Patents
Literature
812 results about "Low-dropout regulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
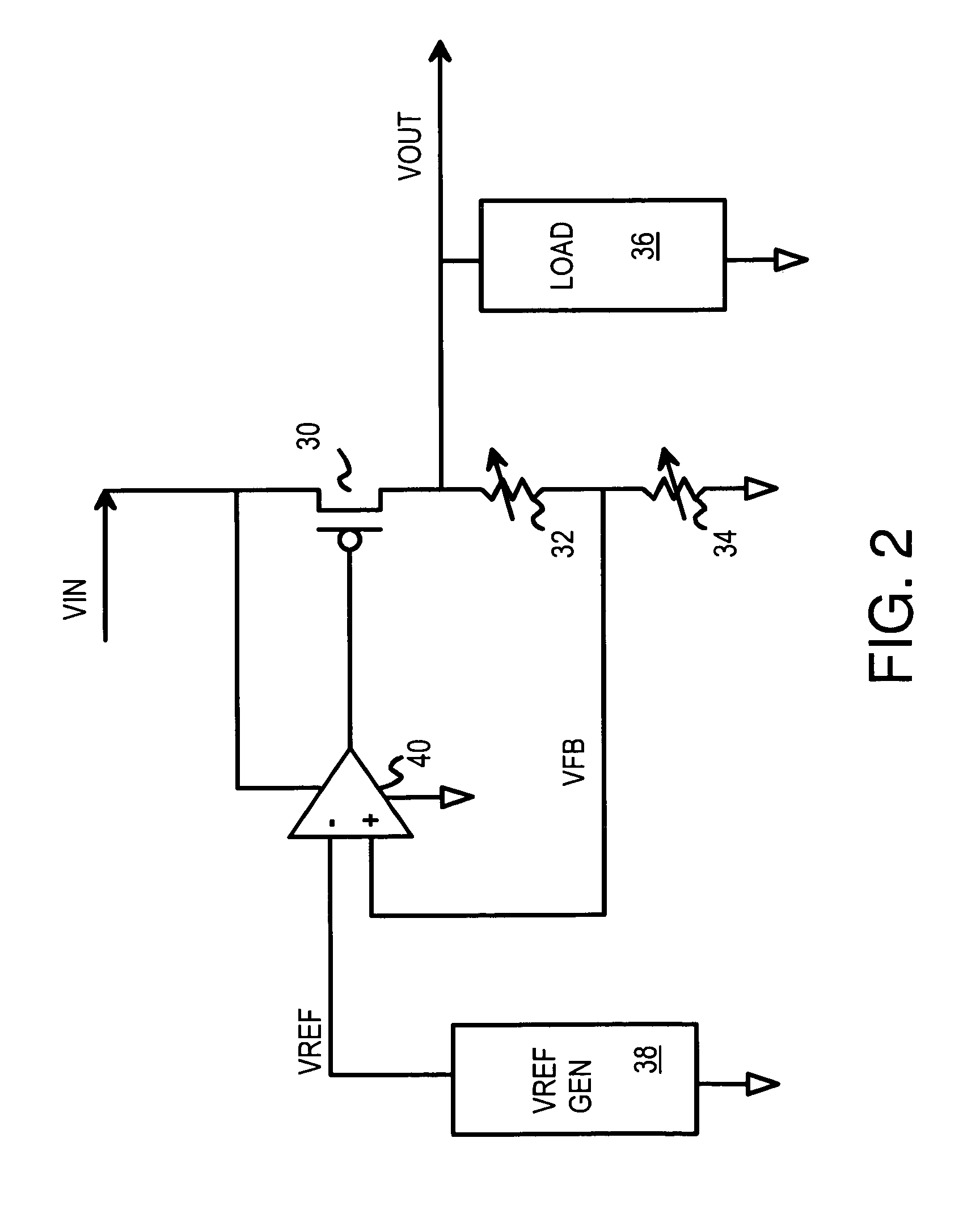
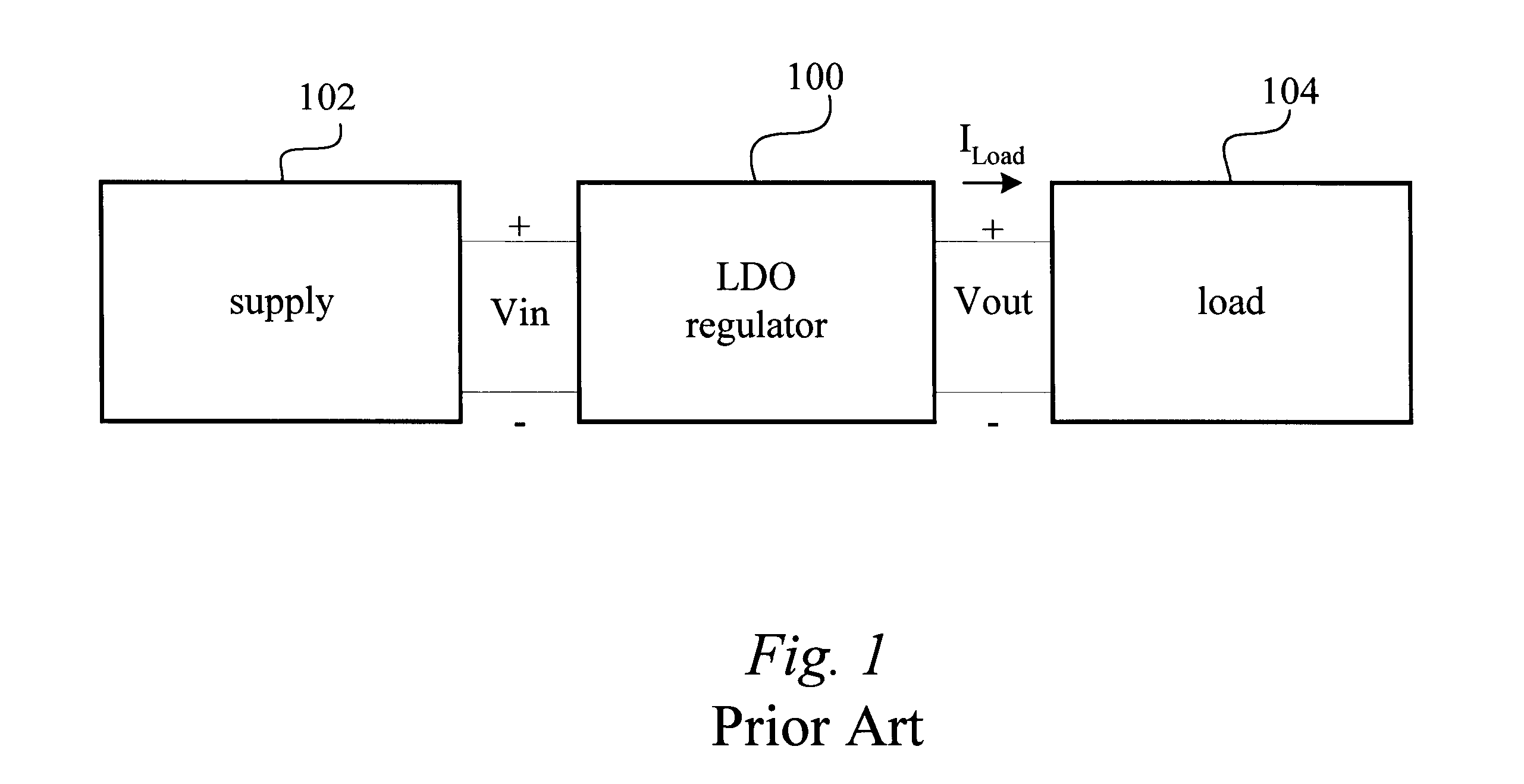
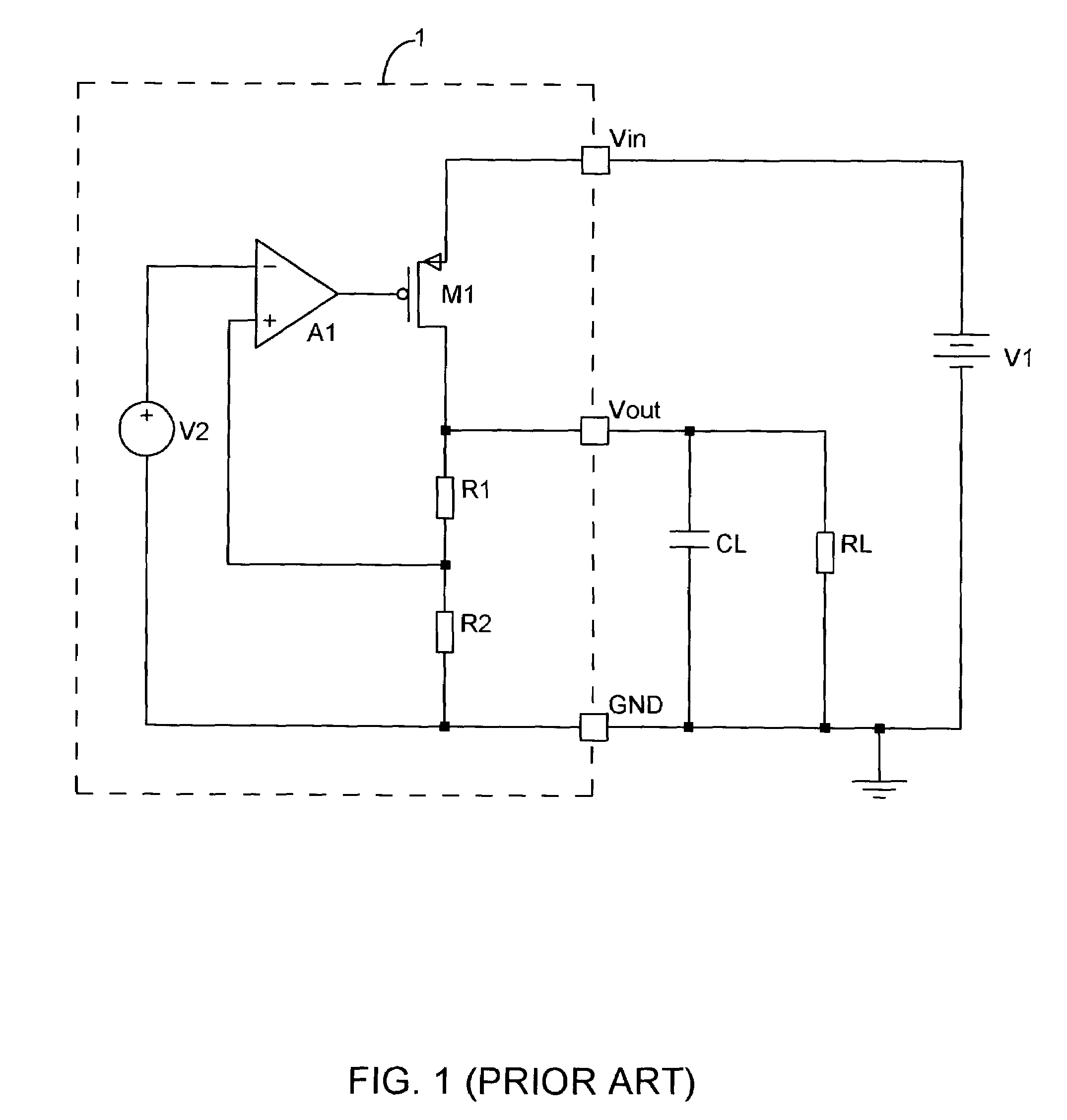
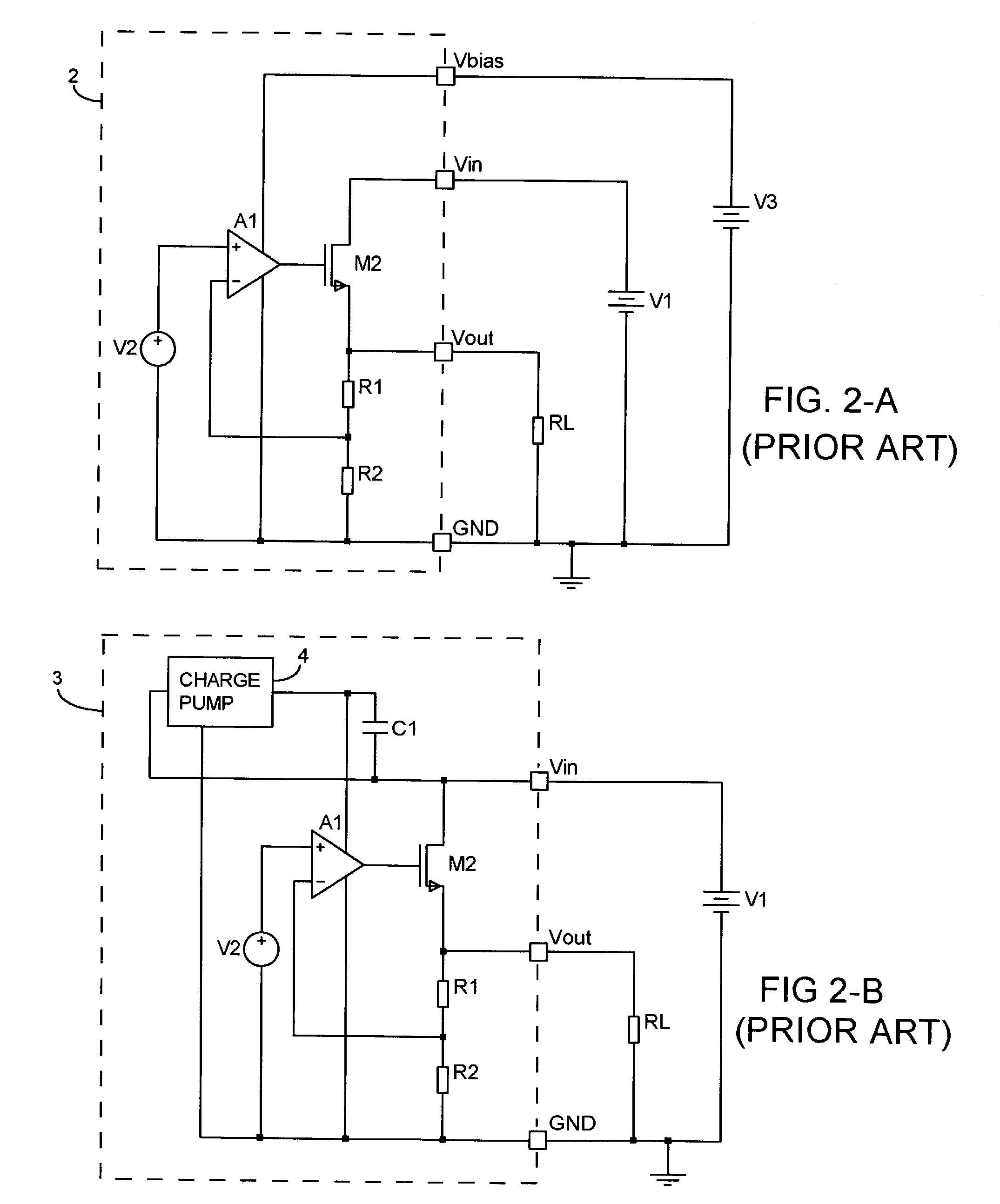
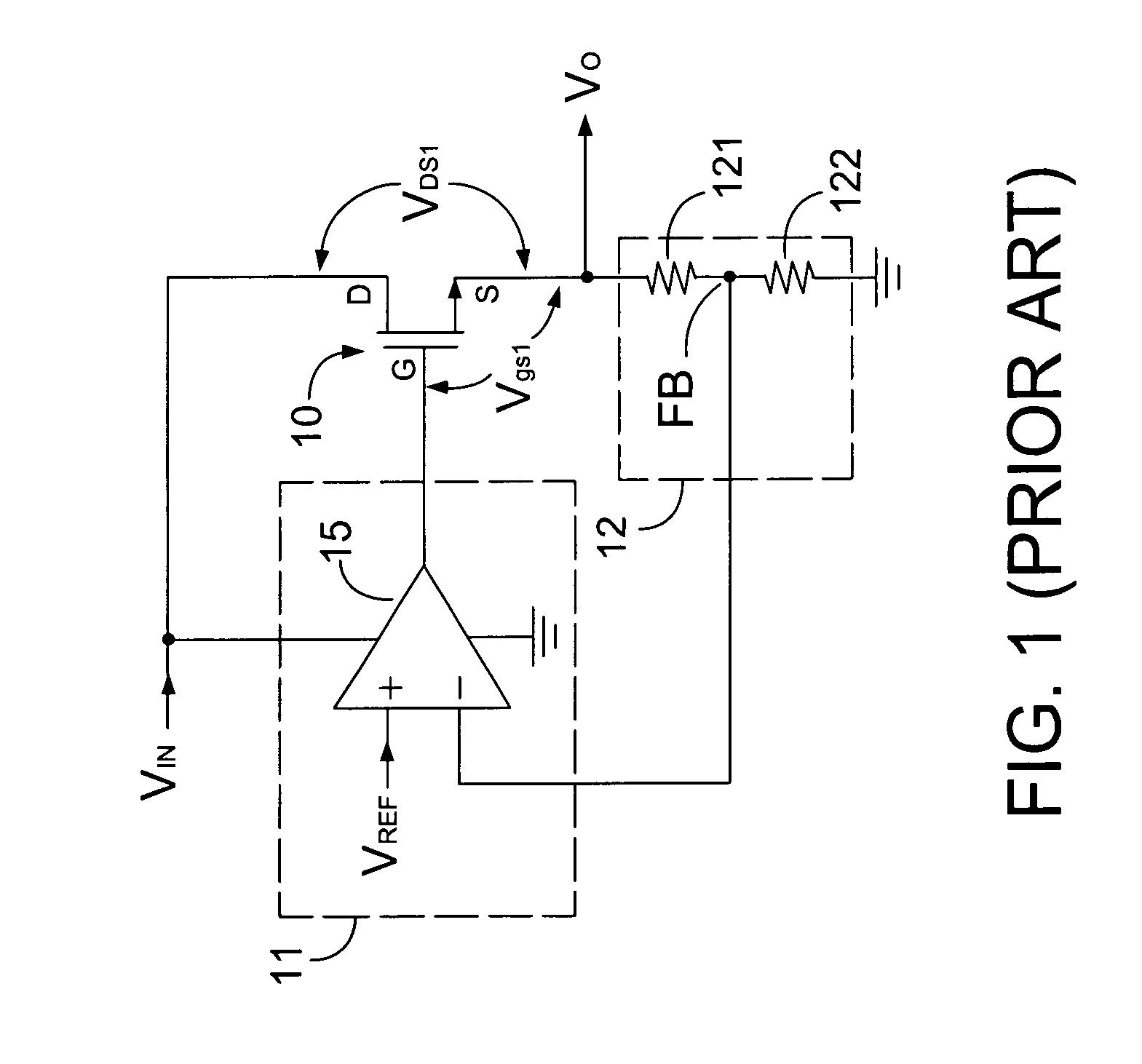
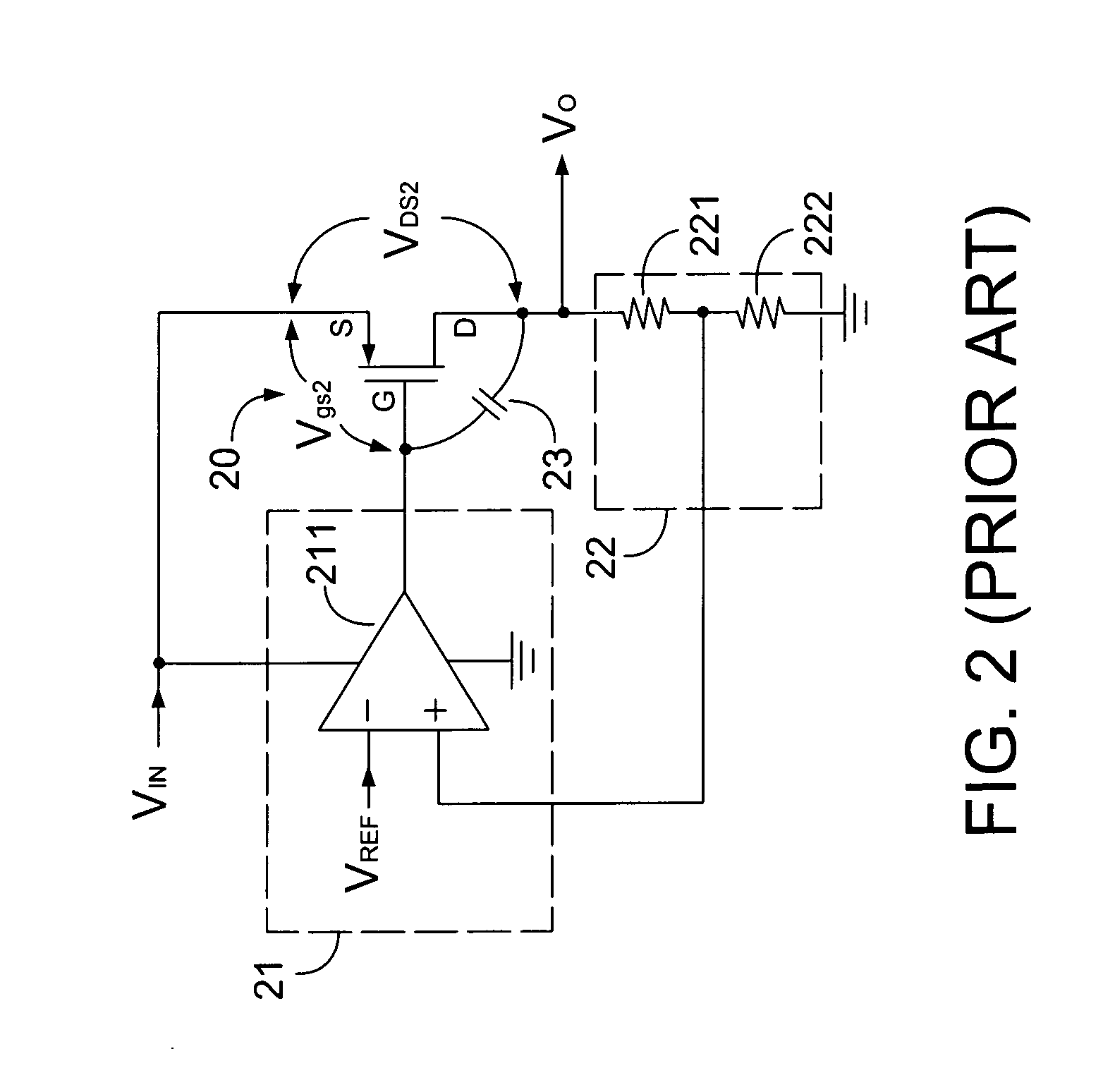
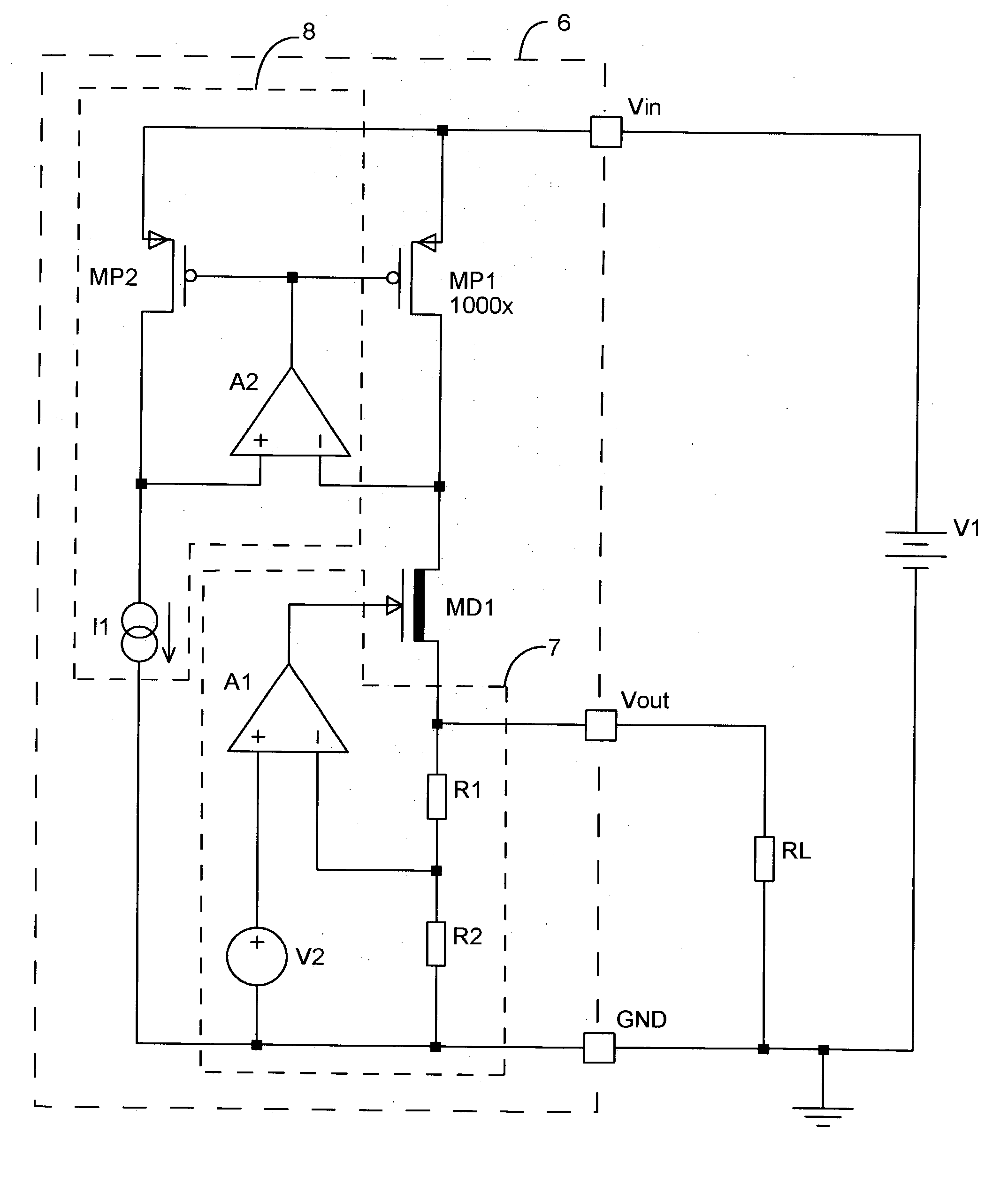
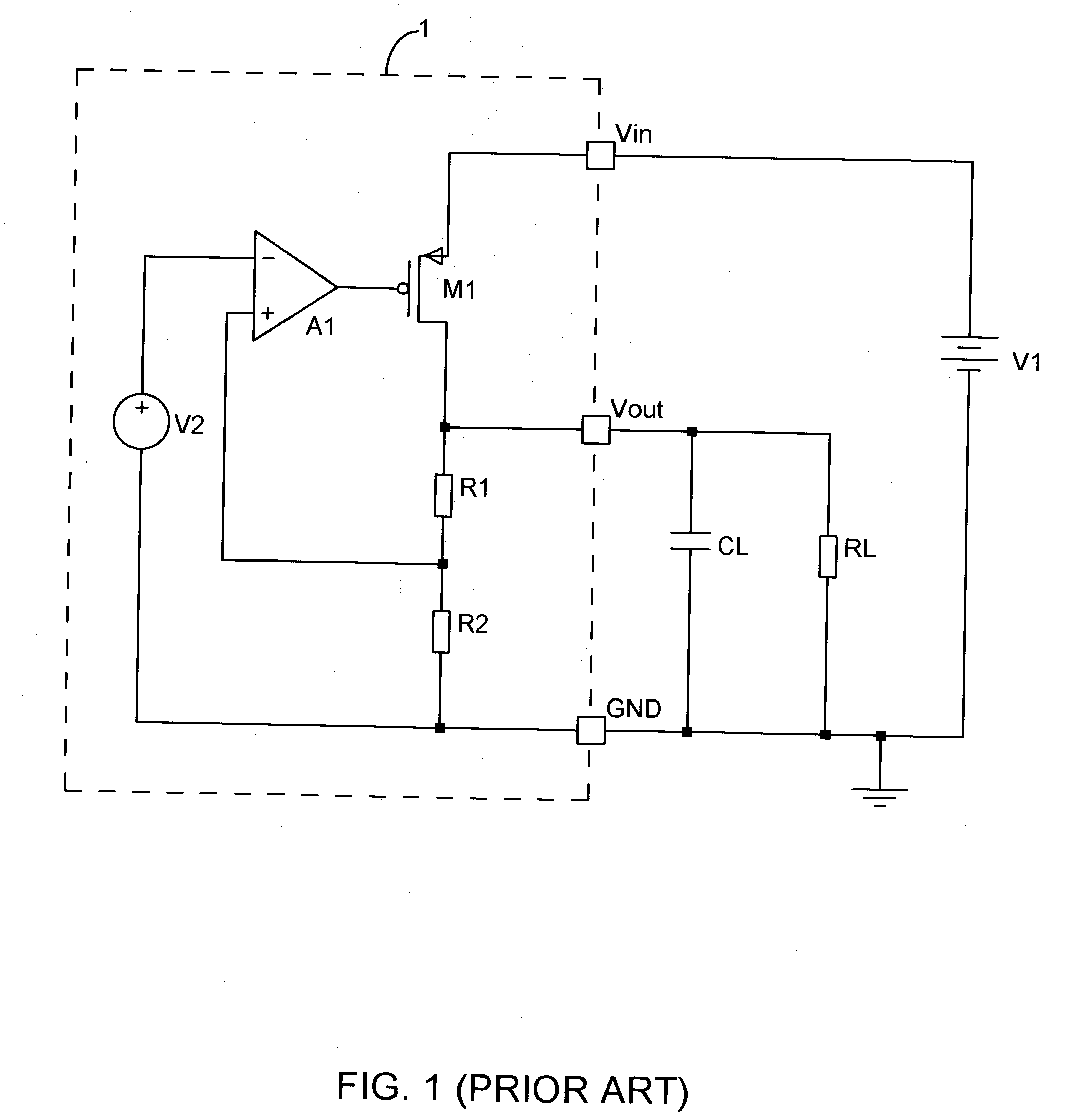
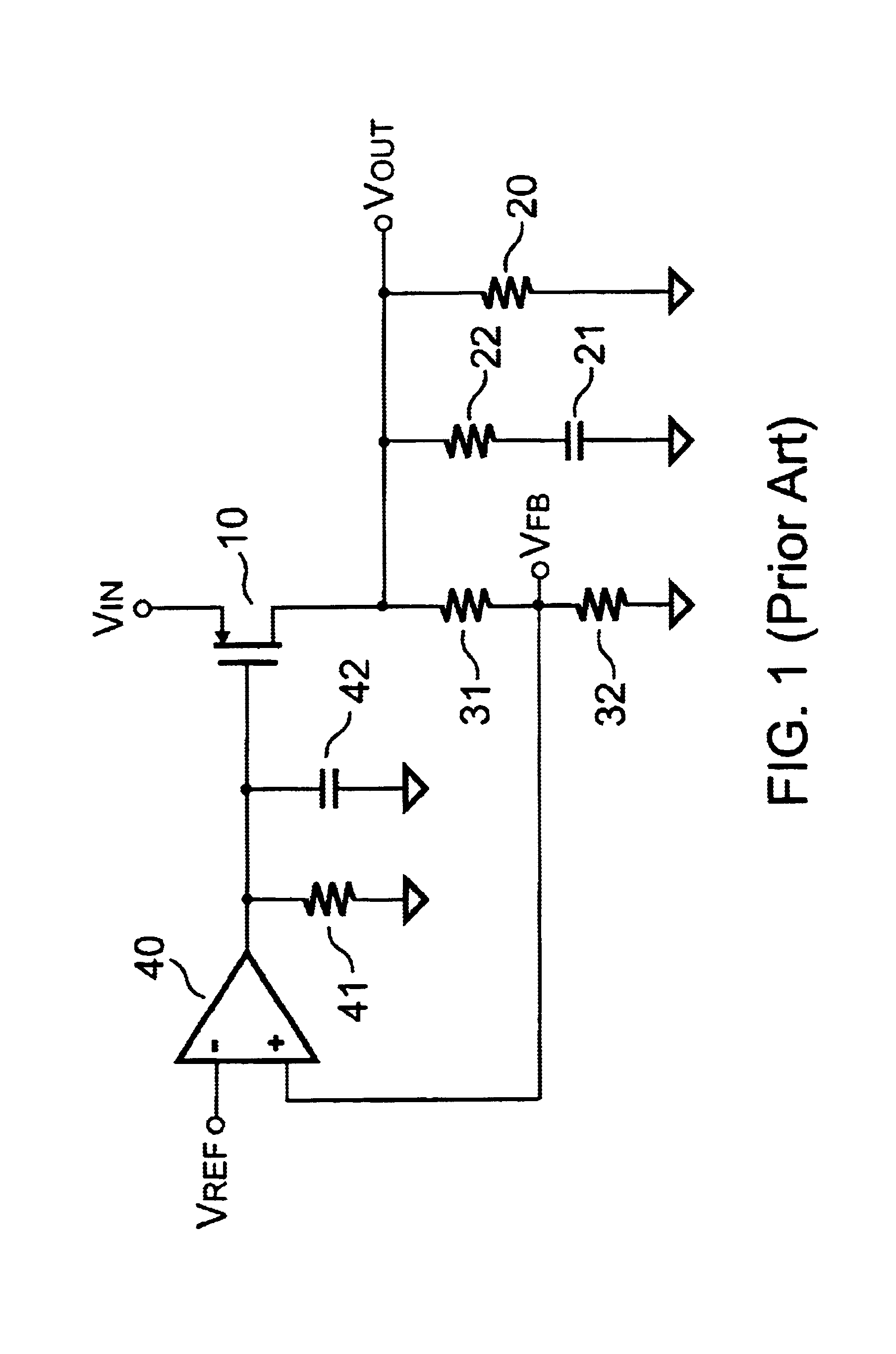
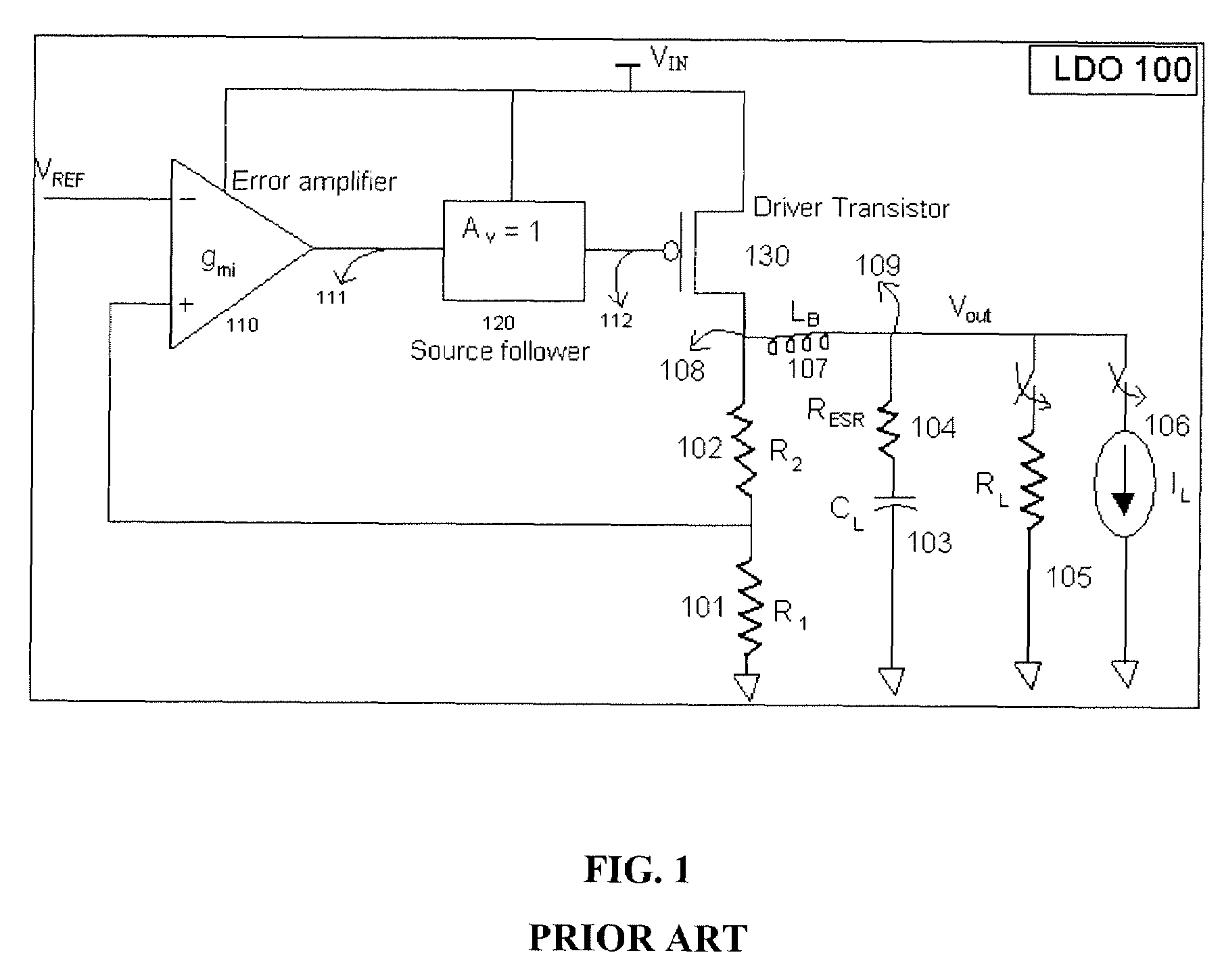
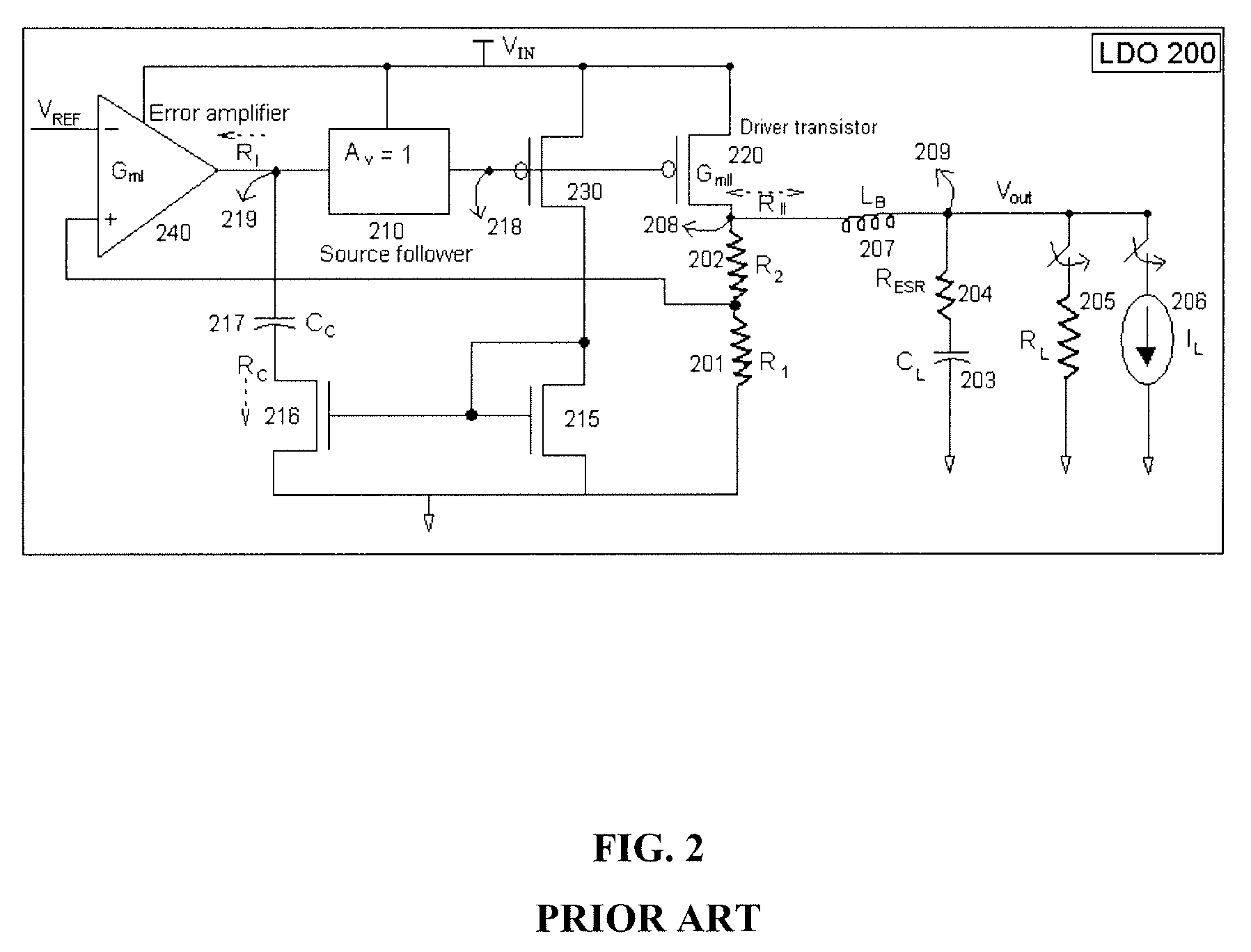
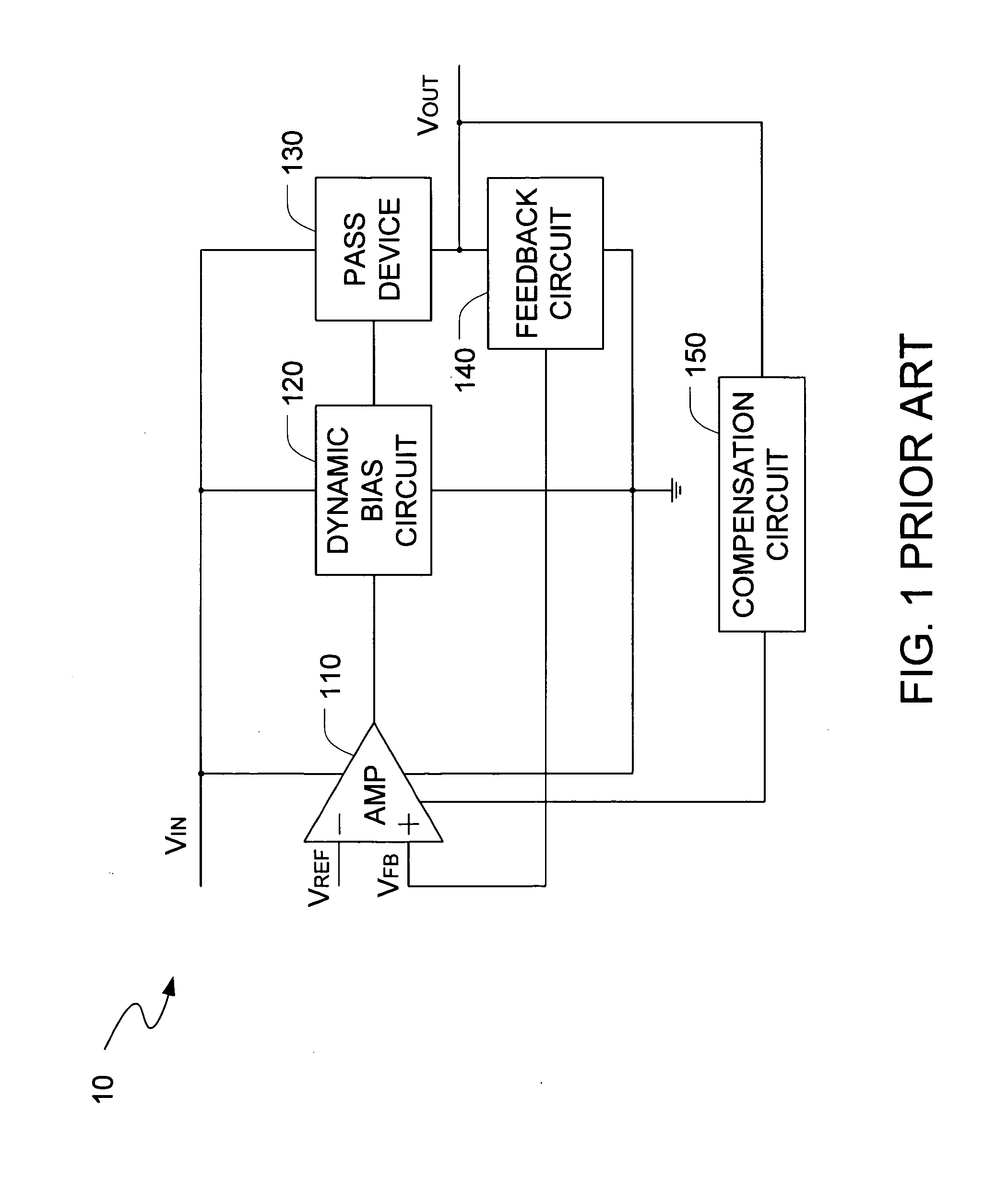
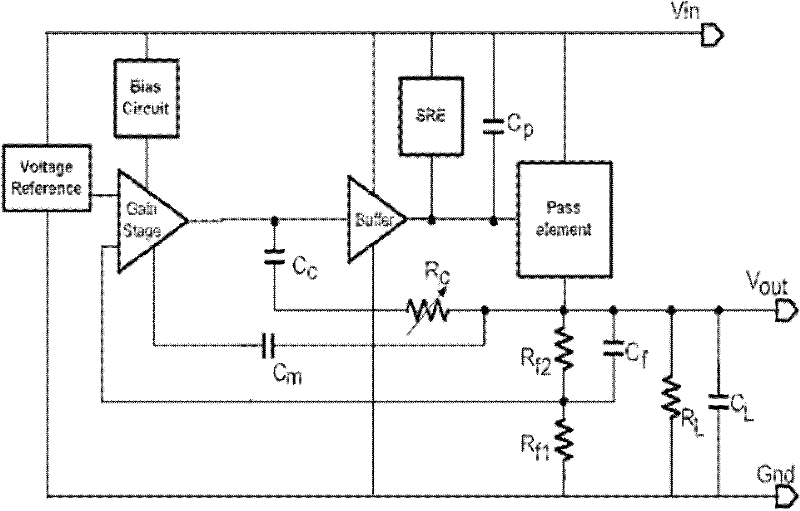
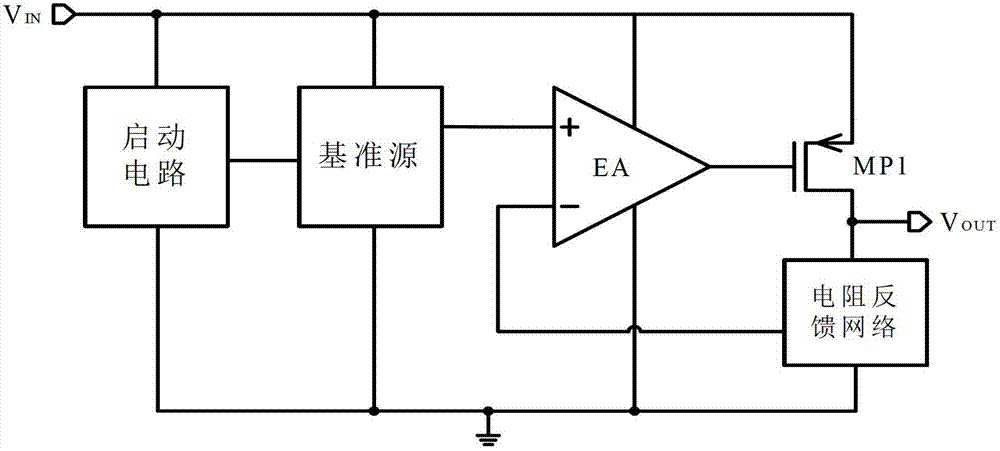
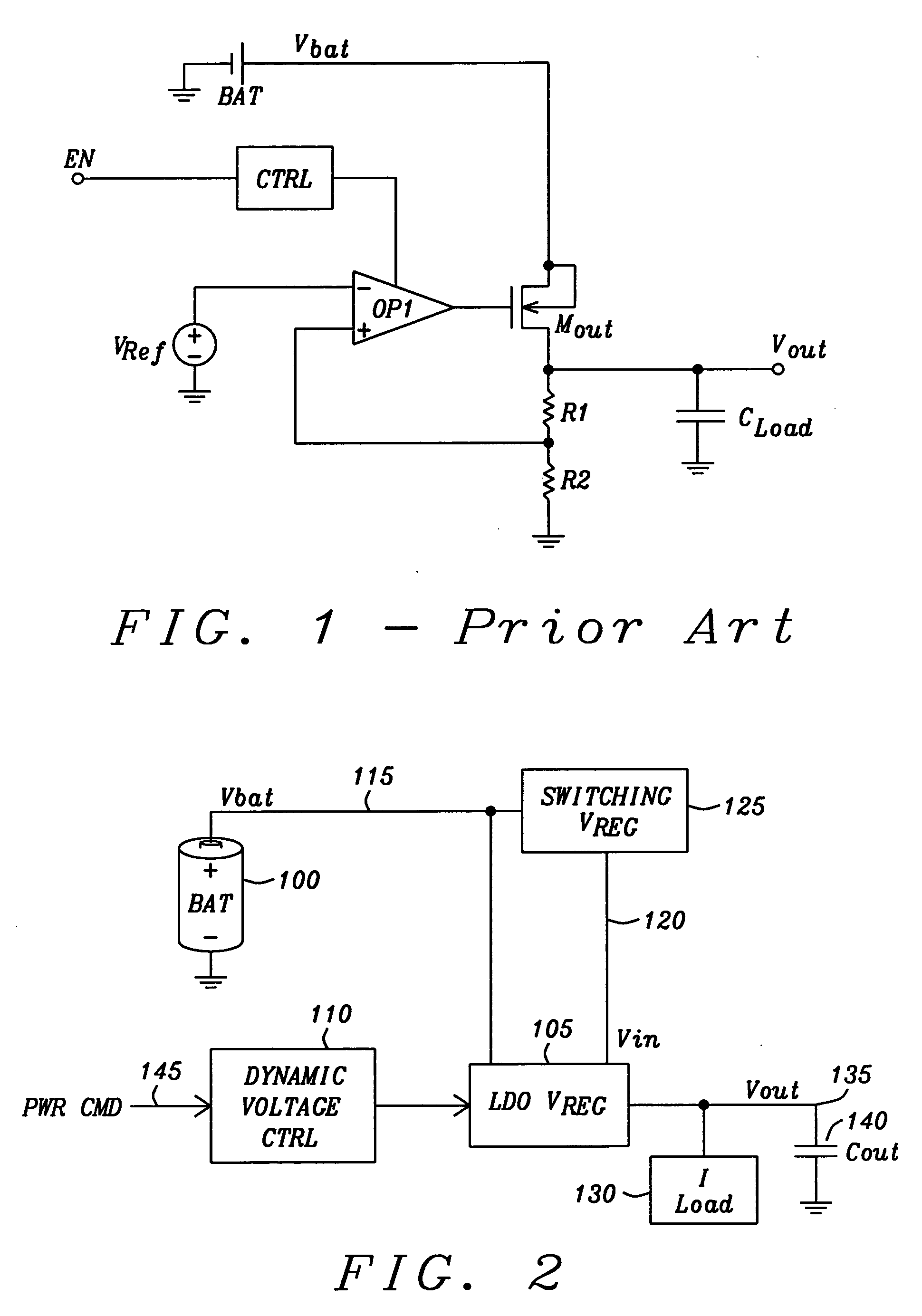
A low-dropout or LDO regulator is a DC linear voltage regulator that can regulate the output voltage even when the supply voltage is very close to the output voltage. The advantages of a low dropout voltage regulator over other DC to DC regulators include the absence of switching noise (as no switching takes place), smaller device size (as neither large inductors nor transformers are needed), and greater design simplicity (usually consists of a reference, an amplifier, and a pass element). The disadvantage is that, unlike switching regulators, linear DC regulators must dissipate power, and thus heat, across the regulation device in order to regulate the output voltage.
Overvoltage sensing and correction circuitry and method for low dropout voltage regulator
InactiveUS6201375B1Reduce severityEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentArrangements responsive to excess voltageOvervoltageElectrical conductor
Owner:BURR-BROWN CORPORATION
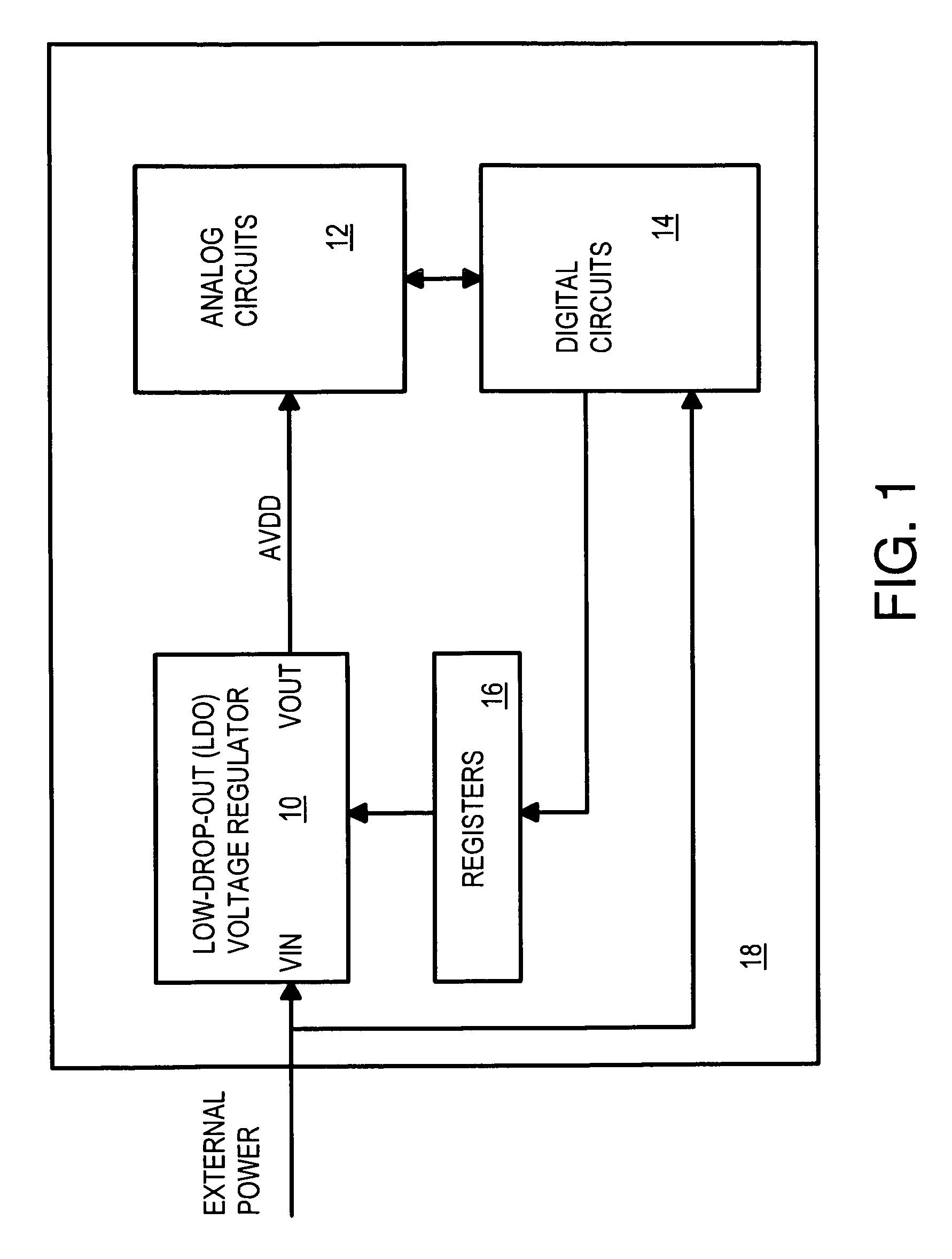
Low dropout voltage regulator with programmable on-chip output voltage for mixed signal embedded applications
ActiveUS7619402B1Multiple-port networksOne-port networksElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
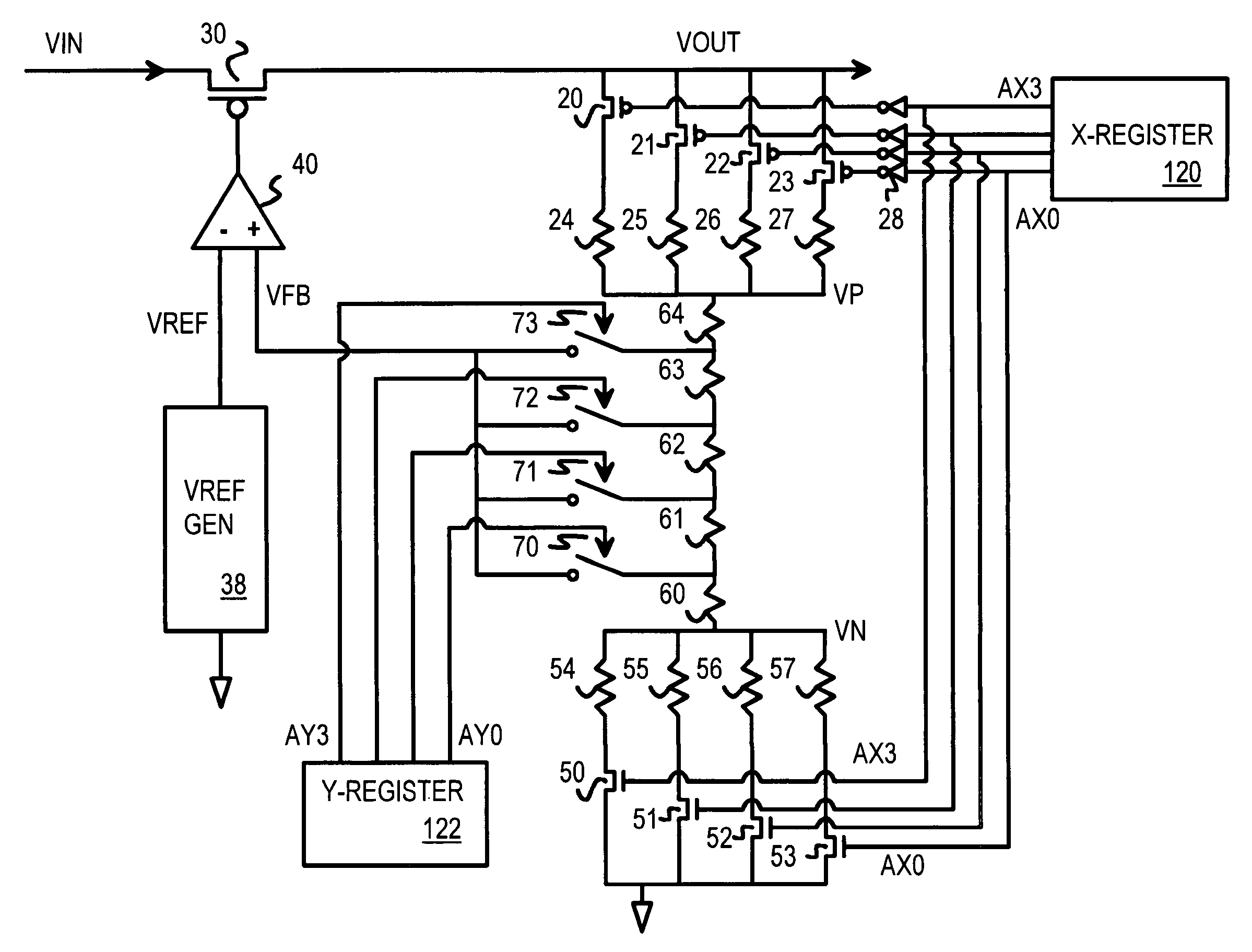
A programmable voltage generator has software-programmable registers that may be decoded to generate control bits that turn on select transistors that control a variable resistor network. An external power voltage is input to a regulator transistor, which has a channel resistance controlled by a gate voltage. The channel resistance of the regulator transistor produces a regulated voltage as an output. An op amp compares a reference voltage to a feedback voltage to generate the gate voltage. The feedback voltage is taken from a tap within the variable resistor network. The variable resistor network has select transistors that select one resistor between the regulated voltage and an upper node, and that select one resistor between a lower node and ground. Switches select a tap within a series of resistors between the upper and lower nodes. Y (fine) control bits select the tap while X (coarse) control bits enable select transistors.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Low drop-out regulator capable of functioning in linear and saturated regions of output driver
