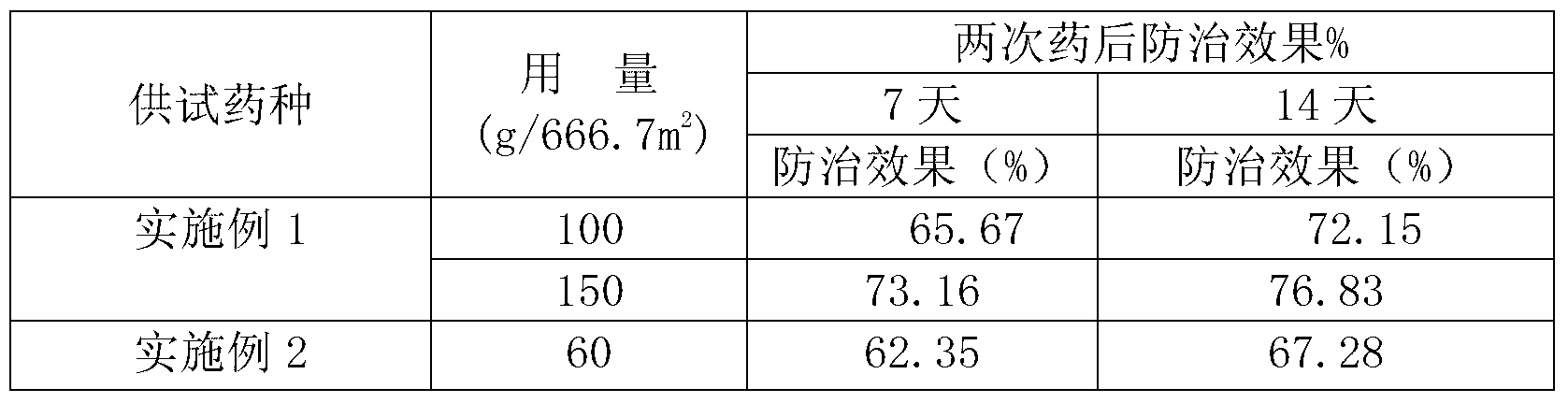
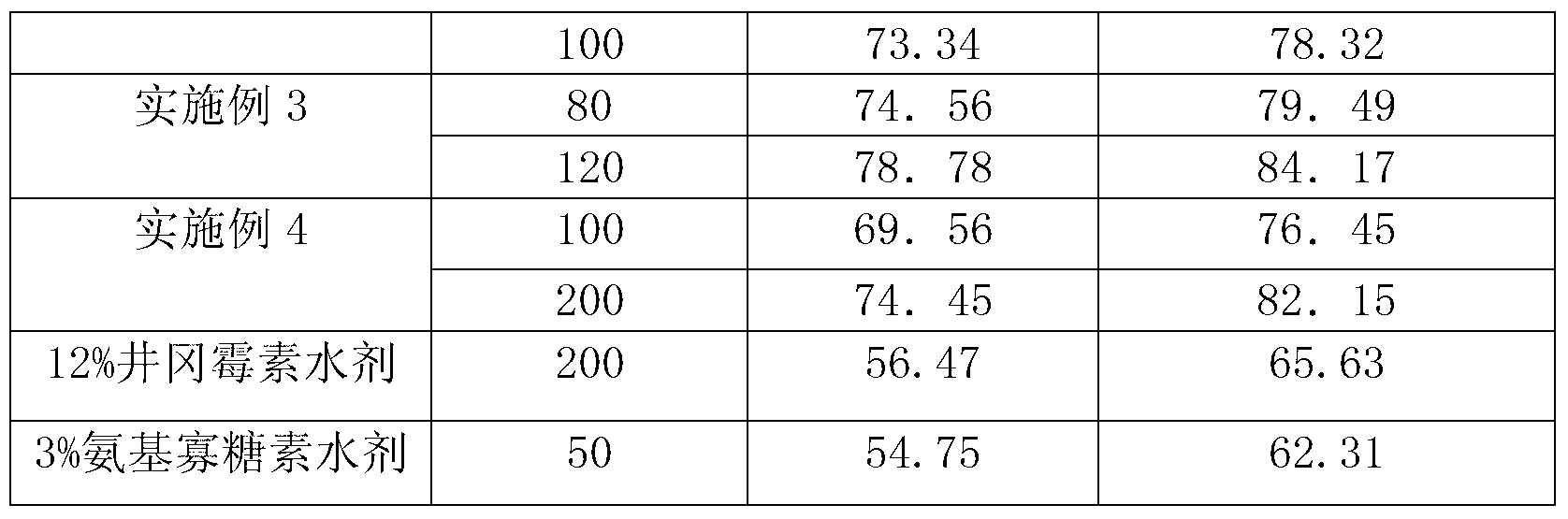
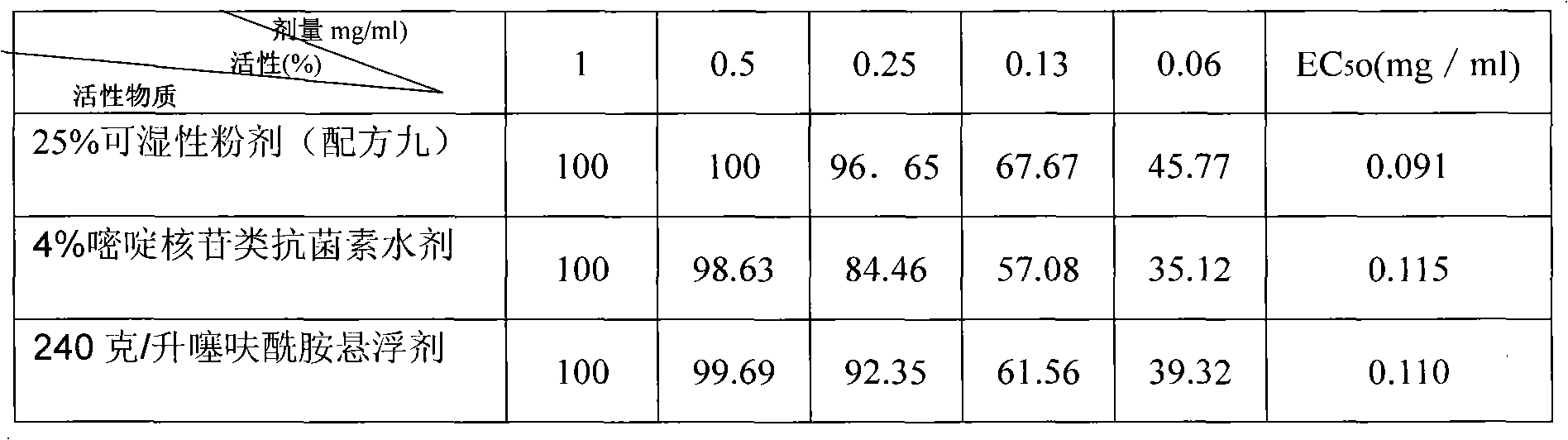
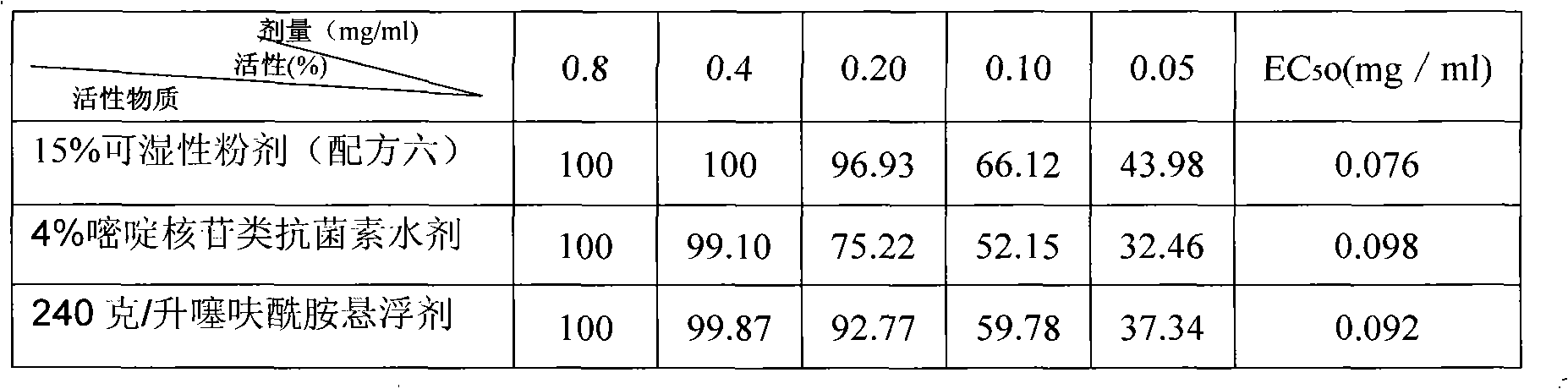
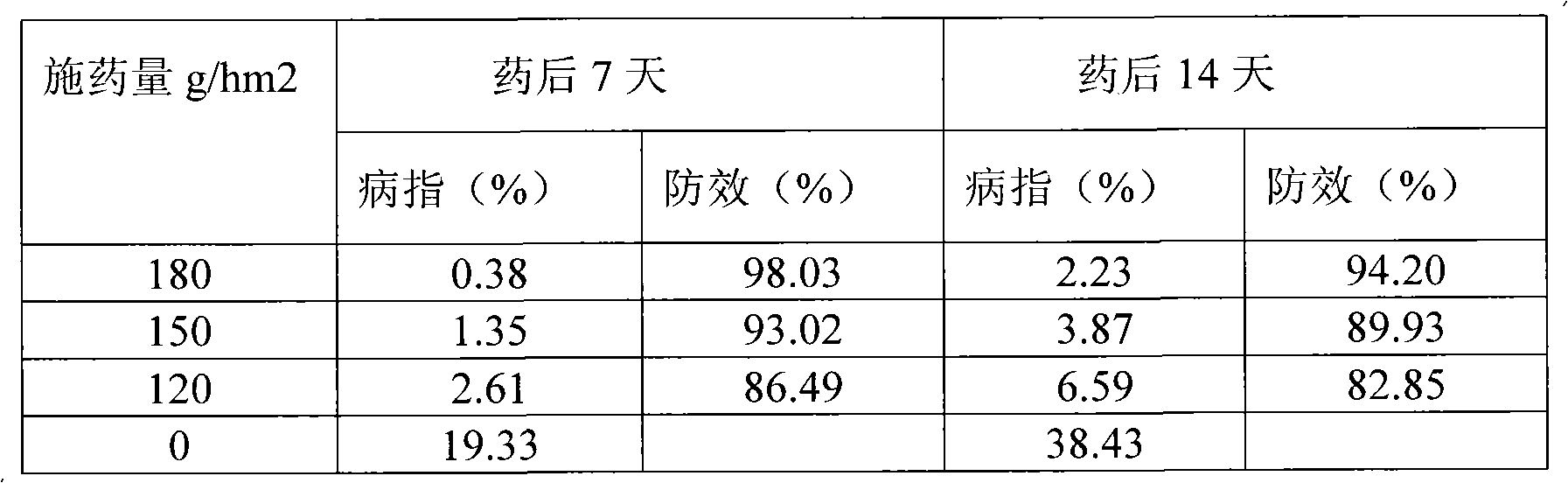
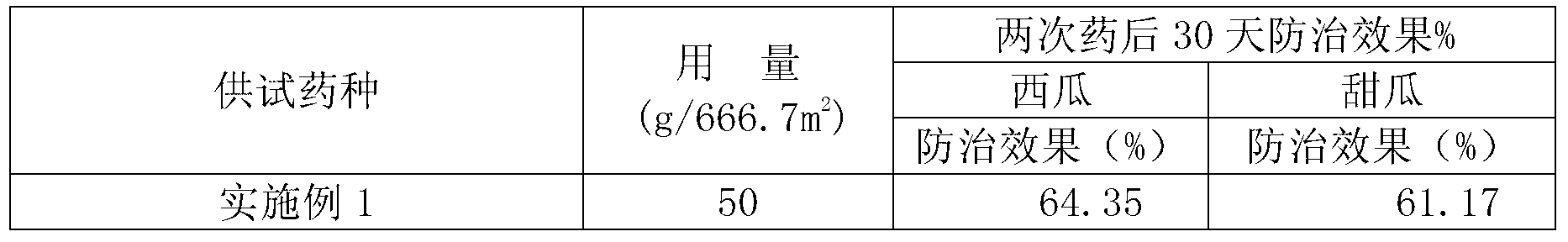
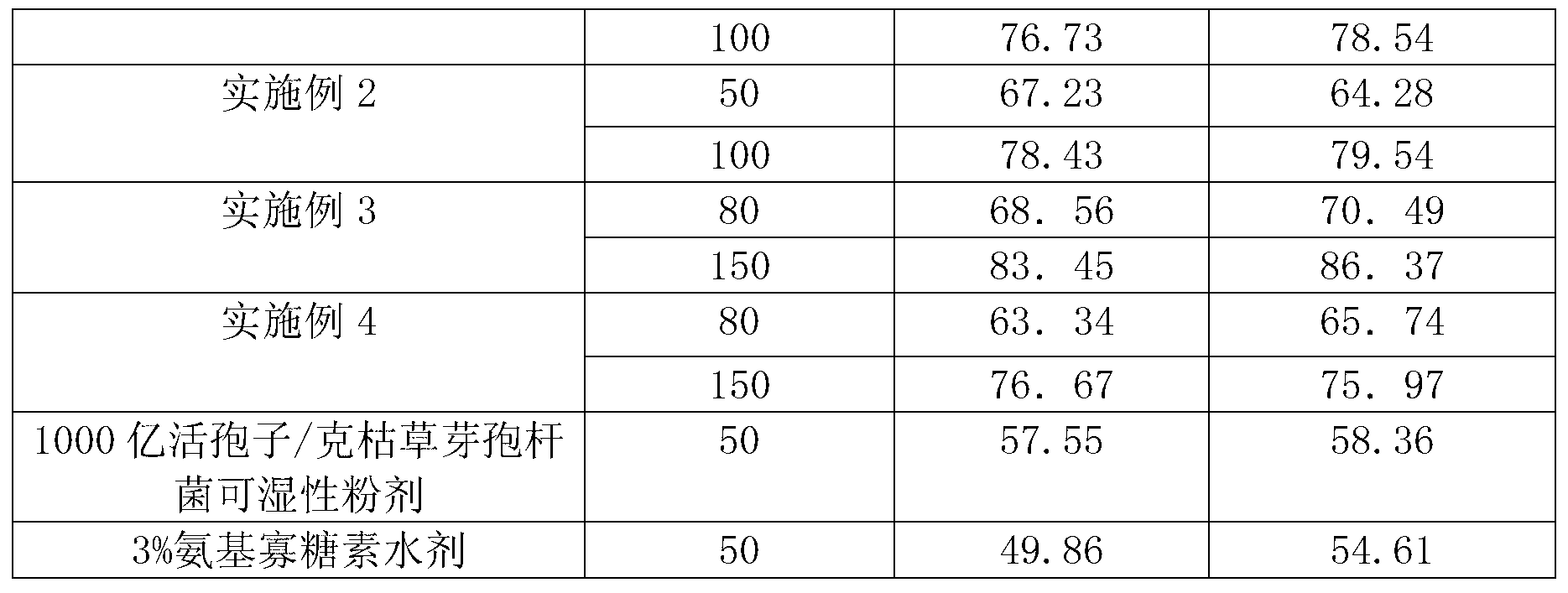
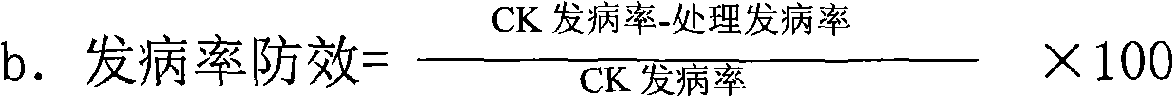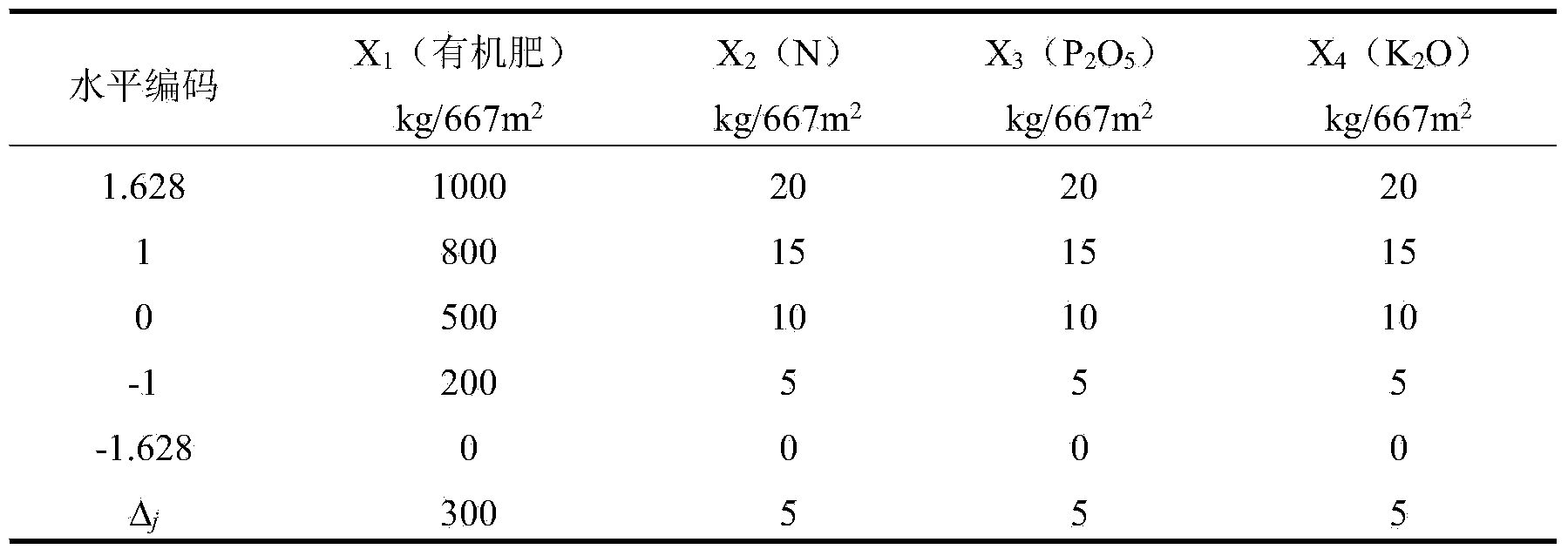Patents
Literature
122 results about "Field trial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A field trial is a competitive event at which dogs compete against one another for placements. There are field trials for retrievers, pointing dogs and flushing dogs. Field trials are usually organized by kennel clubs or other gun dog organizations. Field trials are generally considered more competitive than hunt tests in that success at a field trial requires a higher level of training than simply quailifying to the standard that a hunt test requires. For example, in Retriever Field Trials, dogs retrieve over longer distances with a more complex path than a Retriever Hunt Test would generally provide. Field trial dogs are trained to a much higher degree of training in order to be competitive in the sport. Their purpose is also different, as they compete for 1st-4th, Reserve Judges' Award of Merit and Judges' Award of Merit, while hunting tests are judged on whether the standard is met or not.
