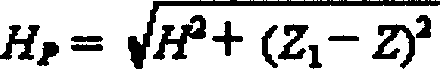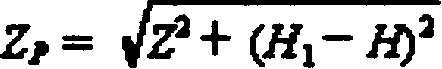Patents
Literature
127 results about "Crossover frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
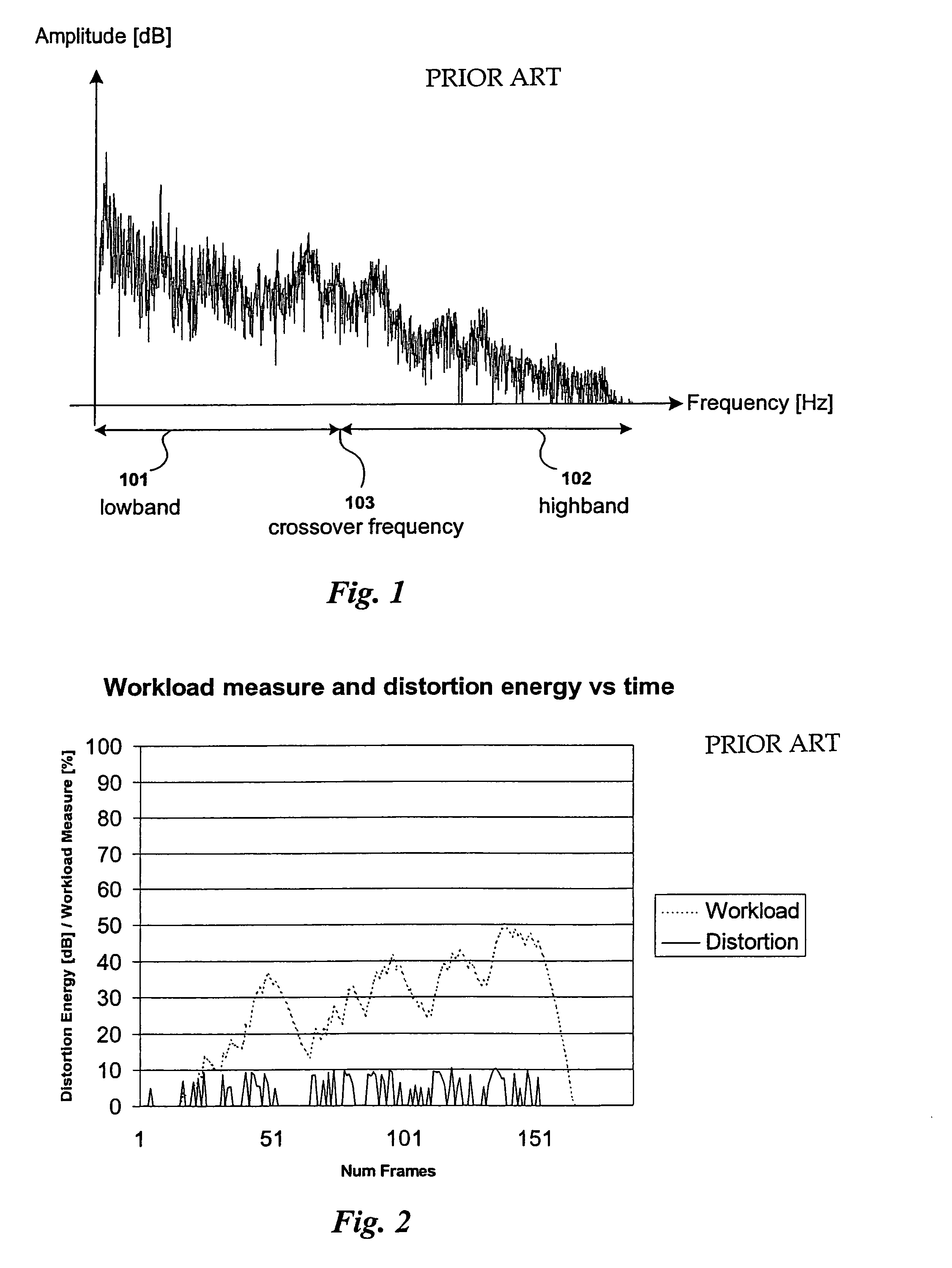
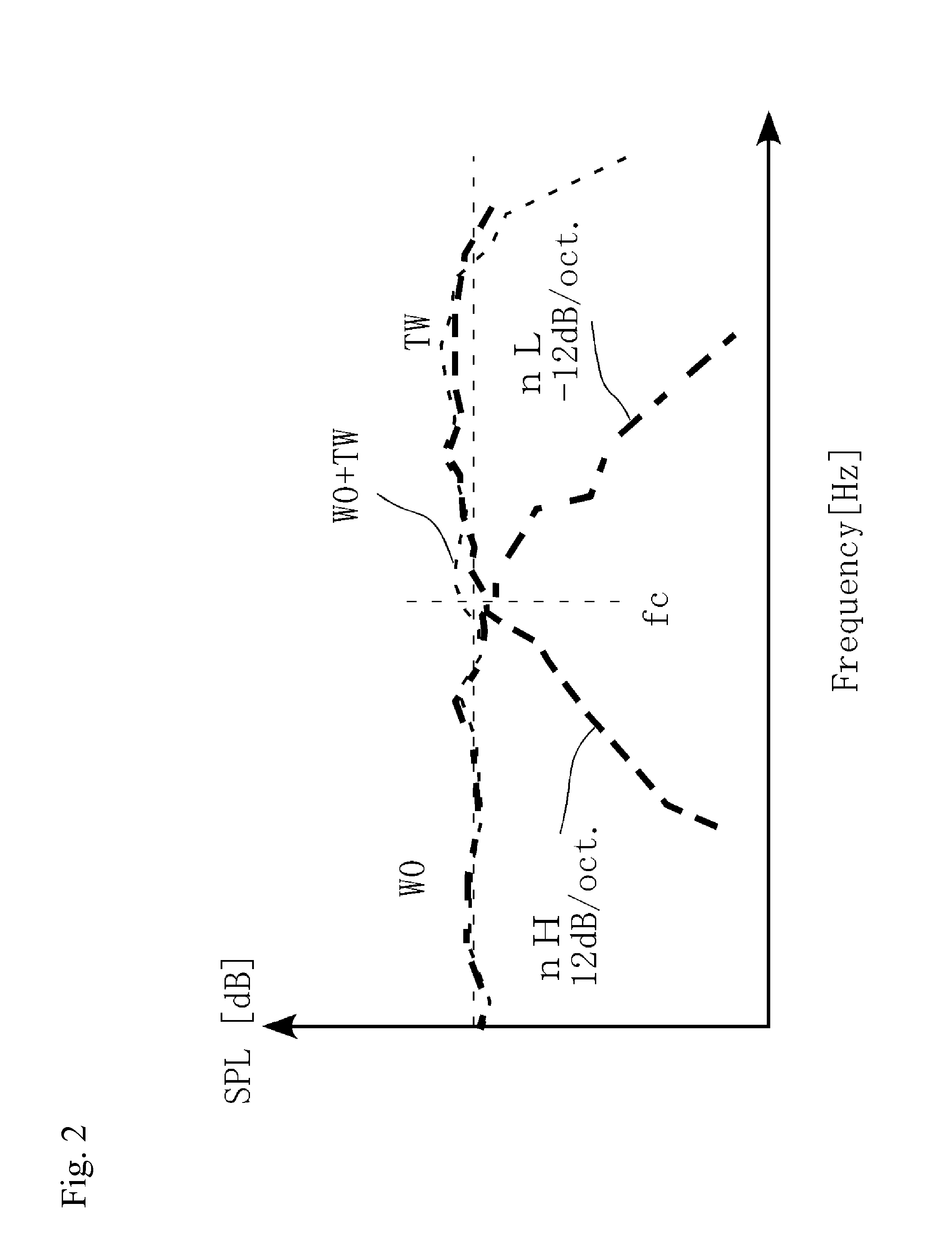
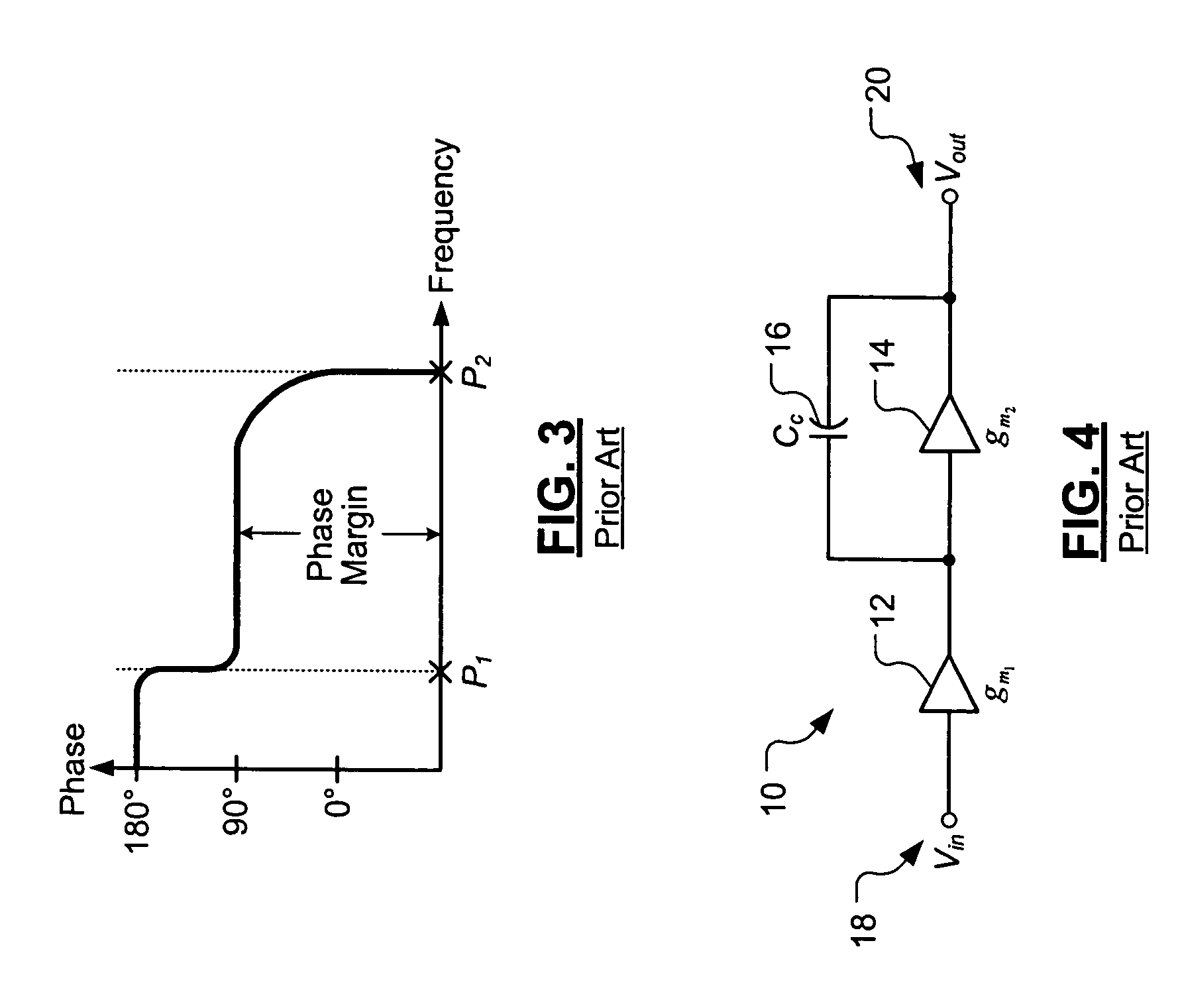
Crossover frequency. [′krȯs‚ō·vər ‚frē·kwən·sē] (engineering acoustics) The frequency at which a dividing network delivers equal power to the upper and lower frequency channels when both are terminated in specified loads.
Enhancing the performance of coding systems that use high frequency reconstruction methods
ActiveUS7050972B2Improve audio qualityBetter trade-offCode conversionSpeech recognitionReconstruction methodComputer module
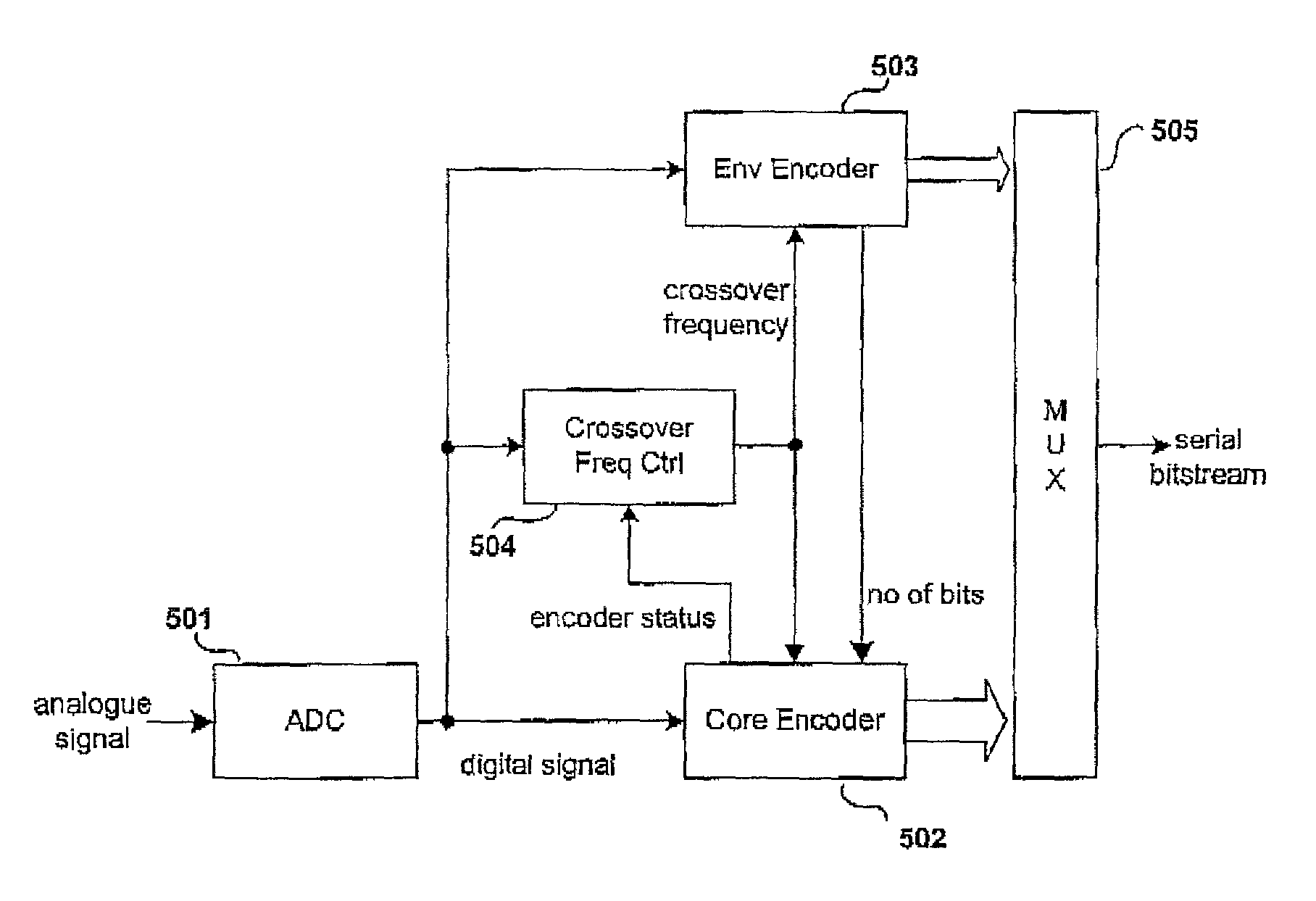
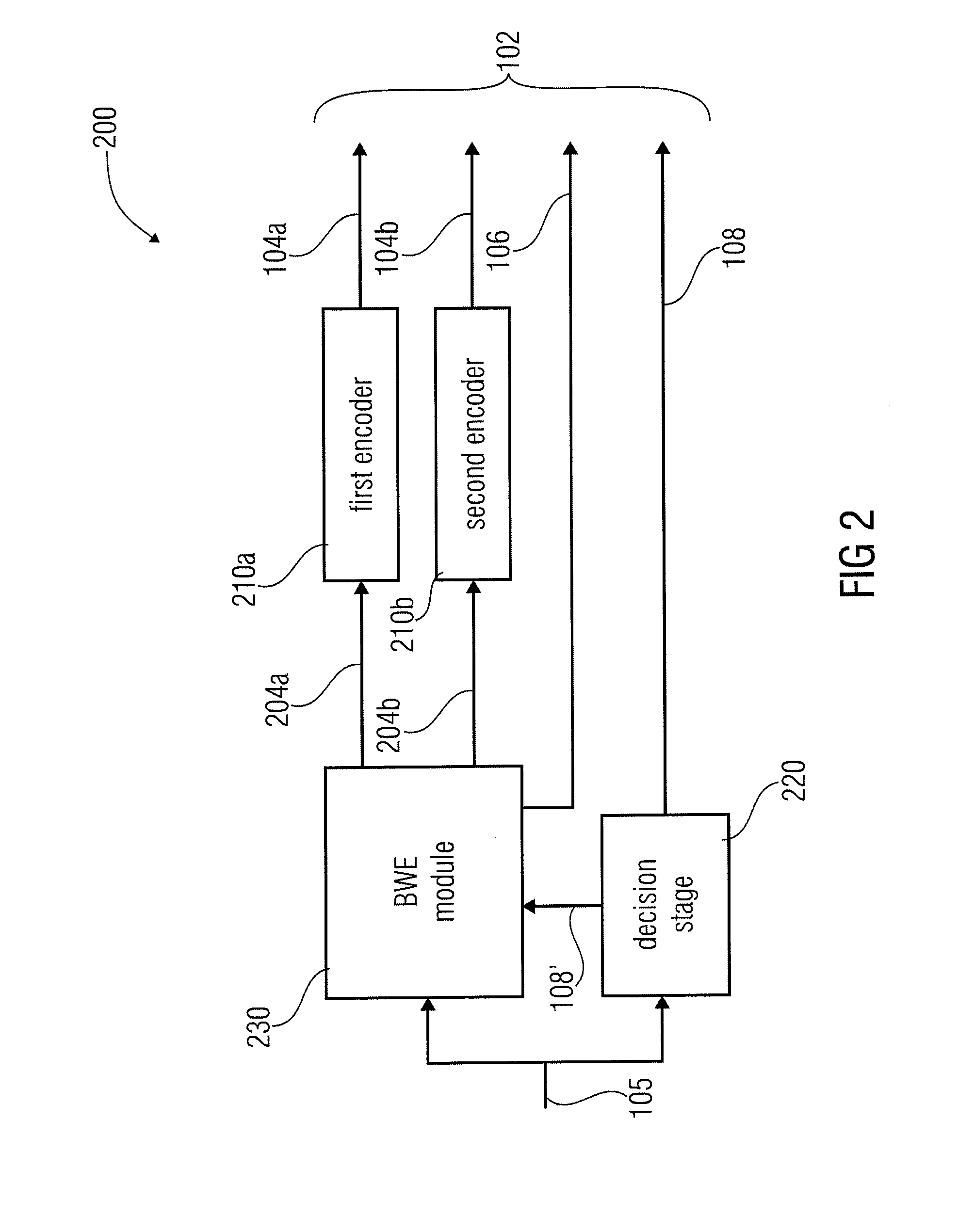
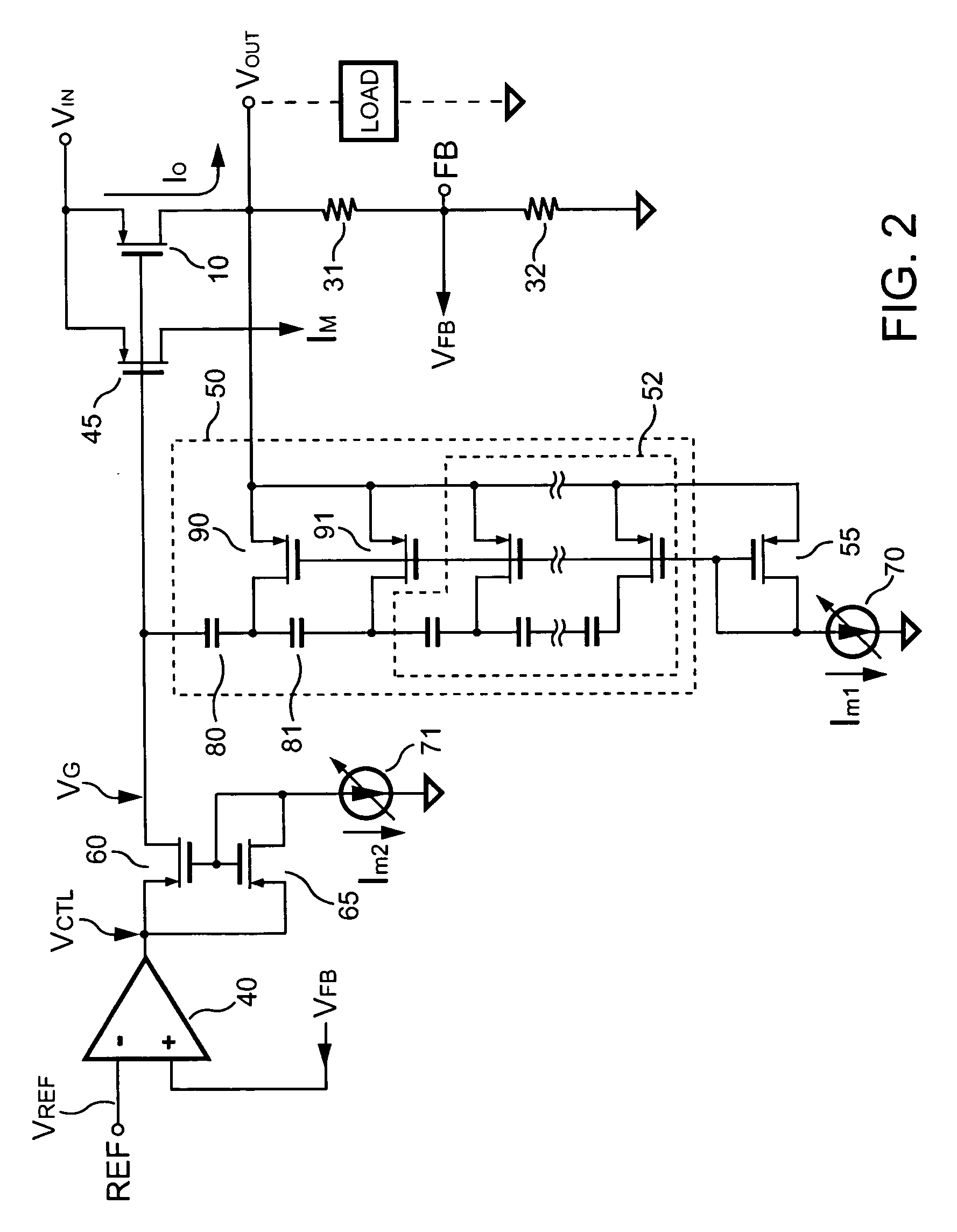
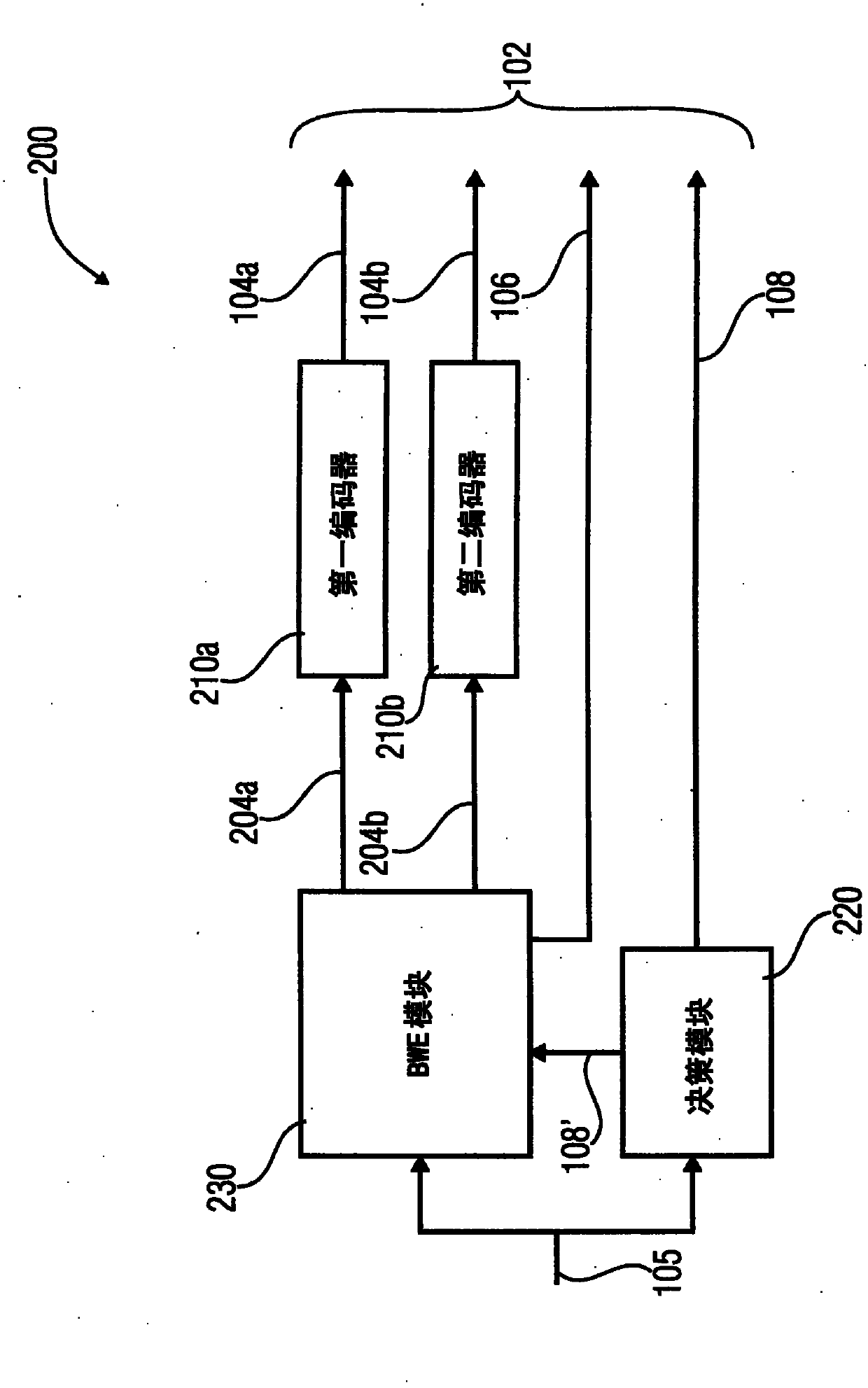
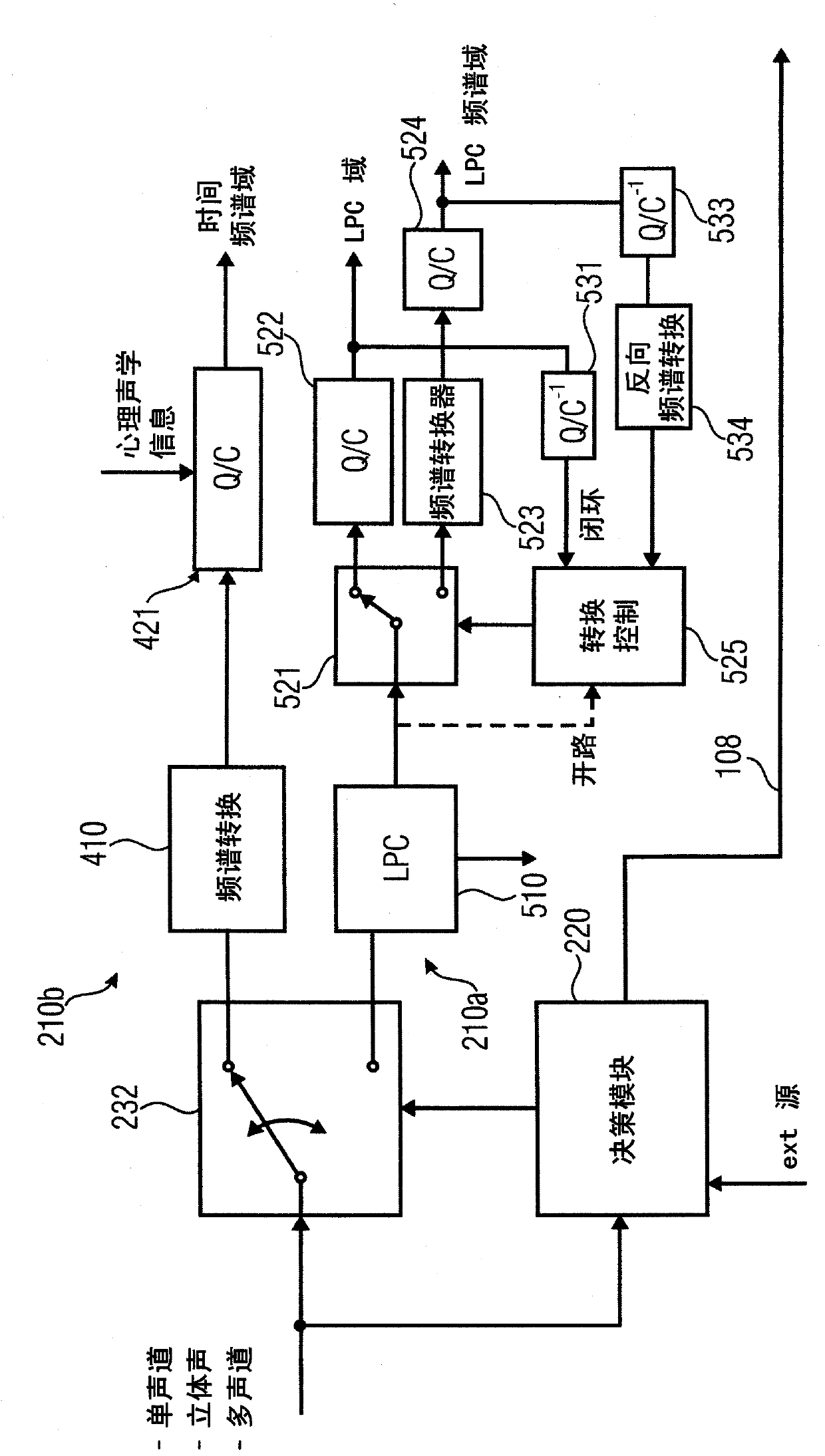
An apparatus for encoding an audio signal to obtain an encoded audio signal to be used by a decoder having a high frequency reconstruction module for performing a high frequency reconstruction for a frequency range above a crossover frequency includes, a core encoder for encoding a lower frequency band of the audio signal up to the crossover frequency, the crossover frequency being variable, and the core encoder being operable on a block-wise frame by frame basis, and a crossover frequency control module for estimating, dependent on a measure of the degree of difficulty for encoding the audio signal by the core encoder and / or a boarder between a tonal and a noise-like frequency range of the audio signal, the crossover frequency to be selected by the core encoder for a frame of a series of subsequent frames, so that the crossover frequency is variable adaptively over time for the series of subsequent frames.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Apparatus and a Method for Decoding an Encoded Audio Signal
ActiveUS20110202353A1Improve perceived qualityHigh resolutionSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBandwidth extensionEncoding algorithm
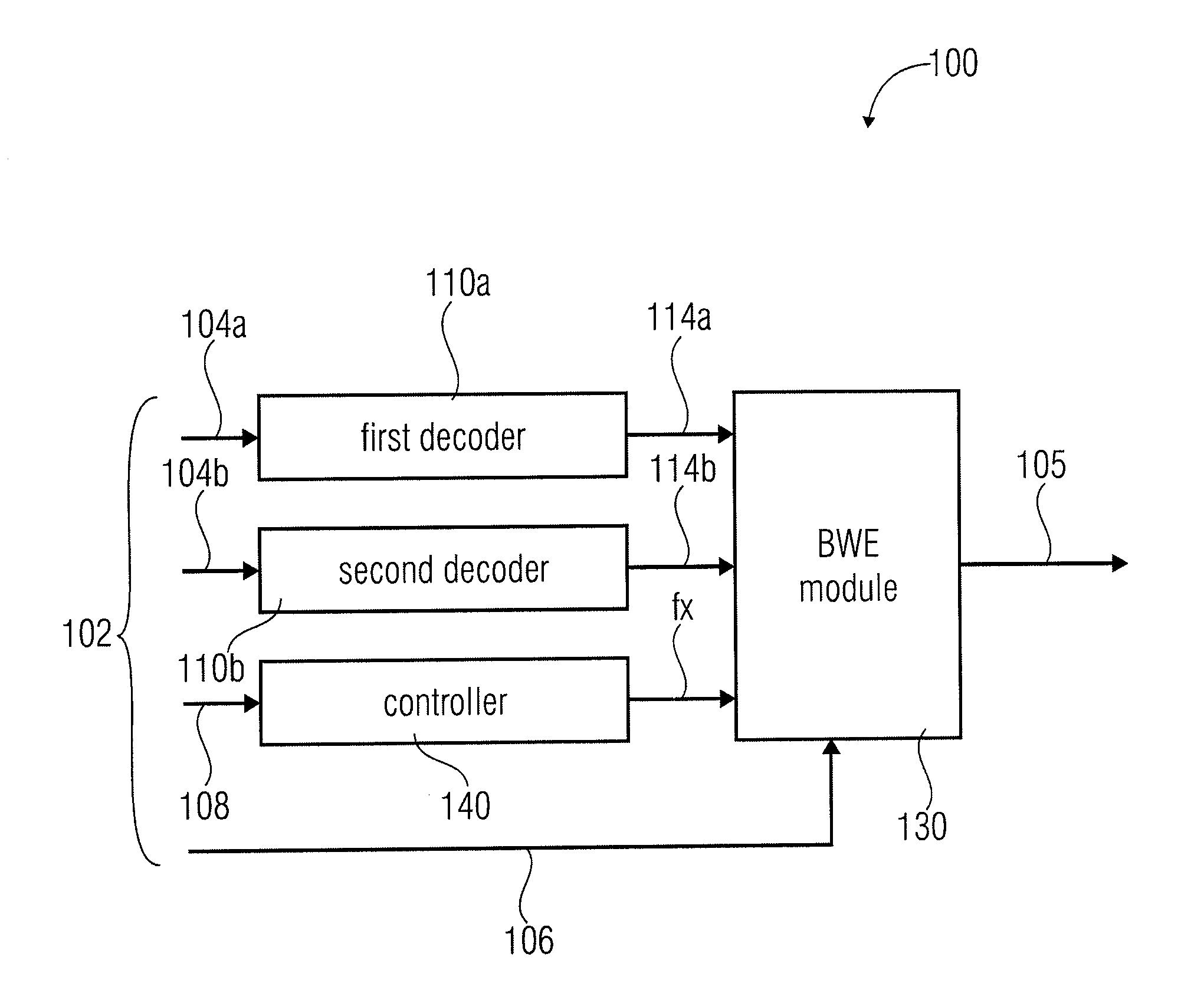
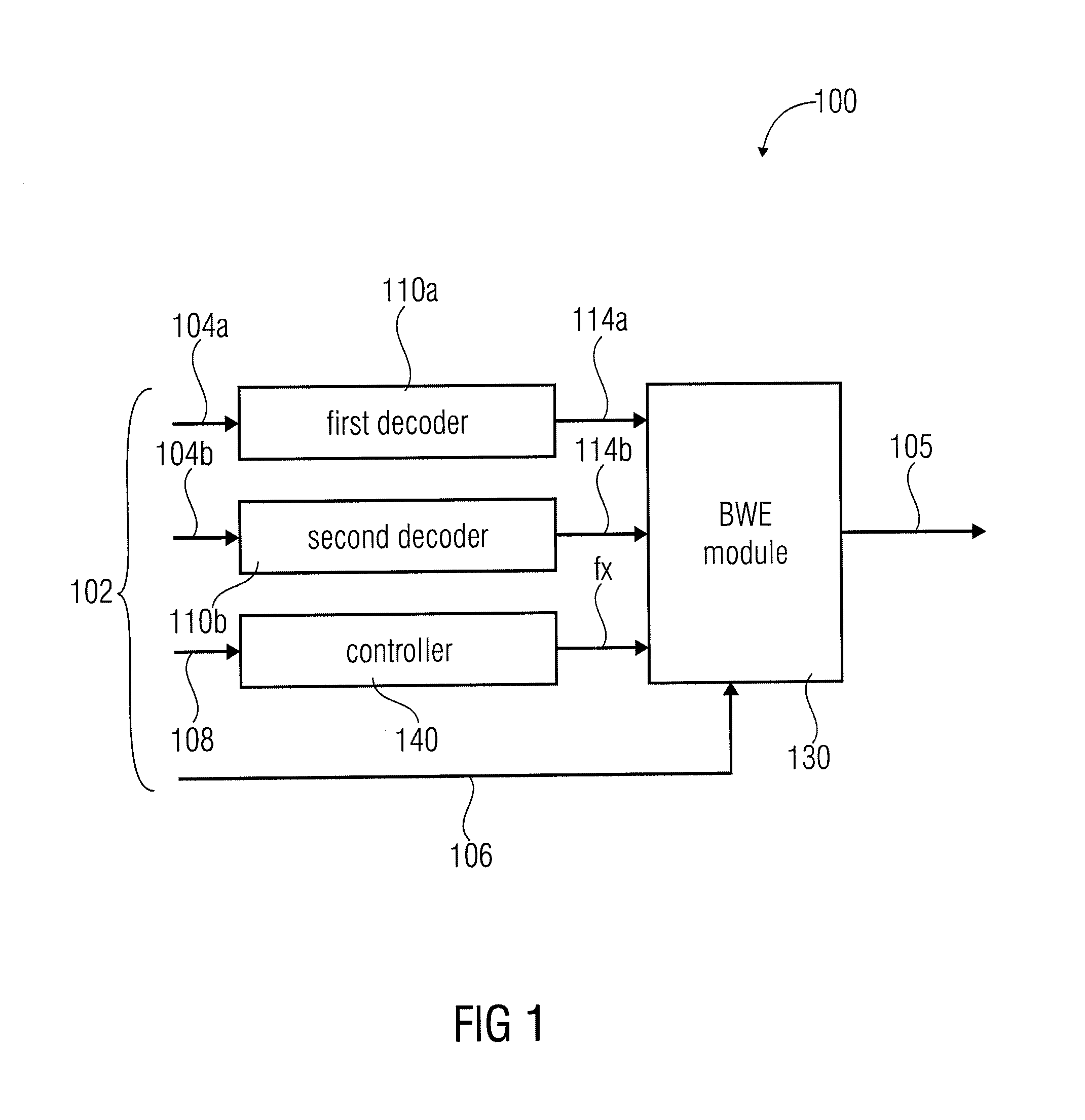
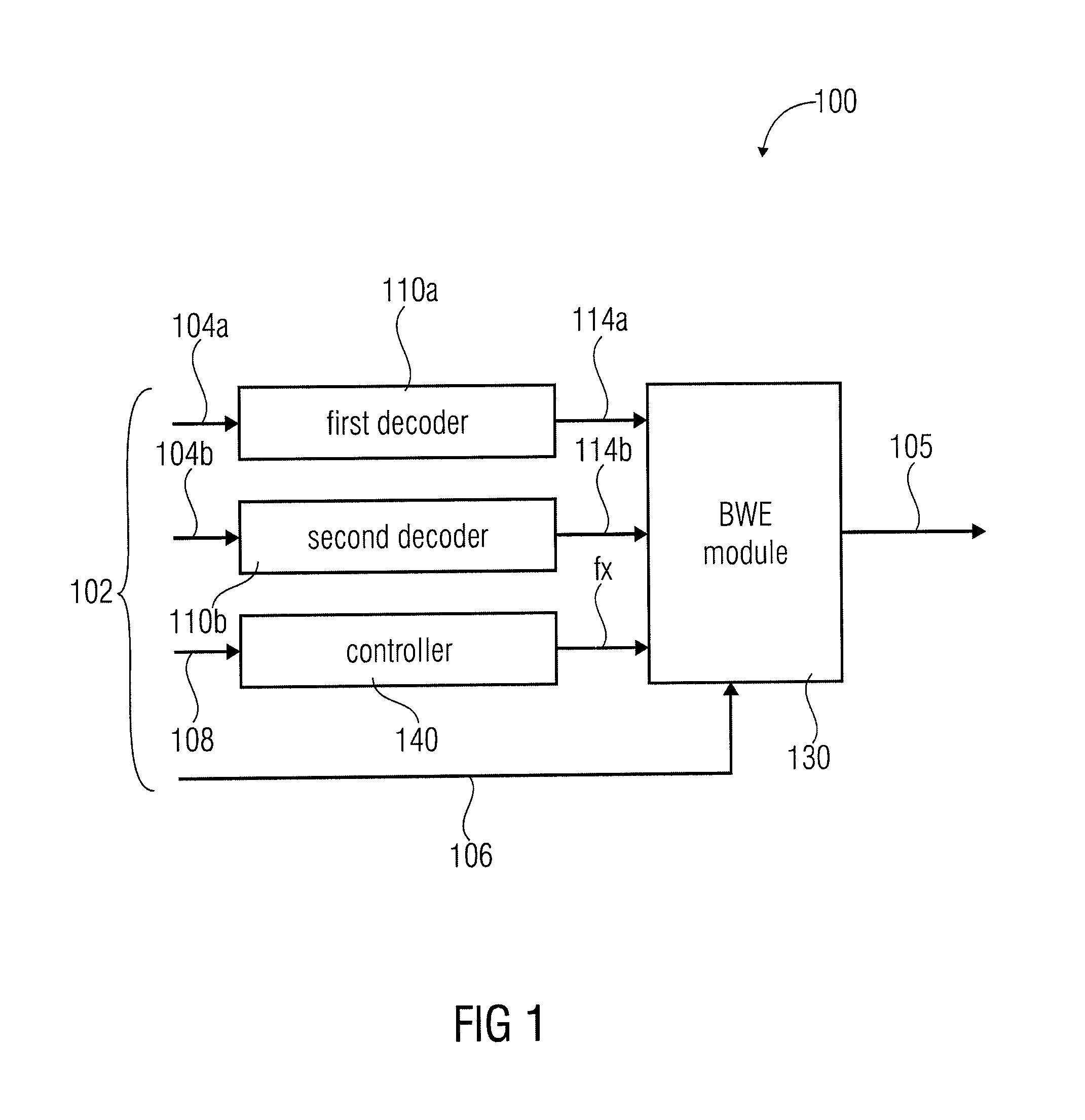
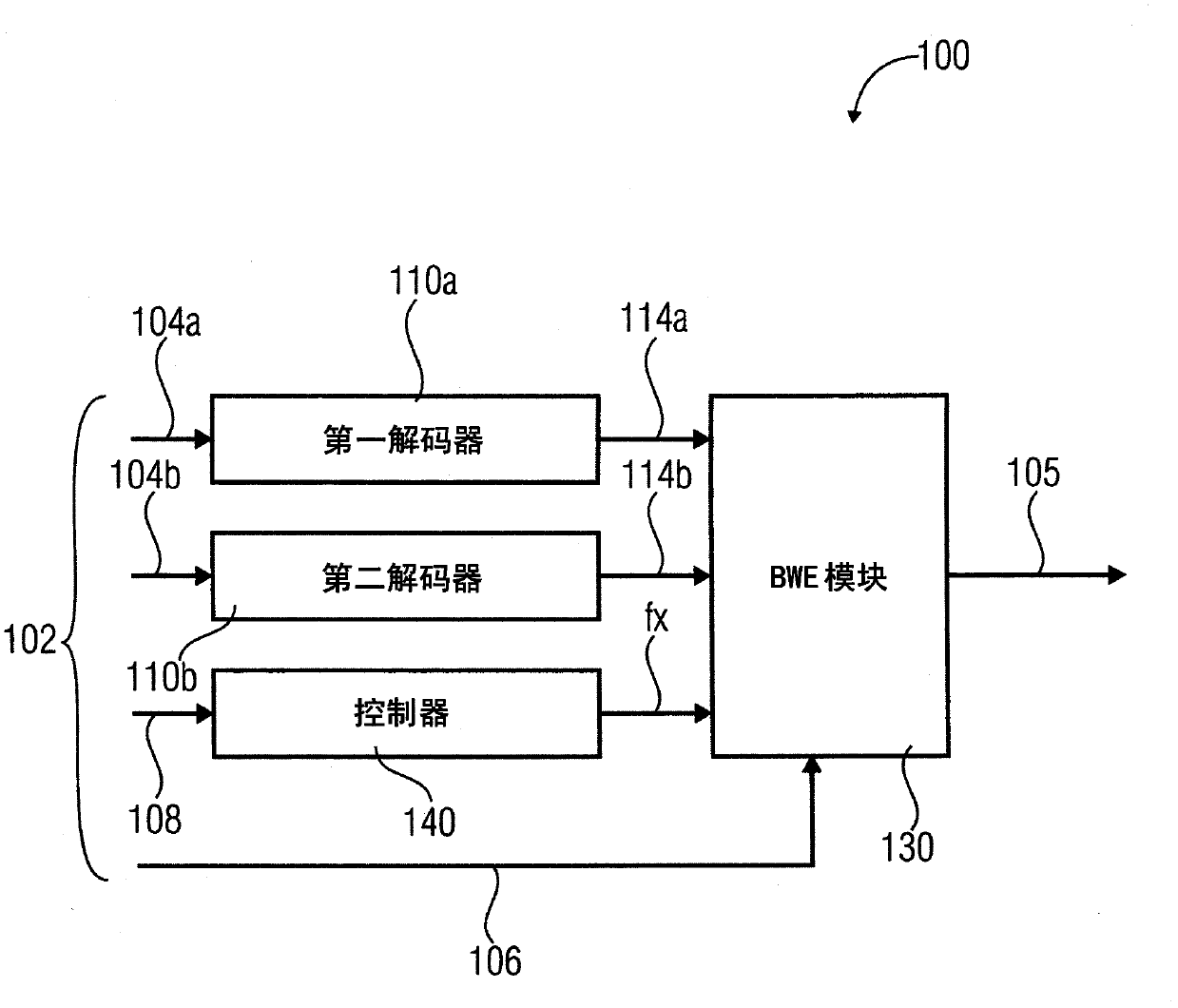
An apparatus for decoding an encoded audio signal having first and second portions encoded in accordance with first and second encoding algorithms, respectively, BWE parameters for the first and second portions and a coding mode information indicating a first or a second decoding algorithm, includes first and second decoders, a BWE module and a controller. The decoders decode portions in accordance with decoding algorithms for time