InactiveUS6285246B1Reduce power consumptionReduce consumptionElectric variable regulationEngineeringCmos process
A low drop-out regulator and methods for producing a low drop-out voltage are provided. A driver transistor adapted for connecting to an input supply voltage and producing an output voltage is provided. In addition, a mirroring transistor is coupled to the driver transistor and a voltage differential between the drain and the source of the driver transistor is mirrored in the mirroring transistor. The low drop-out regulator operates in both linear and saturation regions of the driver transistor. The driver transistor and the mirroring transistor are implemented in a CMOS process.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Low dropout regulator
InactiveUS20070159146A1Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
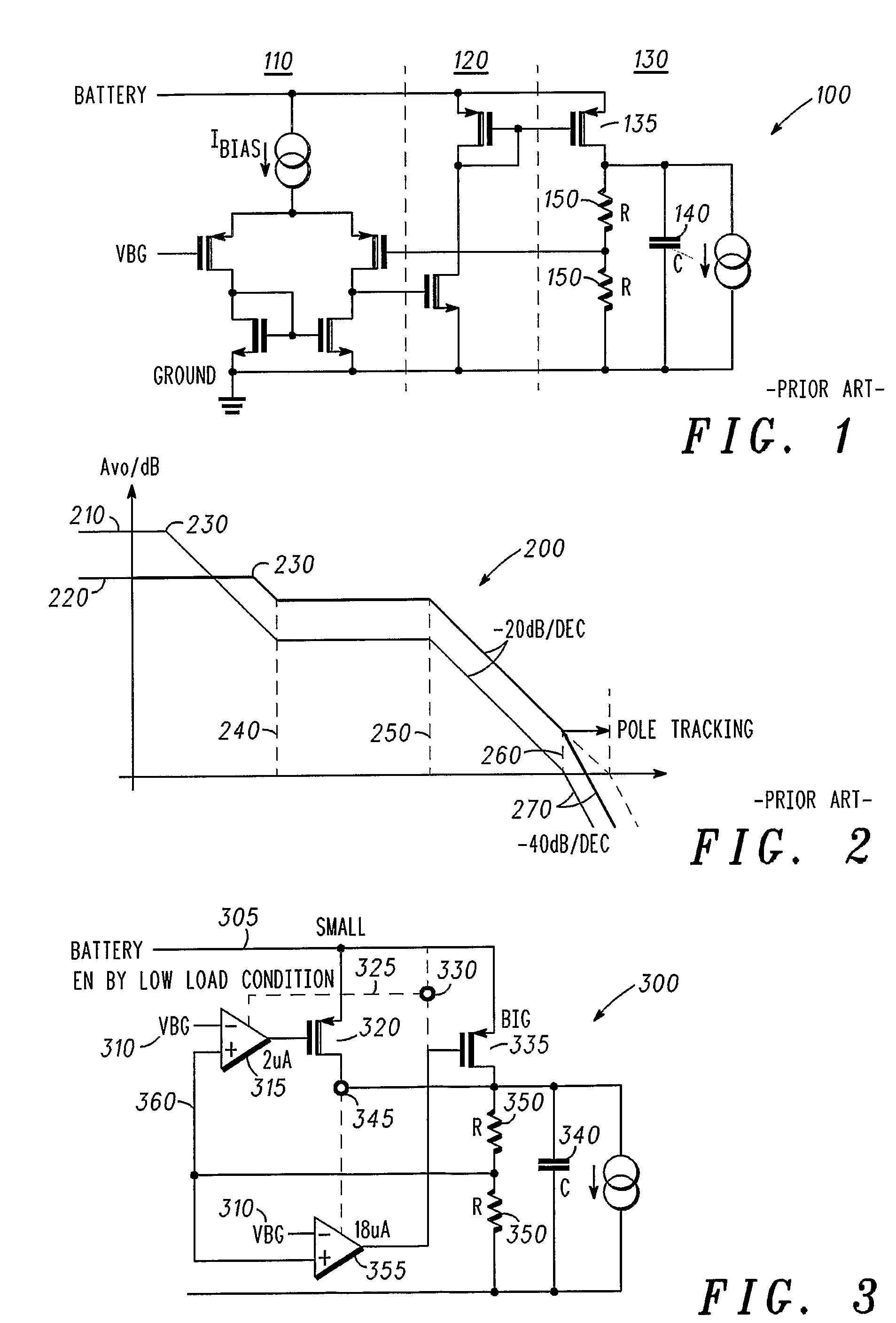
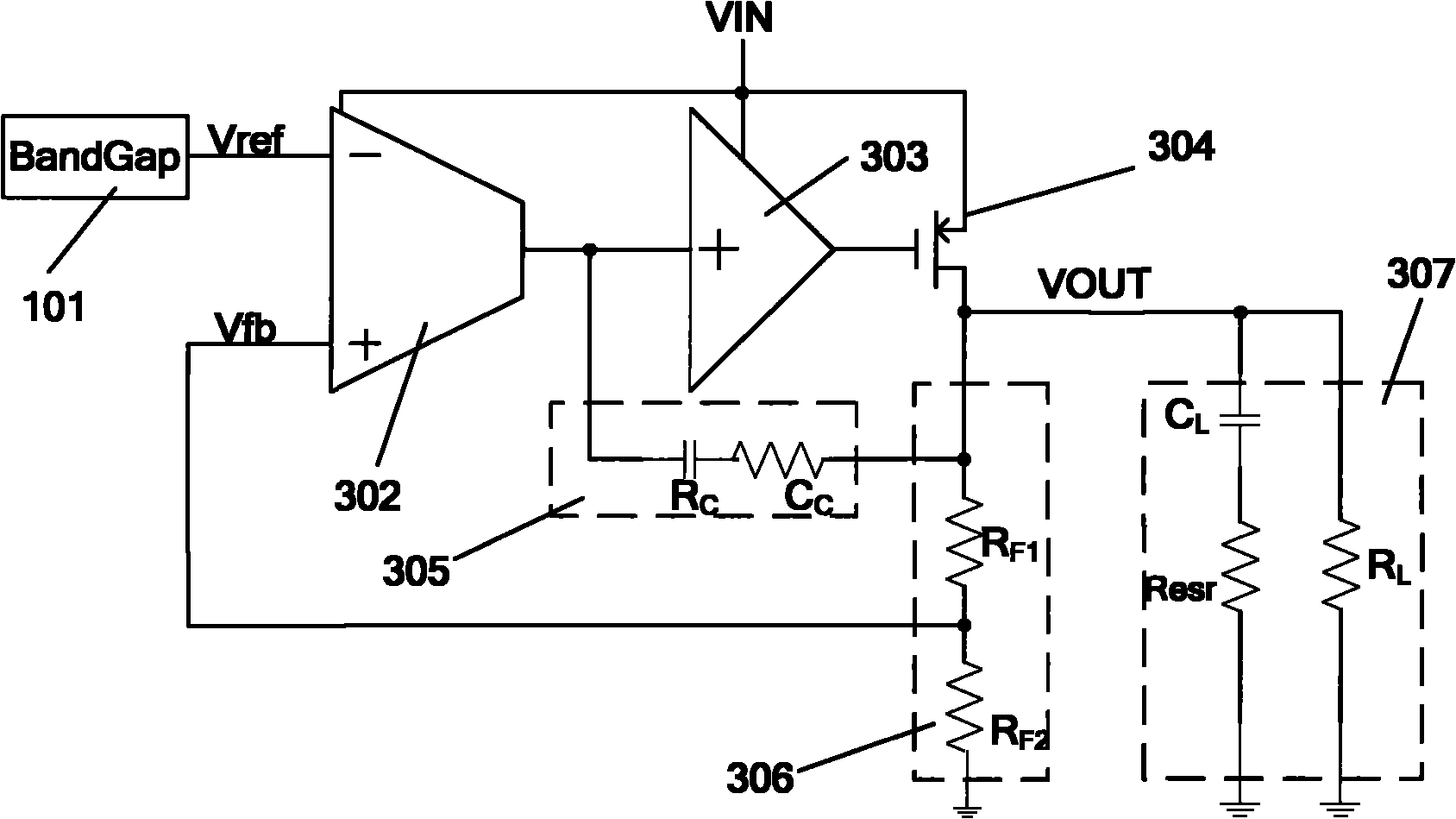
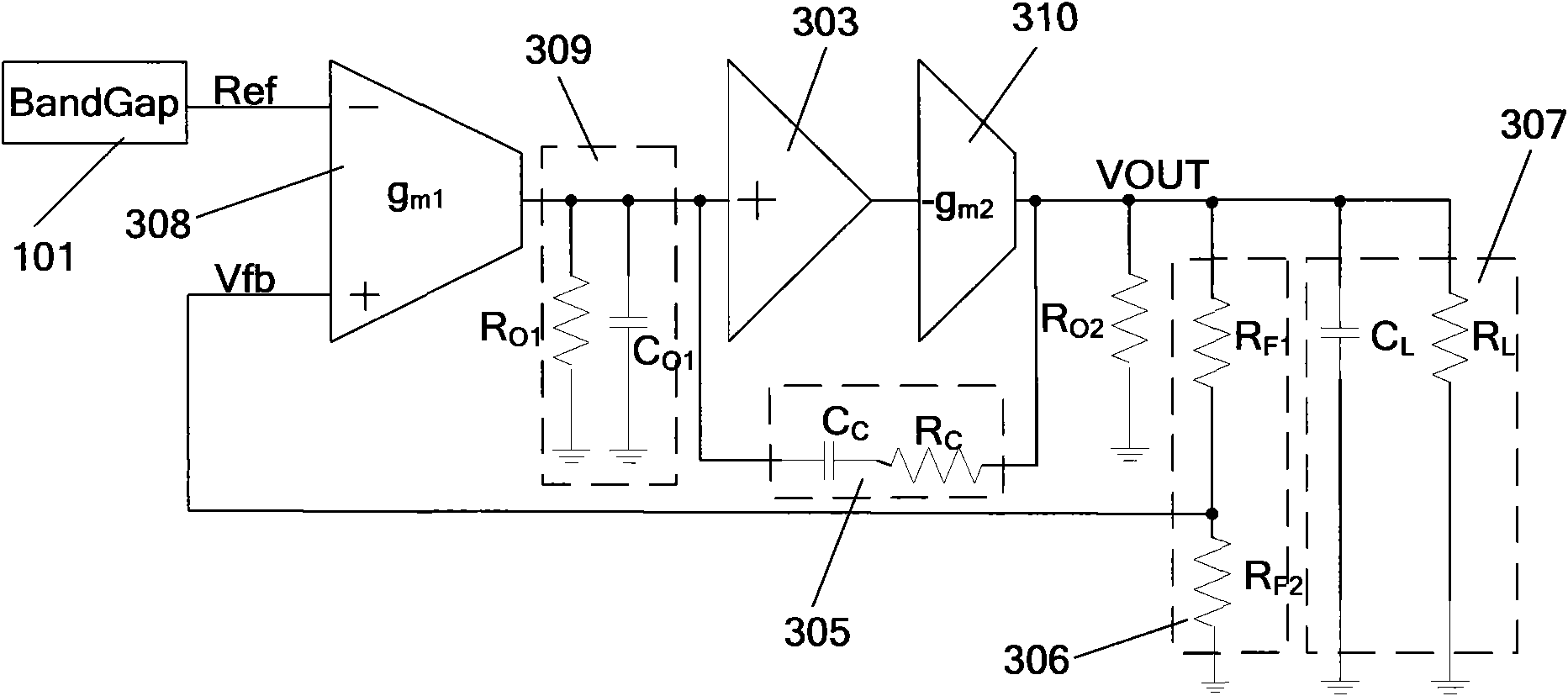
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Low dropout voltage regulator using a depletion pass transistor
InactiveUS6989659B2Improve reliabilityInsensitiveElectric variable regulationEngineeringCurrent regulation
A linear low dropout voltage regulator is described that makes use of a depletion mode NMOS pass transistor and of a PMOS transistor in series to the NMOS transistor and connected to its drain. The depletion NMOS transistor assures low dropout operations, while the series PMOS transistor allows the current regulation even under the condition of shorted load. The same PMOS transistor may be used to disable the current in the load without generating a negative voltage at the gate of the depletion pass transistor. This regulator is inherently stable without the need for an output capacitor in parallel to the load.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
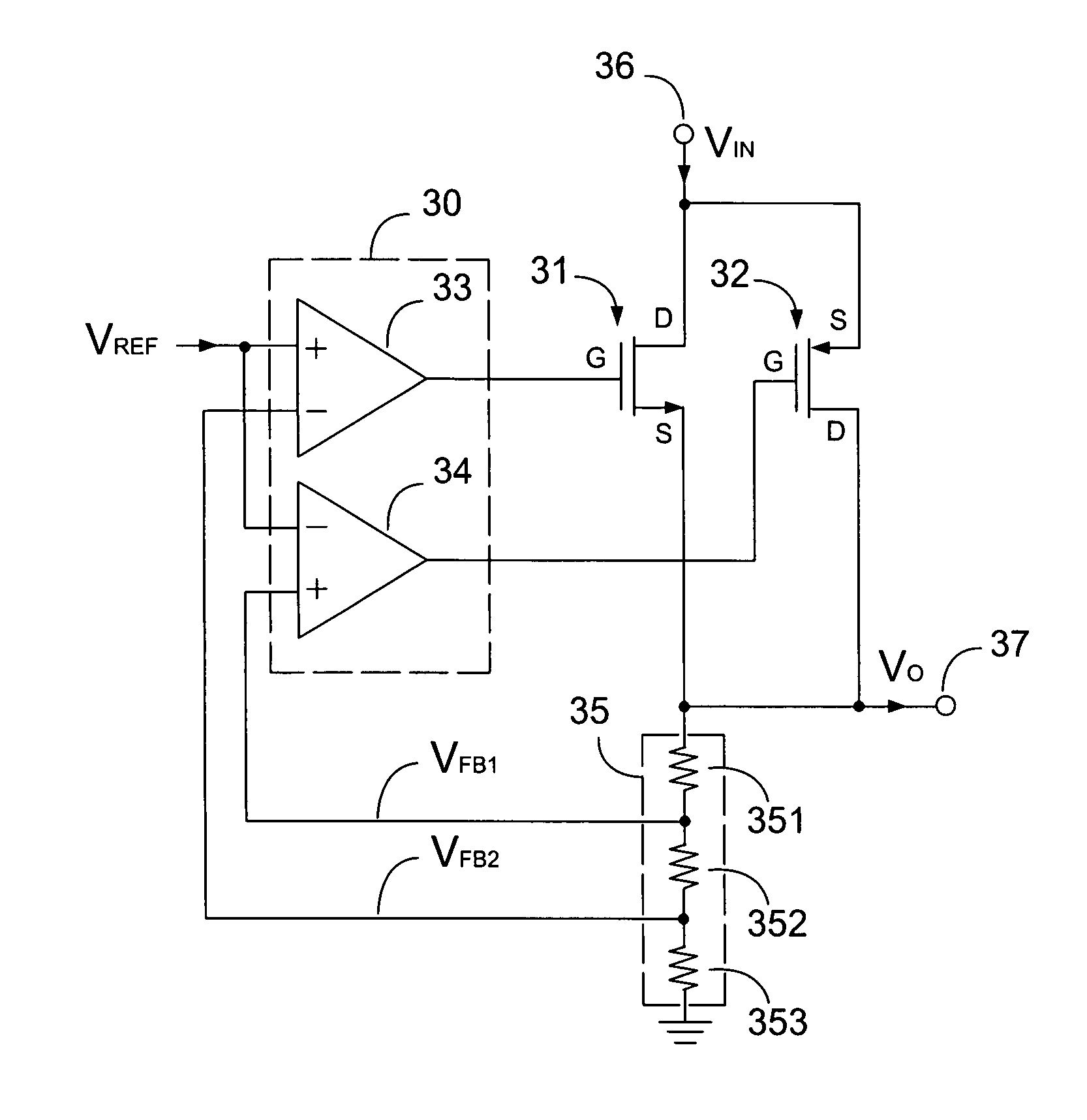
Low dropout regulator with wide input voltage range
ActiveUS20080116862A1Improve loop stabilityLow dropout voltageElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage range
A low dropout (LDO) regulator operates in wide input range. The LDO includes an N-type pass transistor and a P-type pass transistor for supplying power to the output terminal. The P-type pass transistor is connected with N-type pass transistor in parallel. Two error amplifiers control the gate terminals of the N-type pass transistor and P-type pass transistor to generate a first output voltage and a second output voltage. Thus, the first output voltage is generated when the input voltage is higher than a threshold voltage, and the second output voltage is generated when the input voltage is lower than the threshold voltage.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Low dropout voltage regulator using a depletion pass transistor
