Patents
Literature
335 results about "Leakage current reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
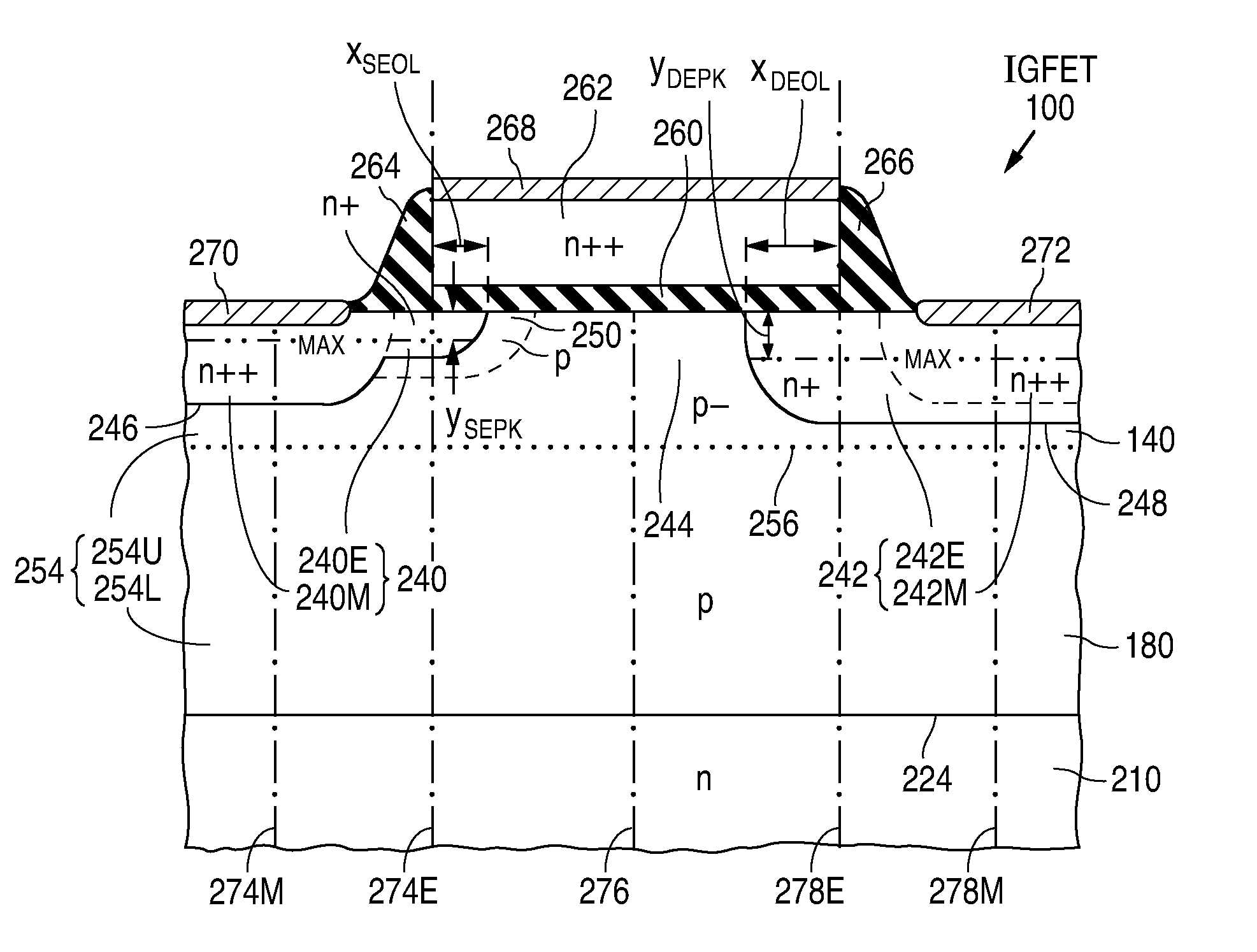
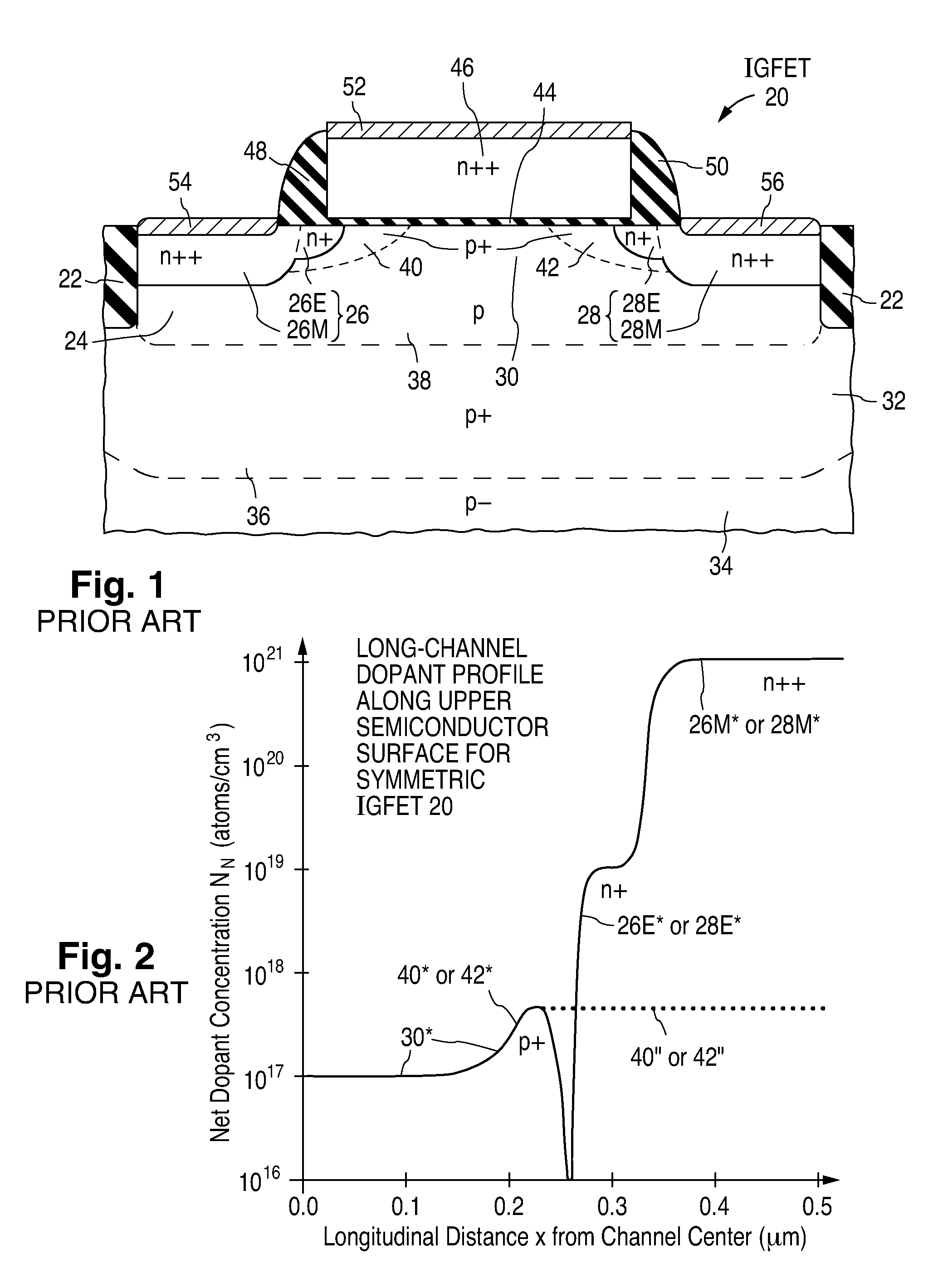
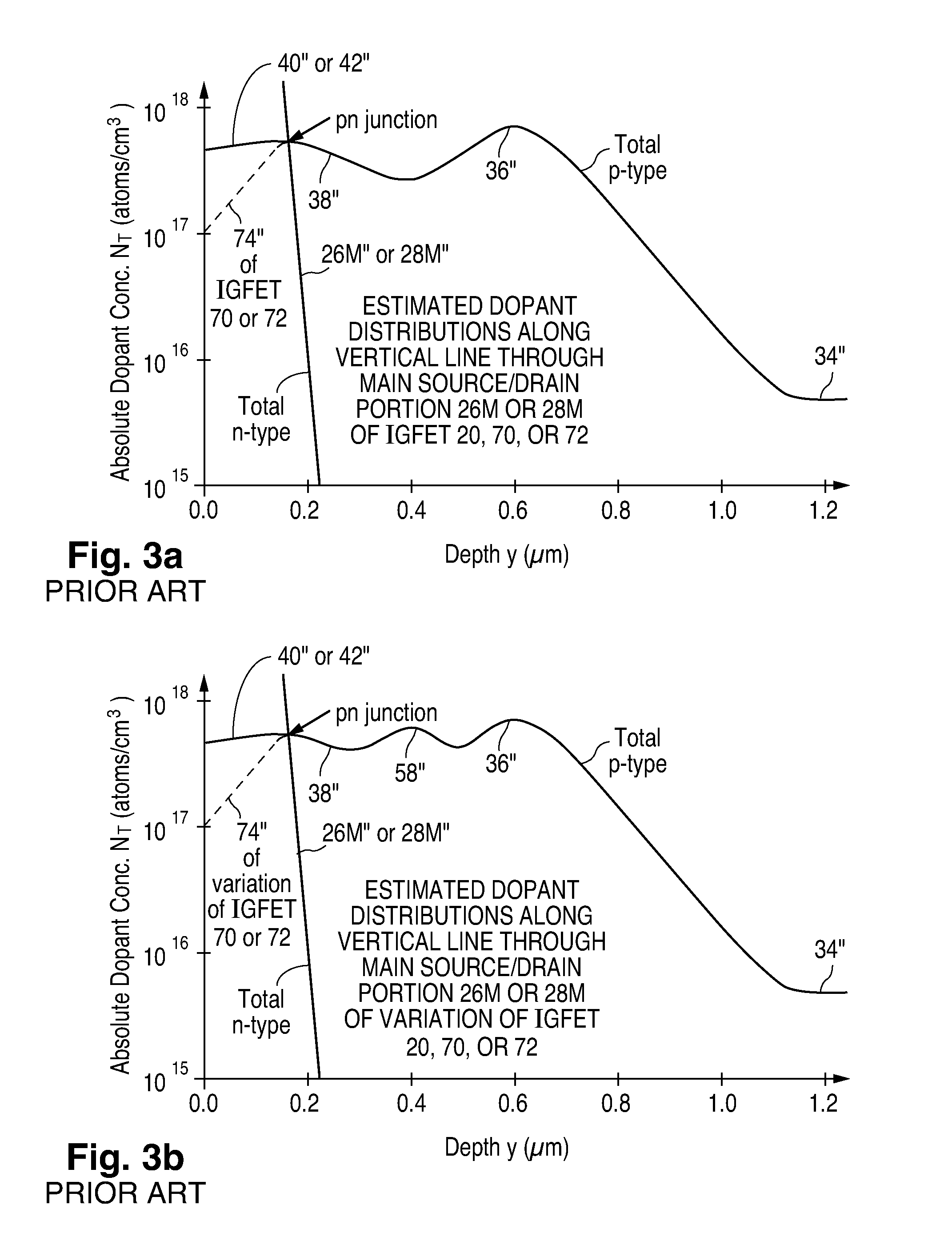
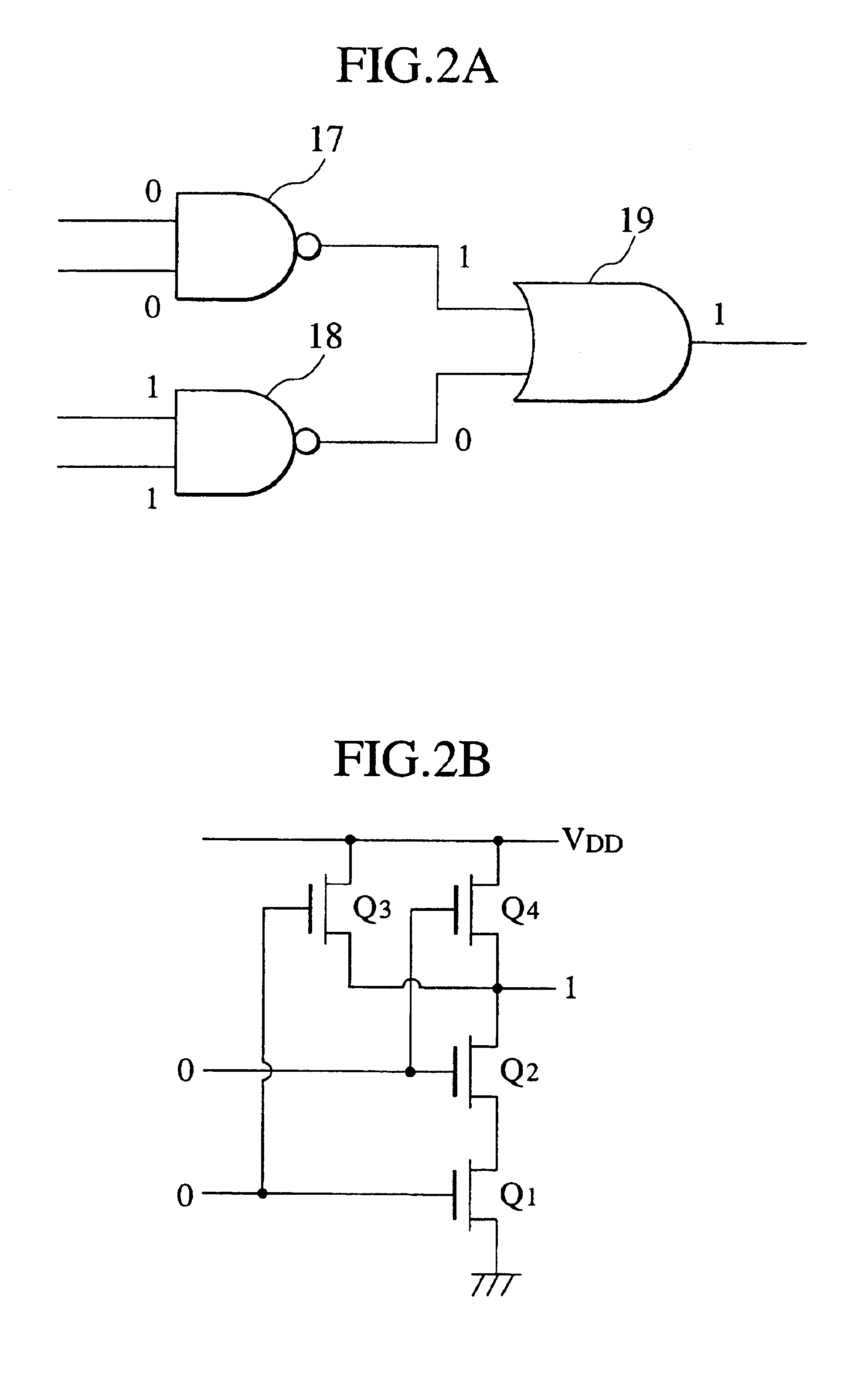
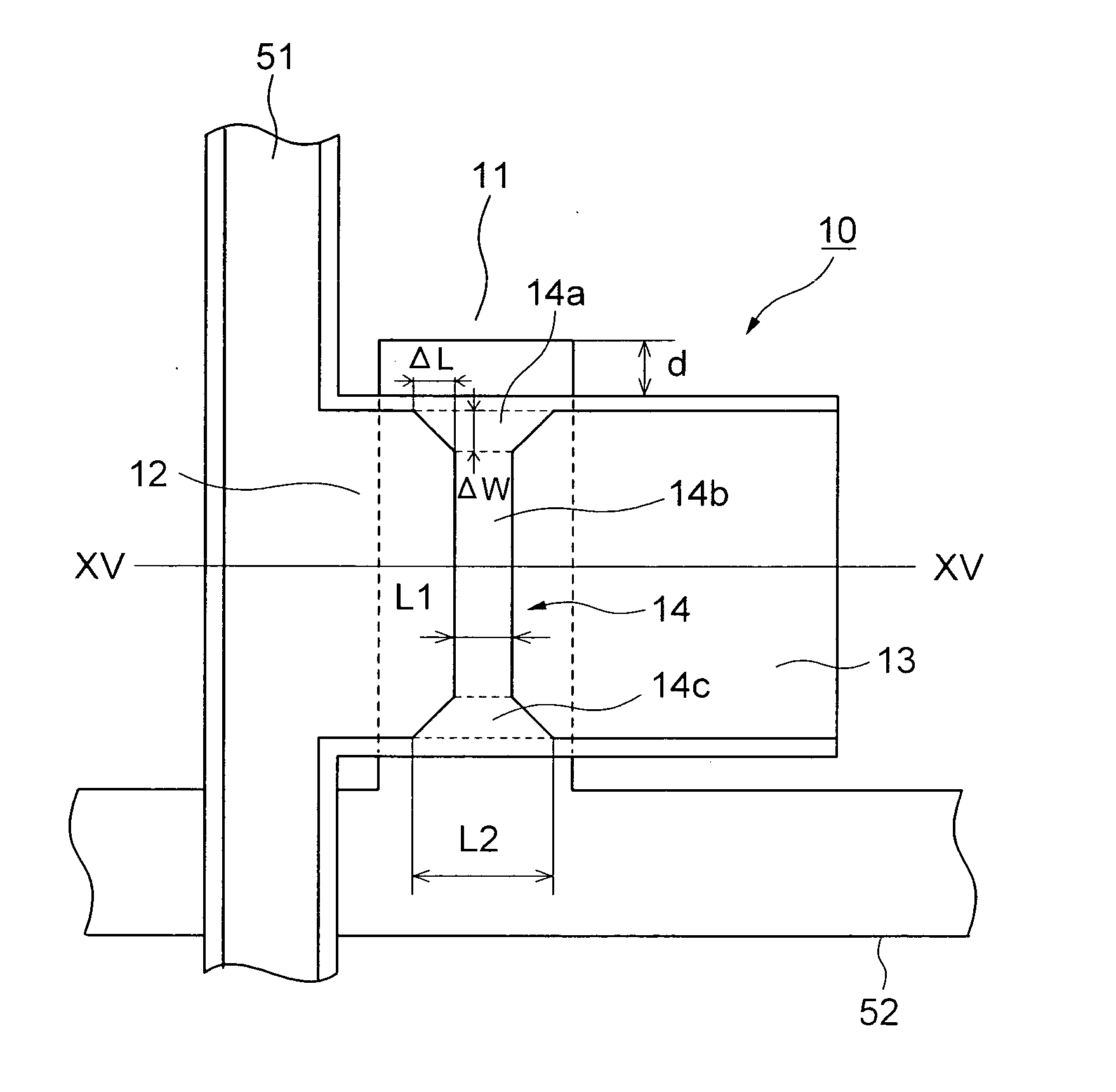
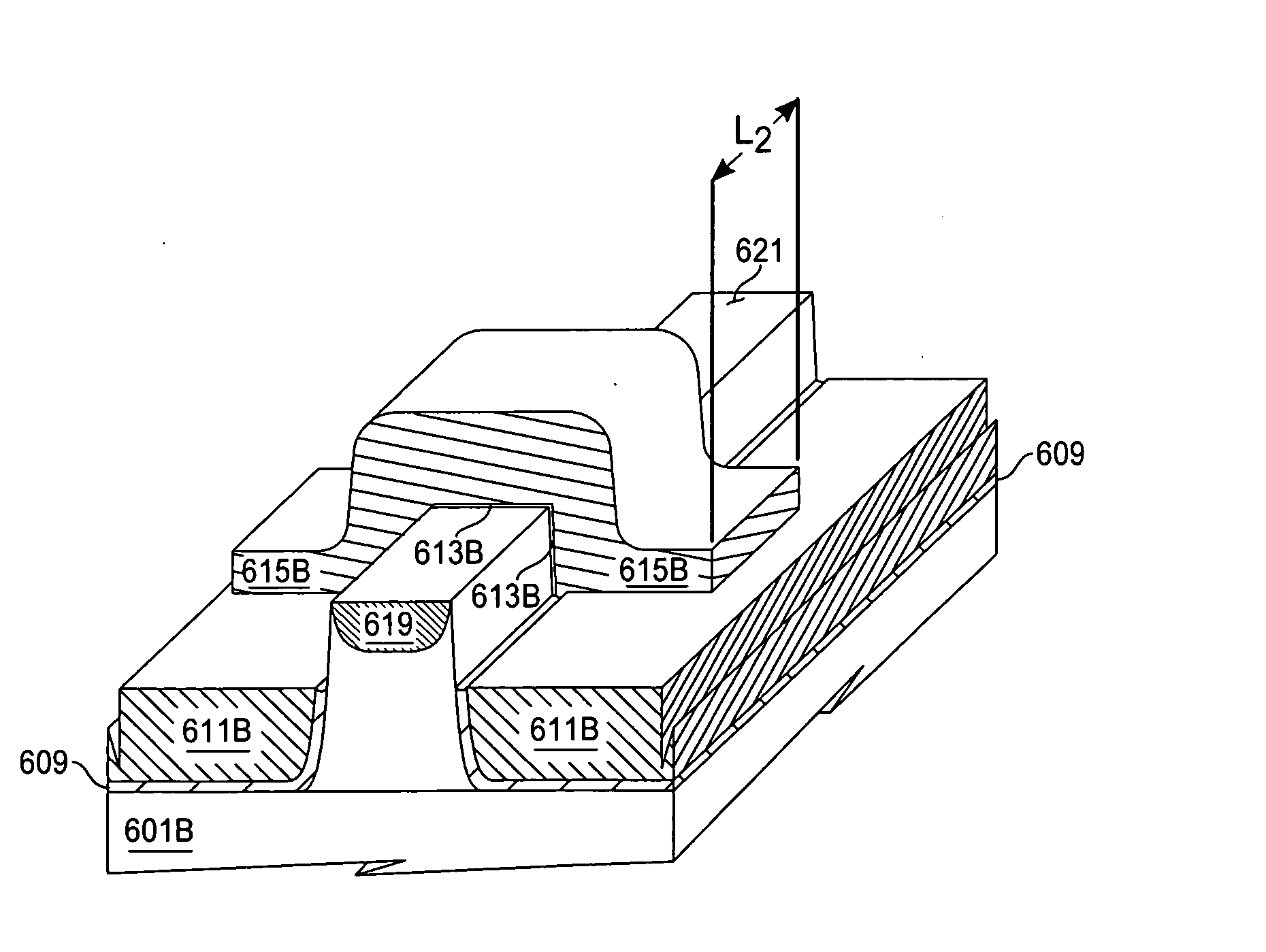
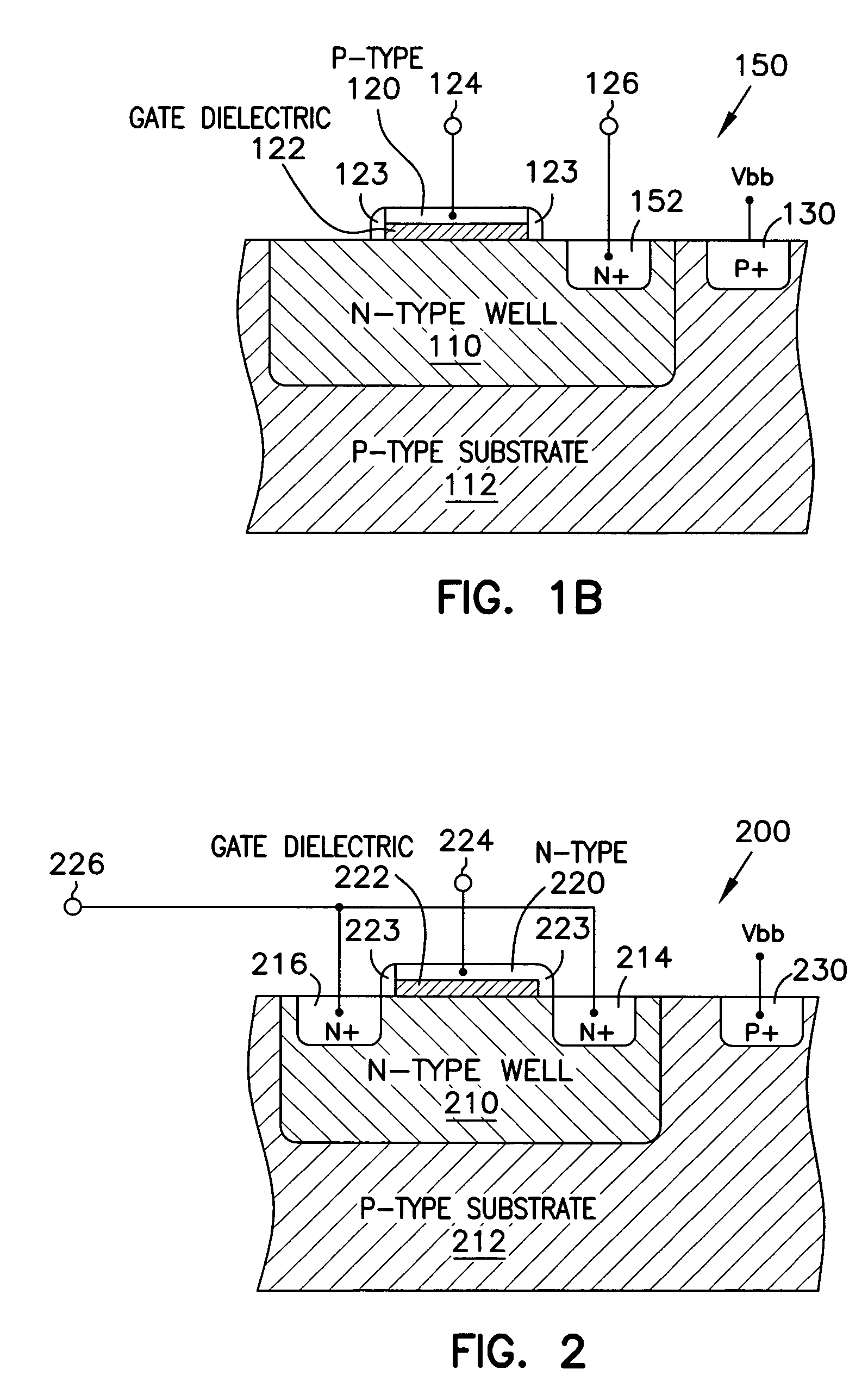
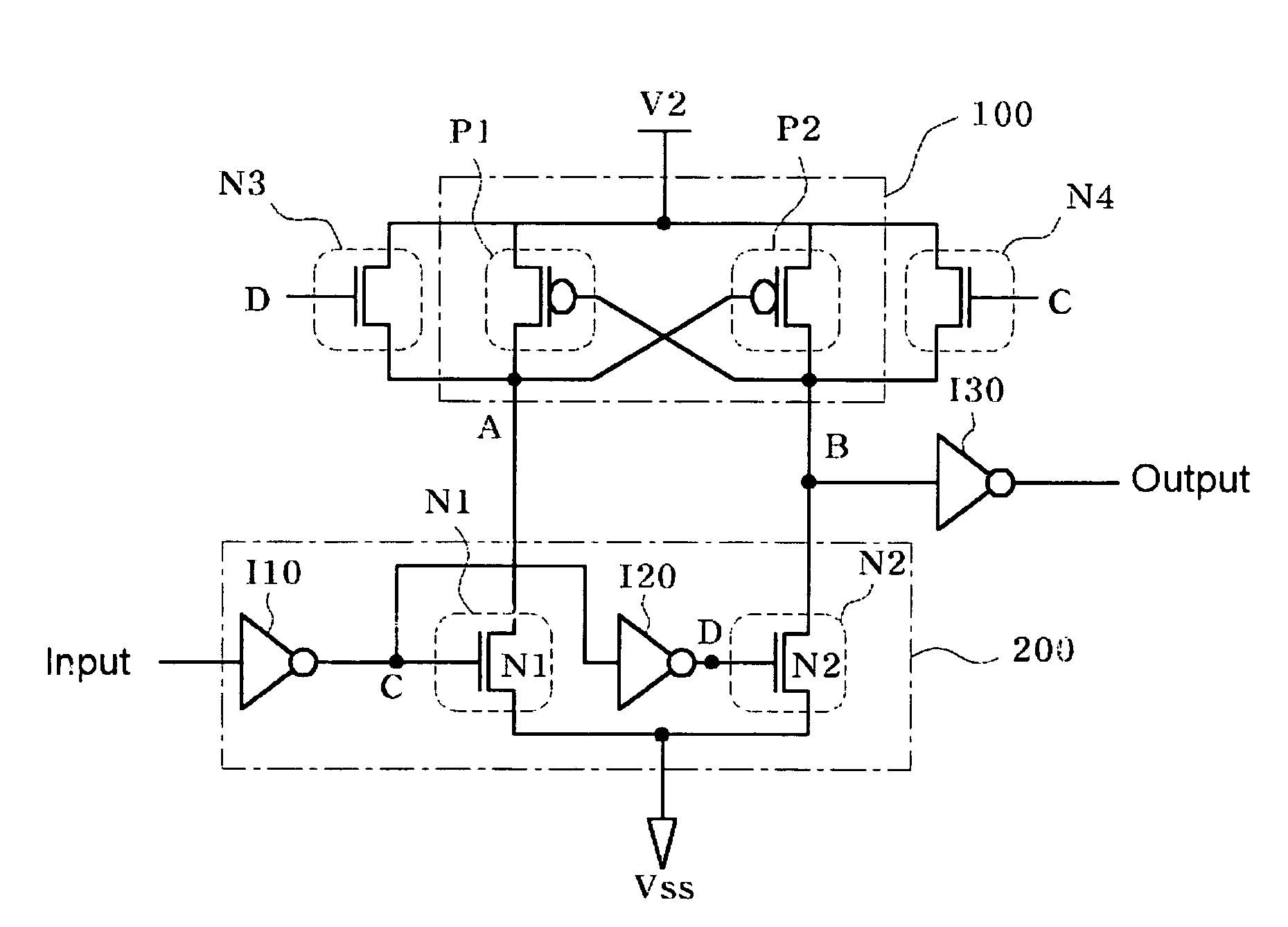
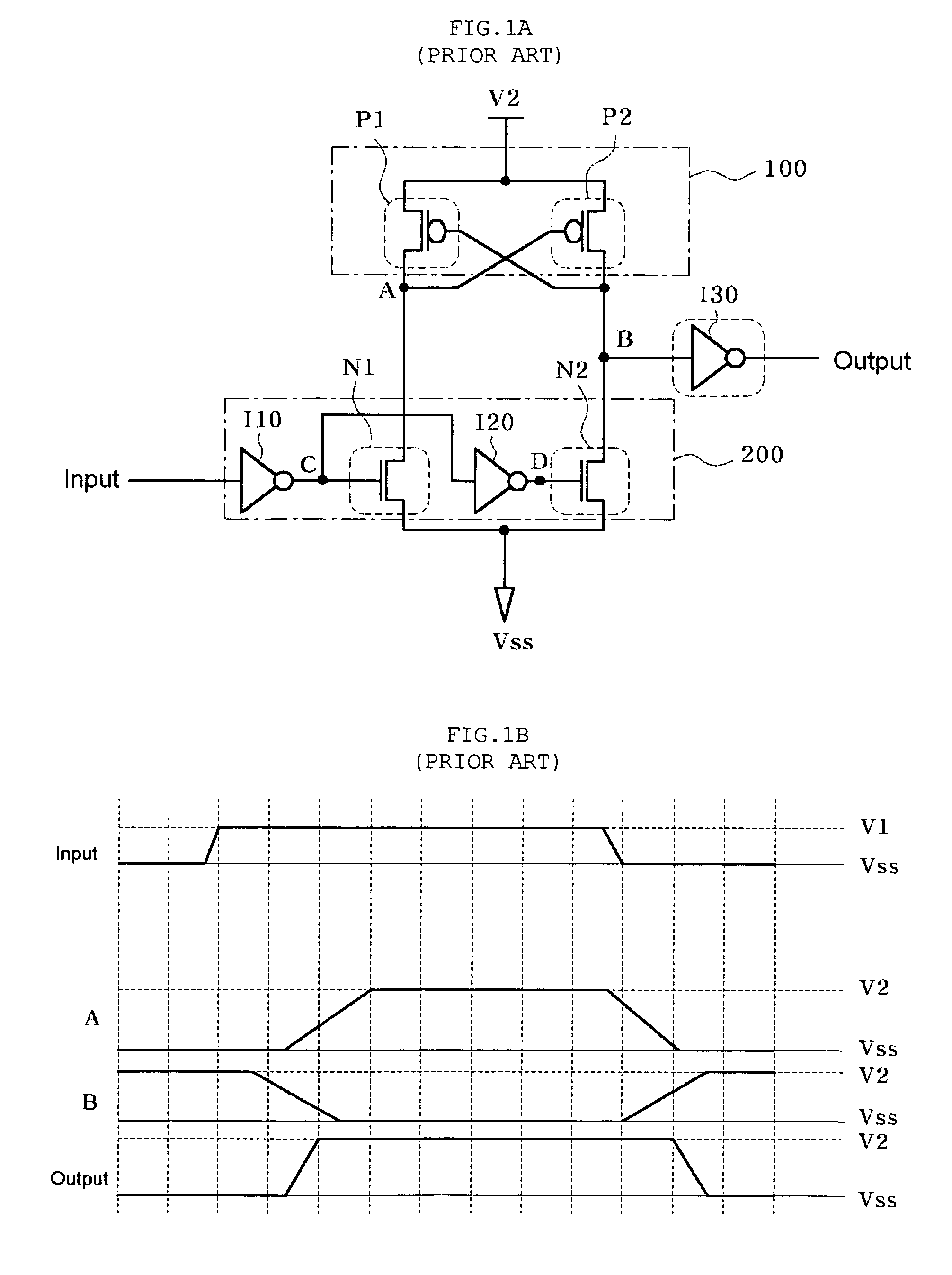
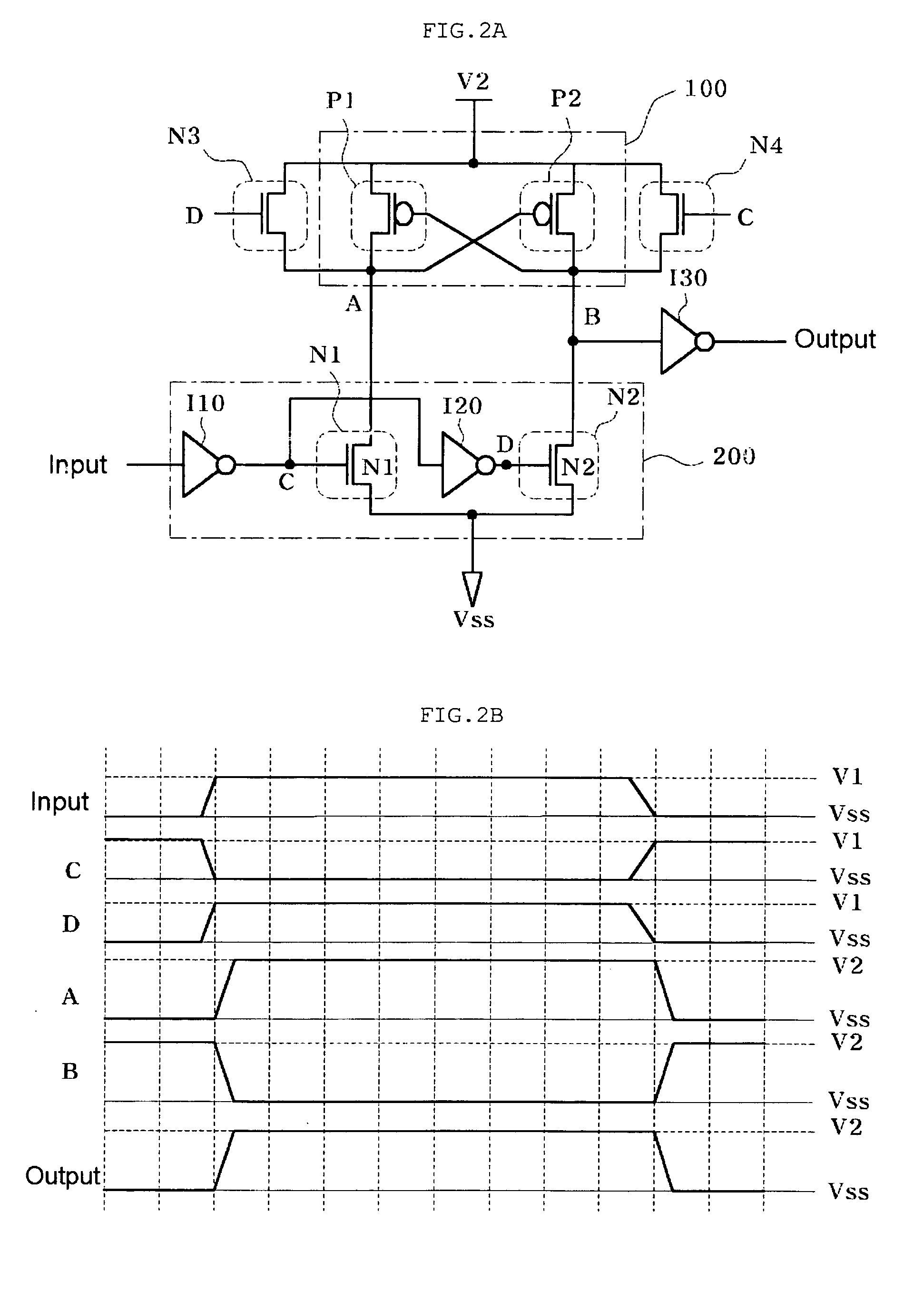
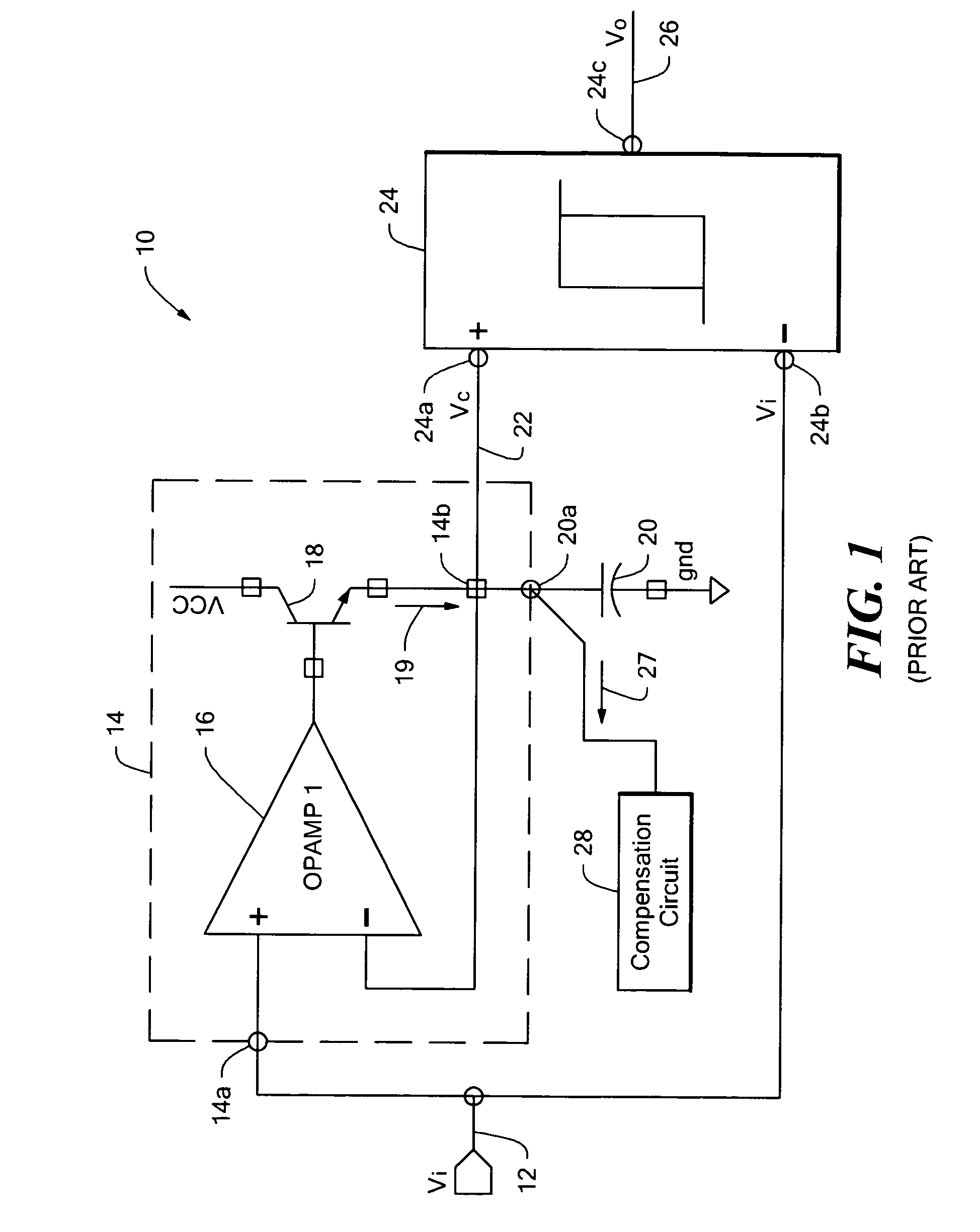
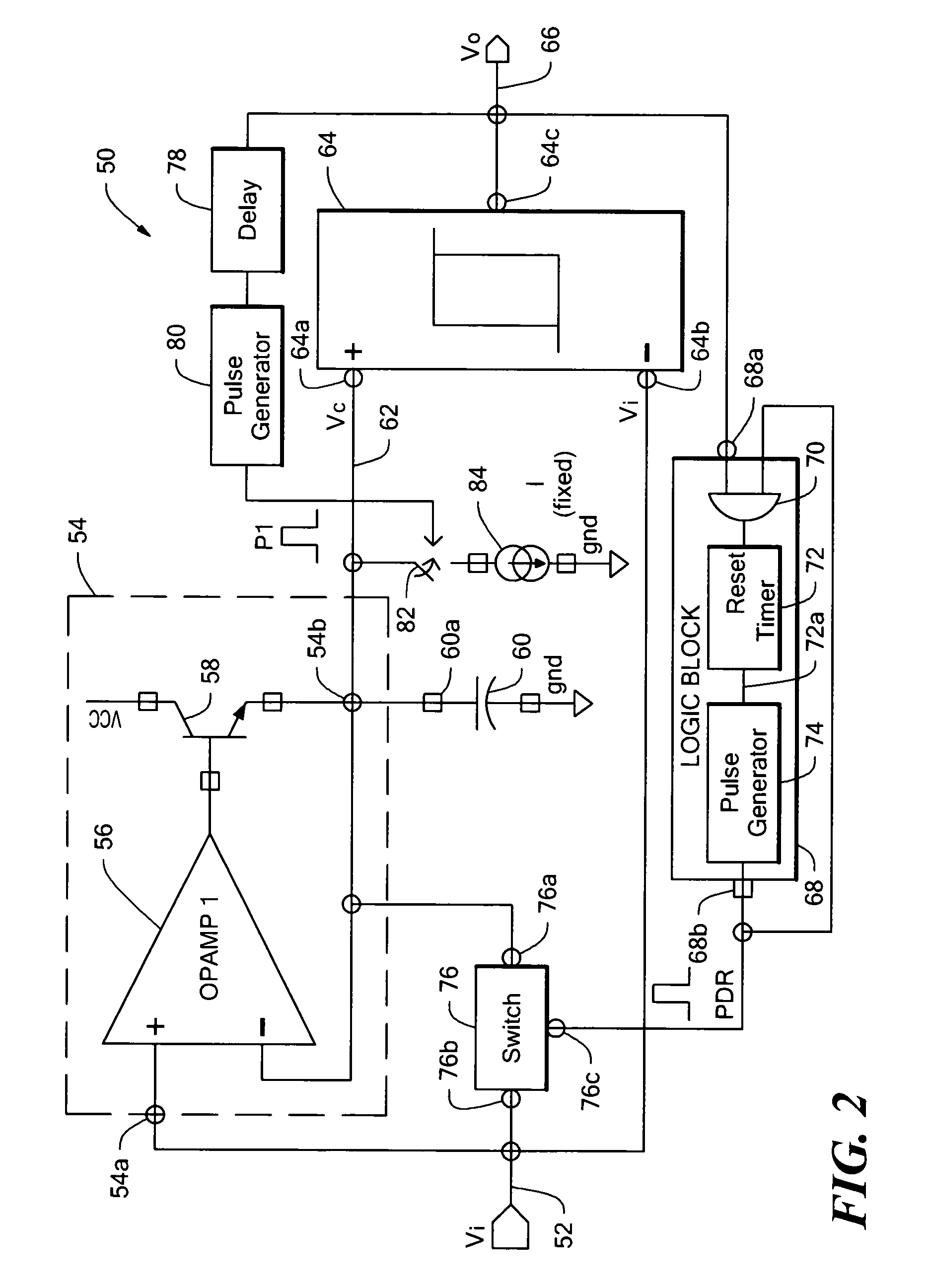
Fabrication of semiconductor structure having asymmetric field-effect transistor with tailored pocket portion along source/drain zone
ActiveUS8163619B2Good analog characteristicReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGate dielectric
An asymmetric insulated-gate field effect transistor (100U or 102U) is provided along an upper surface of a semiconductor body so as to have first and second source / drain zones (240 and 242 or 280 and 282) laterally separated by a channel zone (244 or 284) of the transistor's body material. A gate electrode (262 or 302) overlies a gate dielectric layer (260 or 300) above the channel zone. A pocket portion (250 or 290) of the body material more heavily doped than laterally adjacent material of the body material extends along largely only the first of the S / D zones and into the channel zone. The vertical dopant profile of the pocket portion is tailored to reach a plurality of local maxima at respective locations (PH-1-PH-3-NH-3) spaced apart from one another. This typically enables the transistor to have reduced current leakage.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
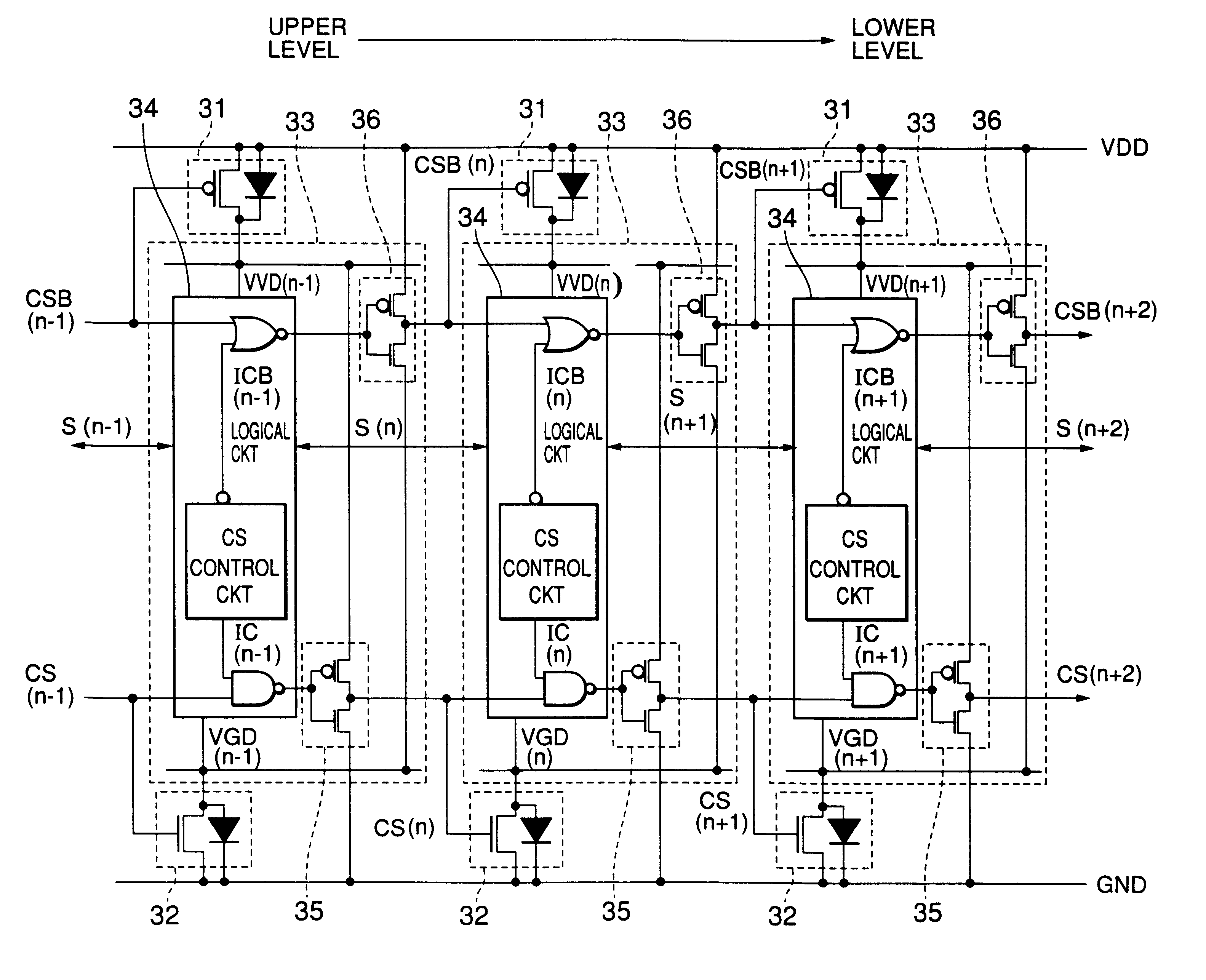
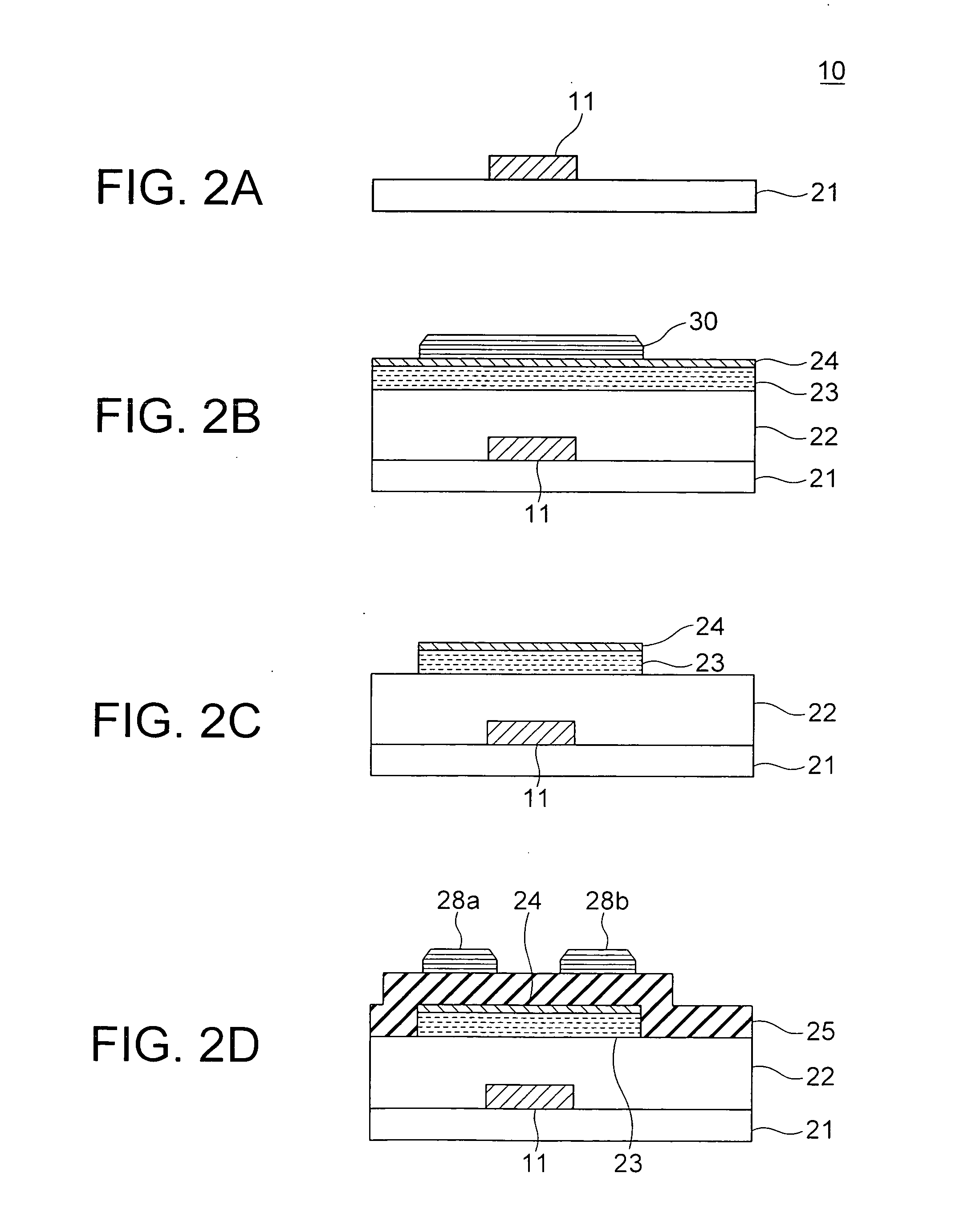
Semiconductor integrated circuit device with low power consumption and simple manufacturing steps
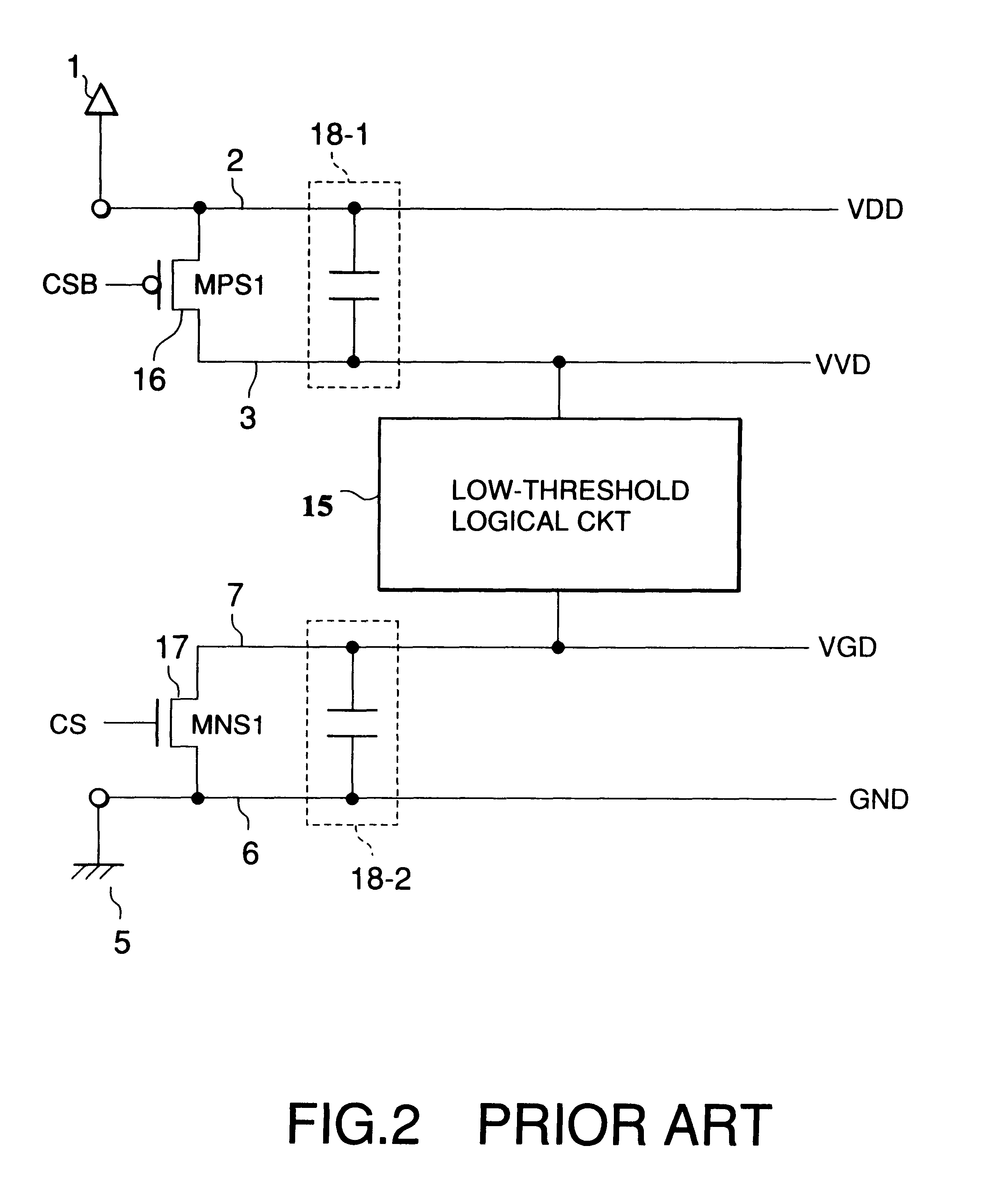
InactiveUS6208171B1Reduce manufacturing stepsProduction costPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionPotential clampBack bias
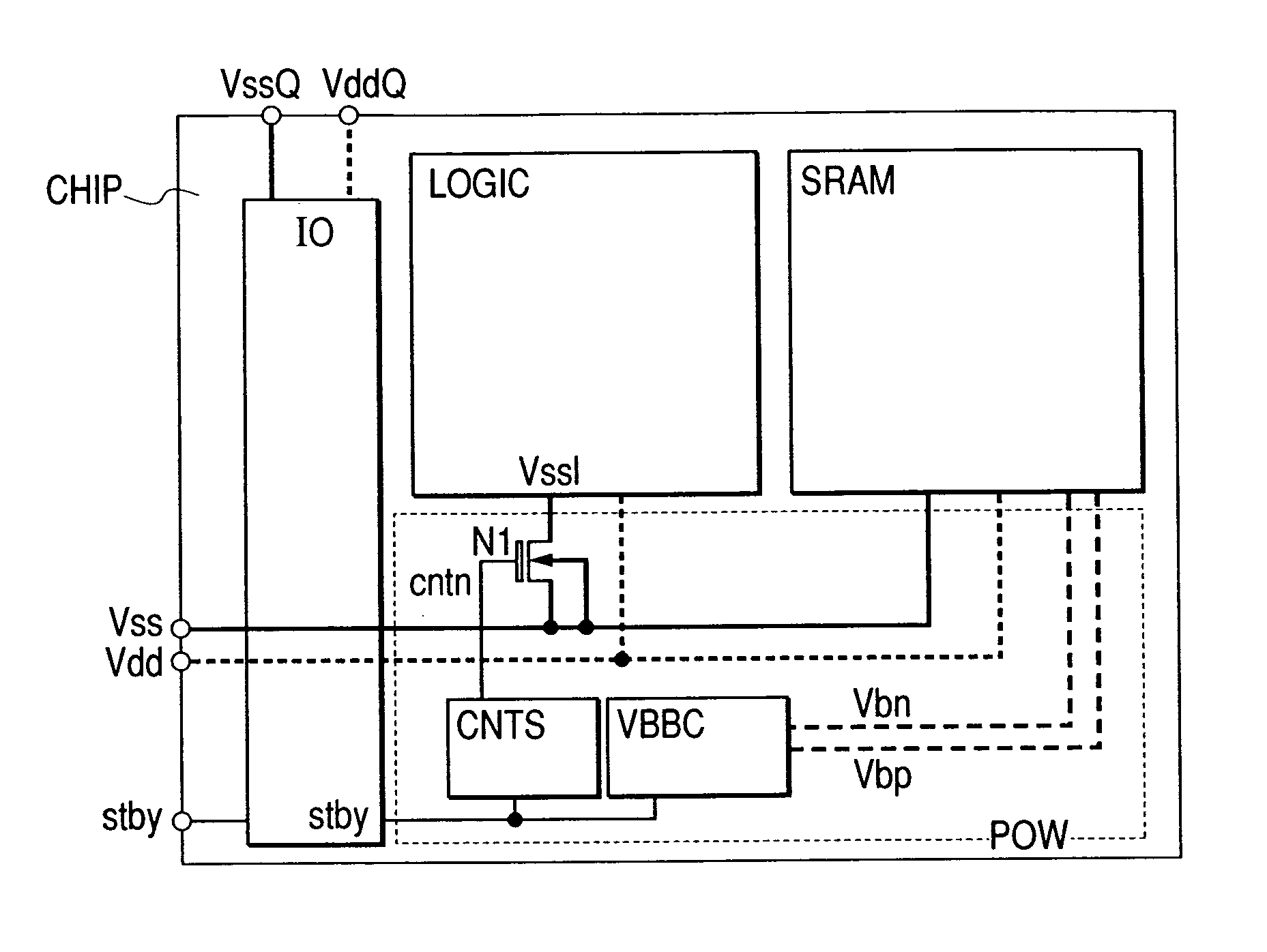
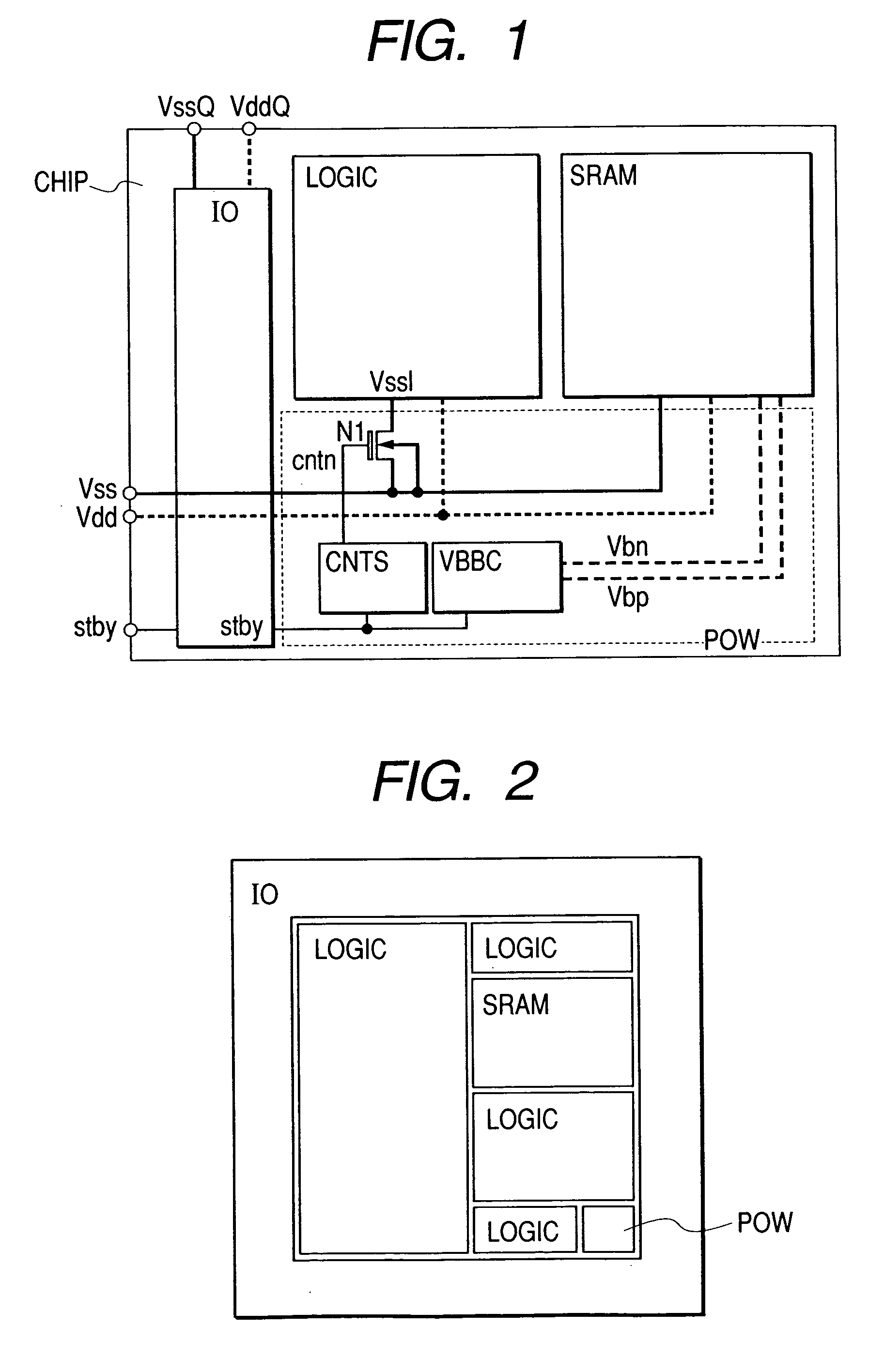
