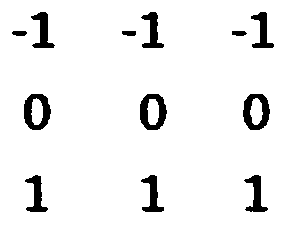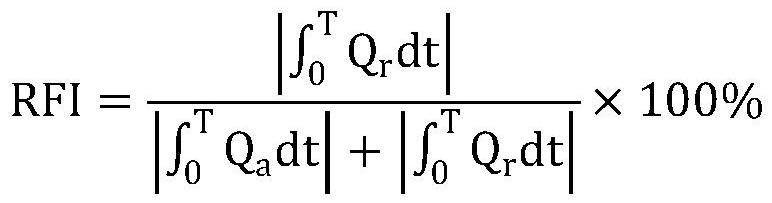Patents
Literature
36 results about "Arterial lumen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
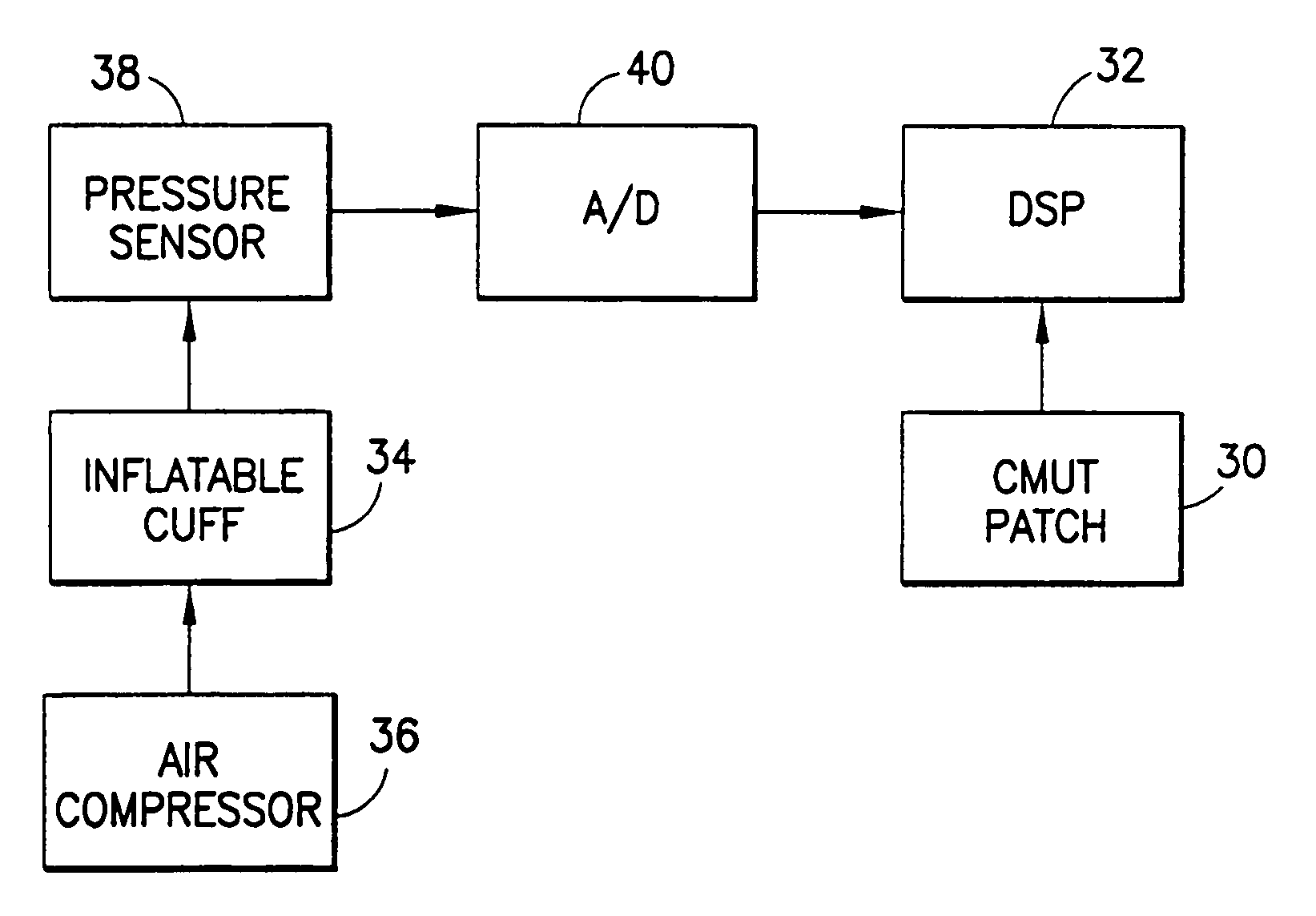
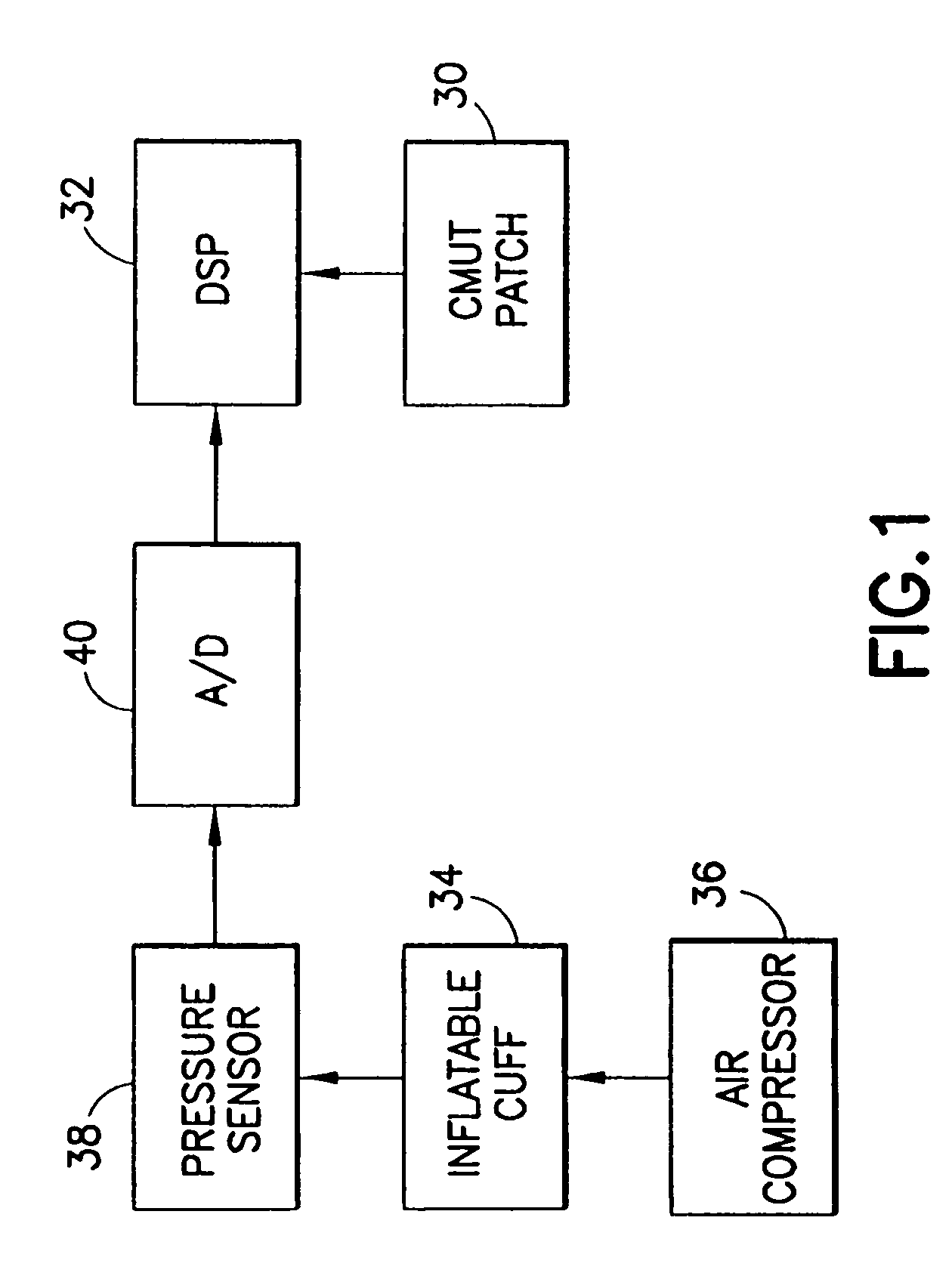
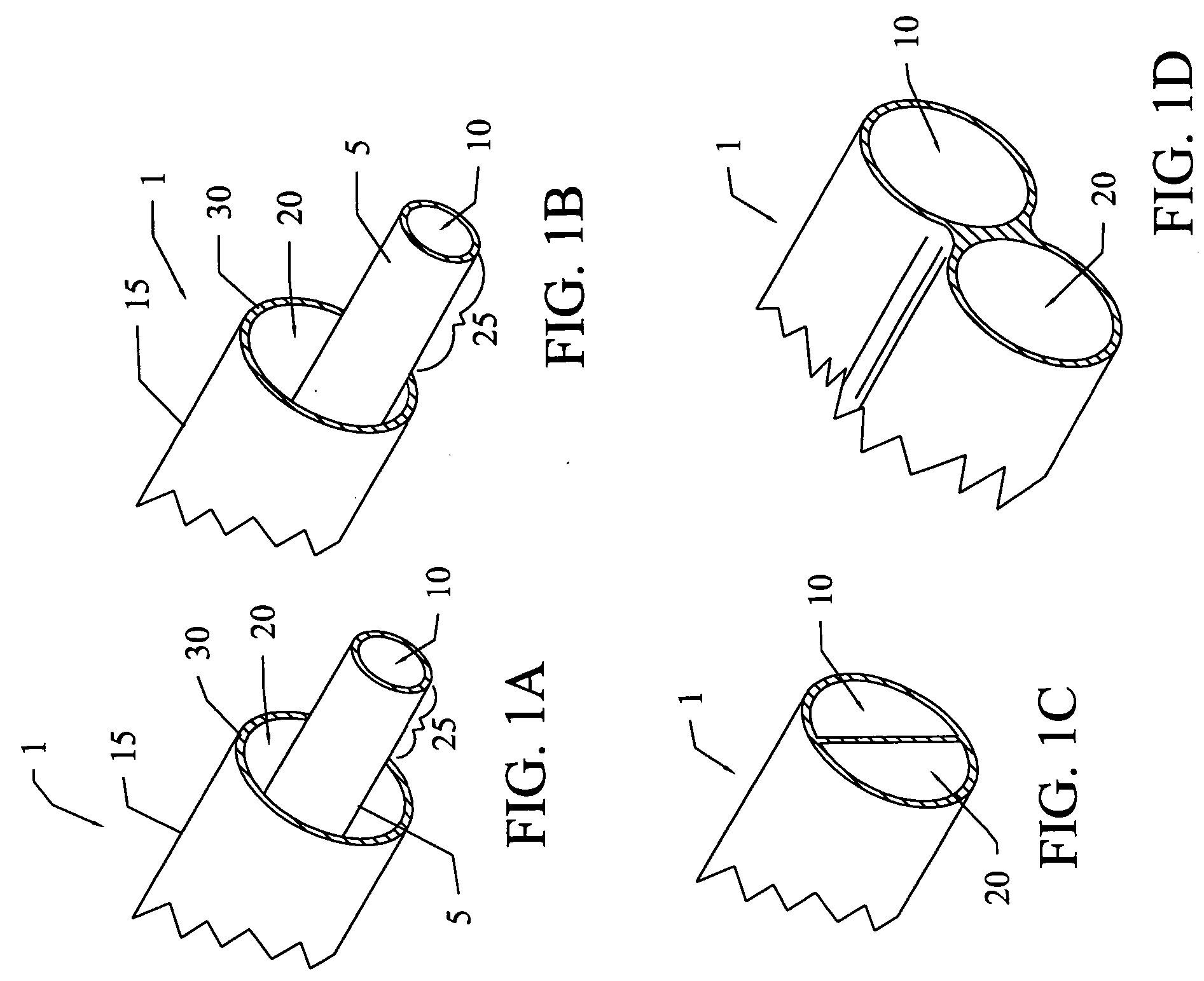
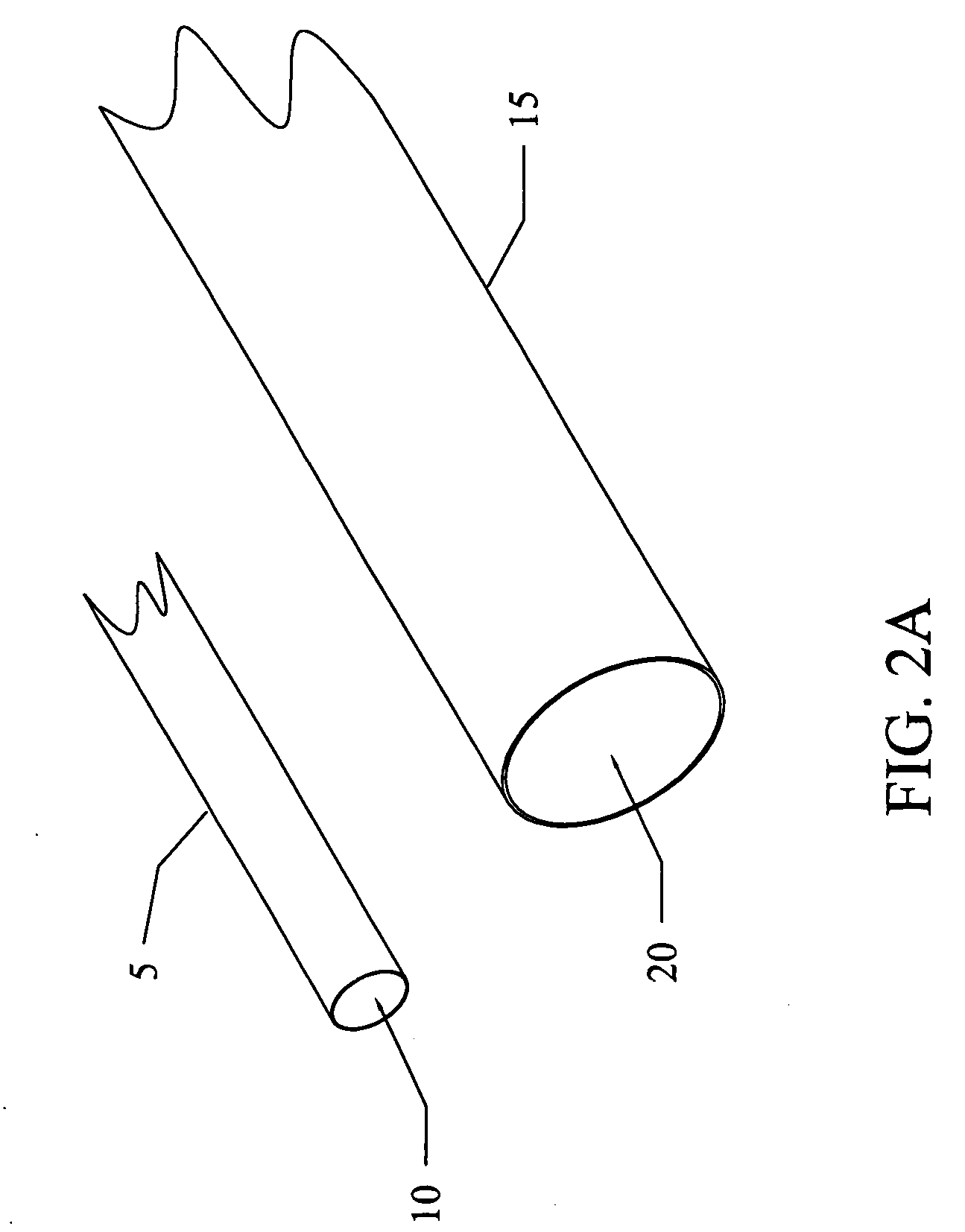
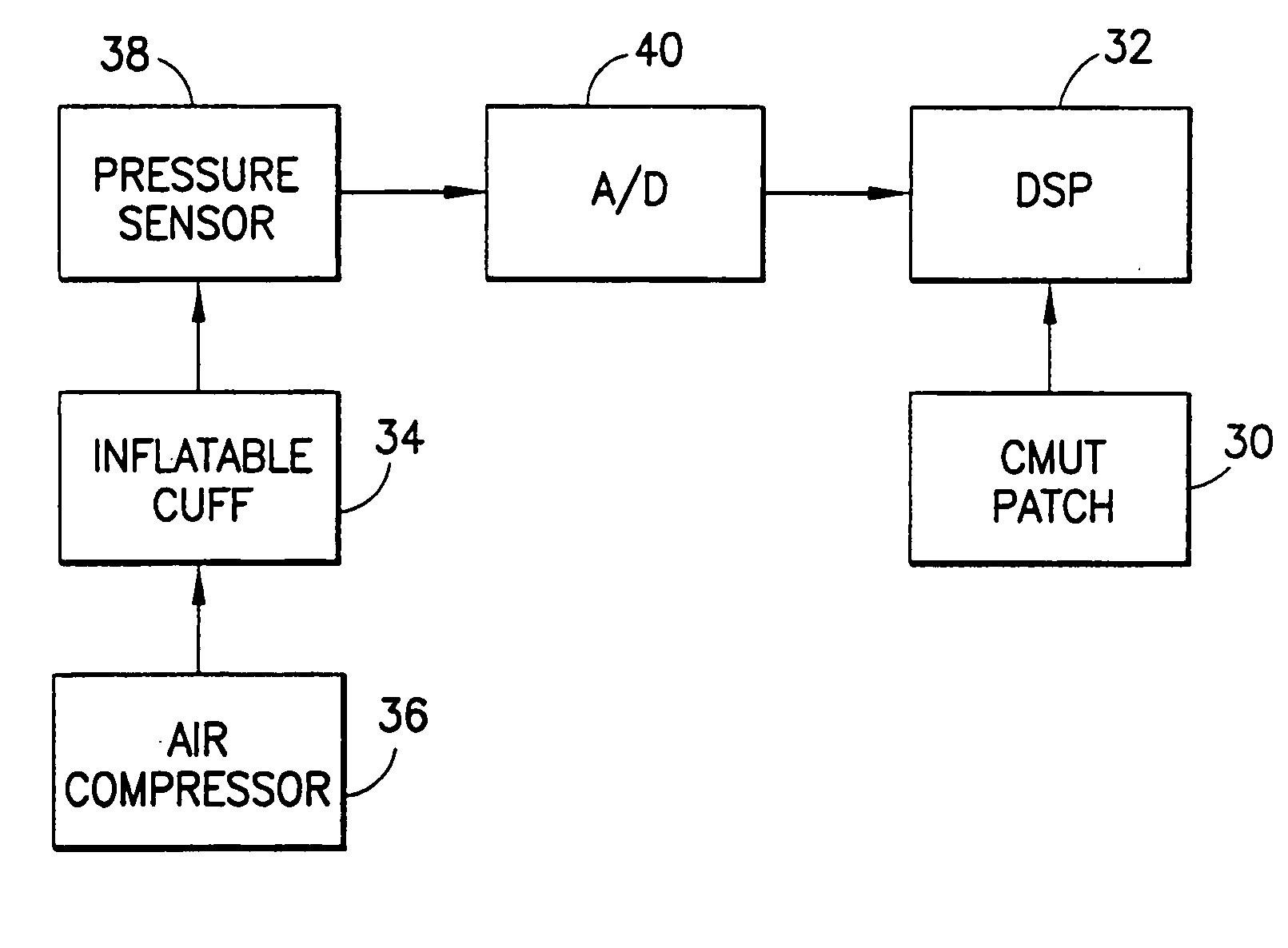
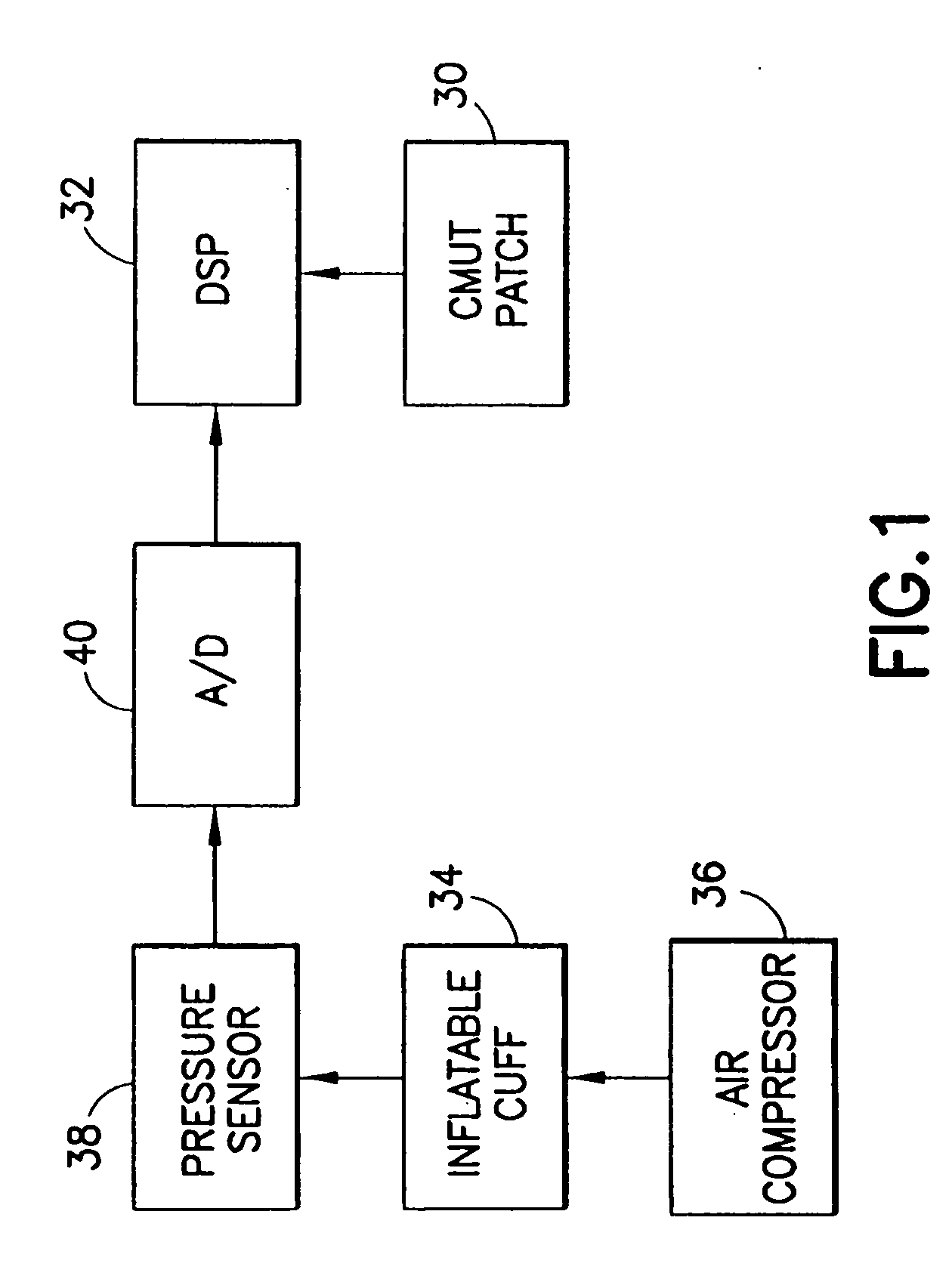
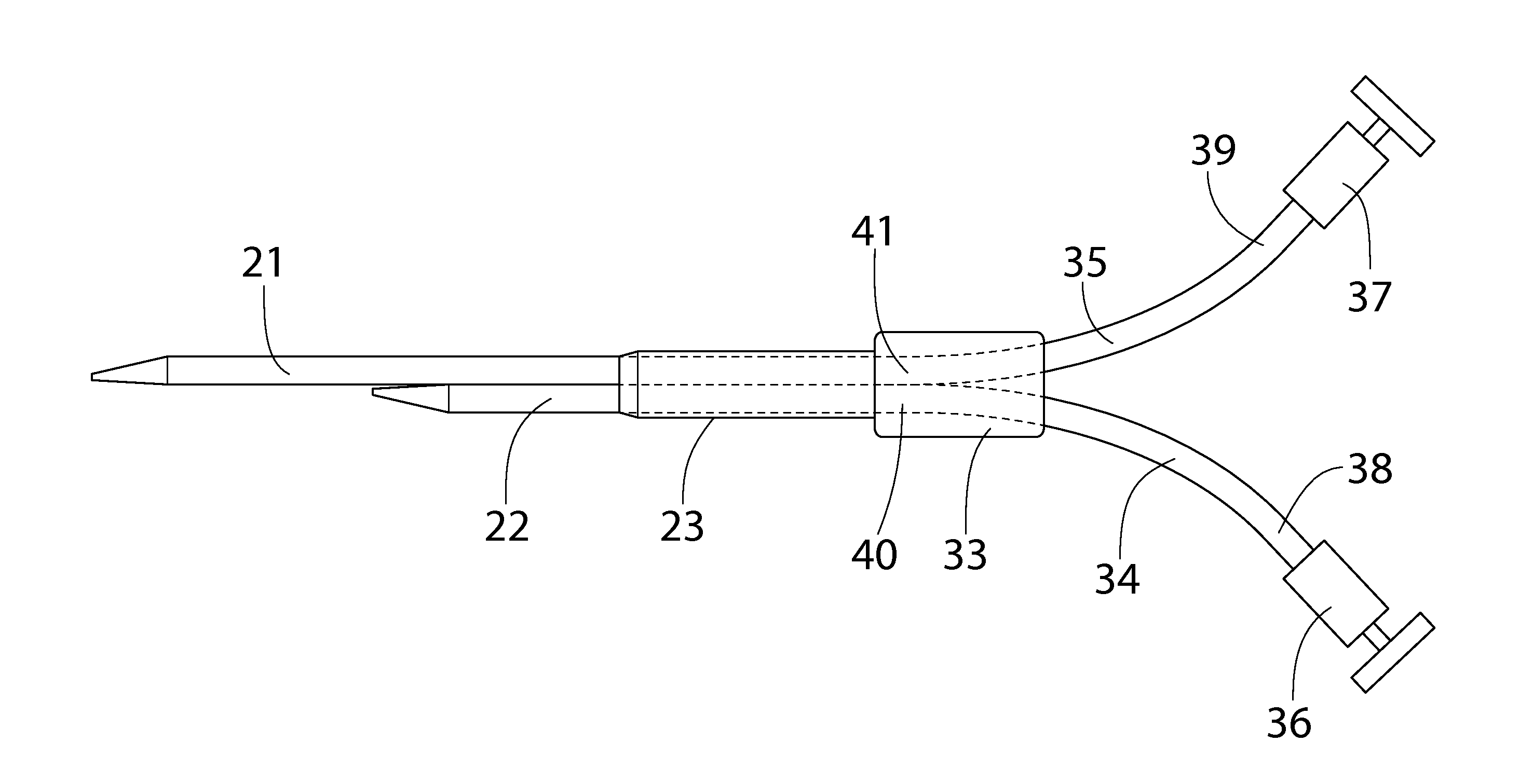
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
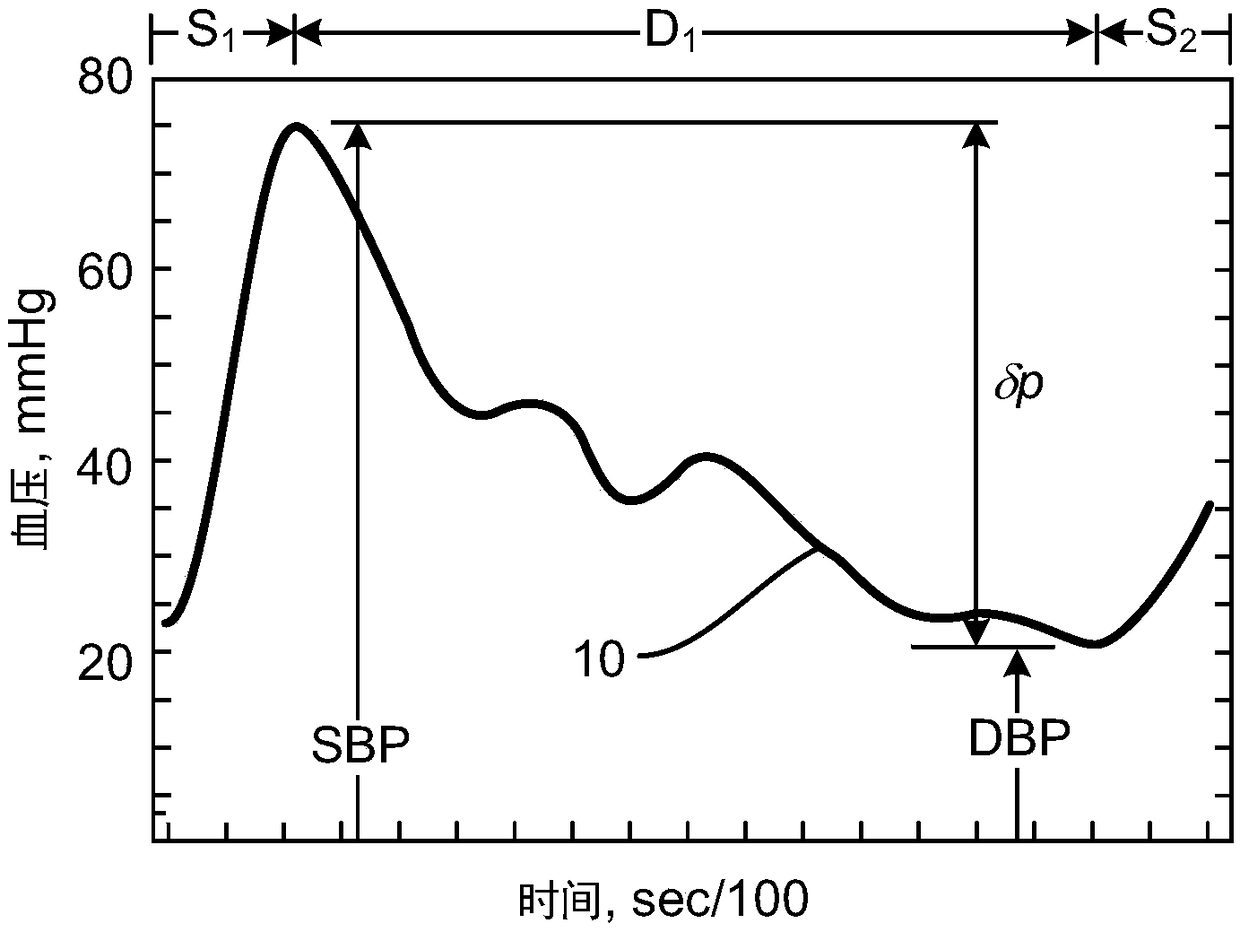
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Dialysis catheter system
InactiveUS20040210180A1Reduce and prevent likelihoodIncrease flow rateMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesArterial canalSuperior vena cava
The present invention provides a dialysis catheter that is designed to function in reverse-flow, having a dual lumen configuration. An embodiment of the present invention includes two lumen cooperatively configured in a co-axial design. The arterial lumen is circular or oval and extends beyond the termination of the venous lumen. The arterial lumen extracts the blood from the blood vessel for hemodialysis treatment. The venous lumen is also circular or oval. Terminating at a proximal point to the distal end of the arterial lumen, this configuration of the venous lumen aids in preventing recirculation. The venous lumen returns dialyzed blood back into the patient. The venous lumen can further include a plurality of apertures to aid in reducing the risk of fibrin sheath growth. In a method of use, the arterial lumen of the invention preferably resides within the right atrium with the venous lumen positioned within the superior vena cava.
