Patents
Literature
64results about "Frequency demodulator arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
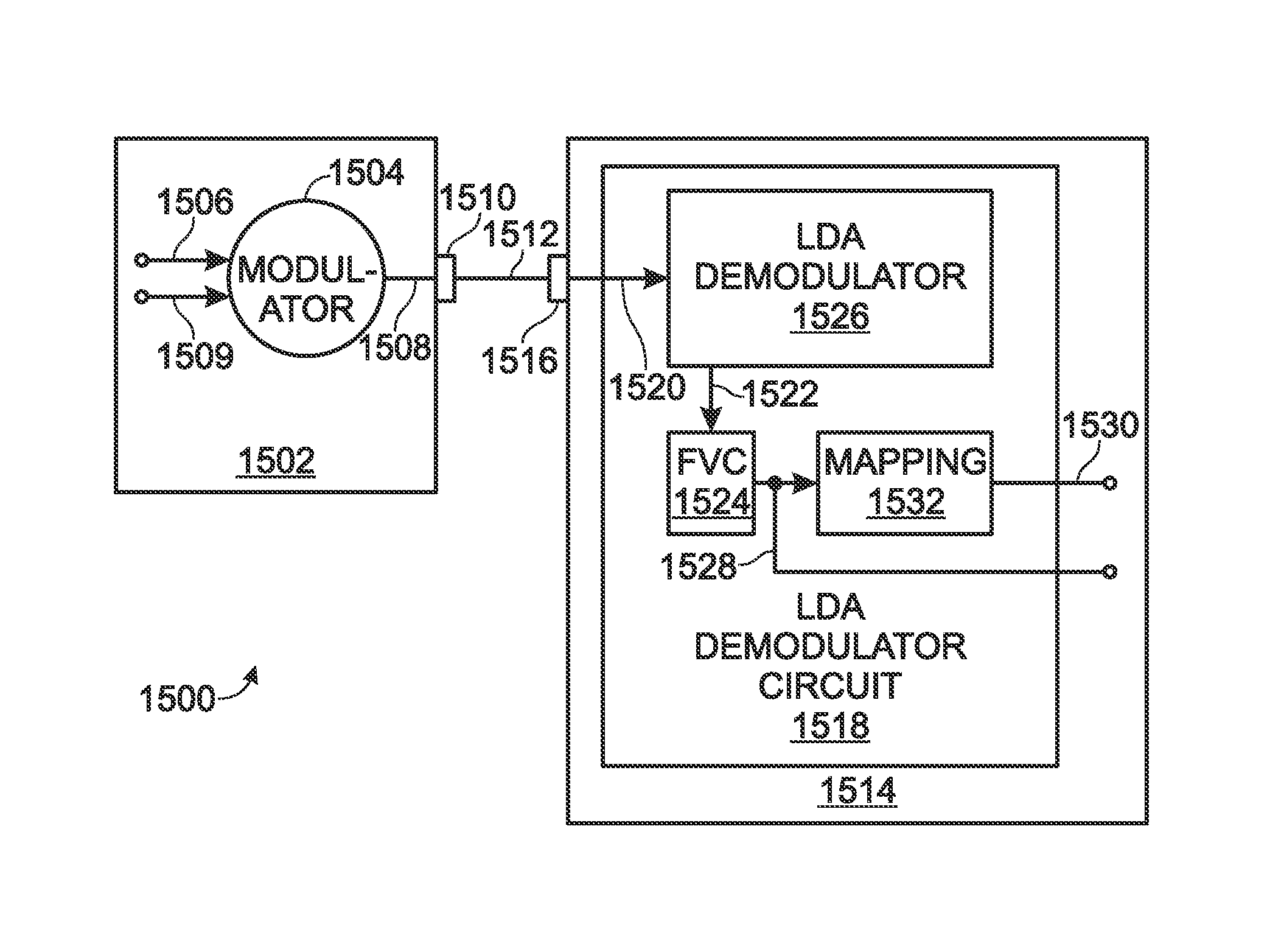
Low-Power, Noise Insensitive Communication Channel using Logarithmic Detector Amplifier (LDA) Demodulator
ActiveUS20140269972A1Reduce generationMinimize power consumptionFrequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsEngineeringFrequency modulation
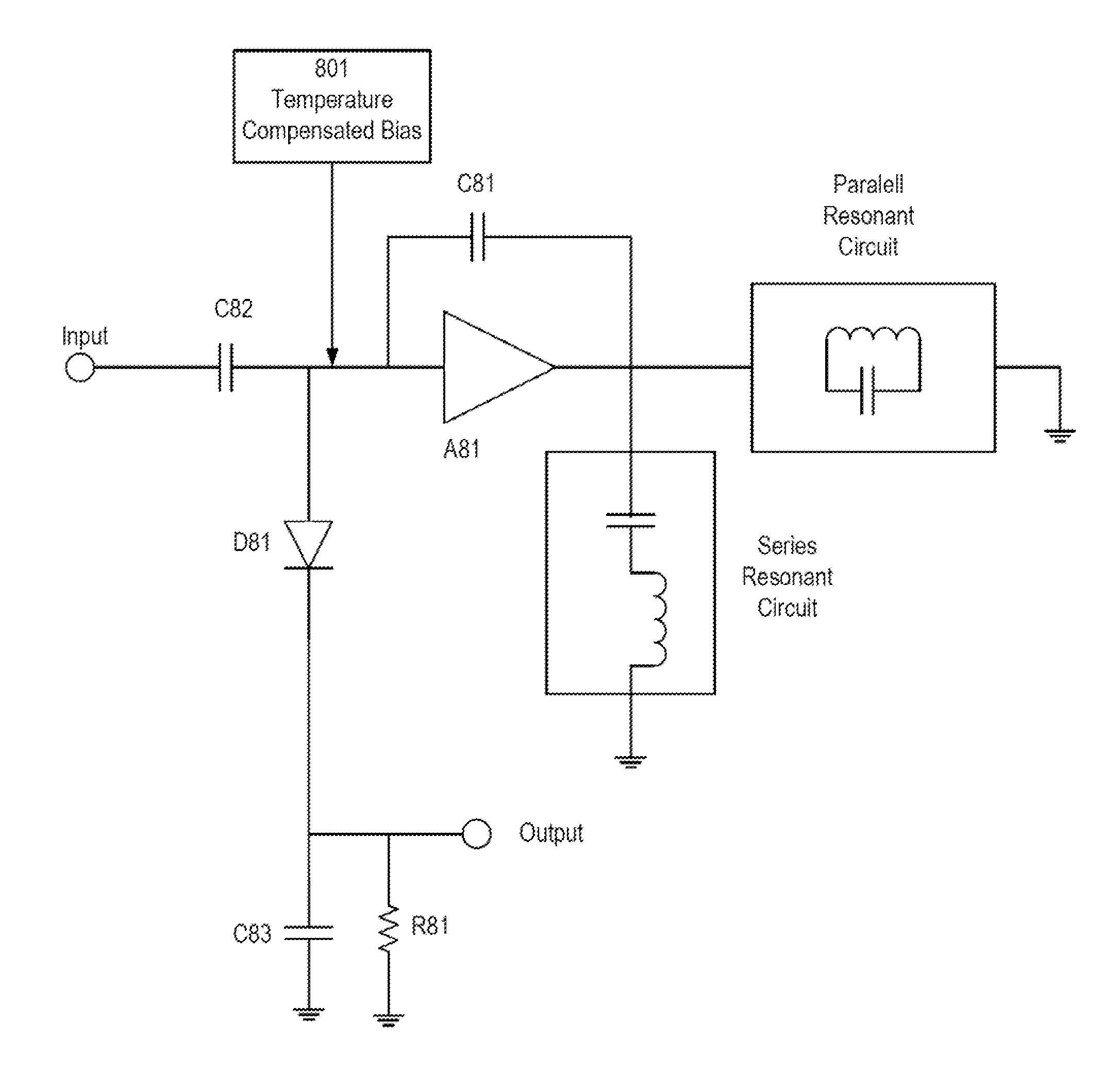
A method is provided for communicating signals at a low power level in an electromagnetic interference (EMI) environment. A first device transmits a modulated signal having a first carrier frequency, including the encoded information via a hardwire transmission medium. In one aspect, the power level of the modulated signal can be adjusted to minimize power consumption or reduce the generation of EMI. The modulated signal may be in one of the following formats: frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) to name a few examples. A second device including a logarithmic detector amplifier (LDA) demodulator circuit receives the signal, which may be mixed with EMI. The LDA demodulator circuit amplifies the modulated signal, without amplifying the EMI, to supply a demodulated baseband signal, which may be an n-ary digital signal, or an audio signal. A low-power, noise insensitive communication channel is also provided.
Owner:DOCKON
Signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
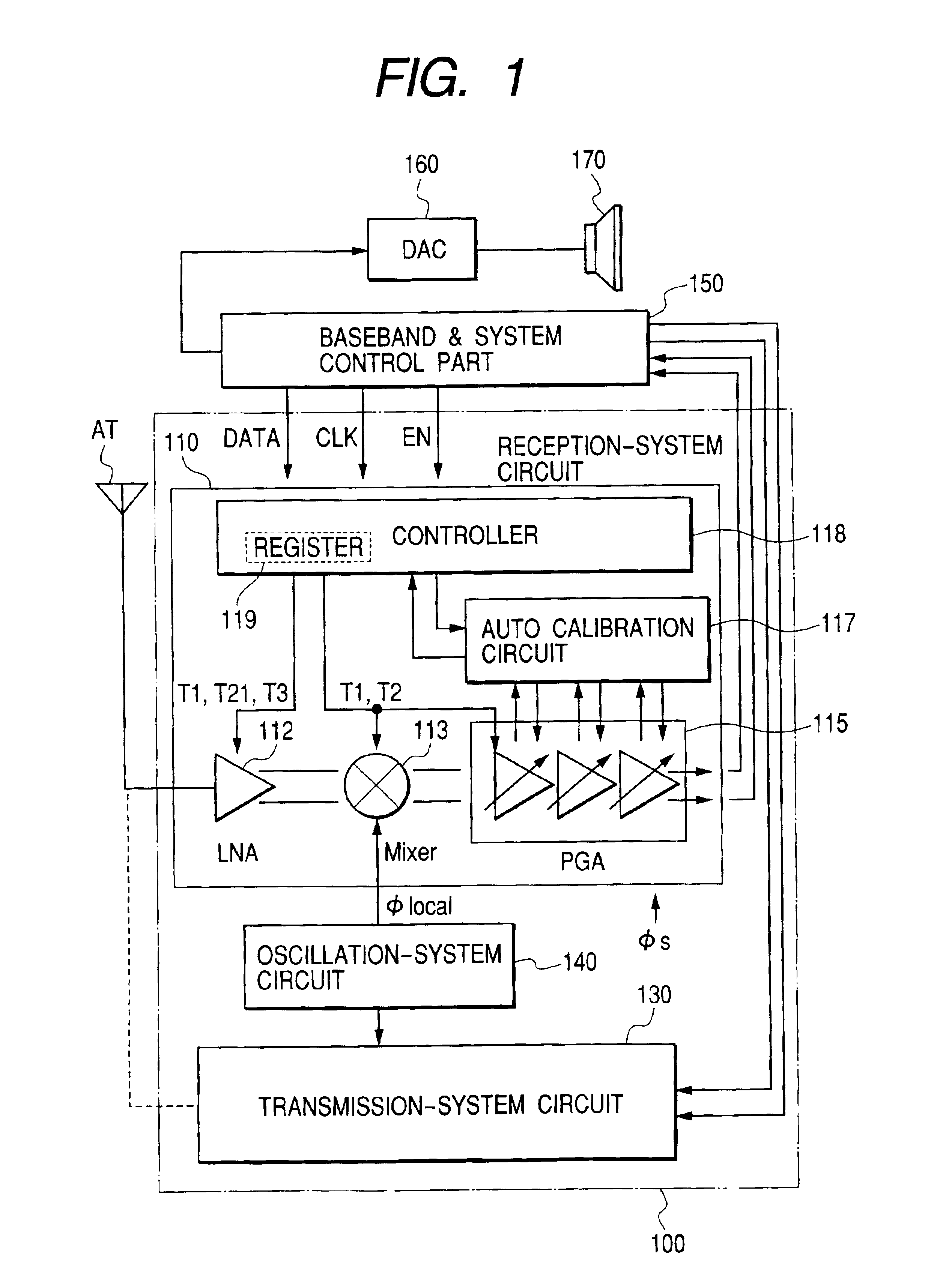
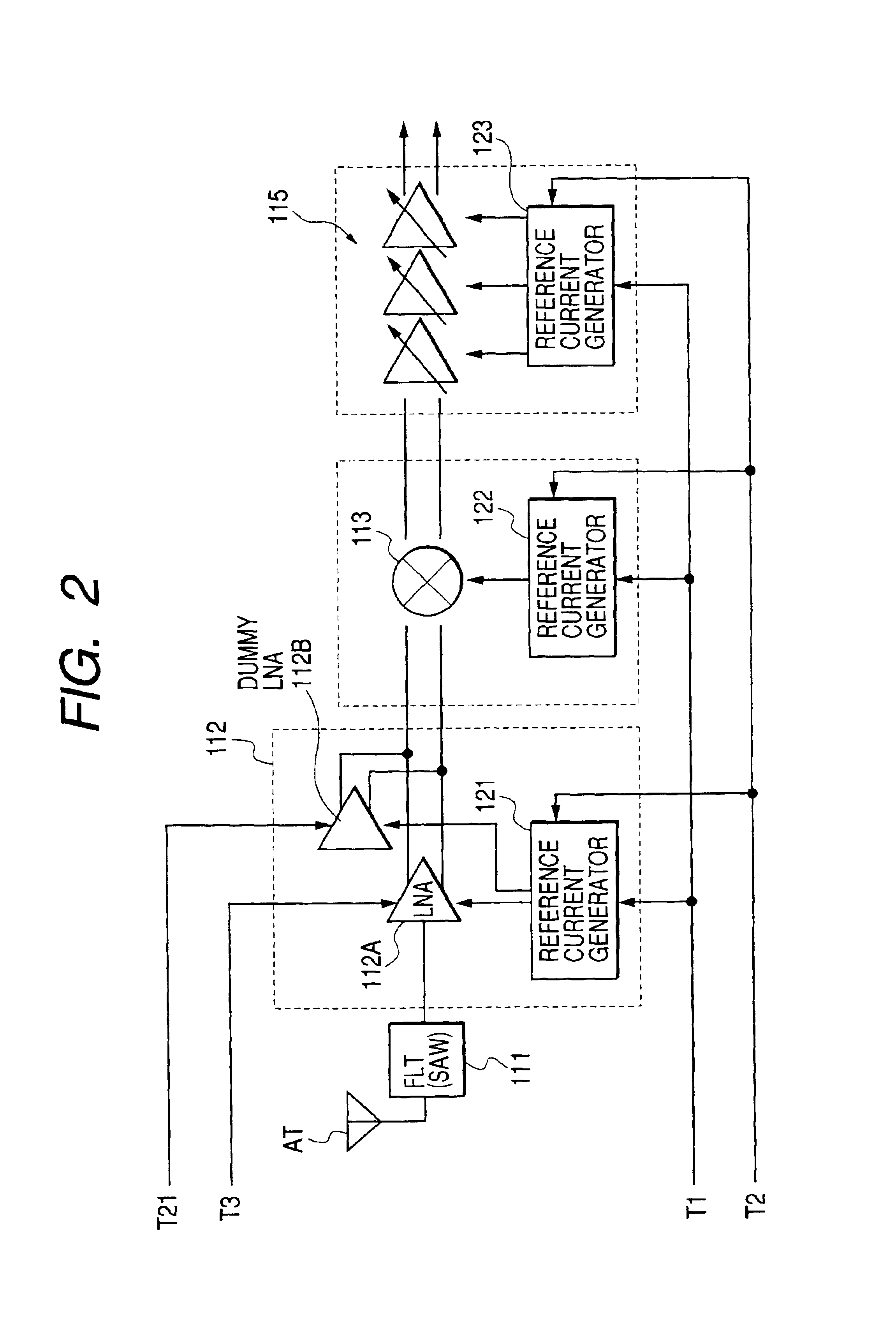
InactiveUS7085587B2Reduce the number of partsHigh bulk densityResonant long antennasFrequency demodulator arrangementsCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
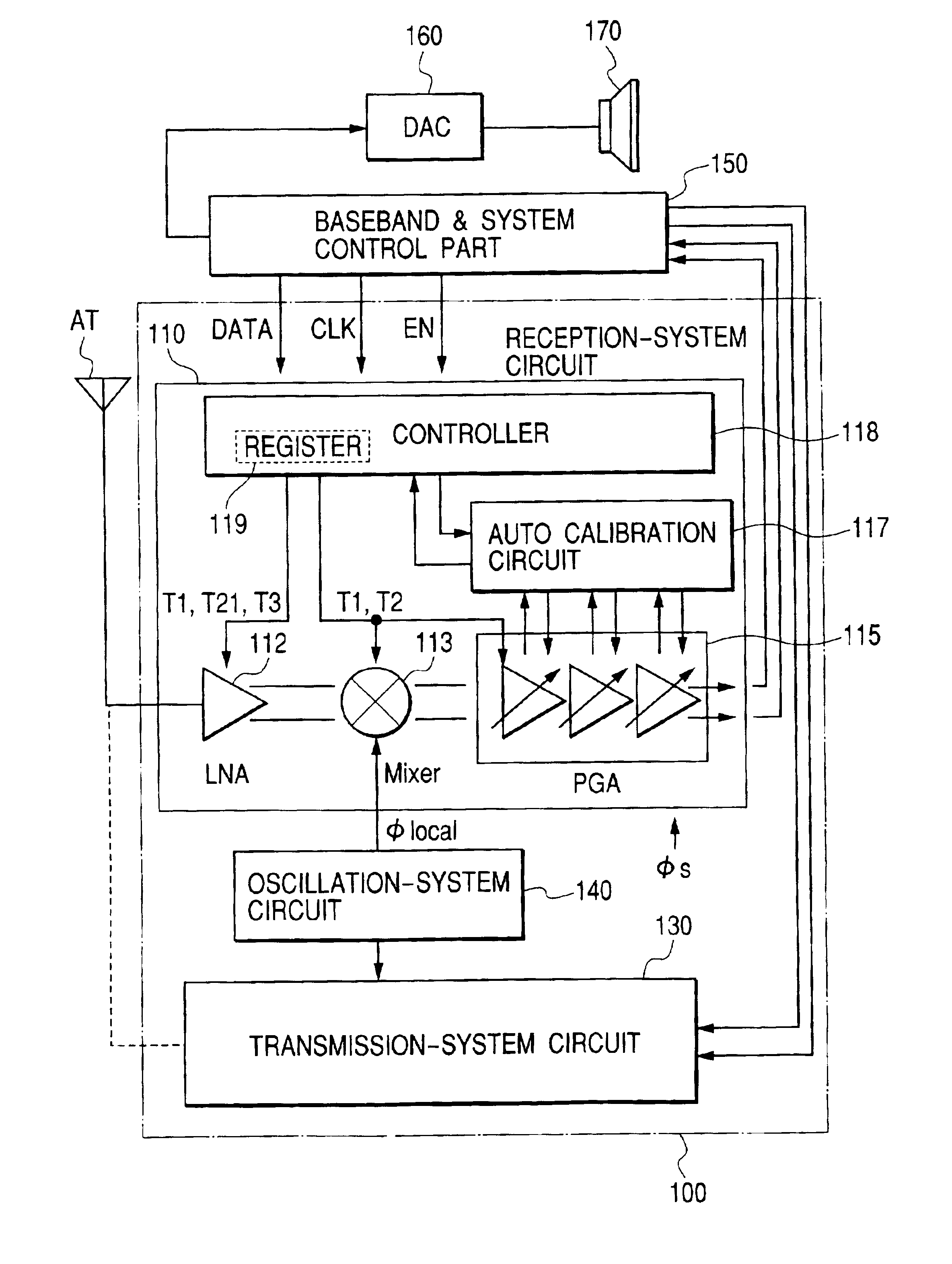
Disclosed herein is a direct conversion type signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit device capable of suppressing a DC voltage variation in the output of a variable gain amplifier upon the transition to a reception mode, reproducing stable receiving characteristics and improving receiving sensitivity. In the signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit device, voltage reference circuits for generating reference voltages for controlling or restricting currents for current sources for supplying operating currents for amplifiers constituting a reception-system circuit are boosted upon the transition from an idle mode or the like to the reception mode to allow the currents to flow into the constant-current sources of the amplifiers after the stabilization of the generated reference voltages.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Near field RF communicators and near field RF communications-enabled devices
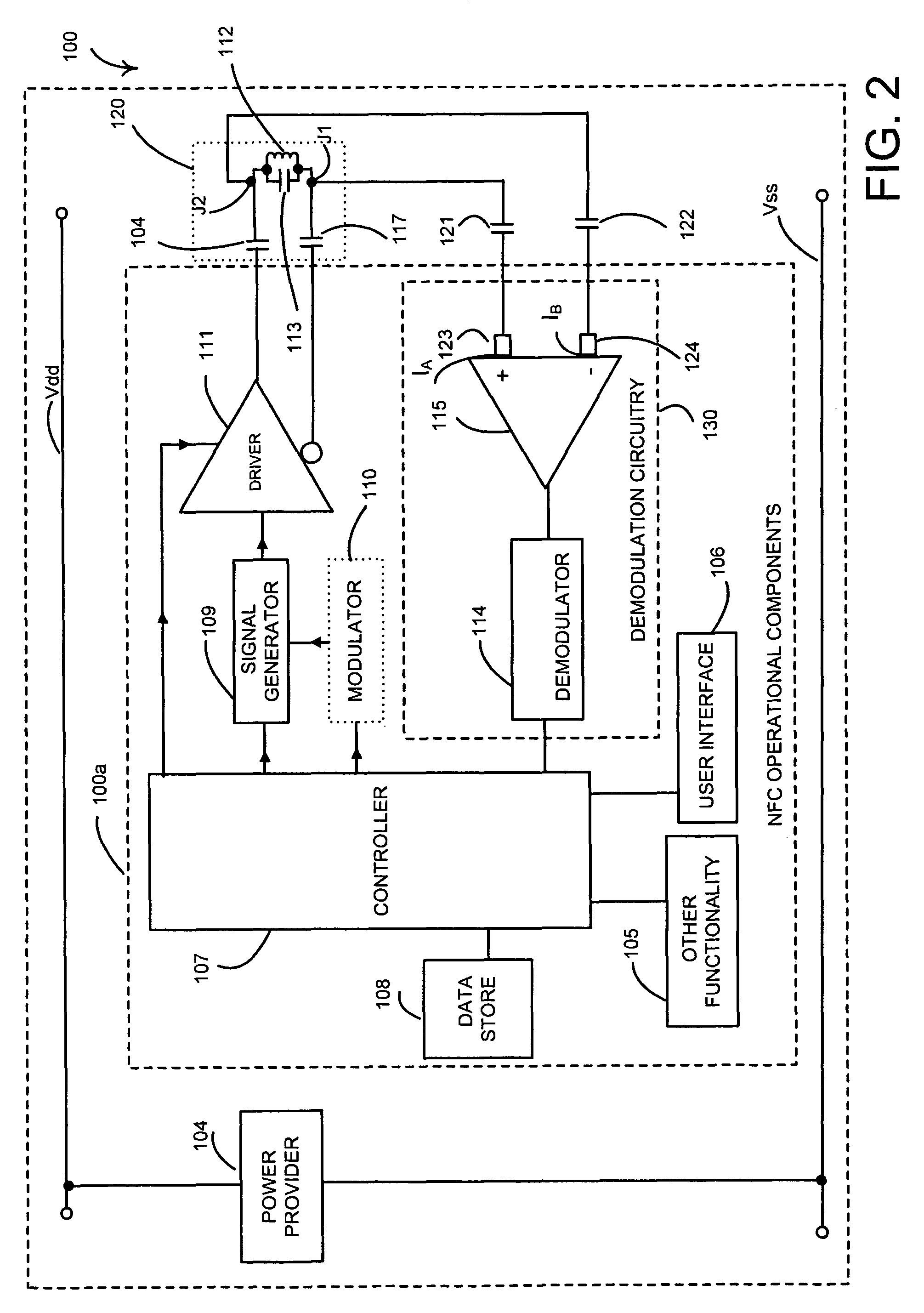
ActiveUS8565675B2Less noise sensitiveMinimisationFrequency demodulator arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
A near field RF communicator has an antenna circuit (120) to receive a modulated radio frequency signal by inductive coupling and demodulation circuitry (130 or 131) to extract the modulation from a received modulated radio frequency signal inductively coupled to the antenna circuit. The demodulation circuitry has a virtual earth input comprising a current mirror. The demodulation circuitry may be formed by an amplifier (115 or 116) and a demodulator (114) coupled to an output of the amplifier. The amplifier may be a single input amplifier (116) coupled to an output of the antenna circuit or may be a differential amplifier (115) having first and second inputs to receive the modulated radio frequency signal from first and second outputs of the antenna circuit, with each amplifier input providing a virtual earth input.
