Patents
Literature
221 results about "Thorax+Lungs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
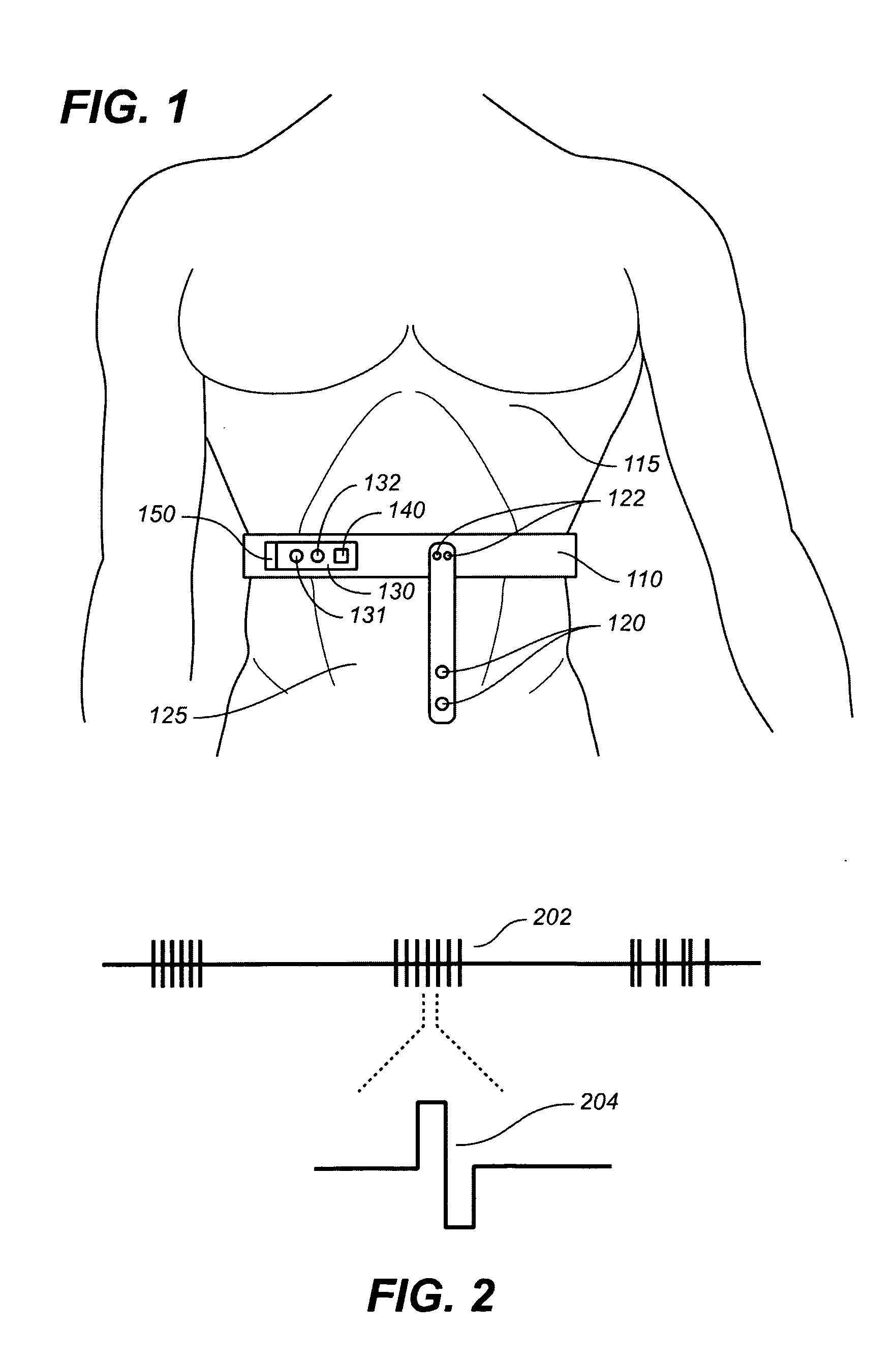
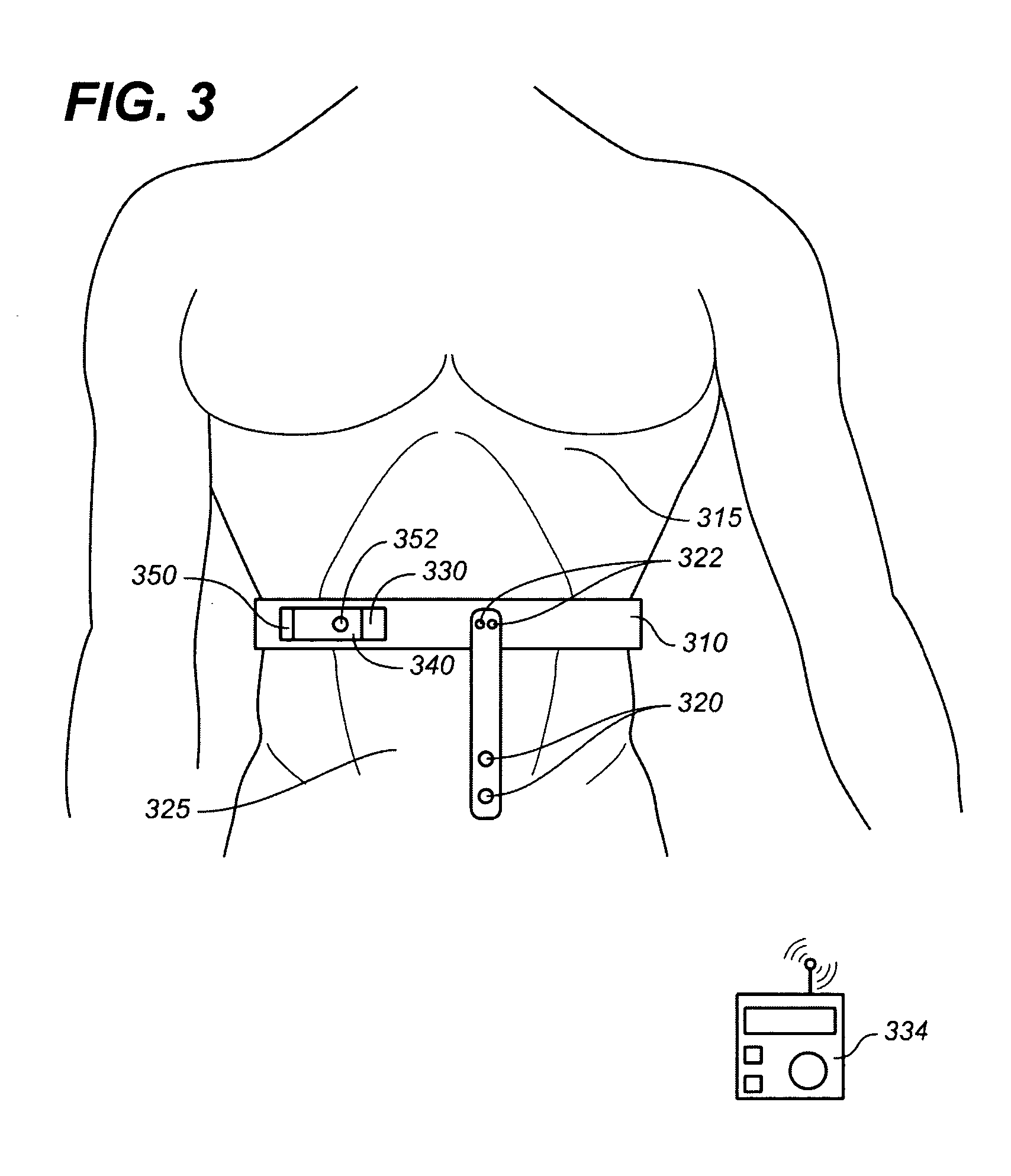
The contents of the thorax include the heart and lungs and the thymus gland); the (major and minor pectoral muscles, trapezius muscles and neck muscle); internal structures such as the diaphragm, esophagus, trachea and a part of the sternum known as the xiphoid process).
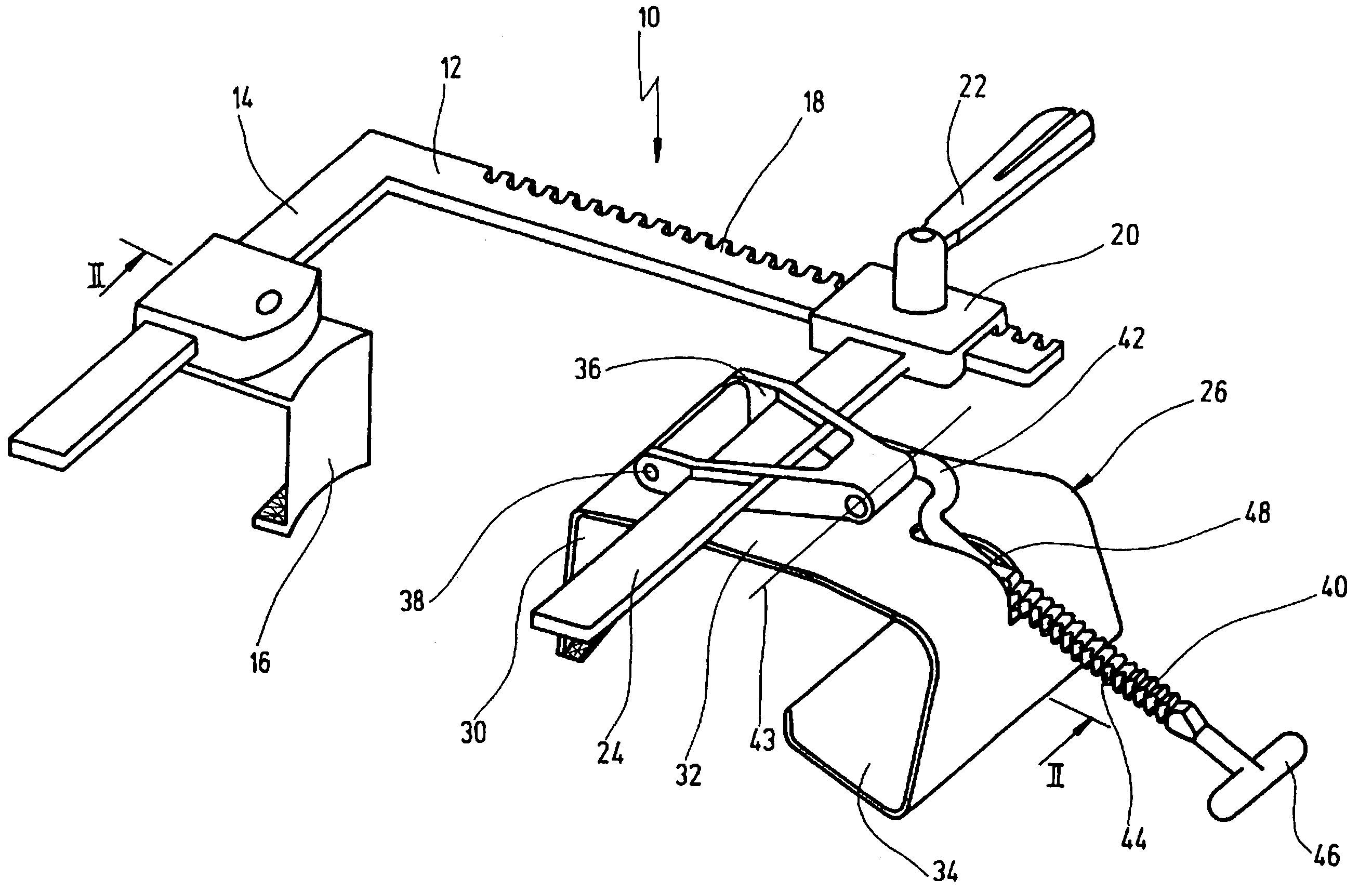
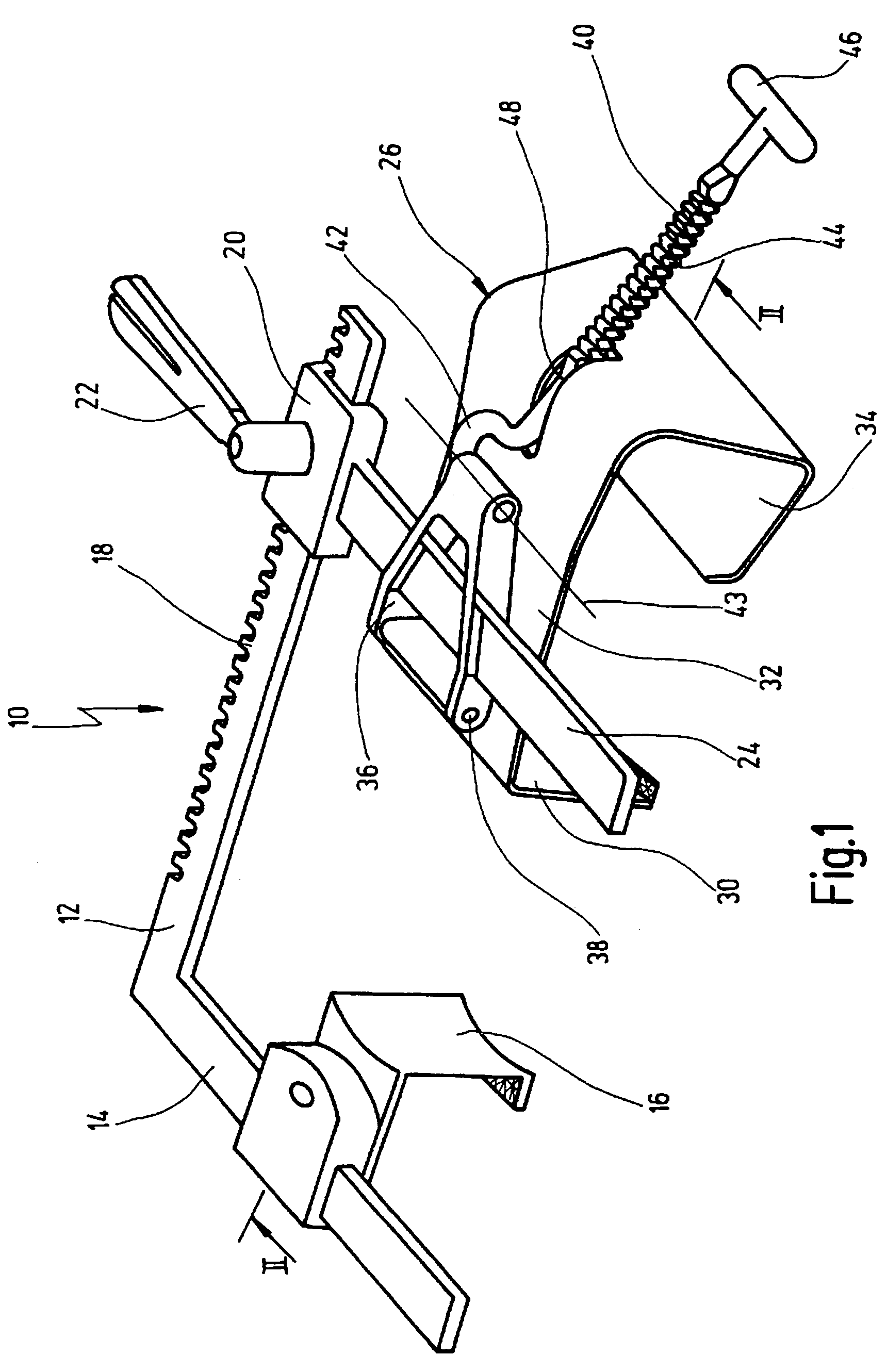
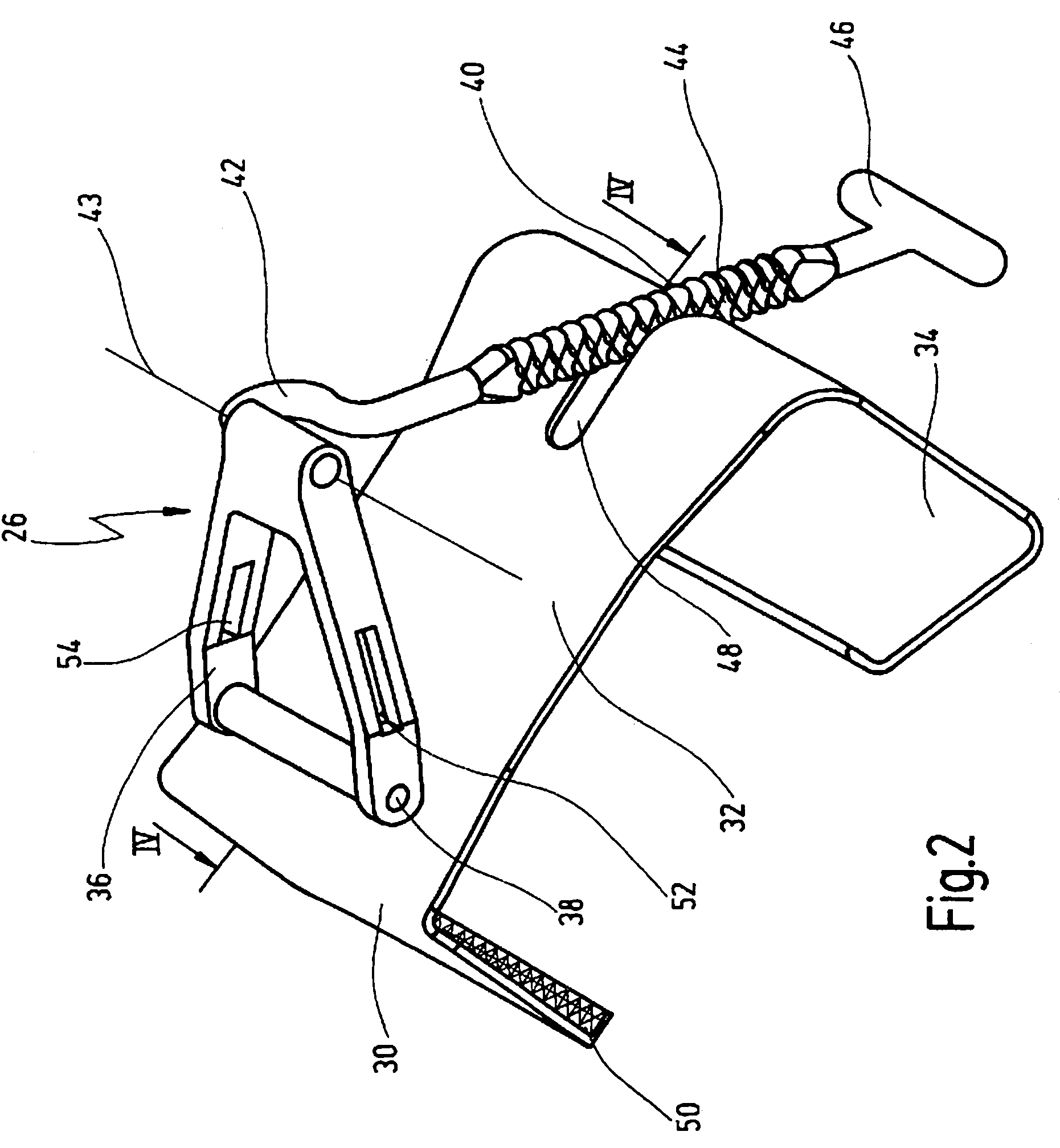
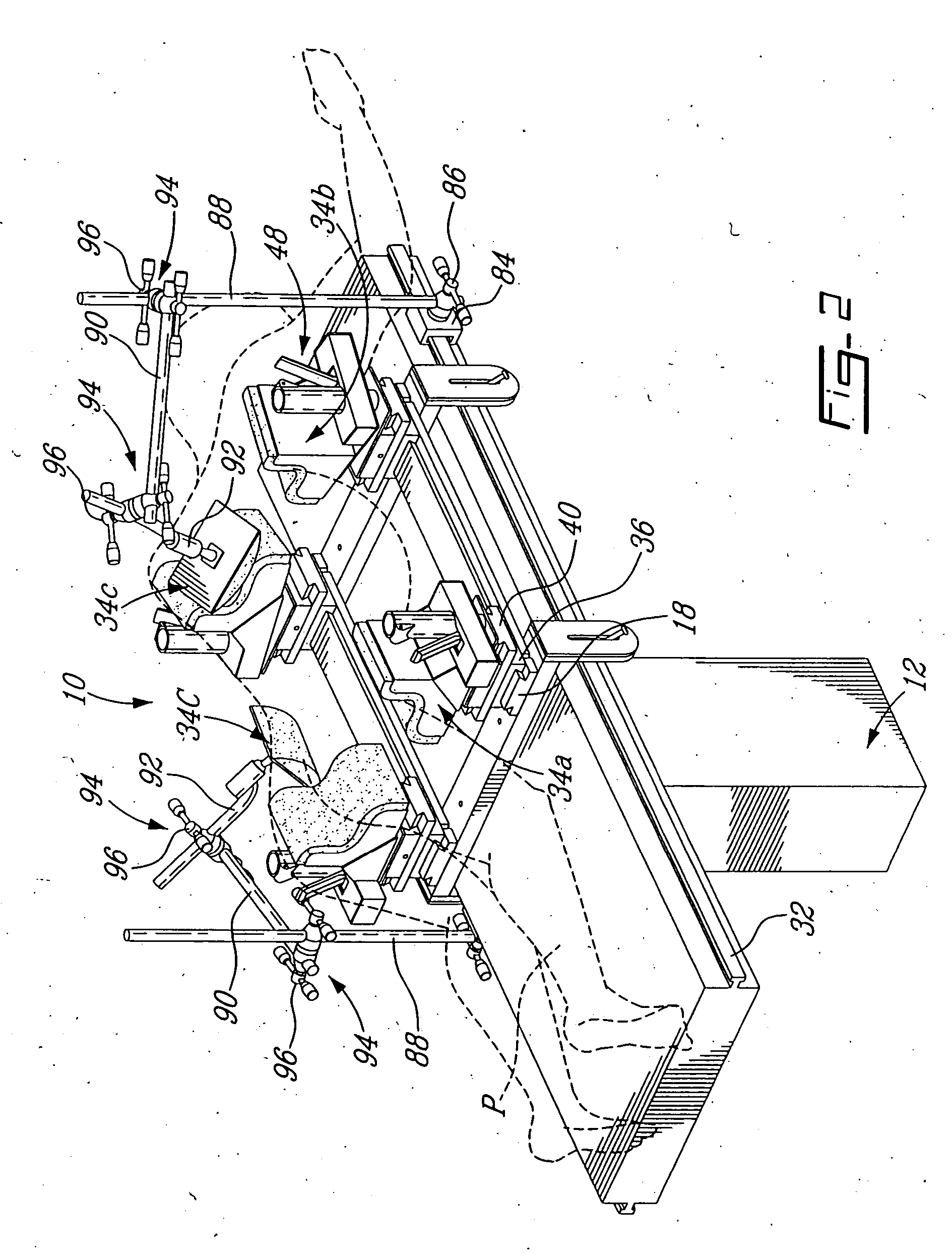
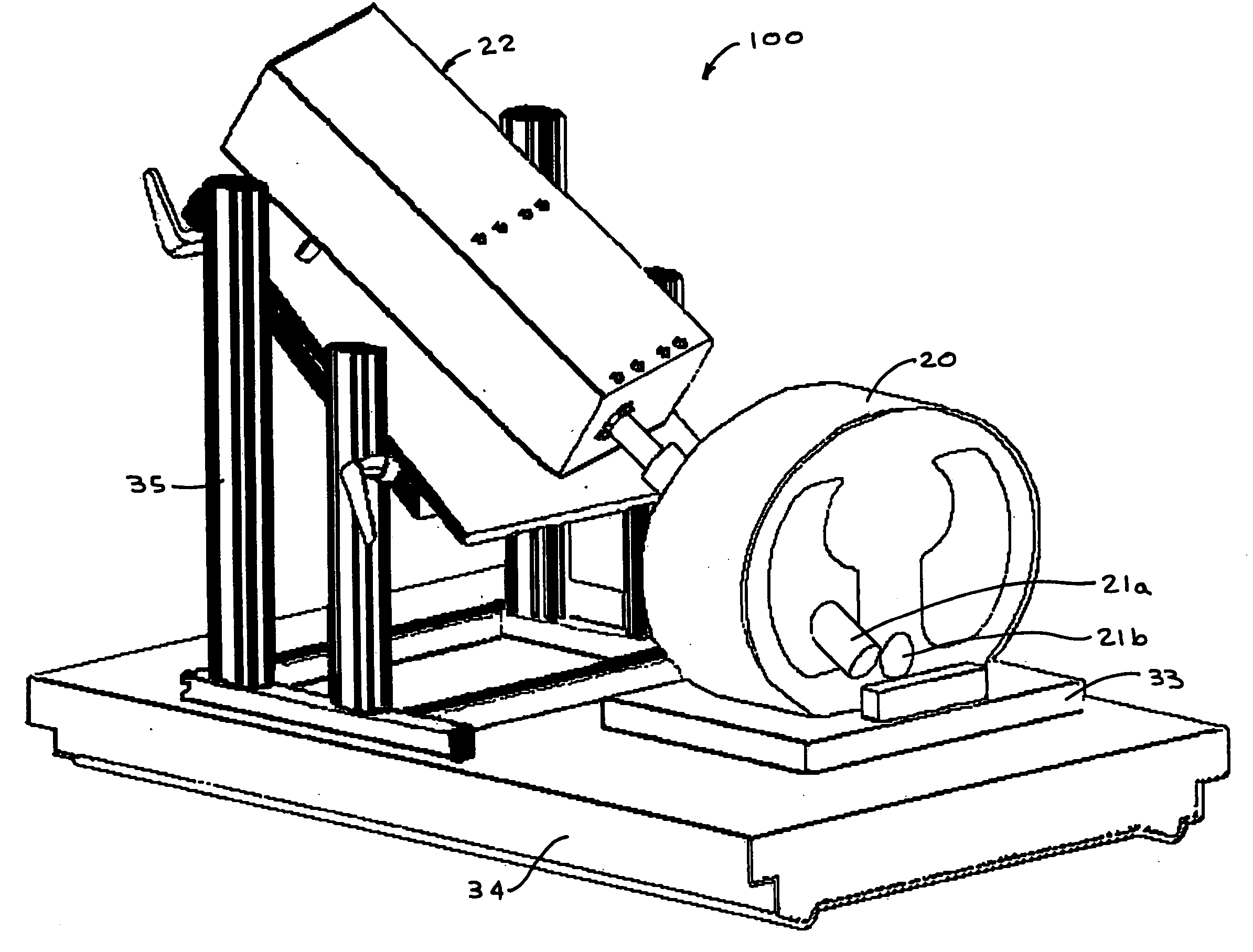
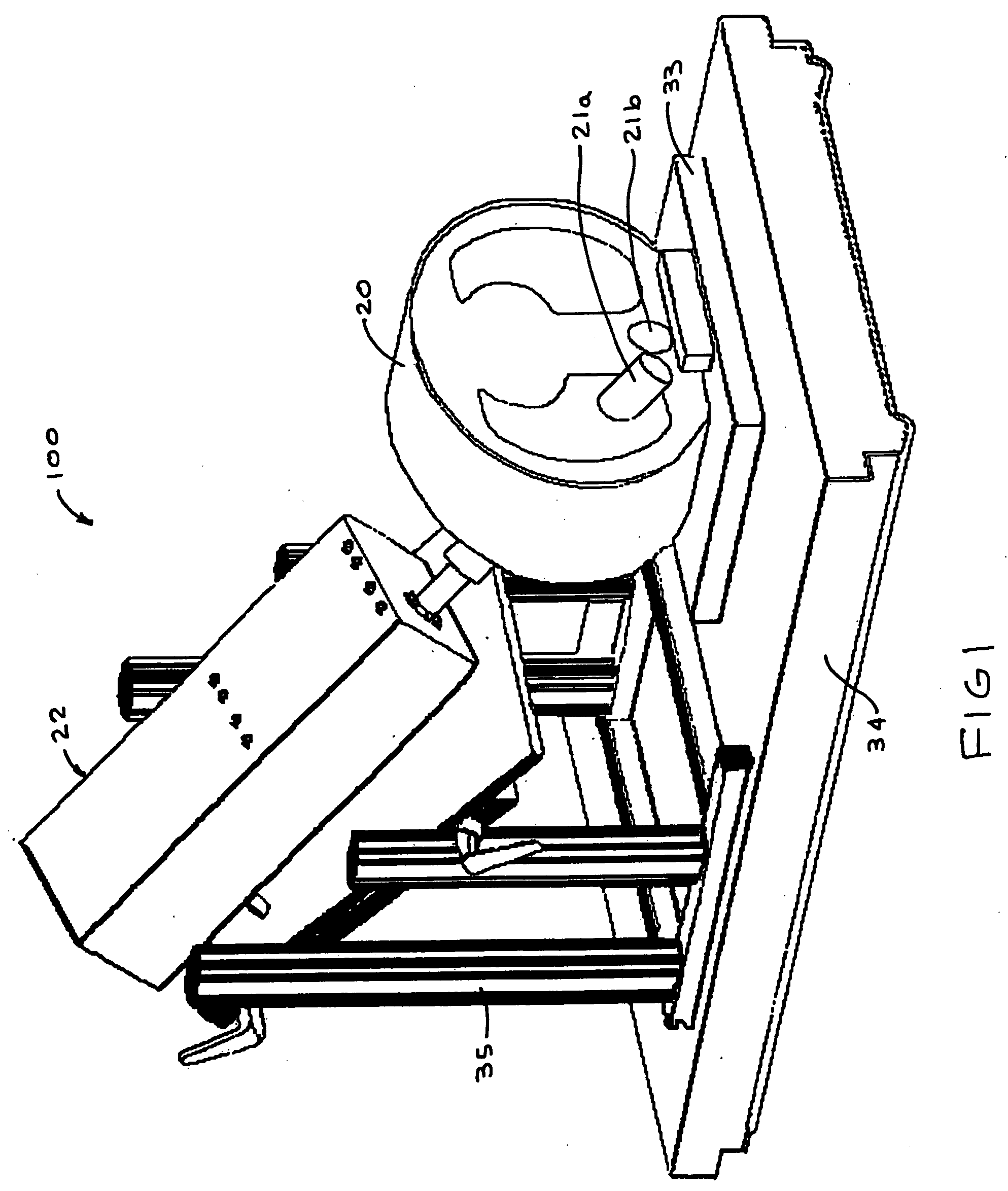
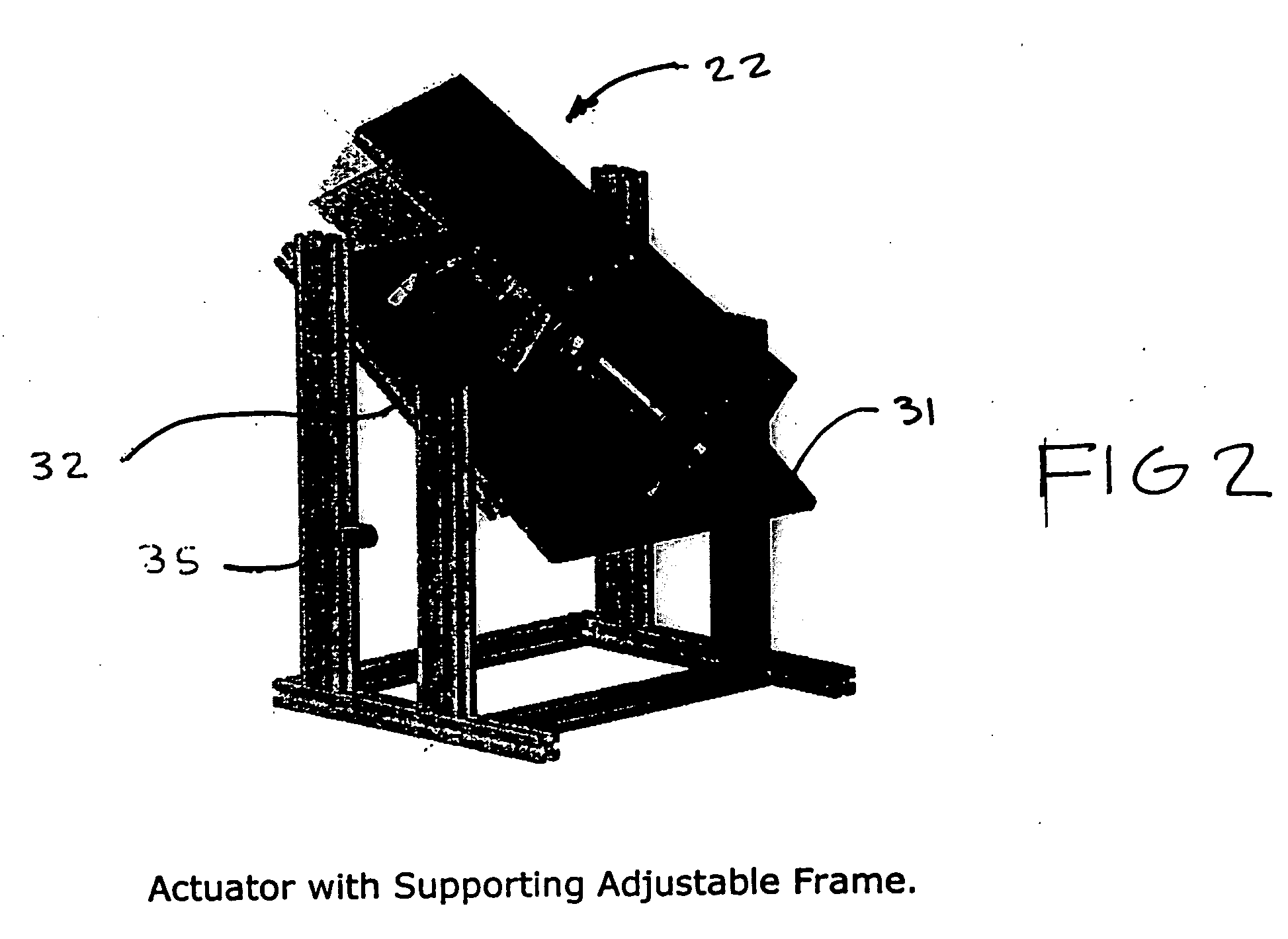
Retractor for performing heart and thorax surgeries
A retractor has a rail, a first holding arm protruding from this rail at an angle at a second holding arm extending approximately parallel to the first holding arm. A distance between the two arms being modifiable. At least one functional element is mounted on one of these holding arms, which functional element has a section extending transversely to the holding arms and a swivel bracket protruding from this transverse section. The functional element being pivotable about a pin extending roughly parallel to the arms via the swivel bracket, a swiveled position can be set by grasping the function element with a hand. A locking mechanism serves for locking the functional element in a swiveled position.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
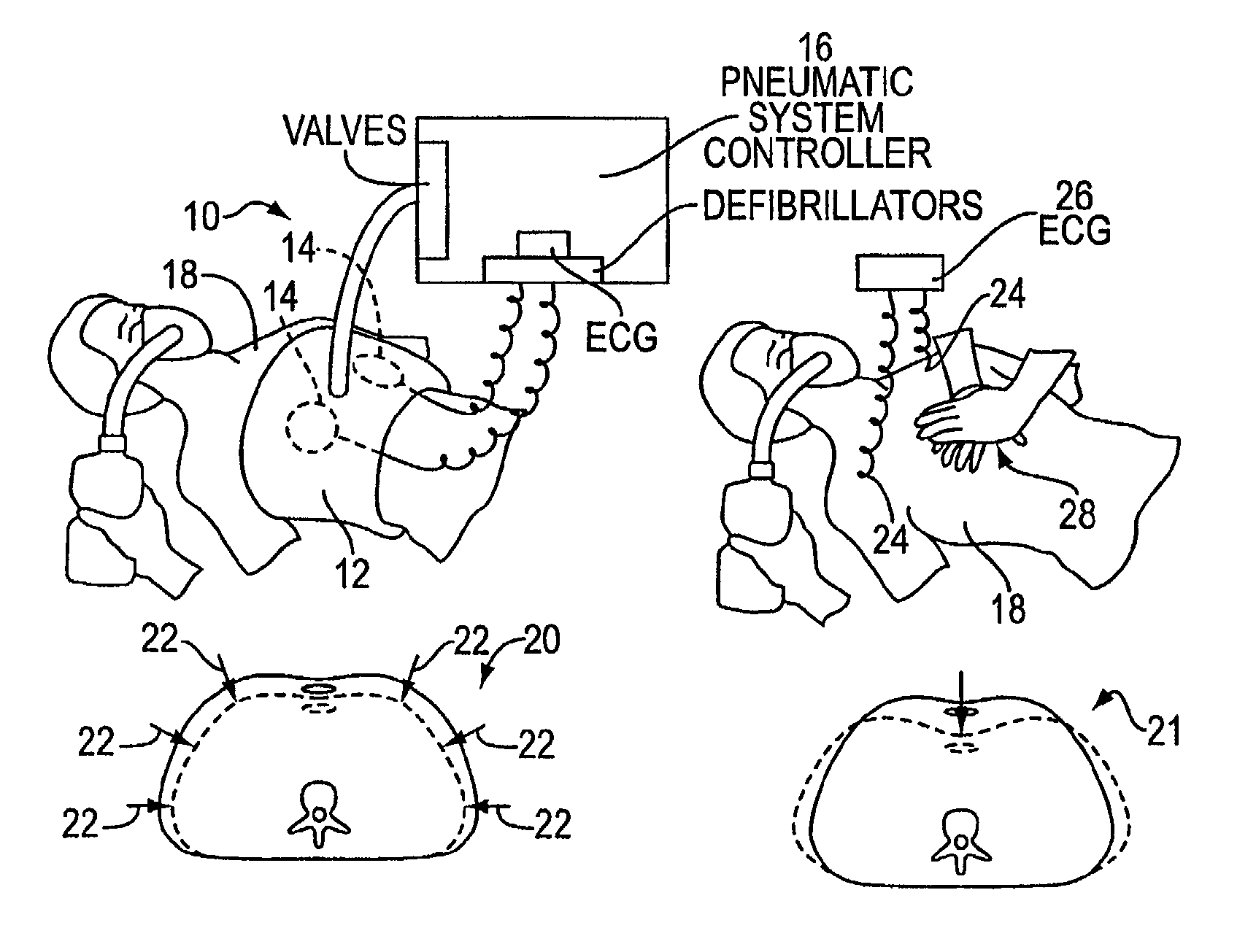
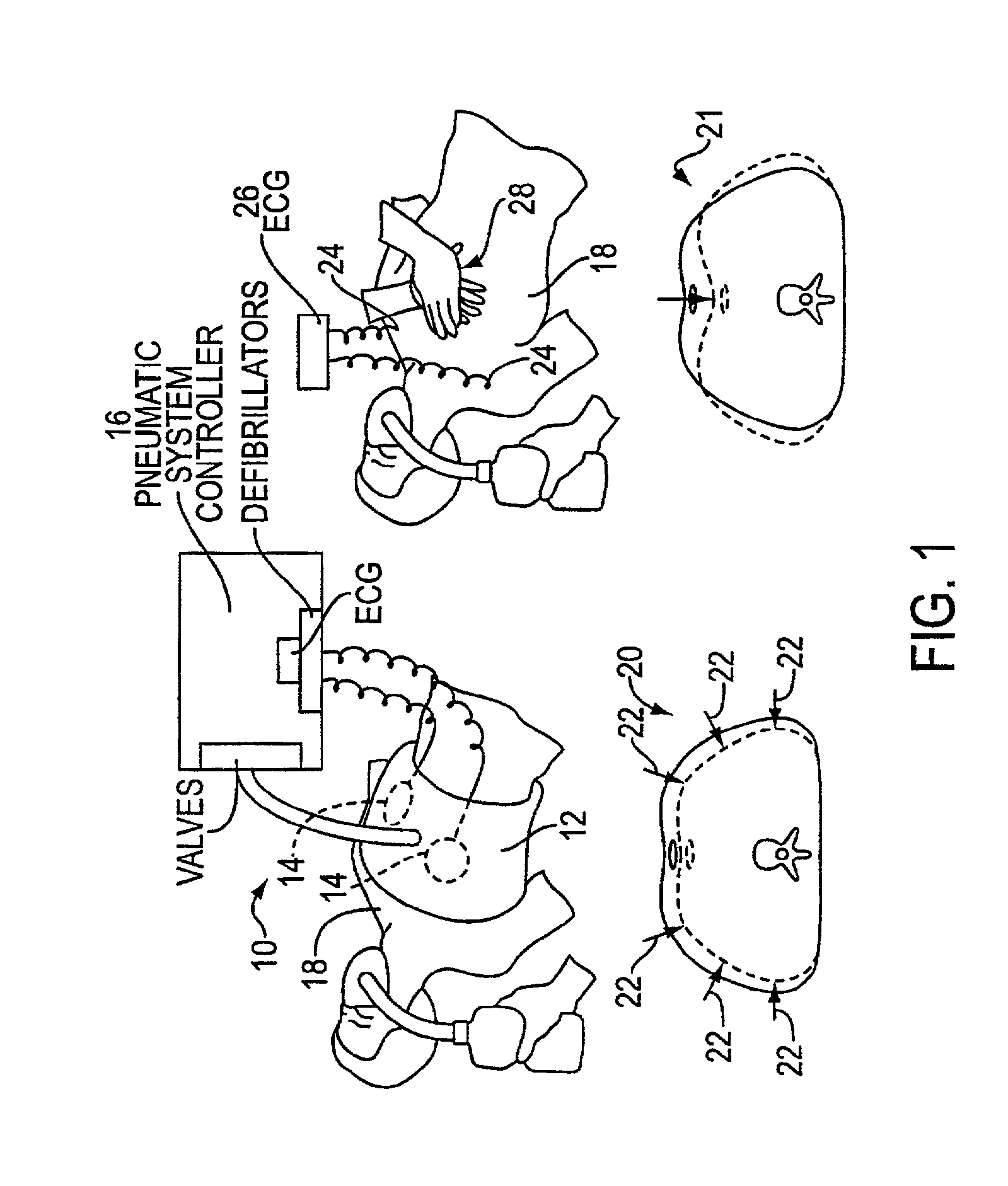
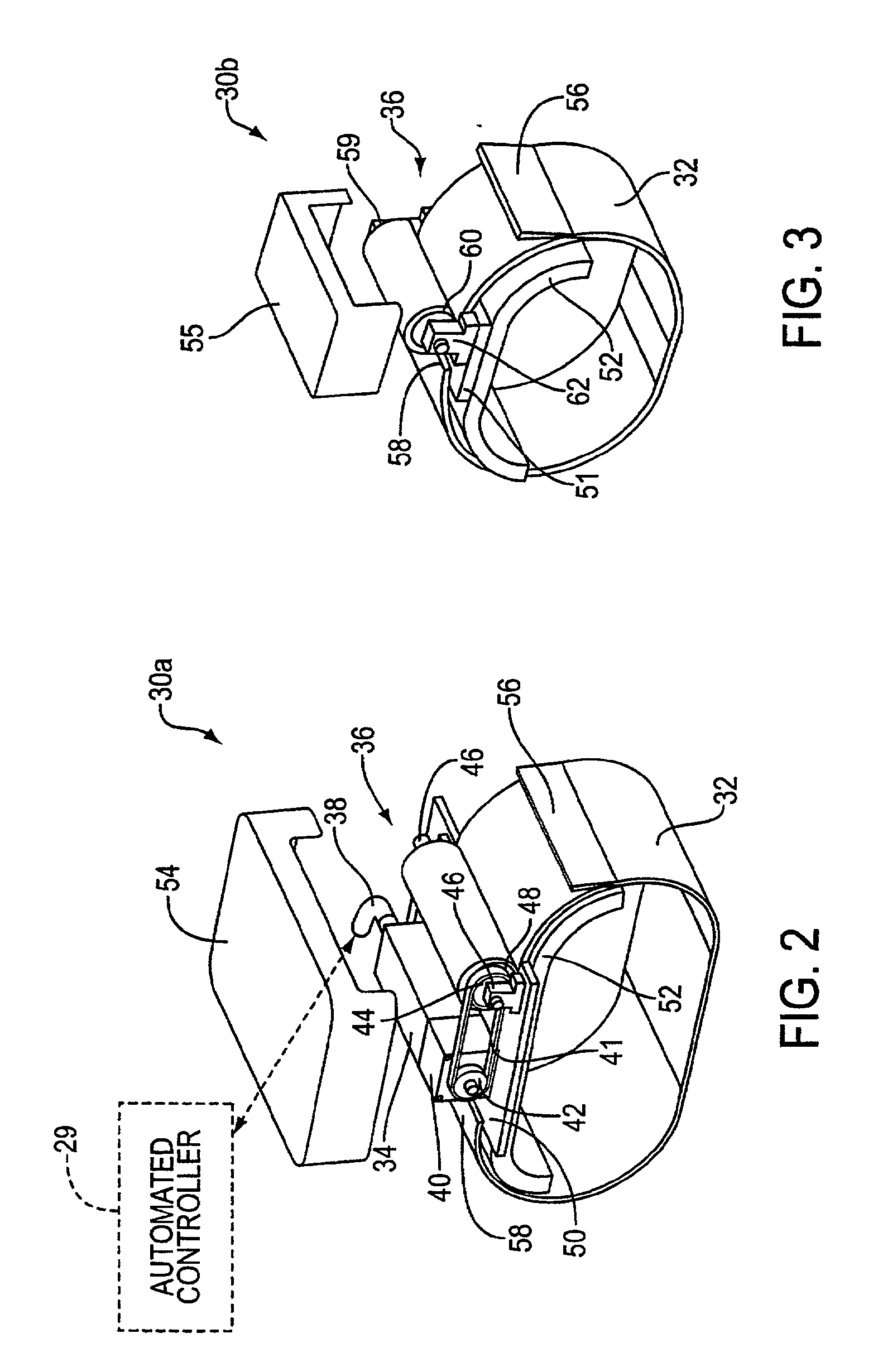
Automated chest compression apparatus
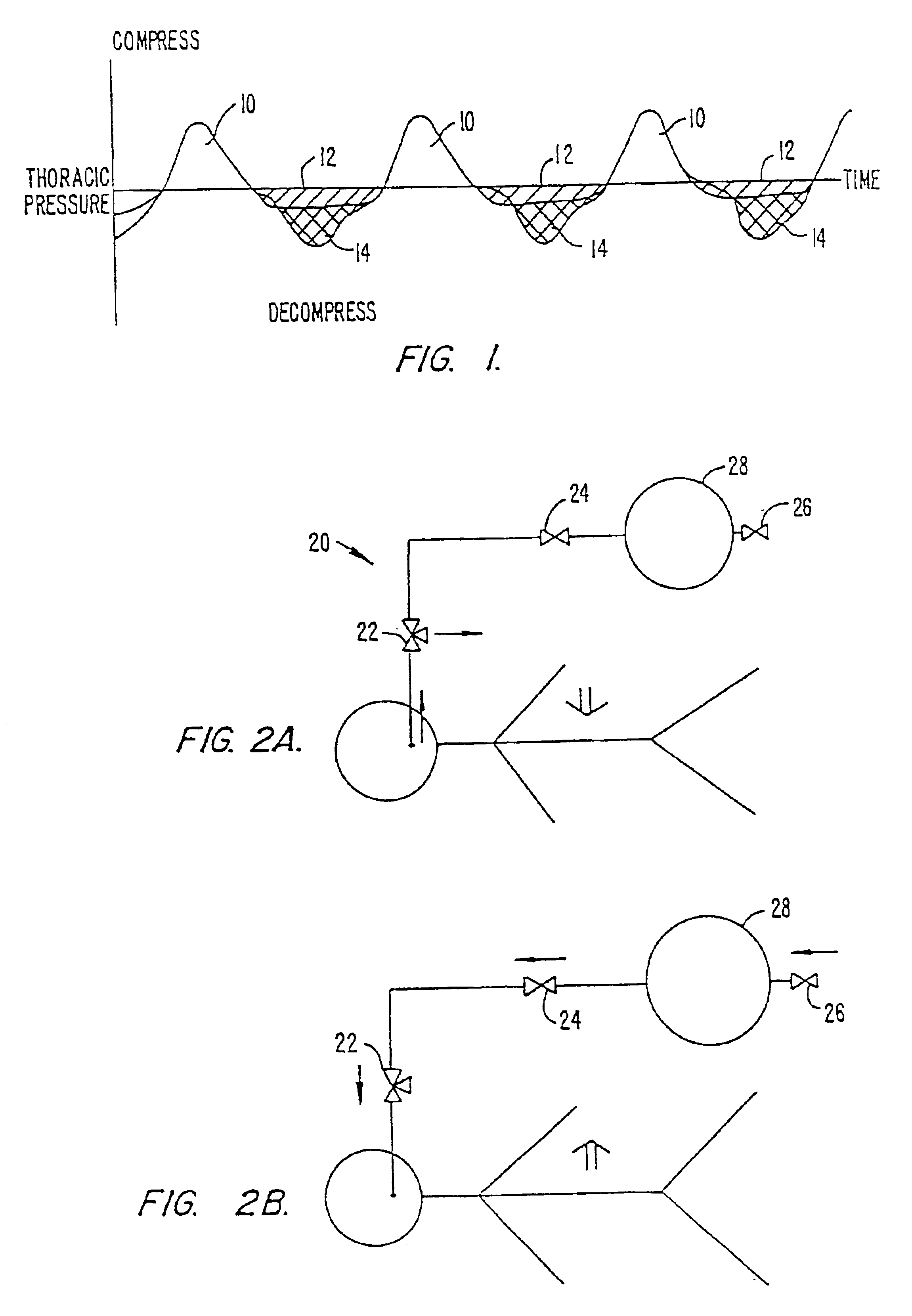
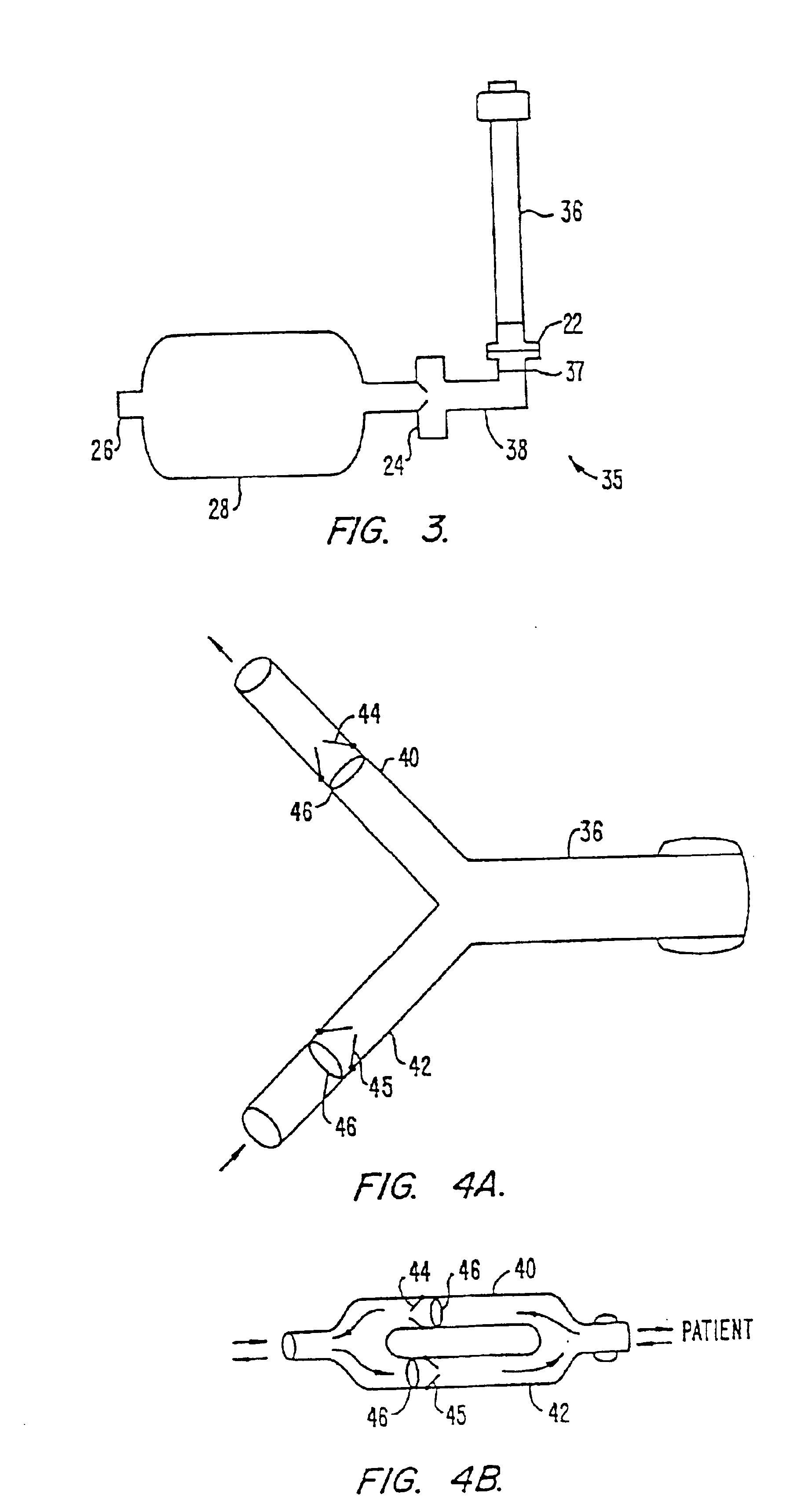
A system applies cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to a recipient. An automated controller is provided together with a compression device which periodically applies a force to a recipient's thorax under control of the automated controller. A band is adapted to be placed around a portion of the torso of the recipient corresponding to the recipient's thorax. A driver mechanism shortens and lengthens the circumference of the band. By shortening the circumference of the band, radial forces are created acting on at least lateral and