Owner:ALTMAN SANFORD D
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Drug delivery device
InactiveUS20050187607A1Reduce inflammationReduce proliferationStentsBlood vesselsGrowth retardantProgenitor
A medical device for drug delivery is provided which includes a stent structure and a biologically active structure attached to the stent structure. The biologically active structure is comprised of a plurality of layers, including a first layer having a first biologically active compound, such as an anti-proliferative, cytostatic or cytotoxic drug, for delivery at a first target site, such as the vascular tissue; a second layer having a second biologically active compound, such as a growth factor, for delivery into the arterial lumen and capable of promoting engraftment and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells and / or endothelial progenitor cells at a second site of myocardial injury; and a third, middle layer which is substantially or selectively impermeable to both the first and second biologically active compounds.
Owner:AKHTAR ADIL JAMAL +1
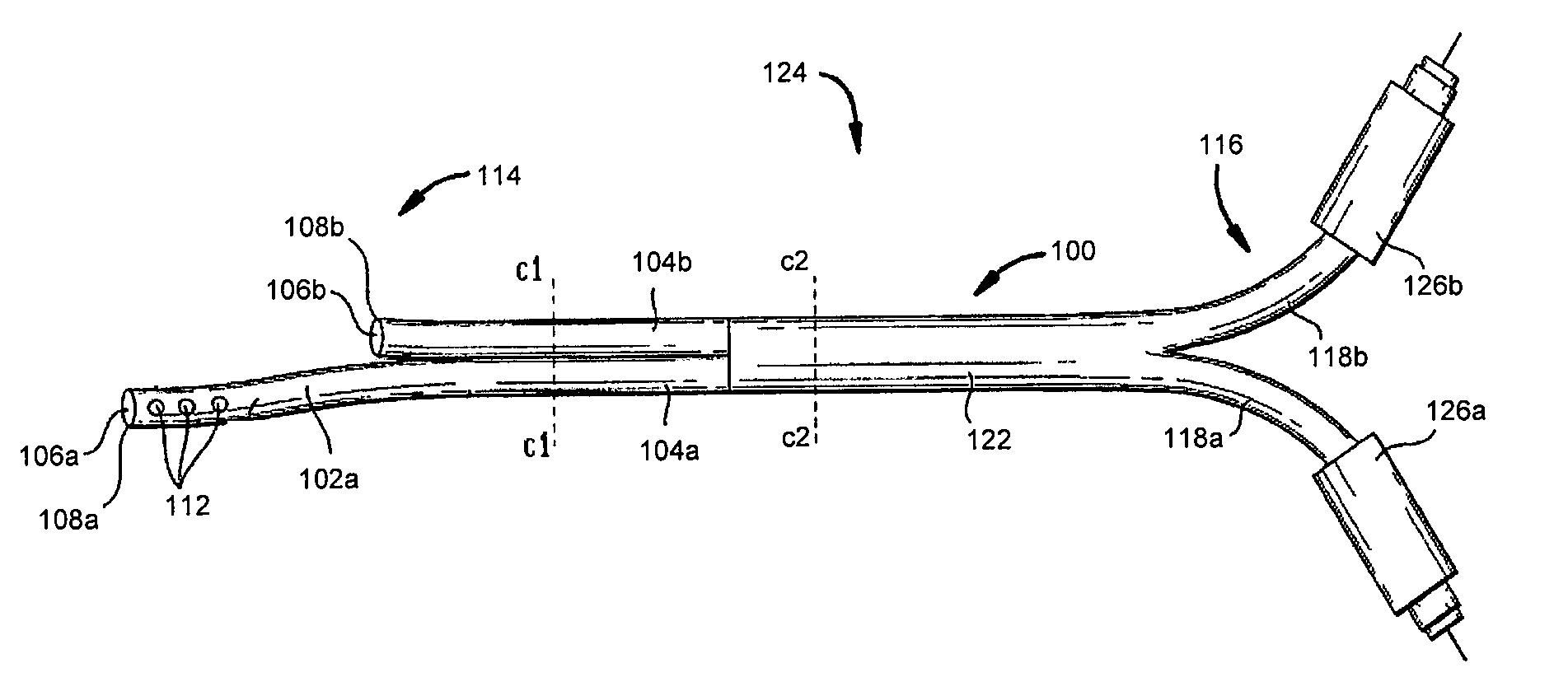
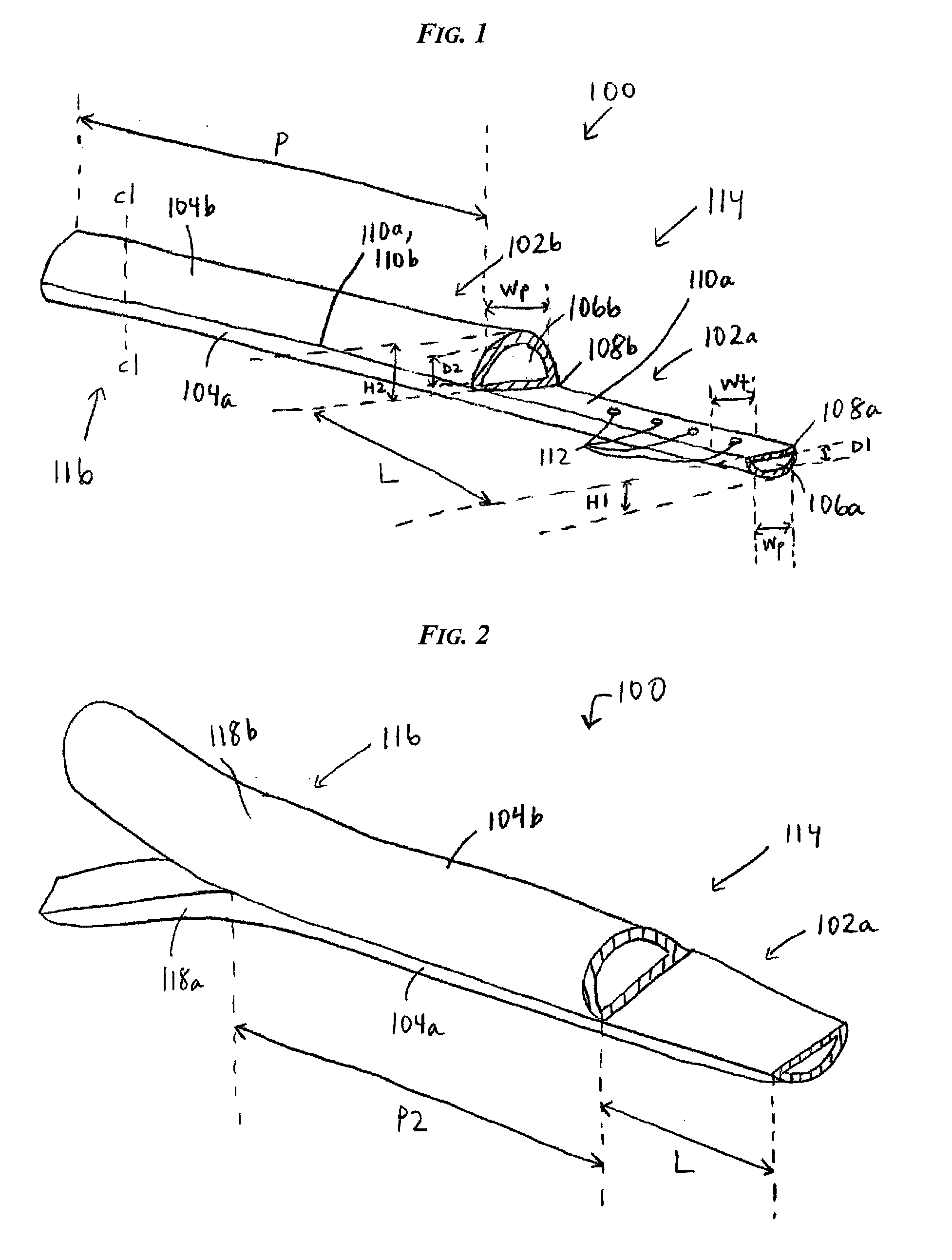
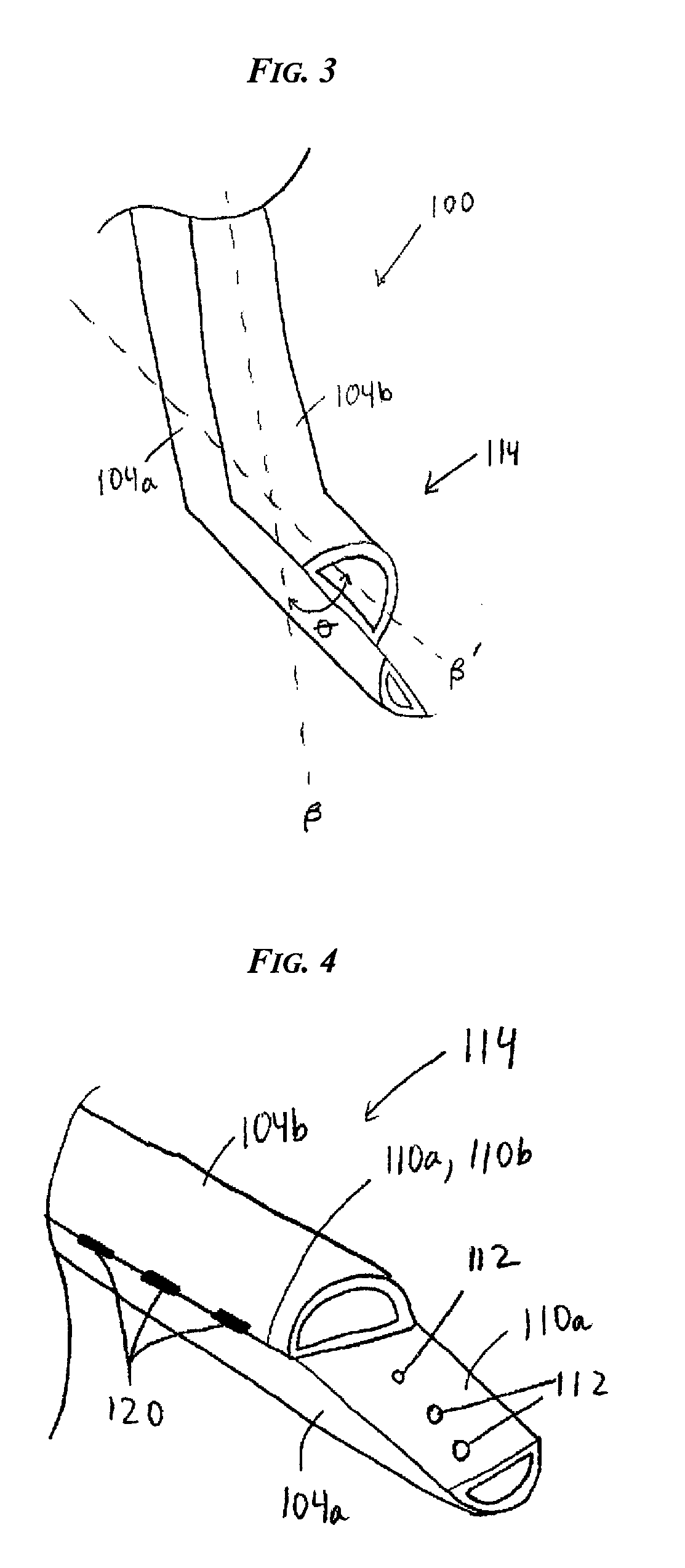
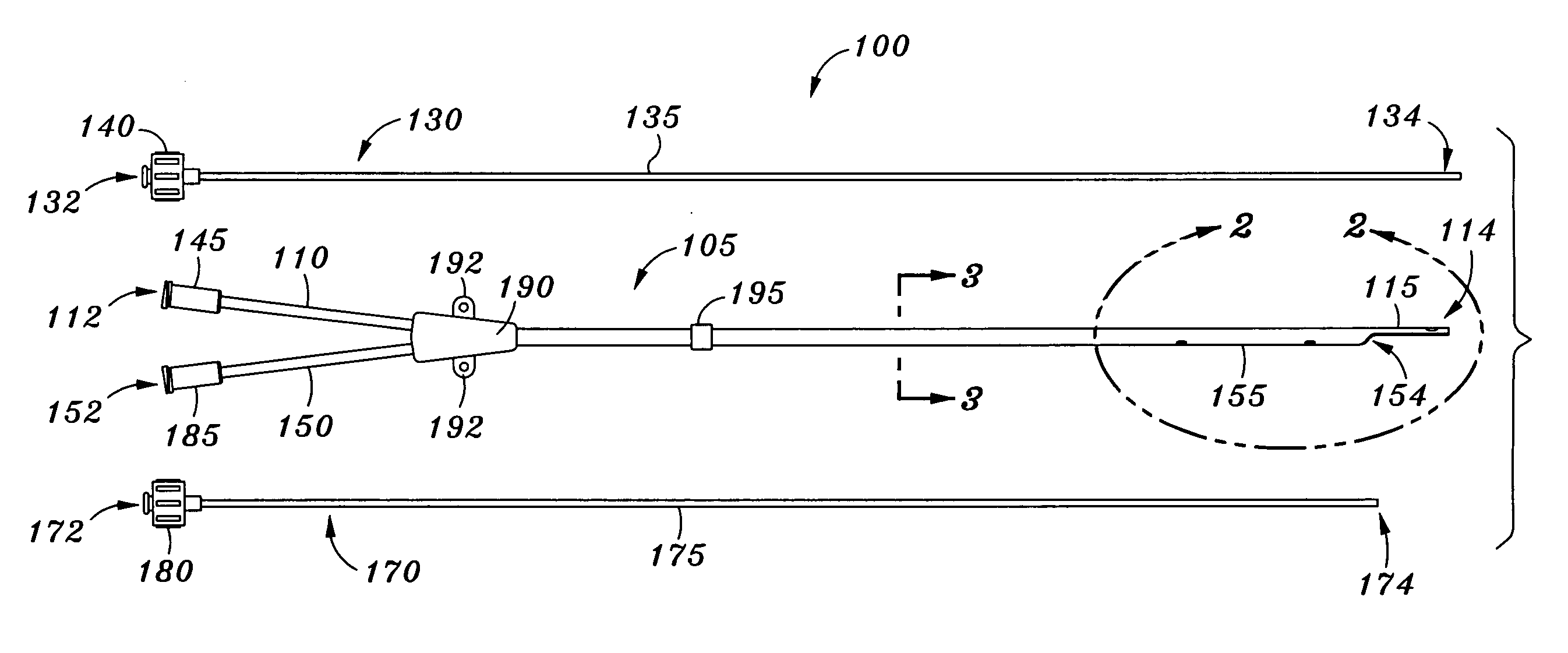
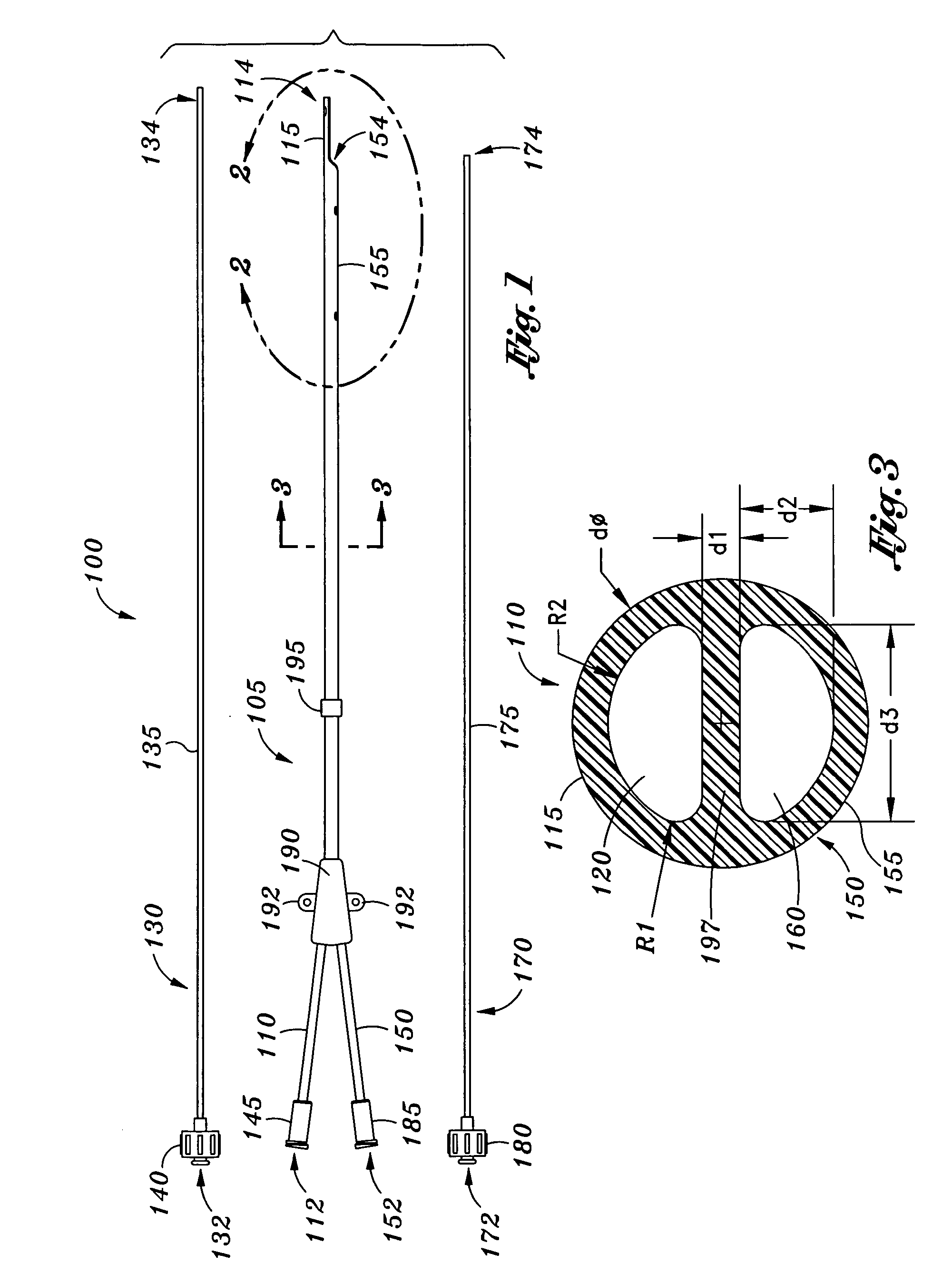
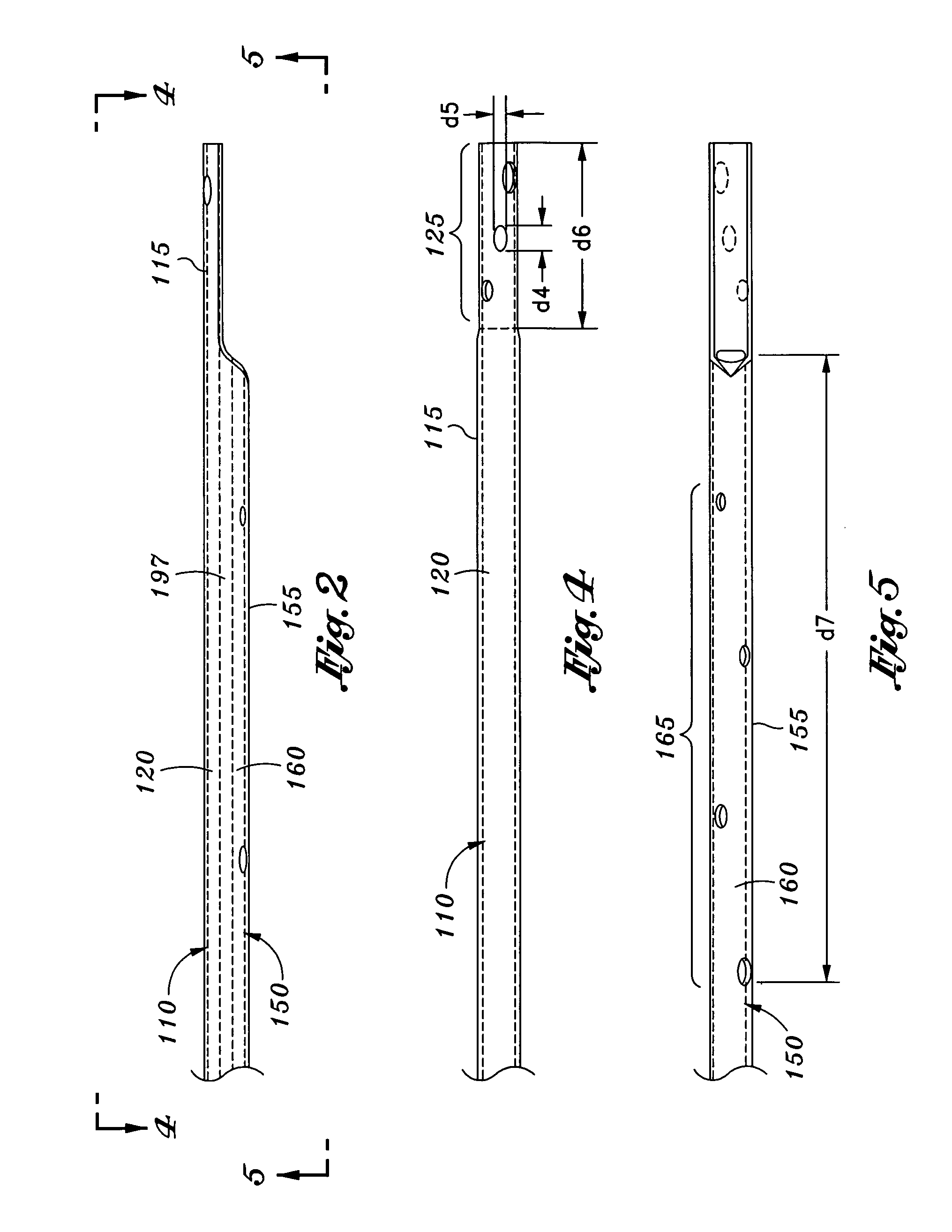
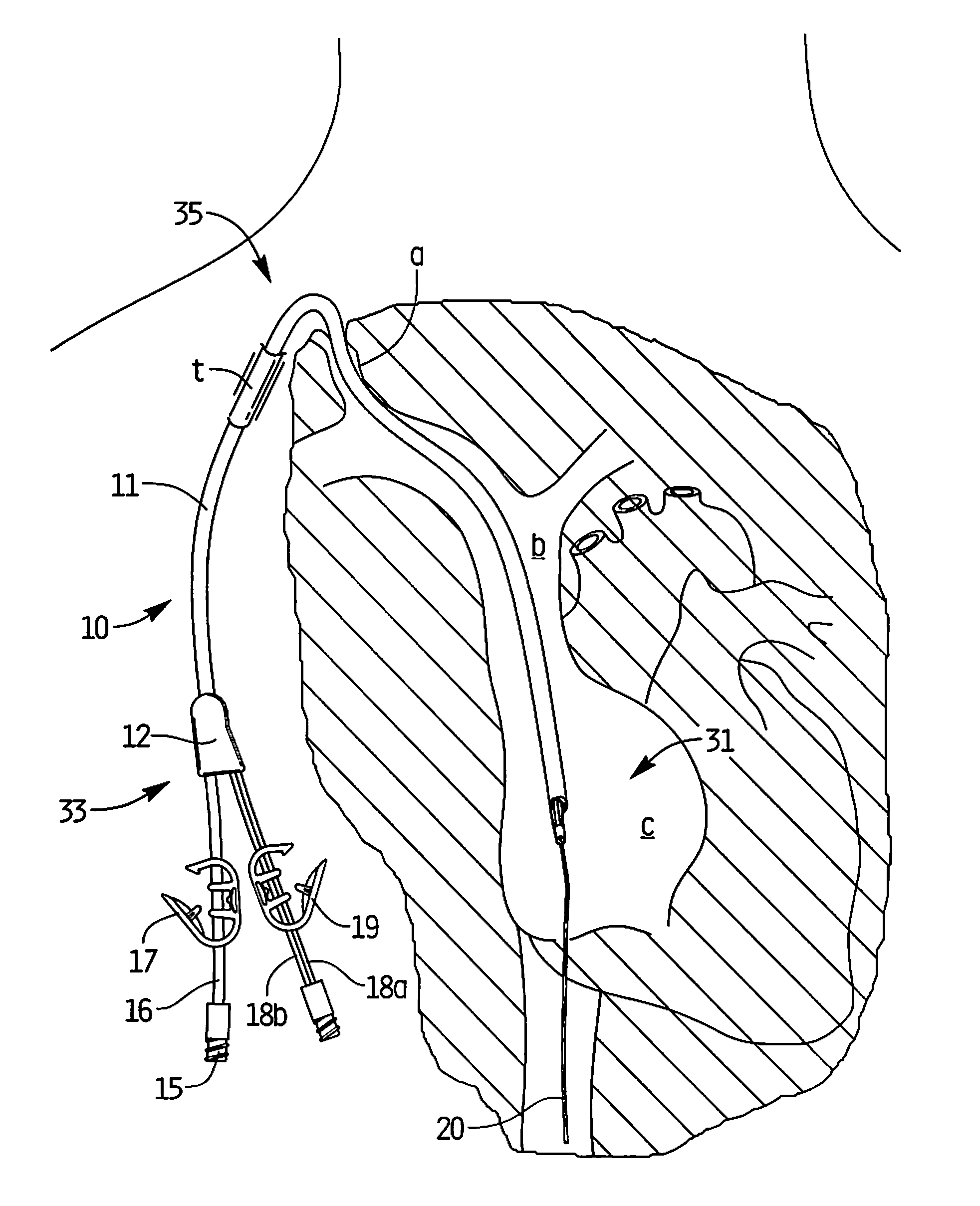
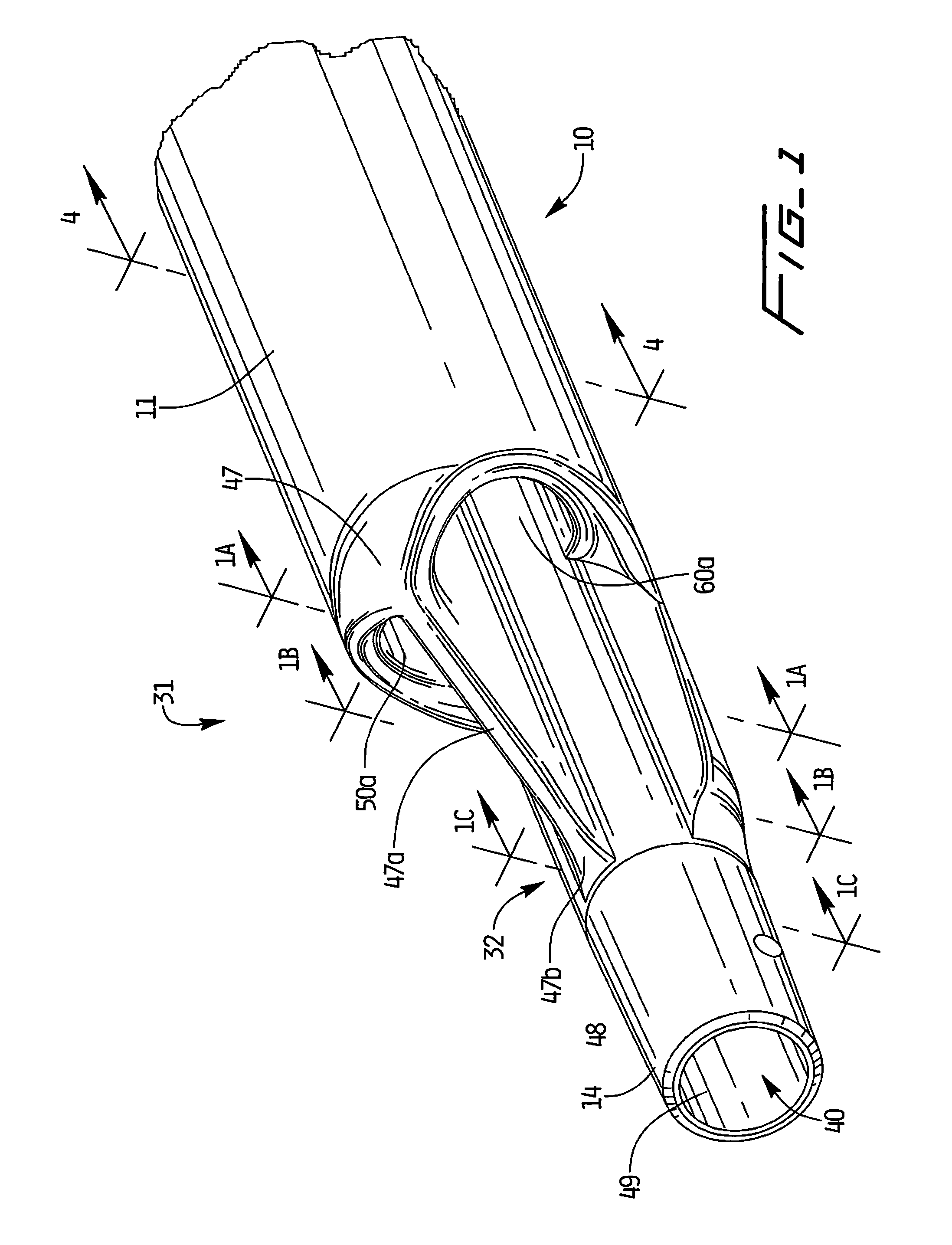
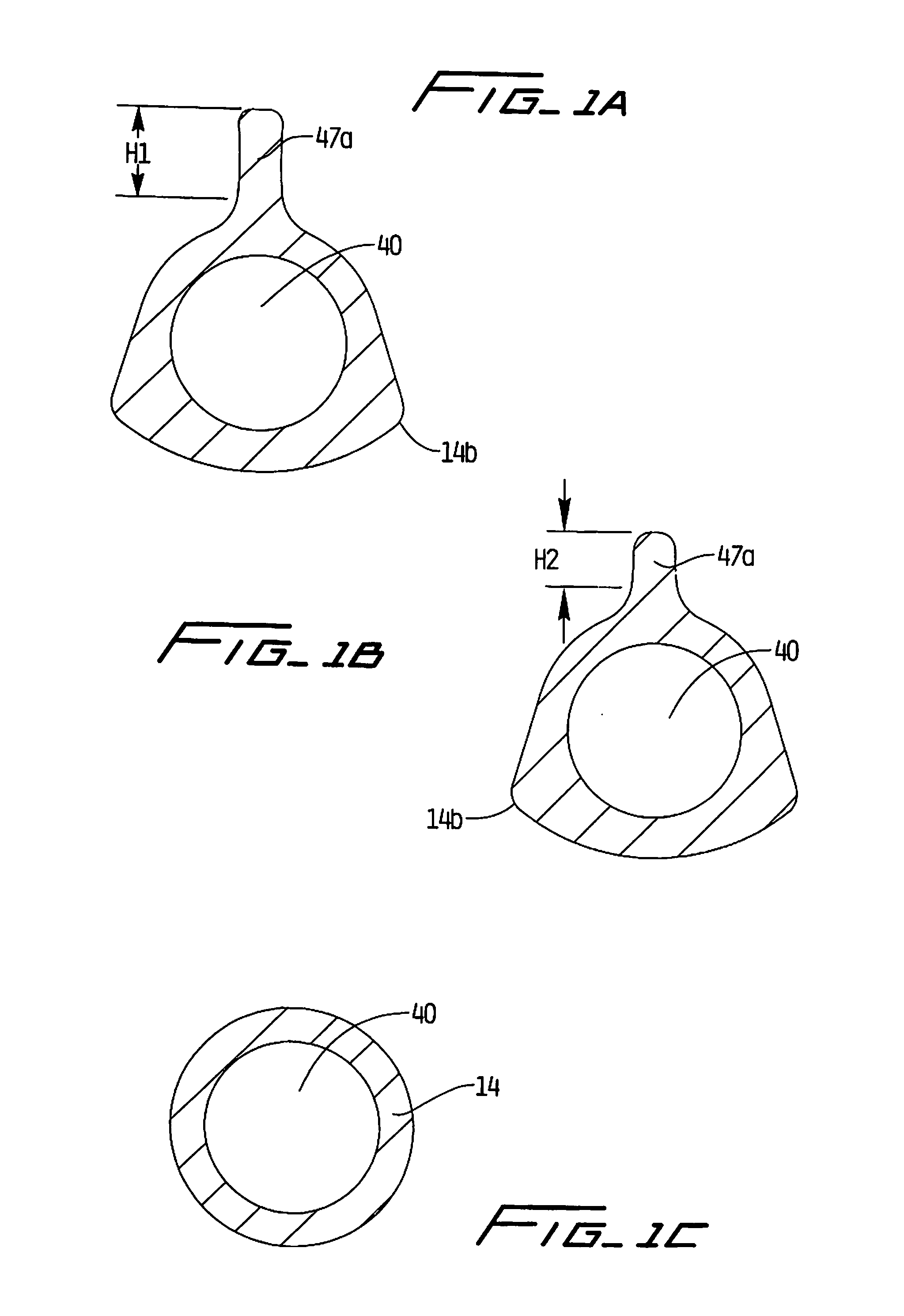
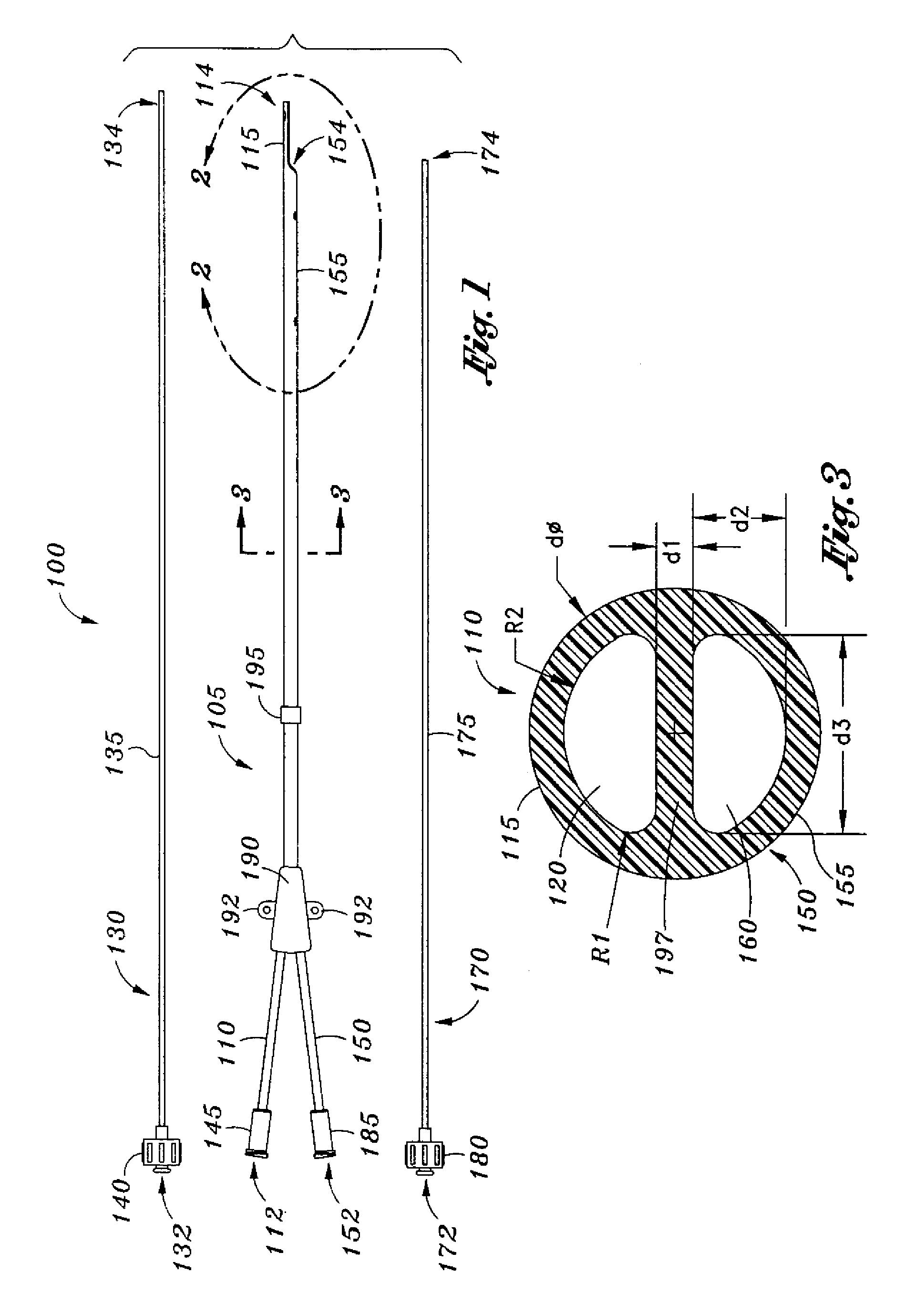
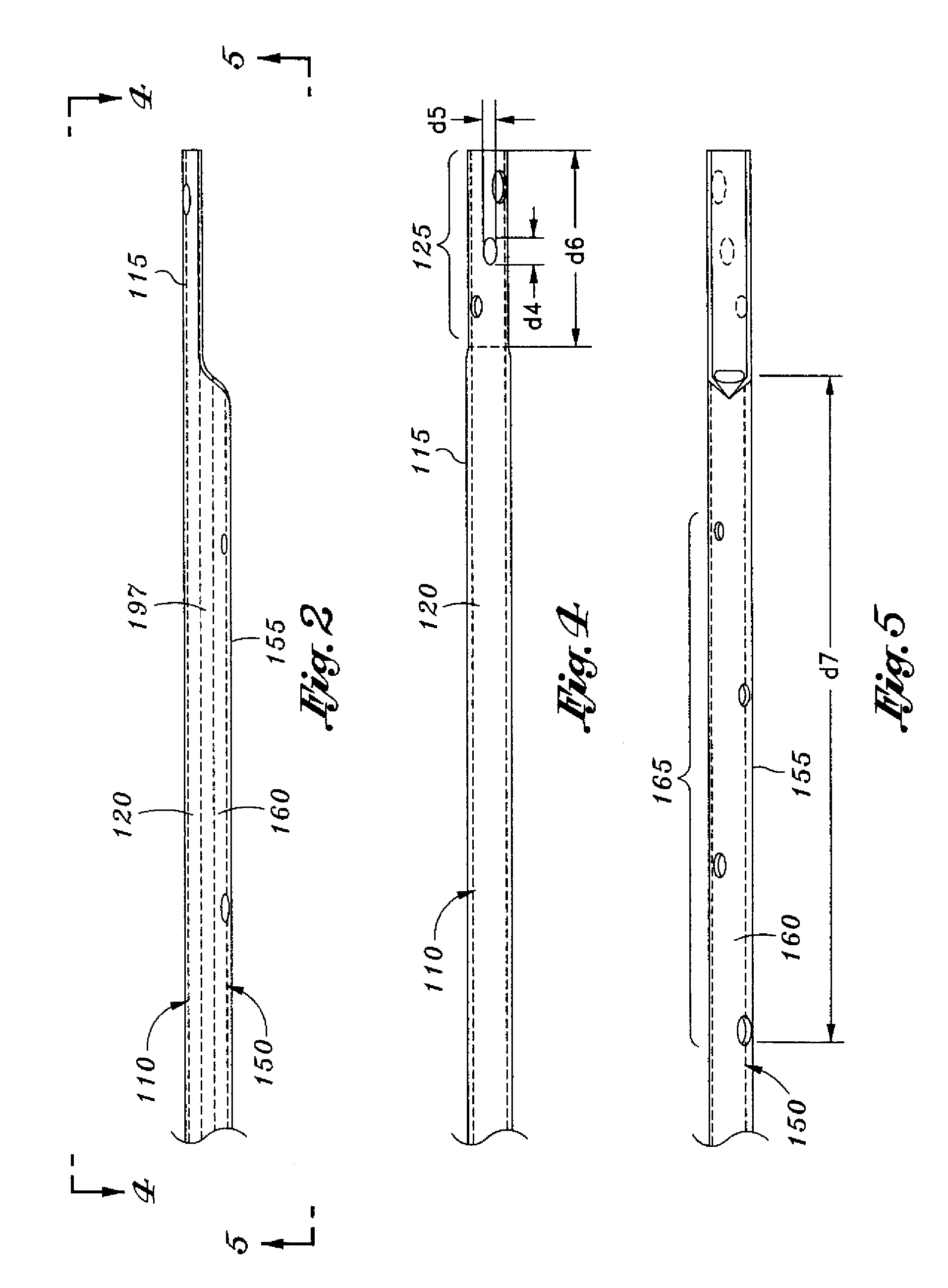
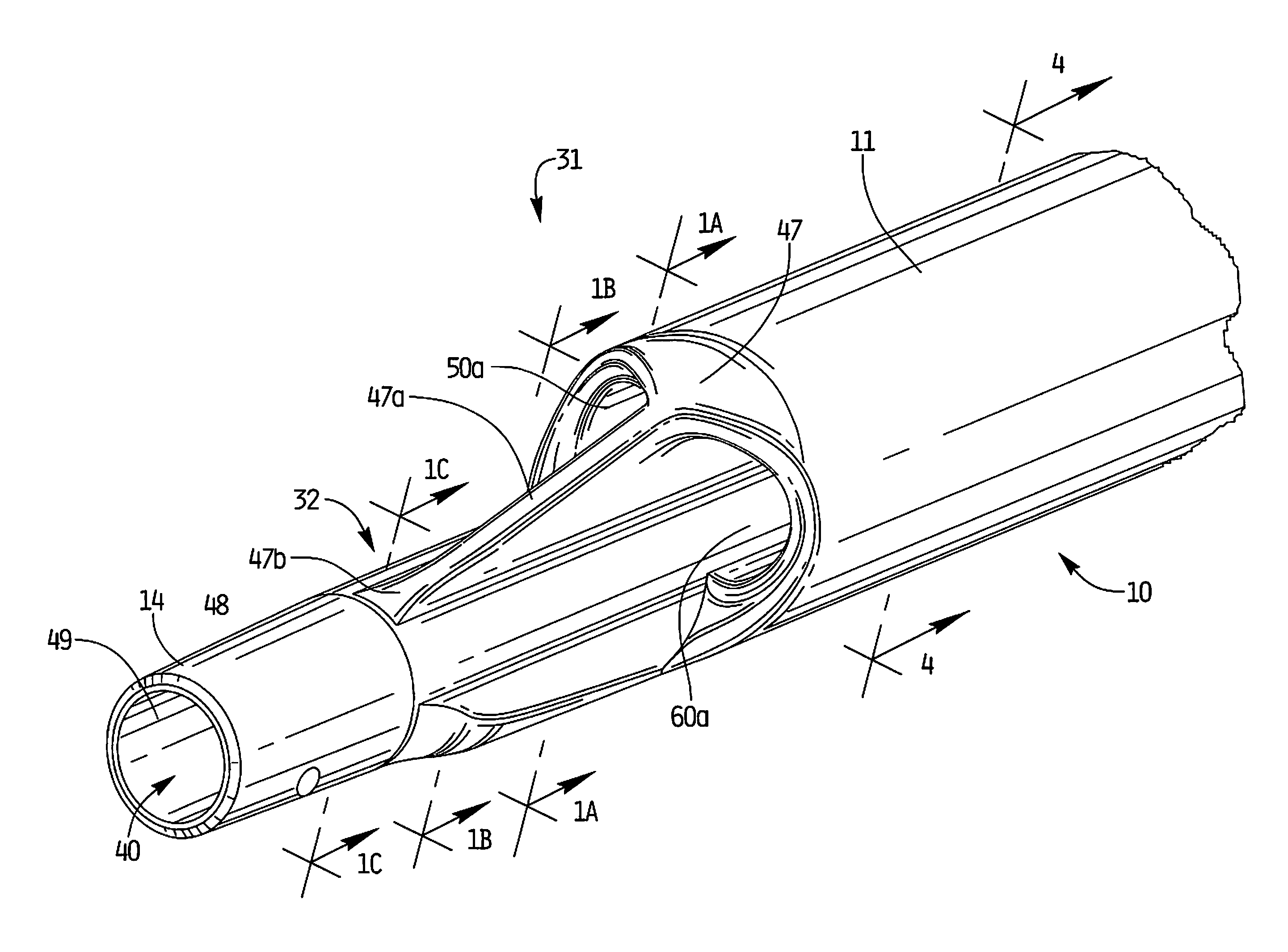
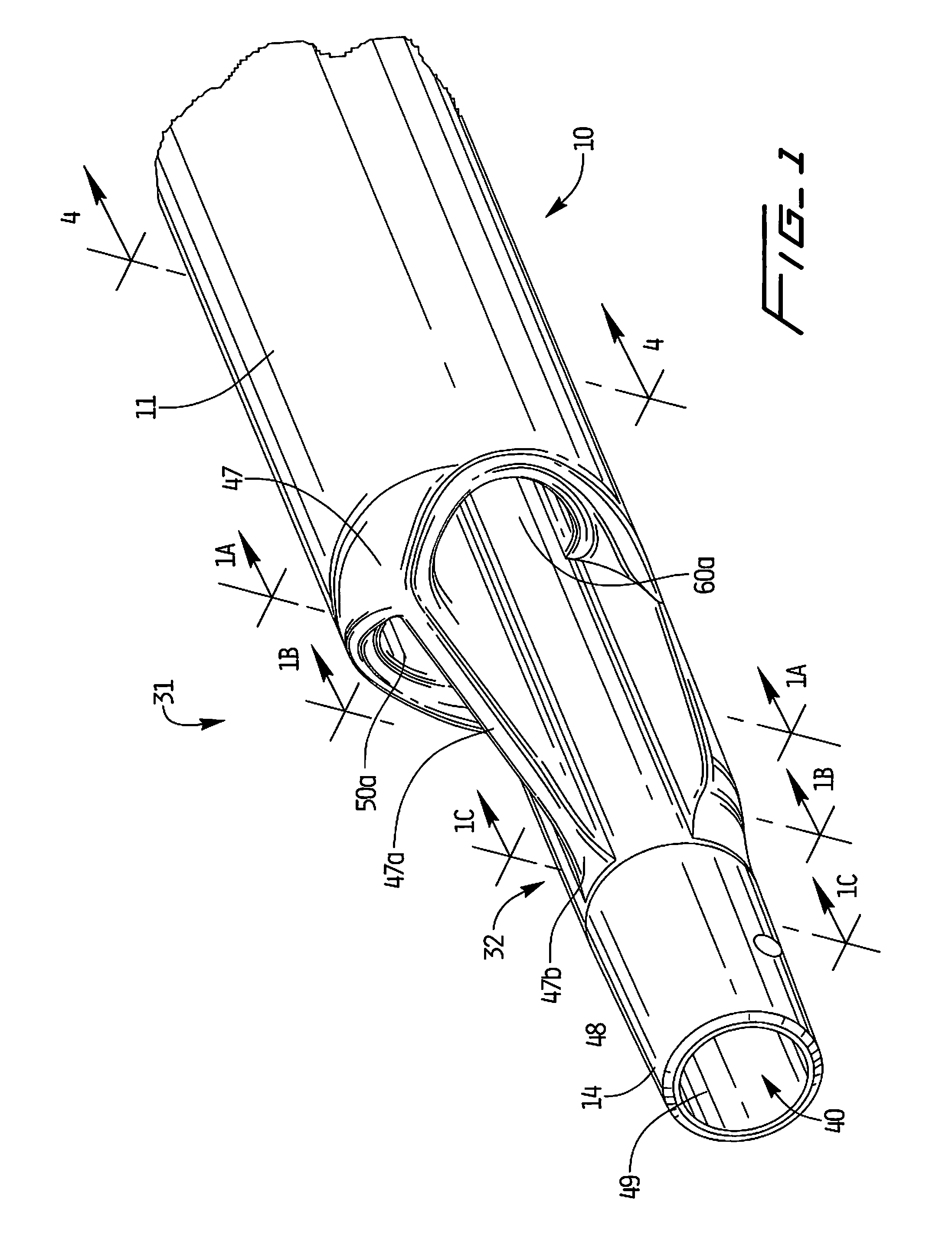
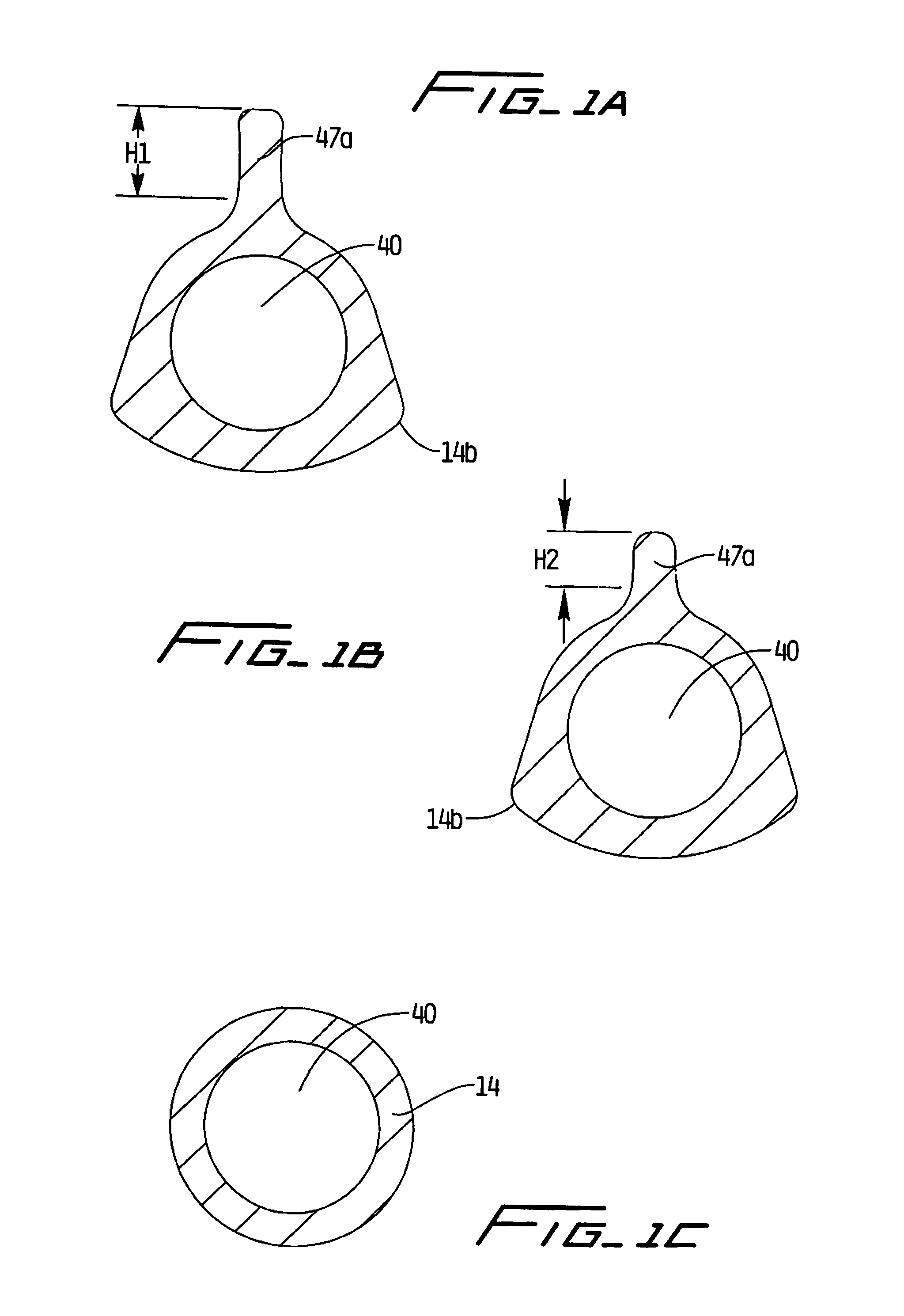
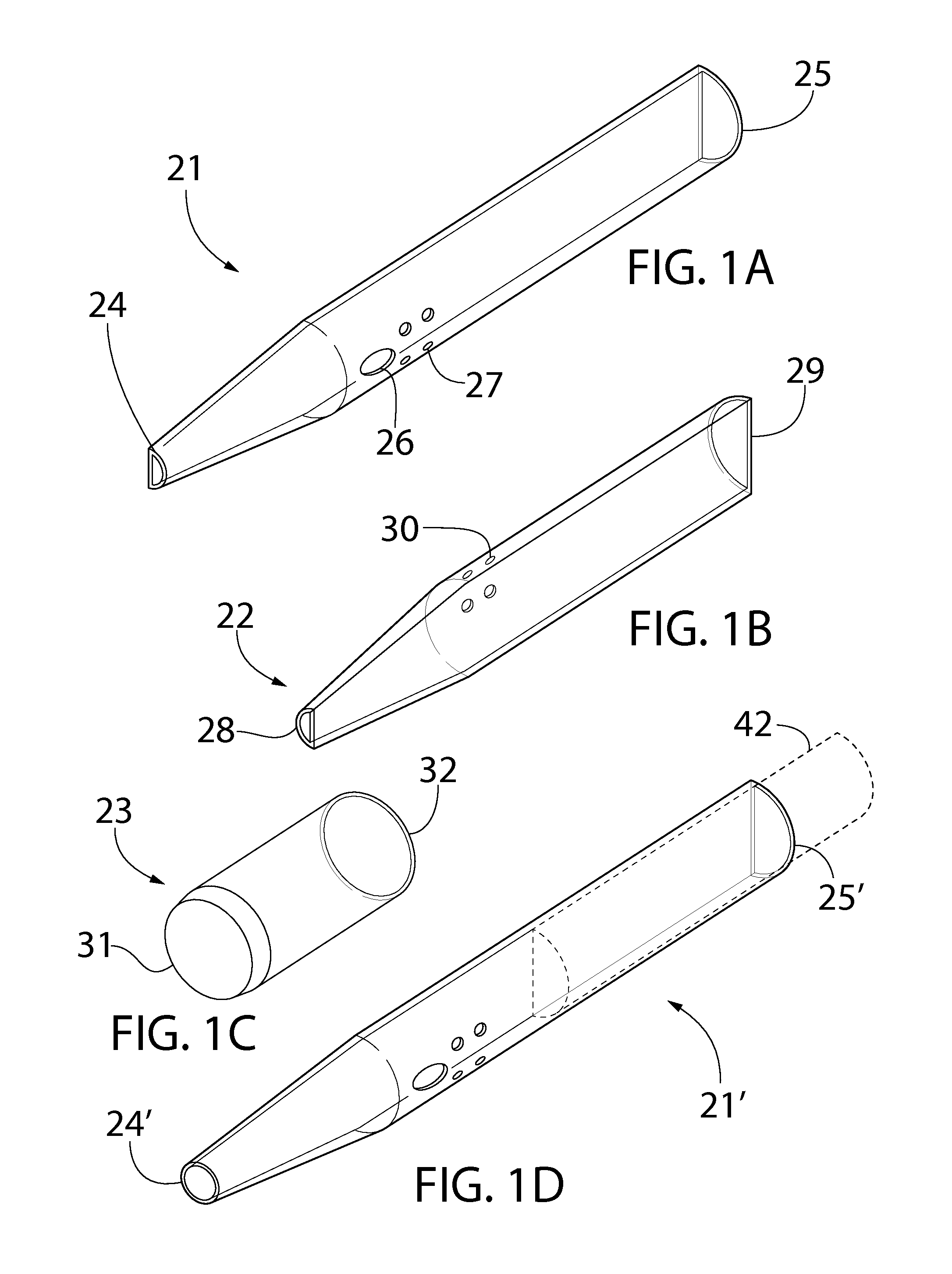
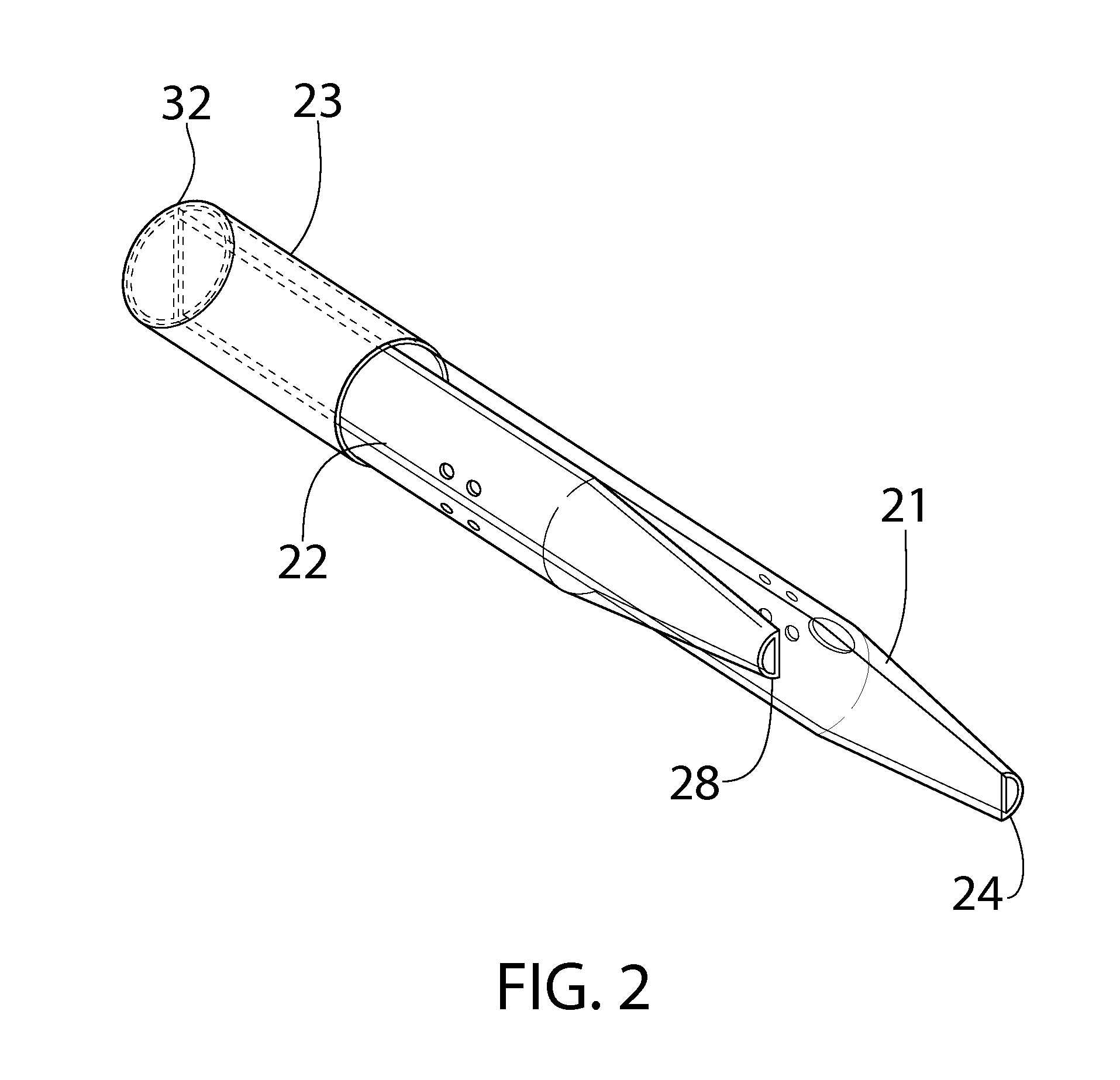
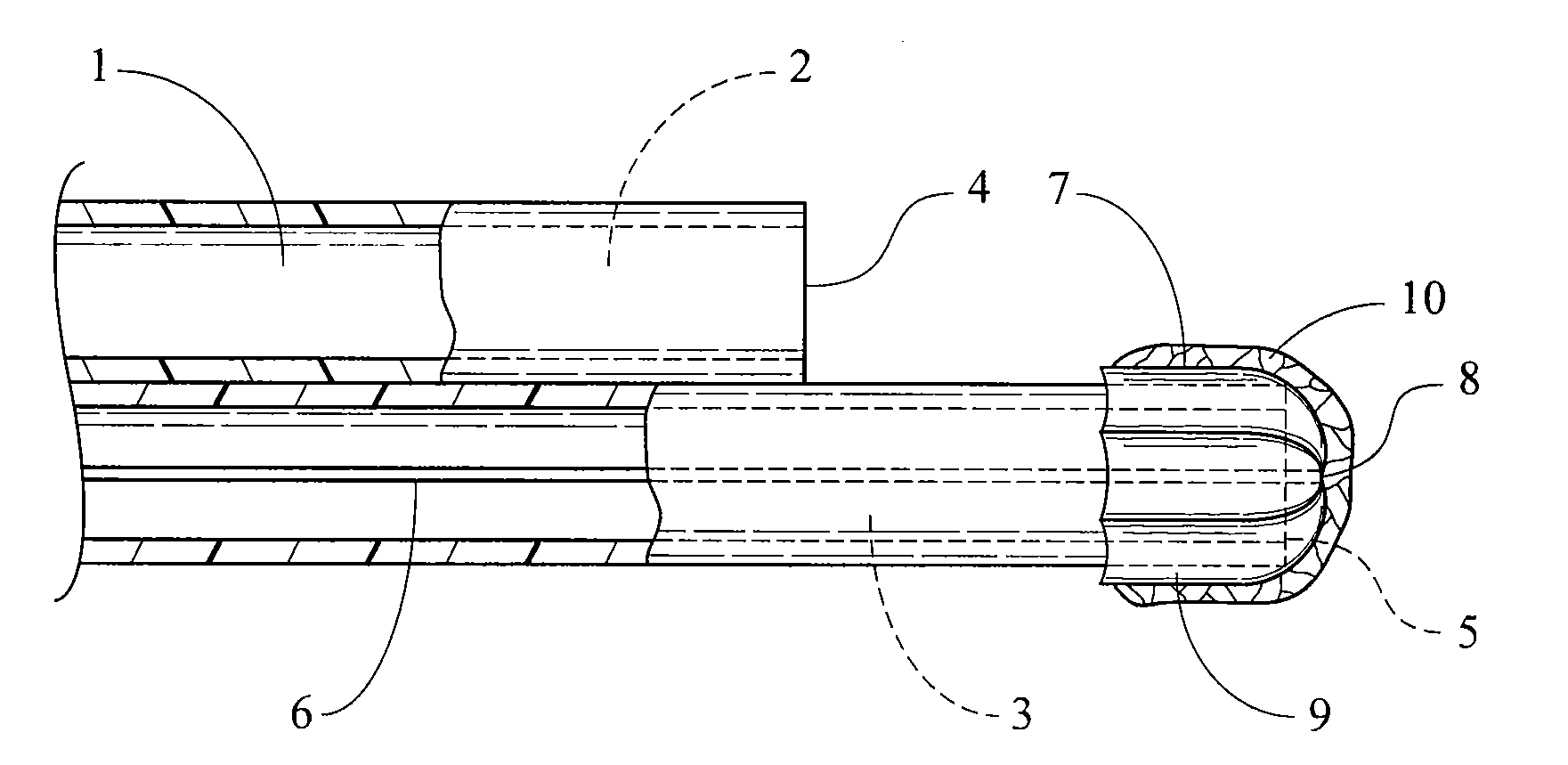
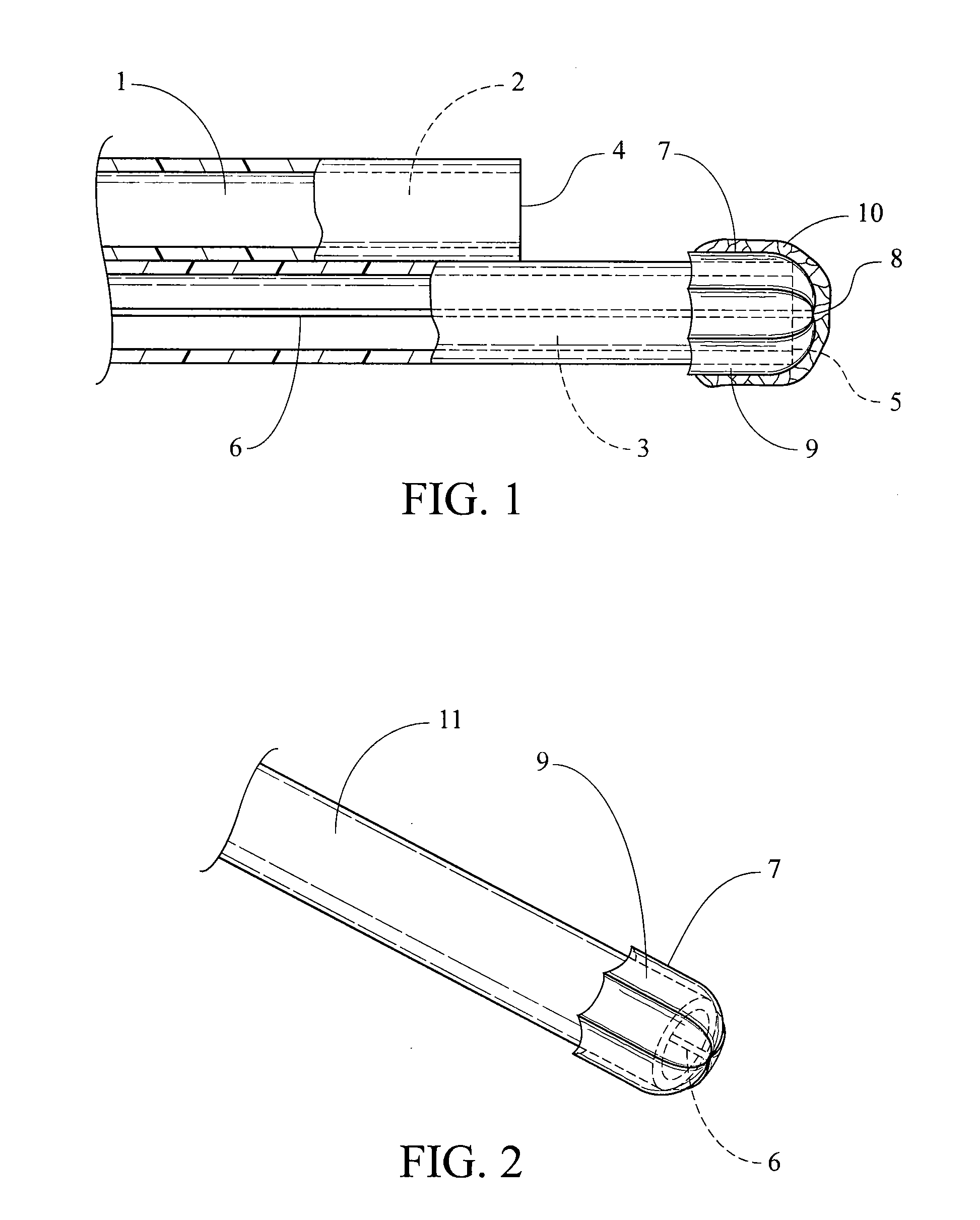
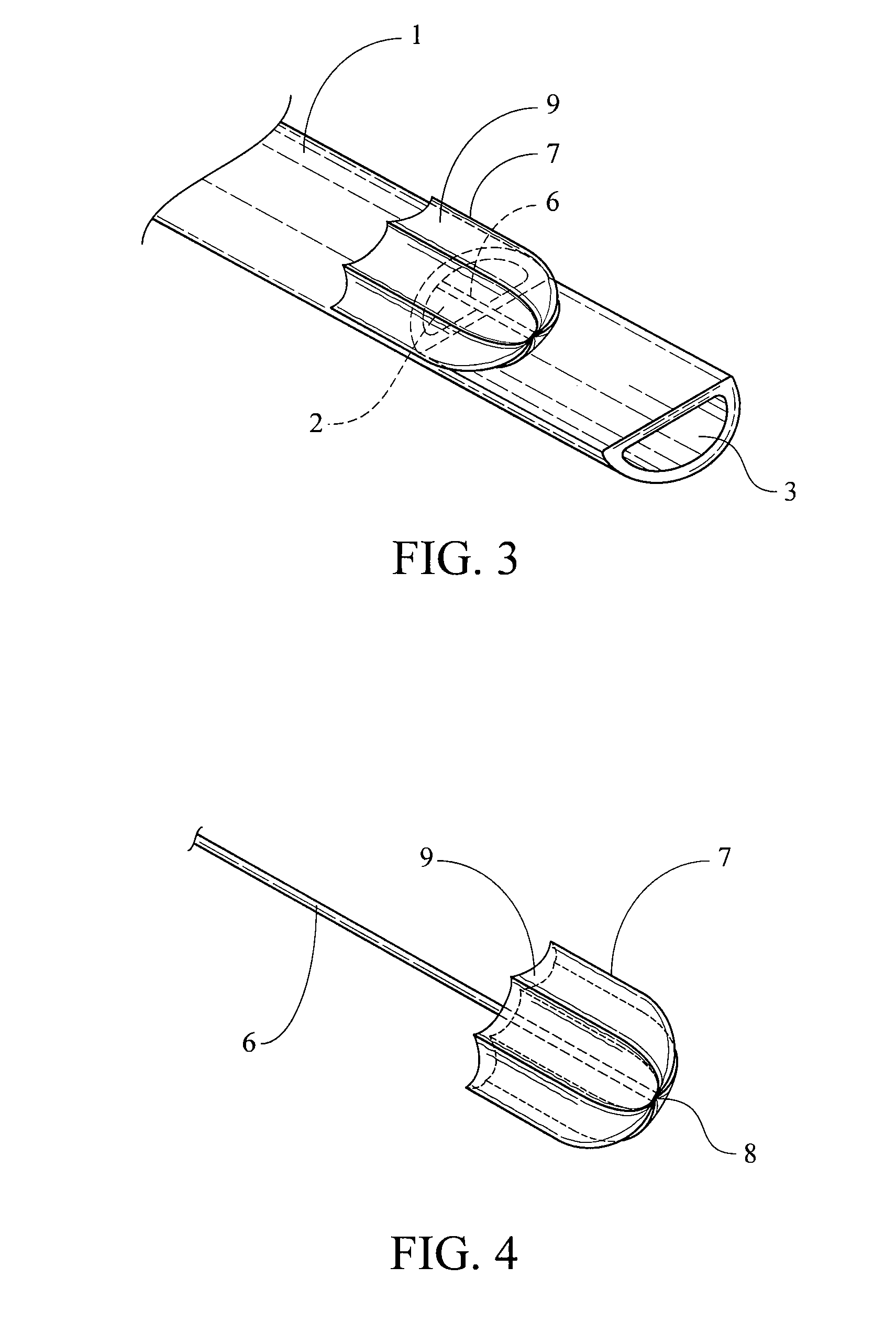
Catheters with enlarged arterial lumens
Asymmetric lumen catheter devices are disclosed. In one aspect of the invention, a catheter assembly includes a first catheter tube having a first lumen extending longitudinally through the first catheter tube and a second catheter tube attached to the first catheter tube. The second catheter tube extends a longitudinal length beyond a distal end of the first catheter tube and has a second lumen extending longitudinally therethrough. The first lumen has a larger cross-sectional size than the second lumen.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
Method and system for balloon counterpulsation during aortic valve replacement
Methods and systems for regulating aortic regurgitation during aortic valve replacement or repair procedures utilize a temporary aortic valve (TAV) catheter and a controller. The temporary aortic valve catheter has an expandable occlusion device which can partially occlude the aortic lumen during ventricular diastole with a lesser occlusion during ventricular systole. Exemplary balloon structures include multiple, independently inflatable balloons which are inflated in synchrony with the cardiac cycle by the controller. By controlling aortic regurgitation, the repair or replacement protocols can be conducted with less interference from blood flow.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
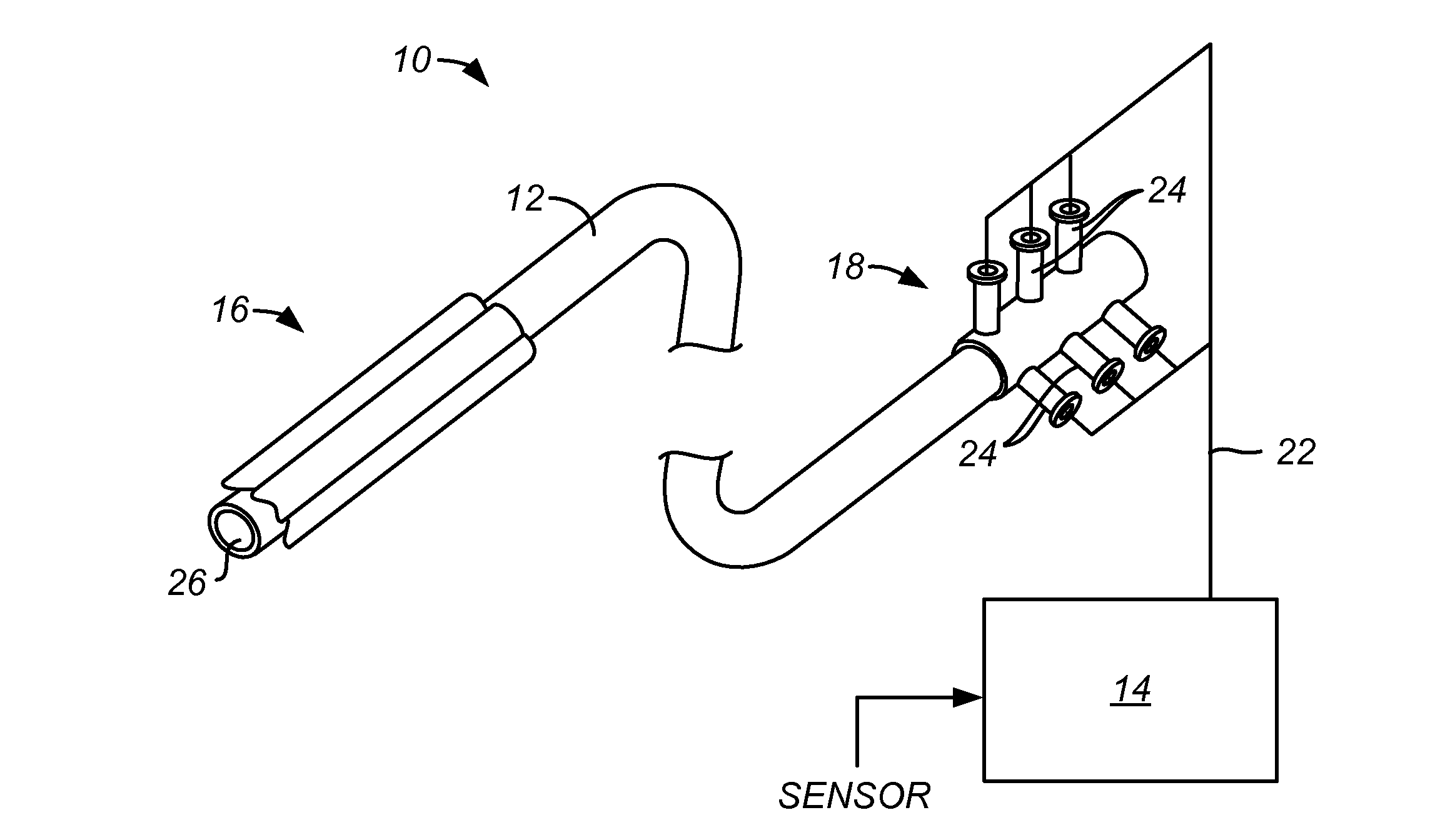
Hemodialysis catheter apparatus