In a semiconductor integrated circuit, a control transistor 4 and a potential clamp circuit 9 are arranged between a power supply line 2 and a virtual power supply line 3. Even in a sleeve mode where the control transistor 4 is turned off, the potential clamp circuit 9-1 clamps the virtual power supply line 3 at a certain potential to hold a potential state (high level or low level) of each node of a logical circuit. At this time, each FET forming the logical circuit is applied with a back bias so that a threshold voltage Vt becomes higher than that in an active mode. Therefore, a leakage current can be decreased. In the semiconductor integrated circuit, the threshold voltage Vt of the control transistor 4 can be selected to be equal to that of one FET of the complementary FET forming the logical circuit. Therefore, the layout area and the number of manufacturing steps can be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
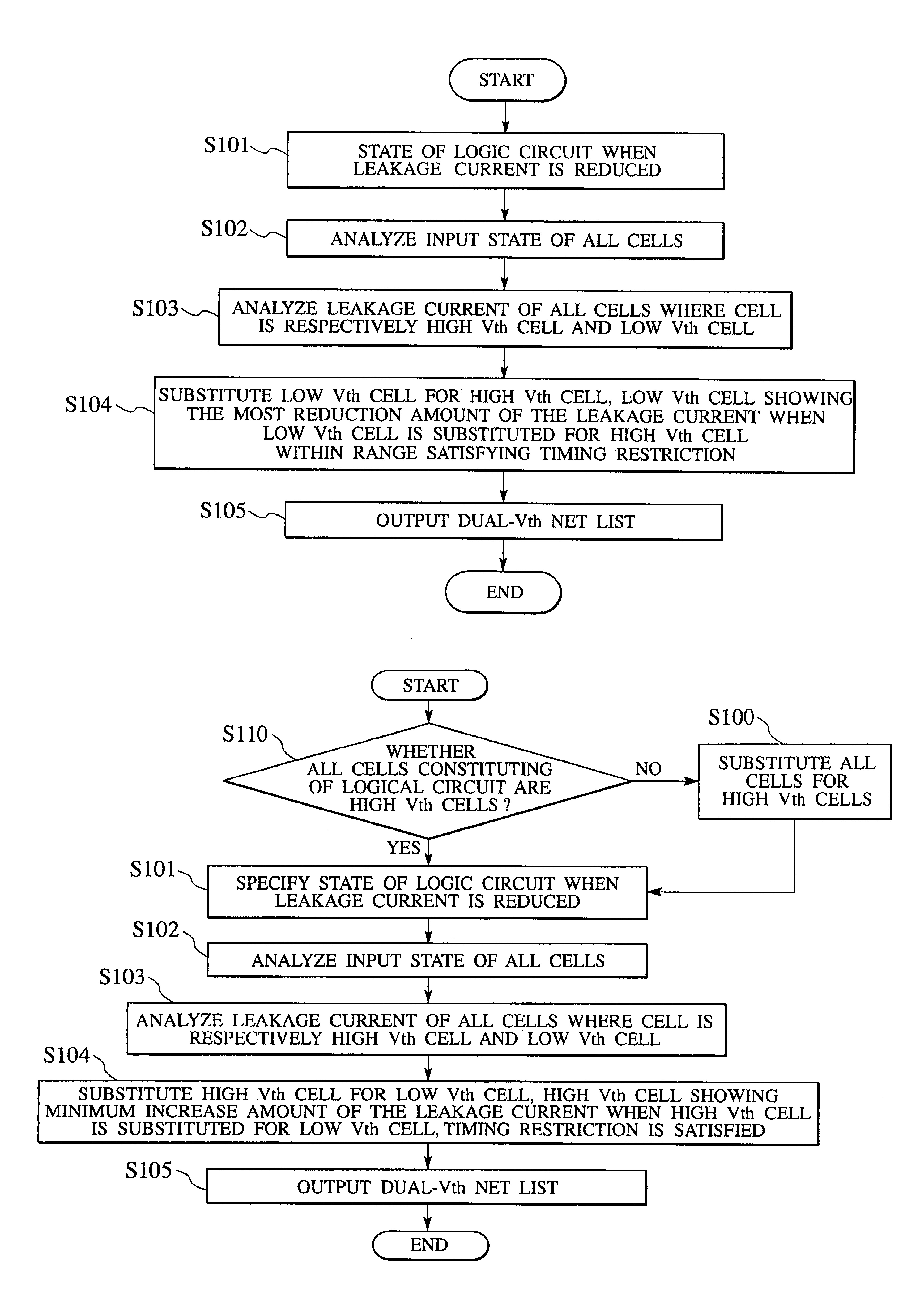
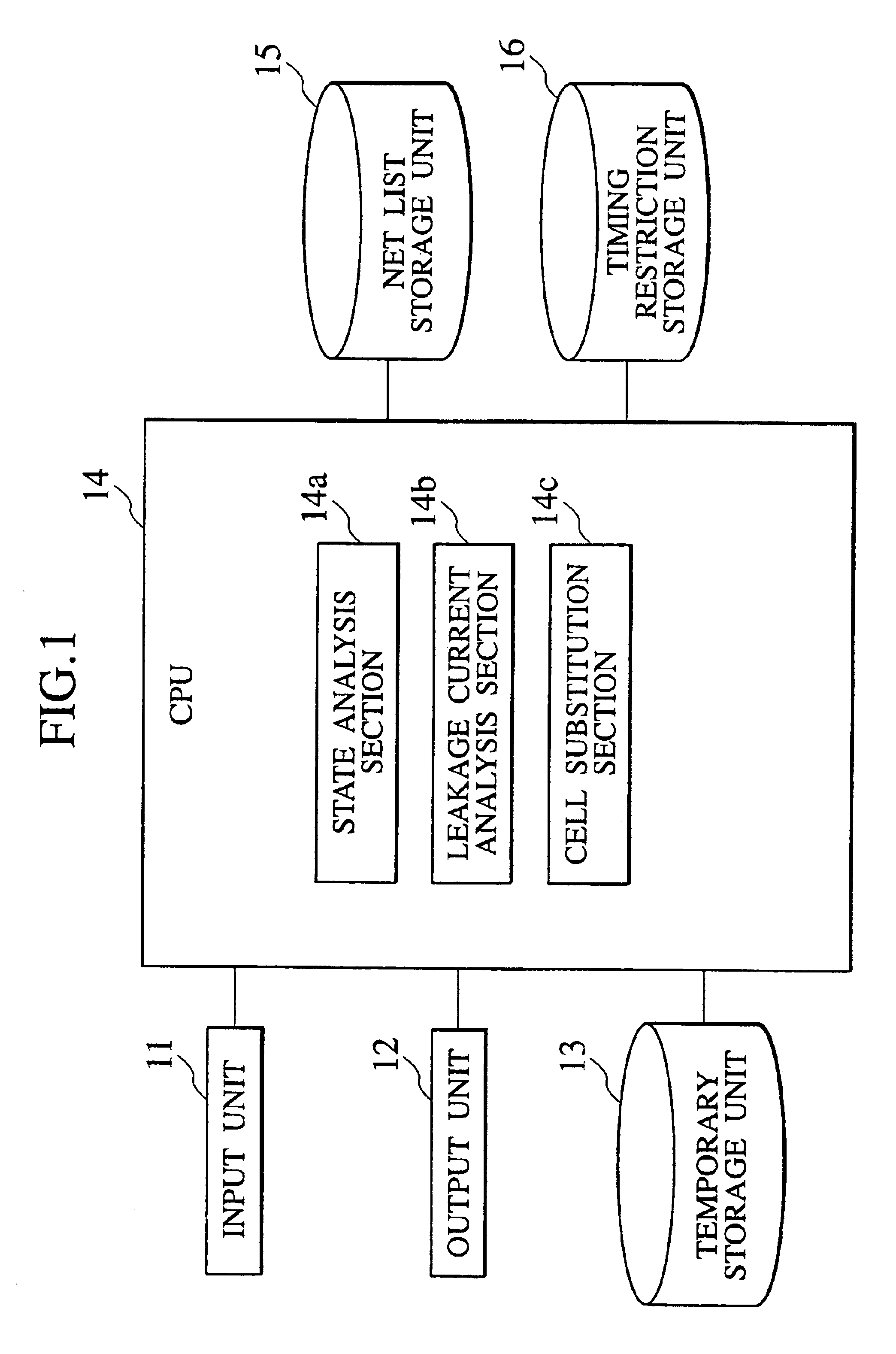
Logic circuit design equipment and method for designing logic circuit for reducing leakage current
A logic circuit design equipment and a logic circuit design method include analyzing input states of all of first cells, respectively, analyzing leakage currents of all of first cells in a case where each first cell is high Vth cell showing a small leakage current at a low speed operation and low Vth cell showing a large leakage current at a high speed operation, respectively, and substituting the first cells for second cells within a range satisfying a timing restriction. Herein, a threshold of the second cell is different from a threshold of the first cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device with reduced leakage current, and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20060118824A1Minimize current leakagePrevent leakageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium nitrideElectron mobility
