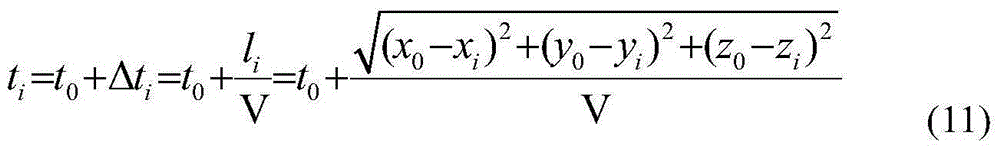Patents
Literature
192 results about "Pulse wave velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pulse wave velocity (PWV) is the velocity at which the blood pressure pulse propagates through the circulatory system, usually an artery or a combined length of arteries. PWV is used clinically as a measure of arterial stiffness and can be readily measured non-invasively in humans, with measurement of carotid to femoral PWV (cfPWV) being the recommended method. cfPWV is highly reproducible, and predicts future cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality independent of conventional cardiovascular risk factors. It has been recognized by the European Society of Hypertension as an indicator of target organ damage and a useful additional test in the investigation of hypertension.
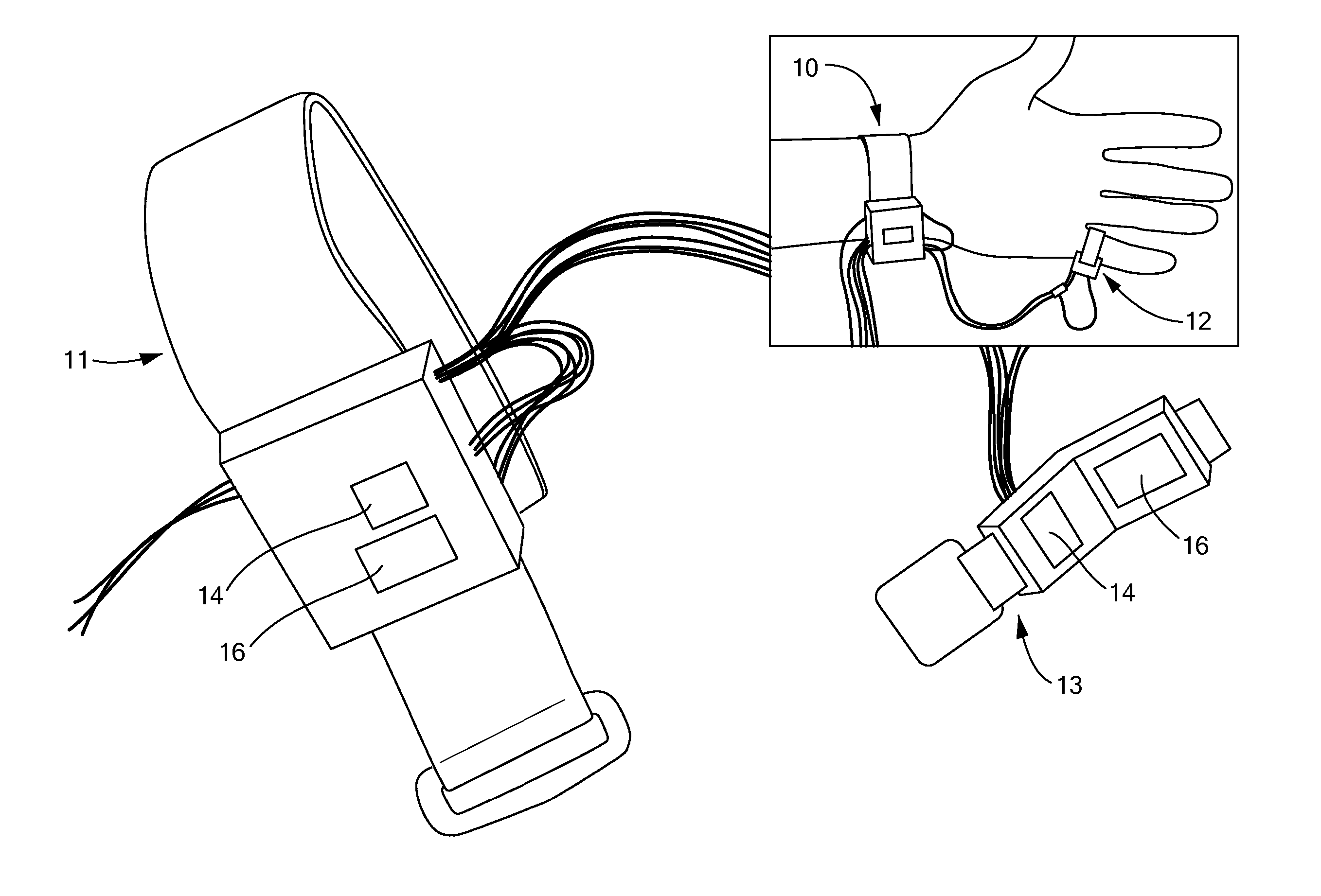
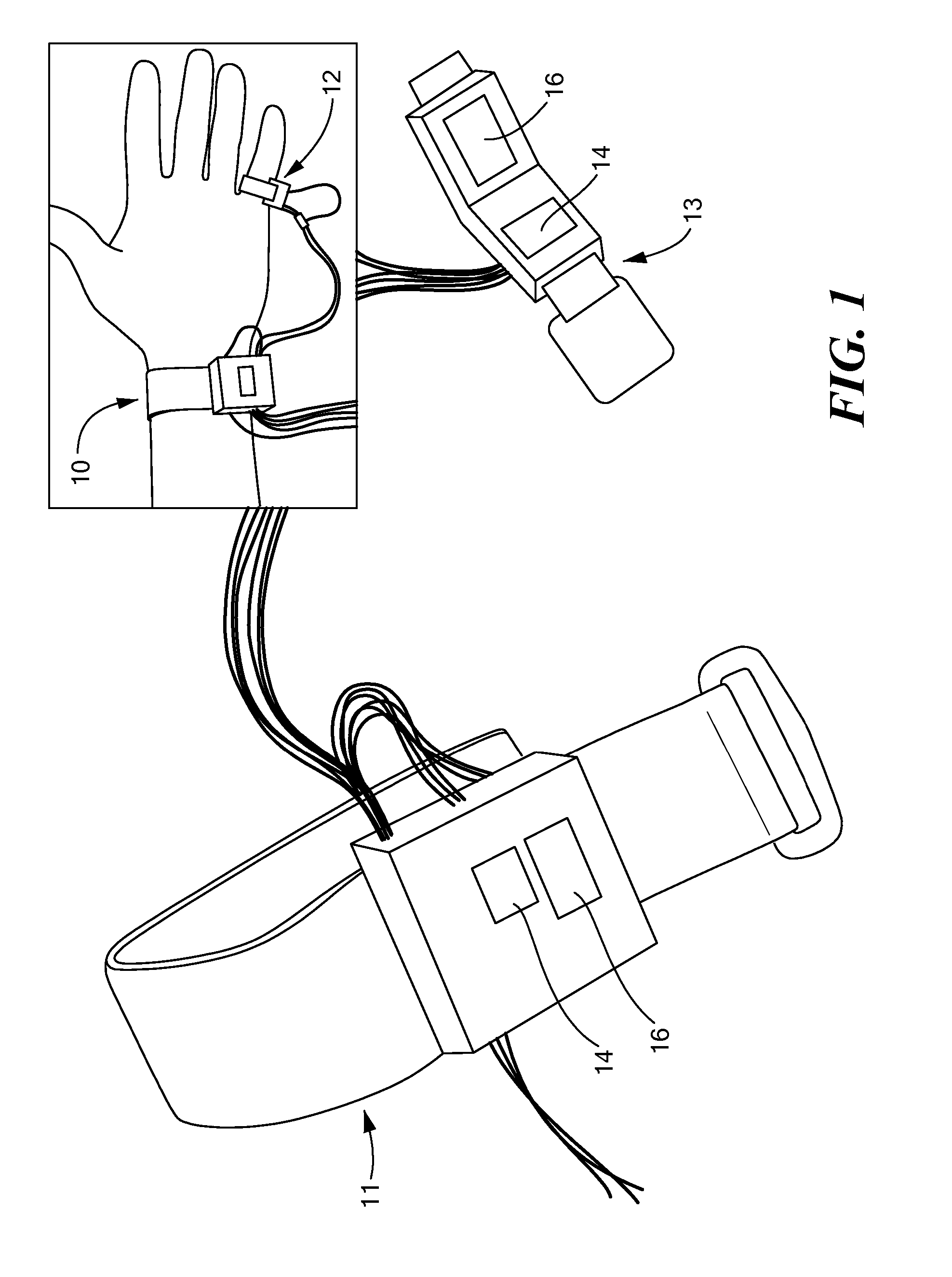
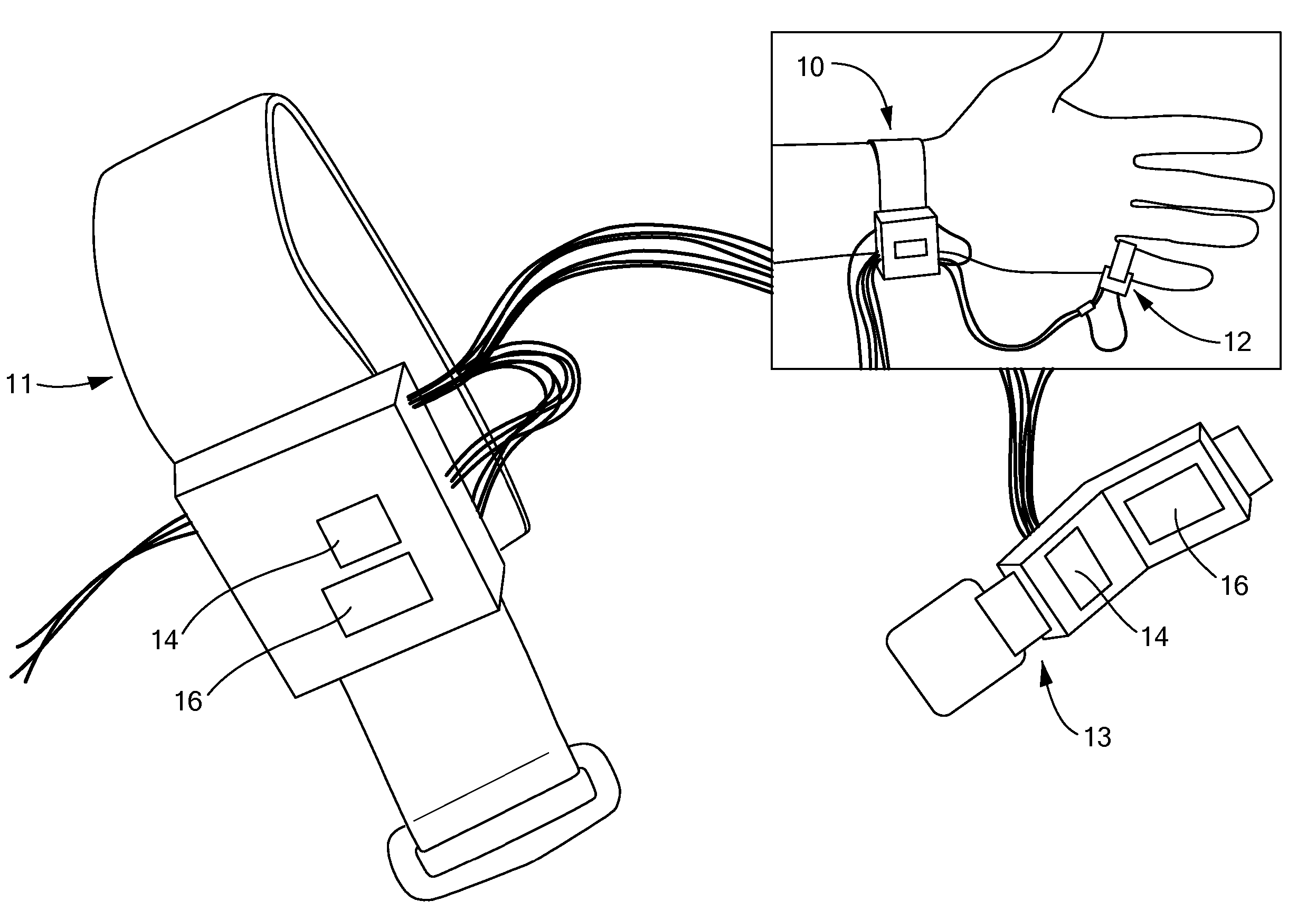
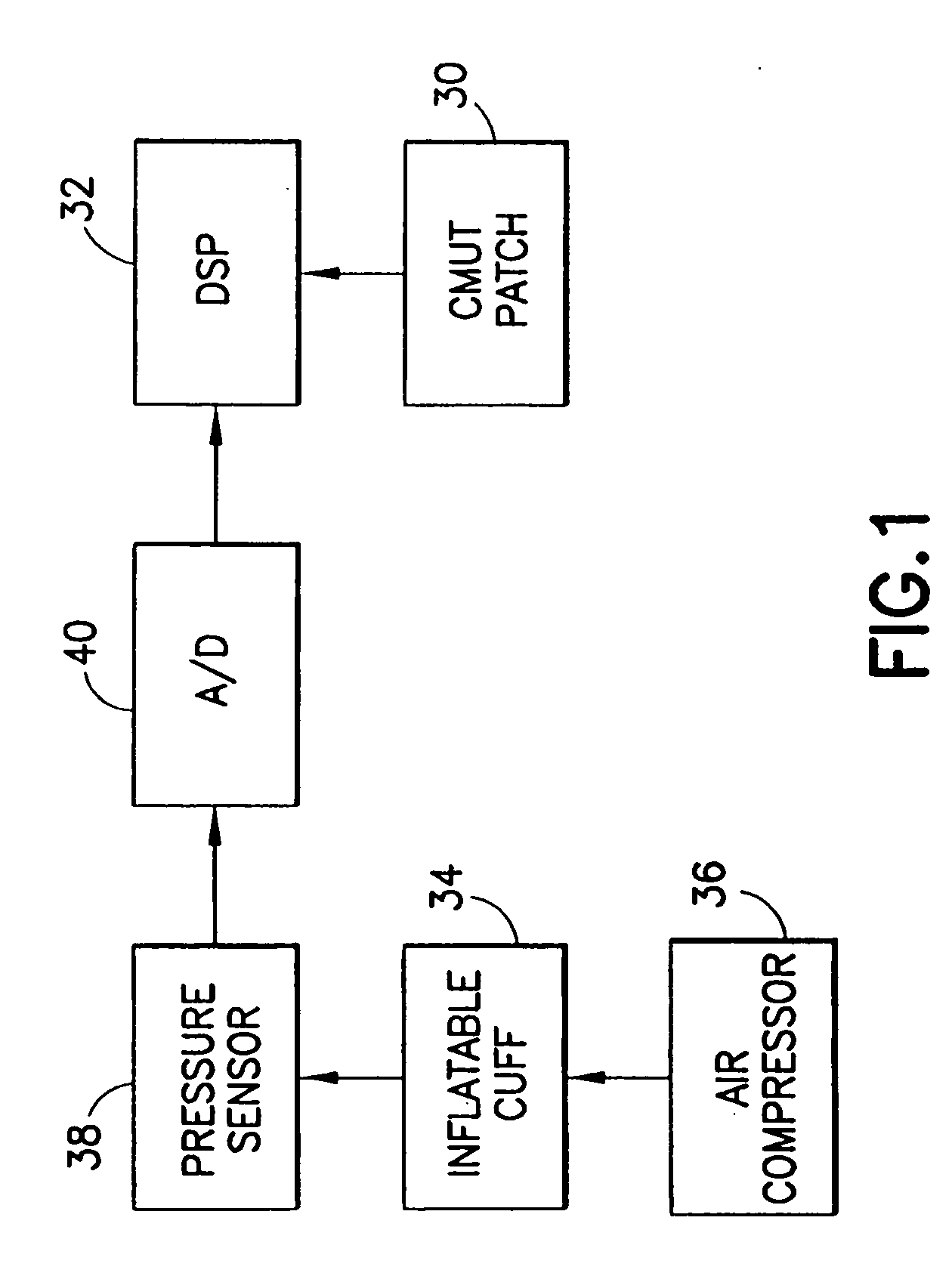
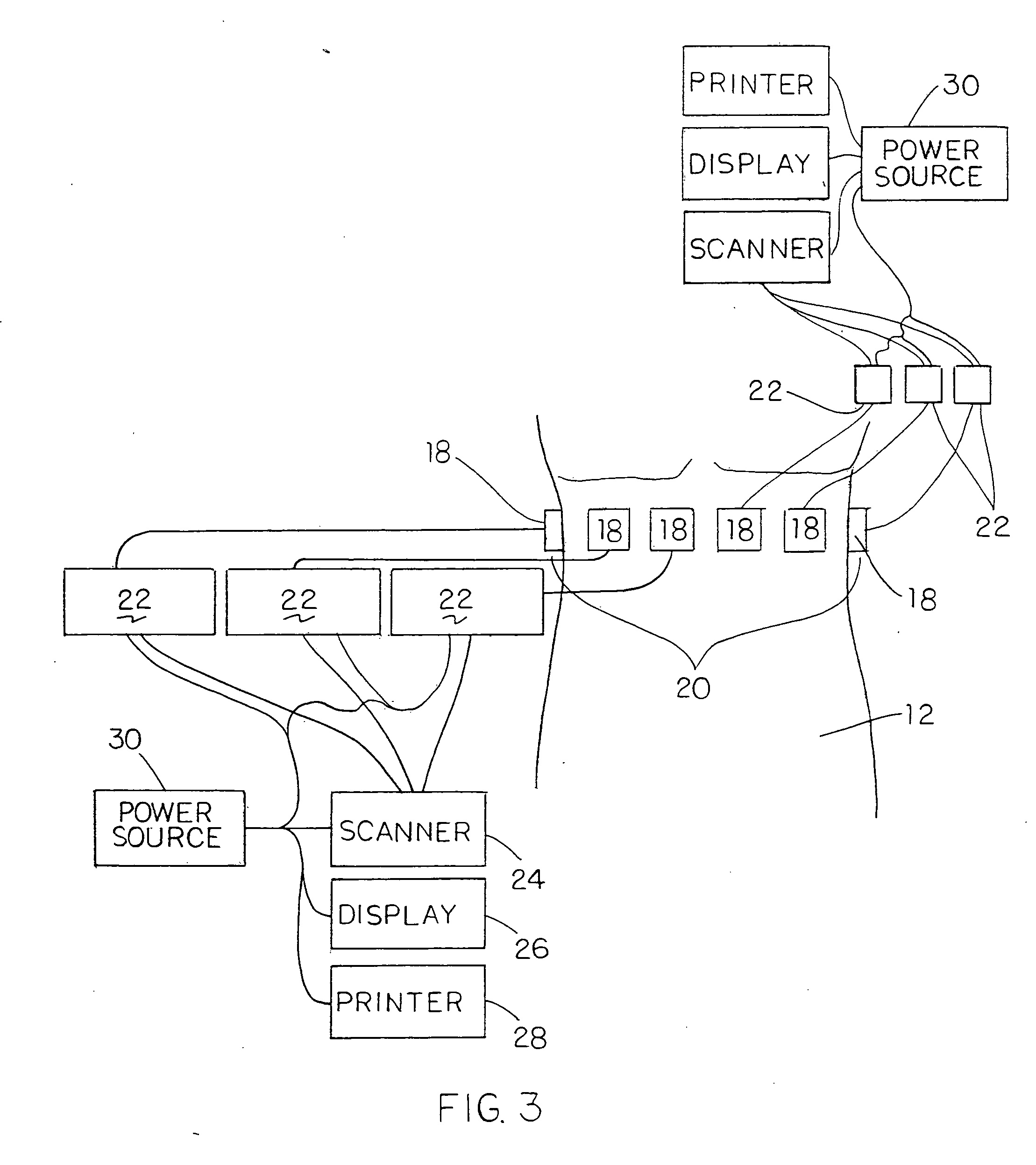
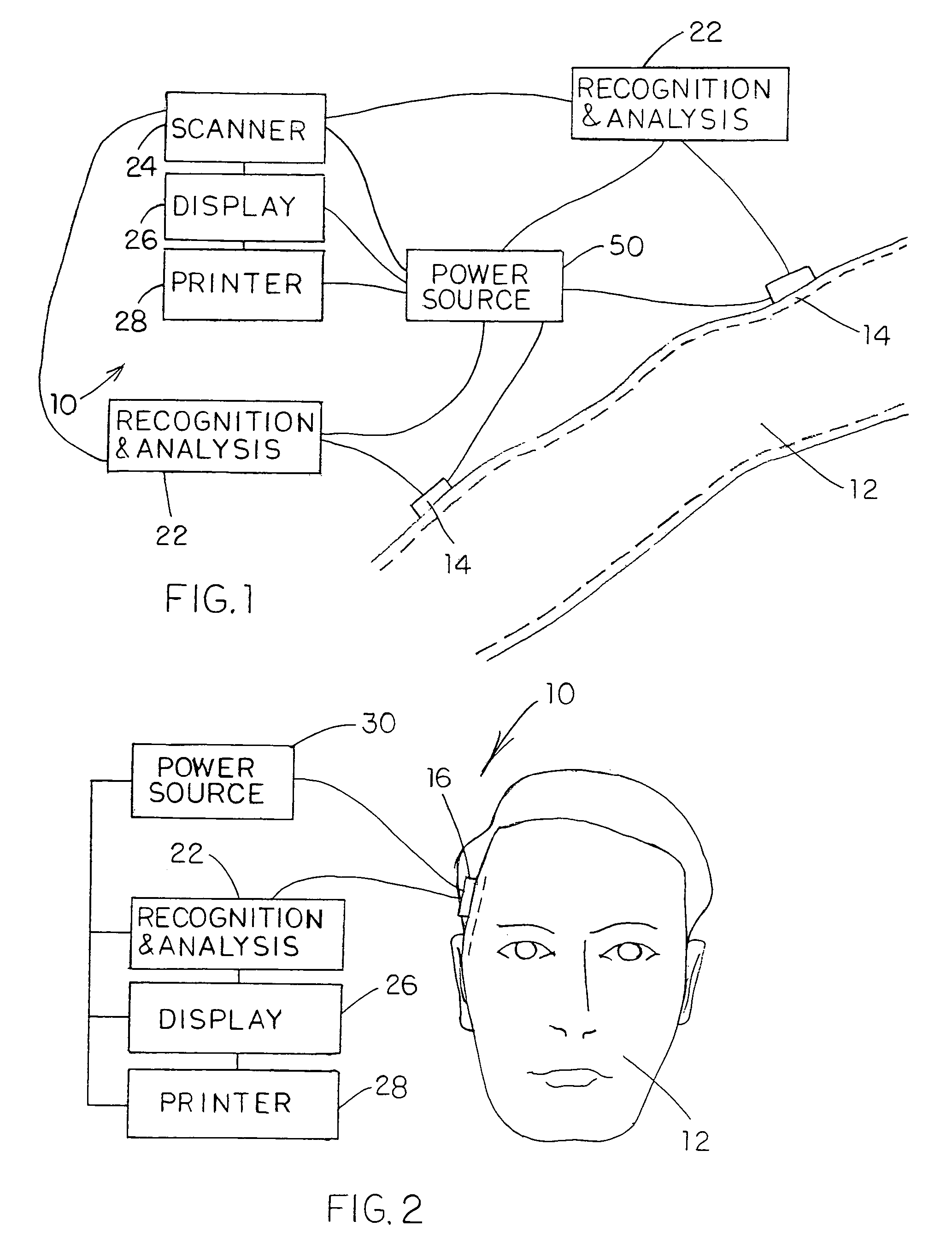
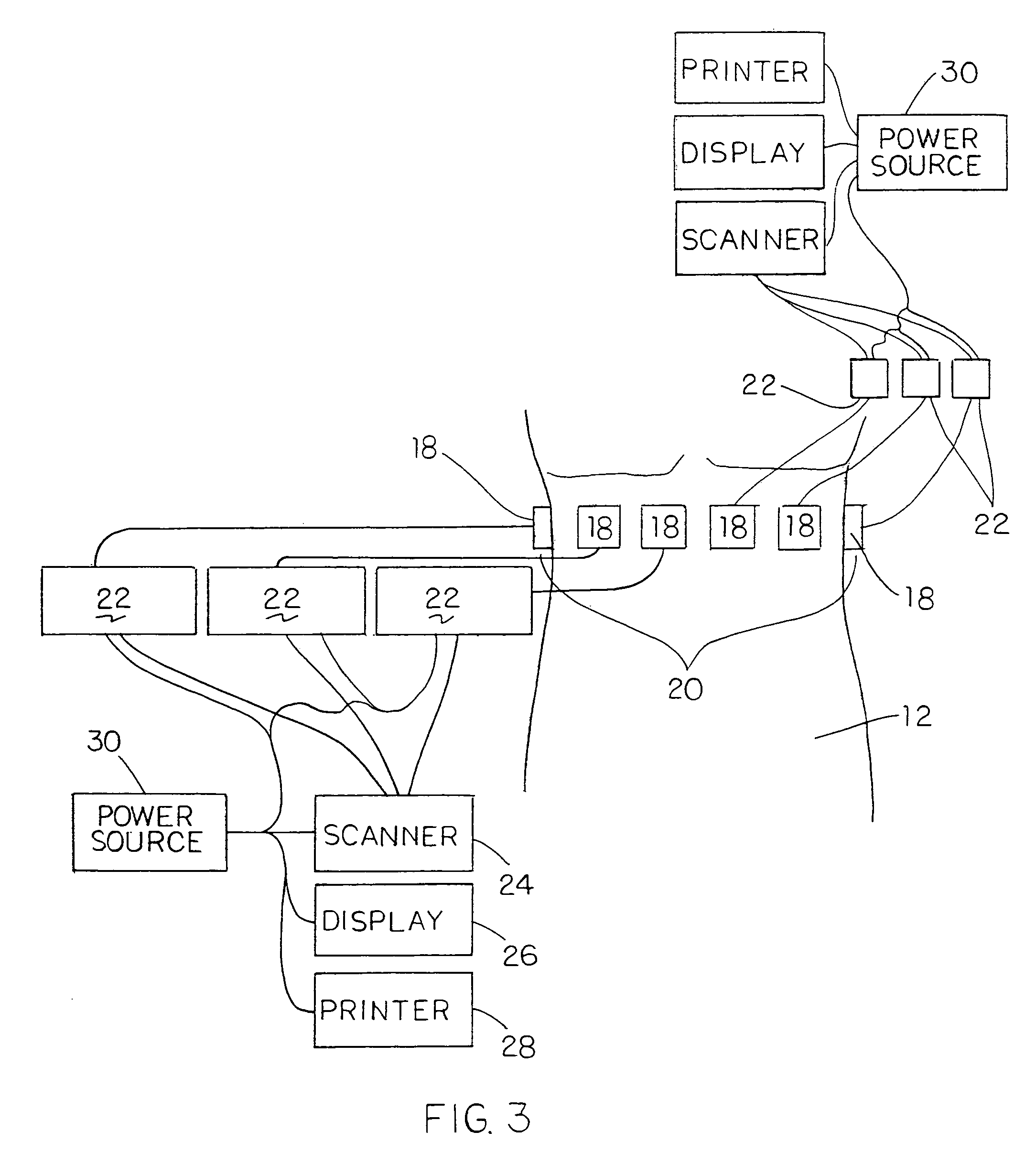
Wearable Pulse Wave Velocity Blood Pressure Sensor and Methods of Calibration Thereof
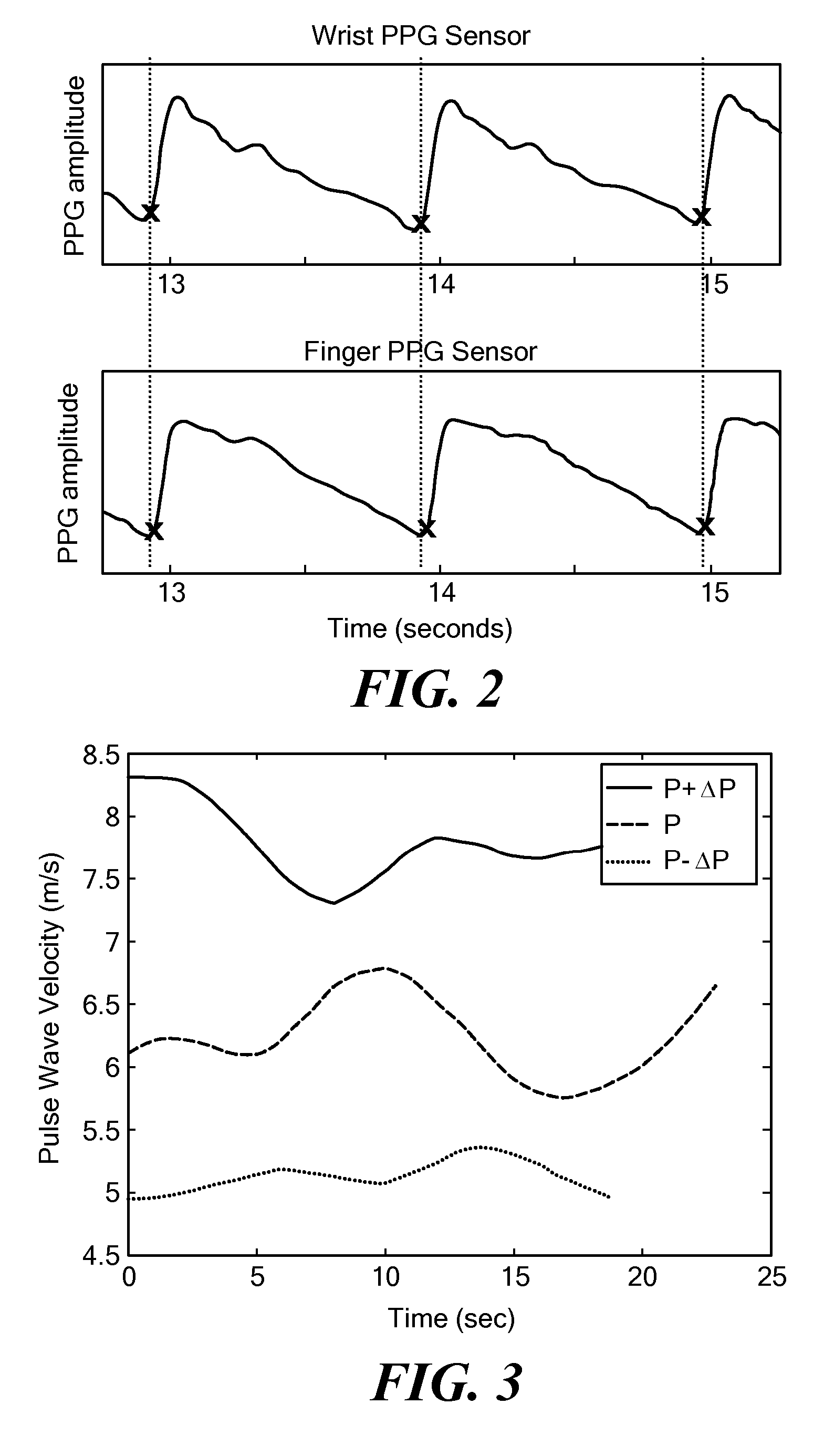
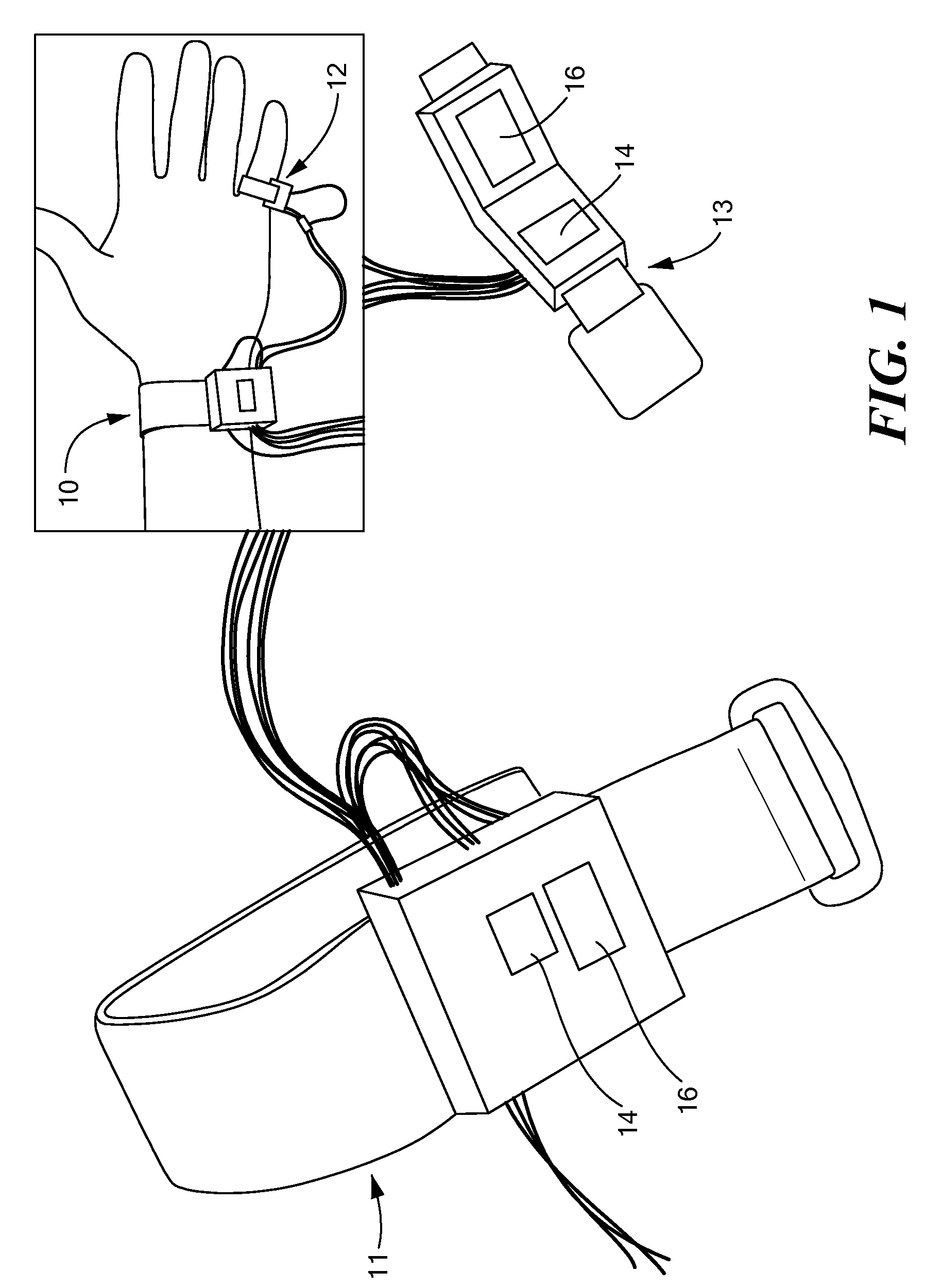
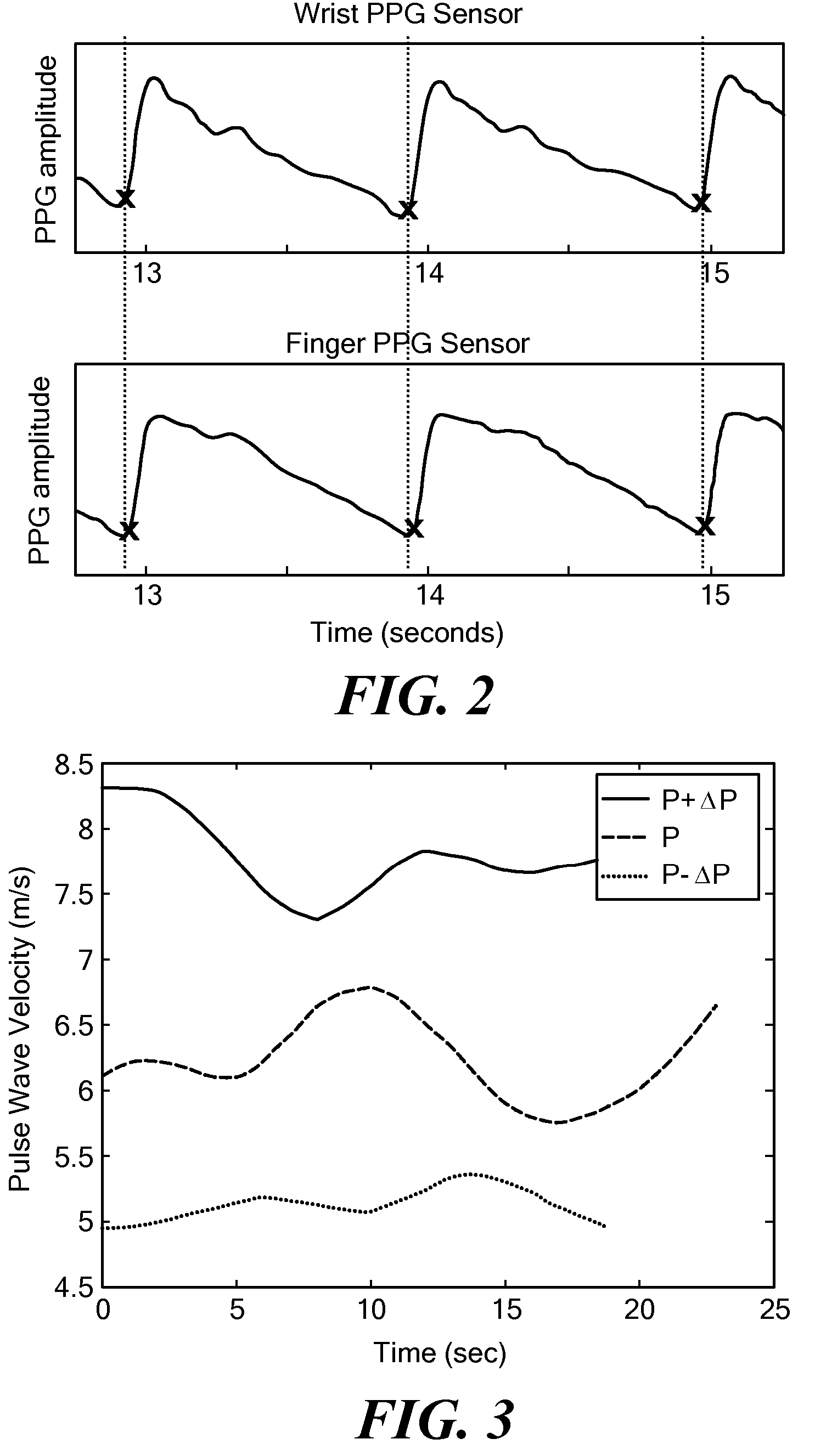
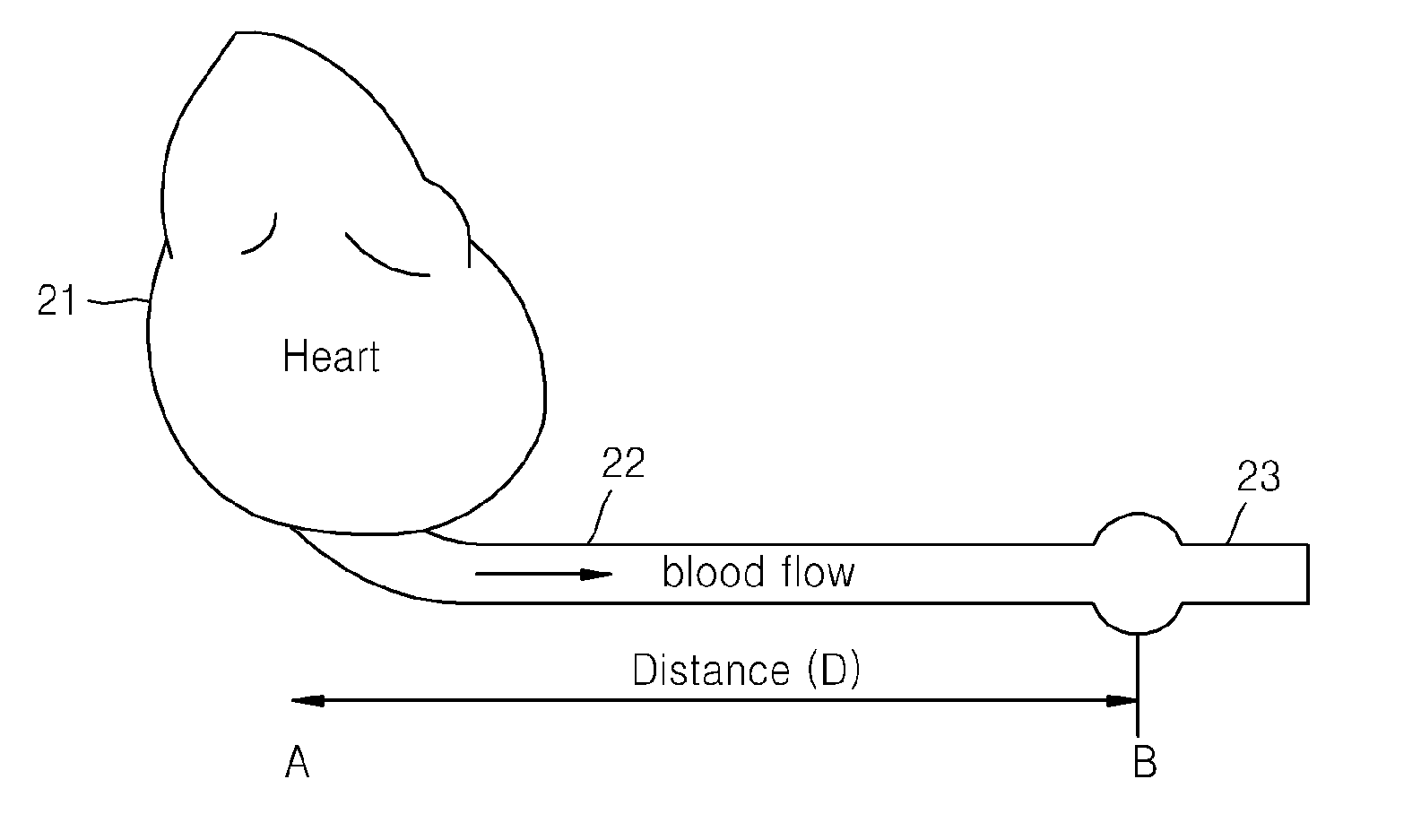
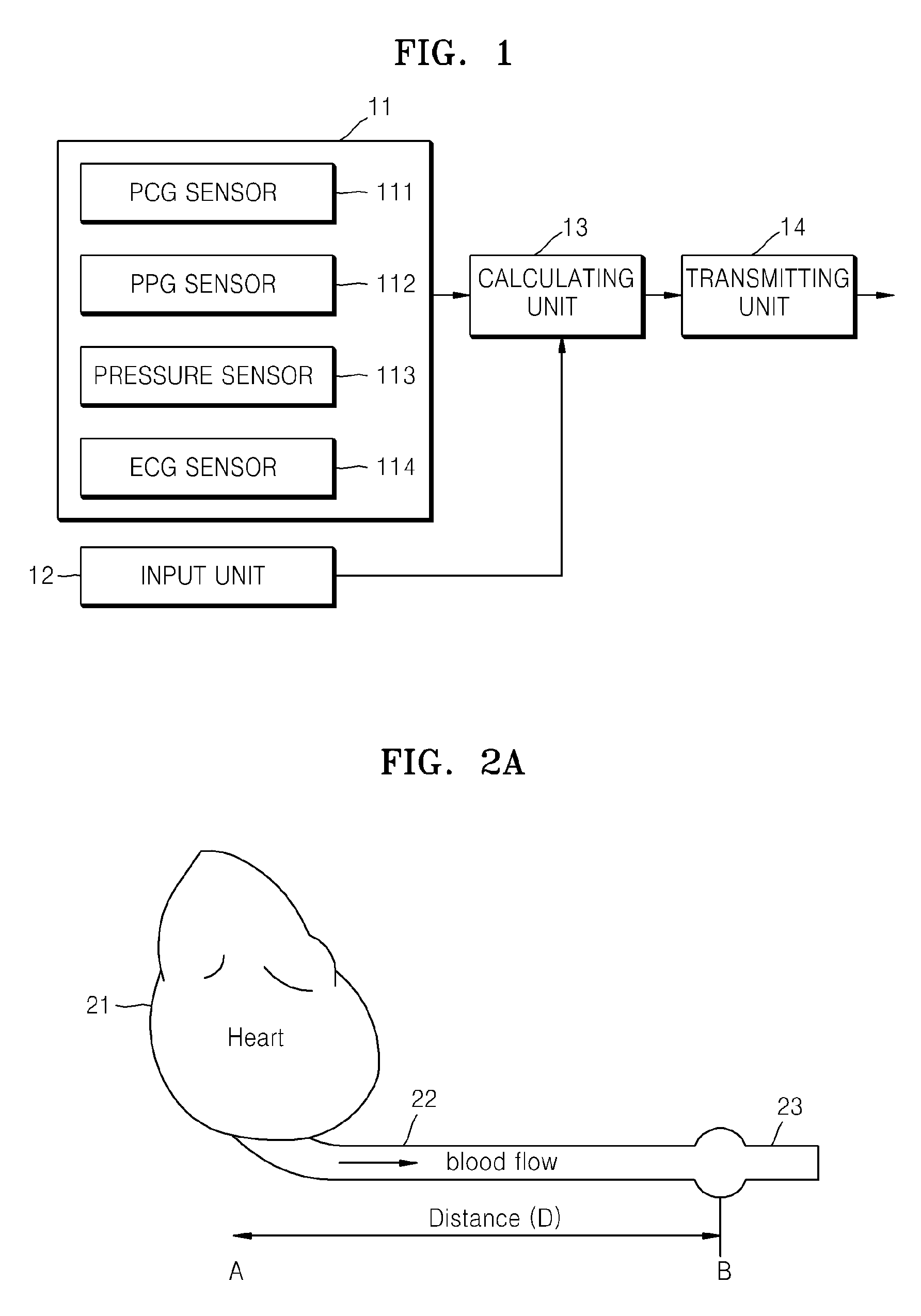
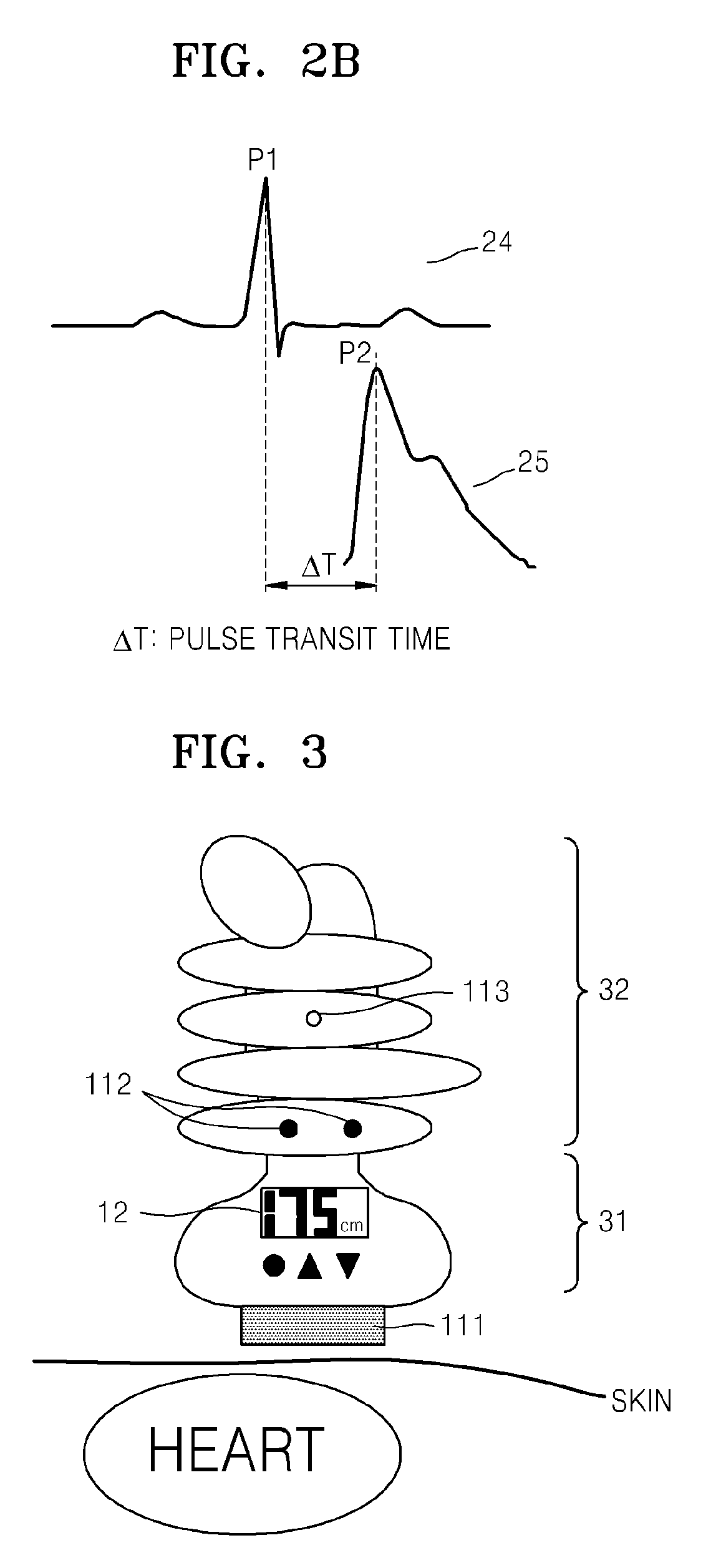
An apparatus and methods for performing a circulatory measurement on an extremity, such as a hand, of a subject. The circulatory measurement results in the derivation of an output circulatory metric that may encompass blood pressure or various other circulatory metrics. An indicator of an input circulatory metric at a locus on the extremity is measured, such as a pulse transit time. To determine the pulse transit time, a first plethysmographic signal may be obtained at a first position on the extremity, while a second plethysmographic signal may be obtained at a second position on the extremity of the subject. A transit time characterizing a circulatory pressure wave is calculated based on the first and second plethysmographic signals, leading to derivation of a wave speed. A calibration is then applied to provide the circulatory measurement based at least on the derived wave speed and a measured indicator of a hydrostatic component of blood pressure. Calibration is provided, in certain described embodiments, by derivation of two calibration parameters, a gain and a pulse transit time at zero pressure. Methods for deriving the calibration parameters include performing measurements under distinct hydrostatic pressure conditions, and based upon a measured derivative with respect to pressure of the pulse wave velocity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Wearable pulse wave velocity blood pressure sensor and methods of calibration thereof