A catheter apparatus is provided for reducing blood clotting in connection with hemodialysis treatment. The catheter apparatus can comprise a first conduit defining an arterial lumen and a second conduit defining a venous lumen. Large staggered apertures can be provided in side walls of the conduits with at least one of the apertures having a cross-sectional area equal or greater than a cross-sectional area of one of the lumens. The catheter apparatus can further include first and second removable obturators adapted for axial insertion into the conduits and for occluding the apertures while so inserted. Advantageously, the obturators can wipe the apertures during removal, causing blood clots incident on the apertures to be dislodged from the apertures. Related methods for using the catheter apparatus in performing hemodialysis treatment are also provided.
Owner:INTERVENTION INNOVATIONS
Dialysis catheter
ActiveUS20110301522A1Increase stiffnessEasy to insertMulti-lumen catheterDialysis systemsShortest distanceDistal portion
A dialysis catheter including a first portion having an outer wall having a first diameter, an elongated distal portion having a second diameter smaller than the first diameter, and a transition region between the first portion and distal portion. A first longitudinally extending venous lumen is configured to deliver blood. First and second independent longitudinally extending arterial lumens are configured to withdraw blood from a patient. The venous lumen and arterial lumen have first and second regions each positioned a first distance from the outer wall of the catheter and a third region positioned a second shorter distance from the outer wall of the catheter to form an arch shaped wall portion progressively increasing in thickness from the third region toward the first region and from the third region to the second region.
Owner:ARGON MEDICAL DEVICES
Hemodialysis catheter apparatus
A catheter apparatus is provided for reducing blood clotting in connection with hemodialysis treatment. The catheter apparatus can comprise a first conduit defining an arterial lumen and a second conduit defining a venous lumen. Large staggered apertures can be provided in side walls of the conduits with at least one of the apertures having a cross-sectional area equal or greater than a cross-sectional area of one of the lumens. The catheter apparatus can further include first and second removable obturators adapted for axial insertion into the conduits and for occluding the apertures while so inserted. Advantageously, the obturators can wipe the apertures during removal, causing blood clots incident on the apertures to be dislodged from the apertures. Related methods for using the catheter apparatus in performing hemodialysis treatment are also provided.
Owner:INTERVENTION INNOVATIONS
High coverage and low profile electrode assembly for angioplasty shockwave catheter
The invention discloses a shock wave generating system for an angioplasty catheter. The system includes an elongate member, wire electrodes, a non-conductive gap, each wire electrode attached to an electrical output terminal of a high voltage power source by an electrical wire extending from a terminal on an outer surface of the elongate member to the wire electrode. The system is an electrode assembly of a shock wave generating angioplasty catheter for treating calcified arteries. Shock waves are impact in nature and can impact and decompose hard calcified platelets deposited on the inner wall of the artery. Once these deposits are fragmented, the space of the arterial lumen expands, thereby improving blood flow.
Owner:谱创医疗科技(上海)有限公司
Continuous calibration of a blood pressure measurement device
