Patents
Literature
89results about How to "Read operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
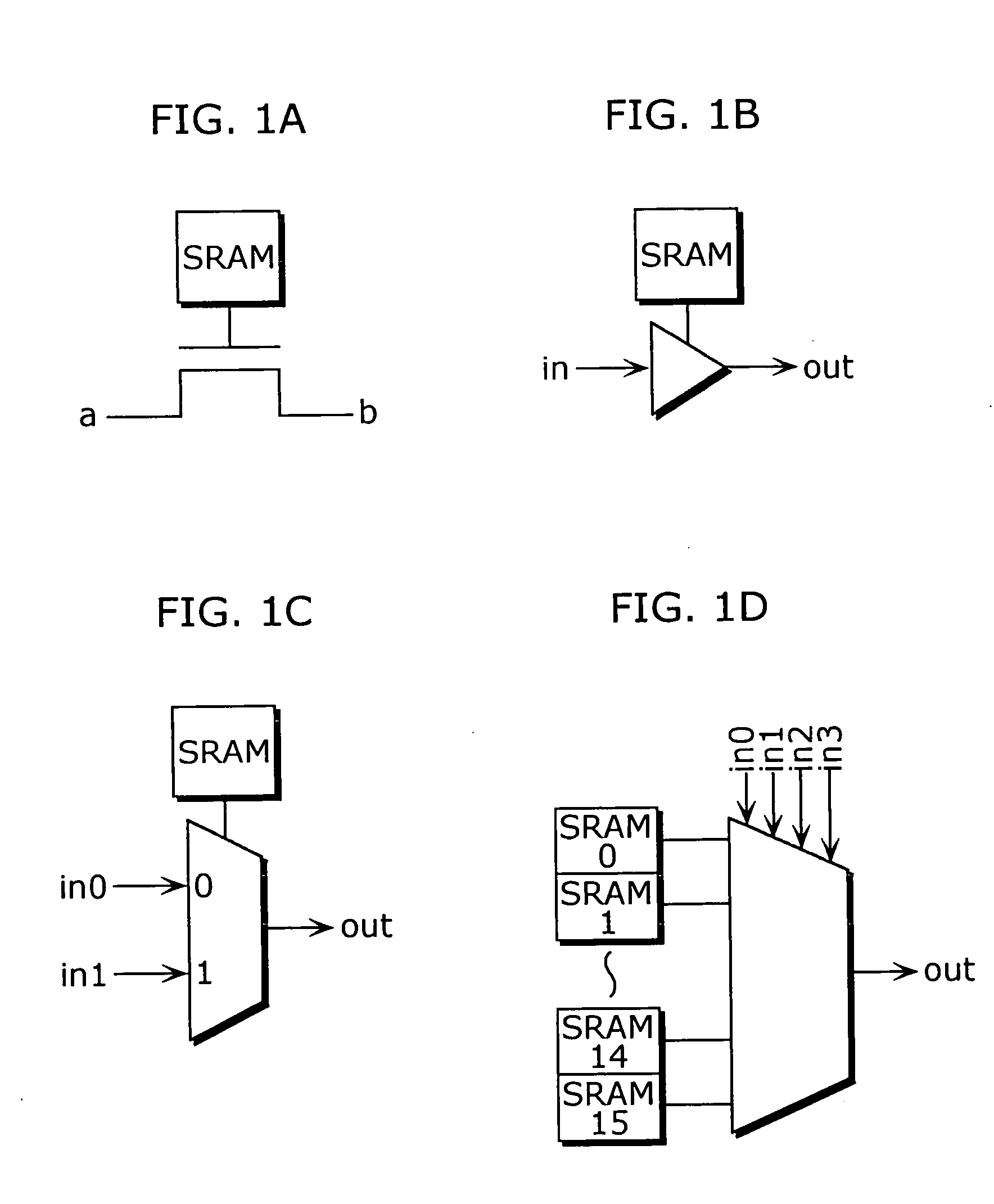
Method for reducing latency in a solid-state memory system while maintaining data integrity
ActiveUS8661218B1Easy accessReduce energy consumptionError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsSolid-state storageFault tolerance
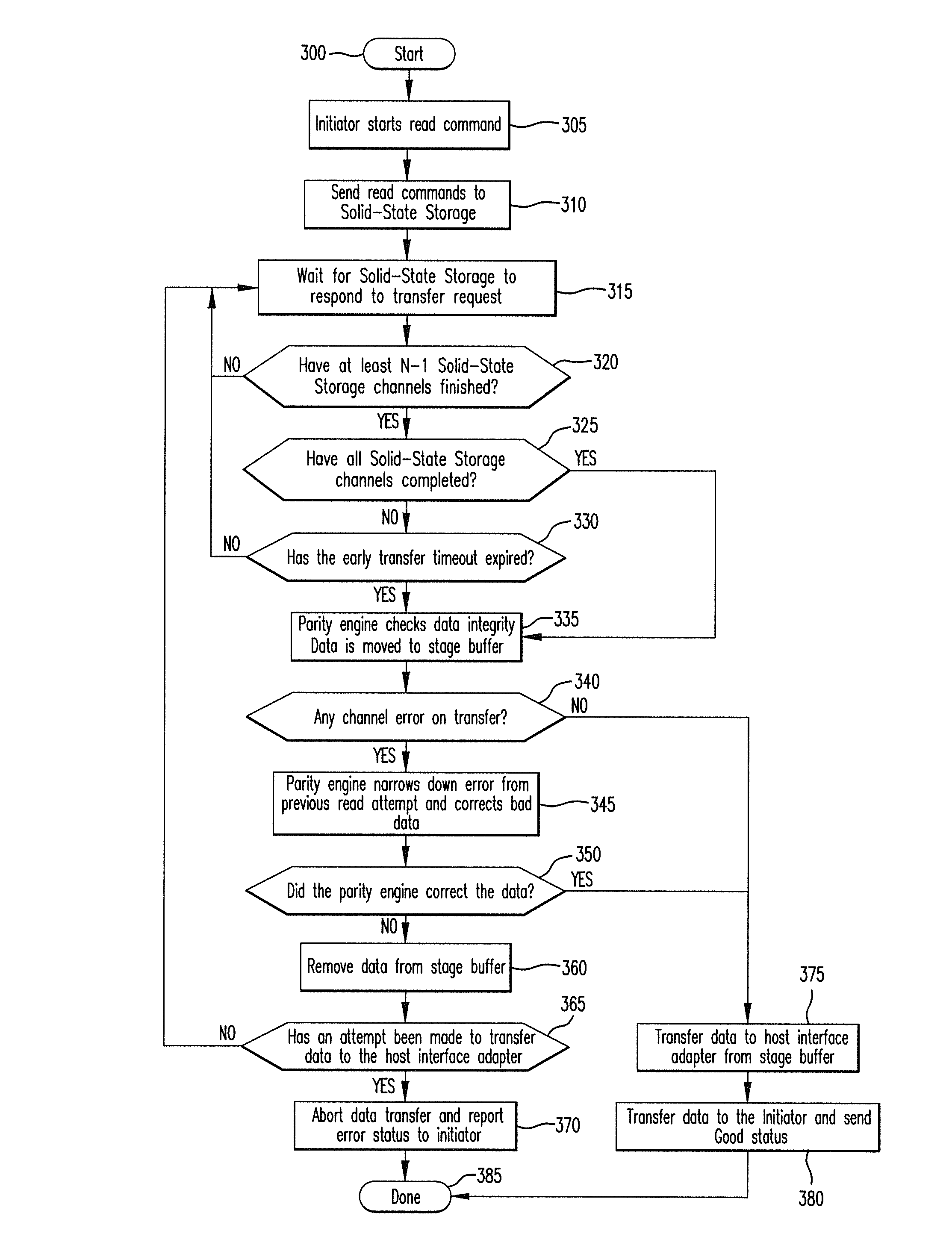
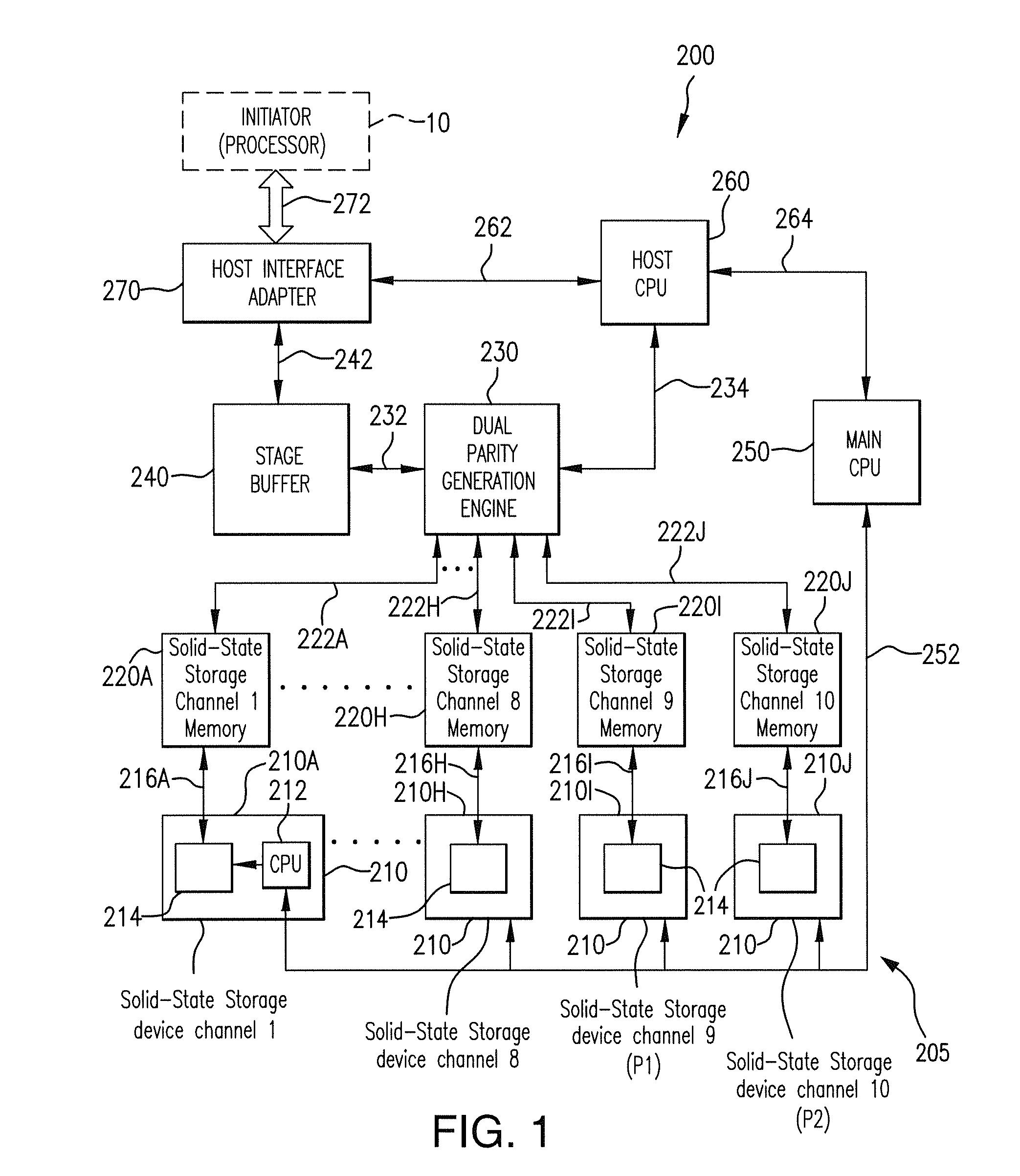
A latency reduction method for read operations of an array of N solid-state storage devices having n solid-state storage devices for data storage and p solid-state storage devices for storing parity data is provided. Utilizing the parity generation engine fault tolerance for a loss of valid data from at least two of the N solid-state storage devices, the integrity of the data is determined when N−1 of the solid-state storage devices have completed executing a read command. If the data is determined to be valid, the missing data of the Nth solid-state storage device is reconstructed and the data transmitted to the requesting processor. By that arrangement the time necessary for the Nth solid-state storage device to complete execution of the read command is saved, thereby improving the performance of the solid-state memory system.
Owner:DATADIRECT NETWORKS
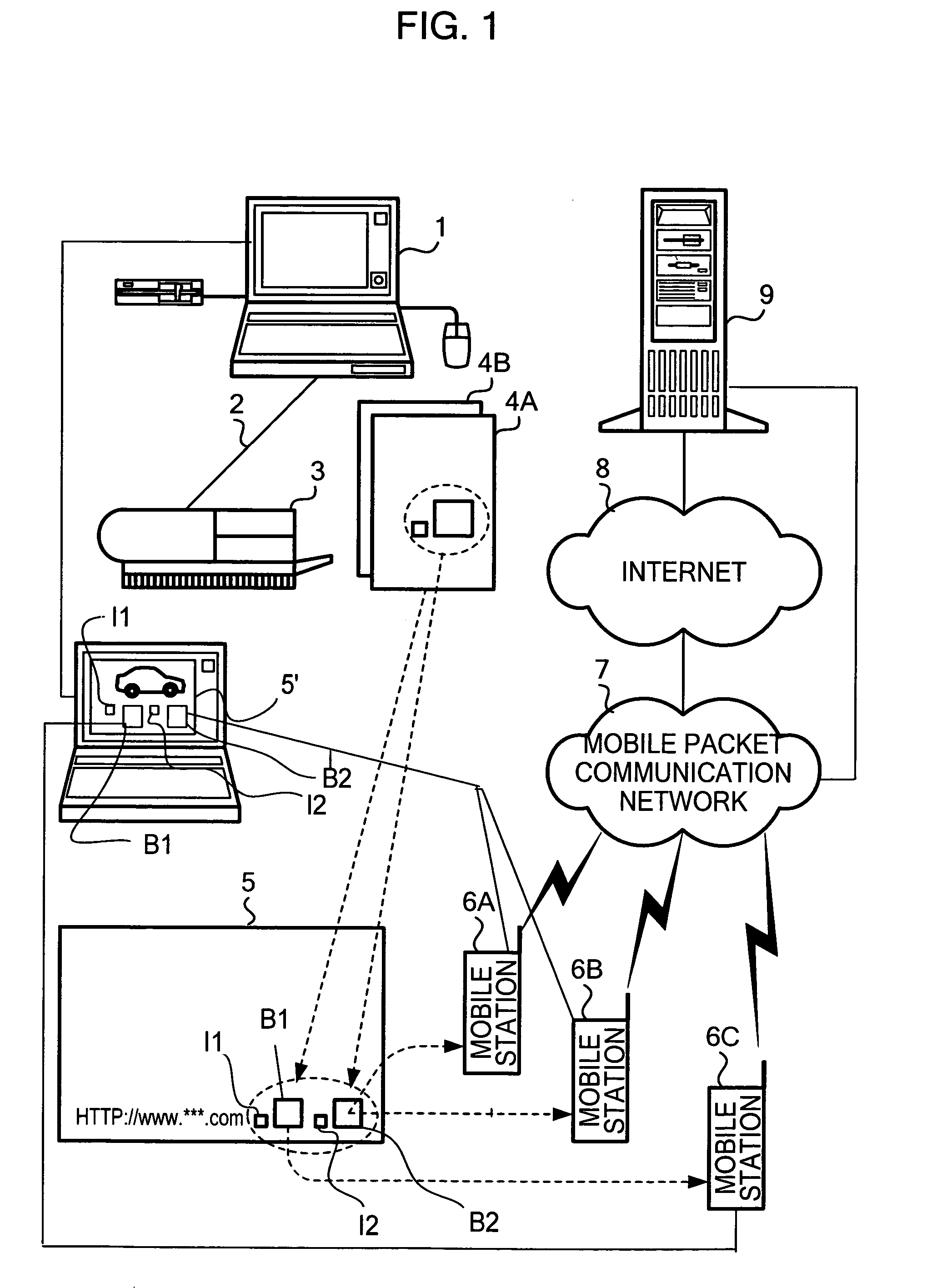
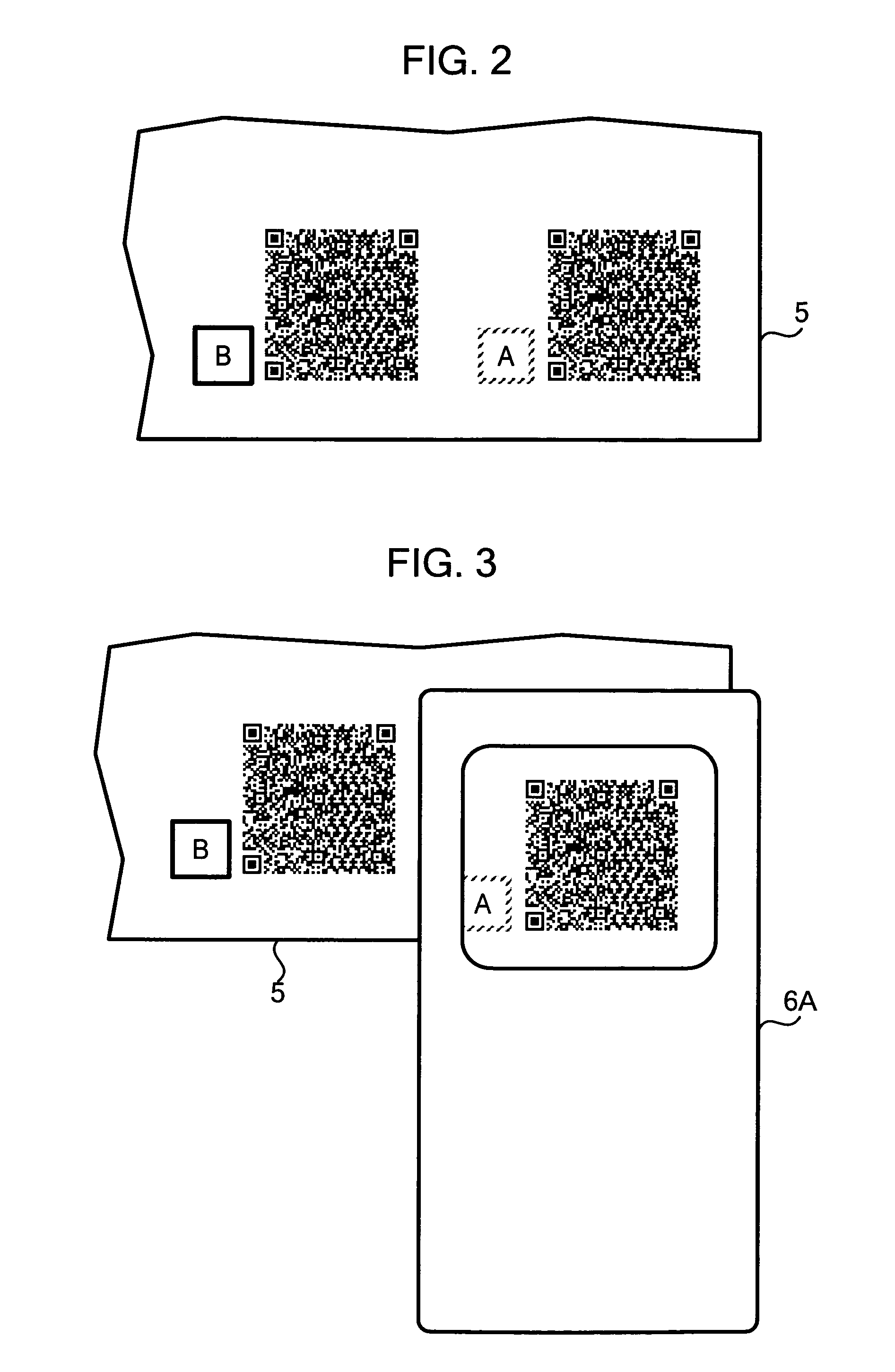
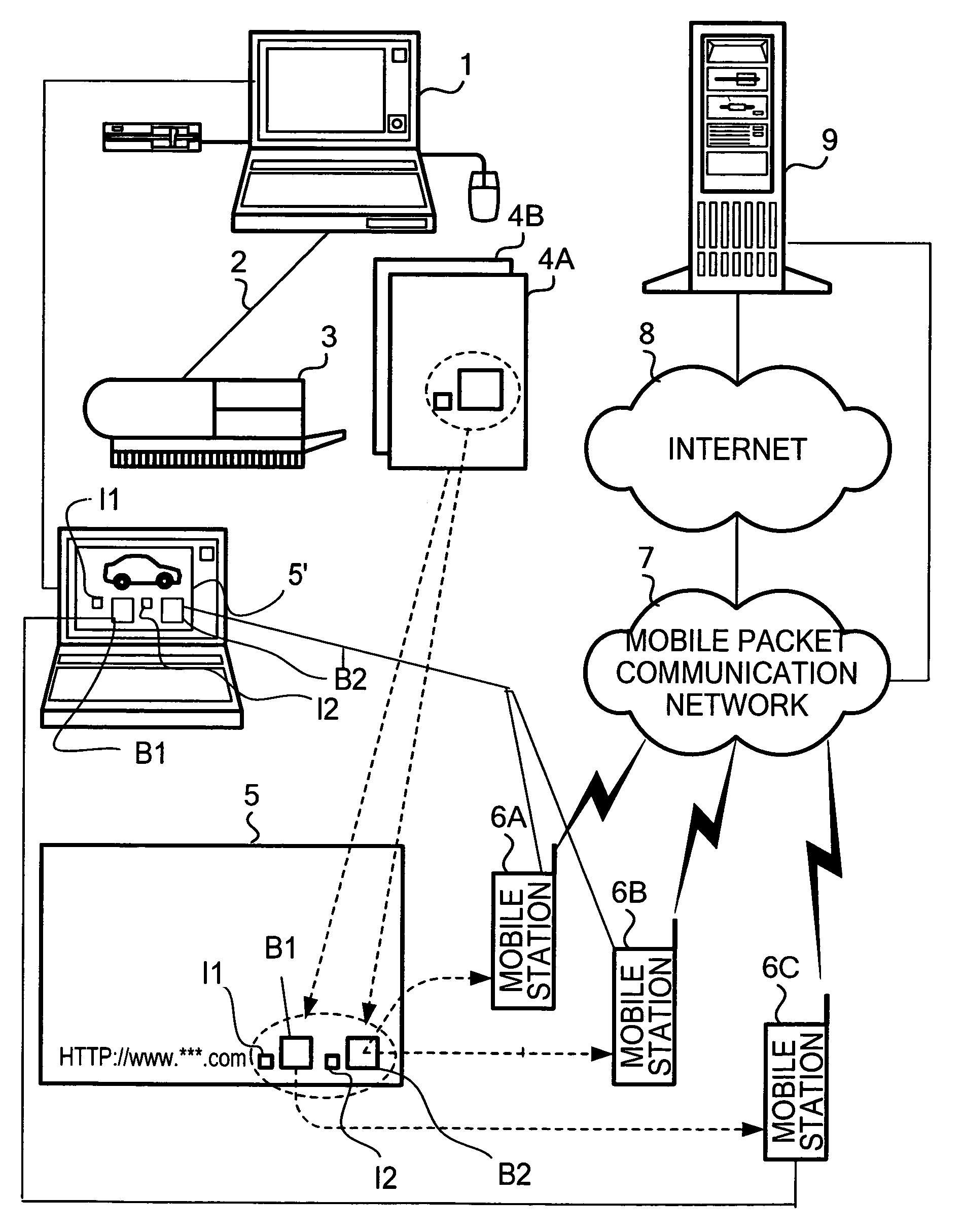
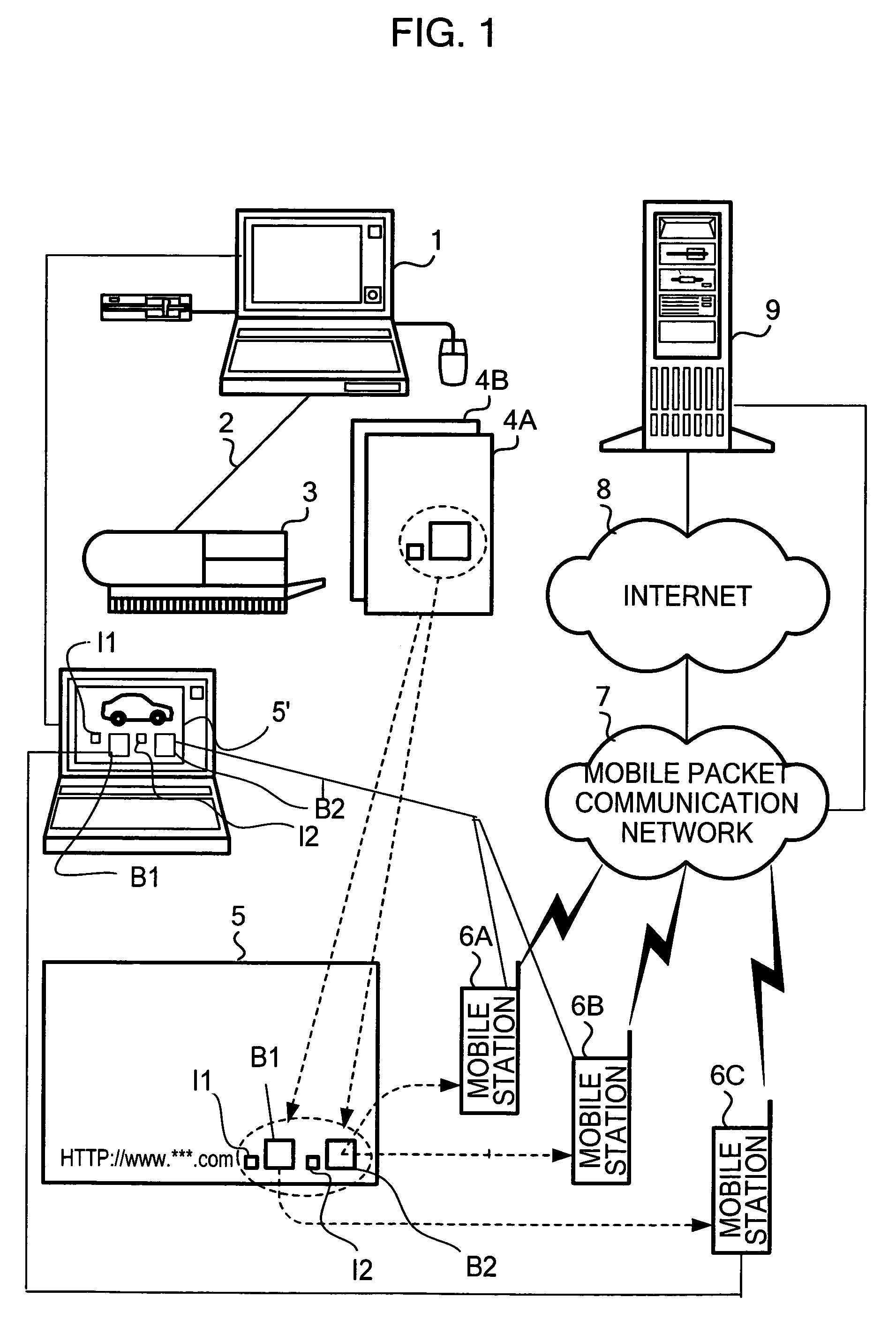
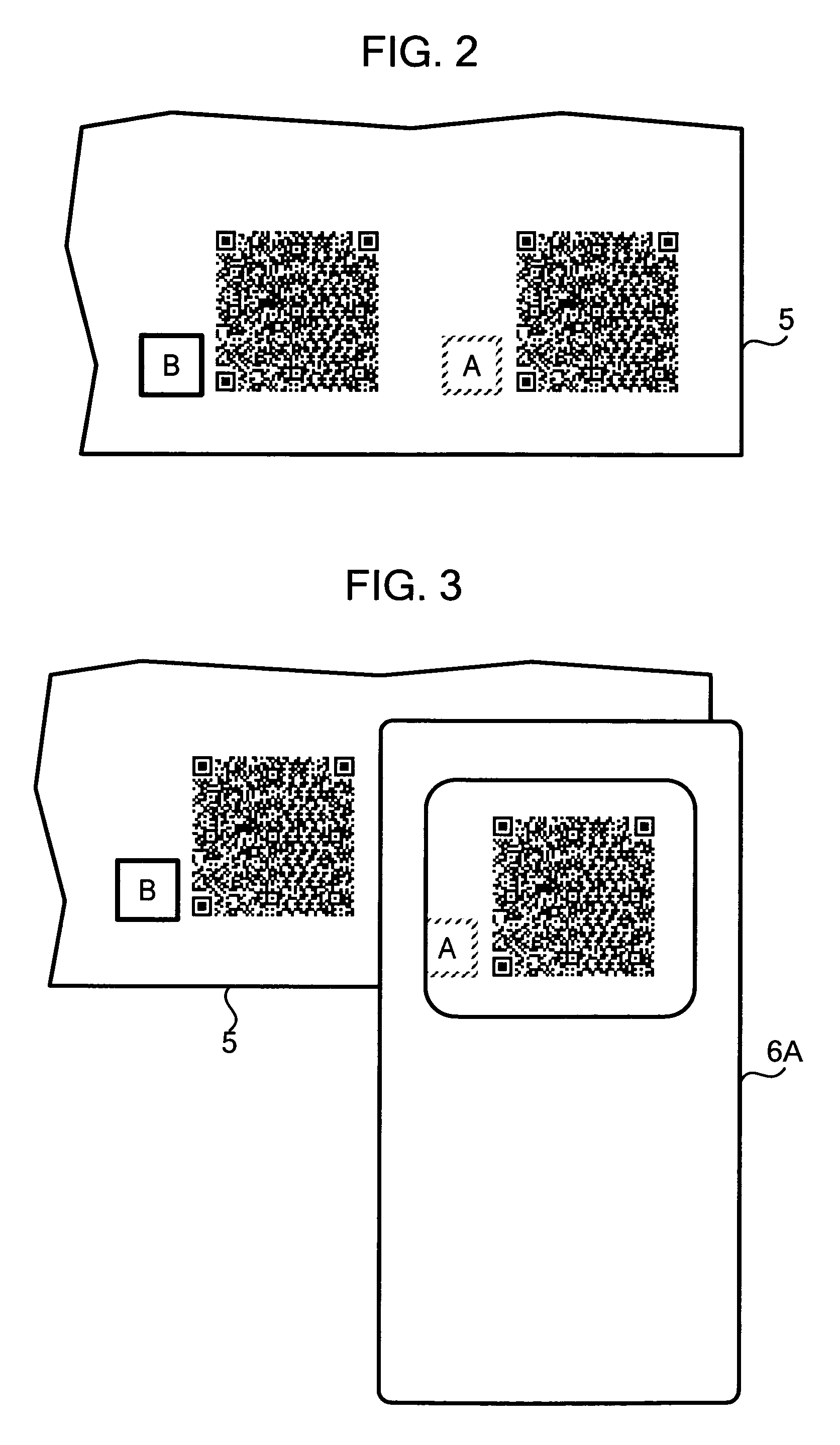
Apparatus and method for reading and decoding information contained in a barcode
ActiveUS20050011958A1Efficient supplyRead operationDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionBarcodeOutput device
An image output device inputs content information, generates a barcode by encoding input content information, and outputs print data so that a sign visually indicating a property of the content information is printed adjacent to the generated barcode or by superimposing the sign on the generated barcode.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Apparatus and method for reading and decoding information contained in a barcode
ActiveUS7410099B2Efficient supplyRead operationDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionBarcodeOutput device
An image output device inputs content information, generates a barcode by encoding input content information, and outputs print data so that a sign visually indicating a property of the content information is printed adjacent to the generated barcode or by superimposing the sign on the generated barcode.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
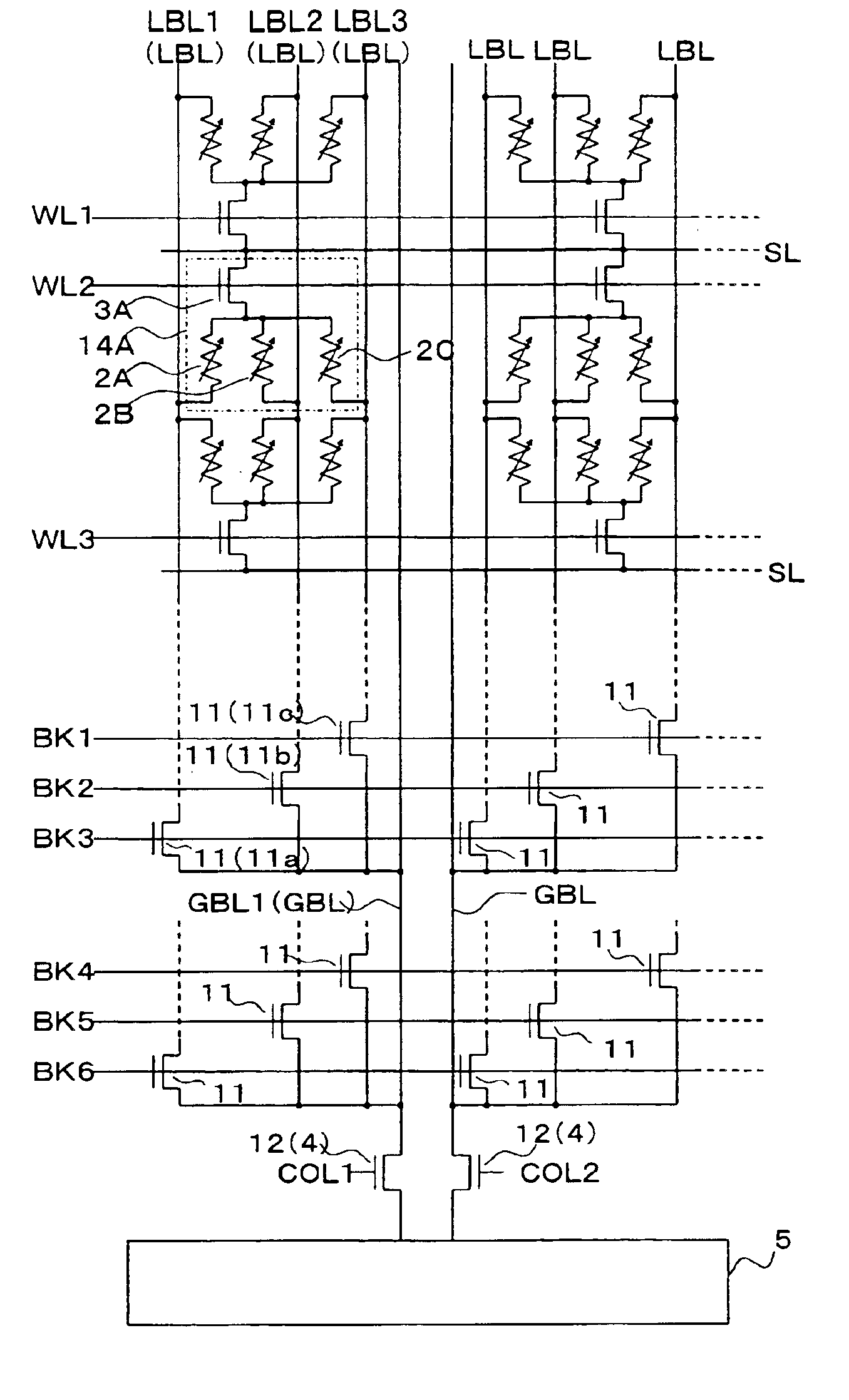
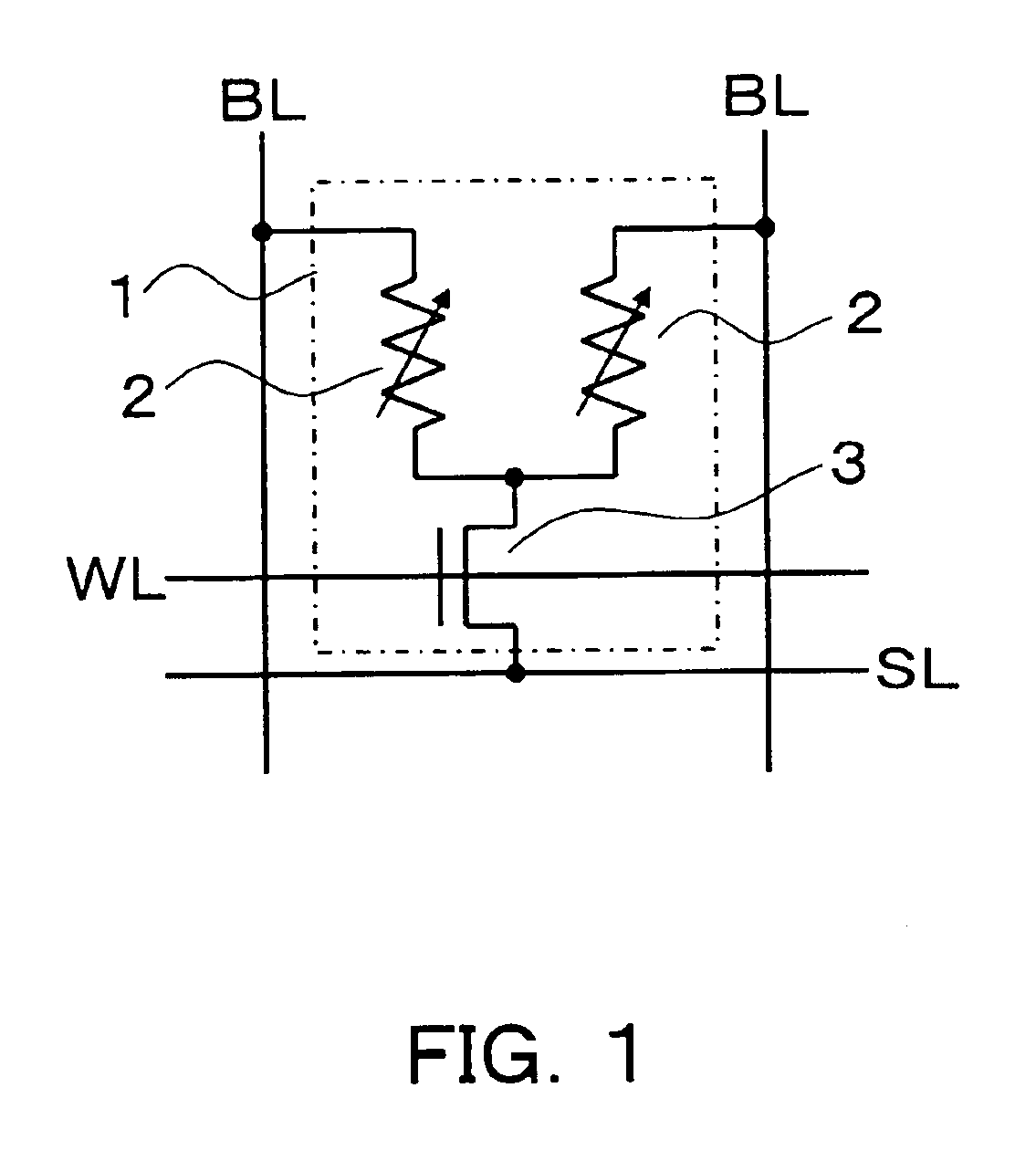
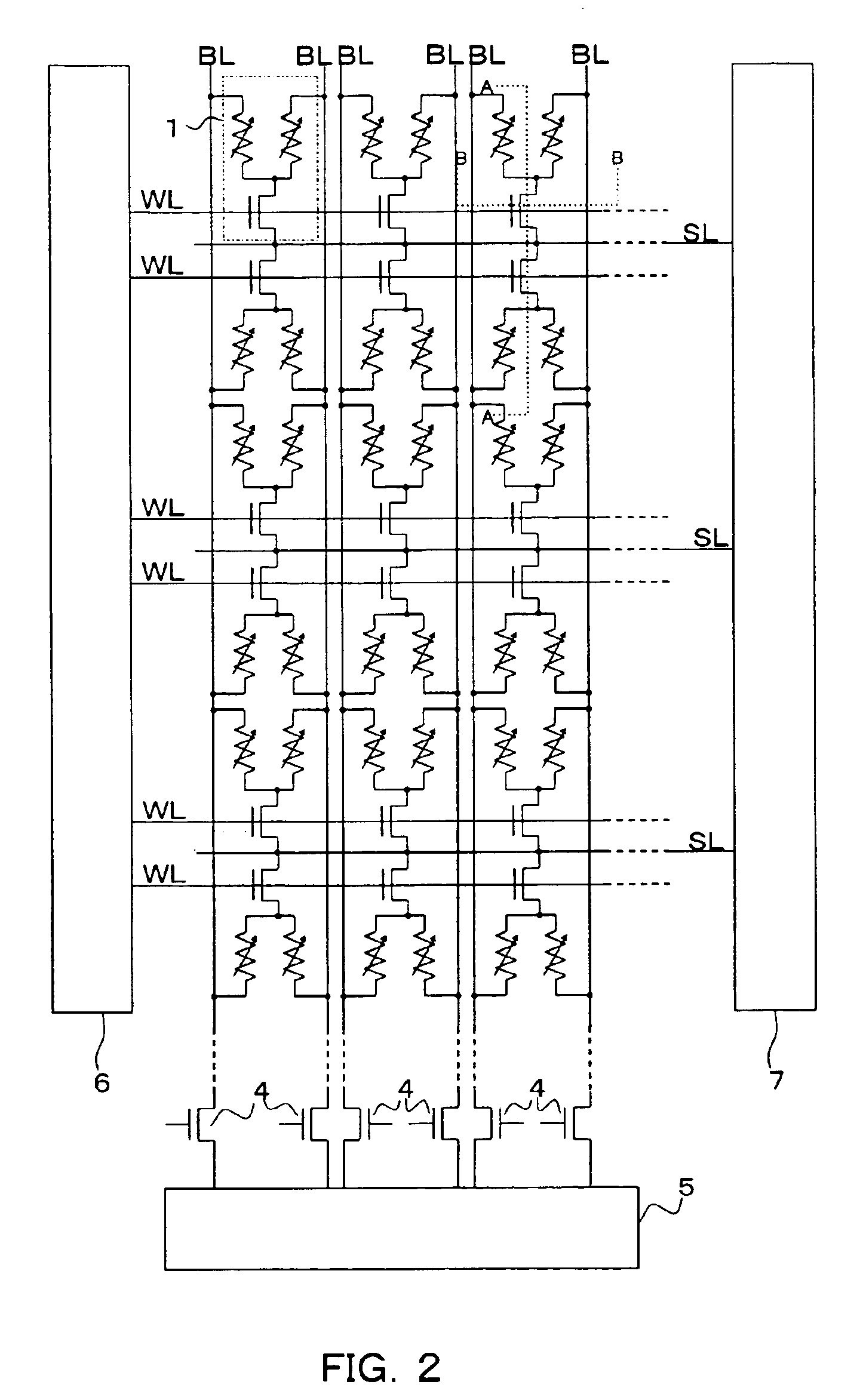
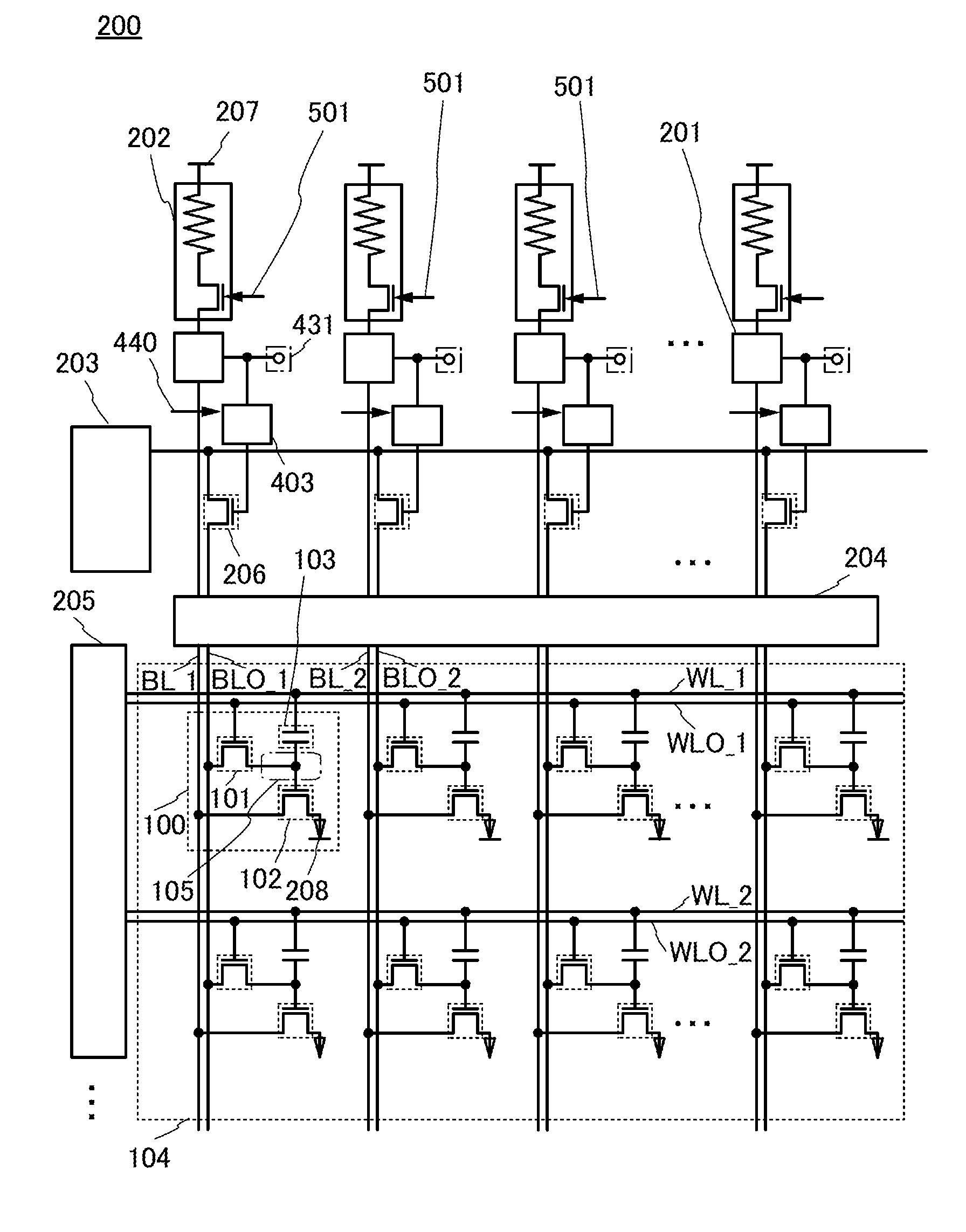
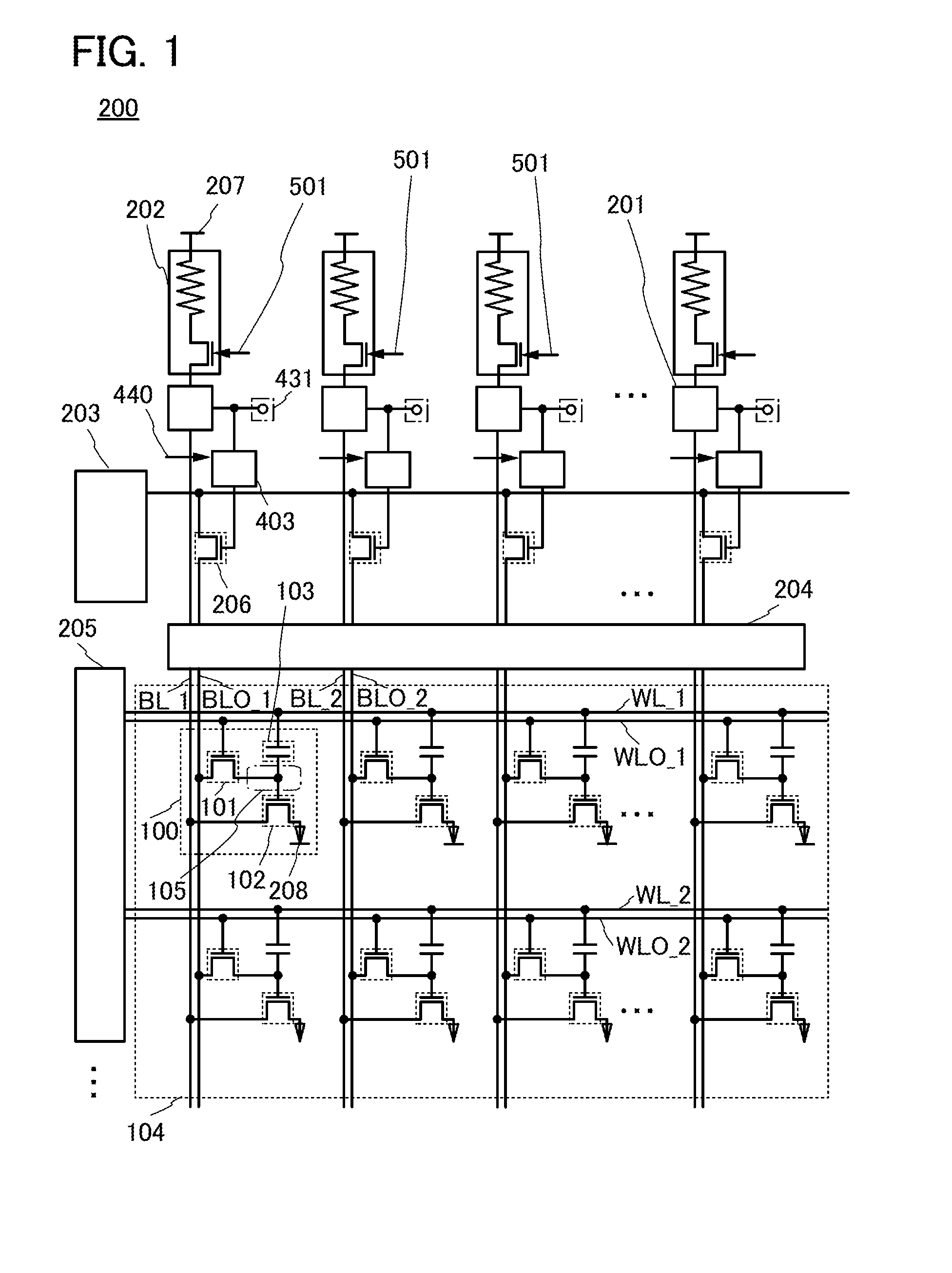
Nonvolatile memory cell and nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS6937505B2Decrease influenceLower on-state resistanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesResistive elementMOSFET