portions of the encoded signal to obtain decoded signals. The BWE module has a controllable crossover frequency and is configured for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the first decoded signal and the BWE parameters for the first portion, and for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the second decoded signal and the bandwidth extension parameter for the second portion. The controller controls the crossover frequency for the BWE module in accordance with the coding mode information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Local oscillator leakage control in direct conversion processes
InactiveUS6960962B2Automatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displaySpatial transmit diversityIntermediate frequencyLocal oscillator
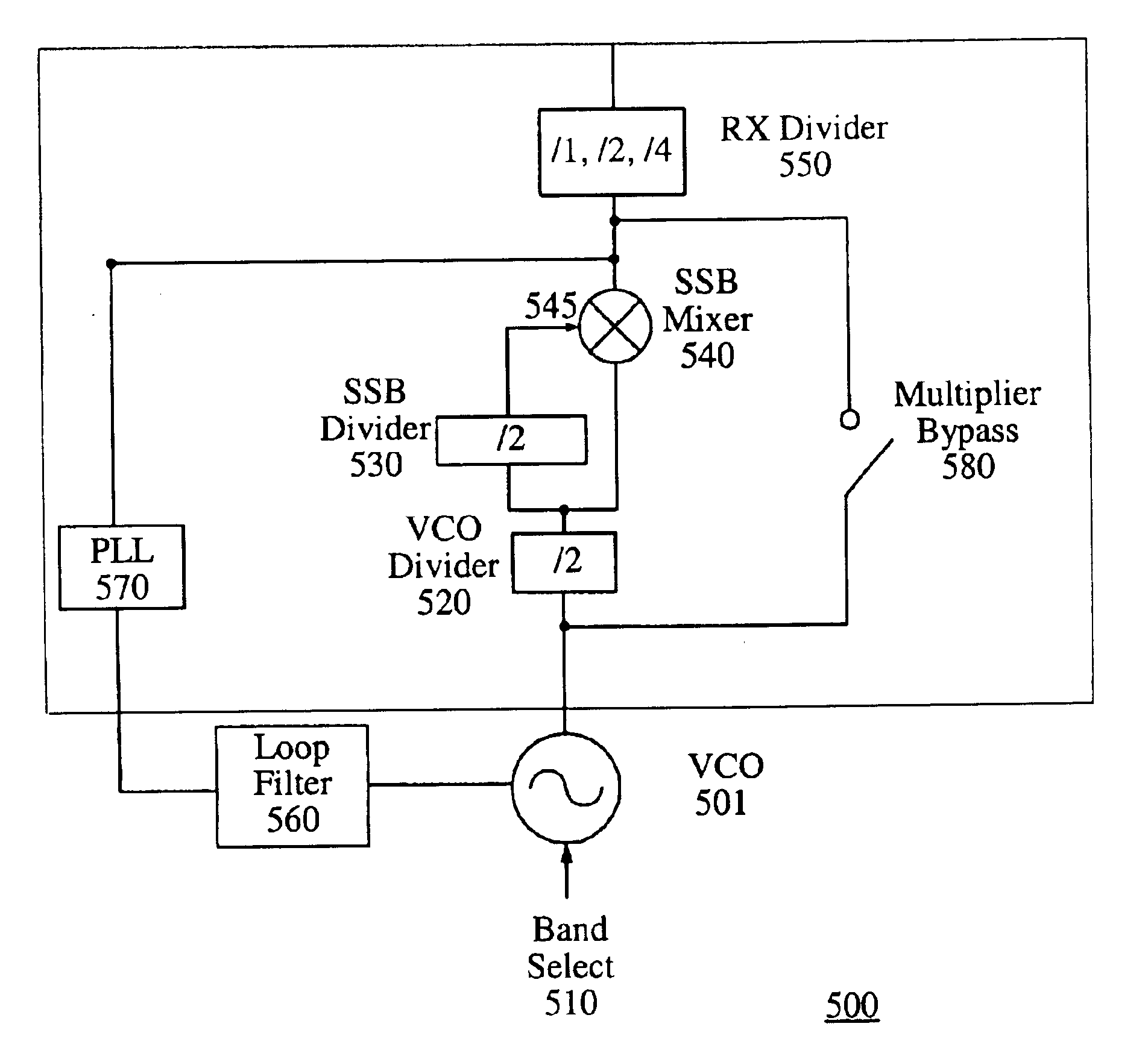
A system and method for generating a local oscillator (LO) frequency in a zero intermediate frequency (IF) receiver or transmitter is presented. A signal is received from a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). The signal has a VCO frequency. The VCO frequency is divided by a number N to produce a signal having a divided-down frequency. The signal having the VCO frequency is then mixed with the signal having the divided-down frequency to produce an output signal having an output frequency. Local oscillator leakage is reduced. Thus, the receiver or transmitter may operate in multiple wireless communication bands and modes and meet the associated specifications.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
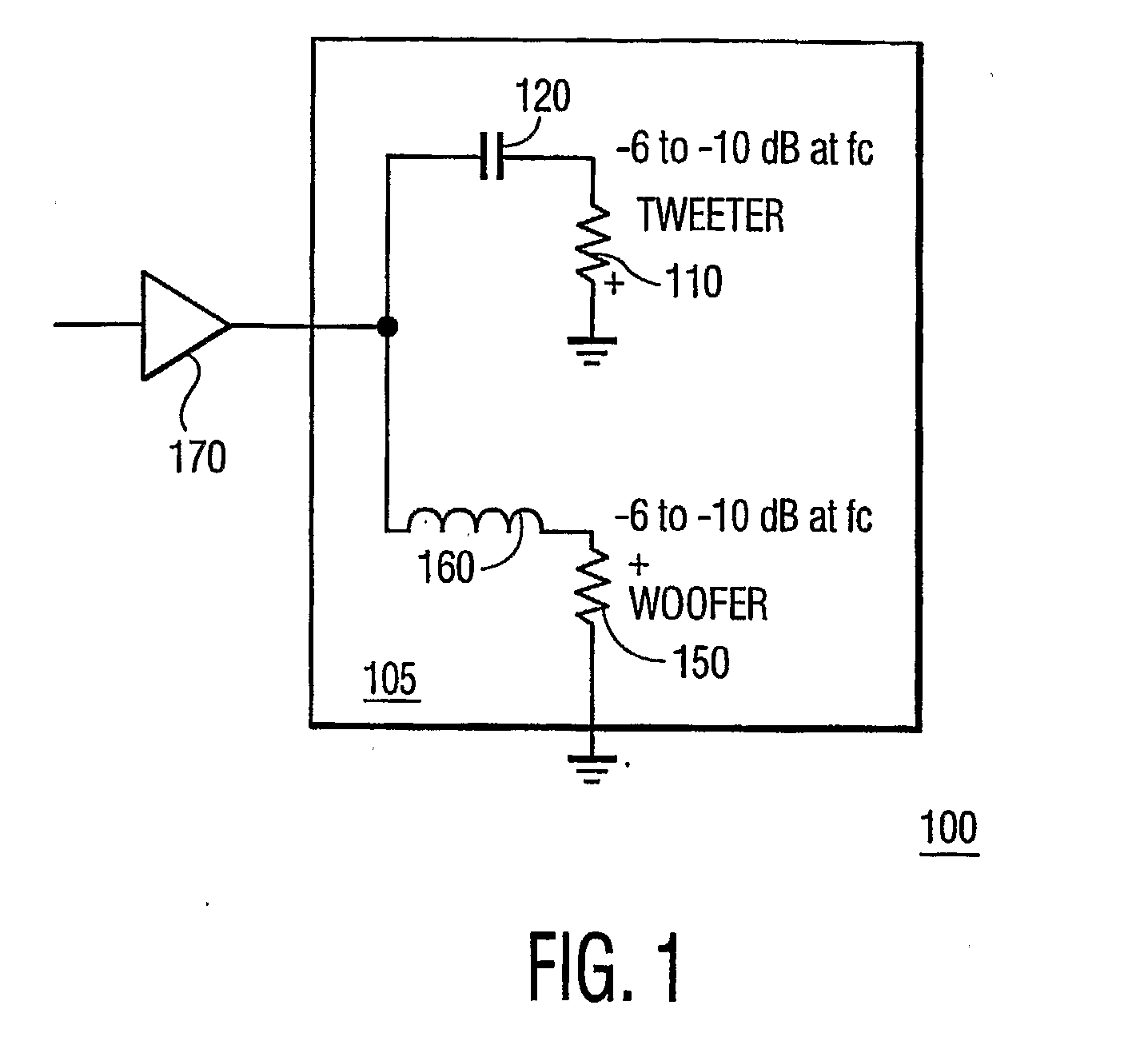
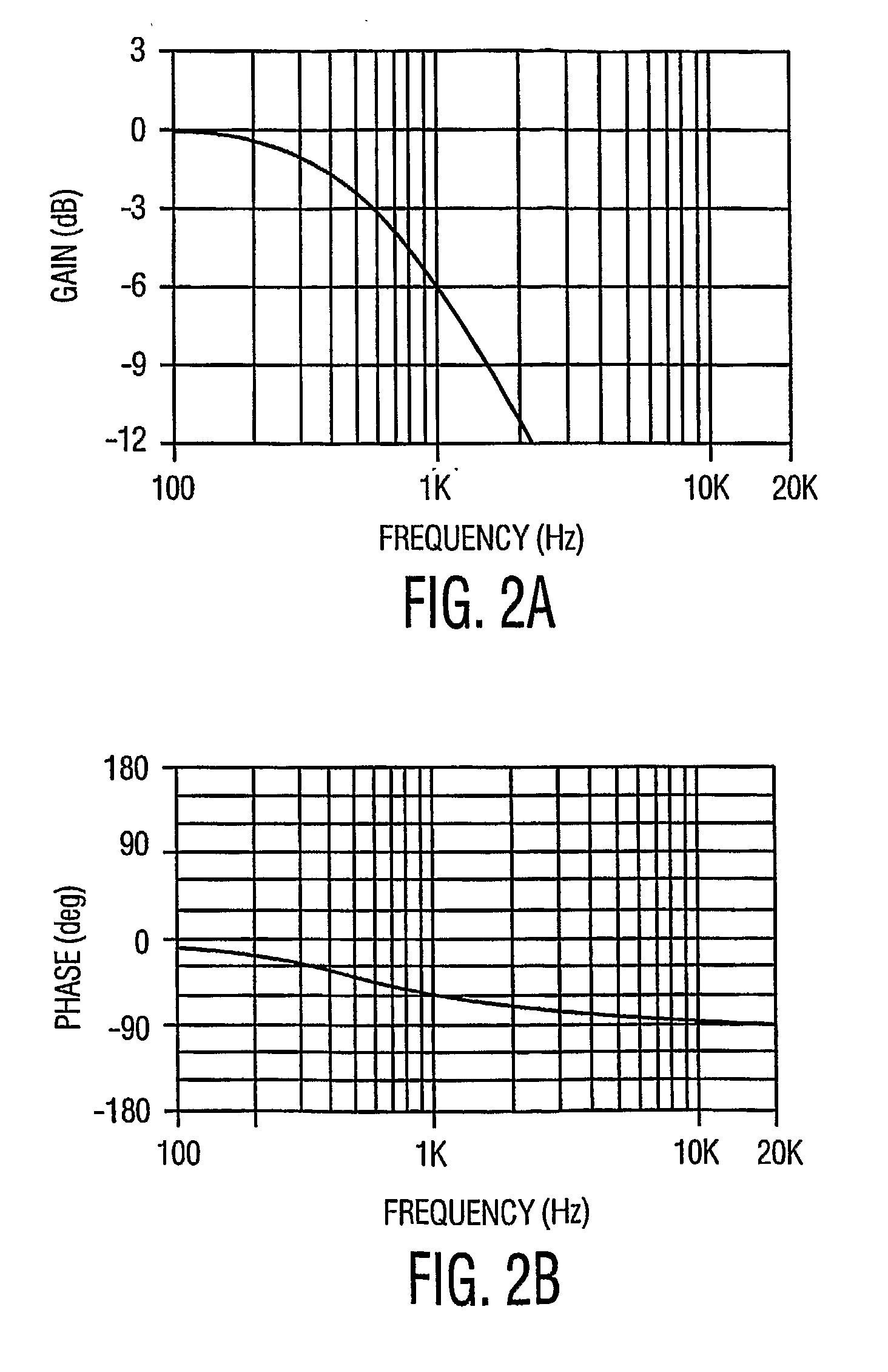
Crossover filter system and method
InactiveUS6854005B2Increased and steep roll offImproved amplitude responseElectric/magnetic computingLoudspeaker signals distributionFilter systemEngineering
A filter system including a low pass filter having a response which rolls off towards a crossover frequency and a high pass filter having a complementary response which rolls off towards the crossover frequency. The responses are arranged such that the combined response of the filters is substantially constant in amplitude at least in the region of the crossover frequency. The response of the low pass filter is defined by a low pass complex transfer function having a first numerator and a first denominator. The response of the high pass filter is defined by a high pass complex transfer function having a second numerator and a second denominator. The desired response is obtained when the second denominator is substantially the same as the first denominator and the sum of the first and second numerators has substantially the same squared modulus as the first or second denominator.
