Patents
Literature
286results about "Digital signal tone/bandwidth control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
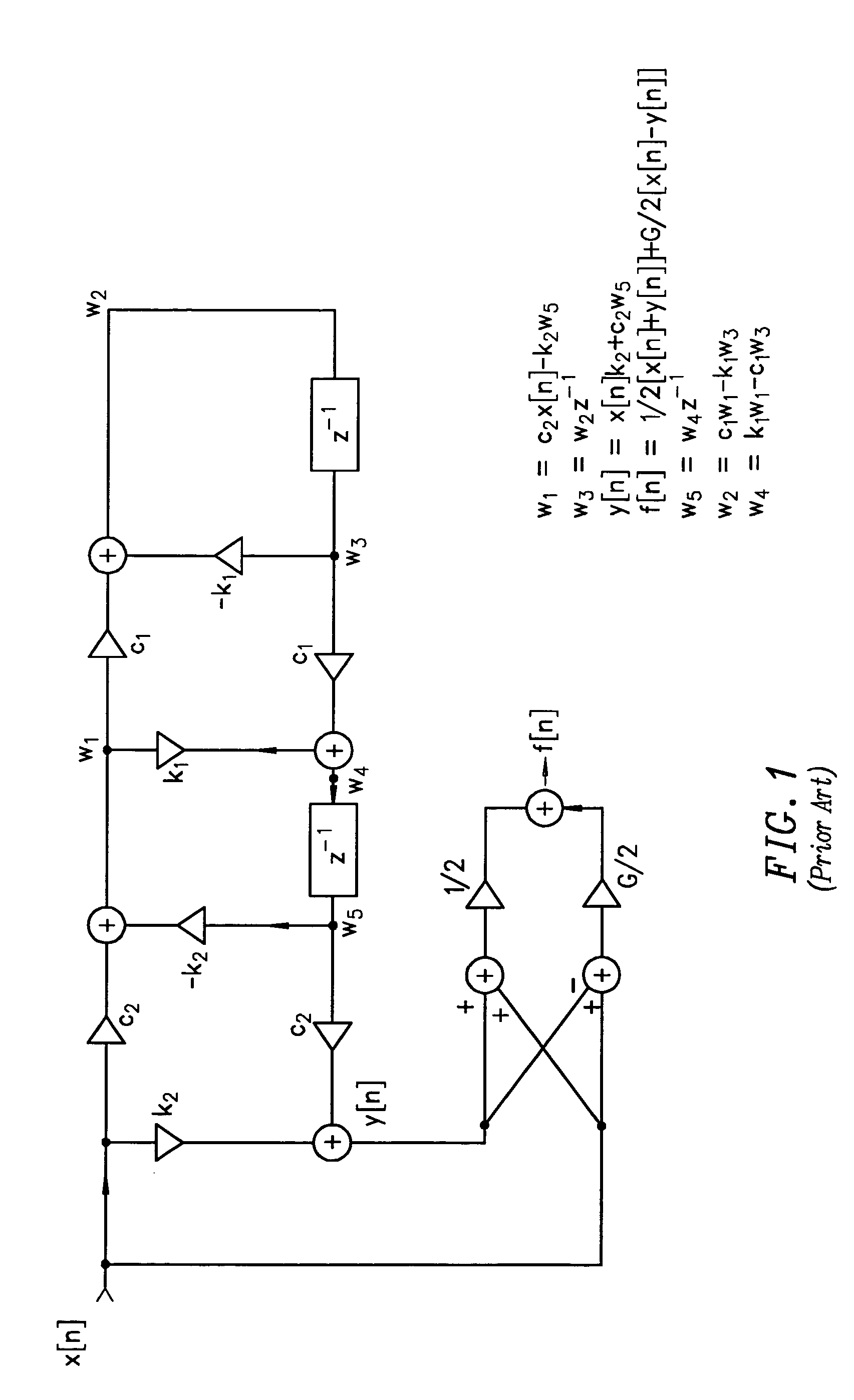
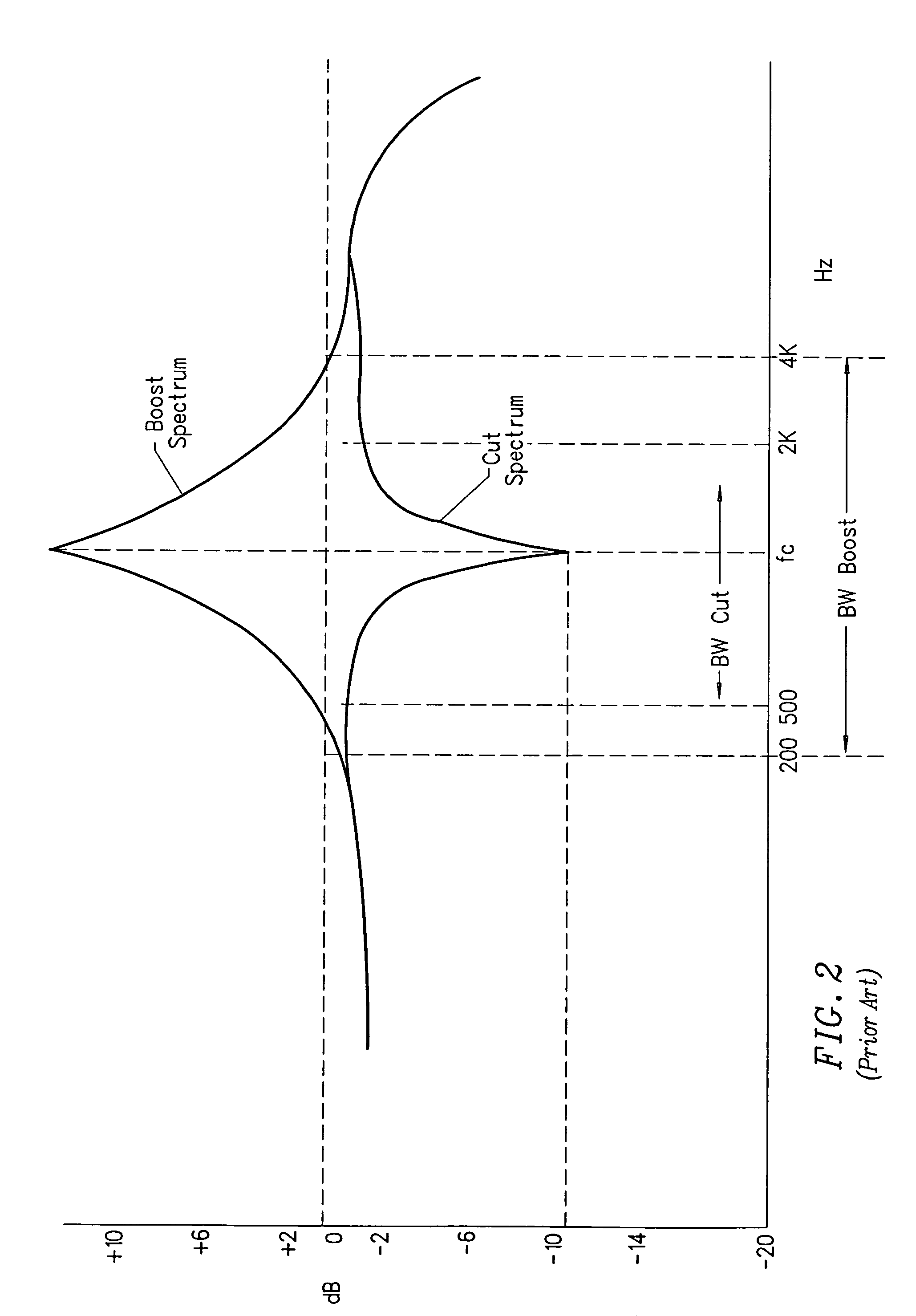
Compensating filters
InactiveUS6760451B1Eliminate phase distortionAdaptive networkAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal processingAmplitude response
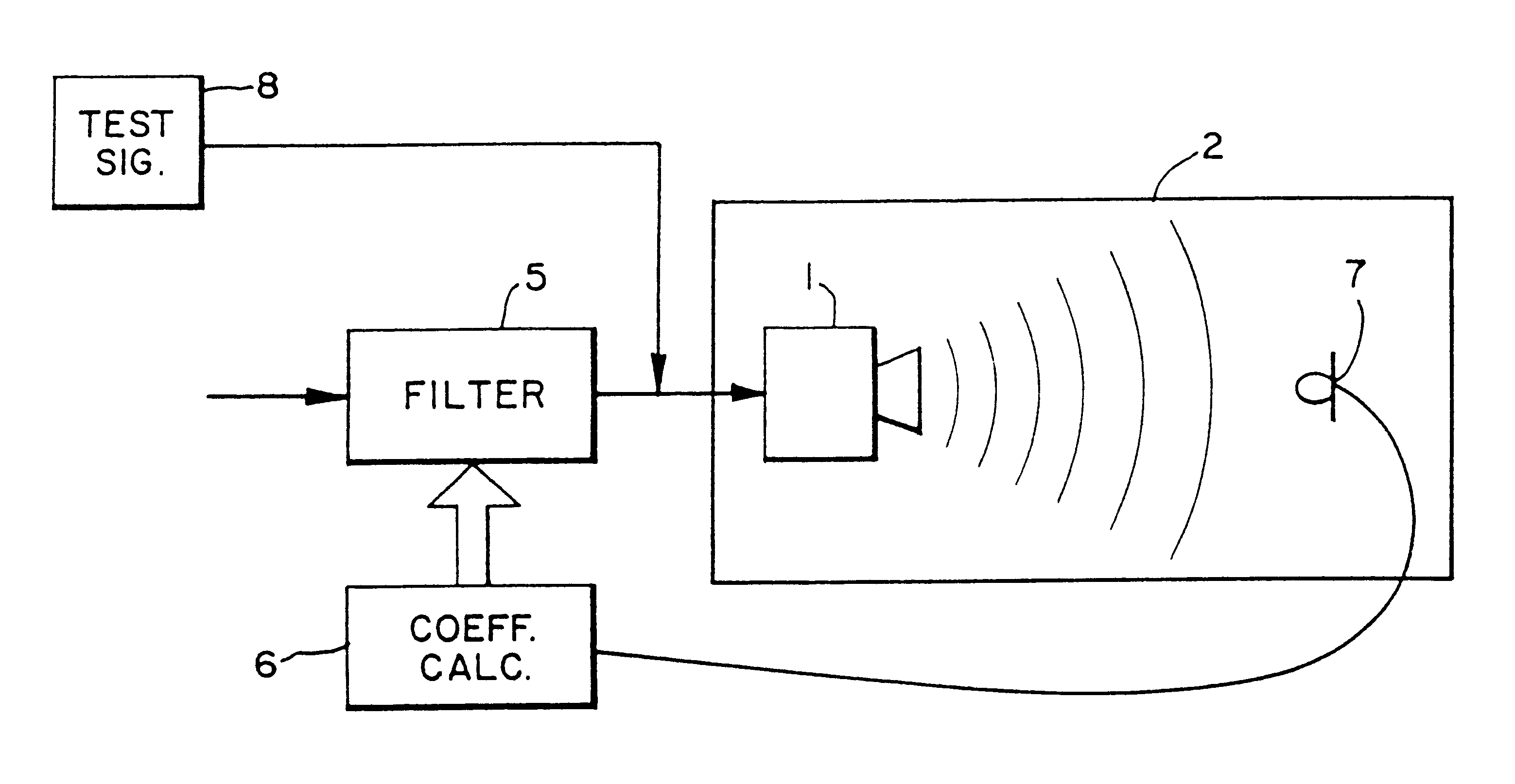
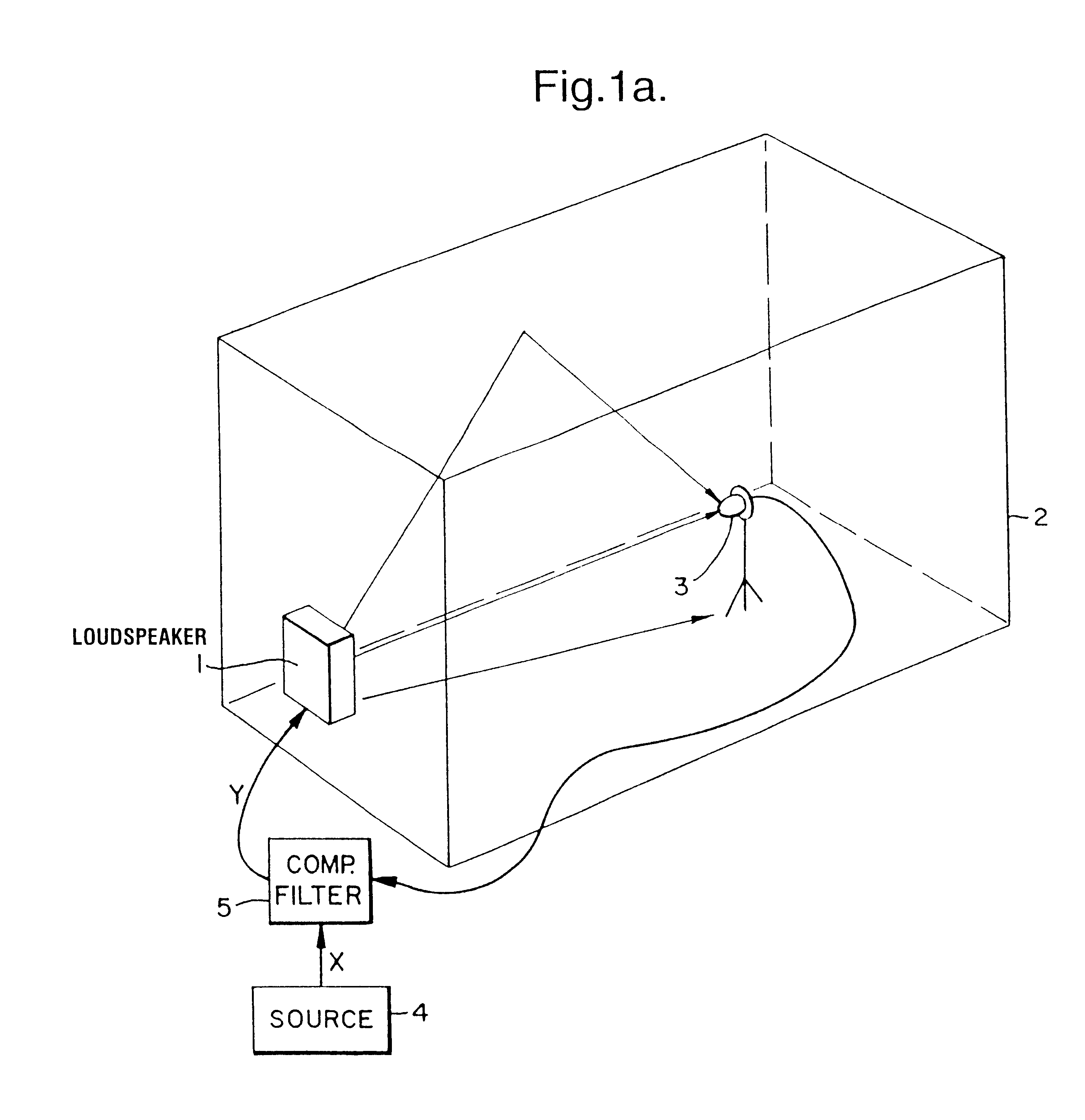
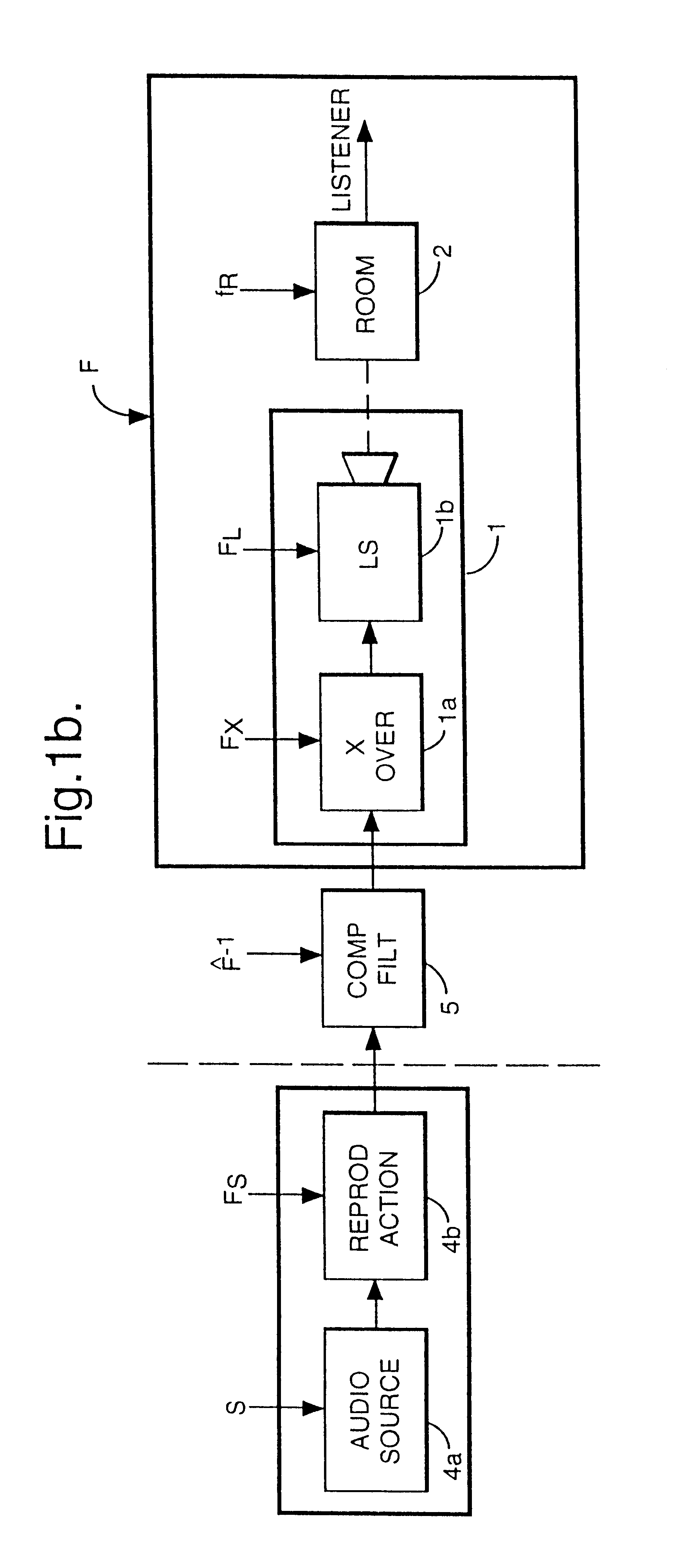
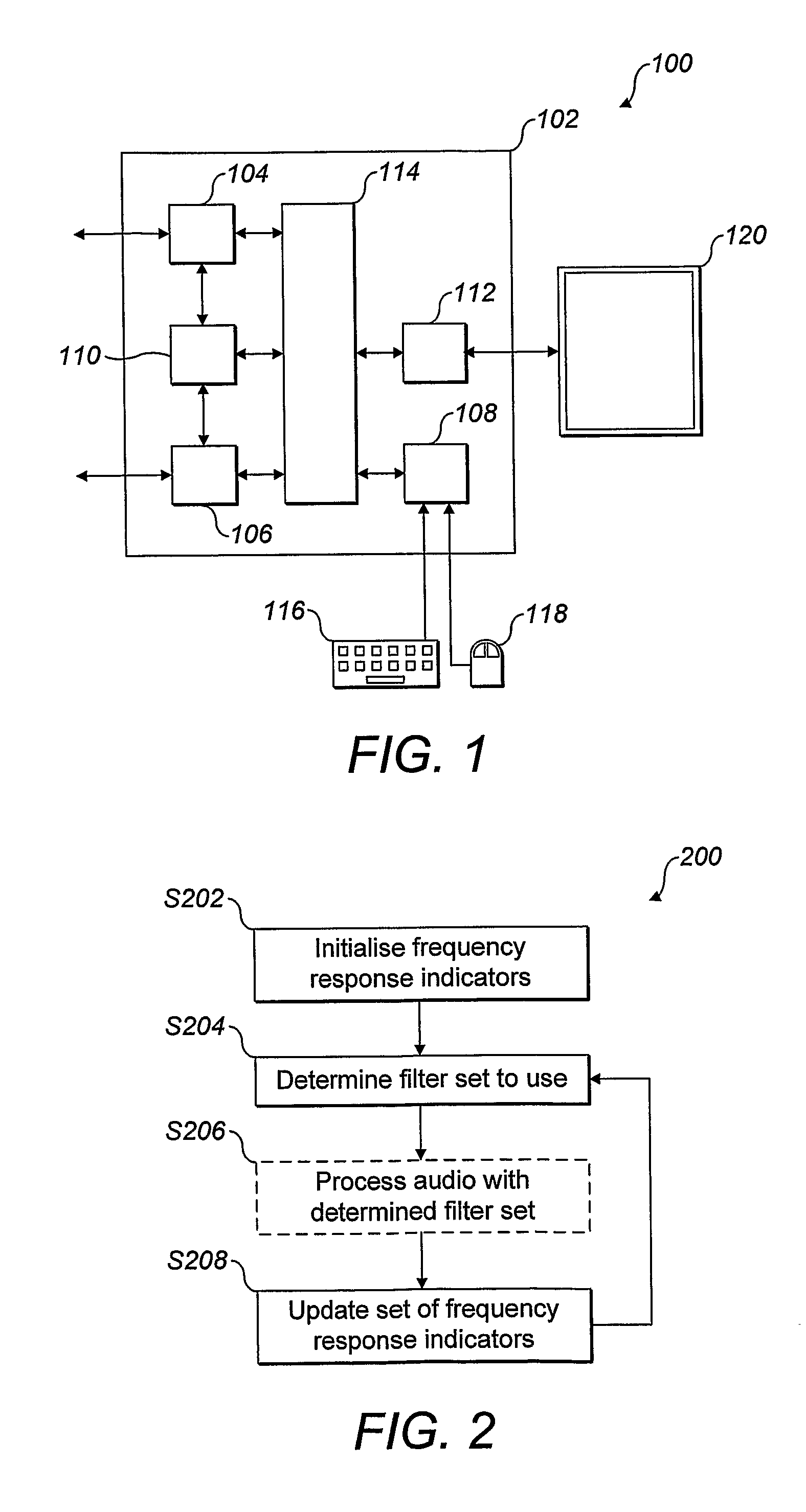
A prefilter (5) for an audio system comprising a loudspeaker (1) in a room (2), which corrects both amplitude and phase errors due to the loudspeaker (1) by a linear phase correction filter response and corrects the amplitude response of the room (2) whilst introducing the minimum possible amount of extra phase distortion by employing a minimum phase correction filter stage. A test signal generator (8) generates a signal comprising a periodic frequency sweep with a greater phase repetition period than the frequency repetition period. A microphone (7) positioned at various points in the room (2) measures the audio signal processed by the room (2) and loudspeaker (1), and a coefficient calculator (6) (e.g. a digital signal processor device) derives the signal response of the room and thereby a requisite minimum phase correction to be cascaded with the linear phase correction already calculated for the loudspeaker (1). Filter (5) may comprise the same digital signal processor as the coefficient calculator (6). Applications in high fidelity audio reproduction, and in car stereo reproduction.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER GRAHAM +1
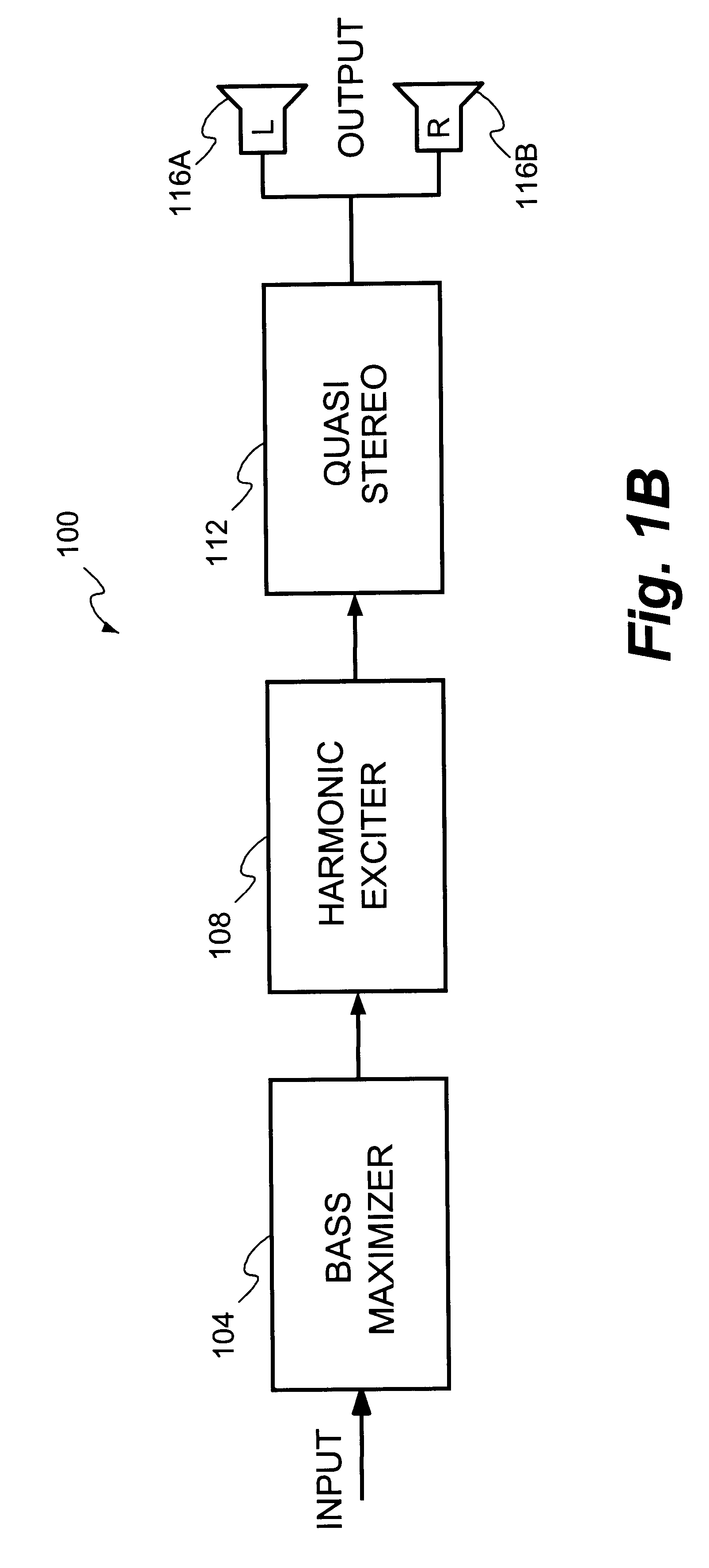
Method and system for enhancing audio signals
InactiveUS6606388B1Facilitates separate modificationFacilitates enhancementElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlHarmonicComputer module
A technique for enhancing audio signals generated from compressed digital audio files is described. The technique uses a Bass Maximizer module, a Harmonic Exciter module and a Quasi Stereo module. The Bass Exciter module enhances the intensity, depth and punch of the bass audio content by creating harmonic sequences from low frequency components contained in the original input signal. The Harmonic Exciter module adds to the treble audio content of the original input signal by generating harmonic series from the high frequency components contained in the input signal. The Quasi Stereo Module creates a stereo image of the enhanced input signal by adding and subtracting delayed and filtered versions of the enhanced input signal with itself to create left and right channeled stereo-like outputs. The technique provides a useful tool to regenerate from an audio signal more pleasant and joyful sounds.
Owner:ARBORETUM SYST
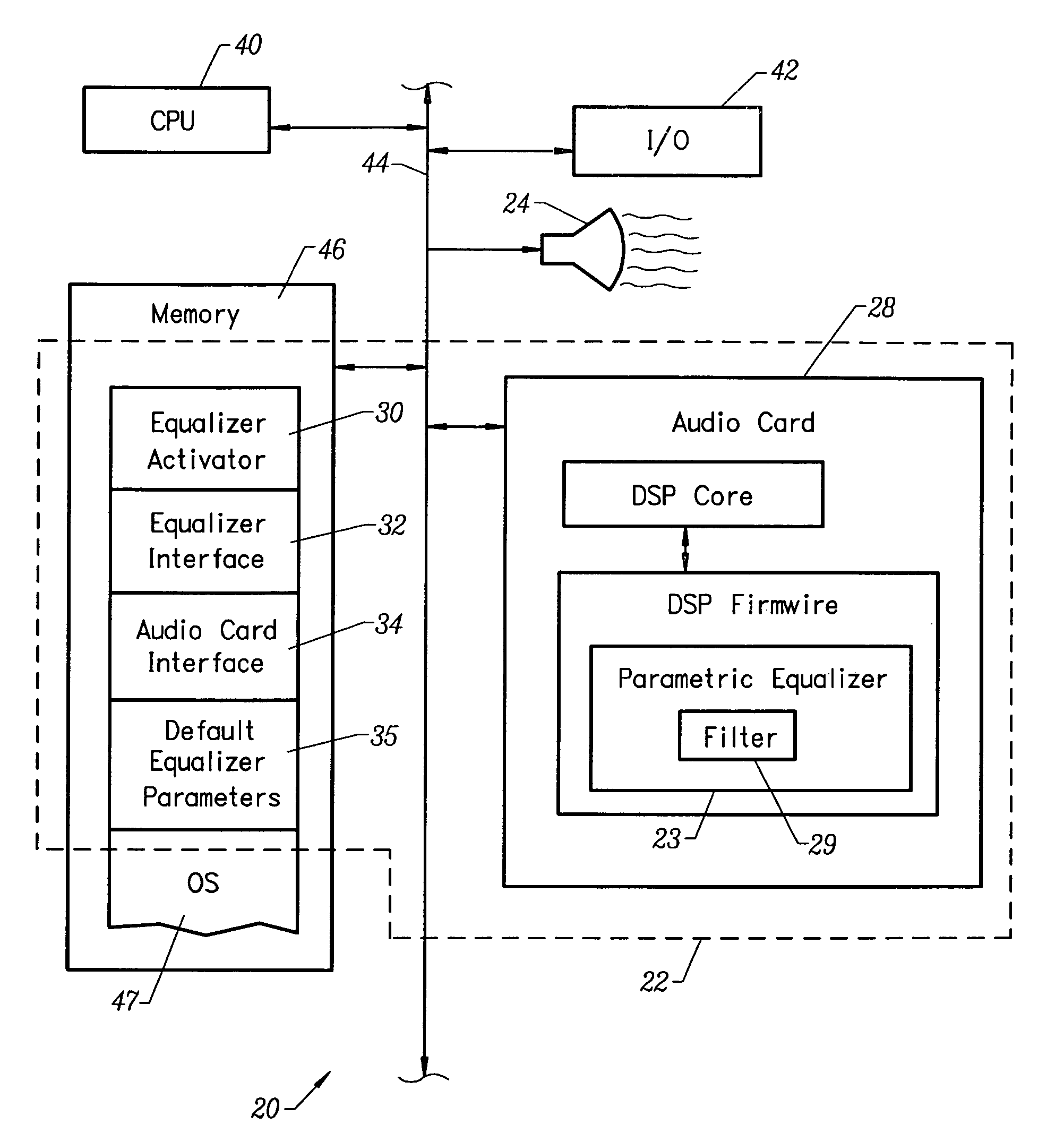
Apparatus and method for improved PC audio quality
InactiveUS6999826B1Improve speaker qualityImprove perceived qualityDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlAmplifiersDigital filterLoudspeaker
A computer readable memory to direct a computer to improve the perceived audio quality of a speaker included in that computer. The computer readable memory stores a first, second and third set of instructions. The first set of instructions causes the computer to determine the speaker type. The second set of instructions causes the computer to select a set of default filter coefficients for a digital filter based upon the speaker type. Finally, the third set of instructions causes the computer to realize a digital parametric equalizer using a digital filter and the set of default filter coefficients. Thus, the digital filter alters the audio signal that is input to the speaker, thereby improving the perceived quality of the speaker.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Enhancing audio using a mobile device
ActiveUS20160035337A1Gain controlVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersNoise levelSound quality
Embodiments disclosed herein enable detection and improvement of the quality of the audio signal using a mobile device by determining the loss in the audio signal and enhancing audio by streaming the remainder portion of audio. Embodiments disclosed herein enable an improvement in the sound quality rendered by rendering devices by emitting an test audio signal from the source device, measuring the test audio signal using microphones, detecting variation in the frequency response, loudness and timing characteristics using impulse responses and correcting for them. Embodiments disclosed herein also compensate for the noise in the acoustic space by determining the reverberation and ambient noise levels and their frequency characteristics and changing the digital filters and volumes of the source signal to compensate for the varying noise levels.
