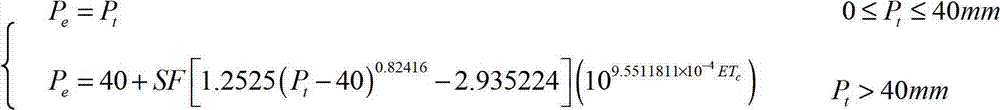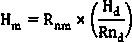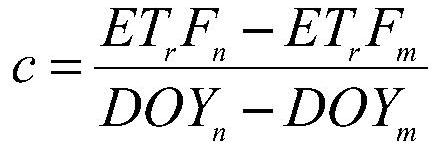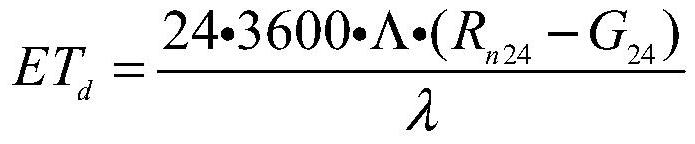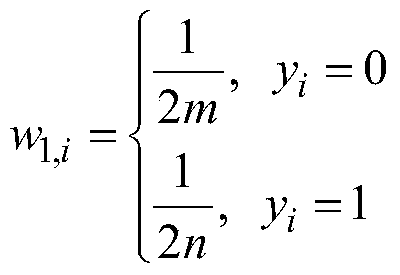Patents
Literature
45 results about "Crop coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Crop coefficients are properties of plants used in predicting evapotranspiration (ET). The most basic crop coefficient, Kc, is simply the ratio of ET observed for the crop studied over that observed for the well calibrated reference crop under the same conditions. PET=Kc*RET Potential evapotranspiration (PET), is the evaporation and transpiration that potentially could occur if a field of the crop had an ideal unlimited water supply.
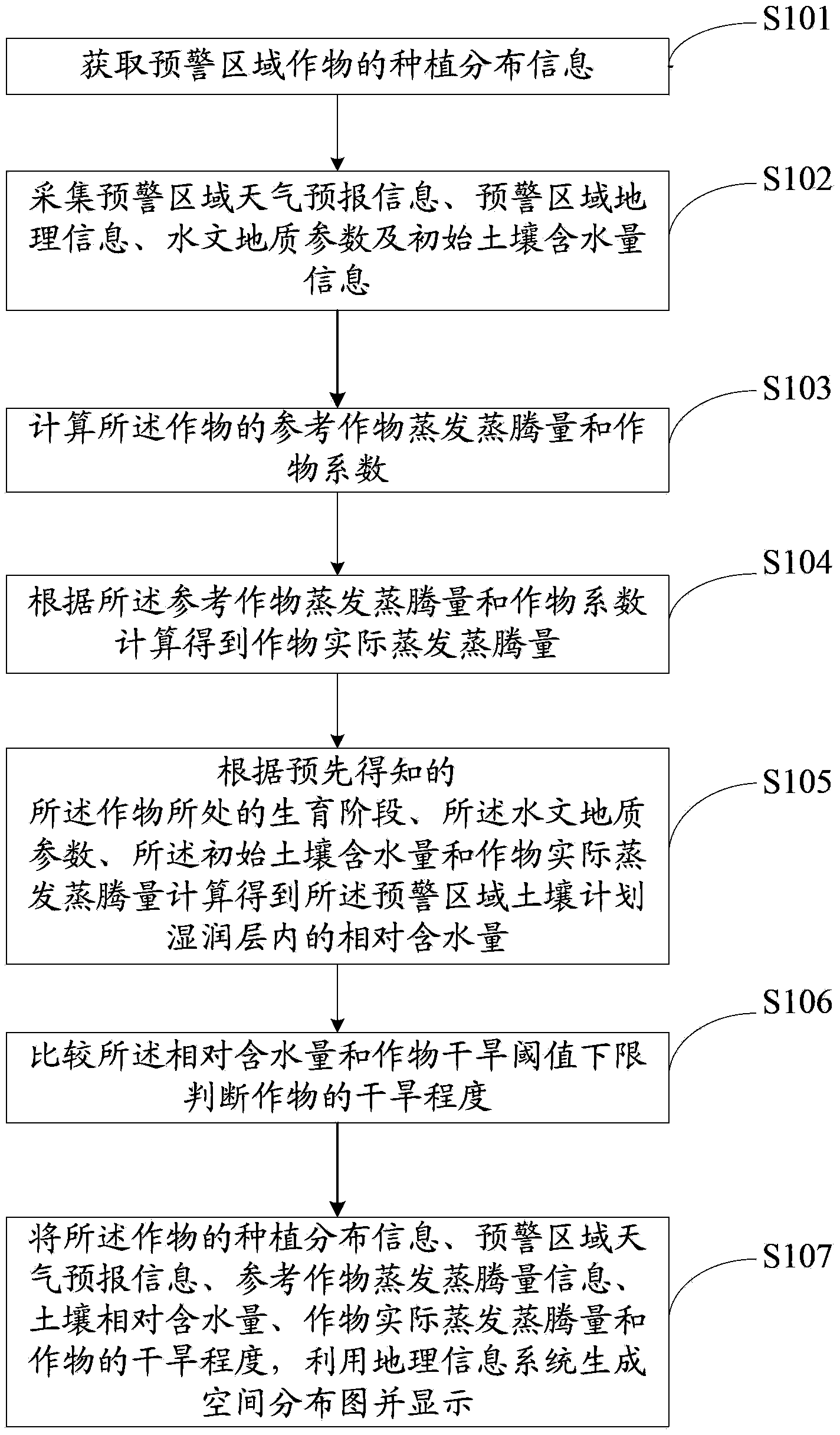
Drought early-warning method and drought early-warning system
ActiveCN102779391ADrought early warning is accurate and reasonableTimely drought and disaster prevention workEarth material testingAlarmsGeographic information systemWater content
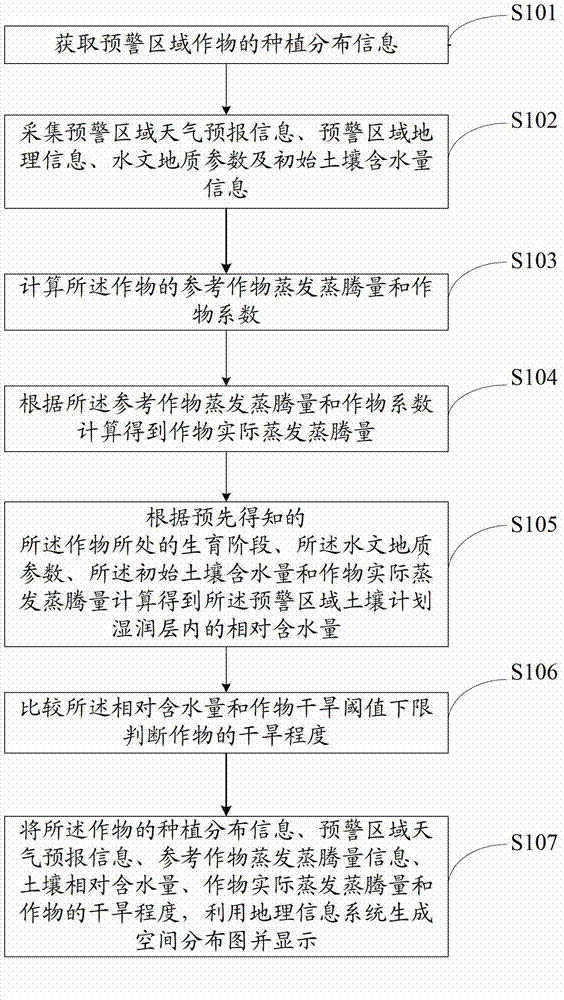
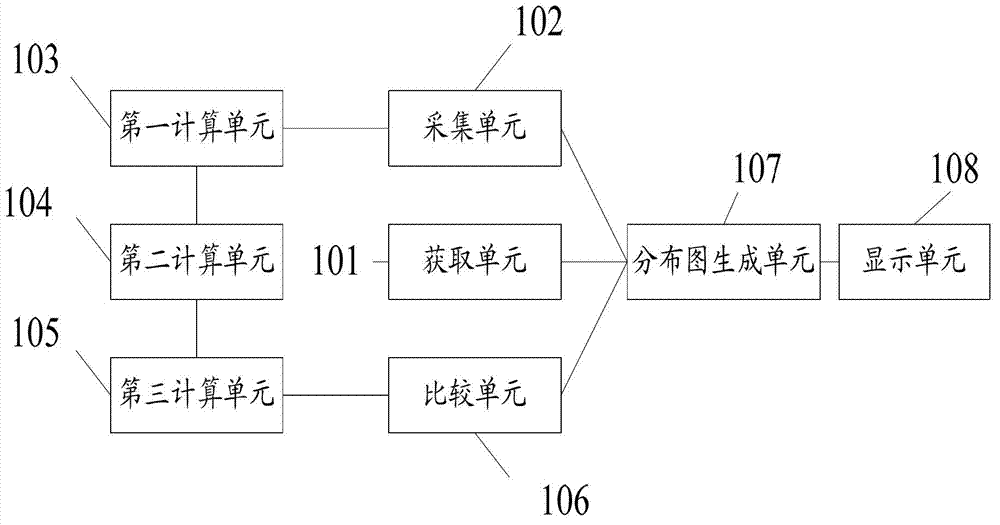
The invention discloses a drought early-warning method. The drought early-warning method includes acquiring plant distribution information of crops in an early-warning area; acquiring information of weather forecasting and the like in the early-warning area; calculating actual evapotranspiration of the crops; calculating to acquire relative water content in a planned moist layer in soil according to information of the actual evapotranspiration of the crops and the like; and comparing the relative water content in the planned moist layer in soil and lower limit of a drought threshold value, and judging drought degree of the crops. Therefore, information from multiple types of sources, such as growth condition of the crops, water in soil, weather forecasting information, geographic information in the early-warning area, is considered comprehensively, the drought degree of the crops is judged, and accordingly early warning of drought of the crops is more accurate and reasonable, and unreasonable utilization and waste of water resources are unlikely to cause during irrigation. Finally, related information of the drought degree of the crops and the like is used to generate and display a space distribution map by a geographic information system, and accordingly optimized allocation of the water resources in agriculture and early warning of drought in an area range are achieved.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Control method and control system for automatic irrigation of interplanted crops
InactiveCN105868864AHigh yieldOvercoming the Limitations of Buried SensorsWatering devicesForecastingControl systemCrop coefficient
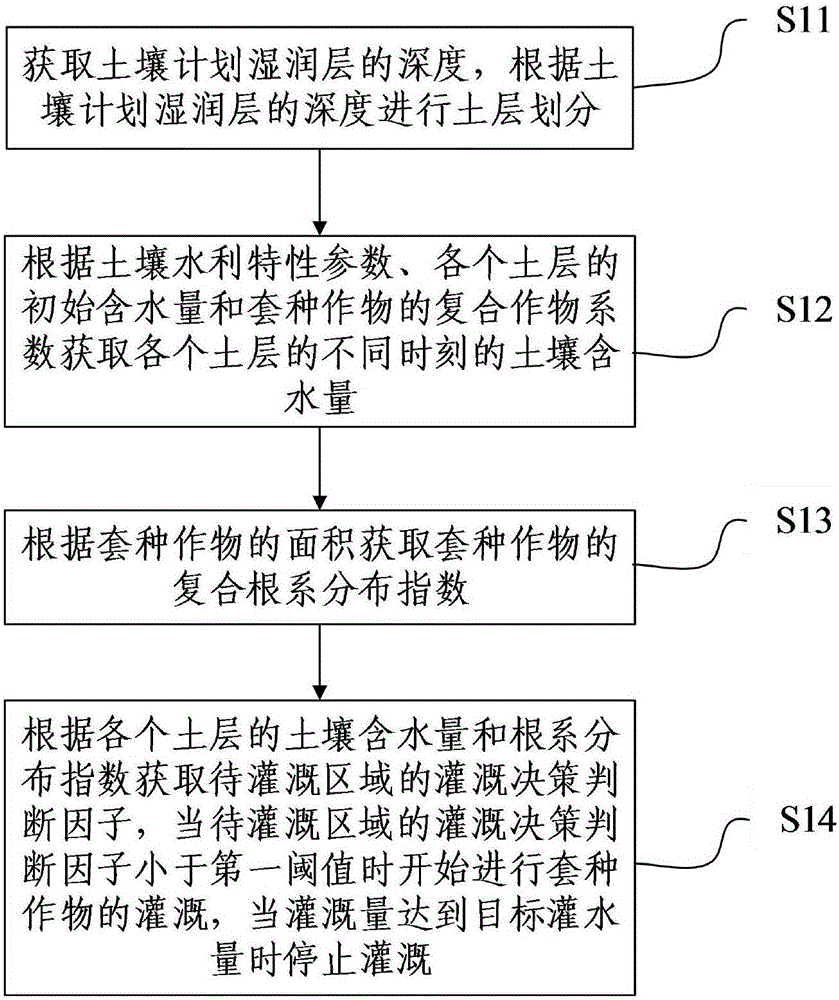
The invention relates to a control method for automatic irrigation of interplanted crops. The method comprises the steps of acquiring depth of a soil designed moisting layer, and performing soil dividing according to the depth of soil designed moisting layer; acquiring soil water contents of each soil layer at different time points according to water characteristic parameters of the soil, initial water content of each soil layer and a composite crop coefficient of the interplanted crops; acquiring a composite root system distribution coefficient of the interplanted crops according to the area of the interplanted crops; acquiring an irrigation decision determination factor of a to-be-irrigated area according to the soil water content and the root system distribution coefficient of each soil layer, starting irrigation of the interplanted crops when the irrigation decision determination factor is smaller than a first threshold, and stopping irrigation when the irrigation amount reaches a target irrigation amount. The control method can be used for performing automatic irrigation on the interplanted crops based on accurate acquiring for soil water conteint information in an interplant mode. The control method has advantages of ensuring high yield of the crops and realizing water content utilization efficiency maximization.
Owner:NINGXIA HUI AUTONOMOUS REGION TANGLAI DRAINAGE MANAGEMENT
Winter wheat water consumption predicting method based on weather forecast information
InactiveCN103886392AIncrease profitImprove utilization efficiencyForecastingField trialWater requirement
The invention provides a winter wheat water consumption predicting method based on weather forecast information. With comprehensive consideration of influences of the crop self-growth-and-development situation and the environment factors including the meteorological condition, the soil condition and the like, a prediction model for estimating the reference crop water requirement (ET0) based on the weather forecast information and a model for estimating a winter wheat crop coefficient based on accumulative temperature are established through field trials and numerical simulation, the prediction model and the model for estimating the winter wheat crop coefficient are coupled into a water balance equation, real-time prediction is conducted on the soil moisture content of winter wheat in a Guangli irrigated area and a people victory canal irrigated area, and irrigation date and irrigating water quota are determined according to irrigating index of different growth periods of the winter wheat so that real-time monitoring of the soil moisture content, drought severity comprehensive analysis and real-time prediction of crop irrigation are achieved. The visual decision basis is provided for an irrigation management layer and a decision maker, timely and appropriate amount of irrigation is instructed for the irrigated areas, and the utilization rate and utilization efficiency of an irrigation water resource of the irrigated areas are improved.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Crop irrigation water requirement calculation method on future climatic conditions
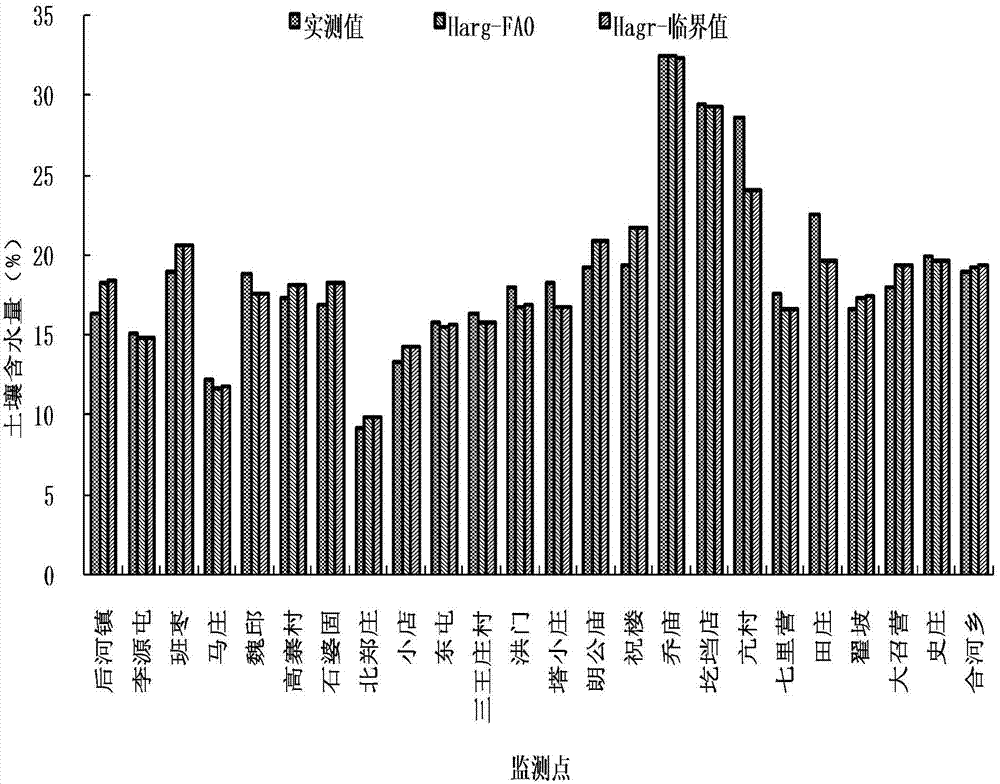
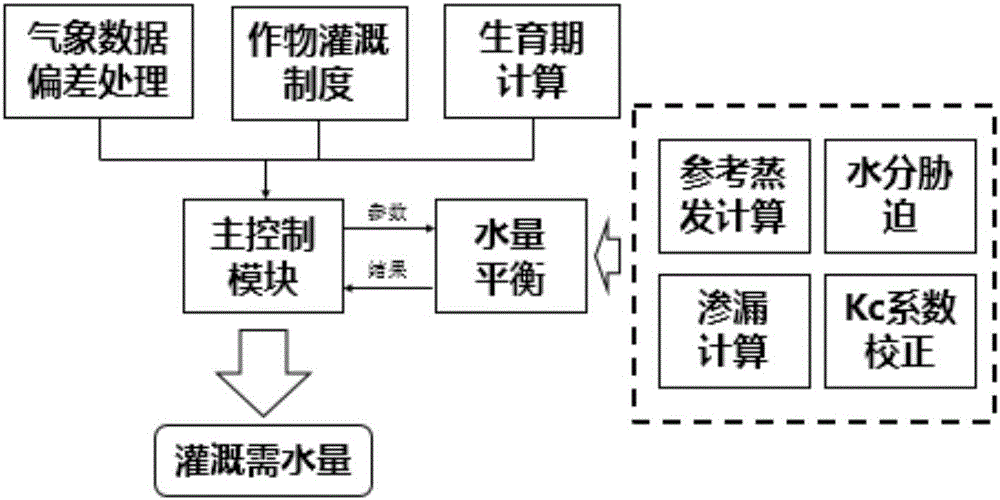
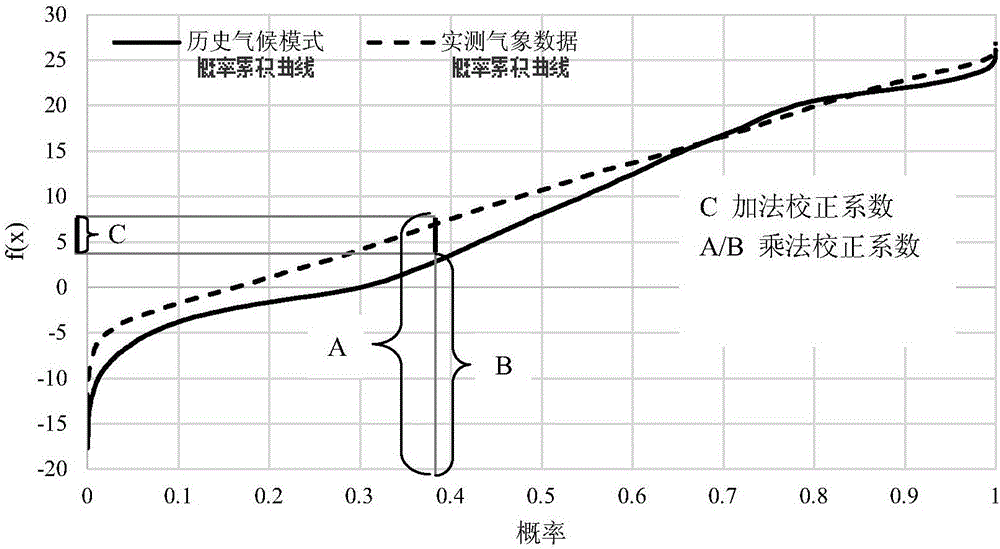
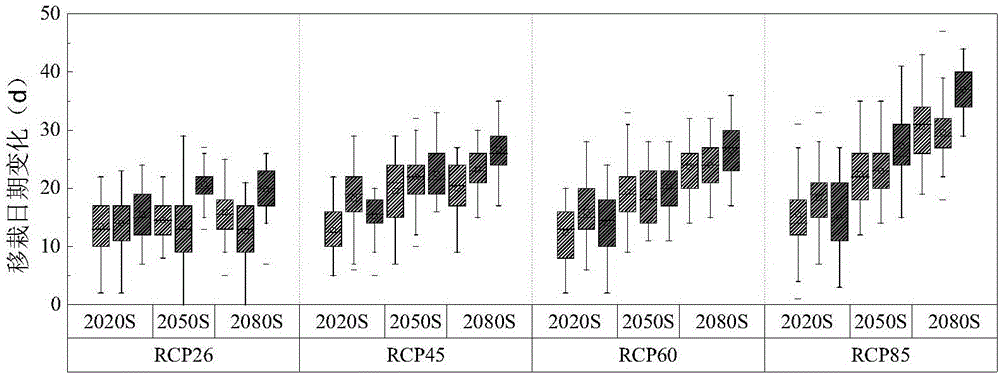
The present invention discloses a crop irrigation water requirement calculation method on future climatic conditions. The method comprises the steps of collecting the future climatic mode data, and correcting the future climatic mode data based on the historical actually measured meteorological data to enable the future climatic mode data to be suitable for the climatic change influence evaluation of a region or station scale; according to the growth period data of a crop field test and an accumulated temperature formula, constructing a response model of the crop planting date and the crop growth period length to the temperature; utilizing a penman formula to combine a single crop coefficient method and a soil moisture stress coefficient to calculate the crop daily water requirement; based on a crop irrigation system and a water balance principle to calculate the crop daily irrigation water requirement. Aiming at the influence of the climatic change on the agricultural water resource security, the method of the present invention considers the change of the crop planting date and the growth period caused by the global warming, so that a water resource planning management department can forecast the regional future agricultural water resource utilization amount more accurately, and accordingly, a water resource planning scheme is proposed more reasonably.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Automatic irrigation control method based on water balance model