Owner:IMMERSION TECH PROPERTY
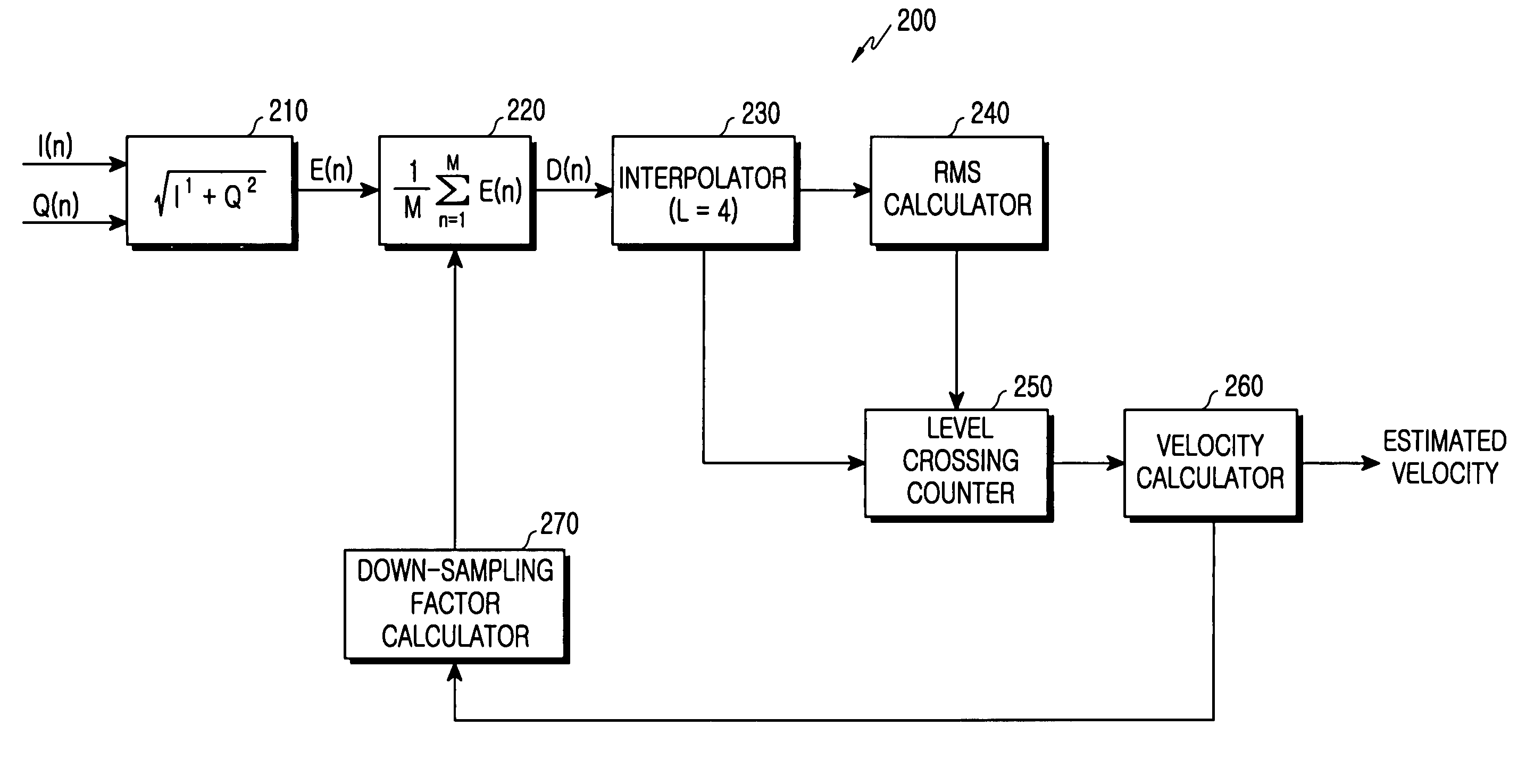
Velocity estimation apparatus and method using level crossing rate
ActiveUS7120440B2Improve accuracyMinimizing influence of noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSubstation equipmentLevel crossingCrossover frequency
Disclosed is a velocity estimator using a level crossing rate. The velocity estimator comprises a power calculator for calculating power values of a signal received from a mobile terminal; a mean power calculator for calculating mean power values for M power values according to a predetermined down-sampling factor M; an interpolator for interpolating the mean power values according to a predetermined interpolation ratio L; a root mean square calculator for calculating a root mean square value using an output of the interpolator; a level crossing counter for counting a level crossing frequency representing how many times the output of the interpolator crosses a level crossing threshold determined according to the root mean square value, for a predetermined time period; and a velocity calculator for calculating a velocity estimation value of the mobile terminal using the level crossing frequency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
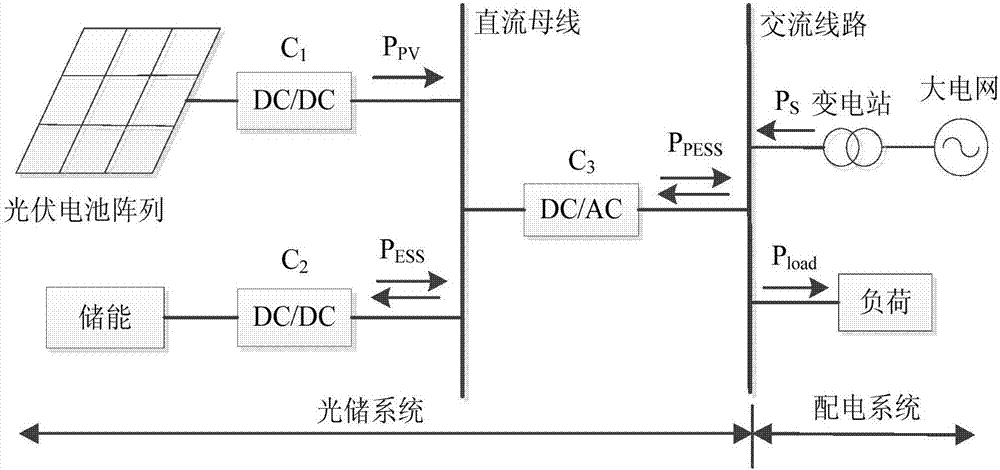
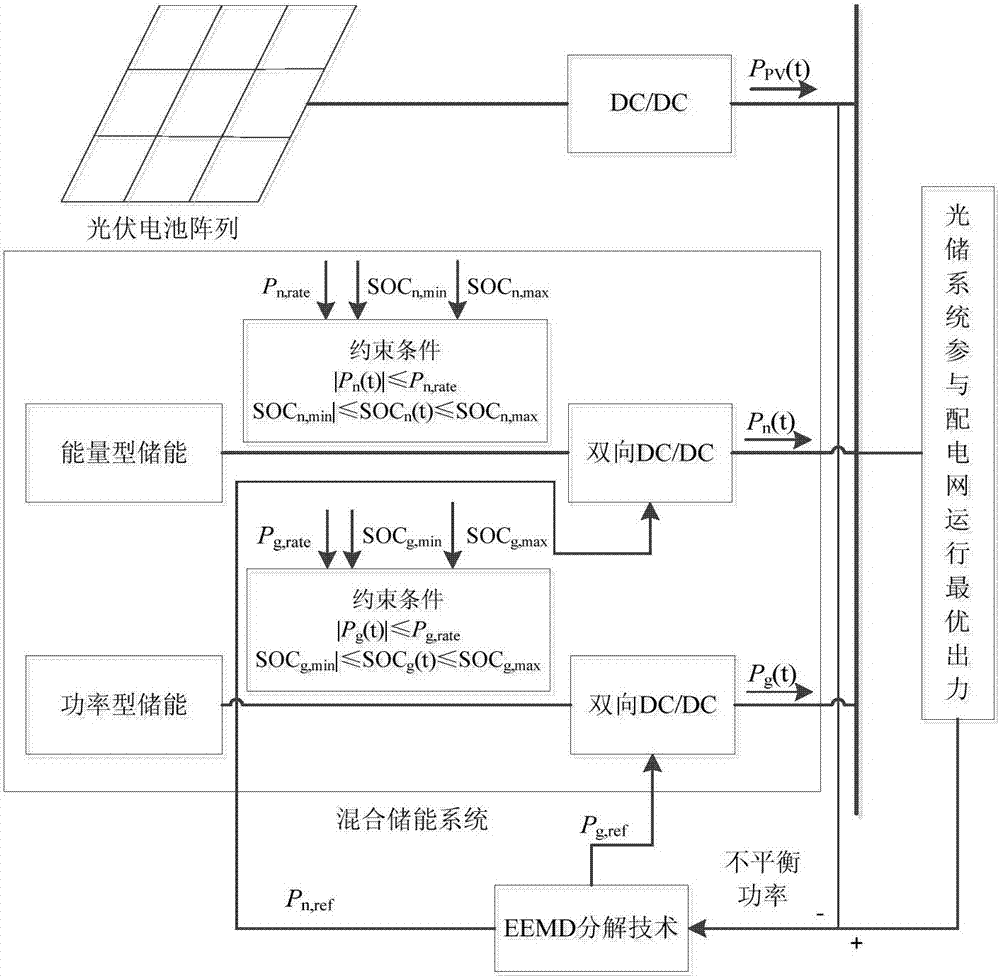
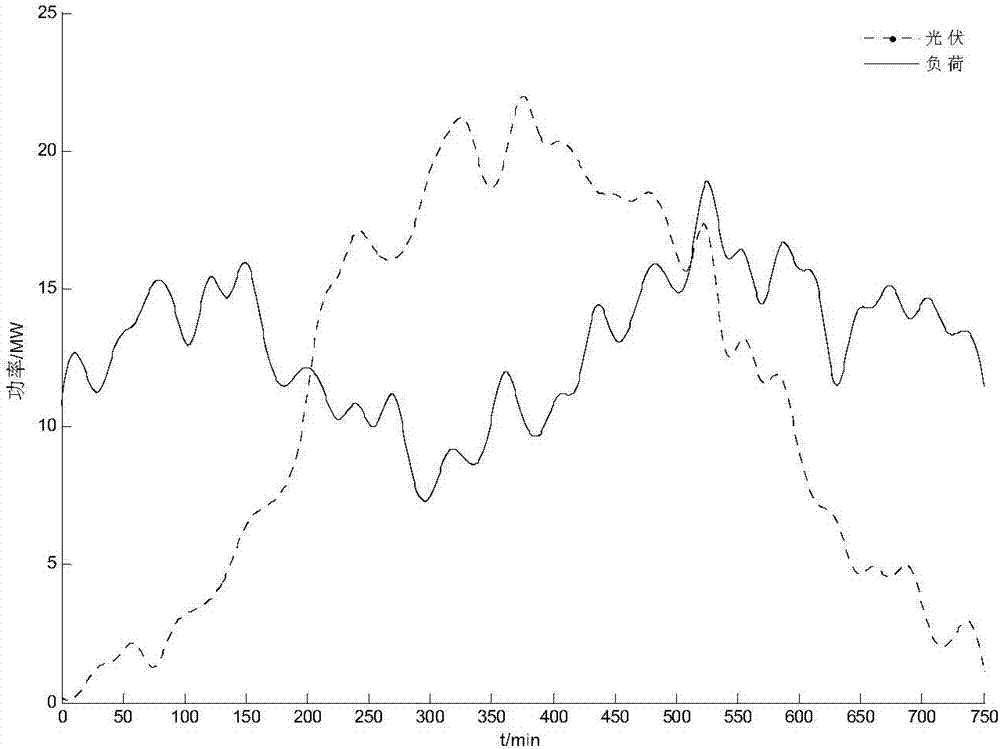
Capacity optimization configuration method for hybrid energy storage system orientating optimization operation of power distribution network
InactiveCN106998072AImprove economyImprove reliabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageSystem capacityNew energy
The invention discloses a capacity optimization configuration method for a hybrid energy storage system orientating optimization operation of a power distribution network. The capacity optimization configuration method comprises the steps of obtaining imbalance power between the optimal output and photovoltaic actual output when an optical storage system participates in operation of the power distribution network firstly, taking the imbalance power as a hybrid energy storage reference power, adopting ensemble empirical mode decomposition to decompose the imbalance power into a series of intrinsic mode functions, and performing recursion Hilbert conversion to obtain an instantaneous frequency-time curve of each intrinsic mode function separately; according to power type and energy type energy storage characteristics, determining crossover frequency by taking least aliasing of the instantaneous frequency-time curves as a principle, and stabilizing the high-frequency components and low-frequency components of the imbalance power by adopting power type energy storage and energy type energy storage respectively; and finally, by considering charging-discharging efficiency, state of charge and life cycle cost, a power type and energy type energy storage rate power and rate capacity economic optimal configuration scheme is proposed. Compared with a conventional method, new energy output can be compensated, consumption capability to new energy can be improved, and active participation to the optimization operation of the power distribution network can be realized.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
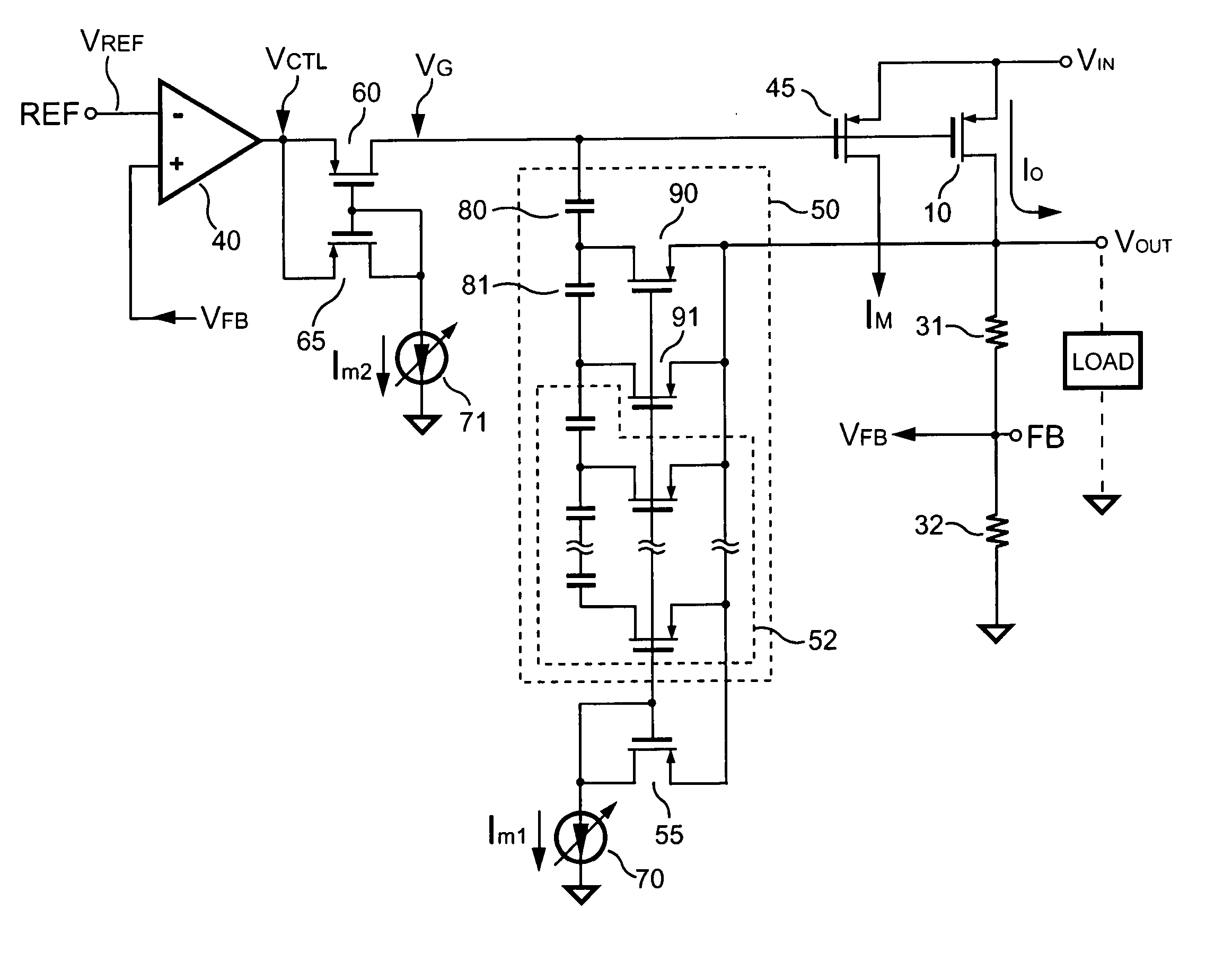
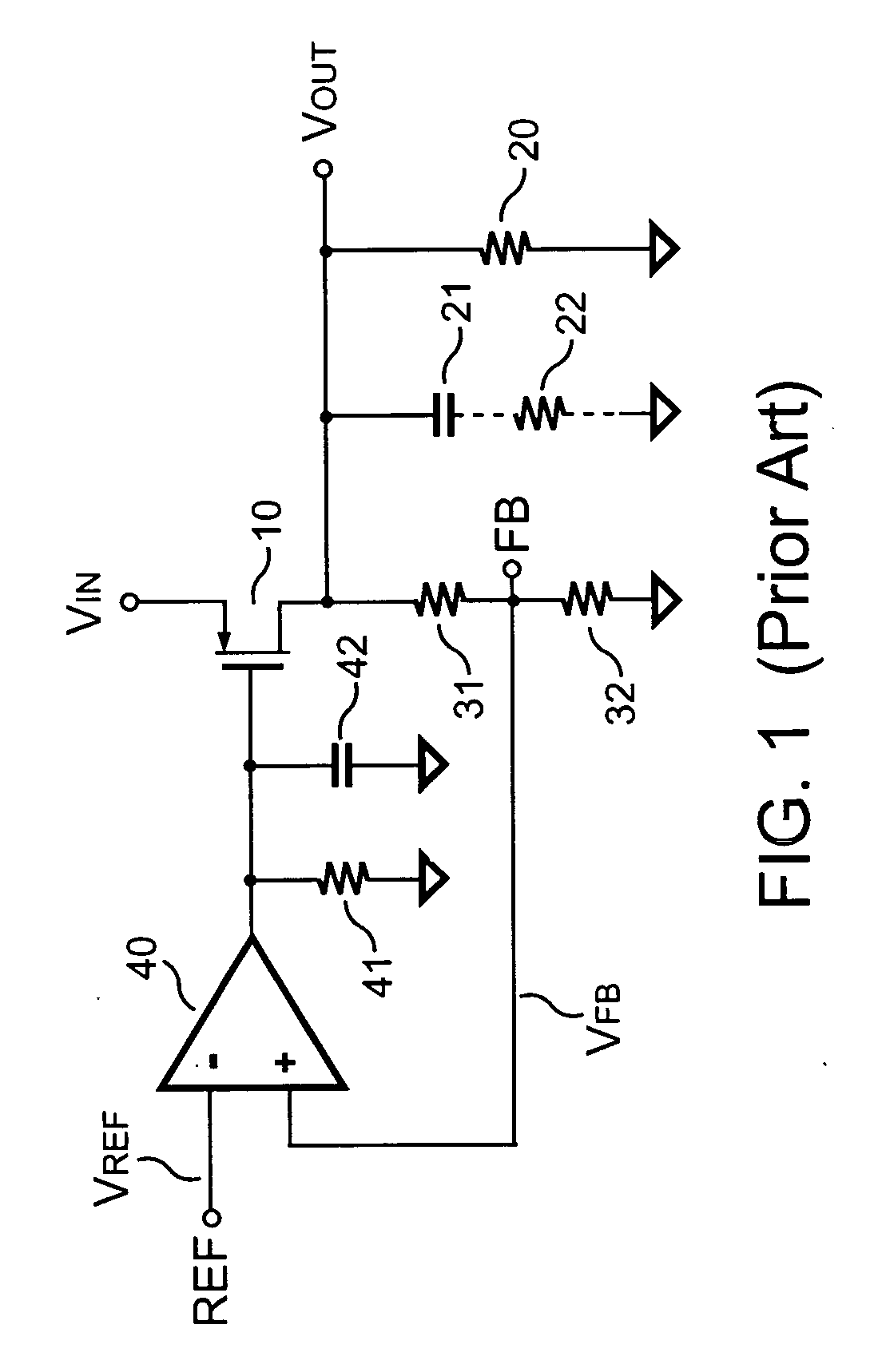
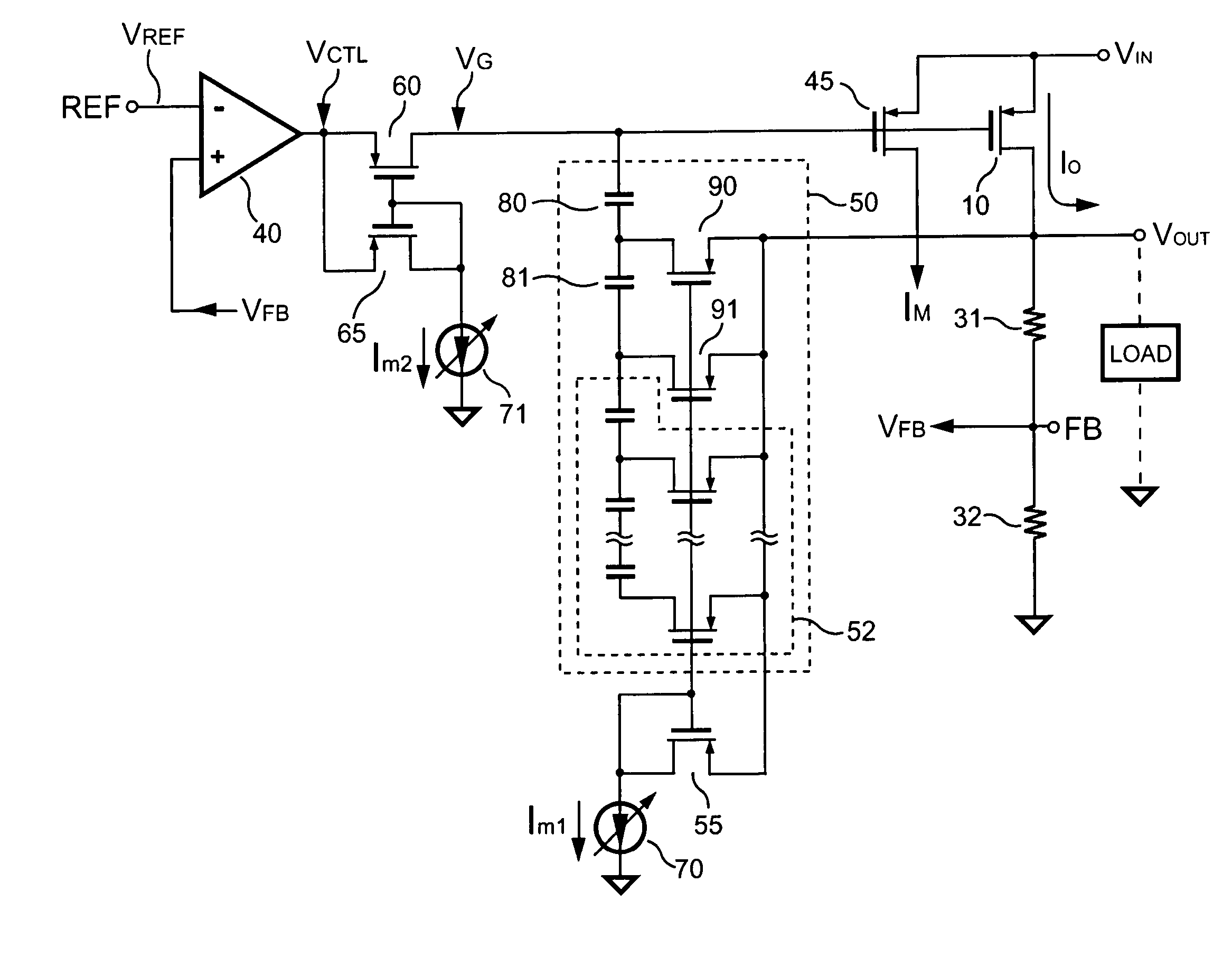
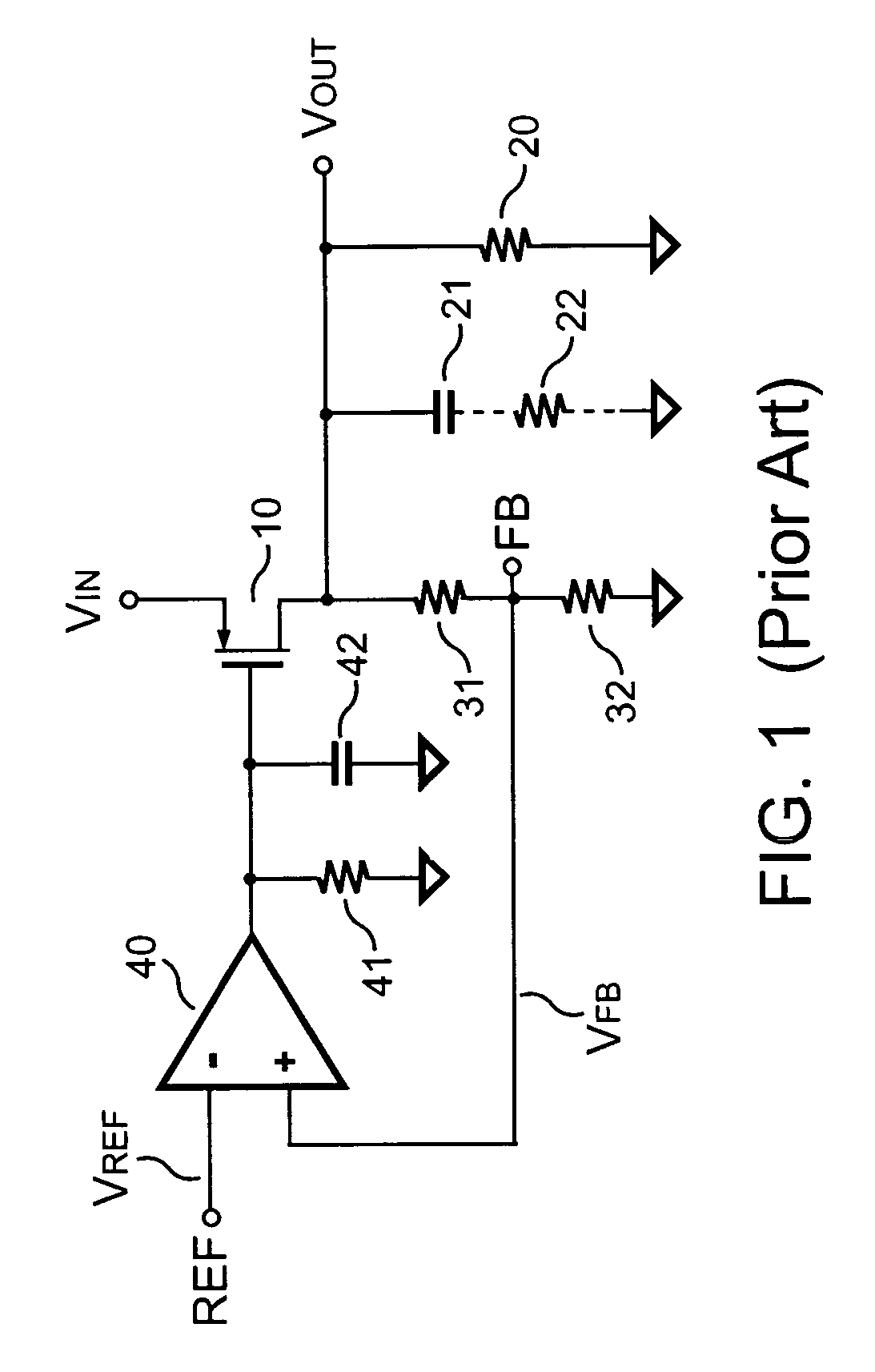
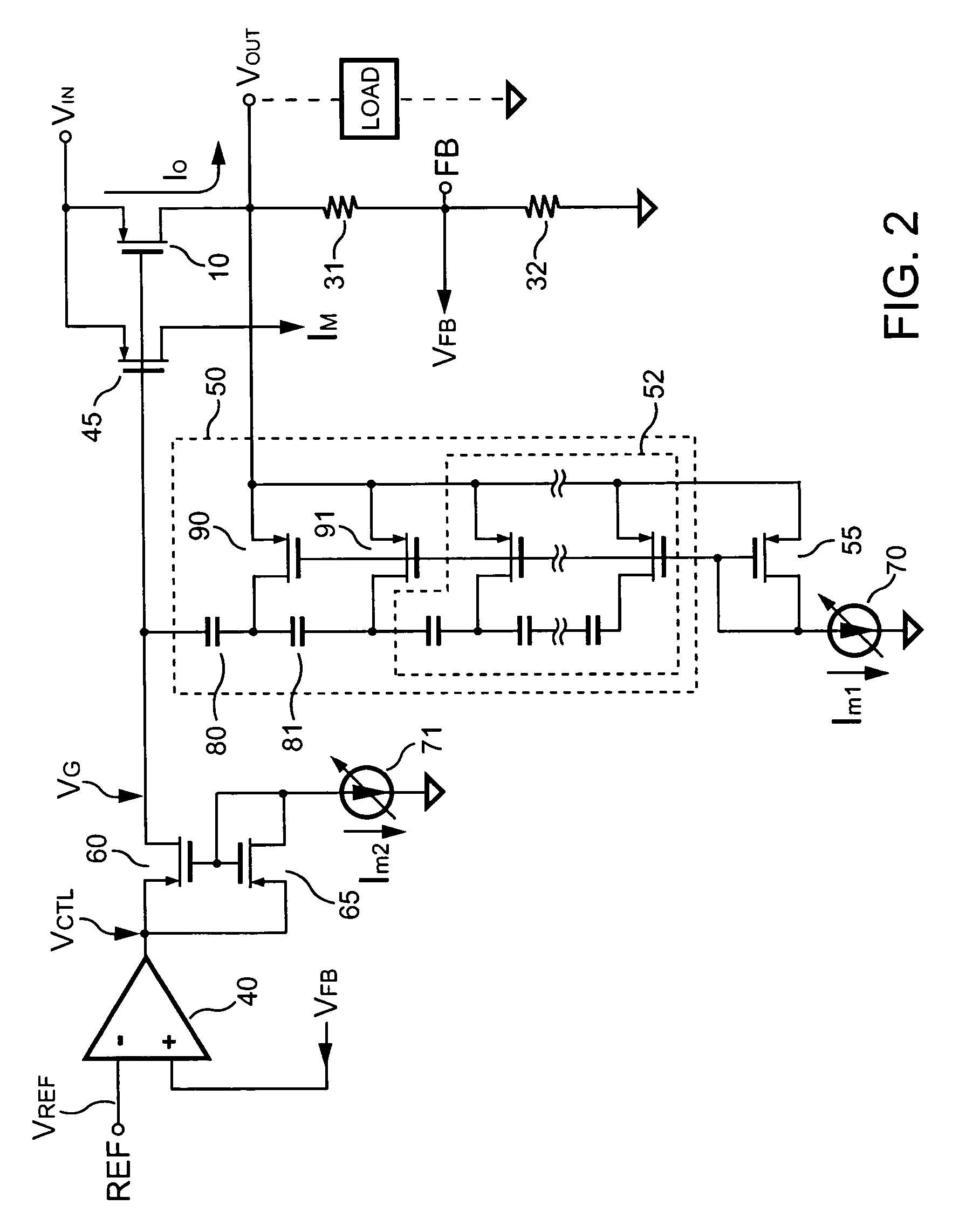
Low dropout voltage regulator providing adaptive compensation
InactiveUS20050242796A1Improve transient responseHigh bandwidthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shiftedEngineering
A method and apparatus to dynamically modify internal compensation of a low dropout (LDO) voltage regulator is provided. The LDO voltage regulator includes an output pass transistor, an error amplifier, a bias transistor and a compensation network. The compensation network is connected between a gate and a drain of the output pass transistor to compensate for the feedback loop. The compensation network and the bias transistor generate pole-zero pairs to perform a maximum 45 degrees phase shift before reaching the crossover frequency in the LDO voltage regulator. Therefore a minimum 45 degrees phase margin is provided for the feedback loop in various load conditions. Furthermore, the pole-zero pairs produced in the LDO voltage regulator are adaptively adjusted according to load conditions, so that the bandwidth is optimized and faster transient response is achieved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Apparatus and a method for decoding an encoded audio signal
ActiveUS8275626B2Quality improvementSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBandwidth extensionEncoding algorithm
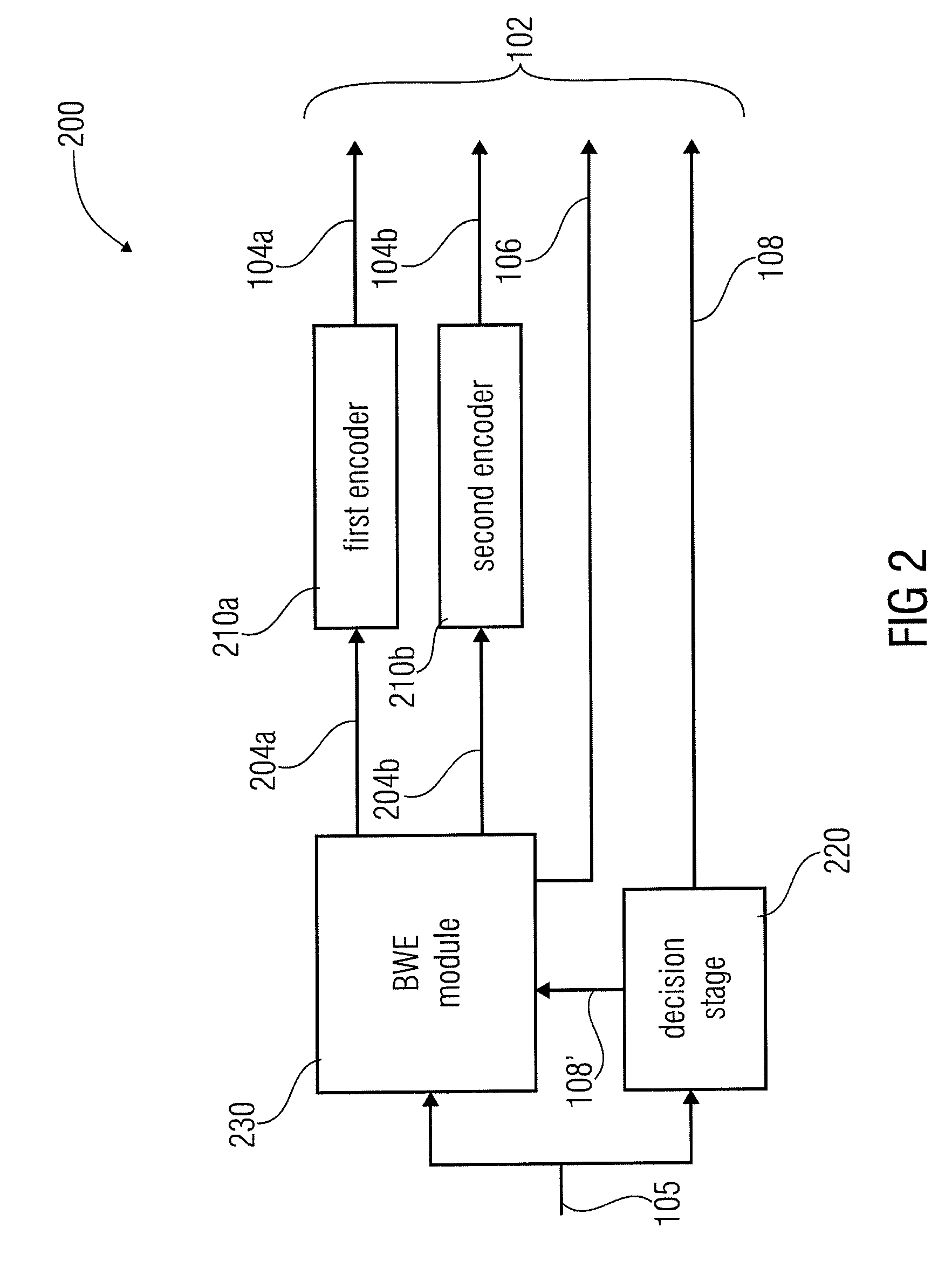
An apparatus for decoding an encoded audio signal having first and second portions encoded in accordance with first and second encoding algorithms, respectively, BWE parameters for the first and second portions and a coding mode information indicating a first or a second decoding algorithm, includes first and second decoders, a BWE module and a controller. The decoders decode portions in accordance with decoding algorithms for time portions of the encoded signal to obtain decoded signals. The BWE module has a controllable crossover frequency and is configured for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the first decoded signal and the BWE parameters for the first portion, and for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the second decoded signal and the bandwidth extension parameter for the second portion. The controller controls the crossover frequency for the BWE module in accordance with the coding mode information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
An apparatus and a method for decoding an encoded audio signal
ActiveCN102089814AImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionBandwidth extensionAlgorithm
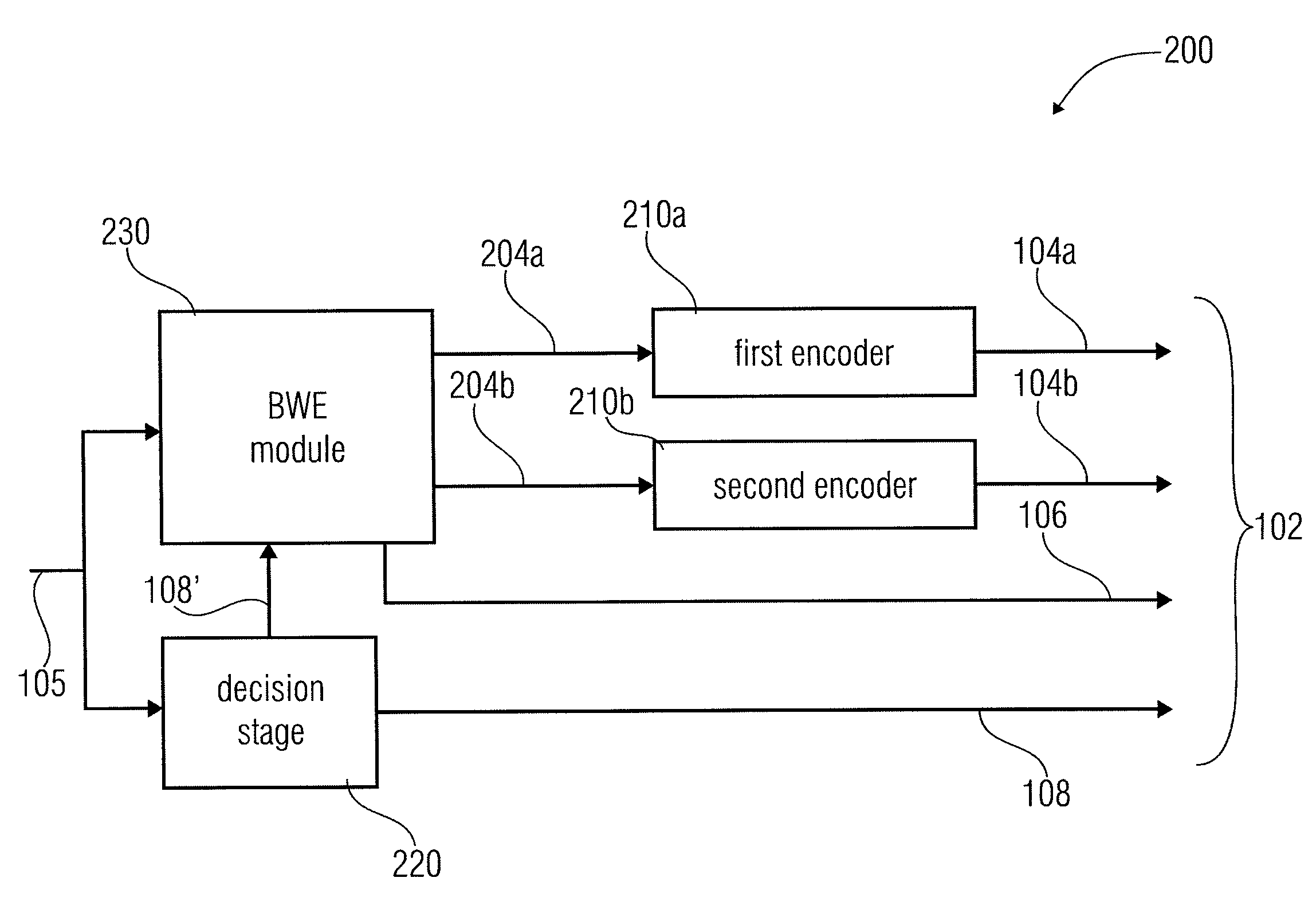
An apparatus for decoding an encoded audio signal, the encoded audio signal comprising a first portion encoded in accordance with a first encoding algorithm, a second portion encoded in accordance with a second encoding algorithm, BWE parameters for the first portion and the second portion and a coding mode information indicating a first decoding algorithm or a second decoding algorithm, comprises a first decoder, a second decoder, a BWE module and a controller. The first decoder decodes the first portion in accordance with the first decoding algorithm for a first time portion of the encoded signal to obtain a first decoded signal. The second decoder decodes the second portion in accordance with the second decoding algorithm for a second time portion of the encoded signal to obtain a second decoded signal. The BWE module has a controllable crossover frequency (fx) and is configured for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the first decoded signal and the BWE parameters for the first portion, and for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the second decoded signal and the bandwidth extension parameter for the second portion. The controller controls the crossover frequency (fx) for the BWE module in accordance with the coding mode information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Noise reduction apparatus, systems, and methods
InactiveUS8232799B2Reduce scan timeReduce data noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFrequency spectrumNoise reduction
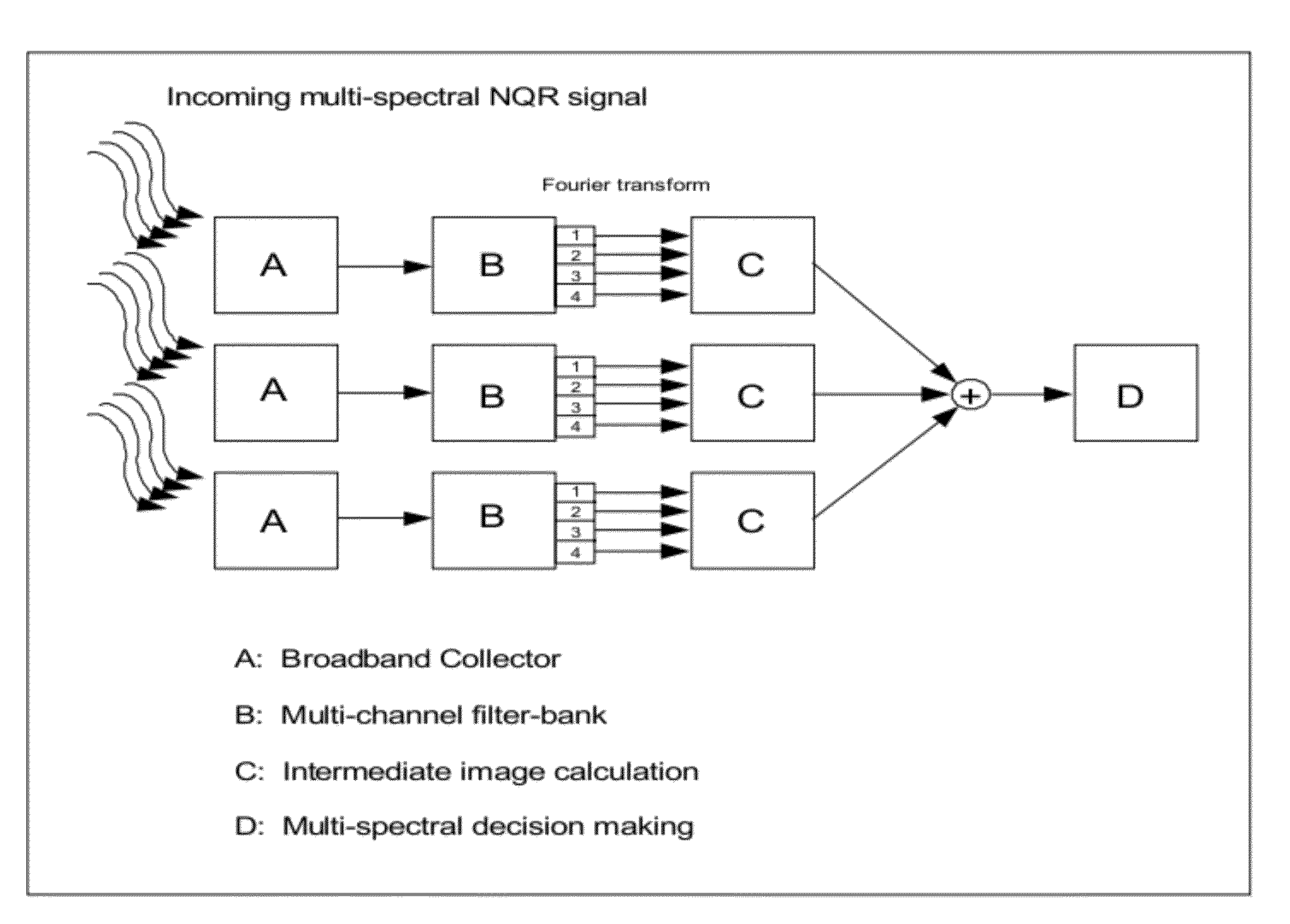
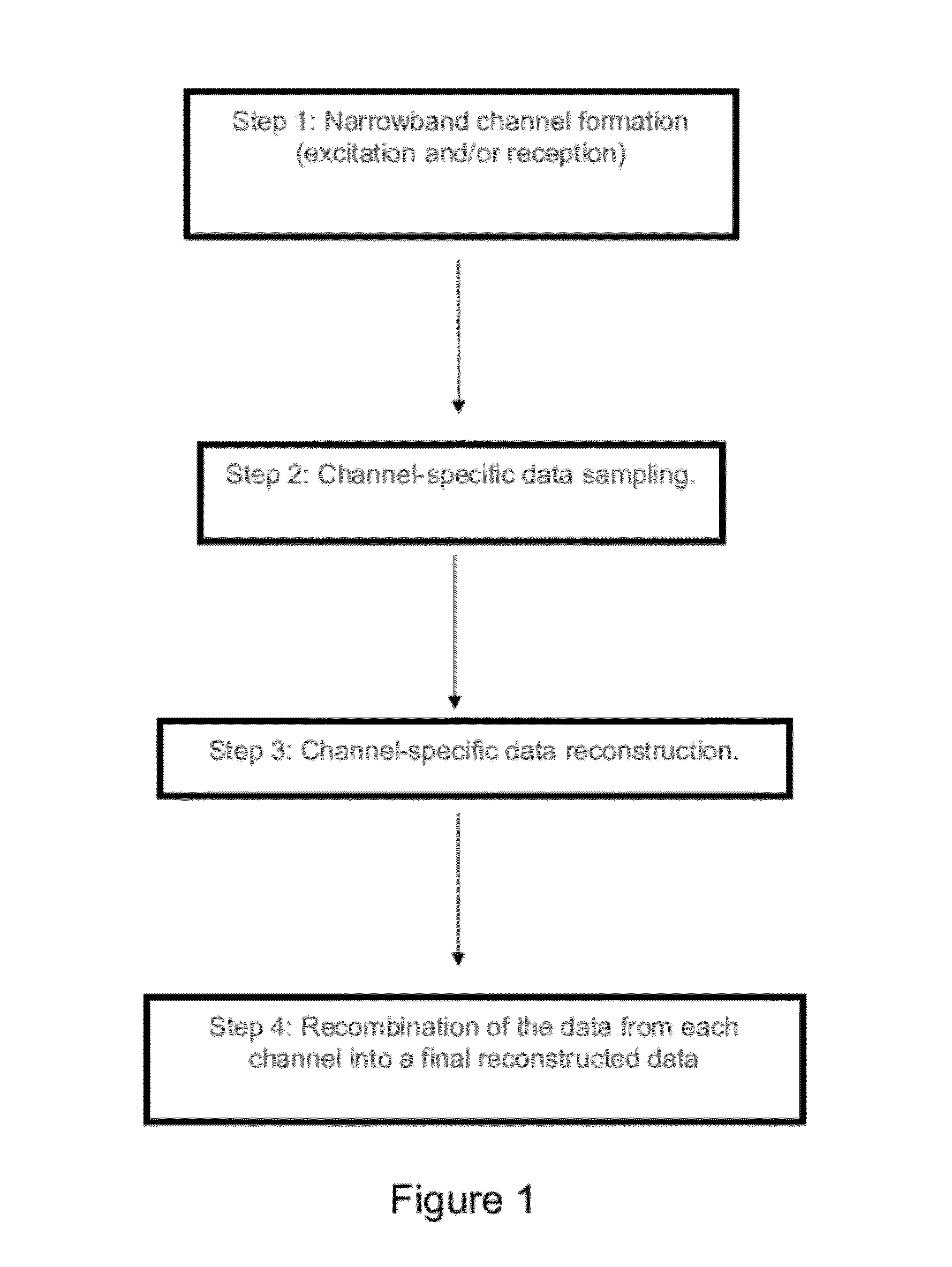
This document describes a general system for noise reduction, as well as a specific system for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR). The general system, which is called Calculated Readout by Spectral Parallelism (CRISP), involves reconstruction and recombination of frequency-limited broadband data using separate narrowband data channels to create images or signal profiles. A multi-channel CRISP system can perform this separation using (1) frequency tuned hardware, (2) a frequency filter-bank (or equivalent), or (3) a combination of implementations (1) and (2). This system significantly reduces what we call cross-frequency noise, thereby increasing signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR). A multi-channel CRISP system applicable to MRI and NQR are described.