It is an object of the present invention to make it possible to decrease the on-state resistance of a selection transistor of a memory cell without increasing the whole area of a memory cell array and accelerate and stabilize the reading operation of data stored in the memory cell. Therefore, a plurality of variable resistive elements capable of storing information in accordance with a change of electrical resistances is included, one ends of the variable resistive elements are connected each other, and an electrode of a selection element constituted by a MOSFET or diode element for selecting the variable resistive elements in common is connected with one end of each of the variable resistive elements to constitute a memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
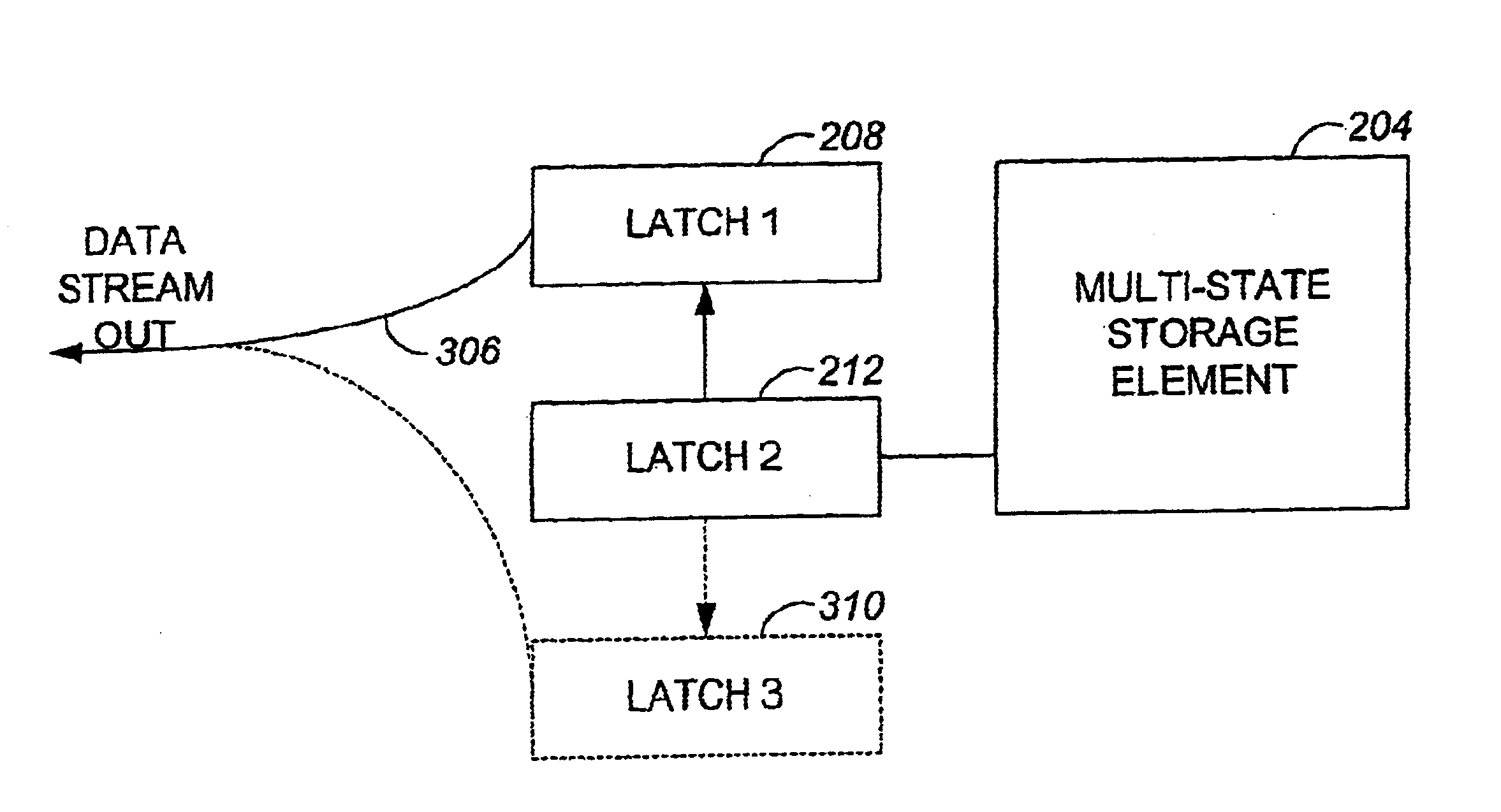
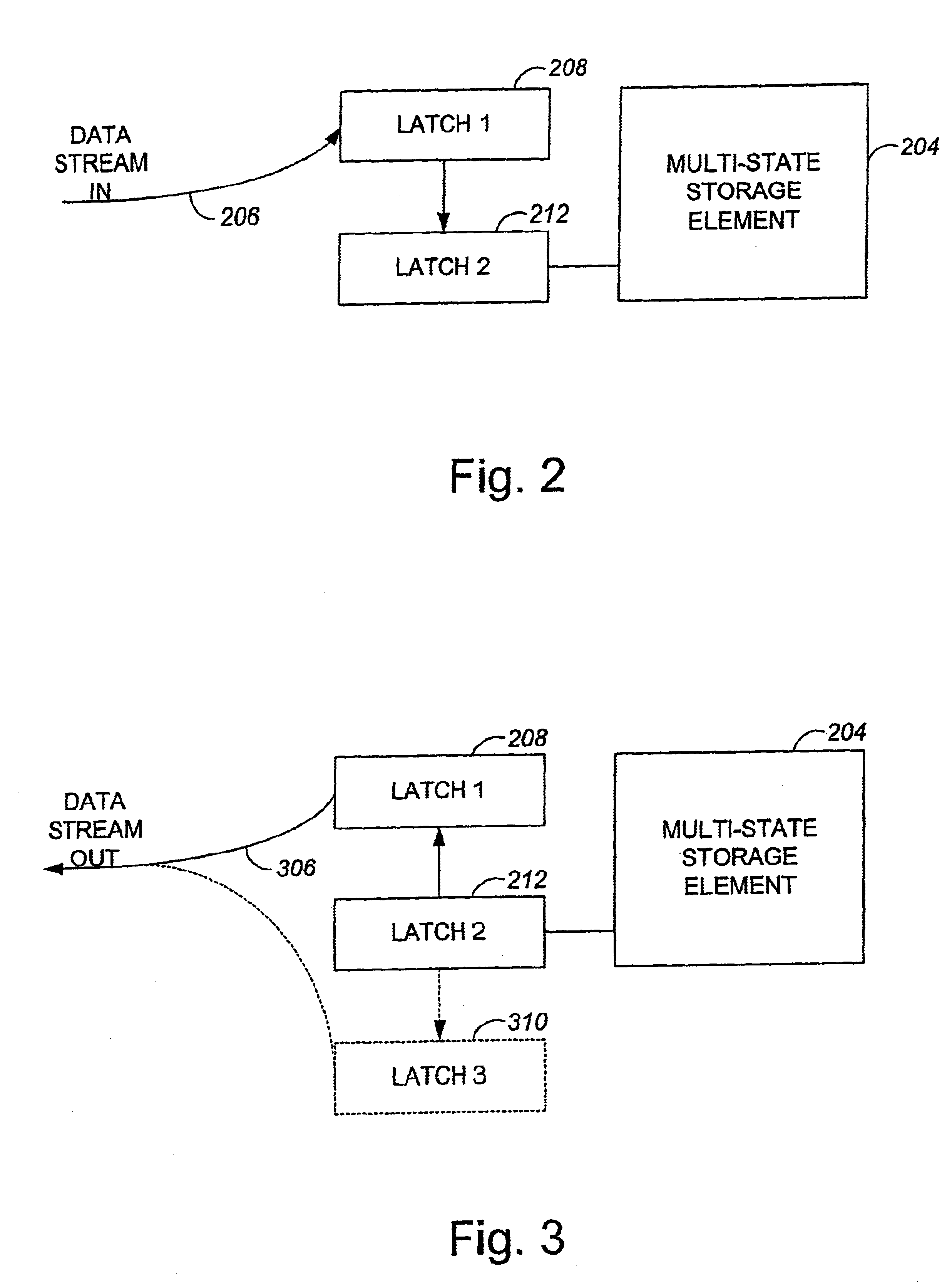
Efficient read, write methods for multi-state memory
InactiveUS6751129B1Read operationOccur more efficientlyRead-only memoriesConcurrent instruction executionComputer hardwareData source
Methods and apparatus for efficiently writing data to and reading data from multi-state memory cells. According to one aspect of the present invention, a memory system includes a first storage element, a data source, a first element, a second element, and a ripple clock. The data source provides a plurality of bits to be stored in the first storage element, and the first element receives a first bit from the data source, and also clocks the first bit into the second element. The first element then receives a second bit of the plurality of bits from the data source substantially while the first bit is being stored into the first storage element. The ripple clock enables access to the first element and the second element such that the first bit and the second bit may be pipelined.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
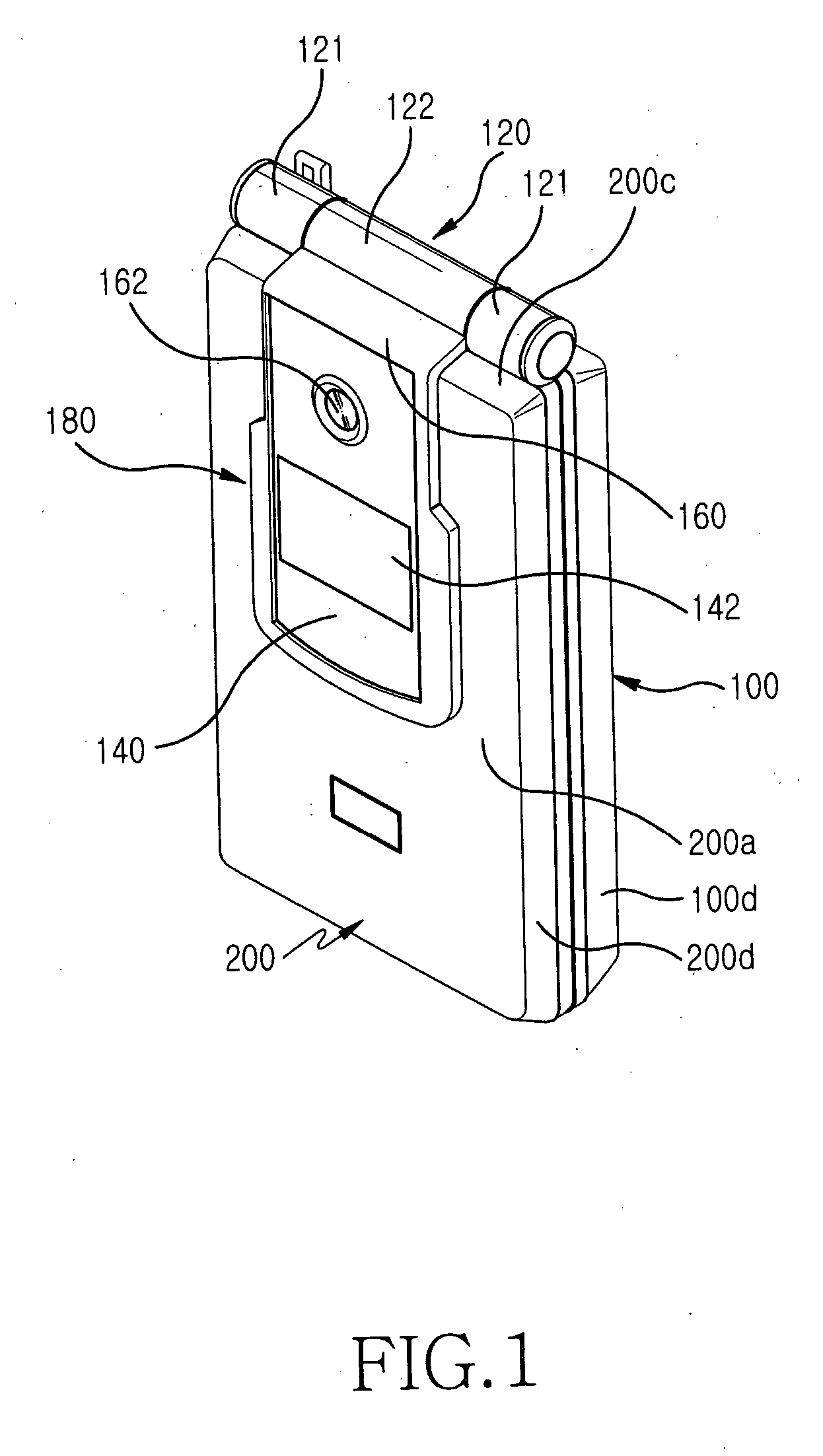
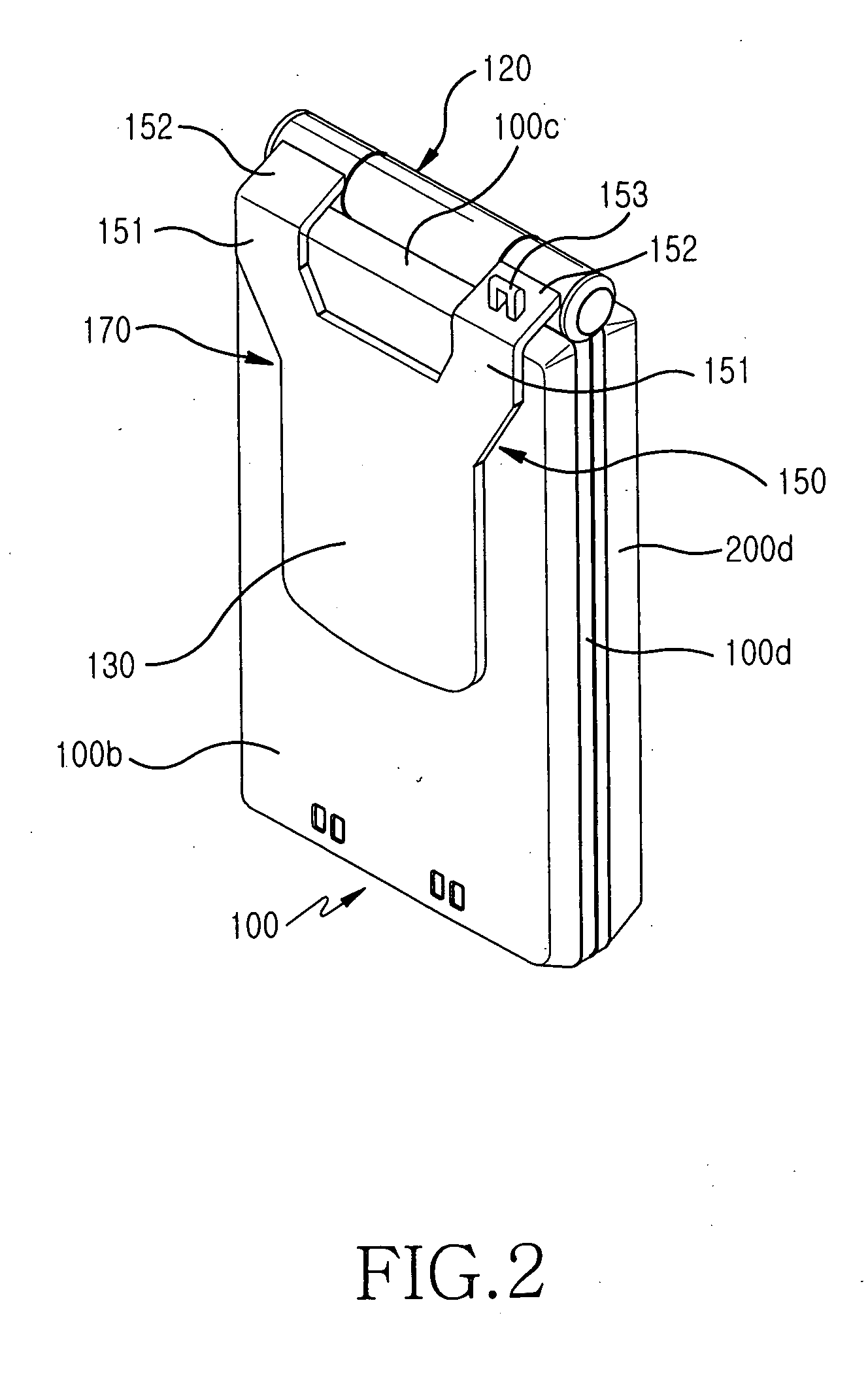
Portable digital communication apparatus having sliding/rotational hinge means
InactiveUS20050113156A1Easy to useRead operationDetails for portable computersTransmissionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
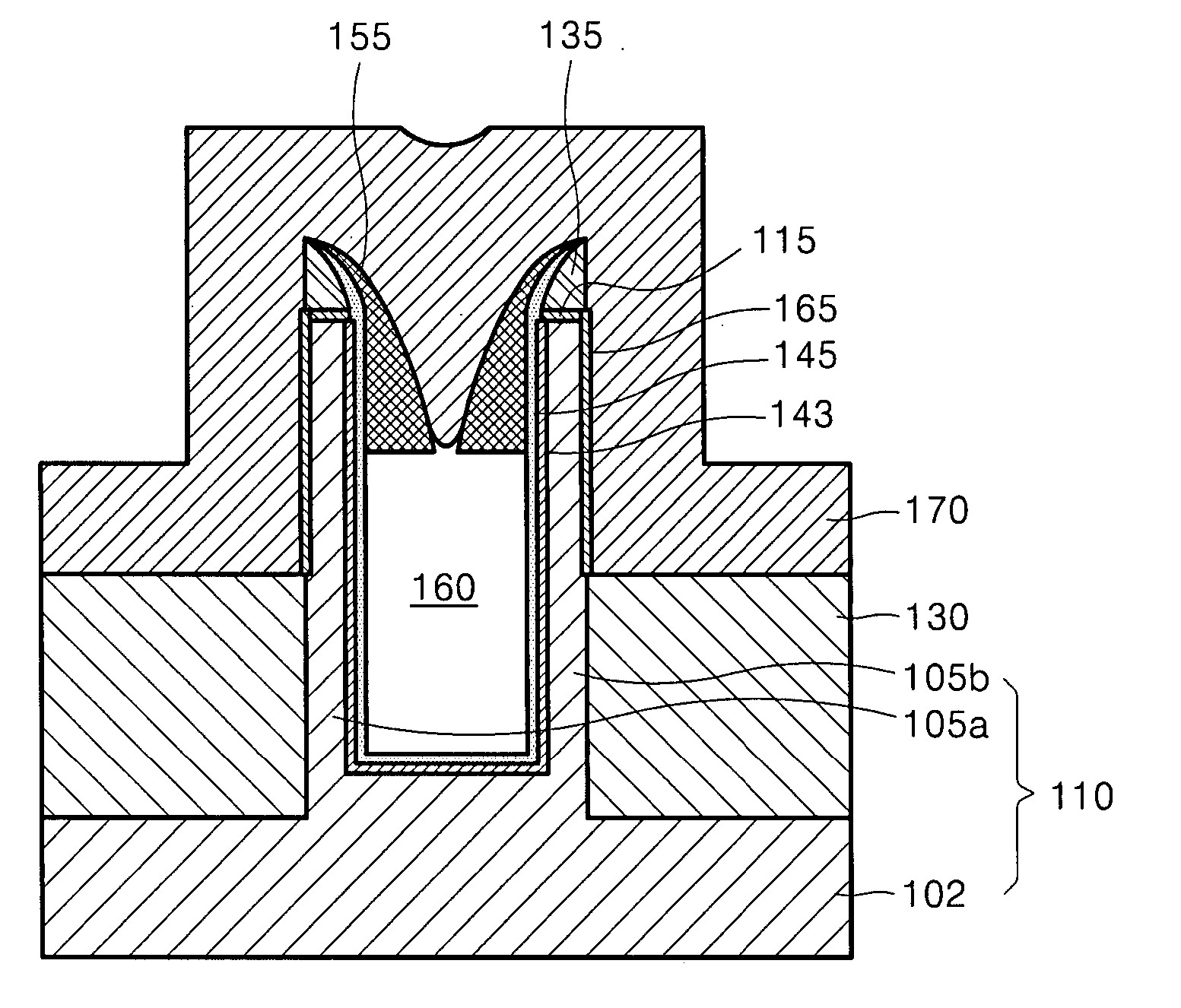
Semiconductor device having a pair of fins and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080111199A1Read operationSuppression of short channel effectsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
Example embodiments relate to a semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same. A semiconductor device according to example embodiments may have reduced disturbances during reading operations and a reduced short channel effect. The semiconductor device may include a semiconductor substrate having a body and a pair of fins protruding from the body. Inner spacer insulating layers may be formed on an upper portion of an inner sidewall of the pair of fins so as to reduce the entrance to the region between the pair of fins. A gate electrode may cover a portion of the external sidewalls of the pair of fins and may extend across the inner spacer insulating layers so as to define a void between the pair of fins. Gate insulating layers may be interposed between the gate electrode and the pair of fins.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pressure activated fingerprint input apparatus
InactiveUS20050213799A1Simply and reliably readingClear readingPrint image acquisitionComputer scienceFingerprint