An apparatus and methods for performing a circulatory measurement on an extremity, such as a hand, of a subject. The circulatory measurement results in the derivation of an output circulatory metric that may encompass blood pressure or various other circulatory metrics. An indicator of an input circulatory metric at a locus on the extremity is measured, such as a pulse transit time, and calibrated to account for the hydrostatic component of blood pressure arising due to vertical displacement of the extremity with respect to the heart.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
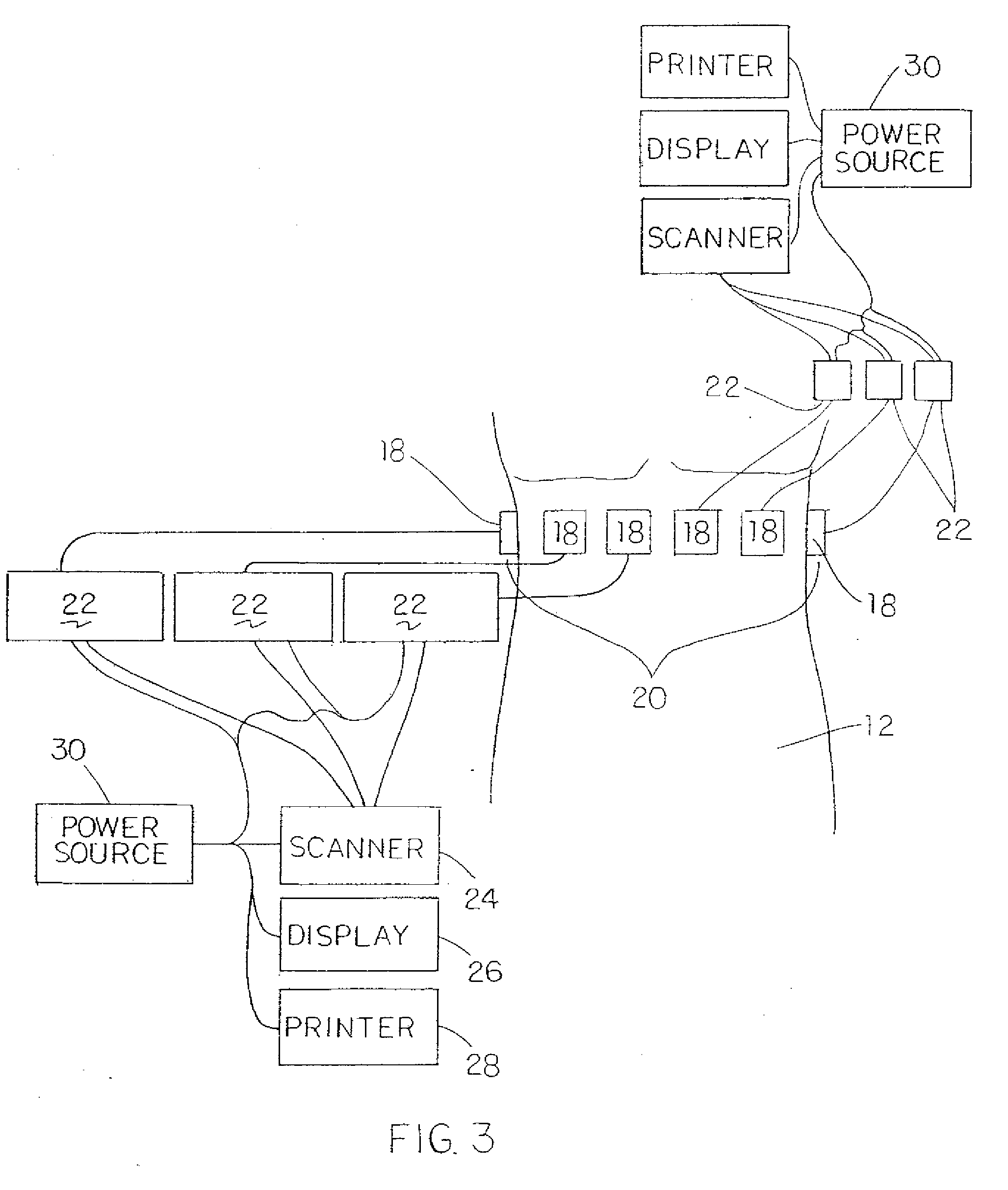
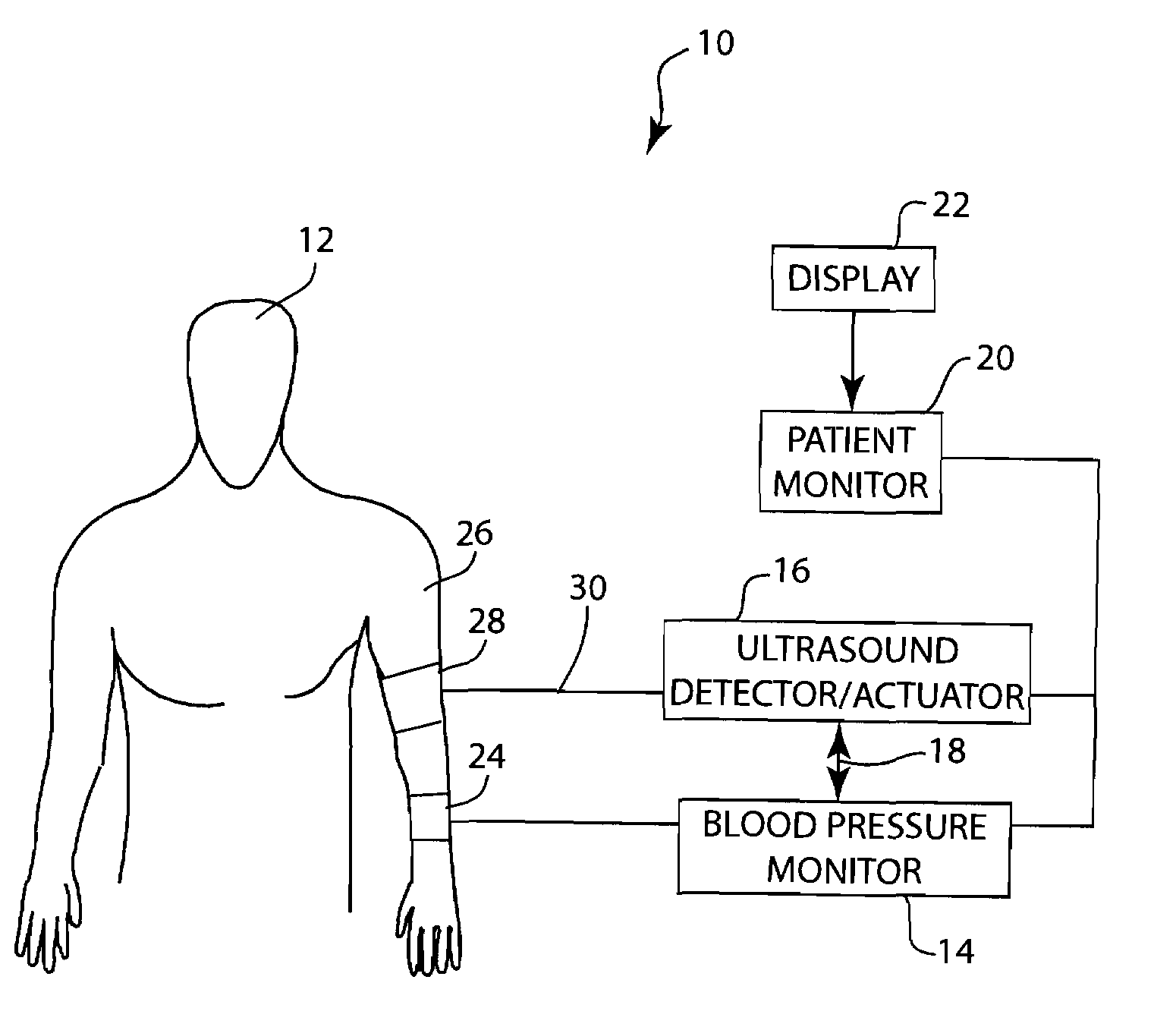
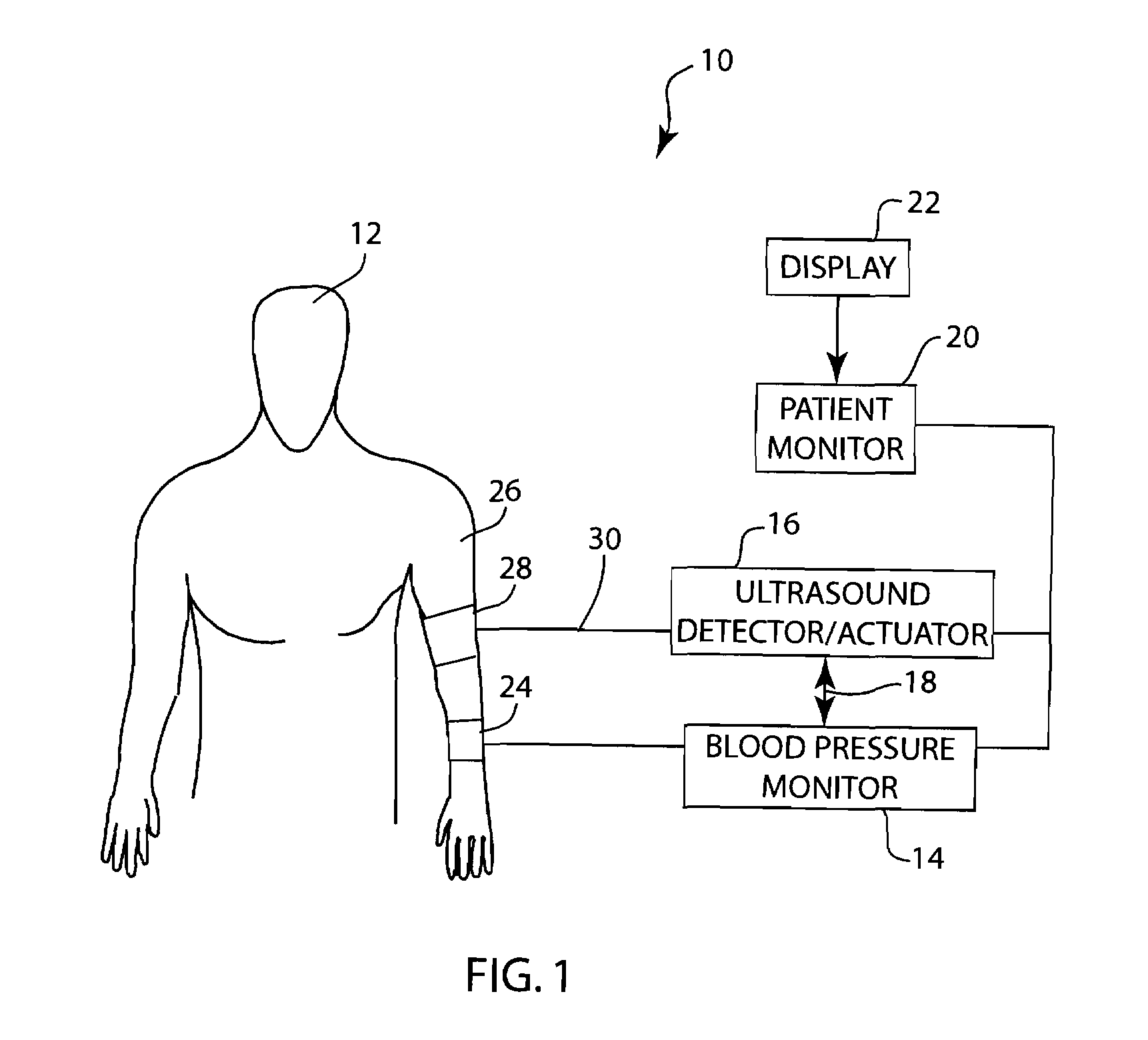
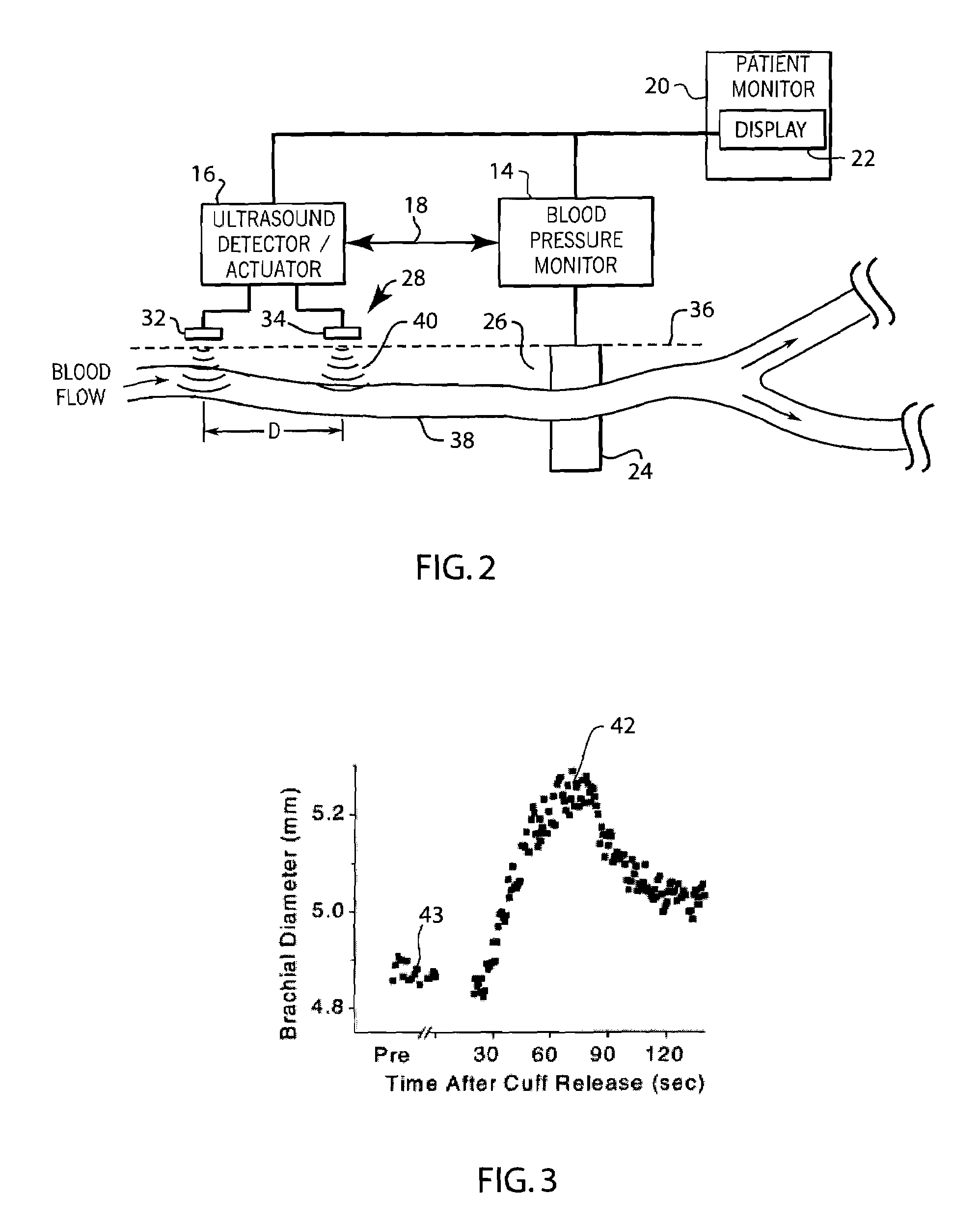
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
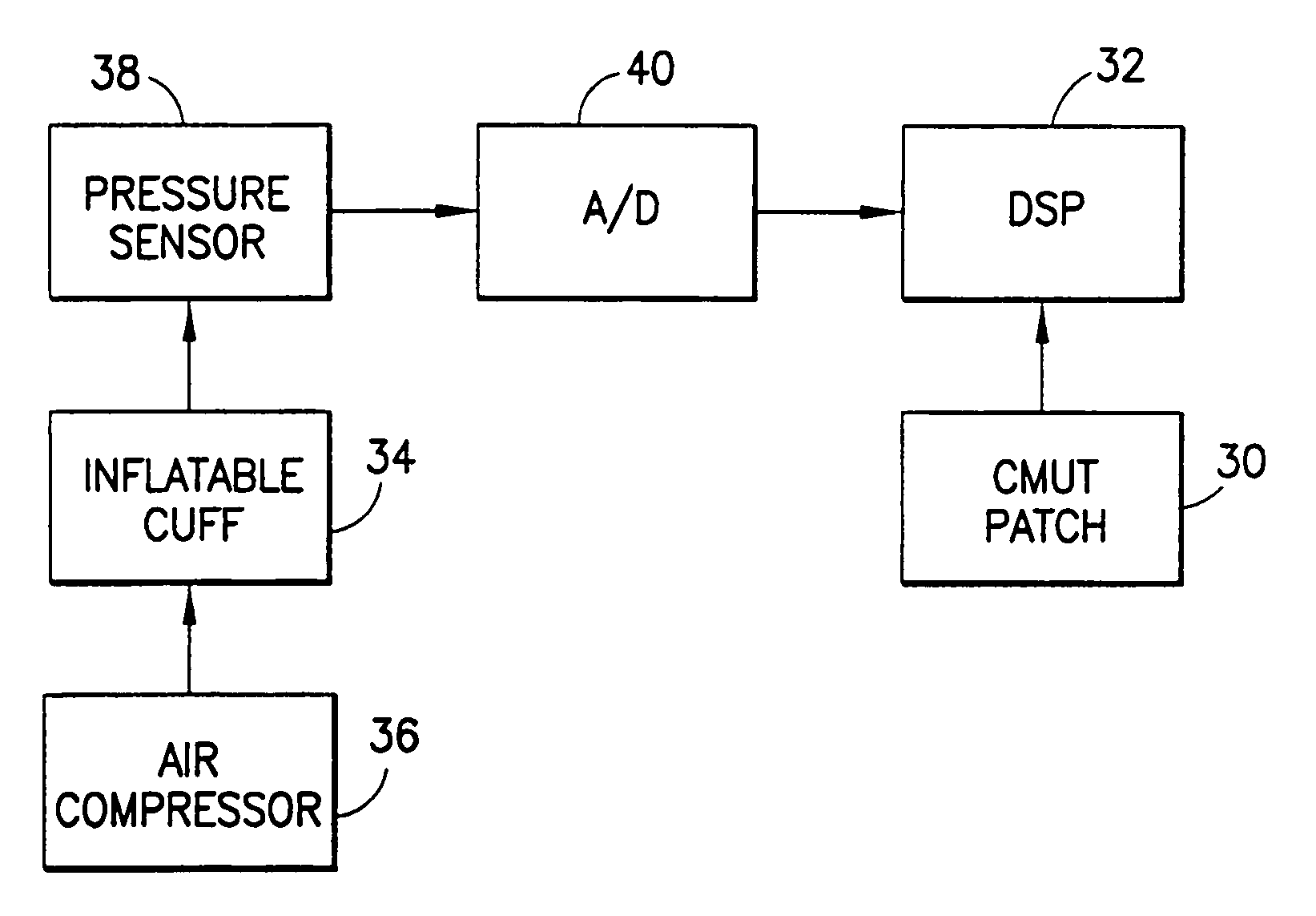
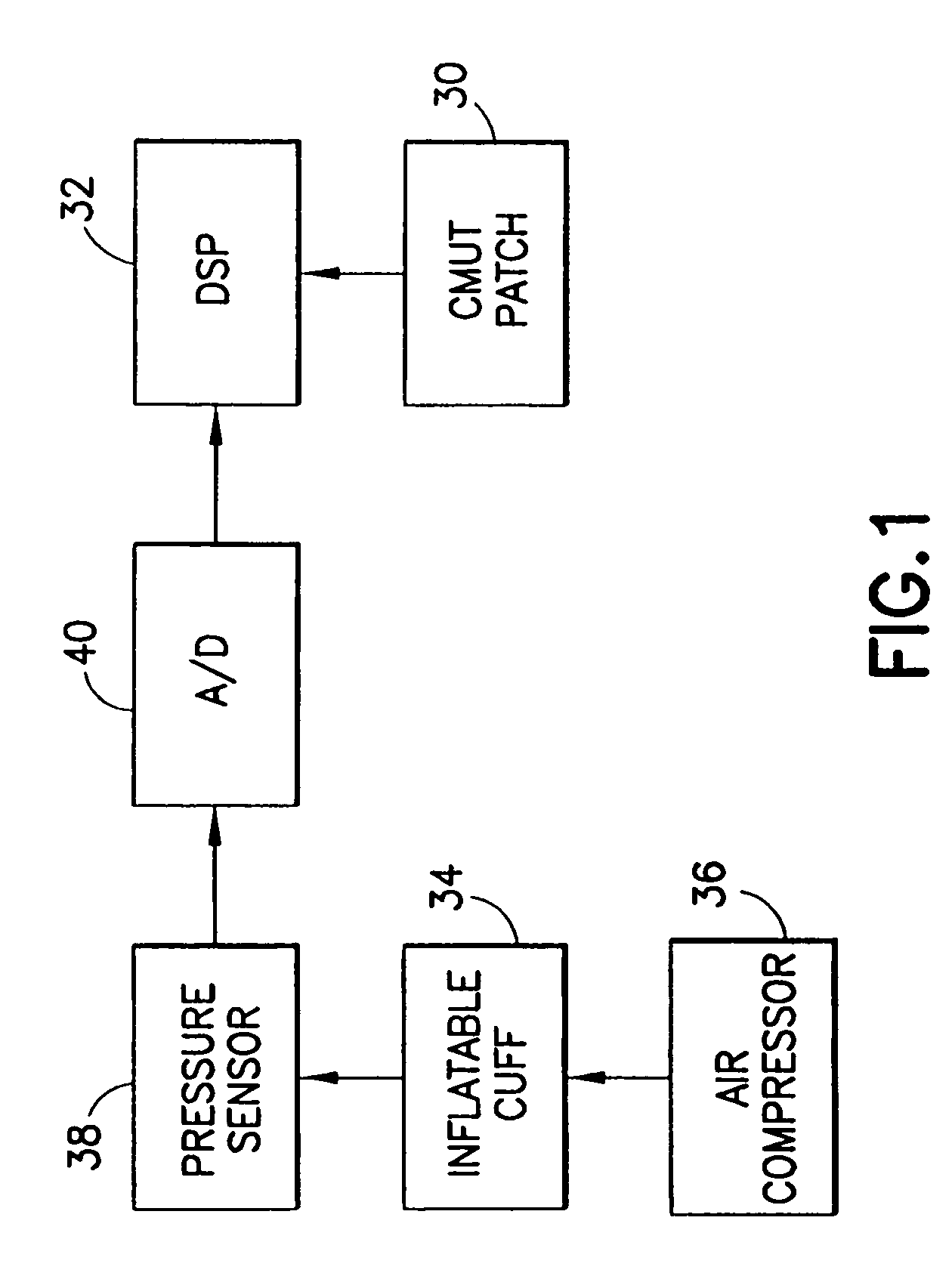
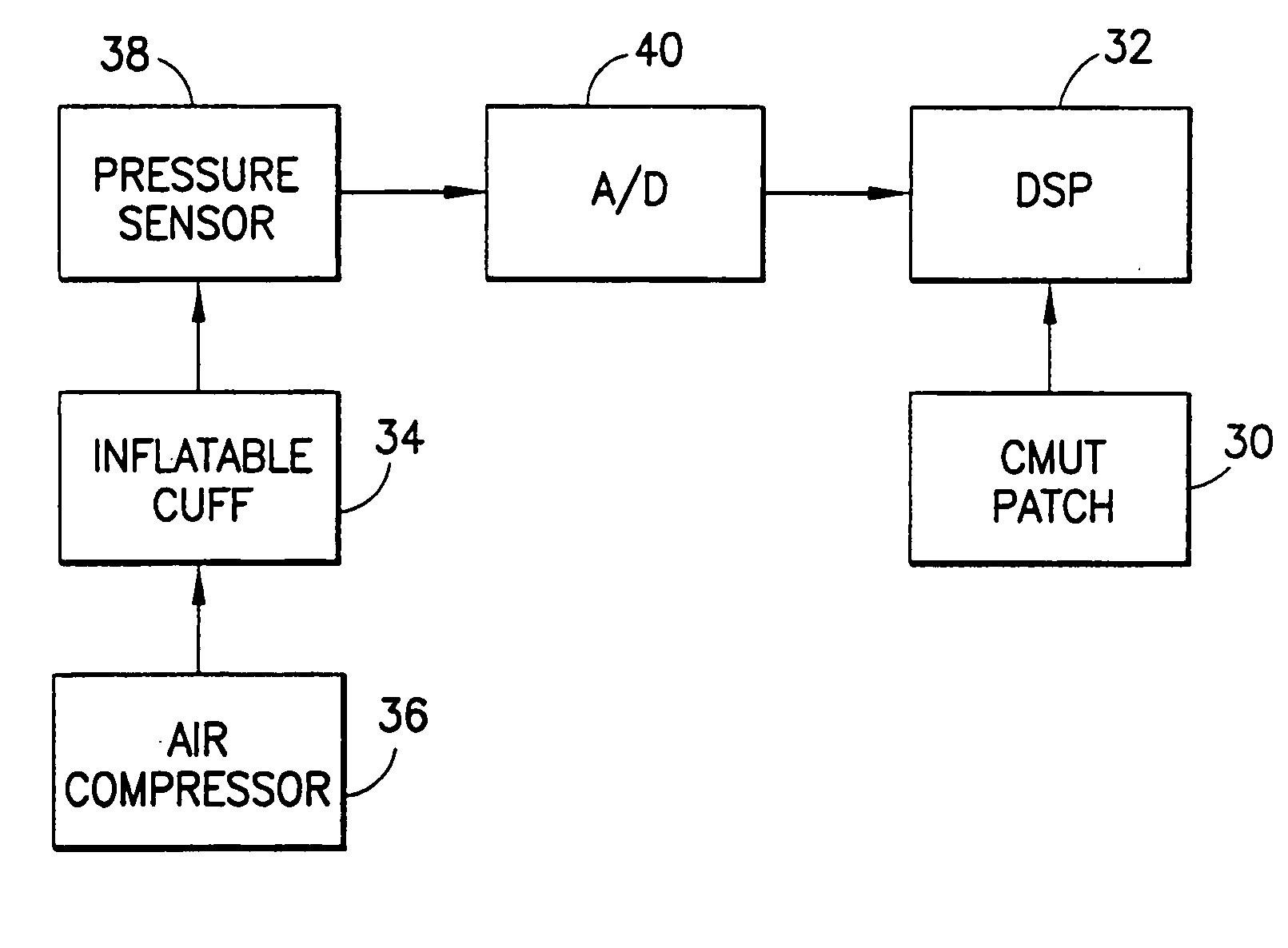
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
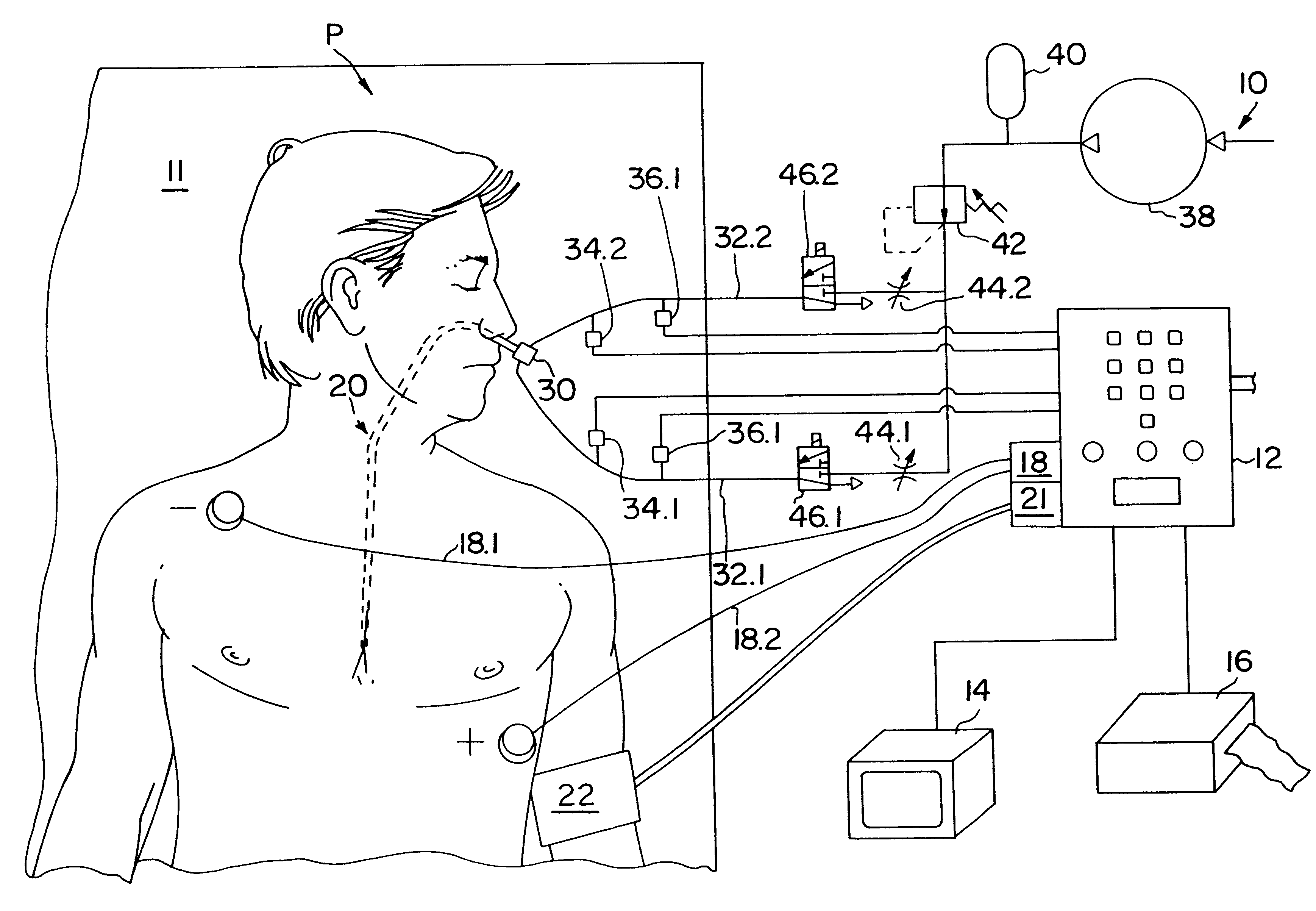
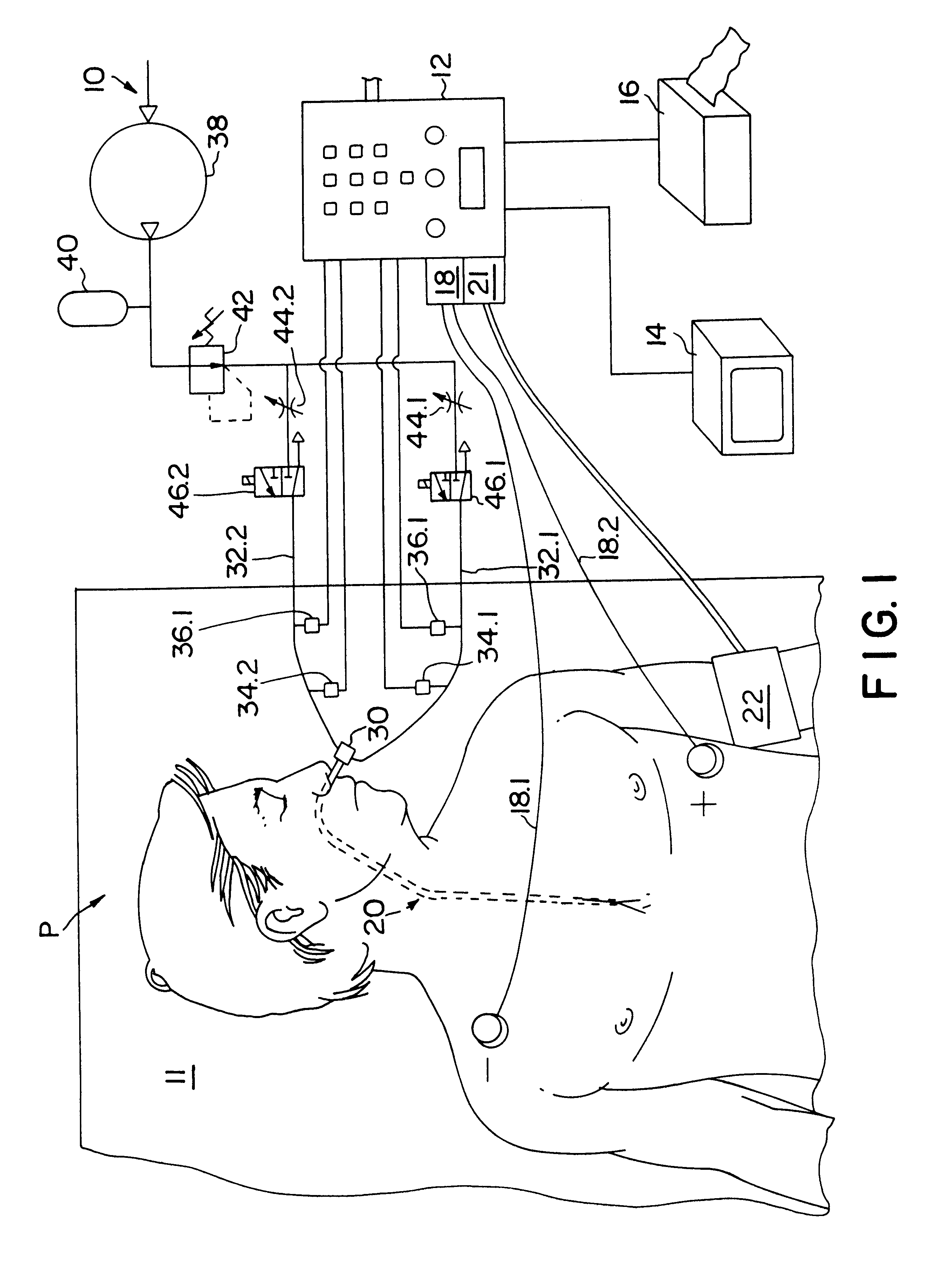
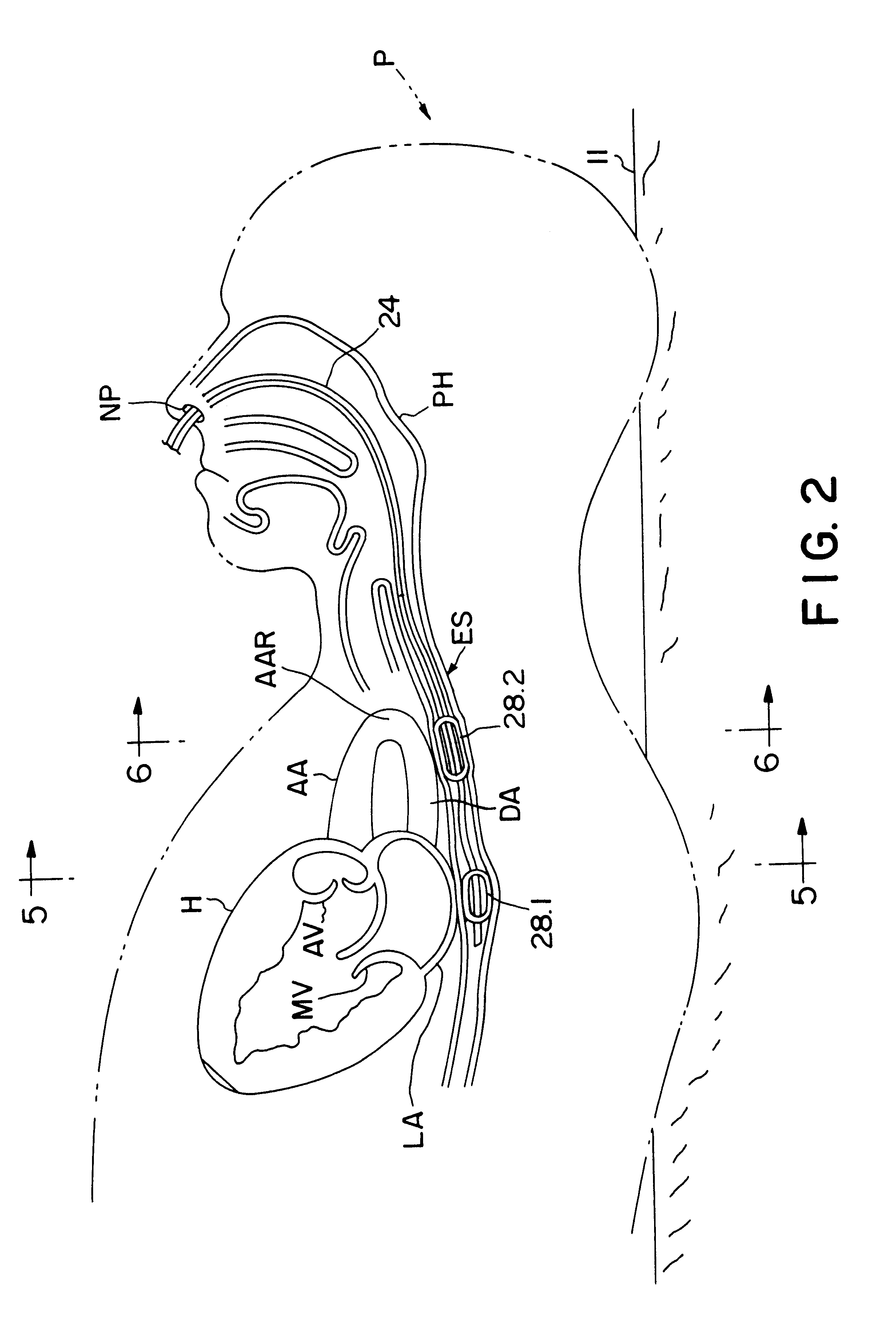
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
InactiveUS6120442AInexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
Apparatus and method for noninvasively determining cardiac performance parameters including 1) lengths of systolic time intervals, (2) contractility index, (3) pulse amplitude ratios while performing the Valsalva maneuver, (4) cardiac output index, and (5) a pulse wave velocity index. A catheter having at least one balloon is inserted into the esophagus and pressurized and positioned adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure. The effects of aortic pressure on the balloon are utilized to determine at least one of the cardiac performance parameters. The catheter may include a second balloon which is spaced from the aortic balloon a distance such that when the second balloon is in a position adjacent the left atrium to sense left atrial pressure the aortic balloon is in a position adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure, this distance being related to the distance between the left atrium and aortic arch in most adult persons.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Continuous blood pressure measuring device
InactiveCN102397064AAvoid the cumbersome calibrationHigh precisionEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyArterial velocityFeature extraction