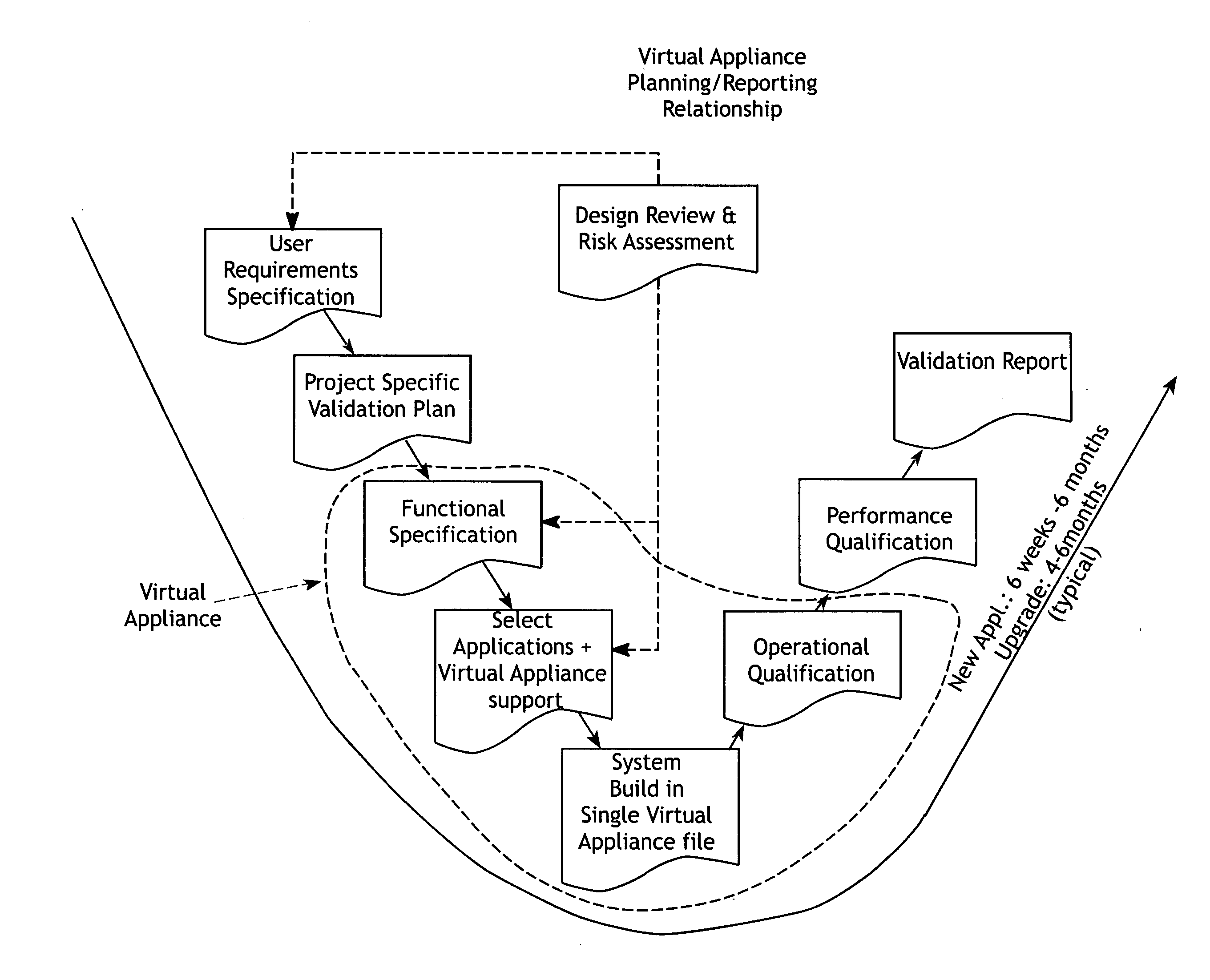
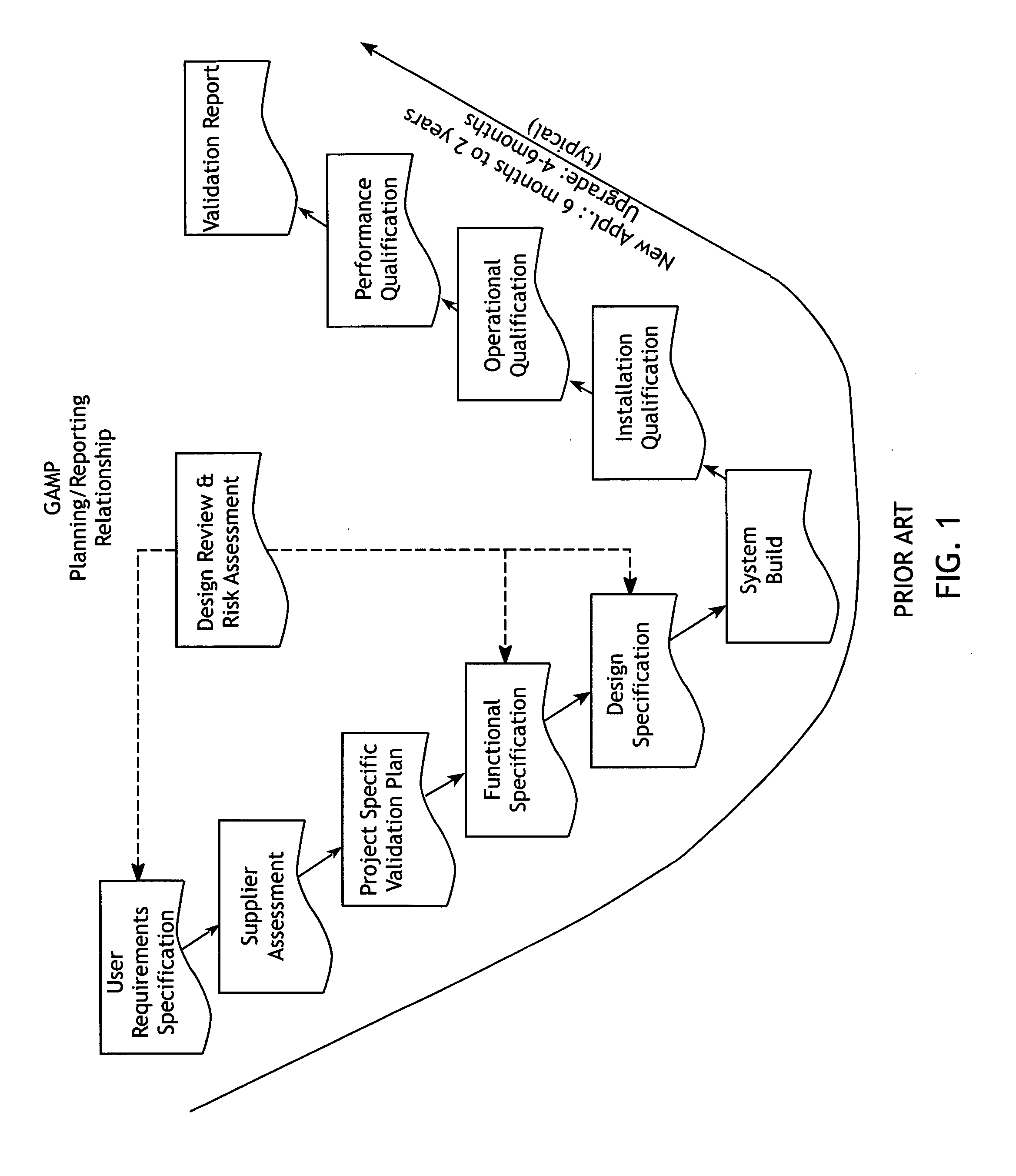
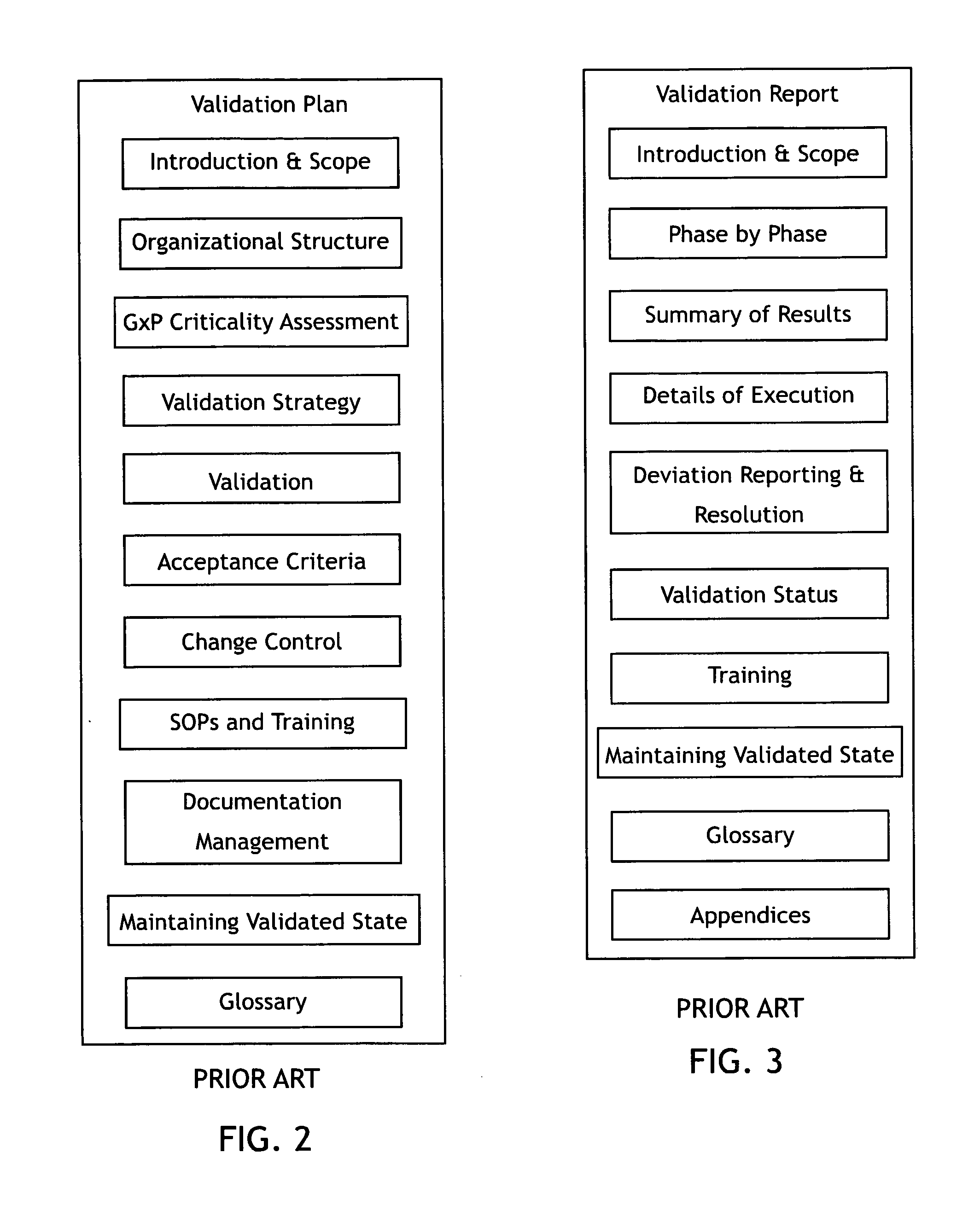
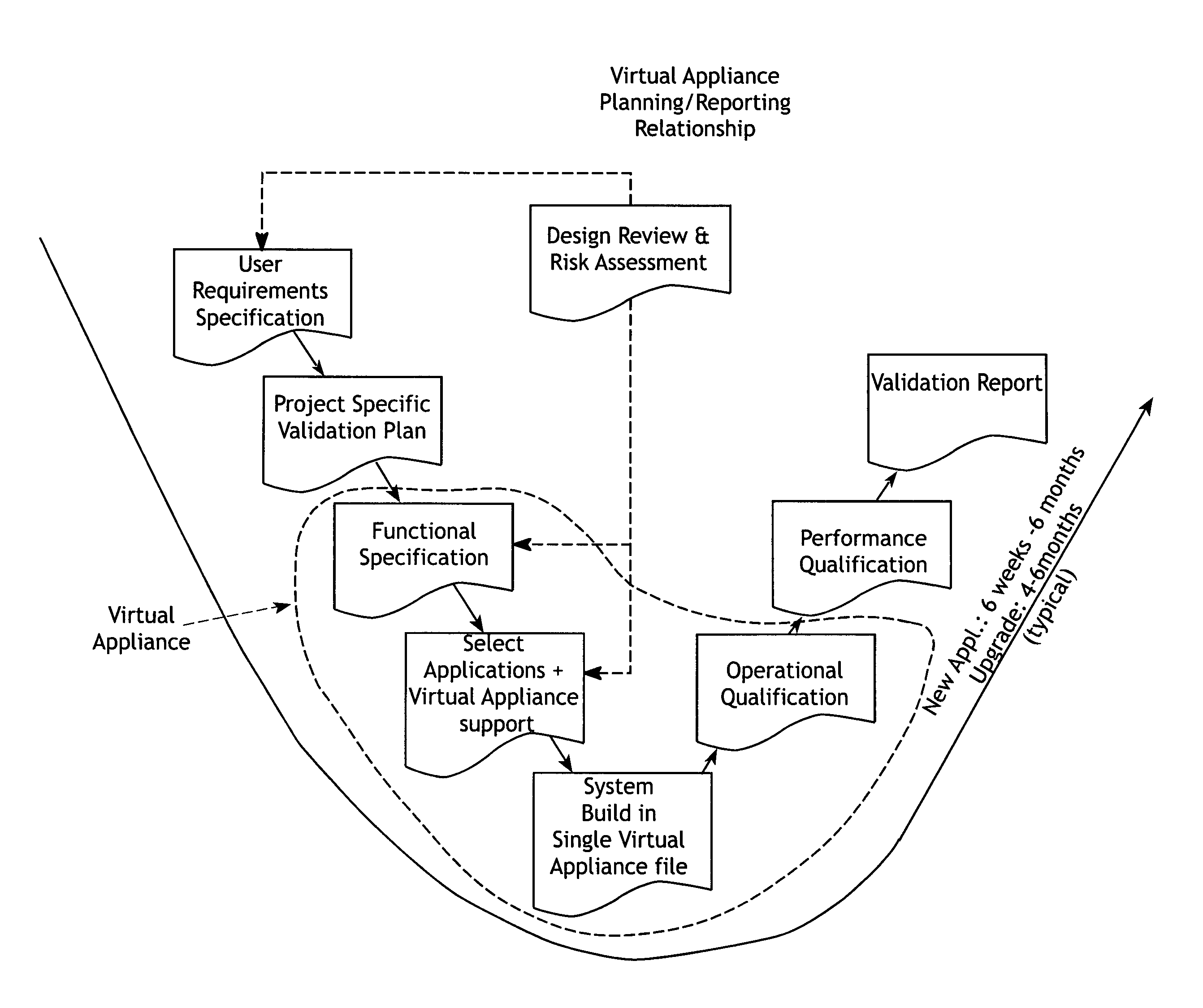
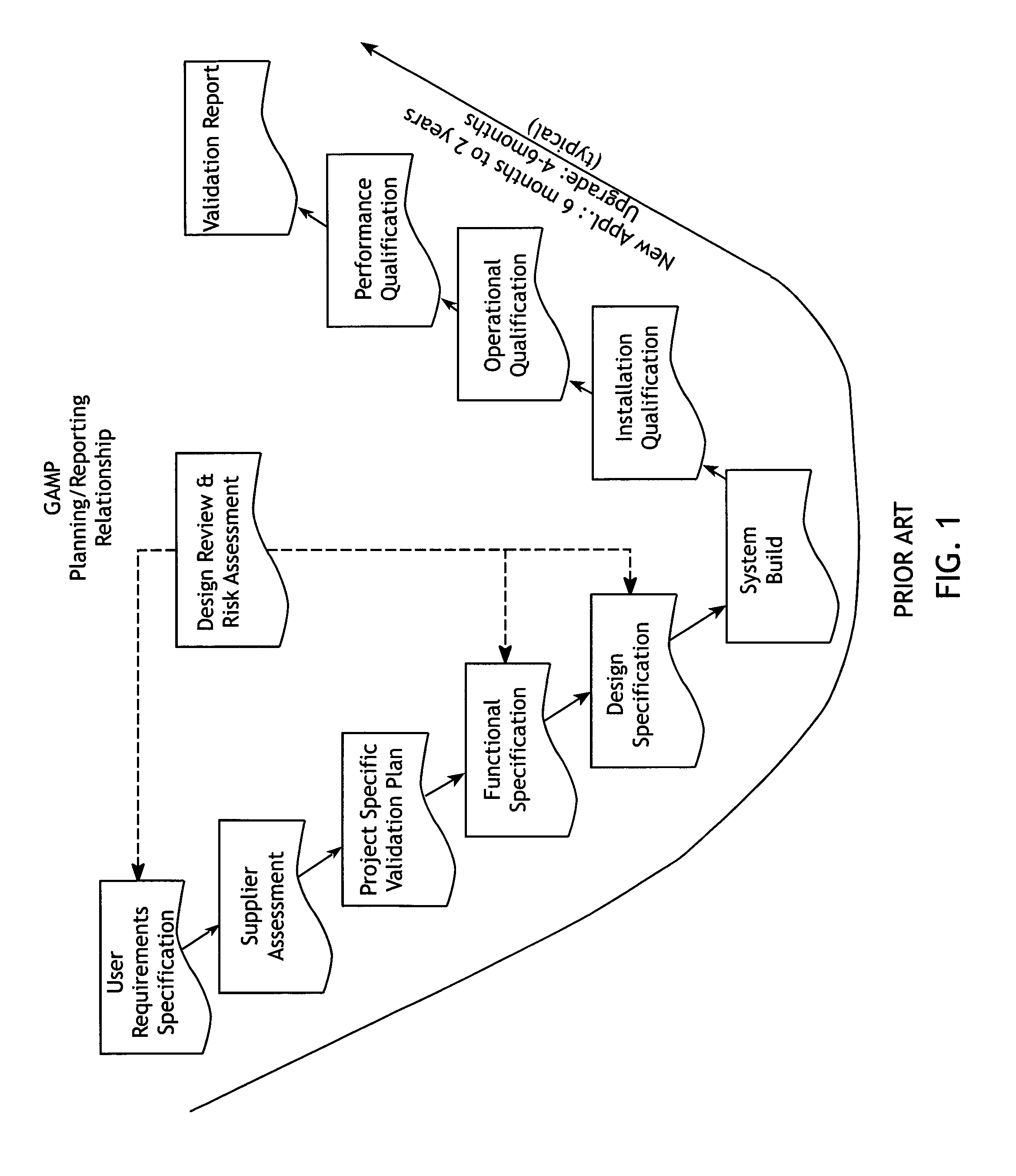
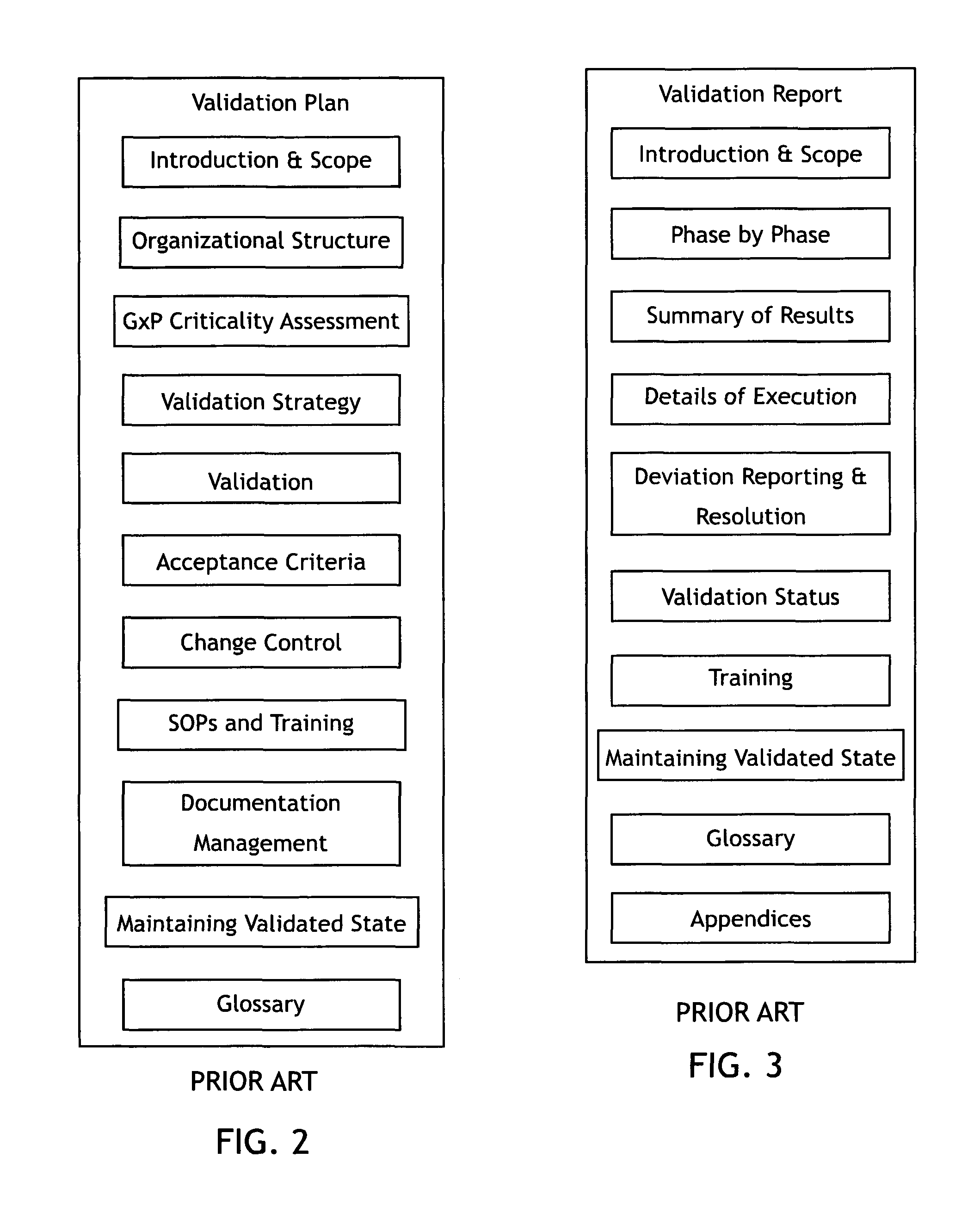
Virtual validation of software systems
InactiveUS20080178144A1Shorten the timeReduces time and effortError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsRegulated IndustrySoftware system
A method for building and verifying and validating a software system that is used for regulated industry software related activities, such as FDA trials, field trials, biomedical data gathering, and similar efforts includes building the application into a virtual appliance using, for example, Vmware. The application and the supporting software are encapsulated in a single virtual file to create a virtual appliance that is independent of hardware and dependent only on virtual appliance support.
Owner:VIRTUAL PURPLE +1
Winter wheat water consumption predicting method based on weather forecast information
InactiveCN103886392AIncrease profitImprove utilization efficiencyForecastingField trialWater requirement
The invention provides a winter wheat water consumption predicting method based on weather forecast information. With comprehensive consideration of influences of the crop self-growth-and-development situation and the environment factors including the meteorological condition, the soil condition and the like, a prediction model for estimating the reference crop water requirement (ET0) based on the weather forecast information and a model for estimating a winter wheat crop coefficient based on accumulative temperature are established through field trials and numerical simulation, the prediction model and the model for estimating the winter wheat crop coefficient are coupled into a water balance equation, real-time prediction is conducted on the soil moisture content of winter wheat in a Guangli irrigated area and a people victory canal irrigated area, and irrigation date and irrigating water quota are determined according to irrigating index of different growth periods of the winter wheat so that real-time monitoring of the soil moisture content, drought severity comprehensive analysis and real-time prediction of crop irrigation are achieved. The visual decision basis is provided for an irrigation management layer and a decision maker, timely and appropriate amount of irrigation is instructed for the irrigated areas, and the utilization rate and utilization efficiency of an irrigation water resource of the irrigated areas are improved.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
