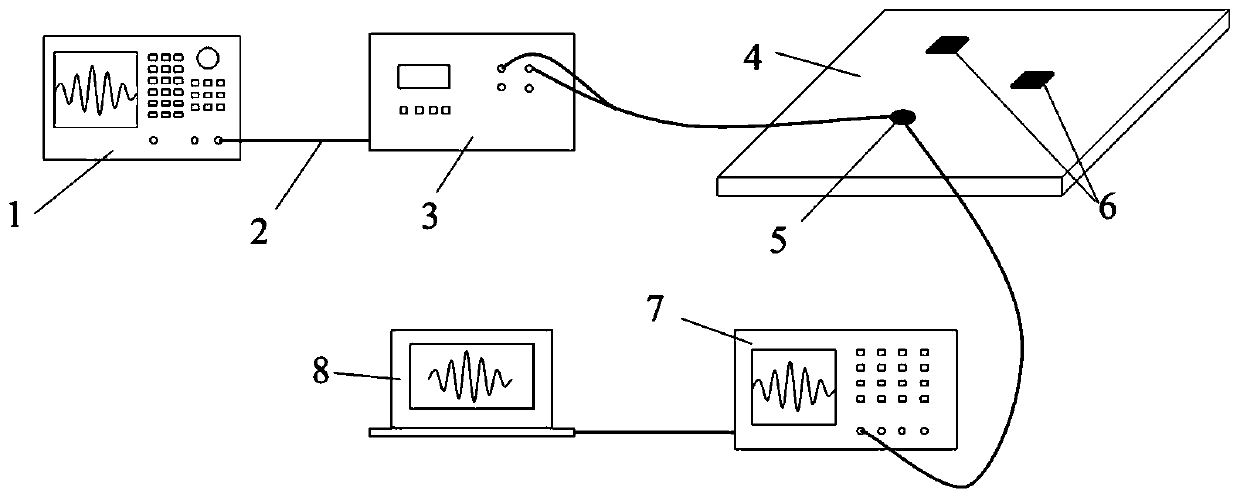
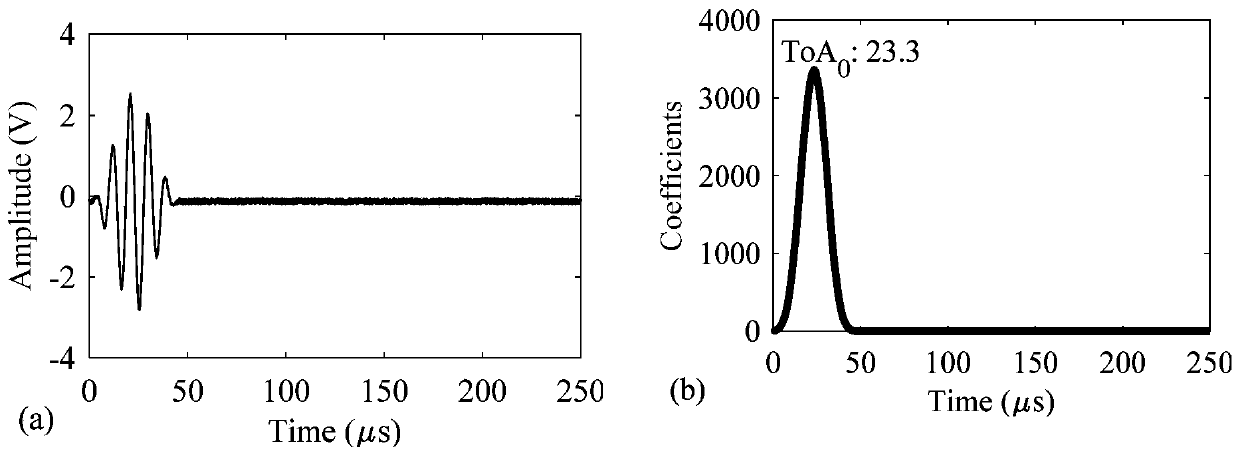
