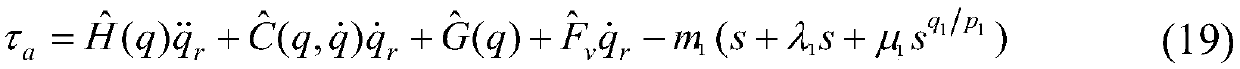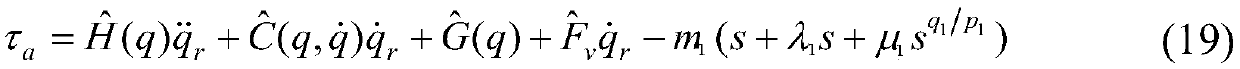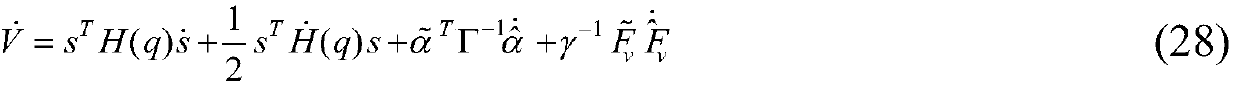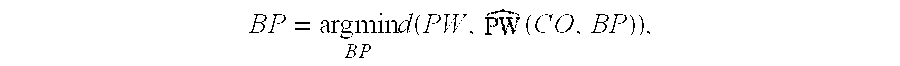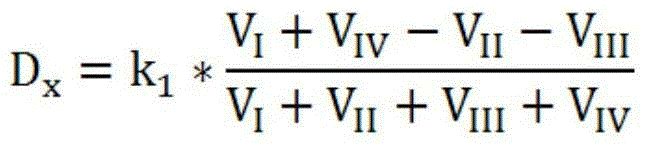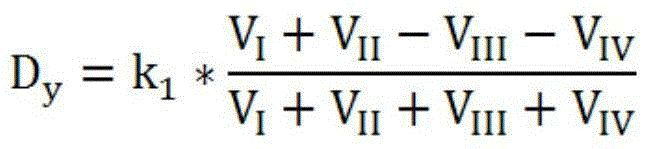Patents
Literature
50results about How to "Continuous tracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
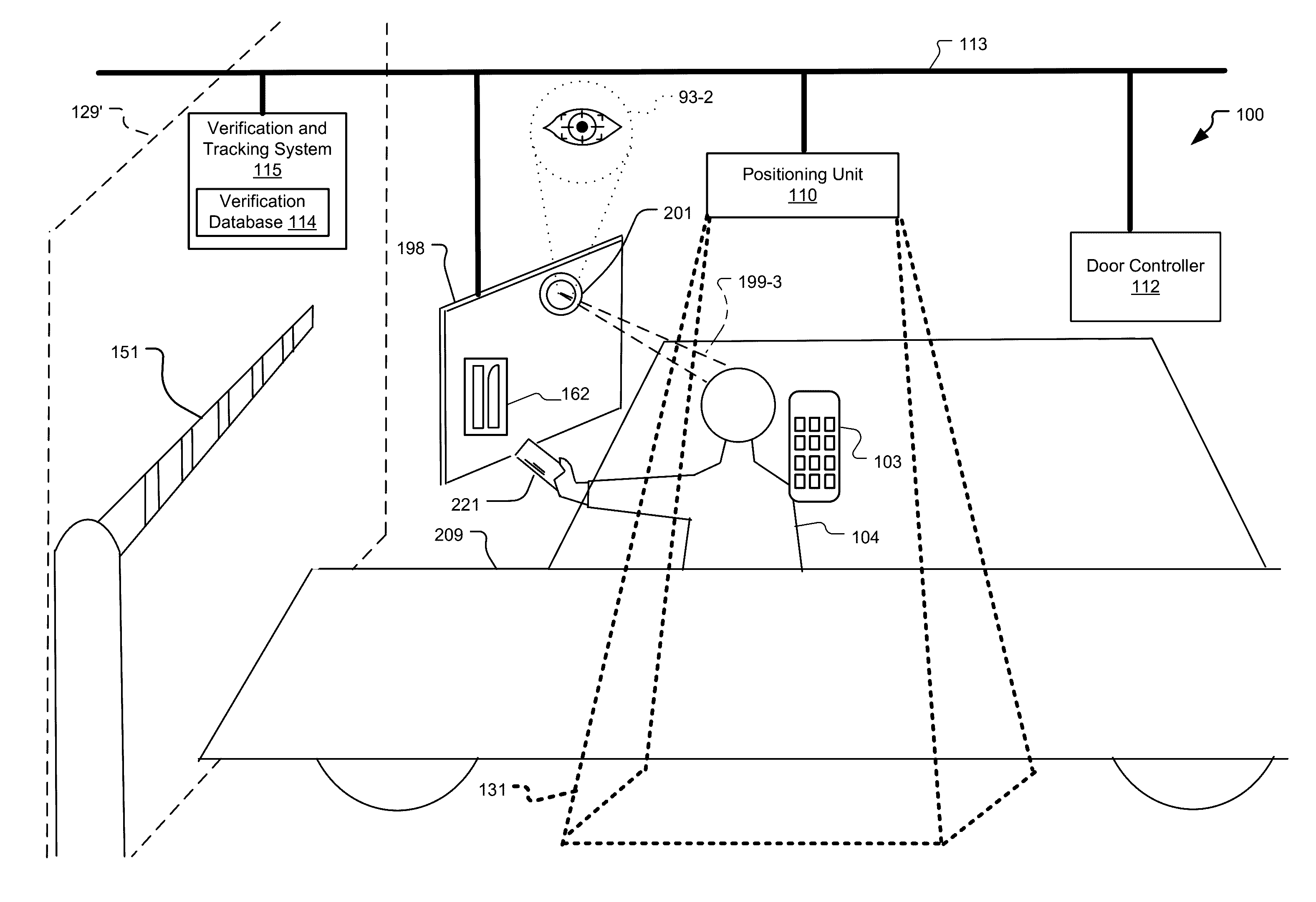
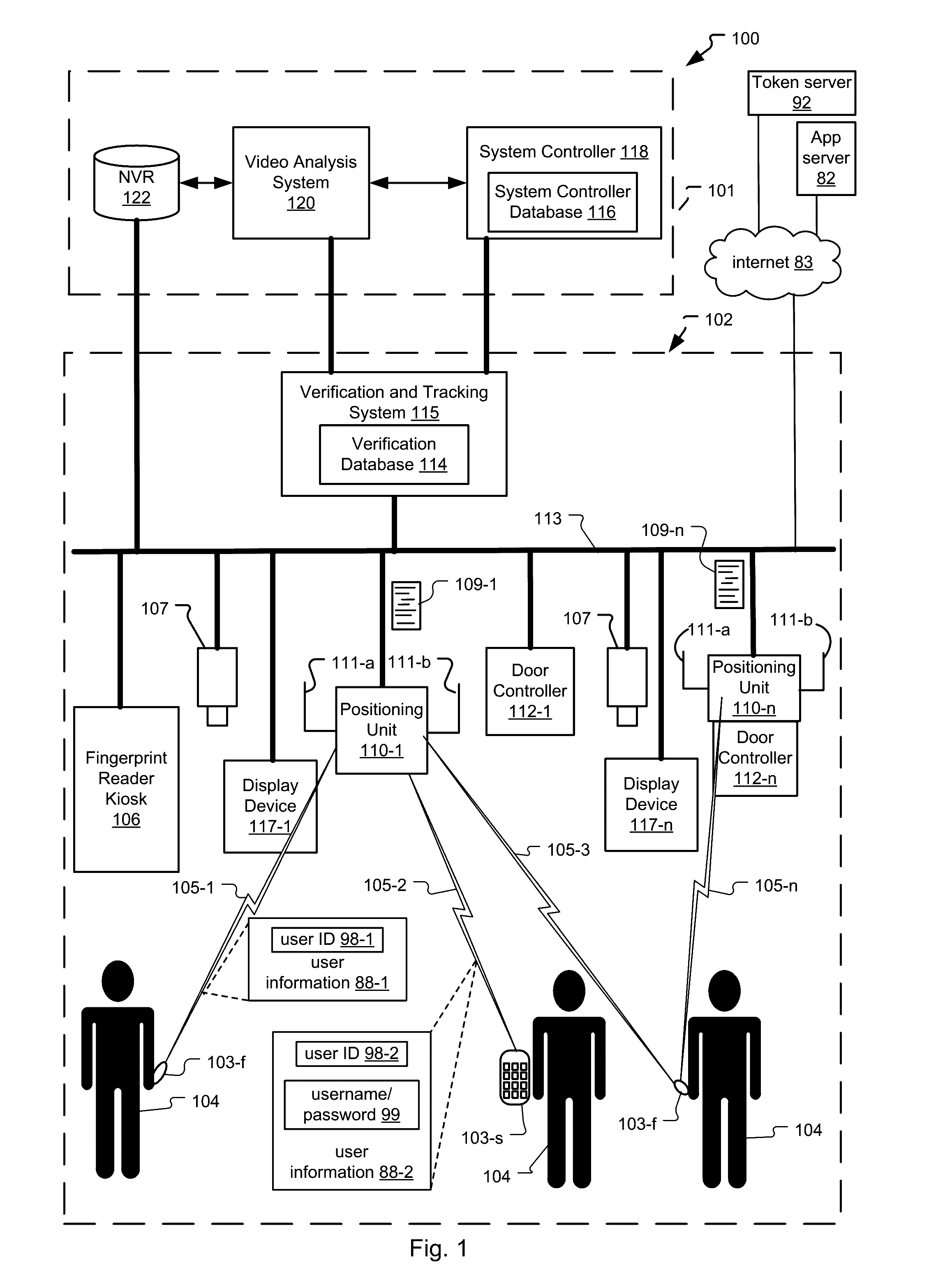
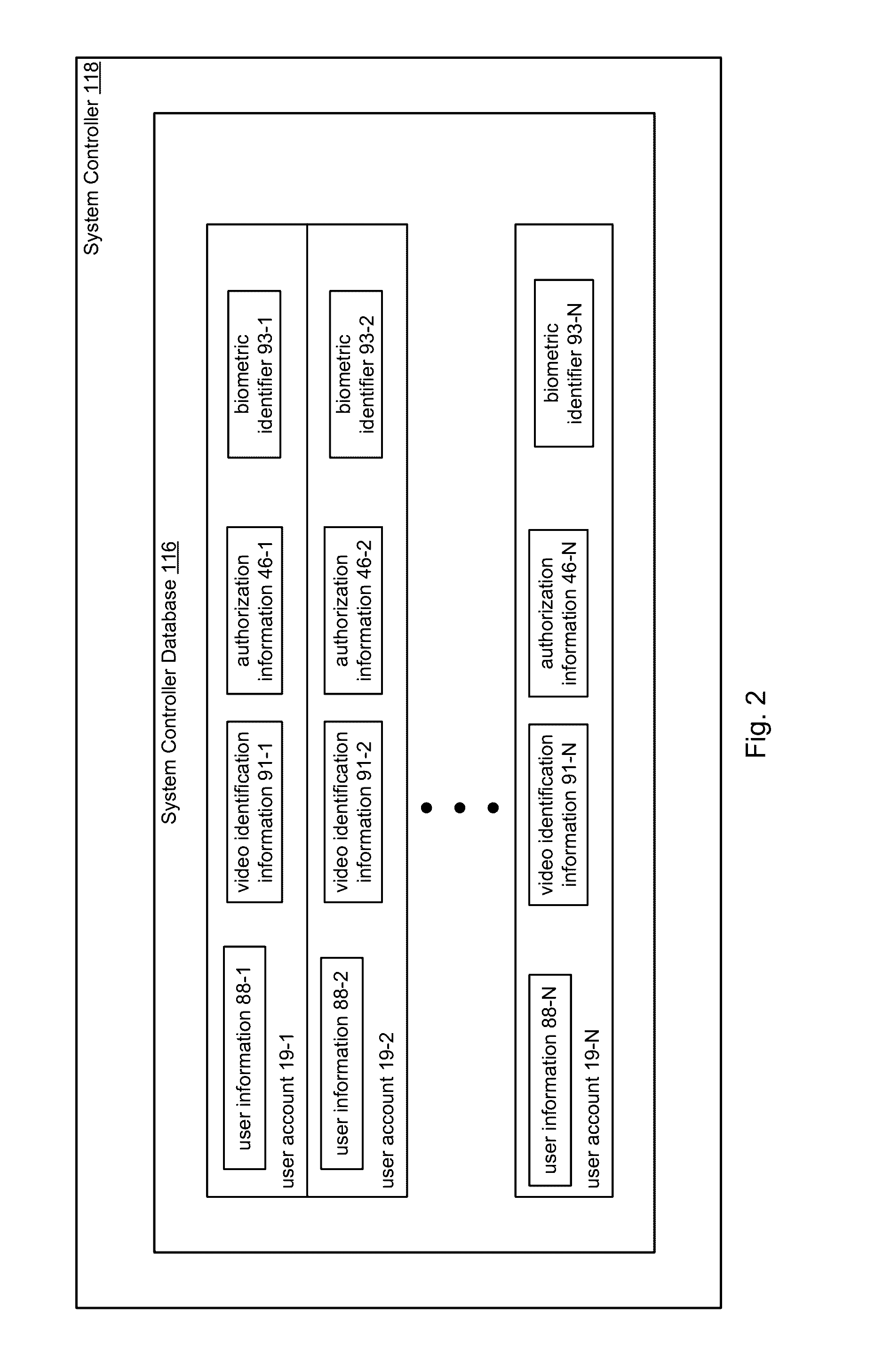
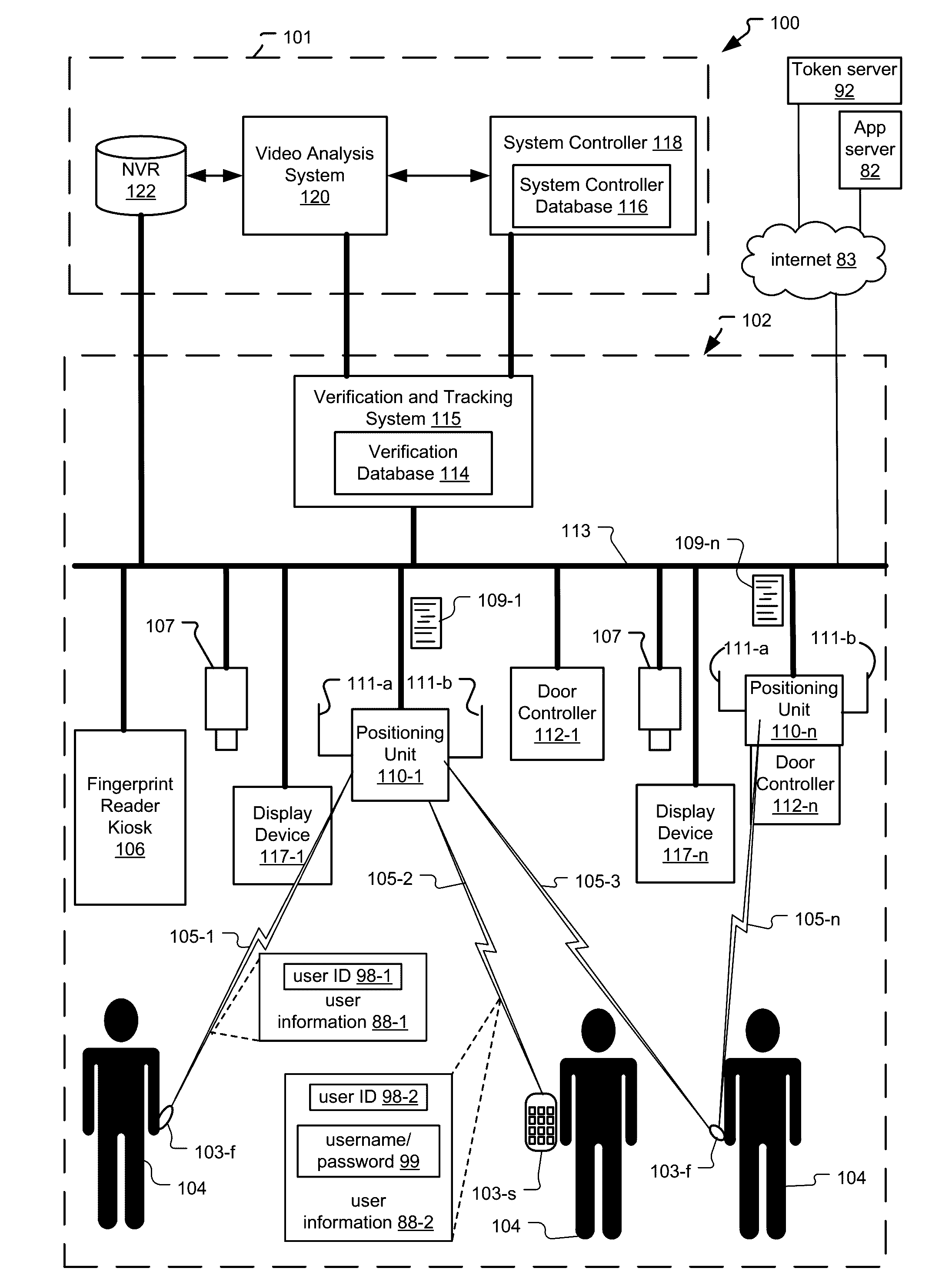
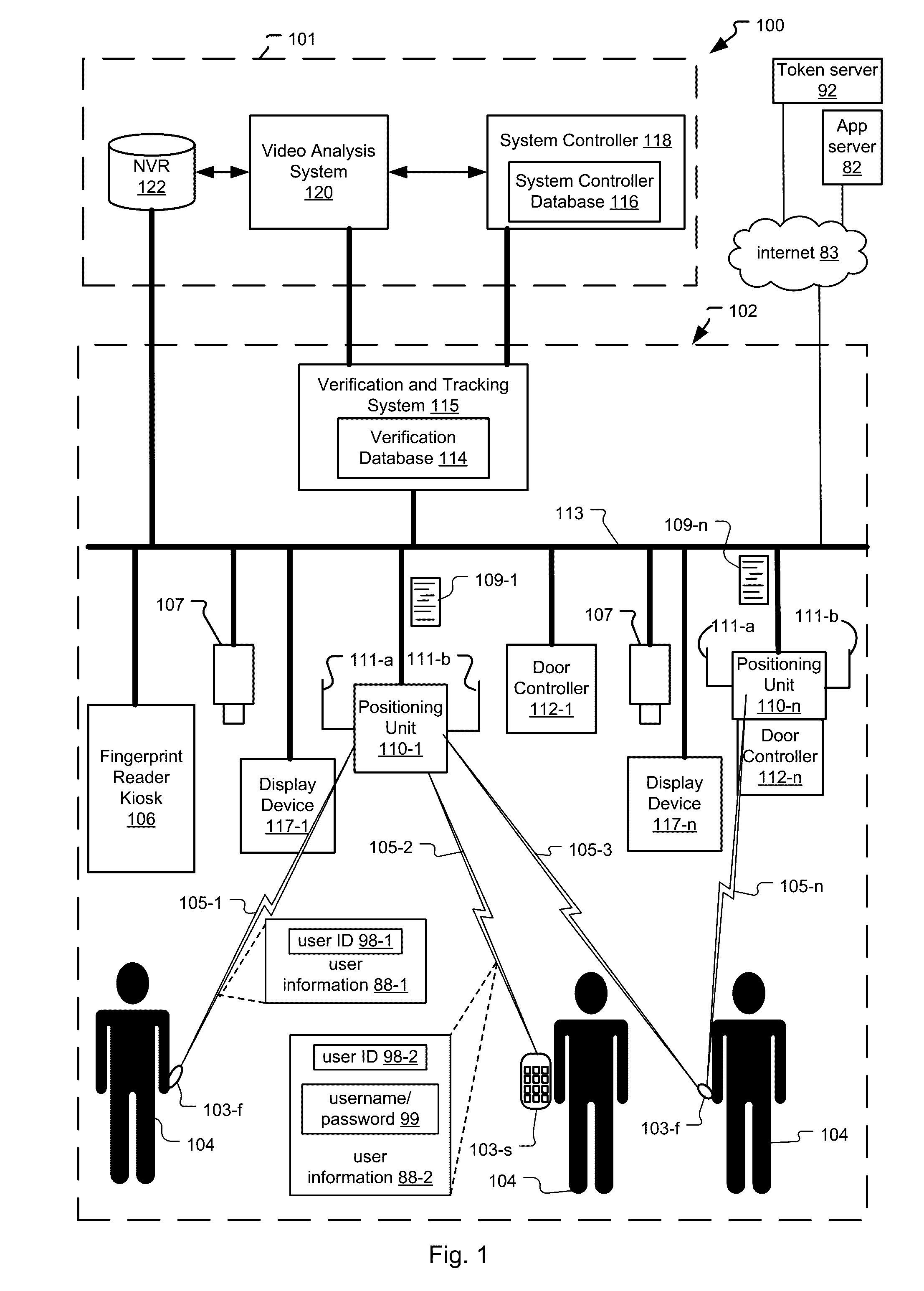
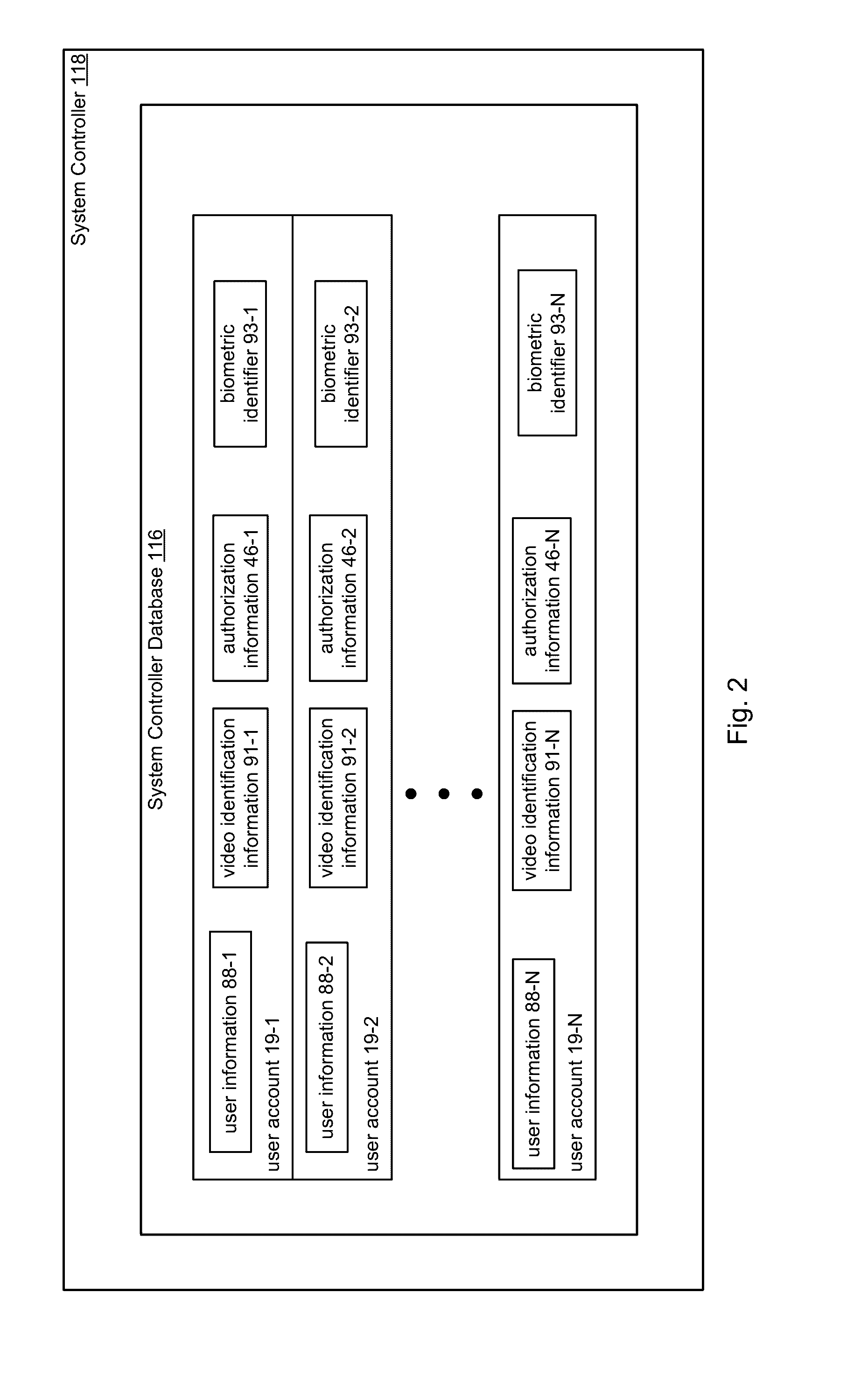
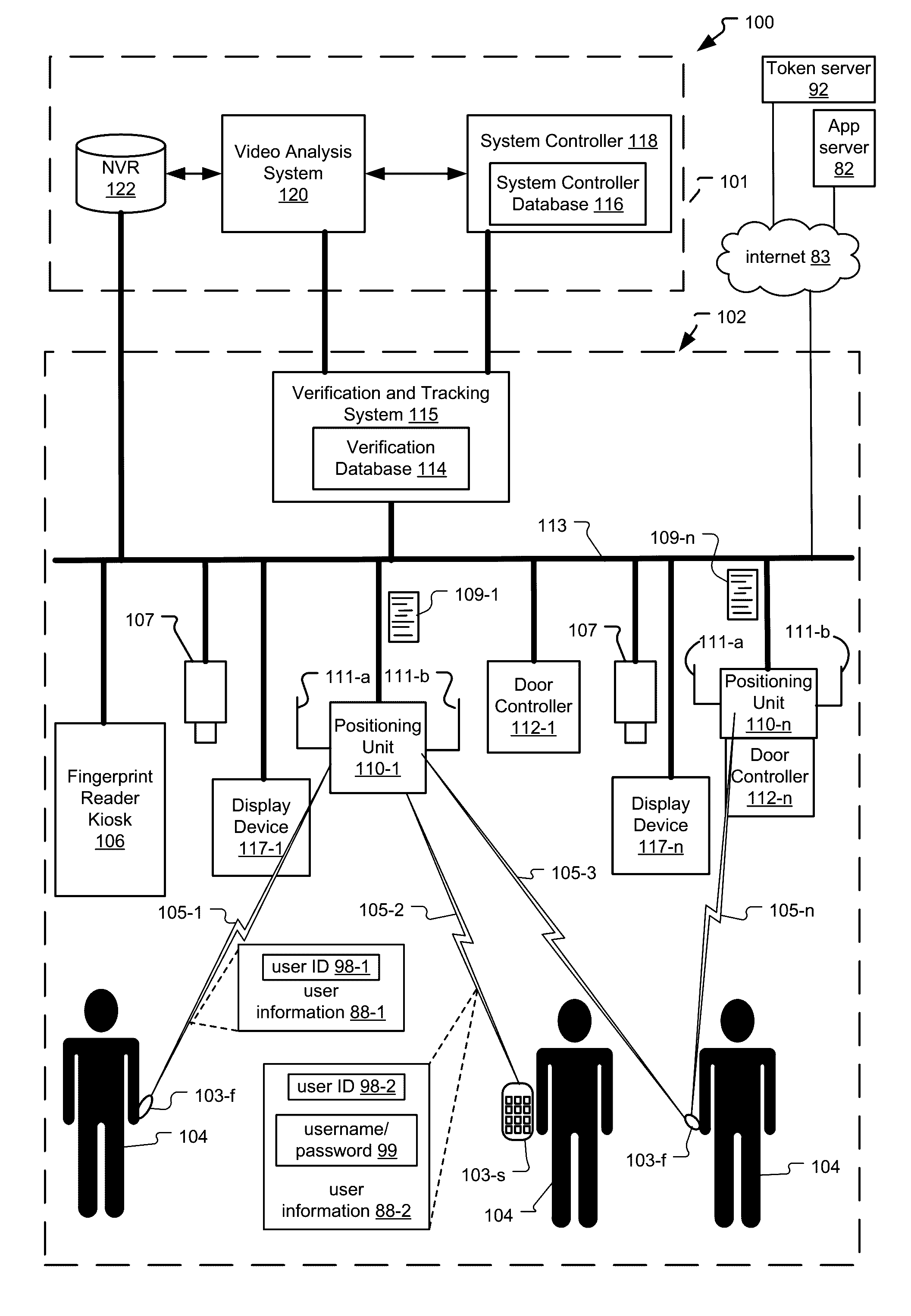
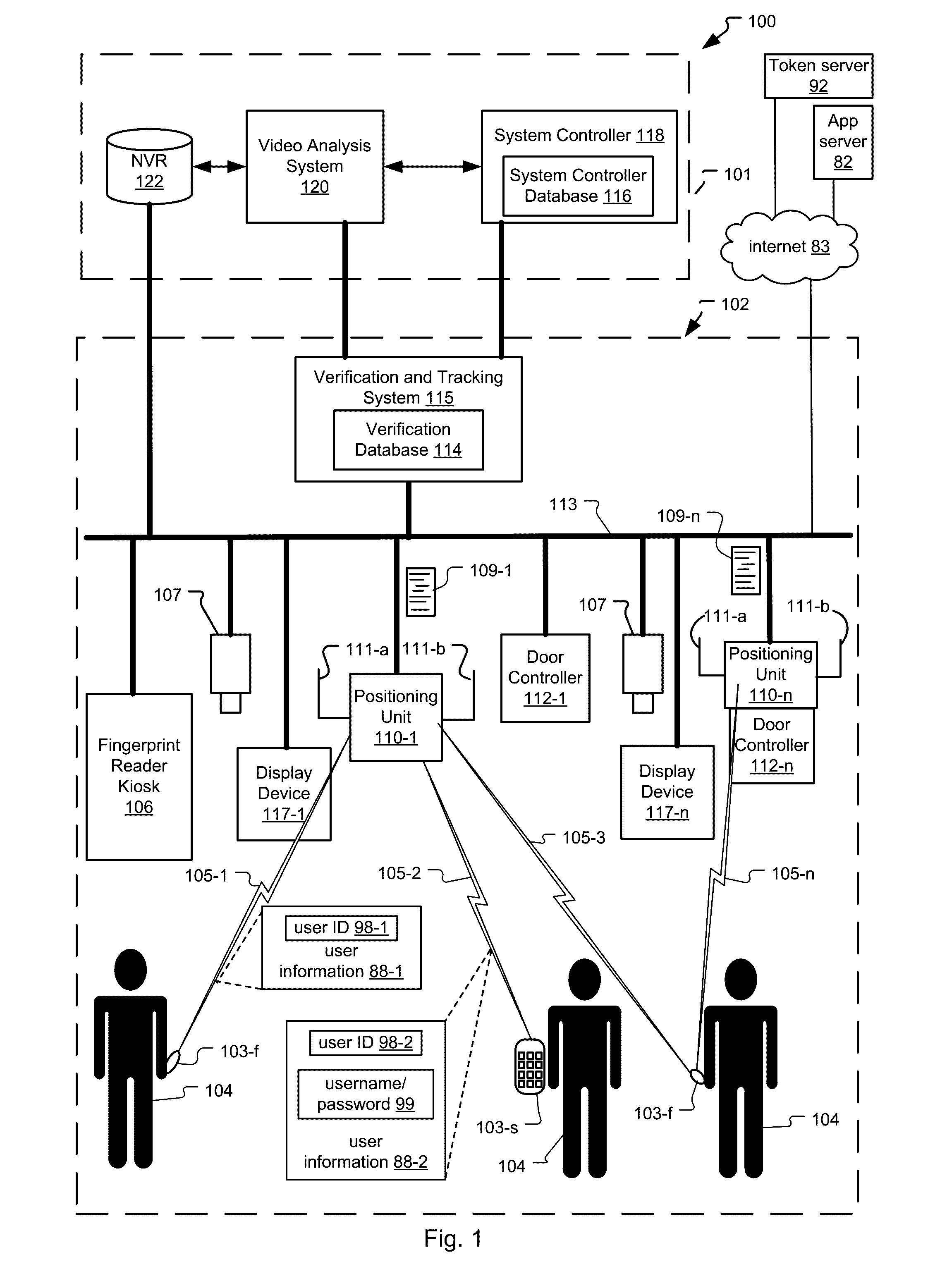
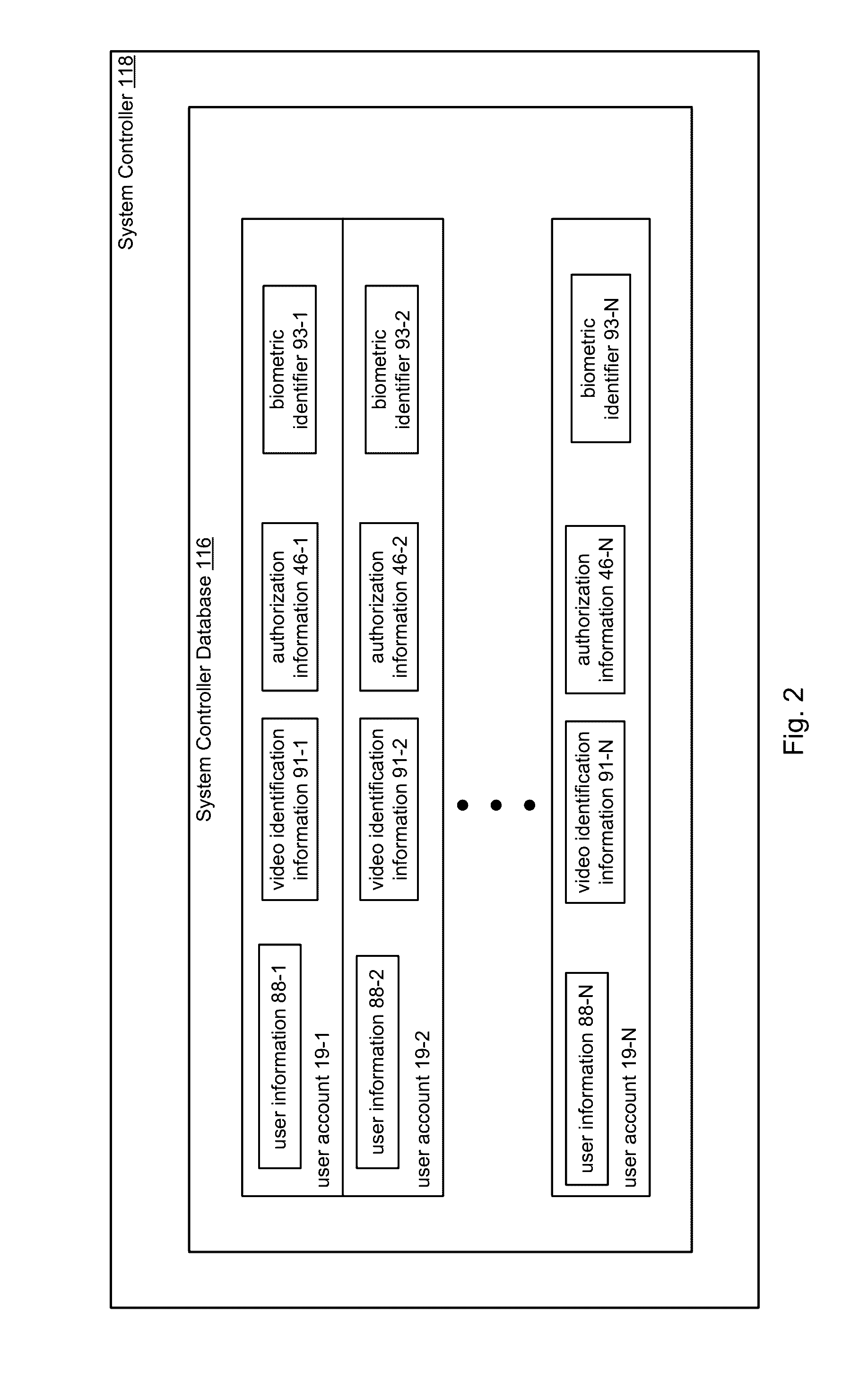
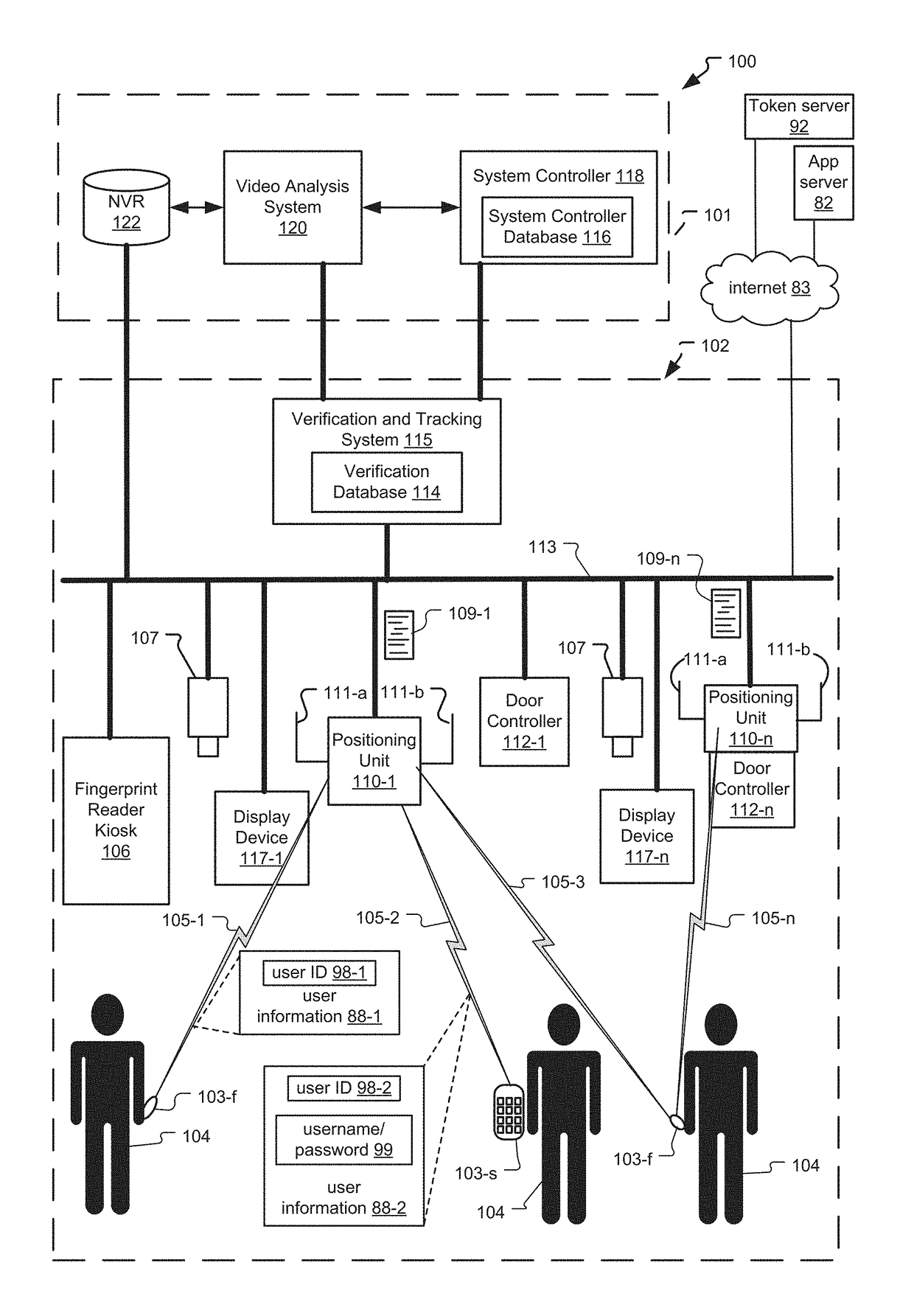
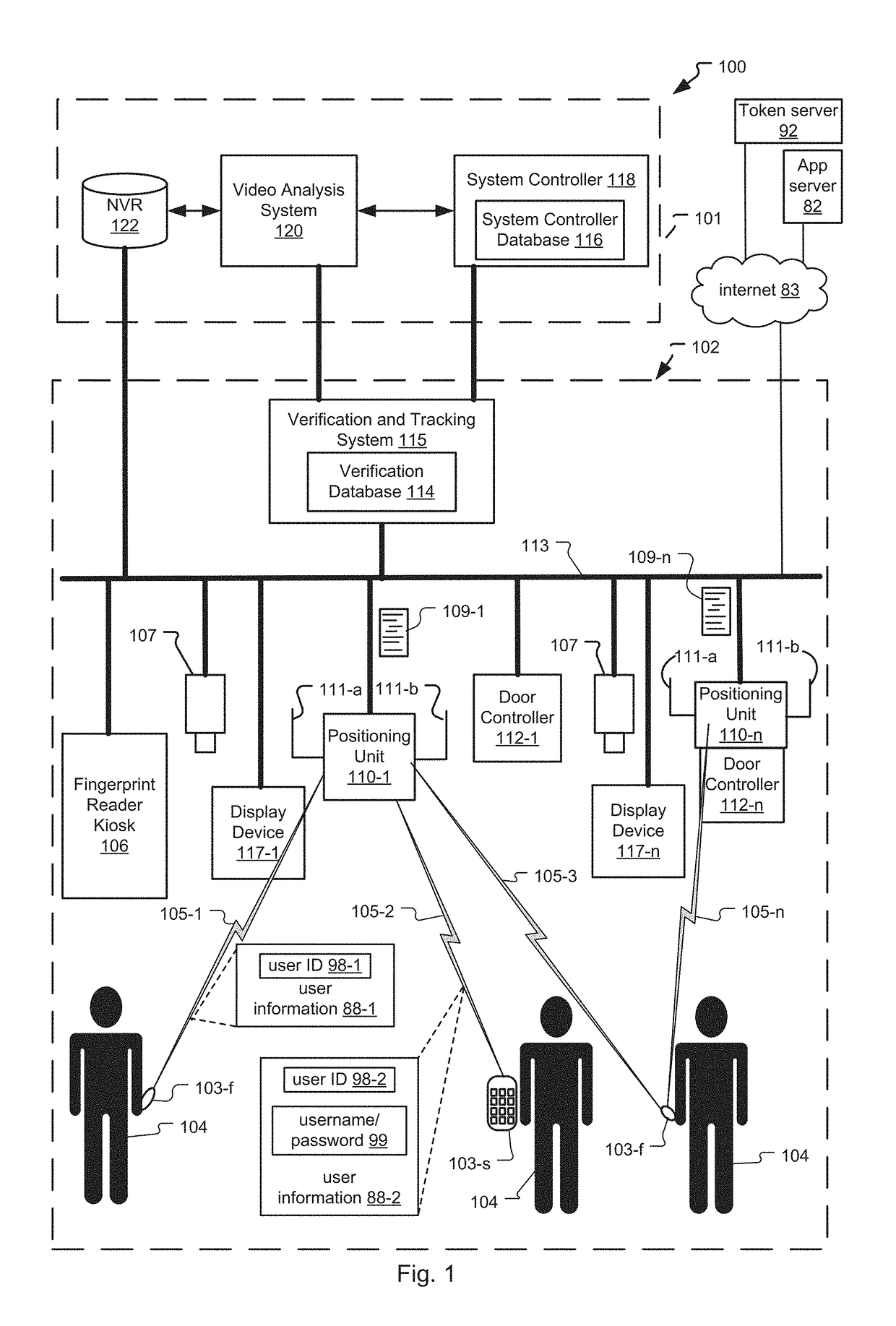
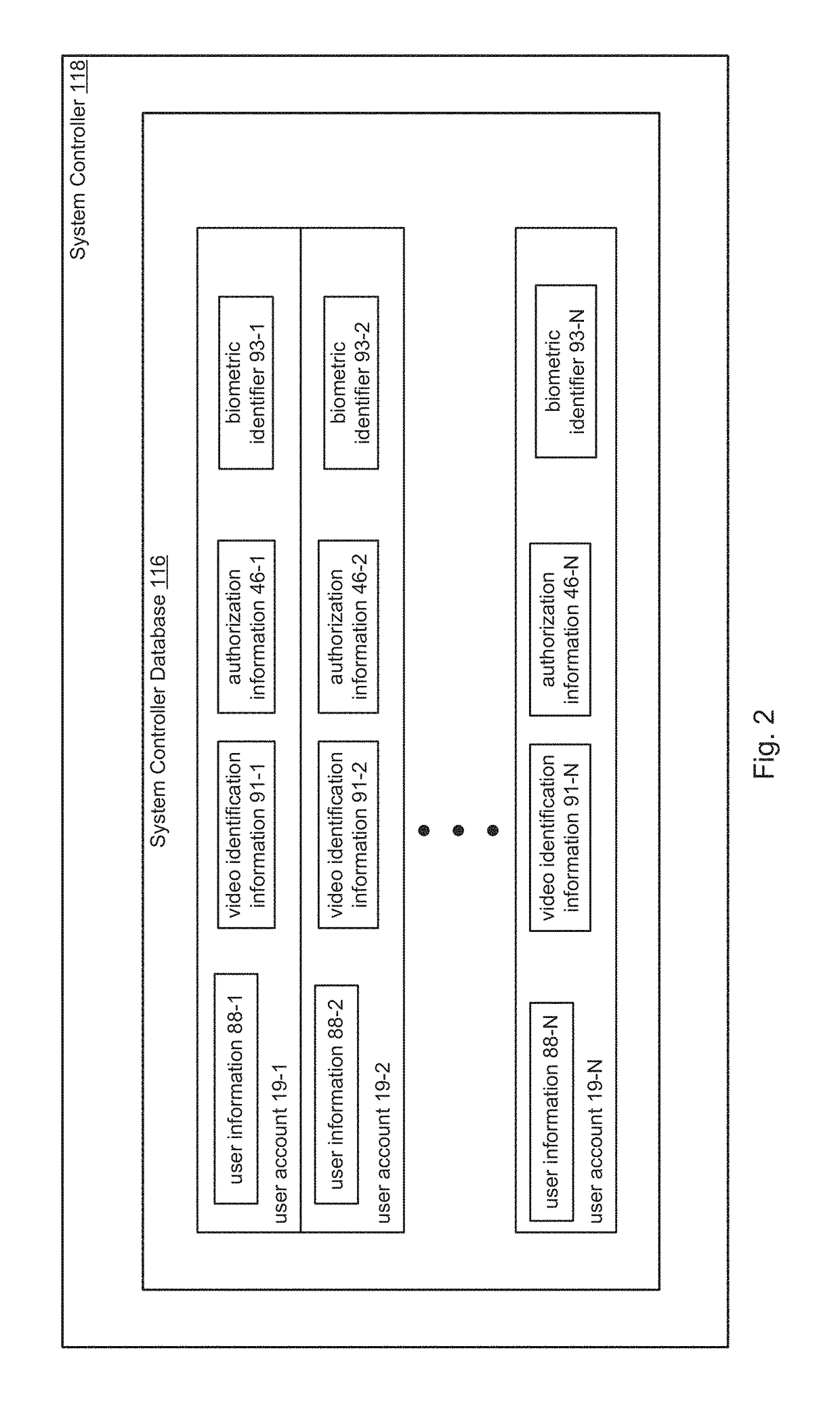
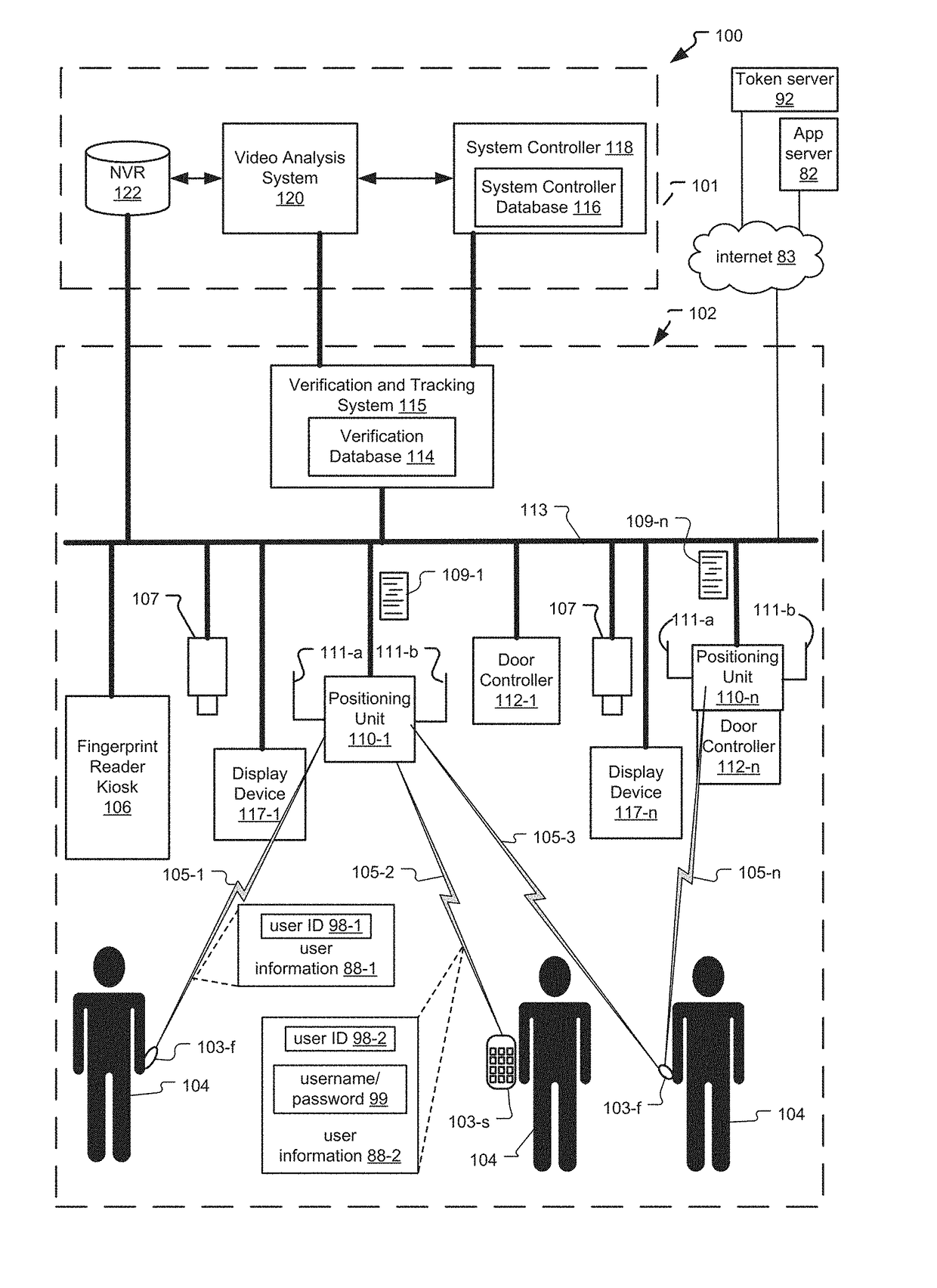
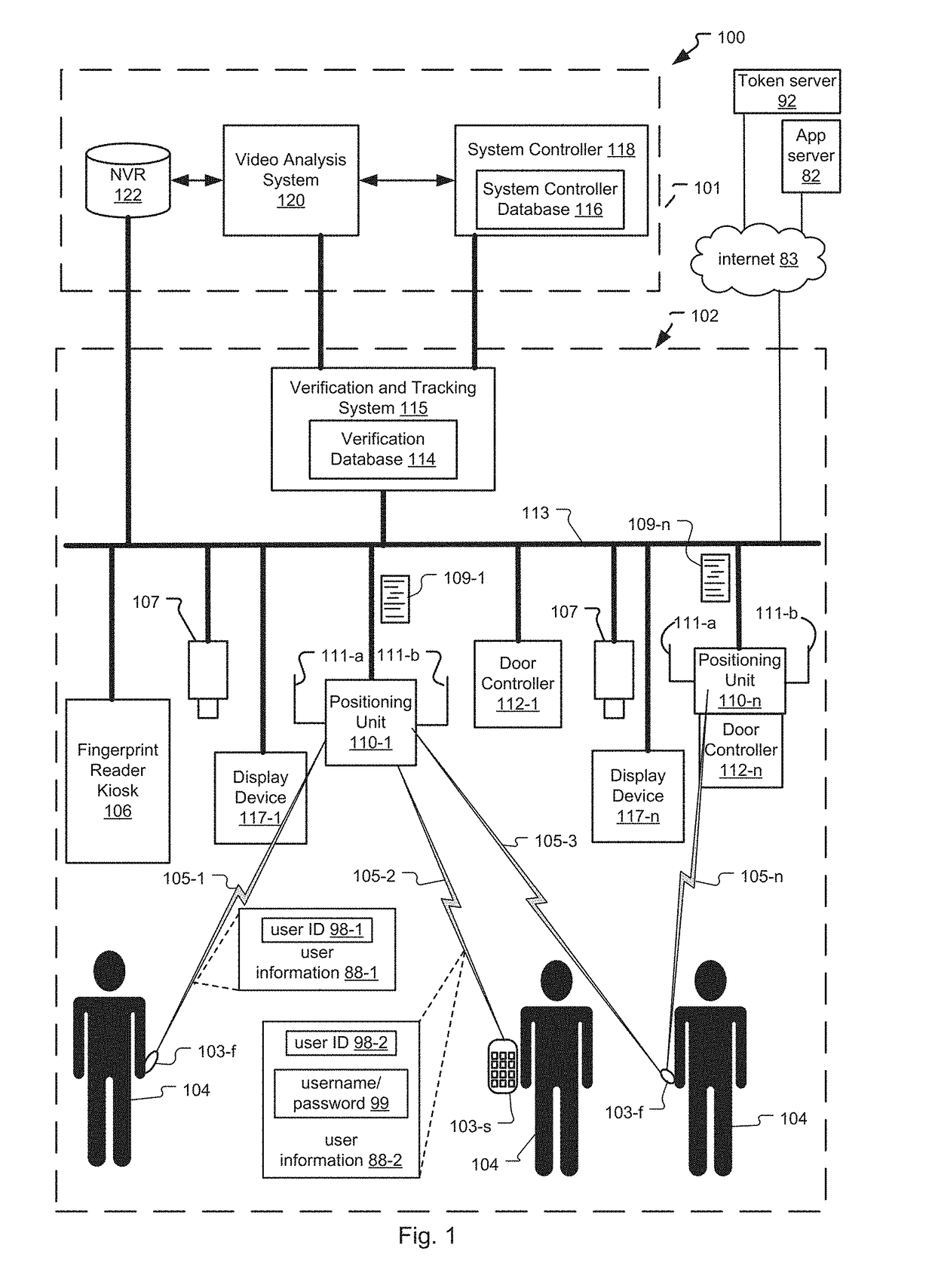
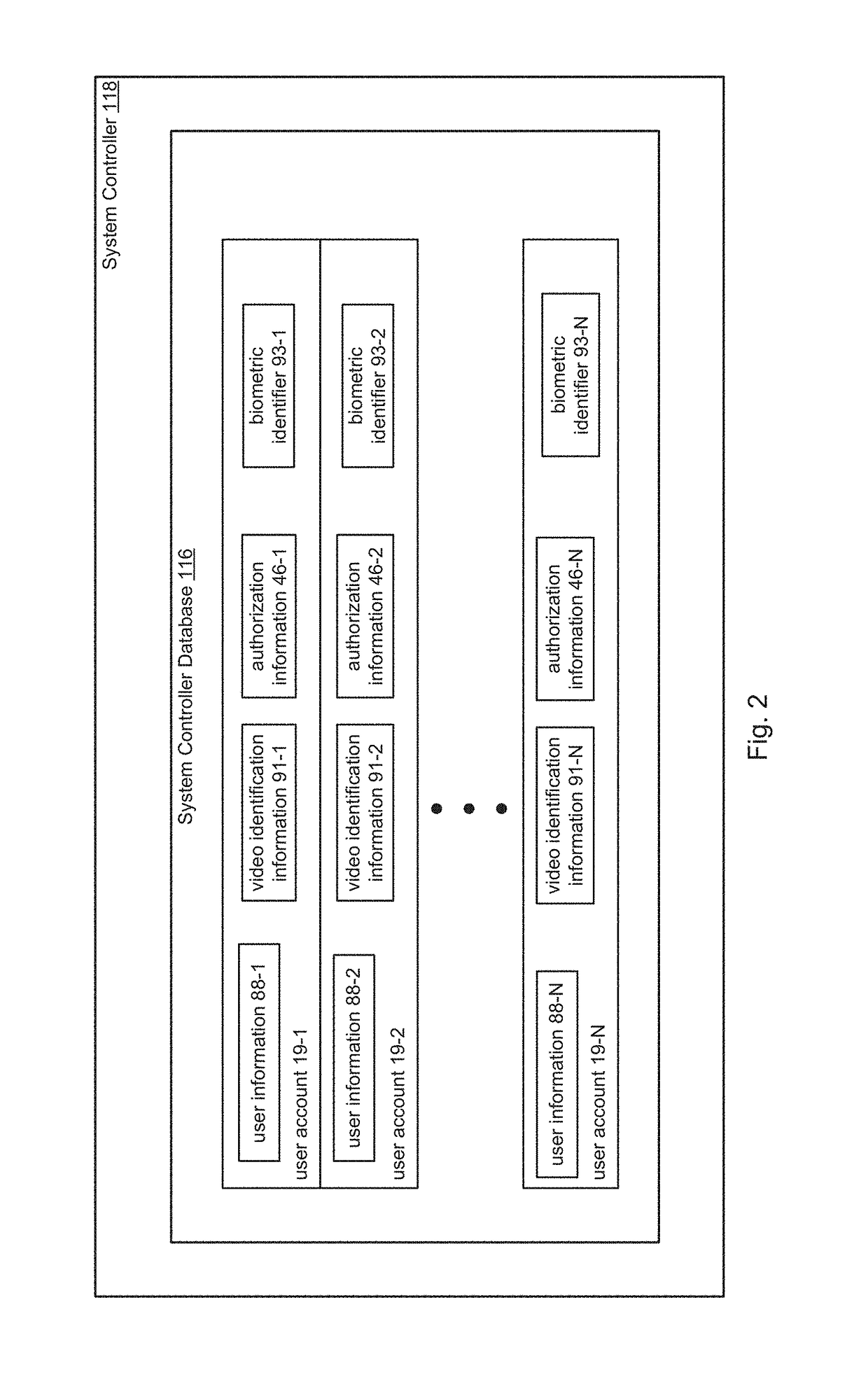
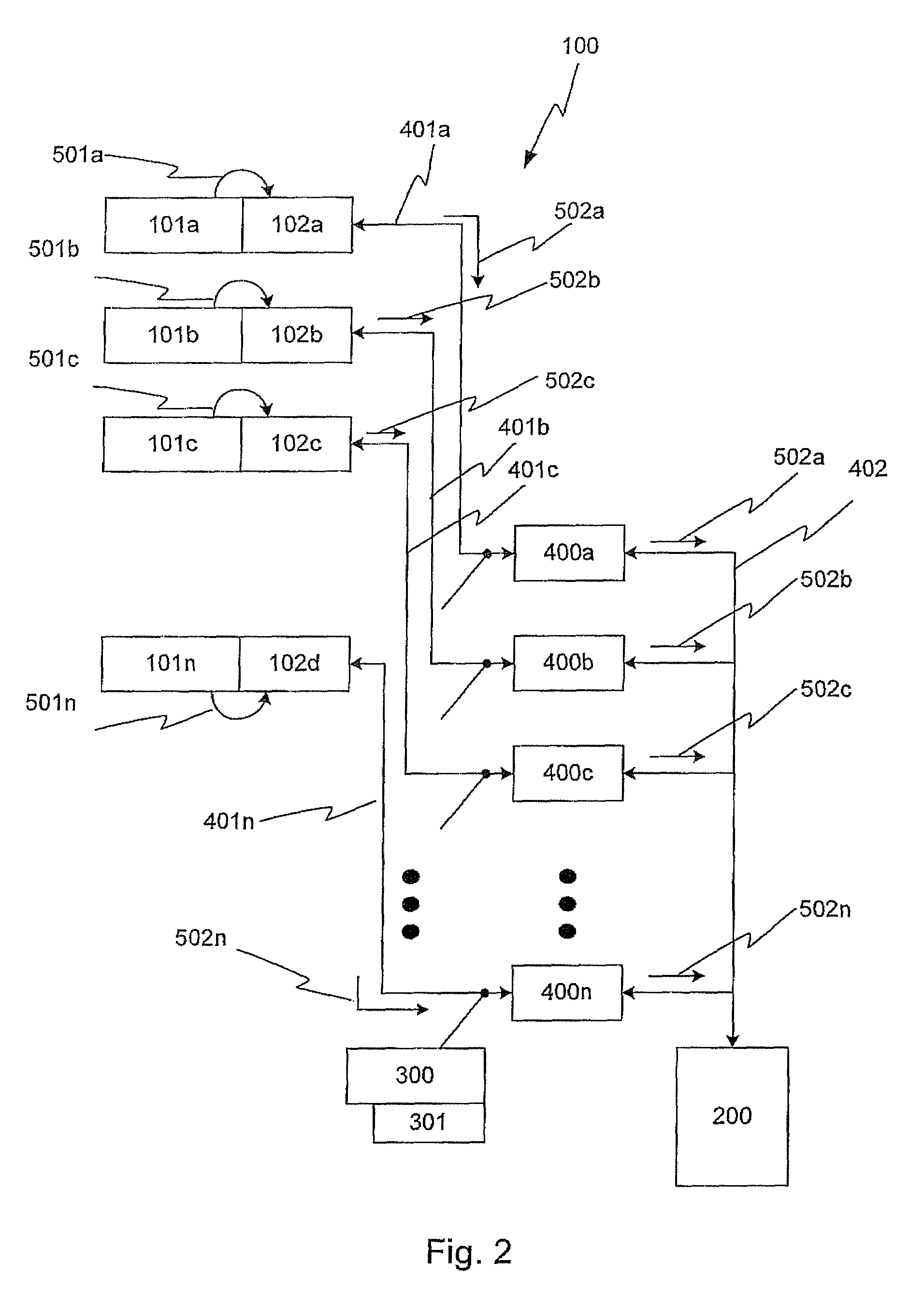
Frictionless Access System for Public Access Point
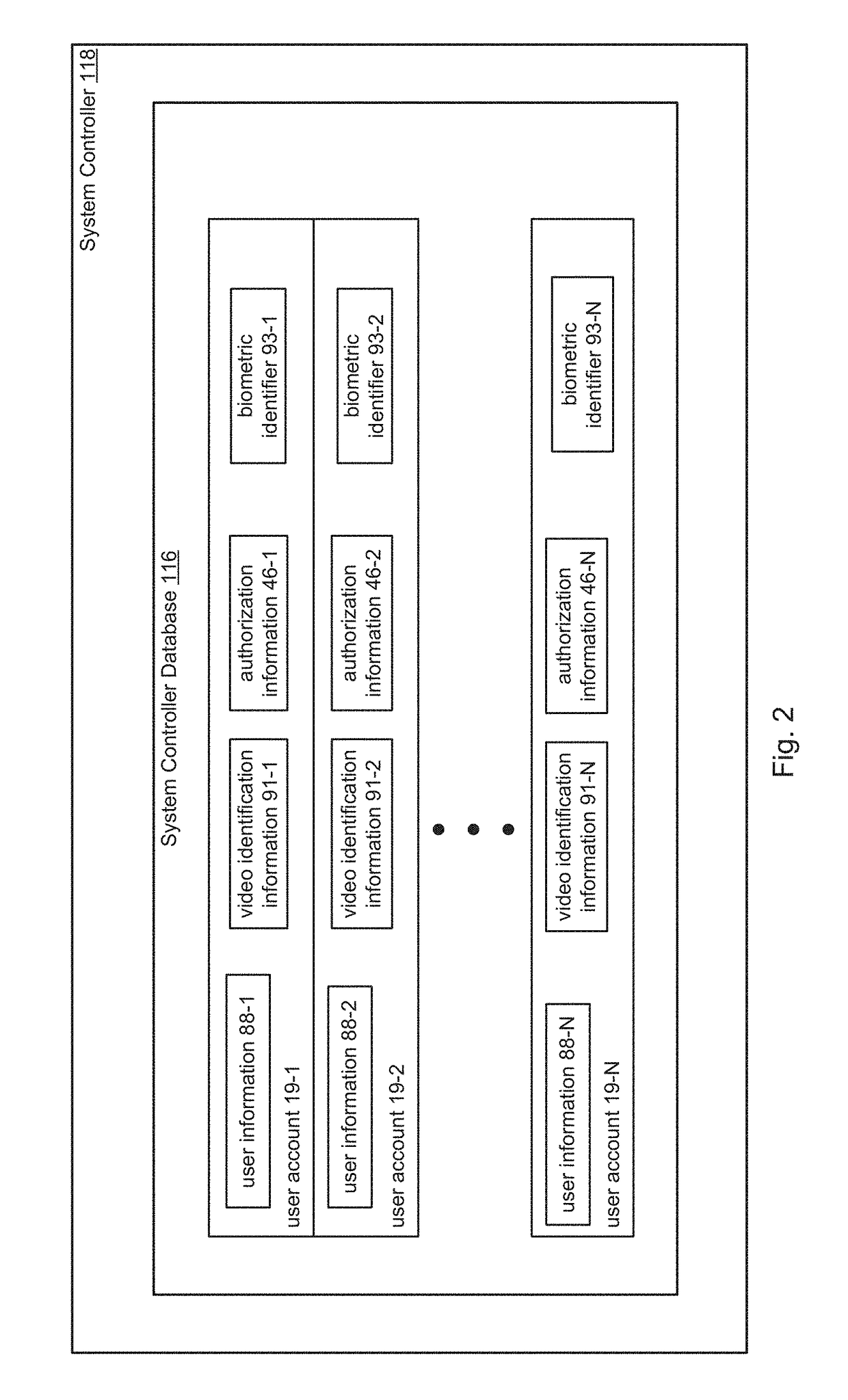
ActiveUS20160343187A1Improve securityContinuous trackingAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsUser deviceControl system
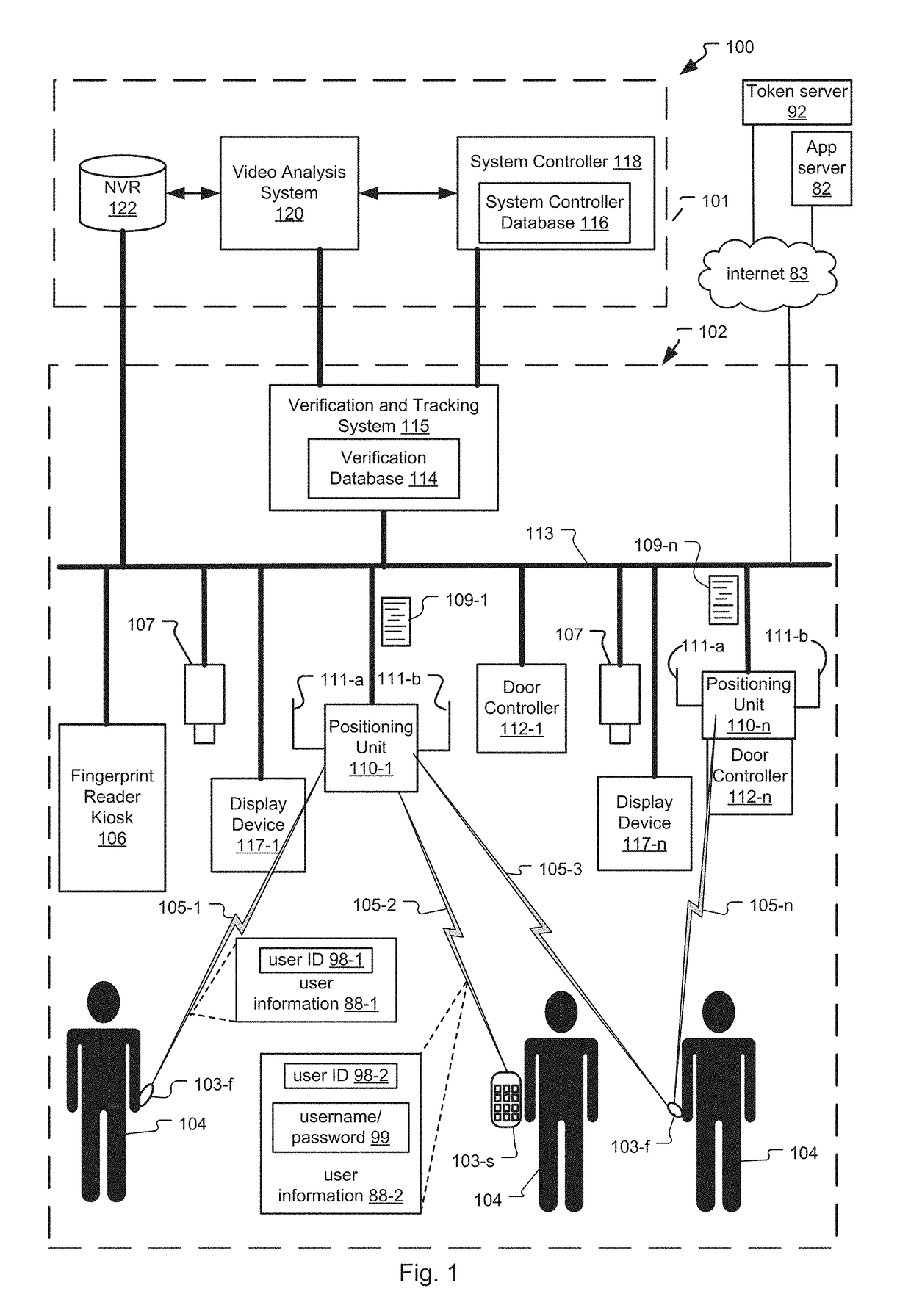
An access control system and method for monitoring a public access point are disclosed. The system includes a positioning unit that tracks locations of users carrying user devices relative to the public access point, where the user devices transmit user information identifying the users via wireless signals. The system determines whether the users are authorized to pass through the access point based on the wireless signals from the user devices. Public access points include security checkpoints at government buildings, airports, amusement parks, and universities, in examples. In embodiments, biometric identifiers are obtained from the users when the users are preferably located within a threshold area of the public access points, and the system confirms the identity of the authorized users via the biometric identifiers to enable the users to pass through the public access points. Additionally, the system can assist in evacuation of users based on their tracked locations.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
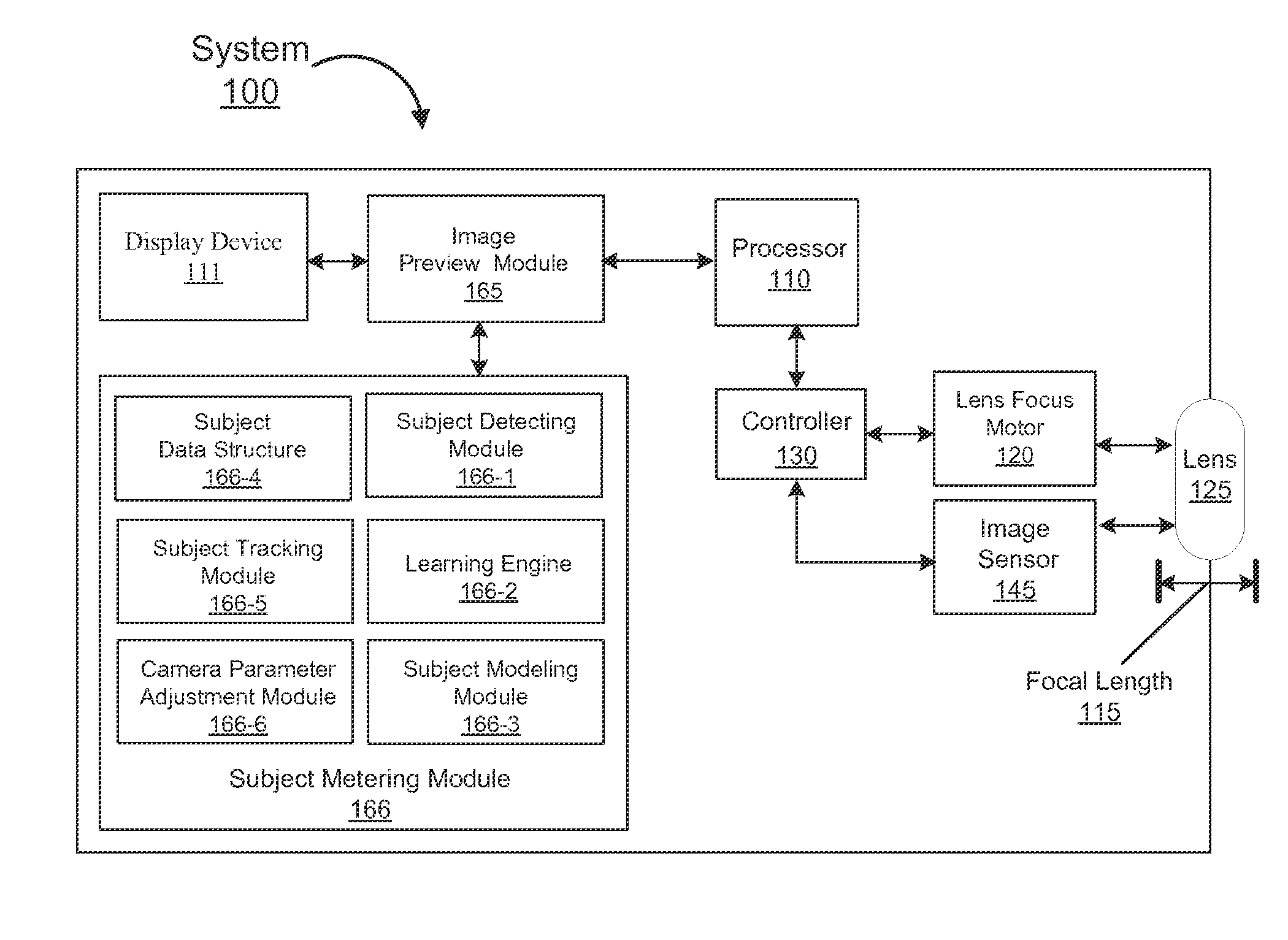
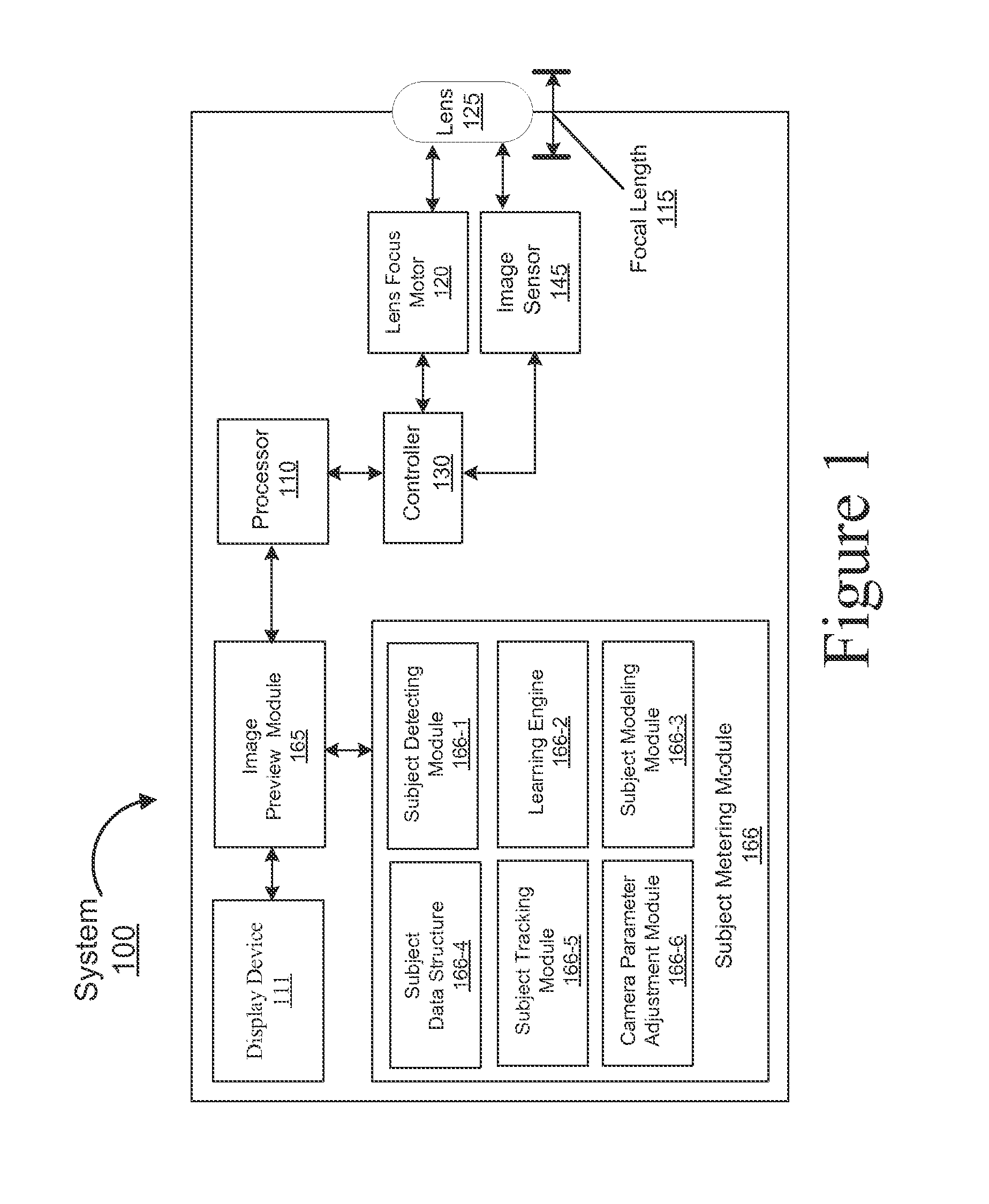
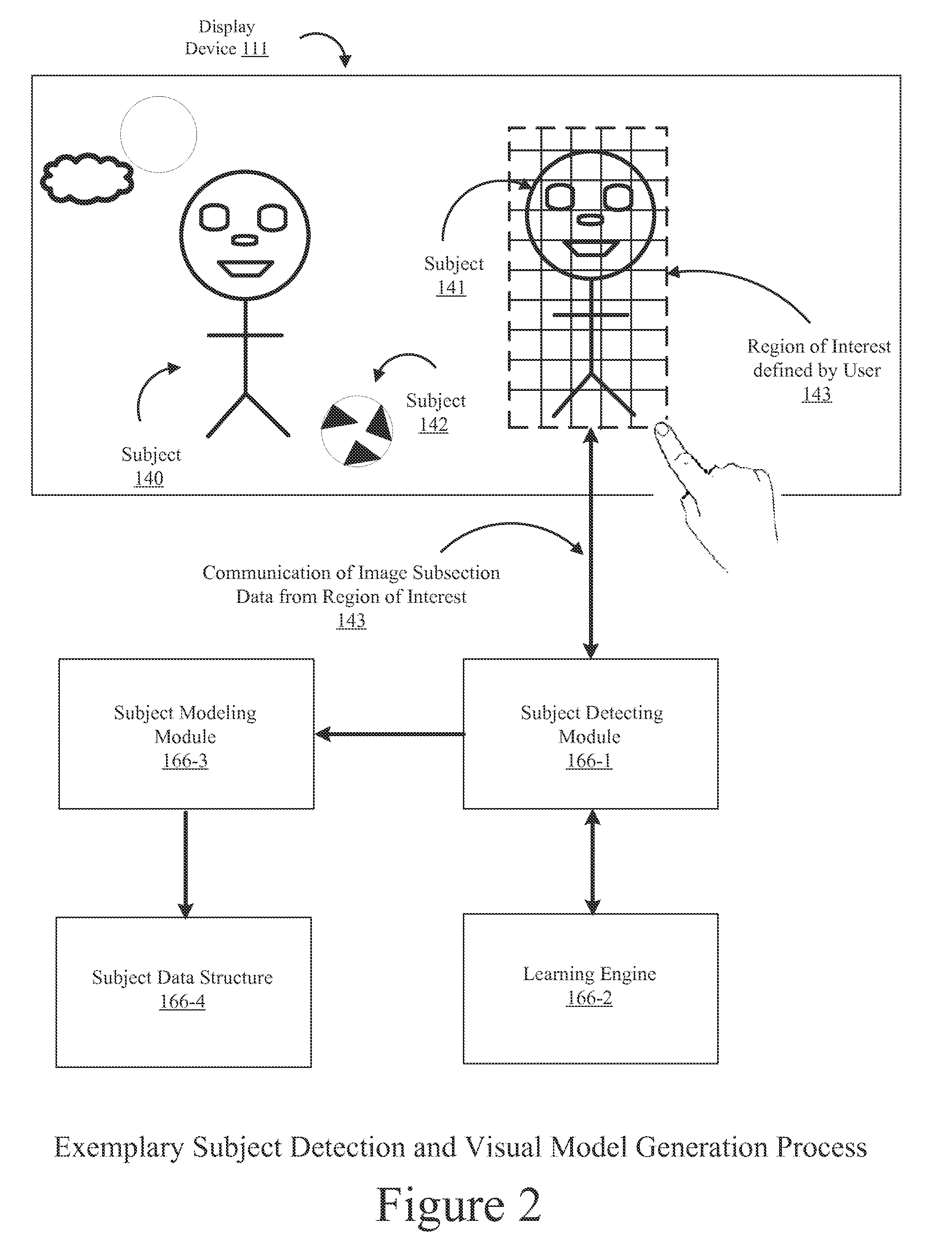
Method and system for visual tracking of a subject for automatic metering using a mobile device
InactiveUS20150103184A1FocusContinuous trackingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOnline learningSubject specific