An image input apparatus includes an image reading assembly positioned below a placement surface on which an object to be examined is placed, and a sensing circuit for sensing that the object is placed on the placement surface, in accordance with a pressure applied to the placement surface.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device
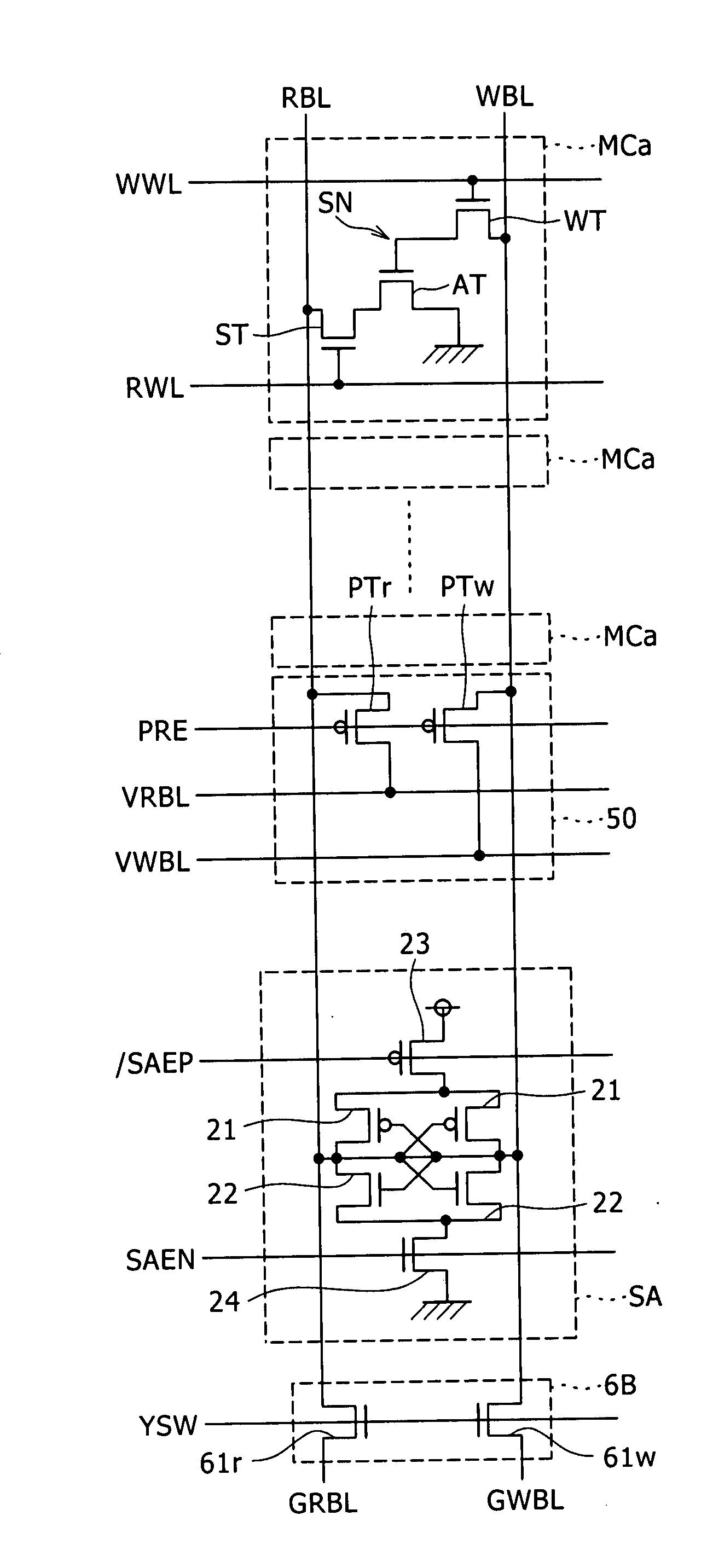
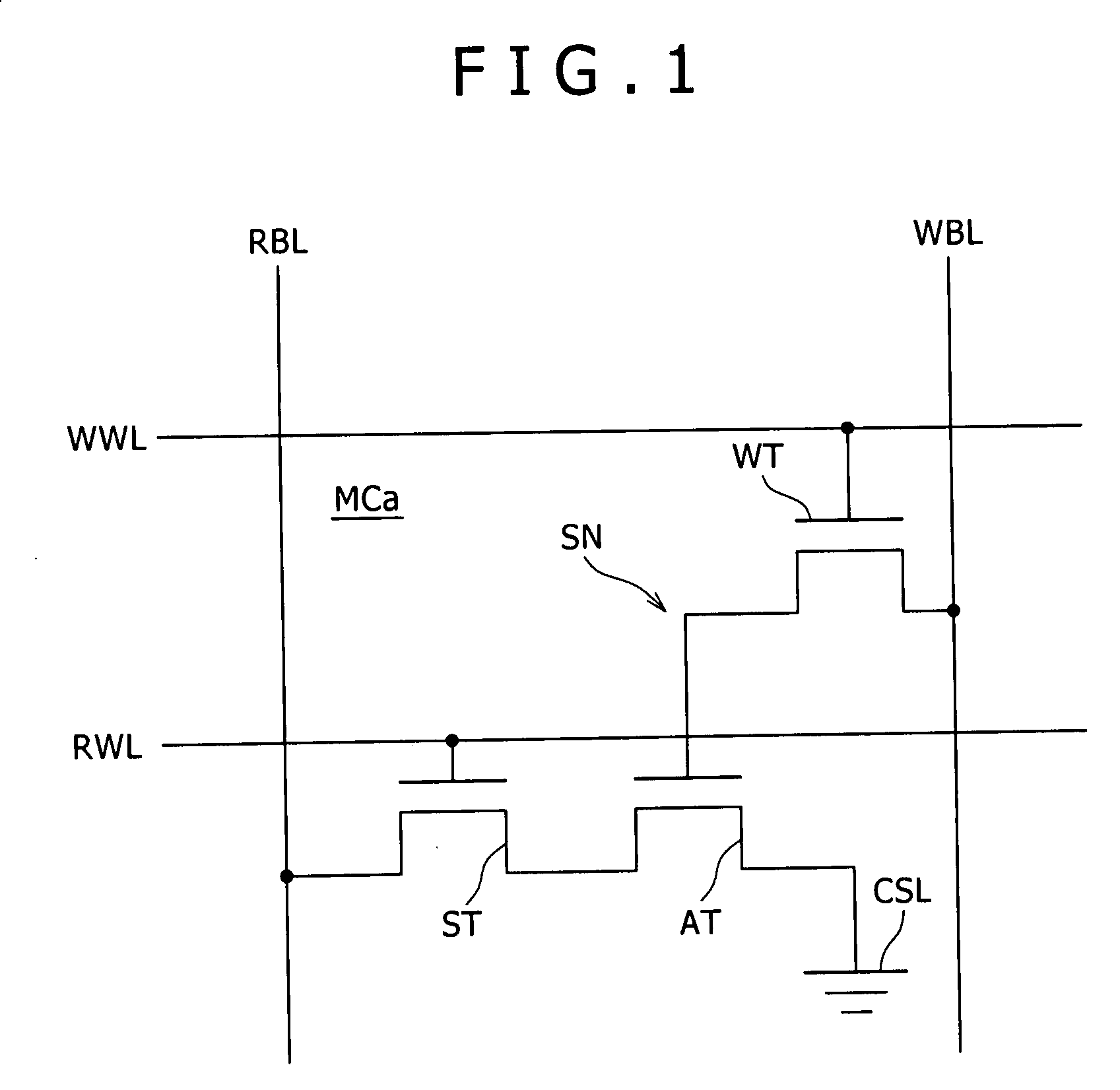
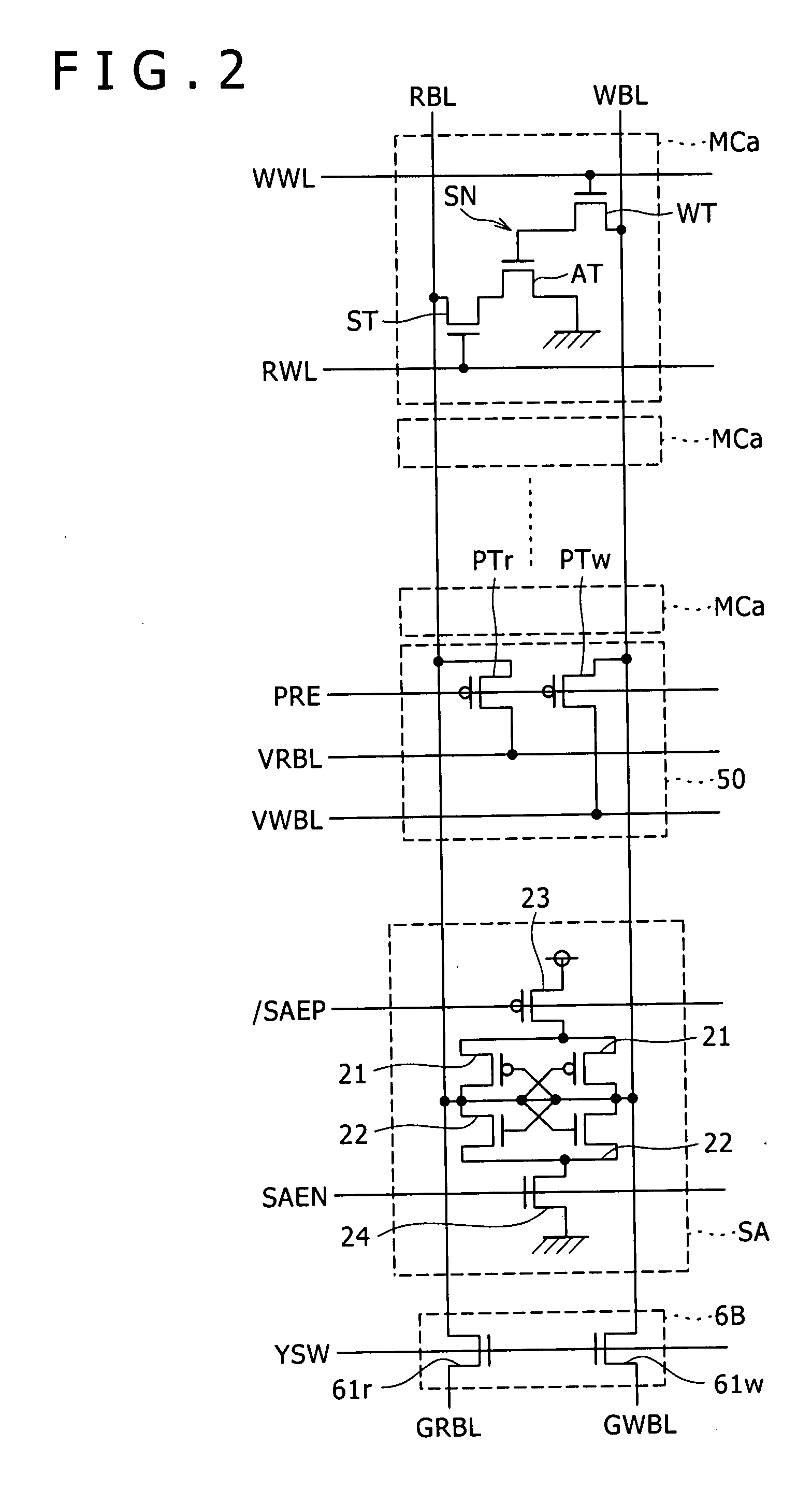
InactiveUS20080025113A1Speedup of readSpeedup of write operationDigital storageWrite bitWrite buffer
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor memory device including, a memory array with memory cells array-like arranged, a read bit line connected to a data output node of the memory cells and shared by a plurality of the memory cells arranged in one direction in the memory array, a write bit line connected to a data input node of the memory cells and shared by a plurality of the memory cells, a sense amplifier for sensing a voltage of the reading bit line, a first sense line and a second sense line connected to the sense amplifier, a read bit line switch for controlling electrical connection and disconnection between the first sense line and the read bit line, a write buffer connected between the second sense line and the write bit line, capable of controlling electrical connection and disconnection between the second sense line and the write bit line.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050190597A1Less deterioration in capabilityRead operationDigital storageFerroelectric capacitorSemiconductor
The semiconductor device of the present invention includes a volatile latch circuit which holds data, a nonvolatile ferroelectric capacitor circuit which holds data, and a switch circuit which connects and disconnects between the latch circuit and the ferroelectric capacitor circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
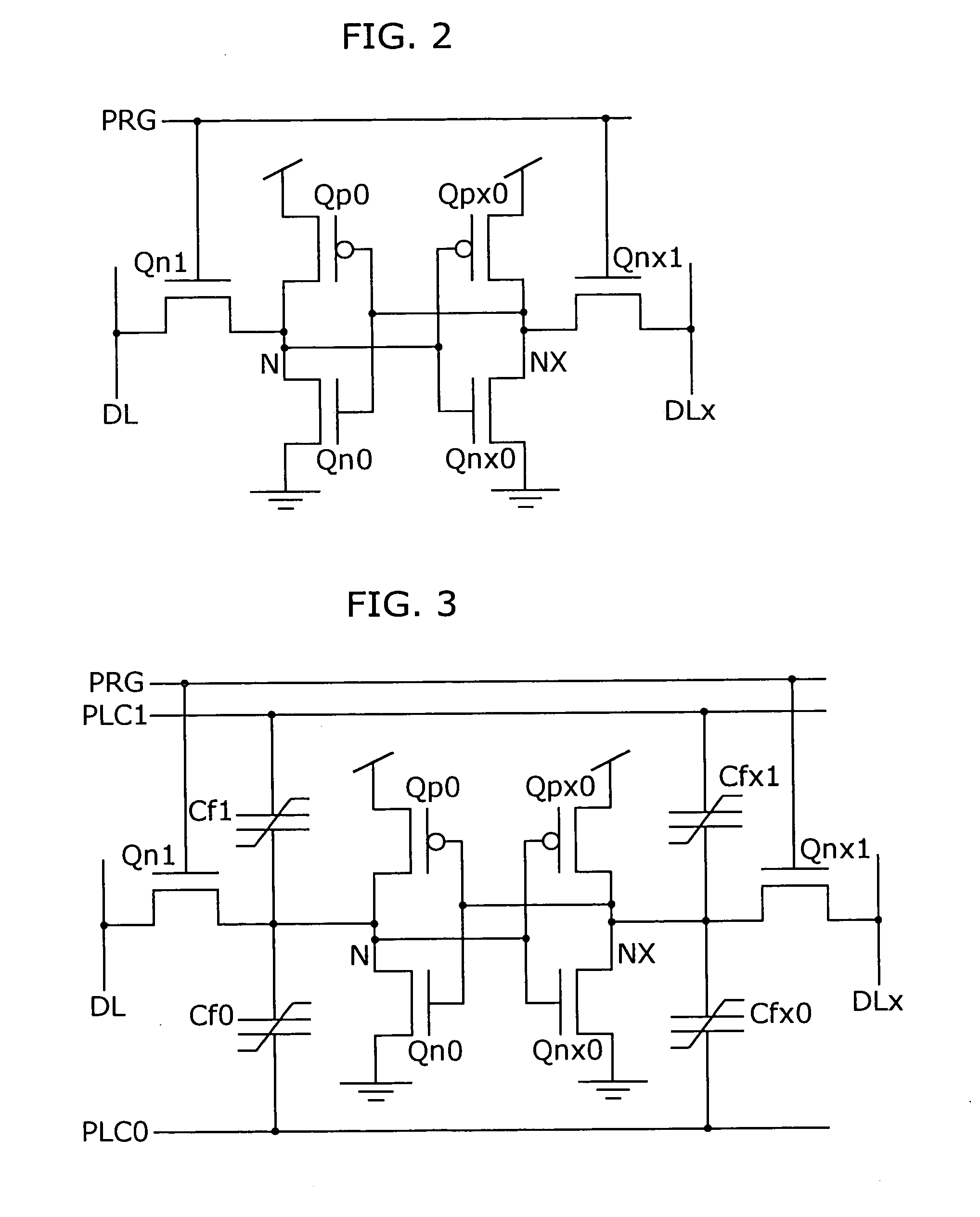
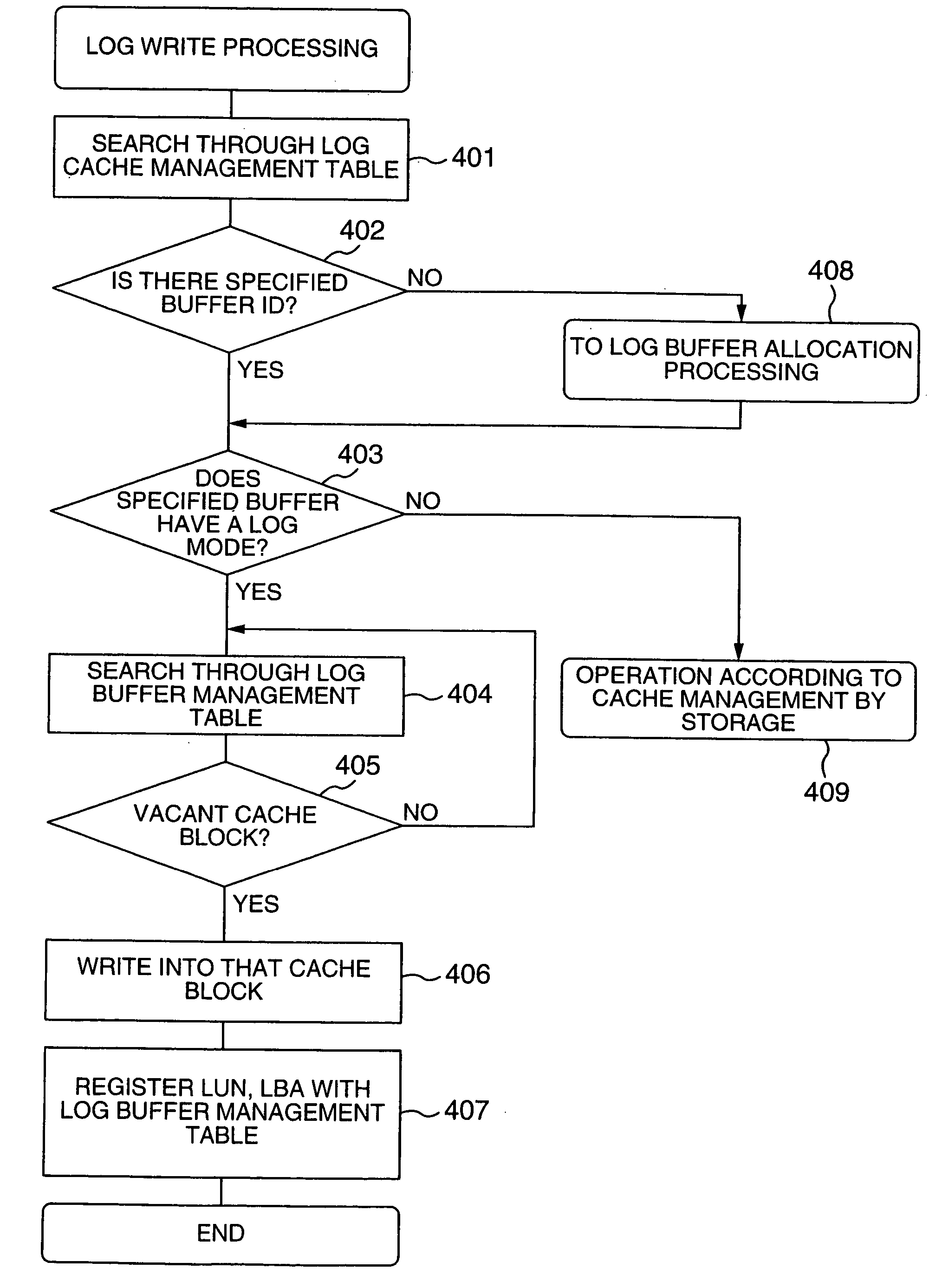
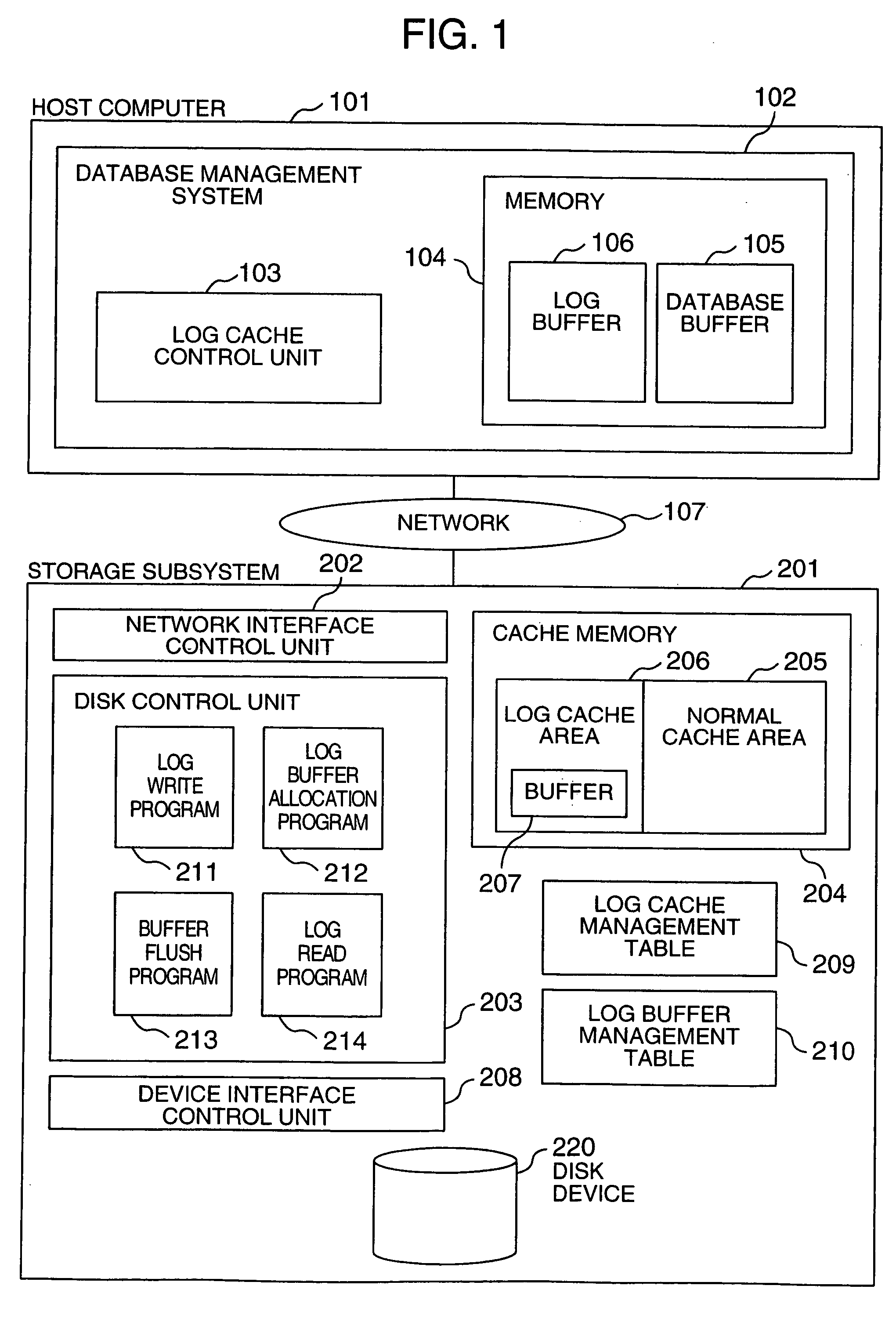
Method and system for data processing with recovery capability
InactiveUS20050251625A1Reduce system recovery timeTime necessaryInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemComputer failure
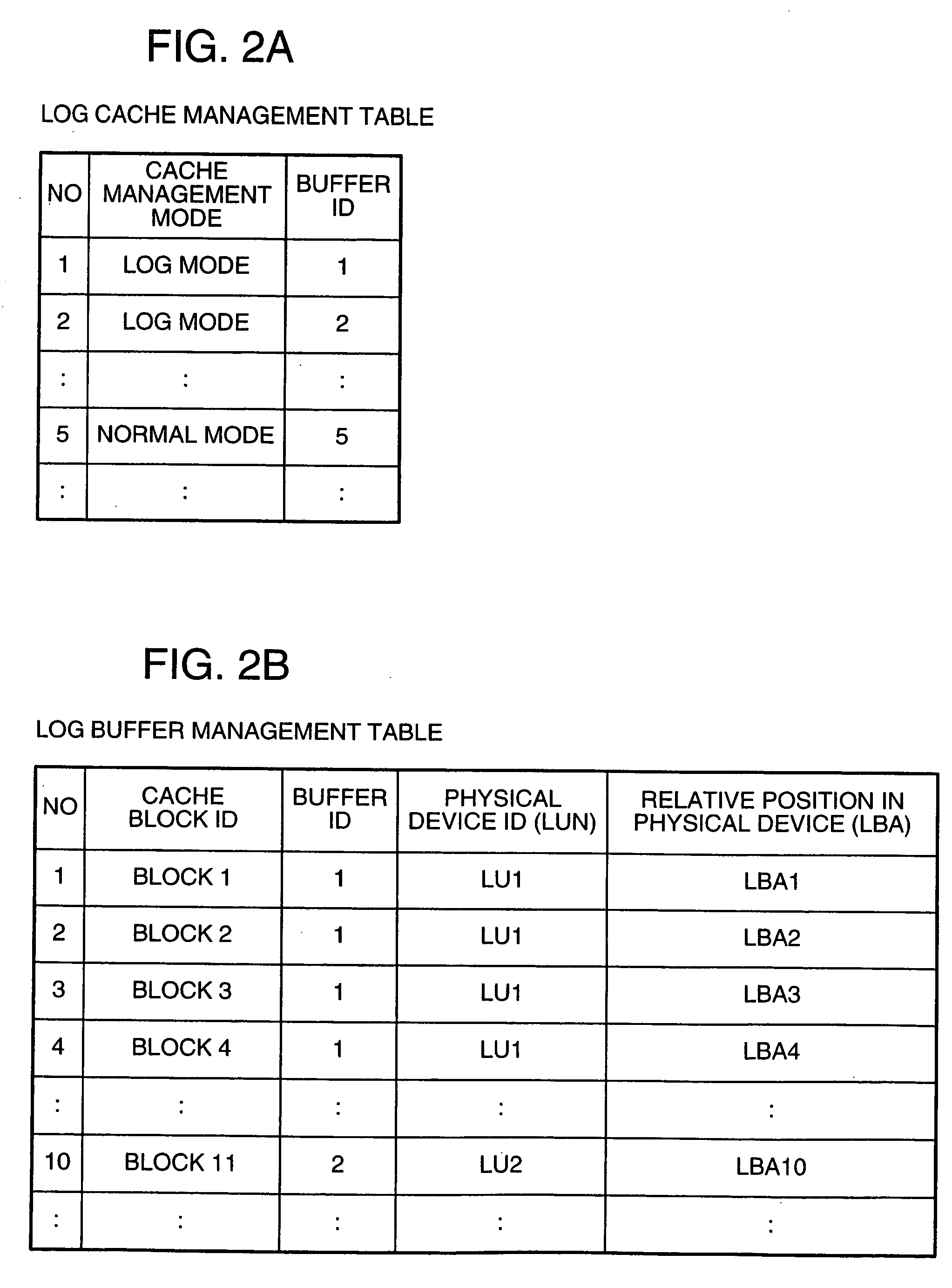
The data processing system controls, from the database management system on a host computer, the storage device subsystem which stores log data supplied from the database management system; allocates on a disk cache in the storage device subsystem in advance a log-dedicated buffer area of a size equal to that of the log data output between checkpoints; writes log data into the buffer area; and, in the event of a host computer failure, reads out the log data from the disk cache without making access to a disk device. Since the log information required for the recovery of the data processing device is cached on the storage device side, the time it takes to read the necessary log information can be shortened, which in turn reduces the system recovery time.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
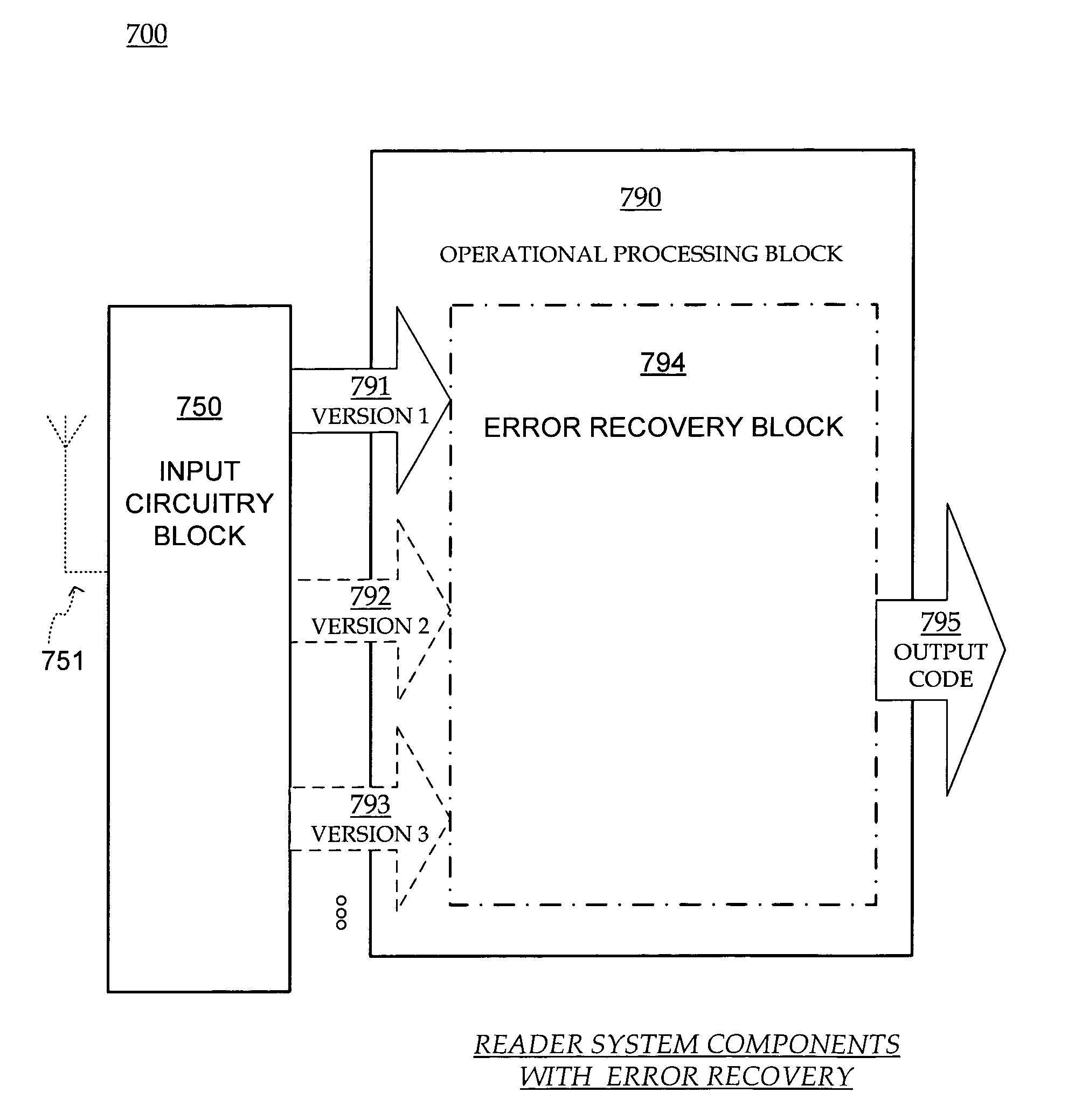
Error recovery in RFID reader systems
ActiveUS20060236203A1Read operationMemory record carrier reading problemsCode conversionComputer hardwareFinal version