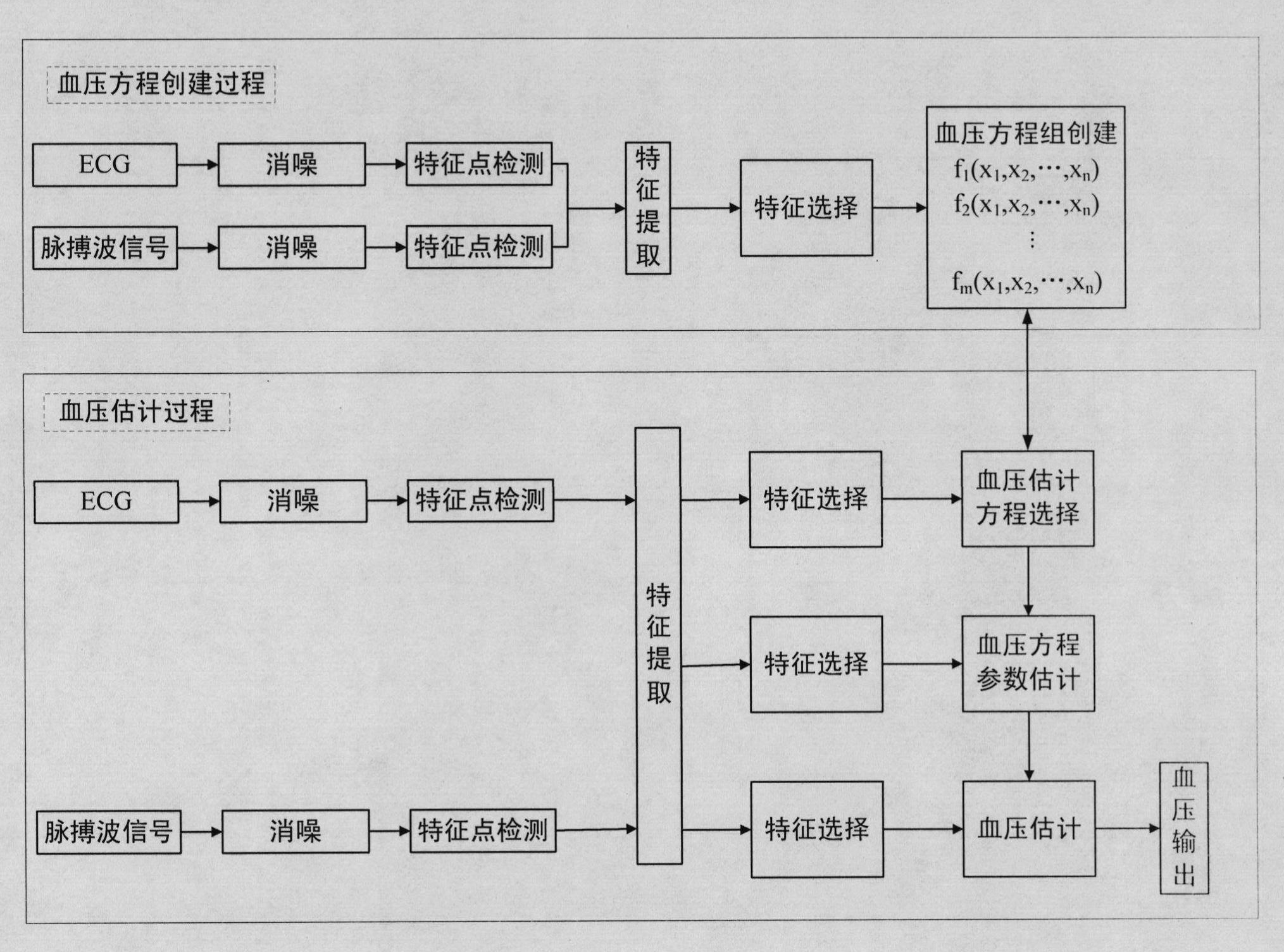
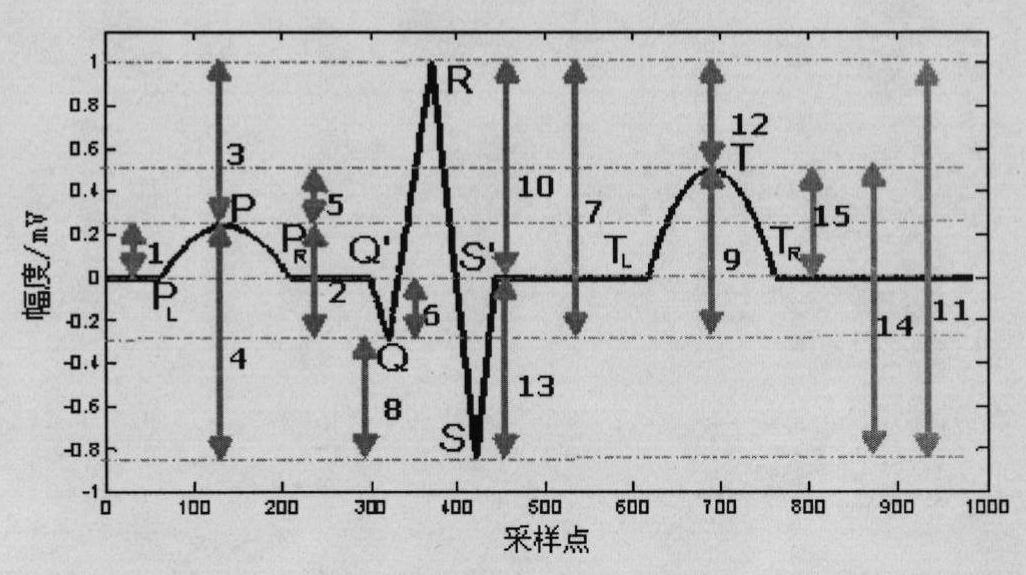
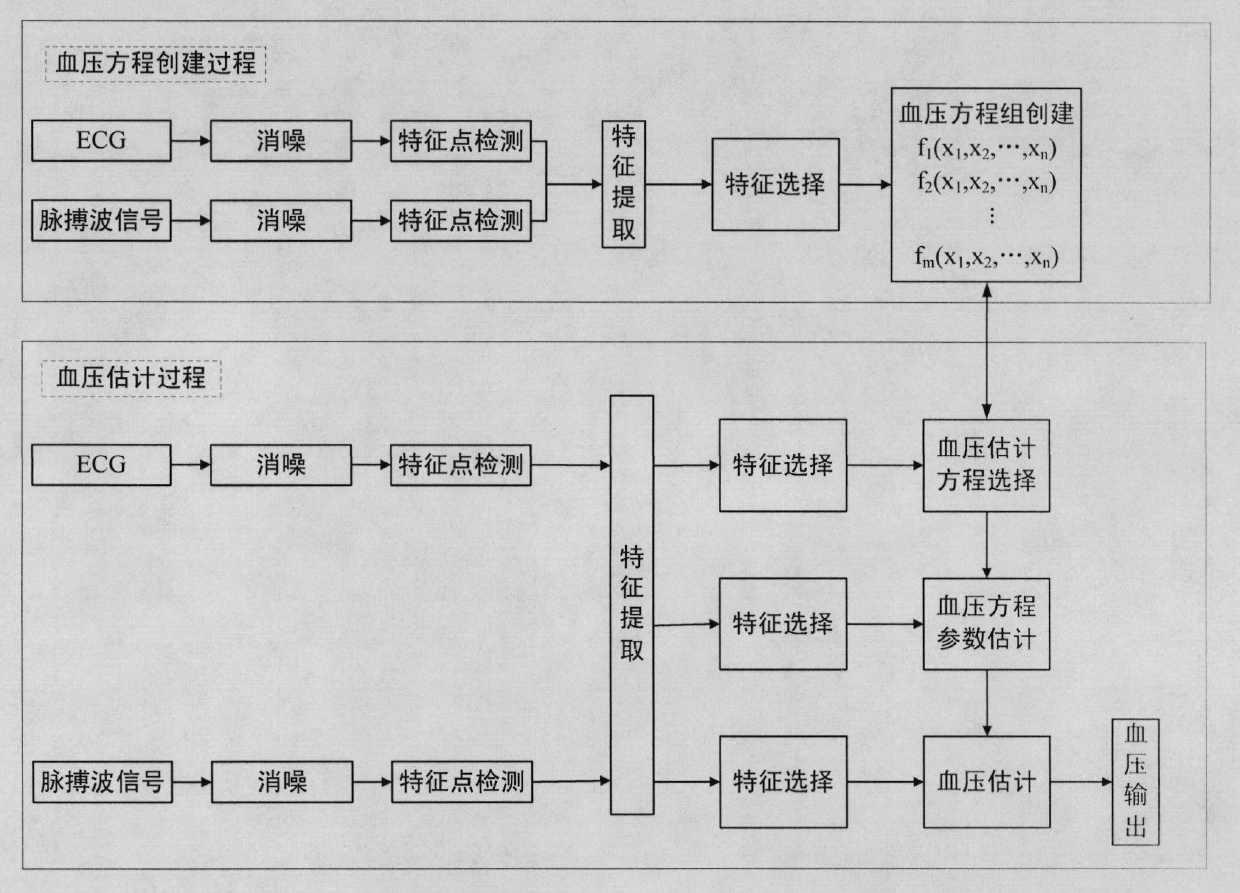
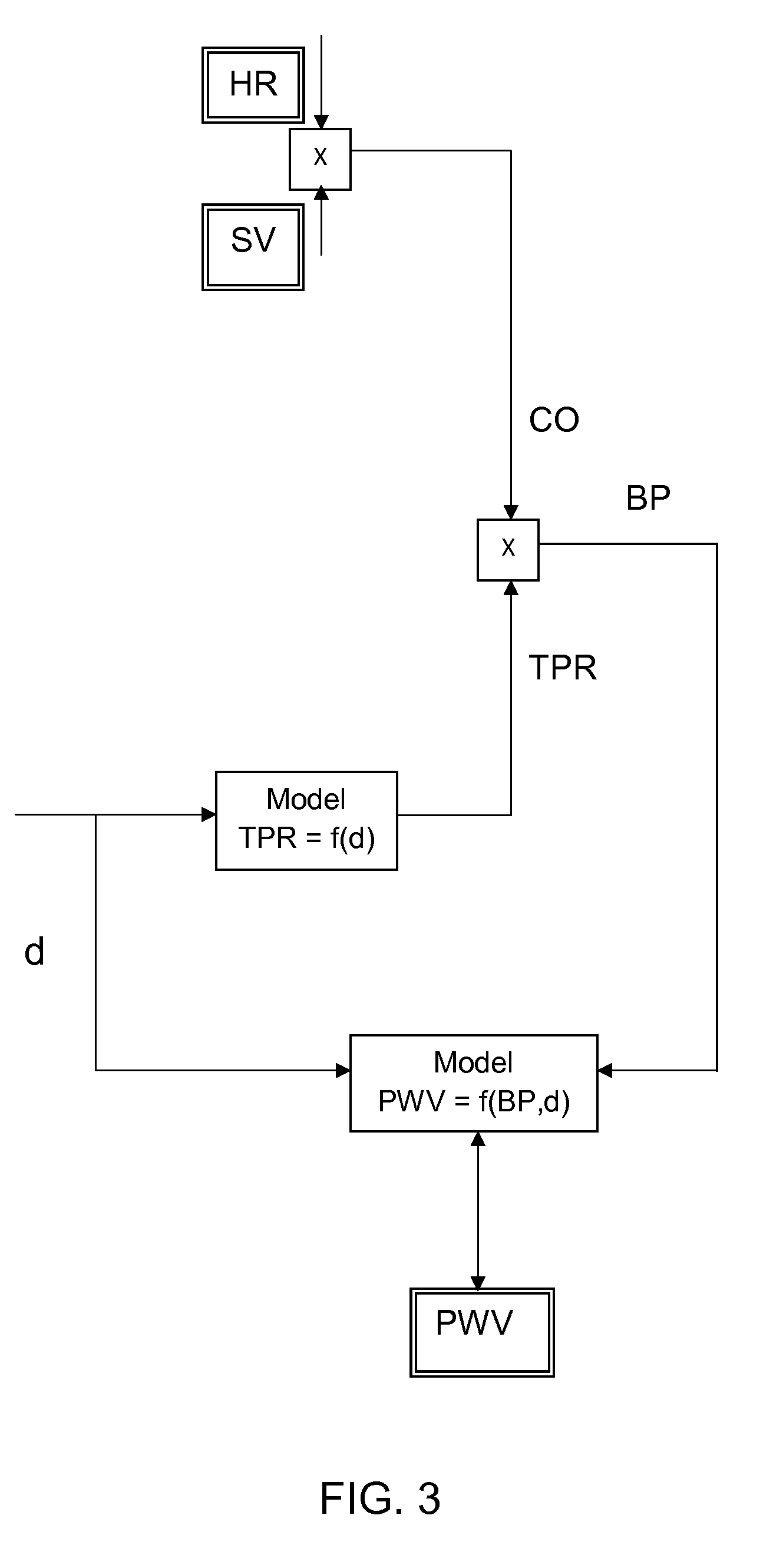
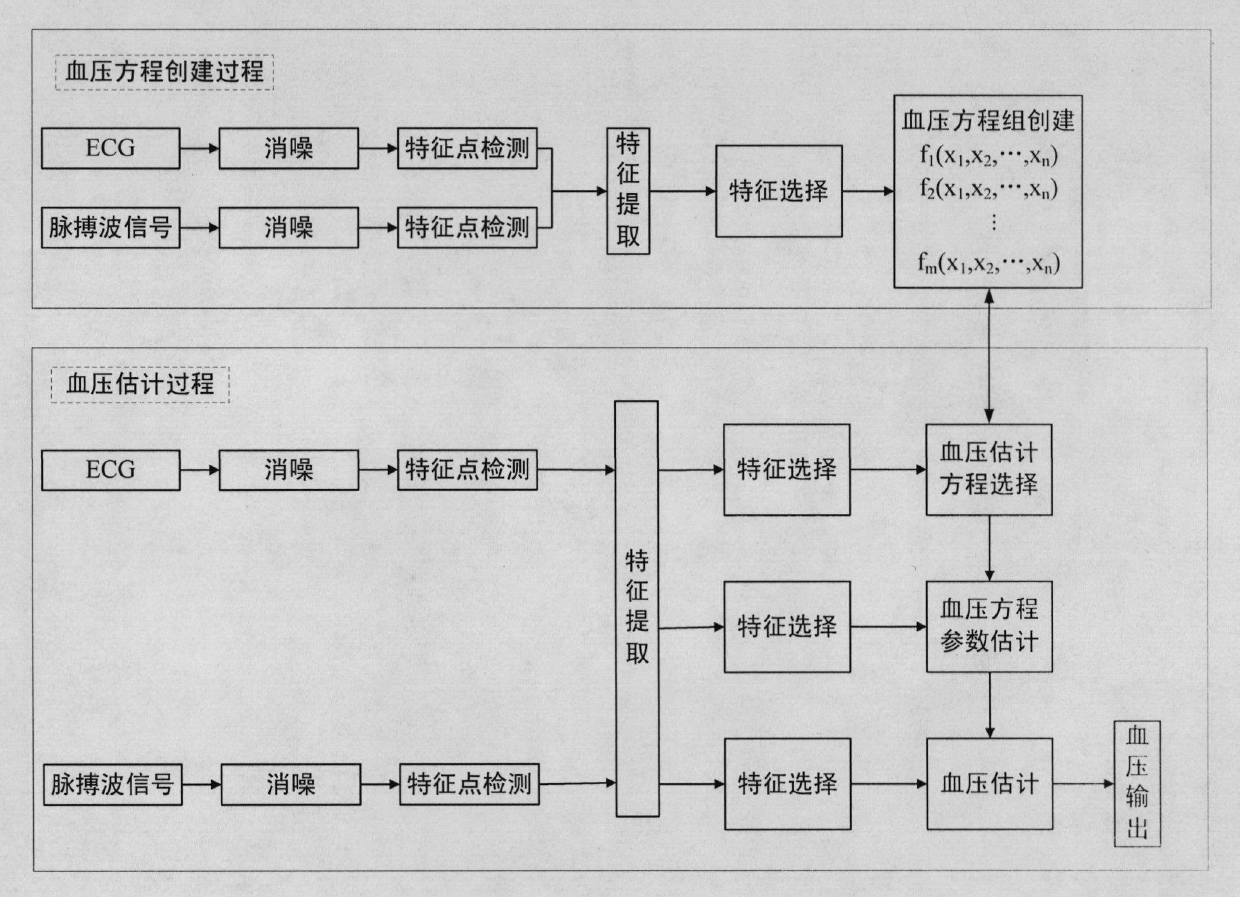
The invention provides a continuous blood pressure measuring device. The method for measuring blood pressure by the device comprises the following steps of: selecting features used for blood pressure equation estimation from a large number of extracted features by feature selection, sending the selected features into a decision system, and determining equations used for estimating the blood pressure from blood pressure simultaneous equations; selecting the features used for estimating coefficients of the blood pressure equations from the features which are extracted from feature extraction by feature selection, and estimating the coefficients of the blood pressure equations by statistical estimation, digital computation and other methods; and finally selecting the features used for estimating the blood pressure from the features which are extracted from the feature extraction by feature selection, and substituting the selected features into the blood pressure equations to estimate blood pressure. By a multi-feature-based pulse wave velocity method and a blood pressure simultaneous equation establishment method, the blood pressure estimation is performed by artificial intelligence, pattern recognition and other ways to ensure that not only the measurement accuracy of the blood pressure estimation is improved but also a complicated parameter calibrating process is avoided.
Owner:SCI RES TRAINING CENT FOR CHINESE ASTRONAUTS
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiparameter whole blood monitor and method
InactiveUS20090270695A1Increase turnaround timeRemove uncertaintyBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsPulse pressureIntravascular catheter
Owner:NEW PARADIGM CONCEPTS
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
InactiveUS6238349B1Inexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
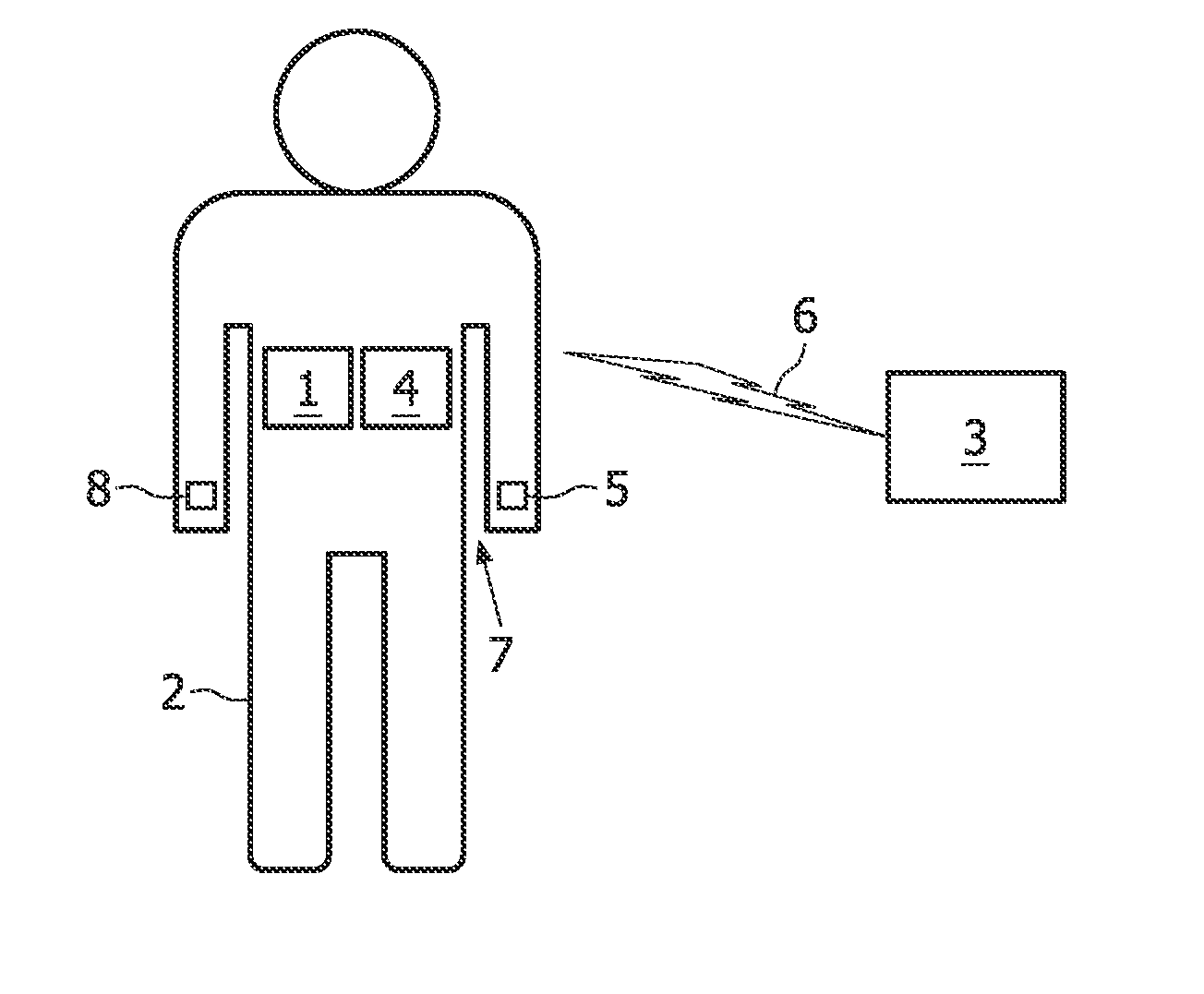
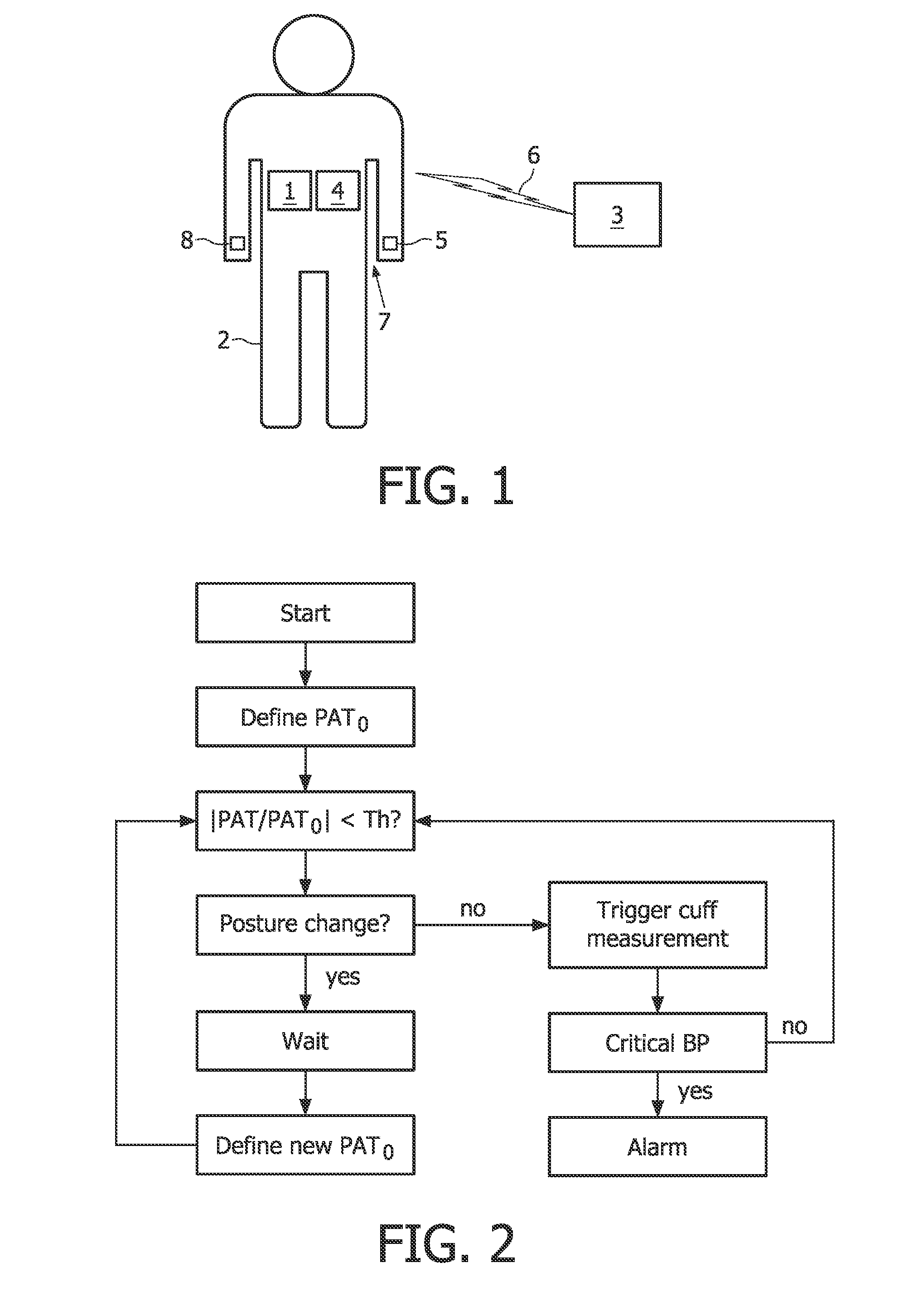
Monitoring the blood pressure of a patient
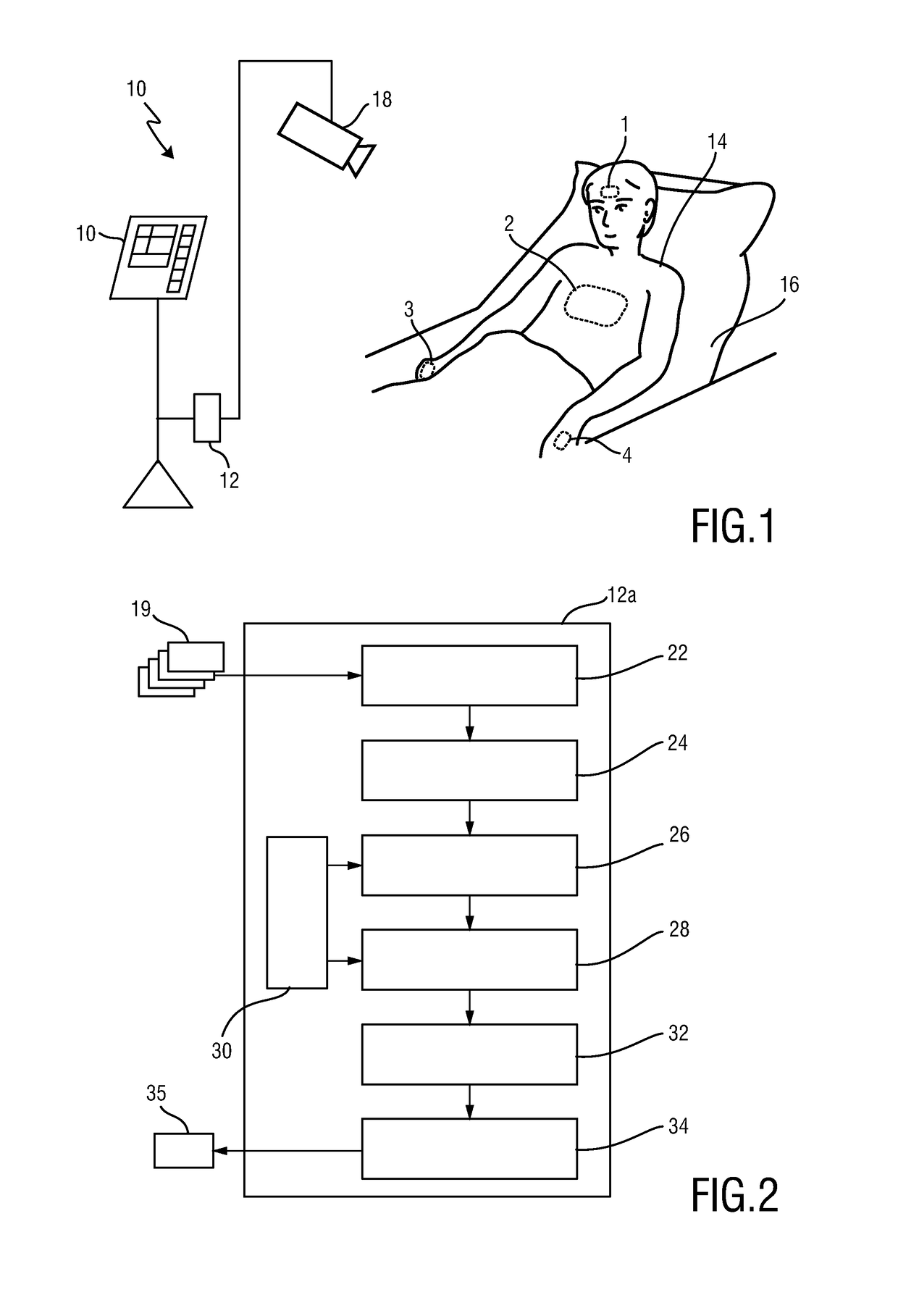
A method for monitoring the blood pressure of a patient, comprising the following steps: determining a pulse arrival time signal from the patient 2 based on the pulse wave velocity method; determining an accelerometer signal from the patient 2; and triggering an additional measure or deriving a blood pressure value, taking into account the pulse arrival time signal and a DC component of the accelerometer signal. In this way, a possibility for monitoring the blood pressure of a patient is provided with which false alarms and / or unnecessary additional cuff-based blood pressure measurements can be avoided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Multiparameter whole blood monitor and method
