Patents
Literature
49 results about "Apolygus lucorum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
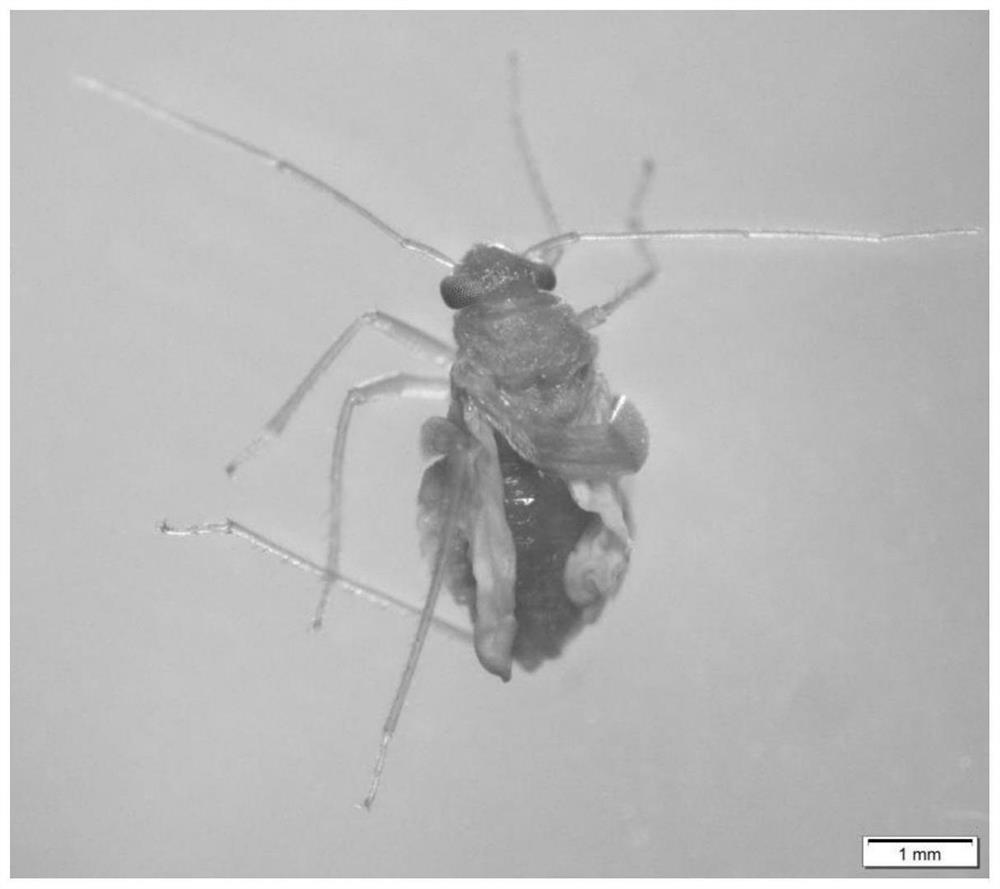
Apolygus lucorum is a species of true bug in the Miridae family. It can be found everywhere in Europe except for Albania, Bulgaria, Iceland, Malta, and Portugal. and much of the Mediterranean basin.Then East across the Palearctic to China and Japan.
Injection method for realizing RNA interference on Apolygus lucorum and application of same in gene screening
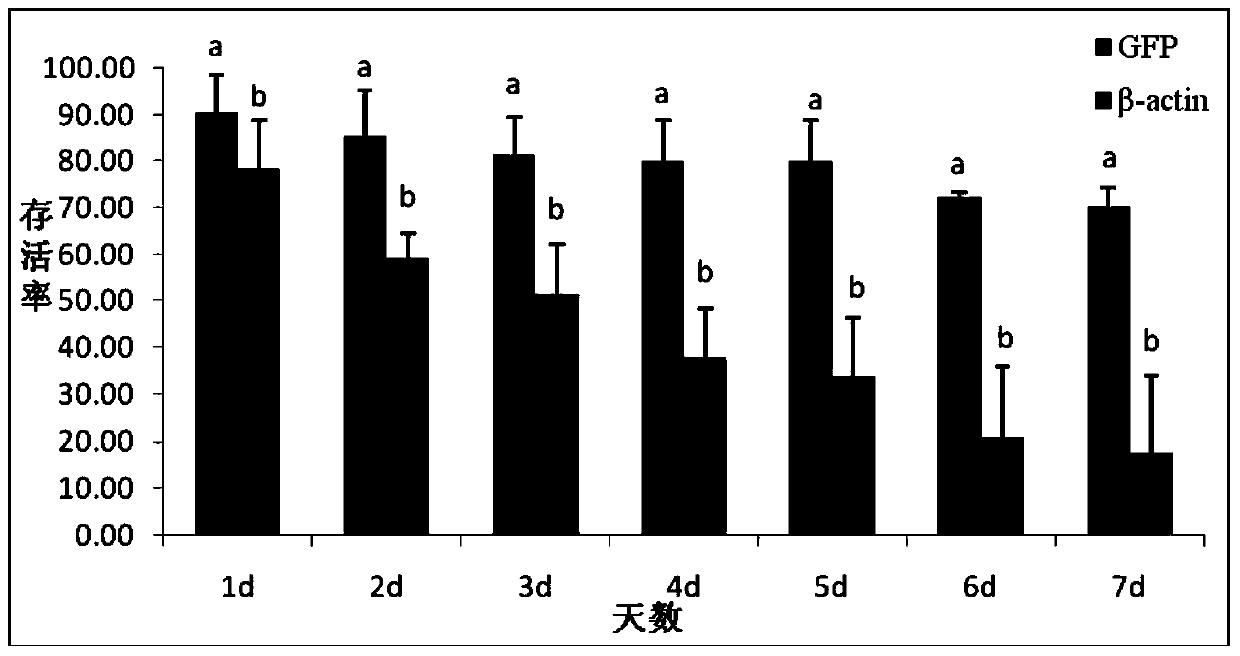
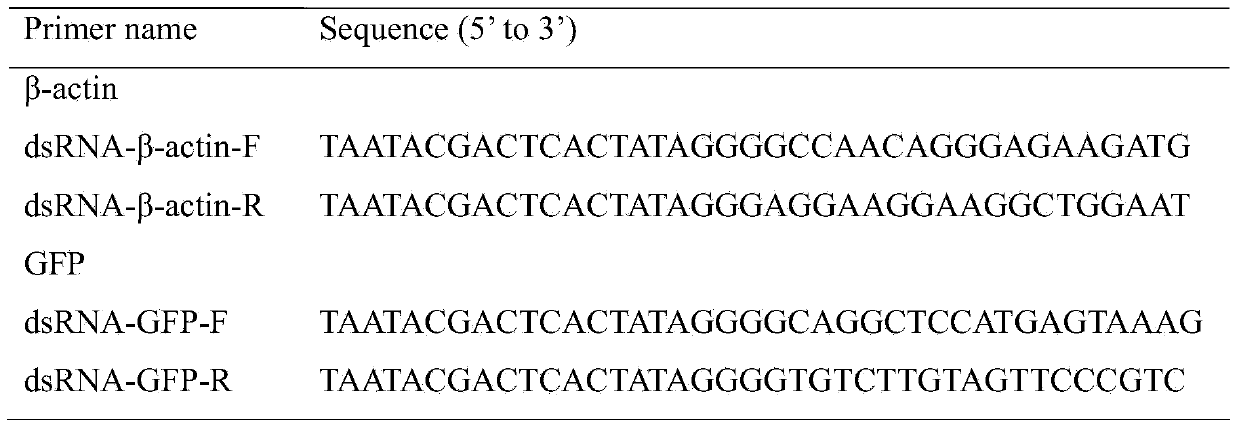
The invention relates to an injection method for realizing RNA interference on Apolygus lucorum and application of the same in gene screening, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The injection method for realizing RNA interference on Apolygus lucorum is characterized in that the outmost side of an intersegmental membrane of metastethidium and an abdomen is the position for injection of dsRNA. An RNAi platform used for researching gene functions of Apolygus lucorum is established for the first time; an injection method is creatively used to determine an optimal injection position for RNAi of Apolygus lucorum and an optimal injection volume at a specific dsRNA concentration, and changes of the phenotype of Apolygus lucorum after injection is detected and recorded. The method provides a novel technological means and a novel technological platform for screening of novel pest-resistant genes and novel gene resources for development of anti-Apolygus lucorum transgenic crops, thereby realizing development of an economic, effective, environment-friendly and novel method for controlling of harm of Apolygus lucorum.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
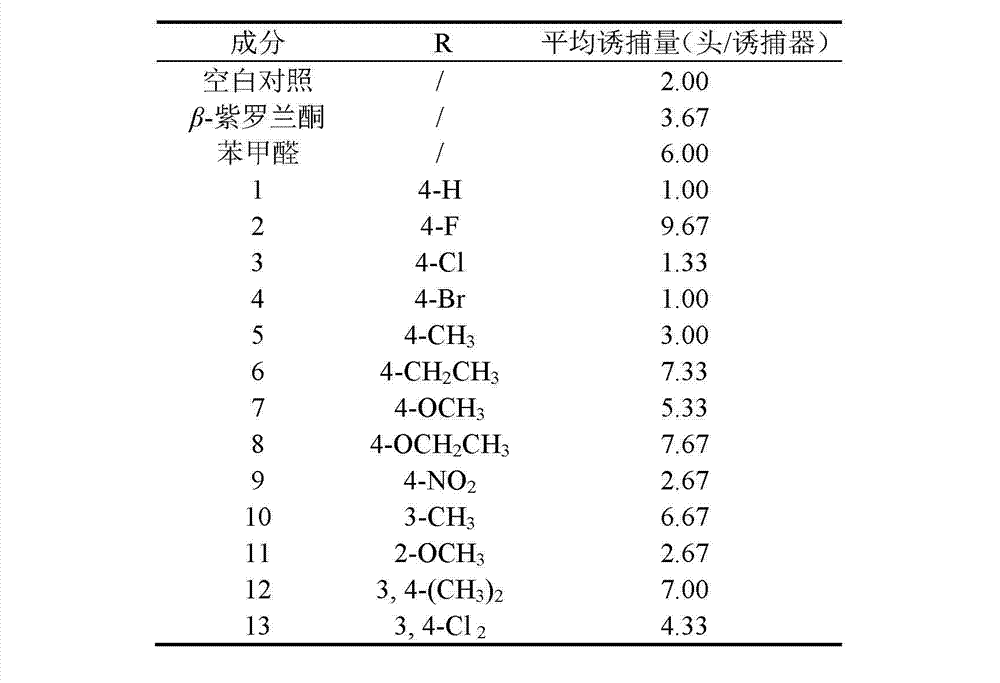
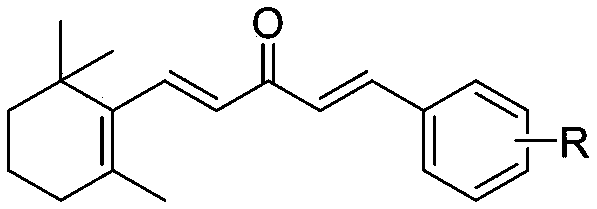
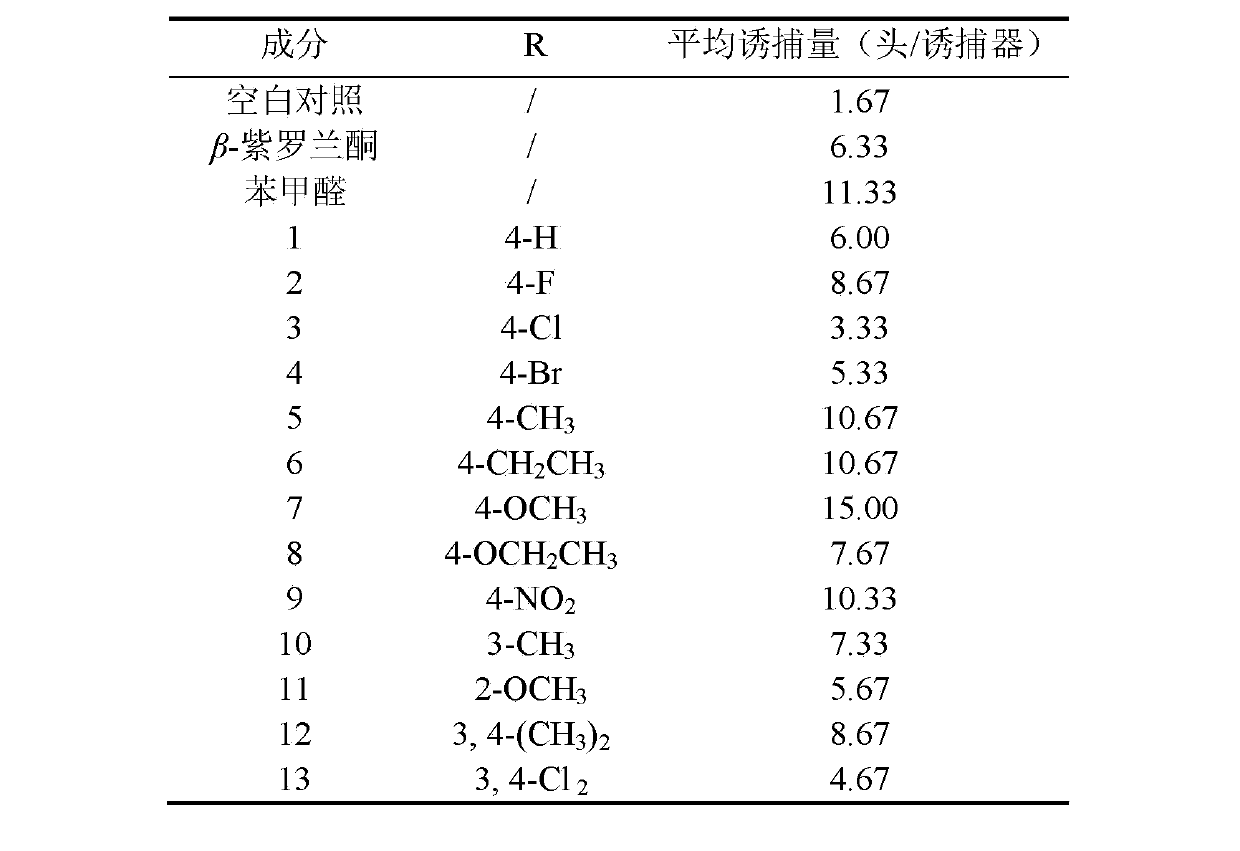
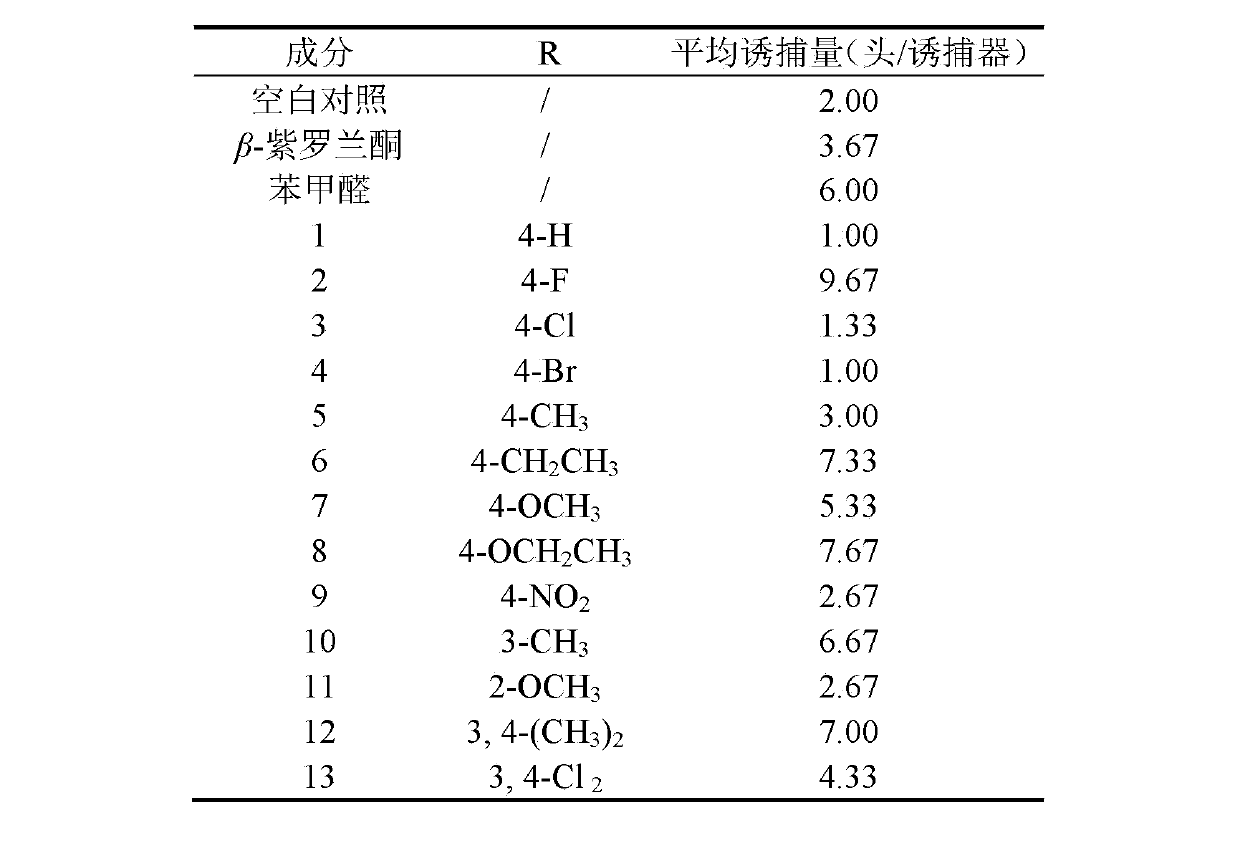
Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant and application thereof
ActiveCN103109808AEasy to prepareEasy to applyPlant growth regulatorsBiocideAdelphocoris suturalisKetone
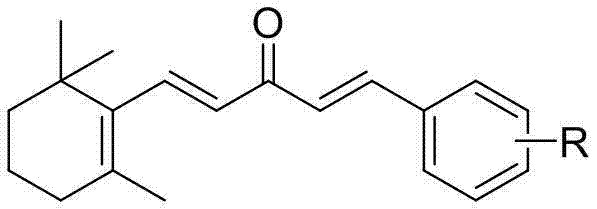
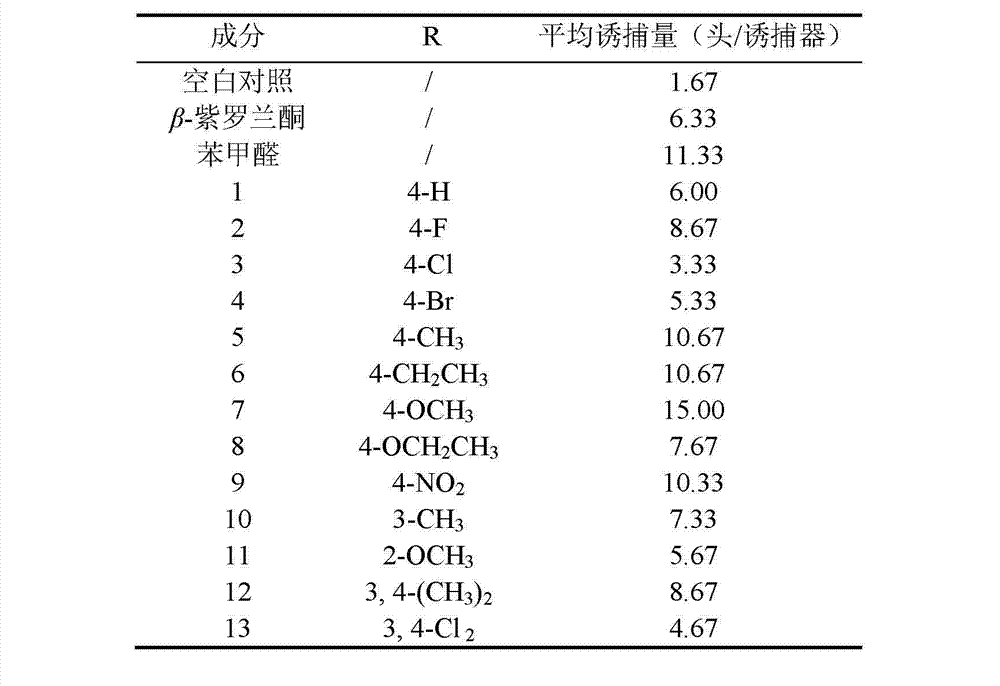
The invention discloses an Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant belonging to the technical field of insect attractant preparation. The Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant is a 1-substituted phenyl-5-(beta- ionone ring)-1, 4-diene 3-ketone compound and is shown in formula (I). The invention provides a synthetic method of the 1-substituted phenyl-5-(beta- ionone ring)-1, 4-diene 3-ketone compound, the preparation method and application of Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant lure. The Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant is simple in preparation method and has the advantageous effects of being efficient, inexpensive and pollution-free to trap and kill.
Owner:SHENZHEN BIOGLOBAL AGRI SCI
Apolygus lucorum trapping method
InactiveCN105961094APurpose of harm reductionReduce in quantityPlant protectionTrappingInflorescence
The invention relates to an Apolygus lucorum trapping method comprising the following steps: planting Artemisia argyi in field edges of an economical crop plantation field, and using strong attractive force of flowering Artemisia argyi on the Apolygus lucorum to trap the Apolygus lucorum. The method is suitable for trapping cotton field Apolygus lucorum imago; the Apolygus lucorum imago likes to feed on Artemisia argyi capitulum, lays eggs and breeds; a plurality of capitulums of the Artemisia argyi can arrange a miniature spike or multiple spikes on branches, the flowering period is long, and Apolygus lucorum trapping period is long, so the Apolygus lucorum can breed on the Artemisia argyi flower for one generation, thus greatly