anterior portions of the thorax. A translating mechanism may be. provided for translating the radial forces to increase the concentration of anterior radial forces acting on the anterior portion of the thorax. The driver mechanism may comprise a tension device for applying a circumference tensile force to the band. The driver mechanism may comprise an electric motor, a pneumatic linear actuator, or a contracting mechanism defining certain portions of the circumference of the band. The contracting mechanism may comprise plural fluid-receiving cells linked together along the circumference of the band. The width of each of the fluid-receiving cells becomes smaller as each cell is filled with a fluid. This causes the contraction of the band and a resulting shortening of the circumference of the band.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
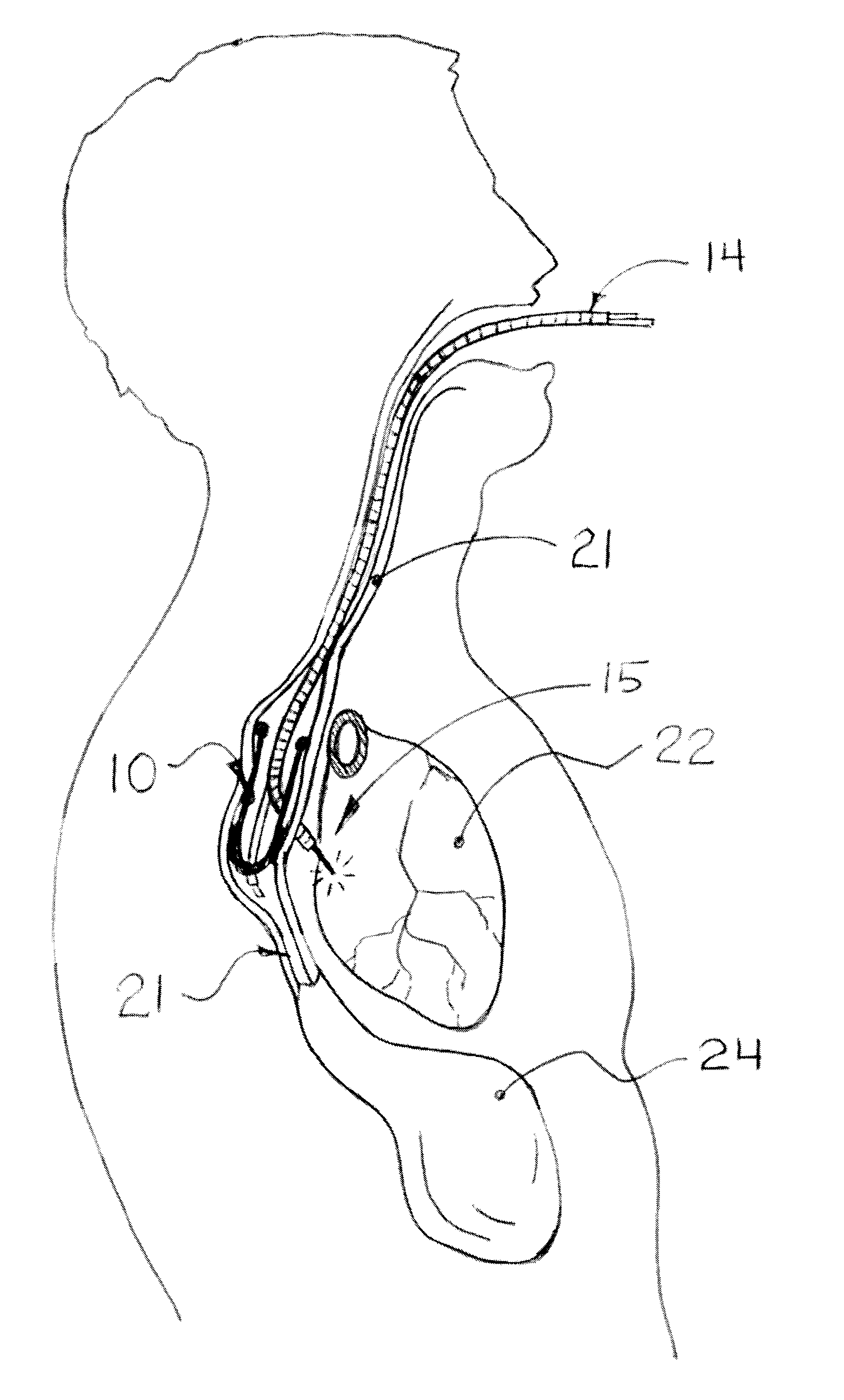
Methods and apparatus for transesophageal microaccess surgery
The current invention describes methods of transesophageal access to the neck and thorax to perform surgical interventions on structures outside the esophagus in both the cervical and the thoracic cavity. It describes a liner device made of a complete or partial tubular structure, or a flat plate, the liner having means to facilitate creation of a side opening, which may include a valve. The liner with its side opening form a port structure inside the esophageal lumen. The port structure allows elongated surgical devices to pass through a perforation across the full thickness of the esophageal wall to outside location, in a controlled way. The elongated surgical devices can be diagnostic scopes, therapeutic scopes, manual elongated surgical devices, robotic arms or the like. After being deployed outside the esophagus, the surgical devices can access structures outside the esophagus, in the neck and thorax in 360 degrees of freedom around the esophageal circumference. These structures can be bony, cartilaginous, spinal, vascular, soft tissue, deep tissues, lymph nodal, cardiac, pulmonary, tracheal, nervous, muscular or diaphragmatic, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the neck, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior chest wall, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the skin of the back, and skin and layers of the breast.