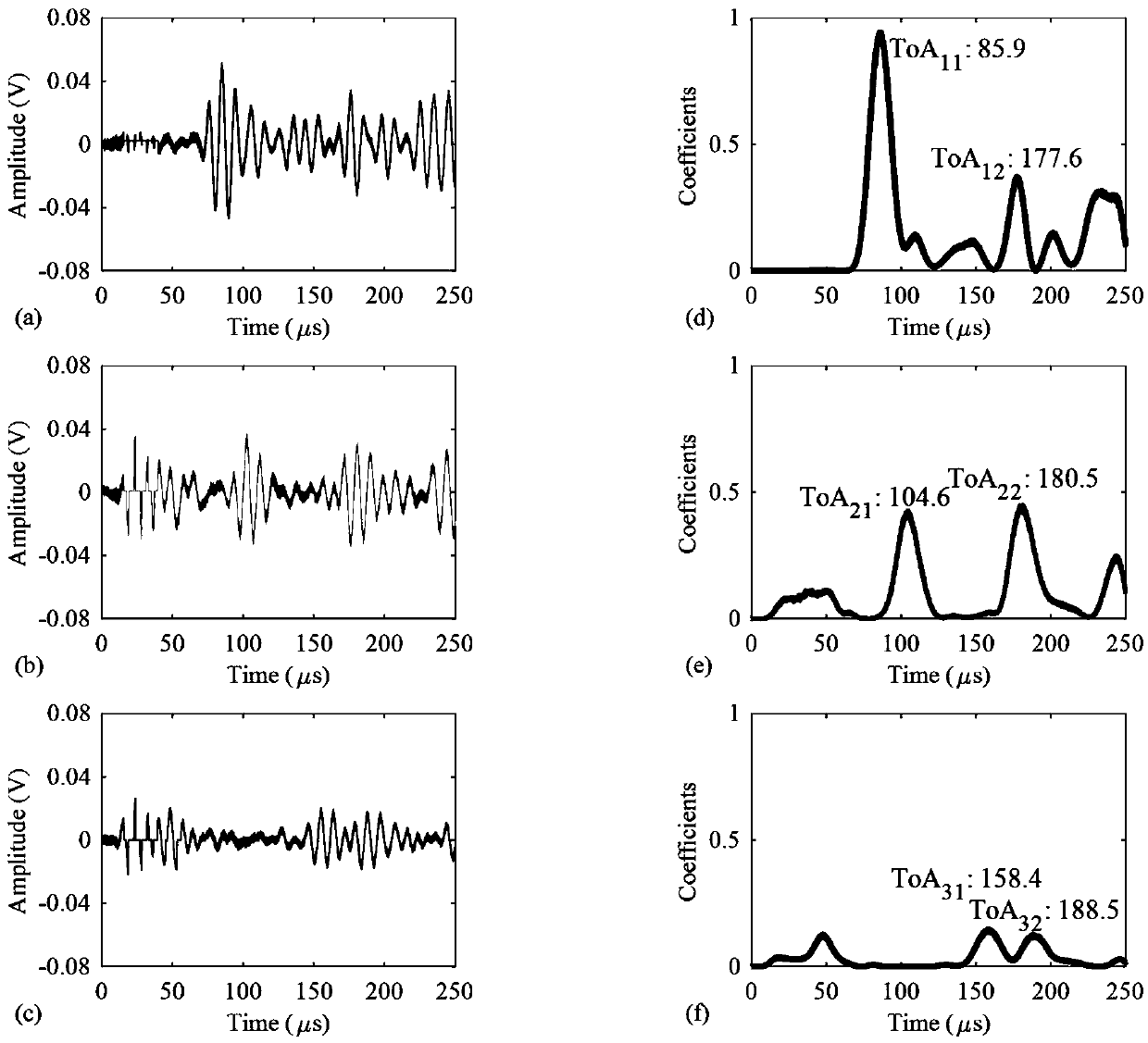
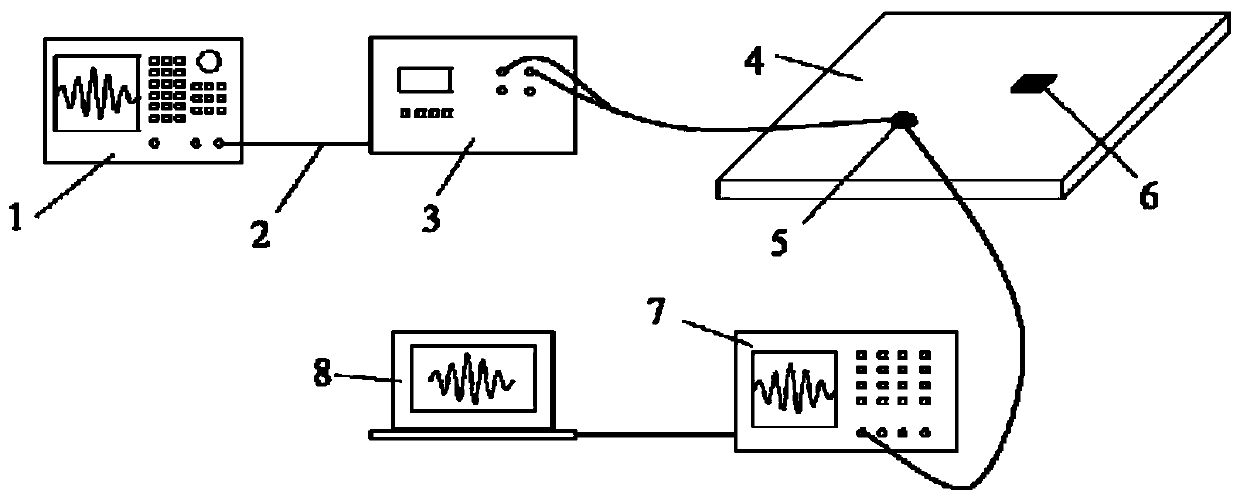