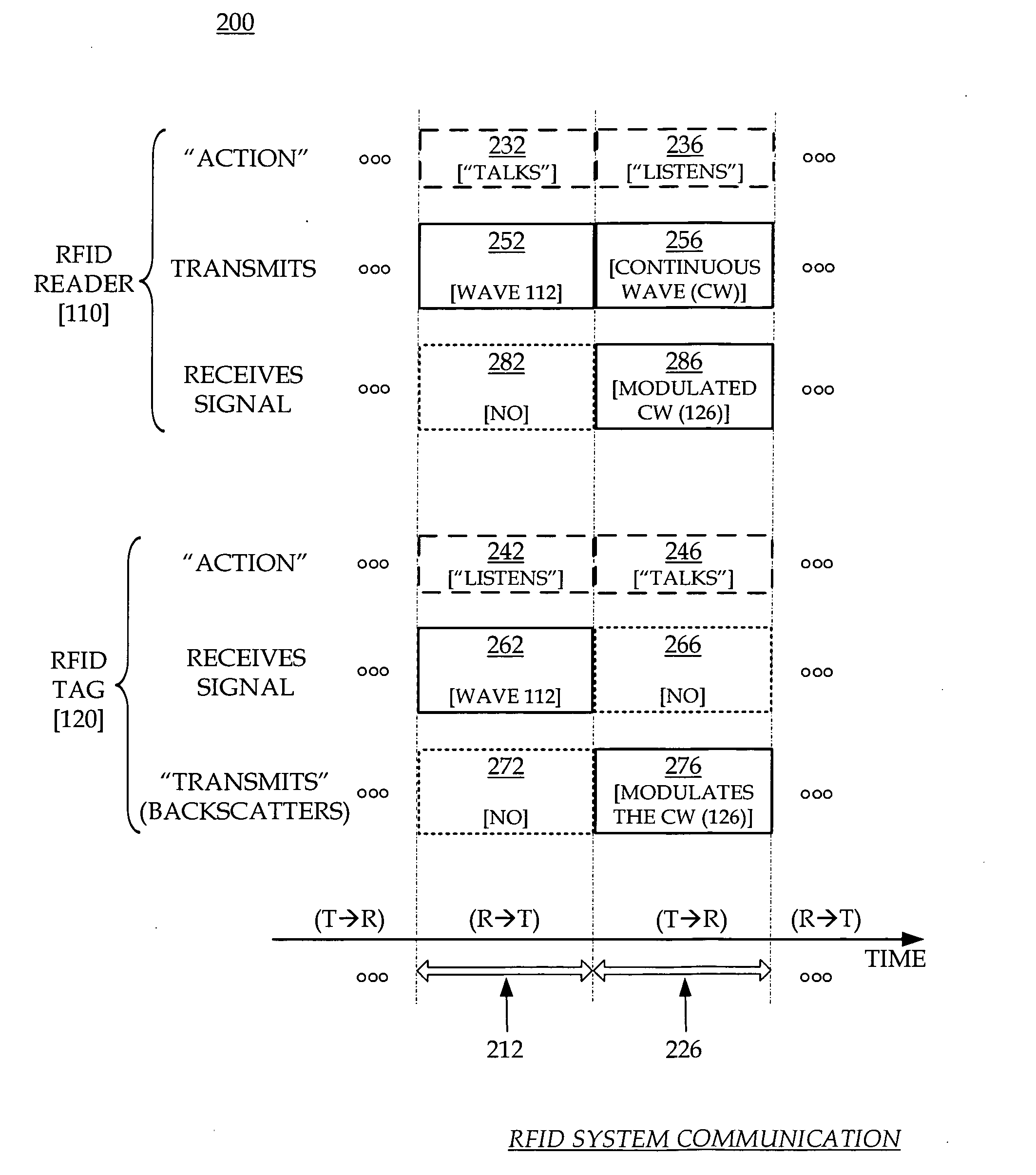
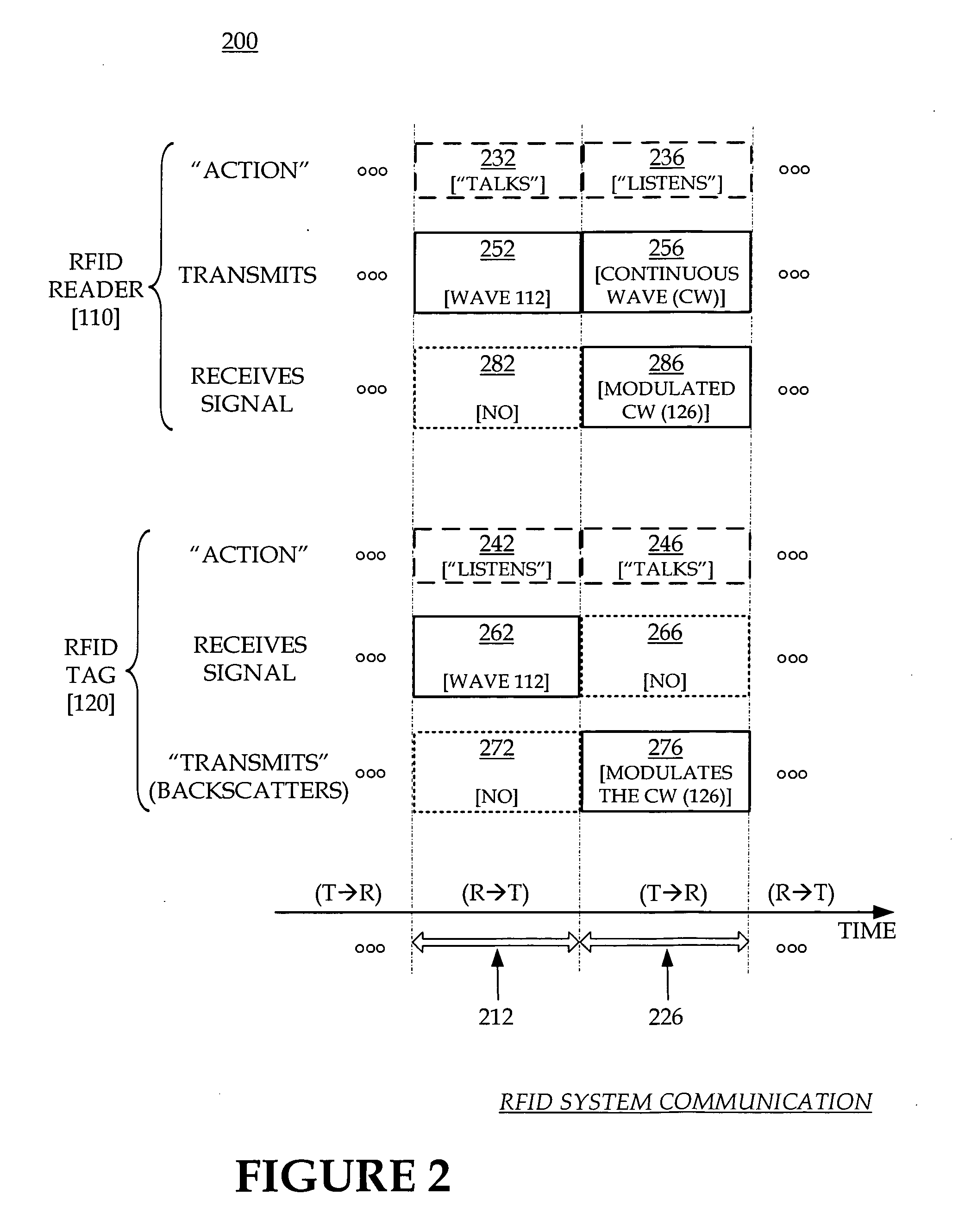
RFID systems, devices, software and methods are adapted for receiving from an RFID tag at least waves that communicate at least a first version of its code. An output tag code is output that is the same as the first version, if a fidelity criterion is met regarding the first version. If not met, the output tag code is instead a final version that is reconstructed from the first version, and also from any additionally optionally subsequently received versions. In some embodiments, an error recovery block includes a subcomponent fidelity criterion checking block that can determine whether the fidelity criterion is met, and a code reconstruction block that can derive the final version.
Owner:IMPINJ
Error recovery in RFID reader systems
ActiveUS7405660B2Read operationMemory record carrier reading problemsCode conversionComputer hardwareFinal version
RFID systems, devices, software and methods are adapted for receiving from an RFID tag at least waves that communicate at least a first version of its code. An output tag code is output that is the same as the first version, if a fidelity criterion is met regarding the first version. If not met, the output tag code is instead a final version that is reconstructed from the first version, and also from any additionally optionally subsequently received versions. In some embodiments, an error recovery block includes a subcomponent fidelity criterion checking block that can determine whether the fidelity criterion is met, and a code reconstruction block that can derive the final version.
Owner:IMPINJ
Portable digital display hardness tester
ActiveUS20140224003A1Simple structureConvenience in operation and readingInvestigating material hardnessRotary encoderMeasurement device
The invention relates to a material hardness testing instrument, specifically to a portable digital display hardness tester, comprising a magnetic chuck, a support, a force measuring device, an indenter, an electronic circuit board, a digital display, and a force applying and indentation depth measuring device consisting of a hand wheel, a rotary encoder and a micrometric screw pair. The support is equipped with the rotary encoder, The micrometric nut is installed in a hole. The digital display is located in the front. The support is fixed on the magnetic chuck. The micrometric nut is internally provided with the micrometric screw. The rotating shaft of the rotary encoder is connected with the micrometric screw and rotates along with the micrometric screw. The upper end of the micrometric screw is connected with the hand wheel, while the lower end is connected with the force measuring device. The lower end of the force measuring device is connected with the indenter. The hand wheel, the micrometric screw, the force measuring device and the indenter are connected and coaxial, capable of moving axially along with the rotation of the hand wheel. The invention is simply structured, convenient in reading, easy to operate, high in accuracy, capable of being applied to the onsite, quick hardness testing of large parts, and capable of testing the Brinell hardness and Vickers hardness through depth measurement.