Owner:ARJAE SPECTRAL ENTERPRISES
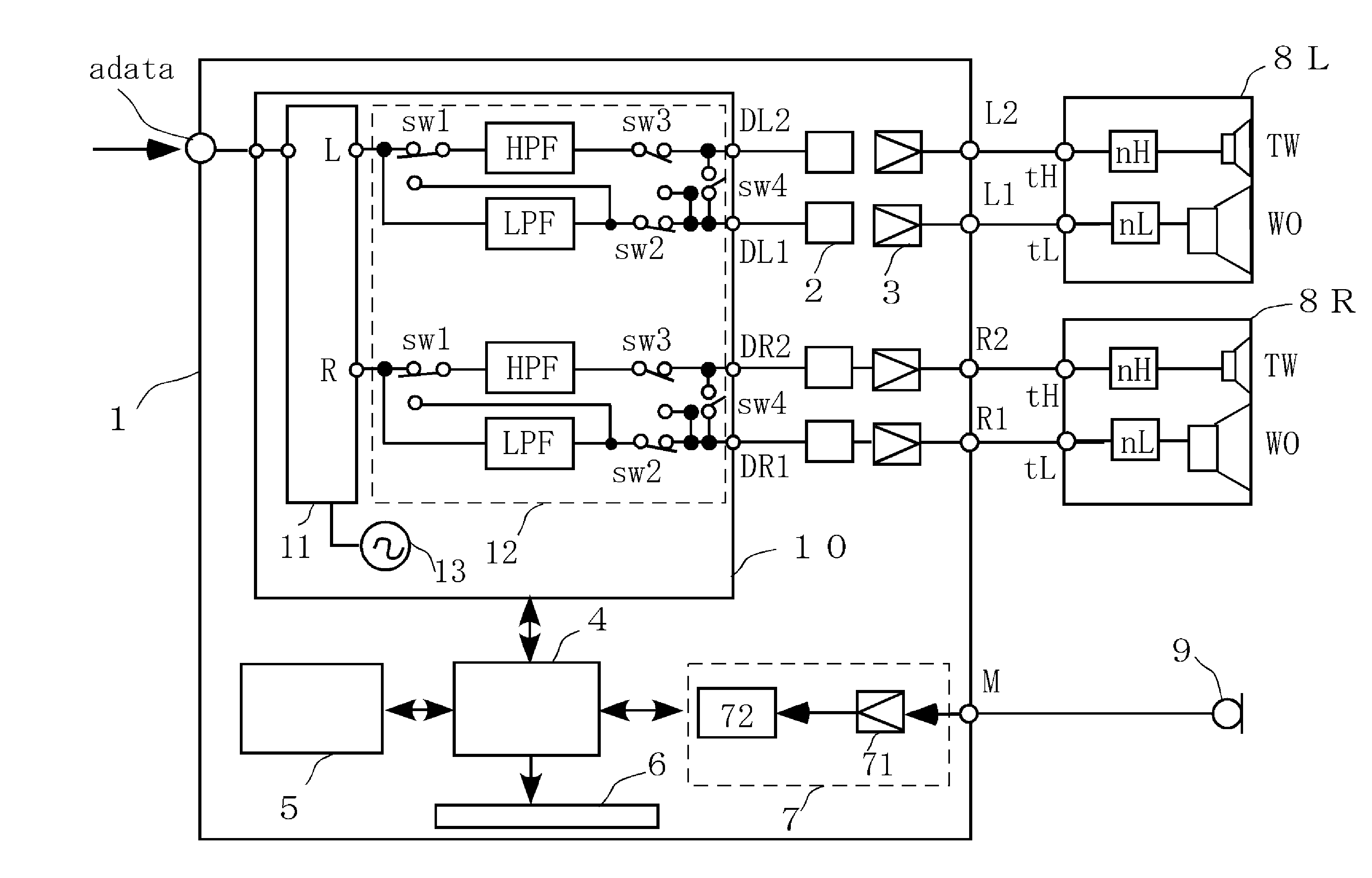
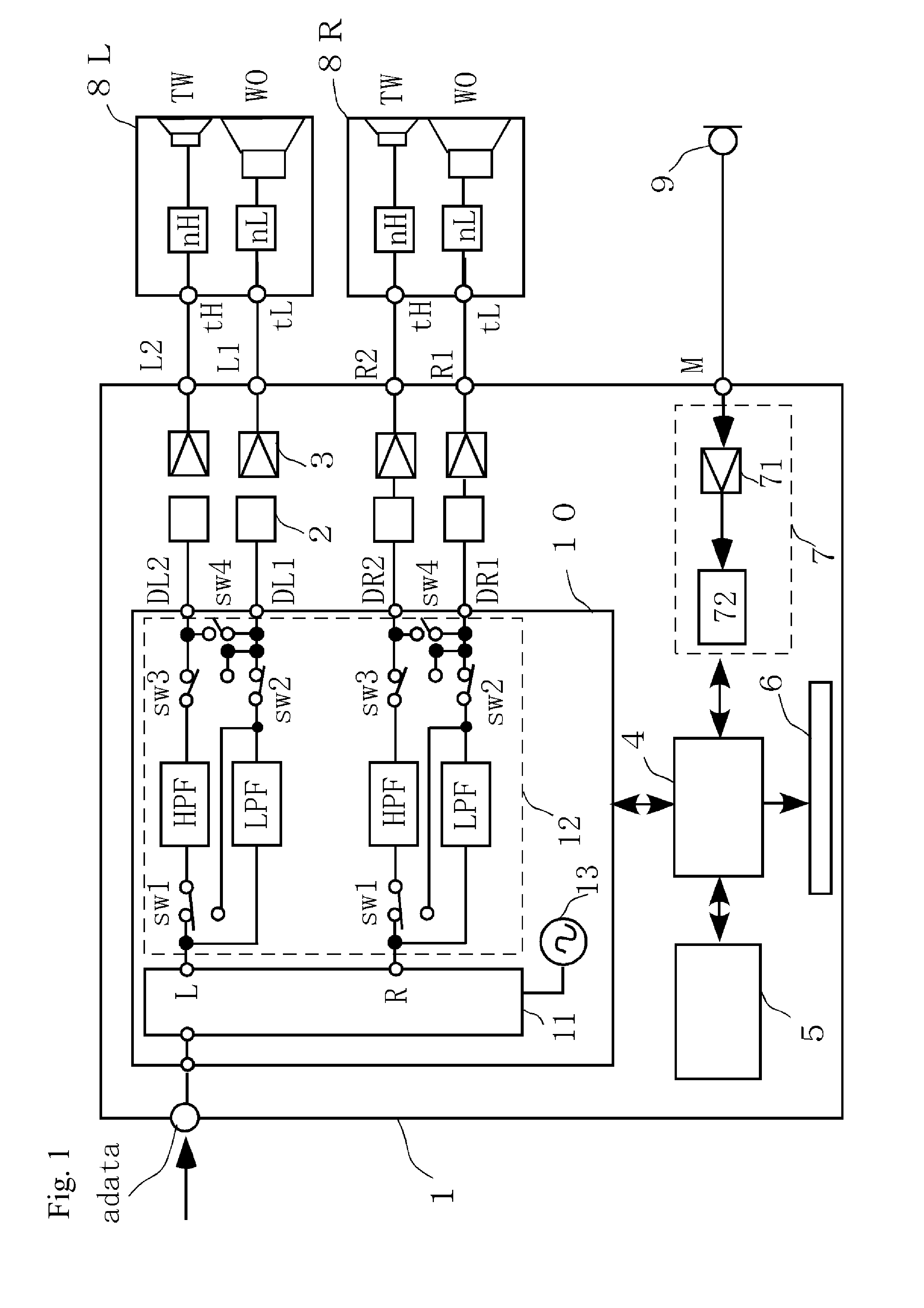
Channel divider, sound reproducing system including the channel divider, and method for setting crossover frequency of the channel divider
InactiveUS20130163770A1Sound pressure frequency characteristic can be preventedAvoid dippingLoudspeaker signals distributionFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEngineeringCrossover frequency
A channel divider that can suitably set a crossover frequency when a biwiring-connectable multiway speaker system including network circuits are used is provided. The channel divider includes a low-pass filter LPF and a high-pass filter HPF for dividing a band of a sound signal into a first output signal and a second output signal so as to output the signals, and a control circuit for controlling the filters. The channel divider has a sound output mode in which the control circuit sets a cutoff frequency fcL of LPF to a value higher than fc0 by about ⅙ to 1 Oct., sets a cutoff frequency fcH of HPF to a value lower than fc0 by about ⅙ to 1 Oct., and outputs the first output signal and the second output signal including frequency bands fcL to fcH when any crossover frequency fc0 for defining the band division is specified.
Owner:ONKYO KK
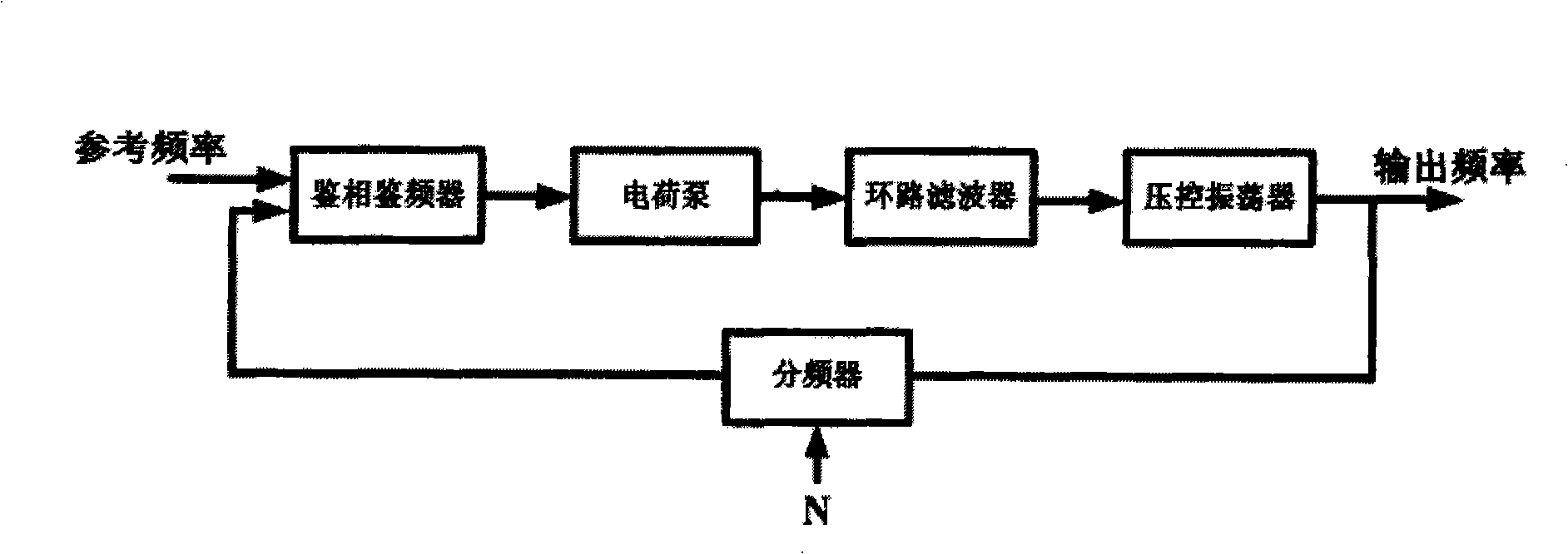
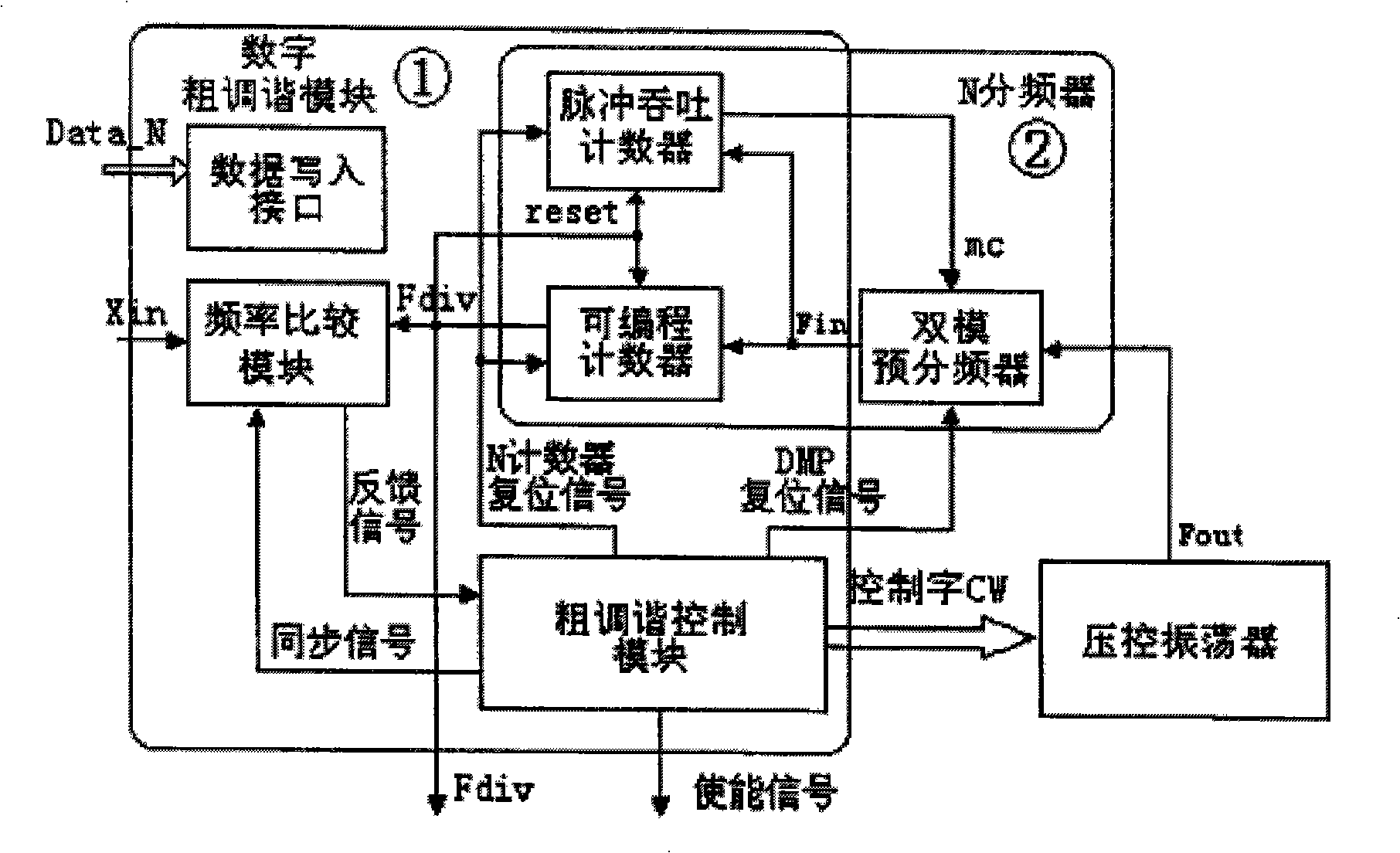
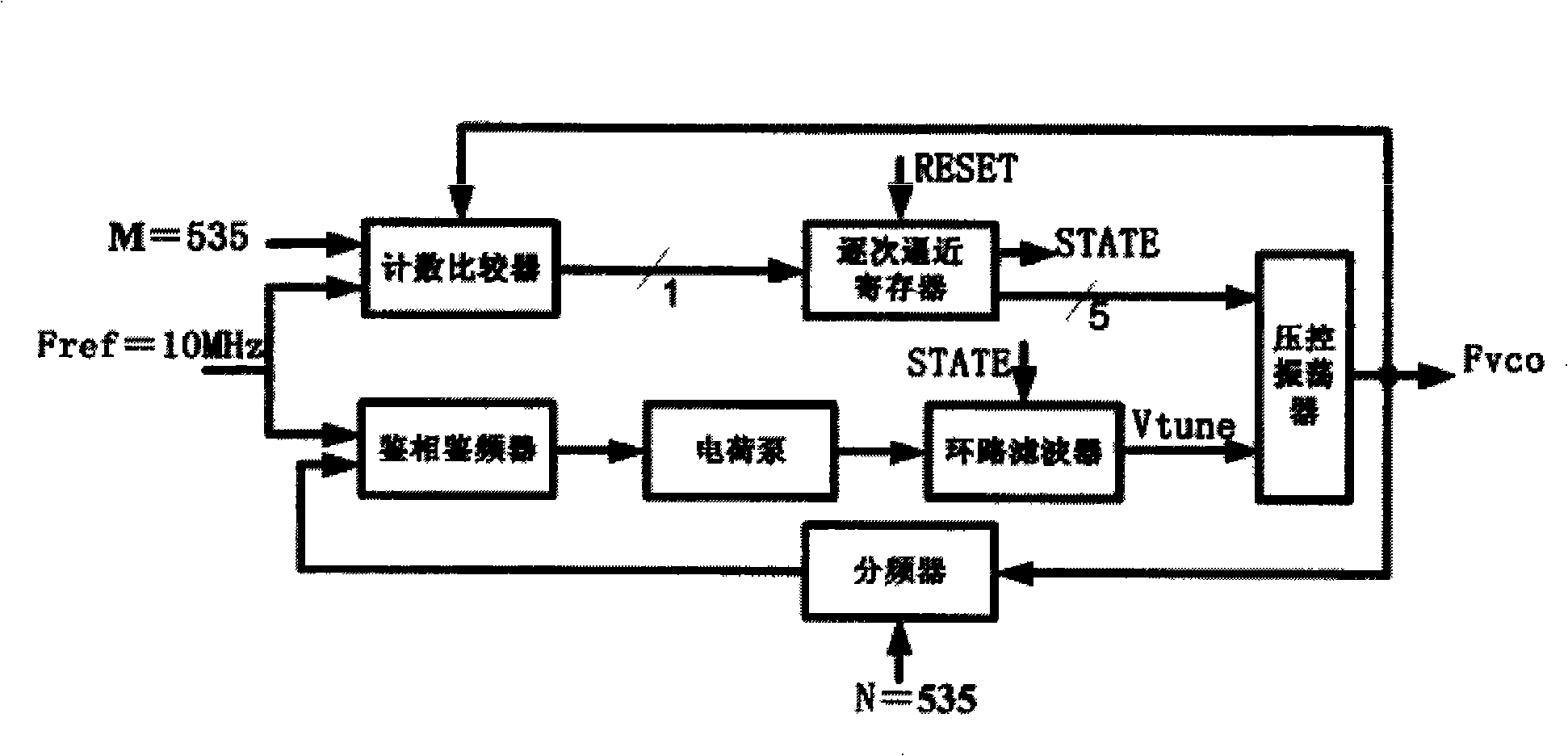
Double-loop circuit frequency synthesizer and method for tuning gross adjustment loop circuit
The invention discloses a dual-loop frequency synthesizer and a tuning method of rough adjustment loop thereof, belonging to the field of frequency synthesizer in wireless transceiver. The frequency synthesizer consists of a rough adjustment loop and a fine adjustment loop, wherein the rough adjustment loop comprises a crossover frequency counter, a frequency reference counter, a shifter, a comparator and a finite state machine. The input end of the crossover frequency counter is connected with frequency dividing signal Fdiv of a voltage controlled oscillator of the fine adjustment loop, the shifter is connected with the crossover frequency counter or the frequency reference counter for leftwards shifting the counting value of the crossover frequency counter or the frequency reference counter, the counting values of the crossover frequency counter and the frequency reference counter are respectively output to the comparator, the compare result of which is input to the finite state machine. Compared with prior art, the invention reduces the time of rough tuning as well as provides higher tuning precision according to the needs.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Digital component proton magnetic instrument
InactiveCN1553218AHigh measurement accuracyEnsure reliabilityElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationDigital controlDigitization
A magnetometer which is composed of digitization frequency-selecting amplifier circuit, digital control current source, single chip computer, clock circuit, communication circuit and relevant control software applies measuring method of frequency in equal period frequency division to carry on measurement for magnetic field intensity according to prin ciple of proton precession. It can carry out measurement for multitype component conbination of F, Z, H, Fe, FH, FHD and FZD under the condition of manual operation or automatic operation according to the setting and it can carry out some other functions based on above principle.