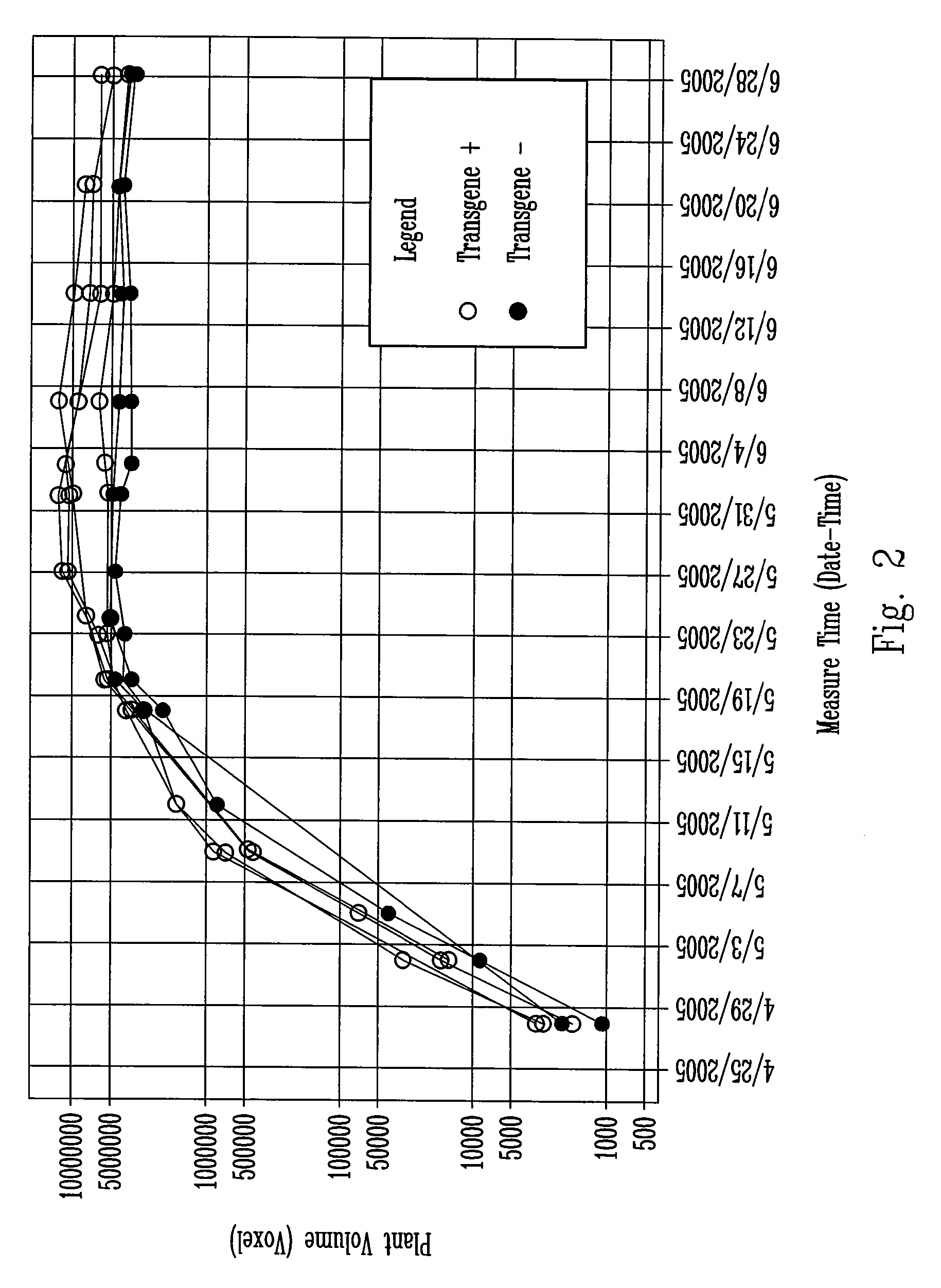
Method for high throughput transgene function analysis for agronomic traits in maize
InactiveUS20070186313A1Determine effectRapid assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisGermplasmField trial
A method for the rapid evaluation of transgene function in maize plants. The method combines high throughput gene construction methods and high efficiency plant transformation techniques in a specifically developed germplasm. In one as aspect, the method uses quantitative, non-destructive imaging technology applied in a portion or throughout the entire life cycle of a test plant to evaluate agronomic traits of interest in a controlled, statistically relevant greenhouse environment. The method reports transgene function early in the transgenic variety development process, eliminating the need to generate seed necessary for multi-location replicated field trials.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for preparing water-soluble fertilizer containing humic acid
InactiveCN103964945ANutritional diversityReduce the amount of solutionFertilizer mixturesField trialMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing a water-soluble fertilizer containing humic acid. The method mainly comprises the following steps: pre-treating peat, extracting humic acid from the pre-treated peat, and adding dissolved urea, monopotassium phosphate, boric acid, ammonium molybdate and microelements subjected to complexation; the water-soluble fertilizer containing humic acid, prepared withthe method provided by the invention, is complete and balanced in nutrition, good in suspension property, and convenient to apply. The results of a field trial prove that the yield of cucumbers, to which the water-soluble fertilizer containing humic acid is applied, is higher than that of a comparison group, the input-output ratio of an area, to which the water-soluble fertilizer containing humic acid is applied, is 1:9.22, and the input-output ratio of an area, to which the water and conventional fertilizer are applied, is 1:5.23.