InactiveCN106508622AHigh control precisionSmall amount of calculationClimate change adaptationWatering devicesSoil typeCrop coefficient
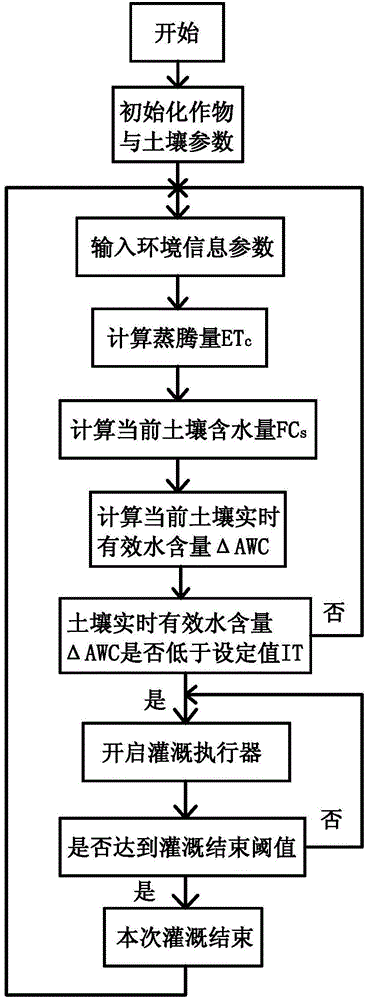
The invention discloses an automatic irrigation control method based on a water balance model. The method comprises the steps of A, initializing parameters, wherein the type and the planting date of the planted crops are determined, and a corresponding crop coefficient Kc is obtained; the soil type is determined, and corresponding wilting water content WP, field capacity WHC and irrigation threshold value IT are obtained; B, calculating current soil water content FCs; C, calculating effective water content AWC of current soil; D, calculating actual evapotranspiration ETc; E, calculating soil real-time effective water content delta AWC; F, judging whether the soil real-time effective water content delta AWC is lower than the irrigation threshold value IT, if the soil real-time effective water content delta AWC is lower than the irrigation threshold value IT, conducting irrigation; if the soil real-time effective water content delta AWC is not lower than the irrigation threshold value IT, turning to the step E to continue calculation. According to the automatic irrigation control method based on the water balance model, defects of the prior art can be overcome, and precision and flexibility of the irrigation control can be improved.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Method and device for determining irrigation system
InactiveCN109819882AAccurately determineTroubleshoot technical issues with poor accuracyWatering devicesResourcesCrop coefficientUltimate tensile strength
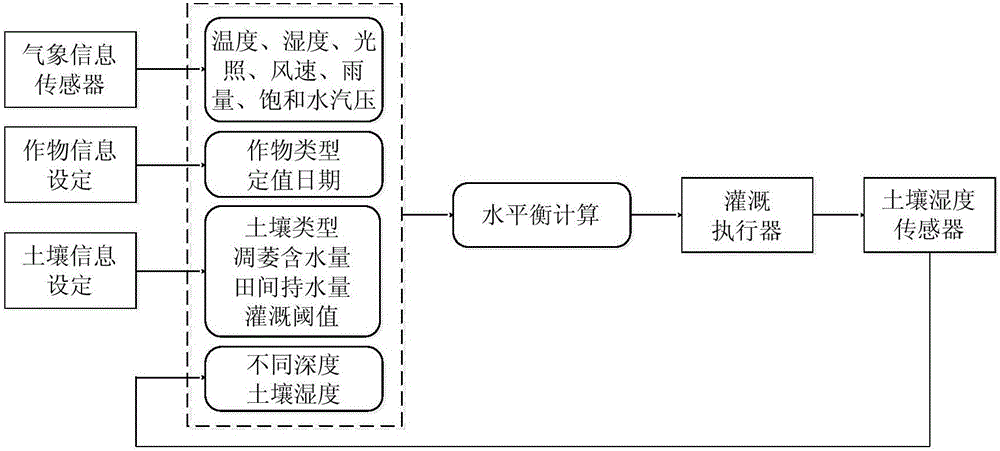
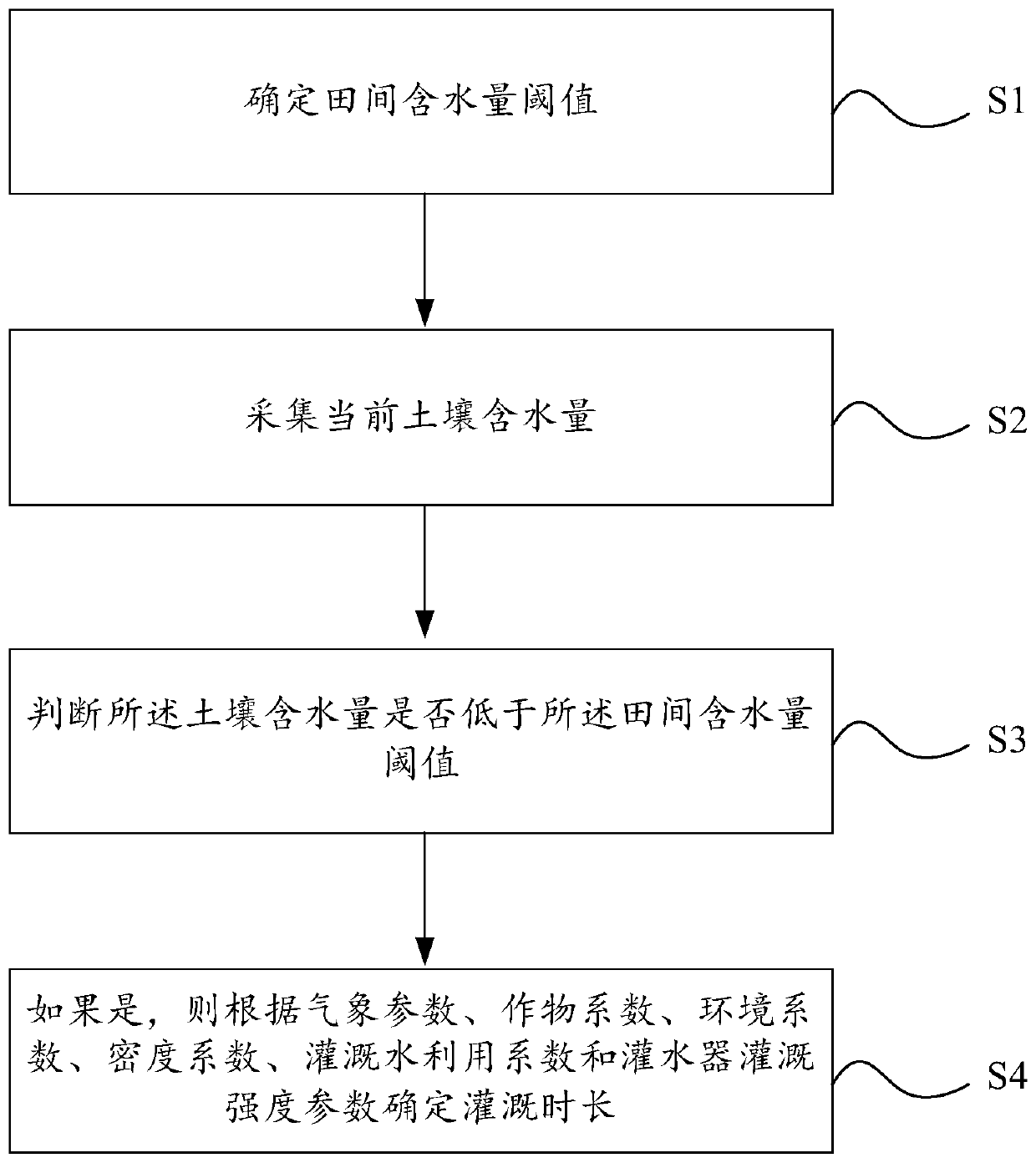
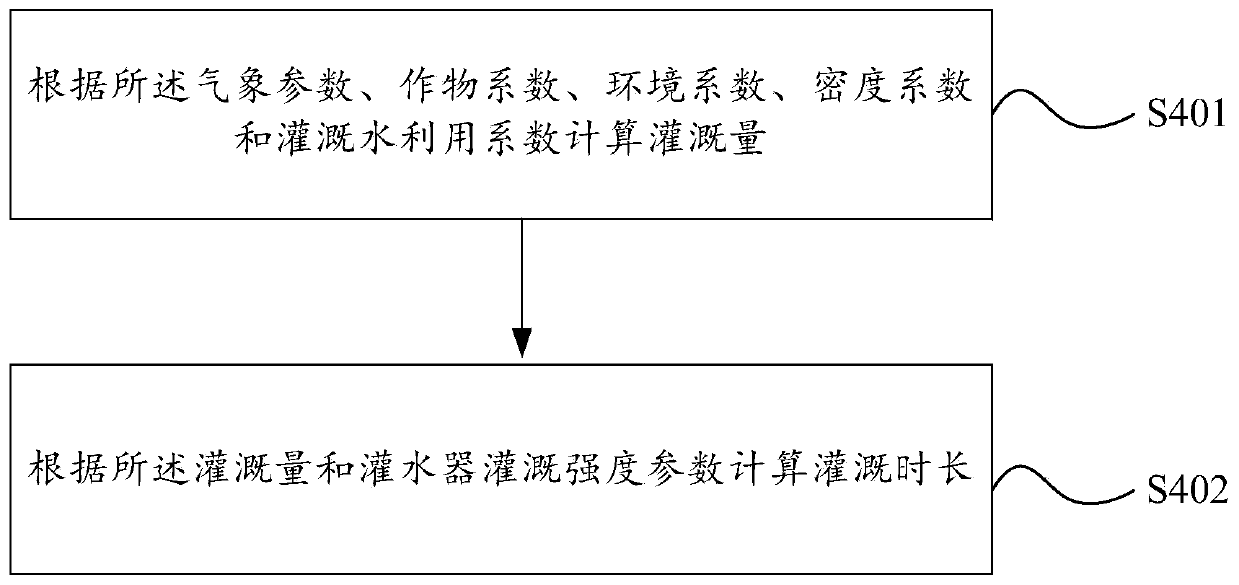
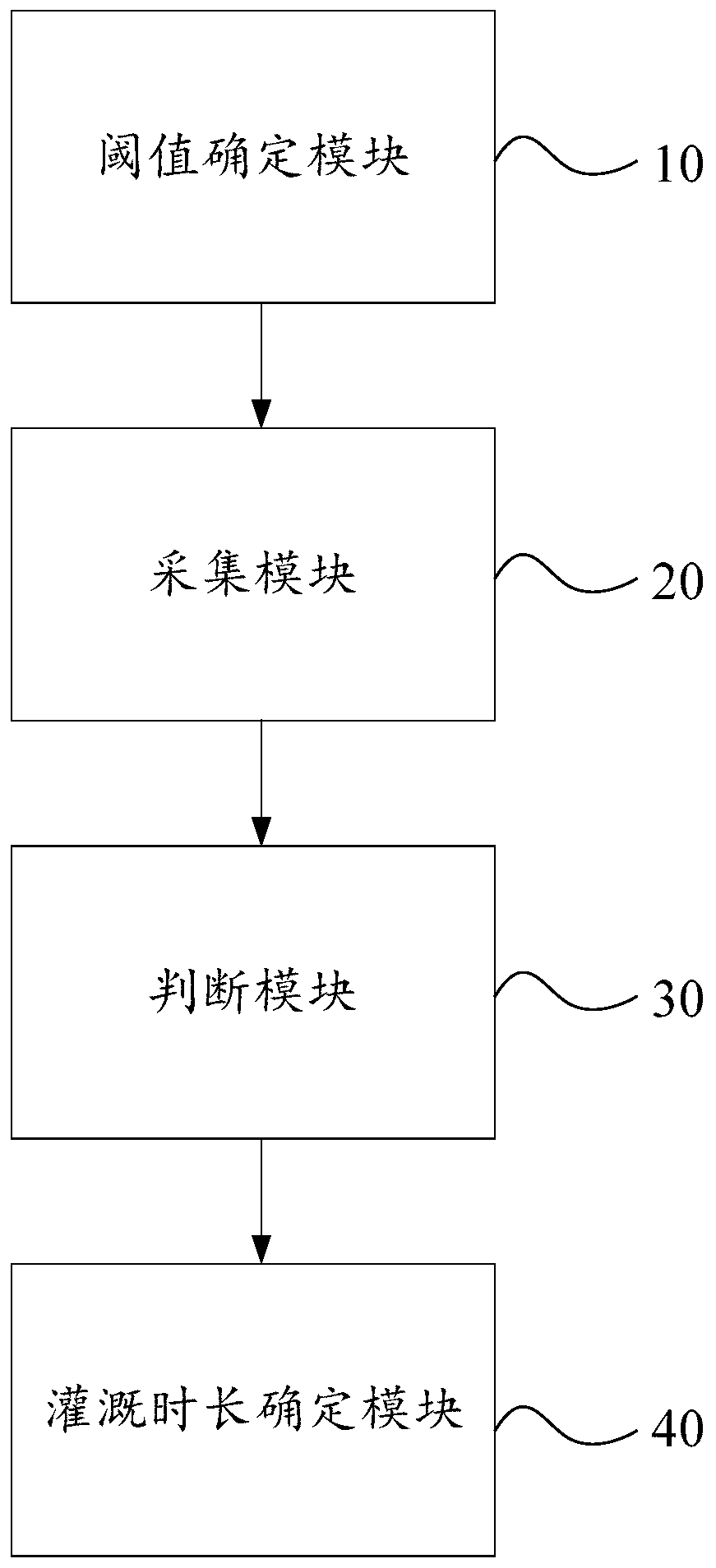
The invention discloses a method and device for determining the irrigation system. The method comprises the following steps that a threshold value of the content of water in a farming area is determined; the current content of water in soil is collected; whether or not the current content of the water in the soil is lower than the threshold value of the content of the water in the farming area isjudged; if yes, the irrigation time is determined according to meteorological parameters, a crop coefficient, an environment coefficient, a density coefficient, an irrigation water utilization coefficient and irrigation intensity parameters of an irrigation emitter. The device for determining the irrigation system comprises a threshold value determining module, a collection module, a judging module and an irrigation time determining module. The method and device solve the technical problem in the prior art that multiple influencing factors in the actual environment are not considered, so thatthe accuracy of the irrigation system is poor.
Owner:HAONONGYI E COMMERCE CO LTD
Irrigation method based on dynamic multilayer extreme learning machine
ActiveCN107466816AImprove generalization abilityImprove stabilityWatering devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning machineIrrigated crops
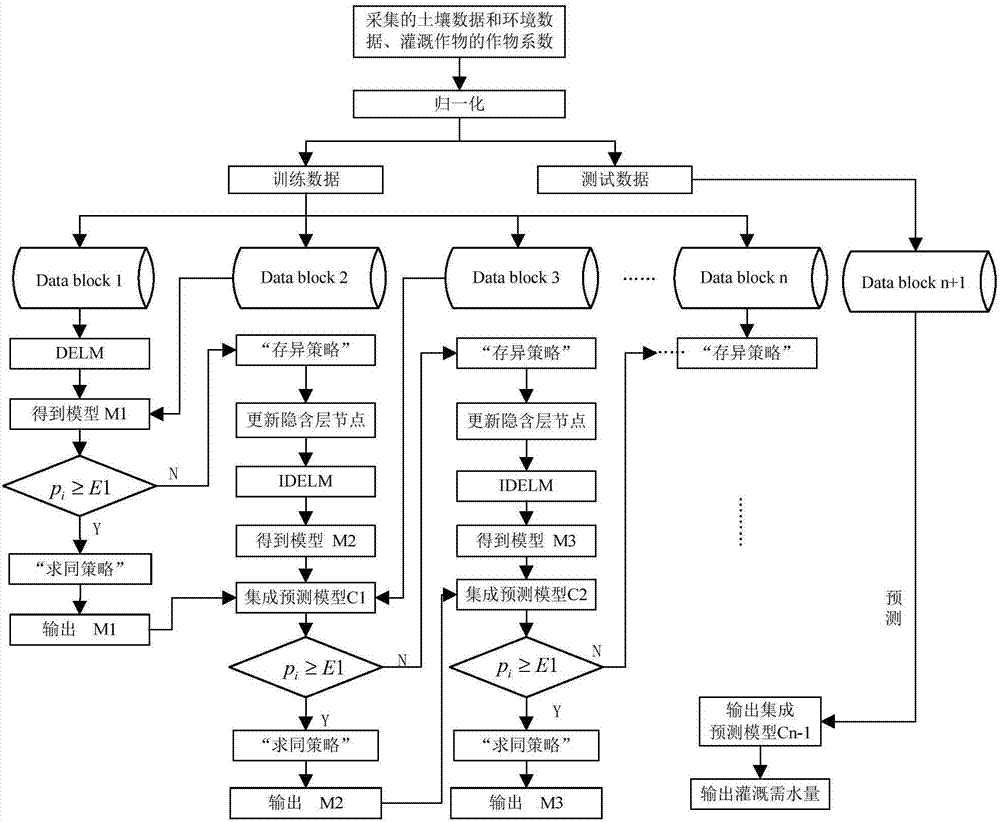
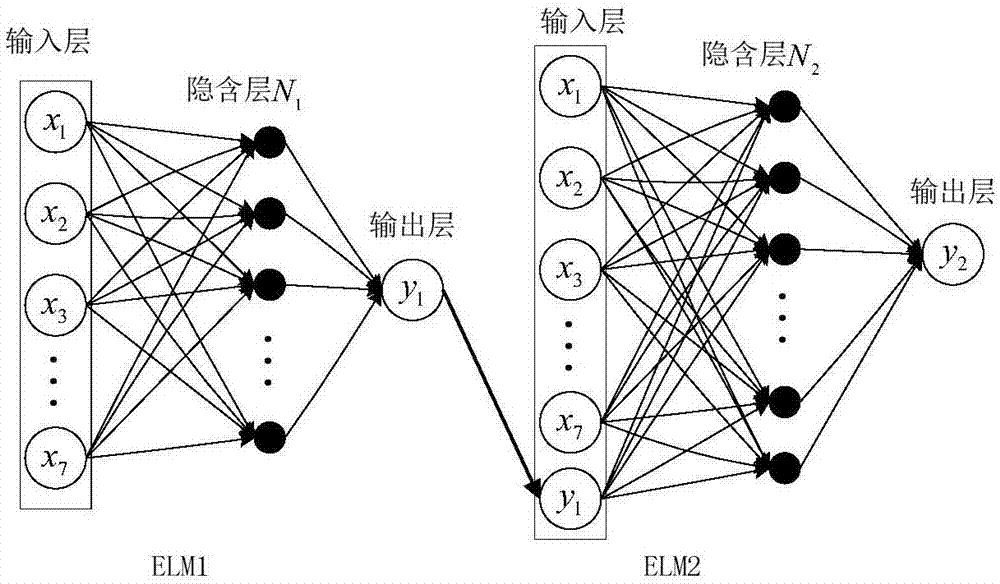
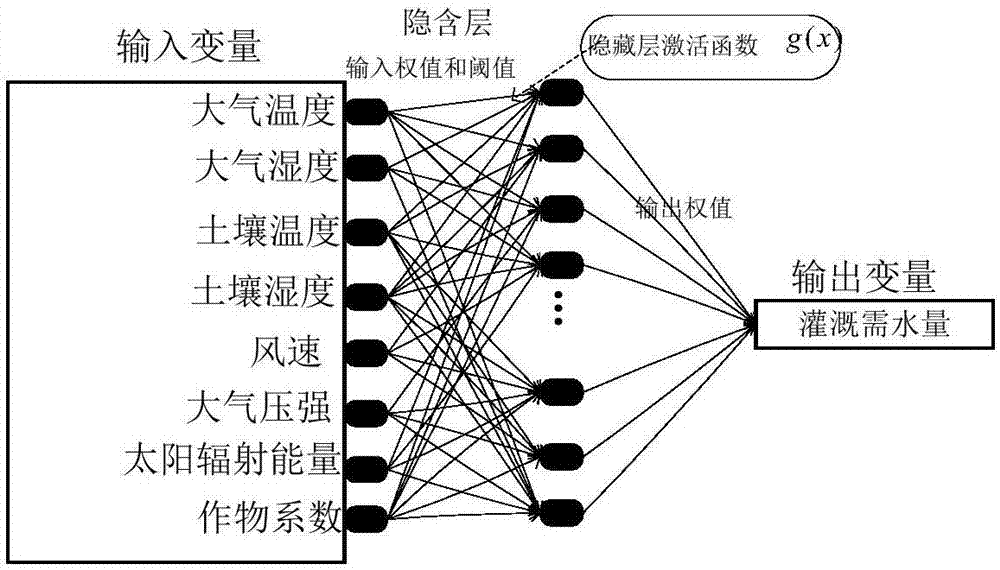
The invention relates to an irrigation method based on a dynamic multilayer extreme learning machine. The irrigation method comprises first collecting a plurality of training data, which comprises soil environment data, meteorological data and crop coefficients of irrigated crops; then performing normalization processing on each group of the training data to form a training set; training the multilayer extreme learning machine by using the training set to obtain a final model; and finally collecting test data, performing normalization processing on the test data, inputting the processed test data into the final model so as to obtain a predicted water amount required by irrigation, and performing irrigation according to the predicted water amount required by irrigation. In the irrigation method provided by the invention, a strategy of ''seeking common points while reserving difference'' is adopted according to calculation accuracy. If the calculation result of the re-input data by using a model meets the accuracy requirement, the model is output, otherwise incremental learning training is performed on the basis of the existing model to obtain a dynamically adjusted model. The irrigation method provided by the invention increases the calculation accuracy of water volumes required by irrigation, reduces the time consumption and calculation cost of prediction of the water volumes required by irrigation, and reaches the goals of reasonable use of water resources and reasonable irrigation of crops.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Irrigation decision-making method and irrigation decision-making device based on weather forecast
ActiveCN110754344AEasy to implementGuaranteed accuracyWeather condition predictionWatering devicesCrop evapotranspirationSoil science
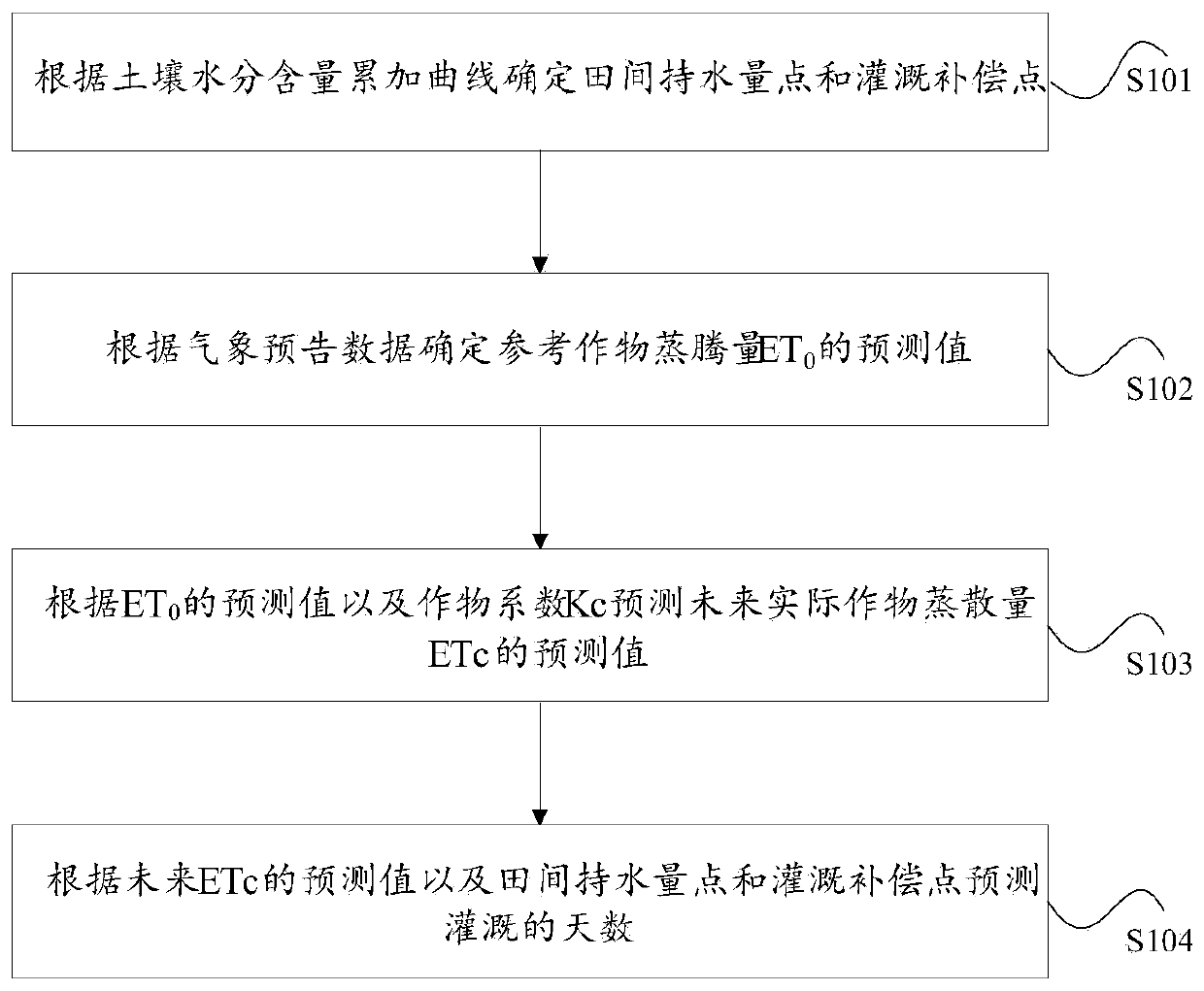
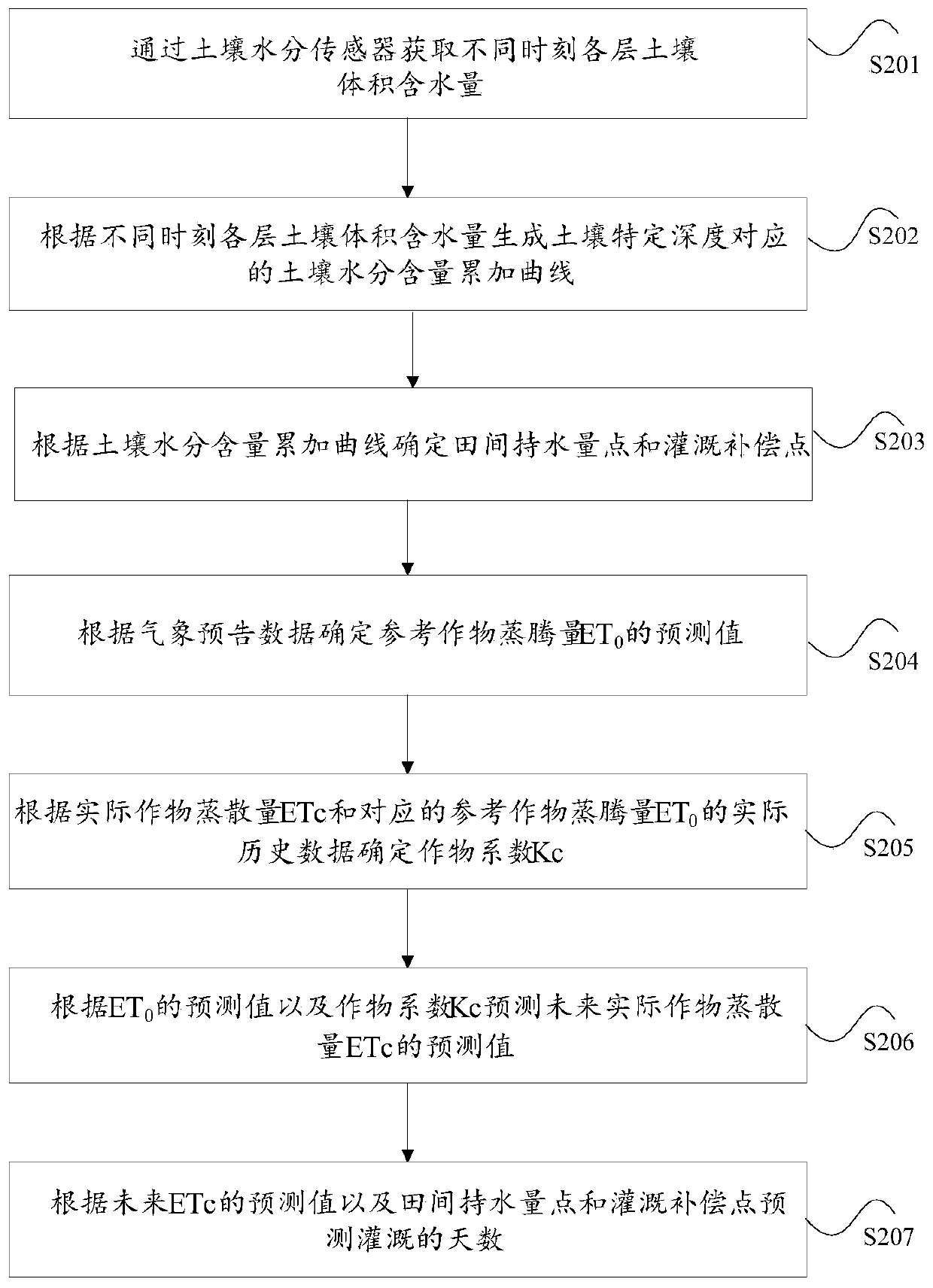
The invention discloses an irrigation decision-making method and an irrigation decision-making device based on weather forecast. The method includes determining a field water holding point and an irrigation compensation point according to a soil moisture content accumulation curve, wherein the soil moisture content accumulation curve is a curve showing time-dependent changes of the soil volumetricwater content corresponding to a specific soil depth; determining a predicted value of reference crop evapotranspiration ET0 according to weather forecast data; predicting a predicted value of actualcrop evapotranspiration ETc in the future according to the predicted value of the ET0 and a crop coefficient Kc; and predicting the number of irrigation days according to the predicted value of the ETc in the future, the field water holding point and the irrigation compensation point. By the method and the device, the problem of complexity of related irrigation forecasting ways is solved.