Owner:CAAVO INC
Reduced latency low frequency equalization system
ActiveUS20070019826A1Reduce frequencyImprove responseGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlEngineeringEqualization
A frequency equalization system is provided that substantially equalizes the room frequency responses generated by at least one loudspeaker within a listening area so that the frequency responses in the listening area are substantially constant and flat within a desired frequency range with minimum signal latency. The frequency equalization system may use multiple microphones to measure the audio signals of one or more subwoofers to achieve an improved bass response that is flat across the relevant frequency range. The system employs an algorithm that is a closed-form, non-iterative, mathematical solution and features short computation time with reduced delays.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
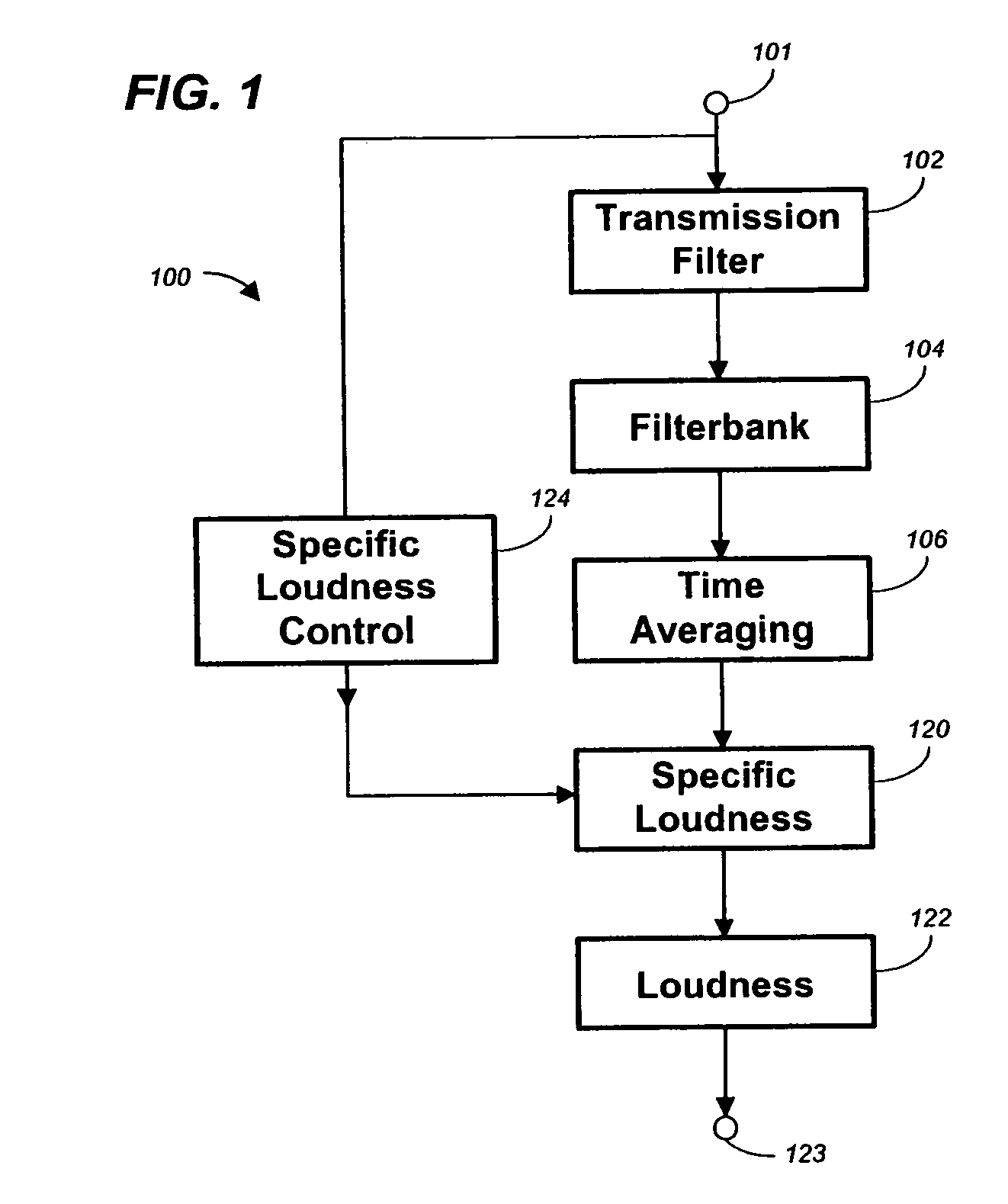
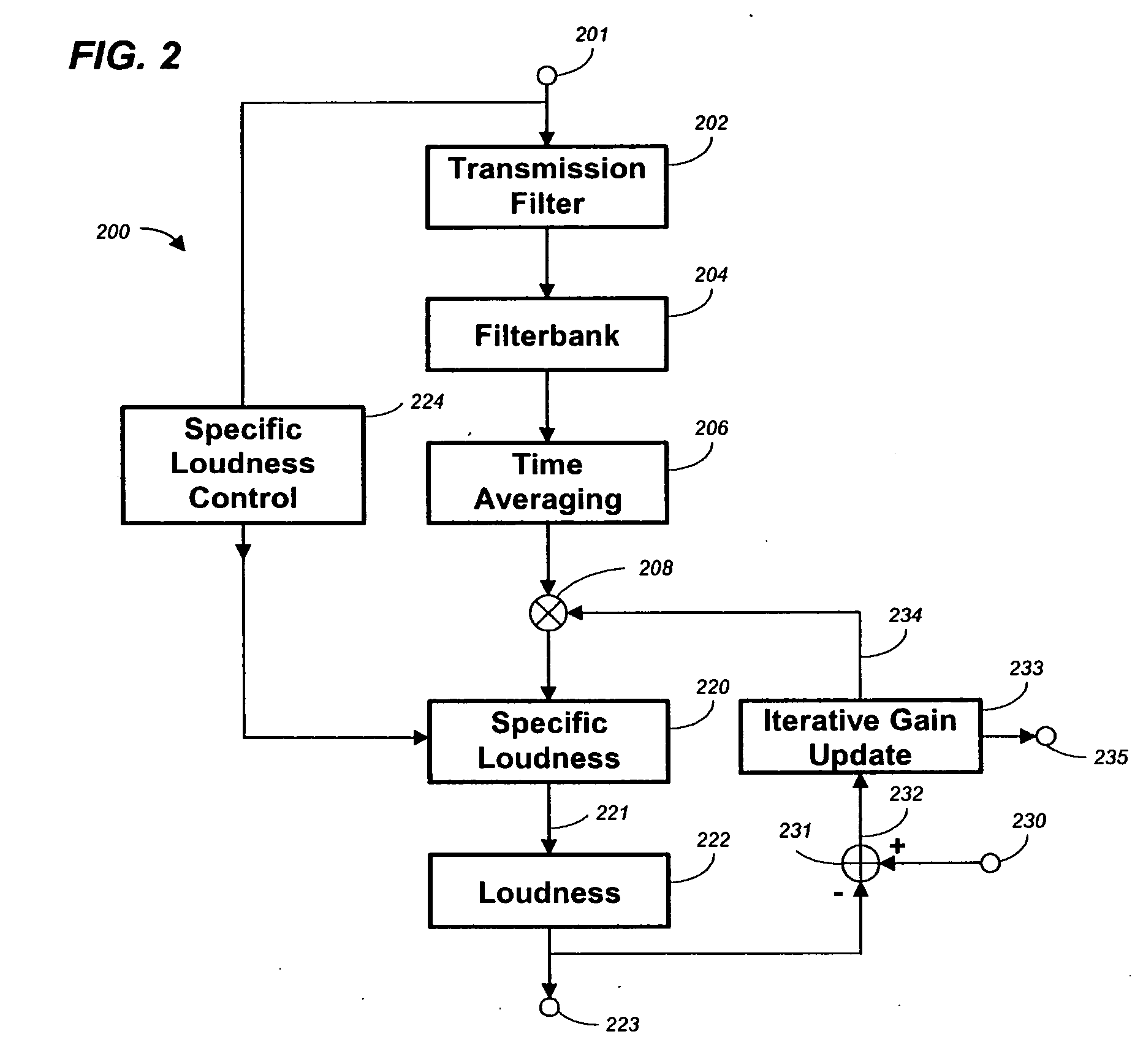
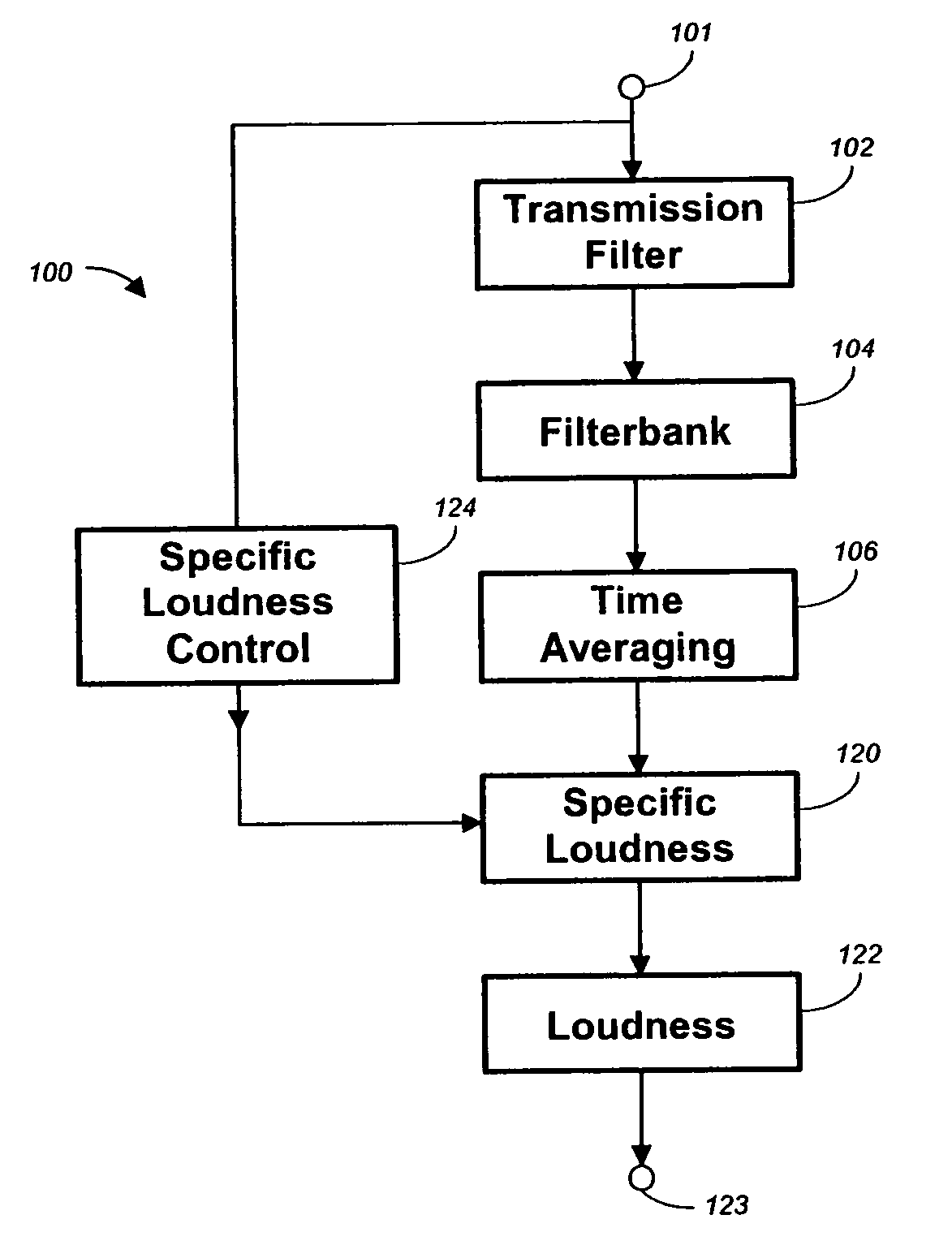
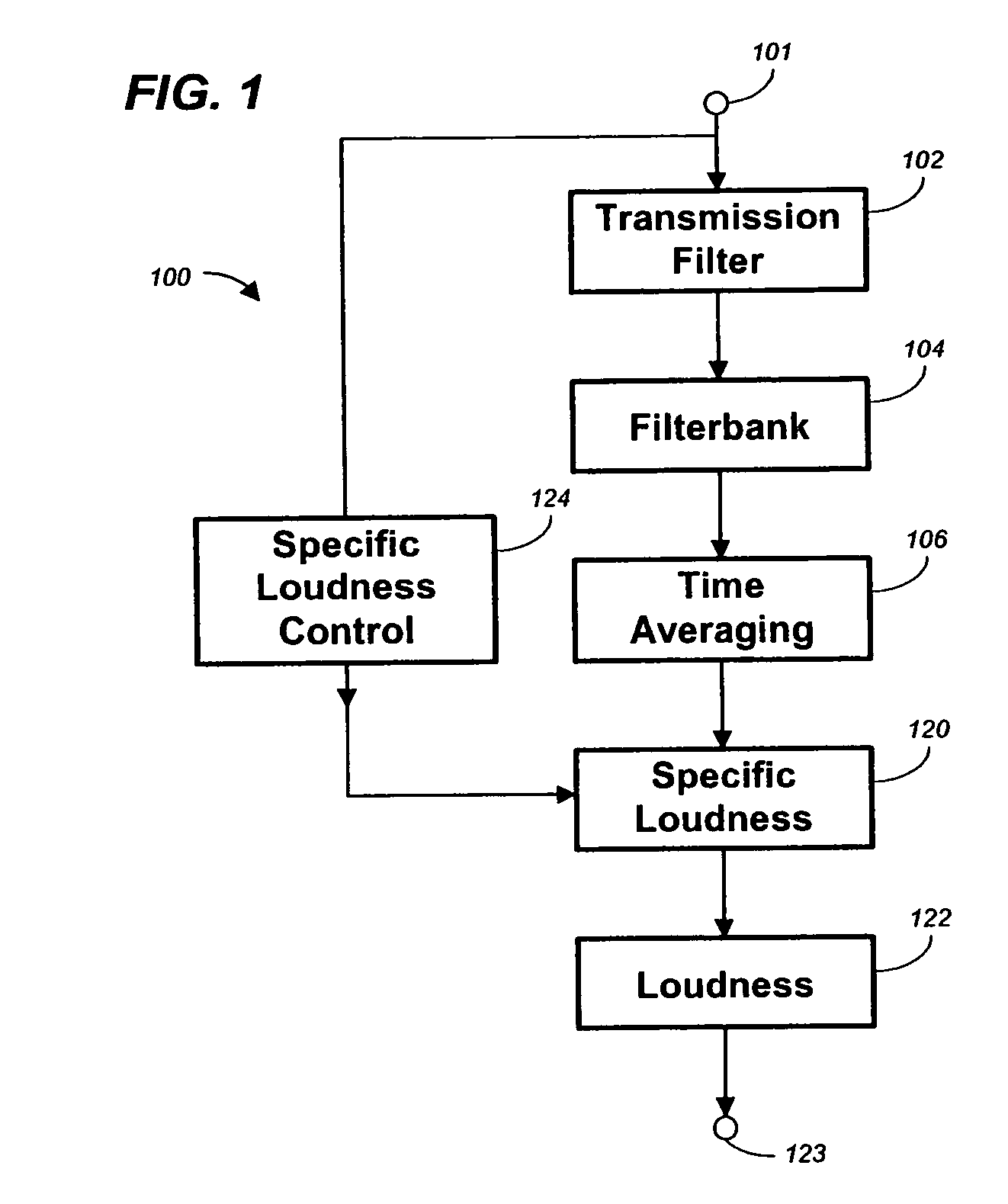
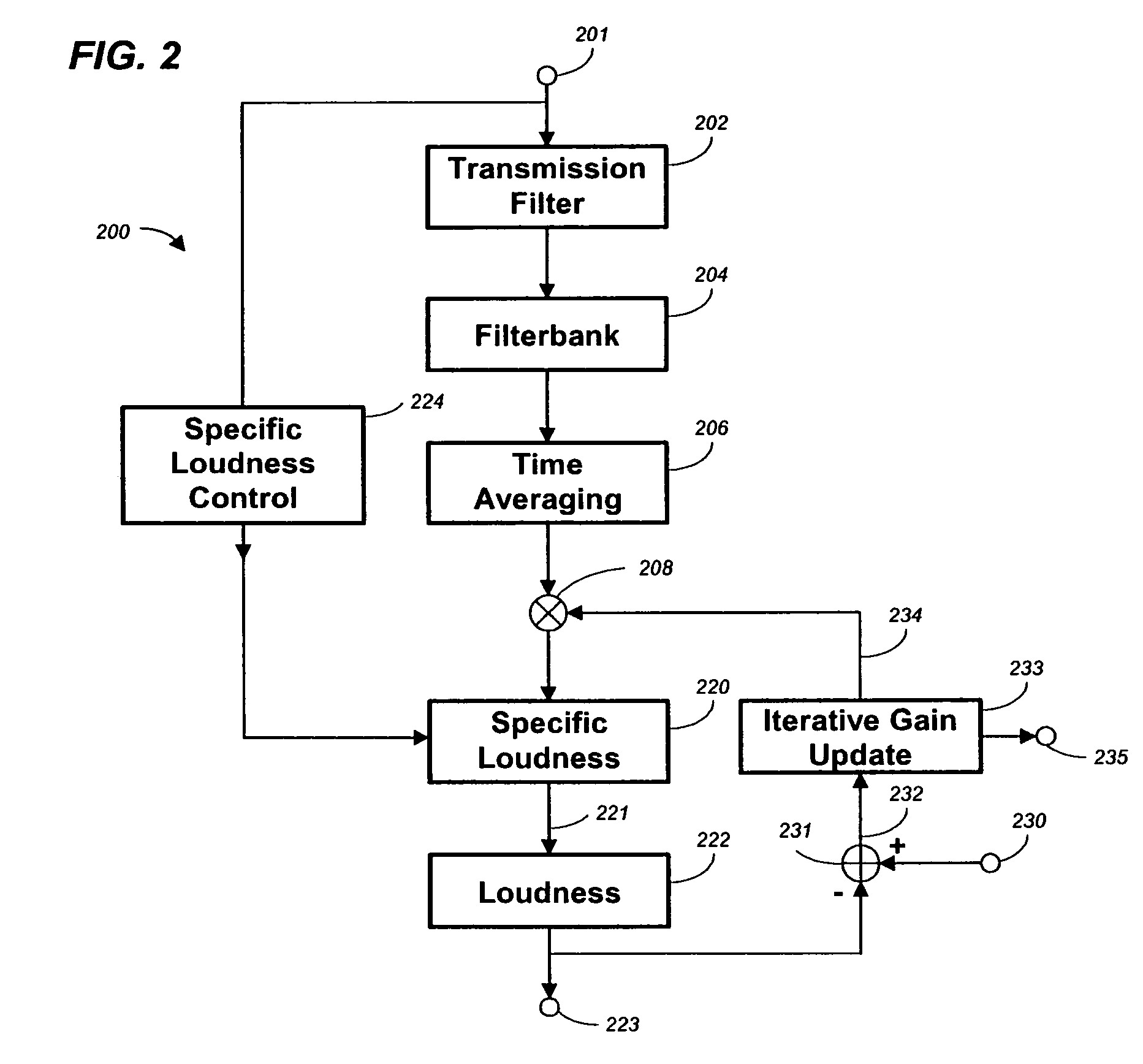
Method, apparatus and computer program for calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness of an audio signal
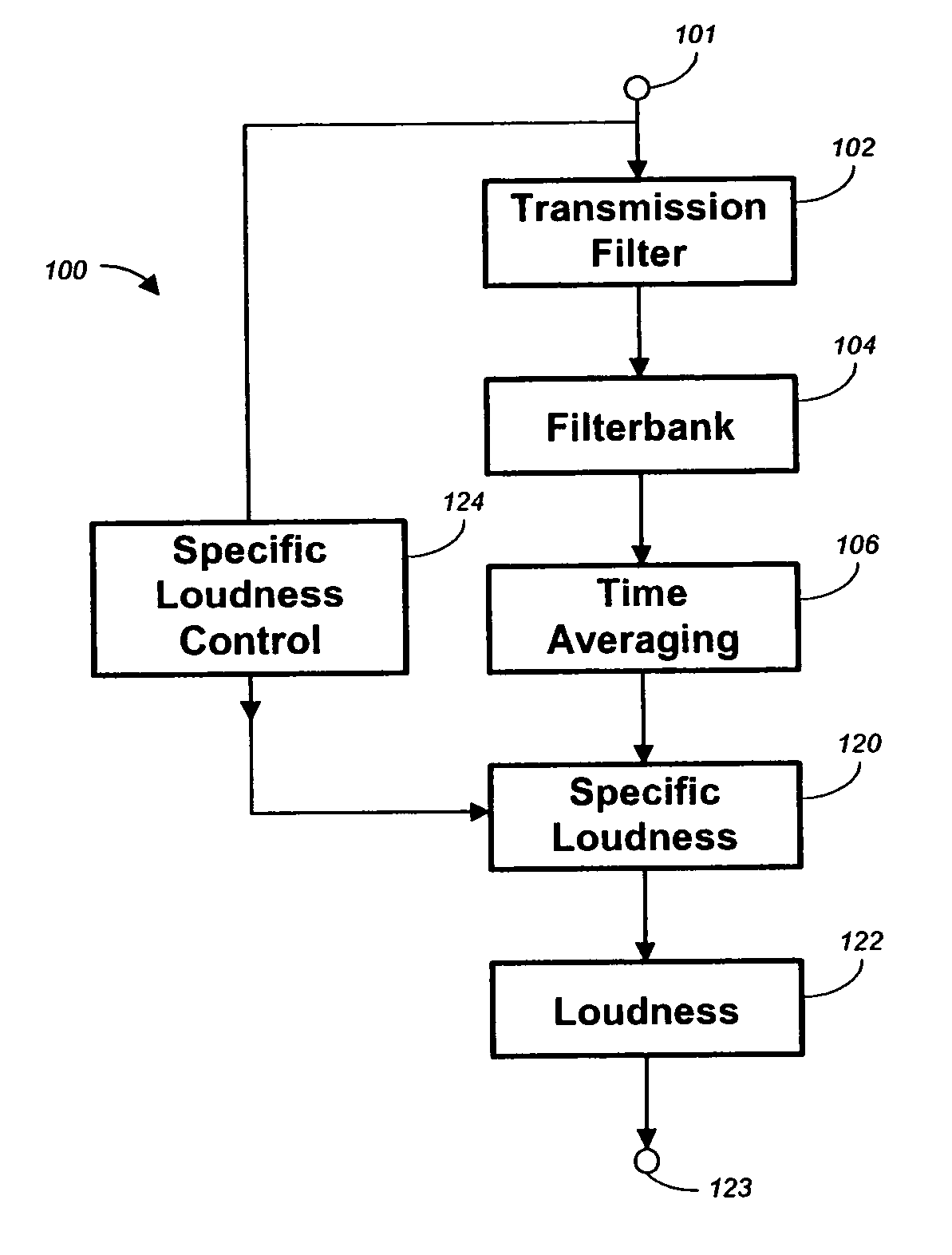
One or a combination of two or more specific loudness model functions selected from a group of two or more of such functions are employed in calculating the perceptual loudness of an audio signal. The function or functions may be selected, for example, by a measure of the degree to which the audio signal is narrowband or wideband. Alternatively or with such a selection from a group of functions, a gain value G[t] is calculated, which gain, when applied to the audio signal, results in a perceived loudness substantially the same as a reference loudness. The gain calculating employs an iterative processing loop that includes the perceptual loudness calculation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
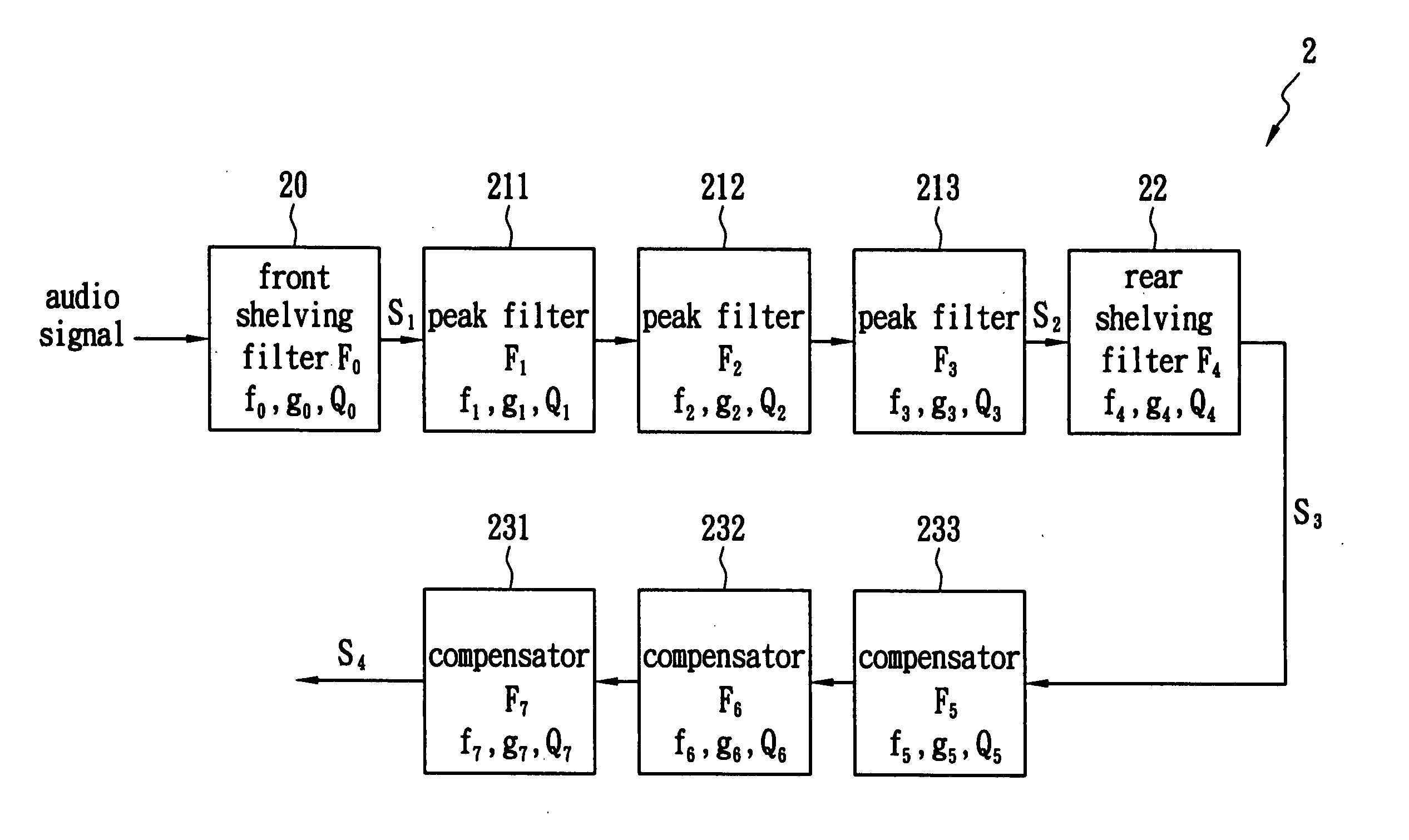
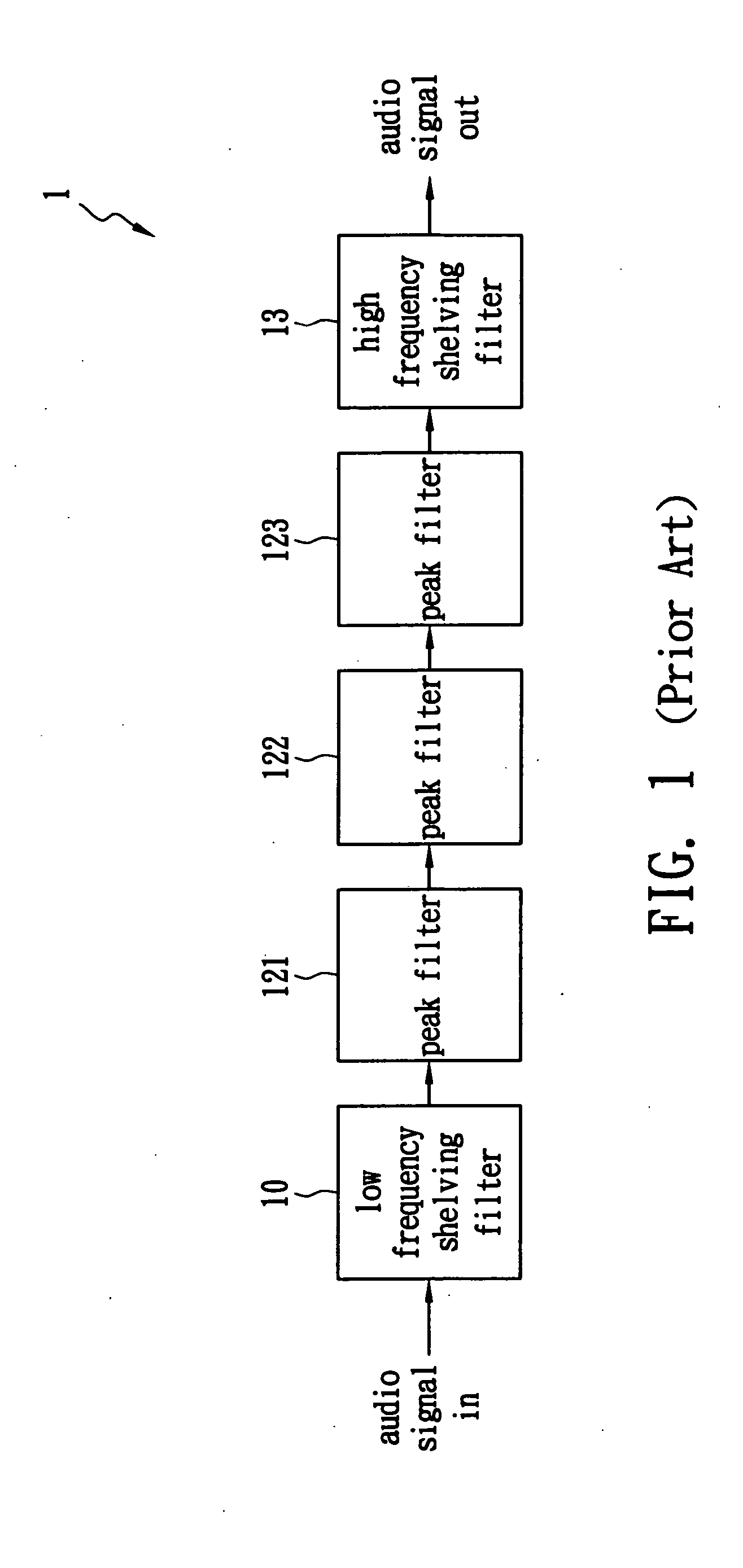
Equalizer bank with interference reduction
InactiveUS20070253577A1Low costEffectively equalizedTransmission control/equlisationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEngineeringPeak value
An equalizer bank with interference reduction is disclosed. The equalizer bank with interference reduction comprises a front-shelving filter, a plurality of peak filters, a rear-shelving filter and a plurality of compensators. The center frequency and the quality factor of each compensator are designed intentionally to be identical to those of the corresponding peak filter. When a user selects a specific gain level, the corresponding parameters that determine the peak filter and the compensator are retrieved directly and a complex calculation is skipped. Therefore, an audio signal can be equalized more efficiently with lower hardware cost.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Compensation system and method for sound reproduction
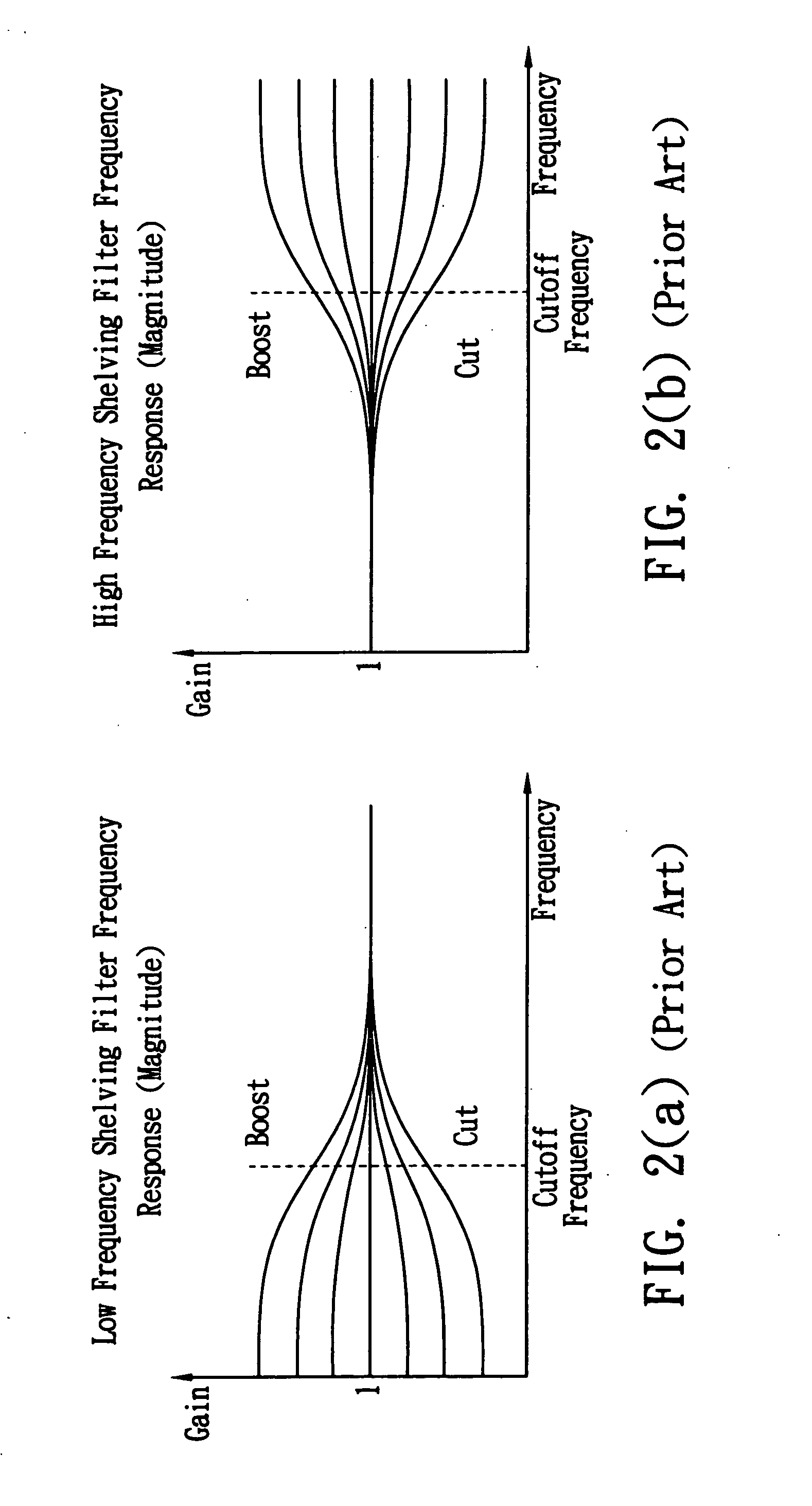
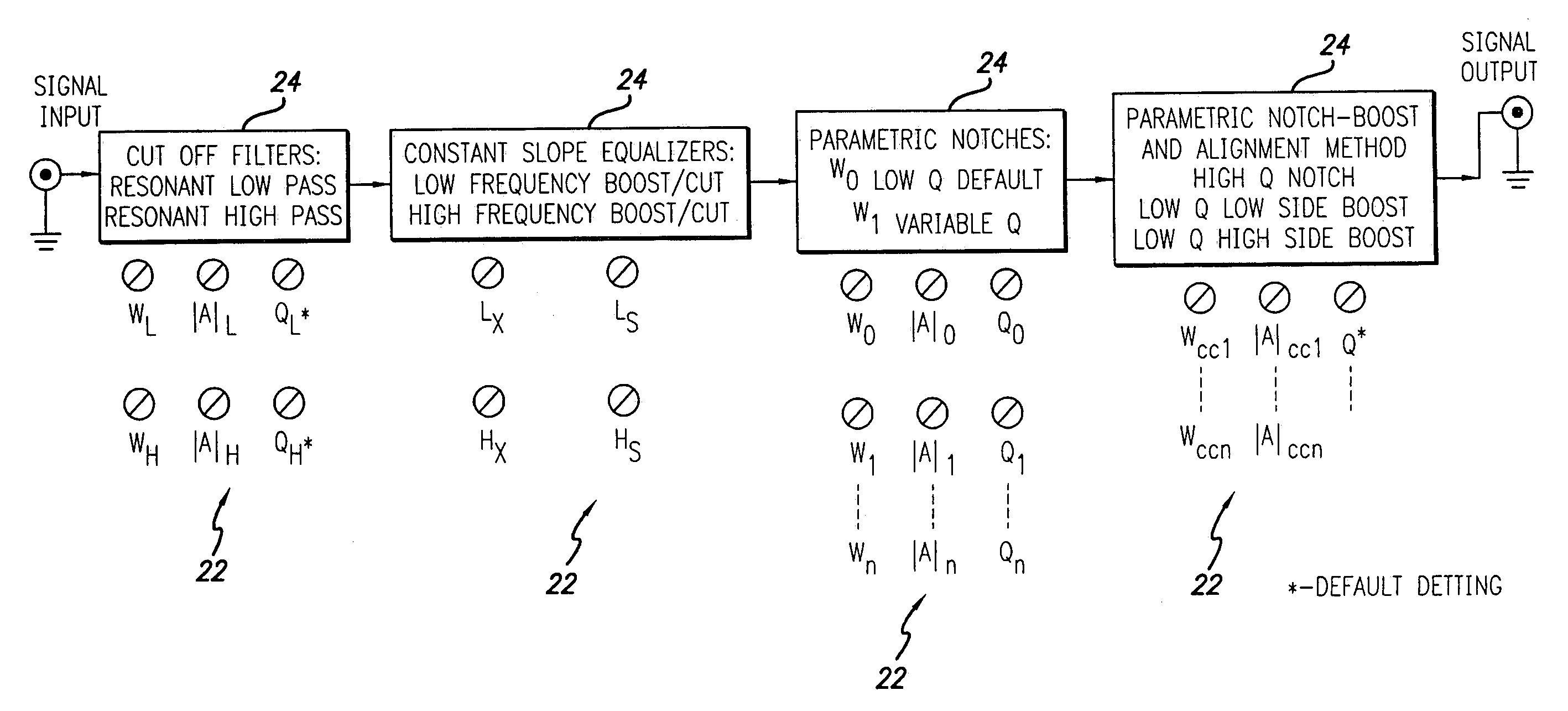
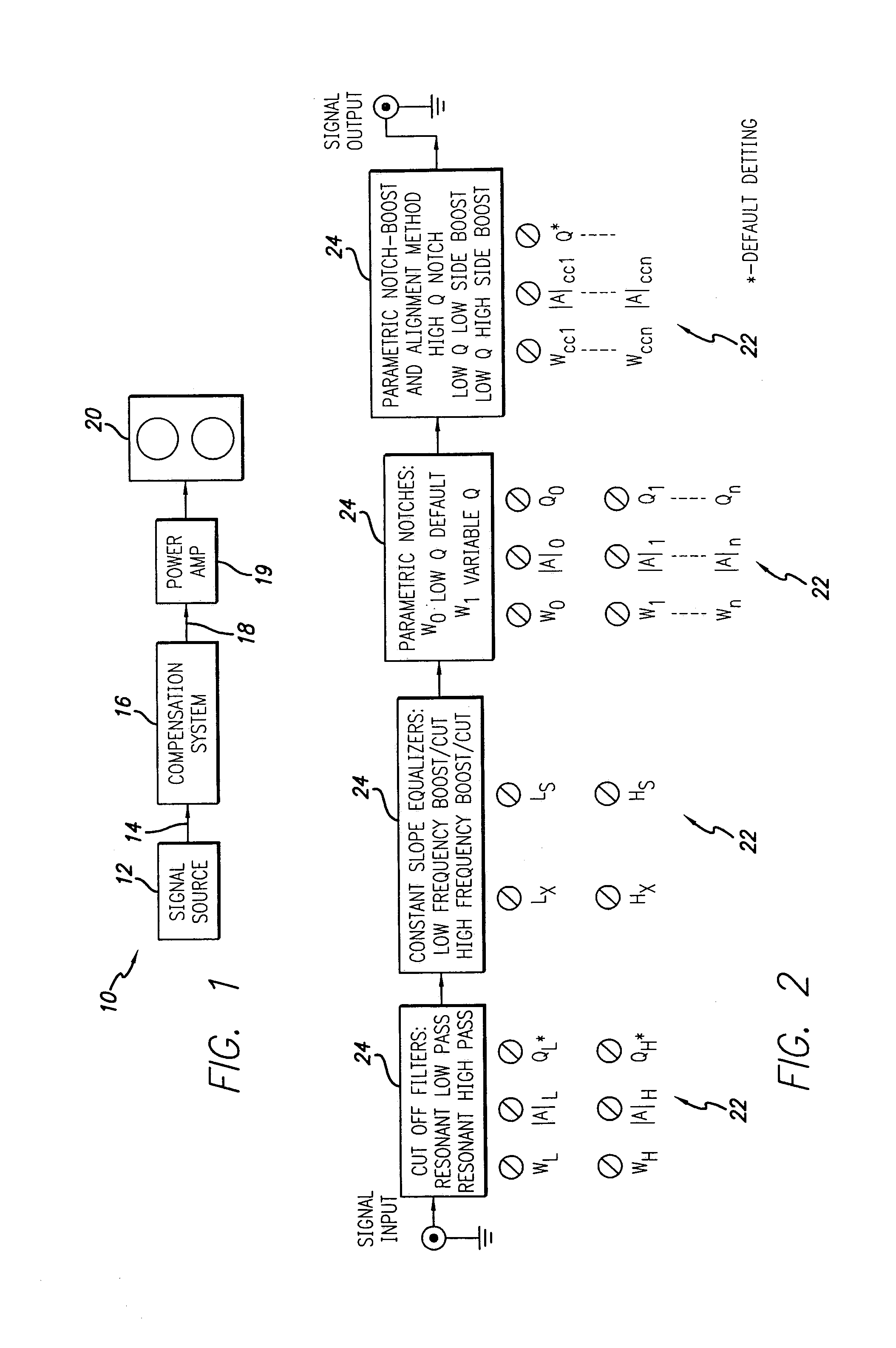
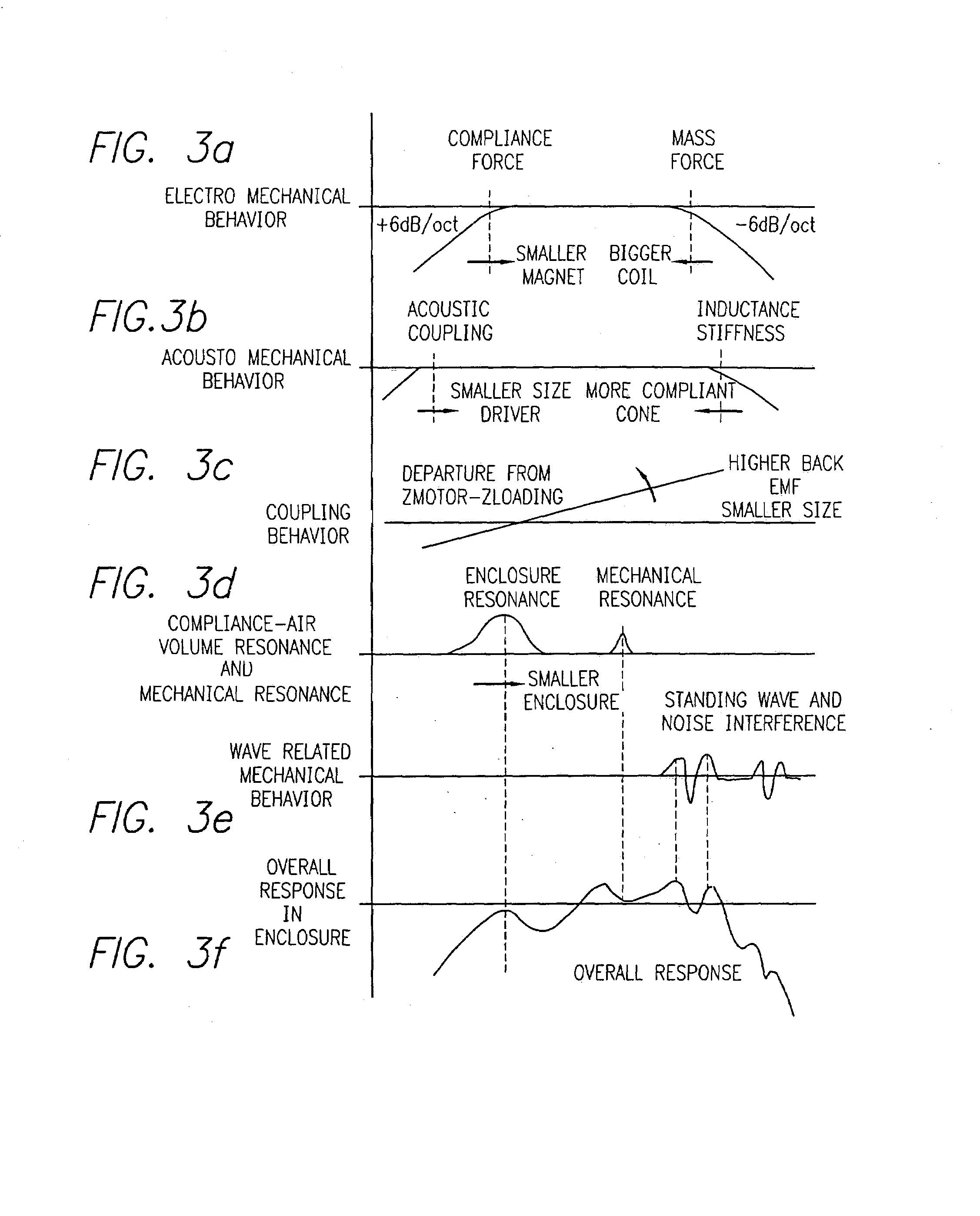
InactiveUS7184556B1Reduce distortion problemsEnhance the imageGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlElectricityDigital signal processing
A sound compensation system alters an electrical audio signal for input to a sonic reproduction device having associated behavioral characteristics. The behavior characteristics of the device are defined by individual or groups of individual components of the sonic reproduction device and include mechanical, acoustic and electromagnetic behaviors. The model includes a plurality of filters that simulate at least one of the behavior characteristics of the sonic reproduction device. The filters are defined by digital signal processes or by analog circuits and are characterized by one or more of an associated frequency, time, phase and transient response. These responses combine to define an overall response for the model. The filters include adjustable parameters which are used to alter filter responses to produce responses that are conjugates to the responses of the unaltered filters and thus the sonic reproduction device. A controller modifies the parameters.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods for transducer calibration and tuning