A linear low dropout voltage regulator is described that makes use of a depletion mode NMOS pass transistor and of a PMOS transistor in series to the NMOS transistor and connected to its drain. The depletion NMOS transistor assures low dropout operations, while the series PMOS transistor allows the current regulation even under the condition of shorted load. The same PMOS transistor may be used to disable the current in the load without generating a negative voltage at the gate of the depletion pass transistor. This regulator is inherently stable without the need for an output capacitor in parallel to the load.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
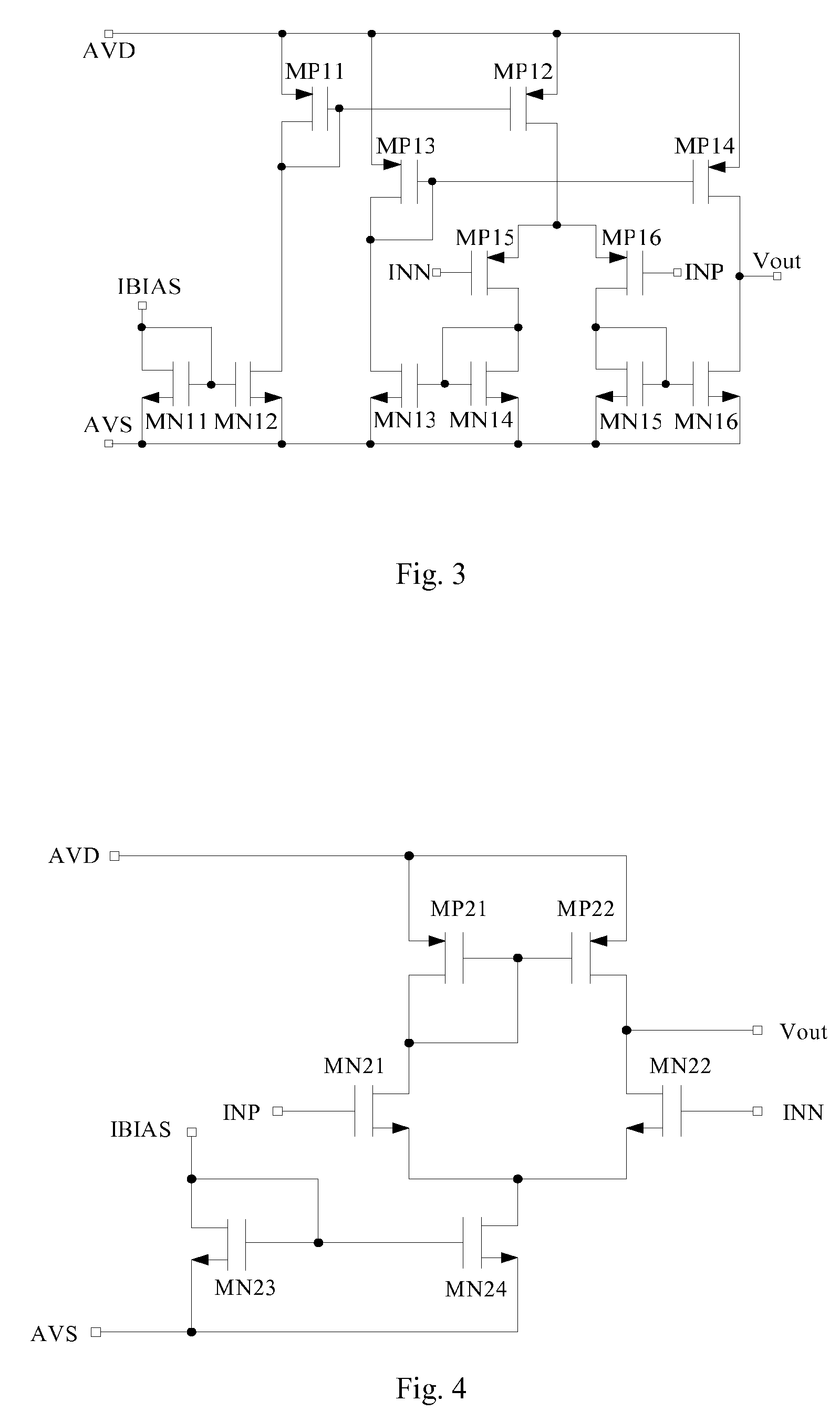
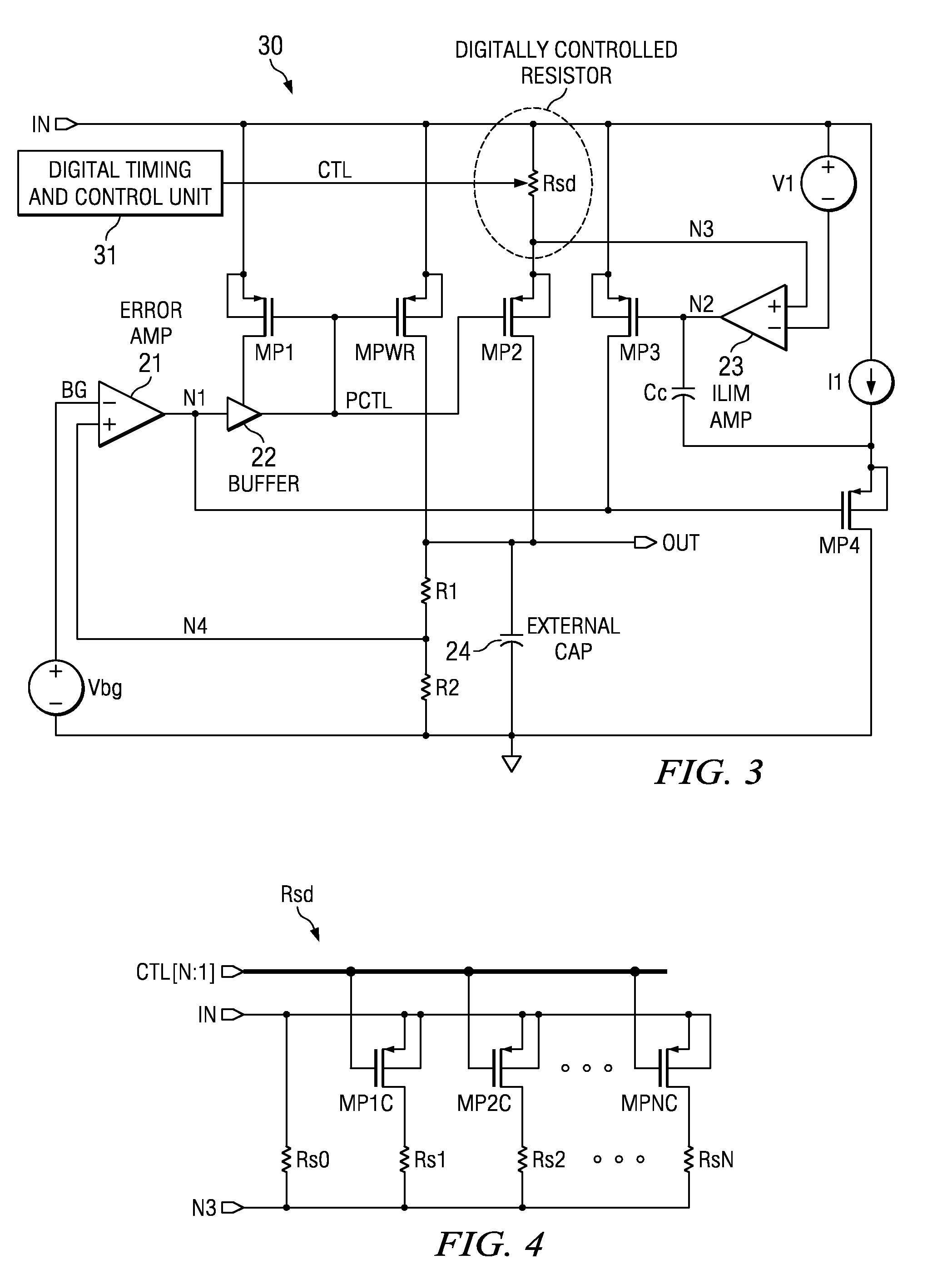
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
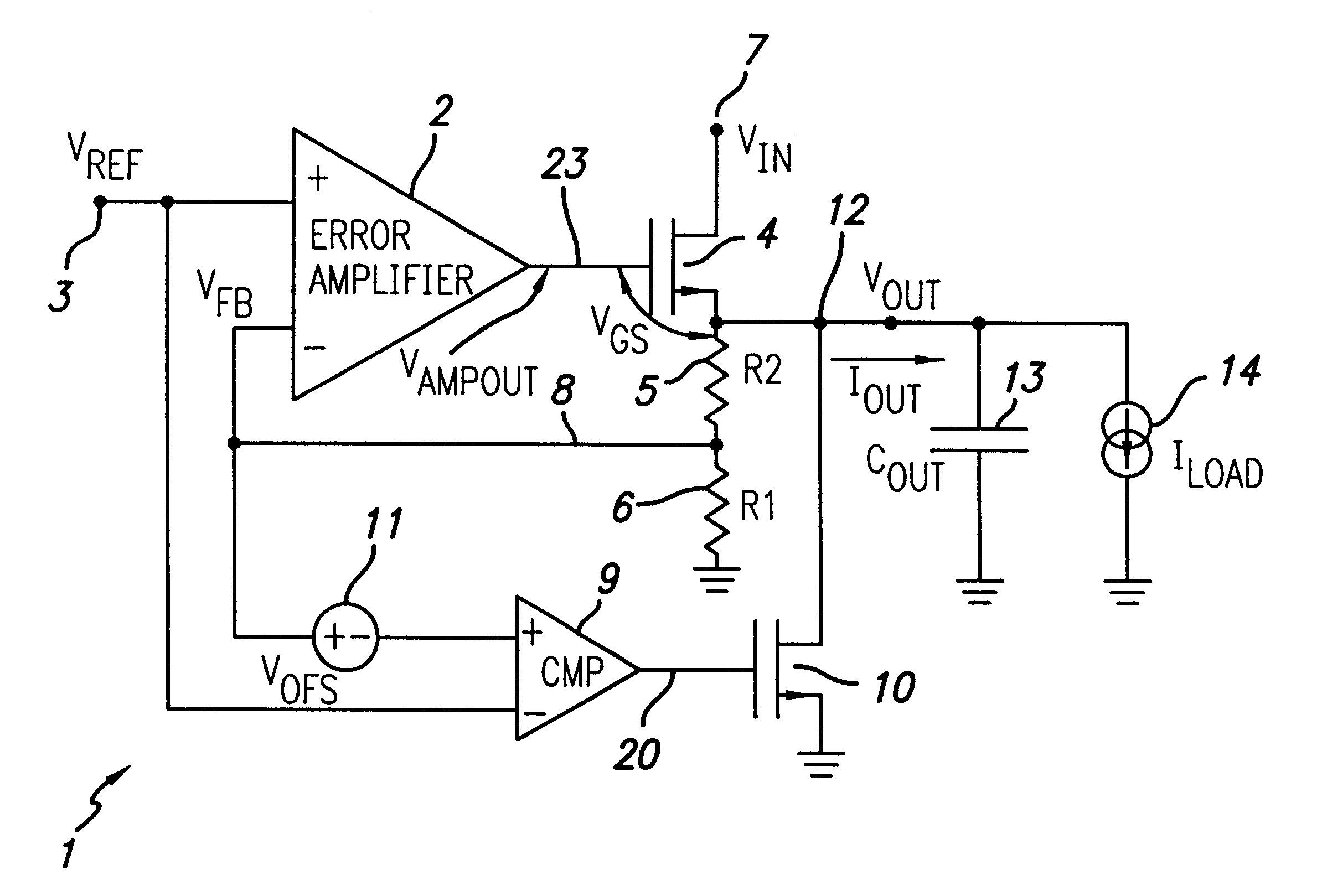
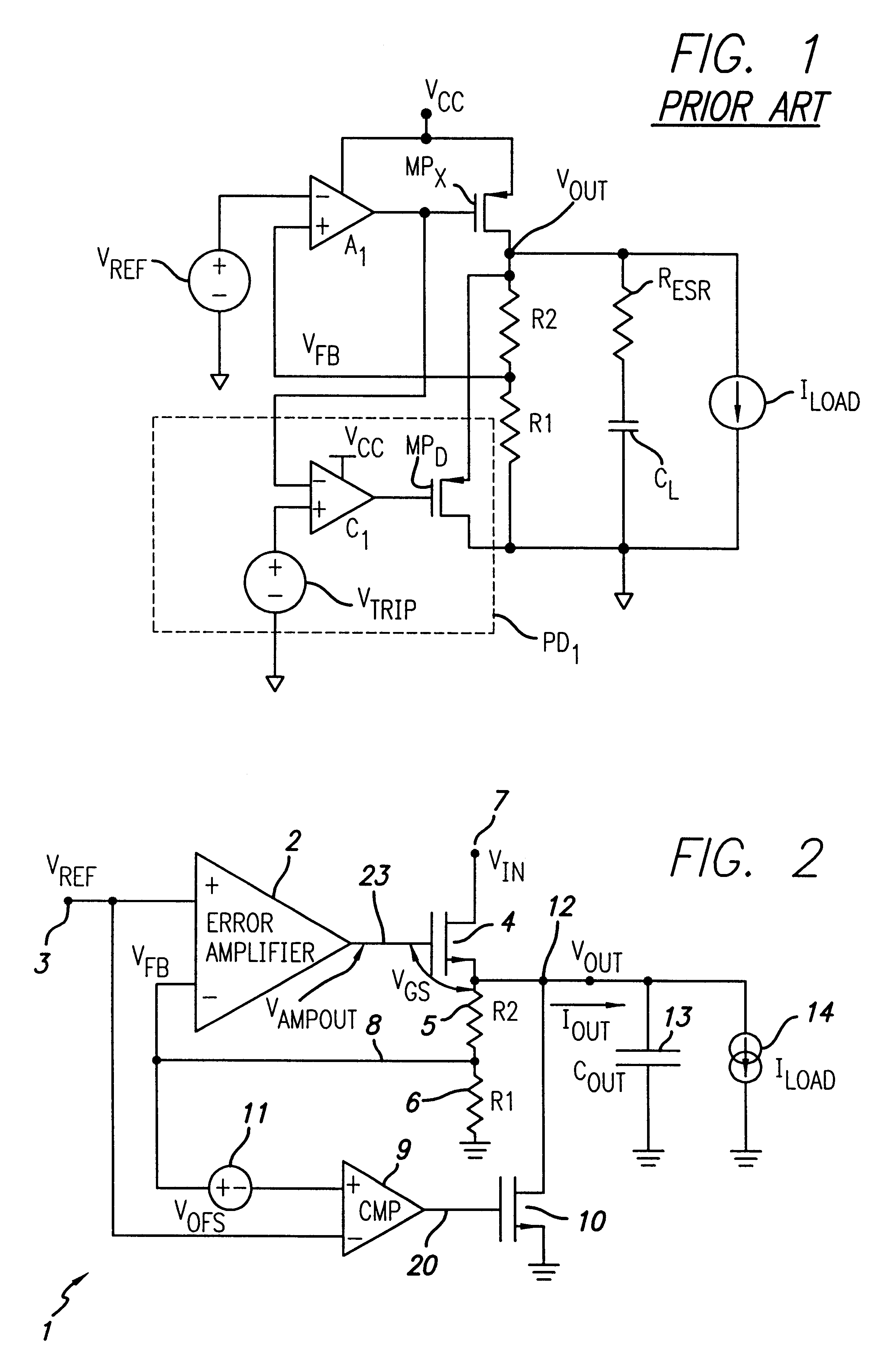
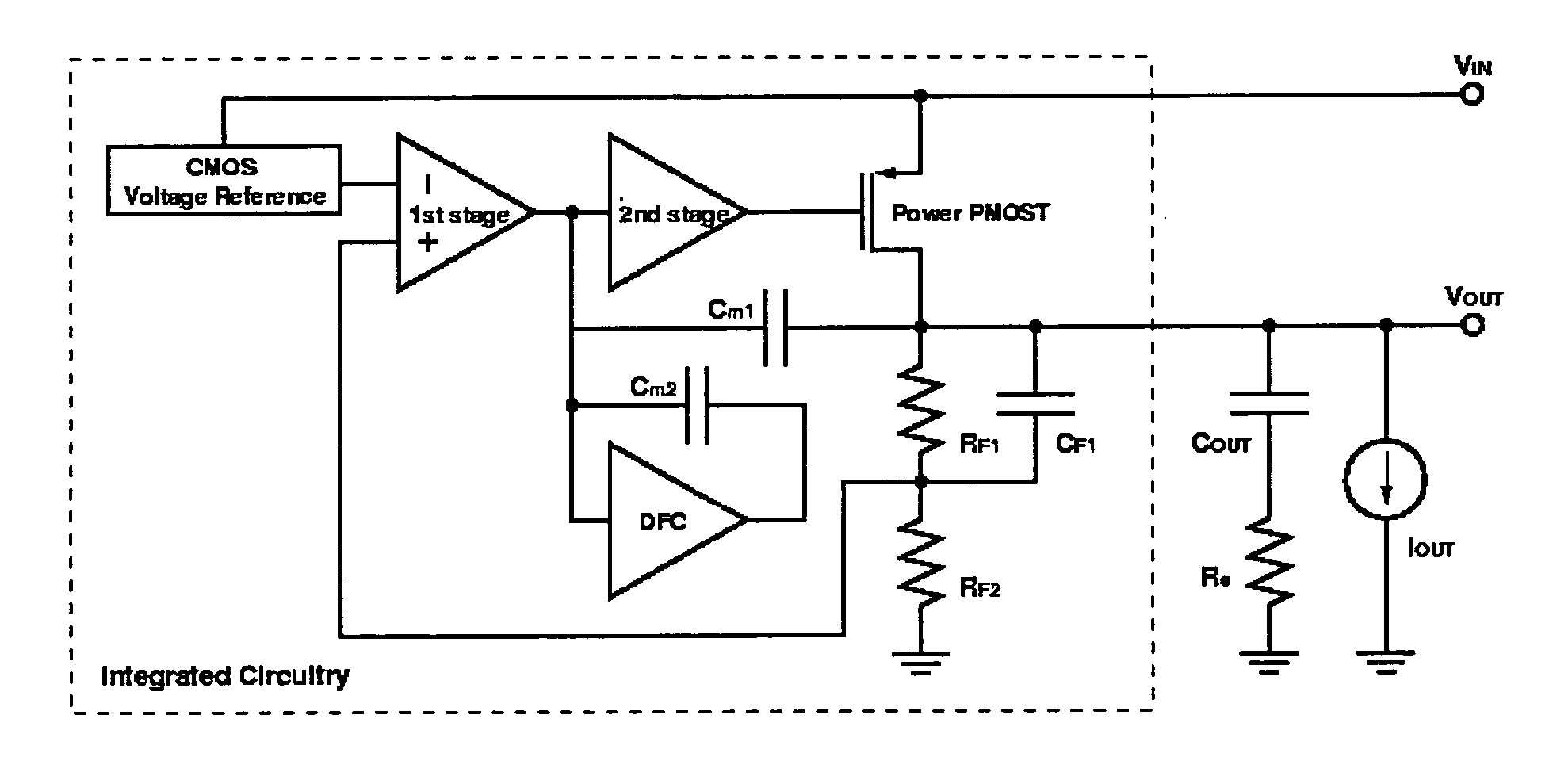
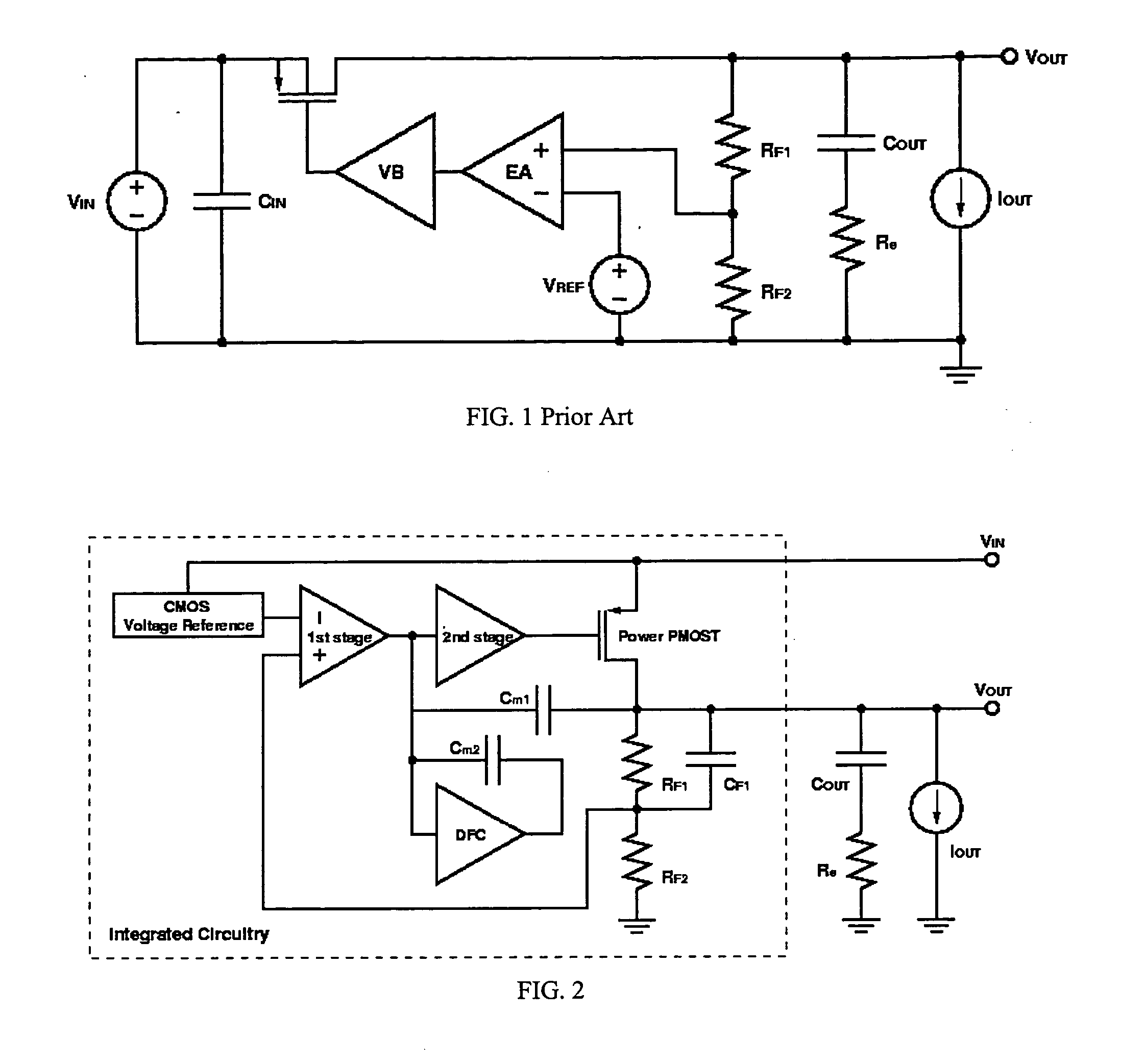
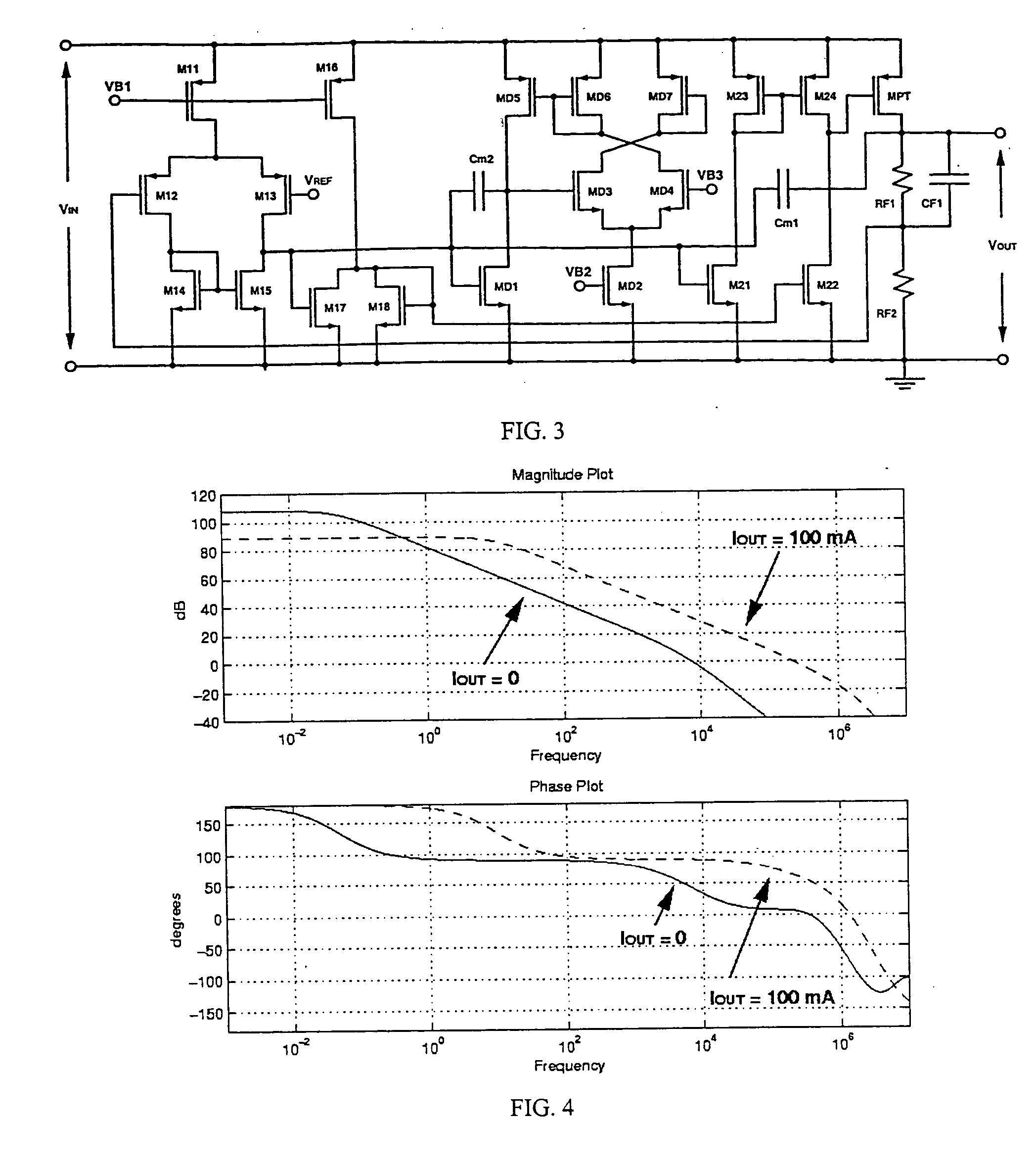
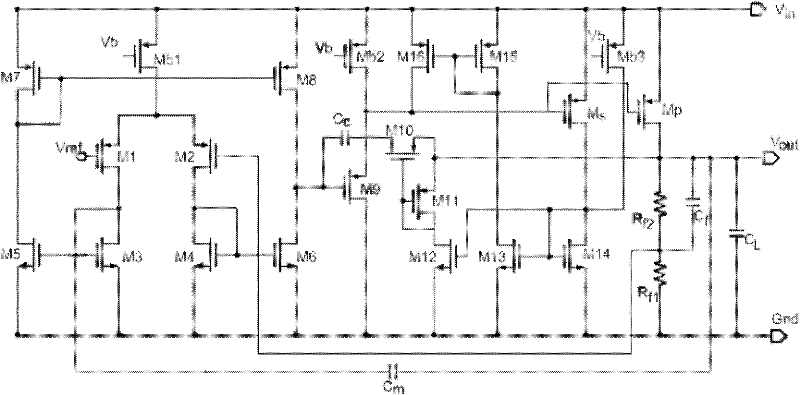
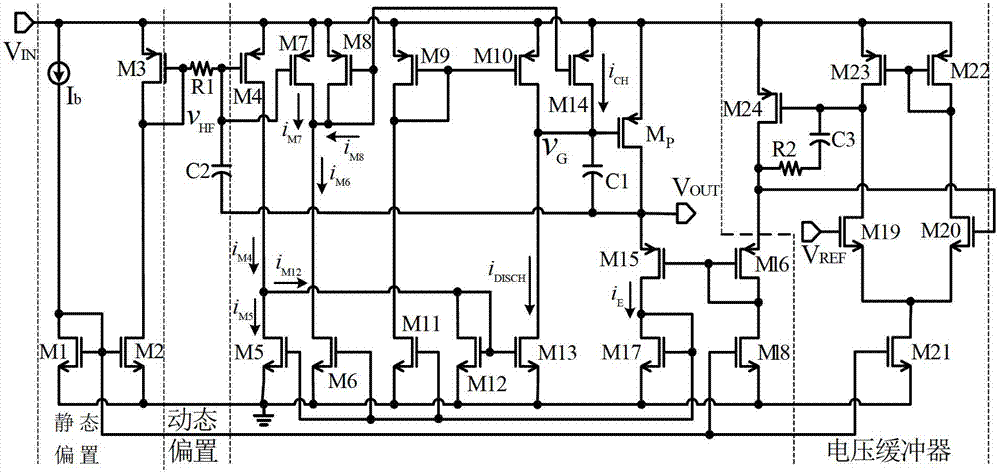
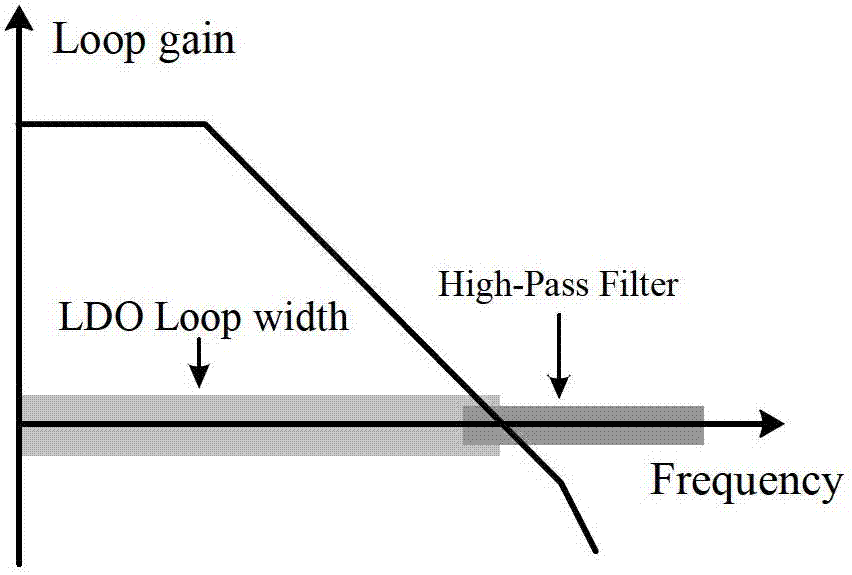
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
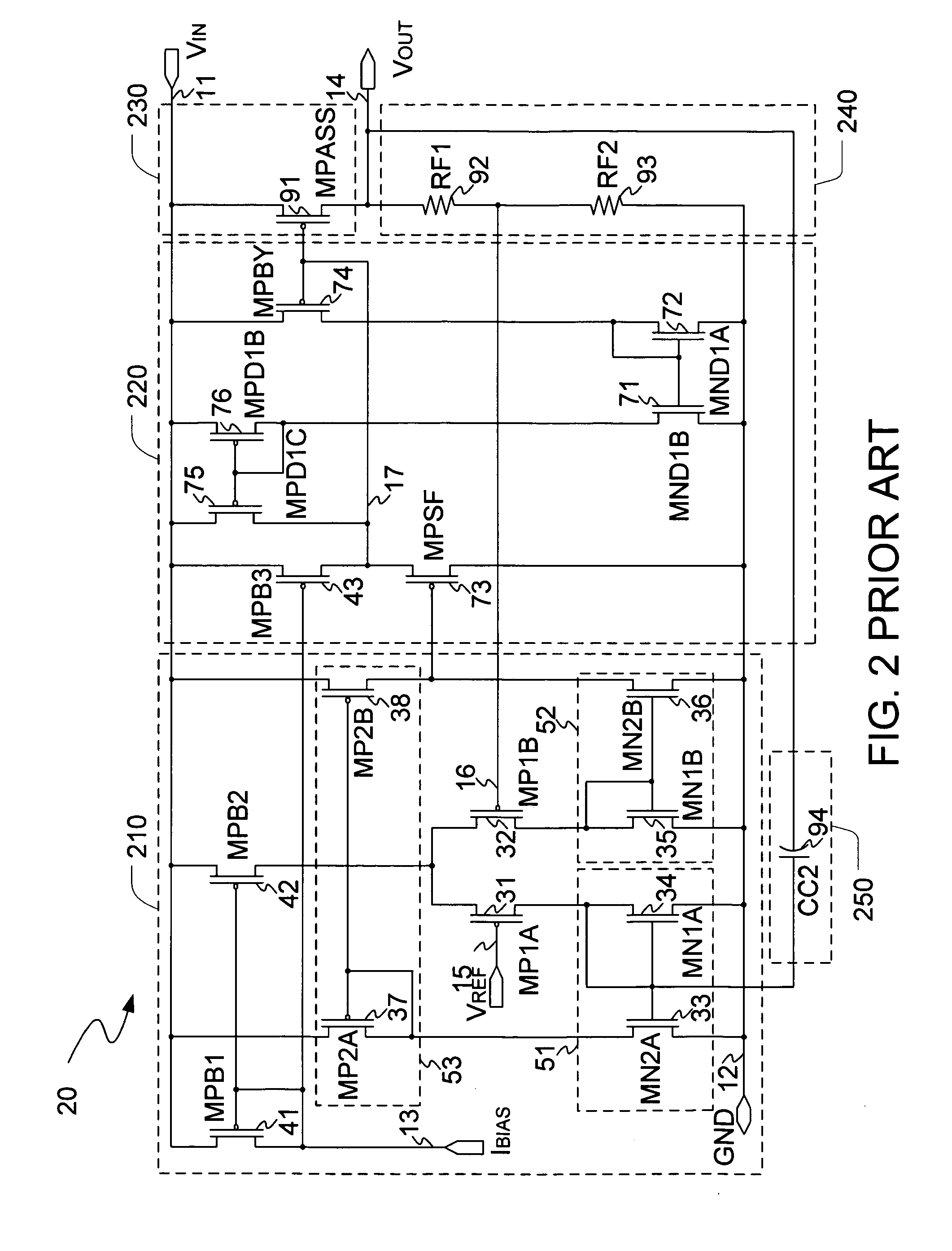
Low dropout regulator
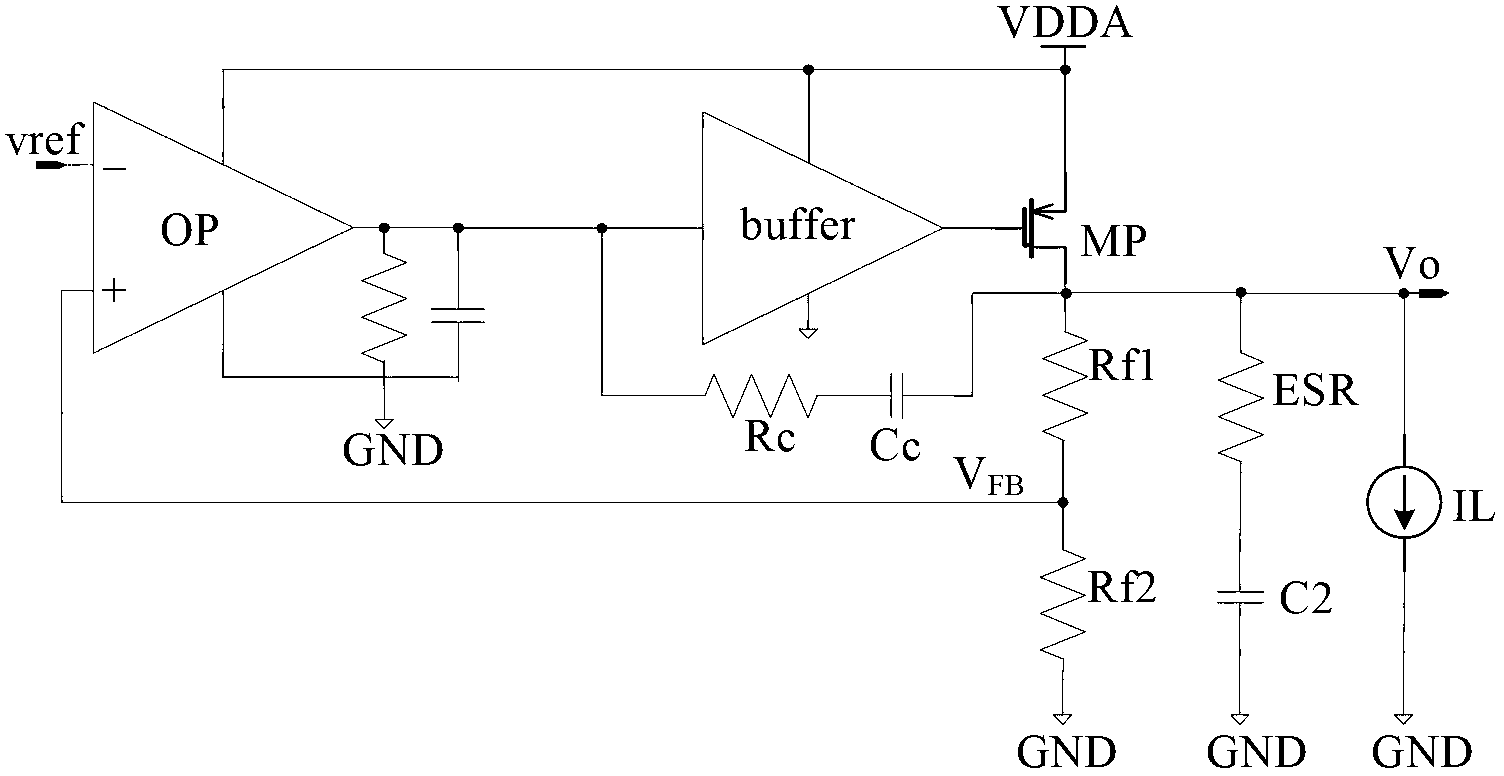
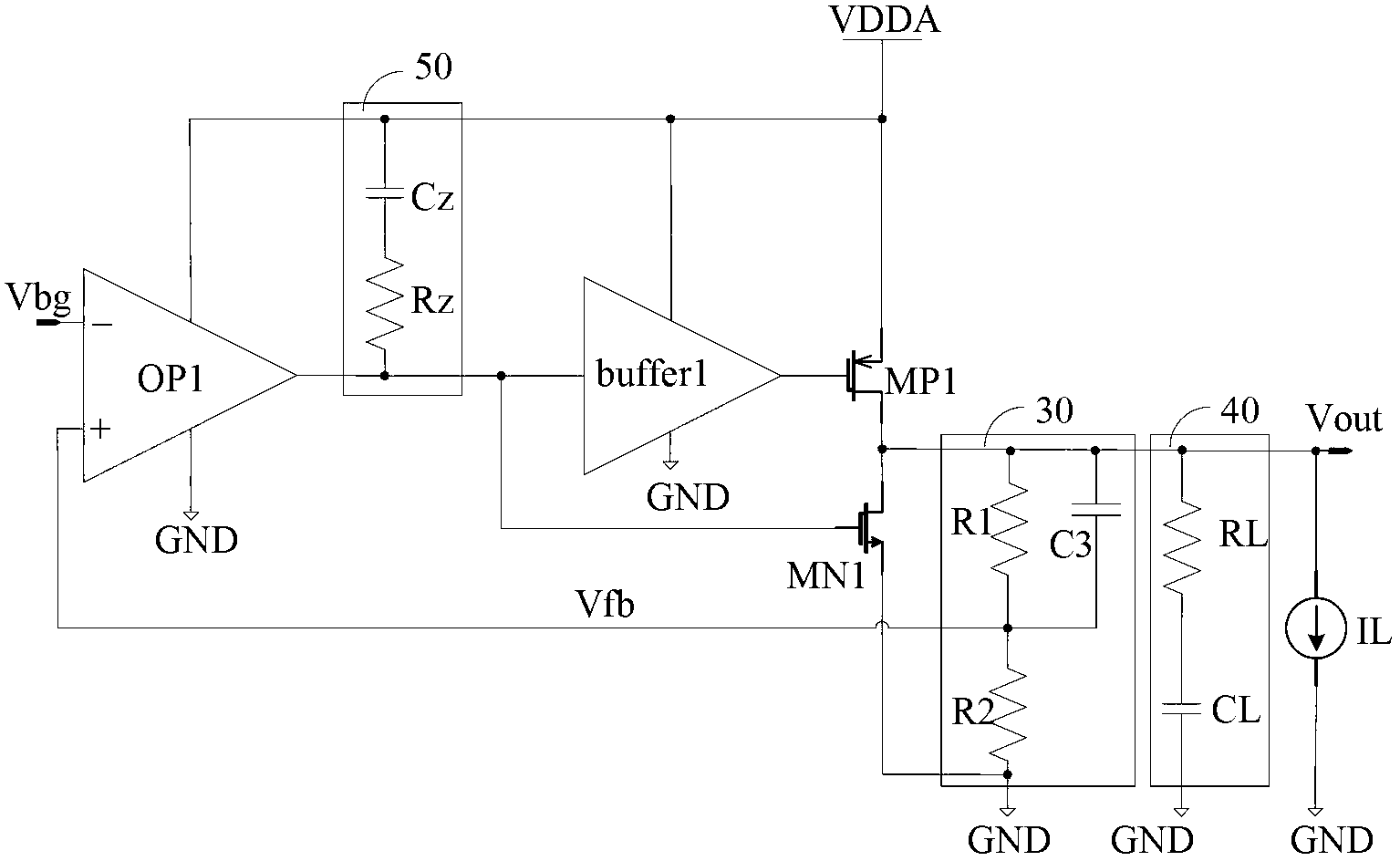
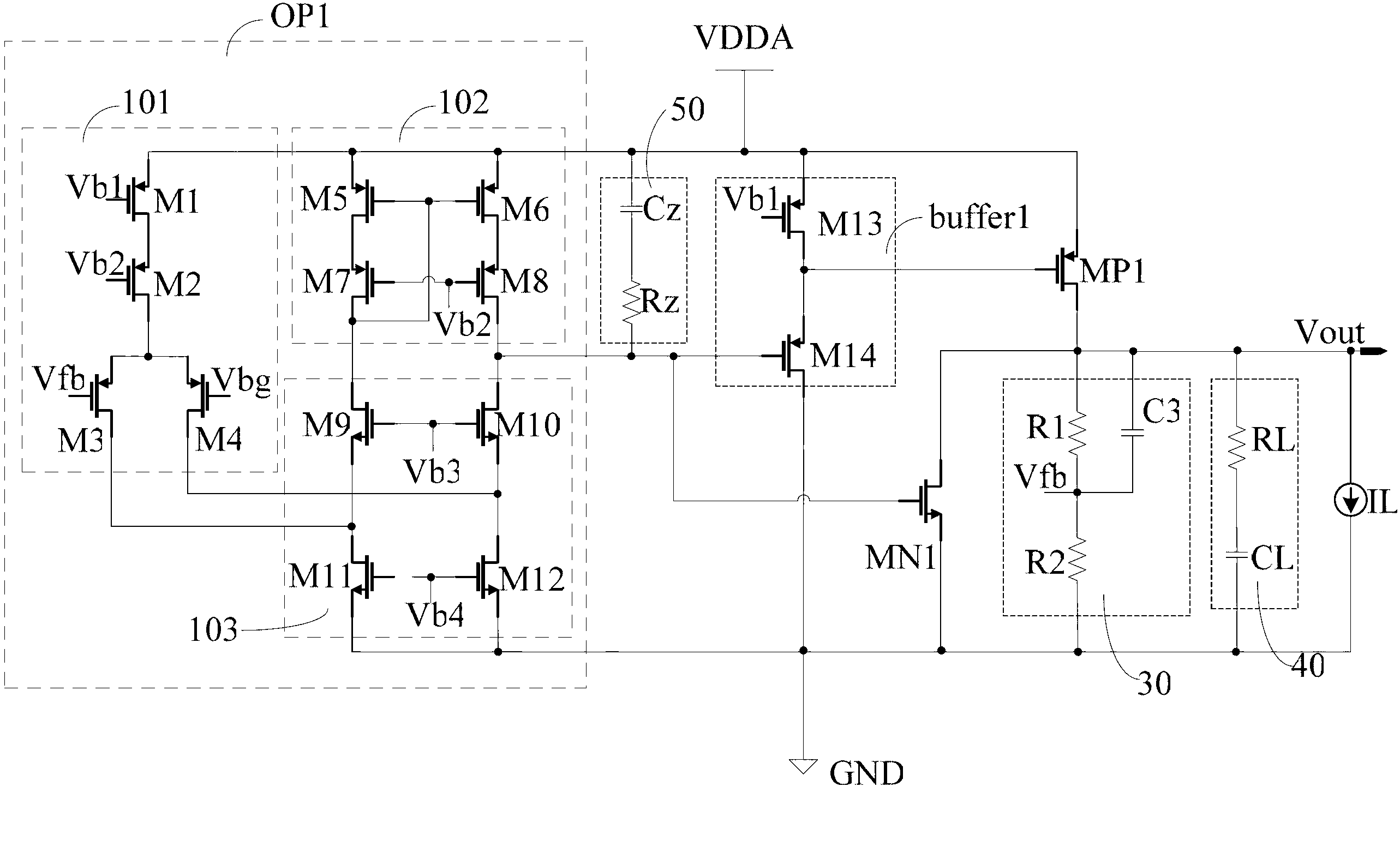
ActiveCN102707754AImprove transient response speedHigh precisionElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierFeedback circuits
The invention discloses a low dropout regulator, which comprises an error amplifier, a buffer circuit, a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) regulation transistor, an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) push-pull tube, a voltage division feedback circuit, a compensation circuit and an output circuit, wherein the gate of the PMOS regulation transistor is connected with the output end of the buffer circuit, the source of the PMOS regulation transistor is connected with power voltage, and the drain of the PMOS regulation transistor is used as the output end of the low dropout regulator; the gate of the NMOS push-pull tube is connected with the output end of the error amplifier, the drain of the NMOS push-pull tube is connected with the drain of the PMOS regulation transistor, and the source of the NMOS push-pull tube is grounded; and the error amplifier, the compensation circuit, the buffer circuit, the PMOS regulation transistor, the voltage division feedback circuit and an output circuit form a main control loop, and the error amplifier, the compensation circuit, the NMOS push-pull tube, the voltage division feedback circuit and the output circuit form an auxiliary control loop. According to the low dropout regulator, the transient response of the regulator can be quickened, and the accuracy of output voltage can be improved.