Systems, methods, and devices of the various embodiments enable continuous non-invasive monitoring of blood pressure with a minimum of interference. The various embodiments may provide a method for adaptation for the calibration for continuous measurements of blood pressure, wherein the measured quantity may be related to an arterial lumen or arterial cross sectional area comprising calibrating the conversion for incremental variations of arterial properties and absolute value adaptation by exploitation of the exponential decay during the diastole. In various embodiments, continuous calibration of a non-interfering blood pressure measurement device may be initiated based on a change in mean arterial pressure being greater than a threshold value, such as a pressure value associated with an actual measured distension of a patient's artery.
Owner:PHILIPS HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS INC
Dialysis catheter
ActiveUS8591450B2Increase stiffnessEasy to insertMulti-lumen catheterMedical devicesShortest distanceDistal portion
Owner:ARGON MEDICAL DEVICES
Split Tip Catheter for Dialysis Treatment
InactiveUS20150320927A1Easy to makeInexpensive materialsMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesBlood arterialOuter Cannula
Disclosed is a split tip catheter having a tapered venous lumen and a tapered arterial lumen, wherein each of the lumens includes a D-shaped cross section. In one embodiment, the length of the venous lumen is greater than the length of the arterial lumen. The venous lumen and the arterial lumen are secured in a side-by-side configuration via an outer sleeve such that the proximal end of the outer sleeve is aligned with the proximal ends of the venous lumen and the arterial lumen, leaving the distal ends of the venous lumen and the arterial lumen free. The proximal ends of the outer sleeve, the venous lumen, and the arterial lumen are insert molded to a hub to connect the lumens to extensions such as venous and arterial blood lines for dialysis treatments.
Owner:VASCUTECH MEDICAL
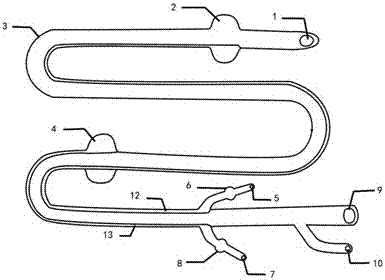
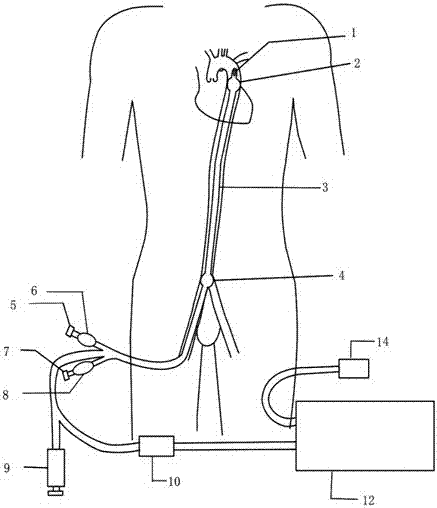
Aortic intracavitary double-horizontal-sacculus blockage pressurized infusion system
PendingCN106924862AImprove recovery effectEasy to primeBalloon catheterSurgeryAorta partMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an aortic intracavitary double-horizontal-sacculus blockage pressurized infusion system. The system comprises a main catheter, an aortic arch sacculus, an aortic arch sacculus injecting catheter, an aortic distal sacculus and an aortic distal sacculus injecting catheter, wherein a main catheter infusion outlet is formed in the top end of the main catheter, and the tail end, introduced to the outside of the body, of the main catheter is a first tail end injecting hole; the aortic arch sacculus is connected to the part below the top end of the main catheter; the aortic arch sacculus injecting catheter attaches to the main catheter; the top end of the aortic arch sacculus injecting catheter communicates with the aortic arch sacculus; the bottom end, introduced to the outside of the body, of the aortic arch sacculus injecting catheter is a second tail end injecting hole; the aortic distal sacculus is connected to the middle section part of the main catheter; the aortic distal sacculus injecting catheter attaches to the main catheter; the top end of the aortic distal sacculus injecting catheter communicates with the aortic distal sacculus; and the bottom end, introduced to the outside of the body, of the aortic distal sacculus injecting catheter is a third tail end injecting hole. For the aortic intracavitary double-horizontal-sacculus blockage pressurized infusion system, the rescuing resuscitating success rate for patients suffering from hemorrhagic sudden cardiac arrest can be improved by improving the effective continuous blood perfusion for the important organs including the heart, the brain, the kidney and the like.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