Owner:京蓝物联技术(北京)有限公司
Systems and methods for planning crop irrigation
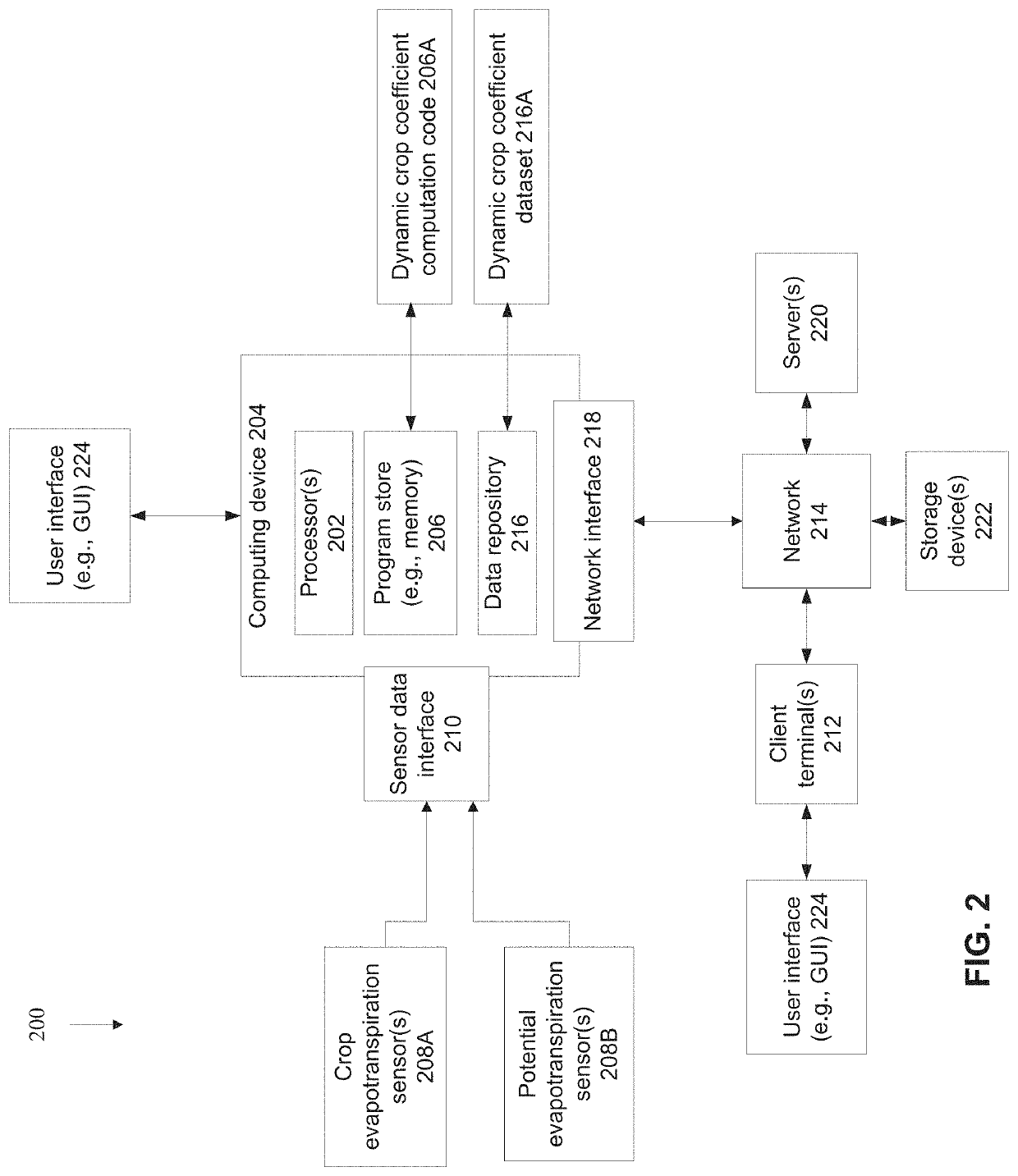
ActiveUS20200241579A1Relieve stressAccurate calculationData processing applicationsComputer controlCrop evapotranspirationAgricultural engineering
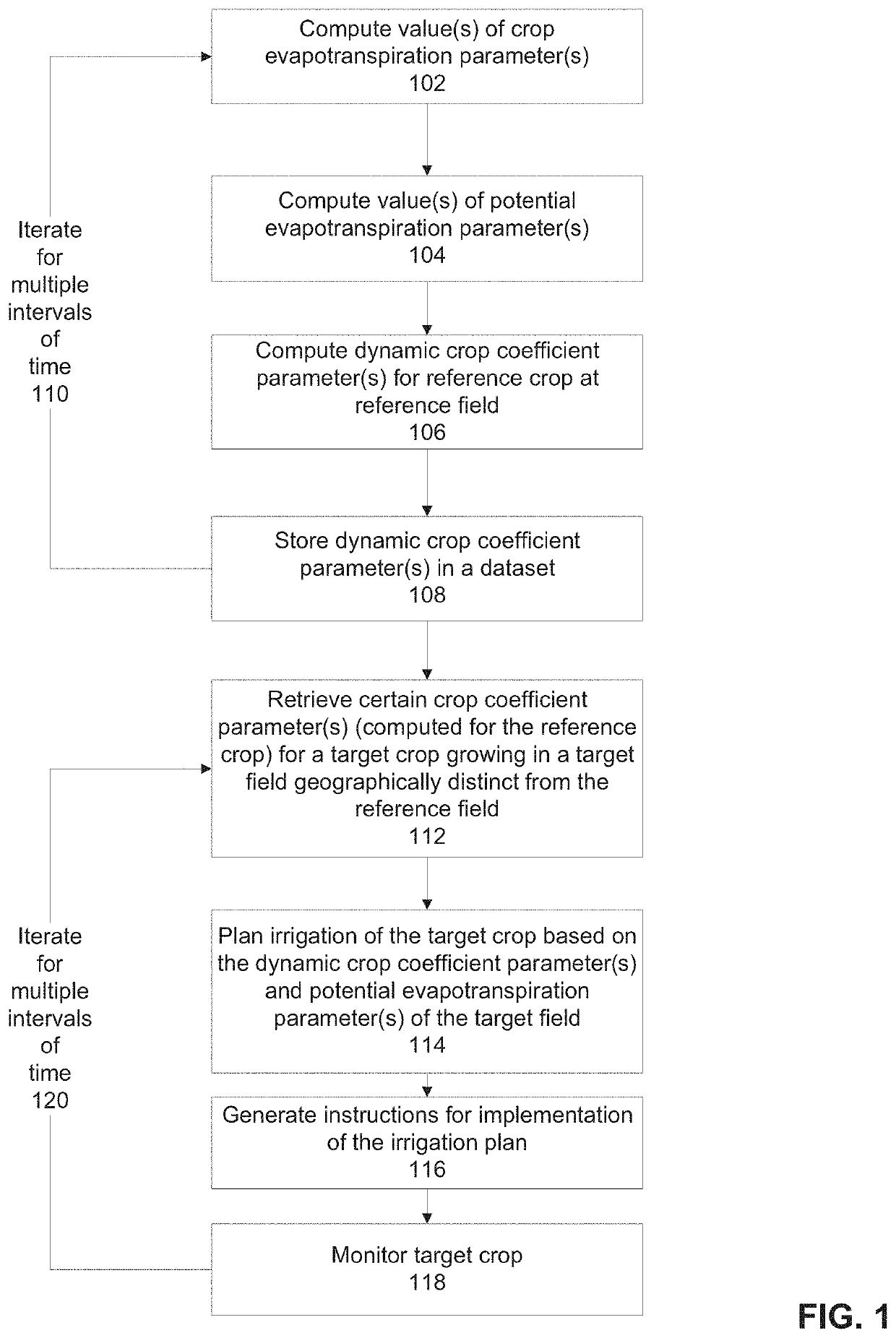
There is provided a method of planning irrigation, comprising: performing for a certain interval of time: computing a value of a crop evapotranspiration parameter indicative of an amount of water consumed by a reference crop, computing a value of a potential evapotranspiration parameter indicative of weather conditions associated with the field of the reference crop, computing a value of a dynamic crop coefficient for the reference crop based on the crop evapotranspiration parameter and the potential evapotranspiration parameter, and providing the dynamic crop coefficient computed for the certain time interval of time of the reference crop that corresponds to a target time interval of a target growing season of the target crop, wherein the target crop is growing in a target field which is geographically distinct from the reference field, and outputting instructions for irrigation of the target crop according to an irrigation plan based on the dynamic crop coefficient.
Owner:SUPPLANT LTD
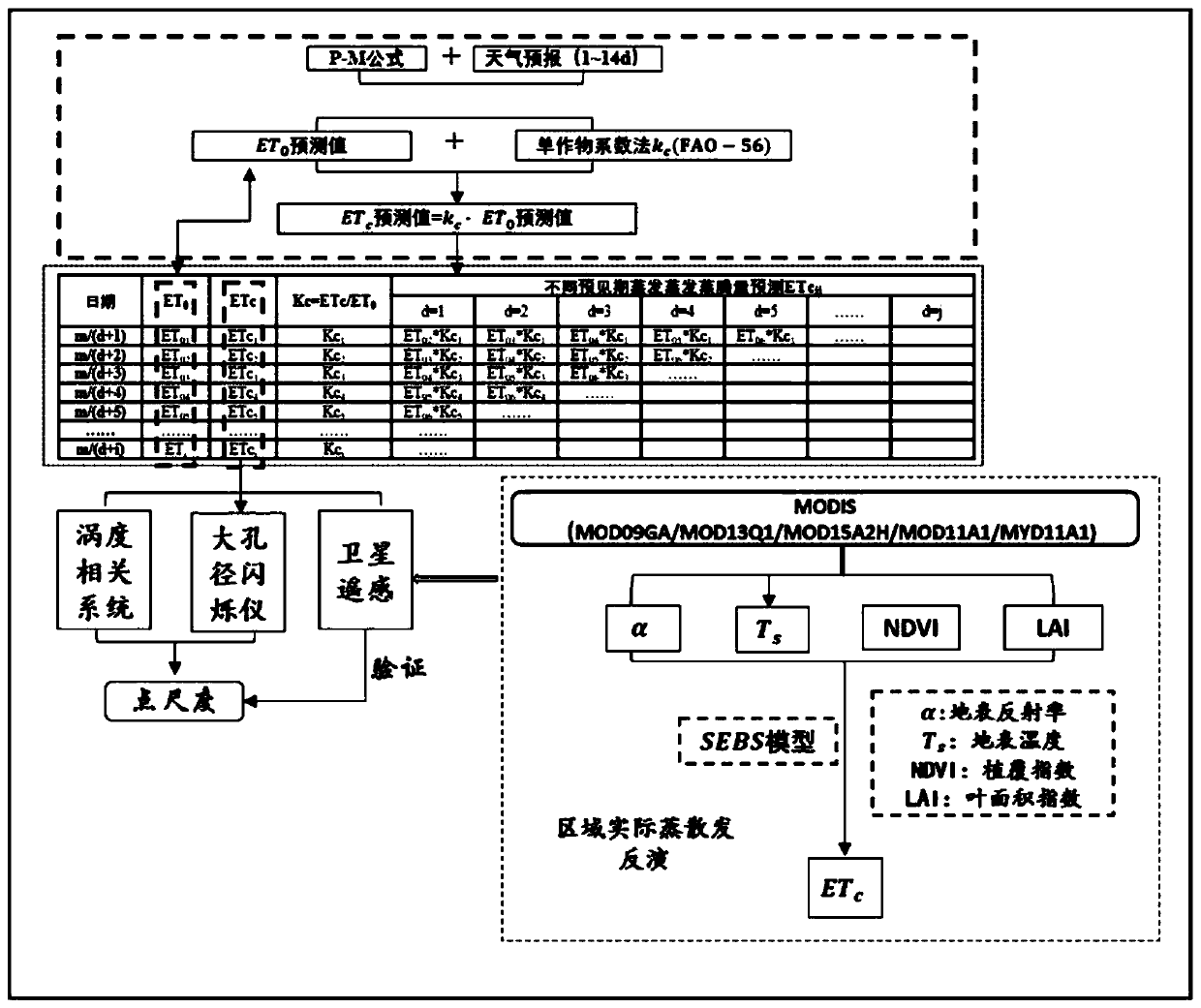
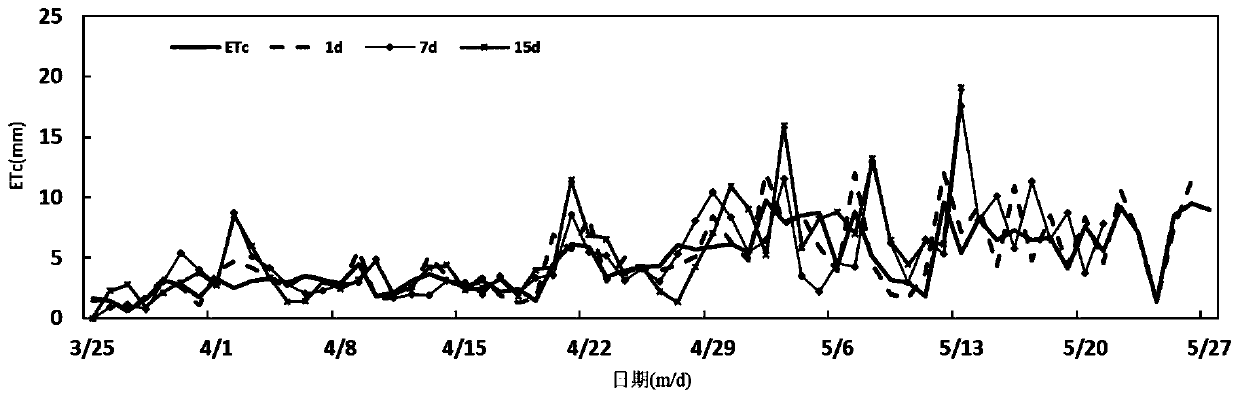
Different-forecast-period area crop ETc prediction and forecast method
ActiveCN110501761AAccurate access to heterogeneityImprove forecast accuracyWeather condition predictionWatering devicesSensing dataCrop coefficient
The invention discloses a different-forecast-period area crop ETc prediction and forecast method. ET0 is calculated by adopting a standard method Penman formula based on meteorological data, a crop ETc is acquired according to a vorticity correlator, and further a crop coefficient Kc is acquired on the basis of an FAO-56 single crop coefficient method. Therefore, in a 1d prediction period of the Etc, the ETc of a (n-1)th day is acquired according to the ET0 of an nth day and the crop coefficient Kc of the (n-1)th day, and the ETc of the nth day is acquired according to the ET0 of the (n+1)th day and Kc of the nth day; and in a 2d prediction period of the ETc, the ETc of a (n-2)th day is acquired according to the ET0 of the nth day and the crop coefficient Kc of the (n-2)th day and the ETcof the nth day is acquired according to the ET0 of the (n+2)th day and the Kc of the nth day. And crop ETc prediction values of different prediction periods are obtained in the same way. Subsequently,remote sensing data is used for improving a regional scale, the method can be used to reduce an influence of uncertainty of weather forecast data on ET0 prediction, and heterogeneity of the ETc of regional crops can be accurately obtained.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Farmland evapotranspiration short-term prediction method
ActiveCN111461909AHigh applicability for short-term forecastingImprove forecast accuracyForecastingSoil scienceCrop evapotranspiration
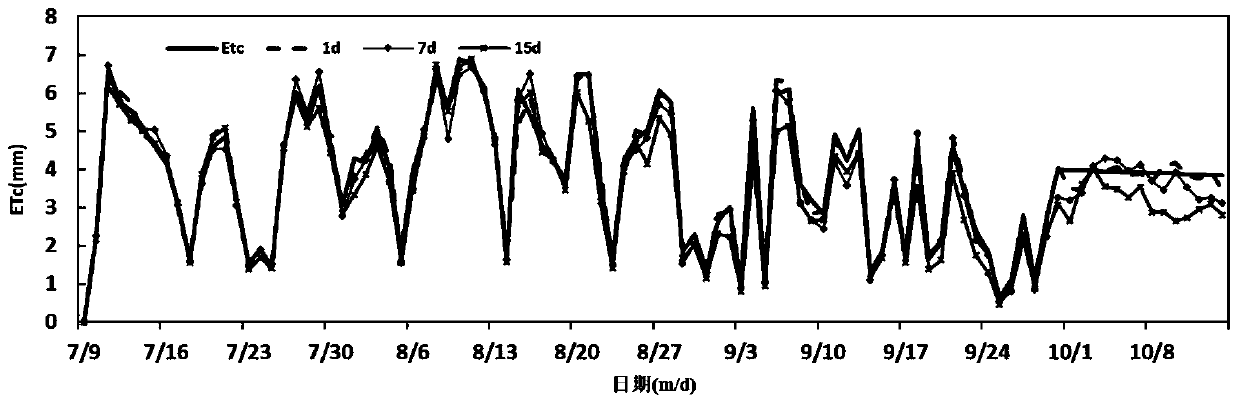
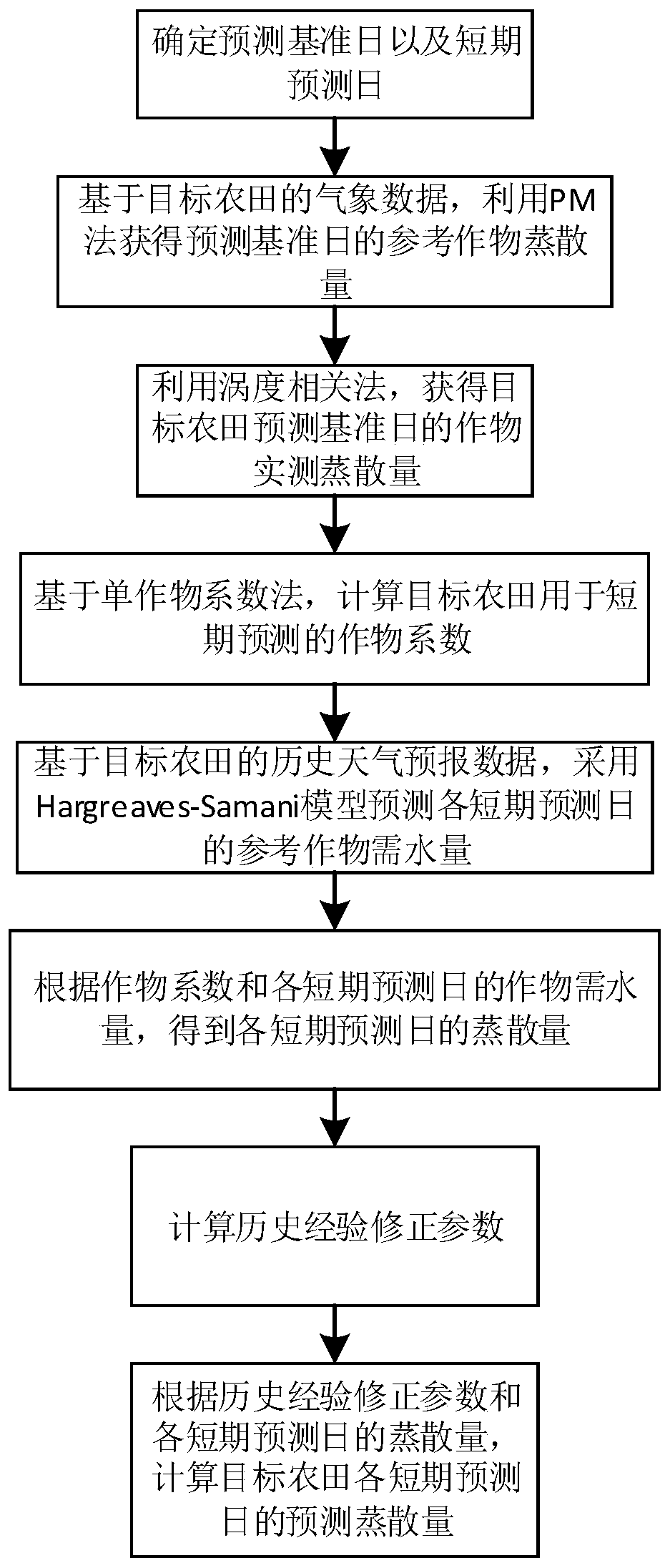
The invention discloses a farmland evapotranspiration short-term prediction method, which relates to the technical field of crop monitoring and comprises the steps of determining a prediction reference date and a short-term prediction date; obtaining a reference crop evapotranspiration ET0 of the prediction reference day by using a PM method; obtaining the actual crop evapotranspiration ETc of thetarget farmland prediction reference date by using a vorticity related system; calculating a crop coefficient Kc of the target farmland for short-term prediction; predicting a reference crop water demand ET '0 of each short-term prediction day by adopting a Hargeavies-Samani model; obtaining evapotranspiration ET'c of each short-term prediction day; calculating a historical experience correctionparameter alpha; and calculating the predicted evapotranspiration ET ''c of each short-term prediction day of the target farmland to complete the short-term prediction of the evapotranspiration of thefarmland. The method is higher in application value, high in prediction precision and good in stability for farmland evapotranspiration short-term prediction, and a scientific basis is provided for farmland moisture management in a plain region in the future.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