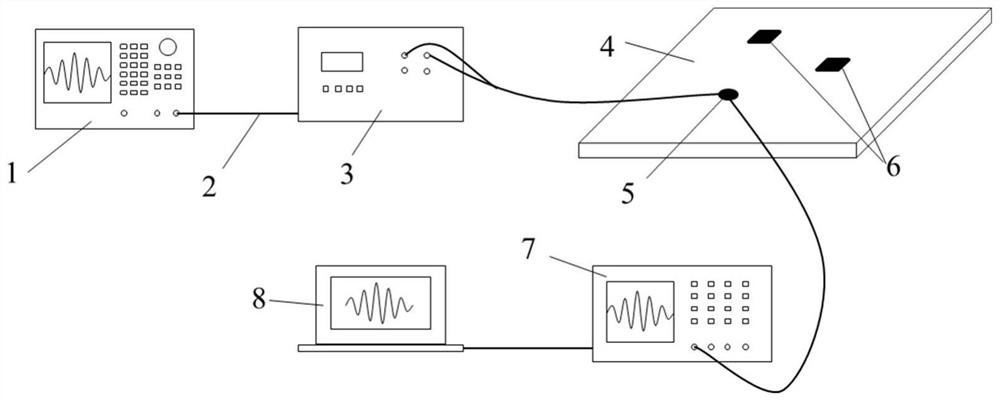
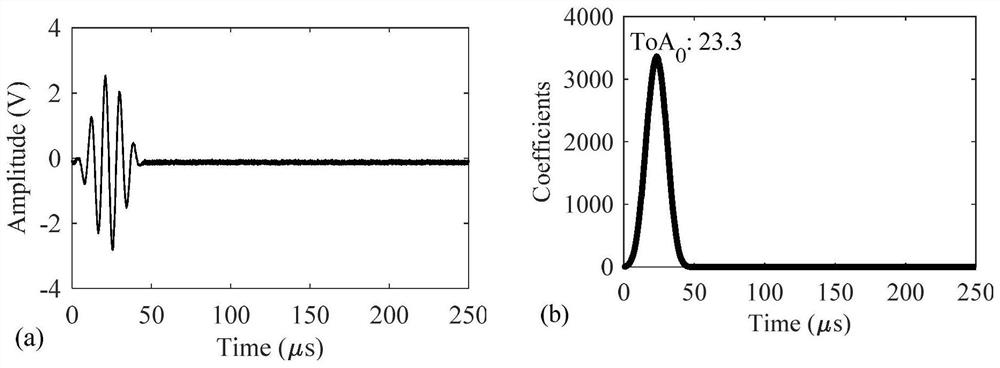