Owner:SINO AGRI SHUNTIAN ECOLOGICAL FERTILIZER CO LTD
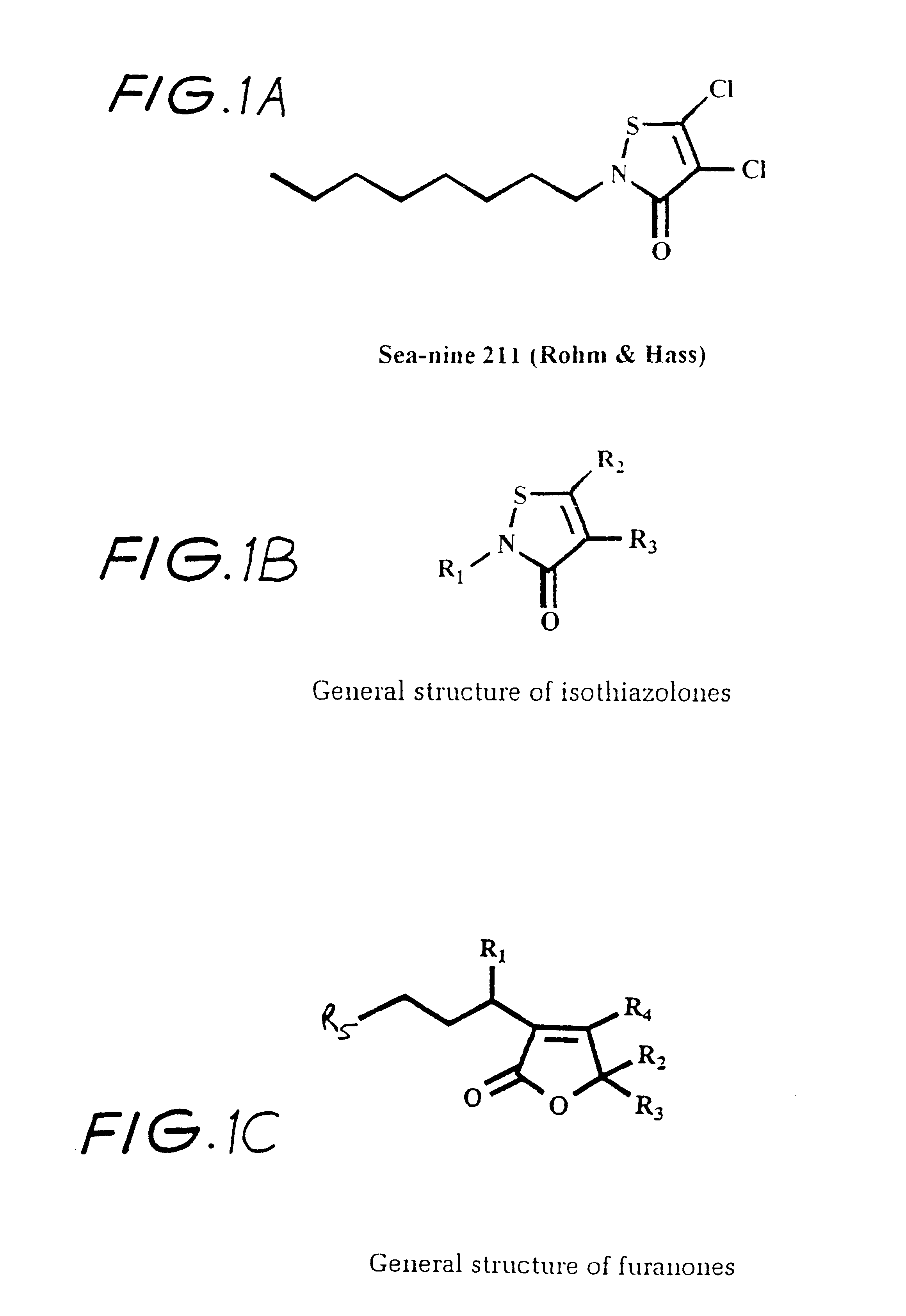
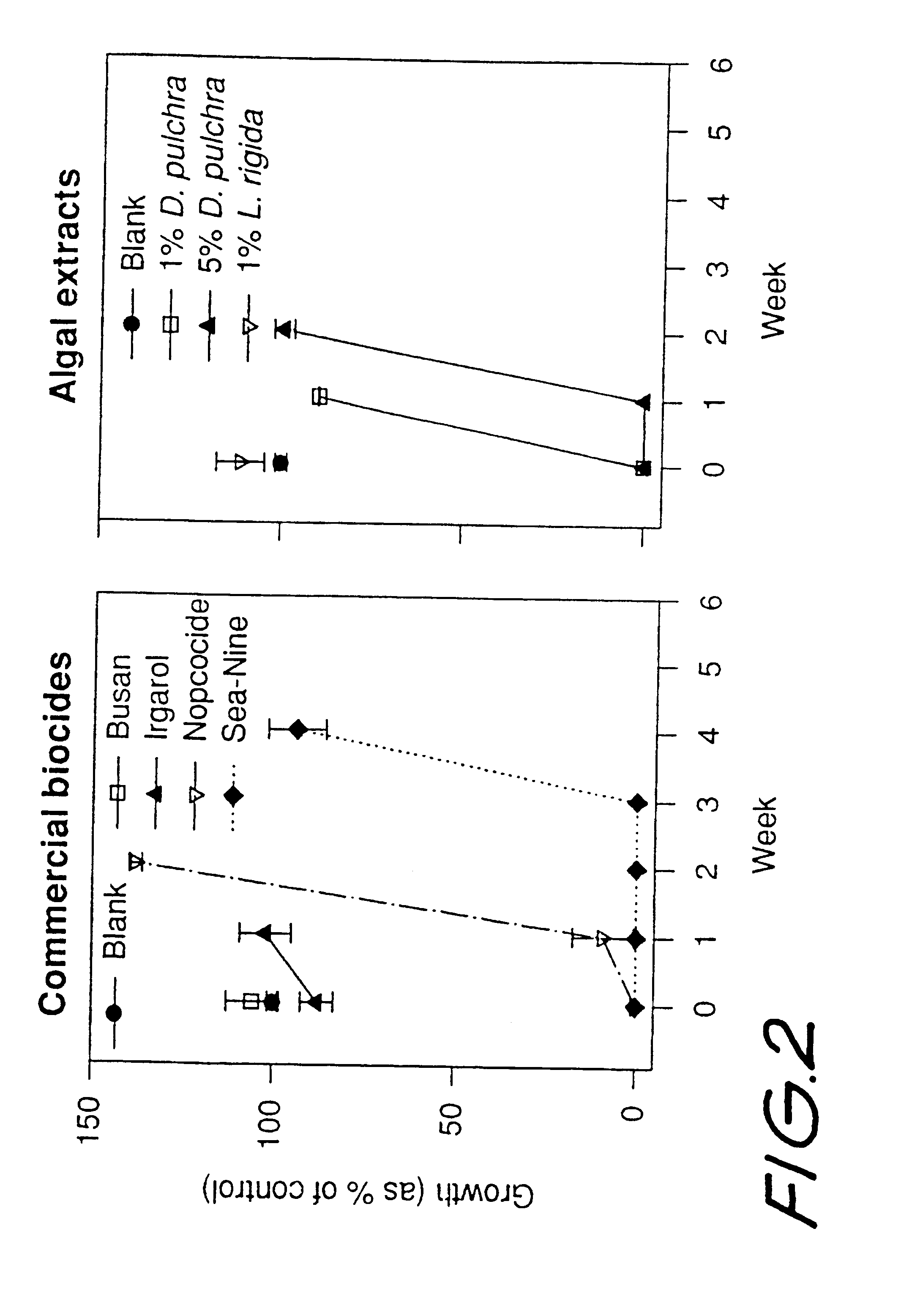
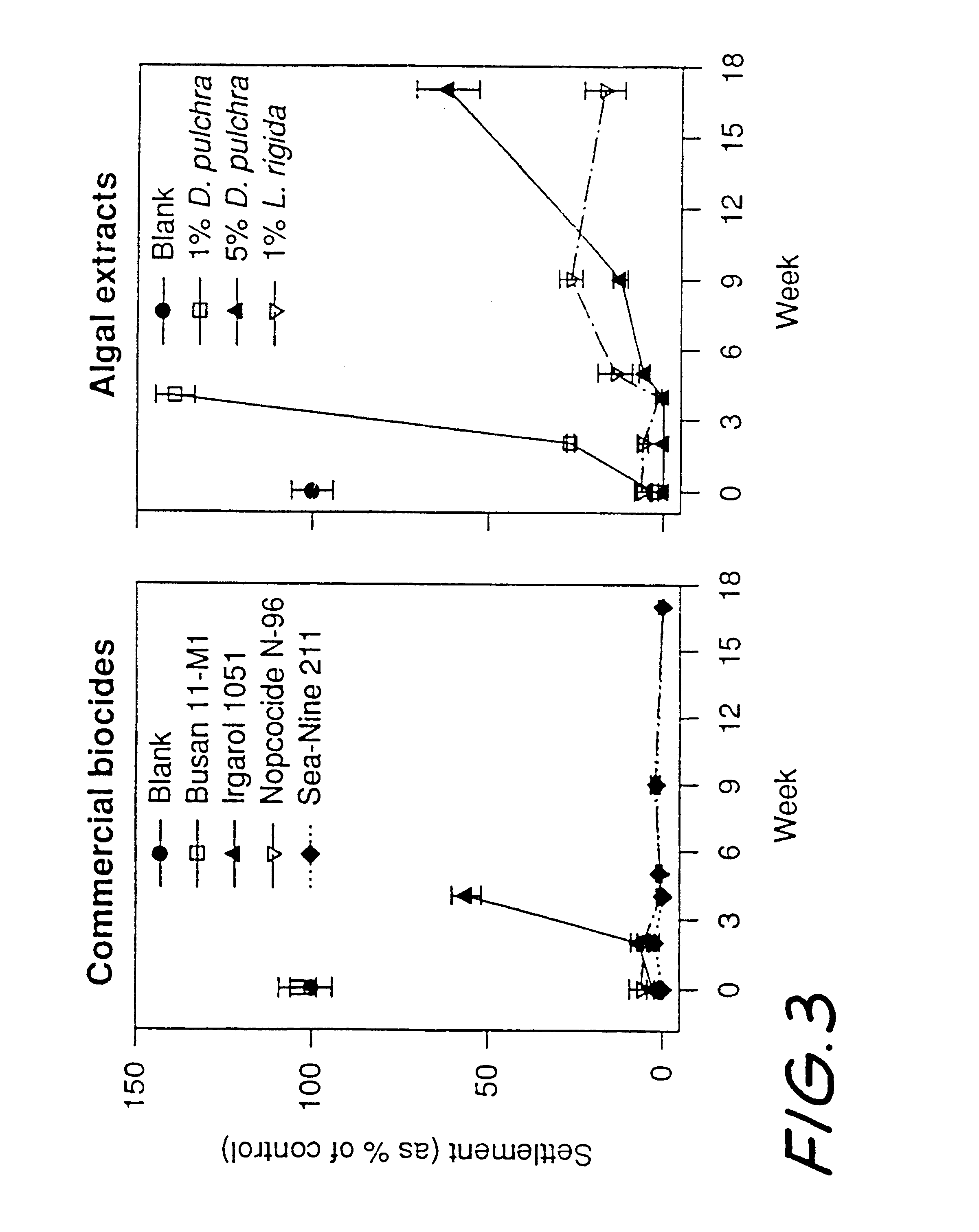
Antifouling polymers
InactiveUS6635692B1Low release rateEfficient mixingBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsField trialSea-Nine 211
A range of extruded polymers incorporating synthetic furanones was manufactured and field tested. Polymers incorporating furanones showed excellent antifouling efficacy and significantly reduced fouling for more than 100 days.The present inventors have developed polymers that release commercial short-lived biocides or analogues of antifouling compounds isolated from marine algae. A range of polymers incorporating either the commercial isothiazolone Sea-Nine 211(TM) or a halogenated furanone were effective antifouling treatments in laboratory and field trials. The efficacy of the polymers was dependant on polymer type and the initial concentration of the antifouling compound. The polymers can be extruded as filaments that can be woven into netting or extruded or molding for other applications.It will be appreciated by persons skilled in the art that numerous variations and / or modifications may be made to the invention as shown in the specific embodiments without departing from the spirit or scope of the invention as broadly described. The present embodiments are, therefore, to be considered in all respects as illustrative and not restrictive.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Stress-resistance multielement quick-acting water-soluble fertilizer
InactiveCN103319242ASolve deficienciesIncrease profitFertilizer mixturesNutrient deficiencyManganese
The invention relates to a stress-resistance multielement quick-acting water-soluble fertilizer and belongs to the technical field of agricultural fertilizers. The stress-resistance multielement quick-acting water-soluble fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 15% of urea, 10% of monopotassium phosphate, 65% of nitrate of potash, 2% of calcium ammonium nitrate, 2% of magnesium sulfate, 1.8% of borax, 0.5% of ammonium molybdate, 0.5% of chelate nickel, 0.5% of chelate iron, 0.5% of chelate zinc, 0.5% of chelate copper, 0.5% of chelate manganese, 1% of chitosan and 0.2% of S-abscisic acid. The fertilizer contains 13 elements which are essential to plants, can be fully dissolved in water, and can be used for solving various nutrient deficiency symptoms of crops, so that the fertilizer utilization rate is increased, resources can be saved, and the condition that the soil is salinized and acidized, is lack of medium trace elements and the like due to over using of fertilizers can be avoided; field trial results prove that the fertilizer is obvious in fertilizer efficiency, can remarkably improve the yield of crops, can improve the quality of fruits, and reduces the occurrence of plant diseases and insect pests; the crops to which the fertilizer is applied can not be subjected to reduction of output under the atrocious weather.
Owner:高晨曦
Compound pesticide for protecting and curing rice sheath blight
Owner:ZHEJIANG TONGLU HUIFENG BIOSCI
Sterilization composition containing amino-oligosaccharin and validamycin and application of pesticide composition
InactiveCN103283725AGood control effectGood prevention effectBiocideFungicidesField trialBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a pesticide composition and application thereof, and particularly relates to a sterilization composition containing amino-oligosaccharin and validamycin A as main active ingredients and application of the pesticide composition. The active ingredients of the sterilization composition are amino-oligosaccharin and validamycin with the weight ratio of 1:1 to 1:50, preferably, 1:2 to 1:10. The sterilization composition containing the amino-oligosaccharin and the validamycin, provided by the invention has an excellent control effect, which is better than that of a single-agent variety, for the rice sheath blight disease through actual field trials, and has no pesticide damage through field observation; the field growth vigour is better than that of a contract single-agent pesticide.
Owner:JIANGSU LVDUN PLANT PROTECTION AGROCHEM EXPERIMENTAL
Pyrimidine nucleotide antibiotic and trifluzamide combined bactericide
The invention discloses a pyrimidine nucleotide antibiotic and trifluzamide combined bactericide, which belongs to the technical field of agrochemicals. The combined bactericide contains 0.1 to 50 percent of pyrimidine nucleotide antibiotic and 0.1 to 70 percent of trifluzamide. The pyrimidine nucleotide antibiotic and trifluzamide combined bactericide combines the pyrimidine nucleotide antibiotic and the trifluzamide together and uses an inhibition effect or a killing effect of the trifluzamide on a germ and a curing effect of an agricultural antibiotic on the germ. The combined bactericide has the advantages of good prevention and control effect on rice sheath blight and wheat sheath blight, over 98 percent of prevention and control ratio according to field trials, strong persistence, over 93 percent of the prevention and control ratio in 14 days after the administration for the prevention and control of the rice sheath blight and the wheat sheath blight, and low production cost which is 50 percent lower than that of singly using the trifluzamide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TONGLU HUIFENG BIOSCI
Biological bactericide composition and application thereof to wilt
The invention relates to a biological bactericide composition and an application thereof to a wilt. The biological bactericide composition comprises active components including amino-oligosaccharin and bacillus subtilis, wherein the weight content of the amino-oligosaccharin is 0.5-5%; the content of the bacillus subtilis is 1.0-1,000.0 hundred million active spores per gram. The biological bactericide composition disclosed by the invention is testified by a field trial and has good prevention and treatment effects on watermelon and melon wilts; meanwhile, all the active components are compounded to further improve the prevention effect and the prevention effect is obviously better than that of a single-dosage variety.
