Patents
Literature
42 results about "Work of breathing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
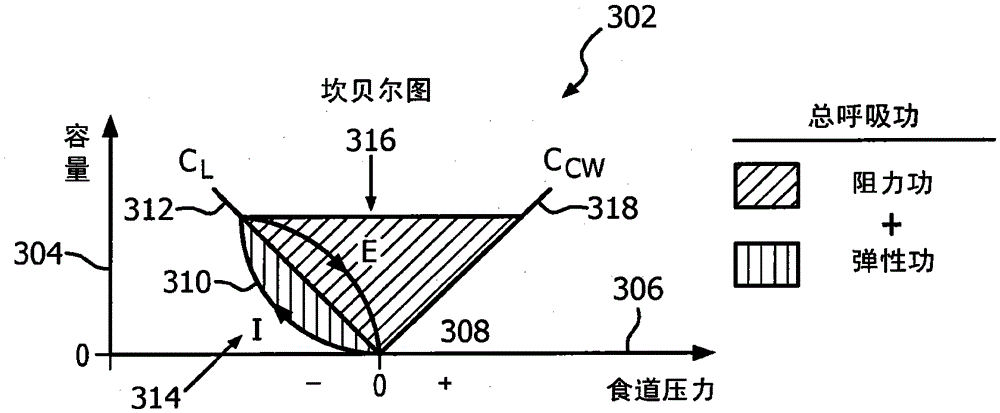
Work of breathing (WOB) is the energy expended to inhale and exhale a breathing gas. It is usually expressed as work per unit volume, for example, joules/litre, or as a work rate (power), such as joules/min or equivalent units, as it is not particularly useful without a reference to volume or time. It can be calculated in terms of the pulmonary pressure multiplied by the change in pulmonary volume, or in terms of the oxygen consumption attributable to breathing. In a normal resting state the work of breathing constitutes about 5% of the total body oxygen consumption. It can increase considerably due to illness or constraints on gas flow imposed by breathing apparatus, ambient pressure, or breathing gas composition.
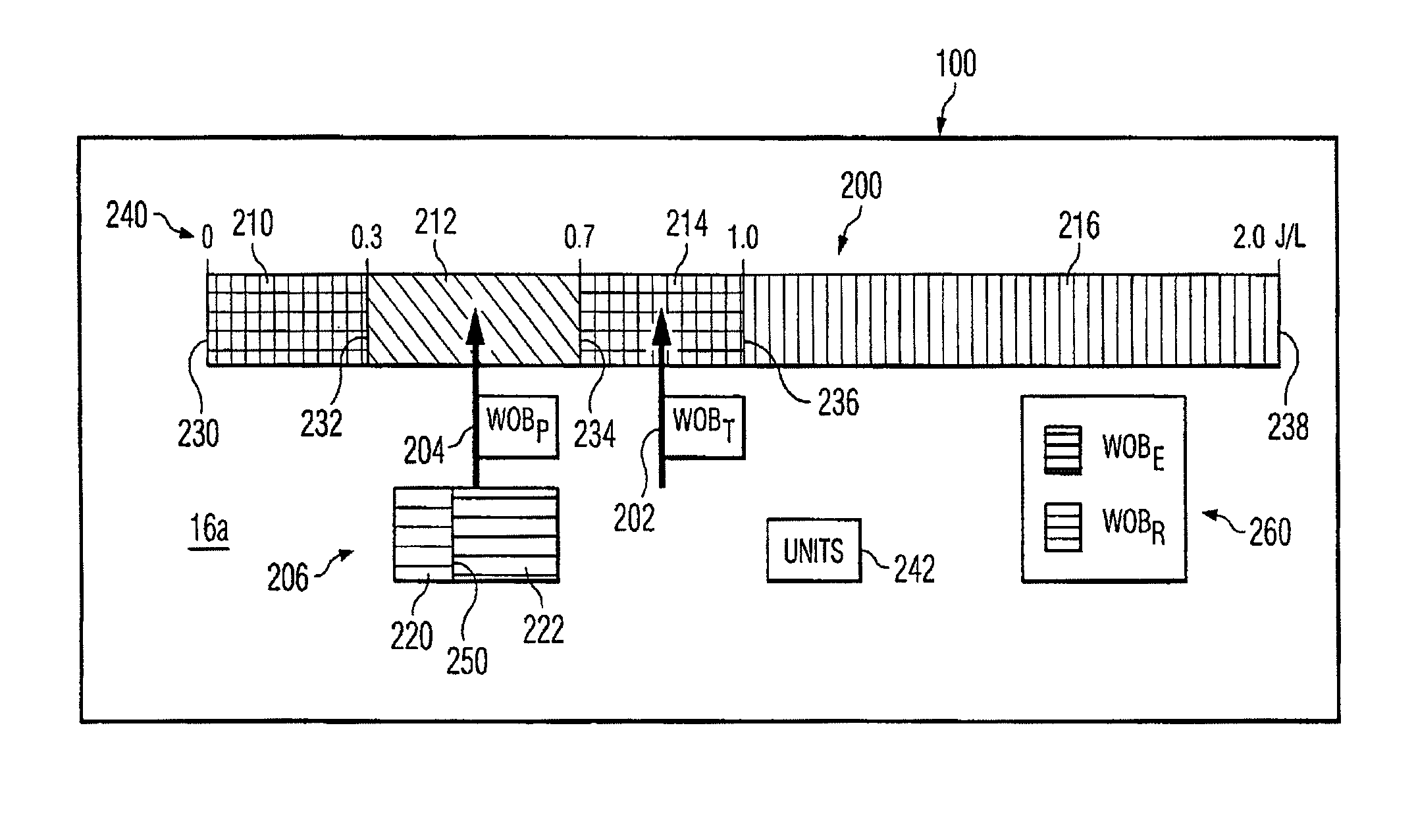
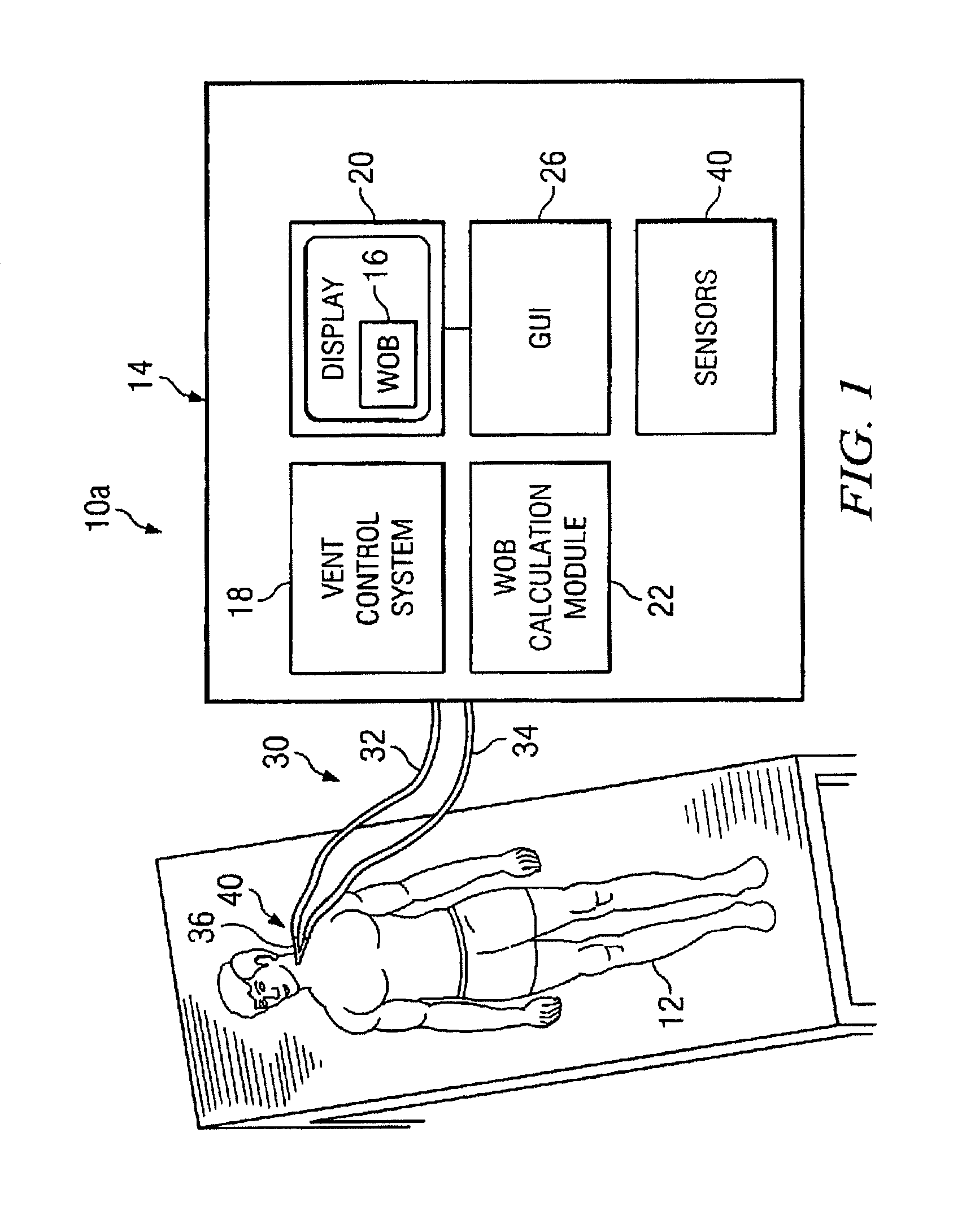
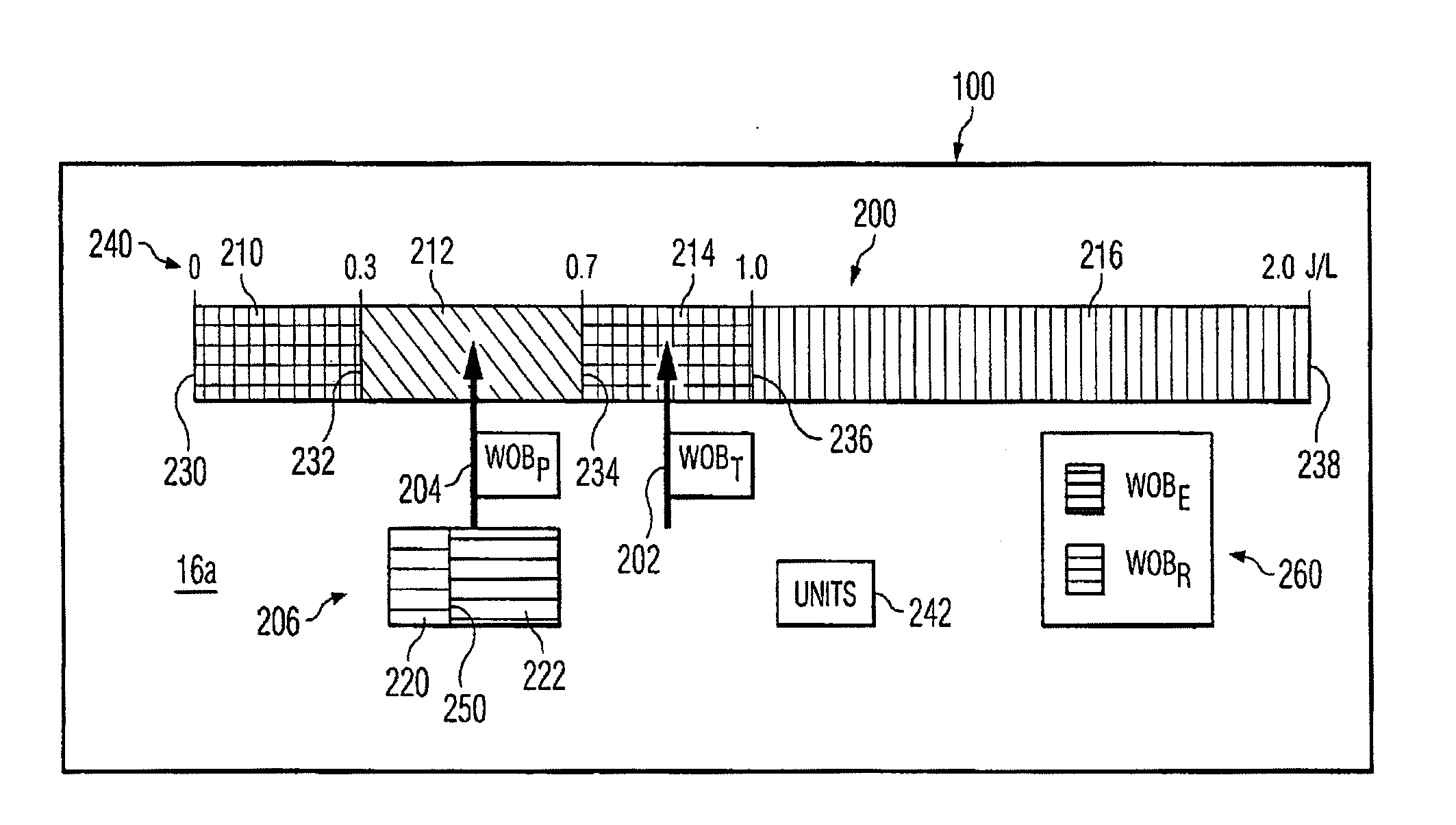
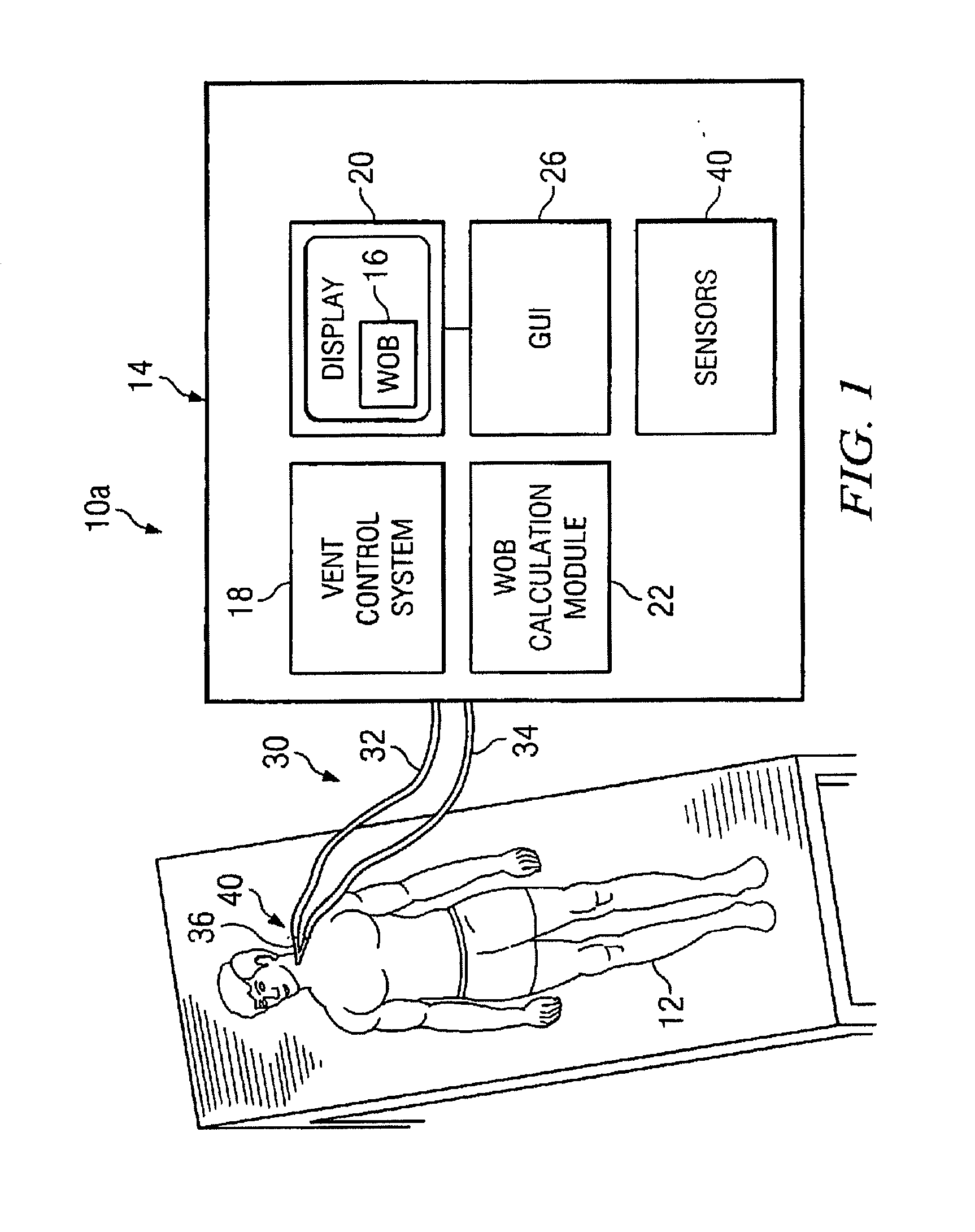
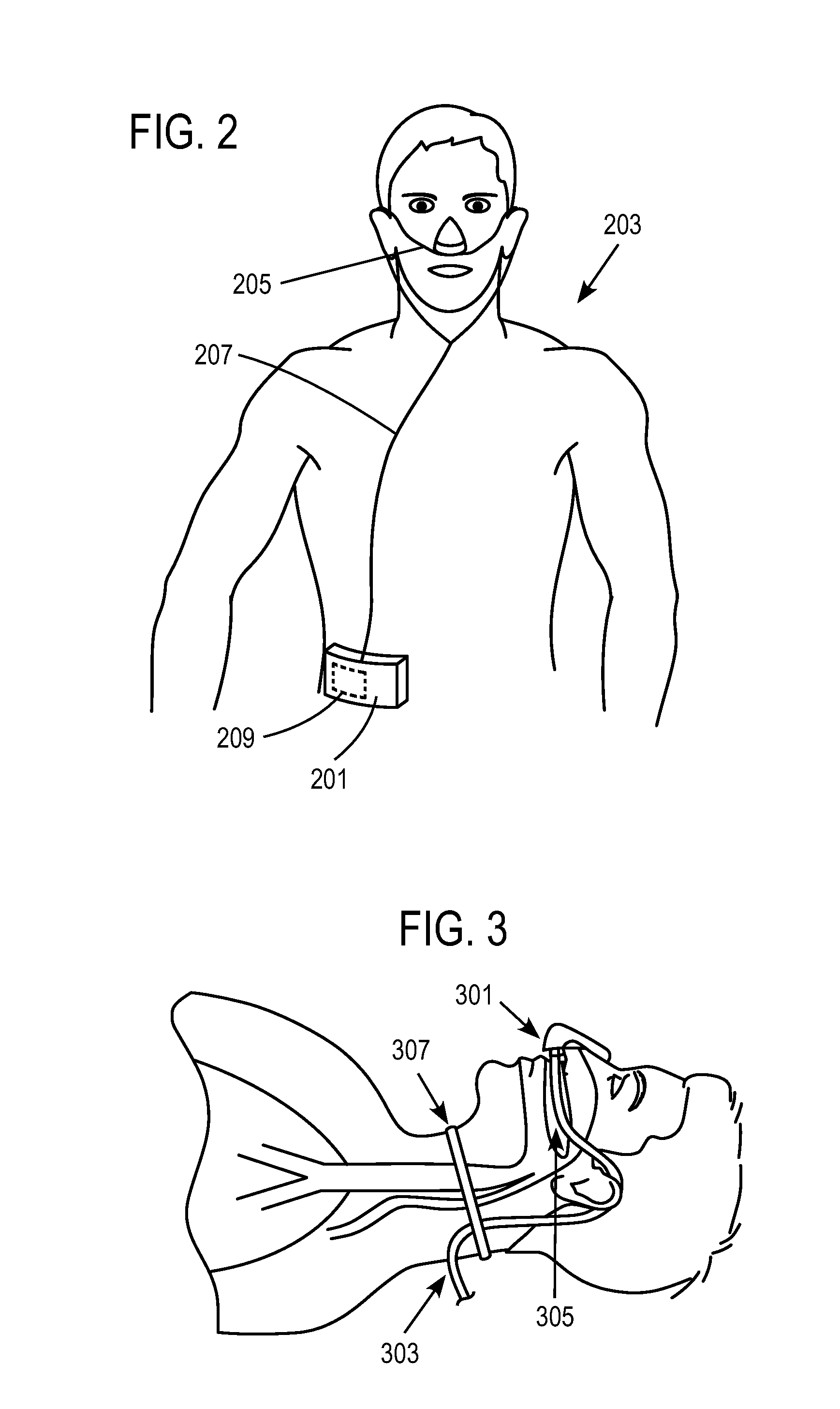
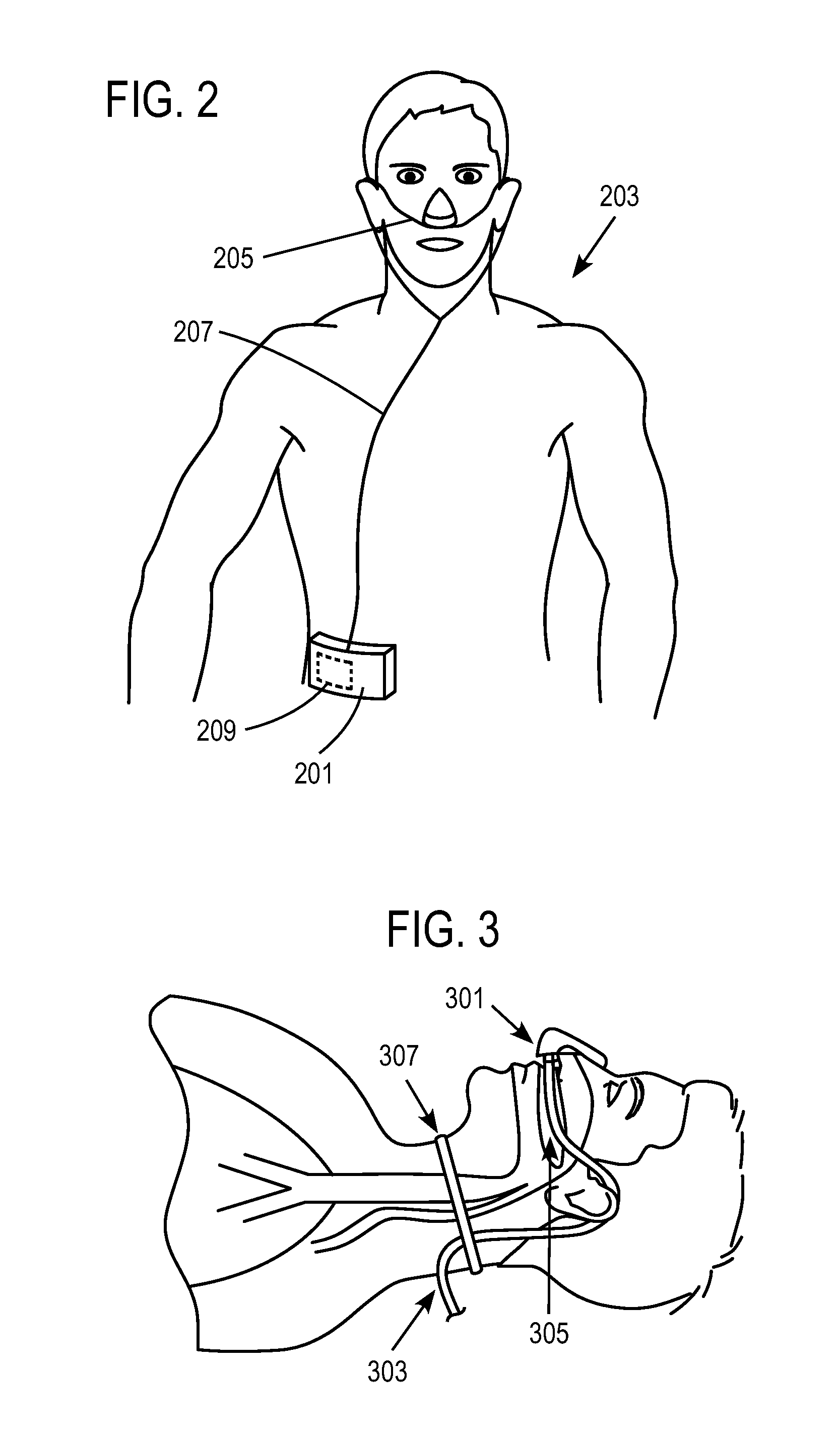
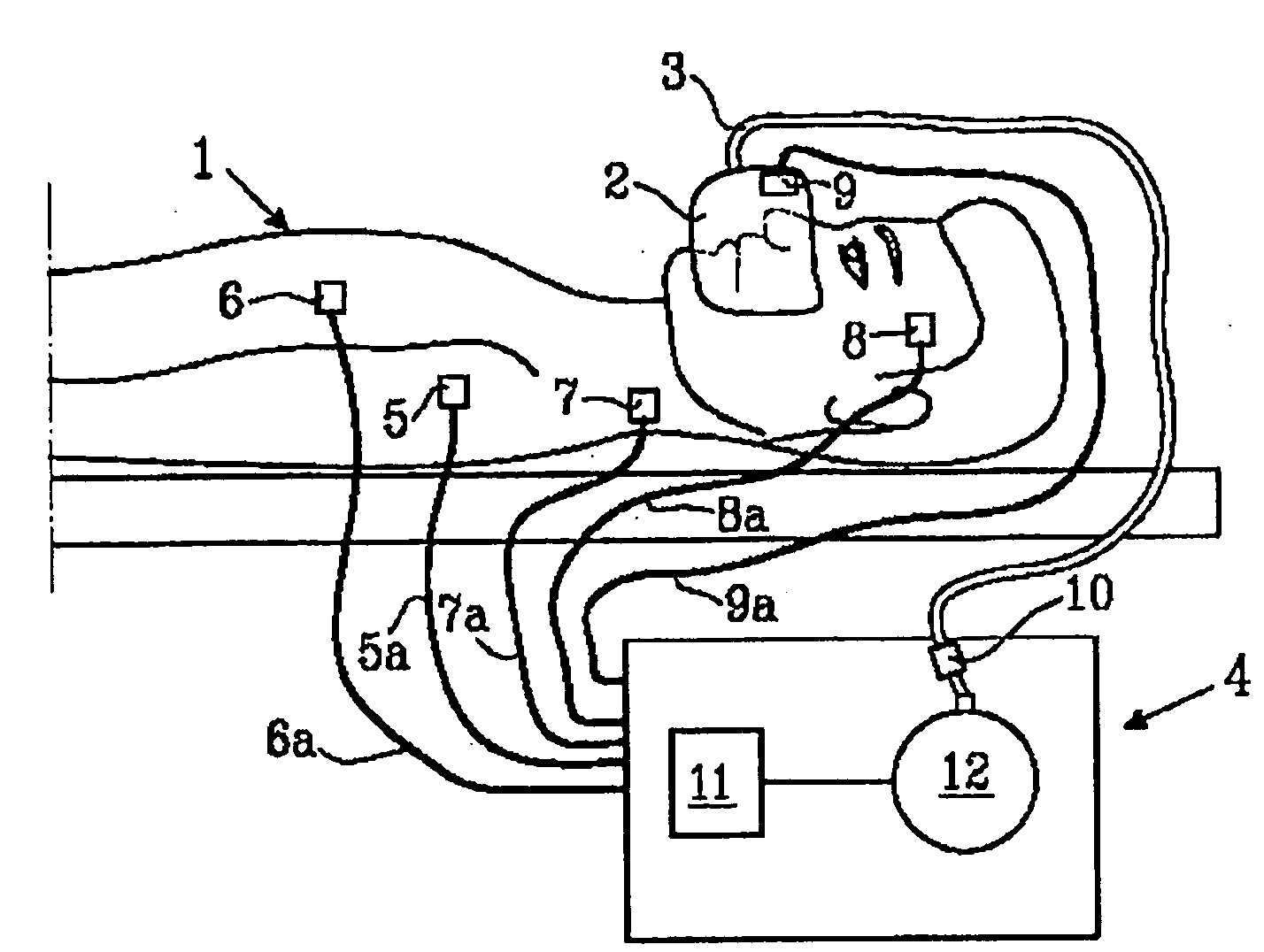
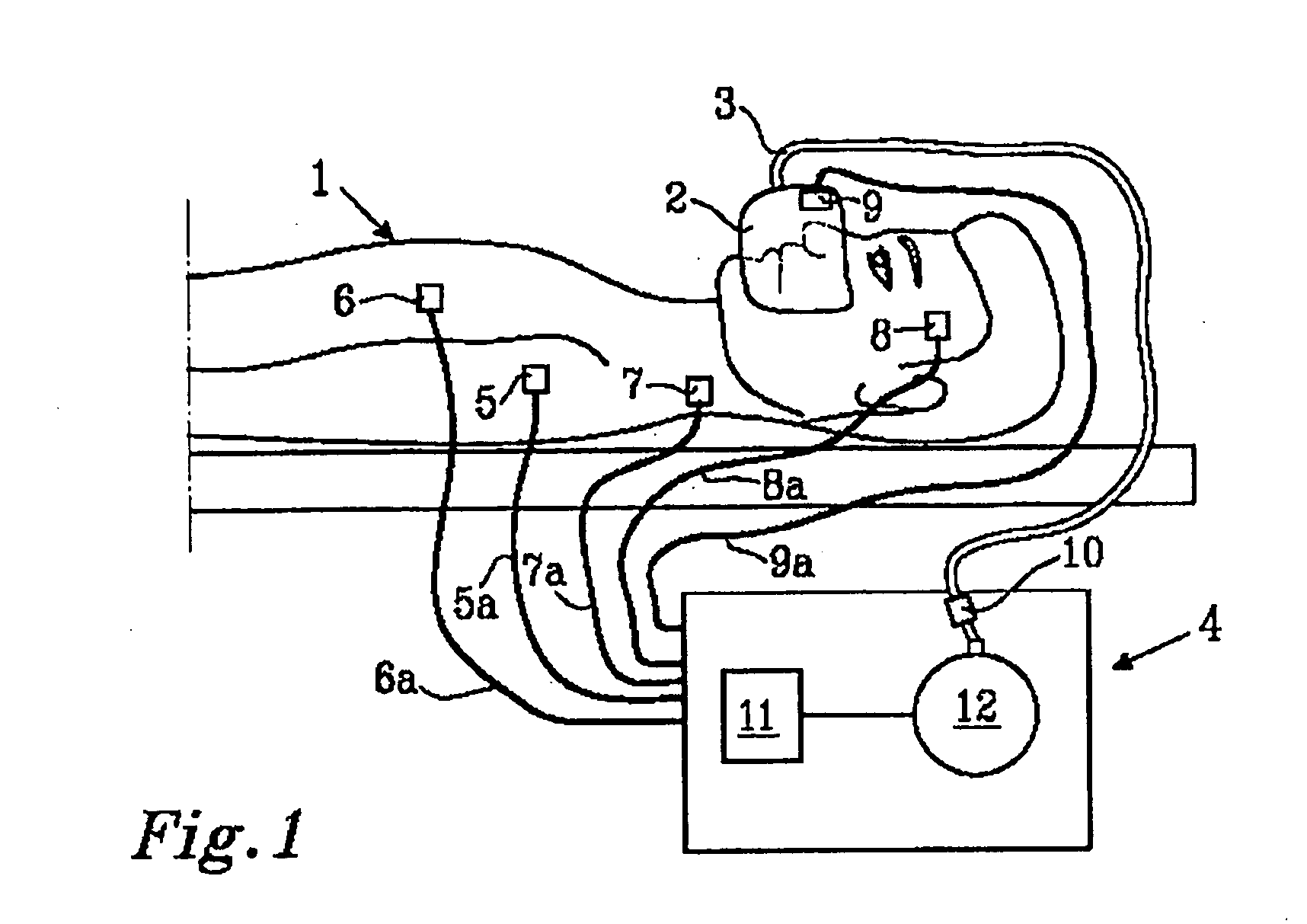
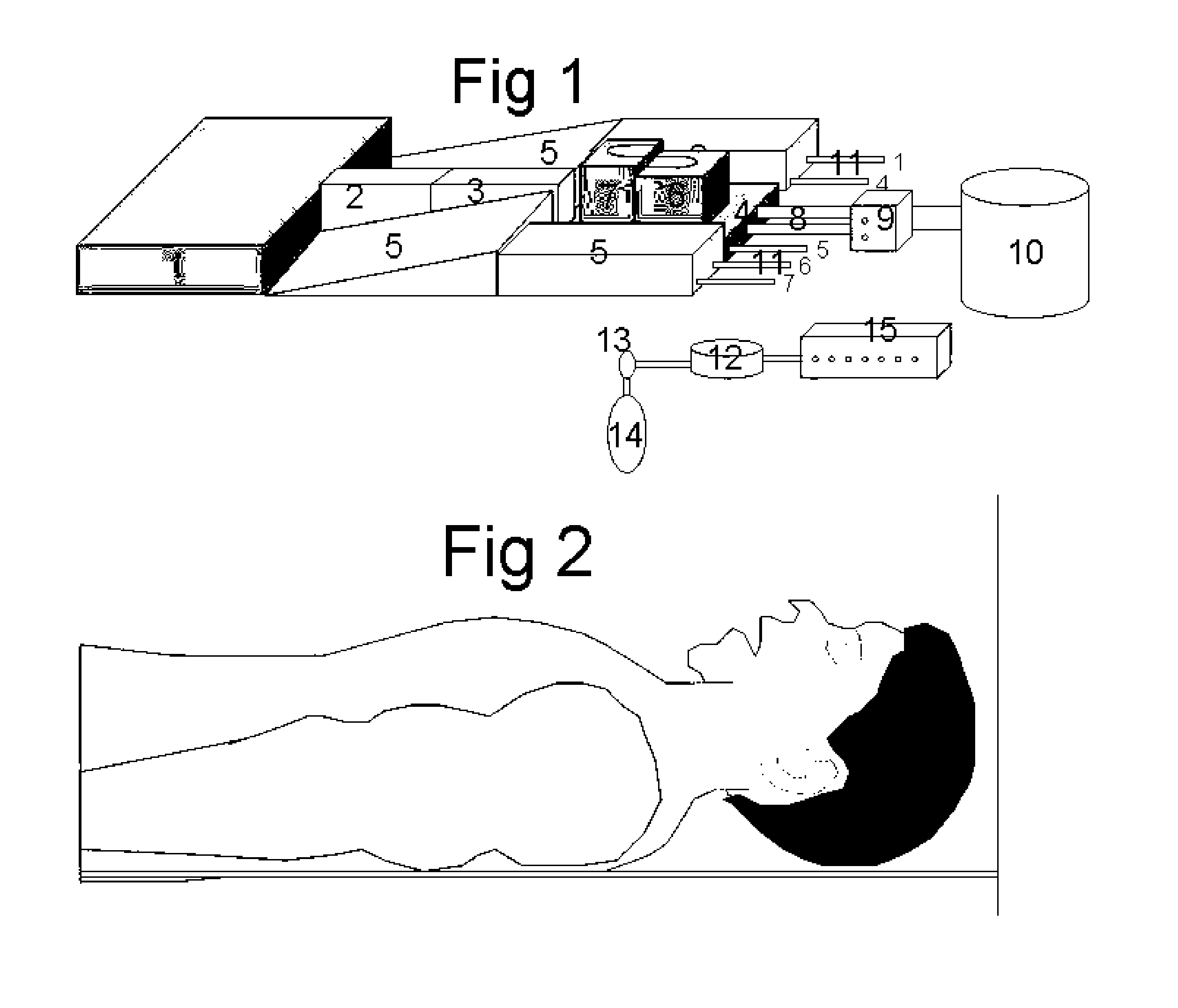
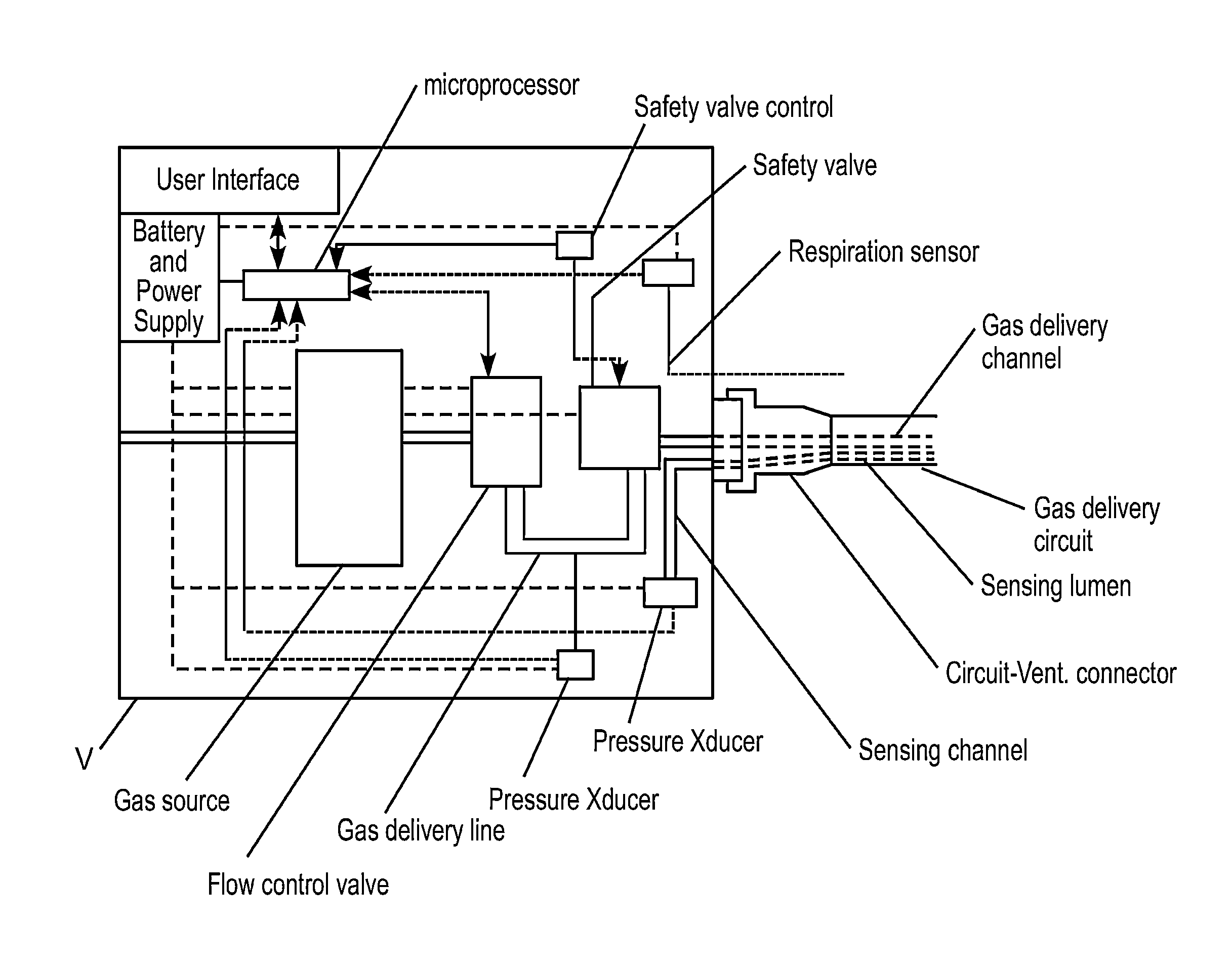
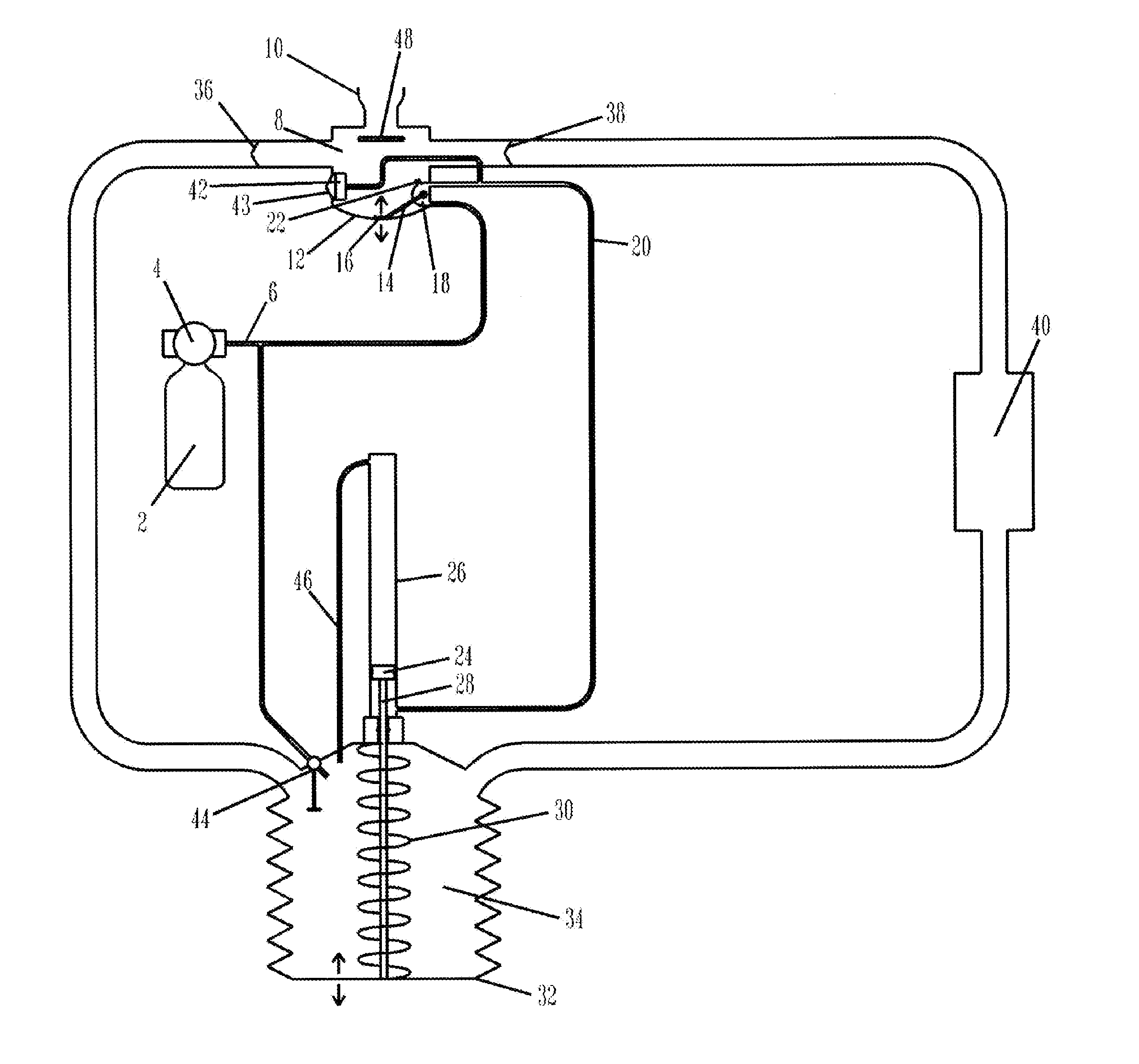
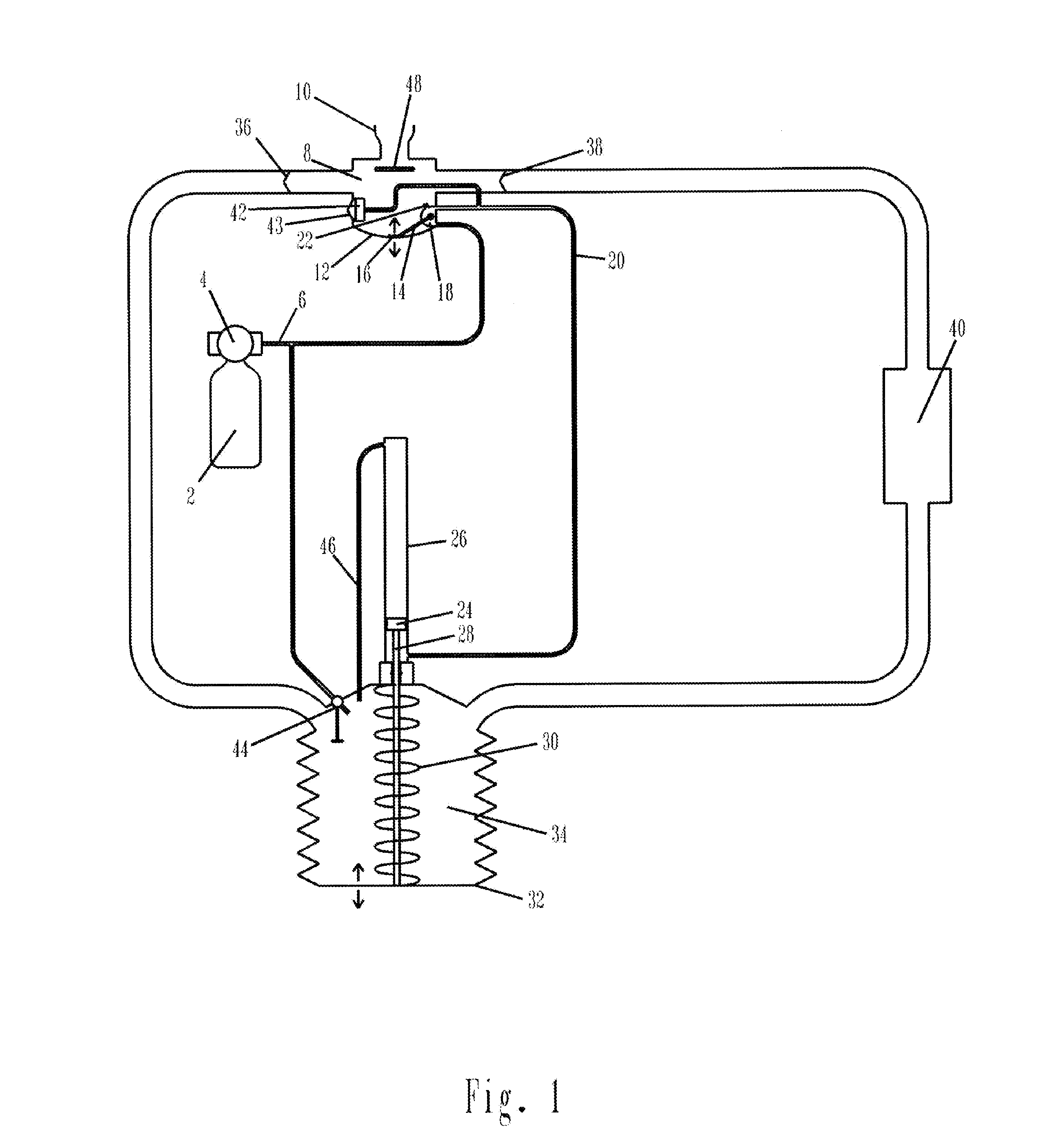
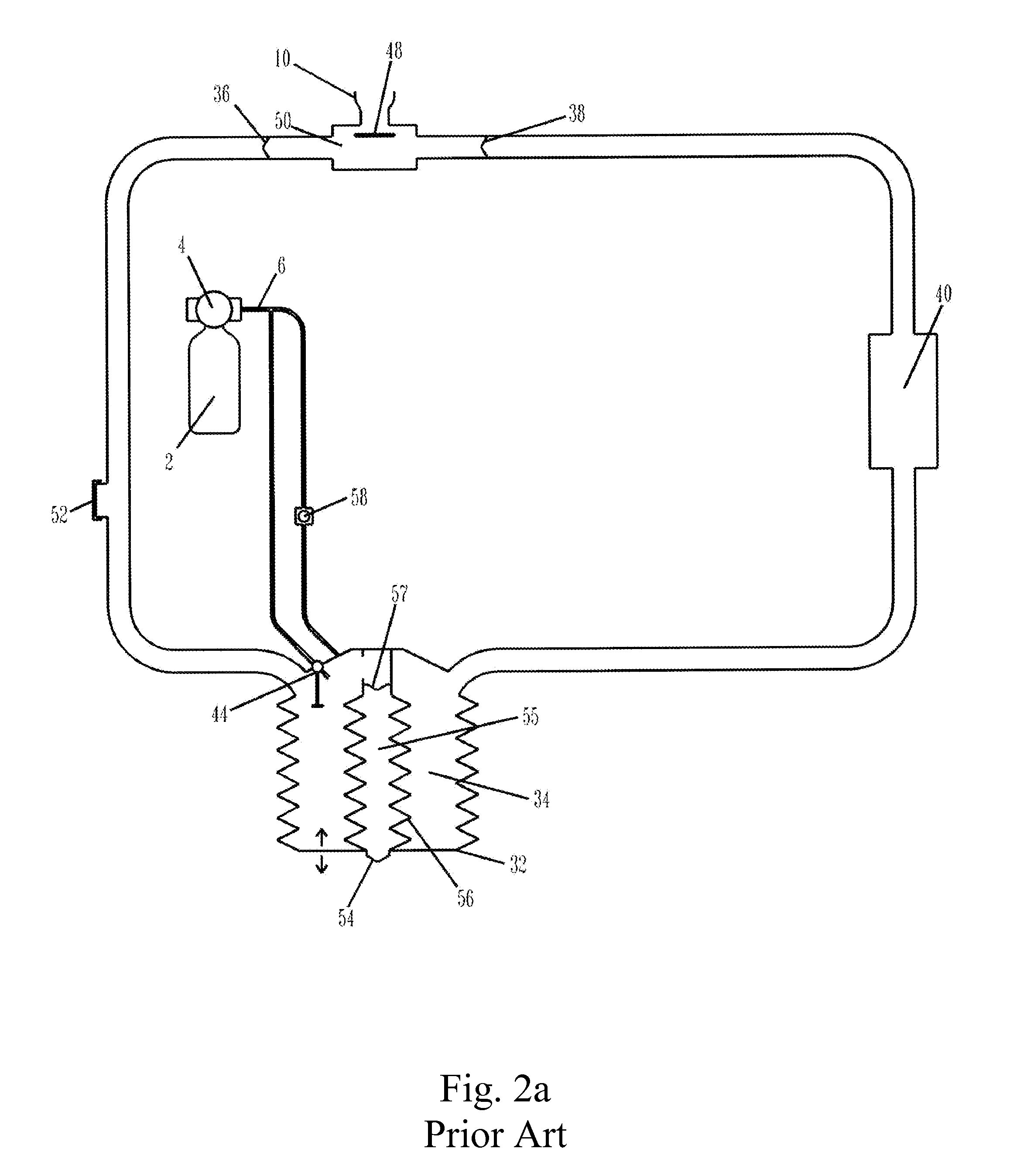
Work of breathing display for a ventilation system
ActiveUS8597198B2Simple processEffectively “ drive ”RespiratorsMedical devicesSupporting systemDisplay device
A breathing support system is provided. The system may include a breathing support device configured to deliver gas to a patient and a display device associated with the breathing support device. The display device may be configured to display a graphic indicating one or more measures regarding the patient's work of breathing.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
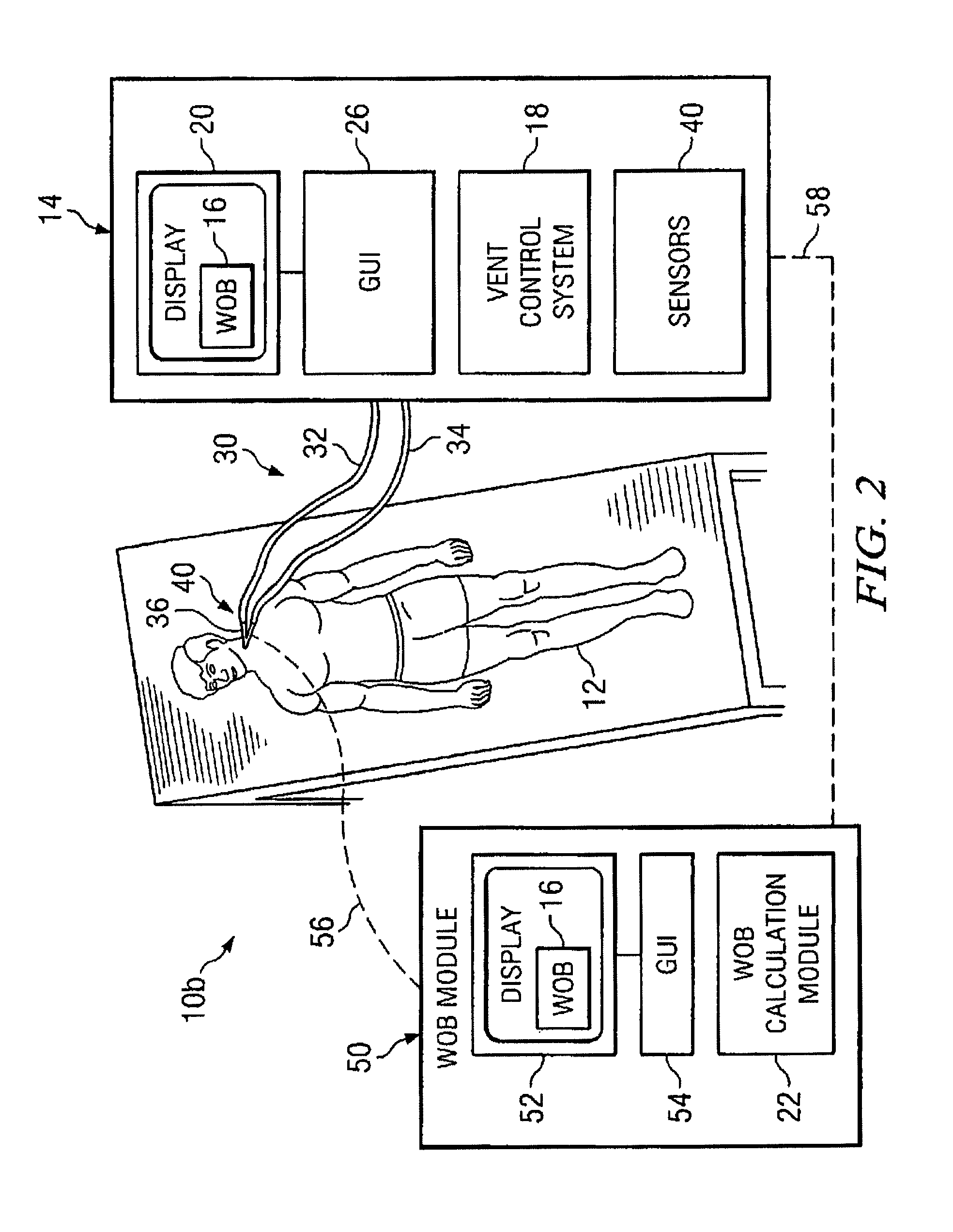
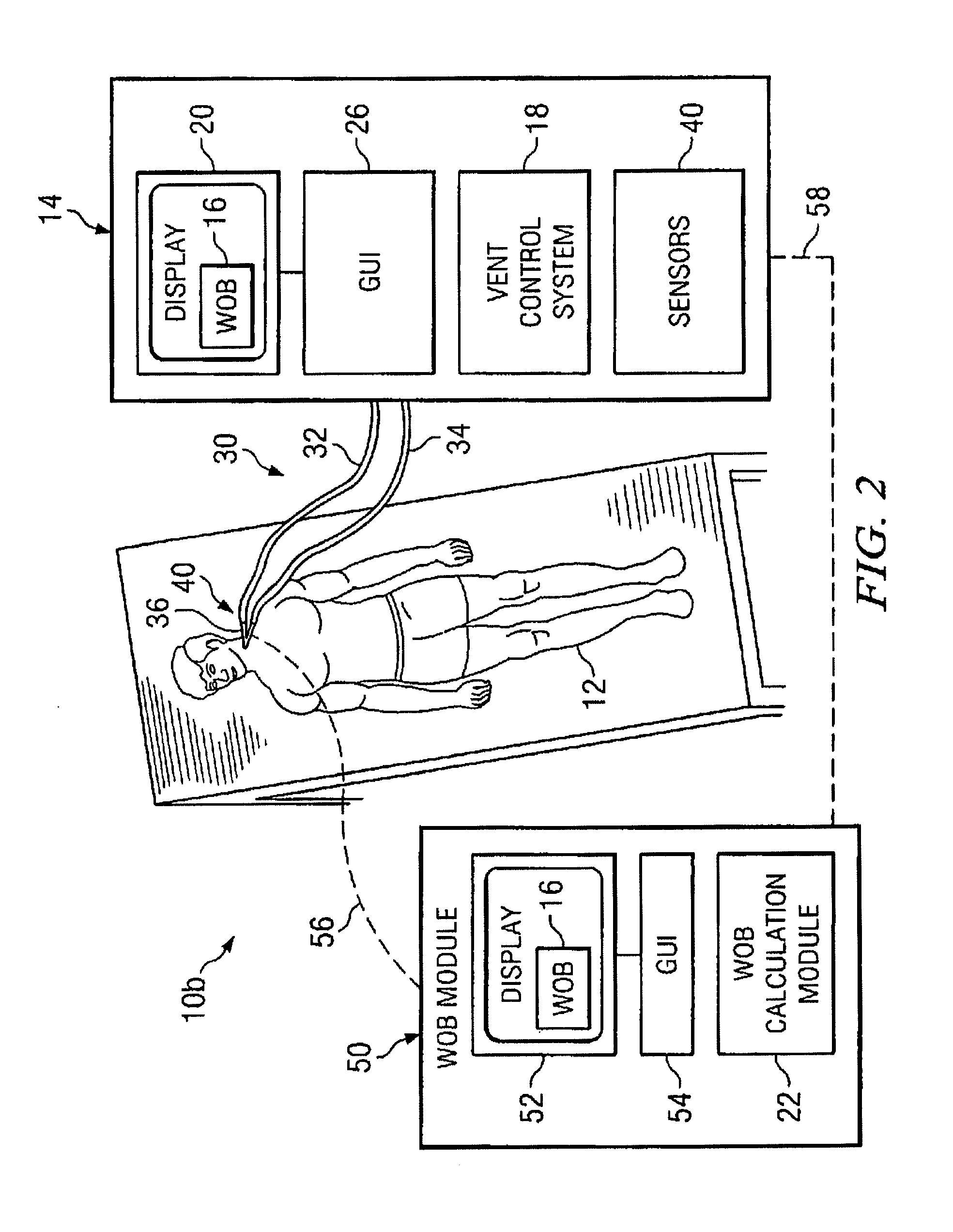
Work of breathing display for a ventilation system
ActiveUS20110230780A1Simple processEffectively “ drive ”RespiratorsMedical devicesSupporting systemDisplay device
A breathing support system is provided. The system may include a breathing support device configured to deliver gas to a patient and a display device associated with the breathing support device. The display device may be configured to display a graphic indicating one or more measures regarding the patient's work of breathing.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
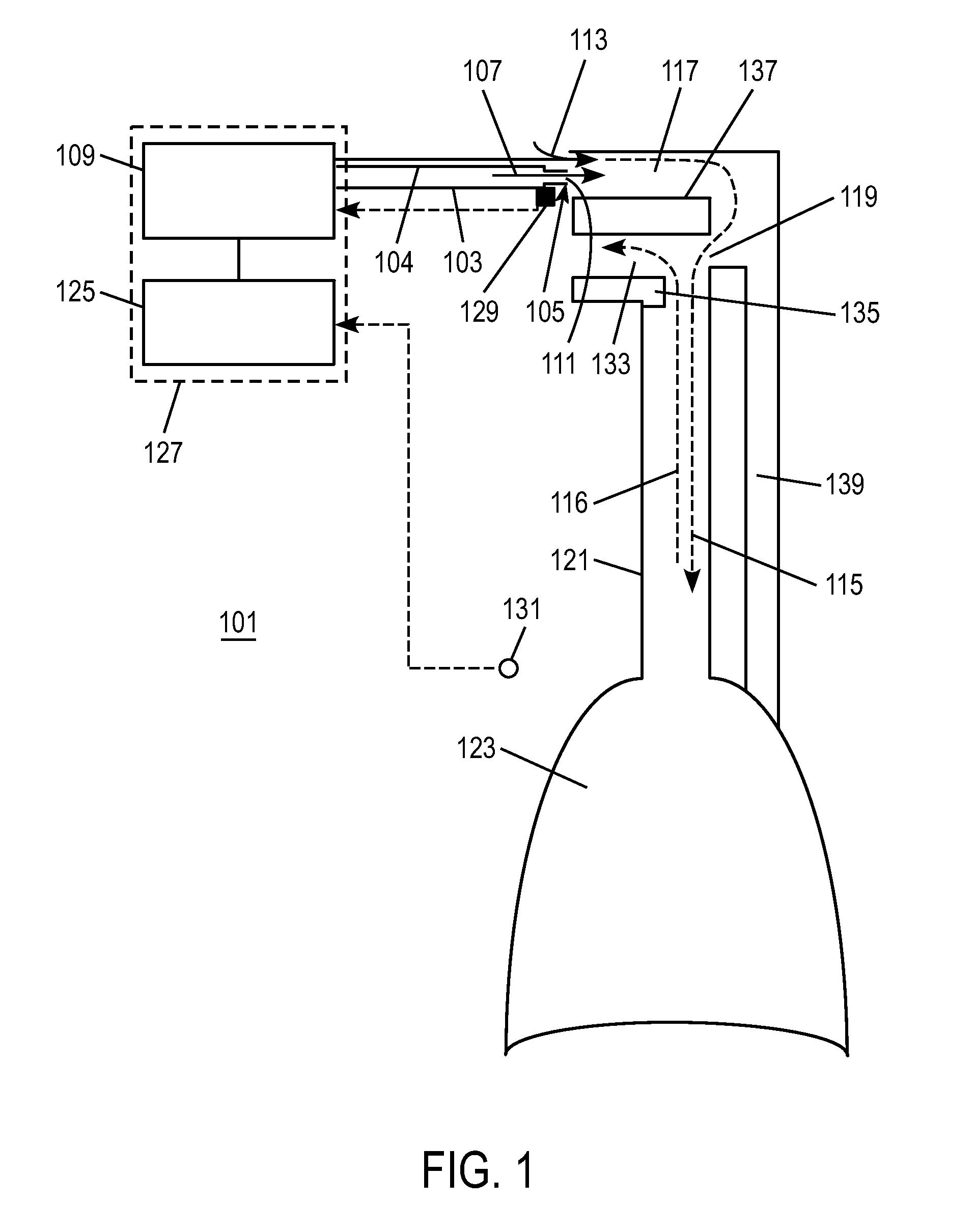
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive open ventilation for providing ventilation support
ActiveUS20100252041A1Work lessIncrease airway pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLung volumesNon invasive
A system for providing ventilation support to a patient may include a ventilator, a control unit, a gas delivery circuit with a proximal end in fluid communication with the ventilator and a distal end in fluid communication with a nasal interface, and a nasal interface. The nasal interface may include at least one jet nozzle at the distal end of the gas delivery circuit; and at least one spontaneous respiration sensor for detecting respiration in communication with the control unit. The system may be open to ambient. The control unit may receive signals from the at least one spontaneous respiration sensor and determine gas delivery requirements. The ventilator may deliver gas at a velocity to entrain ambient air and increase lung volume or lung pressure above spontaneously breathing levels to assist in work of breathing, and deliver ventilation gas in a cyclical delivery pattern synchronized with a spontaneous breathing pattern.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive open ventilation with gas delivery nozzles in free space