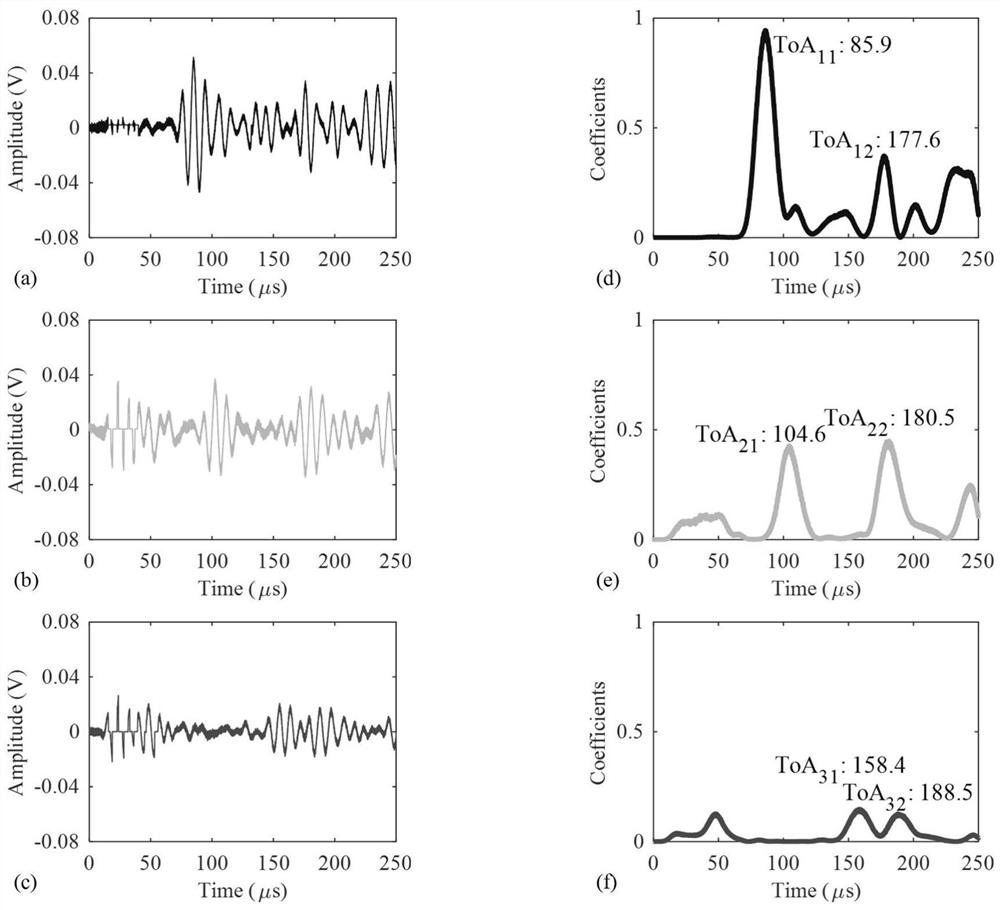