Embodiments of the present invention provide a novel solution that enables mobile devices to continuously track interesting subjects by creating dynamic visual models that can be used to detect and track subjects in-real time through total occlusion or even if a subject temporarily leaves the mobile device's field of view. Additionally, embodiments of the present invention use an online learning scheme that dynamically adjusts tracking procedures responsive to any appearance and / or environmental changes associated with an interesting subject that may occur over a period of time. In this manner, embodiments of the present invention can determine a more optimal focus position that allows movement by either the mobile device or the subject during the performance of auto-focusing procedures and also enables other camera parameters to properly calibrate (meter) themselves based on the focus position determined.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Access Control System with Omni and Directional Antennas
ActiveUS20160284147A1Continuous trackingLower latencySite diversitySpatial transmit diversityControl systemDirectional antenna
An access control system and method for monitoring an access point are disclosed. Preferably, a positioning unit of the system includes a primary antenna and a directional antenna that determine close proximity of users to the access point while also allowing the system to continuously monitor the locations of the users. The primary antenna preferentially receives wireless signals sent from user devices (e.g. mobile phones, fobs) of the users while the directional antenna receives the wireless signals within a threshold area of the access point. The system authorizes users to enter each access point by matching user information of the users extracted from the wireless signals to locally stored user information for the users, and determining that the matched user information is referenced within locally stored authorization information indicating which users can access the access point. The system can pre-authorize the users as they approach the threshold area.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
Robust sliding mode adaptive control method for manipulator system
The invention discloses a robust sliding mode adaptive control method for a manipulator system with progressive tracking performance, which belongs to the field of manipulator control. The control method takes into account structural uncertainties such as parameters of the manipulator system and non-structural uncertainties such as external disturbances, and a parameter estimator is designed for the structural uncertainties such as the parameters; and a continuous robust controller is designed for an upper bound of the non-structural uncertainties such as the external disturbances. The robustadaptive controller designed in the method has good effects on the manipulator system with the structural uncertainties such as the parameters and the non-structural uncertainties such as the external disturbances at the same time, and the position tracking performance of the manipulator system can be ensured. The robust sliding mode adaptive controller is simple and continuous in control outputand is applicable in engineering practice.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tailgating Detection in Frictionless Access Control System