ActiveUS20100252039A1Work lessIncrease airway pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNoseLung volumes
A non-invasive ventilation system may include an interface. The interface may include at least one gas delivery jet nozzle adapted to be positioned in free space and aligned to directly deliver ventilation gas into an entrance of a nose. The at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be connected to a pressurized gas supply. The ventilation gas may entrain ambient air to elevate lung pressure, elevate lung volume, decrease the work of breathing or increase airway pressure, and wherein the ventilation gas is delivered in synchrony with phases of breathing. A support for the at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be provided. A breath sensor may be in close proximity to the entrance of the nose. A patient may spontaneous breathe ambient air through the nose without being impeded by the interface.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Delta Flow Pressure Regulation
InactiveUS20080276939A1Reduce dependenceLittle time differenceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsIntensive care medicine
A method, system, apparatus, and computer program for detecting breathing pattern changes and controlling a mechanical ventilator in accordance to changes of breathing air flow thus reducing the work of breathing for the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
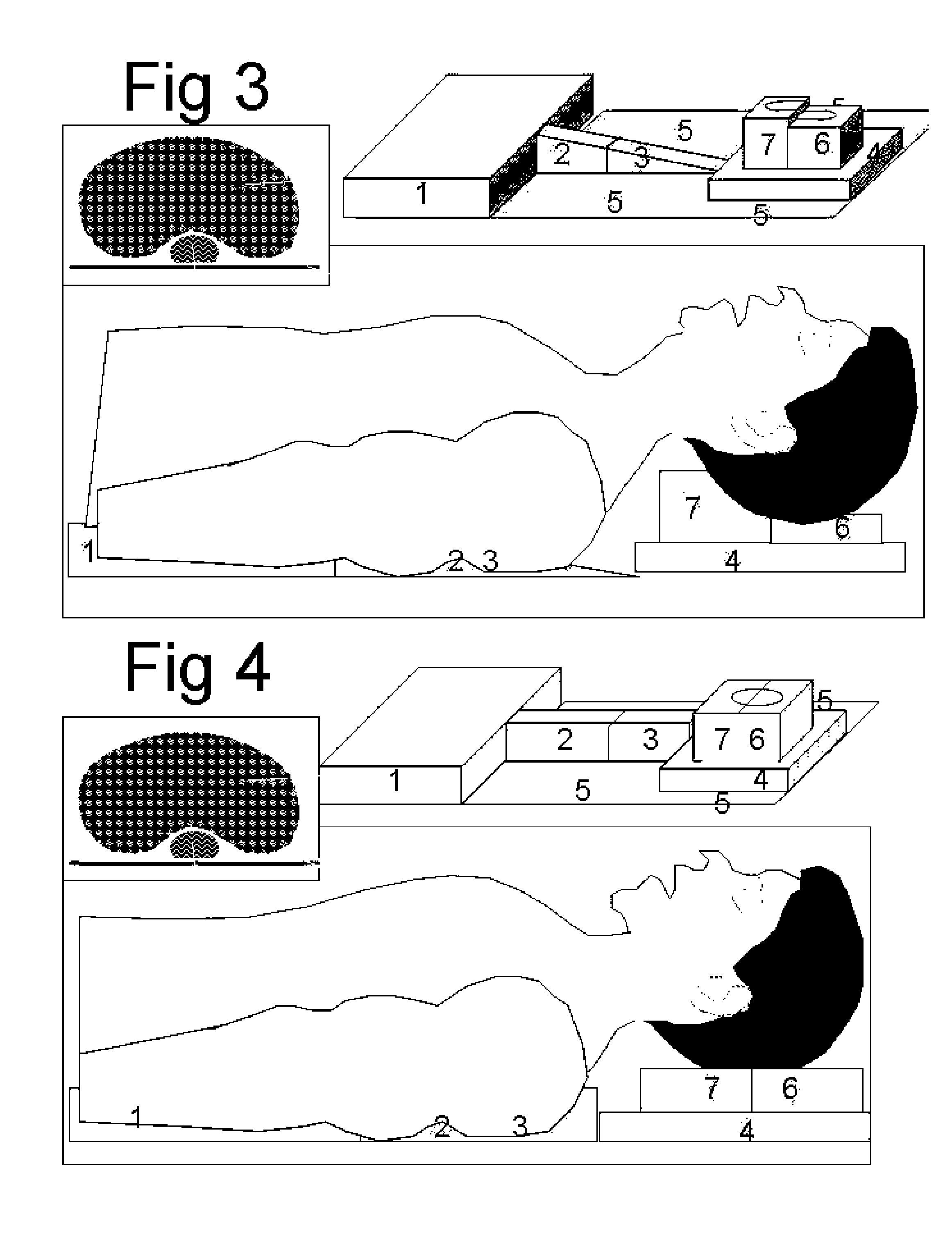
Intubation positioning, breathing facilitator and non-invasive assist ventilation device
InactiveUS20070181122A1Easy intubationEasy alignmentRespiratorsOperating tablesSpinal columnAssisted ventilation
This invention can be used in three different ways for patients who are lying down in bed or on the operating table. First it facilitates the endotracheal intubation, secondly it facilitates the spontaneous breathing of obese patients and thirdly it assists the spontaneous inspiration and expiration in a non-invasive way. This invention device is positioned under the patient before he is asleep without disturbing him. It allows a gradual elevation of the lower and or upper thorax, a gradual elevation of the head giving a flexion of the neck and a gradual hyperextension of the head. After intubation the position is returned to normal without need for removing the invention device. This invention elevates the spinal column and therefore the thorax is no more compressed and the ribs can move free. Inspiration requires less force and the patient can be breathing easier even when lying down. In this invention the spinal column elevation can also be inflated in a synchronized way with the respiration of the patient. During inspiration the spinal column is elevated, facilitating the inspiration. During expiration the elevation is lowered, facilitating the expiration. The work of breathing is reduced for the patient resulting in larger minute volume ventilation or less oxygen consumption.