Owner:稽才建 +1
Low dropout voltage regulator providing adaptive compensation
InactiveUS7091710B2Improve transient responseHigh bandwidthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shiftedCrossover frequency
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
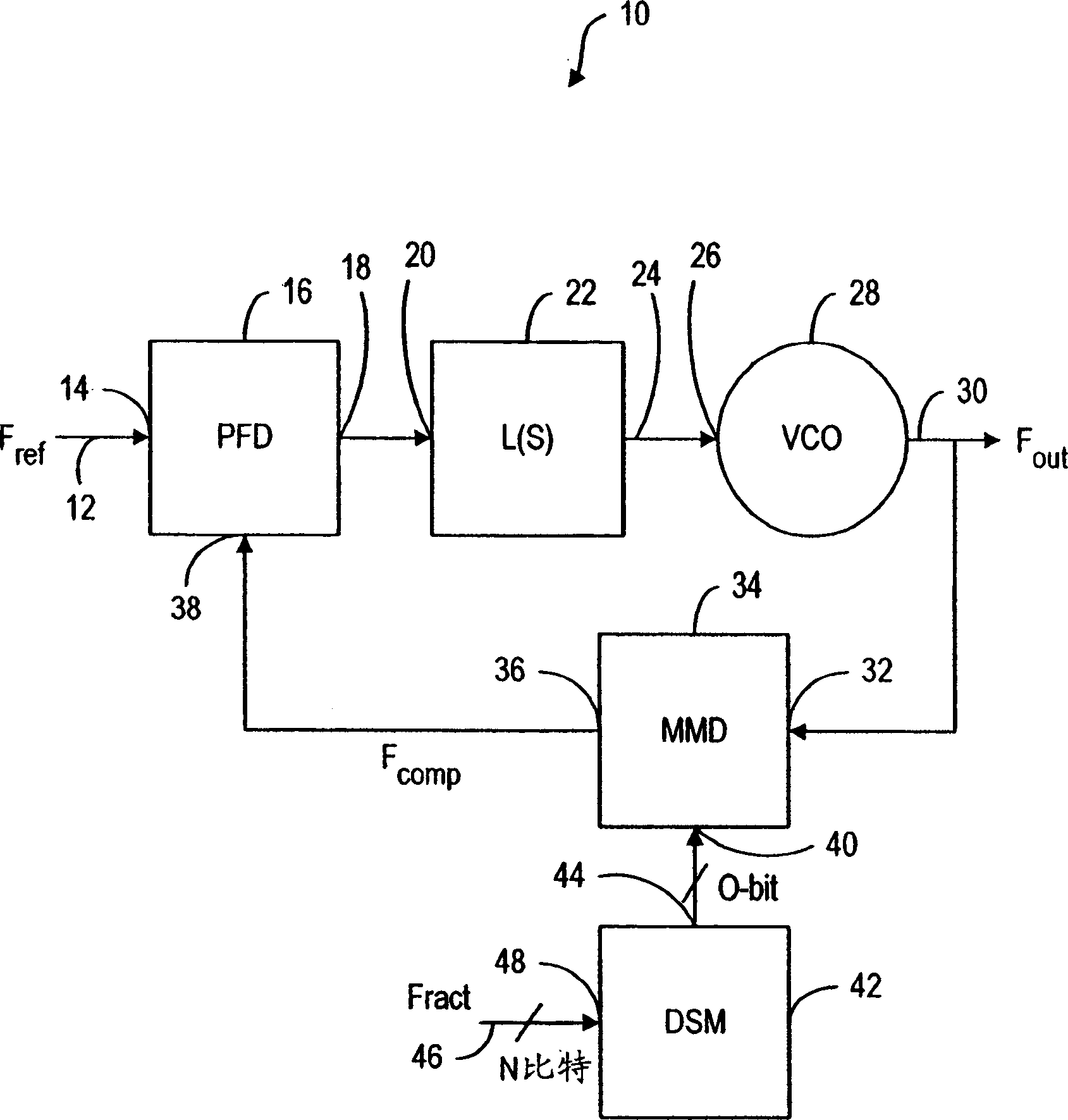
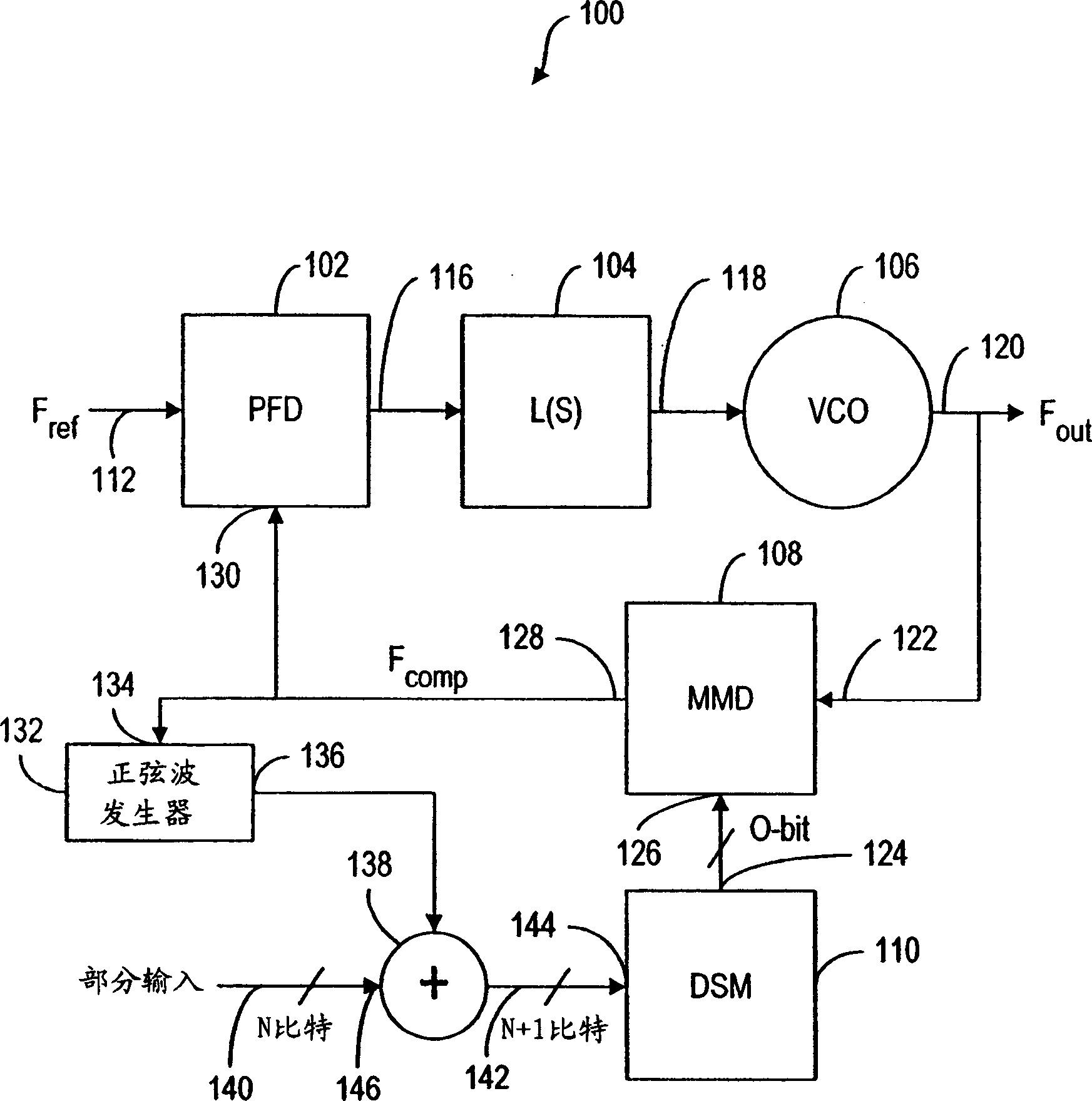
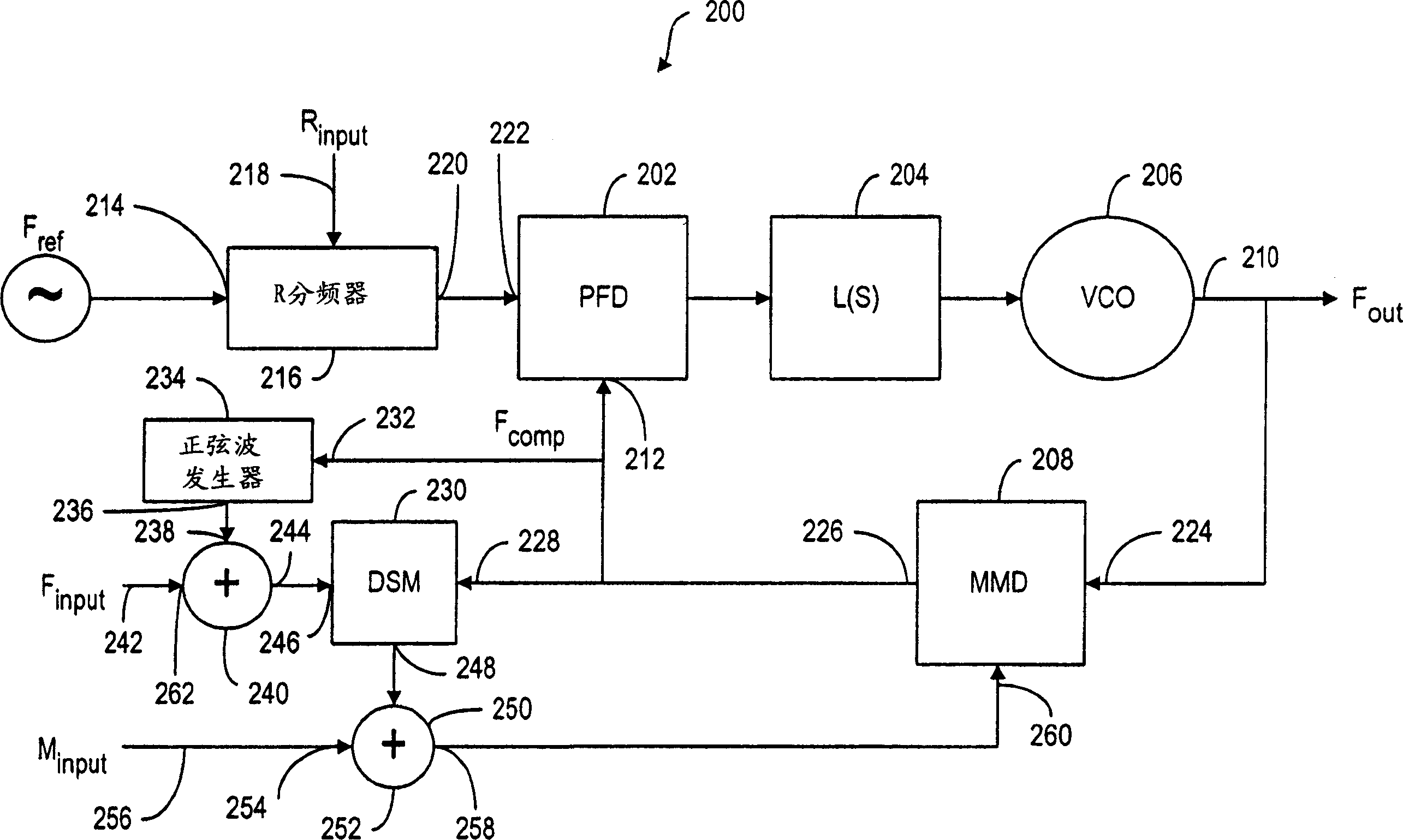
Decimal frequency-dividing synthesizer with sinusoidal generator
A fractional-N frequency synthesizer is disclosed wherein the multi-modulus frequency divider in the feedback path of the phase locked loop is controlled by a delta-sigma modulator to achieve the desired division ratio. The fractional input control signal to the delta sigma modulator is dithered to break any periodicity in the modulator output signal to avoid the generation of fractional spurious frequencies.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method for generating random frequency pulse and method for controlling acceleration and deceleration of stepper motor
InactiveCN101710814APrevent overshootMeet the actual requirementsDynamo-electric converter controlClock rateCrossover frequency
The invention discloses a method for generating random frequency pulse and a method for controlling acceleration and deceleration of a stepper motor, comprising the following steps of: firstly, counting by using a clock control counter provided from an external part ; secondly, demultiplying a clock frequency provided by the external part by using different counting bits, and outputting pulse signals with different demultiplying frequencies through each counting bit; and then extracting the pulse signals with one or several demultiplying frequencies to carry out a combination according to actual needs to generate the pulse signals of the needed frequency. The invention overcomes the defect that the traditional method only can generate pulse signals with integer frequency demultiplication value, thereby satisfying the actual requirement on precision. The invention is used for the field of stepper motor control, at the same time, the generated pulse value is combined with an actual frequency time curve graph of the stepper motor during the acceleration and the deceleration, so that the pulse value on each time point is more coincided with the actual running track and the phenomenon that the lost-step and the overshoot of the stepper motor occur at the starting and the braking phases can be avoided.
Owner:青岛朗讯科技通讯设备有限公司
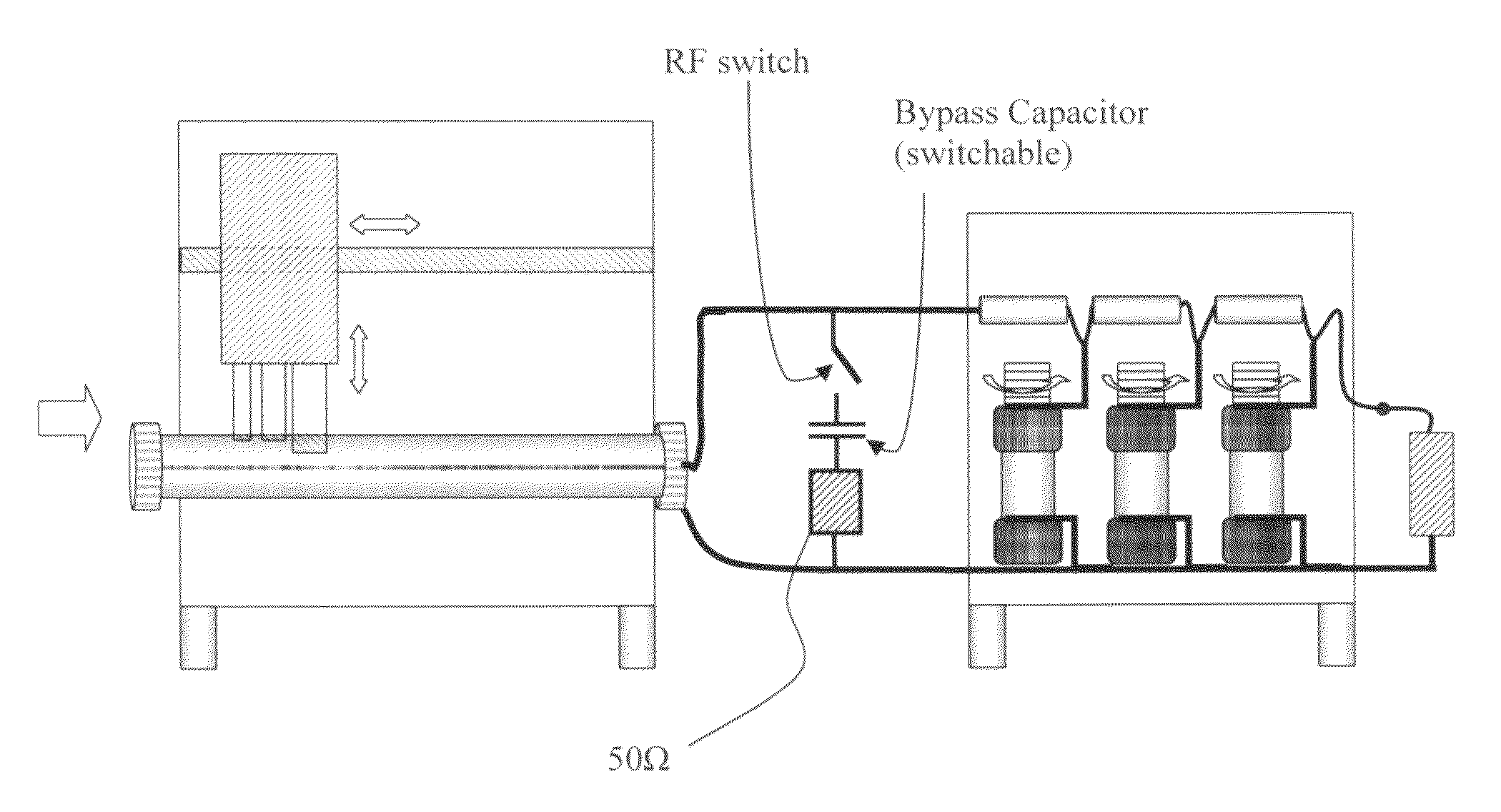
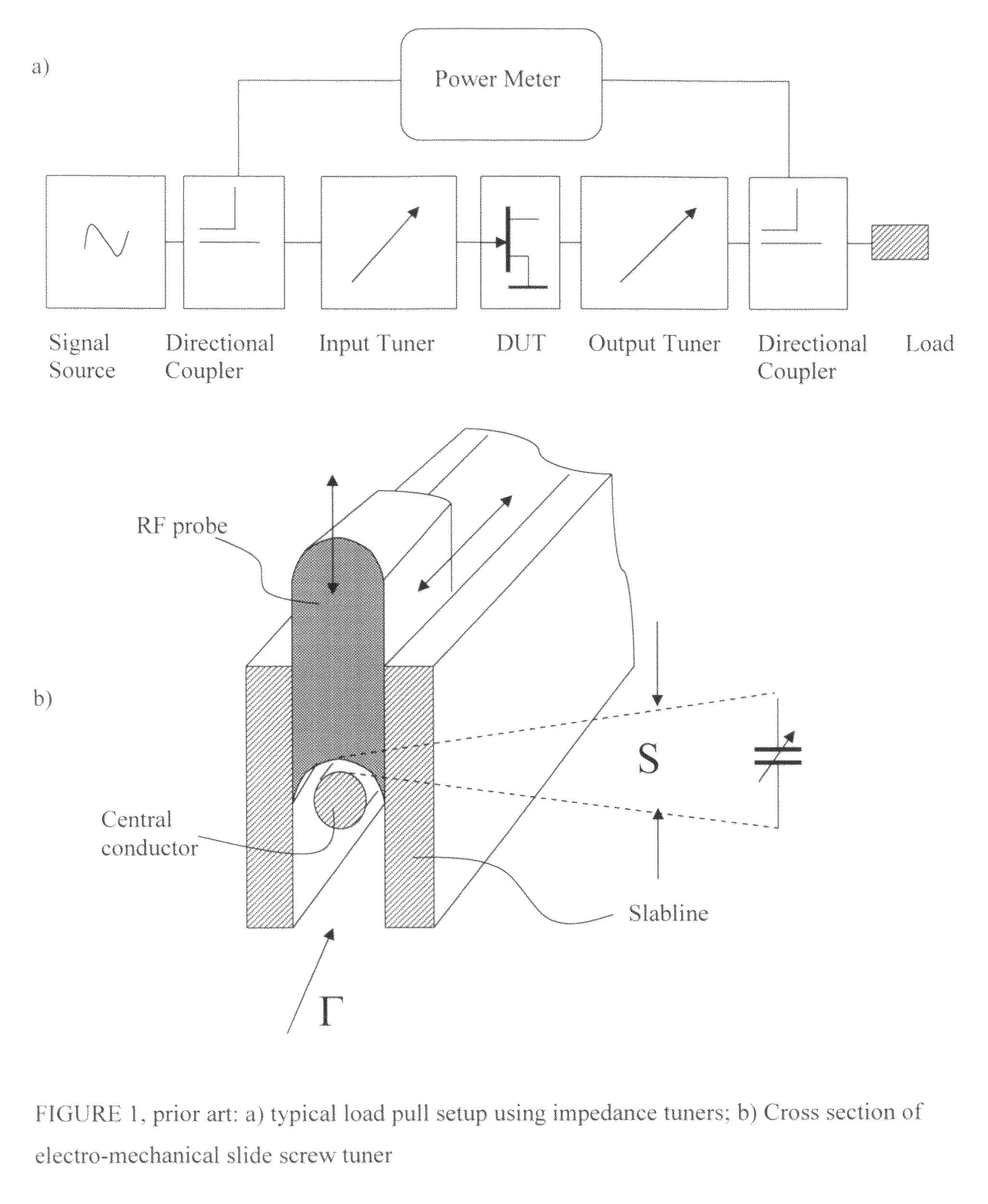
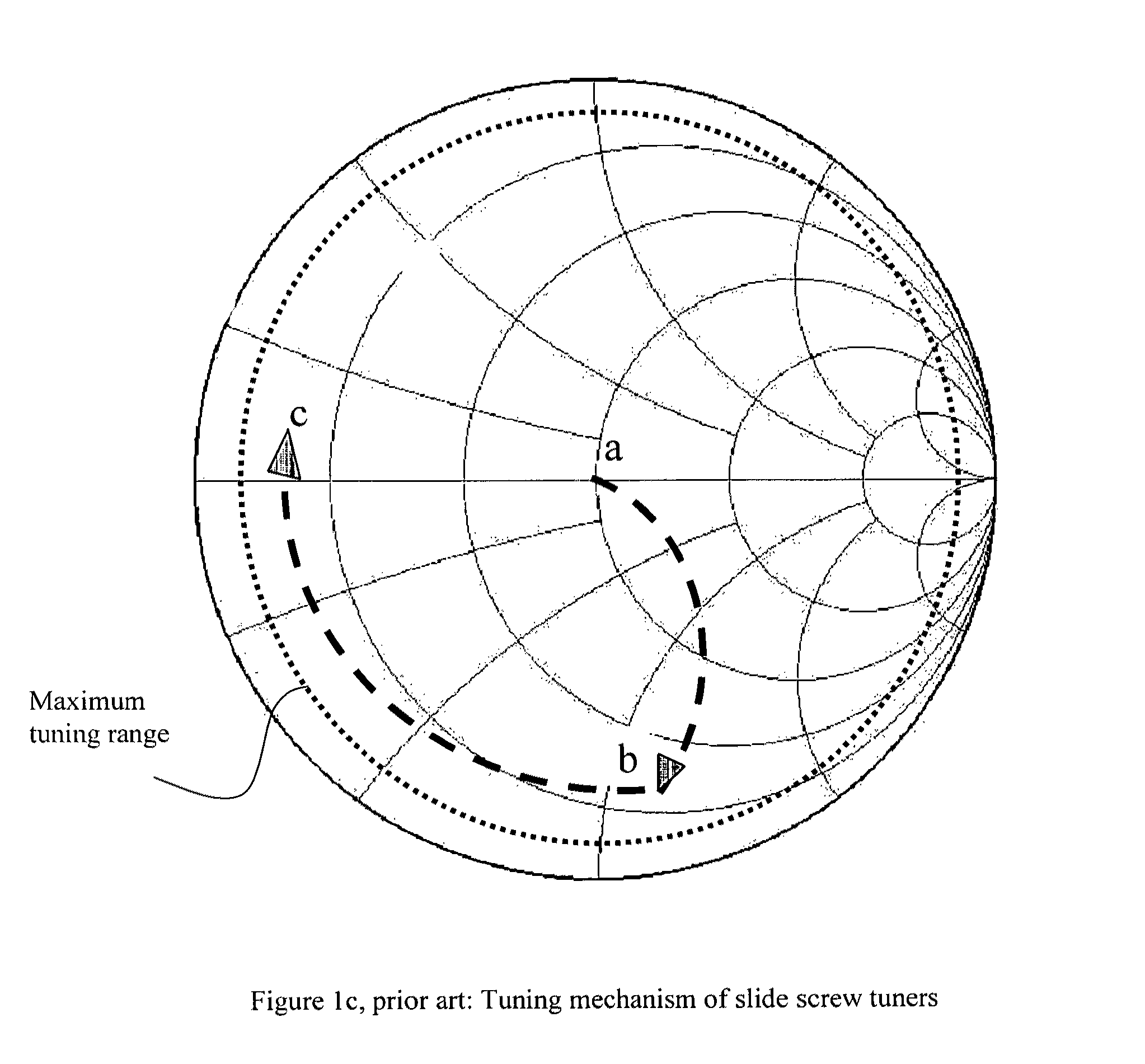
Compact multi frequency-range impedance tuner
An automatic multi frequency-range electro-mechanical impedance tuner covers frequencies from a low megahertz to a high gigahertz range, by combining a high frequency with one or two a low frequency tuner modules; the low frequency module is made using either variable phase shifter-capacitor or multi-capacitor-transmission line tuner structures. The high frequency module is a single, double or triple probe slide screw tuner covering up to 1.5 decades in frequency; the low frequency tuner is using cascades of three or more capacitor-coax cable tuning sections or a low frequency phase shifter combined with a variable shunt capacitor; the low frequency tuner can operate as low as a few megahertz whereas the high frequency tuner can operate up to several gigahertz. Depending on the application, low frequency parallel-blade capacitors or high frequency coaxial trimmers are used. Typical cross-over frequencies between low and high frequency modules range from 200 to 800 megahertz, lowest frequencies can reach below 10 megahertz and highest frequencies 26 to 40 gigahertz. Appropriate calibration, control and tuning procedures allow for a fully integrated operation.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
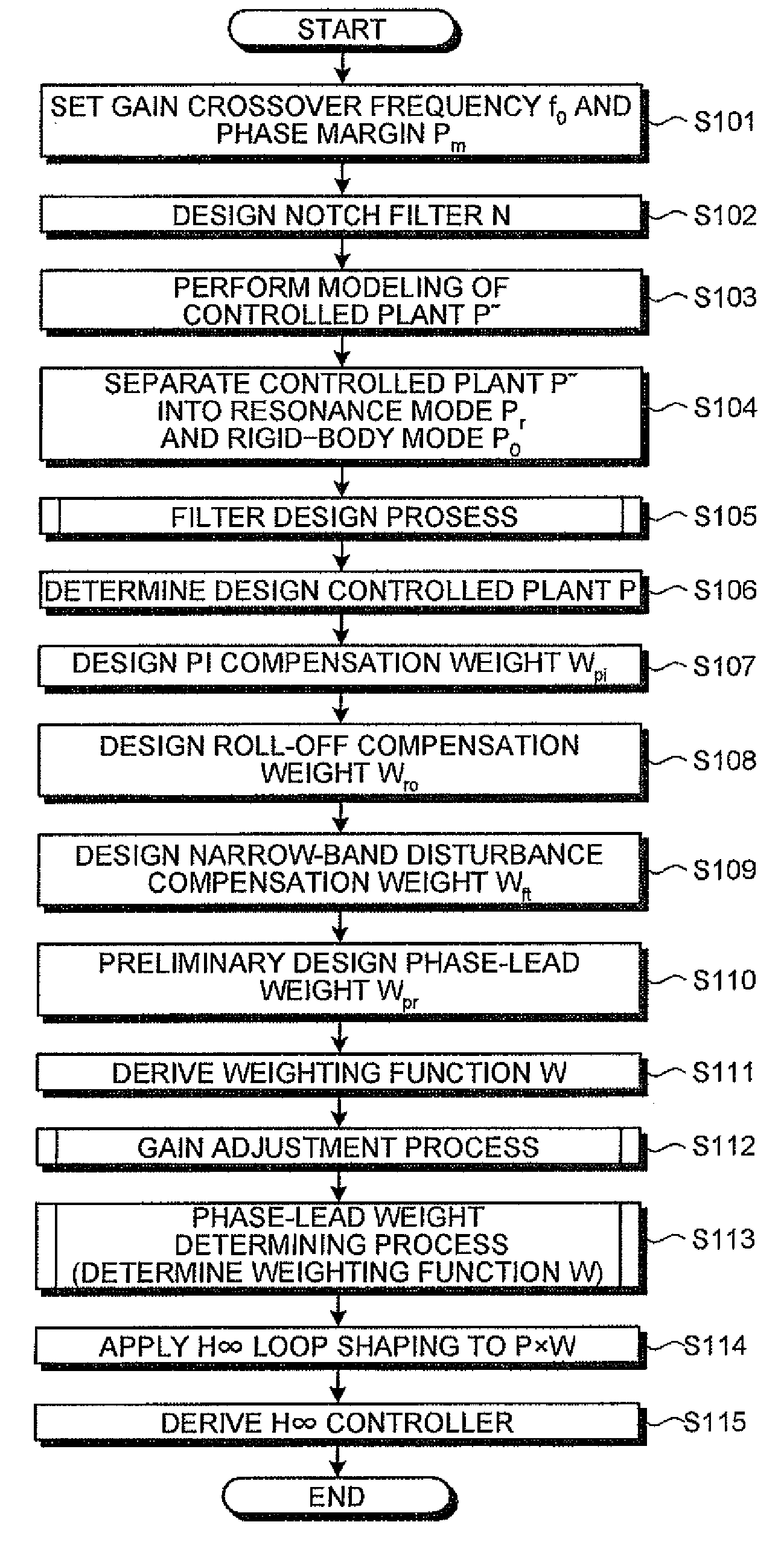
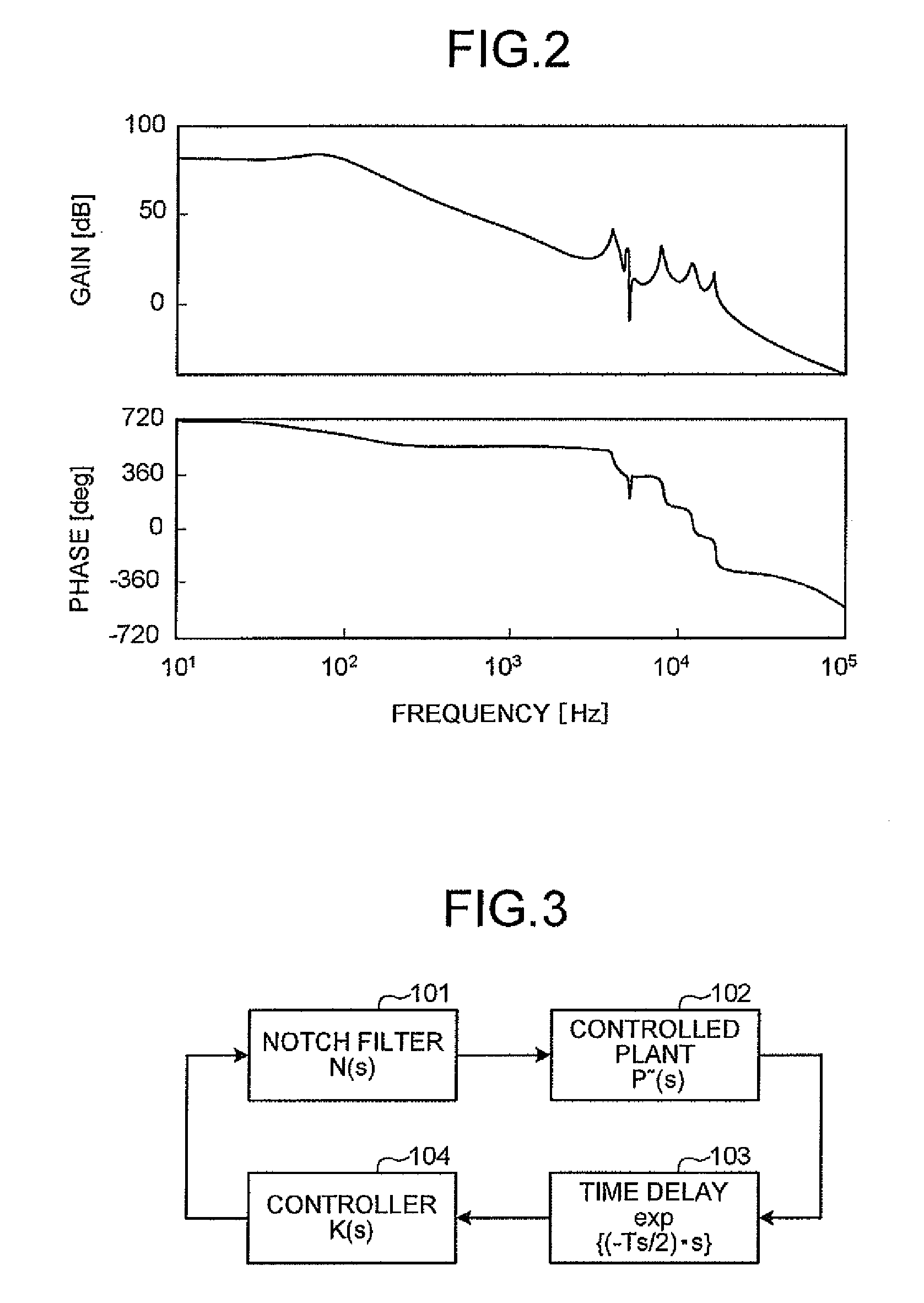
Design method, design support apparatus, and computer product for feedback control system