A high electron mobility transistor is disclosed which has a triple-layered main semiconductor region formed on a silicon substrate via a multilayered buffer region. The multilayered buffer region is in the form of alternations of an aluminum nitride layer and a gallium nitride layer. Whilst the aluminum nitride layers are of n-like conductivity, the gallium nitride layers are doped into p-type conductivity, with the consequent creation of pn junctions between the two kinds of buffer layers. Another pn junction is formed between one p-type gallium nitride layer and the adjoining n-like electron transit layer included in the main semiconductor region. The pn junctions serve for reduction of current leakage.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
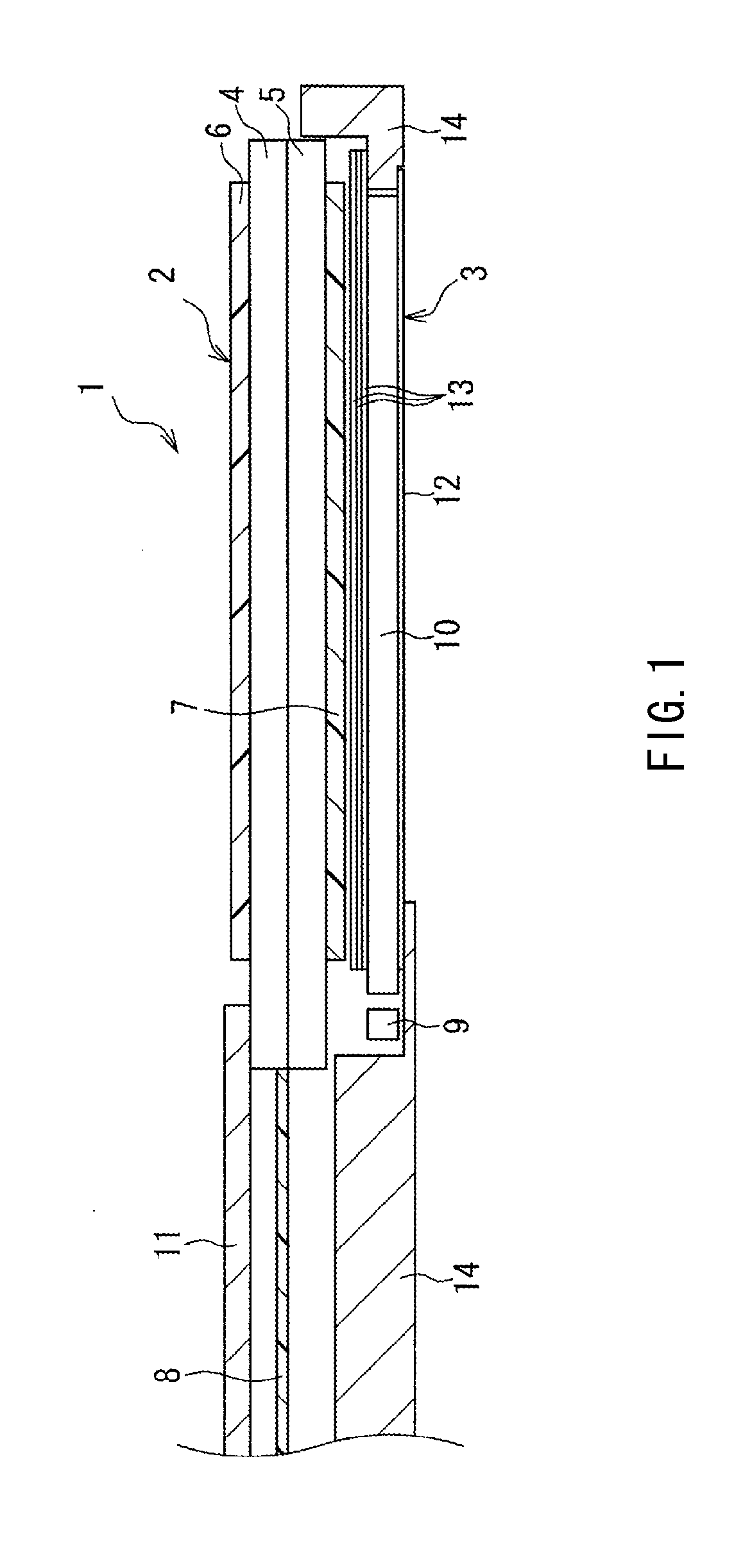
LCD device including a TFT for reducing leakage current
ActiveUS20050041169A1Reduce leakage currentSuppressing increase of TFT areaTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconEngineering
An amorphous-silicon TFT (thin-film-transistor) in an LCD device has a larger channel length at both the edge portions of the channel of the TFT compared to the central portion of the channel by forming chamfers at the corners of the source and drain electrodes. The larger channel length at both the edge portions reduces the leakage current caused by the turned-around light incident onto the channel.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
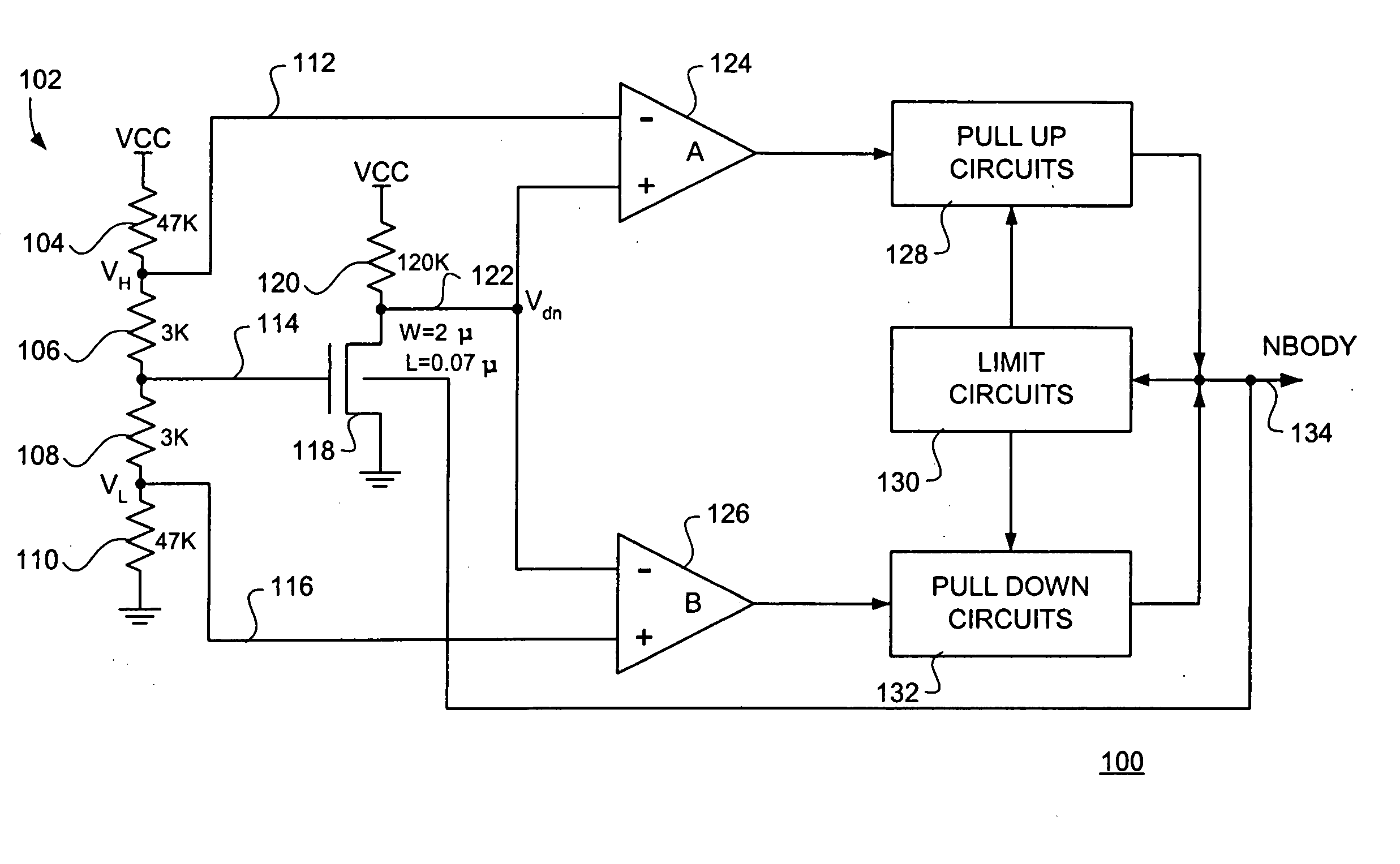
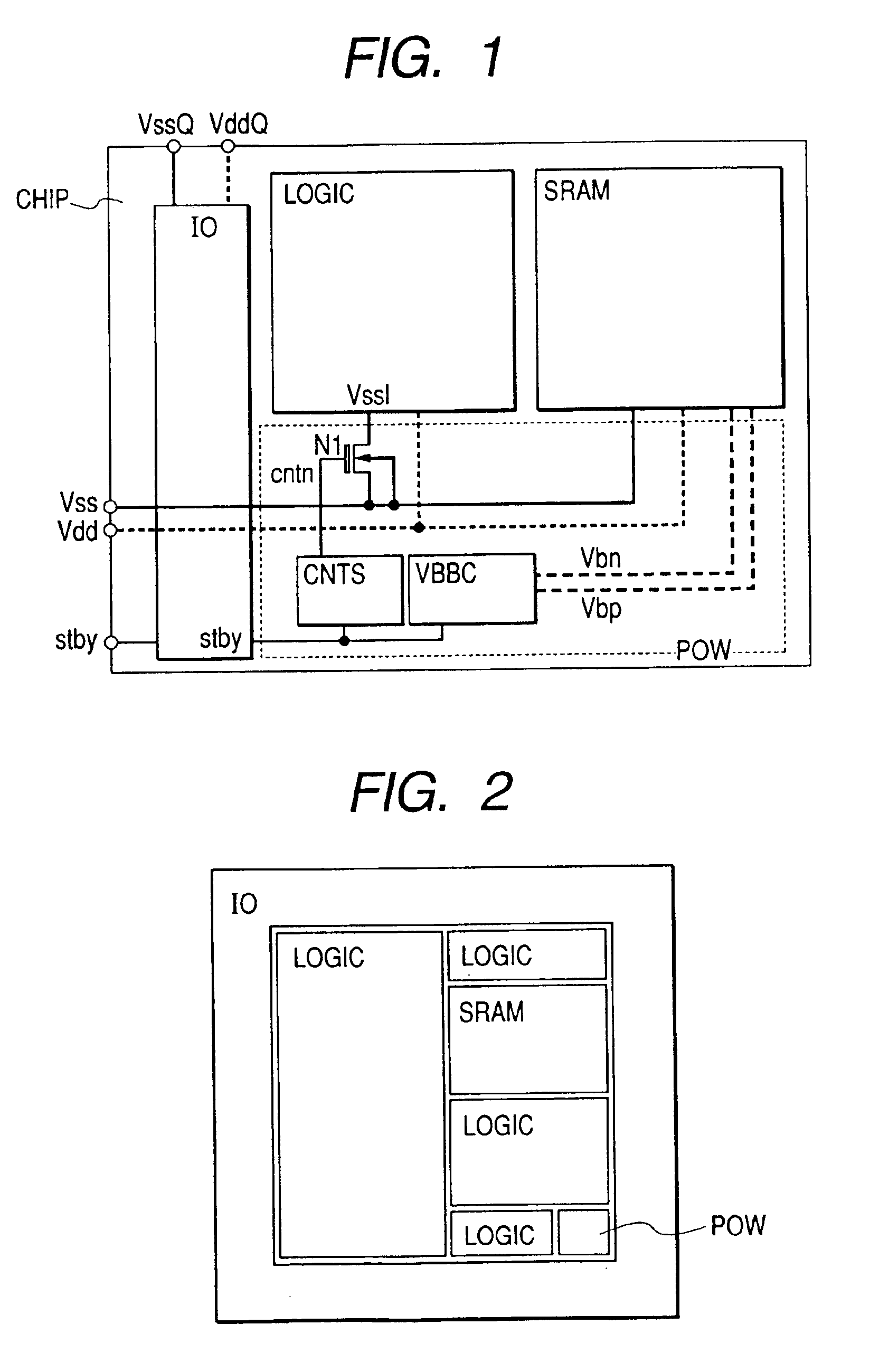
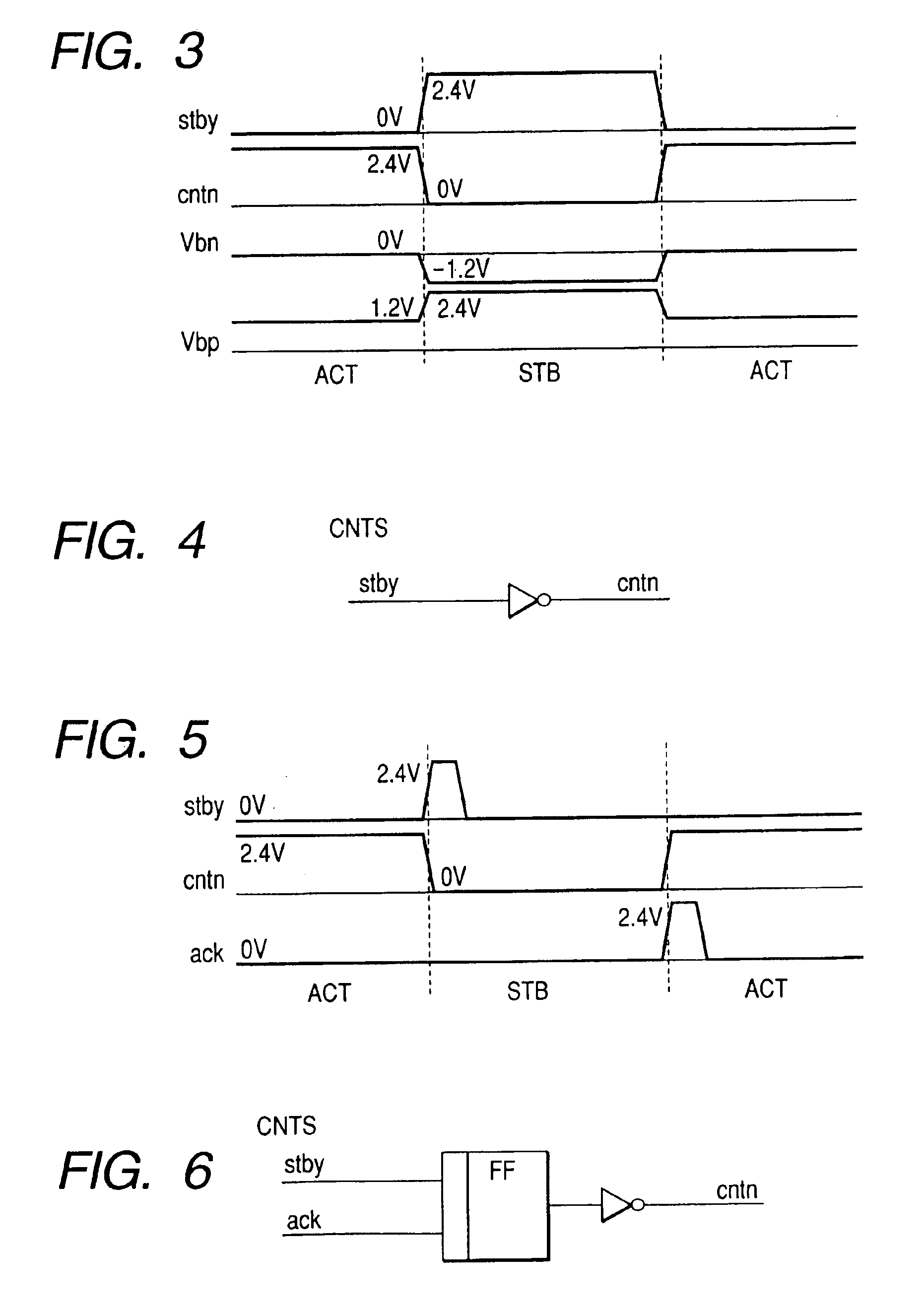
Integrated circuit transistor body bias regulation circuit and method for low voltage applications
InactiveUS20050052219A1Reduce leakage currentMinimizing speed variationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageEngineering
An integrated circuit transistor body bias regulation circuit and method of especial applicability with respect to low voltage applications wherein the threshold voltage (Vt) of certain transistors is lowered at low power supply voltage (VCC) levels, low temperature and / or high Vt process conditions to assure adequate transistor drive but may also be raised at high VCC levels, high temperature and / or low Vt process conditions to reduce leakage current. In this manner, circuit speed that is closer to constant (versus VCC, temperature and process variation) is thereby achieved.