Owner:SHENJAN TJANSIN TESTING INSTR KO LTD
Device including nonvolatile memory element
ActiveUS20110114941A1Stable operation of circuitSmall currentTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsOxide semiconductor
A device including a novel nonvolatile memory element is provided. A device including a nonvolatile memory element in which an oxide semiconductor is used as a semiconductor material for a channel formation region. The nonvolatile memory element includes a control gate, a charge accumulation layer which overlaps with the control gate with a first insulating film provided therebetween, and an oxide semiconductor layer formed using an oxide semiconductor material, which overlaps with the charge accumulation layer with a second insulating film provided therebetween.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
NAND type flash memory array and method for operating the same
ActiveUS20060279991A1Read operationReduces a program disturbance effectivelySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesLow voltageSoi substrate
A NAND type flash memory array which is composed of a plurality of memory cells with a shallow junction on an SOI substrate to make the body region depleted fully when each channel of the memory cells is turned on is provided. The invention improves the efficiency of a reading operation, enables an erasing operation on the SOI structure and enables use of a low voltage VPASS instead of a high voltage VPASS, which is used for a programming operation in a conventional NAND type flash memory array, and therefore it diminishes programming disturbance more effectively than a conventional array.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
Storage system using a rapid storage device as a cache
InactiveUS20110302365A1Avoid missingImprove visit ratePayment architectureSignalling/lighting devicesHard disc driveRandom access memory
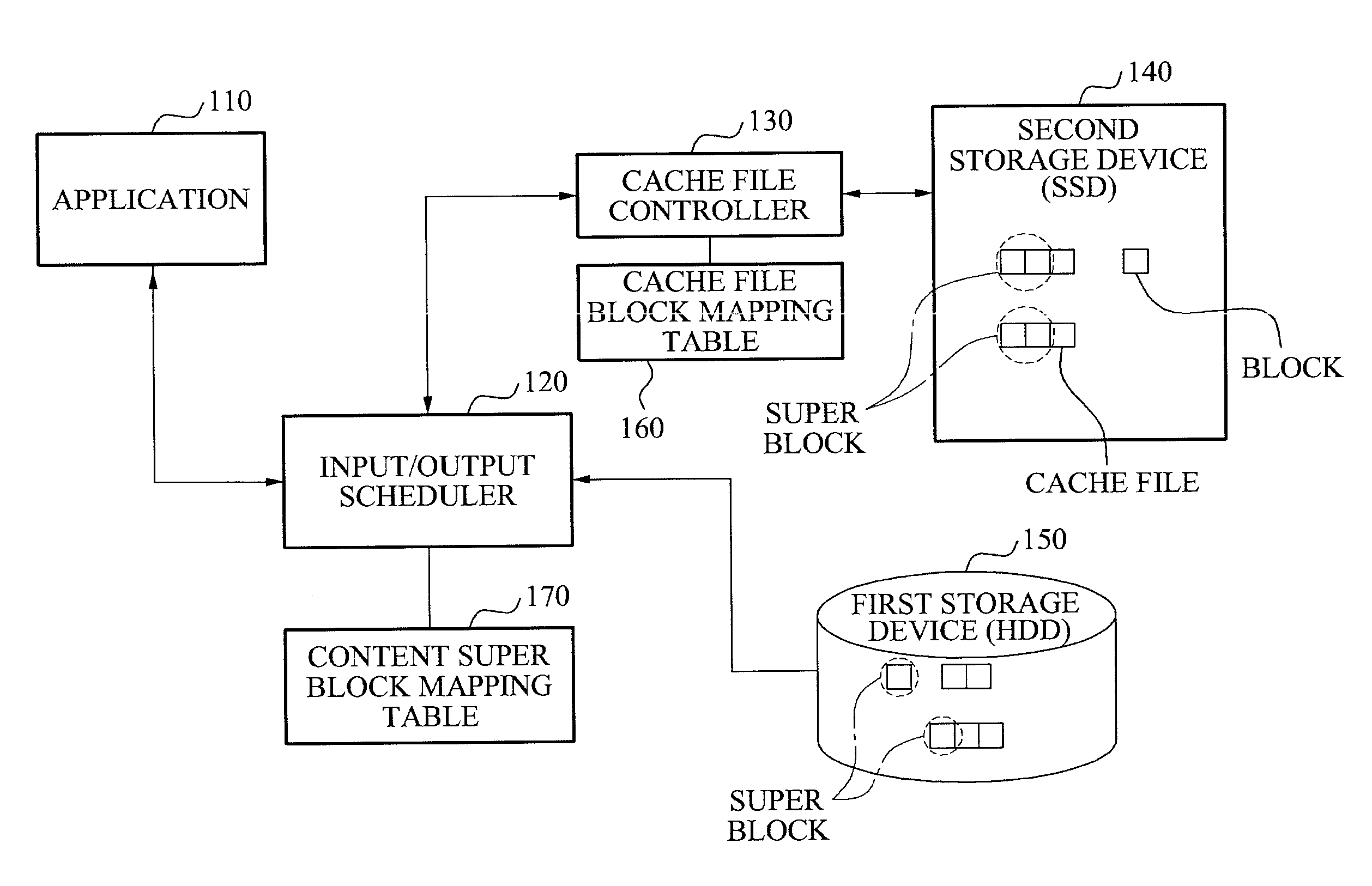
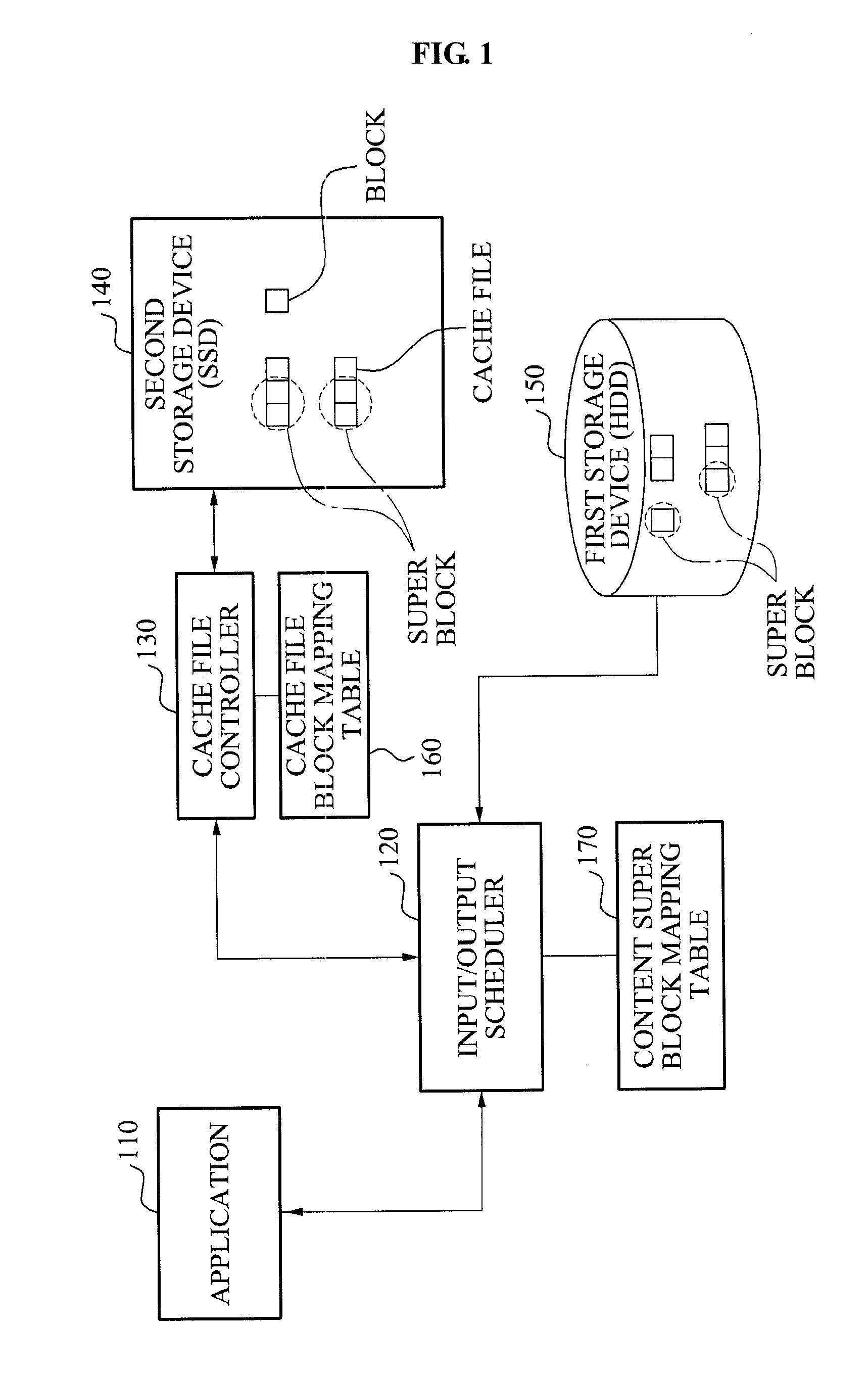
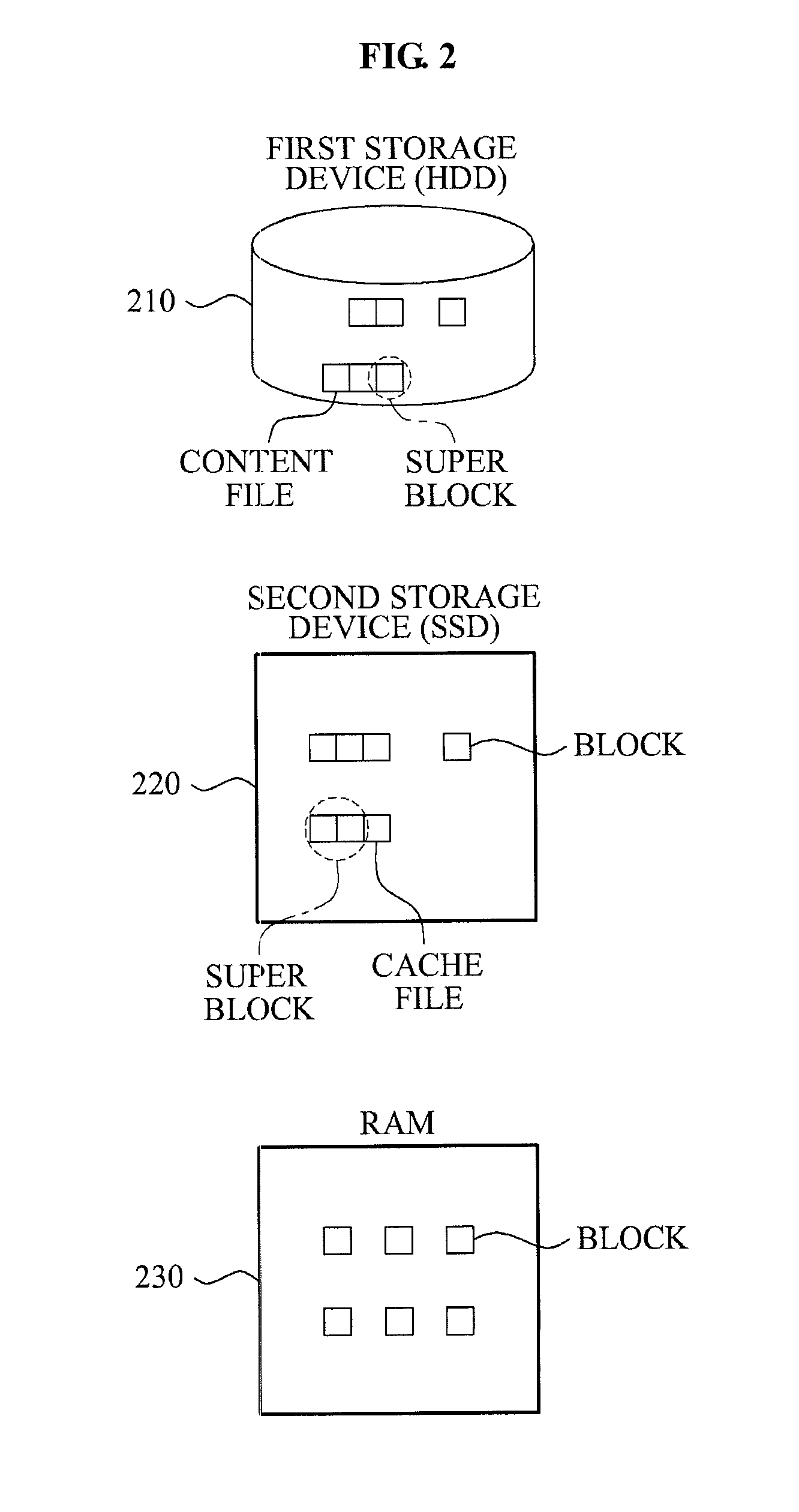
Provided is a storage system using a high speed storage device as a cache. The storage system includes a large-volume of first storage device, a high speed second storage device, and a Random Access Memory (RAM). The large-volume of first storage device corresponds to a Hard Disk Drive (HDD), and the high speed second storage device corresponds to a Solid State Drive (SSD). Also, the high speed second drive is used as a cache. The first storage device manages content files super block by super block, and the second storage device manages cache files block by block.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Apparatus for dividing bank in flash memory
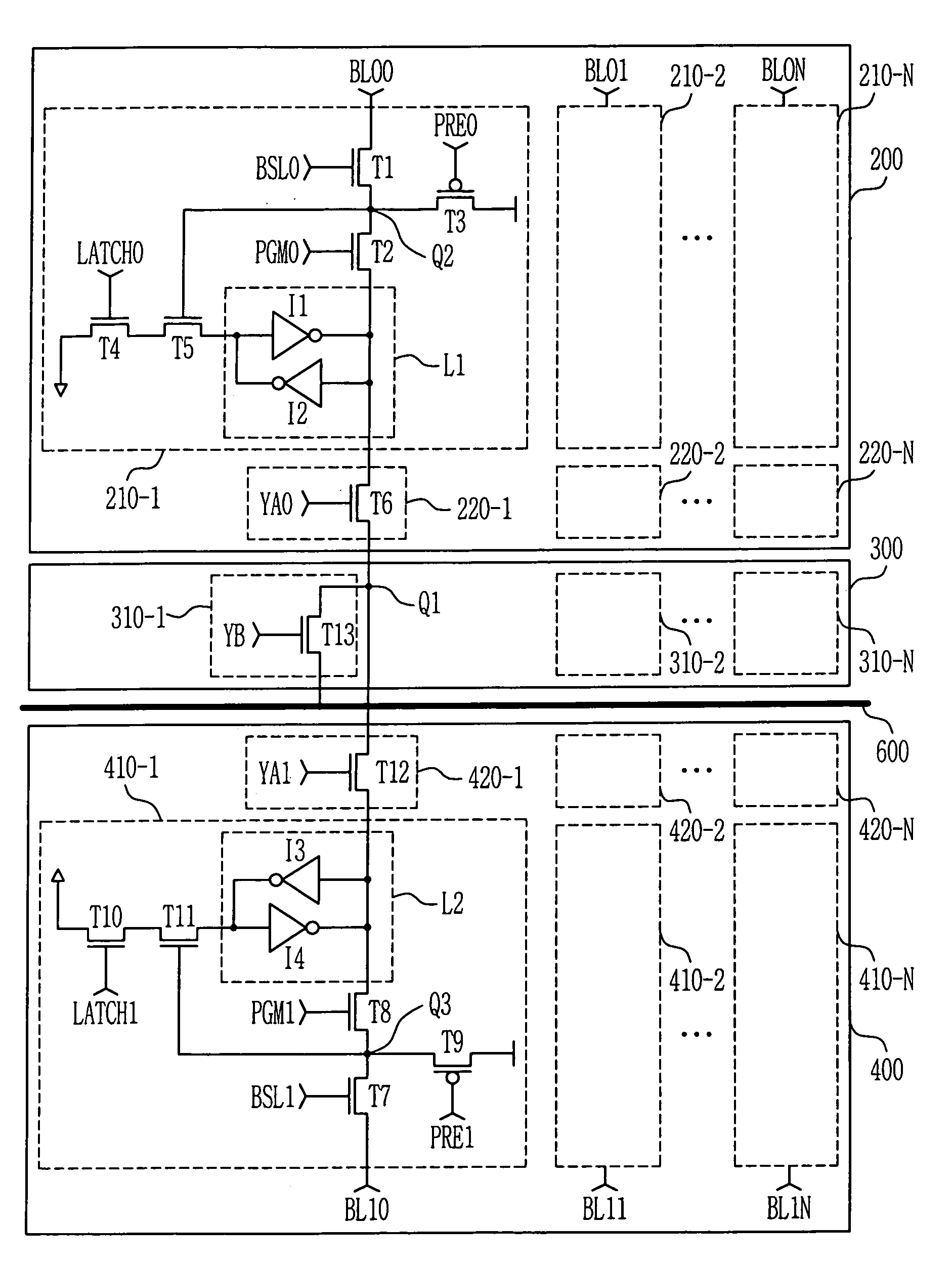
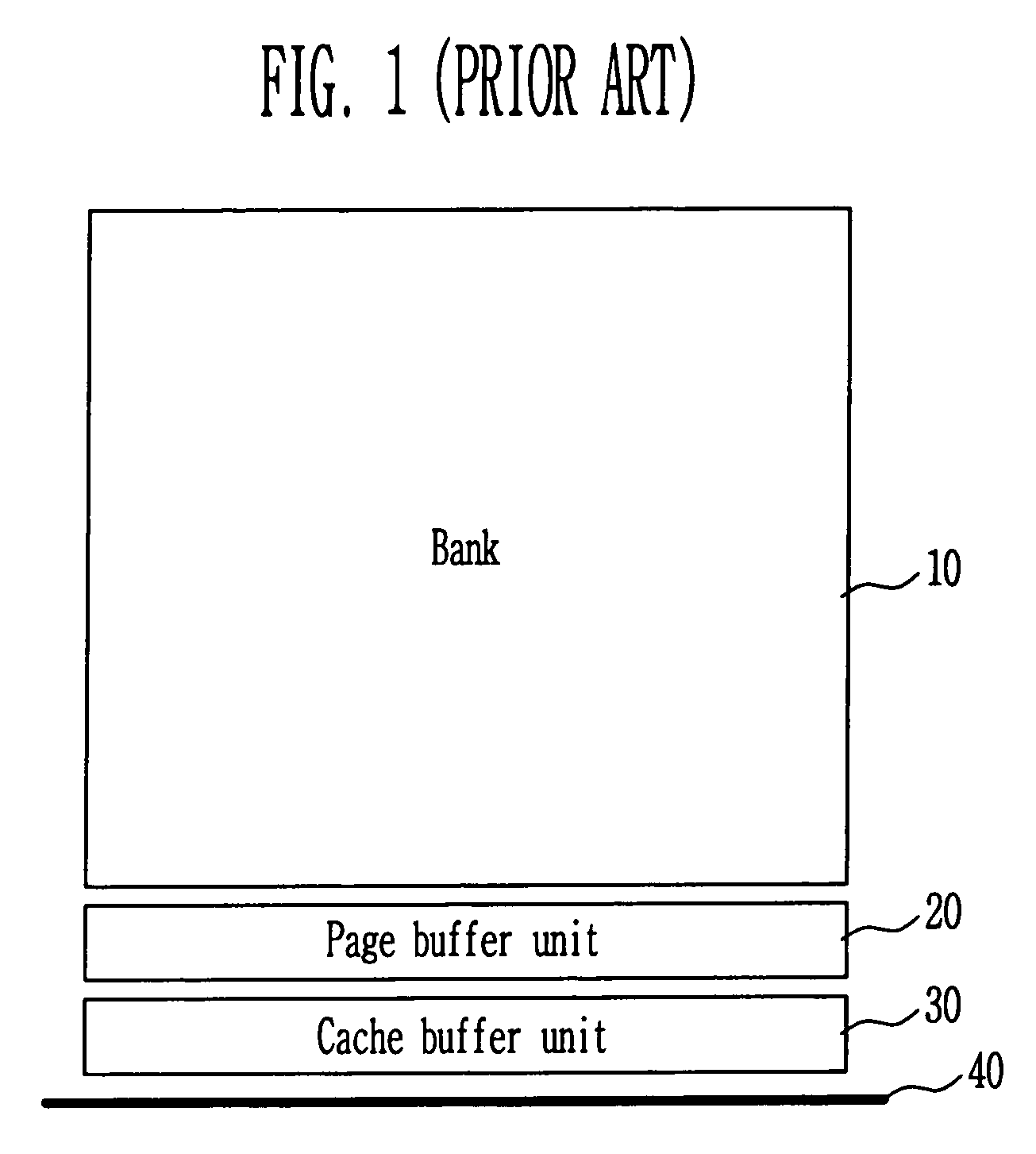
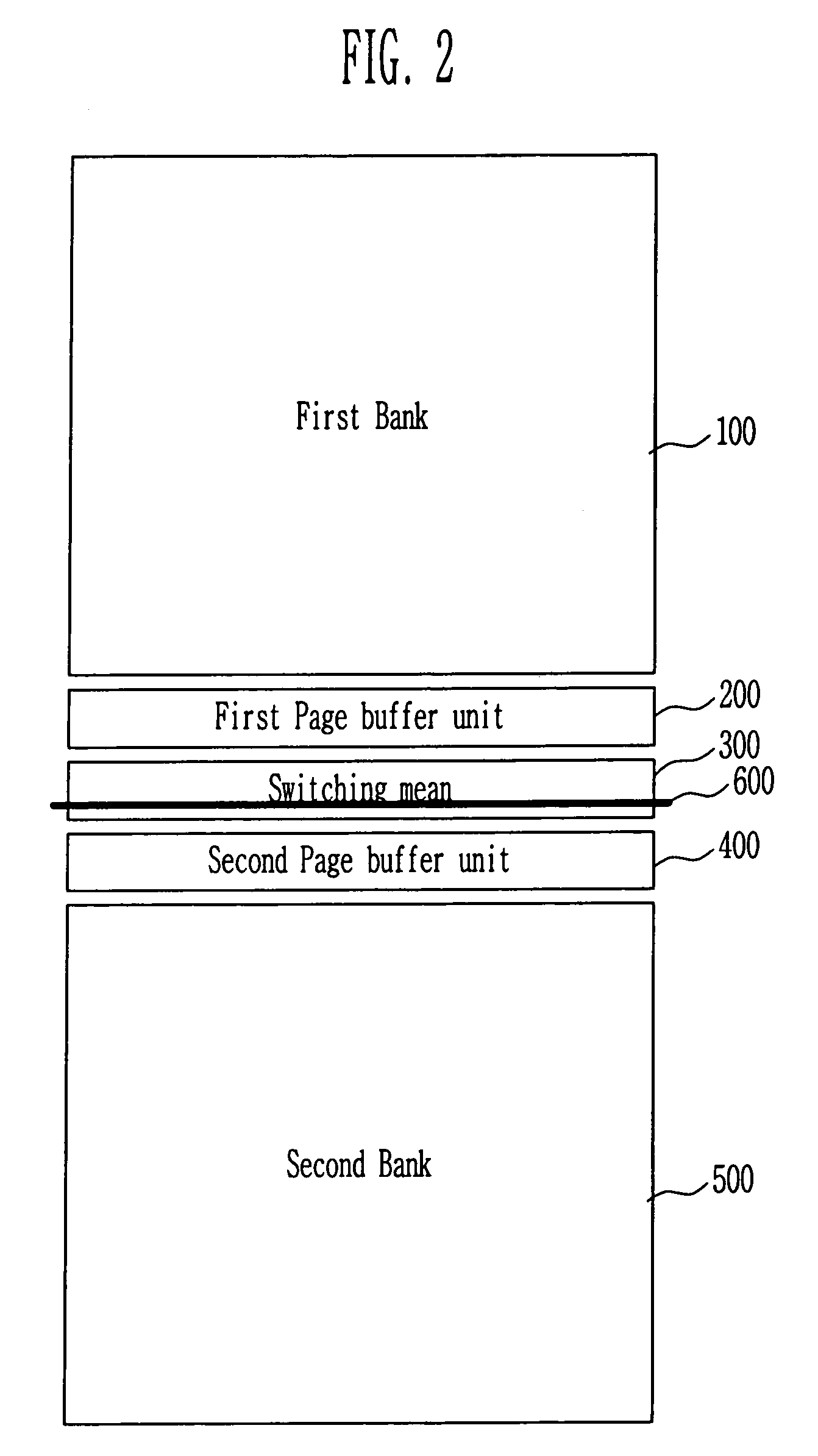
InactiveUS6963502B2Shorten in lengthImprove speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageData bufferInput/output
The present invention relates to an apparatus for dividing a bank in a flash memory. A block of the flash memory is divided into two banks and each page buffer is located between the two banks to share an input / output line. Therefore, it is possible to shorten the length of a bit line, improve a data sensing rate, and allow one bank to perform one operation while the other bank performs a read, write or erase operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
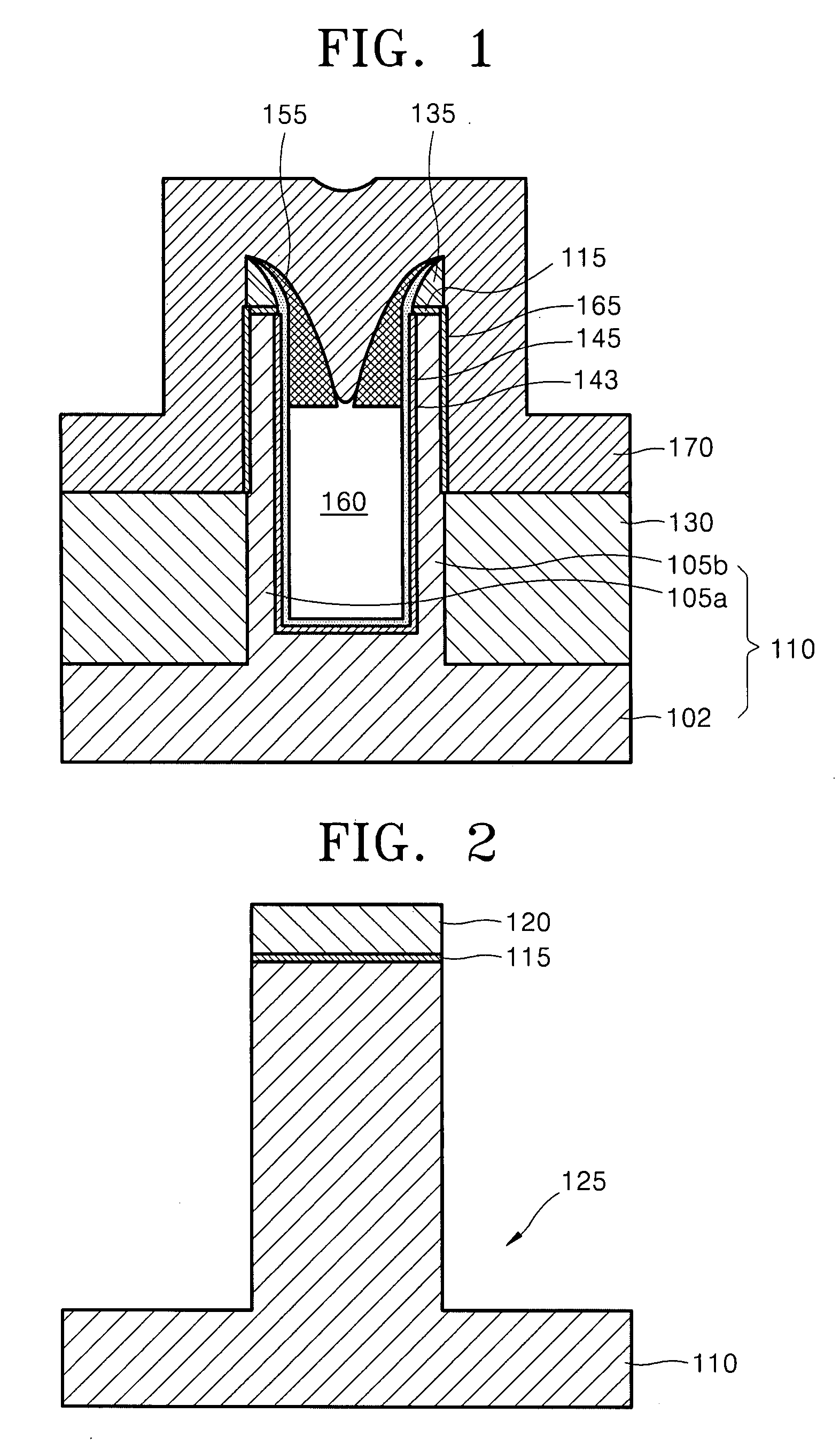
Semiconductor device having a pair of fins and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7560344B2Read operationSuppression of short channel effectsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
Example embodiments relate to a semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same. A semiconductor device according to example embodiments may have reduced disturbances during reading operations and a reduced short channel effect. The semiconductor device may include a semiconductor substrate having a body and a pair of fins protruding from the body. Inner spacer insulating layers may be formed on an upper portion of an inner sidewall of the pair of fins so as to reduce the entrance to the region between the pair of fins. A gate electrode may cover a portion of the external sidewalls of the pair of fins and may extend across the inner spacer insulating layers so as to define a void between the pair of fins. Gate insulating layers may be interposed between the gate electrode and the pair of fins.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and data processing device