InactiveUS20080312891A1Solve problemsProgramme controlDesign optimisation/simulationDesign controlPhase variable
A control system is designed in which a controlled plant is controlled based on output feedback from the controlled plant. An all-pass filter is modeled that is formed of a synthesis of a notch filter compensating for a resonance mode in the control system and the resonance mode. A design controlled plant including the all-pass filter is determined. A controller controls the design controlled plant and includes a weighting function, and, after the weighting function is derived, gain of the weighting function is adjusted using desired gain crossover frequency and phase margin. A phase variable included in a phase-lead weight is determined, and thus the weighting function is determined. H∞ loop shaping is applied to the weighting function and the design controlled plant to obtain an H∞ loop controller.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
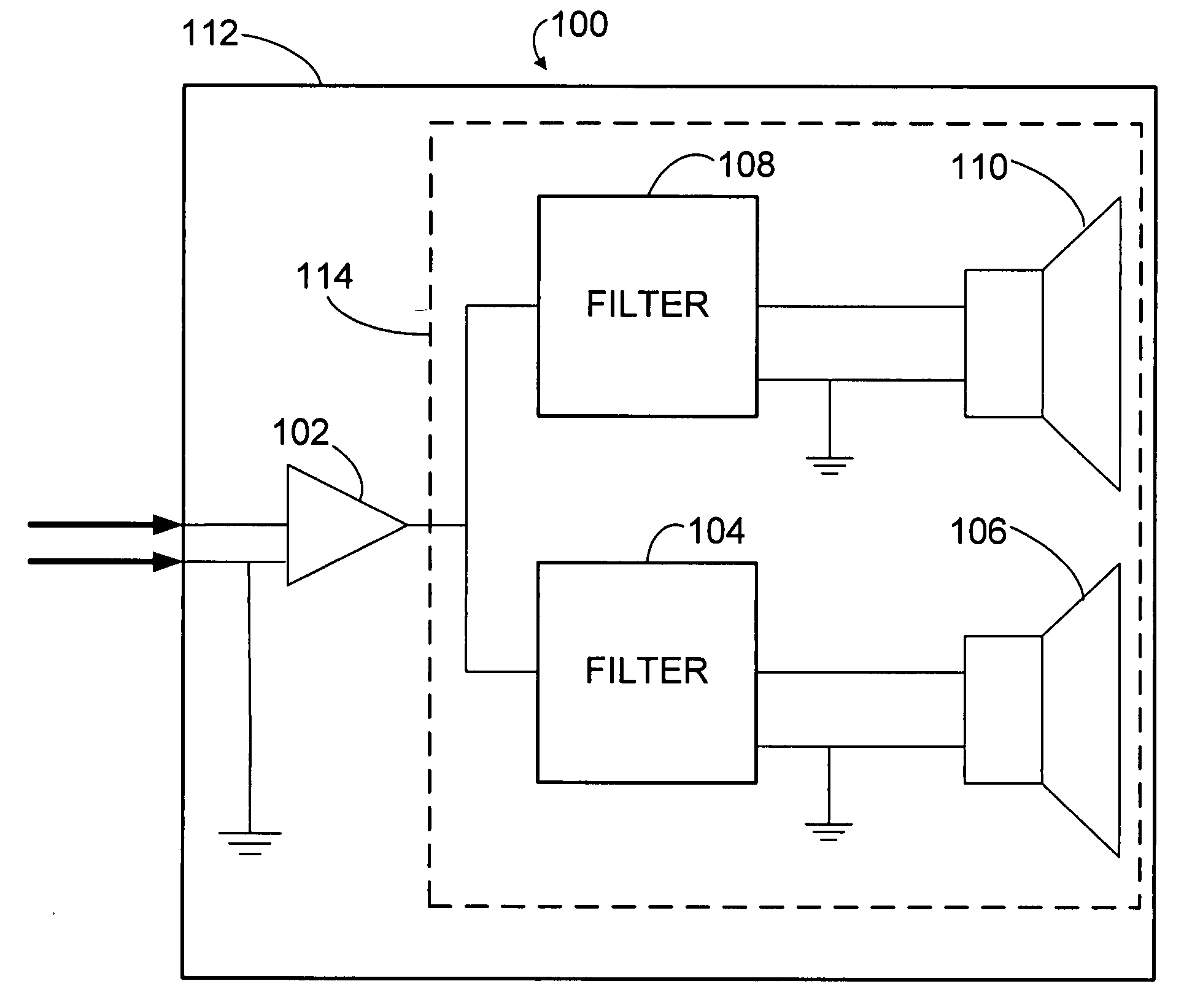
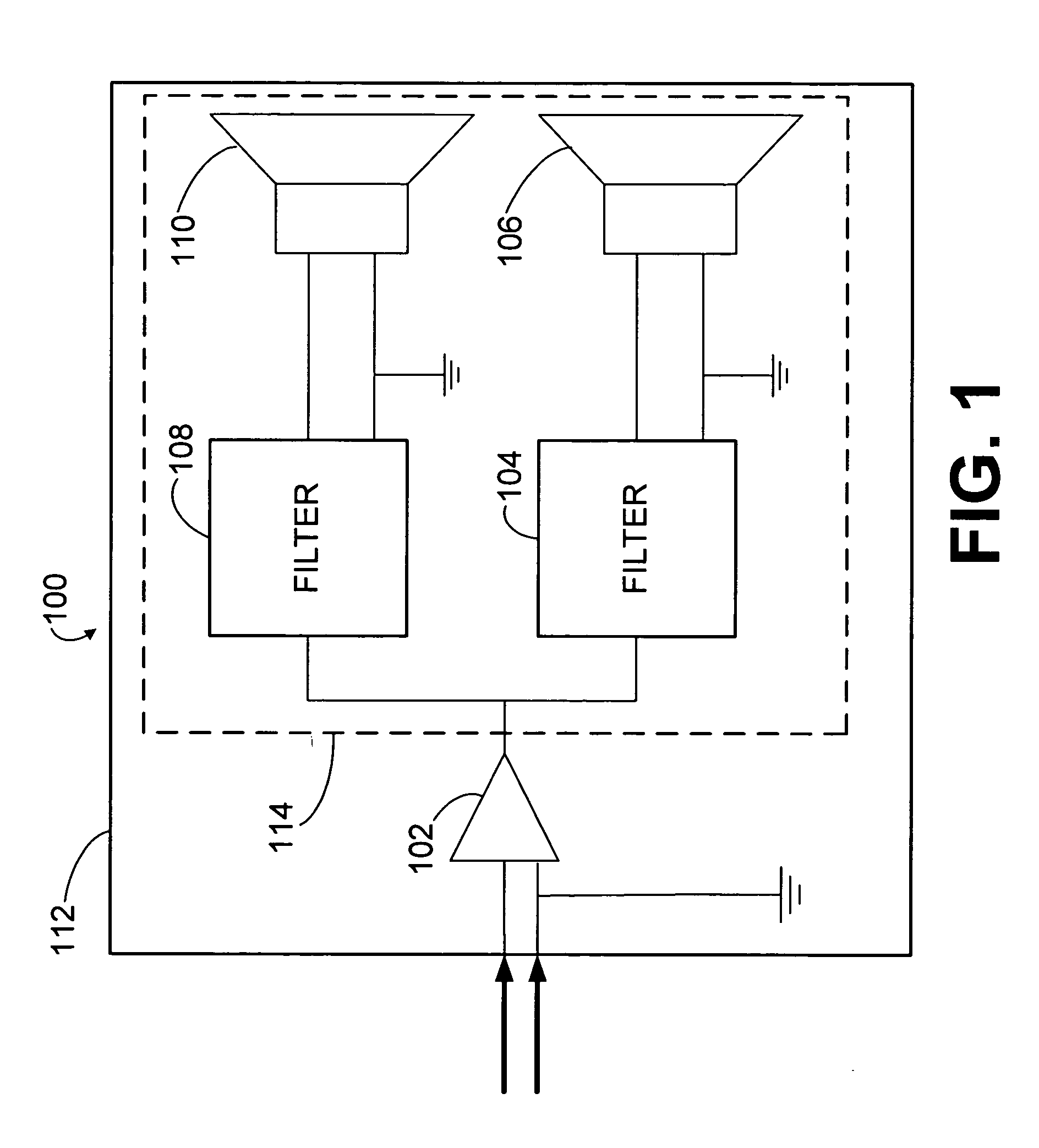
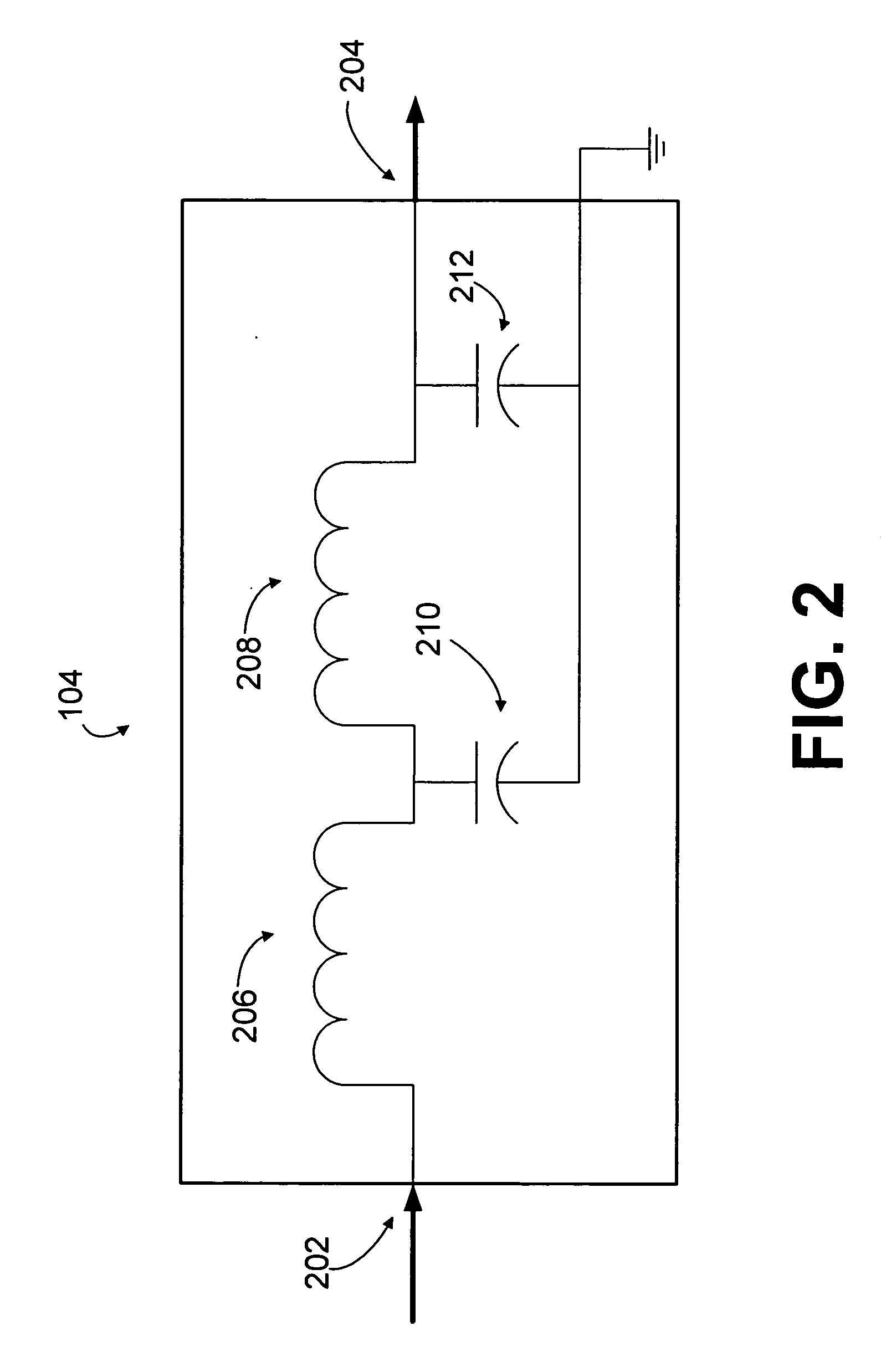
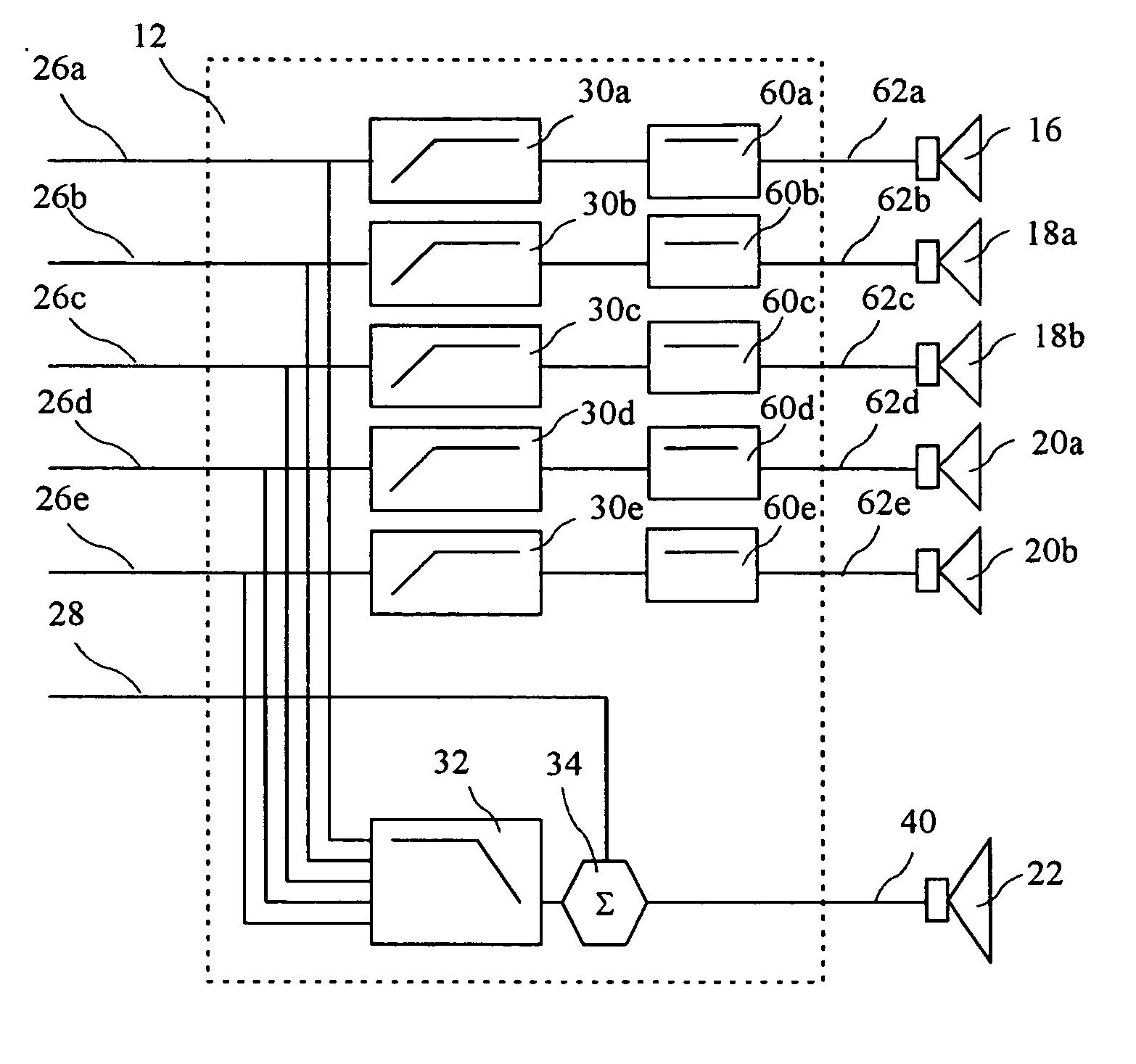
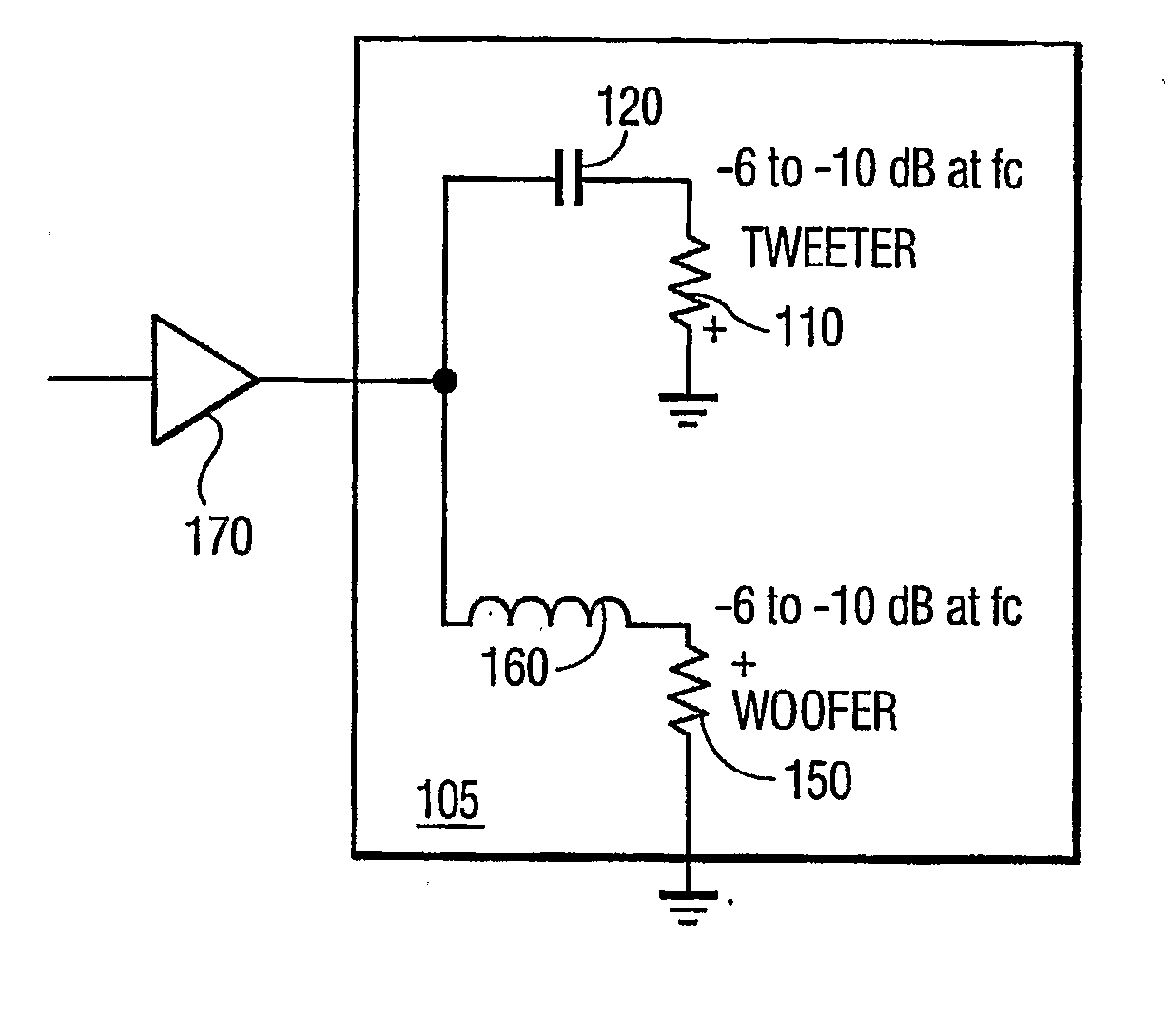
Current feedback system for improving crossover frequency response
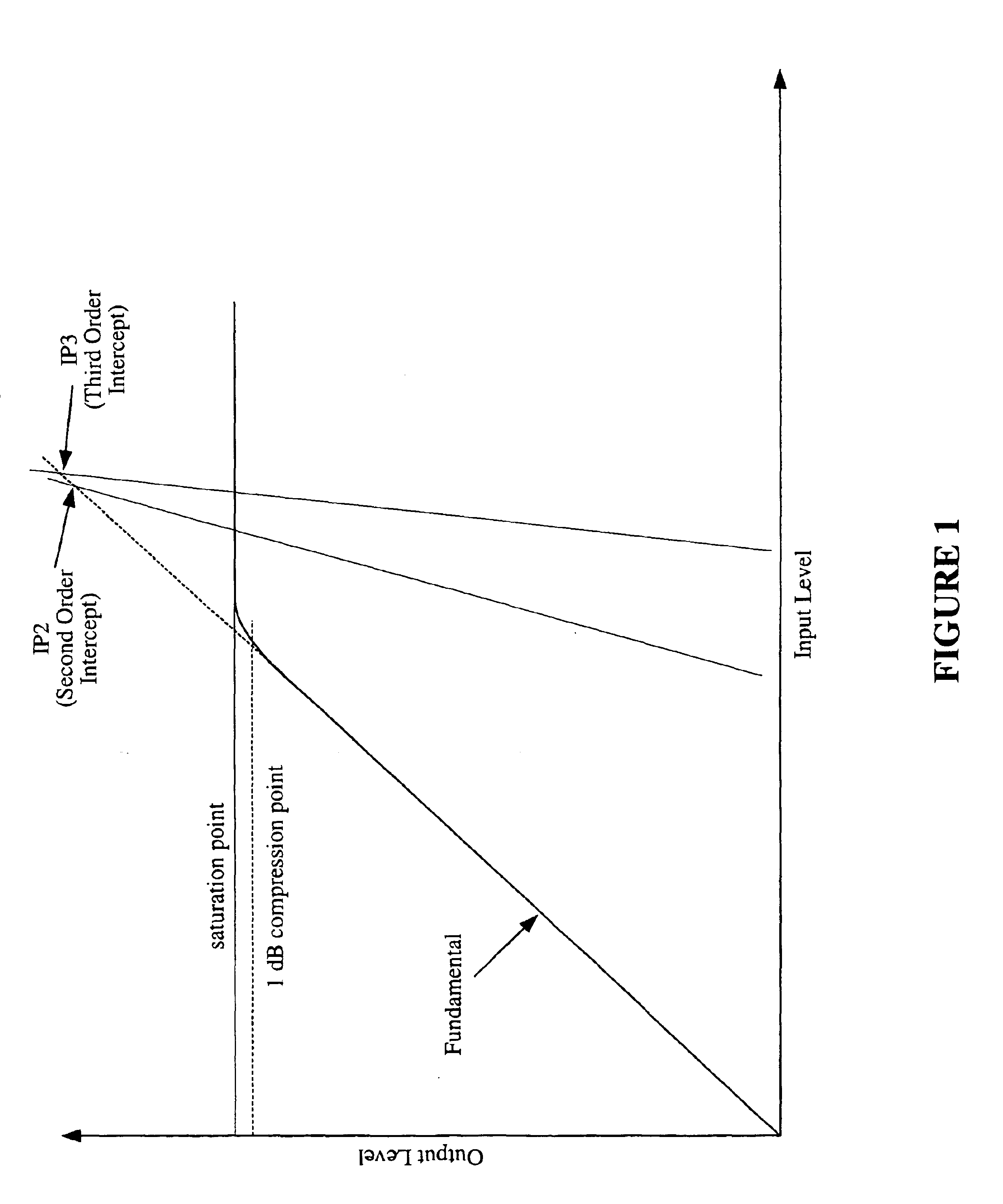
A loudspeaker is provided for receiving an incoming electrical signal and transmitting an acoustical signal. The loudspeaker may include a power amplifier that has an input and an output, where the input receives the incoming electrical signal. The loudspeaker may also include two or more passive filters, such as low-pass, band-pass, and / or high-pass filters, which are coupled to the output of the power amplifier. The passive filters may also be coupled to one or more speaker drivers. The arrangement of passive filters and speaker drivers may have a single input that has a combined input impedance. The output of the amplifier may have an output impedance. The output impedance may be between about 25% and about 400% of the combined input impedance. The power amplifier may include a current-feedback amplifier that is configured to maintain the desired output impedance.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
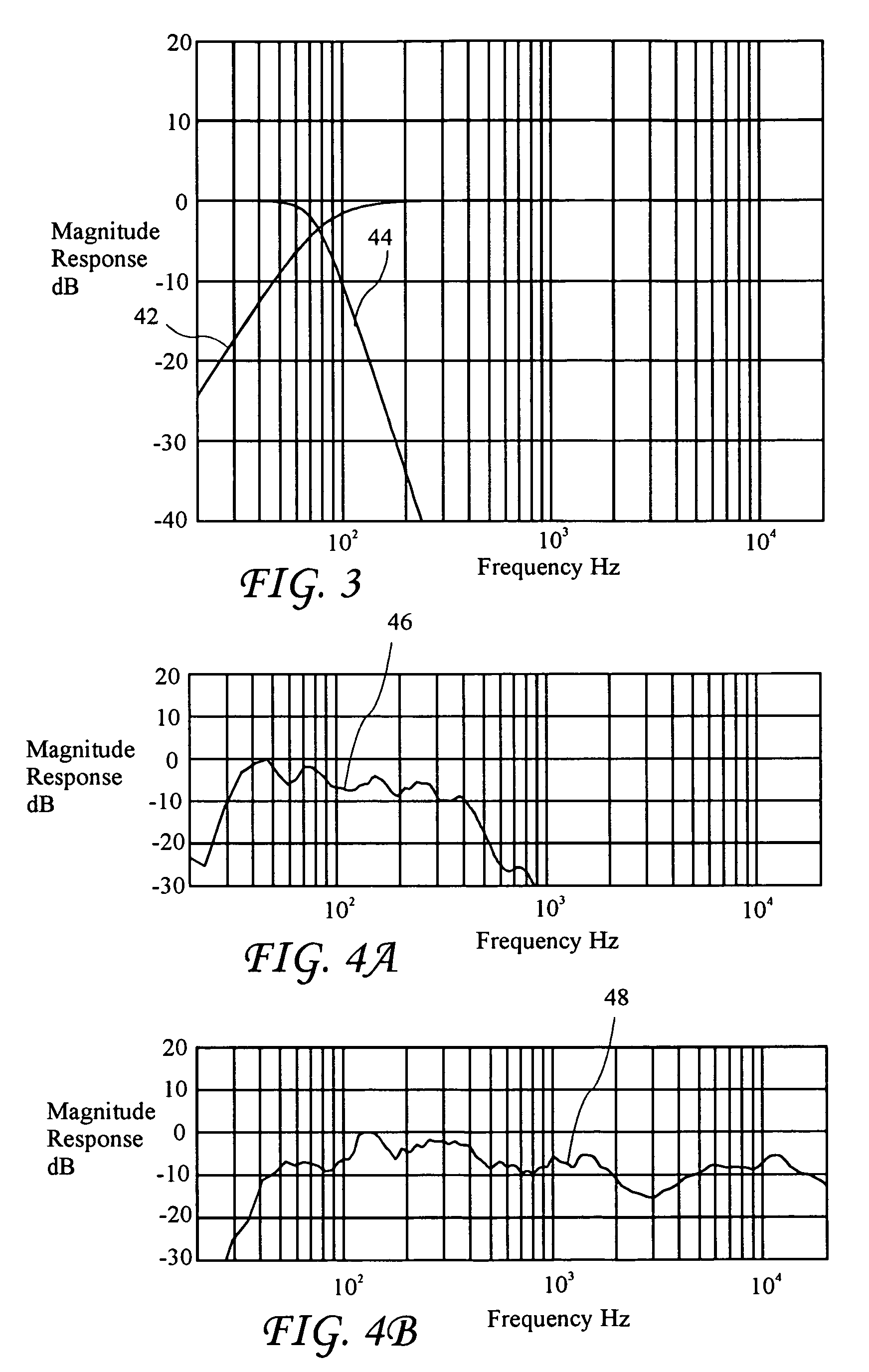
Phase equalization for multi-channel loudspeaker-room responses
ActiveUS20060056646A1Improved magnitude response controlMinimize phase incoherenceFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsLine-transmissionAmplitude responseVocal tract
A system and method for minimizing the complex phase interaction between non-coincident subwoofer and satellite speakers for improved magnitude response control in a cross-over region. An all-pass filter is cascaded with bass-management filters in at least one filter channel, and preferably all-pass filters are cascaded in each satellite speaker channel. Pole angles and magnitudes for the all-pass filters are recursively calculated to minimize phase incoherence. A step of selecting an optimal cross-over frequency may be performed in conjunction with the all-pass filtering, and is preferably used to select an optimal cross-over frequency prior to determining all-pass filter coefficients.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
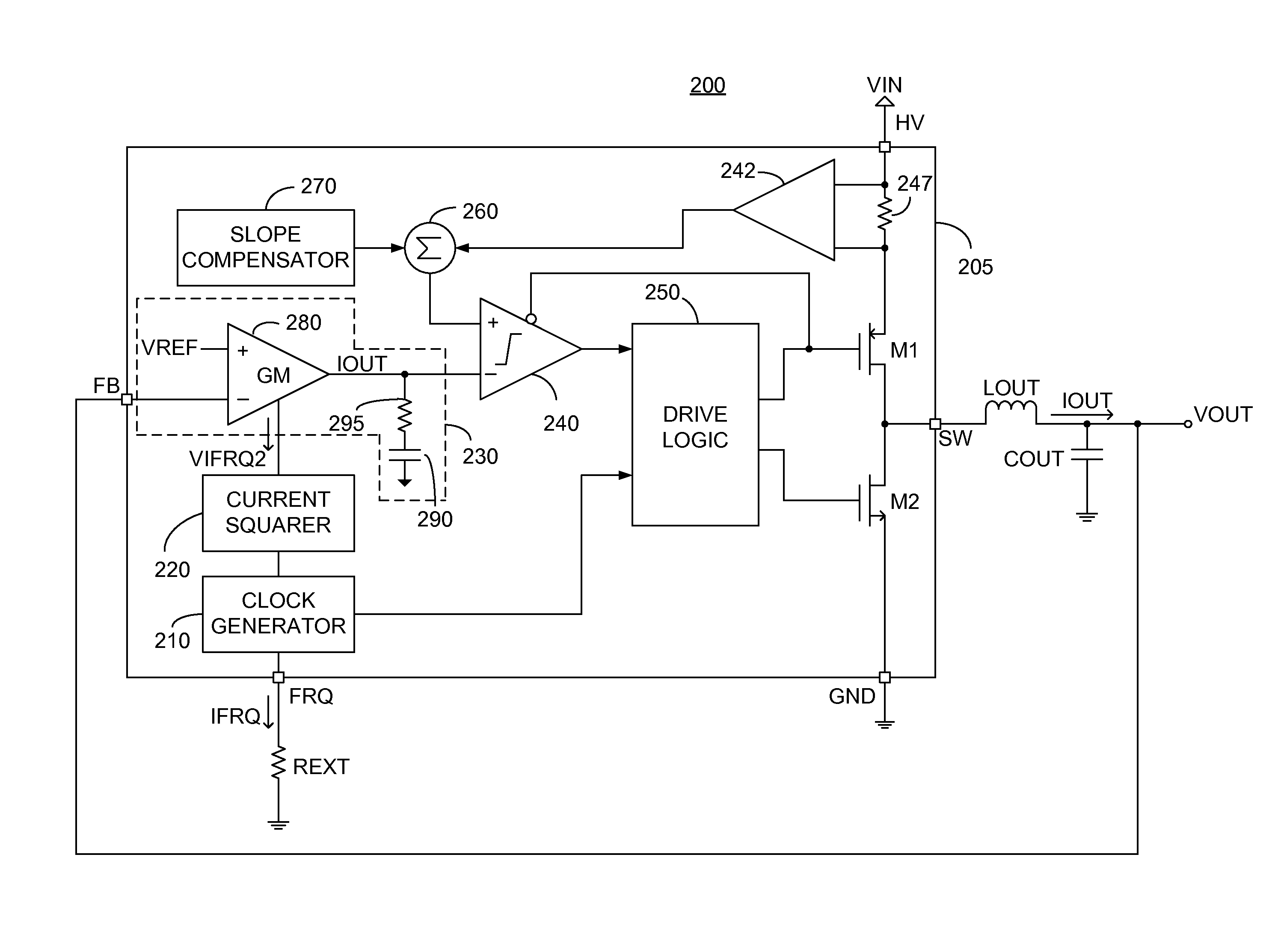
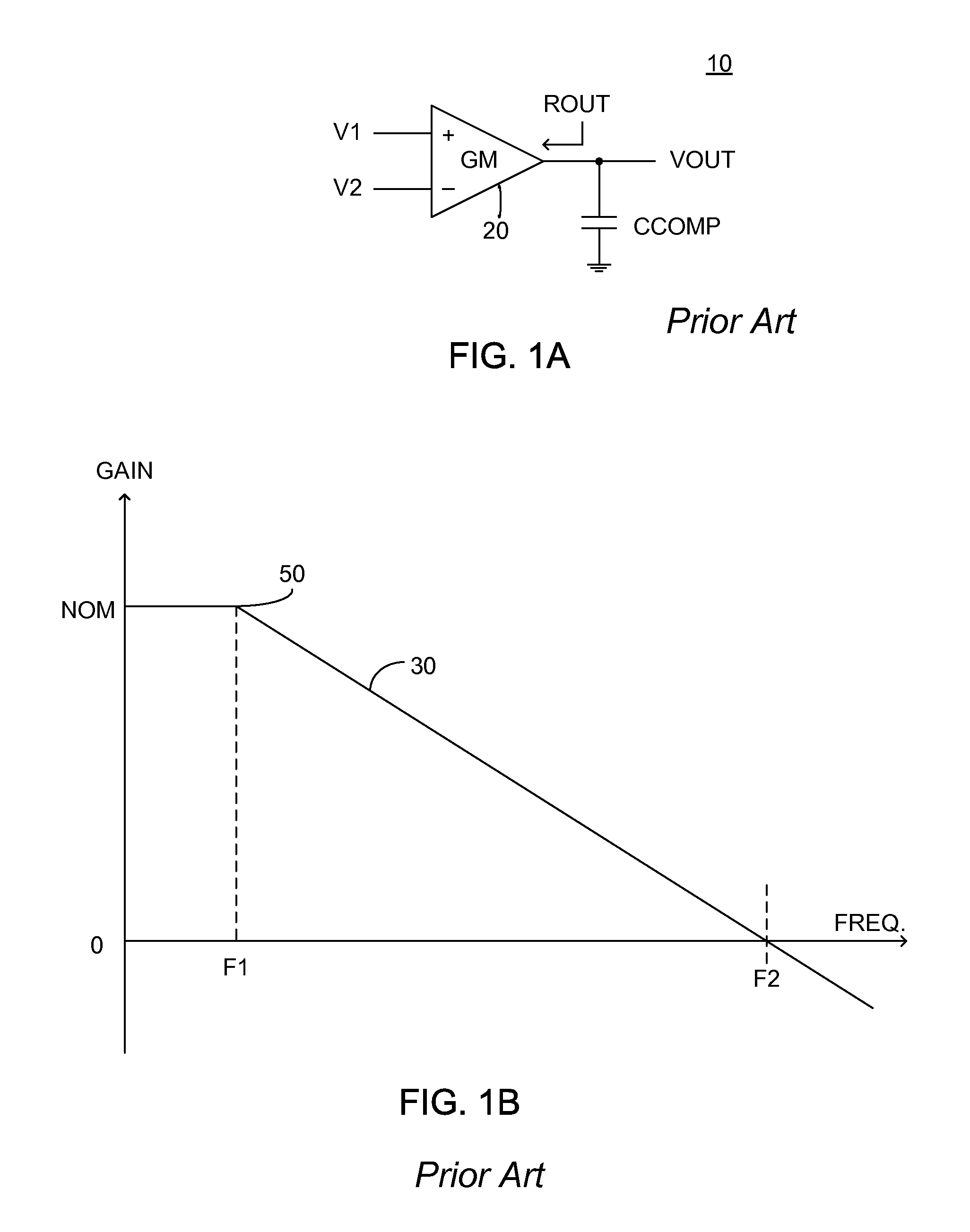
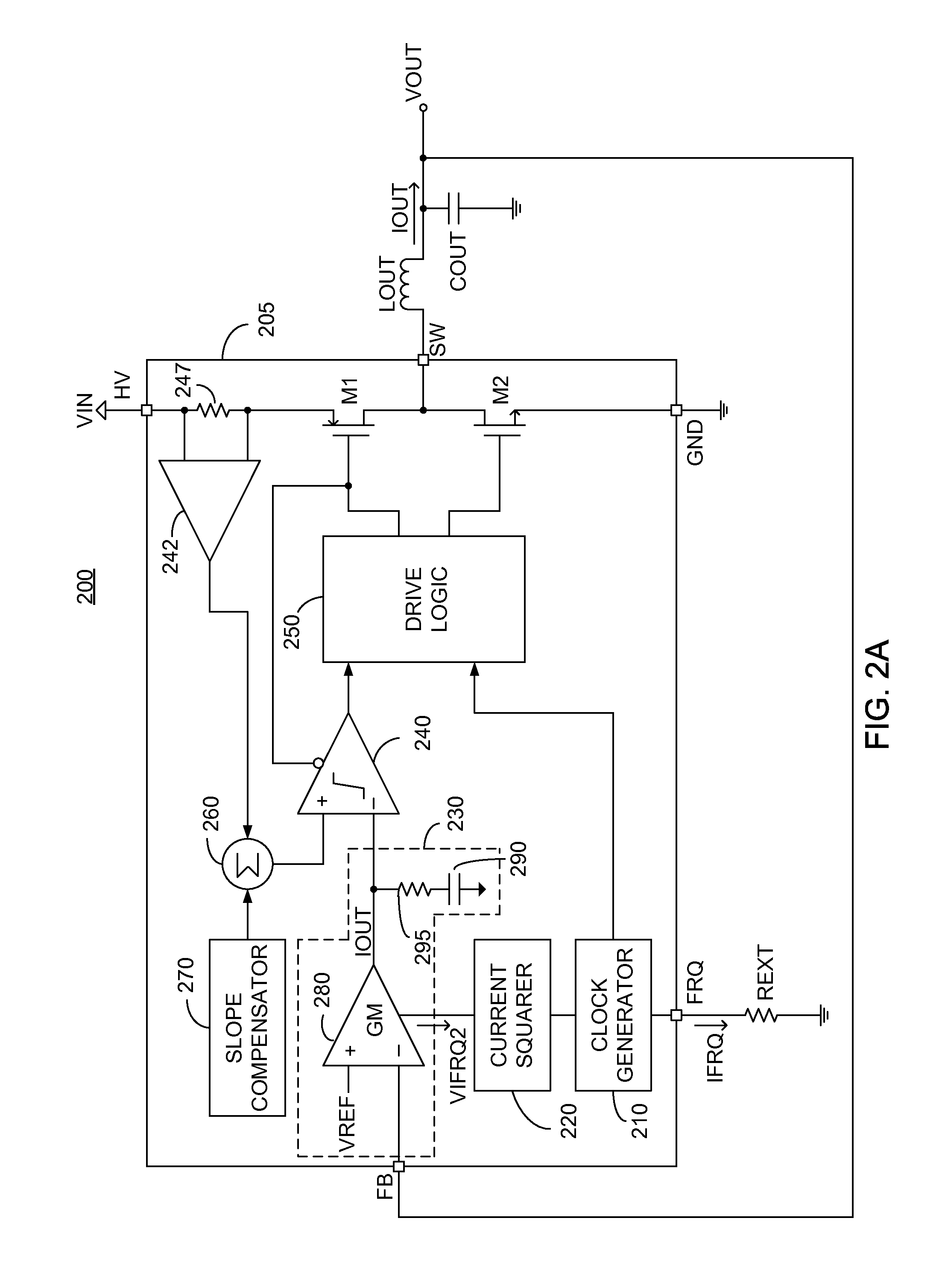
Converter with crossover frequency responsive to switching frequency
A power converter constituted of: a reference source; a clock generator exhibiting a variable frequency output, the value of the frequency of the variable frequency output responsive to an input signal; and an error amplifier in communication with the reference source, the error amplifier exhibiting a gain whose value is responsive to the input signal. Preferably the error amplifier is a transconductance amplifier. In one embodiment the power converter further exhibits a current squarer, arranged to produce a squared value of the input signal and provide the squared value to the transconductance amplifier.