ActiveUS20160284183A1Reduce actionContinuous trackingSpatial transmit diversityParticular environment based servicesTailgatingVideo camera
A system and method for determining tailgating of users in a frictionless access control system are disclosed. The access control system includes a positioning unit that tracks locations of users carrying user devices relative to an access point of a premises, where the user devices transmit user information identifying the users via wireless signals. The access control system then determines whether the users are authorized to pass through the access point based on the wireless signals from the user devices and determines whether non-authorized users are tailgating through the access point with authorized users. In embodiments, the system can also determine tailgating of the users in response to analyzing video data of a scene including the users, where the video data is generated by a video camera positioned to capture the users when the users are within the threshold area.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
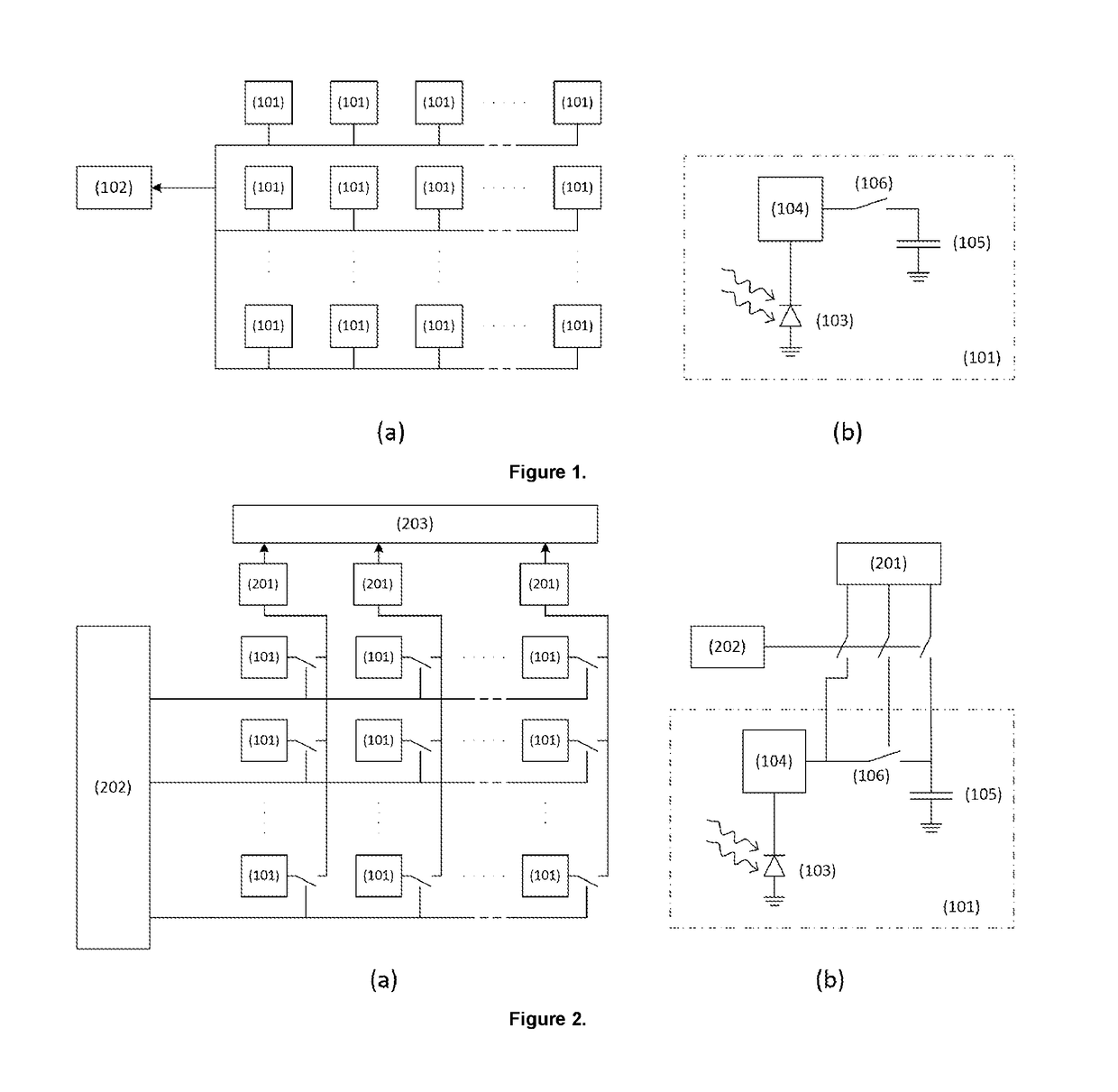
An Event-Based Vision Sensor
ActiveUS20190052820A1Overcome limitationsEfficient codingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
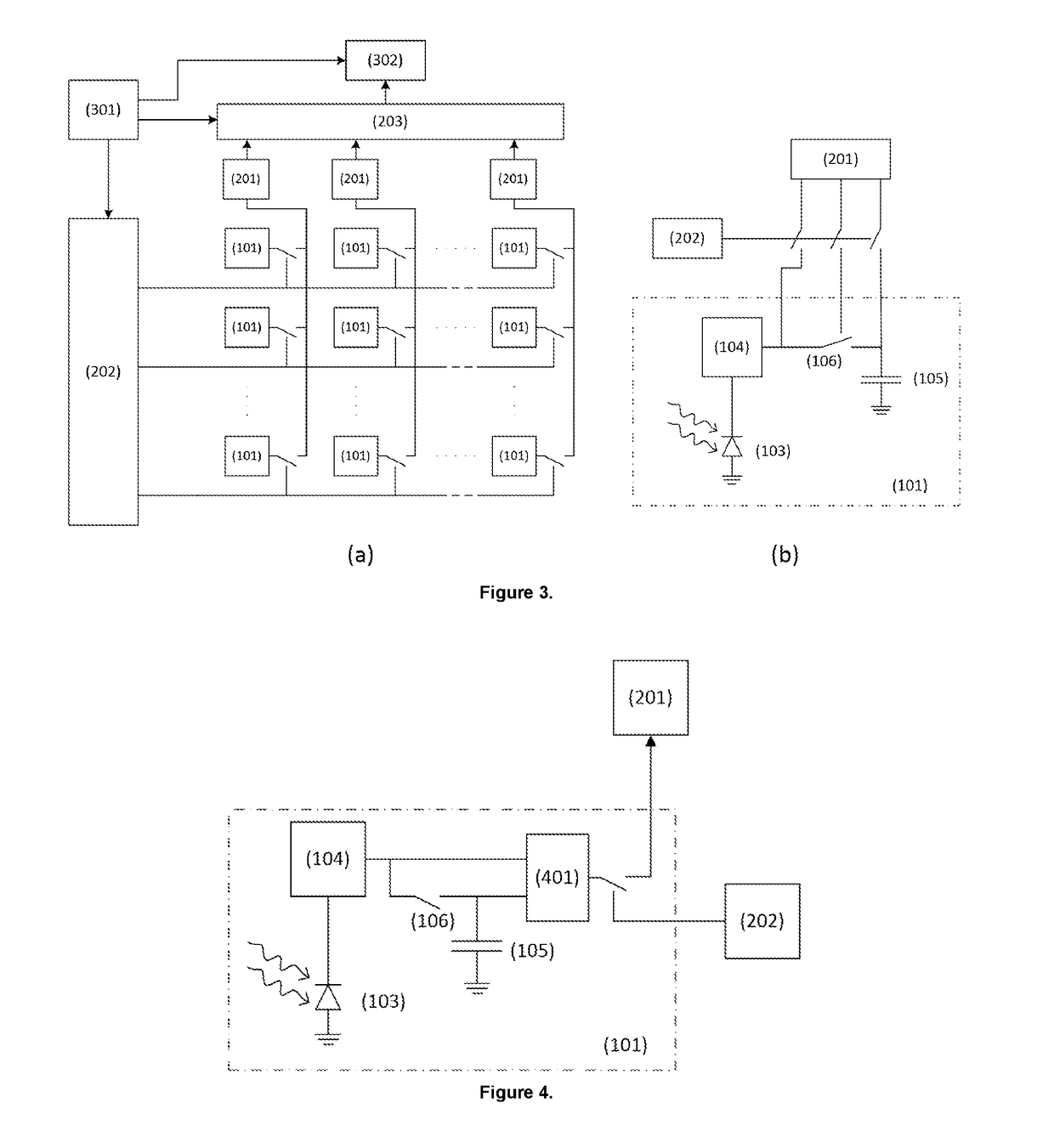
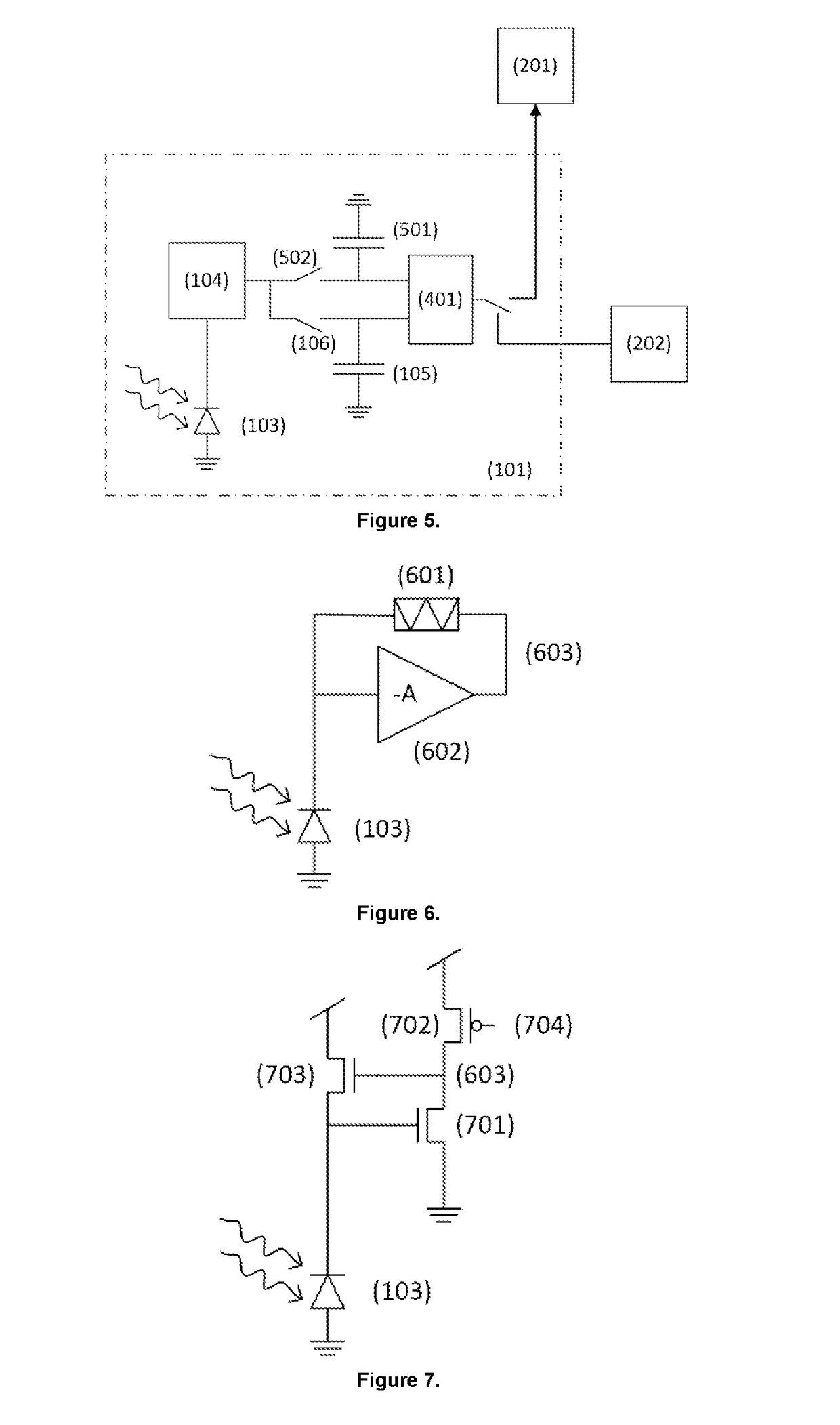
According to the present invention there is provided a vision sensor comprising, an array of pixels (101) comprising rows and columns of pixels, wherein each pixel has an address assigned thereto which represents the position of the pixel in the array, wherein each pixel in the array of pixels comprises a photodiode (103) which can receive light, and which can output current having an amplitude proportional to the intensity of the received light; a photoreceptor circuit (104) which is electronically connected to the photodiode, and which is configured to convert current which it receives from the photodiode into a voltage; a first storage capacitor (105), and at least a first switch which (106) is positioned between the first storage capacitor and an output of the photoreceptor circuit, wherein the first switch can be selectively closed to electronically connect the output of the photoreceptor circuit to the first storage capacitor, or selectively opened to electronically disconnect the output of the photoreceptor circuit from the first storage capacitor; and a circuit (102, 201) which is configured so that it can be selectively electronically connected to a pixel in the array, and to determine if the difference between the voltage output from the photoreceptor circuit and the voltage across the first storage capacitor is greater than a predefined threshold voltage, and to output the address of the pixel to a receiver only if the difference between the voltage output from the photoreceptor circuit and the voltage across the first storage capacitor is greater than a predefined threshold voltage. There is further provided a corresponding method of vision sensing using the vision sensor.