ActiveUS20110002471A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationDigital data processing detailsHard disc driveEarcon
Audio transducers (headphones, speakers, microphones) inherently do not accurately reproduce the signal presented to them at the input. This can be compensated for by taking into account the transducer characteristics and transforming the input signal using a digital signal processor (DSP) to counteract the inaccuracies. However, for the compensation to take place, the DSP needs to know the characteristics of the transducer. For systems with built-in transducers (like laptops with internal speakers) the characteristics of the internal speakers can be stored on the hard-drive of the laptop and the DSP can read this data and make the appropriate compensations. Because a transducer (headphone, speaker, microphone) has its own characteristics that need to be compensated for separately, a profile is supplied to the DSP either by a database lookup based on an identification made by the user or transducer itself or by profile information stored on the transducer. Once the characteristics of a transducer are known, many additional DSP algorithms can be applied in order to improve the audio performance and even safety of the system.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
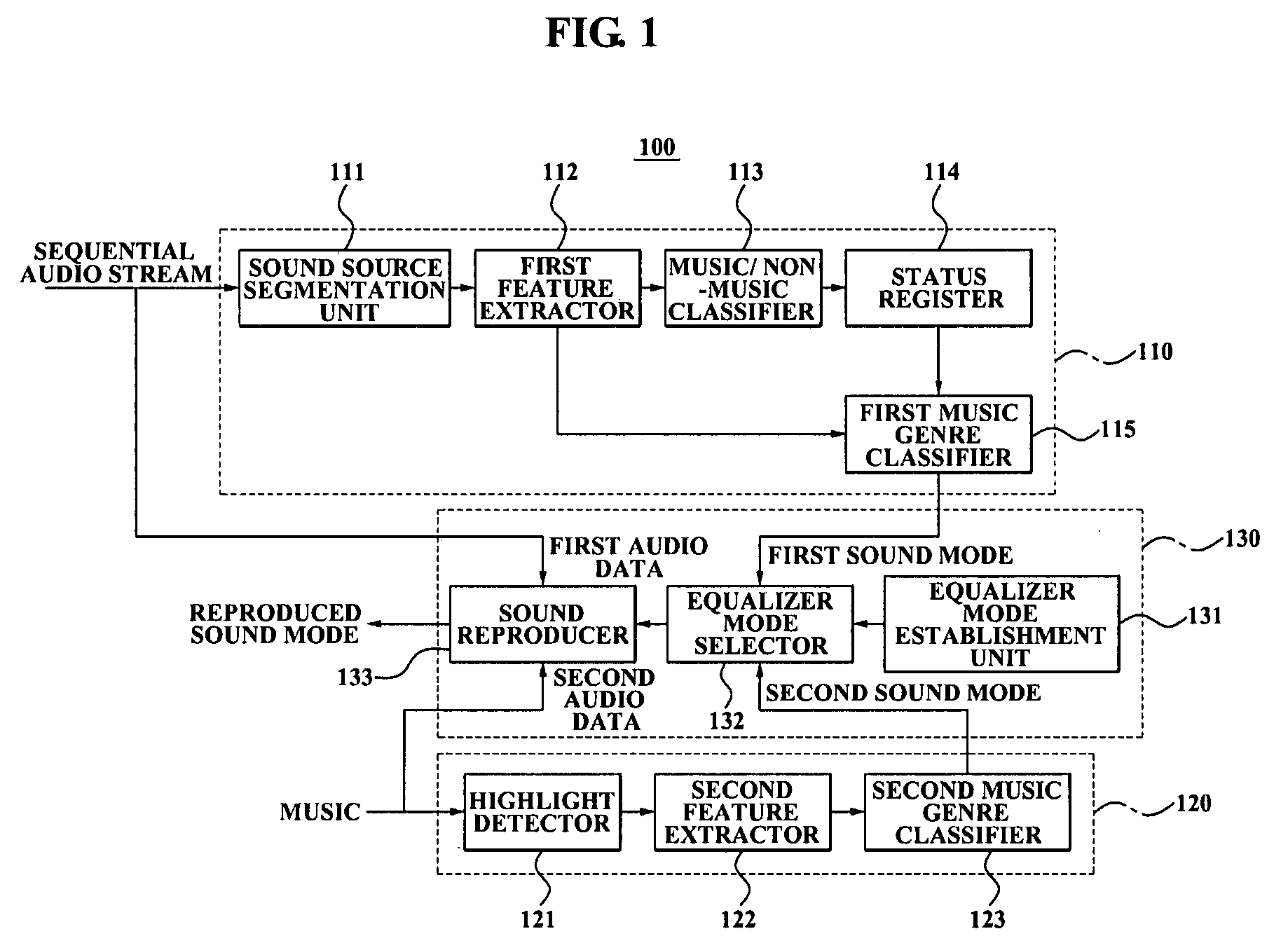
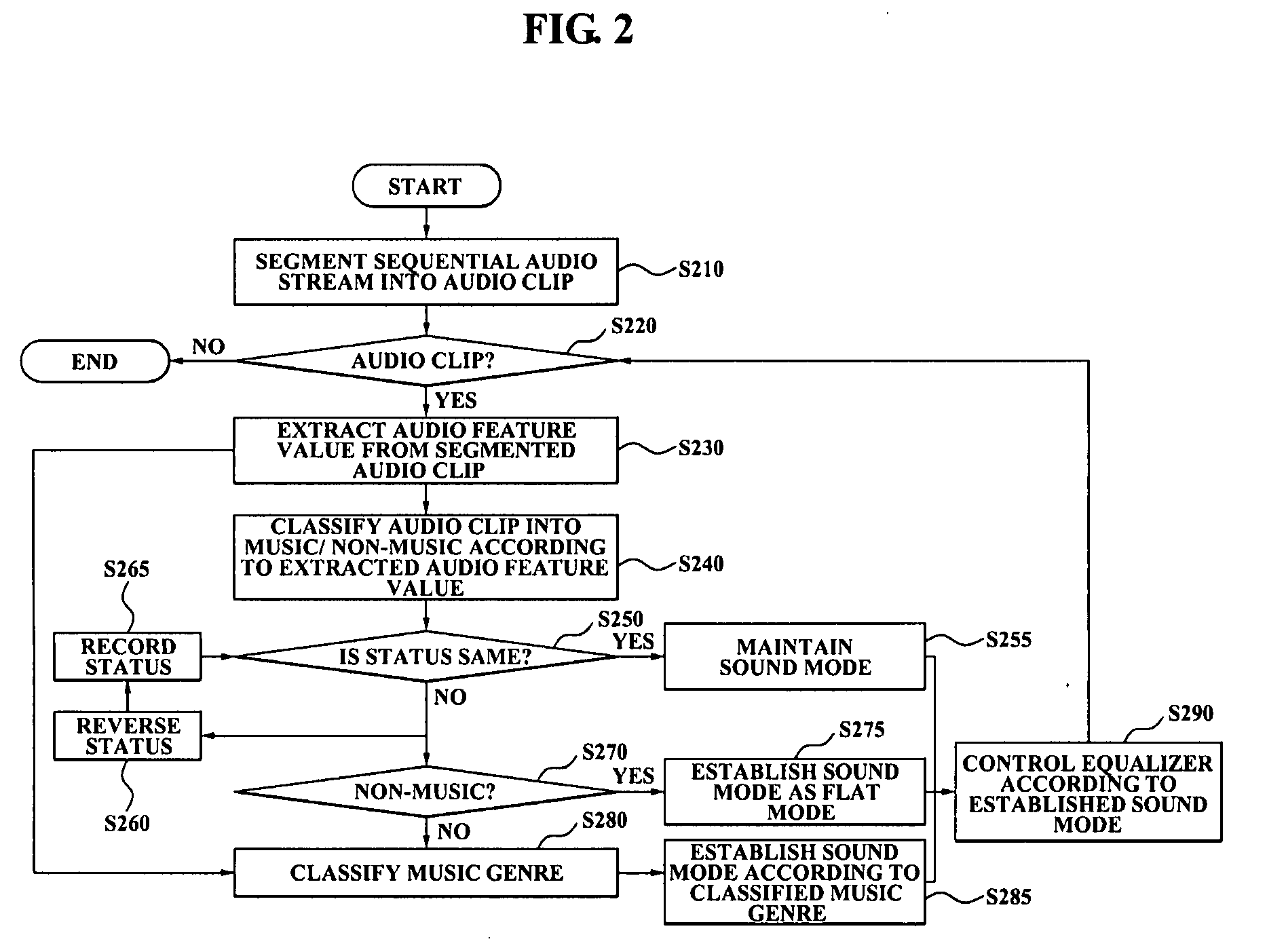
Equalizer control method, medium and system in audio source player
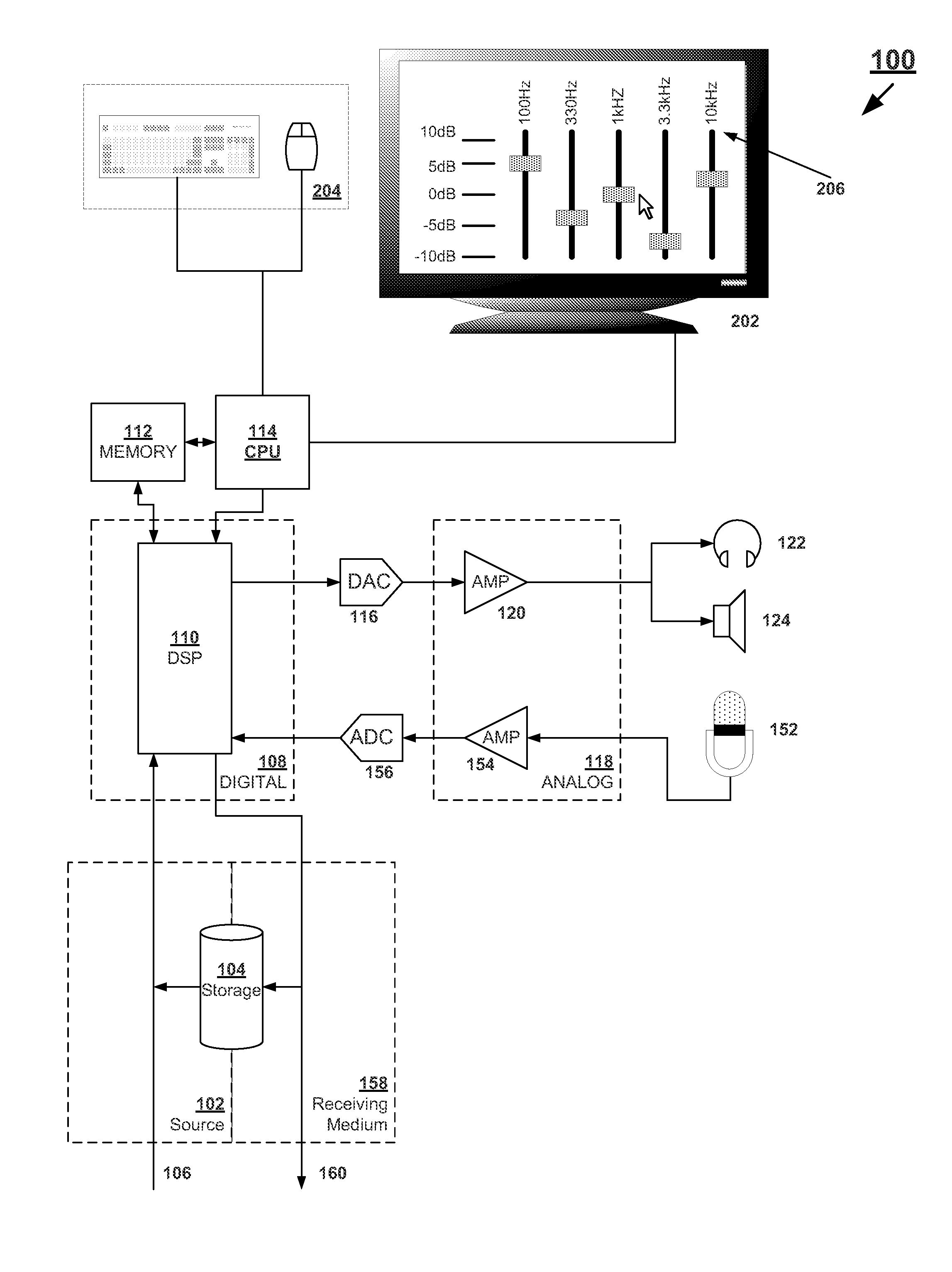
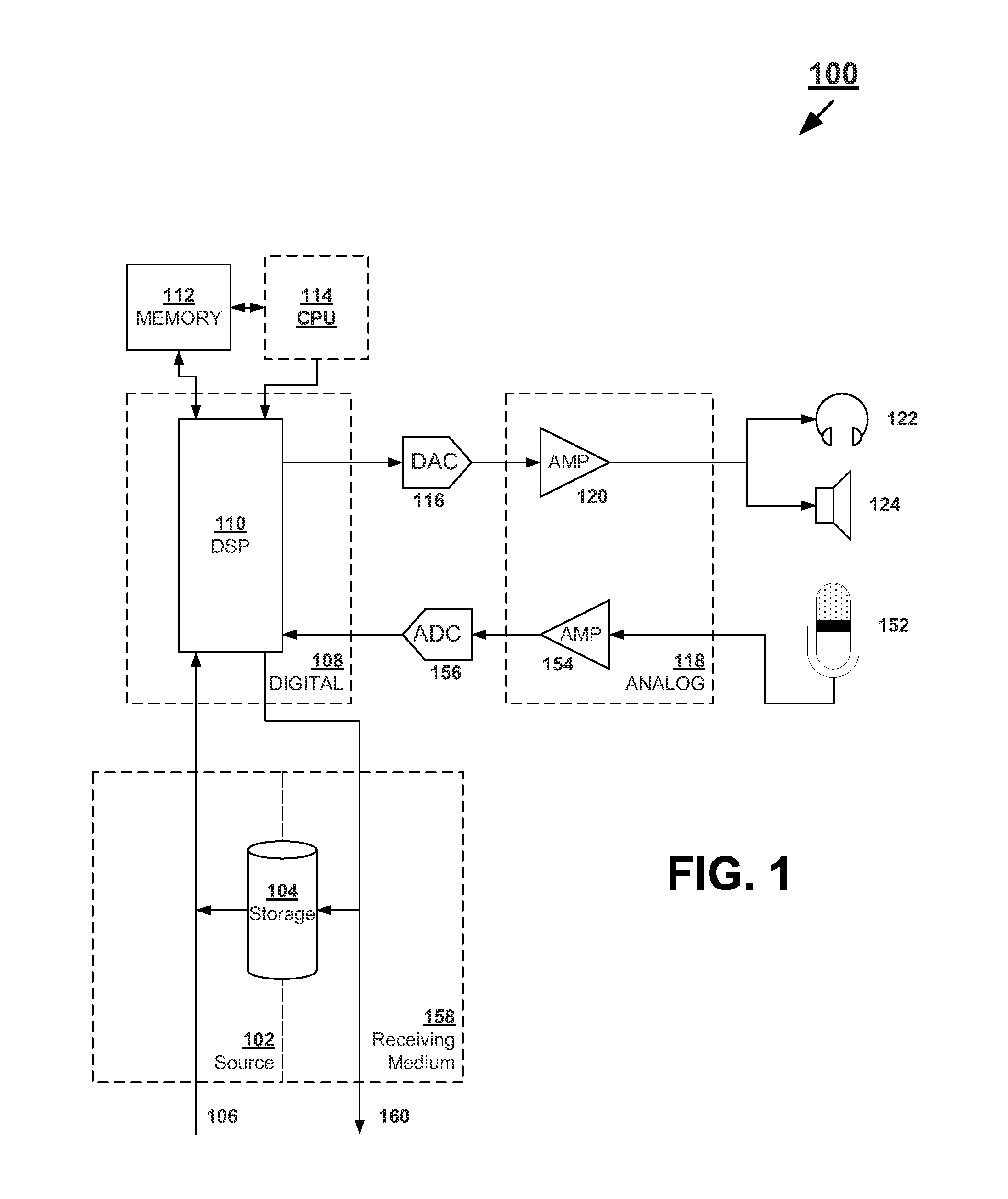
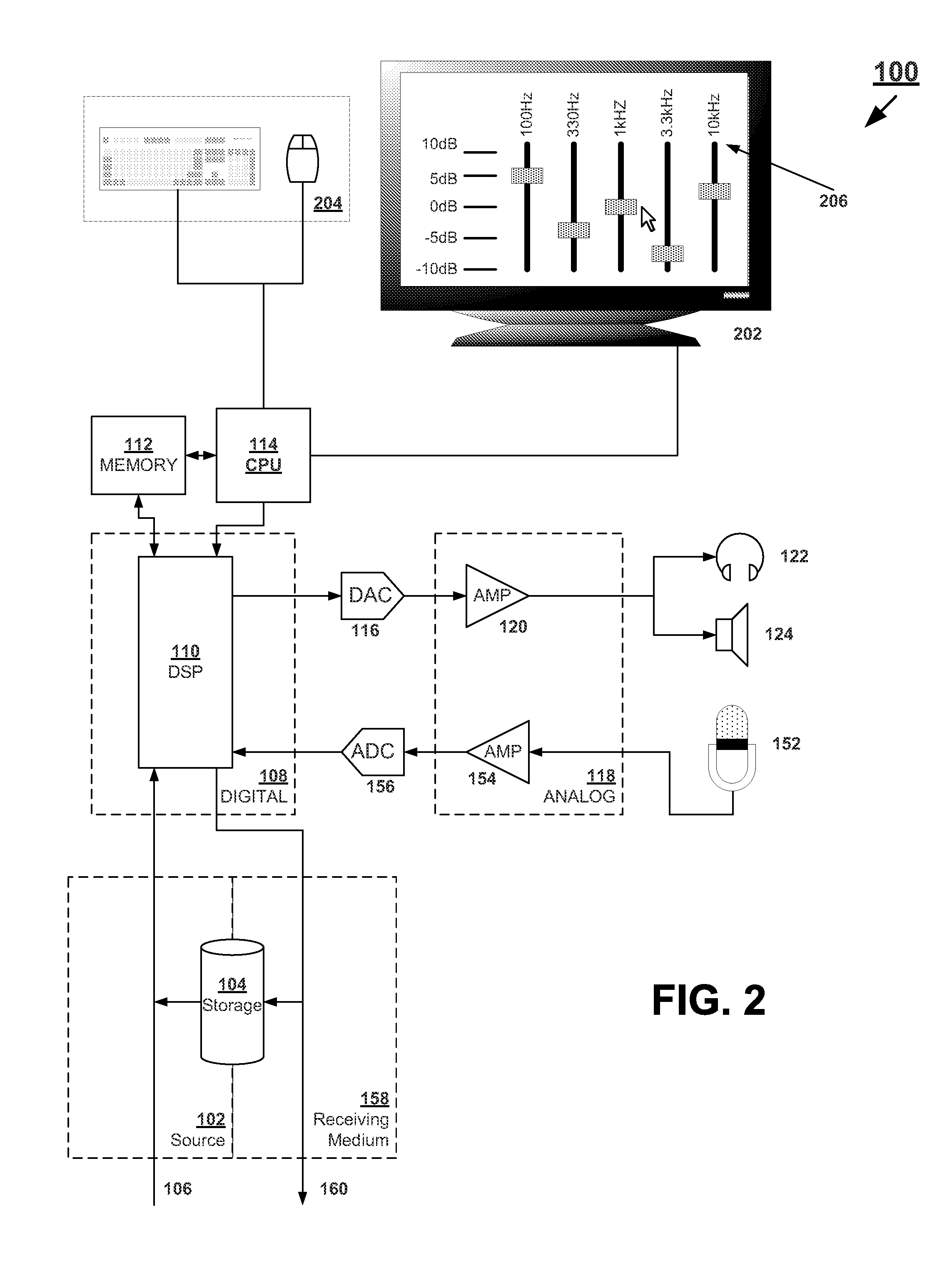
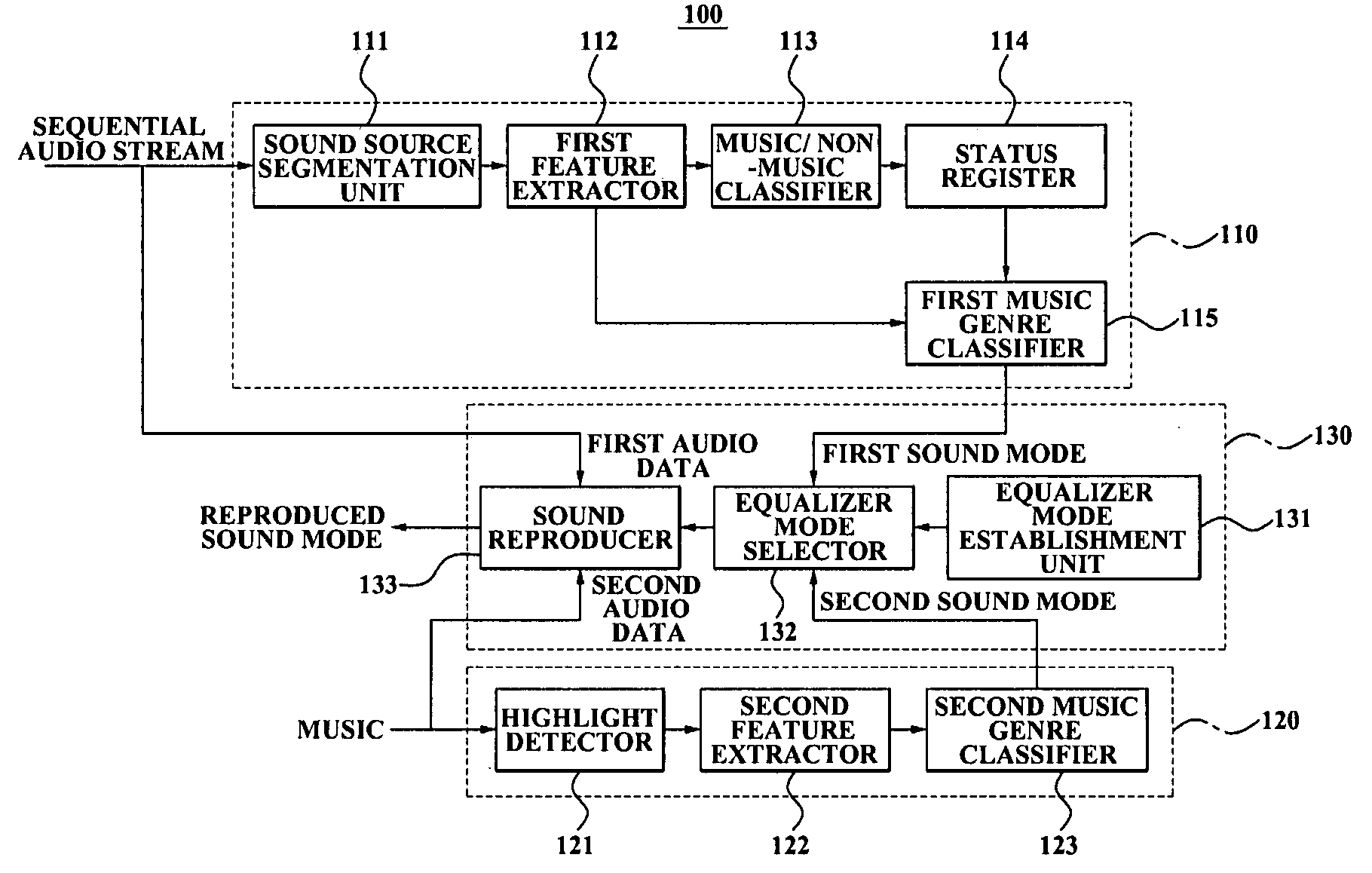
An equalizer control system is provided. The equalizer control system includes a first sound mode identifier to identify a first sound mode for controlling the equalizer from a plurality of sound modes, by classifying an audio feature value, extracted from a sequential audio stream, into a category selected from a plurality of categories, the category corresponding to the first sound mode, a second sound mode identifier to identify a second sound mode for controlling the equalizer, from the plurality of sound modes, by segmenting a sound source into a music genre using a highlight extracted from stored music, and an equalizer controller to analyze the first sound mode and the second sound mode, select one of the first sound mode and the second sound mode, and control the equalizer according to the selected sound mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for transducer calibration and tuning
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
System and method for digital signal processing
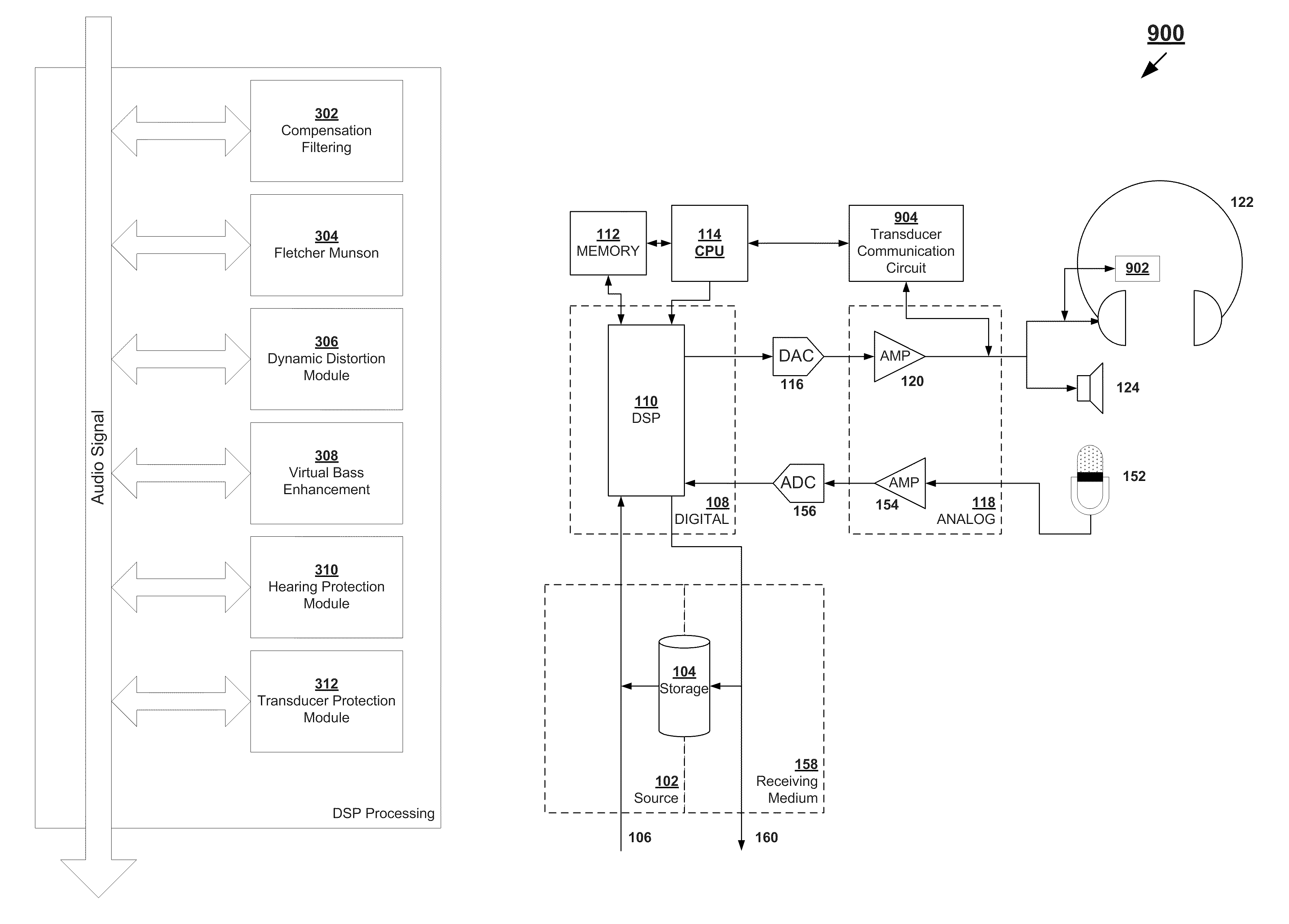
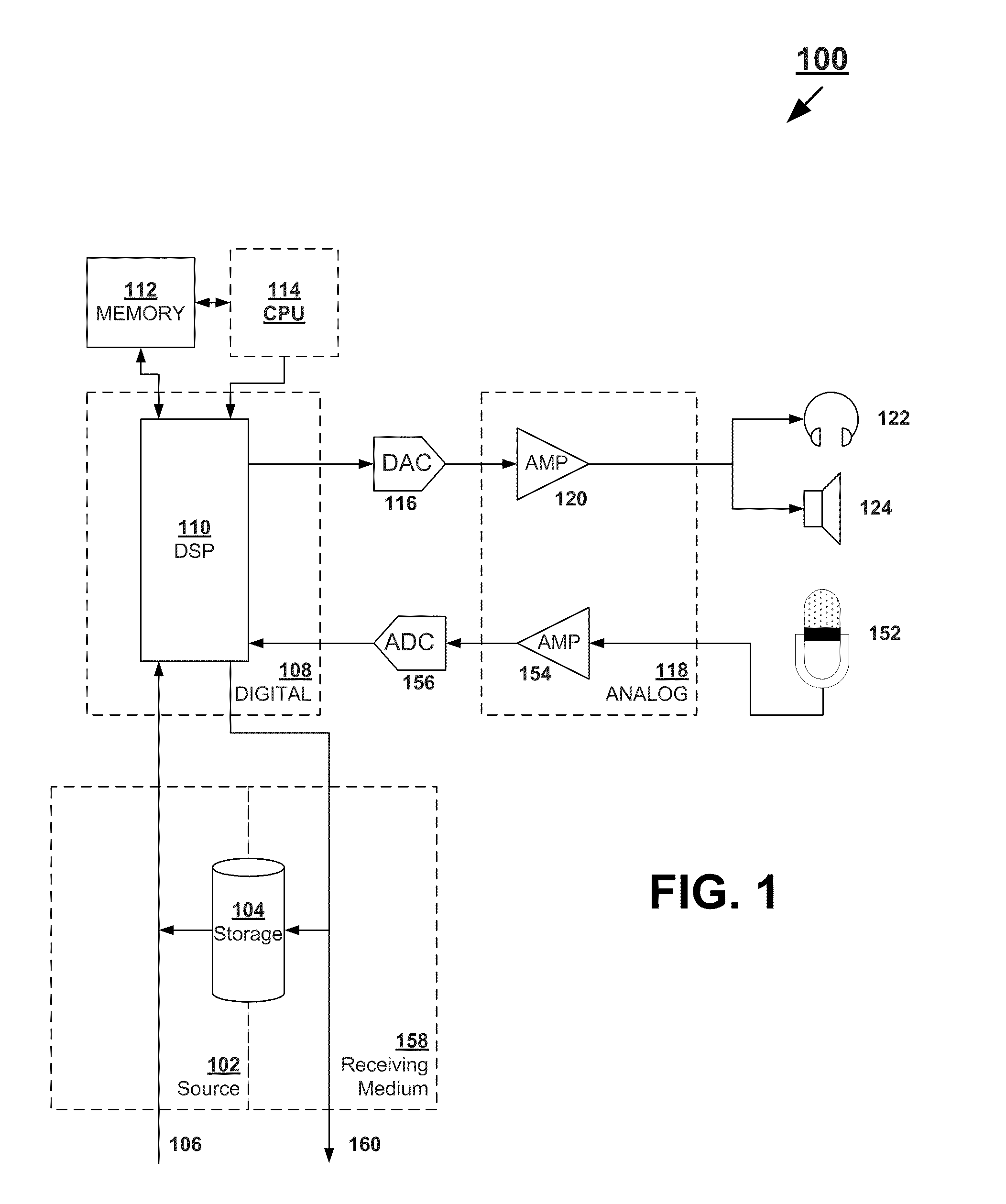
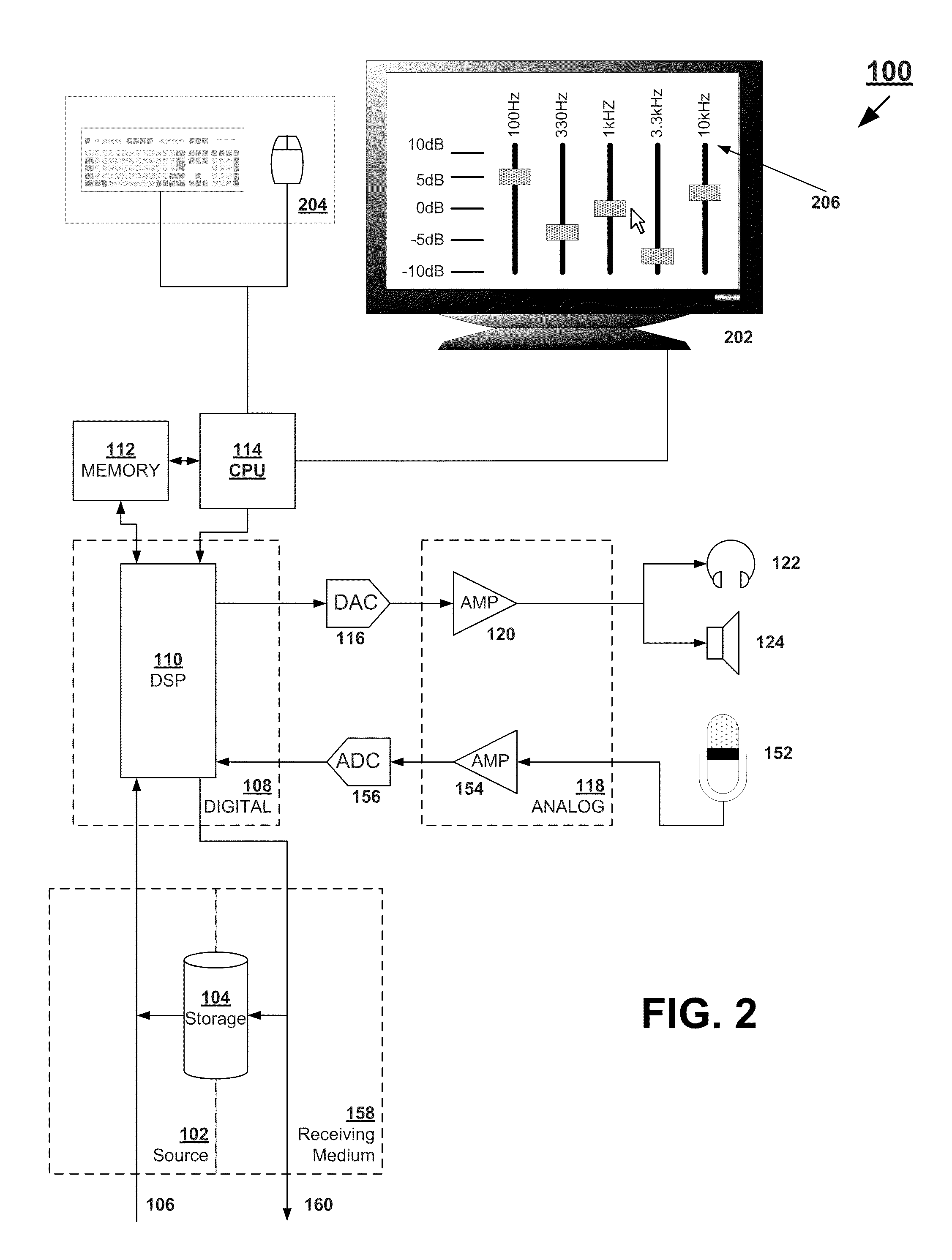
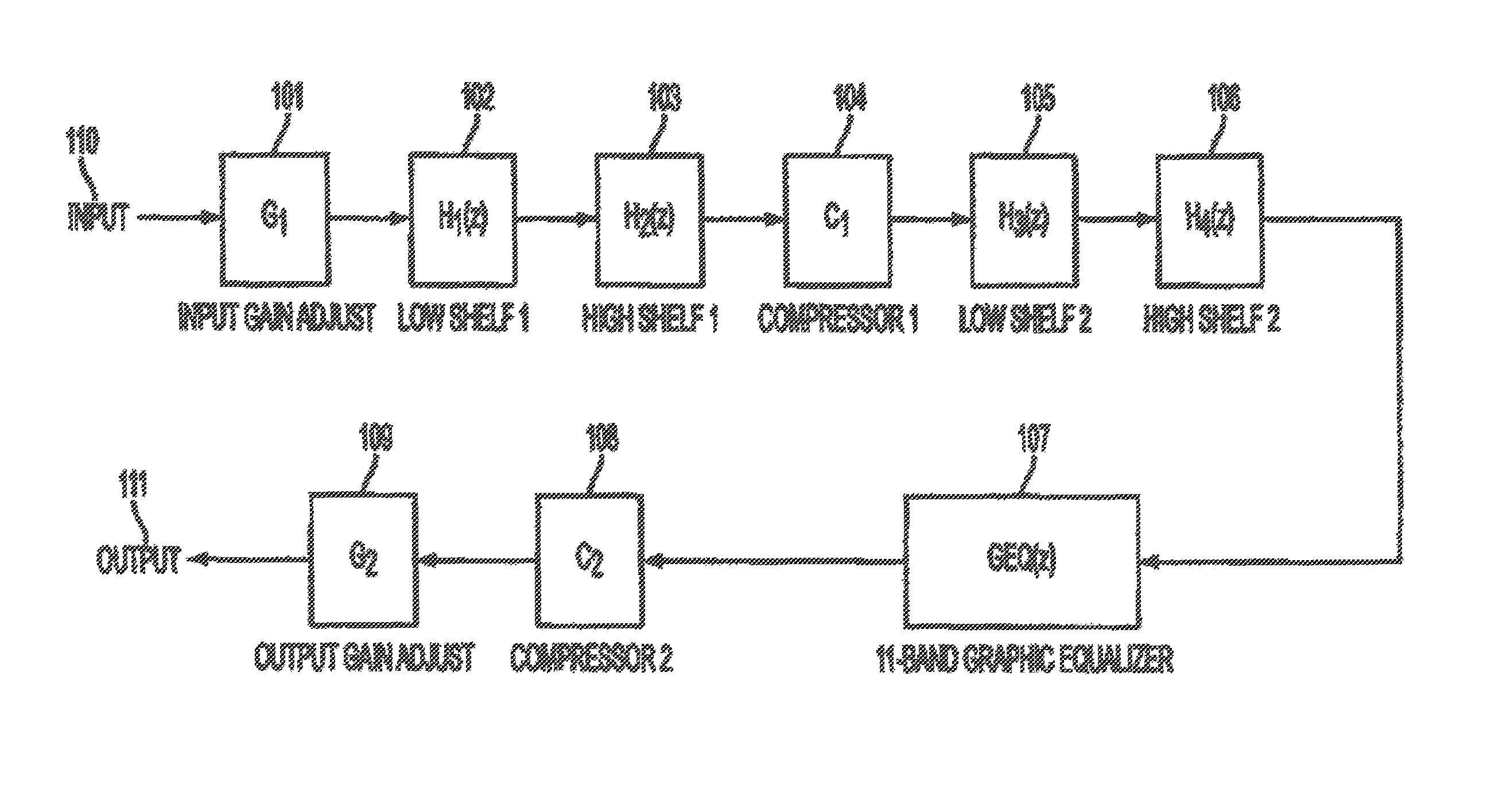
The present invention provides methods and systems for digitally processing audio signals. Some embodiments receive an audio signal and converting it to a digital signal. The gain of the digital signal may be adjusted a first time, using a digital processing device located between a receiver and a driver circuit. The adjusted signal can be filtered with a first low shelf filter. The systems and methods may compress the filtered signal with a first compressor, process the signal with a graphic equalizer, and compress the processed signal with a second compressor. The gain of the compressed signal can be adjusted a second time. These may be done using the digital processing device. The signal may then be output through an amplifier and driver circuit to drive a personal audio listening device. In some embodiments, the systems and methods described herein may be part of the personal audio listening device.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
Method and VLSI circuits allowing to change dynamically the logical behavior
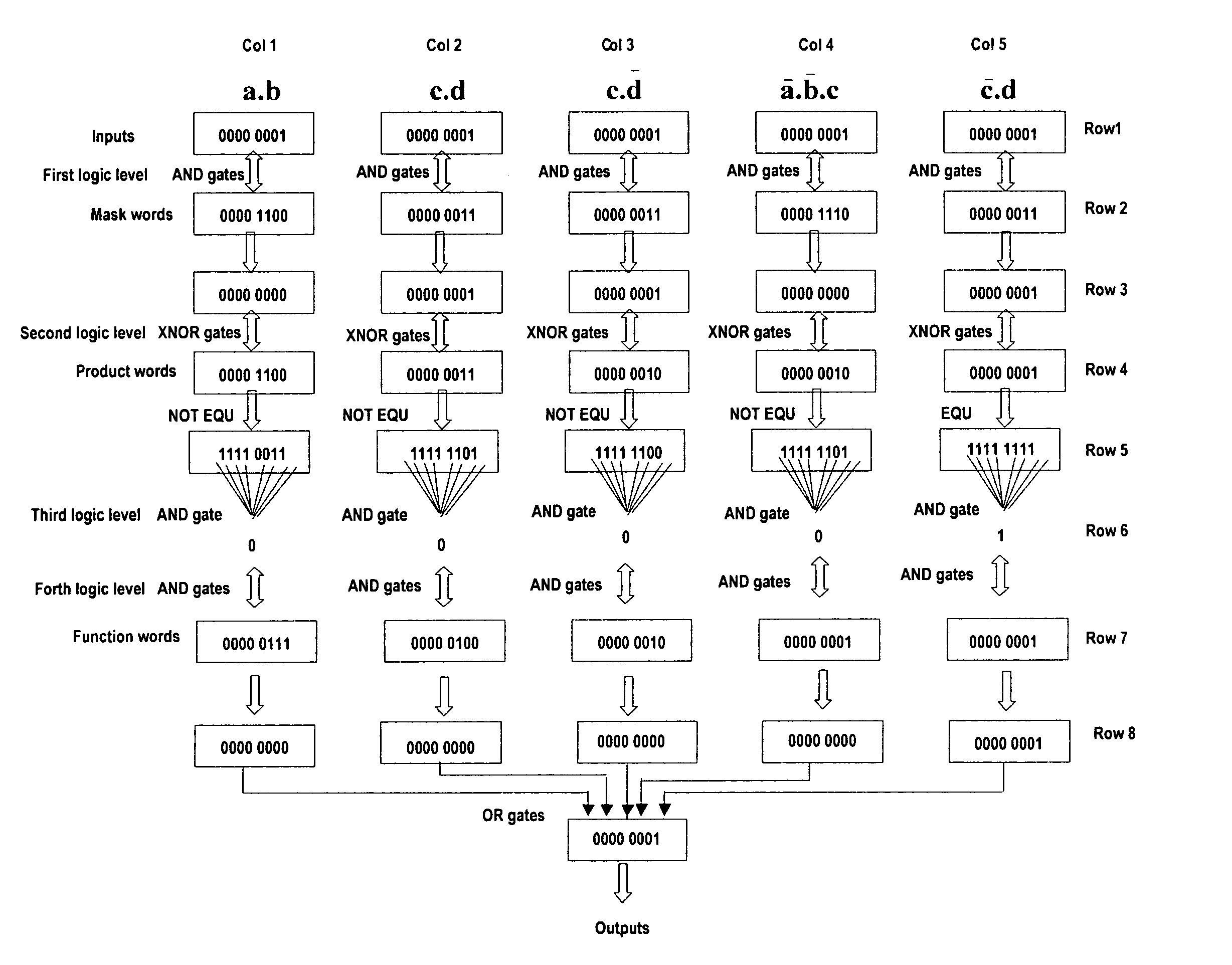