ActiveUS20060287600A1Continuous and precise measurementBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsPulse pressureIntravascular catheter
The present invention provides an apparatus and methods for continuous intravascular measurement of whole blood concentration, blood pressure, and pulse pressure. The intravascular catheter incorporates a sensor to measure whole blood sound velocity, attenuation, backscatter amplitude, and blood flow velocity and also incorporates existing technologies for multiple physiologic measurements of whole blood. Pulse wave velocity and wave intensity are derived mathematically for purposes of estimating degree of local vascular tone.
Owner:NEW PARADIGM CONCEPTS
Continuous blood pressure measuring device
InactiveCN102429649AAvoid the cumbersome calibrationHigh precisionEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyFeature extractionDecision system
The invention provides a continuous blood pressure measuring device. When the device is used for measuring blood pressure, a method comprises the following steps of: firstly, selecting characteristics for blood pressure equation estimation from a lot of extracted characteristics through characteristic selection, feeding the characteristics into a decision system, and determining an equation for estimating the blood pressure from a blood pressure equation set; then, selecting characteristics for estimating a blood pressure equation coefficient from the characteristics extracted based on the characteristic extraction by utilizing the characteristic selection, and estimating a blood pressure equation coefficient by using methods, such as statistical estimation, numerical value calculation and the like; and finally, selecting characteristics for estimating blood pressure from the characteristics extracted based on the characteristic extraction by utilizing the characteristic selection, and substituting the characteristics in the blood pressure equation to carry out blood pressure estimation. A multi-parameter-based pulse wave velocity method and a method for establishing a blood pressure equation set are utilized. the blood pressure estimation is carried out by utilizing methods, such as artificial intelligence, mode identification and the like, and thus, not only is the measurement precision of the blood pressure estimation further increased, but also the complicated parameter calibrating process is avoided.
