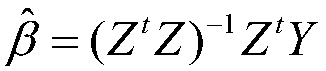Patents
Literature
265results about "Time pulses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
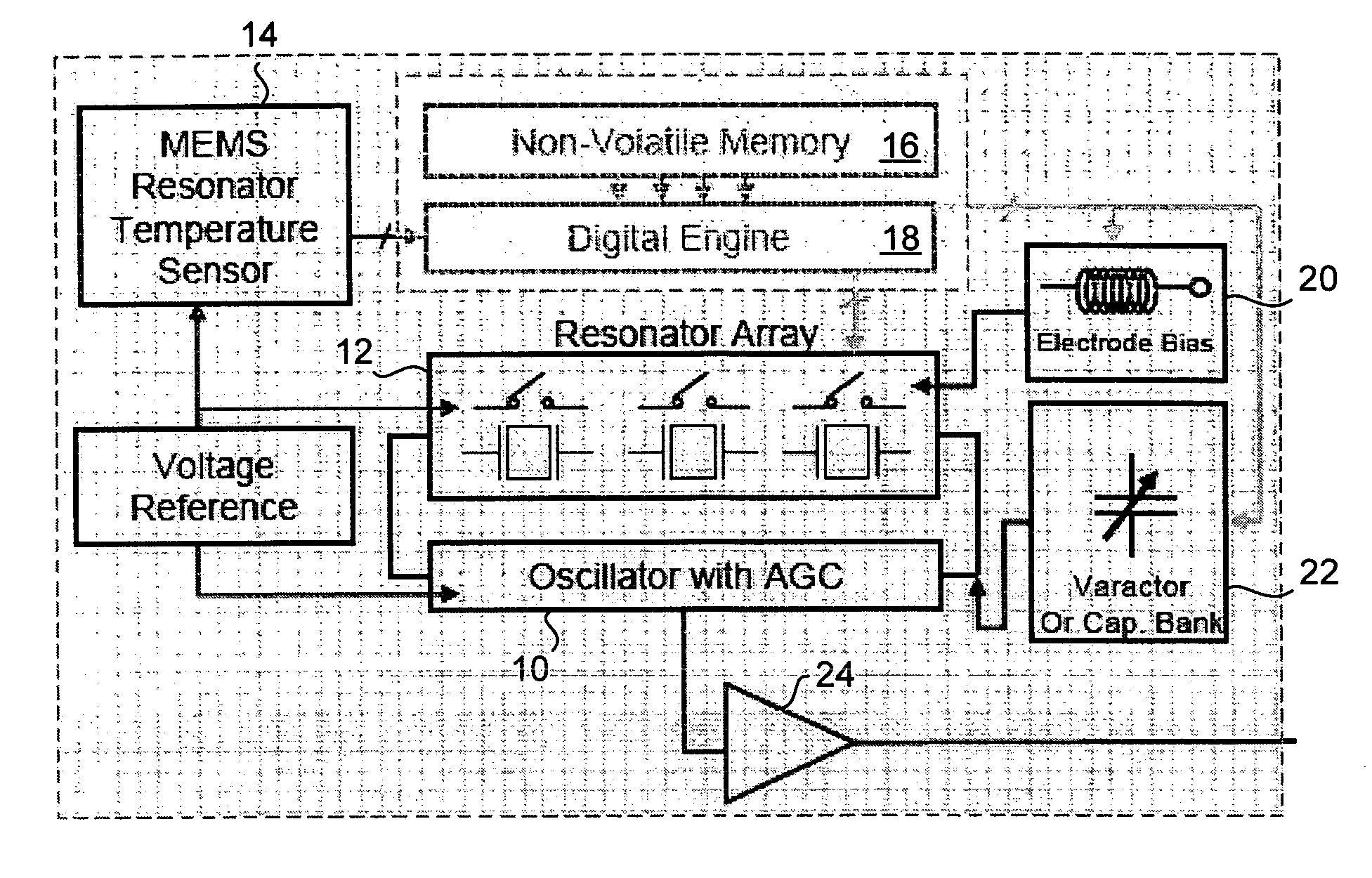
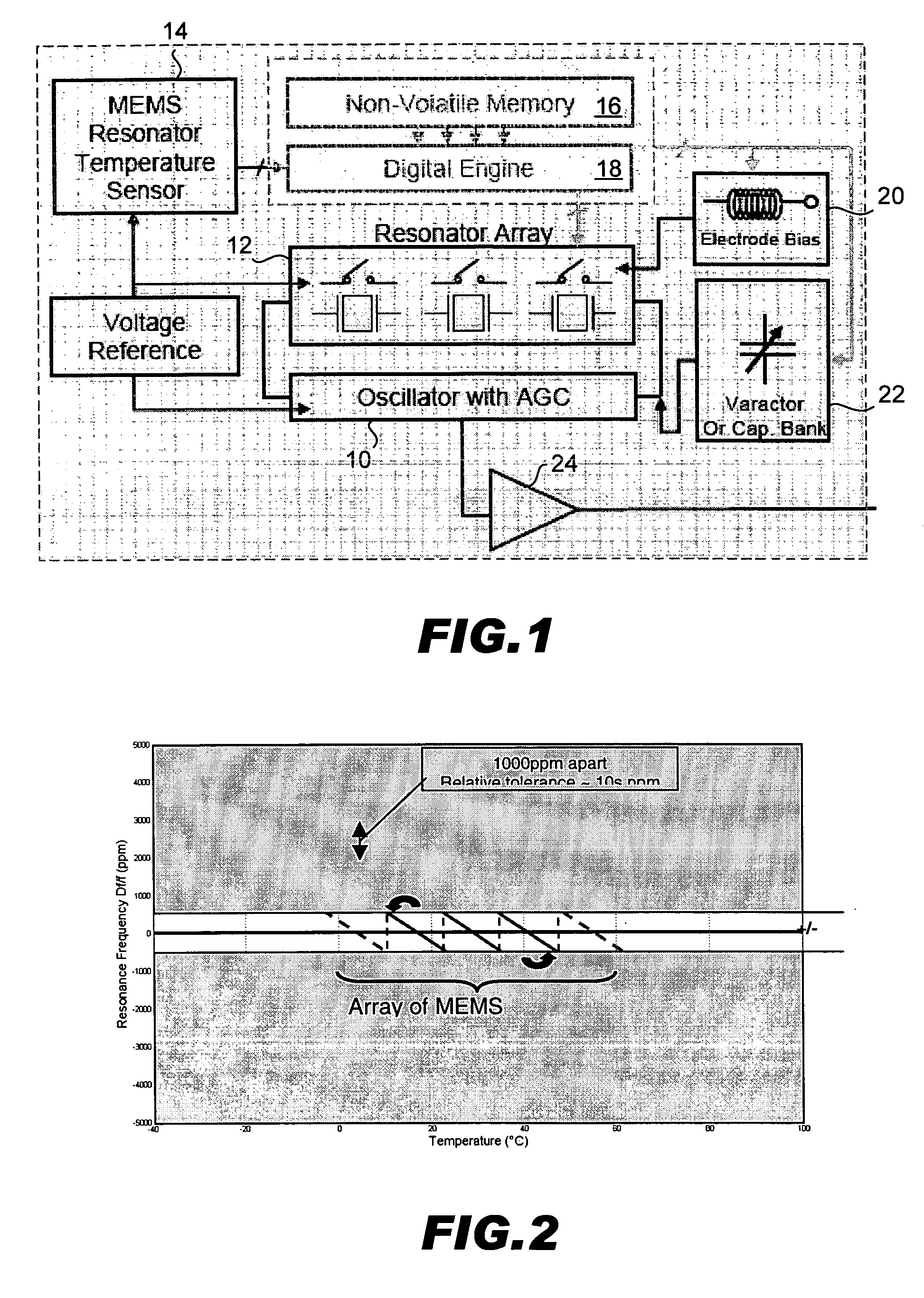
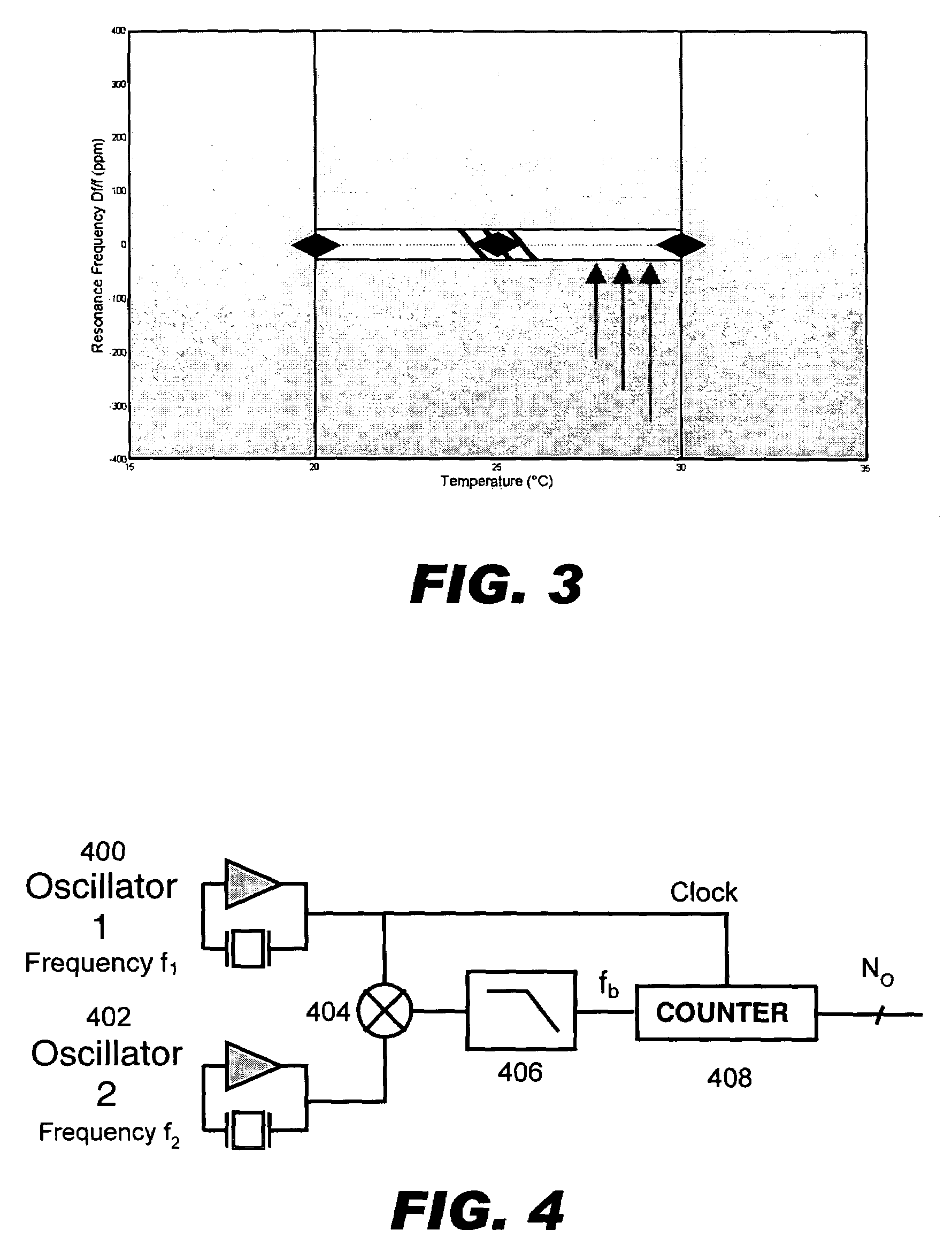
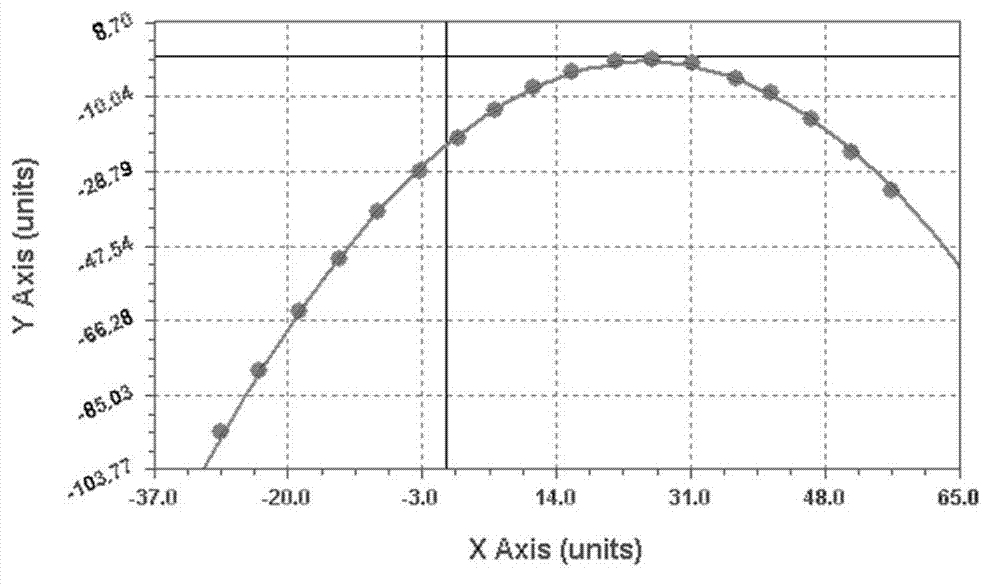
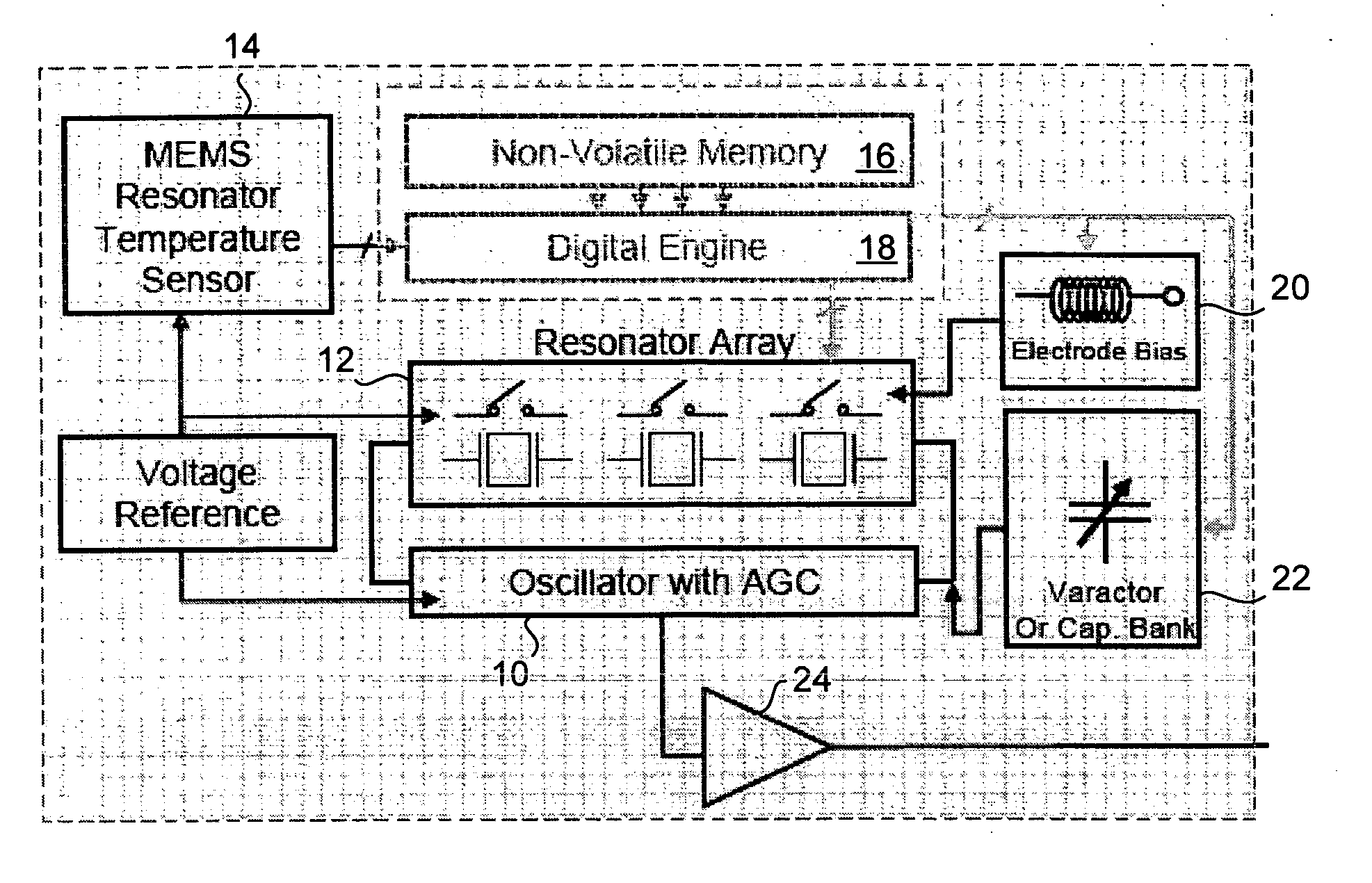
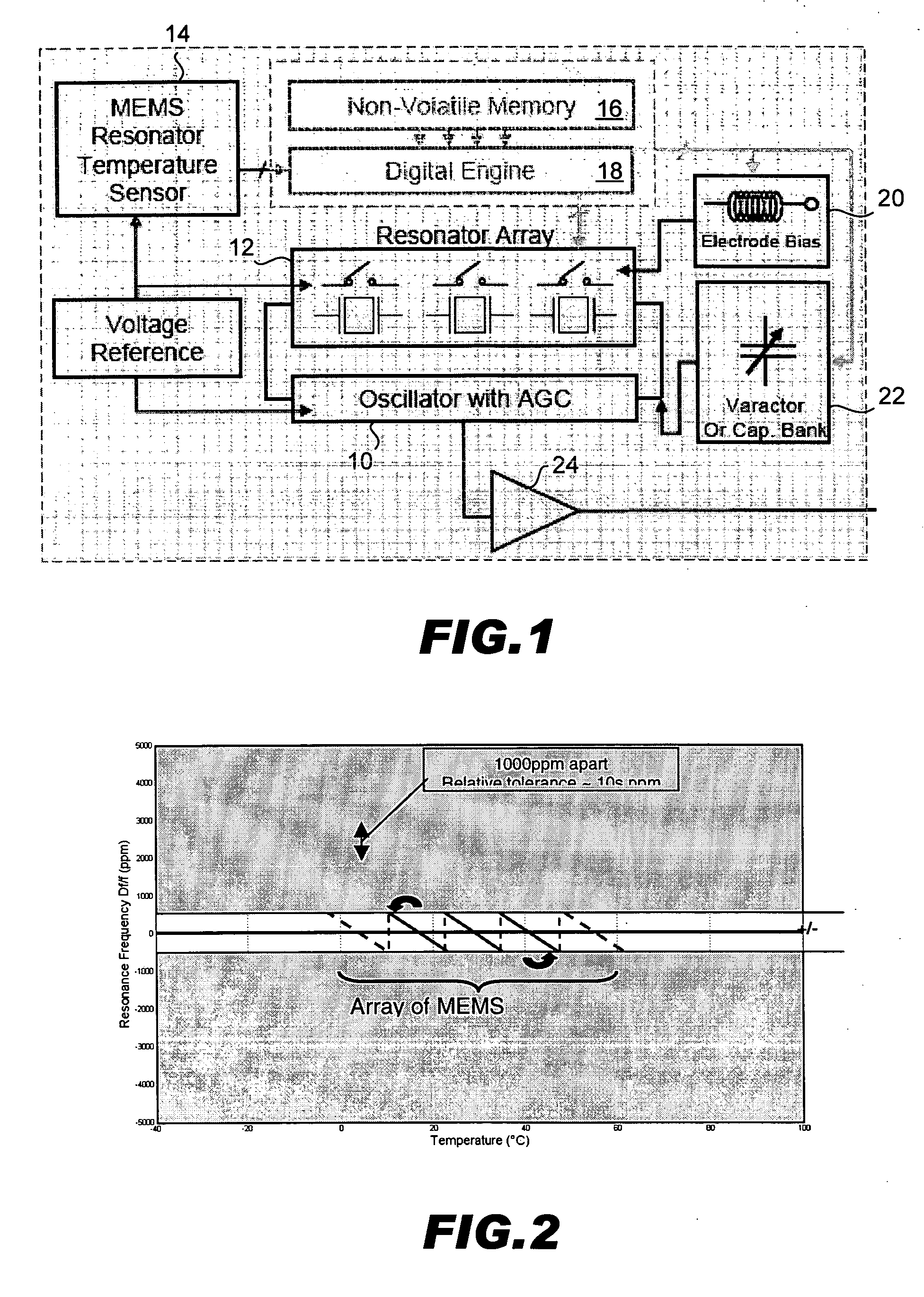
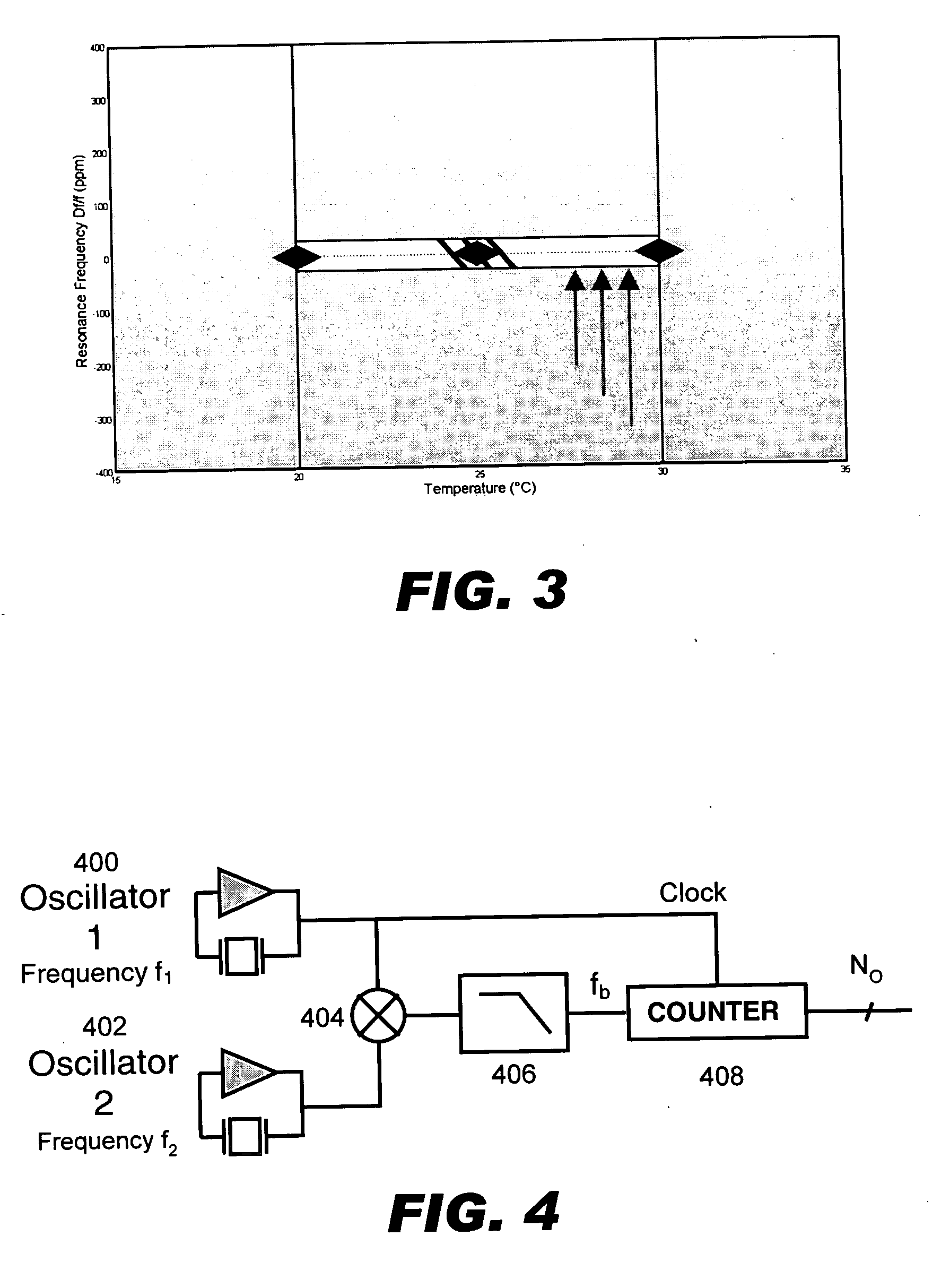
Temperature compensated oscillator including MEMS resonator for frequency control
ActiveUS7211926B2Small deviceLow costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTemperatue controlQuartz resonatorSignal function
Disclosed is an oscillator that relies on redundancy of similar resonators integrated on chip in order to fulfill the requirement of one single quartz resonator. The immediate benefit of that approach compared to quartz technology is the monolithic integration of the reference signal function, implying smaller devices as well as cost and power savings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
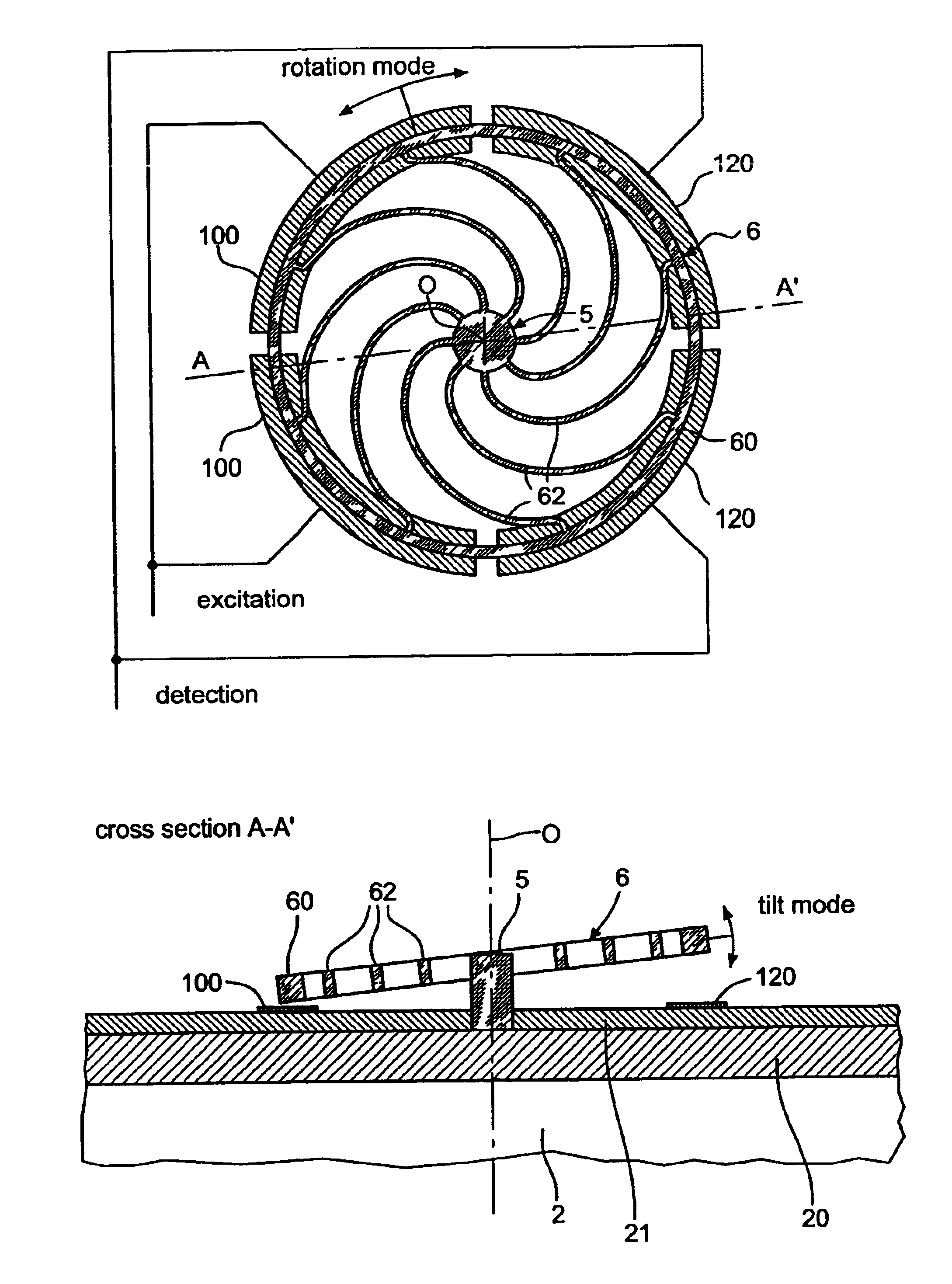
Temperature compensation mechanism for a micromechanical ring resonator
InactiveUS6859113B2Additional requirementAcceleration measurement using interia forcesImpedence networksVIT signalsAtomic physics
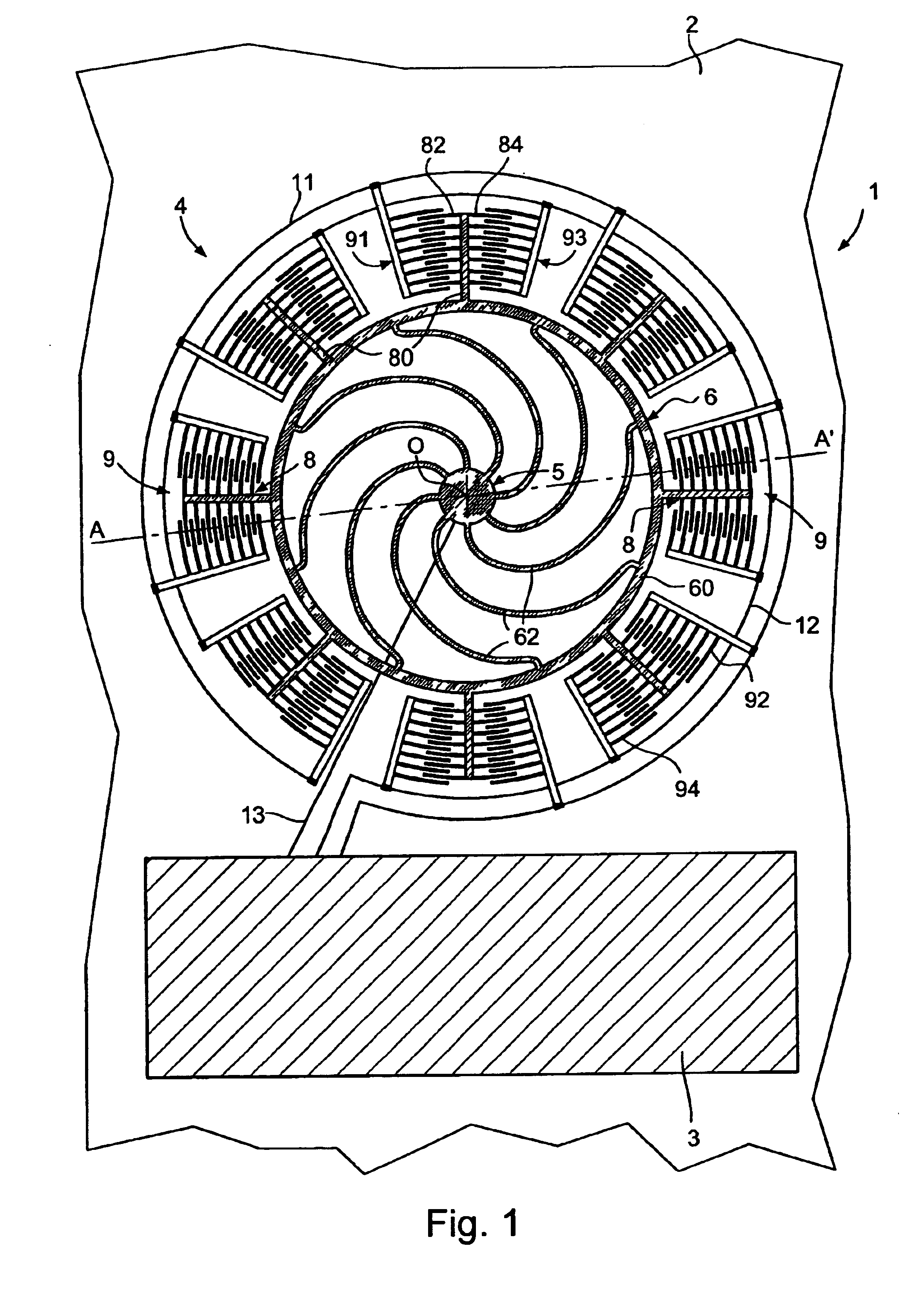
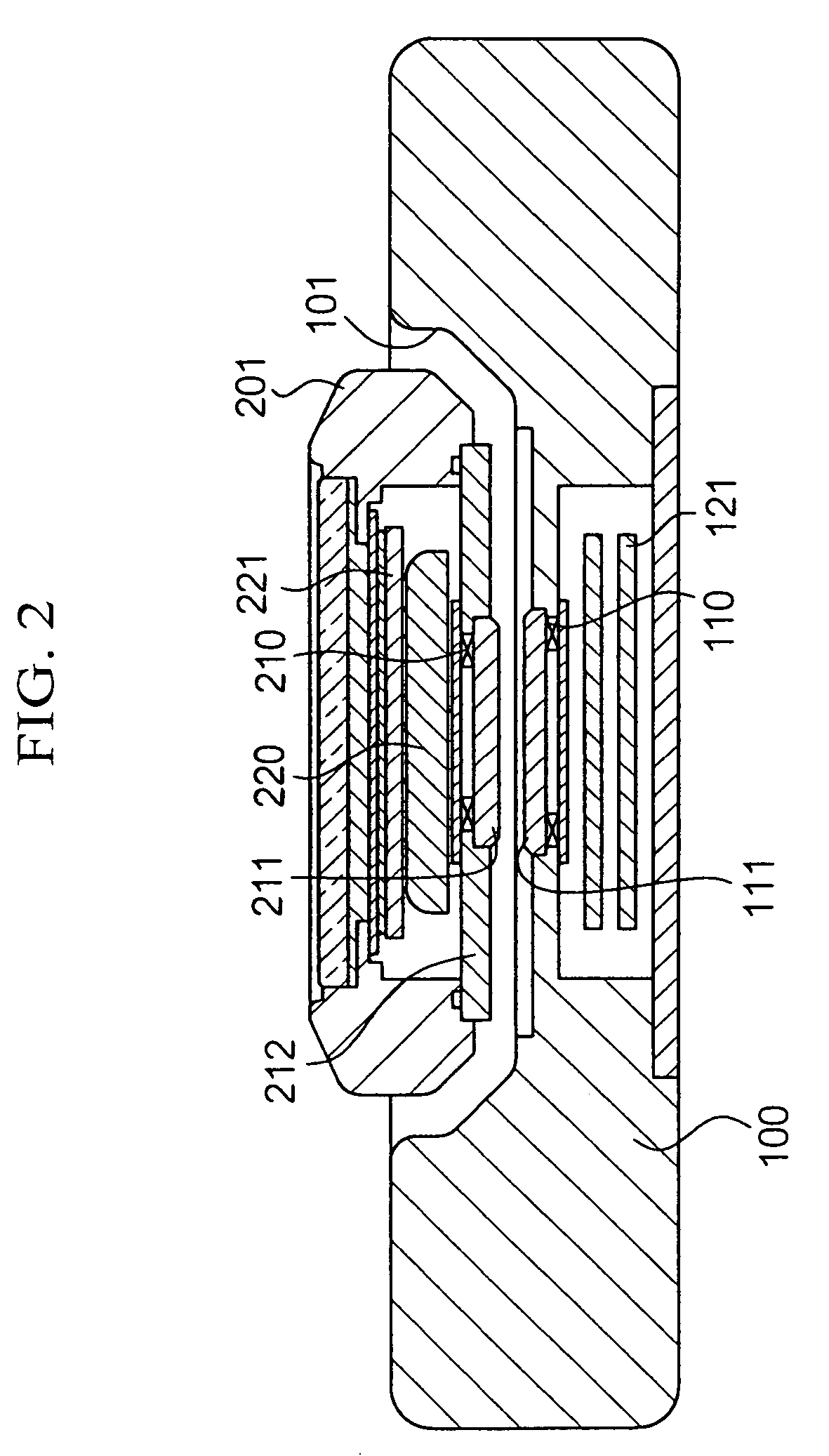
A time base including a resonator (4) and an integrated electronic circuit (3) for driving the resonator into oscillation and for producing, in response to the oscillation, a signal having a determined frequency. The resonator is an integrated micromechanical ring resonator supported above a substrate (2) and adapted to oscillate in a first oscillation mode. The ring resonator includes a free-standing oscillating structure (6). Electrodes (100, 120; 130, 150) are positioned under the free-standing oscillating structure in such a way as to drive and sense a second oscillation mode in a plane substantially perpendicular to the substrate and having a resonant frequency which is different from the resonant frequency of the first oscillation mode, a frequency difference between the resonant frequencies of both oscillation modes being used for compensating for the effect of temperature on the frequency of the signal produced by the time base.