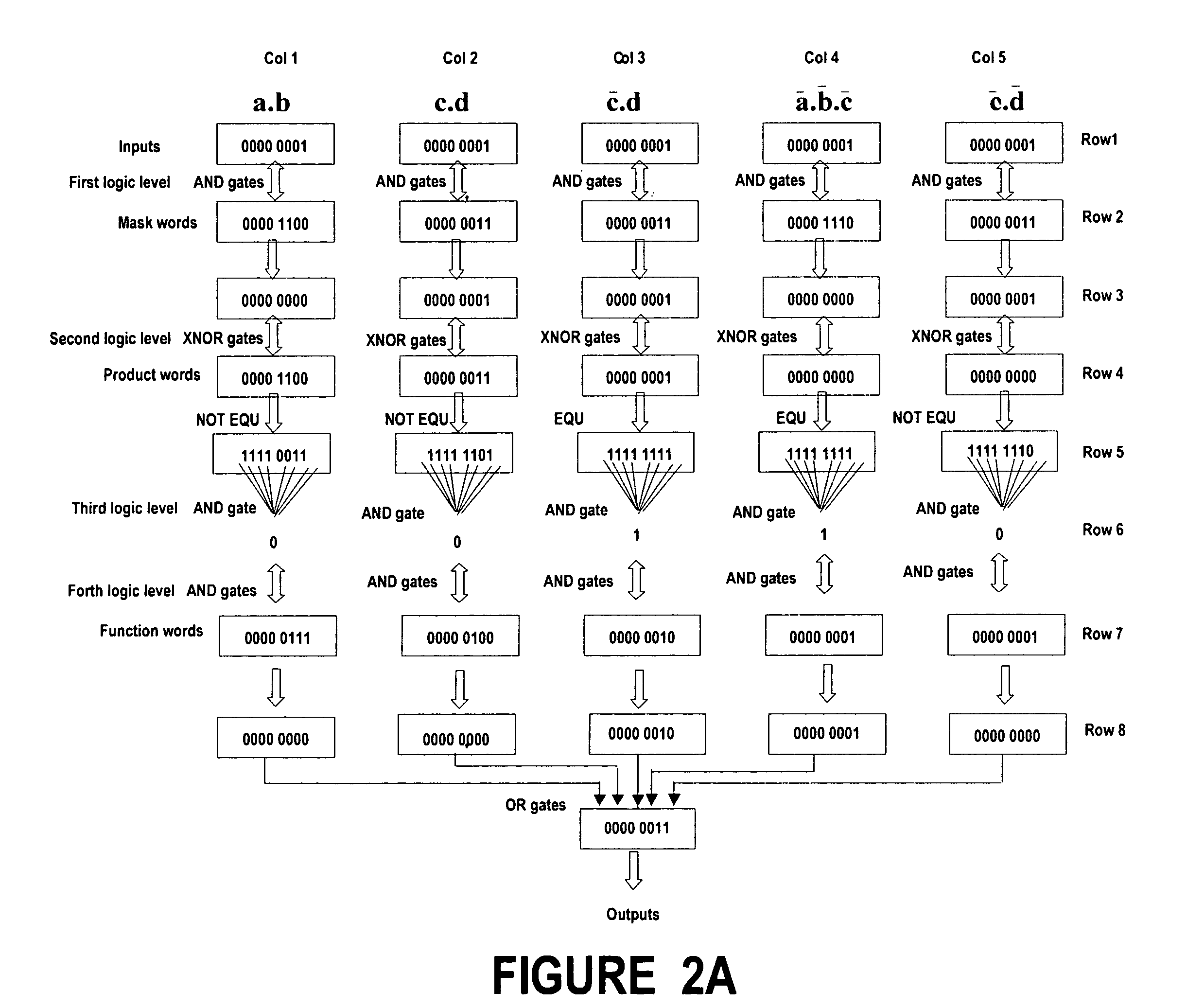
InactiveUS7047166B2Improve accuracyReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusFunction wordHardware structure
A method, named the product terms method that allows to implement and / or to change dynamically the logical behavior of any combinational or synchronous sequential circuits has been presented. The method uses for every product term of logical equations, expressed as a sum-of-product, three memory words: mask word, product word and function word. The words of all product terms are ranged in a table, which characterize the logical behavior of the circuit.The invention provides the hardware structure of several new types of VSLI circuits, having re-configurable logic behaviors. A first embodiment implements any type of multiple output combinational circuit, a second embodiment implements any synchronous sequential circuit with only clock input and, a third embodiment implements any synchronous sequential circuit s with data inputs and clock input.An expert system capable to generate the tables used for the product terms method by interpreting and analysing the logical equations either supplied by the user or found in a database is also provided.
Owner:IOAN DANCEA
Audio processing
ActiveUS20110096933A1Quantity minimizationDigital technique networkGain controlEngineeringAudio frequency
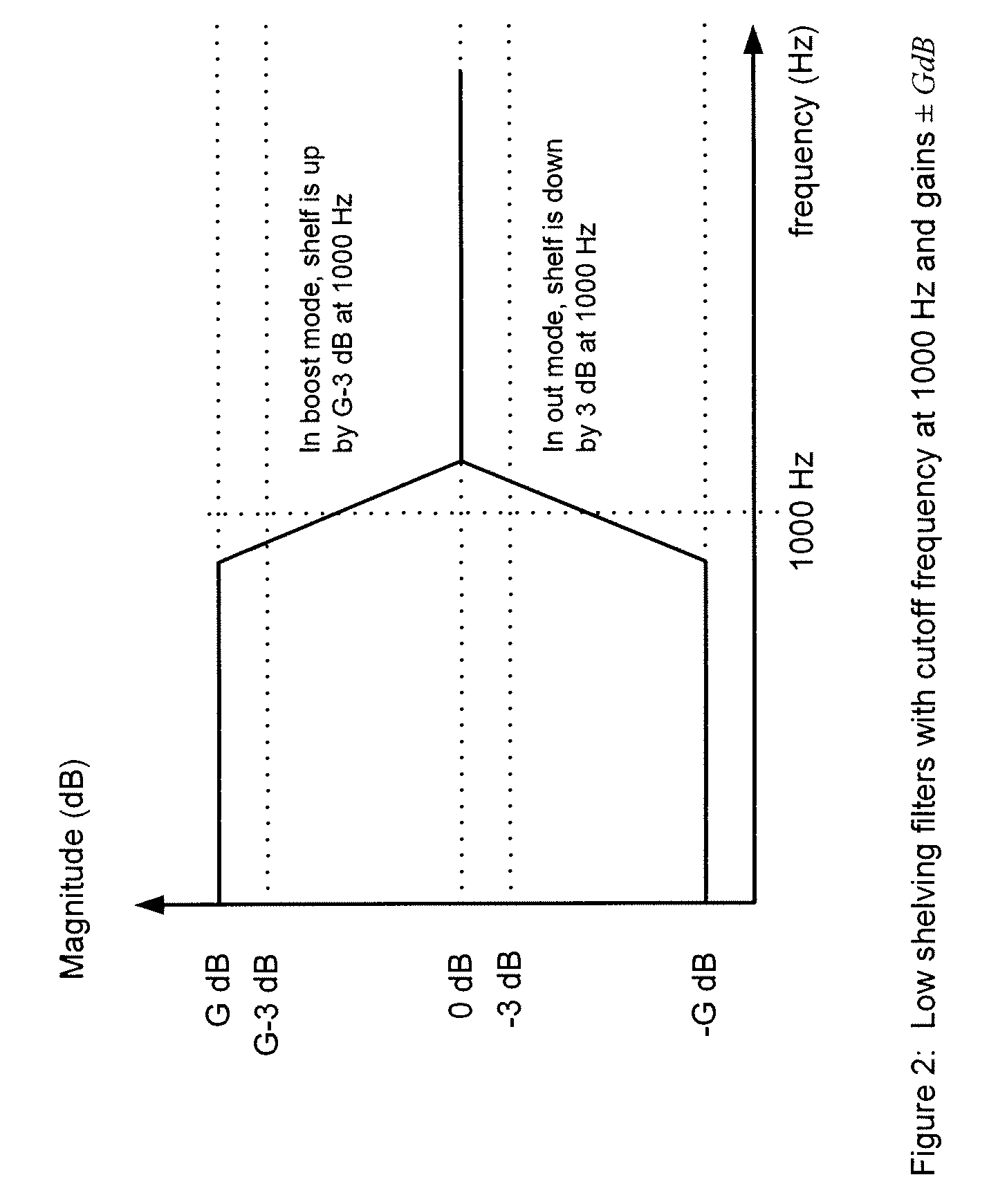
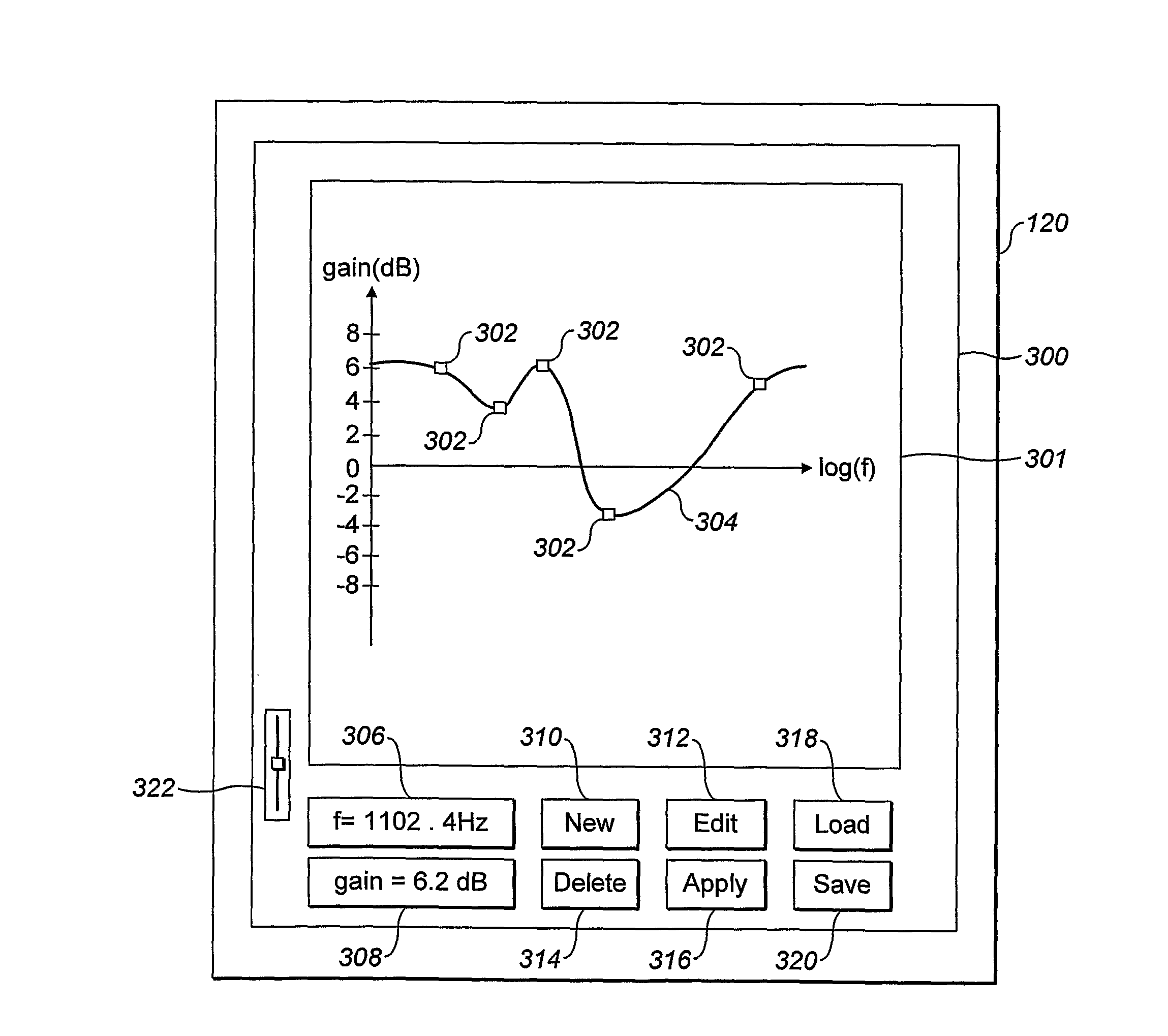
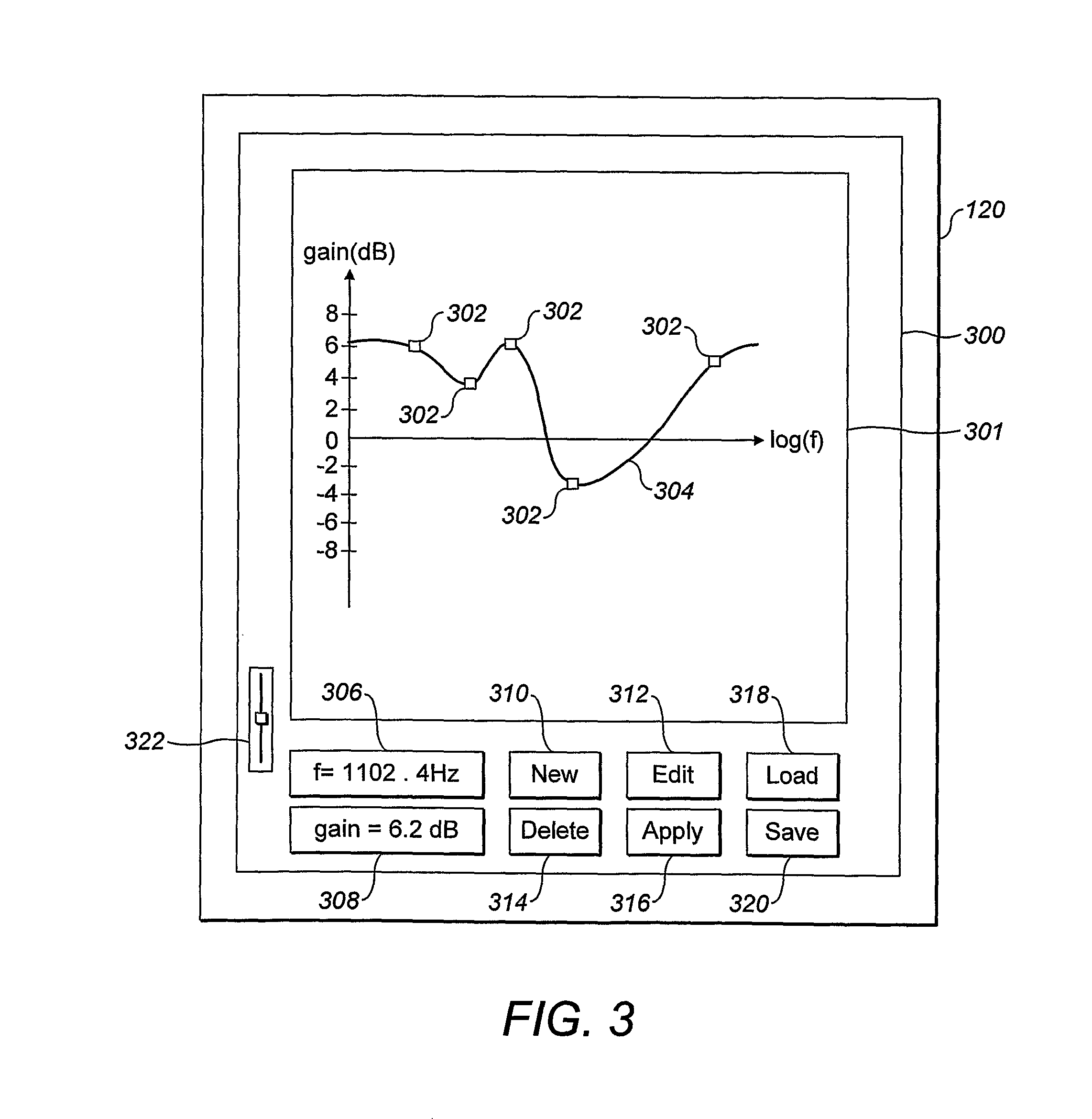
A method of generating a desired shelving filter for audio data, the desired shelving filter having a low-corner frequency U and a high-corner frequency f2, wherein the difference between the gain of the frequency response of the desired shelving filter at f2 and the gain of the frequency response of the desired shelving filter at U is substantially equal to a non-zero desired amount, the method comprising: determining an order for a first shelving filter of a first predetermined type, wherein the low-corner frequency of the first shelving filter is U and the high-corner frequency of the first shelving filter is fΣ, determining, for a second shelving filter of a second predetermined type and of a predetermined order m, a frequency fz for the low-corner frequency of the second shelving filter and a frequency Z4 for the high-corner frequency of the second shelving filter, where h is at least fi, f4 is greater than f3, and f4 is at most fi, and forming the desired shelving filter as a filter combination of the first shelving filter and the second shelving filter; wherein fz, f4 and the order of the first shelving filter are determined such that difference between the gain of the frequency response of the filter combination at fe and the gain of the frequency response of the filter combination at fi is substantially equal to the desired amount.
Owner:OXFORD DIGITAL
Linearized filter band equipment and processes
ActiveUS7266205B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsGraphicsSystems design
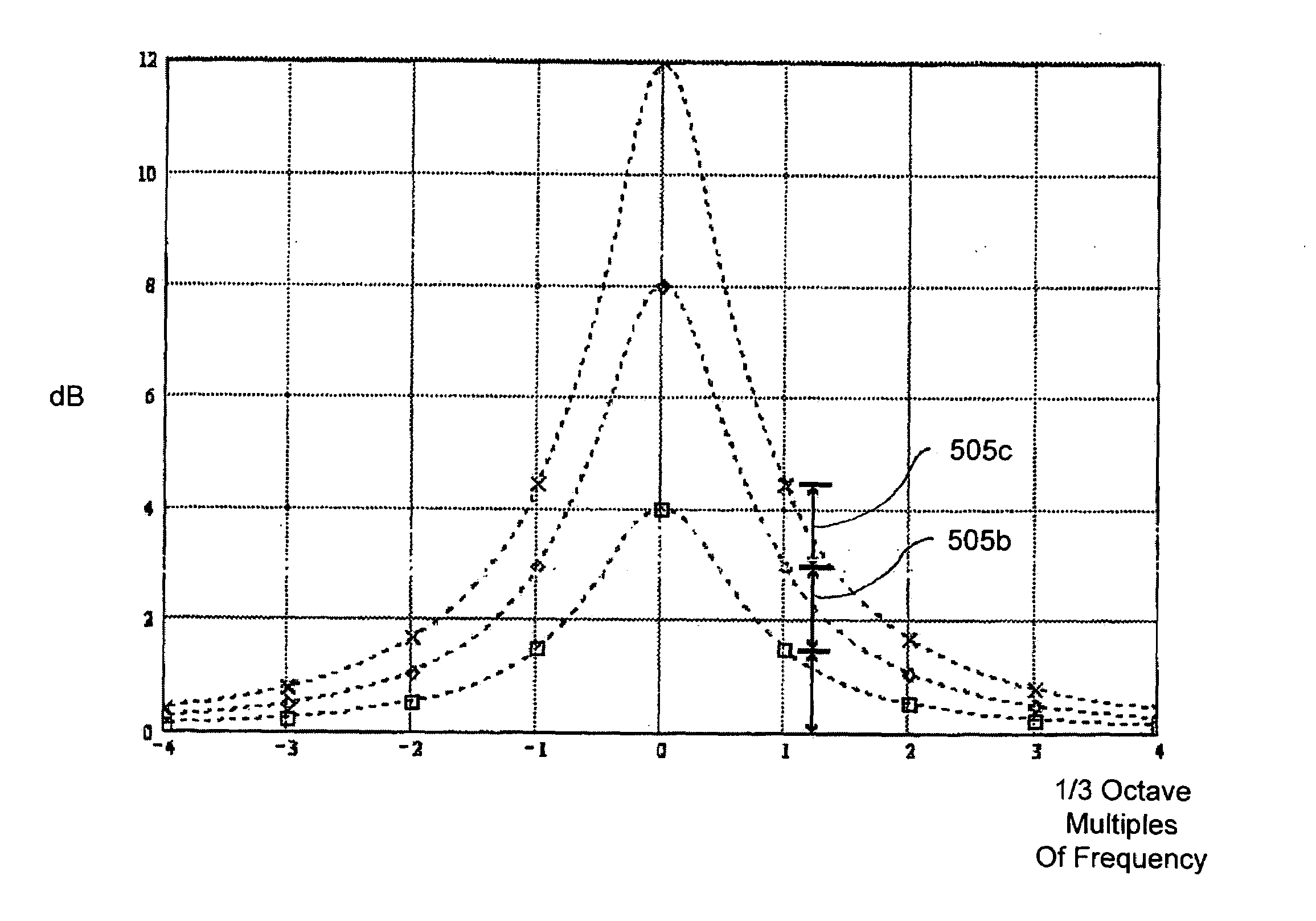
A method for use with equipment having filters, the method characterized by multiplying a matrix having a specified cut-boost setting of a filter of a graphic equalizer by a correction matrix to create a matrix having a corrected cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer; adjusting an actual cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer to be substantially equal to the corrected cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer; and configuring the filter to have a Q value substantially equal to a linearizing Q value. In addition to the foregoing, other method embodiments are described in the claims, drawings, and text forming a part of the present application. In one or more various embodiments, related systems include but are not limited to circuitry and / or programming for effecting the foregoing-referenced method embodiments; the circuitry and / or programming can be virtually any combination of hardware, software, and / or firmware configured to effect the foregoing-referenced method embodiments depending upon the design choices of the system designer.