Owner:BRIGATES MICROELECTRONICS KUNSHAN
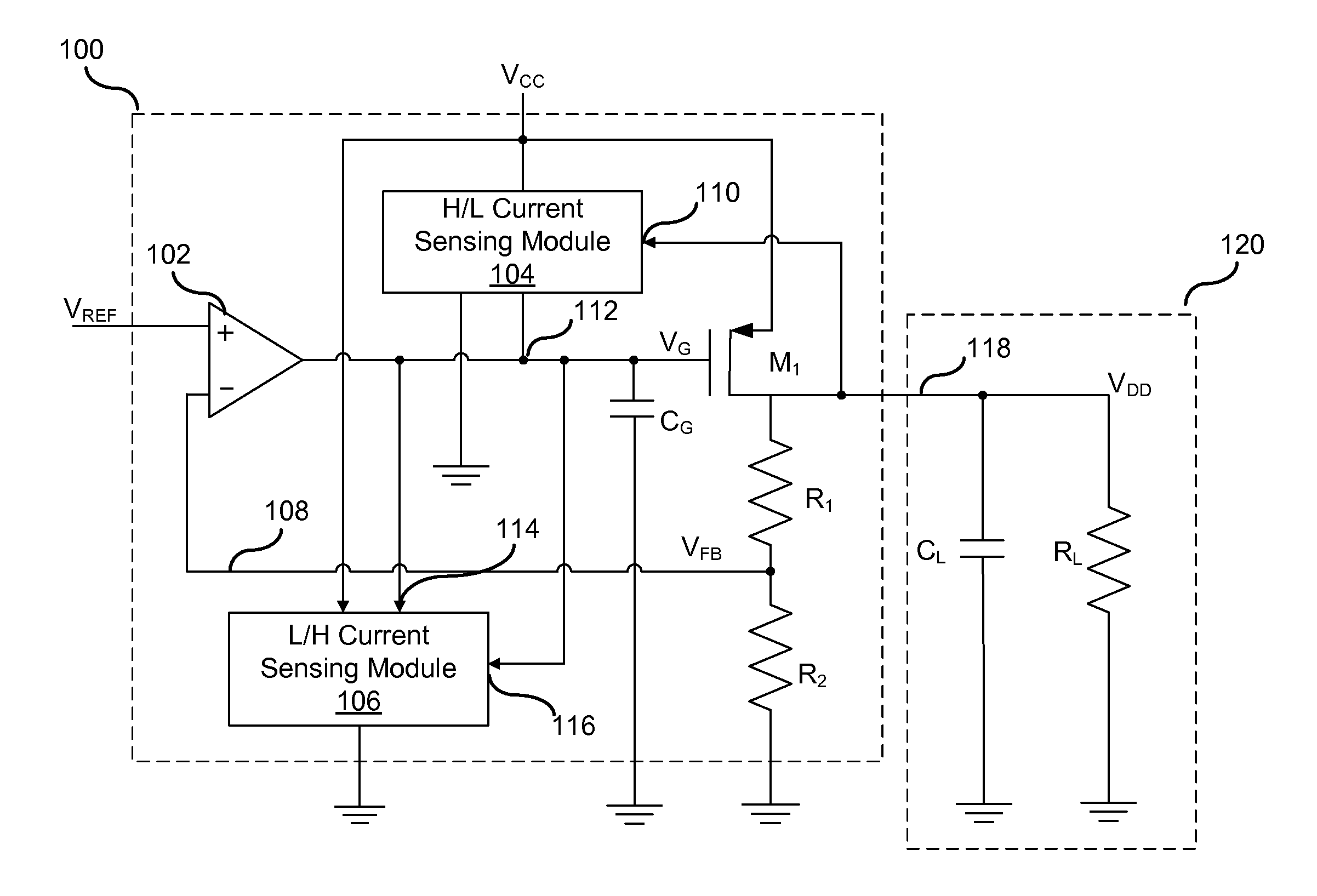
Adaptive transient load switching for a low-dropout regulator
InactiveUS20130119954A1Increase speedTotal current dropElectric variable regulationVoltage regulationSelf adaptive
A low-dropout (LDO) voltage regulator includes a switch to generate an output current, and a first sensing module that increases the speed at which the switch is turned off and the output current is decreased in response to detecting a decreasing load current. The LDO regulator further includes a second sensing module that increases the speed at which the switch is turned on and the output current is increased in response to detecting an increasing load current.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
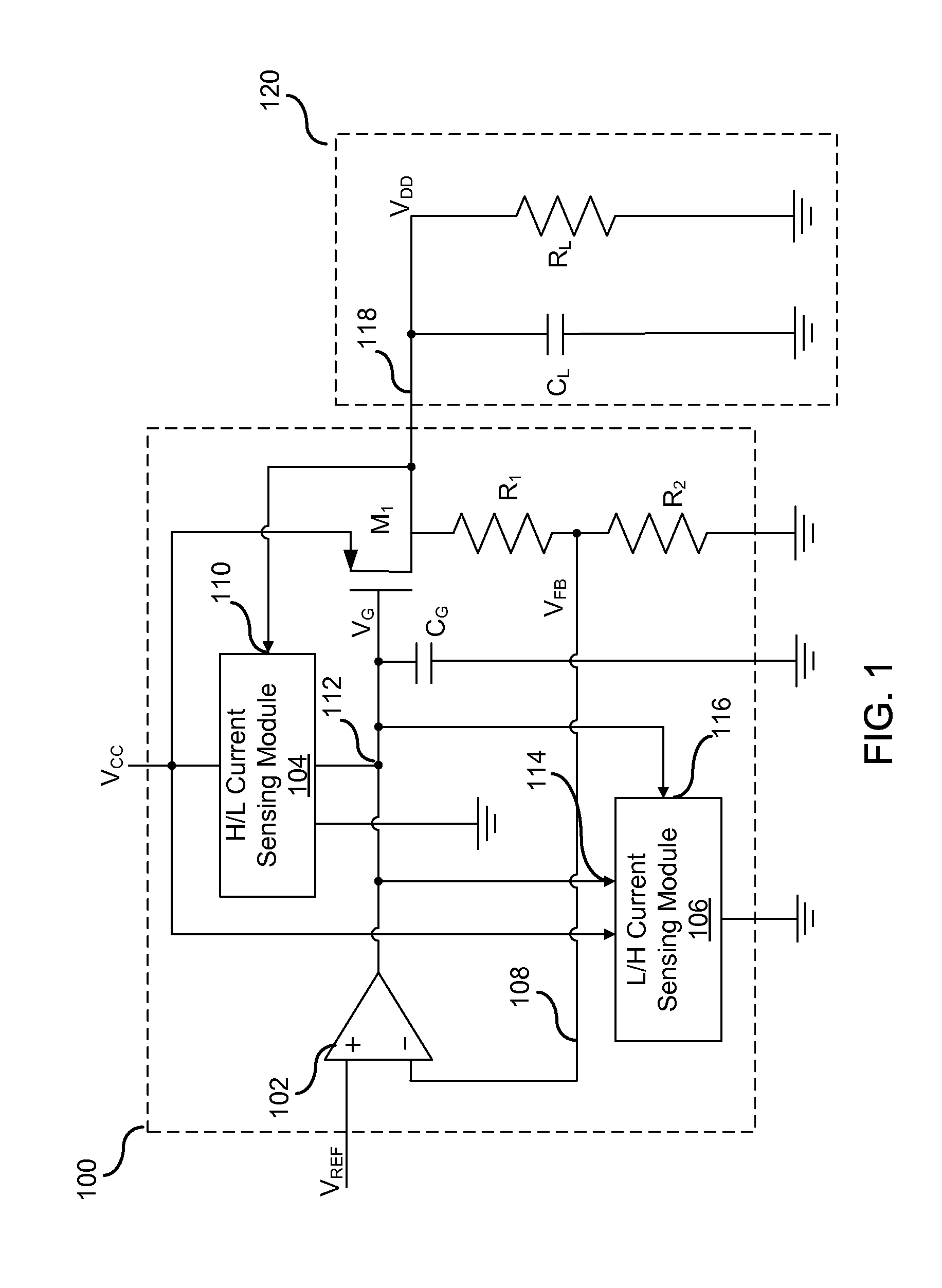
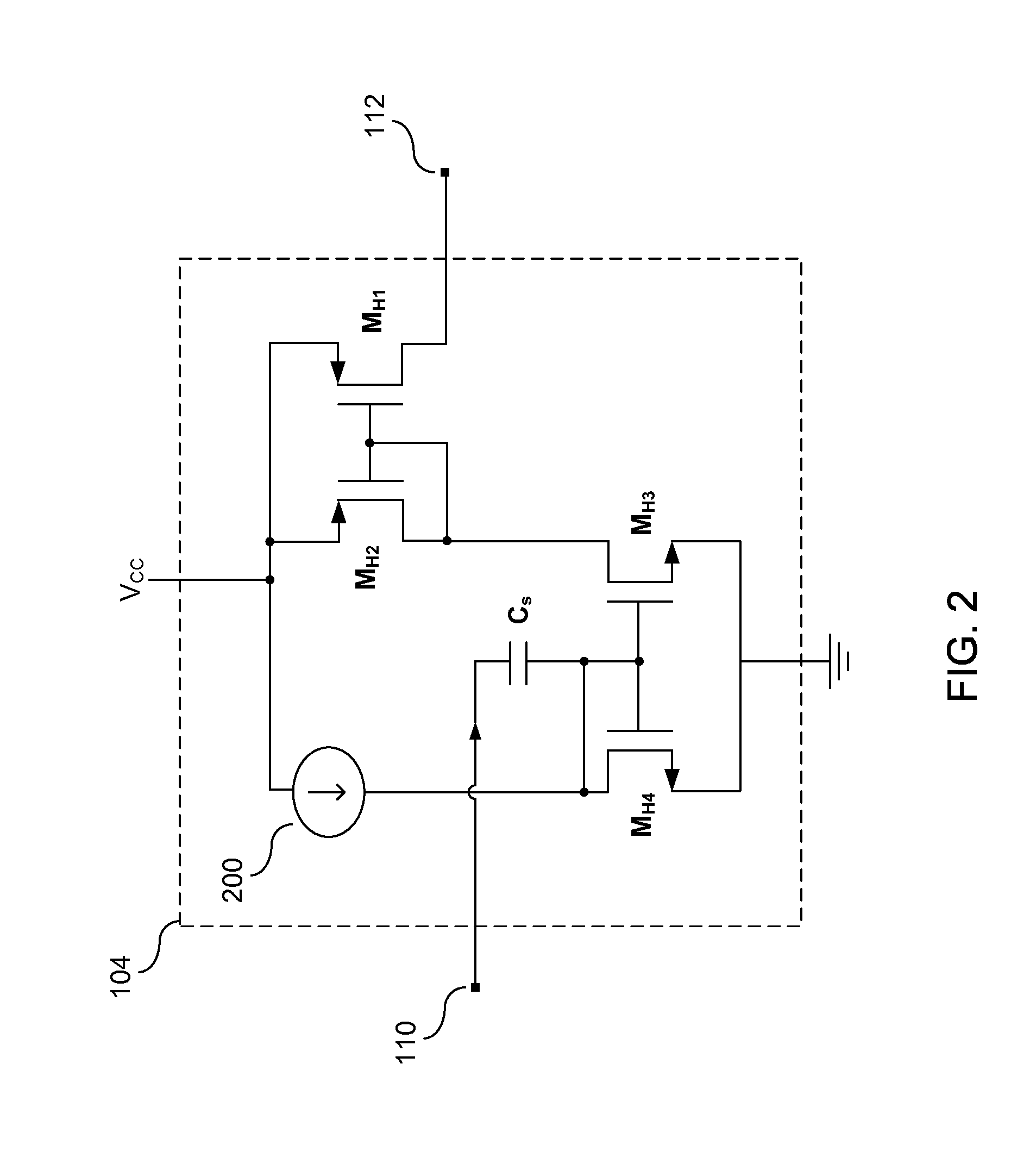
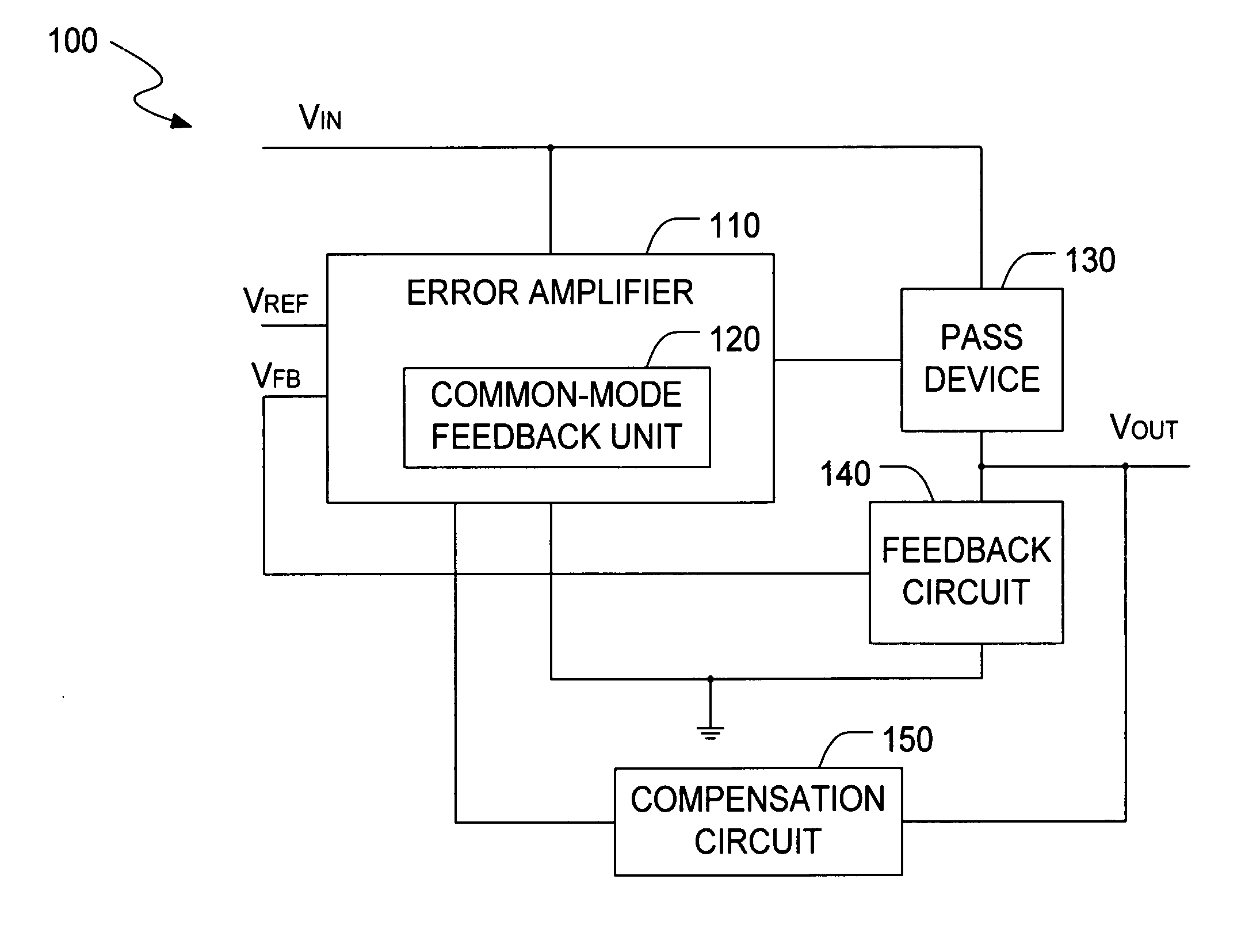
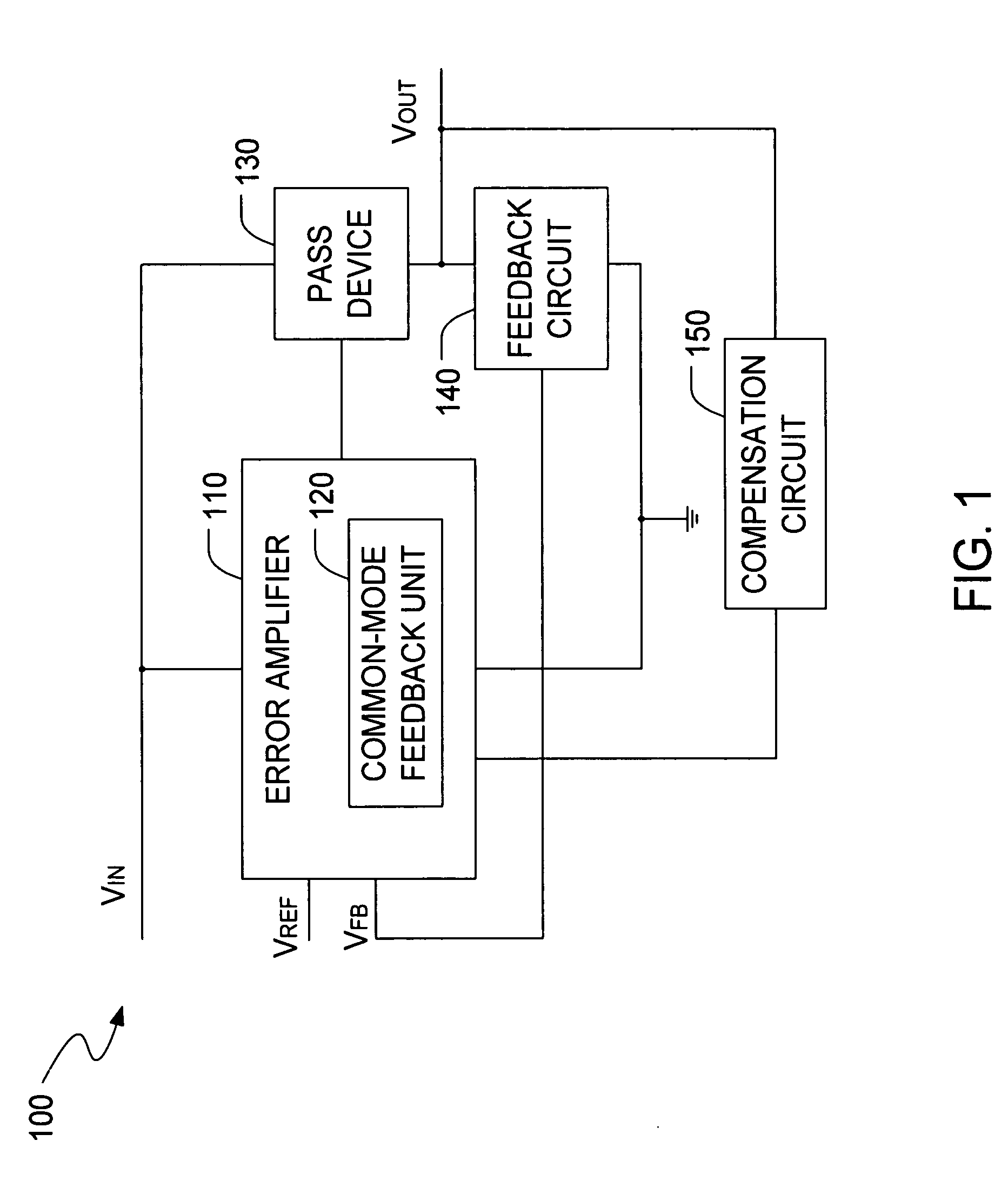
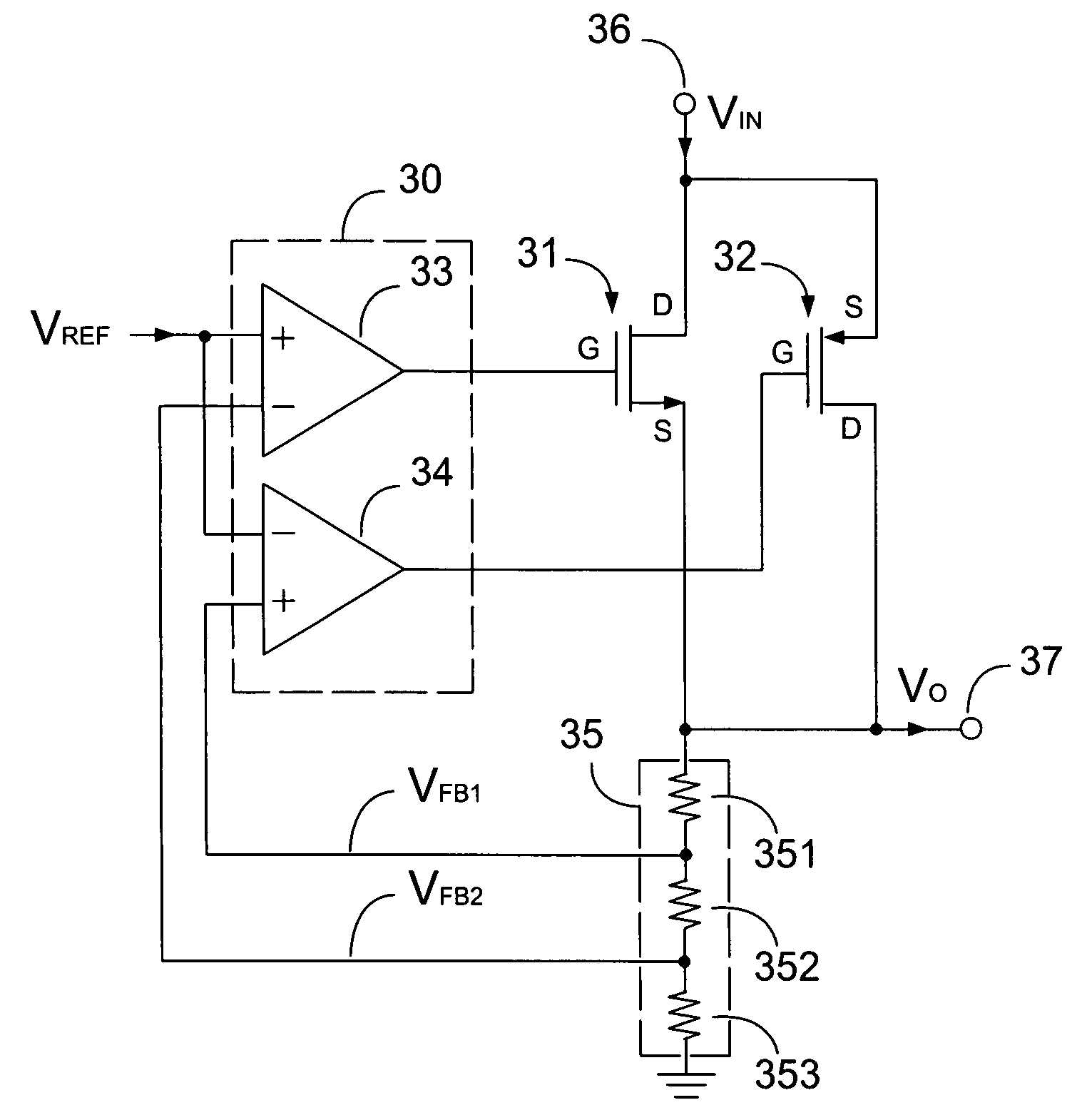
Low drop-out voltage regulator with common-mode feedback
InactiveUS20060197513A1Increase conversion rateStable output voltageAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
The present invention is a LDO voltage regulator circuit with common-mode feedback. The LDO voltage regulator includes an error amplifier with a common-mode feedback unit, a pass device and a compensation circuit. A signal from the pass device acts as an input signal to the error amplifier and is compared with another input signal, producing a differential signal. The differential signal is amplified and then provided to the pass device. A capacitor in the compensation unit provides frequency compensation to the LDO voltage regulator. The common-mode feedback unit incorporated into the error amplifier greatly improves a slew rate of a gate voltage of the pass device.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
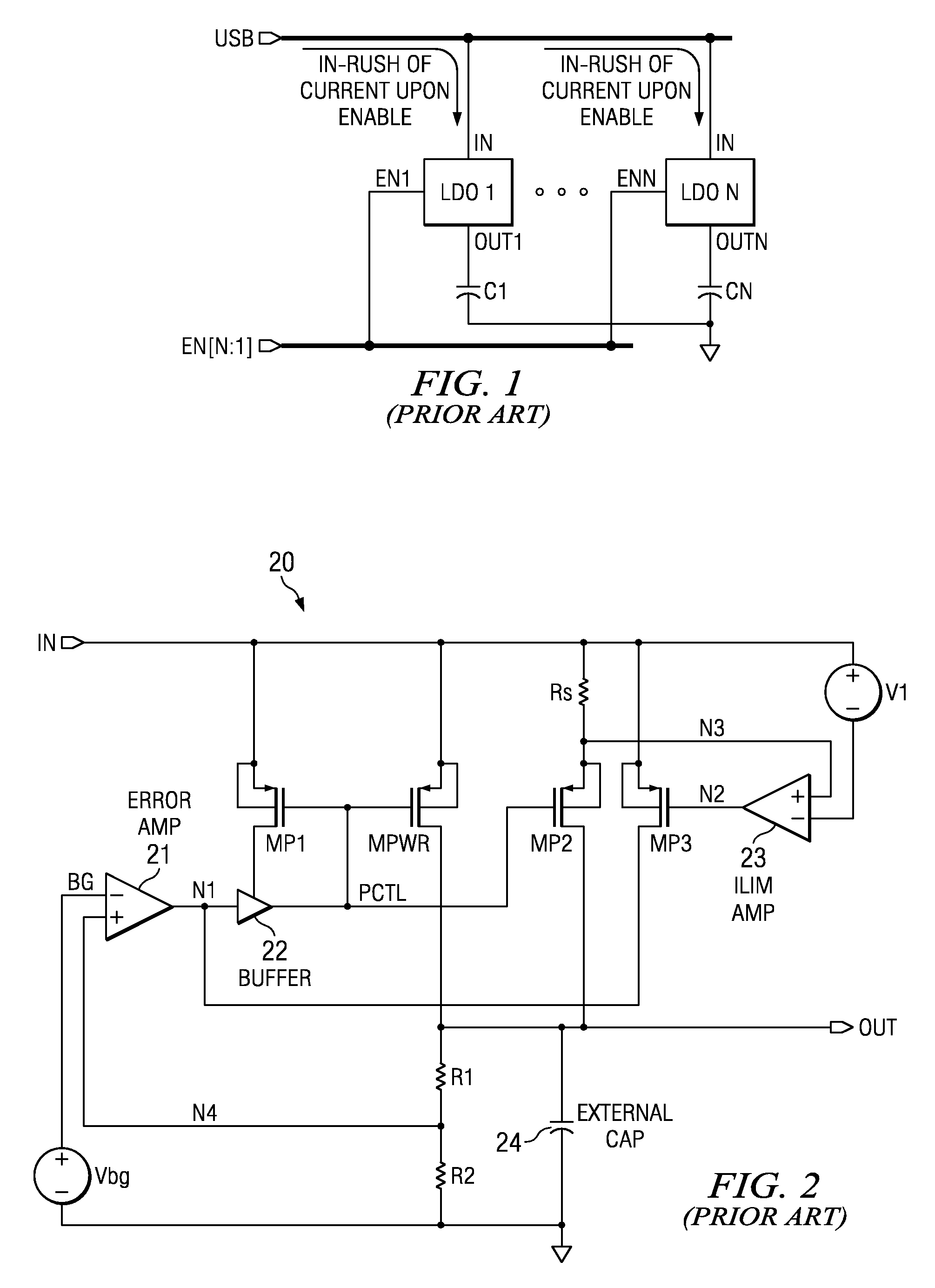
Current Limit Circuit Architecture For Low Drop-Out Voltage Regulators
InactiveUS20130293986A1Reduce output voltageSimple designEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorEngineering
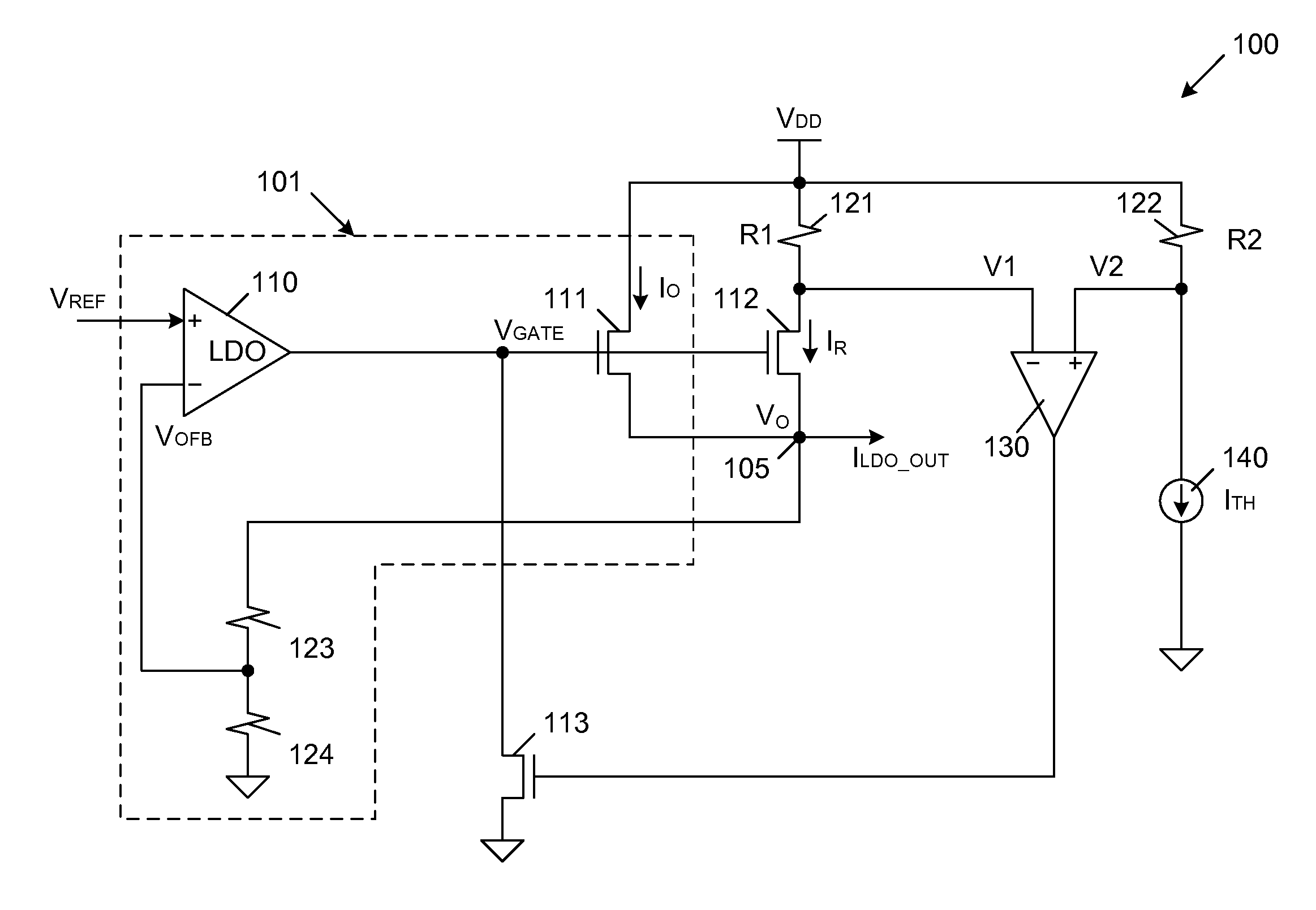
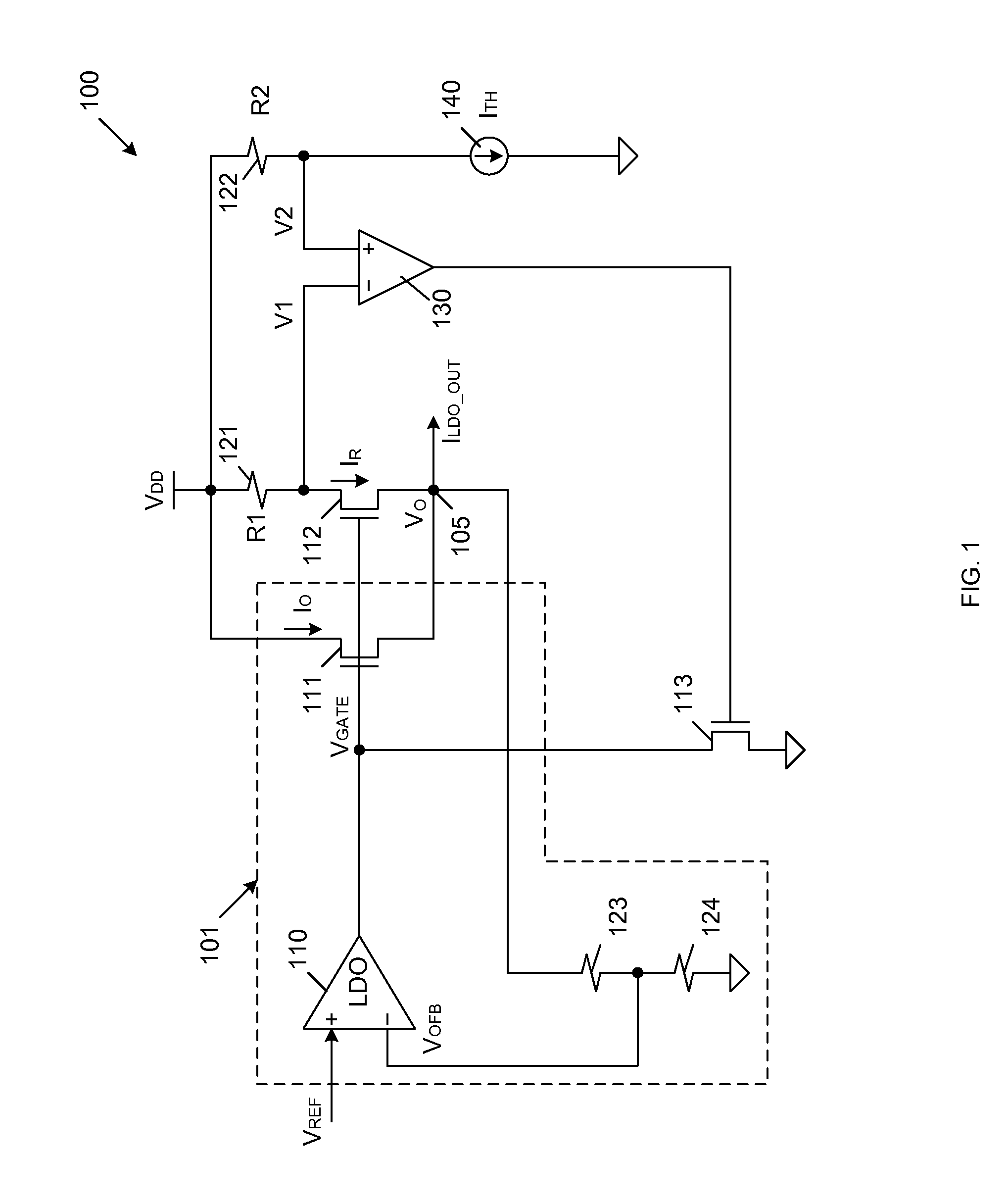
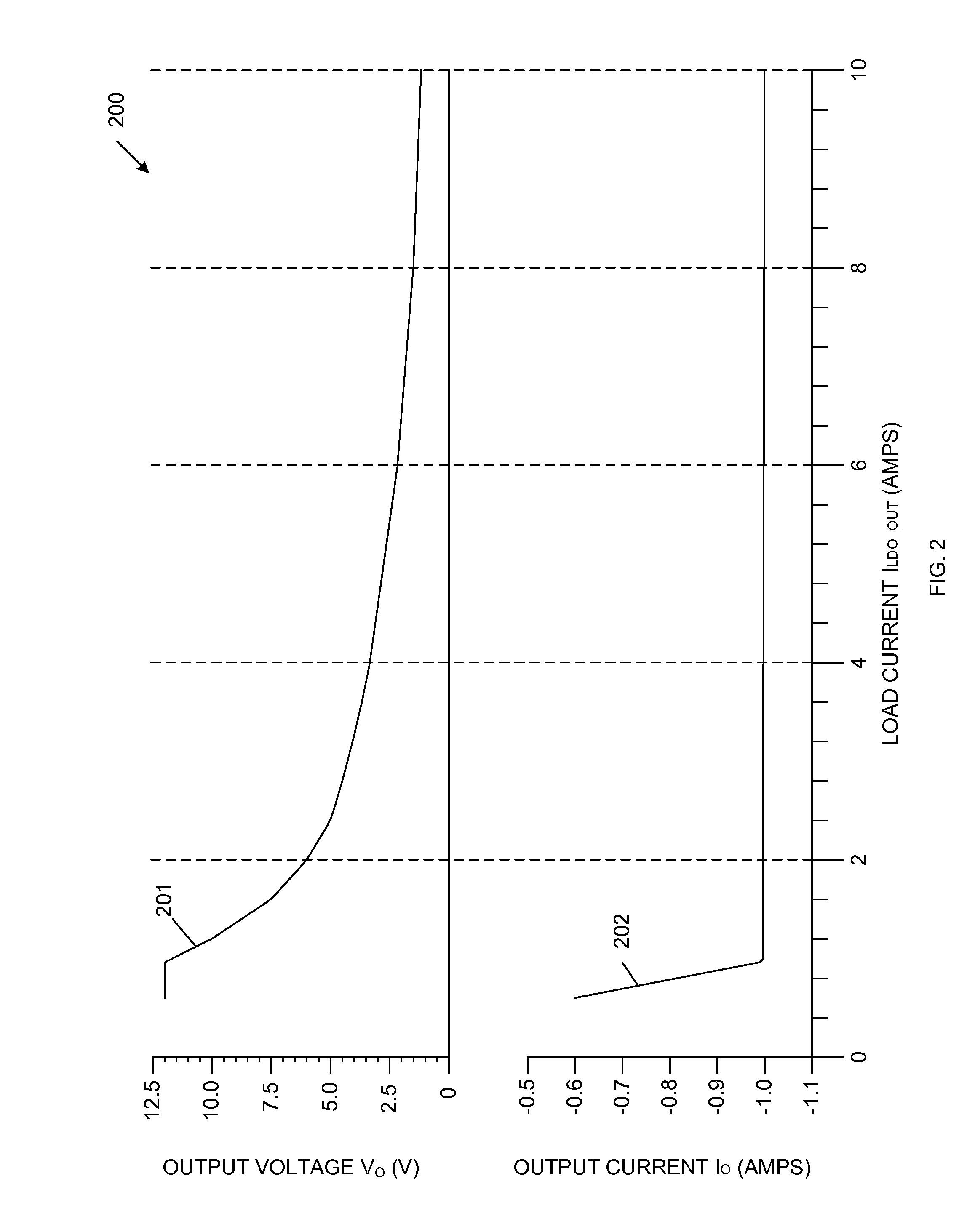
A current limiting circuit for a linear regulator includes an output stage transistor and a replica transistor, which have gates coupled to receive an output voltage from a linear amplifier and sources coupled to load circuitry. A drain of the output stage transistor is coupled to a VDD supply terminal, while a drain of the replica transistor is coupled to the VDD supply terminal through a first resistor. The output stage transistor and replica transistor are operated in saturation, such that proportional currents flow through these transistors. The voltage drop across the first resistor provides a first voltage, which is applied to a second amplifier. A reference voltage is also applied to the second amplifier. When the first voltage becomes less than the reference voltage, a feedback transistor is enabled to pull down the output voltage of the linear amplifier, thereby limiting the output current supplied to the load circuitry.