Owner:UNITED MEMORIES +1
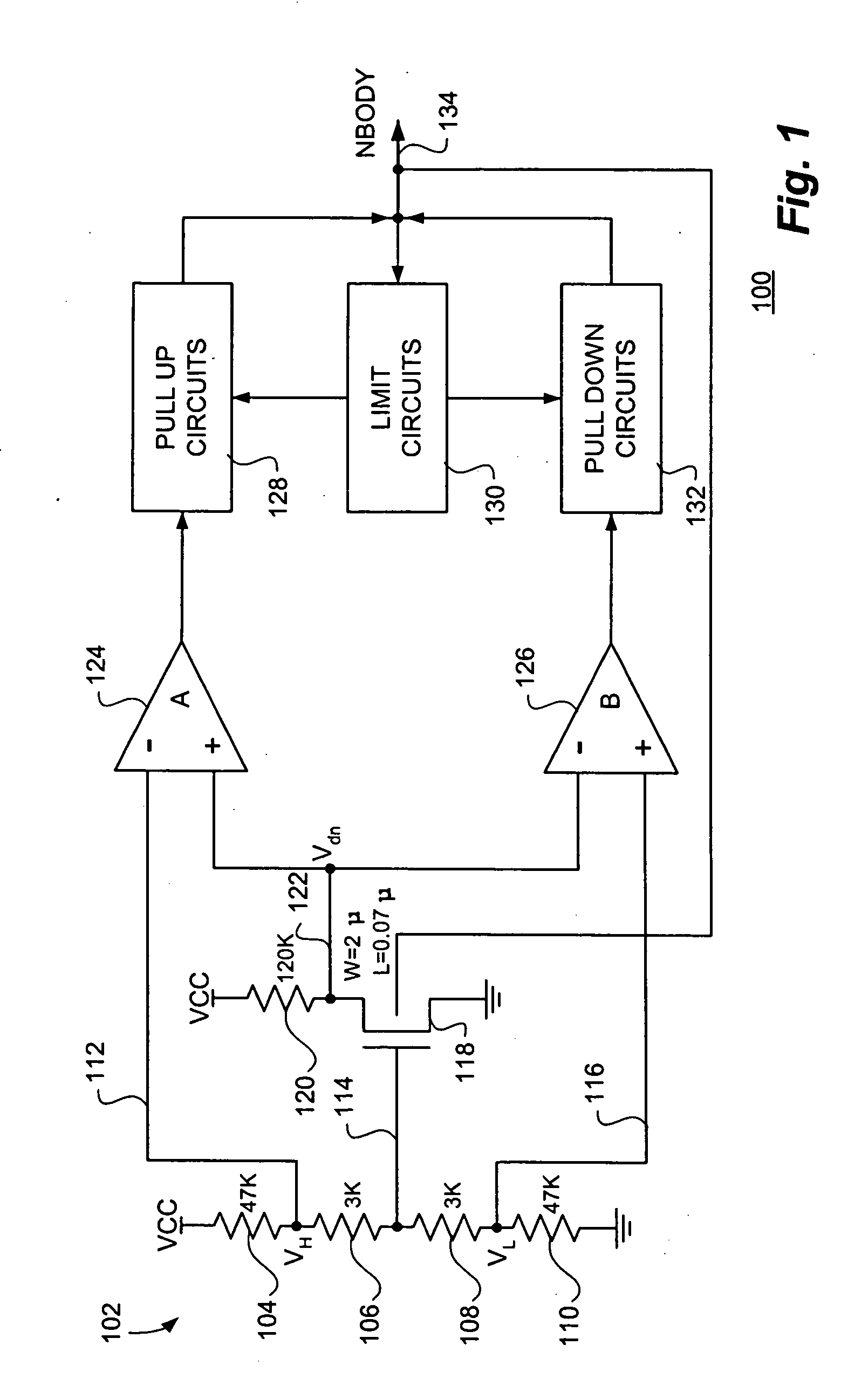
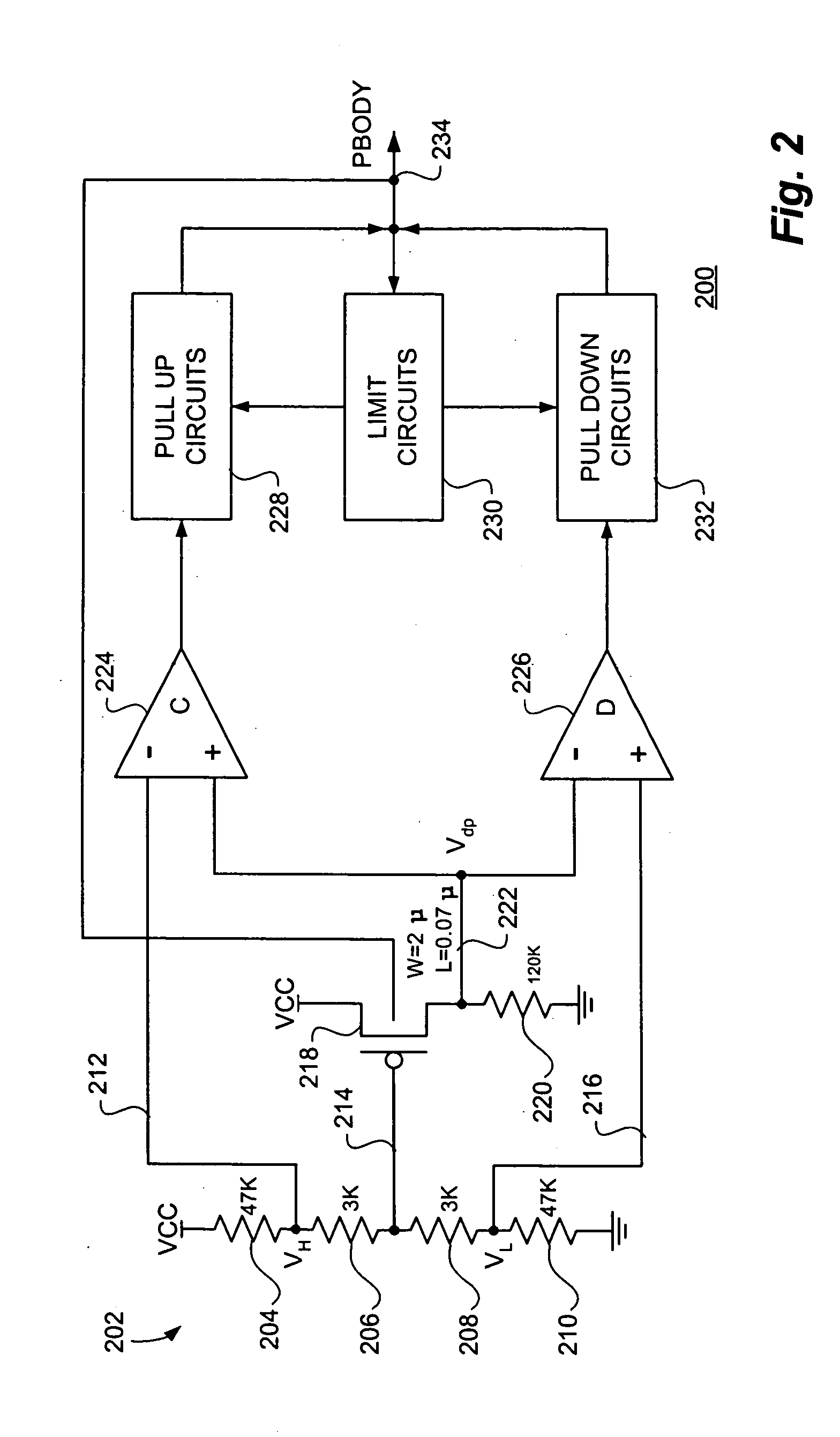
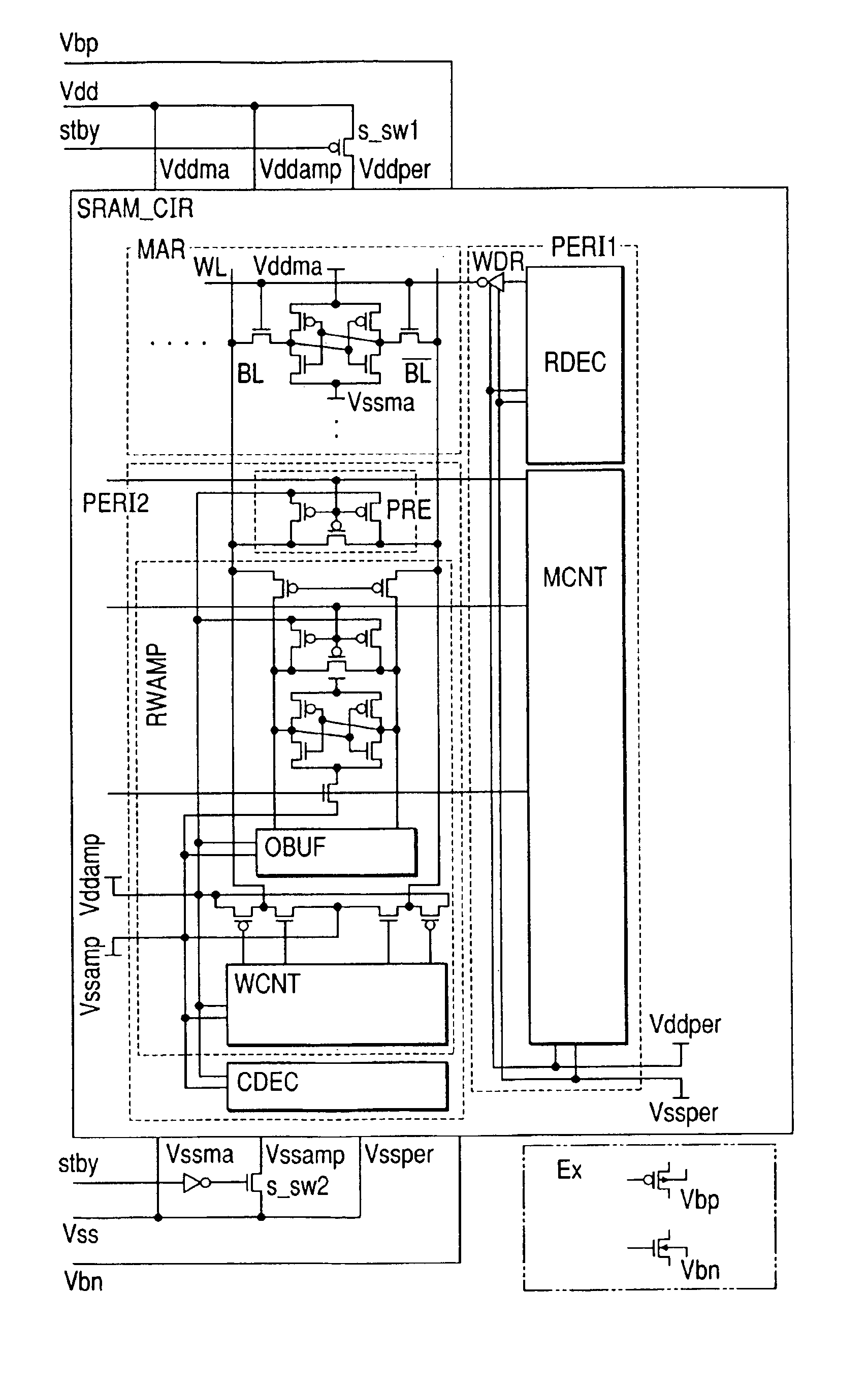
Standby leakage current reduction circuit and semiconductor memory device comprising the standby leakage current reduction circuit
ActiveUS20070147159A1Reduce standby leakage currentReduce excessive power consumptionDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
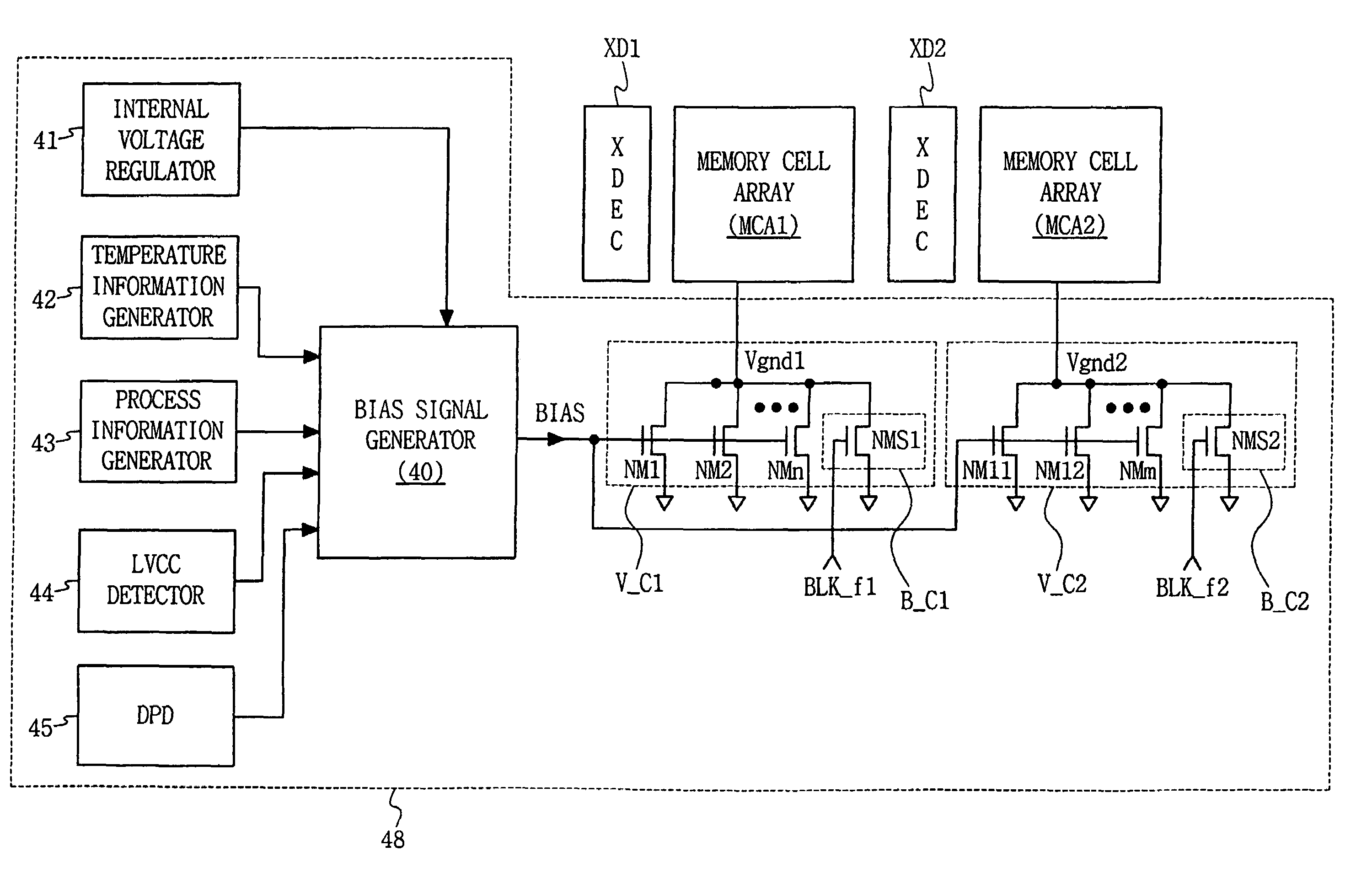
Embodiments of the invention provide a standby leakage current reduction circuit and a semiconductor memory device comprising the standby leakage current reduction circuit. The invention provides a circuit adapted to reduce standby leakage current in a semiconductor memory device comprising memory cells. The circuit comprises a bias signal generator adapted to generate a bias signal, wherein a voltage level of the bias signal is set in accordance with a result of a standby leakage current test. The circuit further comprises a ground voltage controller adapted to receive the bias signal from the bias signal generator and to control a level of a voltage apparent on a virtual ground terminal in response to the bias signal while the semiconductor memory device is in a standby mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
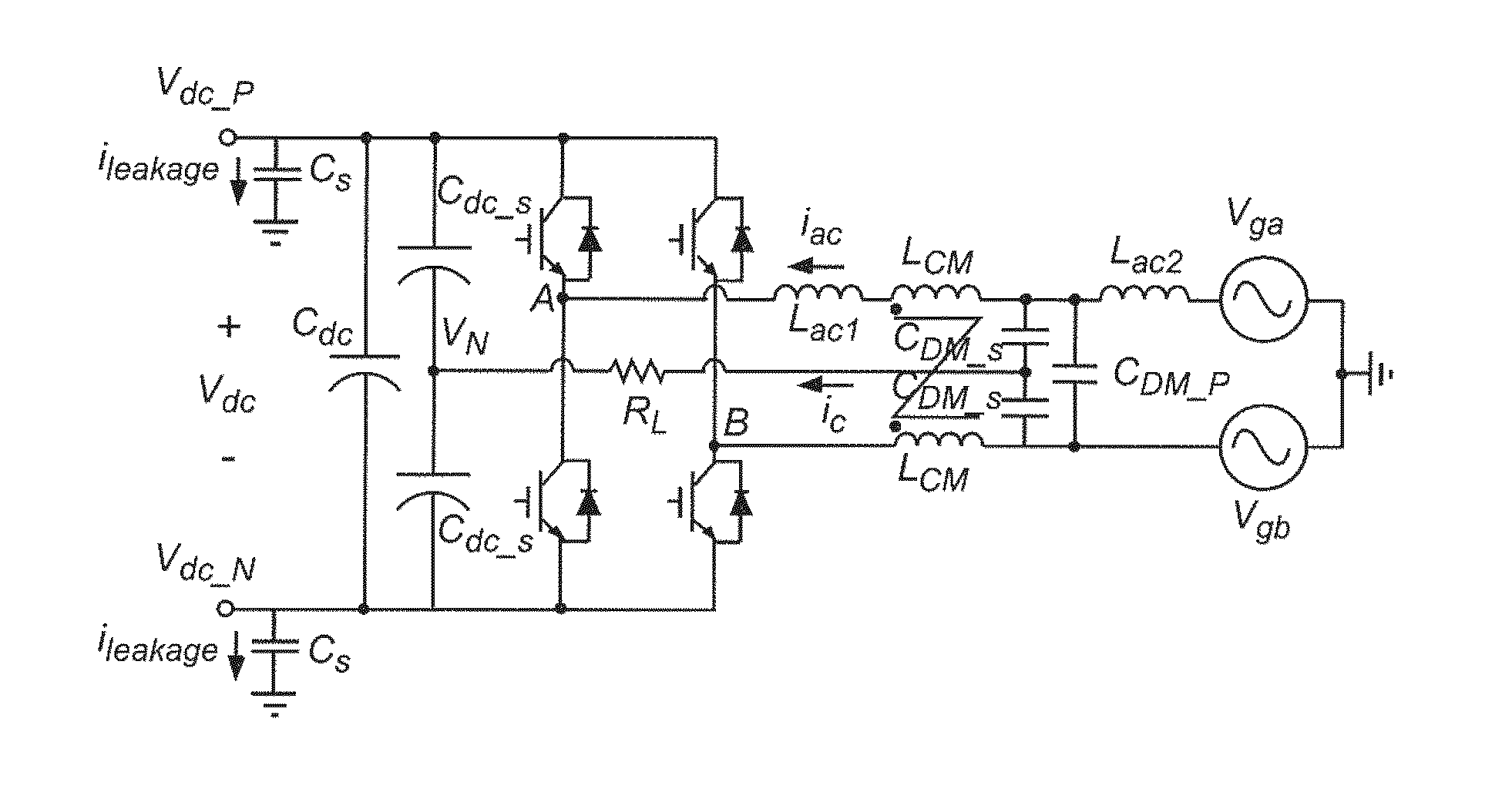
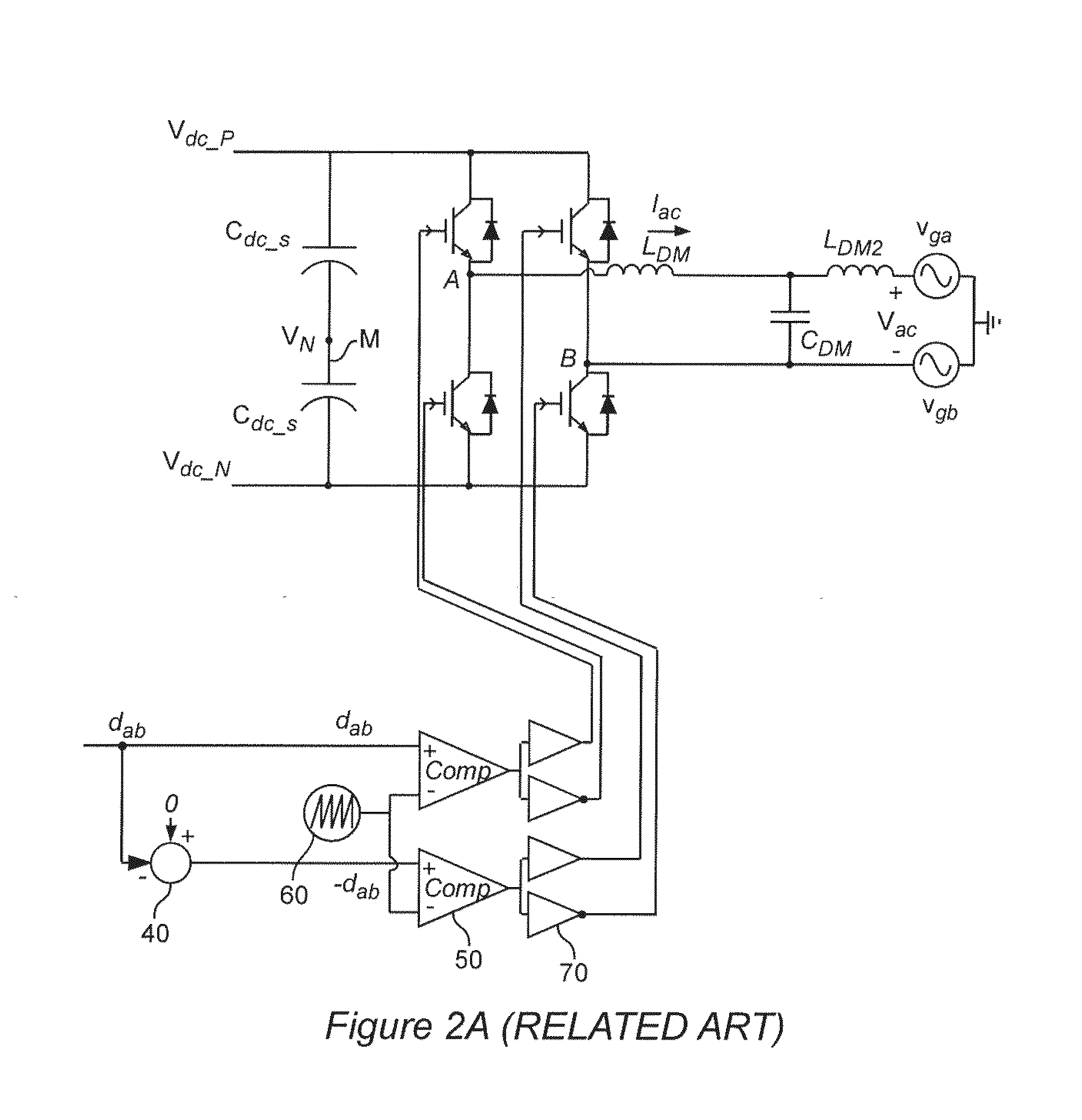
Dc-side leakage current reduction for single phase full-bridge power converter/inverter
ActiveUS20130235628A1Avoid it happening againReduce low frequency common mode noiseLine/current collector detailsAc-dc conversionFull bridgeSinusoidal modulation
Leakage current through stray or parasitic capacitance (which is particularly large in devices such as photovoltaic cell arrays and which are damaged by such leakage currents) due to common mode switching noise in a full bridge single phase power converter is reduced at high frequencies by magnetically coupling the two phase legs on the AC side of the power converter and connecting mid points of the AC and DC sides of the power converter and is reduced at low frequencies by use of a feedback arrangement that modifies sinusoidal modulation of the switches of the full bridge converter to function as an active filter. The magnetic coupling for the two phase legs is designed in a simple manner to avoid saturation based on volt-second considerations.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
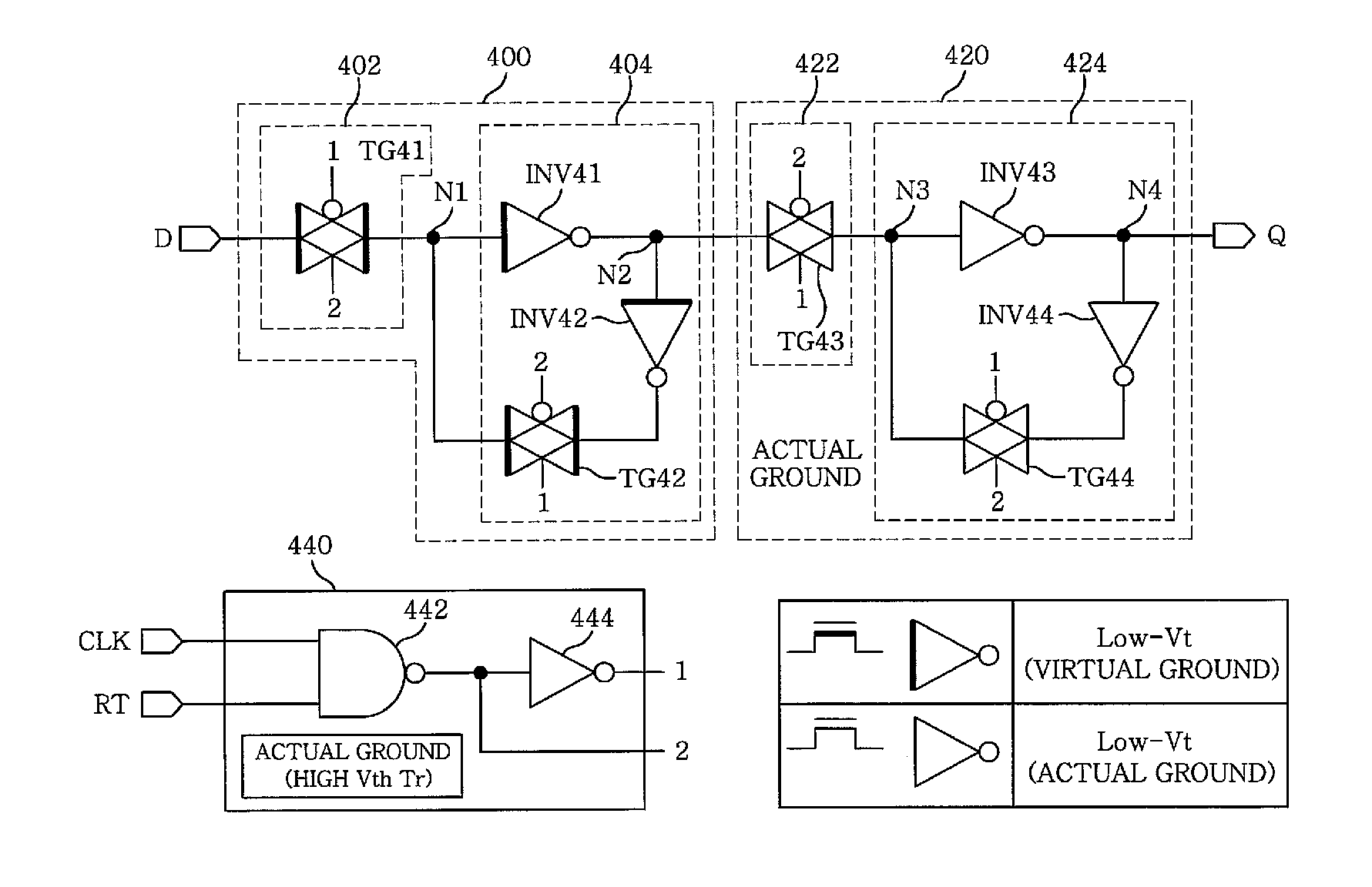
Mtcmos flip-flop with retention function
InactiveUS20090066386A1Reduce leakage currentRun at high speedElectric pulse generatorRetention functionControl signal
There is provided a MTCMOS flip-flop configured to operate at high speed and to reduce leakage current while realizing a retention function in a sleep mode. The MTCMOS flip-flop may include a signal generator adapted to output an internal clock signal or a sleep mode control signal based on changes in a retention signal and an external clock signal, a master latch adapted to latch an input signal and to output a master latch output signal based on the internal clock signal, and a slave latch connected to an actual ground and adapted to latch the master latch signal, to output a slave latch output signal under control of the internal clock signal, and to maintain the latched signal under control of the sleep mode control signal in the sleep mode.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Independent power collapse methodology
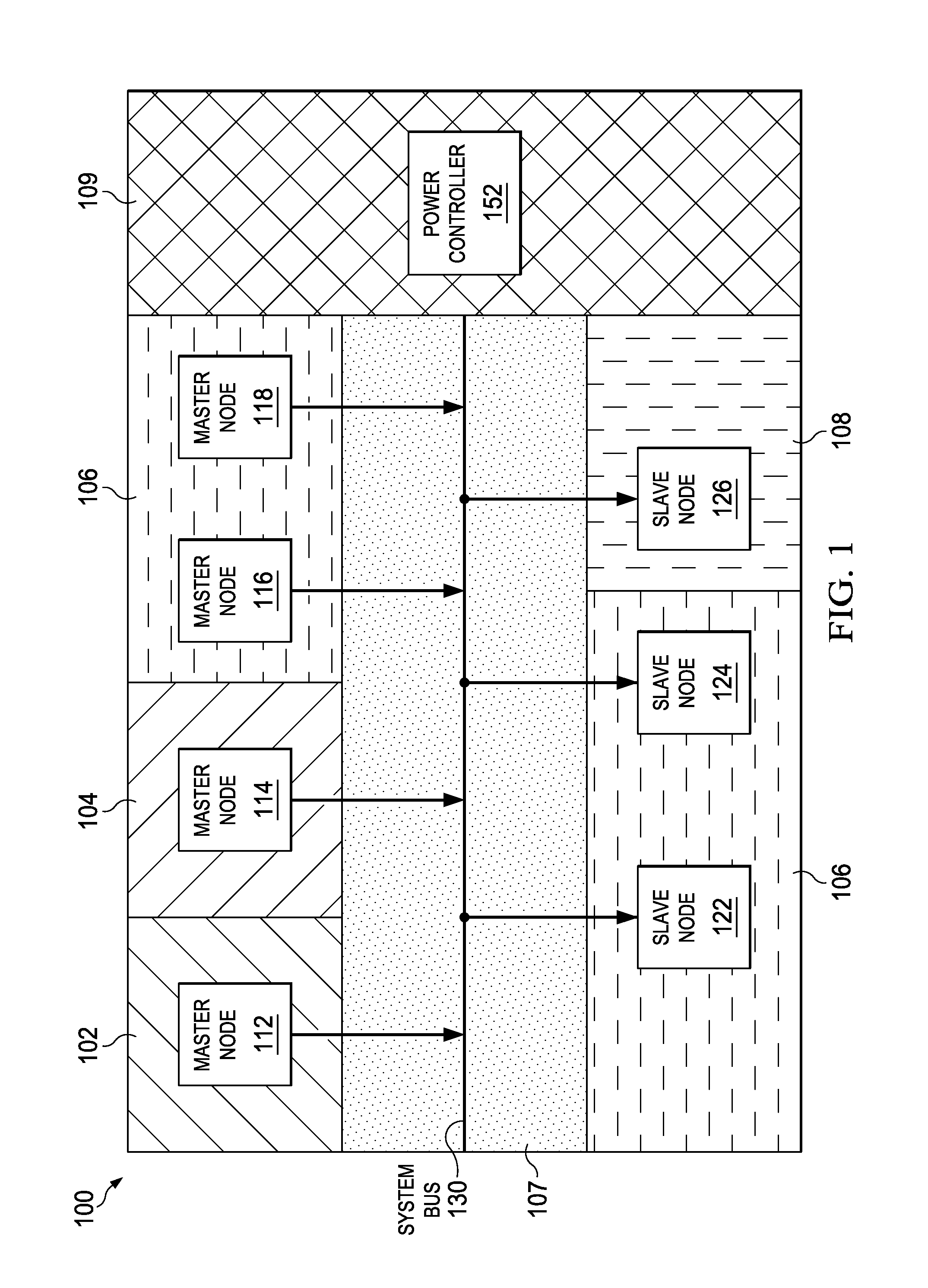
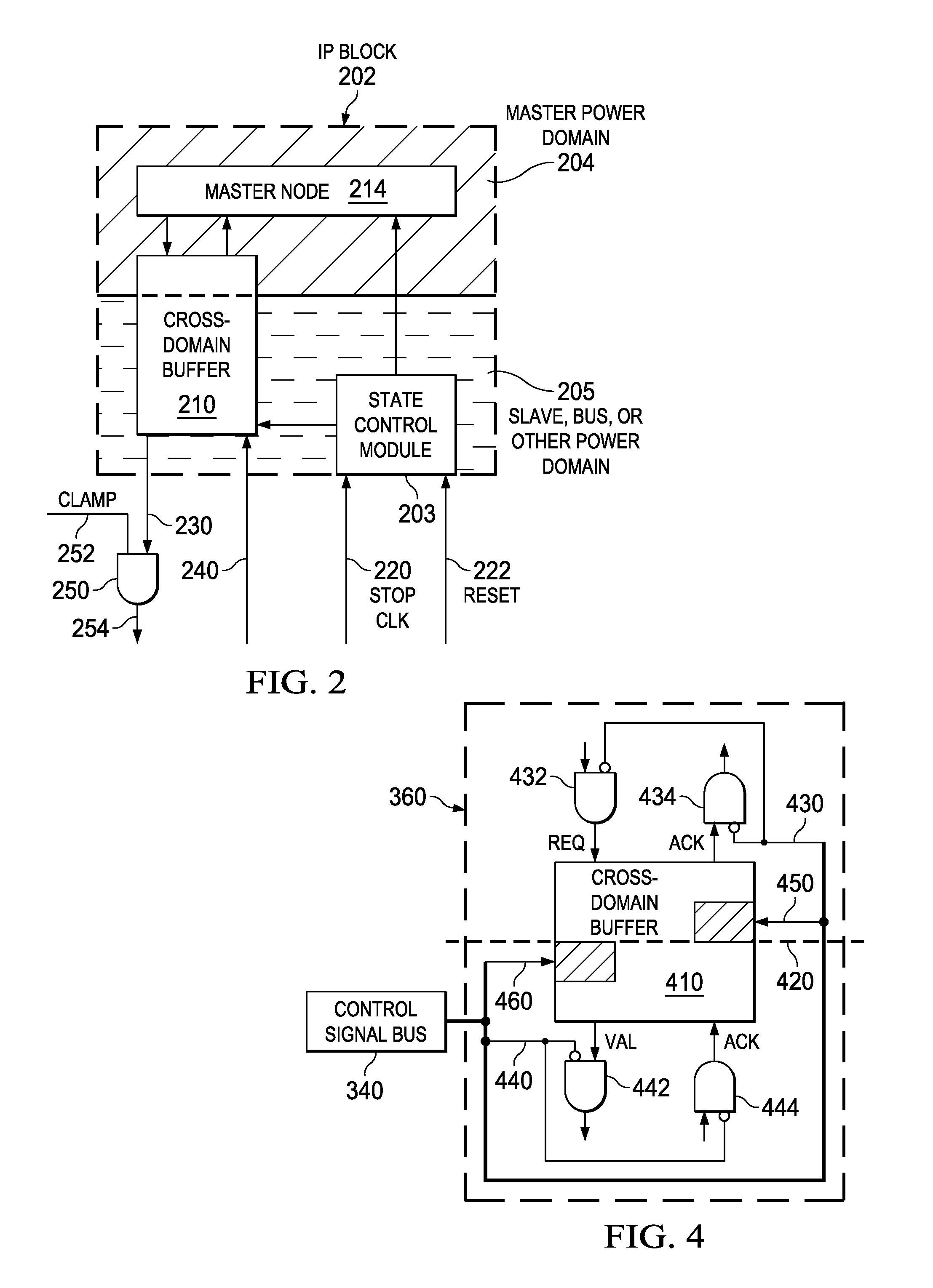
ActiveUS20160239060A1Simplify the design processPromote design reusePower reduction by control/clock signalVolume/mass flow measurementLeakage current reductionEngineering
The feature size of semiconductor devices continues to decrease in each new generation. Smaller channel lengths lead to increased leakage currents. To reduce leakage current, some power domains within a device may be powered off (e.g., power collapsed) during periods of inactivity. However, when power is returned to the collapsed domains, circuitry in other power domains may experience significant processing overhead associated with reconfiguring communication channels to the newly powered domains. Provided in the present disclosure are exemplary techniques for isolating power domains to promote flexible power collapse while better managing the processing overhead associated with reestablishing data connections.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and manufacturing low leakage MOSFETs and FinFETs
InactiveUS20070228425A1Relieve pressureReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETCMOS
By aligning the primary flat of a wafer with a (100) plane rather than a (110) plane, devices can be formed with primary currents flowing along the (100) plane. In this case, the device will intersect the (111) plane at approximately 54.7 degrees. This intersect angle significantly reduces stress propagation / relief along the (111) direction and consequently reduces defects as well as leakage and parasitic currents. The leakage current reduction is a direct consequence of the change in the dislocation length required to short the source-drain junction. By using this technique the leakage current is reduced by up to two orders of magnitude for an N-channel CMOS device.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