Owner:ETA SA MFG HORLOGERE SUISSE
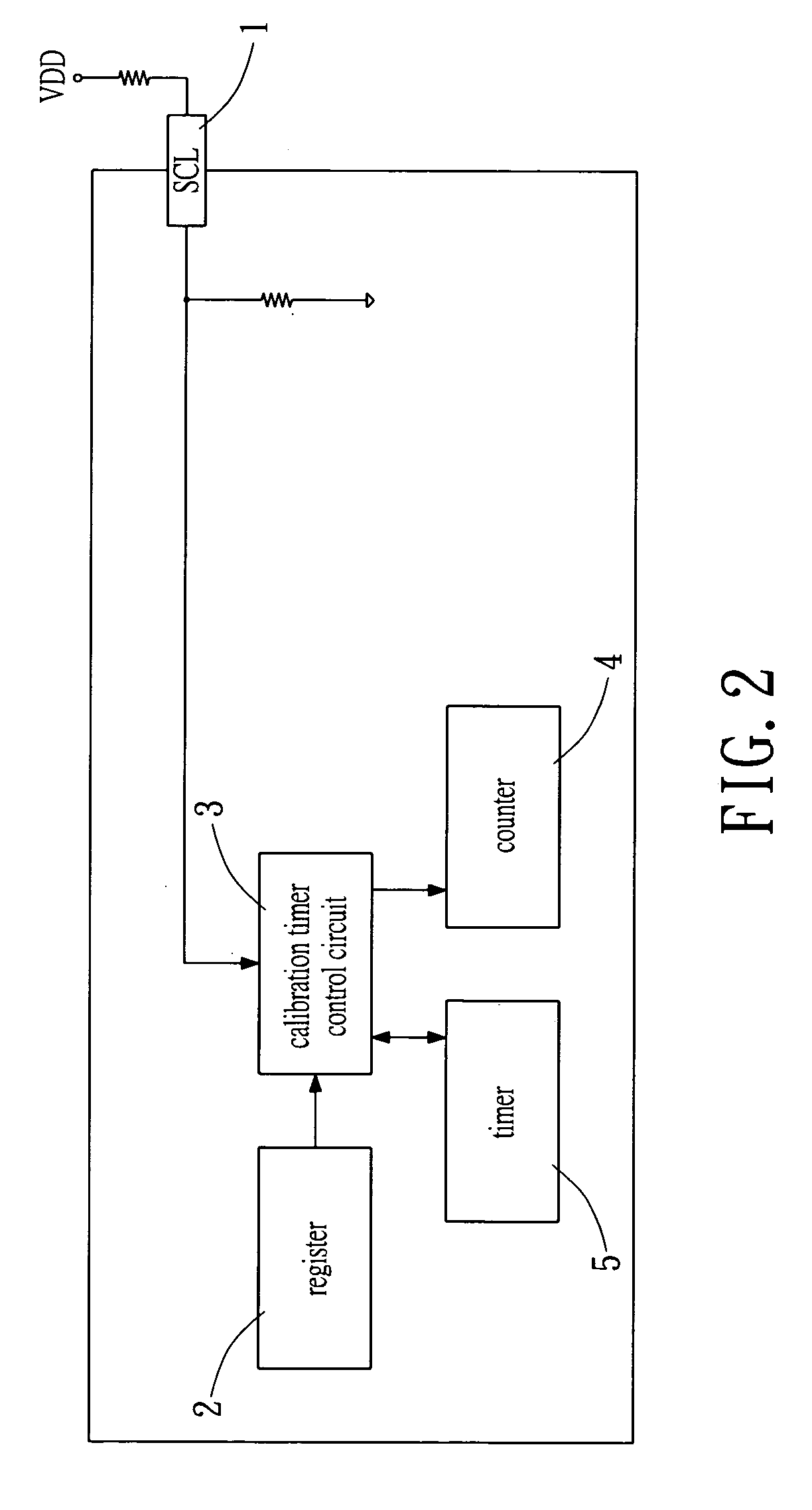
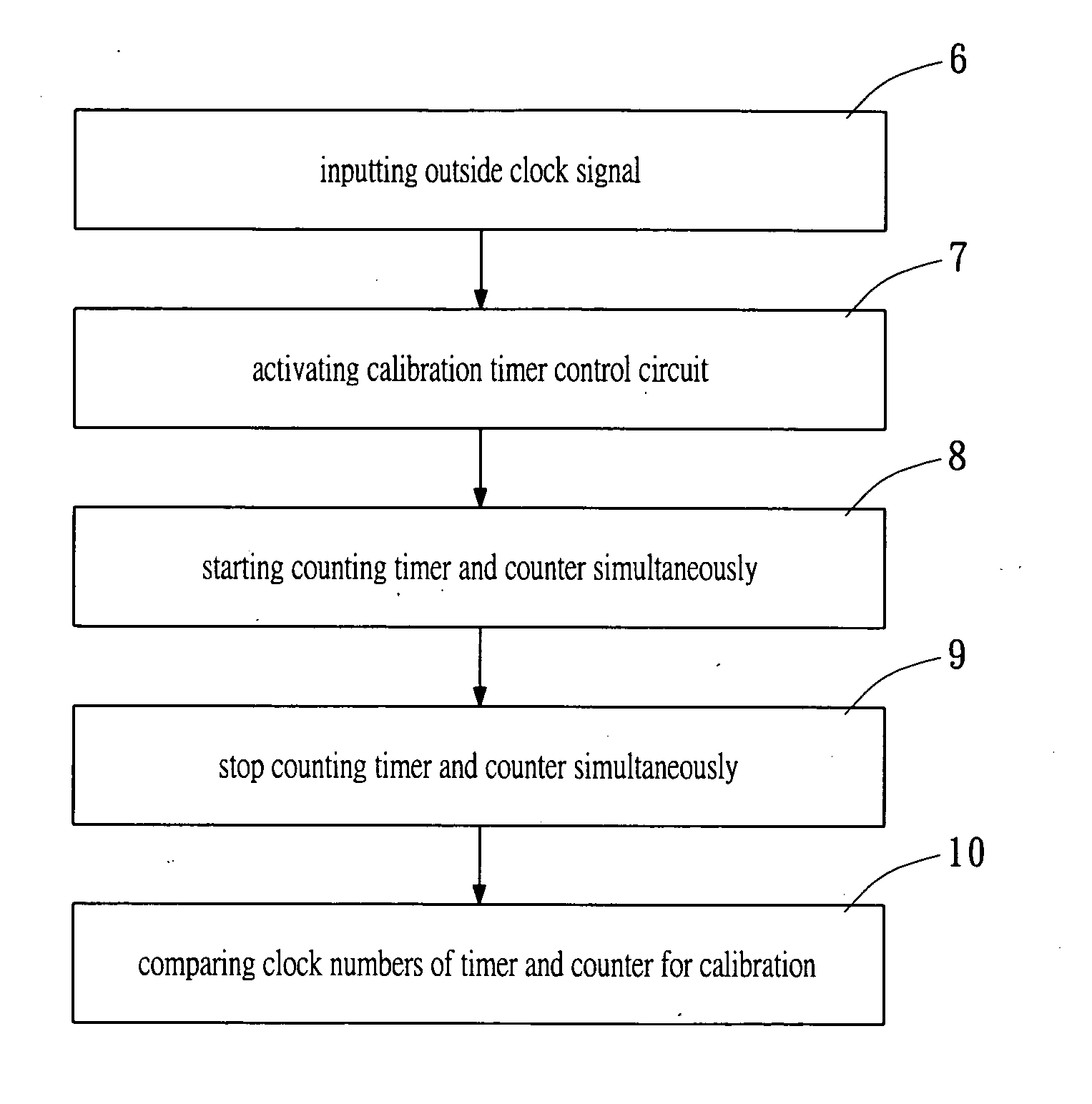
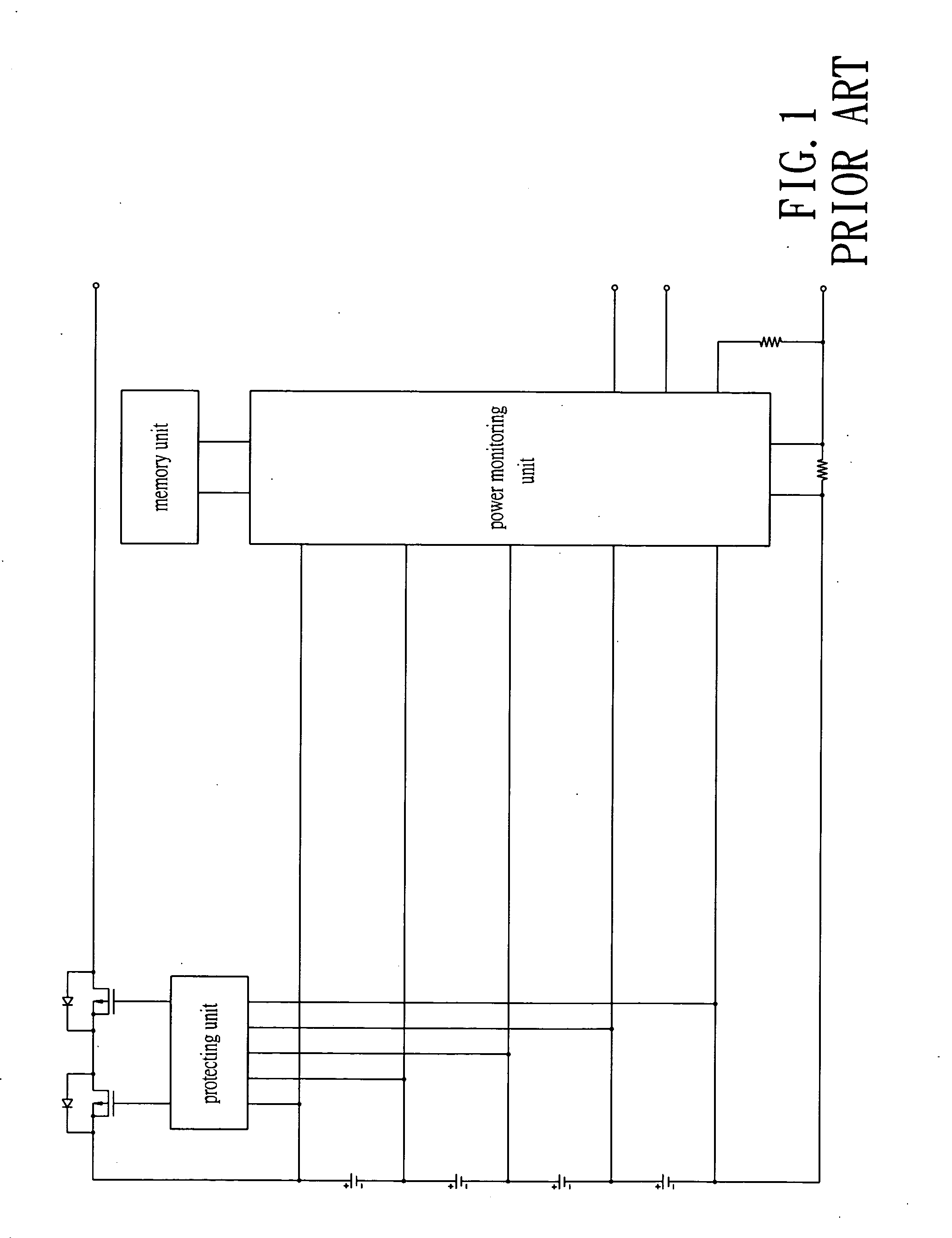
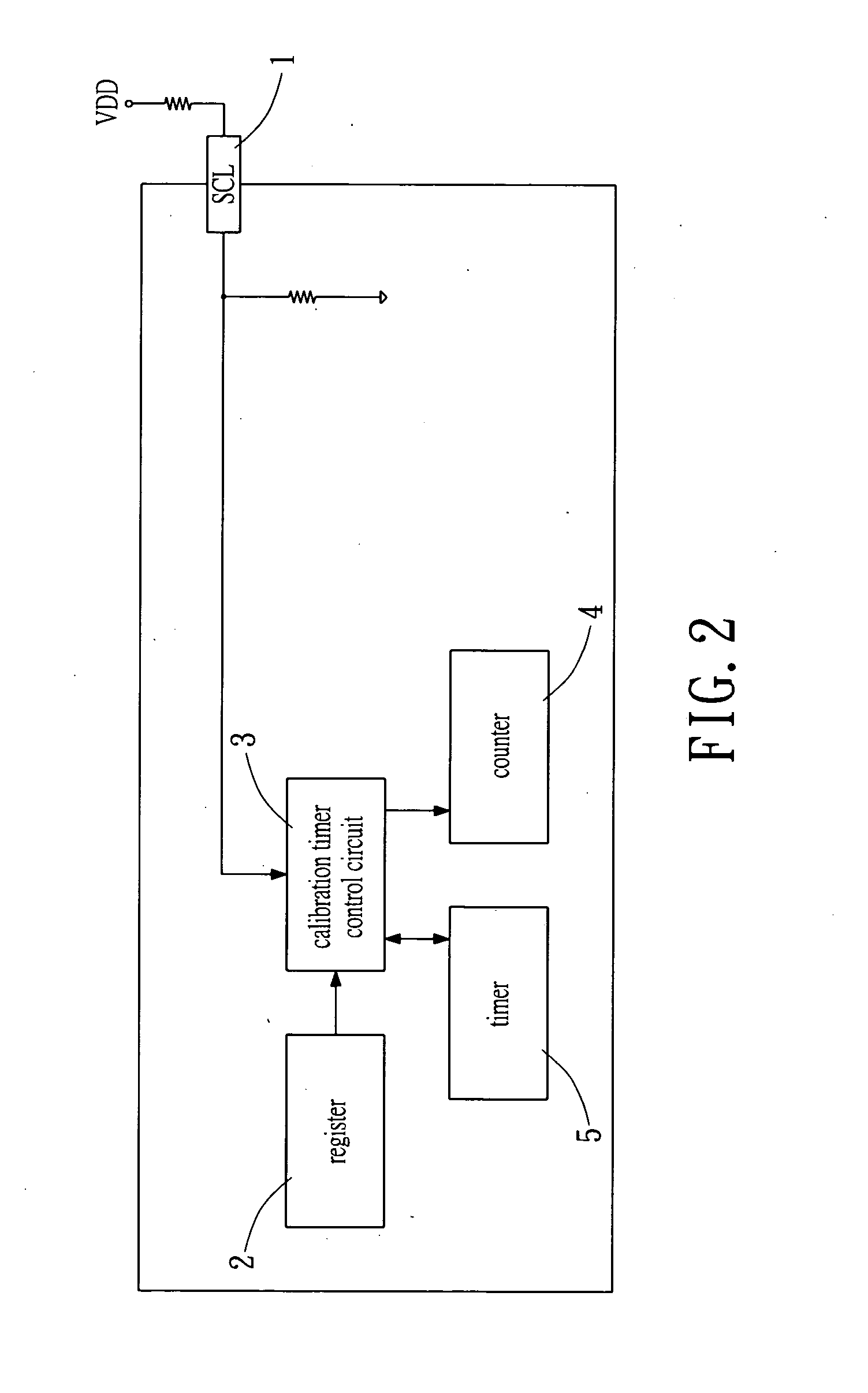
Method and device for clock calibration
InactiveUS7200507B2Batteries circuit arrangementsElectrical measurementsRechargeable cellControl circuit
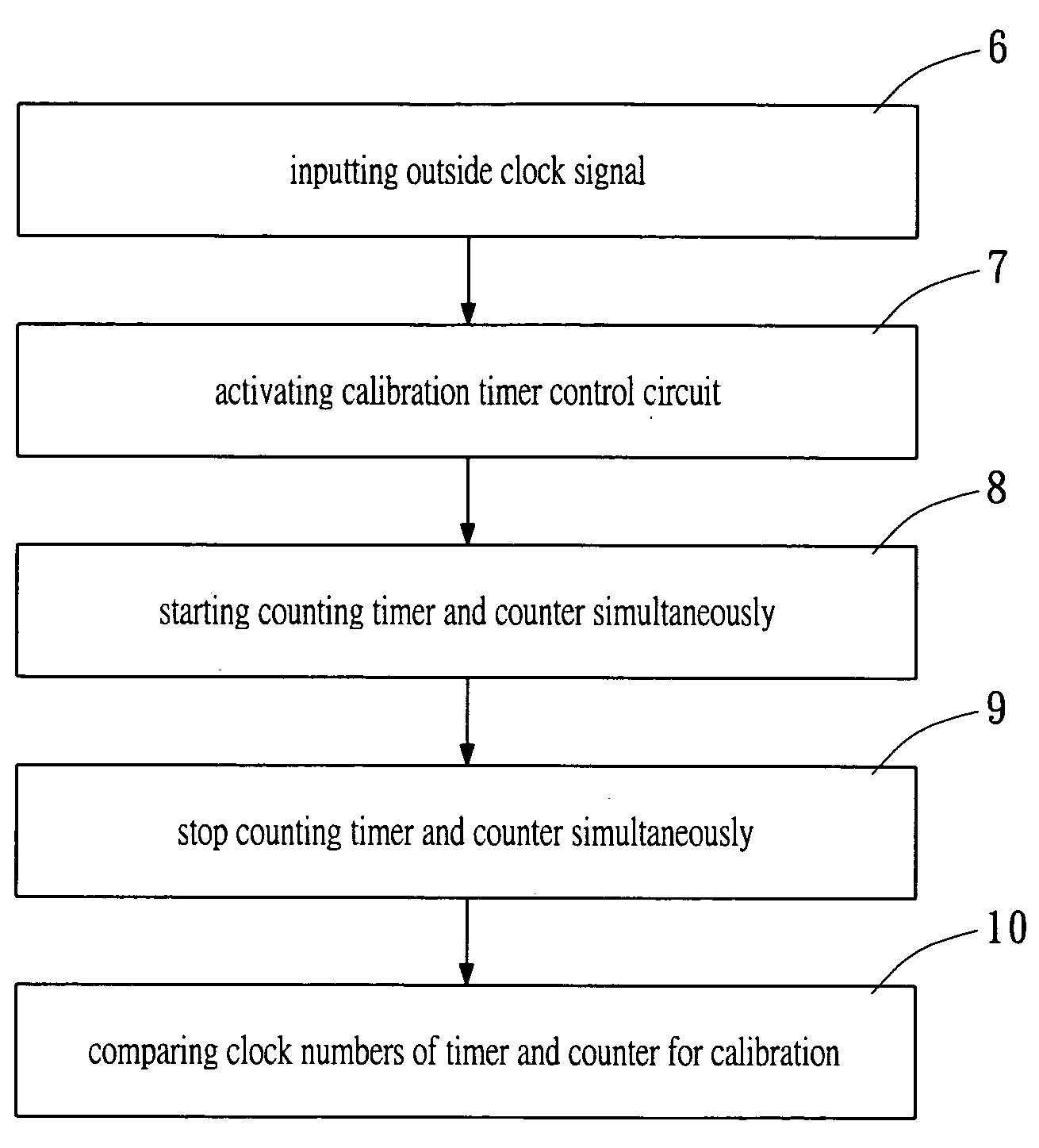
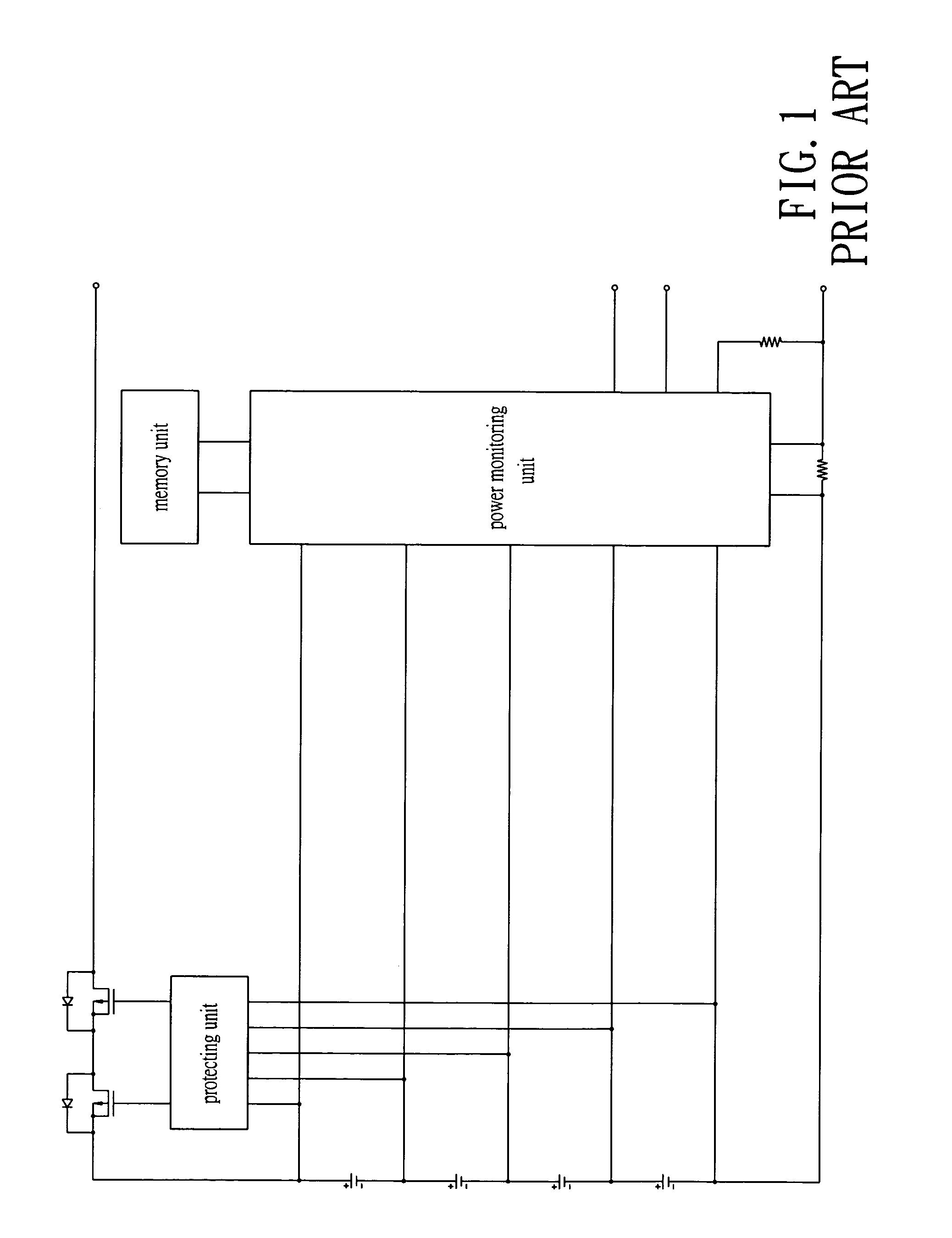
A method and a device for calibrating an interior clock generator installed inside a power monitoring unit of a rechargeable battery. The device includes an input pin for inputting an external clock signal from an exterior clock generator installed outside the power monitoring unit. A calibration timer control circuit is connected to the input pin. A register is connected to the calibration timer control circuit for outputting a start signal to activate the calibration timer control circuit. A counter and a timer are controlled by the calibration timer control circuit to be activated simultaneously therewith to count the outside clock signal and an internal clock signal generated from the interior clock generator, respectively. Such that the timer stops counting when the counter stops counting, a first count of the timer is compared to a second count of the counter to calibrate the interior clock generator.
Owner:FORTUNE SEMICON
Method and corresponding device for taming crystal oscillation frequency of time-keeping device
InactiveCN102436174AReduce manufacturing costSmall device sizeSynchronous motors for clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesNavigation systemFirst generation
The invention discloses a method and corresponding device for taming crystal oscillation frequency of a time-keeping device, which comprises the following steps of: step 1, acquiring the standard time pulse A that is located and output by a navigation satellite; step 2, acquiring the standard time pulse B output by device crystal oscillation fractional frequency; step 3, measuring the clock difference between the standard time pulse A and the standard time pulse B; and step 4, if clock difference exists between A and B, adjusting the crystal oscillation frequency of the device to make the clock difference be in the allowed scope. For the time-keeping equipment with pressure control and temperature compensating crystal oscillation or pressure control crystal oscillation, the frequency deviation of the corrected crystal oscillation can be detected in real time by the method provided by the invention to eliminate the time-keeping error caused by crystal oscillation frequency deviation and avoid accumulation of error. Therefore, the invention is suitable for various satellite navigation systems, such as GPS, Beidou first generation navigation satellite, Beidou second generation navigation satellite, GLONASS, GALILEO and other satellite navigation systems.
Owner:TECHTOTOP MICROELECTRONICS
Chronometric, communication, identification, and tracking tag
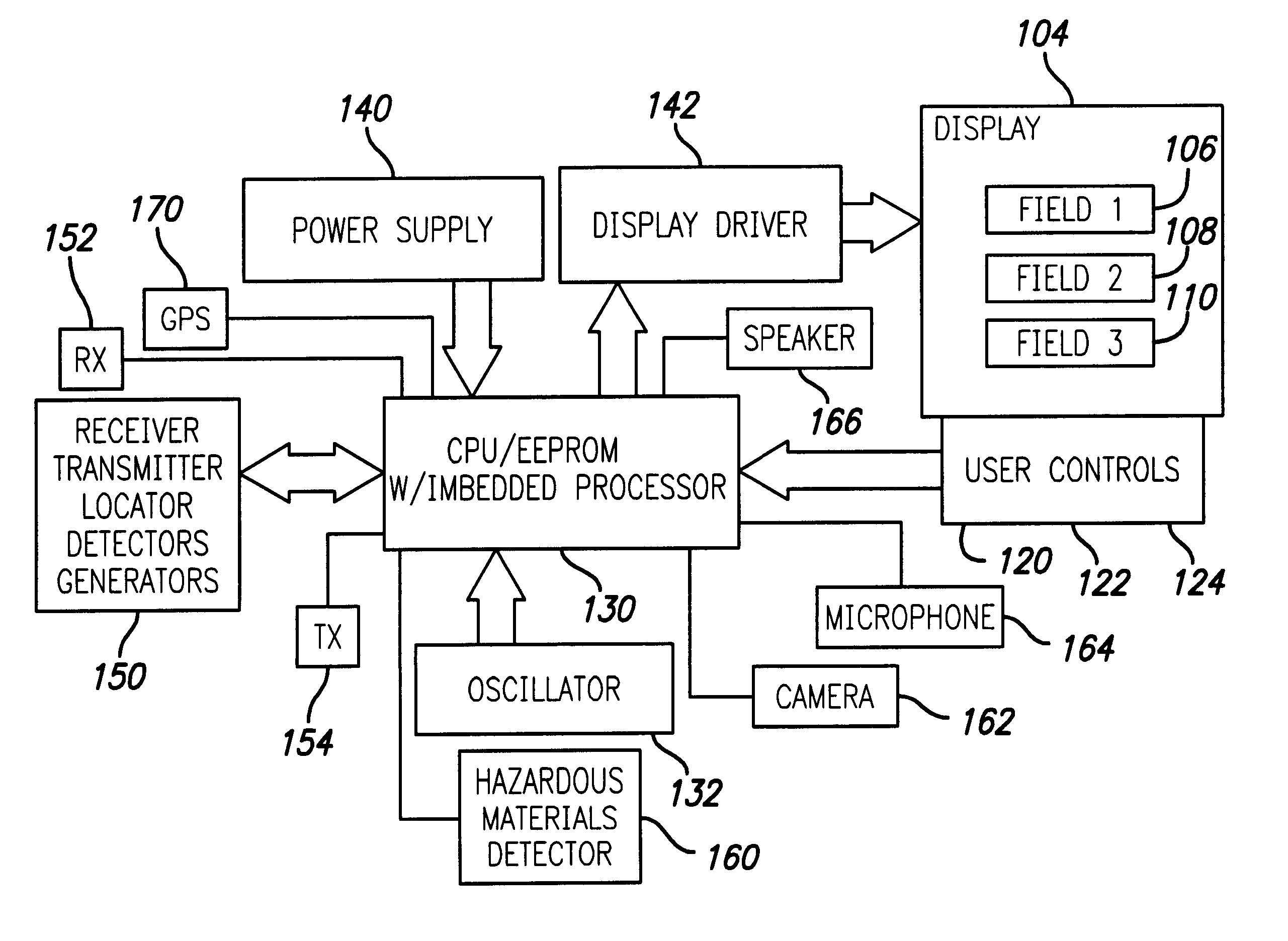
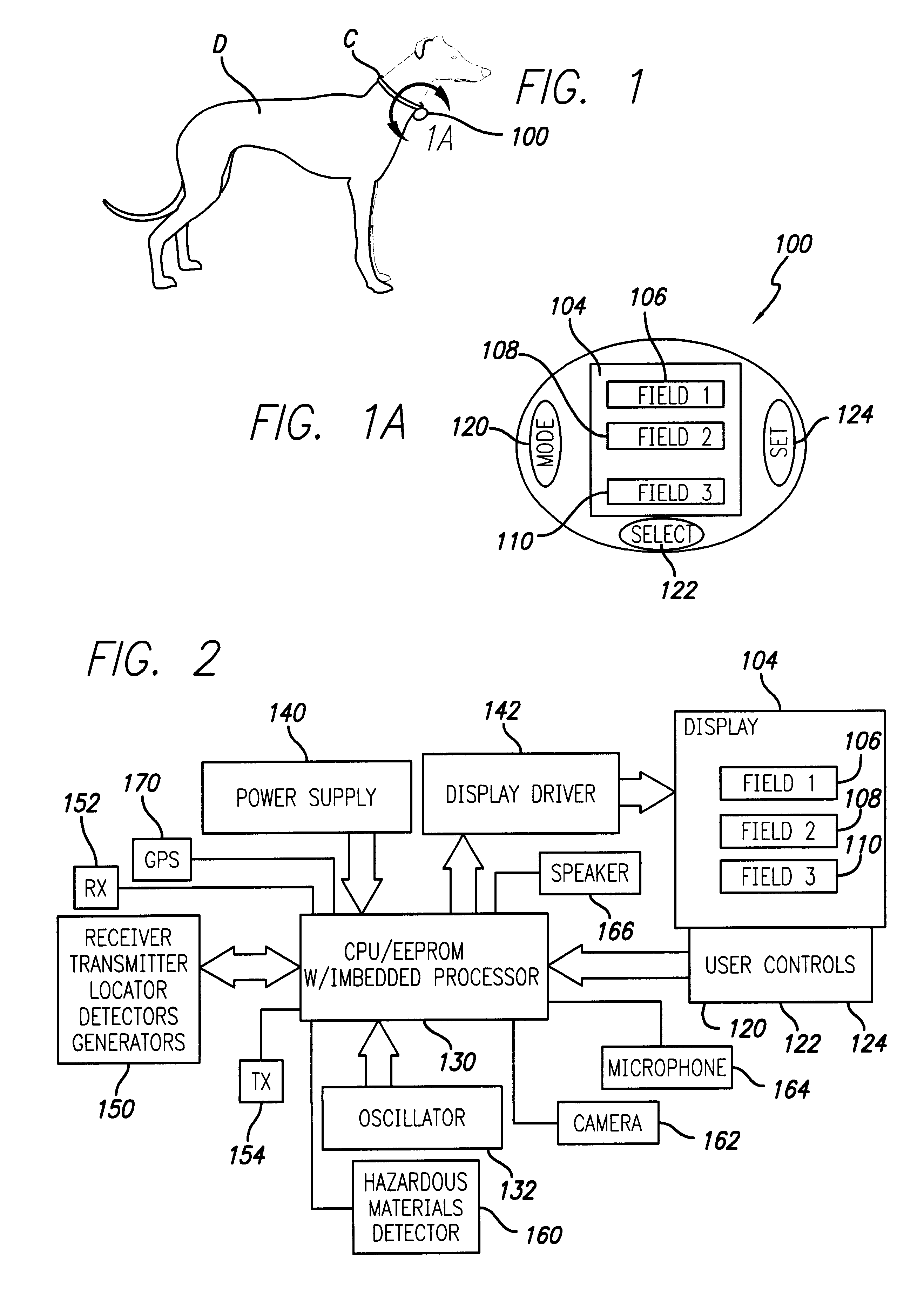
InactiveUS6721681B1Improve effectivenessBetter able to locate suchTime indicationVisual indicationsHazardous substanceCombined use
A chronometric identification and location tag for an animal, such as a dog, that incorporates a variety of detection and sensing functions as well as communication capacities. Assembled in a compact form that allows ready transport on a trainable animal, such as a dog, the chronometer identification and location tag enables the location of the associated animal, as well as the transmission and reception of information and data. Specific embodiments include the use of GPS to provide location data, as well as an alternative location system using temporary or permanent antenna installations. Hazardous material, visual, and acoustic detectors and other sensors and / or generators may be used in conjunction with transmission facilities for providing data regarding the animal's environment. Information and signals may be transmitted to the central controller by a receiver and a speaker can provide for audio signaling to the animal or others close to the animal in an audible range of the speaker.