reducing Apolygus lucorum numbers on cottons, and reducing Apolygus lucorum damages on cottons. The Apolygus lucorum on the cotton can be transferred onto the Artemisia argyi so as to reduce large area drug application in the cotton field for controlling Apolygus lucorum, thus reducing control cost, and providing friendly environment; in addition, the planted Artemisia argyi is perennial herbaceous plant and can serve as herbal medicines, thus providing practical traditional Chinese medicine material; the Apolygus lucorum trapping method is high in value, simple, easy to apply, practical and good in effect.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
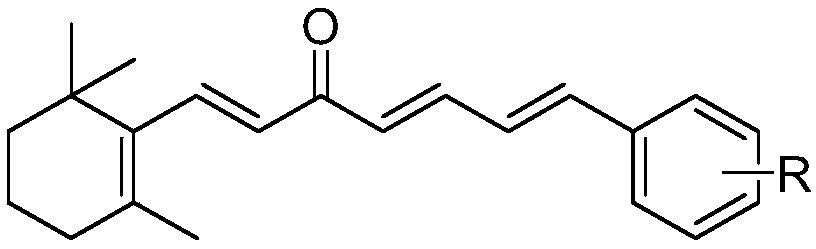
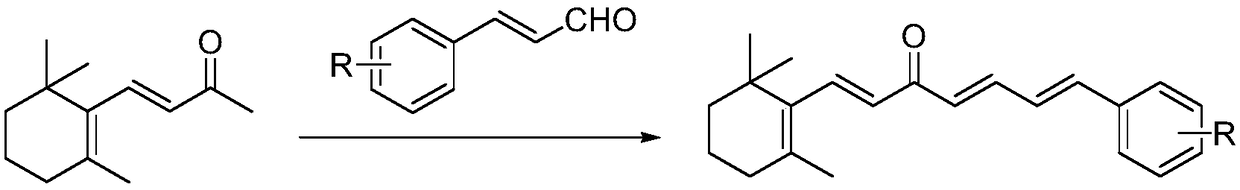
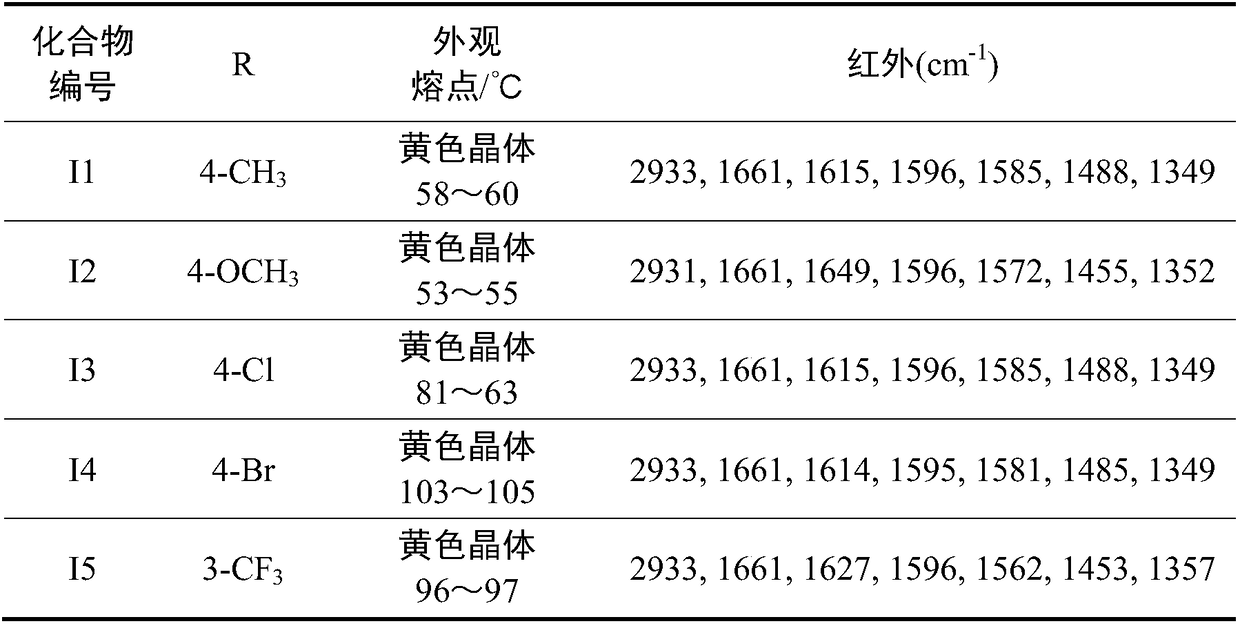
Chalcone compound derived from Beta-ionone and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109053406ASimple processEasy to implementBiocideOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventChalcone
The invention relates to a chalcone compound derived from Beta-ionone and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method for the compound specifically comprises the followingsteps: in an organic solvent, and in the presence of a trapping agent, performing a condensation reaction on the Beta-ionone and substituted cinnamyl aldehyde, to obtain the compound. The provided chalcone compound derived from the Beta-ionone has apparent attractive activity of apolygus lucorum and insecticidal activity of plutella xylostella and tetranychus cinnabrinus, and has the direct control effect to the apolygus lucorum, the plutella xylostella and the tetranychus cinnabrinus. In addition, the preparation method is simple in process, easy to implement, less in by-product, higher in yield, and low in cost, and has a practical application value in agricultural production, and extensive application prospect.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Apolygus lucorum V-ATPaseE gene and application of apolygus lucorum V-ATPaseE gene to aspect of RNAi (ribonucleic acid interfere)-mediated pest control
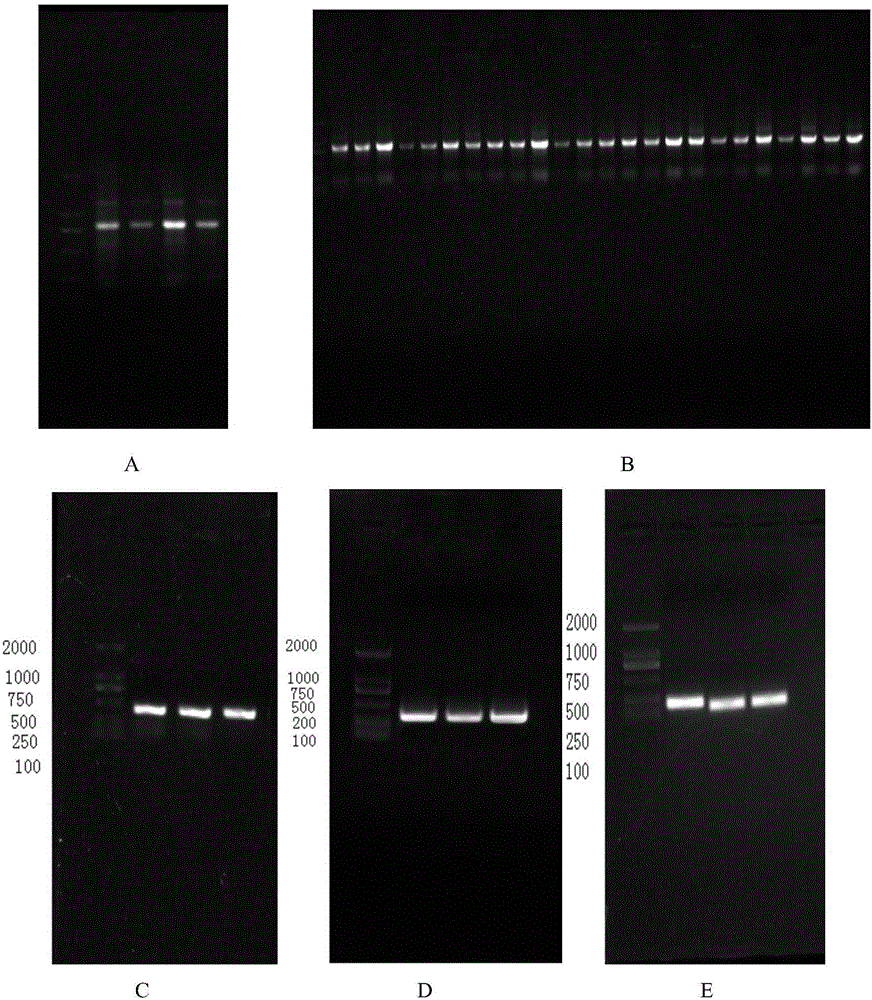
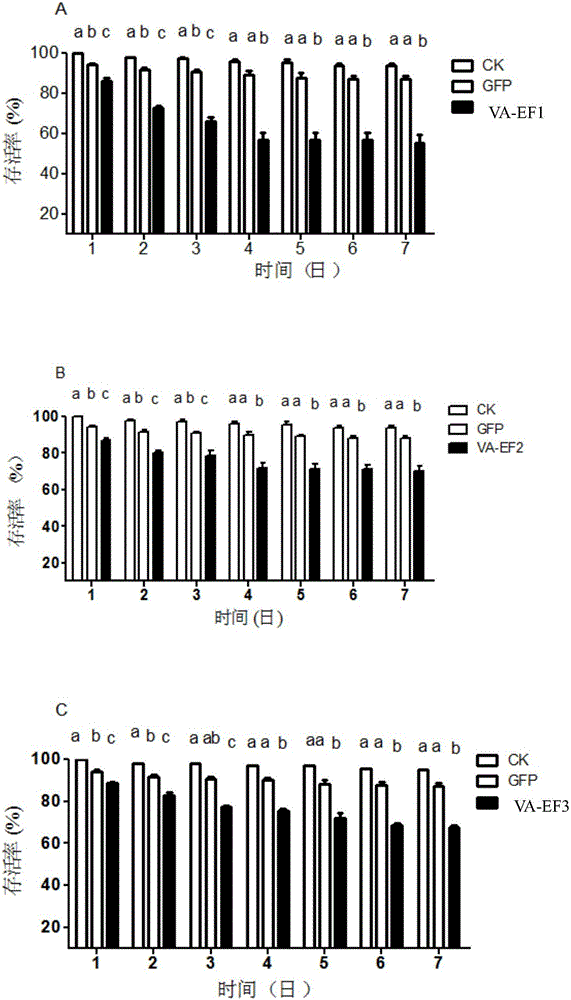
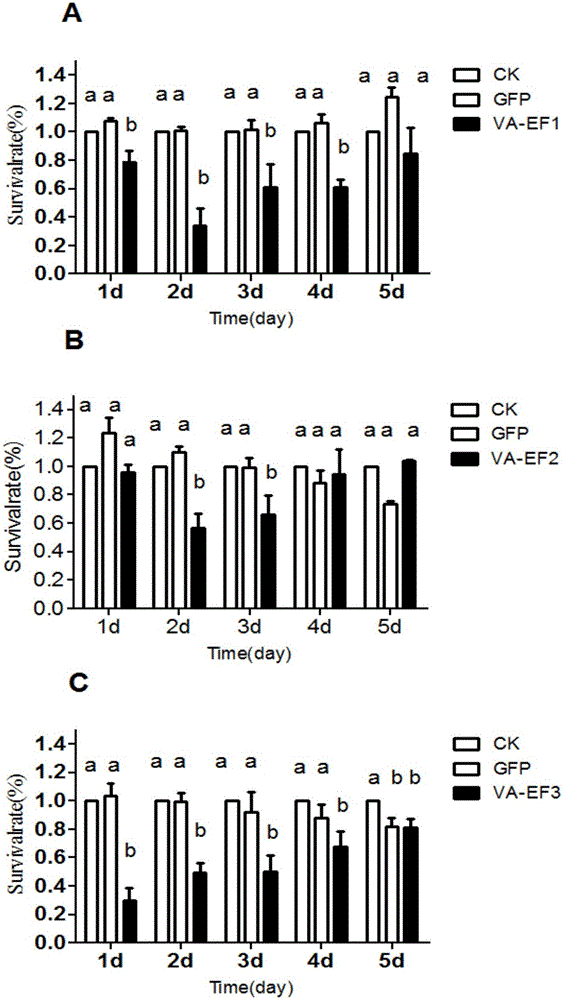
The invention discloses an apolygus lucorum V-ATPaseE gene and application of the apolygus lucorum V-ATPaseE gene to the aspect of RNAi (ribonucleic acid interfere)-mediated pest control. Sequences of the apolygus lucorum V-ATPaseE gene are shown as SEQ ID NO:1. Three different segments of dsRNA (double-stranded RNA) are respectively synthesized at different locations of the apolygus lucorum V-ATPaseE gene and are respectively named as dsVA-EF1, dsVA-EF2 and dsVA-EF3, and then the synthesized dsRNA is transmitted to third-instar lavas of apolygus lucorum by the aid of micro-injection methods. The apolygus lucorum V-ATPaseE gene and the application have the advantages that the survival rates of the third-instar lavas are 55%, 70% and 68% respectively in 7 days after the dsRNA is injected into the third-instar lavas as shown by statistics; target genes are obviously silenced as proved by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) results; RNAi feeding experiments are carried out on selected VA-EF1dsRNA, and the survival rates of the third-instar lavas are 65% in 7 days after the dsRNA is injected into the third-instar lavas as shown by results; candidate genes with good effects can be provided for apolygus lucorum RNA interfere (RNAi)-mediated pest control strategies in the future and are verified.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
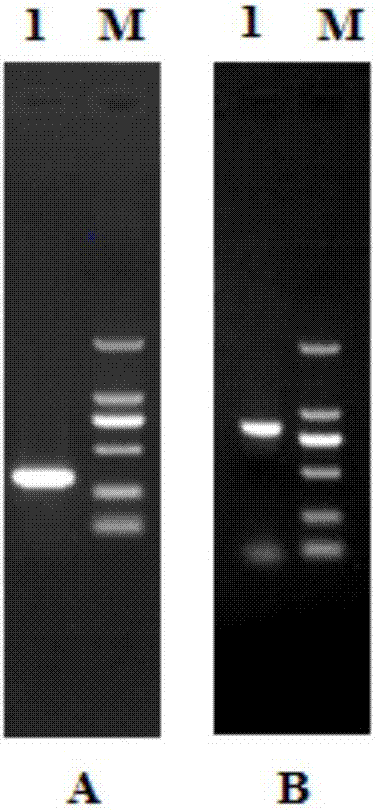
Apolygus lucorum specific COI primer, kit containing apolygus lucorum specific COI primer and application of kit
ActiveCN104611444AHas amplifying effectImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationConserved sequenceGenetics