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Guided wave propagation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
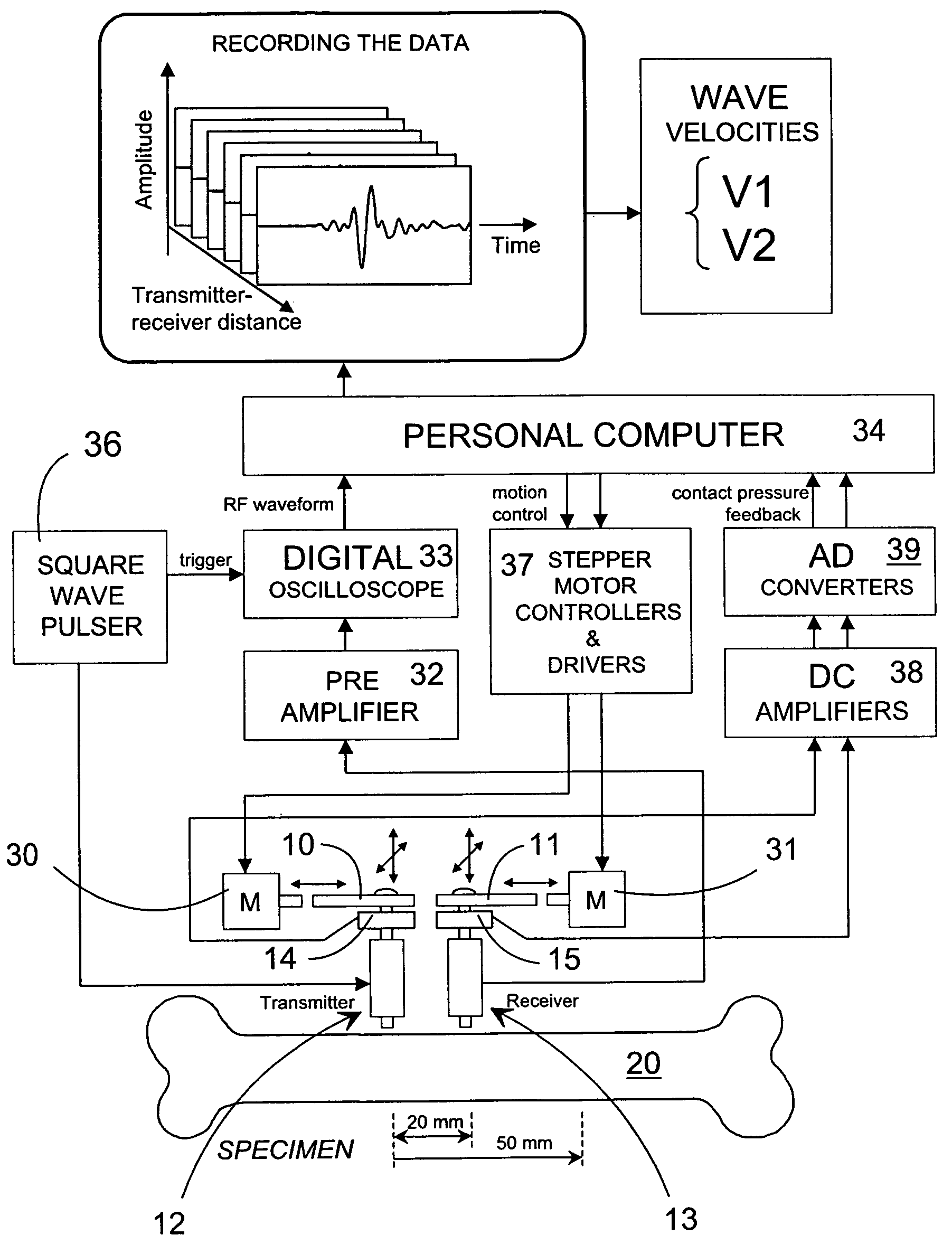