Owner:INMUSIC BRANDS
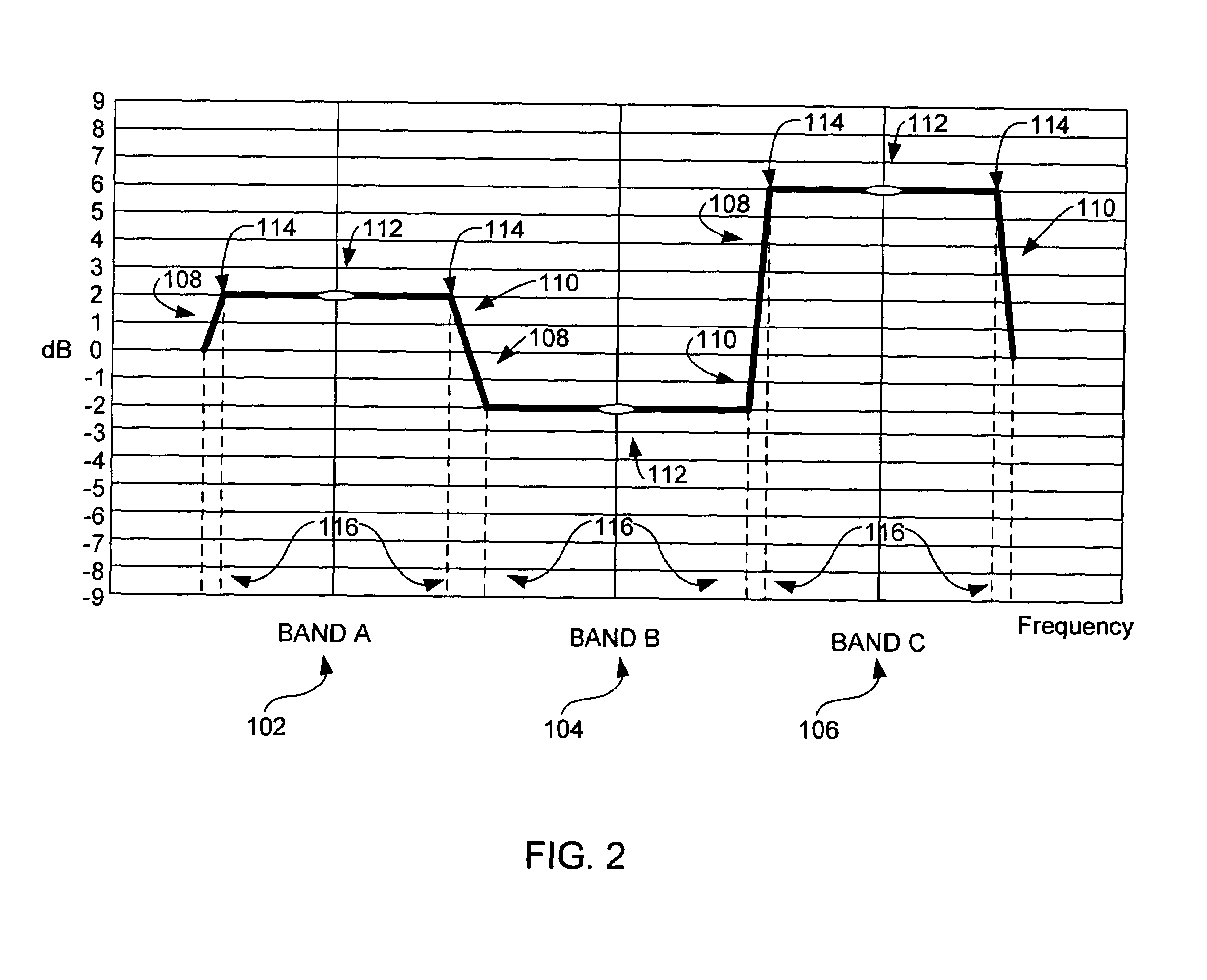
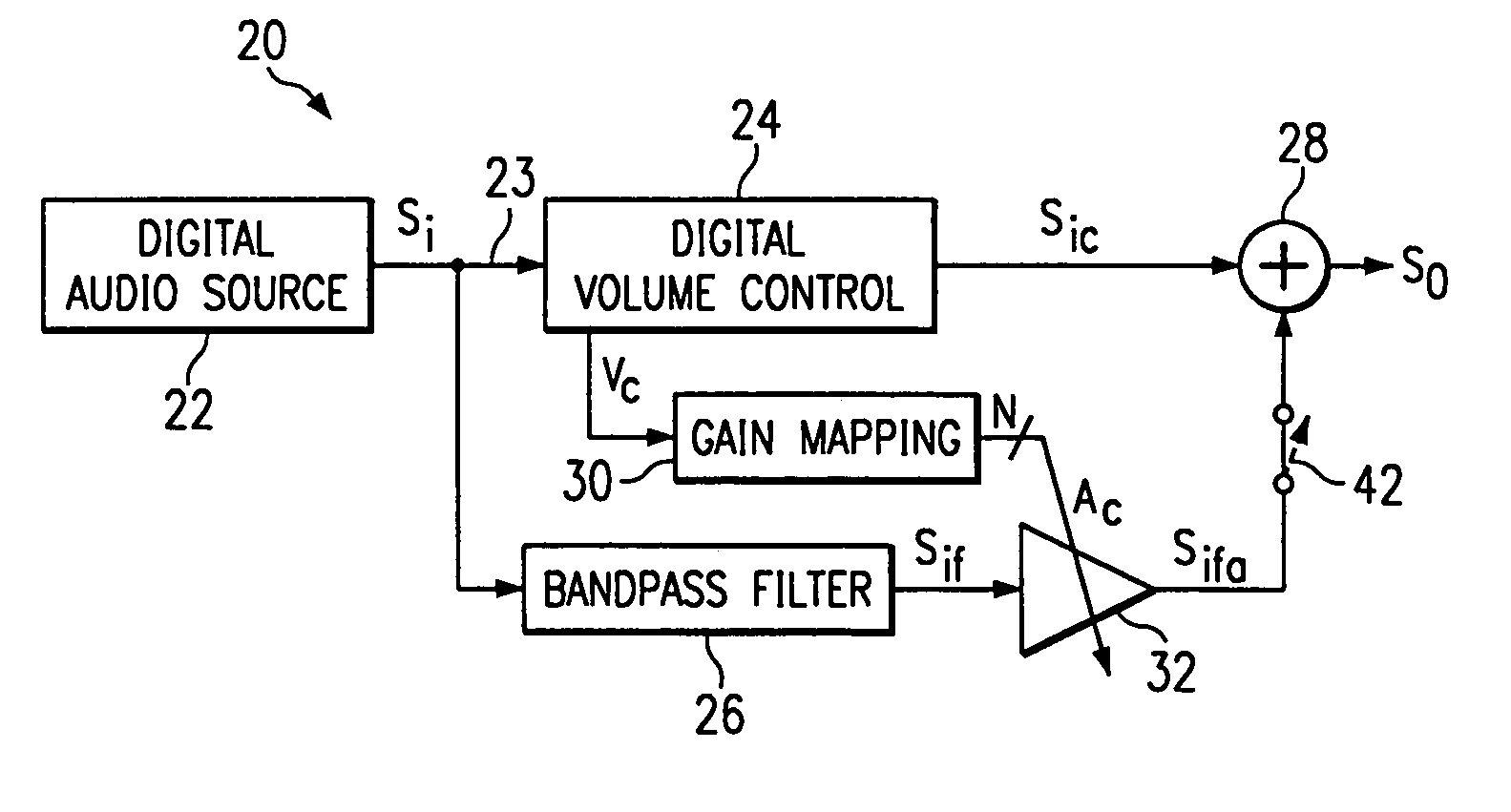
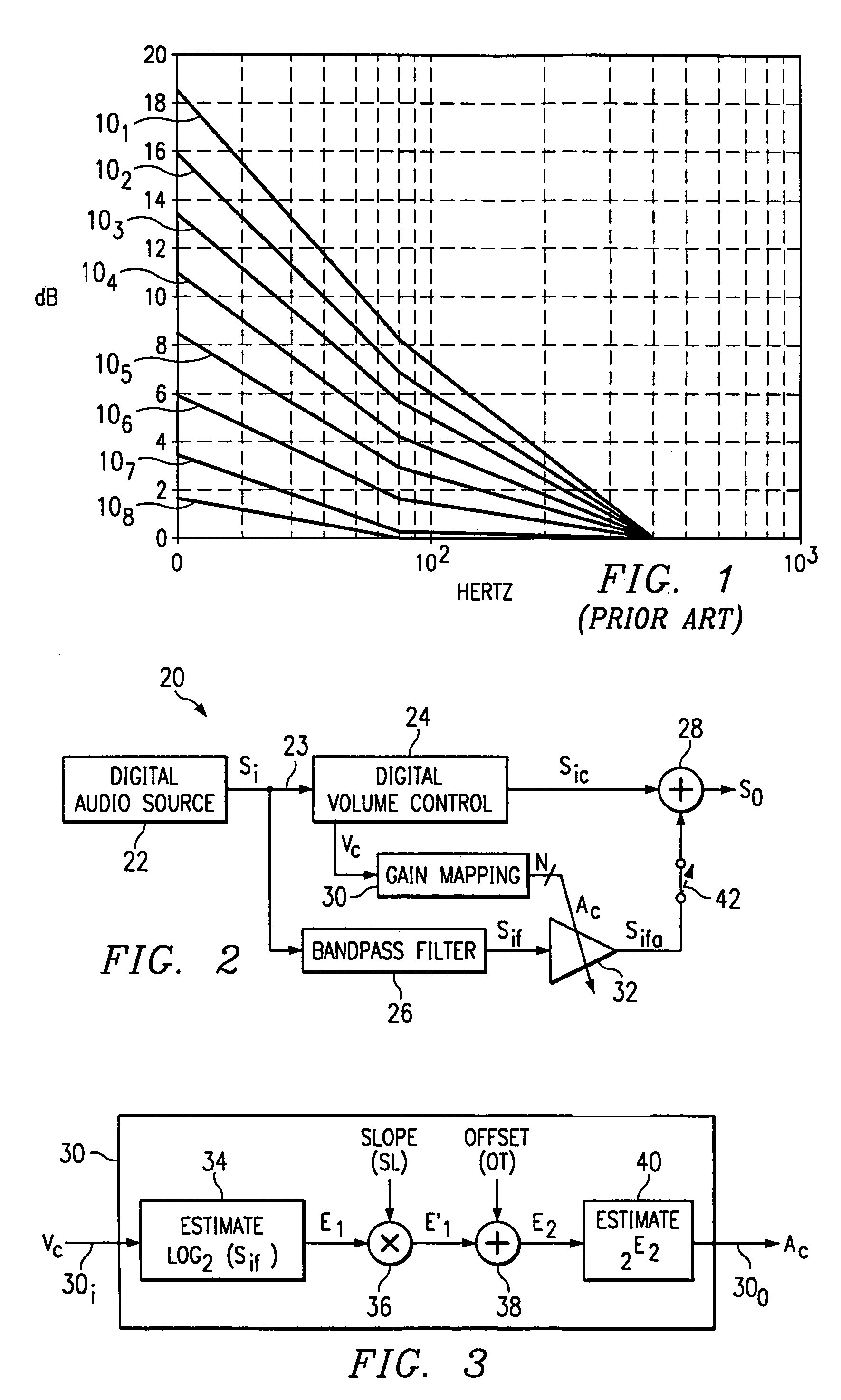
Volume-responsive loudness compensation circuits, systems, and methods
An audio compensation system (20) for producing a sound compensated output signal (So). The system comprises a volume control circuit (24) for producing a volume-adjusted signal (Sic) by applying a volume adjustment to an audio signal in response to a volume setting, wherein the sound compensated output signal is responsive to the volume-adjusted signal. The system also comprises circuitry (26, 30, 32) for producing an amplified signal (Sifa) by amplifying a selected bandwith of signals in response to the volume setting. The sound compensated output signal is also responsive to the amplified signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC +1
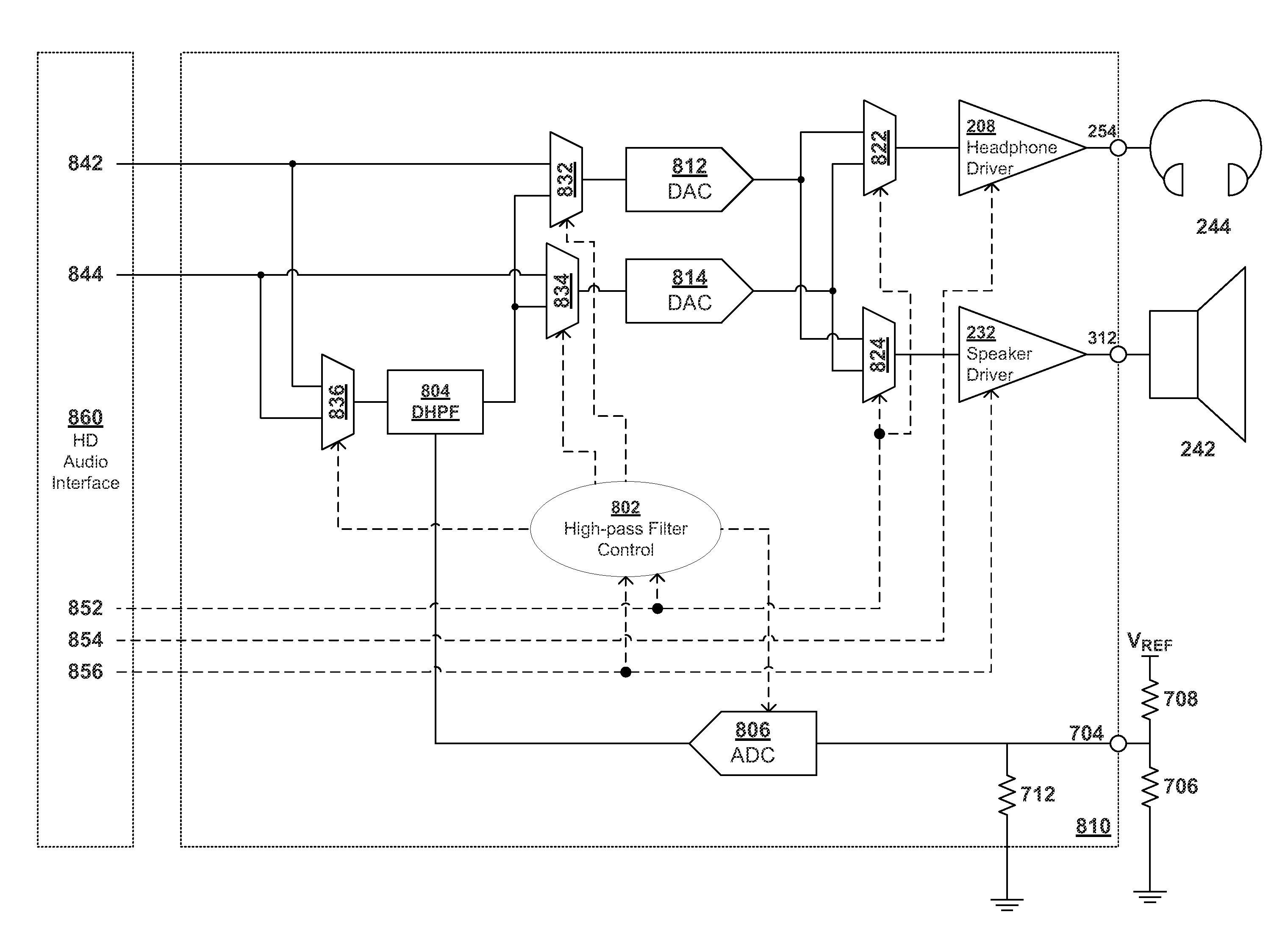
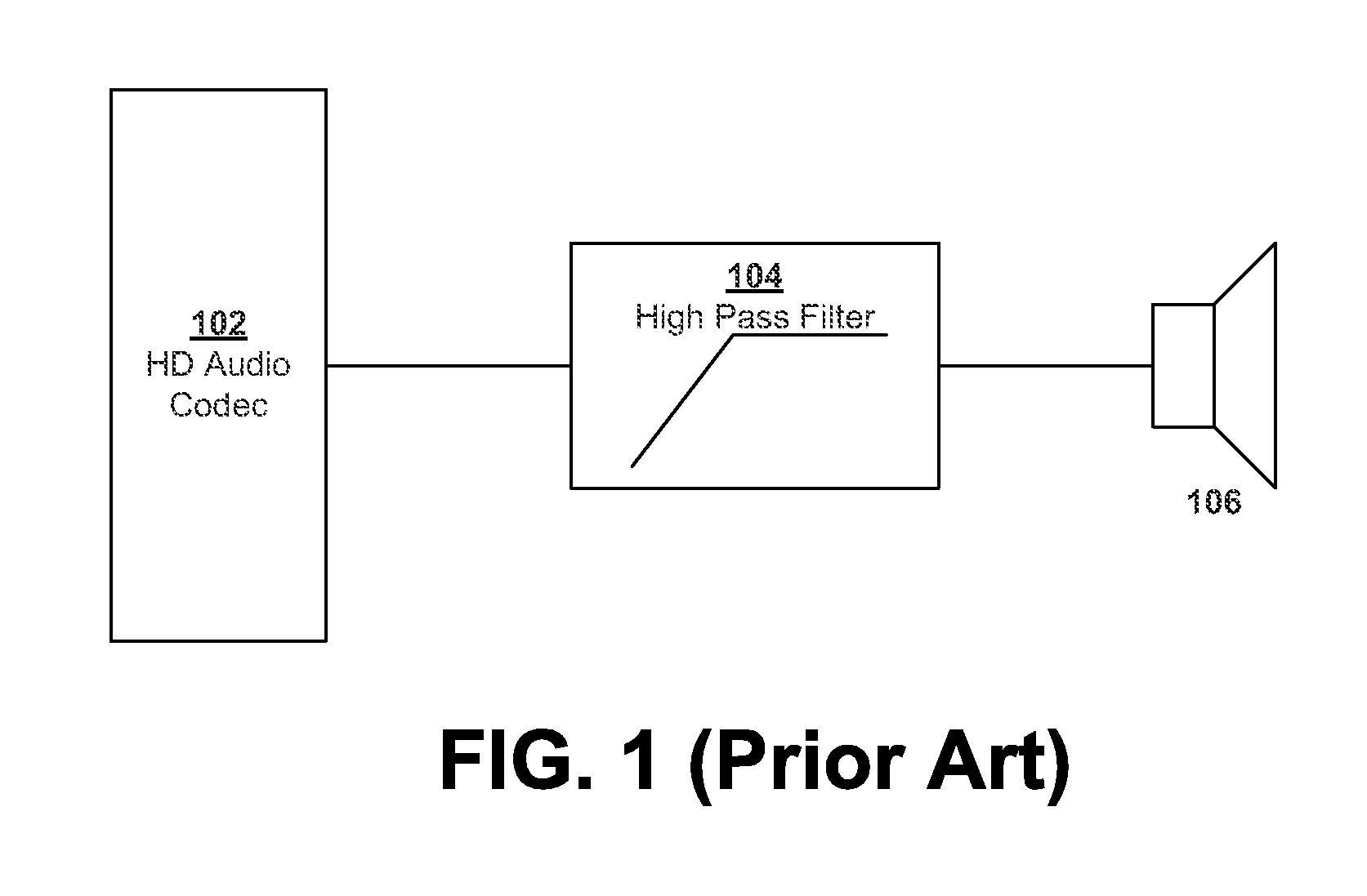
Tuning and DAC Selection of High-Pass Filters for Audio Codecs
ActiveUS20110087346A1Digital signal tone/bandwidth controlSpecial data processing applicationsLoudspeakerCapacitance
An integrated audio codec includes a high-pass filter to prevent damage to personal computer speakers and other components. The audio codec may be compliant with HD audio standards and can operate with generic software drivers. Tuning of the high-pass filter is provided through an external pin-out where either an external capacitor or external resistors provide an ability to tune the high-pass filter. In one implementation, a tuning voltage is digitized into a tuning code used by a digital high-pass filter. In addition, multiplexers can be used to insure only the audio path leading to the speakers is filtered.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
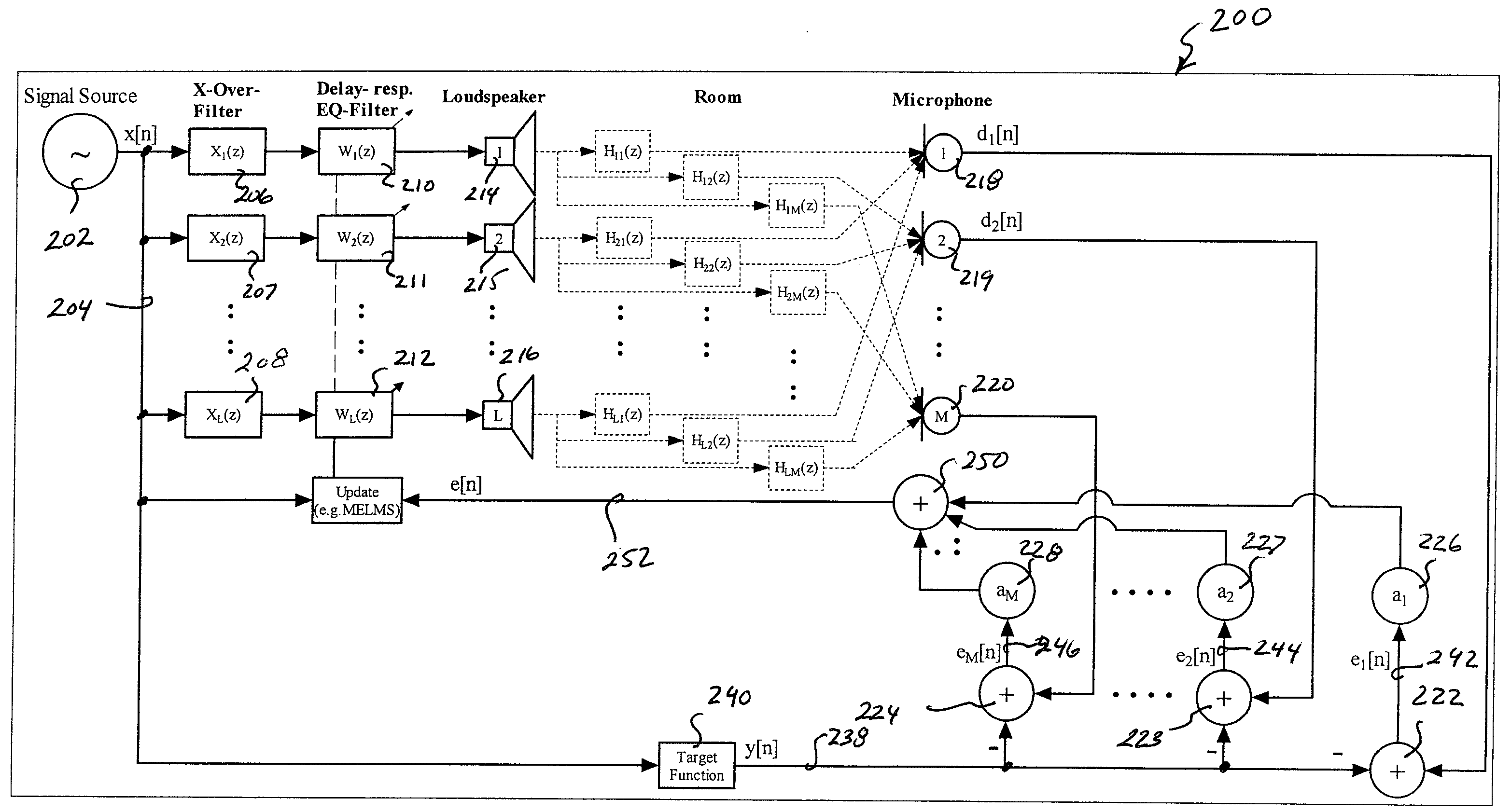
Sound tuning method
The invention relates to a method for automated tuning of a sound system, the sound system comprising delay lines, equalizing filters, and at least two loudspeakers, the method comprising the steps of reproducing a useful sound signal through the loudspeakers, measuring sound pressure values at least one location, providing a target transfer function for tuning the delay lines and the equalizing filters of the sound system, the target transfer function representing a desired transfer characteristics of the sound system, adjusting the delay of the delay lines, and adjusting amplitude responses of the equalizing filters such, that the actual transfer characteristics of the sound system approximates the target function.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Adaptive speaker equalization
InactiveUS20070223736A1Frequency response correctionDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlEqualizationLoudspeaker
A device may include logic configured to detect information about a condition of a speaker in a communications device. The logic may process the information, load equalization logic based on the processed information, and may apply the equalization logic to an input signal of the speaker when the information indicates that a frequency response for the speaker should be changed.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
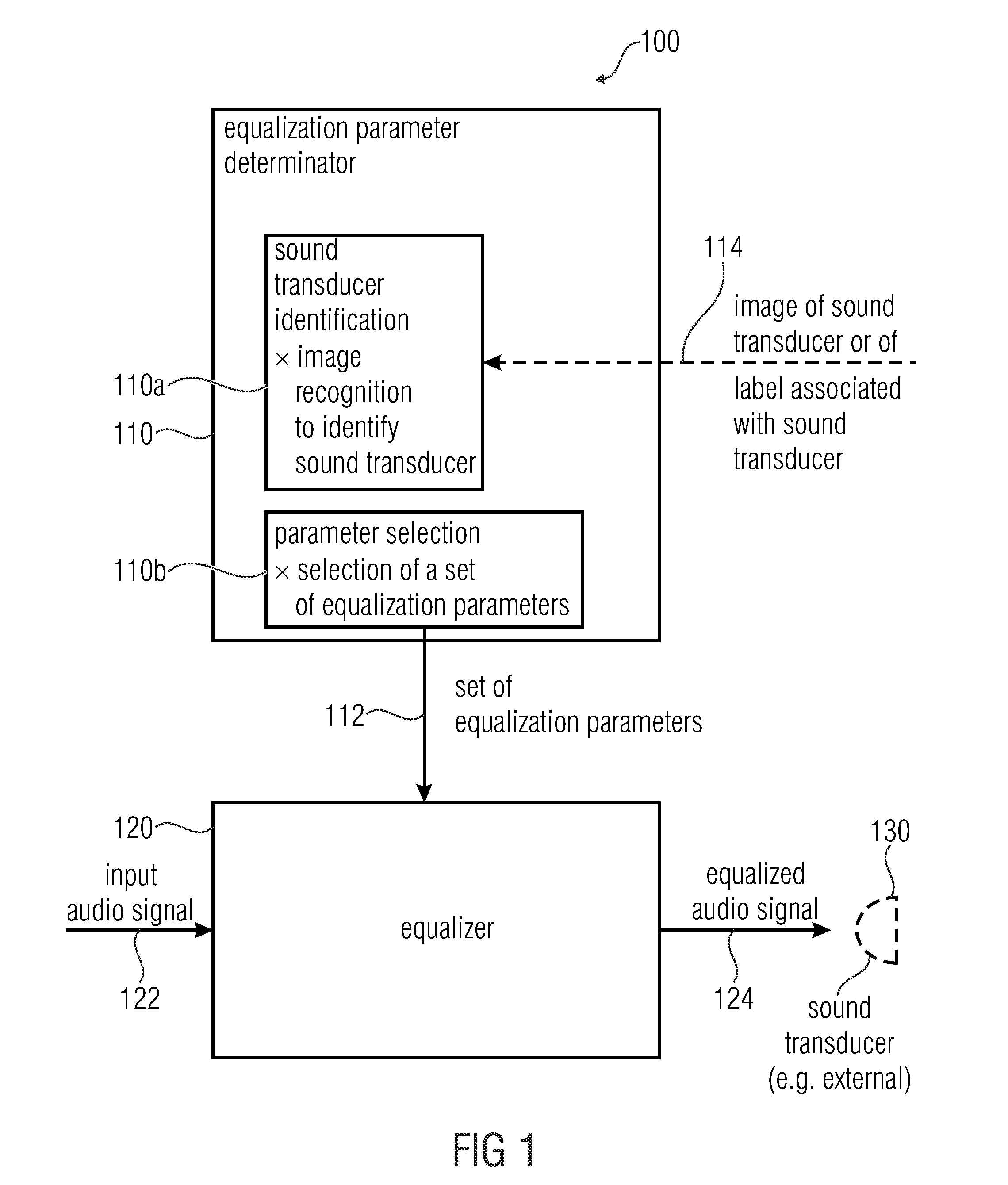
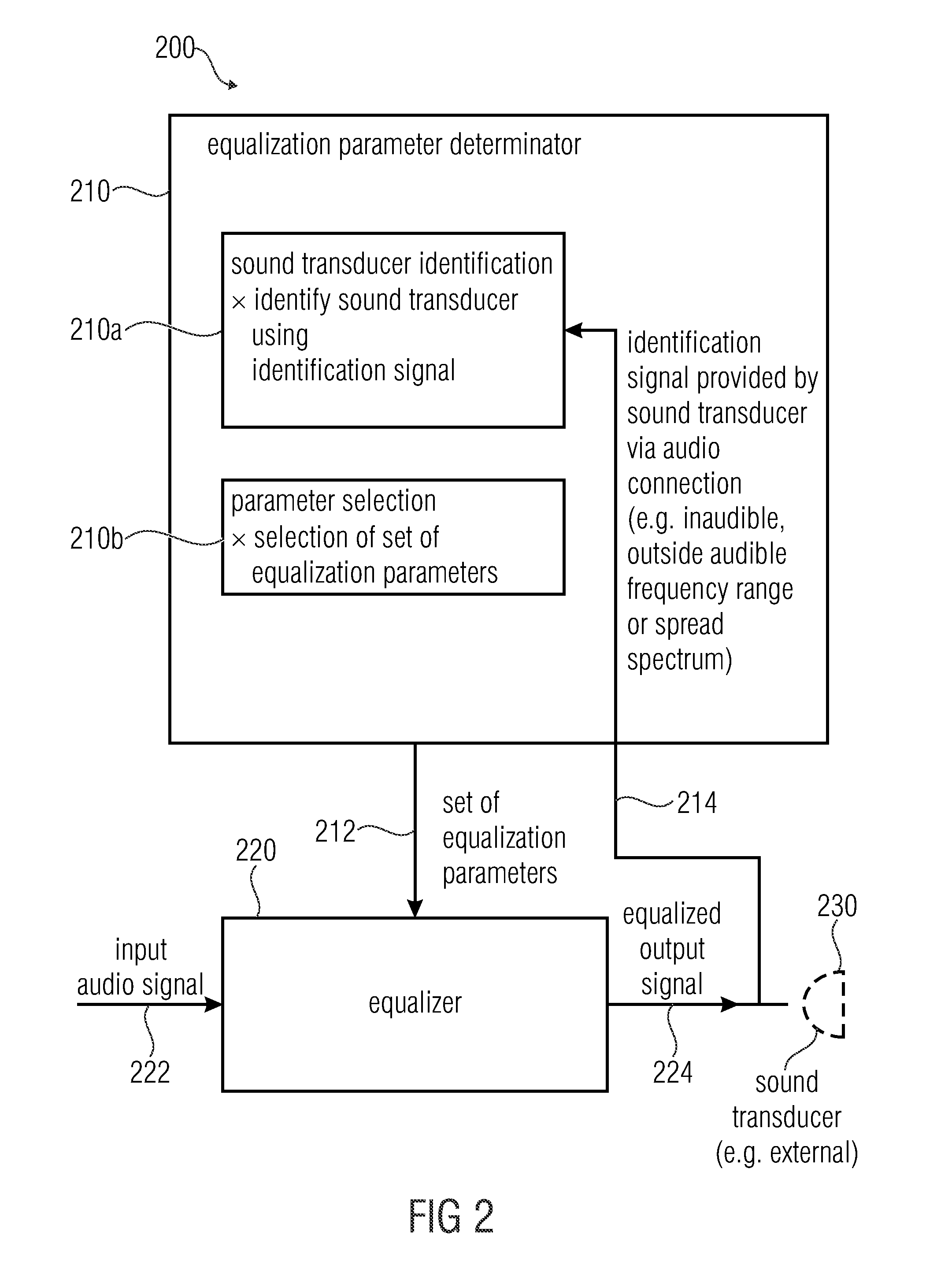
Apparatus for providing an audio signal for reproduction by a sound transducer, system, method and computer program
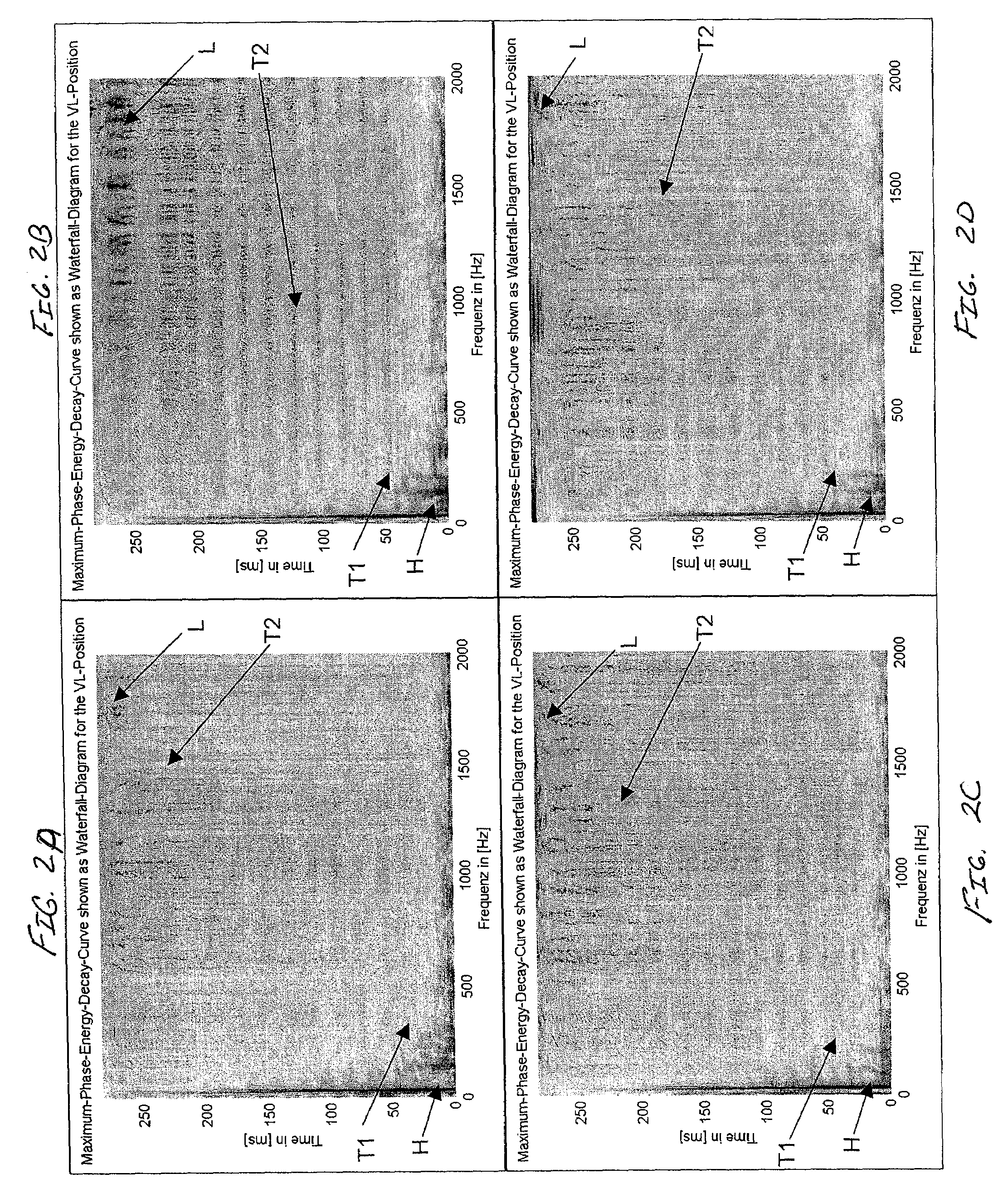
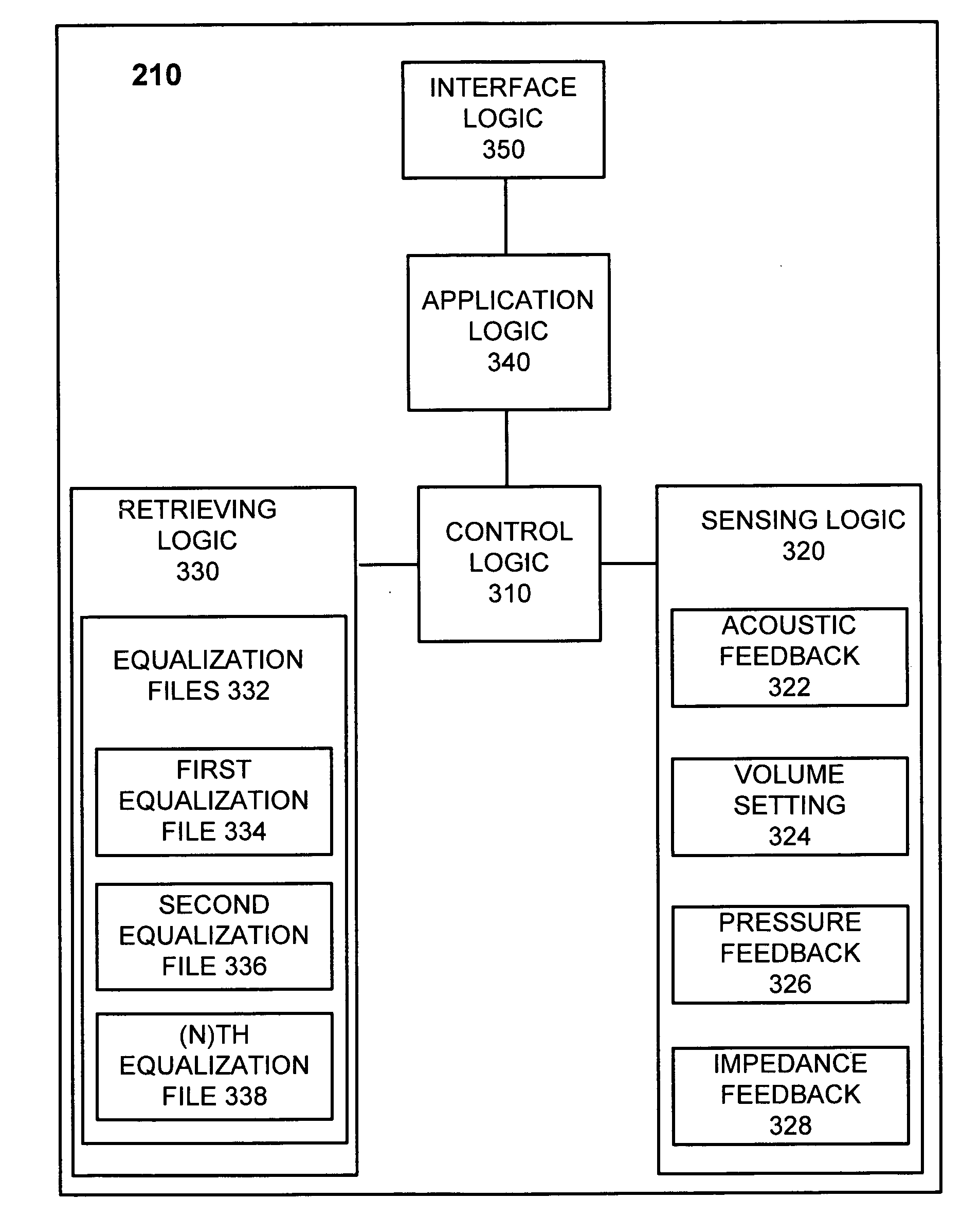
InactiveUS20140369519A1Improve user satisfactionConvenient lifeDigital data information retrievalEarpiece/earphone attachmentsTransducerEqualization
An apparatus for processing an audio signal for reproduction by a sound transducer includes an equalization parameter determinator for determining a set of equalization parameters and an equalizer configured to equalize an input audio signal, to obtain an equalized audio signal. Different concepts for the determination of the set of equalization parameters include an image recognition, an evaluation of an identification signal which is provided by the sound transducer via an audio connection, and a measurement of the impedance of the sound transducer over frequency. Also, an upload functionality and a download functionality are provided.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