The invention relates to the molecular biological field and particularly provides an apolygus lucorum specific COI primer, a kit containing the apolygus lucorum specific COI primer and application of the kit. According to a conserved sequence of apolygus lucorum mtDNA, a pair of apolygus lucorum specific COI primers AluF1 and AluR1 (as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID NO.2) are designed; according to the detection, the pair of primers have specific amplification ability, the size of amplified products is 323bp, and the sensitivity DNA concentration detection limit is 0.15625ng / mu L. By utilizing a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detecting technology, a single specific stripe is obtained by amplifying the specific primers. The apolygus lucorum specific COI primer is simple to operate, and has the characteristics of being efficient, low in price and strong in specificity, so that the detecting accuracy is improved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Apolygus lucorum vitellogenin and specific peptide chain, vector, strain and application thereof
InactiveCN104711265APredicting Outbreak PotentialBacteriaMicroorganism based processesVitellogeninsWestern blot
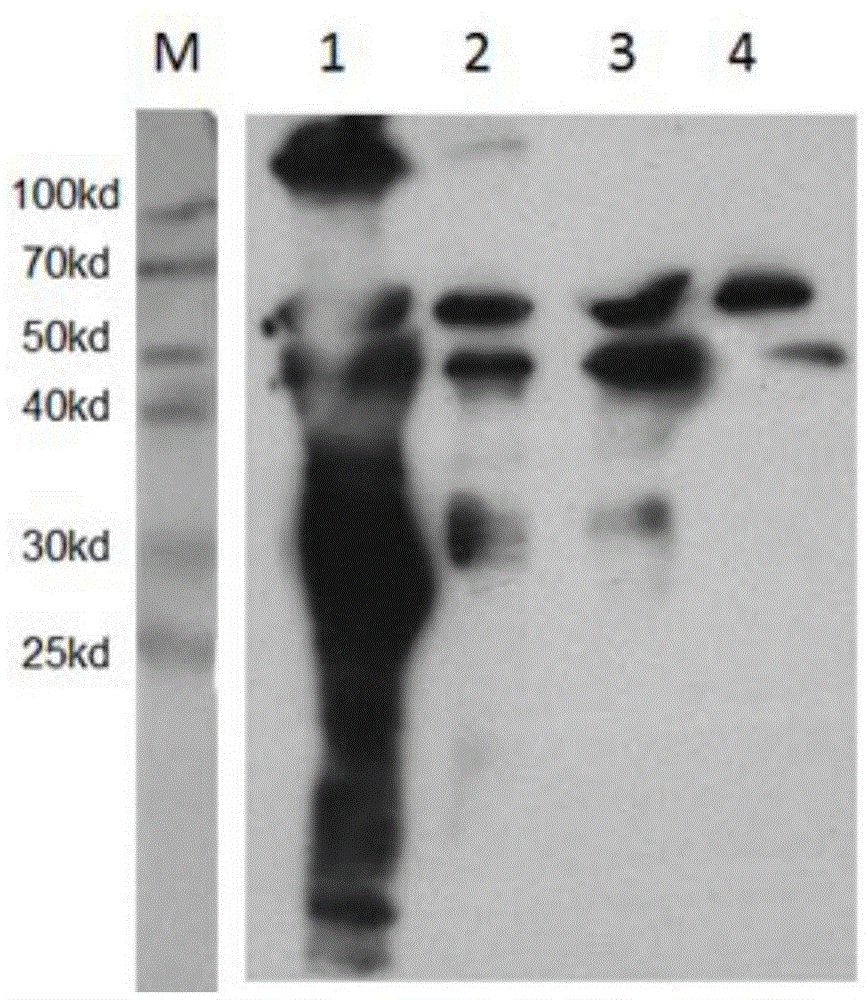
The invention discloses a DNA sequence used for encoding apolygus lucorum vitellogenin. The invention further discloses a specific peptide sequence capable of detecting an AlVg protein expression level by using Western-blot, and the expression difference of AlVg in apolygus lucorum on the protein level is analyzed by utilizing the specificity of the polypeptide. The invention further constructs an atlas of age in days after female adult eclosion and AlVg expression trend. The correlation of AlVg genes and protein expression levels in female adults with single female fecundity is investigated after the female adults are continuously bred on a variety of host plants, in order to construct a related prediction model, which has significant importance on prediction of the spawning potential of the apolygus lucorum. a positive correlation relation between the AlVg expression levels of female apolygus lucorum adults and the single female fecundity after eclosion for 7 days is defined. The specific peptide sequence disclosed by the invention can be used for observing and predicting the population dynamics of the apolygus lucorum in fields, and providing a foundation for research and development of new technology for monitoring field populations of the apolygus lucorum.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
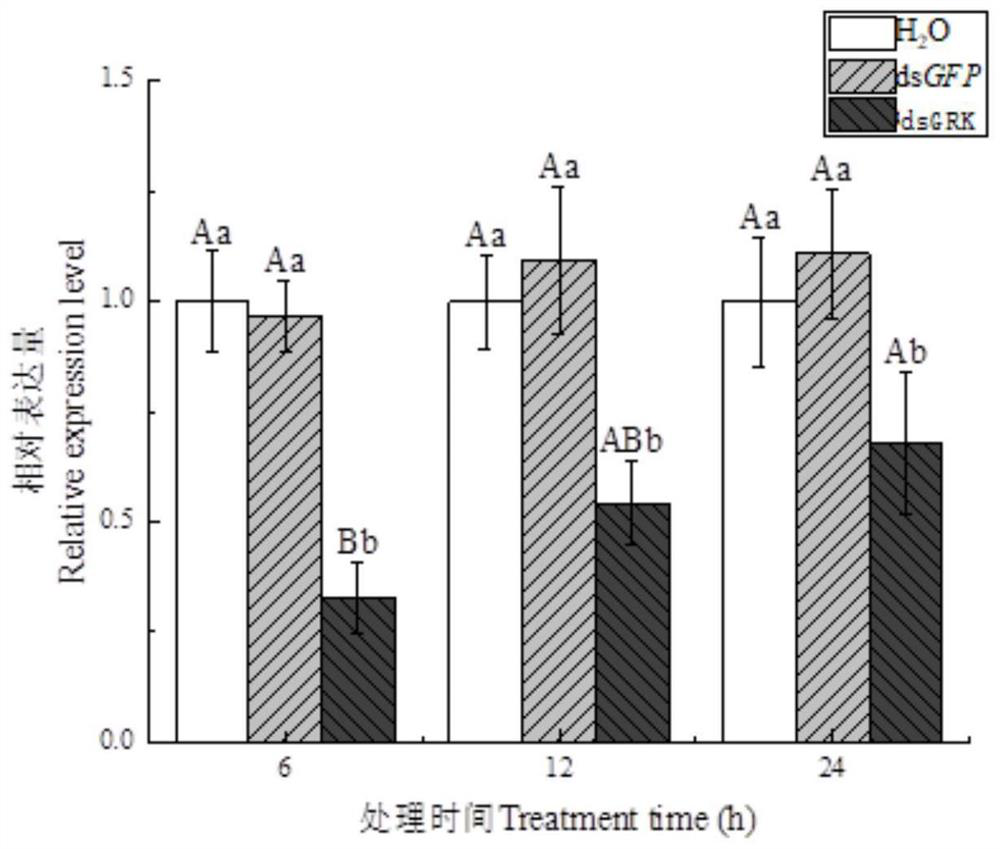
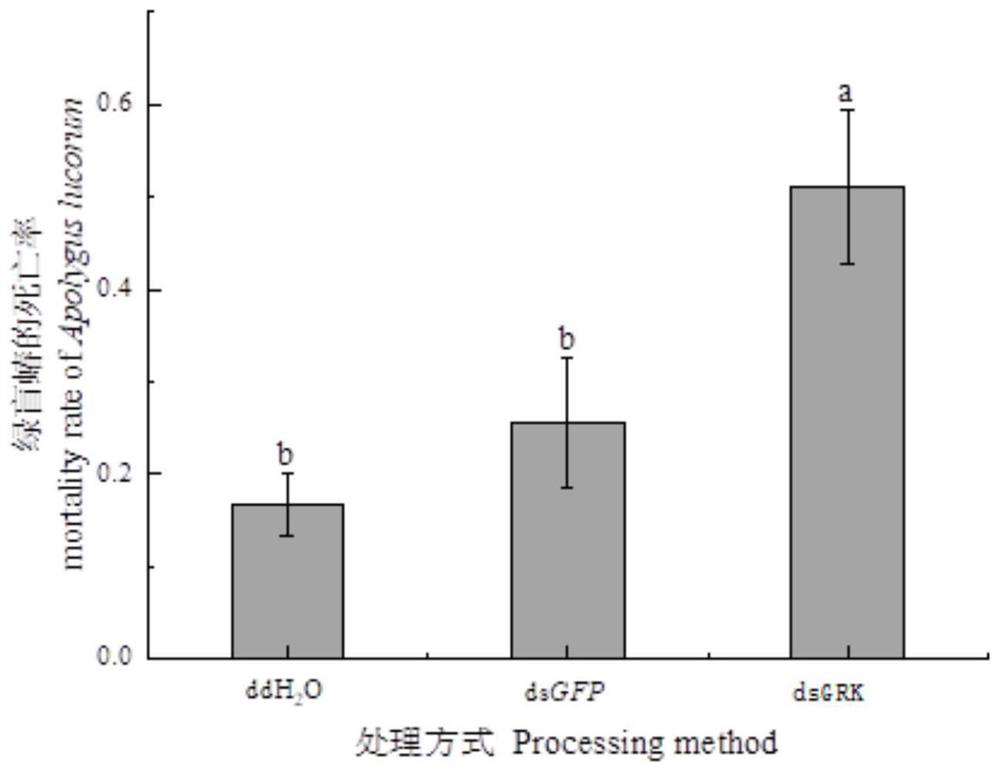
Apolygus lucorum GRK gene, dsRNA thereof, and synthetic method and application thereof
PendingCN113943720ASignificant lethal effectControl populationMicroinjection basedTransferasesEscherichia coliG protein-coupled receptor kinase
The invention discloses apolygus lucorum G protein coupled receptor kinase. The amino acid sequence of the apolygus lucorum G protein coupled receptor kinase is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also discloses a gene for encoding the apolygus lucorum G protein coupled receptor kinase as well as an acquisition method and application thereof. The invention further discloses dsRNA of the apolygus lucorum GRK gene and application thereof. The dsRNA of the synthesized GRK gene has a remarkable lethal effect on the apolygus lucorum, the population number of the apolygus lucorum is effectively controlled, and a new way is provided for pest control. Meanwhile, the dsRNA is synthesized by using escherichia coli, so that a product can be synthesized in a large scale within a short time, and the defect that a kit cannot synthesize a large amount of dsRNA is overcome. Meanwhile, the apolygus lucorum G protein coupled receptor kinase is low in cost, wide in application range, easy to operate, capable of being repeatedly used and free of limitation.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Vigna radiata specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer pair and method for detecting vigna radiata in phytophagous insect bodies