Owner:JIANGSU LVDUN PLANT PROTECTION AGROCHEM EXPERIMENTAL
Evaluation method of tobacco variety on aphid resistance degree
InactiveCN102577795ASimple methodEasy to operateHorticulture methodsEvaluation resultNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop resistance breeding and especially relates to an evaluation method of tobacco variety on aphid resistance degree, which comprises the following steps: (1) setting a verification nursery; (2) selecting tested materials; (3) performing field trial; (4) performing field investigation; (5) dividing aphid resistance degrees of tobacco variety; and (6) repeatedly verifying. The method provided by the invention has the following beneficial effects: the evaluation method is more objective, simple and liable to operate; the method can simultaneously perform resistance evaluation on a plurality of tobacco varieties to improve the efficiency and save the test time; the method can reduce the error of the evaluation result caused by non-uniform aphid generation; and a uniform aphid resistance index is used in the method to reduce the evaluation result difference of different regions.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Maize machine direct sowing method under condition of smashed wheat straw incorporation in Shajiang black soil area
ActiveCN106982640ALand levelingIncrease productionFertilising methodsCereal cultivationBiotechnologyAtrazine
The invention provides a maize machine direct sowing method under the condition of smashed wheat straw incorporation in the Shajiang black soil area. The method comprises the steps that wheat straw is harvested; the obtained wheat straw is smashed by means of a straw smashing device and then uniformly scattered, and covers the ground surface; base fertilizers with the nitrogenous fertilizer as a main is applied on the soil with the smashed wheat straw; maize sowing is conducted; after sowing or around stem pushing, ditching is conducted in an interlacing mode; 40% of Acetochlor Atrazine or 48% of ametryn and 50% of acetochlor and other or other weed killers are mixed with water for closed weeding; from the stem pushing period to the small horn mouth period of maize, nitrogenous fertilizer topdressing is conducted, and secondary nitrogenous fertilizer topdressing is conducted in the big horn mouth period. The inventor continually verifies and improves the method through field trials on different test field in nearly ten years, the results show that by means of the method, it can be ensured that the yield of maize is not affected in the wheat straw incorporation process, and even the yield is improved, and the greatest concern of farmers about reduction of the yield in the early incorporation stage is solved.
Owner:河南沃丰农业开发有限公司
Engineering design and construction of earthen fills
InactiveUS20080004809A1Earth material testingElectric/magnetic detectionField trialMethod development
Owner:EARTHWORK SOLUTIONS
Microbial organic fertilizer special for organic kiwi fruit and preparation method for microbial organic fertilizer
InactiveCN102503607AMeet absorption requirementsIncrease productionBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationActinidiaField trial
The invention relates to a microbial organic fertilizer special for organic kiwi fruit and a preparation method for the microbial organic fertilizer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding a microbial inoculant, namely an effective micooorganisms (EM) compound inoculants into raw materials such as soybean oil residue, ginger plant, cushaw stem, wax gourd stem and greenhouse cucumber stem, and preparing a fermented material by using a batch-charging fermentation composting method; and airing or drying the fermented material to obtain a powdery product. The microbial organic fertilizer special for the organic kiwi fruit fully meets the absorption requirement of the kiwi fruit in two aspects, namely nutrient proportioning and periodic nutrient supply, has high nutrient content, can effectively improve the yield of the kiwi fruit, and can reach the standard of producing organic kiwi fruit. Through field trial, a good effect of increasing the yield of the organic fruit is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG GUANGDA FERTILIZER INDAL TECHCO
Virtual validation of software systems
InactiveUS8266578B2Reduces time and effortReduce buildError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsRegulated IndustrySoftware system
Owner:VIRTUAL PURPLE +1
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof in preparation of antibacterial agents for plant pathogenic fungi. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens LM-Y is separated from rhizosphere soil of diseased peach plants. Compared with the common biocontrol fungi, the bacillus amyloliquefaciens does not produce sensitization spores and is safe to humans, livestock, fruits and vegetables and environmental-friendly. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens LM-Y disclosed by the invention has obvious antagonistic effects on multiple pathogenic fungi such as monilinia fruticola, gibberella zeae, grey mould germs of strawberry and the like, has an inhibition rate of 80% or higher on the monilinia fruticola, has the antibacterial rate higher than that of the conventional biocontrol fungi by about 10% and has great research and development potential. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens LM-Y disclosed by the invention has an obvious effect for controlling the monilinia fruticola, has the field trial control effect of 78.5%, is simple in production process and has very wide application prospects in biocontrol of plant diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cold-resistant agent for rice
InactiveCN103183569AImprove cold resistanceReduce permeabilityFertilizer mixturesBound waterPhosphate