Owner:KLT TECH LLC
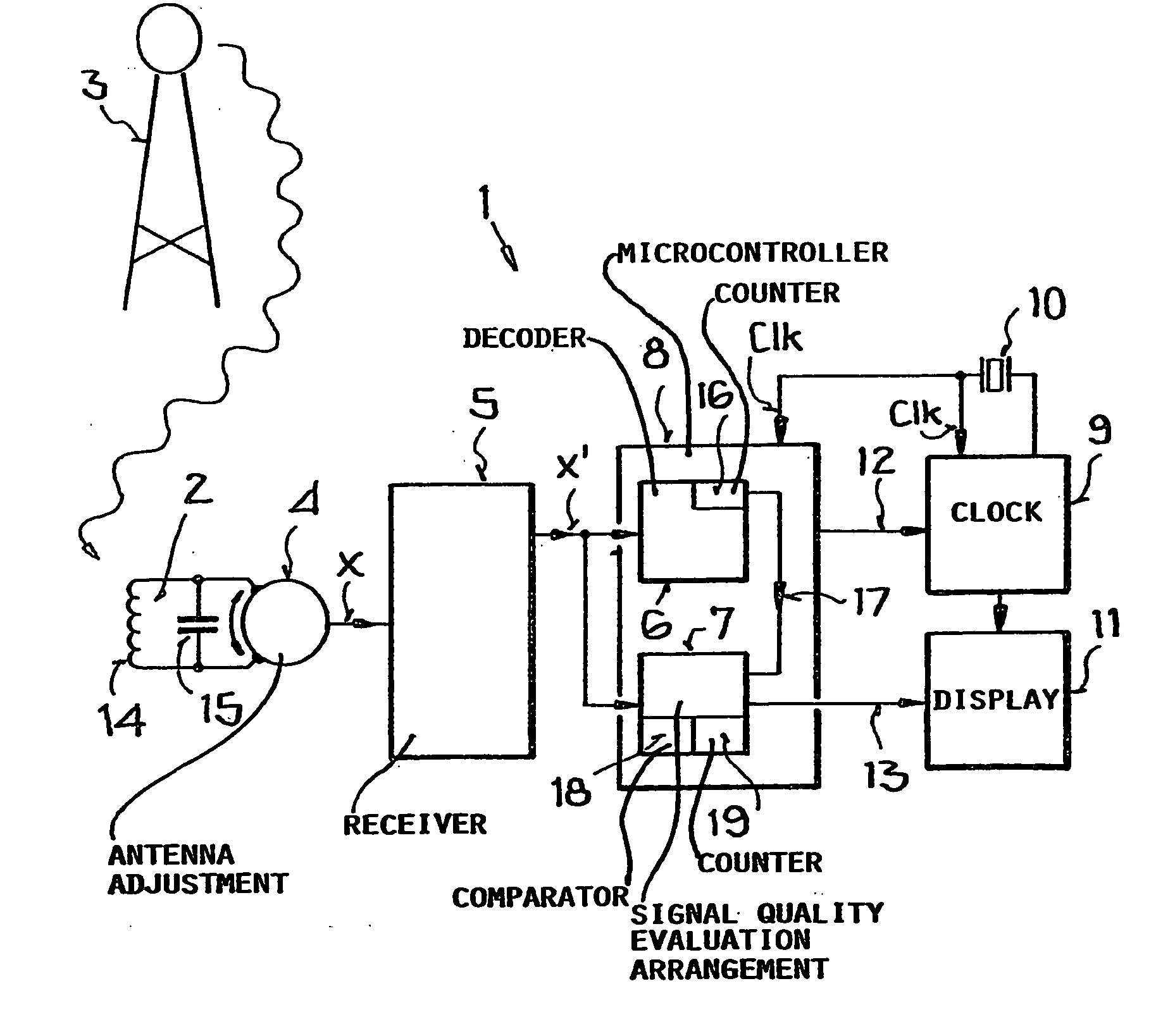
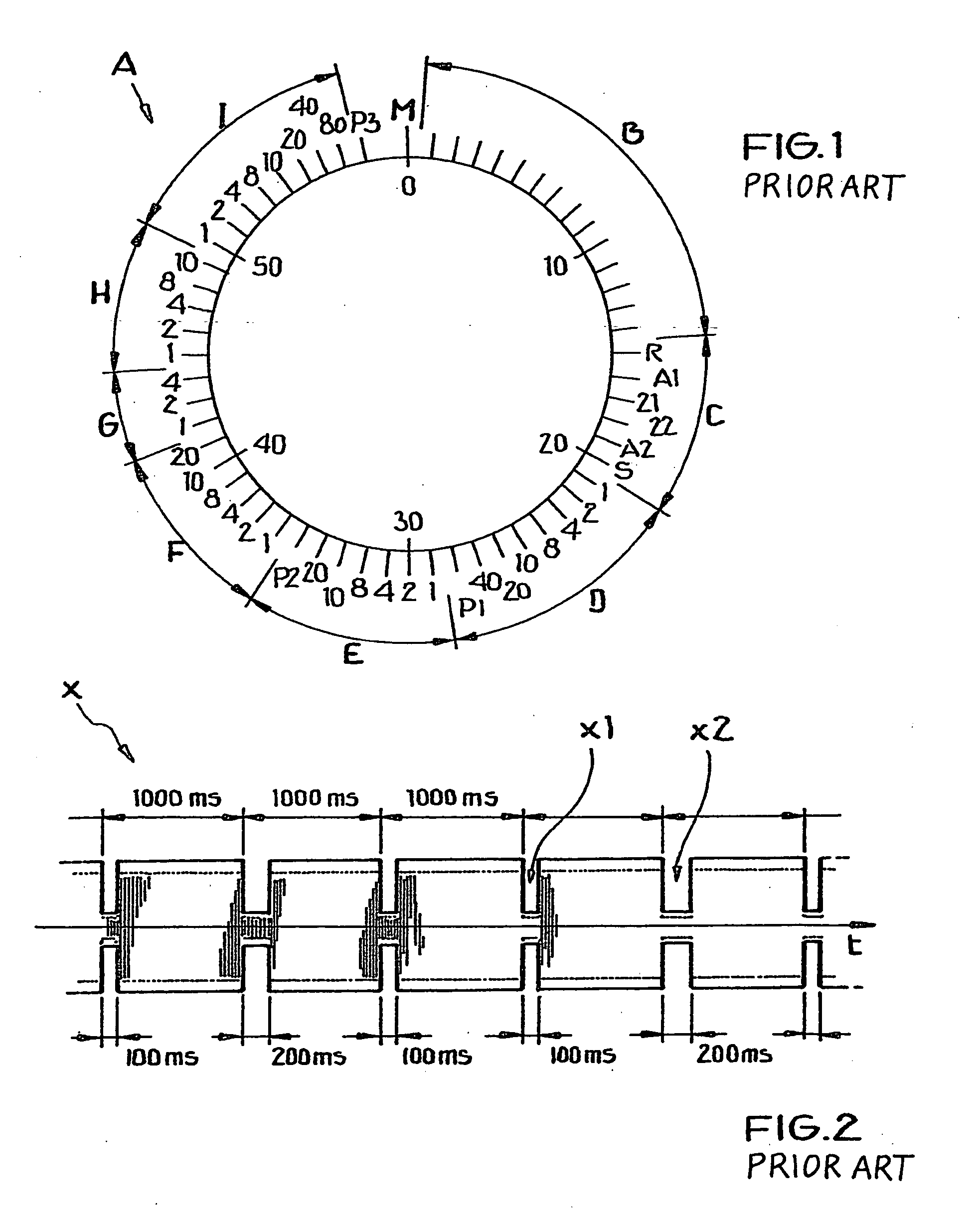
Radio-controlled clock and method for determining the signal quality of a transmitted time signal
InactiveUS20050175039A1Simple wayImprove signal qualityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTemporal informationActual Duration
A transmitted time signal carries time information encoded bit-wise by signal variations in a succession of constant duration time frames, with at least one bit in each time frame. A signal quality is determined and allocated to a respective bit, e.g. depending on the extent of deviation of an actual duration from prescribed durations of a signal variation representing the bit. Thus, a respective signal quality may be allocated to a respective decoded data bit per time frame. Successive data bits can be categorized as interference-free or interference-burdened, and a signal quality of the received time signal can alternatively be determined from the number or ratio of the interference-free bits and the interference-burdened bits. A radio-controlled clock circuit includes a receiving circuit, a bit value decoding arrangement and a signal quality evaluating arrangement.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY +1
Method and apparatus for frequency correcting a periodic signal
InactiveUS20060045215A1Pulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal generatorPhysics
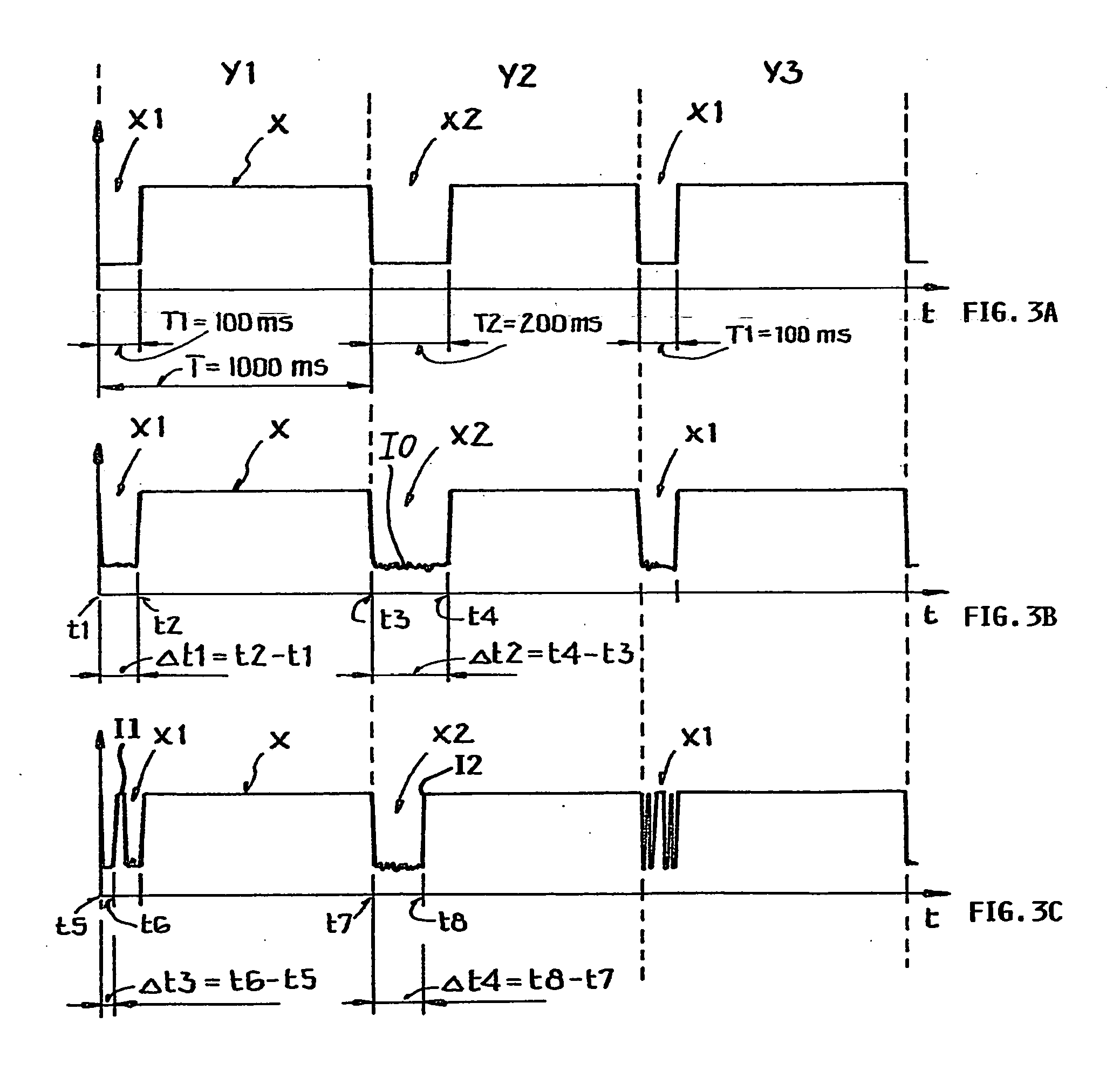
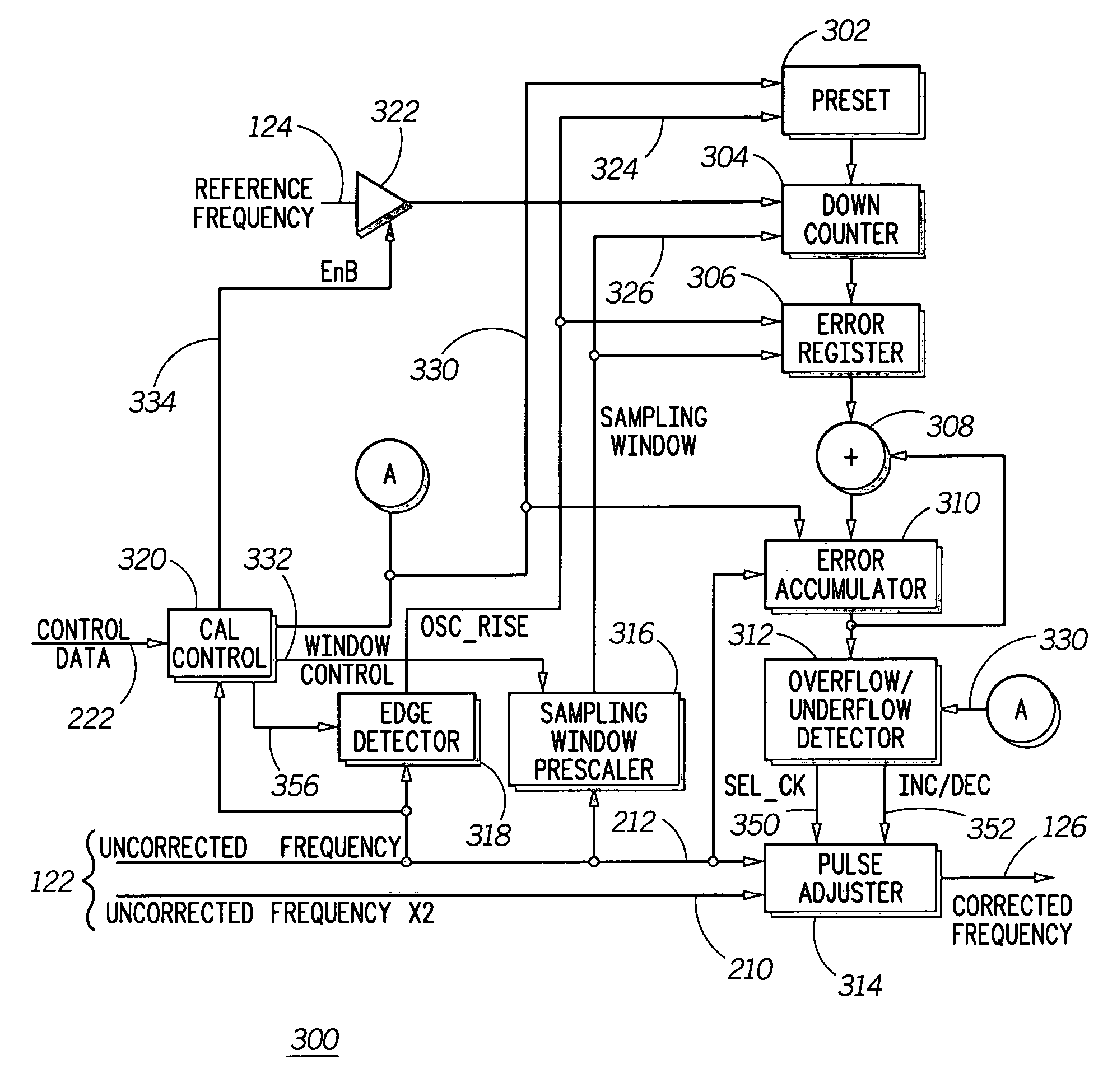
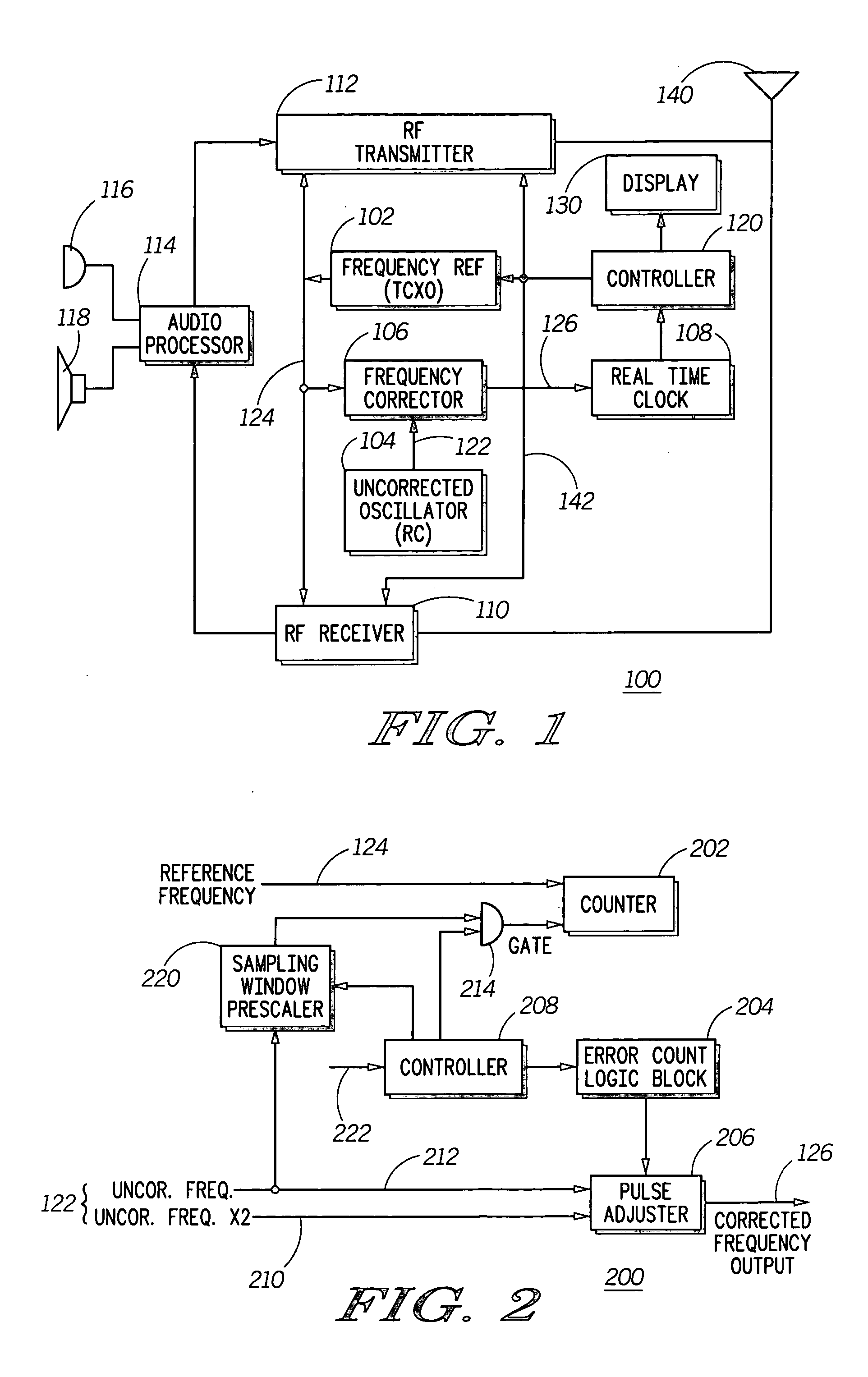
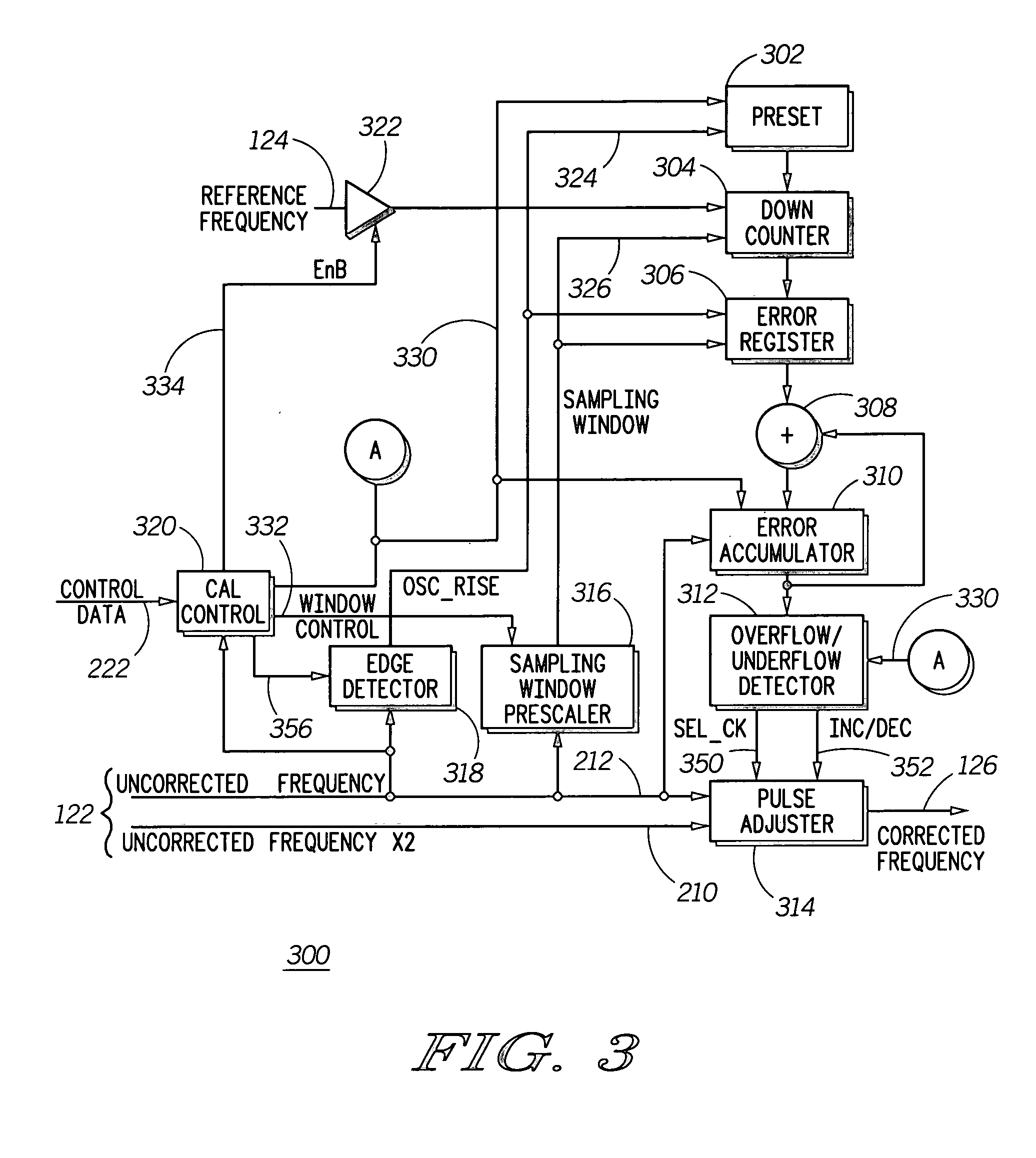
A method and apparatus to correct a periodic signal, such as a frequency reference, based upon another frequency reference. A lower accuracy frequency signal generator (104) provides an uncorrected frequency reference signal (122) to a frequency corrector (106). Frequency corrector (106) counts cycles of a frequency reference signal (124), as generated by a higher accuracy reference generator (102) for a time period derived from the uncorrected frequency signal. Based upon the cycles counted, pulses are added or removed from the uncorrected frequency signal (122) to produce a corrected frequency signal (126). A ratio of pulses to be removed from the uncorrected frequency signal (122) is determined from the number of cycles counted and a counter arrangement is provided to automatically remove the required ratio of pulses from the uncorrected frequency signal (122).
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
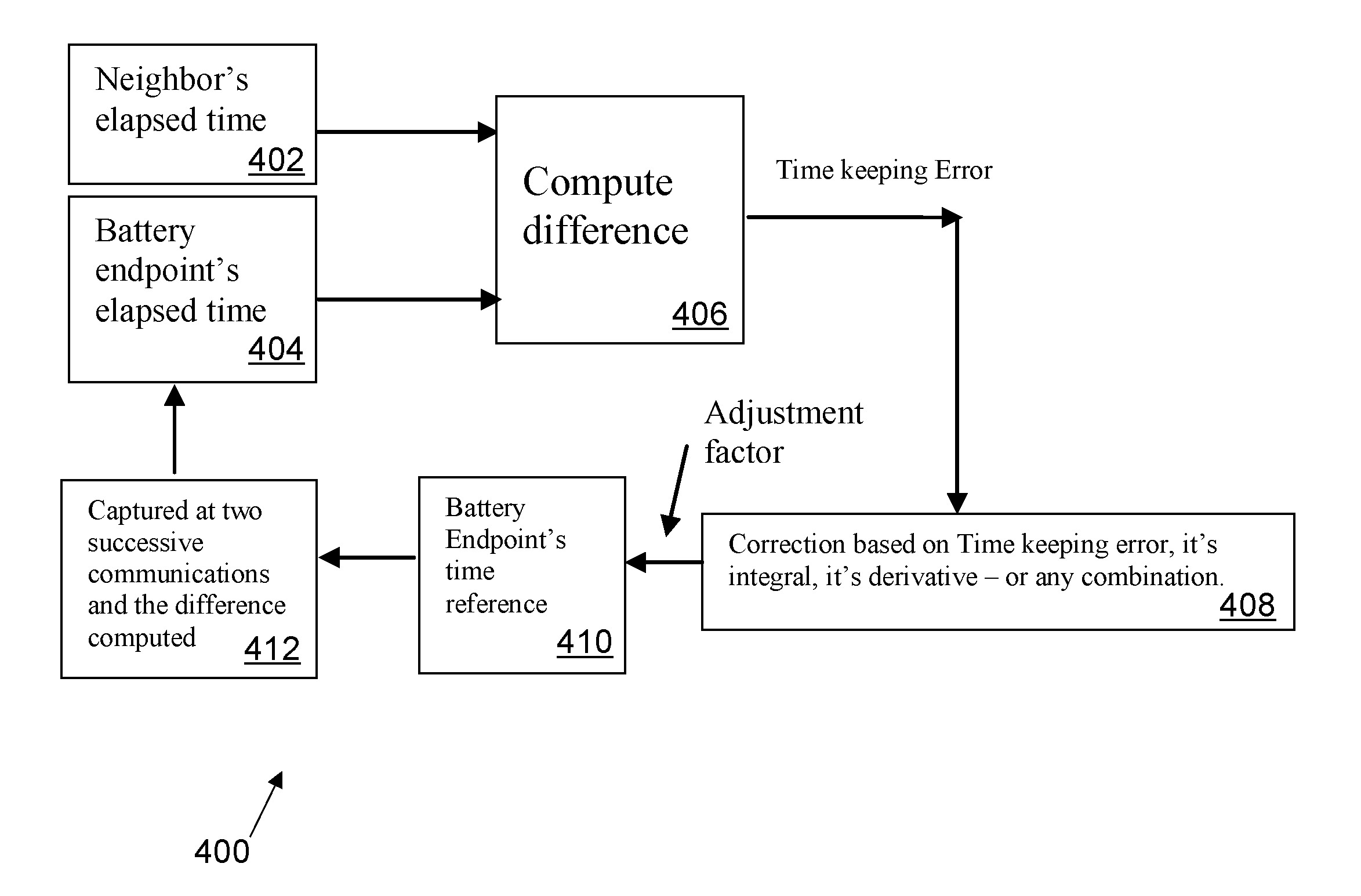
Methods and Systems for Accurate Time-Keeping on Metering and other Network Communication Devices
ActiveUS20090179771A1Accurately keep track of timeAccurate trackingElectric signal transmission systemsMechanical clocksRadio networksNetwork communication
Methods and systems for providing accurate time-keeping on battery-powered communication devices used in AMI systems, mesh networks, and multi-channel radio networks. One embodiment allows the use of low power (and low cost) crystals in battery-powered endpoints by periodically correcting the poor timing of these crystals using communications with a nearby, non-battery-powered device. Such communications allow the battery-powered devices to align their timing with that of their non-battery neighbors, among other things.