Owner:SONY ADVANCED VISUAL SENSING AG
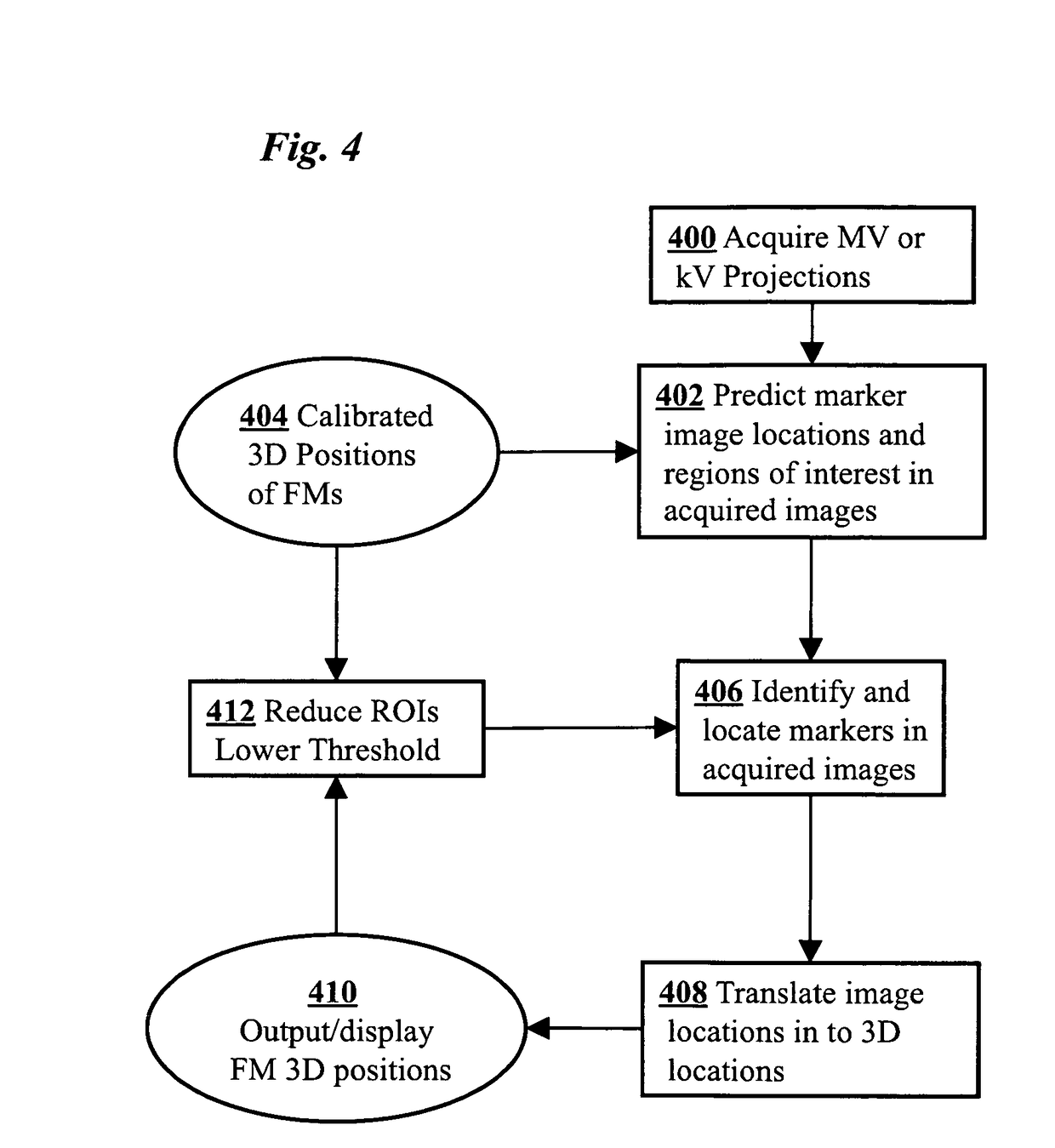
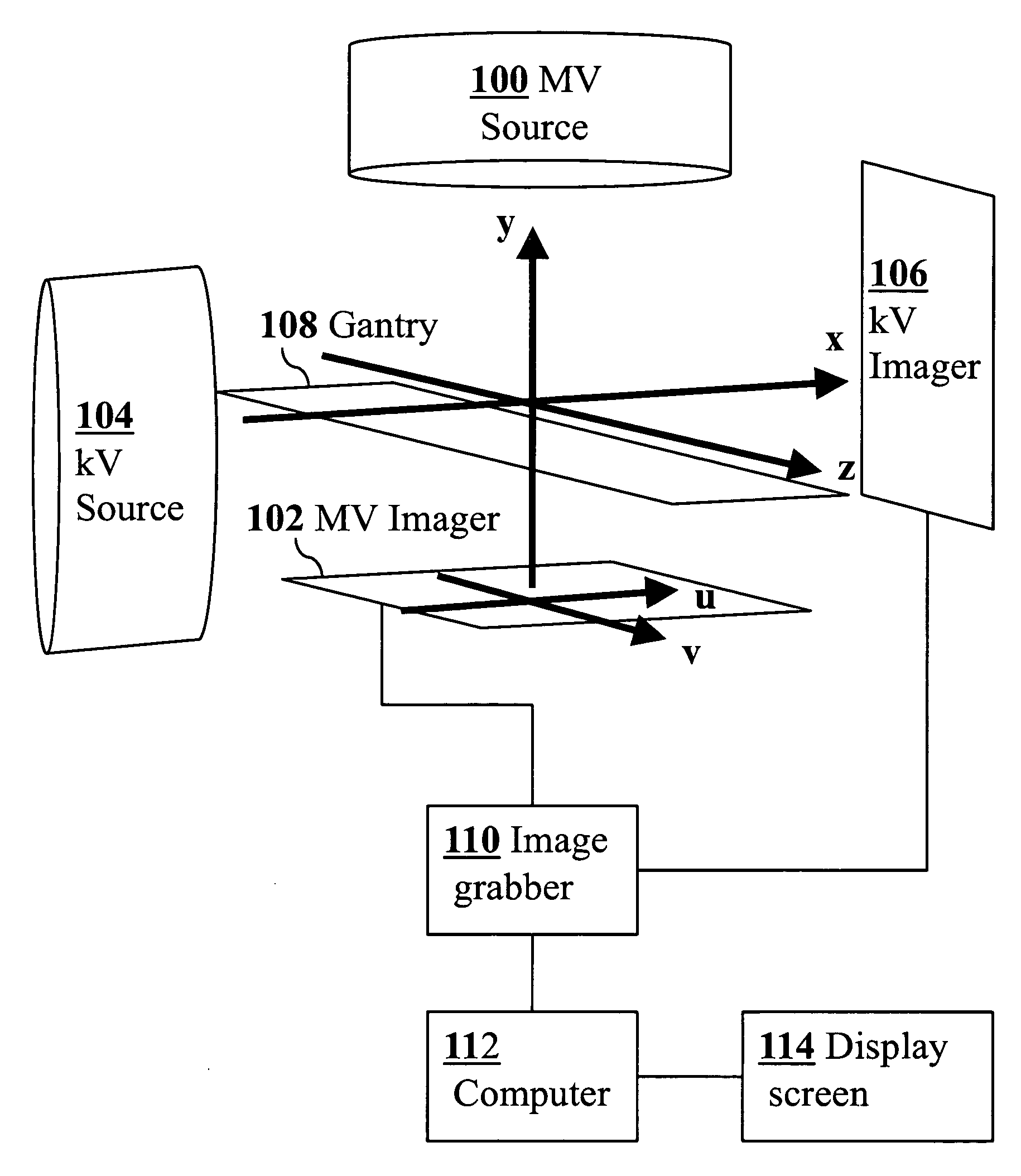
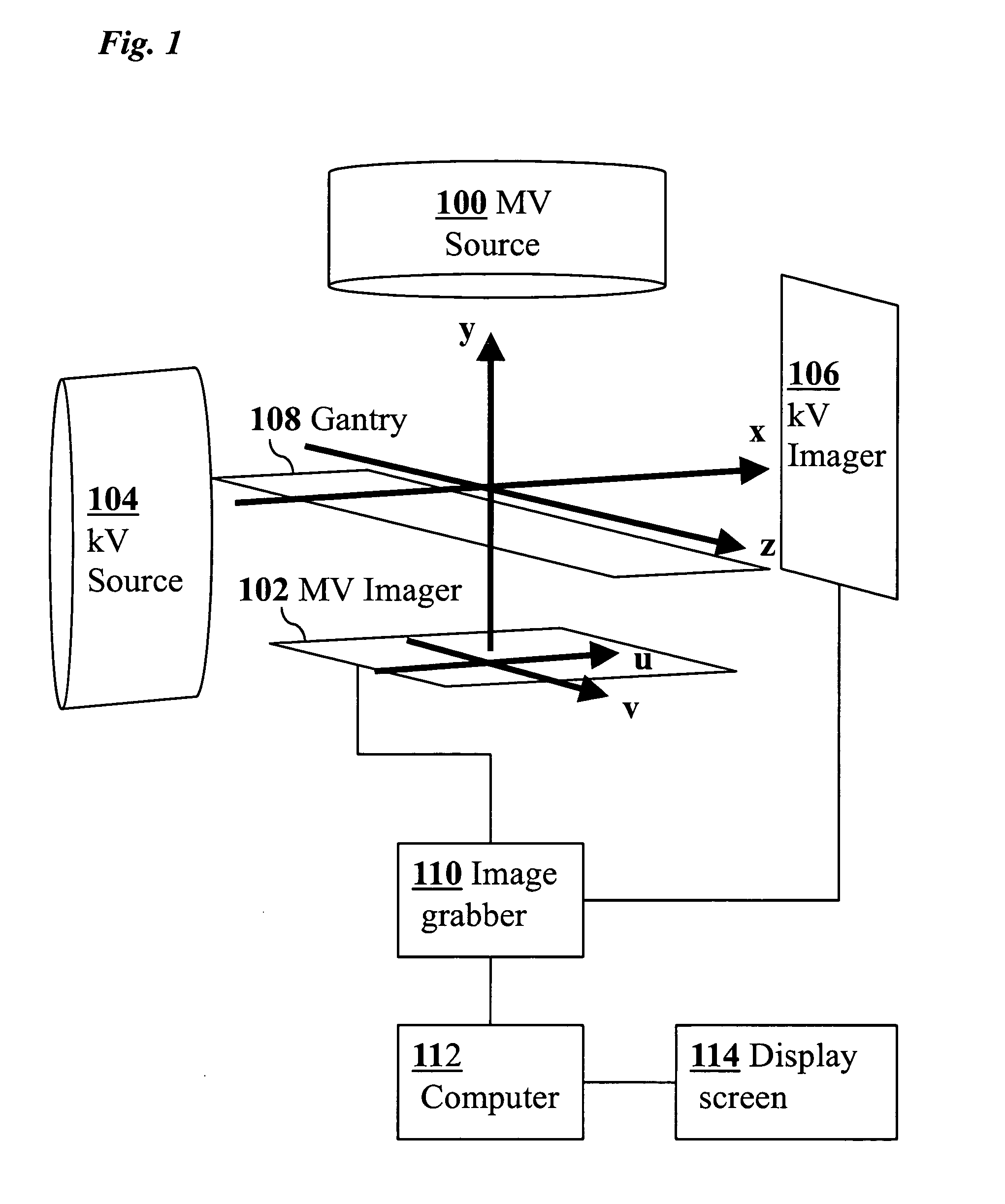
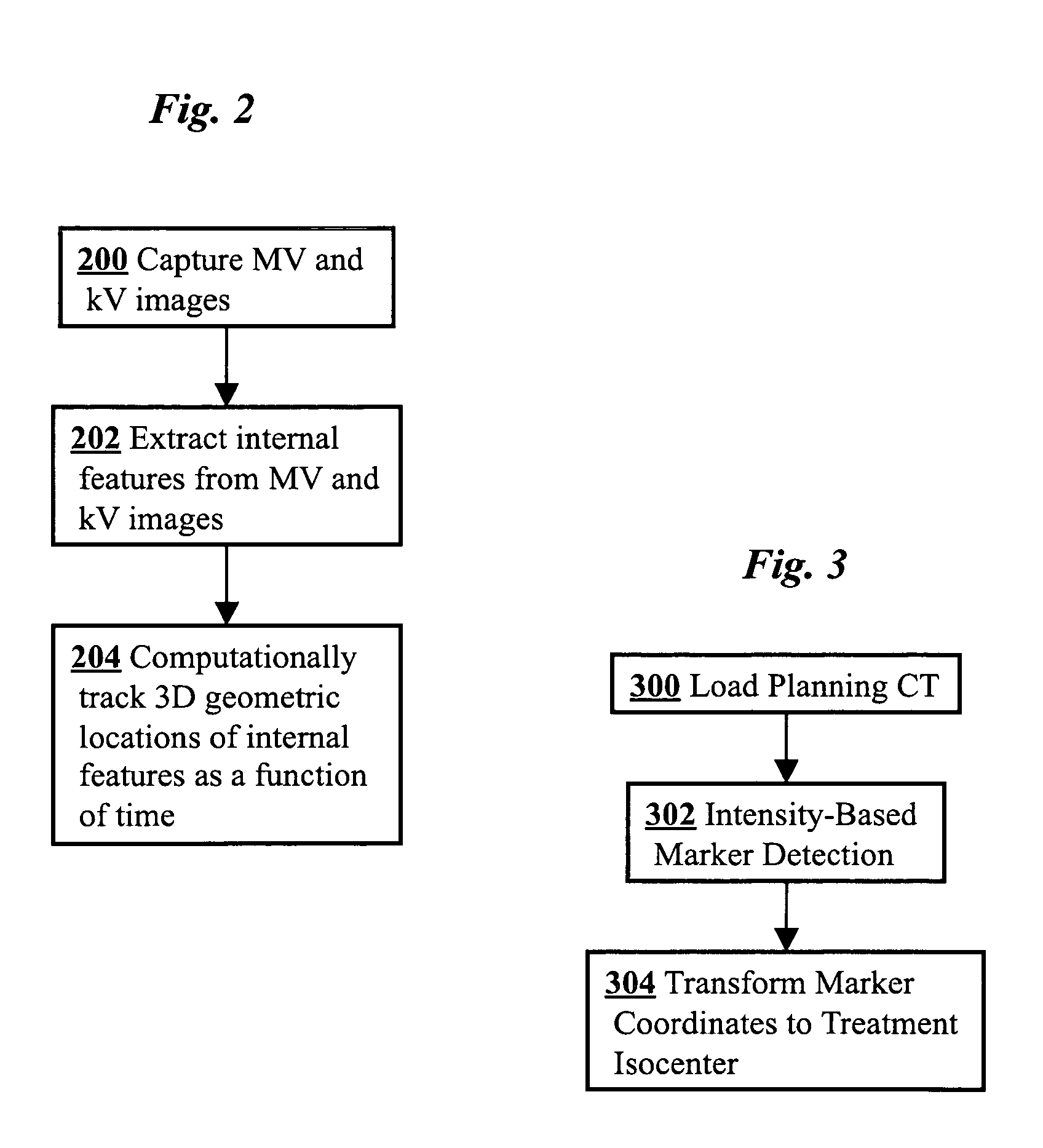
3D real-time tracking of human anatomy using combined kV and MV imaging
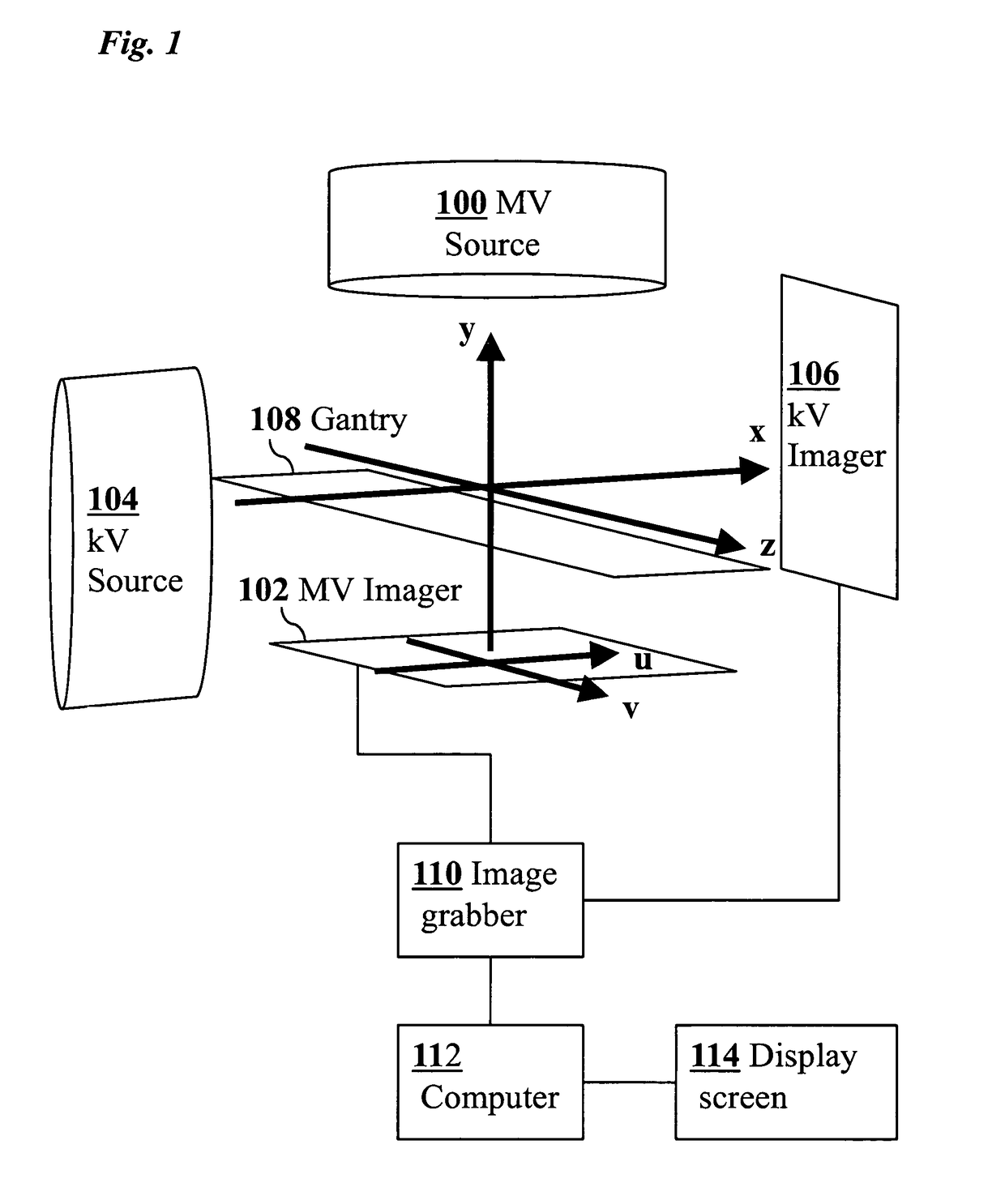
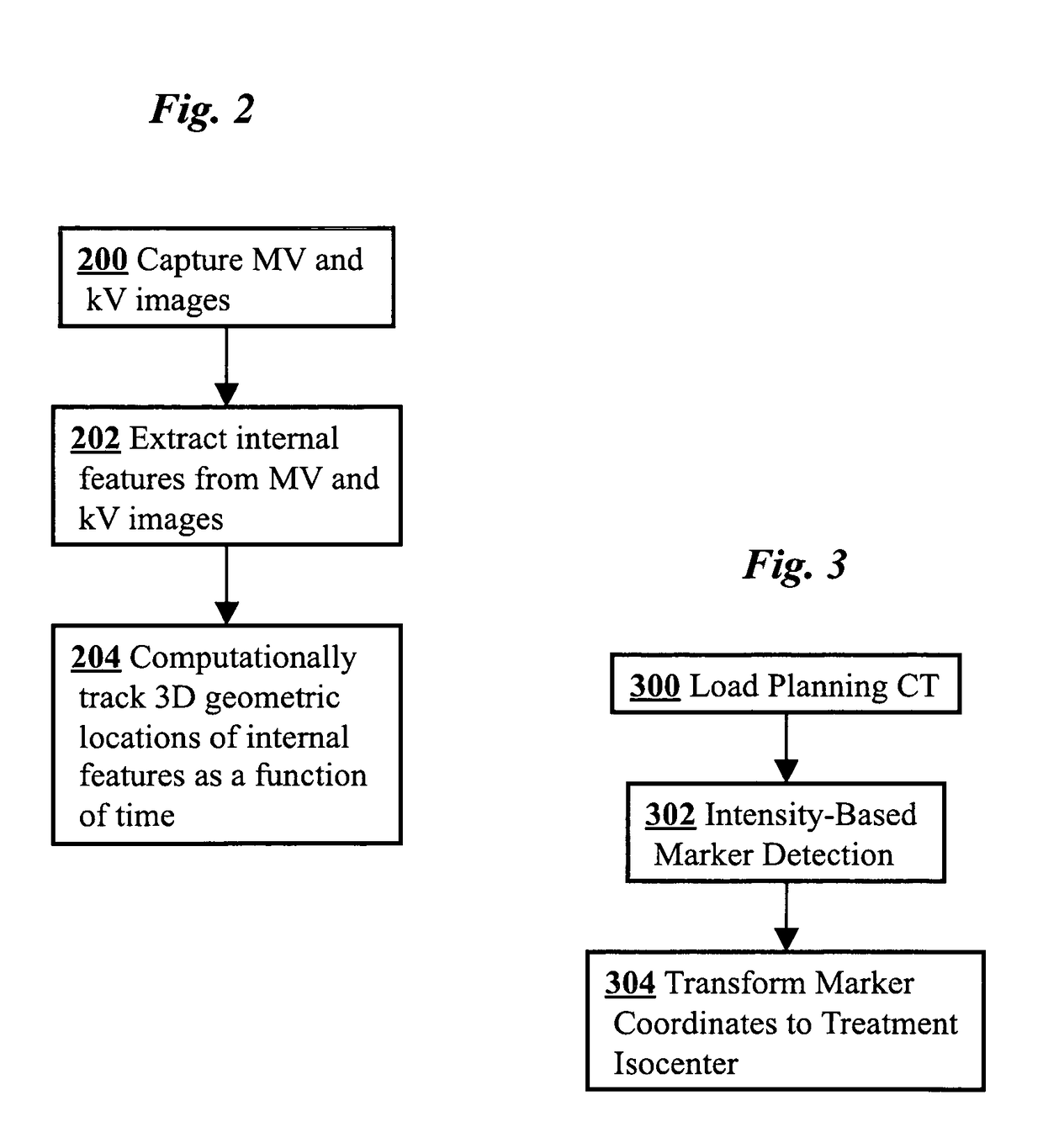
ActiveUS8121368B2Reduce radiationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisHuman anatomy3d tracking
A medical imaging-based system and method uses both kV and MV images captured during a treatment period for organ motion tracking. 3D geometric locations of internal features are computationally tracked as a function of time from internal features, such as natural biological features or implanted fiducials, which are computationally extracted from the captured kV and MV images. A partial information method allows 3D tracking to be maintained in the event that imaging information is temporarily not available.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Frictionless access system for public access point
ActiveUS9947155B2Continuous trackingEnhanced advantageAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesControl systemPublic access
An access control system and method for monitoring a public access point are disclosed. The system includes a positioning unit that tracks locations of users carrying user devices relative to the public access point, where the user devices transmit user information identifying the users via wireless signals. The system determines whether the users are authorized to pass through the access point based on the wireless signals from the user devices. Public access points include security checkpoints at government buildings, airports, amusement parks, and universities, in examples. In embodiments, biometric identifiers are obtained from the users when the users are preferably located within a threshold area of the public access points, and the system confirms the identity of the authorized users via the biometric identifiers to enable the users to pass through the public access points. Additionally, the system can assist in evacuation of users based on their tracked locations.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
3D real-time tracking of human anatomy using combined kV and MV imaging
ActiveUS20090208074A1Reduce radiationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisHuman anatomy3d tracking
A medical imaging-based system and method uses both kV and MV images captured during a treatment period for organ motion tracking. 3D geometric locations of internal features are computationally tracked as a function of time from internal features, such as natural biological features or implanted fiducials, which are computationally extracted from the captured kV and MV images. A partial information method allows 3D tracking to be maintained in the event that imaging information is temporarily not available.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
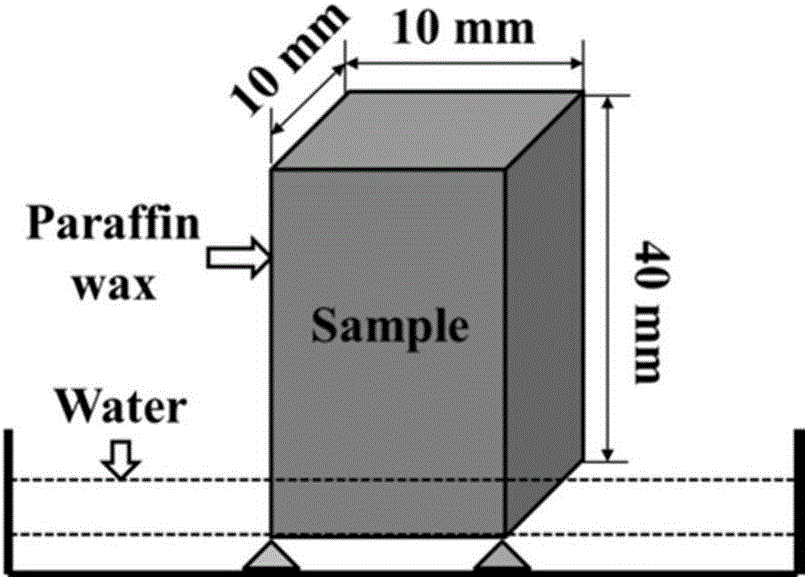
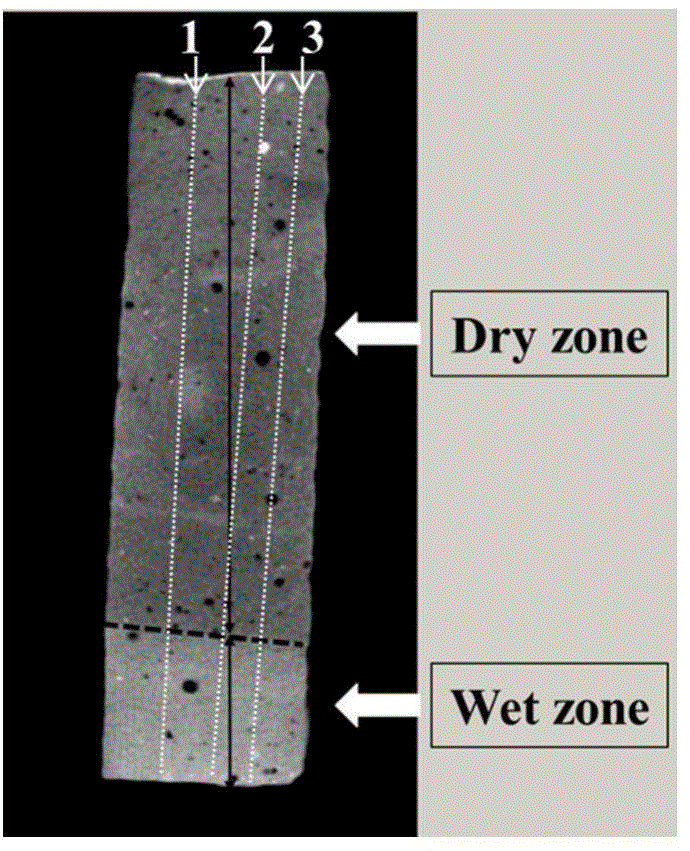
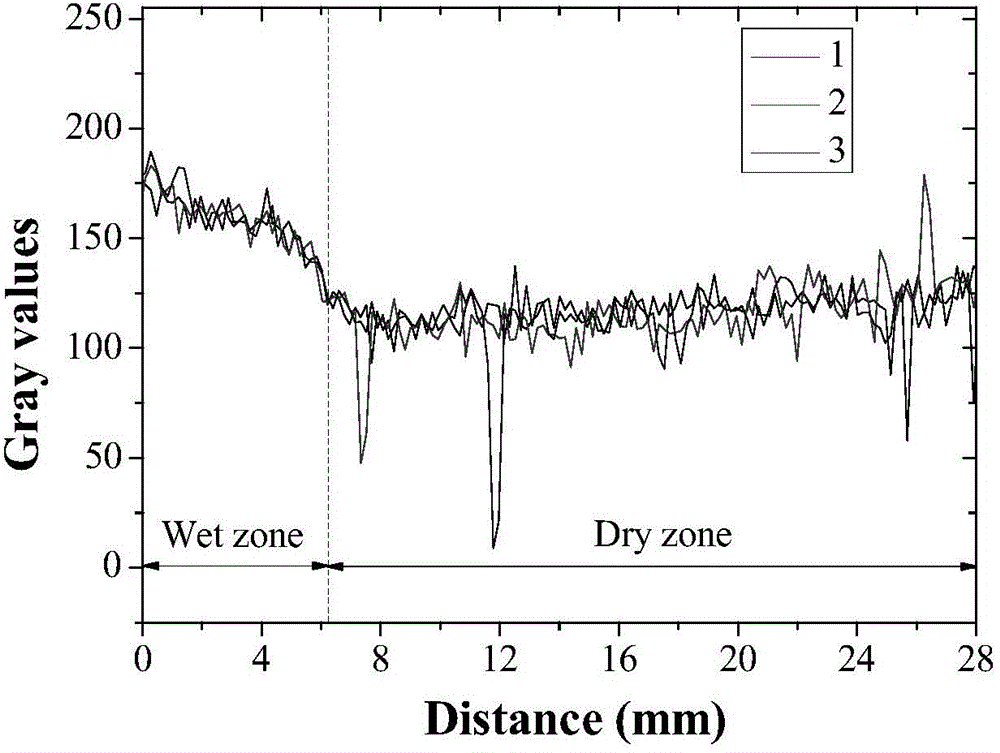
Method for visually representing spatial distribution and content of water in cement-based material
ActiveCN104483334AAccurately predict changes in absorbent massContinuous trackingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCapillary water absorptionEngineering
The invention discloses a method for visually representing spatial distribution and content of water in a cement-based material. The cement-based material which has good forming property and is maintained for a certain age is taken and dried to obtain a sample; all end surfaces and side surfaces, excluding a wetted surface, of the sample are sealed by paraffin; the sample is put in a flat-bottom container, and the wetted surface is supported by small cushion blocks; the flat-bottom container is put on an X-CT (X-Ray computed tomography) imaging device table, water is injected into the flat-bottom container until the water surface is higher than the wetted surface of the sample for a certain distance, a capillary water absorption experiment is performed, meanwhile, an X-CT imaging device is started, and the water soaked sample is subjected to X-CT imaging; an X-CT image is subjected to gray scale analysis, and change of capillary water absorption depth of the sample is obtained; the capillary water absorption depth coefficient is obtained by means of capillary water absorption depth and time; and change of capillary water absorption quality of the sample is obtained by means of the capillary water absorption depth coefficient and sample porosity. According to the method, change of the water soaked depth can be quantitatively represented, and the capillary water absorption quality change can be accurately predicted.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