Owner:MICROACCESS
Positive pressure systems and methods for increasing blood pressure and circulation
InactiveUS20050165334A1Enhance blood flow blackEnhances vital organ circulationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyBlood flowPositive pressure
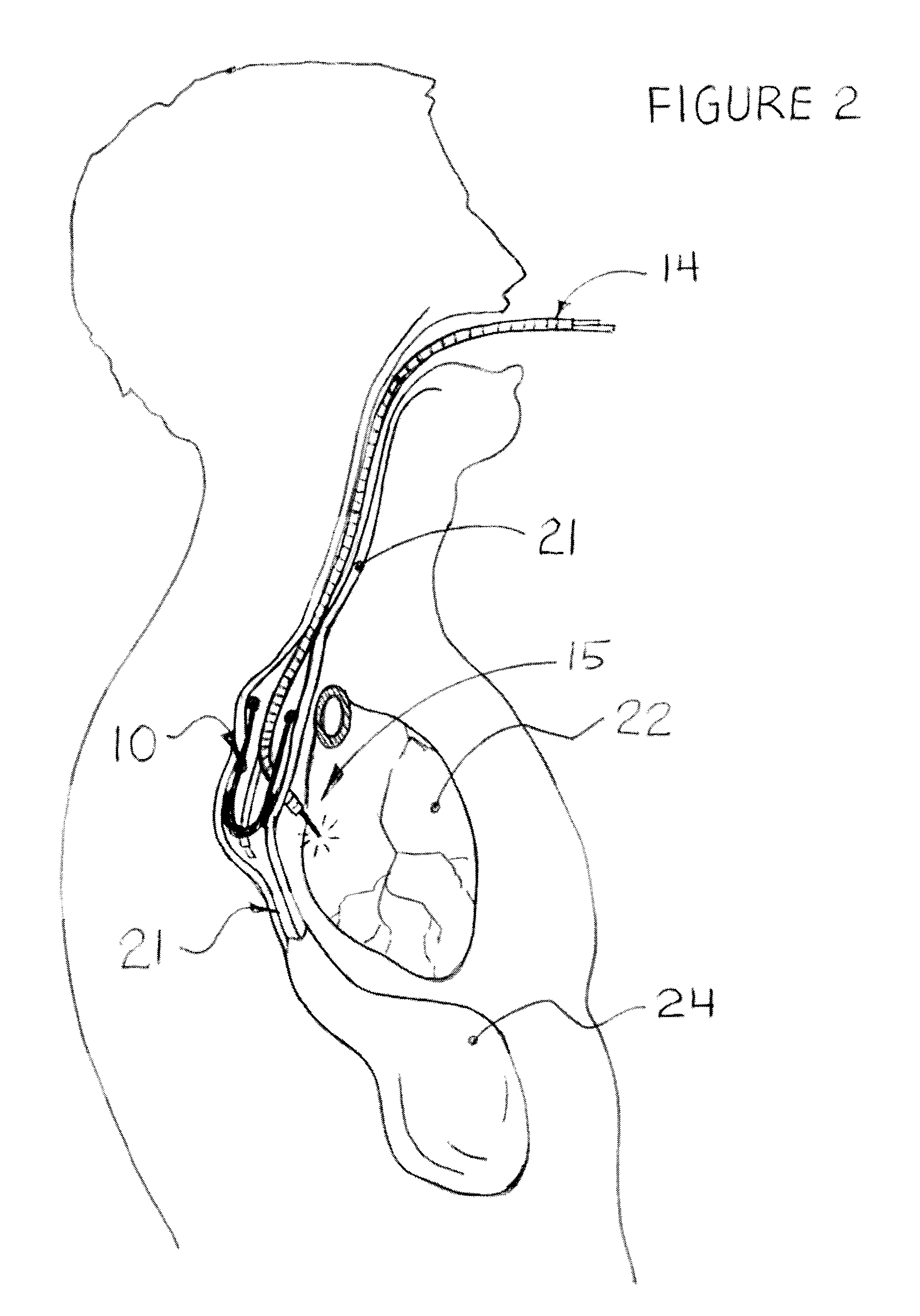
In one embodiment, the invention provides a medical method for treating a person and comprises repeatedly compressing the person's chest. While repeatedly compressing the person's chest, the method further includes repeatedly delivering a positive pressure breath to the person and extracting respiratory gases from the person's airway using a vacuum following the positive pressure breath to create an intrathoracic vacuum to lower pressures in the thorax and to enhance blood flow back to the heart.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
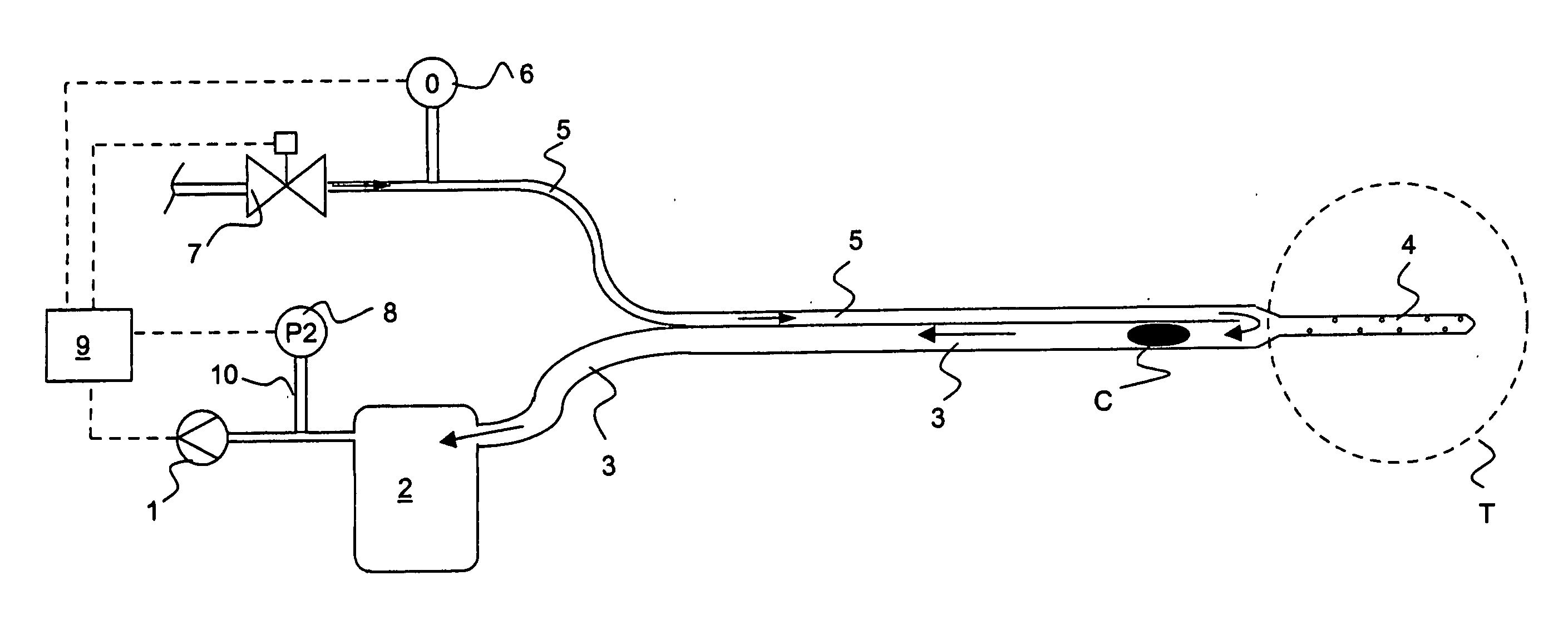
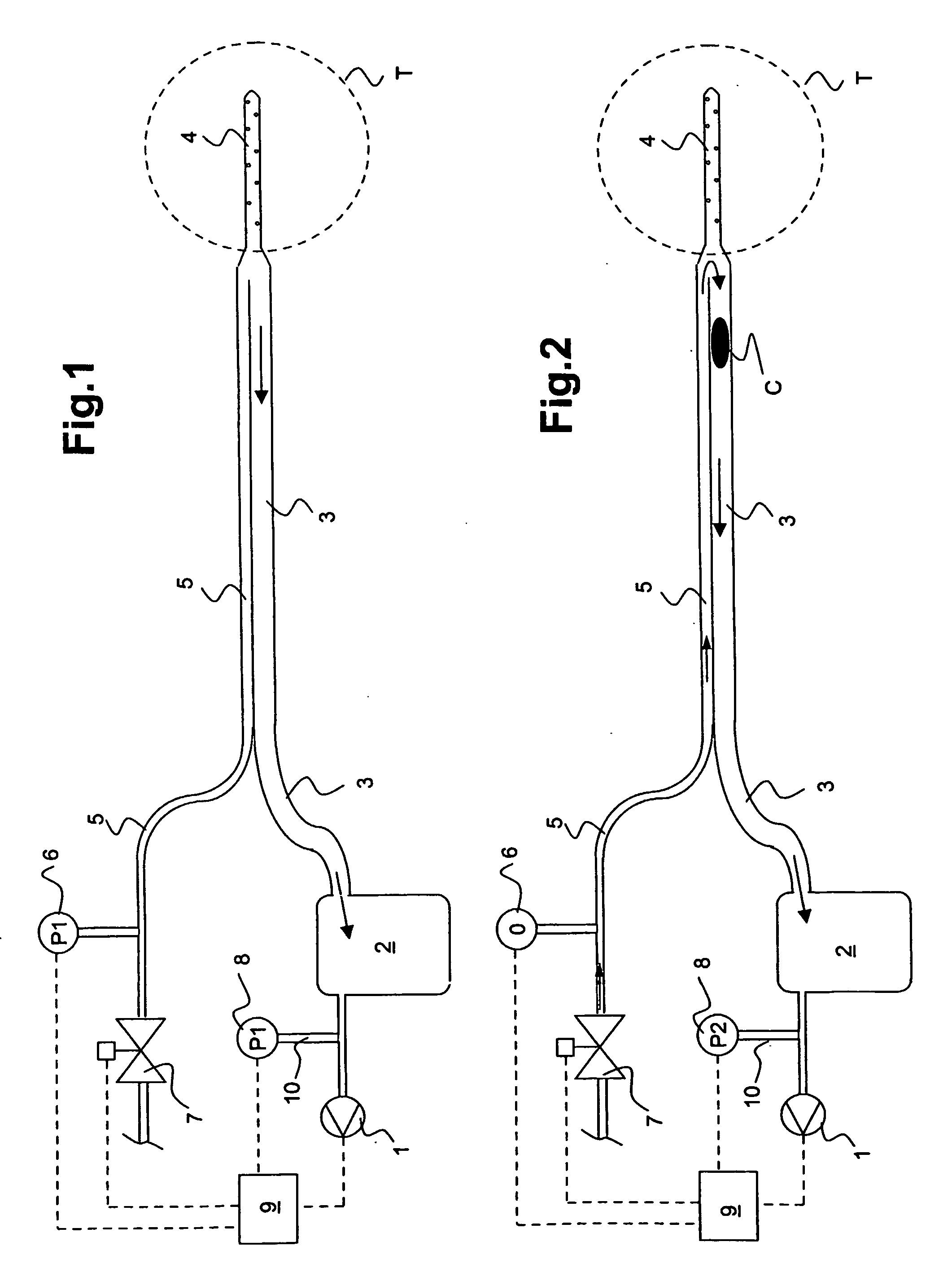
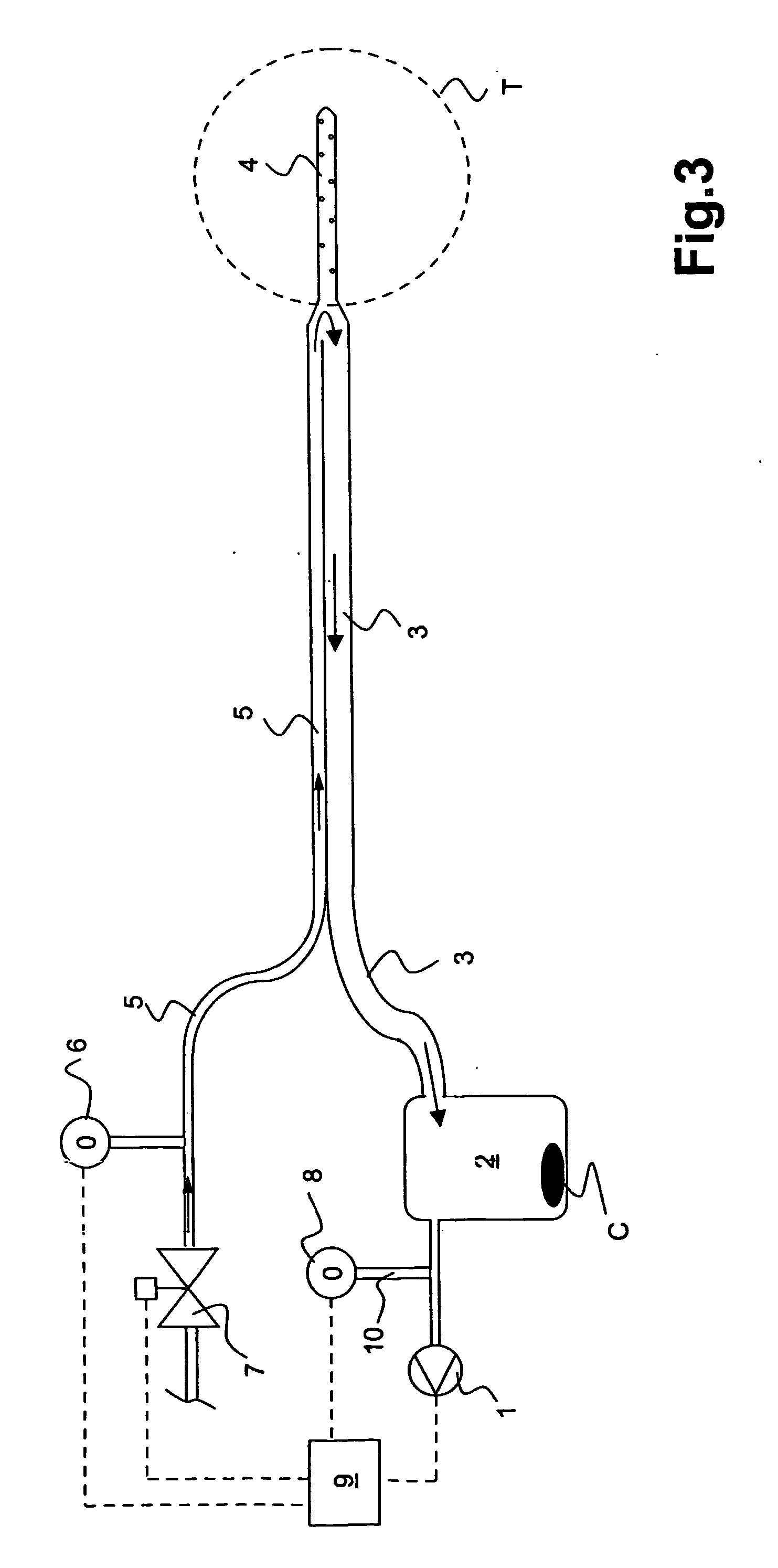
Drainage apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070078444A1The process is simple and convenientGreat suctionInfusion syringesSurgeryThoracic cavityPressure difference
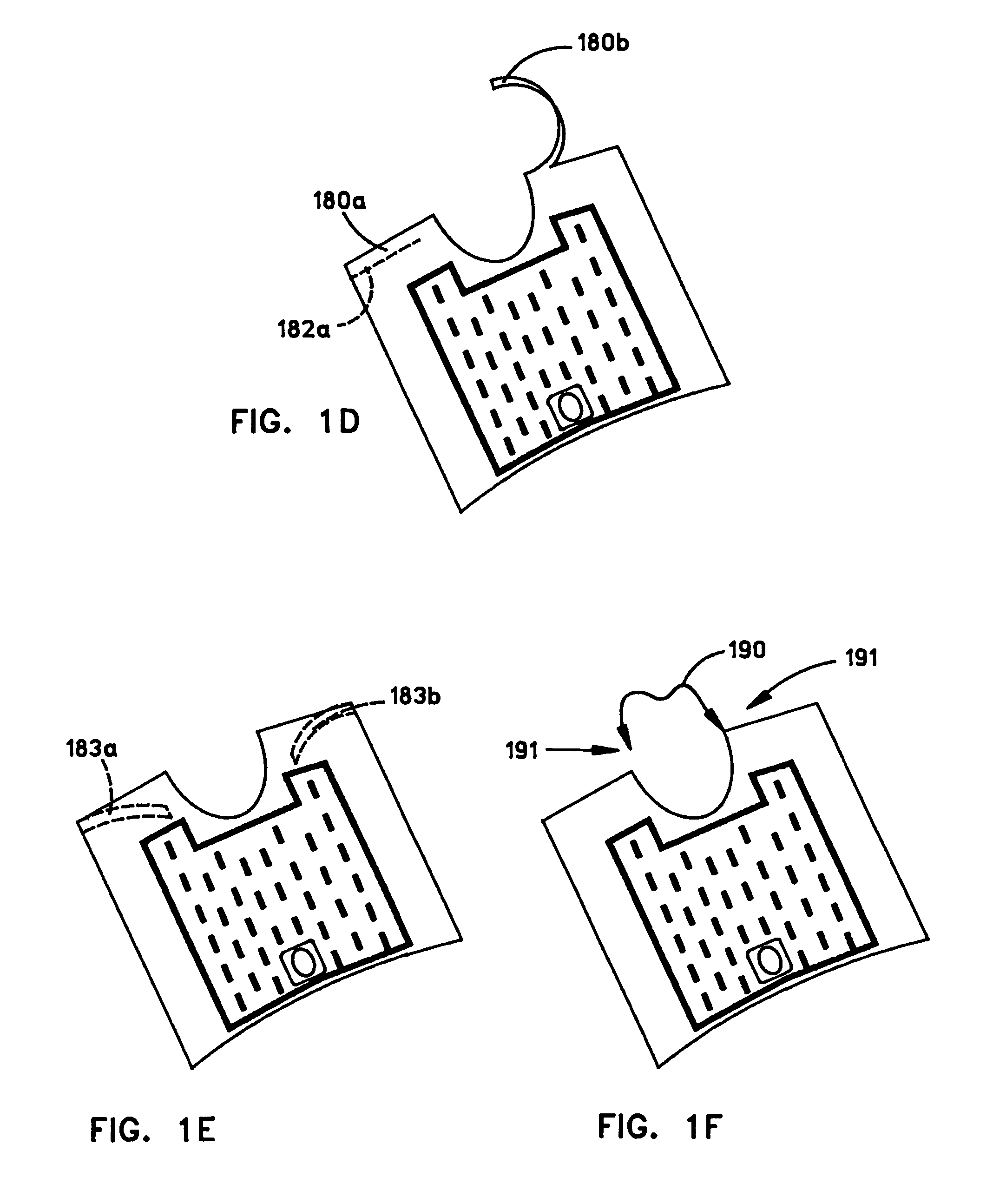
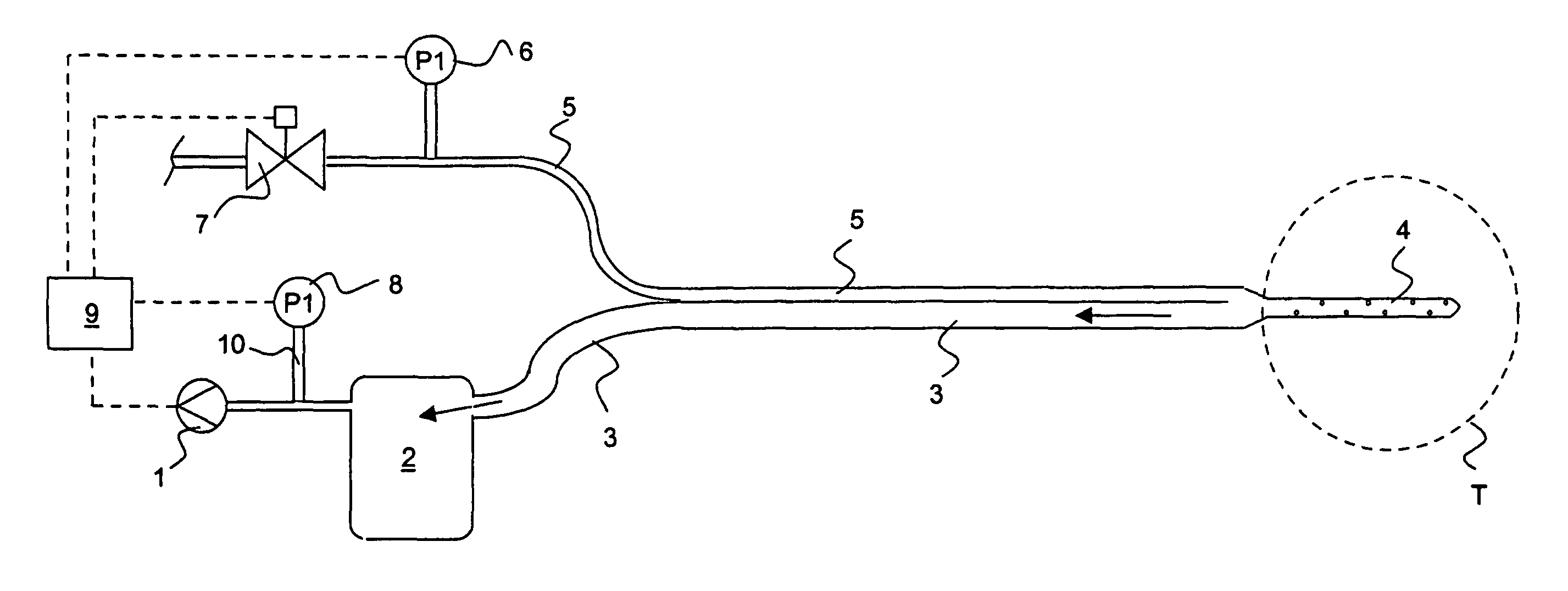
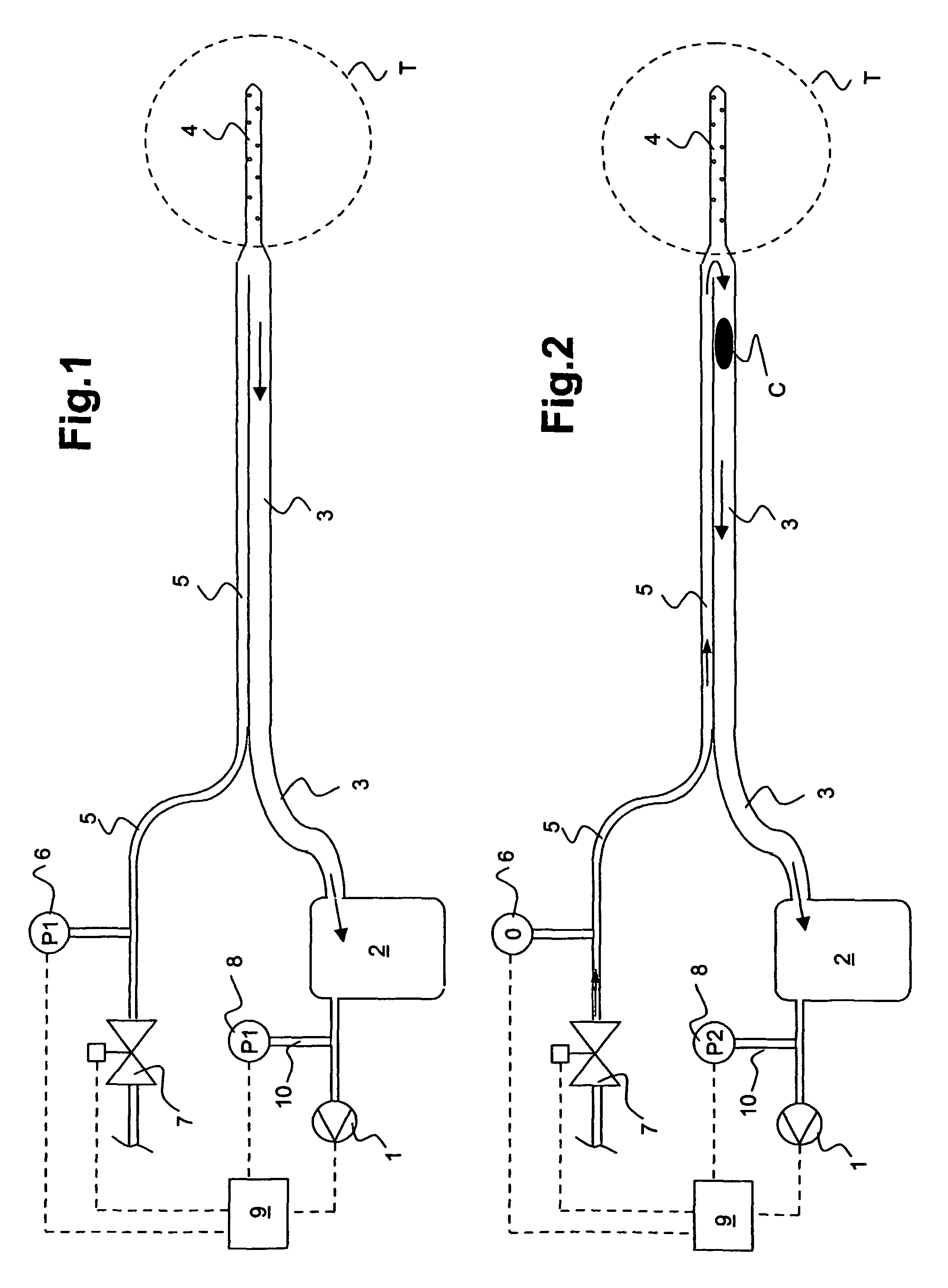
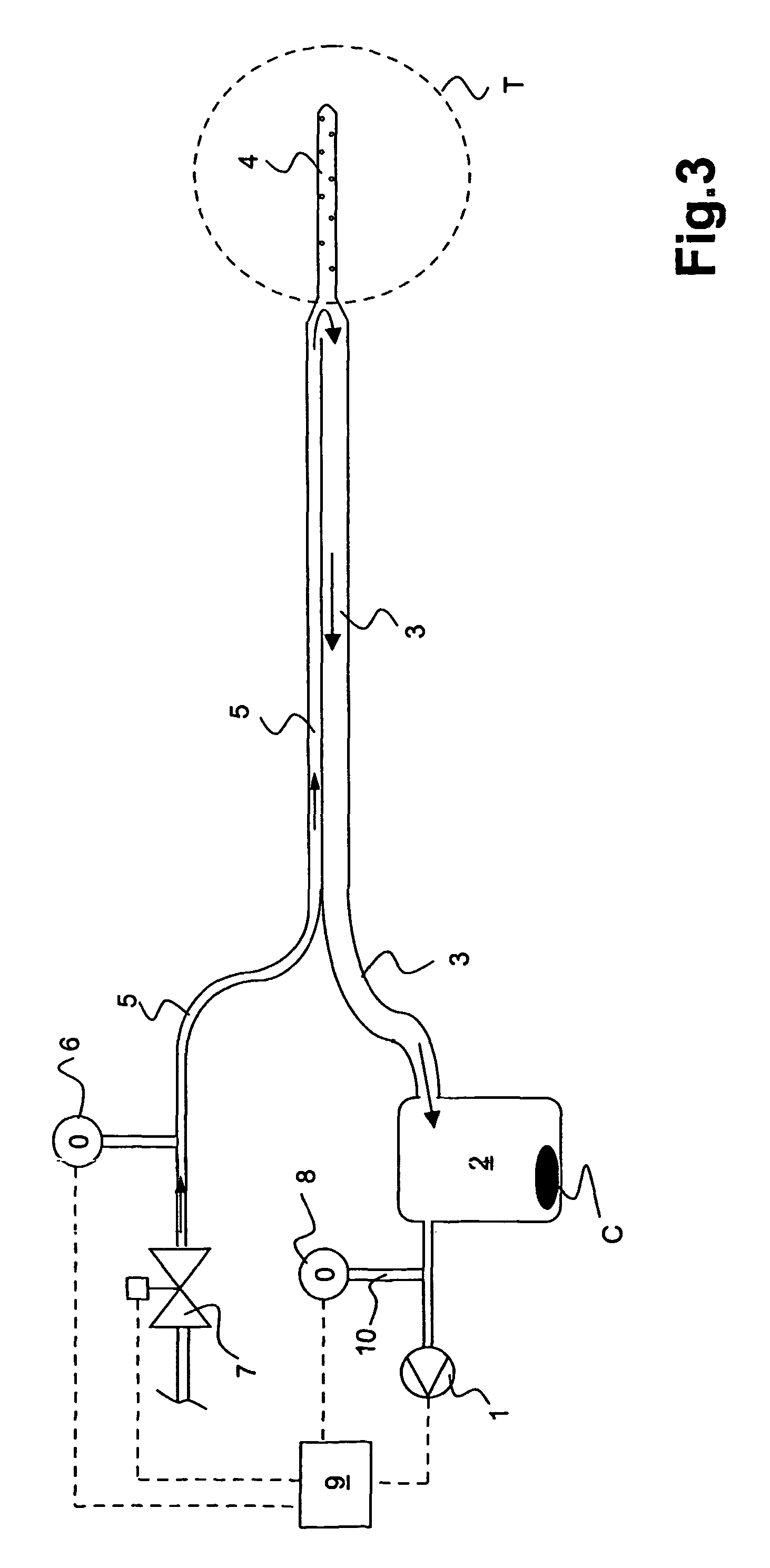
An apparatus for removing body fluids from a body cavity by suction, such as a thorax, gastric or any other human body cavity or a wound, comprises means (9) to increase the pressure difference between a pressure in a drainage lumen (3) and a pressure in the atmosphere when an auxiliary lumen (5) is open. The apparatus enables removal of clots or other plugs of the catheter and drainage tube in an efficient and not patient disturbing way.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
Systems and methods for enhancing blood circulation
InactiveUS6986349B2Increase loopDecrease and prevent flowCompressorElectrotherapyHeart rightInhalation
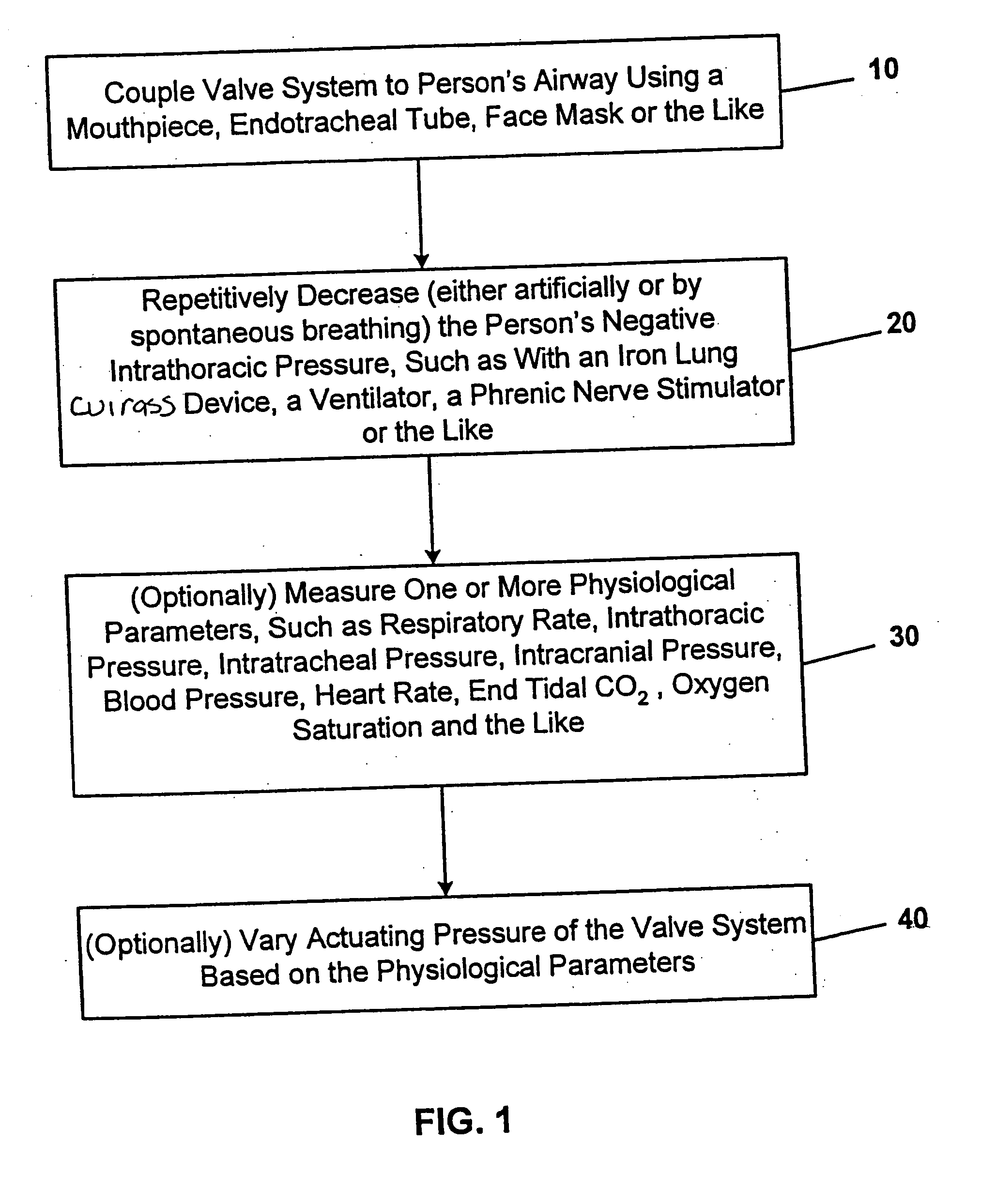
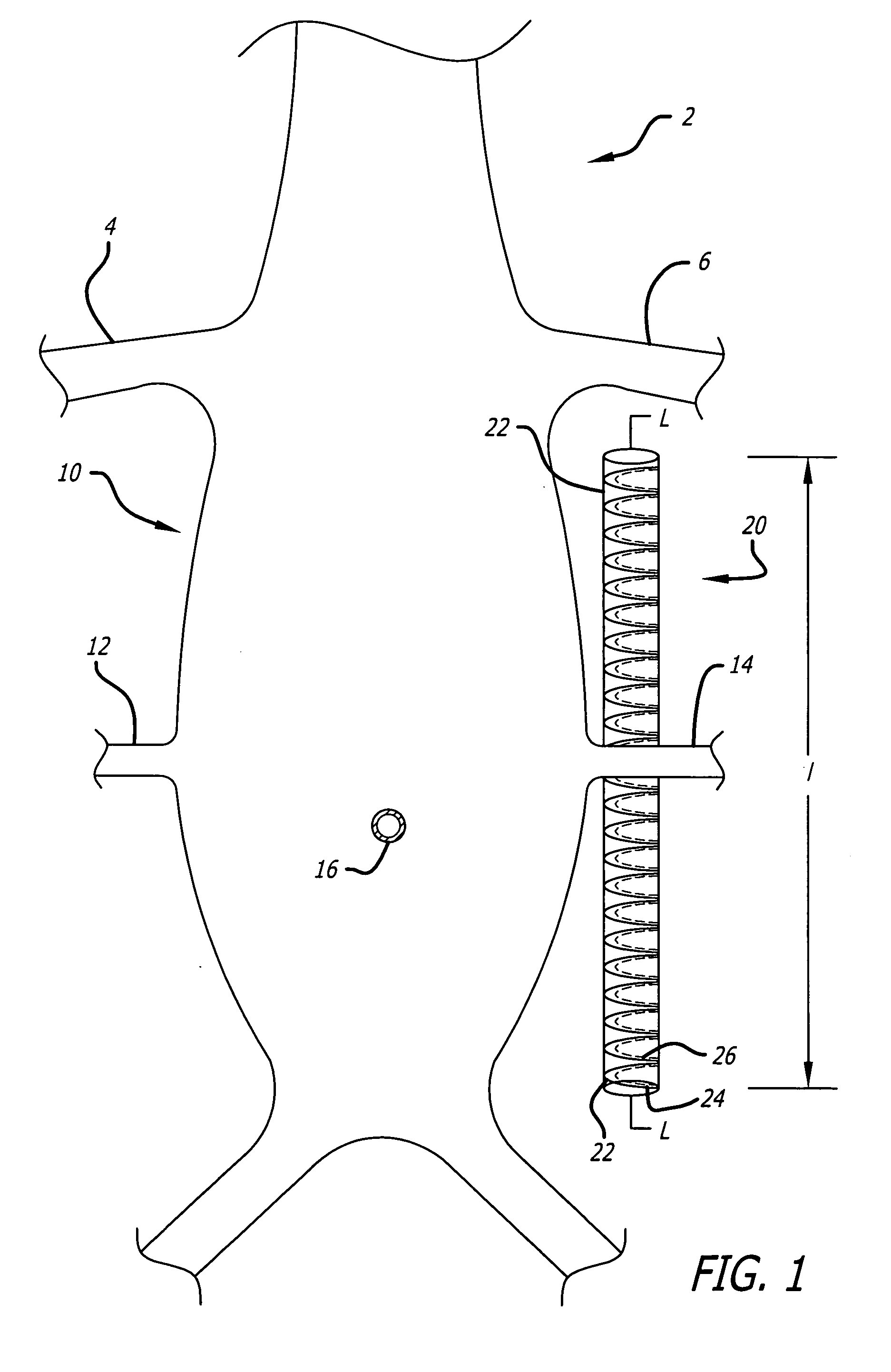
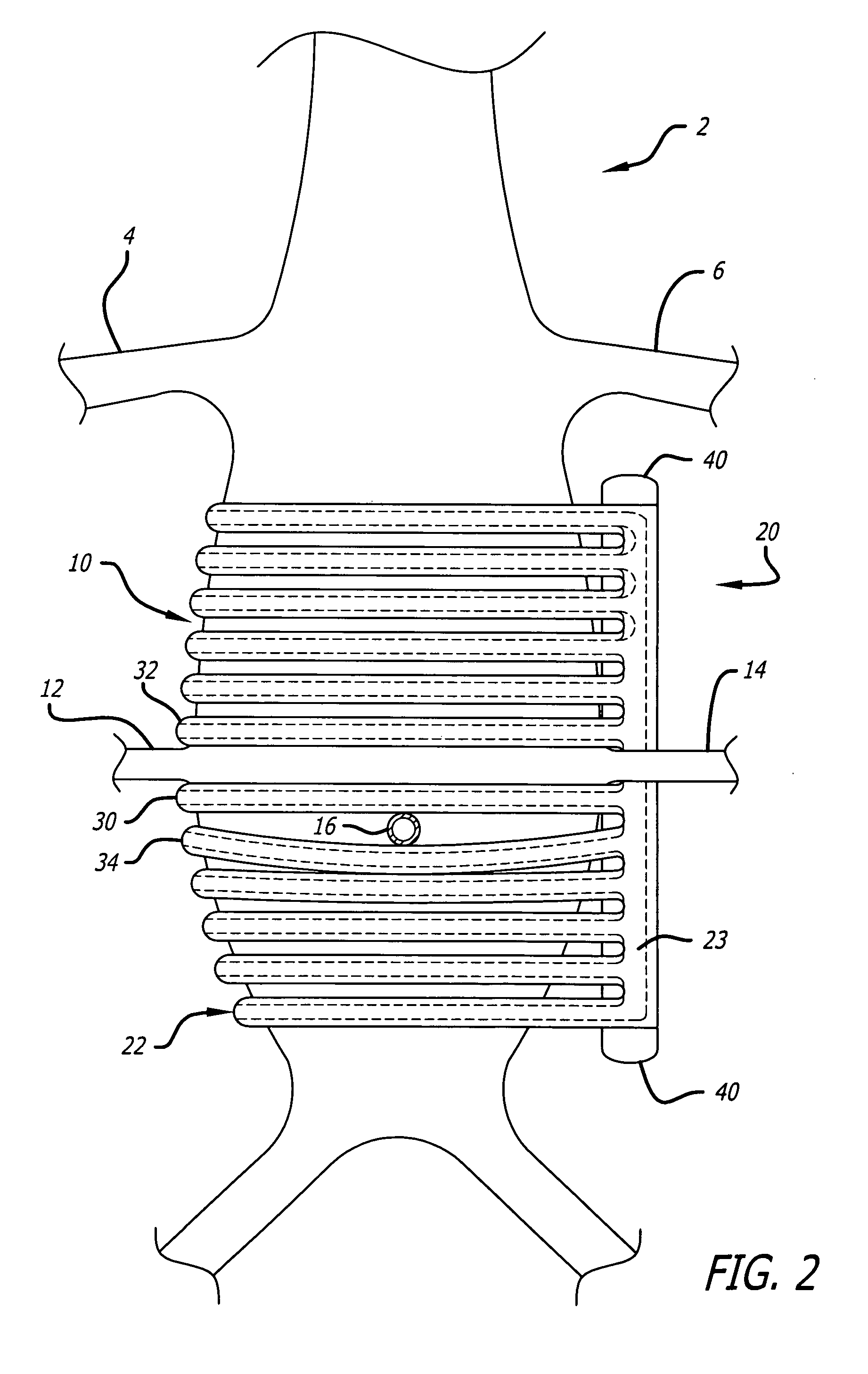
A method for increasing circulation in a breathing person utilizes a valve system that is interfaced to the person's airway and is configured to decrease or prevent respiratory gas flow to the person's lungs during at least a portion of an inhalation event. The person is permitted to inhale and exhale through the valve system. During inhalation, the valve system functions to produce a vacuum within the thorax to increase blood flow back to the right heart of the person, thereby increasing cardiac output and blood circulation.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Patient comfort apparatus and system