Owner:NXP USA INC
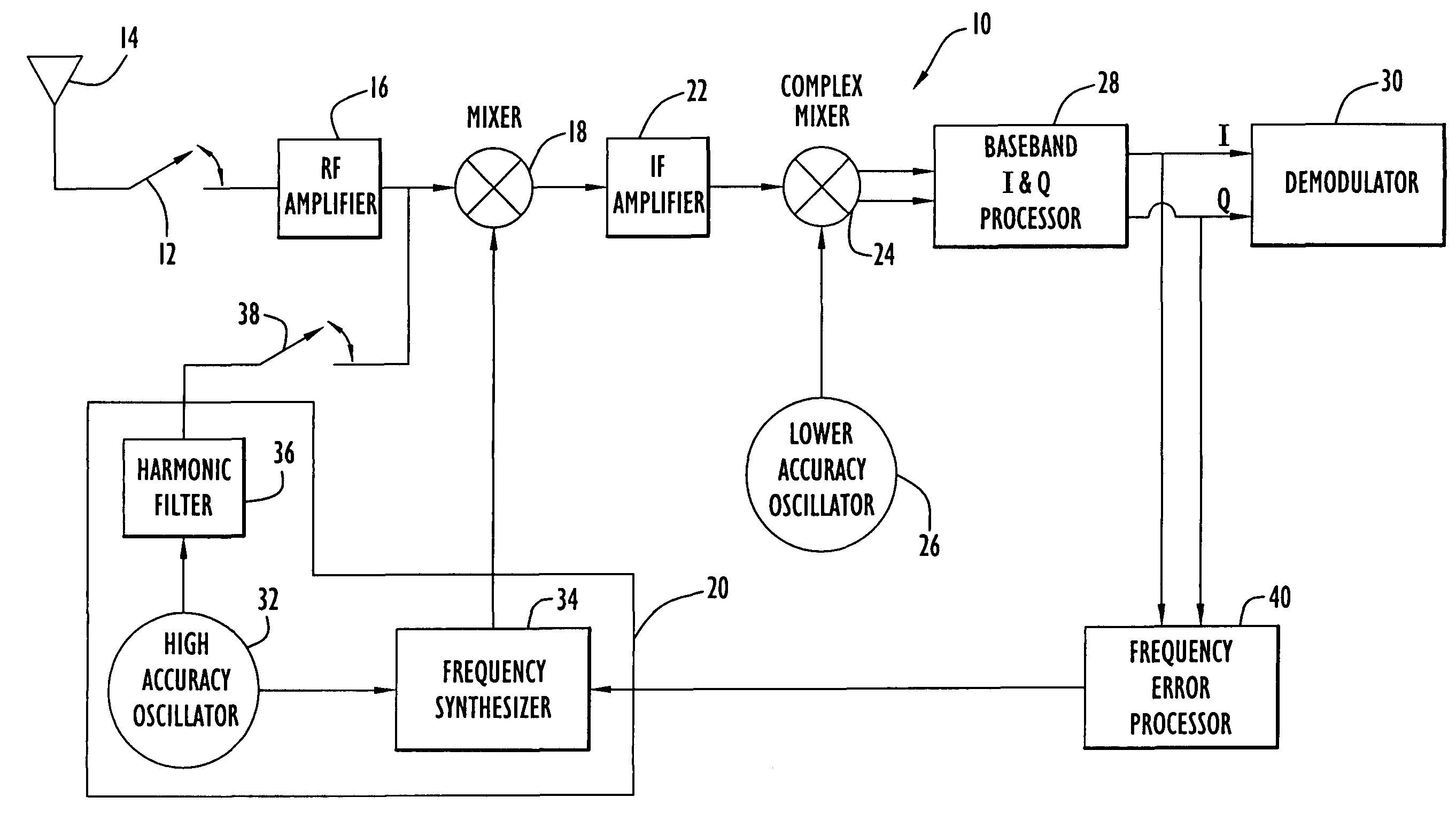
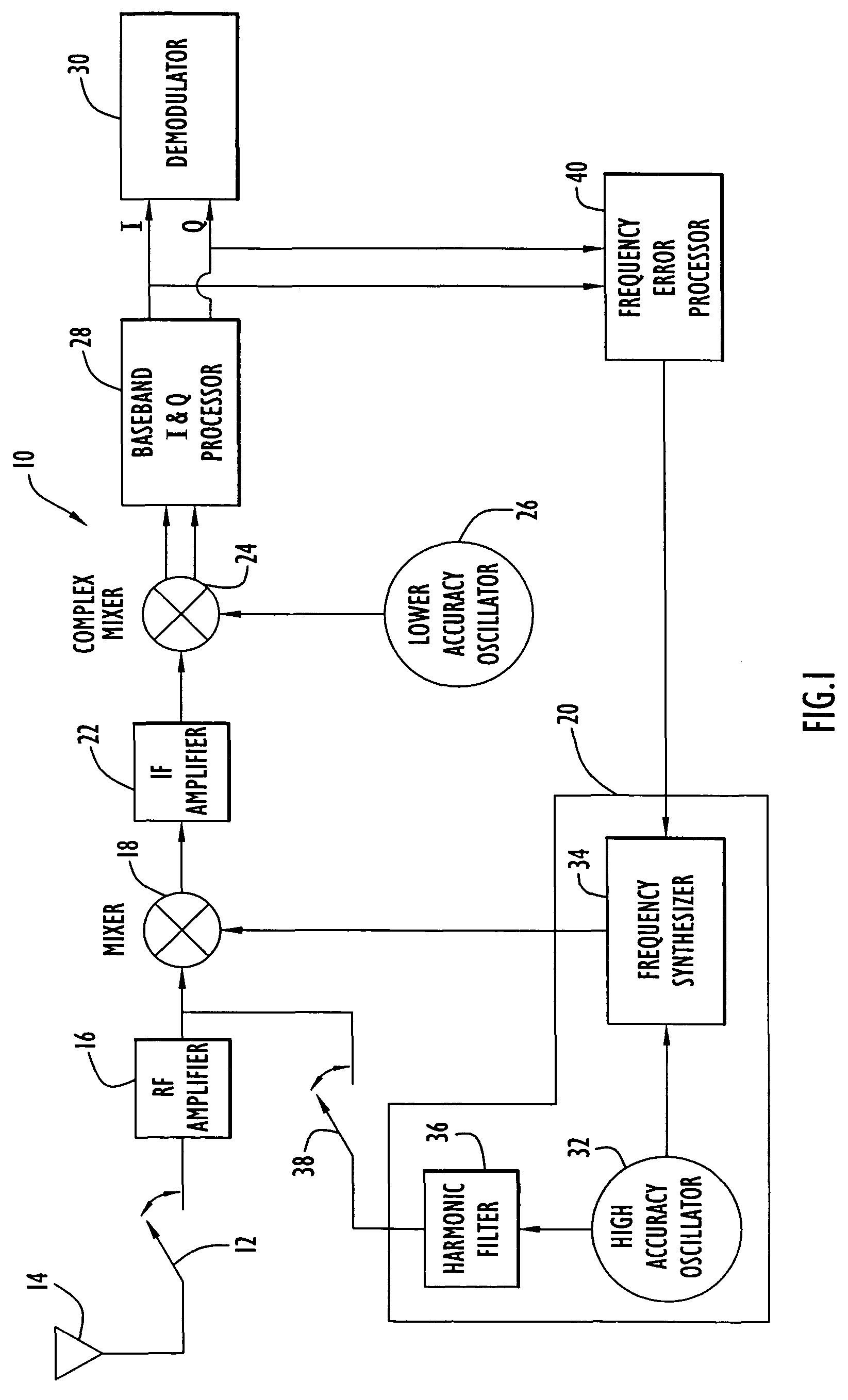
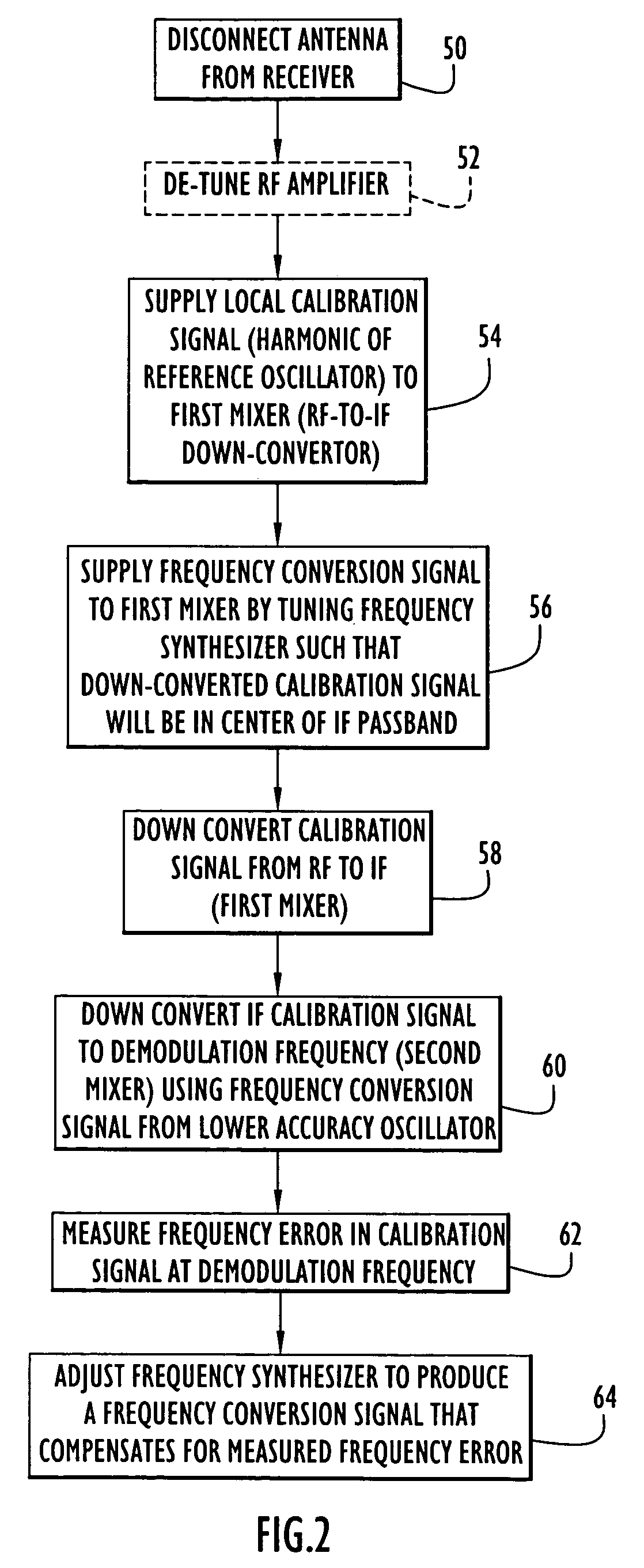
Methods and apparatus for calibrating oscillators in a receiver
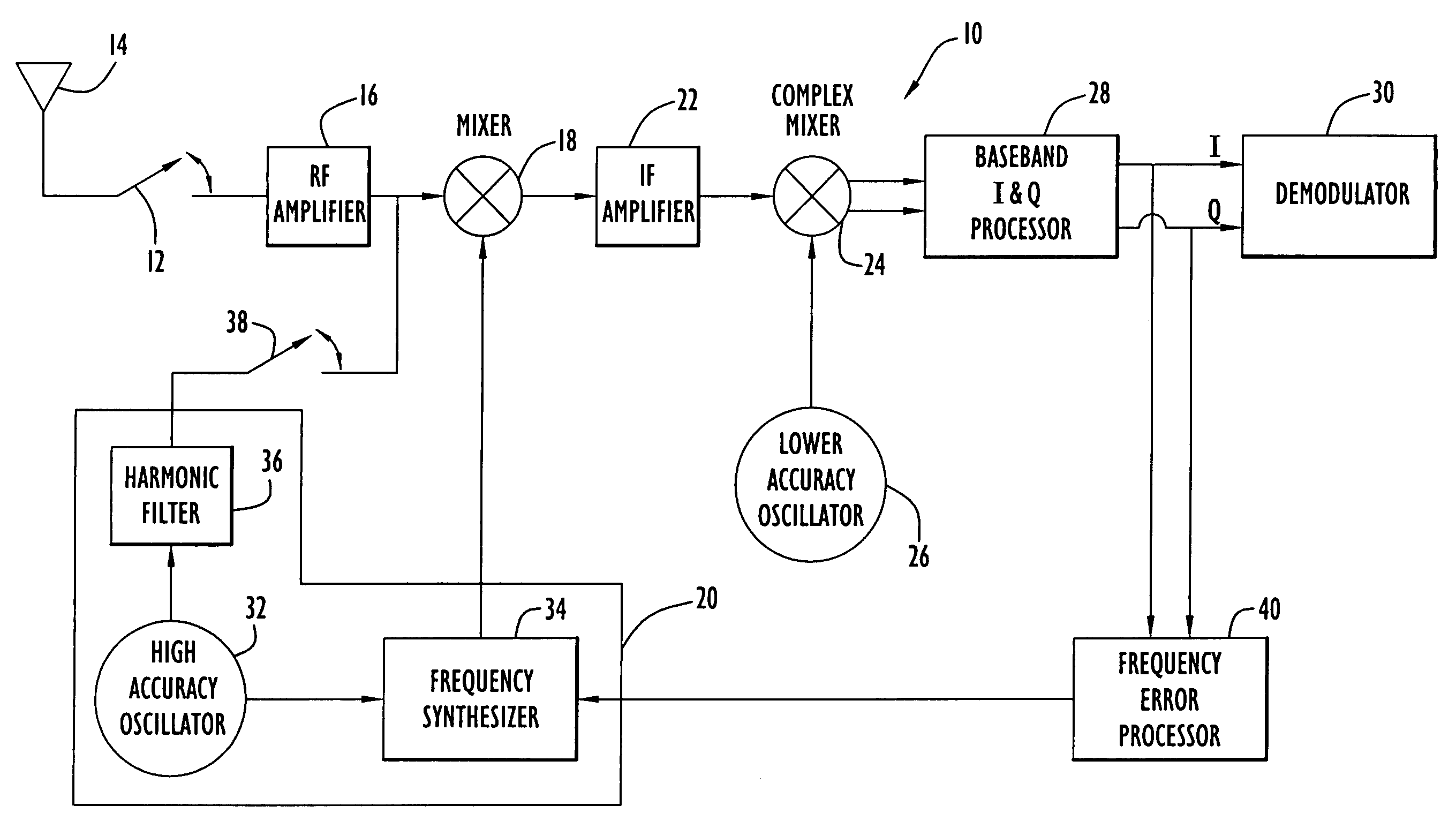
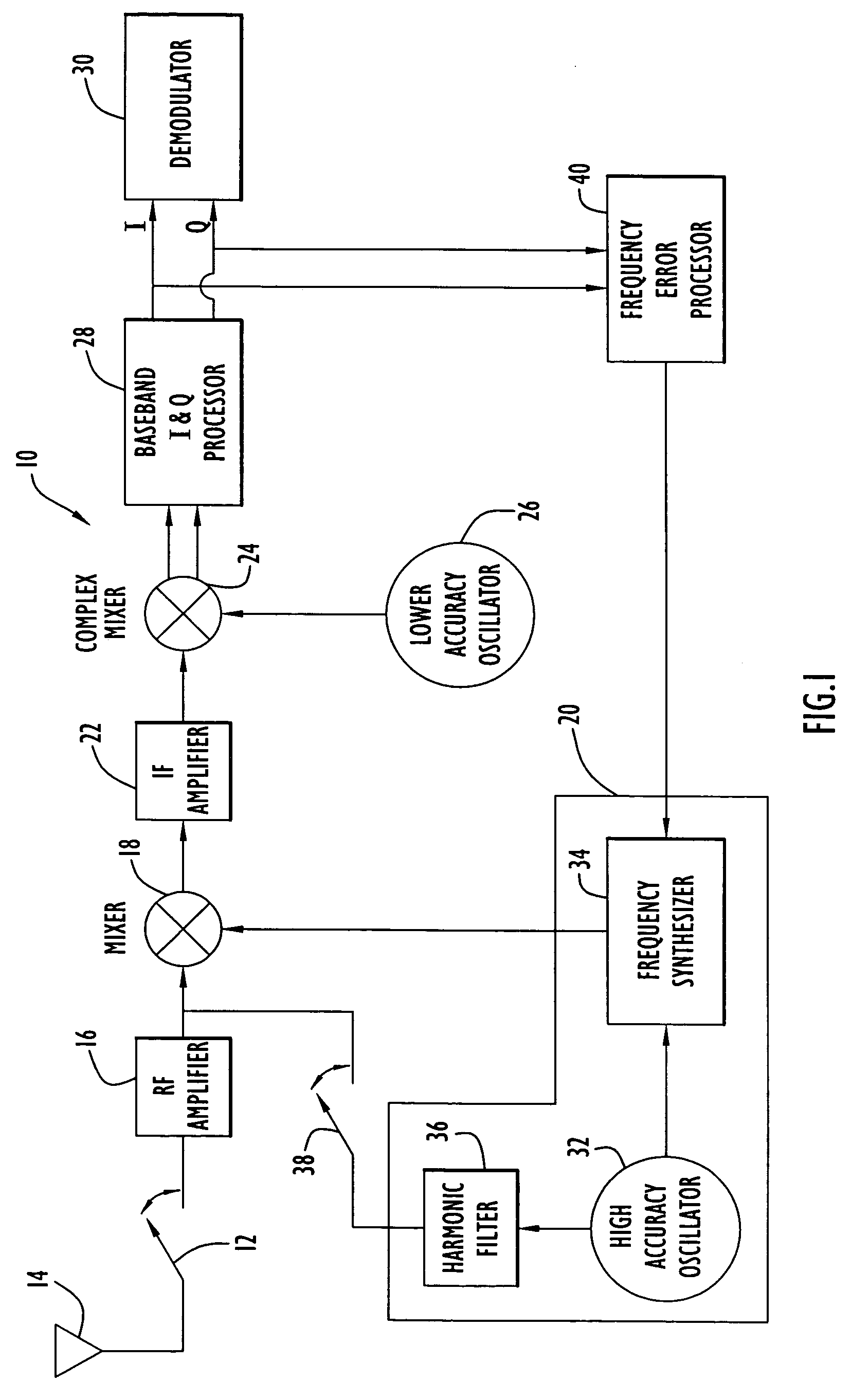
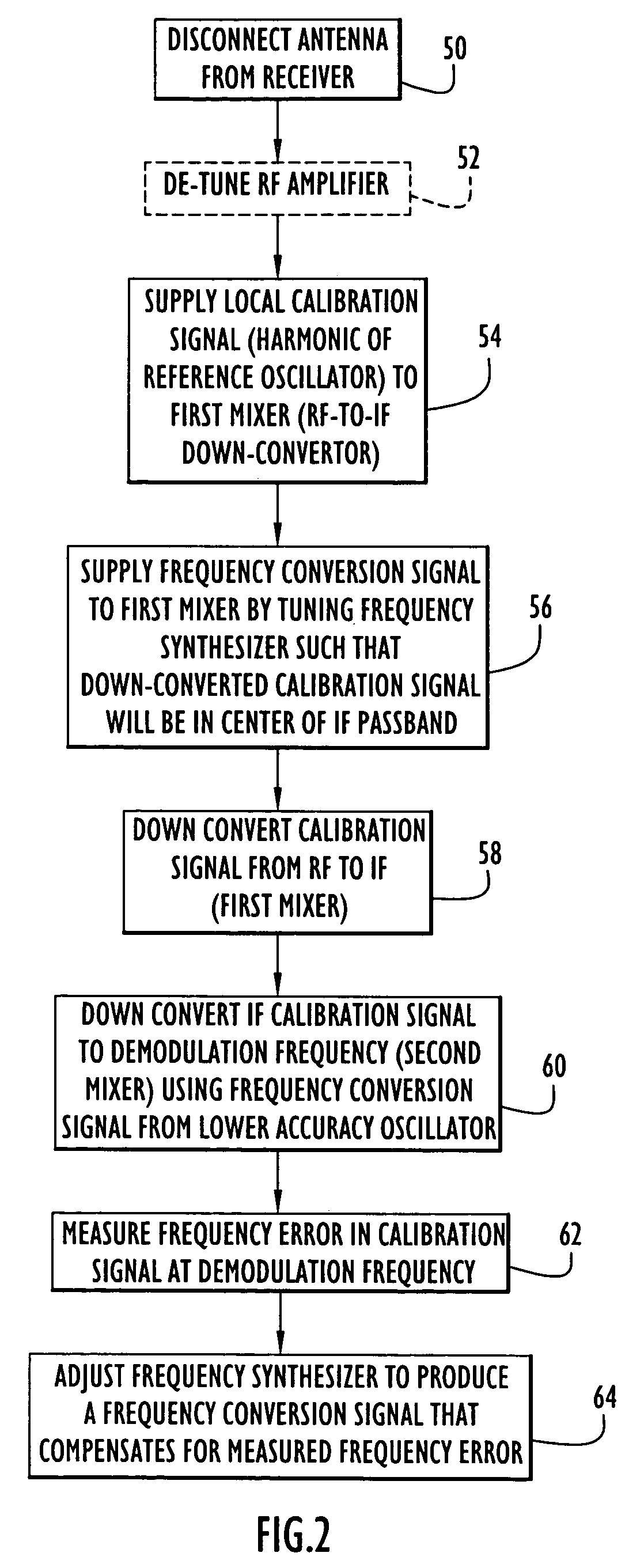
ActiveUS20060121864A1Frequency errorCarrier regulationRadio transmissionFrequency conversionEngineering
A receiver includes a first oscillator supplying a reference frequency signal; a reference signal generator producing a first frequency conversion signal and a local calibration signal from the reference frequency signal; a first frequency converter responsive to the first frequency conversion signal to down-convert the received signal during normal receive operation and to down-convert the local calibration signal during calibration processing; a second frequency converter responsive to a second frequency conversion signal from a second oscillator to further down-convert the received signal and the local calibration signal; a demodulator that demodulates the received signal at a demodulation frequency; and a frequency error processor that determines a frequency error from the local calibration signal at the demodulation frequency, wherein the reference signal generator adjusts a frequency of the first frequency conversion signal used during normal receive operation in response to the frequency error to compensate for the frequency error.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
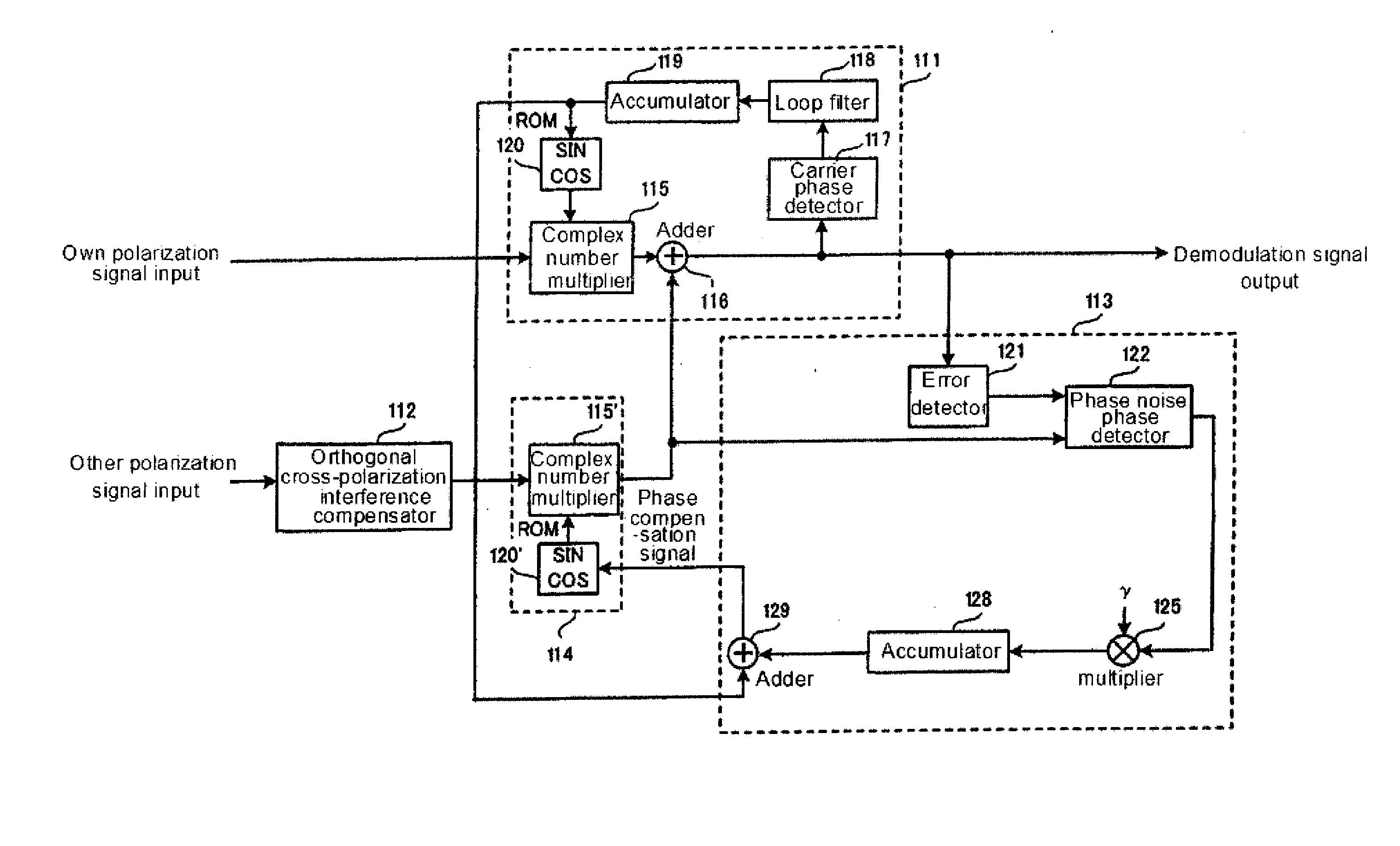
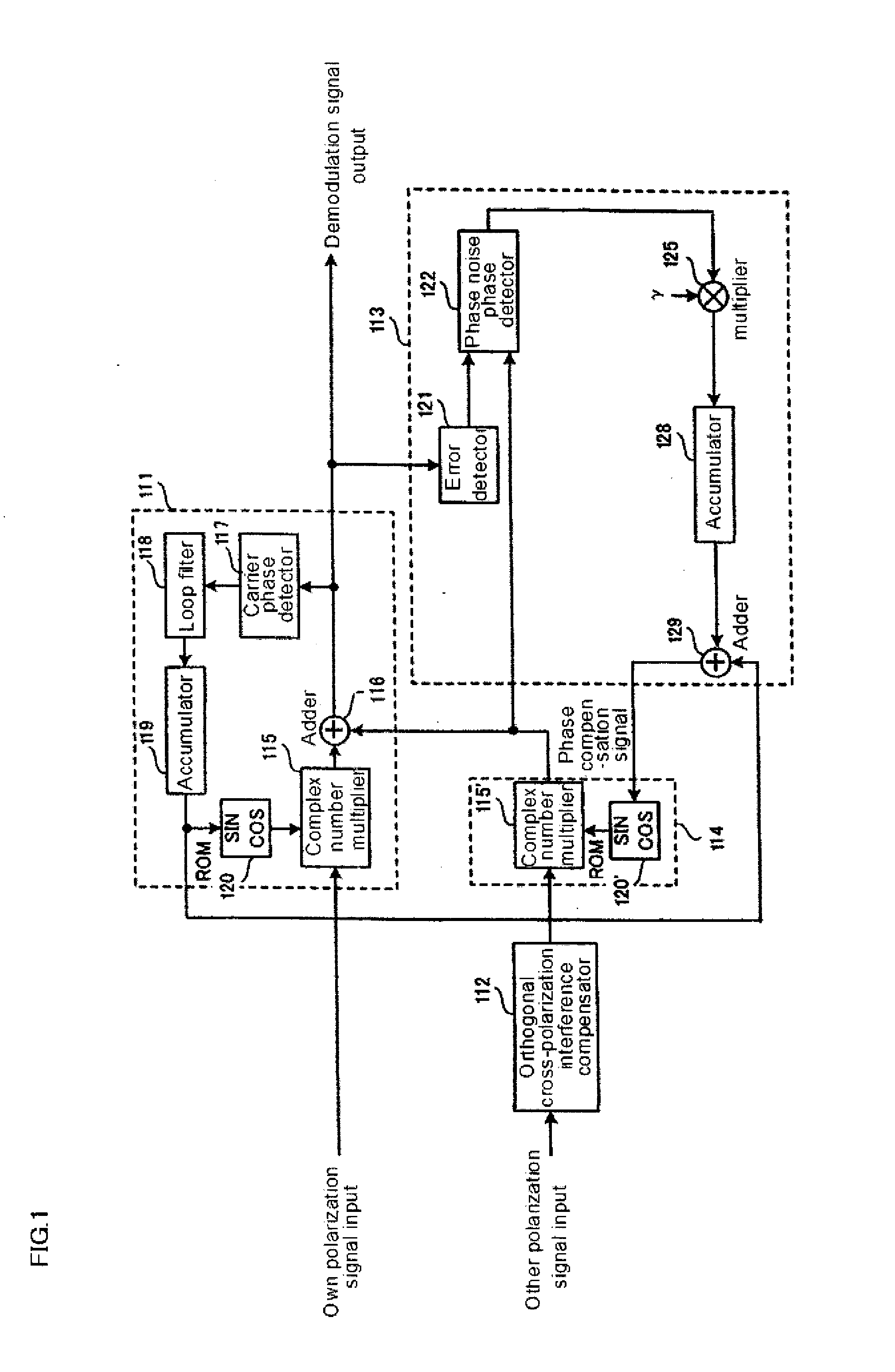
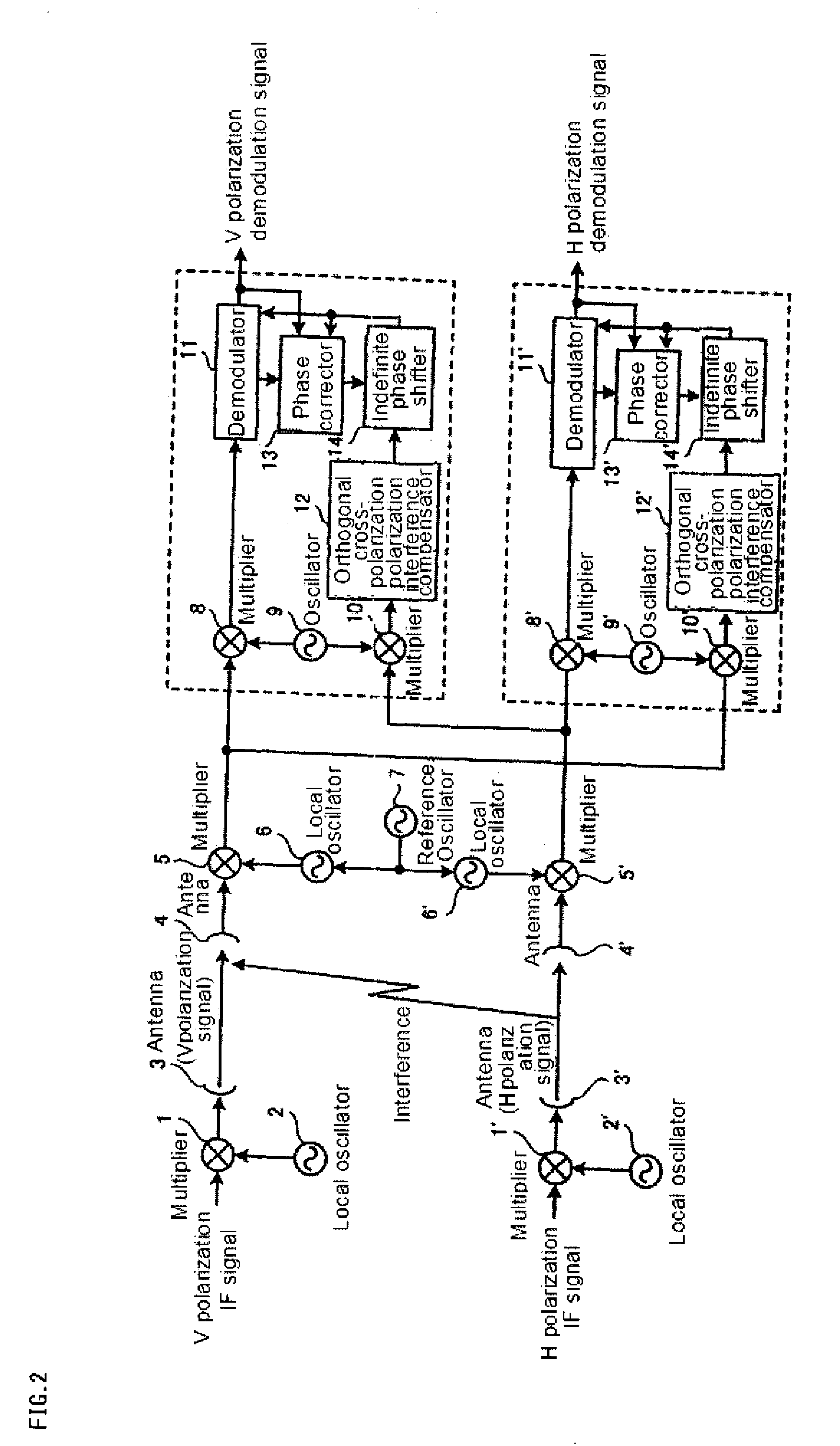
Orthogonal cross polarization interference compensating device, demodulator, receiving station, and method of compensating cross-polarization interference
ActiveUS20100136916A1Frequency demodulator arrangementsModulation transferencePhase detectorPhase noise
An orthogonal cross-polarization interference compensating device for solving the problem tin which integration contents of an integration circuit are indefinite when a control loop is cut. An orthogonal cross-polarization interference compensator generates a compensation signal for compensating phase noise included in an own polarization signal. A demodulator compensates for orthogonal cross-polarization interference based on the compensation signal for the phase noise included in the own polarization signal. An error detector generates an error signal indicating phase difference between the own polarization signal compensated by the demodulator and a proper own polarization signal. A phase noise phase detector generates a differential signal indicating phase difference between the own polarization signal and other polarization signals based on the compensation signal and the error signal. An integration circuit integrates the differential signal and generates an integration signal. An infinite phase-shifter adjusts the compensation signal based on the integration signal. A control circuit determines whether or not orthogonal cross-polarization interference is present based on the compensation signal adjusted by the infinite phase-shifter, and adjusts the integration value indicated by the integration signal to be a predetermined value when there is no orthogonal cross-polarization interference.