External cavity laser light source
ActiveUS20100238962A1High gainLower conditionsOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity laserLeakage current reduction
Provided is an external cavity laser light source. The light source includes a substrate, an optical waveguide, and a current blocking layer. The optical waveguide includes a passive waveguide layer, a lower clad layer, an active layer, and an upper clad layer that are sequentially stacked on the substrate and is divided into regions including a linear active waveguide region, a bent active waveguide region, a tapered waveguide region, and a window region. The current blocking layer was formed an outside of the active layer to reduce leakage current. The linear and bent active waveguide regions have a buried heterostructure (BH), and the tapered waveguide region and the window region have a buried ridge stripe (BRS) structure. The passive waveguide layer a width substantially equal to a maximal width of the tapered waveguide region at least in the bent active waveguide region, the tapered waveguide region, and the window region.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
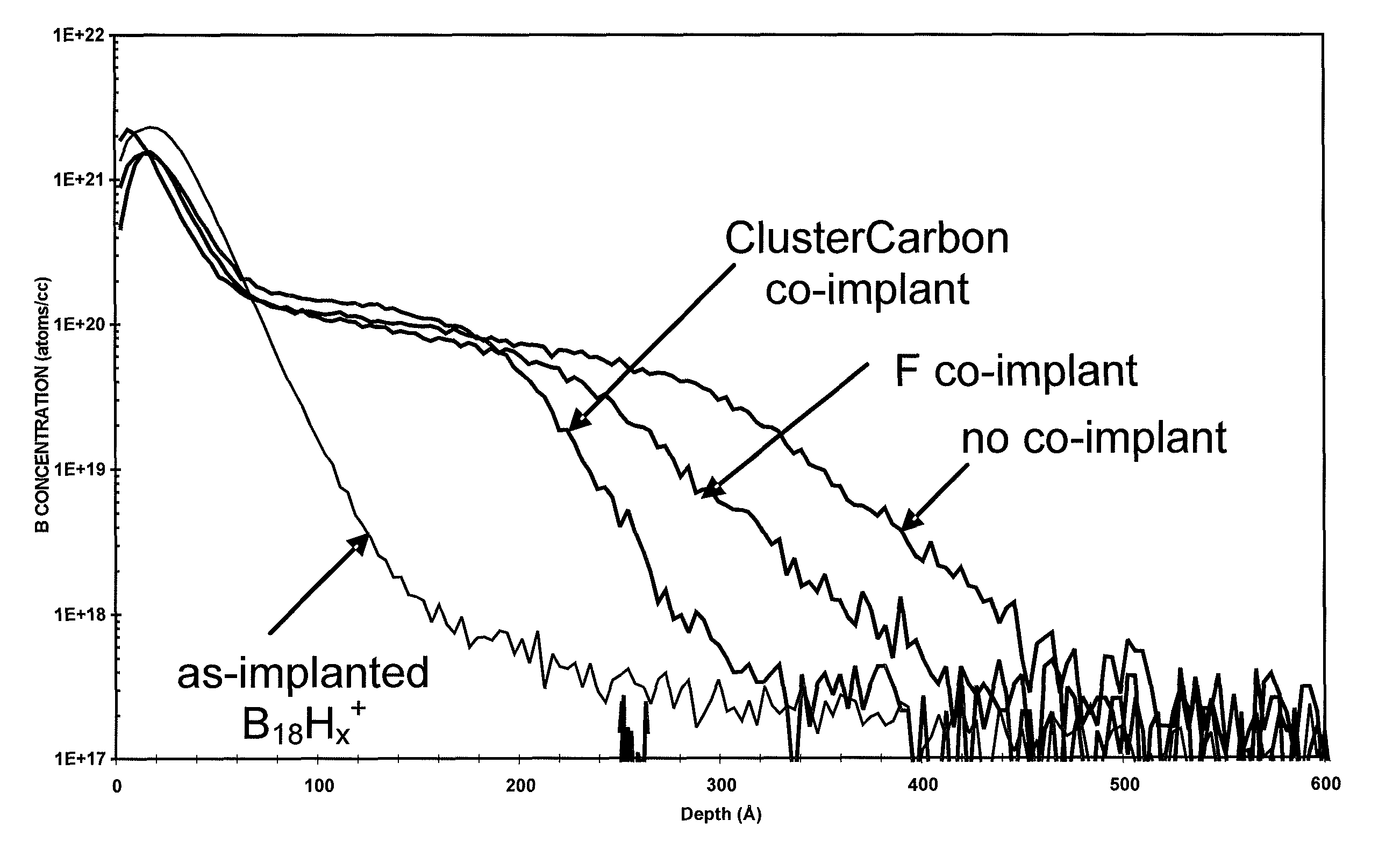
Cluster ion implantation for defect engineering
InactiveUS20080299749A1Easily annealed outEffective controlElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolecular clusterCrystallographic defect
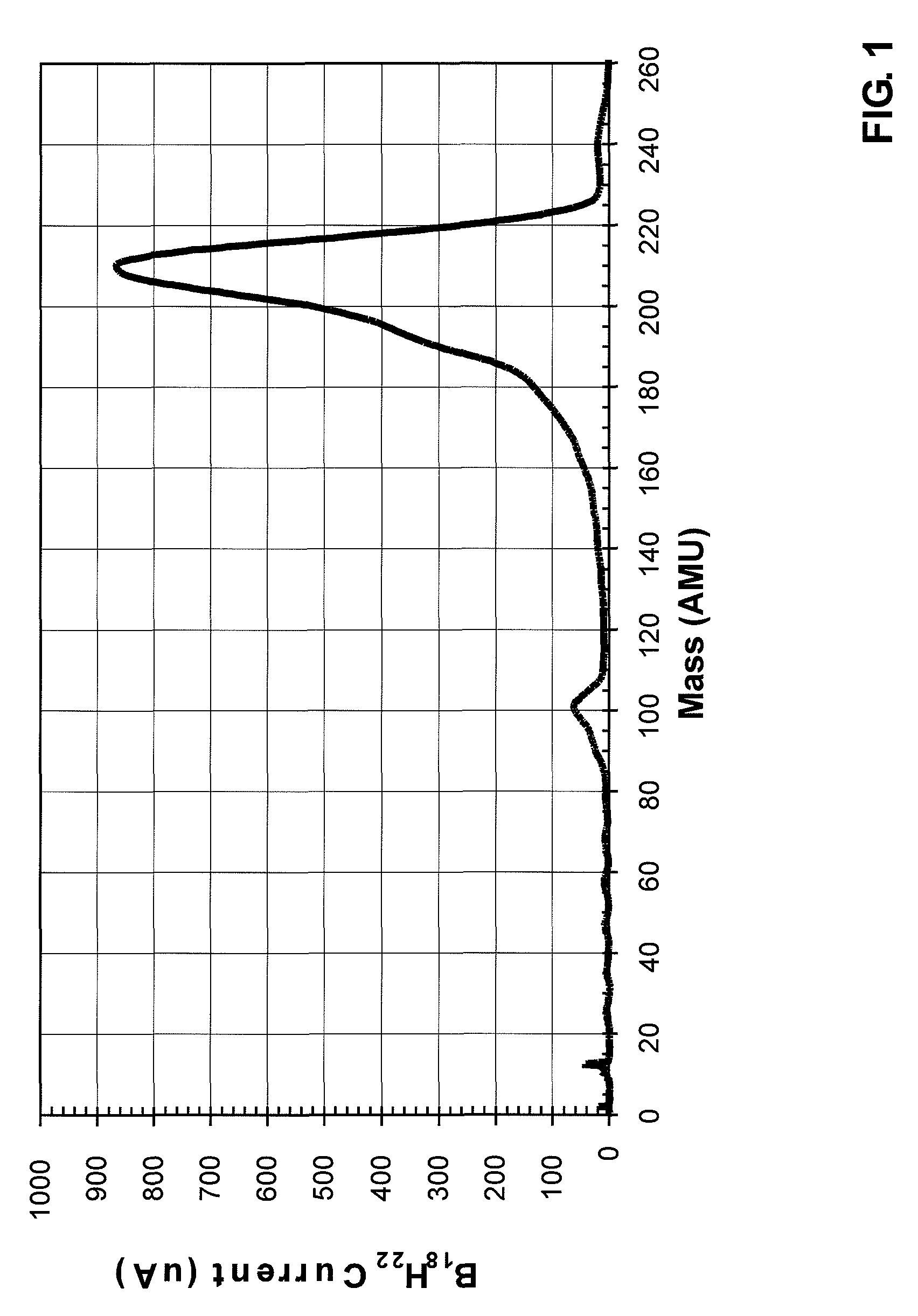
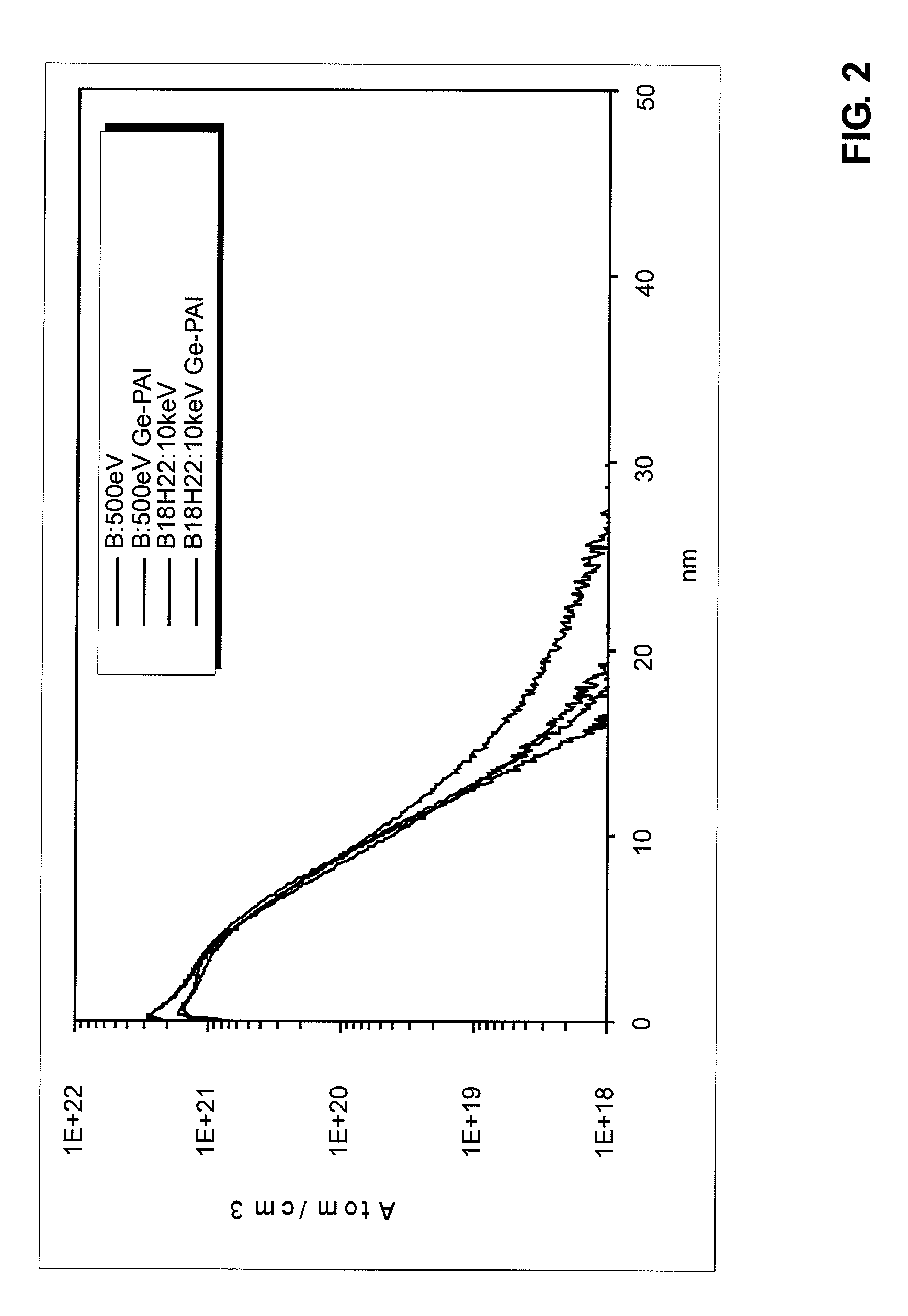
A method of semiconductor manufacturing is disclosed in which doping is accomplished by the implantation of ion beams formed from ionized molecules, and more particularly to a method in which molecular and cluster dopant ions are implanted into a substrate with and without a co-implant of non-dopant cluster ion, such as a carbon cluster ion, wherein the dopant ion is implanted into the amorphous layer created by the co-implant in order to reduce defects in the crystalline structure, thus reducing the leakage current and improving performance of the semiconductor junctions. Dopant ion compounds of the form AnHx+ and AnRzHx+ are used in order to minimize crystal defects as a result of ion implantation. These compounds include co-implants of carbon clusters with implants of monomer or cluster dopants or simply implanting cluster dopants. In particular, the invention described herein consists of a method of implanting semiconductor wafers implanting semiconductor wafers with carbon clusters followed by implants of boron, phosphorus, or arsenic, or followed with implants of dopant clusters of boron, phosphorus, or arsenic. The molecular cluster ions have the chemical form AnHx+ or AnRzHx+, where A designates the dopant or the carbon atoms, n and x are integers with n greater than or equal to 4, and x greater than or equal to 0, and R is a molecule which contains atoms which, when implanted, are not injurious to the implantation process (for example, Si, Ge, F, H or C). These ions are produced from chemical compounds of the form AbLzHm, where the chemical formula of Lz contains R, and b may be a different integer from n and m may be an integer different from x and z is an integer greater than or equal to zero.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Semiconductor device, active matrix substrate, and display device
InactiveUS20120146043A1Easy to makeReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceActive matrix
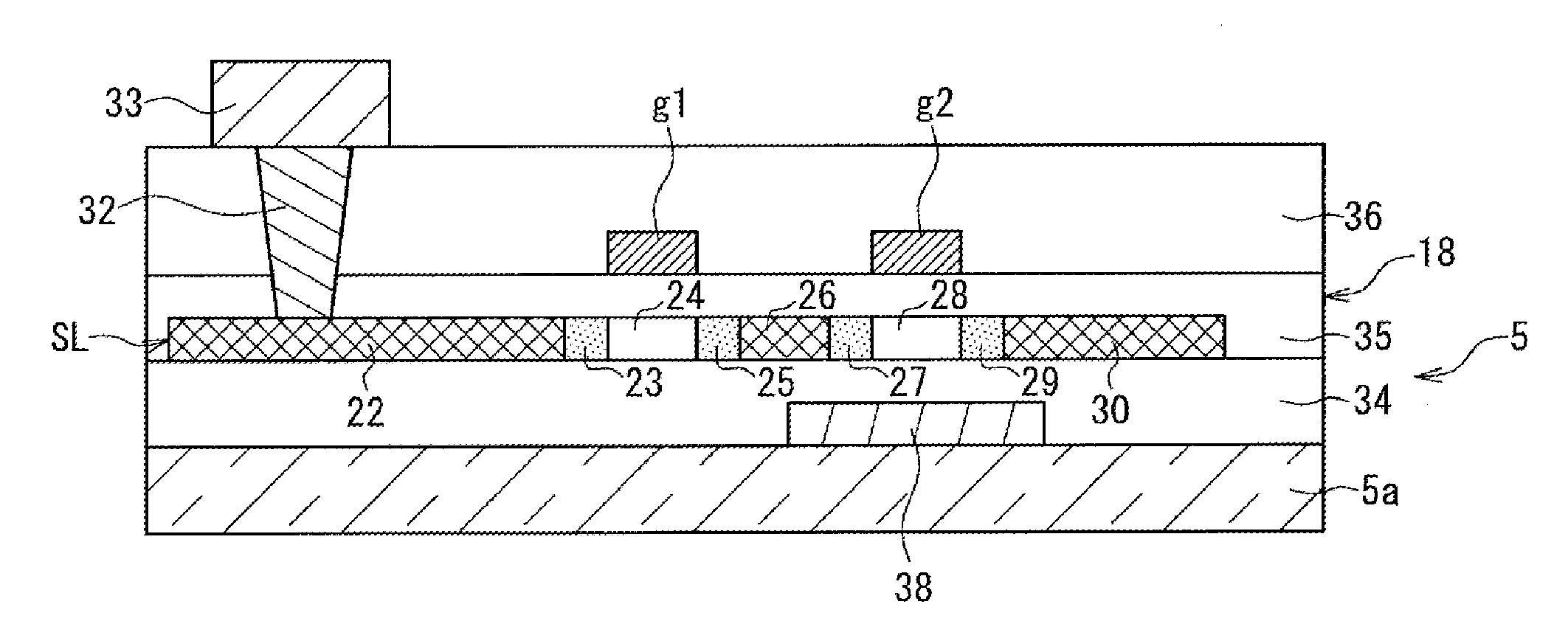
Provided are a semiconductor device that can be fabricated easily and can achieve leakage current reduction, without its structure becoming complex or the device becoming bulky; an active matrix substrate in which the device is used; and a display device in which the device is used. A switching portion (18) (semiconductor device) provided with thin film transistors (Tr1, Tr2) having a top gate electrodes (g1, g2) (main gate electrodes) and a bottom gate electrode (21) (auxiliary gate electrode) includes a silicon layer (SL) (semiconductor layer) provided between the top gate electrodes (g1, g2) and the bottom gate electrode (21); and a light shielding film that shields a carrier generation region formed in the silicon layer from light. A potential of the top gate electrodes (g1, g2) is controlled by a gate signal supplied via a signal line, and a potential of the bottom gate electrode (21) is determined depending on capacity coupling between the bottom gate electrode (21) and the top gate electrodes (g1, g2).
Owner:SHARP KK
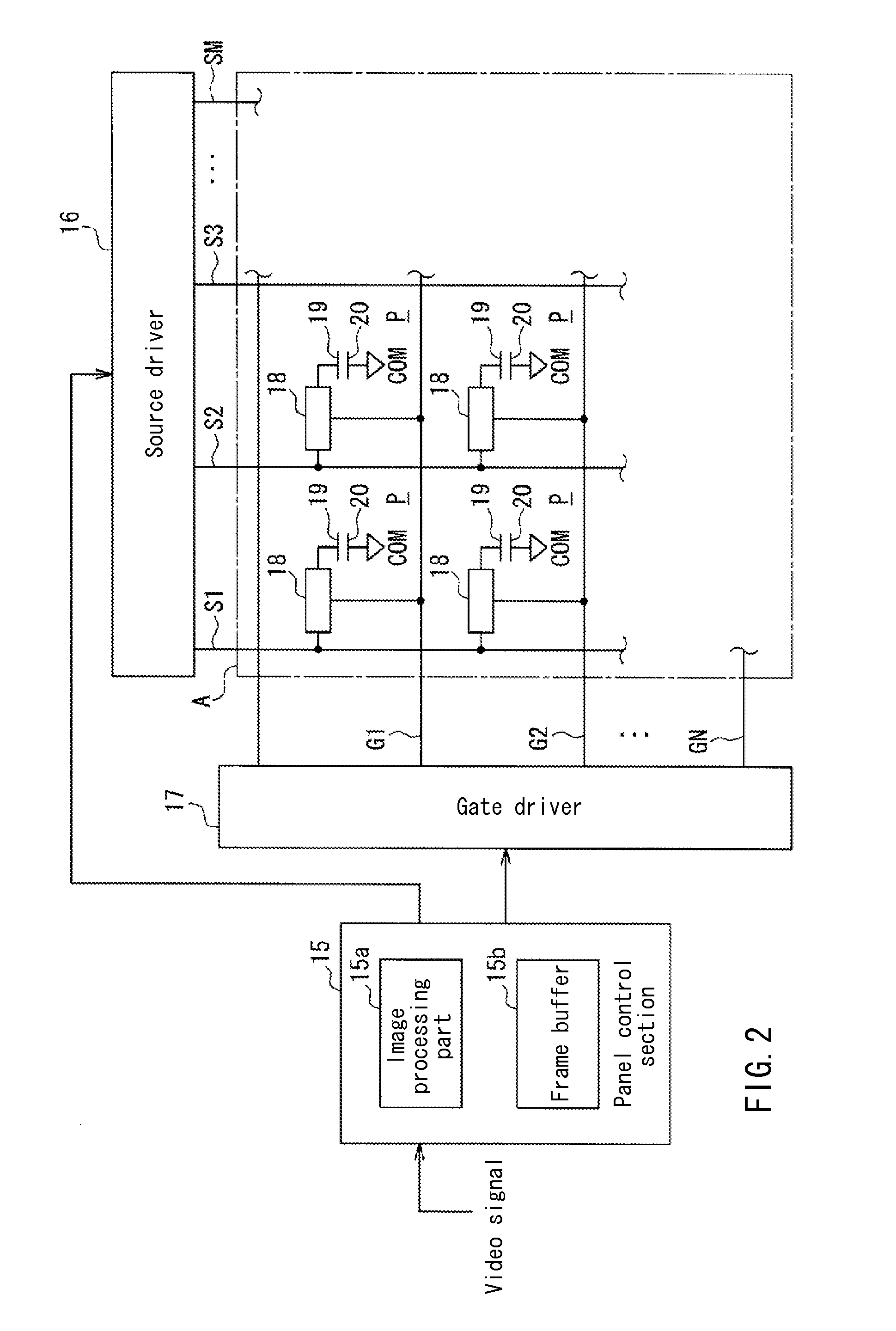
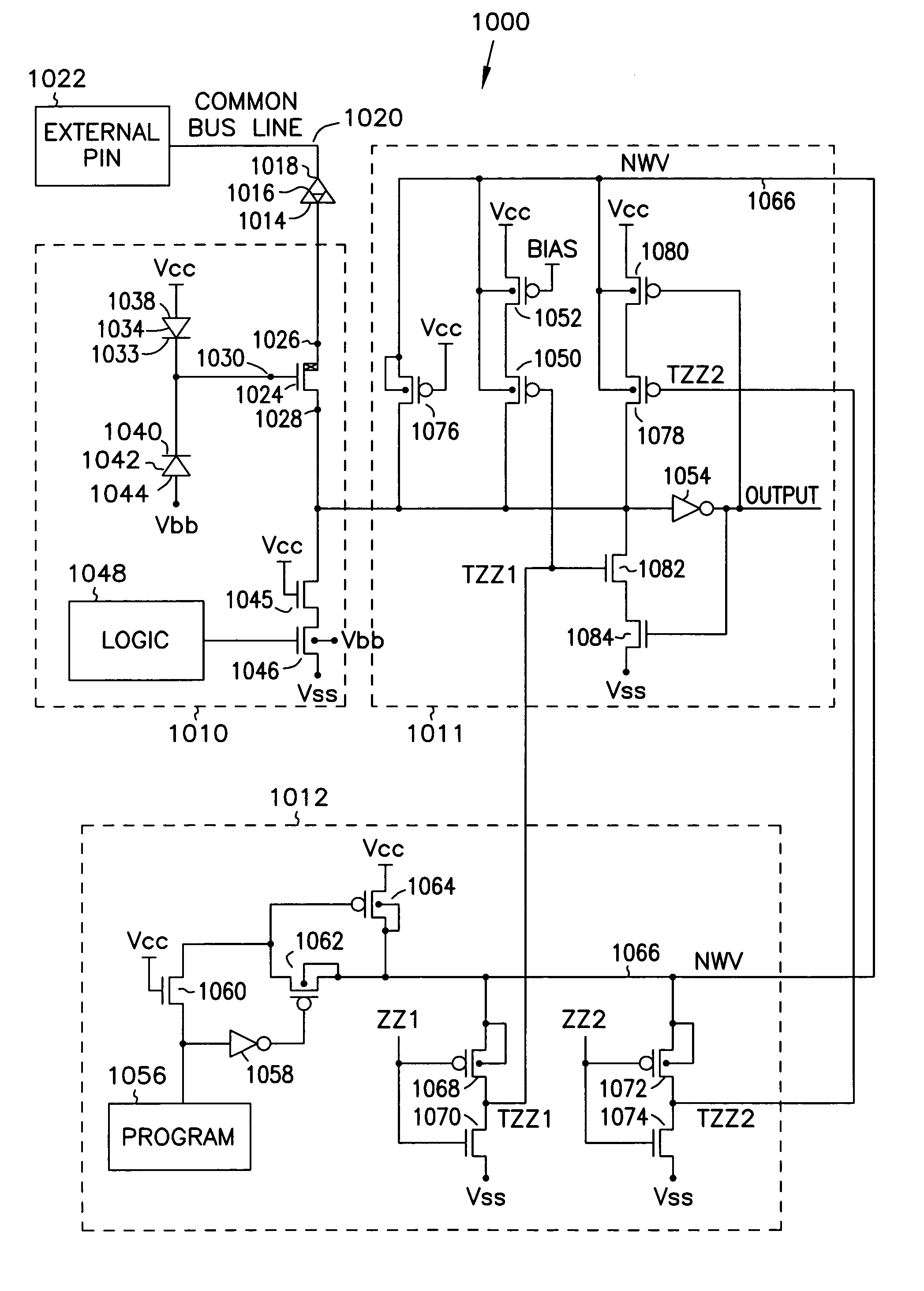
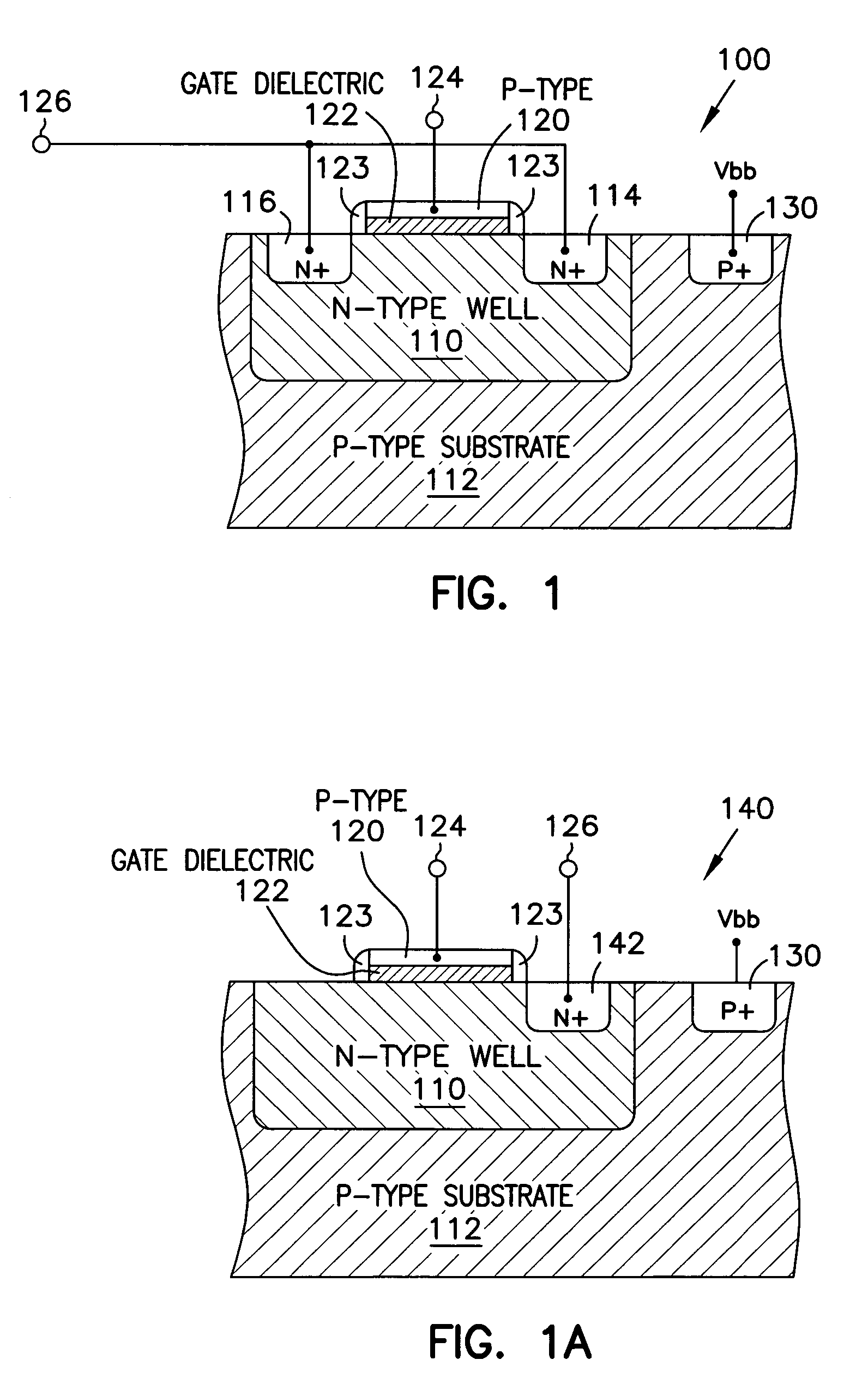
Gate dielectric antifuse circuits and methods for operating same
InactiveUS7030458B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGate dielectricHigh voltage transistors