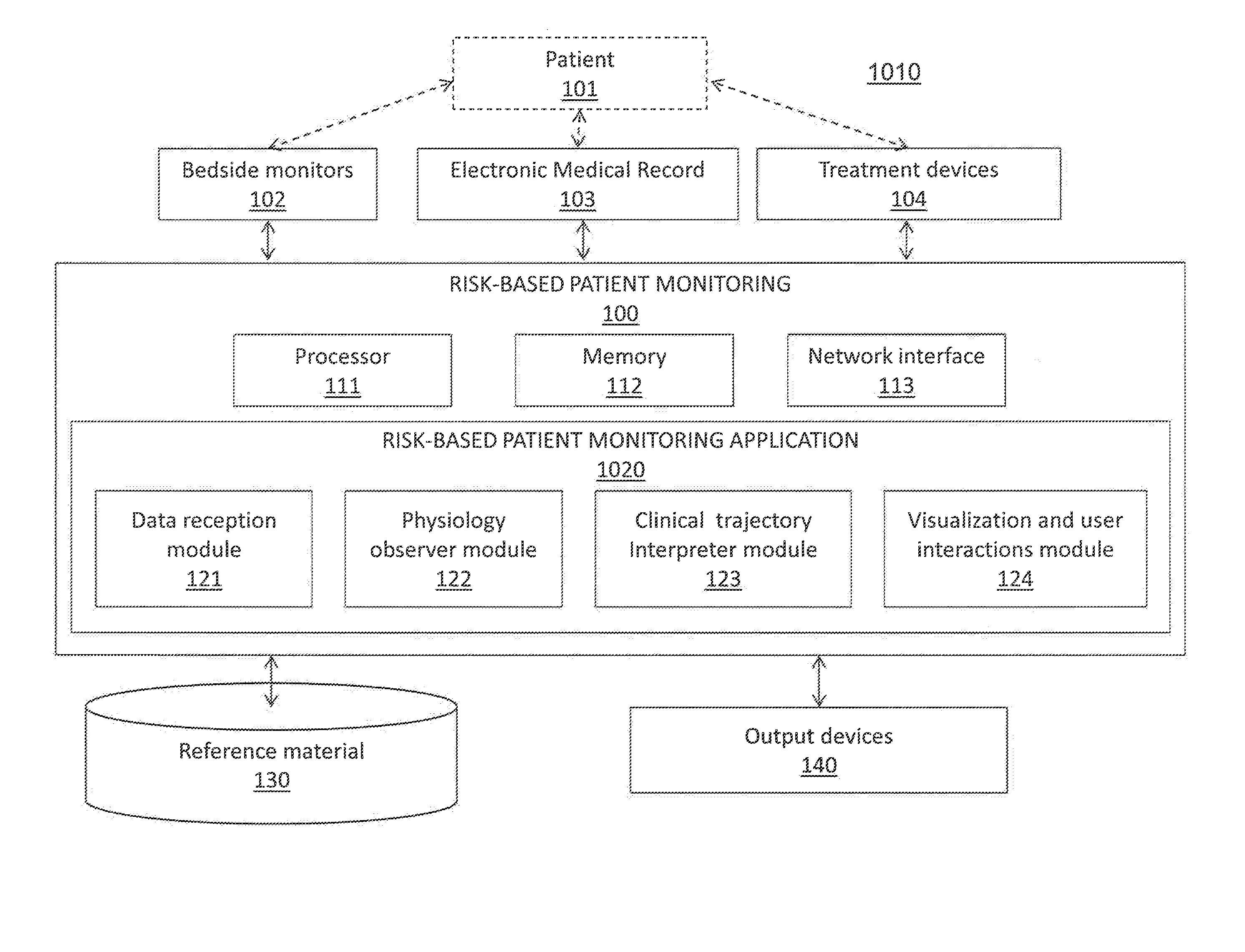
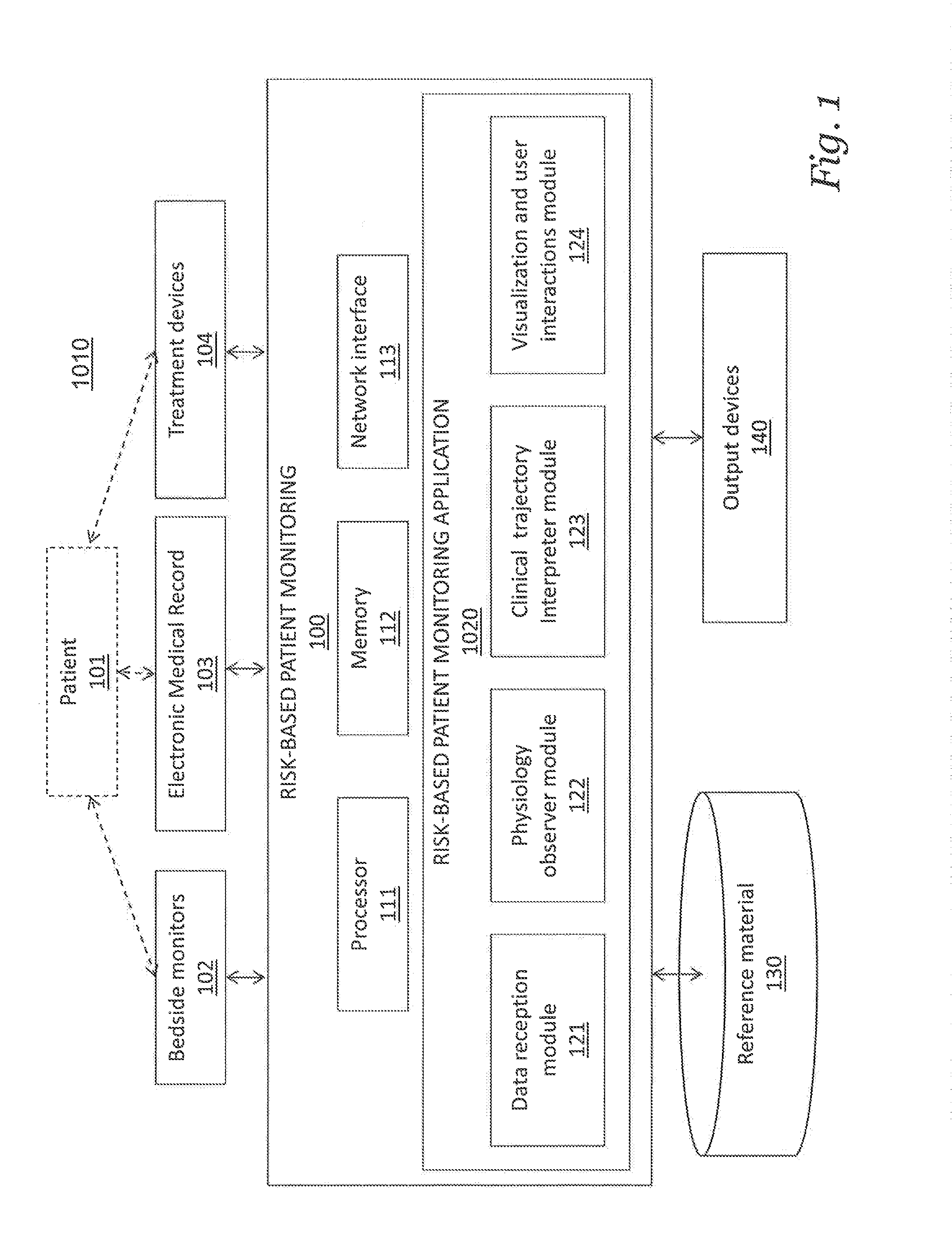
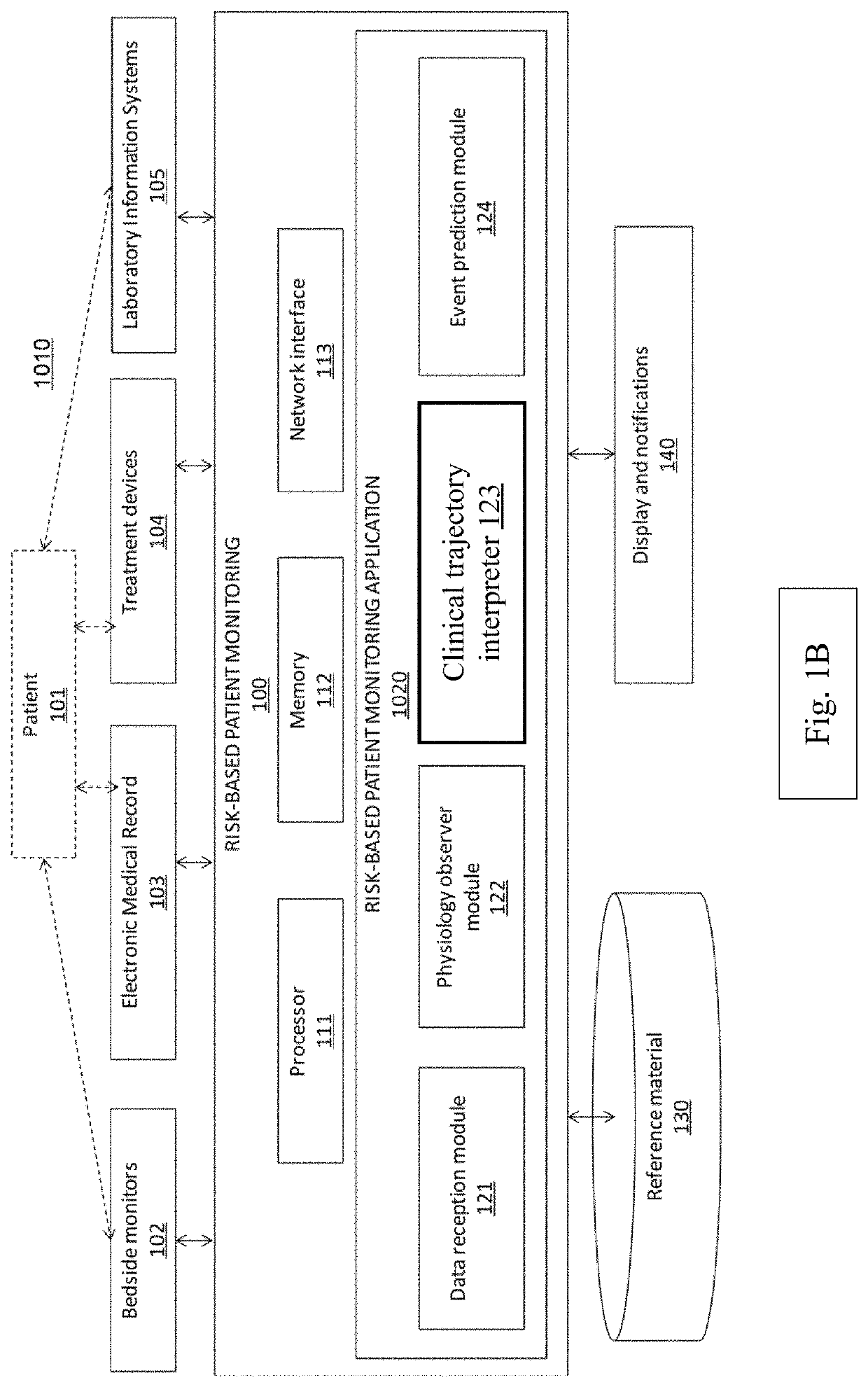
Systems and methods for transitioning patient care from signal-based monitoring to risk-based monitoring
PendingUS20130231949A1Continuous trackingProvide supportMedical simulationElectrocardiographyPatient treatmentCvd risk
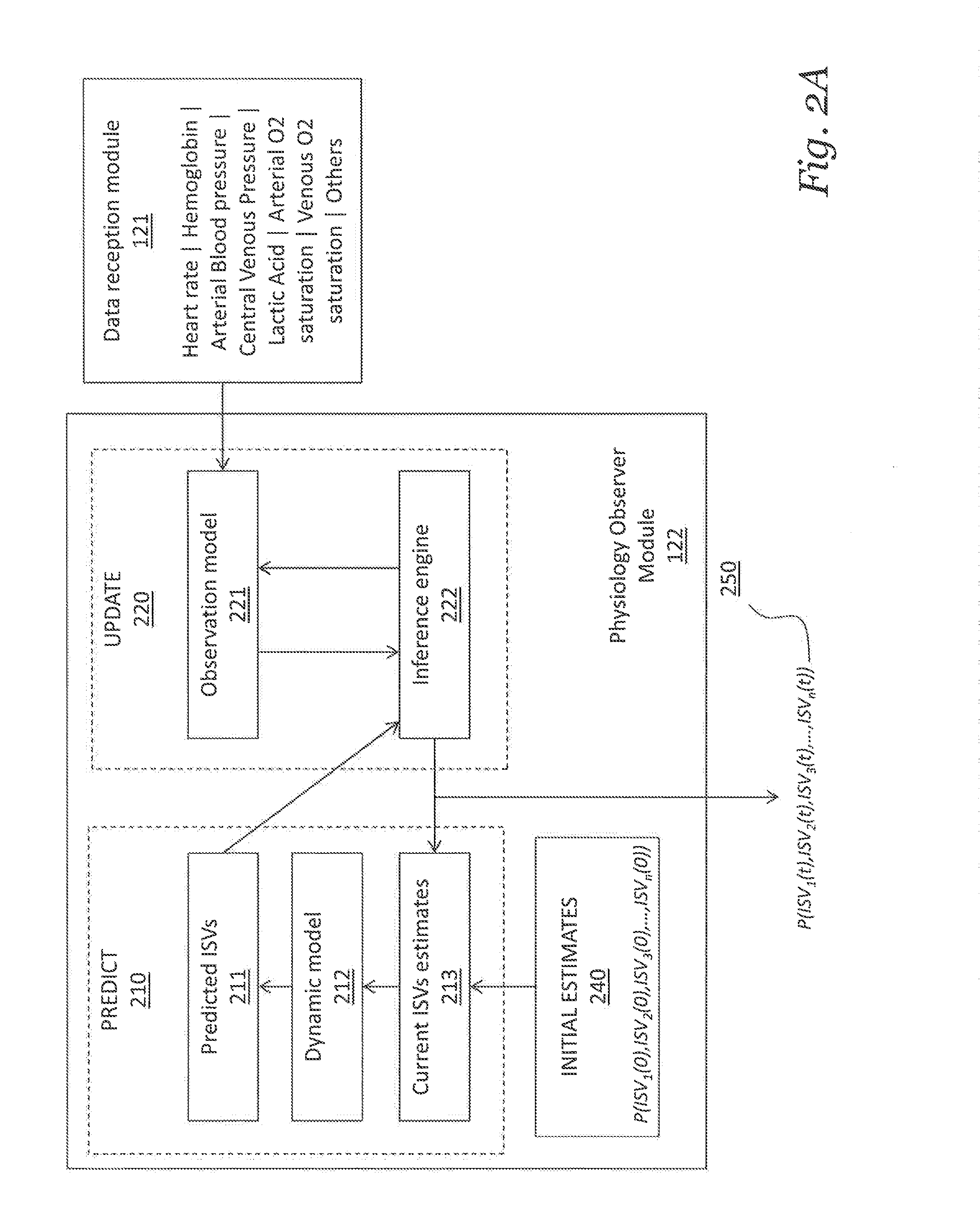
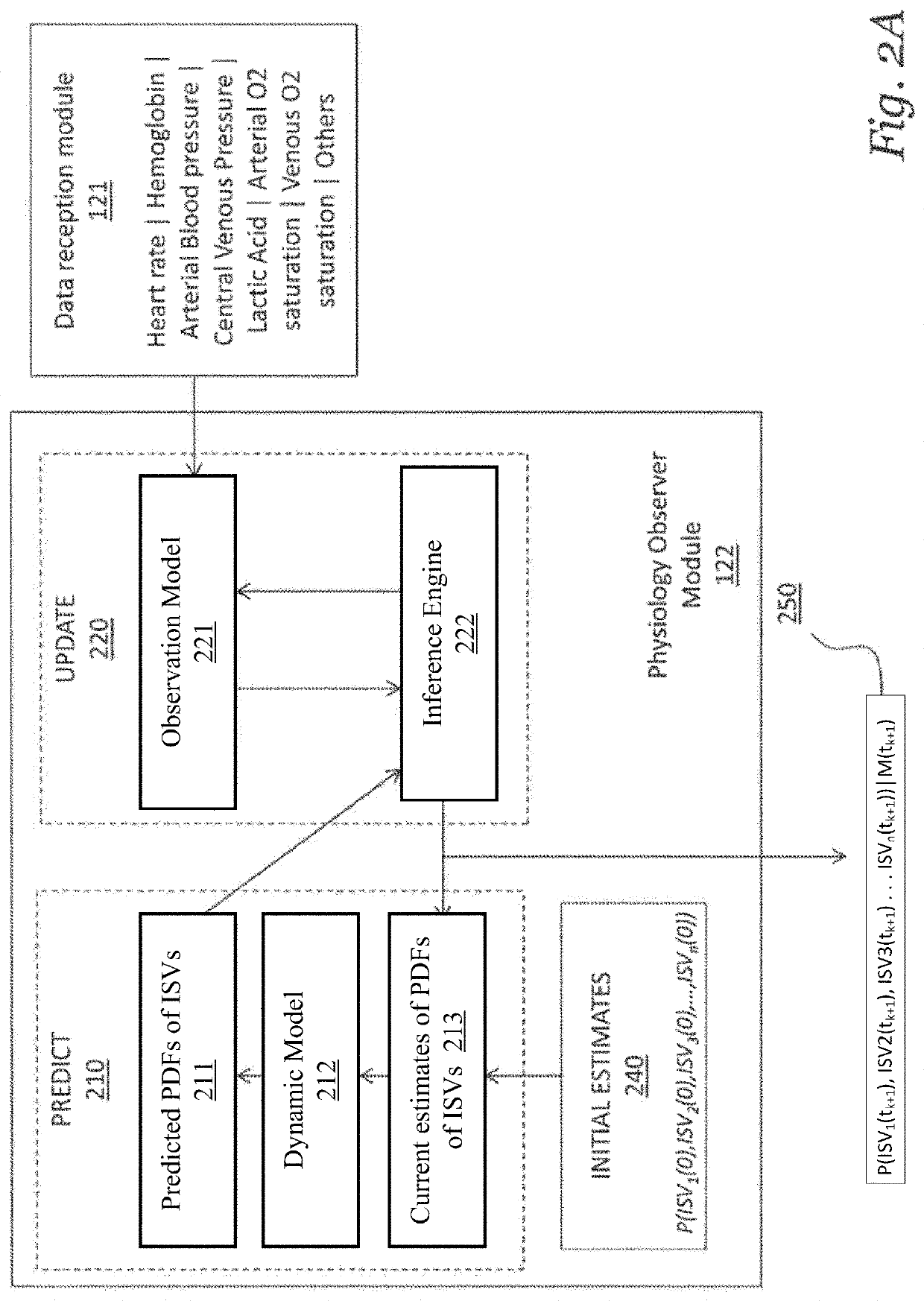
A risk-based patient monitoring system for critical care patients combines data from multiple sources to assess the current and the future risks to the patient, thereby enabling providers to review a current patient risk profile and to continuously track a clinical trajectory. A physiology observer module in the system utilizes multiple measurements to estimate Probability Density Functions (PDF) of a number of Internal State Variables (ISVs) that describe a components of the physiology relevant to the patient treatment and condition. A clinical trajectory interpreter module in the system utilizes the estimated PDFs of ISVs to identify under which probable patient states the patient can be currently categorized and assign a probability value that the patient will be in each of the identified states. The combination of patient states and their probabilities is defined as the clinical risk to the patient.
Owner:ETIOMETRY
Method and apparatus for a continuous non-invasive and non-obstrusive monitoring of blood pressure
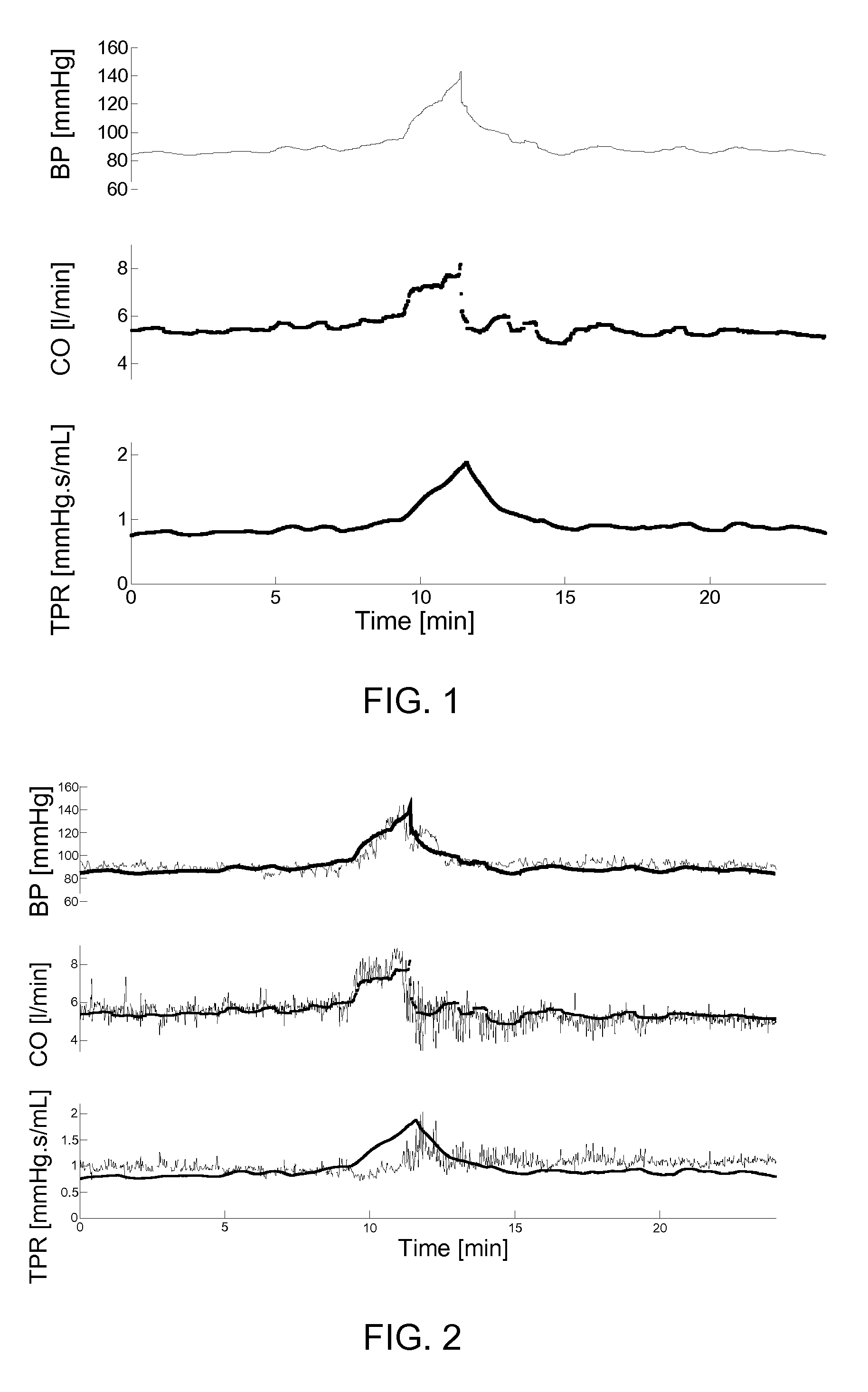
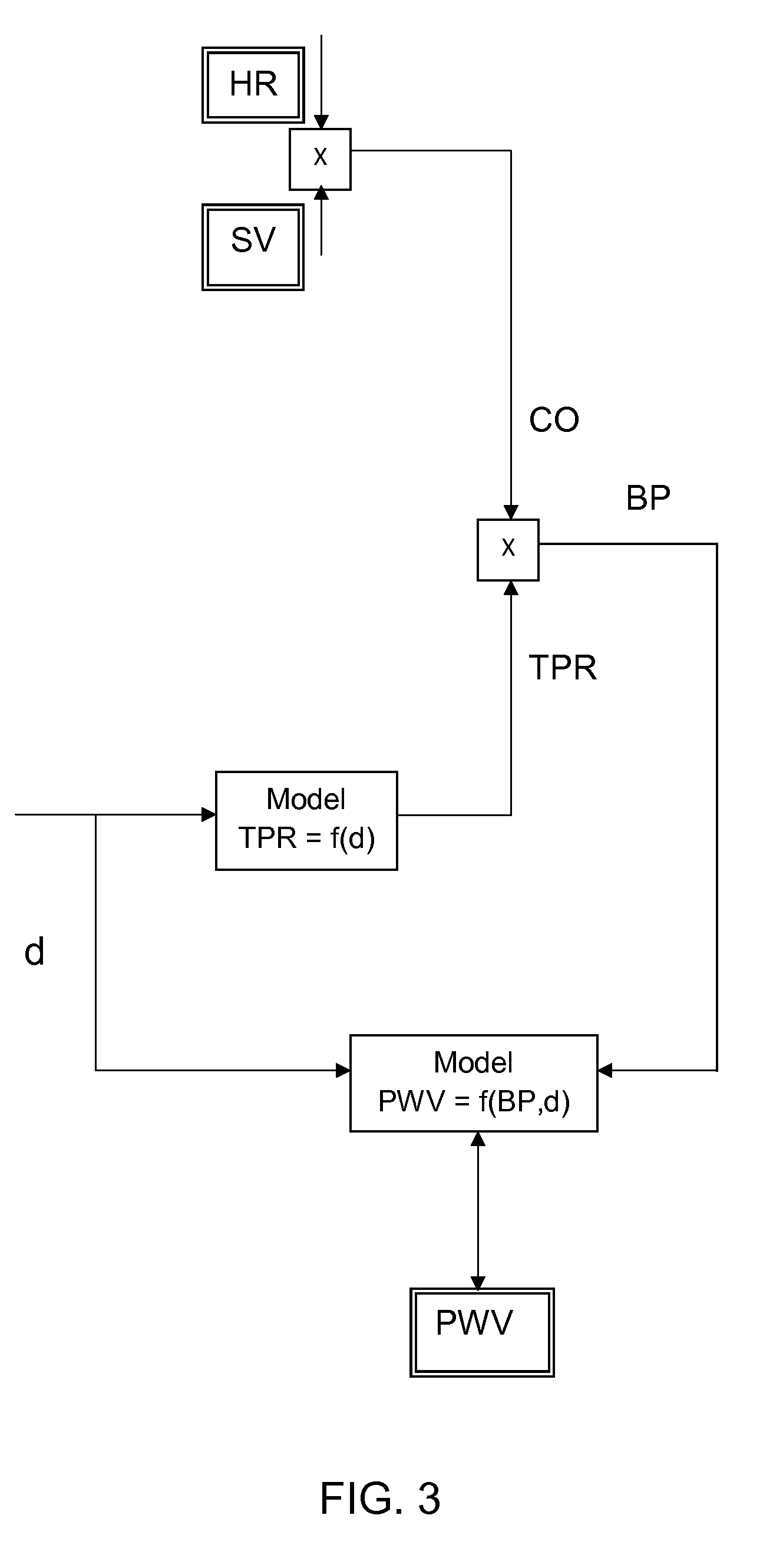
ActiveUS8585605B2Improve accuracyContinuous trackingElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsArterial velocityArterial tree
The invention provides a method and an apparatus for a continuous non-invasive and non-obstrusive monitoring of blood pressure. The method comprises the steps of: a) measuring the value (PW) of a Pulse Wave parameter, equal to or derived from the Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) parameter of a segment of the arterial tree of a subject, b) measuring the value (CO) of the Cardiac Output parameter, and c) determining the value (BP) of the blood pressure that satisfiesBP=argminBPd(PW,(CO,BP)),where PW is the value measured in step a), (CO, BP) corresponds to a predicted value of the Pulse Wave parameter computed according to a model of the segment of the arterial tree, the value (CO) of the Cardiac Output parameter measured in step b) and an hypothesized value of the blood pressure.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
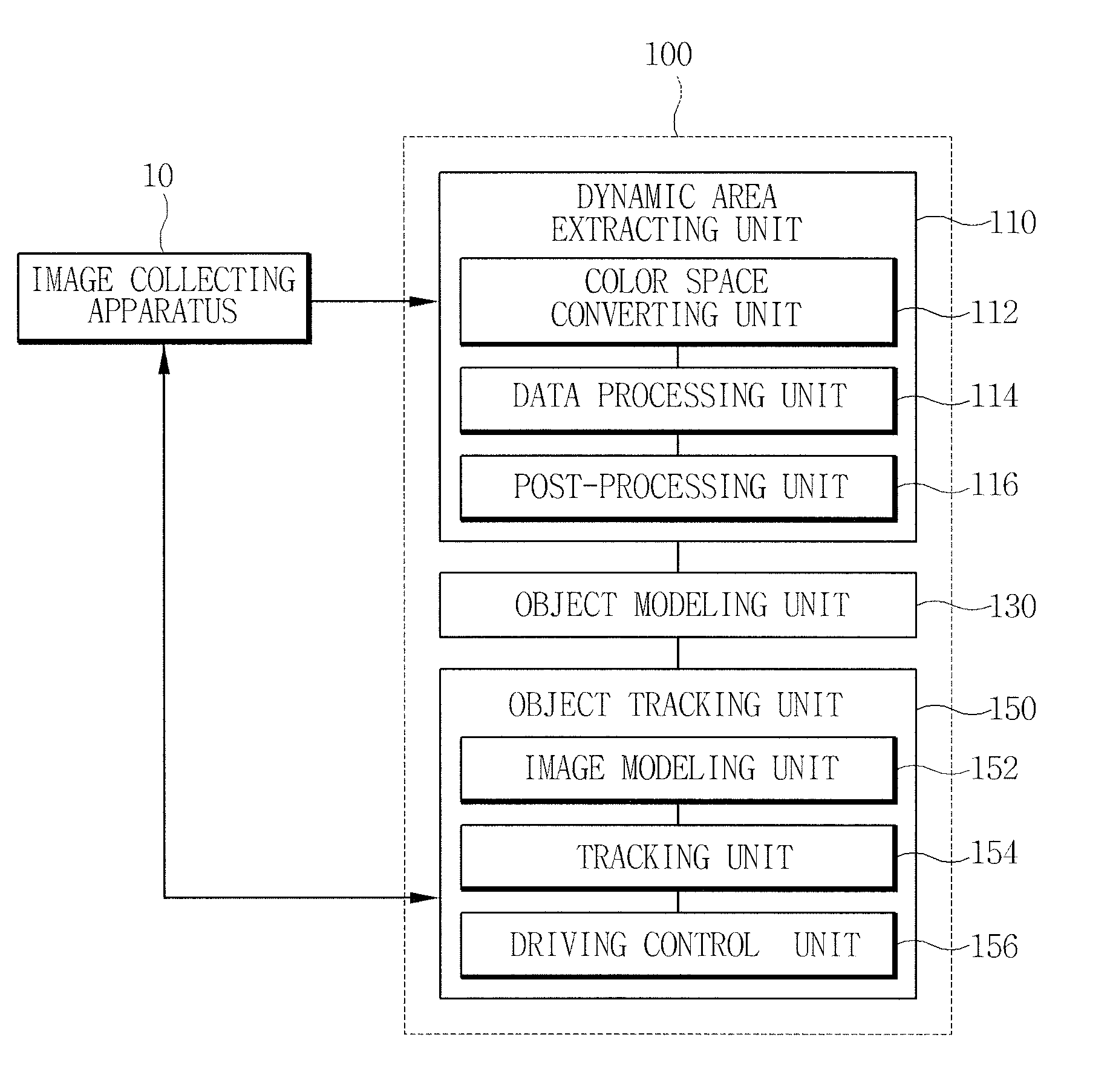
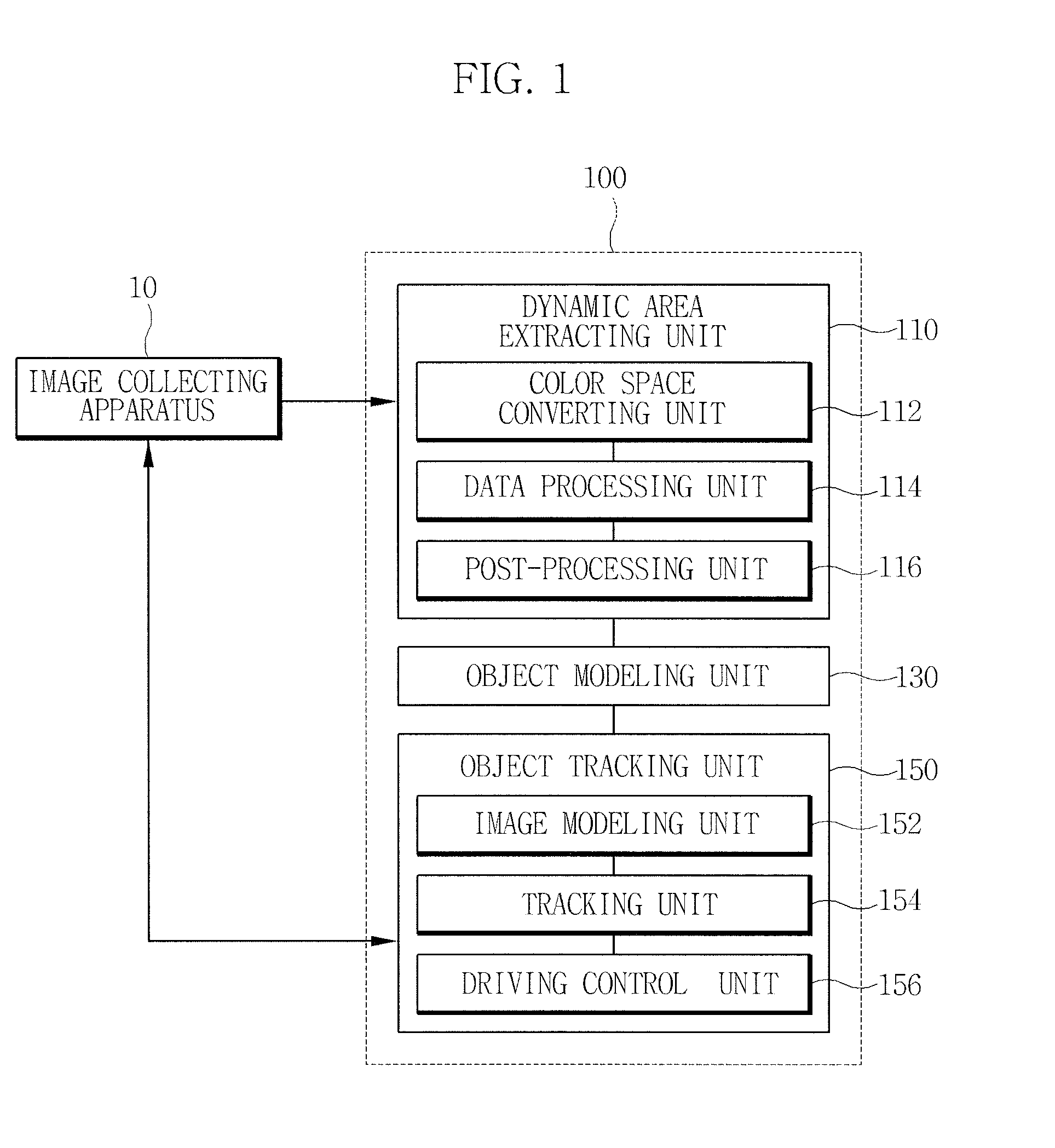
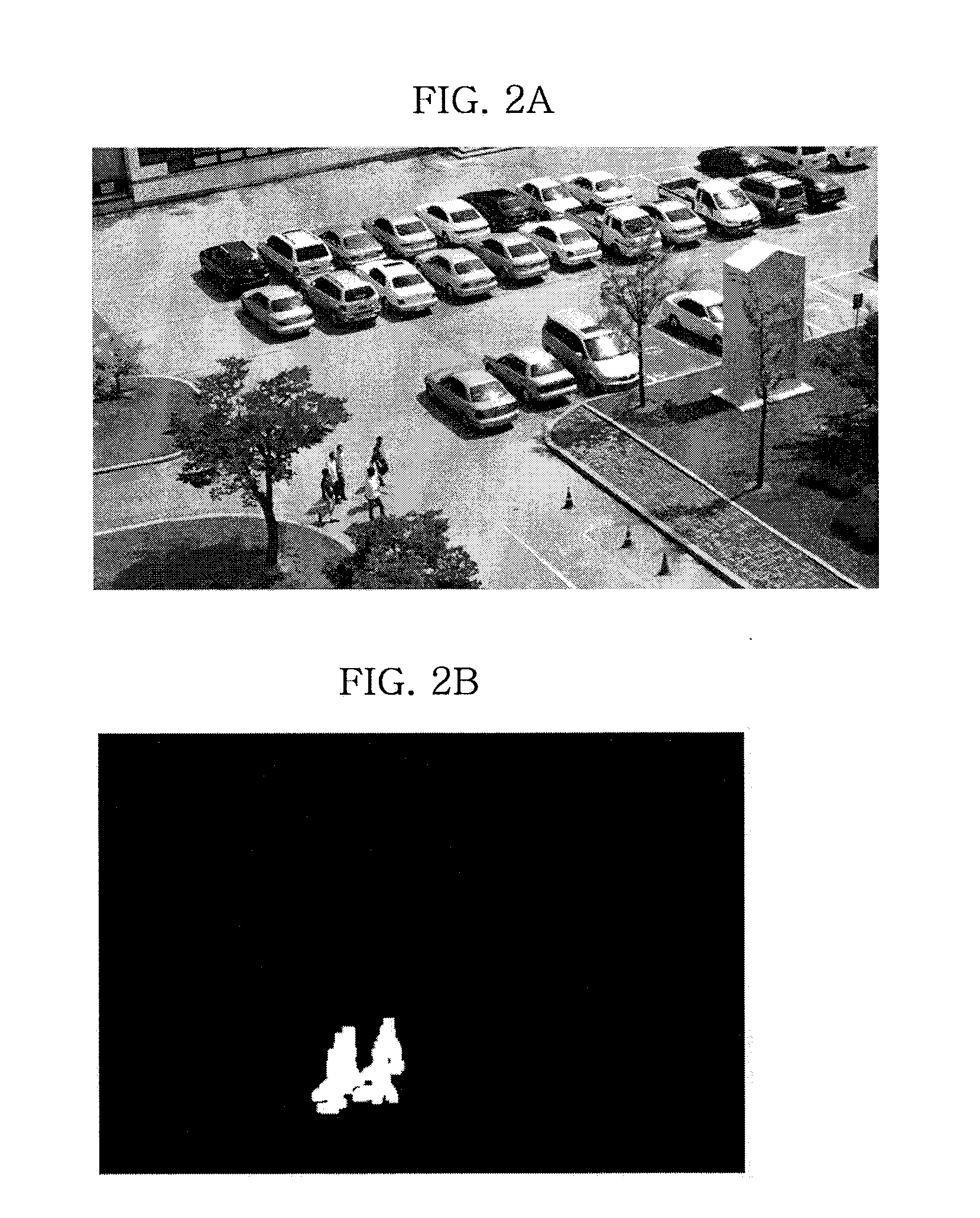
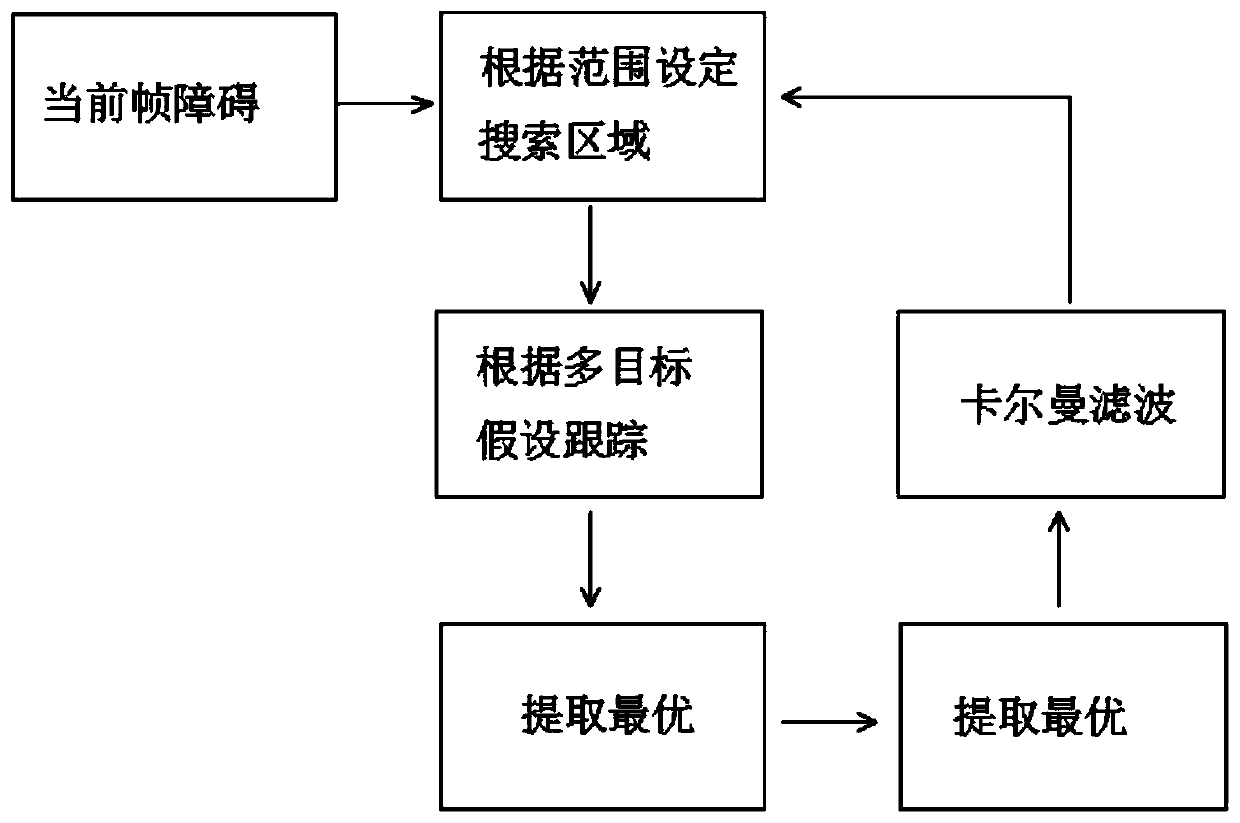
Apparatus for tracking an object using a moving camera and method thereof
InactiveUS20100134632A1Improve reliabilityCancel noiseTelevision system detailsImage analysisPosterior probabilityImage acquisition
Provided is an apparatus for tracking an object, including: a dynamic area extracting unit that extracts an object to be tracked from an image frame collected through an image collecting apparatus; an object modeling unit that models the object to be tracked extracted through the dynamic area extracting unit to calculate the color distribution of the object to be tracked; and an object tracking unit that calculates the color distribution of a next image frame collected through the image collecting apparatus, after calculating the color distribution of the object to be tracked, and calculates a posterior probability that each pixel belongs to the object to be tracked in the next image frame based on the calculated color distribution of the next image frame and the color distribution of the object to be tracked to track the object to be tracked.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
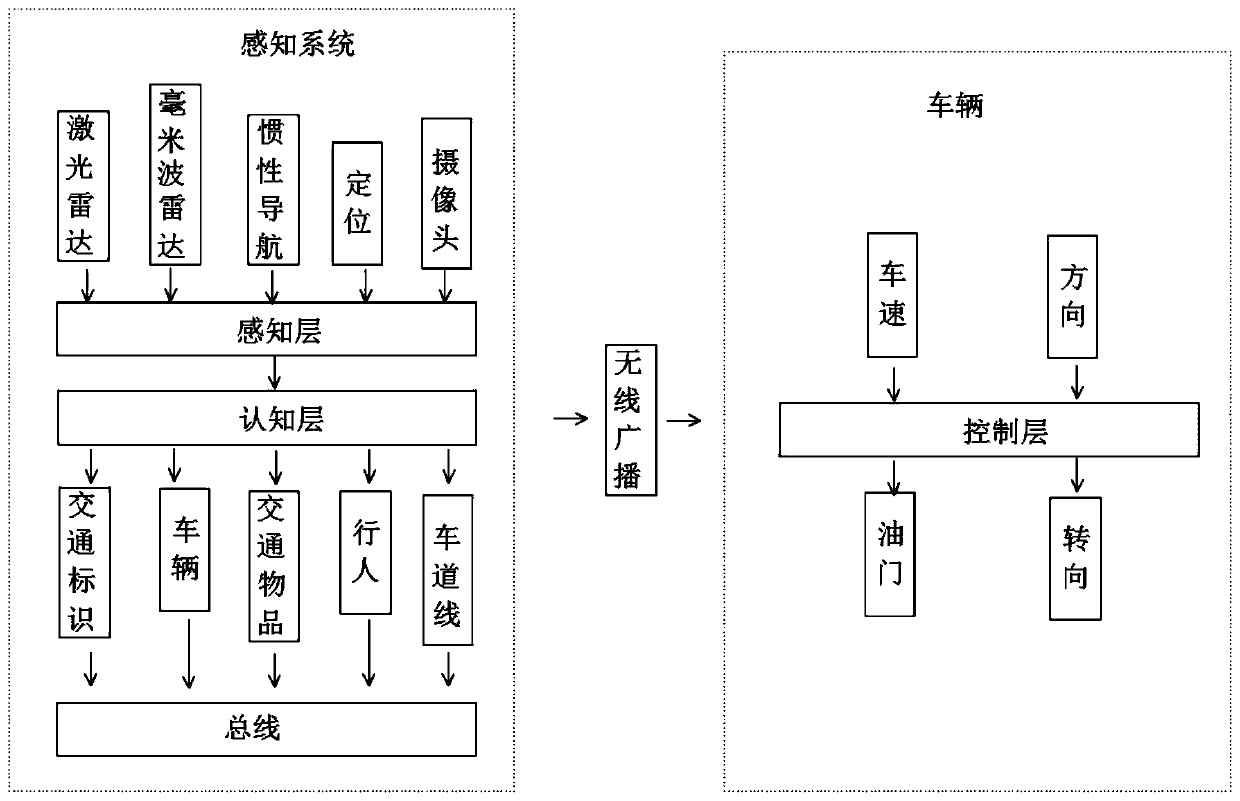
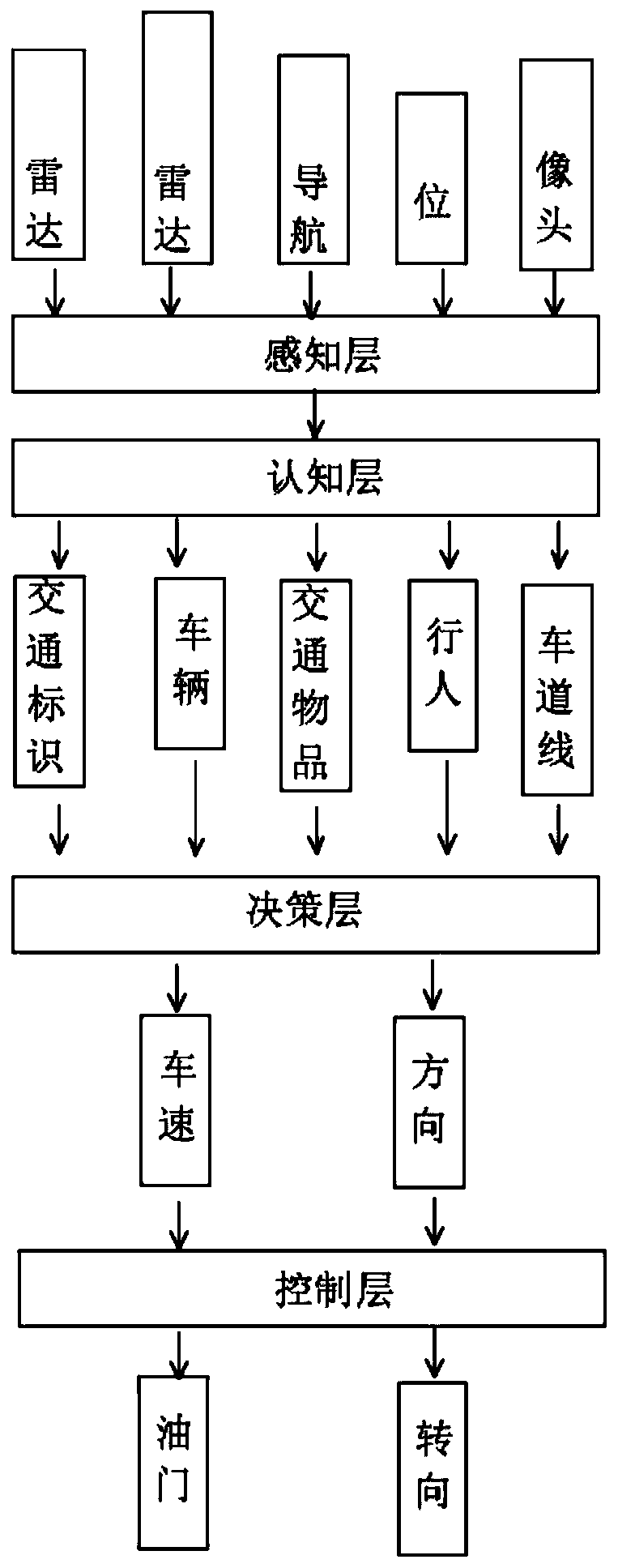
Deep learning type intelligent driving environment perception system based on Internet of Things
InactiveCN110091875AImprove securityImprove stabilityRoad vehicles traffic controlExternal condition input parametersControl layerData information
The invention discloses a deep learning type intelligent driving environment perception system based on the Internet of Things and belongs to the field of intelligent perception systems. According tothe invention, the system comprises a perception system and an intelligent driving vehicle, and the perception system comprises a perception layer and a cognition layer. A decision-making layer and acontrol layer are arranged on the intelligent driving vehicle. The perception layer is used for data acquisition, the decision-making layer is used for planning the information and routes transmittedby the cognition layer, carrying out processing by use of algorithms, and outputting an instruction for adjusting the vehicle speed and direction to the control layer, and the control layer receives the instruction of the decision-making layer and controls a brake, an accelerator and gears of the vehicle. According to the scheme, the implementation mode of unmanned driving is improved, all movingand static obstacles on a road are collected through the perception system, data information of the obstacles is sent to all intelligent driving vehicles running on the road, and the technical difficulty and the production cost are reduced while the safety and the stability of unmanned driving are improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