Owner:SCI RES TRAINING CENT FOR CHINESE ASTRONAUTS
Method and apparatus for automated vascular function testing
ActiveUS20080119741A1Improve performanceAutomatically determineBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood pressure cuffsUltrasonic sensor
A method and system for use in measuring the endothelial dysfunction utilizing flow mediated dilation and determining arterial health of a patient. The system includes a non-invasive blood pressure monitor, an ultrasound system and a pulse oximeter monitor that all communicate with each other to perform the flow mediated dilation. Initially, the ultrasound transducer, blood pressure cuff and pulse oximeter sensor are positioned on an arm of the patient. The blood pressure cuff is inflated to occlude an artery for an occlusion period. Following the occlusion period, the ultrasound system is automatically signaled to begin determining a parameter of the artery, such as diameter, and the flow rate of blood through the artery without any operator intervention. At the same time, the pulse wave velocity PWV is calculated between the ultrasound transducer and the finger probe of the pulse oximeter following the occlusion period. Based upon the detected characteristics of the artery before and after occlusion, as well as the PWV, the system can determine the endothelial dysfunction and arterial health of the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
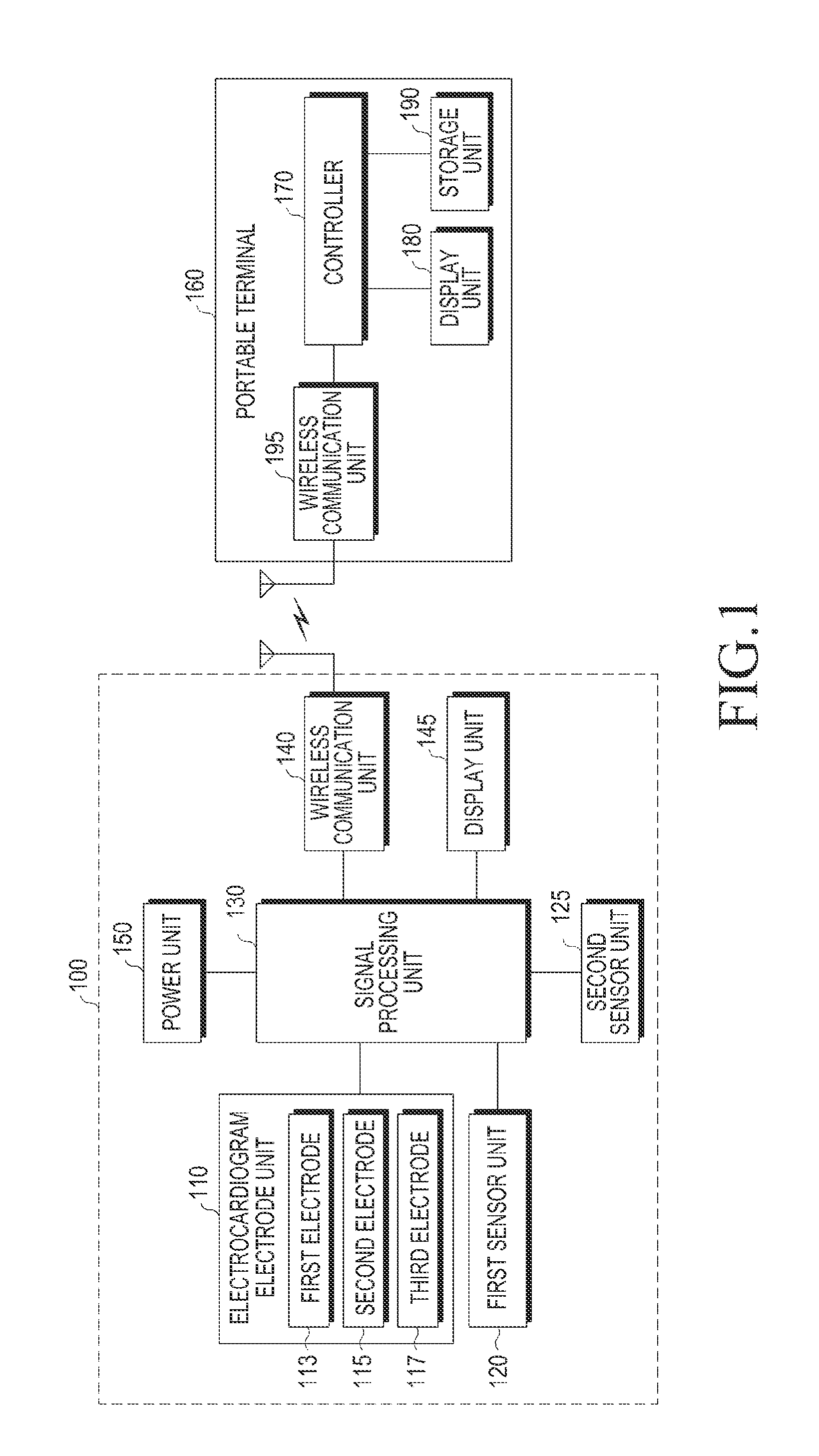
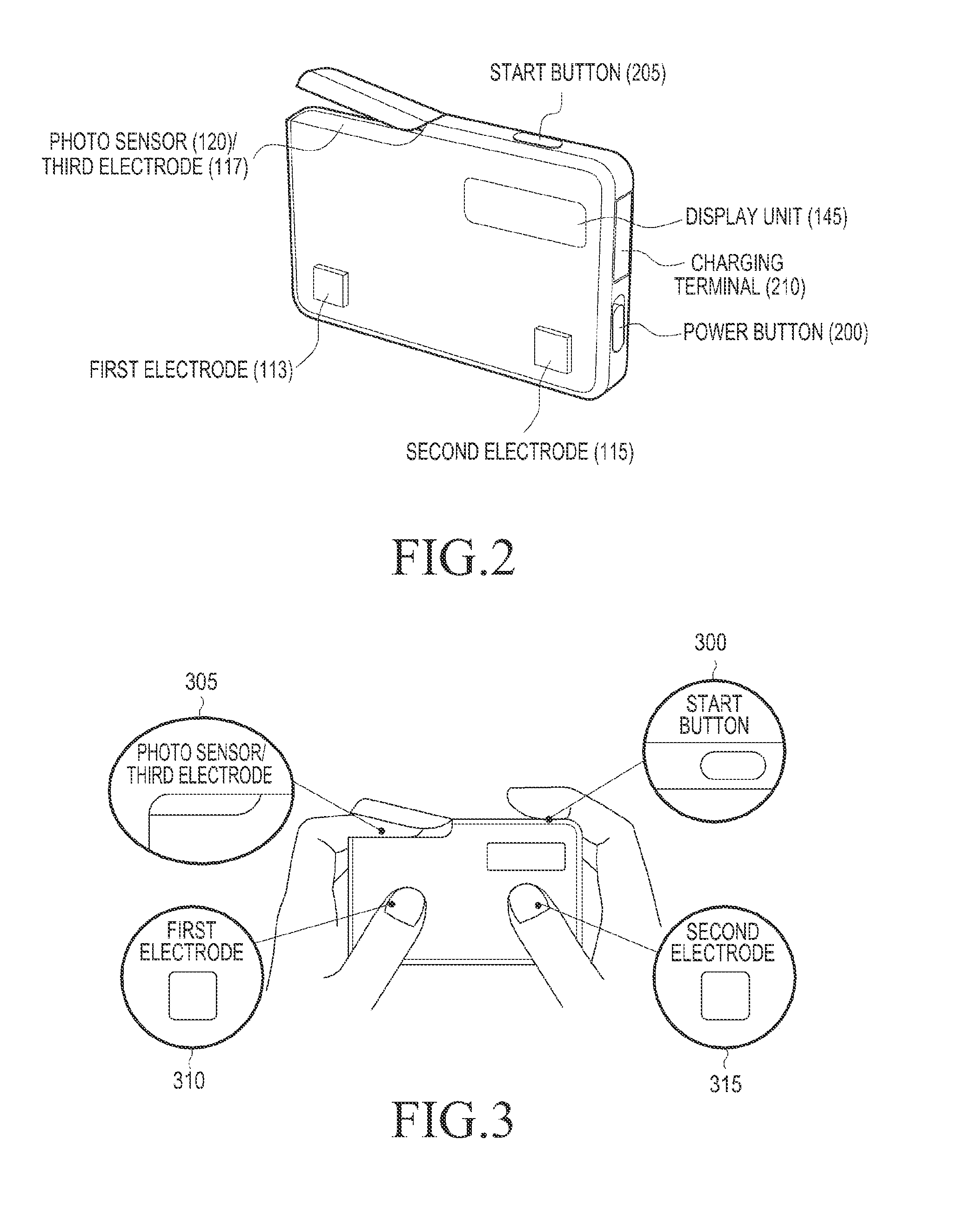
Portable blood pressure measuring apparatus and blood pressure measuring method in portable terminal
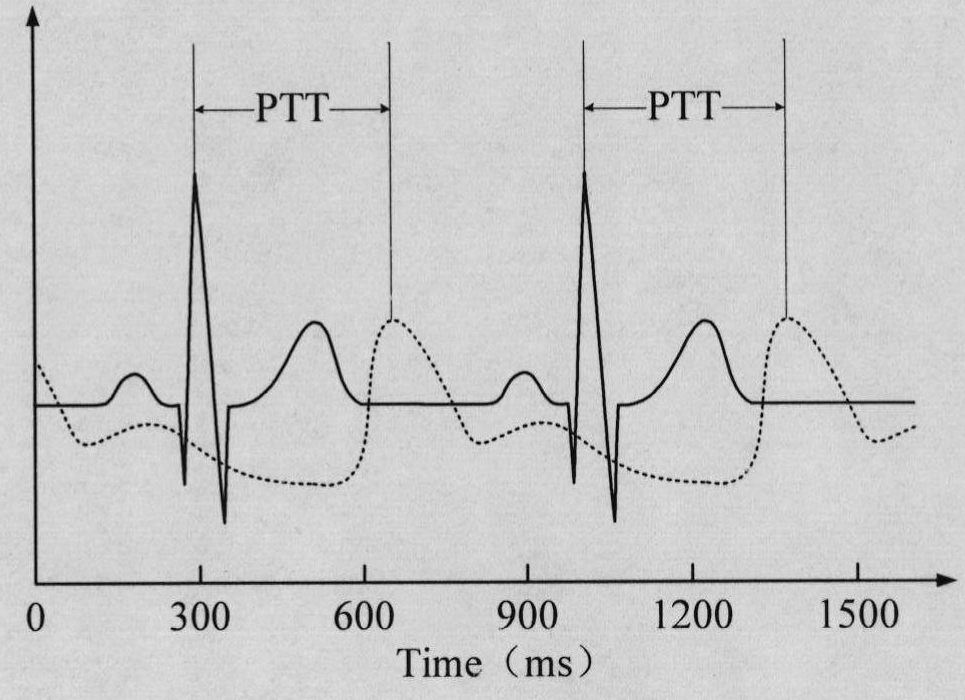
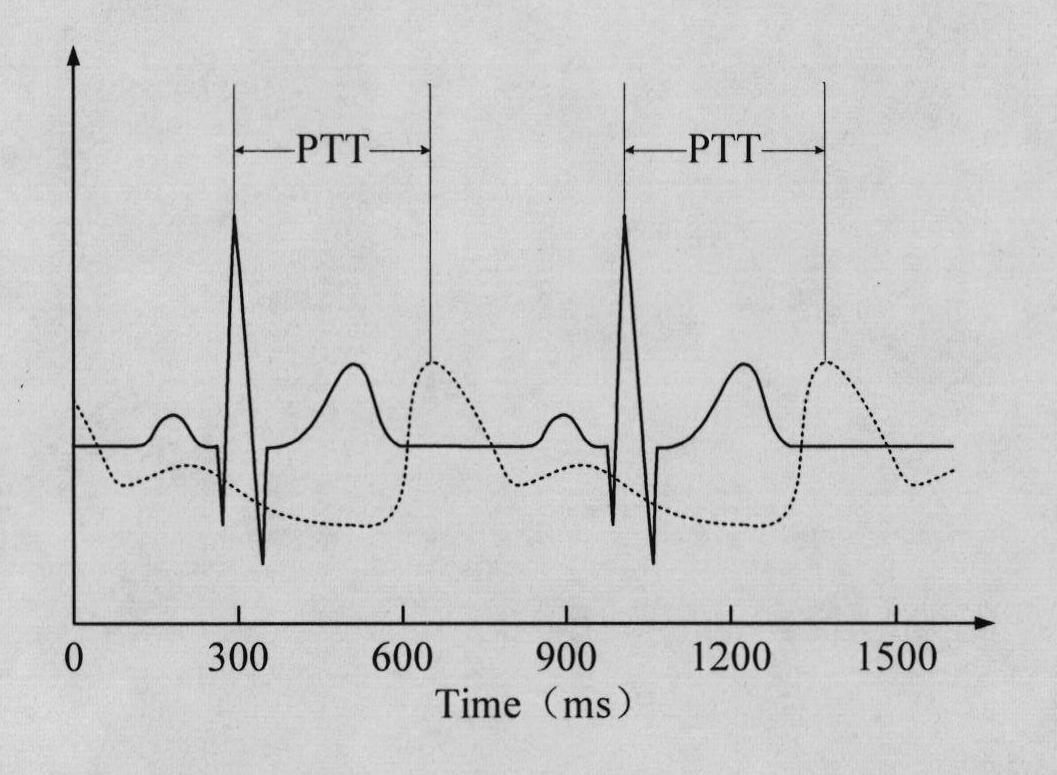
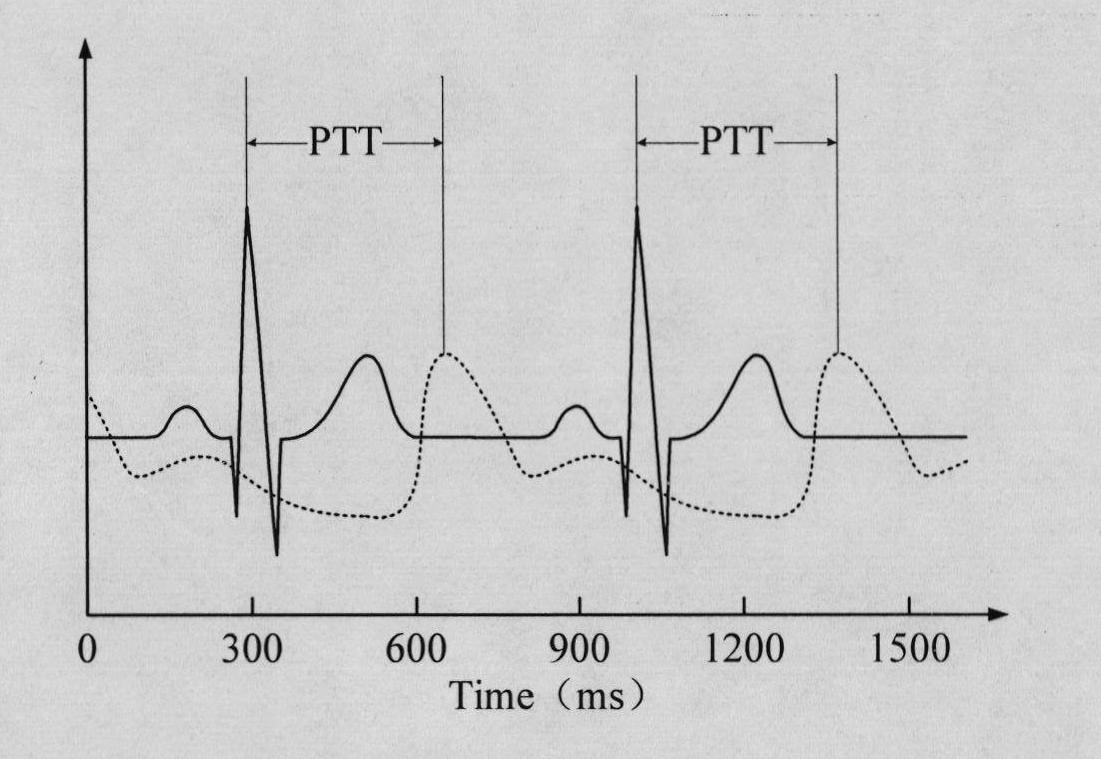
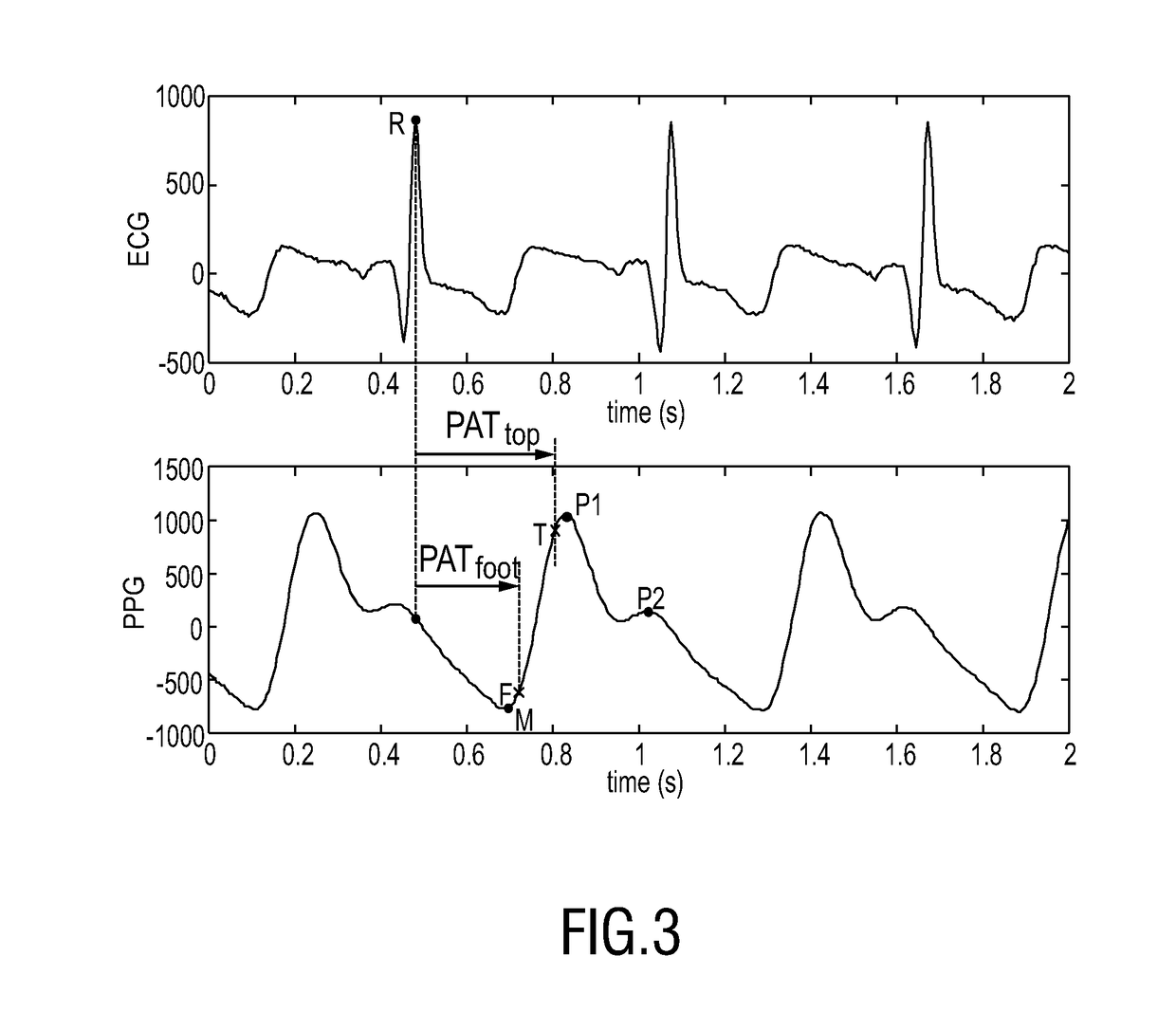
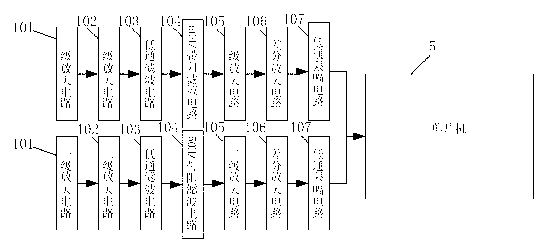
A method and apparatus for readily measuring a blood pressure without using a cuff includes measuring, by a portable blood pressure measuring apparatus, an electrocardiogram signal and a pulse wave signal, transmitting the measured electrocardiogram signal and pulse wave signal to a portable terminal, calculating, by the portable terminal, a Pulse Transit Time (PTT) and a Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) using the transmitted electrocardiogram signal and the pulse wave signal, and calculating a blood pressure value based on the PTT and the PWV. Therefore, users may readily measure a blood pressure at any time and place and may be provided with a customized blood pressure measurement result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for a continuous non-invasive and non-obstrusive monitoring of blood pressure
ActiveUS20090163821A1Improve accuracyContinuous trackingElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsArterial velocityArterial tree
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Continuous blood pressure measurer
InactiveCN102488503AAvoid the cumbersome calibrationHigh precisionEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyArterial velocityFeature extraction
The invention provides a continuous blood pressure measurer. When the continuous blood pressure measurer is used for measuring blood pressure, features used for blood pressure equation estimate are selected from a large quantity of extracted feathers and are transmitted to a decision system, and an equation for estimating blood pressure is determined from a blood pressure equation set; then features for estimating coefficients of the blood pressure equation are selected from extracted features in feature extraction by the aid of feature selection, and the coefficients of the blood pressure equation are estimated via methods such as statistical estimation, numeric calculation and the like; and finally, features for estimating blood pressure are selected from the extracted features in feature extraction by the aid of feature selection, and are substituted into the blood pressure equation for realizing blood pressure estimate. A pulse wave velocity method based on multiple parameters and a method for creating the blood pressure equation set are utilized, blood pressure estimate is realized by the aid of a manual intelligent method, a mode recognition method and the like, measurement precision of blood pressure estimate is further improved, and a troublesome parameter calibration process is avoided.
Owner:SCI RES TRAINING CENT FOR CHINESE ASTRONAUTS
Automatic blood pressure measuring system
ActiveCN103908236AOvercoming the Effects of Motion ArtifactsToleranceEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsVideo recordEngineering
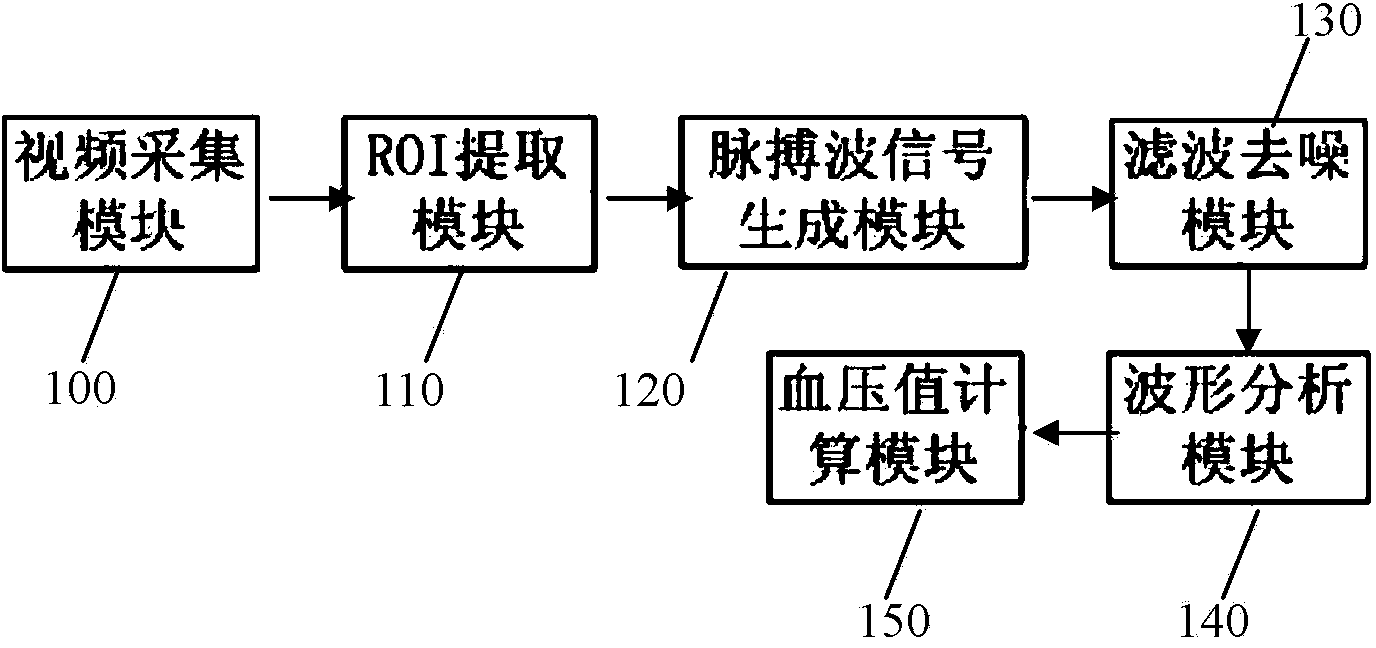
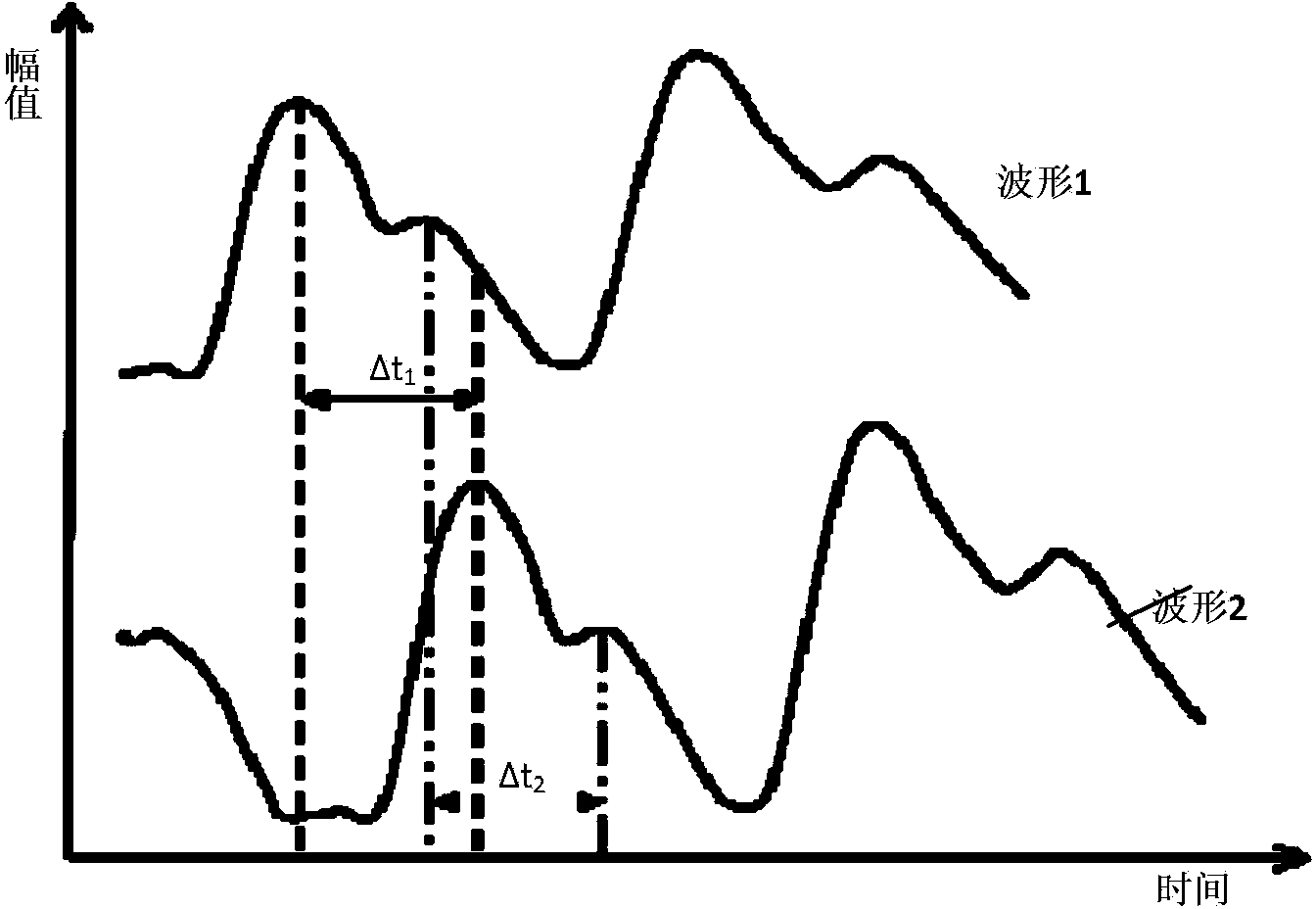
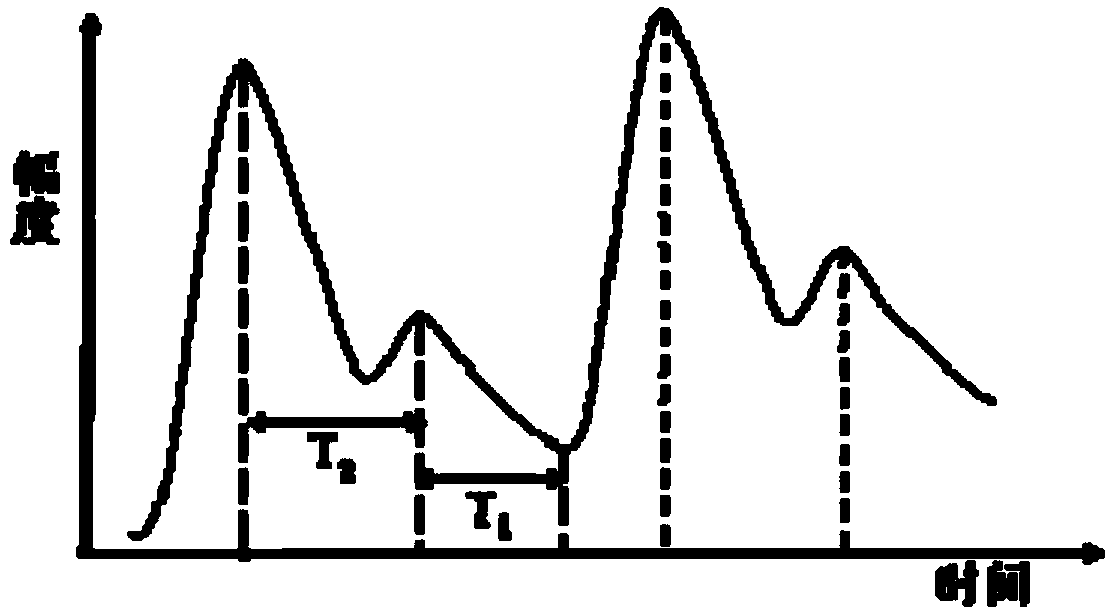
The invention discloses a non-contact type automatic blood pressure measuring system. Blood pressure of a measured person is measured by video recording. The non-contact type automatic blood pressure measuring system comprises a video acquiring module, an ROI extracting module, a pulse wave signal generating module, a filtering and noise reduction module, a waveform analyzing module and a blood pressure value calculating module. An automatic blood pressure measuring method comprises the following steps of acquiring a video of a finger tip; positioning the position of a tracked finger by using contour tracing of the finger tip; acquiring images of the finger; performing primary color separation and ROI segmentation on the images of the finger; respectively taking all pixel mean values of the filtered images as feature values to generate two time-varying pulse wave signal waveforms; performing comparison analysis on the two pulse wave waveforms to obtain transmission time of pulse; calculating the wave velocity of the pulse waves along an artery according to an image center distance d; and calculating a blood pressure value by using a conversion relation between pulse wave velocity and blood pressure. By using a noninvasive and non-contact type remote physiological signal detecting method, interference of motion artifact in a video record is overcome, the measuring precision is high, and blood pressure of a plurality of persons can be measured simultaneously.