InactiveCN105132549ACapable of amplificationStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRadiataBiology
The invention provides a vigna radiata specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer pair which is a pair of specific primers designed according to a vigna radiata rbcL sequence (AP014692.1) published in GenBank. The primer pair which is high in specificity has an amplification function for vigna radiata only and has no amplification products for other sympatric species. The invention further provides a method of using the primer pair for detecting trace amount of vigna radiata in phytophagous insect bodies. By adoption of the method and the primers for detecting vigna radiata, high accuracy and simplicity, quickness and high efficiency in operation are realized, detection can be generally finished within five hours, sensitivity is high, and plasmid concentration detection limit is 4.49E+03. By DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) amplification of apolygus lucorum eating the vigna radiata, the detection rate reaches 100%, so that feasibility of the method is proved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wild cotton or semi-wild cotton mirid resistance identification method
InactiveCN104719013AEliminate distractionsIdentification results are stableHorticulture methodsPlant protectionOperabilitySquare meter
The invention discloses a wild cotton or semi-wild cotton mirid resistance identification method. The method specifically comprises the steps that identified varieties are planted in a net house; the net house is covered with a nylon net ranging from 80 meshes to 100 meshes; apolygus lucorum mixed populations are inoculated manually during 10-12 leaf stage of cotton growing with the density being one per square meter; a cage is cleared ten days before mirids are released, and 1500-fold phoxim is sprayed in the net house; the damage degrees of all the identified varieties to three leaves at the top of each cotton plant, the total number of lateral branches of each cotton plant and the number of damaged lateral branches are investigated in seven to ten days after the apolygus lucorum mixed populations are inoculated; the leaf damaged index, the lateral branch damage rate and the lateral branch damage reducing rate are calculated; the resistance levels of the identified varieties are judged. By means of the method, interference of the factors such as other pests and natural enemies is eliminated, the identification result is stable and reliable, and the practicality and operability are high.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Apolygus lucorum soluble trehalase (AlTre-1) monoclonal antibody as well as preparation method and application of thereof
InactiveCN104829722AHigh sensitivityBiological testingImmunoglobulins against enzymesWestern blotSpecific immunity
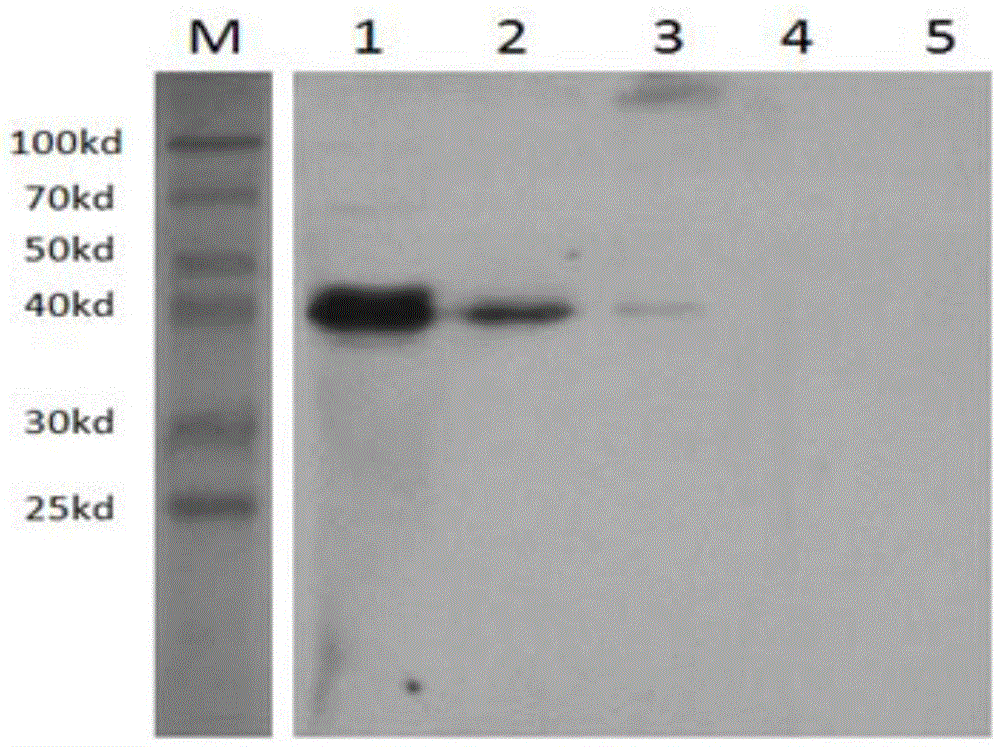