A number of antifuse support circuits and methods for operating them are disclosed according to embodiments of the present invention. An external pin is coupled to a common bus line in an integrated circuit to deliver an elevated voltage to program antifuses in a programming mode. An antifuse having a first terminal coupled to the common bus line is selected to be programmed by a control transistor in a program driver circuit coupled to a second terminal of the antifuse. The program driver circuit has a high-voltage transistor with a diode coupled to its gate to bear a portion of the elevated voltage after the antifuse has been programmed. The program driver circuit also has an impedance transistor between the high-voltage transistor and the control transistor to reduce leakage current and the possibility of a snap-back condition in the control transistor. A read circuit includes a transistor coupled between a read voltage source and the second terminal to read the antifuse in an active mode. The common bus line may be coupled to a reference voltage through a common bus line driver circuit in the active mode to pass current to or from the read circuit. The common bus line driver circuit has a control transistor and a high-voltage transistor with a diode coupled to its gate to bear the elevated voltage on the common bus line during the programming mode. The read circuit may have a latch circuit to latch a state of the antifuse in a sleep mode. A floating well driver logic circuit raises the voltage potential of wells and gate terminals of p-channel transistors in the read circuit during the programming mode to reduce current flow from the common bus line.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, liquid crystal display device, RFID tag, light emitting device, and electronic device
InactiveUS20070069401A1Improve featuresTotal current dropVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesLiquid-crystal displayDevice material
There is provided a semiconductor device, in which characteristics of the semiconductor device are improved by thinning a gate insulating film and a leak current can be reduced, and a manufacturing method thereof. An aluminum film which is a metal film is formed over a polycrystalline semiconductor film, and plasma oxidizing treatment is performed to the aluminum film, whereby an aluminum oxide film is formed by oxidizing the aluminum film, and a silicon oxide film is formed between the polycrystalline semiconductor film and the aluminum oxide film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
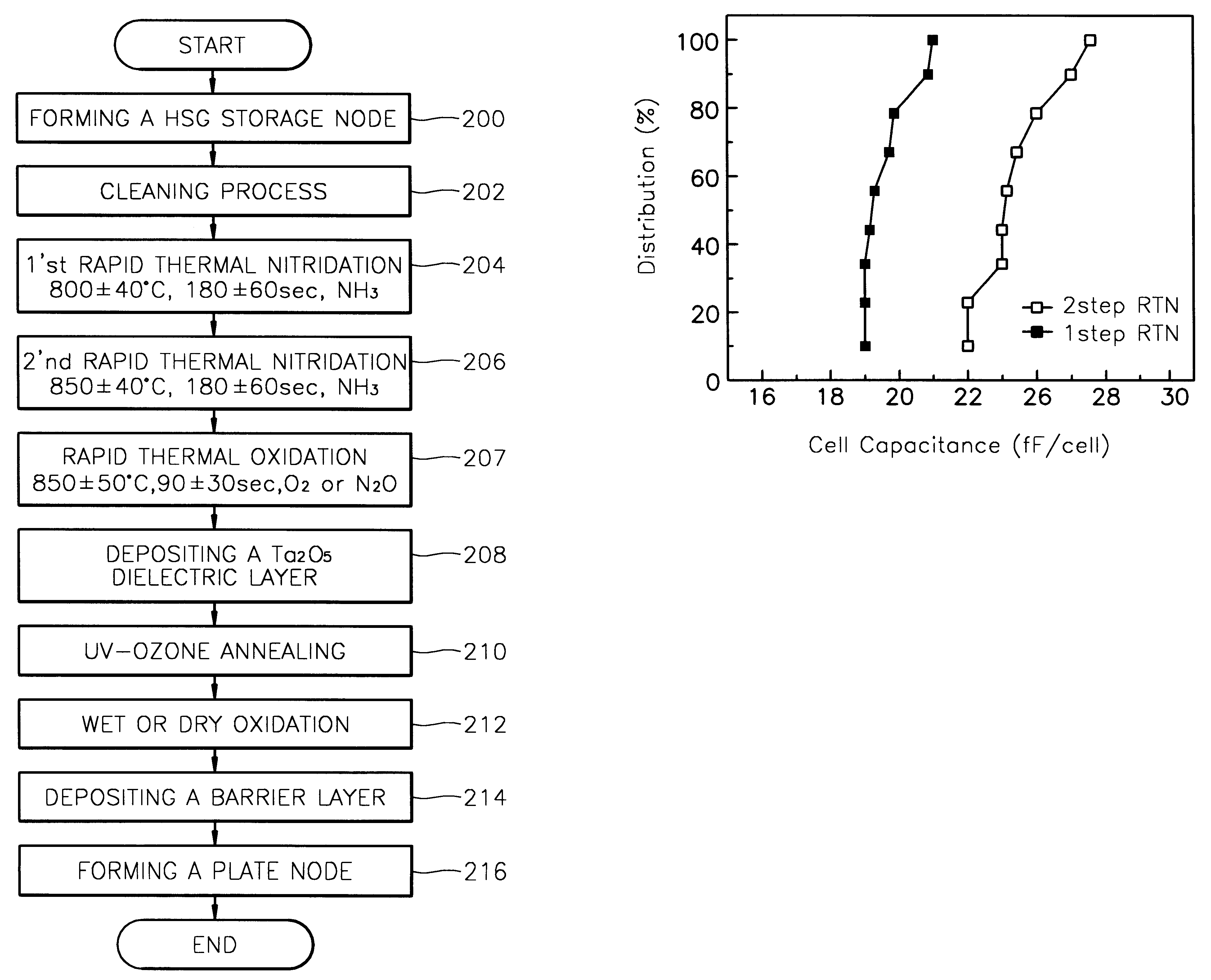
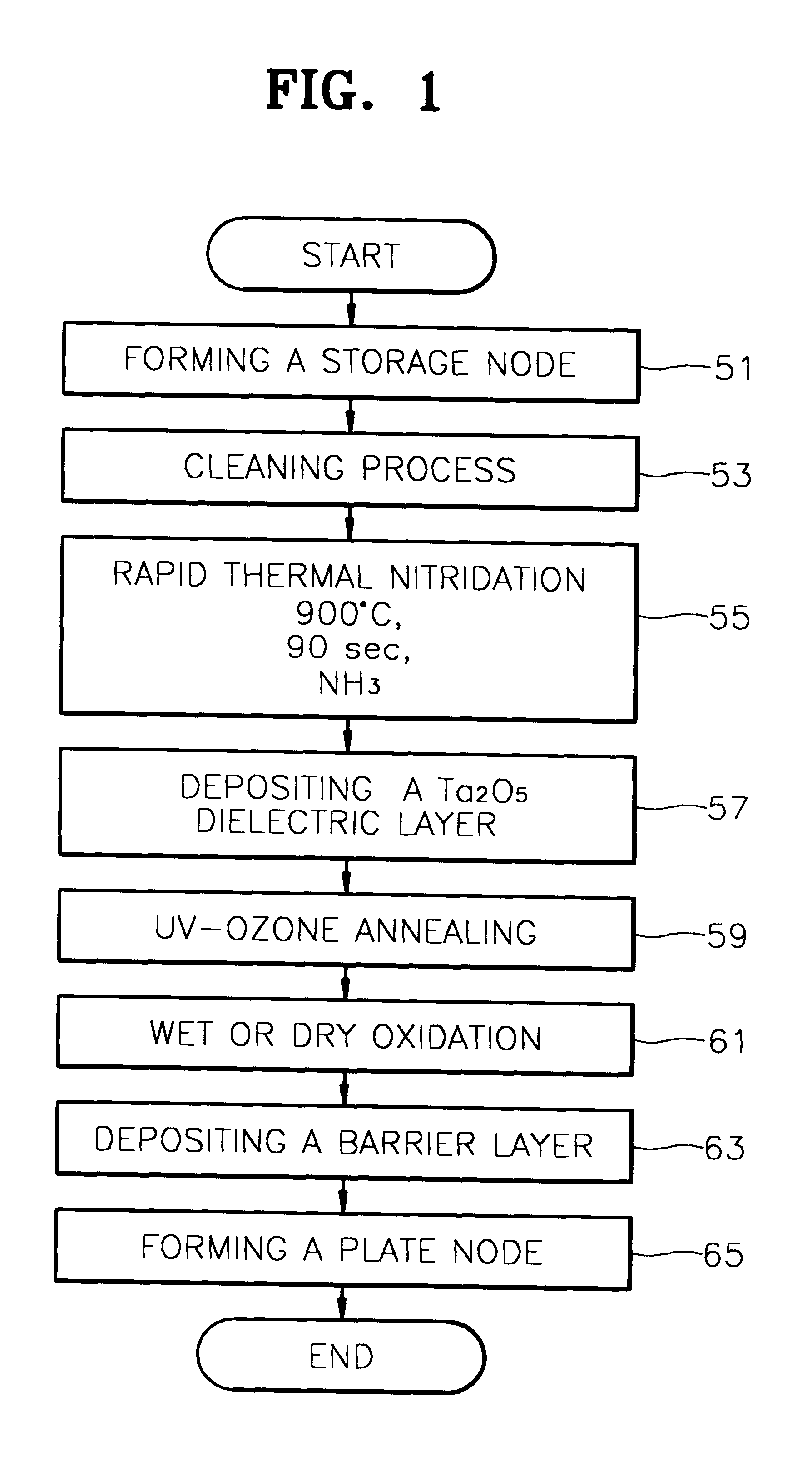
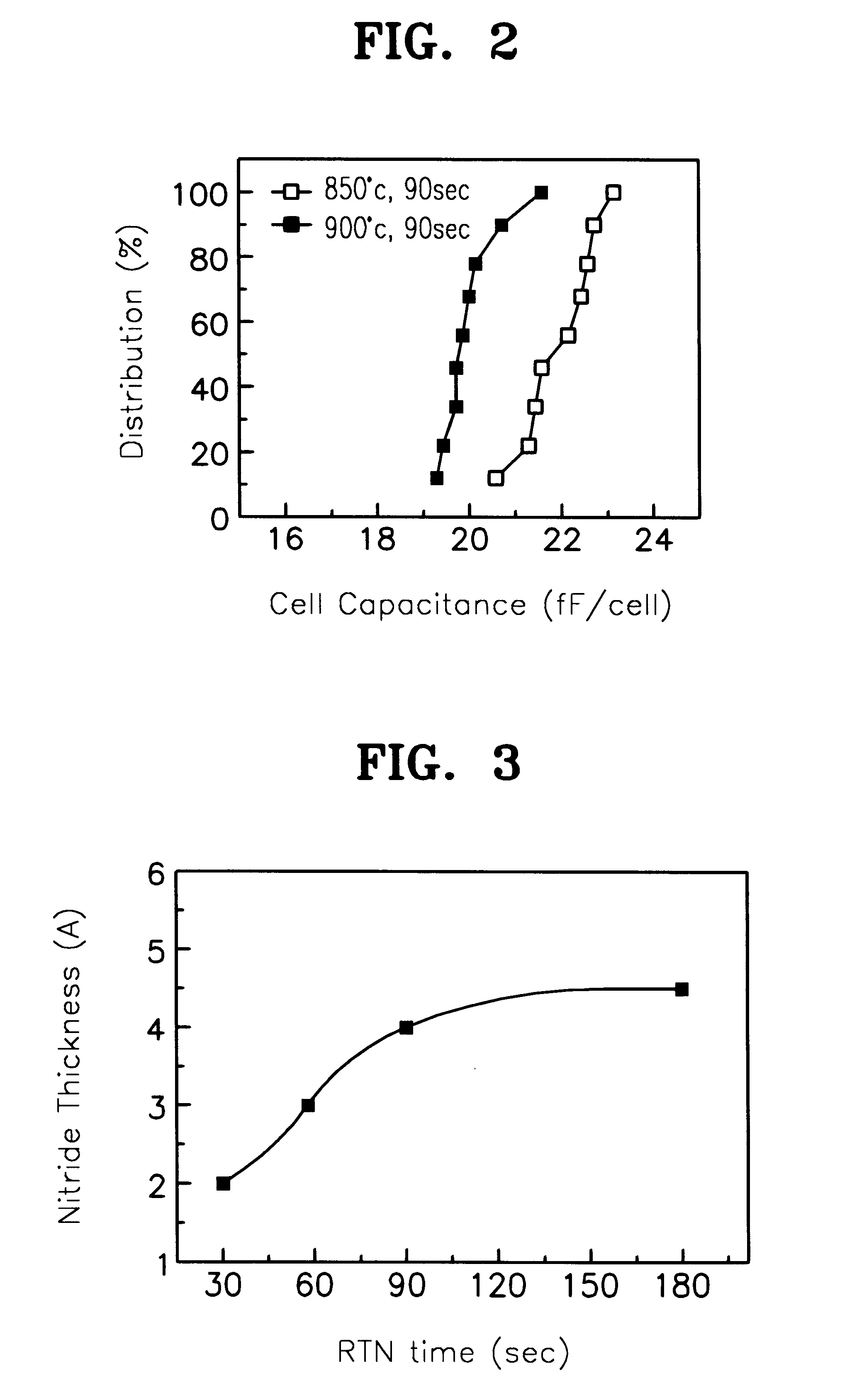
Method for forming a tantalum oxide capacitor using two-step rapid thermal nitridation
A method for forming a Ta2O5 capacitor on a semiconductor device reduces leakage current and increases cell capacitance by utilizing a two-step rapid thermal nitridation (RTN) process to form a nitride layer on a hemi-spherical grain (HSG) storage node. The first RTN process is performed in a NH3 atmosphere at 800±40° C. for 180±60 seconds, thereby forming a nitride layer having a thickness of about 4 Å. The second RTN process is performed in a NH3 atmosphere at 850±40° C. for 180±60 seconds, thereby increasing the thickness of the nitride layer to at least about 7 Å. Therefore, a nitride layer that is thick enough to act as an oxidation barrier is achieved, but agglomeration of the HSGs on the storage node due to high process temperatures is prevented. To make the structure more readily adaptable to process for manufacturing DRAMs with Ta2O5 dielectric layers, a rapid thermal oxidation (RTO) process can then be performed in an O2 or N2O atmosphere at 850±50° C. for 90±30 seconds to thereby form a combined layer comprising a nitride layer and an oxide layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Charge pump circuit and PLL circuit using same
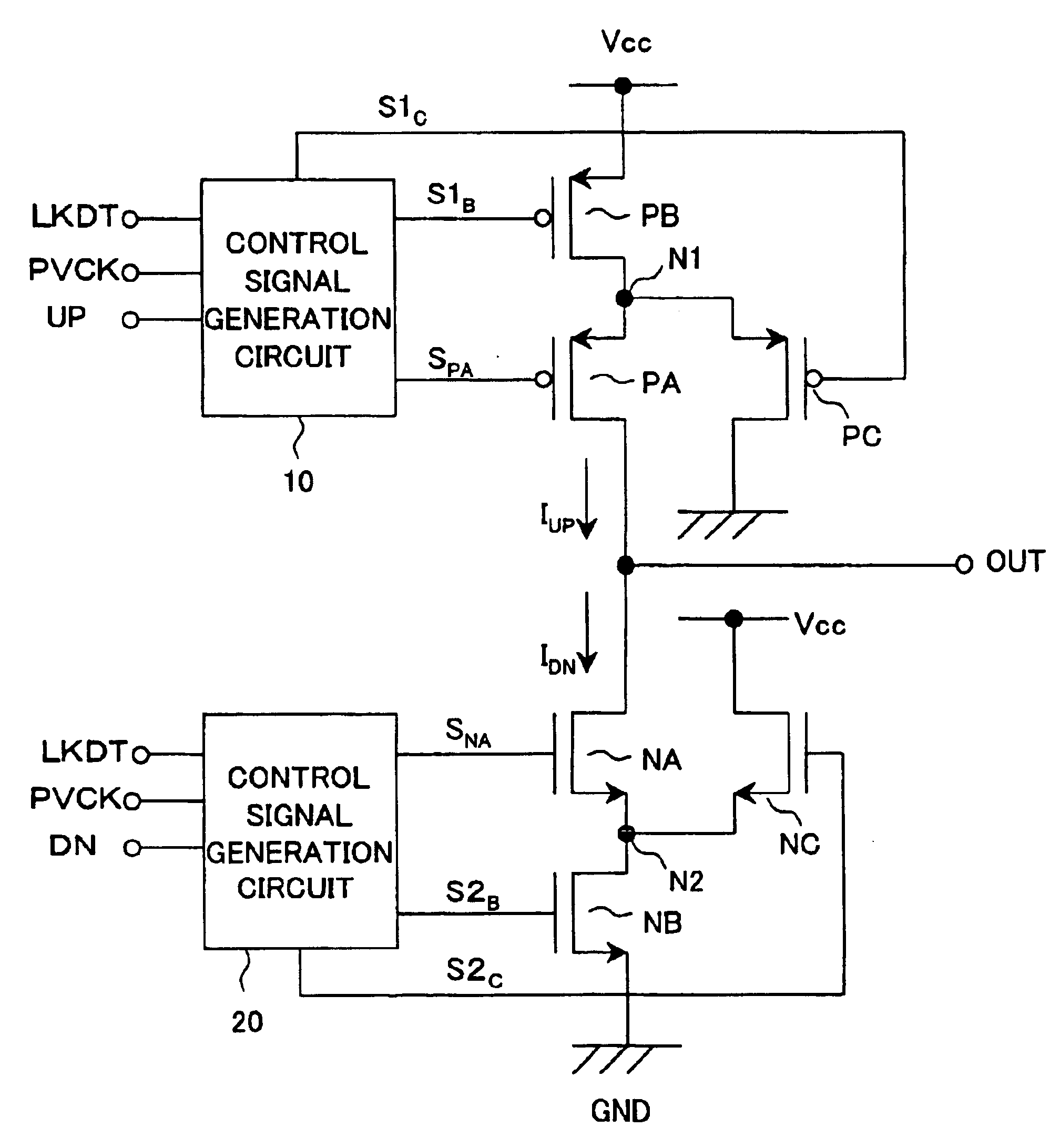
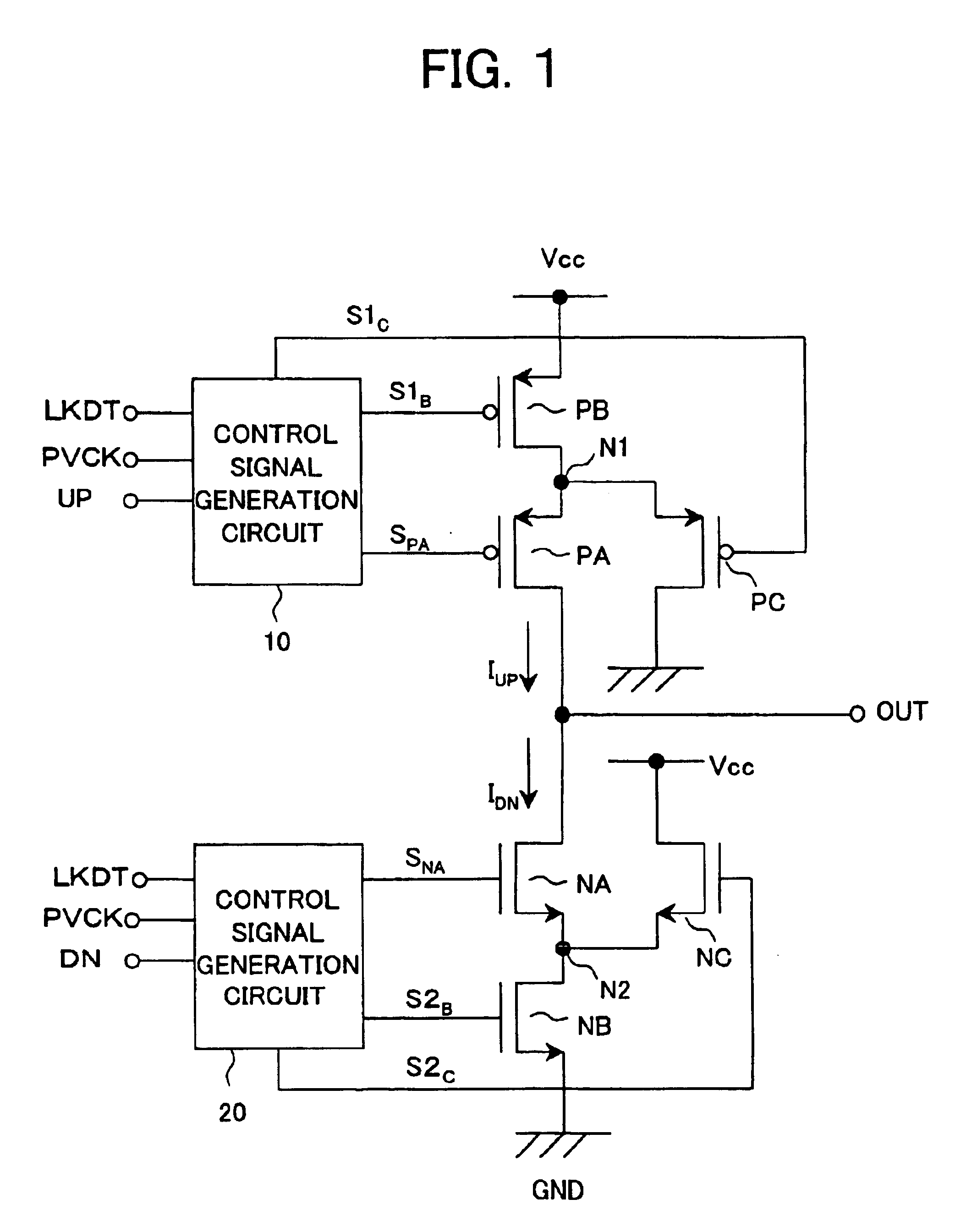
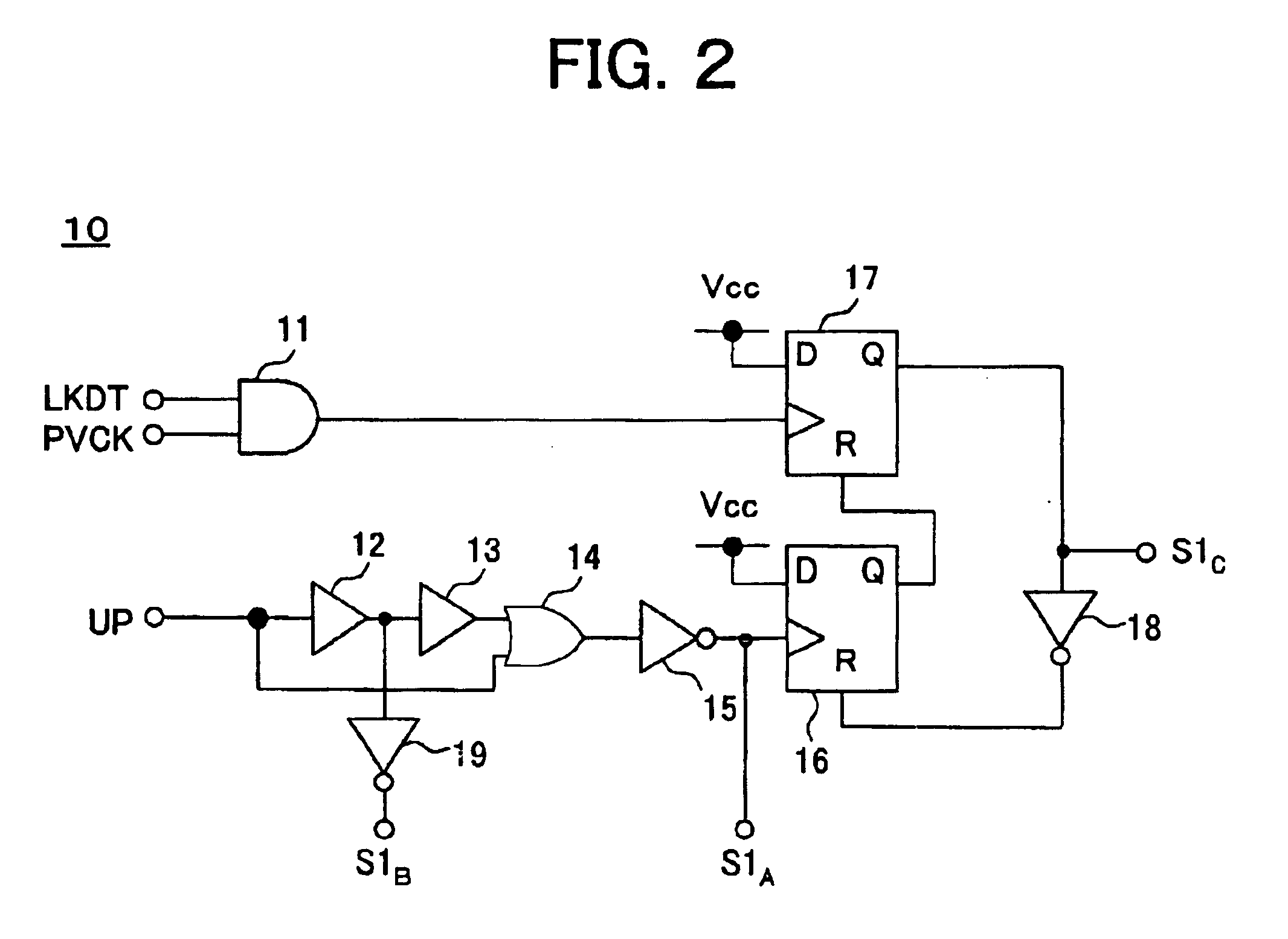
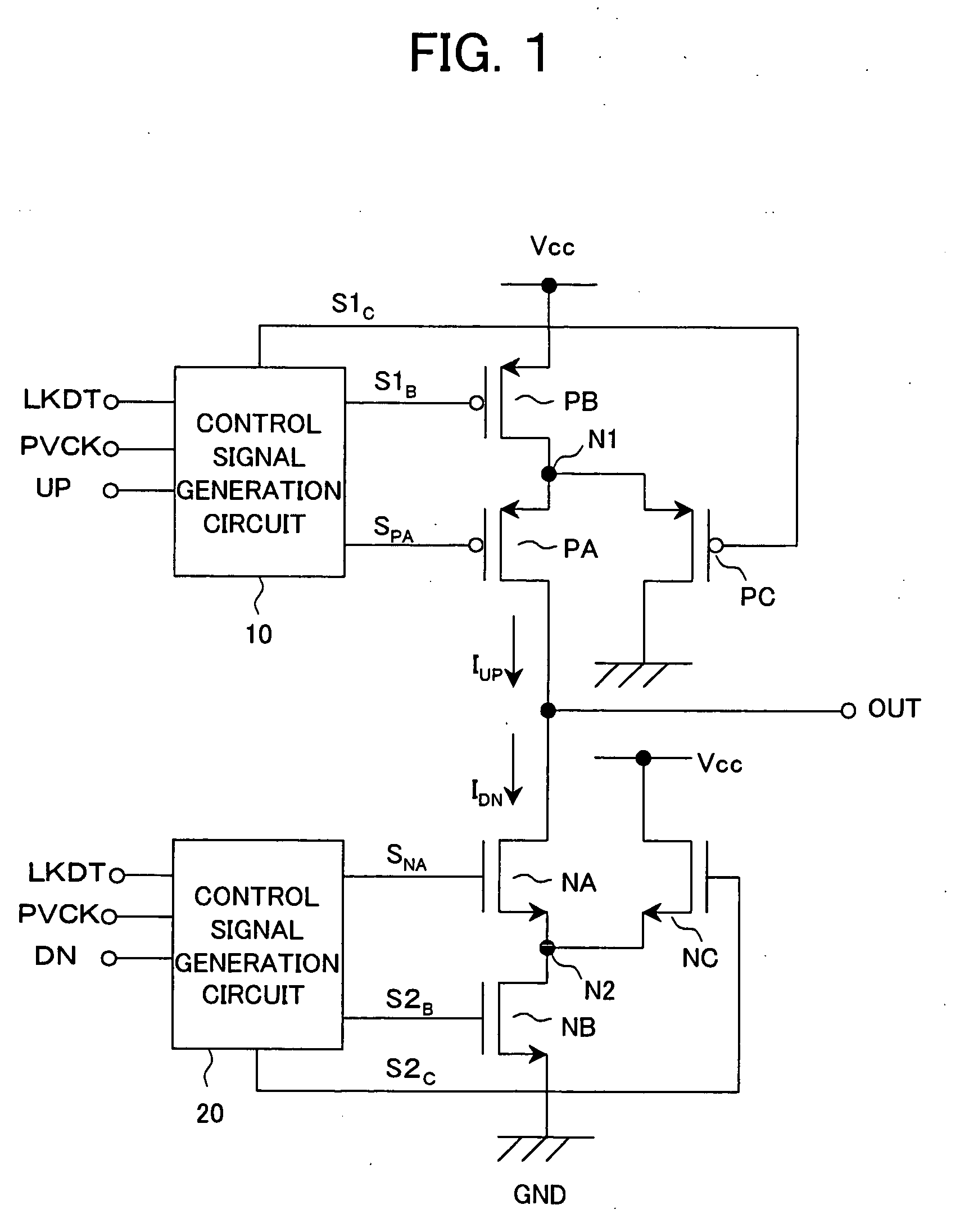
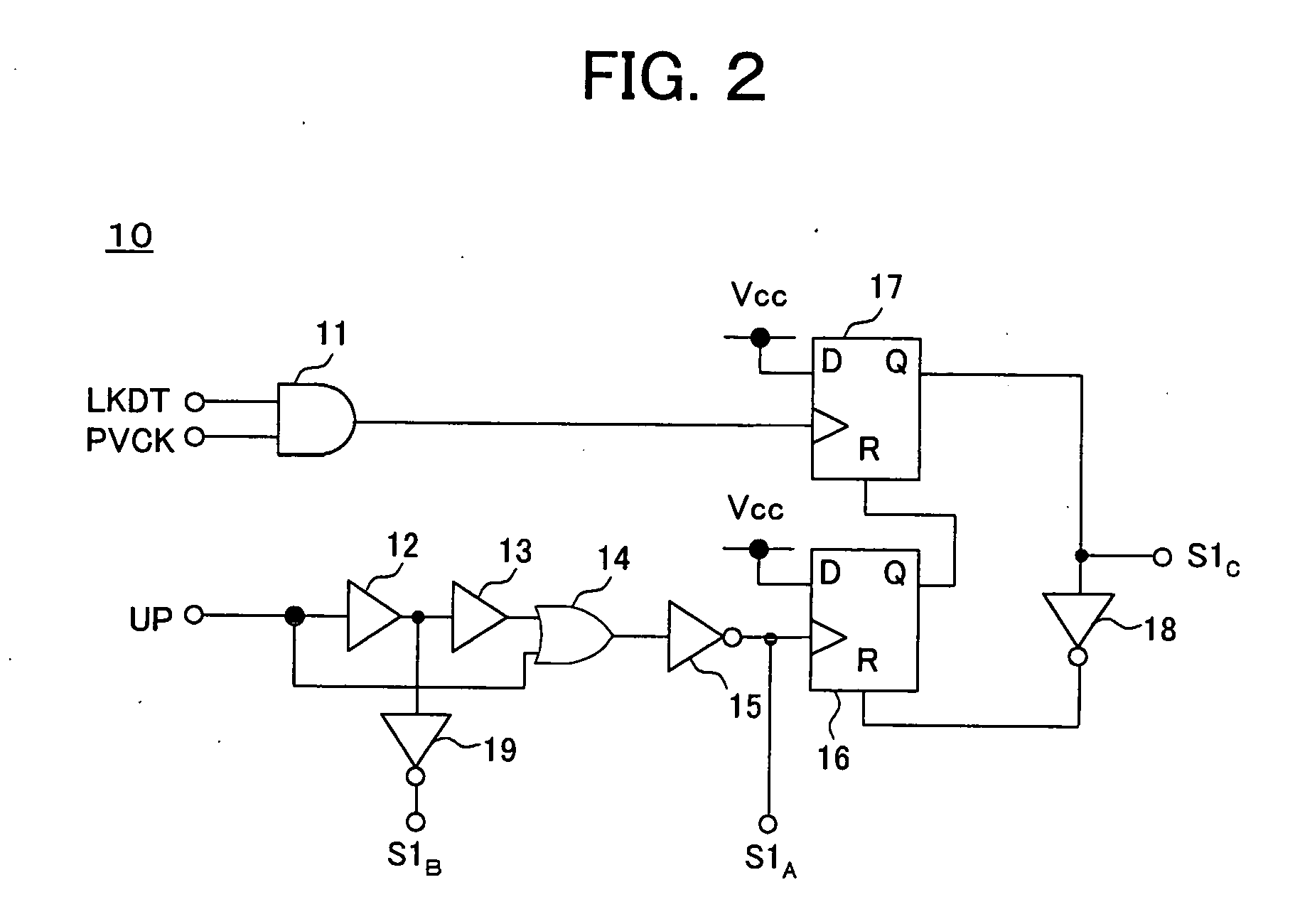
ActiveUS6919746B2Enhance rising and falling characteristicReduce leakage currentPulse automatic controlAc-dc conversionCharge currentControl signal
A charge pump circuit able to enhance the rising and falling characteristics of a current output, drive the current output with a short pulse, reduce leakage current at the OFF time when a current is not output, and realize a reduction of a power consumption and a PLL circuit using same. By outputting a charge current or a discharge current in accordance with an up signal or a down signal and turning on a third transistor (PC, NC) at the OFF time when the current is not output, an inverse bias voltage is supplied between a gate and a source of the second transistor (PA, NA), whereby a reduction of the leakage current can be realized. When the second or third transistor is switched in accordance with the up signal or the down signal, the timing of the control signal is appropriately controlled, simultaneous turning on of the second and third transistors can be avoided, release or injection of charges from and to the output terminal of the charge pump circuit can be prevented, and the stability of an oscillation frequency of a VCO can be improved.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
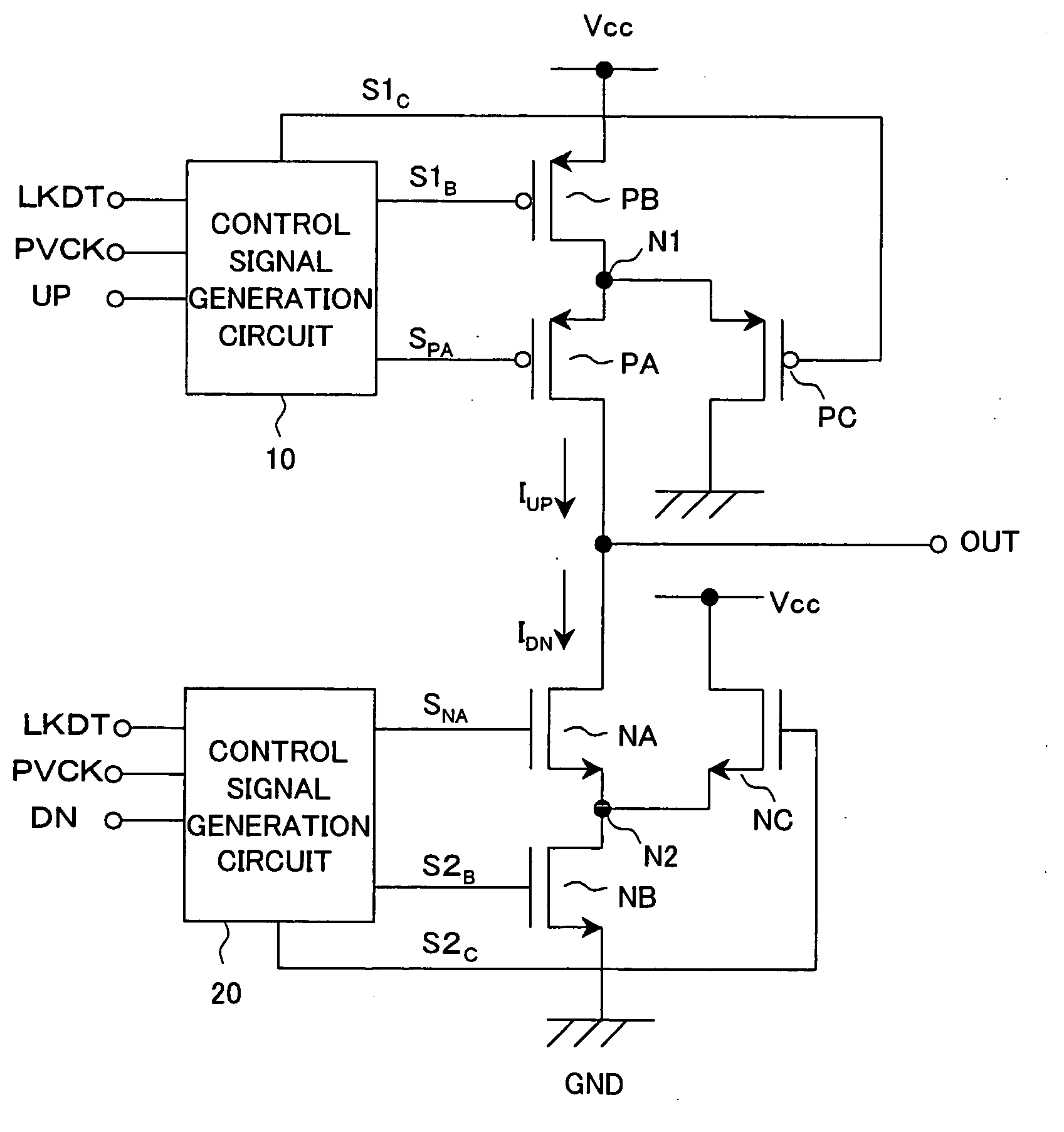
Charge pump circuit and PLL circuit using same