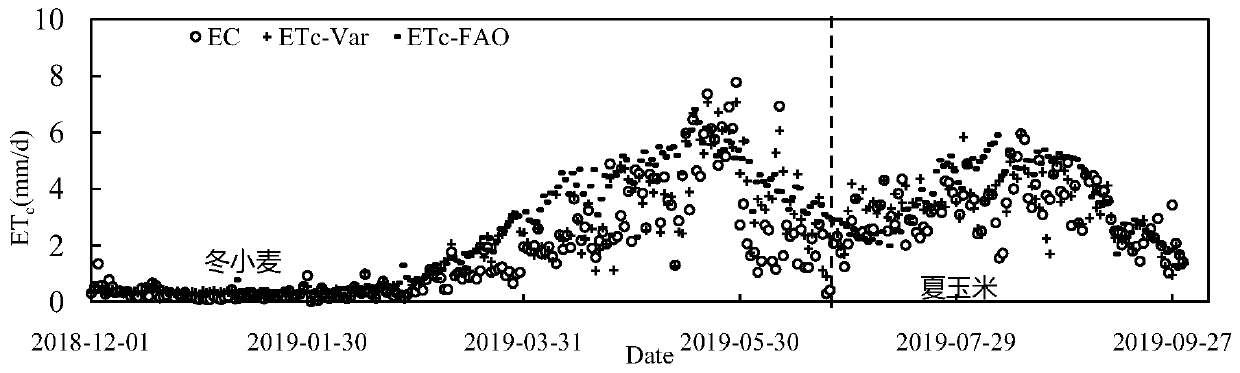
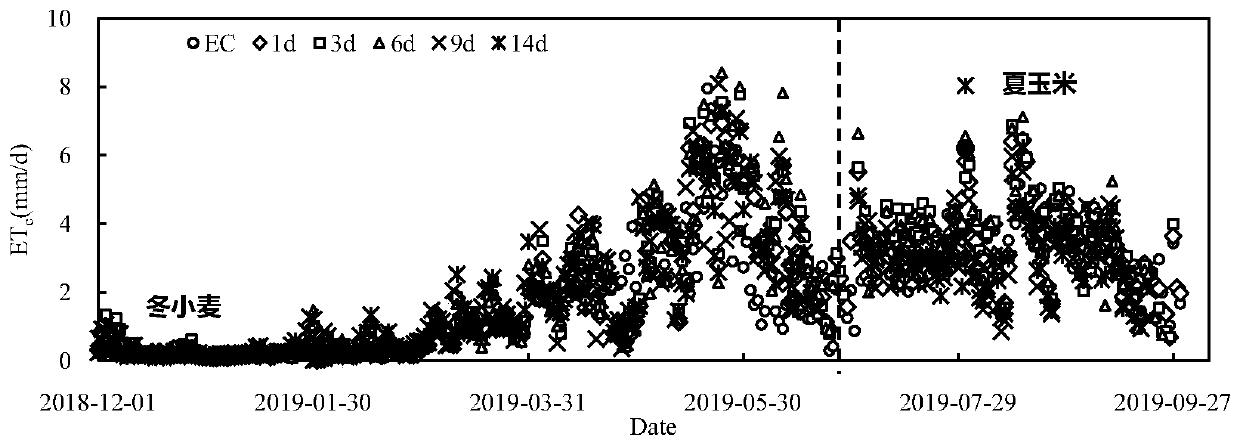
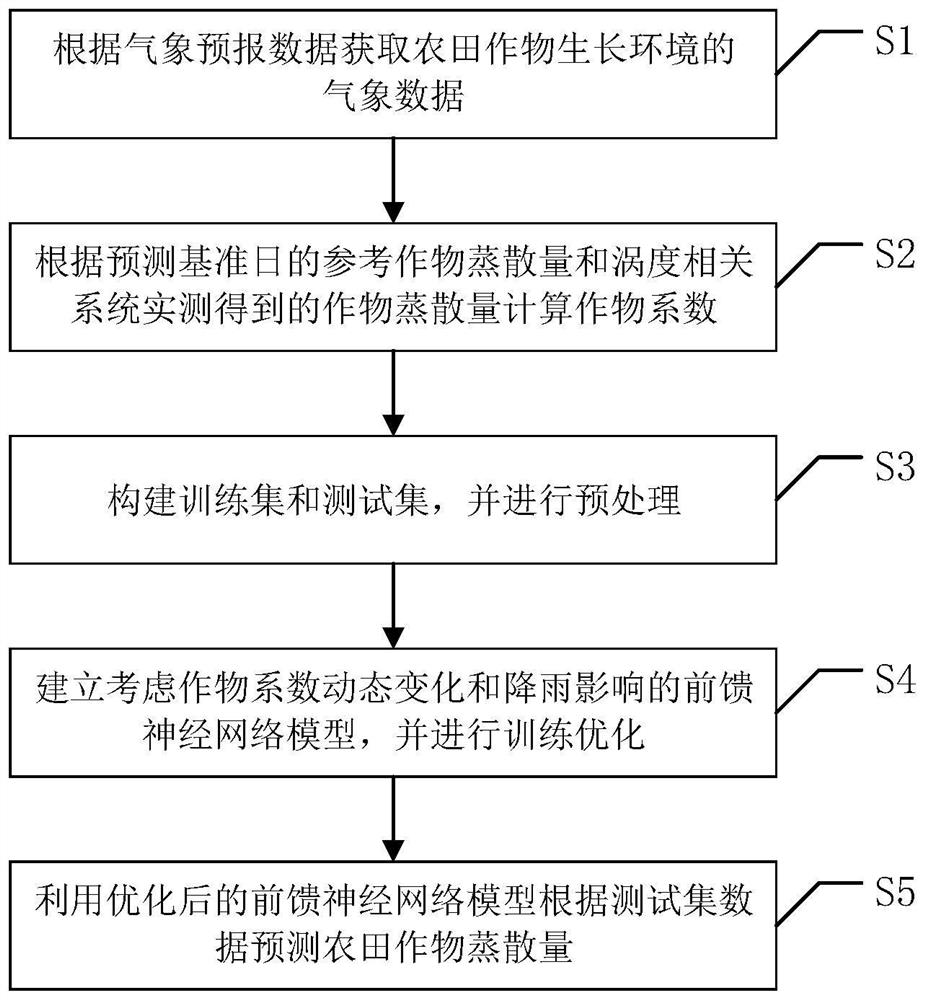
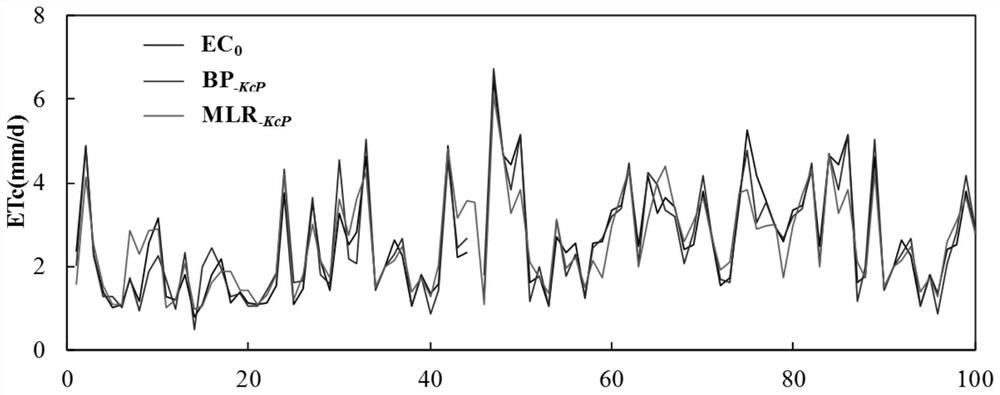
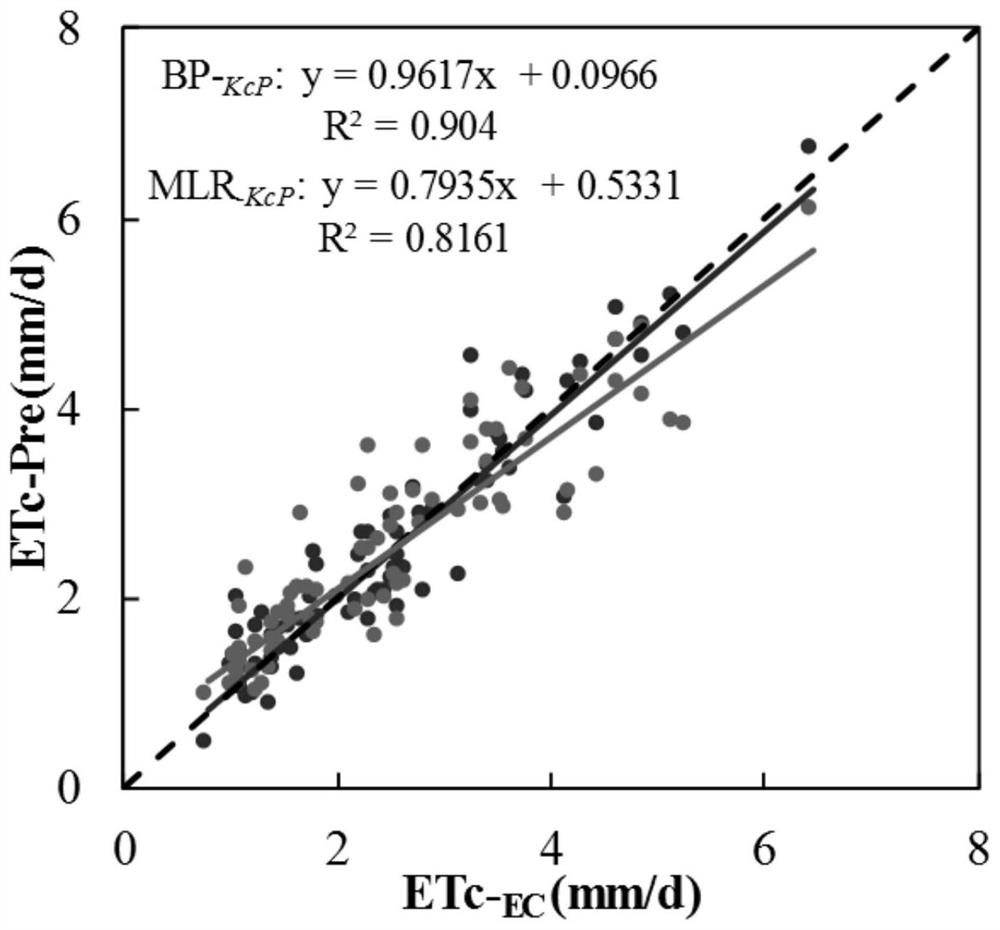
Farmland evapotranspiration short-term prediction method considering crop coefficient dynamic change and rainfall
ActiveCN111833202AEvapotranspiration meetsIn line with the actual growth conditionsForecastingNeural architecturesCrop evapotranspirationNerve network
The invention discloses a farmland evapotranspiration short-term prediction method considering crop coefficient dynamic change and rainfall. The method comprises the steps of obtaining meteorologicaldata of a farmland crop growth environment; calculating a crop coefficient of the prediction reference date according to the reference crop evapotranspiration of the prediction reference date and theactually measured evapotranspiration of the farmland; respectively constructing a training set and a test set, and carrying out preprocessing; establishing a feedforward neural network model considering crop coefficient dynamic change and rainfall influence, and performing training optimization; and utilizing the optimized feedforward neural network model to predict the evapotranspiration of the farmland crops in a short term according to the test set data. The influence of crop coefficient change and rainfall on the farmland crop evapotranspiration is considered, the nonlinear relation between the farmland reference crop evapotranspiration and driving factors of the farmland reference crop evapotranspiration is effectively constructed, accordingly, the crop evapotranspiration better meeting the actual growth condition of crops can be obtained, and a scientific basis is provided for future moisture management of the farmland underlying surface.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Crop coefficient estimation method based on crop stress index
InactiveCN106771056AWell formedAddressing the limitations of adequate water supply requirementsEarth material testingTesting plants/treesAgricultural scienceCrop evapotranspiration
The invention discloses a crop coefficient estimation method based on crop stress index. According to the estimation method, a crop water stress index (CWSI) and a crop coefficient (Kc) calculation formula are combined to obtain a theoretical model that utilizes a practical crop evapotranspiration (Eta) and CWSI to estimate Kc. The method has the advantages that the Eta data is easy to obtain; the sufficient water supply condition, which is required in conventional crop coefficient calculation, is not needed; and the whole calculation of crop coefficient is simplified.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Accurate irrigation method and system for crops, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114698535AHigh precisionReduce wasteWatering devicesForecastingSoil scienceCrop coefficient
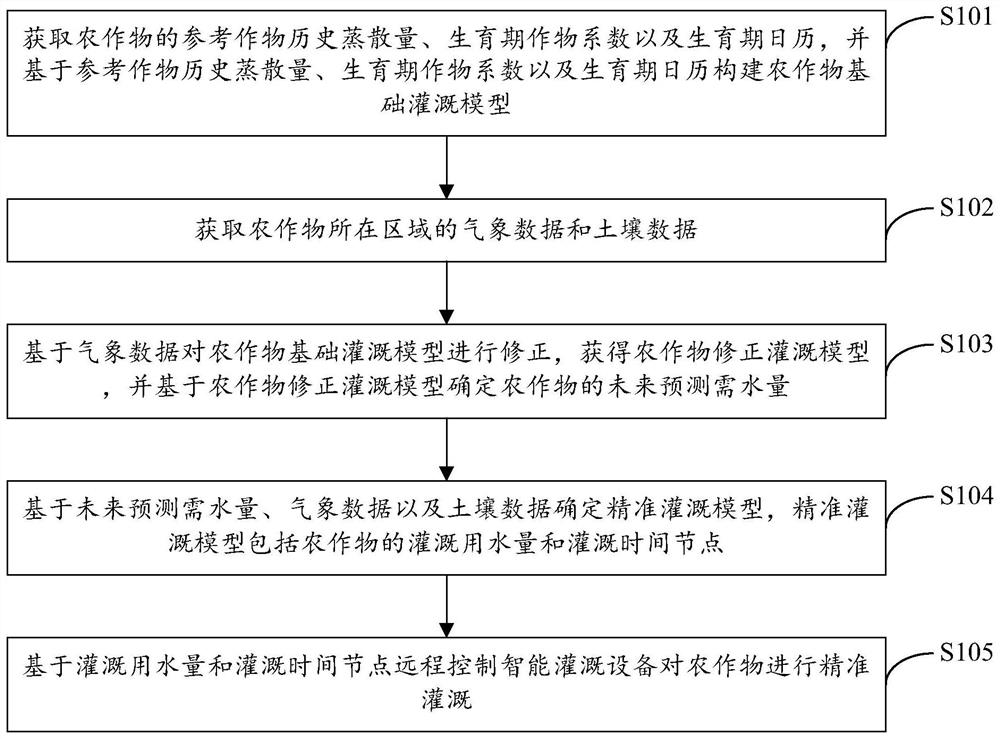
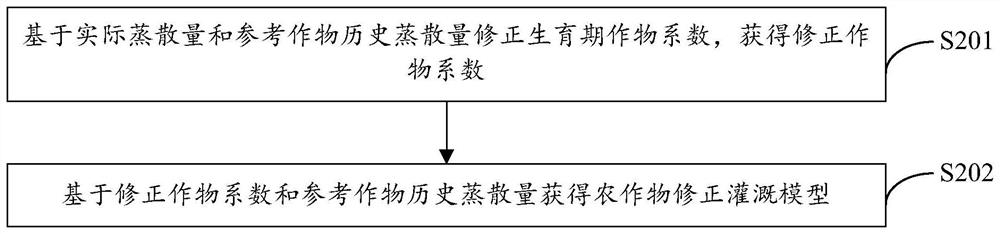
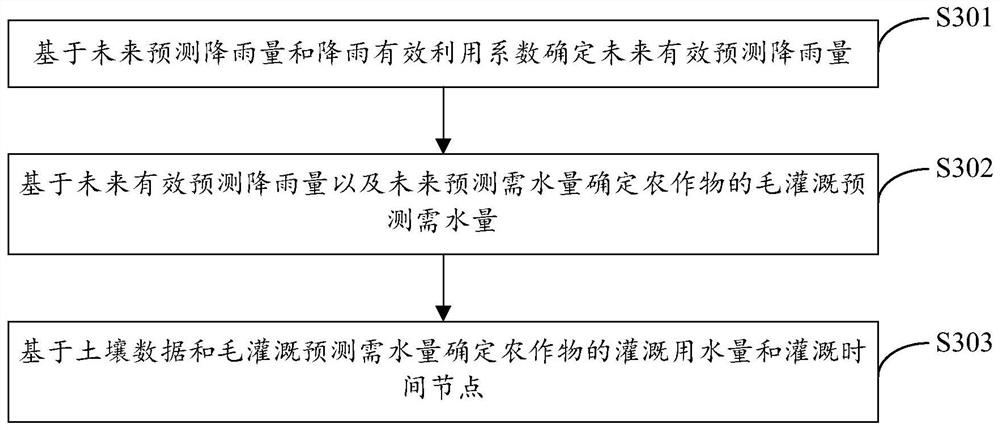
The invention provides a crop precise irrigation method and system, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a reference crop historical evapotranspiration, a growth period crop coefficient and a growth period calendar of a crop, and constructing a crop basic irrigation model based on the reference crop historical evapotranspiration, the growth period crop coefficient and the growth period calendar; acquiring meteorological data and soil data of an area where crops are located; correcting the crop basic irrigation model based on the meteorological data to obtain a crop corrected irrigation model, and determining the future predicted water demand of the crops based on the crop corrected irrigation model; determining a precise irrigation model based on the future predicted water demand, the meteorological data and the soil data, wherein the precise irrigation model comprises irrigation water consumption and irrigation time nodes of crops; and based on the irrigation water consumption and the irrigation time node, the intelligent irrigation equipment is remotely controlled to accurately irrigate crops. According to the invention, the accuracy of irrigating crops can be improved.