Owner:LANDISGYR INNOVATIONS INC
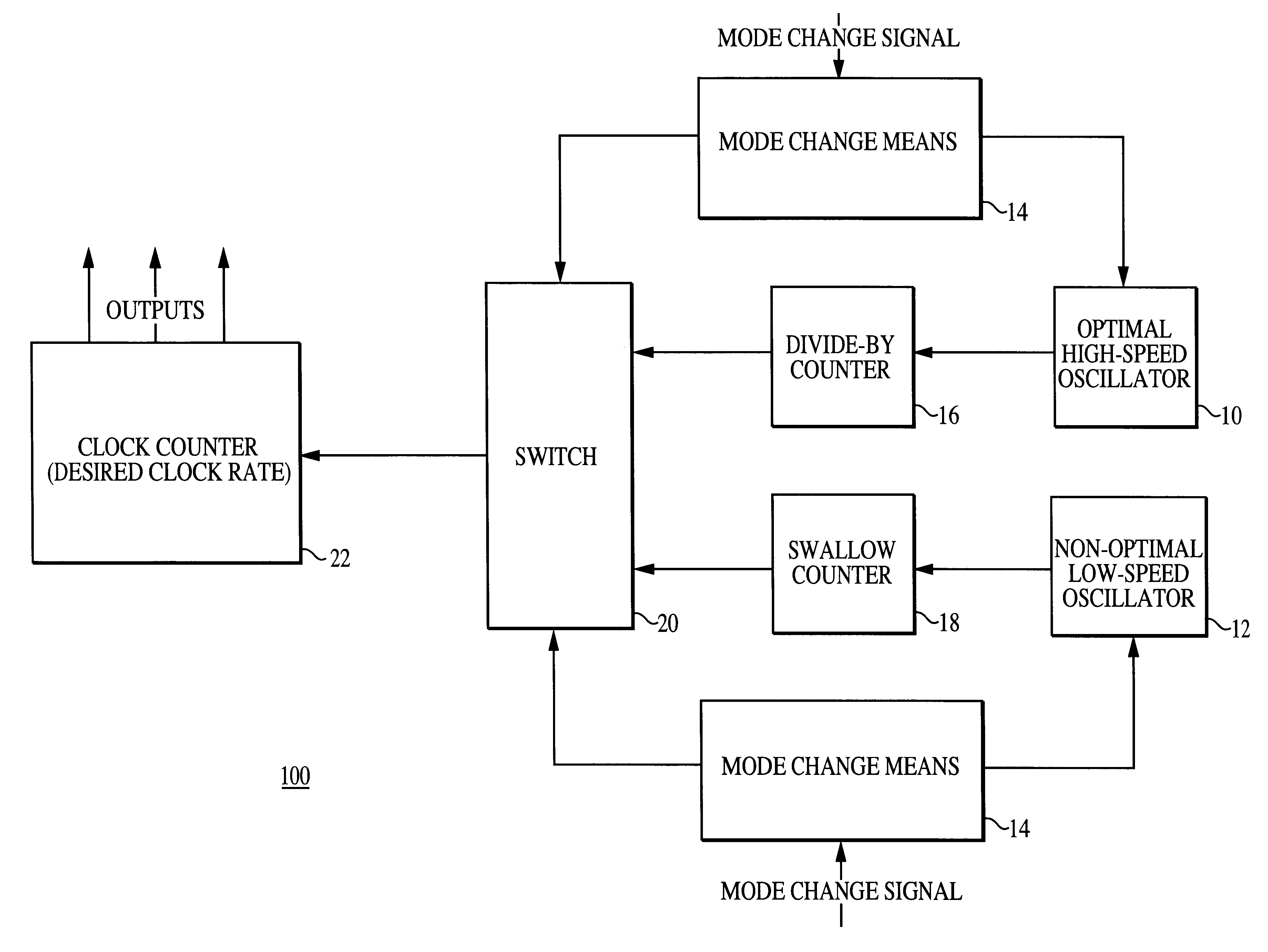
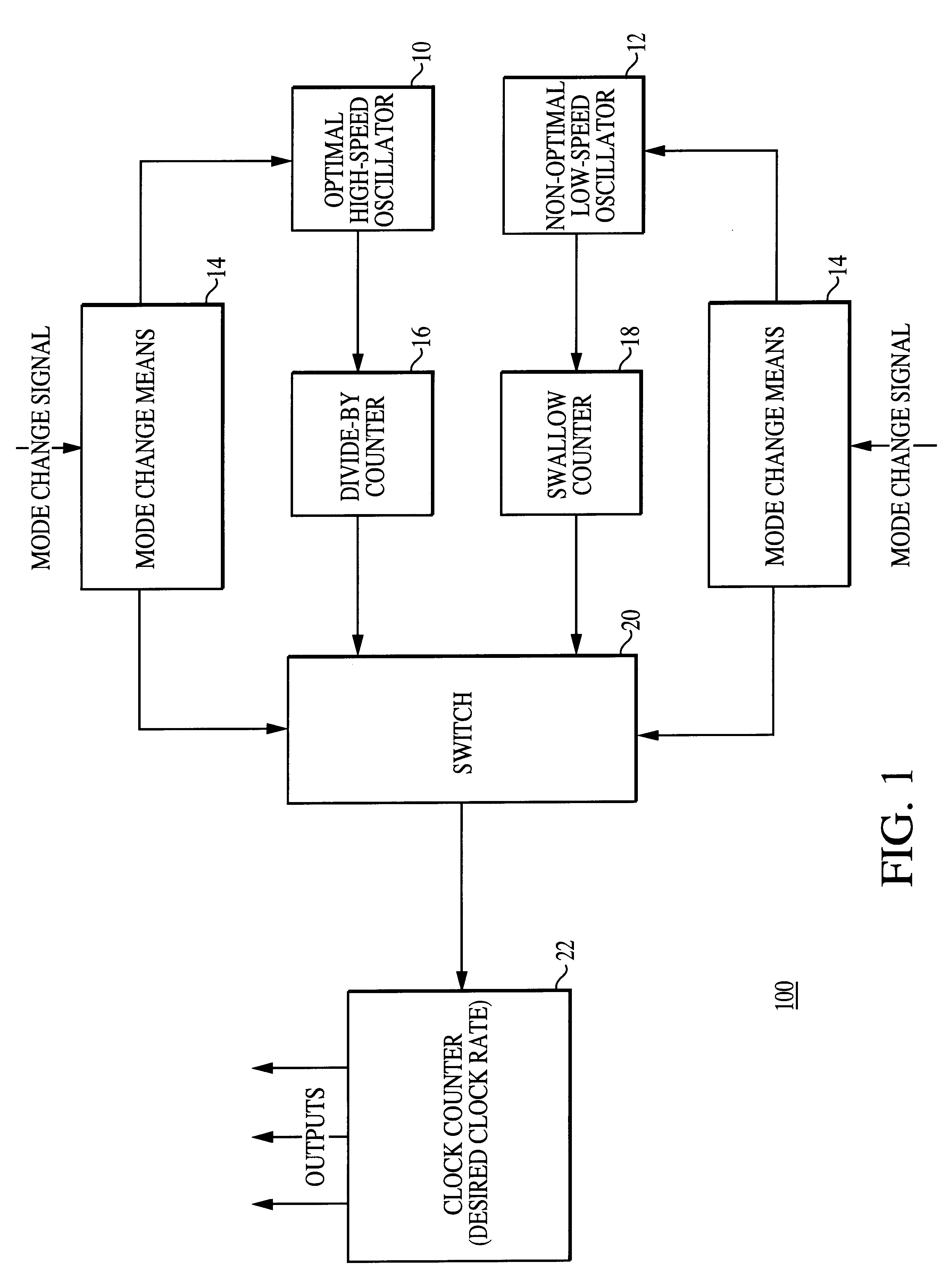
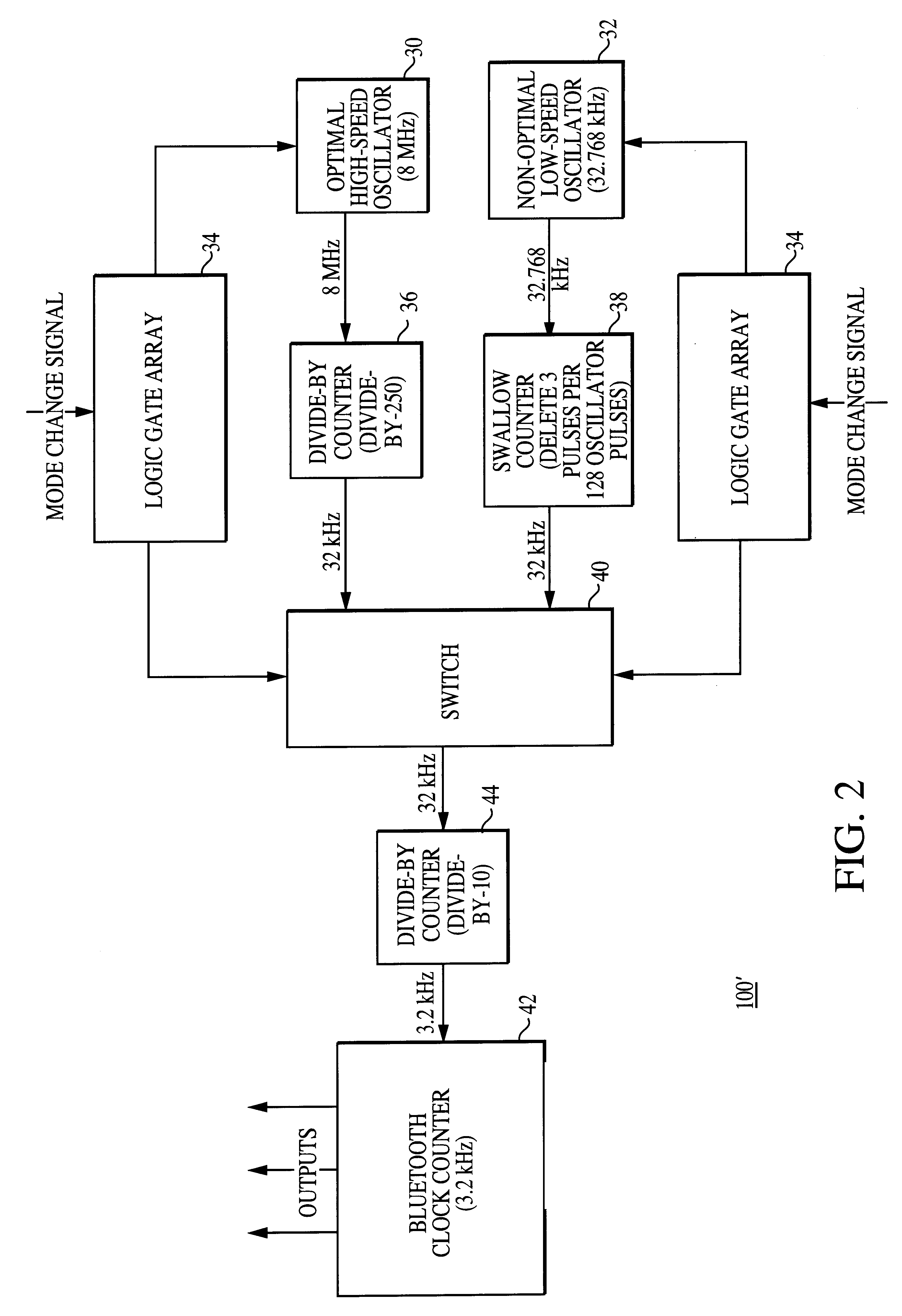
Method and apparatus for implementing a high-precision interval timer utilizing multiple oscillators including a non-optimal oscillator
InactiveUS6292062B1Reduce power consumptionImplement switchPulse automatic controlError detection/correctionLow speedTwo step
The present invention is a novel method and apparatus for implementing a high-precision timer utilizing a non-optimal oscillator and a high-speed oscillator wherein only one oscillator is enabled at a given moment in time. The high-precision timer method and apparatus comprises a timer and an error-correction technique. In one embodiment, the timer of the present invention is constructed from a high-speed oscillator and a low-speed non-optimal oscillator. The timer operates from the high-speed oscillator during on-the-air modes of operation and from the low-speed non-optimal oscillator during sleep modes of operation. The present inventive method corrects errors that are introduced by the non-optimal oscillator and a swallow counter. The errors are corrected using an error-correction technique having two steps: an error-determination step and an error-correction step. In the preferred embodiment of the error-determination step, a total error for a time interval is determined by performing the following steps: (1) calculating an individual error that occurs at each pulse; (2) multiplying the individual error by the number of pulses occurring during the time interval; and (3) adjusting for a non-optimal counter. Once an error has been determined, the error-correction step adjusts a clock counter accordingly. Depending upon the error-correction technique used, the error-correction step can correct the total error at one of several locations within a timer counter chain that is used to practice the present invention. The implementation of the present invention allows a straightforward realization of multiple timers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Clock-temperature-error compensation method and system thereof
InactiveCN102591197ALow priceReduce manufacturing costSynchronous motors for clocksSynchronisationCrystal oscillatorCompensation methods
The invention relates to the field of related clock error compensation technology, and in particular relates to a clock-temperature-error compensation method and a system thereof. The clock-temperature-error compensation method comprises the following steps of: measuring the temperature at initial time, obtaining and storing a first temperature value, and storing the first temperature value; after measuring time T, measuring the temperature again and obtaining a second temperature value; adopting the first temperature value or the second temperature value as the measuring temperature, and according to the relation between the measuring temperature and the clock crystal-oscillator error, calculating and obtaining an error value of a clock; calculating a clock error of the measuring time T; repeatedly executing the steps from step 2 to step 4, till the clock error accumulated value is larger than a preset clock adjusting threshold, adding the value same as the clock adjusting threshold for the clock, and executing the steps from step 2 to step 4 again. The clock-temperature-error compensation method has the advantages that the clock compensation can be realized only by using the common circuit and algorithm without needing to use GPS or a function clock chip with expensive price and adjustable oscillating circuit frequency, so that the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUIZHOU DESAY SV AUTOMOTIVE
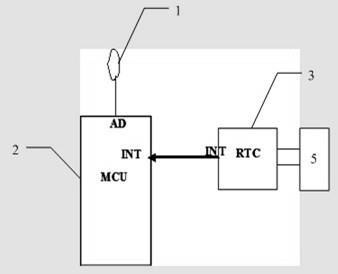
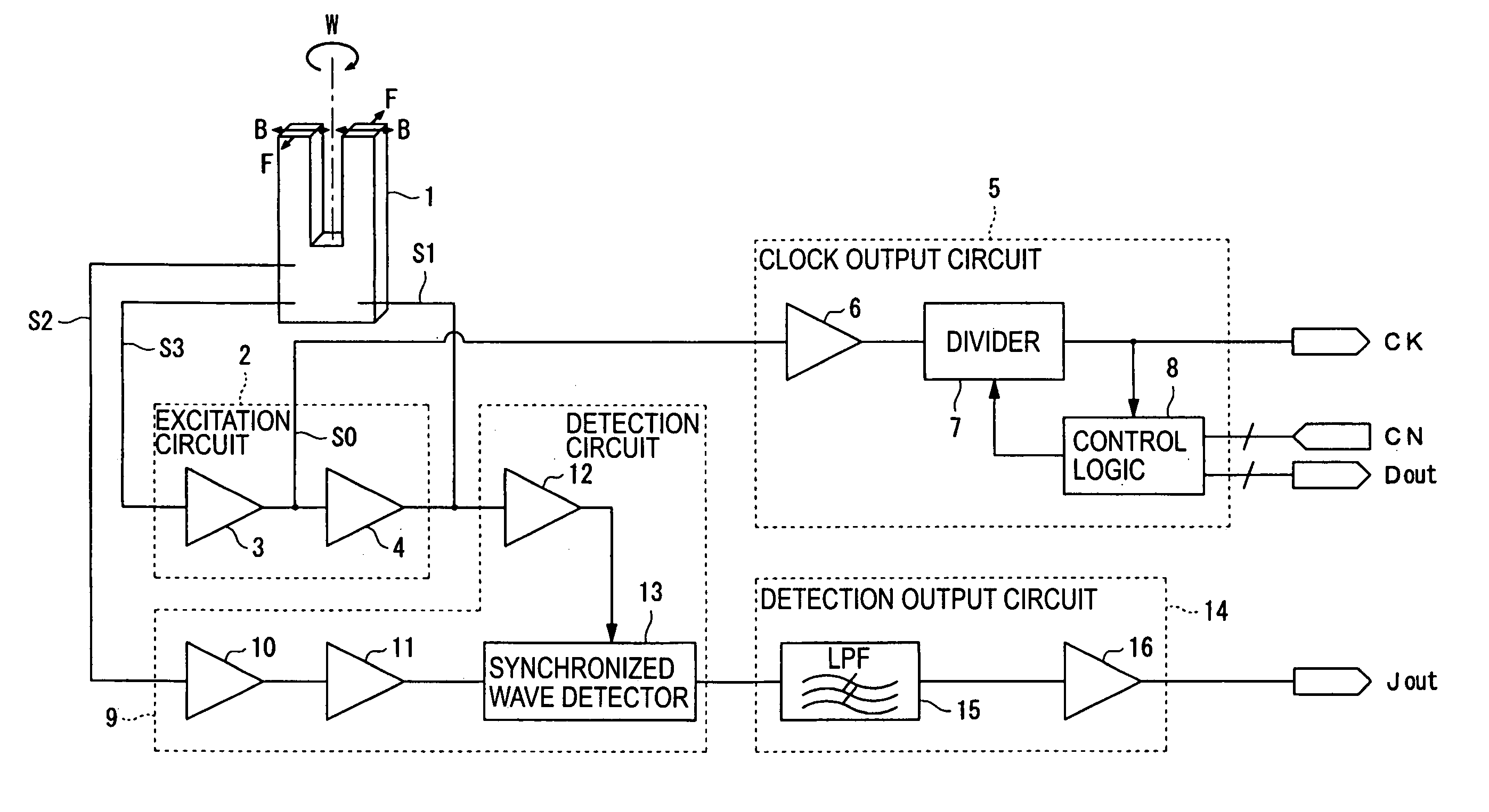
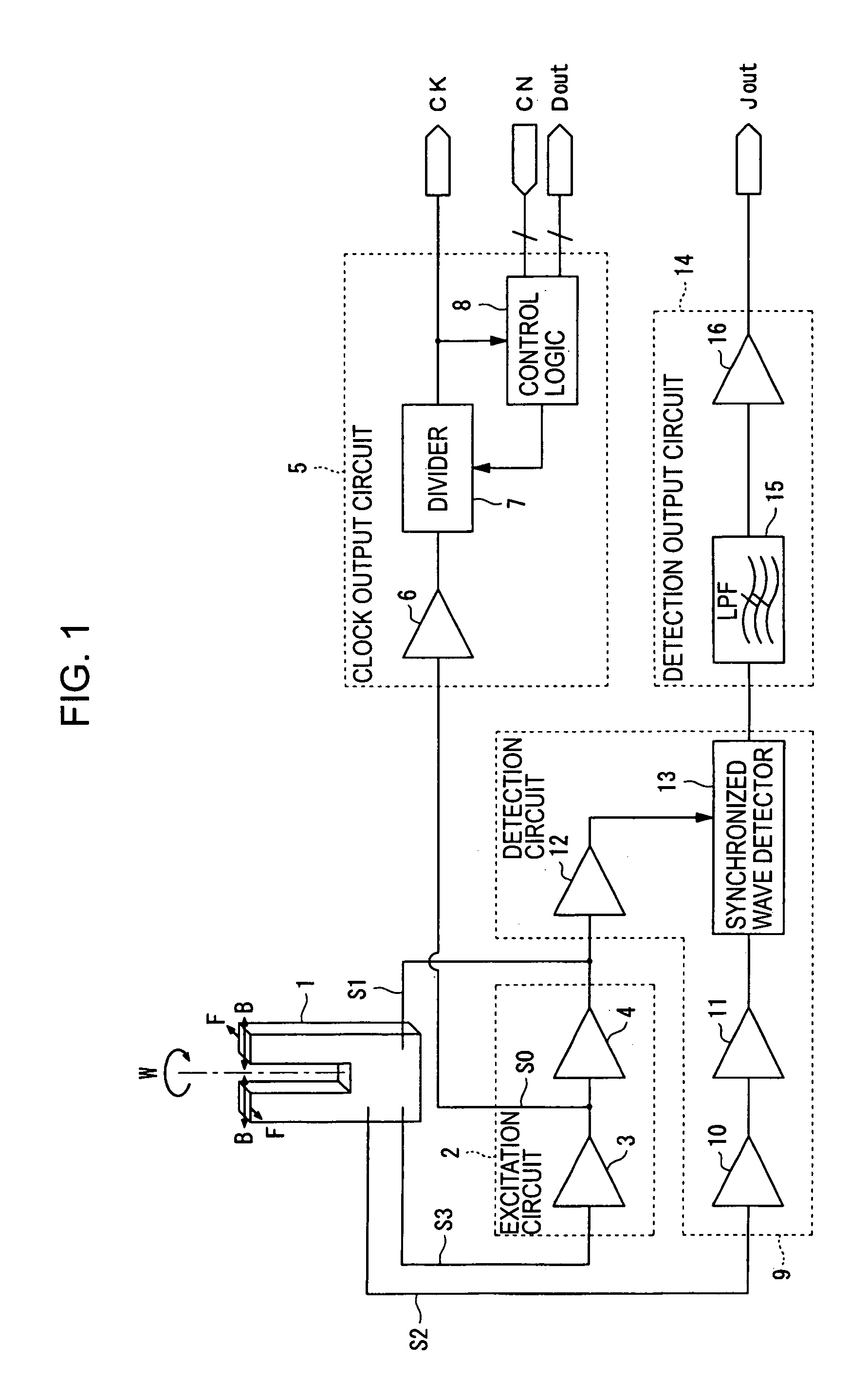
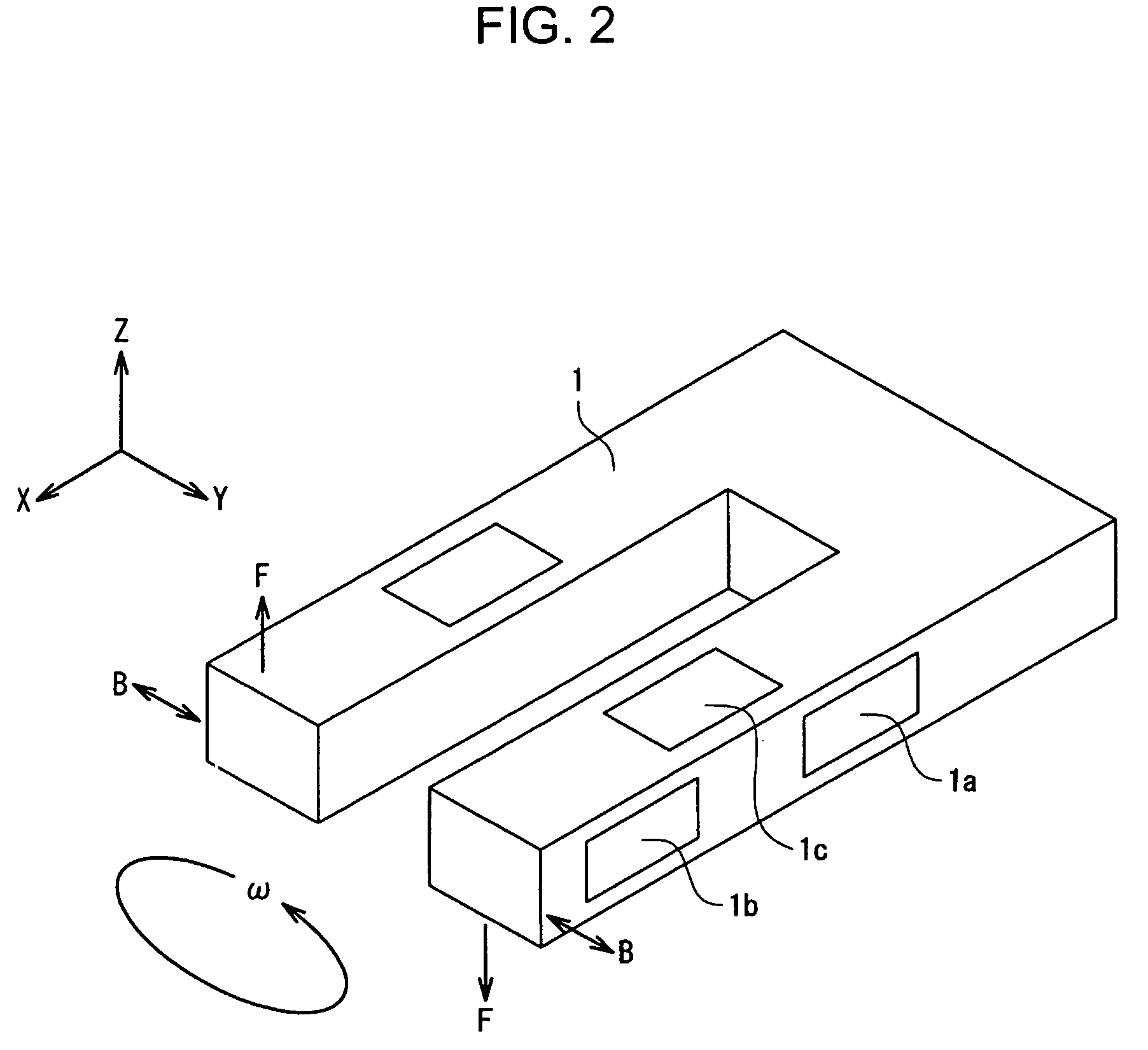
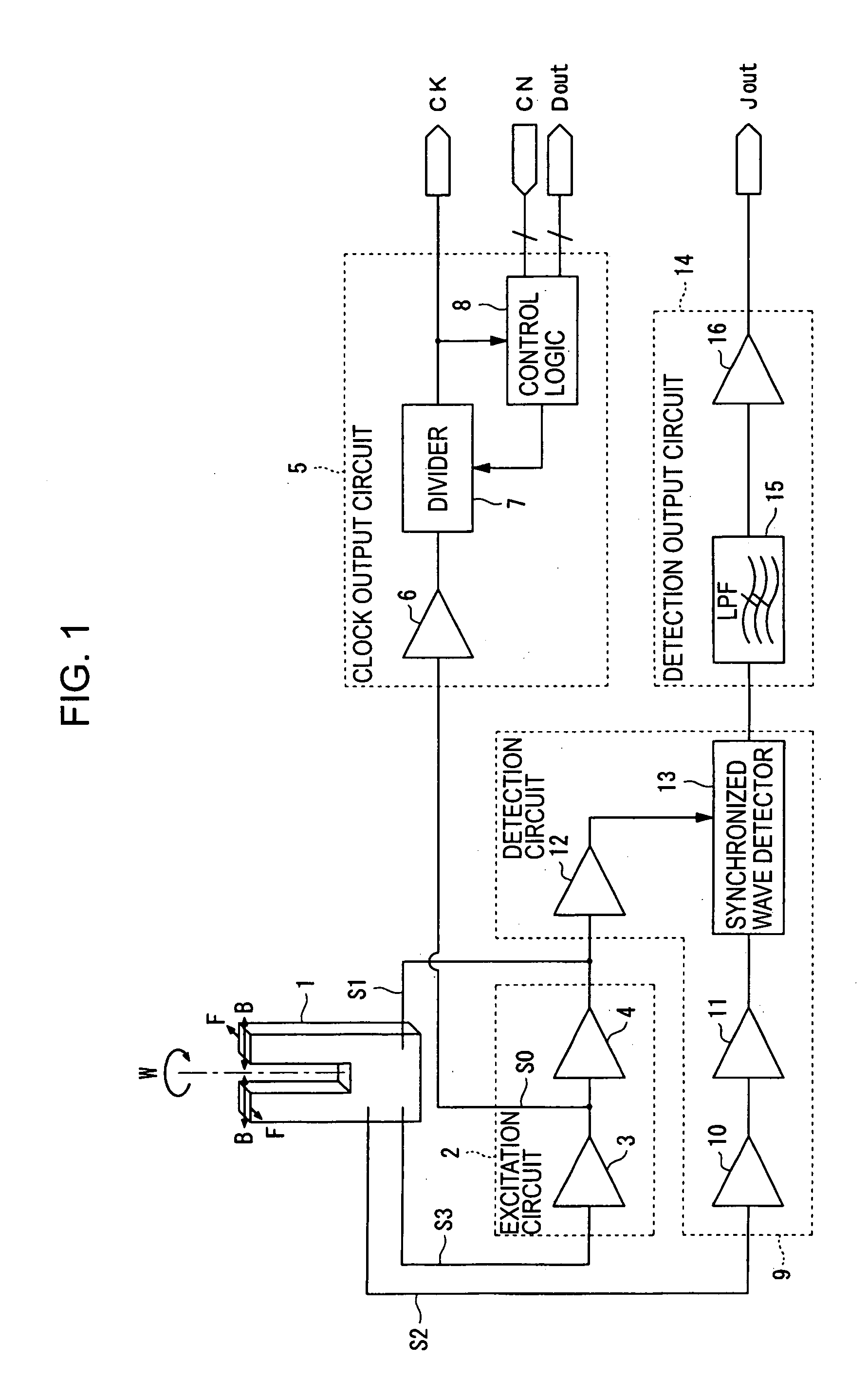
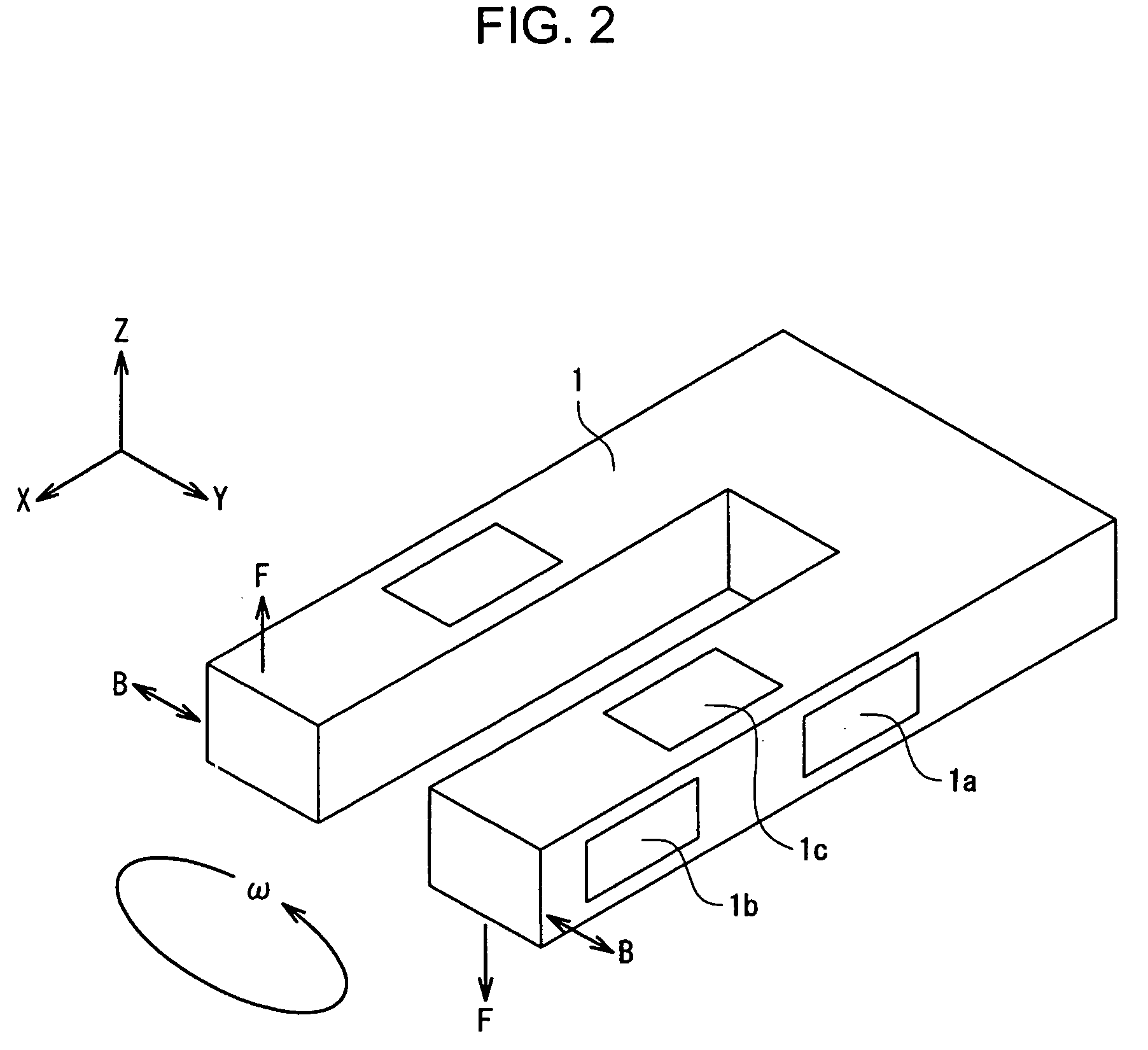
Clock generating device, vibration type gyro sensor, navigation device, imaging device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7258009B2Suppressing the device from being largeSubject to movementTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationTime informationGyroscope
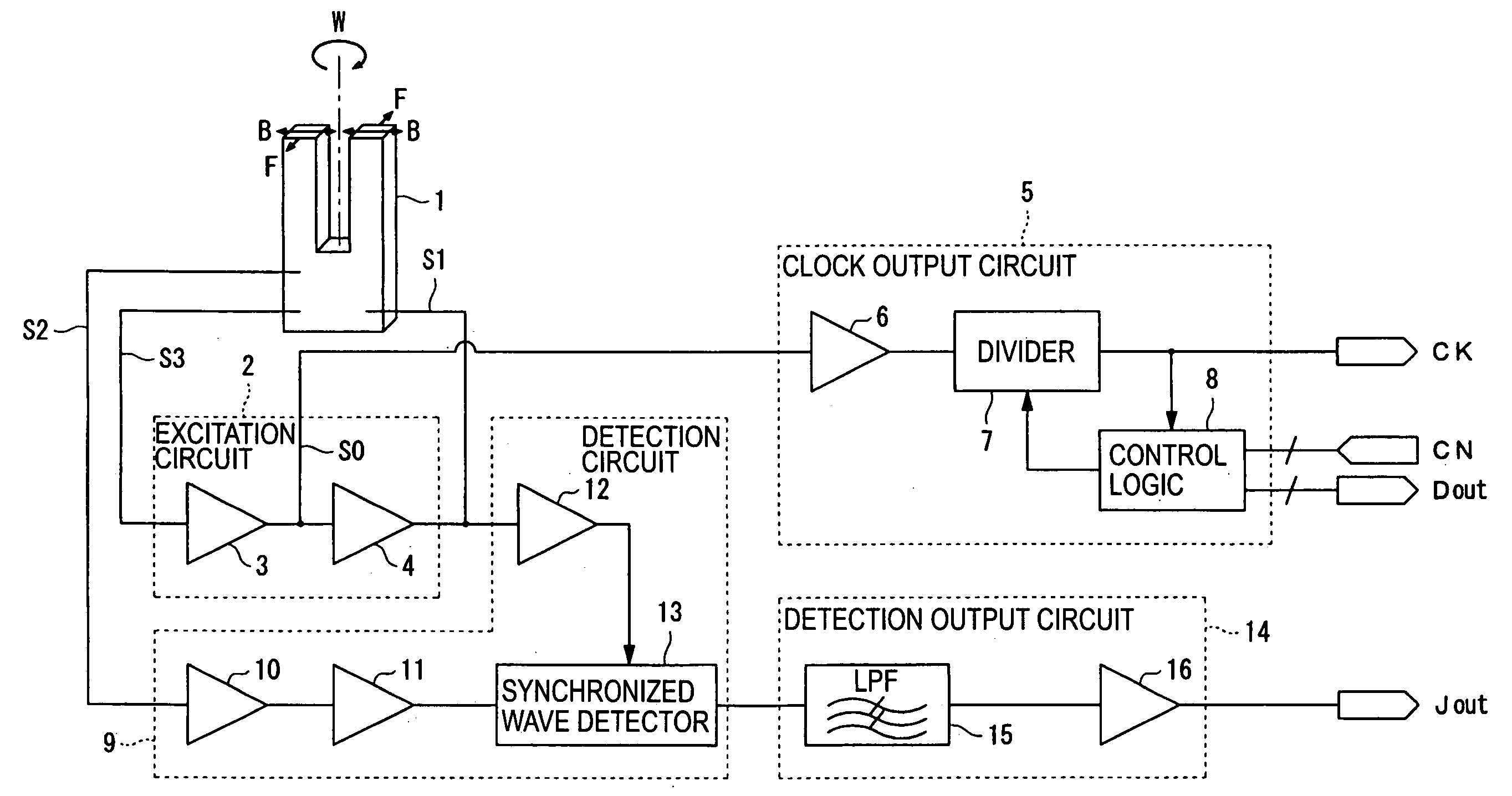
A vibration gyro sensor is provided which is capable of generating time information and detecting an angular velocity. A driving signal for driving a tuning fork piezoelectric vibrating reed is generated based on an excitation signal generated by an oscillation circuit. An angular velocity signal is obtained based on a detection signal generated by a detection electrode of the tuning fork piezoelectric vibration reed. The excitation signal generated by the oscillation circuit is input to a divider such that a timer clock signal is generated.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
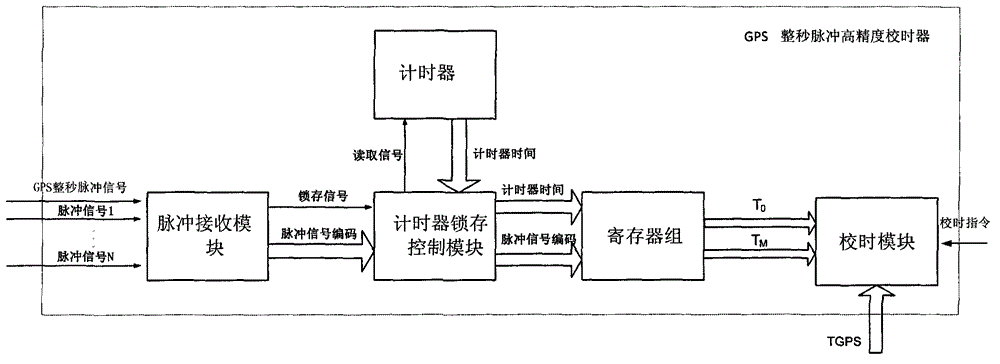
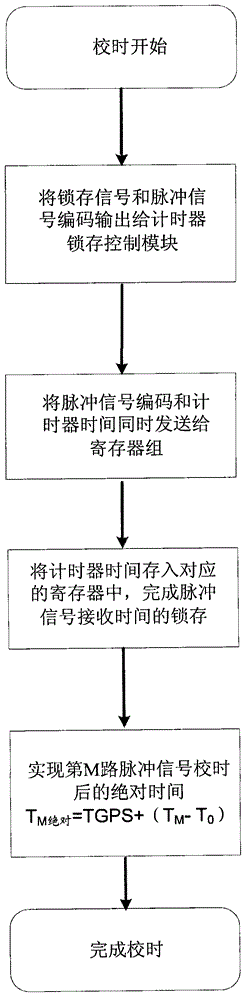
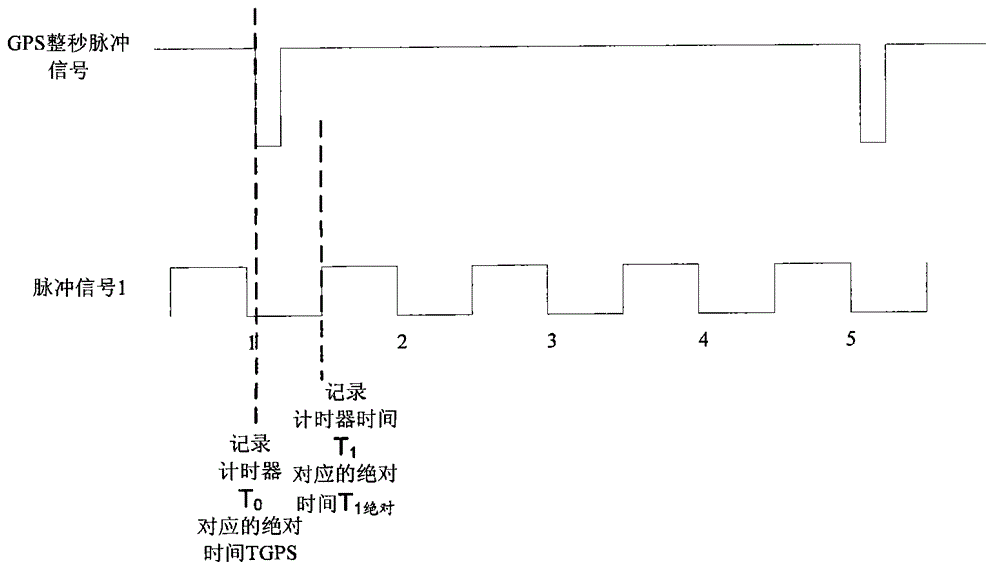
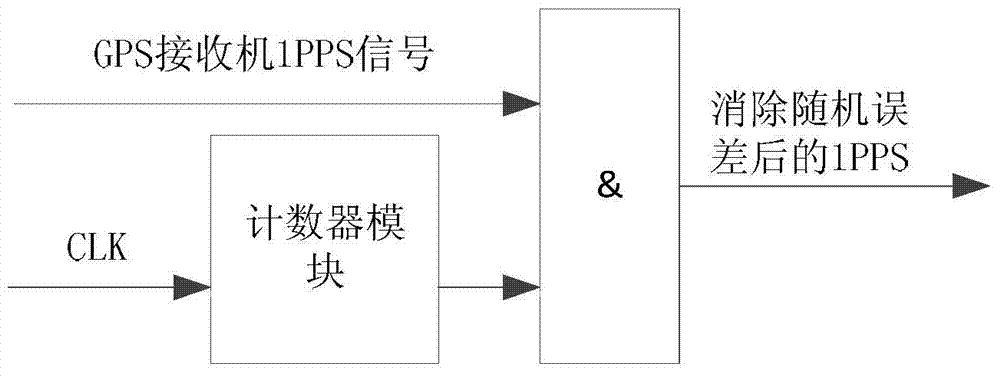
High-precision GPS (Global Positioning System) 1pps (1 Pulse Per Second) timer and timing method of spacecraft
ActiveCN102866621AHigh precisionHigh precision requirementsSynchronous motors for clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesTime errorProcessor register
The invention relates to a high-precision GPS (Global Positioning System) 1pps (1 Pulse Per Second) timer of a spacecraft. Time is recorded by a system timer according to relevant pulse signals with a hardware latch technology. For the first time, a pulse receiving module, a timer latch control module, a register block, a timing module and a timer are all utilized for timing of the pulse signals. Signal timing is realized by a hardware latch mode instead of a traditional software interrupt way. A time error is only limited to a hardware transmission error, and the hardware transmission error can be neglected in comparison to interrupt response time. The accuracy and the stability of the utilization of the GPS 1pps signal in timing are largely improved, and the requirement of the spacecraft on high precision signal timing is met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Intelligent ammeter clock calibration method
ActiveCN103176400AHigh precisionProtection against temporary unreliabilitySetting time indicationElectrical measurementsMicrocontrollerMicrocomputer
The invention relates to an intelligent ammeter clock calibration method aims at utilizing conventional resources of a single chip microcomputer to realize wide-range high-precision error correction. The technical scheme includes: a, measuring frequency deviation values of different temperature points, and simulating a temperature-frequency deviation curve; b, determining a minimum correction value of coarse tuning, and utilizing a formula obtained in step a to calculate out frequency deviation at current temperature as a compensation value; c, if the compensation value is smaller than the minimum correction value of the coarse tuning, executing step g, or executing step d; d, if M is 2, 3, 4 or 5, executing step e, or executing step f; e, using an internal pulse counter to perform pulse counting to signals output by a crystal oscillator, coarse tuning, and executing step g; f, performing frequency multiplication or frequency demultiplication to the signals output by the crystal oscillator to obtain a signal Ft; and g, arranging a controllable capacitor array at an output end of the crystal oscillator.