Owner:TOWER SEMICONDUCTOR
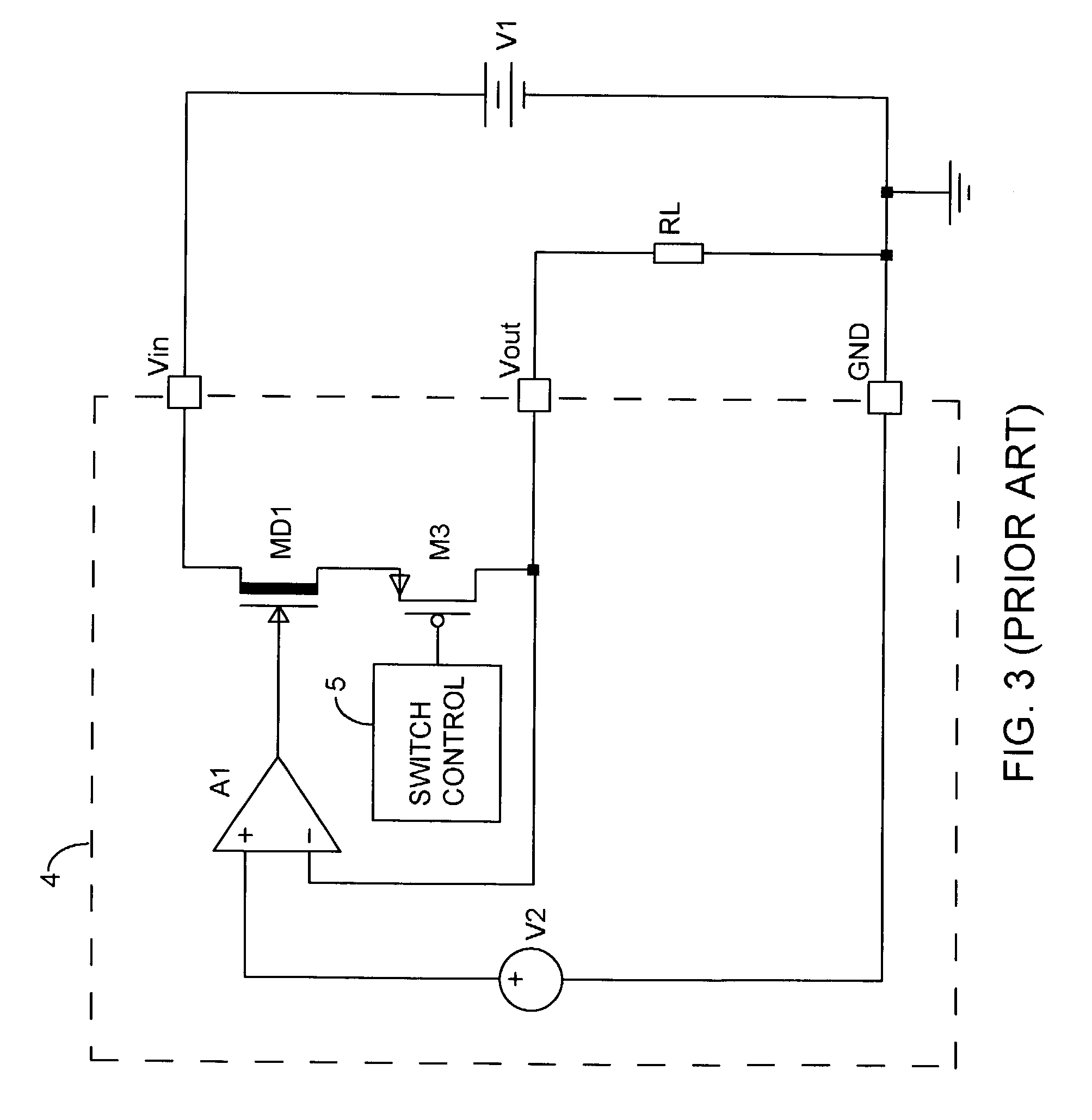
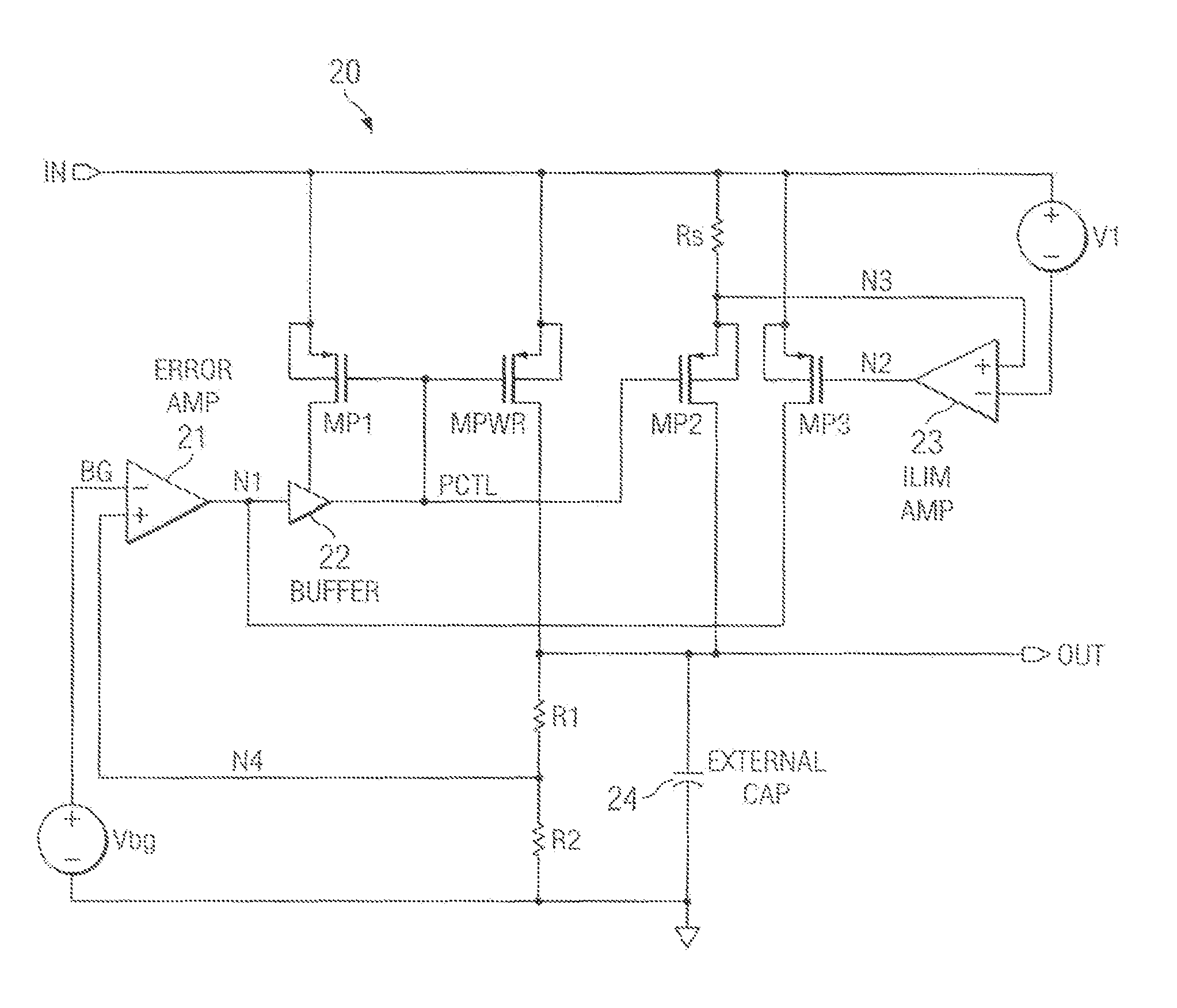
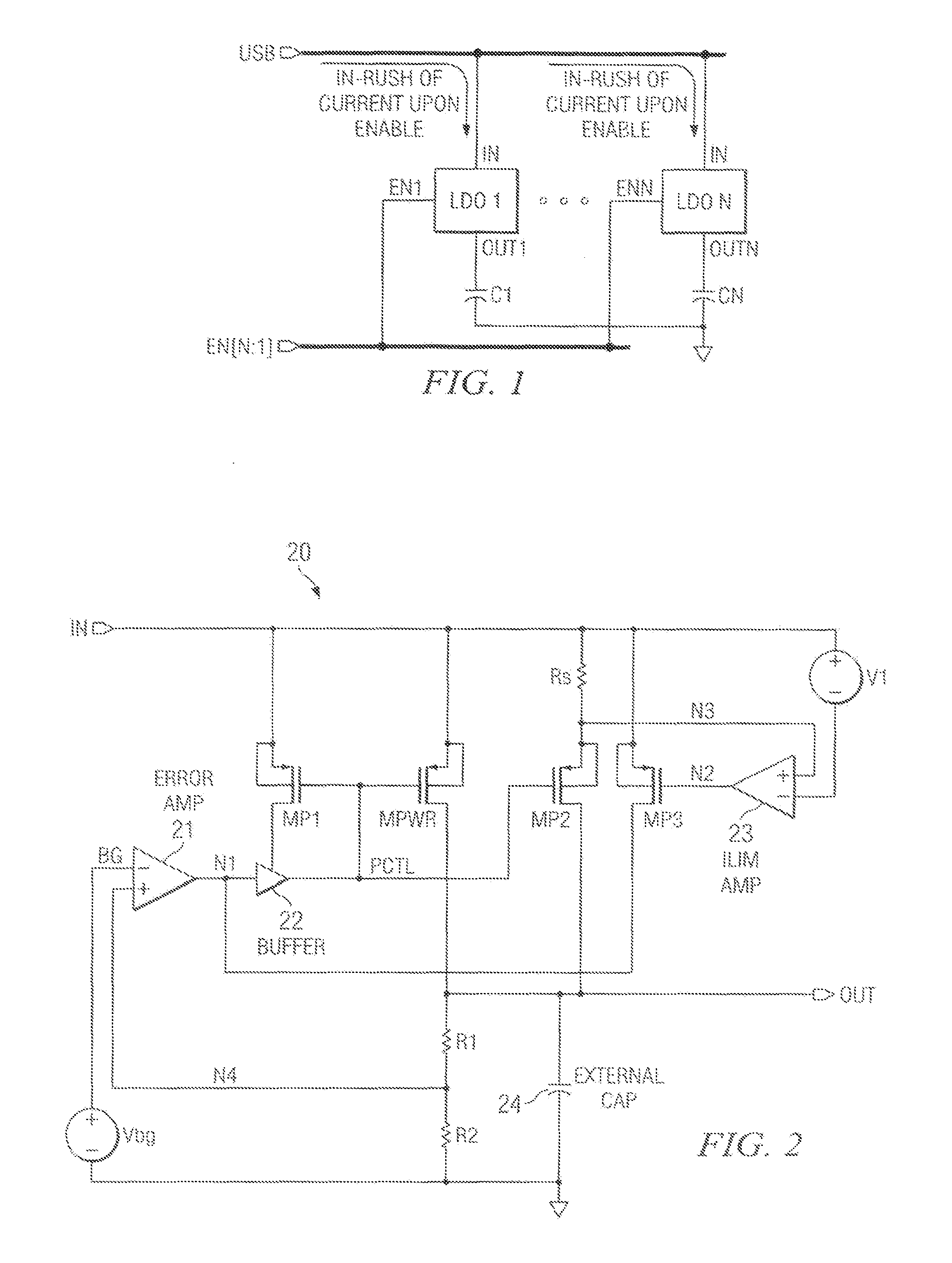
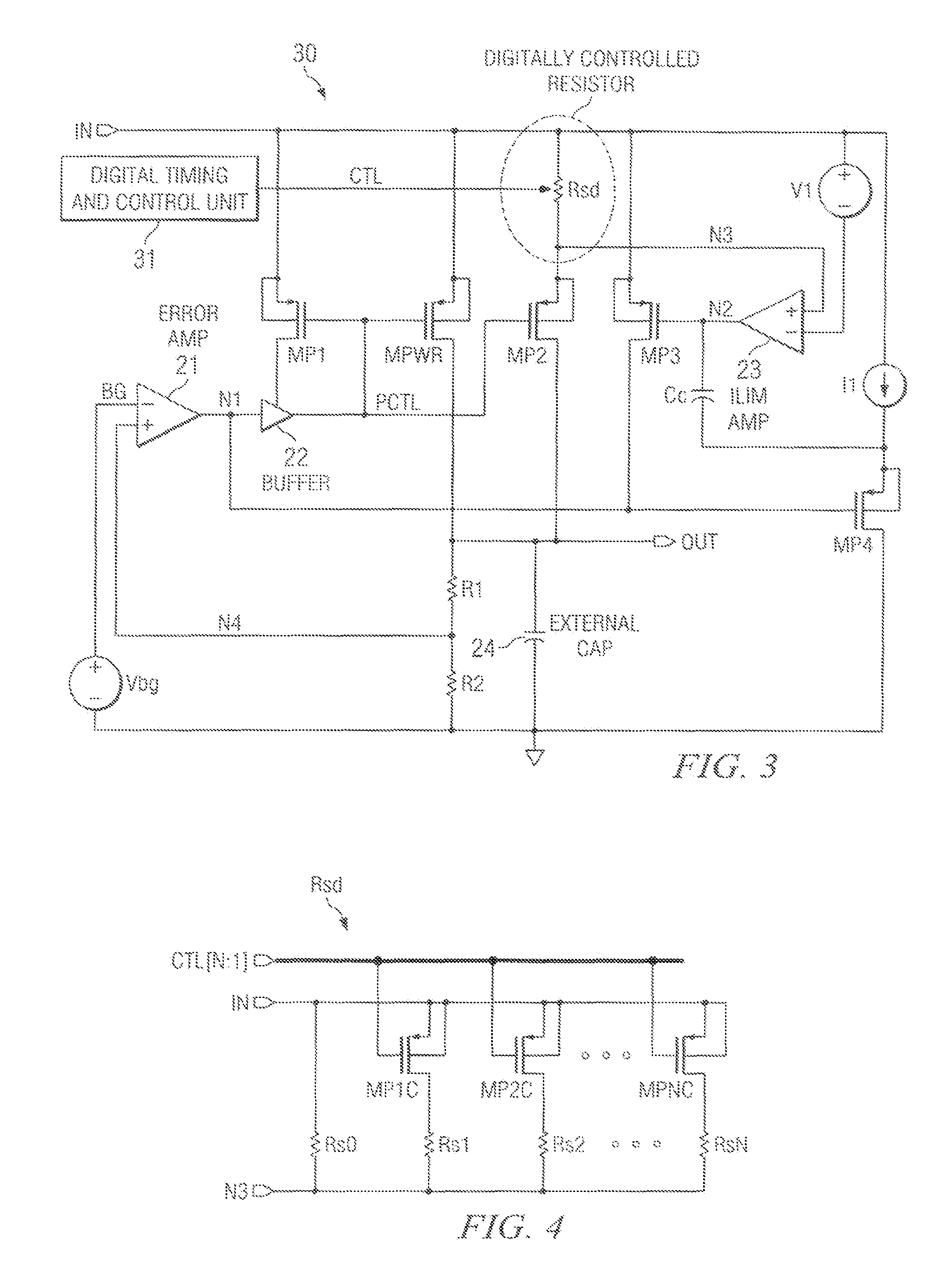
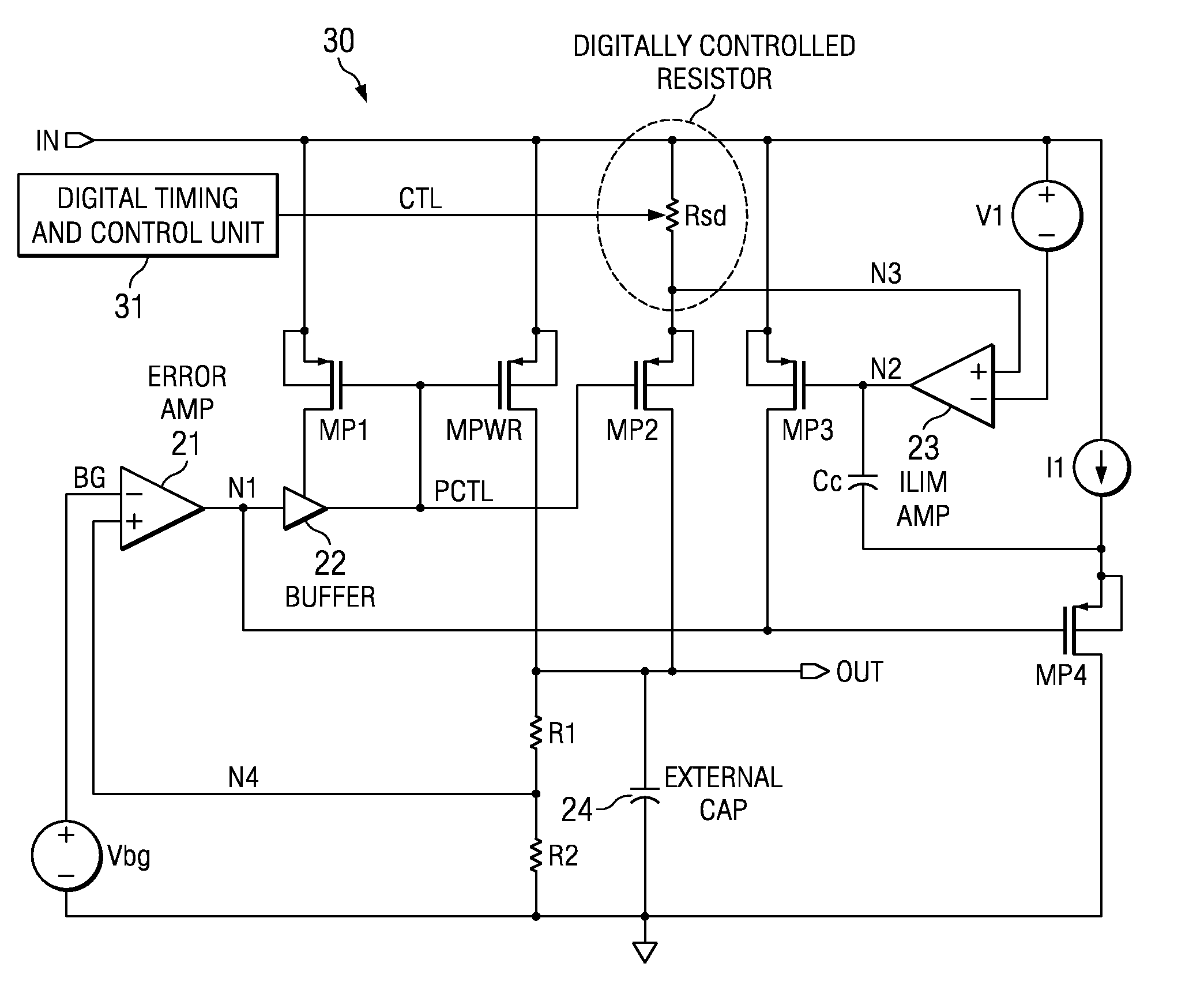
Soft-start circuit and method for low-dropout voltage regulators
ActiveUS20070216383A1Easily customizable controlMinimal die areaPower supply linesElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent limiting
A low drop-out voltage regulator having soft-start. A low drop-out regulator circuit is provided having an input node, an output node, a power FET connected by a source and drain between the input node and the output node, and a feedback circuit having an output connected and providing a control signal to a gate of the power FET. A current limit circuit is configured to control the power FET to limit the current through it when the voltage across a controllable sense resistor connected to conduct a current representing the current through the power FET exceeds a predetermined limit value. At start-up, control unit provides a control signal to the controllable resistor to cause the resistance value of the controllable resistor to decrease incrementally in value at respective predetermined incremental times during a predetermined time interval.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Low dropout regulator with wide input voltage range
ActiveUS7531996B2Improve loop stabilityReduce voltageElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage range
A low dropout (LDO) regulator operates in wide input range. The LDO includes an N-type pass transistor and a P-type pass transistor for supplying power to the output terminal. The P-type pass transistor is connected with N-type pass transistor in parallel. Two error amplifiers control the gate terminals of the N-type pass transistor and P-type pass transistor to generate a first output voltage and a second output voltage. Thus, the first output voltage is generated when the input voltage is higher than a threshold voltage, and the second output voltage is generated when the input voltage is lower than the threshold voltage.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Low dropout regulator circuit without external capacitors rapidly responding to load change
InactiveUS20110121802A1Low dropout regulatorImprove load responseAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
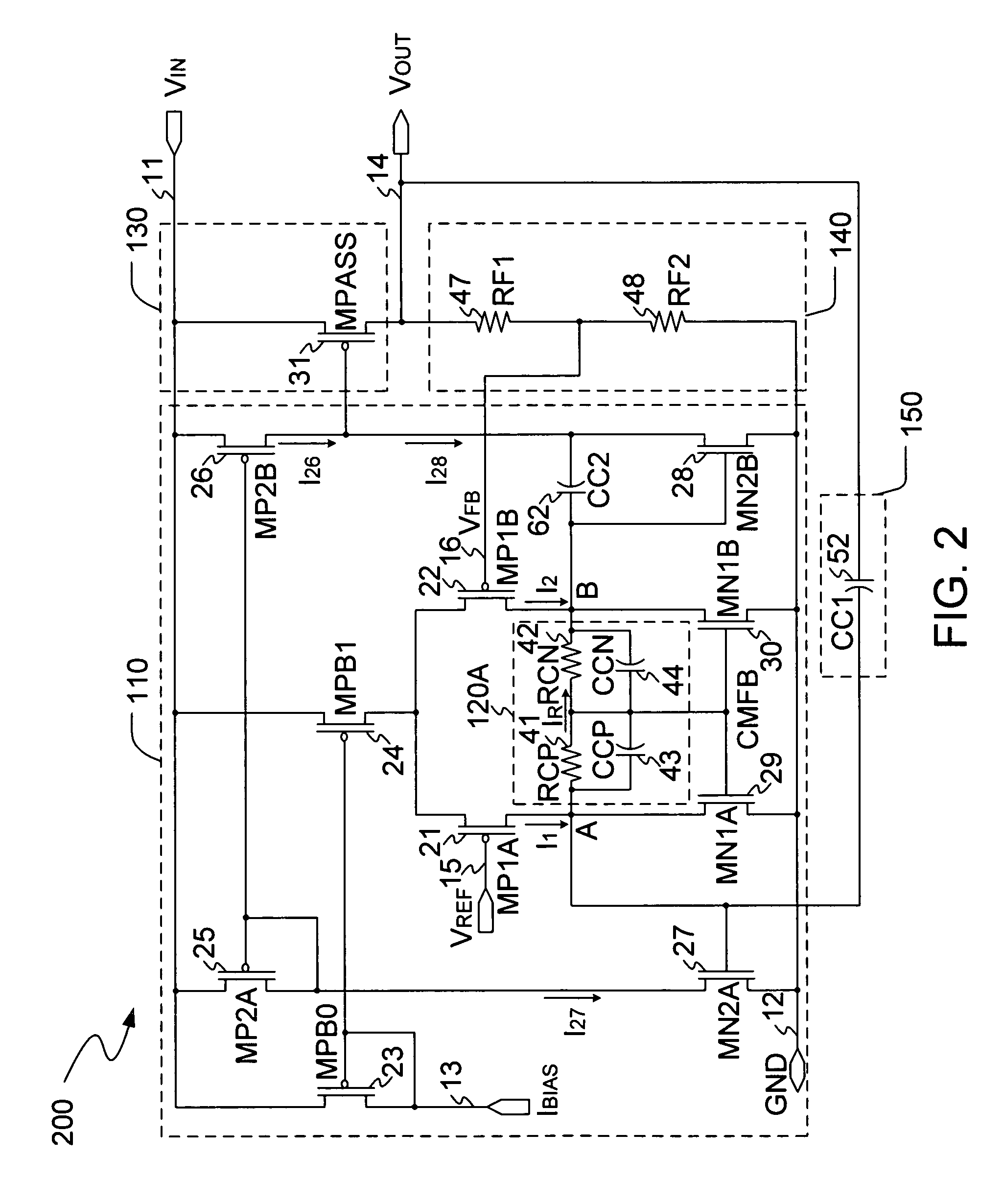
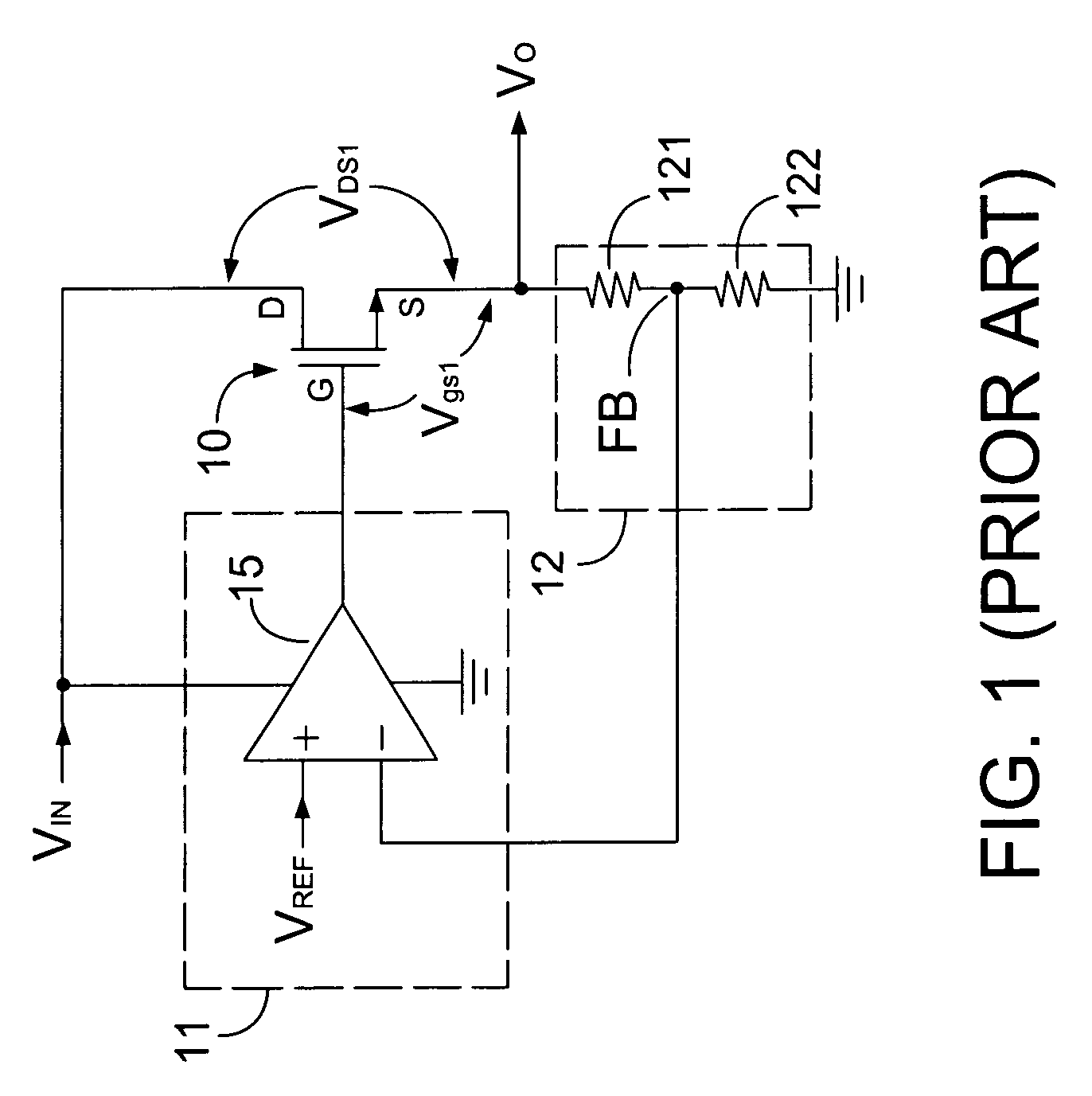