Owner:NEC CORP
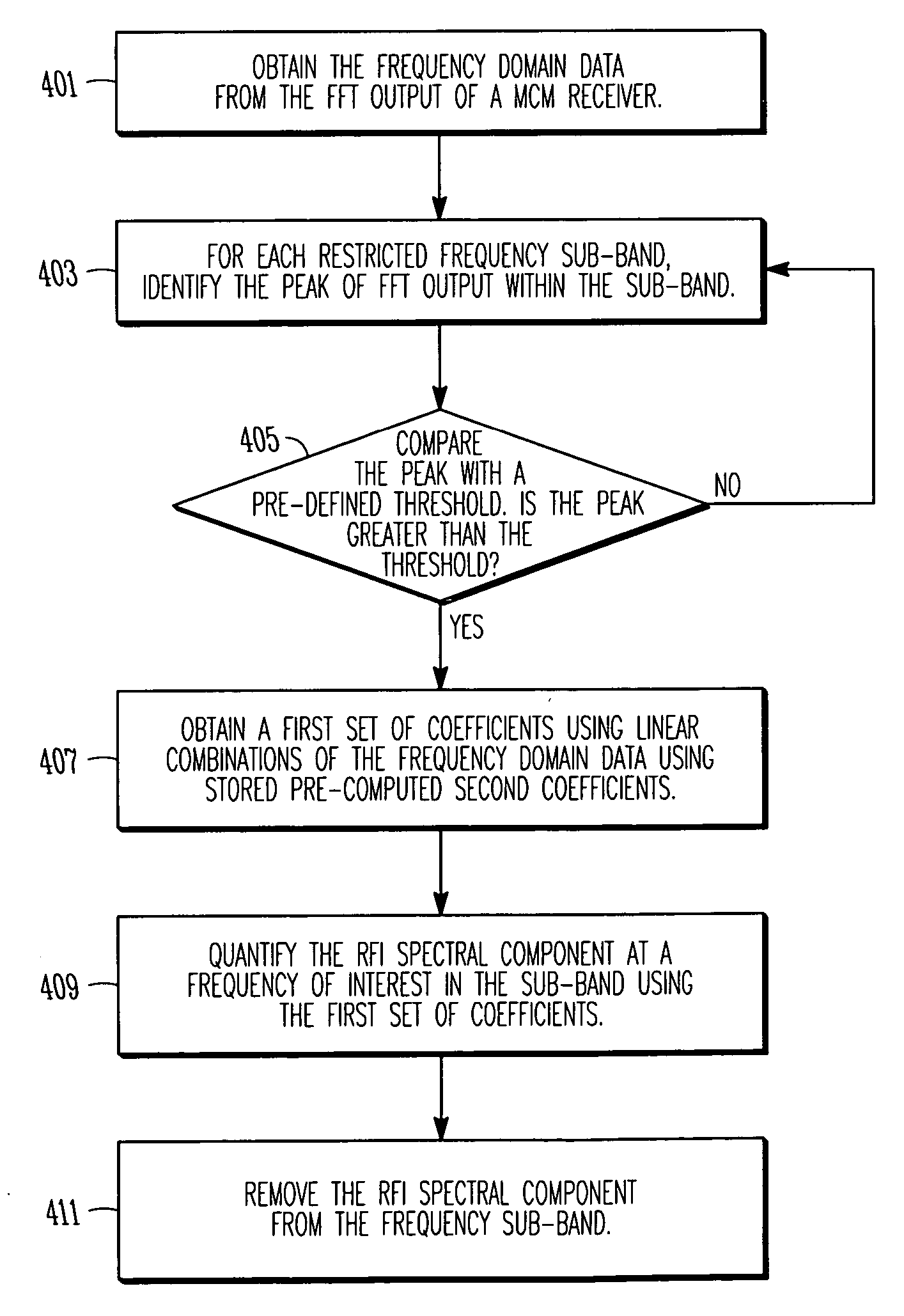
Digital cancellation of radio frequency interference
ActiveUS20060215775A1Less computational complexityImprove performanceFrequency demodulator arrangementsError preventionFrequency spectrumEngineering
A method and system of canceling radio frequency interference (RFI) sourced from a narrow-band radio frequency transmitter to interfere with the operation of a multi-carrier modulation system. The spectral components of the RFI can be represented as a Taylor series of 1 / (m−1 / 2) where m is an integer and (m−1 / 2) is a normalized approximate distance between the frequency of interest and the center frequency of the RFI. The coefficients of the Taylor series are obtained by solving a set of linear equations using the Fourier output at several properly chosen frequencies where the RFI components dominate. The coefficients for the Taylor series are formulated as linear combinations of the FFT output at the chosen frequencies and are computed and stored beforehand. Simple multiplications and additions are needed for obtaining the Taylor series coefficients from the FFT output at the chosen frequencies. The coefficients of the Taylor series can be obtained for any frequency, and the spectral component of the RFI can be estimated and removed from the MCM signals.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
FM receiver and method for improving receiving performance thereof
InactiveCN101471679AFrequency demodulator arrangementsAutomatic frequency control detailsWireless handheld devicesSignal quality
An FM receiver including an FM antenna that receives continuous wavelength signals, where the FM receiver is coupled to the FM antenna and operable to alter a center frequency of a gain profile of the FM antenna. The FM receiver includes a low noise amplifier module that is coupled to amplify the continuous wavelength signal to produce an amplified RF signal therefrom. A down conversion module is coupled to mix the amplified RF signal with a local oscillation to produce an information signal. A filter module is coupled to filter the information signal to produce a filtered information signal. A demodulation module is coupled to capture audio information from the filtered information signal. A signal monitoring module is coupled to monitor the FM signal quality of a received continuous wavelength signal. The signal monitoring module produces a signal quality indication therefrom. An antenna control module produces a signal value based upon the signal quality indication, wherein the signal value operates to alter the center frequency of a gain profile of the FM antenna. The present invention also provides a wireless hand-held device having the FM receiver.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
Low if radio receiver
InactiveUS20070165748A1Frequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsLocal oscillator signalRadio reception
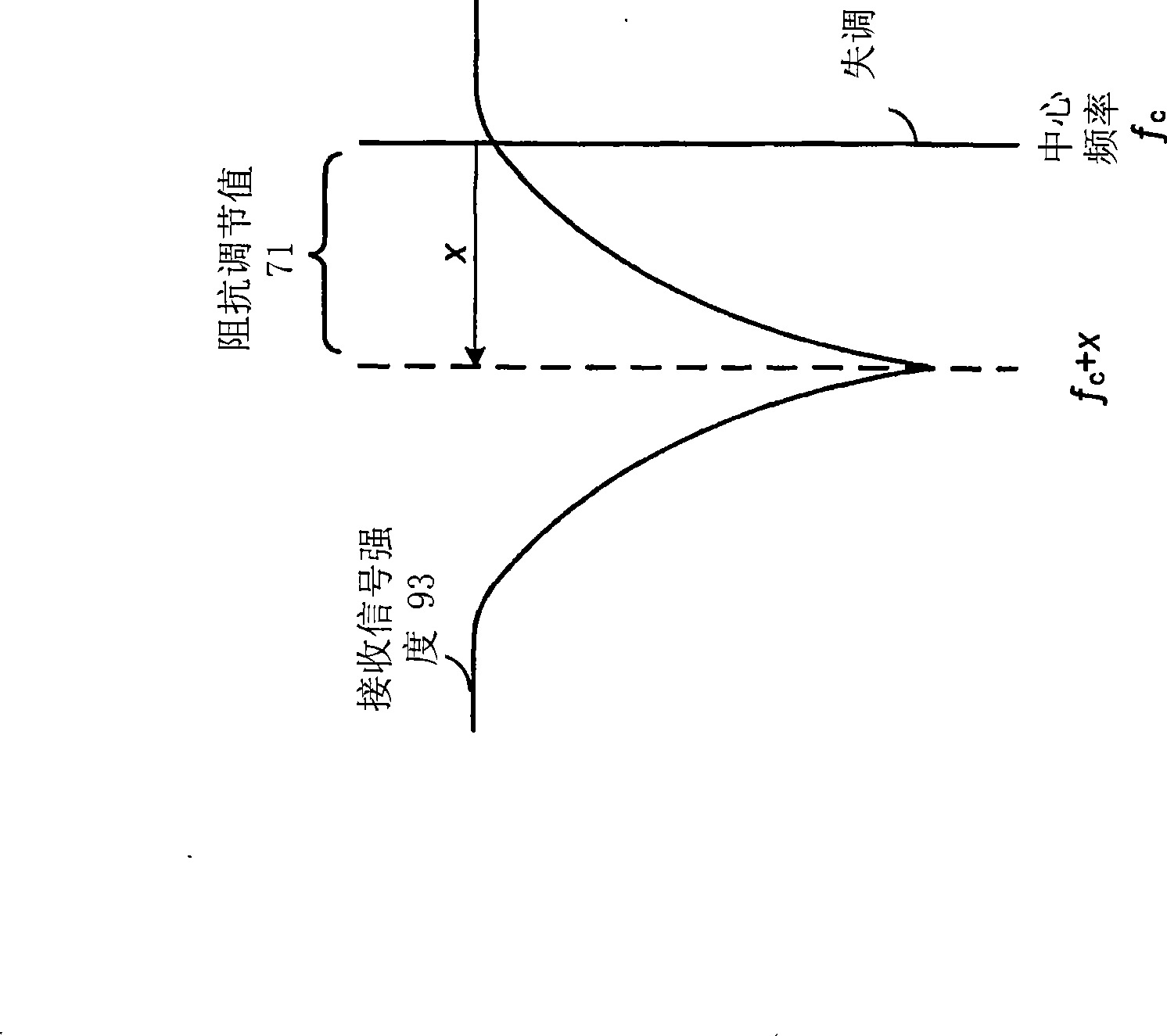
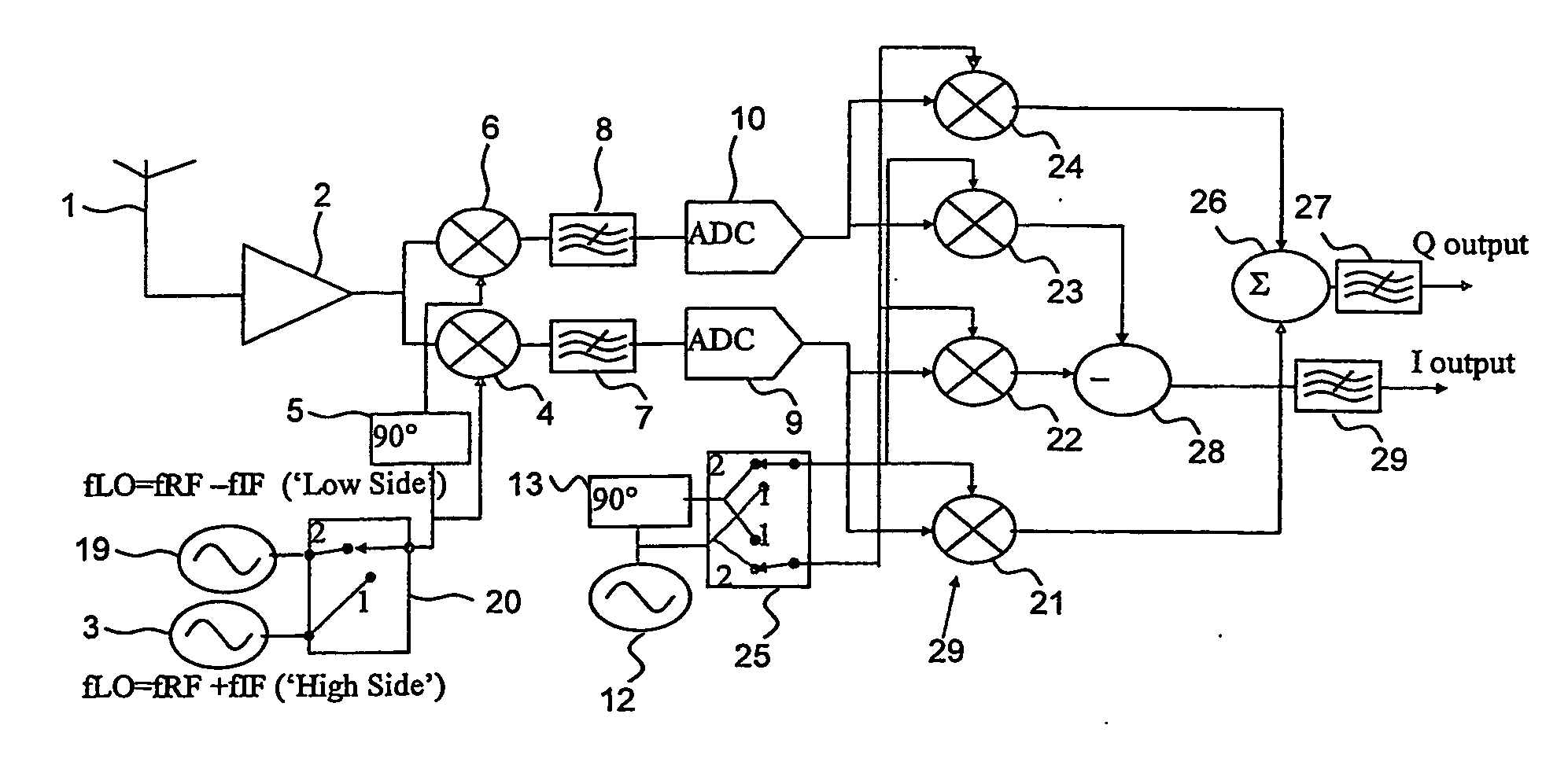
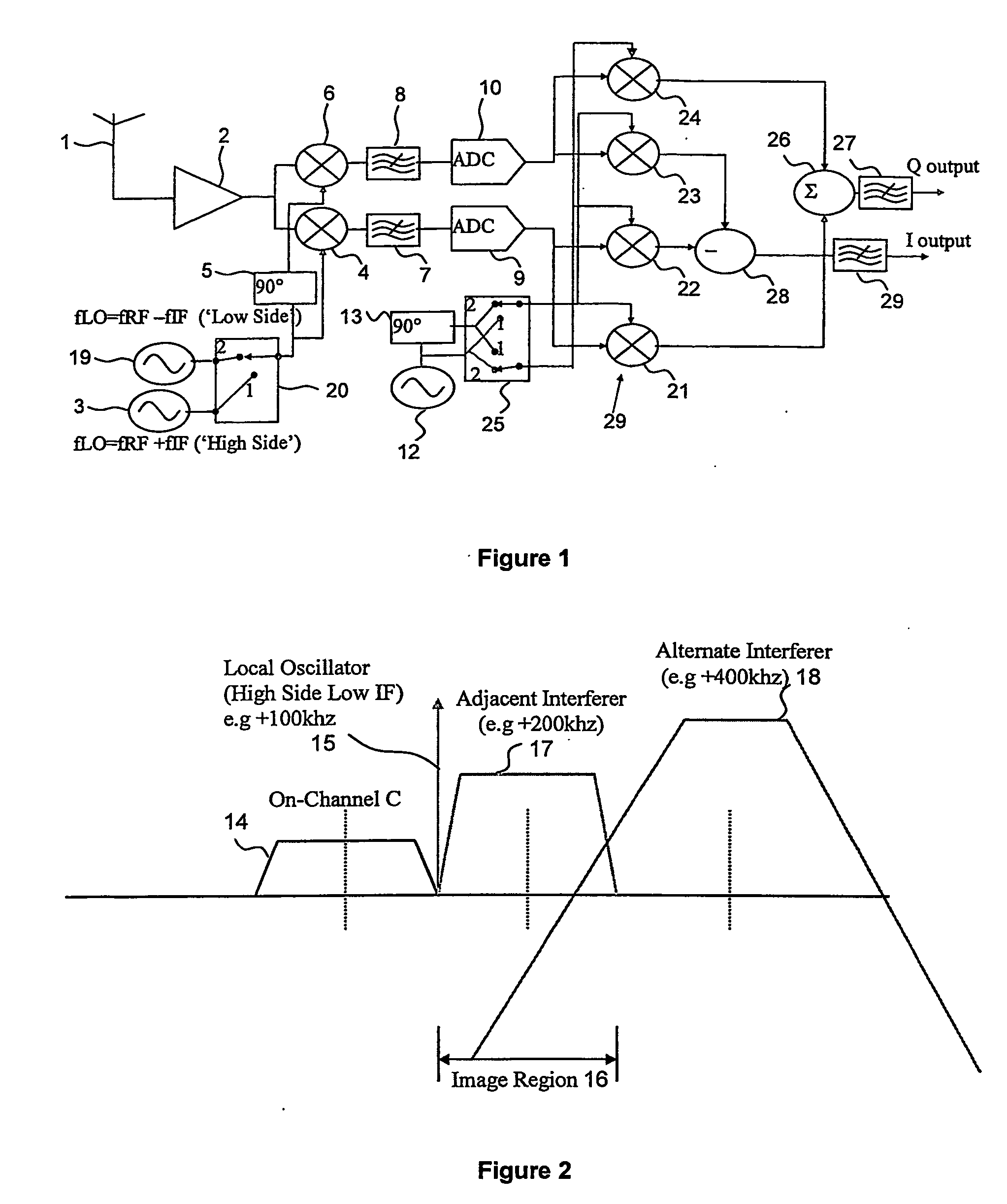
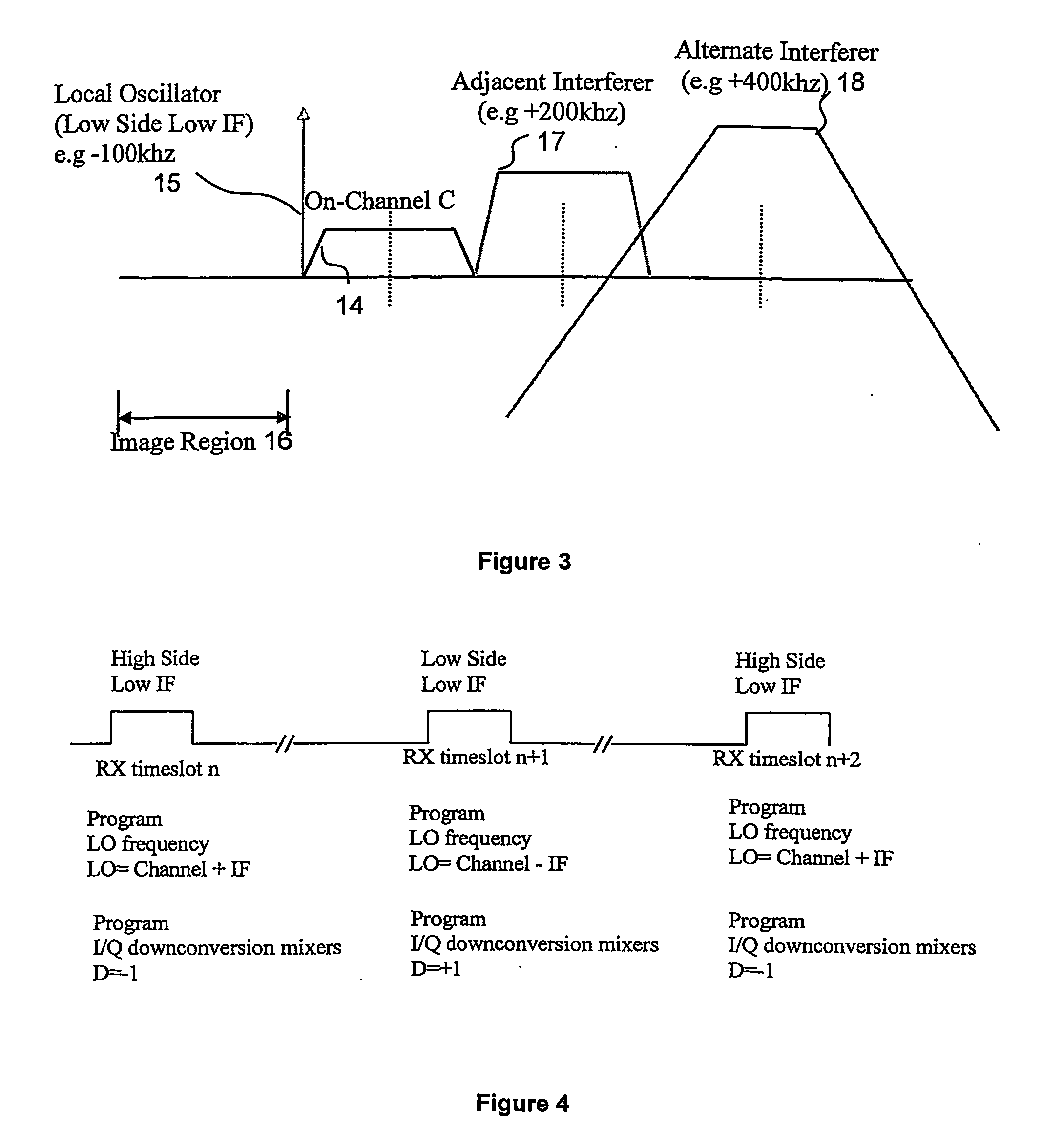
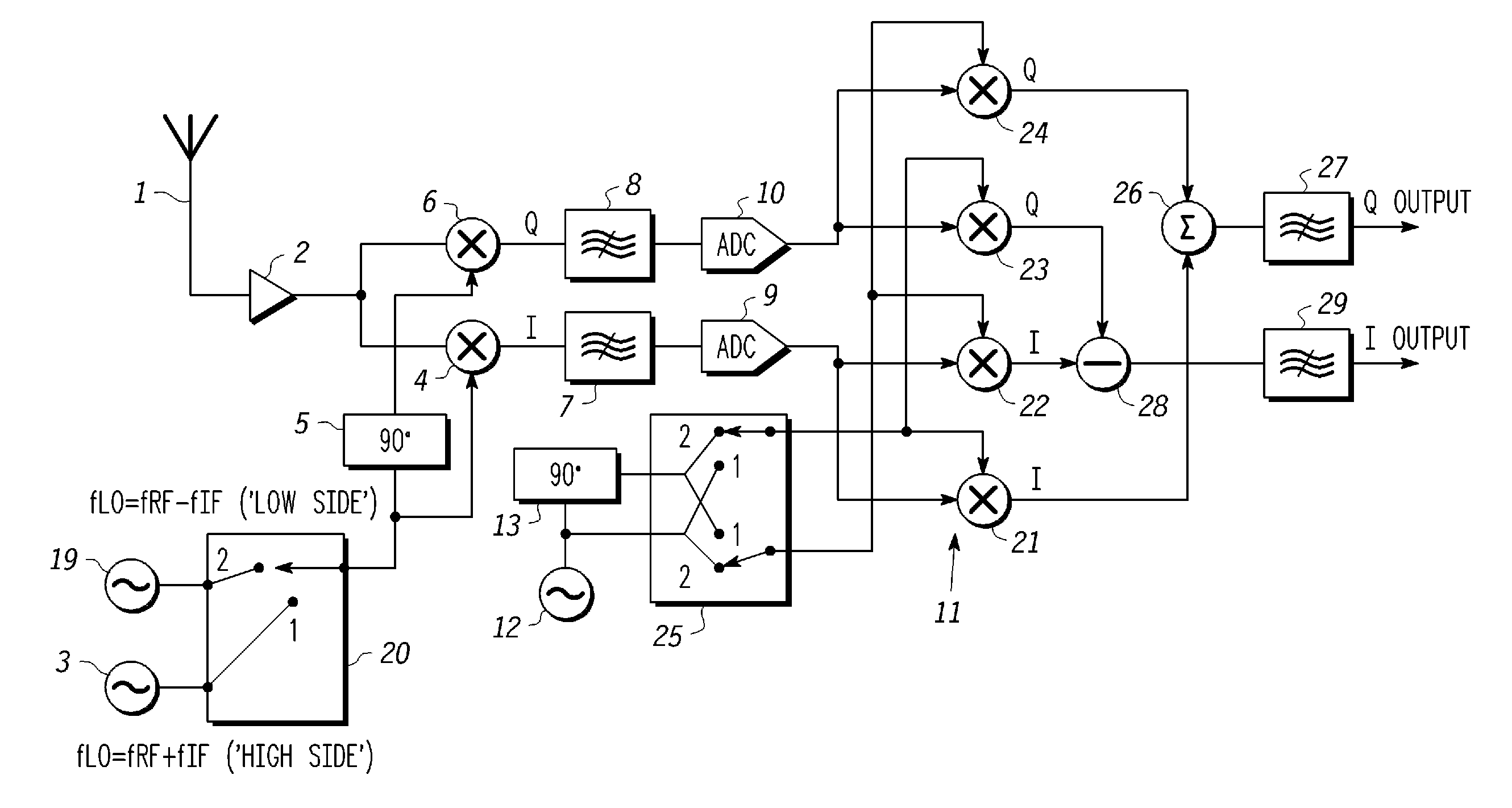
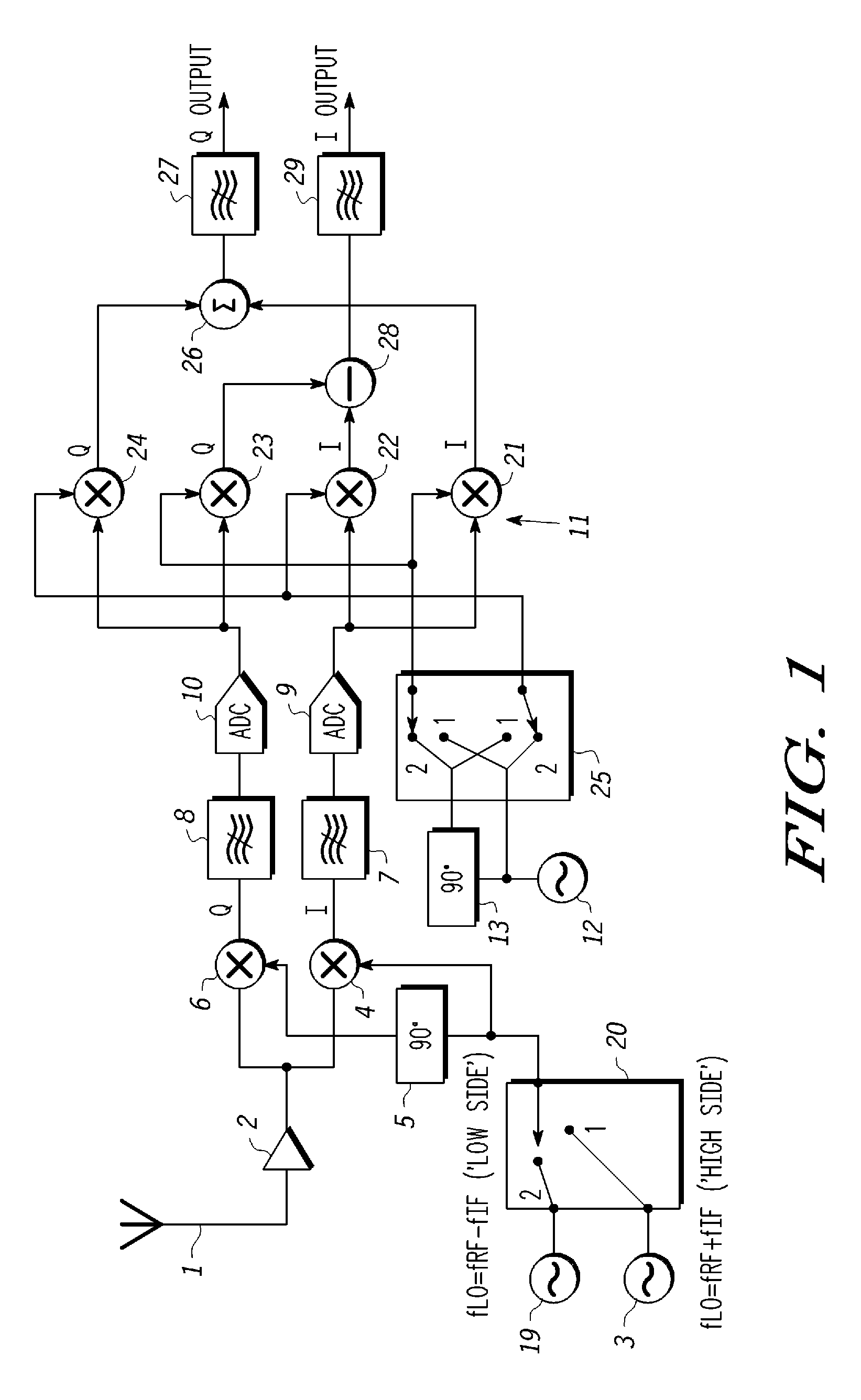
A slot-based low Intermediate Frequency (‘IF’) radio receiver comprises an IF local oscillator for producing I and Q IF local oscillator signal components in phase quadrature, I and Q mixer channels for mixing the input signal with the I and Q IF local oscillator signal components to produce I and Q IF signal components. The IF local oscillator includes frequency alternation means for causing the IF local oscillator frequency to alternate a plurality of times during each frame between first and second values, one of which is greater and the other smaller than the desired carrier frequency of the input signal so as to reduce the effect of adjacent and alternate interferers. The phase of the baseband local oscillator is alternated in synchronism with the alternation of the IF local oscillator frequency.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