The invention discloses a cold-resistant agent for rice. The cold-resistant agent is formed by mixing and uniformly stirring the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-25 of allantoin, 10-20 of proline, 10-20 of glycine, 10-20 of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 10-15 of boric acid, 10-15 of zinc sulfate and 5-10 of manganese sulfate. After the raw materials are scientifically combined, the effect is composited; and field trials prove that after the rice is sprayed by 1000 times of solution of the product, the bound water and the chlorophyll of plants can be improved, the permeability of cell membranes is reduced, the cold tolerance of rice seedlings and plants is obviously improved, the damage of cold dew wind is effectively avoided, the ripening rate and the thousand seed weight are improved, the ageing of functional leaves and branches of rice can be delayed, and the lodging-resistance effect is obvious.
Owner:李启荣 +1
Methods in the engineering design and construction of earthen fills
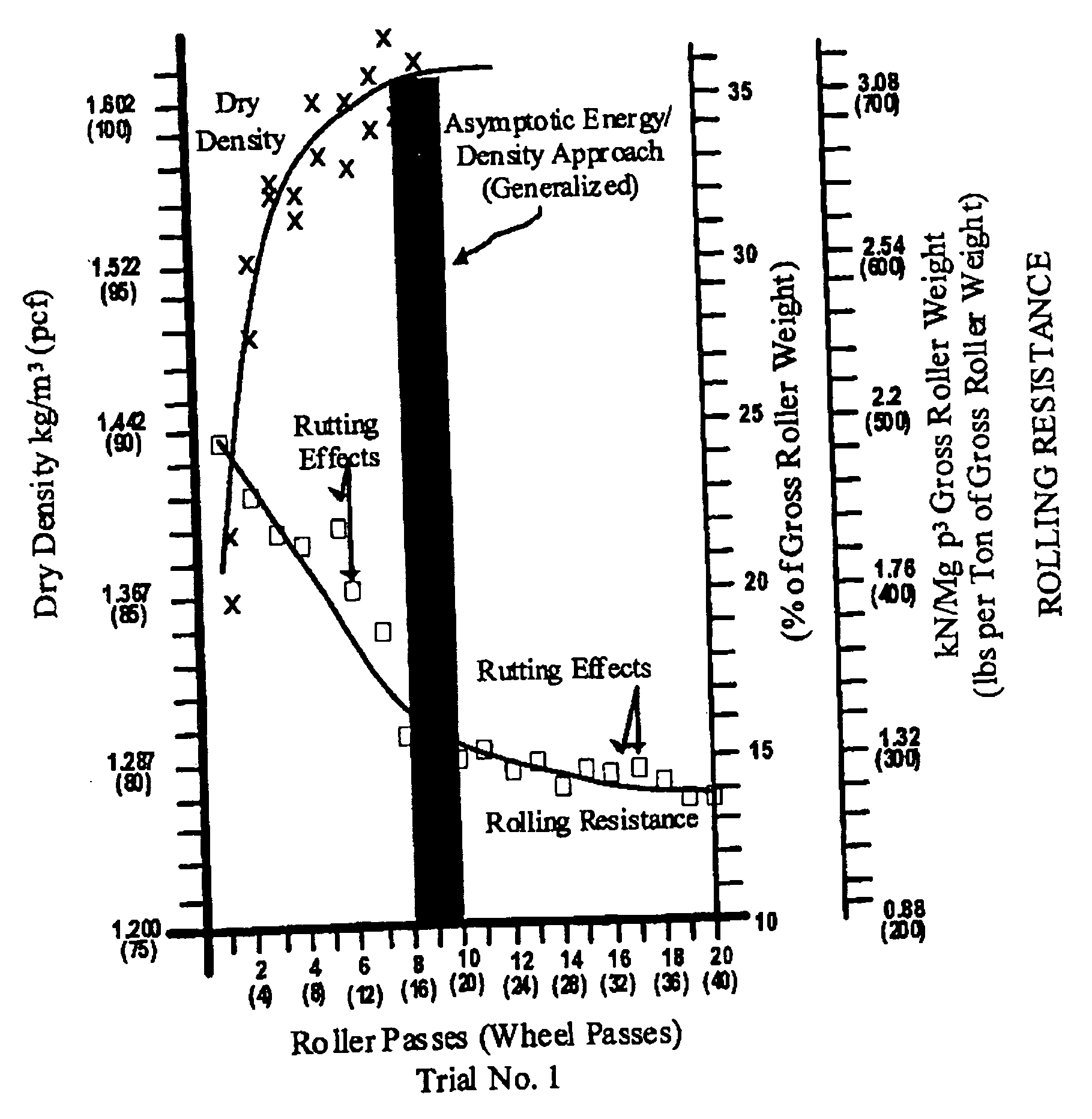
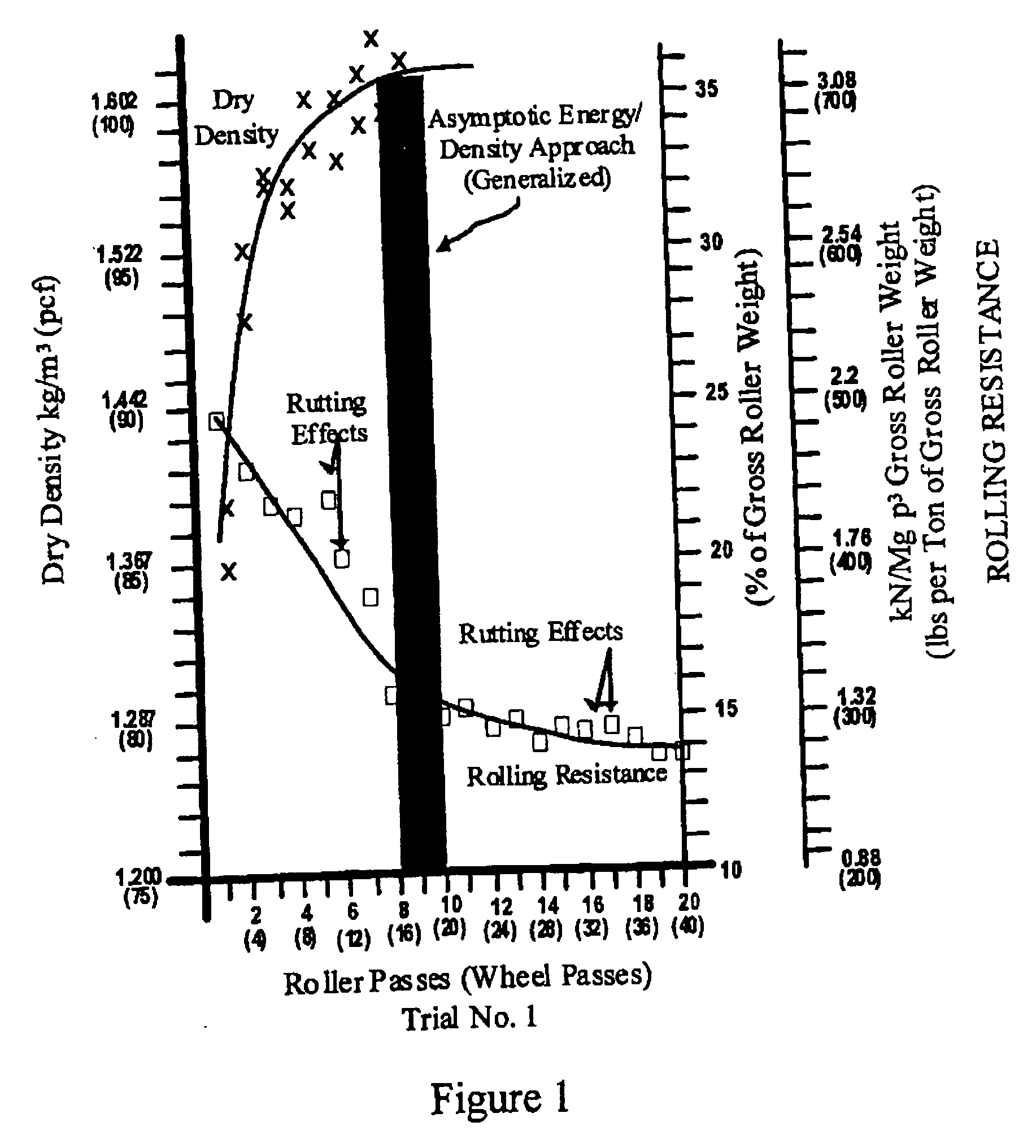
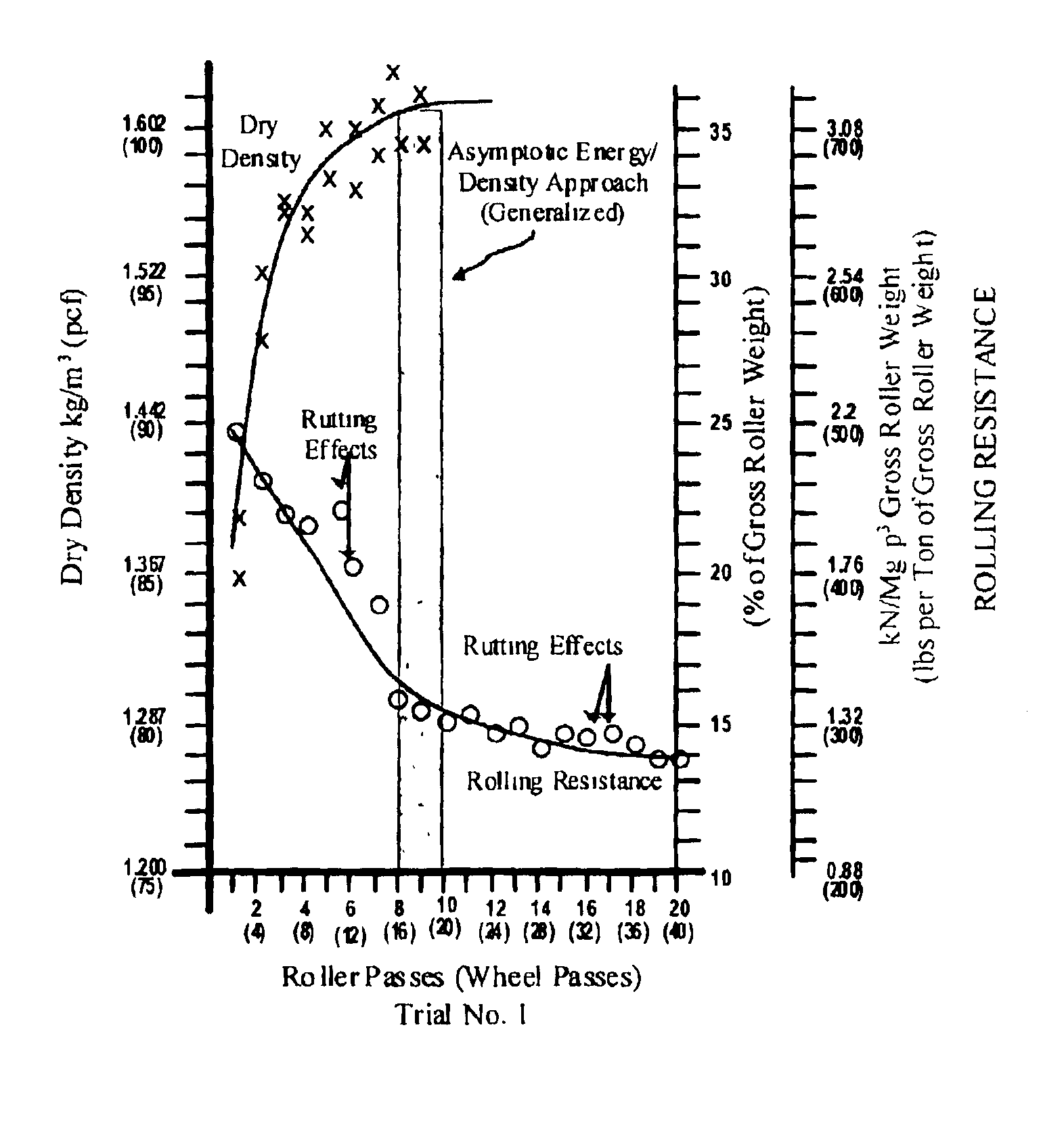
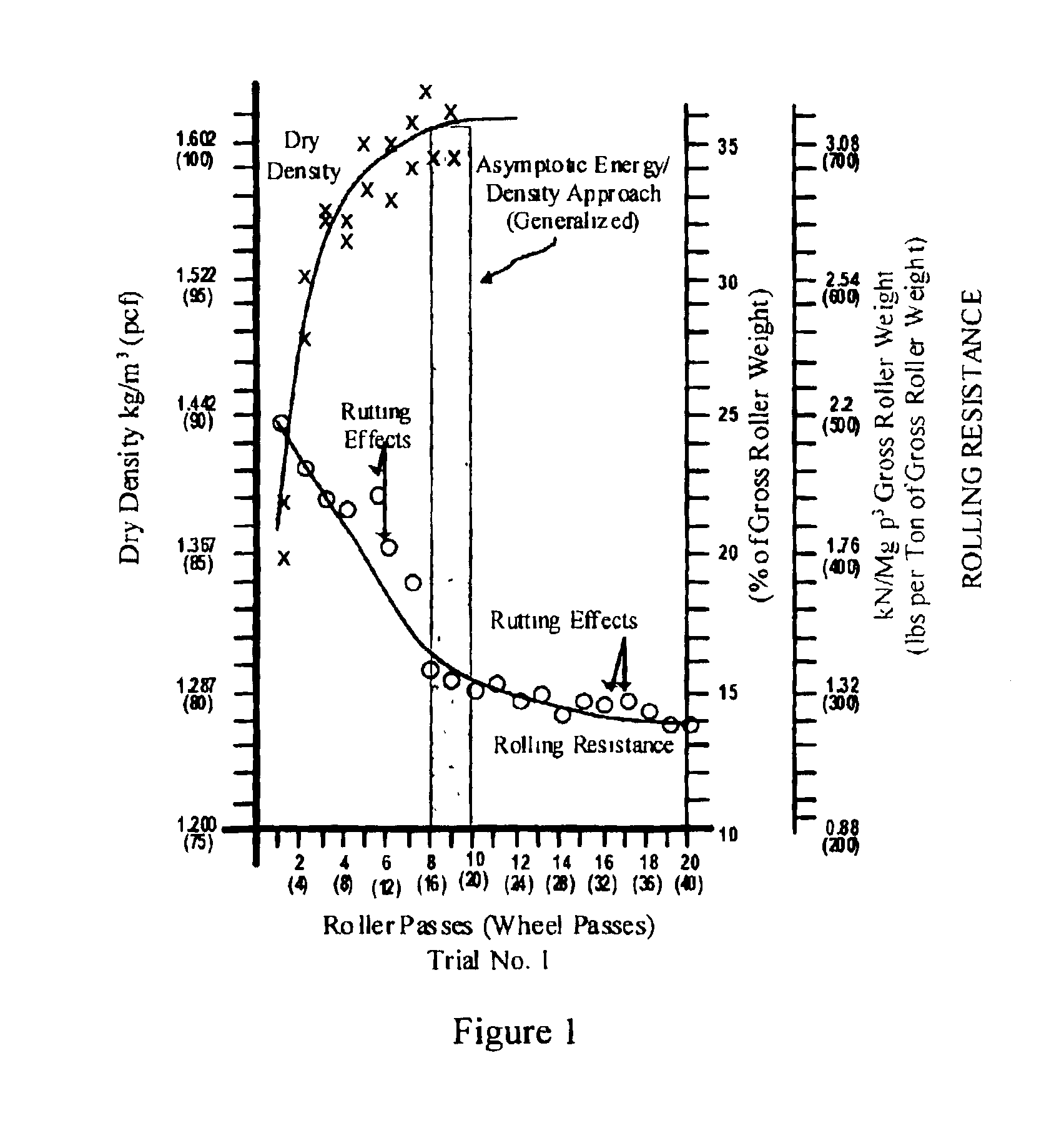
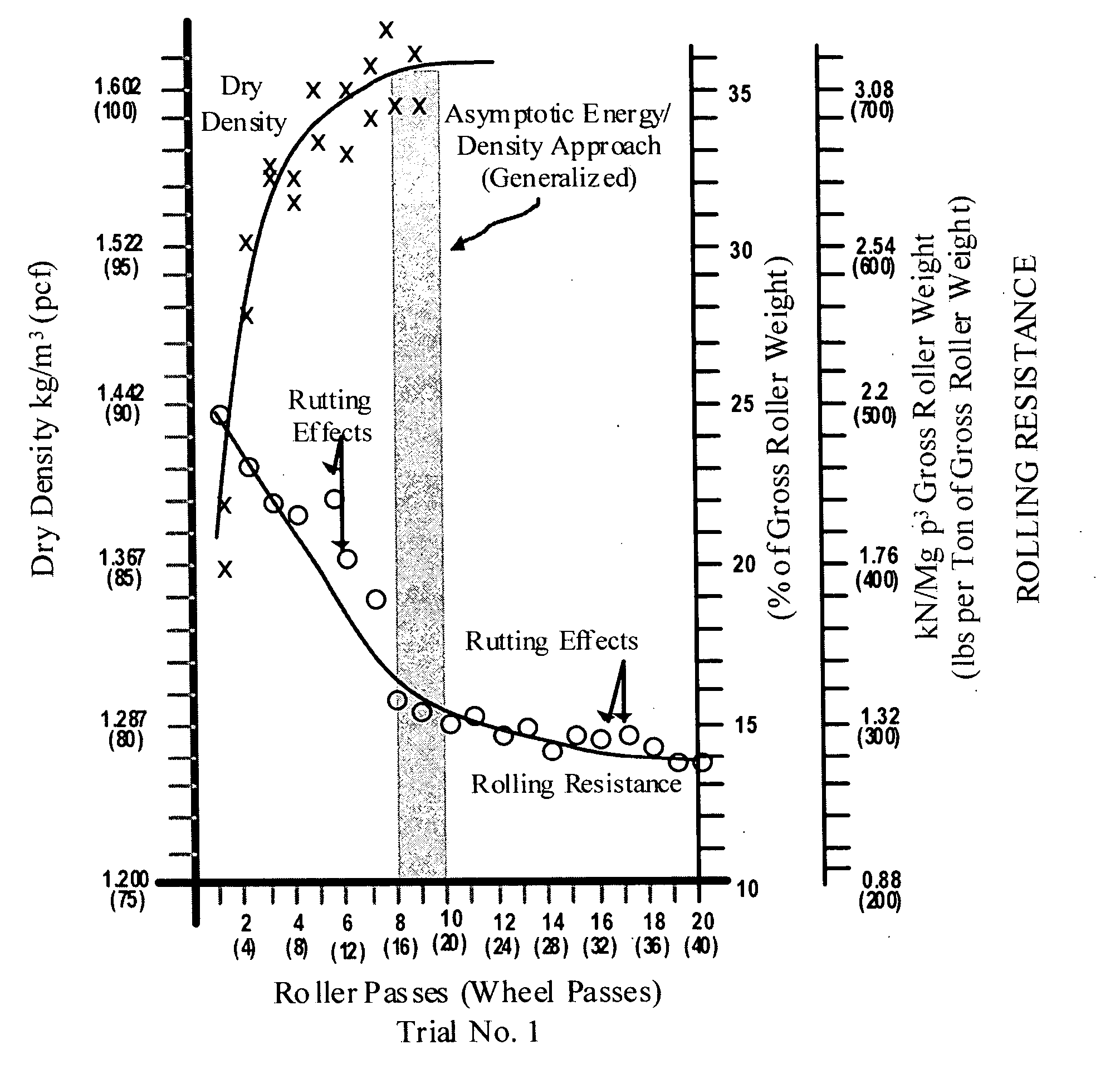
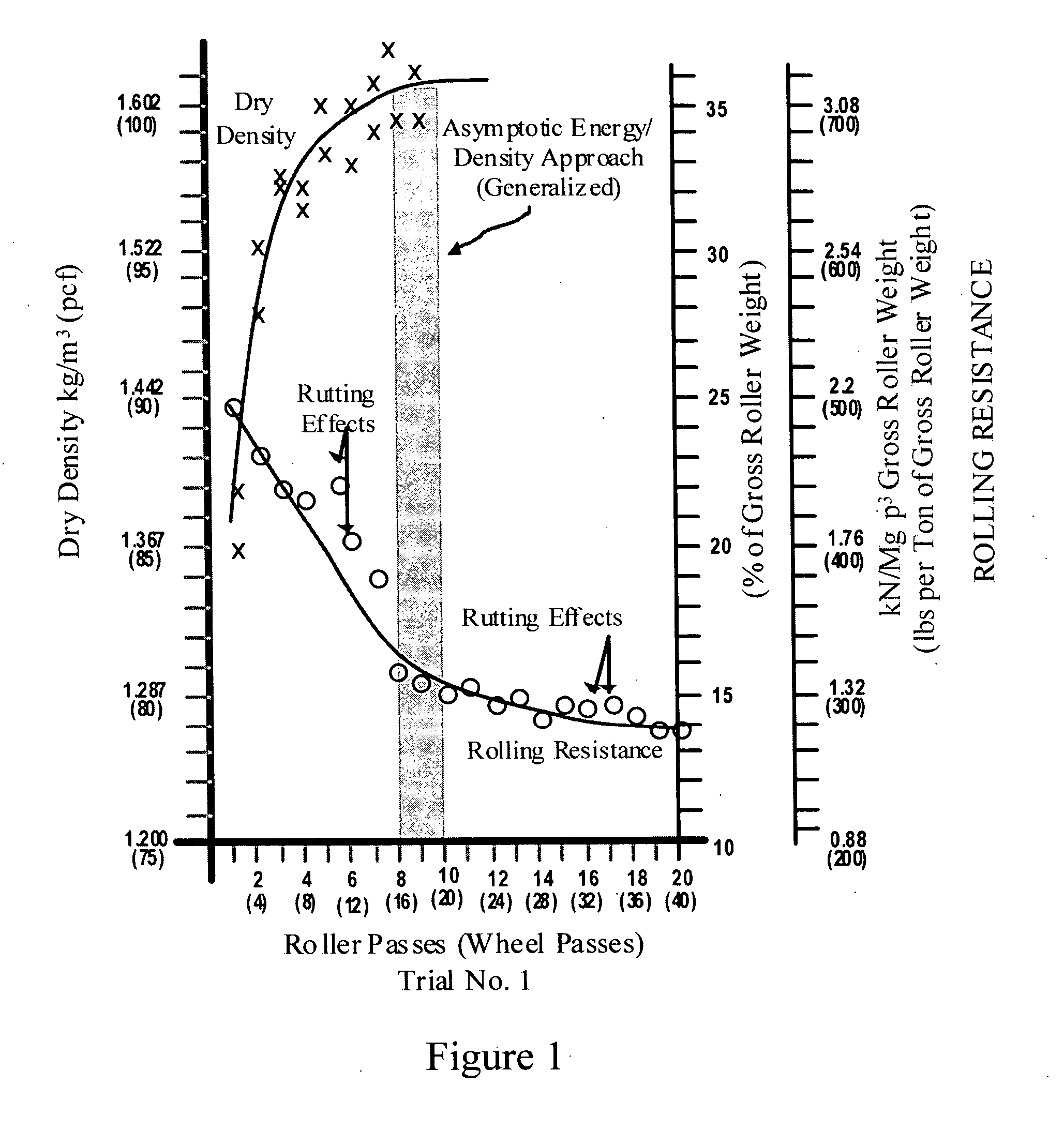
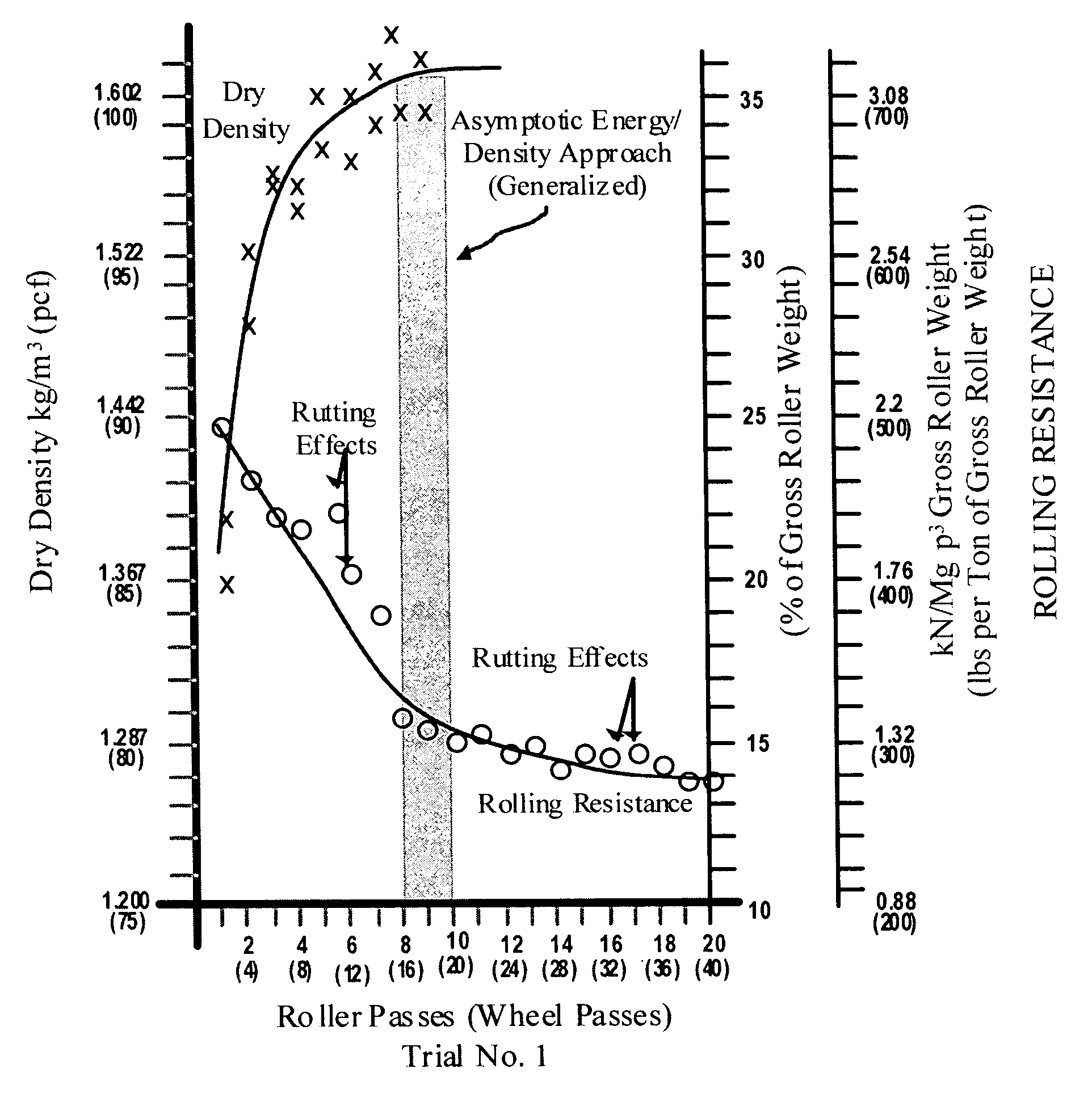
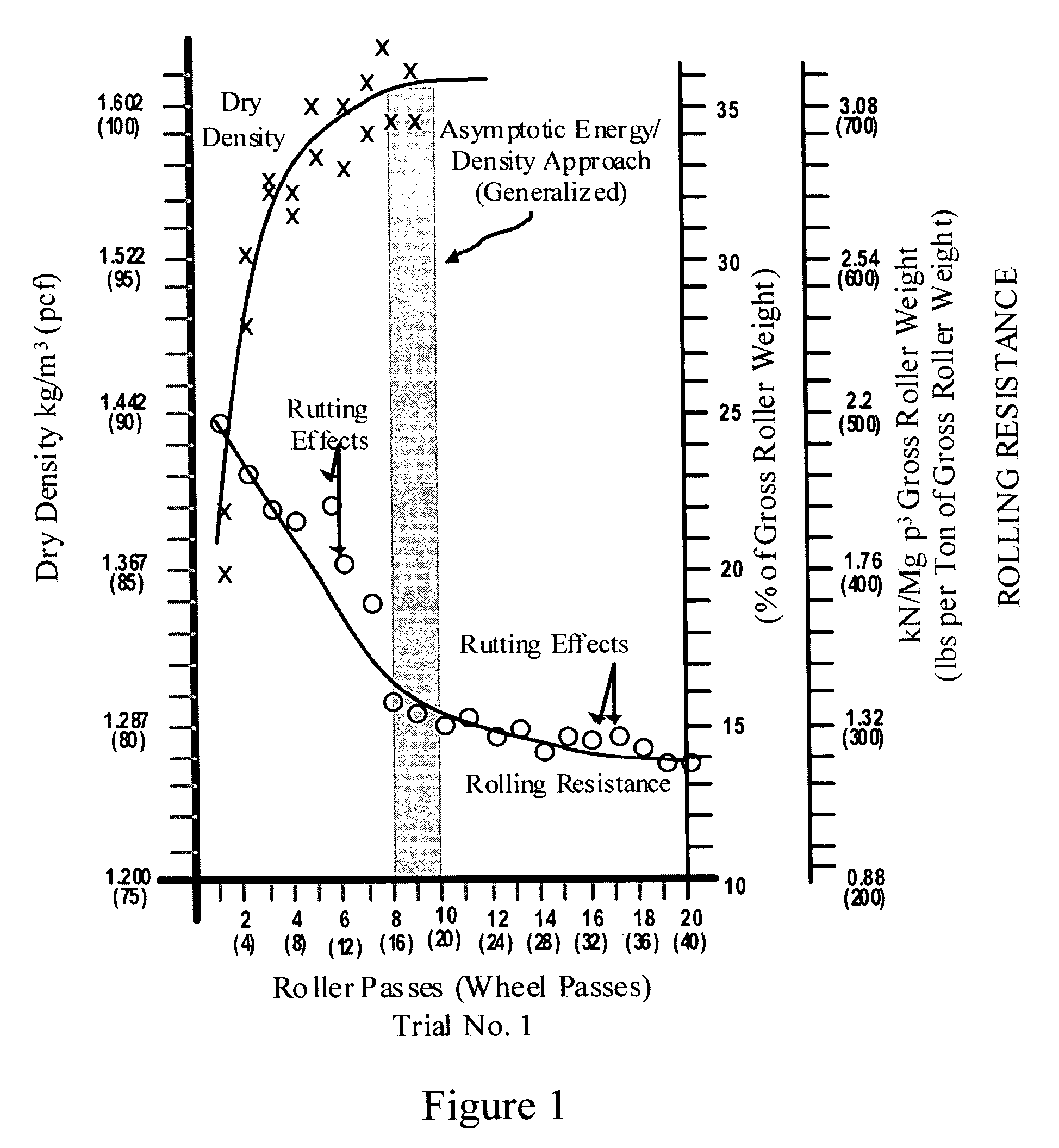
The invention is a composite of interdependent engineering methods for earthen fill engineering and construction. The invention includes the development, utilization, and correlation of actual, cumulative field compaction energies, unique to and based on field combination-specific variables of any combination but including all of the following: soil type, compactor type, lift thickness, moisture content, and soil amendment type and mix. Interdependent development of the field combination-specific compaction energies includes the following combination-specific steps: novel rolling resistance energy versus dry density field trials, novel generation and direct curvalinear utilization of parabolic rolling resistance energy curves with roller passes, novel determination of asymptotic energy-density approach ranges, novel selection and application of percentage density sectors on novel moisture-density curves, and novel projection of said percentage density sectors onto corresponding roller compaction energy curves for selection and use of design compaction energy levels. Interdependent correlation of the combination-specific energy values is made with all physical and engineering properties of all soil types and amended soil types in the compacted state that corresponds to and is the product of the specific combination of field variables. In addition to interdependent utilization of the energy and corresponding engineering properties in method development, the energy and corresponding engineering properties are tabulated within cross-matrices of all field combinations for use in engineering design, engineering correction, laboratory compaction testing, and construction controls. The cross-matrix values are related in a manner that permits determining values for additional field combinations that have not been tested on a full scale.
Owner:EARTHWORK SOLUTIONS
Methods in the engineering design and construction of earthen fills
InactiveUS20050019105A1Earth material testingElectric/magnetic detectionRolling resistanceField trial
The invention is a composite of interdependent engineering methods for earthen fill engineering and construction. The invention includes the development, utilization, and correlation of actual, cumulative field compaction energies, unique to and based on field combination-specific variables of any combination but including all of the following: soil type, compactor type, lift thickness, moisture content, and soil amendment type and mix. Interdependent development of the field combination-specific compaction energies includes the following combination-specific steps: novel rolling resistance energy versus dry density field trials, novel generation and direct curvalinear utilization of parabolic rolling resistance energy curves with roller passes, novel determination of asymptotic energy-density approach ranges, novel selection and application of percentage density sectors on novel moisture-density curves, and novel projection of said percentage density sectors onto corresponding roller compaction energy curves for selection and use of design compaction energy levels. Interdependent correlation of the combination-specific energy values is made with all physical and engineering properties of all soil types and amended soil types in the compacted state that corresponds to and is the product of the specific combination of field variables. In addition to interdependent utilization of the energy and corresponding engineering properties in method development, the energy and corresponding engineering properties are tabulated within cross-matrices of all field combinations for use in engineering design, laboratory compaction testing, and construction controls. The cross-matrix values are related in a manner that permits determining values for additional field combinations that have not been tested on a full scale.
Owner:EARTHWORK SOLUTIONS
Notoginseng soil treatment agent and use method thereof
InactiveCN101584331AReduce residual toxicityGood control effectBiocideFungicidesDiseaseSoil treatment