Owner:MULIER JAN PAUL
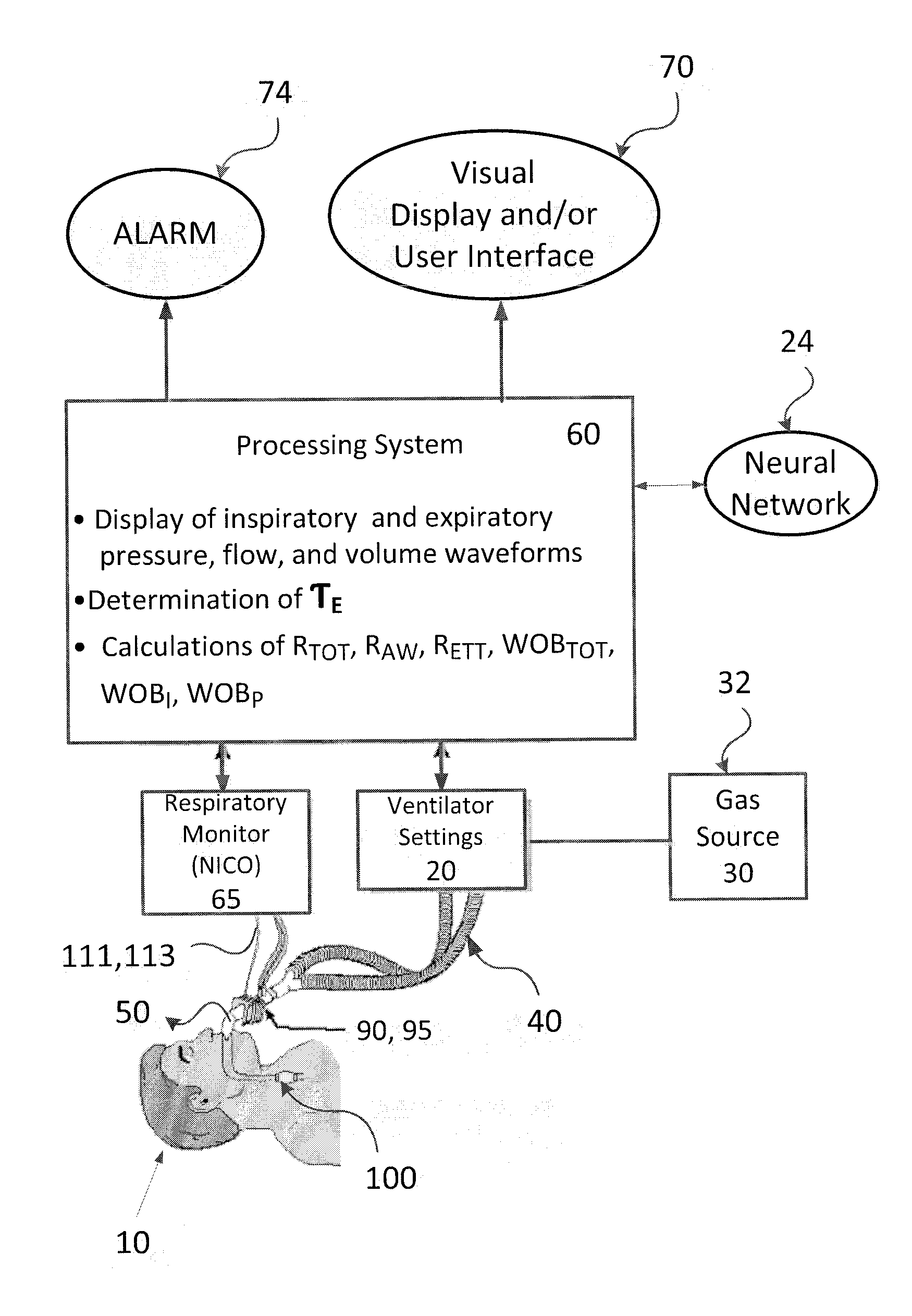
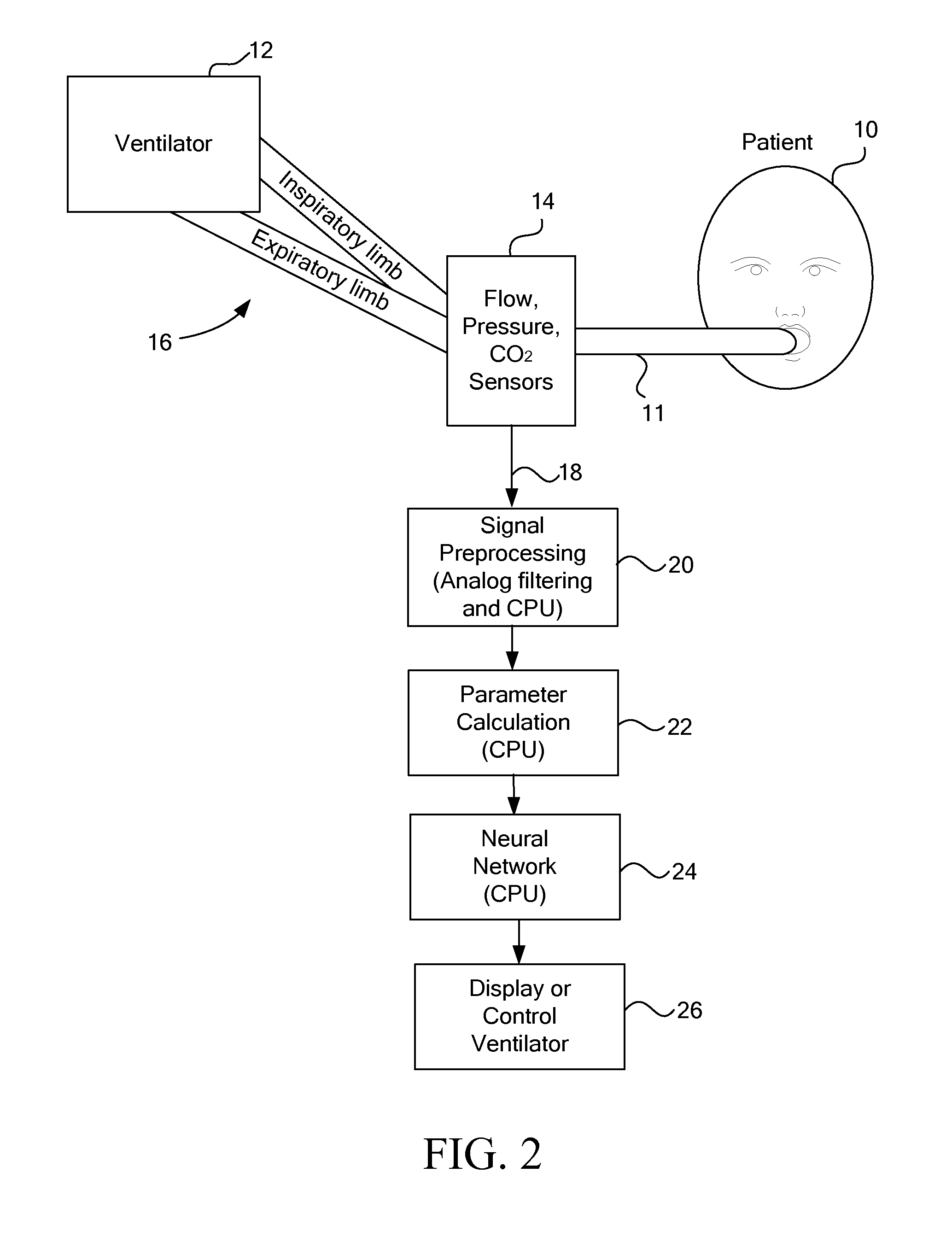
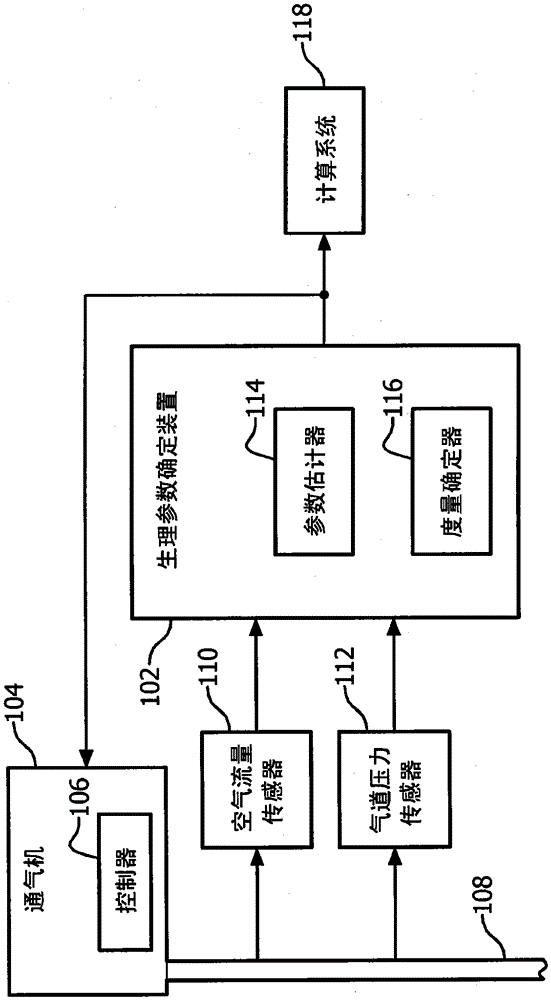
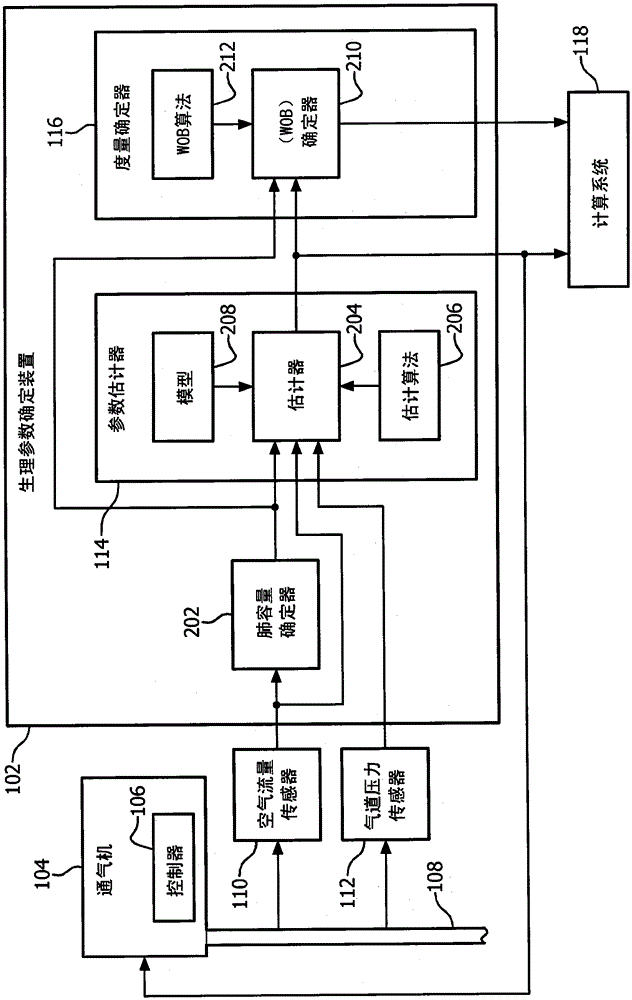
Methods and systems for monitoring resistance and work of breathing for ventilator-dependent patients
ActiveUS20140276173A1Avoids inspiratory muscle fatigue muscleAppropriate treatmentTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMathematical modelTherapeutic effect
Methods for non-invasively and accurately estimating and monitoring resistance and work of breathing parameters from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the ventilator-dependent patient using an adaptive mathematical model are provided. These methods are based on calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors. The resistance and work of breathing parameters are important for: assessing patient status and diagnosis, appropriately selecting treatment, assessing efficacy of treatment, and properly adjusting ventilatory support.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +1
Method and Apparatus for Predicting Work of Breathing
ActiveUS20120215081A1Avoids respiratory muscle fatigue respiratory muscleAvoids respiratory muscle respiratory muscle deconditioningRespiratorsMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMathematical model
A method of creating a noninvasive predictor of both physiologic and imposed patient effort of breathing from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the patient using an adaptive mathematical model. The patient effort is commonly measured via work of breathing, power of breathing, or pressure-time product of esophageal pressure and is important for properly adjusting ventilatory support for spontaneously breathing patients. The method of calculating this noninvasive predictor is based on linear or non-linear calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