InactiveUS20100265754A1Avoid adverse effectsUnnecessary currentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringData processing
When writing into an antifuse memory element finishes, a value of resistance of the memory element rapidly decreases; accordingly, an output voltage of a boosting circuit which produces a writing voltage rapidly decreases. By detecting a change in the output voltage of the boosting circuit to control a writing command, the writing operation can be stopped immediately after the memory element is shorted. Thus, unnecessary current consumption caused by continuing a writing operation on the shorted memory element can be suppressed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Image reading device
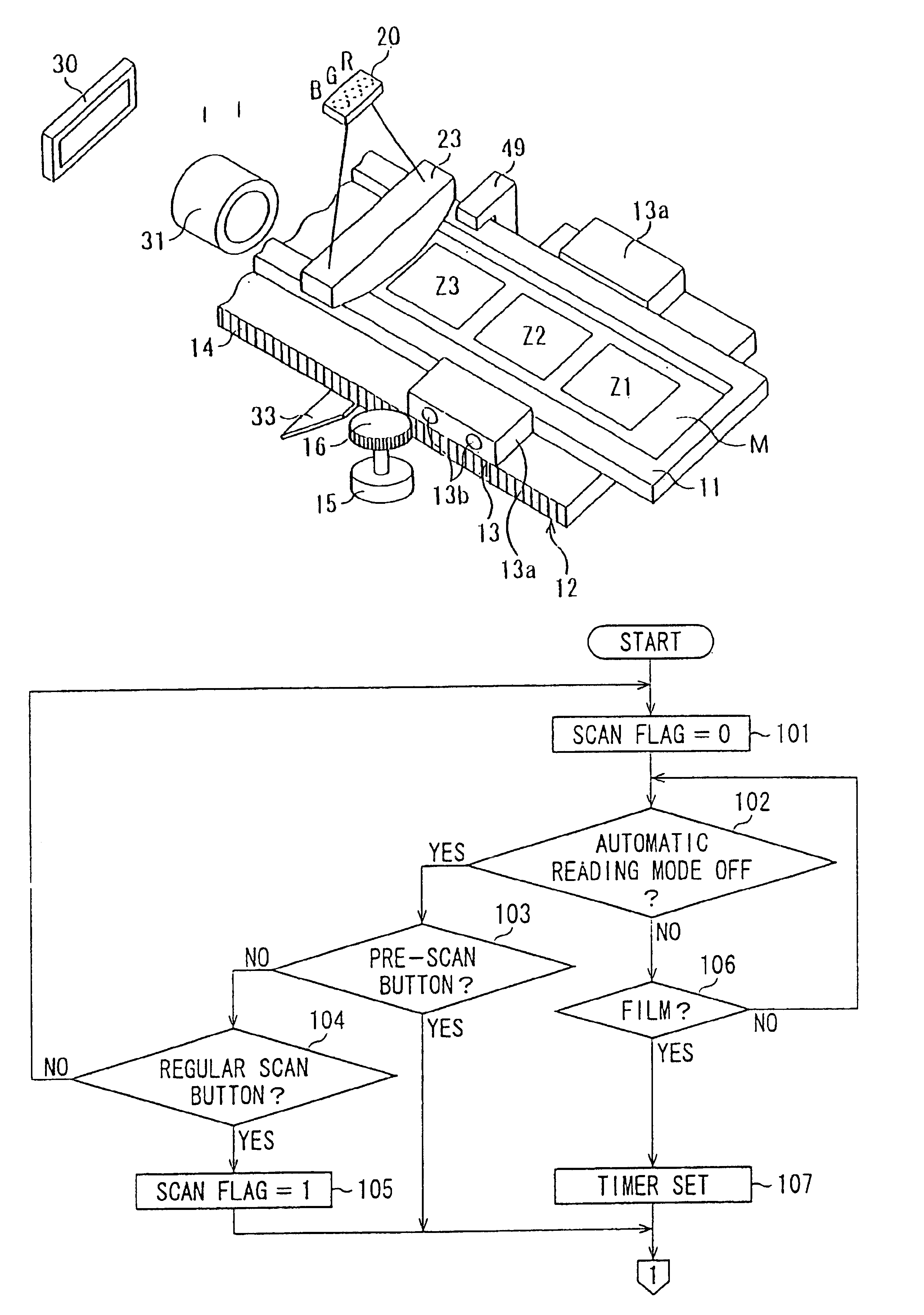
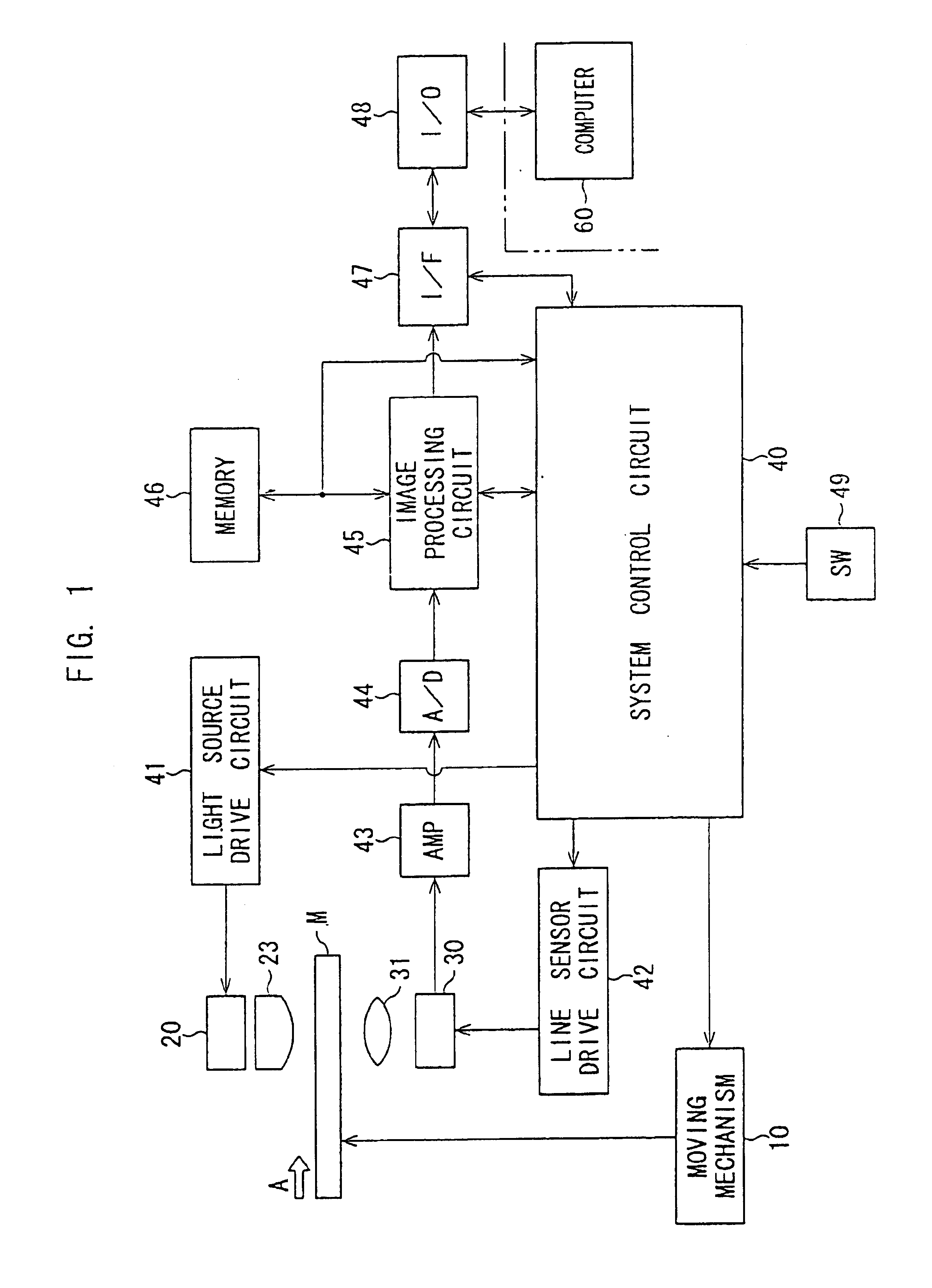
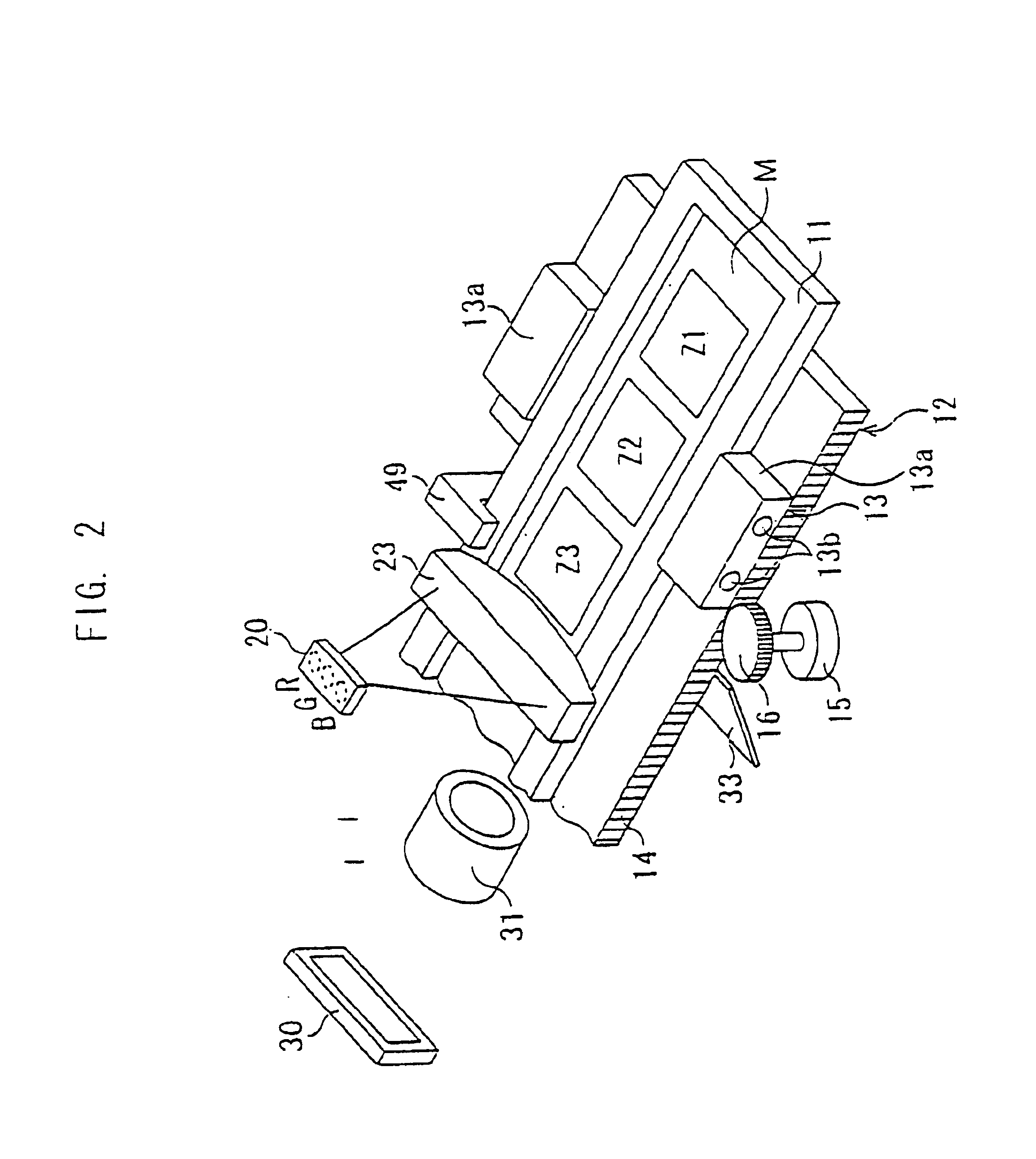
InactiveUS6862119B1Read operationReduce processing timeCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationWaiting timeComputer engineering
The image reading device has a reading operation control processor that automatically starts a reading operation. In the reading operation, first, it is determined whether a film is attached to the image reading device. When the film is not attached to the image reading device, the reading operation is not proceeded. Conversely, when the film is attached to the image reading device, a pre-scanning operation is performed in which an image recorded in a film is read with a relatively coarse pitch, after a waiting time has passed. Then, a regular scanning operation is performed in which the image is read with a pitch finer than that of the pre-scanning operation.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Device including nonvolatile memory element
ActiveUS8319267B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall currentTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsOxide semiconductor
A device including a novel nonvolatile memory element is provided. A device including a nonvolatile memory element in which an oxide semiconductor is used as a semiconductor material for a channel formation region. The nonvolatile memory element includes a control gate, a charge accumulation layer which overlaps with the control gate with a first insulating film provided therebetween, and an oxide semiconductor layer formed using an oxide semiconductor material, which overlaps with the charge accumulation layer with a second insulating film provided therebetween.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
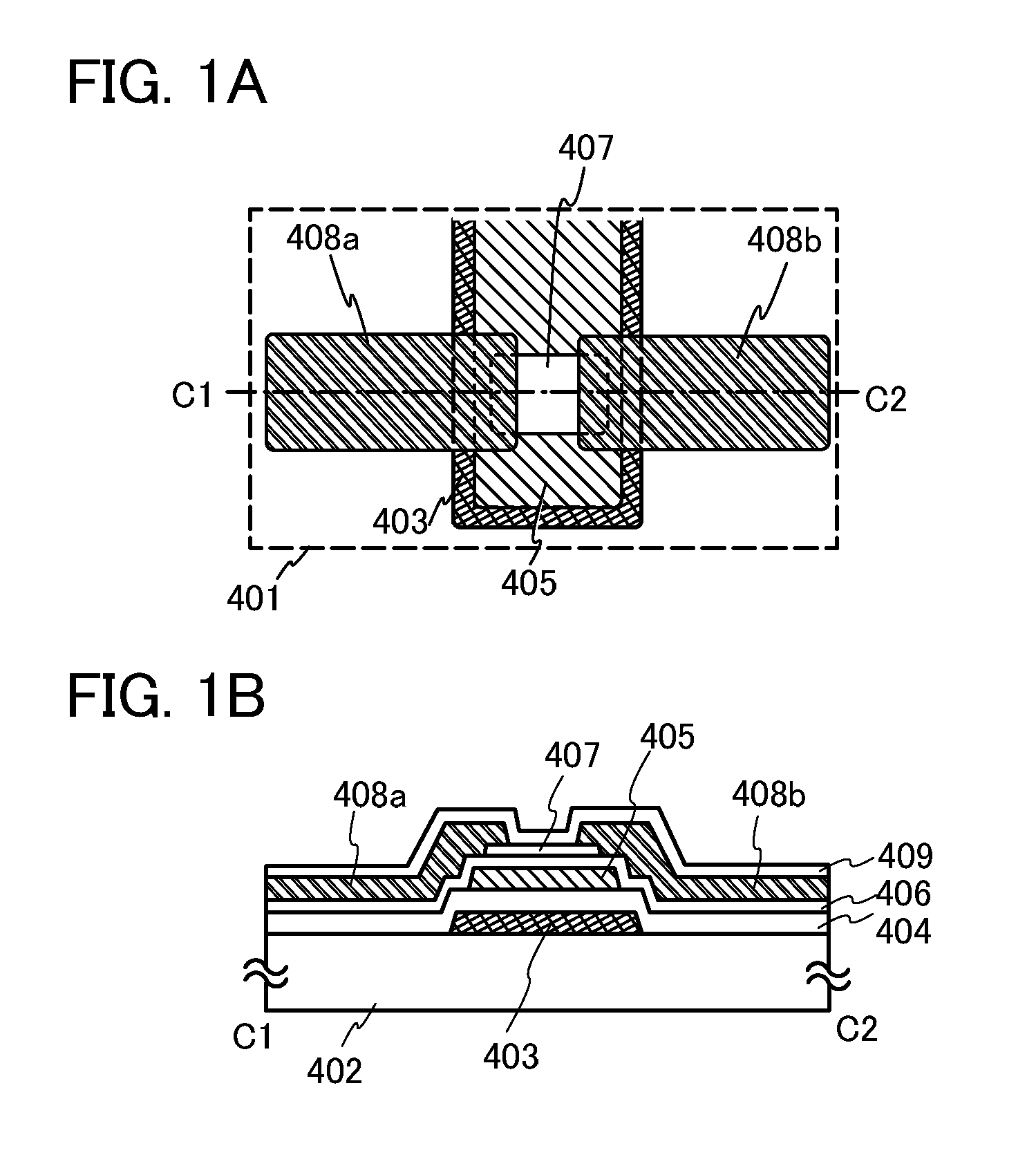
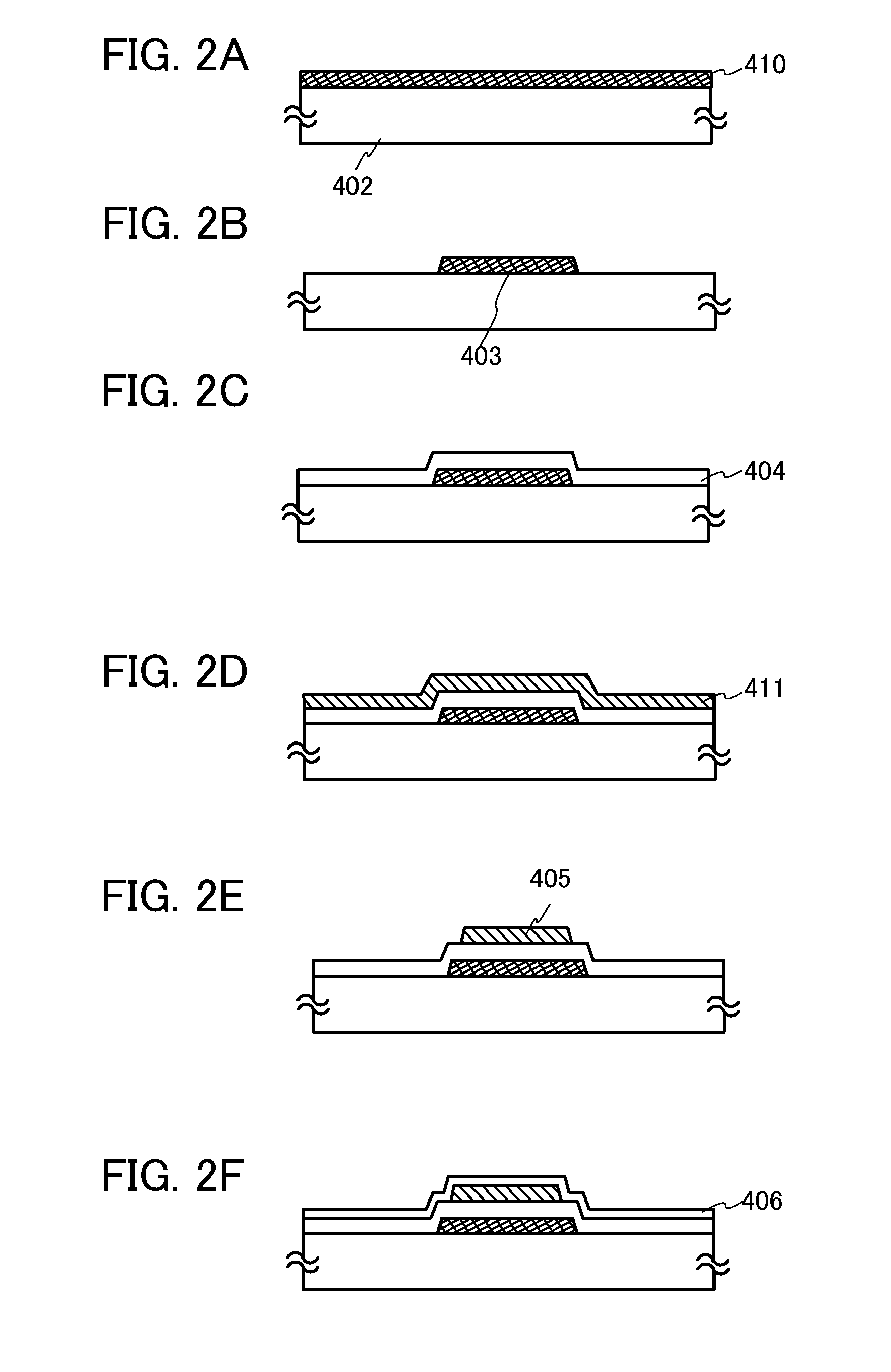
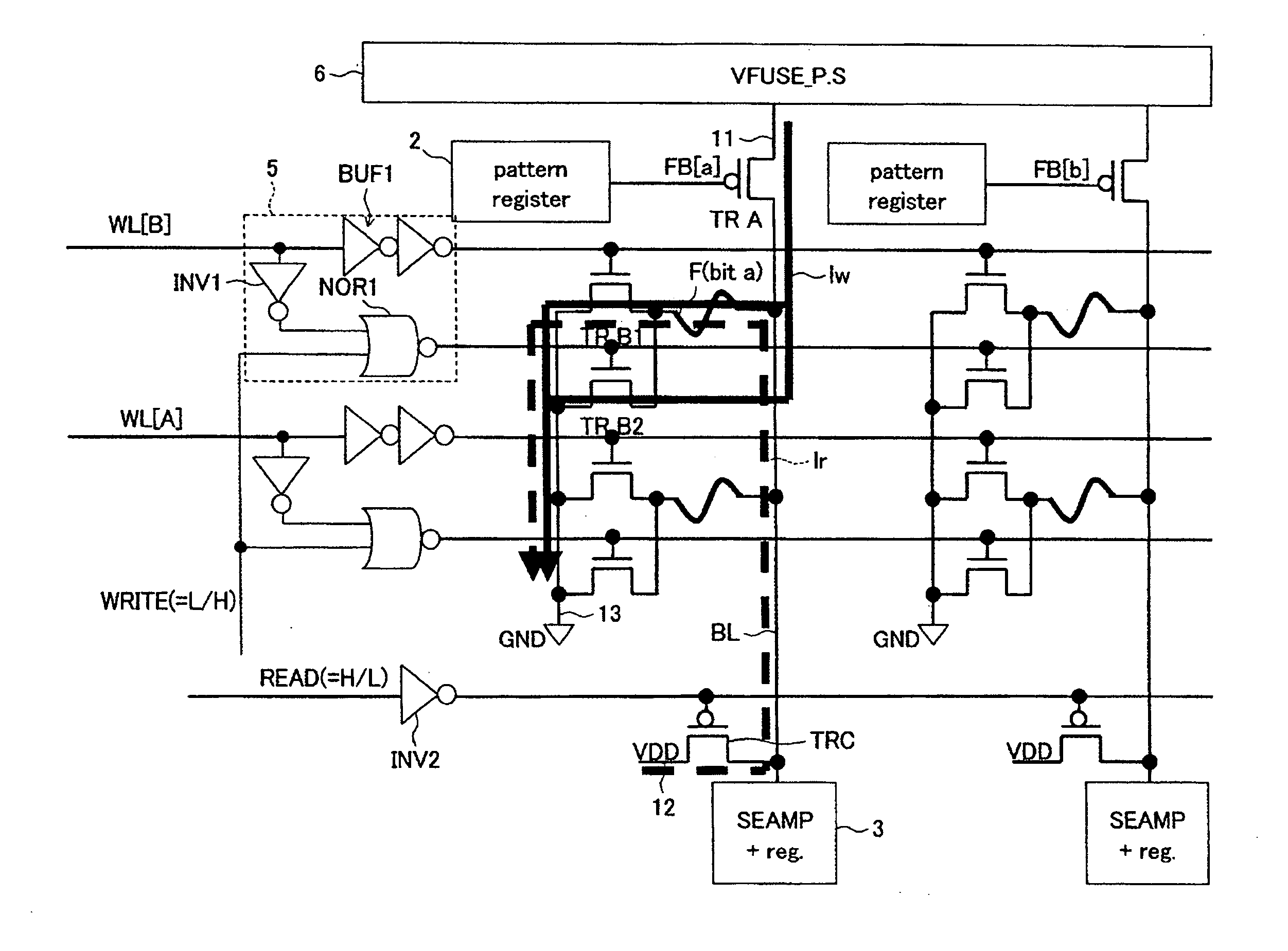
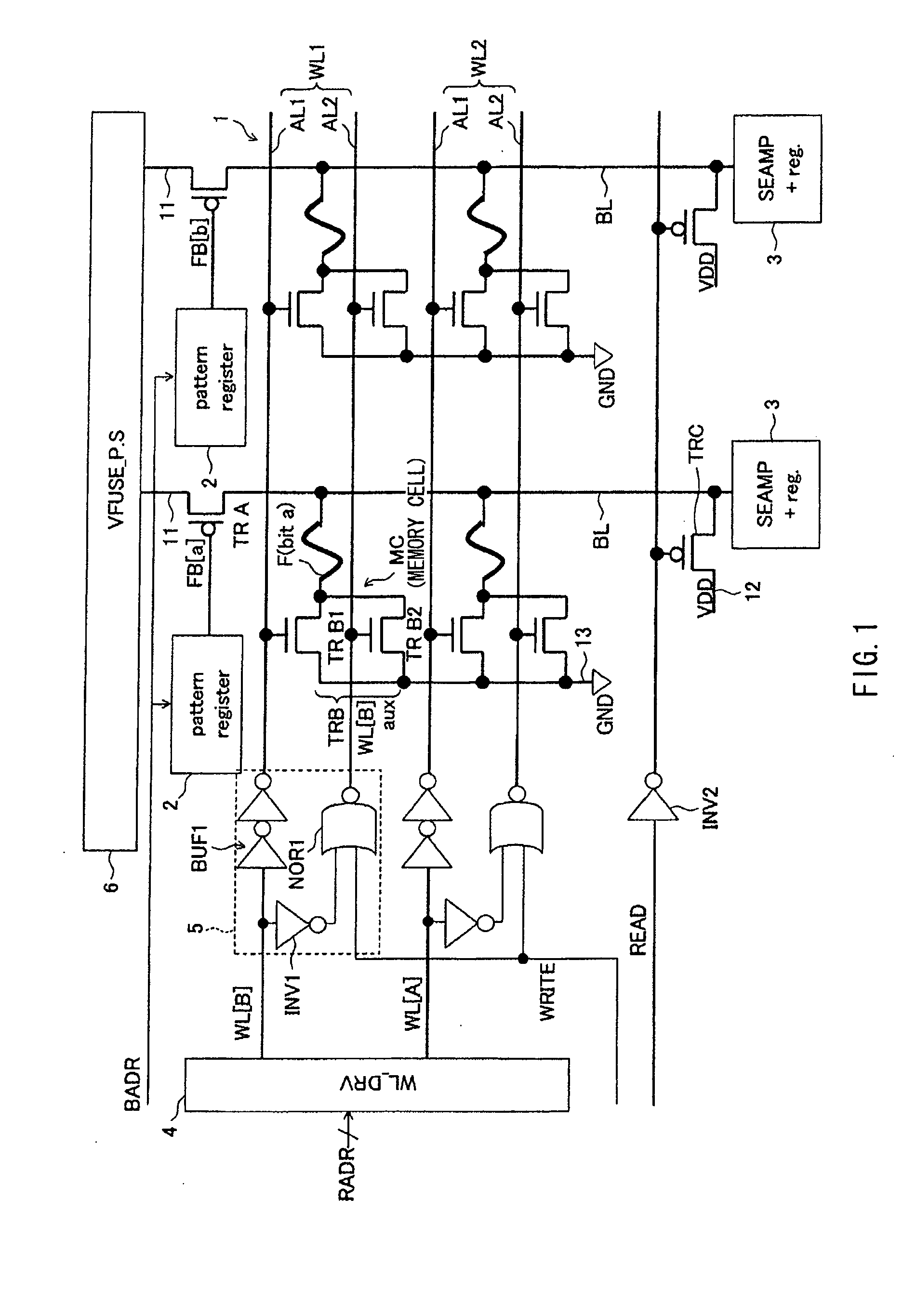
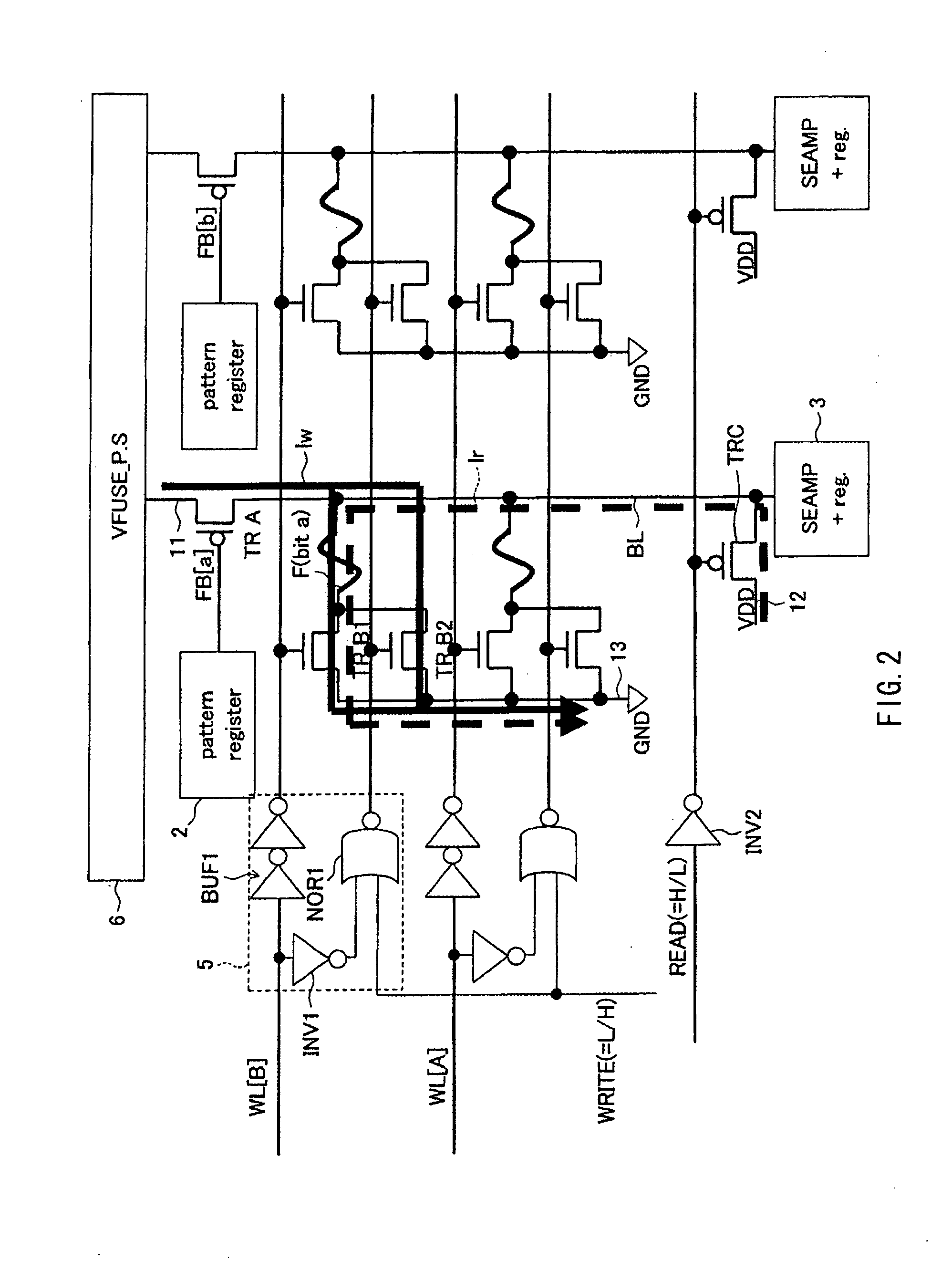
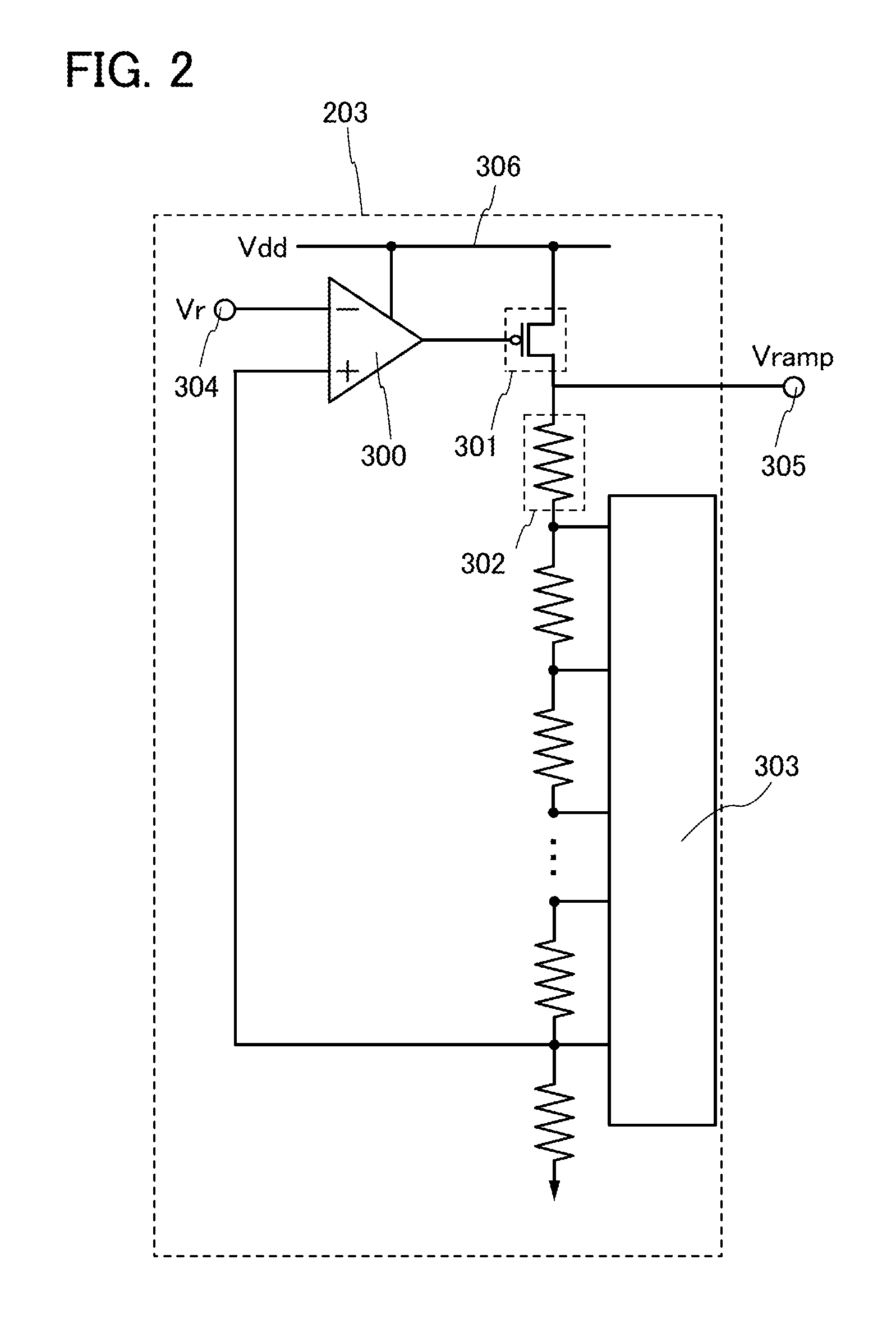
Semiconductor device
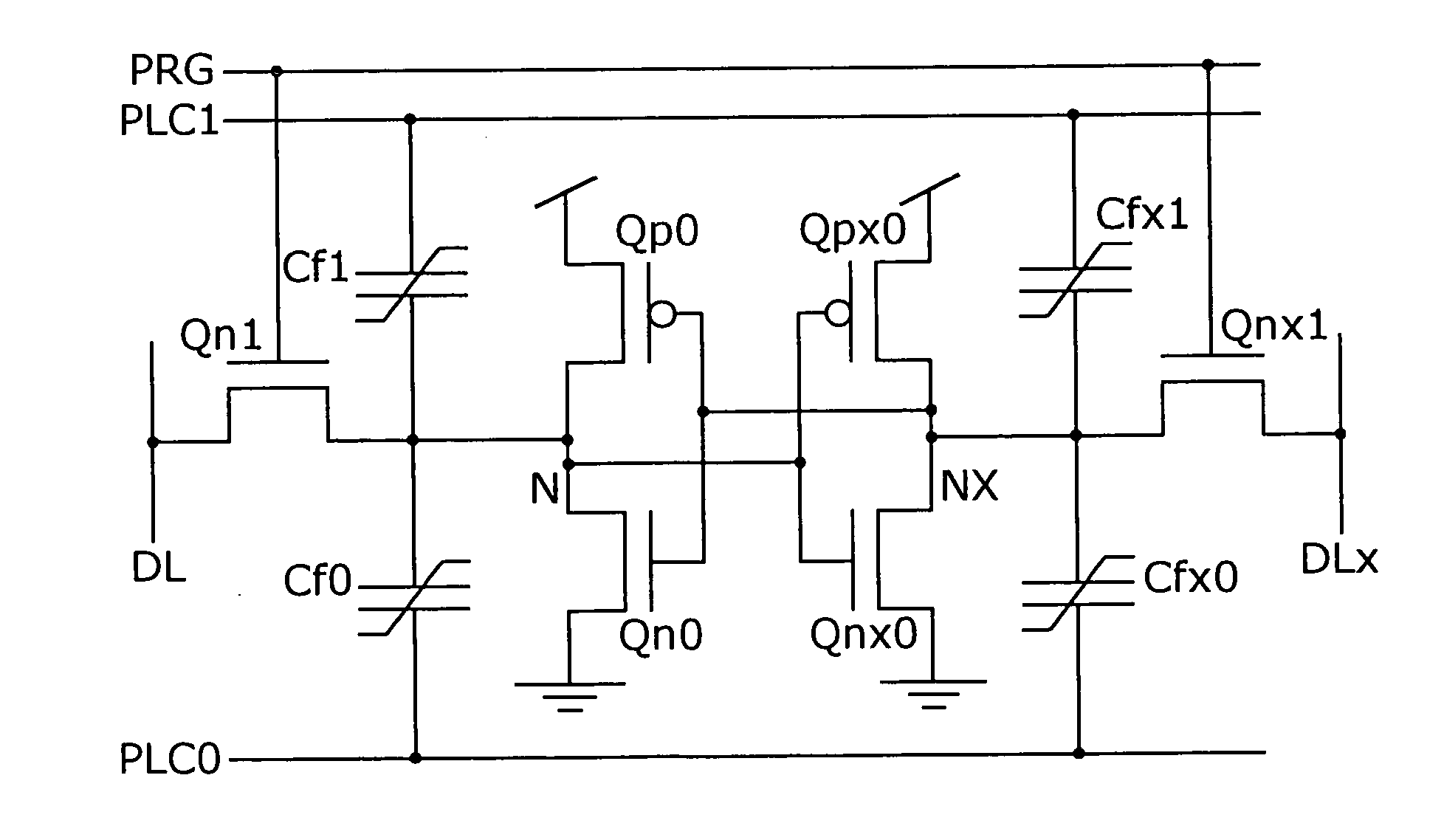
InactiveUS20120039105A1Shorten operation timeReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesInternal logicAccess time
Both decreasing access time and power consumption and improving storage bit count per one word line are compatibly attained. A memory cell array 1 has a configuration in which at least one row of memory cells MC having a fuse device F with a resistance value variable according to a flowing current and a plurality of cell transistors (TRB1 and TRB2) connected in parallel with respect to the fuse device F is arranged. In the relevant semiconductor device, out of the plurality of cell transistors (TRB1 and TRB2), the number of cell transistors turned ON is controllable by a writing control signal (WRITE) inputted from outside and an internal logic circuit 5 (and a word line drive circuit 4).