The invention relates to a notoginseng soil treatment agent and a use method thereof. The notoginseng soil treatment agent contains 50% of carbendazol wettable powder, 95% of hymexazol wettable powder, 25% of metalaxyl, propamocarb wettable powder and 72% of agricultural use streptomycin wettable powder. The soil treatment agent has good effects to prevent major fungus diseases caused by ascomycetes, deuteromycetes, oomycetes in fungus and diseases caused by pseudomonas and xanthomonas bacteria; soil treatment is carried out on soil which is used for continuously planting for four years with the soil treatment agent 20 days before notoginseng transplanting and a notoginseng seed dressing. Rate of emergence of a field trial is 87.22% which is 63.63% higher than that of a comparison without using the soil treatment agent of 23.59 percent. The soil treatment agent has low toxicity to human and livestock and less vestigital, and not only can be used for preventing and treating bad rot, stump rot, bud-rot and diseases of the notoginseng, but also can be used for treating the soil of various crops of other traditional Chinese medical materials and vegetables.
Owner:文山壮族苗族自治州三七科学技术研究所
Method for remote sensing quantitative assessment of yield loss of rapeseed under waterlogging damage stress based on satellite data
The invention discloses a method for the remote sensing quantitative assessment of the yield loss of rapeseed under a waterlogging damage stress based on satellite data. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out plot-scale rapeseed waterlogging damage field trials to obtain ground rapeseed yield data of different varieties in different development stages under different waterlogging damage treatments; obtaining and preprocessing satellite image data with a high spatial resolution; calculating the rape waterlogging damage induced yield loss rate and the vegetation index change rateunder the waterlogging damage stress; analyzing the correlation coefficient of the rapeseed yield and the yield reduction rate to the vegetation index and the vegetation index change rate under the waterlogging damage stress; and establishing a model for the remote sensing quantitative estimation of the plot-scale rapeseed yield reduction under the waterlogging damage stress by using a multiple regression technology, and performing accuracy test. The method can be used to provide services for the accurate management of water and fertilizers in farmers' rapeseed fields and provide a basis forthe insurance company to develop disaster loss evaluation and loss assessment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of composite oligosaccharide fruit and vegetable root nourishing element
PendingCN108271787AFlexible locationReduce energy consumptionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideDiseaseField trial
The invention relates to a preparation method of composite oligosaccharide fruit and vegetable root nourishing element. The preparation method comprises the following four steps: crushing a chitosan raw material, acid-dissolving chitosan powder, performing enzymolysis on a high-viscosity chitosan solution, and compositing carboxymethyl chitosan and oligosaccharide. A field trial proves that a product has the effect of promoting the growth of fruit and vegetable roots, nourishing and protecting the roots and strengthening the roots and seedlings; and the composite oligosaccharide fruit and vegetable root nourishing element has the effects of improving and restoring soil, optimizing a rhizospheric microorganism ecological system, and inhibiting the occurrence and development of soil-borne disease, and is suitable for the green-house fruit and vegetable cultivation. By applying the product disclosed by the invention, the use amount of chemical fertilizer and pesticides can be reduced, thepesticide residue pollution of an agricultural product can be reduced, and the quality and the economic benefit of the agricultural product can be improved.
Owner:济南高新区阿波罗甲壳素工程技术研究中心
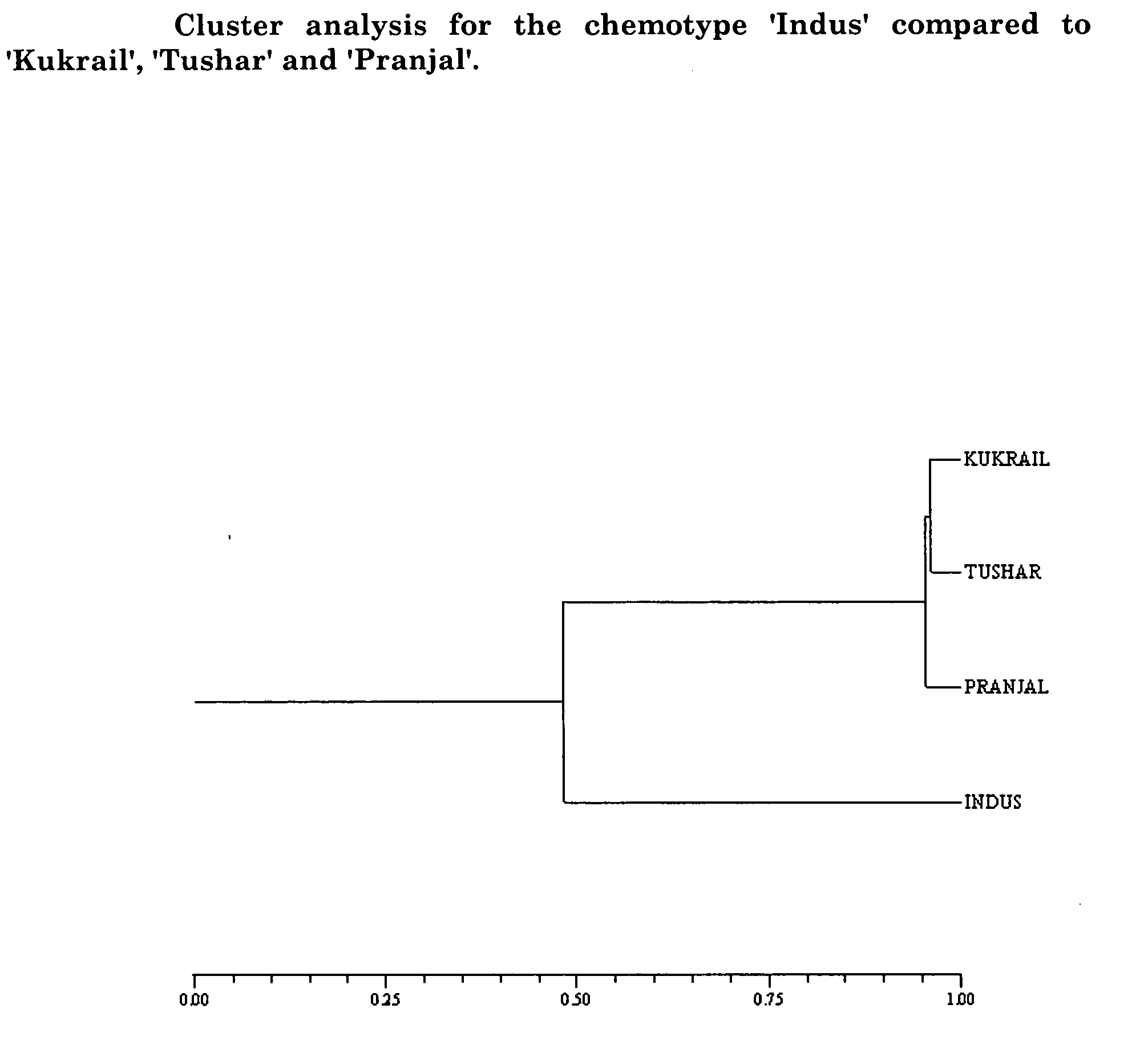
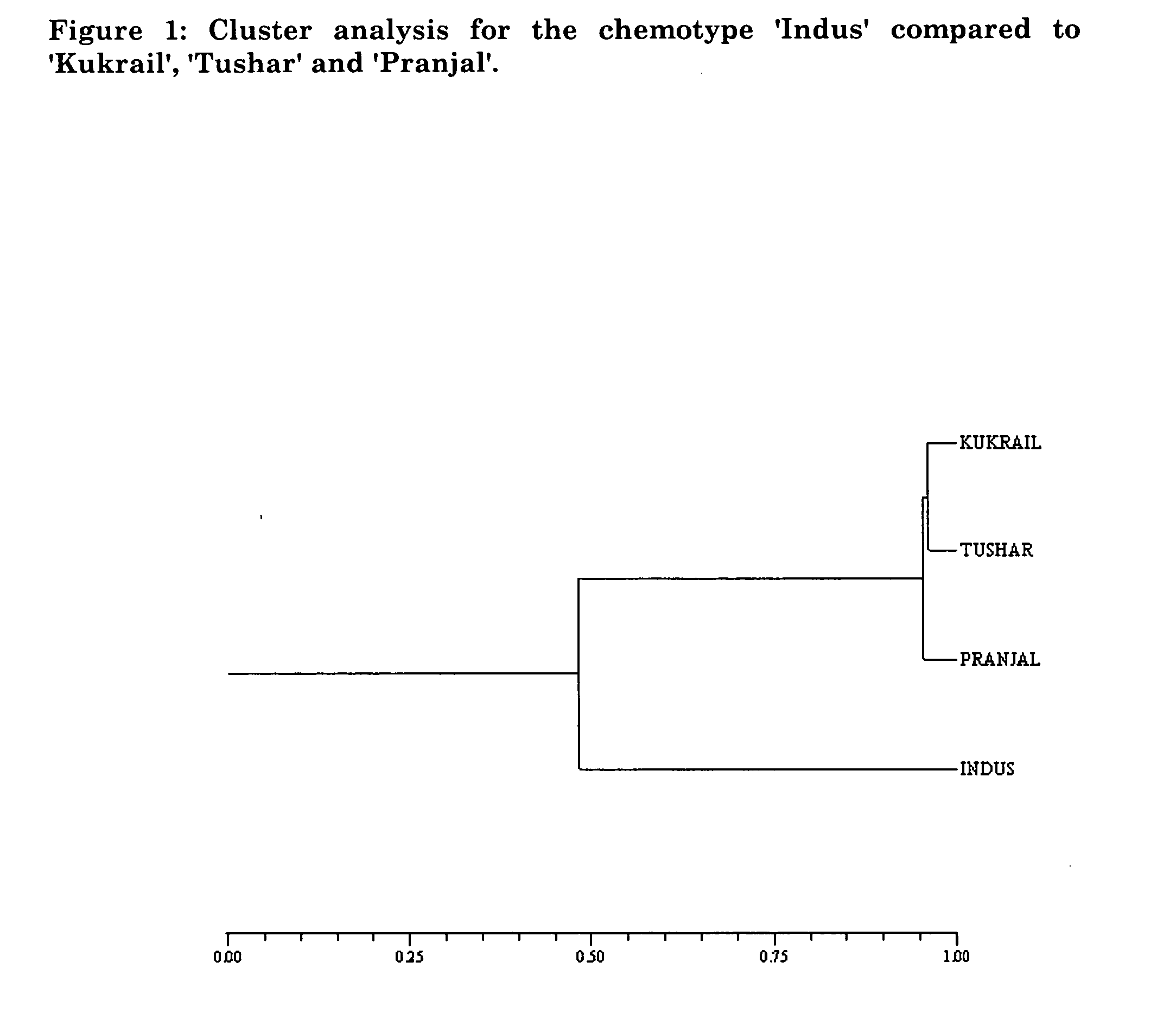
Mint plant 'Indus'
ActiveUS20050150027P1High amount of menthofuranReduce the amount of solutionAngiosperms/flowering plantsMenthofuranField trial
The present invention relates to a new and distinct mint plant of Mentha piperita ‘Cim Indus’, selected through screening, field trial and analysis of monoterpene constituents of the essential oil of the germplasm, possessing the characters of producing high amount of menthofuran ranging between 22 to 30% of total oil content, high amount pulegone ranging between 9.0 to 18% of total oil content, with essential oil content ranging between 0.32 to 0.40% of the total oil content.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Sterilizing composition containing benzothiostrobin and triazole fungicide and application thereof
InactiveCN103503883AGood control effectDelay drug resistanceBiocideFungicidesField trialBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a sterilizing composition containing benzothiostrobin and triazole fungicide. The sterilizing composition comprises active ingredients and auxiliary elements of a pesticide preparation, wherein the active ingredients comprise benzothiostrobin and triazole fungicide; the mass ratio of the benzothiostrobin to the triazole fungicide is (1:50)-(50:1); the triazole fungicide is one of tebuconazole, flutriafol, triadimefon, propiconazole and hexaconazole. The benzothiostrobin and the triazole fungicide of the sterilizing composition are two sterilizing agents having different mechanisms and are not subjected to conflicts after being compounded, a remarkable synergistic effect on the resistant bacteria is achieved within a certain scope, the sterilizing composition has a remarkable control effect, is safe and does not damage crops, the acute toxicity on a mammal is reduced after the benzothiostrobin and the triazole fungicide are compounded, and the safety is improved. The field trial shows that the sterilizing composition expands the bacteriocidal spectrum and has special effects on diseases of the crops such as powdery mildew, leaf spot disease, false smut, scab, banded sclerotial blight, damping-off and the like, and the use amount of the sterilizing composition is less.