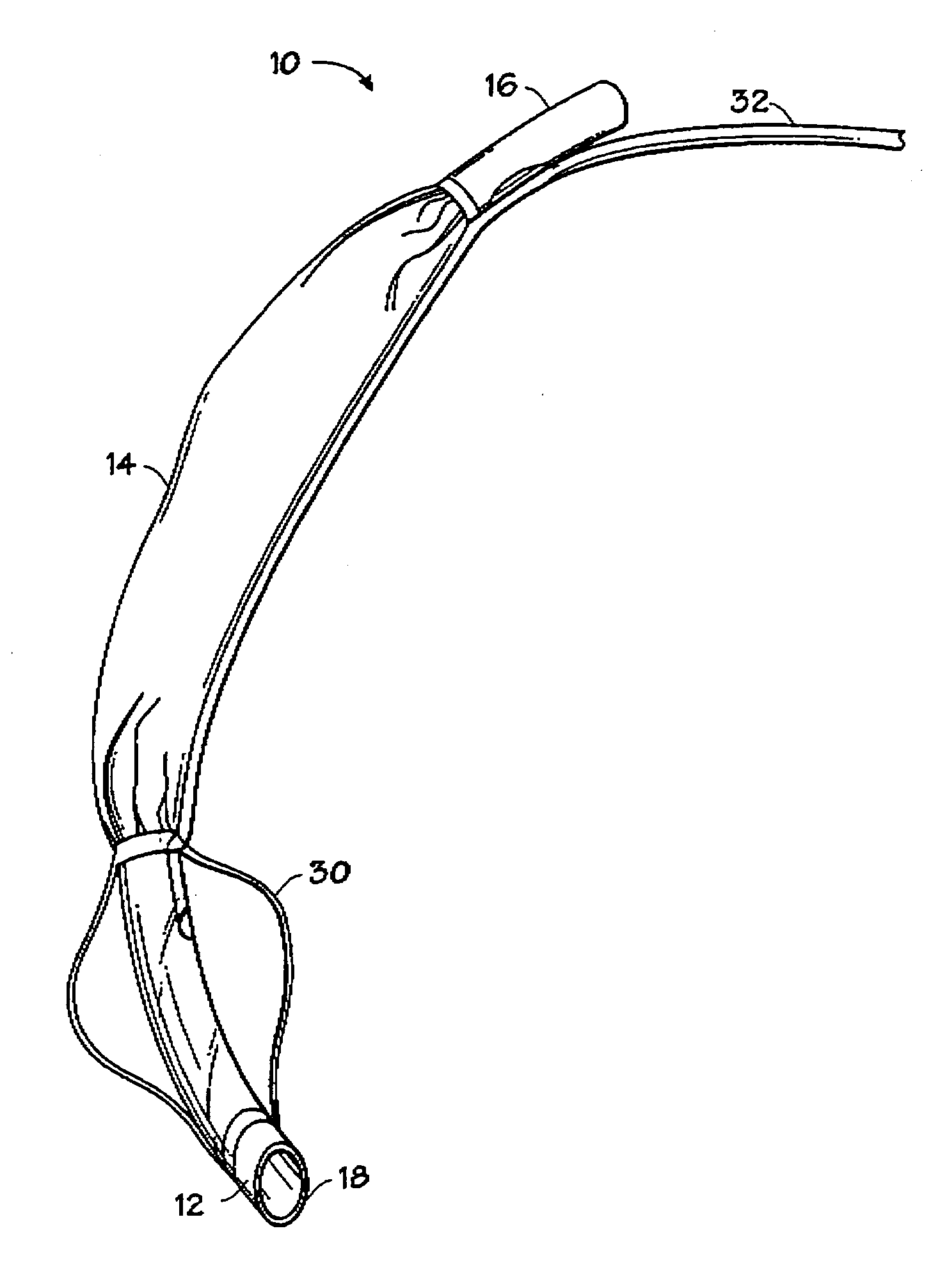
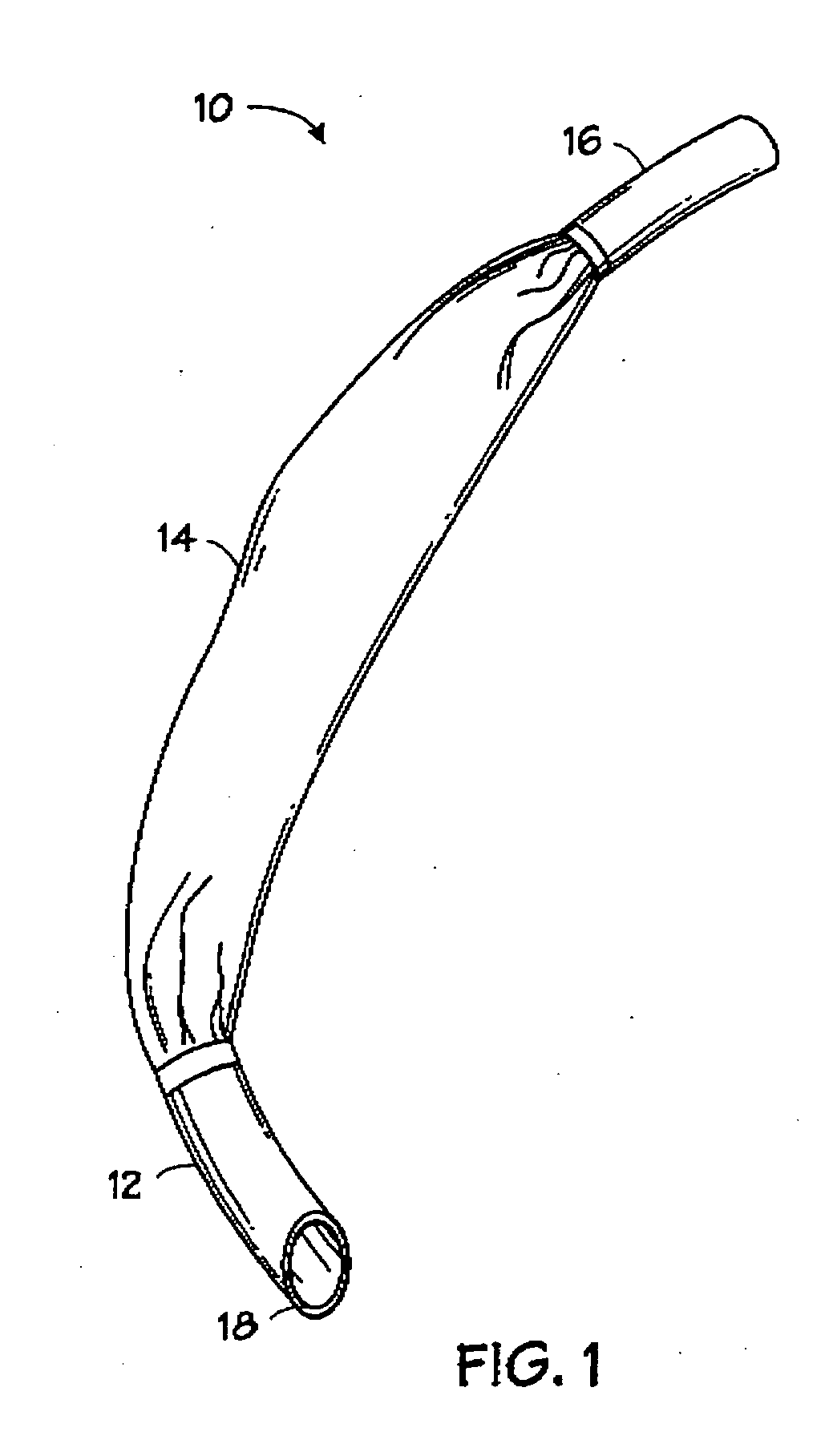
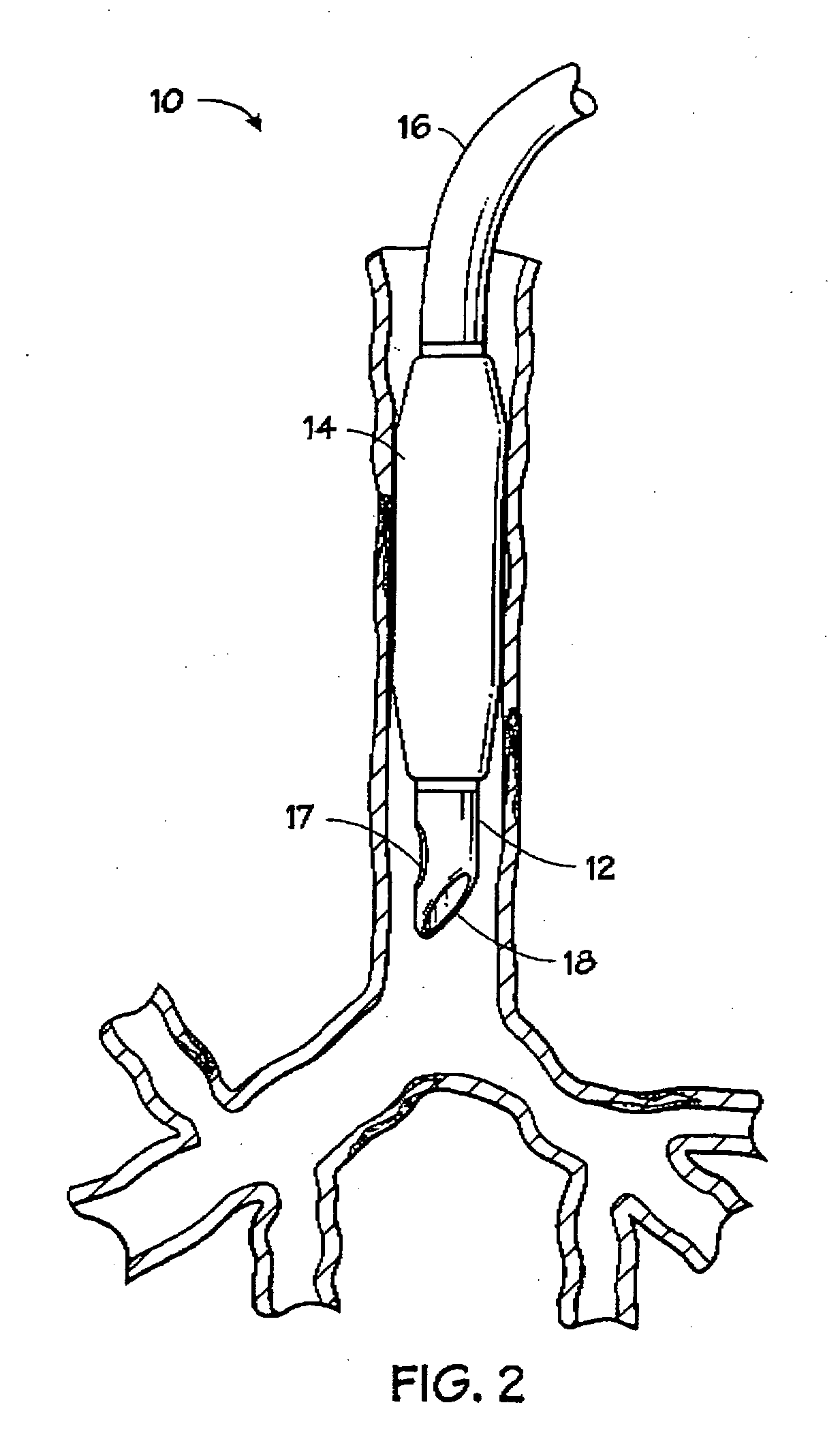
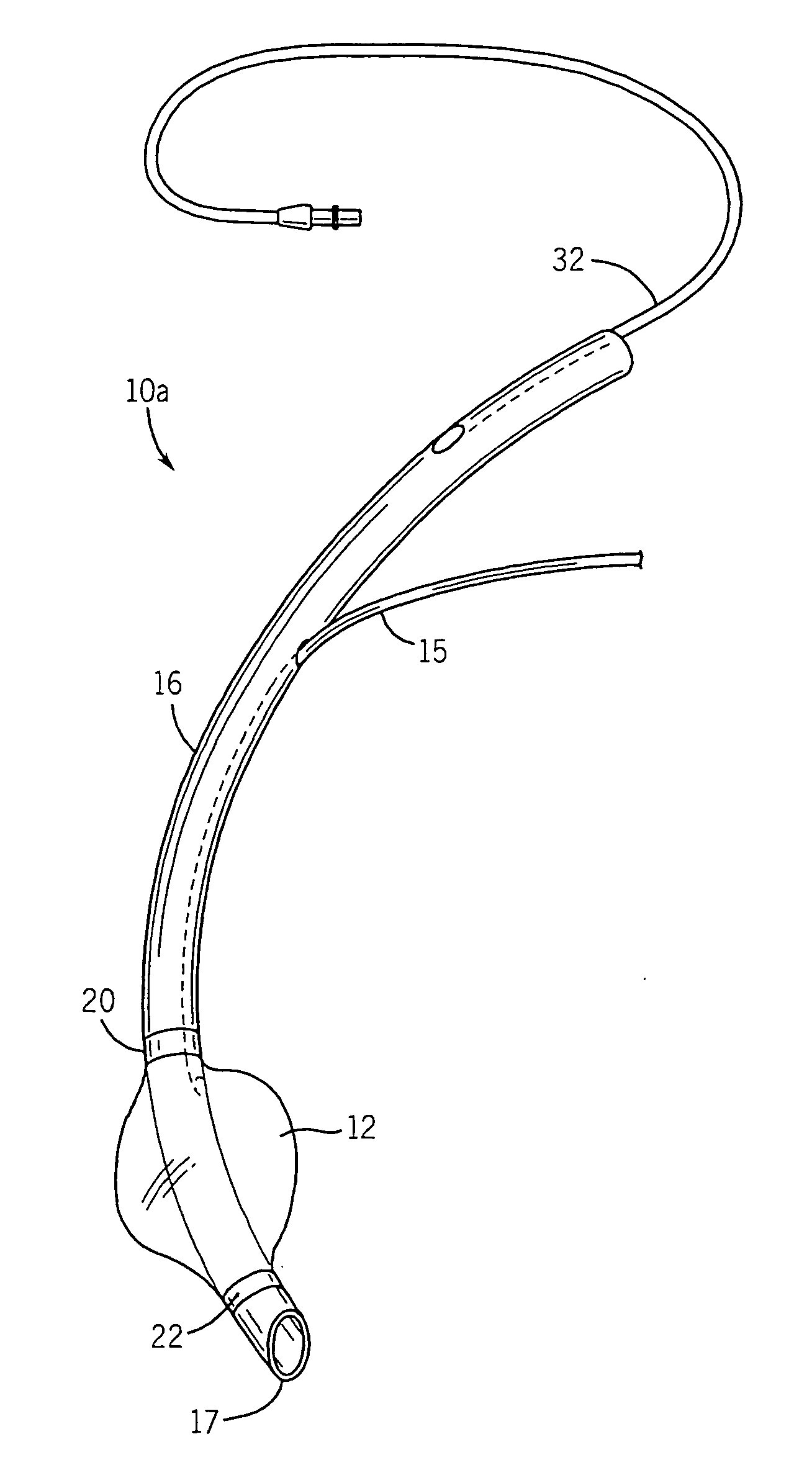
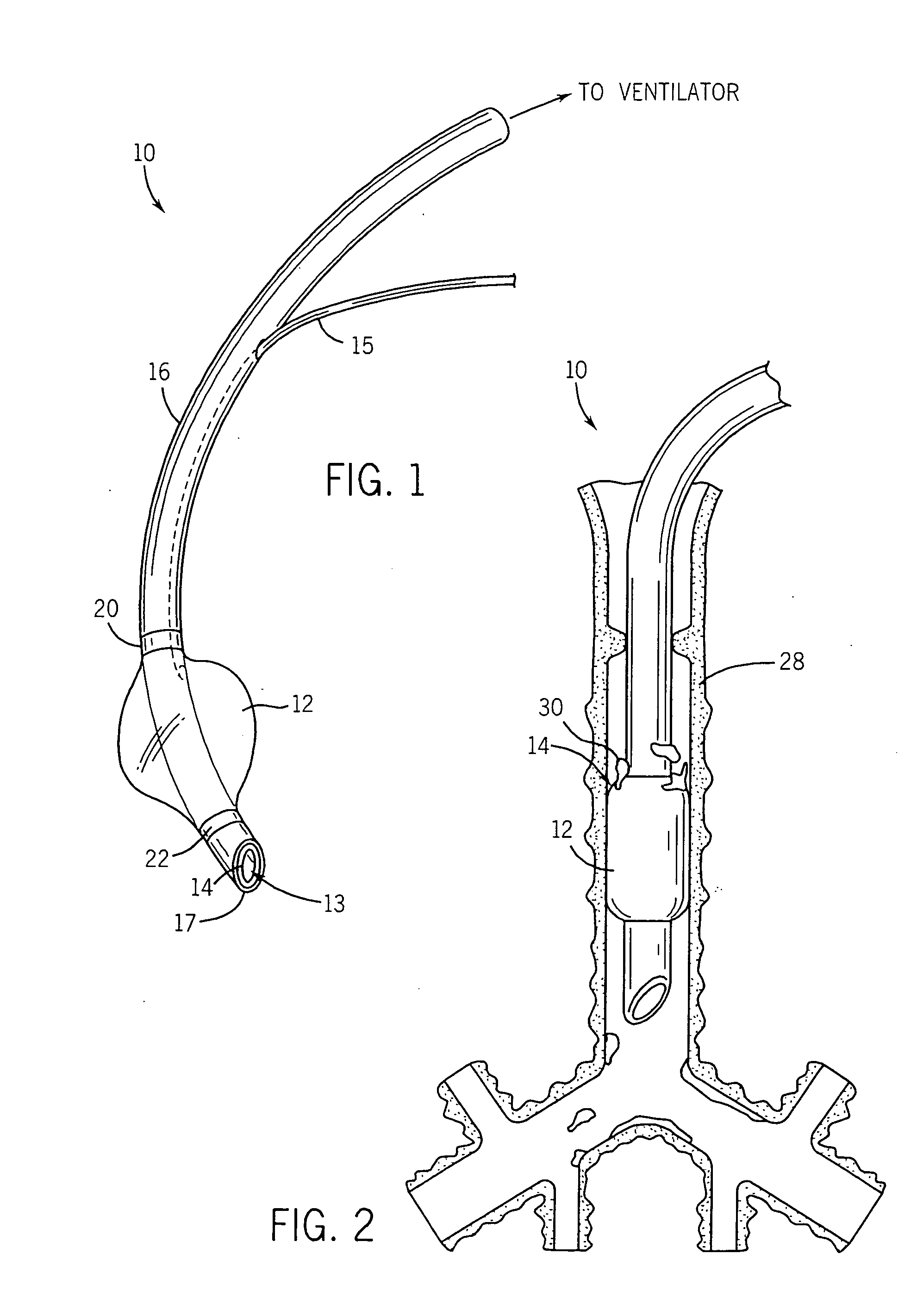
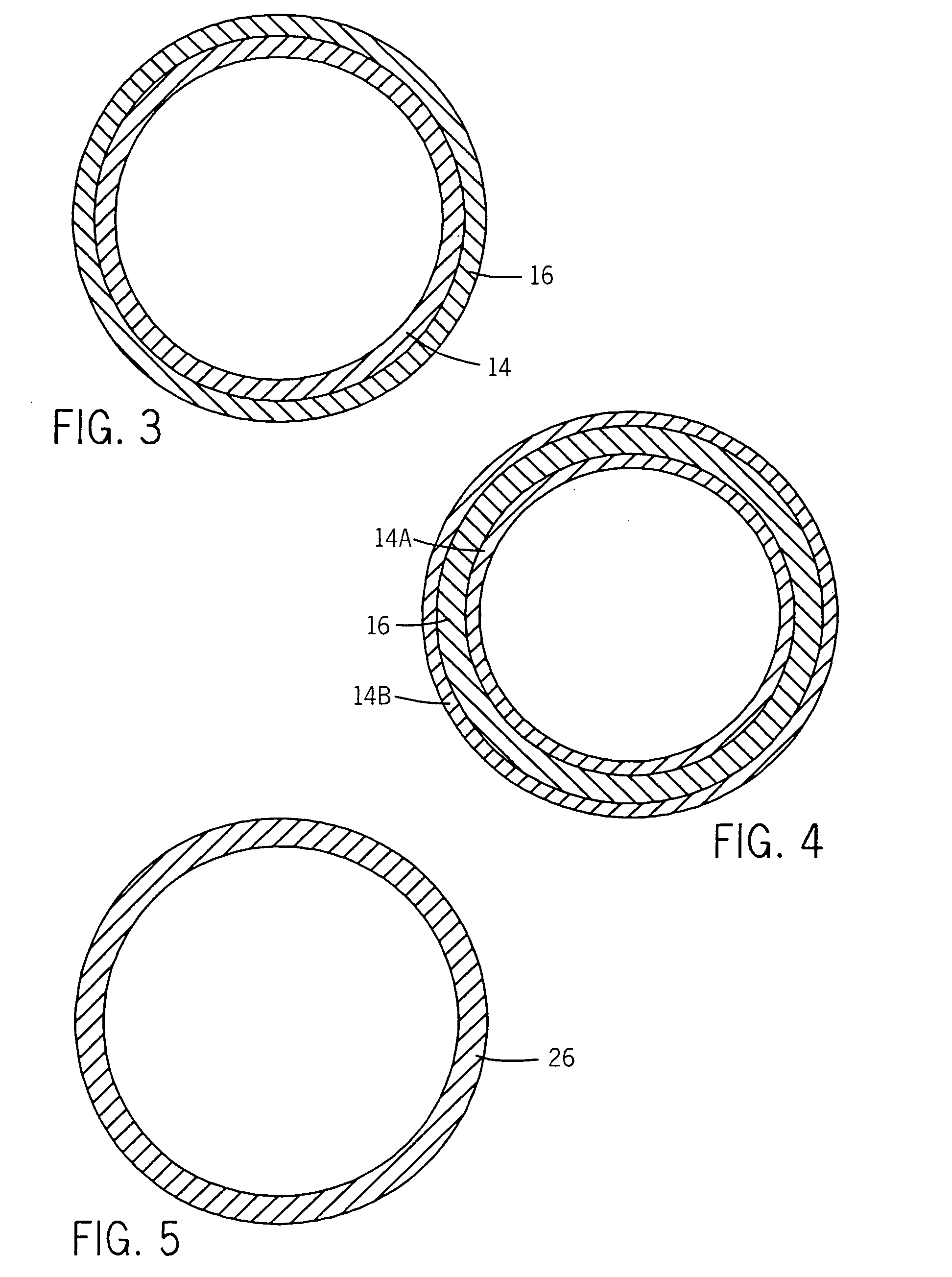
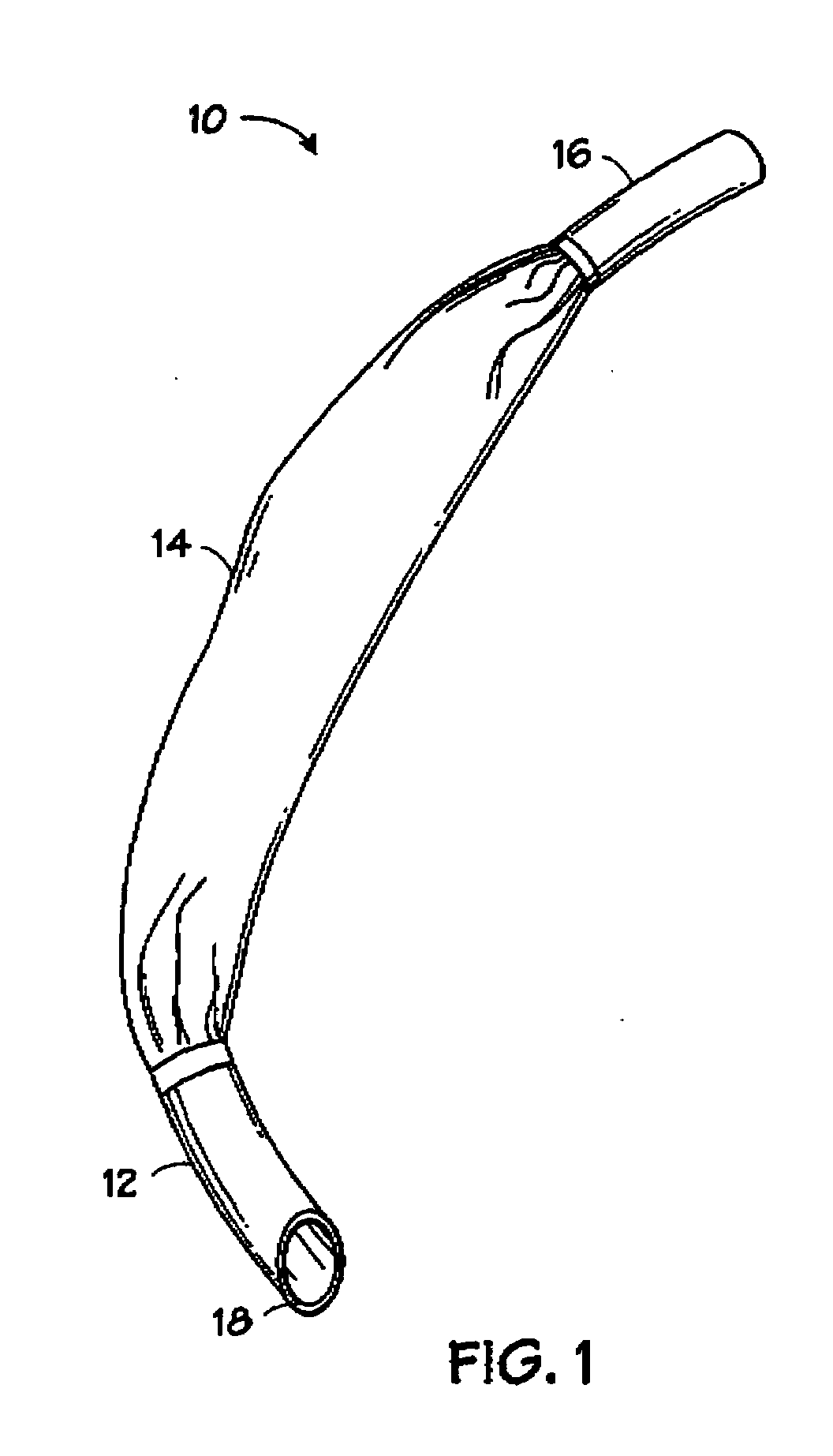
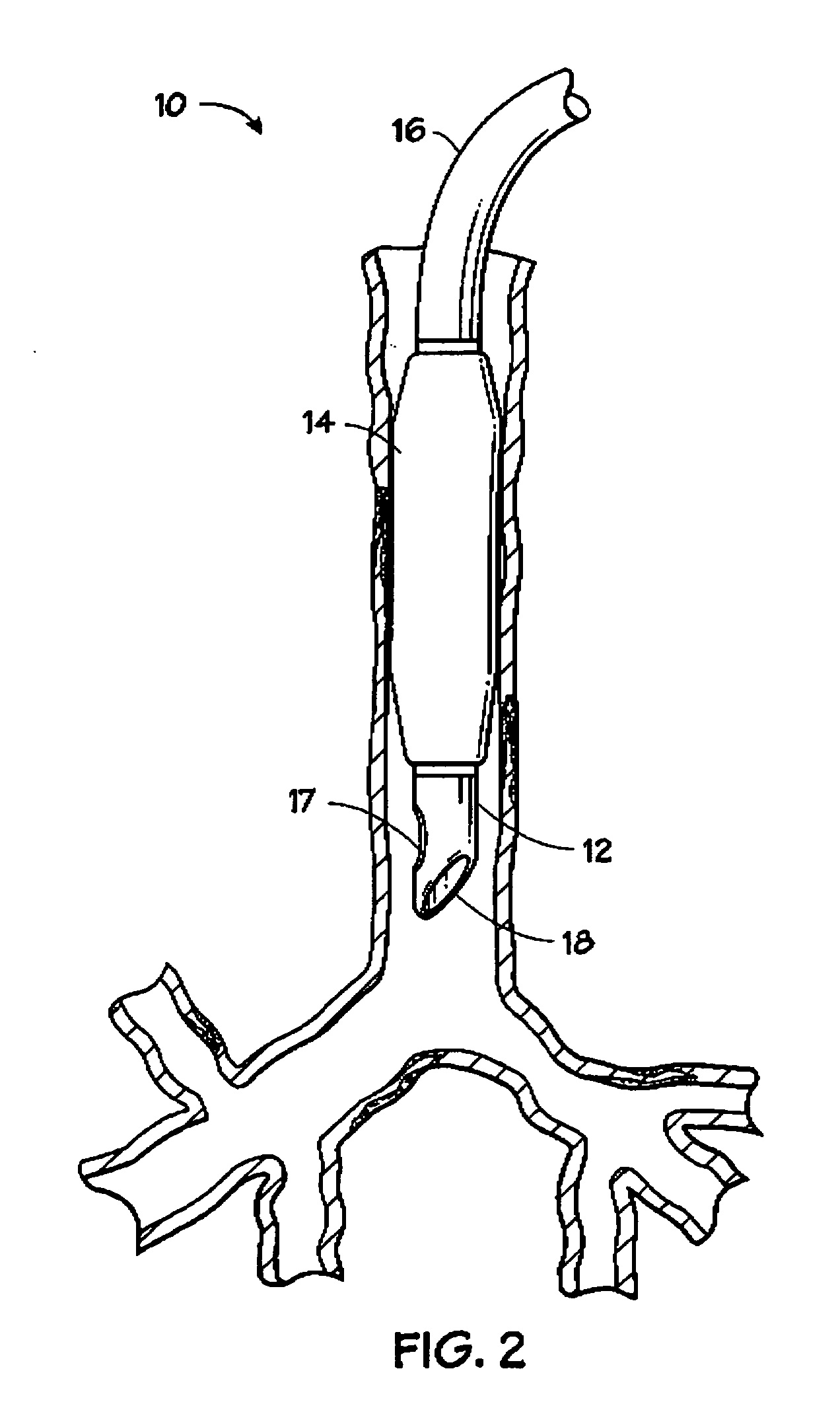
Self-sizing adjustable endotracheal tube
There is disclosed an endotracheal tube which has a minimal cross-sectional profile for easy viewing of anatomical features during intubation. After the tube is placed into the trachea, the tube is adapted to increase the diameter. In this manner the tube diameter may be expanded to allow for decreased Work of Breathing (WOB) for patient, while not having so large a diameter as to cause tracheal discomfort.
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
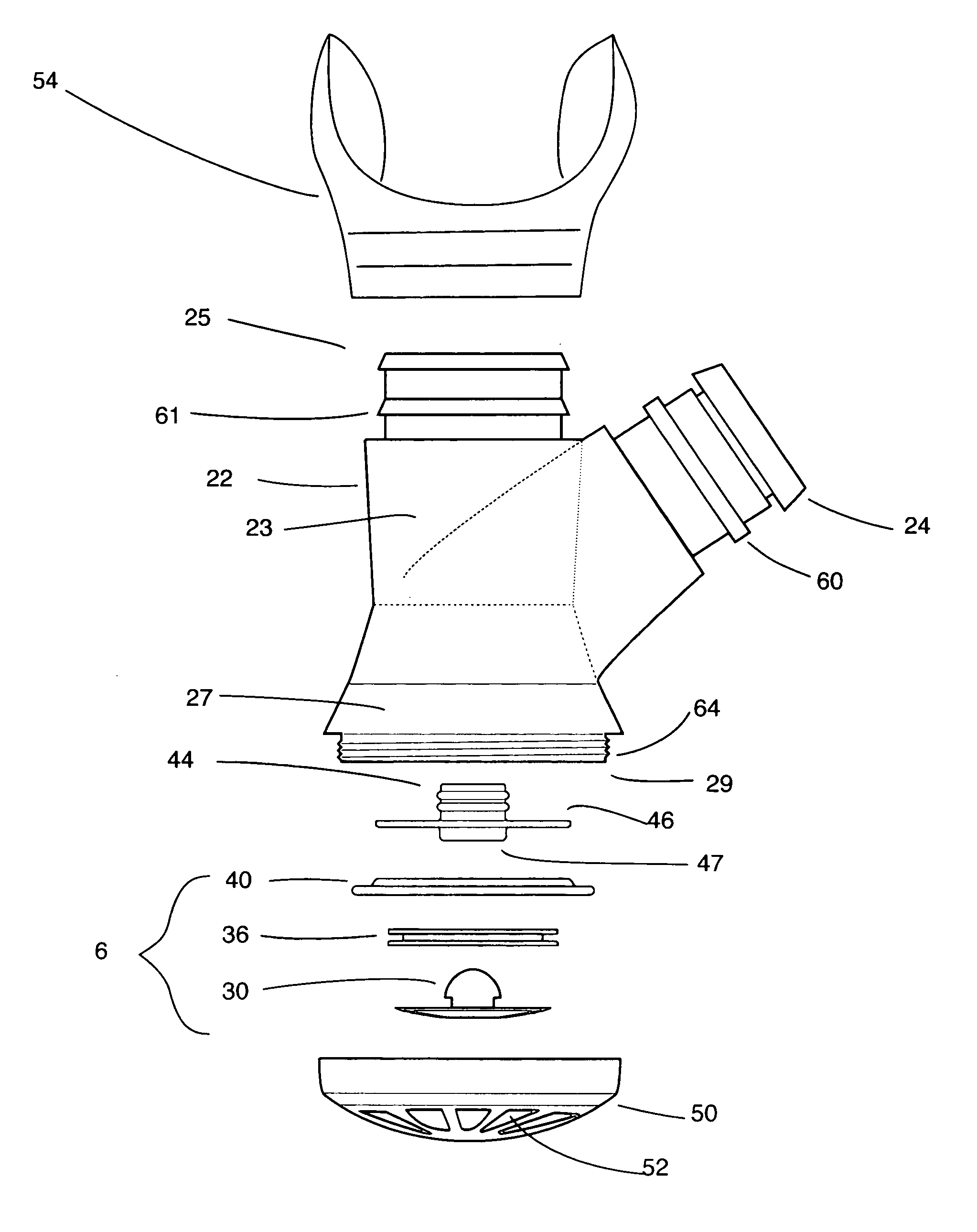
Underwater breathing devices and methods
InactiveUS7793656B2Improve balanceMinimizeBreathing masksRespiratory apparatusBreaths/minAmbient water
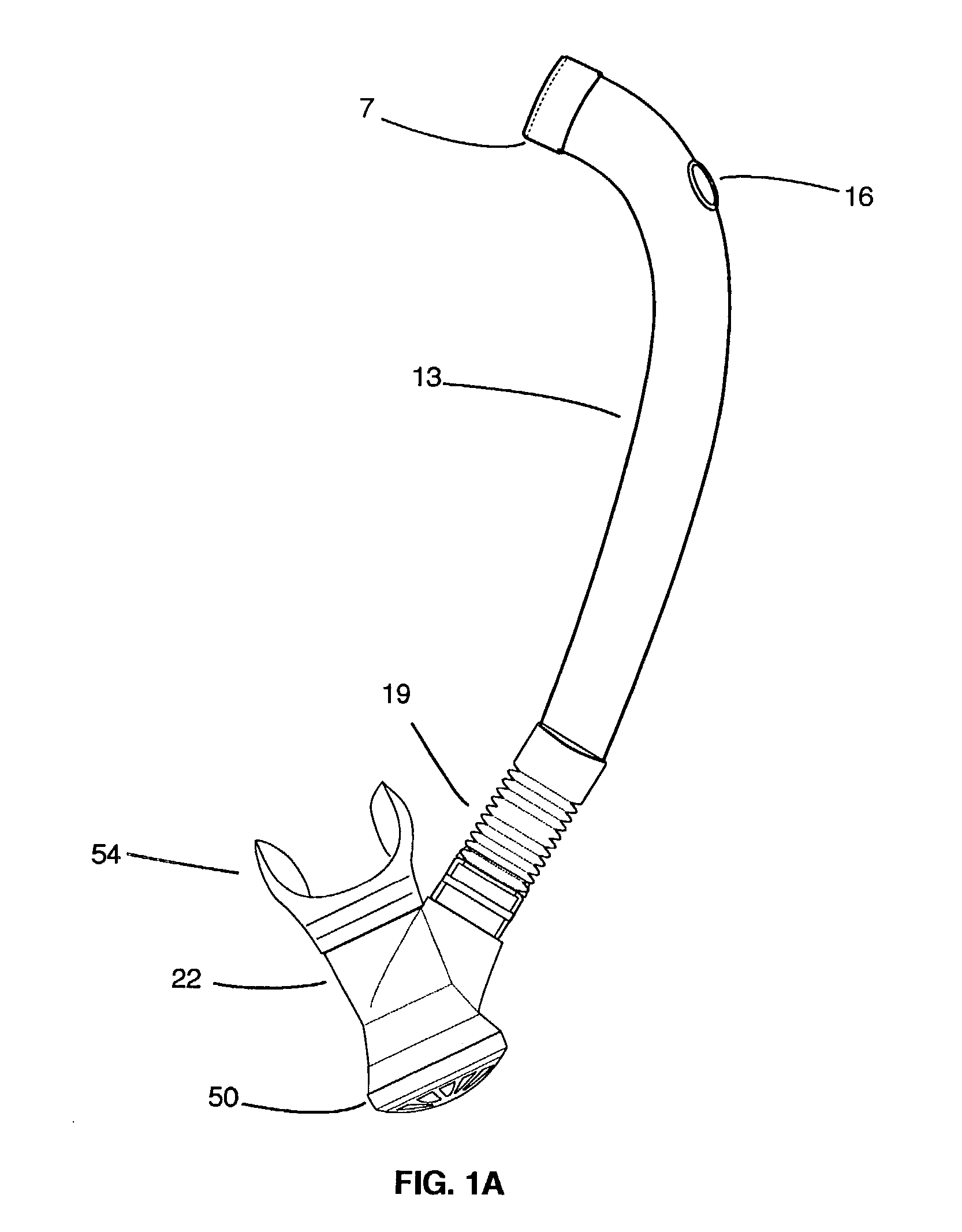
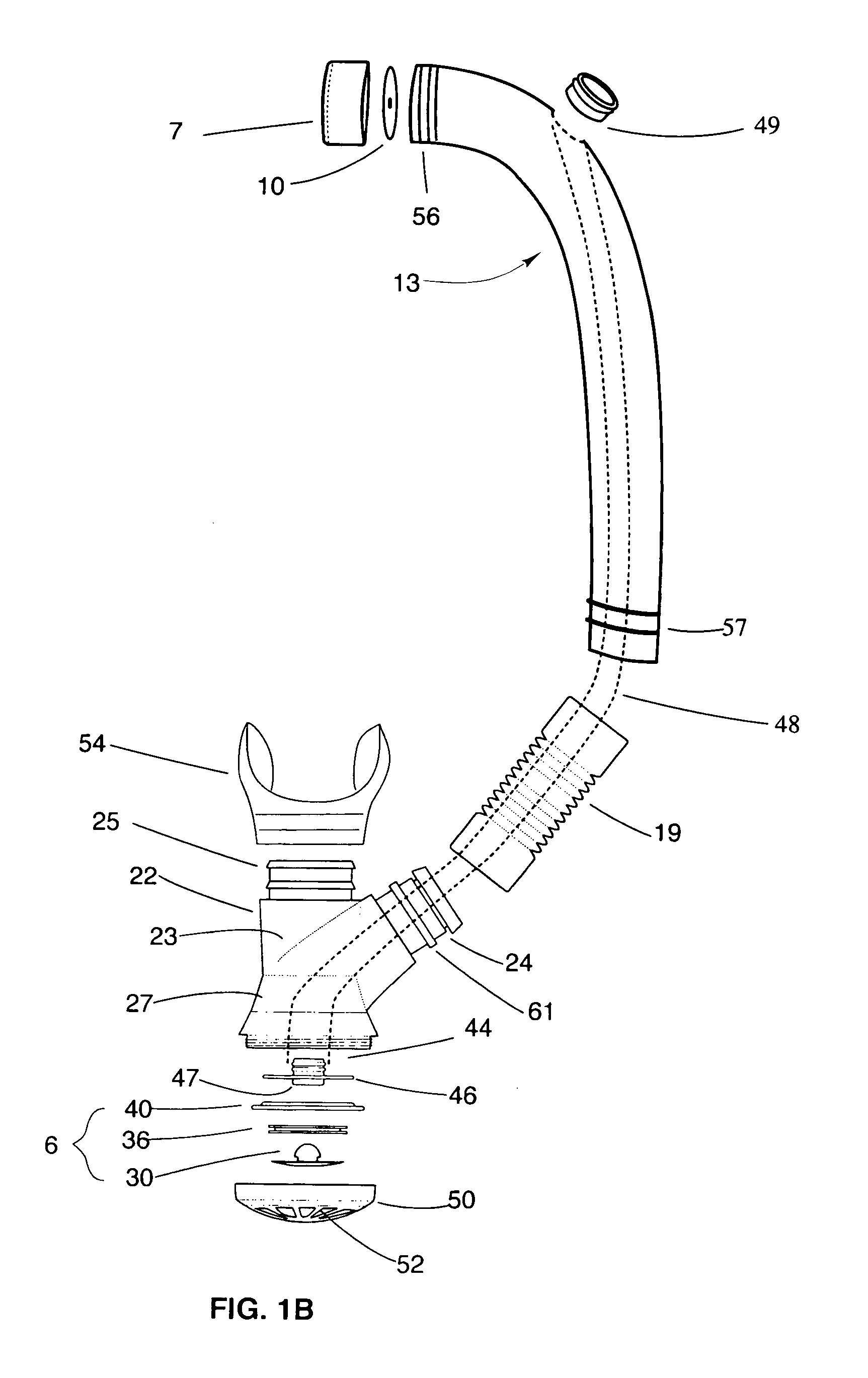
A swim and skin-dive snorkel for providing positive end-expiratory pressure for pressure-balanced exhalation.The snorkel may include inhalation and exhalation conduits. Air can be exhaled into a chamber and released when exhalation pressure within the chamber exceeds a threshold pressure. The threshold pressure that must be overcome to achieve exhalation may be balanced against the compressive forces of the ambient water pressure acting against the user's chest and lungs, which may greatly reduce the resting expiratory flow rate, the minute respiratory rate, and therefore the overall work of breathing. The exhalation pressure may be linearly matched to the ambient water pressure as a function of dive depth, thereby discouraging exhalation while diving. A purge valve may also be placed at the lower aspect of the snorkel.