Owner:武汉禾大科技有限公司
Fuzzy control irrigation method for rice seedling raising in hard land
PendingCN114002951ARealize water saving and energy savingSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationAgricultural engineeringDrip irrigation
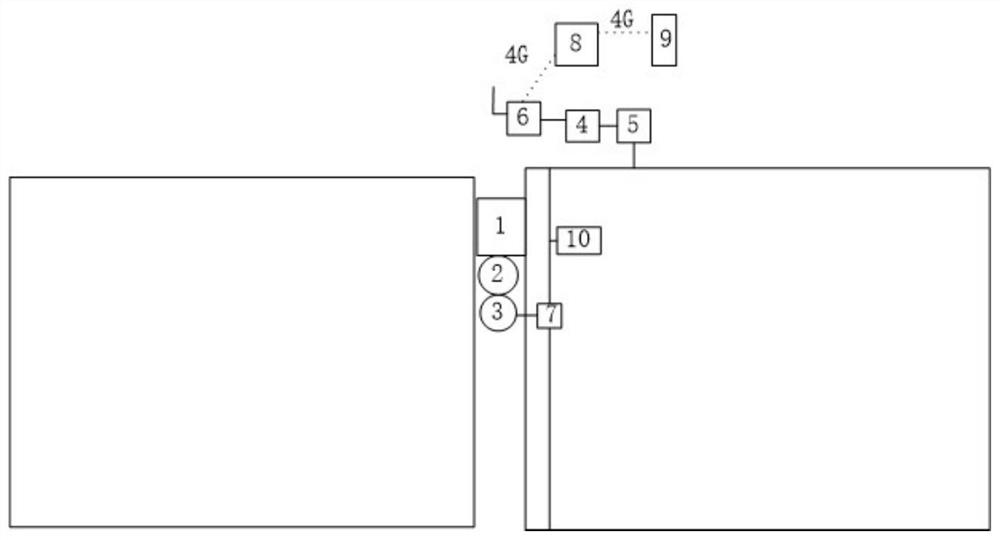
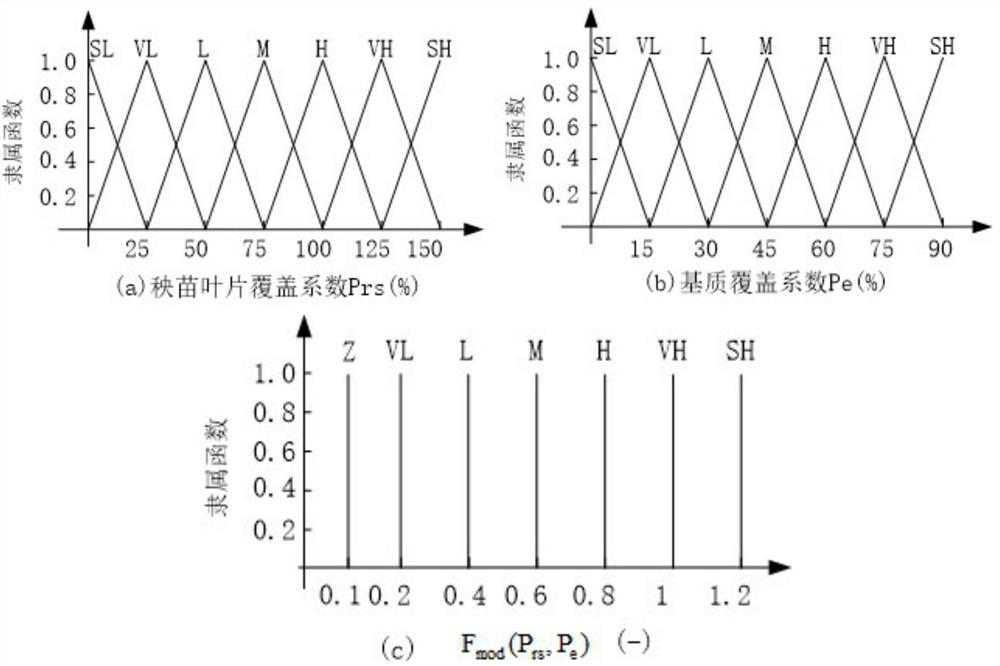
The invention discloses a fuzzy control irrigation method for rice seedling raising in hard land. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating the evapotranspiration of seedlings; carrying out fuzzy double-coefficient evapotranspiration calculation on the seedlings by considering a basic crop coefficient and a soil evaporation coefficient; monitoring the growth state of seedlings through a camera carried by an unmanned aerial vehicle, and adopting a movable sprinkling irrigation head to achieve precise irrigation of seedling trays. The sprinkling irrigation system is composed of a camera, a sprinkling irrigation pump, a fixed nozzle, a main control unit, a 4G network module, a cloud server and an APP. The paste logic fully considers the evapotranspiration effect of crop moisture, the evapotranspiration required by a seedling tray on the day is estimated through illumination, humidity, atmospheric pressure and temperature values of 24-hour weather forecast and seven-stage fuzzification, and then the basic irrigation amount is formed through correction of a fuzzification double-crop coefficient method. According to the invention, low-cost precise drip irrigation is realized, and the method has wide application prospect and feasible practical value.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Construction and application of summer corn drought disaster loss quantitative evaluation model
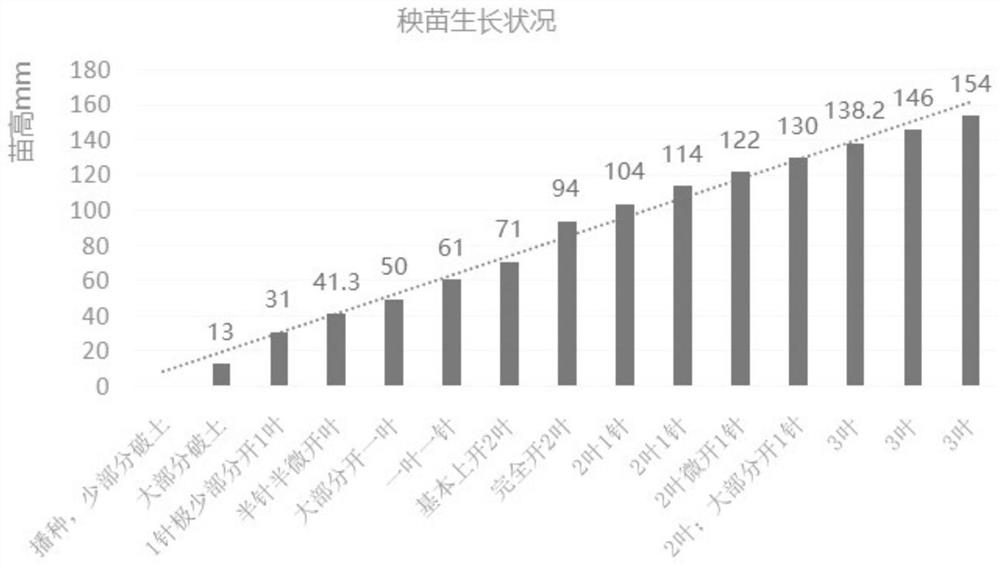
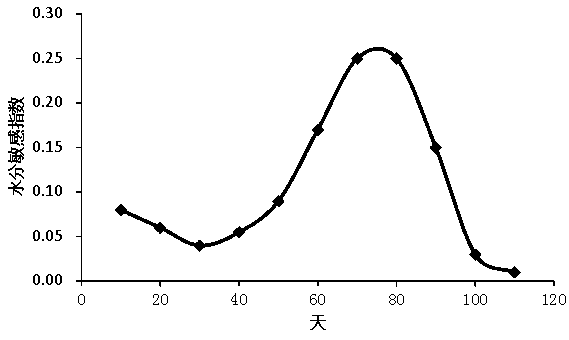
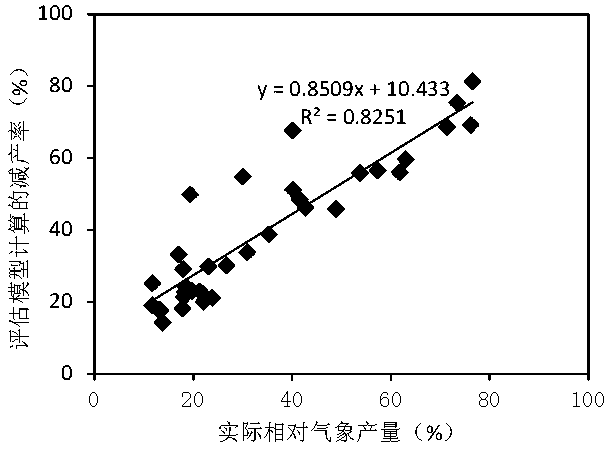
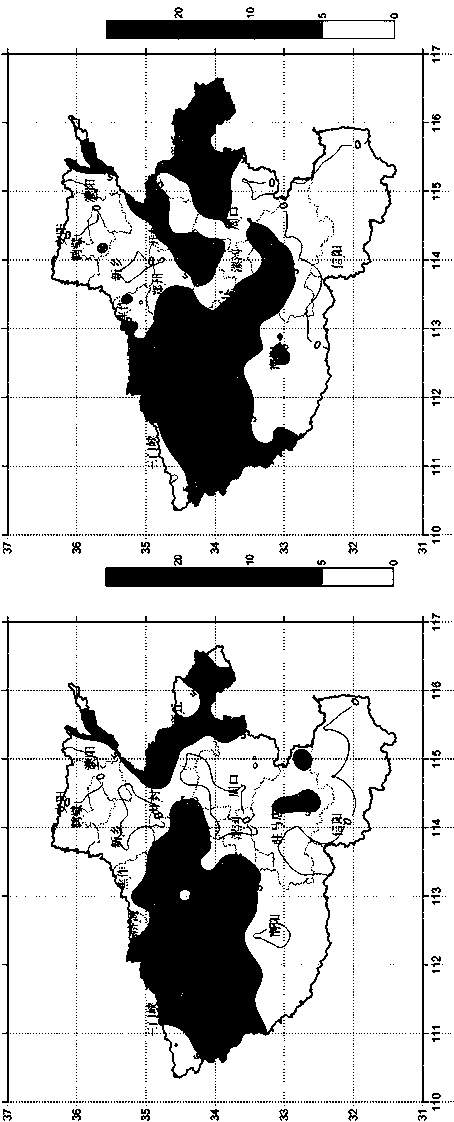
The invention discloses construction and application of a summer corn drought disaster loss quantitative evaluation model, and aims to solve the technical problem that the influence of field drought disasters on the yield cannot be accurately restored and detected in the prior art. The method comprises: constructing a summer corn drought disaster damage loss model by the following steps: determining n growth stages of the summer corn in the whole growth period by taking 10 days or the number of local habitual days as a step length; according to summer corn field irrigation test data, calculating a moisture sensitivity index [lambda]i of the summer corn in the ith growth stage by utilizing an interpolation method; calculating a crop coefficient Kci of each stage according to a local irrigation test; and establishing a summer corn drought disaster loss quantitative evaluation model. The summer corn drought disaster loss quantitative evaluation model established by the invention can accurately restore and detect the influence of field drought disasters on the yield, is low in cost and strong in timeliness, can provide a basis for drought resistance and disaster reduction, and promotesthe development of agricultural economy.
Owner:HENAN INST OF METEOROLOGICAL SCI
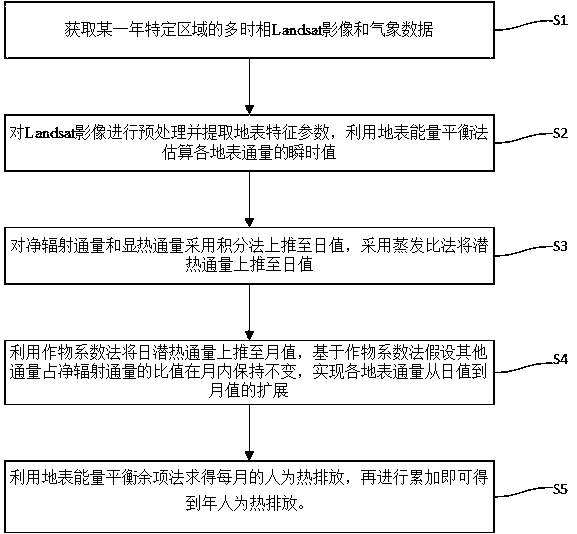
Remote sensing-based anthropogenic heat emission time scale upscaling method
The invention provides a remote sensing-based anthropogenic heat emission time scale upscaling method. The method includes the following steps that: the multi-time phase Landsat images of a specific region are acquired; surface fluxes are estimated through using a surface energy balance method; a net radiant flux and a sensible heat flux are up-scaled to daily values through an integral method; alatent heat flux is up-scaled to a daily value through an evaporation ratio method; the daily latent heat flux is up-scaled to a monthly value through a crop coefficient method, the surface fluxes canbe extended to monthly values from daily values on the basis of the crop coefficient method provided that the proportion of the other fluxes to the net radiant flux is constant monthly; and monthly anthropogenic heat emissions are obtained through a remainder term method, and the monthly anthropogenic heat emissions are accumulated, so that annual anthropogenic heat emissions can be obtained. With the remote sensing-based anthropogenic heat emission time upscaling method of the invention adopted, the problem of the time upscaling during anthropogenic heat emission calculation can be solved; and long-time scale anthropogenic heat emissions are of great significance for fields such as energy resource management, climate numerical value simulation and urban environmental change.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