InactiveUS7001416B2Stay comfortableEffective convective warmingGarment special featuresCouplingsPatient comfortThermal treatment
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
Drainage apparatus and method
InactiveUS7976533B2The process is simple and convenientGreat suctionInfusion syringesWound drainsPressure differenceThoracic cavity
An apparatus for removing body fluids from a body cavity by suction, such as a thorax, gastric or any other human body cavity or a wound, comprises means (9) to increase the pressure difference between a pressure in a drainage lumen (3) and a pressure in the atmosphere when an auxiliary lumen (5) is open. The apparatus enables removal of clots or other plugs of the catheter and drainage tube in an efficient and not patient disturbing way.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
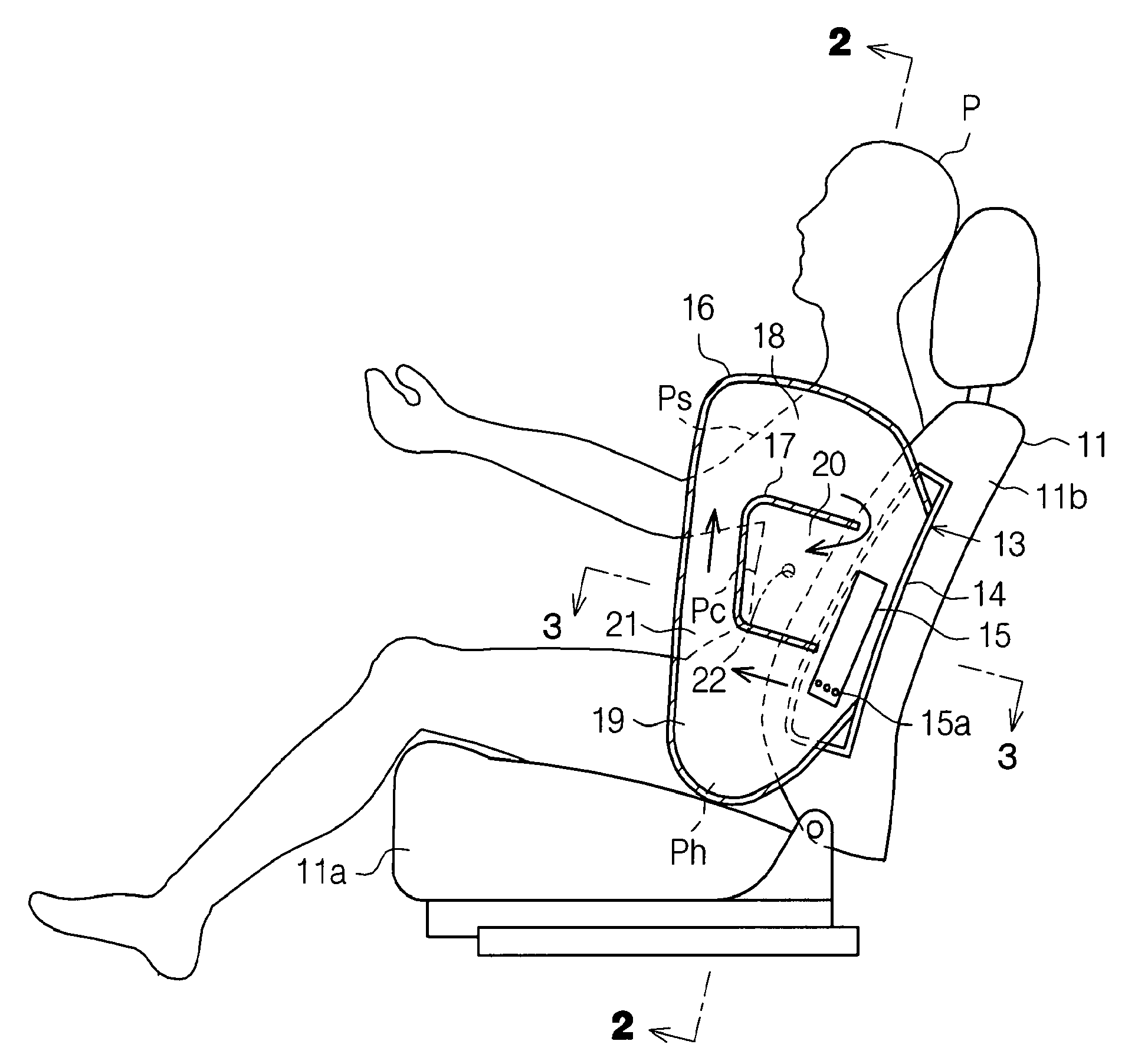
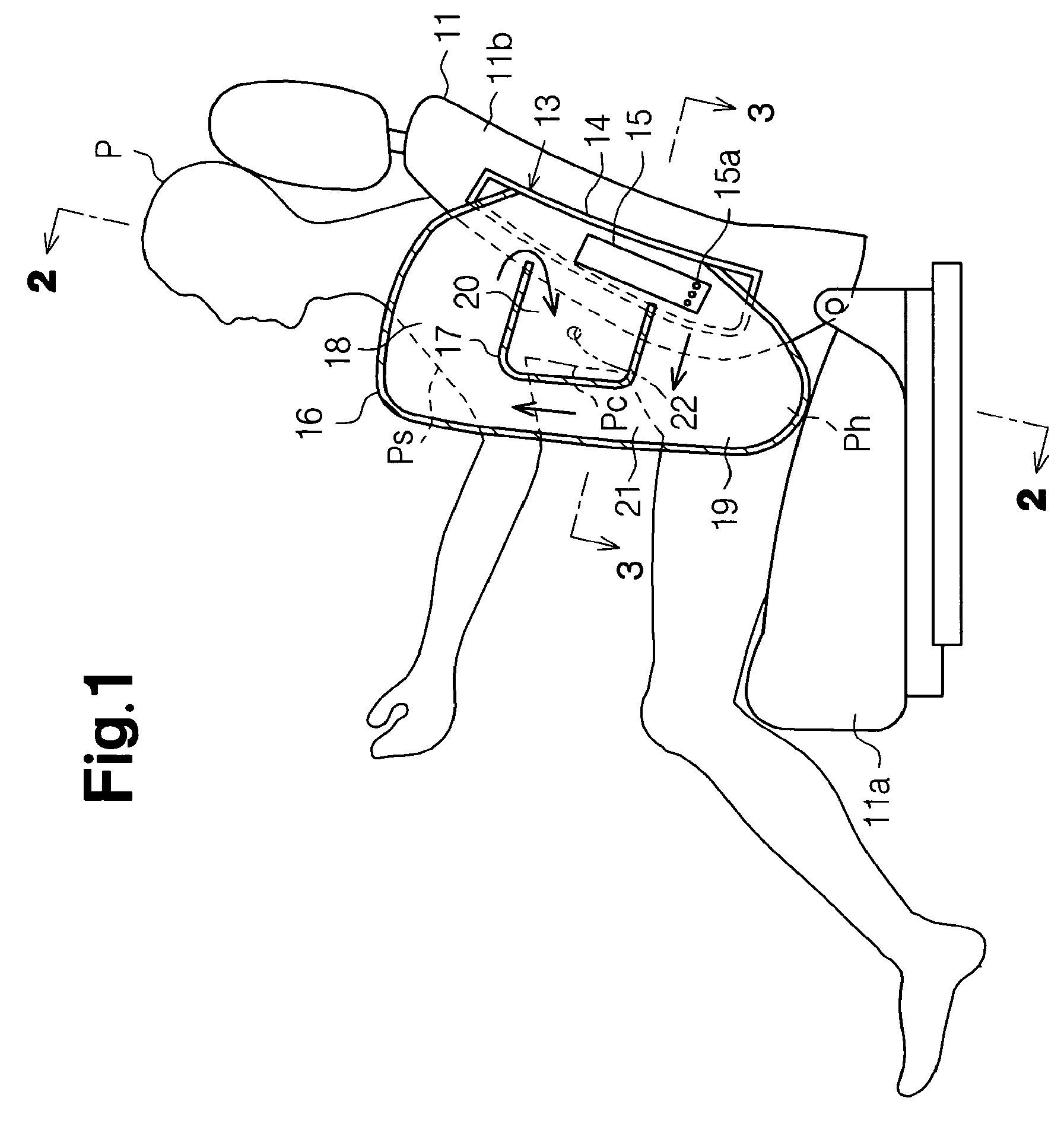
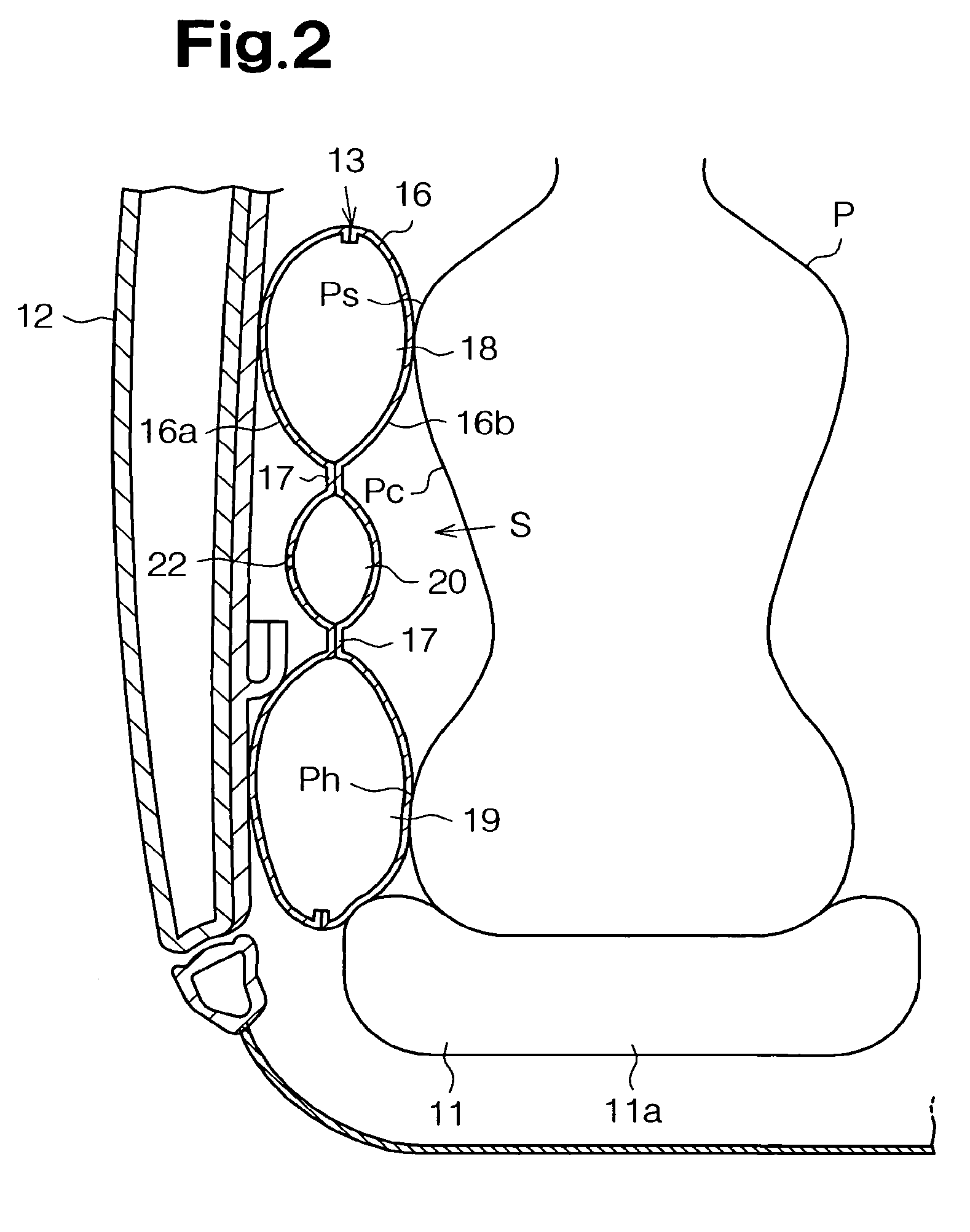
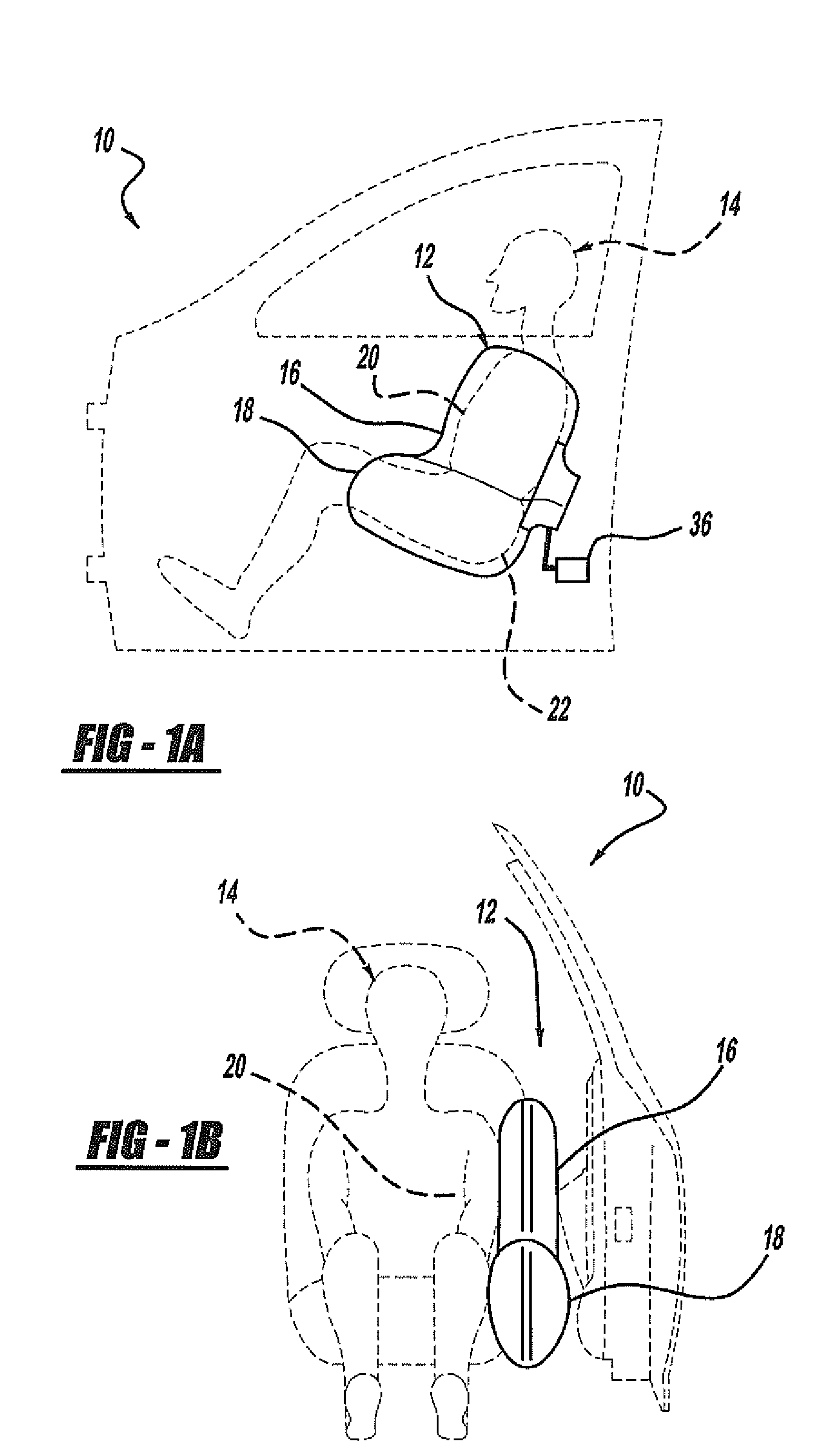
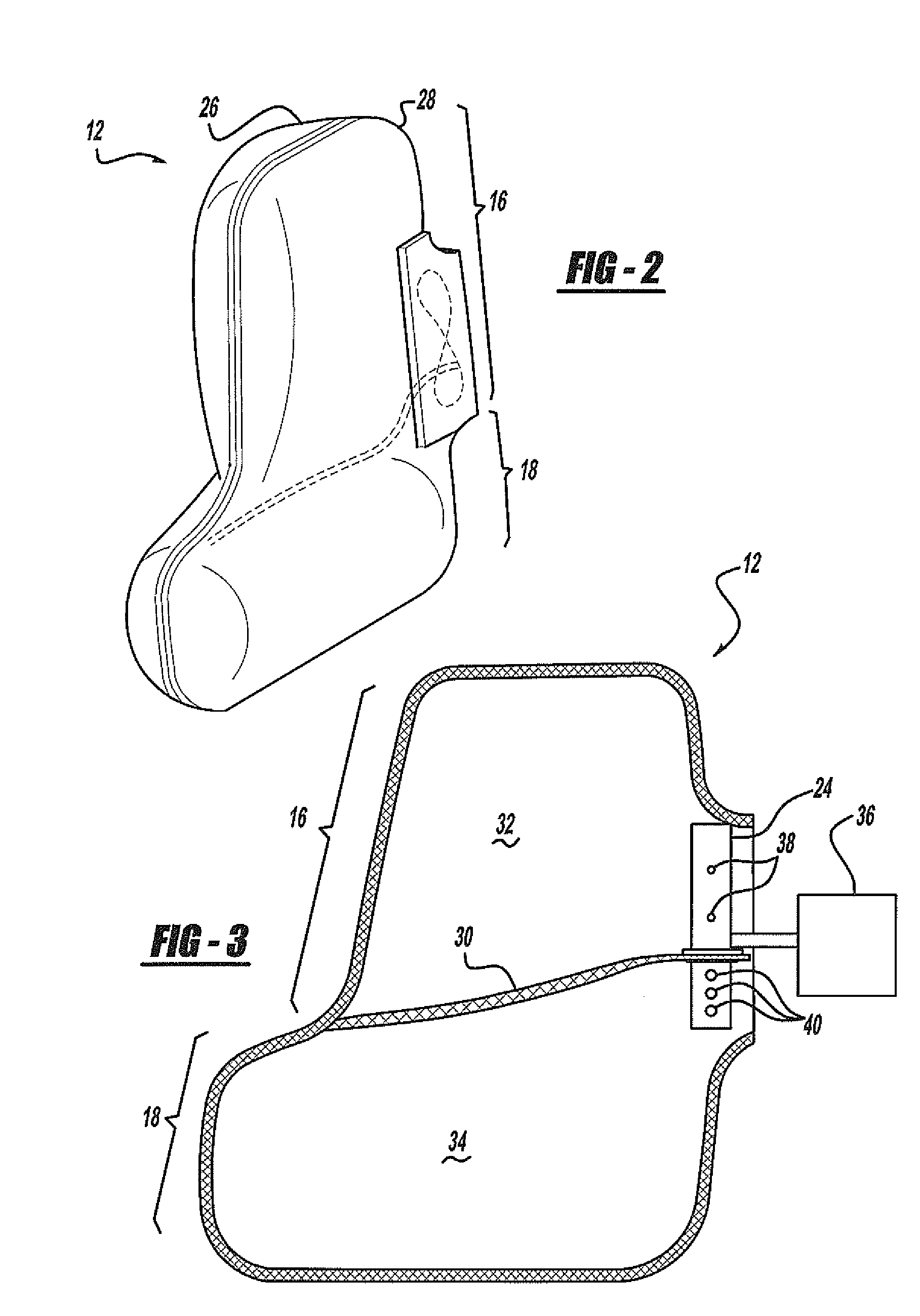
Side airbag apparatus
InactiveUS7793973B2Effective protectionFacilitate inflationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringAirbag
A side airbag apparatus for vehicle has an airbag and an inflator. An upper chamber, a lower chamber, and an intermediate chamber are defined by a seam in the airbag. When the airbag is deployed, the upper chamber corresponds to a shoulder of an occupant, the lower chamber corresponds to a lumbar region of the occupant, and the intermediate chamber corresponds to a thorax of the occupant. The seam guides gas from the inflator to the upper and lower chambers such that the upper and lower chambers are substantially simultaneously inflated, and the intermediate chamber is inflated after a delay. The thickness of the intermediate chamber is less than the thicknesses of the upper and lower chambers. As a result, the occupant of the vehicle is effectively protected.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Apnea treatment device
Treatment or control of sleep apnea by achieved using a device or method for stimulation of expiration muscles. Somatic or expiratory muscle stimulation instead of a mask during sleep may regularize breathing. An apnea belt around the thorax may detect respiration by monitoring stretch and provide electrical stimulation to muscles used for expiration.