Owner:HEXING ELECTRICAL
Temperature compensated oscillator including MEMS resonator for frequency control
ActiveUS20060261703A1SmallLow costRadiation pyrometryPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesQuartz resonatorSignal function
Disclosed is an oscillator that relies on redundancy of similar resonators integrated on chip in order to fulfill the requirement of one single quartz resonator. The immediate benefit of that approach compared to quartz technology is the monolithic integration of the reference signal function, implying smaller devices as well as cost and power savings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Temperature compensation mechanism for a micromechanical ring resonator
InactiveUS6894576B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesImpedence networksMass momentElectronic circuit
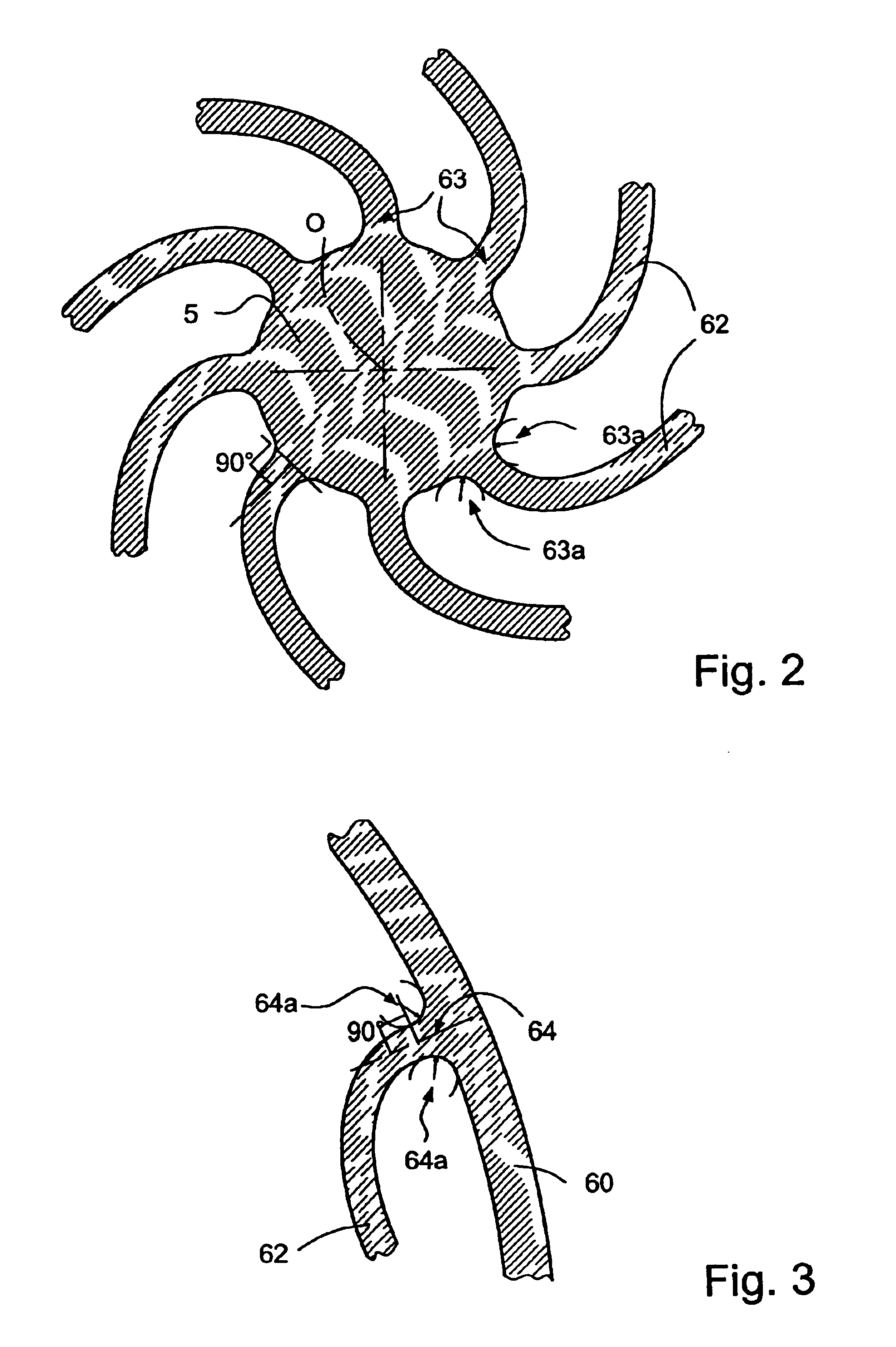
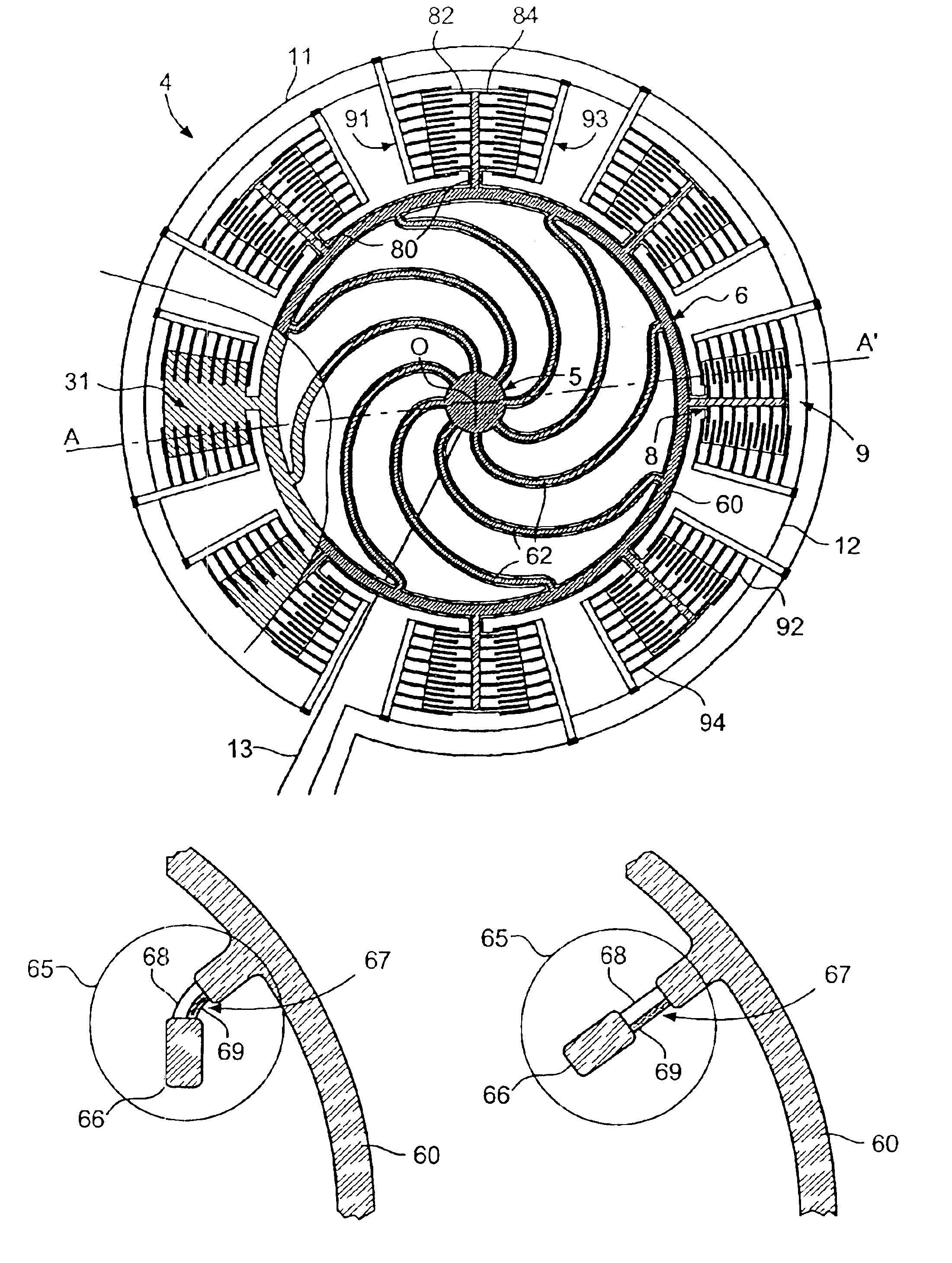
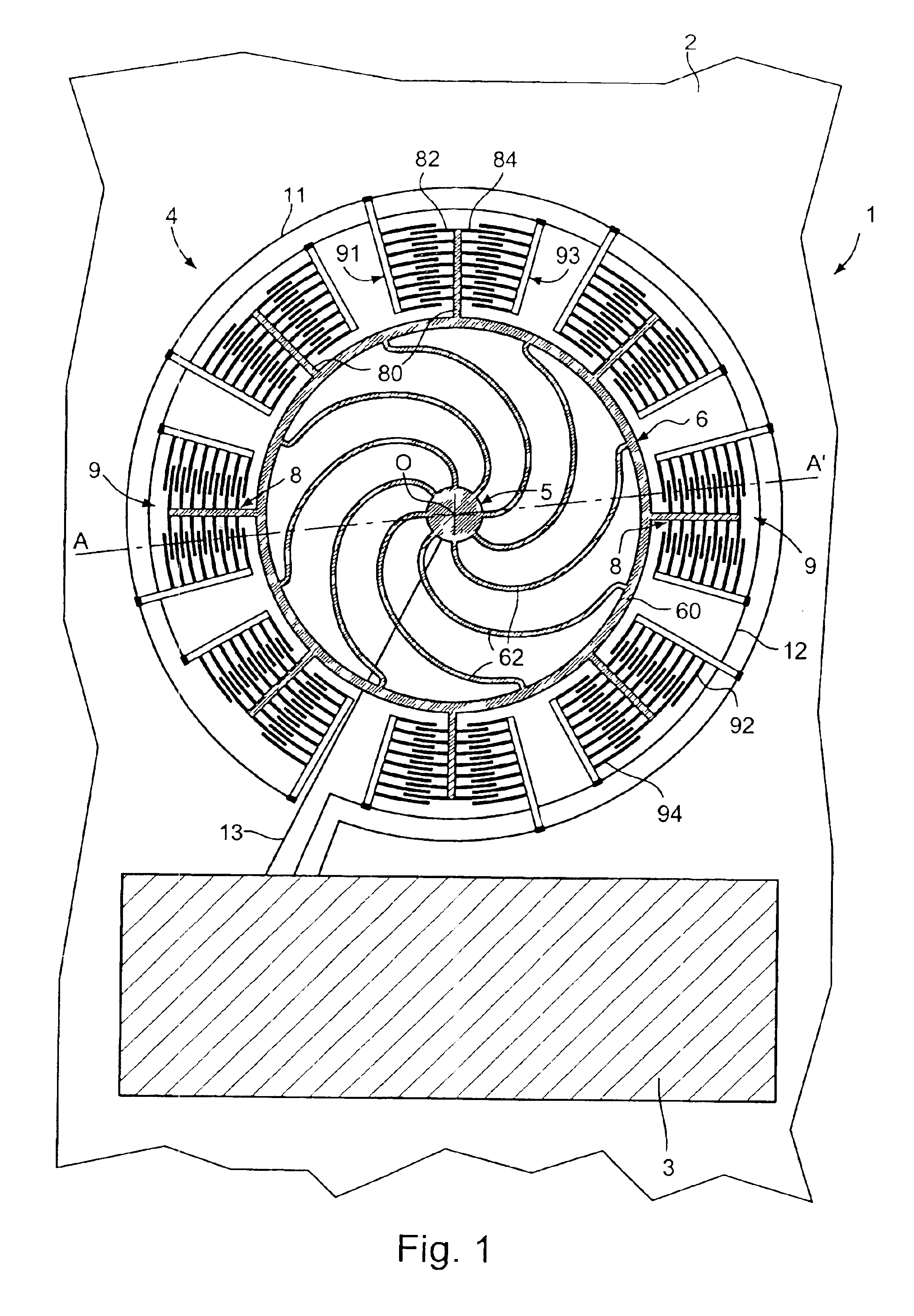
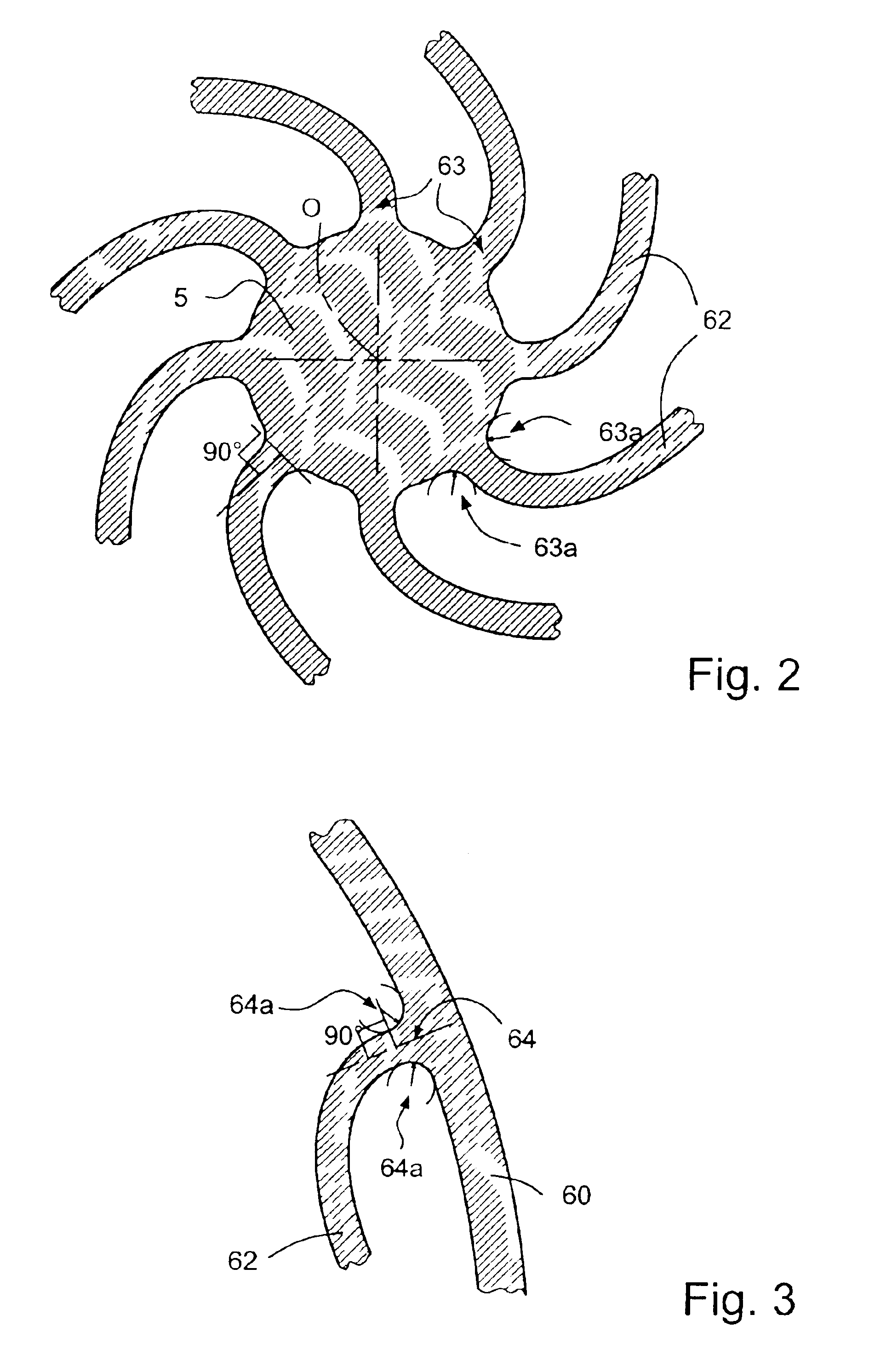
A time base including a resonator (4) and an integrated electronic circuit (3) for driving the resonator into oscillation and for producing, in response to the oscillation, a signal having a determined frequency. The resonator is an integrated micromechanical ring resonator supported above a substrate (2) and adapted to oscillate around an axis of rotation (O) substantially perpendicular to the substrate. The ring resonator includes a free-standing oscillating structure having a plurality of thermally compensating members (65) which are adapted to alter a mass moment of inertia of the free-standing oscillating structure as a function of temperature so as to compensate for the effect of temperature on the resonant frequency of the ring resonator.
Owner:ETA SA MFG HORLOGERE SUISSE
Clock generating device, vibration type gyro sensor, navigation device, imaging device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20050160813A1Subject to movementGood precisionTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationTime informationGyroscope
A vibration gyro sensor is provided which is capable of generating time information and detecting an angular velocity. A driving signal for driving a tuning fork piezoelectric vibrating reed is generated based on an excitation signal generated by an oscillation circuit. An angular velocity signal is obtained based on a detection signal generated by a detection electrode of the tuning fork piezoelectric vibration reed. The excitation signal generated by the oscillation circuit is input to a divider such that a timer clock signal is generated.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
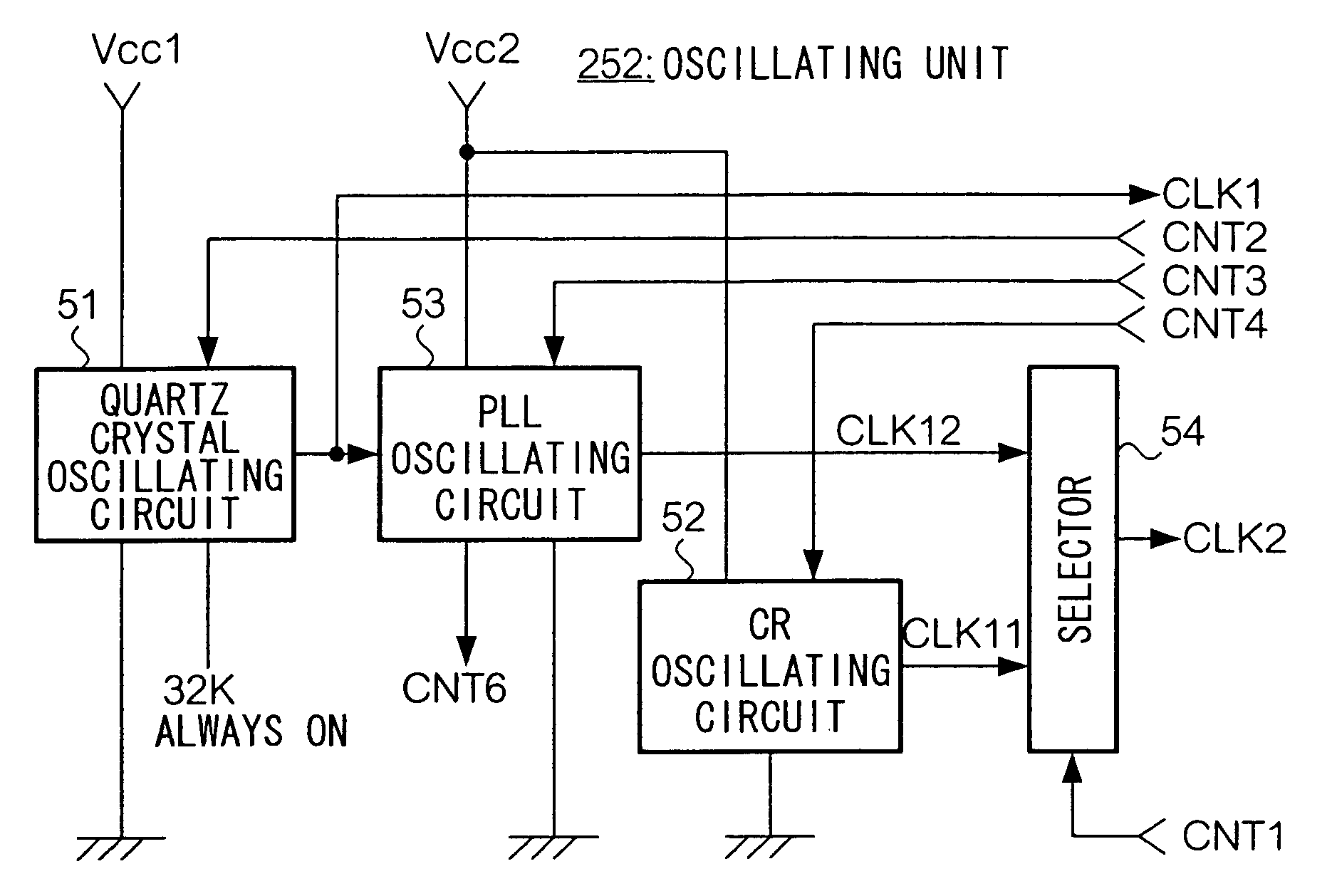
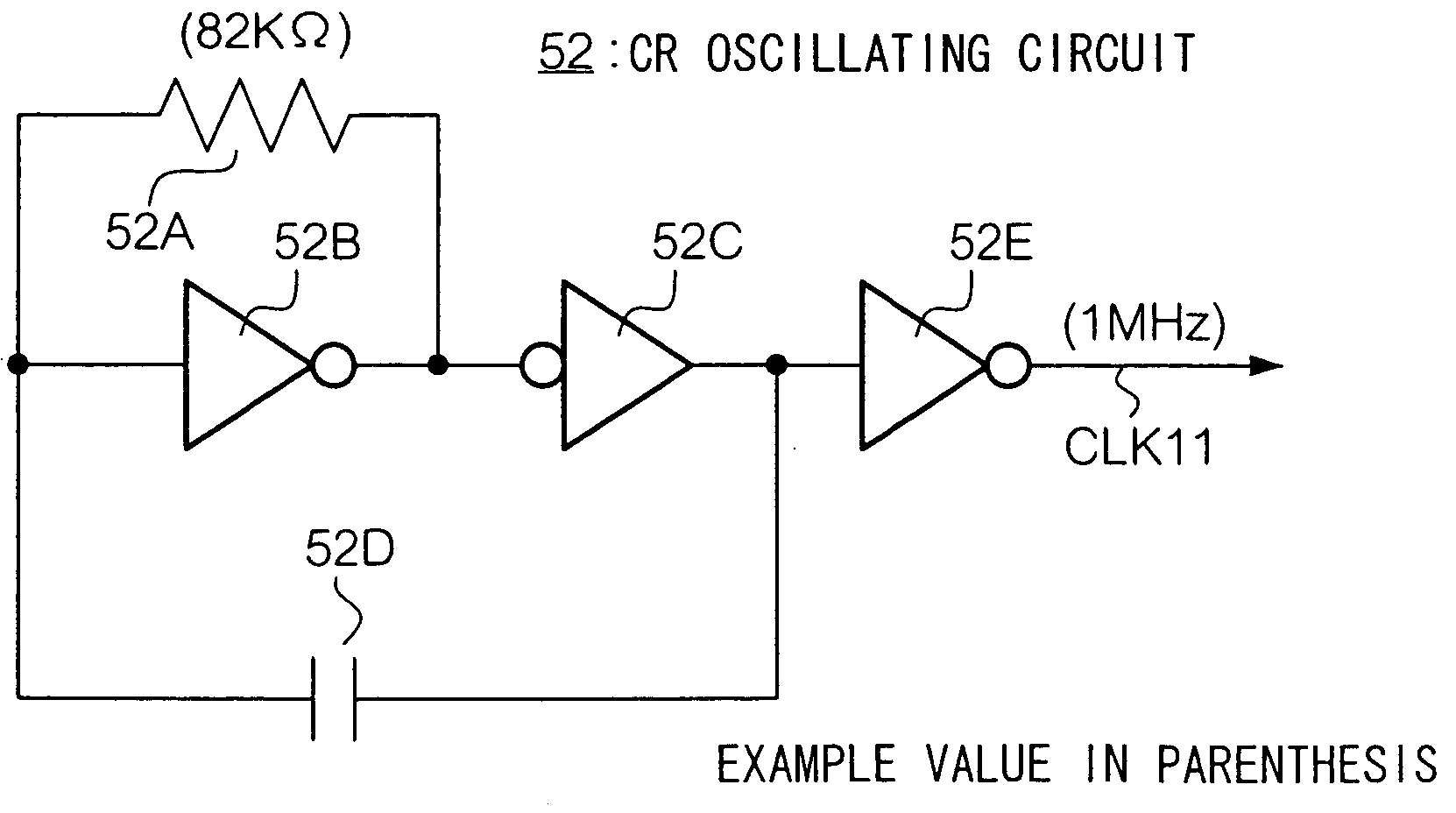
Apparatus for selecting and outputting either a first clock signal or a second clock signal
InactiveUS7065668B2Reduce power consumptionHigh speed informationInput/output for user-computer interactionPulse generation by logic circuitsOperating voltageWaiting time
By using a CR oscillating circuit and a PLL oscillating circuit selectively, these two oscillating circuits are used as a high frequency, low power consumption, short waiting time for stable oscillation, and low operating voltage oscillating circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Adaptive time synchronization method based on temperature compensation
ActiveCN108449791AImprove performanceImprove energy efficiencySynchronisation arrangementSynchronous motors for clocksClock driftWireless mesh network
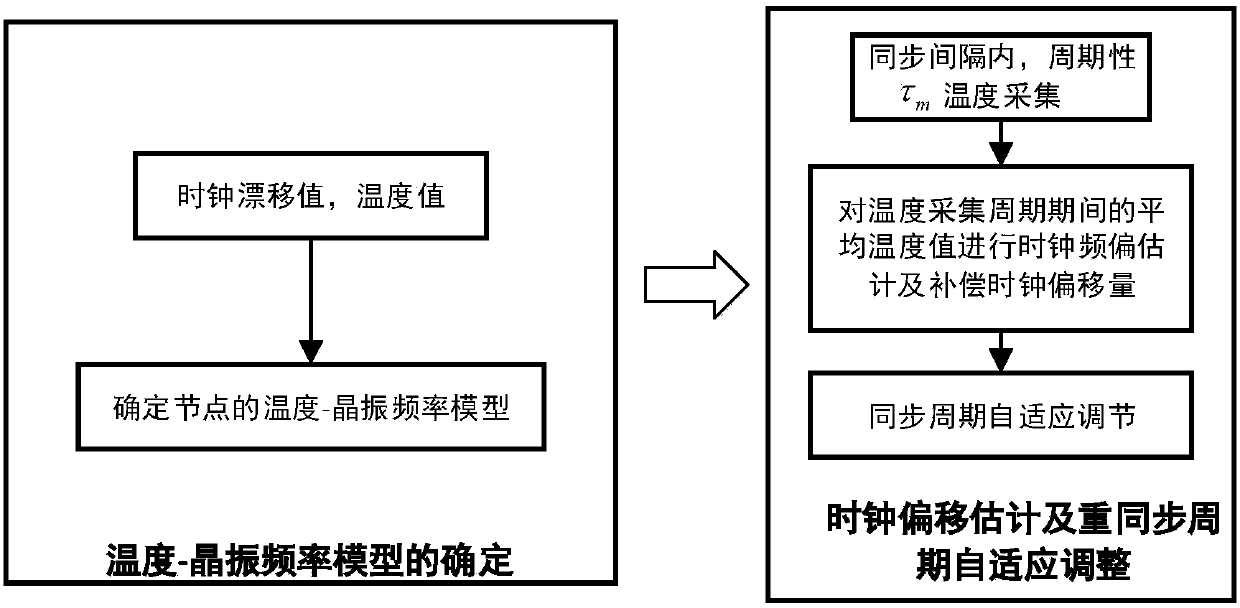
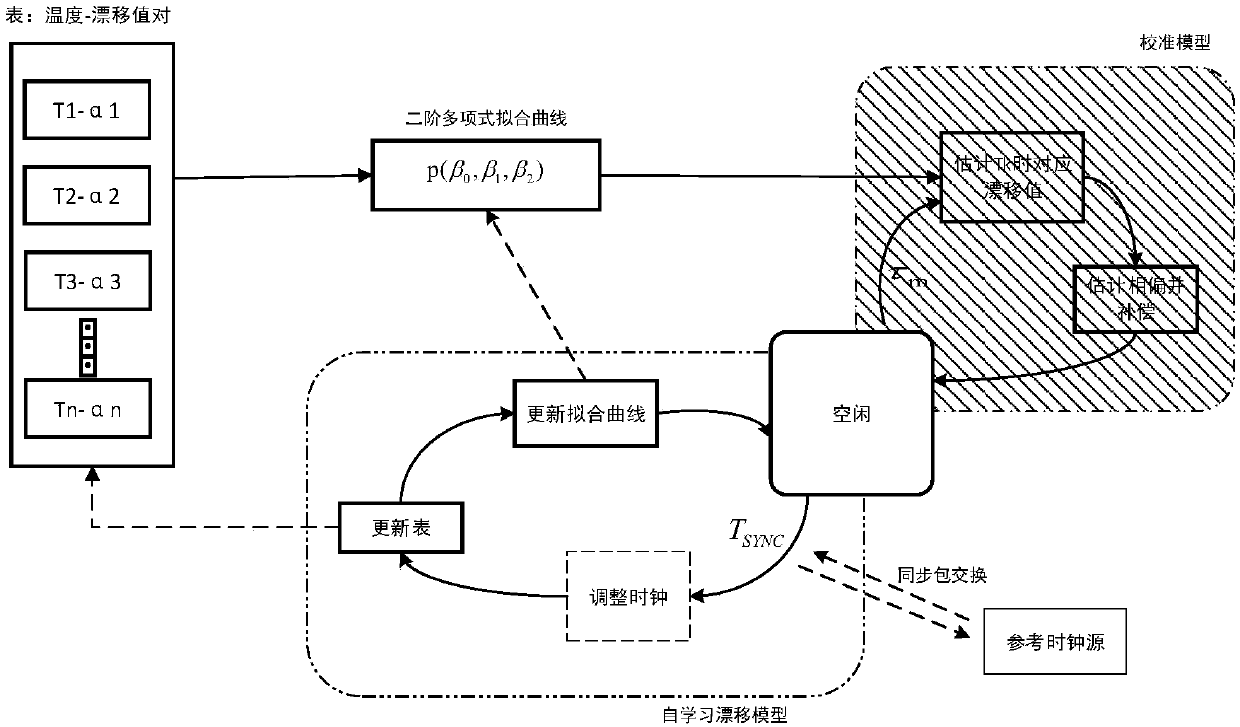
The invention relates to an adaptive time synchronization method based on temperature compensation, belonging to the technical field of wireless sensor networks. In consideration of the large influence of the environmental temperature on a clock crystal oscillator frequency, the method includes the following steps: firstly, a temperature-crystal oscillator frequency model is established by using the correlation between the clock drift and temperature, and nodes can compensate for the offset of a clock according to the temperature changes under the model to improve the accuracy of synchronization between the nodes; and secondly, in the case that the network delay is a Gaussian model, and in combination with the relevant theory of probability time synchronization, the nodes can compensate for the current time according to a maximum synchronization error allowed by the network and the accumulated clock offset, and estimate a corresponding resynchronization interval. According to the method, the nodes can reduce the energy consumption to the greatest extent on the basis of meeting the specific synchronization accuracy, and the network load can be reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Information processing apparatus
InactiveUS20050030112A1Reduce power consumptionHigh speed informationInput/output for user-computer interactionPulse generation by logic circuitsInformation processingWaiting time
By using a CR oscillating circuit and a PLL oscillating circuit selectively, these two oscillating circuits are used as a high frequency, low power consumption, short waiting time for stable oscillation, and low operating voltage oscillating circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
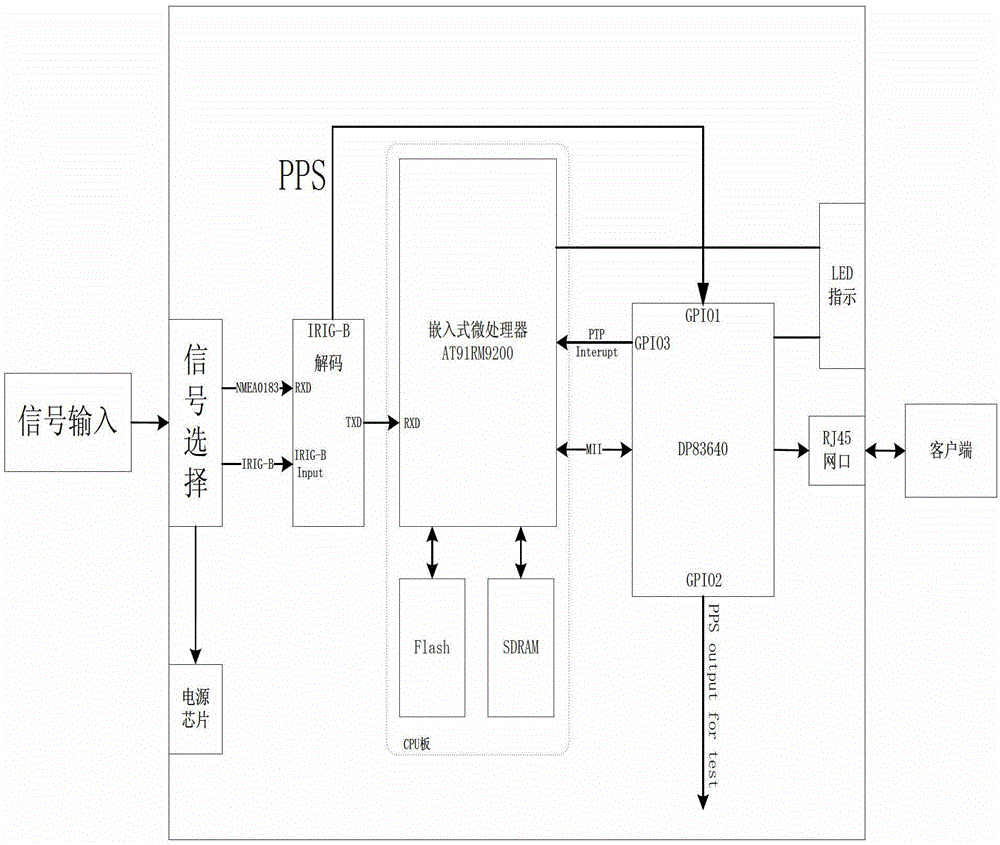
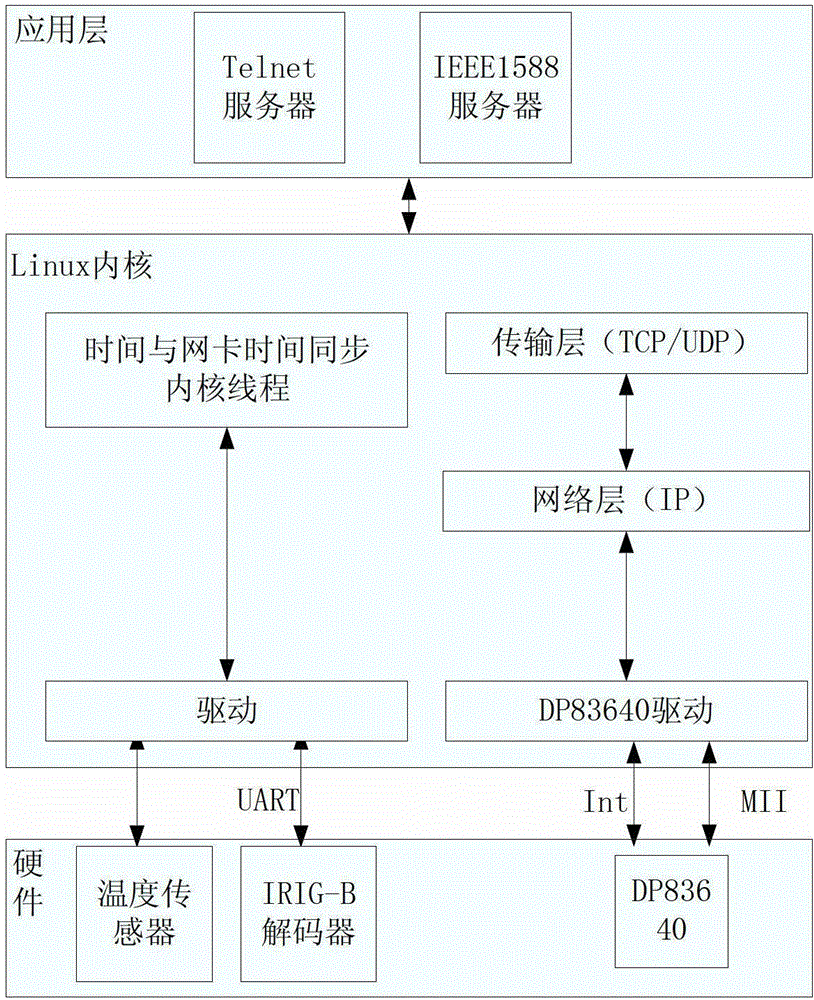
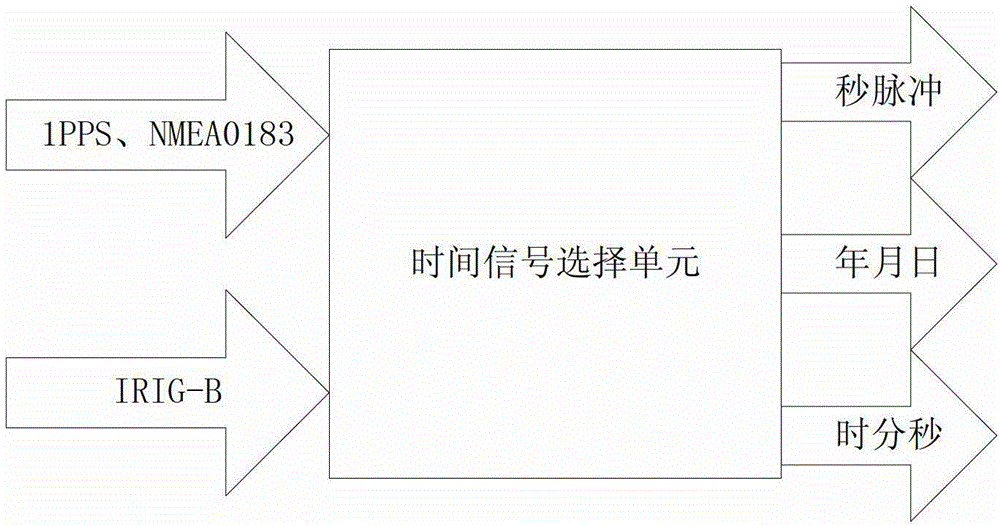
B code decoding technology fused institute of electrical and electronic engineers 1588 (IEEE1588) intelligent power grid time transmission method and device
InactiveCN102882626AImprove time accuracyImprove long-term stabilitySynchronous motors for clocksTime-division multiplexTimestampTransformer
The invention discloses a B code decoding technology fused institute of electrical and electronic engineers 1588 (IEEE1588) intelligent power grid time transmission method. The time signal input end of an embedded processor and network interface module on an intelligent power grid transformer substation time transmission device has two groups of input signals, one group comprises 1 pulse per second (PPS) signals and national marine electronics association 0183 (NMEA0183) signals, and the other group comprises inter-range instrumentation group-B (IRIG-B) signals; a signal selection module is used for selecting a group of signals with the highest time accuracy, and the priorities of the 1PPS and NMEA0183 signals are higher than that of the IRIG-B signals; a decoding module deserializes the signals selected by the signal selection module, and provides a timestamp for the embedded processor and network interface module; and a time protocol for time message resolution in an IRIG-B decoding module is an NMEA0183 protocol, and a global positioning system (GPS) receiver transmits position and speed information to a processor through a serial port according to the standard specification of the NMEA0183 protocol which is a standard protocol of the GPS receiver.