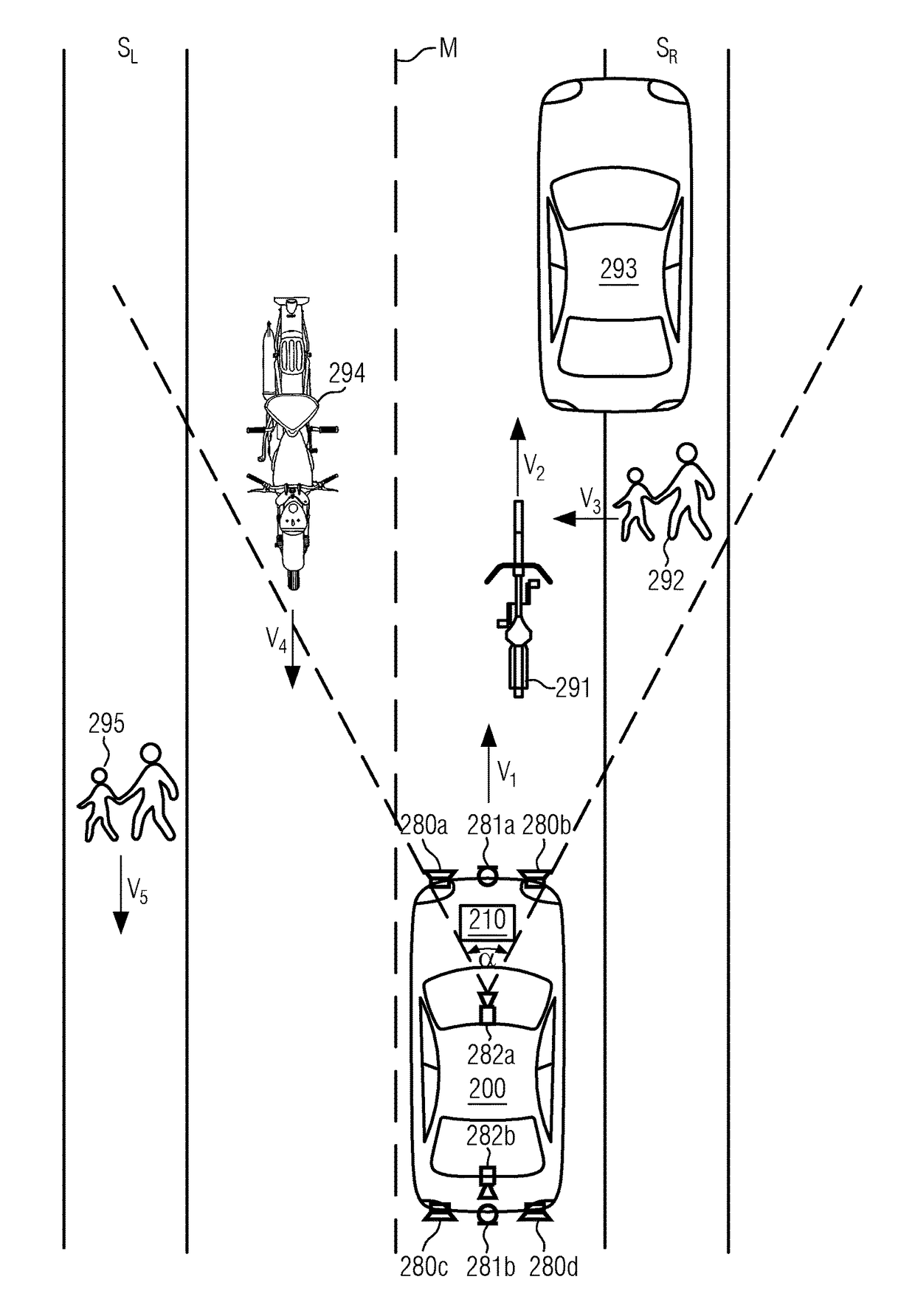
System and method for external sound synthesis of a vehicle
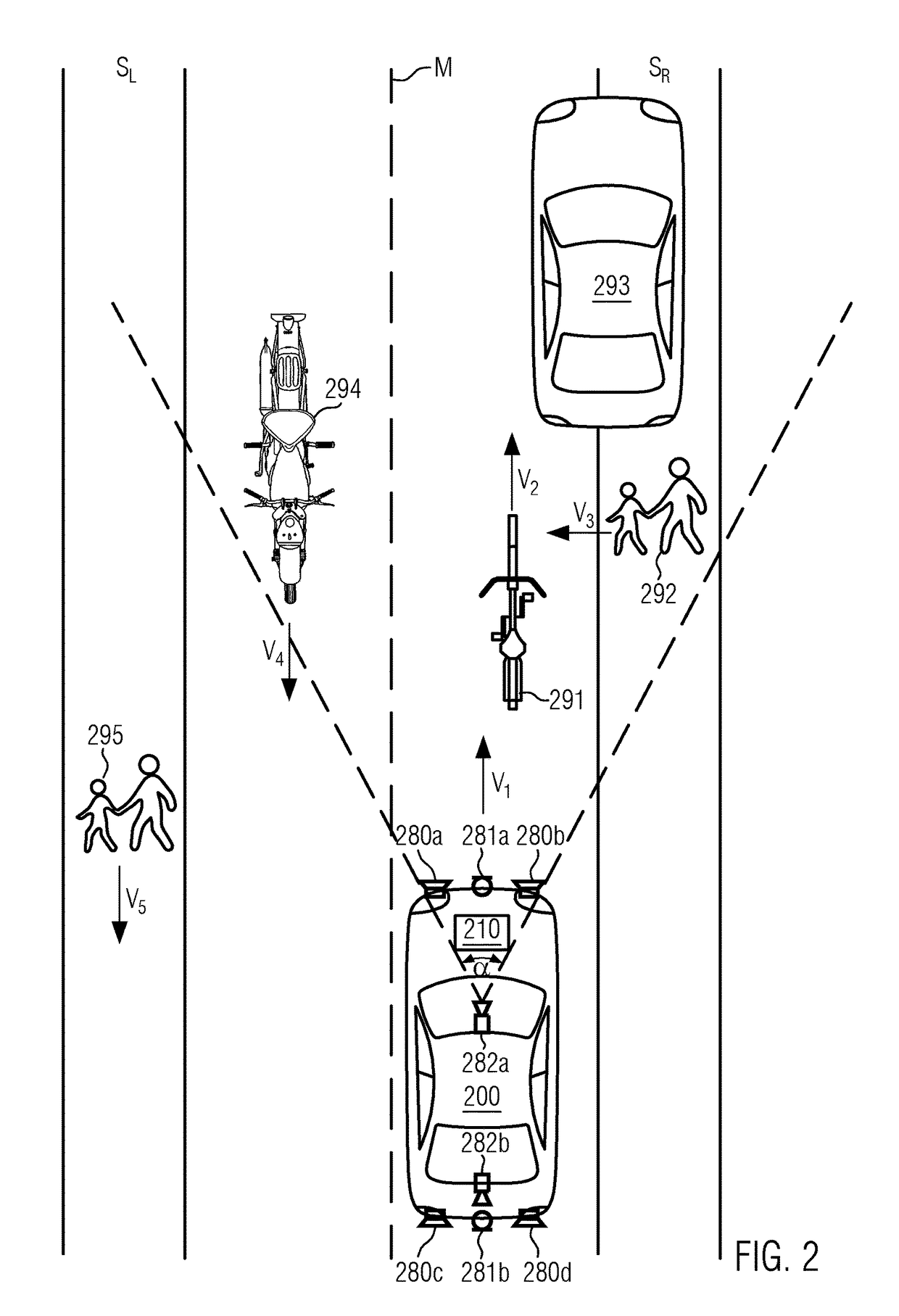
ActiveUS20170222612A1Minimize synthetic noise emissionImprove passive safetySignal processingAcoustic signal devicesRoad userTransducer
The present disclosure provides a system for the synthesis of external sound of a vehicle, the system comprising a hazard analysis unit configured to detect a collision hazard between the vehicle and at least one further road user, in particular an outside traffic participant; at least one electroacoustic transducer; and a sound processing unit configured to generate an audio signal representing an, in particular vehicle dependent, synthetic noise signal and to control the at least one electroacoustic transducer to output a synthetic external sound based on the audio signal, wherein the sound processing unit is configured to modify the audio signal to enhance the perceptibility of the synthetic external sound by the further road user upon detection of the collision hazard.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
System and method for narrow bandwidth digital signal processing
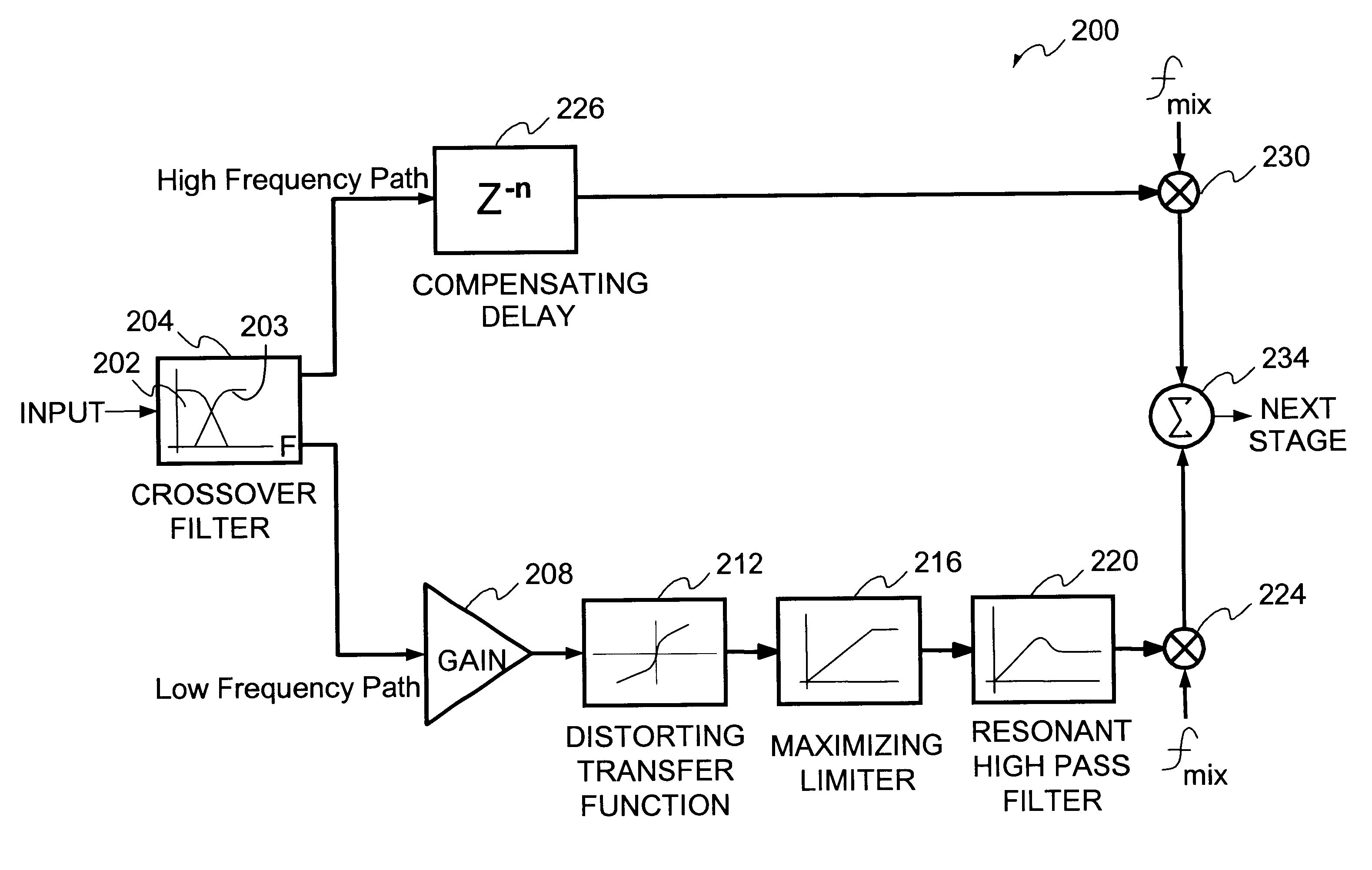
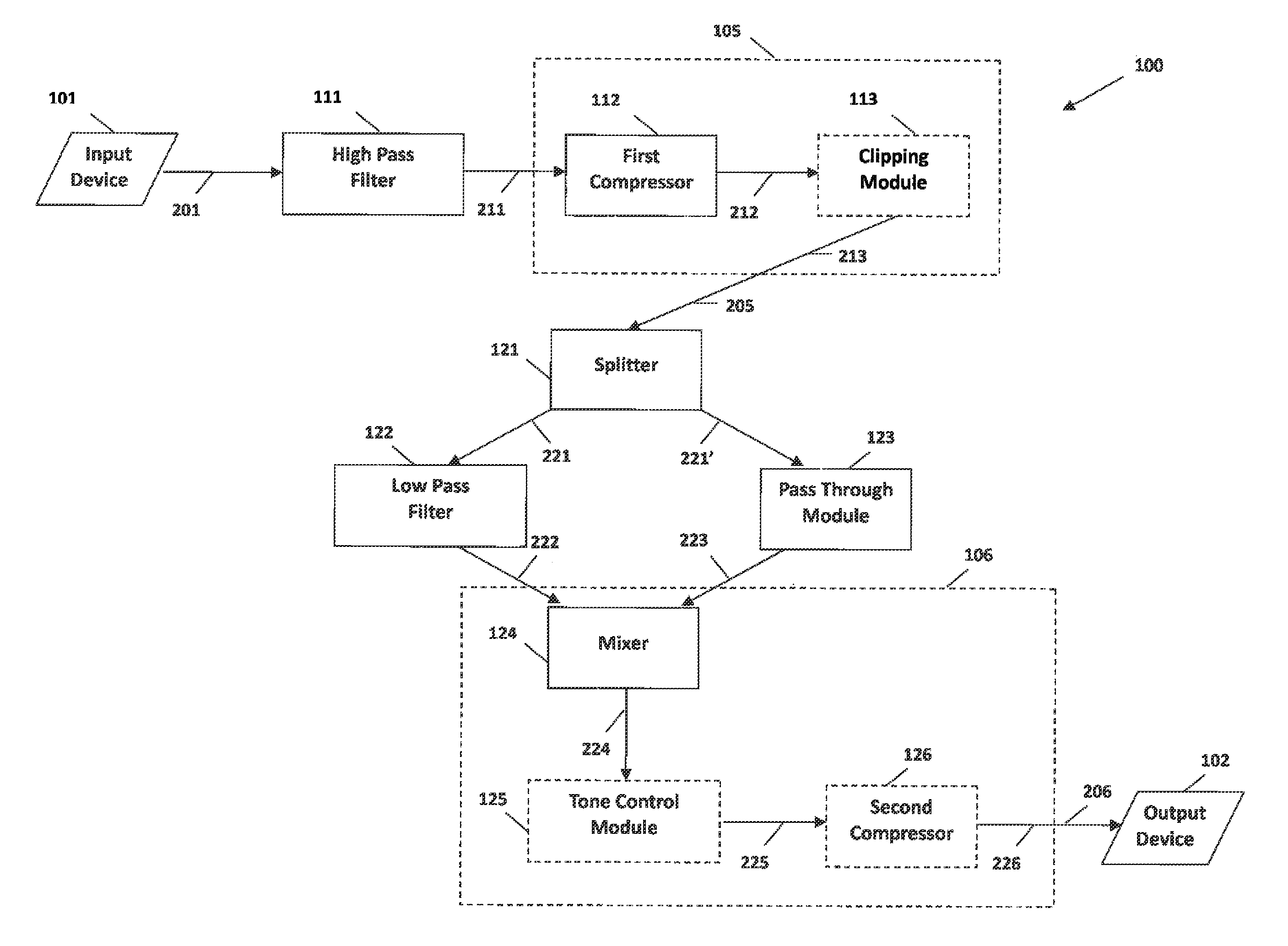
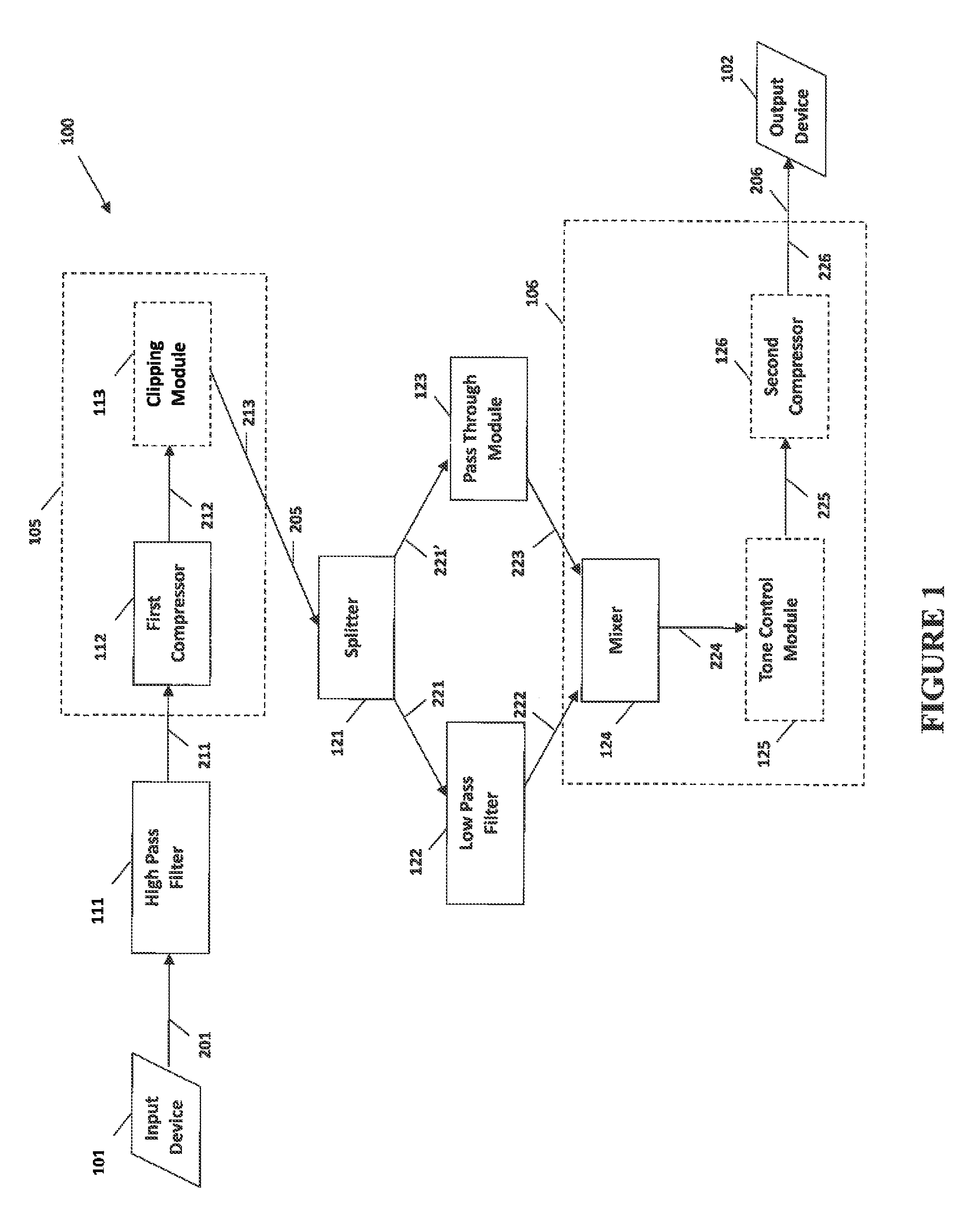
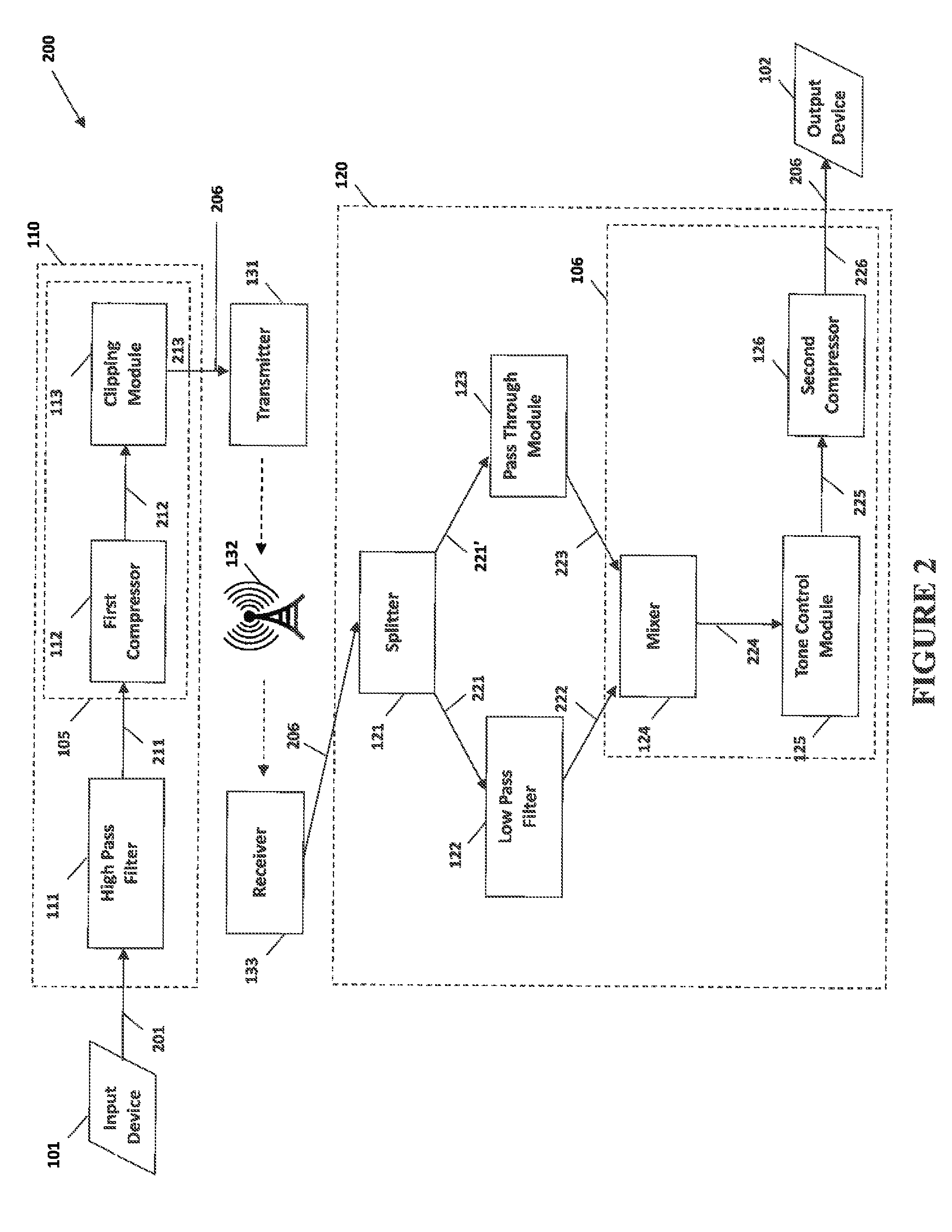
The present invention provides methods and systems for narrow bandwidth digital processing of an input audio signal. Particularly, the present invention includes a high pass filter configured to filter the input audio signal. A first compressor then modulates the filtered signal in order to create a partially processed signal. In some embodiments, a clipping module further limits the gain of the partially processed signal. A splitter is configured to split the partially processed signal into a first signal and a second signal. A low pass filter is configured to filter the first signal. A pass through module is configured to adjust the gain of the second signal. A mixer then combines the filtered first signal and the gain-adjusted second signal in order to output a combined signal. In some embodiments, a tone control module further processes the combined signal, and a second compressor further modulates the processed signal.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
Method of enhancing sound for hearing impaired individuals
InactiveUS20090074206A1Improve functionalityImprove usabilitySignal processingGain controlDigital signal processingTransceiver
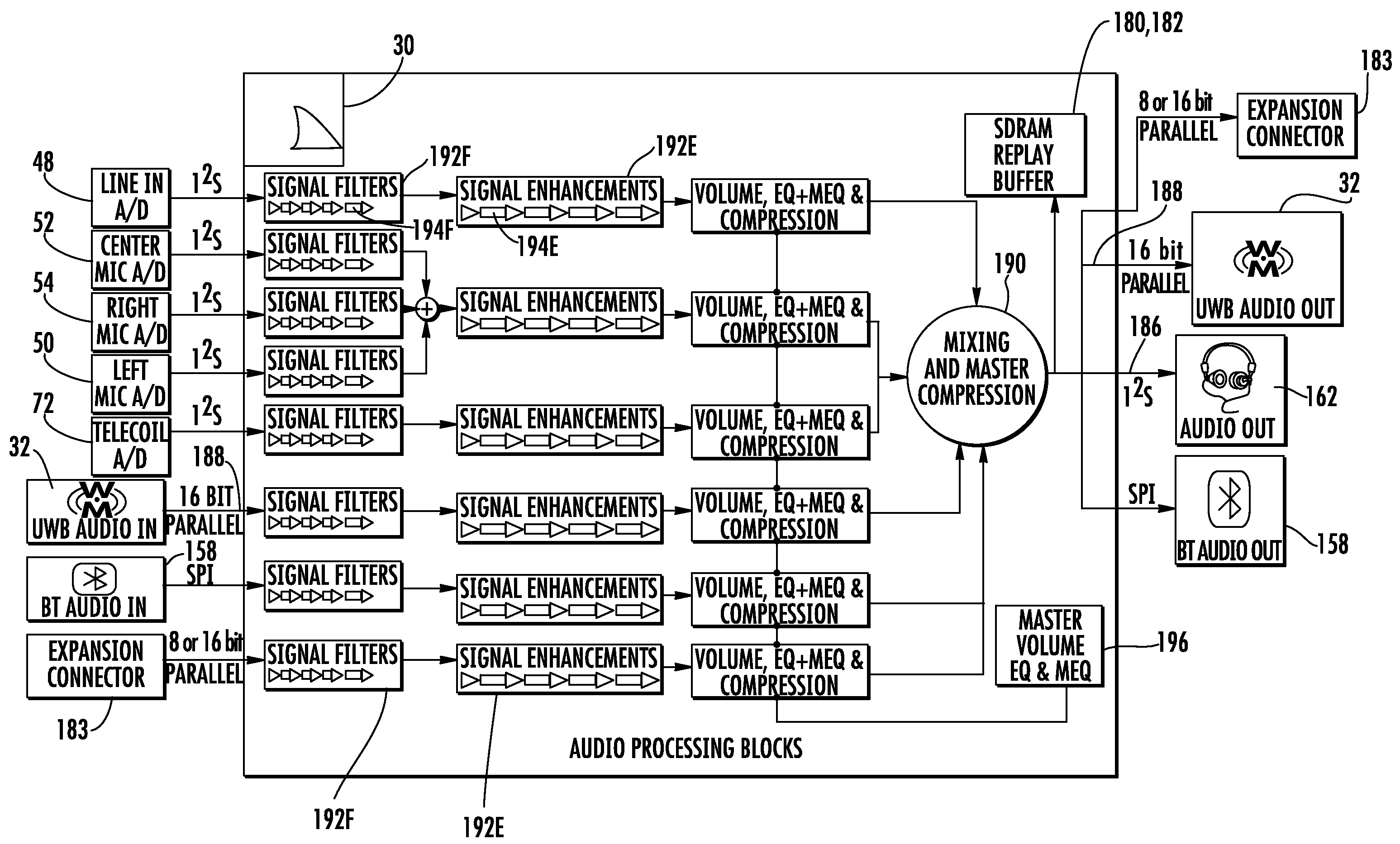
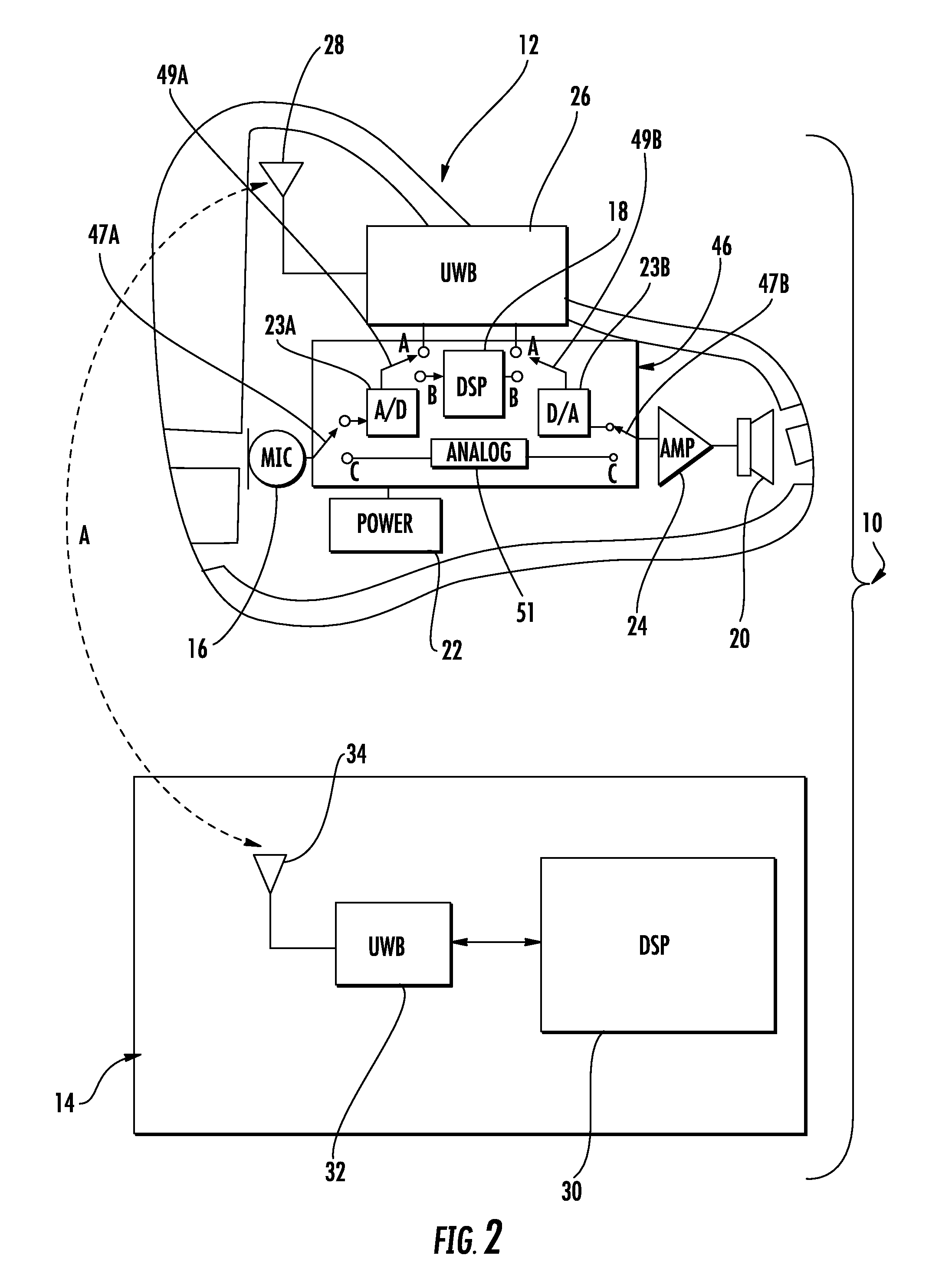
A portable assistive listening system for enhancing sound for hearing impaired individuals includes a fully functional hearing aid and a separate handheld digital signal processing (DSP) device. The focus of the present invention is directed to the handheld DSP device and a unique method of processing incoming audio signals. The DSP device includes a programmable digital signal processor, a UWB transceiver for communicating with the hearing aid and / or other wireless audio sources, an LCD display, and a user input device (keypad). The handheld device is user programmable to apply different sound enhancement algorithms for enhancing sound signals received from the hearing aid and / or other audio source. The handheld device is capable of receiving audio signals from multiple sources, and gives the user control over selection of incoming sound sources and selective enhancement of sound. Specifically, the invention focuses on a proprietary method of adjusting the master volume and equalization of each of the multiple incoming audio signals prior to mixing all of the enhanced signals for output. Applying a Master Volume and Equalization setting prior to mixing provides for a more evenly enhanced sound and better overall sound intelligibility, as well as reducing processing power drained from the system during use.