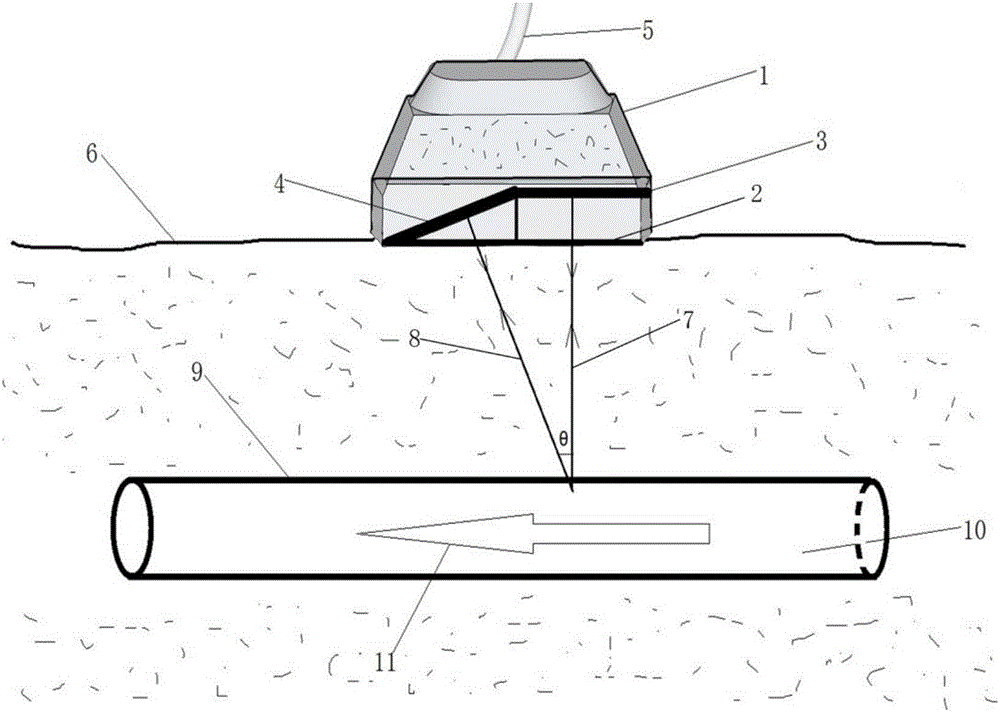
Ultrasonic probe for collecting arterial pulse signals and lumen internal wall face blood signals in corresponding positions
ActiveCN106344072AImprove accuracyEliminate wall pulsation interferenceBlood flow measurement devicesHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSonificationSkin surface
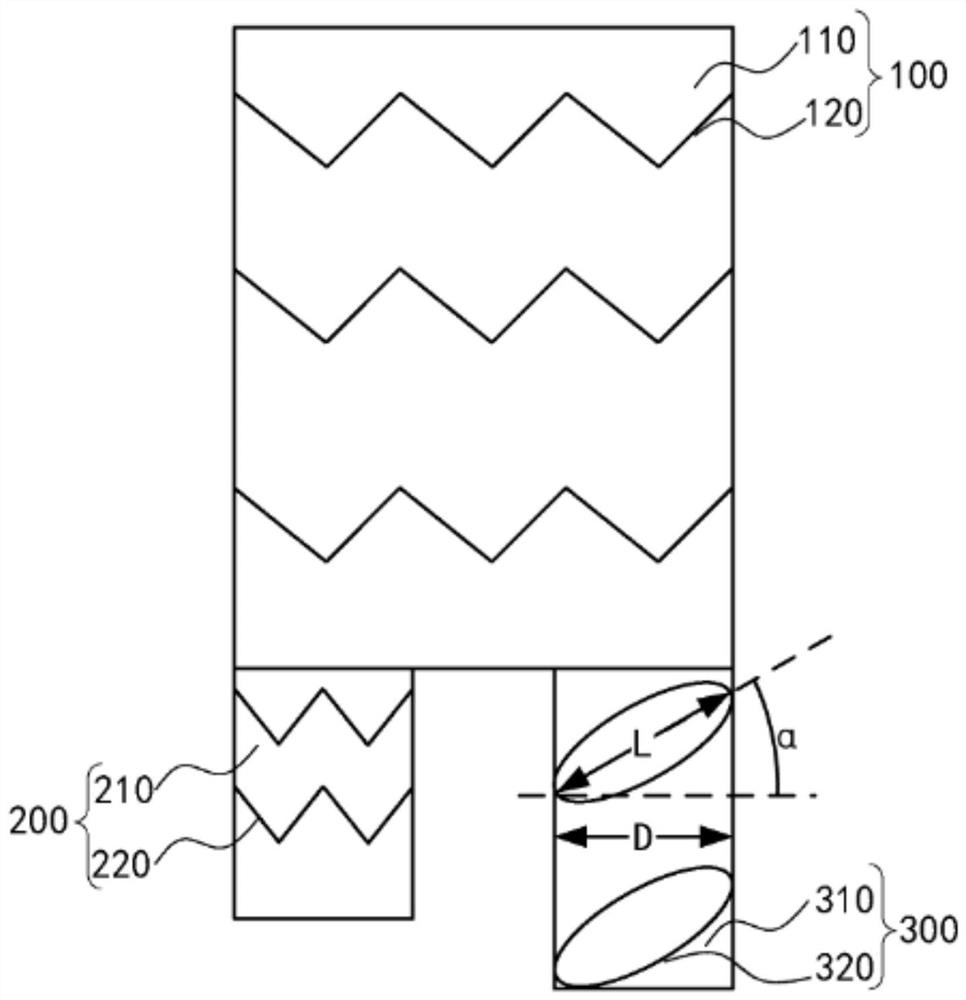
An ultrasonic probe for collecting arterial pulse signals and lumen internal wall face blood signals in corresponding positions comprises a casing (1) with supporting and protecting functions, a parallel piezoelectric patch (3) arranged in the casing (1) and parallel to a probe detection surface (2), an inclined piezoelectric patch (4) arranged at an included angle theta ranging from 30 degrees to 60 degrees with the probe detection surface (2) and an electric cable (5) used for transmitting emitting and receiving signals. During using, the probe is placed on the skin surface (6), the parallel piezoelectric patch (3) emits and receives vertical acoustic beams (7) which are focused to the internal wall face of an arterial blood vessel (9); the inclined piezoelectric patch (4) emits and receives acoustic beams (8) forming an included angle being 90 degrees-theta, and the acoustic beams are focused to the position, close to the blood vessel internal wall face by 0.1-0.5 mm, of an arterial lumen (10). The ultrasonic probe has the advantages of being simple and convenient to operate and high in accuracy; independent vessel wall pulse signals and the blood signals containing the vessel wall pulse information can be detected simultaneously, and the accurate blood vessel wall surface blood speed is obtained through elimination of vessel wall pulse interference of mixed signals.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Systems and methods for navigating, opening and cleaning plaque or total occlusion in arteries
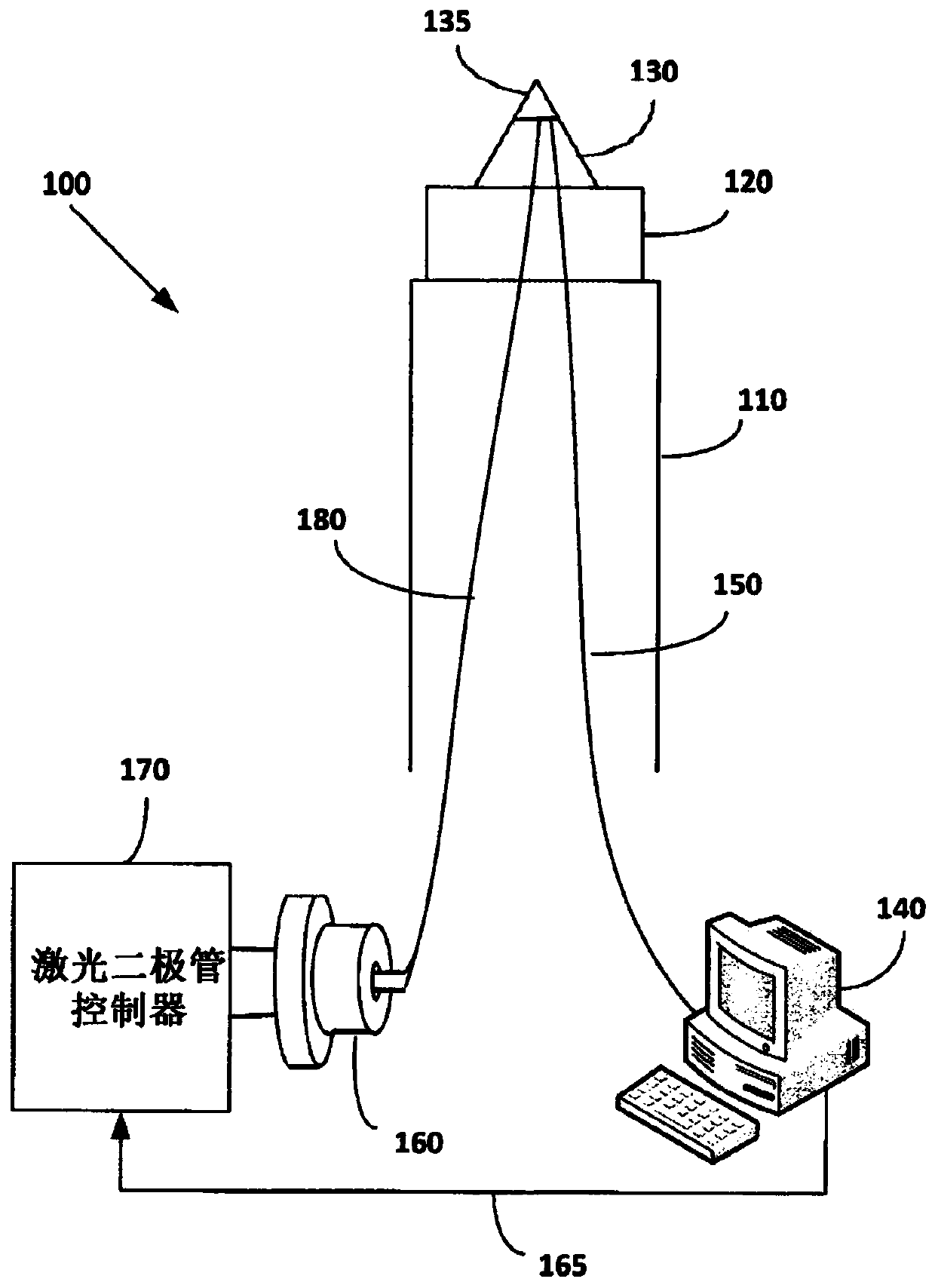
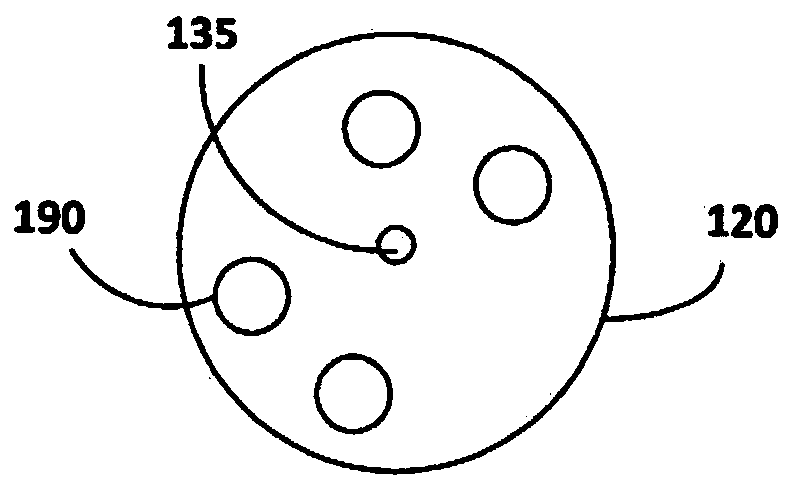
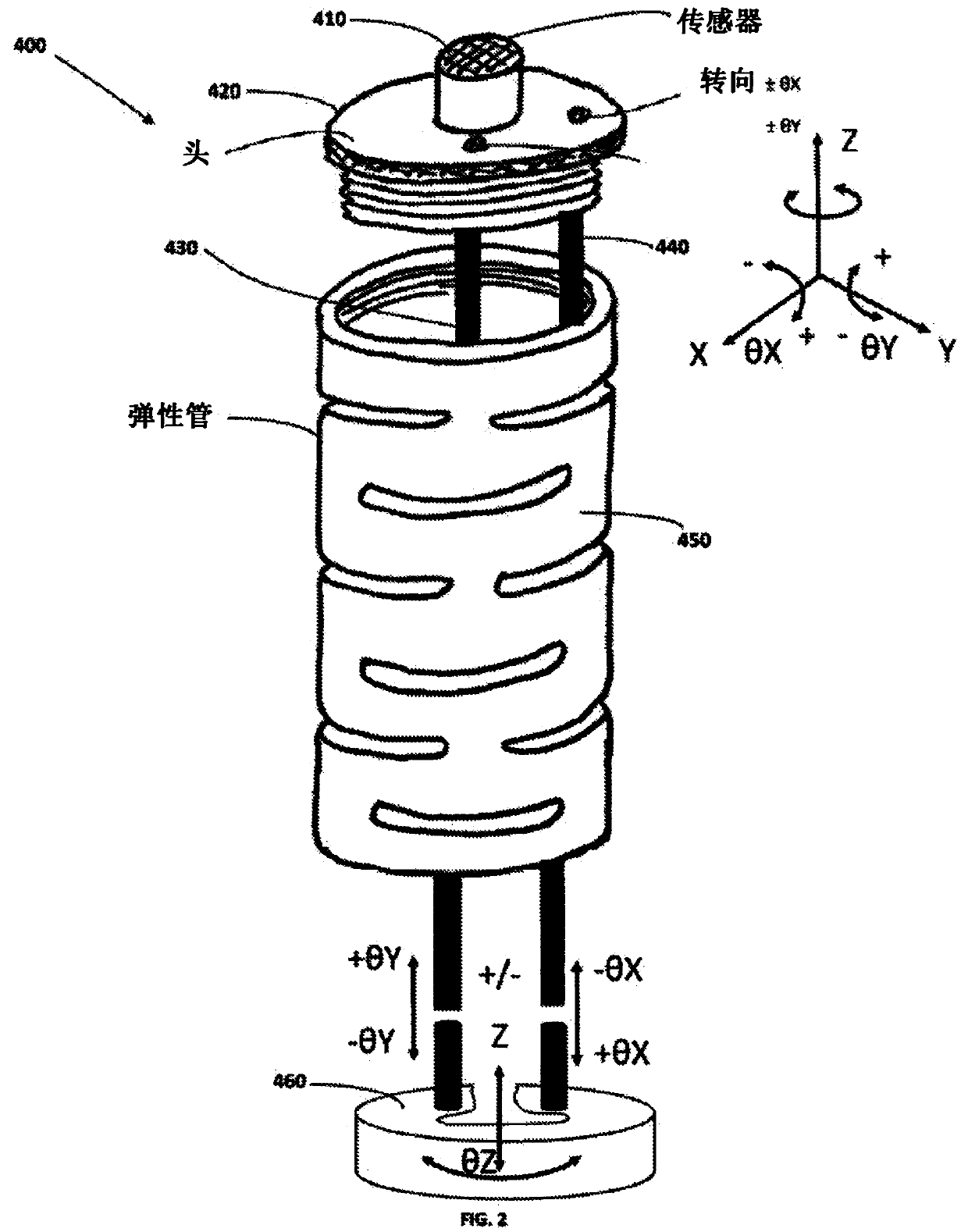
A vascular guide wire device comprising: a guide wire comprising a guide wire head and a laser-acoustic head sensor configured to navigate in a patient's blood vessel, said laser-acoustic head sensorconnected via an optic fiber threaded through said guide wire device with a laser-acoustic diode controlled by a laser-acoustic diode controller; a computerized system electronically communicating with said laser-acoustic head sensor, said computerized system comprising a computer, image processing means and display means and configured to provide images and measurements 2- centimeters ahead inside a patient's arteries occlusions therein purposing to move and navigate safely into the right artery lumen; first steering means connected with said guide wire head and configured to navigate said laser-acoustic head sensor according to said image processing results; and opening means connected with said guide wire head for opening total occlusion of said artery.