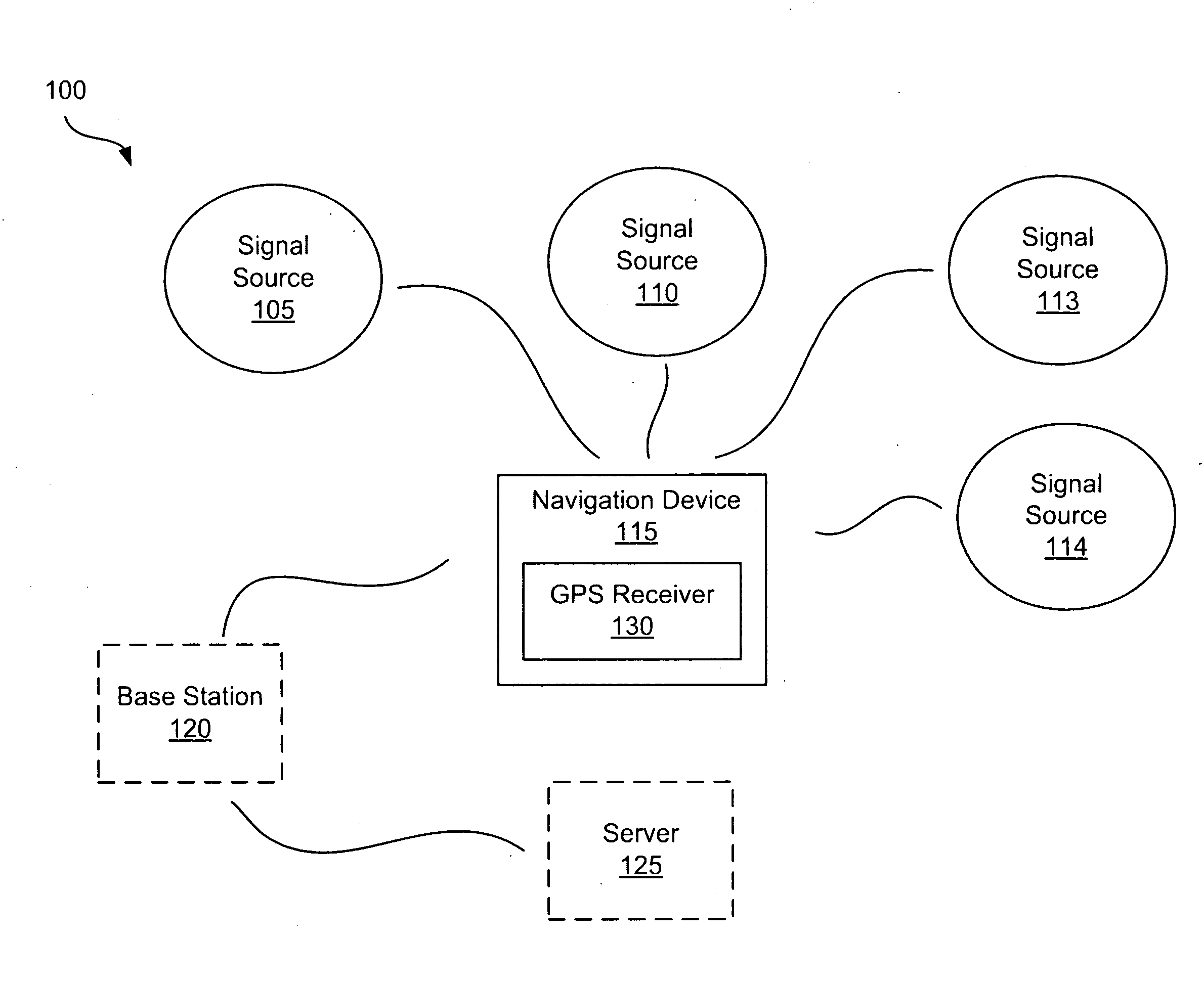
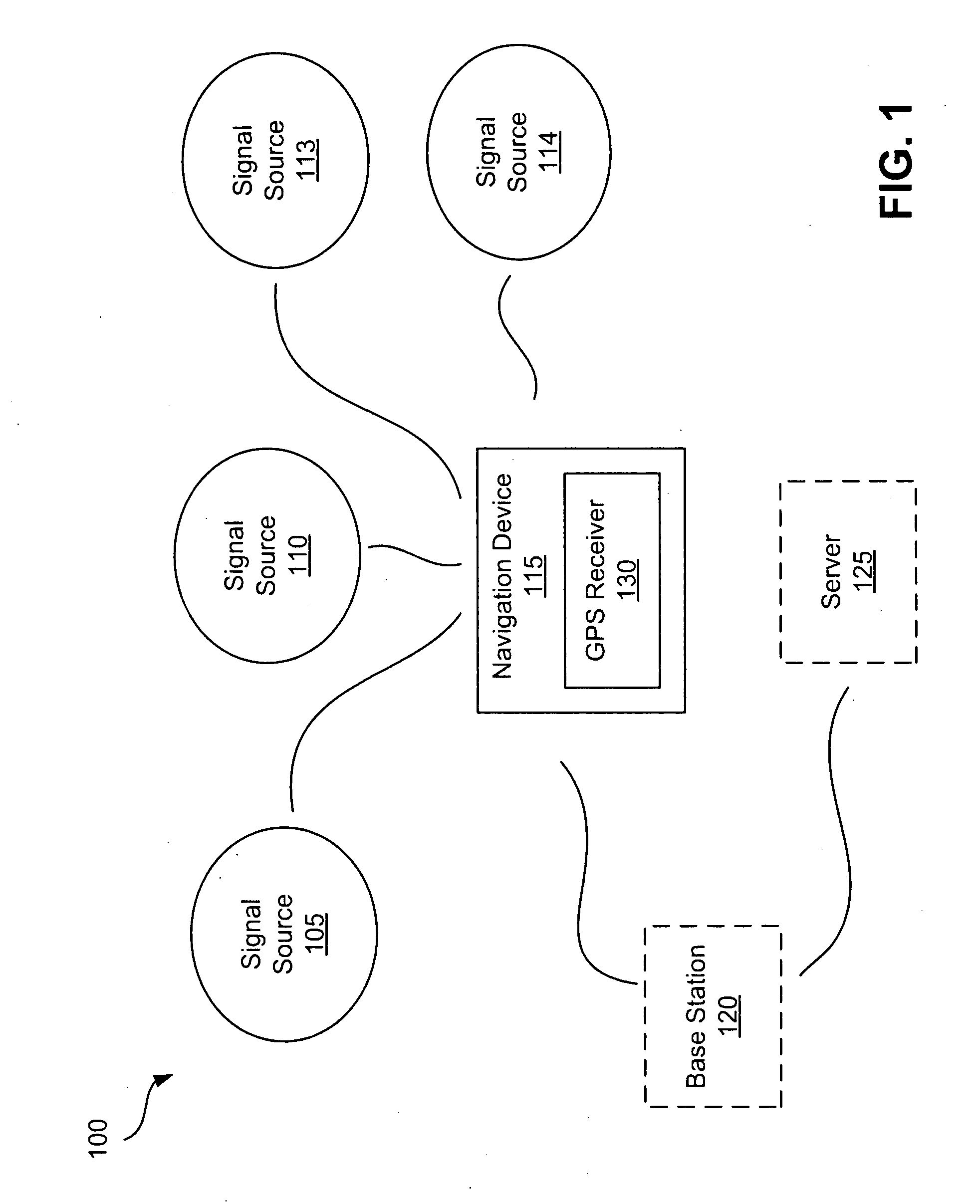
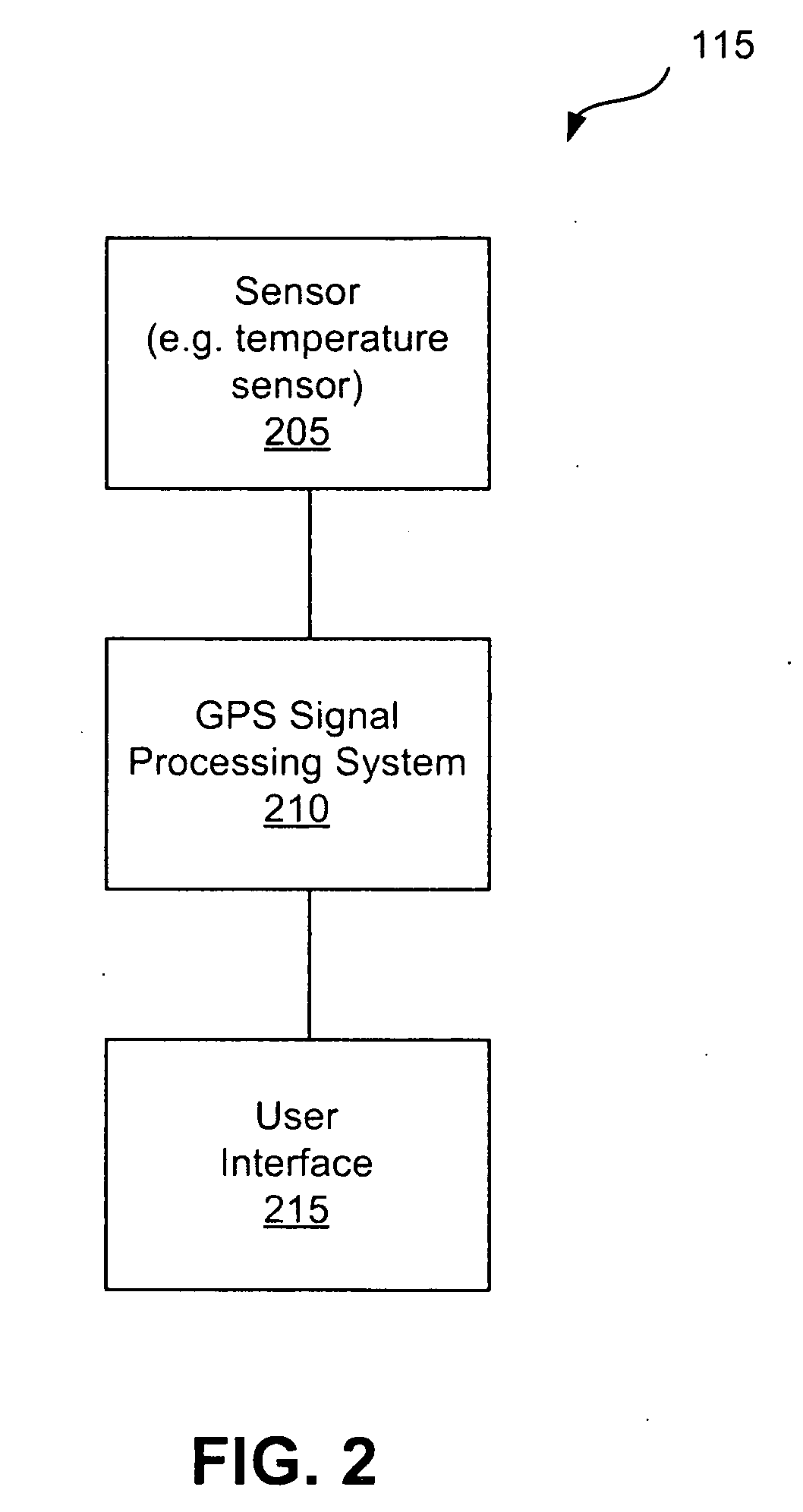
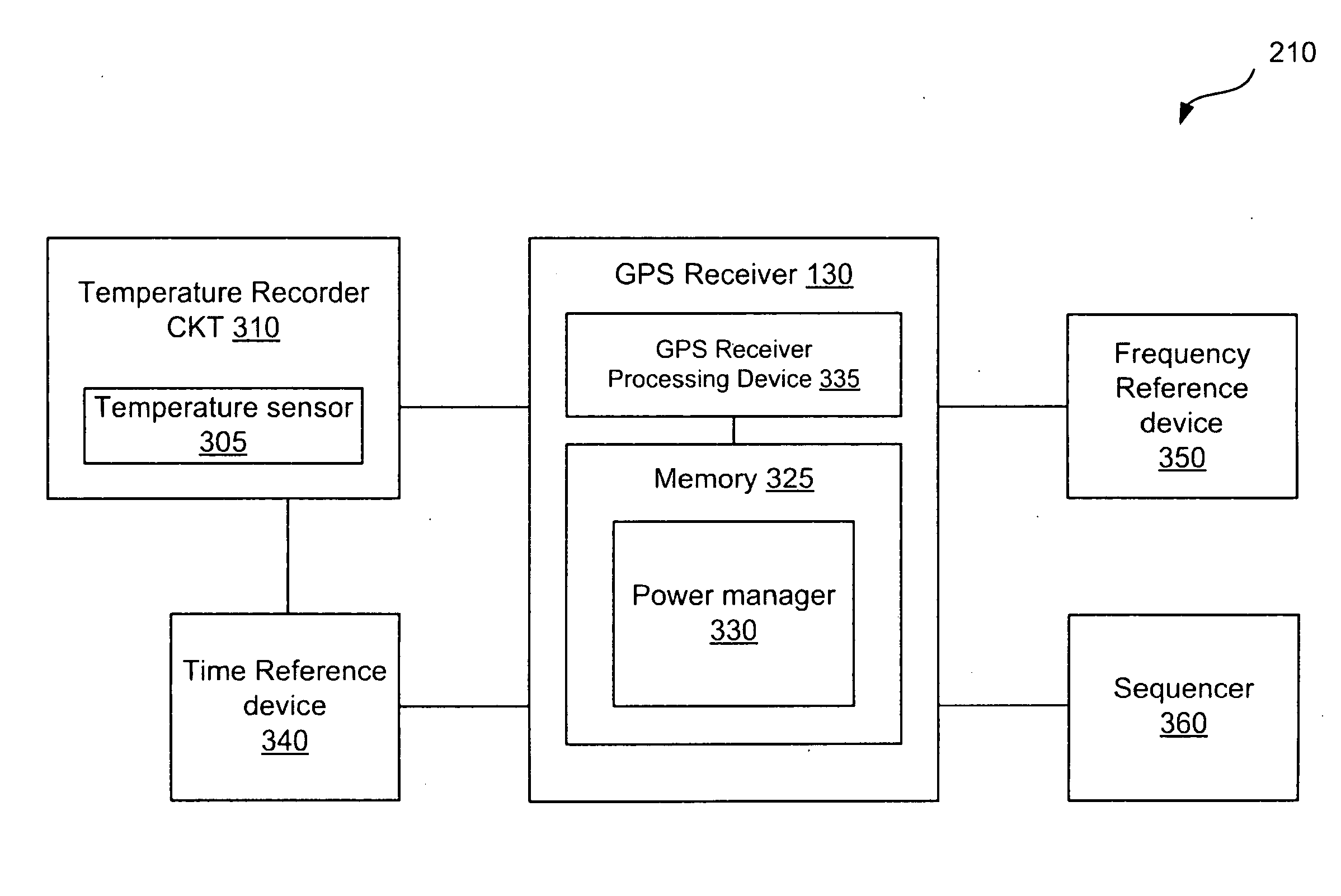
Systems and methods for managing power consumption
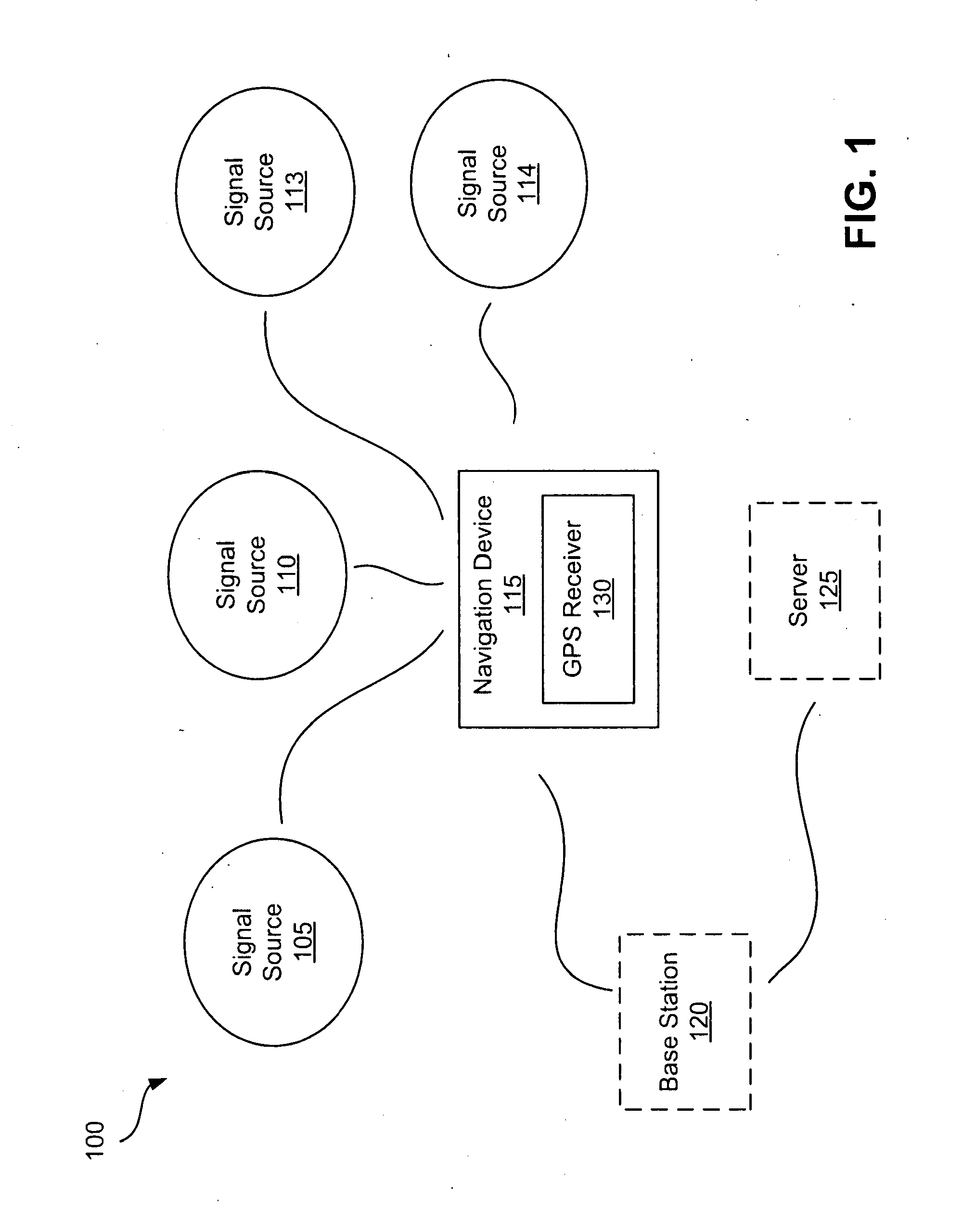
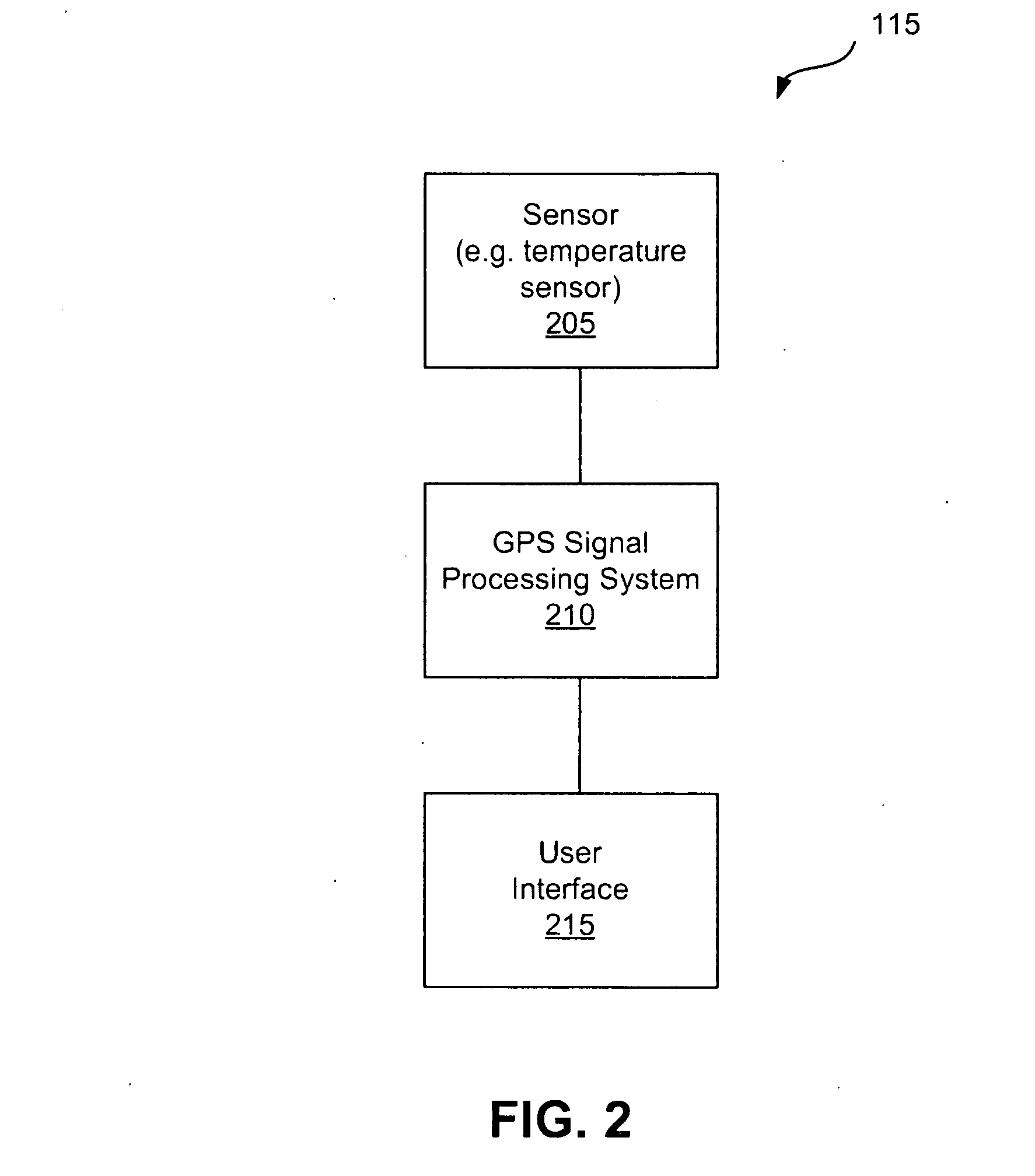
ActiveUS8185083B2Consumes less powerExtend battery lifeFrequency demodulator arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsGps receiverGps navigation
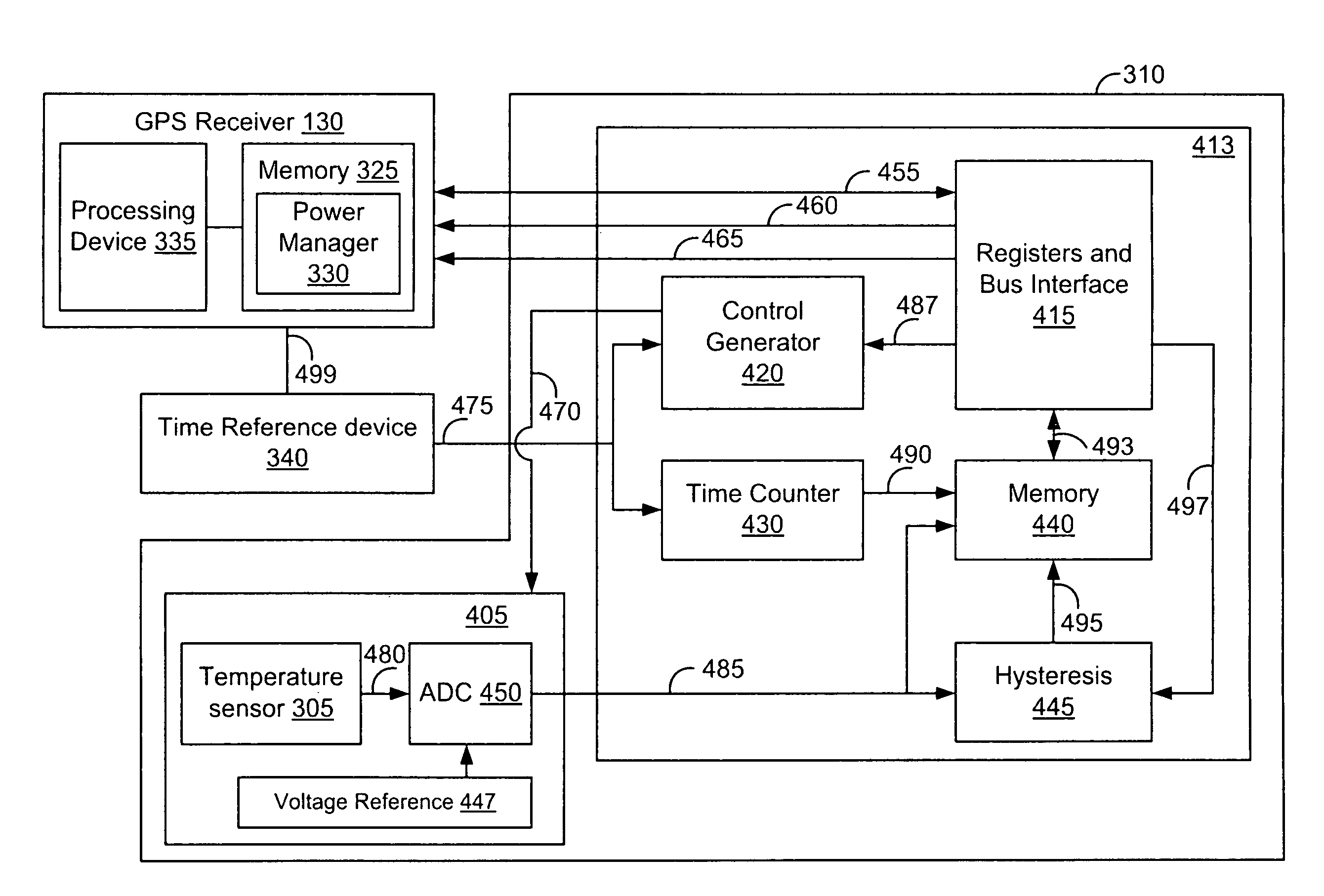
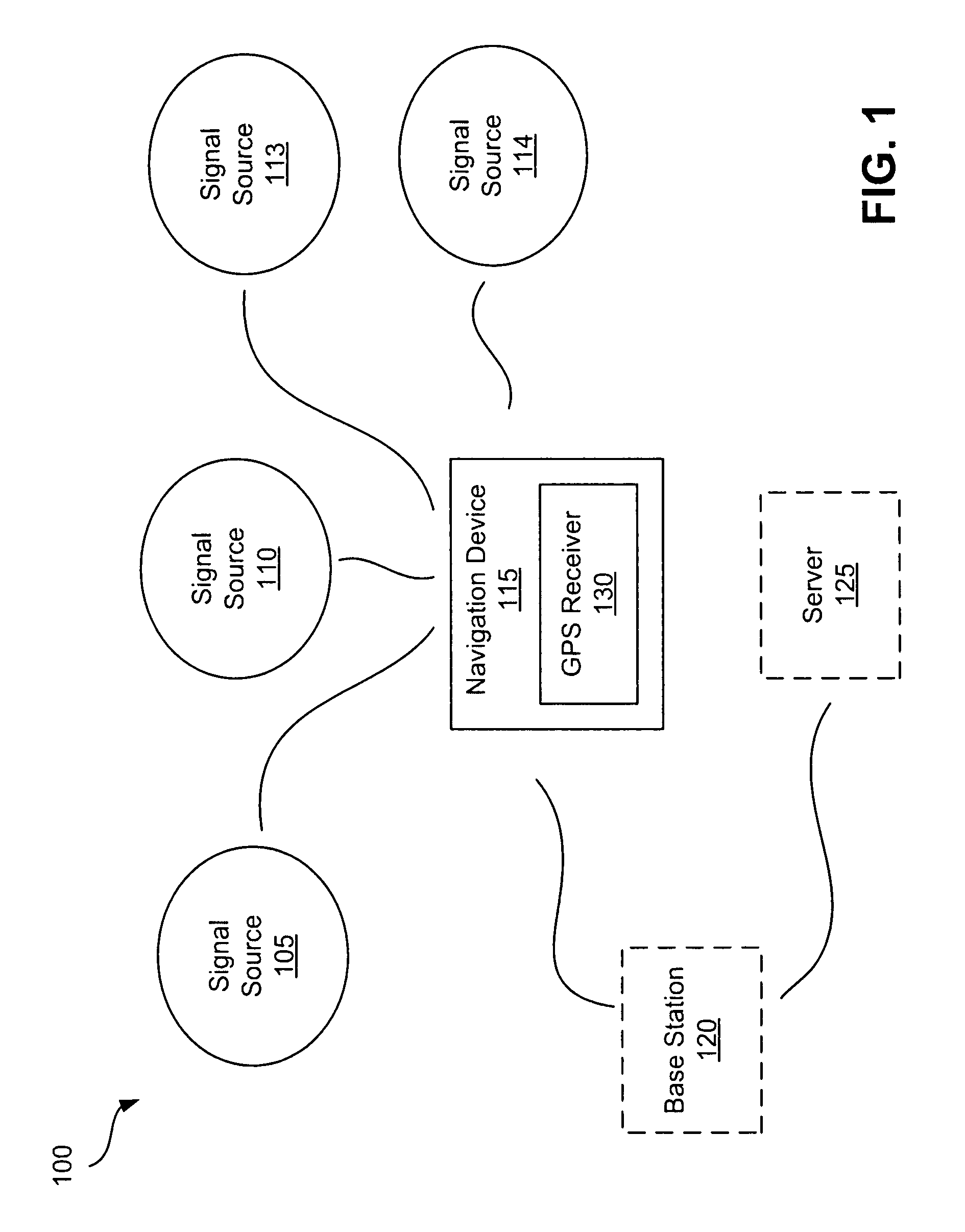
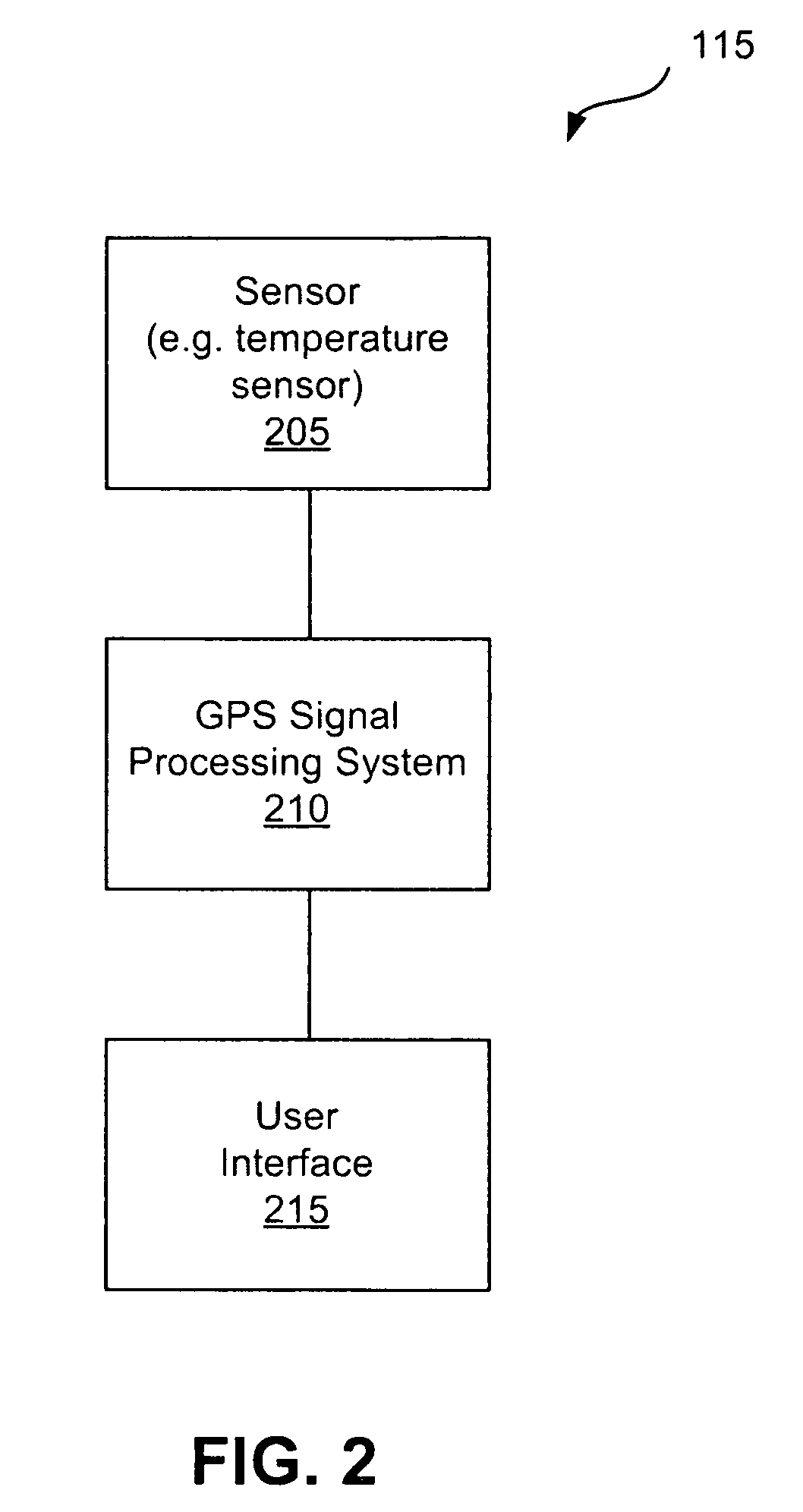
GPS navigation devices or GPS receivers can consume less power by using a temperature recorder circuit and / or a power manager in maintaining the accuracies of the GPS receiver time and reference frequency to improve battery life. A representative receiver includes a time reference device and the temperature recorder circuit that operate while the receiver hibernates. The time reference device generates clock signals and the temperature recorder circuit receives and operates using the clock signals from the time reference device. The temperature recorder senses the temperature of the time reference device. The temperature recorder circuit is designed to send a wake-up signal to at least one electrical component of the receiver to wake up the electrical component of the receiver. The electrical component of the receiver includes at least one of the following: a GPS signal processing system and a frequency reference device.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
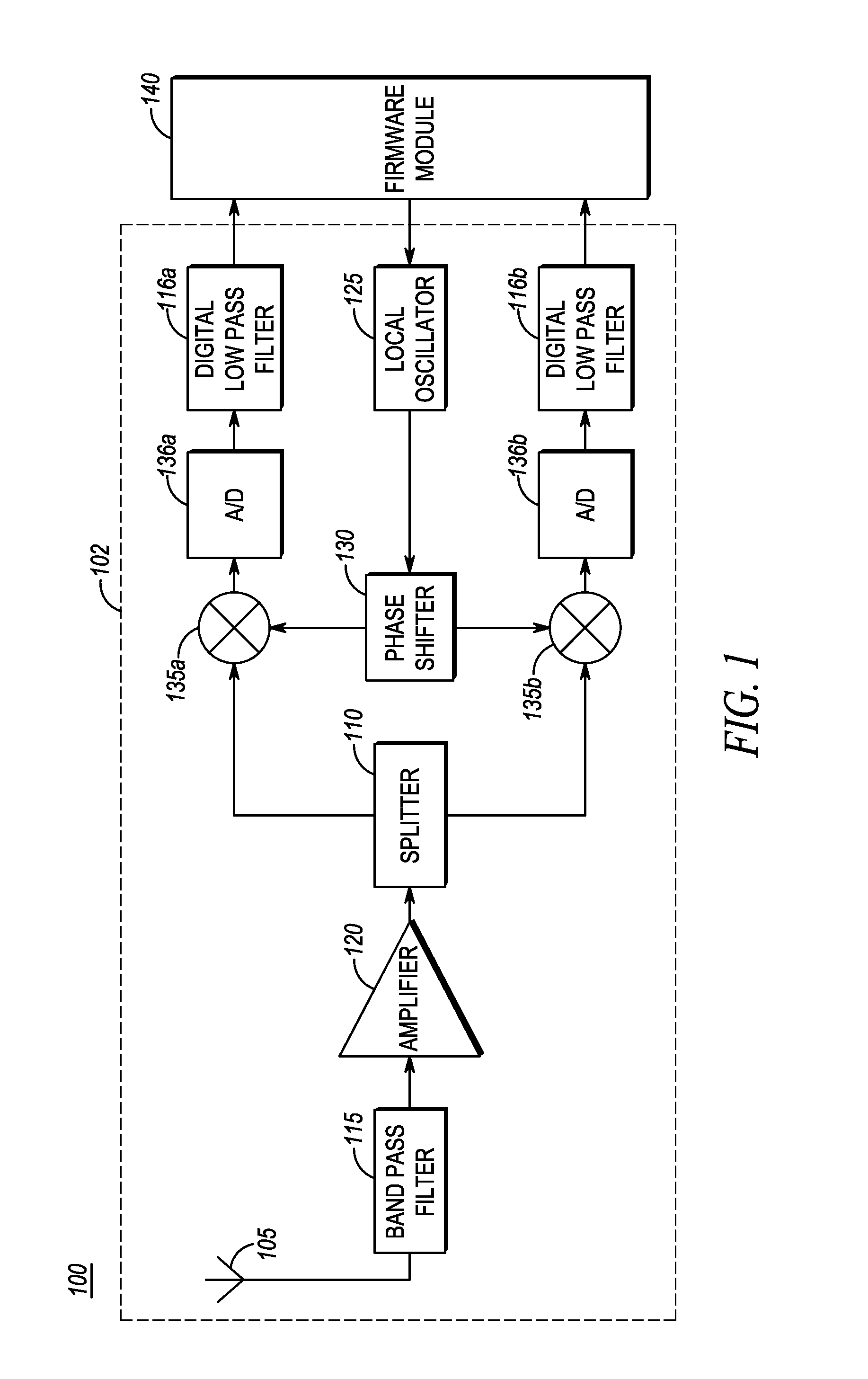
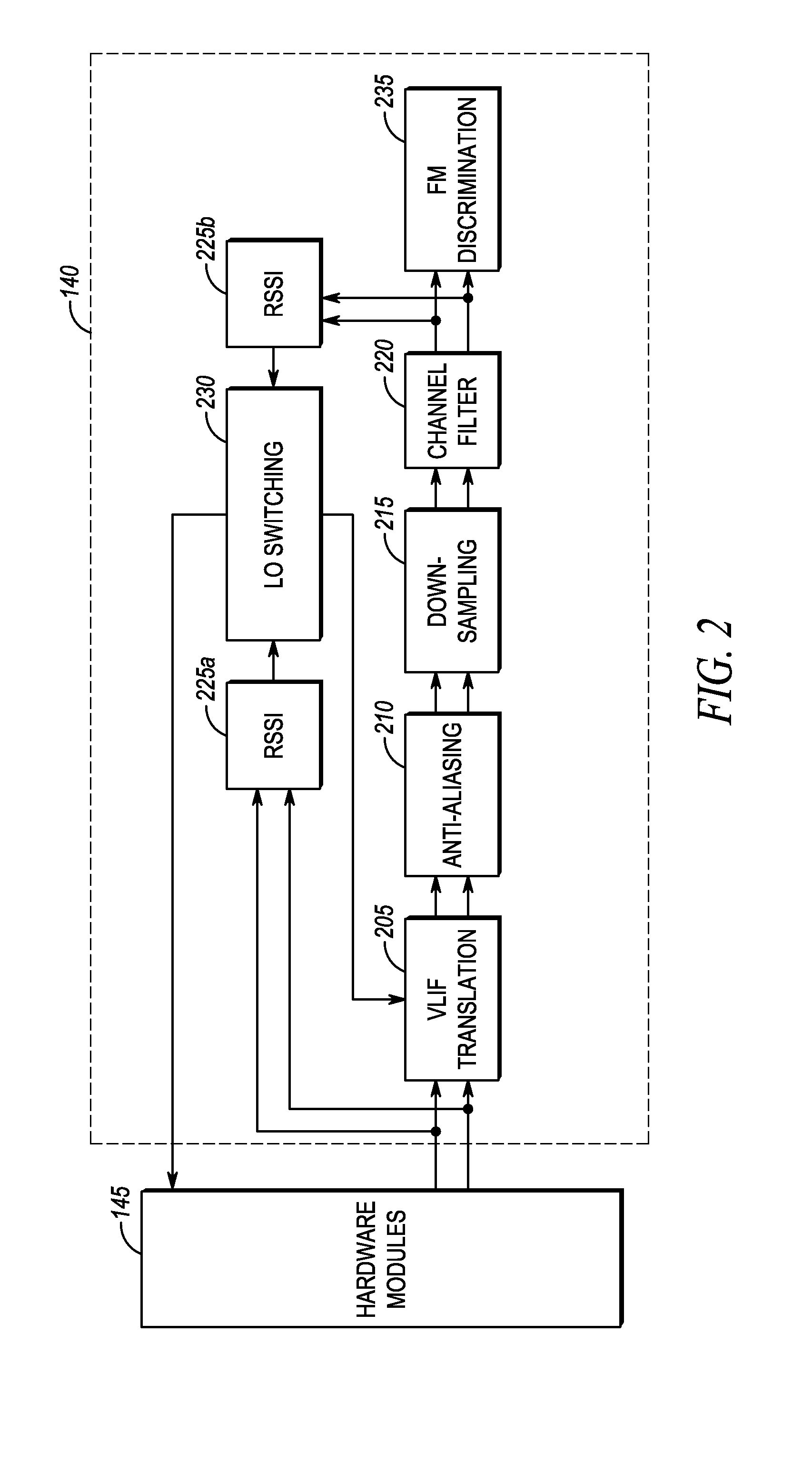
Very low intermediate frequency (VLIF) receiver and a method of controlling a VLIF receiver
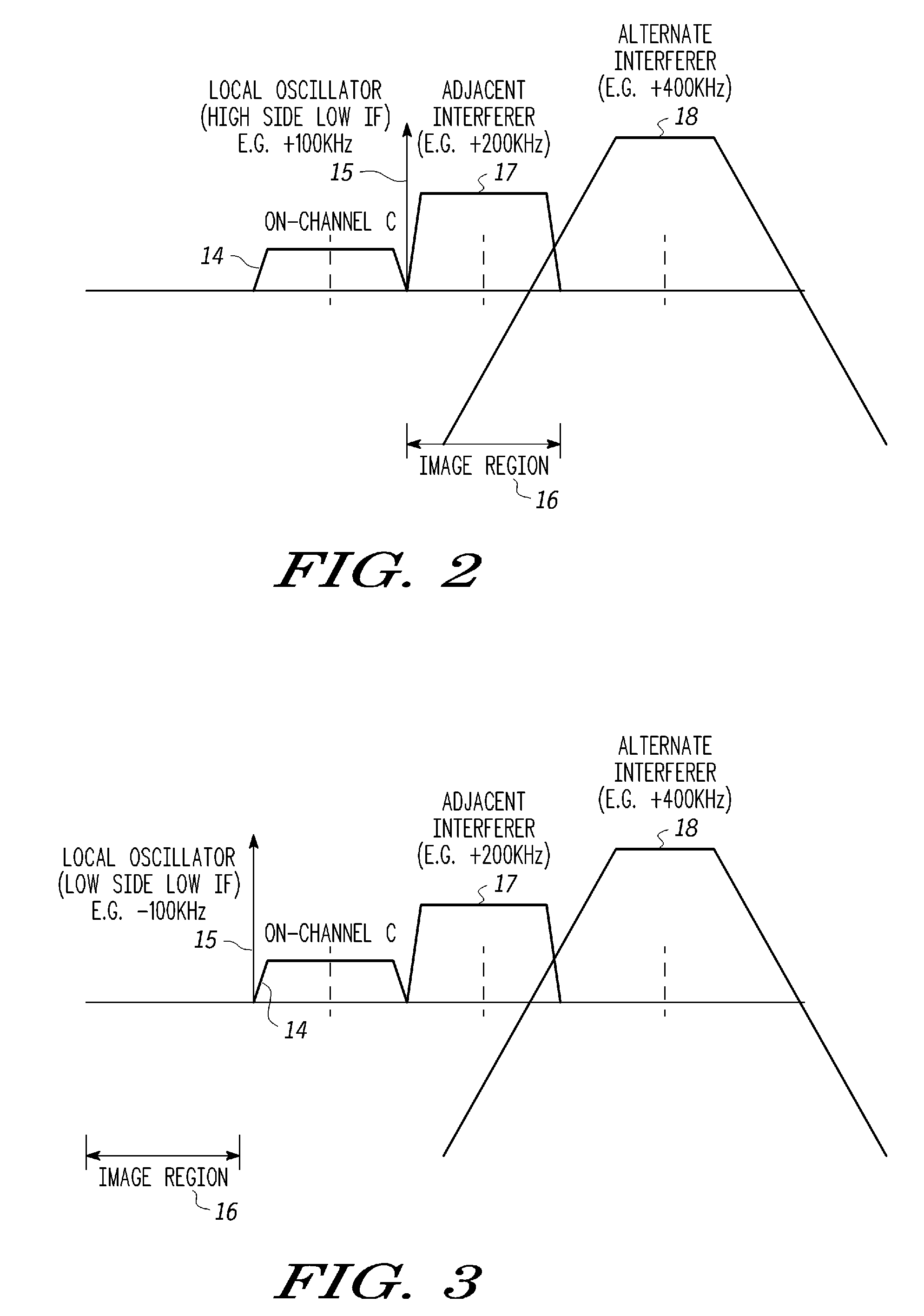
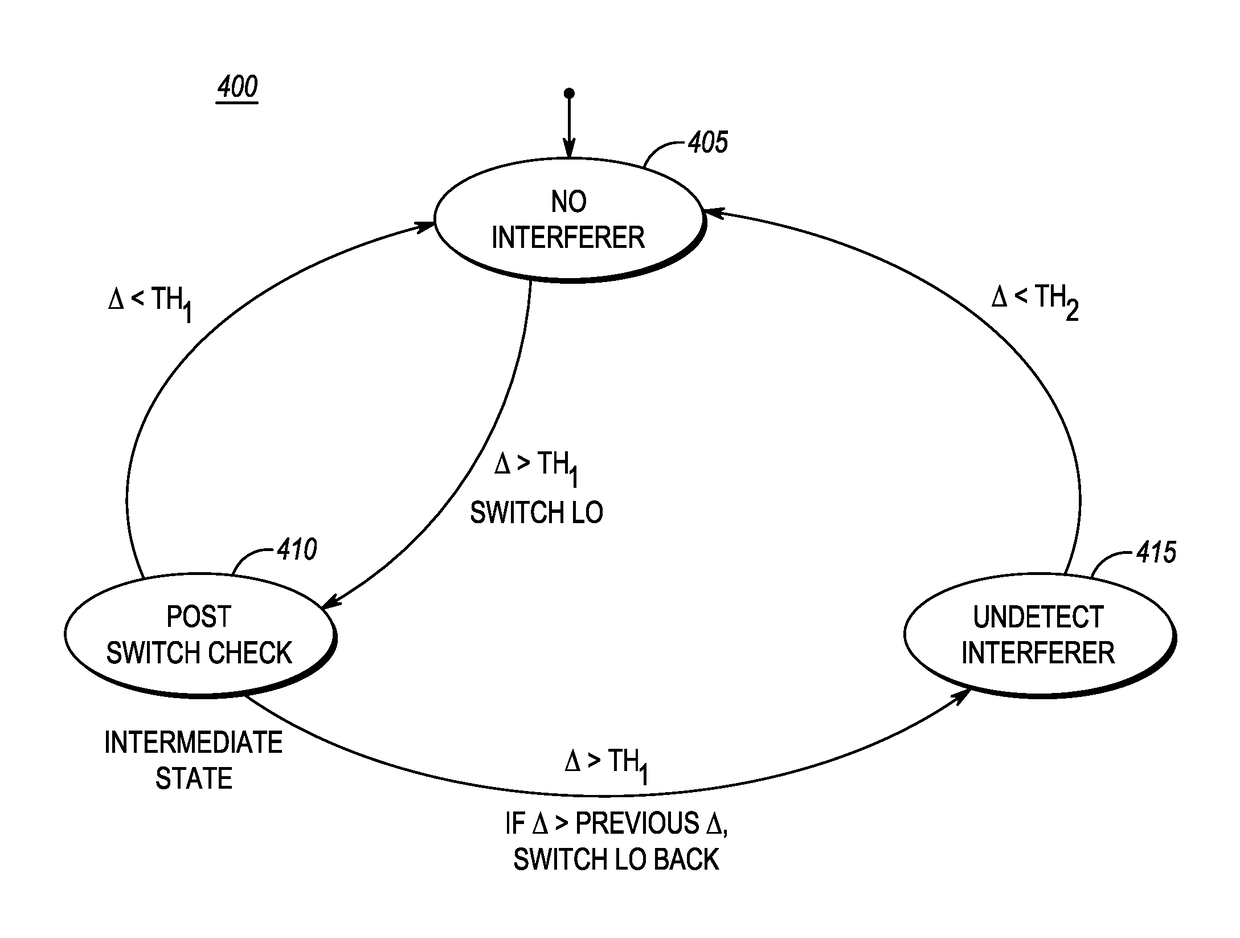
ActiveUS20150295604A1Frequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsAdjacent-channel interferenceIntermediate frequency
A very low intermediate frequency (VLIF) receiver and a method of controlling a VLIF receiver. The method comprises estimating energy levels in first and second signals and detecting interference from a first adjacent channel interferer based upon a difference in energy in the first and second signals. The first signal comprising a first on-channel portion and an adjacent channel portion and the second signal comprises an intermediate frequency translation of the first on-channel portion. The energy levels are estimated for corresponding time instances and the adjacent channel interferer is of the adjacent channel portion. The VLIF receiver is then controlled based upon the detected interference.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
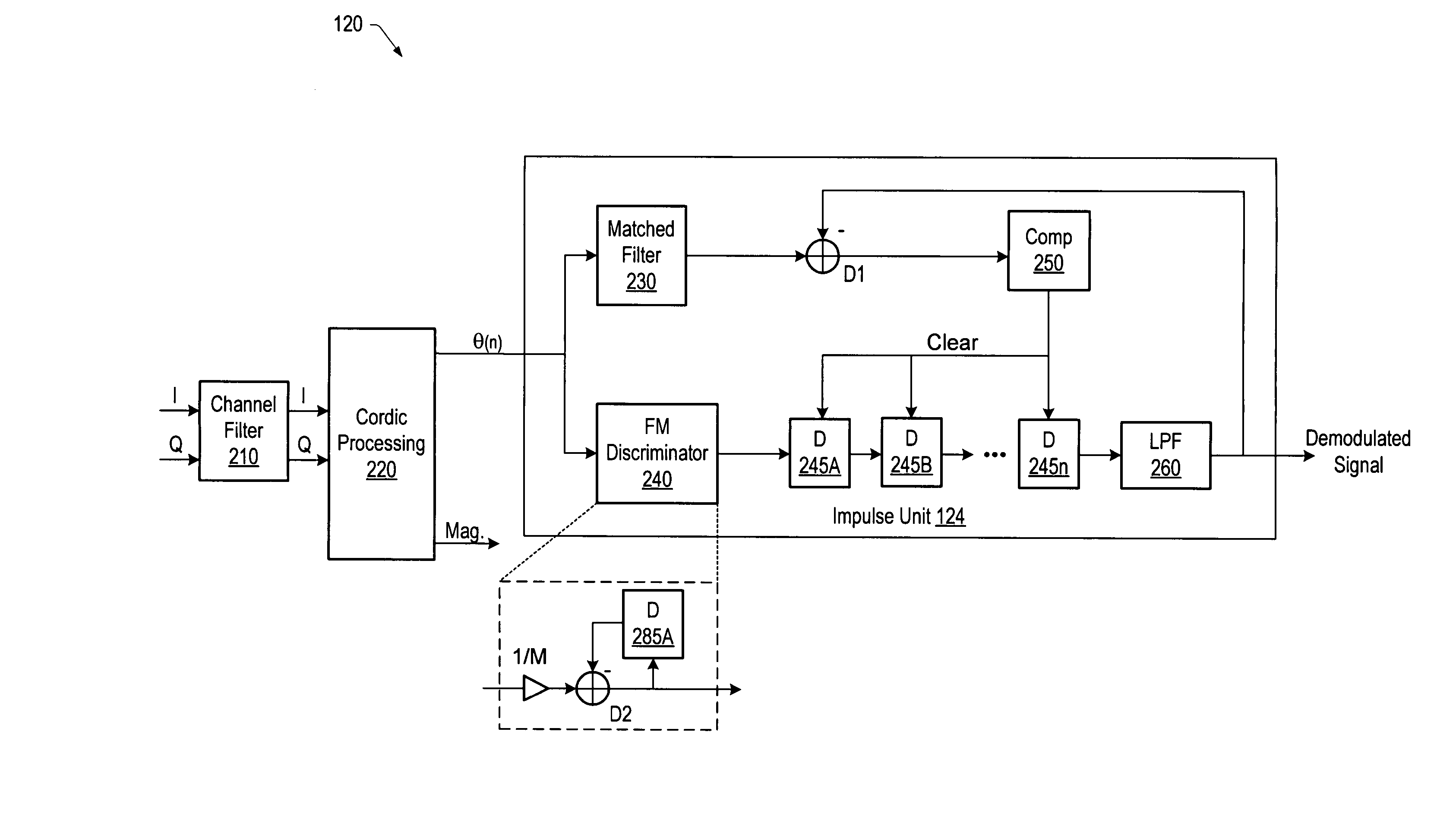
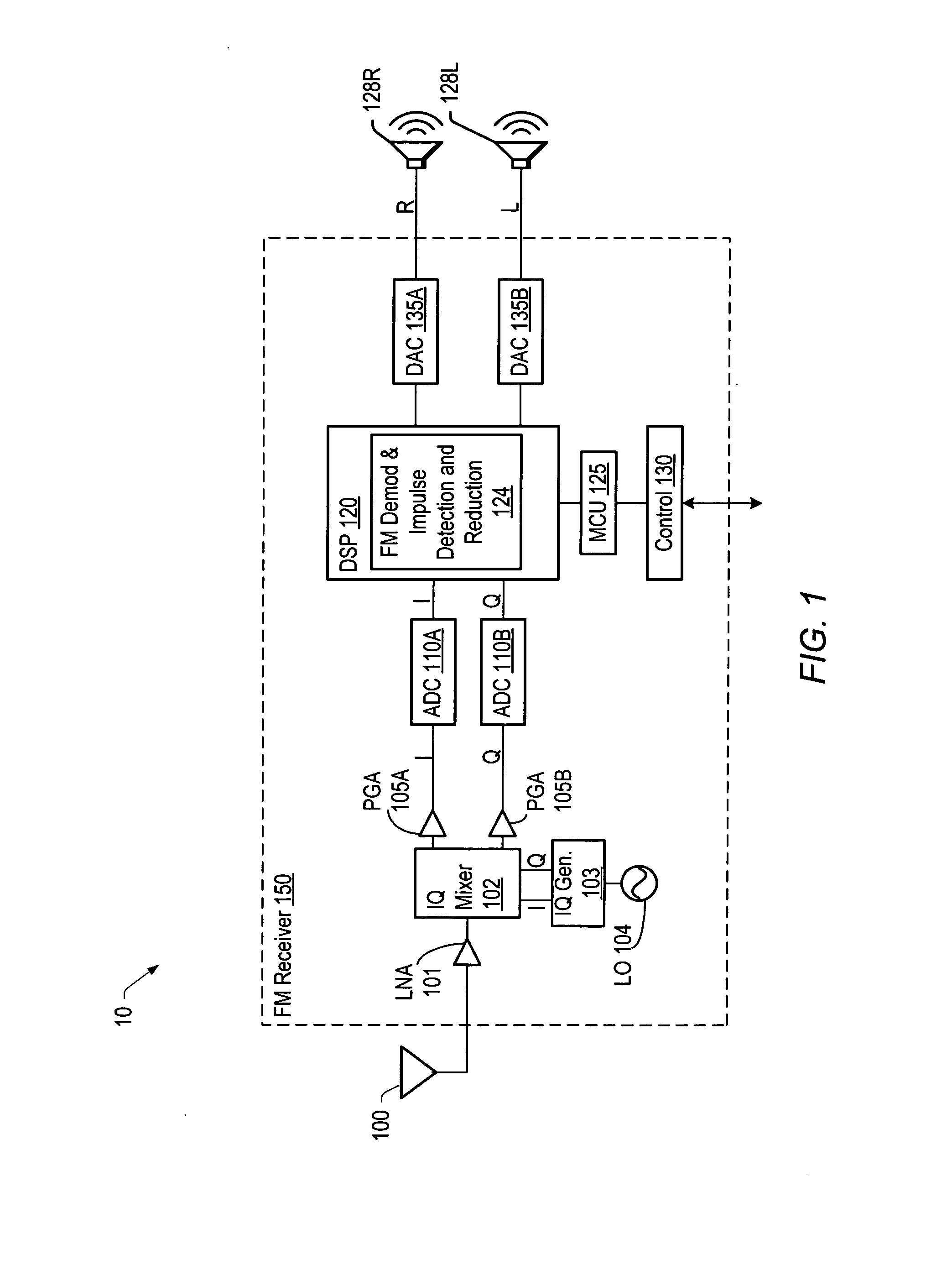
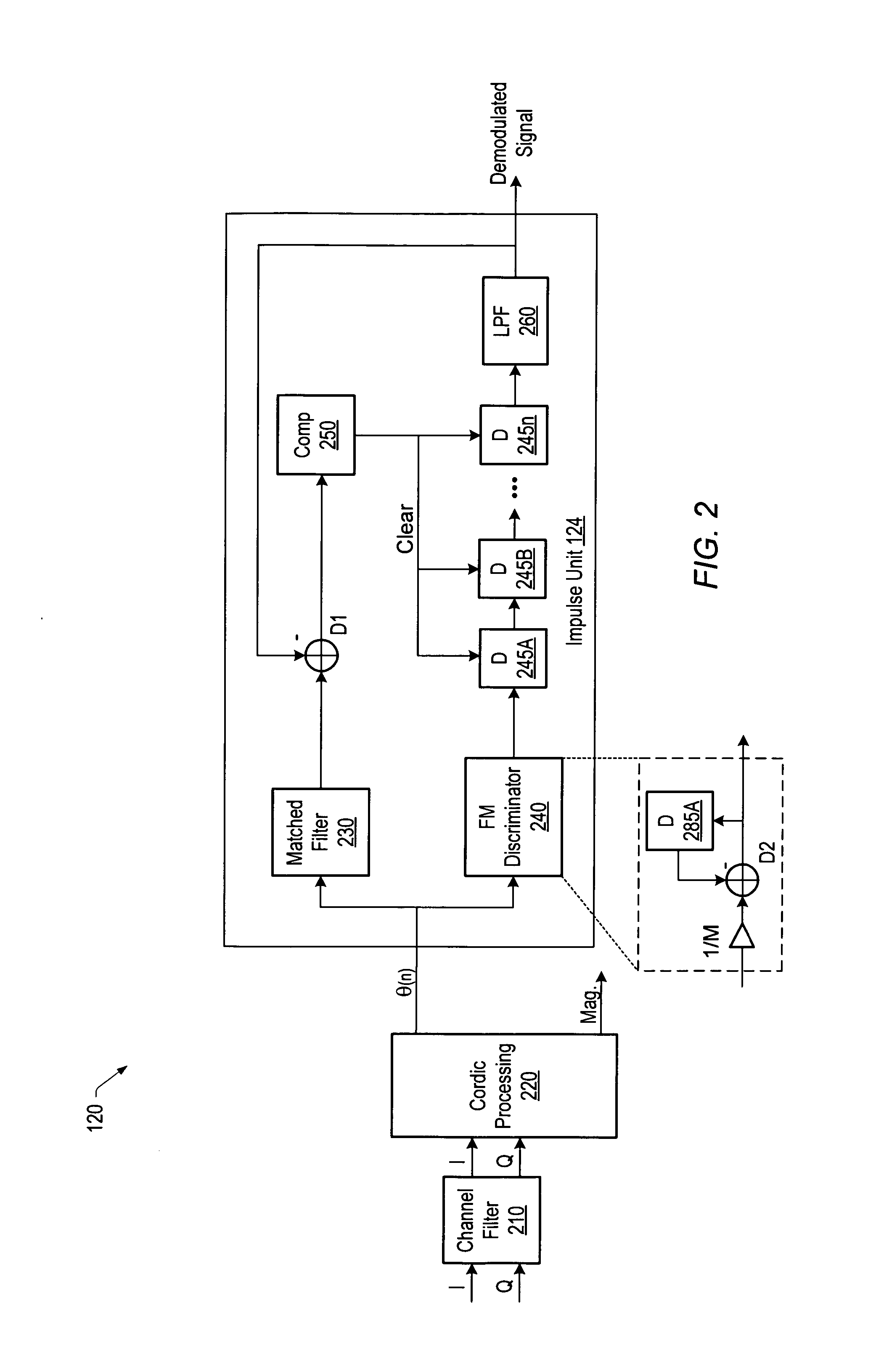
Impulse detection and reduction in a frequency modulation radio receiver
InactiveUS20070211830A1Frequency demodulator arrangementsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationCurrent sampleDiscriminator
A radio receiver includes a processing unit that may generate a respective phase value corresponding to each of a plurality of digital samples of a received complex frequency modulation (FM) signal. The receiver also includes an impulse unit that may detect whether a linear combination of a phase value of a current sample and a phase value of one or more previous samples will produce an impulse at an output of an FM demodulator. If the impulse unit detects that an impulse will be produced at the output, the impulse unit may replace the output of the FM discriminator with a predetermined value.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Systems and methods for managing power consumption