Owner:TIANJIN DIANKANG TECH
Device and method for obtaining pulse transit time and/or pulse wave velocity information of a subject
ActiveUS20170164904A1Fast but reliable determinationFast but reliable monitoringImage enhancementMedical imagingArterial velocityClassical mechanics
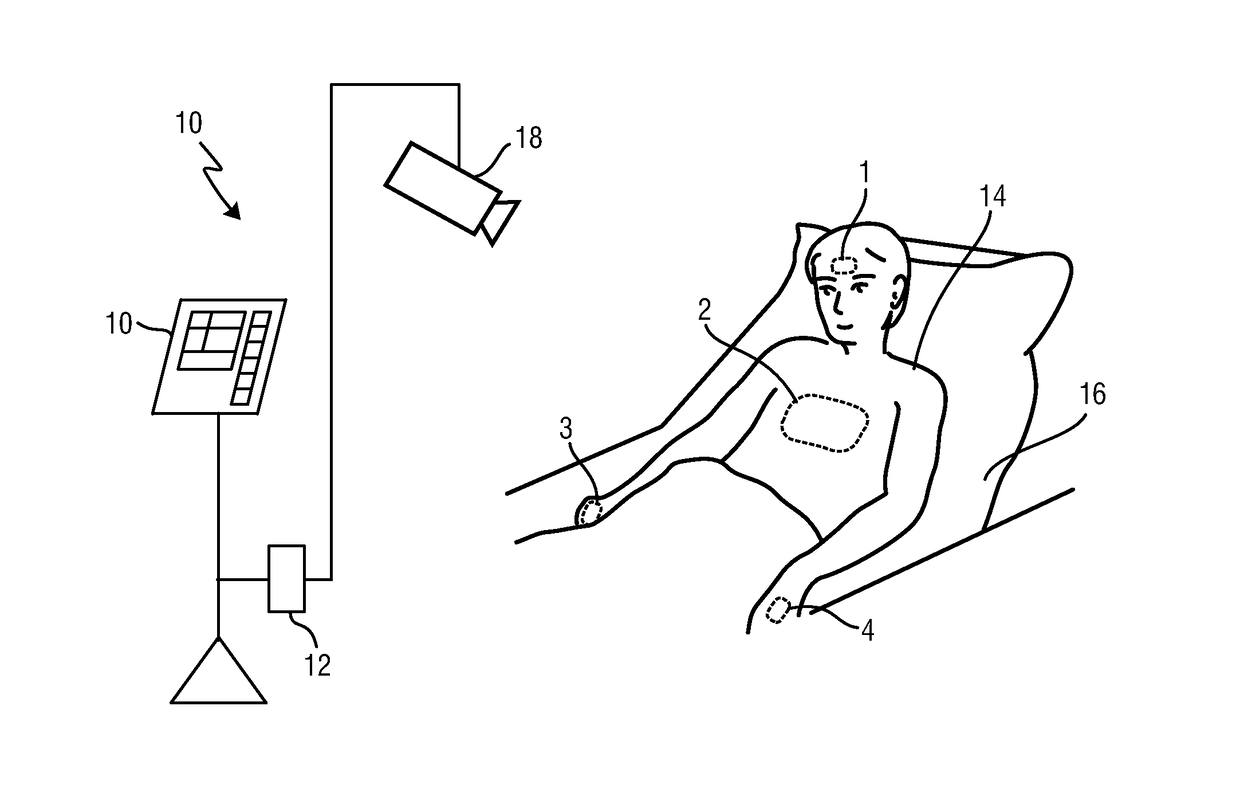
The present invention relates to a device and method for obtaining pulse transit time and / or pulse wave velocity information of a subject (14). Based on a set of image frames (19) of a subject (14) and detected motion of body parts of the subject (14) regions of interest are selected from different non-moving body parts and pulse transit time and / or pulse wave velocity information is obtained from acquired PPG signals extracted from different regions of interest and the respective determined physical distance between the respective regions of interest.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
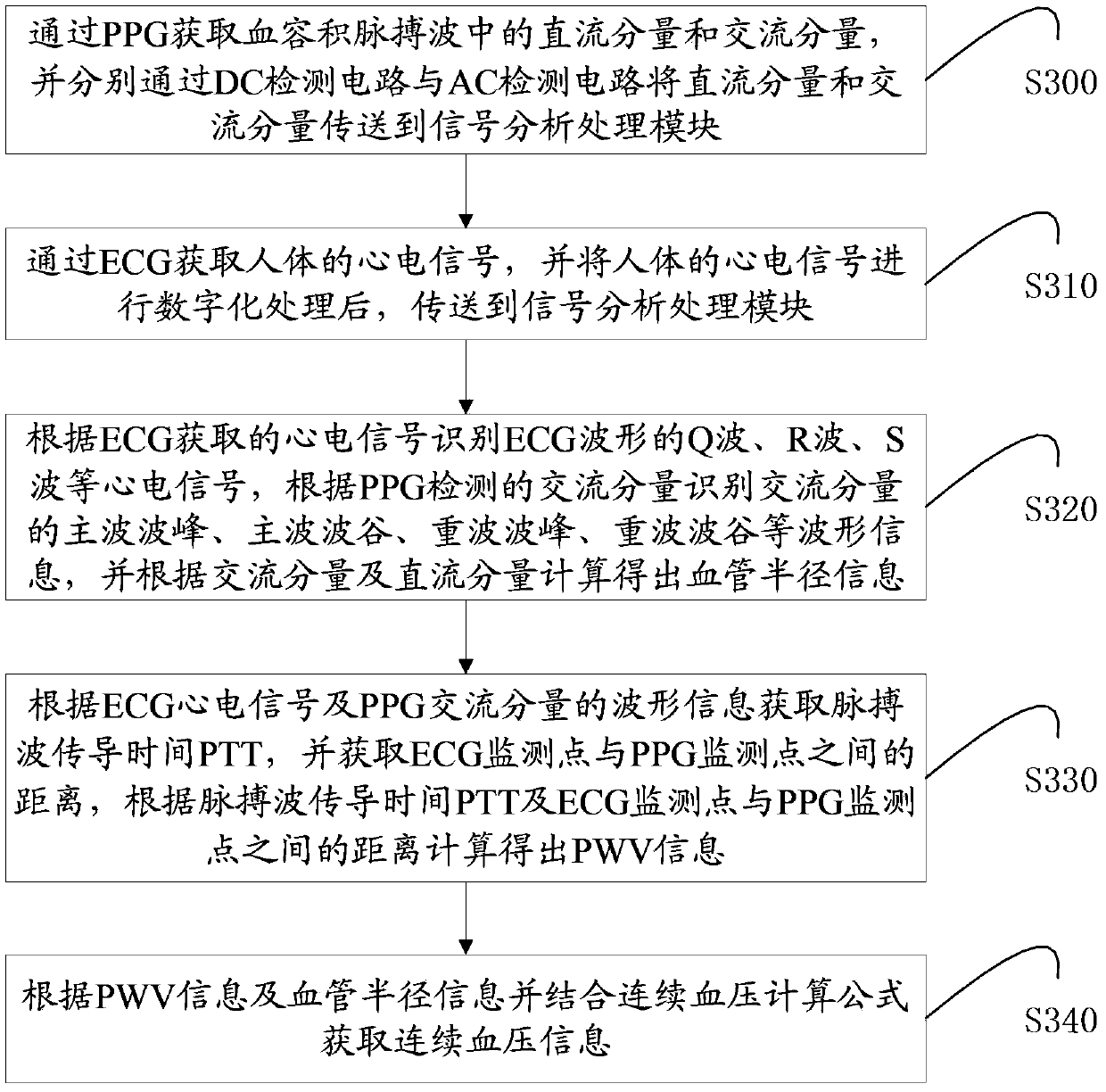
Non-invasive blood pressure continuous detection device and method
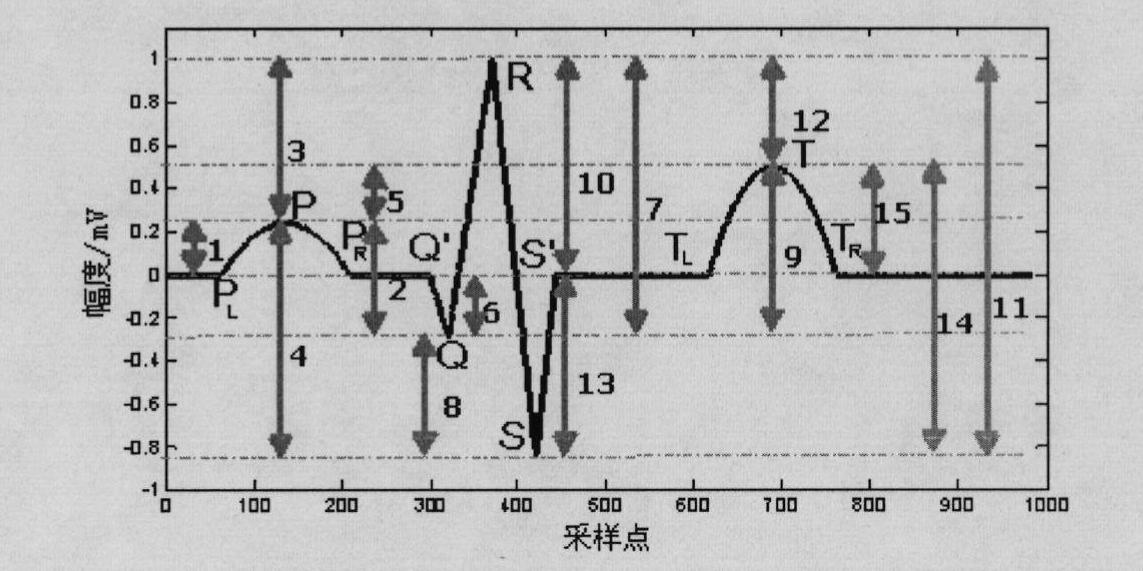
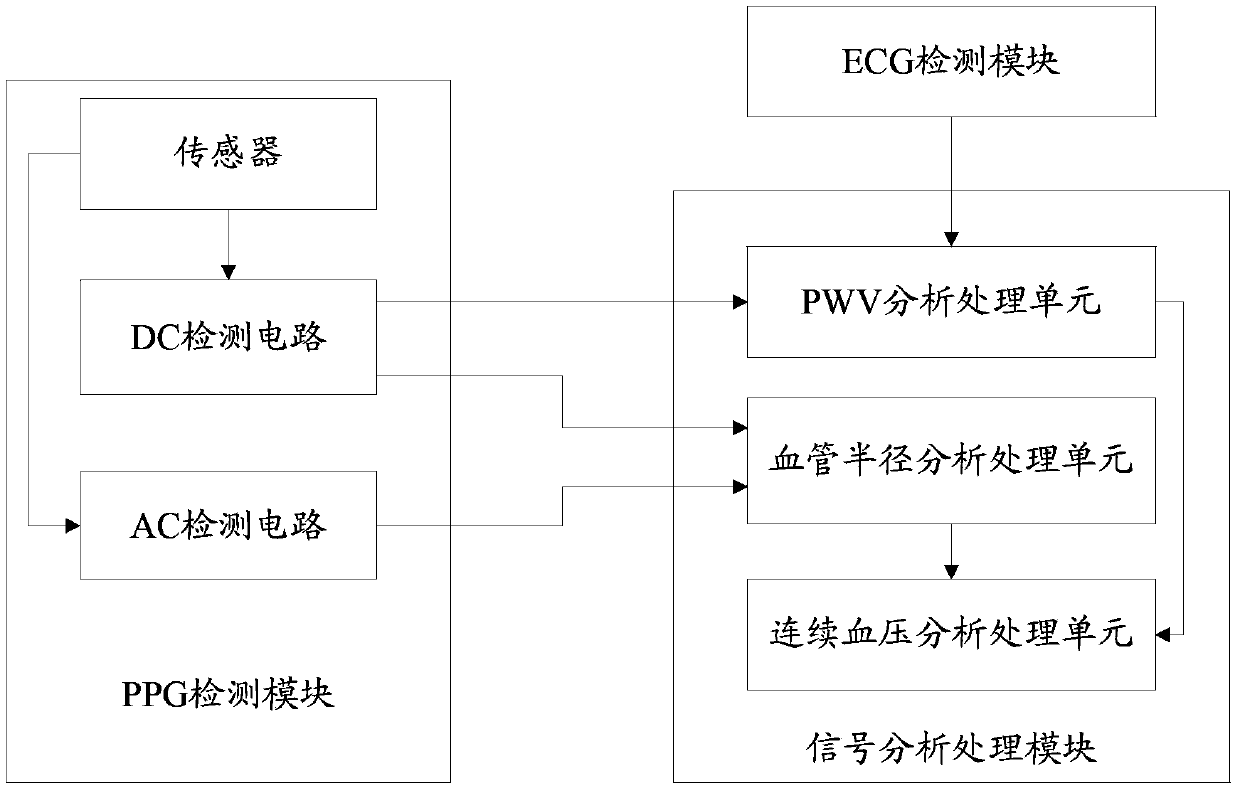
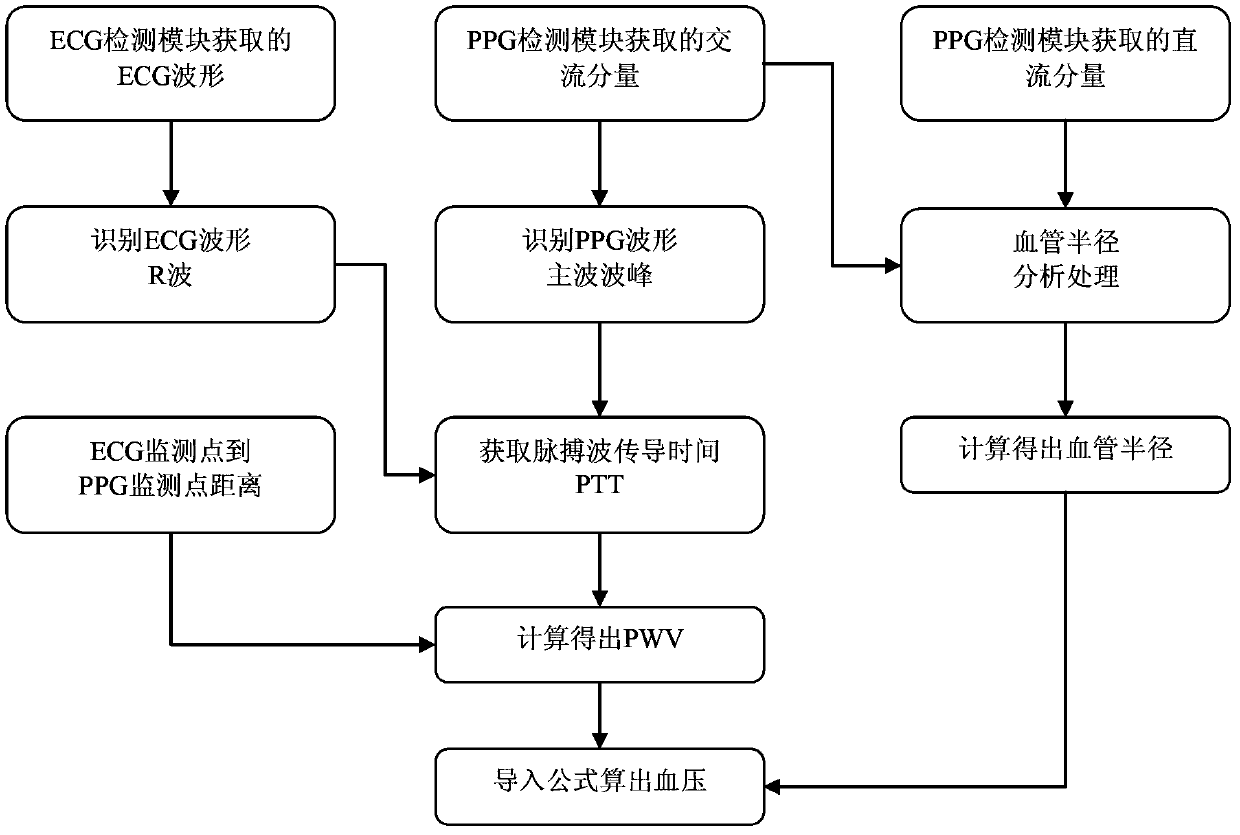
ActiveCN103385702AReduce the number of calibrationsImprove accuracyEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyEcg signalBlood volume pulse
The invention belongs to the technical field of non-invasive blood pressure detection and particularly relates to a non-invasive blood pressure continuous detection device and a non-invasive blood pressure continuous detection method. The non-invasive blood pressure continuous detection device comprises a volume pulse wave image detection module, an electrocardiogram detection module and a signal analysis processing module; the volume pulse wave image detection module is used for acquiring a direct current component and an alternate current component in a blood volume pulse wave; the electrocardiogram detection module is used for acquiring an electrocardiosignal of a human body; and the signal analysis processing module is used for acquiring PWV (Pulse Wave Velocity) information according to the electrocardiosignal acquired by the electrocardiogram detection module and the alternate current component detected by the volume pulse wave image detection module, acquiring blood vessel radius information according to the alternate current component and the direct current component and acquiring continuous blood pressure information according to the PWV information and the blood vessel radius information. Due to implementation of the non-invasive blood pressure continuous detection device and the non-invasive blood pressure continuous detection method which are disclosed by the invention, influence of variation of the blood vessel radius on the blood pressure in the long-term non-invasive blood pressure measurement process is removed, accuracy of long-term detection is improved, and times of continuously calibrating the blood pressure are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
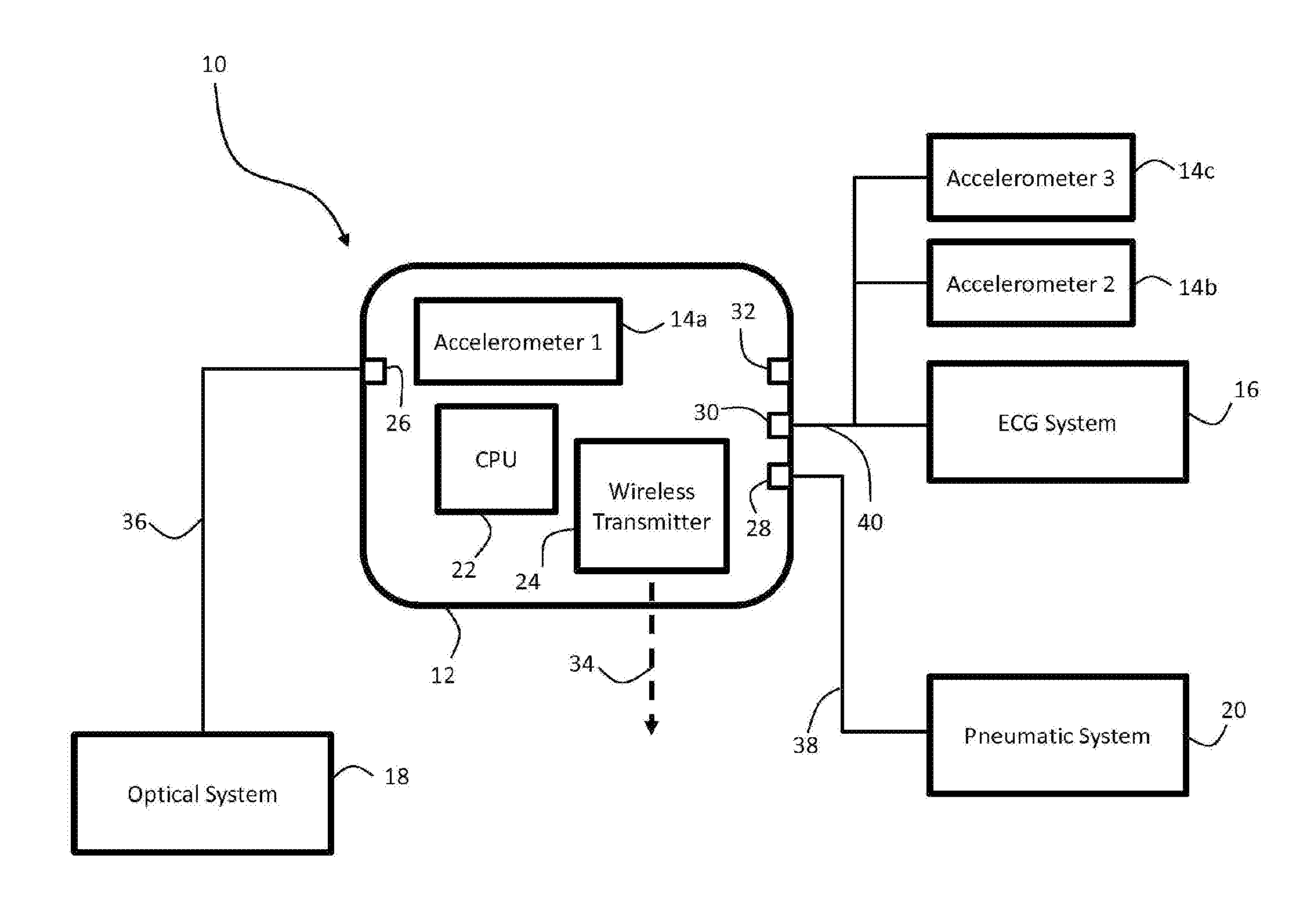
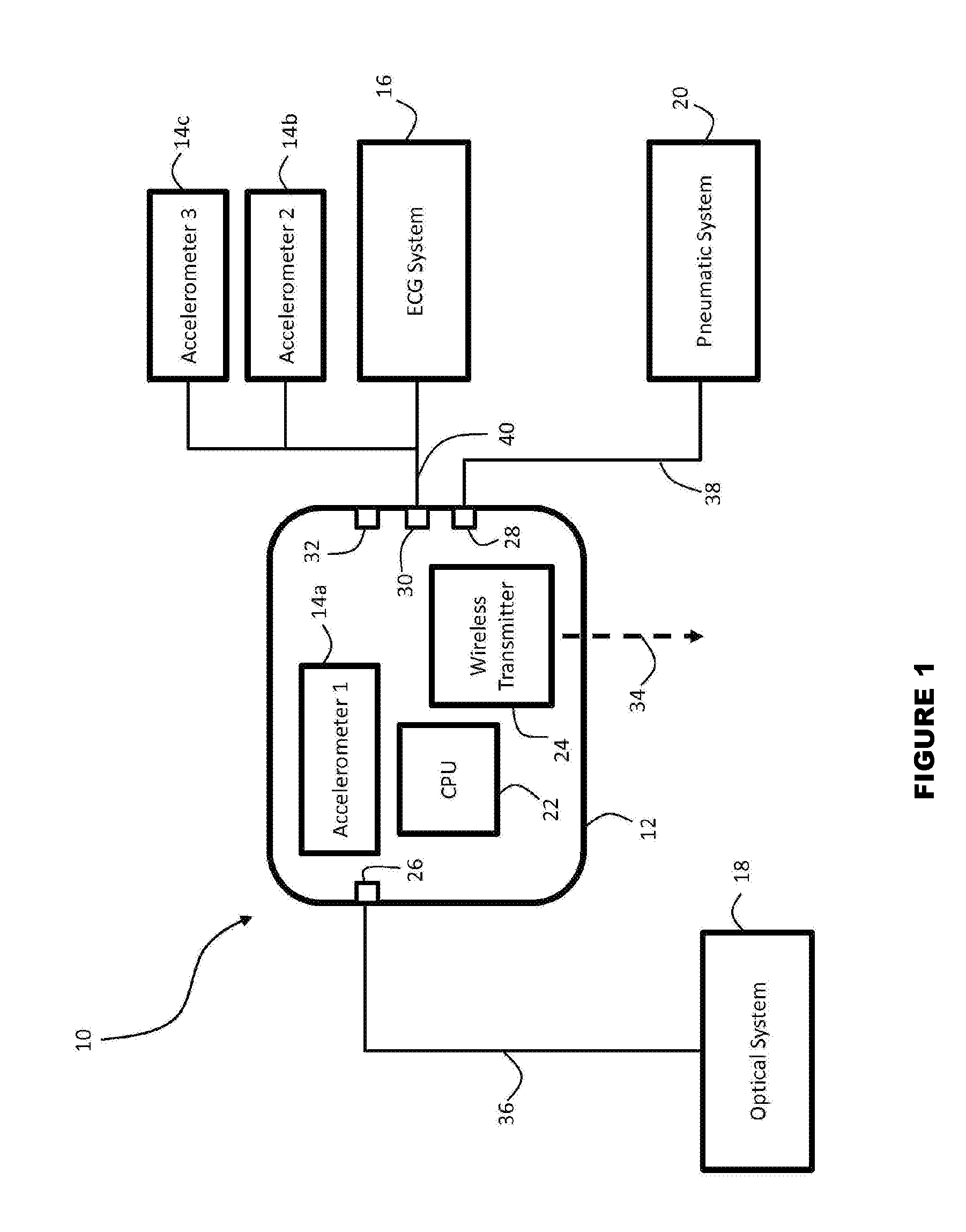
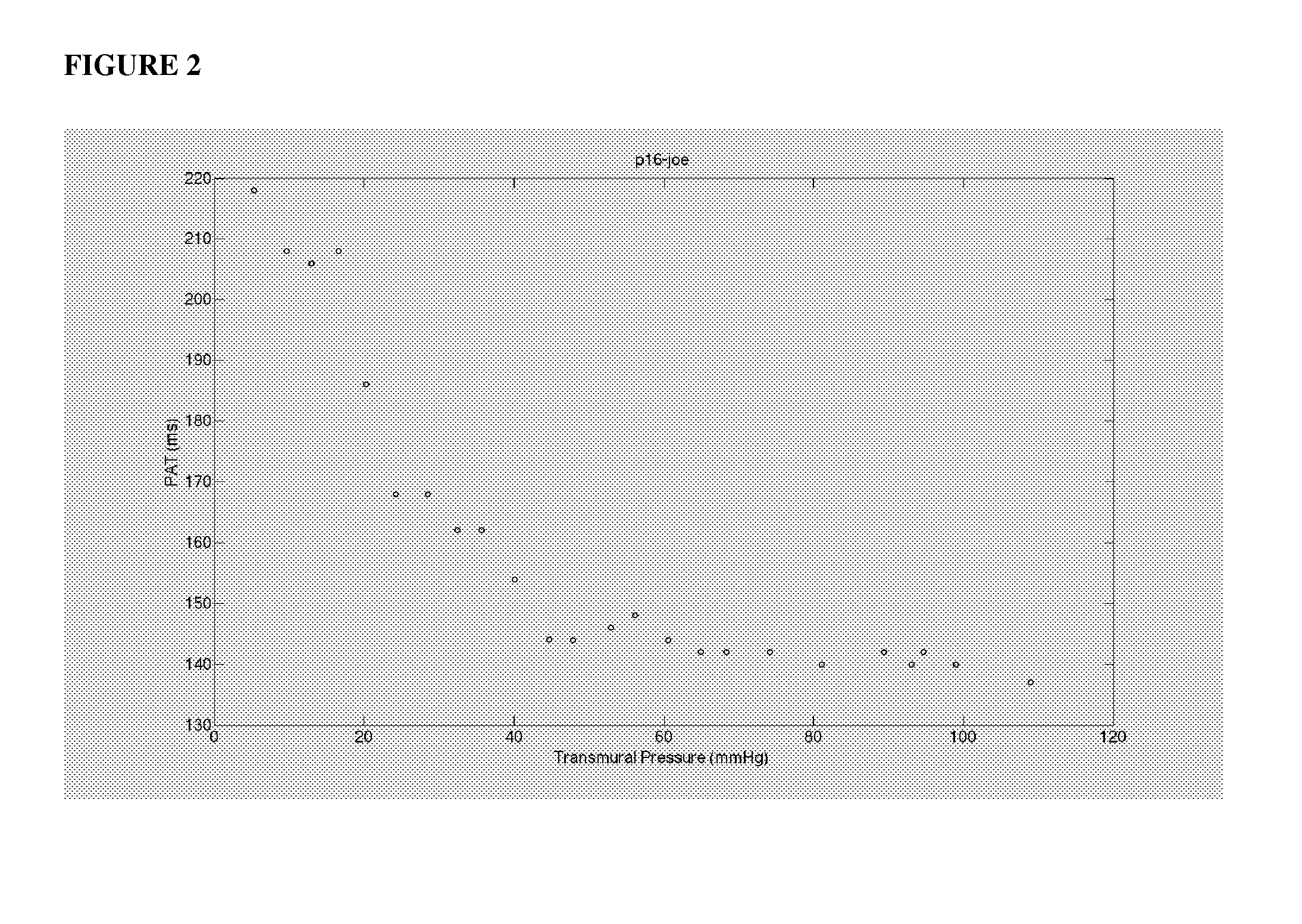
System for calibrating a blood pressure measurement based on vascular transit of a pulse wave
The invention provides a system and method for measuring vital signs (e.g. SYS, DIA, SpO2, heart rate, and respiratory rate) and motion (e.g. activity level, posture, degree of motion, and arm height) from a patient. The system features: first and second sensors configured to independently generate time-dependent waveforms indicative of one or more contractile properties of the patient's heart; and a cuff-based oscillometric module. A processing component, typically worn on the patient's body and featuring a microprocessor, receives the time-dependent waveforms generated by the different sensors and processes them to determine patient-specific calibration values for use in a continuous blood pressure measurement based on pulse wave velocity (PWV).