Owner:PRC CARDIO OPTIC
Arterial intracavity ultrasonic image processing method and related device
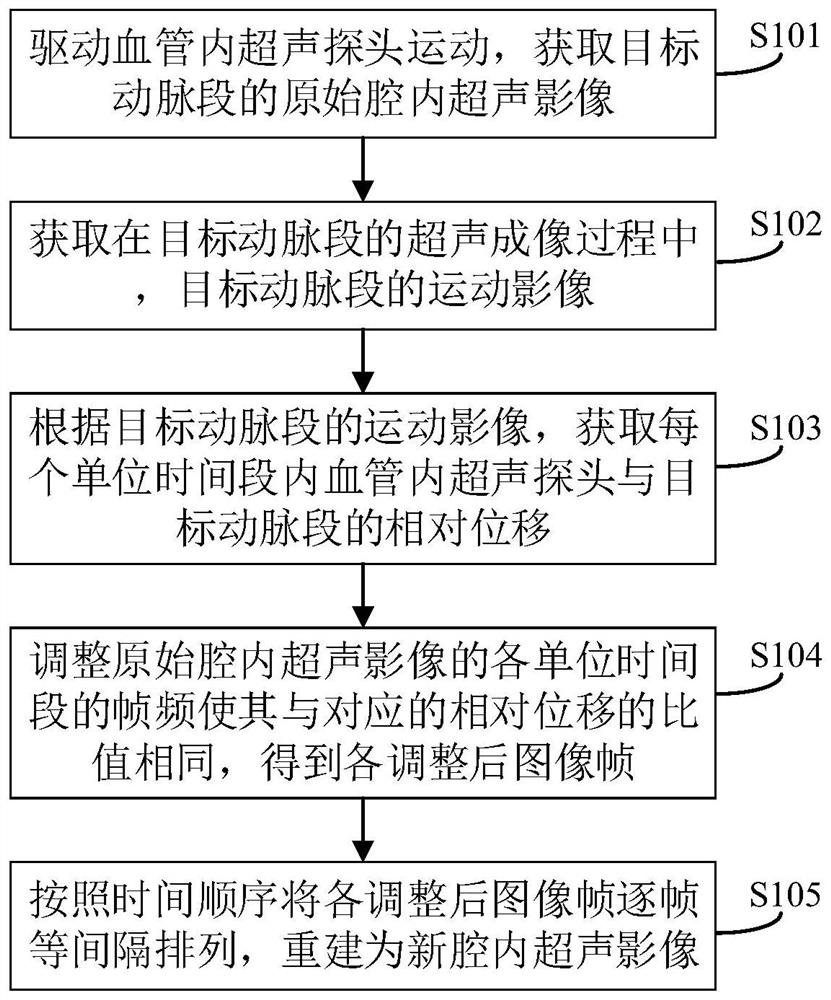
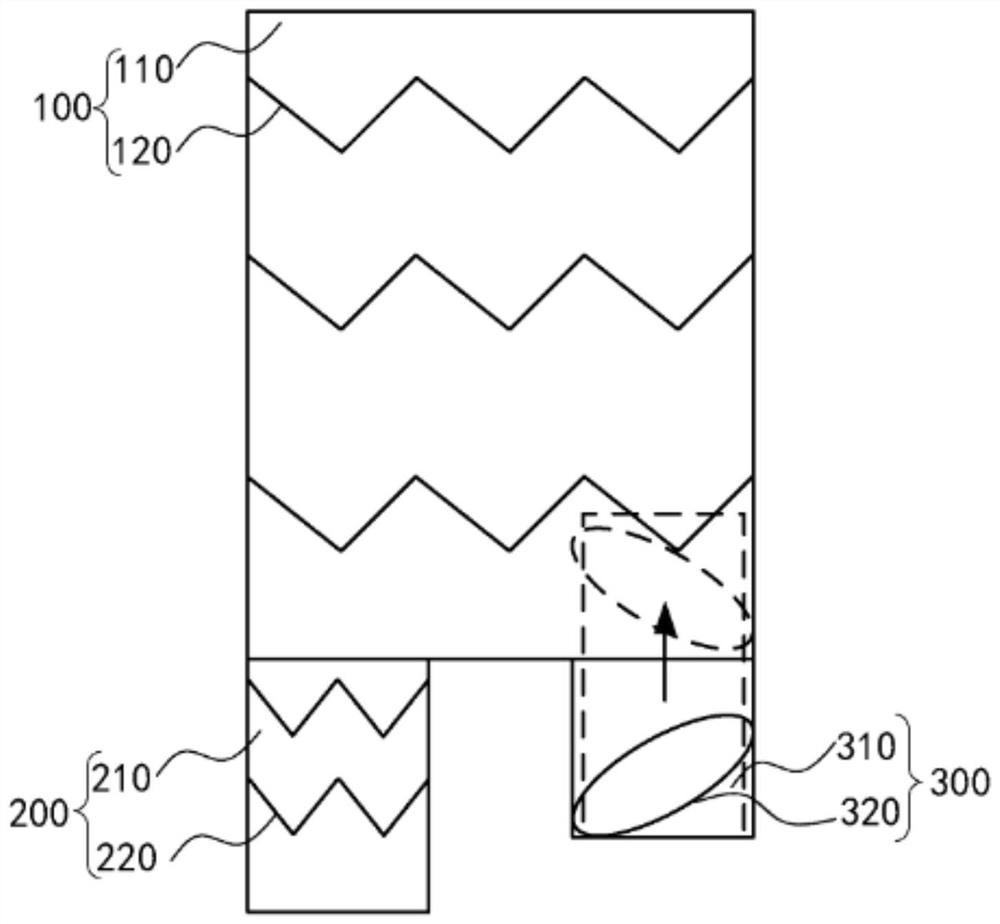
ActiveCN113116388AIntuitive and true severityNo measurement inaccuraciesOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryImaging processingDiagnostic ultrasound
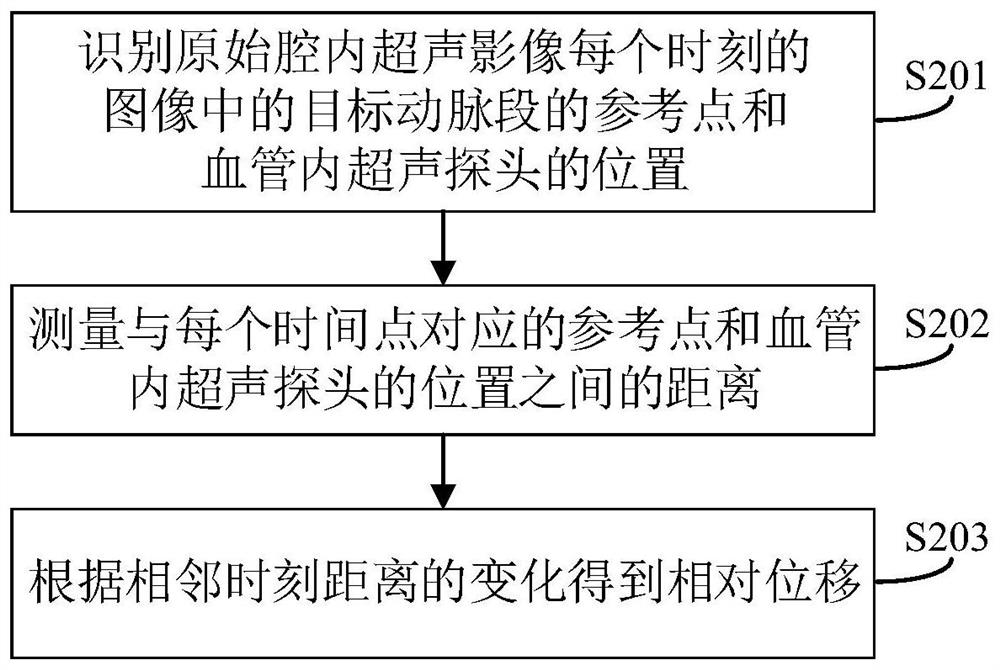
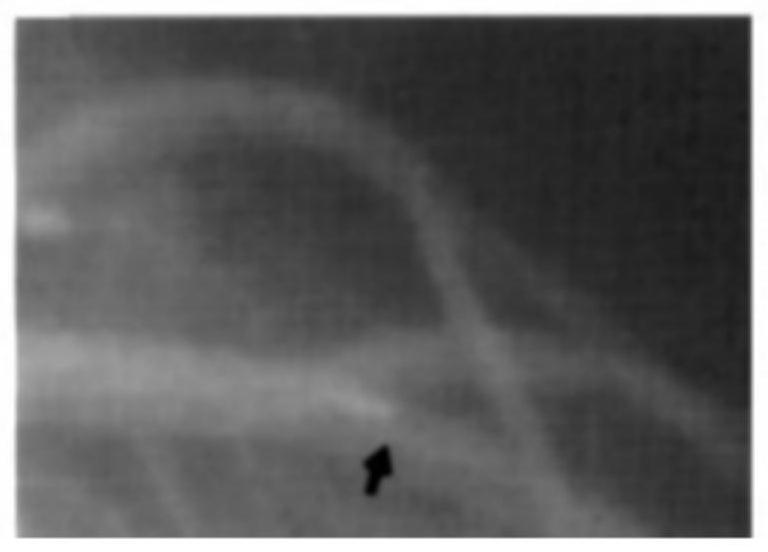
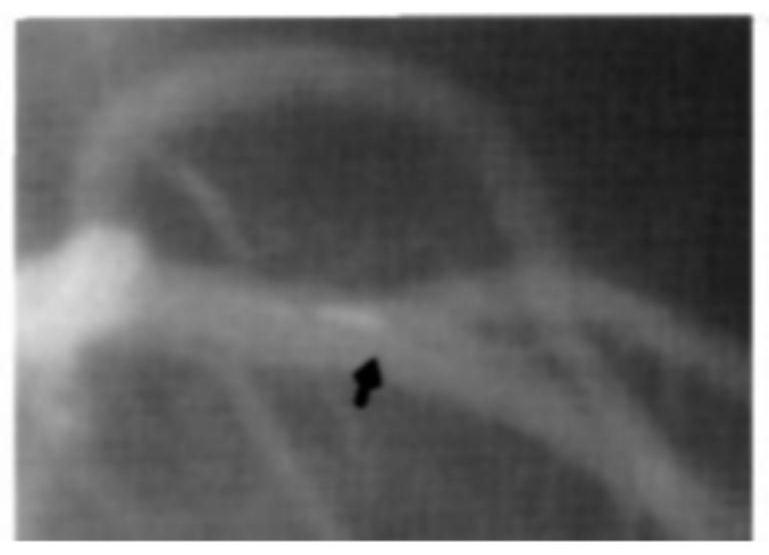
The invention discloses an arterial intracavity ultrasonic image processing method. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring relative displacement between an intravascular ultrasonic probe and a target artery section within each unit time period according to a motion image of a target artery section, and taking the relative displacement as a basis for guiding the adjustment of the frame frequency within each unit time period, i.e., making targeted adjustment to same original frame frequency within each unit time period of the original intracavity ultrasonic image: adjusting the frame frequency within each unit time of ultrasonic images in an original cavity to enable the ratio of the frame frequencies to the corresponding relative displacement to be the same. In this way, new arterial intracavity images obtained through reconstruction on the adjusted frame images can visually and truly reflect the severity degree of the pathological tissue when replayed, and meanwhile, the situation of inaccurate measurement of long-axis images directly generated in the collection process is avoided. The invention further discloses an arterial intracavity ultrasonic image processing device and equipment, a readable storage medium and an ultrasonic diagnosis system, all of which have the foregoing beneficial effects.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
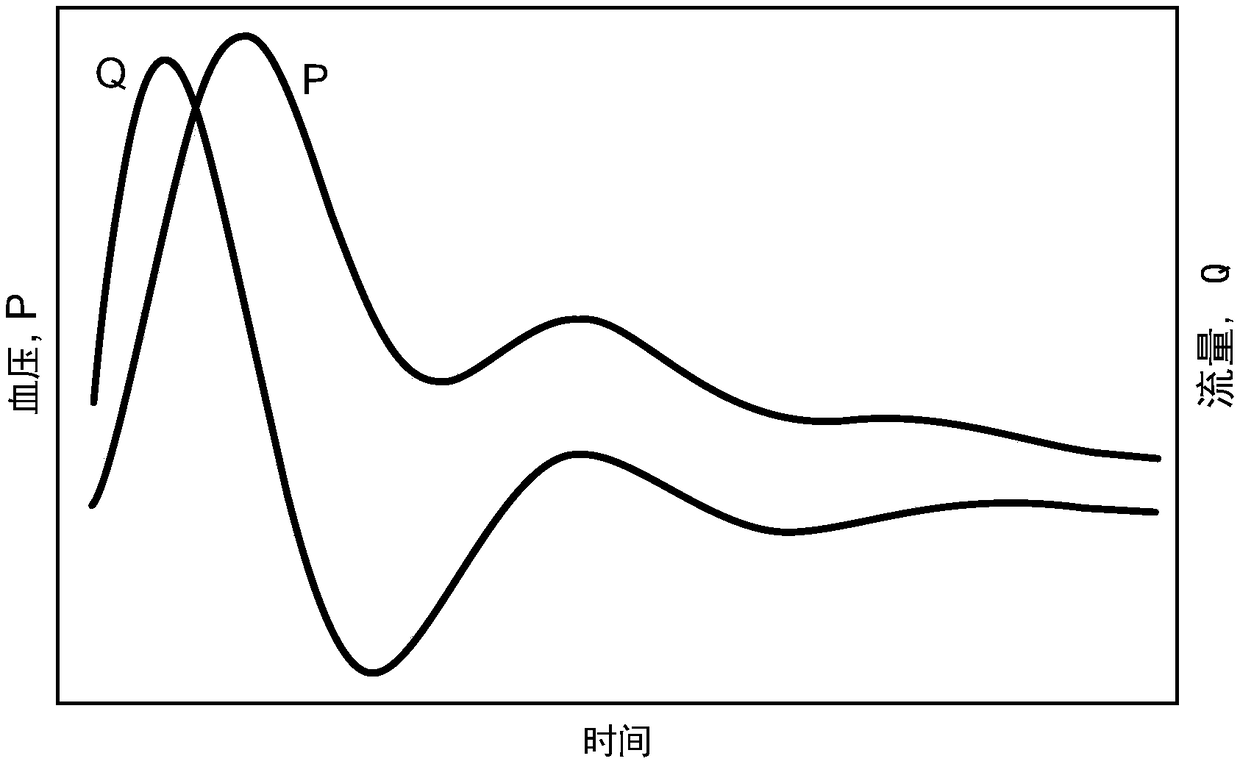
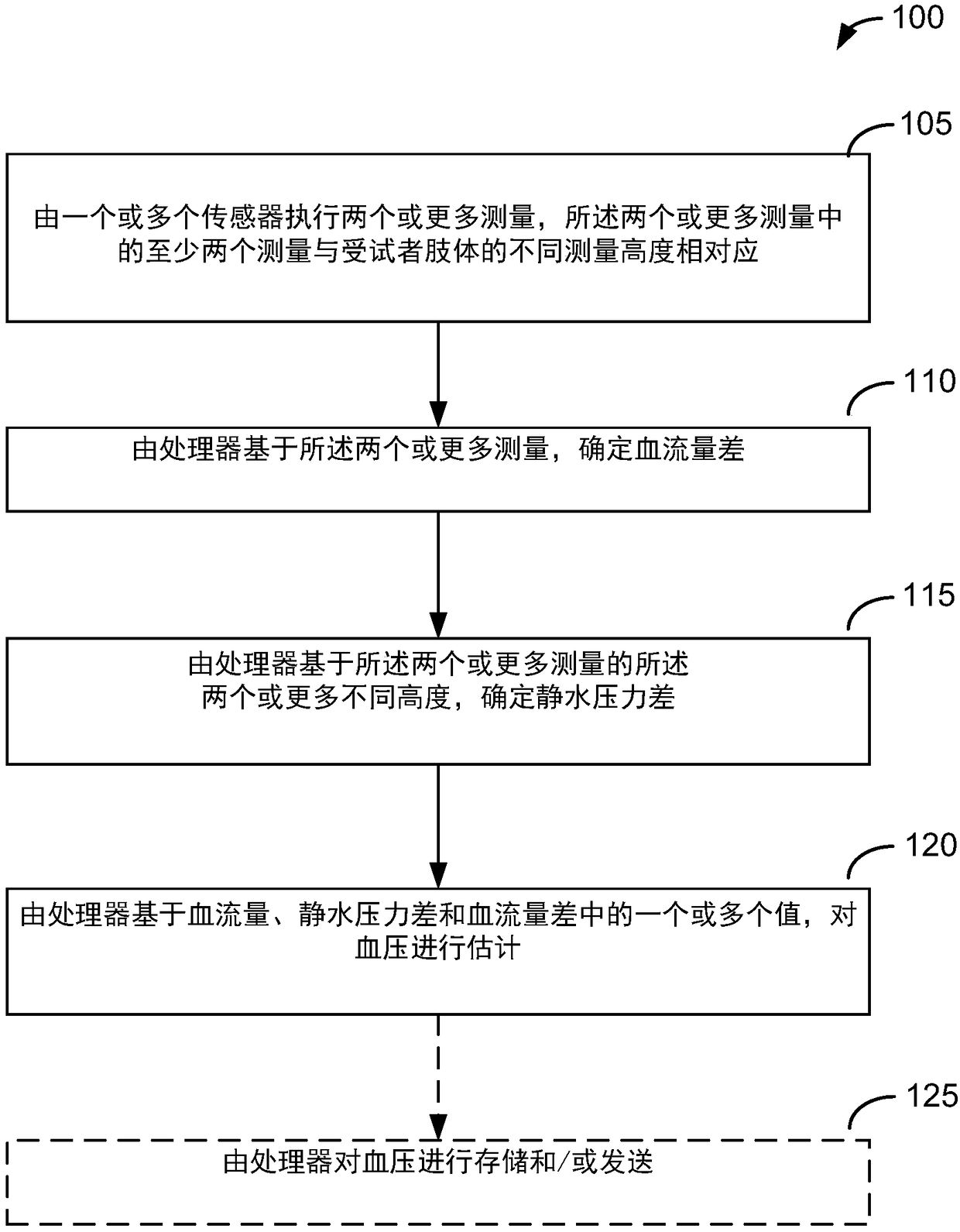
Methods and devices for calculating blood pressure based on measurements of arterial blood flow and arterial lumen
A system for calculating blood pressure may include a sensor system and a control system. The control system may be capable of controlling one or more sensors of the sensor system to take at least twomeasurements, the at least two measurements including at least one measurement taken at each of two or more different measurement elevations of a subject's limb. In some examples, the control systemmay be capable of determining a blood flow difference based on the at least two measurements, of determining a hydrostatic pressure difference based on the two or more different elevations of the at least two measurements and of estimating a blood pressure based on one or more values of blood flow, the hydrostatic pressure difference and the blood flow difference.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Vascular catheter
InactiveUS20190001099A1Avoid trackingMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesTransverse planeIliac artery
Owner:AYRSHIRE & ARRAN HEALTH BOARD
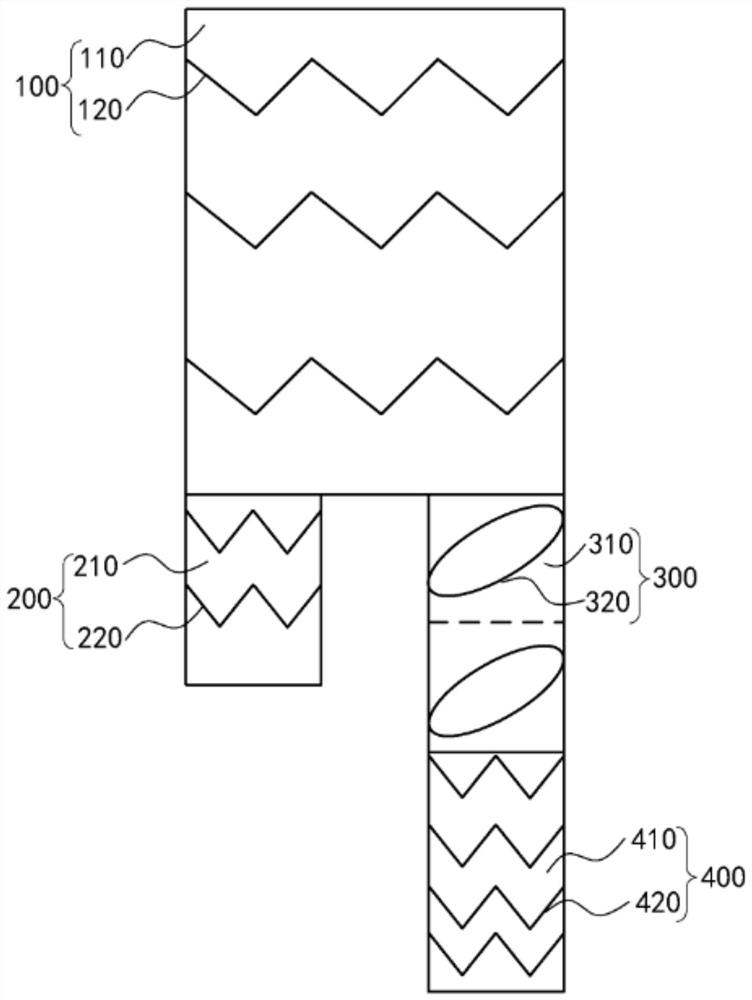
Artery intracavity image reconstruction method, device and equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114680817AExact lesion lengthImprove accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryCatheterComputer vision
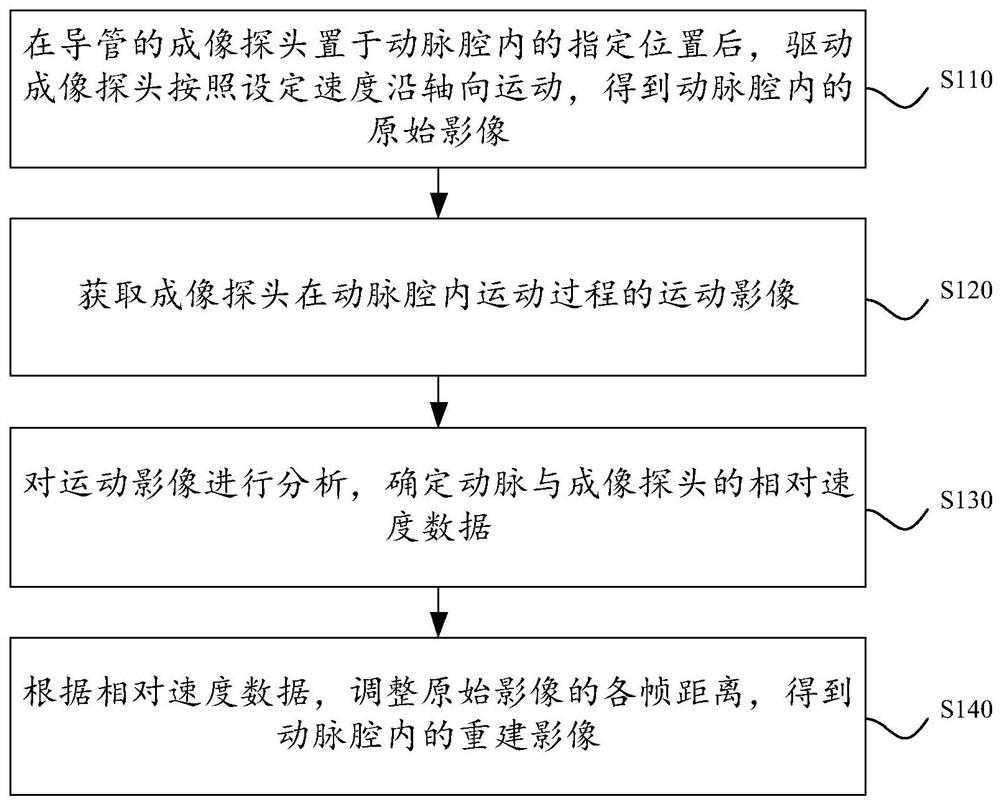
The invention discloses an image reconstruction method in an artery cavity, which comprises the following steps of: after an imaging probe of a catheter is arranged at a specified position in the artery cavity, driving the imaging probe to move along the axial direction according to a set speed to obtain an original image in the artery cavity; acquiring a motion image of the imaging probe in the motion process in the artery cavity; analyzing the motion image, and determining relative speed data of the artery and the imaging probe; and according to the relative speed data, adjusting the distance of each frame of the original image to obtain a reconstructed image in the artery cavity. By applying the technical scheme provided by the invention, the accuracy of the reconstructed image in the artery cavity is higher, and the artery lesion length measured by the reconstructed image is more accurate, so that reliable numerical evidence can be provided for clinicians to diagnose and determine related treatment schemes. The invention further discloses an artery intracavity image reconstruction device and equipment and a storage medium, which have corresponding technical effects.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
Stent artificial blood vessel
InactiveCN111956369AMaintain physiological lengthAdjustable lengthStentsBlood vesselsAnatomyIliac artery
The invention provides a stent artificial blood vessel. The stent artificial blood vessel comprises an inflow section, a fixed side bifurcated outflow section and a movable side bifurcated outflow section; the inflow section comprises a first artificial blood vessel body and a first stent, and the first artificial blood vessel body is provided with a first outlet and a second outlet; the fixed side bifurcated outflow section is connected to the first outlet and comprises a second artificial blood vessel body and a second stent; and the movable side bifurcated outflow section is connected to the second outlet and comprises a third artificial blood vessel body and an annular stent, and the annular stent is arranged on the third artificial blood vessel body, so that at least part of the movable side bifurcated outflow section is adjustably folded in the first artificial blood vessel body. By means of the design, through the design that the movable side bifurcated outflow section is adjustably folded, the length of the outflow section can be adjusted, so that the use requirements of application environments in artery cavities such as abdominal aorta and bilateral iliac arteries are met, the physiological length of the abdominal aorta is kept, and the endoleak risk caused by sleeve connection is avoided.
Owner:AORTEC MEDICAL TECH
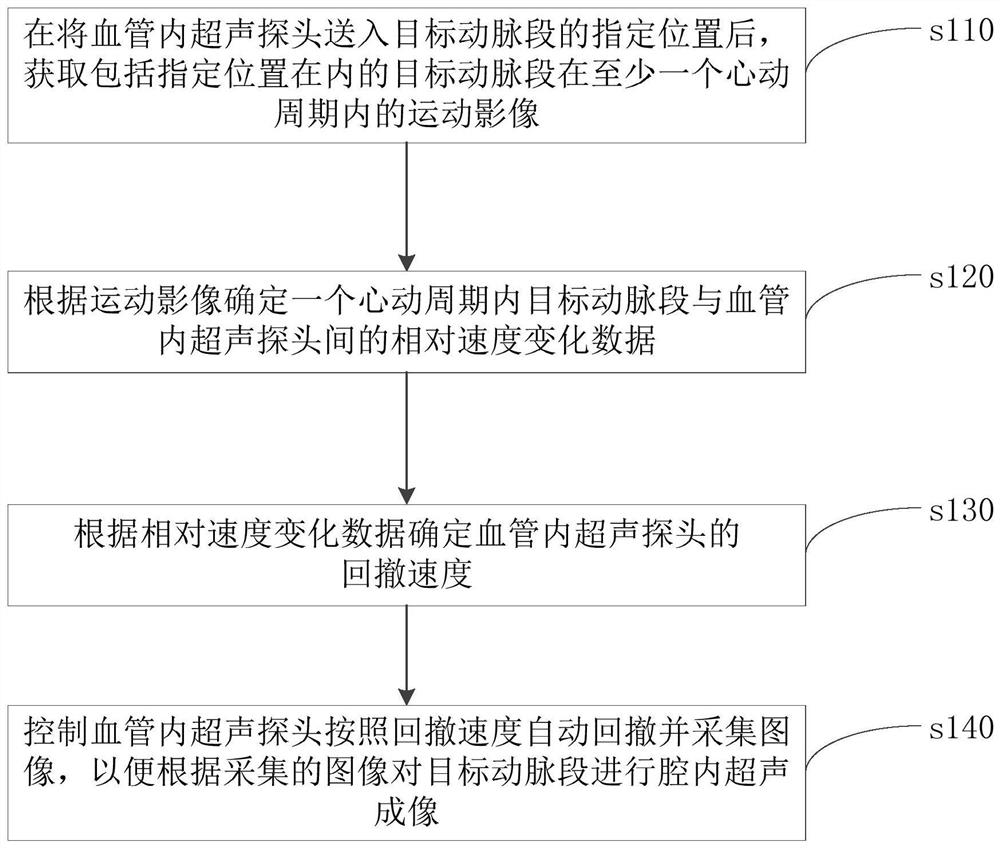
Artery intracavity ultrasound imaging method, artery intracavity ultrasound imaging device, equipment and artery intracavity ultrasound imaging system
ActiveCN113116385AAvoid lossImprove accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound probeImage acquisition
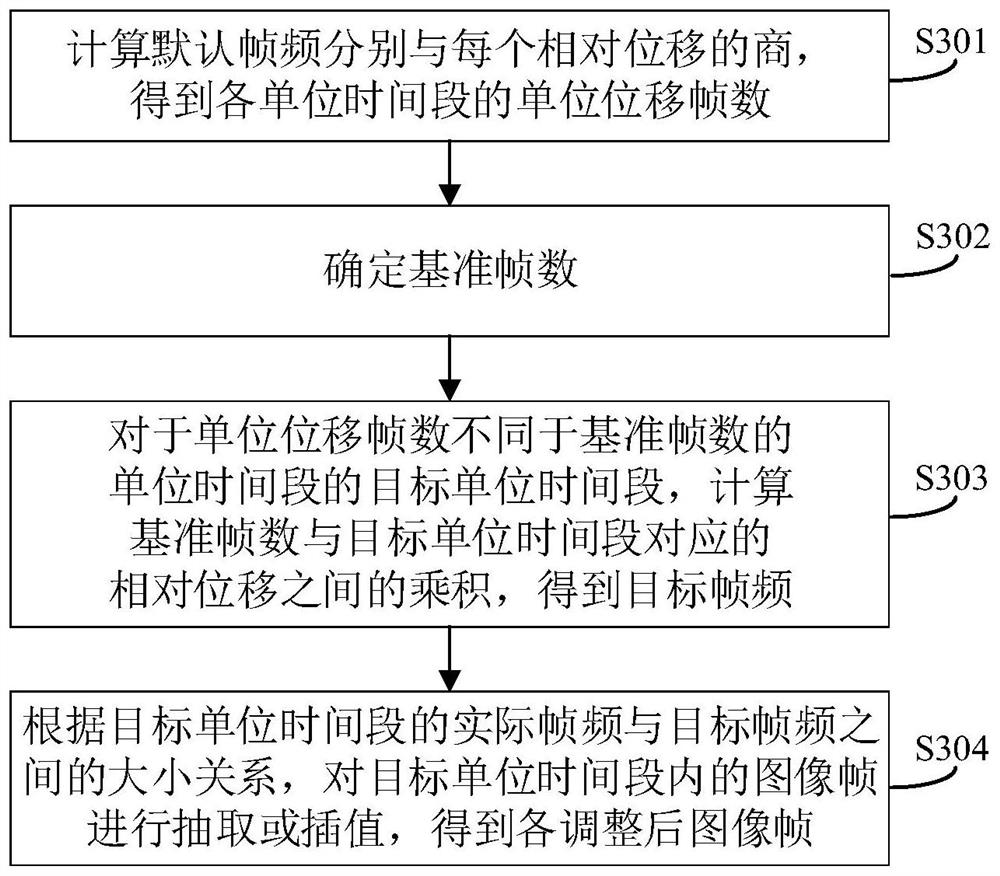