ActiveUS20100248678A1Consumes less powerExtend battery lifeFrequency demodulator arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsGps receiverGps navigation
GPS navigation devices or GPS receivers can consume less power by using a temperature recorder circuit and / or a power manager in maintaining the accuracies of the GPS receiver time and reference frequency to improve battery life. A representative receiver includes a time reference device and the temperature recorder circuit that operate while the receiver hibernates. The time reference device generates clock signals and the temperature recorder circuit receives and operates using the clock signals from the time reference device. The temperature recorder senses the temperature of the time reference device. The temperature recorder circuit is designed to send a wake-up signal to at least one electrical component of the receiver to wake up the electrical component of the receiver. The electrical component of the receiver includes at least one of the following: a GPS signal processing system and a frequency reference device.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
System and method for eliminating single-frequency interference and multi-frequency interference
ActiveCN101729461AReduce computational complexityImprove tracking accuracyFrequency demodulator arrangementsAmplitude demodulation detailsComputation complexityInterference elimination
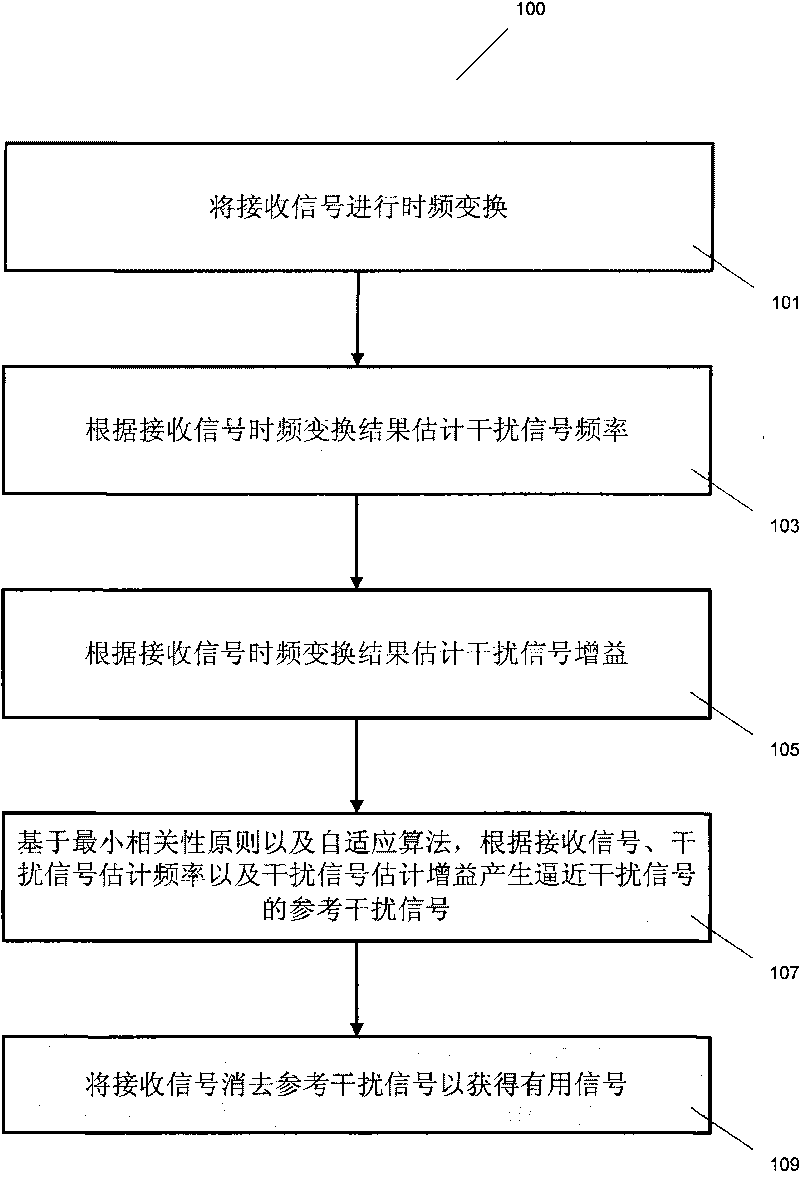
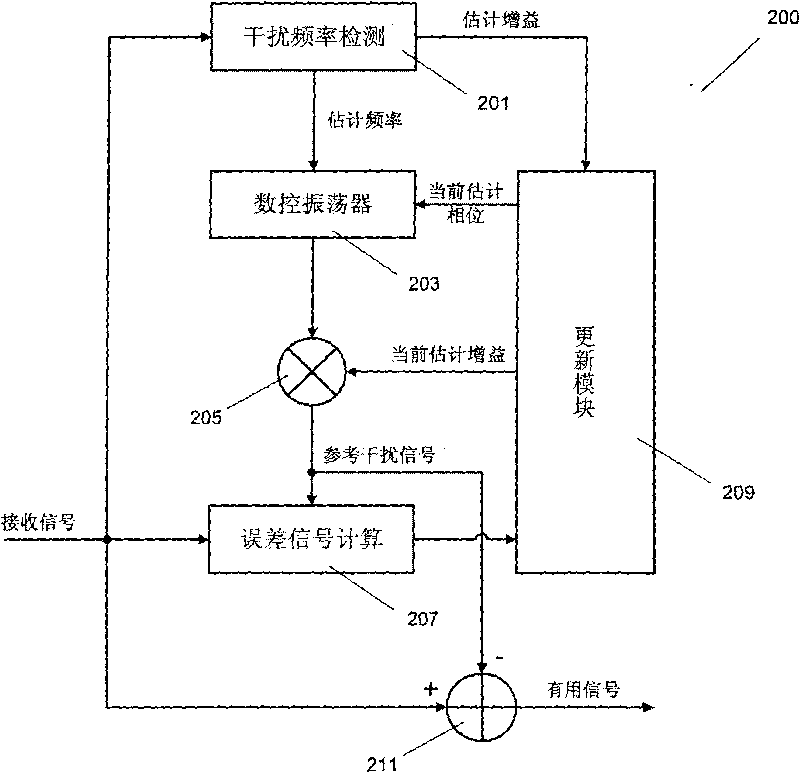
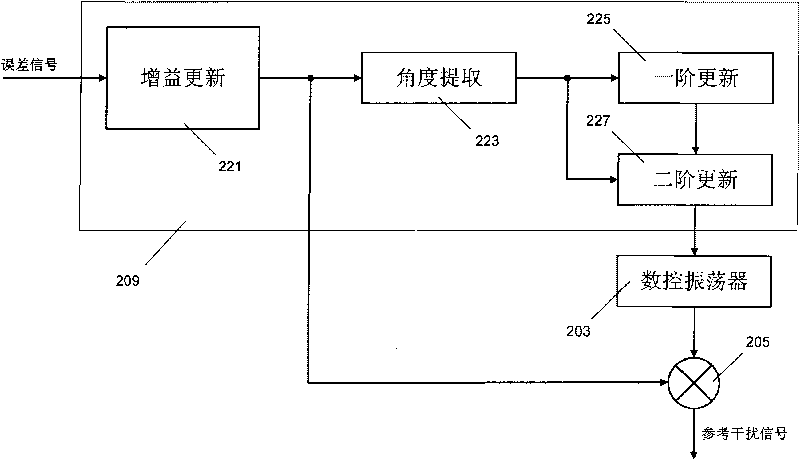
The invention relates to a system and a method for eliminating single-frequency interference and multifrequency interference, which comprises the following steps: acquiring an estimated frequency and an estimated gain of an interfering signal through low-precision time-frequency transformation; producing a reference interfering signal according to the estimated frequency and the estimated gain; based on a minimum relevance principle, calculating to obtain an error signal according to a received signal and the reference interfering signal; and based on an adaptive algorithm, updating the reference interfering signal according to the error signal. The method of the invention has the advantages of low computational complexity, high convergence speed and high tracking accuracy, and the like.
Owner:MONTAGE TECH CHENGDU CO LTD +1
Demodulator and communication device using the same
InactiveUS6850113B2High sensitivityReduce circuit sizeFrequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsCapacity valueEngineering
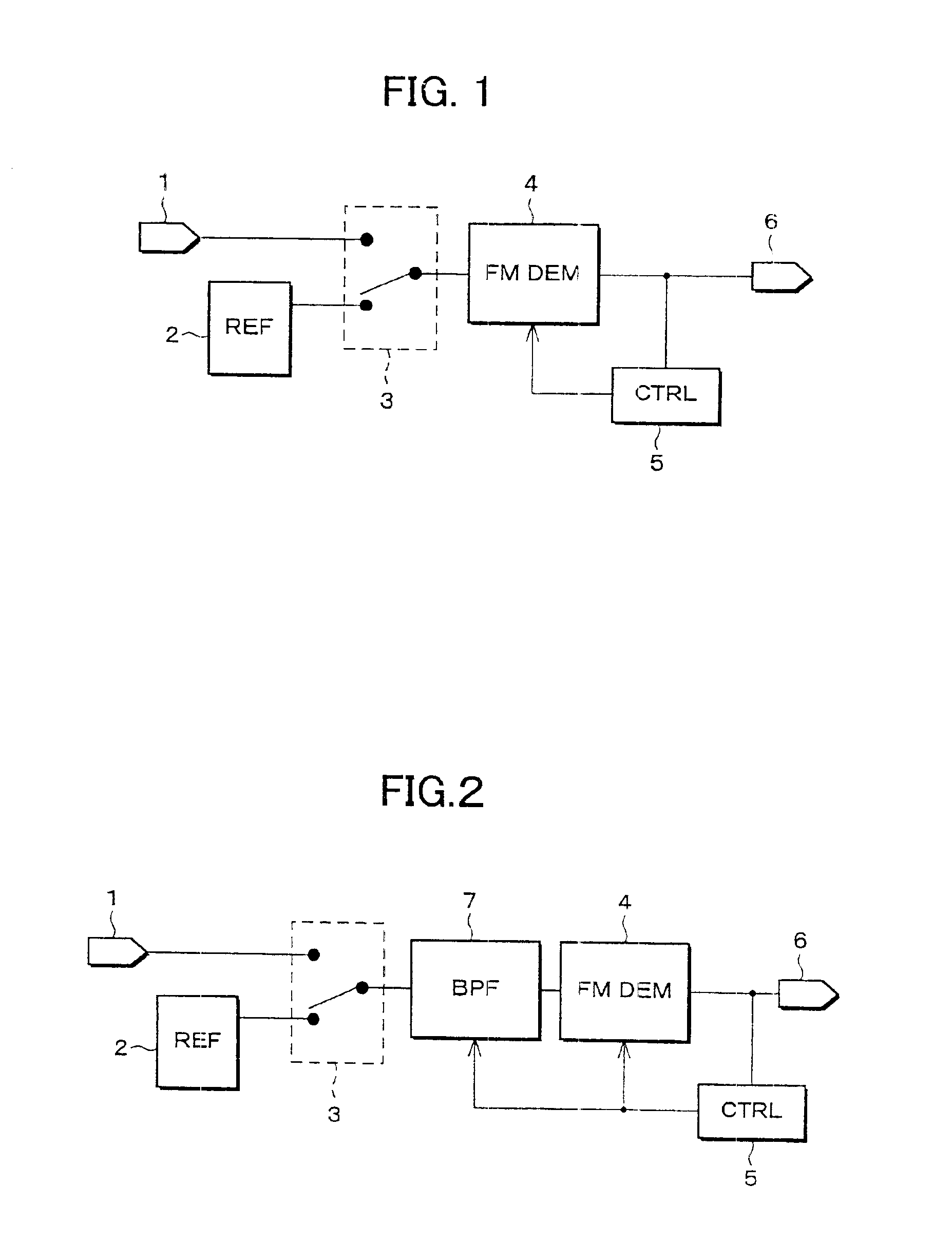
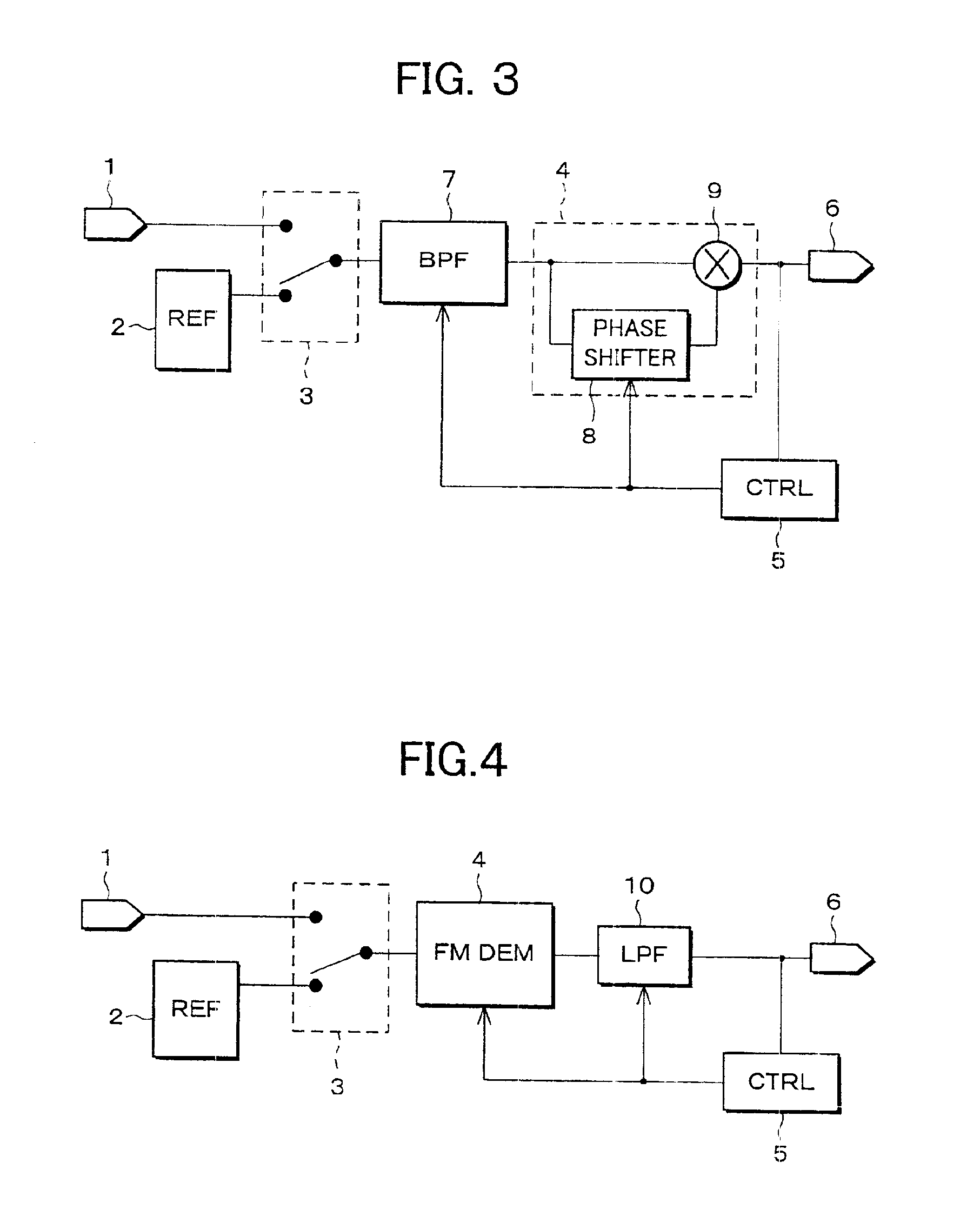
A demodulator includes a reference signal generator for generating a reference signal, an FM demodulation circuit for demodulating a modulated signal, and a control circuit for controlling demodulation sensitivity of the FM demodulation circuit. The control circuit controls the demodulation sensitivity of the FM demodulation circuit so that an output signal, obtained when the reference signal from the reference signal generator is inputted to the FM demodulation circuit, becomes a specified value. This structure can stabilize the demodulation sensitivity of the demodulation circuit while restraining increases in circuit scale and current consumption, and can adjust dispersions in the demodulation sensitivities of the respective ICs due to relative errors of a resistance value of a resistor and a capacity value of a condenser in an IC, the resistor and the condenser constituting the demodulator.