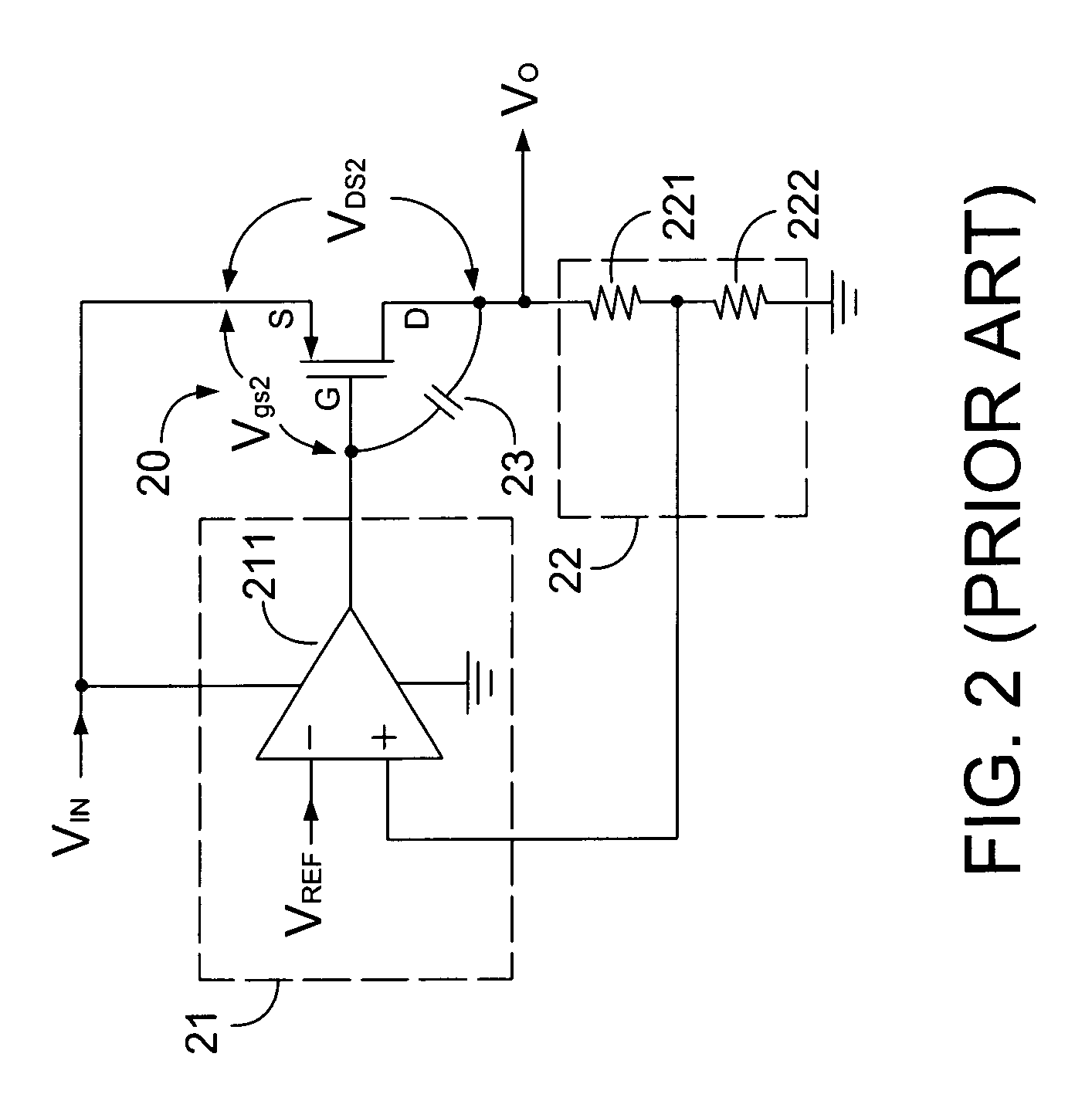
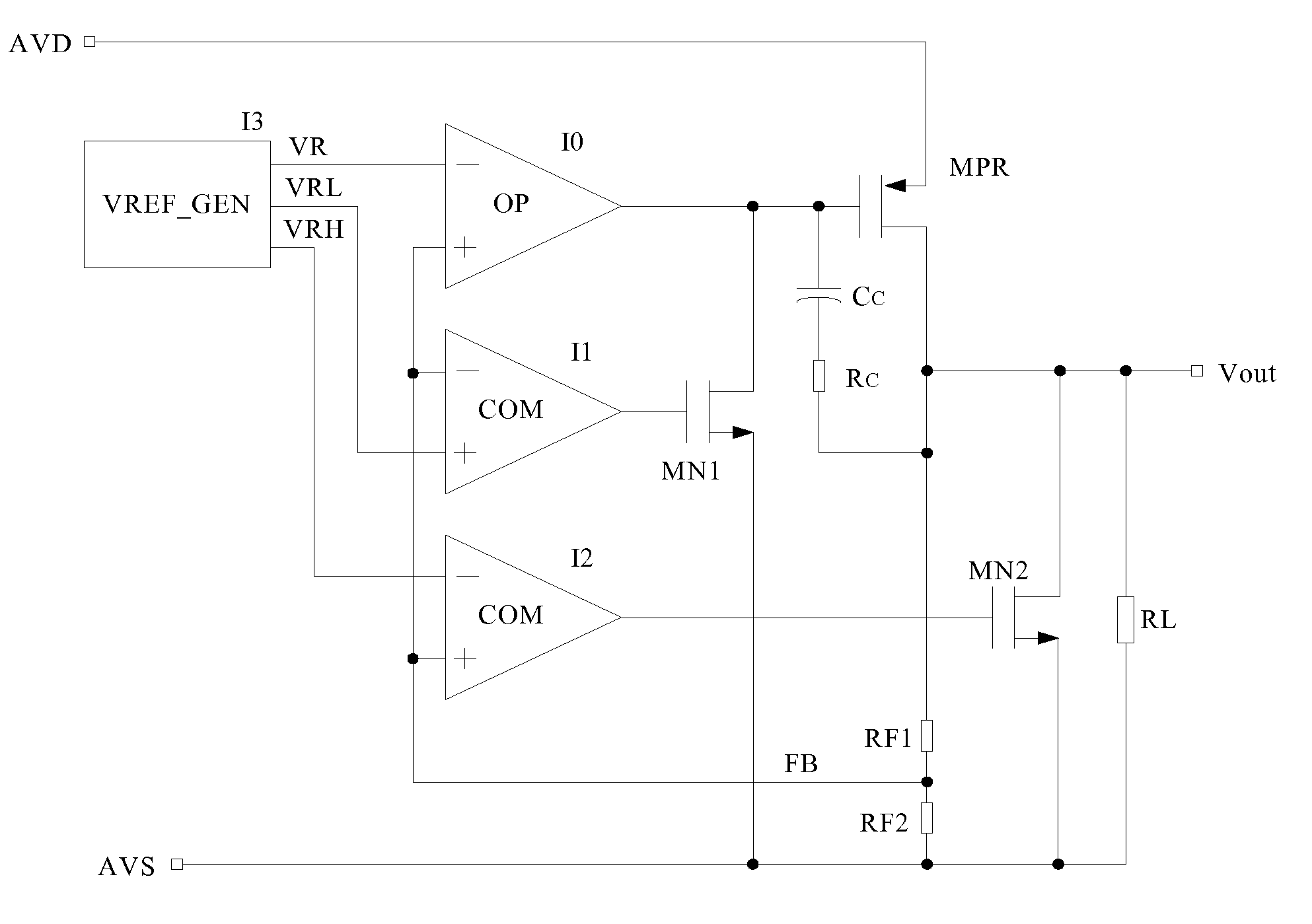
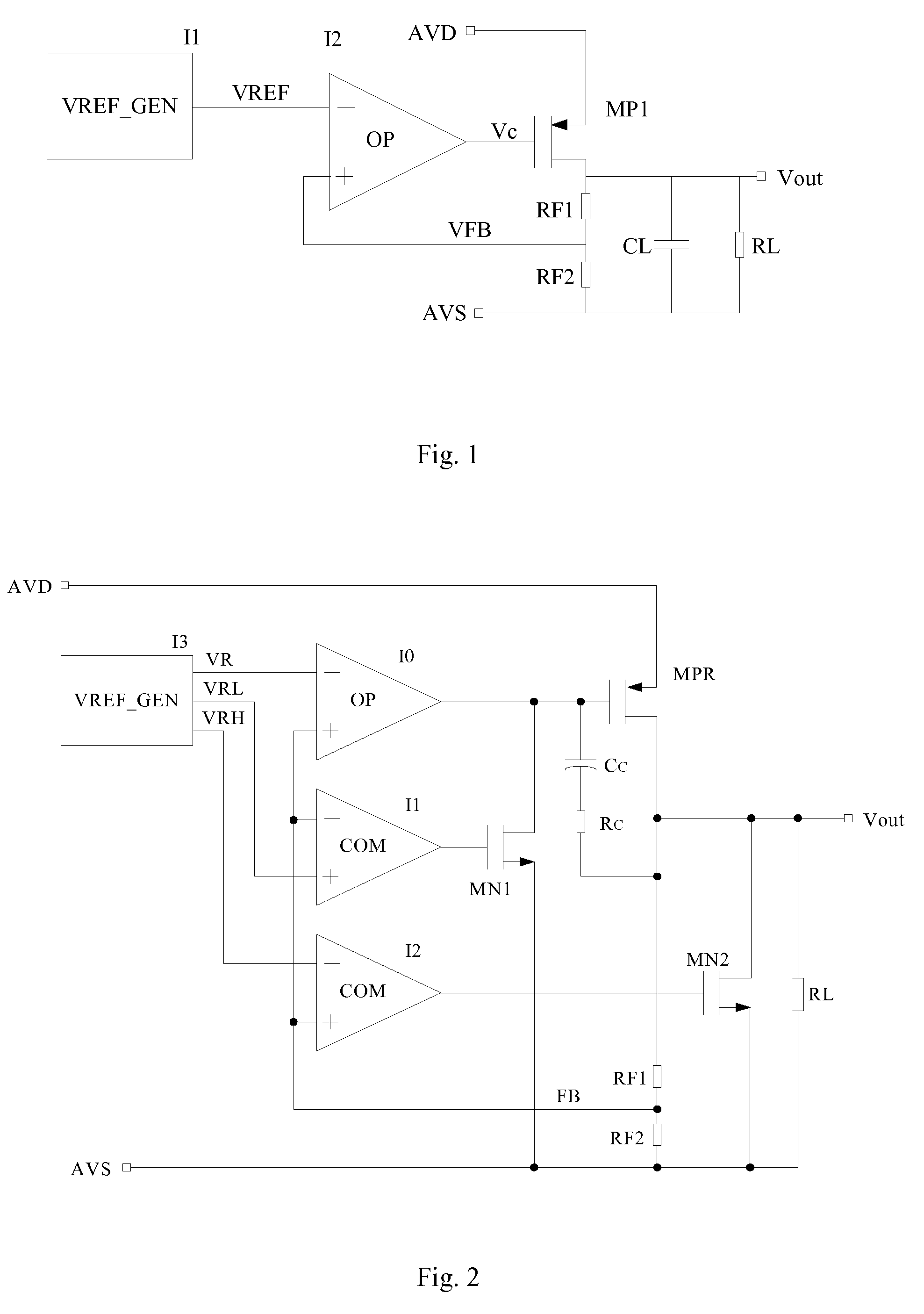
A low dropout regulator (LDO) circuit without external capacitors rapidly responding to load change includes a slow pathway and a fast pathway for controlling voltage, wherein the slow pathway for providing precise output voltage includes an operational amplifier I0, a driving transistor MPR, a resistor RF1 and a resistor RF2 forming an operational amplifier loop, and the fast pathway for responding to rapid load change includes a comparator I1, a comparator I2, a field effect transistor MN1, a field effect transistor MN2, a driving transistor MPR, a resistor RF1 and a resistor RF2 forming a comparator loop. The circuit is capable of controlling the output voltage by the slow operational amplifier loop and fast comparator loop, so that the load response speed of the LDO is greatly improved without the increase of the system power consumption and external big capacitors.
Owner:IPGOAL MICROELECTRONICS (SICHUAN) CO LTD
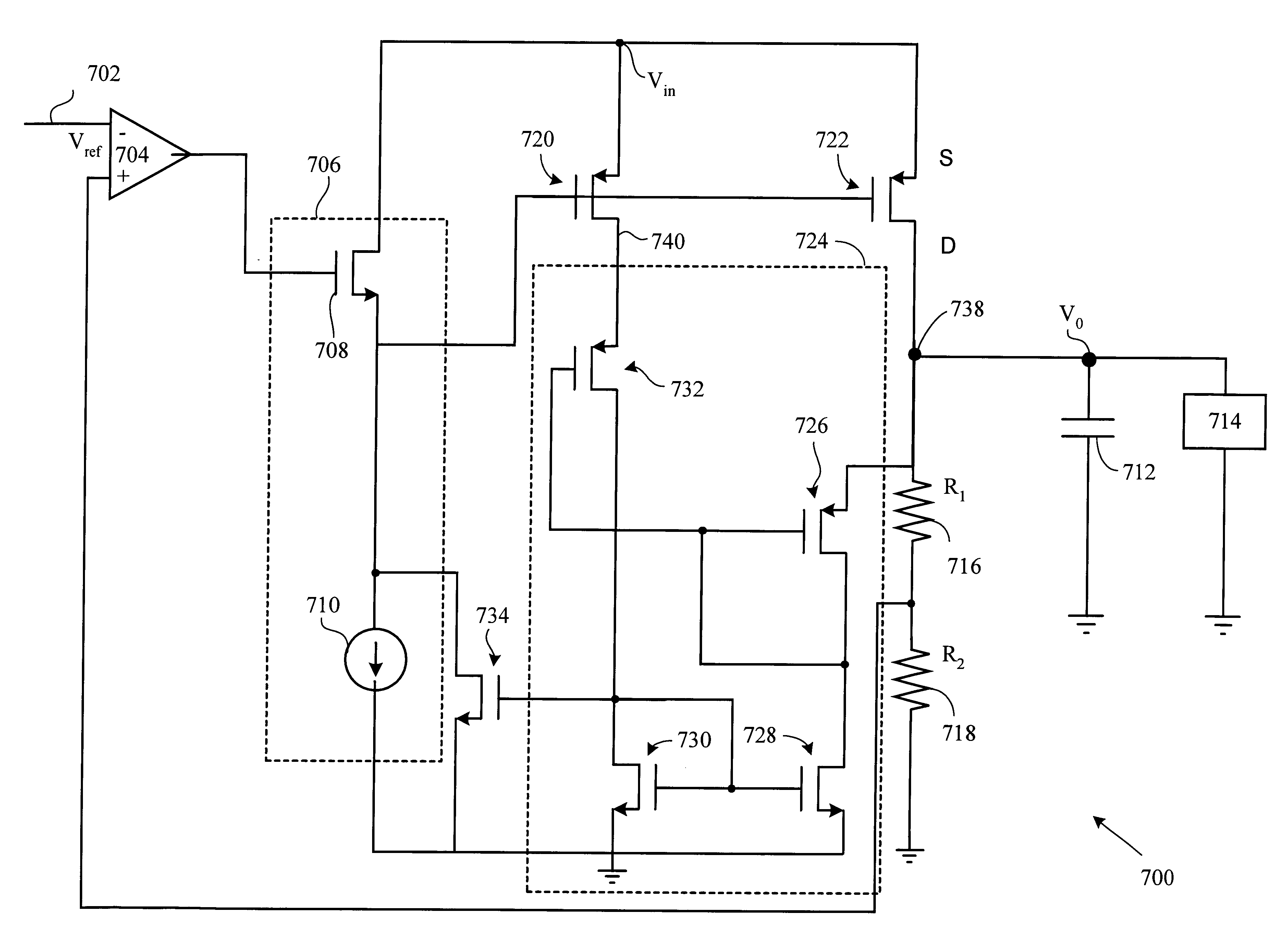
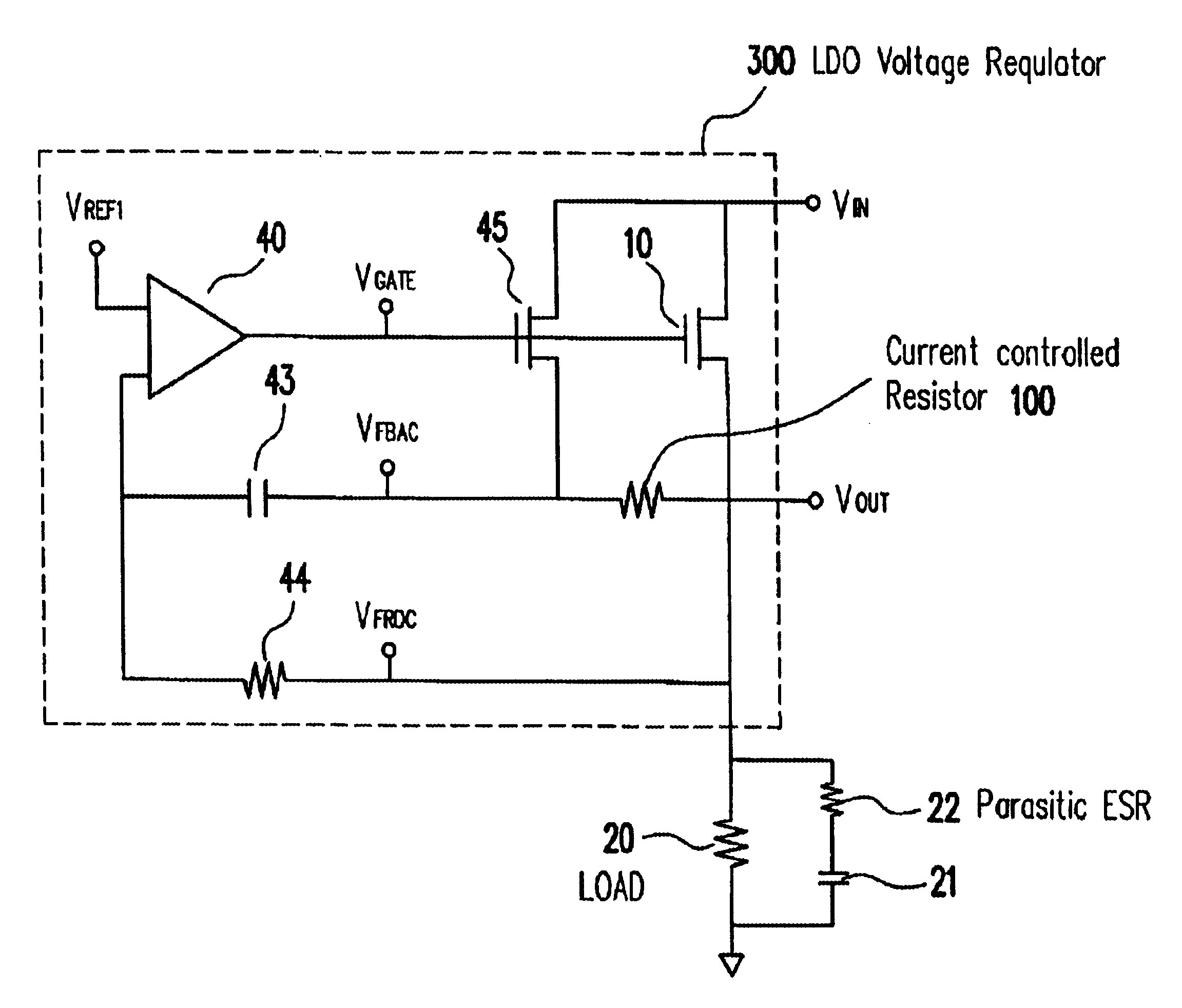
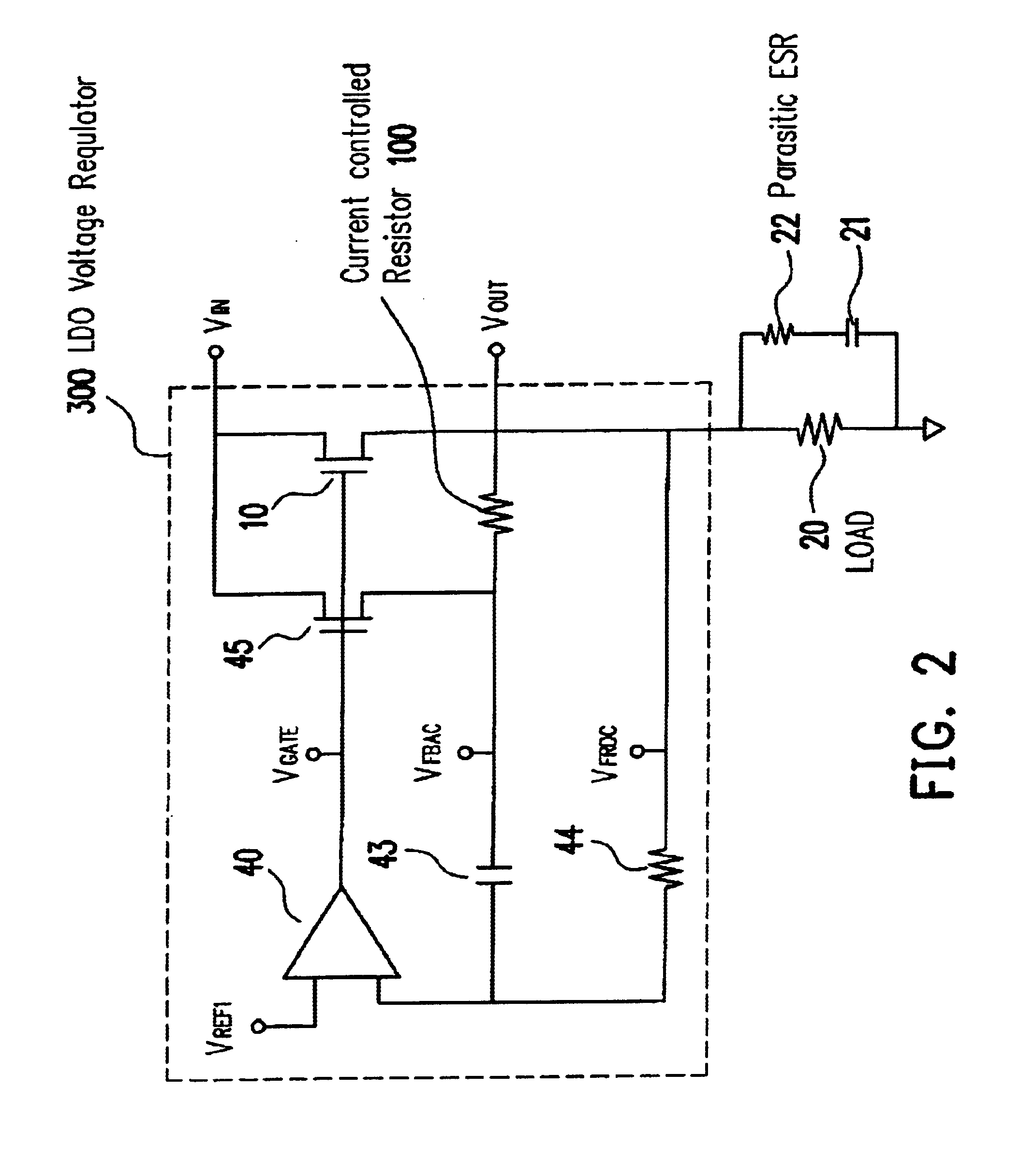
Low drop-out voltage regulator and an adaptive frequency compensation
InactiveUS6861827B1Lower overall pressure dropTight output controlElectric variable regulationCapacitanceFrequency compensation
A method and apparatus to dynamically modify the internal compensation of a low drop-out (LDO) voltage regulator is presented. The process involves creating an additional equivalent series resistance (ESR) from an internal circuit. The additional ESR of the internal circuit is sufficient to ensure the DC output stability. This allows the ESR of the output capacitance to be reduced to zero if desired, for improved transient response.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
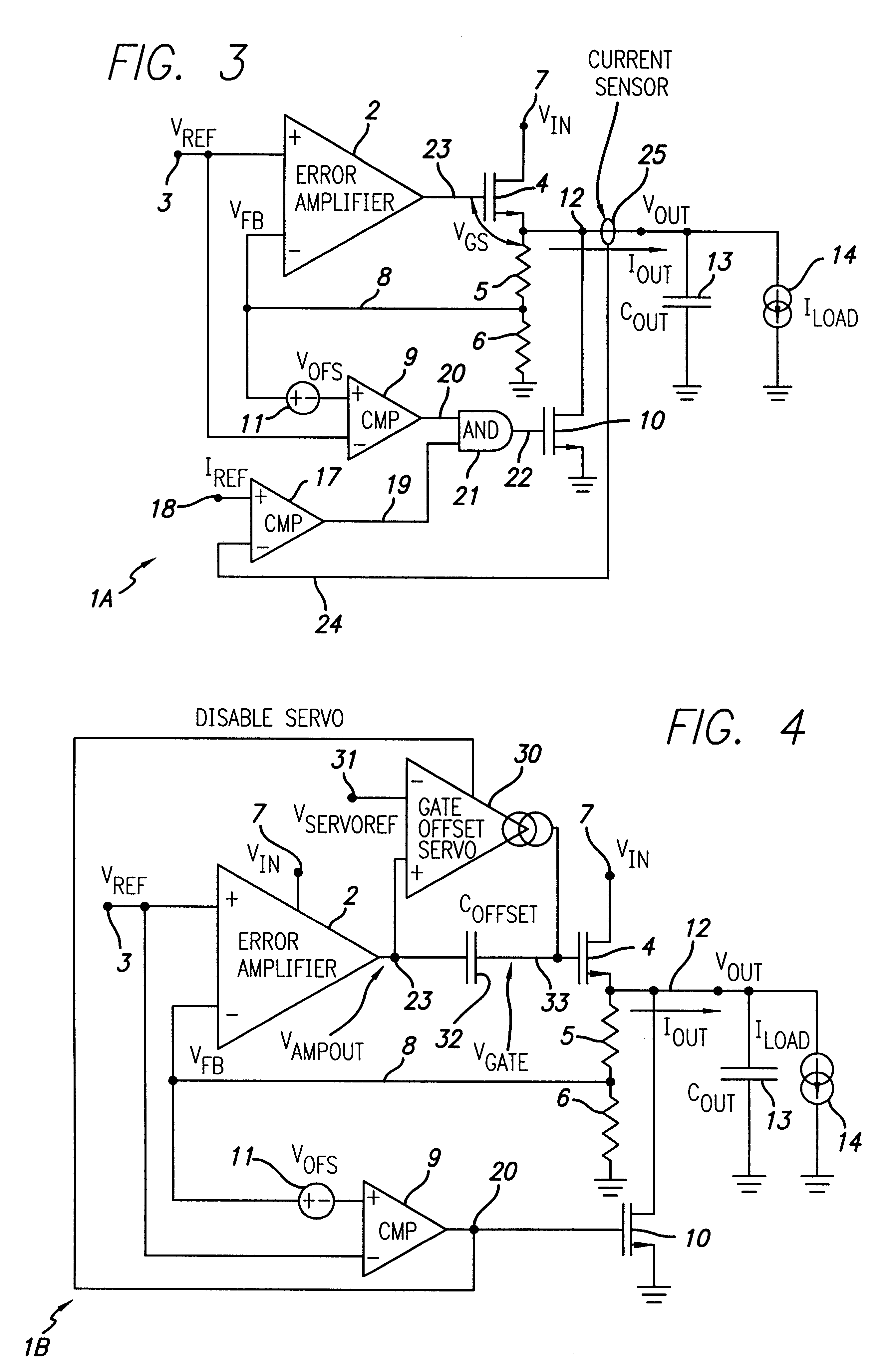
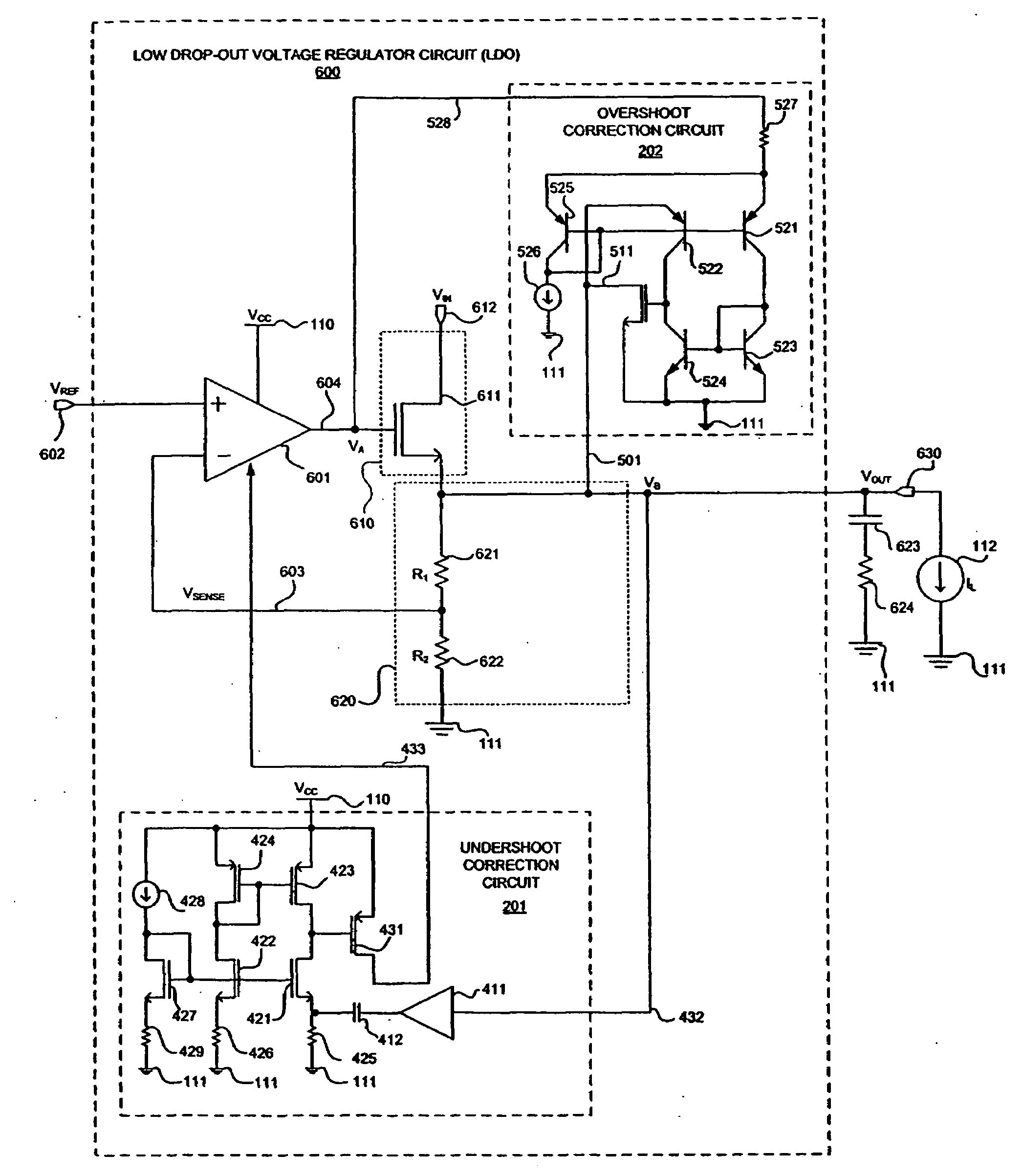
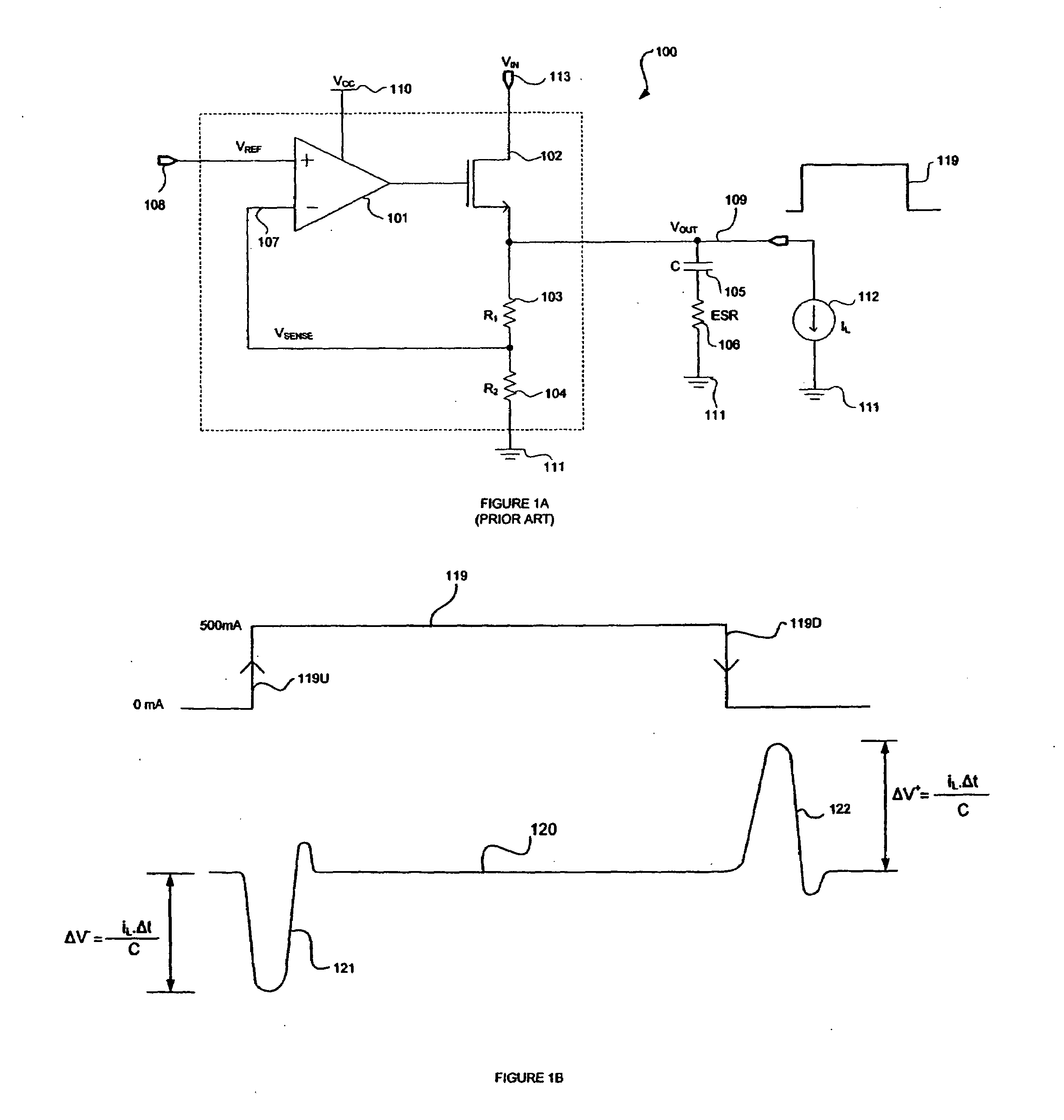
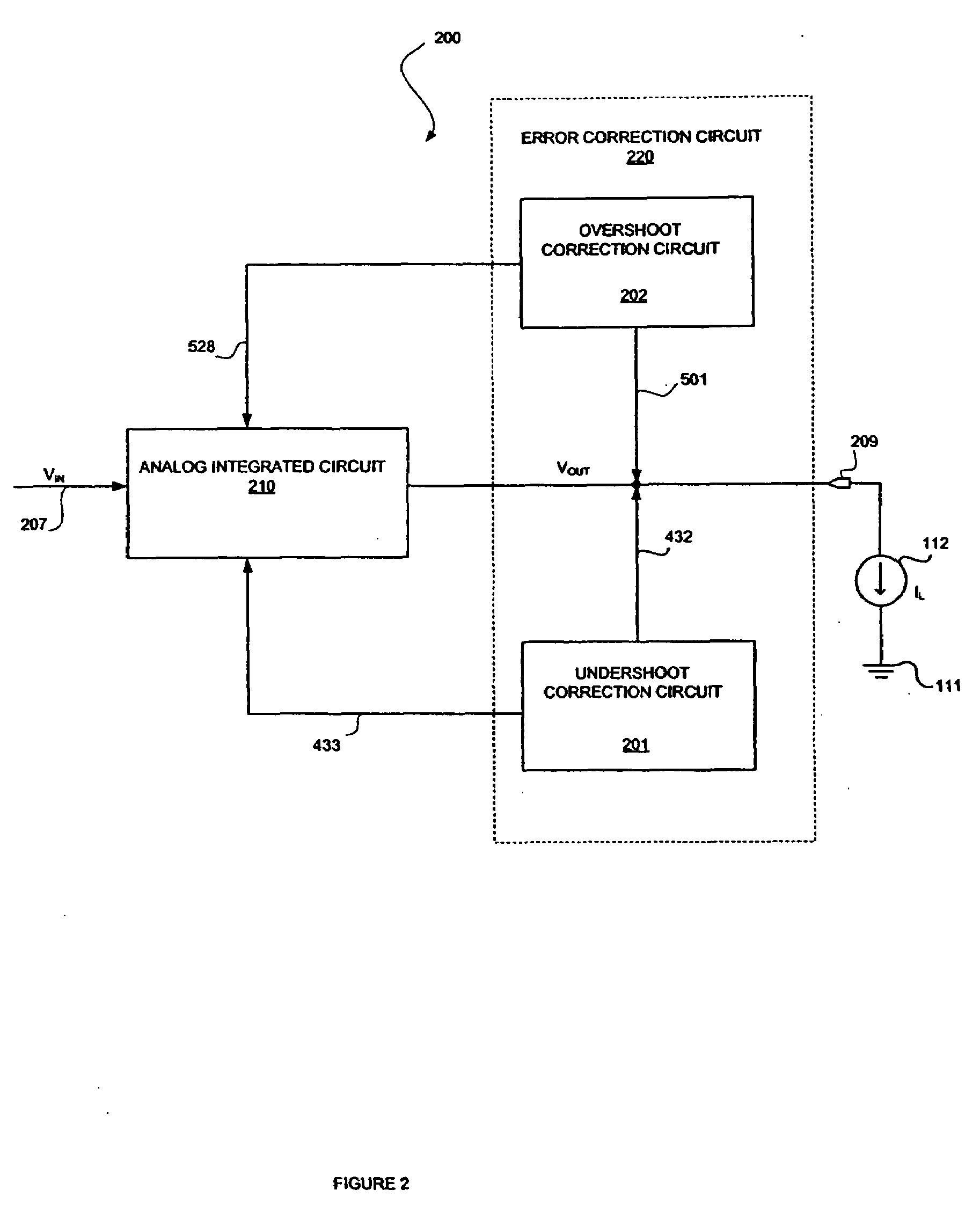
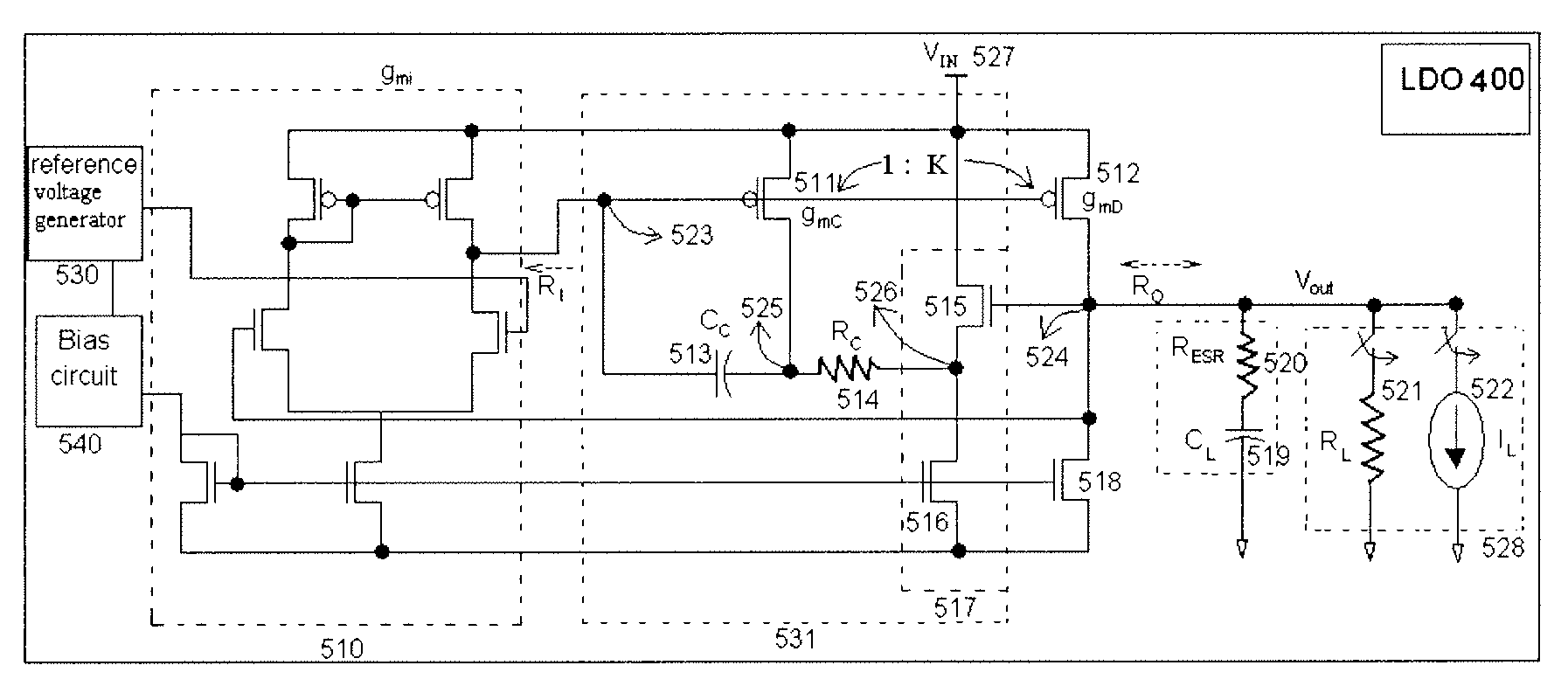
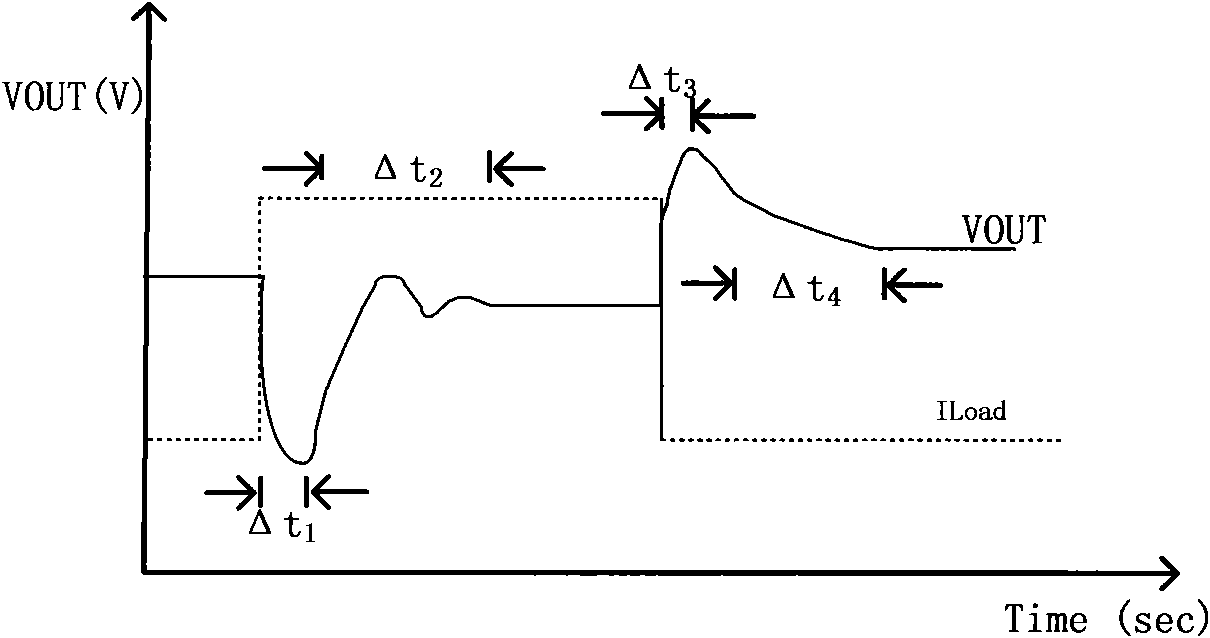
Method and apparatus for overshoot and undershoot errors correction in analog low dropout regulators
ActiveUS20080180071A1Reduce overshootReducing undershootPulse automatic controlDigital computer detailsLow-dropout regulatorIntegrated circuit
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for dynamically correcting overshoot and undershoot errors in an analog integrated circuit by improving the reaction time (Δt) of the analog integrated circuit. Equivalently, an error correction circuit is disclosed including an overshoot correction circuit and an undershoot correction that are only activated to reduce overshoot and undershoot errors by increasing the bandwidth of the integrated circuit when either undershoot or overshoot errors are detected.