A charge pump circuit able to enhance the rising and falling characteristics of a current output, drive the current output with a short pulse, reduce leakage current at the OFF time when a current is not output, and realize a reduction of a power consumption and a PLL circuit using same. By outputting a charge current or a discharge current in accordance with an up signal or a down signal and turning on a third transistor (PC, NC) at the OFF time when the current is not output, an inverse bias voltage is supplied between a gate and a source of the second transistor (PA, NA), whereby a reduction of the leakage current can be realized. When the second or third transistor is switched in accordance with the up signal or the down signal, the timing of the control signal is appropriately controlled, simultaneous turning on of the second and third transistors can be avoided, release or injection of charges from and to the output terminal of the charge pump circuit can be prevented, and the stability of an oscillation frequency of a VCO can be improved.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
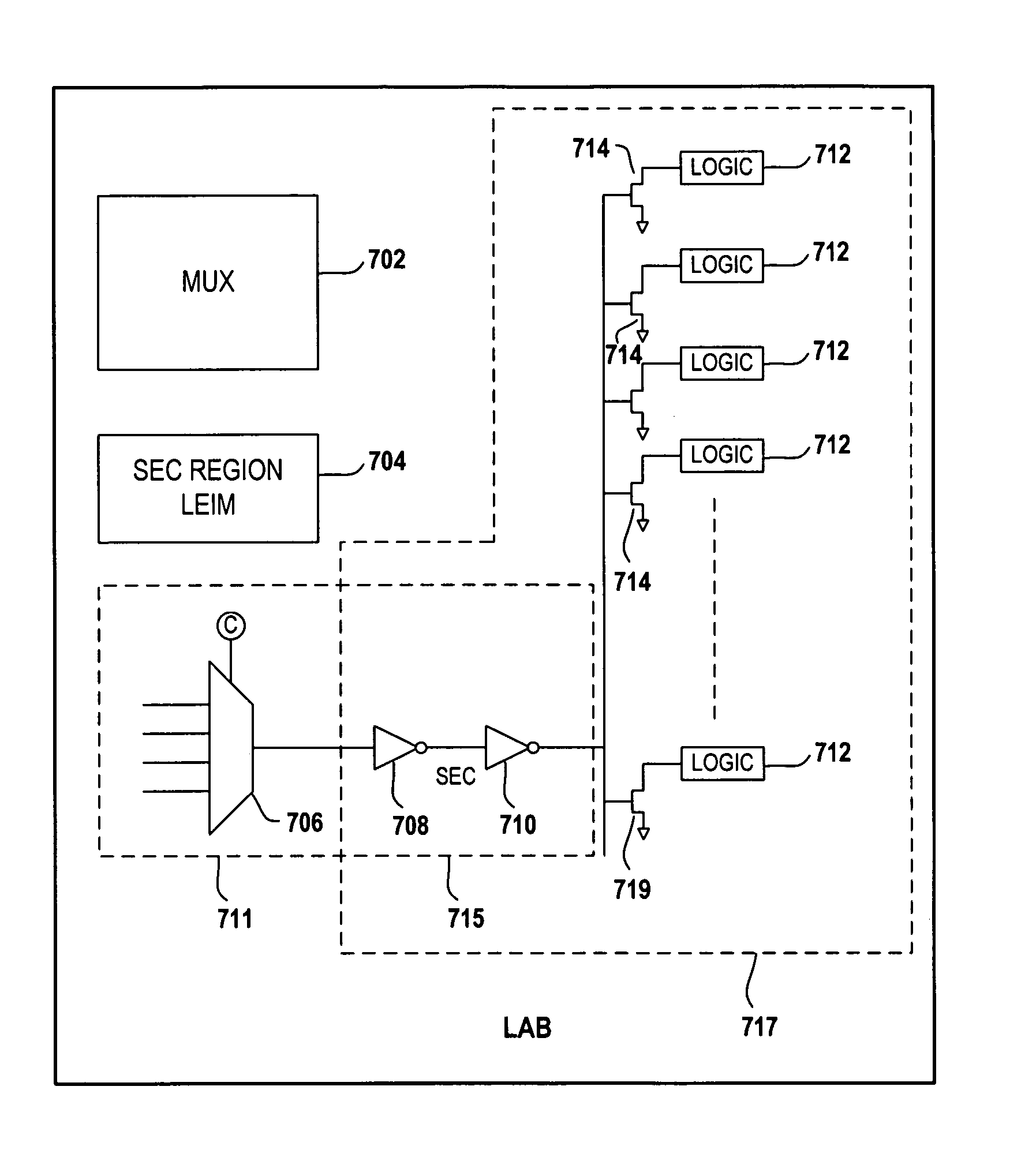
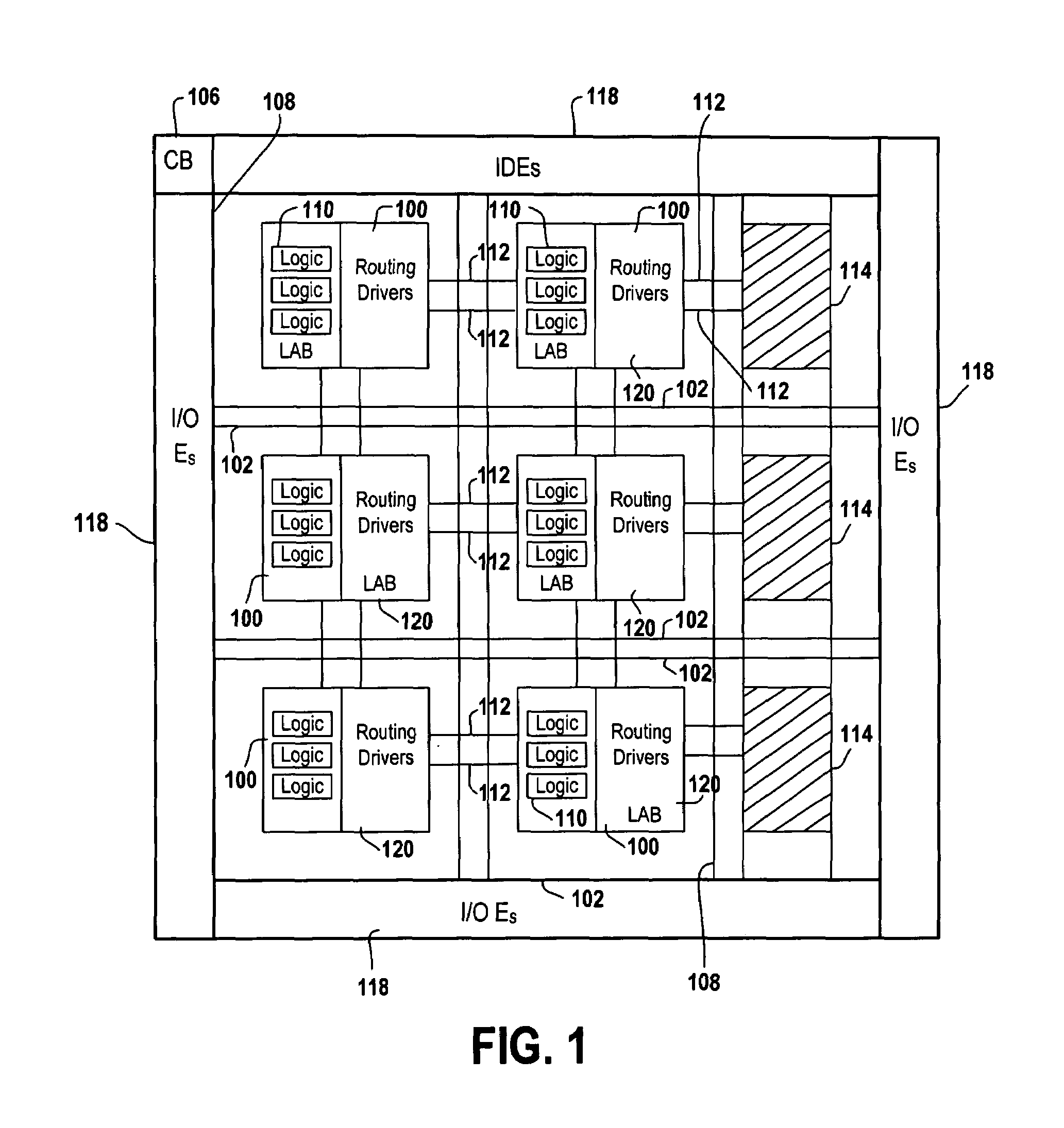
Method of reducing leakage current using sleep transistors in programmable logic device
InactiveUS7355440B1Reduce leakage currentTotal current dropPower reduction by control/clock signalSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceErasable programmable logic device
A programmable logic device (PLD) having minimal leakage current for inactive logic blocks is provided. The PLD includes an array of logic blocks. Among the array of logic blocks, one of the array of logic blocks monitors the level of activity of each of the remaining logic blocks. The level of activity may be monitored by observing the input and output pin of the logic blocks. The PLD further includes a plurality of driven wires defining a routing pattern between the array of logic blocks. When one of the array of logic blocks detect inactivity in any one of the remaining logic blocks for a certain duration, the one of the array logic blocks transmits a signal invoking a sleep mode for the inactive logic blocks. A sleep transistor with a threshold voltage level that is capable minimizing the leakage current is associated with each of the remaining block. The gate of the sleep transistor receives the signal transmitted by one of the array logic blocks and the signal switches off the sleep transistor.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Level shifter
ActiveUS7145363B2Reduce leakage currentAvoid delayHeat storage plantsElectric pulse generatorEngineeringLeakage current reduction
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Cluster ion implantation for defect engineering
InactiveUS7919402B2Reduce defectsMinimize crystal defectsElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon implantationMonomer
A method of semiconductor manufacturing is disclosed in which doping is accomplished by the implantation of ion beams formed from ionized molecules, and more particularly to a method in which molecular and cluster dopant ions are implanted into a substrate with and without a co-implant of non-dopant cluster ion, such as a carbon cluster ion, wherein the dopant ion is implanted into the amorphous layer created by the co-implant in order to reduce defects in the crystalline structure, thus reducing the leakage current and improving performance of the semiconductor junctions. These compounds include co-implants of carbon clusters with implants of monomer or cluster dopants or simply implanting cluster dopants. In particular, the invention described herein consists of a method of implanting semiconductor wafers implanting semiconductor wafers with carbon clusters followed by implants of boron, phosphorus, or arsenic, or followed with implants of dopant clusters of boron, phosphorus, or arsenic.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
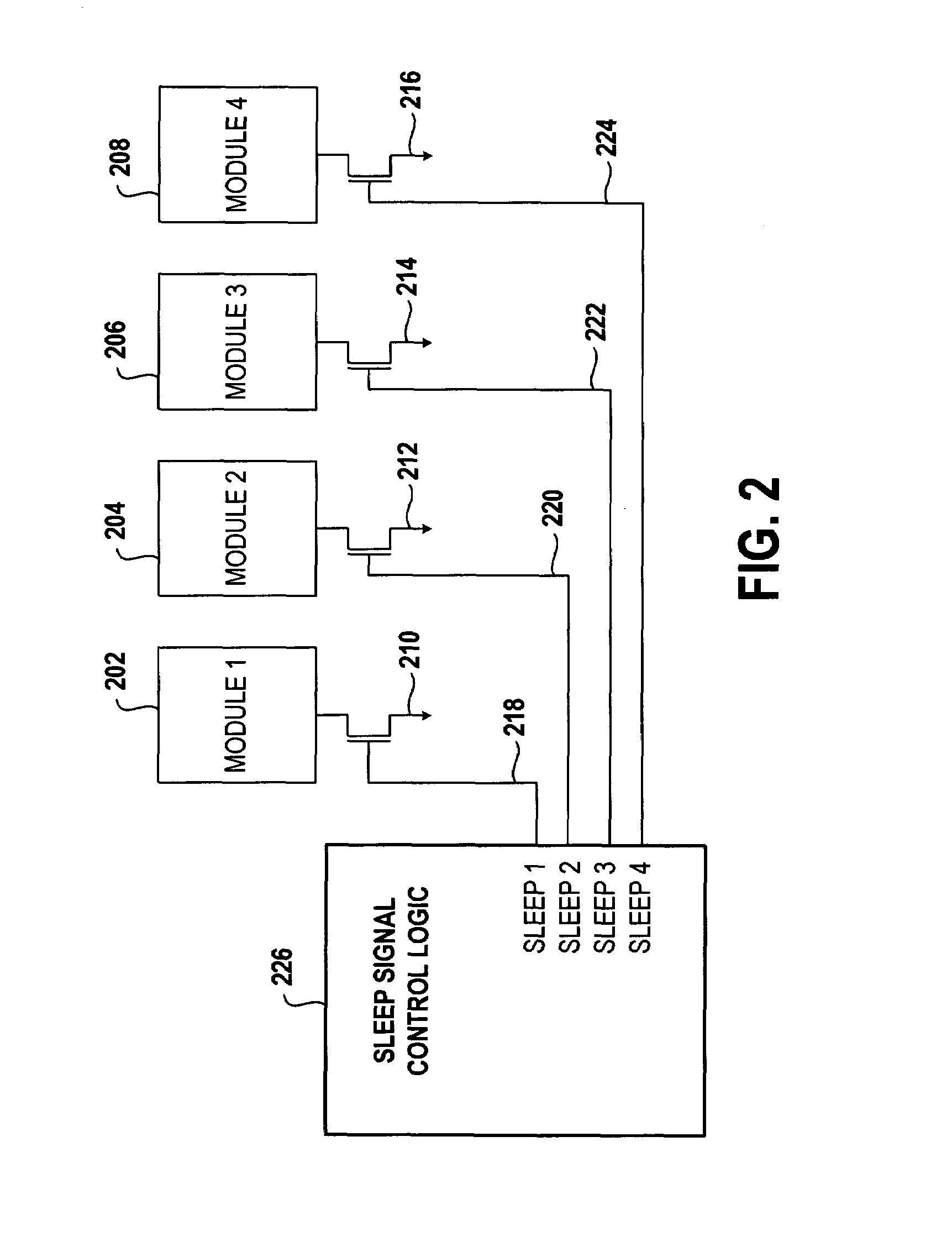
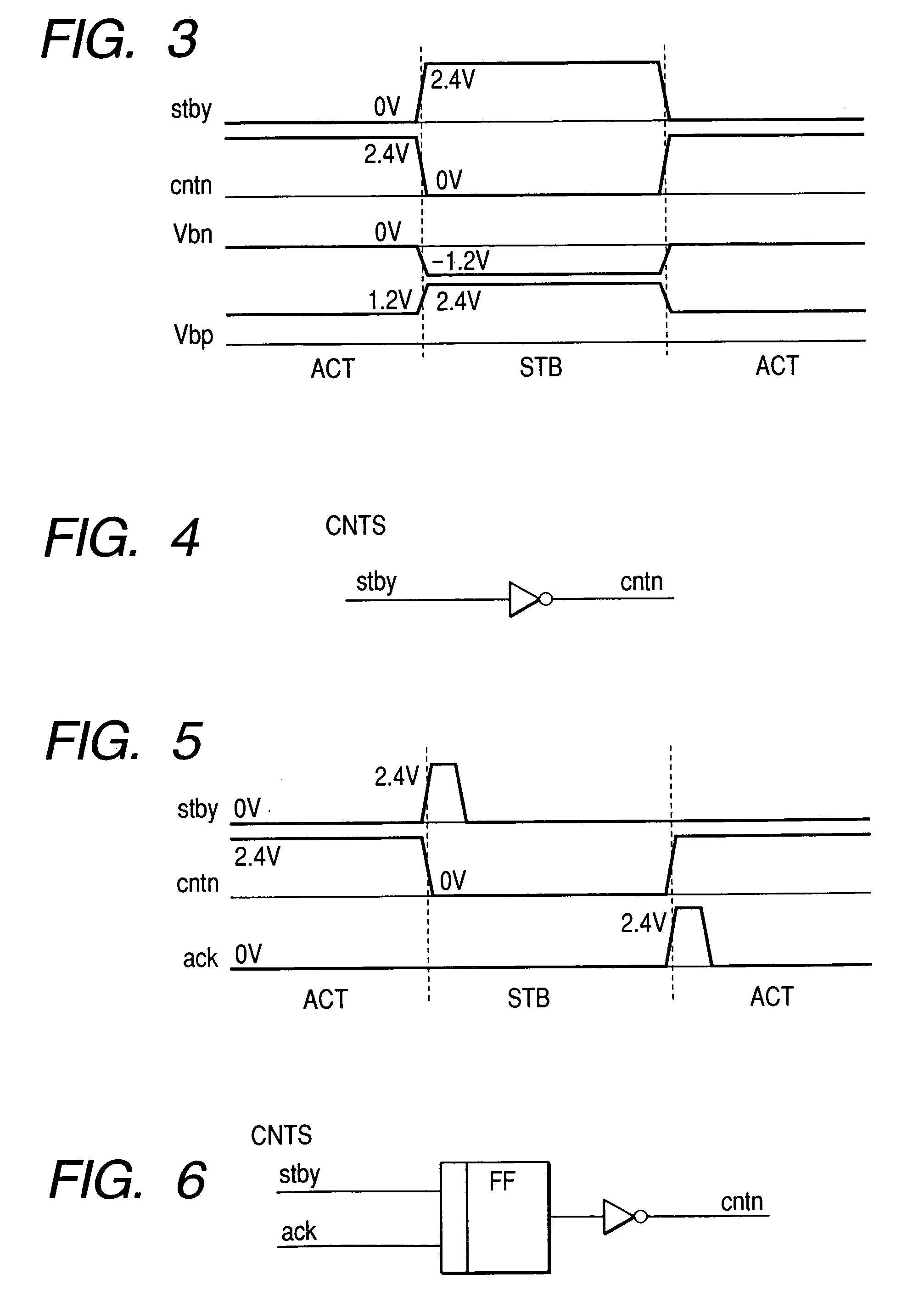
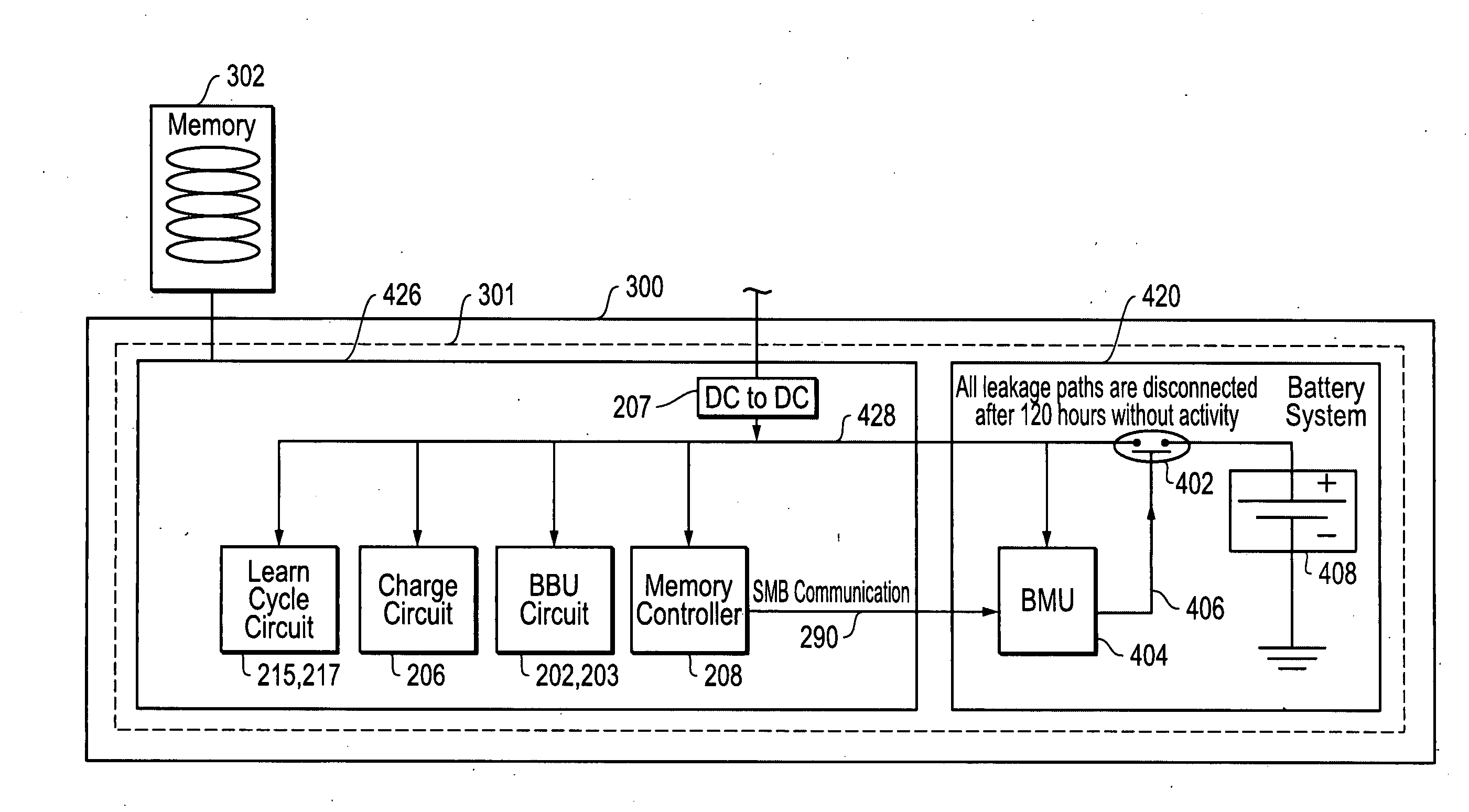
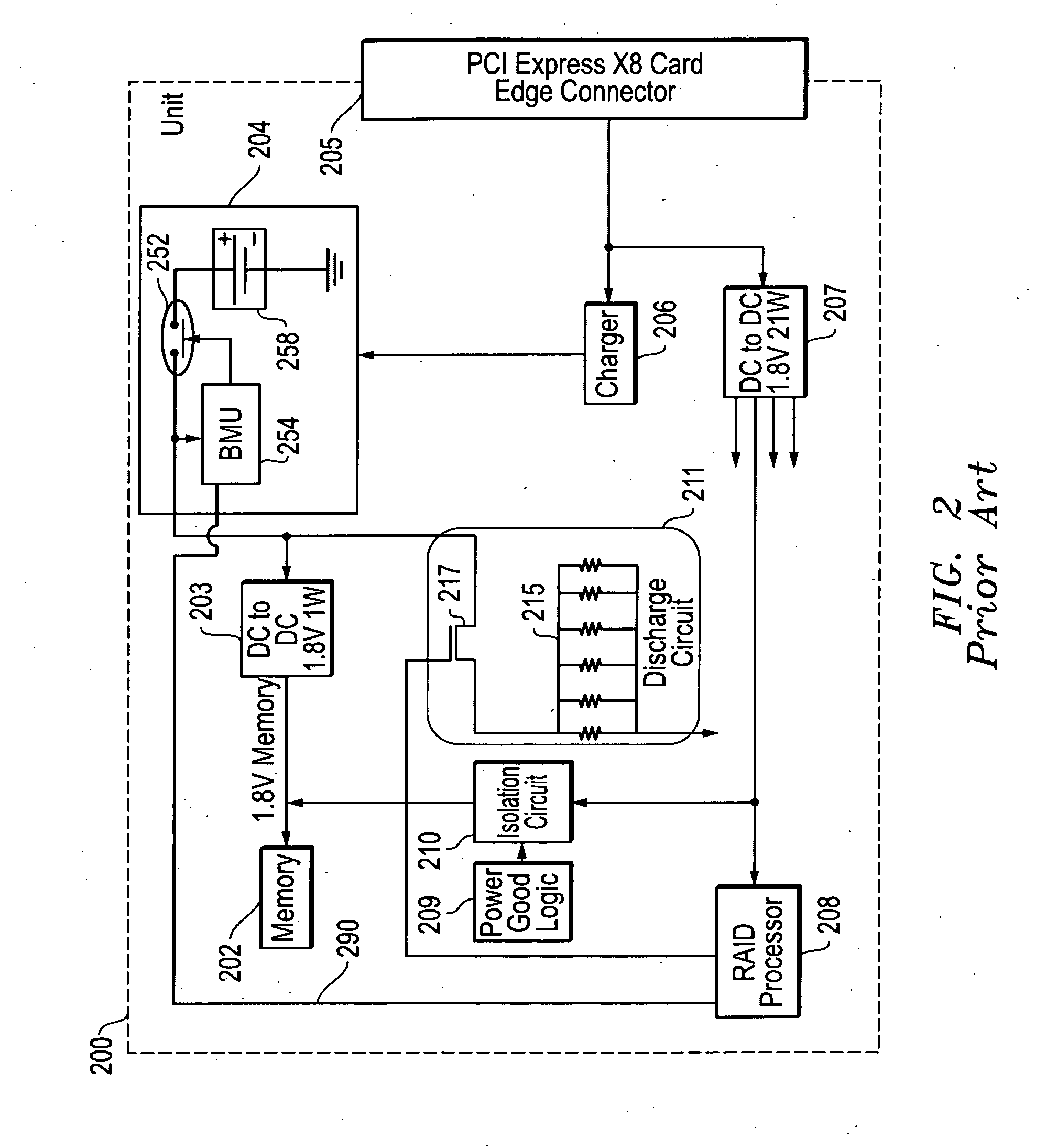
Systems and methods for time-based management of backup battery life in memory controller systems
ActiveUS20110072280A1Save energyReduce the impactEnergy efficient ICTBatteries circuit arrangementsRAIDMemory controller
Systems and methods that may be implemented for time-based management of storage memory controller (e.g., RAID controller) backup battery life in information handling systems by limiting the backup battery system operation time in order to save energy, reduce the impact of leakage current, and prolong memory controller backup battery shelf life while at the same time meeting requirements of back-up time for storage / server applications. The disclosed systems and methods may be implemented, for example, by providing a battery system controller that implements a pre-set memory controller backup battery operation time, in combination with a hardware-controlled mechanism that extends backup battery system operation time by disabling one or more current leakage paths within the storage memory controller circuitry.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Standby leakage current reduction circuit and semiconductor memory device comprising the standby leakage current reduction circuit