Owner:SHARP KK
Low IF radio receiver
InactiveUS7697632B2Frequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsRadio receiver designLocal oscillator signal
A slot-based low Intermediate Frequency (‘IF’) radio receiver comprises an IF local oscillator for producing I and Q IF local oscillator signal components in phase quadrature, and I and Q mixer channels for mixing the input signal with the I and Q IF local oscillator signal components to produce I and Q IF signal components. The IF local oscillator frequency alternates a plurality of times during each frame between first and second values, one of which is greater and the other smaller than the desired carrier frequency of the input signal so as to reduce the effect of adjacent and alternate interferers. The phase of the baseband local oscillator is alternated in synchronism with the alternation of the IF local oscillator frequency.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
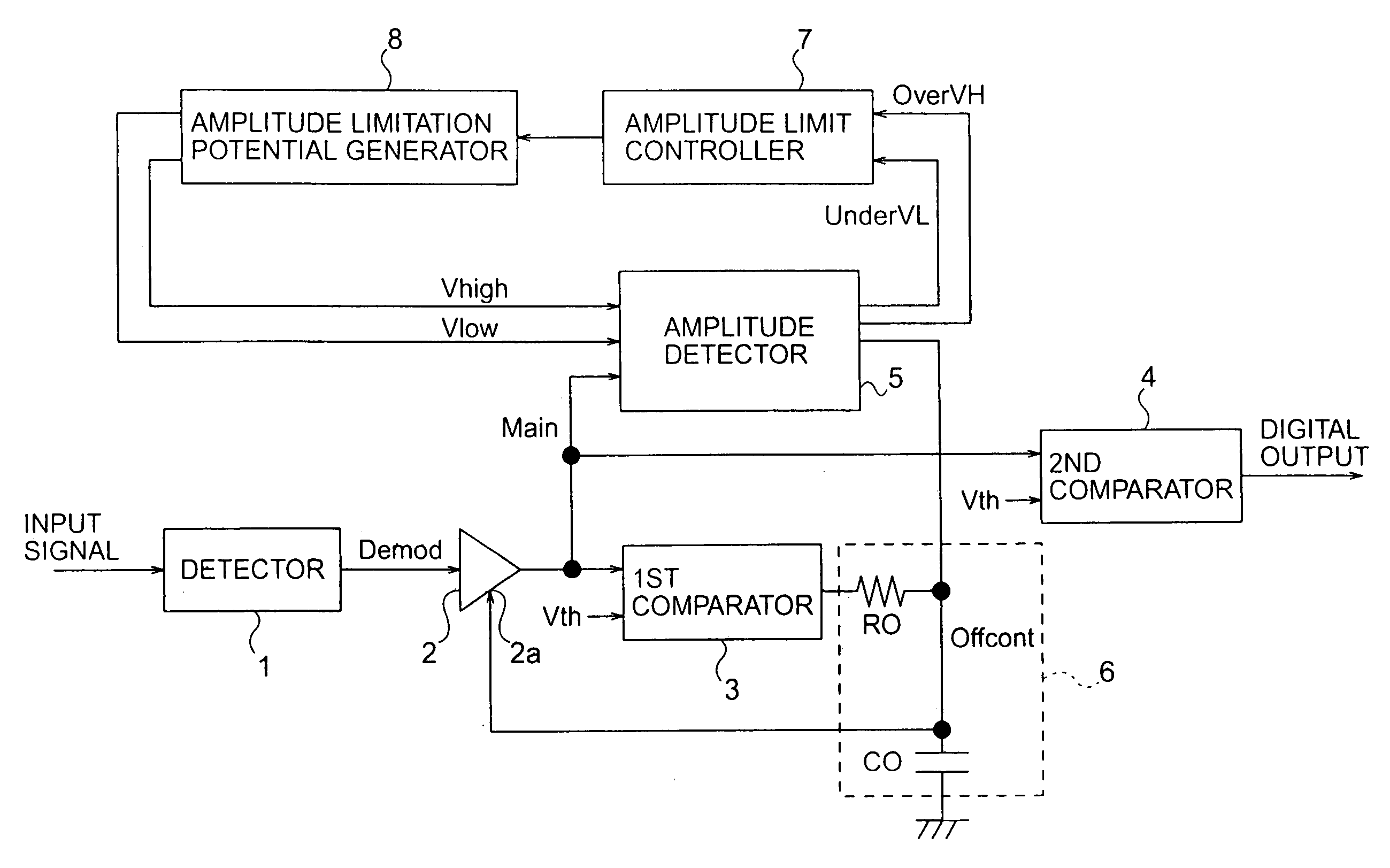
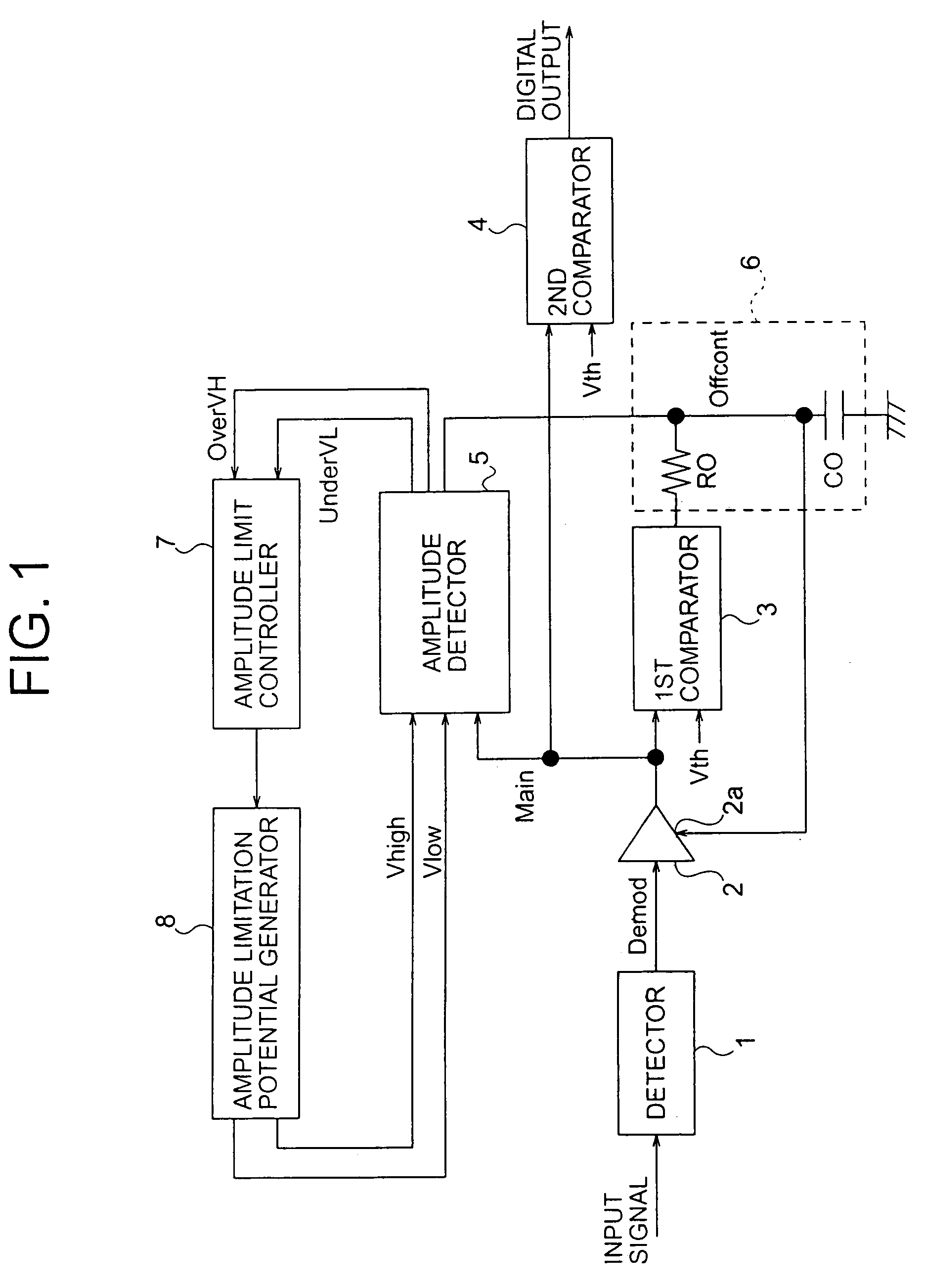
Signal compensation circuit and demodulating circuit with high-speed and low-speed feedback loops
InactiveUS7035349B2Quick compensationThe output signal is accurateDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
A signal compensation circuit compensates for direct-current offset of an input signal by amplifying the input signal with an amplifier having a variable direct-current offset. A low-speed negative feedback loop charges and discharges a capacitor in an integrating circuit according to the direct-current component of the amplified signal. A high-speed negative feedback loop charges and discharges the same capacitor at a faster rate when the amplified signal goes outside an allowable amplitude range. The capacitor potential is used to control the direct-current offset of the amplifier. The allowable amplitude range is adjusted according to the amplitude of the amplified signal. High-speed compensation can thus be combined with a tolerance for runs of identical code levels in the input signal.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Very low intermediate frequency (VLIF) receiver and a method of controlling a VLIF receiver
ActiveUS9608679B2Frequency demodulator arrangementsTransmissionAdjacent-channel interferenceIntermediate frequency
A very low intermediate frequency (VLIF) receiver and a method of controlling a VLIF receiver. The method comprises estimating energy levels in first and second signals and detecting interference from a first adjacent channel interferer based upon a difference in energy in the first and second signals. The first signal comprising a first on-channel portion and an adjacent channel portion and the second signal comprises an intermediate frequency translation of the first on-channel portion. The energy levels are estimated for corresponding time instances and the adjacent channel interferer is of the adjacent channel portion. The VLIF receiver is then controlled based upon the detected interference.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Methods and apparatus for calibrating oscillators in a receiver
ActiveUS7720451B2Frequency demodulator arrangementsModulation transferenceFrequency conversionEngineering
A receiver includes a first oscillator supplying a reference frequency signal; a reference signal generator producing a first frequency conversion signal and a local calibration signal from the reference frequency signal; a first frequency converter responsive to the first frequency conversion signal to down-convert the received signal during normal receive operation and to down-convert the local calibration signal during calibration processing; a second frequency converter responsive to a second frequency conversion signal from a second oscillator to further down-convert the received signal and the local calibration signal; a demodulator that demodulates the received signal at a demodulation frequency; and a frequency error processor that determines a frequency error from the local calibration signal at the demodulation frequency, wherein the reference signal generator adjusts a frequency of the first frequency conversion signal used during normal receive operation in response to the frequency error to compensate for the frequency error.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
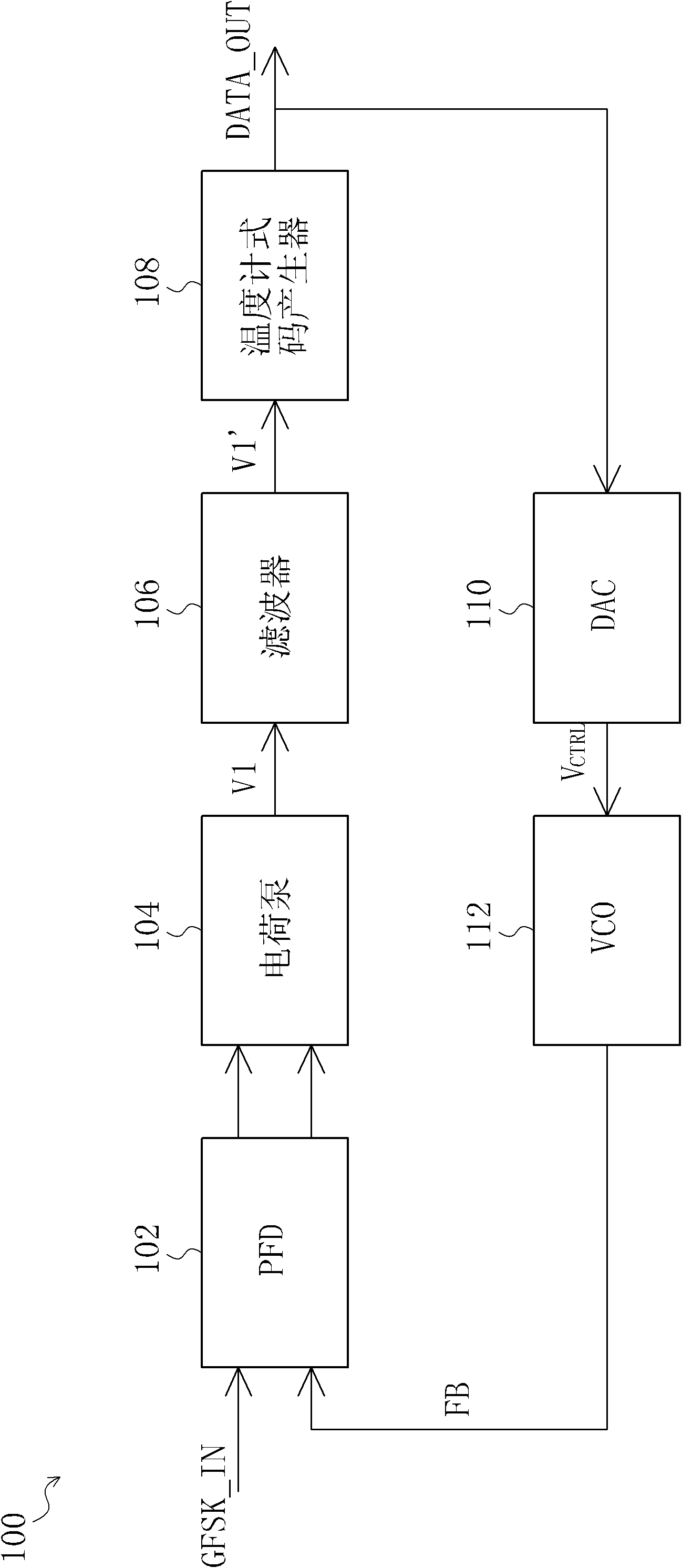
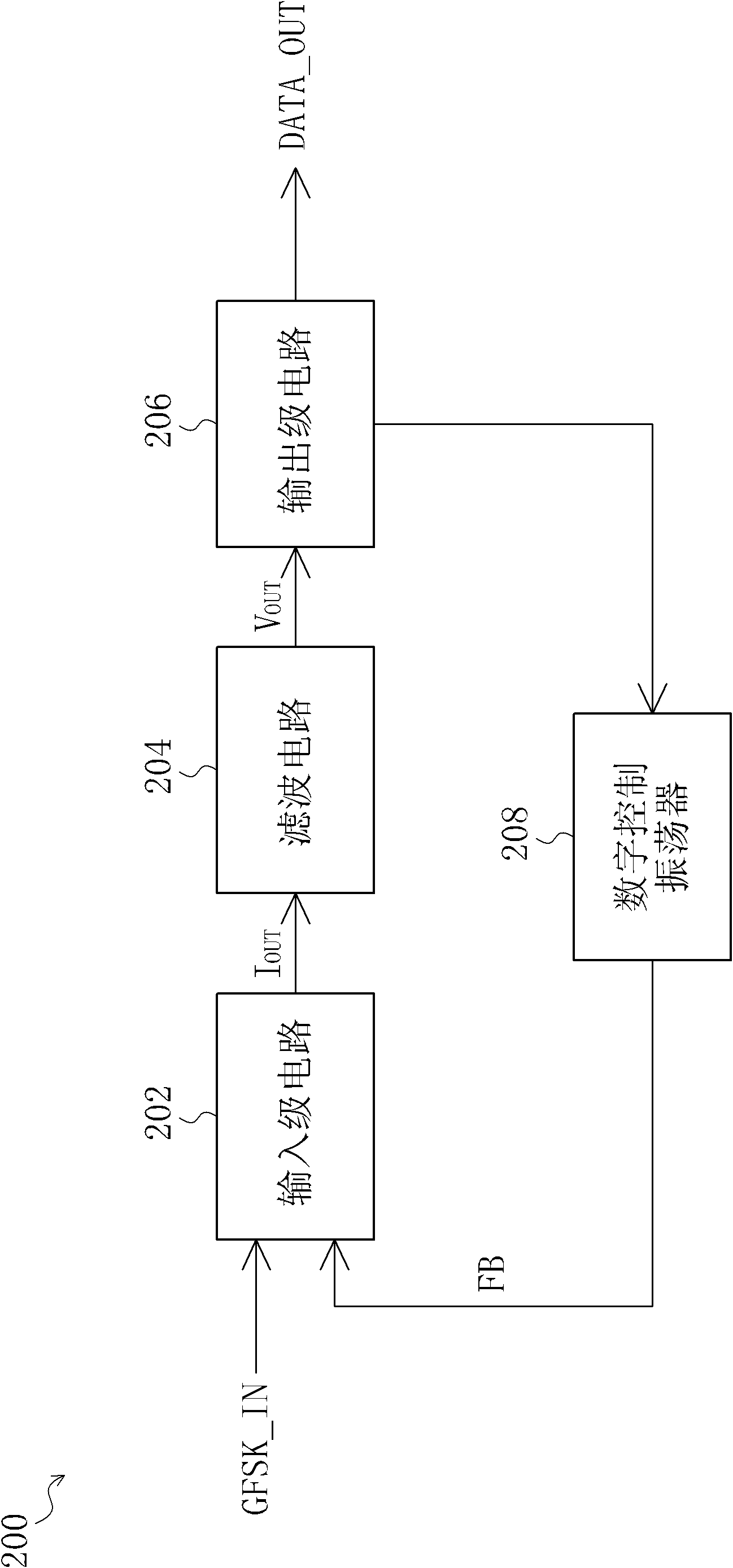
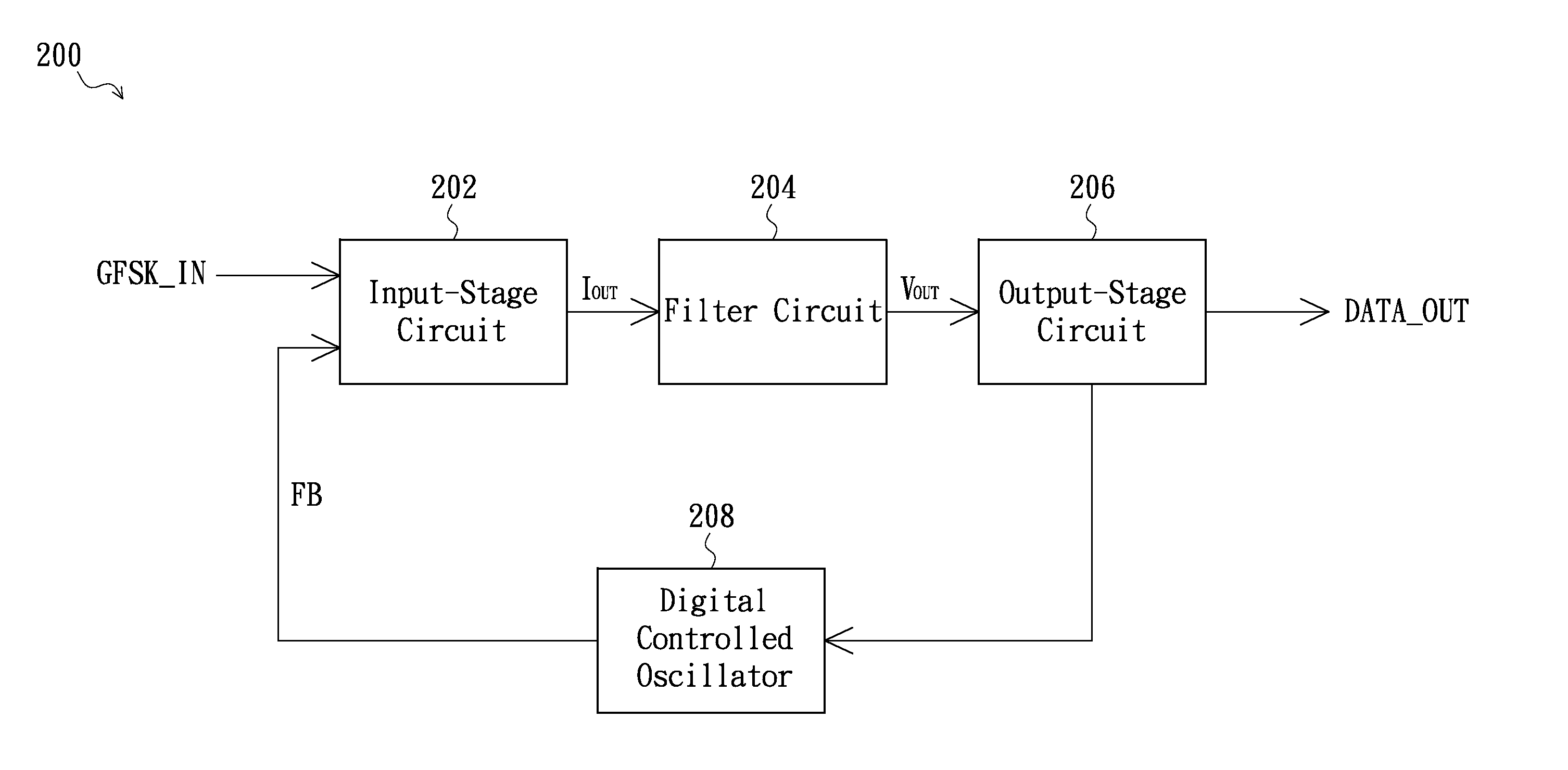
Receiver
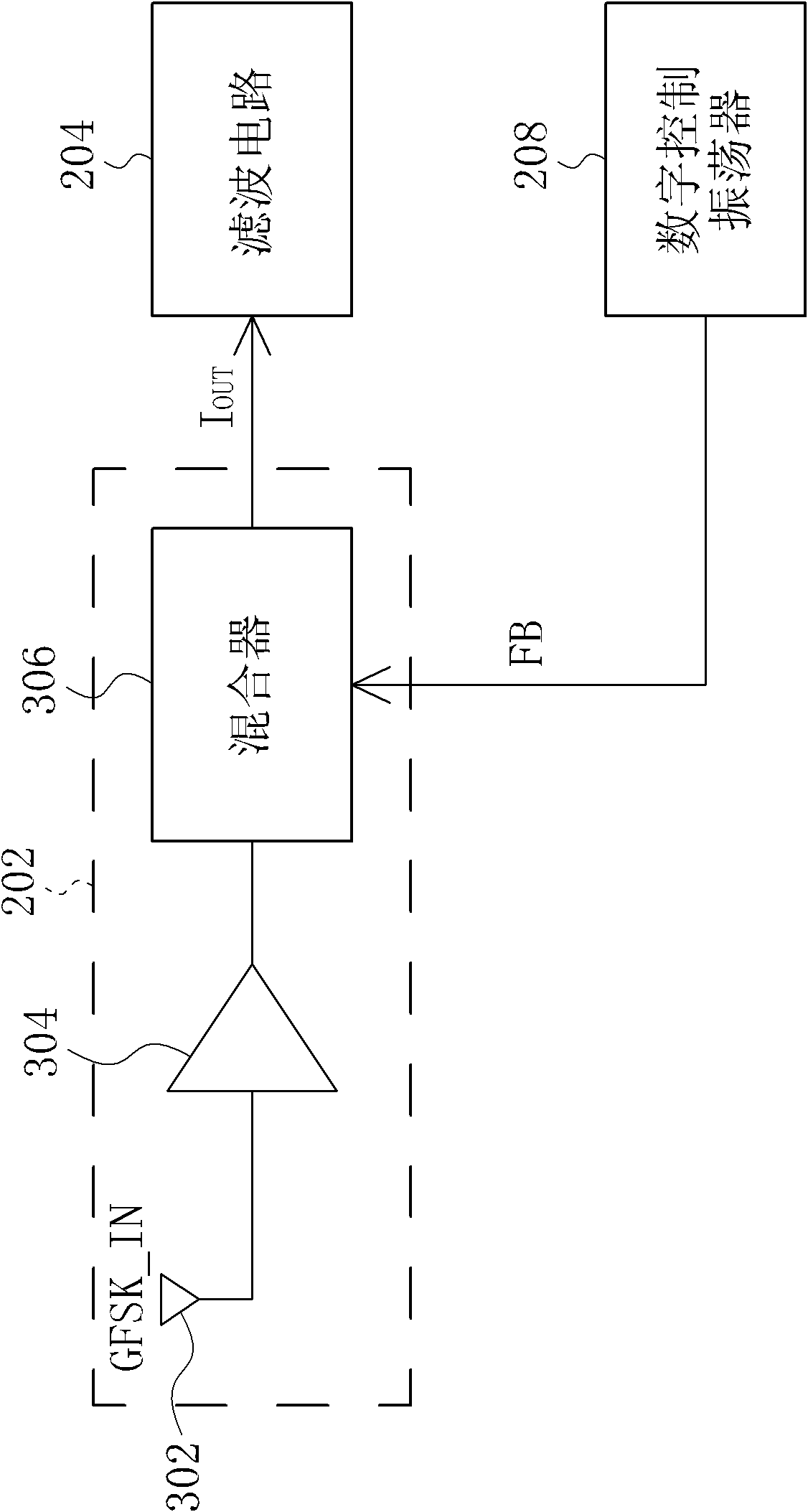
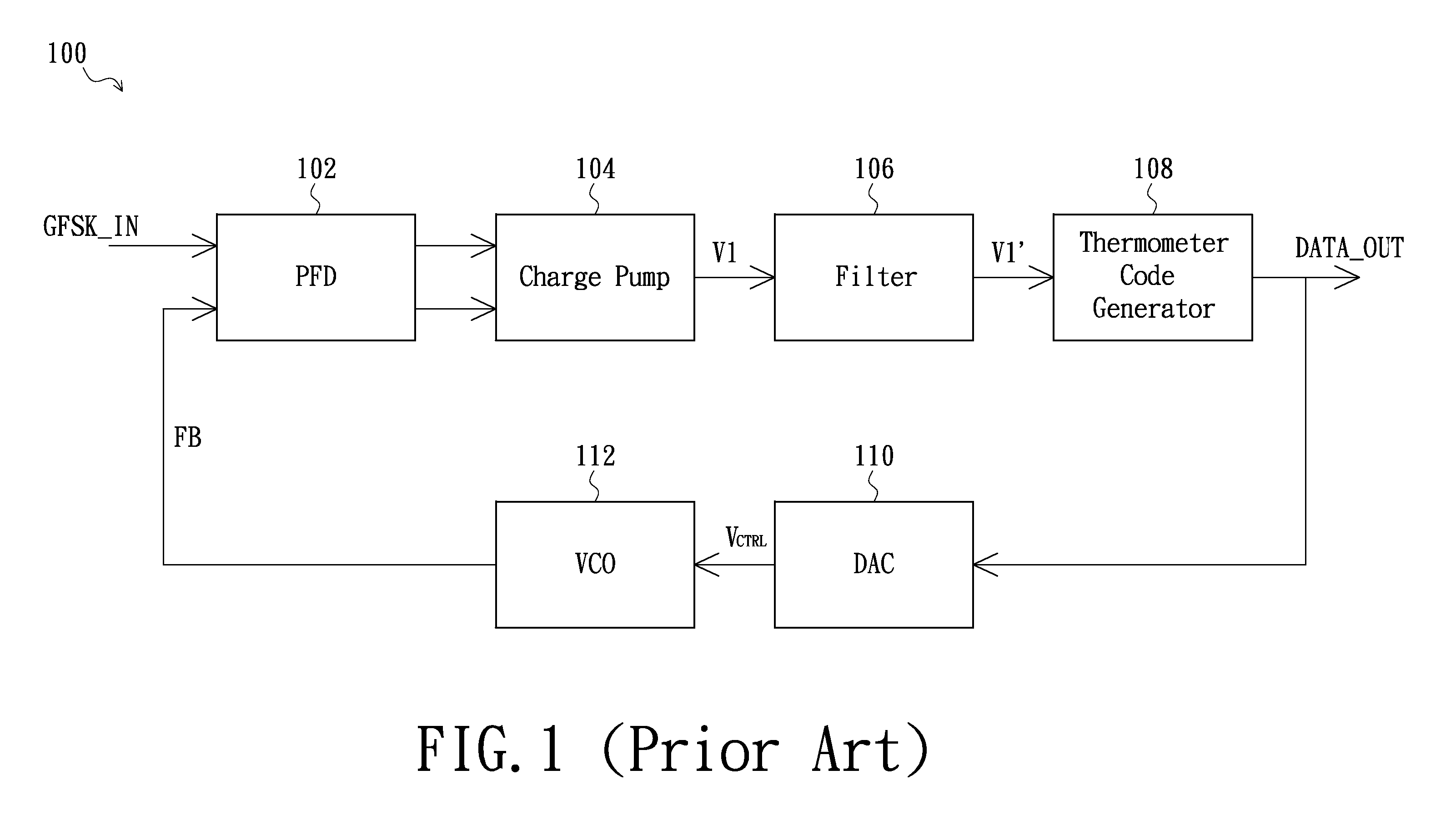
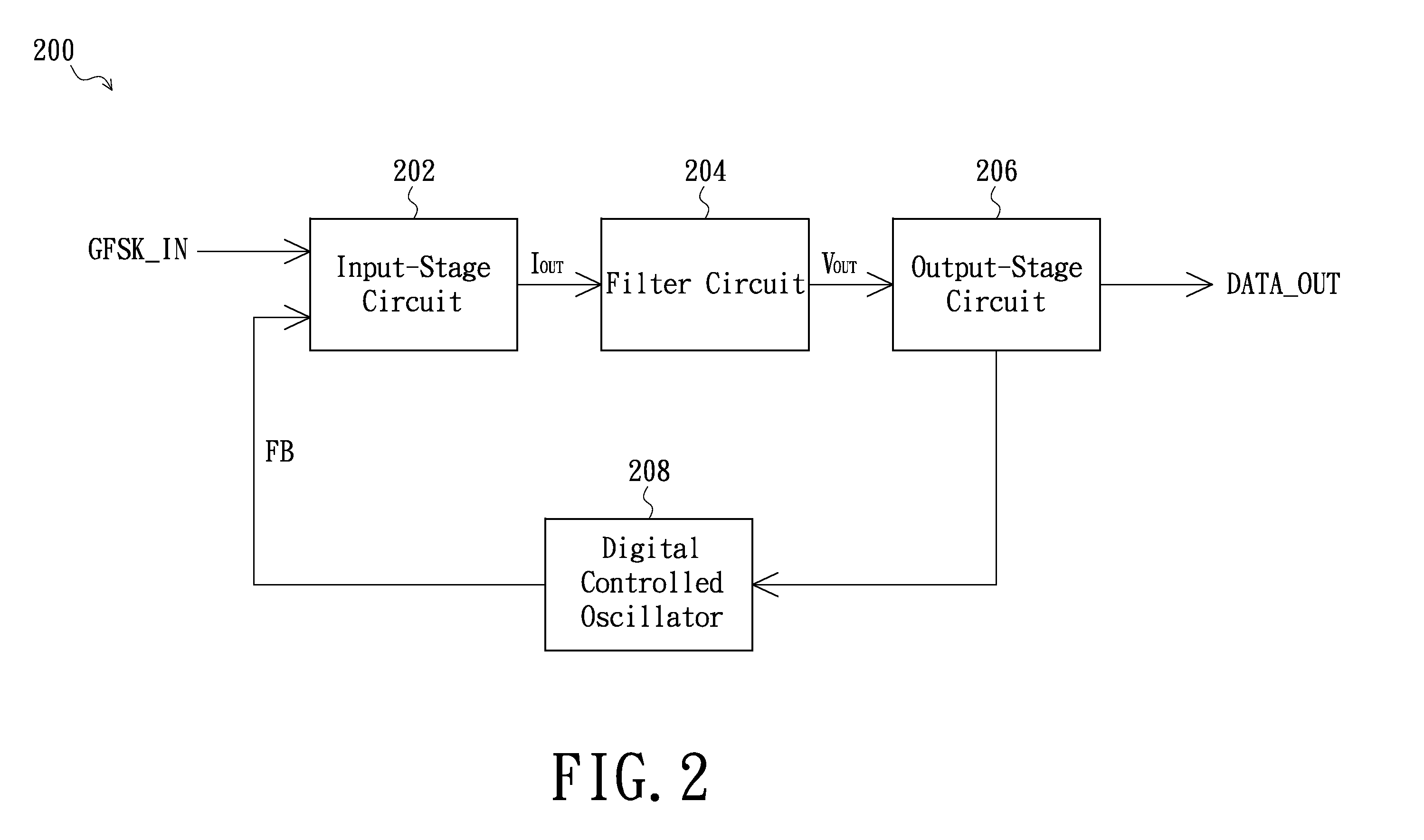
InactiveCN102594751AFrequency demodulator arrangementsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsPower flowDigital controlled oscillator
A receiver comprises an input-stage circuit, a filter circuit, an output-stage circuit and a digital control oscillator. The input-stage circuit has a mixer configured for mixing the GFSK signal and a feedback signal to generate an input-stage current signal to the filter circuit. Then the filter circuit filters the input-stage current signal, and converts it into a voltage signal. The output-stage circuit is coupled to the filter circuit, for converting the voltage signal into a digital output data. In addition, the digital control oscillator is coupled to the output-stage circuit, for outputting the feedback signal based on the digital output data.