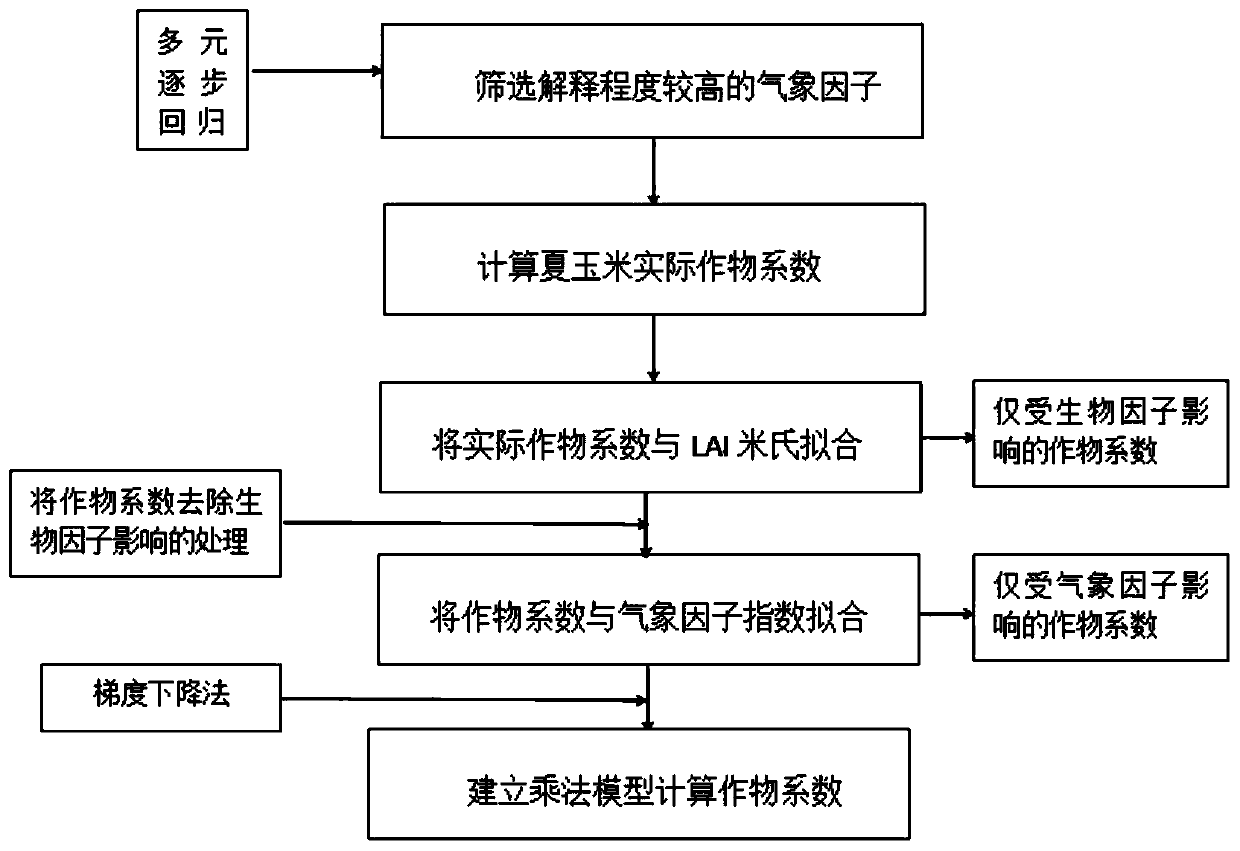
Method for calculating summer corn actual crop coefficient based on weather and biological factors
InactiveCN111080465AAccurate estimation of actual evapotranspirationData processing applicationsSoil scienceCrop coefficient
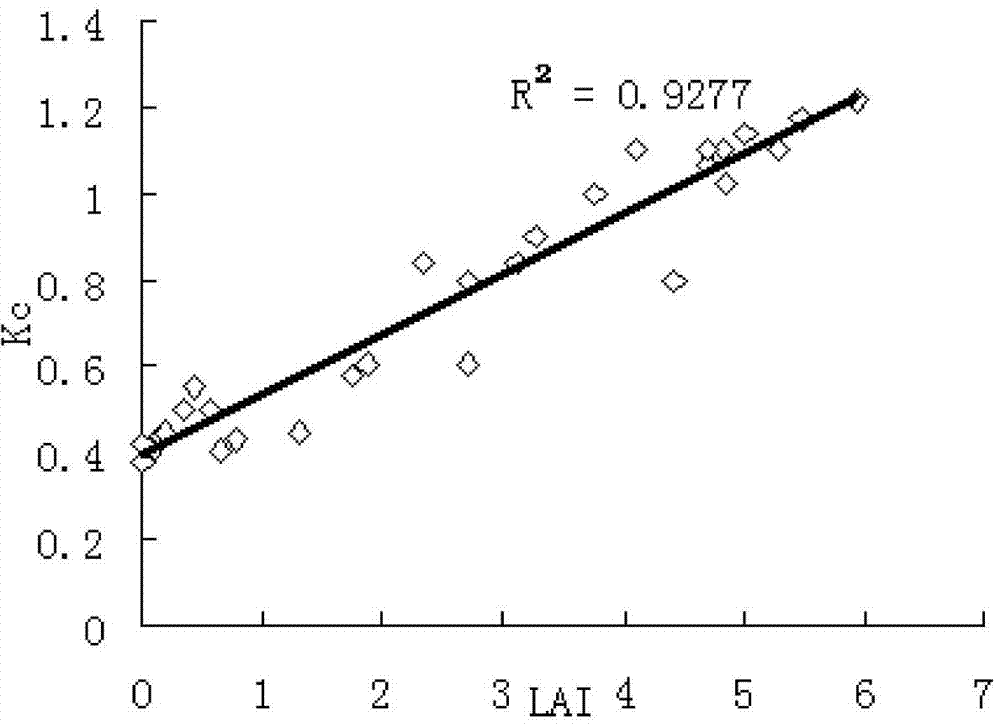
The invention relates to a method for calculating the actual crop coefficient of summer corn based on weather and biological factors. Firstly, a large weighing lysimeter is used for actually measuringevapotranspiration data and a series of meteorological data to calculate an actual crop coefficient; fitting the crop coefficient and the leaf area index by using a Mie equation to obtain a crop coefficient influenced by the biological factor; secondly, surface temperature is screened out through multiple regression to serve as meteorological factors influencing crop coefficients; and finally, model parameters are solved through a gradient descent method, a calculation result is evaluated based on actually measured data, and the method has important significance in mastering dynamic change characteristics of crop coefficients in the summer corn growth period and accurately estimating the actual evapotranspiration of crops.
Owner:安徽省(水利部淮河水利委员会)水利科学研究院(安徽省水利工程质量检测中心站)
Crop irrigation method, device and system and readable storage medium
PendingCN112329212AAddressing Inadequate IrrigationThe solution is the problem of over-irrigationSelf-acting watering devicesDesign optimisation/simulationSoil scienceCrop coefficient
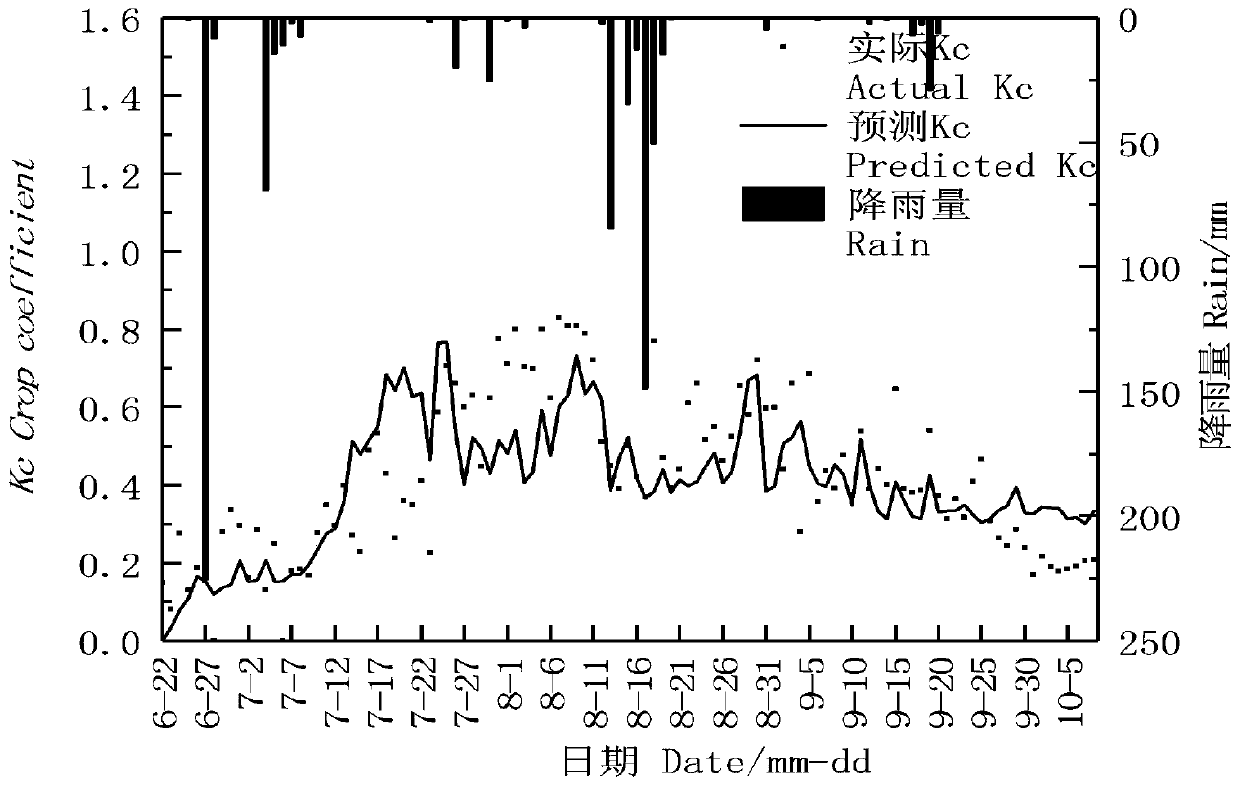
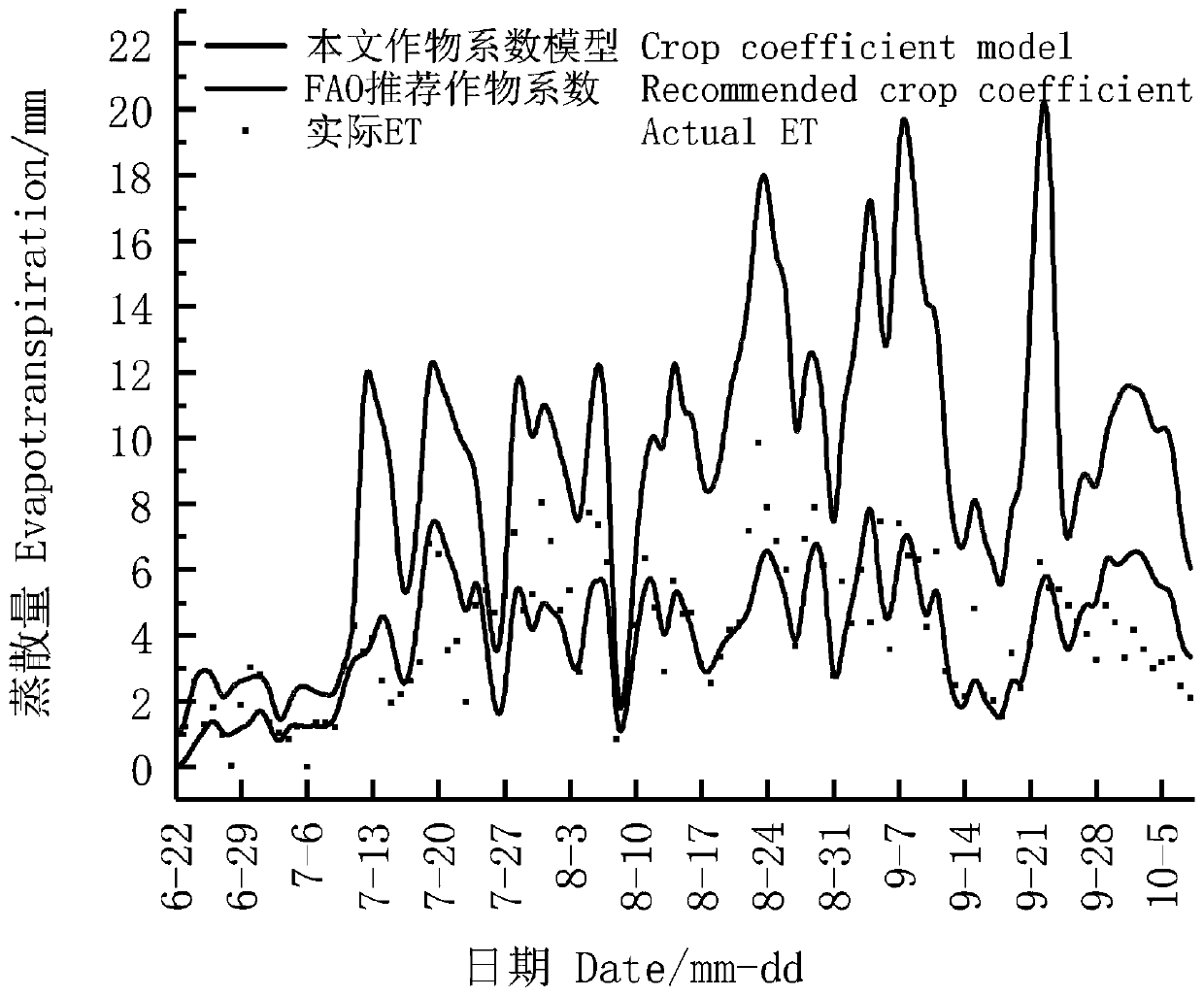
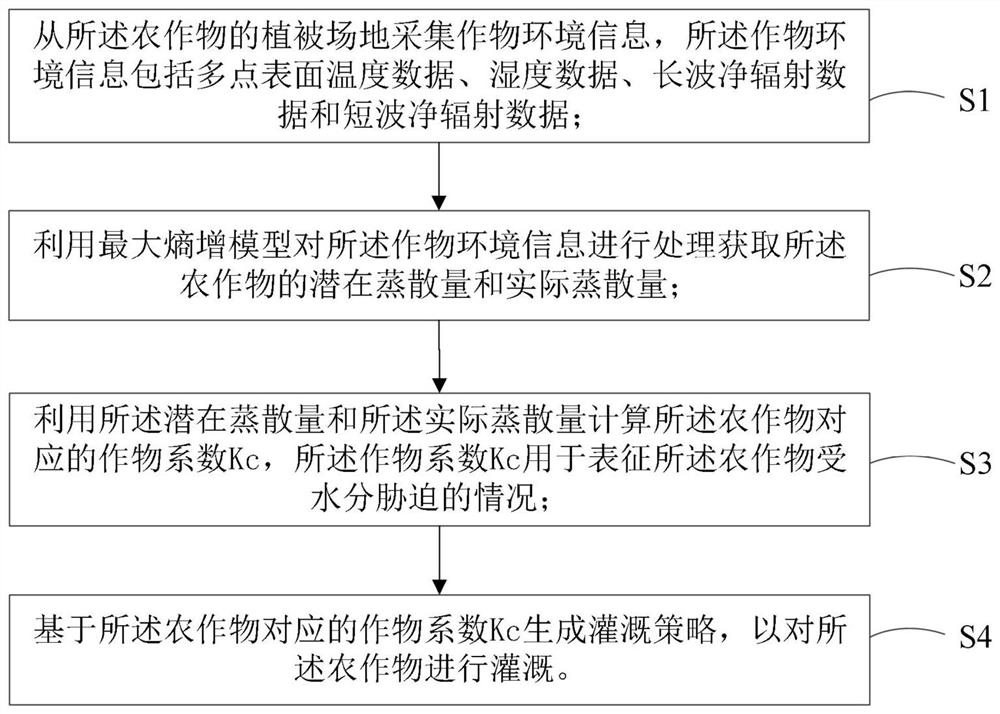
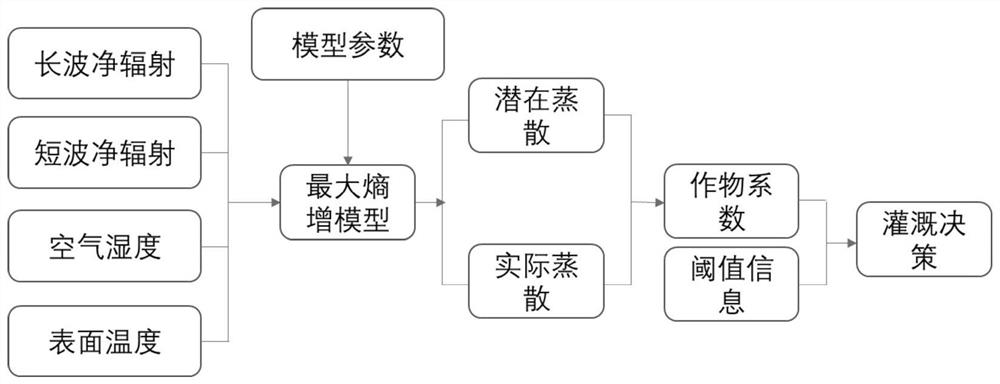
The invention discloses a crop irrigation method, device and system and a readable storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of agriculture, and the method comprises the steps: S1, collectingcrop environment information from a vegetation field of a crop, wherein the crop environment information comprises temperature data, humidity data, long-wave net radiation data and short-wave net radiation data; s2, processing the crop environment information by using a maximum entropy increase model to obtain a potential evapotranspiration amount and an actual evapotranspiration amount of the crop; S3, calculating a crop coefficient Kc corresponding to the crop by utilizing the potential evapotranspiration and the actual evapotranspiration, wherein the crop coefficient Kc is used for representing the condition that the crop is subjected to water stress; and S4, generating an irrigation strategy based on the crop coefficient Kc corresponding to the crop so as to irrigate the crop. Crops are irrigated in a targeted mode, the irrigation reliability is good, the irrigation accuracy is high, and the problem that the crops are not fully irrigated or excessively irrigated can be effectivelysolved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
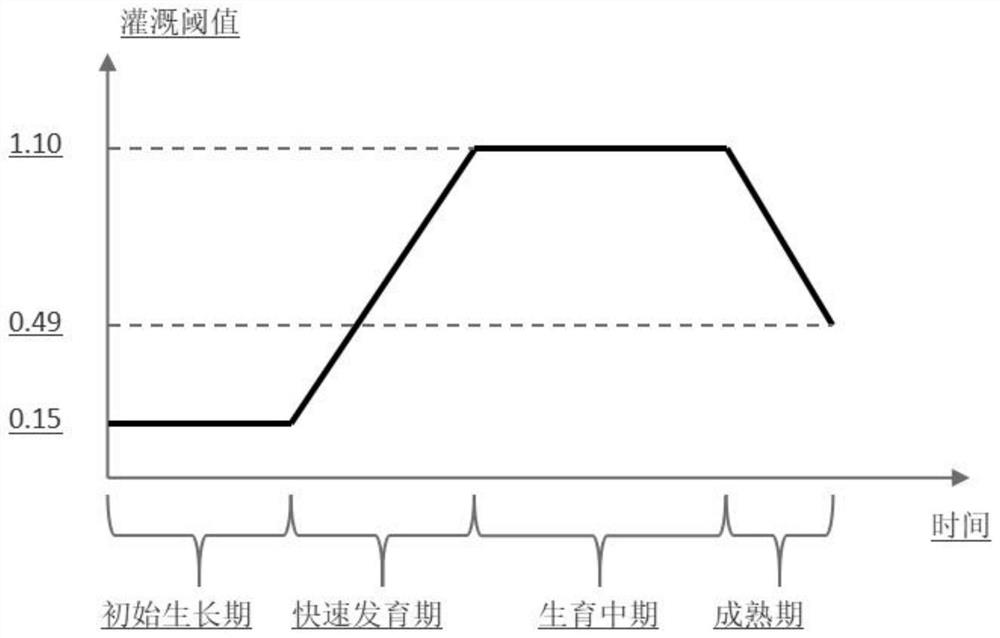
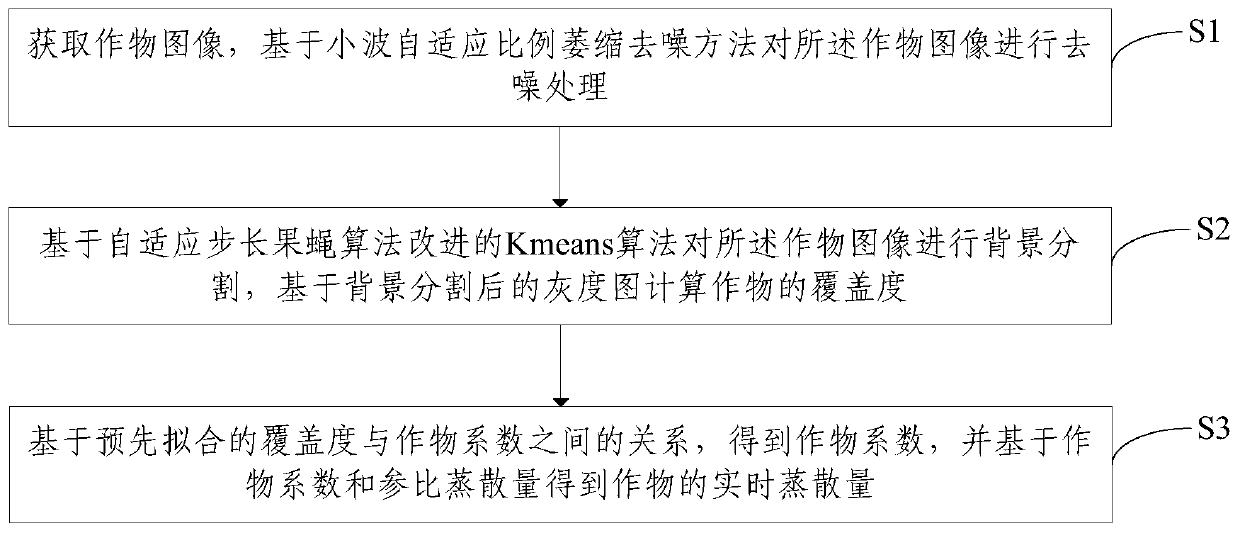
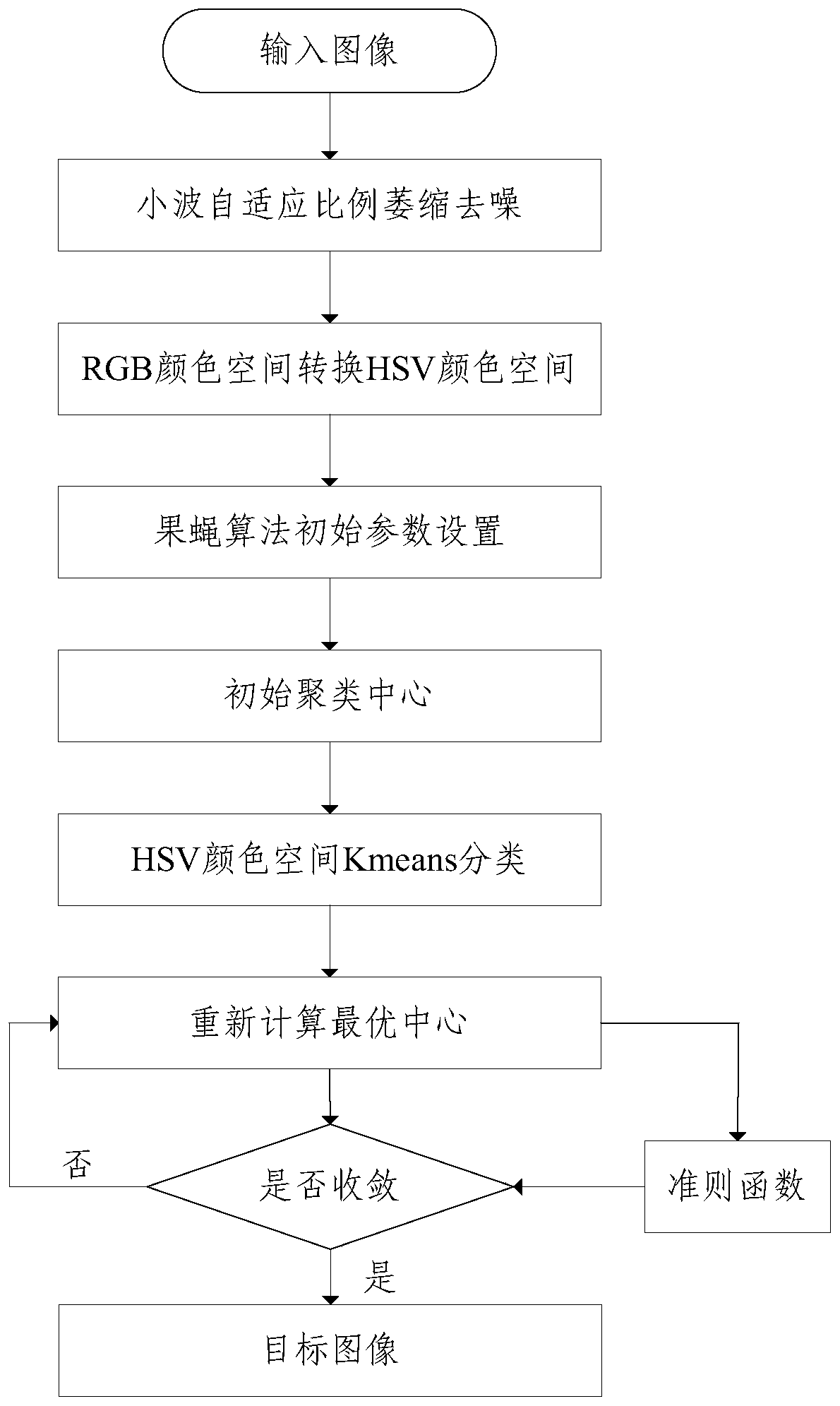
A crop real-time water consumption monitoring method and device based on machine vision
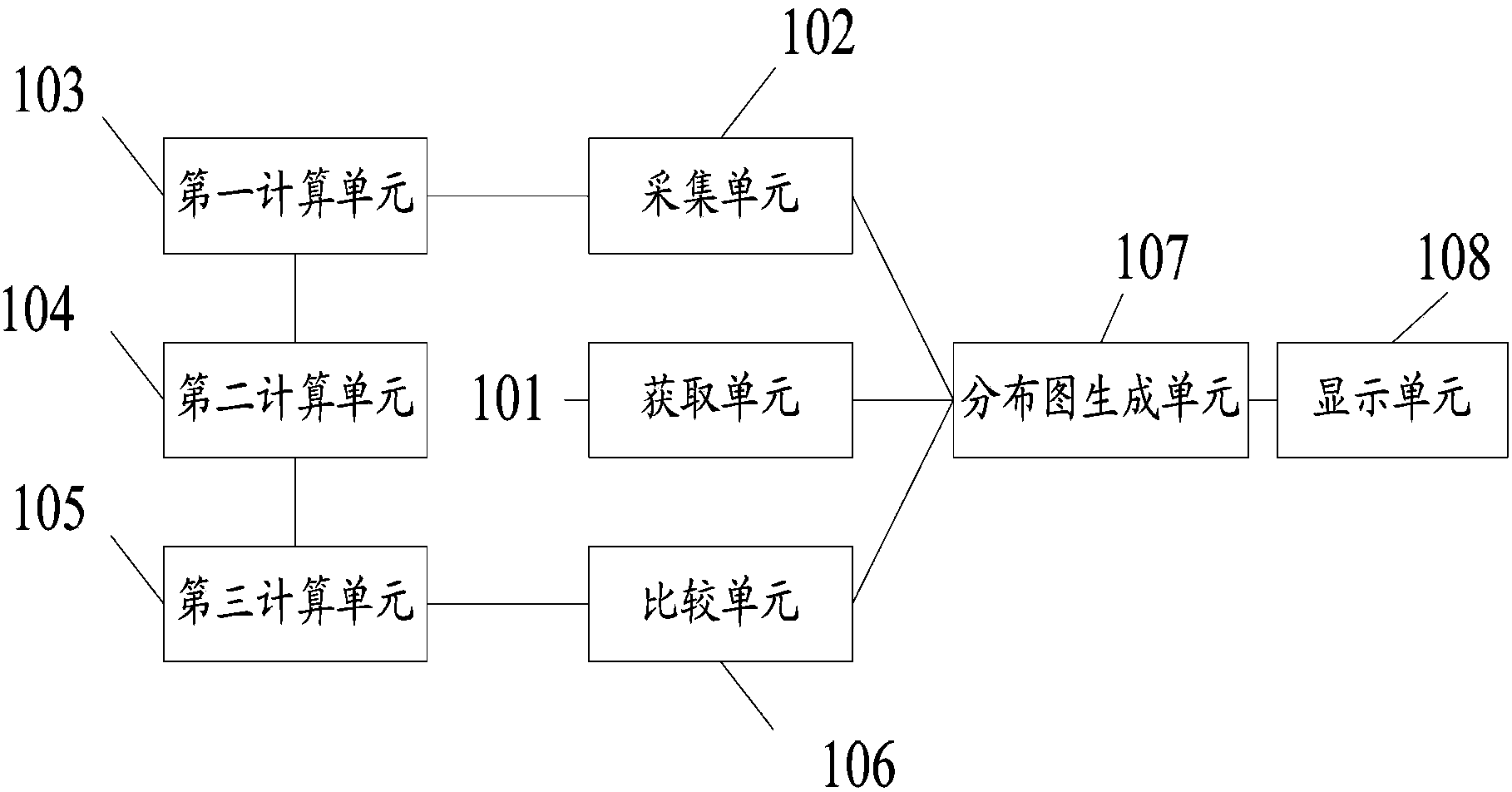
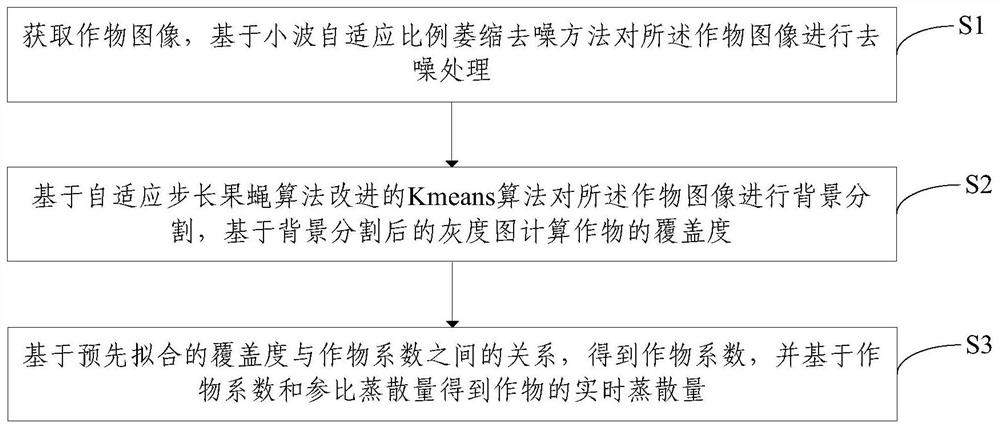
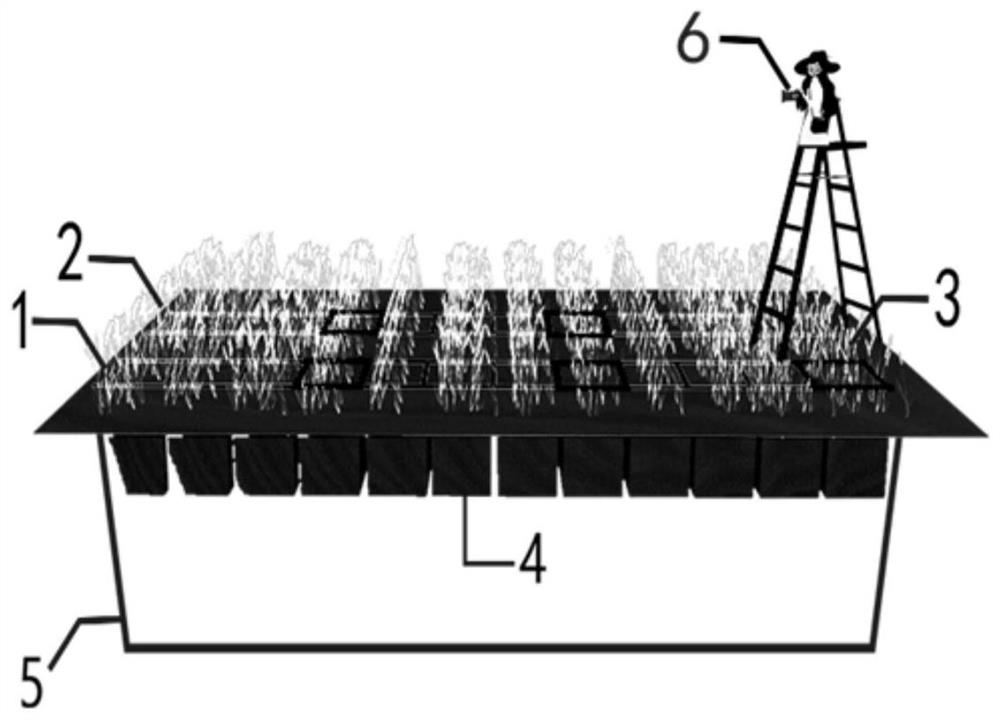
ActiveCN109712110AImprove utilization efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisWater storageMachine vision
The embodiment of the invention provides a crop real-time water consumption monitoring method and device based on machine vision. The coverage is obtained in a lossless image mode, the relation between the real-time crop coefficient and the coverage is obtained by means of professional lysimeter equipment, the method can be expanded to other planting fields to measure the real-time water storage capacity and crop coefficient of crops, and supports are provided for scientific research and production. Image recognition and artificial intelligence technologies such as an information image preprocessing technology, a segmentation technology, an image feature extraction and selection algorithm and the like are applied to monitor and obtain crop growth and physiological state information such ascrop leaf area, coverage degree and canopy temperature which are closely related to yield and quality, so that the water utilization efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT OF INTELLIGENT EQUIP FOR AGRI