Owner:RMX
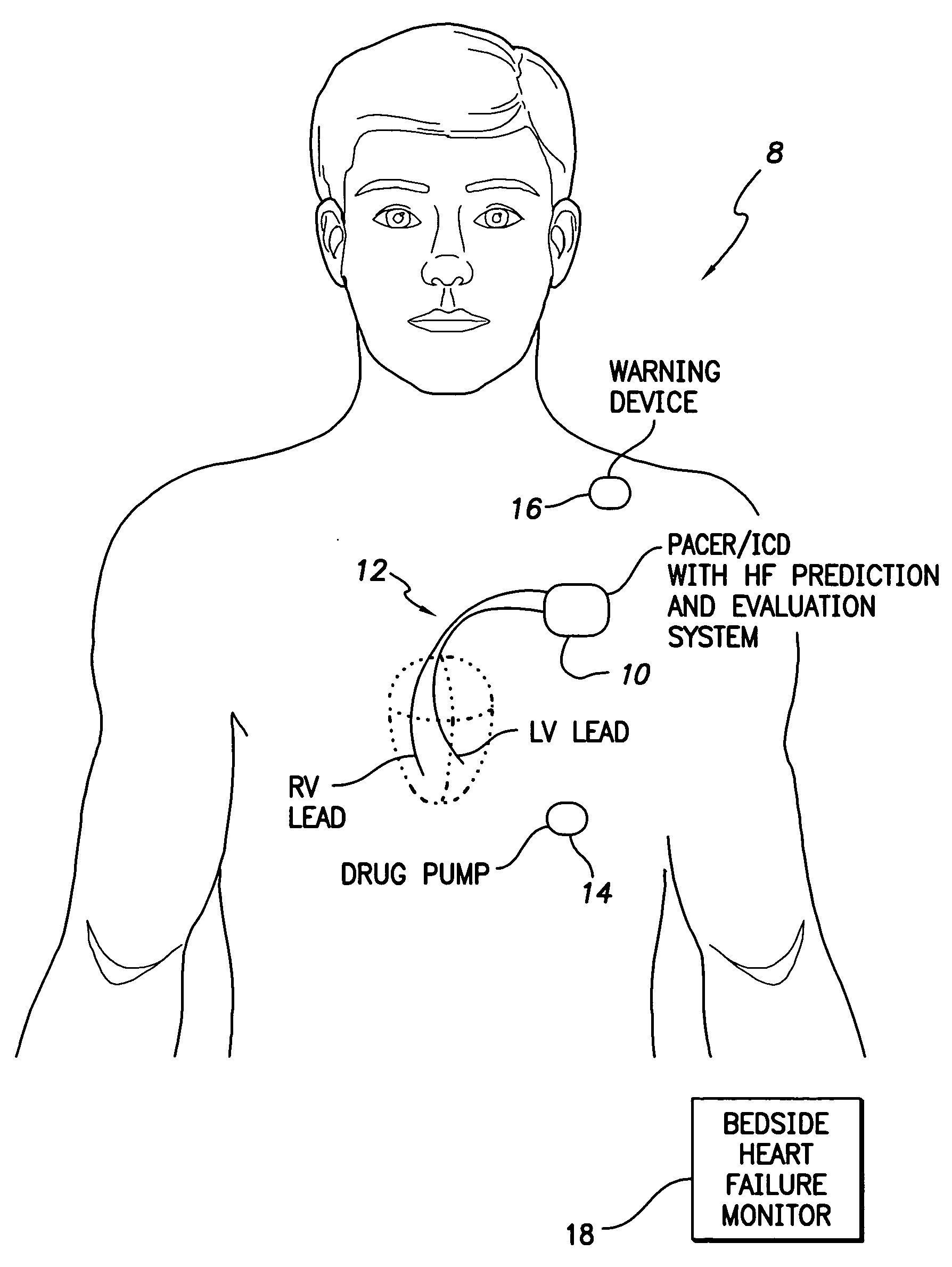
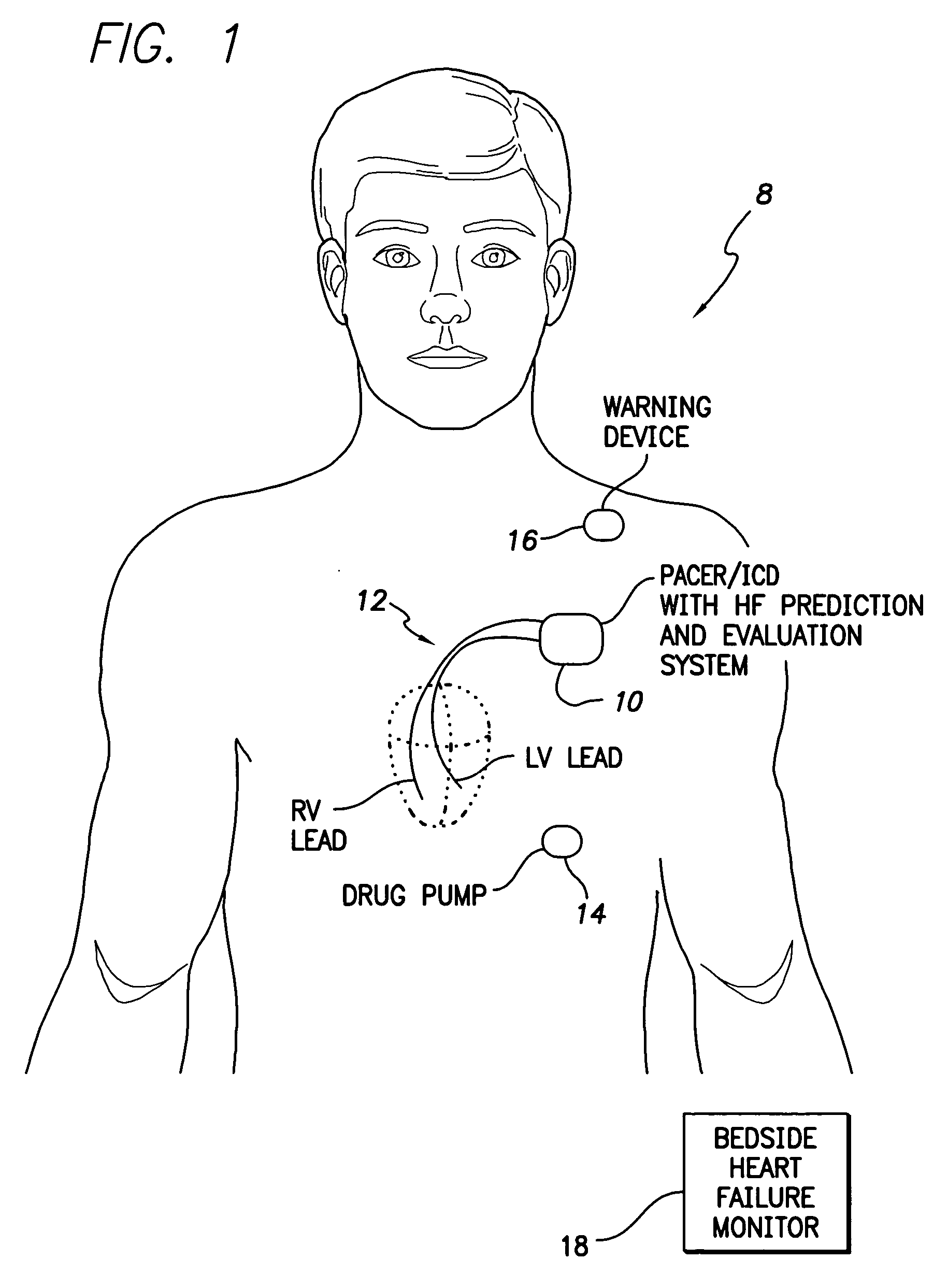
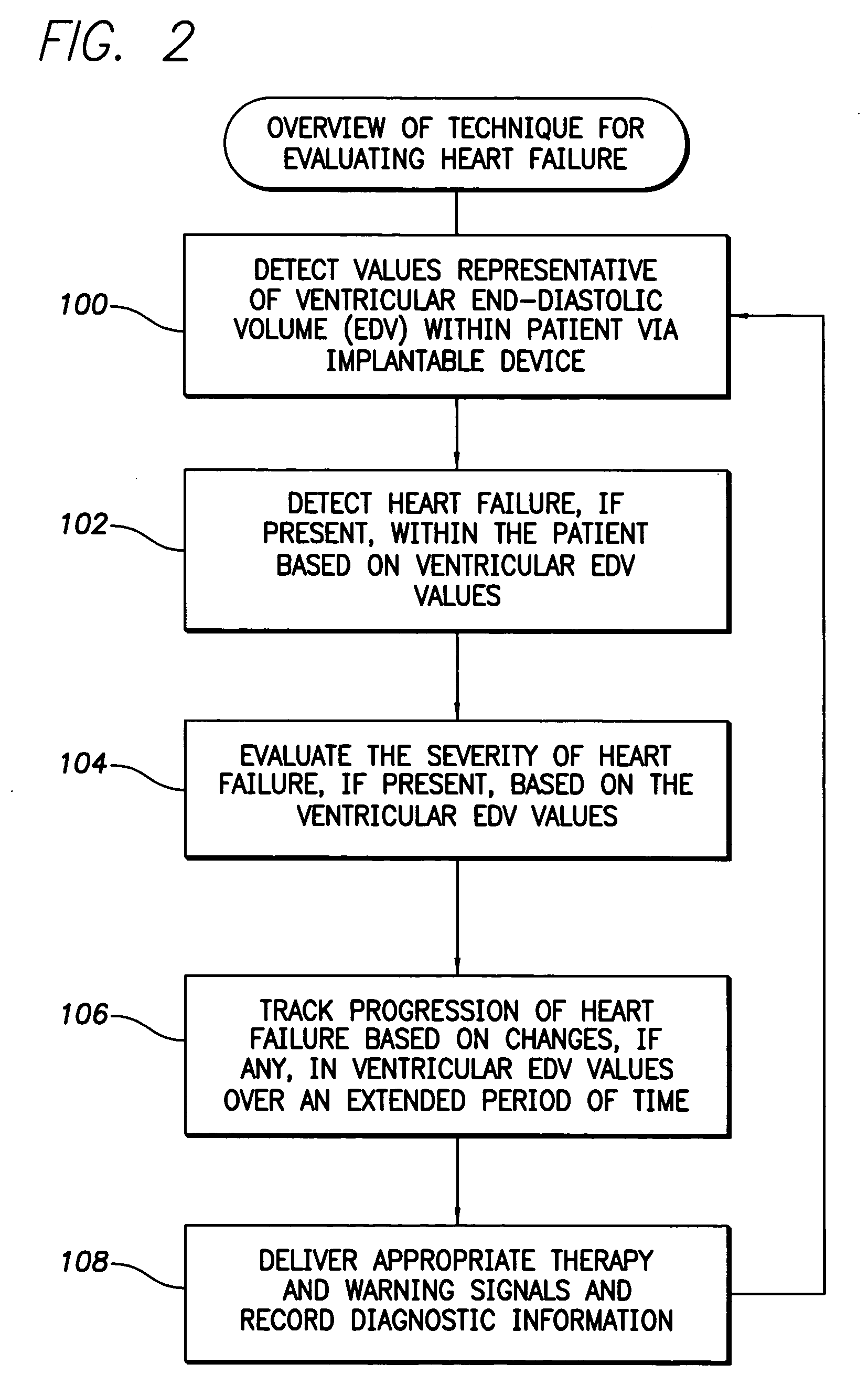
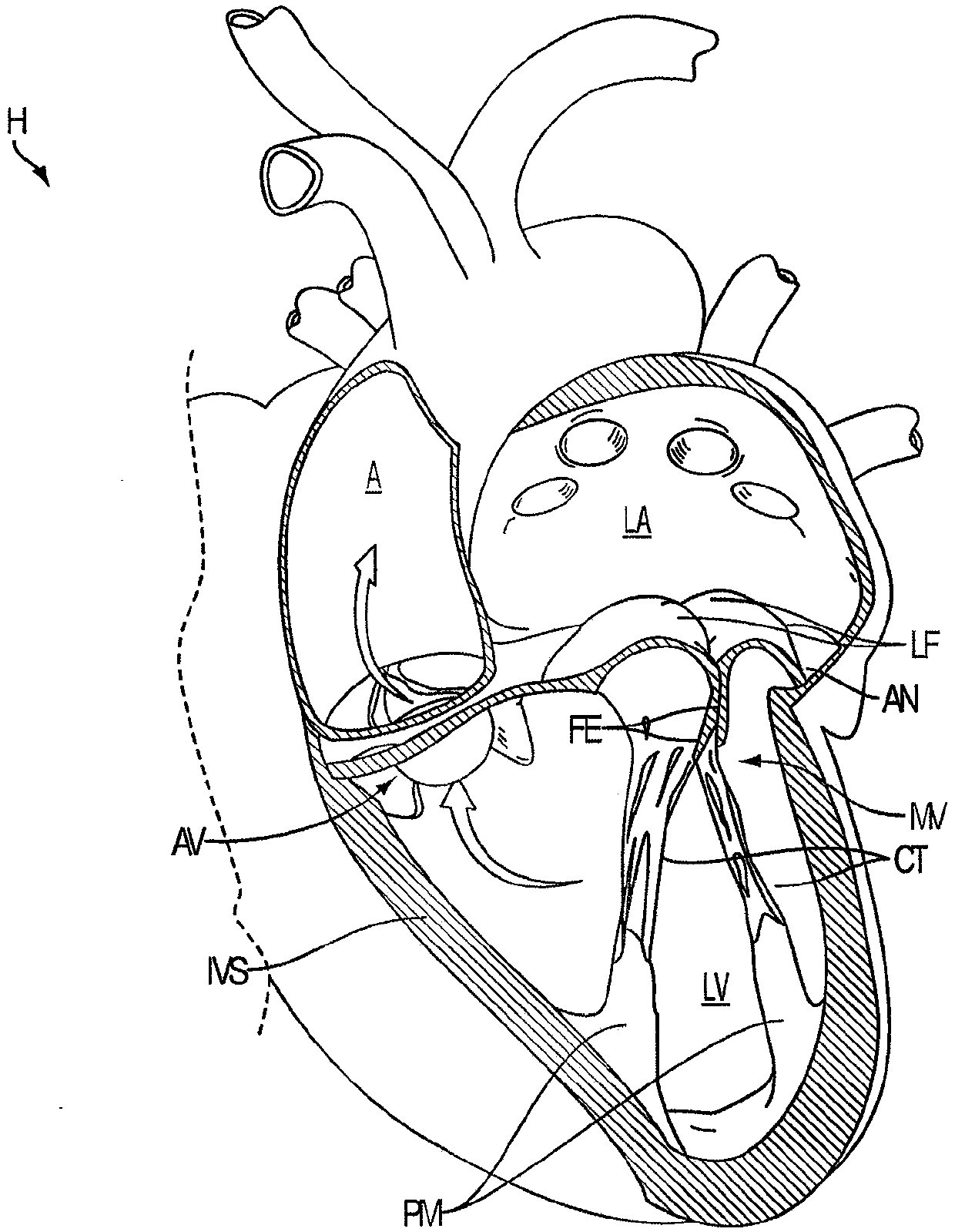
System and method for predicting a heart condition based on impedance values using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20050216067A1Reliably predict onset of heart conditionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulmonary edemaThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for predicting the onset of a heart condition within a patient based on impedance measurements. Briefly, overloads in fluid levels in the thorax and in ventricular myocardial mass within the patient are detected based on impedance signals sensed using implanted electrodes. The onset of certain heart conditions is then predicted based on the overloads. For example, pulmonary edema arising due to diastolic heart failure is predicted based on the detection of on-going overloads in both fluid levels and ventricular mass. Ventricular hypertrophy is detected based on an on-going ventricular mass overload without a sustained fluid overload. Various other heart conditions may also be predicted based on specific combinations of recent or on-going overloads. Evoked response is exploited to corroborate the predictions. Appropriate warning signals are generated and preemptive therapy is initiated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Sleep staging based on cardio-respiratory signals
A method for diagnosis of a sleep-related condition of a patient having a thorax. The method includes receiving physiological signals from sensors coupled to the thorax of the patient, and analyzing the physiological signals, independently of any electroencephalogram (EEG) or electro-oculogram (EOG) signals, in order to identify sleep stages of the patient.
Owner:WIDEMED
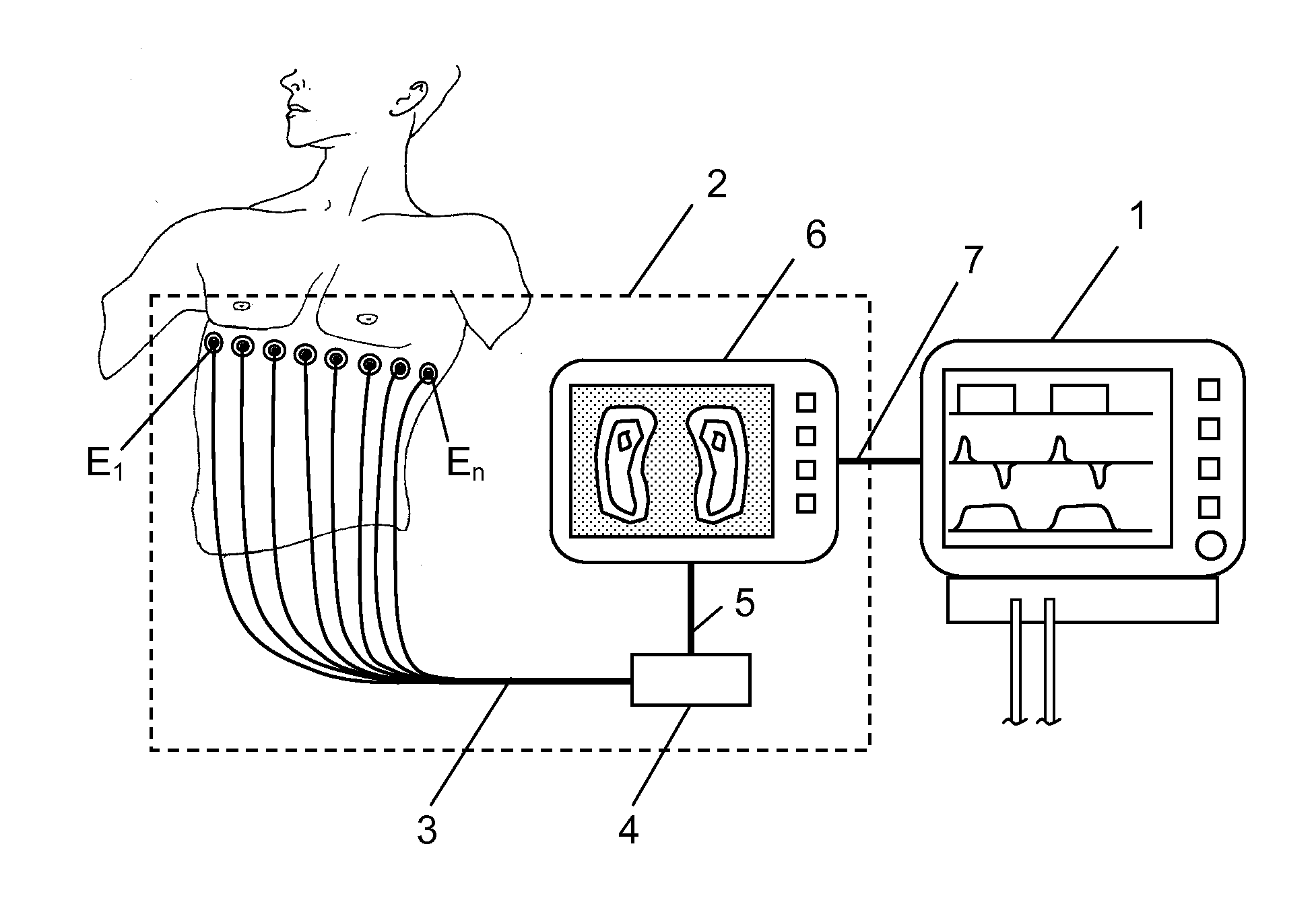
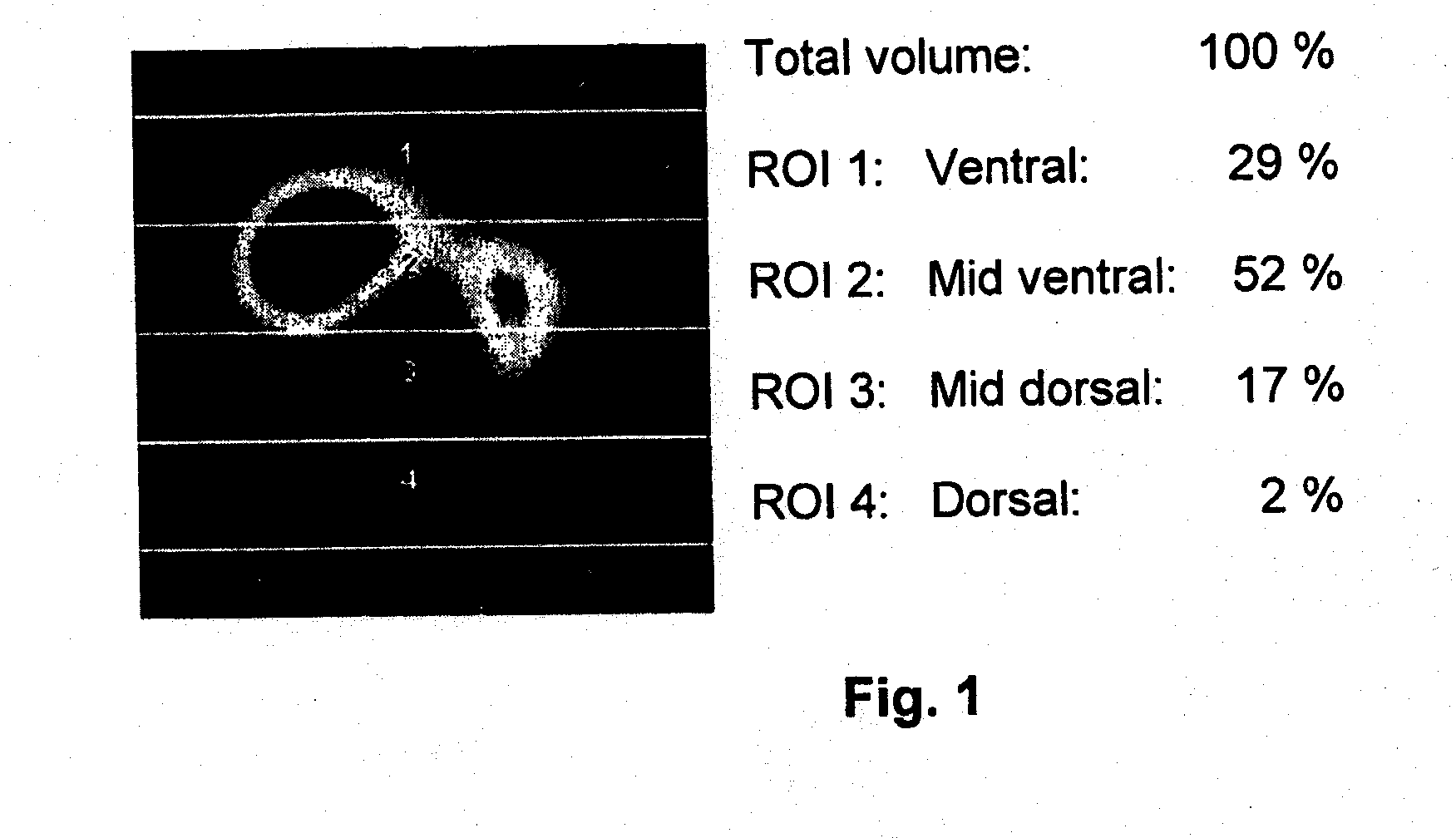
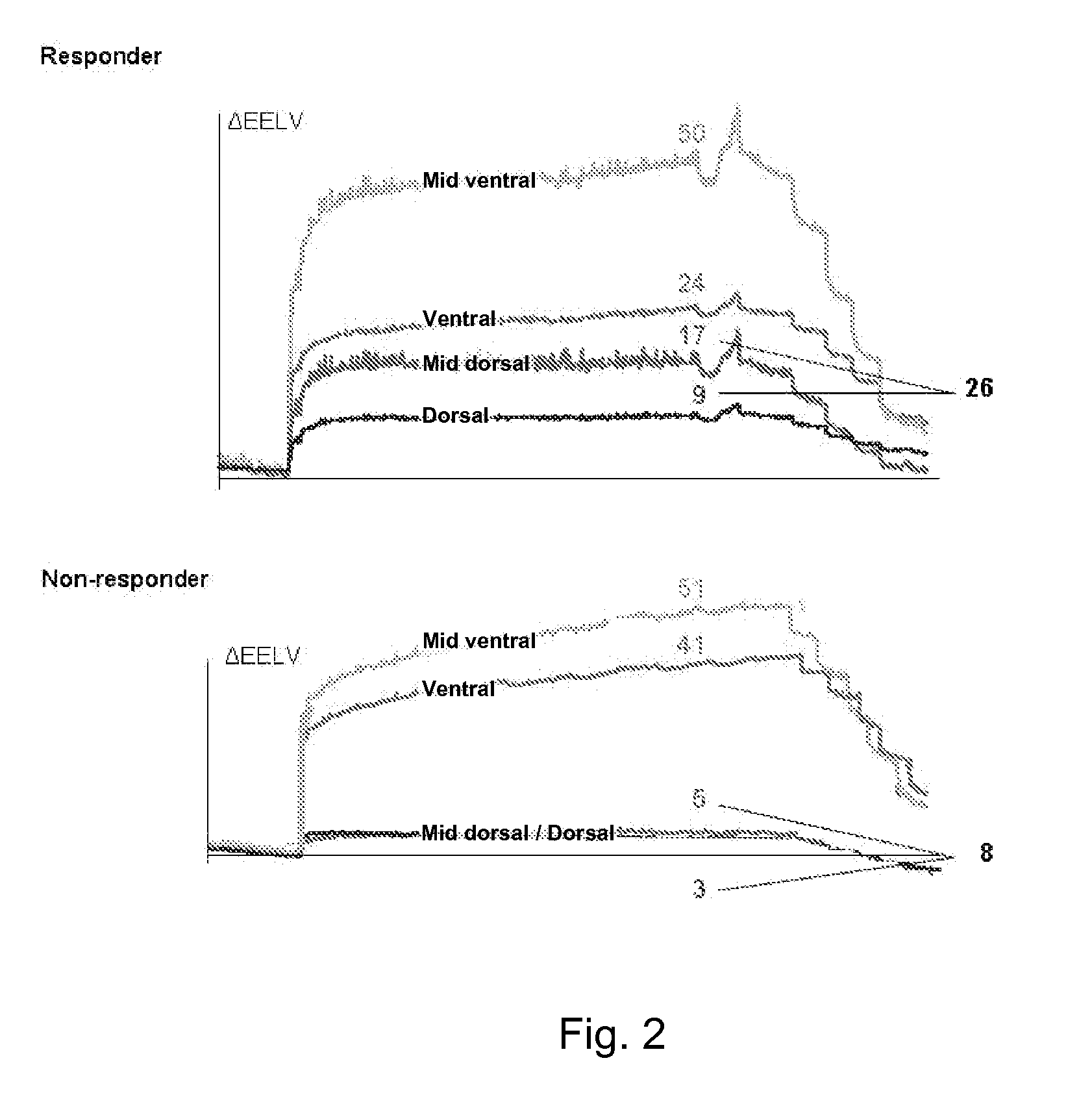
Apparatus and method to determine functional lung characteristics
InactiveUS20100228143A1Easy to interpretEasy to perceiveRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesImpedance distributionBreathing cycle
An apparatus for determining functional lung characteristics of a patient includes an electrical impedance tomography (EIT) imaging device adapted to record the impedance distribution within a plane of the thorax of the patient. The EIT imaging device includes a control and analysis unit for performing the impedance measurement and deriving the impedance distribution within the plane of the thorax. The control and analysis unit automatically performs steps including determining a global impedance change, defined as the impedance change with respect to an earlier measured reference impedance distribution integrated over the electrode plane, and recording the global impedance change curve as a function of time, performing breath detection in order to identify a breathing cycle, subdividing each breathing cycle to define a plurality of intratidal intervals, subdividing an EIT image from each interval into a plurality of regions of interest and calculating for each region of interest the ratio of the integrated impedance change within this region of interest to the global impedance change of this EIT image, for each intratidal interval presenting indications of the ratios determined for the regions of interest to provide an intratidal gas distribution representation for each interval.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Aneurysm treatment system and method
InactiveUS20060281966A1Reduce dilationShorten the progressStentsSurgeryAneurysm treatmentBlood vessel
An external aneurysm support scaffold is implanted around an exterior surface of an aneurysm and prevents substantial dilation or progression of the AAA. Minimally invasive delivery is used via port-access, i.e. for aortic aneurysms along the back, abdomen, or thorax, to a location externally adjacent the aneurysm, such as via laparascopic delivery. The scaffold is unwound or unfolded in-situ to extend partially (e.g. about 270 degrees) or completely circumferentially around the aneurysm. Unique delivery devices allow for deployment around the aneurysm. Gaps between an array of transverse fingers of the scaffold may accommodate branch vessels extending from the aneurismal vessel, such as aortic perforators. An agent is injected to treat an aneurysm, such as by providing support, cell retention or recruitment, and / or angiogenesis. Living cells are delivered to treat an aneurysm. An adjustable graft polymerizes in-situ to support an aneurysm conformed therewith.