Owner:LIFETIME PRODUCTS
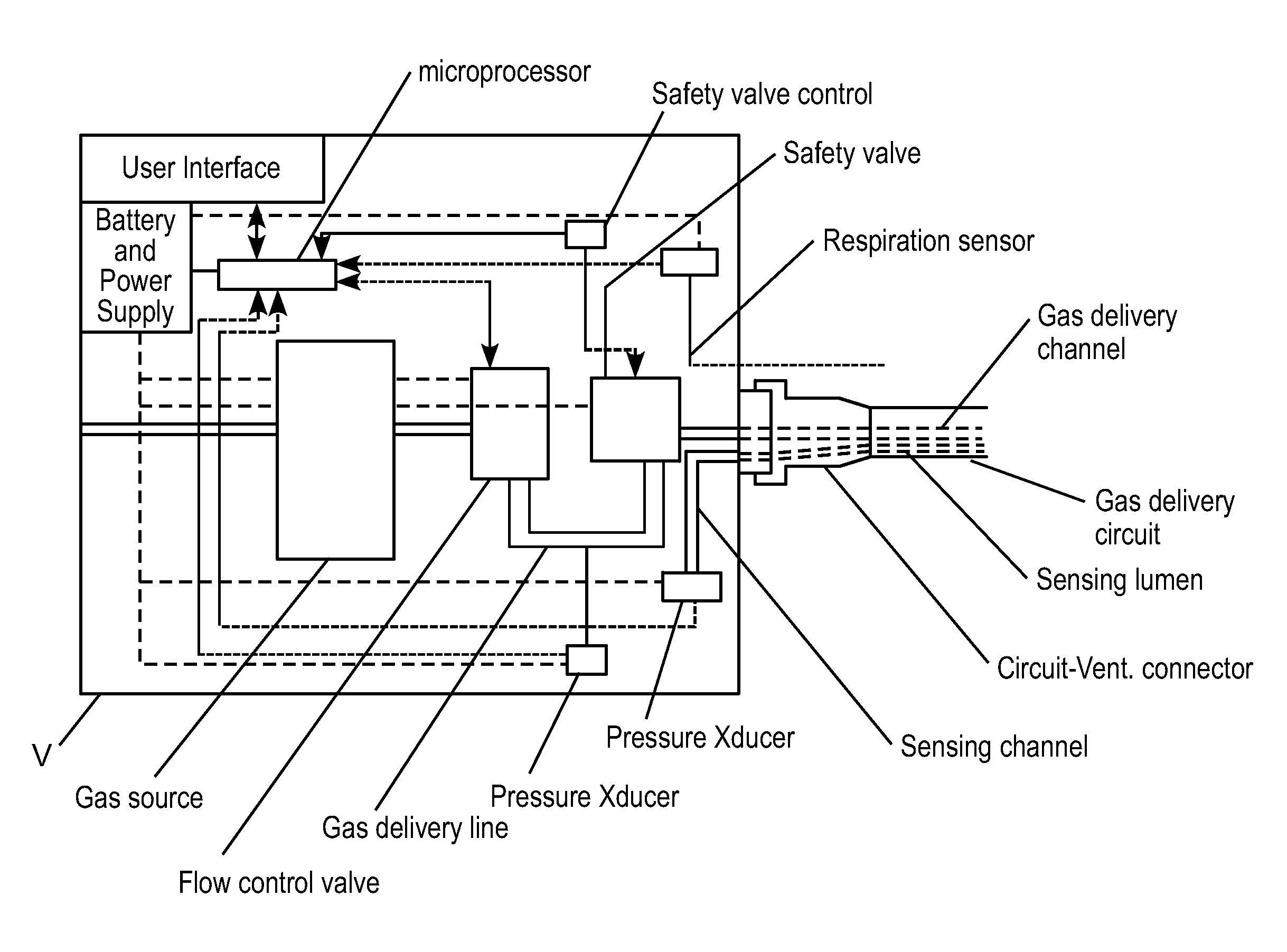
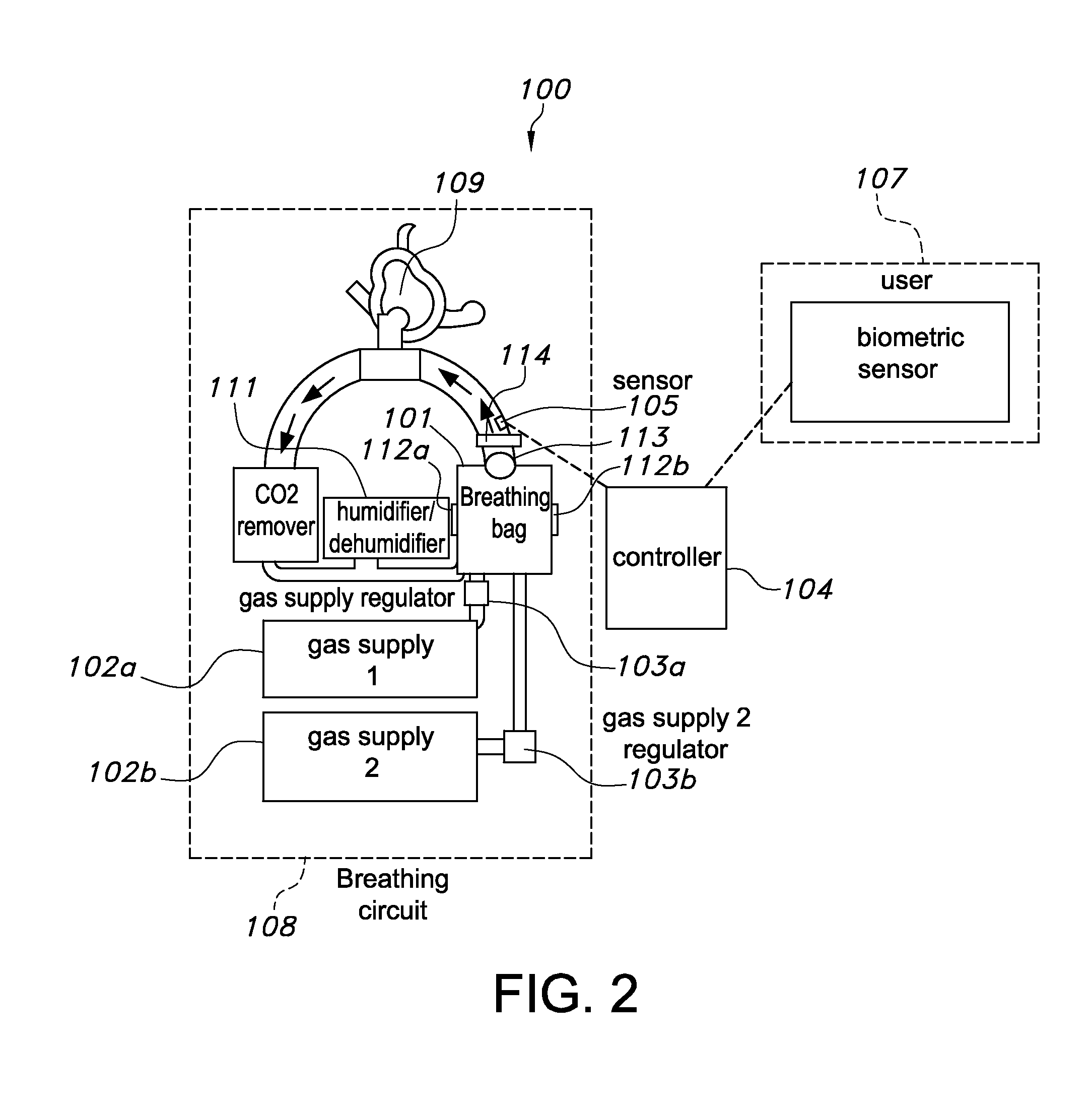
A home-based heliox system with carbon dioxide removal
ActiveUS20160213879A1Simple for individual operationSufficiently compactRespiratorsElectrocardiographyHelioxHome based
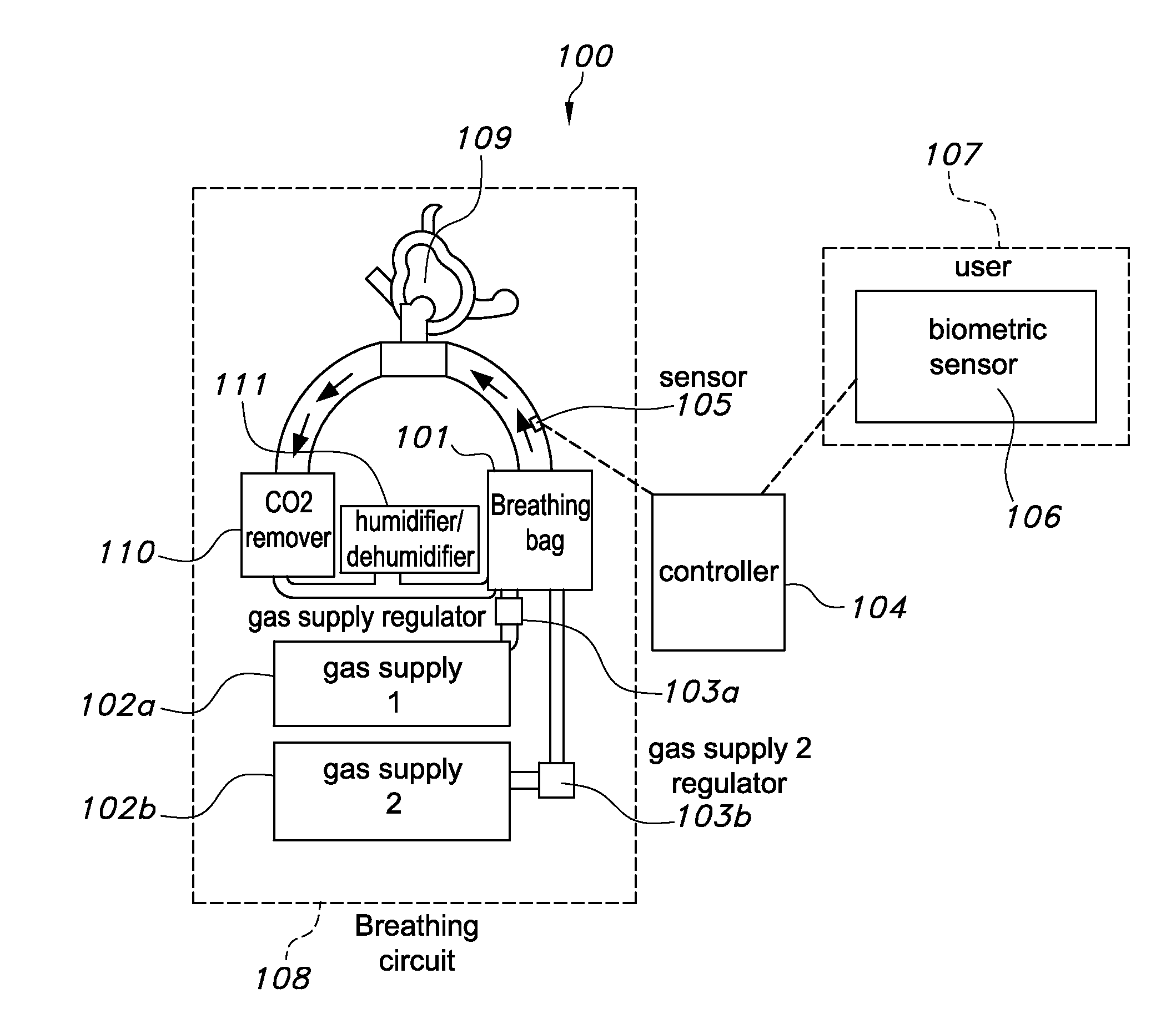
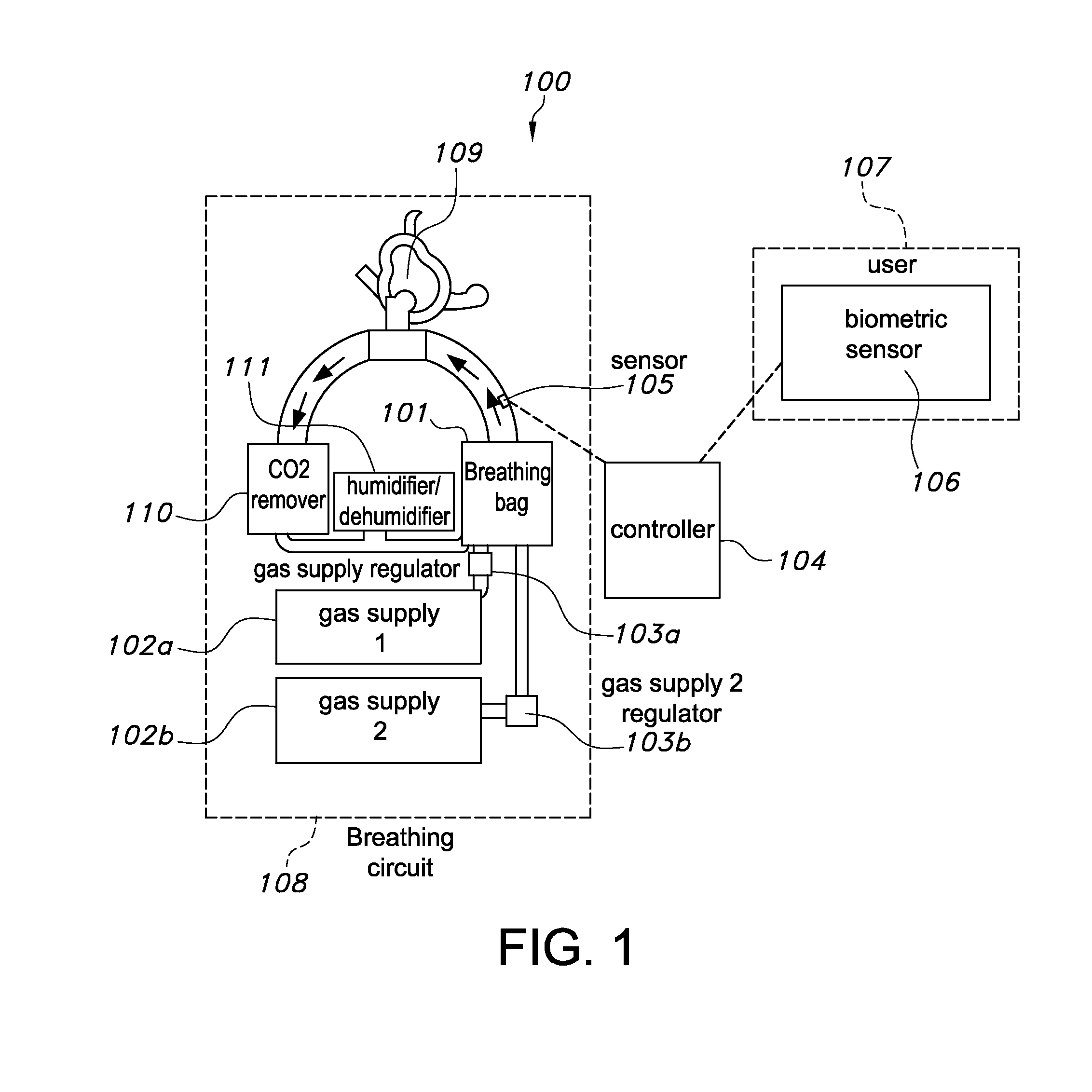
A closed-circuit heliox delivery system and methods for alleviating symptoms of COPD and related disorders are provided. The system is self-monitoring and can be used outside of a hospital environment. The system contains a gas supply fluidly connected to a breathing circuit. The breathing circuit contains an upper airway device, such as a mask. The system contains a sensor(s) and controller. The sensors measure parameters in the system, the ambient environment, or related to the physiological state of the user. The controller can adjust the system to maintain parameters within the device, i.e. pressure, temperature, humidity, within predetermined ranges. The controller can adjust the system to maintain a target physiological state of the user, i.e. target blood oxygen levels or Work of Breathing (WOB).
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
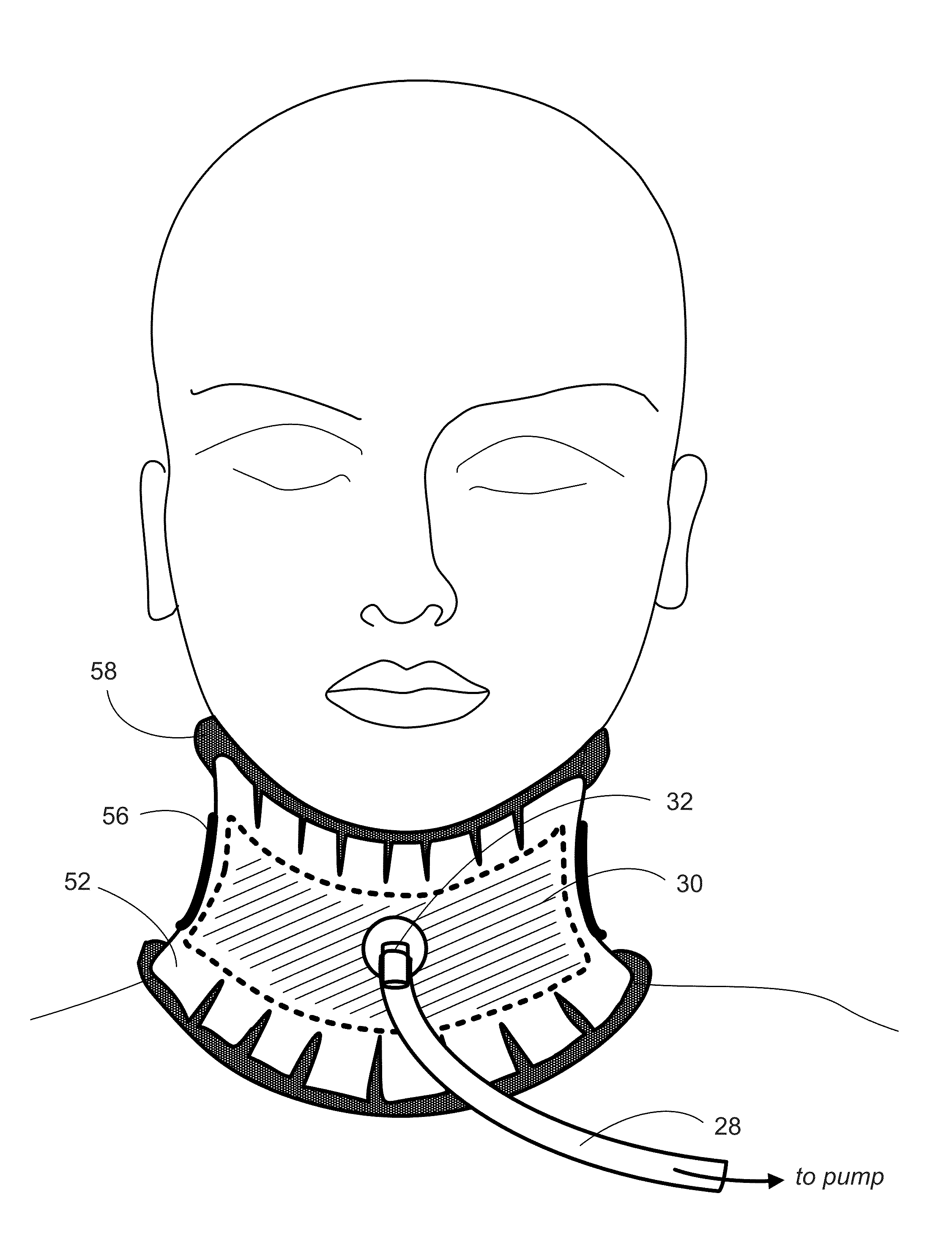
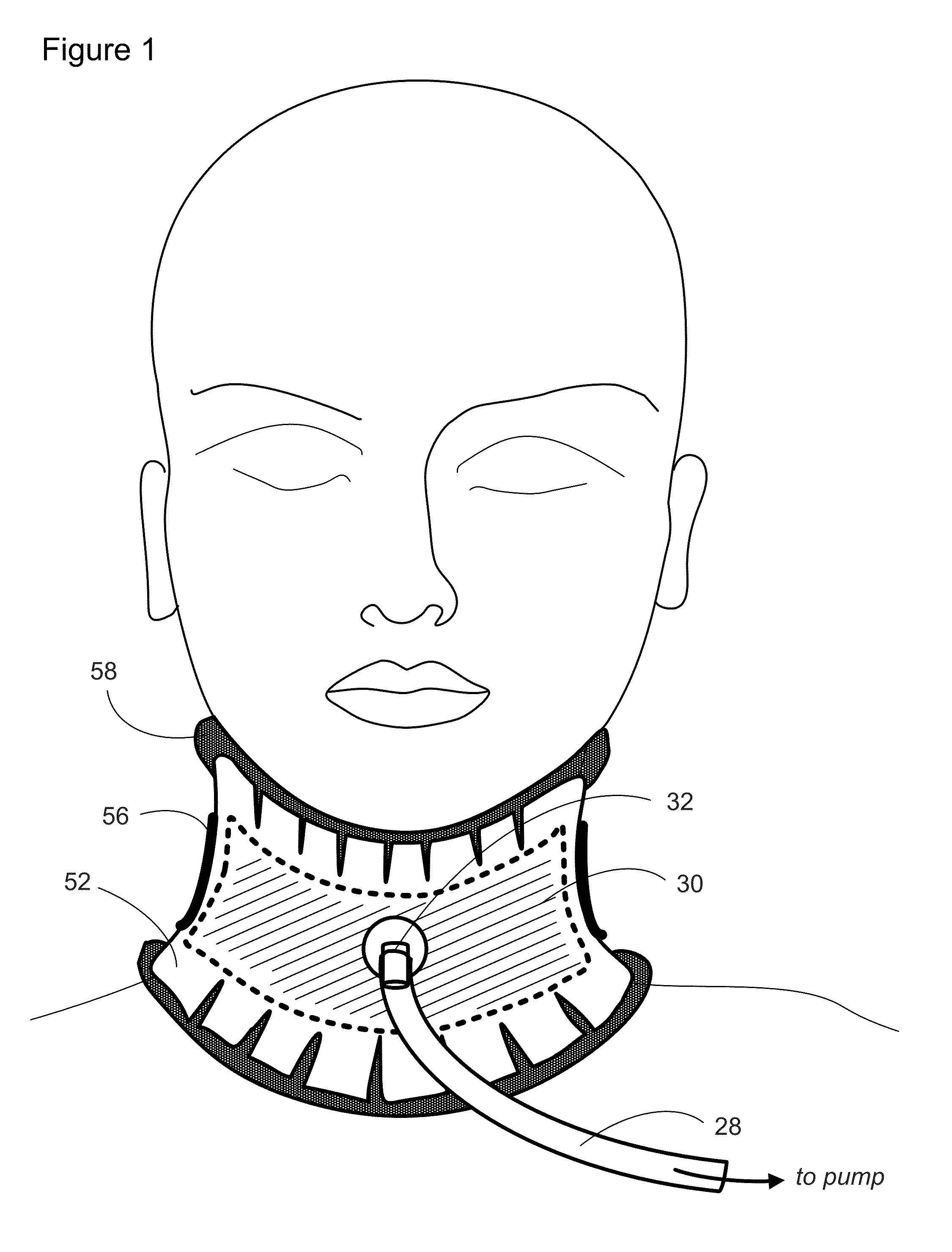
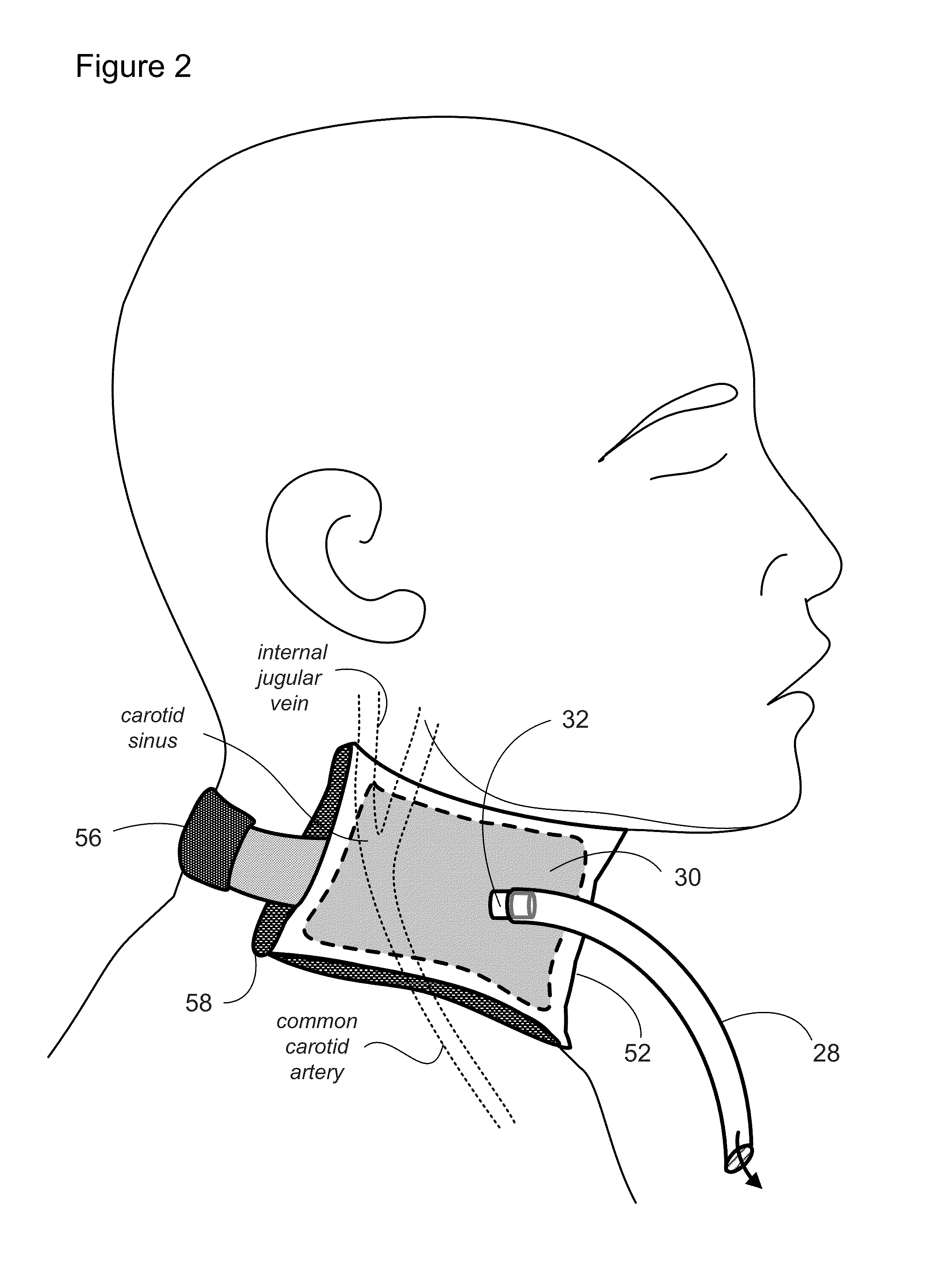
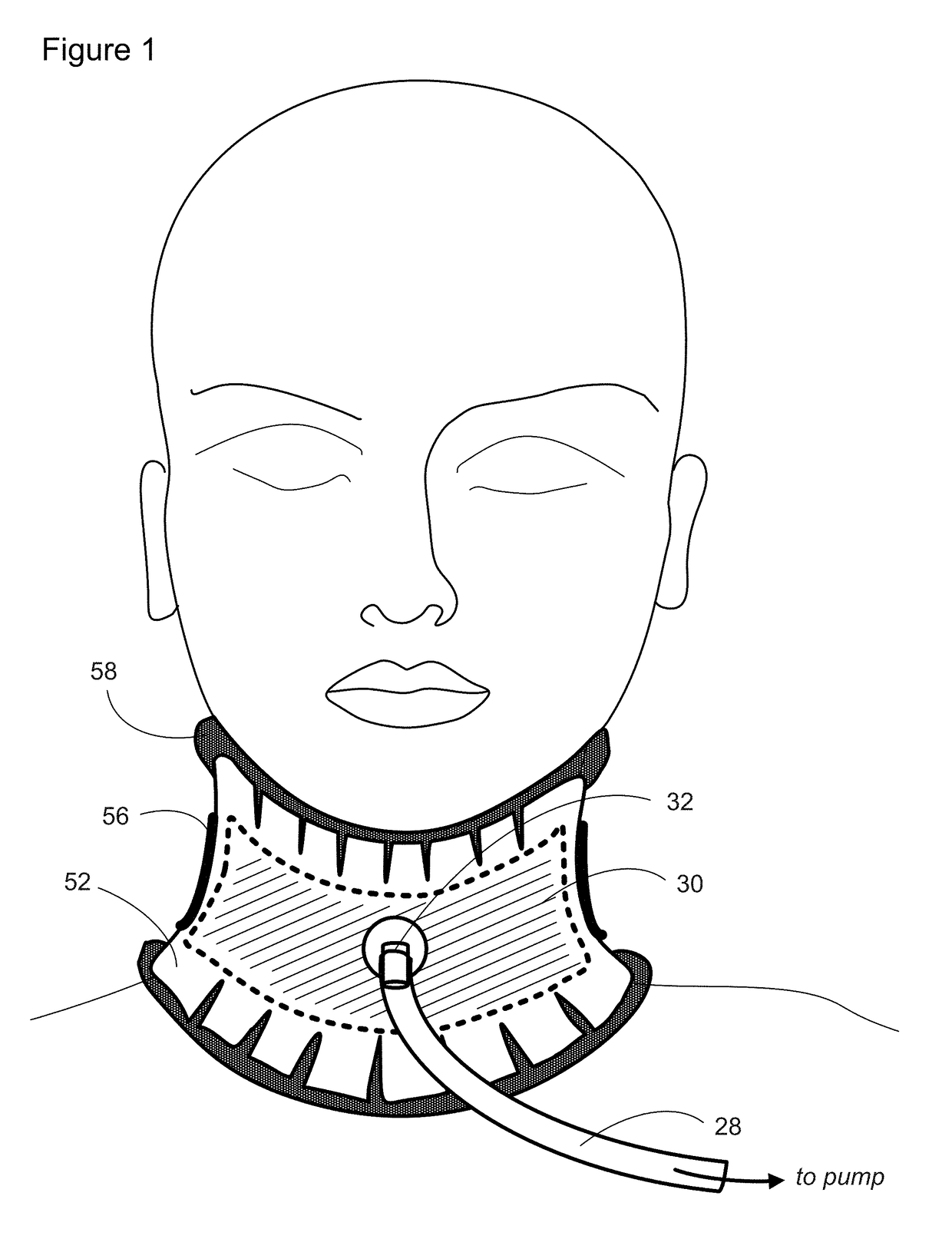
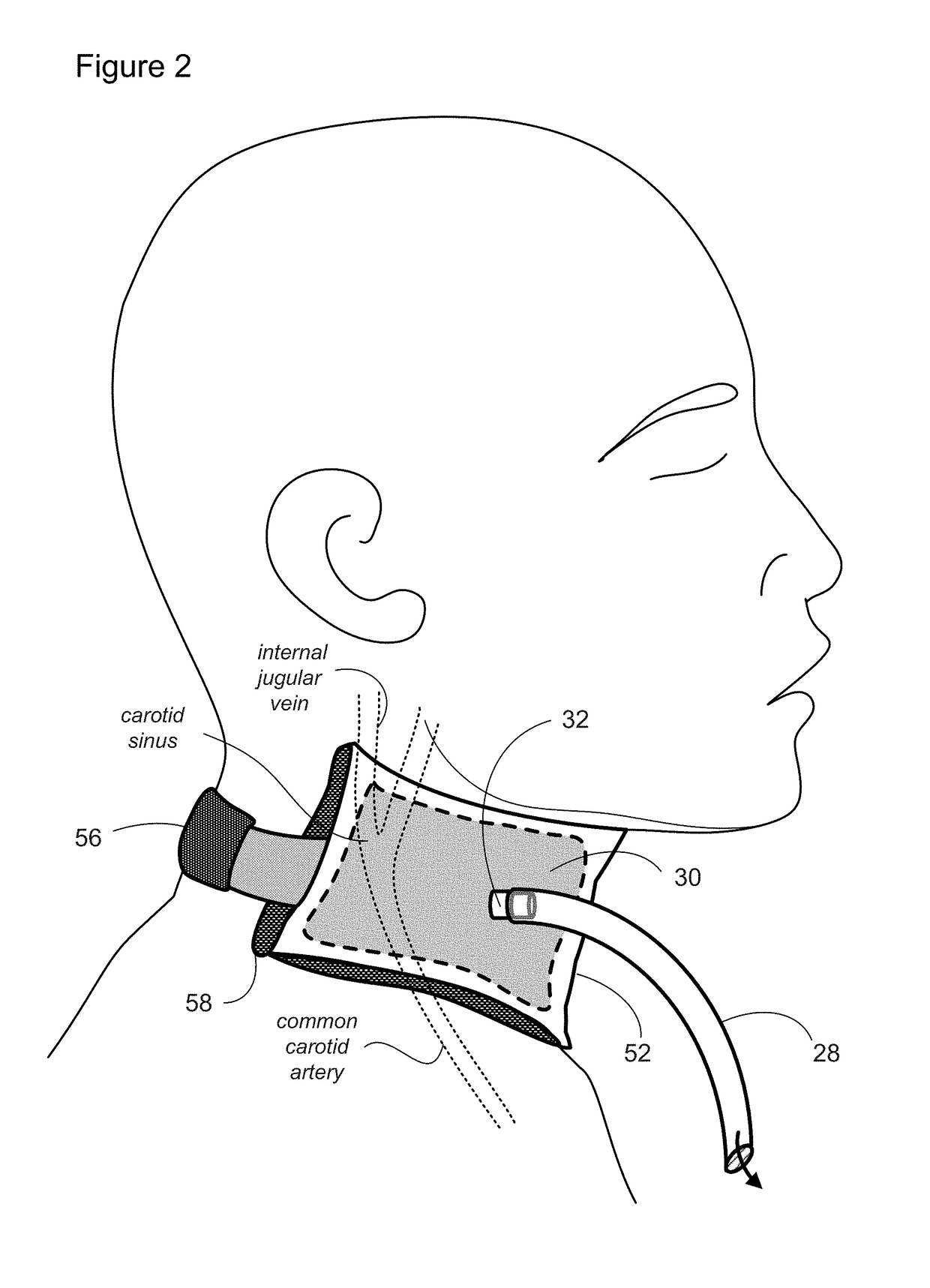
Methods and apparatus for lowering intracranial and intraspinal cord pressure
ActiveUS20130274638A1Lower intracranial pressureAvoid placingRespiratorsPneumatic massageSpinal cordVALVE PORT
Apparatus and methods are provided for applying negative pressure to tissues of a patient that are transmitted to the vertebral venous system of the patient and thereby lowering intracranial pressure. Intracranial pressure is thus lowered easily without increasing the work of breathing, without needing to be intubated, and without breathing through a valve in patients with elevated increased intracranial pressure.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for reducing the work of breathing
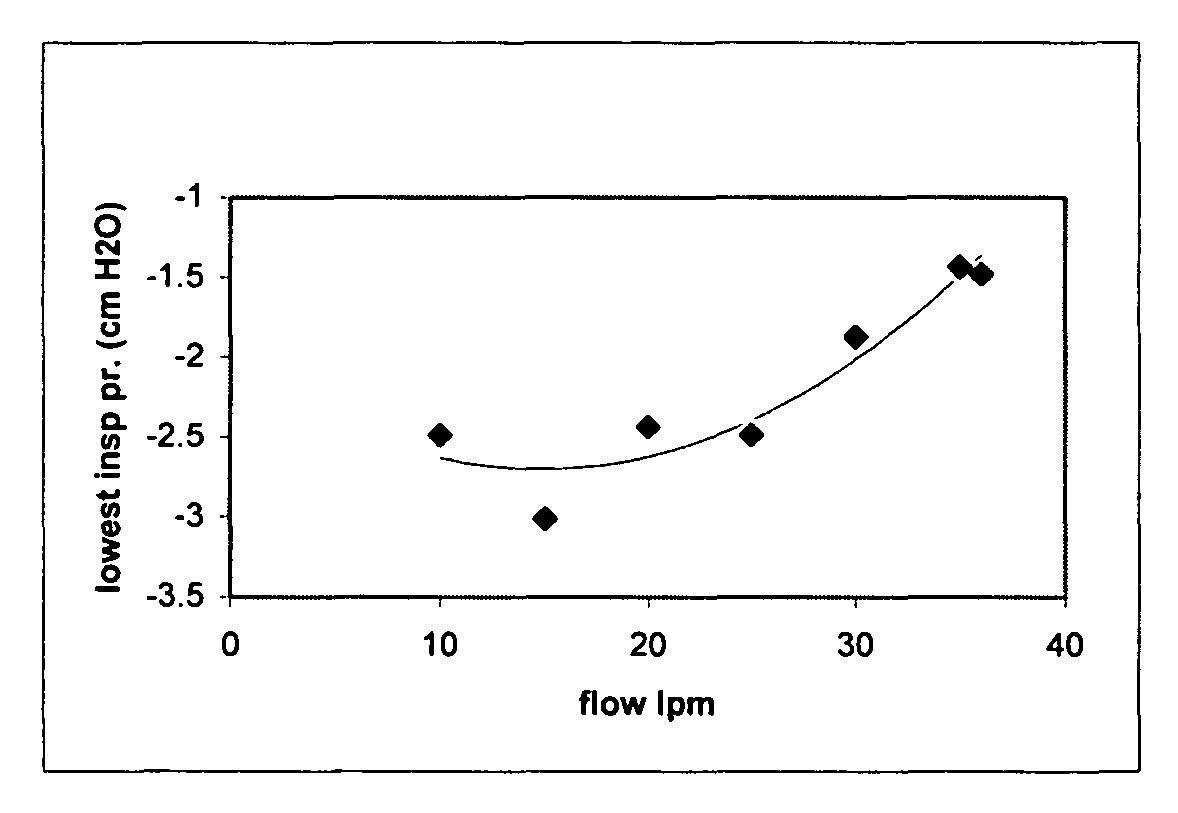
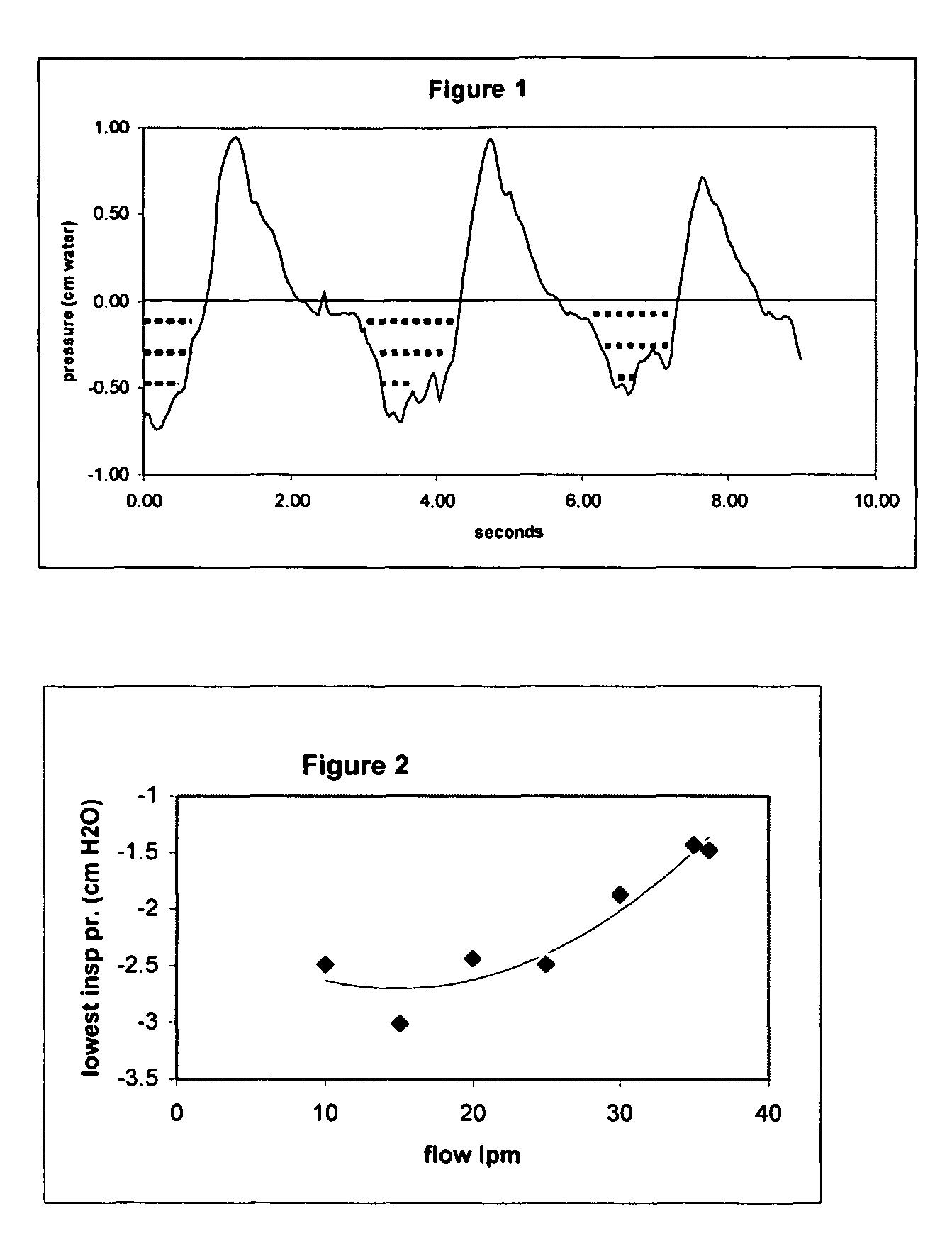
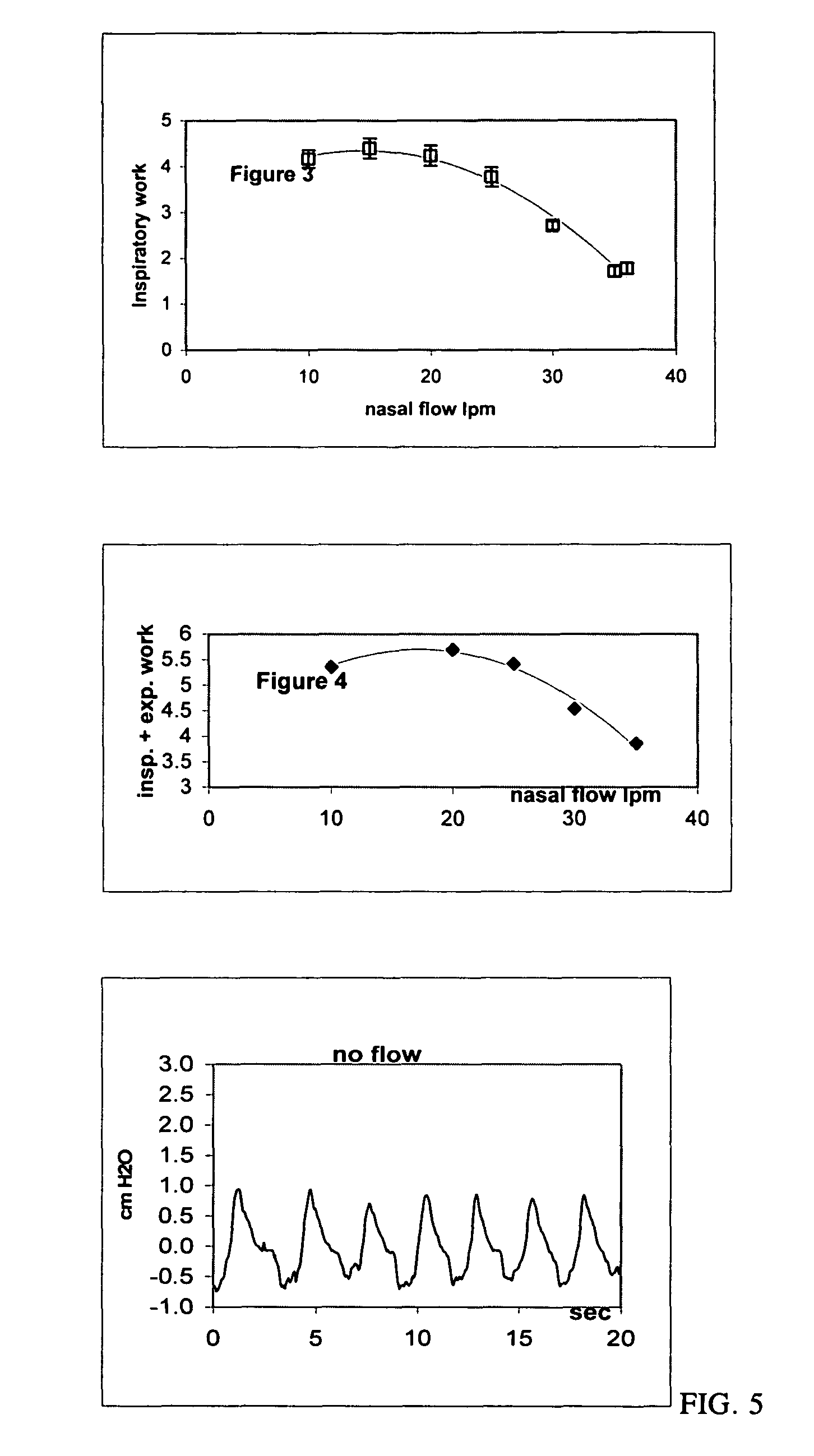
The present invention relates to a method for reducing the work of breathing. Heated and humidified air is delivered through a nasal cannula to the nasal passageway of a patient at a flow rate above 20 liters / min thereby reducing inspiratory work.
Owner:BRIDGE BANK NAT ASSOC
Endotracheal tube and technique for using the same
InactiveUS20080078406A1Decreasing microbe adhesionTracheal tubesMedical devicesTracheal tubeMedicine
There is disclosed an endotracheal tube to which an adhesion-resistant material, adhesion-resistant material is applied. Several techniques are disclosed for applying the adhesion-resistant material, adhesion-resistant material, including surface treatments, co-extrusion, and compounding. The adhesion-resistant material, adhesion-resistant material helps prevent the adhesion of microbes to the surface of the endotracheal tube. In this manner the cross-sectional area through which the patient may breathe is increased, effectively decreasing the work of breathing for the patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
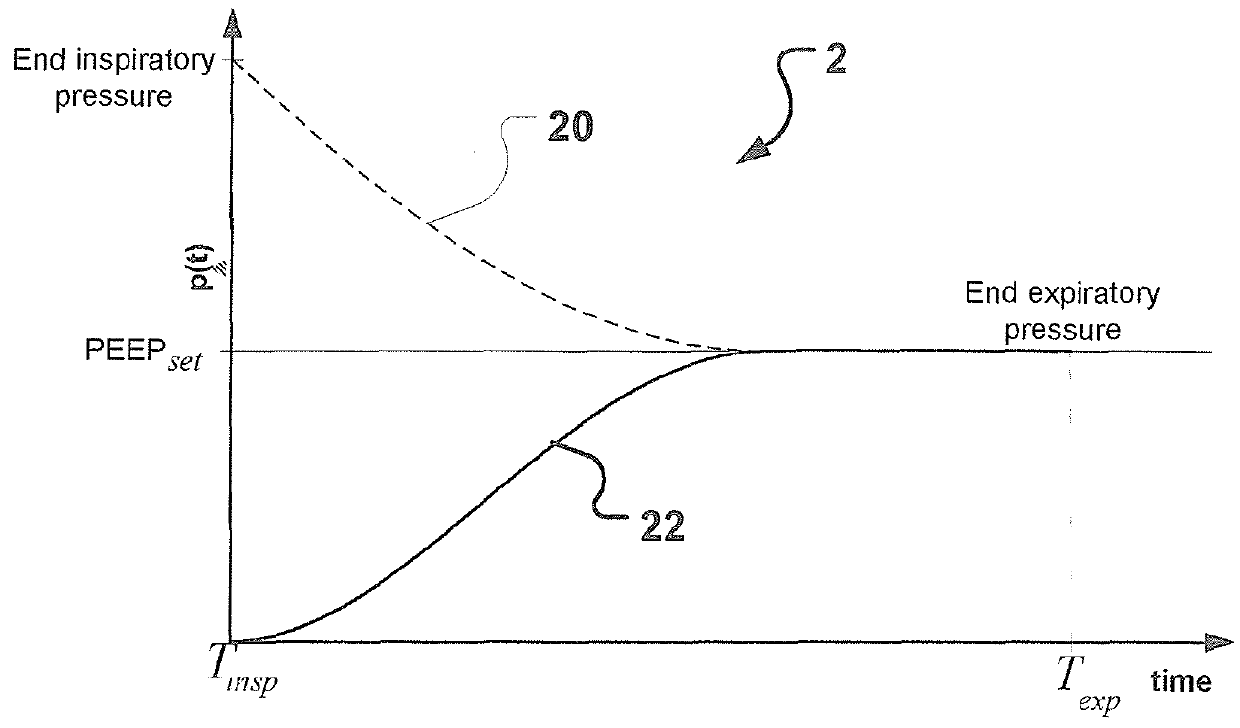
Peep regulation for a breathing apparatus
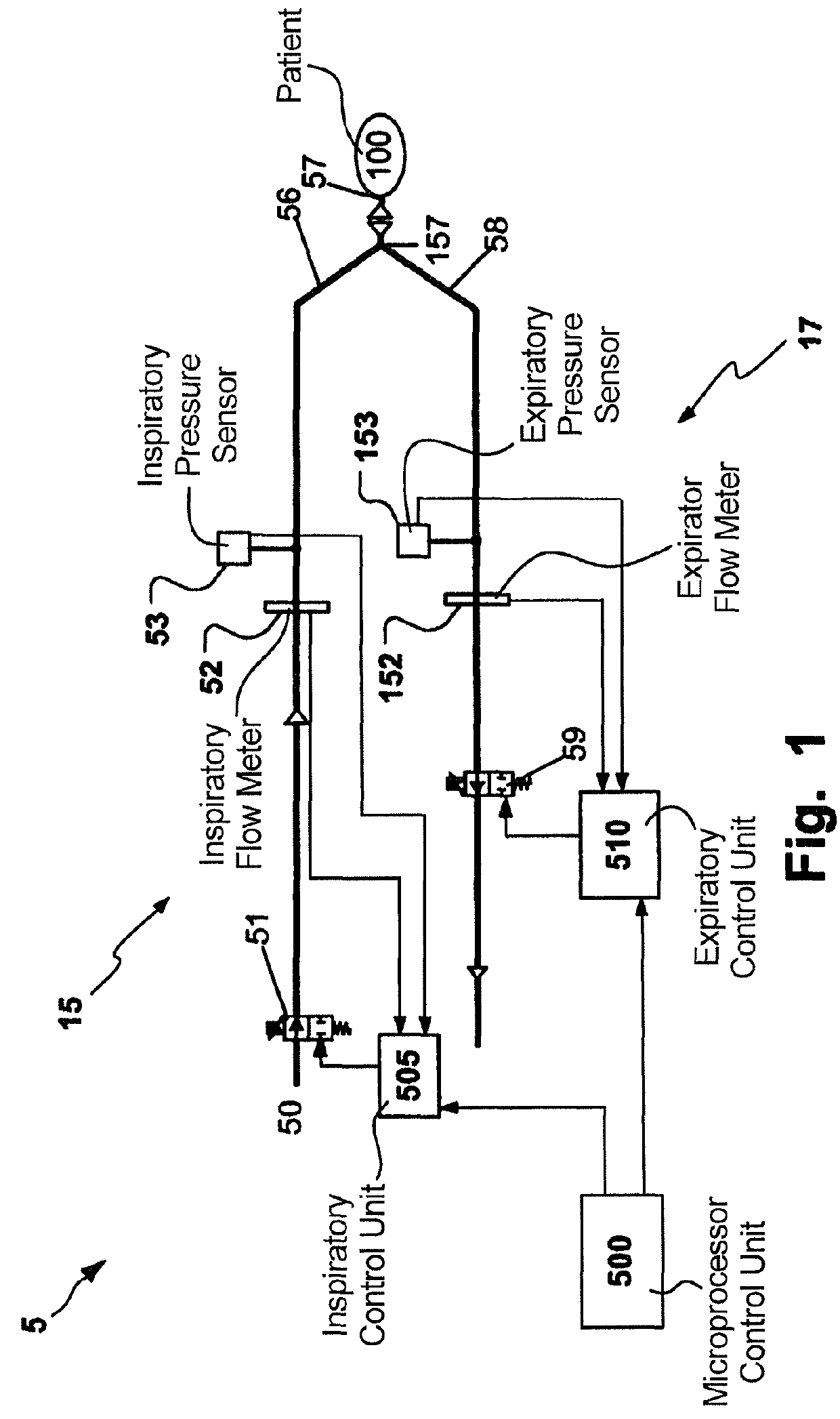
ActiveUS20120167884A1Minimize workReliable considerationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFeedback controlBreathing cycle
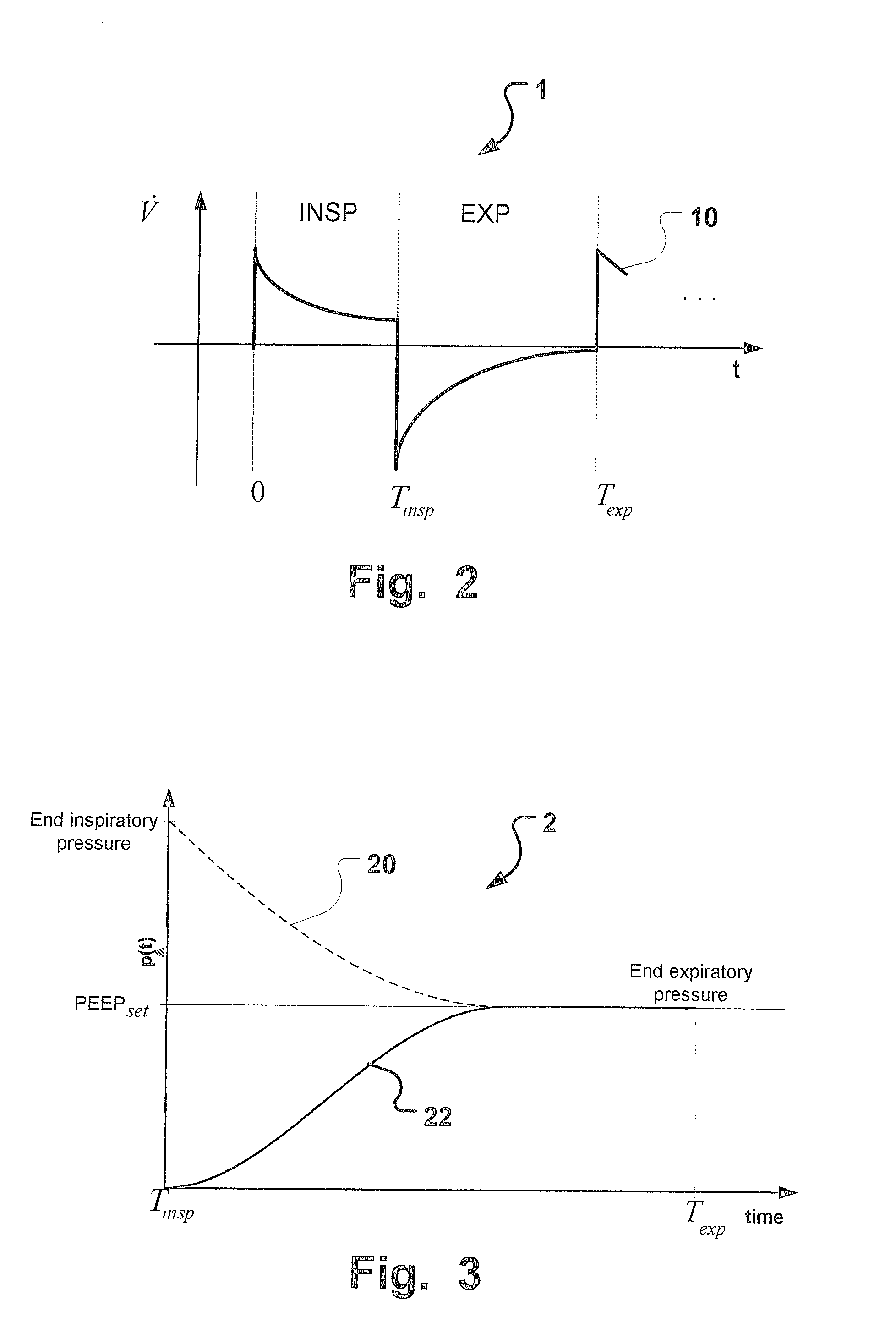
A breathing apparatus has an expiratory flow sensor unit, an expiratory pressure sensor unit, an expiratory pressure regulator, and an expiratory control unit operatively connected to the expiratory pressure sensor unit for a feedback control of an expiratory pressure during an expiratory phase of a breathing cycle. The expiratory control unit is adapted to provide a real time target pressure value during the expiratory phase to the expiratory pressure regulator for adjusting a desired positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) level (PEEPset) based on an inspiratory tidal volume of an inspiratory phase of the same breathing cycle and a currently accumulated expiratory tidal volume measured by the expiratory flow sensor unit. In this manner advantageous regulation of PEEP with minimized work of breathing is obtained.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