The invention discloses an Apolygus lucorum soluble trehalase (AlTre-1) monoclonal antibody as well as a preparation method and application of thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, applying AlTre-1 recombinant protein subjected to prokaryotic expression and purification to an immunized mice so as to prepare antiserum, and determining the titer of the antiserum by an indirect ELISA method; and preparing myeloma cells and spleen cells and then performing cell fusion, screening positive porocyte by an ELISA method, then performing subcloning, and picking out positive monoclonal holes for enlarging cultivation and strain fixing, thereby finally obtaining the AlTre-1 monoclonal antibody. Besides, a Western blot method determines that the monoclonal antibody can specifically identify the AlTre-1 recombinant protein and can generate specific immune reaction. By virtue of the application of the AlTre-1 monoclonal antibody, a material base and a technical support can be provided for the tissue distribution of soluble trehalase in Apolygus lucorum and the quick detection and molecular biology study of the protein.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
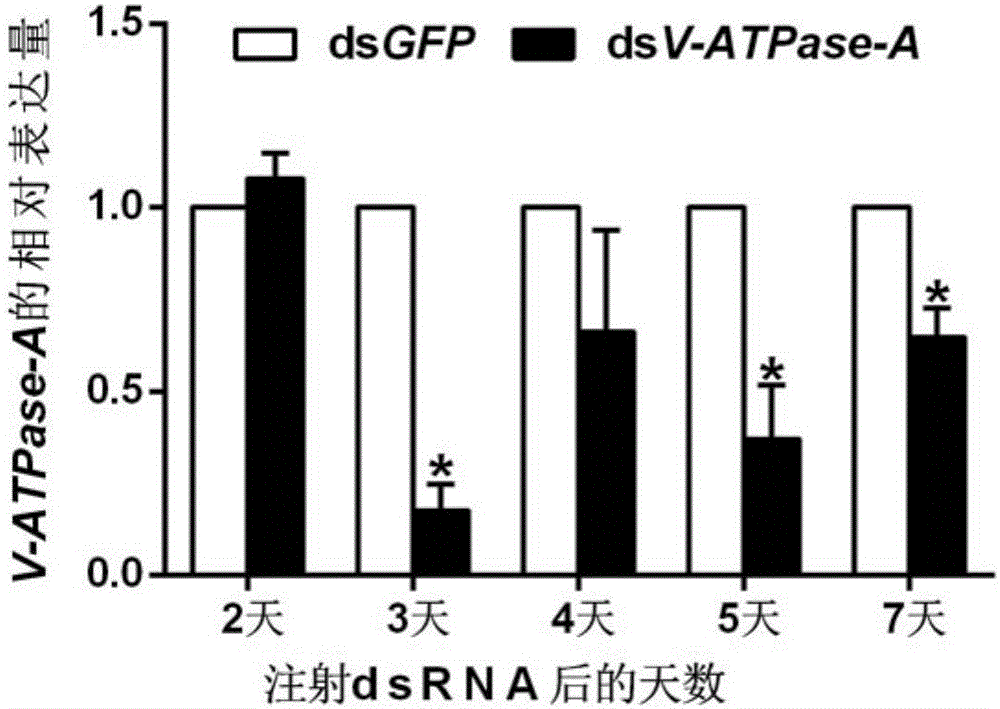
Apolygus lucorum V-ATPase-A gene cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and application thereof
InactiveCN106318956ABiocideHydrolasesComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidCandidate Gene Association Study
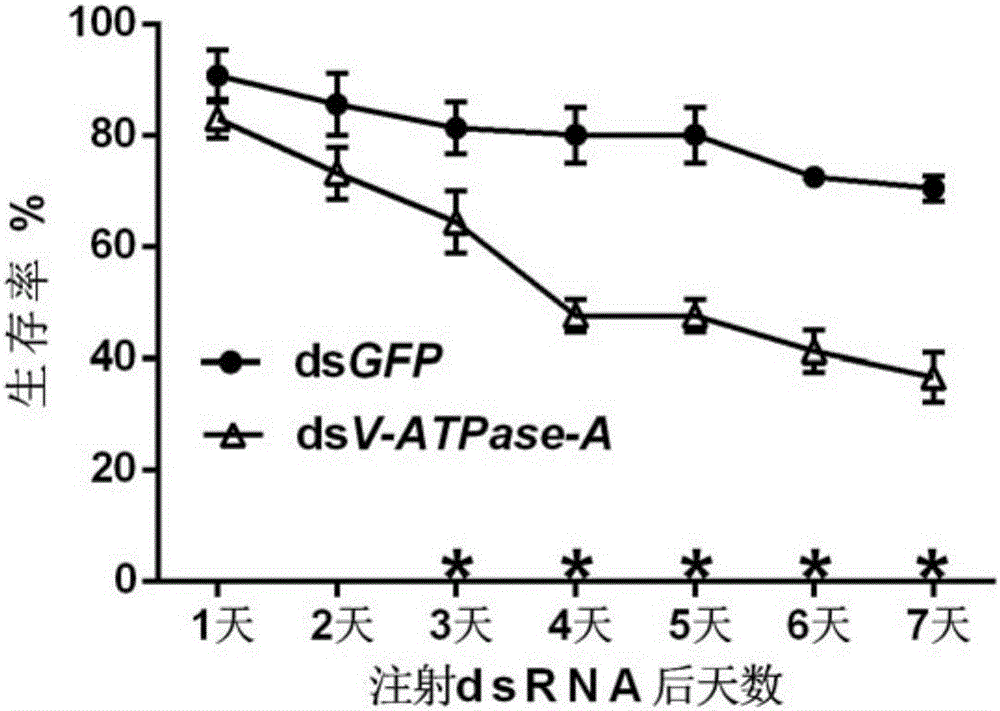
The invention discloses an apolygus lucorum V-ATPase-A gene cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biological control. According to the apolygus lucorum V-ATPase-A gene cDNA disclosed by the invention, a V-ATPase-A gene is obtained by cloning apolygus lucorum for the first time; the sequence of the V-ATPase-A gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the gene is used as a target of RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid interference) to design and synthesize apolygus lucorum V-ATPase-AdsRNA; after dsV-ATPase-A is introduced into apolygus lucorum nymphs by adopting an injection method, the V-ATPase-A gene expressions are respectively blocked, the growth and the metabolism of the apolygus lucorum are inhibited, and the death rate is improved. Experiments show that the apolygus lucorum V-ATPase-A gene provides a candidate gene with a good control effect for a future pest control strategy mediated by apolygus lucorum RNAi.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Green drug for controlling grape apolygus lucorum and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105145668ANo pollution in the processPromote absorptionBiocideAnimal repellantsIndian-lilacPollution
The invention discloses a green drug for controlling grape apolygus lucorum and a preparation method thereof. The green drug for controlling grape apolygus lucorum comprises the following raw materials by weight: 10-15 parts of fructus toosendan, 15-18 parts of fruit of melia azedarach L., 25-30 parts of pyrethrum, 10-15 parts of flos daturae, 5-10 parts of azadirachta Indica, 7-12 parts of fructus cnidii, and 3-5 parts of clothianidin. The green drug for controlling grape apolygus lucorum is capable of effectively controlling grape apolygus lucorum, is high in drug effect, does not facilitate an insect to generate drug resistance, is free of residue, free of environment pollution, free of toxicity and harm to human body, and is capable of promoting grape to absorb nutrients and substantially improving output.
Owner:句容市茅山镇恒泰家庭农场
Novel compound repellent for apolygus lucorum as well as preparation method and application thereof
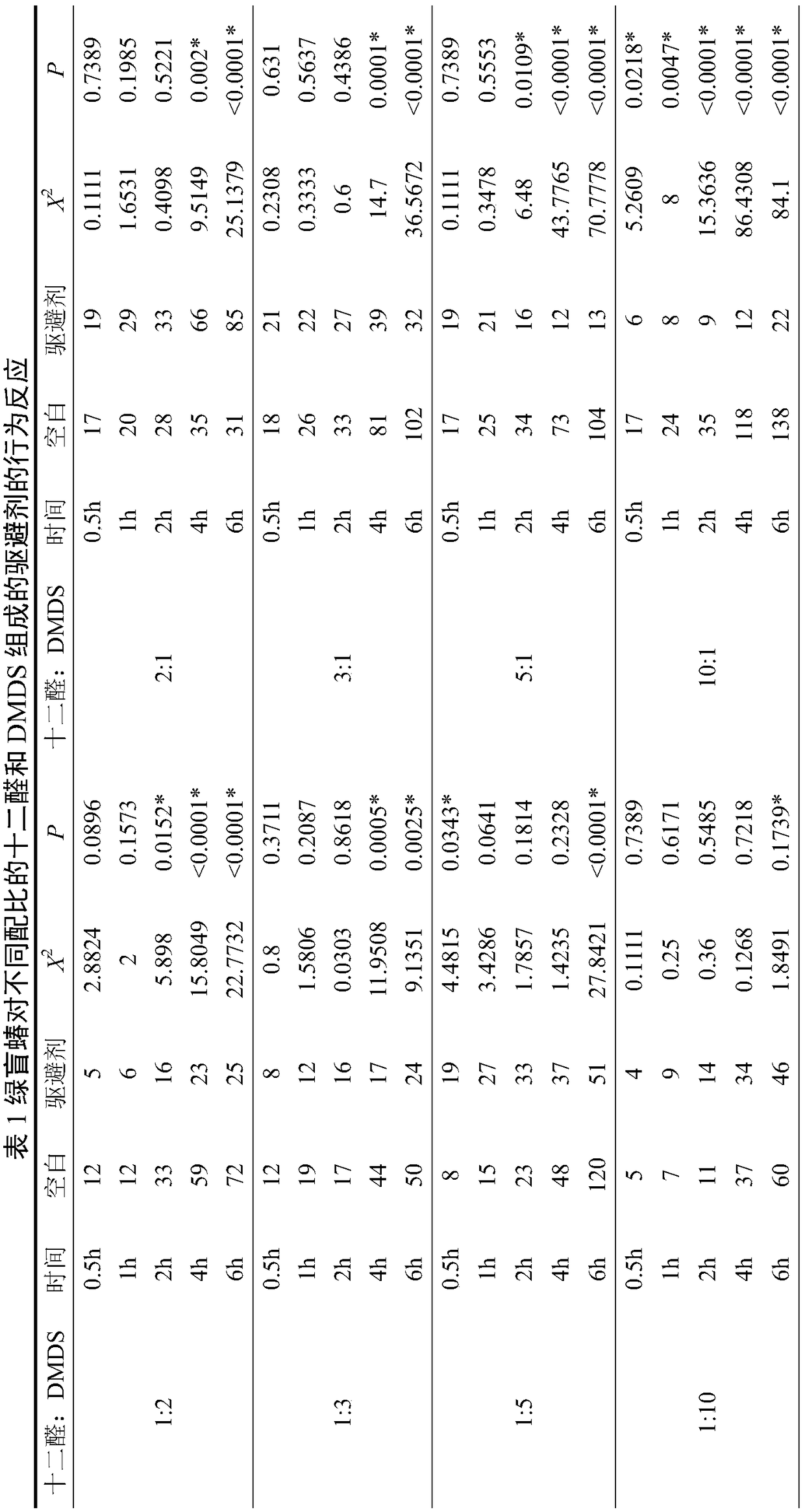
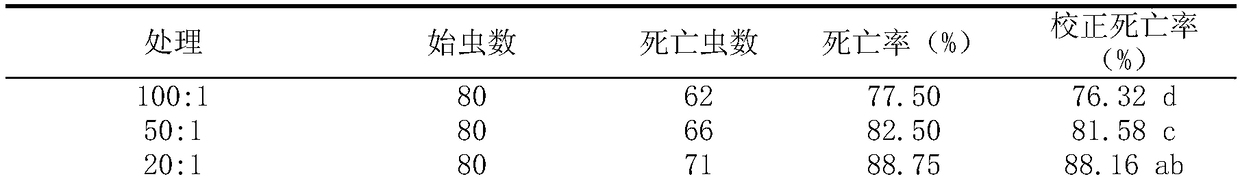
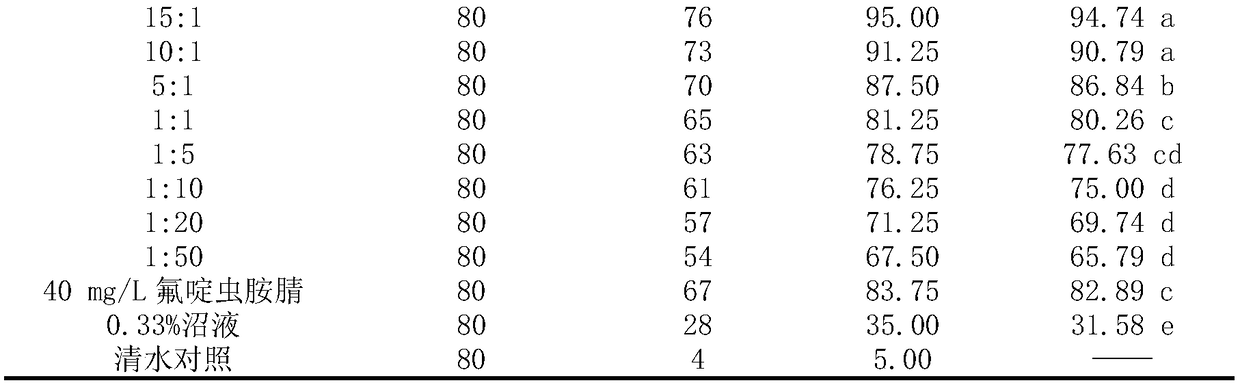
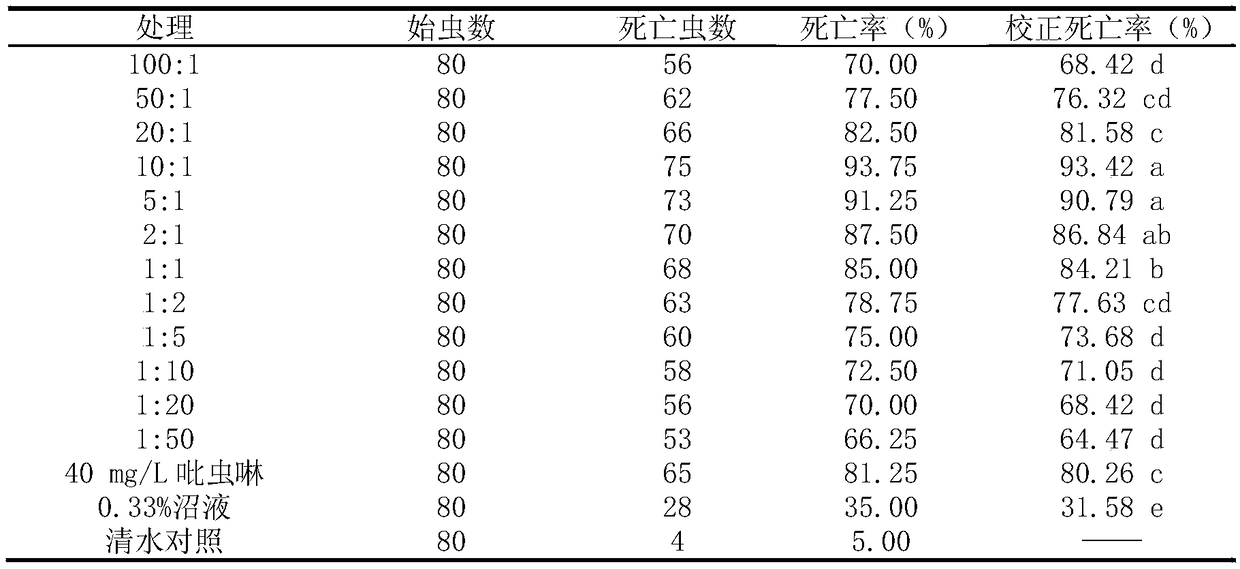
ActiveCN108617651AReduce irritating odorGuaranteed repellent effectBiocidePest repellentsApolygus lucorumMethyl disulfide
The invention relates to a novel compound repellent for apolygus lucorum as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the invention, dodecyl aldehyde is mixed with dimethyl disulfide in a proper ratio, so that the pungent odor of the dimethyl disulfide is reduced, and the repellent effect on the apolygus lucorum (adult insects) is ensured. The novel compound repellent forthe apolygus lucorum provided by the invention is efficient and simple in preparation and use method, low in price, and long in lasting period.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compound composition containing biogas slurry and insecticide and application thereof in crop pest control