Owner:EMERGE MEDSYST
System for sensing, diagnosing and treating physiological conditions and methods
InactiveUS20080108905A1Good effectLower blood pressureCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationThoracic cavityIncreased blood flow
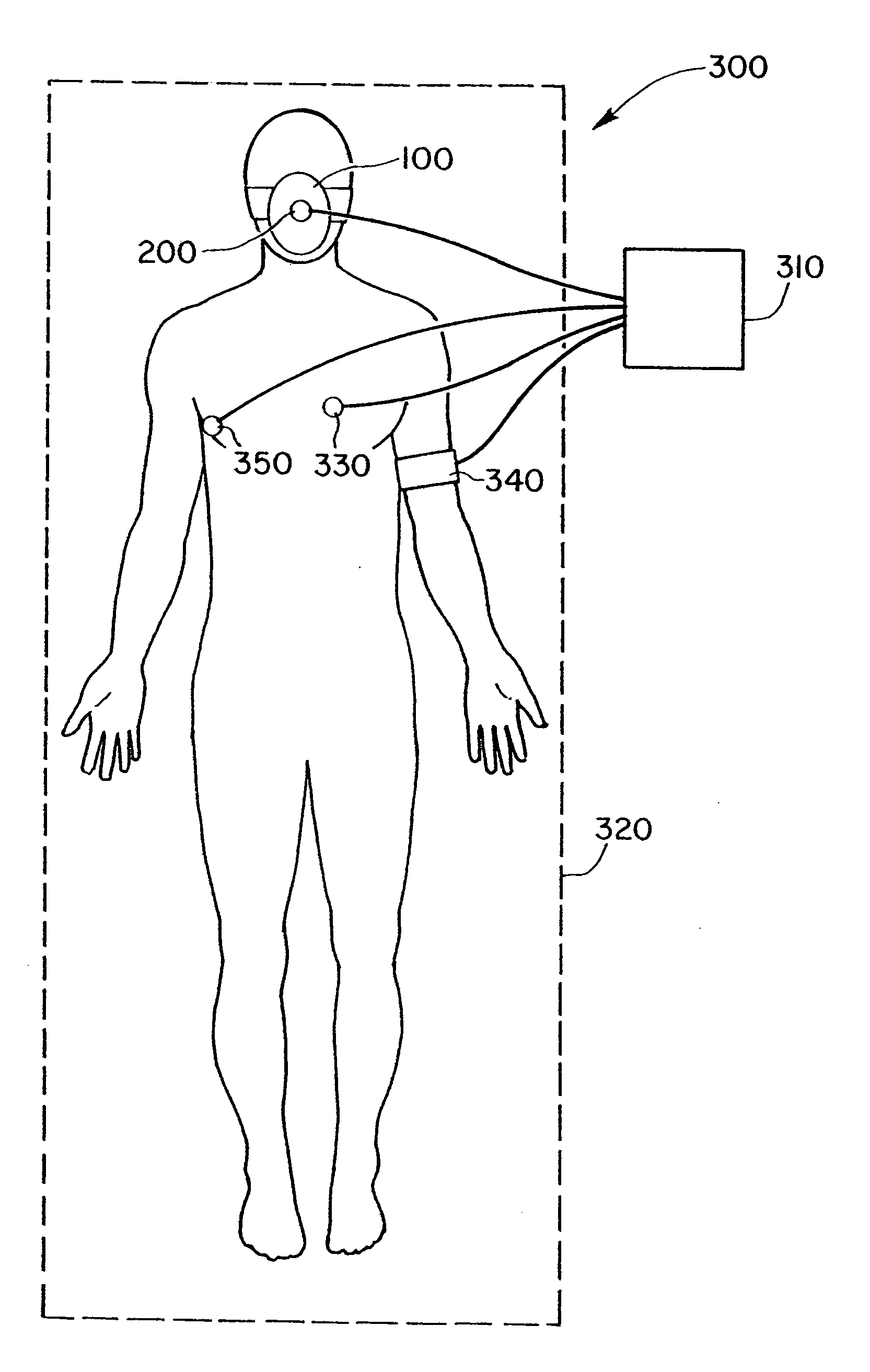
One method for diagnosing a cardiovascular-related condition in a breathing person comprises interfacing a valve system to the person's airway. The valve system is configured to decrease or prevent respiratory gas flow to the person's lungs during at least a portion of an inhalation event. The person is permitted to inhale and exhale through the valve system. During inhalation, the valve system functions to produce a vacuum within the thorax to increase blood flow back to the right heart of the person, thereby increasing blood circulation and blood pressure. Further, at least one physiological parameter is measured both prior to and while the person inhales and exhales through the valve system. The measured parameters are evaluated to confirm the initial diagnosis of a cardiovascular condition.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
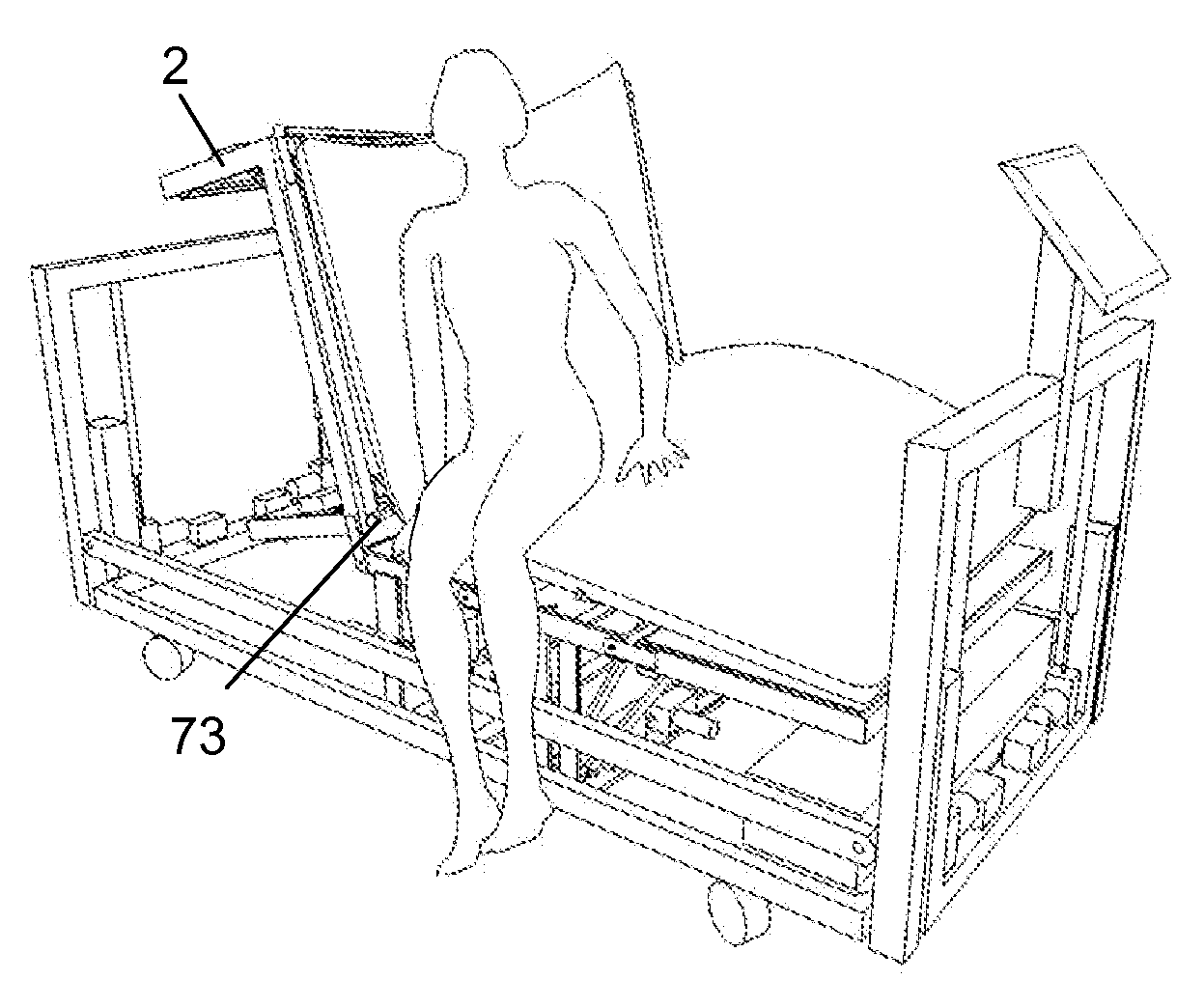
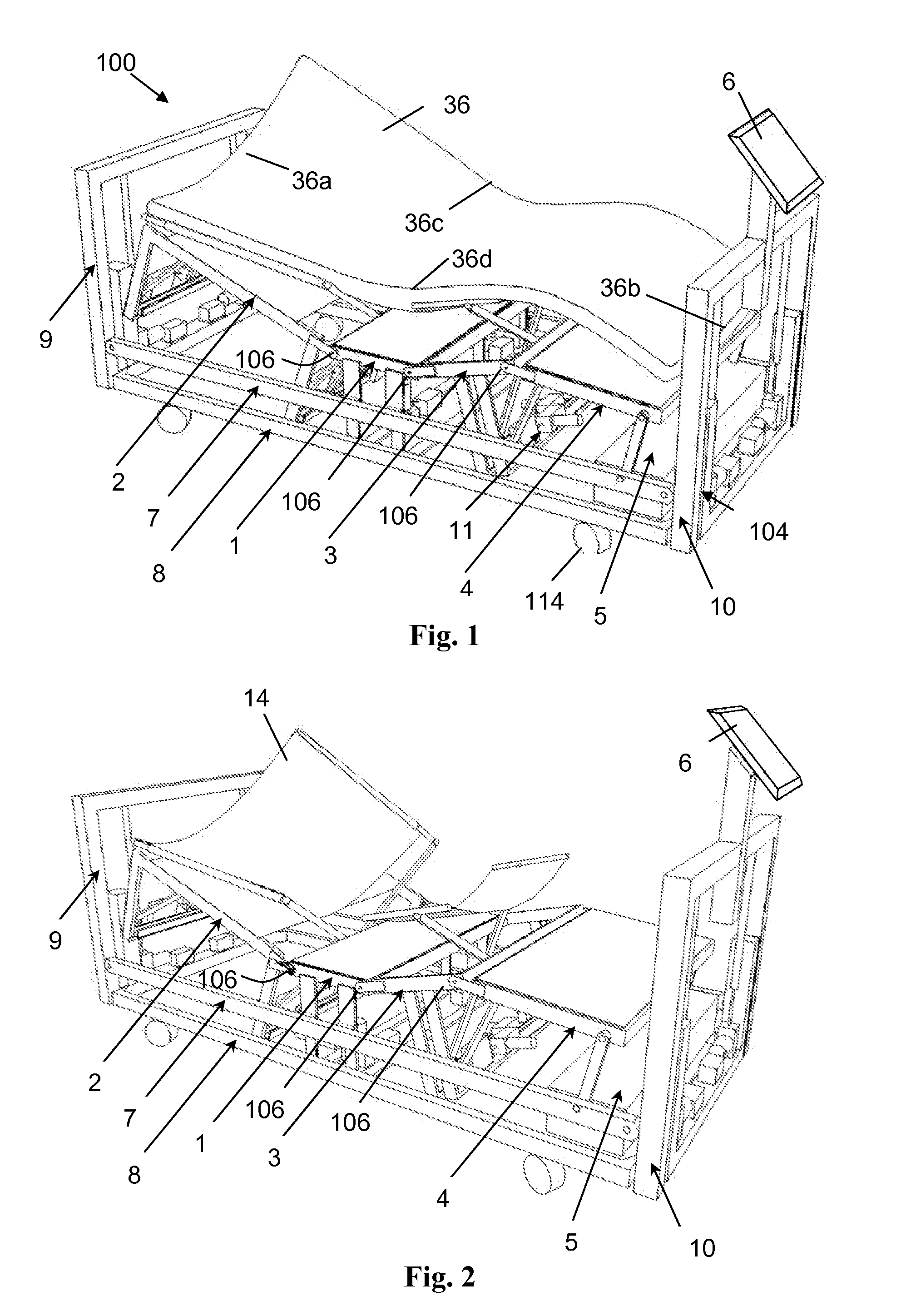
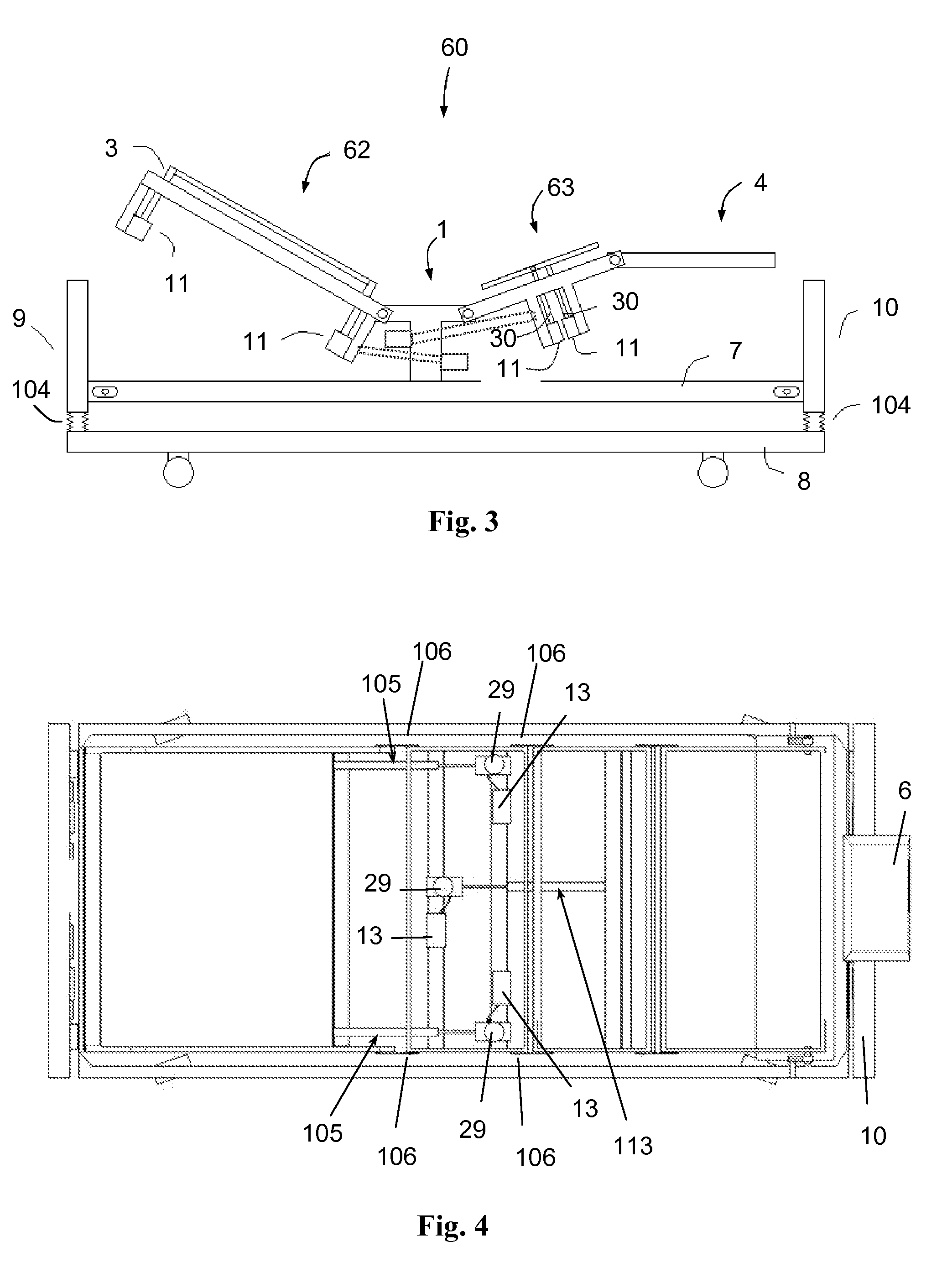
Modulating Support Surface to Aid Patient Entry and Exit
InactiveUS20090094745A1Facilitate egressFacilitate patient entry or exitSofasBedsEngineeringShoulder Support
An adjustable bed comprises separately articulatable and rotatable sections. These sections are operable to be articulated and rotated to facilitate a patient's entrance or exit to or from the bed. To facilitate entrance or exit, the torso section is articulated to a substantially upright or chair-like position. Next, the torso section is tilted, either to the right or to the left, to facilitate patient entry or exit. During the first part of this tilting motion, the lower thorax support region of the torso section is extended more than the shoulder support region to help rotate the patient into an exiting position. During the second part of this tilting motion, the shoulder support region is then hyperextended to help drive the patient off of the bed. A separately rotatable lower leg section may also be tilted in the same direction to further facilitate patient entry or exit.
Owner:BEDLAB
Apparatus for treating gerd
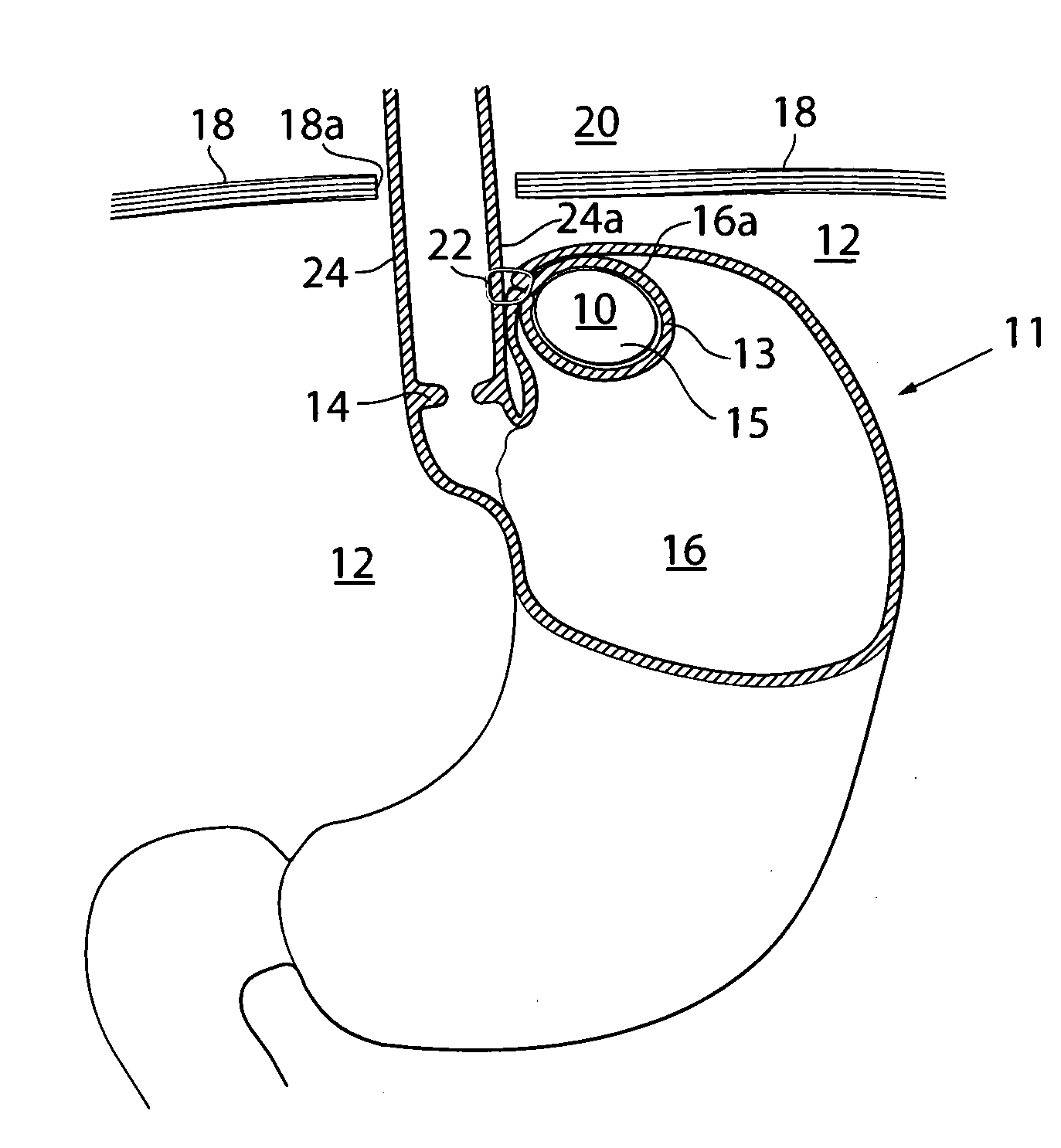
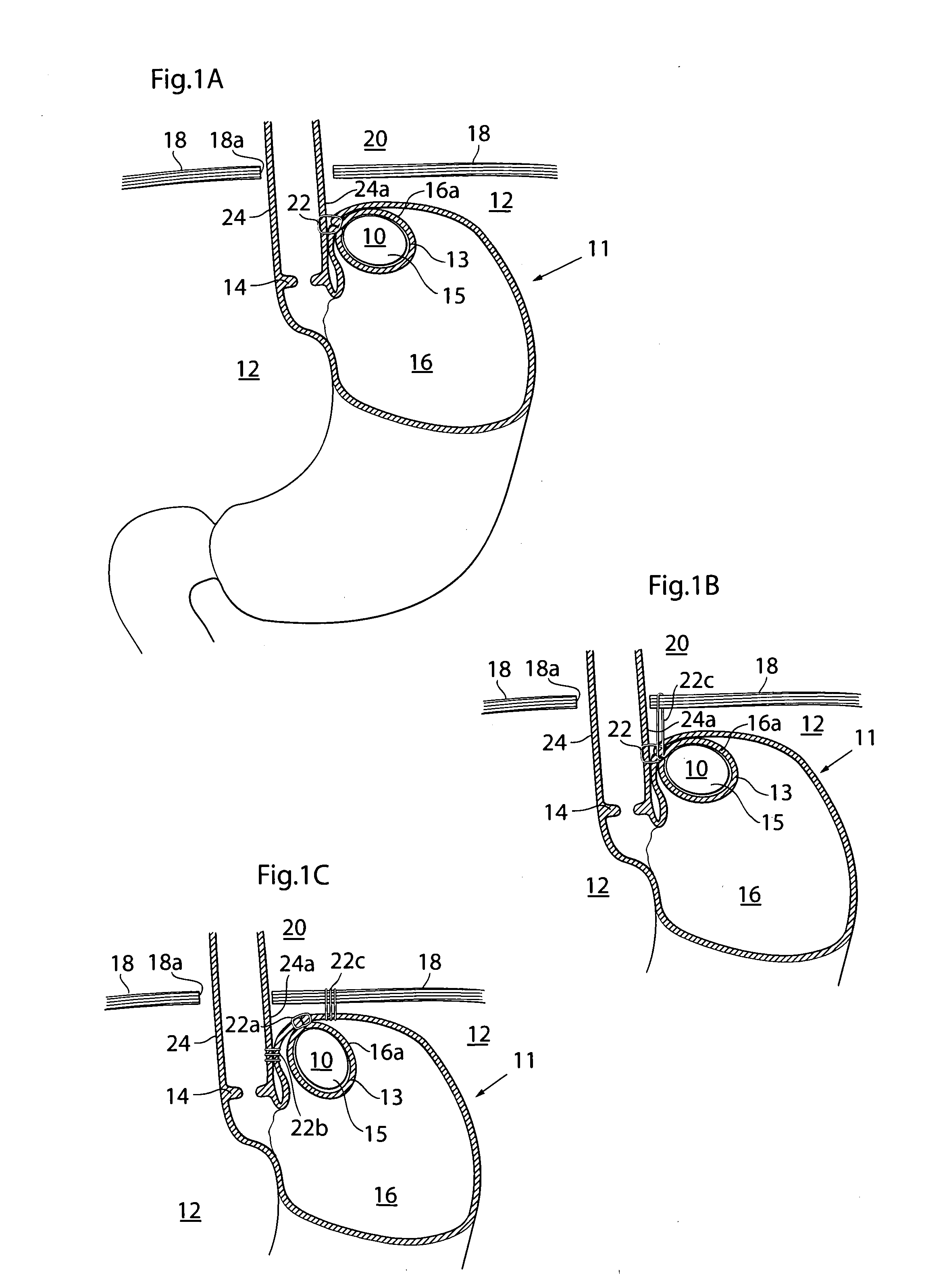
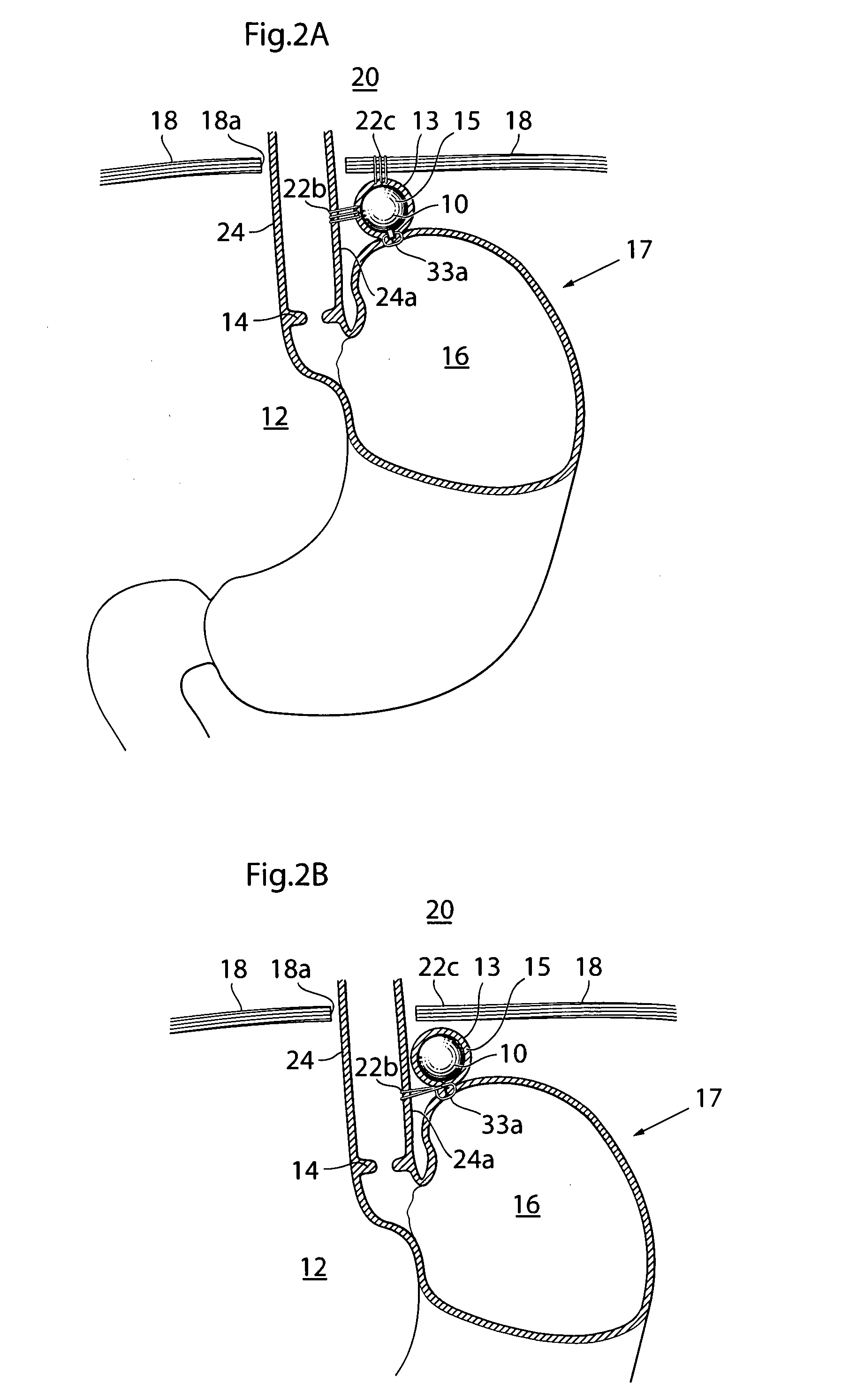
An apparatus for the treatment of acid reflux disease has an implantable movement restriction device adapted to be at least partly invaginated by a patient's stomach fundus wall. A substantial part of the outer surface of the movement restriction device is adapted to rest against the stomach wall without injuring the latter in a position between the patient's diaphragm and at least a portion of the lower part of the invaginated stomach fundus wall, such that movement of the cardiac notch of the patient's stomach towards the patient's diaphragm is restricted, to thereby prevent the cardia from sliding through the patient's diaphragm opening into the patient's thorax, so as to maintain the supporting pressure against the patient's cardia sphincter muscle exerted from the patient's abdomen. The movement restriction device has a size of at least 125 mm3 and a circumference of at least 15 mm.