Self-sizing adjustable endotracheal tube
There is disclosed an endotracheal tube which has a minimal cross-sectional profile for easy viewing of anatomical features during intubation. After the tube is placed into the trachea, the tube is adapted to increase the diameter. In this manner the tube diameter may be expanded to allow for decreased Work of Breathing (WOB) for patient, while not having so large a diameter as to cause tracheal discomfort.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for predicting work of breathing
InactiveUS8672858B2Avoid muscle fatigueAccurate estimateRespiratorsMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMathematical model
A method of creating a noninvasive predictor of both physiologic and imposed patient effort of breathing from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the patient using an adaptive mathematical model. The patient effort is commonly measured via work of breathing, power of breathing, or pressure-time product of esophageal pressure and is important for properly adjusting ventilatory support for spontaneously breathing patients. The method of calculating this noninvasive predictor is based on linear or non-linear calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Self-sizing adjustable endotracheal tube
InactiveUS20080078401A1Reduce pressureIncrease pressureTracheal tubesMedical devicesTracheal tubeGynecology
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
Methods and systems for monitoring resistance and work of breathing for ventilator-dependent patients
ActiveUS10165966B2Accurate monitoringAvoid muscle fatigueTracheal tubesMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
Methods for non-invasively and accurately estimating and monitoring resistance and work of breathing parameters from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the ventilator-dependent patient using an adaptive mathematical model are provided. These methods are based on calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors. The resistance and work of breathing parameters are important for: assessing patient status and diagnosis, appropriately selecting treatment, assessing efficacy of treatment, and properly adjusting ventilatory support.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +1
Self-sizing adjustable endotracheal tube
There is disclosed an endotracheal tube which has a minimal cross-sectional profile for easy viewing of anatomical features during intubation. After the tube is placed into the trachea, the tube is adapted to increase the diameter. In this manner the tube diameter may be expanded to allow for decreased Work of Breathing (WOB) for patient, while not having so large a diameter as to cause tracheal discomfort.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
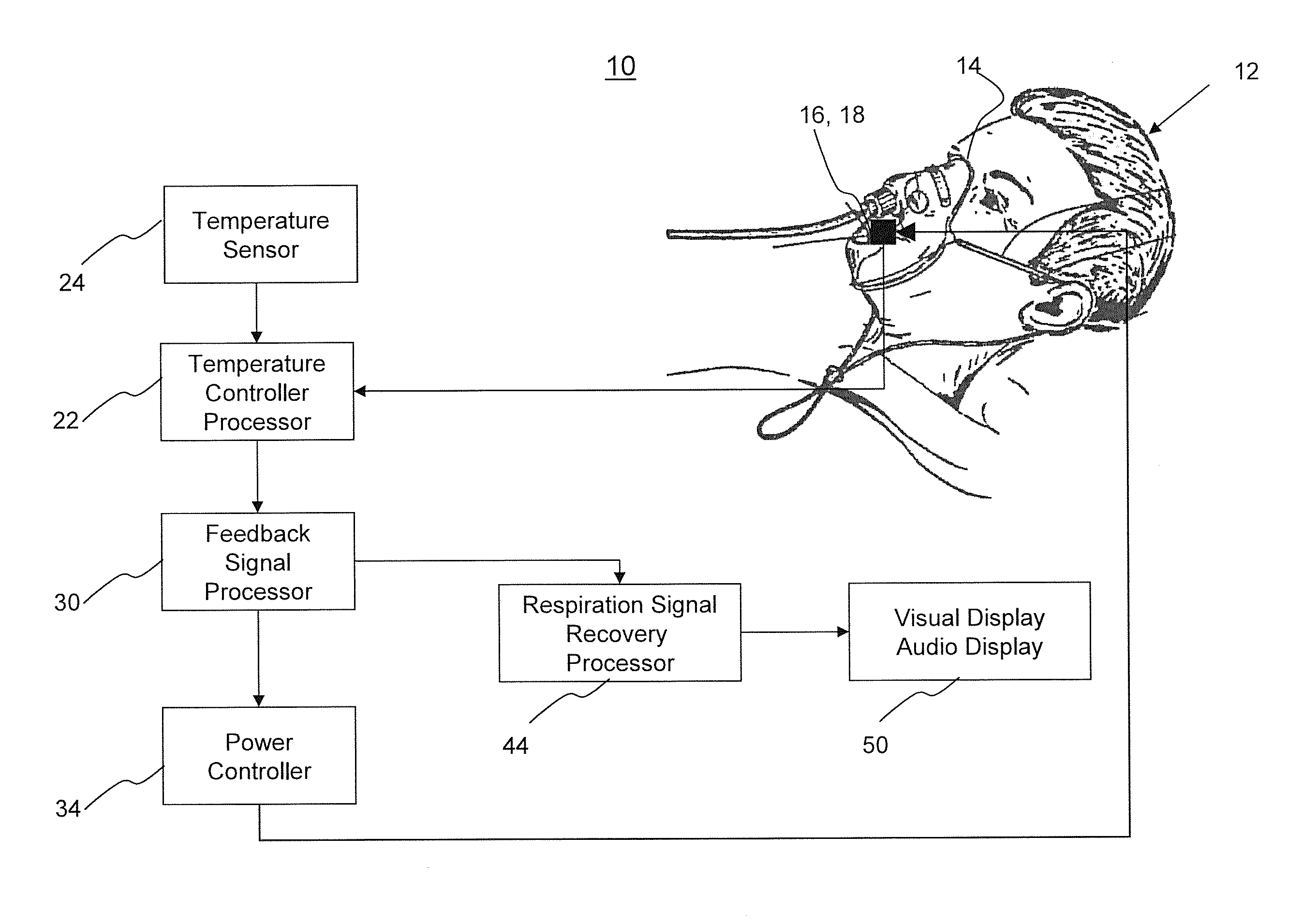
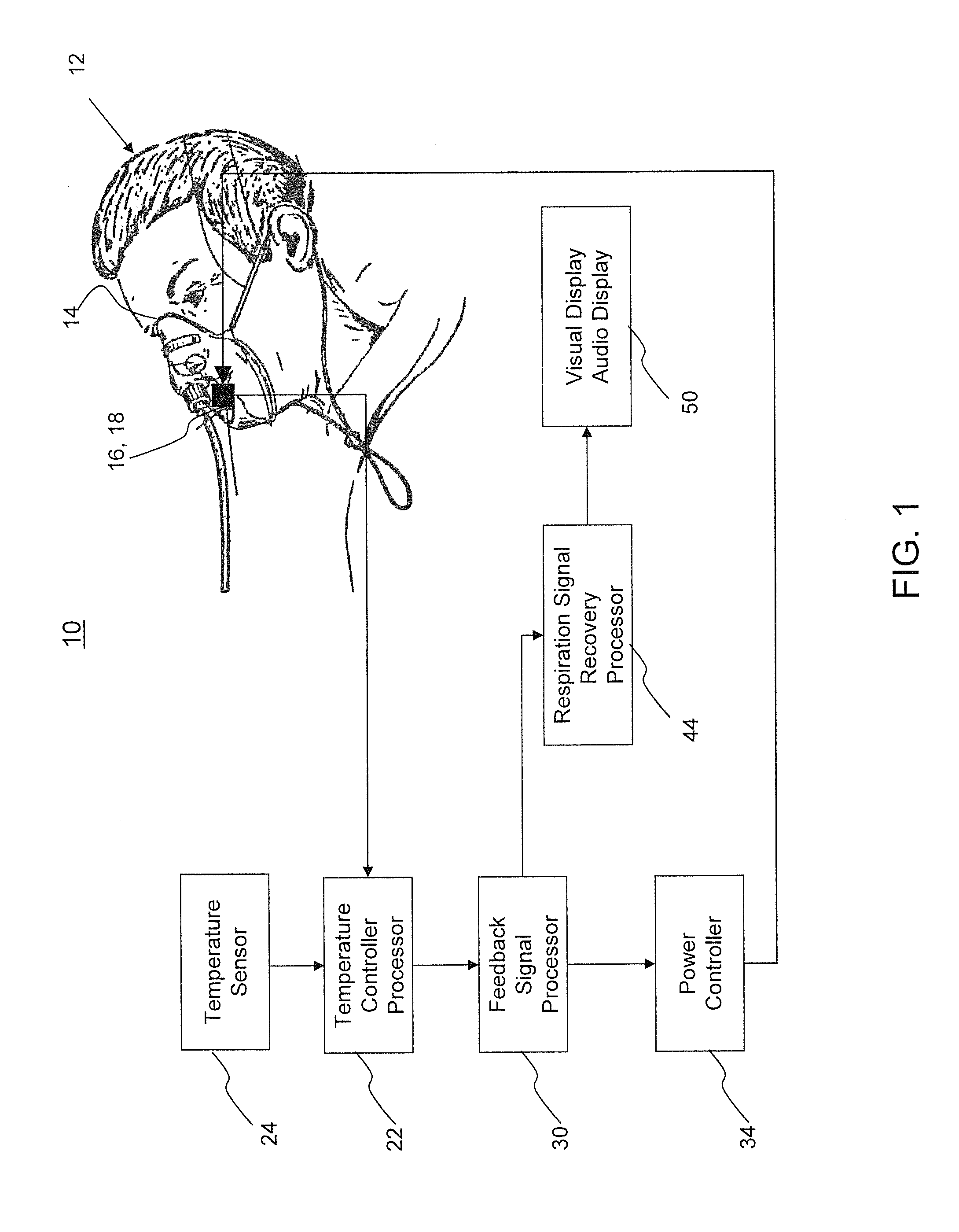
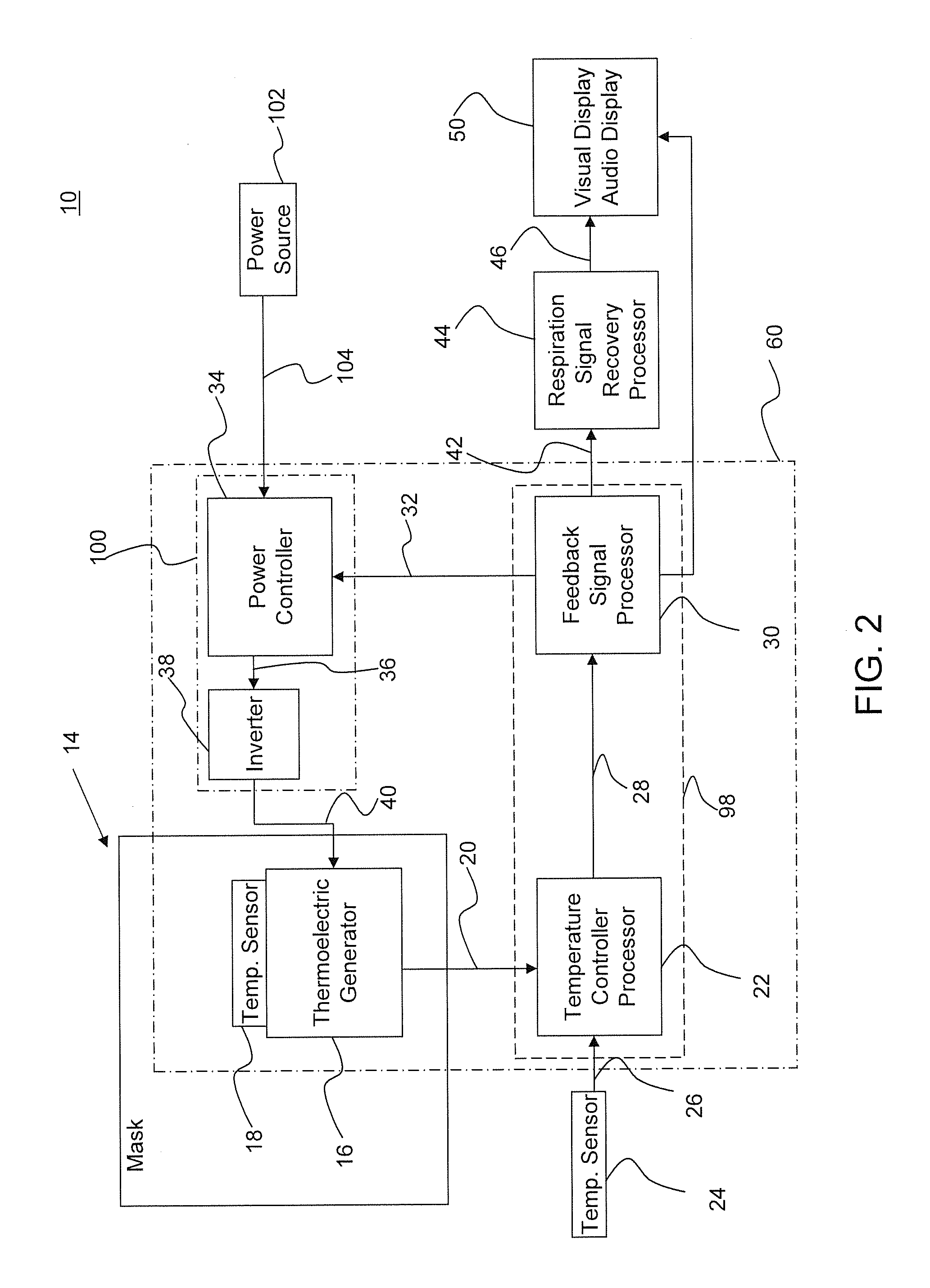
Respiration monitoring system and method
ActiveUS8911380B1Accurate of respirationVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsMedical devicesNoseEngineering
A respiration monitoring system includes a thermoelectric generator that may be mounted within a mask enclosure or free-standing, covering all or part of the nose and / or mouth of a subject. A first temperature sensor is attached to the thermoelectric generator for measuring the subject's breath. A power controller develops a difference between a preset temperature and the subject's breath temperature that is then inserted into a feedback error signal and then into a power controller which regulates the power to the thermoelectric generator to maintain a preset temperature.