The invention discloses an artery intracavity ultrasonic imaging method. The withdrawing speed of a probe is determined according to relative speed change data between a target artery section and an ultrasonic probe when the ultrasonic probe is static, so that the influence of the movement process of the artery cavity along with the heartbeat on the withdrawing image acquisition process of the probe can be reduced; loss of useful data can be avoided while repeated imaging is avoided; an appropriate number of arterial cavity images are enabled to be acquired; the occurrence of image distortion is avoided; the accuracy of withdrawing image acquisition is improved, so that a reliable length value is provided for an arterial intervention doctor in the arterial intervention treatment process, and the accuracy of the arterial lesion length measured according to artery intracavity ultrasonic imaging is improved; and the diagnosis and treatment effect can be effectively improved. The invention also discloses an artery intracavity ultrasonic imaging device, computer equipment, a computer readable storage medium and an artery intracavity ultrasonic imaging system, which have the beneficial effects.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
Abdominal artery remodeling device
The invention provides an abdominal artery remodeling device, which comprises a flexible blood vessel patch and a connection body, wherein one end of the blood vessel patch is a suturing end, and theother opposite end is a cutting end; the cutting end can be cut off by a scalpel; the connection body is installed on the suturing end of the blood vessel patch; the cutting end of the blood vessel patch permits to be bent to one side near the suturing end to be connected with the connection body, a tubular cavity is formed, and the cavity is used for coating the peripheral surface of a blood vessel to serve as a bracket. According to the abdominal artery remodeling device provided by the invention, an artery cavity is externally remodeled so as to be convenient to reduce damage on branch blood vessels.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Hemodialysis catheter with thrombus blocker
ActiveUS20120095416A1Good removal effectPrevent thrombosisMulti-lumen catheterInfusion needlesArterial lumenArterial line
A hemodialysis catheter with a plurality of umbrella-like wire members covered with a film which works as a thrombus blocker and can easily and effectively remove the thrombus is disclosed. The hemodialysis catheter has a proximal lumen, the arterial lumen, and a distal lumen, the venous lumen. An elongate member is longitudinally put in either the proximal lumen or the distal lumen, or two elongate members in both lumens. A plurality of umbrella-like wire members are connected to the end of the elongate member. When the hemodialysis catheter is put in the vessel but not in use, the end of the lumen is capped off by the plurality of umbrella-like wire members covered with a film. When it is ready to use, the doctor can pull the elongate member which connects to the plurality of umbrella-like wire members out off the lumen inverting the plurality of umbrella-like wire members and clearing away any thrombus that has formed.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
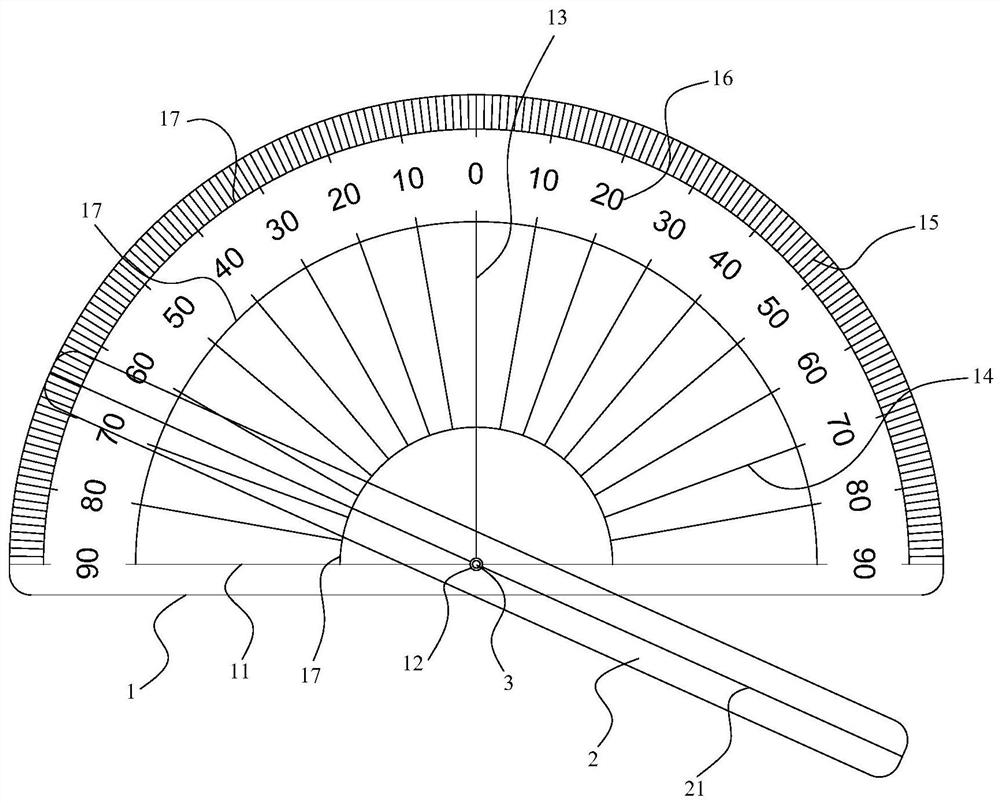
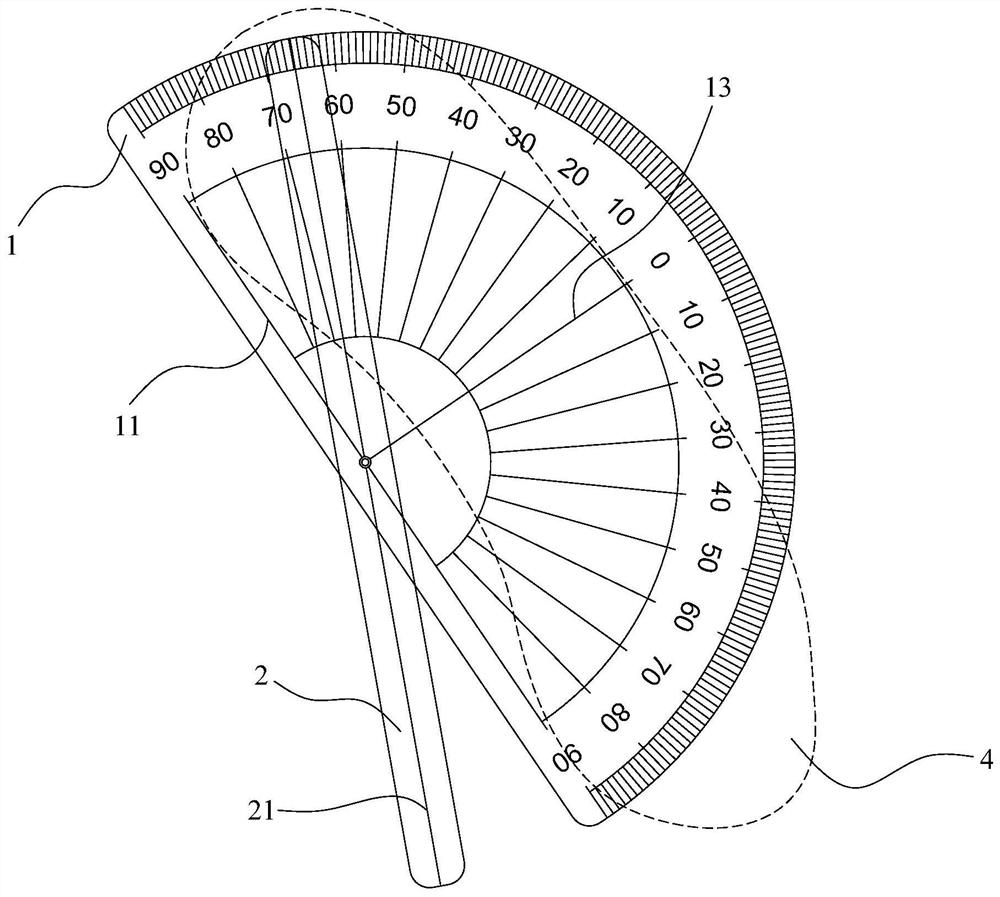
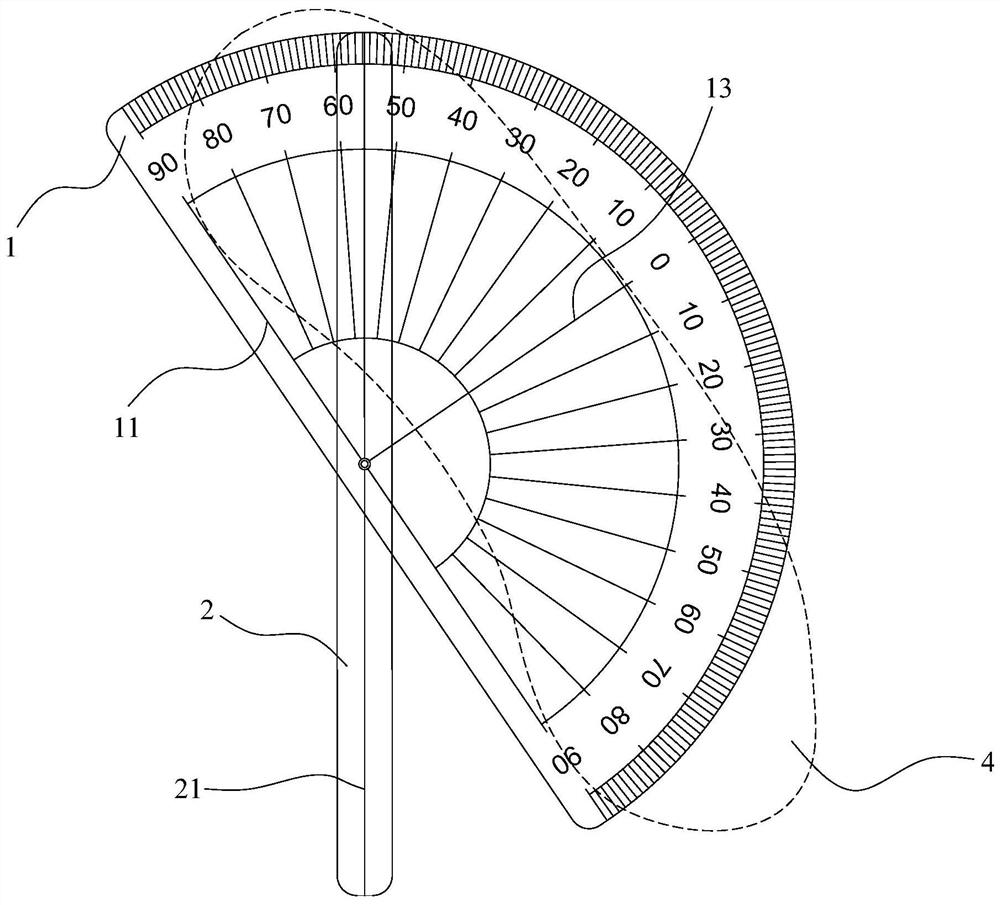
Aortic Arch Tangent Angle Measuring Ruler and Measuring Method
ActiveCN108362192BRealize personalized measurementPinpoint release pointAngles/taper measurementsProtractorGonial angle
The invention provides an arcus aortae tangential position angle measuring scale and measurement method. The measuring scale is provided with a protractor and a positioning ruler. The protractor is provided with a bottom edge indicating line and is provided with a zero degree indicating line perpendicular to the bottom edge indicating line and intersecting with a bottom edge at the middle point. Fine scale lines and scale numerical values are arranged on the inner side of an arc-shaped edge of the protractor. The scale numerical value corresponding to the zero-degree indicating line is 0. Scale numerical values in the clockwise and counter-clockwise directions on two sides of 0 are used for indicating 0-90 degrees. The positioning rule is provided with a long axis indicating line. The longaxis middle point of the long axis indicating line is hinged with a bottom middle part of the bottom edge indicating line via a hinge shaft. The measuring method is using the measuring scale to measure the arcus aortae tangential position angle. The invention solves problems of poor surgical effect and severe complication due to incorrect DSA projection angle in current prosthetics in a thoracicaorta cavity and can realize customized measurement of the projection angle of an arcus aortae part.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
A thrombolytic balloon catheter device
ActiveCN109821139BReduced through outer diameterReduce thrombus sheddingBalloon catheterMedical devicesDecompression chamberEngineering
The invention provides a rapid exchange catheter device that can be used for thrombolysis in coronary artery thrombus and can be used for percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). The device includes a guide wire tube, an inner tube , outer tube and balloon; the middle and distal section of the wire guide tube, the inner tube and the outer tube are coaxially invaginated from the inside to the outside; It opens in the inner cavity of the inner tube; the inner cavity of the inner tube is a connected perfusion cavity, and its proximal end is provided with a drug injection port, and its far part is provided with perfusion side holes and guide wire inlets that open in multiple directions; the outer tube and the inner tube The space between them is the balloon pressure-reduction cavity, the proximal end is provided with the balloon pressure-reduction hole, and the distal end communicates with the balloon cavity. The present invention integrates the functions of the thrombolytic catheter and the balloon catheter into one catheter, can quickly complete the two operations of thrombolysis and PTCA in coronary thrombosis, can reduce the thrombus load, prevent thromboembolism, shorten the operation time, and reduce the number of doctors and doctors. X-ray exposure of the patient.