Owner:SONY CORP
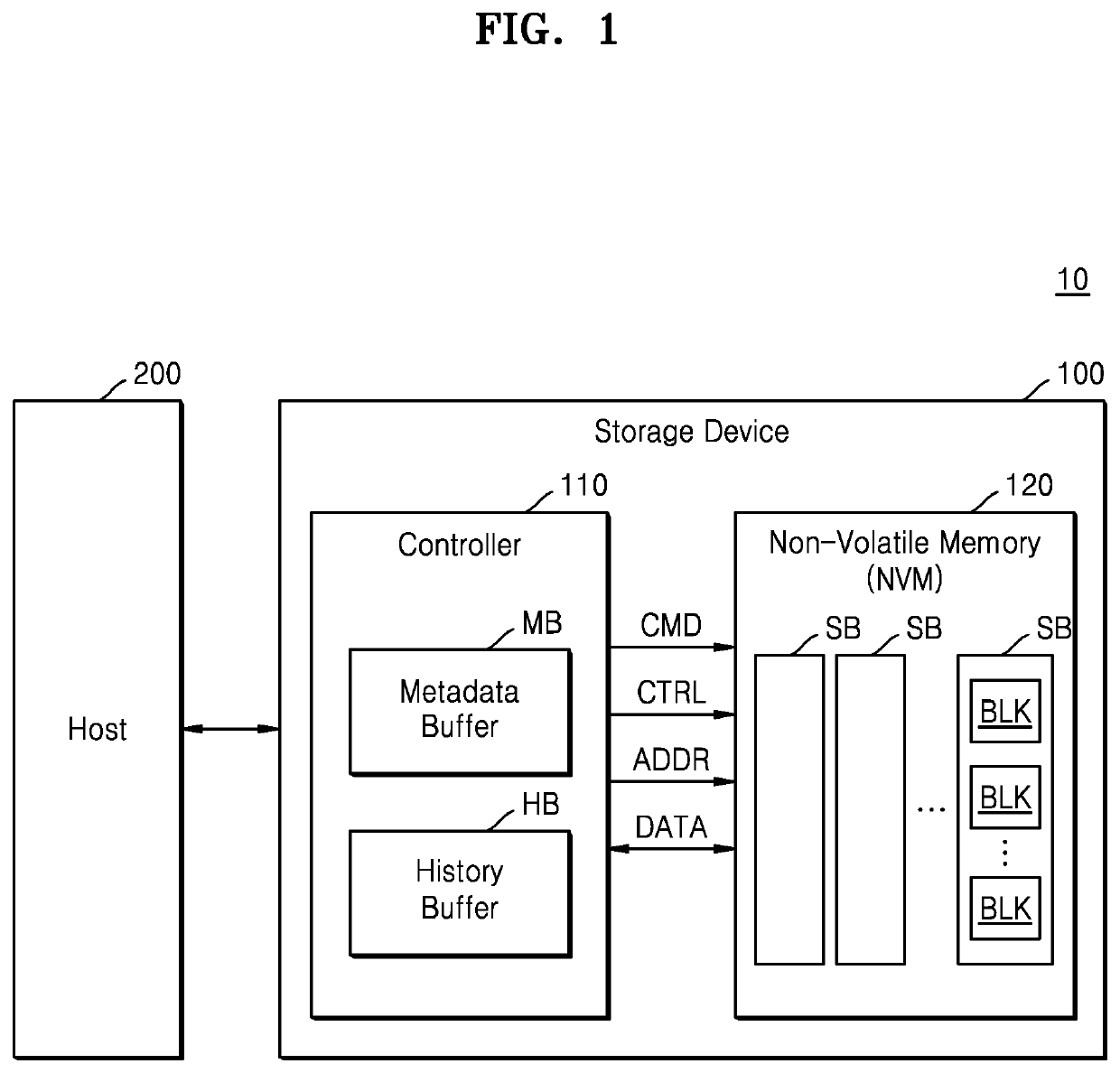
Storage device and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20210166774A1Less read retry operationCapacity history bufferRead-only memoriesMemory systemsEngineeringMetadata
A method of operating a storage device including a non-volatile memory includes storing program and erase counts of the non-volatile memory as metadata in units of super blocks, wherein each of the super blocks includes a pre-defined number of blocks of the non-volatile memory, performing a read operation on a first block included in a first super block based on a first read level, storing the first read level as a history read level of the first super block in a history buffer when the read operation on the first block is successful, receiving a read request for a second block of the first super block and an address of the second block from a host, and performing a read operation on the second block based on the history read level stored in the history buffer. The pre-defined number is at least two.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
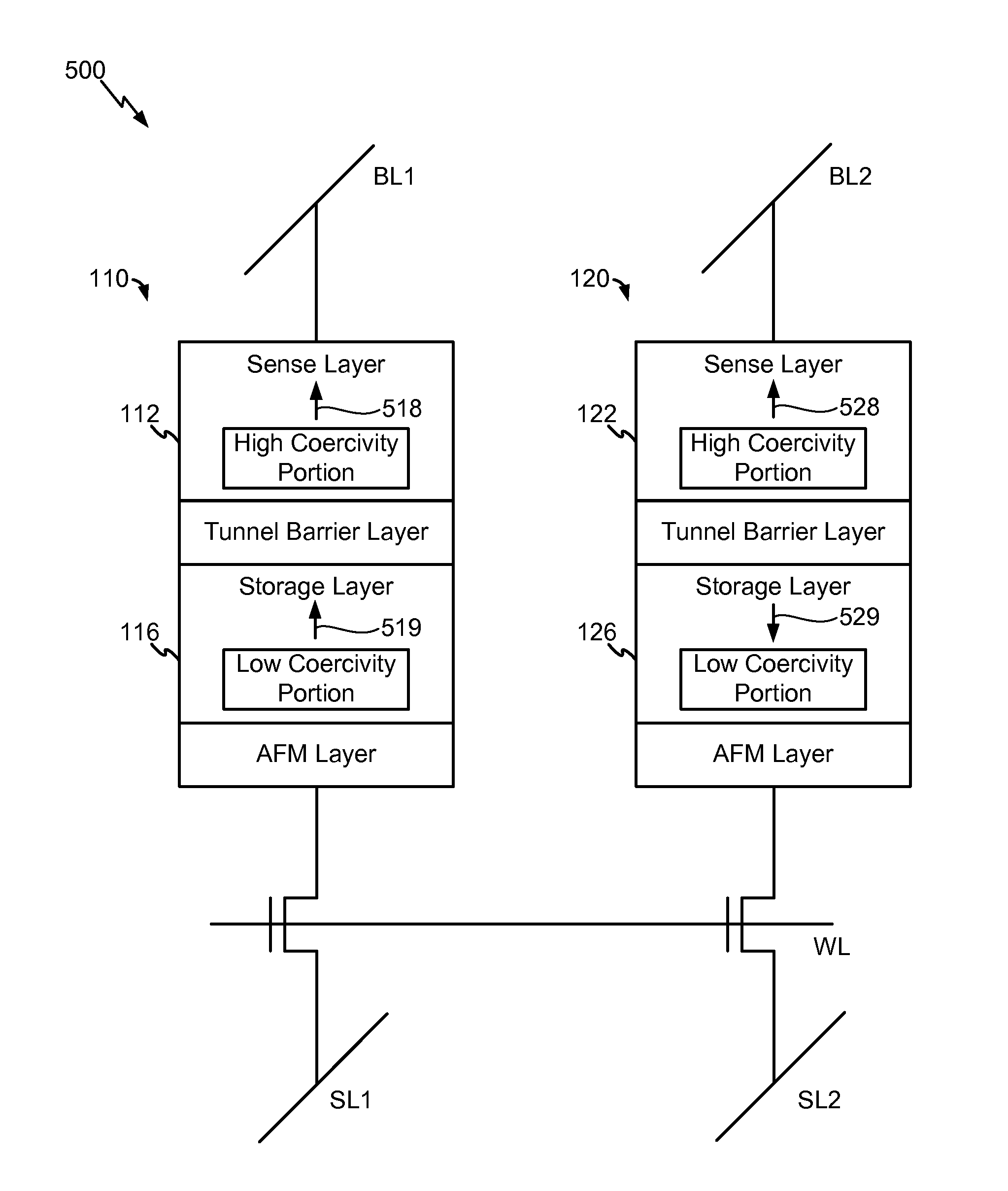
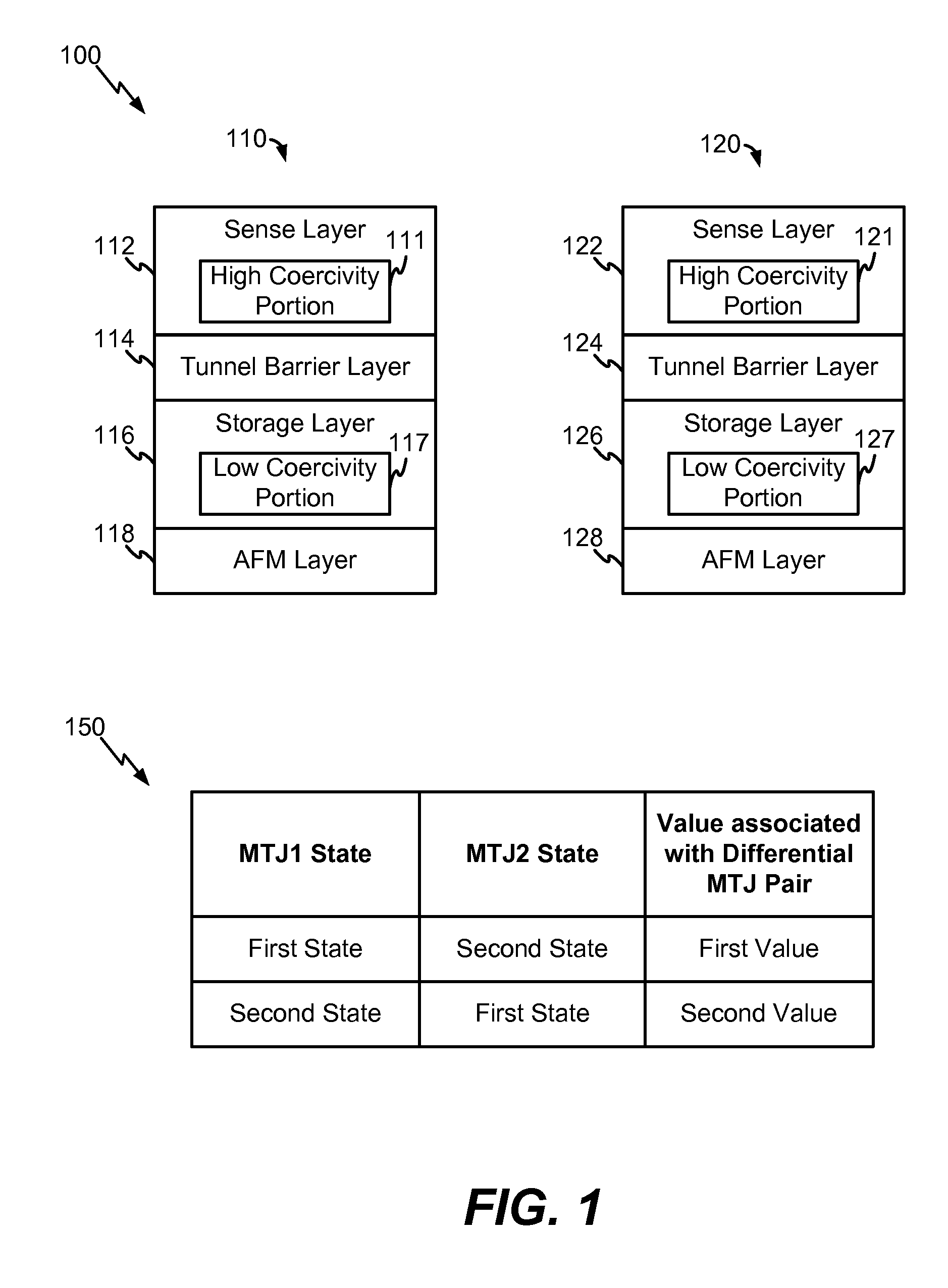
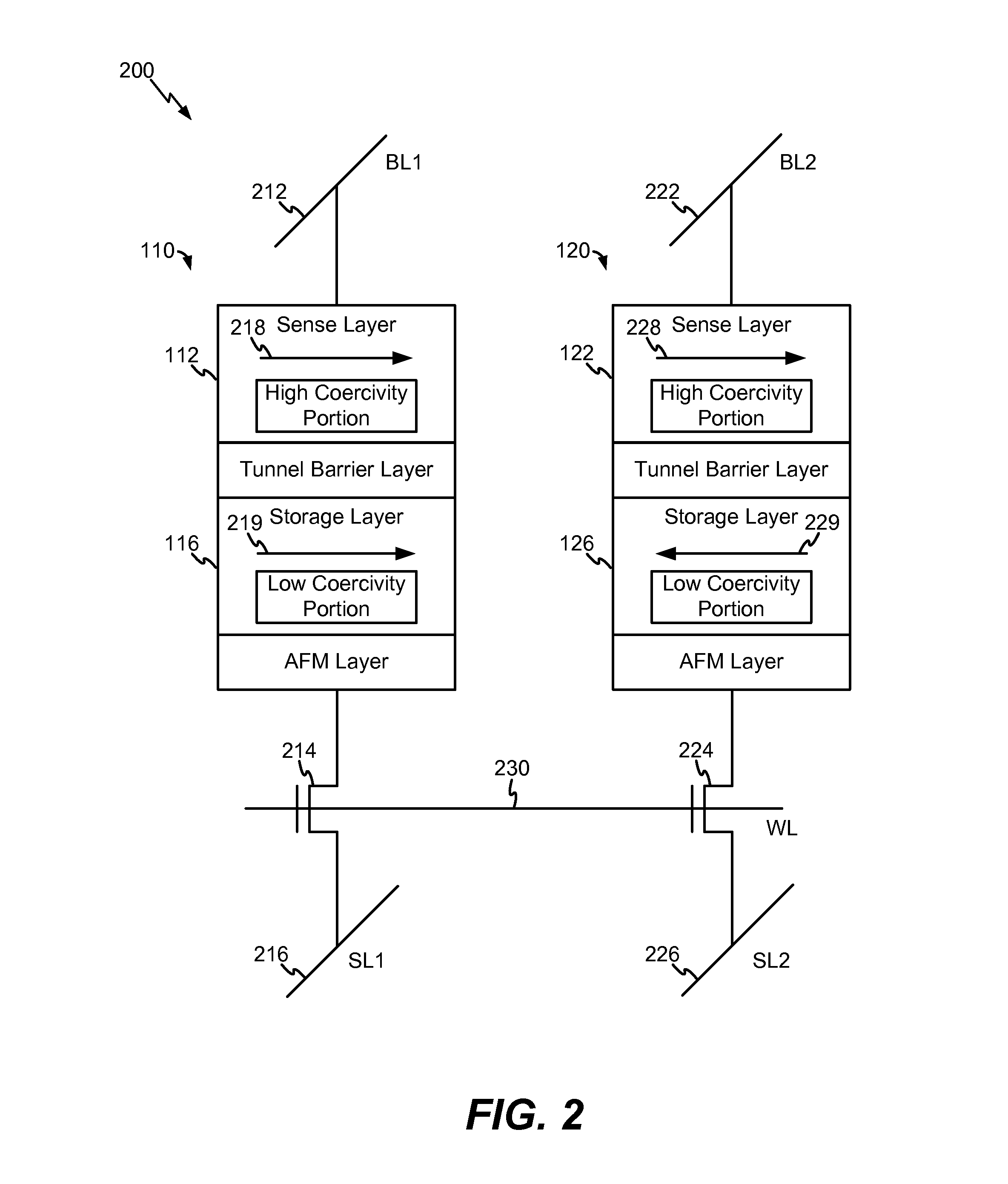
Differential magnetic tunnel junction pair including a sense layer with a high coercivity portion
InactiveUS20160049185A1Improve coercive forceEasy to operateDigital storageEngineeringTunnel junction
An apparatus includes a first magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device of a differential MTJ pair. The apparatus further includes a second MTJ device of the differential MTJ pair. The first MTJ device includes a sense layer having a high coercivity portion.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Operation method for non-volatile memory
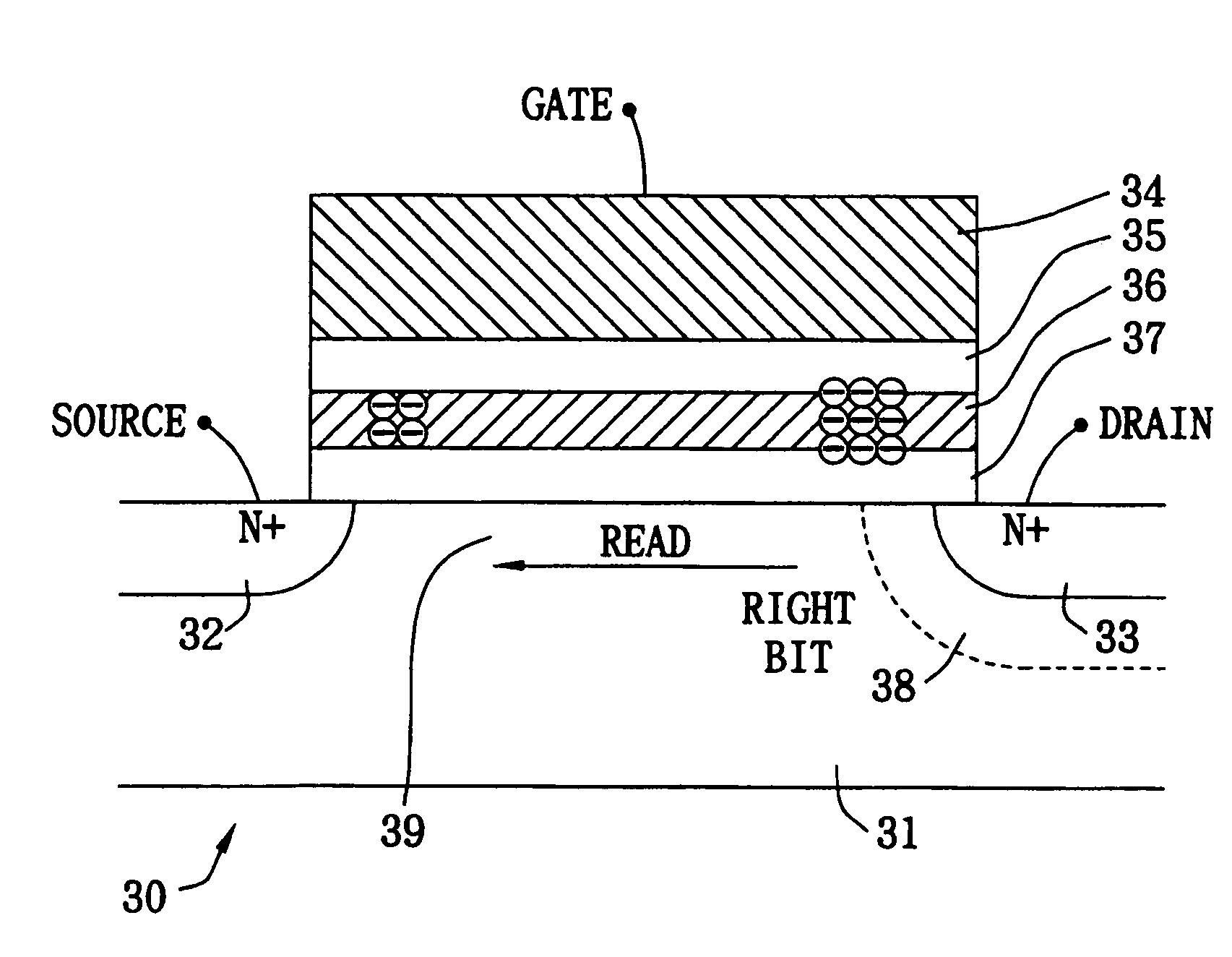
ActiveUS6963508B1Simplifies reading operationEasy to operateRead-only memoriesDigital storageNon-volatile memoryDepletion region
An operation method for non-volatile memory is conducted as follows. First, a non-volatile memory cell capable of storing a first bit and a second bit is provided. The non-volatile memory cell comprises a first region and a second region with a channel therebetween and a gate above the channel but separated therefrom by a charge trapping layer, wherein the first bit and the second bit are positioned close to the first and second regions, respectively. Next, a first programmed voltage for the first bit, a second programmed voltage for the second bit and an erased voltage for the first and second bits are determined, wherein the first programmed voltage is smaller than the second programmed voltage. For reading the first bit, a voltage is applied to the second region, inducing a depletion region around the second region. For reading the second bit, a voltage is applied to the second region, wherein the voltage applied to the second region is smaller than that for reading the first bit.