Owner:LINSHOM MANAGEMENT LLC
Methods, Systems and Devices for Non-Invasive Open Ventilation For Providing Ventilation Support
ActiveUS20130255683A2Work lessIncrease pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLung volumesNon invasive
A system for providing ventilation support to a patient may include a ventilator, a control unit, a gas delivery circuit with a proximal end in fluid communication with the ventilator and a distal end in fluid communication with a nasal interface, and a nasal interface. The nasal interface may include at least one jet nozzle at the distal end of the gas delivery circuit; and at least one spontaneous respiration sensor for detecting respiration in communication with the control unit. The system may be open to ambient. The control unit may receive signals from the at least one spontaneous respiration sensor and determine gas delivery requirements. The ventilator may deliver gas at a velocity to entrain ambient air and increase lung volume or lung pressure above spontaneously breathing levels to assist in work of breathing, and deliver ventilation gas in a cyclical delivery pattern synchronized with a spontaneous breathing pattern.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
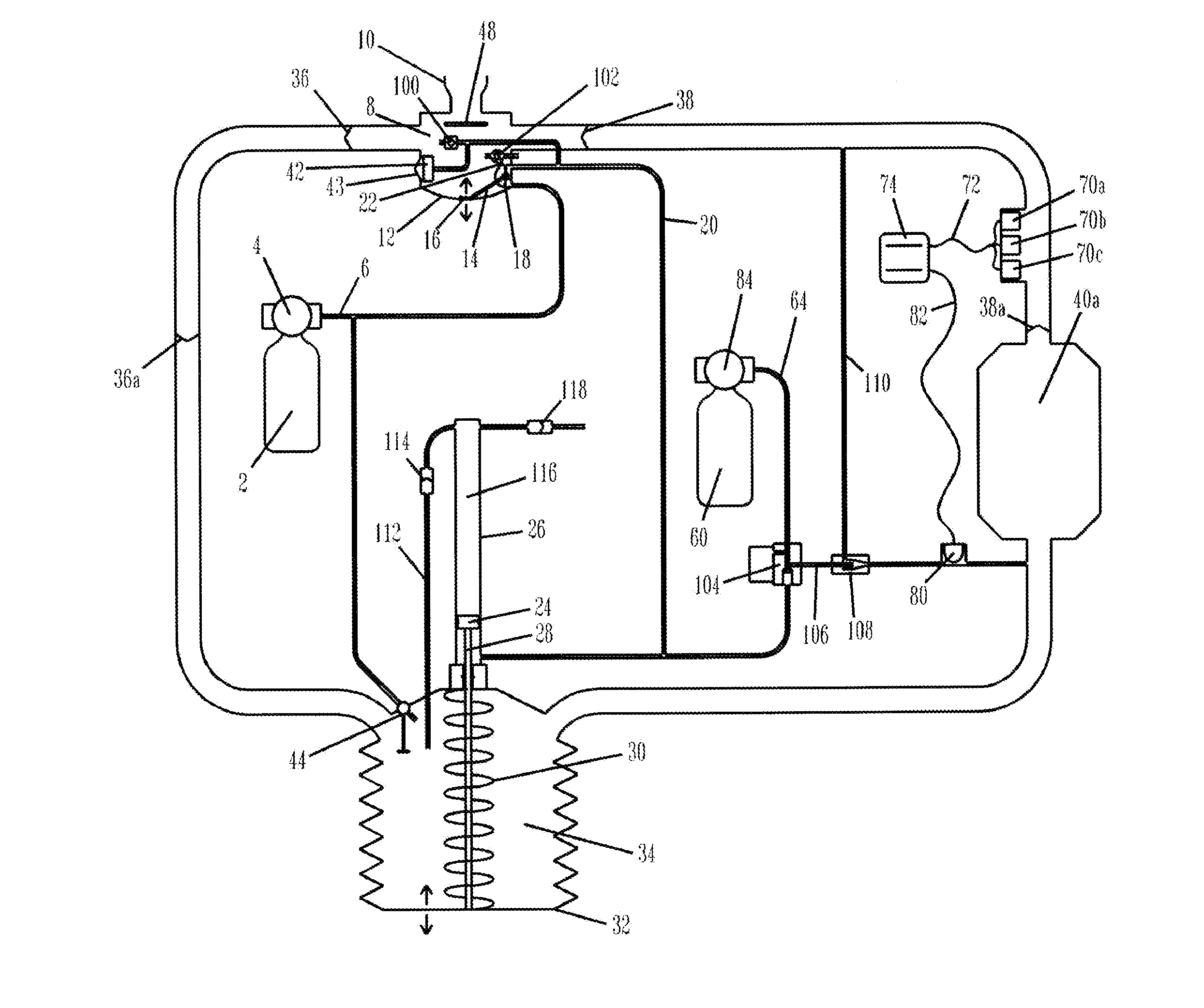
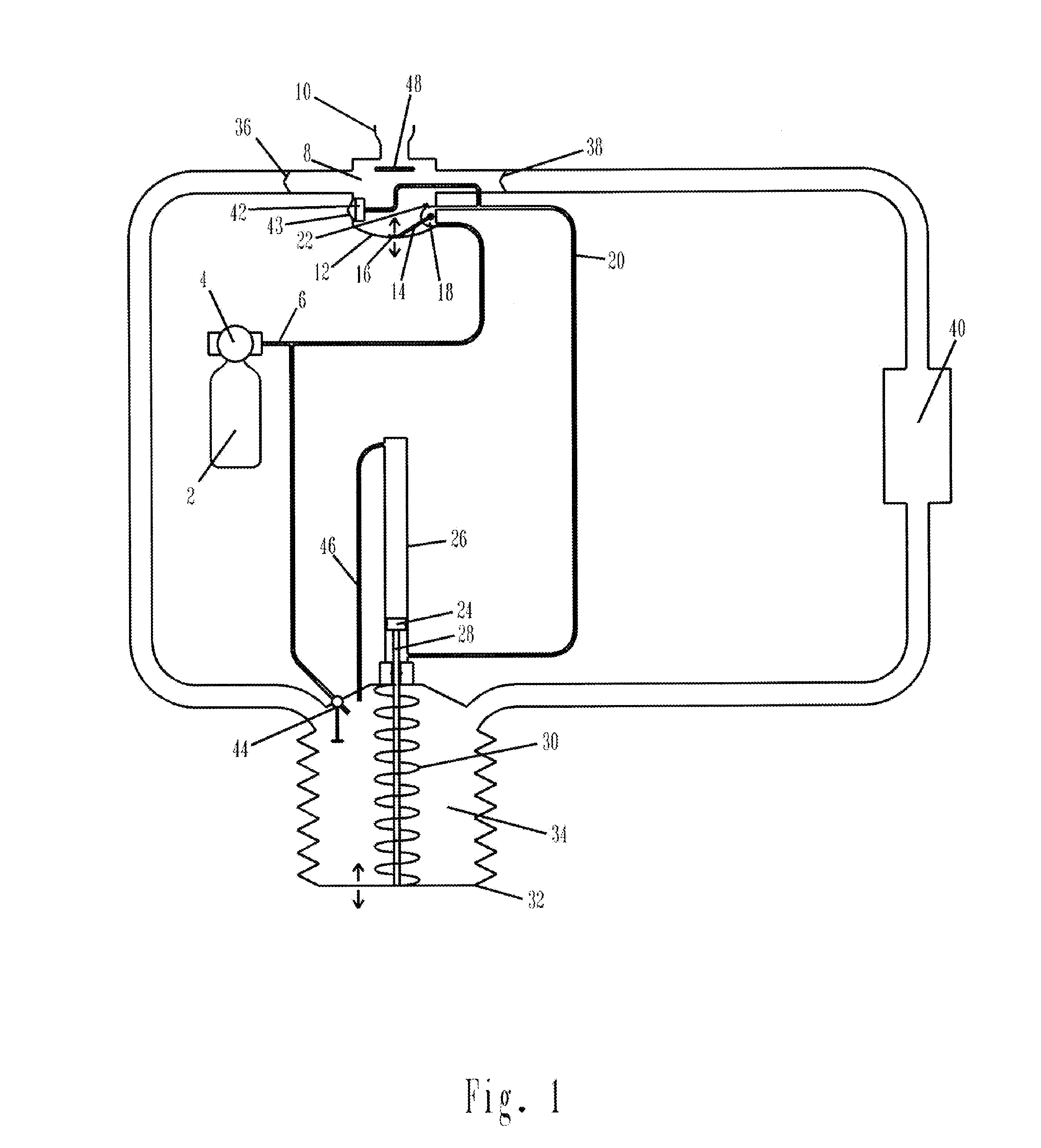
Gas assisted re-breathing device
InactiveUS20120192868A1Prevents premature ventingConvenient introductionRespiratorsRespiratory apparatusBreatherBreathing gas
A gas assisted re-breathing device is disclosed for life support of individuals venturing into harsh environments, particularly the underwater environment, which results in reduced work of breathing. Similar to prior art re-breathers, hoses connect a mouthpiece to direct the flow of breathing gas in a loop like fashion, passing in and out of a flexible gas storage container and a CO2 scrubbing device prior to re-breathing. Disclosed is a pressurized gas assisted re-breathing device, driven by pressurized gas, actuated by the breathing pressure local to the mouthpiece, that acts to move the flexible gas storage container on behalf of the individual and a loop seal valve that is forcibly shut during assisted breathing, which seals the assisted breathing loop to prevent premature venting of breathing gas to the surrounding environment, unless the assisted breathing loop is full, whereupon the loop seal valve opens to allow excess breathing gas to escape into the surrounding environment through forcible exhalation by the individual through one or more conventional one way valves that prevent backflow from the surrounding environment back into the loop. This device significantly reduces work of breathing without unwanted breathing gas loss and further facilitates additional safety features that would otherwise not be practical due to the resultant increase in work of breathing.
Owner:DIVE COBALT BLUE
Self-sizing adjustable endotracheal tube
There is disclosed an endotracheal tube which has a minimal cross-sectional profile for easy viewing of anatomical features during intubation. After the tube is placed into the trachea, the tube is adapted to increase the diameter. In this manner the tube diameter may be expanded to allow for decreased Work of Breathing (WOB) for patient, while not having so large a diameter as to cause tracheal discomfort.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Gas assisted re-breathing device
InactiveUS8770194B2Prevents premature ventingConvenient introductionRespiratorsBreathing masksBreathing gasRespiratory pressure
A gas assisted re-breathing device is provided for life support of individuals venturing into harsh environments, particularly the underwater environment, which results in reduced work of breathing. In the pressurized gas assisted re-breathing device, pressurized gas, actuated by the breathing pressure local to the mouthpiece, acts to move a flexible gas storage container on behalf of the individual and a loop seal valve is forcibly shut during assisted breathing, which seals the assisted breathing loop to prevent premature venting of breathing gas to the surrounding environment, unless the assisted breathing loop is full, whereupon the loop seal valve opens to allow excess breathing gas to escape into the surrounding environment through forcible exhalation by the individual through one or more conventional one way valves that prevent backflow from the surrounding environment back into the loop.
Owner:DIVE COBALT BLUE
Peep regulation for a breathing apparatus