Owner:BIONICA CORP
System and method for digital signal processing
ActiveUS9413321B2Automatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlGraphicsDigital signal processing
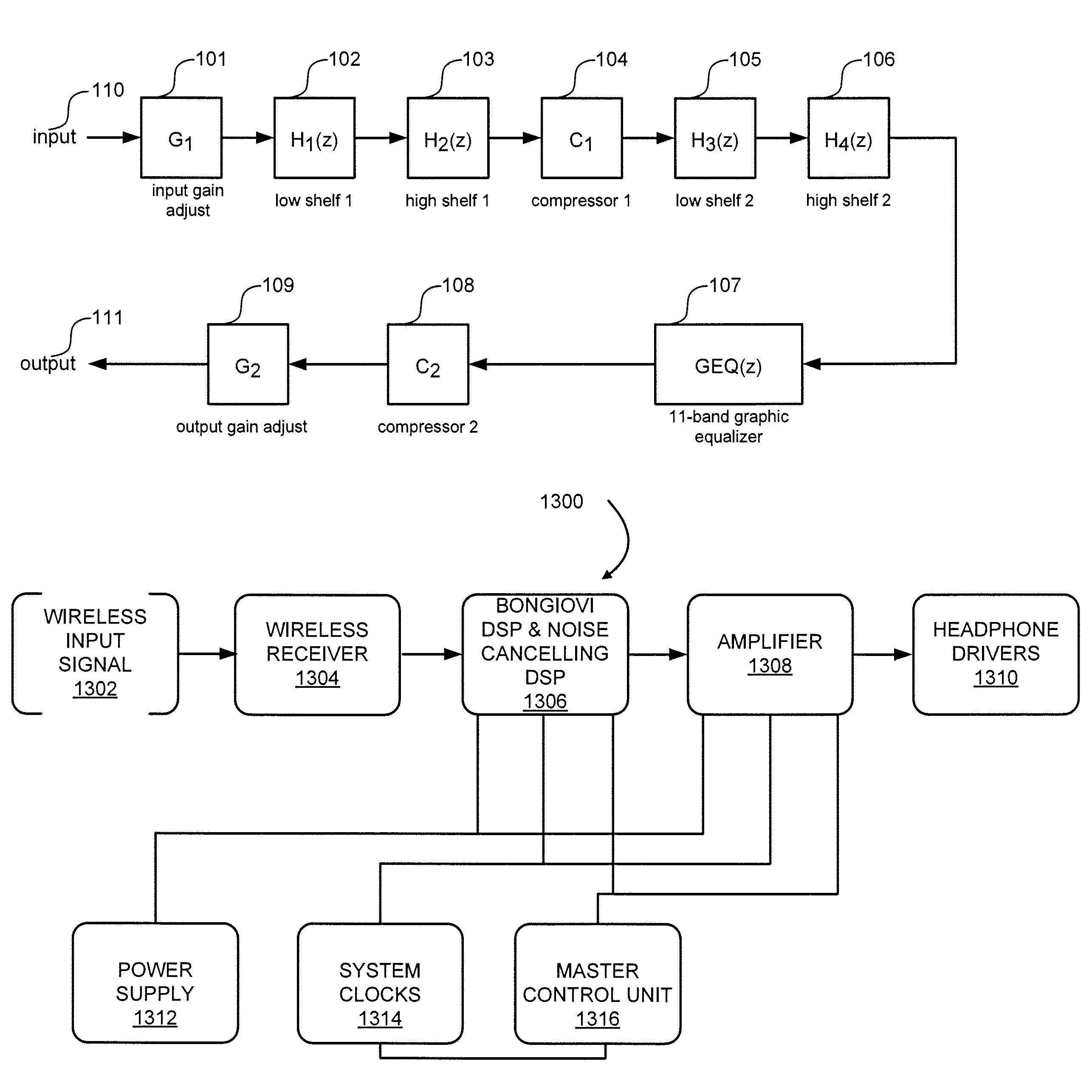
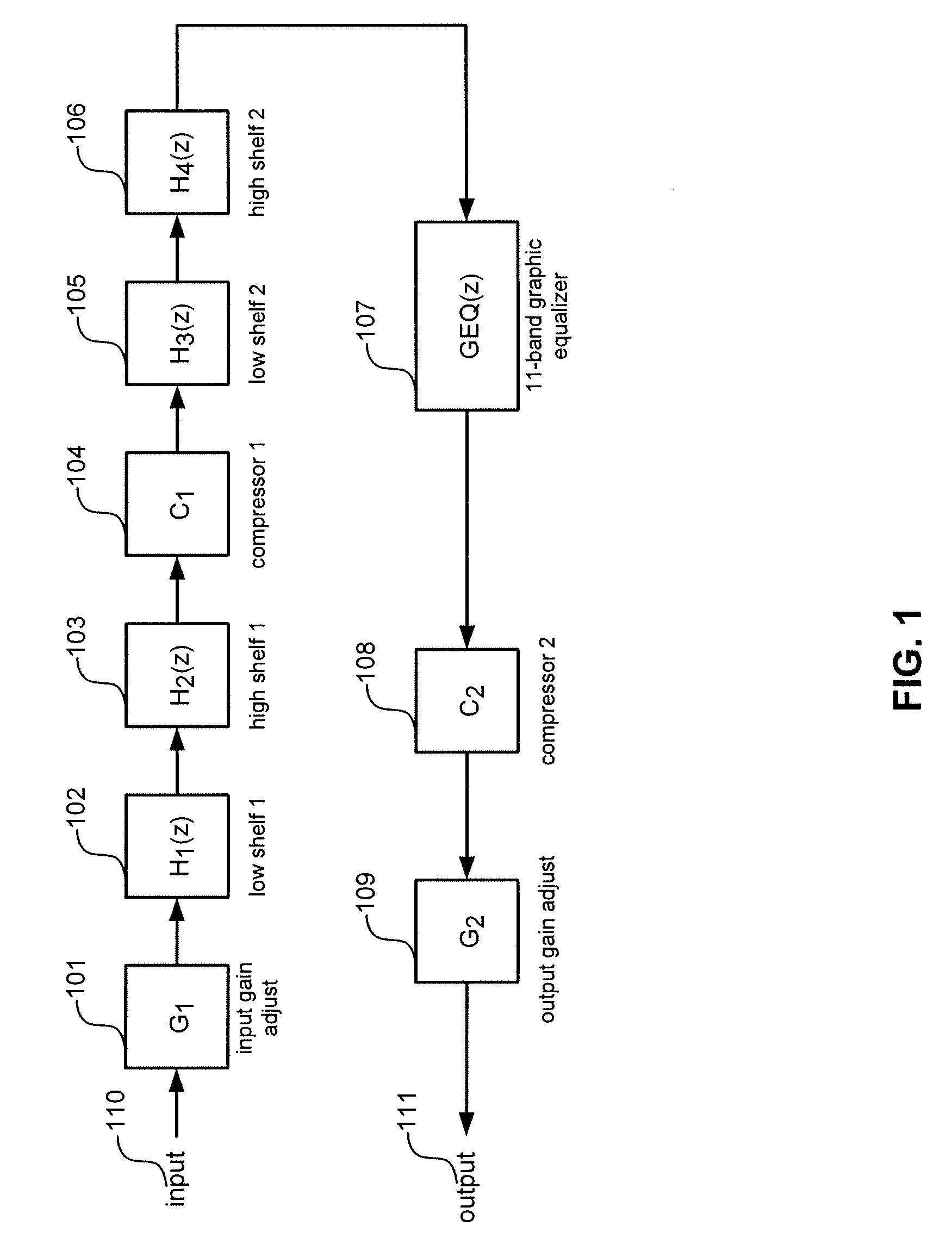
The present invention provides for methods and systems for digitally processing an audio signal to reproduce high quality sounds on various materials. In various embodiments, a method comprises filtering the signal with a low shelf filter and / or high shelf filter, passing the signal through a first compressor that, filtering the signal again with a low shelf filter and / or high shelf filter, processing the signal with a graphic equalizer based on a selected material profile, passing the signal through a second compressor, and outputting the signal to a transducer.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
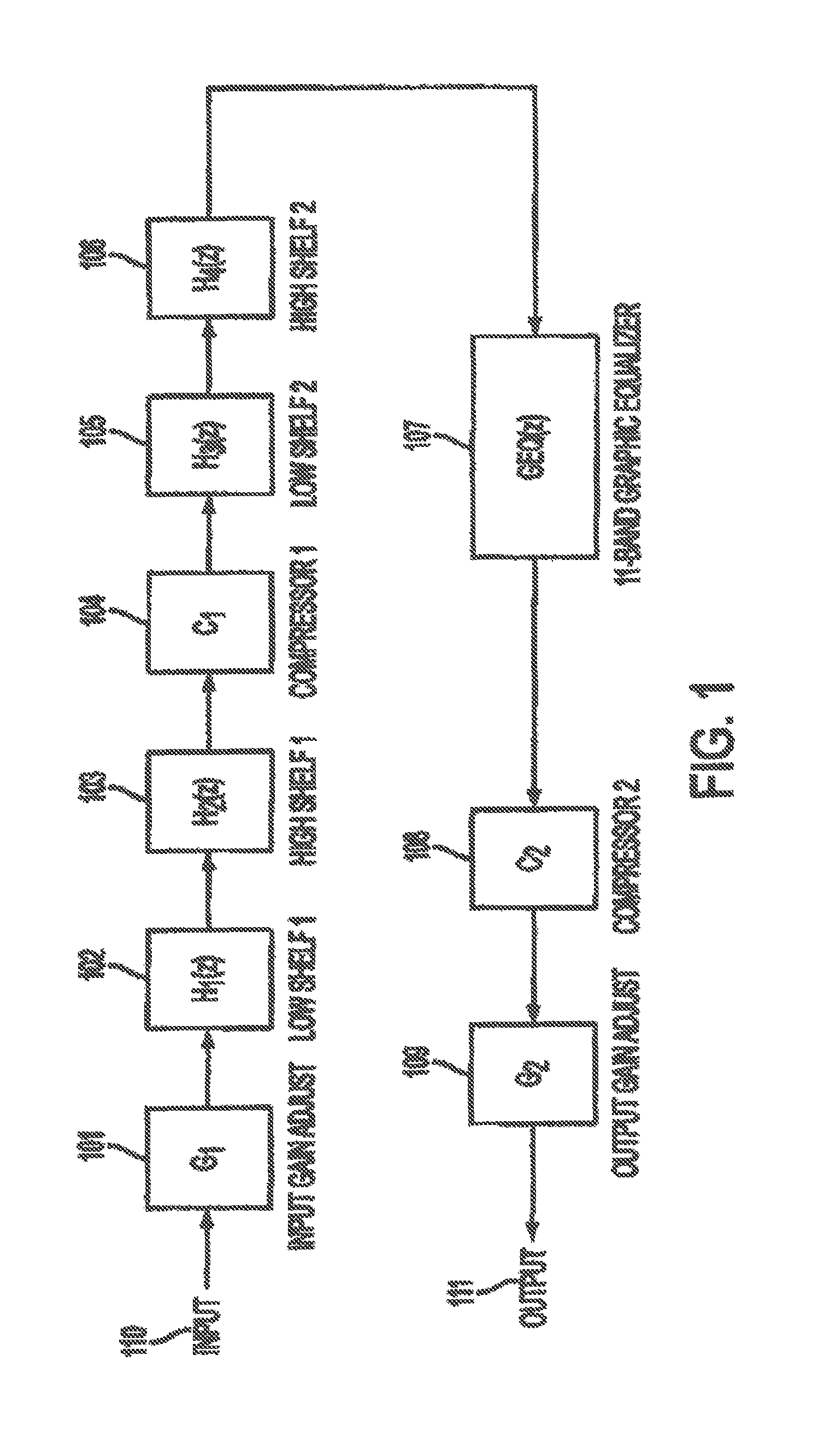
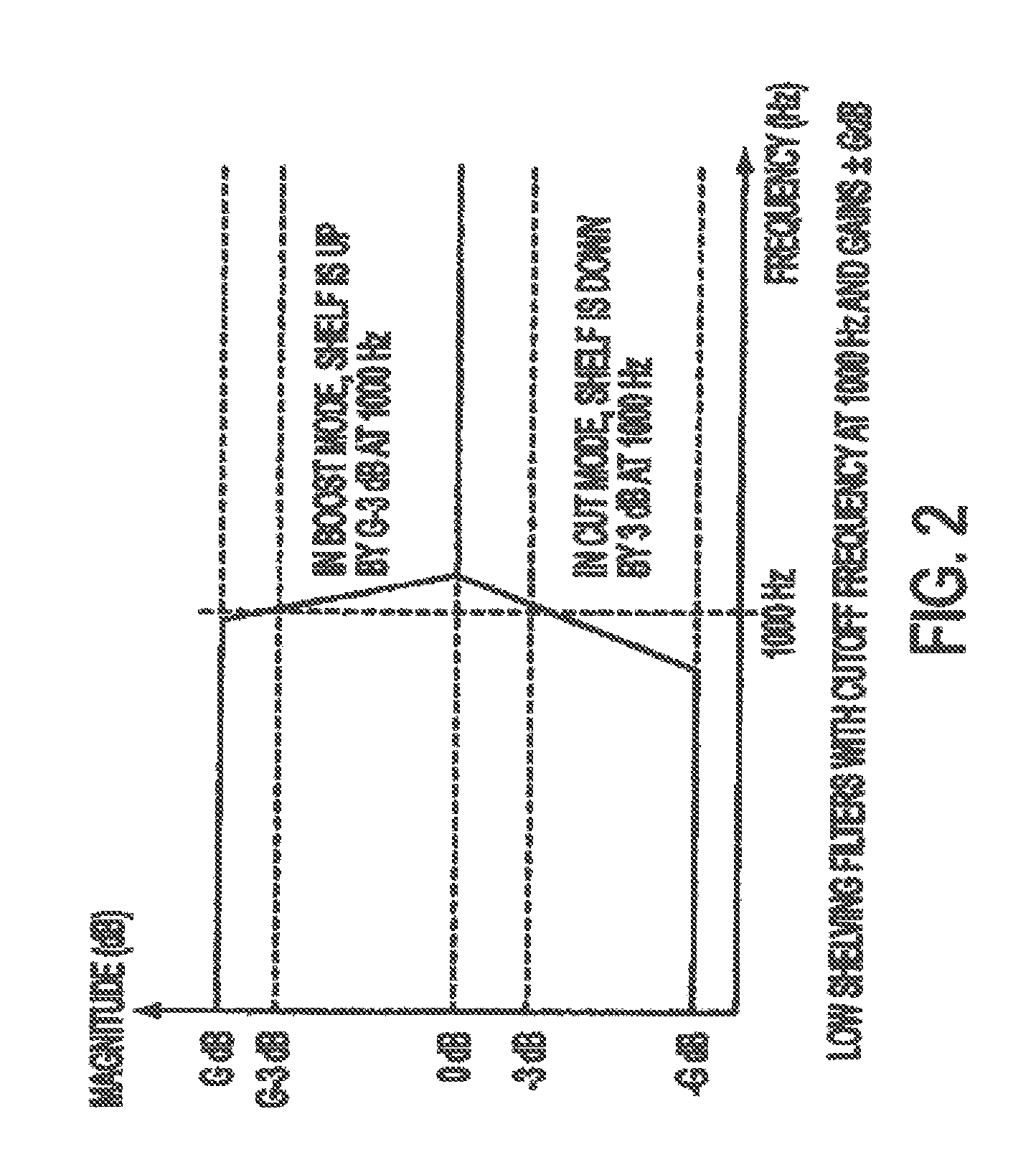
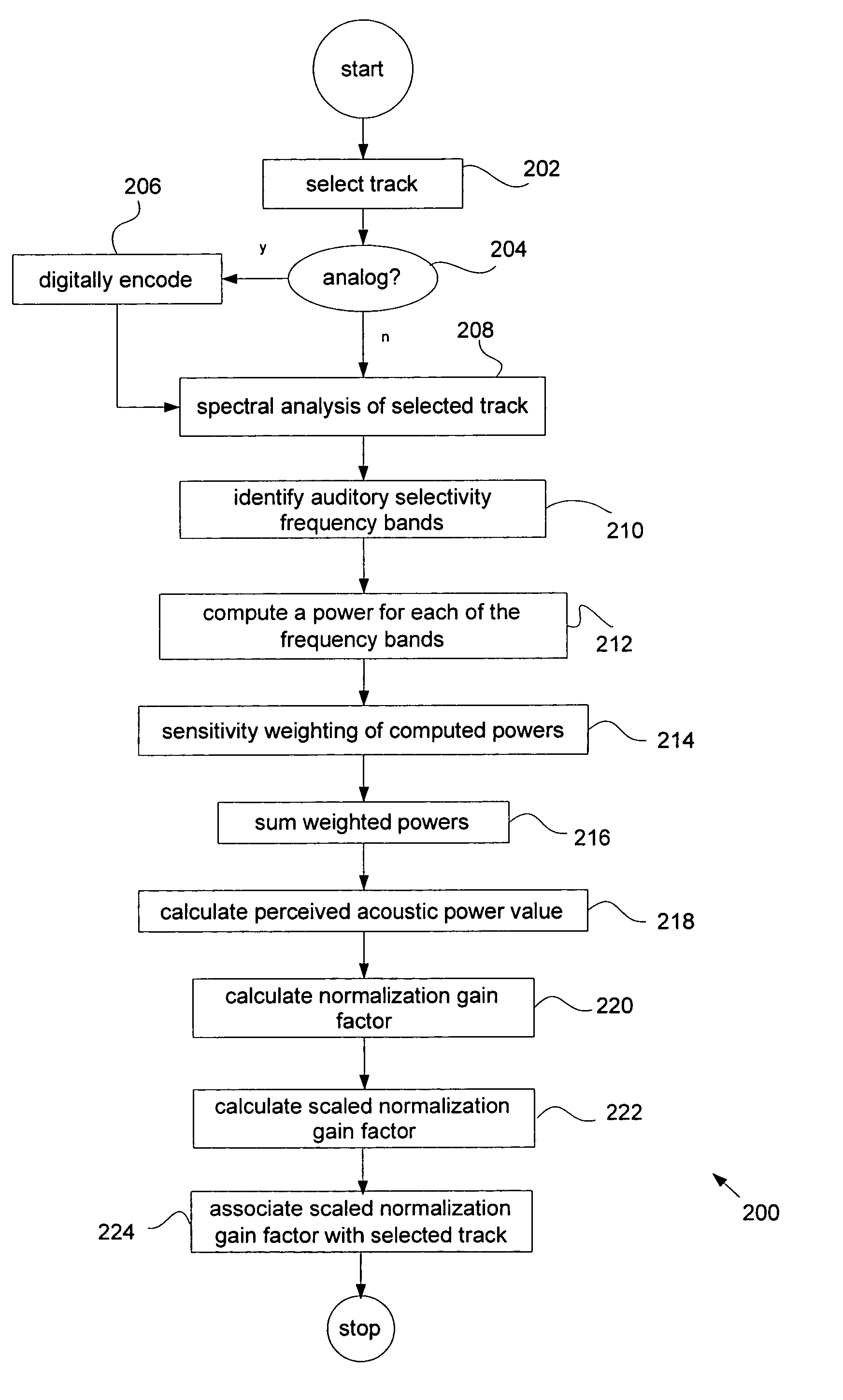
Method and apparatus for automatically normalizing a perceived volume level in a digitally encoded file
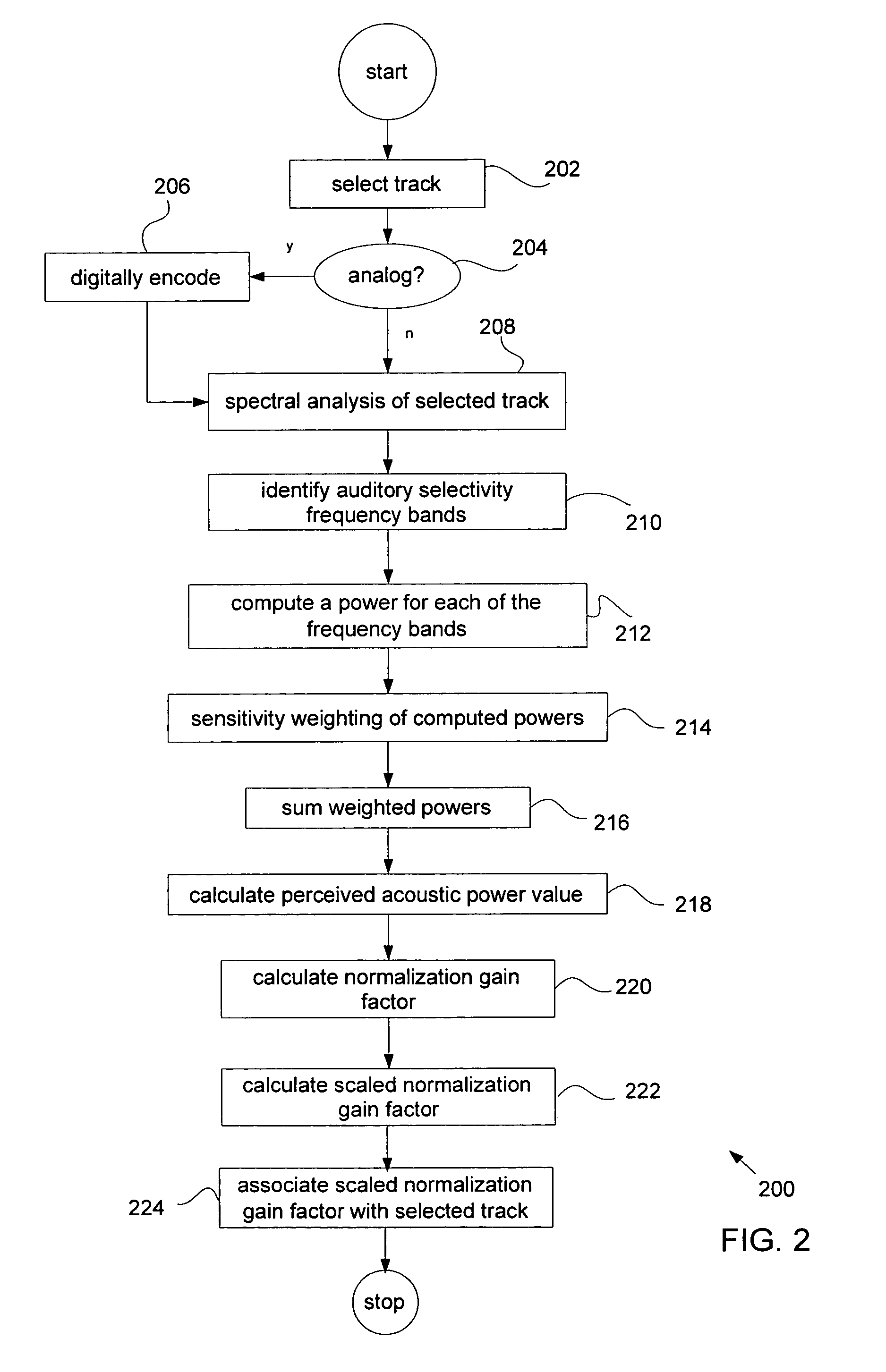
InactiveUS7469208B1Data processing applicationsBroadcast information characterisationLoudnessComputer science
Automatically normalizing a perceived loudness for a digitally encoded audio track formed of a number of channels during playback on a multimedia asset player is described. A number of auditory selectivity frequency bands are selected and for each channel in the track, a power value for each of the number of selectivity frequency bands is computed. Each of the power values is weighted by a sensitivity weighting factor and a sum value of all the weighted power values is then calculated. For the track, a perceived acoustic power value is calculated based upon the sum value for each of the channels and a normalization gain factor based upon the perceived acoustic power is calculated and associated with the track. During playback, the normalization gain factor is applied to the track.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method, apparatus and computer program for calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness of an audio signal
One or a combination of two or more specific loudness model functions selected from a group of two or more of such functions are employed in calculating the perceptual loudness of an audio signal. The function or functions may be selected, for example, by a measure of the degree to which the audio signal is narrowband or wideband. Alternatively or with such a selection from a group of functions, a gain value G[t] is calculated, which gain, when applied to the audio signal, results in a perceived loudness substantially the same as a reference loudness. The gain calculating employs an iterative processing loop that includes the perceptual loudness calculation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
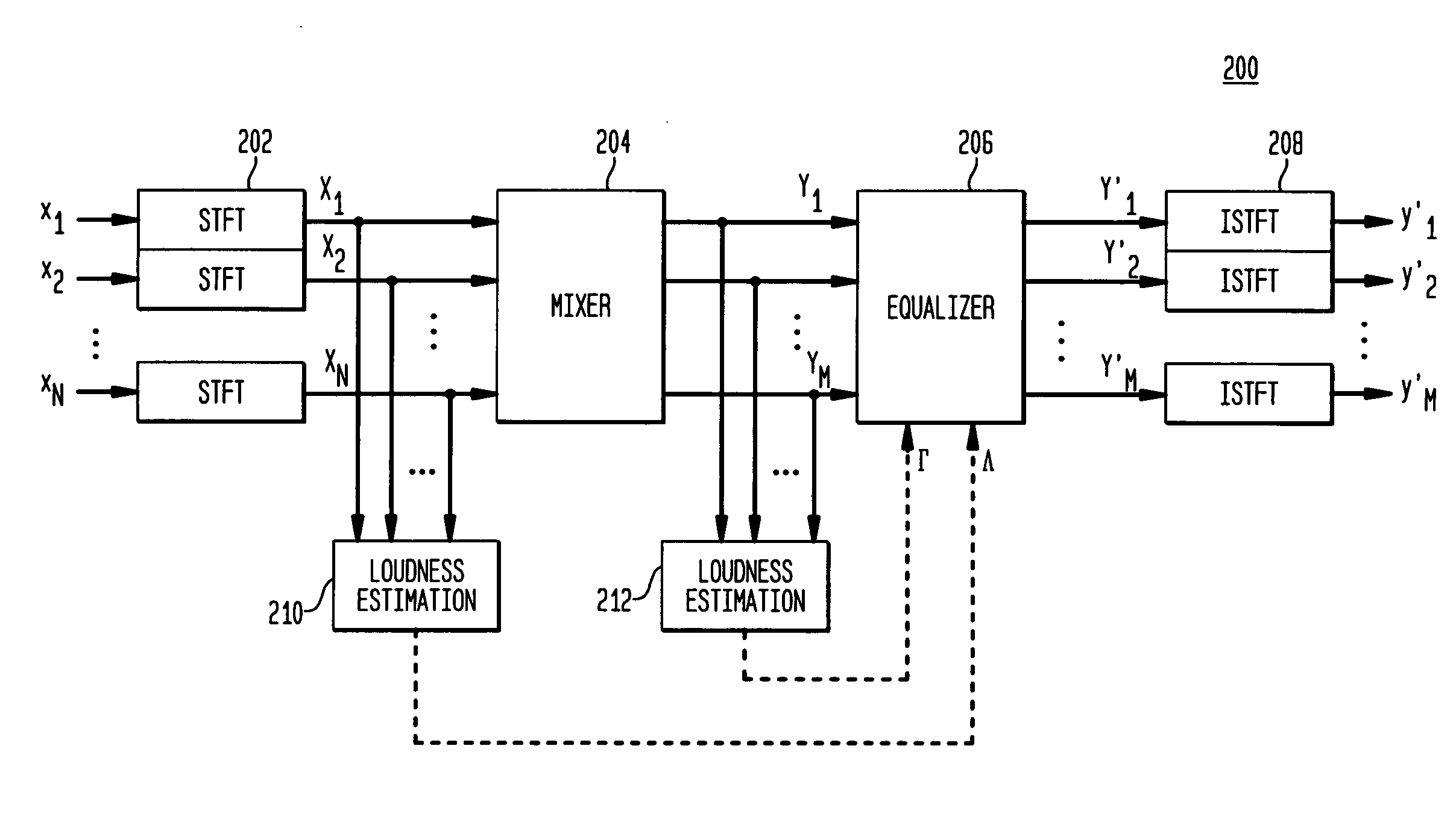
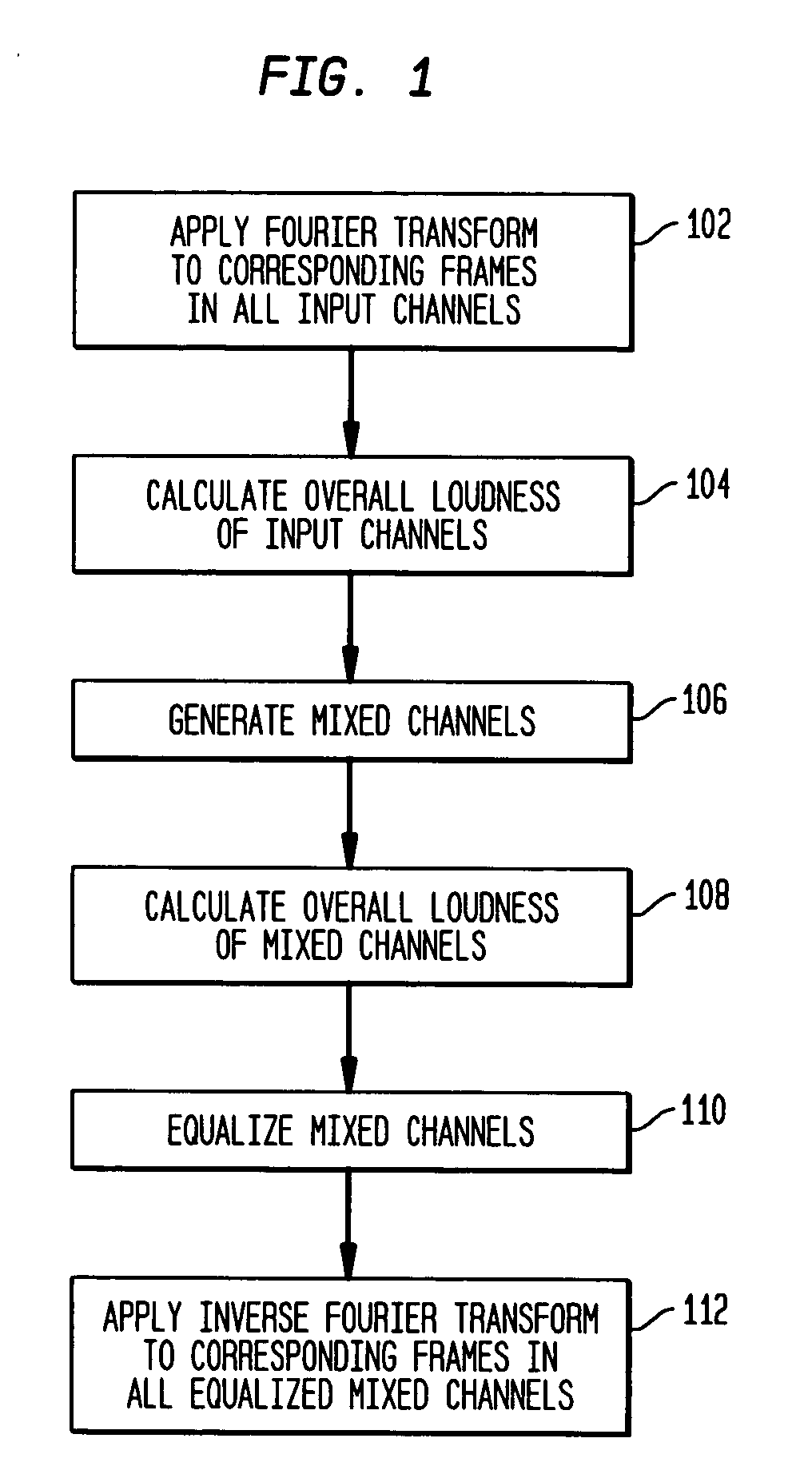
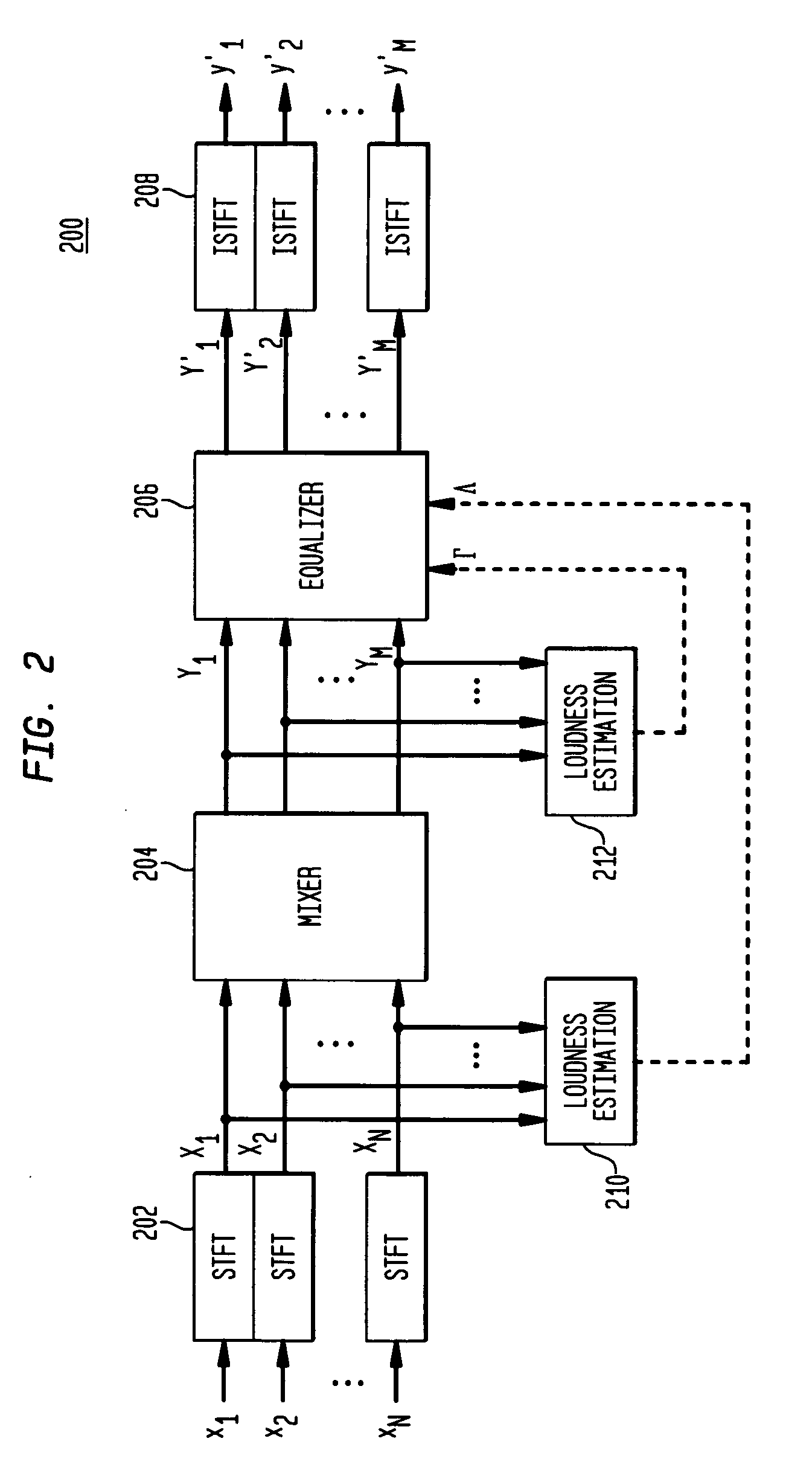
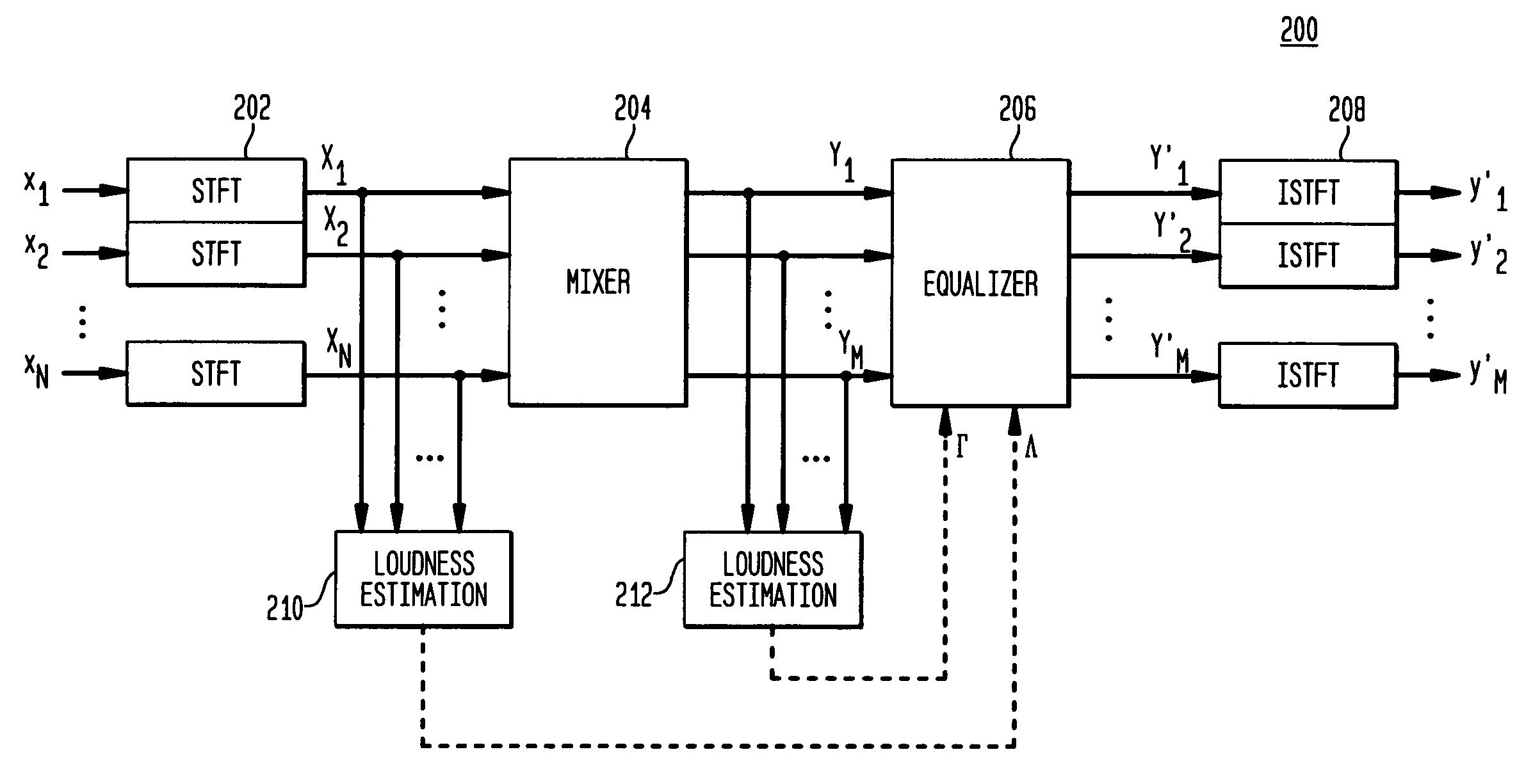
Audio mixing using magnitude equalization
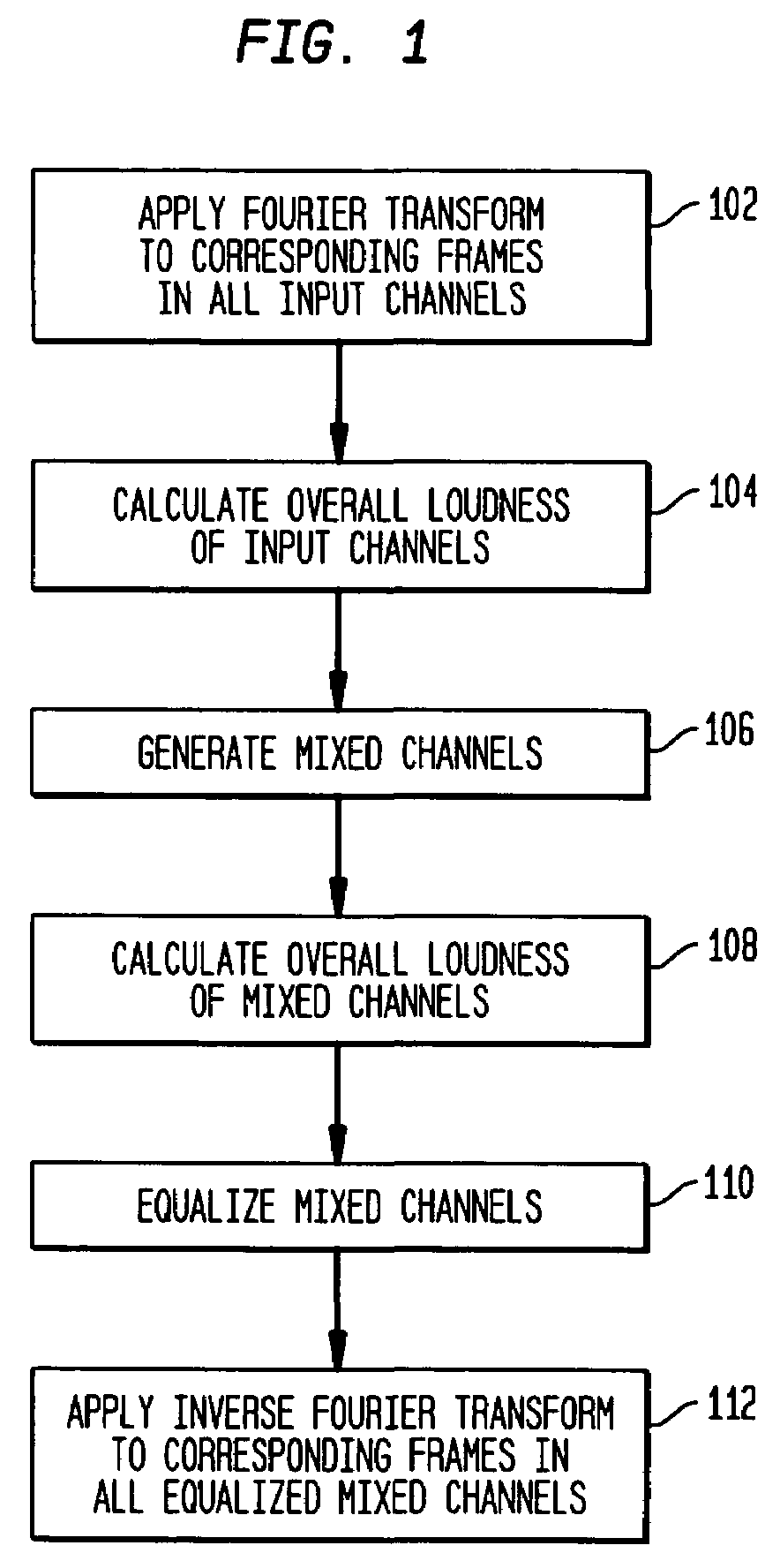
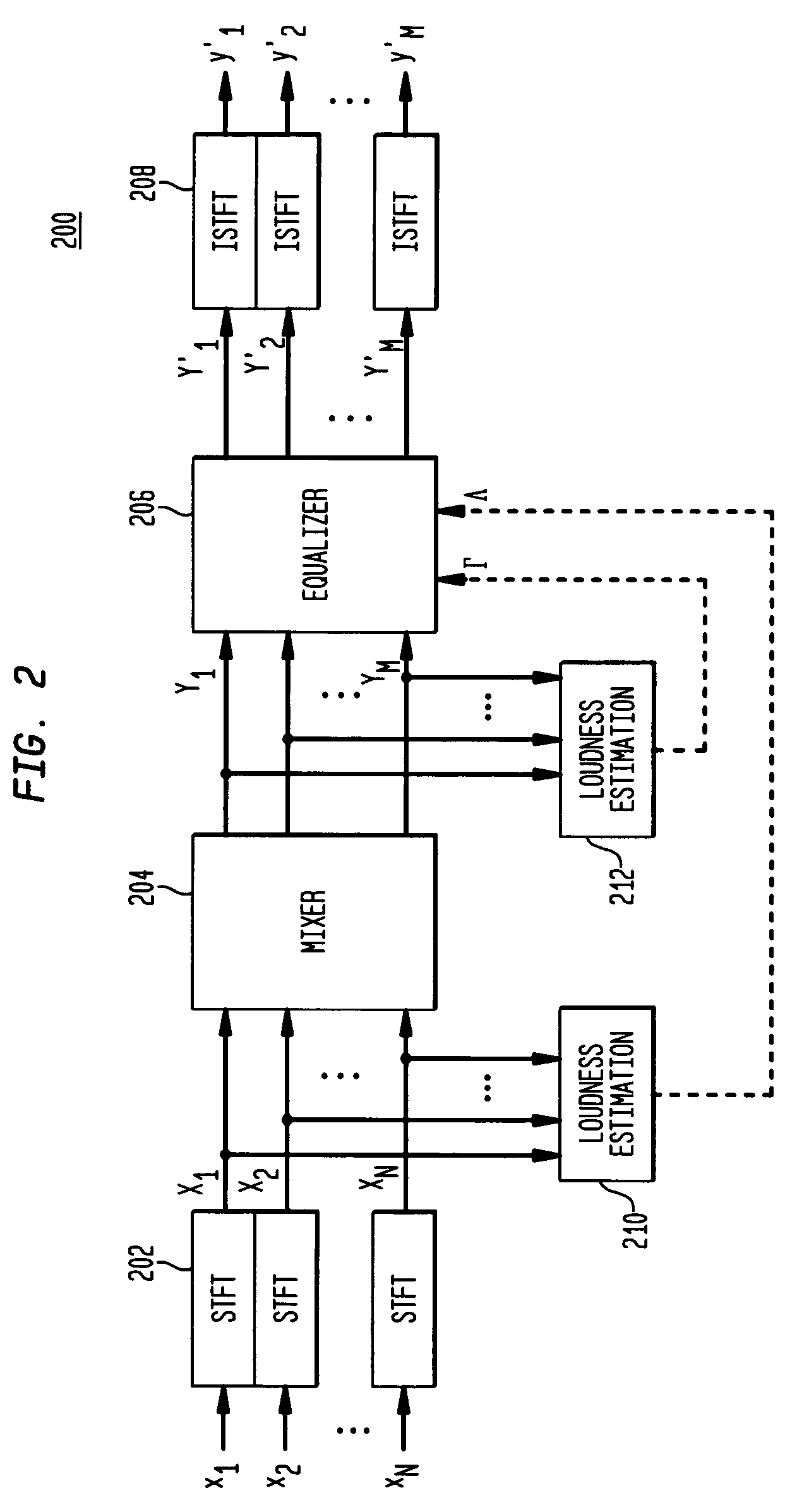
ActiveUS20050195995A1Inhibition effectLoss of loudnessGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlEqualizationPower sharing