Owner:SKYMEDI CORPORATION
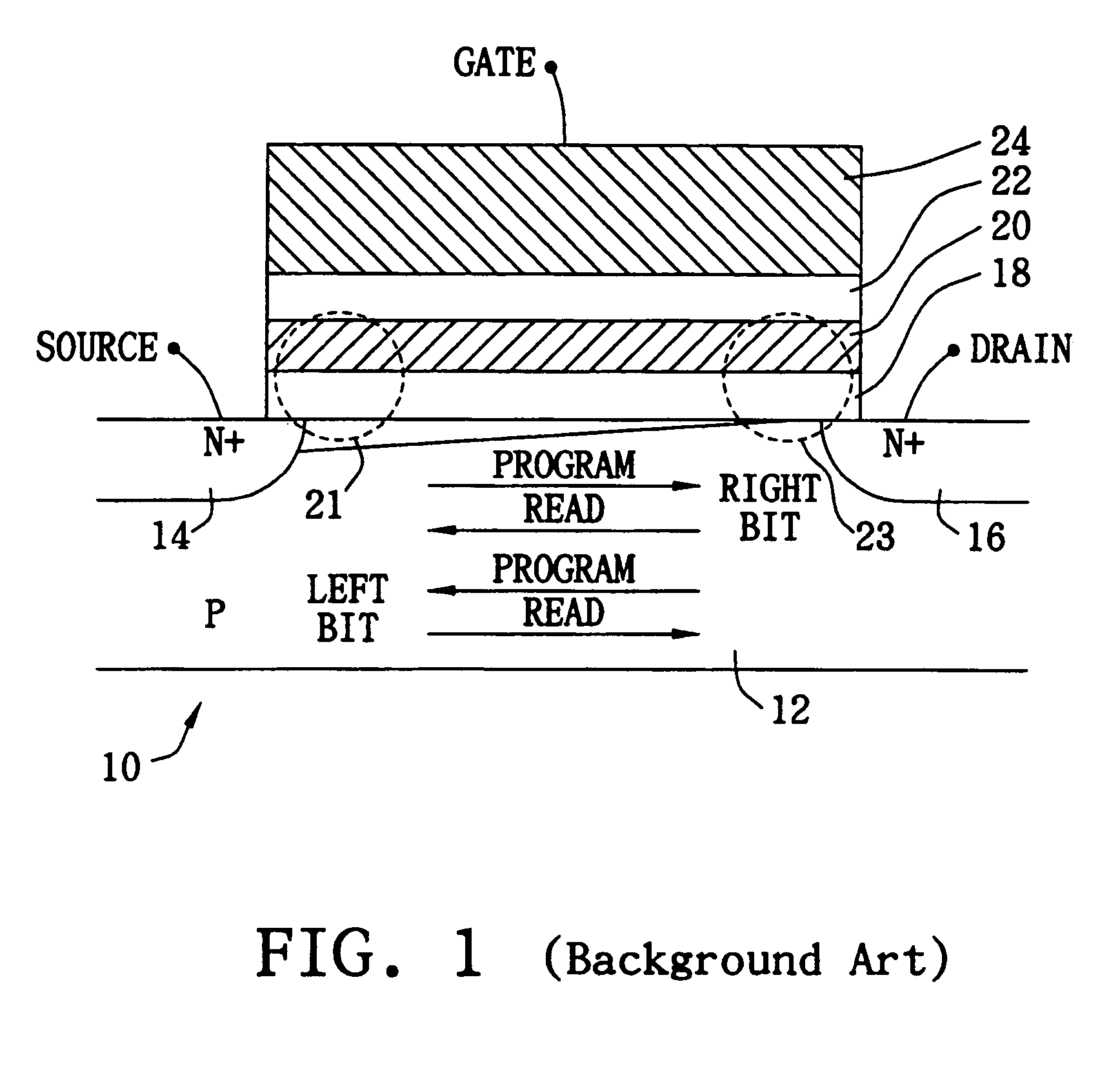
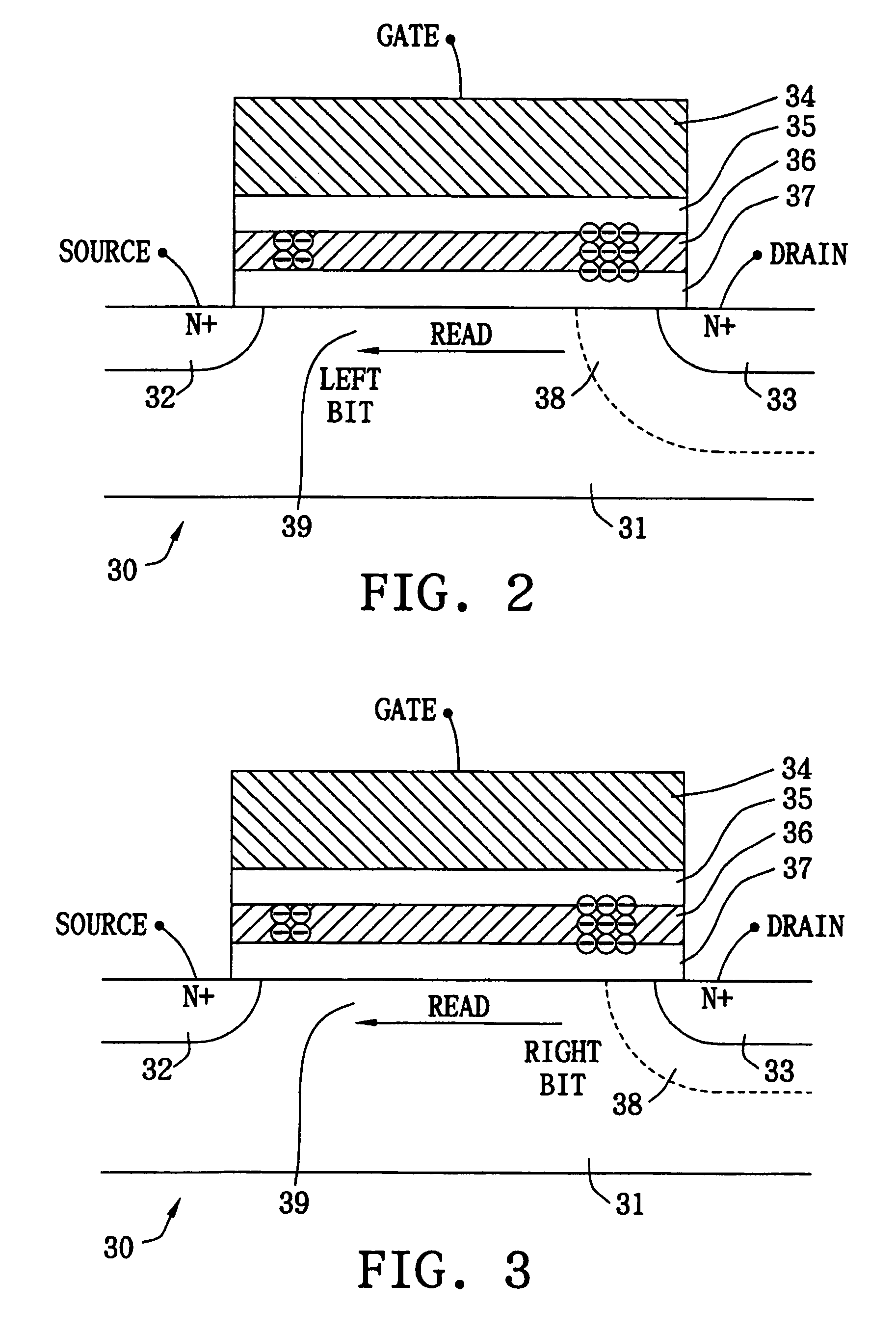
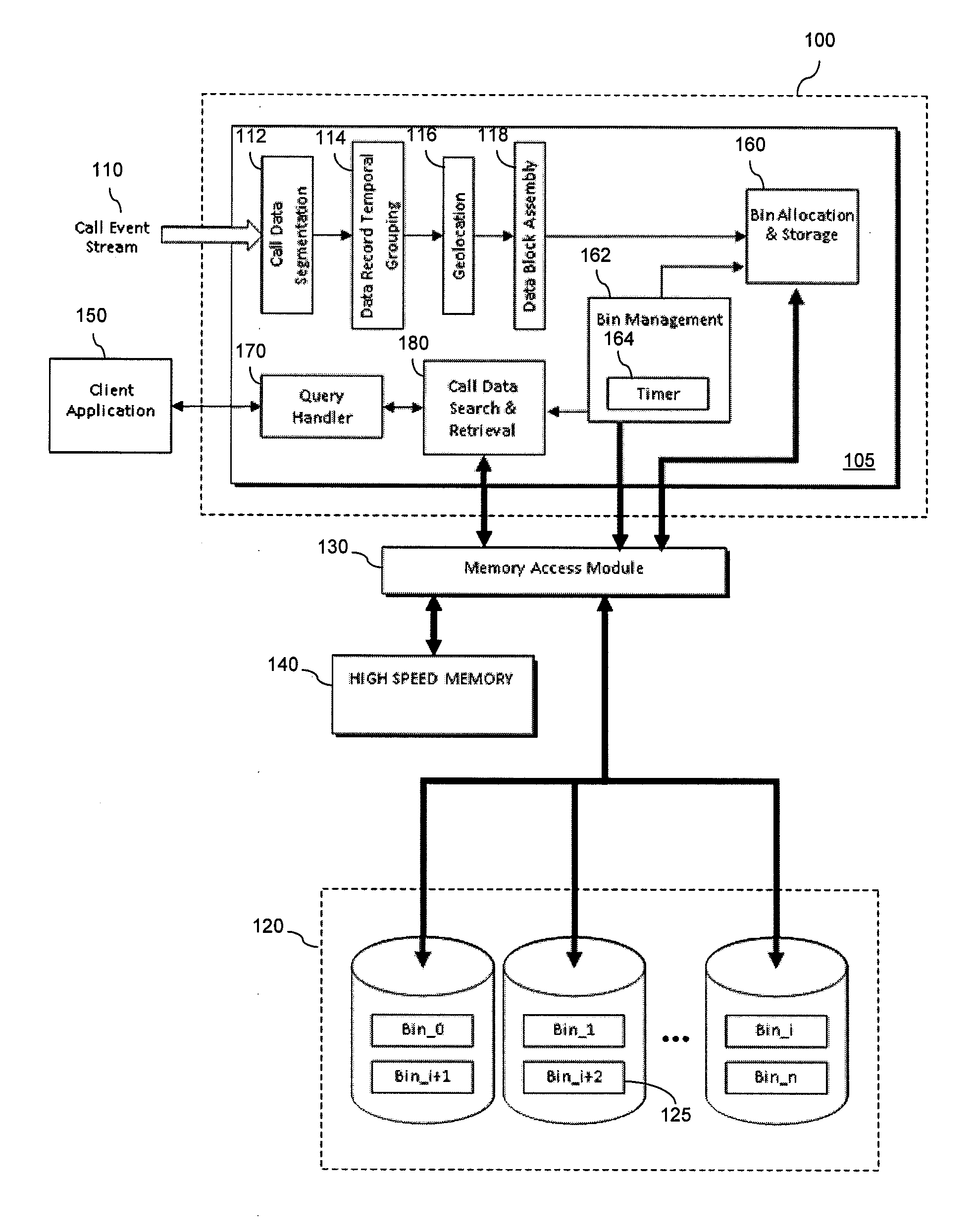
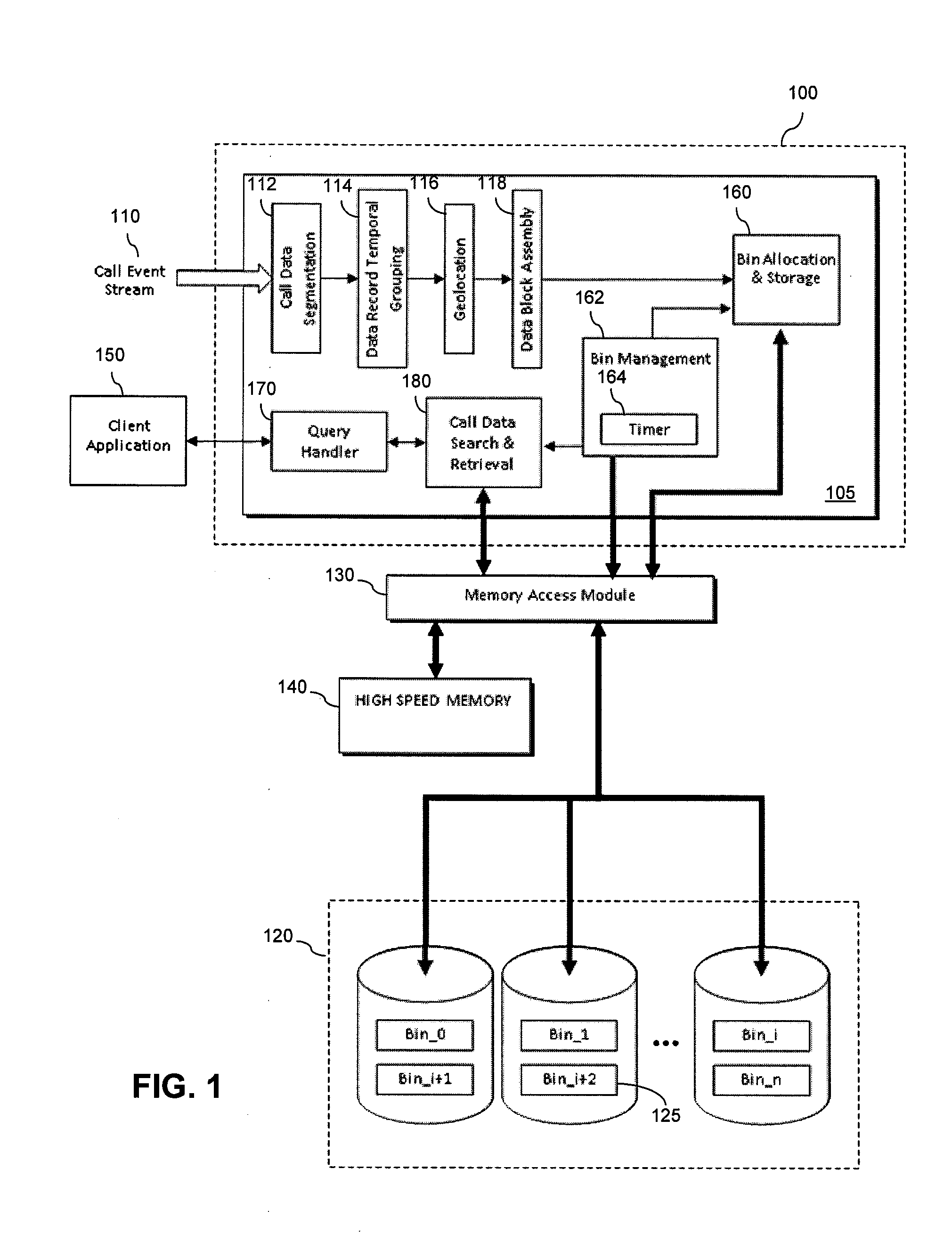
Method and apparatus for managing call data
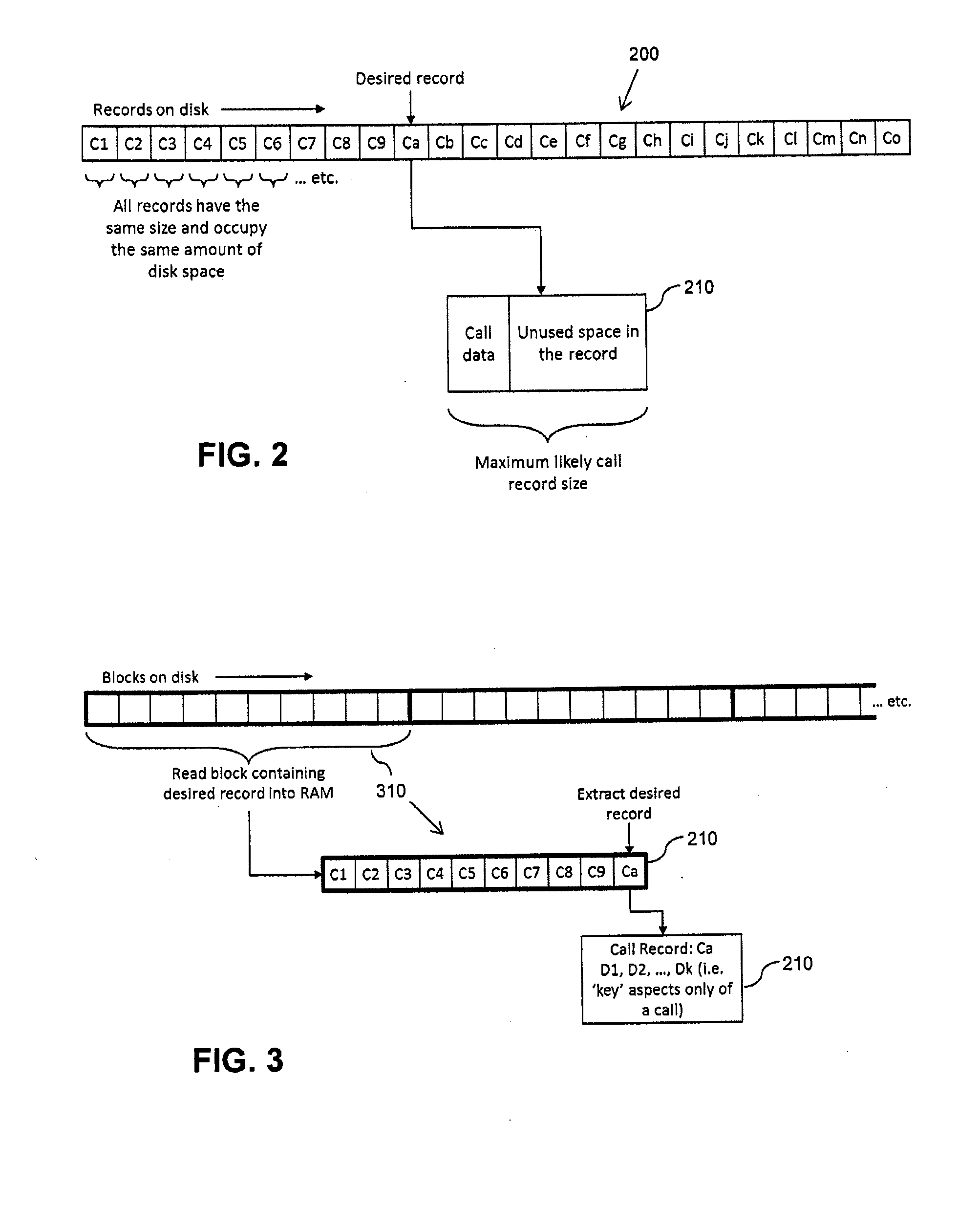
ActiveUS20140287740A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one orRead operationAccounting/billing servicesMultimedia data queryingRadio networksData management
A data management system method of managing call data for at least one radio network element within a cellular communication network. The method comprises receiving call data for at least one call from the at least one radio network element within the cellular communication network, arranging the received call data into call data records, assembling the call data records into at least one data block, and writing the at least one data block to at least one data storage device. The method further comprises, upon receipt of a call data query, retrieving call data records from the at least one data storage device on a per data block basis.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS UK
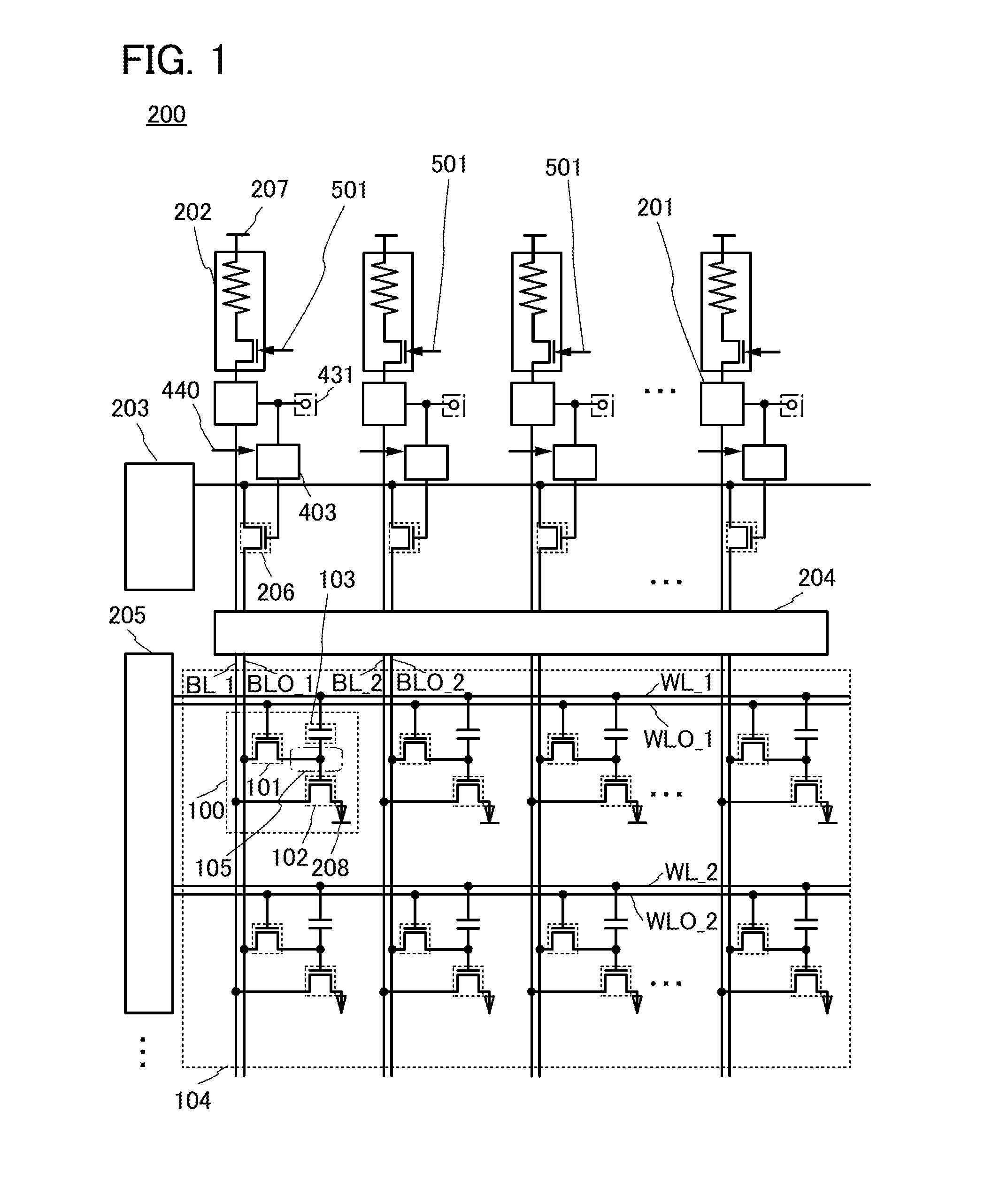
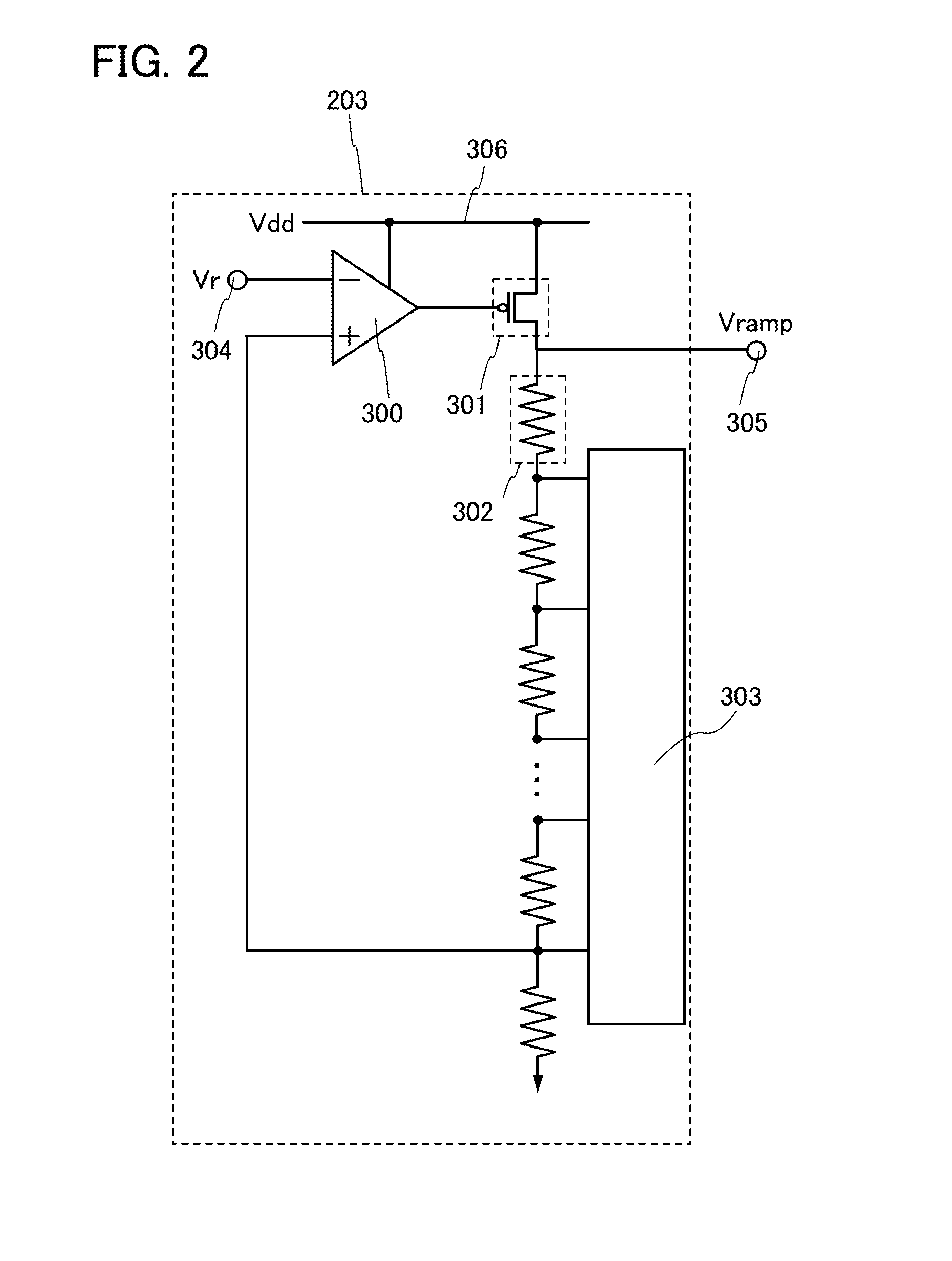
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120153276A1OperationHighly integratedTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceControl circuit
An object is to provide a semiconductor memory device capable of shortening writing operation by concurrently determining potentials of memory cells on one word line. A plurality of transistors having switching characteristics are connected to one potential control circuit, whereby writing potentials are determined concurrently. A potential continues to be changed (raised or decreased) stepwise, a desired potential is determined while changing the potential, and whether data resulted from reading with respect to written data is correct or not is continuously checked, so that high-precision writing operation and high-precision reading operation can be achieved. In addition, favorable switching characteristics and holding characteristics of a transistor including an oxide semiconductor are utilized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
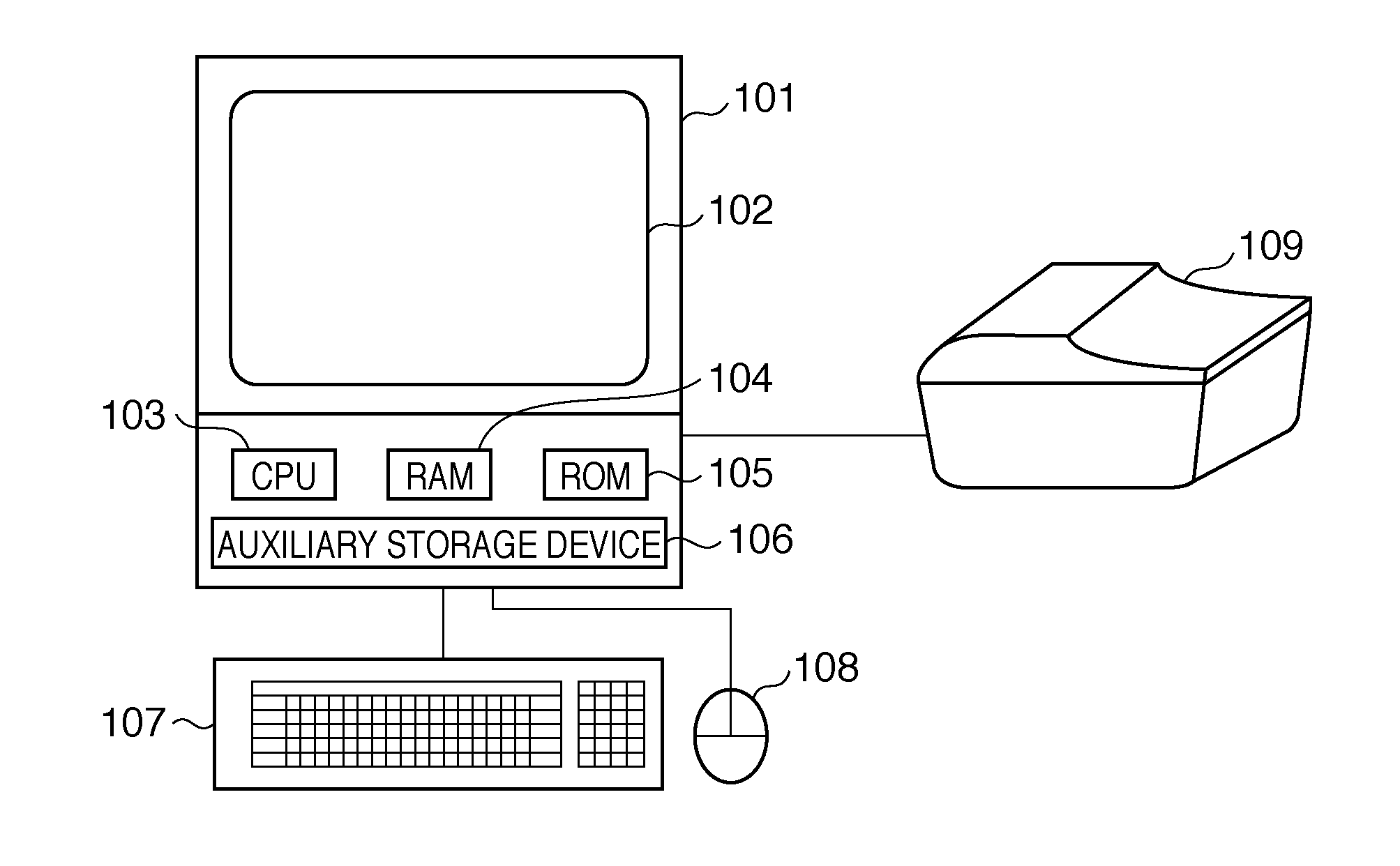
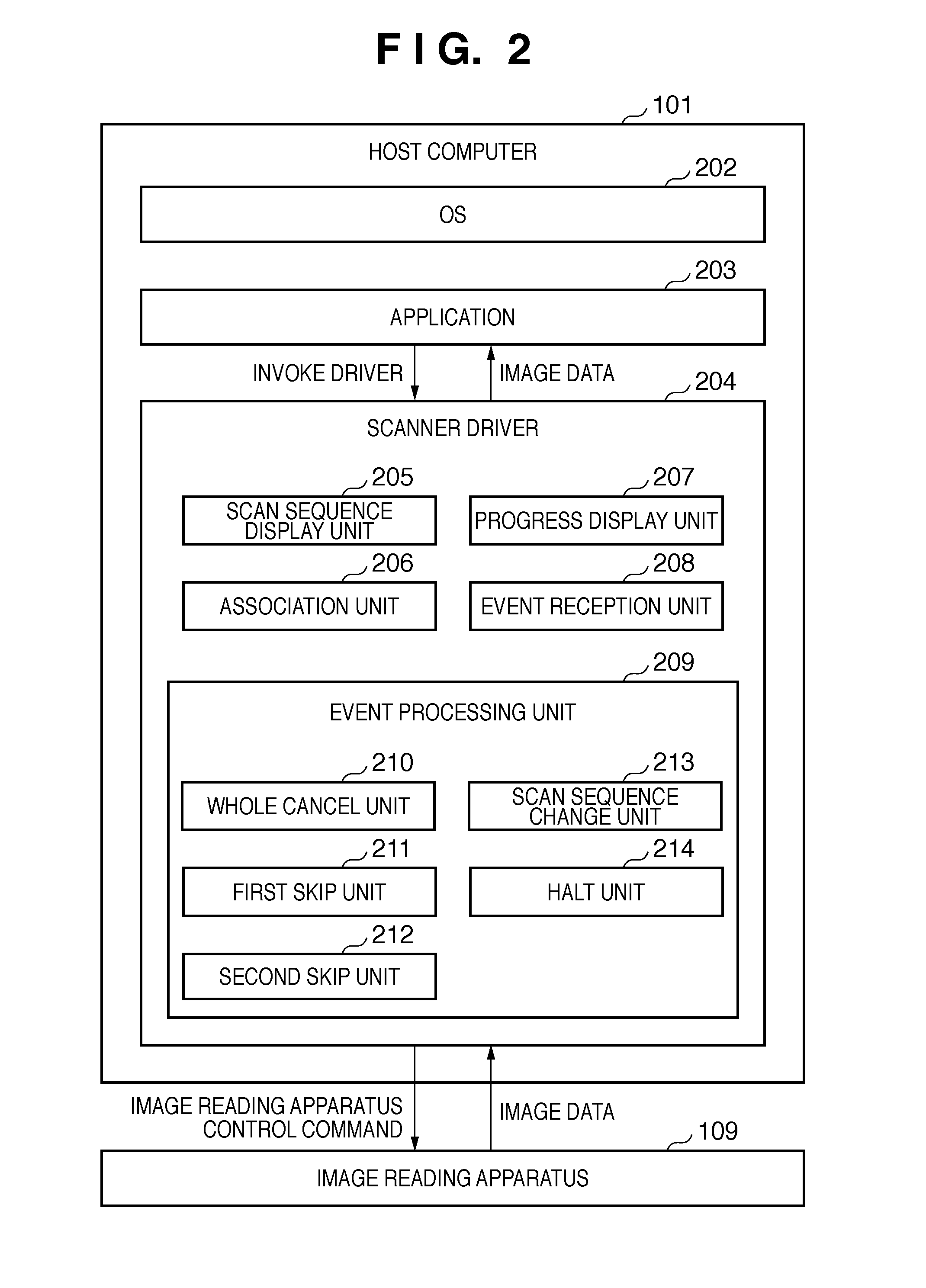
Image reading method, image reading system, and image reading apparatus
InactiveUS20120008176A1Easily progressRead operationPictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Visual perception
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS8686415B2Shorten holding timeHighly integratedTransistorSolid-state devicesControl circuitComputer science
An object is to provide a semiconductor memory device capable of shortening writing operation by concurrently determining potentials of memory cells on one word line. A plurality of transistors having switching characteristics are connected to one potential control circuit, whereby writing potentials are determined concurrently. A potential continues to be changed (raised or decreased) stepwise, a desired potential is determined while changing the potential, and whether data resulted from reading with respect to written data is correct or not is continuously checked, so that high-precision writing operation and high-precision reading operation can be achieved. In addition, favorable switching characteristics and holding characteristics of a transistor including an oxide semiconductor are utilized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com