Owner:钟文
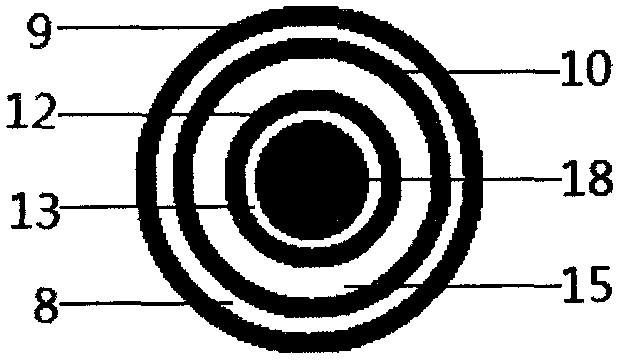
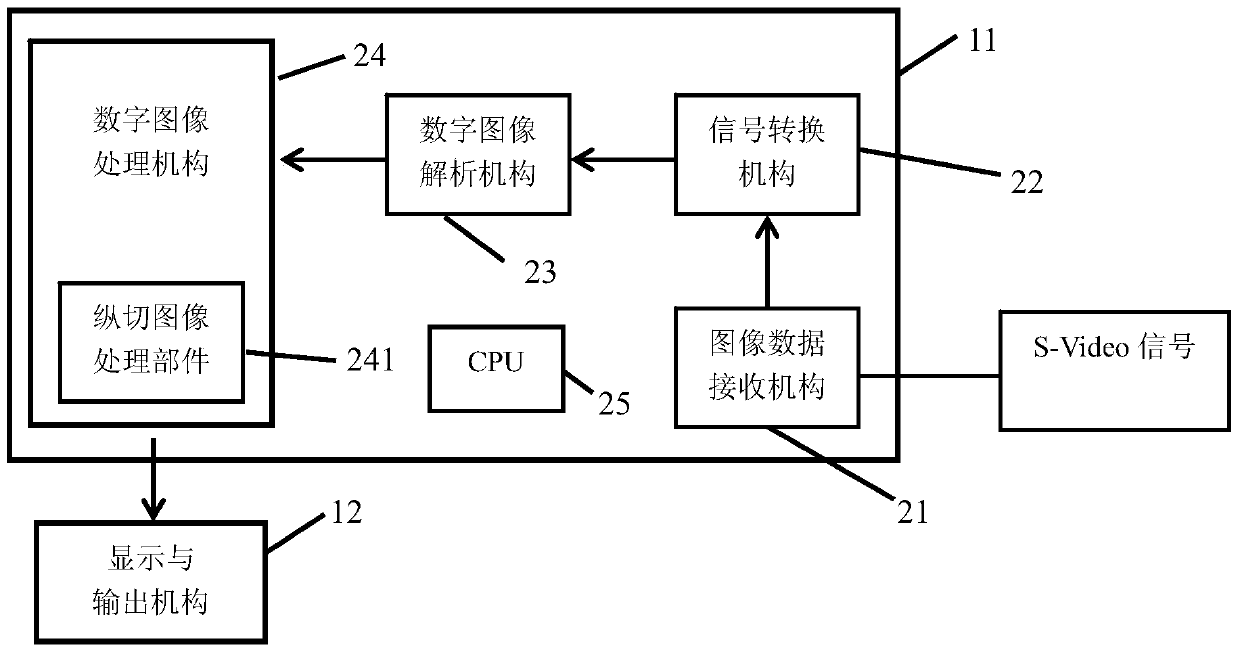
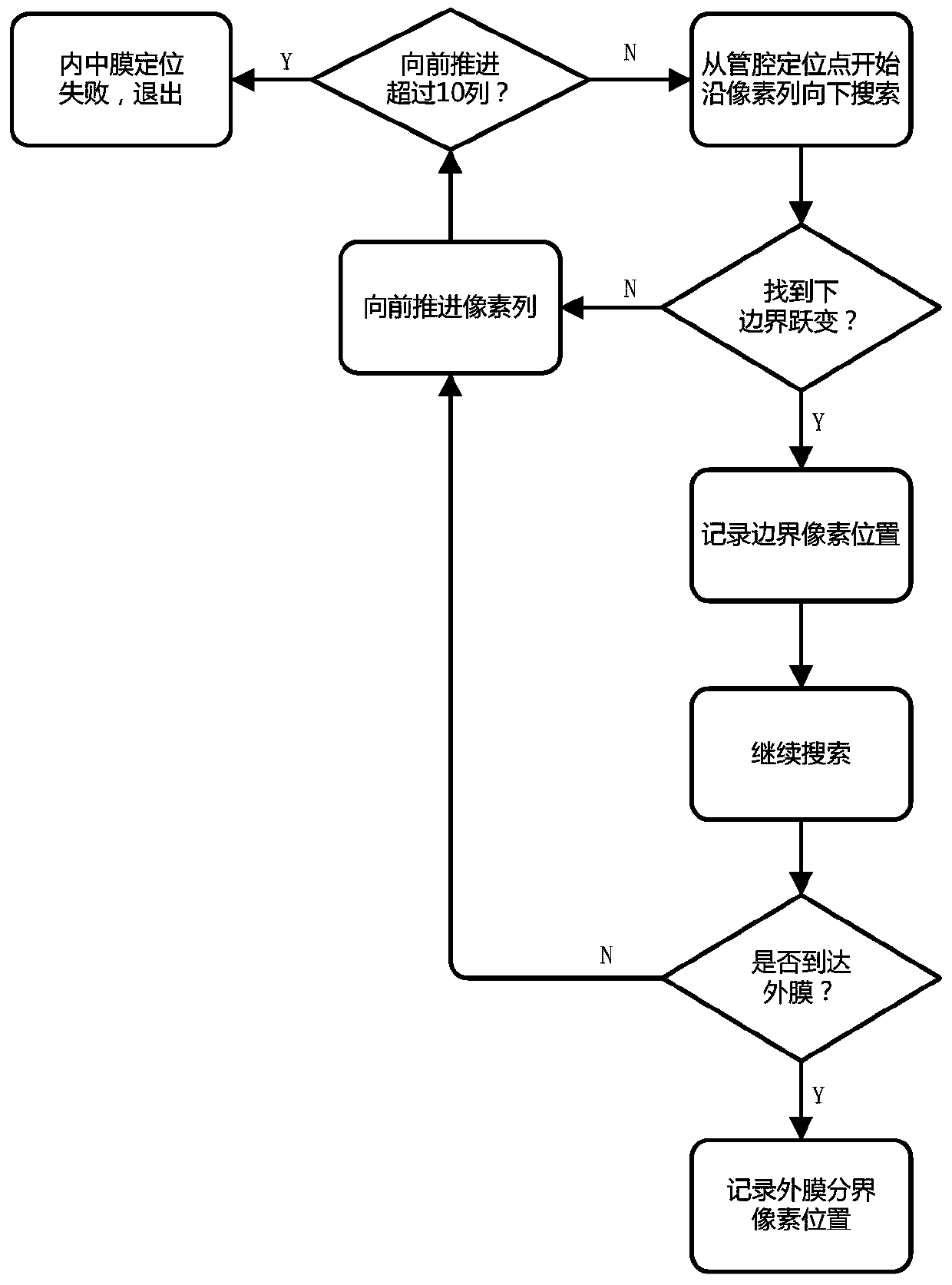
A post-processing device and method for ultrasonic longitudinal section images of common carotid artery
InactiveCN104517277BHigh precisionImprove transmission efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisTunica mediaImaging processing
The invention provides an afterprocessing method of ultrasonic longitudinal-cutting images of the common carotid artery. The afterprocessing method includes determining arterial lumen positioning points, intima positioning points and tunica media positioning points in the ultrasonic longitudinal-cutting images of the common carotid artery, tracking the intima and the tunica media according to the intima positioning points and the tunica media positioning points, and determining the intima boundary and the tunica media boundary and thereby calculating the thickness of the intima and the tunica media of the artery according to boundary position information. The invention further provides a device implementing the method. By the afterprocessing method and device, computer measuring of the thickness of the intima and the tunica media in the carotid artery is realized, accuracy is remarkably improved, and transmission efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Aortic dissection endoluminal repair postoperative false lumen blood flow state evaluation method
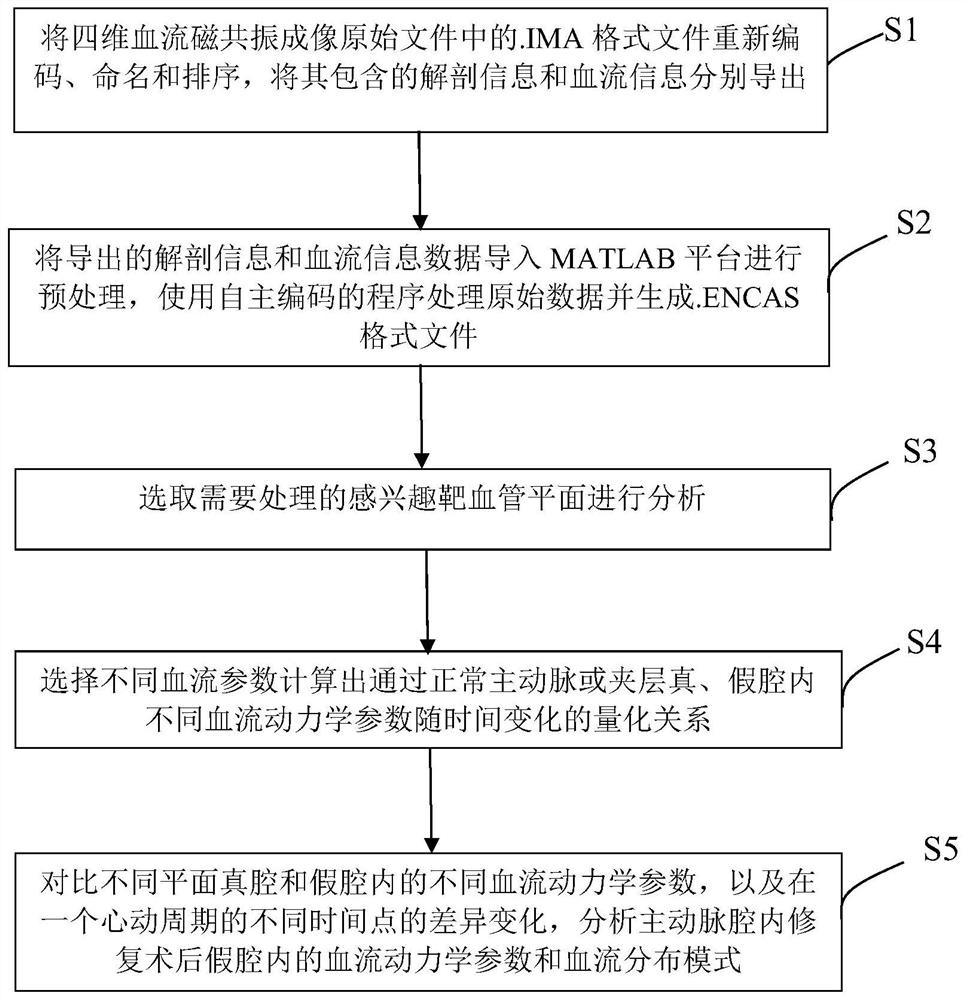
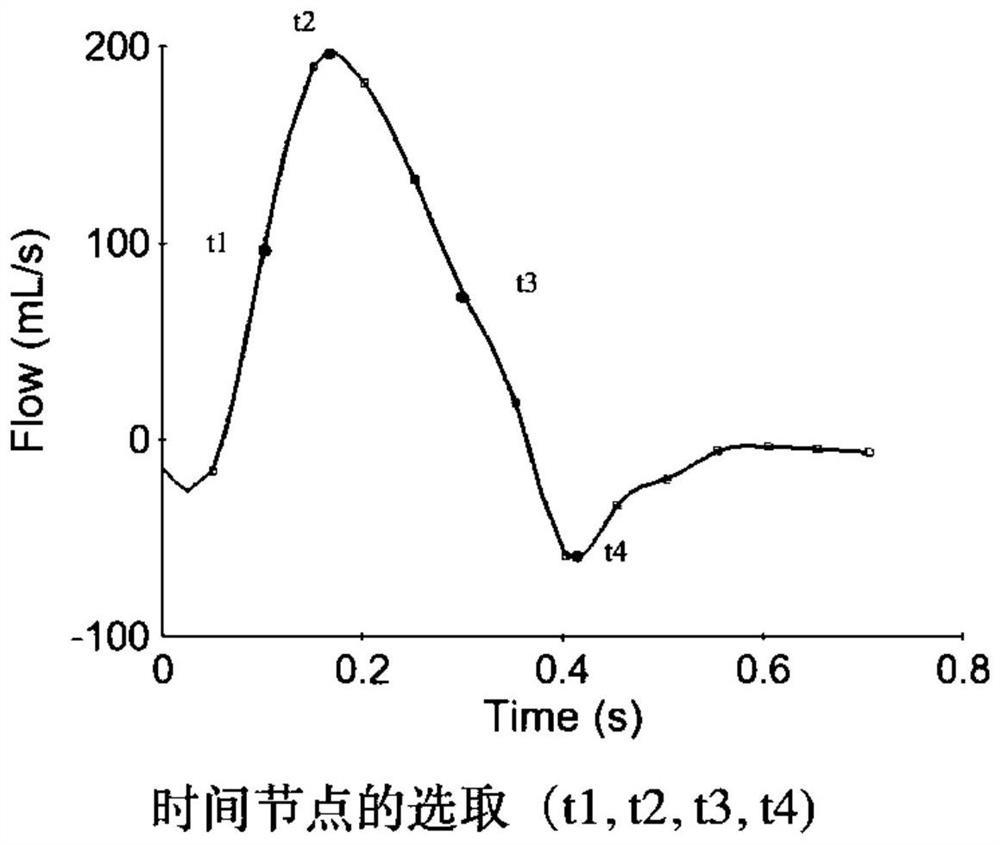
The invention provides an aortic dissection endoluminal repair postoperative false lumen blood flow state evaluation method, which comprises the following steps of: recoding, naming and sequencing a .IMA format file in a four-dimensional blood flow magnetic resonance imaging original file, and respectively exporting anatomical information and blood flow information contained in the .IMA format file; importing exported anatomical information and blood flow information data into an MATLAB platform to be preprocessed, processing original data through an autonomous coding program, and generating an .ENCAS format file; selecting an interested target blood vessel plane needing to be processed for analysis; selecting different blood flow parameters to calculate a time-varying quantitative relation of different blood flow dynamic parameters passing through normal aorta or real and false cavities of a dissection; and comparing different hemodynamic parameters in the true cavity and the false cavity in different planes as well as difference changes at different time points in a cardiac cycle, and analyzing hemodynamic parameters and a blood flow distribution mode in the false cavity after the aortic endoluminal repair.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
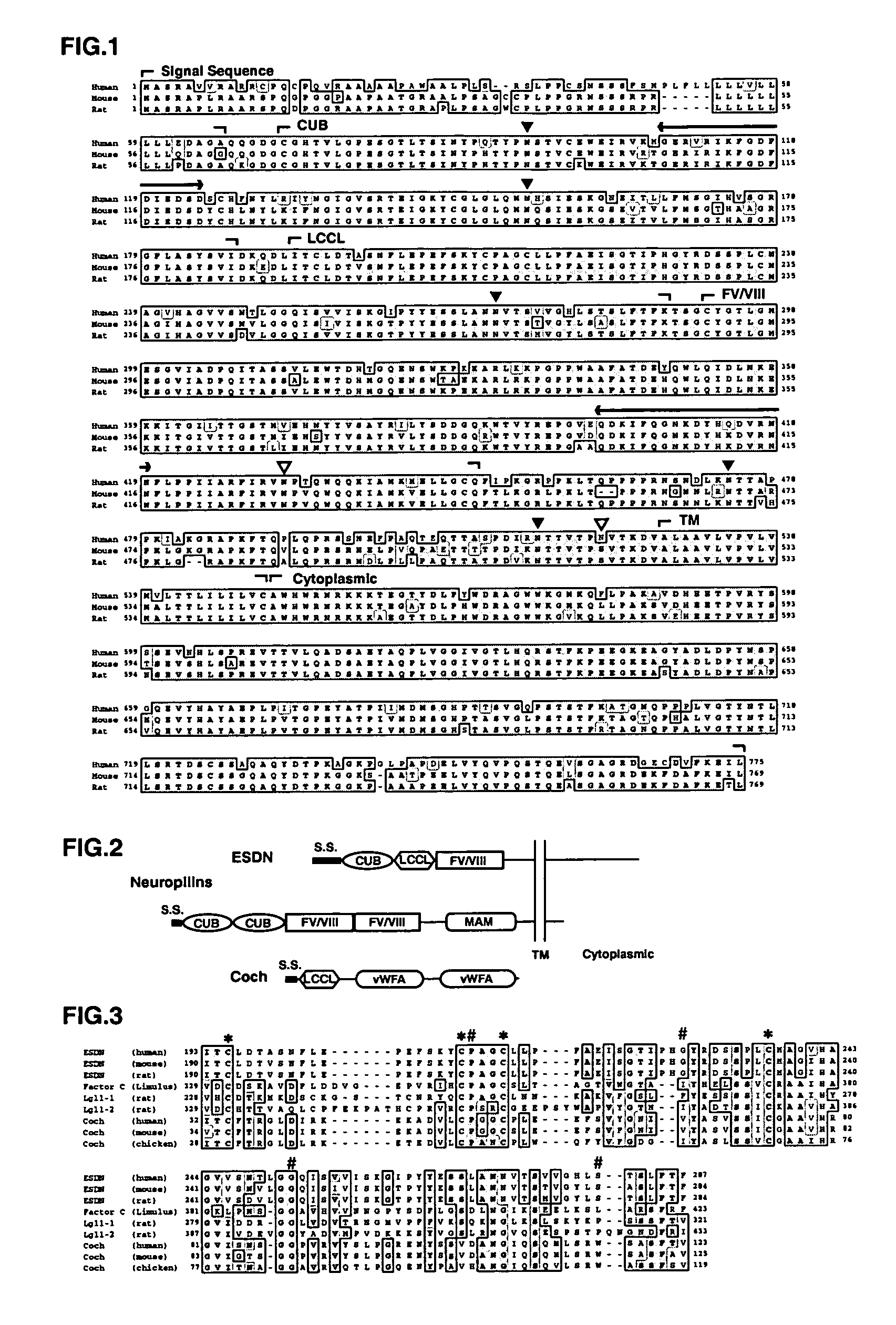
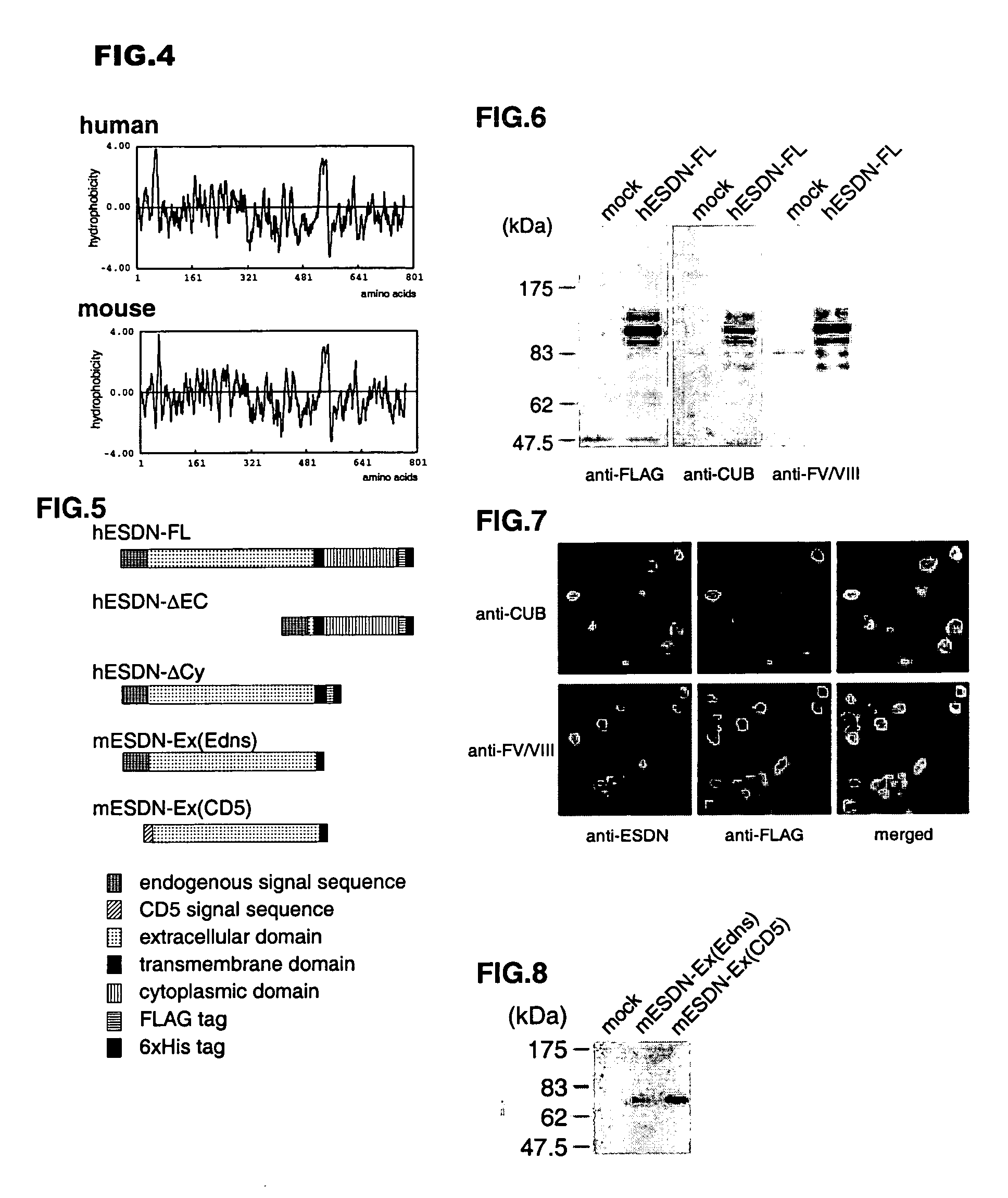
Novel polypeptide ESDN, polynuleotides encoding the polypeptide, and utility of the polypeptide
The invention discloses a useful and novel factor (polypeptide) which plays an important role for morbid vascular smooth muscle in restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronany angioplasty (PTCA) and arterial sclerosis in the field of cardiovascular system.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com