Filtering image data to obtain samples mapped to pixel sub-components of a display device
a display device and image data technology, applied in image enhancement, image analysis, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of luminance accuracy, color errors or lowered resolution, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing color aliasing, reducing color aliasing, and increasing cutoff frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
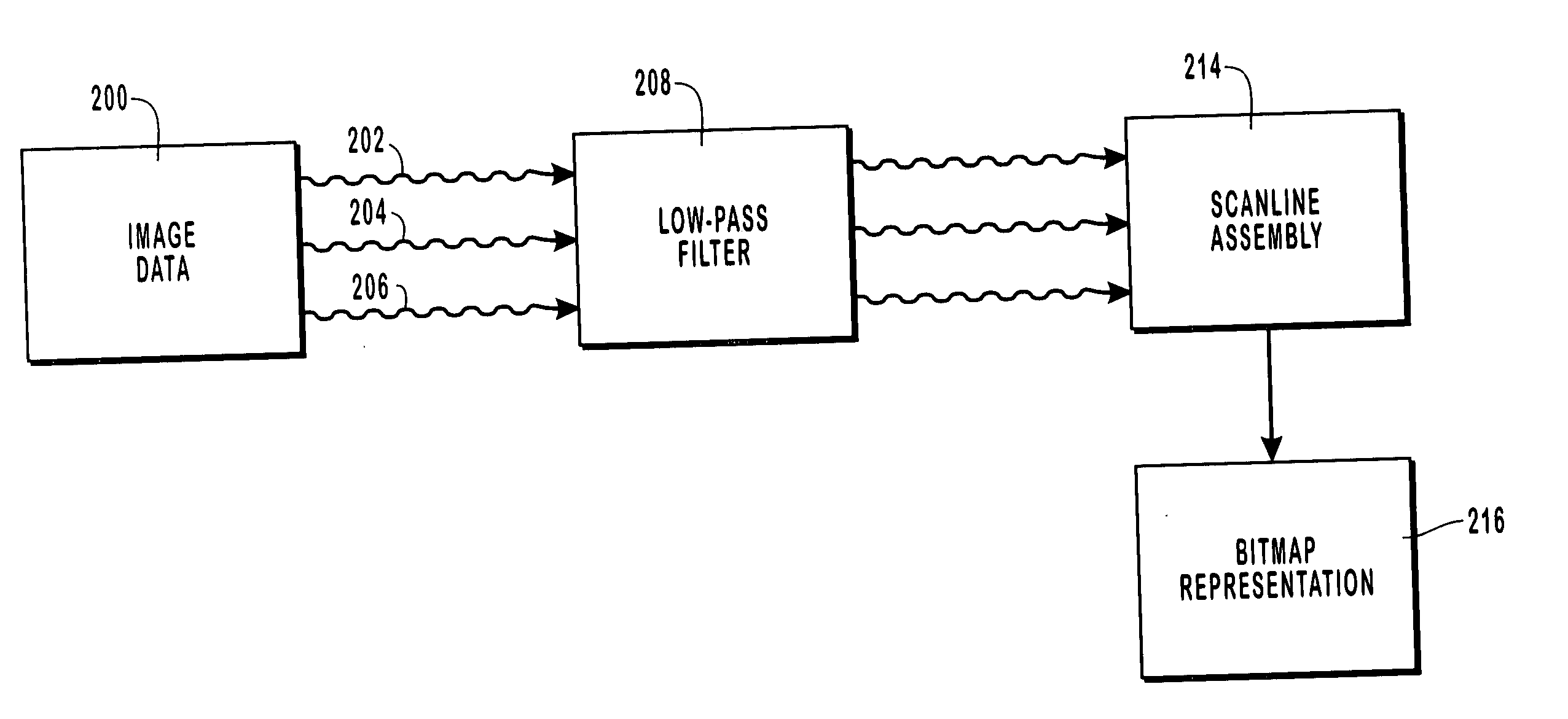
[0026] The present invention relates to image data processing and image rendering techniques whereby image data is rendered on patterned flat panel display devices that include pixels each having multiple separately controllable pixel sub-components of different colors. When applied to display devices, such as conventional liquid crystal display (LCD) devices, the image data processing operations include filtering a three-channel continuous signal representing the image data through filters that obtain samples that are mapped to the red, green, and blue pixel sub-components. The filters are selected to establish a desired tradeoff between color accuracy and luminance accuracy. Generally, an increase in color accuracy results in a corresponding decrease in luminance accuracy and vice versa. The samples mapped to the pixel sub-components are used to generate luminous intensity values for the pixel sub-components.
[0027] The image rendering processes are adapted for use with LCD device...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com