InactiveCN108294003ASynergistic effect is obviousImprove efficacyBiocideAnimal repellantsSlurryPlant Sources
The invention belongs to the technical field of compound compositions of insecticides and particularly relates to a compound composition containing biogas slurry and an insecticide and application thereof in crop pest control. The effective components of the compound composition provided by the invention are prepared from a component I and a component II, wherein the component I is biogas slurry;and the component II is one of sulfone imine insecticides, phenylpyrazole insecticides, anabasine insecticides, picolinamide insecticides, pyrethroid insecticides, novel pyridine methylenimine insecticides, benzoyl urea insecticides, antibiotic insecticides and plant source insecticides. The compound composition containing the biogas slurry and the insecticide is applied to control of apolygus lucorum. The compound composition provided by the invention has the advantages of being obvious in synergistic effect, high in drug effect, good in fast-acting property, low in toxicity, low in residue content, long in lasting period, wide in insecticidal spectrum, capable of avoiding and delaying generation of pest drug resistance, convenient to use, safe, reliable and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG YANTAI AGRI SCI & TECH INST +1
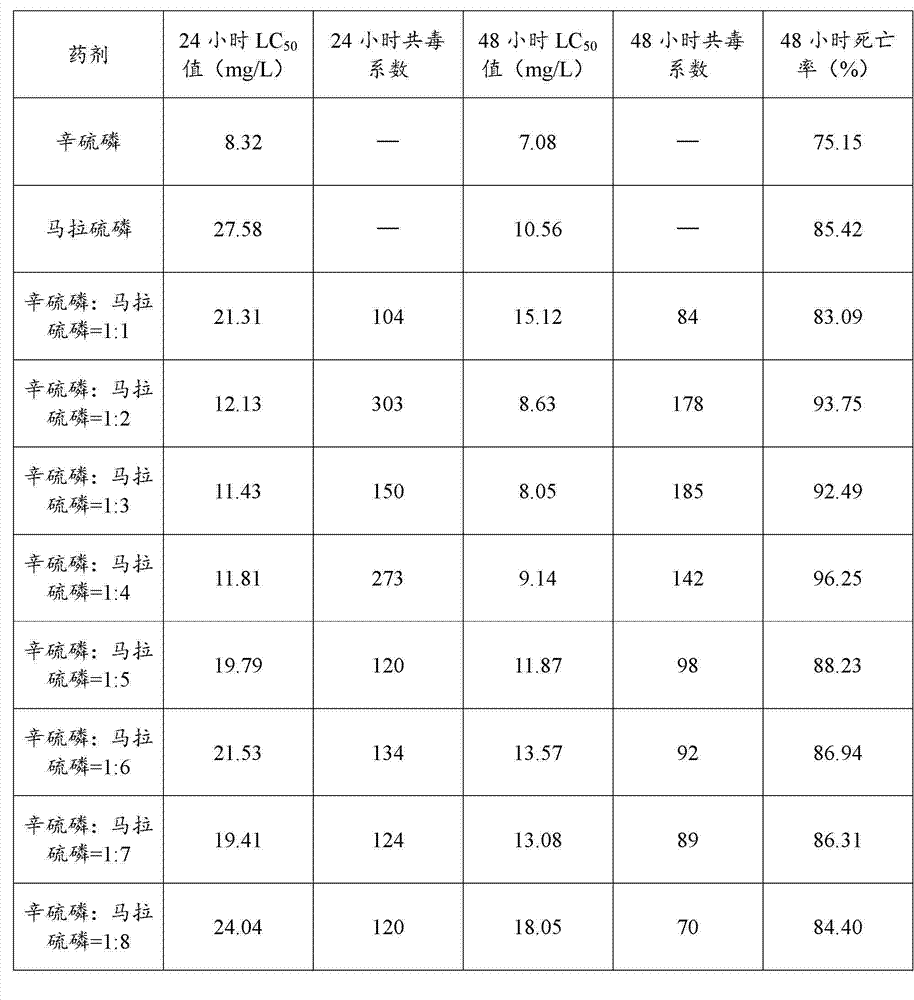
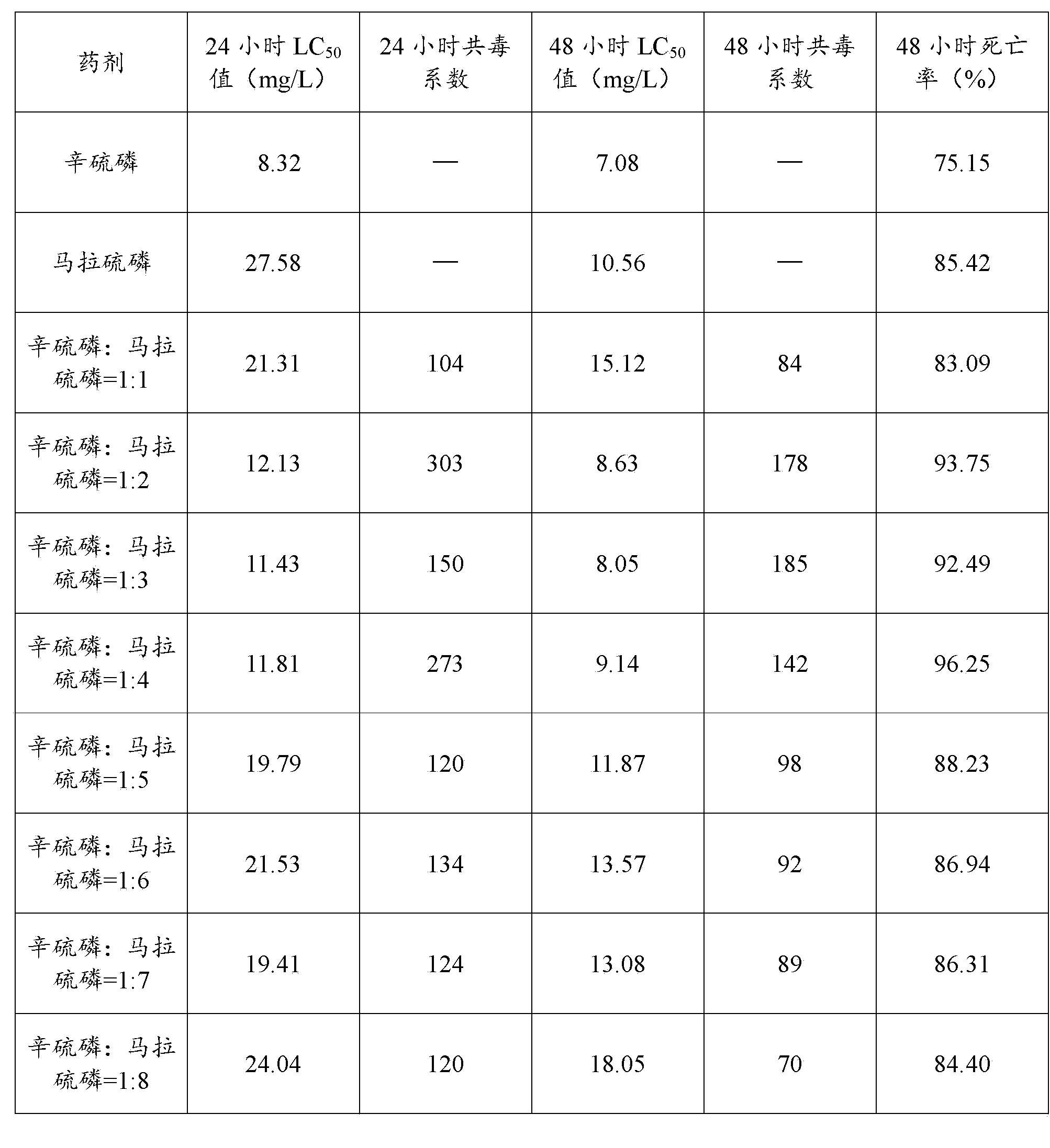
Compound pesticide for controlling apolygus lucorum and preparation method of compound pesticide
The invention belongs to the technical field of compound pesticides, and in particular relates to a compound pesticide for controlling apolygus lucorum and a preparation method of the compound pesticide. According to the preparation method, phoxim and malathion are taken as active ingredients to prepare the compound pesticide, the advantages of the phoxim and the malathion are complemented with each other, not only are the characteristics of good control effect and strong knockdown capacity of the phoxim brought into play, but also the defects of quick photodecomposition and short duration of the phoxim are overcome, the pesticide effect is obviously improved, and the synergistic effect is obvious; and the compound pesticide has an obvious effect on controlling the apolygus lucorum, and the use cost is lowered.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
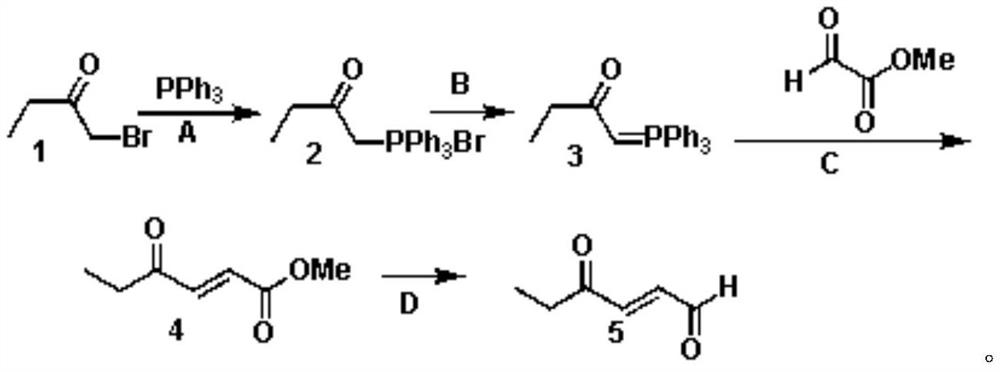
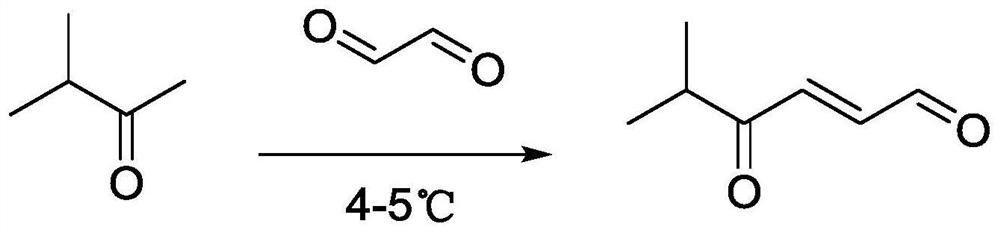
Synthesis method of trans-4-oxo-2-hexenal
PendingCN111747837ALow costEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsButyloneHexene
Owner:SUZHOU HUADAO BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant and application thereof
ActiveCN103109808BEasy to prepareEasy to applyBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAdelphocoris suturalisKetone
The invention discloses an Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant belonging to the technical field of insect attractant preparation. The Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant is a 1-substituted phenyl-5-(beta- ionone ring)-1, 4-diene 3-ketone compound and is shown in formula (I). The invention provides a synthetic method of the 1-substituted phenyl-5-(beta- ionone ring)-1, 4-diene 3-ketone compound, the preparation method and application of Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant lure. The Apolygus lucorum Meyer-Dur and Adelphocoris suturalis jakovlev attractant is simple in preparation method and has the advantageous effects of being efficient, inexpensive and pollution-free to trap and kill.