Owner:FORSELL PETER
Independent gripper
The invention provides devices, systems and methods for tissue approximation and repair at treatment sites. The devices, systems and methods of the invention will find use in a variety of therapeutic procedures, including endovascular, minimally-invasive, and open surgical procedures, and can be used in various anatomical regions, including the abdomen, thorax, cardiovascular system, heart, intestinal tract, stomach, urinary tract, bladder, lung, and other organs, vessels, and tissues. The invention is particularly useful in those procedures requiring minimally-invasive or endovascular access to remote tissue locations, where the instruments utilized must negotiate long, narrow, and tortuous pathways to the treatment site. In addition, many of the devices and systems of the invention are adapted to be reversible and removable from the patient at any point without interference with or trauma to internal tissues.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Intubation positioning, breathing facilitator and non-invasive assist ventilation device
InactiveUS20070181122A1Easy intubationEasy alignmentRespiratorsOperating tablesSpinal columnAssisted ventilation
This invention can be used in three different ways for patients who are lying down in bed or on the operating table. First it facilitates the endotracheal intubation, secondly it facilitates the spontaneous breathing of obese patients and thirdly it assists the spontaneous inspiration and expiration in a non-invasive way. This invention device is positioned under the patient before he is asleep without disturbing him. It allows a gradual elevation of the lower and or upper thorax, a gradual elevation of the head giving a flexion of the neck and a gradual hyperextension of the head. After intubation the position is returned to normal without need for removing the invention device. This invention elevates the spinal column and therefore the thorax is no more compressed and the ribs can move free. Inspiration requires less force and the patient can be breathing easier even when lying down. In this invention the spinal column elevation can also be inflated in a synchronized way with the respiration of the patient. During inspiration the spinal column is elevated, facilitating the inspiration. During expiration the elevation is lowered, facilitating the expiration. The work of breathing is reduced for the patient resulting in larger minute volume ventilation or less oxygen consumption.
Owner:MULIER JAN PAUL
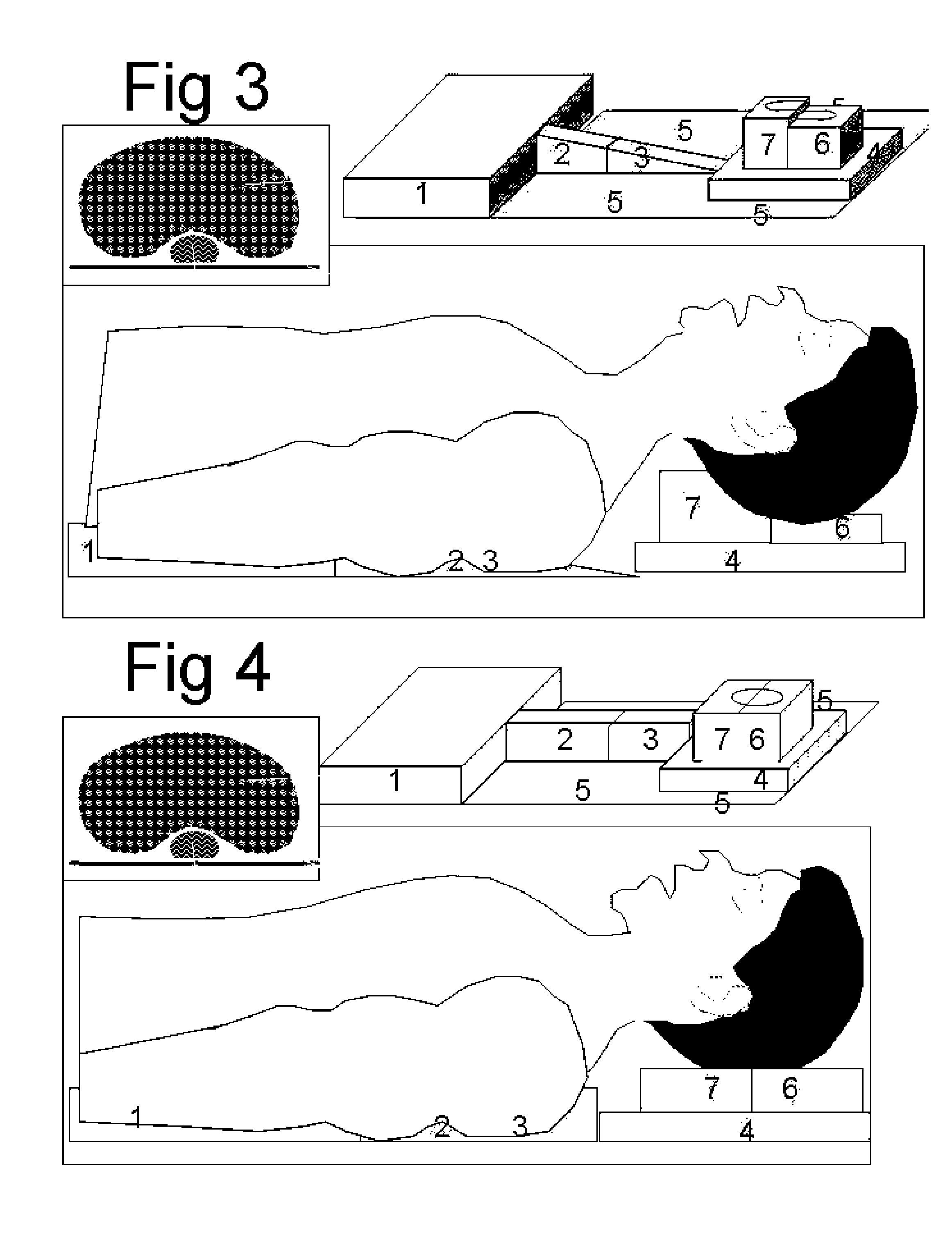
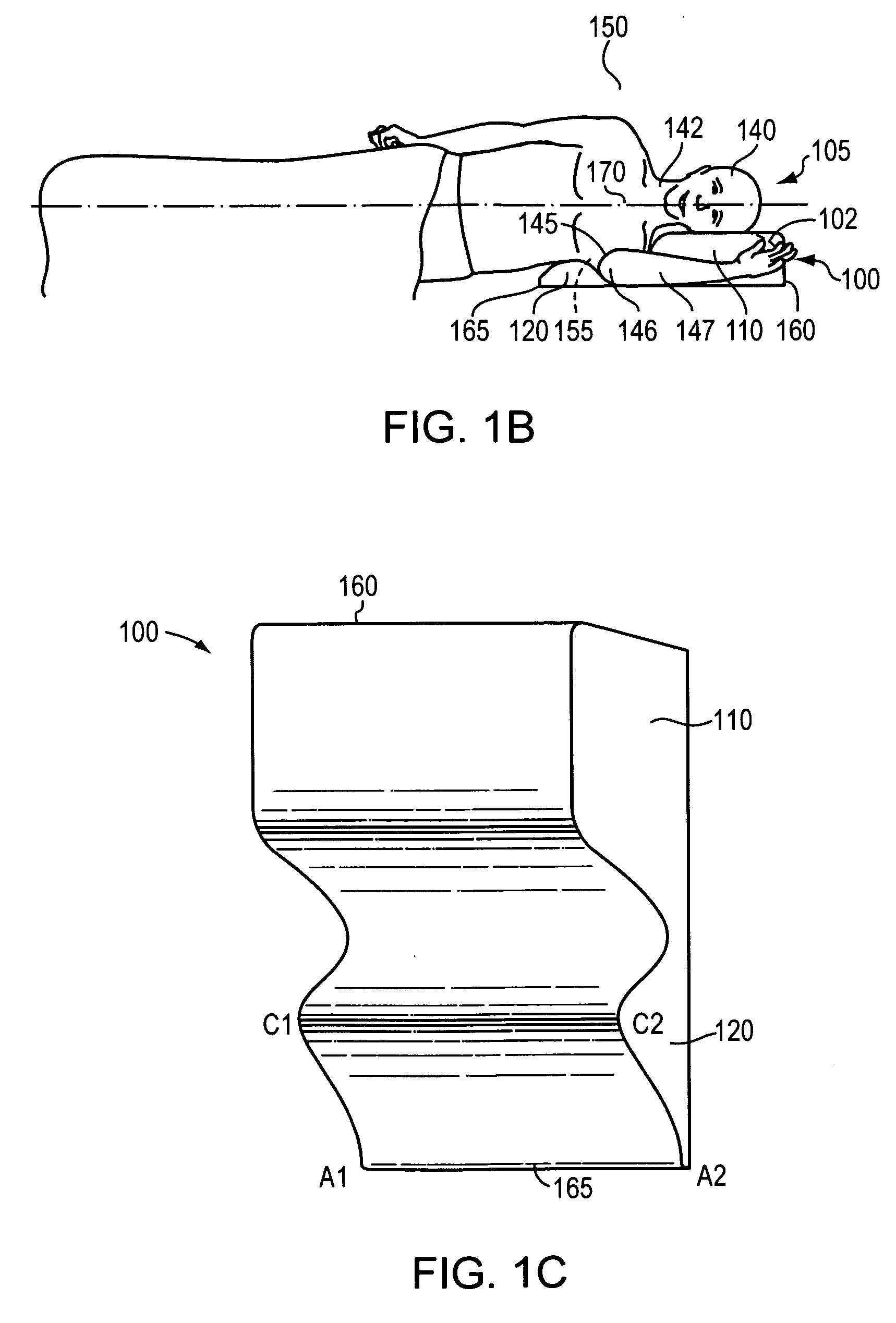
Axillary support device
An axillary support device is provided for decompressing the axilla (armpit) and associated structures in a sidelying position. A thoracic cushion provides firm axillary support to a user at the level of the mid to upper thorax, distal to the axilla. A head cushion connected to the thoracic cushion supports the user's head and may maintain a neutral cervical spine alignment position. A connector connecting the cushions creates a valley to receive an upper arm of the user. A back support may be used to maintain the sidelying position. An inflatable bladder may be used to adjust the axillary support device in order to appropriately relieve pressure on the user's axilla and associated structures. With the axillary support device, the upper arm of the user is relatively free to extend perpendicularly in front of the body in the sidelying position with reduced stress on the lateral shoulder and axilla.
Owner:AXILLAN CORP
Side airbag apparatus
InactiveUS20080174093A1Soft deploymentAvoid shockPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementInternal pressureAirbag
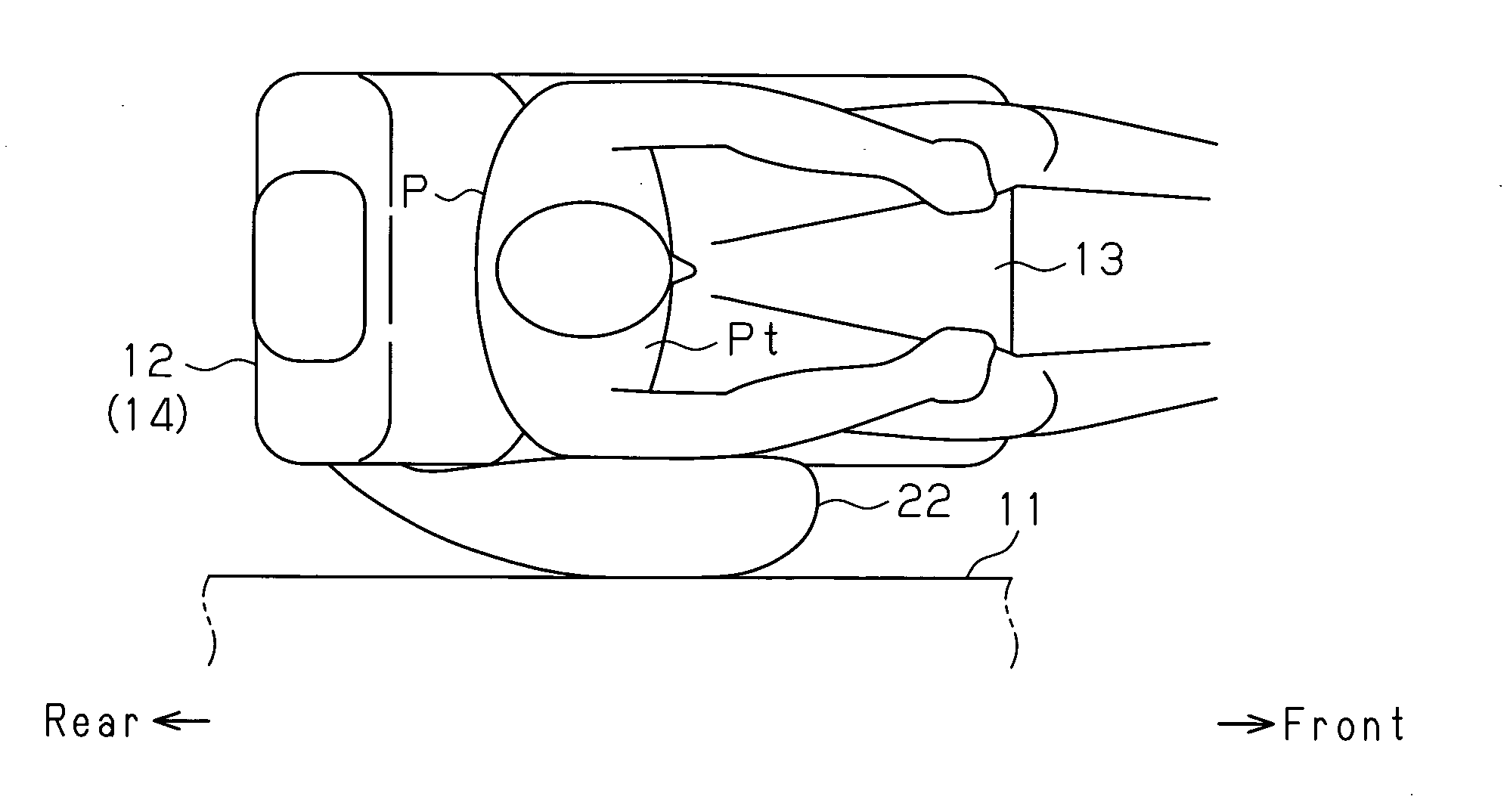
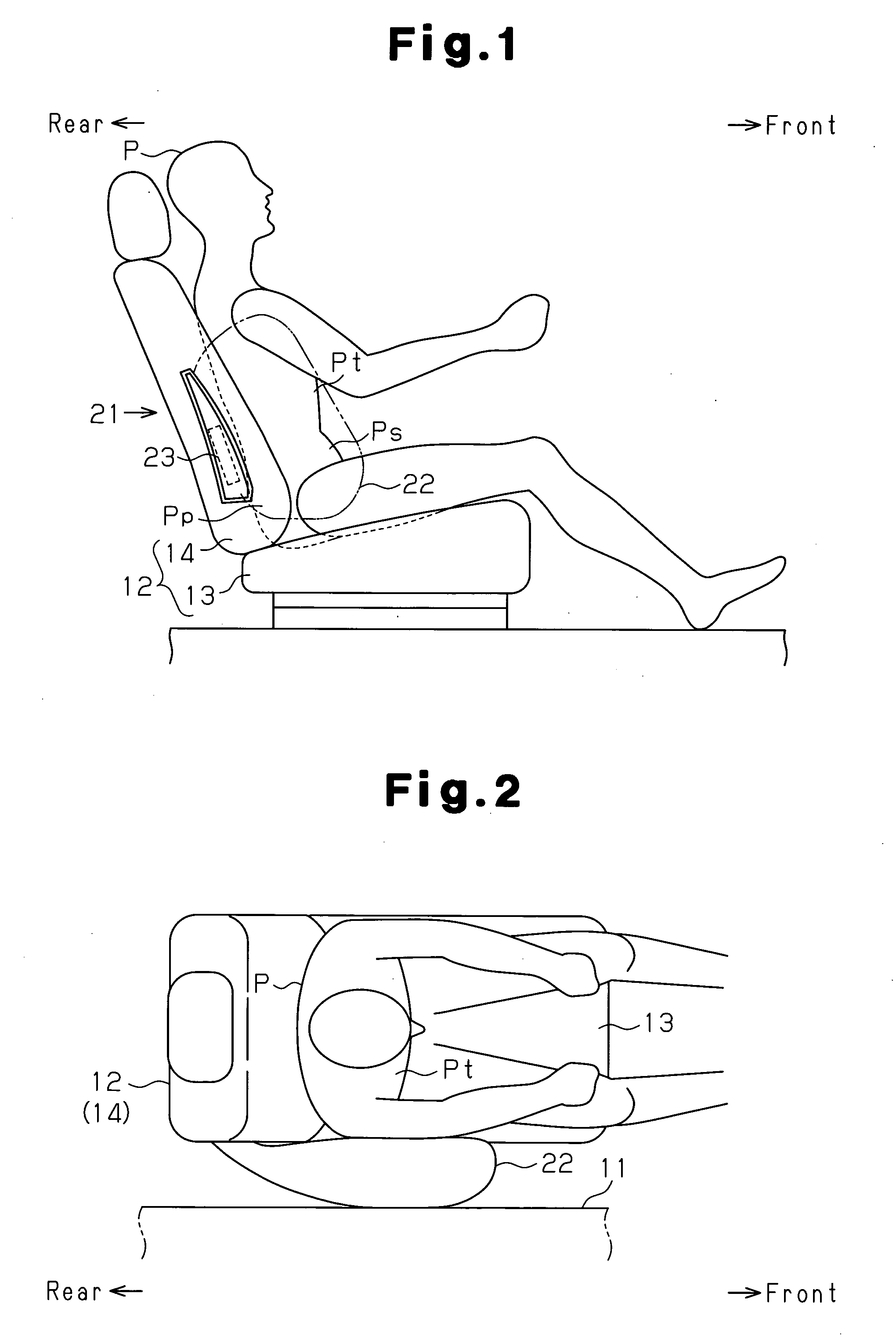
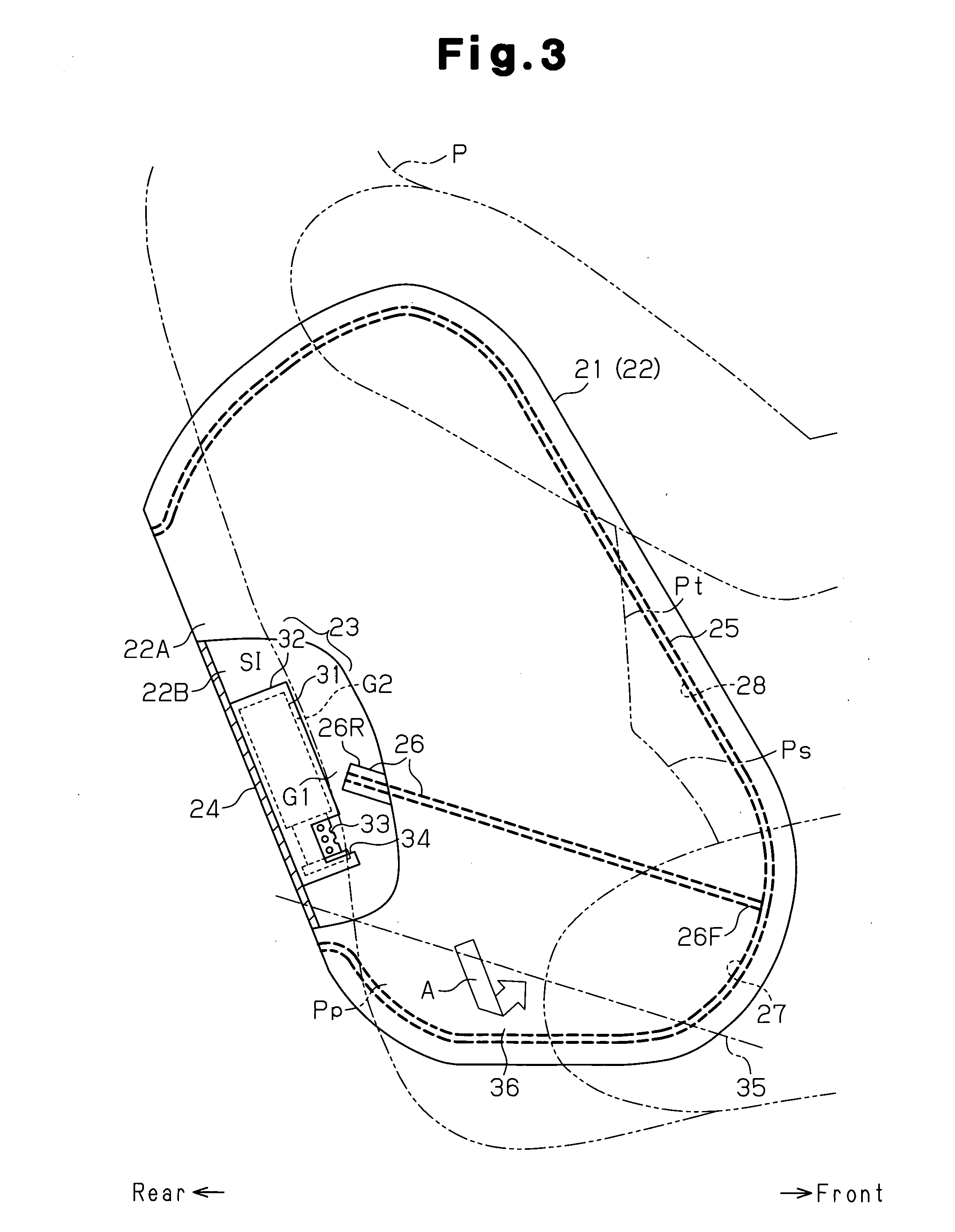
A side airbag apparatus has an inflator 31, an airbag 22, and a tether (partition portion) 26. The tether 26 partitions an internal space SI of the airbag 22 into a lumbar region protection chamber 27 inflated beside lumbar regions Pp of an occupant P and a thorax protection chamber 28 protecting a thorax Pt and an abdominal region Ps. The side airbag apparatus inflates the lumbar region protection chamber 27 at a higher internal pressure than the thorax protection chamber 28. In the side airbag apparatus, the tether 26 is disposed in the internal space SI so as to be inclined downward toward the front of the vehicle. The area corresponding to the lumbar region protection chamber 27 of the airbag 22 is folded along the inclination of the tether 26.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease simulator
InactiveUS20070196780A1Crucible furnacesEducational modelsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesPhysical therapy
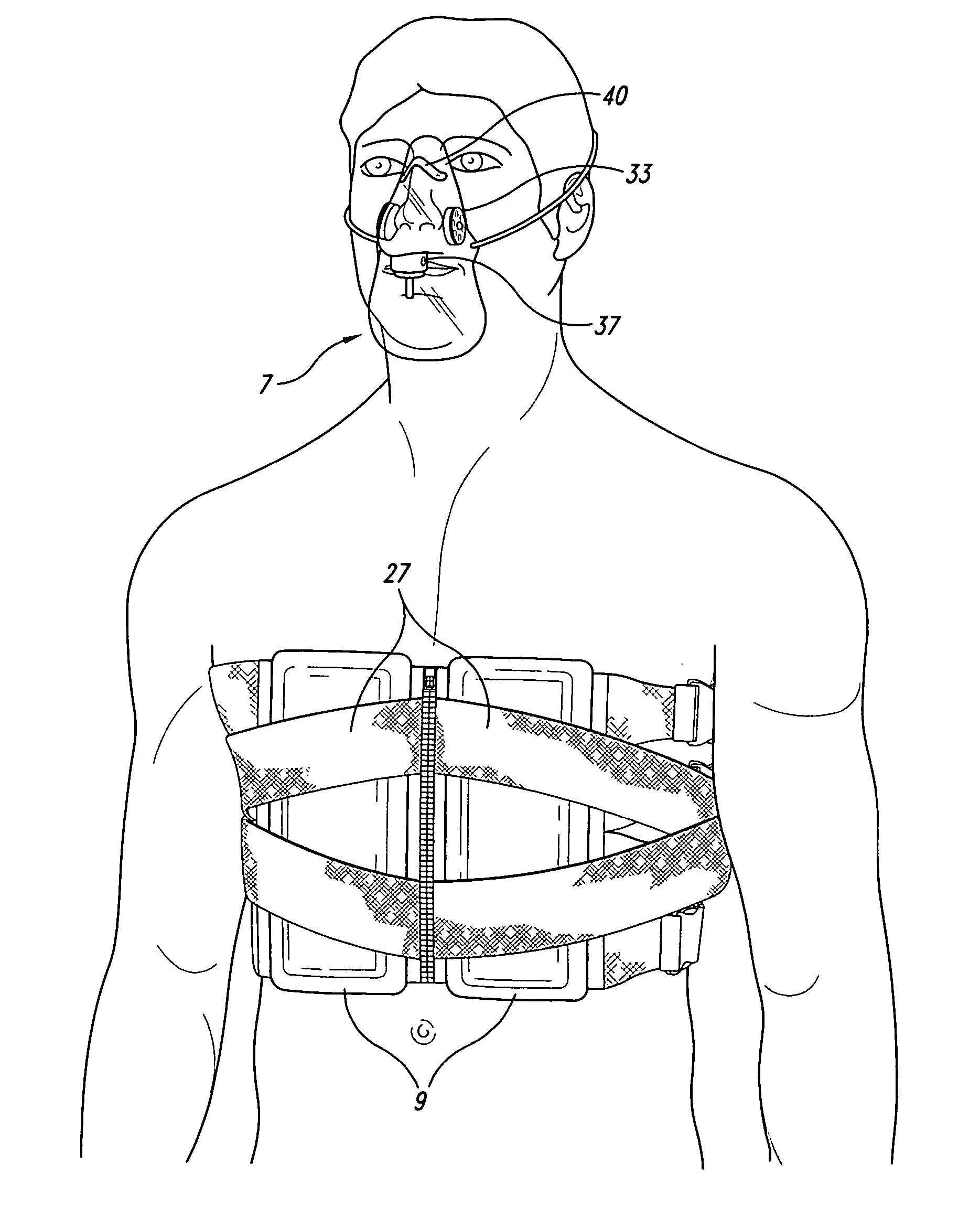
Particular aspects provide a garment for simulating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), comprising a particularly efficacious combination of a thorax-constricting garment portion, and a diaphragm-impeding garment portion, along with an optional restrictive airway mask. The thorax-constricting portion has a frontal abdominal-thoracic plate member and tensioning means extendible around a wearer's thoracic circumference to provide for constrictive thoracic-abdominal tensioning. The diaphragm-impeding portion has a projection (e.g., weighted projection or pouch) projecting away from the wearer-proximal surface of the frontal plate member, which is operative with the thorax-constricting portion to simultaneously constrict thorax expansion while impeding diaphragm contraction and downward movement. Additional aspects provide a method for simulating COPD, comprising tensioning a thoracic-abdominal constricting garment, having diaphragm-impeding means and optional restrictive airway mask, around a wearer's thoracic-abdominal area at a tension, and for a time period sufficient to simulate at least one symptom or effect of COPD.