Owner:林宗贤
Digital cancellation of radio frequency interference
ActiveUS7542531B2Less complexImprove performanceFrequency demodulator arrangementsError preventionFrequency spectrumEngineering
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
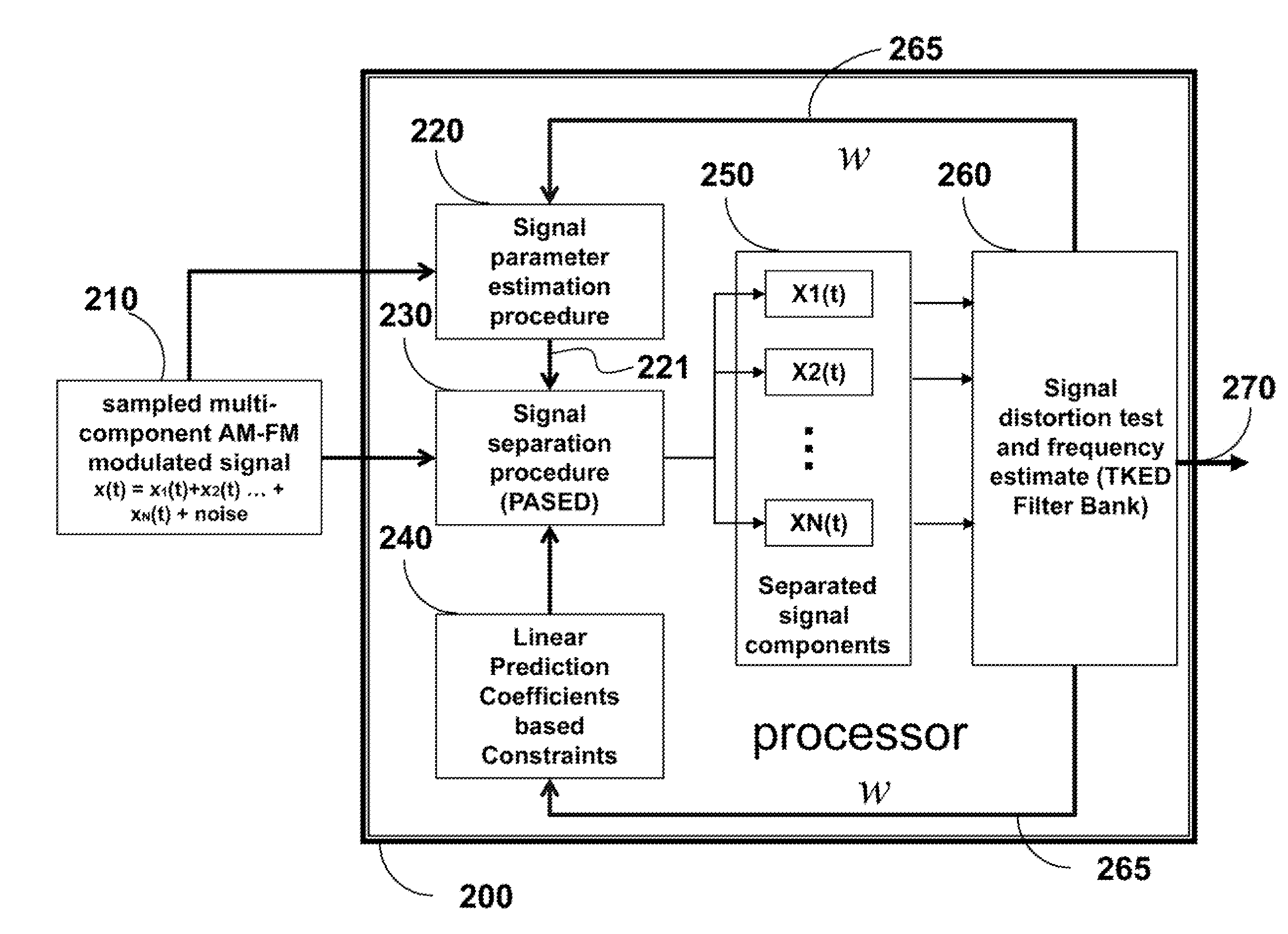
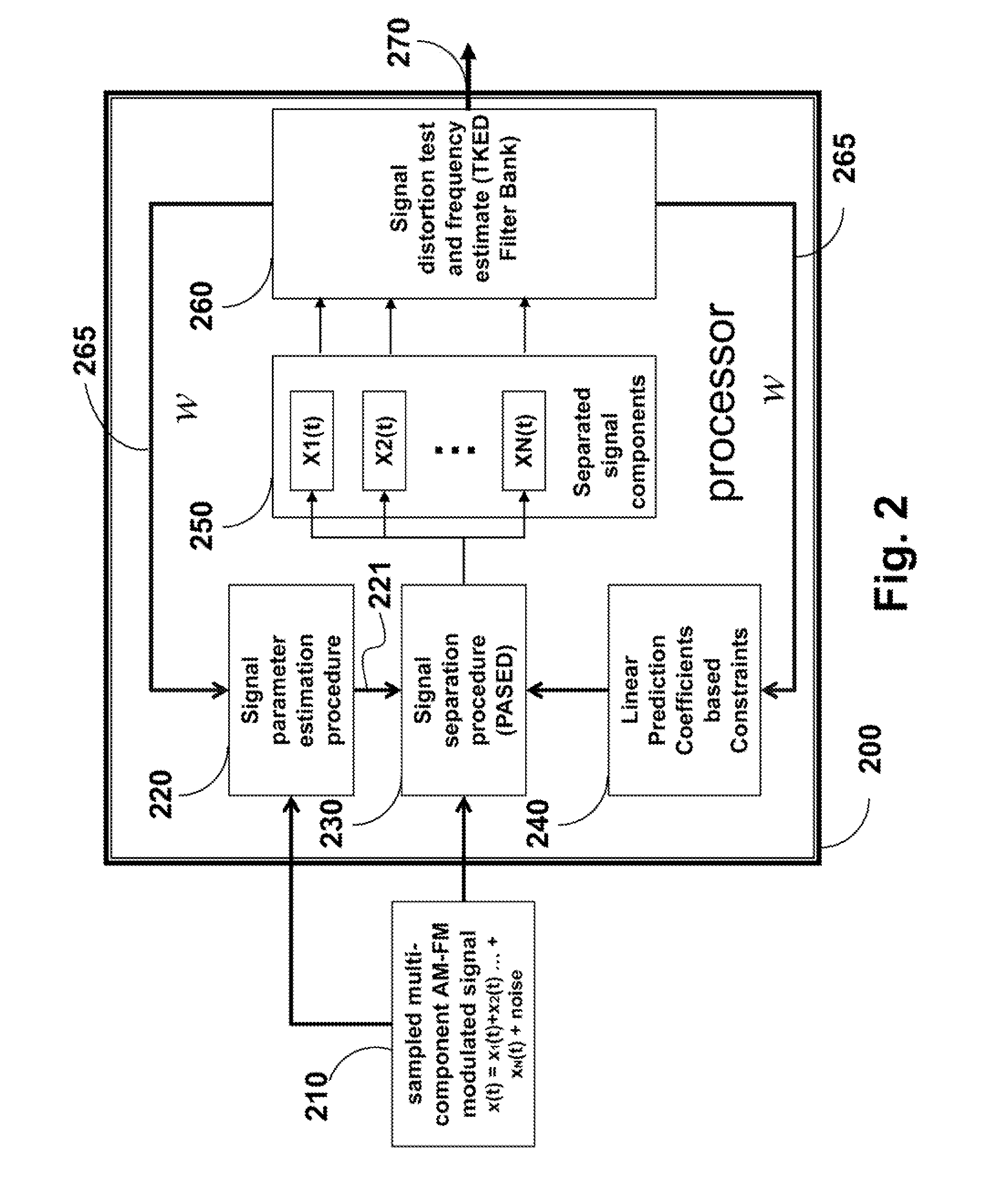
Method for Separating Multi-Component Signals
InactiveUS20150109053A1Enhance separation of signalEasy to separateFrequency demodulator arrangementsSimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationEnergy basedDemodulation
A method separates a multi-component signal by first estimating parameters of the signal. Then, using periodicity-based algebraic separation and energy-based demodulation, the signal is separated into components according to the parameters and constraints. Last, a Teager-Kaiser energy detector is applied to each component to provide a direct current signal for each component, and the constraint for each component used by the separating.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Systems and methods for managing power consumption
InactiveUS20120184236A1Consumes less powerExtend battery lifeFrequency demodulator arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsGps receiverGps navigation
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
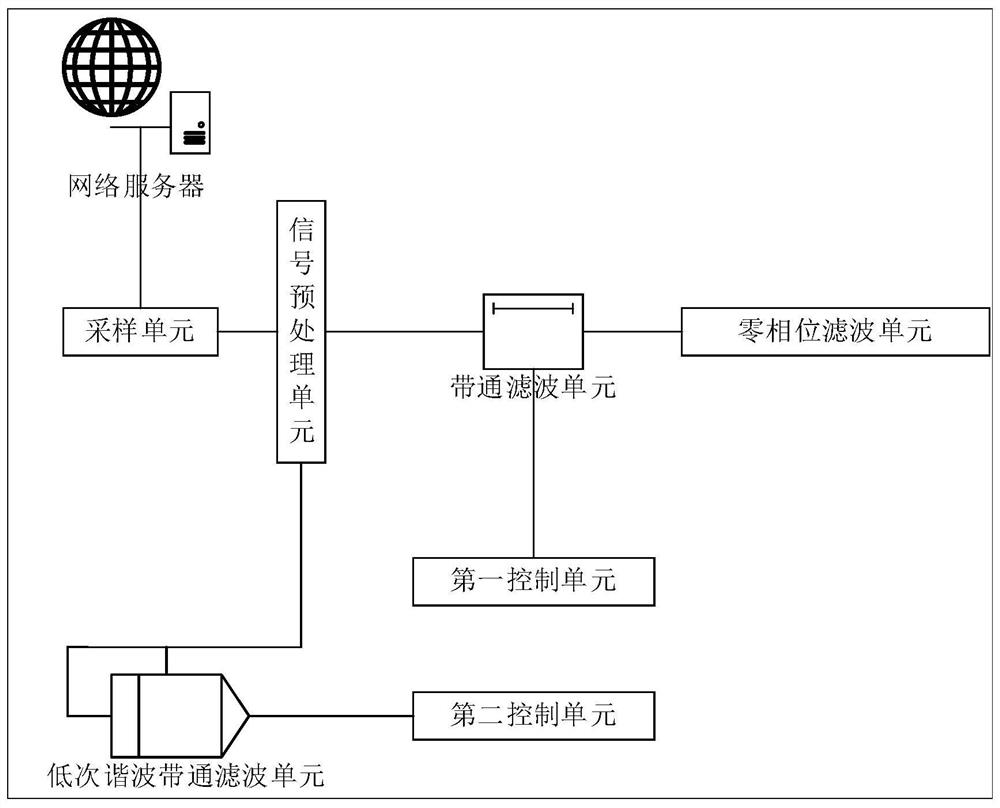
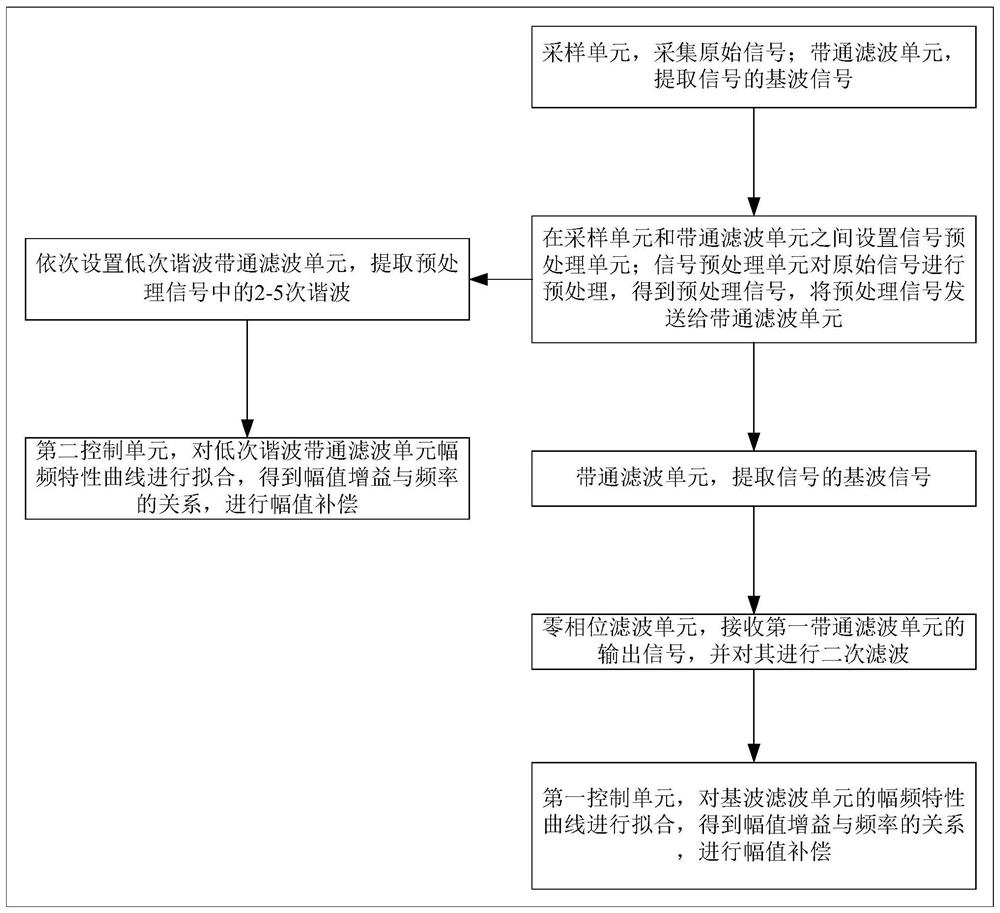
Broadband bandpass filter system and method
InactiveCN111697927AImprove accuracyEasy to filterMultiple-port networksFrequency demodulator arrangementsBandpass filteringSoftware engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication, and particularly relates to a broadband band-pass filter system and method, and the system comprises: a sampling unit which is used for collecting an original signal; ta band-pass filtering unit which is used for extracting fundamental wave signals of the signals; a zero-phase filtering unit which is used for receiving the output signal of the first band-pass filtering unit and carrying out secondary filtering on the output signal; and a first control unit which is used for fitting the amplitude-frequency characteristic curve of the fundamental wave filtering unit to obtain the relationship between the amplitude gain and the frequency, and carrying out amplitude compensation. After an original signal is collected, the originalsignal is preprocessed, when band-pass filtering is carried out on the preprocessed signal, a fundamental wave signal of the preprocessed signal is more easily extracted, and then signal amplitude compensation is carried out on the extracted fundamental wave signal, so that the accuracy of the finally band-pass signal is higher, and meanwhile, the band-pass filtering efficiency is higher.
Owner:HANGZHOU LEGEND INTELLIGENT EQUIP CO LTD
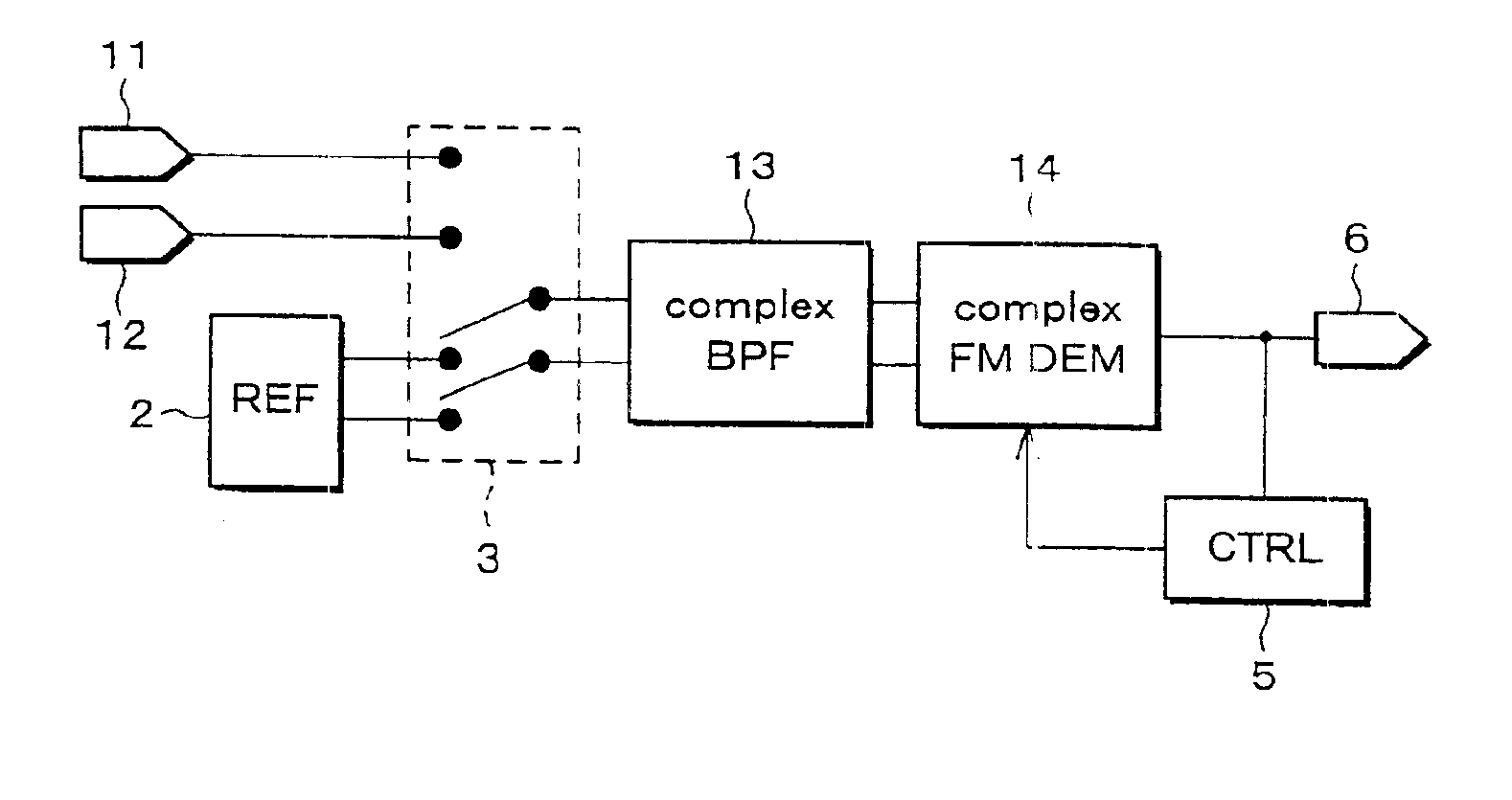
Radio receiver and intermediate frequency signal generation method
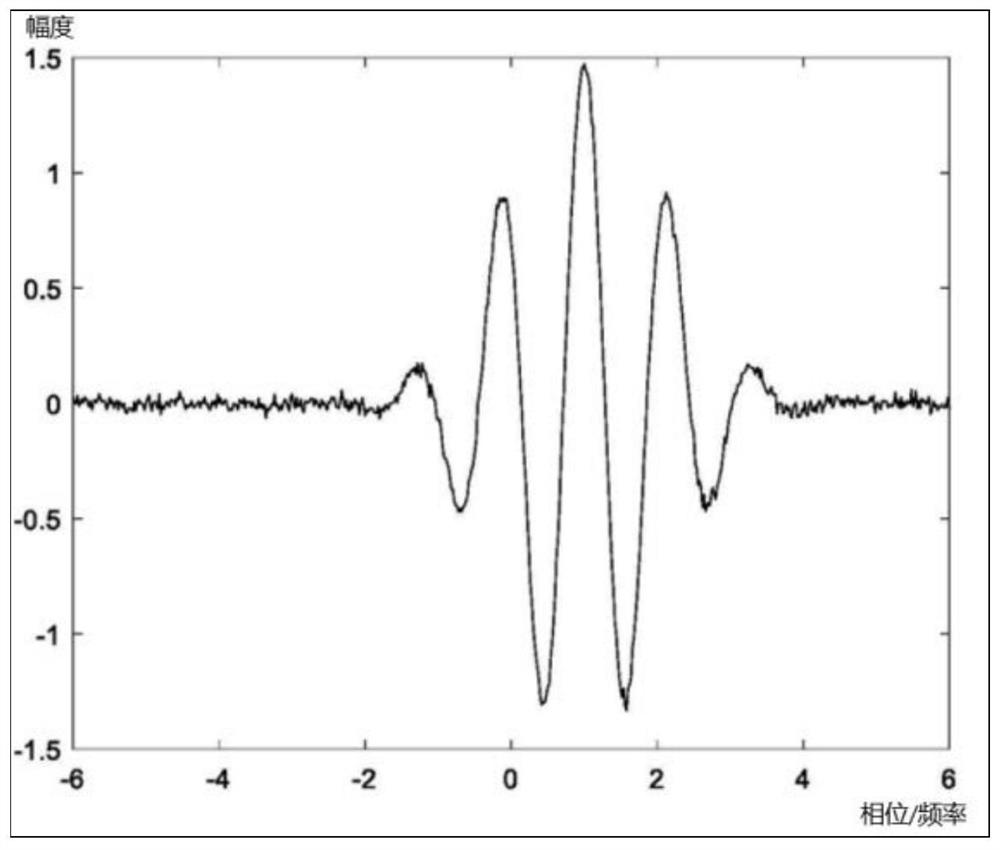
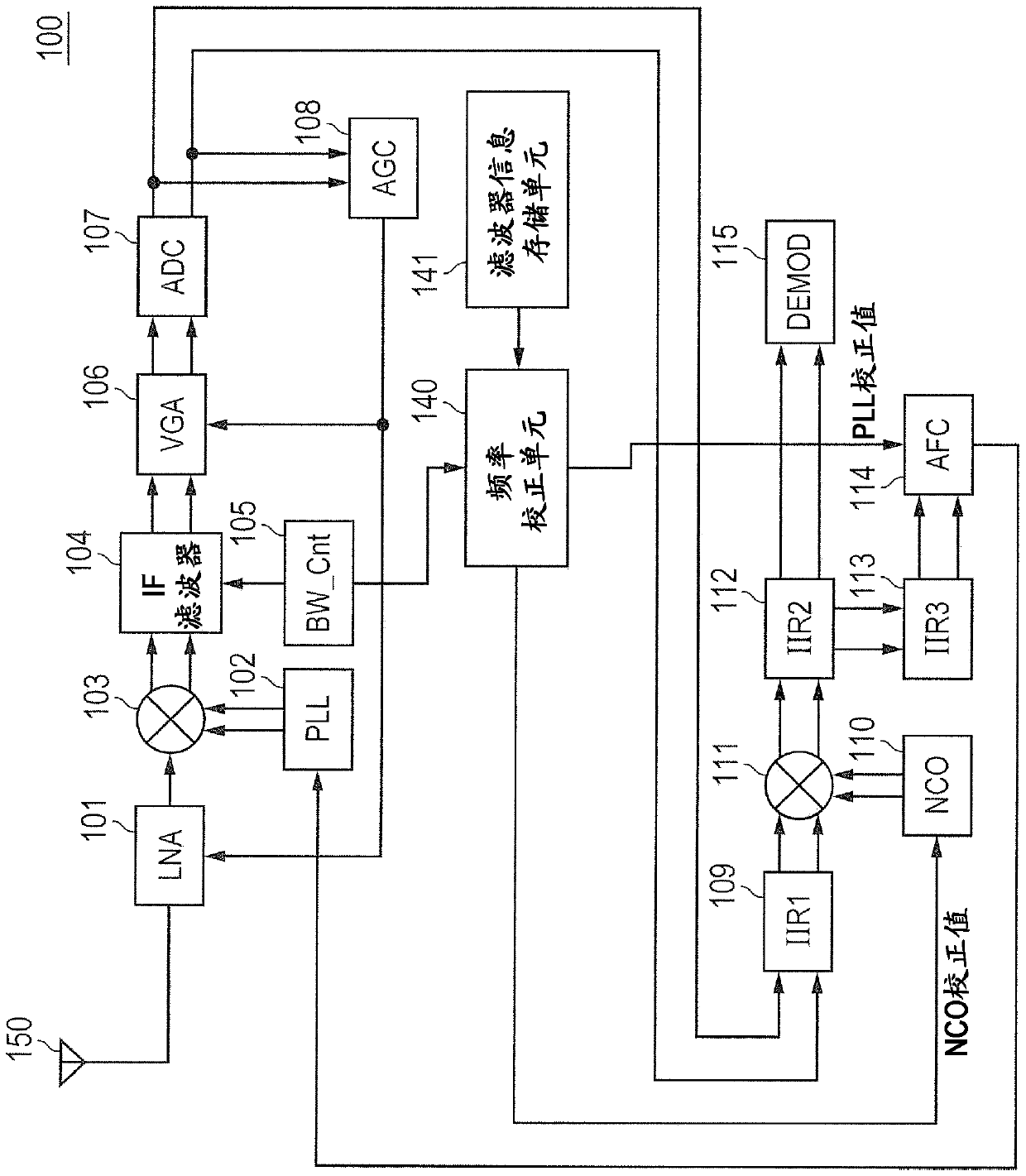
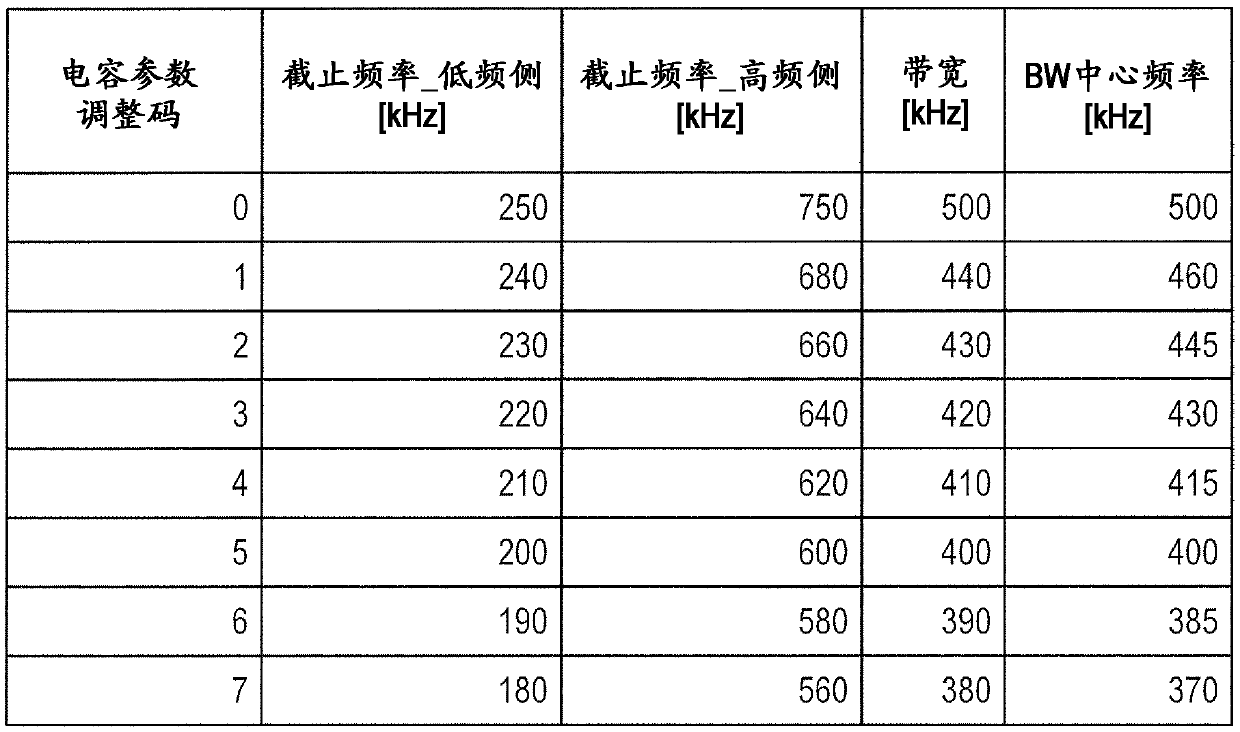
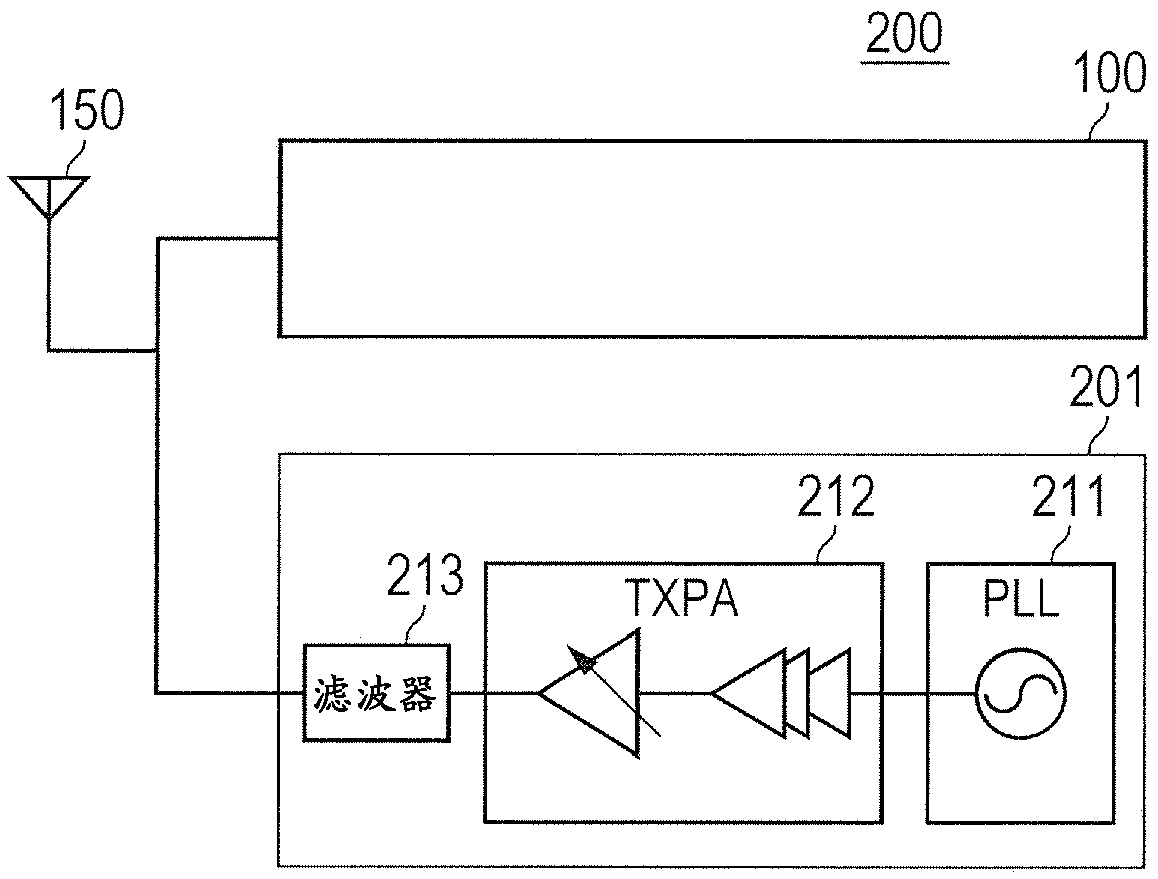
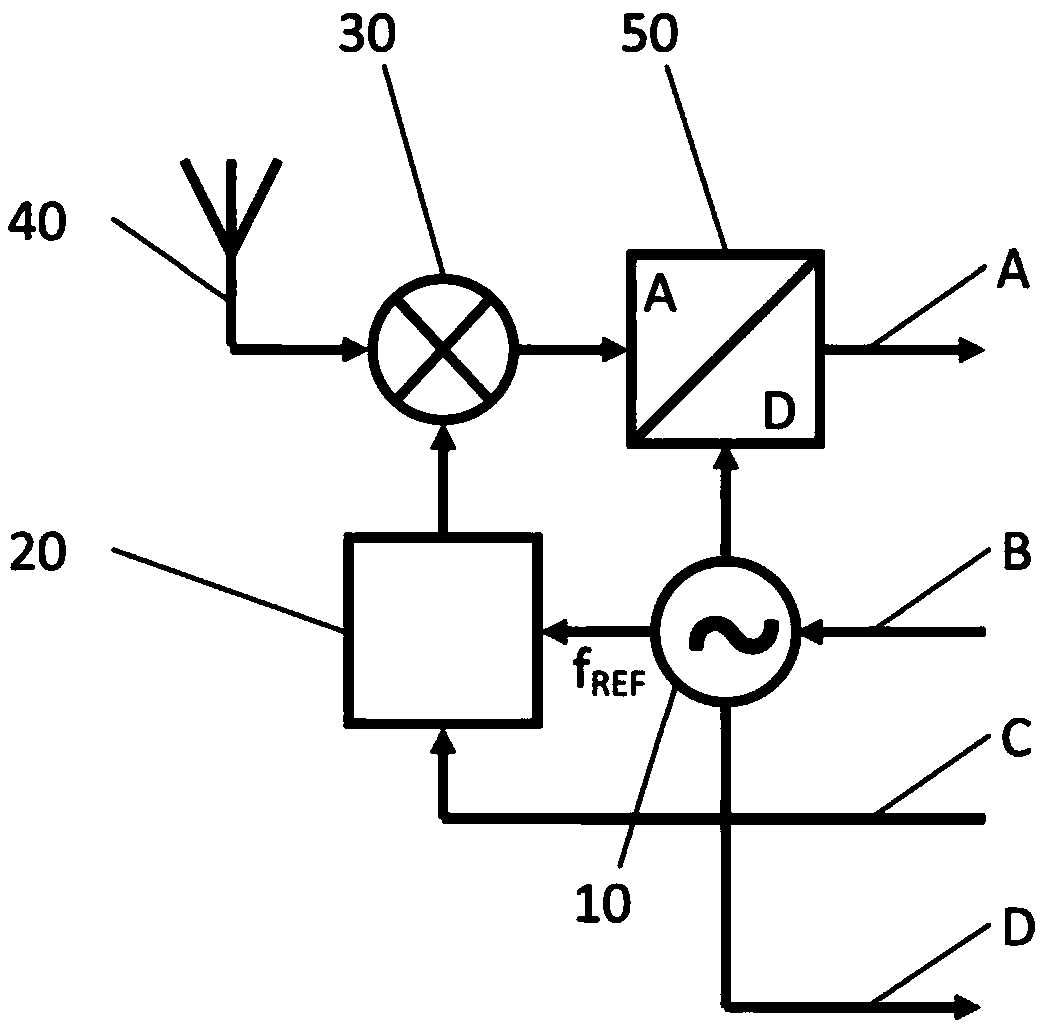
ActiveCN109905138APrevents deterioration of reception performanceFrequency demodulator arrangementsModulation transferenceIntermediate frequencyRadio receiver
The disclosure relates to a radio receiver and an intermediate frequency signal generation method, and specifically relates to an IF filter that band-limits an intermediate frequency signal outputtedfrom a mixer. An AFC unit controls the oscillation frequency of a PLL so that the frequency of the intermediate frequency signal is a predetermined frequency. When the AFC unit controls the oscillation frequency of the PLL, a band control unit controls the passing characteristic of the IF filter to the passing characteristic of a wide band, and after the completion of the control, controls the passing characteristic of the IF filter to the passing characteristic of a narrow band. A frequency correction unit refers to a filter information storage unit, and corrects the oscillation frequency controlled by the AFC unit according to the difference between the center frequency of the passband of the passing characteristic of the wide band and the center frequency of the passband of the passingcharacteristic of the narrow band.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
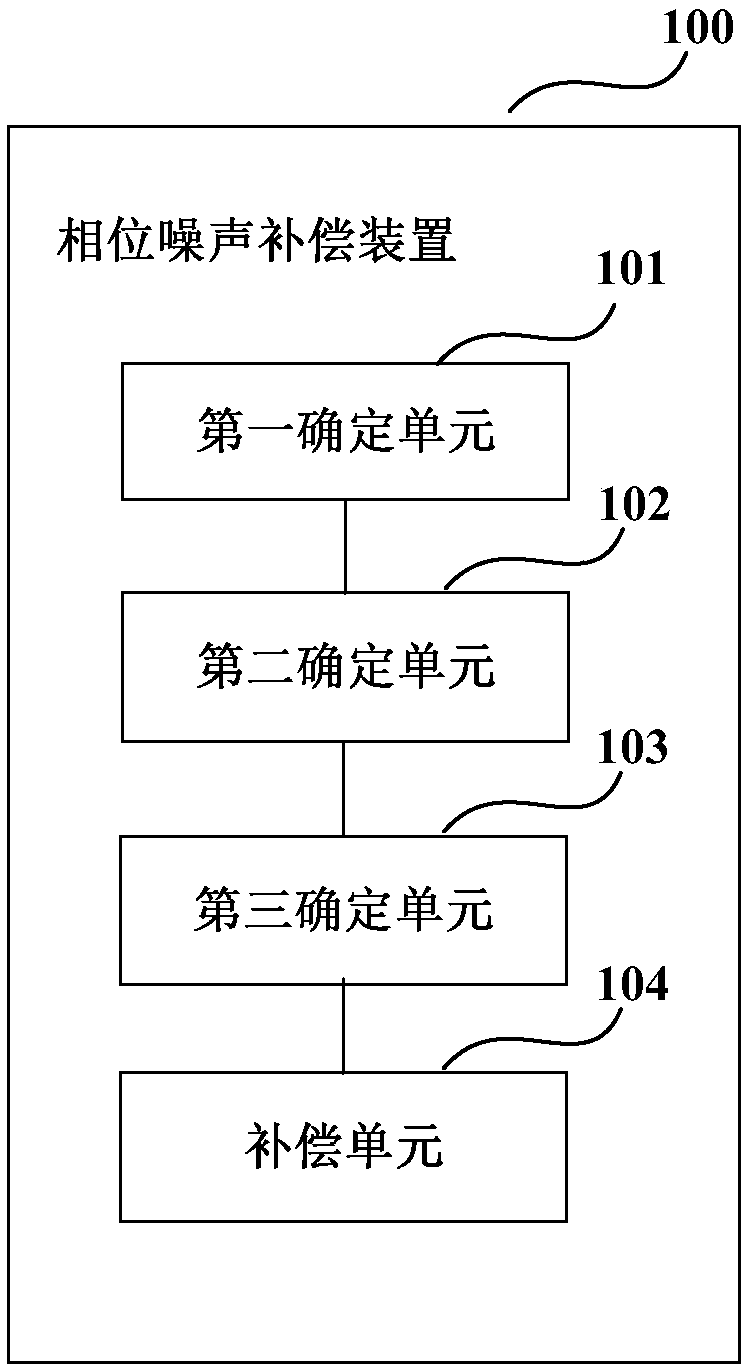
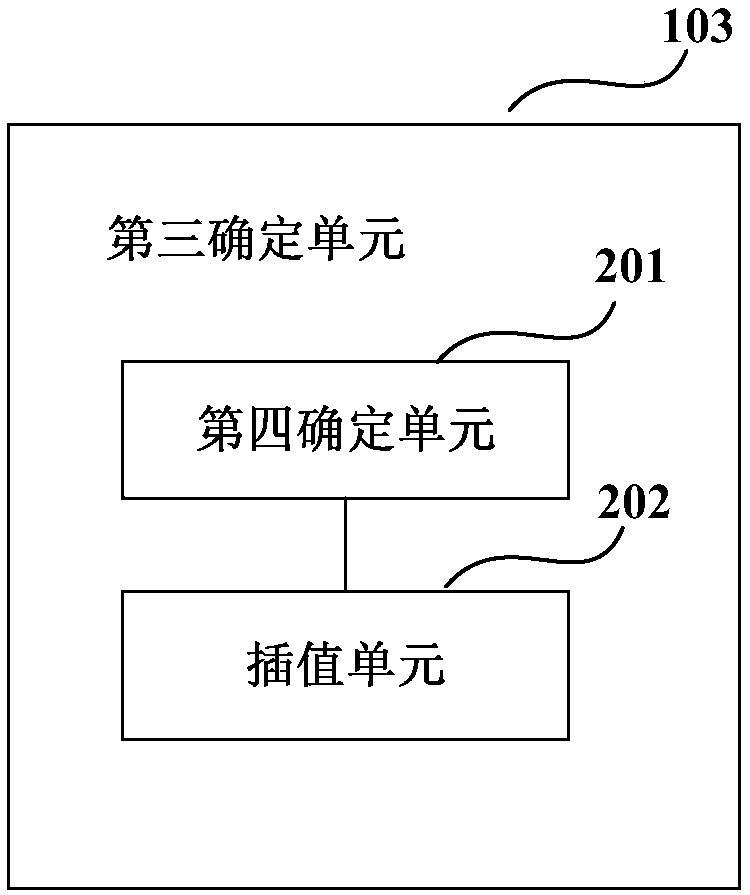
Phase noise compensation device and method and receiver
ActiveCN110460385AAccurate estimateGuaranteed transmission efficiencyFrequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsSequence signalPhase noise
The embodiment of the invention provides a phase noise compensation device, a phase noise compensation method and a receiver. The method comprises steps of determining a correction signal according tothe estimated value of the non-ideal parameter of the transmitter and the training sequence signal in the transmitted signal; and determining the phase noise of the received signal according to the correction signal, so that the influence of the non-ideal transmitter on the phase noise is considered, the phase noise can be accurately estimated, the phase noise can be effectively compensated, andthe transmission efficiency and performance of the system are ensured.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
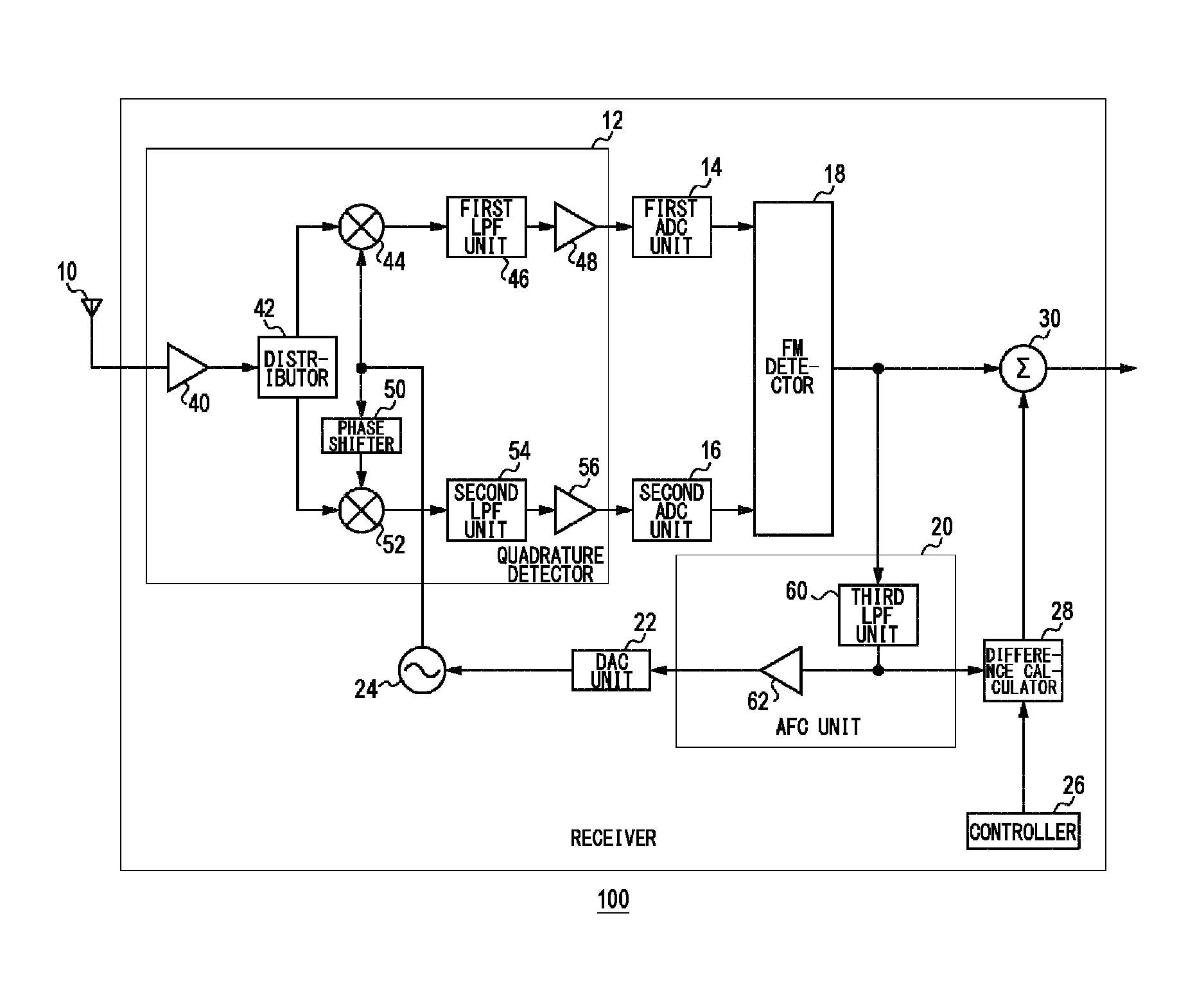
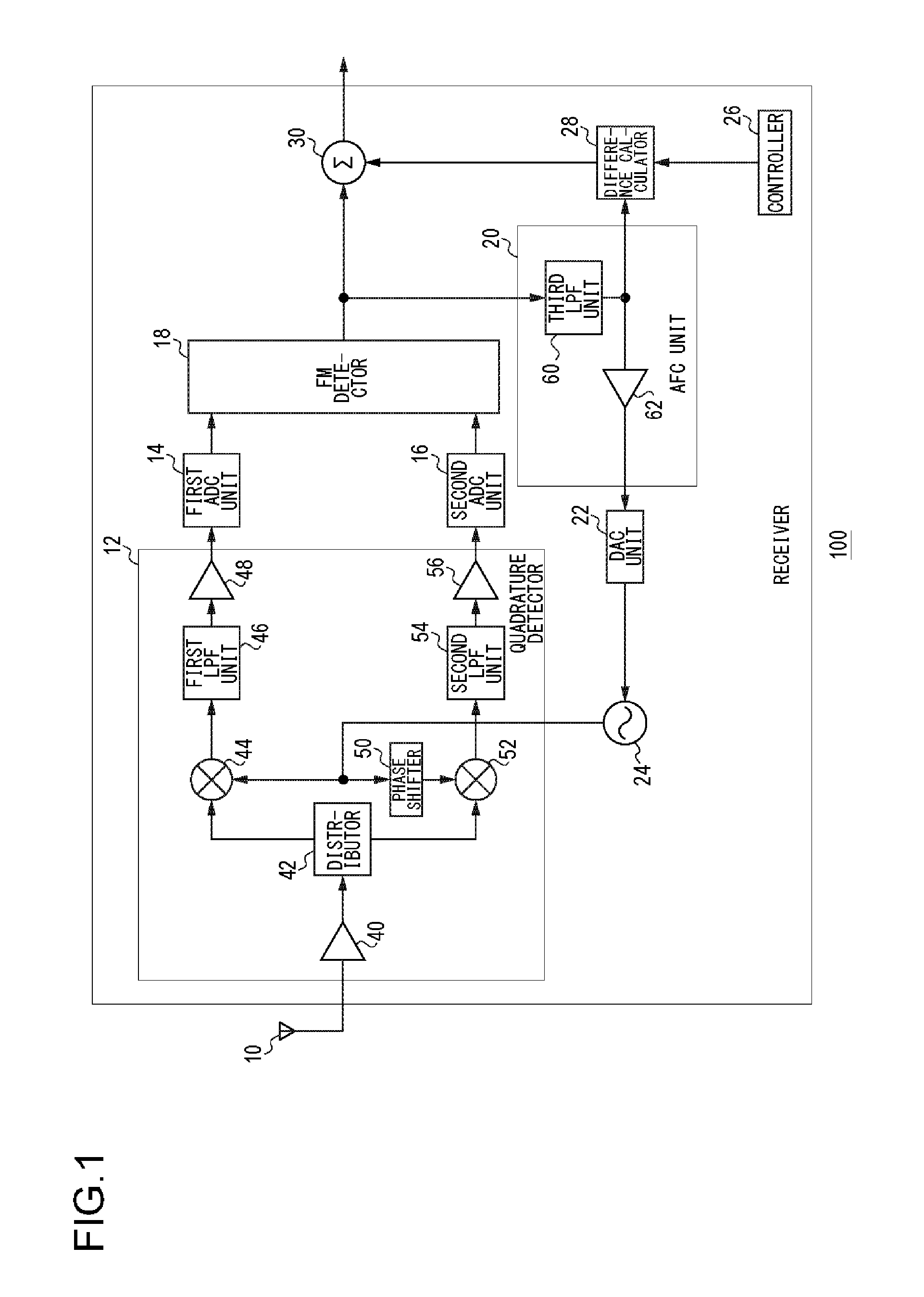
FM receiver that receives fm signal and method for receiving FM signal