Winter wheat regional crop coefficient measuring and calculating method
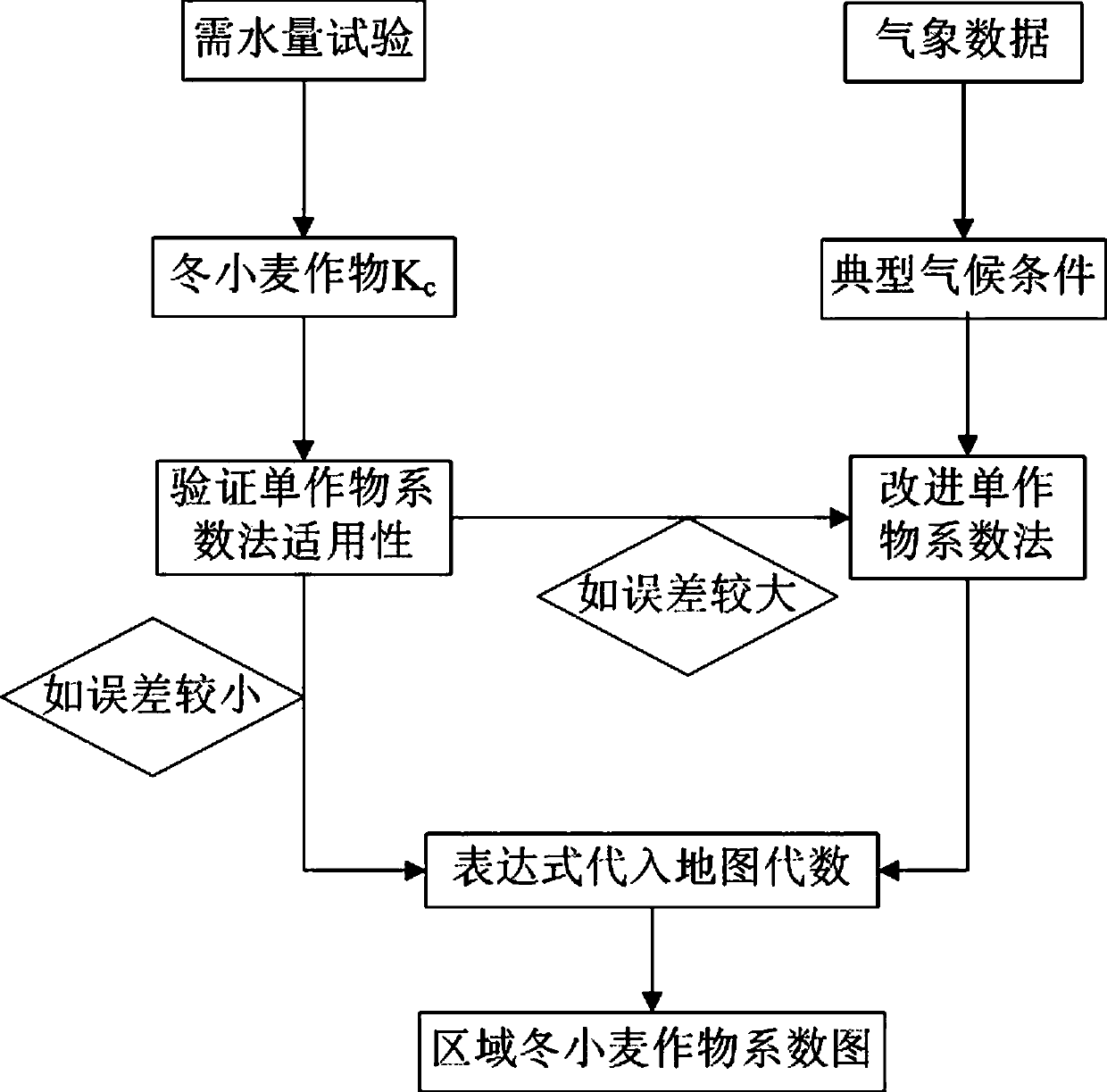
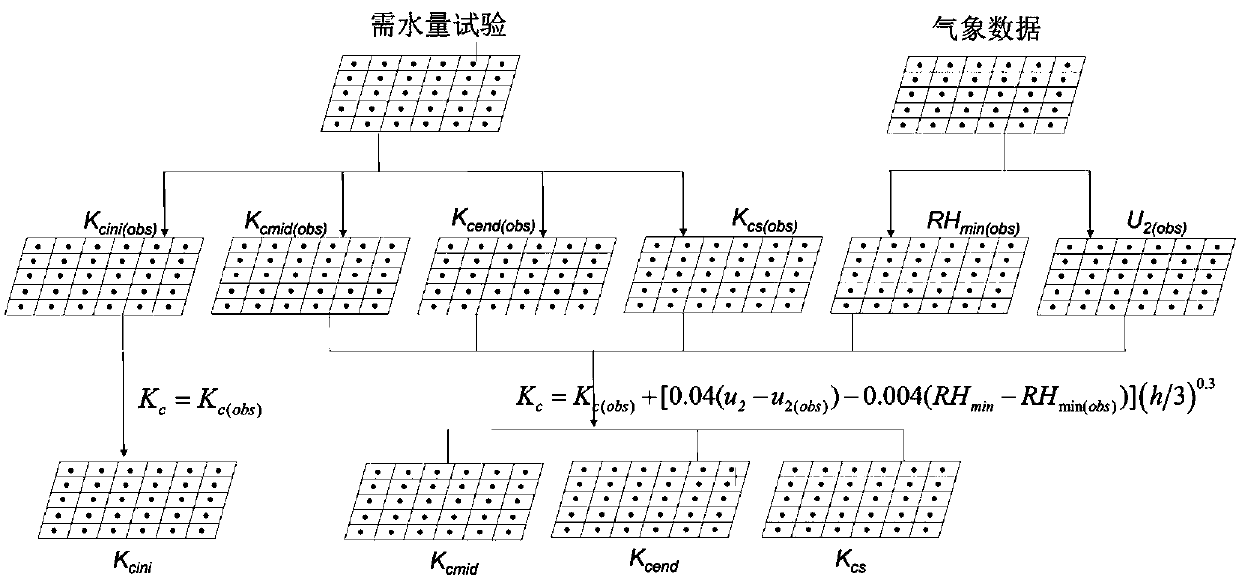
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop coefficient measuring and calculating methods, and particularly relates to a regional winter wheat crop coefficient measuring and calculating method. The method is based on a single-crop coefficient method, the single-crop coefficient method is improved in combination with reality, an improved single-crop coefficient method formula serves as anexpression to be substituted into a map algebra, regional crop coefficient calculation is conducted on each pixel of a grid map, and therefore the regional winter wheat crop coefficient map is obtained. According to the method, a crop coefficient basic recommendation value and a correction formula suitable for Chinese planting subareas are provided; a regional single crop coefficient method is provided by combining with map algebra, and verification is performed by using measured water demand data of winter wheat, so that an effective way is provided for solving the problem of point-to-surfaceconversion of crop coefficients, and technical support is provided for farmland water conservancy engineering planning, design and management, inter-regional water distribution and cross-basin waterdistribution.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
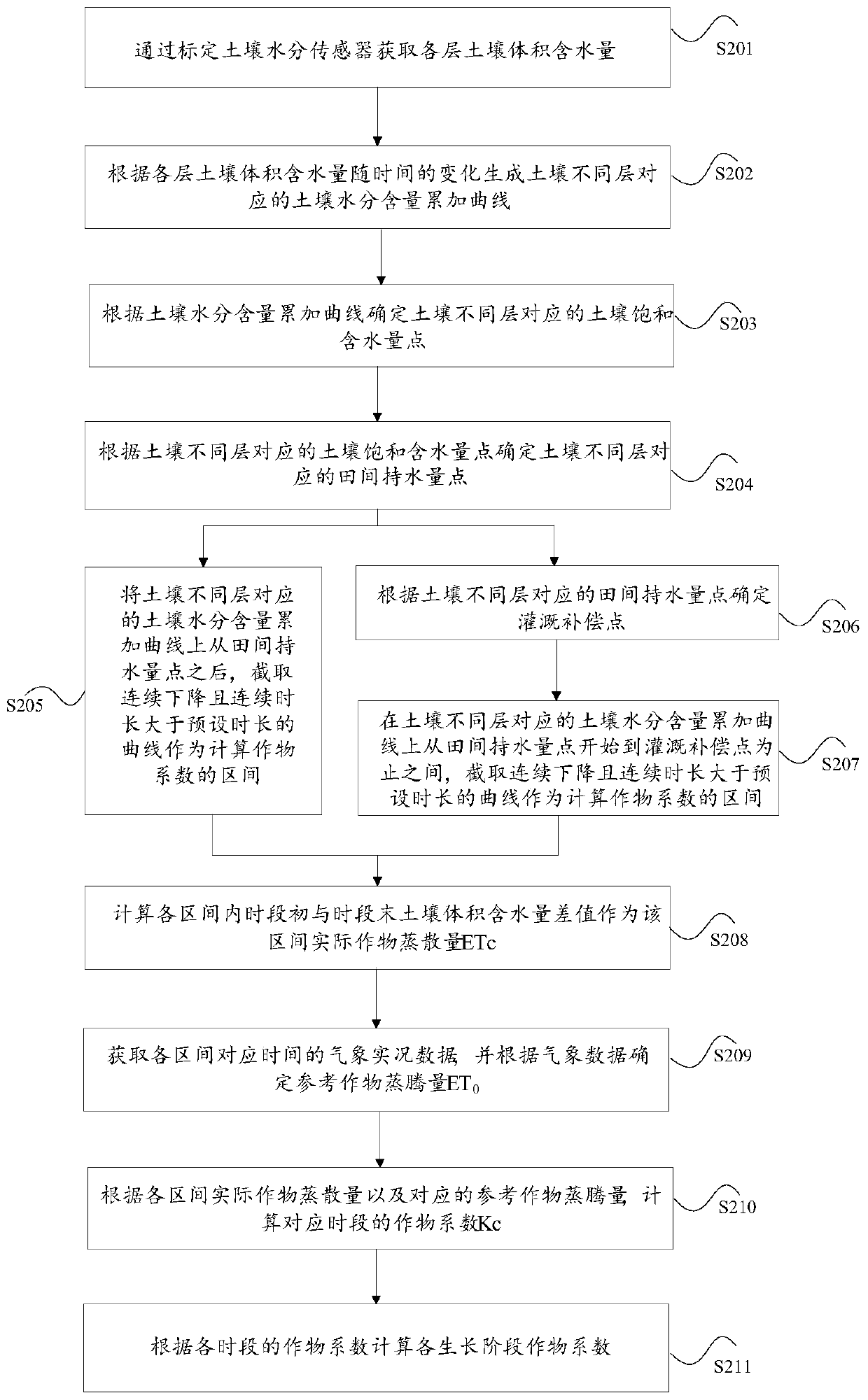
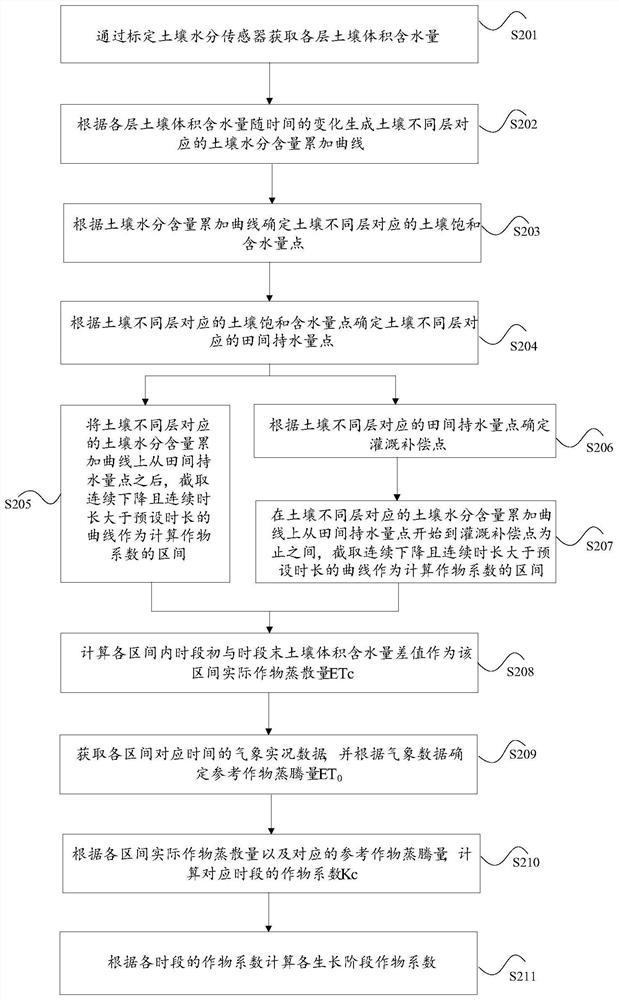
Crop coefficient determination method and device
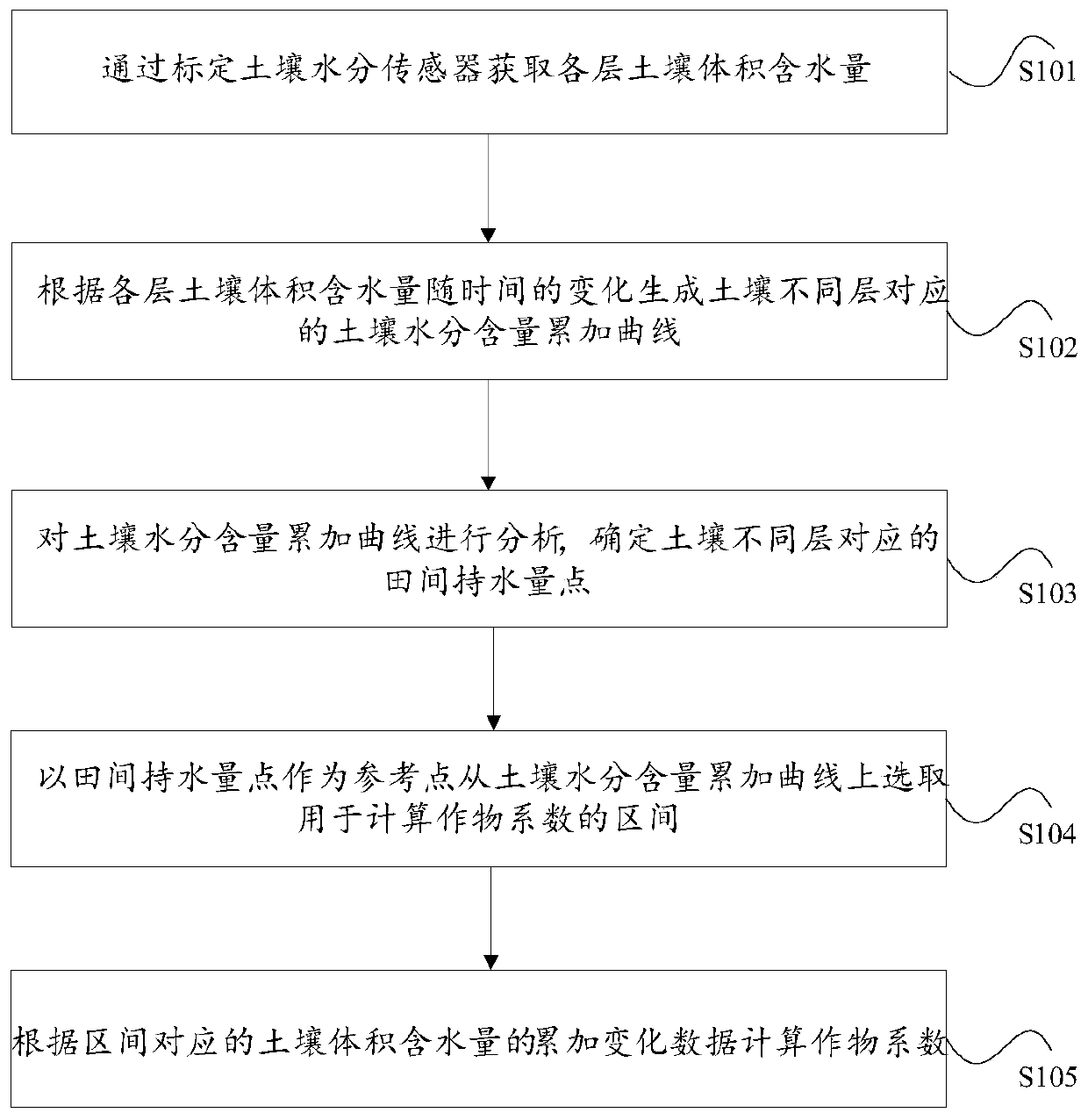
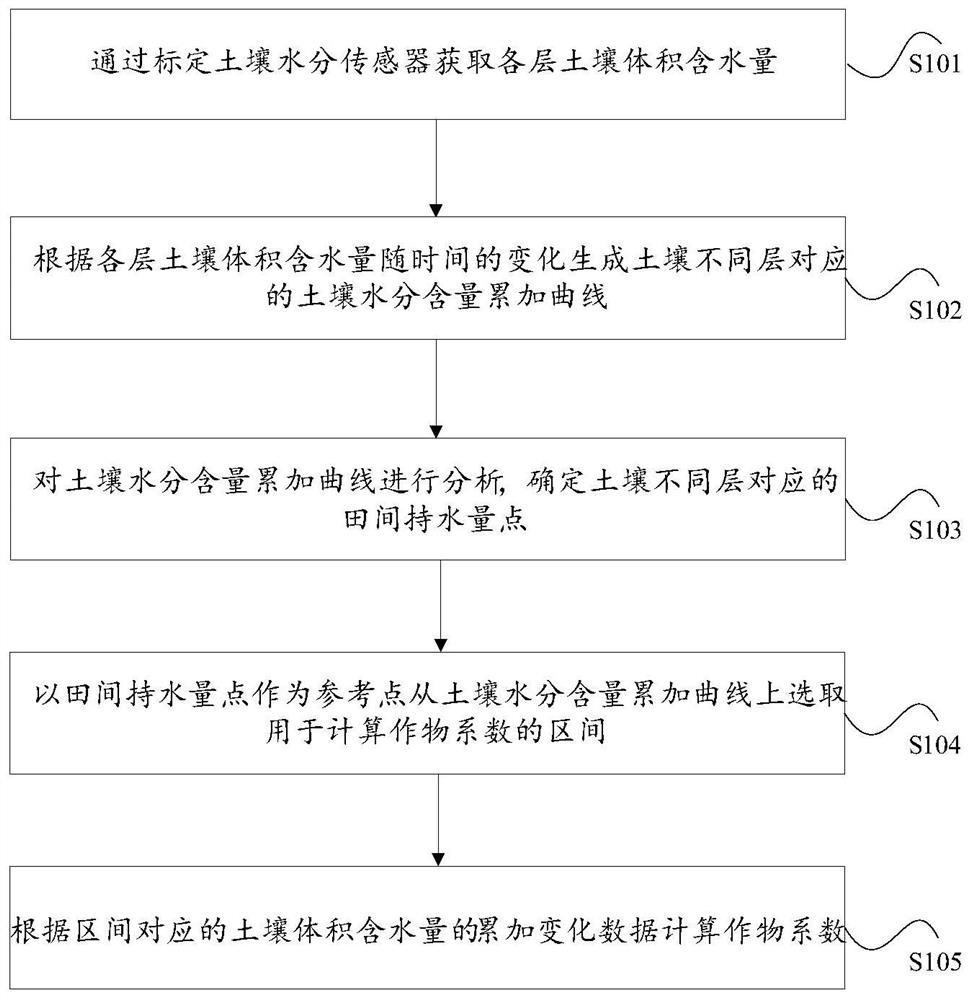
ActiveCN110726807AEasy to operateImprove referenceabilityEarth material testingTesting plants/treesSoil scienceSoil moisture sensor
The invention discloses a crop coefficient determination method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: calibrating a soil moisture sensor to obtain the volumetric water content of each layer of soil; generating a soil moisture content accumulation curve corresponding to different layers of soil according to the change of the volume moisture content of each layer of soil along with time; analyzing the soil moisture content accumulation curve, and determining field water-holding capacity points corresponding to different layers of soil; selecting an interval for calculating a crop coefficient from the soil moisture content accumulation curve by taking the field water-holding capacity points as reference points; and calculating a crop coefficient according to the accumulatedchange data of the soil volumetric water content corresponding to the interval. According to the invention, the problems of the complex crop coefficient determination mode and the low reference are solved.
Owner:京蓝物联技术(北京)有限公司
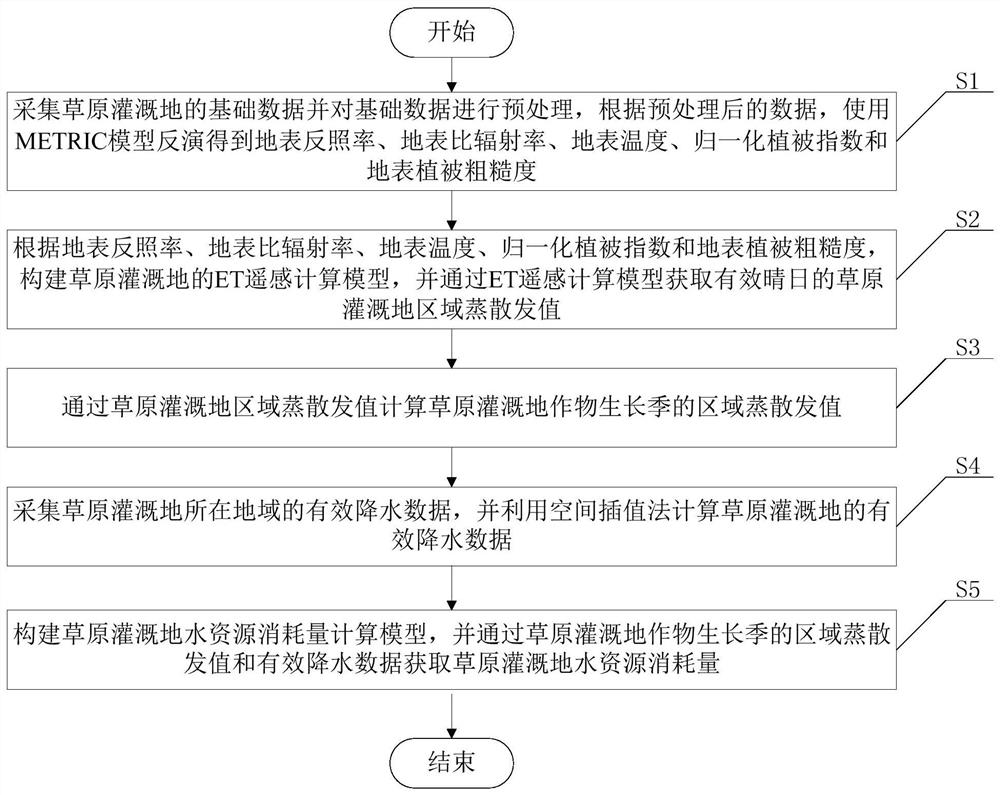
Method for calculating grassland irrigation land water resource consumption
ActiveCN112700089AHigh precisionGeneral water supply conservationResourcesVegetationCrop evapotranspiration
The invention discloses a method for calculating water resource consumption of grassland irrigation land, which comprises the following steps of: performing ET long-sequence expansion on an equivalent decomposition area by utilizing a stable gradual change characteristic of a grassland area reference crop coefficient on a time scale, and coupling area reference crop evapotranspiration by utilizing an improved reference crop coefficient method to calculate the water resource consumption of grassland irrigation land. The grassland region evapotranspiration long sequence extension under remote sensing image missing, especially non-sunny interference, is realized, the problem that remote sensing region evapotranspiration ET calculation is difficult is solved, and the precision of grassland region evapotranspiration ET long sequence calculation is improved. Aiming at the grassland irrigation land water resource consumption calculation problem, the method quantitatively determines the water resource consumption GW value of the grassland area irrigation land crop growth season through the irrigation land water resource consumption calculation model, defines the key area of grassland area underground water resource real-time monitoring and management, and improves the grassland irrigation land water resource utilization rate. Typical case analysis reference is provided for grassland area underground water resource development and utilization management and grassland ecosystem research in irrigated land vegetation construction.