Owner:WARE LINDA M +1
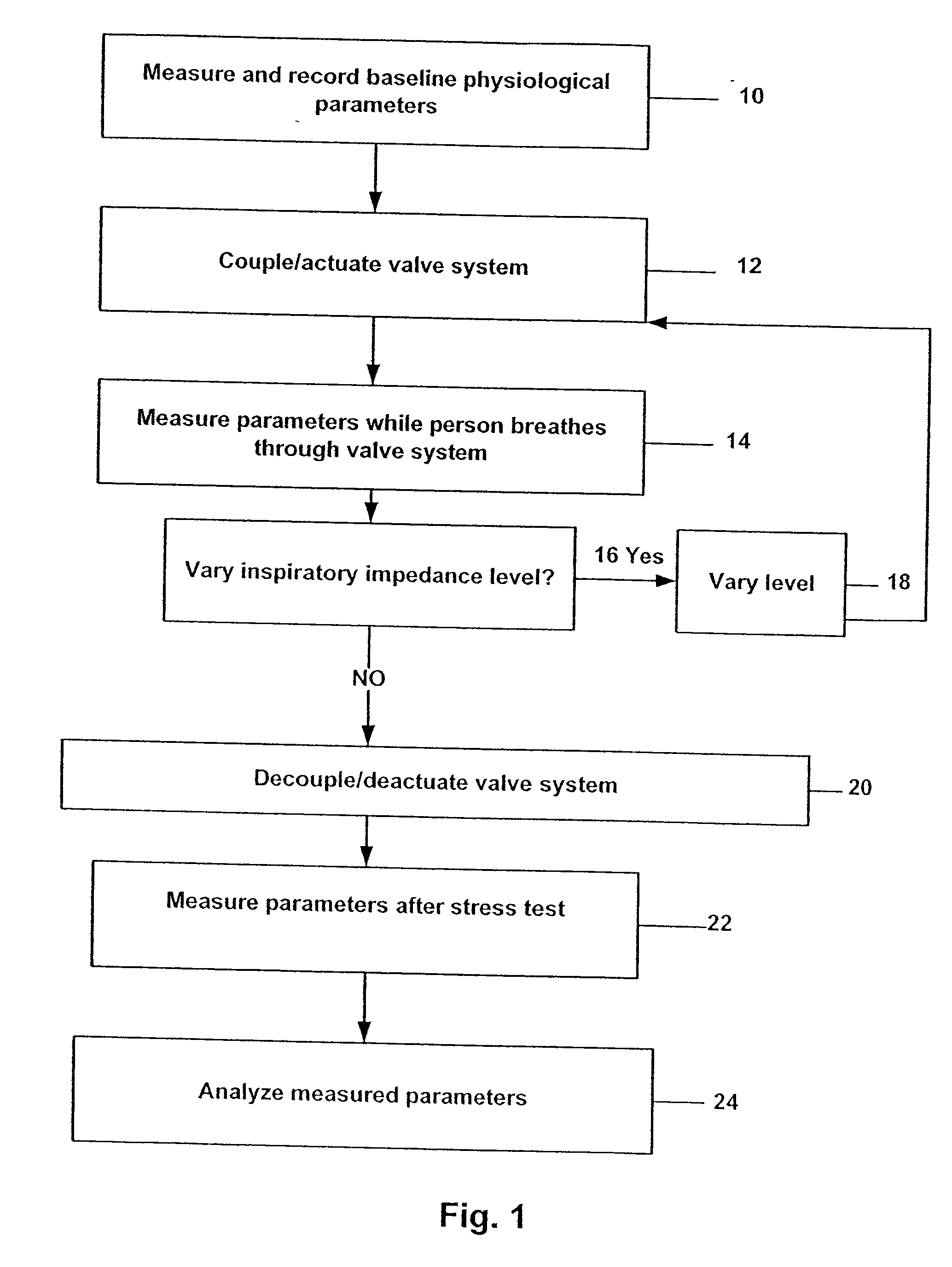
Stress test devices and methods
InactiveUS20050126567A1Good effectLower blood pressureRespiratorsFilling using suctionThoracic cavityIncreased blood flow
One method for diagnosing a cardiovascular-related condition in a breathing person comprises interfacing a valve system to the person's airway. The valve system is configured to decrease or prevent respiratory gas flow to the person's lungs during at least a portion of an inhalation event. The person is permitted to inhale and exhale through the valve system. During inhalation, the valve system functions to produce a vacuum within the thorax to increase blood flow back to the right heart of the person, thereby increasing blood circulation and blood pressure. Further, at least one physiological parameter is measured while the person inhales and exhales through the valve system. The measured parameter is evaluated to diagnose a cardiovascular condition.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for locating and tracking persons
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for locating and tracking persons by use of an implantable device. The described invention is an implant able device composed of biocompatible materials in all areas where contact with organic tissue occurs. The gross anatomic siting of the device includes any limb, the torso, including back and perineum, the neck, and the head. The surgical anatomic siting of the device includes: (1) Supramuscular: for example, deep to the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat, on or attached to muscle and / or muscle fascia. Such a location is currently used for implantation of commercially available buried intravenous access ports, which are positioned on, and attached to, the pectoralis major muscle fascia; (2) Intramuscular: for example, within or between the muscles of a limb; (3) Submuscular: for example, deep to a large muscle. Such a location is currently used for implantation of commercially available artificial urethral and anal sphincter reservoirs, which are positioned deep to the rectus abdominus muscles, within the pre-peritoneal Space of Retzius; (4) Intraluminal: for example, within the lumen of an organ which has a naturally occurring orifice. Such a location is currently used for implantation of commercially available ingested video endoscopy capsule devices, i.e. gastrointestinal tract lumen, and intrauterine contraceptive devices, i.e. uterus lumen; and (5) Intracavitary: for example, intrathoracic or intraperitoneal. Such an intraperitoneal location is currently used for implantation of commercially available intraperitoneal dialysis catheters.
Owner:PERSEPHONE
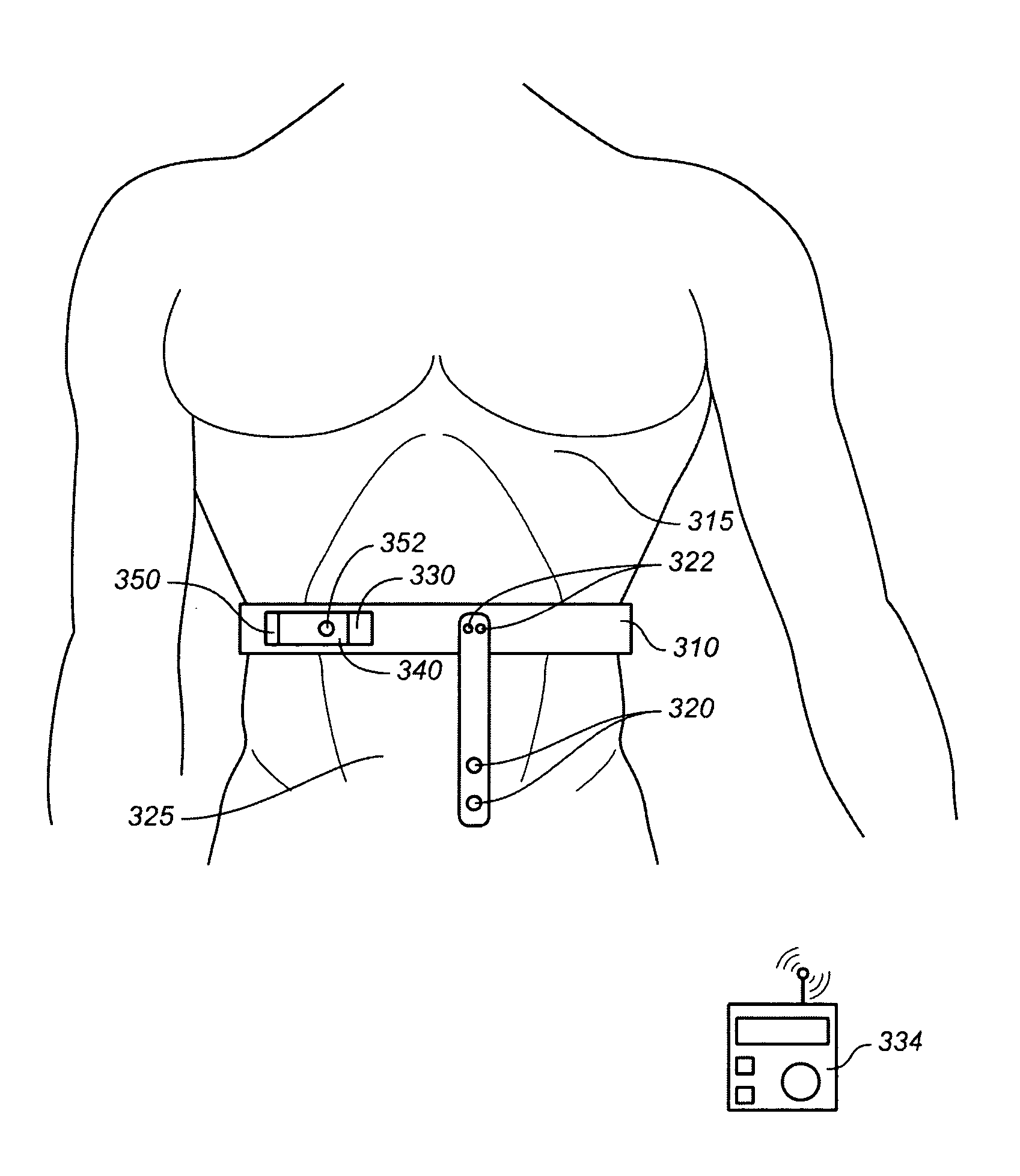
Wearable thorax percussion device
A wearable thorax percussion device for dislodging mucous buildup in the airways of a human patient, the device comprising frame elements and electromechanical actuators retained by the frame elements to intermittently percuss the thorax, and an electronic controller and power source for generating and modulating an electrical signal to energize the actuator. The frame elements may be interconnected by a garment, or fasteners and elastic or adjustable strapping.
Owner:HILL ROM SERVICES
An improved side airbag
InactiveUS20050104342A1Easy constructionMinimizing manufacturing cycle timePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementCushioningLateral airbag
An improved side airbag (10) is provided for enhancing protection of a vehicle occupant's thorax and simultaneously displacing the vehicle occupant (14) away from door intrusion. This improved side airbag (12) is an inflatable bag having a thorax-cushioning portion (16) and a pelvis-pushing portion (18) adjacent to the thorax-cushioning portion (16). The thorax-cushioning portion (16) has a first predetermined stiffness for cushioning a thorax region of the vehicle occupant (14) while the pelvis-pushing portion (18) has a second predetermined stiffness for displacing the vehicle occupant (14) away from the door intrusion. The second predetermined stiffness of the pelvis-pushing portion (18) is greater than the first predetermined stiffness of thorax-cushioning portion (16).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Dynamic frame for prone surgical positioning
ActiveUS20050081865A1Improve patient positioningPrecise positioningInternal osteosythesisOperating chairsSurgery procedureSurgical department
A dynamic trunk positioning device comprises a frame adapted to be removably mounted to an operating table. A number of pads are provided for engaging the trunk of a patient. Each pad is independently adjustably mounted to the frame for movements along three independent directions in order to permit 3-D manipulation thereof by a surgeon either before the surgery while a patient is being positioned or during the surgery when additional corrective forces on the patient's thorax are needed, thereby providing not only for stable positioning of the patient on the operating table but also providing for active application of individual corrective forces at different locations on the patient's trunk.
Owner:HUBERT LABELLE +6
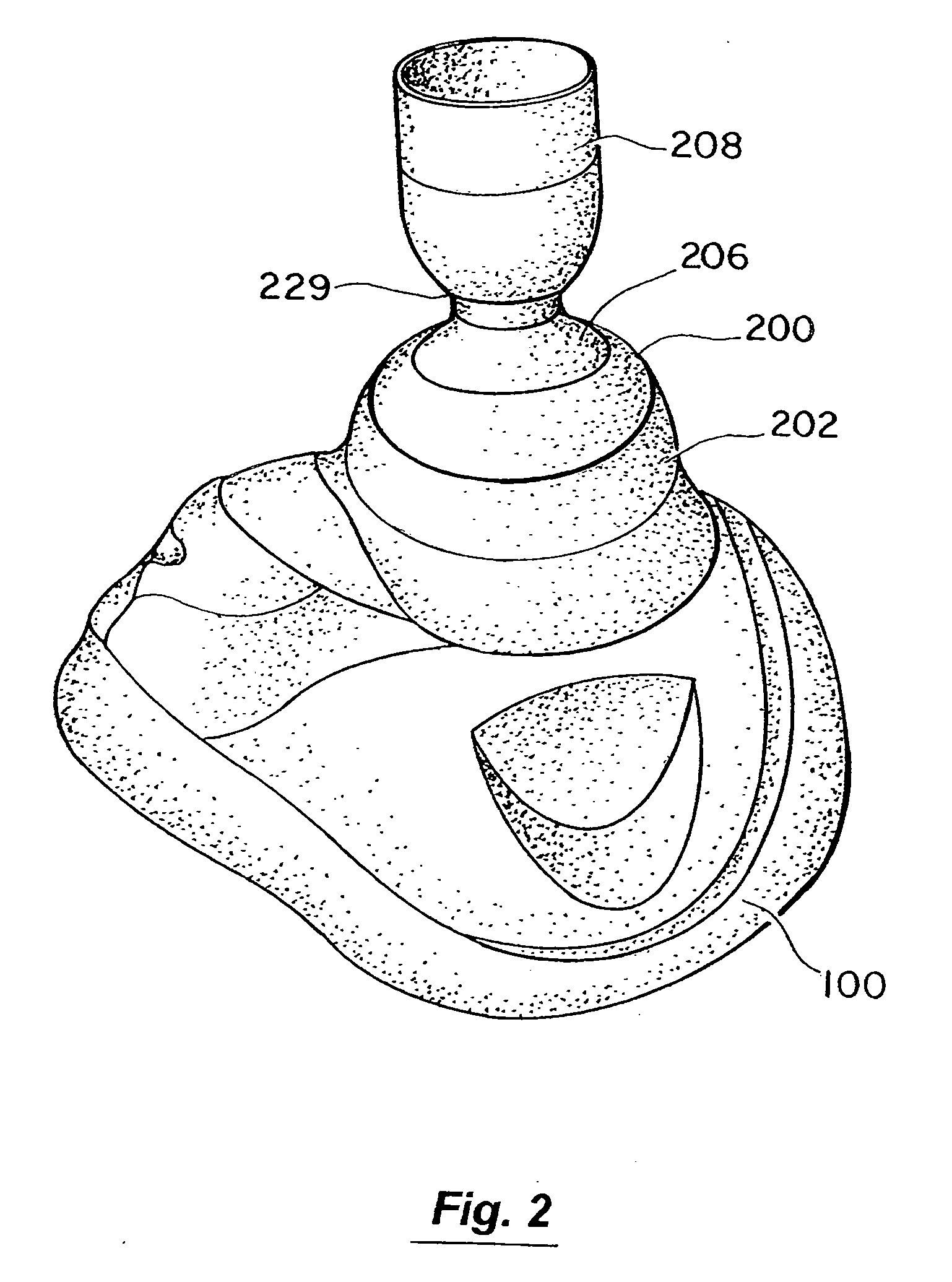
Breast Reconstruction Device And Methods
A novel human breast implant and method for using the same comprising a bioabsorbable implant into which native, autologous vascularized tissue and autologous fat is placed and propagated within a patient's chest as a breast implant.
Owner:BIOSTRUXS
Dynamic phantom for radiation therapy
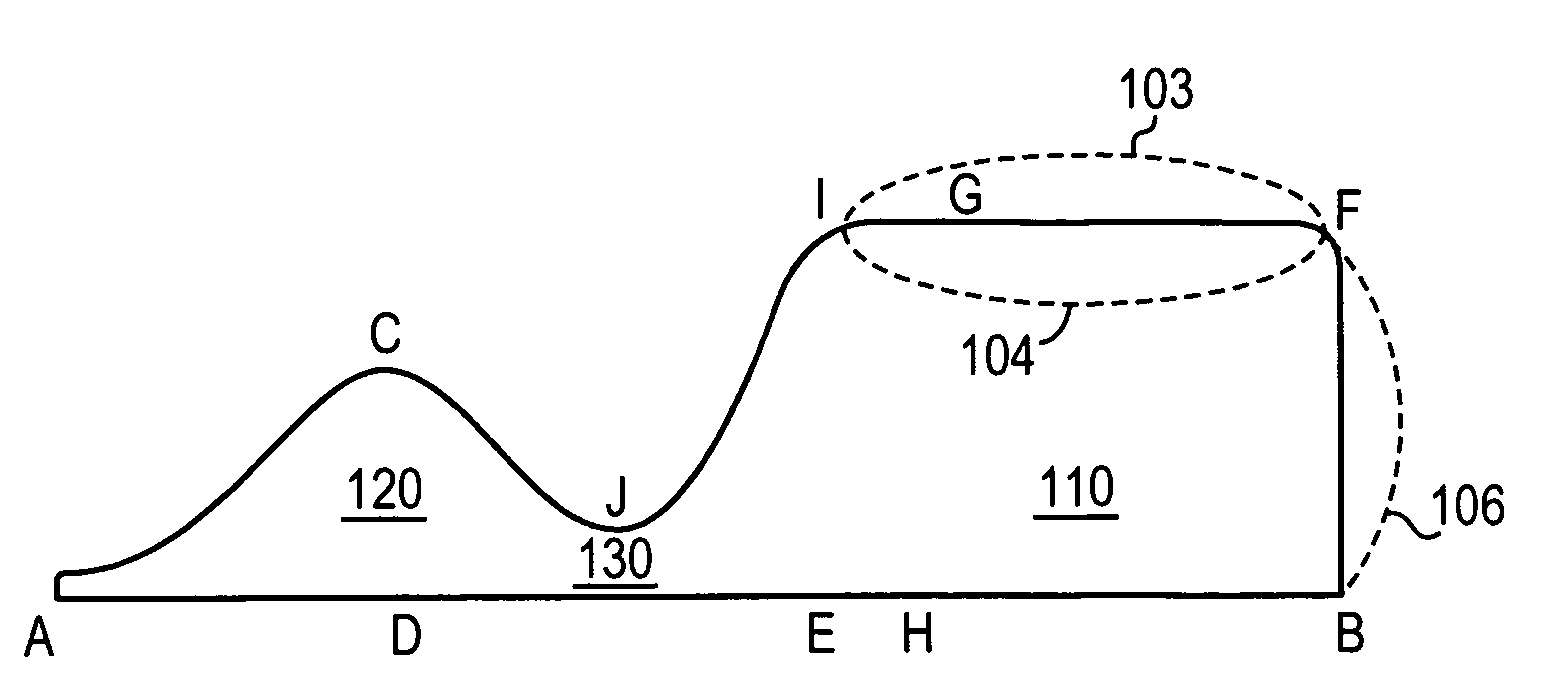
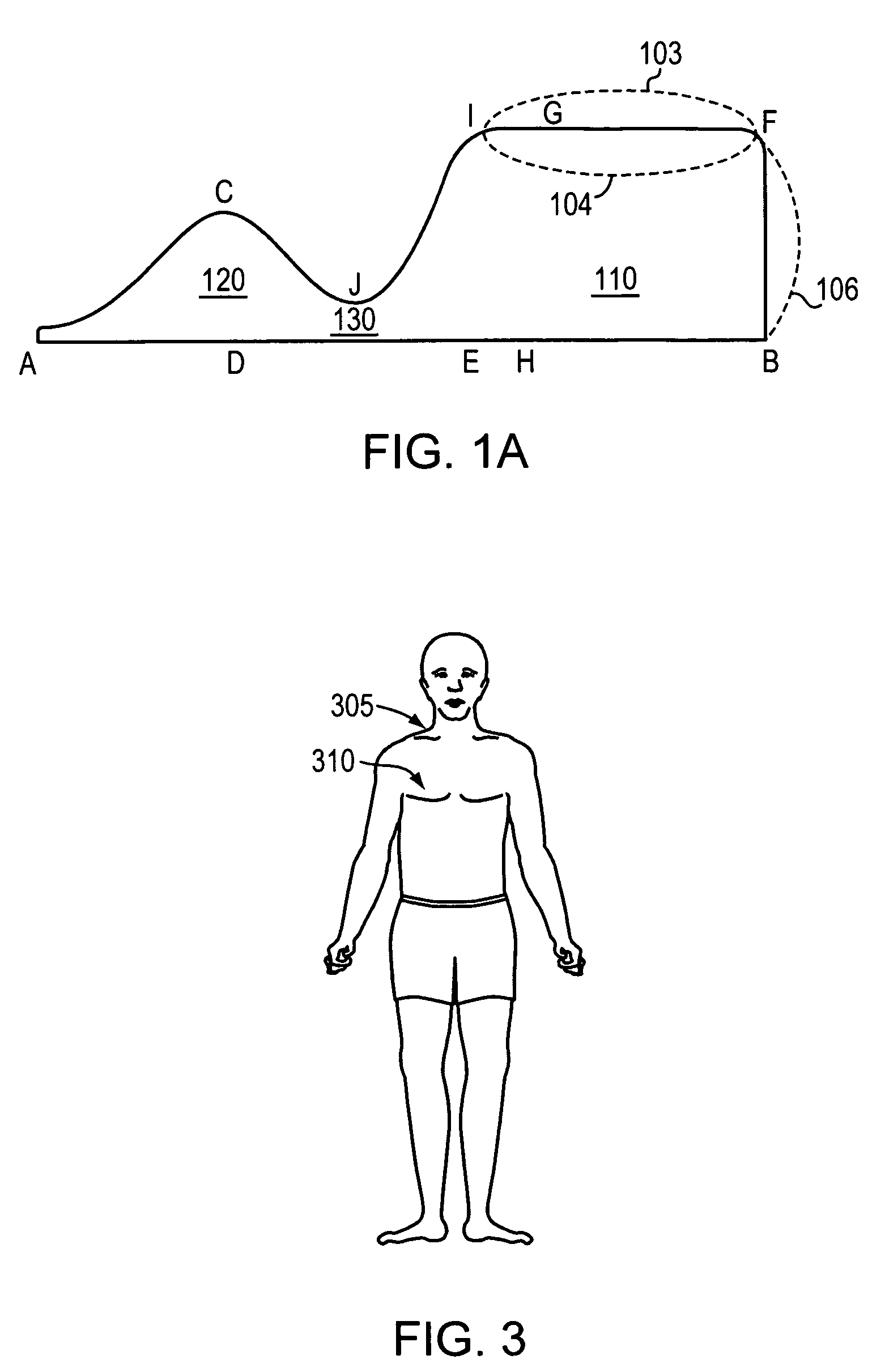
ActiveUS20050211889A1Facilitates three-dimensional motionPromotes relative motionMagnetic measurementsCalibration apparatusAbnormal tissue growthTumor target
The present invention is a thorax phantom that enables simulation of tumor motion within a tissue equivalent material. The system consists of a tissue equivalent epoxy phantom representing a 15 cm axial section of the human thorax that includes simplified spine and lung anatomies. Within the phantom are thru rods of similar tissue density. The rods are attached to a computer-controlled actuator that facilitates both linear and rotational motion of the rods within the phantom. A plurality of tumor targets and radiation detectors can be placed within the rods at various locations thereby enabling the simulation of respiratory and cardiac induced tumor motions within the phantom and assessment of the effects of these motions on image acquisitions, treatment planning and radiation treatment delivery.
Owner:COMPIZED IMAGING REFERENCE SYST
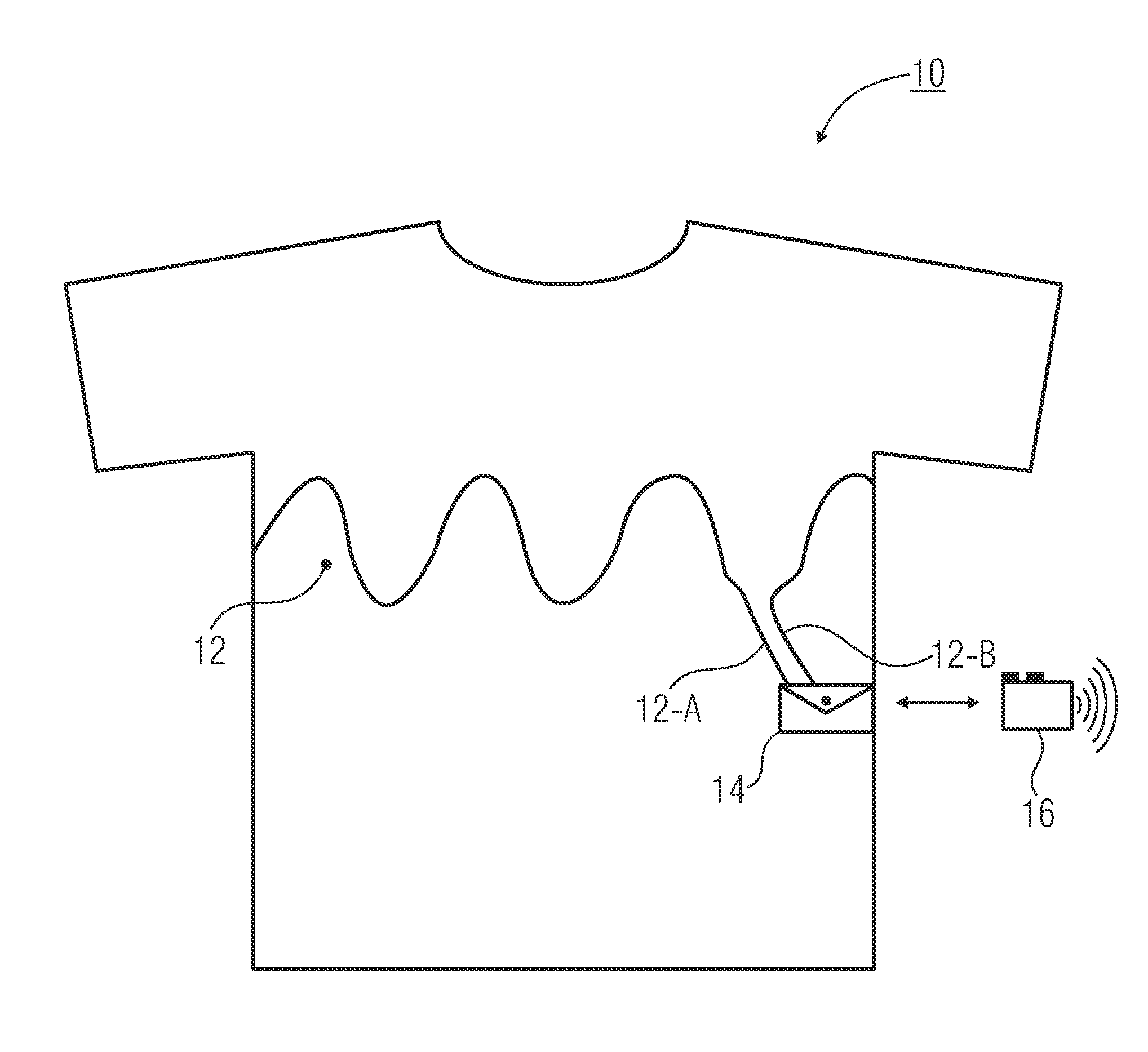
Garment for detecting respiratory movement
InactiveUS20100286546A1Avoid formingPrevent slippingRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsElectricityRESPIRATORY MOVEMENTS
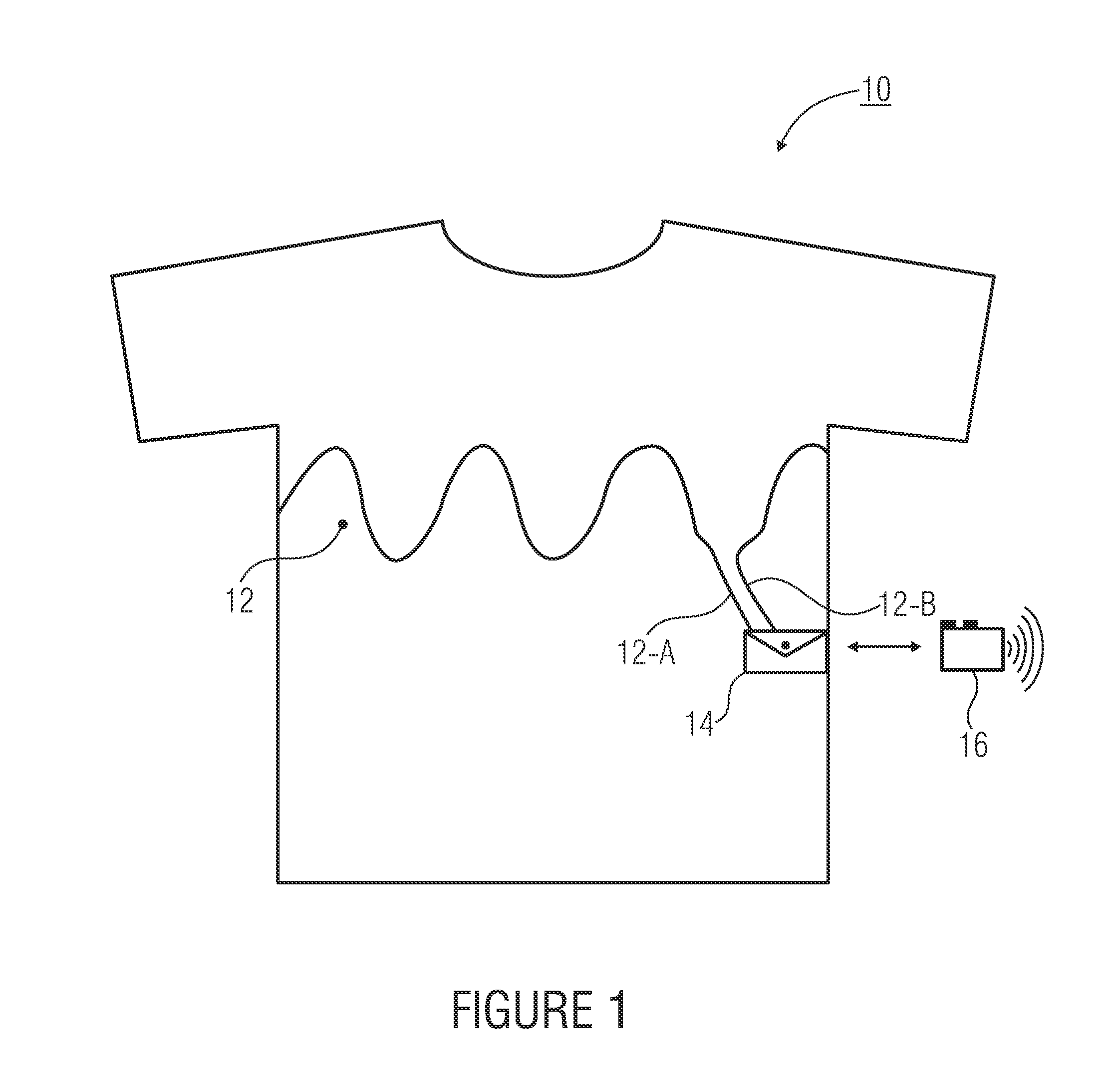
A garment for detecting respiratory movement of a living being, wherein the garment can be pulled over the thorax of the living being, including an electric conductor integrable at the height of the thorax of the living being into the garment, which is attached to the garment in order to change an electrically measurable characteristic in dependence on the respiratory movement of the thorax, and a holder for fixing evaluation electronics integrable into the garment, which can be coupled to the electric conductor and which is implemented to detect the electrically measurable characteristic and which further includes an interface for outputting or storing data derived from the electrically measurable characteristic.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com