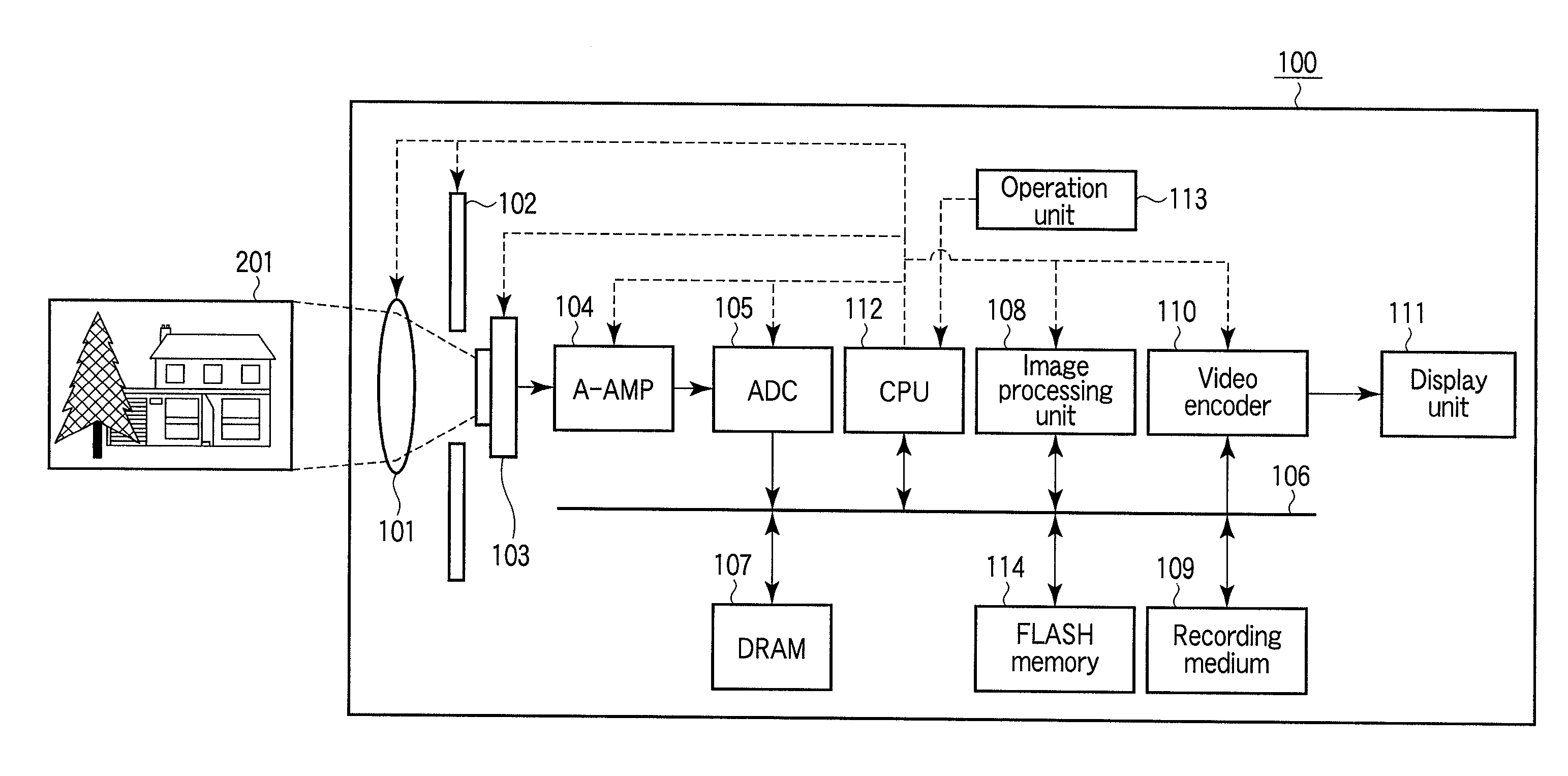
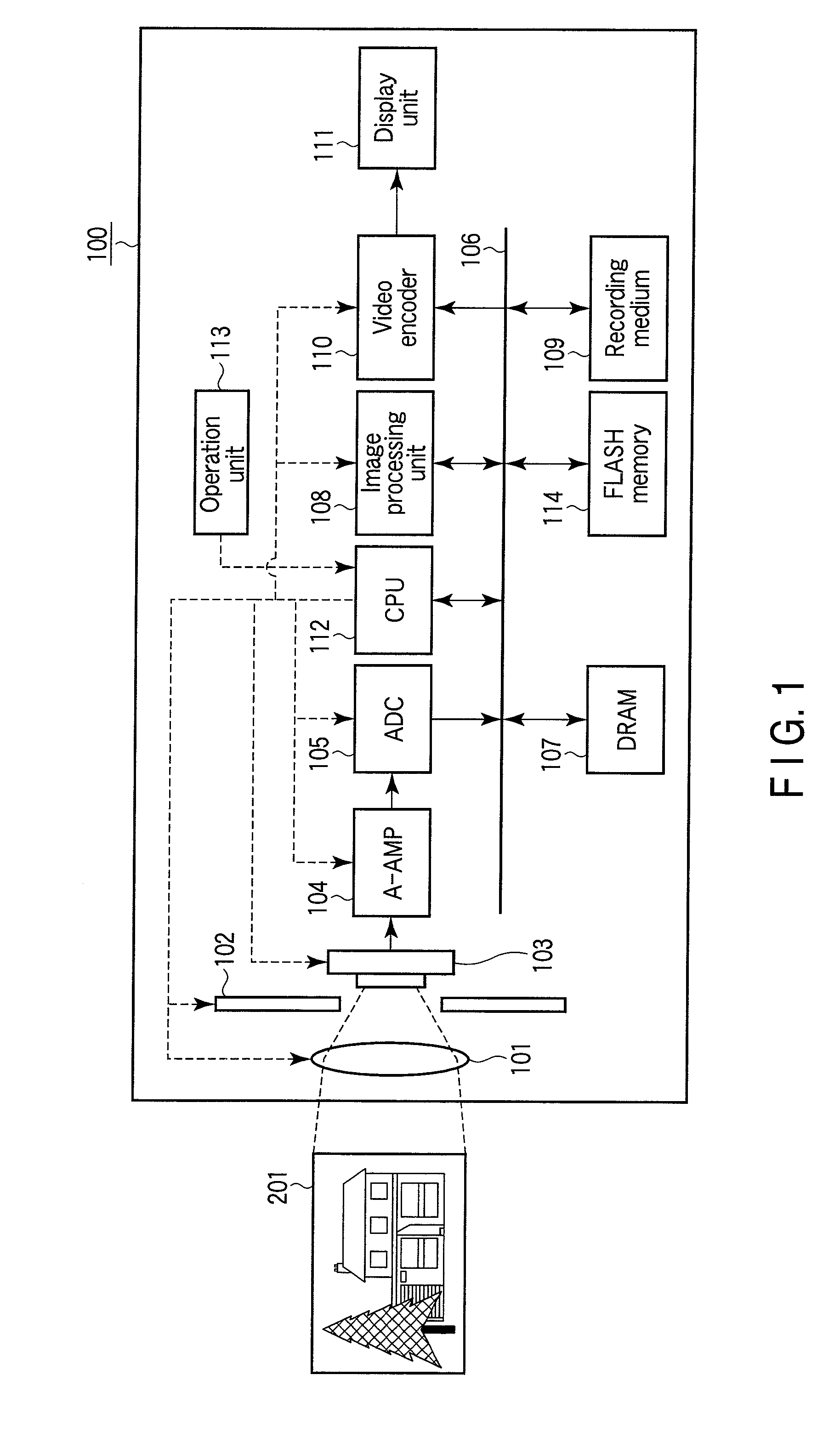
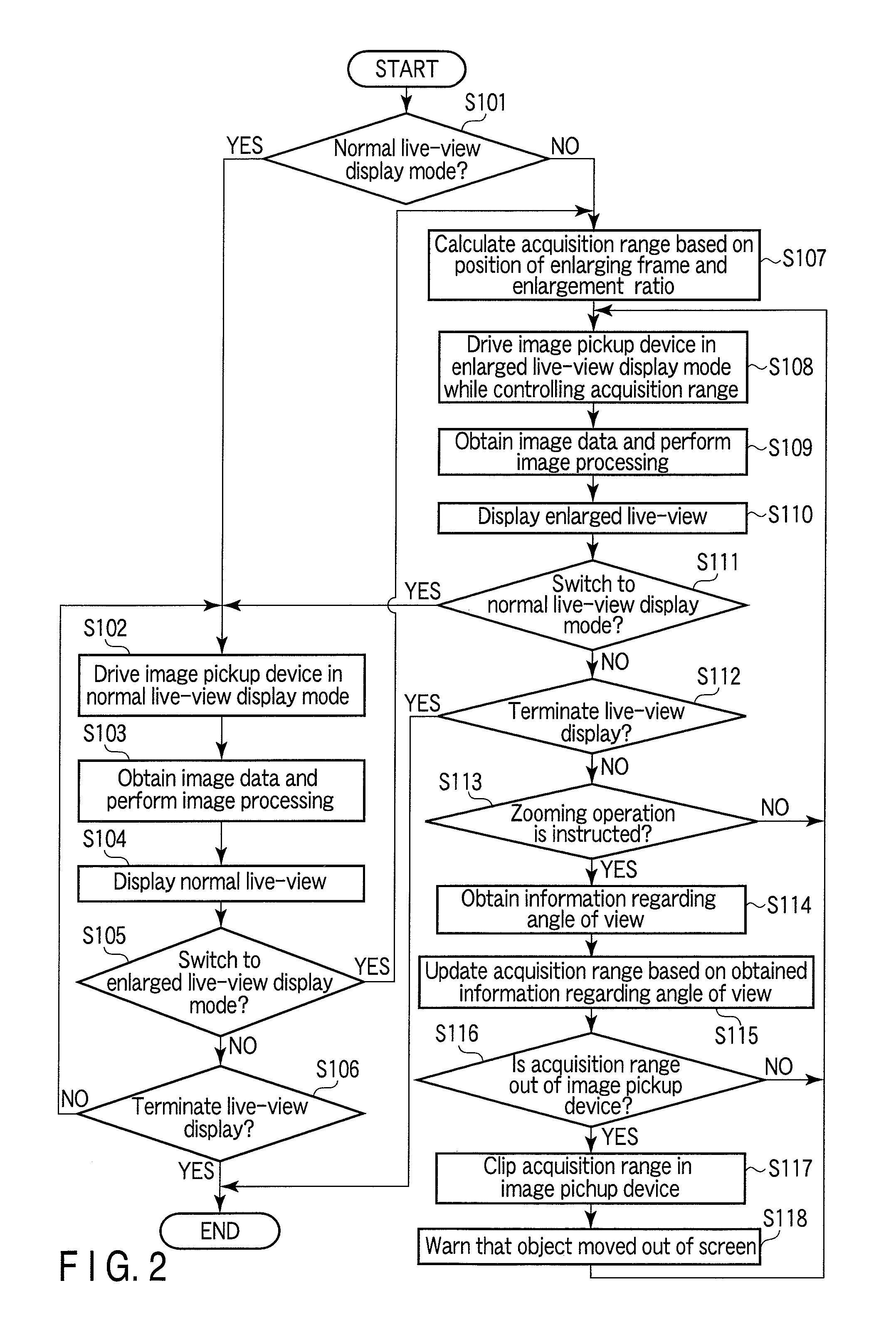
Image capturing appratus and image capturing method
InactiveUS20110109771A1Continuous trackingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage signalAngle of view
An image capturing apparatus is provided which can continuously keep track of an object even under changes of the angle of view during enlarged live-view display, as well as an image capturing method for such an image capturing apparatus. Acquisition range of image signals is controlled by the CPU to crop a portion of an object image formed on the image pickup device. Subsequently, the enlarged live-view display is performed in which the image based on the obtained image signals is enlarged and displayed on the display unit. If a zooming operation is performed during the enlarged live-view display, the CPU obtains information regarding the angle of view and updates the acquisition range of the image signals according to the information regarding the angle of view after the change.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method for rapidly measuring radon concentration by zero-order approximation
InactiveCN102141527AContinuous trackingEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentFiltrationHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for rapidly measuring radon concentration by zero-order approximation, comprising measurement and calculation. At first, a radon measurement instrument is enabled to work under a scale mode, radon concentration is reversely deduced by using the counting of a long-time 218Po peak in a standardized radon chamber to obtain a scale factor, which is therefore equivalent to an RAD7 radon measurement instrument working under a sniff mode; the radon measurement instrument is then switched to work under a zero-order approximation mode, measurement cycle and cycle times are set, and after the radon measurement instrument is started up, the air outside is subjected to the filtration of radon daughter element by a high-efficiency filter, then continuously pumped into a measurement chamber and discharged to the outside; new daughter element 218Po generated by radon decay in the measurement chamber is adsorbed to the surface of a semiconductor detector under the action of strong electric field, electric signals, which are generated by high energy alpha particles released by the further decay of the 218Po, is subjected to energy identification and then counted to obtain the concentration of the 218Po so as to obtain radon concentration; and the data of radon concentration obtained by measurement is then calculated by applying a specific algorithm, thus the change of radon concentration can be rapidly measured.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
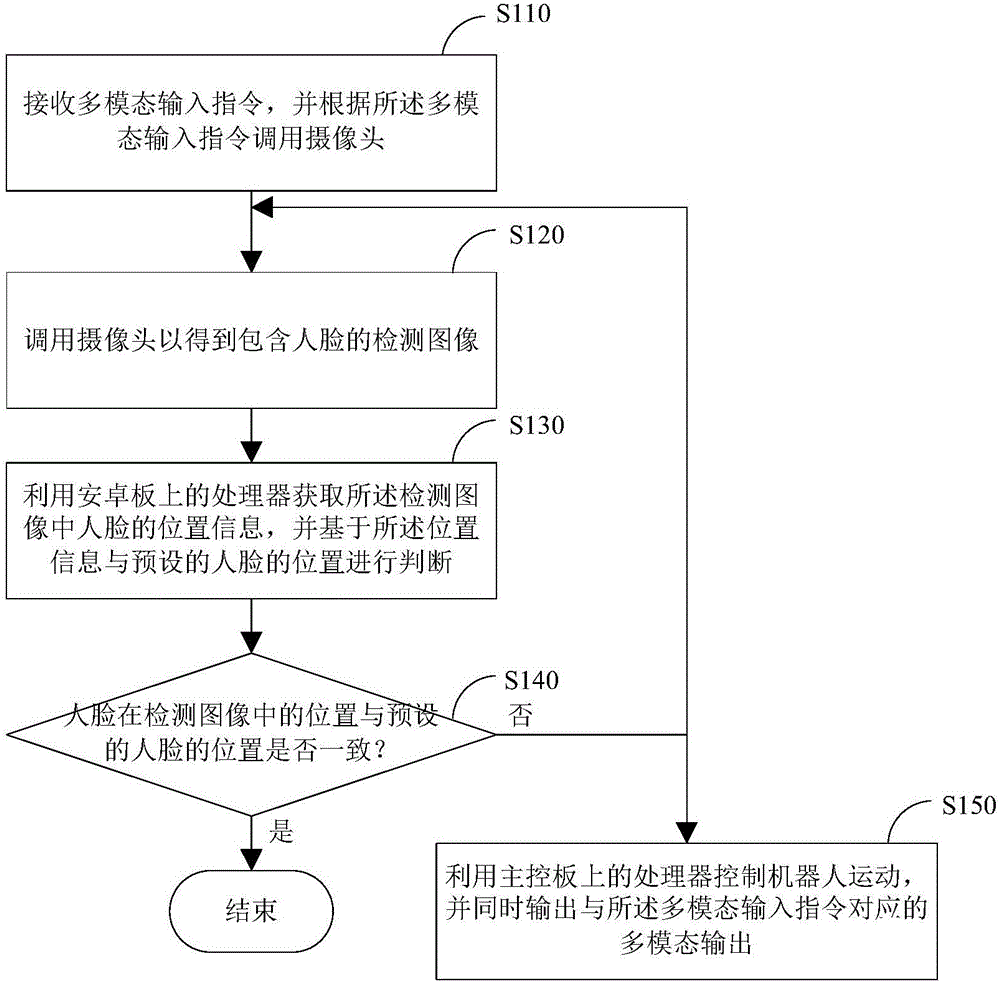
Method used for intelligent robot system to achieve real-time face tracking
InactiveCN105759650AReal-time trackingTrack real-time continuousCharacter and pattern recognitionProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersTrack algorithmIntelligent robots
The invention discloses a method used for an intelligent robot system to achieve real-time face tracking, comprising the steps of: receiving a multi-modal input command, calling a camera according to the multi-modal input command to obtain a detection image containing a face; utilizing a processor on an Android board to obtain position information of the face in the detection image, and performing judgment based on the position information and a preset face position; when the position of the face in the detection image is not consistent with the preset face position, utilizing a processor on a main control board to control a robot to move, and simultaneously outputting multi-modal output corresponding to the multi-modal input command; and re-acquiring a detection image containing a face, obtaining position information of the face in the detection image, and performing judgment based on the position information and the preset face position until the position of the face in the detection image is consistent with the preset face position. The method simplifies a tracking algorithm, reduces system cost, and achieves real-time and continuous tracking for the face.