Owner:SHENZHEN BIOGLOBAL AGRI SCI
Compound pesticide for controlling apolygus lucorum and preparation method of compound pesticide
The invention belongs to the technical field of compound pesticides, and in particular relates to a compound pesticide for controlling apolygus lucorum and a preparation method of the compound pesticide. According to the preparation method, phoxim and malathion are taken as active ingredients to prepare the compound pesticide, the advantages of the phoxim and the malathion are complemented with each other, not only are the characteristics of good control effect and strong knockdown capacity of the phoxim brought into play, but also the defects of quick photodecomposition and short duration of the phoxim are overcome, the pesticide effect is obviously improved, and the synergistic effect is obvious; and the compound pesticide has an obvious effect on controlling the apolygus lucorum, and the use cost is lowered.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Using method of sticky traps
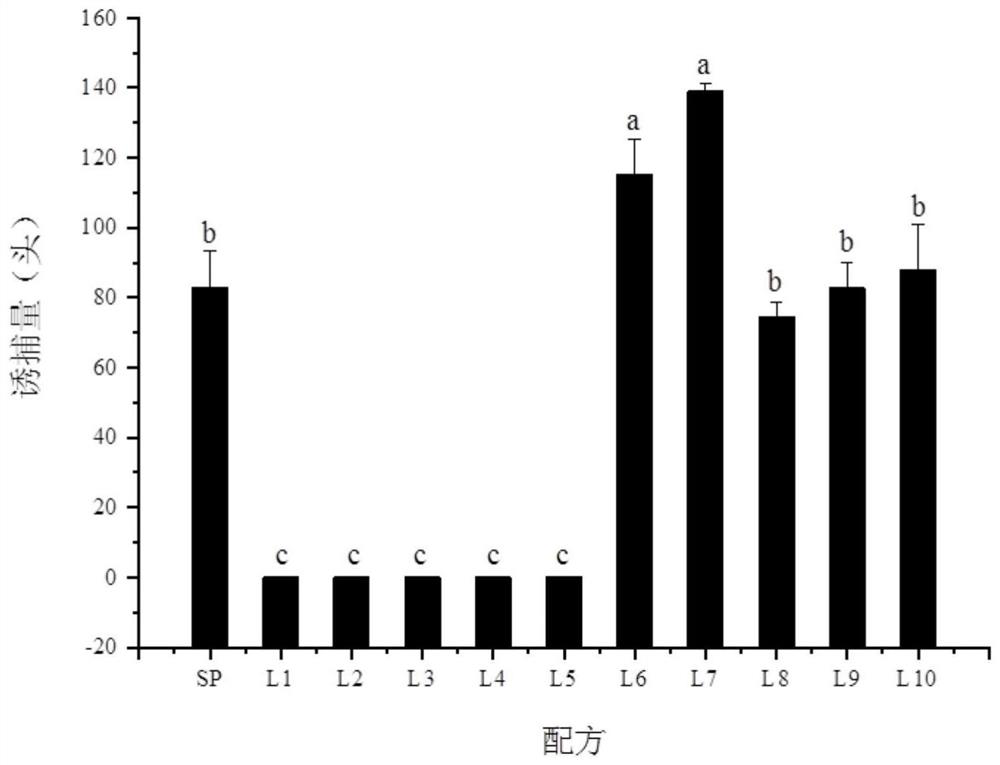
InactiveCN105850943AImprove booby effectBooby avoidancePlant protectionInsect catchers and killersTrappingField trial
The invention discloses a using method of sticky traps. The using method includes the following steps: hanging one sticky trap in tea field every 25-64m<2>. The using method has the advantages that field trial proves that the sticky traps have good imago trapping and killing effect on major tea pests (such as empoasca pirisuga matumura, dendrothrips minowai priesner, aleurocanthus spiniferus and apolygus lucorum meyer-dur), and trapping and killing of major natural enemies of tea gardens are avoided.
Owner:GUIZHOU TEA RES INST
Attractant composition using apolygus lucorum attractant synergist as well as application and attractant core of attractant composition
ActiveCN112514900AFlexible usageStrong autonomyBiocidePest attractantsBenzaldehydeAdelphocoris suturalis
The invention discloses an attractant composition using an apolygus lucorum attractant synergist as well as application and an attractant core of the attractant composition. The adelphocoris suturalisattractant composition comprises adelphocoris suturalis aggregation pheromone and a synergist, and the weight ratio of the adelphocoris suturalis aggregation pheromone to the synergist is 0.25-4: 1.The synergist is selected from three of benzaldehyde, linalool and linalool oxide in different proportions. The attractant composition provided by the invention can be prepared into an attractant coreso as to be matched with the existing apolygus lucorum aggregation pheromone for use. The invention provides an attractant core containing an apolygus lucorum attractant composition component. The attractant core is used for preventing, controlling and detecting the occurrence of apolygus lucorum. According to the invention, the defects of high cost and difficulty in popularization of imported and domestic apolygus lucorum aggregation pheromone lure cores in the prior art are overcome, the cost is low, the use is flexible, and the trapping efficiency is higher.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI +1
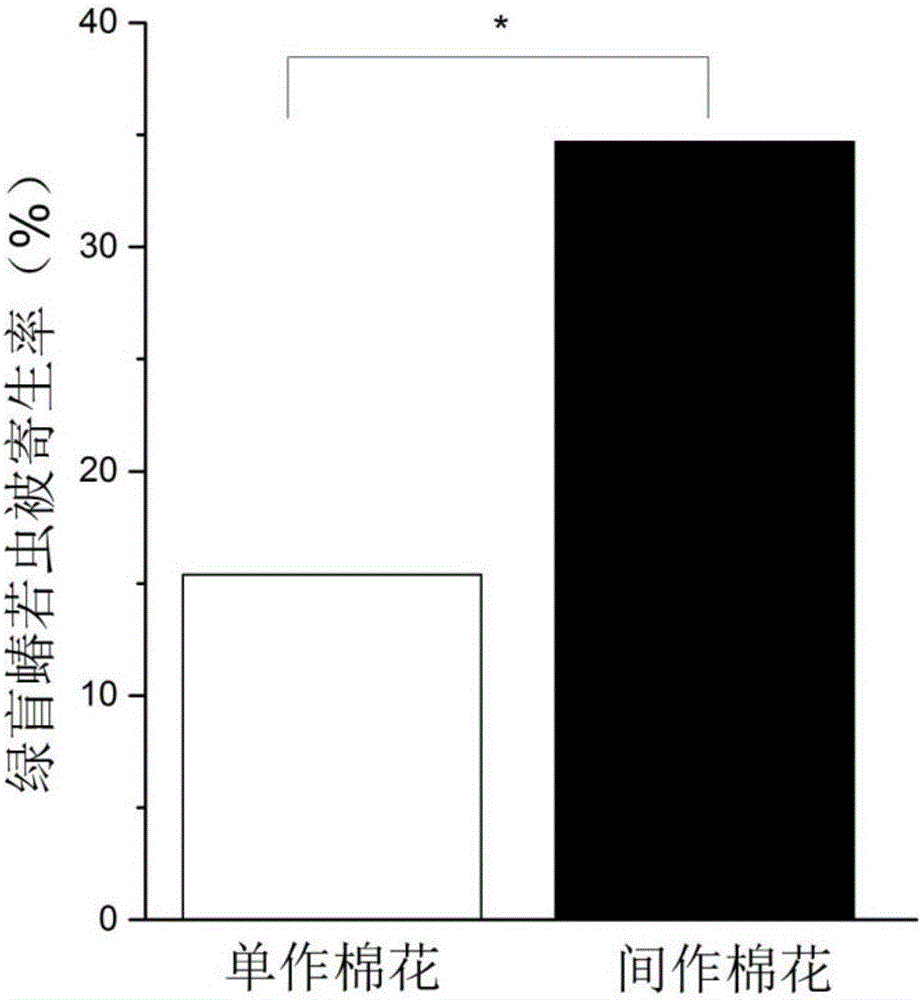
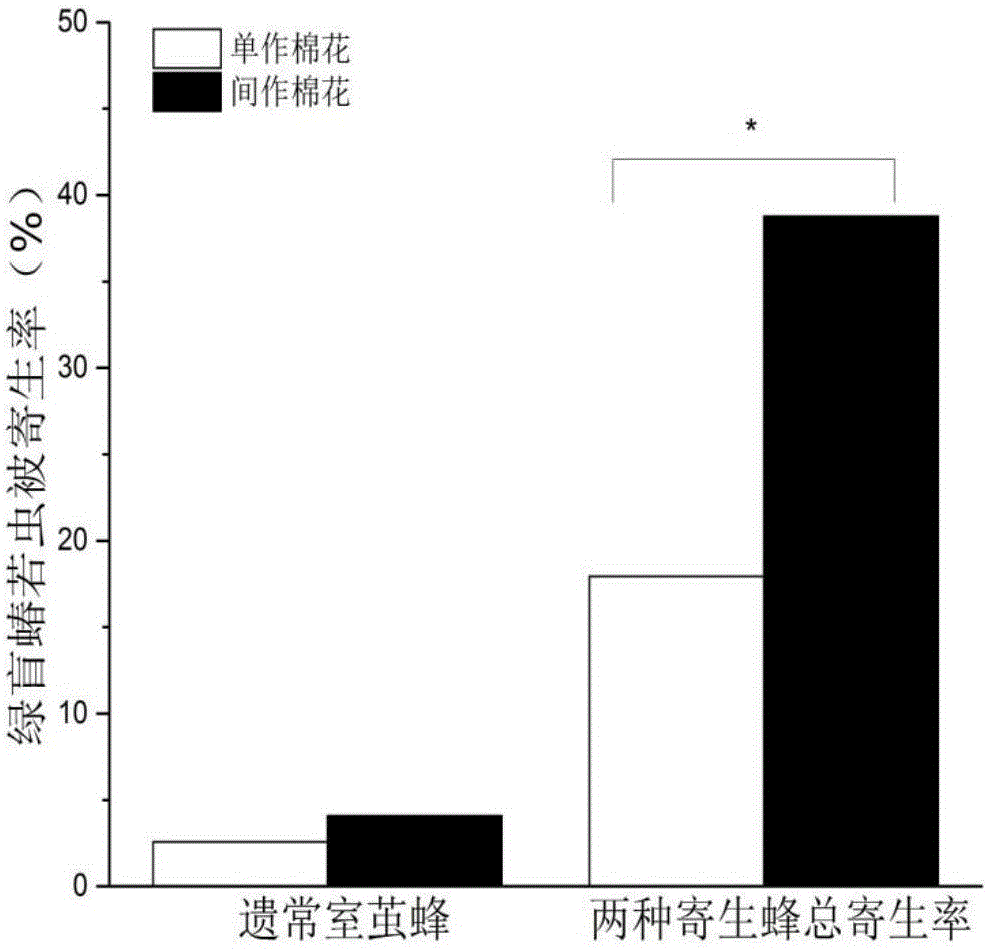
Method for increasing parasitized rate of apolygus lucorum in cotton field
ActiveCN106688601AImprove controlHelp to establishPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsPolygonum fagopyrumApolygus lucorum
The invention relates to a method for increasing the parasitized rate of apolygus lucorum in a cotton field. Buckwheat is intercropped in the cotton field in a strip-sowing mode. According to the method for removing the apolygus lucorum, the buckwheat is intercropped in the cotton field, parasitic-wasp population establishment is promoted, and therefore the apolygus-lucorum-nymph parasitism rate of parasitic wasps is increased; occurrence of apolygus-lucorum populations is naturally controlled, pesticide does not need to be applied, and overmuch manual control is not required; the method is environmentally friendly, easy to operate and remarkable in pest removing effect.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
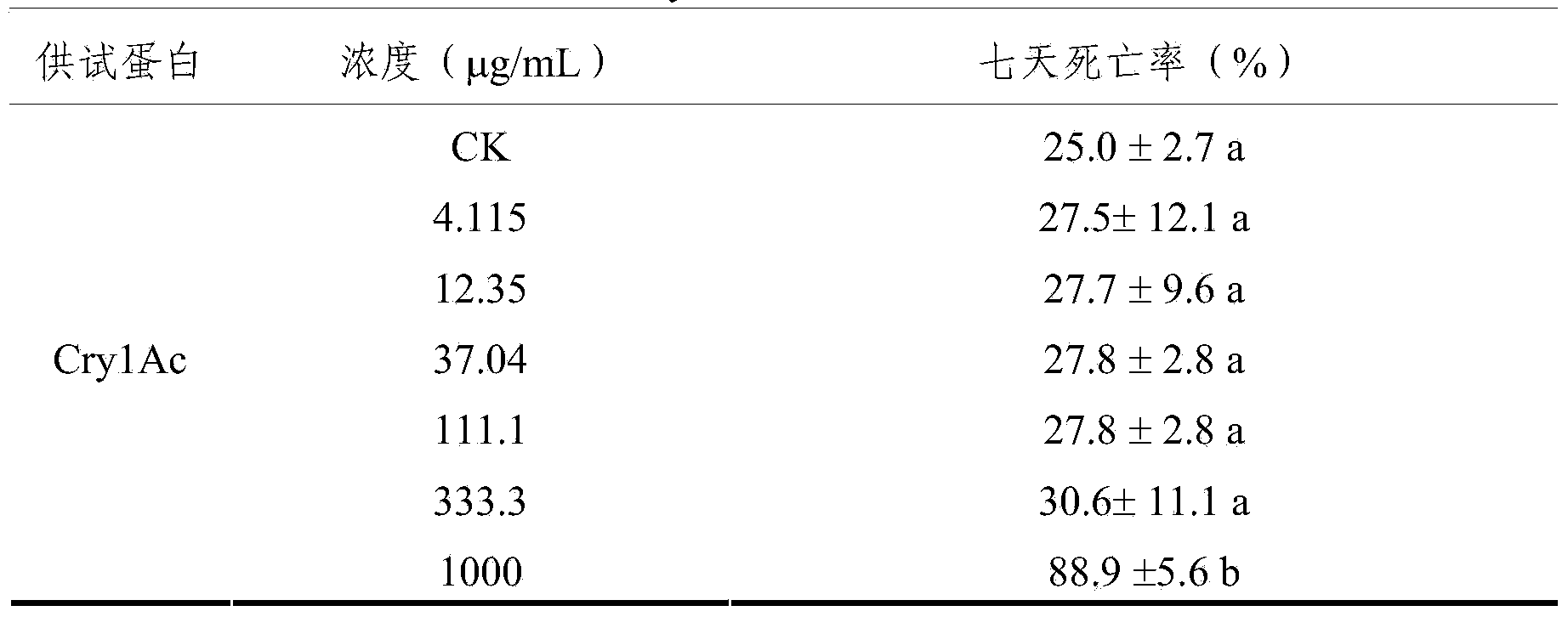
Method for evaluating influences of biological protein on apolygus lucorum
InactiveCN103609529AEfficient determinationAccurate measurementAnimal feeding stuffArthropod mouthpartsFodder
The invention provides a method for evaluating influences of biological protein on apolygus lucorum. The method includes the steps of firstly, diluting biological protein to be measured to obtain biological protein with different concentrations, mixing the biological protein with apolygus lucorum artificial fodders to obtain biological protein measurement fodders, and taking fodders where biological protein is not added as a contrast; secondly, wrapping the measurement fodders and the contrast fodders with extended sealing films respectively to obtain capsules; thirdly, adhering the capsules to the side wall of a raising box without cover; fourthly, inoculating nymphs of apolygus lucorum into the raising box, sealing the opening of the raising box through gauze, and conducting cultivation; fifthly, recording the death condition of apolygus lucorum or the weight changes of apolygus lucorum from the day 0, and thereby evaluating the influences of biological protein on apolygus lucorum. The method is wide in application range, agents with stomach toxicity and systemic action and chemical substances dissolved in the artificial fodders can be effectively measured, the problem that piercing-sucking mouthpart insects including apolygus lucorum can hardly make direct contact with biological protein with different concentrations is solved, the influences of biological protein on apolygus lucorum can be accurately measured, and the method has high practicability.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Apolygus lucorum ultraspiracle protein specific polyclonal antibody as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103992404AHigh sensitivitySerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansWestern blotSpecific immunity
The invention discloses a specific polyclonal antibody of an apolygus lucorum ultraspiracle protein (ALUSP) as well as a preparation method and application thereof. An ALUSP recombinant protein after prokaryotic expression and purification is applied to an immune rabbit to prepare a polyclonal antibody; after determining titer of the polyclonal antibody by utilizing an ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) method, the inventor adopts a Western blot method to determine that the polyclonal antibody can specifically recognize the ALUSP recombinant protein and can produce specific immunity reaction. On such as a basis, the inventor further establishes an efficient, high-sensitivity and accurate Western blot method, so that apolygus lucorum ultraspiracle protein can be specifically detected out from an apolygus lucorum polypide. The specific polyclonal antibody can be applied to providing a material basis and a technical support for tissue distribution of the ultraspiracle protein in the apolygus lucorum, rapid detection of the protein and molecular biology study.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
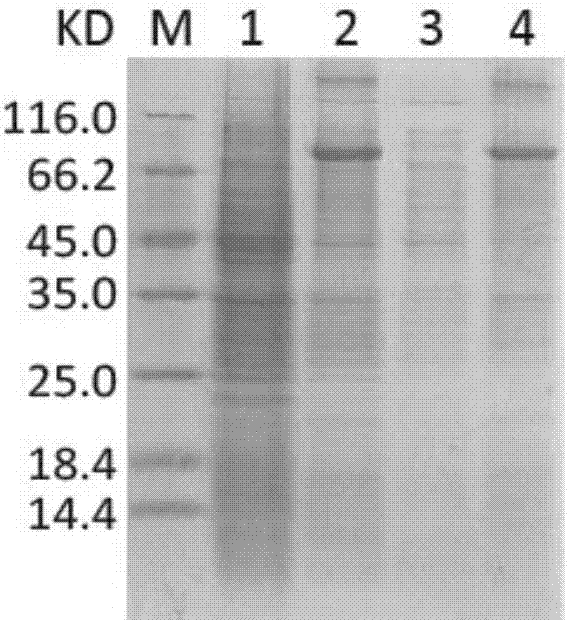
Apolygus lucorum cell nucleus hormone receptor E75, coding sequence thereof, carrier and bacterial strain