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Determining a propagation velocity for a surface wave
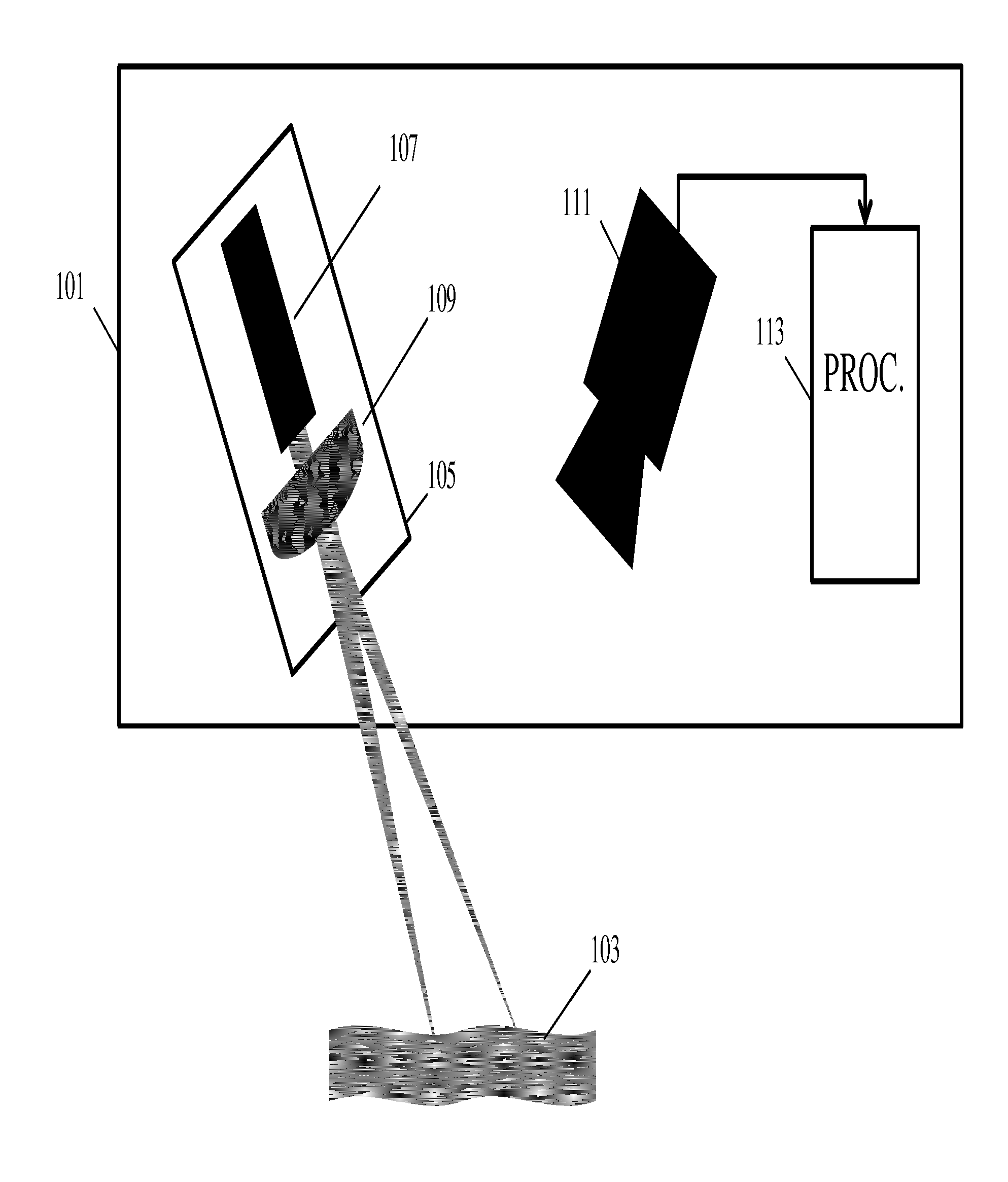
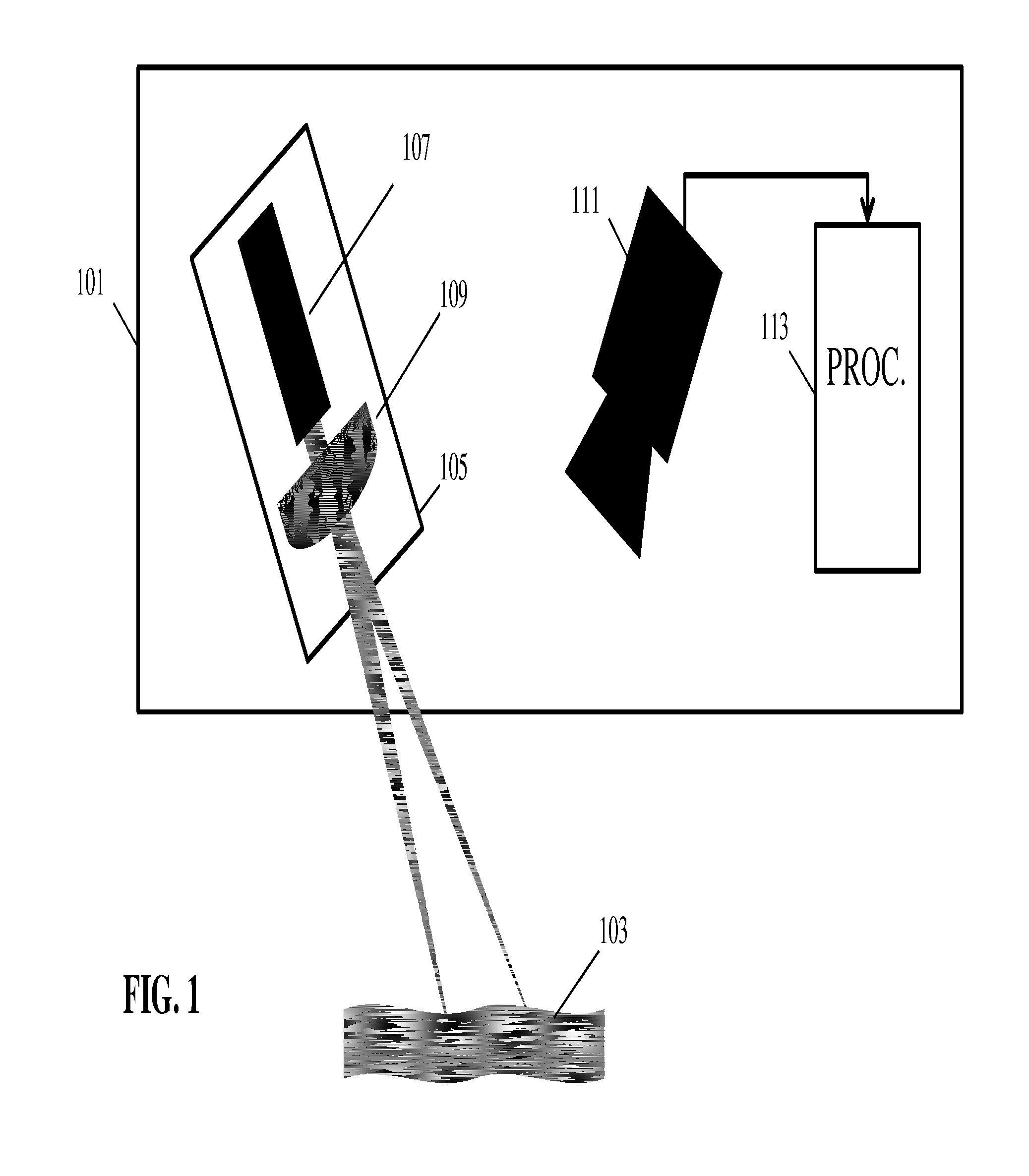
ActiveUS20150323311A1Improved and facilitated determinationAccurately determineDiagnostics using lightUsing optical meansLight spotSpatial analysis
An apparatus for determining a propagation velocity for a surface wave comprises a coherent light source (105) for generating at least a first and a second light spot on a surface (103). A camera (111) captures at least one out-of-focus image of at least a part of the surface (103) comprising the light spots. The out-of-focus image comprises light spot image objects for the light spots where the light spot image objects have speckle patterns. An analyzer (113) determines the propagation velocity in response to a time difference between speckle pattern changes in the two speckle patterns. The camera may specifically use a rolling shutter allowing the determination of the propagation velocity to be based on a spatial analysis of the speckle patterns. The approach may in particular allow an efficient remote measuring of pulse wave velocities e.g. in animal tissue and in particular, in human tissue.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Devices and Methods for Monitoring Directional Blood Flow and Pulse Wave Velocity with Photoplethysmography
Provided according to embodiments of the invention are methods of monitoring the direction of blood flow that include processing with a computer photoplethysmography (PPG) signal streams from a sensor array on a body site of the individual to determine the direction and / or velocity of the blood flow at the body site of the individual. In some embodiments, direction of the blood flow at the body site is determined by the phase difference between at least three PPG signal streams from the sensor array, wherein the at least three PPG signal streams are generated from emissions of the at least three emitters.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
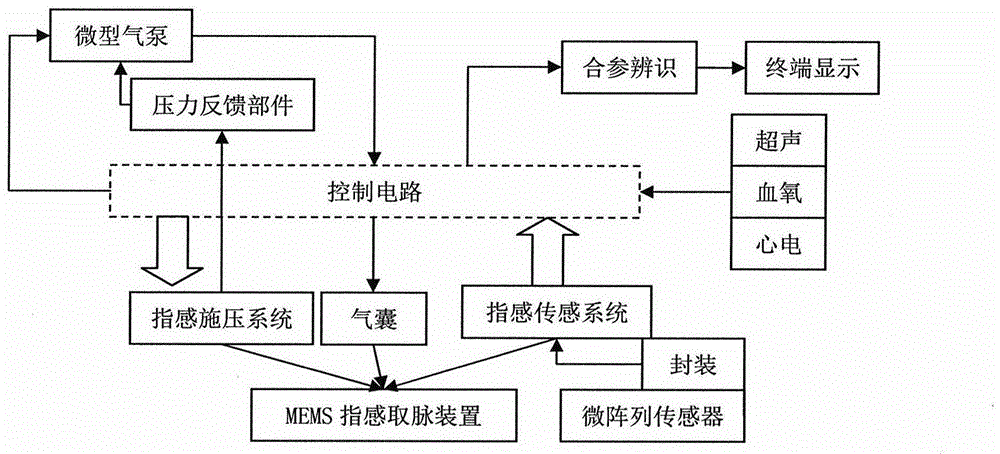
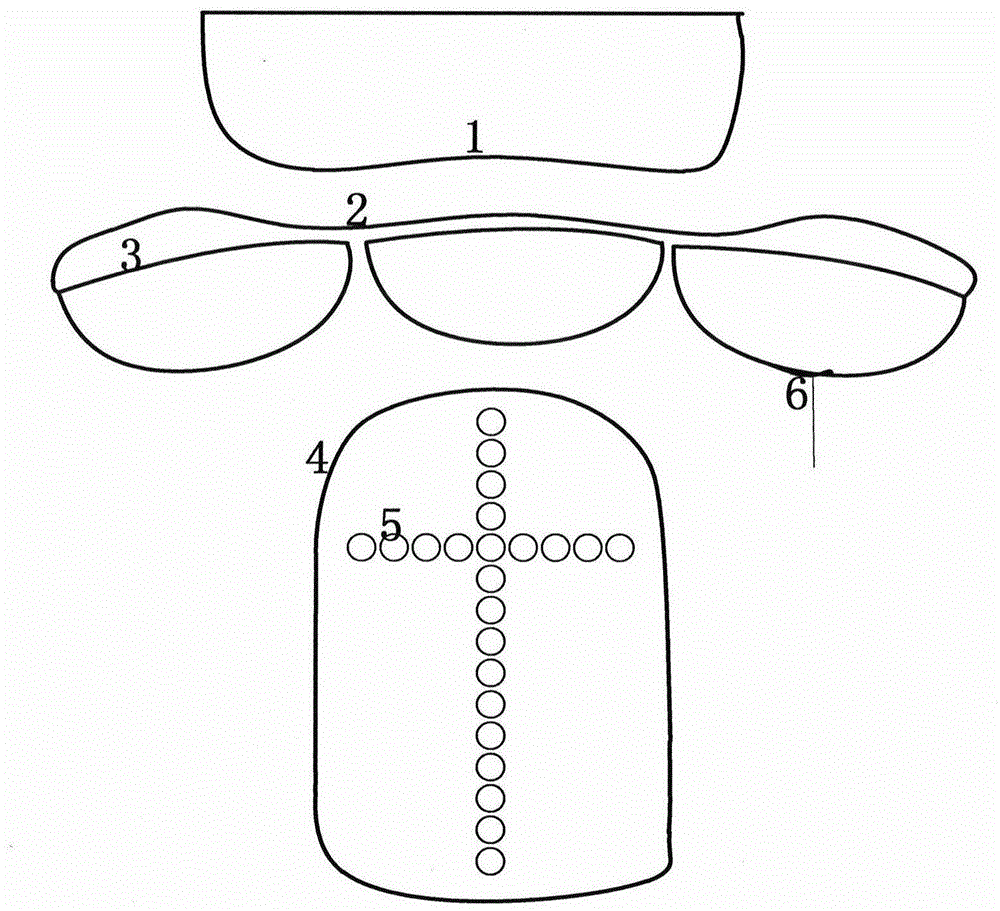
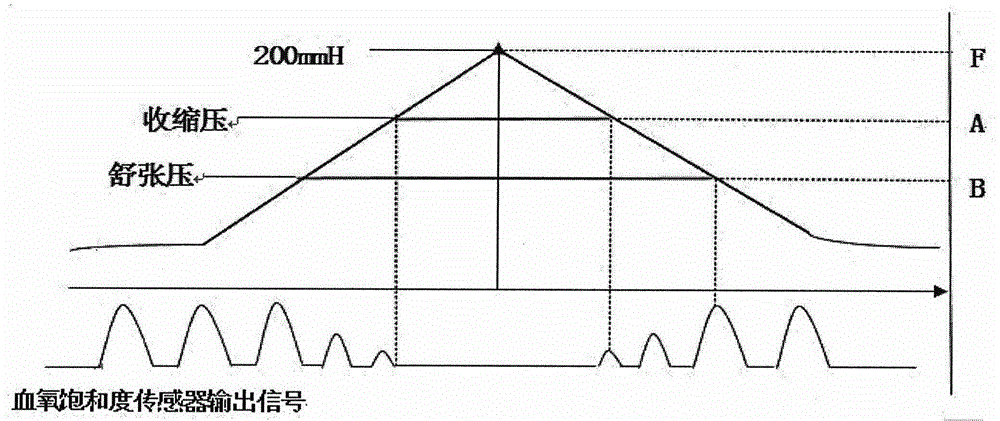
Three-position and nine-indicator multi-information acquisition and recognition device based on finger feel pressure application and microarray sensing
InactiveCN105030195AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTouch PerceptionSonification
The invention relates to a three-position and nine-indicator multi-information acquisition and recognition device based on finger feel pressure application and microarray sensing. The device is integrated with an MEMS microarray sensing contact probe, a miniature air pump, a standard II lead electrocadiography sensor and a detection electrode, a finger photoplethysmography senor and a bionic finger pressure probe, an air pressure finger cot, an air pressure wristlet, a miniature inflator pump, a wireless transmission device, an integrated circuit chip, a touch screen and a button lithium battery. According to the device, by adopting the MEMS technology, a microarray pressure sensor is designed to simulate the human under-finger touch information, acquire the properties in the aspects of position, pace, form, and dynamic of the pulse-taking information, and the properties and parameters, including pulse wave velocity (PWV), the blood pressure, the oxyhemoglobin saturation, the electrocardio, and the ultrasound, which can embody the physiological status of the organism form a dynamic synchronous data set. According to the theory of synthesis of the four diagnostic methods of the traditional Chinese medicine, the data is translated into relevant information such as vision, touch and the temperature sensation acquired by the traditional Chinese medical doctor, and so that the purpose of simulating the process of the synthesis of the four diagnostic methods of the traditional Chinese medicine is achieved by utilizing the digitized and quantized traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis.
Owner:牛欣
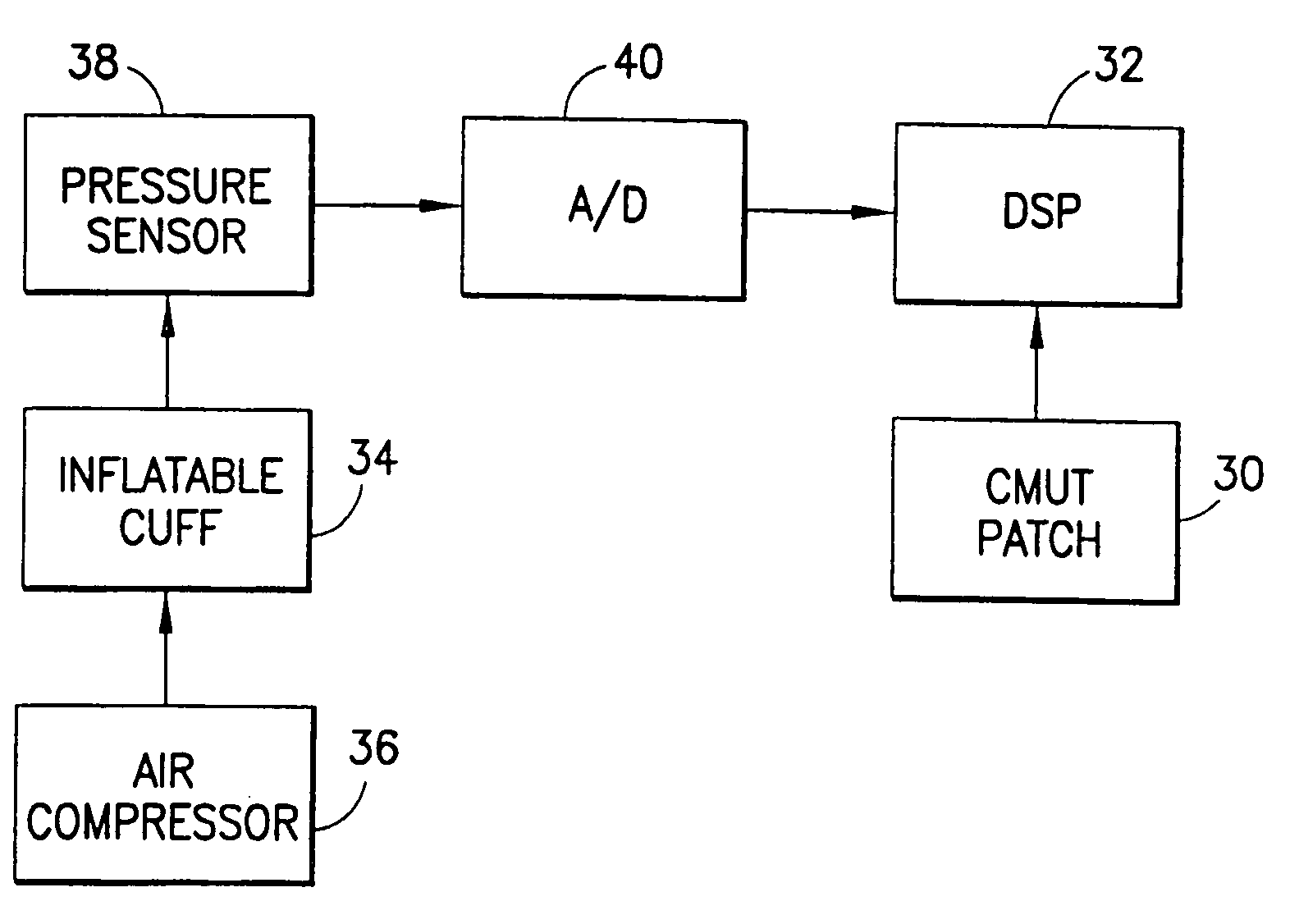
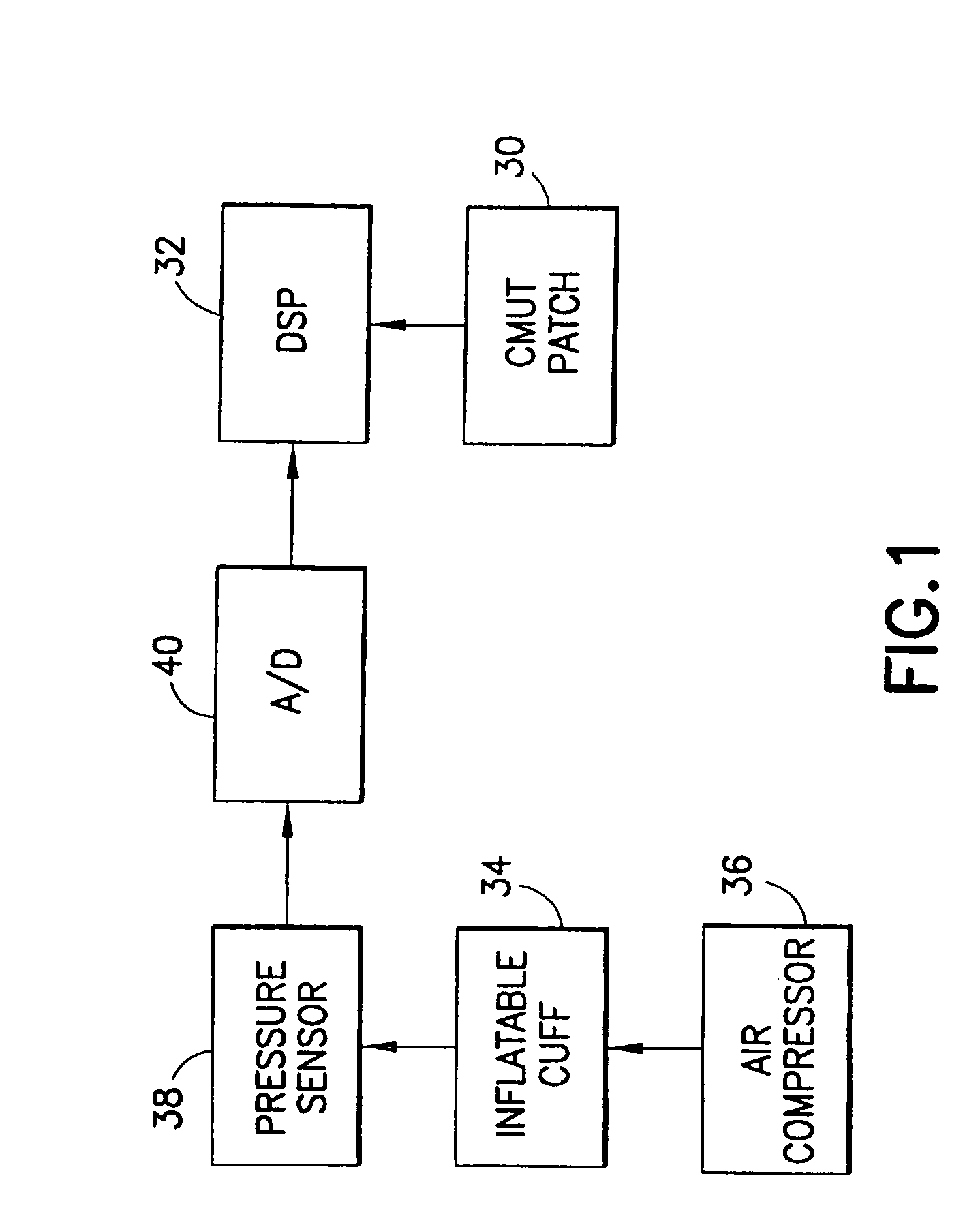
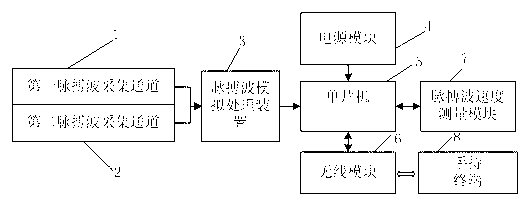
Measurement device and method for pulse wave velocity physiological parameters based on photoelectric plethysmography
The invention provides a measurement device and a measurement method for pulse wave velocity physiological parameters based on photoelectric plethysmography. The measurement device comprises a first pulse wave collecting channel and a second pulse wave collecting channel which are connected with a pulse wave analog processing device; the pulse wave analog processing device is also connected with a single chip microcomputer through a signal; the single chip microcomputer is electrically connected with a power module and is connected with a handheld terminal through a wireless module by utilizing the signal; the single chip microcomputer is also connected with a pulse wave velocity measurement module in a communication way; the single chip microcomputer is a central control processing unit and internally comprises a clock circuit, a storage, a timer, an A / D (Analog / Digital) converter and an I / O (Input / Output) interface which are controlled to connect through a single chip microcomputer processor; and the delay error can be effectively reduced by adopting the measurement device together with the measurement method.