Owner:南京澳德思电气有限公司
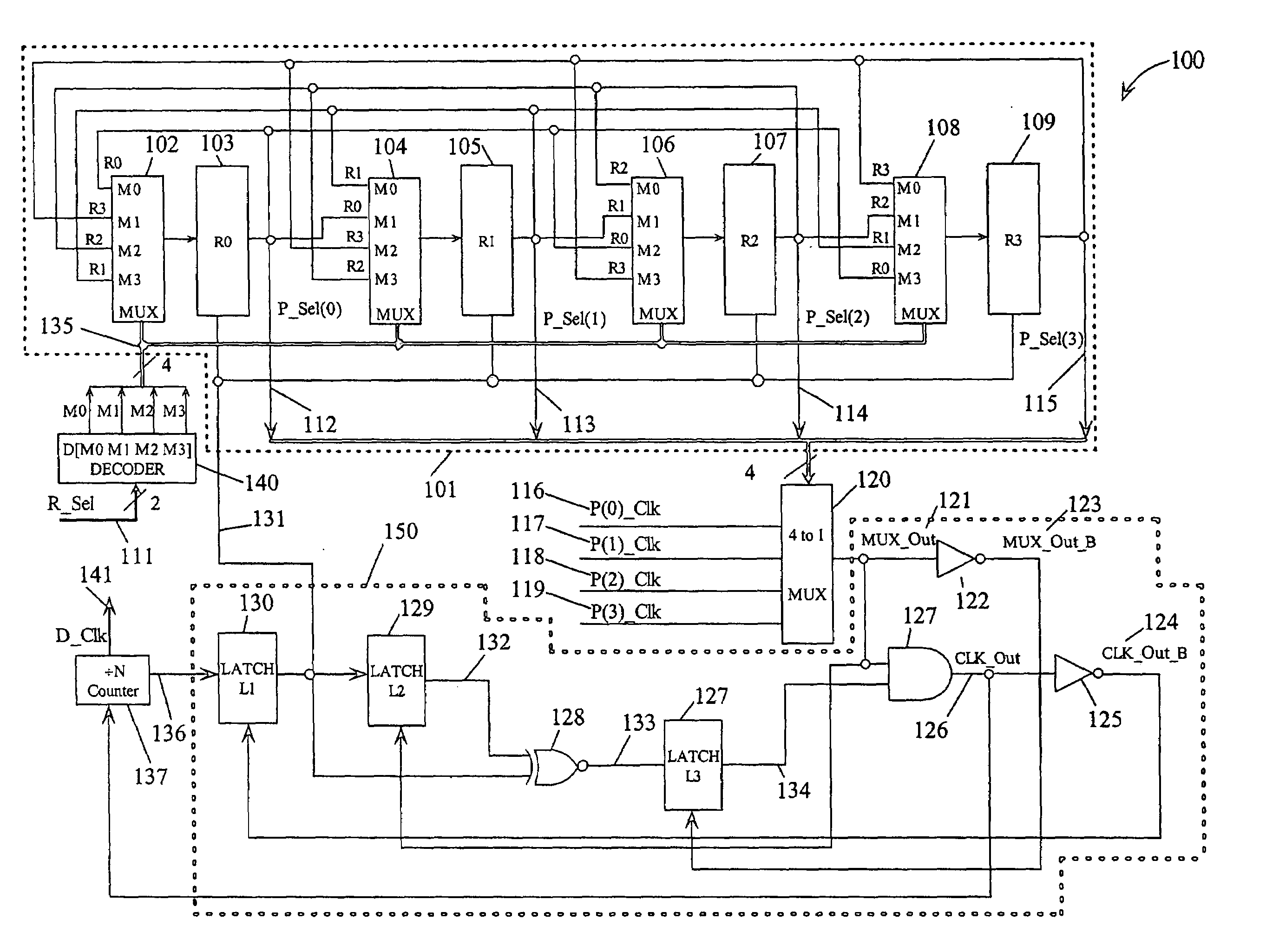
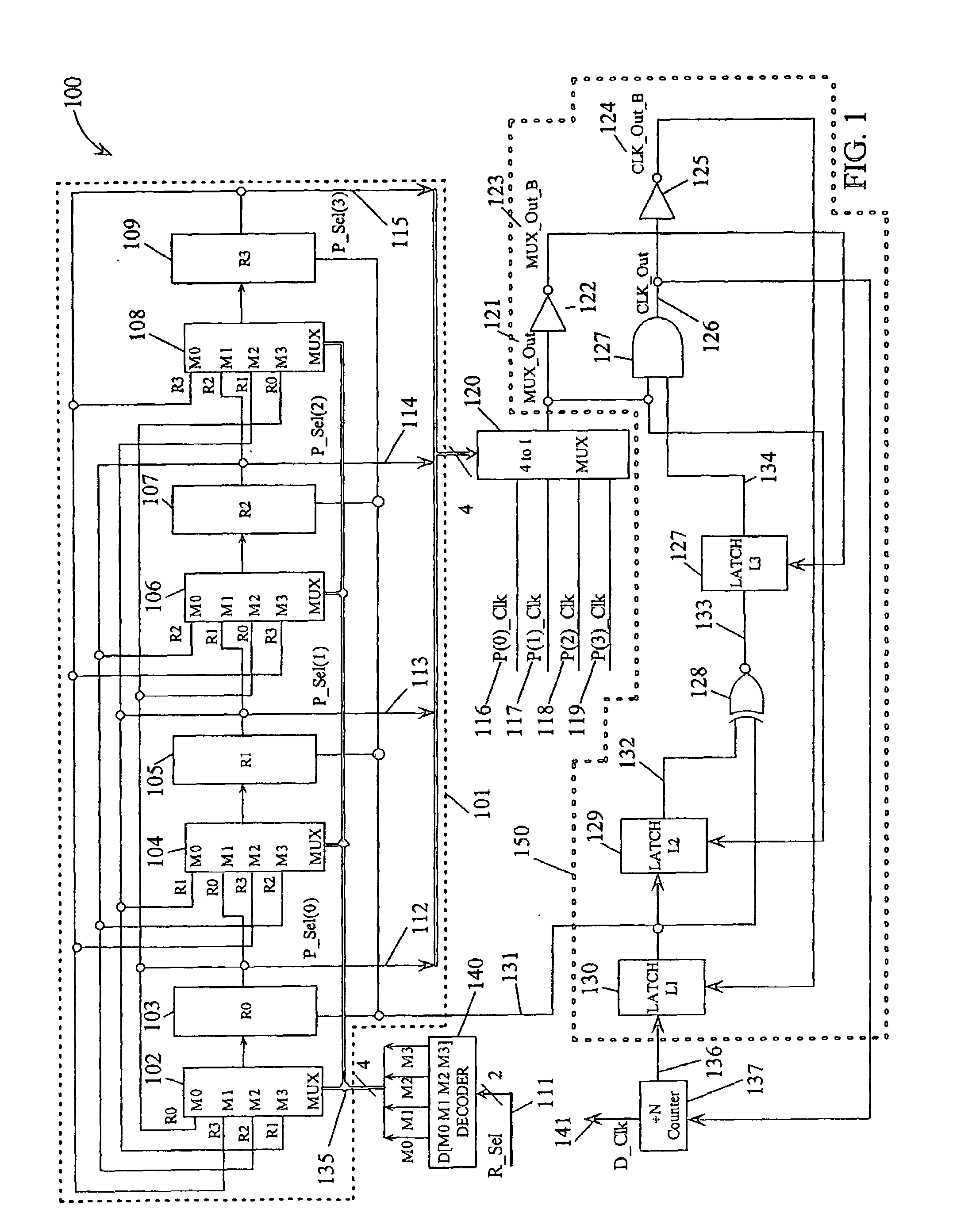
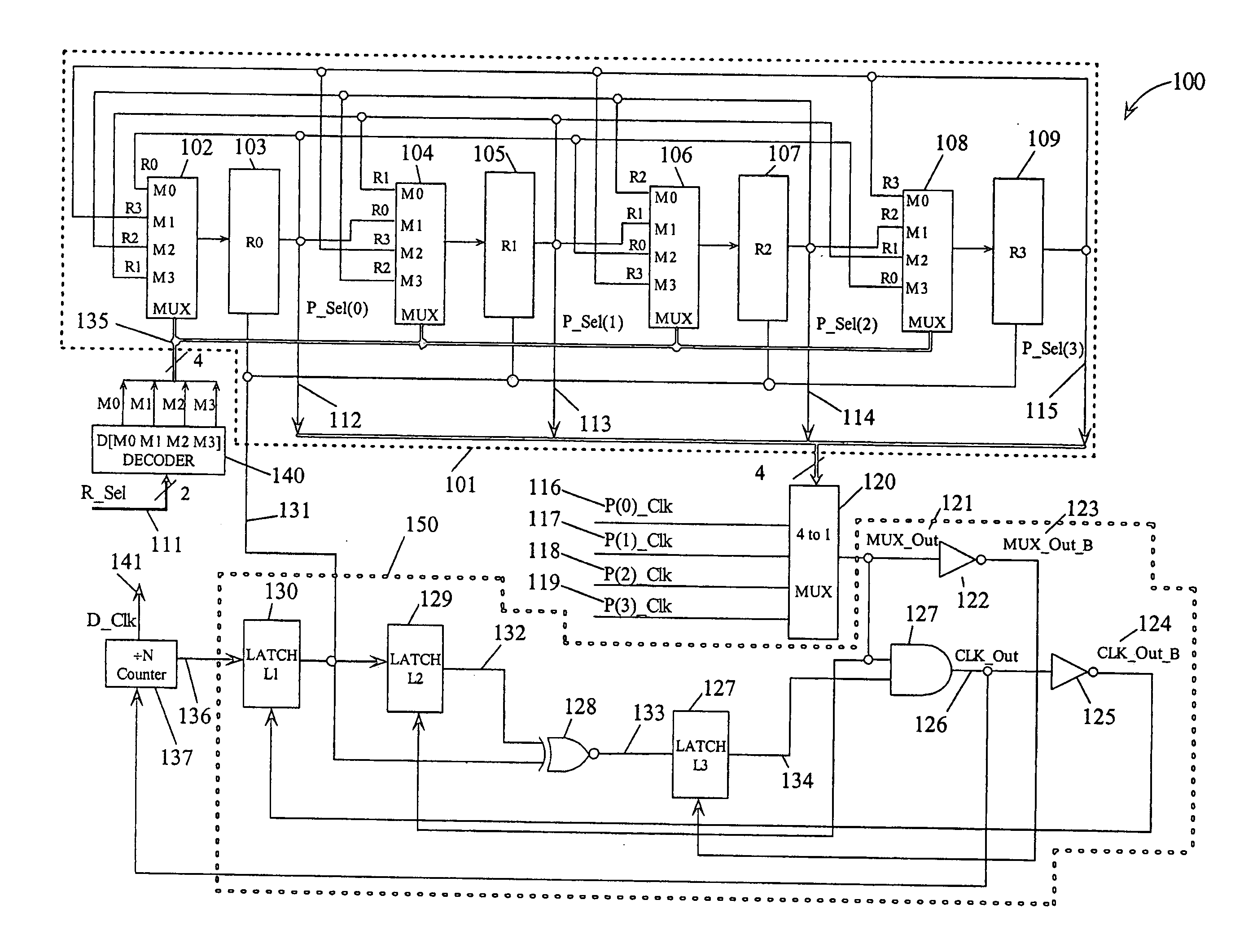
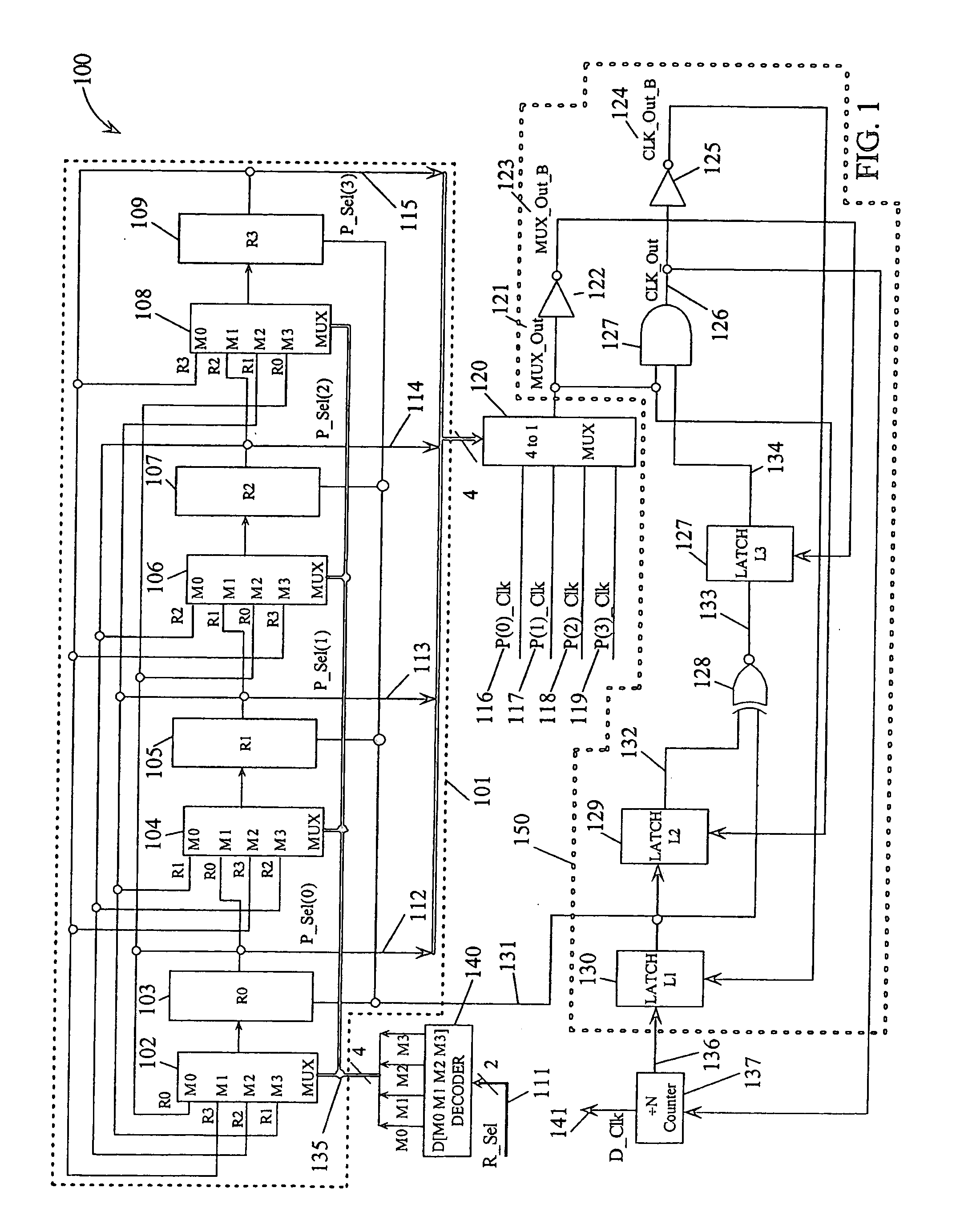
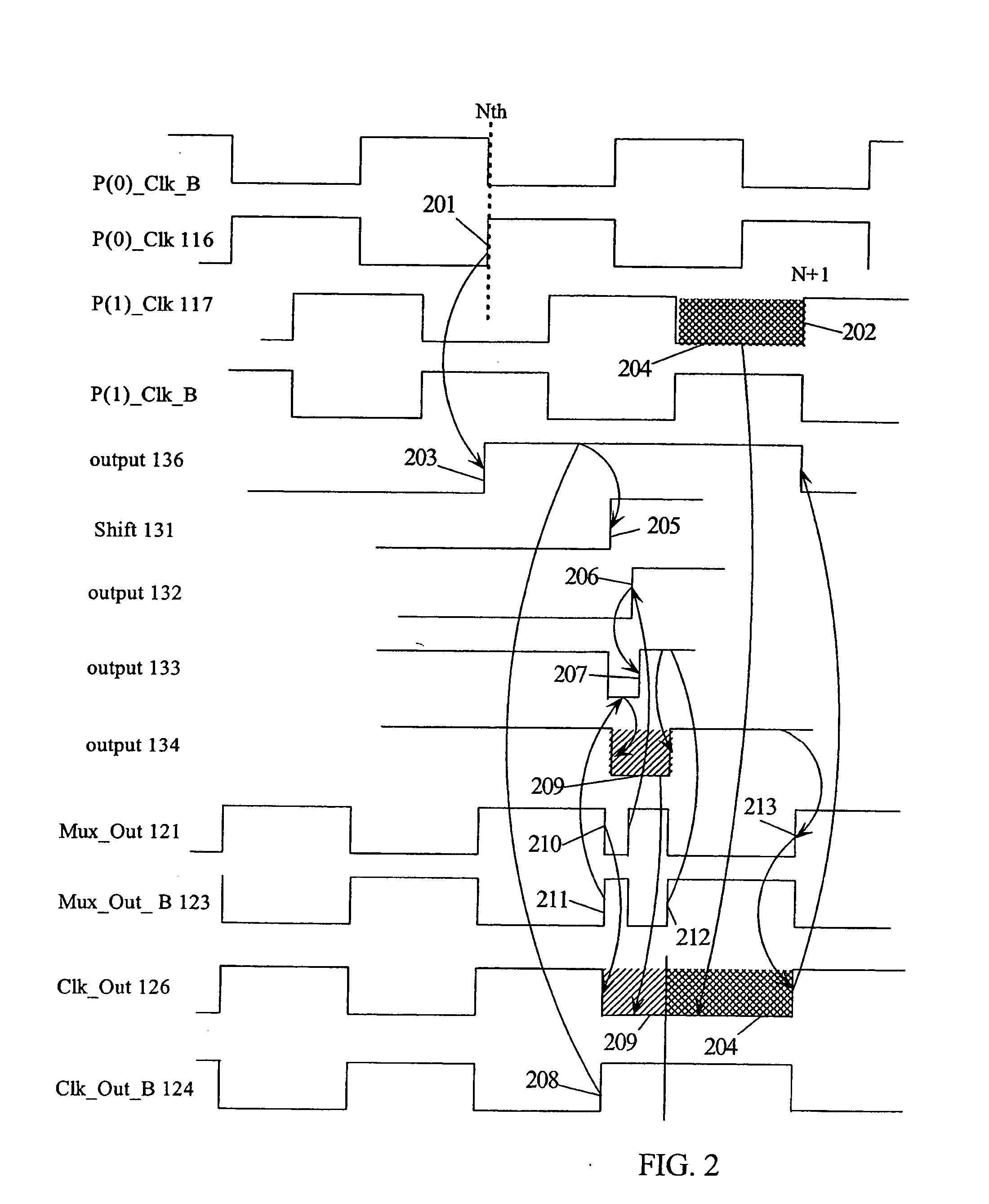
Phase clock selector for generating a non-integer frequency division
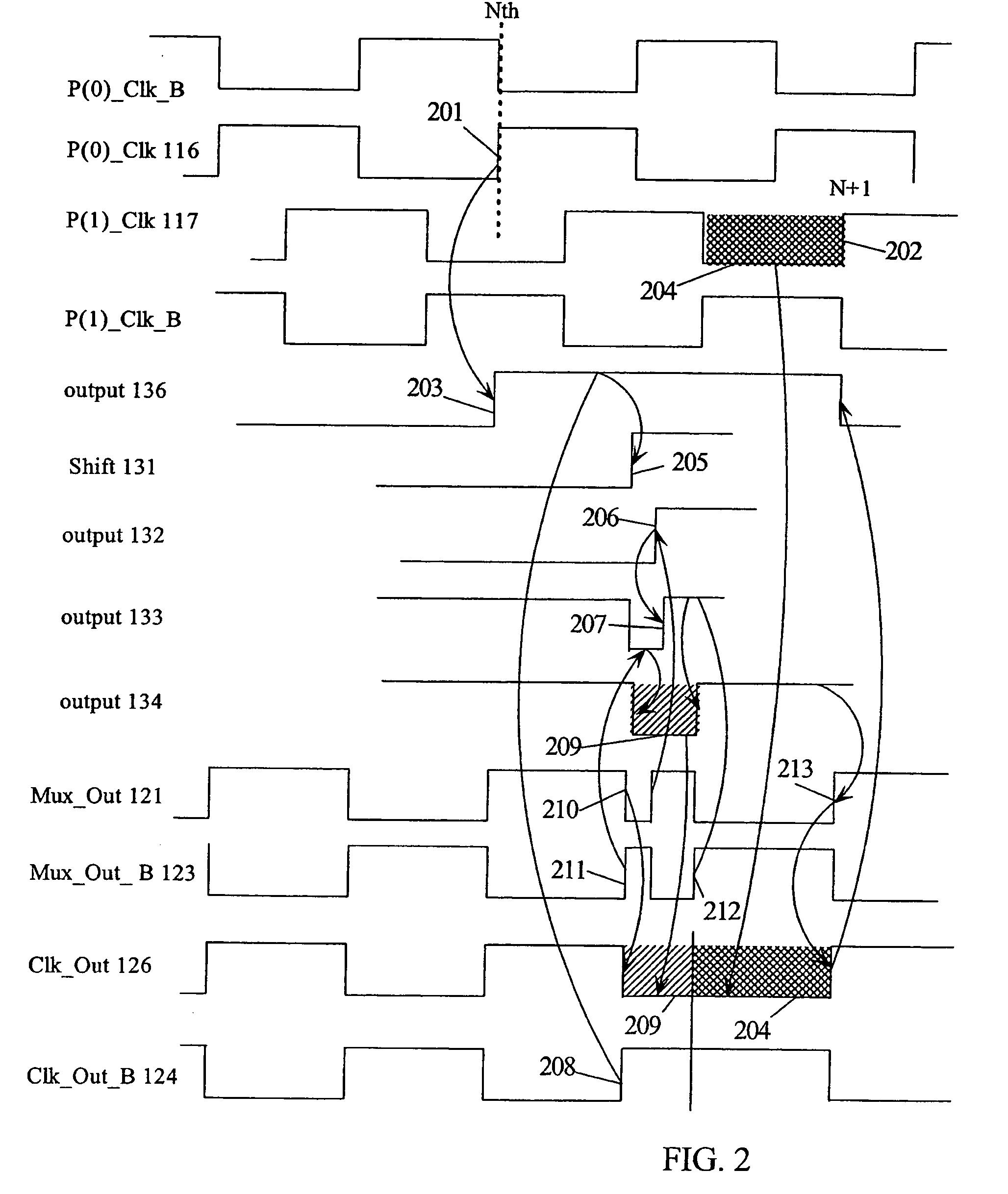
A frequency divider circuit uses a base counter to frequency divide a clock signal with period T by an integer value N and employs a cyclic rotational select circuit to select among multiple equally phase shifted signals of a multiple phase clock to generate a fractional term P / k where P is variable from 0 to k−1. The counter counts an output clock that corresponds to the output of a multiplexer selecting from among the multiple clock phases. Depending on the desired fractional term, after N counts of the output clock phases of the multiple phase clock are selected glitch free by rotationally selecting a first phase, and skipping either 0, 1, 2 . . . up to k−1 sequential phases to generate fractional terms 0, 1 / k, 2 / k, 3 / k . . . k−1 / k, respectively, thus providing frequency division corresponding to N+P / k where P may be varied from 0 to k−1.