The invention discloses a DNA sequence for coding an apolygus lucorum cell nucleus hormone receptor E75. The invention further discloses the apolygus lucorum cell nucleus hormone receptor E75, a recombinant expression vector used for coding the DNA sequence for coding the apolygus lucorum cell nucleus hormone receptor E75, and a transgenic cell system or a transgenosis recombinant bacterium, application of the recombinant expression vector, the transgenic cell system or the transgenosis recombinant bacterium in producing the apolygus lucorum cell nucleus hormone receptor E75 as well as a preparation method of the apolygus lucorum cell nucleus hormone receptor E75. A gene of the apolygus lucorum cell nucleus hormone receptor E75 is utilized to construct a pCzn-E75 recombinant plasmid; the pCzn-E75 recombinant plasmid is transferred into a TOP 10 clone strain, and can generate an inclusion body of protein after being induced through IPTG in an Arctic Express expression bacterial strain, the protein can be formed through denaturation and renaturation, and purifying is performed to prepare the protein. The prepared protein has molecular weight of about 75 KD and has protein concentration of 0.4 mg / ml.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for detecting insecticide resistance of apolygus lucorum
InactiveCN103675253ASolve operational problemsEasy to operateDisease diagnosisBiological testingChlorpyrifosMalathion
The invention provides a method for detecting the insecticide resistance of apolygus lucorum. Under the diagnostic dose of an insecticide, a diagnostic glass tube is manufactured for rapidly detecting the resistance level of an apolygus lucorum field population to the insecticide, wherein the insecticide is malathion, chlorpyrifos, methomyl, cyhalothrin, imidacloprid or endosulfan; the diagnostic dose of the insecticide as follows: 67 ng / cm<2> of malathion, 560 ng / cm<2> of chlorpyrifos, 620 ng / cm<2> of methomyl, 3,046 ng / cm<2> of cyhalothrin, 886 ng / cm<2> of imidacloprid and 1,092 ng / cm<2> of endosulfan. The method disclosed by the invention is convenient to use and is suitable for rapidly detecting the resistance level of the apolygus lucorum in the field; results are intuitive and clear; the disadvantages that the conventional bioassay method has a large number of samples, tedious operation, time waste and the like are overcome; the method can be used for rapidly detecting the resistance level of the apolygus lucorum field population.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
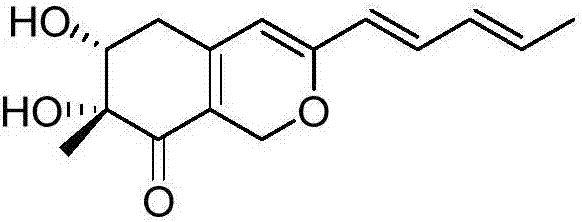
Application of compound Harziphilone
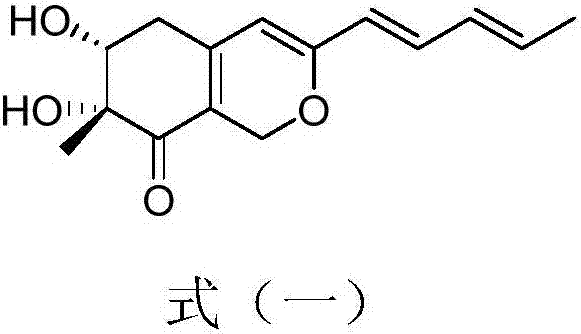
InactiveCN106889069AHigh insecticidal activityLow toxicityBiocideAnimal repellantsMicroorganismNatural product
The invention discloses application of a compound Harziphilone. The structure of the compound is shown in a formula (I) and has better insecticidal activity for apolygus lucorum, the median lethal concentration (LC50) is 18.5 [mu]g / mL, and the compound can be taken as a novel pesticide ingredient with an insecticidal effect or a lead compound. The compound shown in the formula (I) is taken as a natural products derived from a microorganism, and is easy for large-scale fermentation preparation and easy to degrade in an environment.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
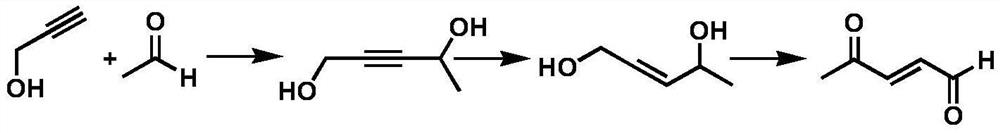
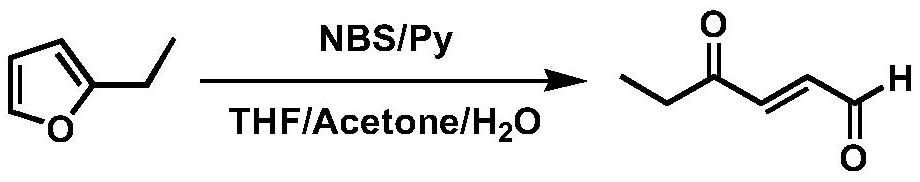
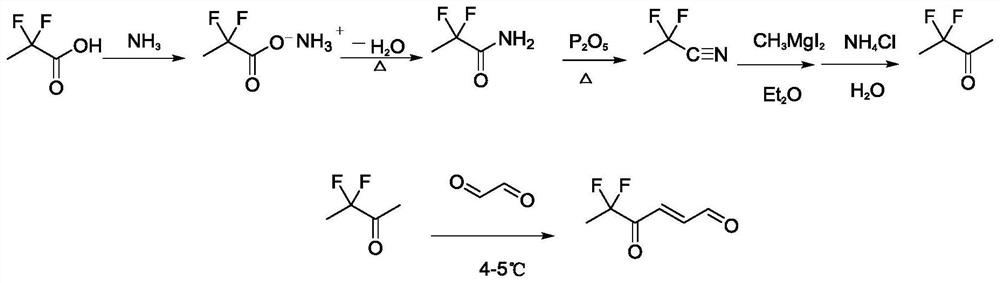
Synthesis method and application of 4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal analogue
ActiveCN112094181AHigh trapping activityImprove stabilityPreparation by organometalhalide reactionBiocideHexacosenoic acidMethyl palmoxirate
The invention discloses a synthesis method and application of a 4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal analogue, and belongs to the technical field of biological prevention and control. The analogues comprise 5-methyl-4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal, 5, 5-difluoro-4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal, 4-oxo-trans-2-hexenoic acid, 4-oxo-trans-2-hexenol and 4-hydroxy-trans-2-hexenal. One or more of the five compounds completely replace 4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal in sex pheromone components of apolygus lucorum, lygus pratensis and apolygus lucorum. The synthesis methods of the 5-methyl-4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal and the 5, 5-difluoro-4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal are found for the first time, the application composition can significantly reduce the release rate of the lure, prolong the trapping time and save the cost, the problem that the 4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal is unstable in the field can be avoided, and the application range of the 5-methyl-4-oxo-trans-2-hexenal is widened. Male insects such as apolygus lucorum, herbage miridae and apolygus lucorum can be trapped and killed more effectively.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Apolygus lucorum membrane-bound trehalase, its coding sequence, vector and strain of sequence, and application of vector or strain
InactiveCN103275999AReduce manufacturing costTaller than aliveBacteriaHydrolasesAgricultural scienceTrehalase
The invention discloses an Apolygus lucorum membrane-bound trehalase coding DNA sequence. The invention also discloses an Apolygus lucorum membrane-bound trehalase, a recombinant expression vector or a transgenic cell system or a transgenic transgenic bacterium of the Apolygus lucorum membrane-bound trehalase coding DNA sequence, an application of the recombinant expression vector or the transgenic cell system or the transgenic transgenic bacterium in the production of the Apolygus lucorum membrane-bound trehalase, and a preparation method of the Apolygus lucorum membrane-bound trehalase. The molecular weight of zymoprotein prepared in the invention is 60KD, and zymoprotein can degrade trehalose to form glucose at an optimal temperature of 50DEG C under an optimal pH value of 7.0. Purified trehalase can be used for the qualitative and quantitative content detection of trehalase in industries and other fields, and provides a foundation for the research and development of insect trehalase inhibitors.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for creating cotton apolygus lucorum-resistant germplasm by using plant-mediated RNAi
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a method for creating cotton apolygus lucorum-resistant germplasm by using plant-mediated RNAi. According to the invention, a RNAi vector is constructed by taking a conserved sequence of apolygus lucorum LIM gene as a target sequence, and the apolygus lucorum LIM gene is successfully introduced into a cotton host by utilizing an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method, so that transgenic cotton for expressing the double-stranded RNA of the apolygus lucorum LIM gene is obtained. The transgenic cotton is planted in an outdoor net room, and insect inoculation experiments show that the transgenic cotton can cause down-regulation of the expression quantity of the apolygus lucorumLIM gene, further cause death of apolygus lucorum due to incapability of completing normal eclosion, and finally cause reduction of the population quantity of apolygus lucorum, so that the insect-resistant effect is achieved. The transgenic cotton provided by the invention has resistance to apolygus lucorum. And the transgenic cotton can be hybridized with BT cotton to produce new germplasm of multi-insect-resistant cotton.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com