Owner:MICROSEMI
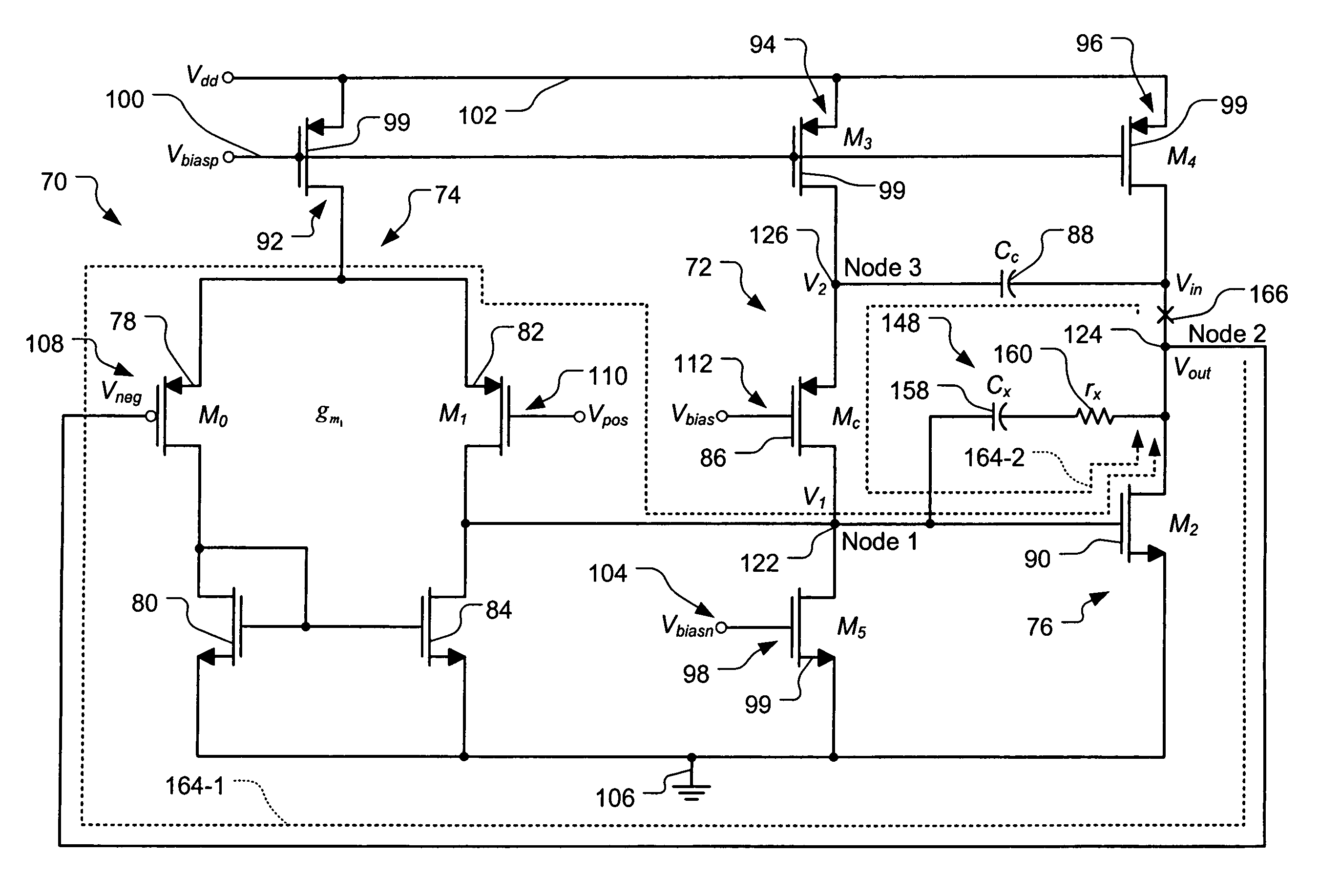
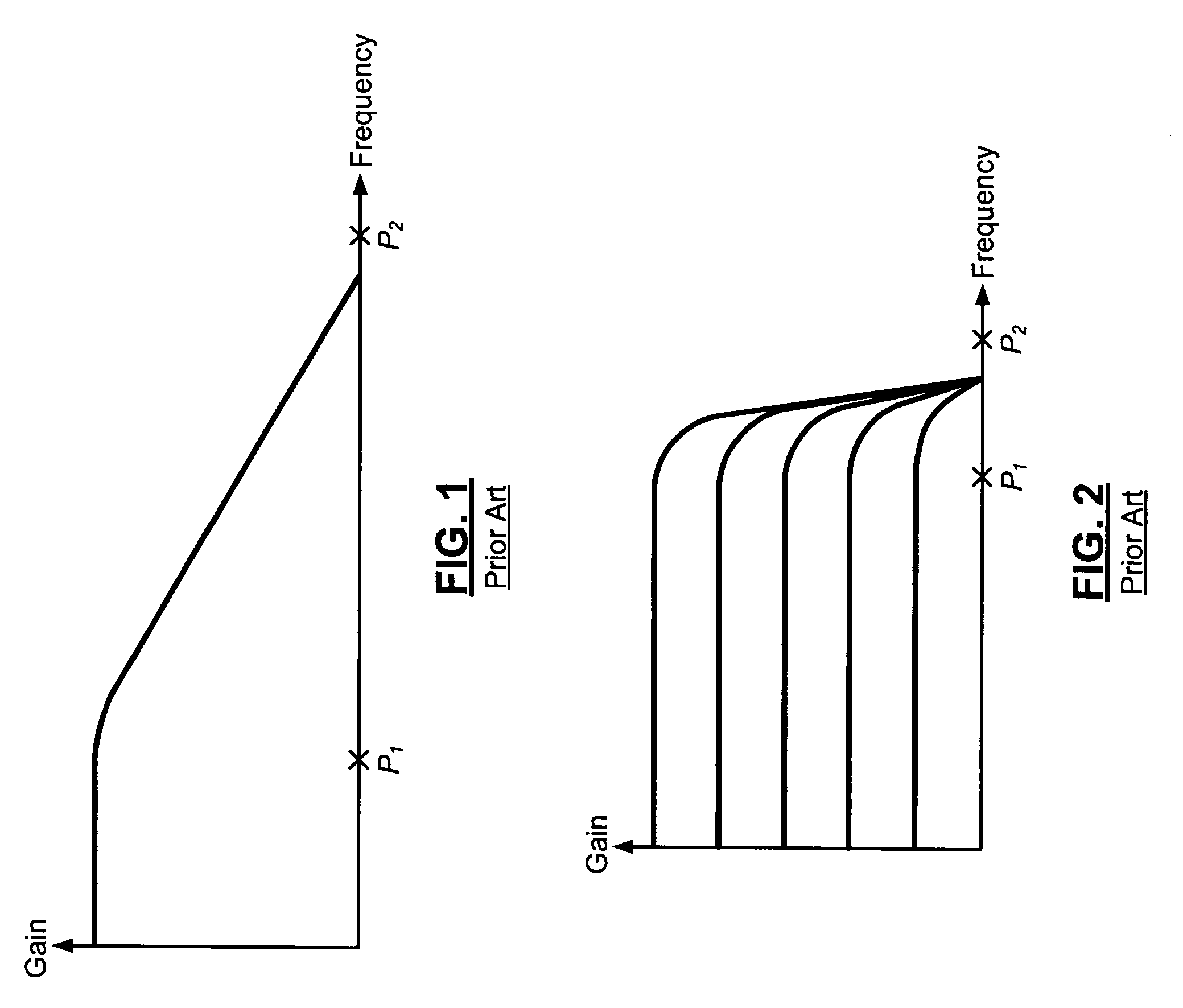
Frequency compensation architecture for stable high frequency operation
InactiveUS7248117B1Cancellation effectDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
An operational transconductance amplifier includes a first amplifier circuit that generates a first bias. A second amplifier circuit receives the first bias and generates a feedback signal. The first amplifier circuit also receives the feedback signal. A Miller compensation circuit receives the feedback signal and generates a second bias. An Ahuja compensation circuit receives the first and second biases and the feedback signal and generates a third bias. The second amplifier circuit receives the third bias. A feedback loop has an open loop response with first and second poles and a zero that are located below a crossover frequency. The Miller compensation circuit increases a frequency difference between the first and second poles. The Miller compensation circuit also adjusts a frequency of one of the poles so that the zero cancels an effect of the pole on the open loop response.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
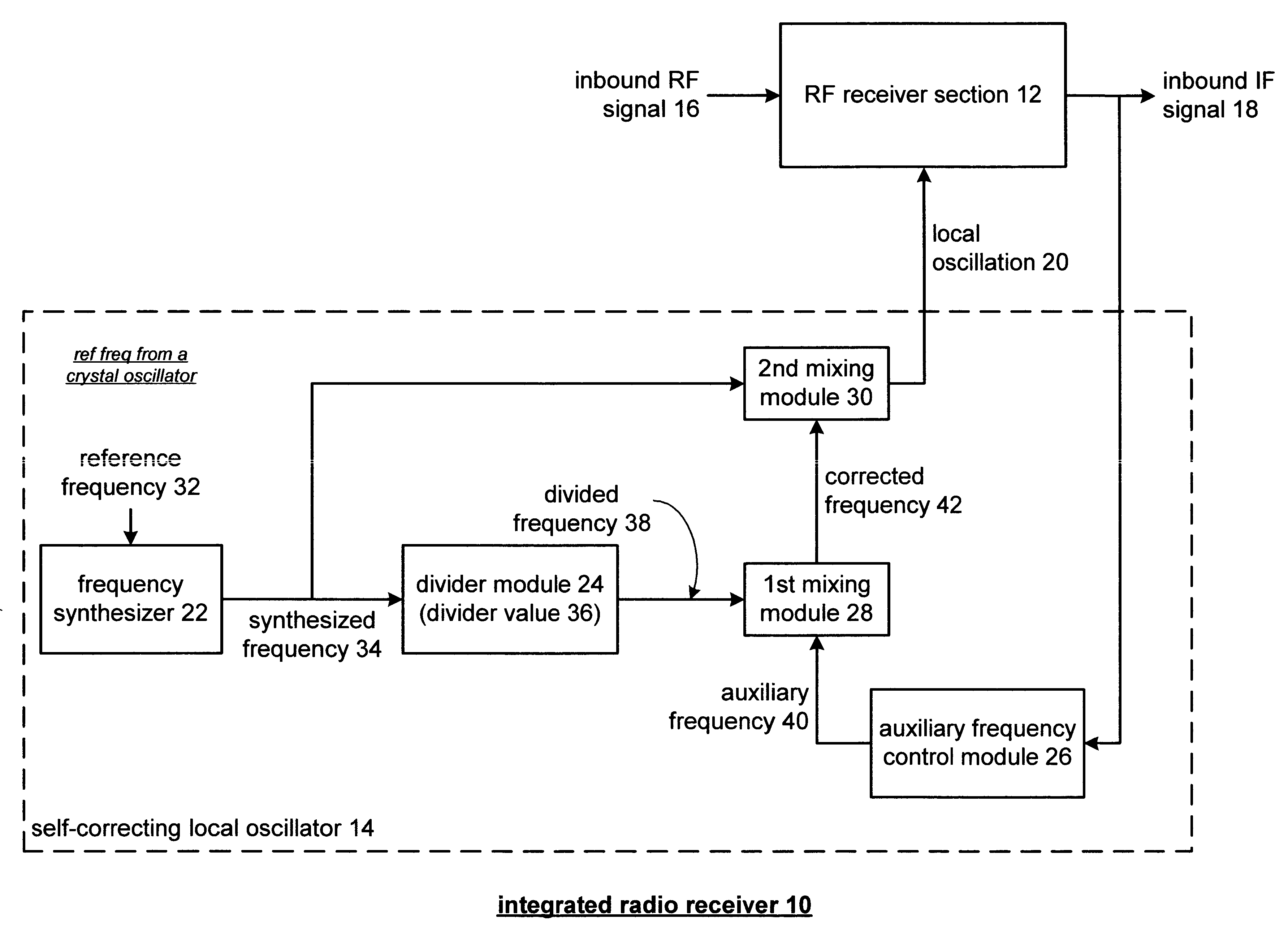
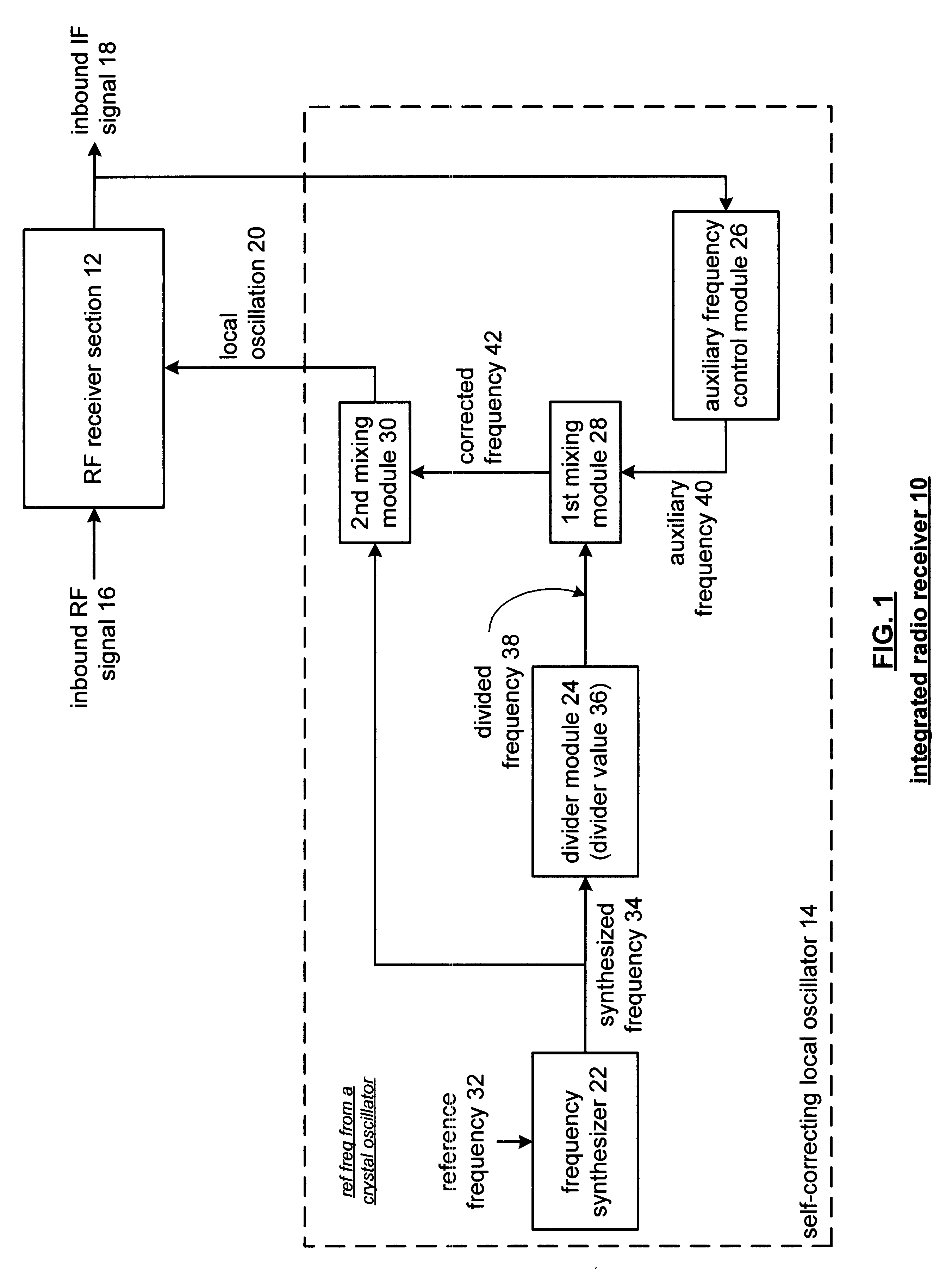
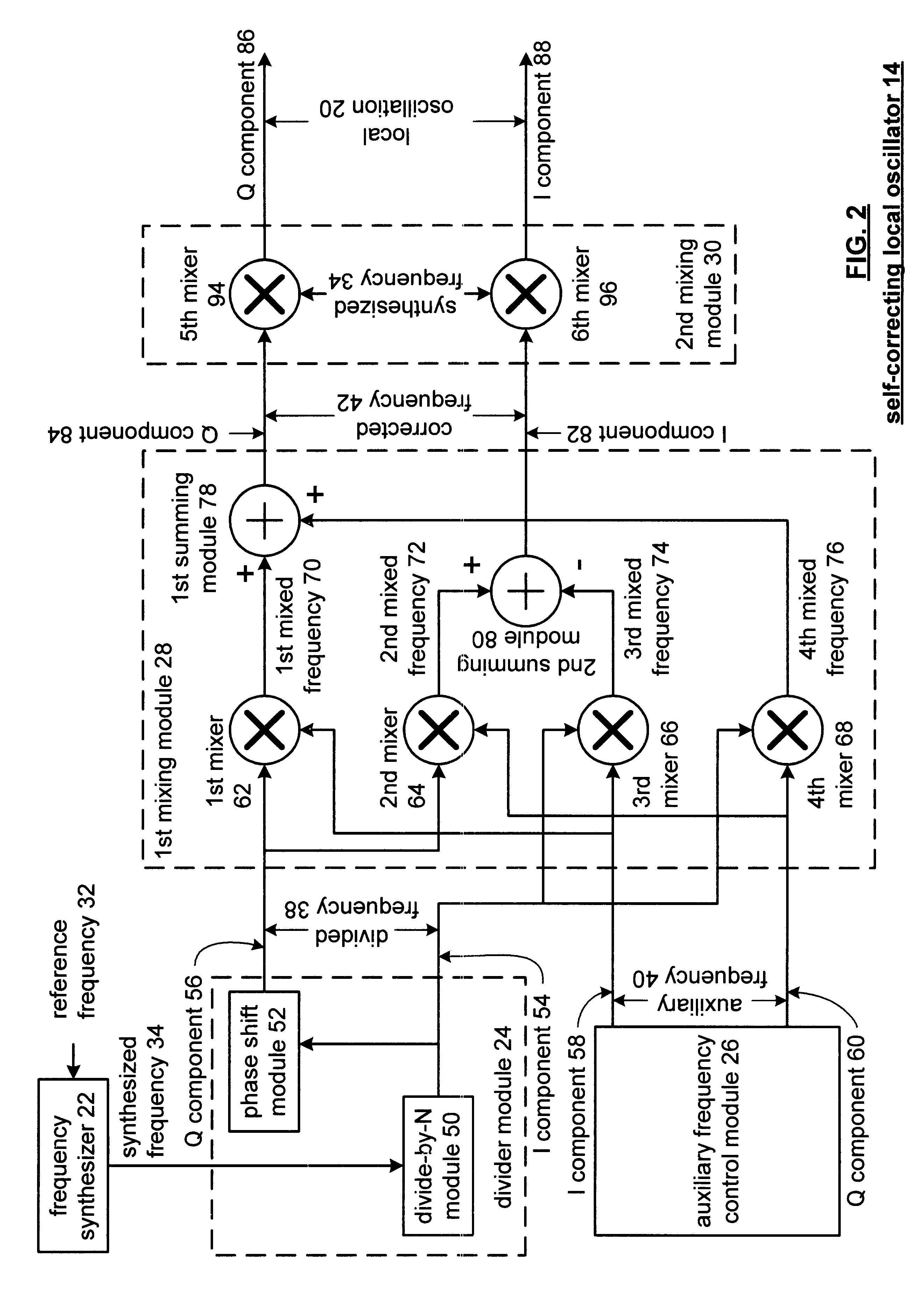
Method and apparatus for generating a self-correcting local oscillation
InactiveUS6850745B2Easy to adjustPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionEngineeringCrossover frequency
A method and apparatus for generating a self-correcting local oscillation includes processing that begins by generating a synthesized frequency from a reference frequency. The processing then continues by dividing the synthesized frequency by a divider value to produce a divided frequency. The processing continues by generating an auxiliary frequency and mixing the auxiliary frequency with the divided frequency to produce a corrected frequency. The processing then continues by mixing the corrected frequency with the synthesized frequency to produce a local oscillation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
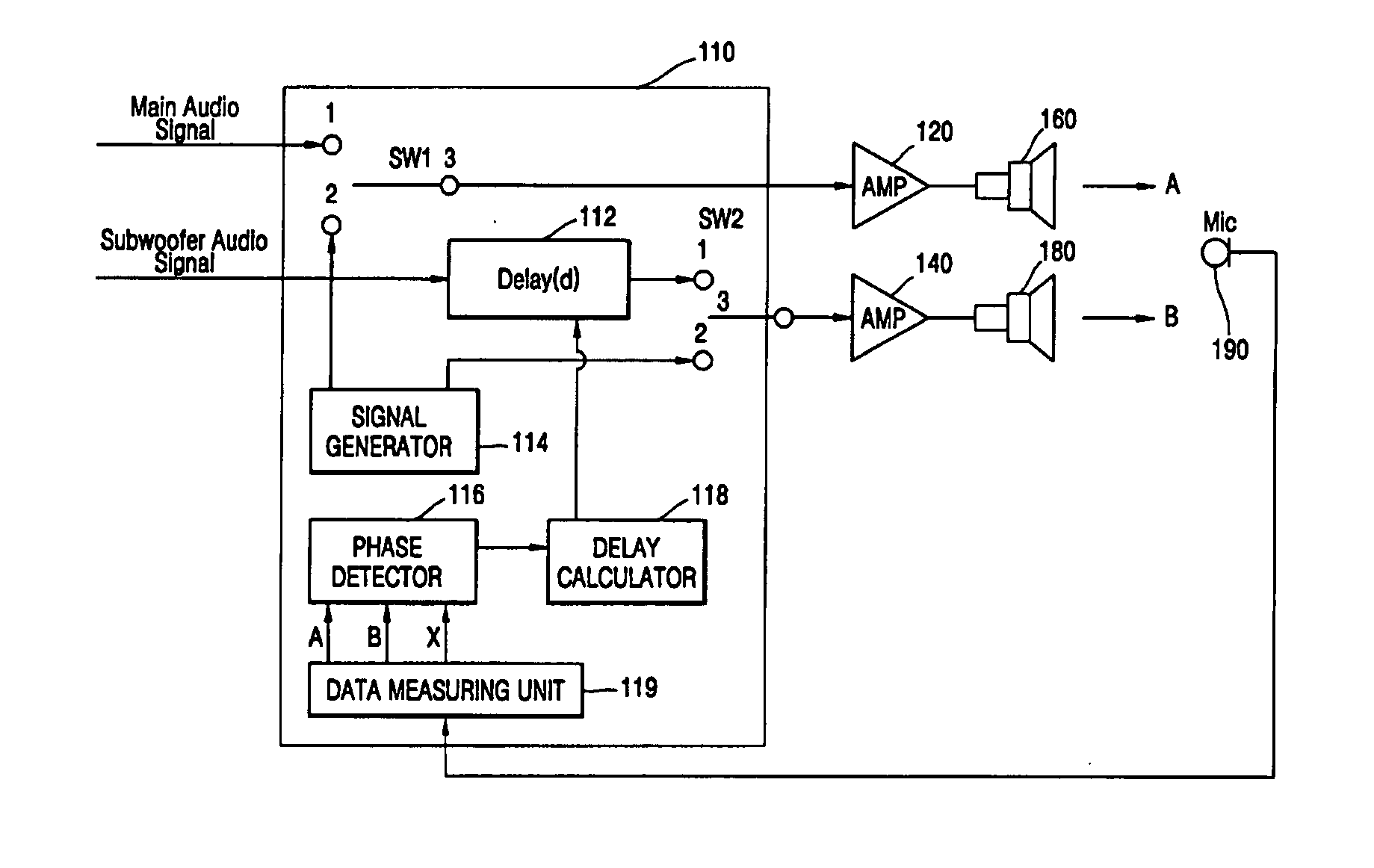
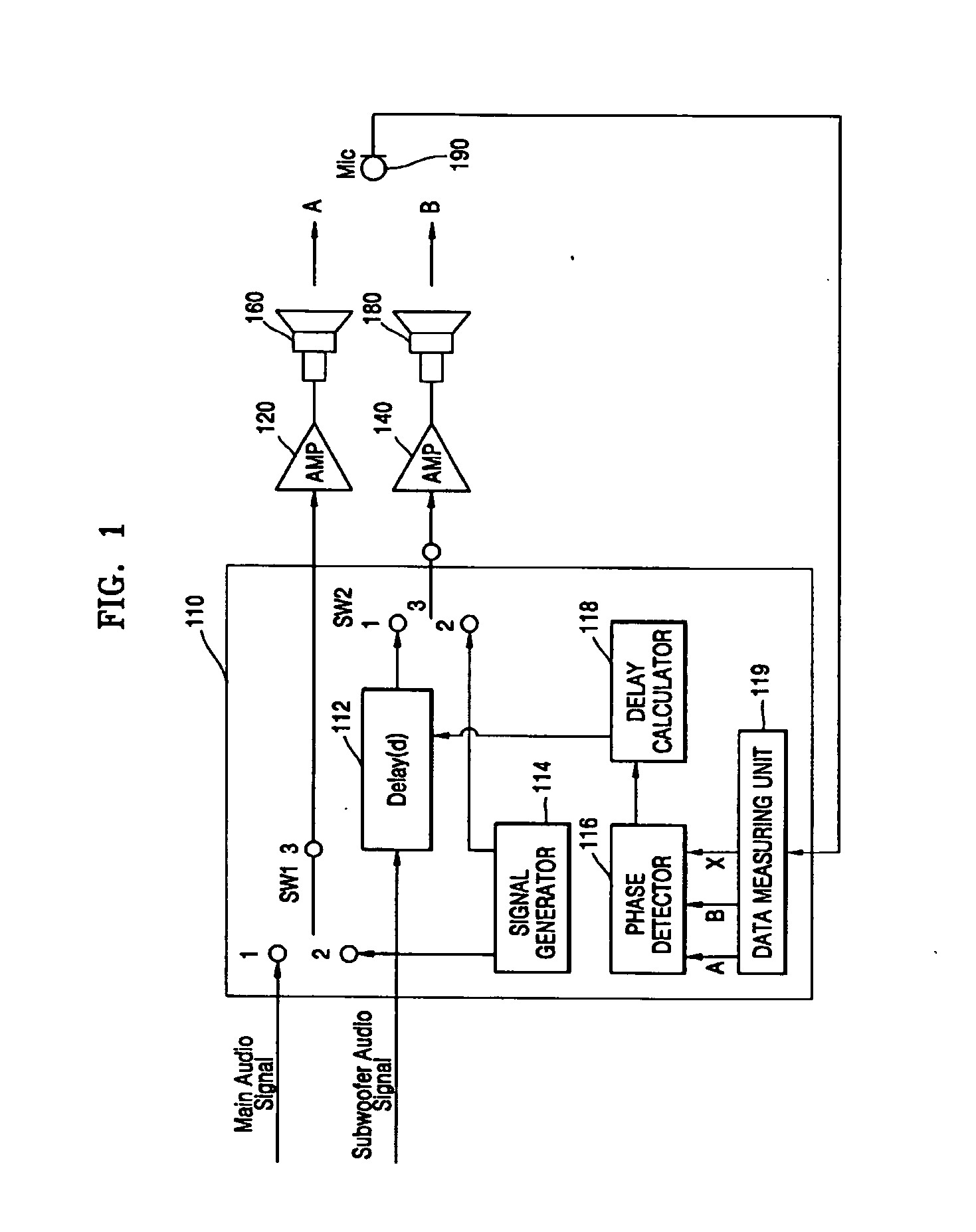
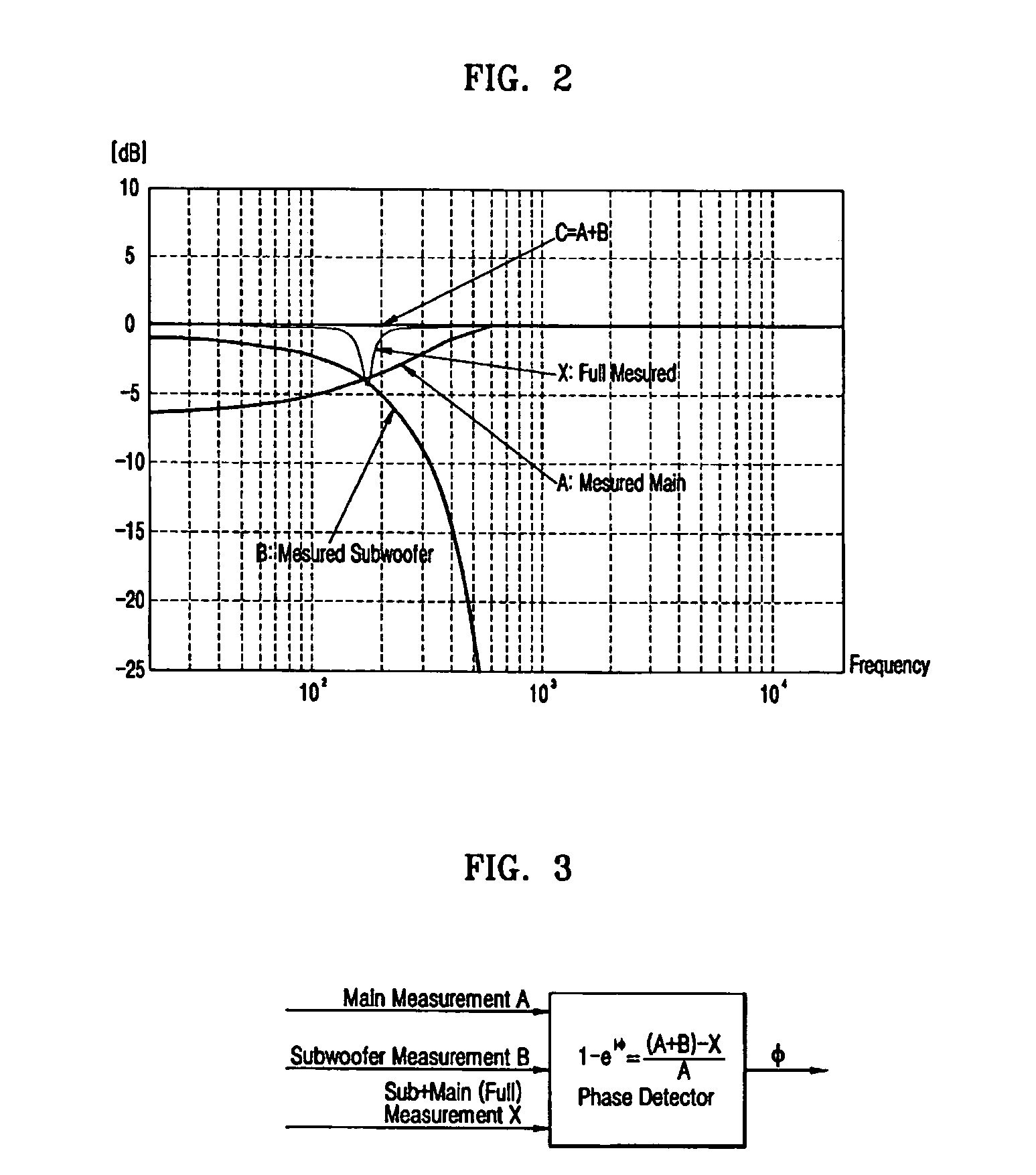
Method and apparatus to compensate a phase of a subwoofer channel signal
InactiveUS20060050896A1Pseudo-stereo systemsLoudspeaker signals distributionPhase differenceEngineering
A method and an apparatus to adjust a phase of a subwoofer channel signal in order to compensate for a phase difference generated at a crossover point between a subwoofer response and a main speaker response. The method includes: measuring a first response characteristic of a signal output from the subwoofer, a second response characteristic of a signal output from the main speaker, and a third response characteristic of a test signal simultaneously output from the subwoofer and the main speaker, detecting a phase difference between the subwoofer and the main speaker according to a difference value between the first, second, and third response characteristics at a crossover frequency, calculating a delay value of the subwoofer according to the detected phase difference, and compensating for the detected phase difference at the crossover point between the subwoofer and the main speaker using the calculated delay value of the subwoofer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
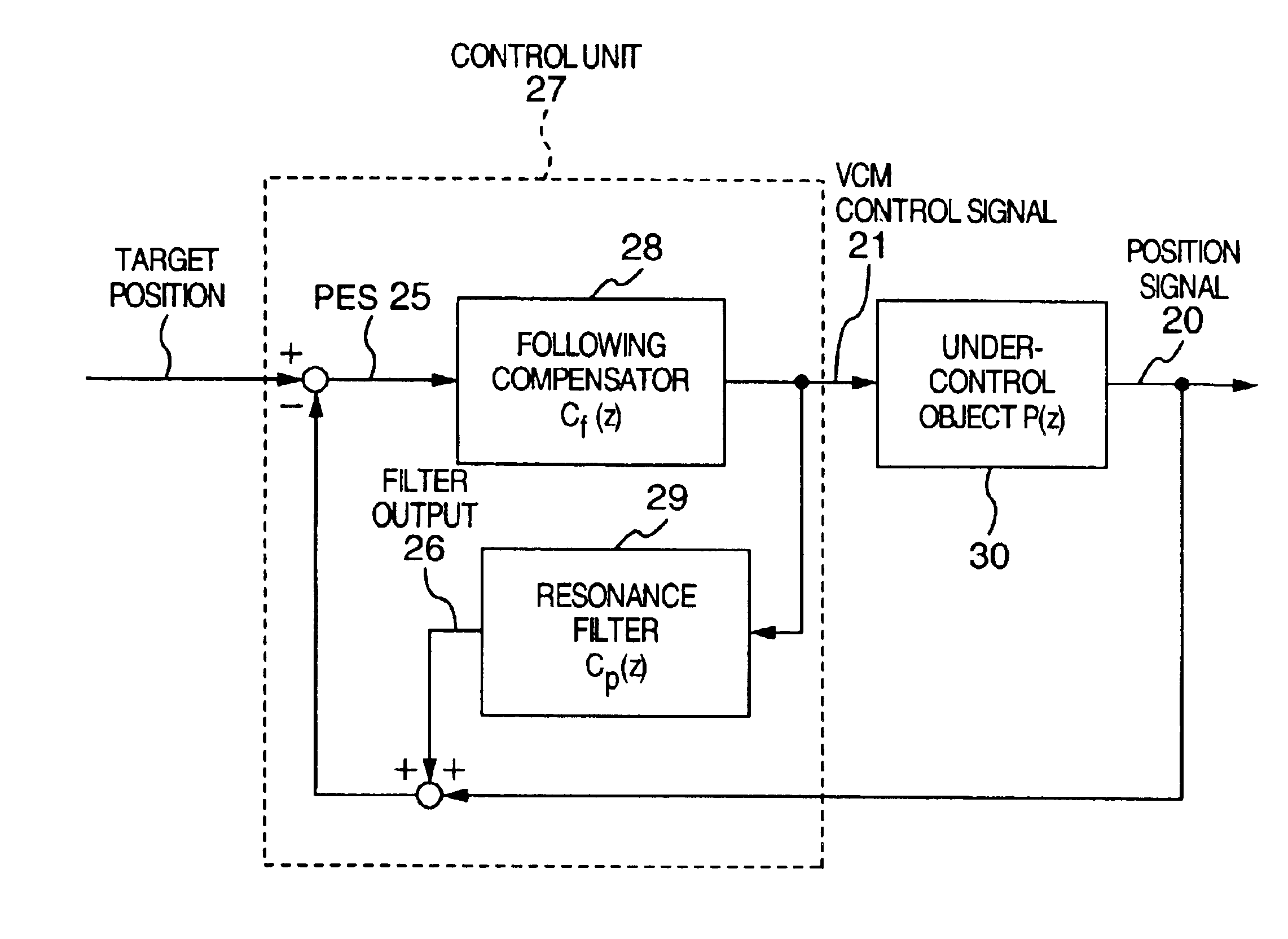
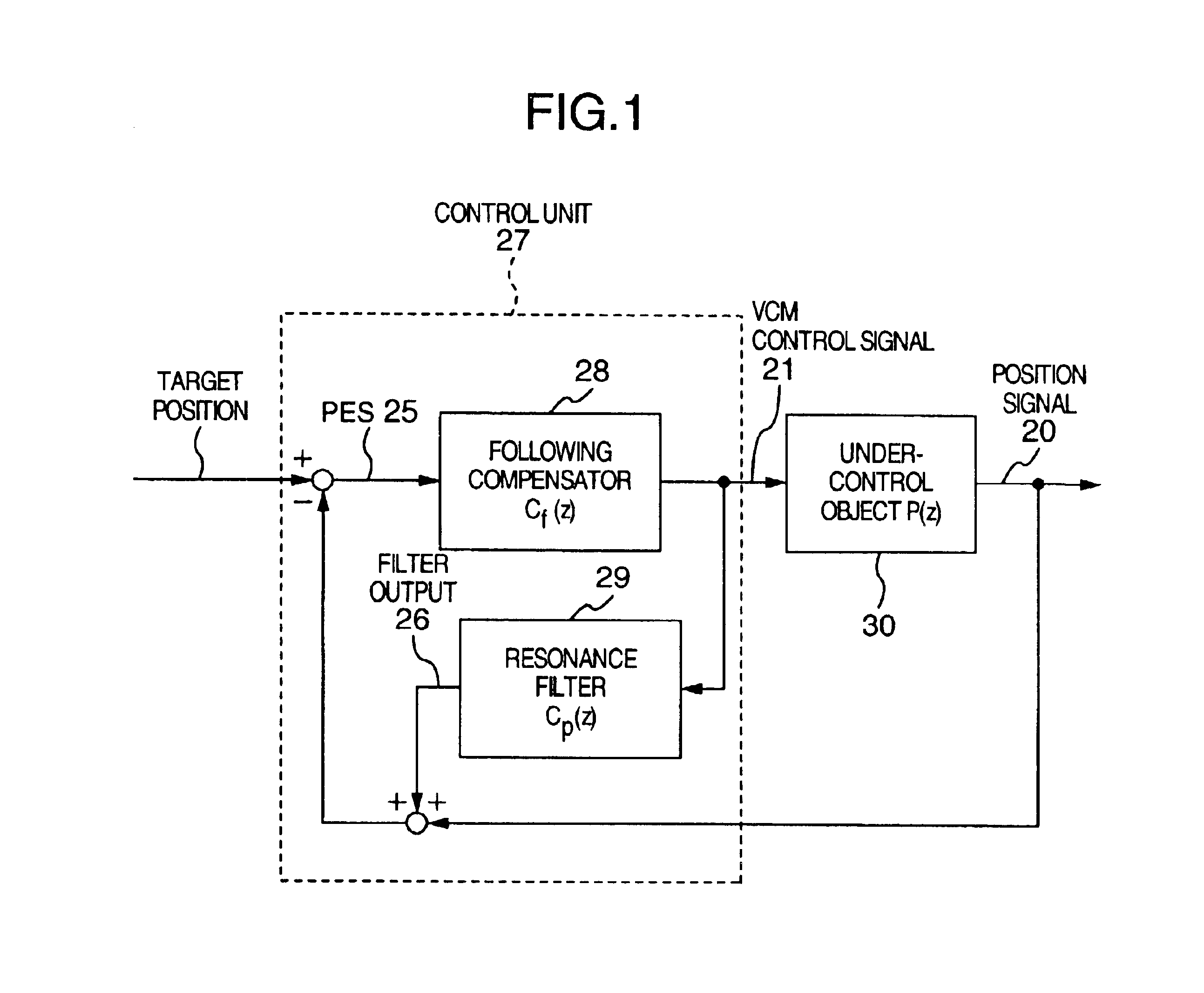
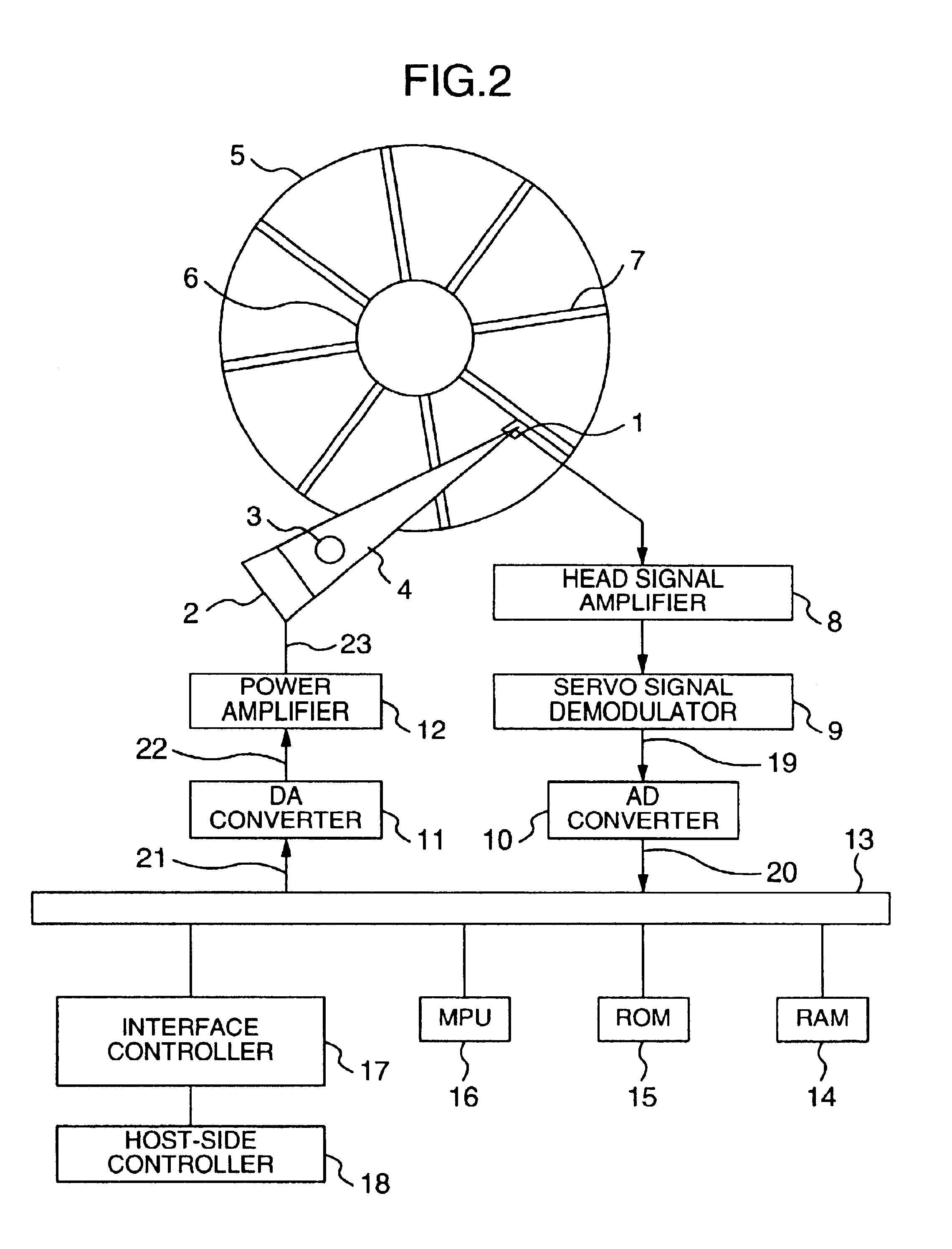
Magnetic disk apparatus
A magnetic disk apparatus includes a following compensator for measuring a frequency characteristic of an under-control object to stabilize a vibration mode of the under-control object with phase condition and a resonance filter having a resonance point in the vicinity of a frequency at which positioning accuracy is to be enhanced, being coupled in parallel to the under-control object. Polarity of mode constant of the resonance filter is so determined as to stabilize a vibration mode brought about by the resonance filter on the basis of a relation between the frequency stabilized by a control system and the phase-180° crossover frequency. Positioning accuracy at a specific frequency can be enhanced without involving unstability in the control system even in a frequency range where sensitivity function of the control system is higher than 0 dB inclusive.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
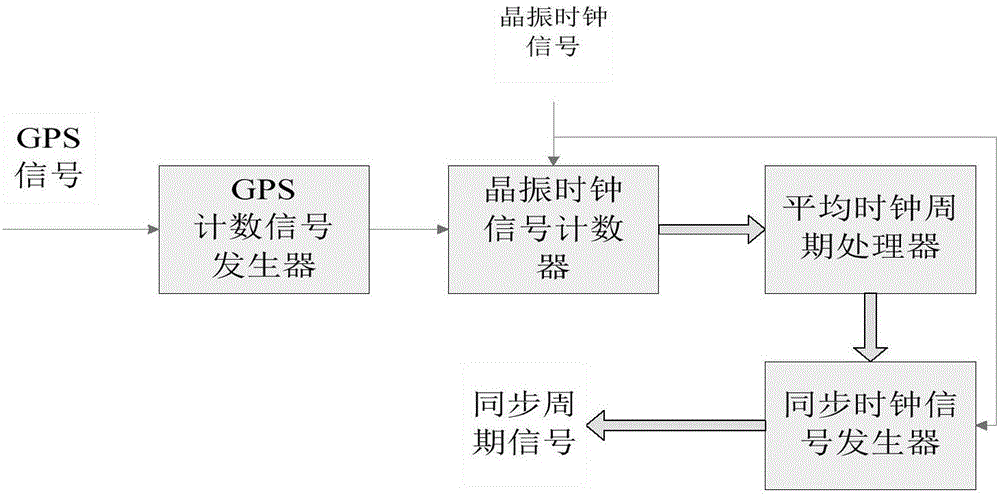
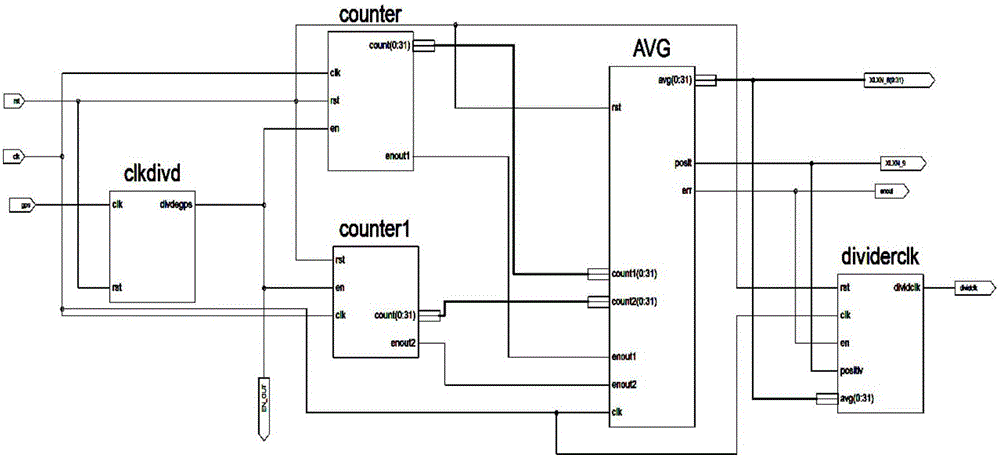
GPS (Global Positioning System) synchronizing signal frequency source circuit
InactiveCN106027187AHigh stability requirementsEnsure a high degree of synchronicityFrequency-division multiplex detailsSignal generatorAlternating current
The invention provides a GPS (Global Positioning system) synchronizing signal frequency source circuit. The GPS synchronizing signal frequency source circuit at least comprises the following signal synchronization processing modules: a GPS counting signal generator, a crystal oscillation clock signal counter, an average clock period processor and a synchronous clock signal generator. The GPS synchronizing signal frequency source circuit is characterized in that the GPS counting signal generator performs frequency division on a crystal oscillation signal by taking a GPS pulse per second as a trigger signal; the crystal oscillation clock signal counter is used for receiving the crystal oscillation clock signal, and calculating an average frequency error of the crystal oscillation clock signal through average clock period processing; and the synchronous clock signal generator is used for generating a frequency signal which is synchronous to the GPS pulse per second and correcting a crystal oscillation frequency error in order to output a frequency division frequency signal which is synchronous to the GPS pulse per second. Through adoption of the GPS synchronizing signal frequency source circuit, the problems that a crystal oscillation frequency signal cannot be synchronous to the GPS pulse per second and an output alternating-current signal is distorted in an existing throughput pulse method are solved, and a technical basis is laid for the realization of a time synchronization standard source.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