Owner:MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Low dropout regulator with stability compensation
InactiveUS7589507B2Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Soft-start circuit and method for low-dropout voltage regulators
ActiveUS7459891B2Easily customizable controlMinimal die areaPower supply linesElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent limiting
A low drop-out voltage regulator having soft-start. A low drop-out regulator circuit is provided having an input node, an output node, a power FET connected by a source and drain between the input node and the output node, and a feedback circuit having an output connected and providing a control signal to a gate of the power FET. A current limit circuit is configured to control the power FET to limit the current through it when the voltage across a controllable sense resistor connected to conduct a current representing the current through the power FET exceeds a predetermined limit value. At start-up, control unit provides a control signal to the controllable resistor to cause the resistance value of the controllable resistor to decrease incrementally in value at respective predetermined incremental times during a predetermined time interval.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
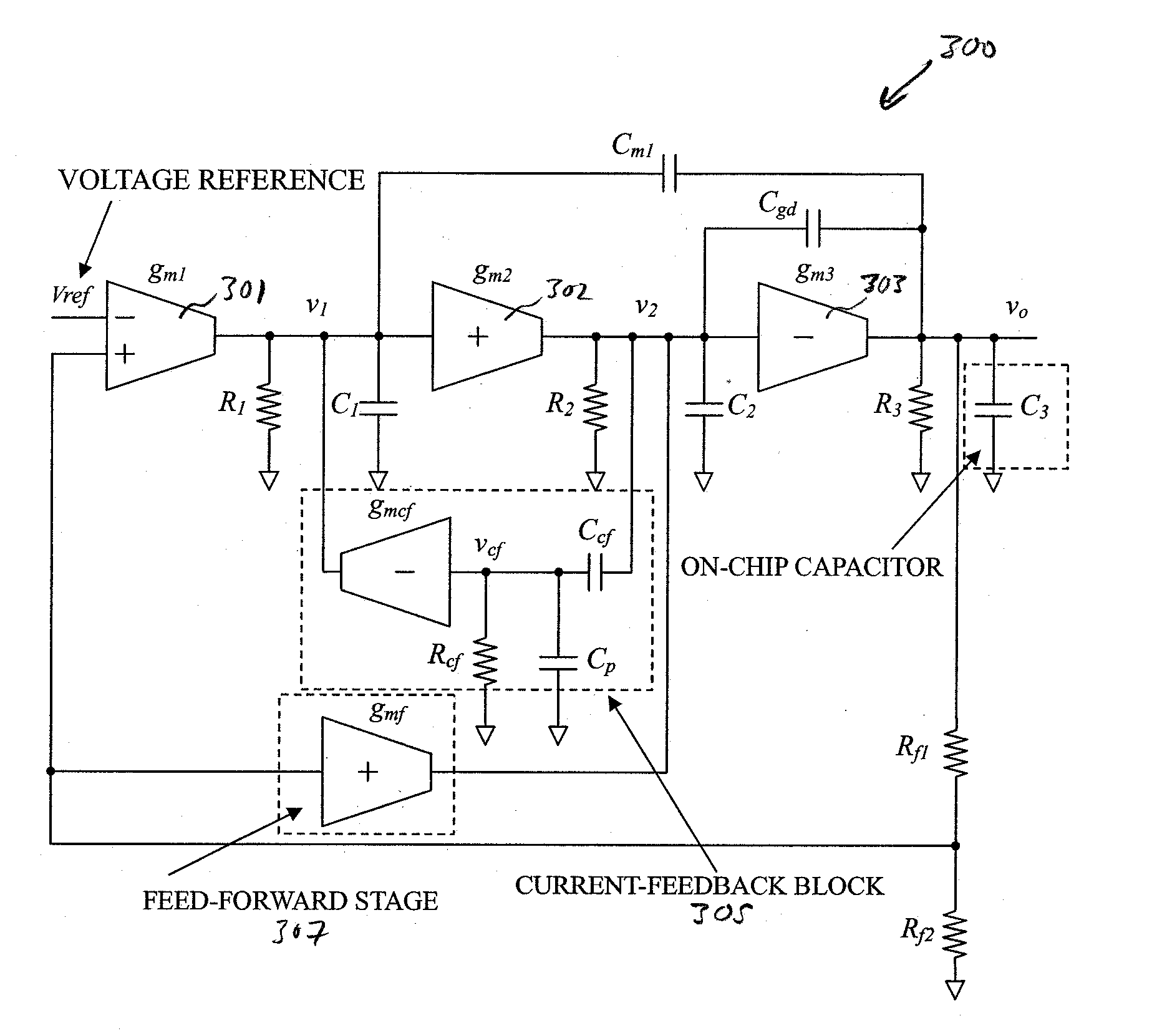
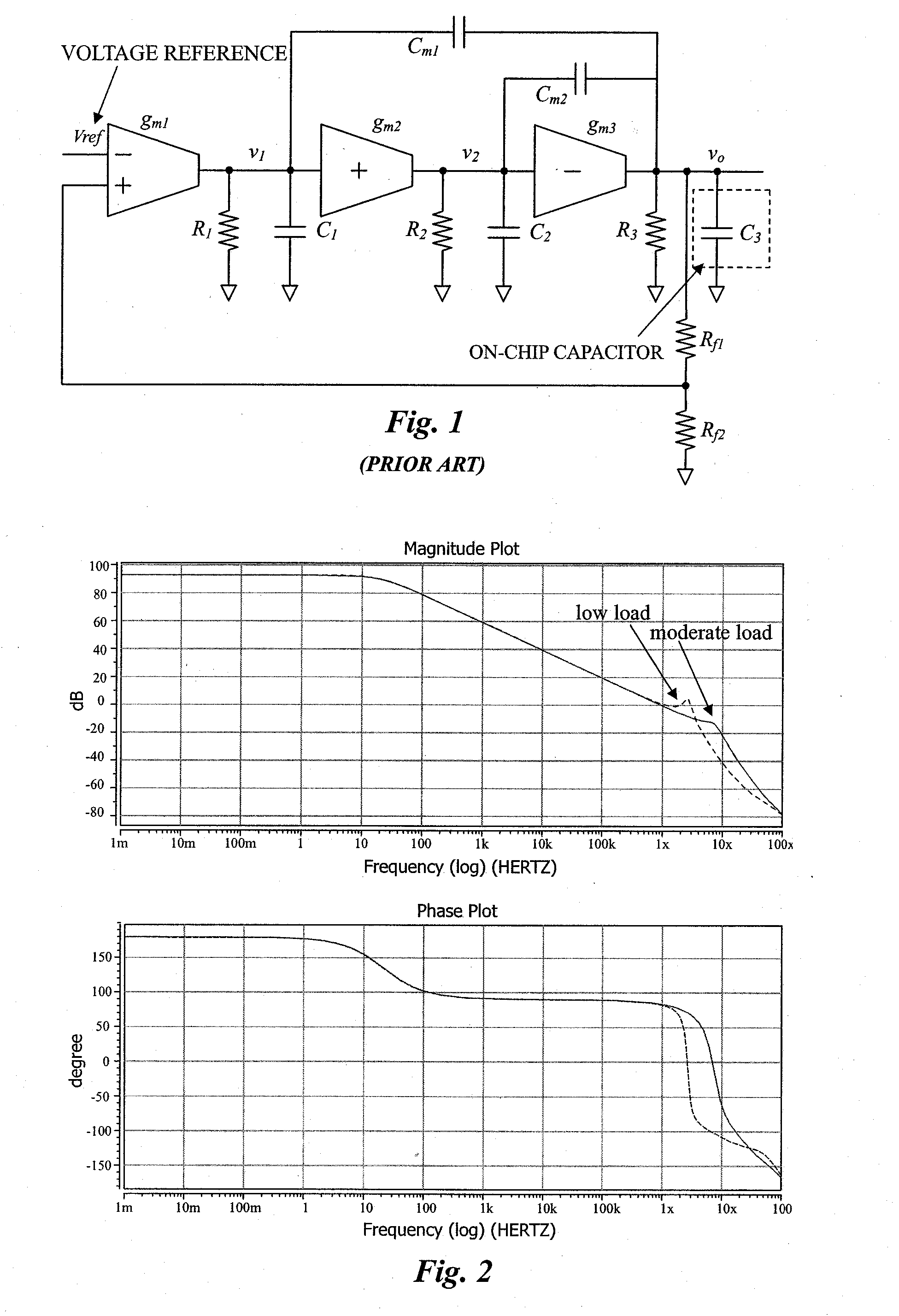
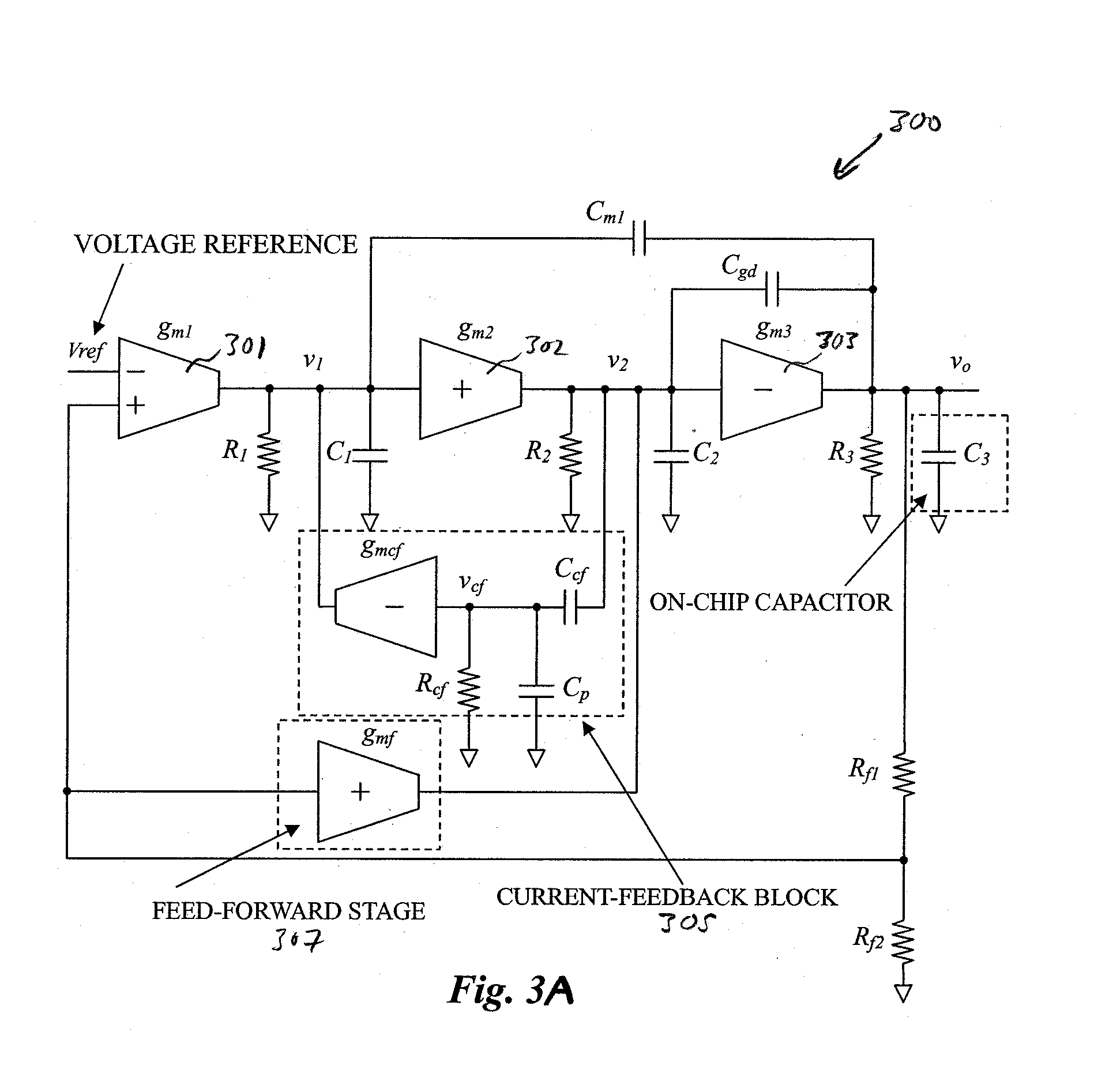
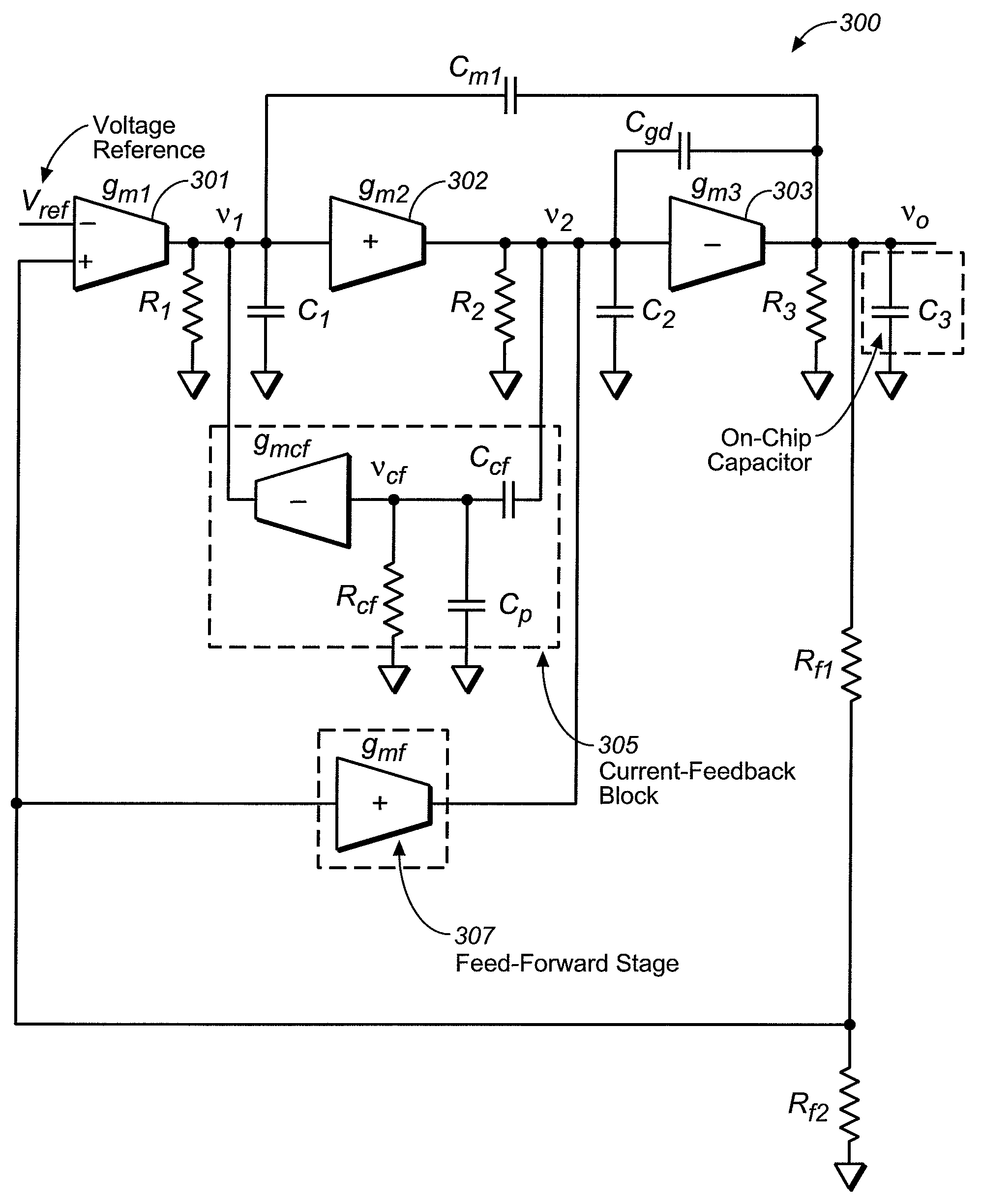
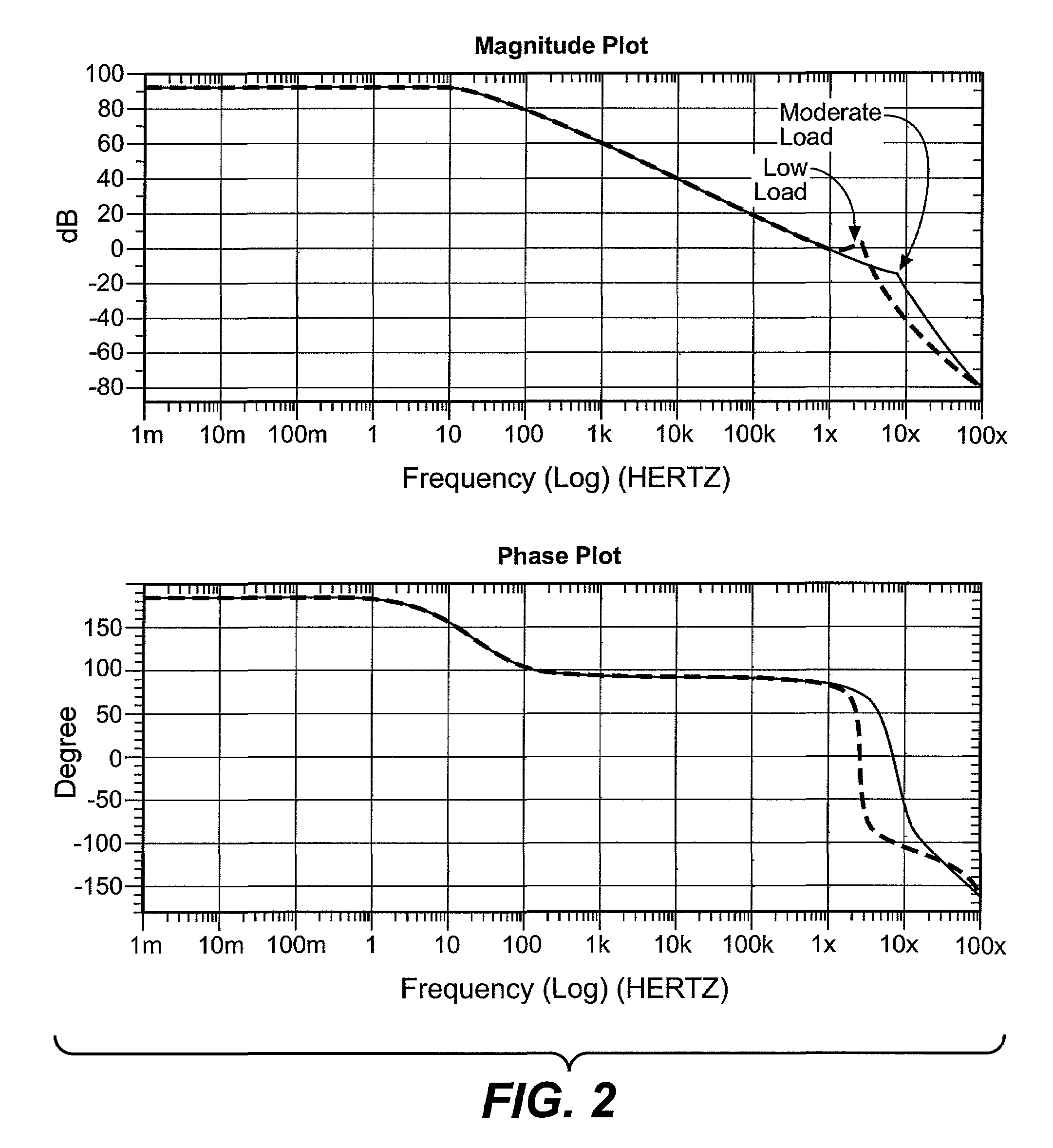
Area-Efficient Capacitor-Free Low-Dropout Regulator
ActiveUS20070018621A1Improve stabilitySacrificing performanceElectric variable regulationCapacitanceFrequency compensation
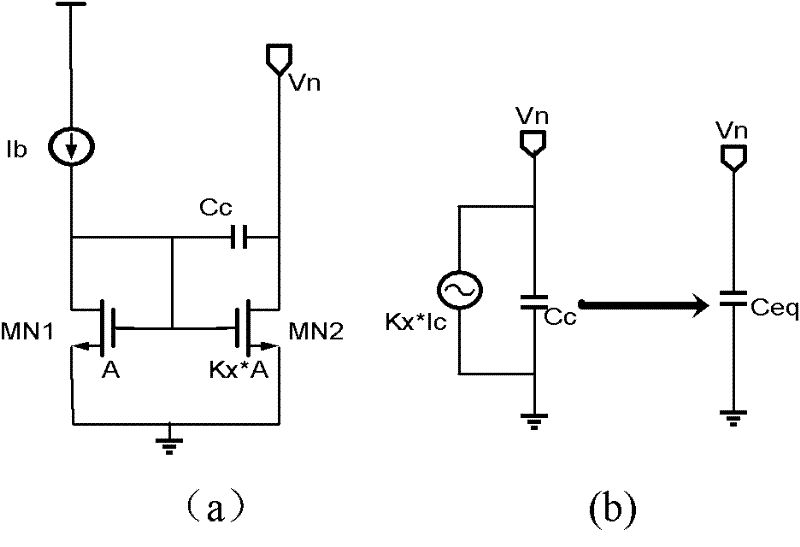
An area-efficient capacitor-free low-dropout regulator based on a current-feedback frequency compensation technique is disclosed. An implementation of a current feedback block with a single compensation capacitor is used to enable capacitance reduction. The resultant low-dropout regulator does not generally require an off-chip capacitor for stability and is particularly useful for system-on-chip applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Area-efficient capacitor-free low-dropout regulator
ActiveUS7495422B2Improve stabilitySacrificing performanceElectric variable regulationCapacitanceFrequency compensation
An area-efficient capacitor-free low-dropout regulator based on a current-feedback frequency compensation technique is disclosed. An implementation of a current feedback block with a single compensation capacitor is used to enable capacitance reduction. The resultant low-dropout regulator does not generally require an off-chip capacitor for stability and is particularly useful for system-on-chip applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
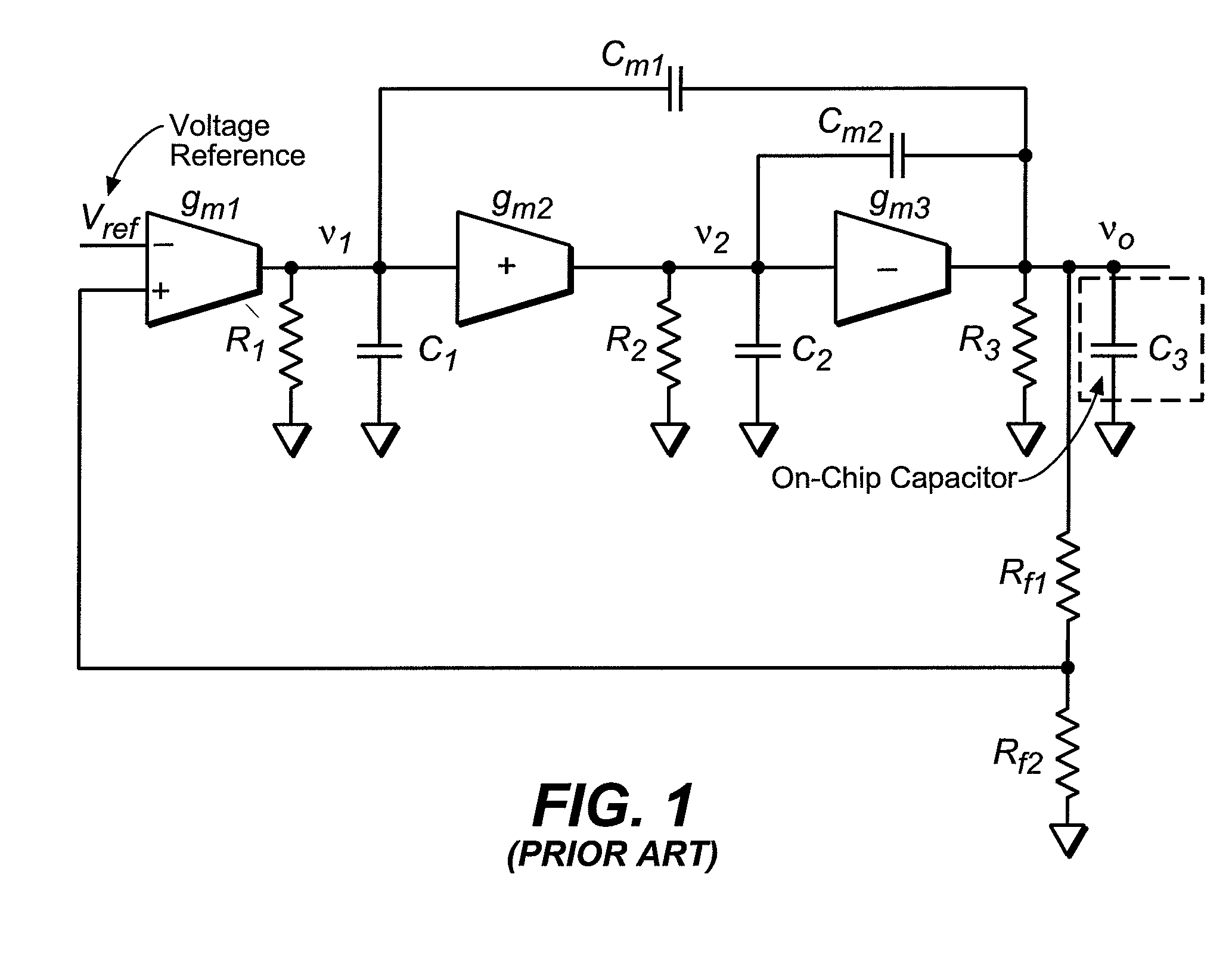
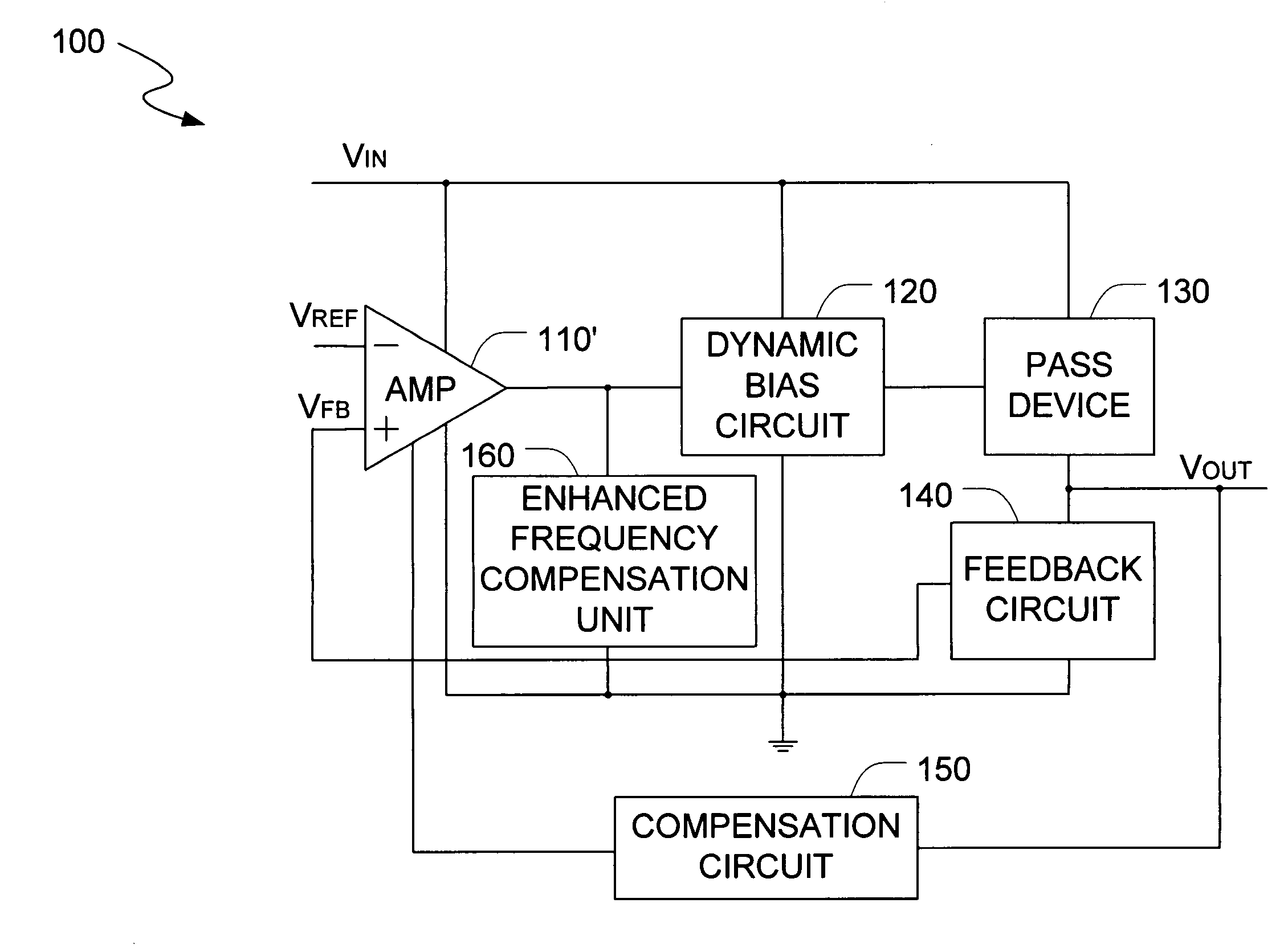
Low drop-out voltage regulator with enhanced frequency compensation
InactiveUS20060192538A1Enhanced frequency compensation capacityIncrease conversion rateElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
The present invention is a voltage regulator circuit with enhanced frequency compensation. The voltage regulator includes an error amplifier, a dynamic bias circuit, an enhanced frequency compensation unit, a pass device and a compensation circuit. A signal from the pass device acts as an input signal of the error amplifier and is compared with another input signal, producing a differential signal. The differential signal is amplified and then provided to the dynamic circuit and the enhanced frequency compensation unit. The enhanced frequency compensation unit is provided such that a zero reference value in a left-hand plane can be generated to optimize the compensation for the voltage regulator circuit. The error amplifier includes a capacitor for compensating an output voltage of the voltage regulator circuit.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
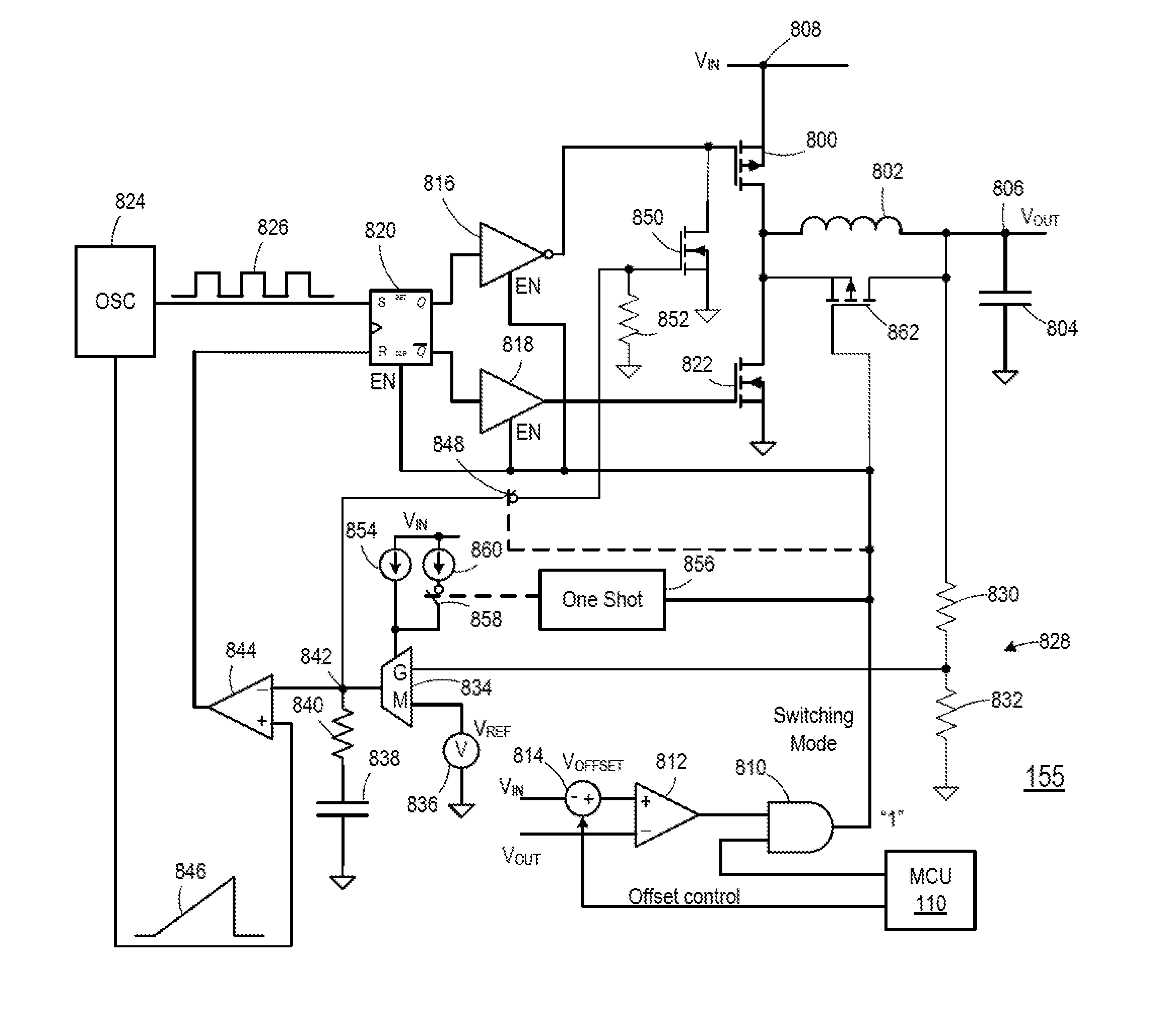
Voltage regulator with switching and low dropout modes
ActiveUS20150042300A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage dropVoltage regulation
A voltage regulator includes an input terminal, an output terminal, a control circuitry, a buck mode switching converter, and a low dropout regulator circuit. The buck mode switching converter is arranged to convert a voltage signal received at the input terminal to a first voltage signal at the output terminal responsive to a first predetermined signal output from the control circuitry. The buck mode switching converter includes an electronically controlled switch in communication with an energy storage element. The low dropout regulator circuit is coupled between the input terminal and the output terminal and includes a linear circuit and is arranged to control a voltage drop across the linear circuit so as to provide a second voltage signal at the output terminal responsive to a second predetermined signal output from the control circuitry.