Owner:INST OF WATER RESOURCES FOR PASTERAL AREA MINIST OF WATER RESOURCES P R C
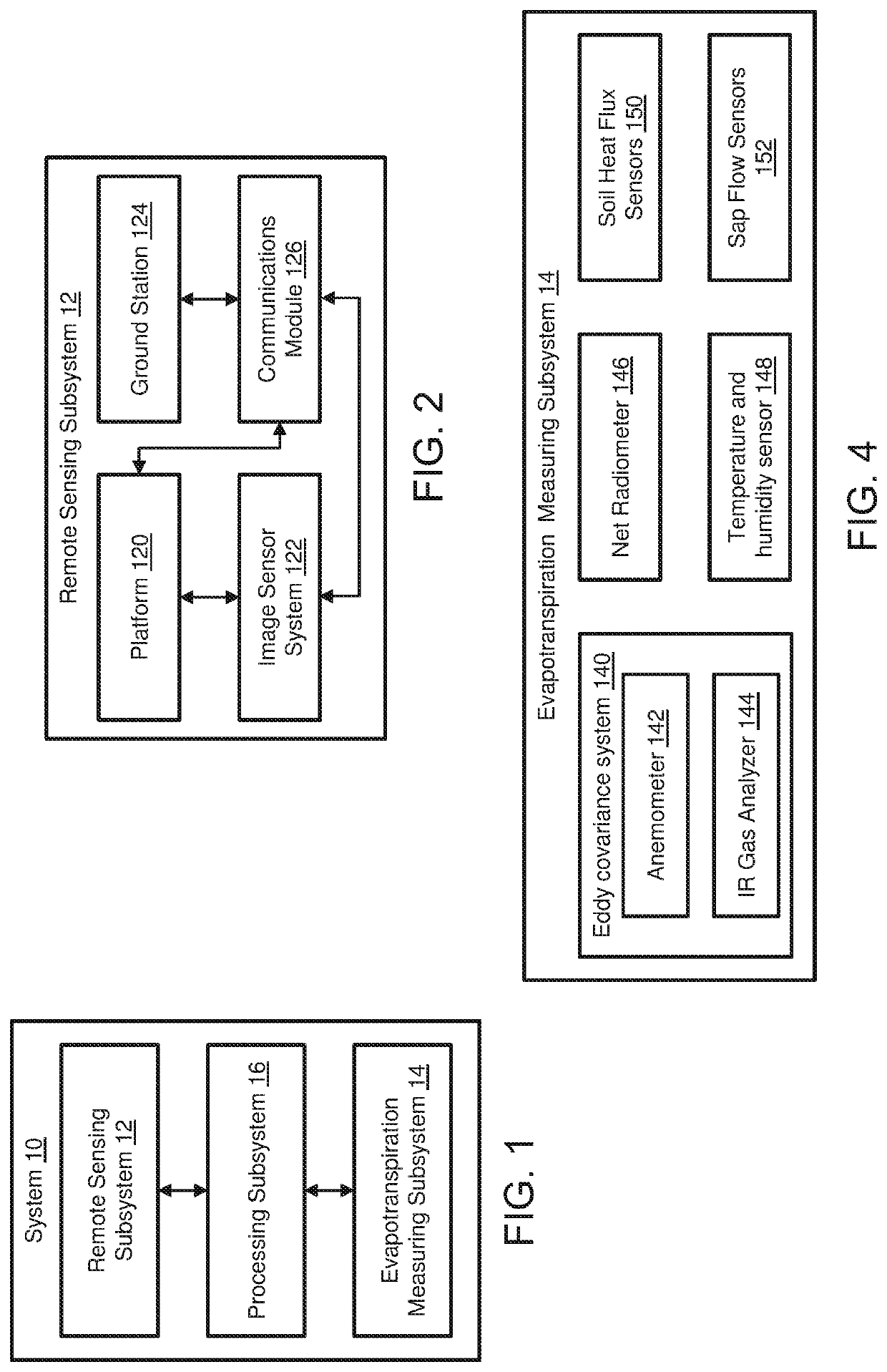
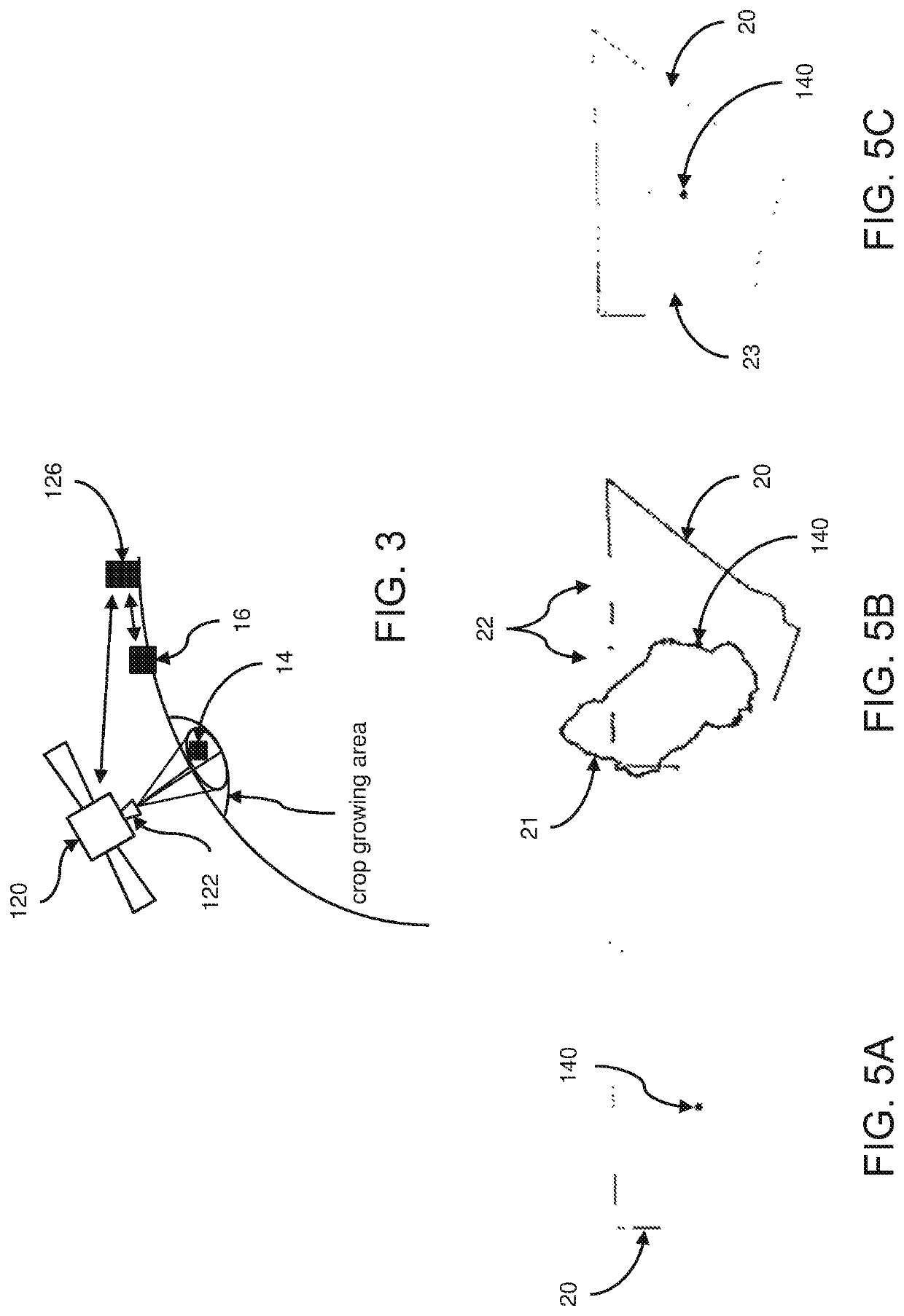
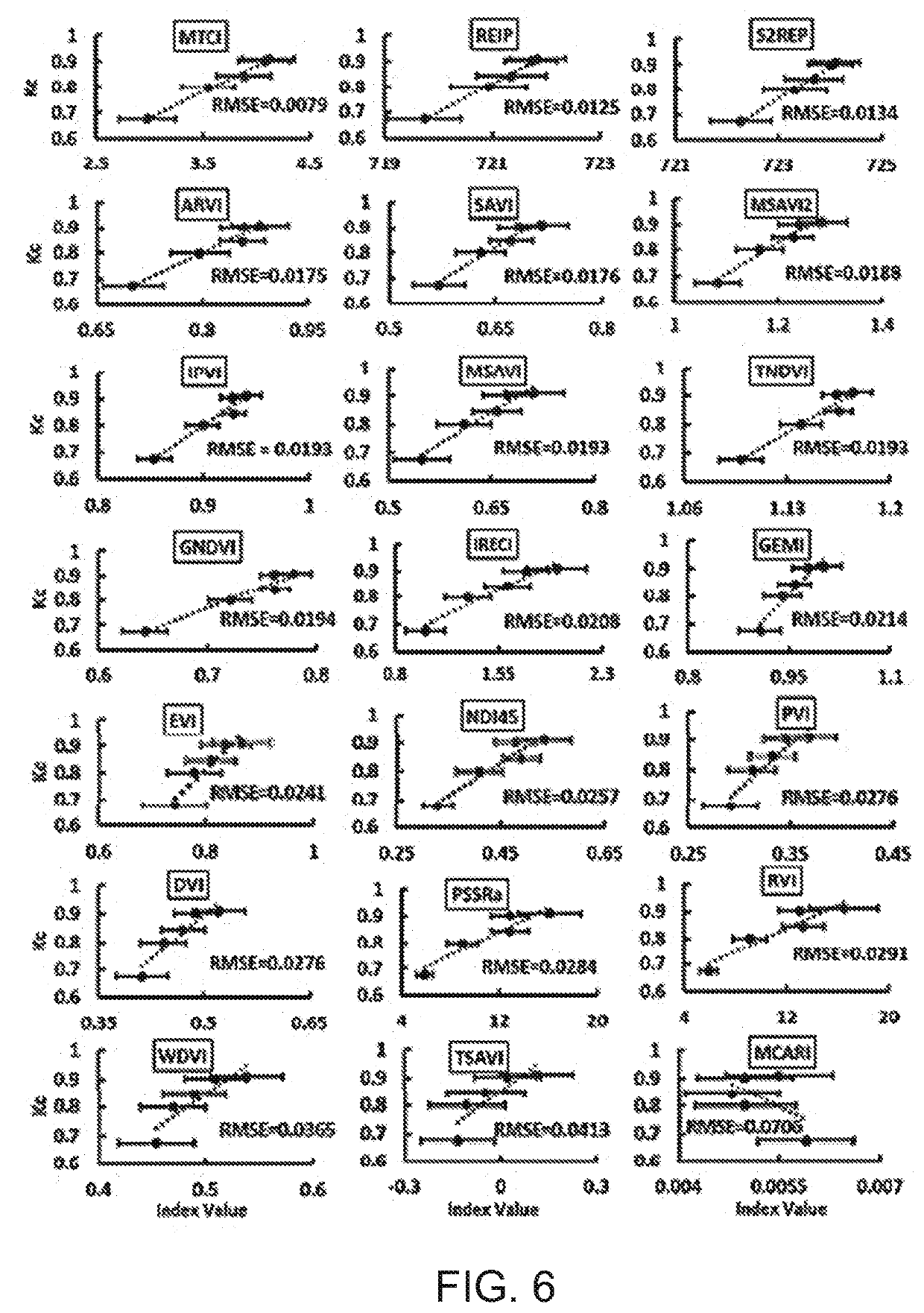
Method and system for estimating crop coefficient and evapotranspiration of crops based on remote sensing
Methods and systems estimate crop coefficients of a crop. At least one image sensor system captures a plurality of multispectral images of the crop and image data is derived from the multispectral images, At least one vegetation index of the crop is determined based on image data in at least a first spectral band. The reflectance of the crop monotonically increases and reaches a reflectance of at least 20% for at least one wavelength in the first spectral band. A crop coefficient of the crop is estimated based on the determined at least one vegetation index.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT
A Calculation Method of Water Resources Consumption in Grassland Irrigated Land
ActiveCN112700089BHigh precisionGeneral water supply conservationResourcesVegetationCrop evapotranspiration
The invention discloses a method for calculating the consumption of water resources in grassland irrigated land, which uses the stable and gradual change characteristics of the reference crop coefficient in the grassland area on the time scale, and expands the ET long sequence of the equivalent decomposition area, and uses the improved reference crop coefficient method to couple The regional reference crop evapotranspiration realizes the expansion of the long sequence of evapotranspiration in the grassland region under the absence of remote sensing images, especially under the interference of non-sunny days, and solves the difficult problem of ET calculation in the remote sensing region, and improves the accuracy of the long sequence calculation of evapotranspiration in the grassland region. Aiming at the calculation problem of water resource consumption in grassland irrigated land, the present invention quantifies and determines the GW value of water resource consumption in crop growing season in irrigated grassland area through the calculation model of water resource consumption in grassland area, and defines the real-time monitoring and management of groundwater resources in grassland area It provides a typical case analysis reference for the development and utilization management of groundwater resources in grassland areas and grassland ecosystem research.
Owner:INST OF WATER RESOURCES FOR PASTERAL AREA MINIST OF WATER RESOURCES P R C
Method and device for determining crop coefficient
ActiveCN110726807BEasy to operateImprove referenceabilityEarth material testingTesting plants/treesSoil scienceSoil moisture sensor
The application discloses a method and a device for determining a crop coefficient. The method of this application includes obtaining the soil volumetric water content of each layer by calibrating the soil moisture sensor; generating the soil moisture content cumulative curve corresponding to different layers of soil according to the change of the soil volumetric water content of each layer with time; analyzing the soil moisture content cumulative curve, Determine the field water capacity points corresponding to different soil layers; use the field water capacity points as reference points to select the interval for calculating the crop coefficient from the soil moisture content accumulation curve; calculate according to the cumulative change data of the soil volume water content corresponding to the interval crop factor. This application solves the problems of complex determination methods of crop coefficients and low referentiality.
Owner:京蓝物联技术(北京)有限公司
Dynamic percentage feature cropping adaboost face detection algorithm
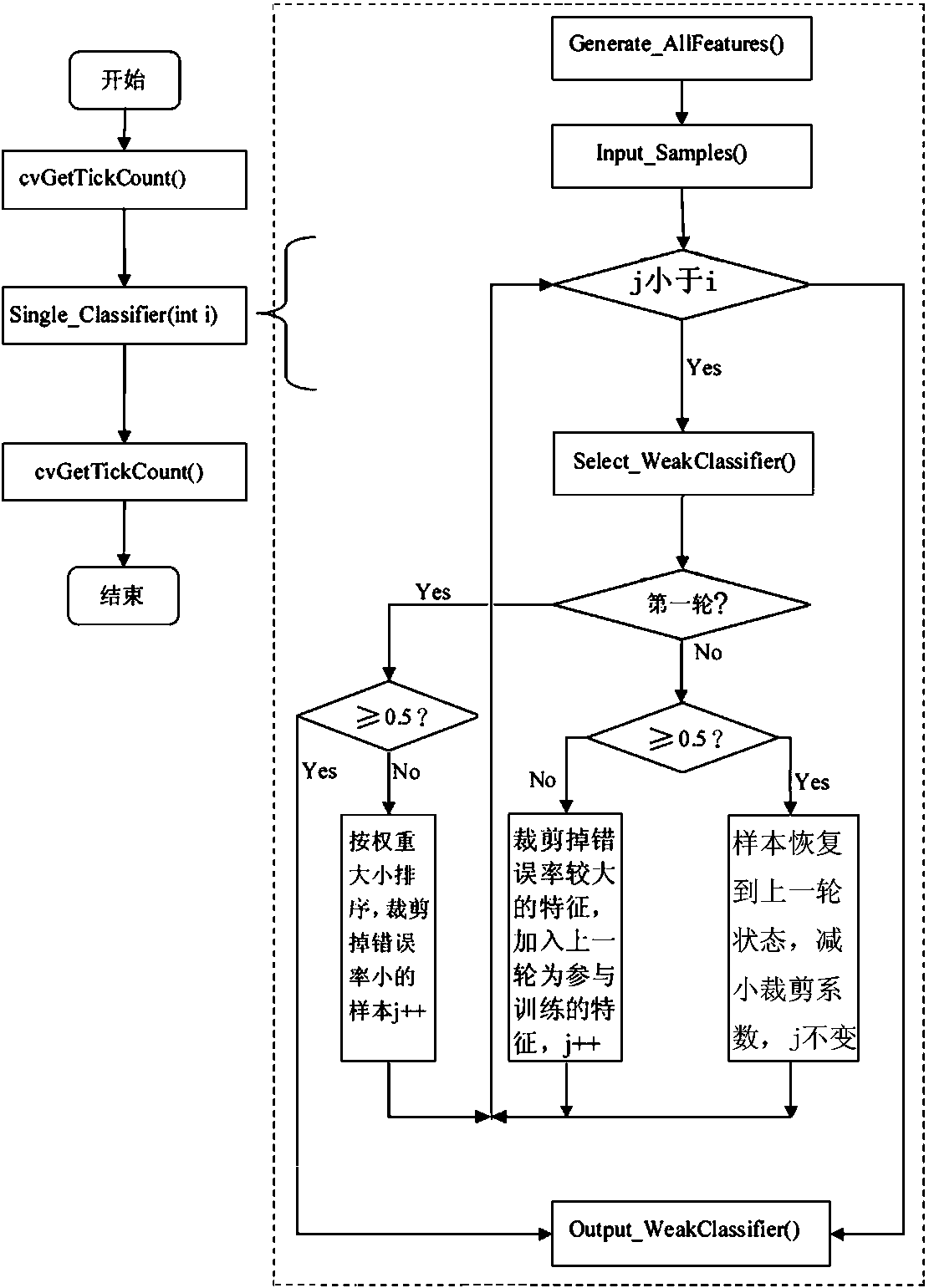
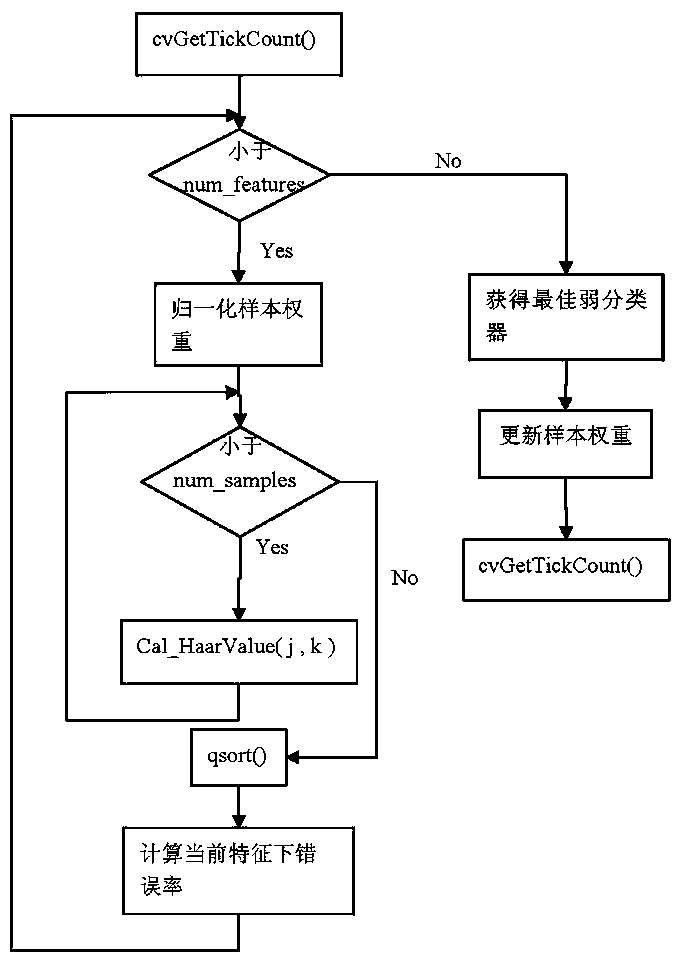
InactiveCN105069396BReduce training timeCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionCrop coefficient
The invention discloses a dynamic percentage feature clipping AdaBoost face detection algorithm, specifically: at the beginning of each iteration, first determine the percentage f of the number of features to be clipped, and then select features with better classification performance to participate in the next step rounds of training; when the error rate of the best weak classifier in this iteration obtained from training is greater than the random extraction value, the number of features participating in training is expanded by reducing the clipping coefficient of this iteration; if all features are used for training, If the error rate still exceeds 0.5, stop the iteration. The present invention is applicable to when there are too many features participating in the training, and the purpose of saving training time is achieved by selecting features with a lower error rate in the previous round to participate in the next round of training.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
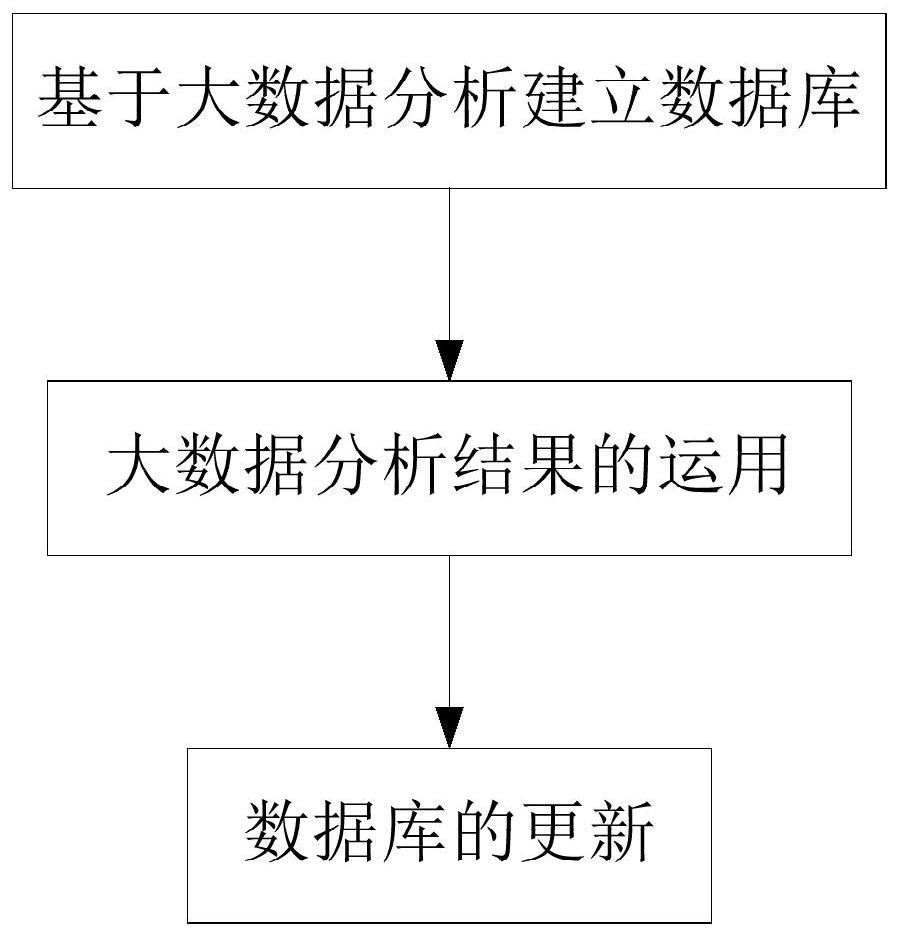
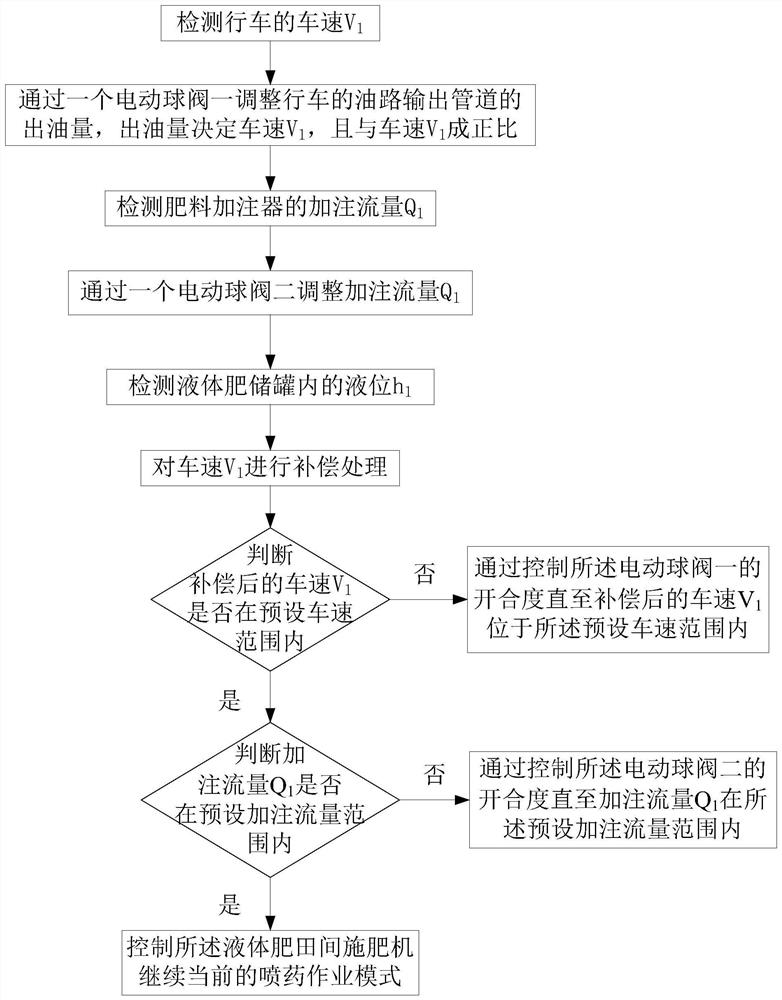
A field fertilization method of liquid fertilizer based on big data analysis
ActiveCN110720287BReduce real-time errorsImprove fertilization efficiencyLevel controlFertilising methodsAgricultural engineeringCrop coefficient
The invention discloses a liquid fertilizer field fertilization method based on big data analysis, which specifically includes three steps: establishing a database based on big data analysis, using big data analysis results, and updating the database; the invention discloses a liquid fertilizer field based on big data analysis The method of fertilization in between, through big data analysis, the same soil quality coefficient, the same crop coefficient, and the idealized parameter group under different liquid levels can be obtained, so that farmers can directly select the operating parameters of the fertilizer machine according to the soil quality coefficient and crop coefficient, during the fertilization process The medium fertilization machine will directly and automatically adjust other parameter values according to the difference in liquid level, which is more convenient for farmers to operate, reduces the difficulty of operation, and thus improves the efficiency of fertilization.
Owner:ANHUI RUILING GAUGE MFG CO LTD
Drought early-warning method and drought early-warning system
ActiveCN102779391BDrought early warning is accurate and reasonableTimely drought and disaster prevention workEarth material testingAlarmsGeographic information systemWater content
The invention discloses a drought early-warning method. The drought early-warning method includes acquiring plant distribution information of crops in an early-warning area; acquiring information of weather forecasting and the like in the early-warning area; calculating actual evapotranspiration of the crops; calculating to acquire relative water content in a planned moist layer in soil according to information of the actual evapotranspiration of the crops and the like; and comparing the relative water content in the planned moist layer in soil and lower limit of a drought threshold value, and judging drought degree of the crops. Therefore, information from multiple types of sources, such as growth condition of the crops, water in soil, weather forecasting information, geographic information in the early-warning area, is considered comprehensively, the drought degree of the crops is judged, and accordingly early warning of drought of the crops is more accurate and reasonable, and unreasonable utilization and waste of water resources are unlikely to cause during irrigation. Finally, related information of the drought degree of the crops and the like is used to generate and display a space distribution map by a geographic information system, and accordingly optimized allocation of the water resources in agriculture and early warning of drought in an area range are achieved.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method and device for monitoring real-time water consumption of crops based on machine vision
ActiveCN109712110BImprove utilization efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisWater storageEnvironmental resource management
The embodiment of the invention provides a crop real-time water consumption monitoring method and device based on machine vision. The coverage is obtained in a lossless image mode, the relation between the real-time crop coefficient and the coverage is obtained by means of professional lysimeter equipment, the method can be expanded to other planting fields to measure the real-time water storage capacity and crop coefficient of crops, and supports are provided for scientific research and production. Image recognition and artificial intelligence technologies such as an information image preprocessing technology, a segmentation technology, an image feature extraction and selection algorithm and the like are applied to monitor and obtain crop growth and physiological state information such ascrop leaf area, coverage degree and canopy temperature which are closely related to yield and quality, so that the water utilization efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT OF INTELLIGENT EQUIP FOR AGRI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com