Owner:IBM CORP
Oscillation circuit and electronic equipment comprising semiconductor integrated device with clock function including the oscillation circuit
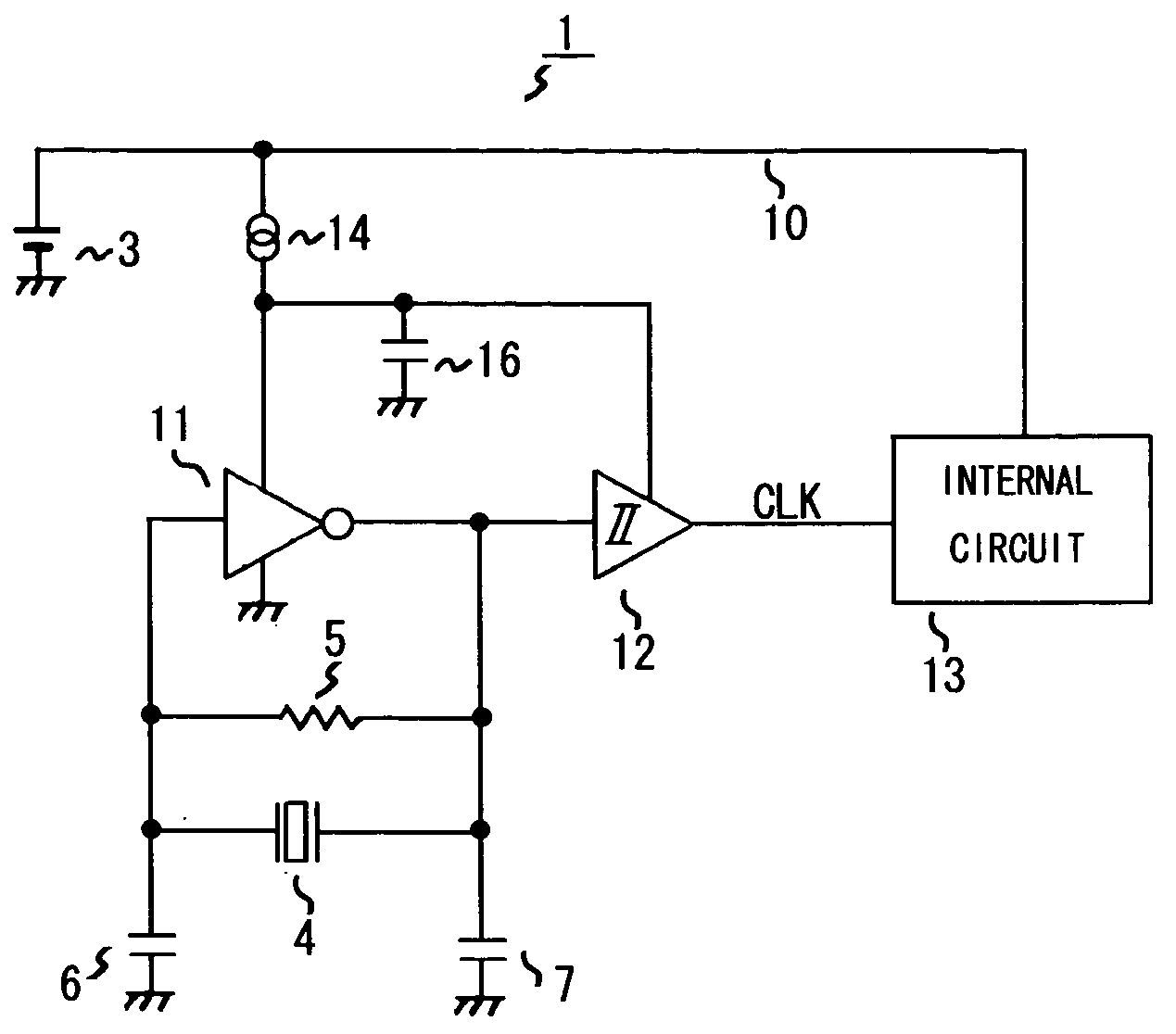
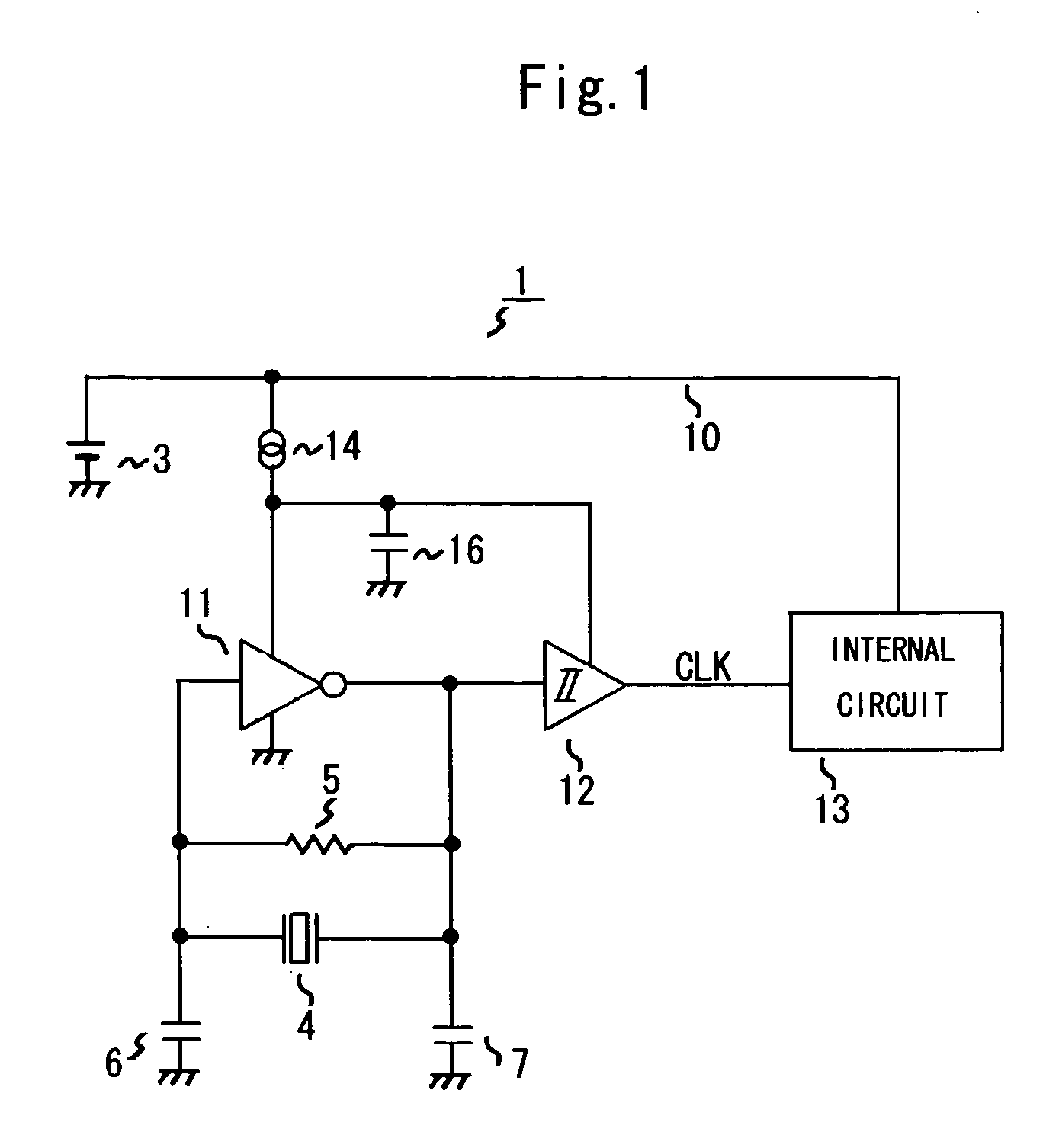
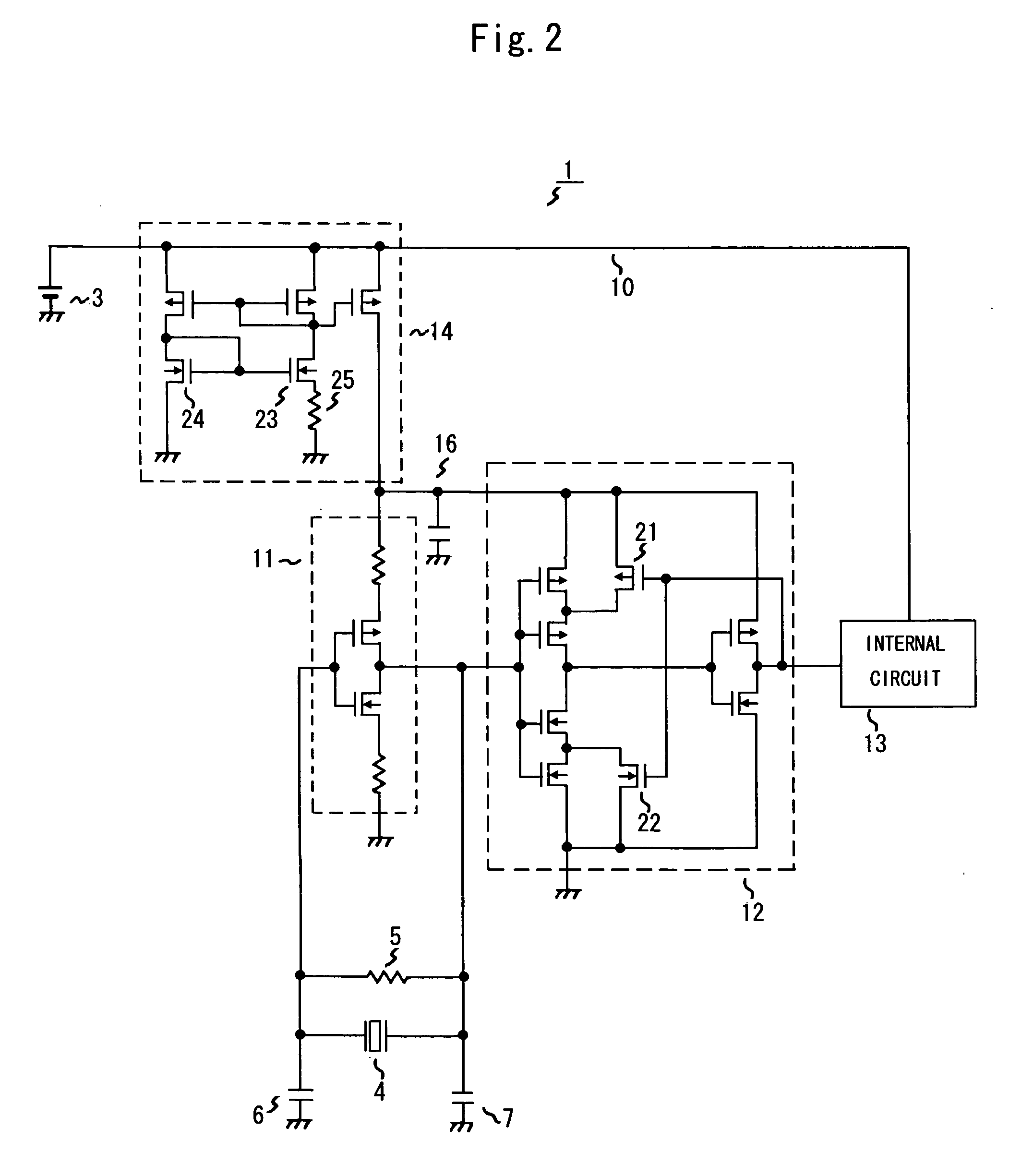
InactiveUS20050017812A1Total current dropReduce power consumptionPulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsSchmitt triggerElectrical battery
The present invention provides an oscillation circuit which enables a further decrease of power consumption. The oscillation circuit comprises a piezoelectric oscillator, such as a quartz oscillator, for generating voltage that oscillates at a natural frequency, an inverter for amplifying this oscillation voltage, a Schmitt trigger circuit for shaping the waveform of the output of the inverter and outputting oscillation output signals, and a constant current source which is connected to a power supply line from a battery and supplies current to the power supply of the inverter and the Schmitt trigger circuit.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Phase clock selector for generating a non-integer frequency division
A frequency divider circuit uses a base counter to frequency divide a clock signal with period T by an integer value N and employs a cyclic rotational select circuit to select among multiple equally phase shifted signals of a multiple phase clock to generate a fractional term P / k where P is variable from 0 to k−1. The counter counts an output clock that corresponds to the output of a multiplexer selecting from among the multiple clock phases. Depending on the desired fractional term, after N counts of the output clock phases of the multiple phase clock are selected glitch free by rotationally selecting a first phase, and skipping either 0, 1, 2 . . . up to k−1 sequential phases to generate fractional terms 0, 1 / k, 2 / k, 3 / k . . . k−1 / k, respectively, thus providing frequency division corresponding to N+P / k where P may be varied from 0 to k−1.
Owner:IBM CORP
Clock signal output apparatus and control method of same, and electric apparatus and control method of same
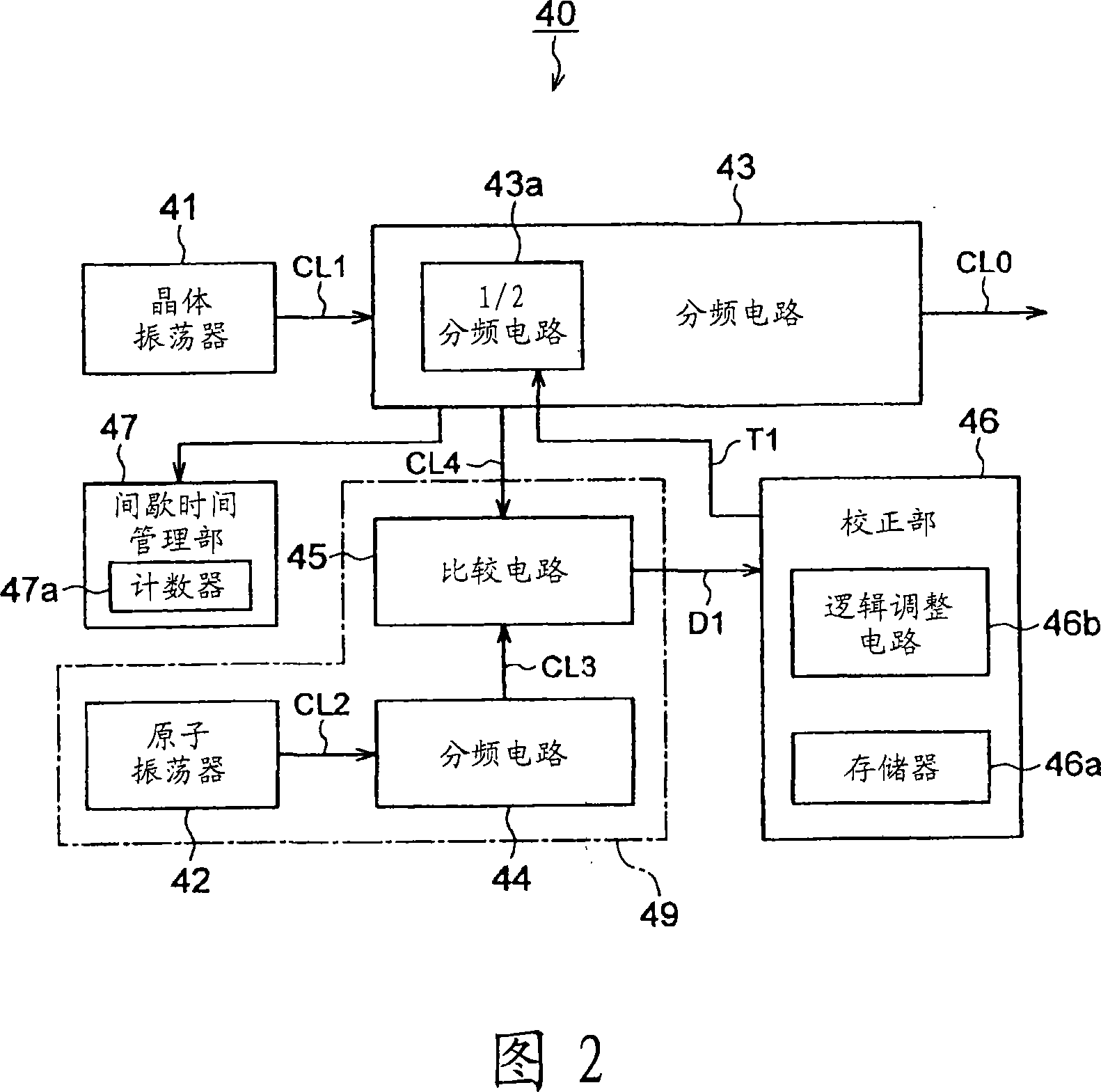
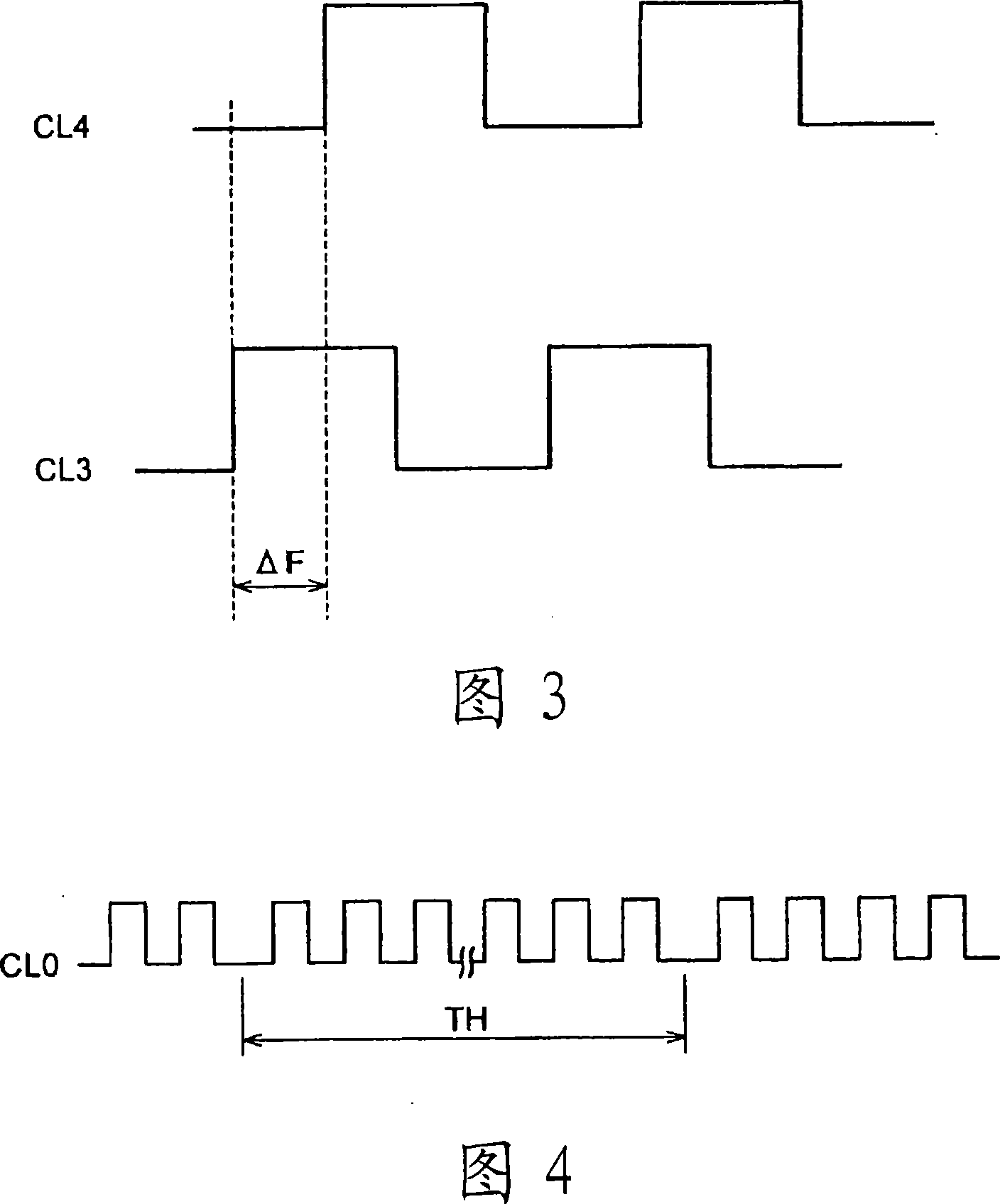
InactiveCN101128780AHigh precisionAvoid increased power consumptionApparatus using atomic clocksMaster clocksTime managementOutput device
Provided are a clock signal outputting device and its control method, and an electronic device and its control method, which can enhance the precision of a clock signal while avoiding an increase in the entire power consumption even if a highly precise oscillator of a relatively high power consumption is used. The clock signal output device includes a quartz oscillator (41) for generating a reference clock signal (CL1), and generates and outputs an outputted clock signal (CL0) of a predetermined frequency from the reference clock signal (CL1). The clock signal output device further includes an atomic oscillator (42) for generating a clock signal (CL2) of a higher precision than that of the quartz oscillator (41), an intermittent time managing unit (47) for driving the atomic oscillator (42) intermittently, and a correction unit (46) for acquiring correction data to correct the displacement of the outputted clock signal (CL0) with reference to the clock signal (CL2), each time the atomic oscillator (42) is driven, thereby to correct the outputted clock signal (CL0) on the basis of that correction data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
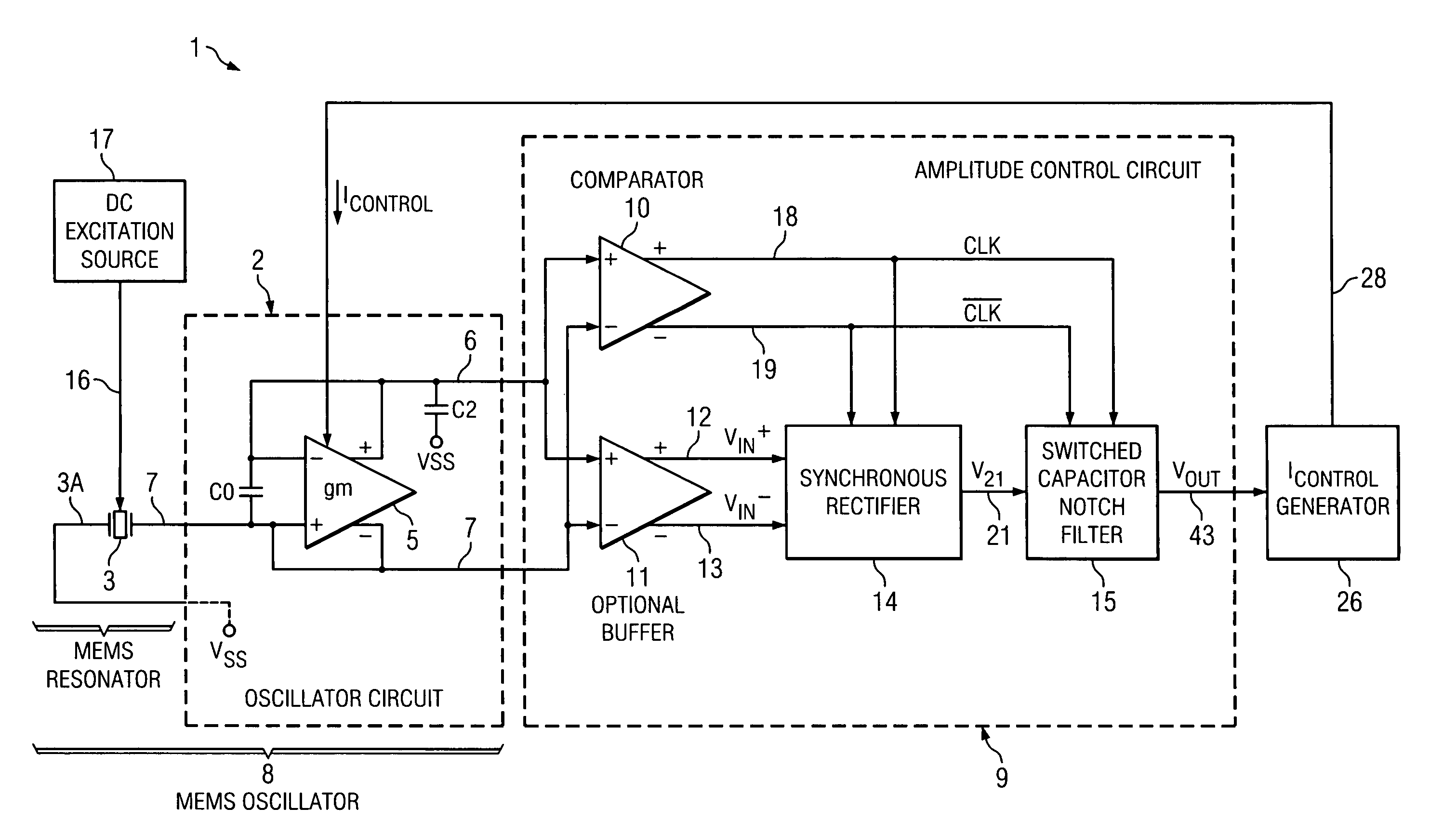
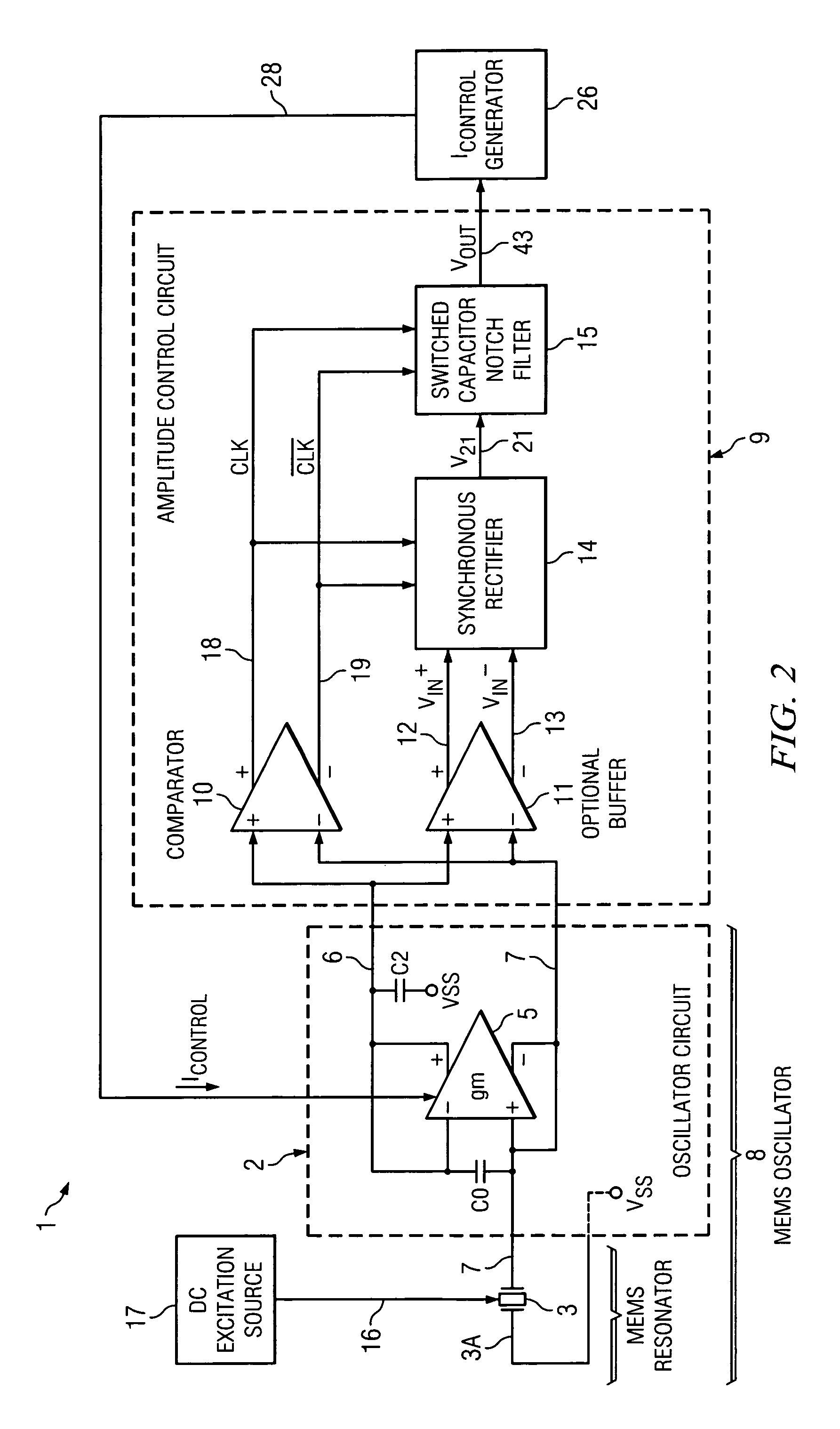
Circuitry and method for precision amplitude control in quartz and MEMS oscillators
ActiveUS8228130B1Improve performanceAccurate supervisionPulse automatic controlImpedence networksNegative phaseAmplitude control
An oscillator includes oscillator circuitry (8) including a transconductance stage (2) and a resonator (3). A comparator (10) produces first (CLK) and second ( / CLK) clock signals which indicate the timing of positive and negative phases of a differential output signal (VIN+-VIN−) produced by the transconductance circuit in response to the resonator. A synchronous rectifier (14) converts the differential output signal to a current (IRECT) in response to the first and second clock signals. A switched capacitor notch filter (15) filters the current in response to the first and second clock signals. A control current (ICONTROL) which controls the transconductance of the transconductance circuit is generated in response to the notch filter. The resonator may be a MEMS resonator.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
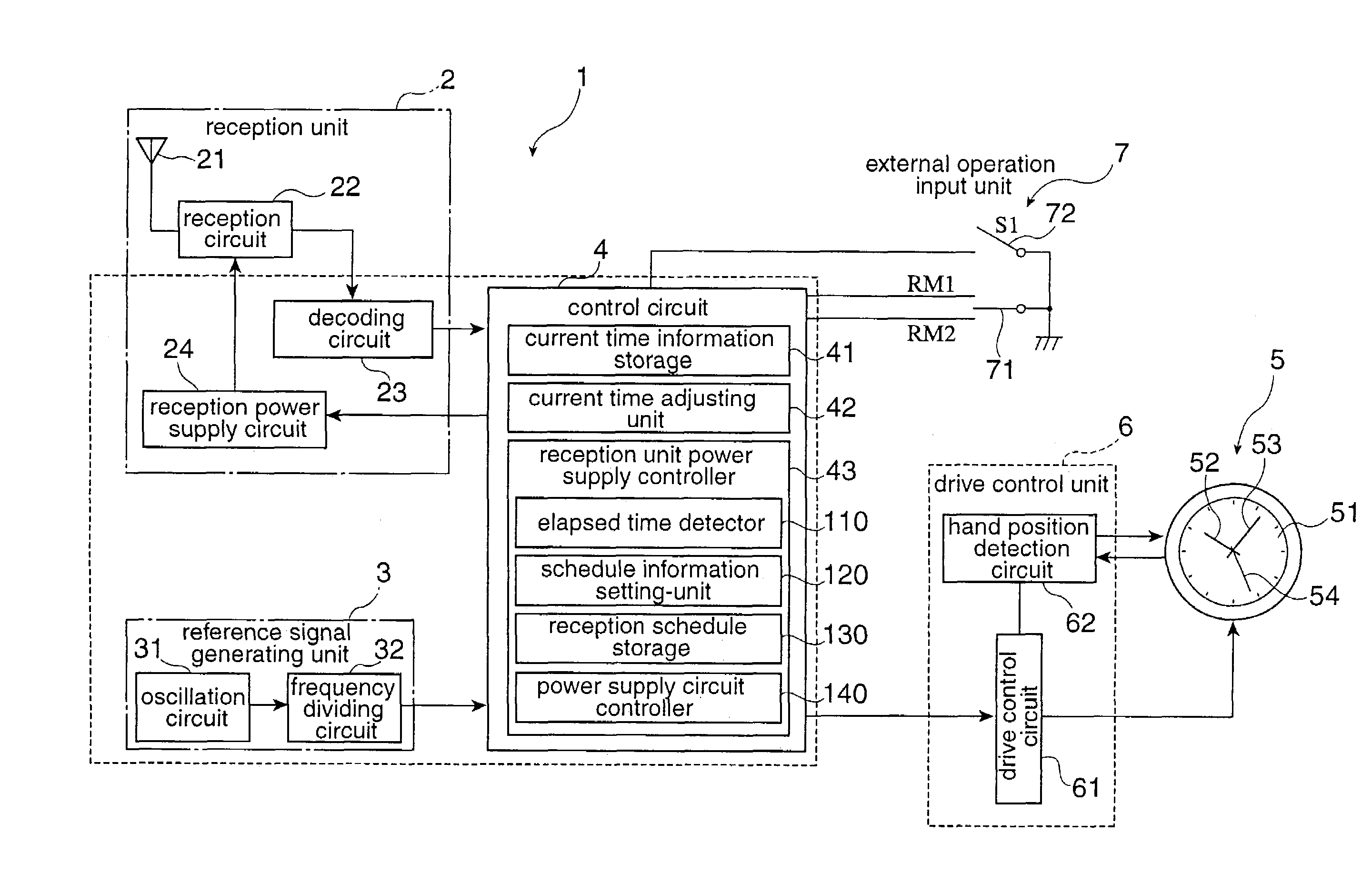
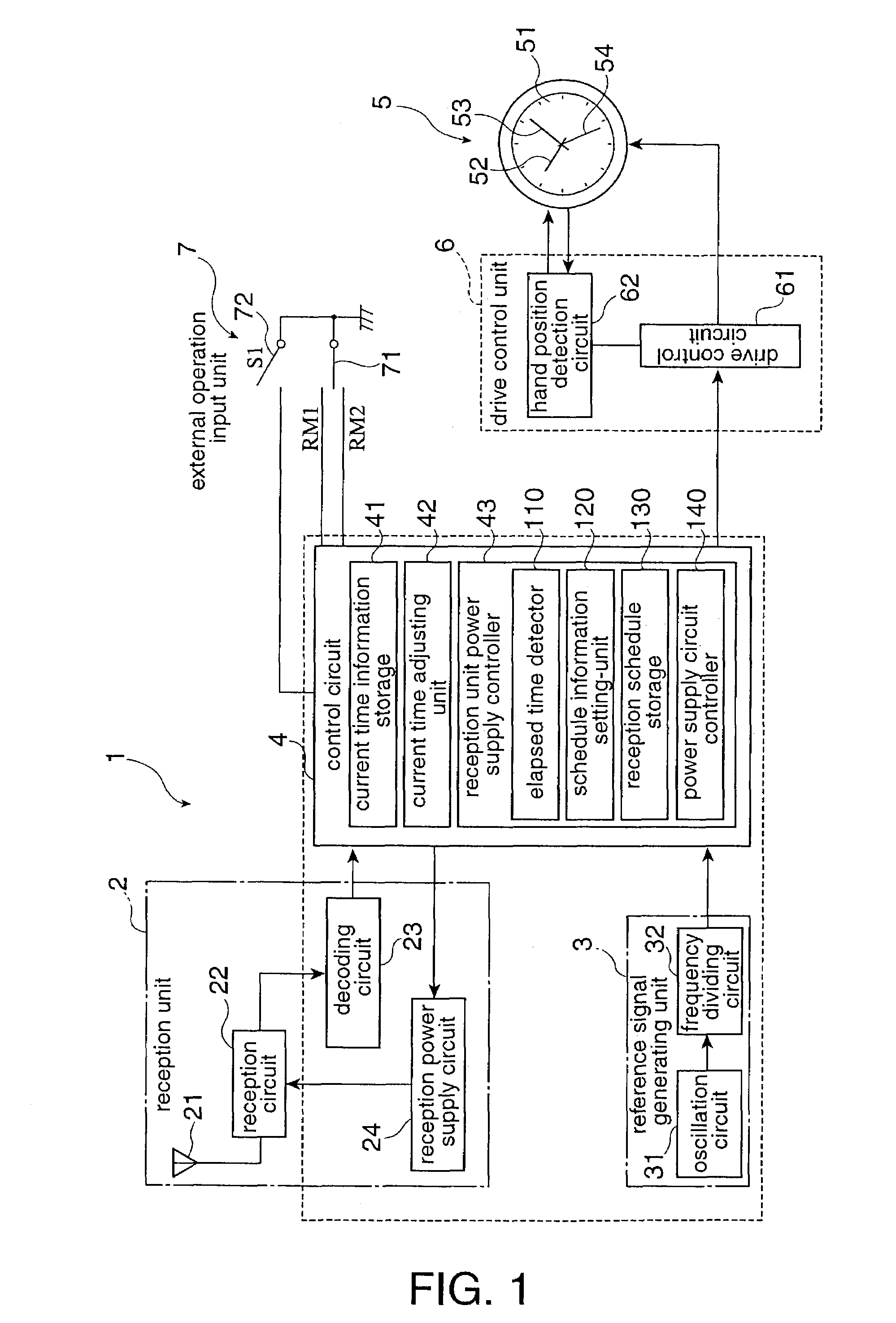
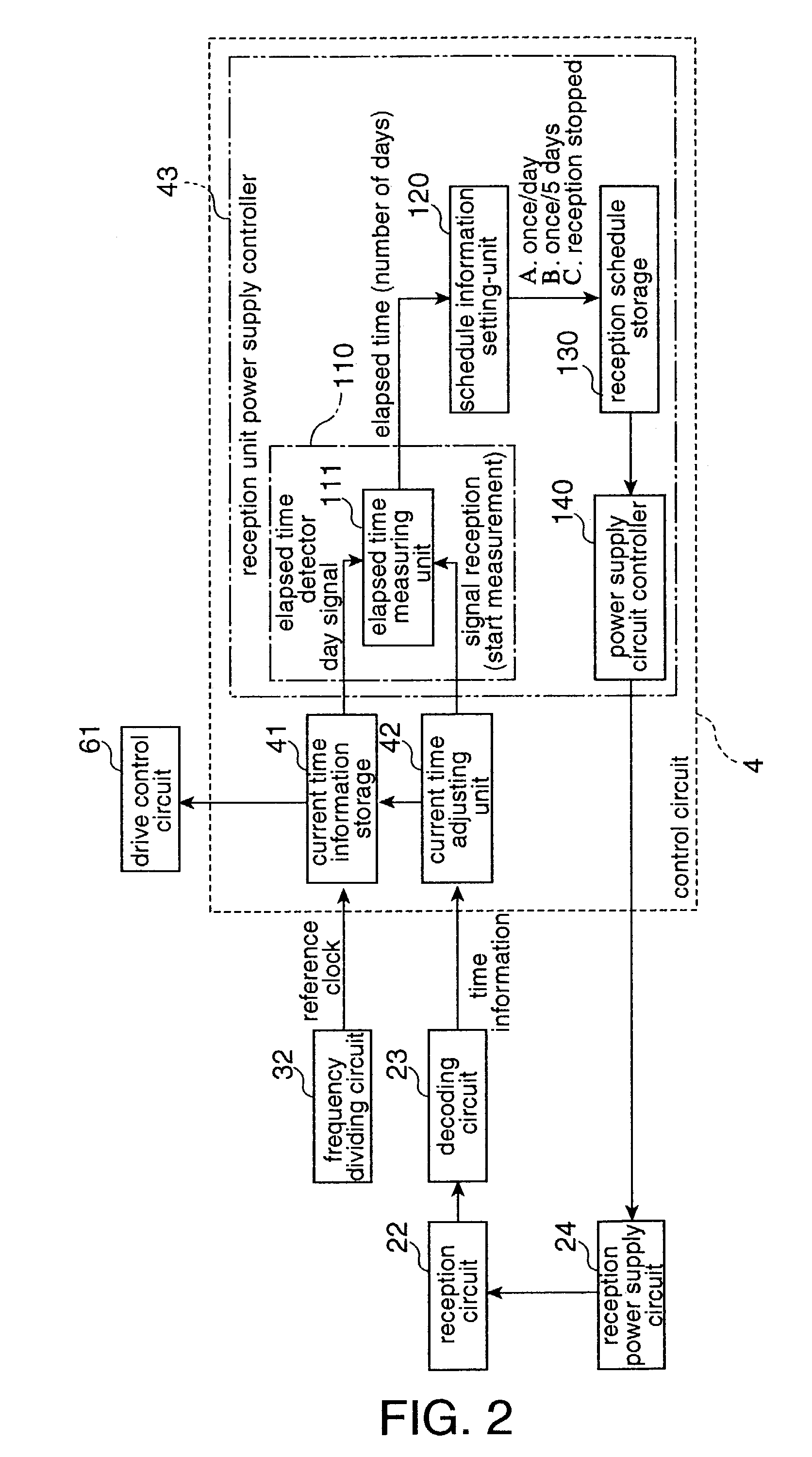
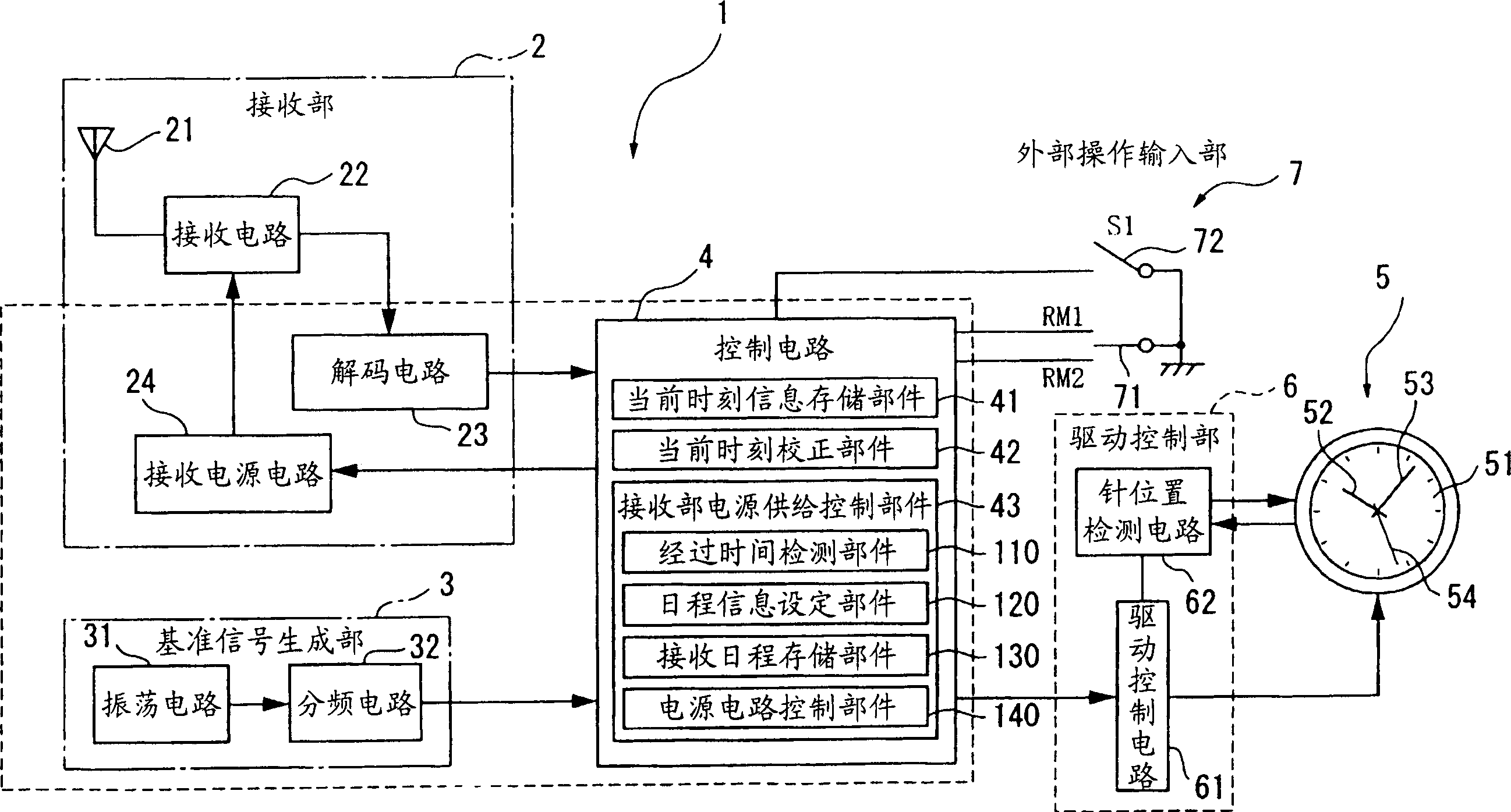
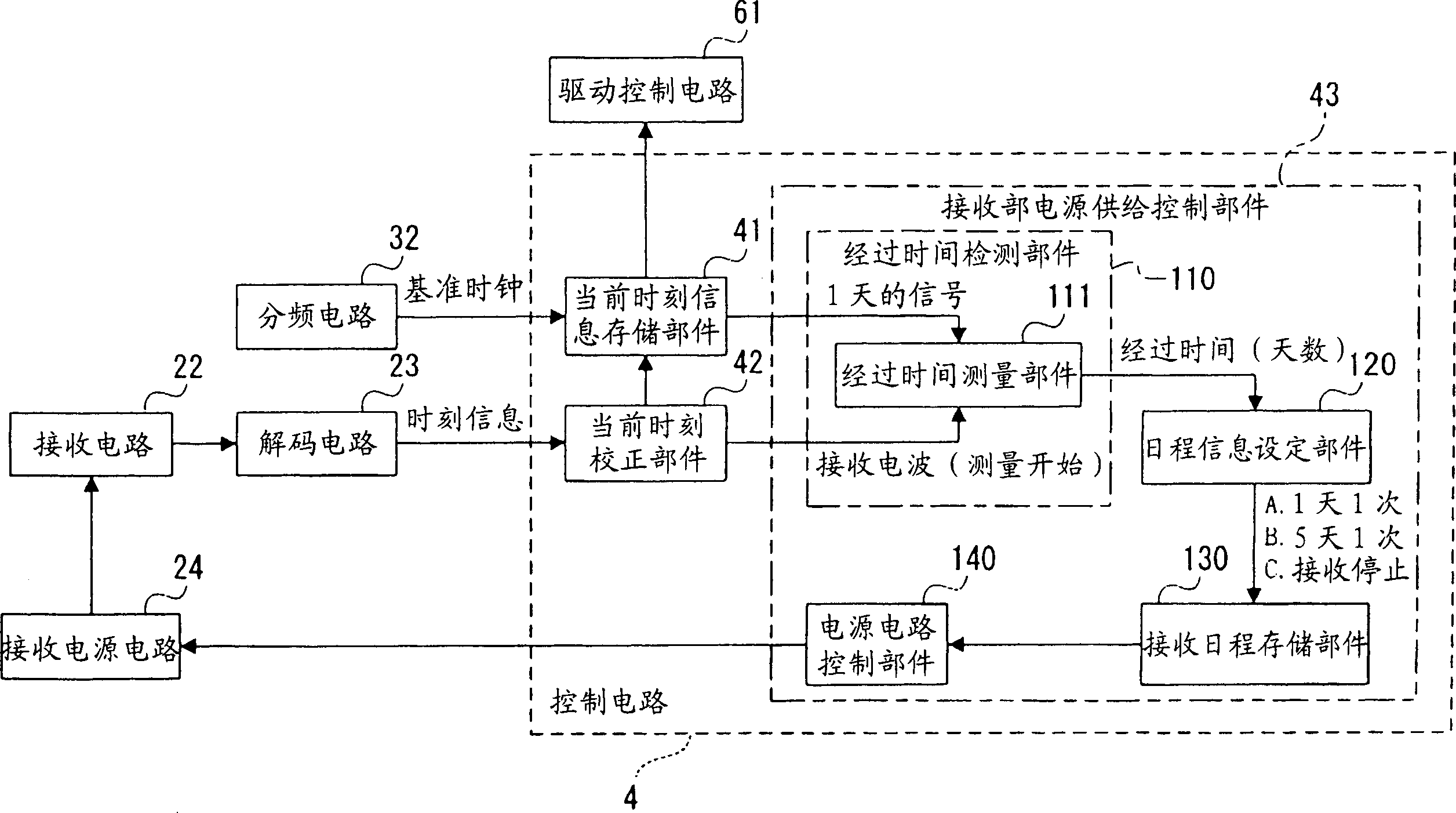
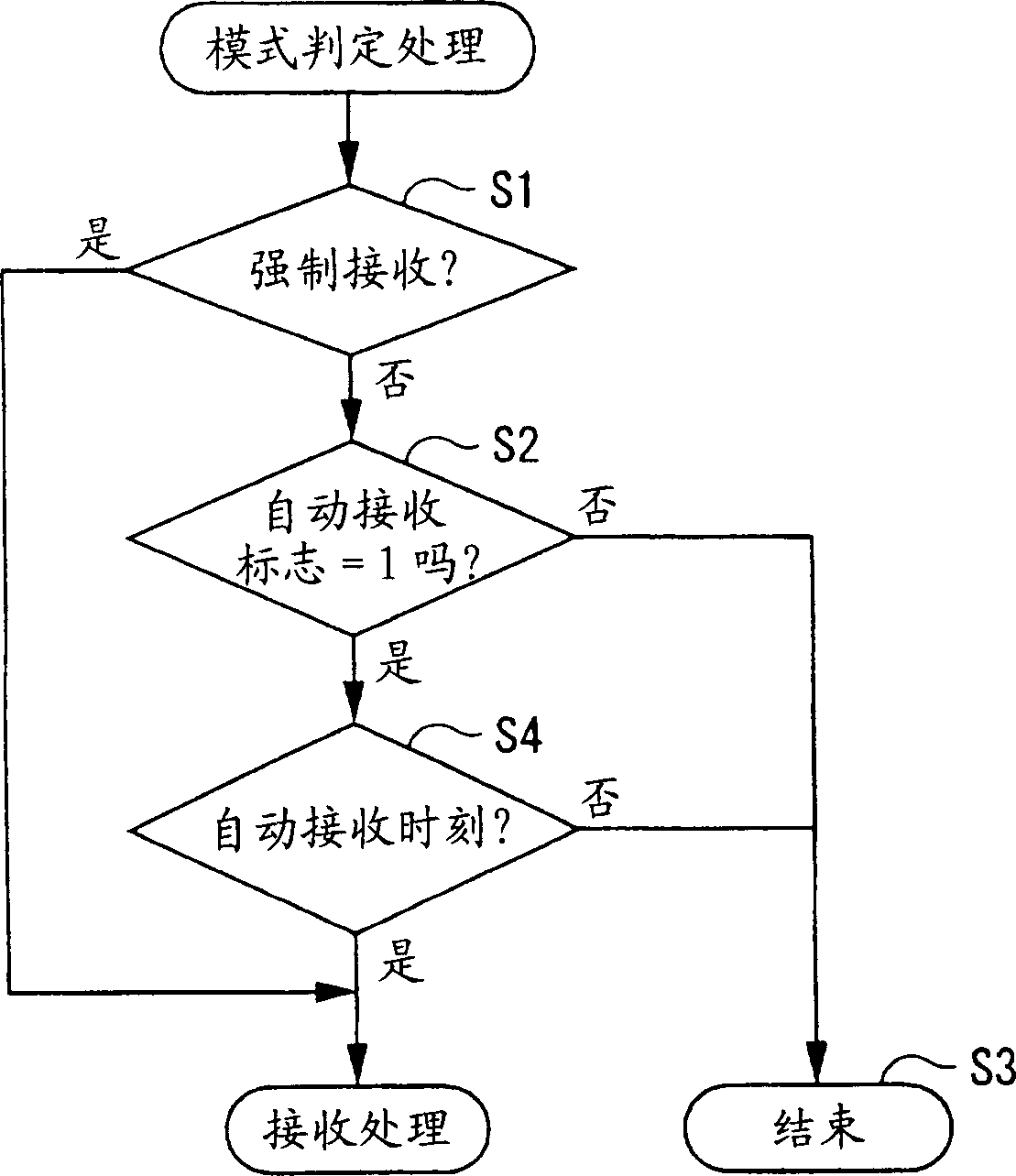
Radio-controlled timepiece and control method for a radio-controlled timepiece
ActiveUS6967901B2Improve energy efficiencySuppressing unnecessary power consumptionMechanical clocksTime-pieces with integrated devicesTime informationPower controller