Owner:BEIJING GUANGNIAN WUXIAN SCI & TECH
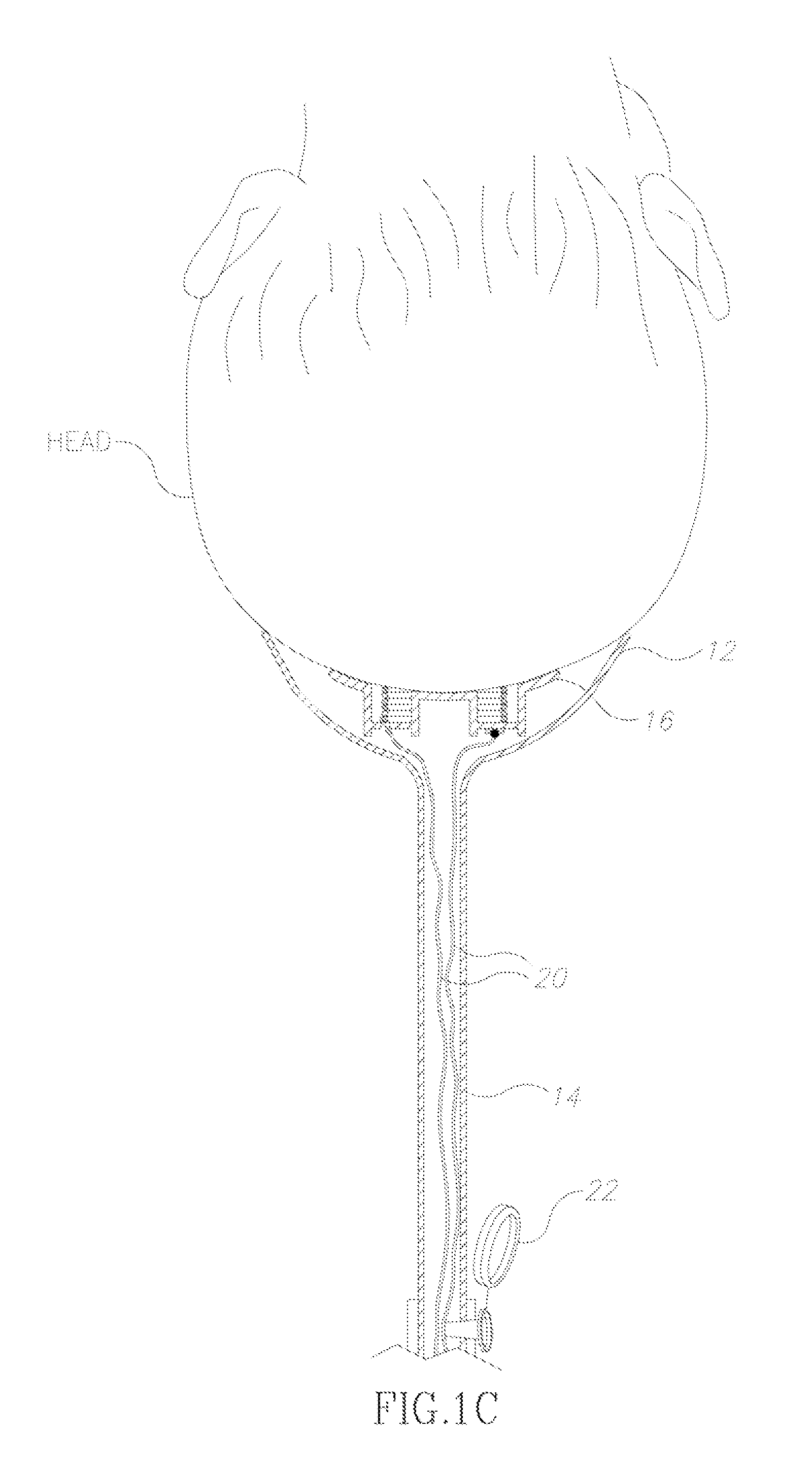
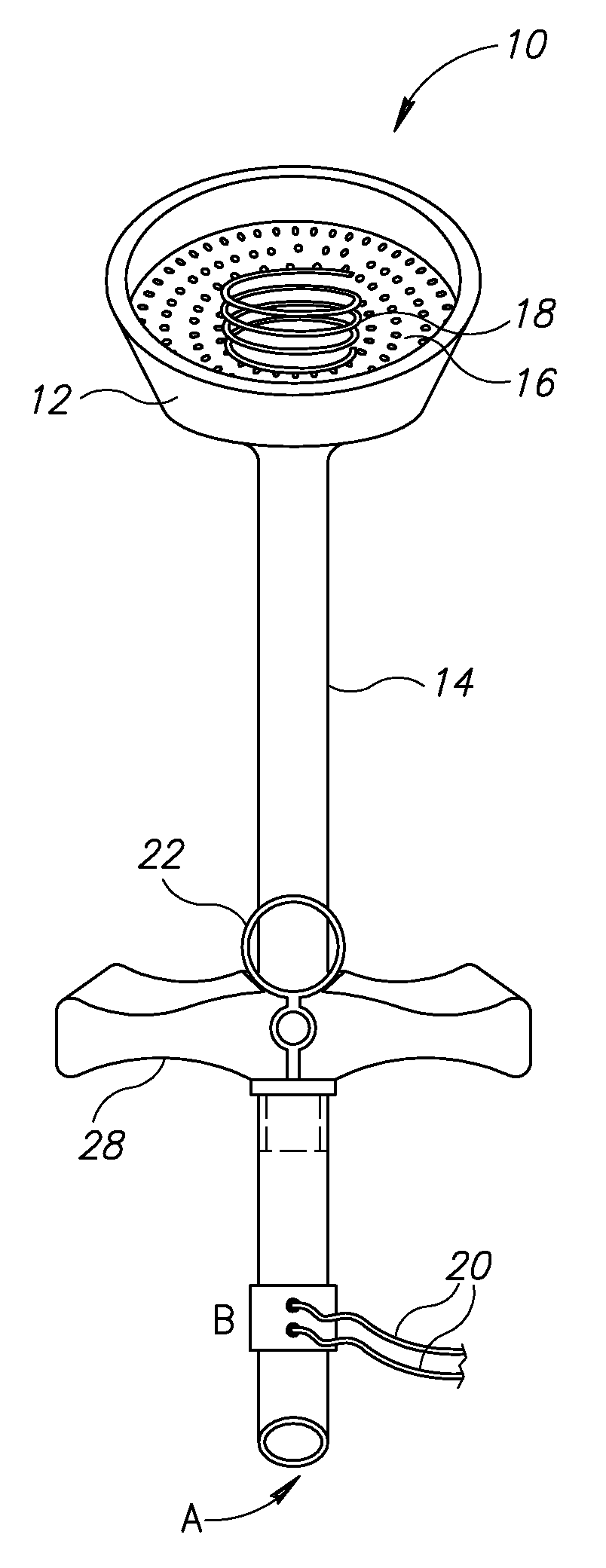
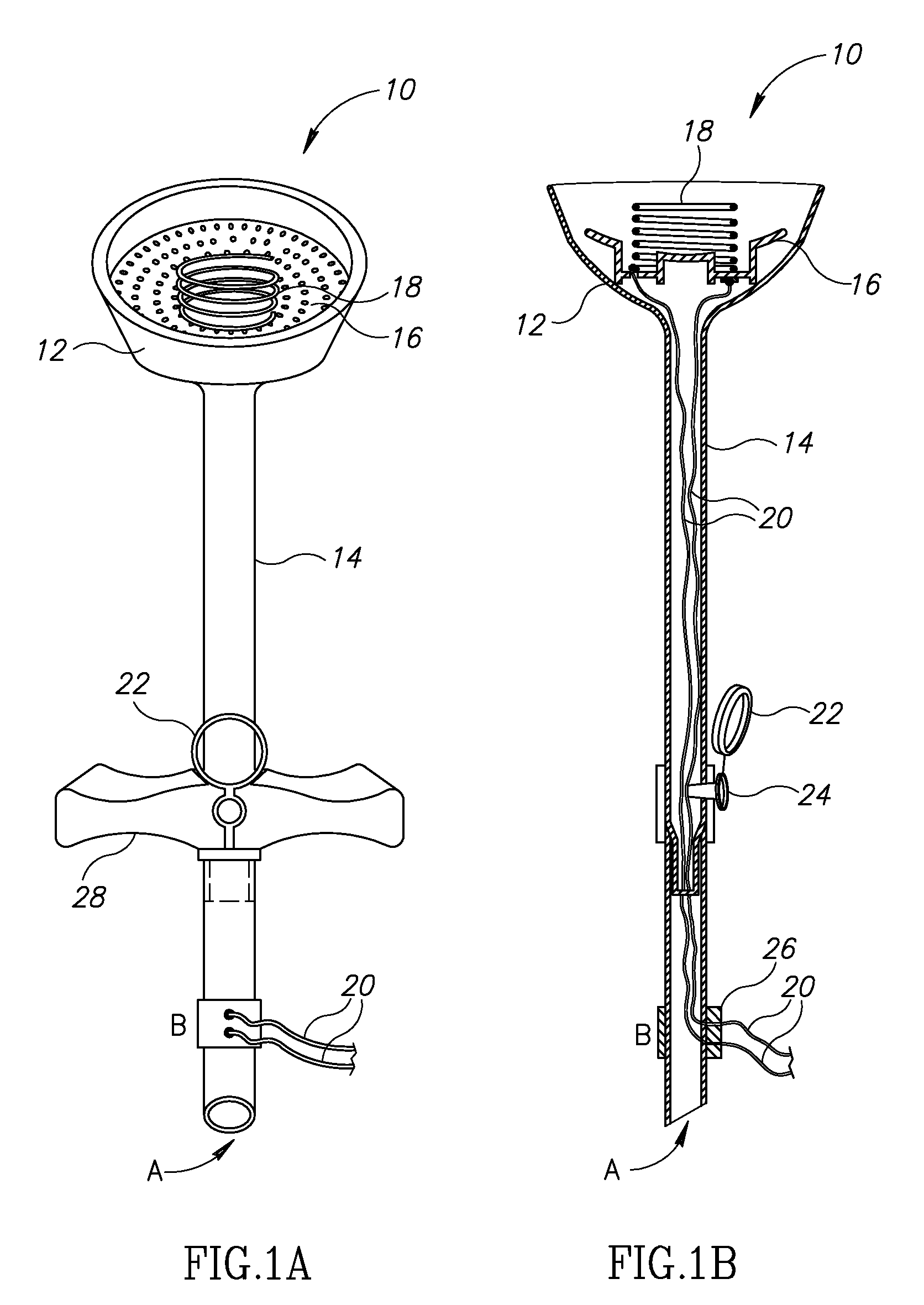
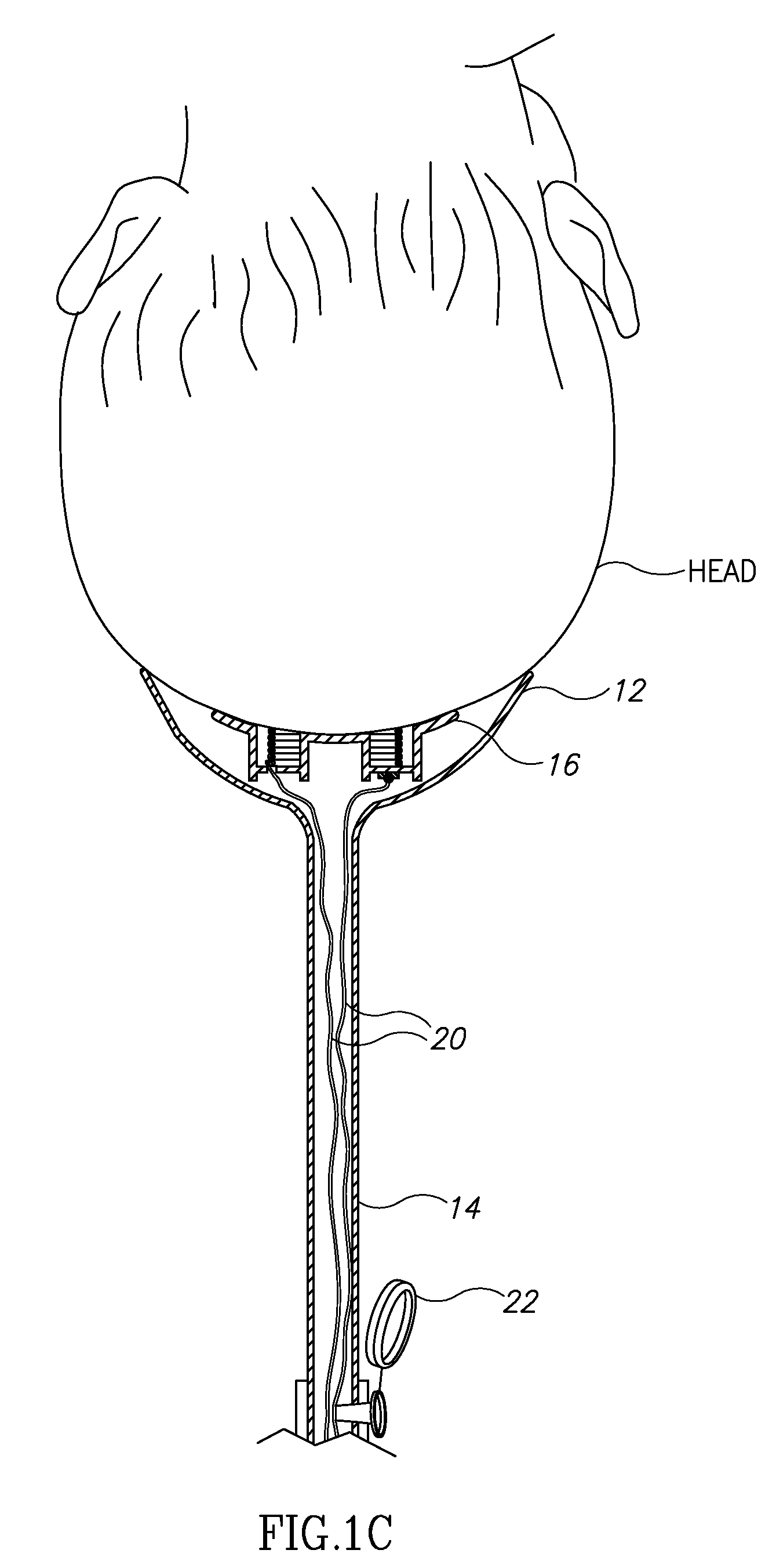
Vacuum delivery extractor
A delivery extractor for use with a suction source and at least one monitor in vacuum assisted deliveries. The extractor comprises a cup-shaped element and a tubular stem joined to the cup-shaped element and in pneumatic communication with the suction source. The extractor also includes at least one noninvasive sensor positioned on a sensor support so as to continuously contact the scalp of a fetus when the head of the fetus is positioned in the cup-shaped element. The sensor support is depressible within the cup-shaped element. The at least one sensor is in communication with the monitor(s) which monitors at least one physiological indicator of the well-being of the fetus during its transit through the birth canal. In other cases, the aforementioned noninvasive sensor(s) detects direct waves while other noninvasive sensors positioned on the rim of the cup-shaped element detect surface waves related to the same phenomenon.
Owner:ASSOC FOR PUBLIC HEALTH
Video recognition in frictionless access control system
ActiveUS9865144B2Continuous trackingSpatial transmit diversityCharacter and pattern recognitionUser deviceControl system
A system and method for video recognition of users in a frictionless access control system are disclosed. The access control system includes a positioning unit that tracks locations of users carrying user devices relative to an access point of a premises, where the user devices transmit user information identifying the users via wireless signals. The system determines whether the users are authorized to pass through the access point based on the wireless signals from the user devices. One or more video cameras also capture video data of the users when the users are preferably located within a threshold area of the access point. Then, the system confirms the identity of each authorized user by comparing video identification information of the user determined from the video data, such as facial recognition information, to stored video identification information for each user. Confirmed users can then pass through the access point.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
Video monitoring method, video monitoring device and video monitoring system
InactiveCN104349143AGuaranteed continuityGuaranteed accuracyImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringVideo tracking
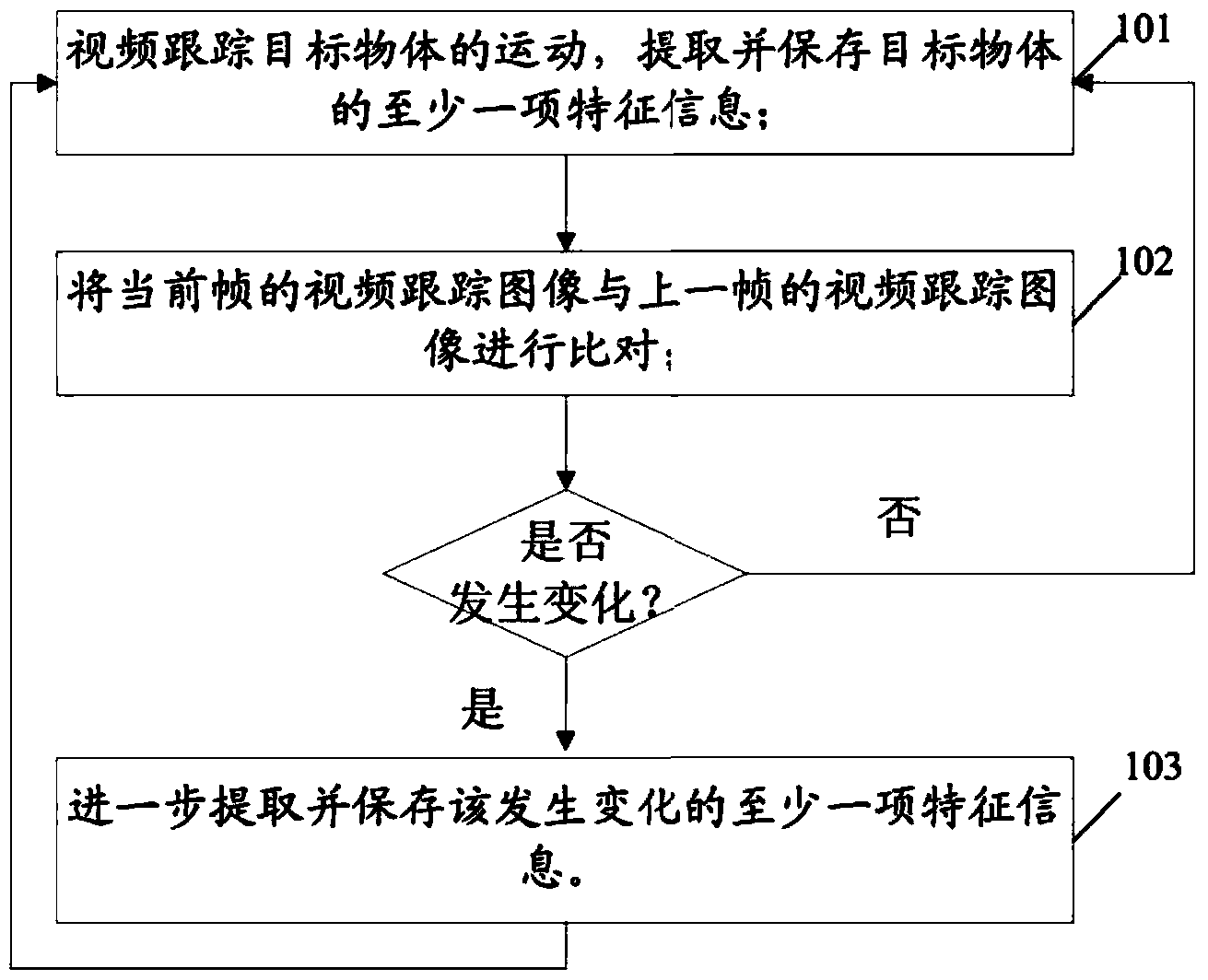
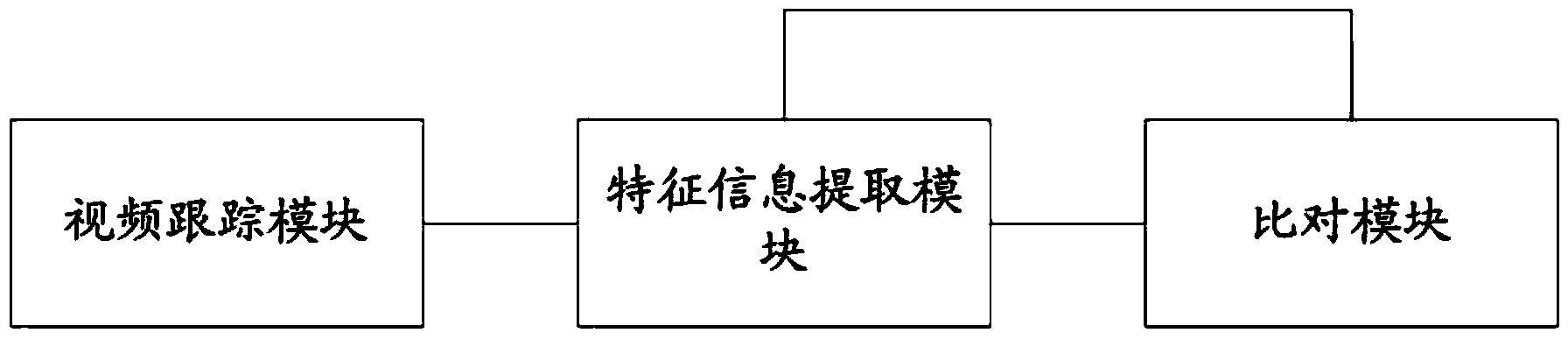
The embodiment of the invention provides a video monitoring method, a video monitoring device and a video monitoring system, aiming at solving the problem that in the prior art, video tracking interruption or error is caused by an excessively fixed feature information extraction method. The video monitoring method comprises the steps of tracking the movement of a target object by video, and extracting and storing at least one feature information of the target object; the method further comprises the steps of comparing the video tracking image of the current frame with that of the previous frame; when the at least one feature information of the target object in the video tracking image of the current frame changes relative to that of the previous frame, further extracting and storing the changed at least one feature information.
Owner:GUANGDONG VIMICRO
Tailgating detection in frictionless access control system
ActiveUS10235854B2Continuous trackingReduce actionSpatial transmit diversityParticular environment based servicesUser deviceControl system
A system and method for determining tailgating of users in a frictionless access control system are disclosed. The access control system includes a positioning unit that tracks locations of users carrying user devices relative to an access point of a premises, where the user devices transmit user information identifying the users via wireless signals. The access control system then determines whether the users are authorized to pass through the access point based on the wireless signals from the user devices and determines whether non-authorized users are tailgating through the access point with authorized users. In embodiments, the system can also determine tailgating of the users in response to analyzing video data of a scene including the users, where the video data is generated by a video camera positioned to capture the users when the users are within the threshold area.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
System and methods for transitioning patient care from signal based monitoring to risk based monitoring
PendingUS20210090742A1Continuous trackingProvide supportMedical simulationHealth-index calculationMedical emergencyPatient treatment
A risk-based patient monitoring system for critical care patients combines data from multiple sources to assess the current and the future risks to the patient, thereby enabling providers to review a current patient risk profile and to continuously track a clinical trajectory. A physiology observer module in the system utilizes multiple measurements to estimate Probability Density Functions (PDF) of a number of Internal State Variables (ISVs) that describe components of the physiology relevant to the patient treatment and condition. A clinical trajectory interpreter module in the system utilizes the estimated PDFs of ISVs to identify under which probable patient states the patient can be currently categorized and assign a probability value that the patient will be in each of the identified states. The combination of patient states and their probabilities is defined as the clinical risk to the patient.
Owner:ETIOMETRY
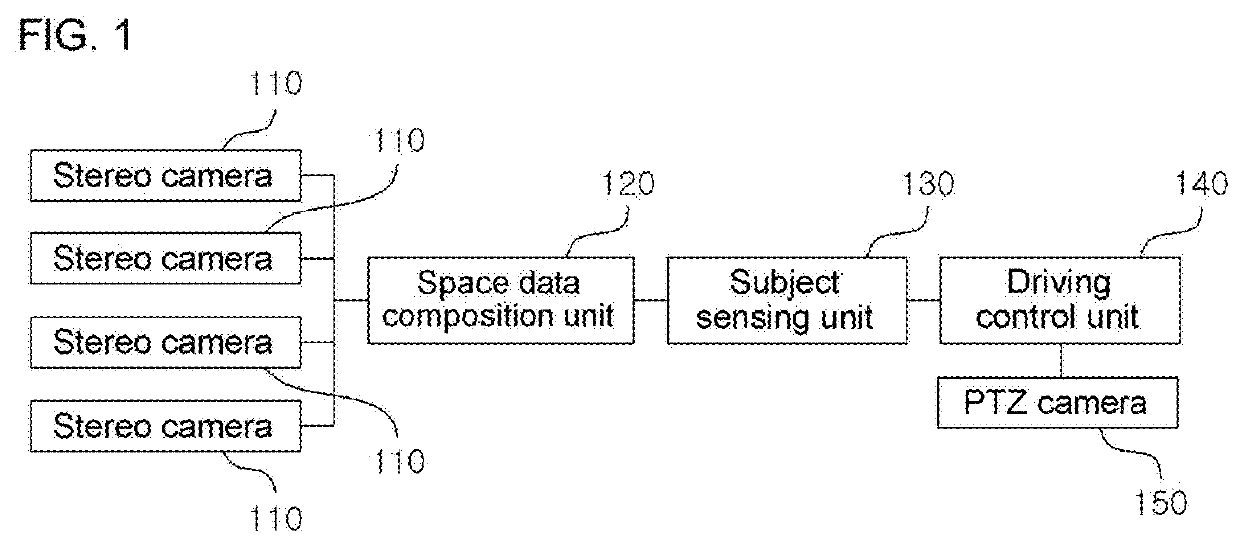
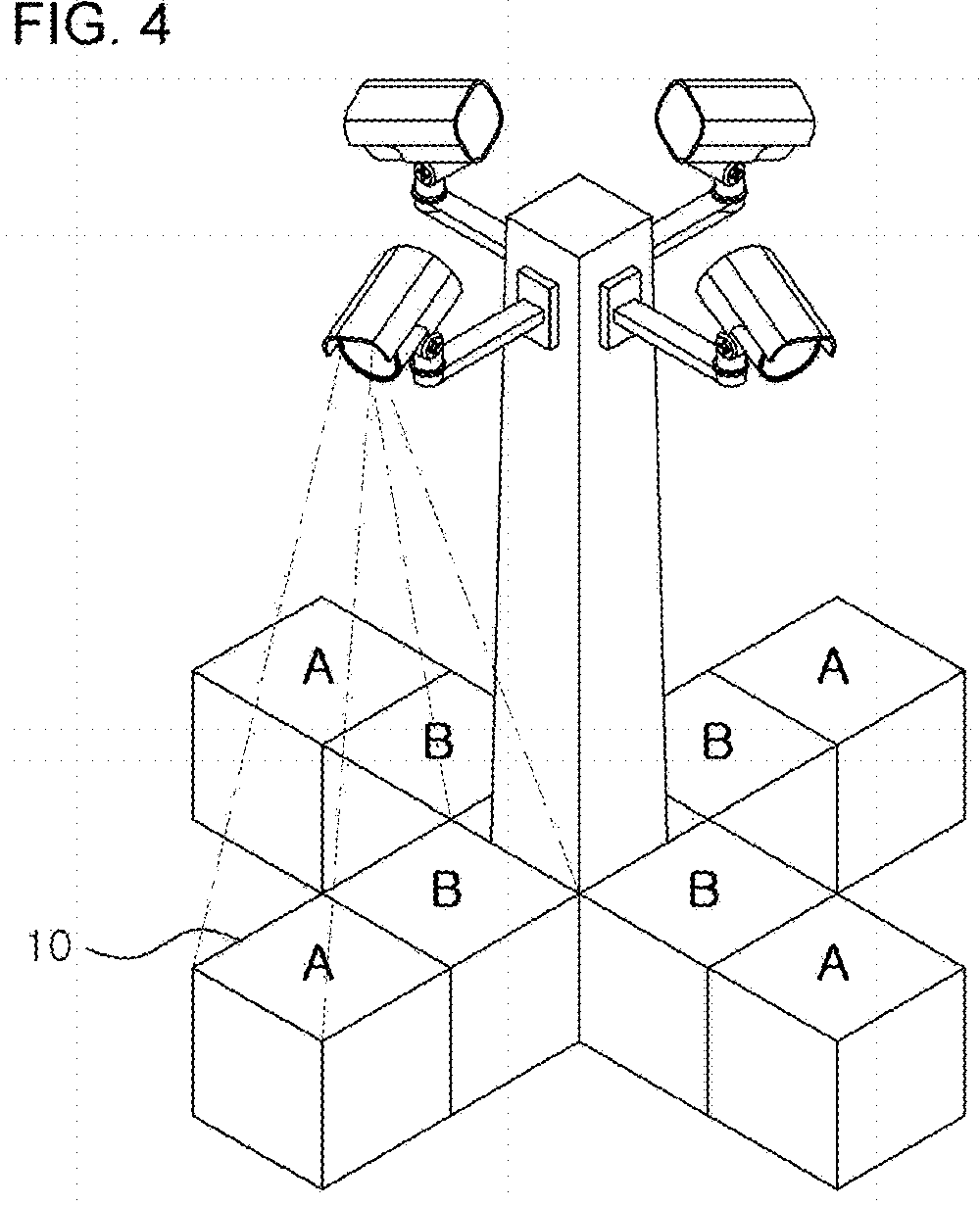
System for tracking subject moving within space using stereo cameras
InactiveUS20180278919A1Continuous trackingAccurate trackingImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudStereo cameras
A system for tracking a subject moving within a space using stereo cameras includes stereo cameras installed in different directions, a space data composition unit forming a space map where information about 3D space is shared by matching depth maps generated in photographing areas of the stereo cameras, a subject sensing unit analyzing point clouds or the space map and determining that the subject is present in a photographing area of a stereo camera corresponding to a point, a PTZ camera moving so that a photographing direction is directed toward the subject, and a driving control unit driving the PTZ camera using a first method for setting an initial value and for driving the PTZ camera and / or a second method for setting the photographing zones of the 3D space, presetting the driving values of the PTZ camera, fetching the preset value of the zone, and driving the PTZ camera.
Owner:GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION TECH
Vacuum delivery extractor
A delivery extractor for use with a vacuum suction source and at least one monitor in vacuum assisted deliveries. The extractor comprises a cup-shaped element and a tubular stem joined to the cup-shaped element and in pneumatic communication with the vacuum suction source. The extractor also includes at least one non-invasive sensor positioned on and in mechanical communication with a sensor support so as to continuously contact the scalp of a fetus when the head of the fetus is positioned in the cup-shaped element. The sensor support is compressible within the cup-shaped element. The at least one sensor is in communication with the at least one monitor which monitors at least one physiological indicator of the well-being of the fetus during its transit through the birth canal. The invention also includes a system and method for using the above extractor.