ActiveUS9461587B2Reduce impactFrequency demodulator arrangementsTransmissionControl signalLocal oscillator
A quadrature detector quadrature-detects an FM signal. An FM detector generates a detection signal by FM detecting an FM signal that has been quadrature-detected. An AFC unit generates a control signal for controlling a frequency of a local oscillation signal used for quadrature detection on the basis of the generated detection signal, and feeds back the control signal to a local oscillator that should output the local oscillation signal. A difference calculator generates a difference signal representing a difference from a reference value on the basis of the generated detection signal. An addition unit adds the generated difference signal and the generated detection signal.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
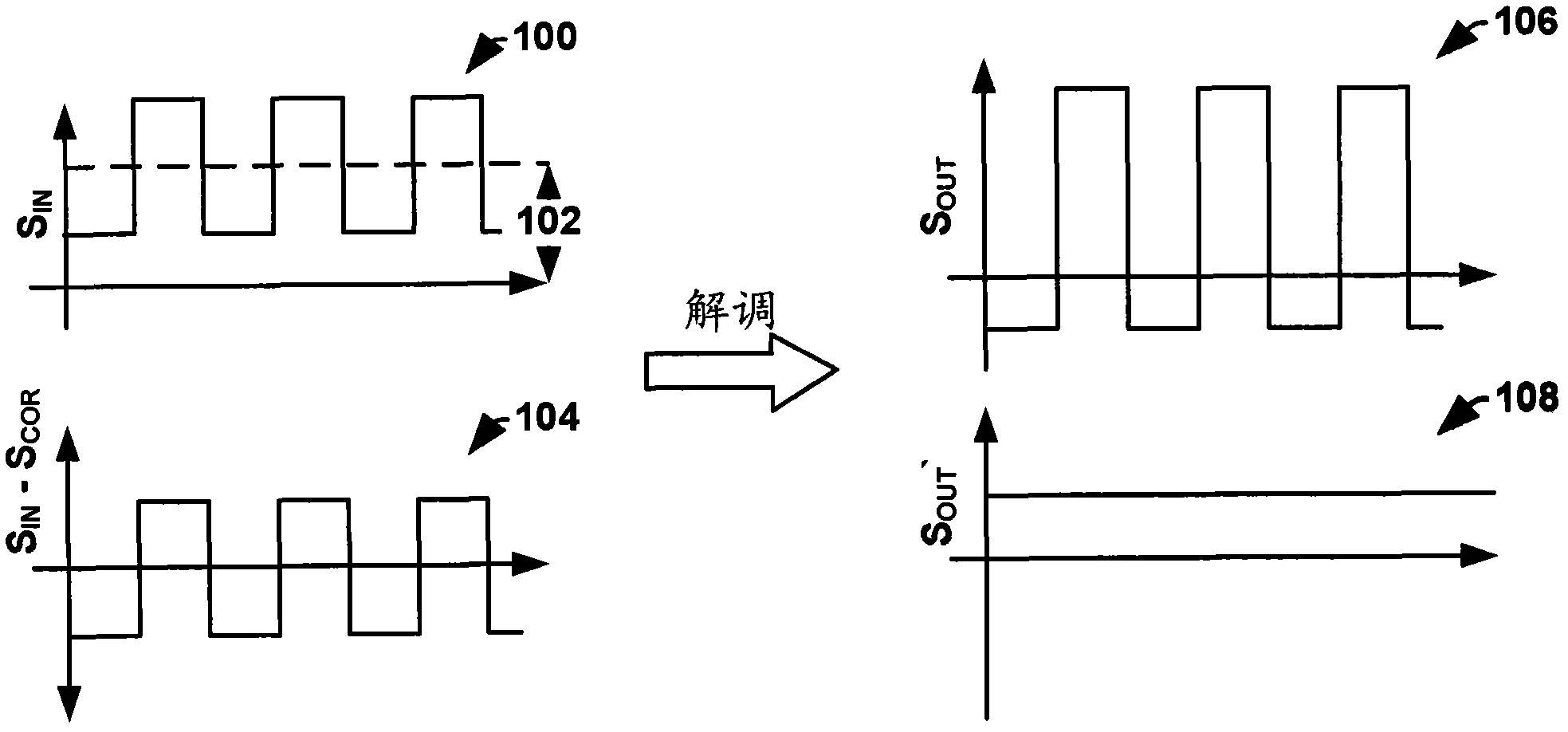
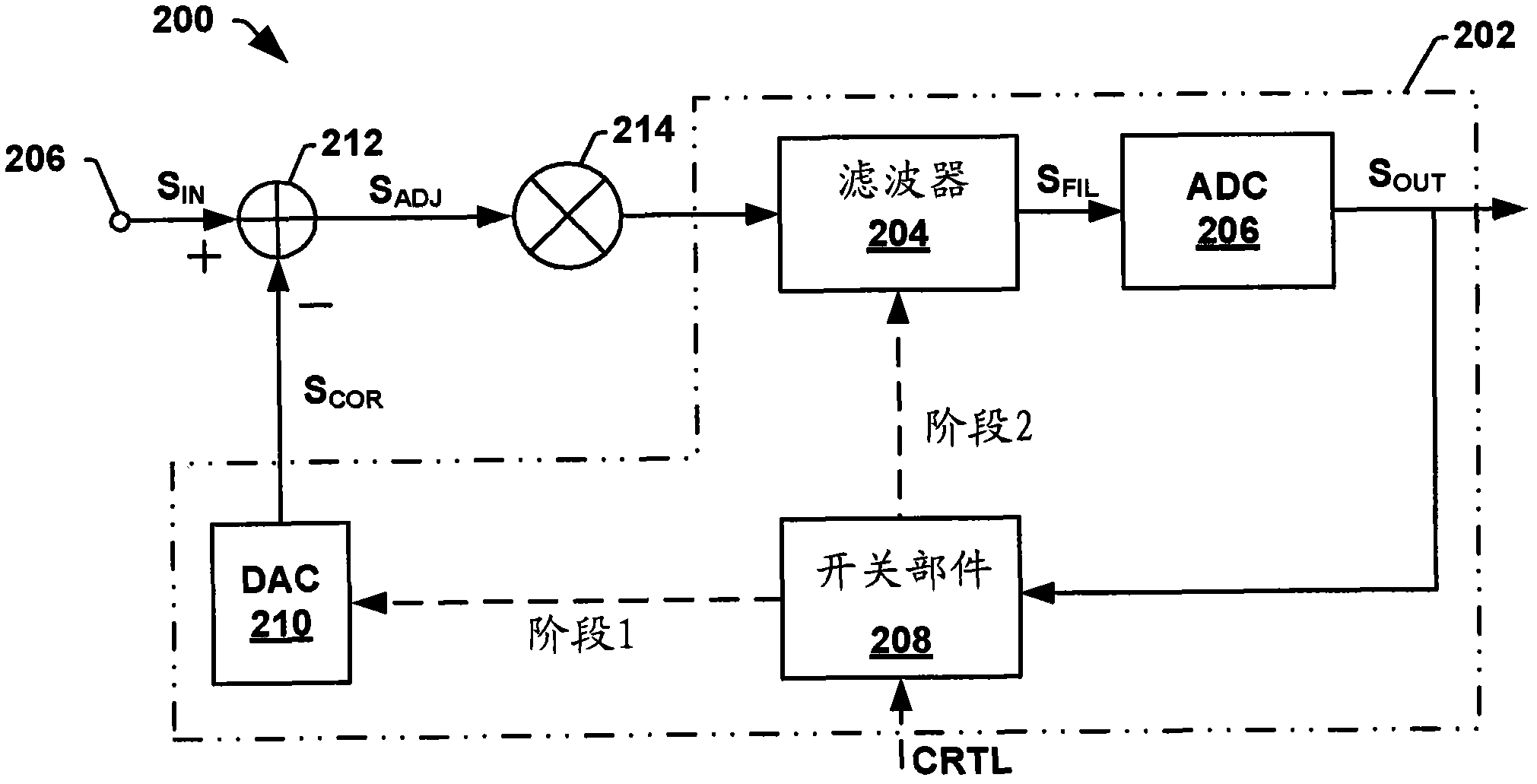
Configurable system for cancellation of the mean value of a modulated signal
ActiveCN102594261AMultiple-port networksFrequency demodulator arrangementsConfigurable systemsVIT signals
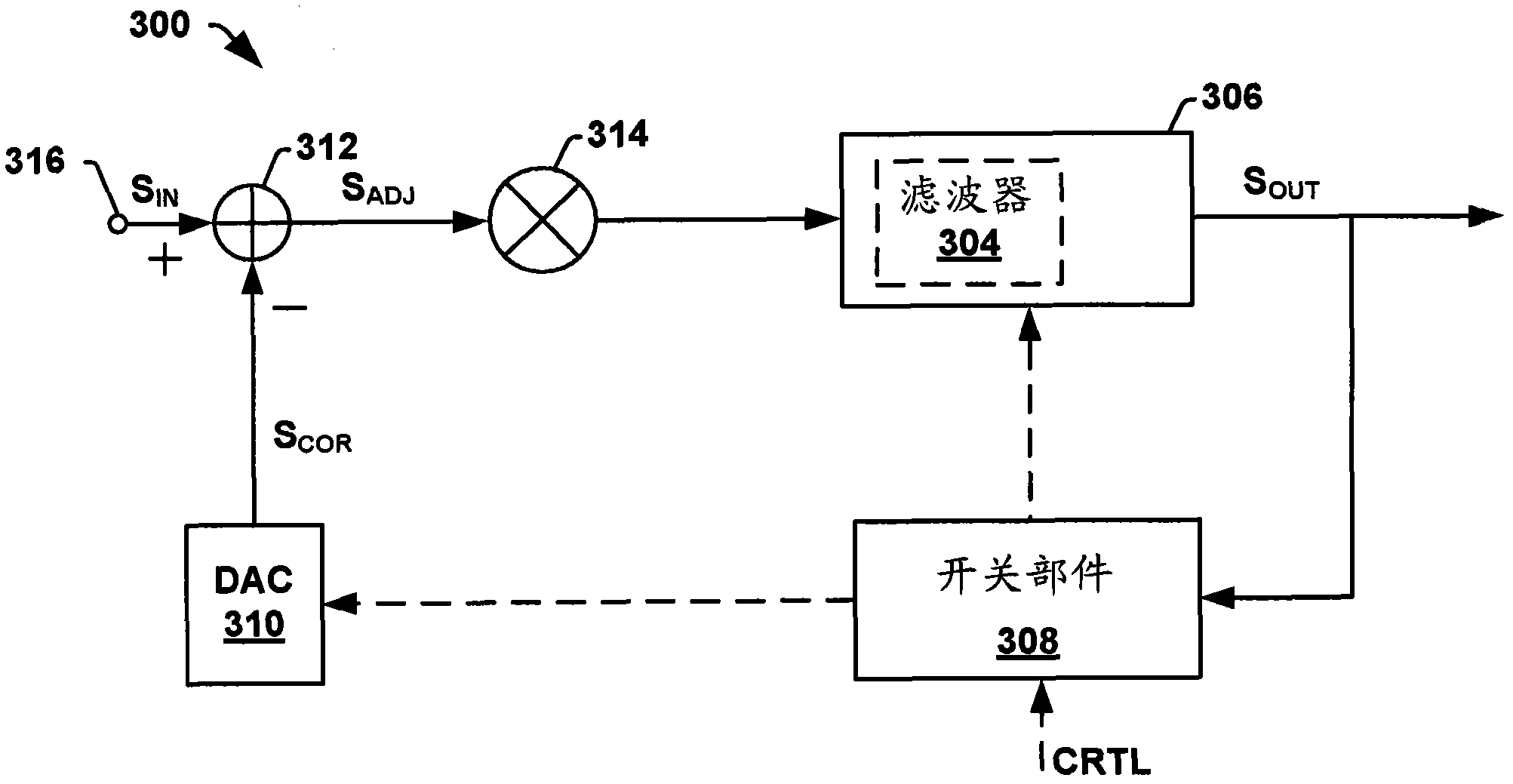
A configurable system for cancellation of the mean value of a modulated signal is disclosed. Some embodiments of the invention relate to a DC offset correction circuit comprising a feedback loop having a DAC controlled by a reconfigurable ADC, which determines (e.g., tracks) the mean value of a modulated input signal. The circuit operates according to two phase process. In a first "pre-modulation" tracking phase, an input signal is tracked by the ADC, which is configured to output the input signal's mean value as a digital code equivalent to the input mean value. The output of the ADC is provided to a DAC, which provides an analog representation of the mean value to an adder that subtracts the mean value from the modulated input signal to generate a bipolar adjusted input signal. In a second "modulation" phase, the estimated mean value is held constant, so that the bipolar adjusted input signal may be provided to an activated modulation circuit for improved system performance.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Method for frequency error correction of oscillator of sensor node of wireless sensor network
InactiveCN108781198AFrequency demodulator arrangementsPulse automatic controlWireless mesh networkWireless sensor networking
The invention relates to a method for the frequency error correction of an oscillator of a sensor node in a sensor network, comprising the following steps: receiving a transmission signal of a transmitter, the signal being modulated by orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM); determining the frequency deviation of the oscillator using the received transmission signal; and determining a correction signal for correcting the frequency deviation of the oscillator and correcting the frequency of the oscillator by means of the correction signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Low-power, noise insensitive communication channel using logarithmic detector amplifier (LDA) demodulator
ActiveUS9048943B2Reduce generationMinimize power consumptionFrequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsEngineeringFrequency modulation
A method is provided for communicating signals at a low power level in an electromagnetic interference (EMI) environment. A first device transmits a modulated signal having a first carrier frequency, including the encoded information via a hardwire transmission medium. In one aspect, the power level of the modulated signal can be adjusted to minimize power consumption or reduce the generation of EMI. The modulated signal may be in one of the following formats: frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) to name a few examples. A second device including a logarithmic detector amplifier (LDA) demodulator circuit receives the signal, which may be mixed with EMI. The LDA demodulator circuit amplifies the modulated signal, without amplifying the EMI, to supply a demodulated baseband signal, which may be an n-ary digital signal, or an audio signal. A low-power, noise insensitive communication channel is also provided.
Owner:DOCKON
receiver
InactiveUS20120177150A1Reduce quality problemsFrequency demodulator arrangementsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsFrequency mixerDigital controlled oscillator
A receiver comprises an input-stage circuit, a filter circuit, an output-stage circuit and a digital control oscillator. The input-stage circuit has a mixer configured for mixing the GFSK signal and a feedback signal to generate an input-stage current signal to the filter circuit. Then the filter circuit filters the input-stage current signal, and converts it into a voltage signal. The output-stage circuit is coupled to the filter circuit, for converting the voltage signal into a digital output data. In addition, the digital control oscillator is coupled to the output-stage circuit, for outputting the feedback signal based on the digital output data.
Owner:LIN TSUNG HSIEN
Popular searches
Substation equipment Transmission noise suppression Line-transmission details Modulation transference balanced arrangements Amplifier details Amplitude demodulation by non-linear multiple-pole elements Near-field in RFID Near-field systems using receivers Transmission monitoring Differential amplifiers
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com