A radio-controlled timepiece reduces unnecessary power consumption and improves energy conservation. The radio-controlled timepiece has a reception unit power supply controller 43 that regularly operates a reception power supply circuit 24 that drives a reception circuit 22 for receiving a radio signal containing time information. The reception unit power supply controller 43 has an elapsed time detector 110 for determining or measuring the elapsed time from the last time a signal was received, a reception schedule storage 130 for storing schedule information for supplying power, a schedule information setting-unit 120 for changing the schedule information to schedule information B with a longer power supply time interval than a default setting A if the elapsed time becomes greater than or equal to a set time, and a power supply circuit controller 140 that controls operation of the reception power supply circuit 24 based on the schedule information. Because the frequency of signal reception is reduced if the period in which signal reception is not possible increases, power consumption can be reduced.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and device for clock calibration
InactiveUS20060122799A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectrical measurementsRechargeable cellControl circuit
A method and a device for calibrating an interior clock generator installed inside a power monitoring unit of a rechargeable battery. The device includes an input pin for inputting an external clock signal from an exterior clock generator installed outside the power monitoring unit. A calibration timer control circuit is connected to the input pin. A register is connected to the calibration timer control circuit for outputting a start signal to activate the calibration timer control circuit. A counter and a timer are controlled by the calibration timer control circuit to be activated simultaneously therewith to count the outside clock signal and an internal clock signal generated from the interior clock generator, respectively. Such that the timer stops counting while the counter stops counting, a first count of the timer is compared to a second count of the counter to calibrate the interior clock generator.
Owner:FORTUNE SEMICON
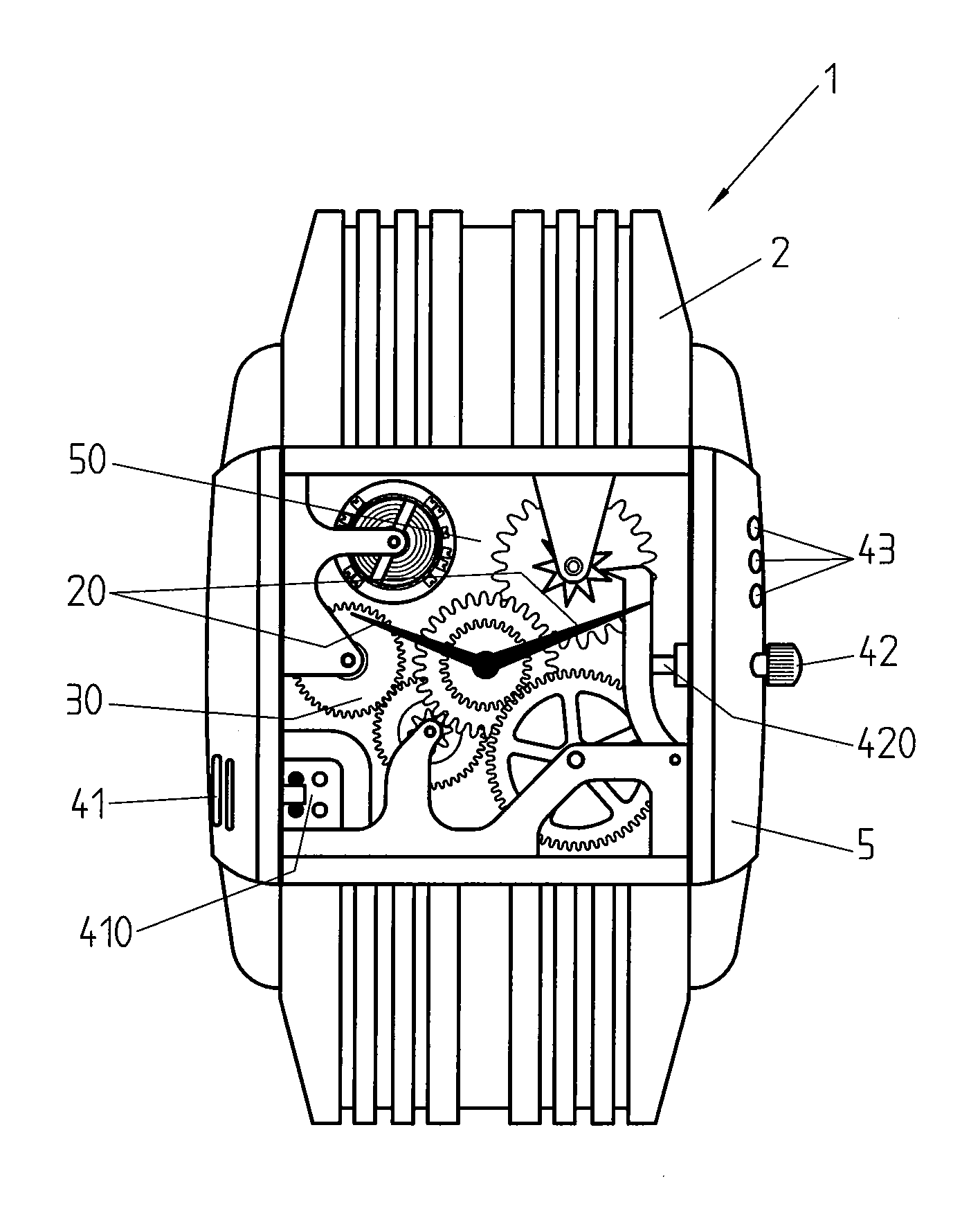
Wristwatch with electronic display
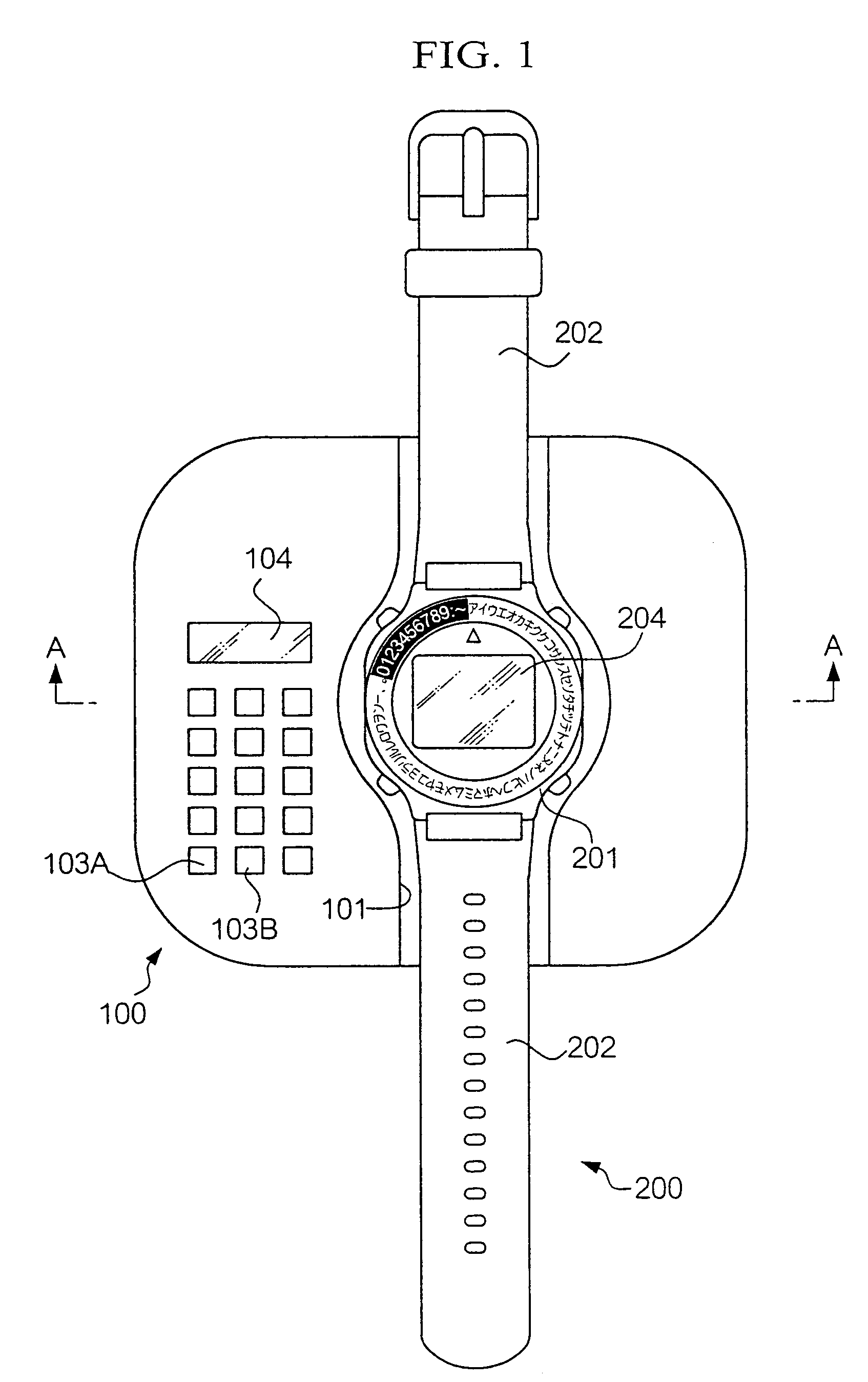
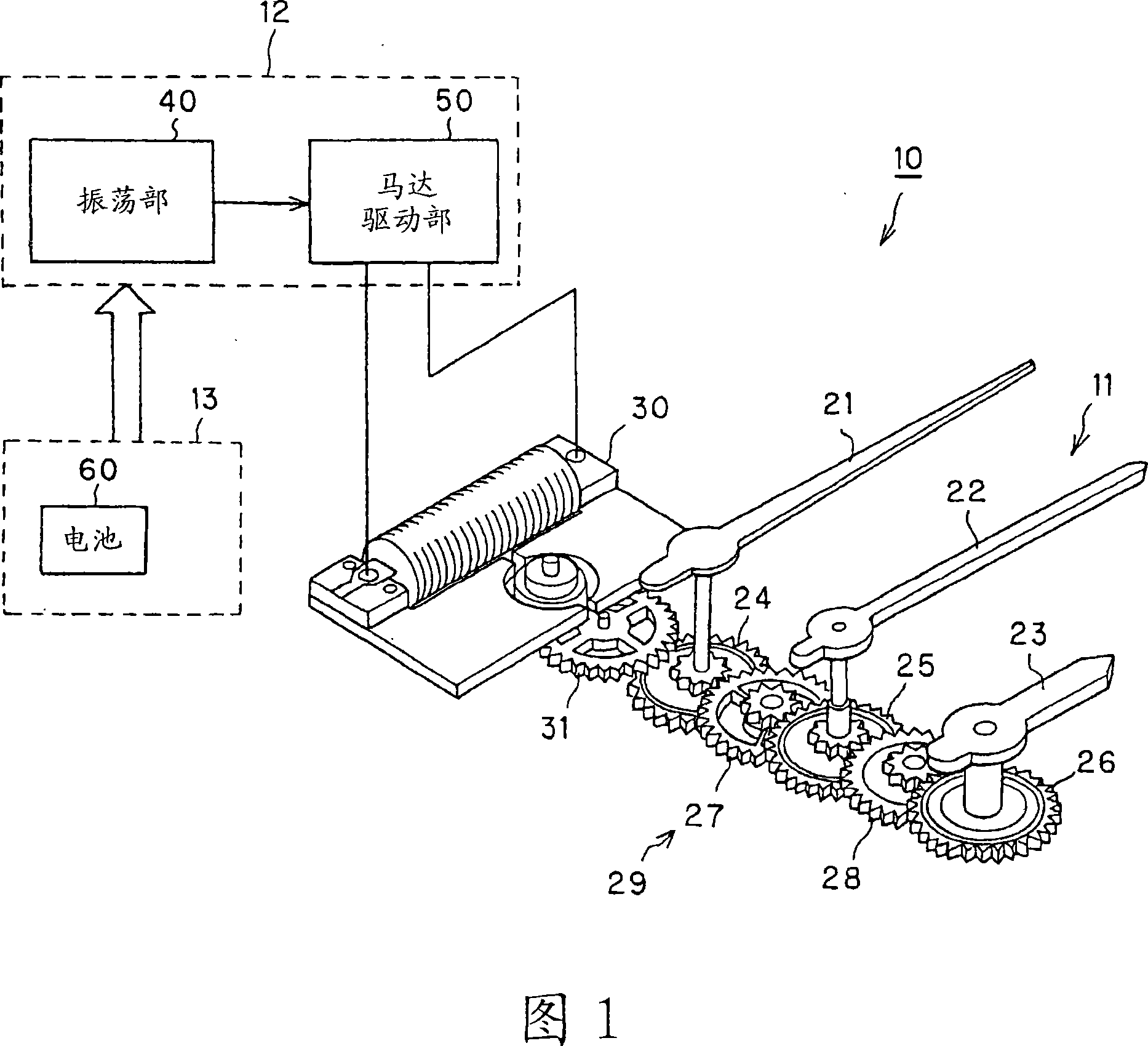
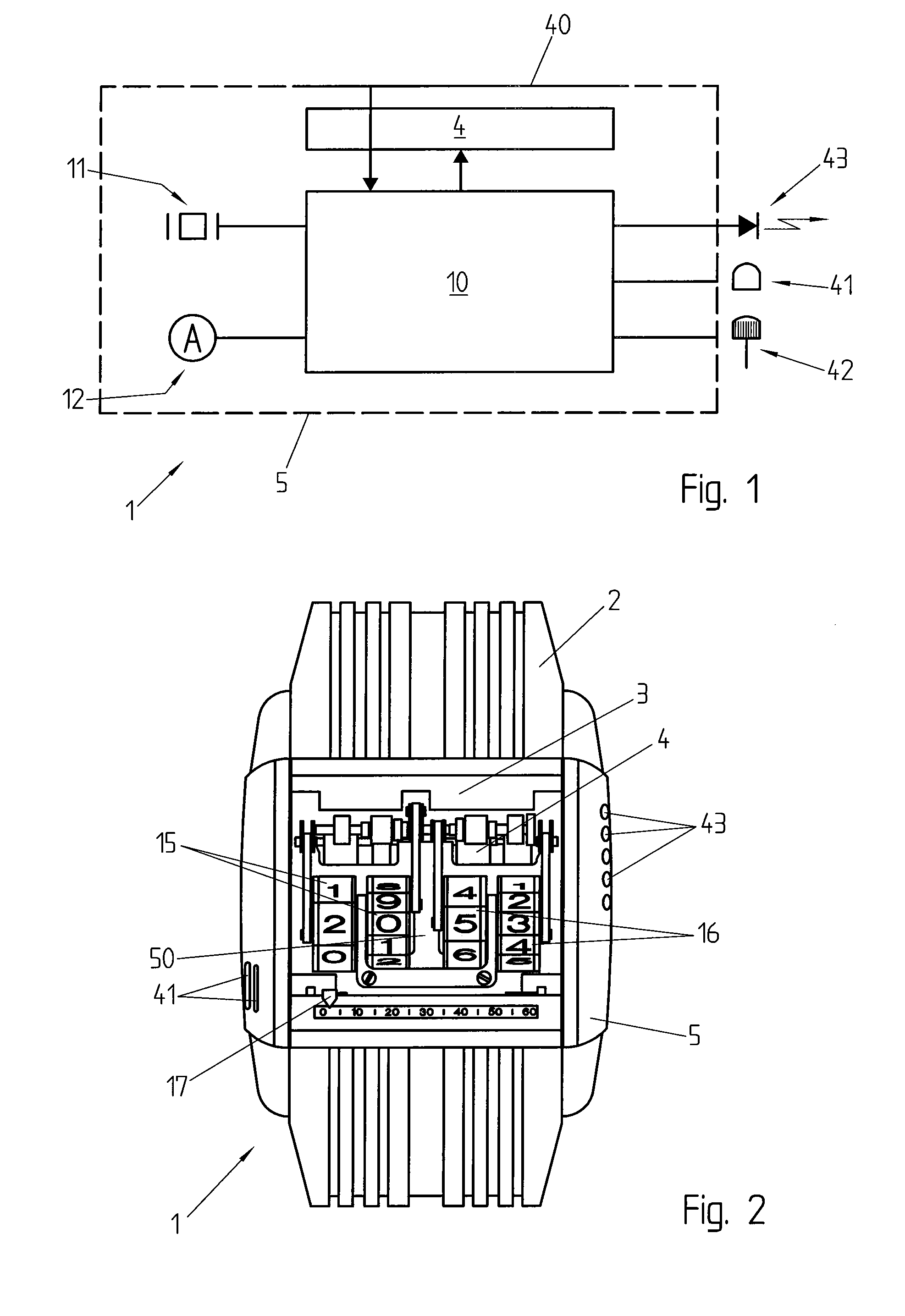
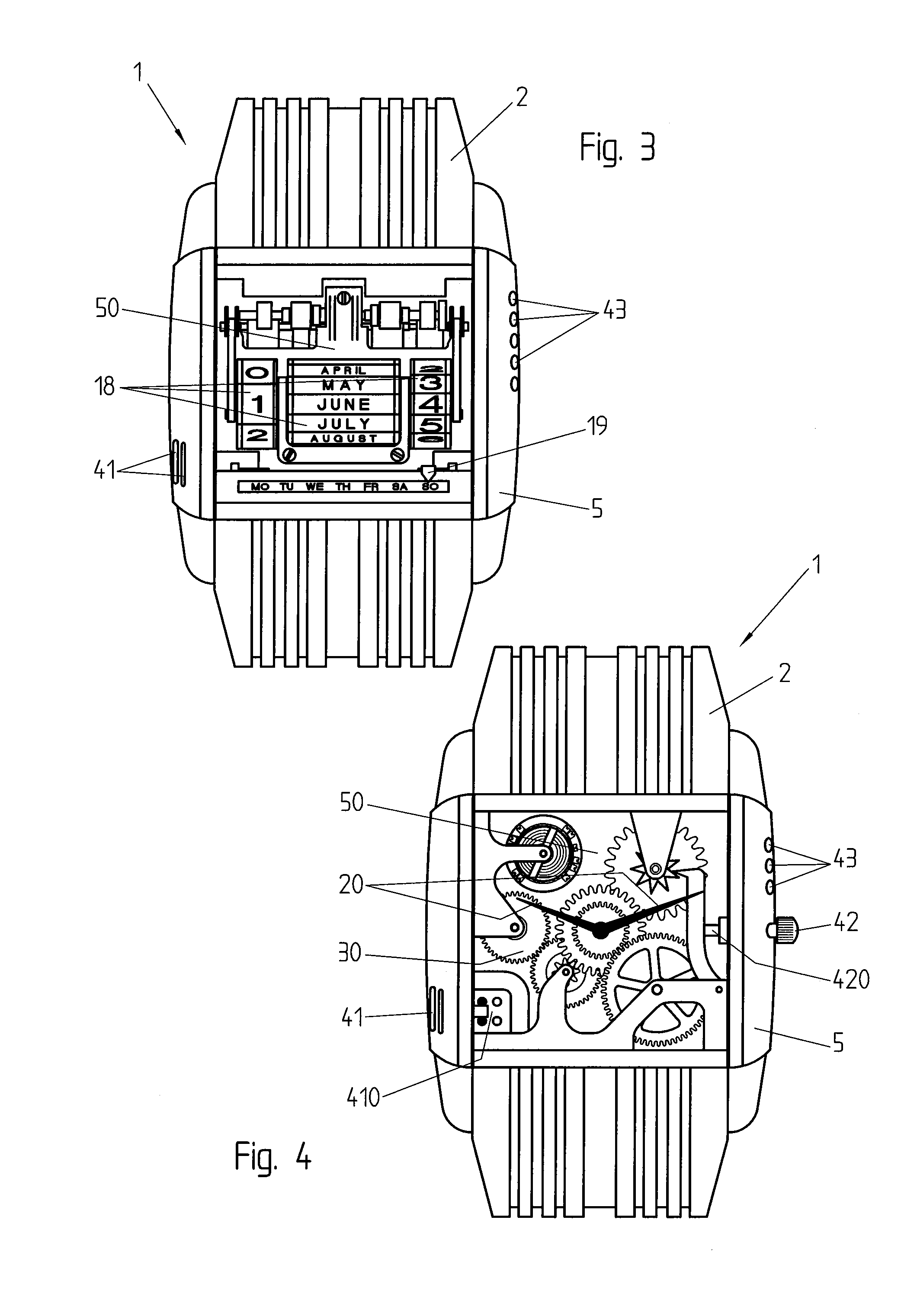
ActiveUS8588033B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove accuracyVisual indicationElectric indicationAccelerometerSimulation
Method for displaying the time in a wristwatch furnished with an electronic display (4) allowing the display of a simulated mechanical watch movement and of time indicators (20) so as to simulate a mechanical watch. The time displayed is advantageously calculated on the basis of the simulation of the movement and depends on the acceleration measured by an accelerometer.
Owner:SLYDE ANALYTICS LLC
High-precision distributed synchronous clock system and method
InactiveCN104122789AHigh precisionImprove stabilitySynchronous motors for clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesData synchronizationTime information
The invention discloses a high-precision distributed synchronous clock system and method. A distributed synchronization method combining GPS (global positioning system) with a constant-temperature crystal oscillator is adopted, that is, a GPS receiver module resolves time information and positioning information and generates 1PPS (pulse per second) signals to rectify local 1PPS signals generated by a constant-temperature crystal oscillator module, so that the local 1PPS signals and the 1PPS signals are synchronous. Thus, a viewer with the high-precision distributed synchronous clock system is capable of realizing multipoint distributed synchronization, high in synchronization accuracy and capable of accurately recording time during synchronous acquisition of data. Furthermore, spatial dimension of data acquiring points can be accurately positioned. After one or more GPSs fail, pulse per second generated by the local constant-temperature crystal oscillator is used for synchronization instead of the 1PPS signals, and effective time of synchronization can reach more than half an hour.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Wave correction clock and control method of wave correction clock
InactiveCN1447198ATo achieve the function and effectSame function and effectSynchronous motors for clocksTime-pieces with integrated devicesTime informationTelecommunications
The invention seeks to provide a radio-controlled timepiece that can suppress unnecessary power consumption and improve energy conservation. <??>The radio-controlled timepiece has a reception unit power supply control means 43 for regularly operating a reception power supply circuit 24 that drives a reception circuit 22 for receiving a radio signal containing time information. The reception unit power supply control means 43 has a elapsed time detection means 110 for determining the elapsed time from the last time a signal was received, a reception schedule storage means 130 for storing schedule information for supplying power, a schedule information setting means 120 for changing the schedule information to schedule information B with a longer power supply time interval than a default setting A if the elapsed time becomes greater than or equal to a set time, and a power supply circuit control means 140 for controlling operation of the reception power supply circuit 24 based on the schedule information. Because the frequency of signal reception is reduced if the period in which signal reception is not possible increases, power consumption can be reduced. <IMAGE>
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Popular searches
Thermometers using electric/magnetic elements Material analysis by electric/magnetic means Electrial characteristics varying frequency control Piezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devices Time pulses Using electrical means Electric pulse generator Electrostatic generators/motors Burglar alarm short radiation actuation Generator stabilization
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com