Owner:ASSOC FOR PUBLIC HEALTH
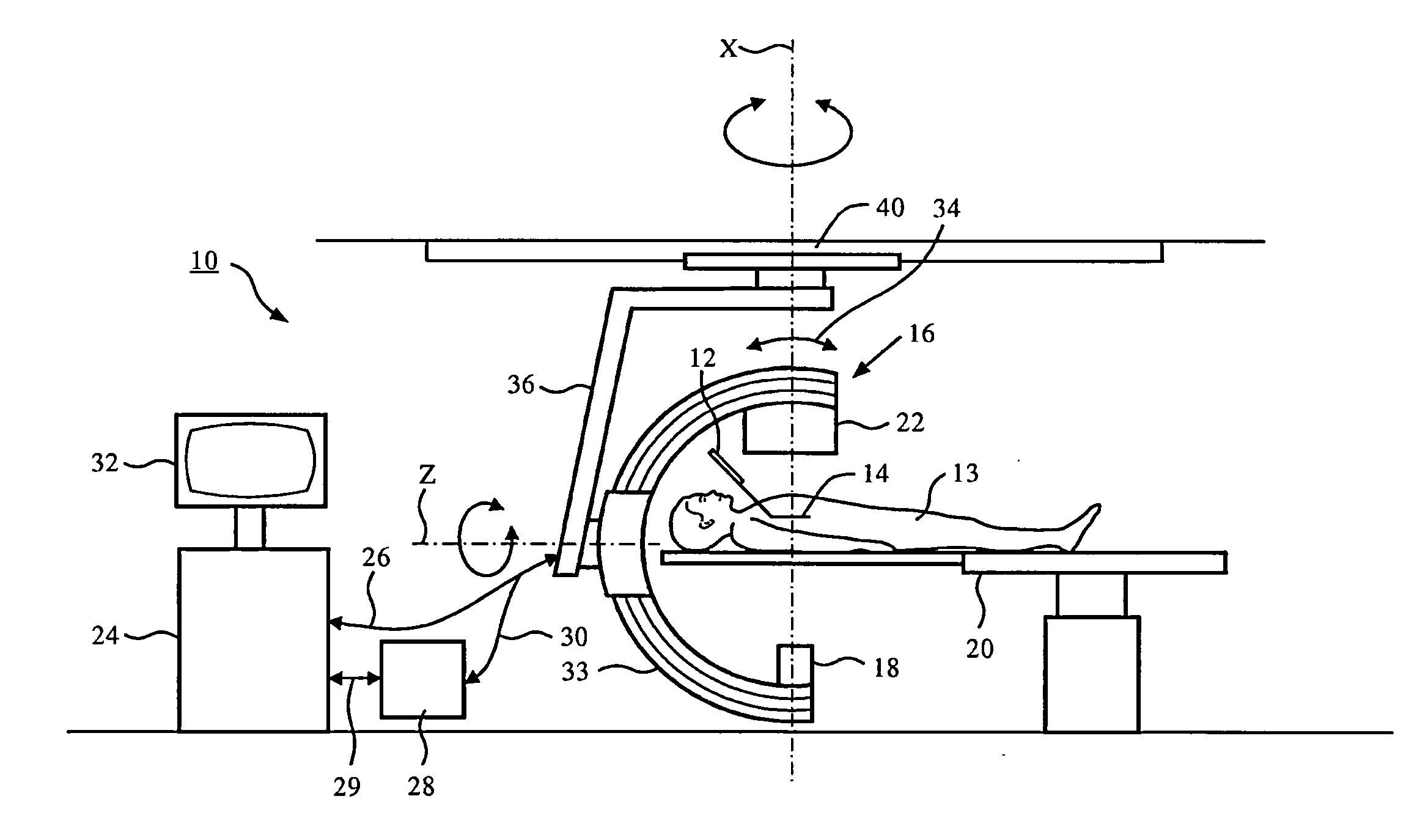
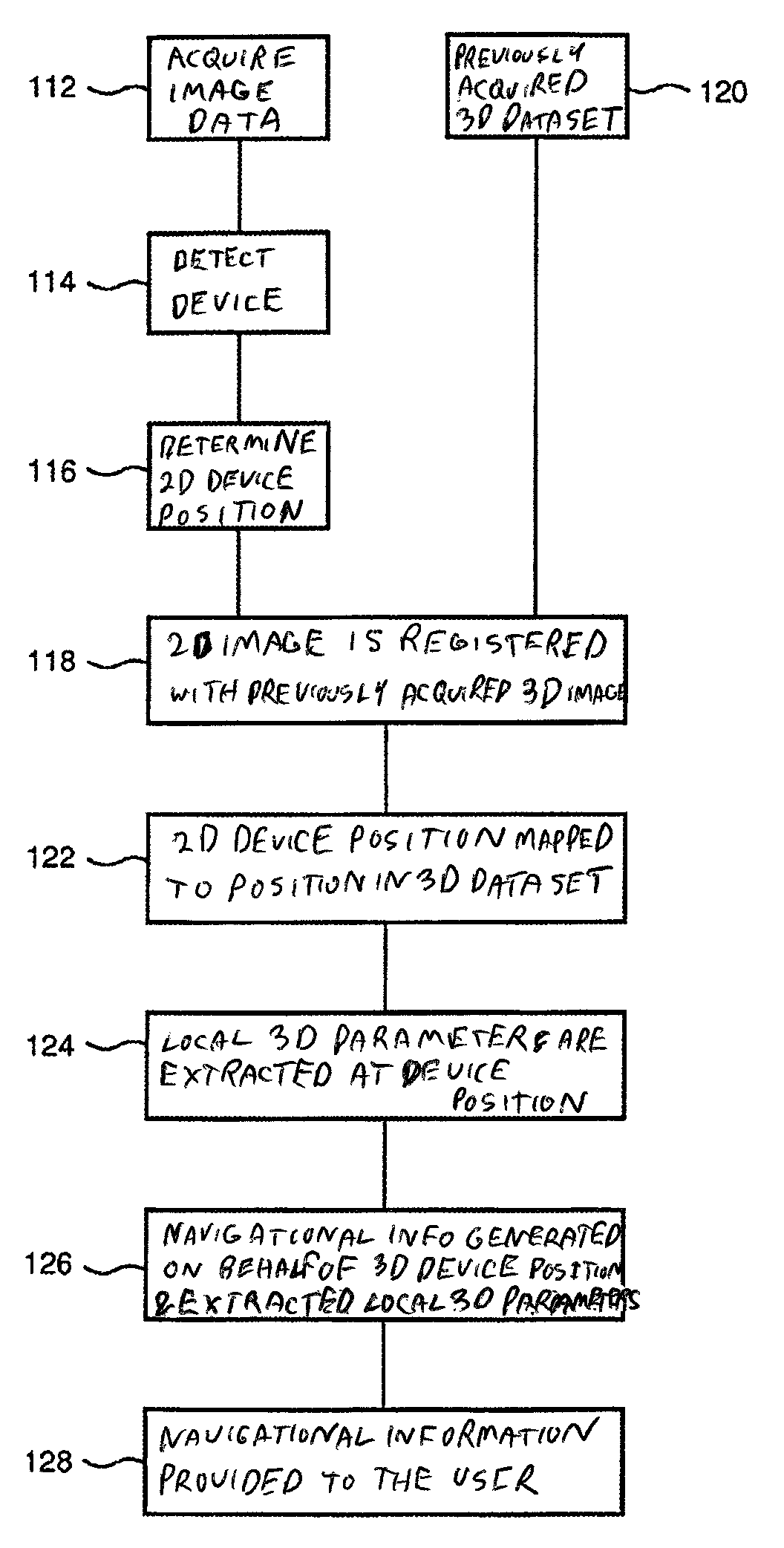
Navigating an interventional device
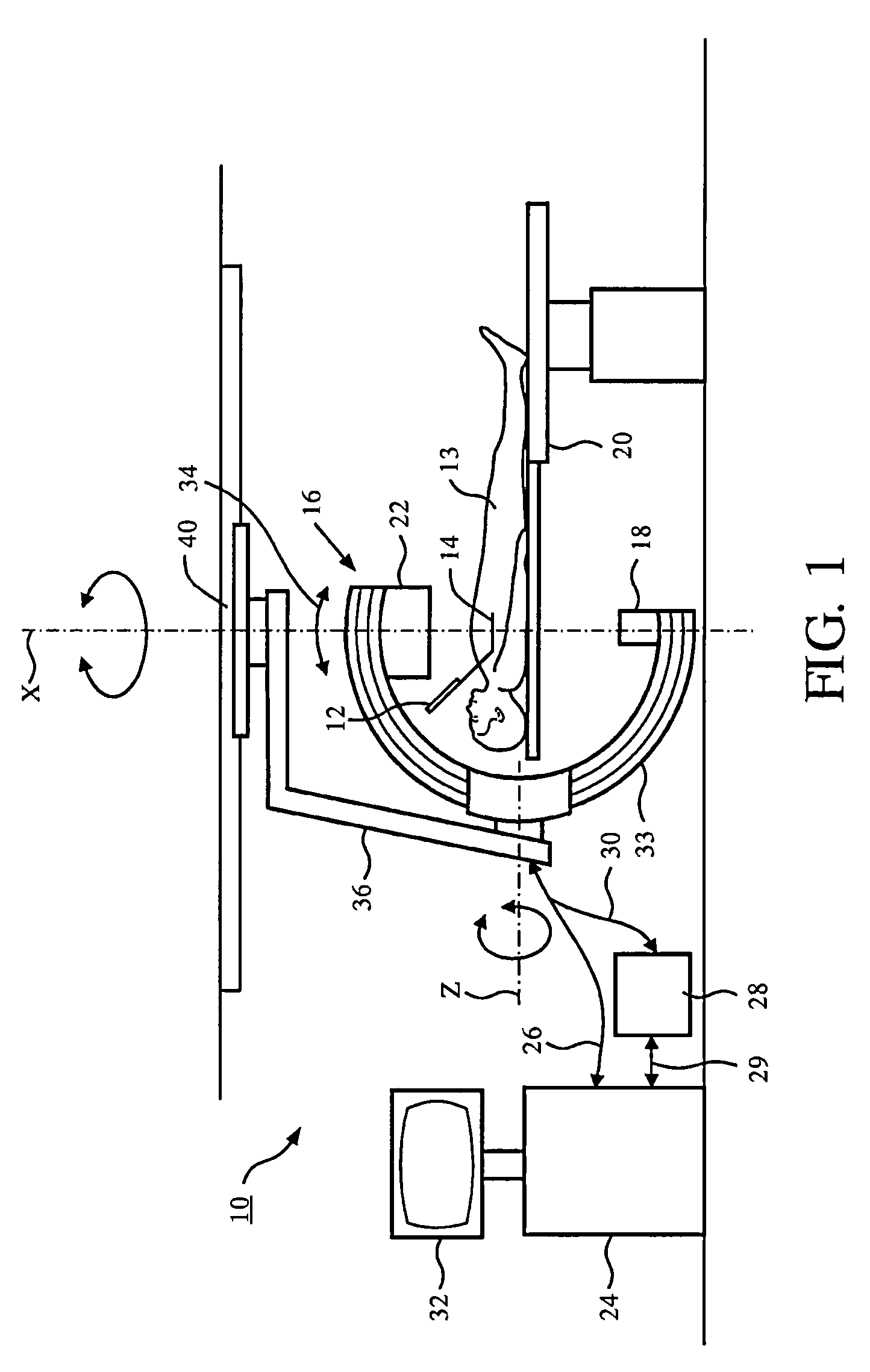
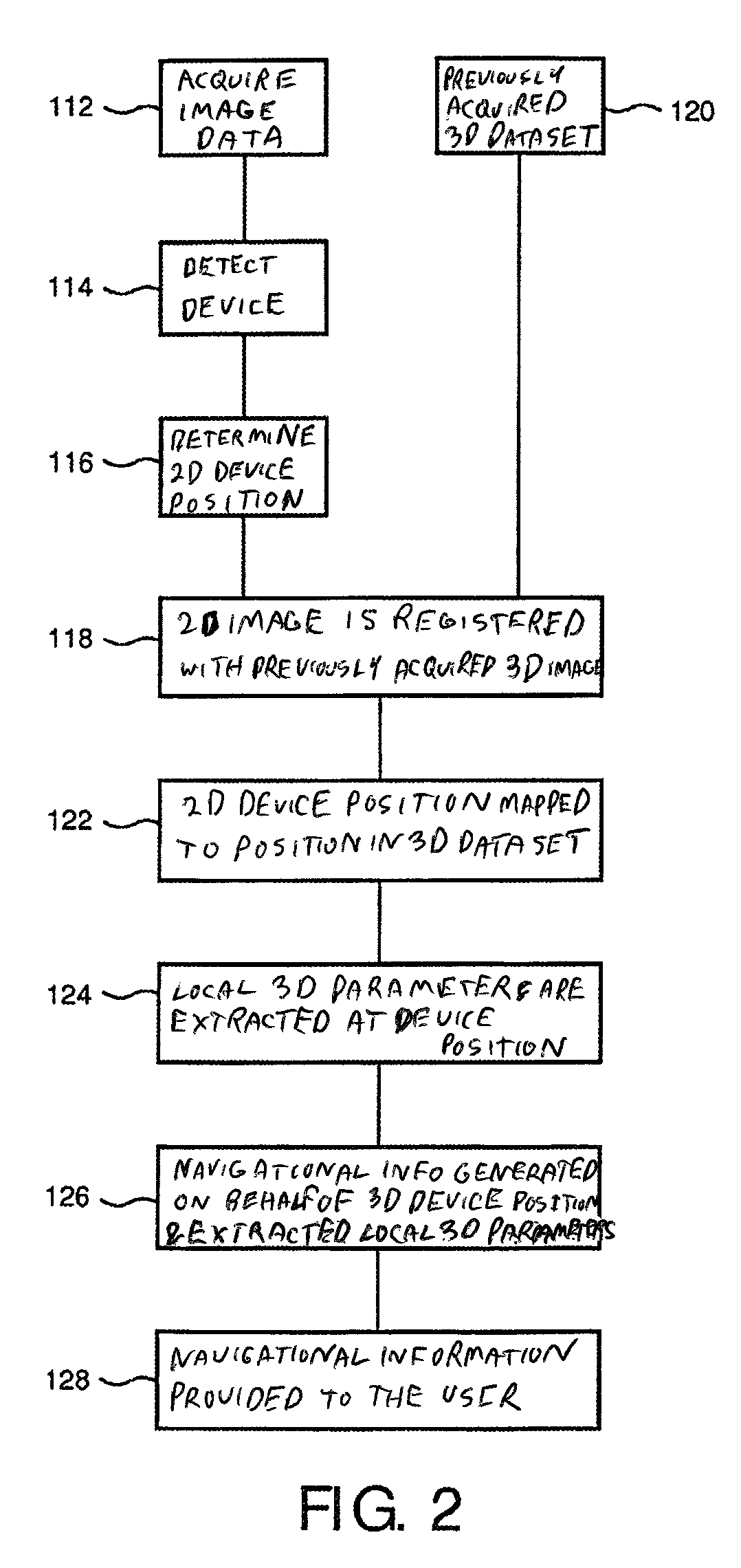
ActiveUS20130101196A1Facilitate interventional procedureEasy to detectImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionX-rayX ray dose
The present invention relates to navigating an interventional device. In particular, the invention relates to a system for navigating an interventional device within a tubular structure of an object, a method for navigating an interventional device within a tubular structure of an object as well as a computer program element and a computer-readable medium. In order to provide enhanced information to the user in an easily comprehensible manner while keeping the X-ray dose to a minimum, a system and a method for navigating an interventional device within a tubular structure of an object are provided, wherein the method comprised the following steps: a) Acquiring 2D X-ray fluoroscopy image data in one projection geometry of a region of interest of the tubular structure; b) detecting the interventional device in the 2D X-ray image; c) determining the 2D position of the interventional device in the 2D X-ray image; d) registering the at least one 2D X-ray image with a previously acquired 3D dataset of the region of interest of the tubular structure; e) mapping the determined 2D position of the interventional device to a position in the 3D dataset; f) extracting local 3D parameters of the tubular structure at the position of the interventional device; g) generating navigational information on behalf of the determined 3D position of the interventional device and the extracted local 3D parameters; and h) providing the navigational information to the user.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
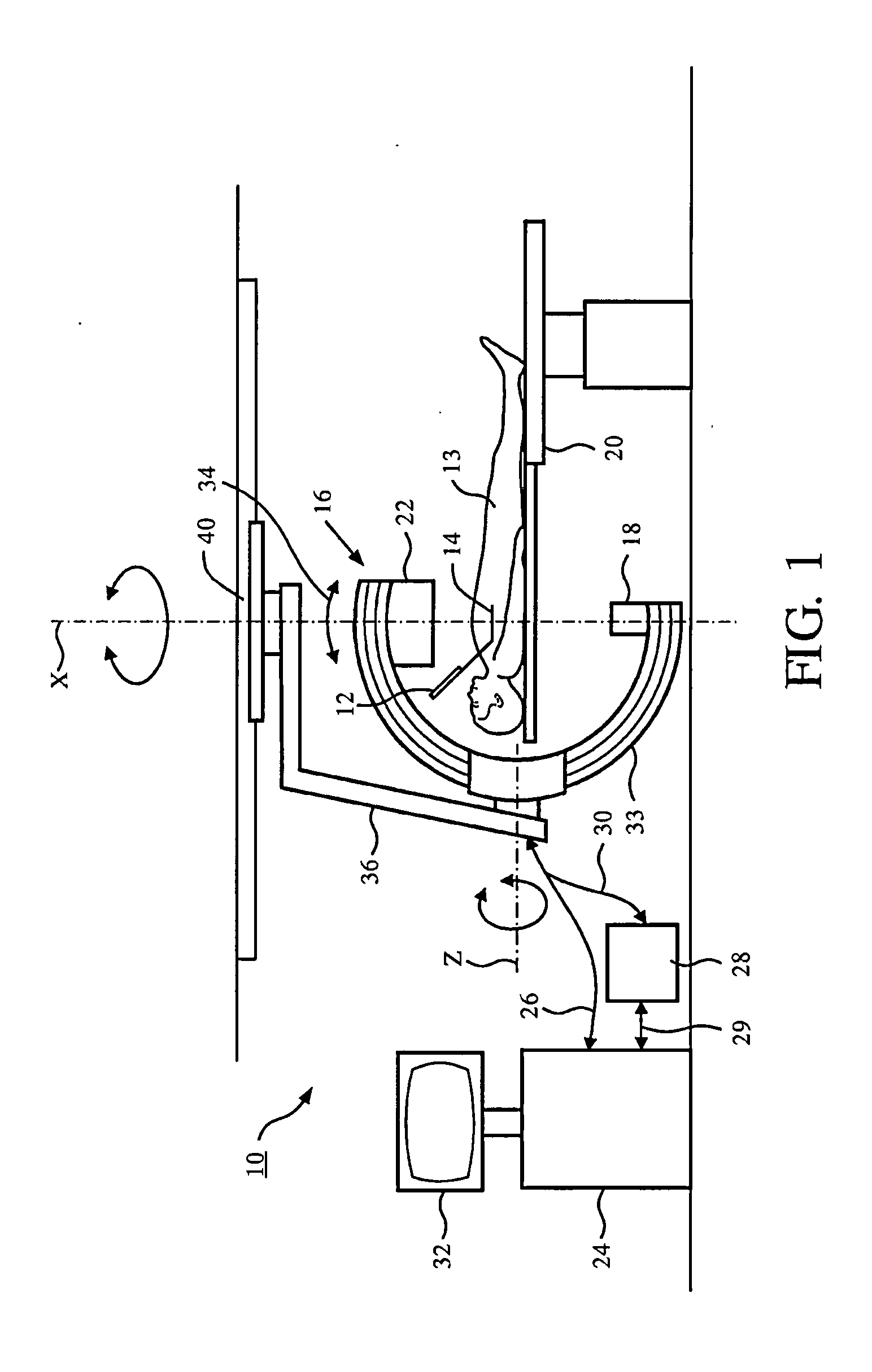
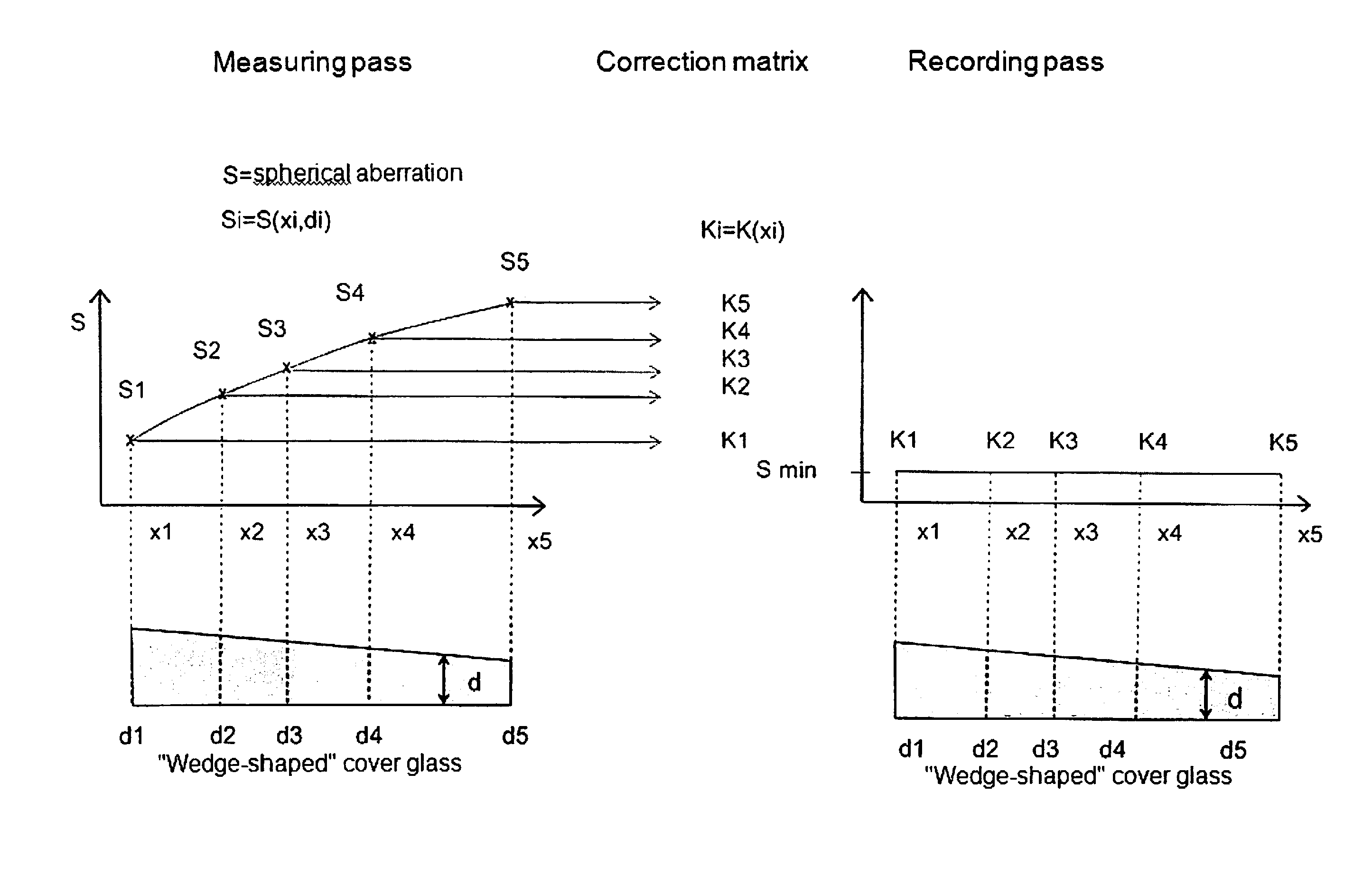
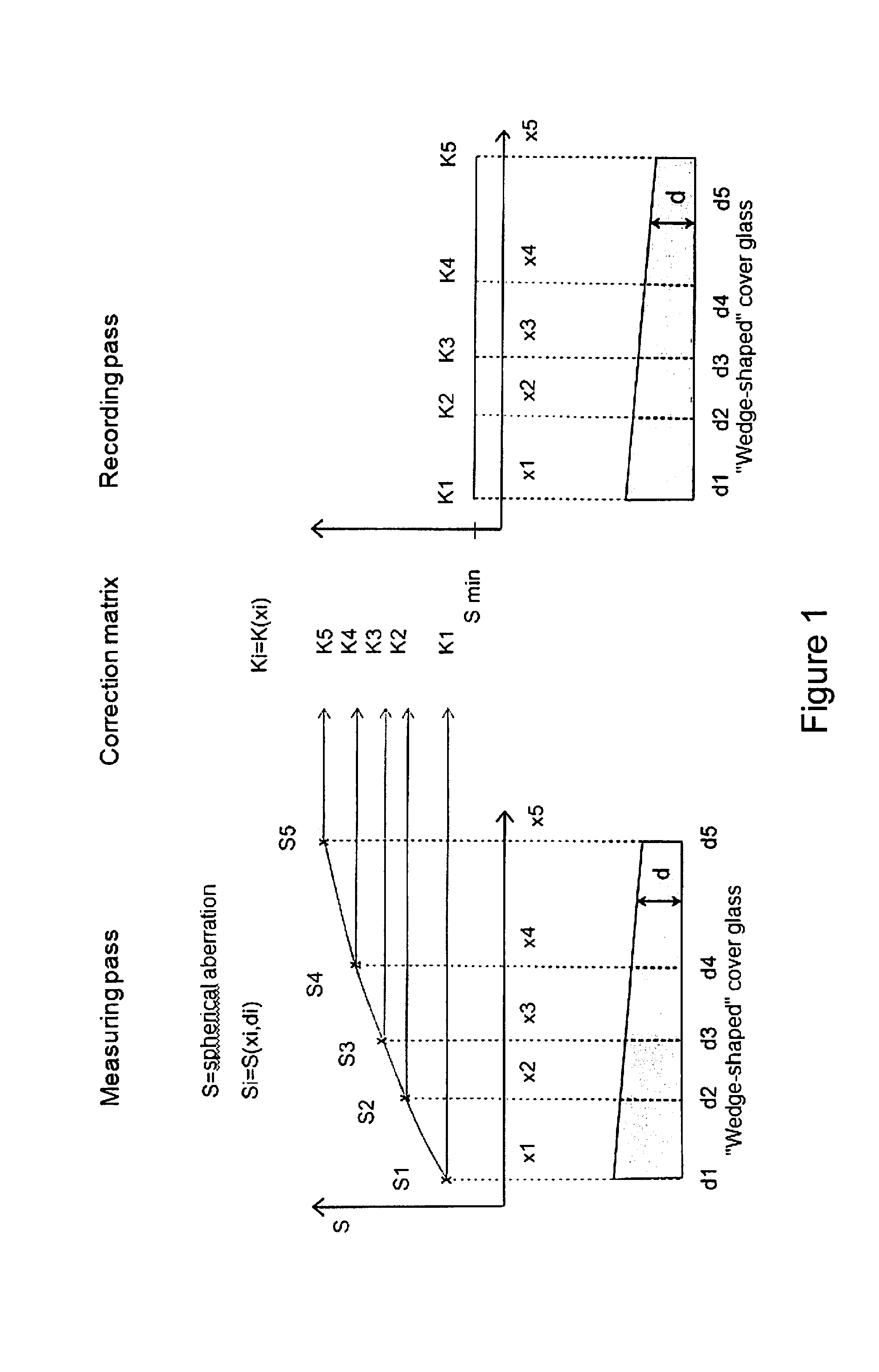
Method for the correction of spherical aberration in microscopic applications
ActiveUS20150253562A1Minimize phototoxicityMinimize time requirementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputational physicsOptic system
A procedure for the correction of spherical aberration in microscopic applications, wherein various recordings of a specimen to be observed are taken and evaluated for the purpose of changing the setting values of the optical system. The correction values are stored in a correction matrix as a function of the recording position, the recording time, the wavelength, and the temperature, wherein the determination and storage of the correction values are carried out in each recording position in the x, y, and z coordinates, and / or the correction values are determined after a selection of grid points by interpolation, so that the correction values of the interpolated correction matrix are the starting values for the subsequent exact determination by measurement.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
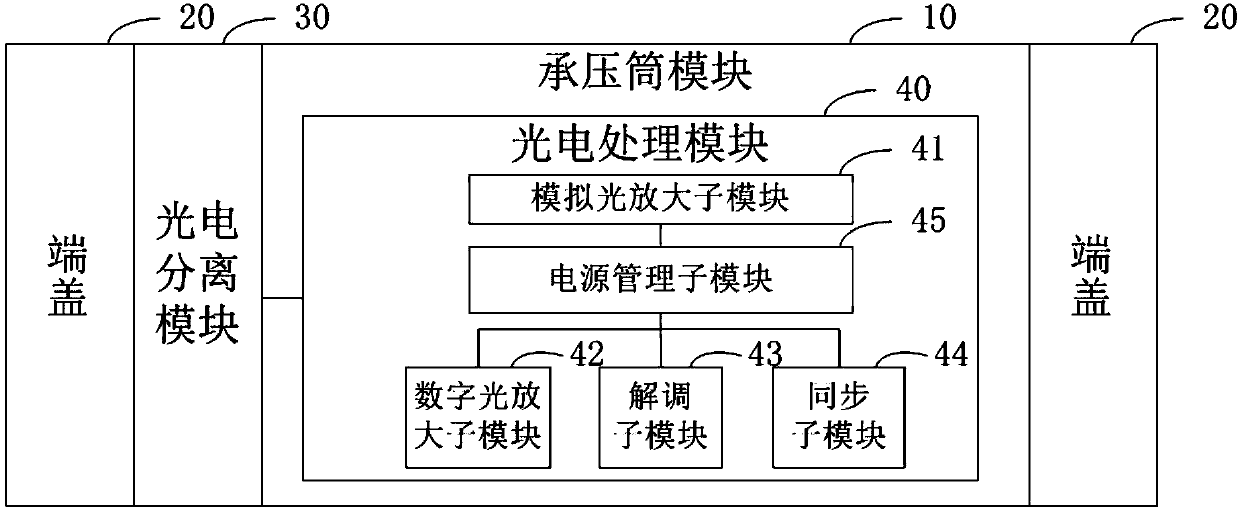
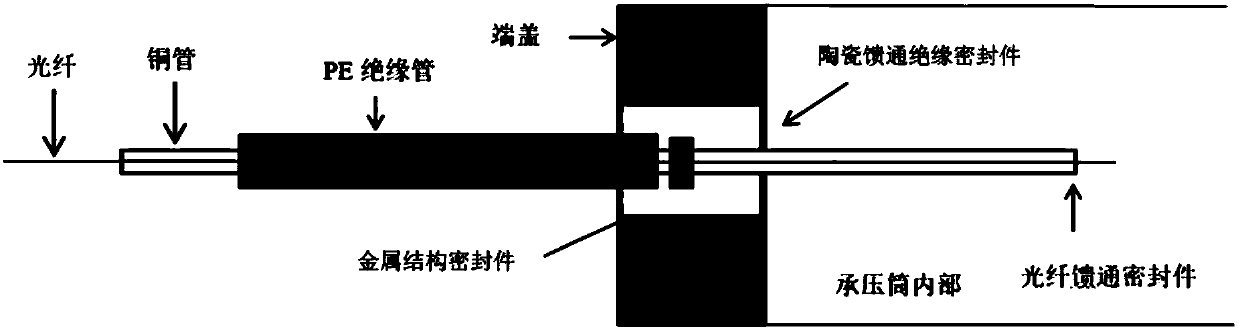
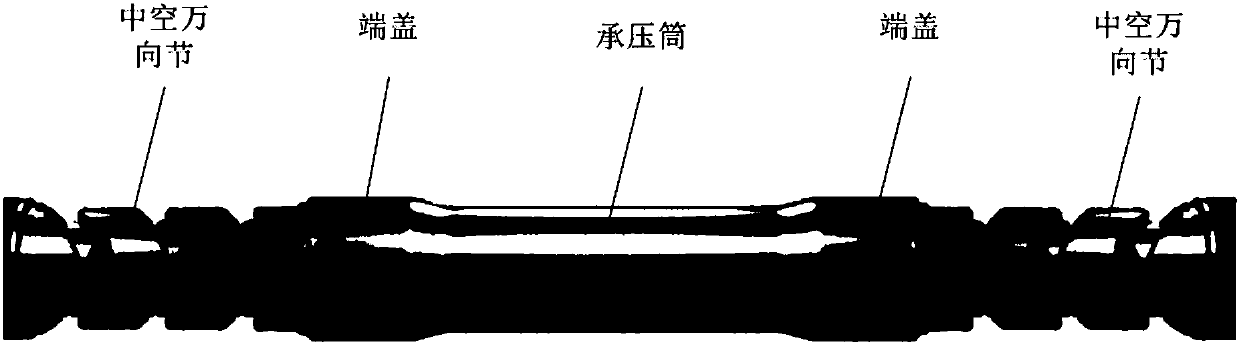
Underwater optical signal amplification relay with demodulation function, and submarine monitoring system
The invention provides an underwater optical signal amplification relay with a demodulation function, and a submarine monitoring system. The underwater optical signal amplification relay comprises a pressure bearing cylinder, end covers, a photoelectric separation module and a photoelectric processing module; wherein the photoelectric processing module is used for performing amplification transmission on a downlink analog optical signal transmitted in a submarine optical cable accessing the relay, converting an uplink analog optical signal into an uplink digital optical signal and performing amplification transmission on the uplink digital optical signal; the end covers are arranged on the two ends of the pressure bearing cylinder; and the photoelectric separation module and the photoelectric processing module are arranged in the pressure bearing cylinder. According to the underwater optical signal amplification relay with the demodulation function provided by the invention, the amplification transmission is performed on the downlink analog optical signal, the uplink analog optical signal is demodulated into the uplink digital optical signal, and then the amplification transmissionis performed on the uplink digital optical signal, thereby improving the signal quality of remote transmission of the submarine optical cable and effectively solving the difficulty that the transmission distance of the analog optical signal in the submarine optical cable is solved.
Owner:CHANGSHA XIANGJI HAIDUN TECH CO LTD +1
Navigating an interventional device
ActiveUS8942457B2Enhanced informationContinuous trackingImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setNuclear medicine
The present invention relates to navigating an interventional device. In particular, the invention relates to a system for navigating an interventional device within a tubular structure of an object, a method for navigating an interventional device within a tubular structure of an object as well as a computer program element and a computer-readable medium. In order to provide enhanced information to the user in an easily comprehensible manner while keeping the X-ray dose to a minimum, a system and a method for navigating an interventional device within a tubular structure of an object are provided, wherein the method comprised the following steps: a) Acquiring 2D X-ray fluoroscopy image data in one projection geometry of a region of interest of the tubular structure; b) detecting the interventional device in the 2D X-ray image; c) determining the 2D position of the interventional device in the 2D X-ray image; d) registering the at least one 2D X-ray image with a previously acquired 3D dataset of the region of interest of the tubular structure; e) mapping the determined 2D position of the interventional device to a position in the 3D dataset; f) extracting local 3D parameters of the tubular structure at the position of the interventional device; g) generating navigational information on behalf of the determined 3D position of the interventional device and the extracted local 3D parameters; and h) providing the navigational information to the user.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Data Recording Apparatus
InactiveUS20090182907A1Continuous trackingProgramme controlComputer security arrangementsData recordingData conversion
A data recording apparatus is disclosed for recording production and product data output from at least one electronic device. A data collector device assigned to the electronic device records the production and product data and converts said data into transmission data to be transmitted, which are subsequently stored in a storage device. A configuration device connected between the data collector device and the storage device controls the storage of the transmission data.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
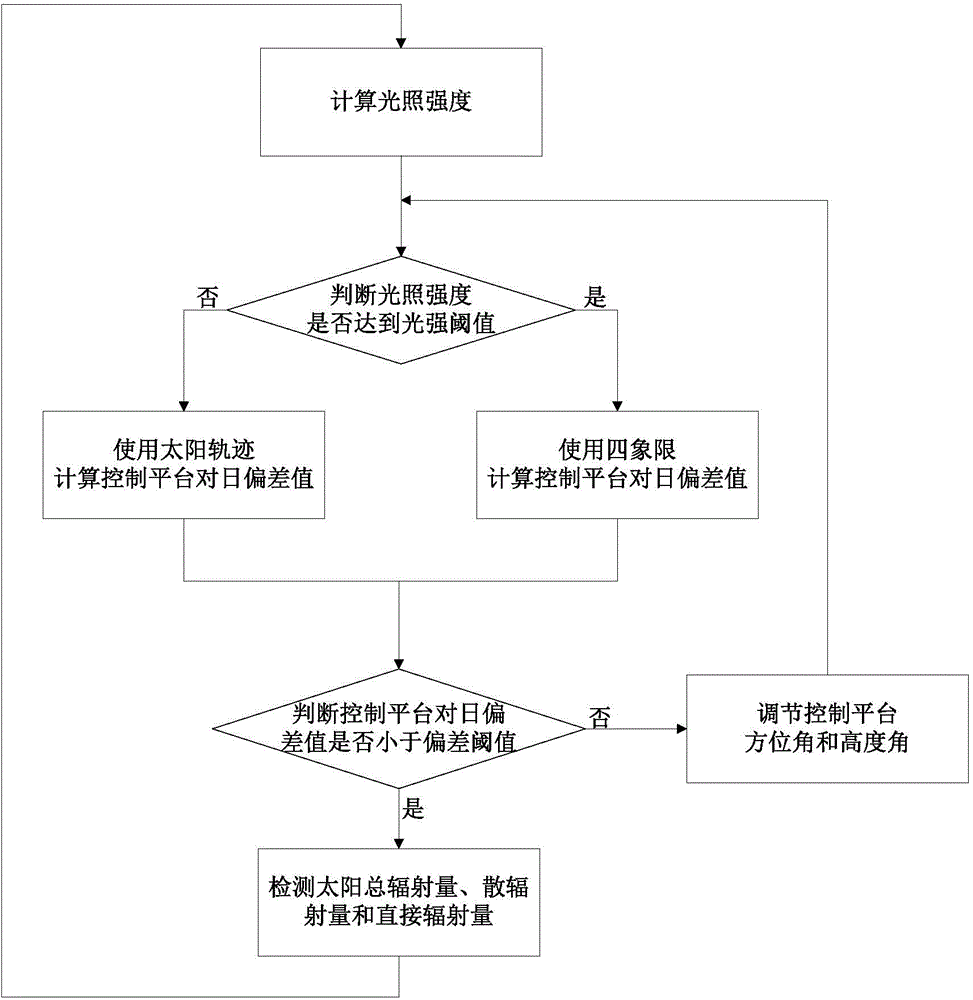
Active sunward tracking type solar resource measuring method
InactiveCN104793634AAccurate trackingContinuous trackingControl using feedbackFour quadrantsRadiation sensor
The invention discloses an active sunward tracking type solar resource measuring method and aims to achieve sunward tracking precision and continuity. Under the condition of sufficient illumination intensity, a four quadrant is used to calculate the sunward deviation of a control platform; under the condition of insufficient illumination intensity, sun trajectory is used to calculate the deviation of the control platform. By the automatic switching of the two control platform sunward deviation calculation methods, control platform sunward tracking accuracy and continuity are achieved. Due to the fact that a radiation sensor aims to the sun at any time, the cosine errors in sun radiation measuring are eliminated, and sun radiation measuring precision is increased. By the two control platform sunward deviation calculation methods, a control platform can accurately track sun trajectories, sun radiation quantity accuracy is guaranteed, and solar resource measuring precision is increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com