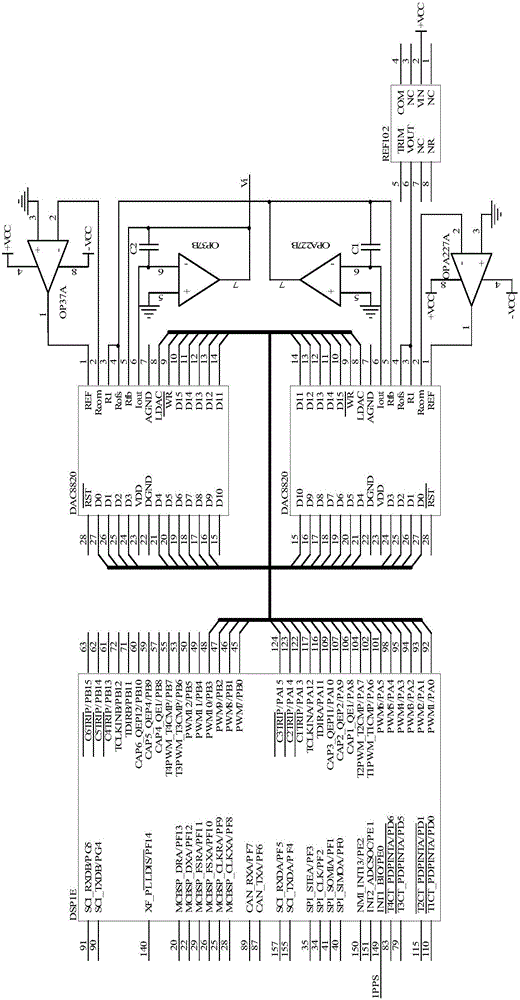
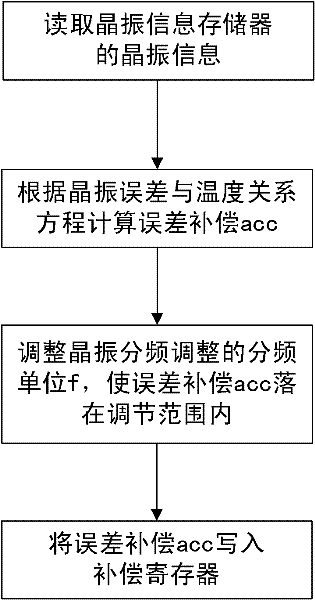
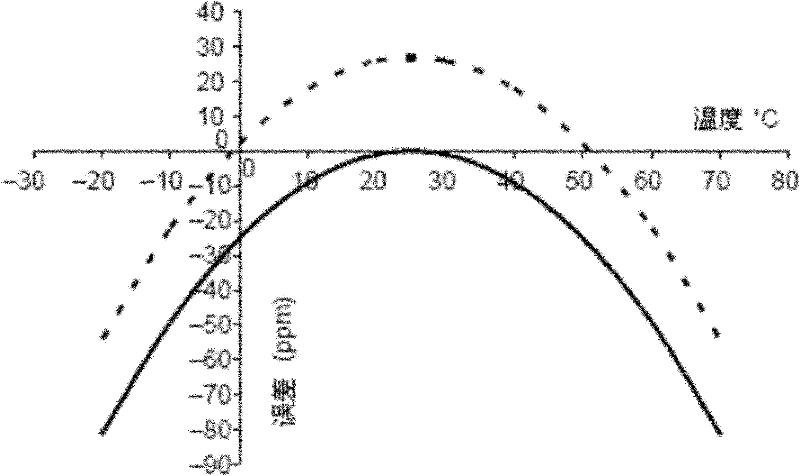
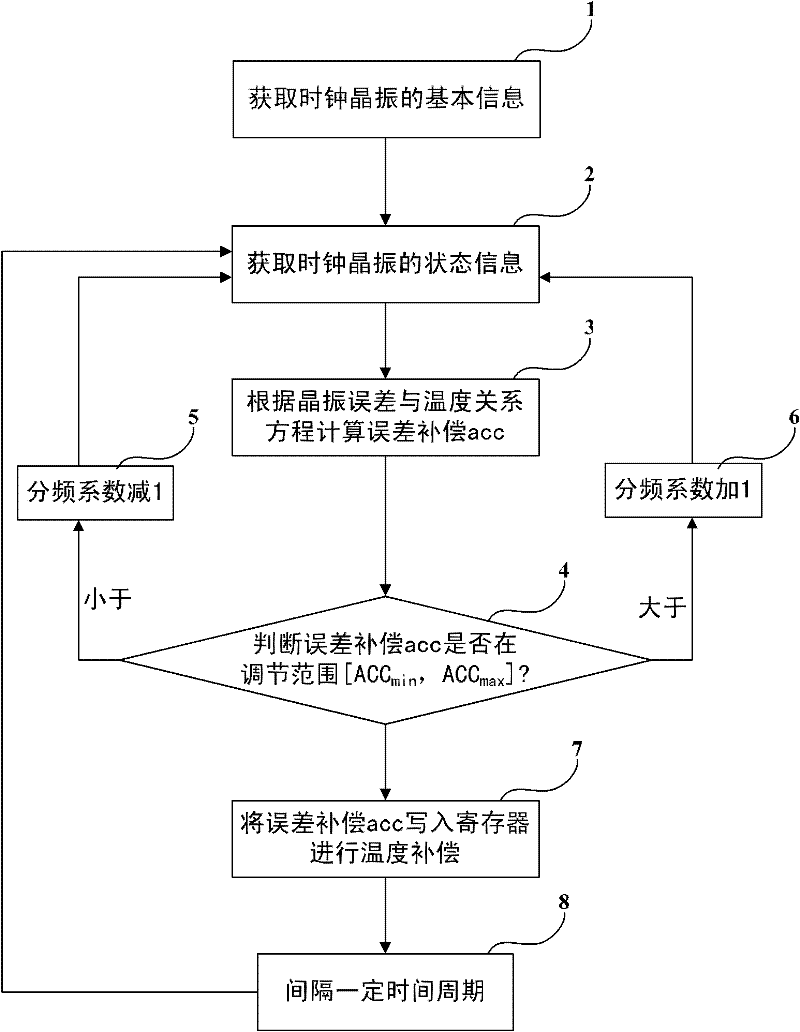
Wide range temperature error compensating method of real-time clock and system thereof
The invention provides a wide range temperature error compensating method of a real-time clock and a system of the real-time clock. The compensating method comprises the following steps of: calculating the needed error compensation acc through acquiring current state information of a quartz crystal oscillator, judging whether the needed error compensation acc is in a regulating range provided by the system, if not, leading in a controllable error through regulating a crossover frequency of the quartz crystal oscillator so as to change the calculating value of the error compensation acc and cause the error compensation acc to be in the regulating range provided by the system, and compensating the temperature. The temperature error compensating method actively leads the controllable constant error amount E to the error compensation acc through regulating the crossover frequency of the quartz crystal oscillator so as to change the value of the error compensation acc and cause the error compensation acc to be in the regulating range provided by the product. Thus, the product is capable of compensating the temperature error without changing the hardware configuration and preventing theregulating range of the error compensation acc influencing the precise compensation.
Owner:BEIJIG YUPONT ELECTRIC POWER TECH
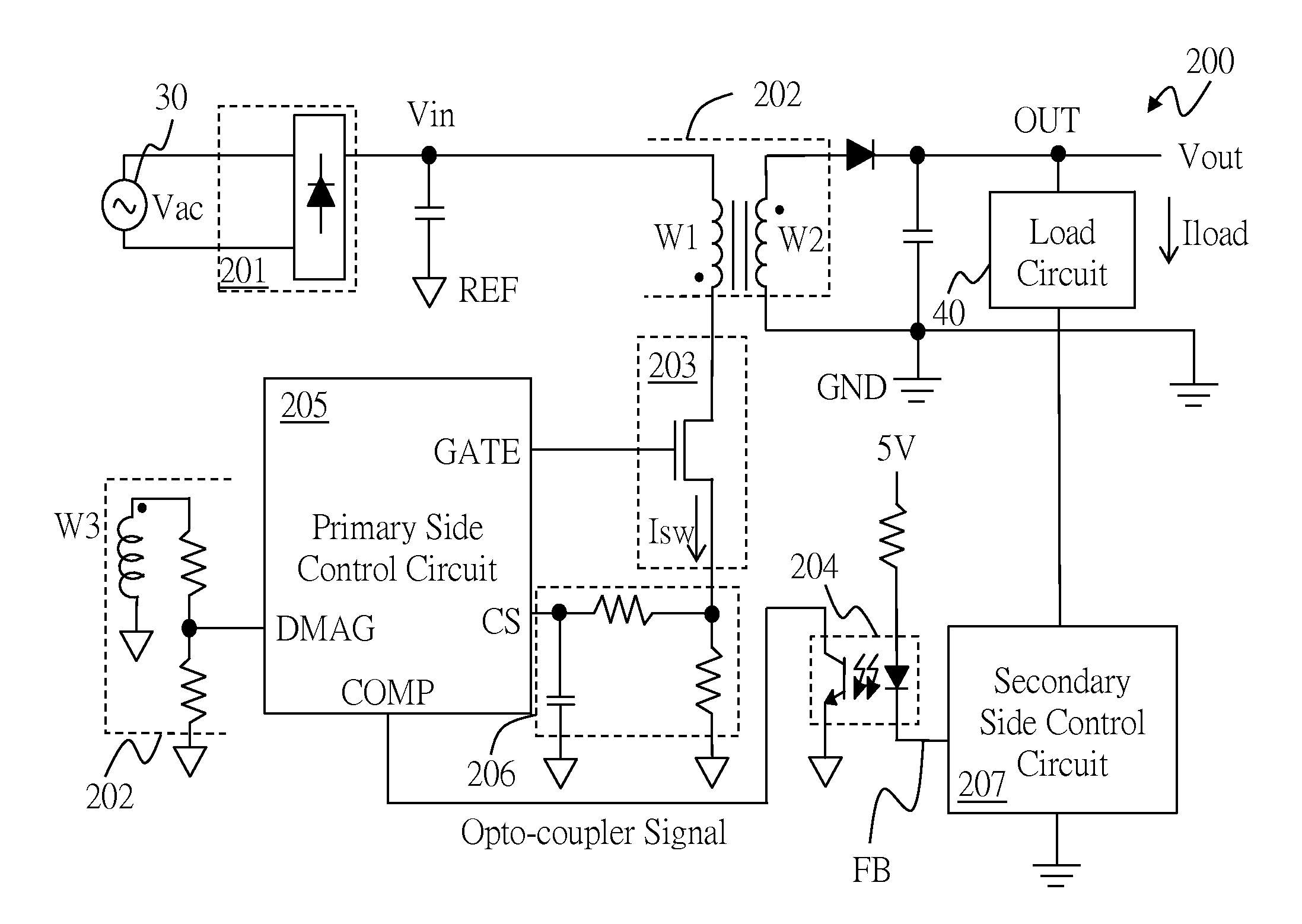
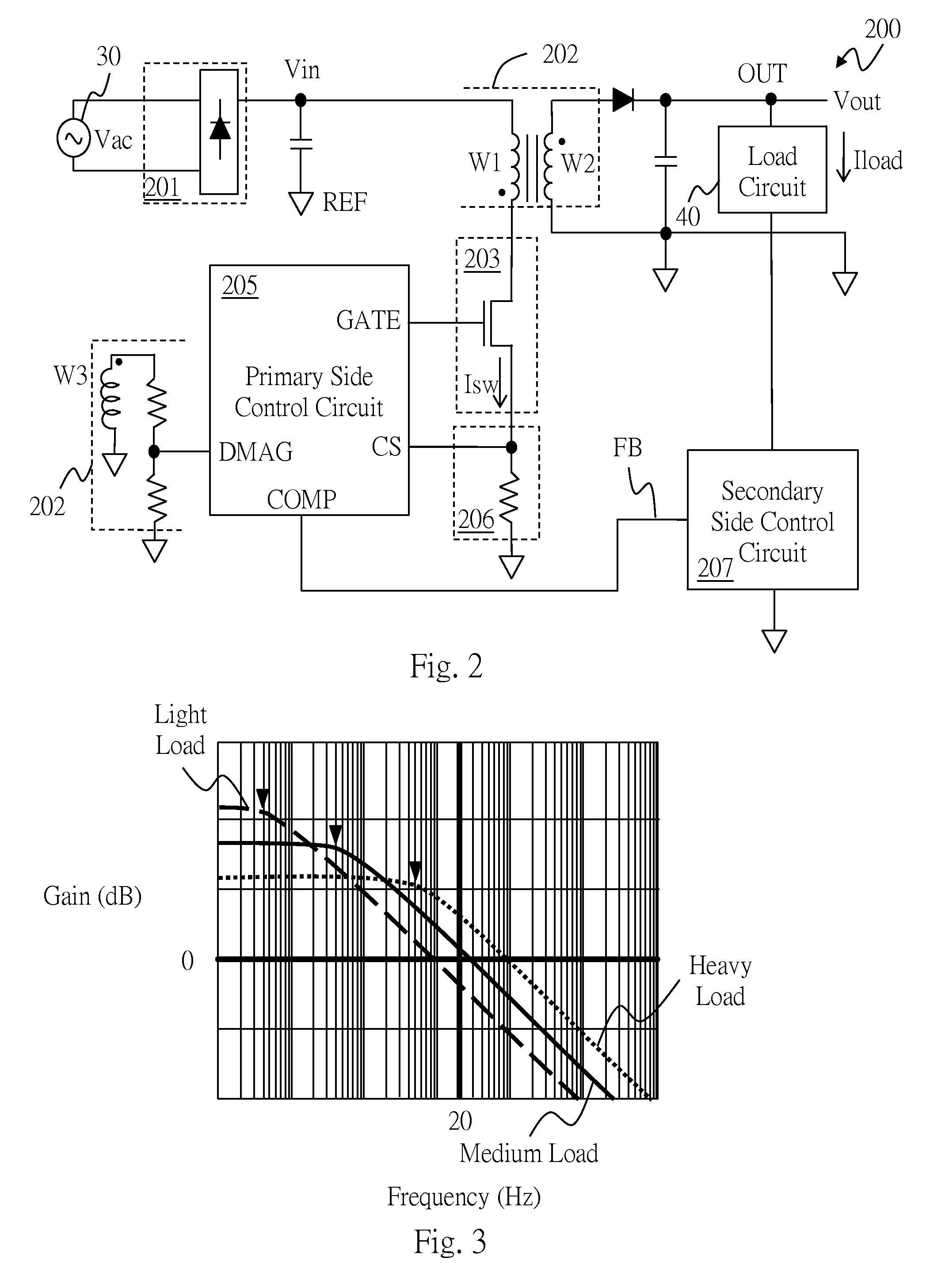
Flyback power converter, secondary side control circuit, and control method thereof
ActiveUS20160141966A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLoad circuitSwitched current
The present invention provides a flyback power converter, a secondary side control circuit, and a control method thereof. The flyback power converter converts an input voltage to an output voltage, and provides a load current to a load circuit. The flyback power converter includes: a transformer circuit, a power switch circuit, a switch current sense circuit, a primary side control circuit, and a secondary side control circuit. The secondary side control circuit adaptively adjusts a frequency of a zero of a compensator gain function and / or a mid-frequency gain of the compensator gain function according to the load current, such that a number of poles of a system open loop gain function of the flyback power converter is at most more than a number of zeroes of the system open loop gain function by one under a crossover frequency.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Discriminator stabilized superconductor/ferroelectric thin film local oscillator
InactiveUS6078223AAlleviating bit error rate degradationReduce loadPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationDiscriminatorFerroelectric thin films
A tunable local oscillator (10) with a tunable circuit (12) that includes a resonator (16) and a transistor (14) as an active element for oscillation. Tuning of the circuit (12) is achieved with an externally applied dc bias (22, 24) across coupled lines (20) on the resonator (16). Preferably, the resonator (16) is a high temperature superconductor microstrip ring resonator with integral coupled lines (20) formed over a thin film ferroelectric material. A directional coupler (38) samples the output of the oscillator (14) which is fed into a diplexer (40) for determining whether the oscillator (14) is performing at a desired frequency. The high-pass and low-pass outputs (42, 44) of the diplexer (40) are connected to diodes (48, 46) respectively for inputting the sampled signals into a differential operational amplifier (50). Amplifier (50) compares the sampled signals and emits an output signal if there is a difference between the resonant and crossover frequencies. Based on the sampled signal, a bias supplied to the ring resonator is either increased or decreased for raising or lowering the resonant frequency by decreasing or increasing, respectively, the dielectric constant of the ferroelectric.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE
First-order loudspeaker crossover network
InactiveUS20070121964A1Loudspeaker signals distributionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsPhase differenceAmplitude response
A first-order crossover network having low-pass and high-pass filters to respectively drive first and second loudspeakers in a loudspeaker system is designed such that the phase difference at a crossover frequency between output signals of the first and second loudspeakers is no greater than 60 degrees, so that the output signals are at least partially in phase. Preferably, the phase difference should be about 40 degrees to create a near in-phase effect. The polarity in which the first loudspeaker is coupled to the first-order crossover network is an inverse of the polarity in which the second loudspeaker is coupled to the crossover network. Optionally, the input signals can be equalized to flatten the magnitude responses of the crossover network.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com