ActiveUS9333312B2Quick releaseMinimizing expiratory resistanceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFeedback controlBreathing cycle
A breathing apparatus has an expiratory flow sensor unit, an expiratory pressure sensor unit, an expiratory pressure regulator, and an expiratory control unit operatively connected to the expiratory pressure sensor unit for a feedback control of an expiratory pressure during an expiratory phase of a breathing cycle. The expiratory control unit is adapted to provide a real time target pressure value during the expiratory phase to the expiratory pressure regulator for adjusting a desired positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) level (PEEPset) based on an inspiratory tidal volume of an inspiratory phase of the same breathing cycle and a currently accumulated expiratory tidal volume measured by the expiratory flow sensor unit. In this manner advantageous regulation of PEEP with minimized work of breathing is obtained.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
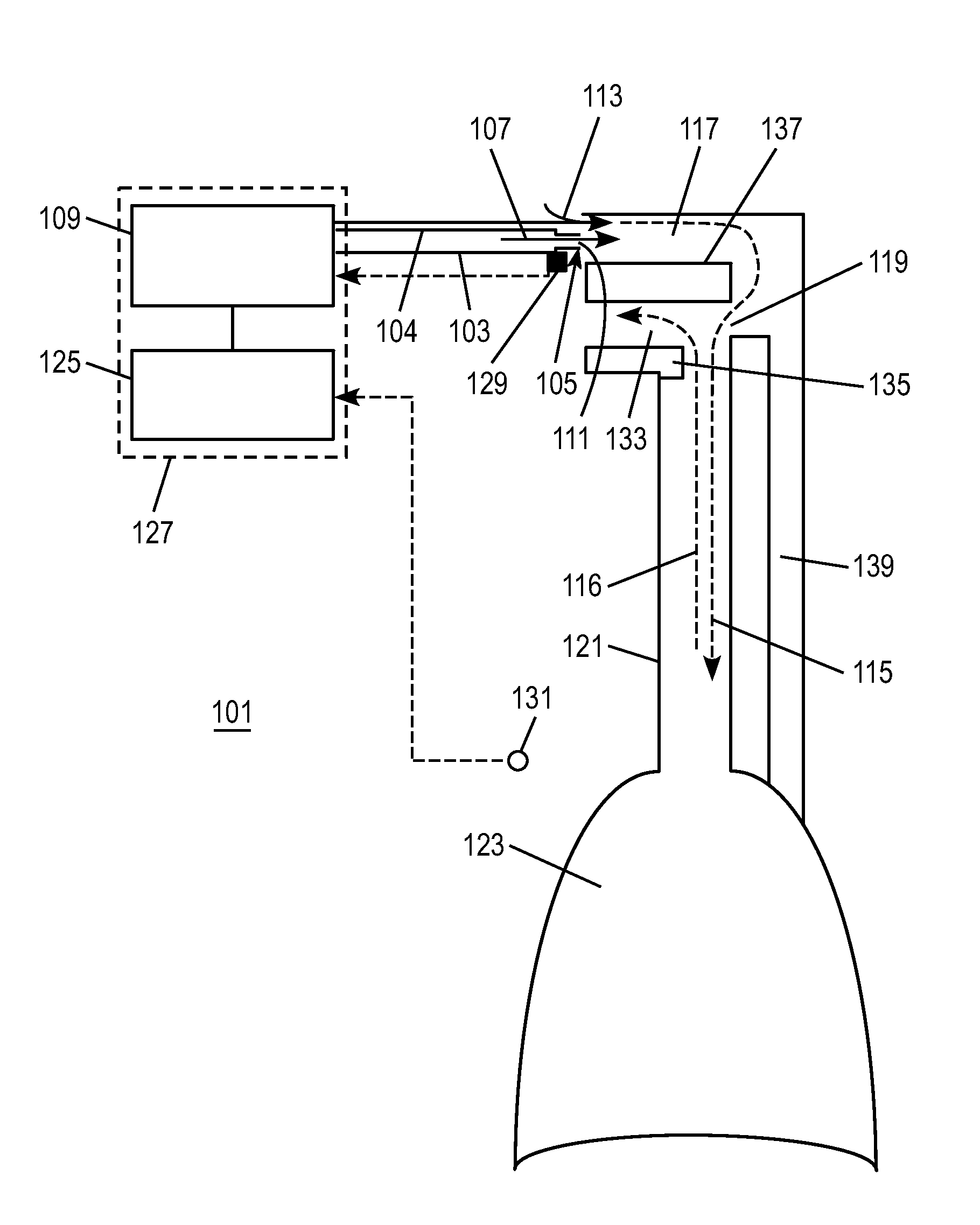
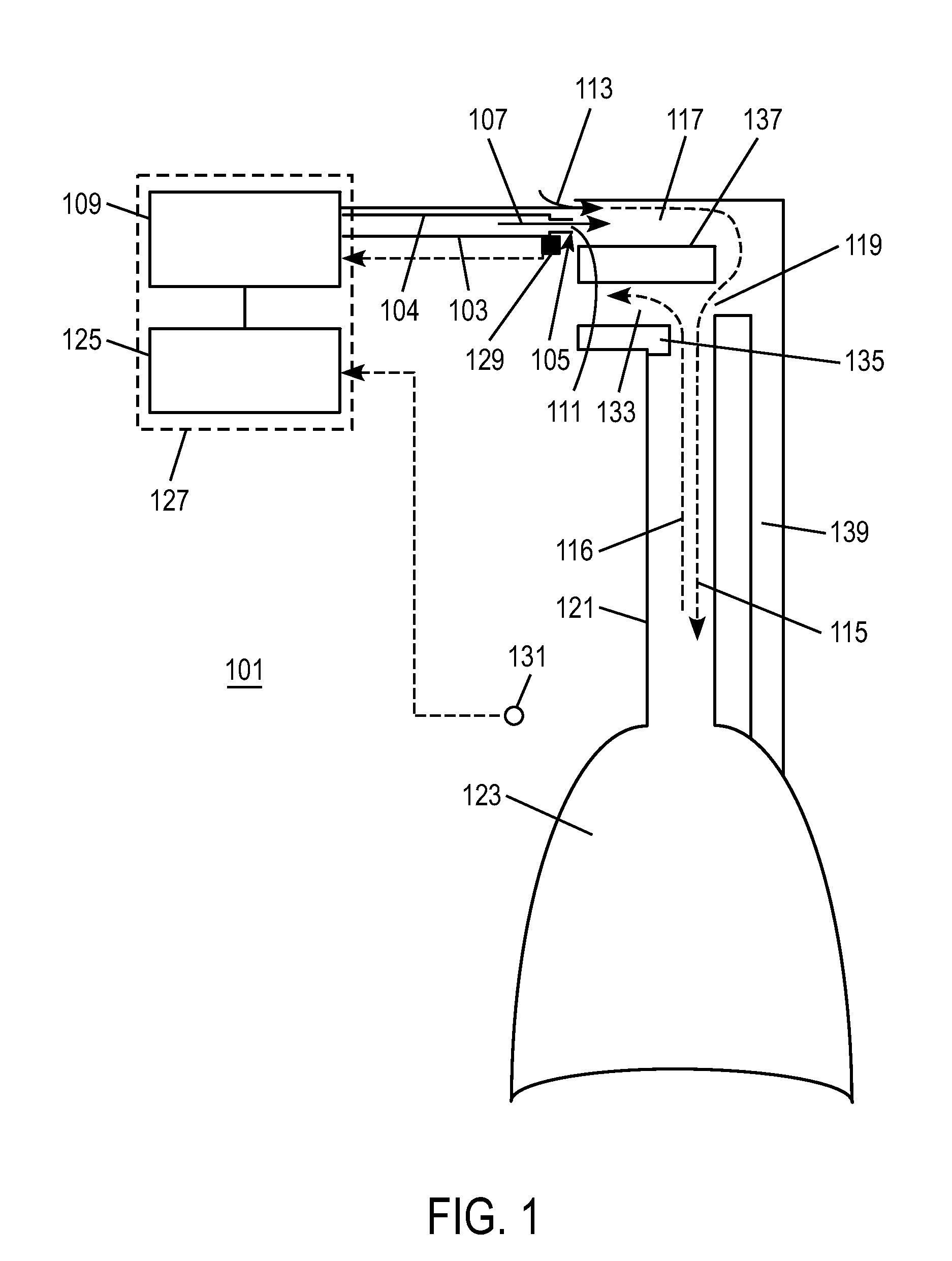
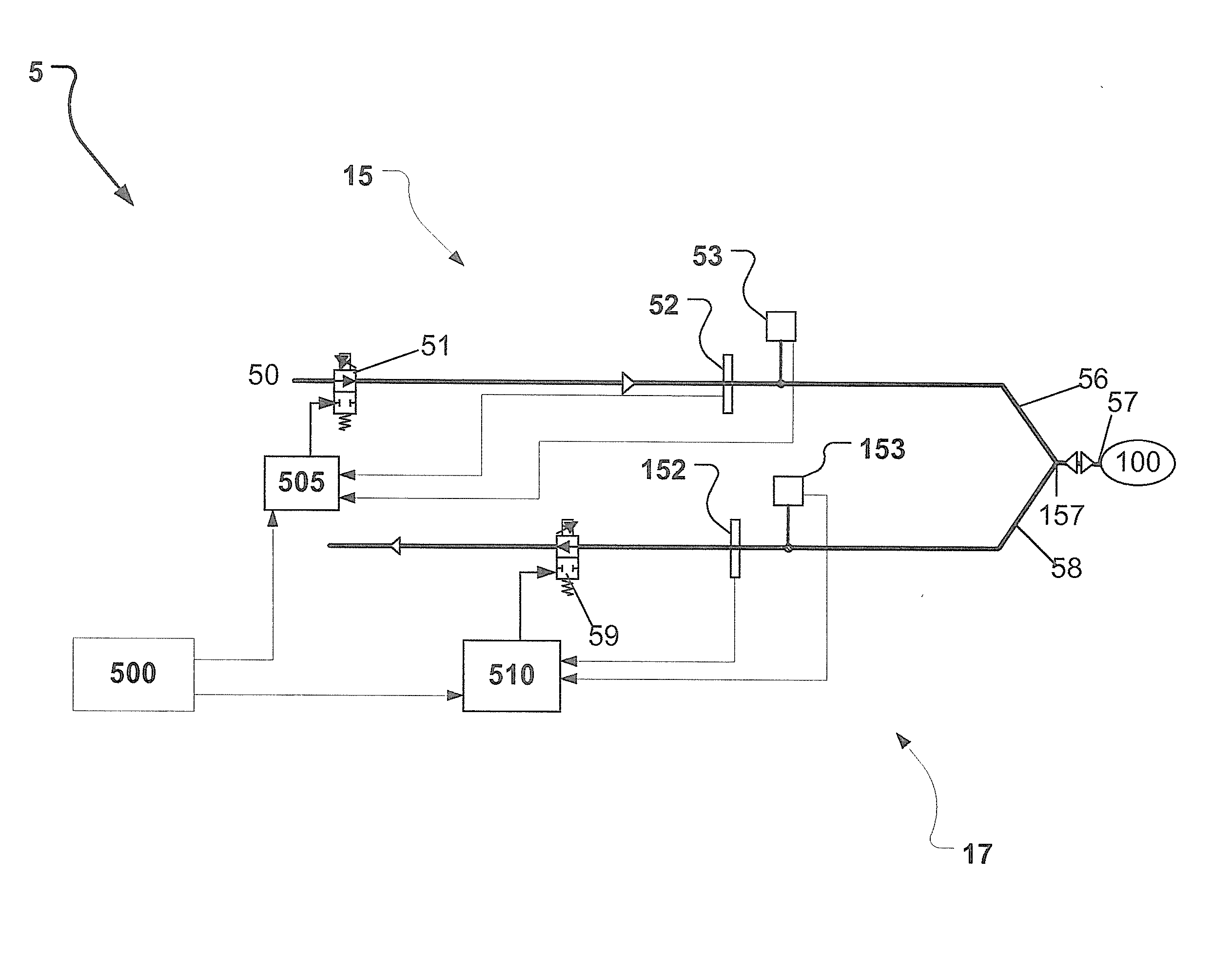
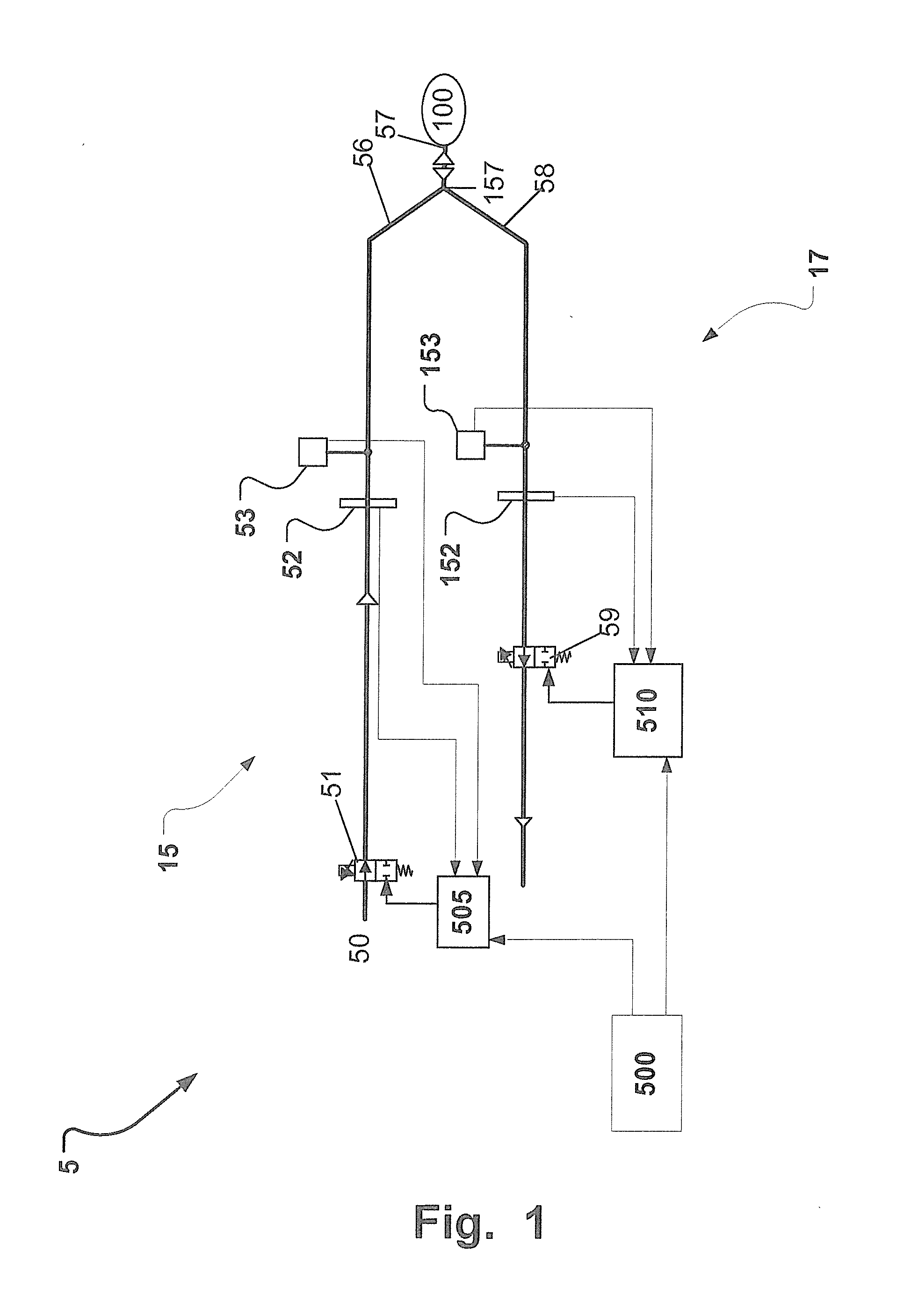
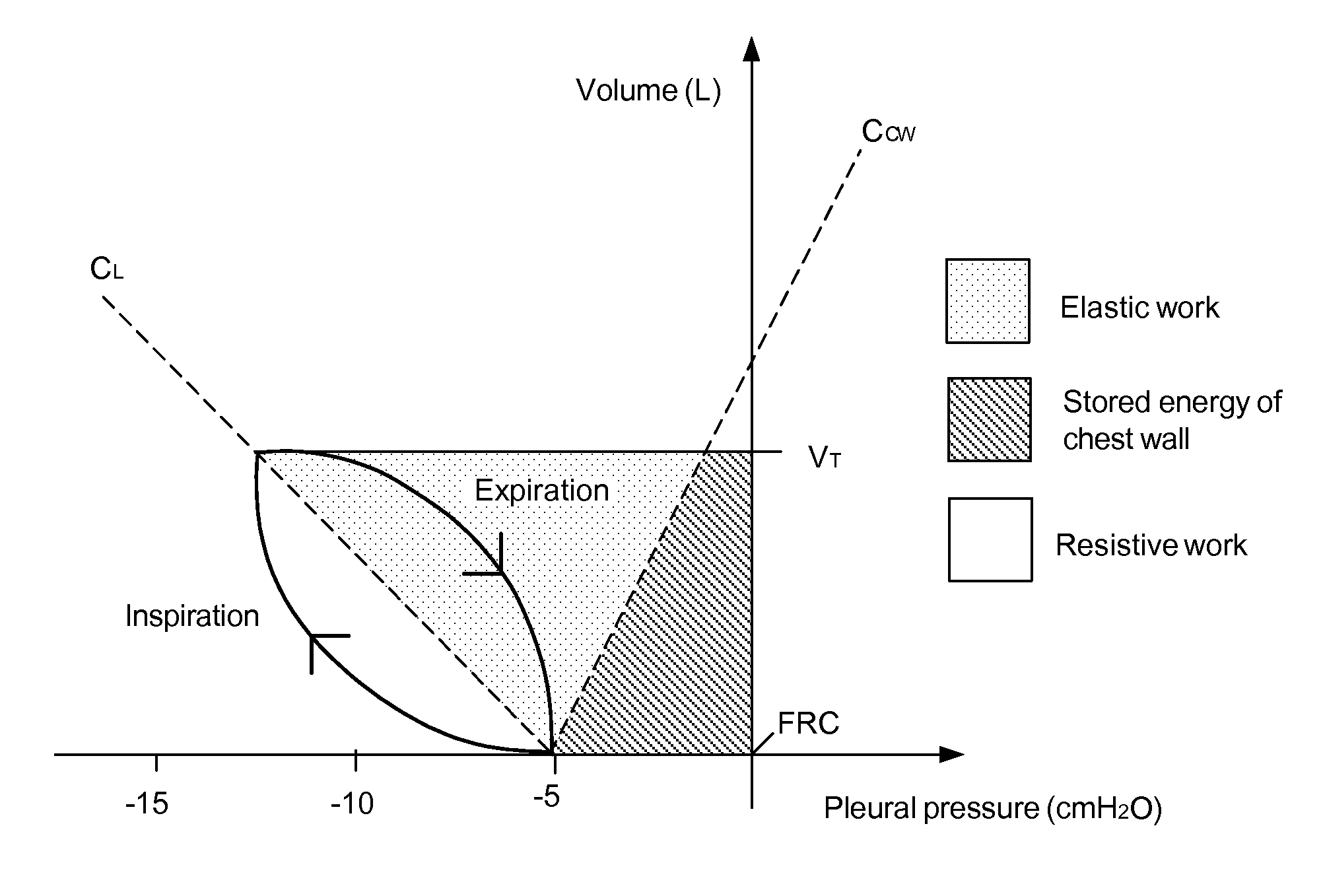
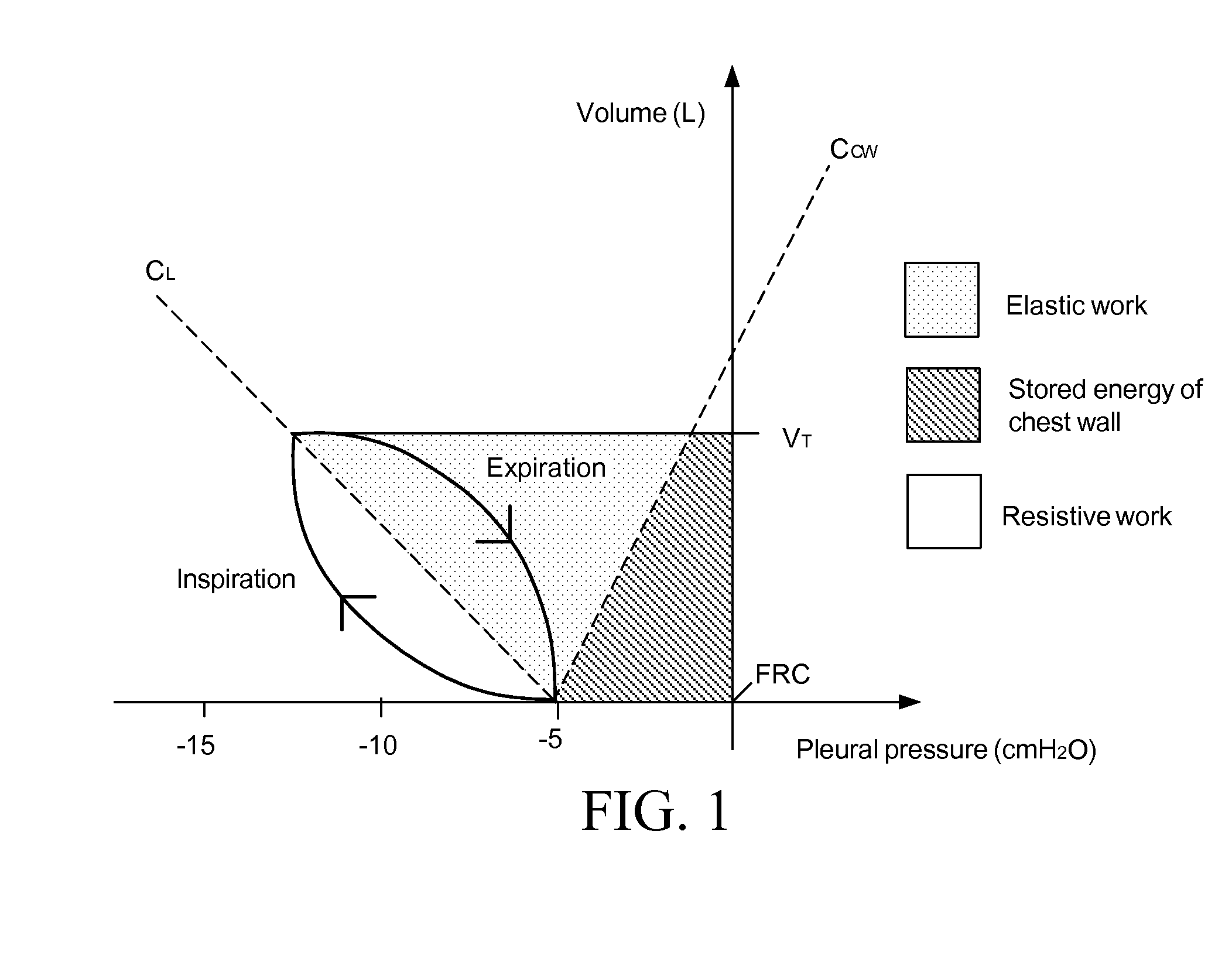
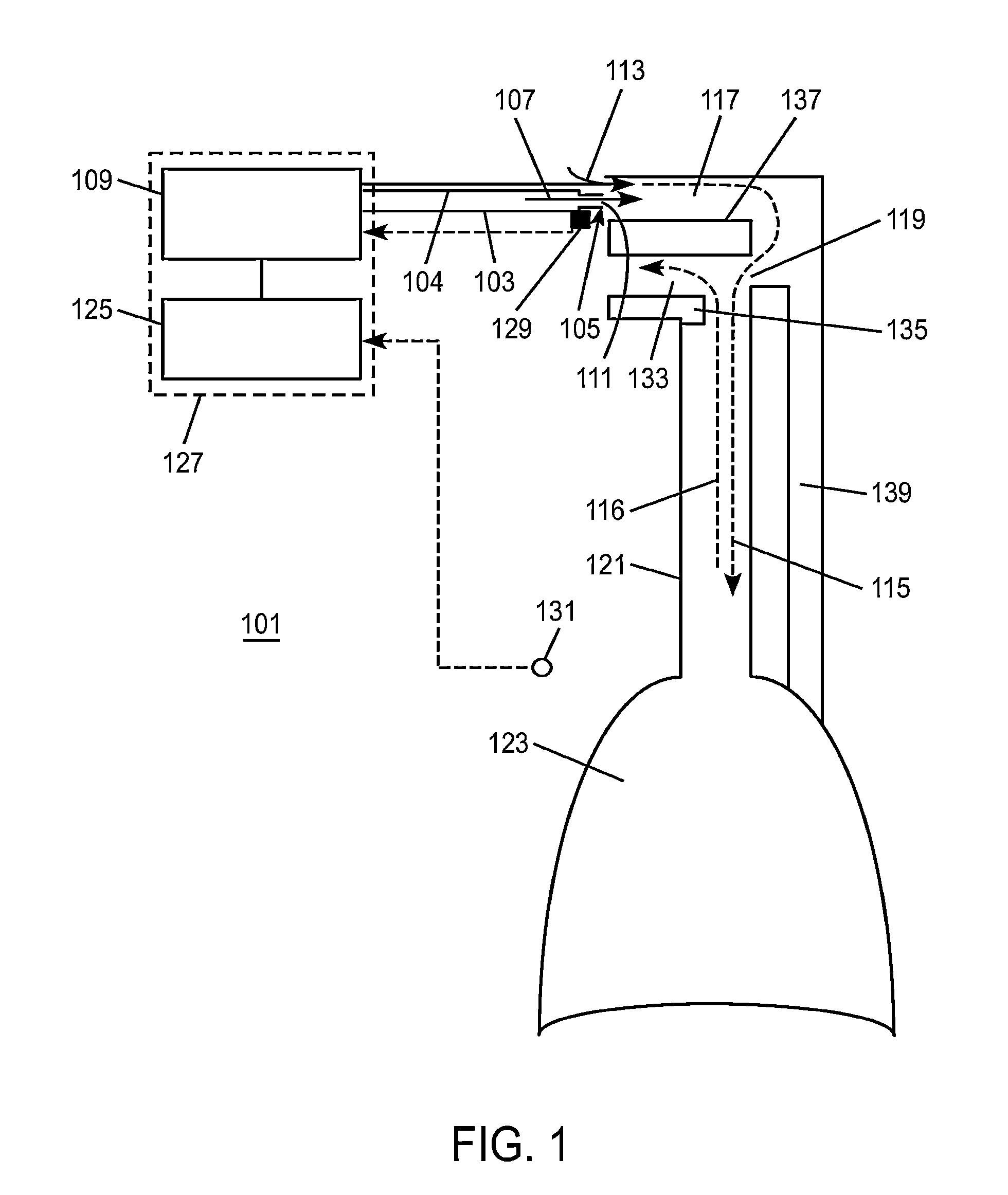
Non-invasive estimation of intra-pleural pressure and/or computation of work of breathing based on a non-invasive estimation of intra-pleural pressure
A method includes obtaining a first physiological parameter indicative of a non-invasively measured airway pressure of a subject, obtaining a second physiological parameter indicative of a non-invasively measured air flow into the lungs of the subject, and estimating a third physiological parameter indicative of an intra-pleural pressure of the subject based on the first and second physiological parameters and generating a signal indicative thereof. An other method includes obtaining a first physiological parameter indicative of a non-invasively estimated intra-pleural pressure of a subject, determining a second physiological parameter indicative of a lung volume of the subject that is based on a third physiological parameter indicative of a non-invasively measured air flow into the lungs of the subject, and determining a work of breathing based on the first and second physiological parameters and generating a signal indicative thereof.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Nasal Insert Impreganted with an Aromatherapy Oil
This invention discloses a novel nasal insert which reduces the effect of upper airway resistance syndrome. The insert comprises a short, hollow, flexible tube with the central portion of one side being removed. The insert is inserted into each nostril to allow increased airflow and reduce the work of breathing. The efficiency of the insert may be increased by its impregnation with aroma-therapy essential oils.
Owner:VOLGYESI GEORGE
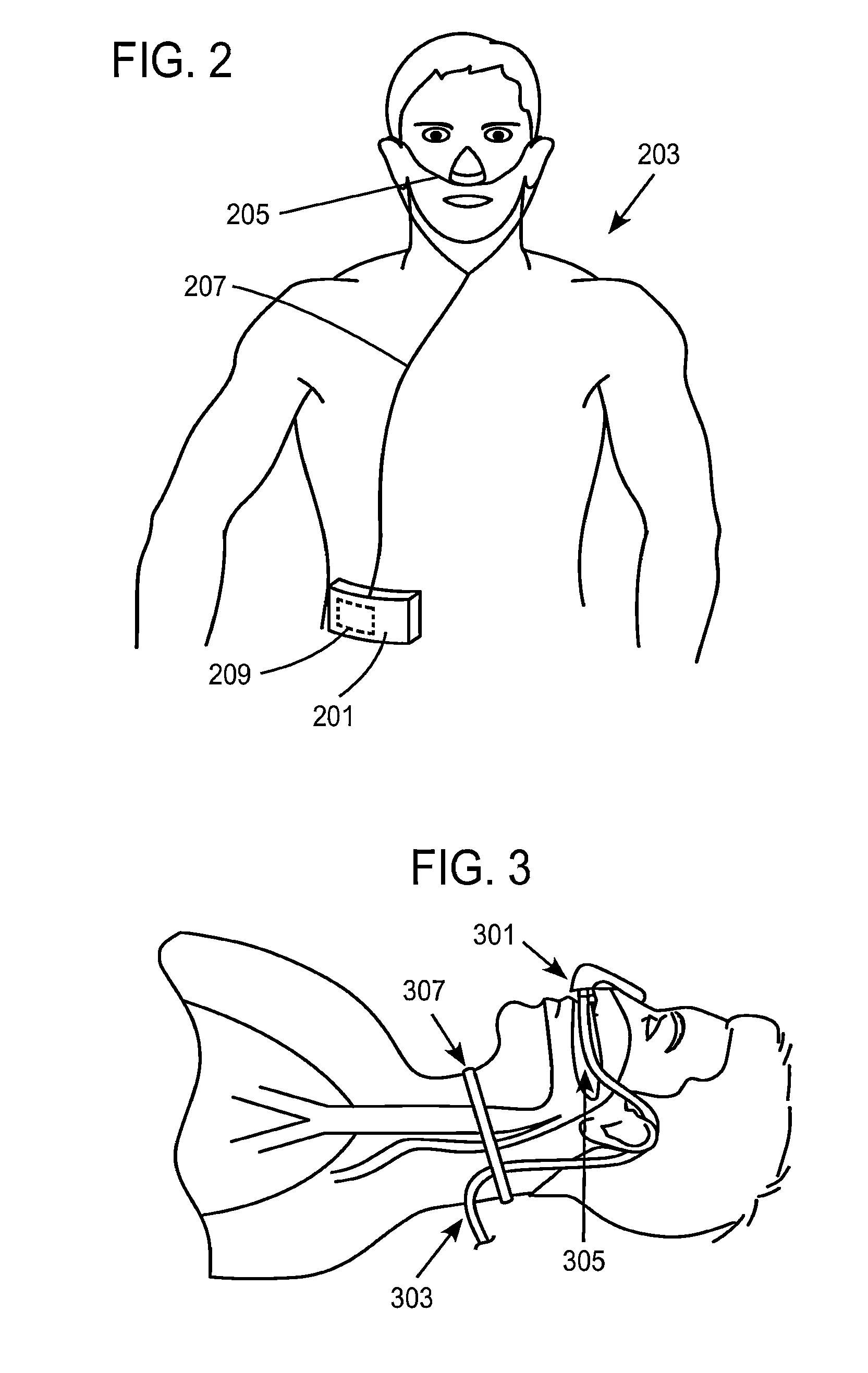
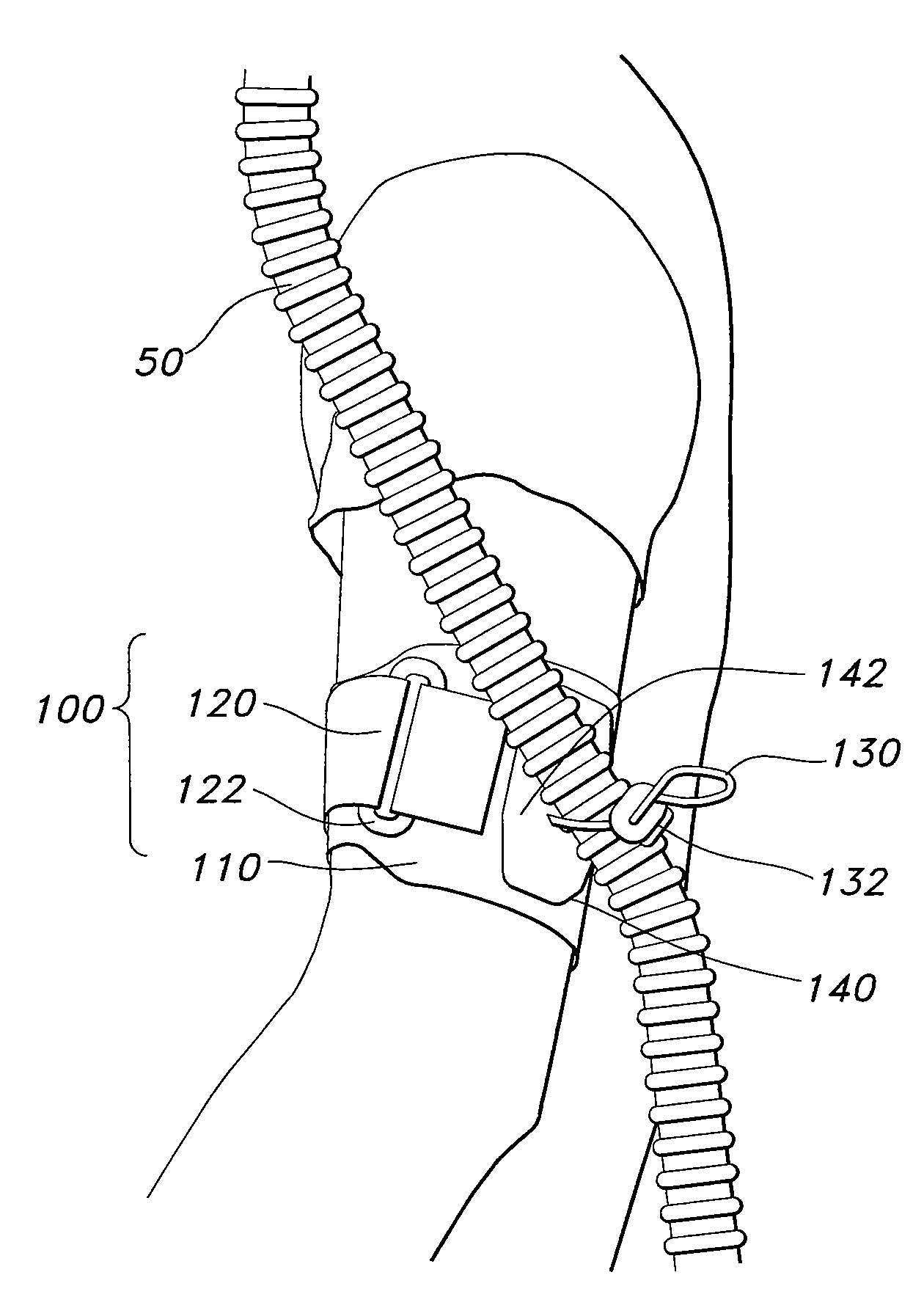
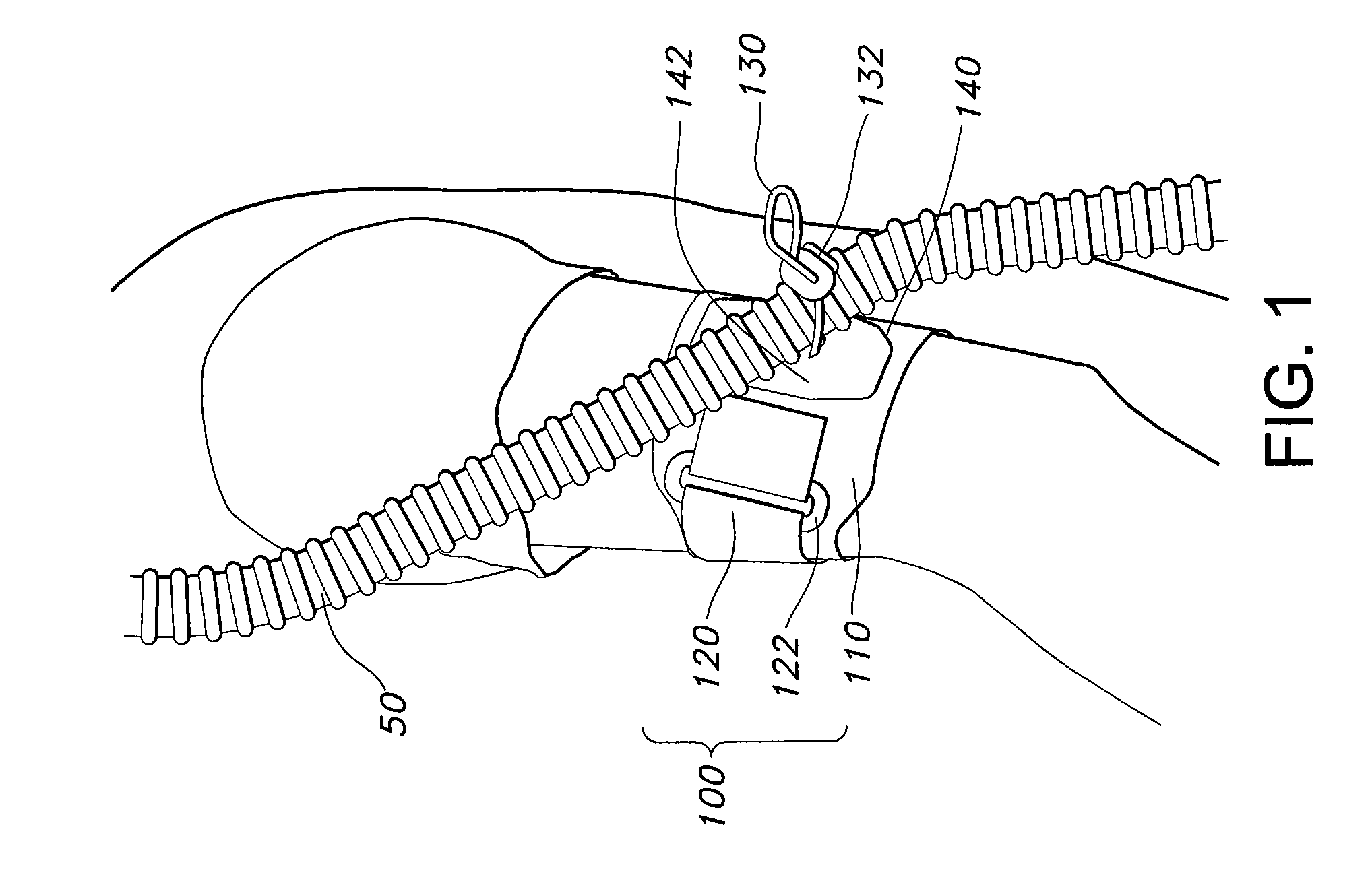
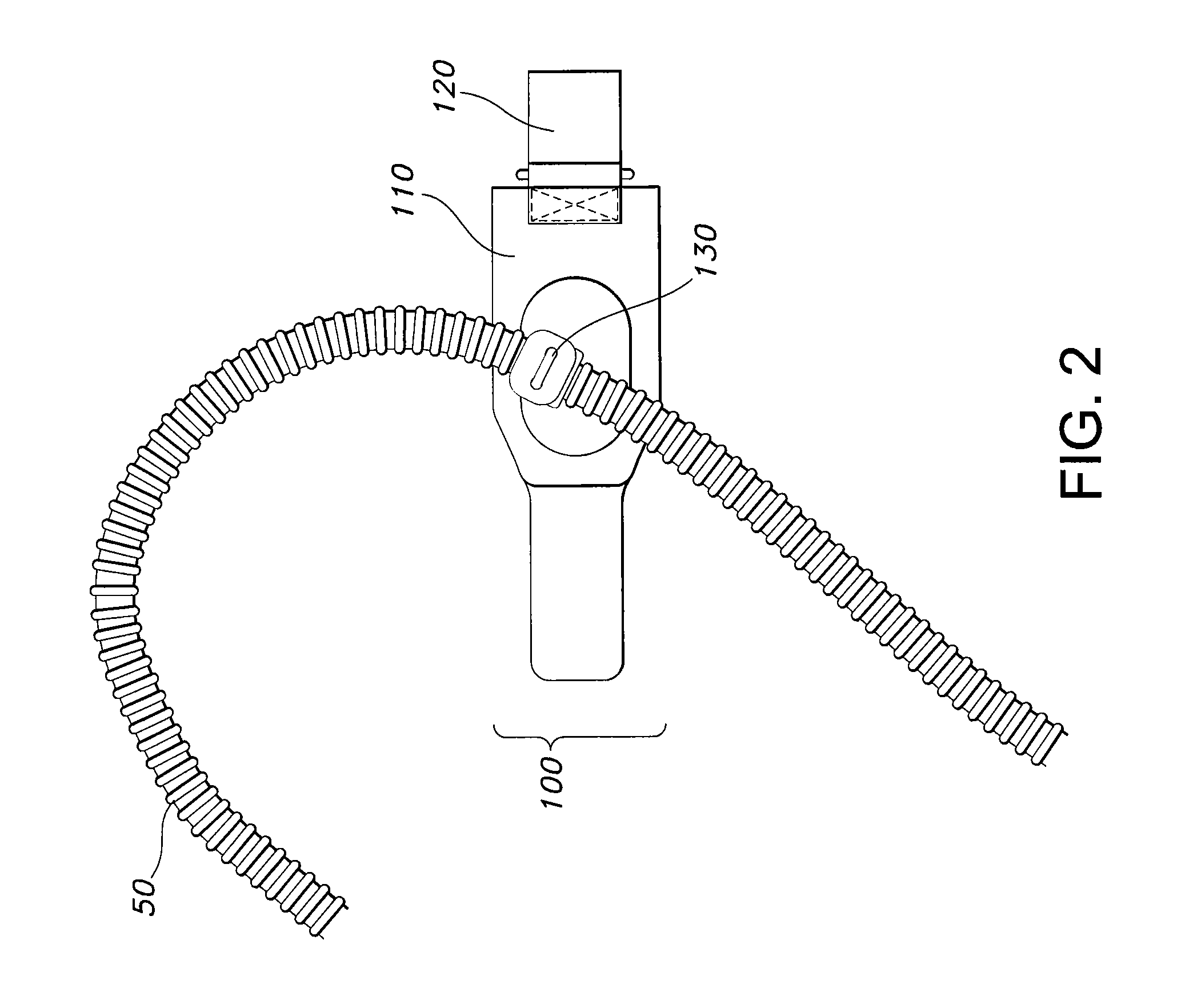
Apparatus, systems, and methods for securing a breathing tube to an arm
Methods, systems, and apparatus for securing a breathing tube to a user are disclosed. An exemplary apparatus is an armband including a strap sized to encircle the arm of the user, a connecting element coupled to the strap to secure the strap around the arm, and at least one loop coupled to the strap, the loop receiving the breathing tube and securing the breathing tube to the arm. In use, the armband may secure a breathing tube to a user by encircling the arm of the user with the strap, securing the strap around the arm with the connecting element, and attaching the breathing tube to the arm. The armband may be used in a system for assisting a user with the work of breathing that includes a source of breathing air, a breathing tube, and a patient interface.
Owner:VAPOTHERM INC
Methods and apparatus for lowering intracranial and intraspinal cord pressure
Apparatus and methods are provided for applying negative pressure to tissues of a patient that are transmitted to the vertebral venous system of the patient and thereby lowering intracranial pressure. Intracranial pressure is thus lowered easily without increasing the work of breathing, without needing to be intubated, and without breathing through a valve in patients with elevated increased intracranial pressure.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com