ActiveUS7397721B2Reduce leakage currentReduce excessive power consumptionDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
Embodiments of the invention provide a standby leakage current reduction circuit and a semiconductor memory device comprising the standby leakage current reduction circuit. The invention provides a circuit adapted to reduce standby leakage current in a semiconductor memory device comprising memory cells. The circuit comprises a bias signal generator adapted to generate a bias signal, wherein a voltage level of the bias signal is set in accordance with a result of a standby leakage current test. The circuit further comprises a ground voltage controller adapted to receive the bias signal from the bias signal generator and to control a level of a voltage apparent on a virtual ground terminal in response to the bias signal while the semiconductor memory device is in a standby mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Track-and-hold peak detector circuit
ActiveUS7053674B1Small in value and size and costReduce operating frequencyCurrent/voltage measurementInstant pulse delivery arrangementsDetector circuitsHemt circuits
A track-and-hold peak detector circuit, which can operate at low input signal frequencies, includes a capacitor to hold a peak voltage of the input signal and logic circuitry that reduces an effect of leakage current into or out of the capacitor, and therefore, provides protection against self-switching of an output signal of the peak detector circuit.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
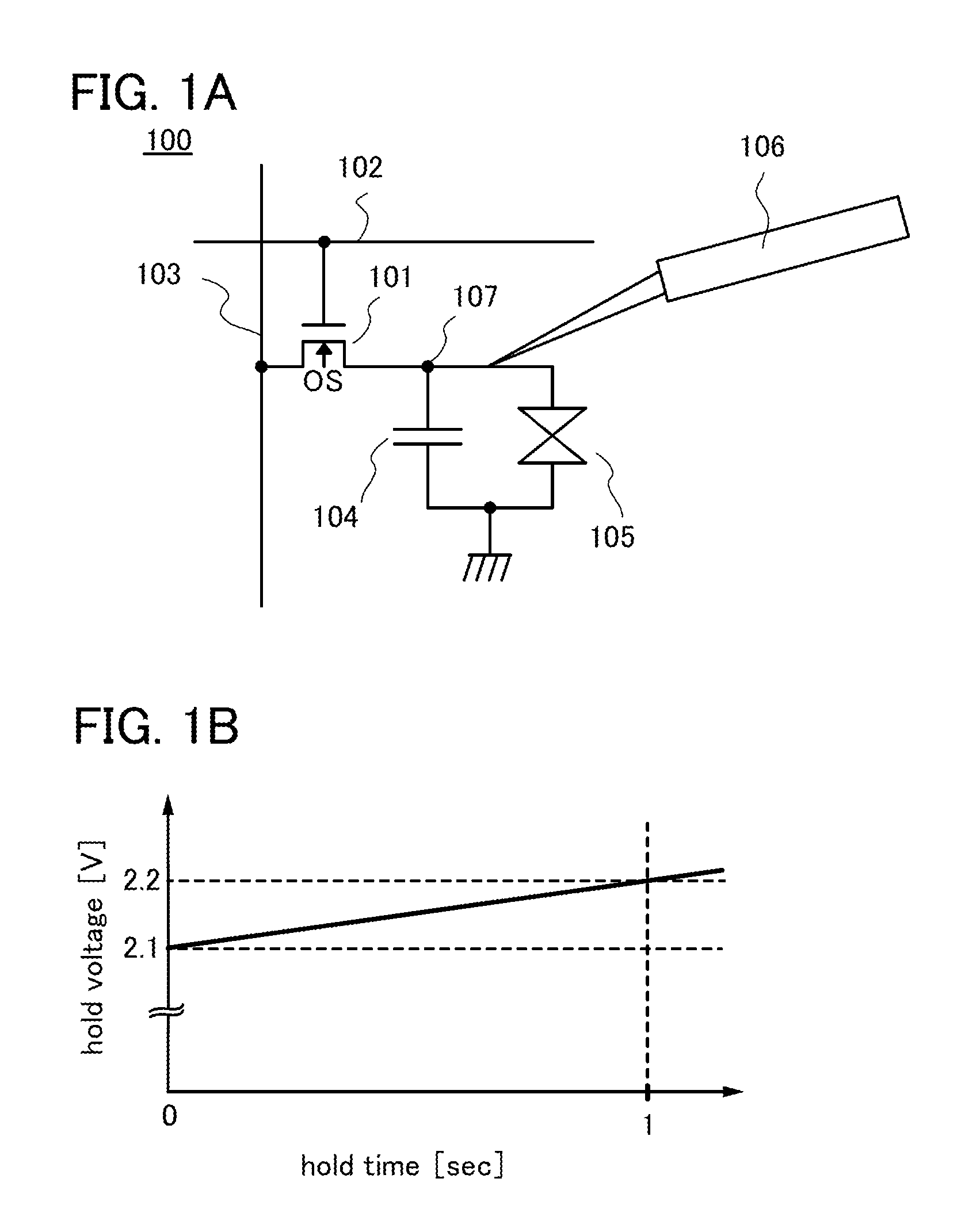
Measurement device
ActiveUS20130314074A1Accurate voltage measurementReduce leakage currentOverload protection arrangementsElectrical testingElectrical resistance and conductanceMeasurement device
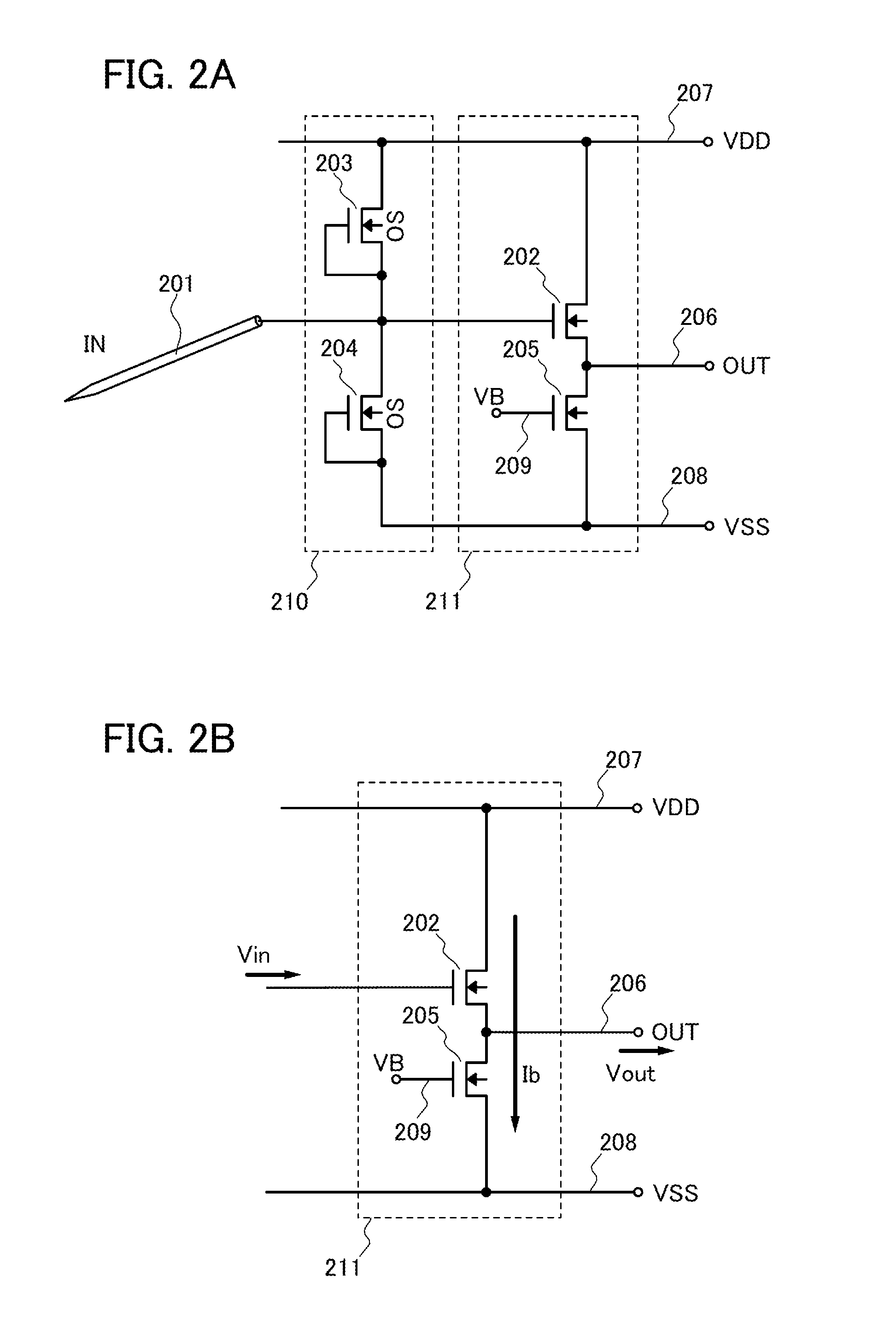
To provide a measurement device which allows long-term accurate measurement of voltage without adversely affecting a device under test, by ensuring a predetermined level of resistance to ESD and reducing leakage current. A measurement device includes a probe needle for contacting a device under test, a first FET for detecting voltage of the device under test, and a protection circuit for protecting the first FET from static electricity. The protection circuit includes a second FET having an oxide semiconductor film as a channel formation region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
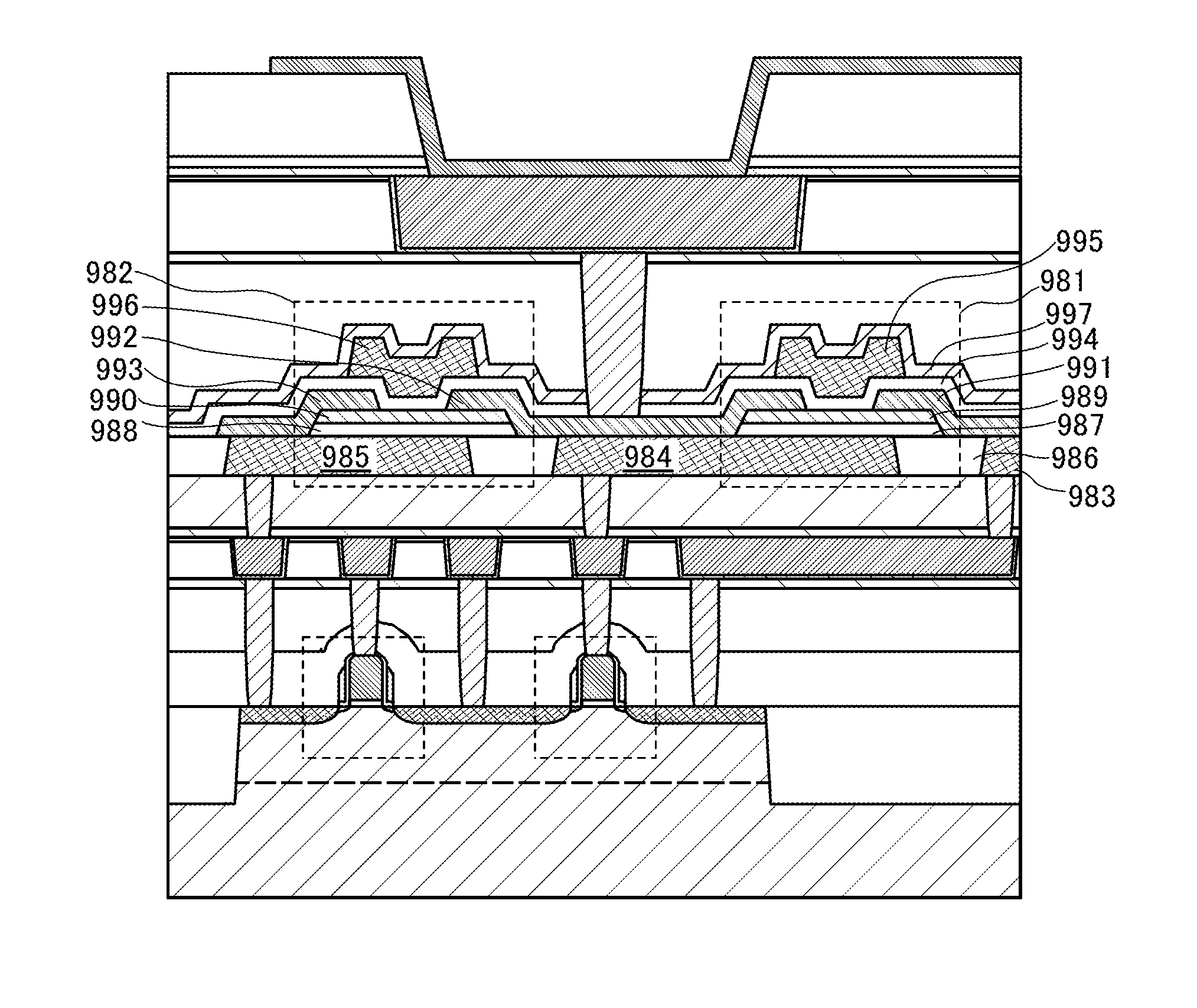
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20120012912A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineDevice material
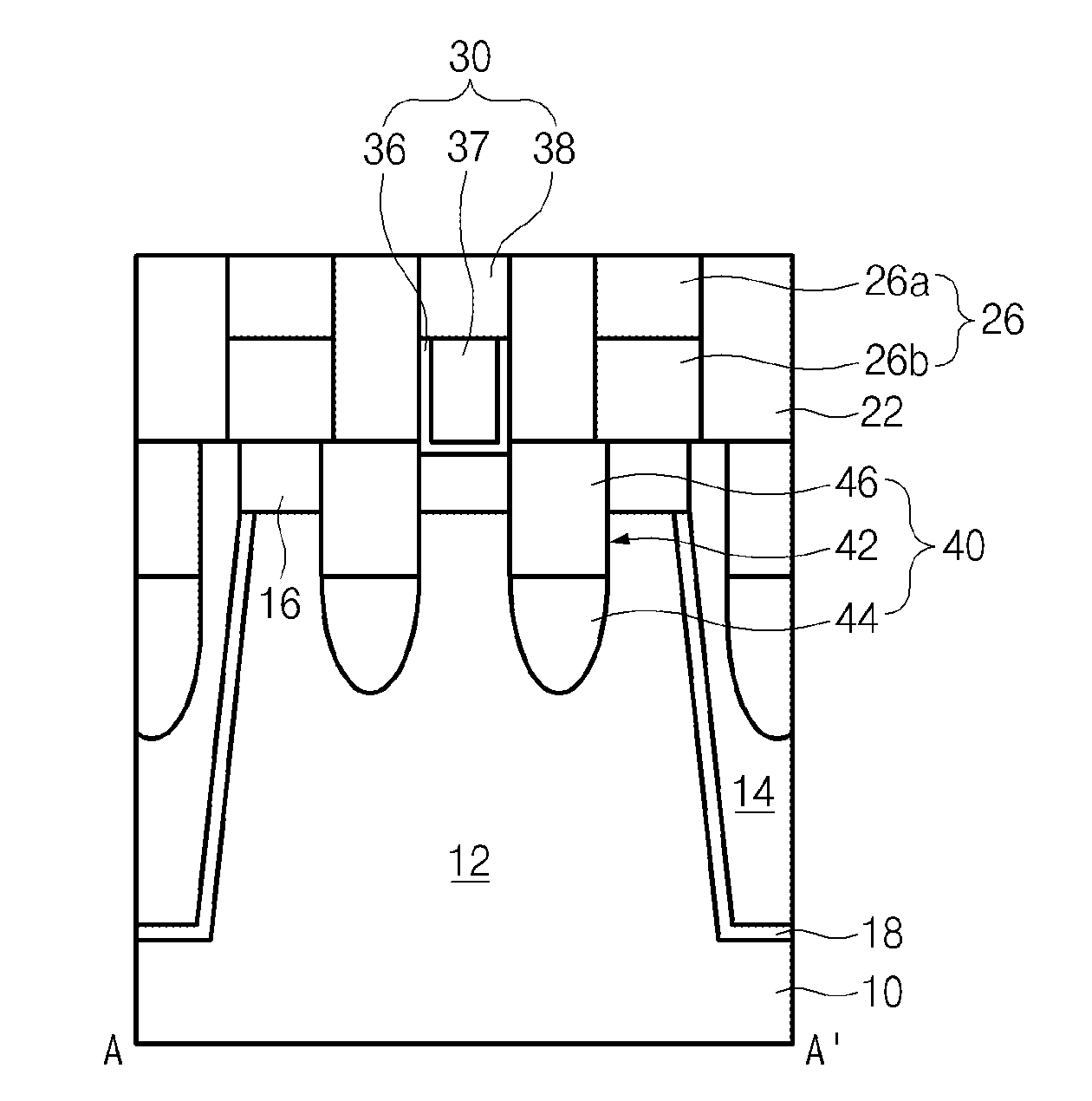
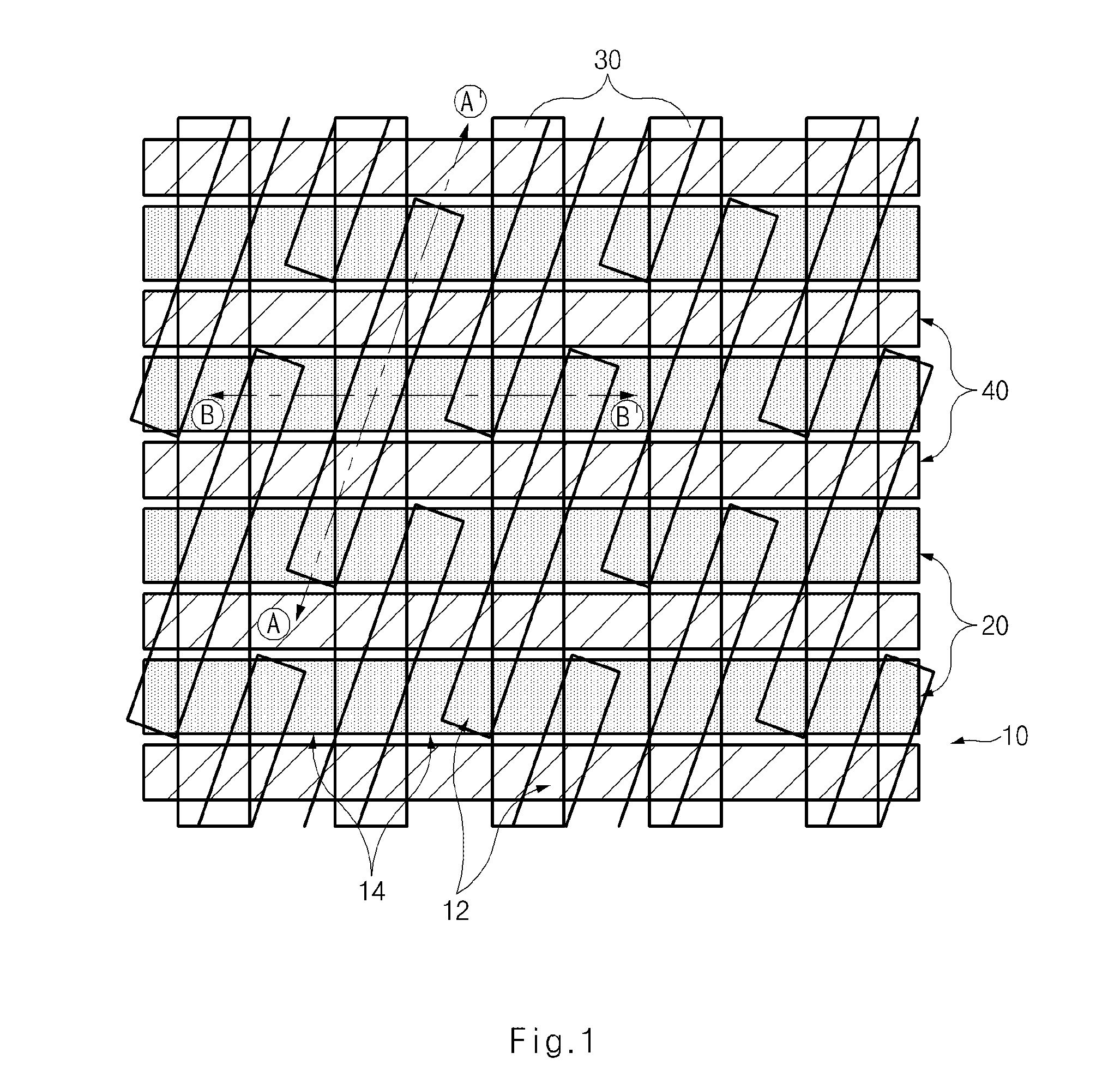
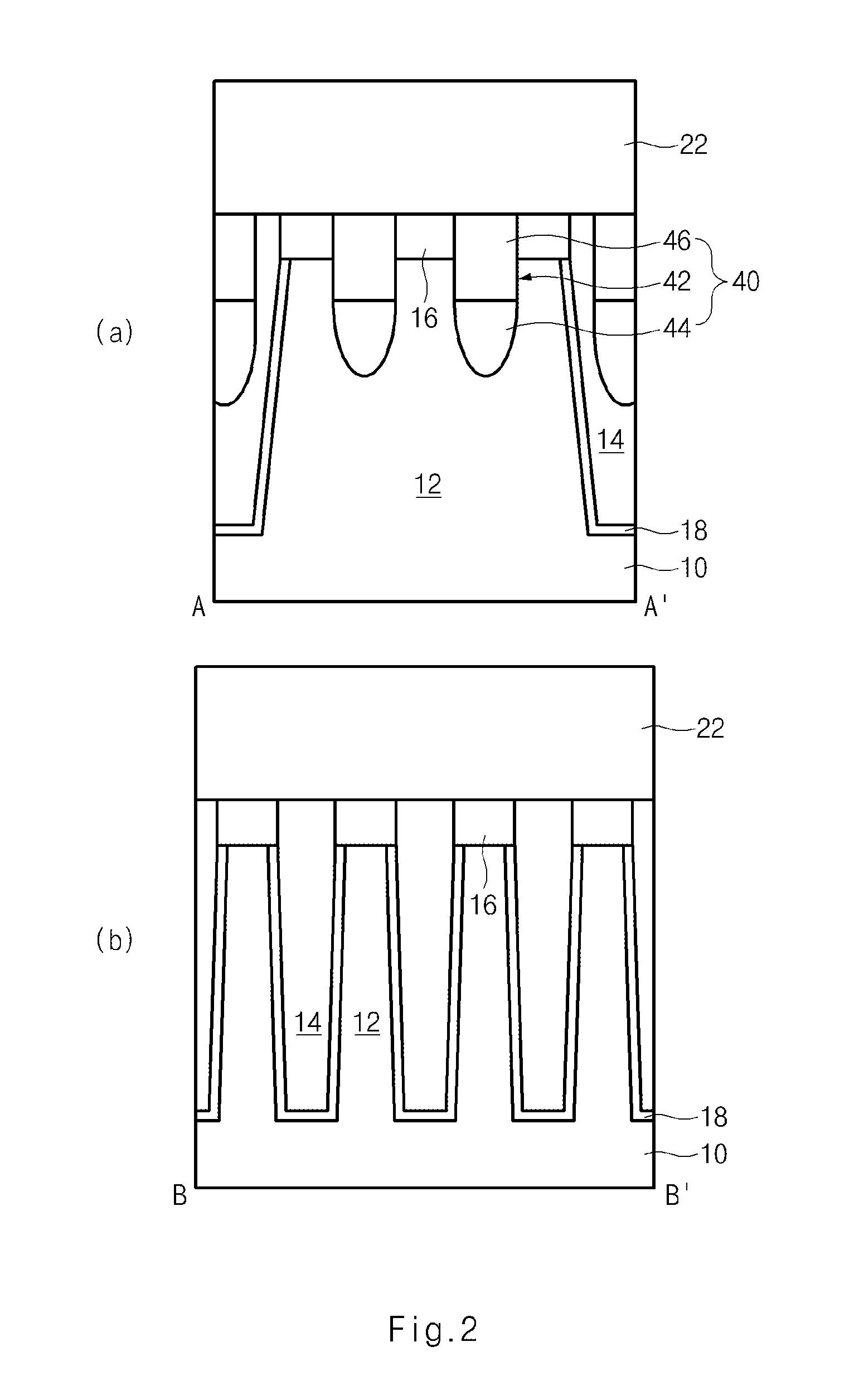
A semiconductor device comprises: a semiconductor substrate including an active region defined as a device isolation film; a bit line hole disposed over the top portion of the semiconductor substrate; an oxide film disposed at sidewalls of the bit line hole; and a bit line conductive layer buried in the bit line hole including the oxide film. A bit line spacer is formed with an oxide film, thereby reducing a parasitic capacitance. A storage node contact is formed to have a line type, thereby securing a patterning margin. A storage node contact plug is formed with polysilicon having a different concentration, thereby reducing leakage current.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Low-power semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS6914803B2Reduce leakage currentReduce power consumptionDigital storageSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
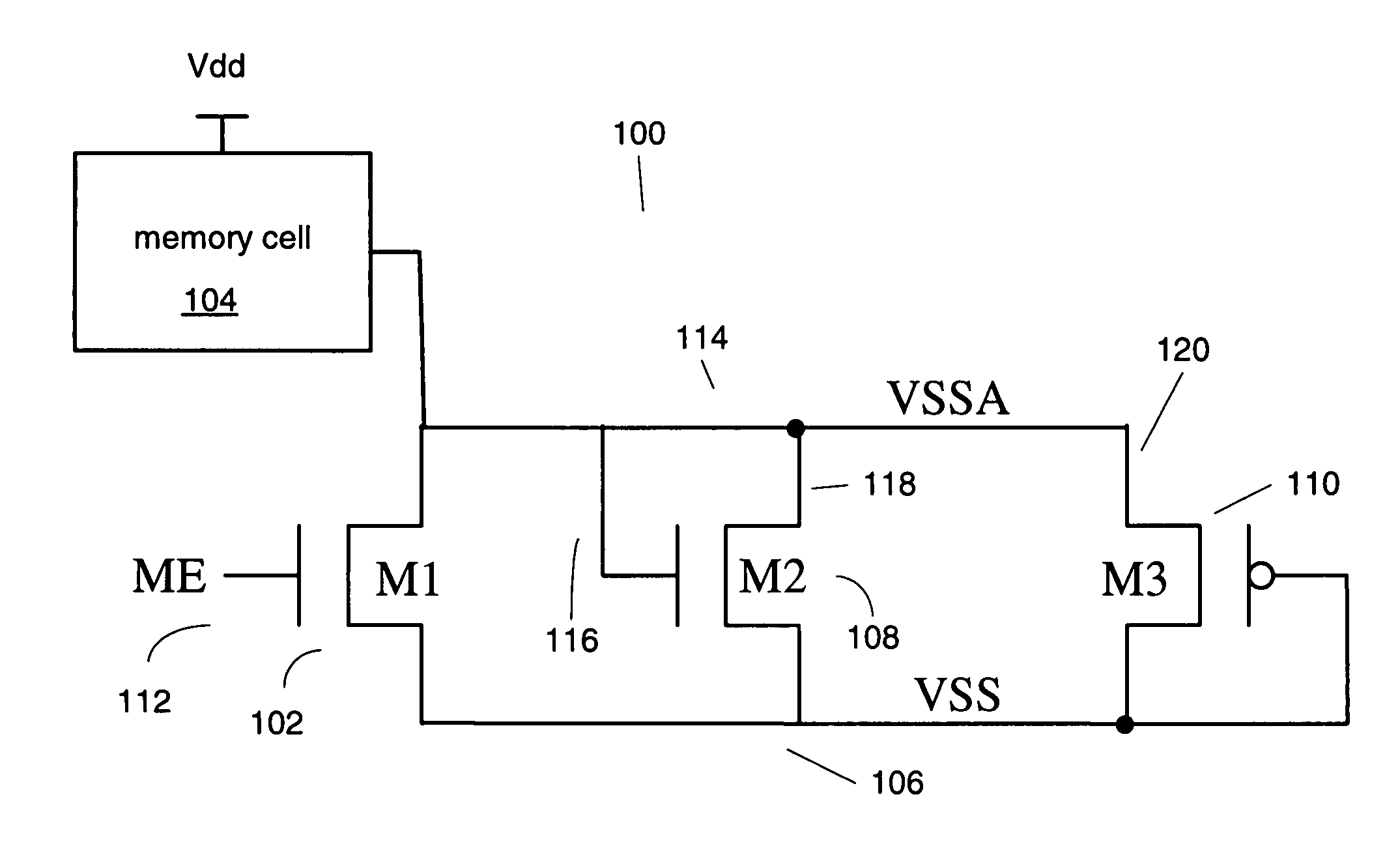
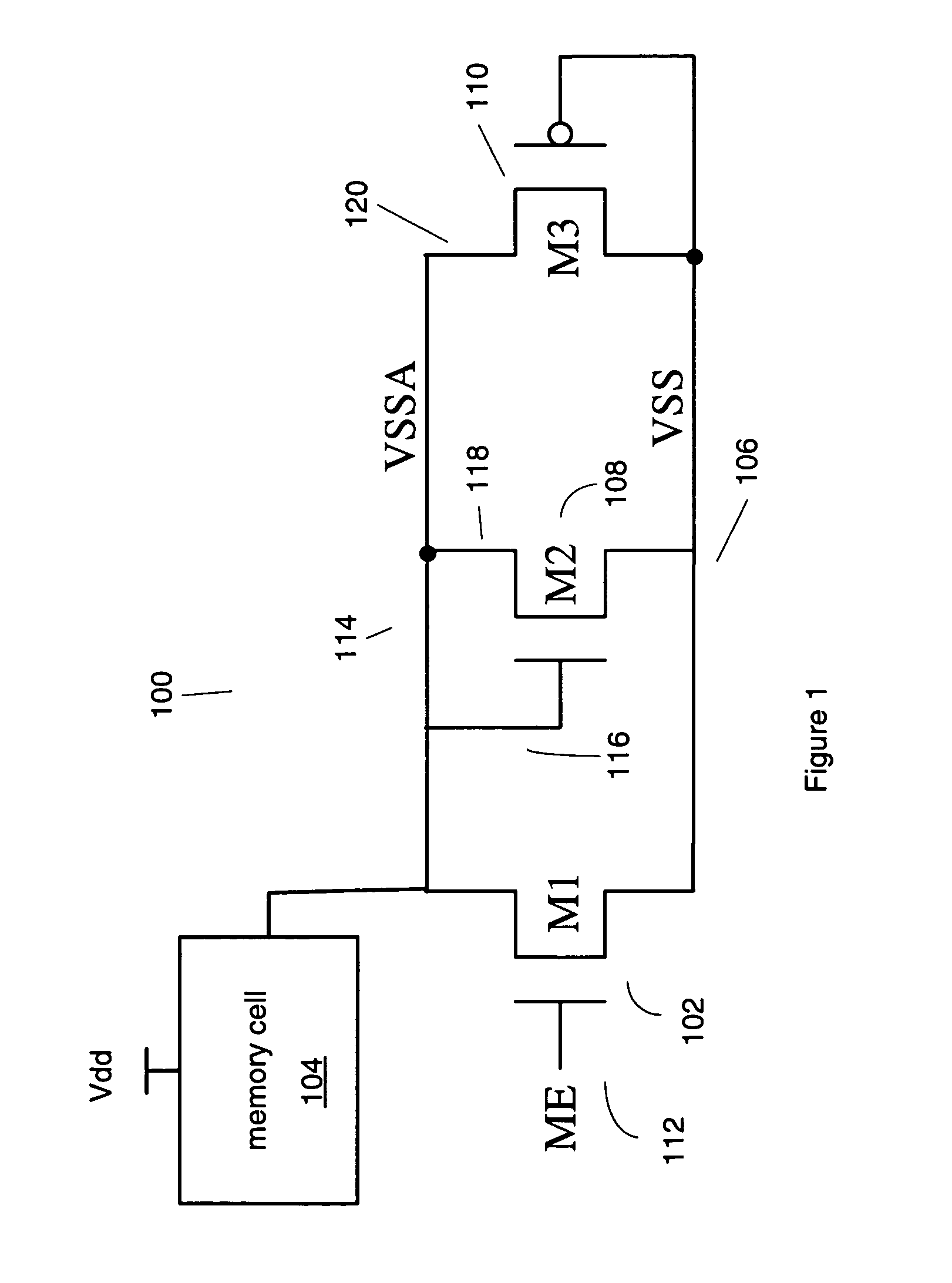
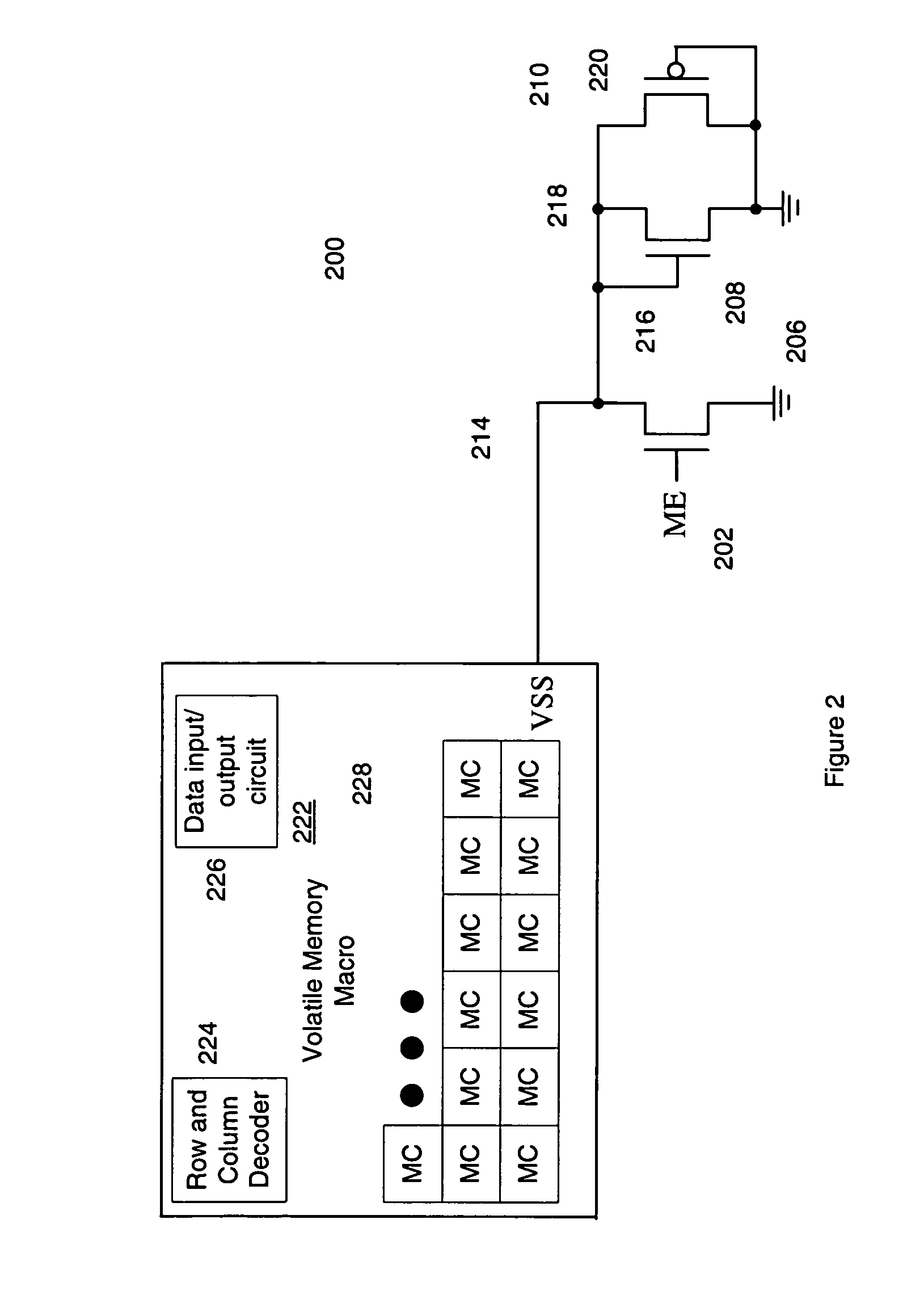
Methods and apparatuses for memory array leakage reduction using internal voltage biasing circuitry
ActiveUS7149142B1Reduce leakage currentReliable maintenanceDigital storageControl powerCurrent limiting
Various methods, apparatuses, and systems are described in which a volatile memory that includes a plurality of volatile memory cells as well as a voltage limiting component and a current limiting component. Power consumption in a standby mode is controlled. The voltage limiting component and the current limiting component couple between the volatile memory cells and the ground voltage potential. One or more rows of memory cells in the memory array are isolated from the ground voltage potential to control power consumption in the standby mode by having the current limiting component stop passing current in the standby mode. A floating ground voltage potential sensed by each memory cell when in the standby mode is controlled by configuring the voltage limiting component to conduct when the floating ground voltage potential is larger than a threshold voltage of the voltage limiting component in order to reduce leakage current but reliably maintain the stored contents of the volatile memory cell. The floating ground voltage potential is internally raised higher than a voltage biasing the bulk of the transistors in the volatile memory cells by coupling the floating ground voltage potential to the voltage limiting component.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com