According to one embodiment, during mixing of an N-channel input signal to generate an M-channel output signal, in at least one frequency sub-band, magnitude equalization is applied to the mixed channel signals such that an amplitude sum magnitude for the N input channels (e.g., the magnitude of a sum of estimated amplitudes of the N input channels) is approximately equal to an amplitude sum magnitude for the M output channels (e.g., the magnitude of a sum of estimated amplitudes of the M output channels). In one implementation, magnitude equalization is applied to one or more sub-bands (e.g., those below 1 kHz), and power equalization is applied to one or more other sub-bands (e.g., those above 1 kHz) to reduce coloration effects in the output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Audio mixing using magnitude equalization
ActiveUS7639823B2InhibitionEnergy lossGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlEqualizationComputer science
According to one embodiment, during mixing of an N-channel input signal to generate an M-channel output signal, in at least one frequency sub-band, magnitude equalization is applied to the mixed channel signals such that an amplitude sum magnitude for the N input channels (e.g., the magnitude of a sum of estimated amplitudes of the N input channels) is approximately equal to an amplitude sum magnitude for the M output channels (e.g., the magnitude of a sum of estimated amplitudes of the M output channels). In one implementation, magnitude equalization is applied to one or more sub-bands (e.g., those below 1 kHz), and power equalization is applied to one or more other sub-bands (e.g., those above 1 kHz) to reduce coloration effects in the output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
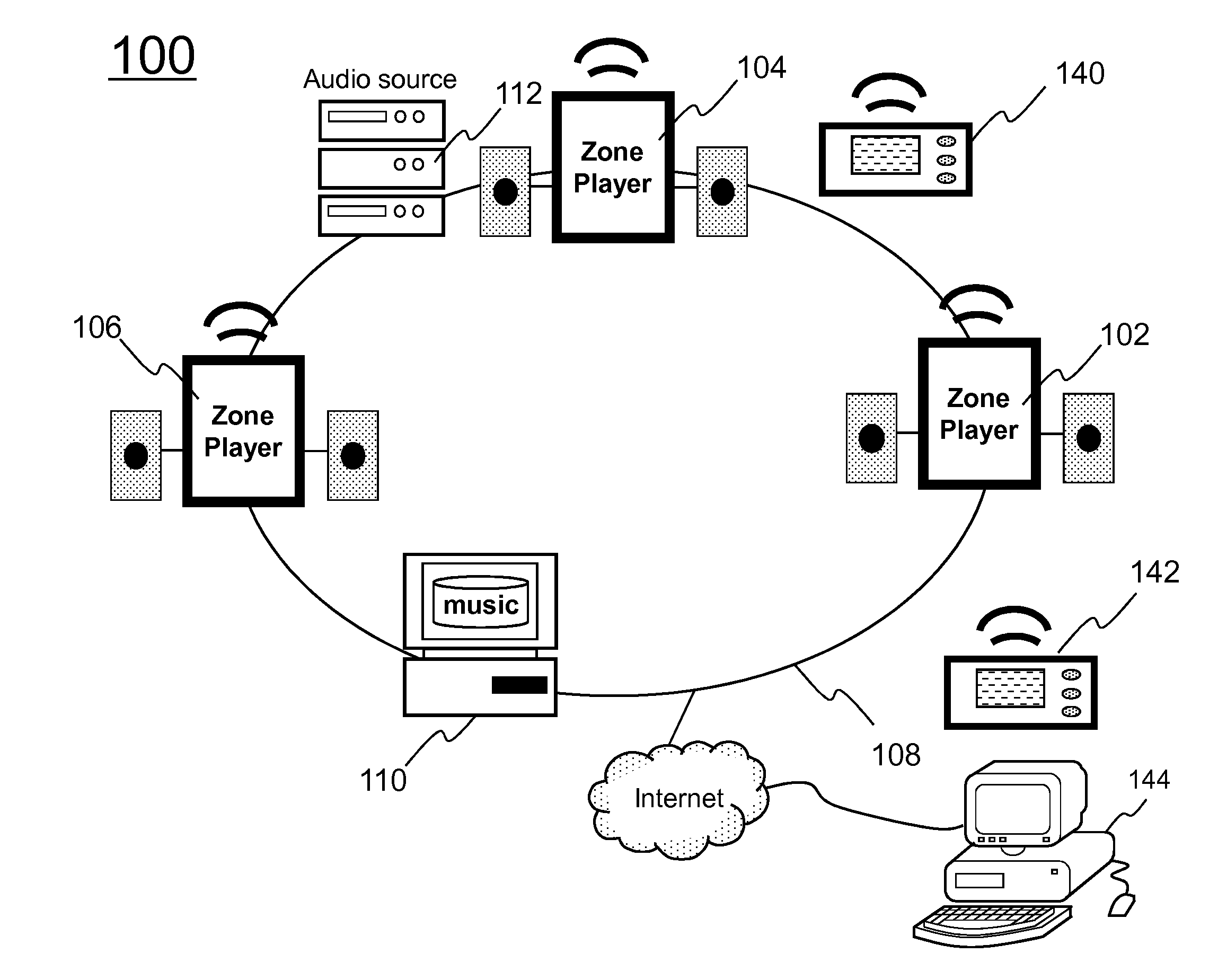
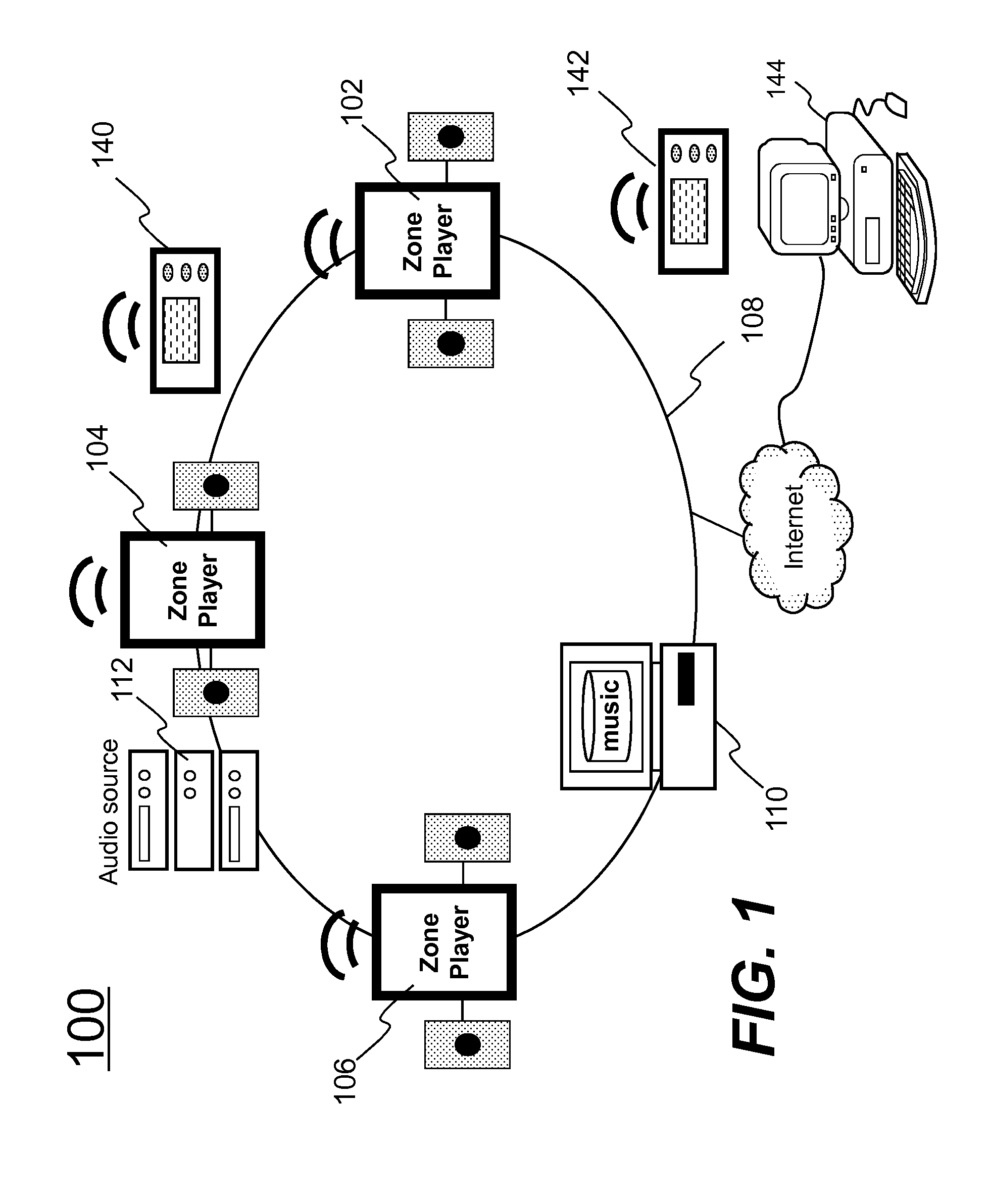
Adjusting a Playback Device
Certain embodiments provide methods and systems for managing a sound profile. An example playback device includes a network interface and a non-transitory computer readable storage medium having stored therein instructions executable by the processor. When executed by the processor, the instructions are to configure the playback device to receive, via the network interface over a local area network (LAN) from a controller device, an instruction. The example playback device is to obtain, based on the instruction, via the network interface from a location outside of the LAN, data comprising a sound profile. The example playback device is to update one or more parameters at the playback device based on the sound profile. The example playback device is to play back an audio signal according to the sound profile.
Owner:SONOS
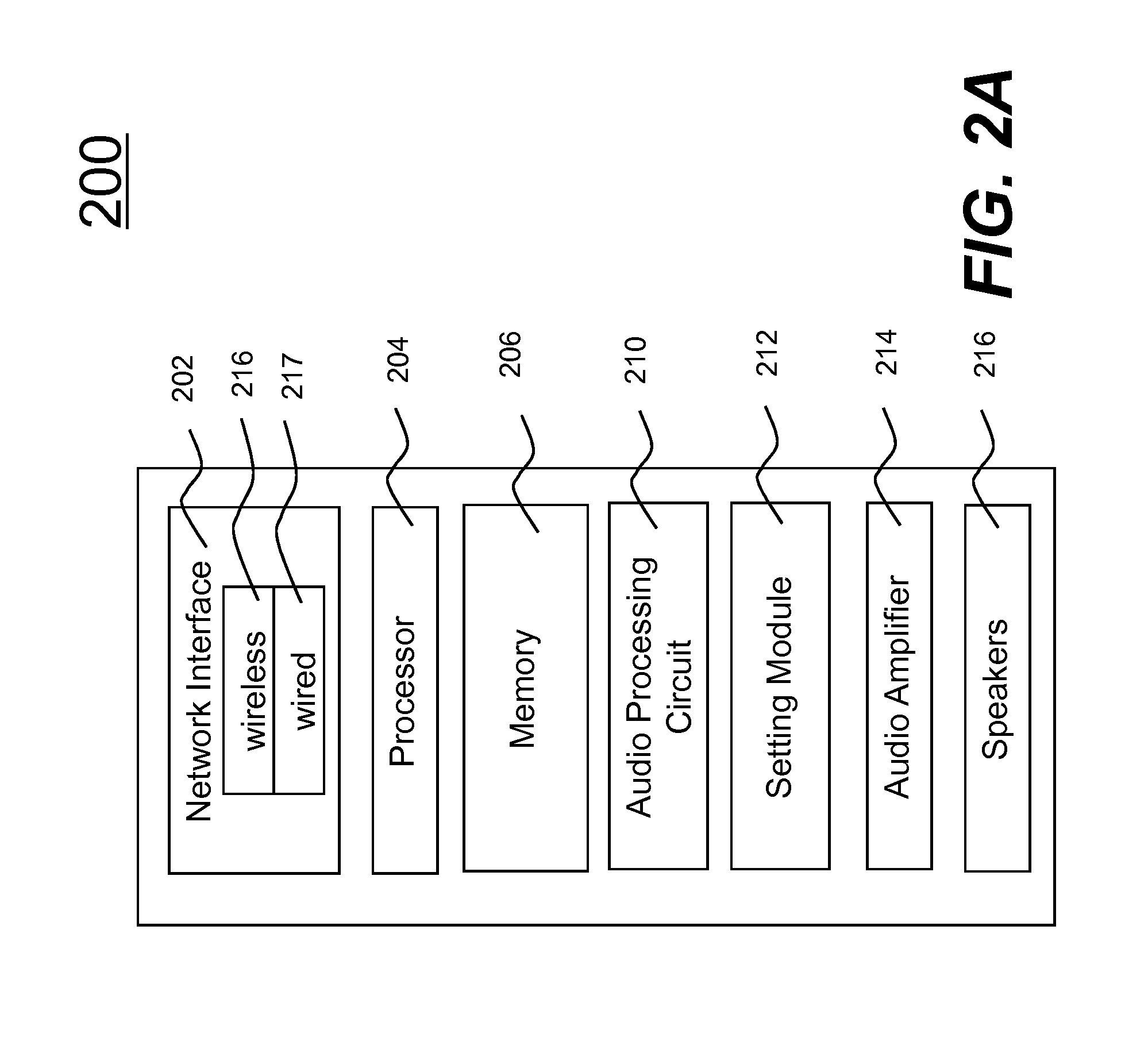
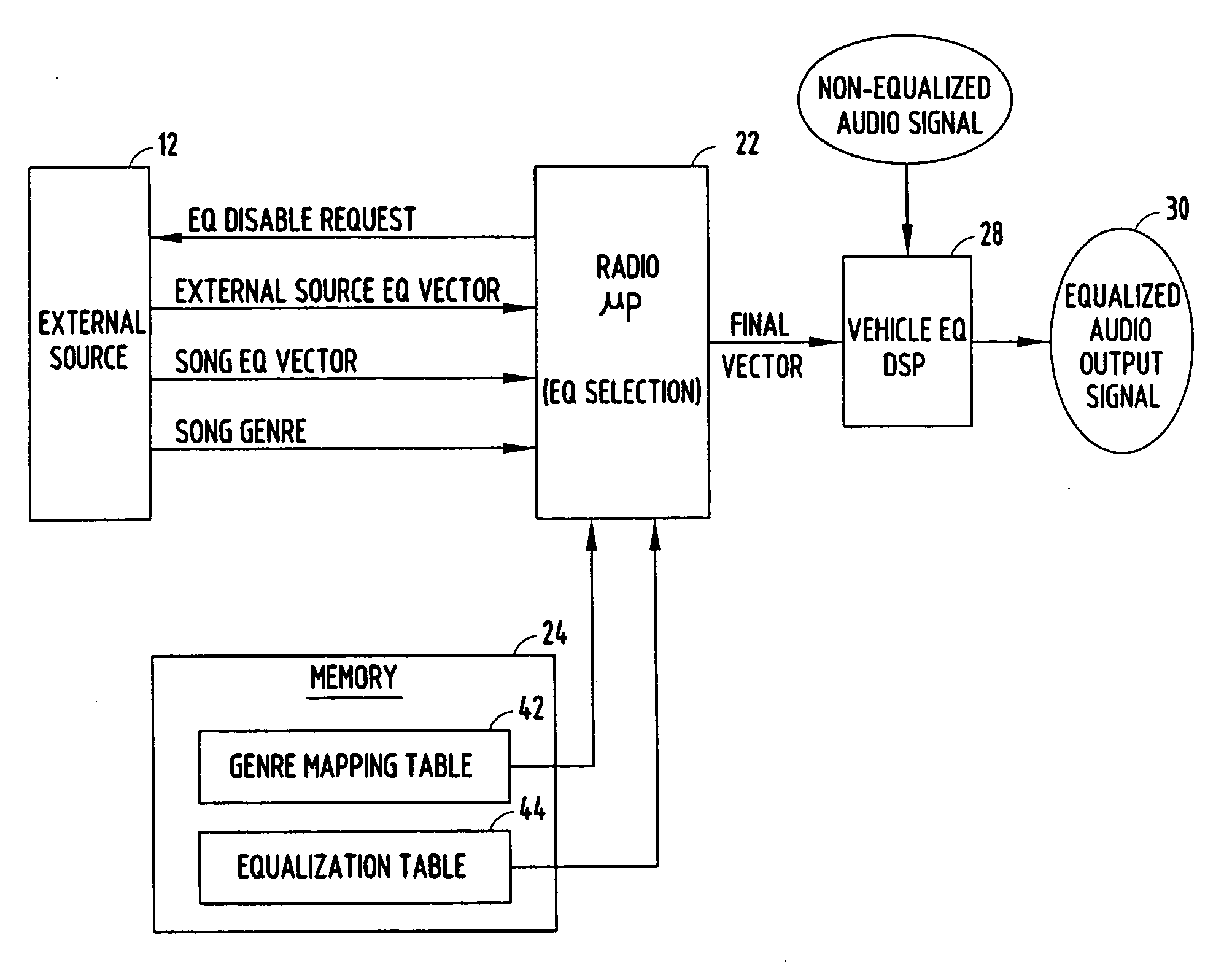
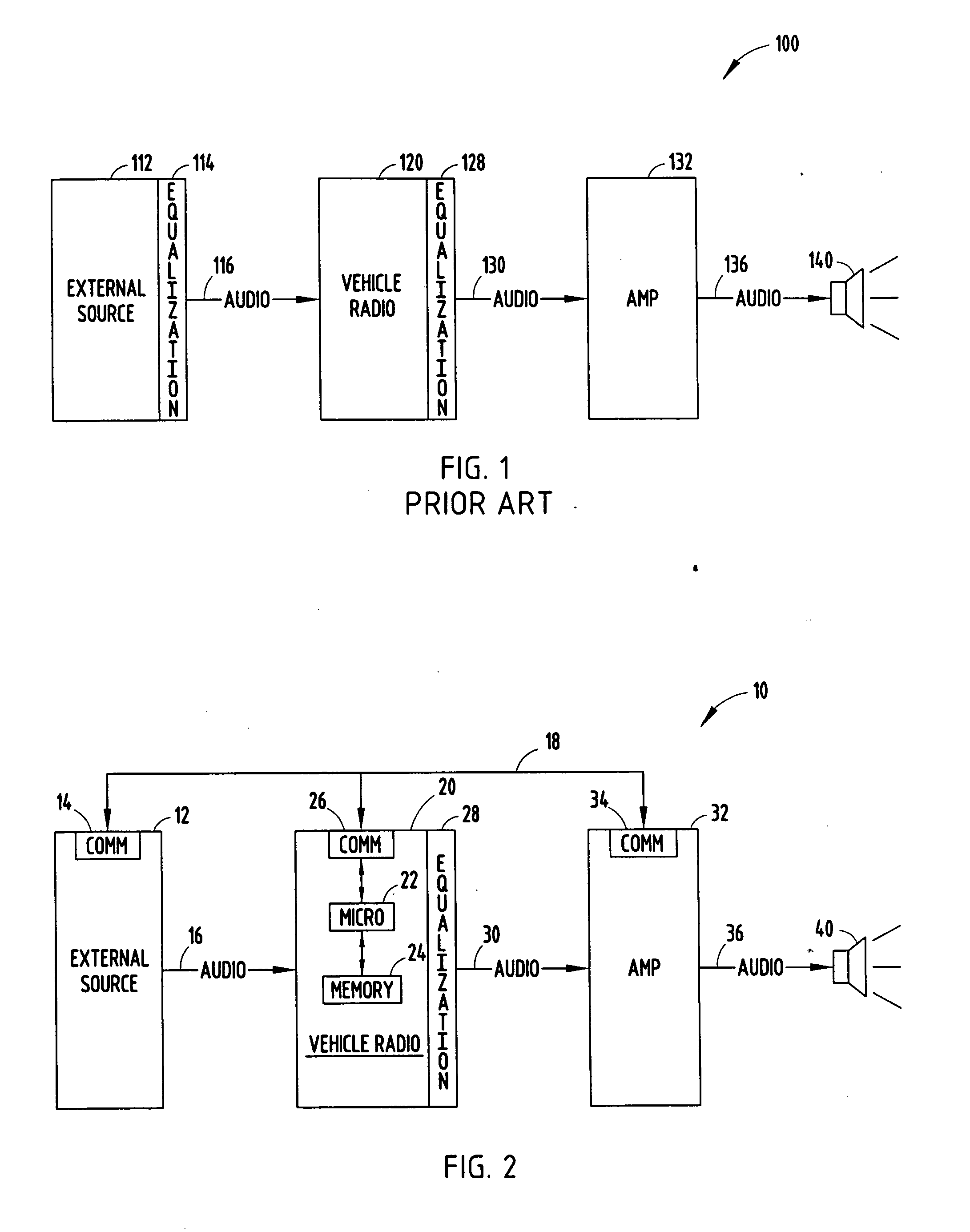
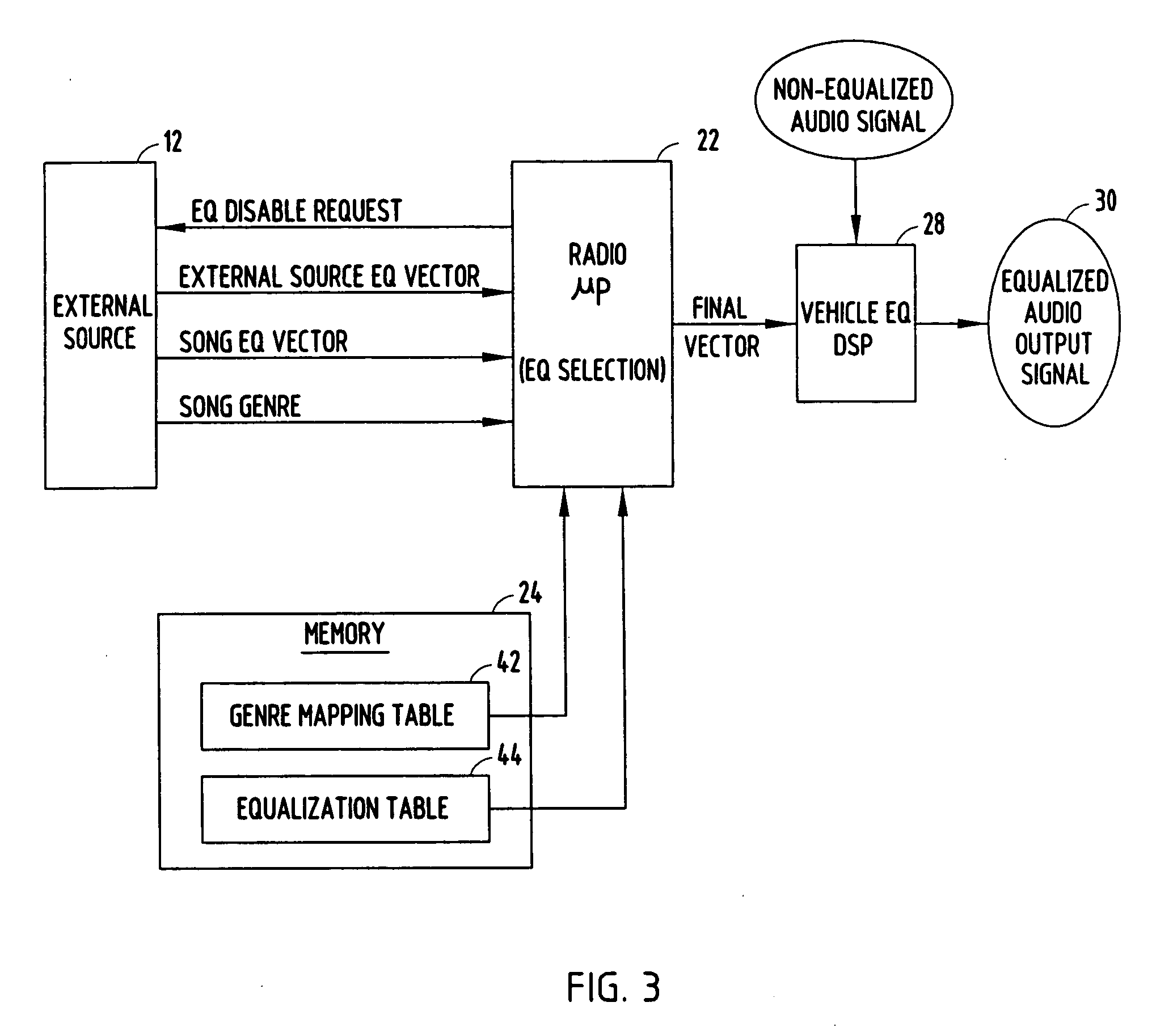
Audio entertainment system equalizer and method
InactiveUS20080013752A1Digital signal tone/bandwidth controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEqualizationComputer science
An audio entertainment system and method for providing controlled equalization of sound from an external source is provided. The audio entertainment system includes a first audio device having an equalizer with first equalization settings and an output for providing an audio output signal. The system also includes an input for receiving audio signals from an external second audio device having second equalization settings. The second audio device inputs to the first audio device second equalization settings. The system further includes a controller for processing the equalization settings and controlling the audio output signal based on the equalization settings.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Popular searches
Stereophonic systems Two-channel systems Stereophonic arrangments Input/output processes for data processing Sets with customised acoustic characteristics Mouthpiece/microphone attachments Sound producing devices Transmission noise suppression Combination control in untuned amplifier Digital/coded signal combination control
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com