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP
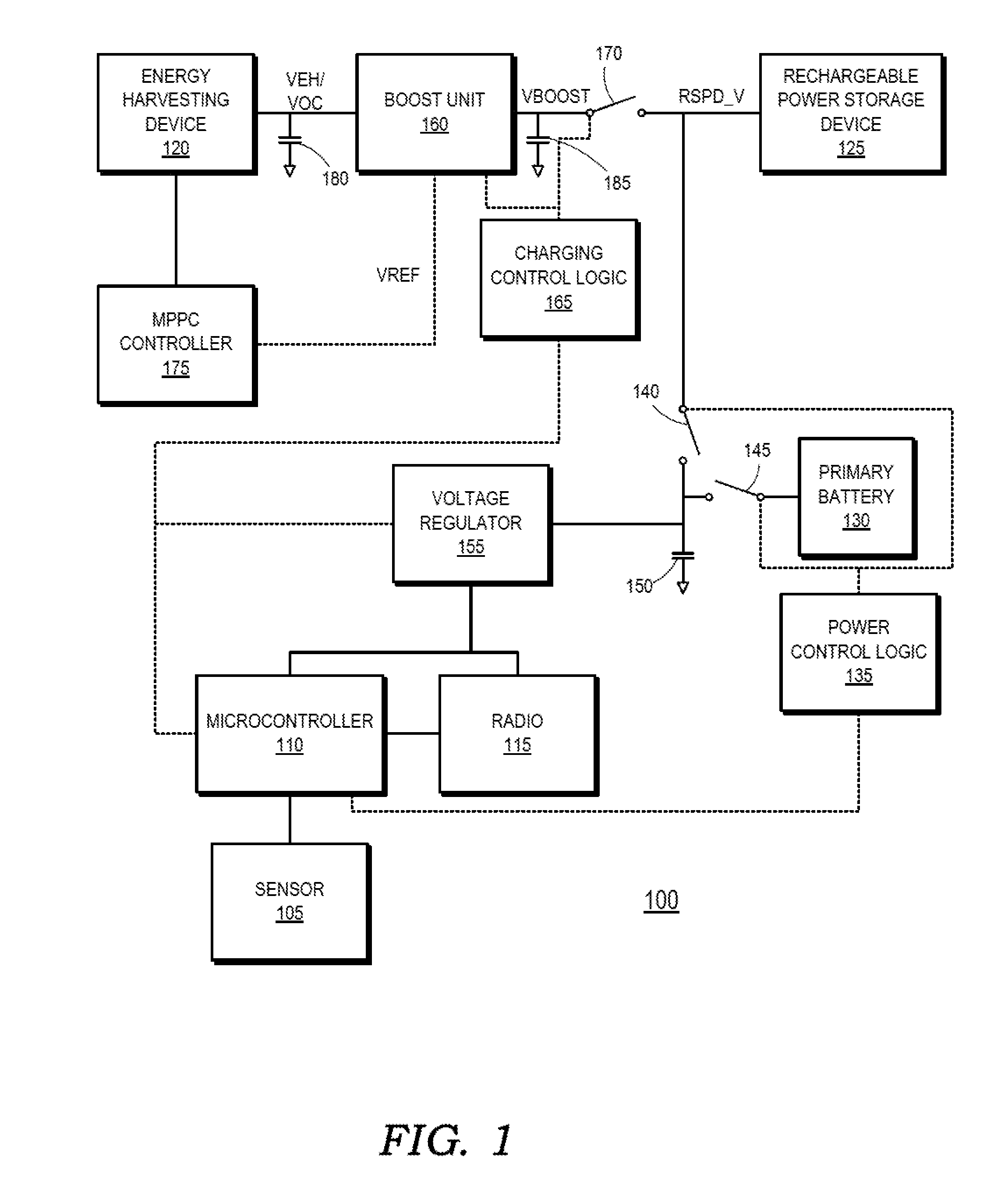
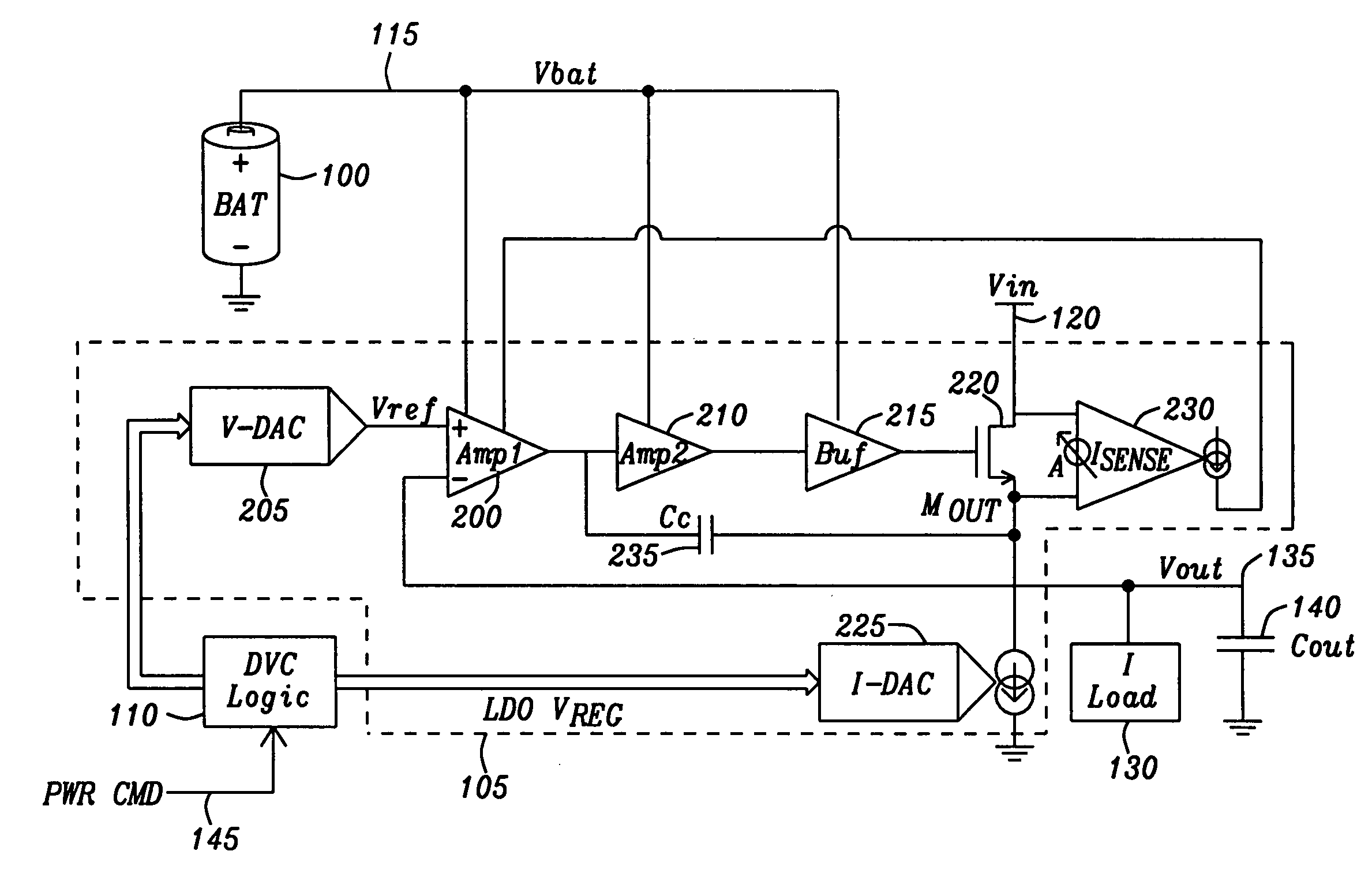
System and method for providing a dynamically configured low drop out regulator with zero quiescent current and fast transient response
A system and a method are disclosed for providing a dynamically configured low drop out regulator that has zero quiescent current and a fast transient response. A power supply control circuit is provided that comprises a switcher circuit and a low drop out regulator and a control signal circuit. When the output voltage of the low drop out regulator is in a steady state condition the control signal circuit generates control signals that turn off the operation of the low drop out regulator to provide zero quiescent current. When the output voltage is not in a steady state condition the control signal circuit generates control signals that turn on the operation of the low drop out regulator to provide a fast transient response.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
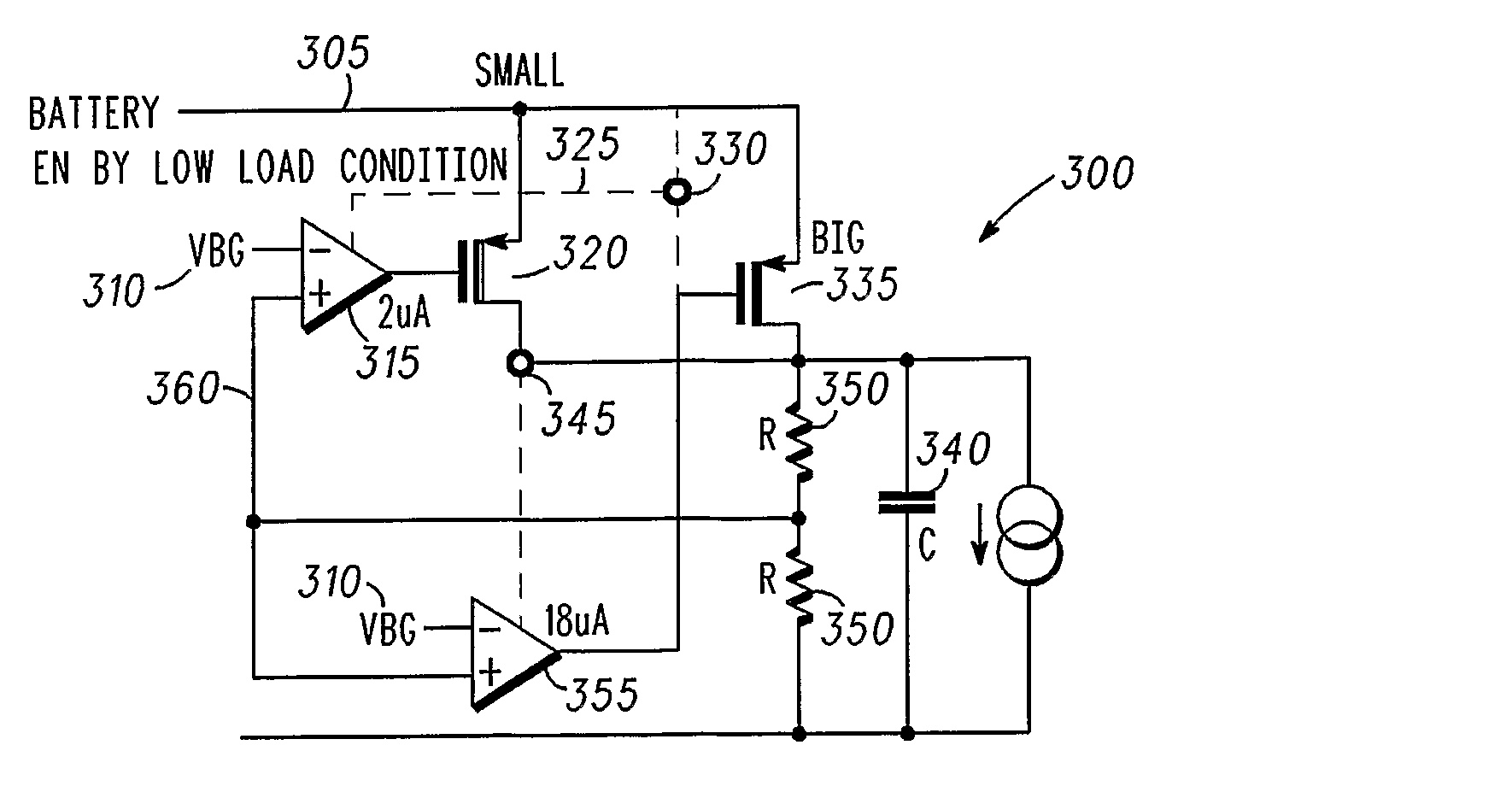
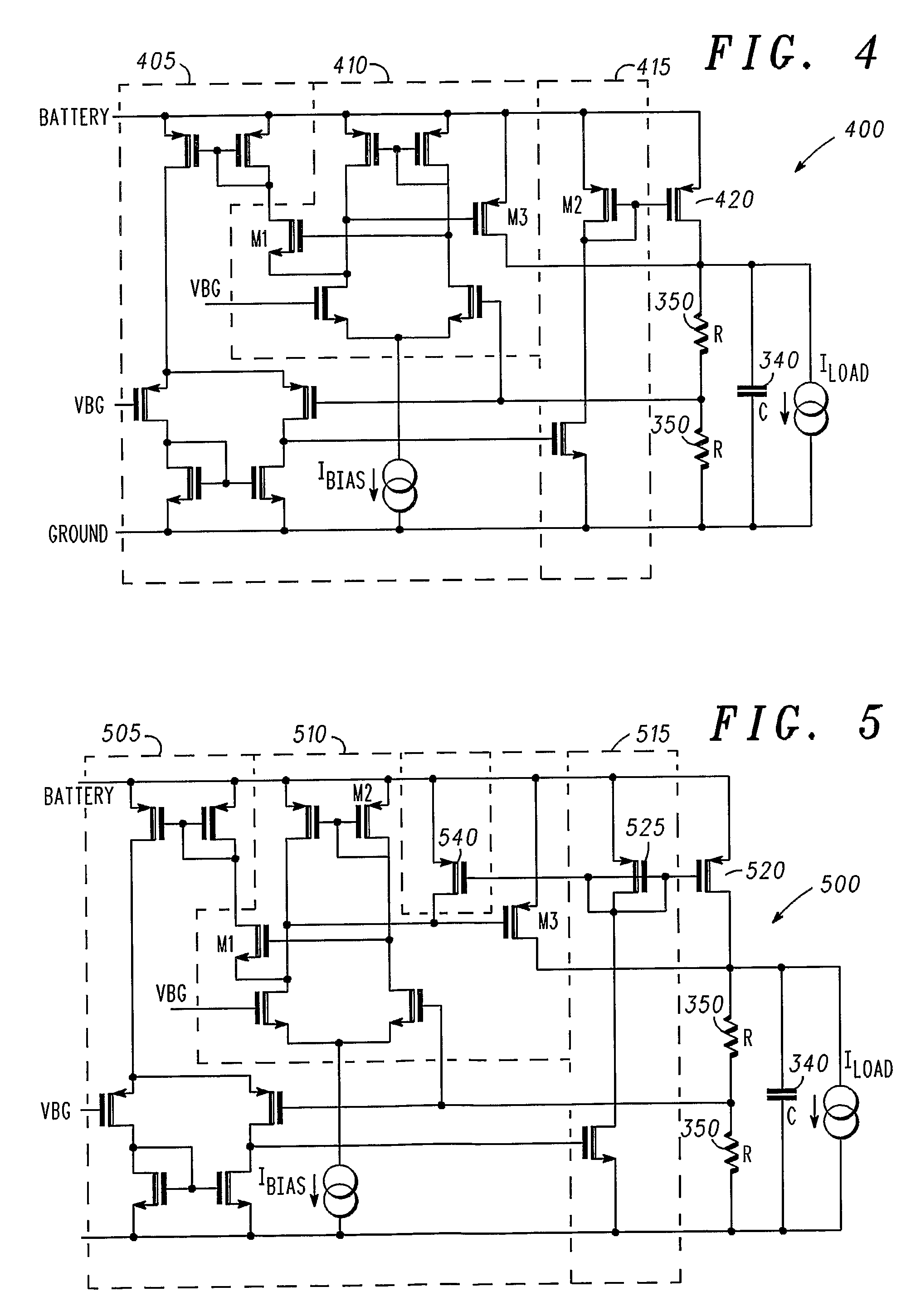
Voltage Regulator With Pass Transistors Carrying Different Ratios Of The Total Load Current And Method Of Operation Therefor
ActiveUS20080191670A1Ac network voltage adjustmentElectric variable regulationLow loadVoltage regulation
A voltage regulator for providing a voltage regulated output to a load comprises a first loop and a second loop. The first loop comprises a first active device coupled to a first pass device and configured to provide a first, relatively high current output to the load. The second loop comprises a second active device coupled to a second pass device and configured to provide a second, relatively low current output to the load.In this manner, when the inventive concept is applied to low drop-out regulators, the provision of two independent loops reduces dramatically the quiescent current provided by the voltage regulator under low load conditions.
Owner:NXP USA INC
LDO (Low DropOut Regulator) based on dynamic zero pole tracking technology
InactiveCN102541134AImprove stabilityElectric variable regulationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses an LDO (Low DropOut Regulator) based on a dynamic zero pole tracking technology, belonging to the field of power supply management. The LDO is provided to solve the problem of the stability of a traditional LDO loop, and specifically comprises an error amplifier, a buffer and a slew-rate enhancement circuit. The LDO is characterized by further comprising a first capacitor, a second capacitor and a variable resistor, wherein one end of the first capacitor is connected with the output end of the error amplifier, the other end of the first capacitor is connected with one end of the variable resistor, one end of the second capacitor is connected with the error amplifier, and the other end of the second capacitor is connected with the other end of the variable resistor and is taken as the output end of the LDO. According to the LDO based on the dynamic zero pole tracking technology, disclosed by the invention, the first capacitor and the variable resistor form a compensative network as a dynamic zero pole of a system; and in addition, a phase margin of the LDO loop is compensated by utilizing the second capacitor in a current multiplication mode so that the stability of the LDO loop is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Filling in/pulling out current rapid response linear voltage regulator and regulating method
ActiveCN101893908AStable output voltageEliminate the problemElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses a filling in / pulling out current rapid response linear voltage regulator and a regulating method. The regulator comprises a reference voltage source, two error amplifiers, an N-channel MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube I, an N-channel MOS tube II and a static current control unit. The static current control unit consists of a current summing unit, a pulling out current subtracting unit and a filling-in current subtracting unit. In the voltage regulating method, two error amplifiers dynamically monitor the voltage variation of a source electrode of the N-channel MOS tube I and a drain electrode of the N-channel MOS tube II when the pulling-out and filling-in current occur and dynamically control the gate-to-source voltage of two N-channel MOS tubes so that the source voltage of the N-channel MOS tube I and the drain voltage of the N-channel MOS tube II vary toward the same direction. The invention has novel and reasonable design, convenient circuit connection, small area of circular bard and good use effect, ensures the large-load stability and greatly improves the transient response of an LDO (Low Dropout Regulator).
Owner:深圳德信微电子有限公司
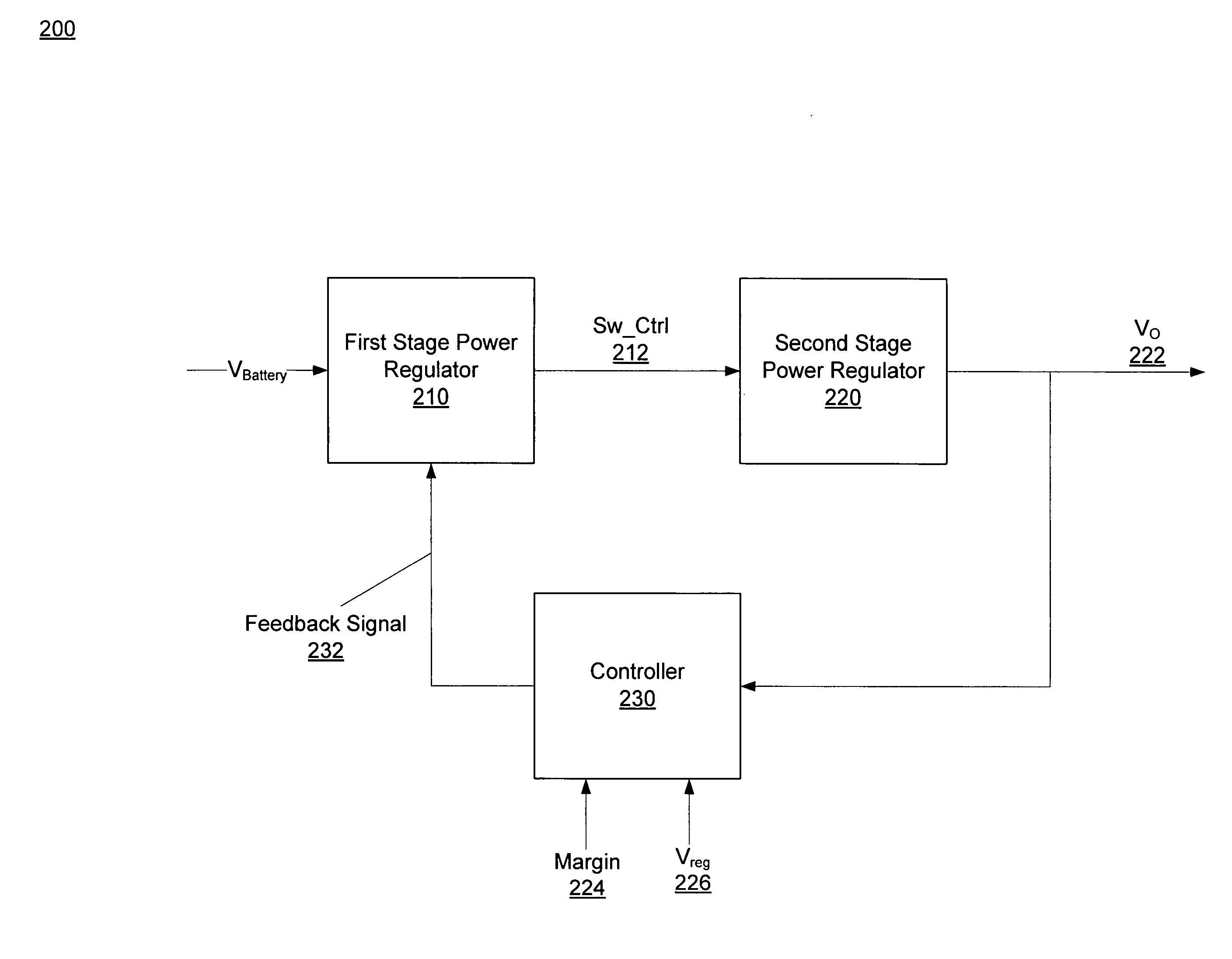
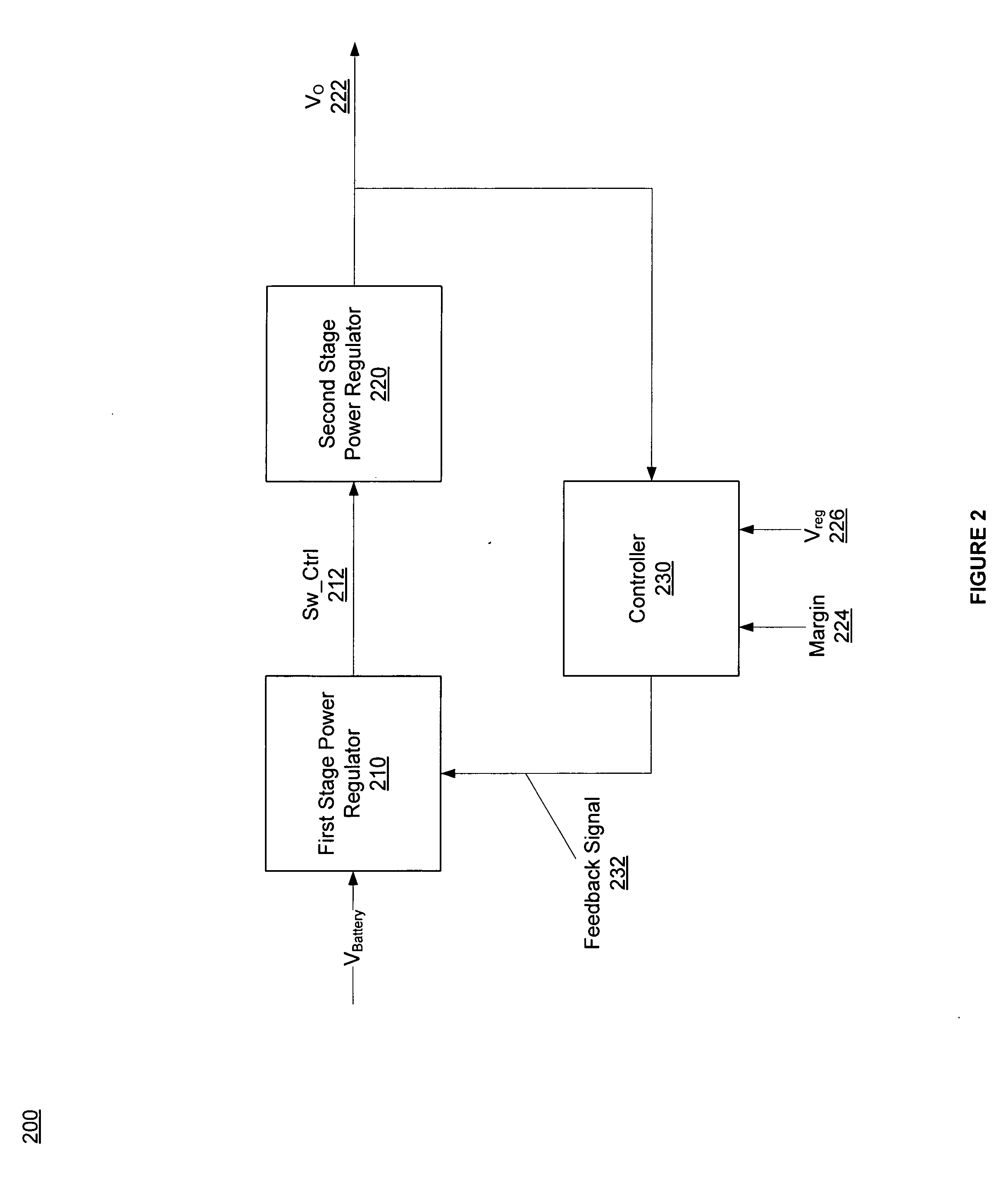
Power management efficiency using DC-DC and linear regulators in conjunction
ActiveUS20090153108A1Effective regulationIncreasing of complexityThree-or-more-wire dc circuitsApparatus with intermediate ac conversionLinear regulatorPower Management Unit
A power management unit for improving power efficiency of an electronic device. The power management unit includes a first and a second stage power regulator and a control circuitry. The first stage power regulator includes a switching regulator to efficiently adjust an input voltage based on a feedback signal. The adjusted input voltage provides the second stage power regulator that includes low dropout voltage regulators with an input voltage close to its output. Thus, power dissipation in the second stage is reduced by reducing the voltage differential between the input and desired output voltages. The second stage turns on / off power to units of the electronic device. The control circuitry generates the feedback signal based on dropout voltages of the low dropout voltages, the desired output voltage and the adjusted input voltage. The largest dropout voltage is selected and adds it to the desired output voltage to generate the feedback signal.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Low dropout regulator
InactiveCN102789257ASmall quiescent currentImprove transient responseElectric variable regulationPower flowEngineering
The invention discloses a low dropout regulator, comprising a current substraction circuit which consists of MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) tubes M4 and M5 and has a load hopping from a light load to a heavy load, a current substraction circuit which consists of M6 and M7 and has a load hopping from a heavy load to a light load, as well as a fast response pathway which consists of M7, M8 and M14 and has a load hopping from a heavy load to a light load. According to the LDO (low dropout regulator) disclosed by the invention, the bias current of an error amplifier is increased only when the circuit is transiently switched, thereby the output transient response is improved, and the quiescent current of the circuit at a steady state is ensured to be very low; when the load hops from the heavy load to the light load, the fast response pathway is increased, the bandwidth of a transient loop is expanded, the output transient characteristic is improved, and the magnitude of output spike voltage is reduced; and furthermore, when the LDO is in a steady state, only an EA main loop is involved in work, thereby the quiescent current of the LDO is not increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low drop-out voltage regulator with dynamic voltage control
ActiveUS20120299564A1Minimize power consumptionLow dropout voltageElectric variable regulationLoad circuitPower flow
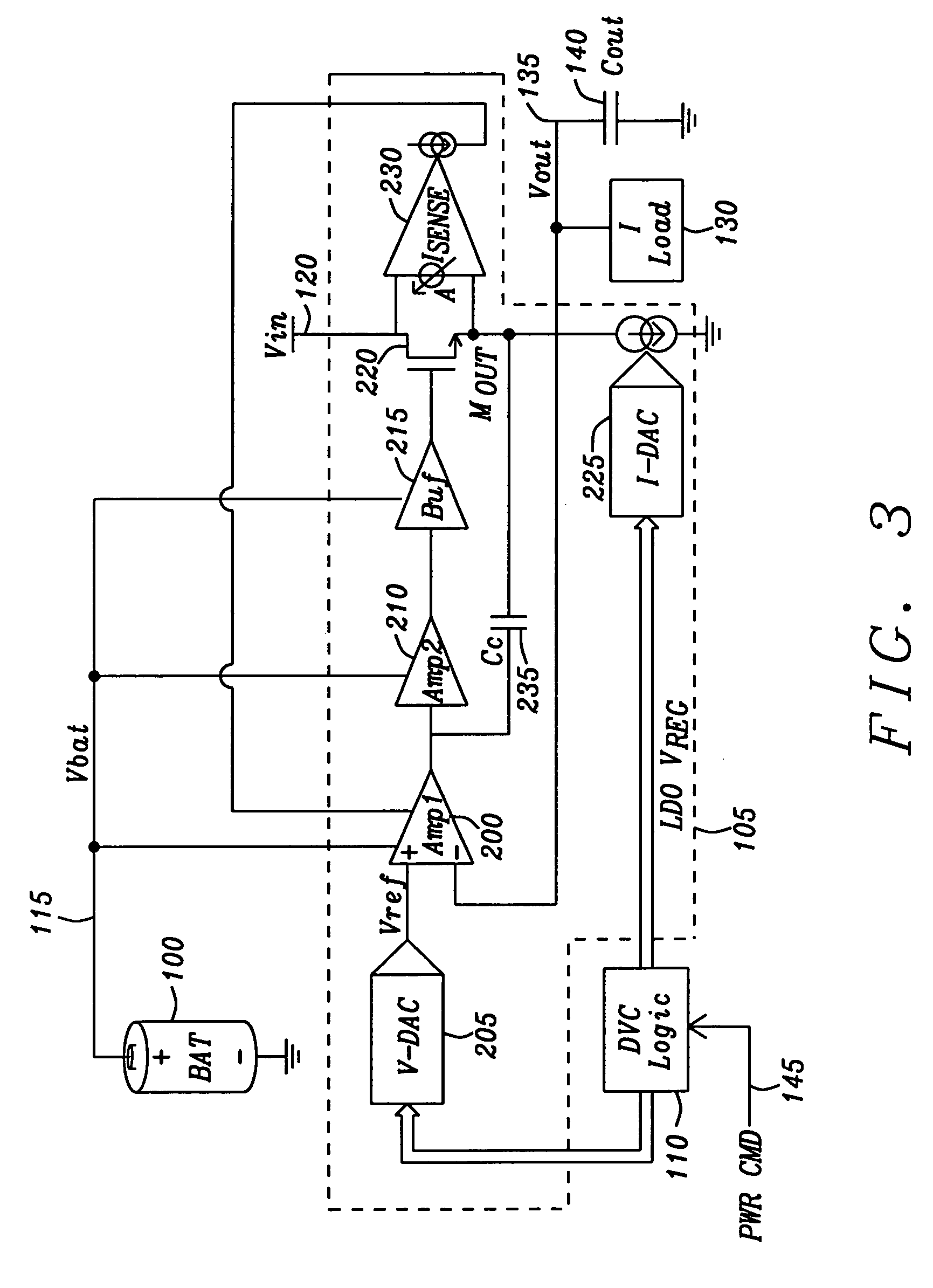
A low dropout voltage regulator circuit that dynamically adjusts its output voltage has a voltage adjustment circuit in communication with a dynamic voltage controlling circuit for modifying the output voltage of the low dropout voltage regulator. A first amplification circuit is connected to receive an adjusted reference voltage from the voltage adjustment circuit and compare it with a feedback signal from the output voltage to provide a drive signal to a signal input terminal of a follower output transistor. An output terminal of the follower output transistor provides the output voltage of the regulation circuit. An adjustable internal load circuit applies a load current to the output terminal of the follower output transistor to increase the bandwidth of the output of the voltage regulation circuit that is sensed by a dynamic biasing sensing circuit to generate a dynamic biasing signal that modifies the bandwidth of the first amplification circuit.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com