Owner:JIANGSU SEVENCONTINENT GREEN CHEM CO LTD
Attractant capable of promoting cross-pollination and improving fruit set percentage of fruit tree
The invention discloses an attractant capable of promoting cross-pollination and improving the fruit set percentage of a fruit tree. The attractant is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 3 to 4 parts of concentrated perfume oil, 5 to 7 parts of inositol, 5 to 7 parts of folic acid, 60 to 100 parts of glucose and 180 to 220 parts of purified water. The attractant tastes sweet, has fragrance and can attract insects like honeybees and butterflies to come to an orchard to assist in pollination. According to field trial results, after spraying of the attractant for about 1 h, a great amount of insects like honeybees and butterflies are attracted to the orchard to gather honey and assist in cross-pollination and the fruit set percentage is increased by 30 to 50% compared with that of a control group; labor and time are saved, and the attractant has low cost and is easy to prepare and convenient to use.
Owner:杨健
Method for assessing rice yield
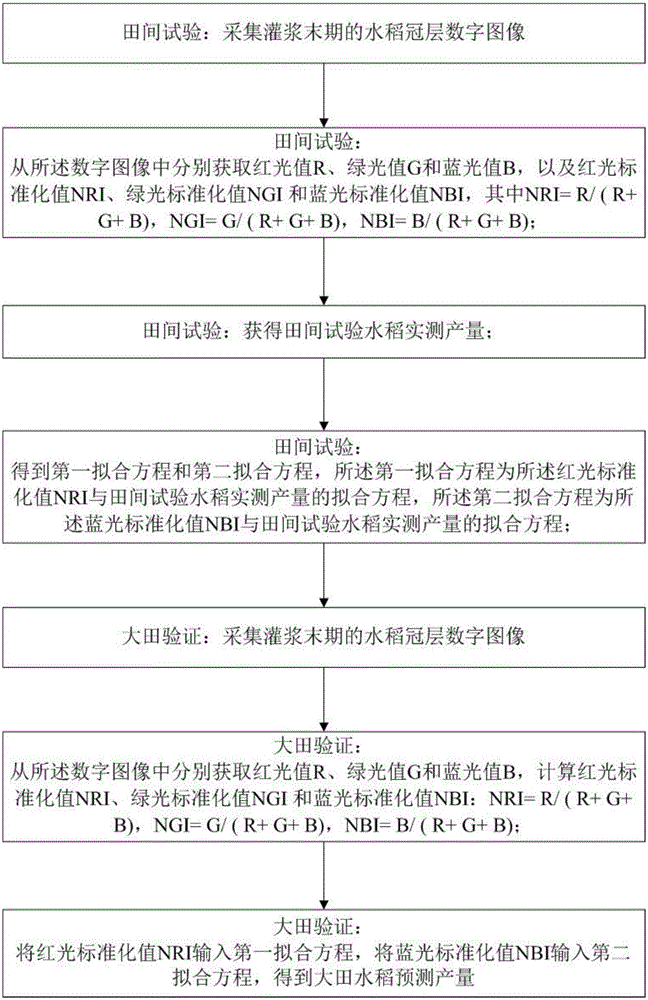
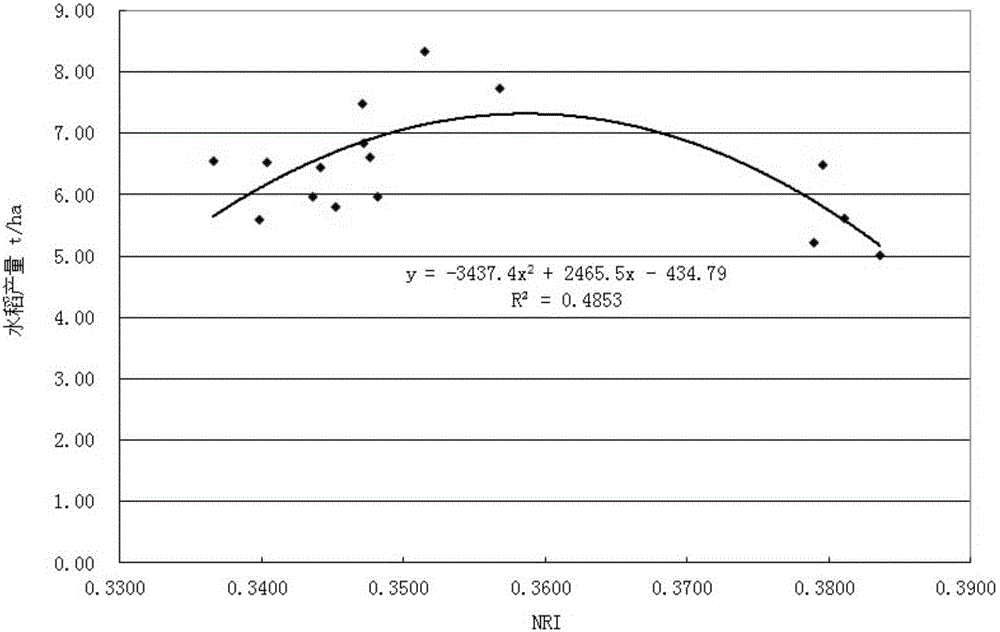
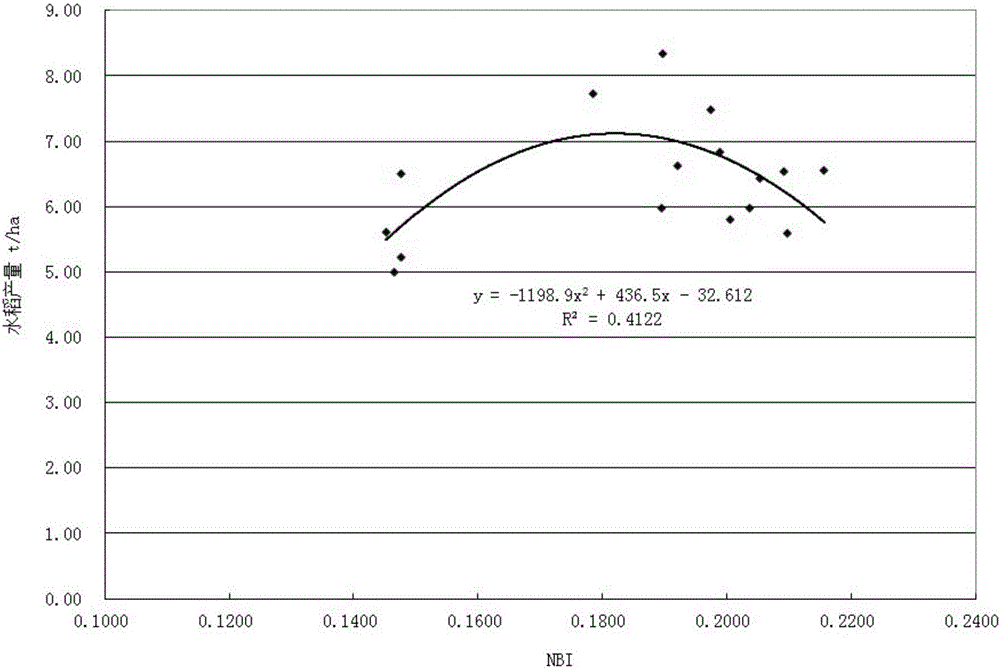
ActiveCN105842245AHigh degree of complianceEasy to predictInvestigation of vegetal materialField trialDigital image
The invention discloses a method for assessing the rice yield. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) in a field trial, collecting a digital image of rice canopy at the last phase of grouting; acquiring a red light standard value NRI, a green light standard value NGI and a blue light standard value NBI; acquiring practically measured yield of field trial rice; acquiring a first fitted equation and a second fitted equation; (2) in a field validation process, collecting the digital image of rice canopy at the last phase of grouting; acquiring the red light standard value NRI, the green light standard value NGI and the blue light standard value NBI; and inputting the red light standard value NRI to the first fitted equation, inputting the blue light standard value NBI to the second fitted equation and acquiring the predicted yield of the field rice. According to the method provided by the invention, the rice yield is predicted, the conformity between the predicted yield and the practically measured yield is higher and the rice grain yield is better predicted. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention is simple and is low in cost.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Compound fertilizer for improving tea yield and preparation method thereof
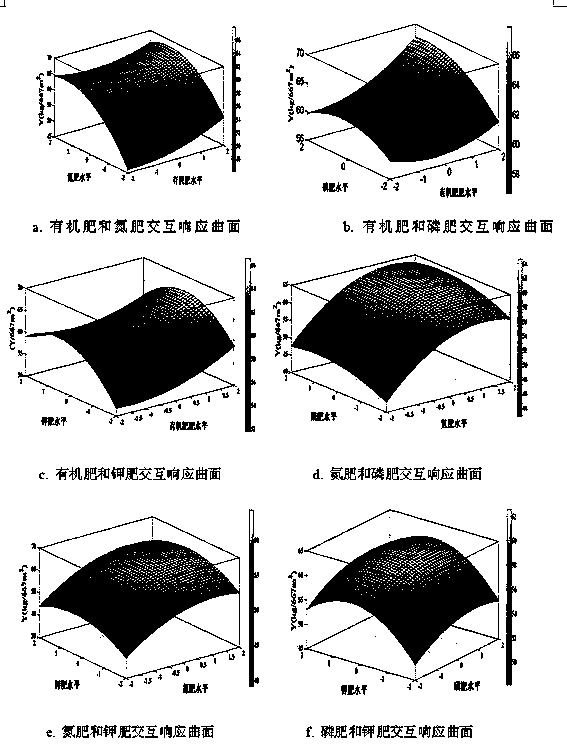
The invention discloses a compound fertilizer for improving a tea yield and a preparation method thereof. According to a field trial with four-factor five-level quadratic regression universal rotational-combination design, a regression effect model of an organic fertilizer, nitrogenous, phosphorous and potassic fertilizers and the tea yield is established, so as to analyze factors and interaction. The compound fertilizer is prepared from the components at a certain ratio: 799.40-928.10kg / 677m<2> of the organic fertilizer, 15.30-16.92kg / 667m<2> of the pure nitrogenous fertilizer, 15.00-17.14kg / 667m<2> of the pure phosphorous fertilizer, 11.38-13.58kg / 667m<2> of the pure potassic fertilizer. With the adoption of the compound fertilizer provided by the invention, the tea yield can be improved. The compound fertilizer can be applied to fertilization of tea trees of a tea garden.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Plant growth regulator containing furfurylaminopurine and brassinolide
InactiveCN104782637AHigh activityConsistent efficacyBiocidePlant growth regulatorsGrowth plantBrassinolide
The invention relates to a plant growth regulator containing furfurylaminopurine and brassinolide. The plant growth regulator comprises furfurylaminopurine, brassinolide and additives, wherein the weight ratio of the furfurylaminopurine to the brassinolide is (1 to 30)-(30 to 1); the total weight of the furfurylaminopurine and the brassinolide accounts for 0.01-20% of the weight of the plant growth regulator. The plant growth regulator can be processed into solutions or soluble powder in practical application; a large quantity of field trials prove that the plant growth regulator has excellent growth-promoting and yield-increasing effects on crops such as rice, wheat, cucumber and tomatoes.
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHONGXUN AGRI TECH
Field trial soil sampling method
InactiveCN103245527AEasy to analyze differencesWithdrawing sample devicesBiological propertyField trial
The invention discloses a field trial soil sampling method and belongs to the field of researches of a crop cultivation technology. The method can carry out respective sampling on soil which has different distances from root surfaces of plants, and comprises the following steps of cleaning impurities, digging roots, shaking the roots, brushing the roots, sampling and the like. After the sampling, the field soil is divided into three types: rhizosphere soil A, non-rhizosphere soil B and non-rhizosphere soil C. Compared with a traditional method for sampling the soil by adopting a soil auger, the method is more delicate, is convenient for scientific research personnel to carry out difference analysis on physiological and biochemical indexes and biological properties of the soil at different parts, and provides evidence for improving the crop cultivation technology.
Owner:JIANGXI TOBACCO LEAF SCI RES INST
Methods in the engineering design and construction of earthen fills
InactiveUS7110884B2Earth material testingSpecial data processing applicationsRolling resistanceField trial
The invention is a composite of interdependent engineering methods for earthen fill engineering and construction. The invention includes the development, utilization, and correlation of actual, cumulative field compaction energies, unique to and based on field combination-specific variables of any combination but including all of the following: soil type, compactor type, lift thickness, moisture content, and soil amendment type and mix. Interdependent development of the field combination-specific compaction energies includes the following combination-specific steps: novel rolling resistance energy versus dry density field trials, novel generation and direct curvalinear utilization of parabolic rolling resistance energy curves with roller passes, novel determination of asymptotic energy-density approach ranges, novel selection and application of percentage density sectors on novel moisture-density curves, and novel projection of said percentage density sectors onto corresponding roller compaction energy curves for selection and use of design compaction energy levels. Interdependent correlation of the combination-specific energy values is made with all physical and engineering properties of all soil types and amended soil types in the compacted state that corresponds to and is the product of the specific combination of field variables. In addition to interdependent utilization of the energy and corresponding engineering properties in method development, the energy and corresponding engineering properties are tabulated within cross-matrices of all field combinations for use in engineering design, laboratory compaction testing, and construction controls. The cross-matrix values are related in a manner that permits determining values for additional field combinations that have not been tested on a full scale.
Owner:EARTHWORK SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com