Owner:BEIJING ANYI TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and sensor for measuring biological signal and apparatus and method for measuring pulse wave velocity
Provided is an apparatus for measuring a biological signal. The apparatus includes a first surface having a first sensor which is attached to a predetermined part of a user's body and measures a first biological signal generated by the predetermined part; and a second surface having a second sensor which is attached to the user's finger and measures a second biological signal generated by the finger. Therefore, a user can easily check his or her health condition without being limited by time or place.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Layered speed positioning method for regional rock microseismic source
InactiveCN105022031AHigh precisionGood forecasting and early warningPosition fixationRectangular coordinatesWave velocity
The invention belongs to the field of geotechnical engineering, and provides a layered speed positioning method for a regional rock microseismic source. The method comprises the following steps: (1), dividing the rock region of a to-be-detected seismic source into different wave velocity layers, building a three-dimensional rectangular coordinate system, and calculating an analytic equation of interfaces of all wave velocity layers; (2), installing sensors in the rock region, and measuring the spatial coordinates of all sensors; (3) carrying out an explosion test in the rock region, and calculating the wave velocities of all wave velocity layers; (4) calculating the spatial coordinates (x0, y0, z0) of the microseismic source. The method provided by the invention achieves high positioning precision of the microseismic source, and can prompt the technology of microseismic monitoring to play a good role in prediction and early warning in engineering practice.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
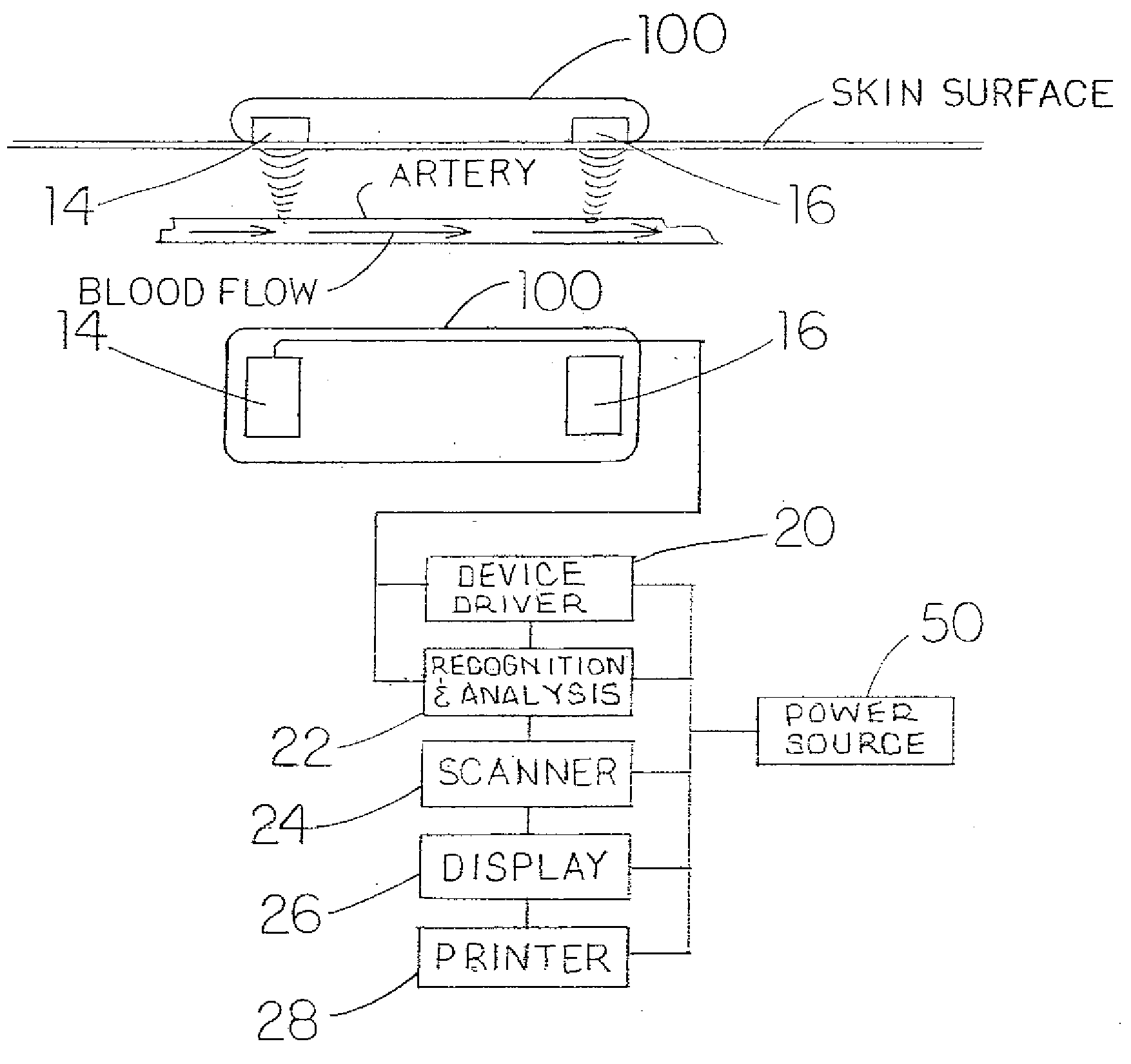
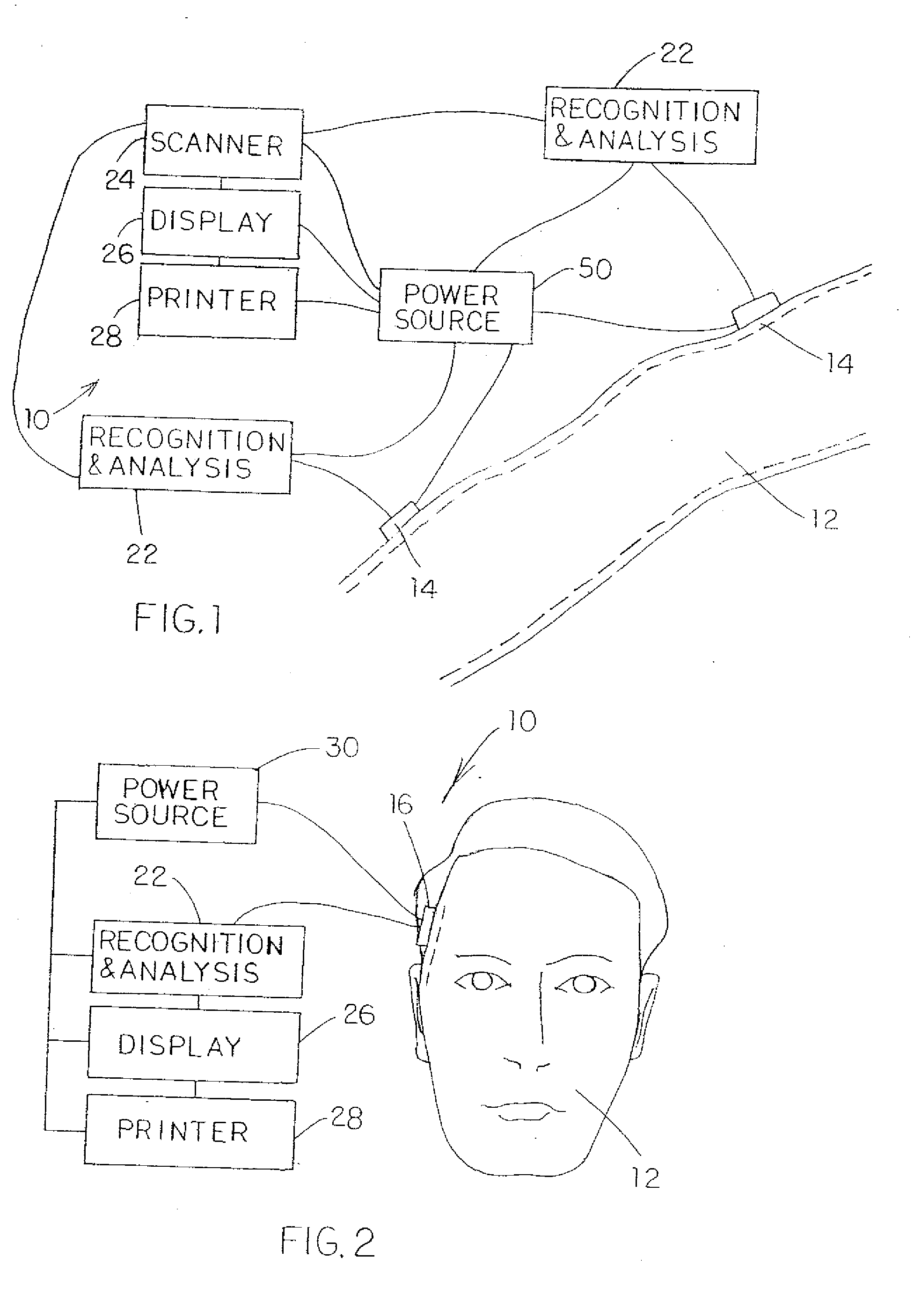
Contactless System and Method For Measuring and Continuously Monitoring Arterial Blood Pressure
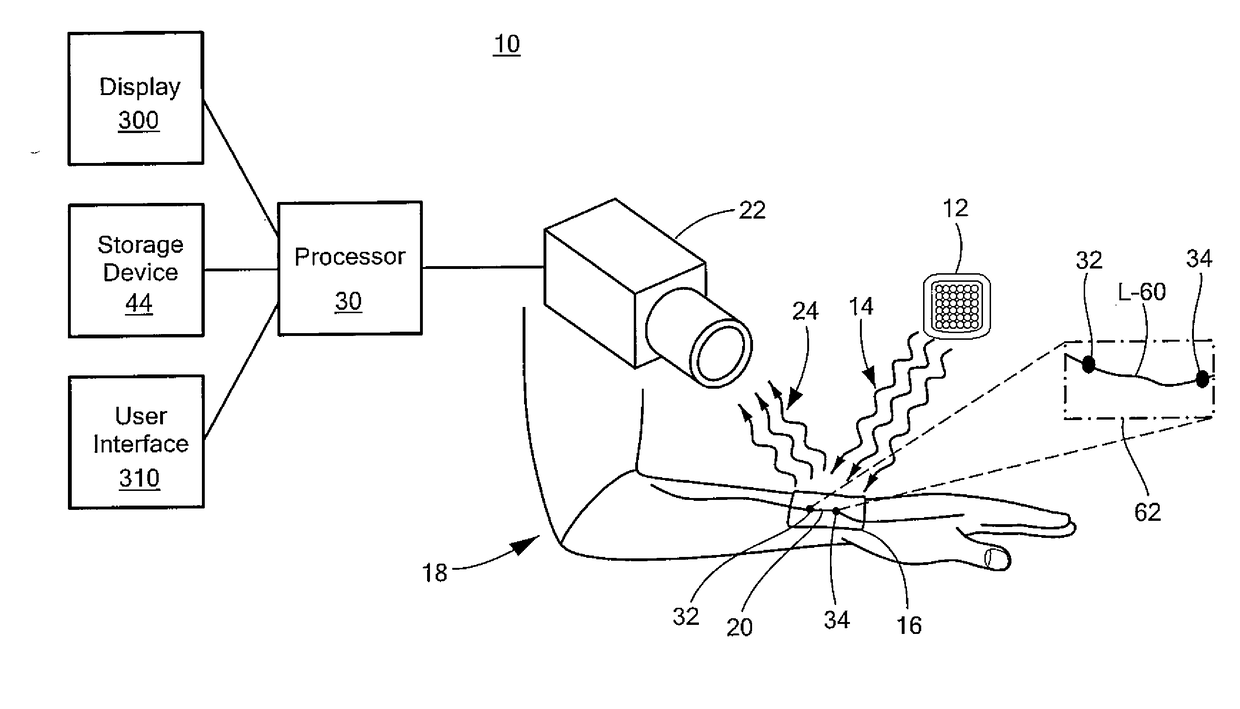
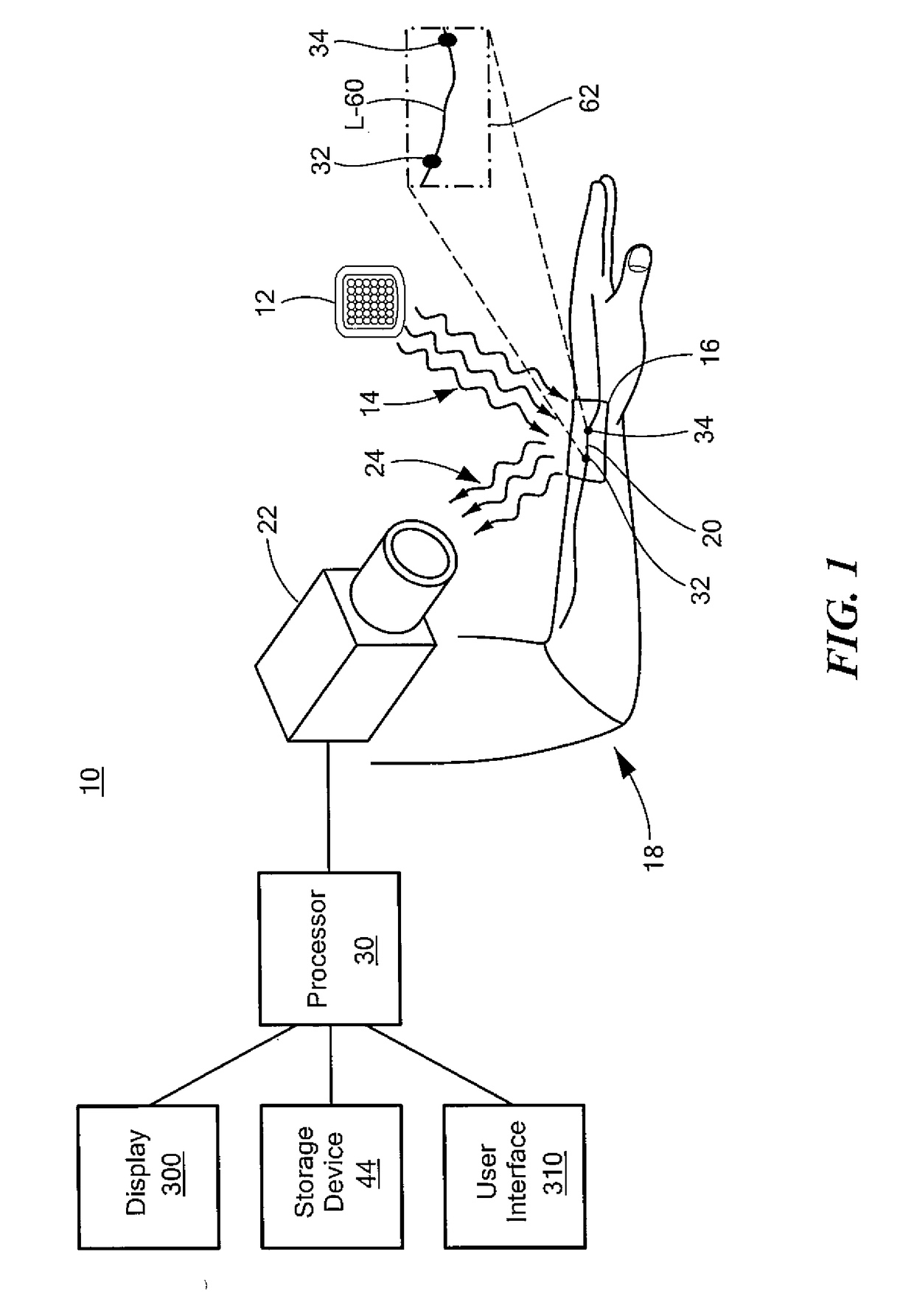
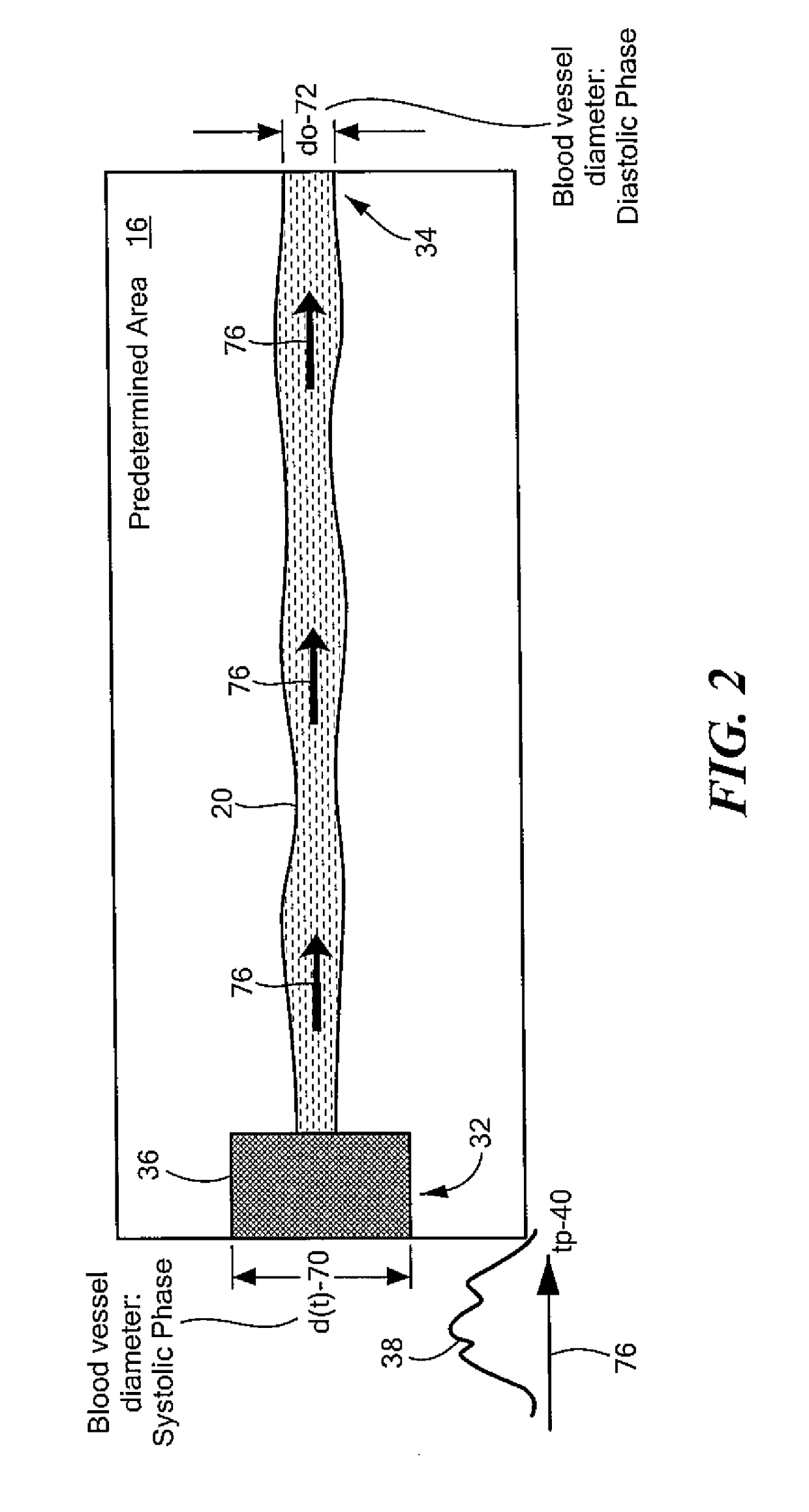
A contactless system for measuring and continuously monitoring arterial blood pressure includes a light source configured to illuminate light having at least one predetermined wavelength at a predetermined area of a human subject having an artery therein. A detector responsive to reflected light from the predetermined area is configured to continuously acquire images of the artery in the predetermined area. A processor is configured to process the images and determine: when an image at a proximal location of the predetermined area is darker indicating transition of a pulse wave into the artery at the proximal location and at a proximal time and when an image at a distal location of the predetermined area is darker indicating transition of the pulse wave into the artery at a distal location at a distal time, determine the difference in time between the distal time and the proximal time to calculate a pulse transit time (PTT), determine a length between the proximal location and the distal location, determine a diameter of the artery during a systolic phase of a cardiac pulse, determine a diameter of the artery during a diastolic phase of a cardiac pulse, calculate a pulse wave velocity of the pulse wave, calculate pulse pressure (ΔP), calculate an elastic modulus (E) of the artery, and contactlessly and continuously calculate the arterial blood pressure for each cardiac cycle of the human subject.
Owner:VIVONICS
Multiparameter whole blood monitor and method
ActiveUS7559894B2Continuous and precise measurementBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsPulse pressureIntravascular catheter
The present invention provides an apparatus and methods for continuous intravascular measurement of whole blood concentration, blood pressure, and pulse pressure. The intravascular catheter incorporates a sensor to measure whole blood sound velocity, attenuation, backscatter amplitude, and blood flow velocity and also incorporates existing technologies for multiple physiologic measurements of whole blood. Pulse wave velocity and wave intensity are derived mathematically for purposes of estimating degree of local vascular tone.
Owner:NEW PARADIGM CONCEPTS
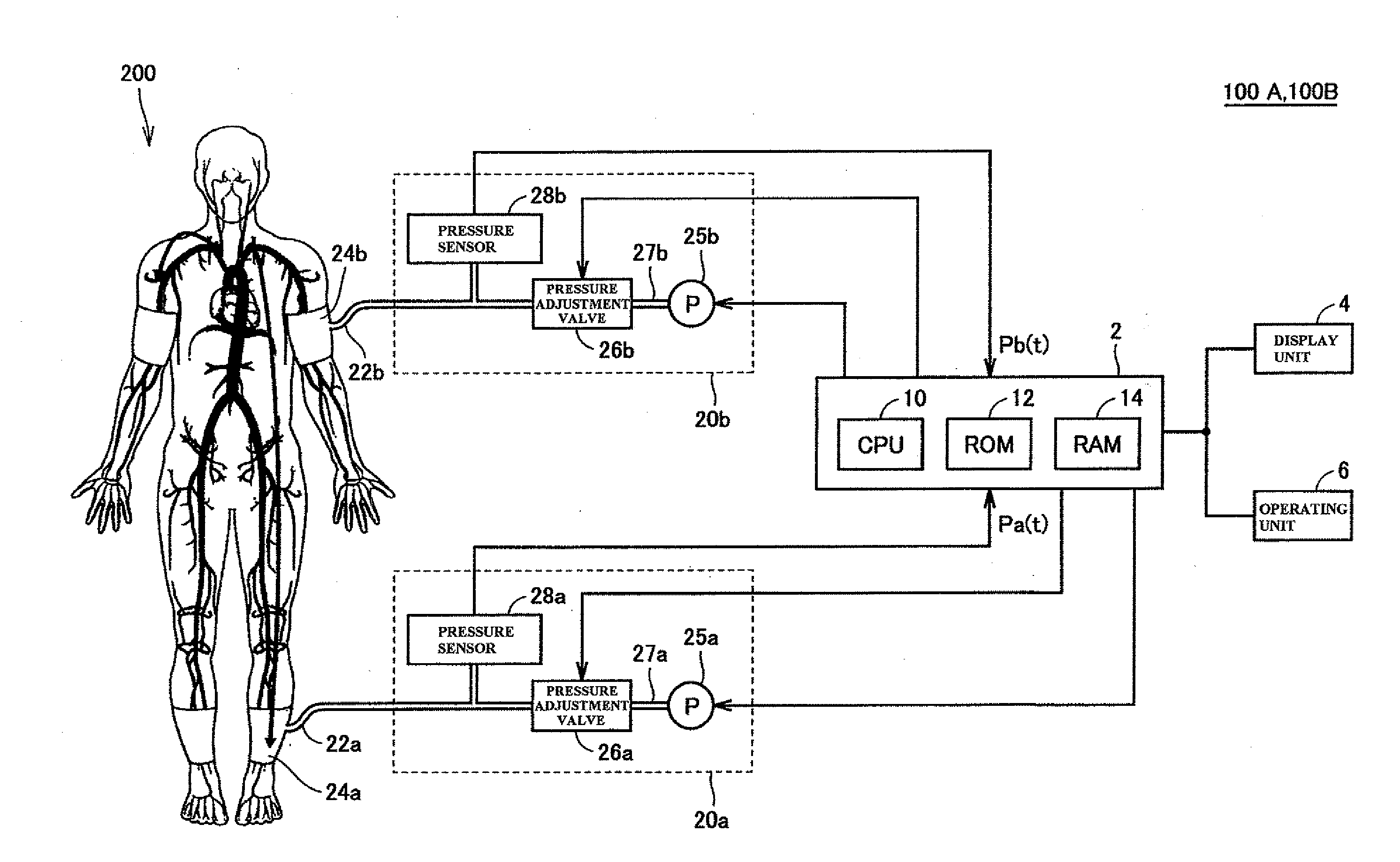
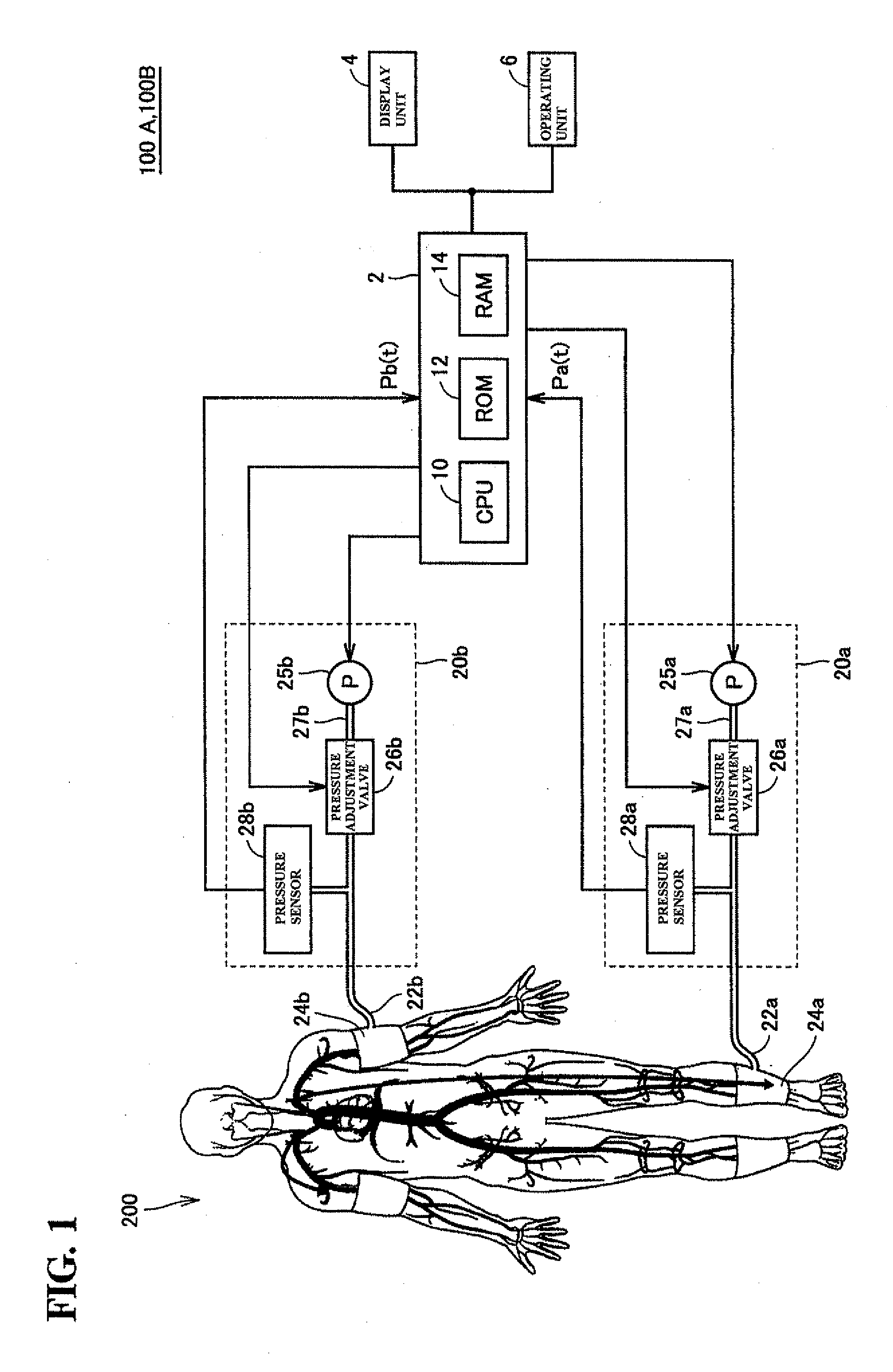
Measurement apparatus
ActiveUS20130109982A1Simple configurationAccurate assessmentCatheterSensorsMeasurement devicePhase difference
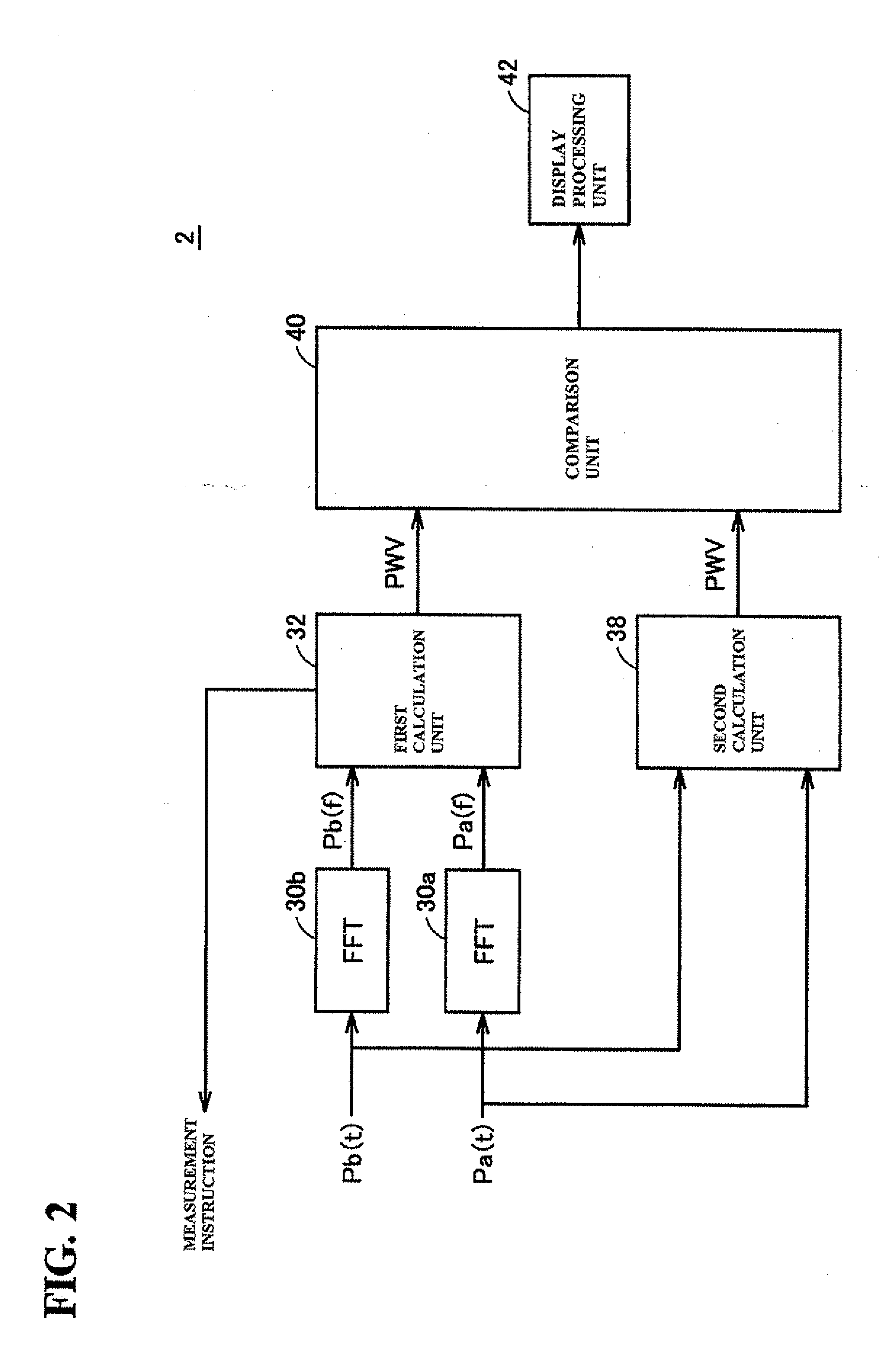
A first calculation unit receives phase characteristics Pa(f) and Pb(f) outputted from frequency transform units, calculates a propagation time difference based on a phase difference between the two phase characteristics in a high-frequency component thereof, and calculates a pulse wave velocity by dividing a difference in the distances of vascular pathways from the heart to respective measurement areas. Meanwhile, a second calculation unit calculates a pulse wave velocity by dividing the stated difference in the distances by a appearance time difference at a predetermined position in respective pulse waveforms obtained by rendering the measurement signals Pa(t) and Pb(t) on a time axis. A comparison unit compares the pulse wave velocities, and in the case where the ratio thereof is outside a predetermined range, an evaluation result indicating that it is possible that a predetermined pathologic change is present in the vascular pathway is outputted to a display processing unit.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Pulse wave velocity measurement method
ActiveUS20150366456A1Low costImprove accuracyDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsPostural orientationWave velocity
The present invention provides a pulse wave velocity measurement method and system as well as an imaging device available for everyday use by general users at low cost with measurement accuracy less affected by posture or the like. The present invention simultaneously images different parts of a human body in a non-contact state by a single visible light camera and acquires continuous time series image data. Then, the present invention detects each pulse wave from the image data in the different parts of the human body based on a temporal change in pixel value of the different parts of the human body, and then calculates a pulse wave velocity of the human body based on a time difference between the pulse waves in the different parts of the human body.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com