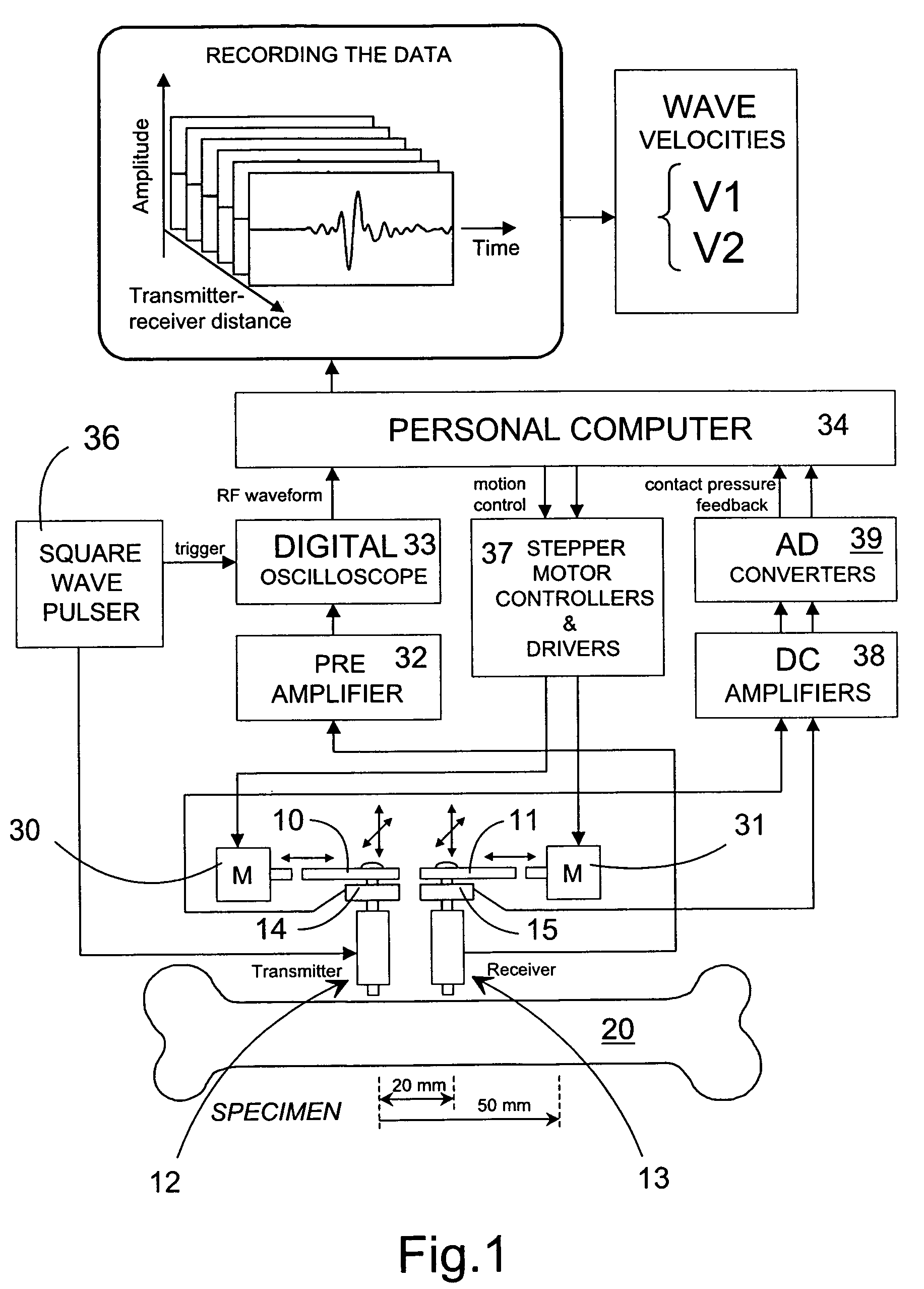
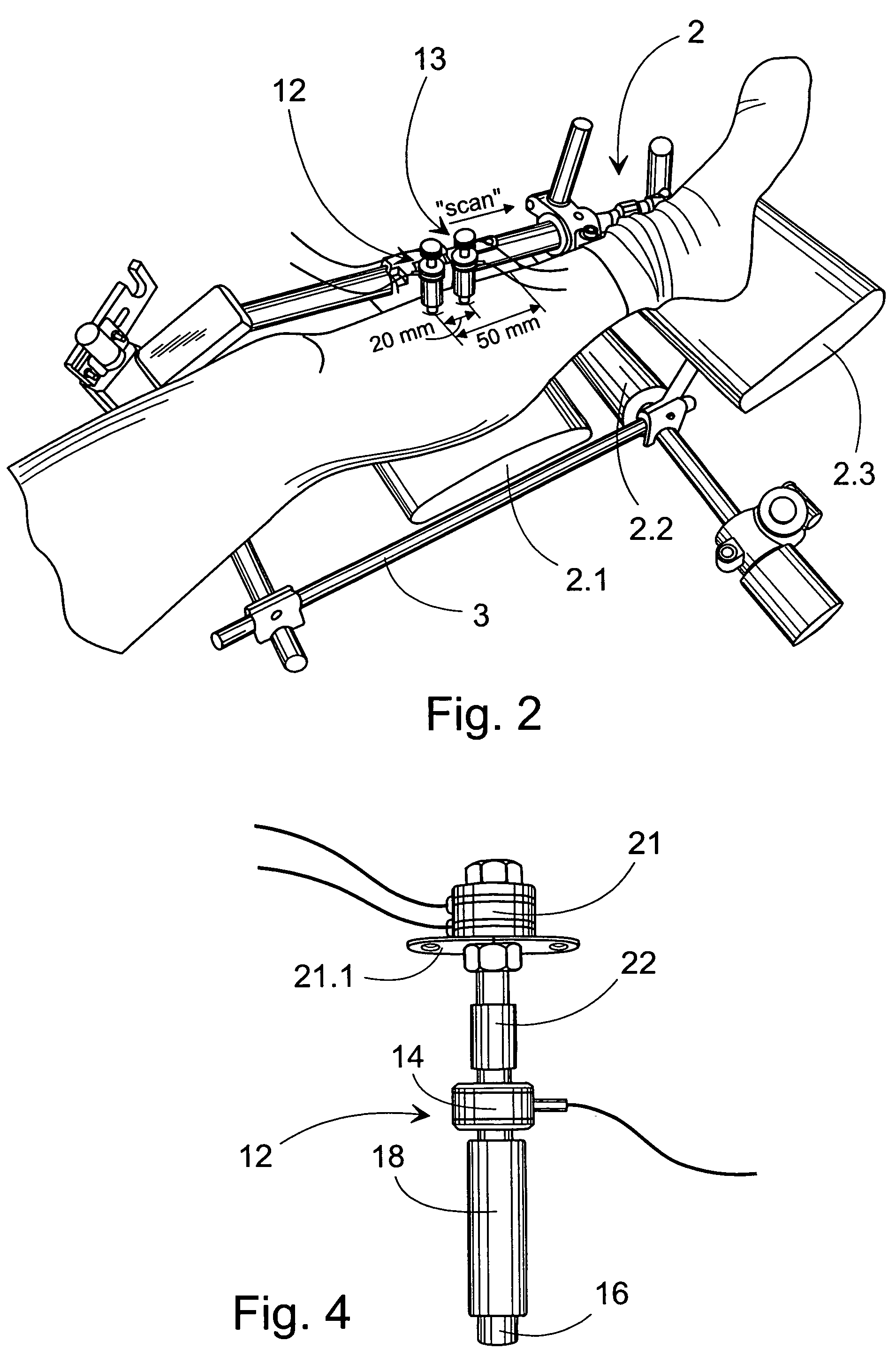
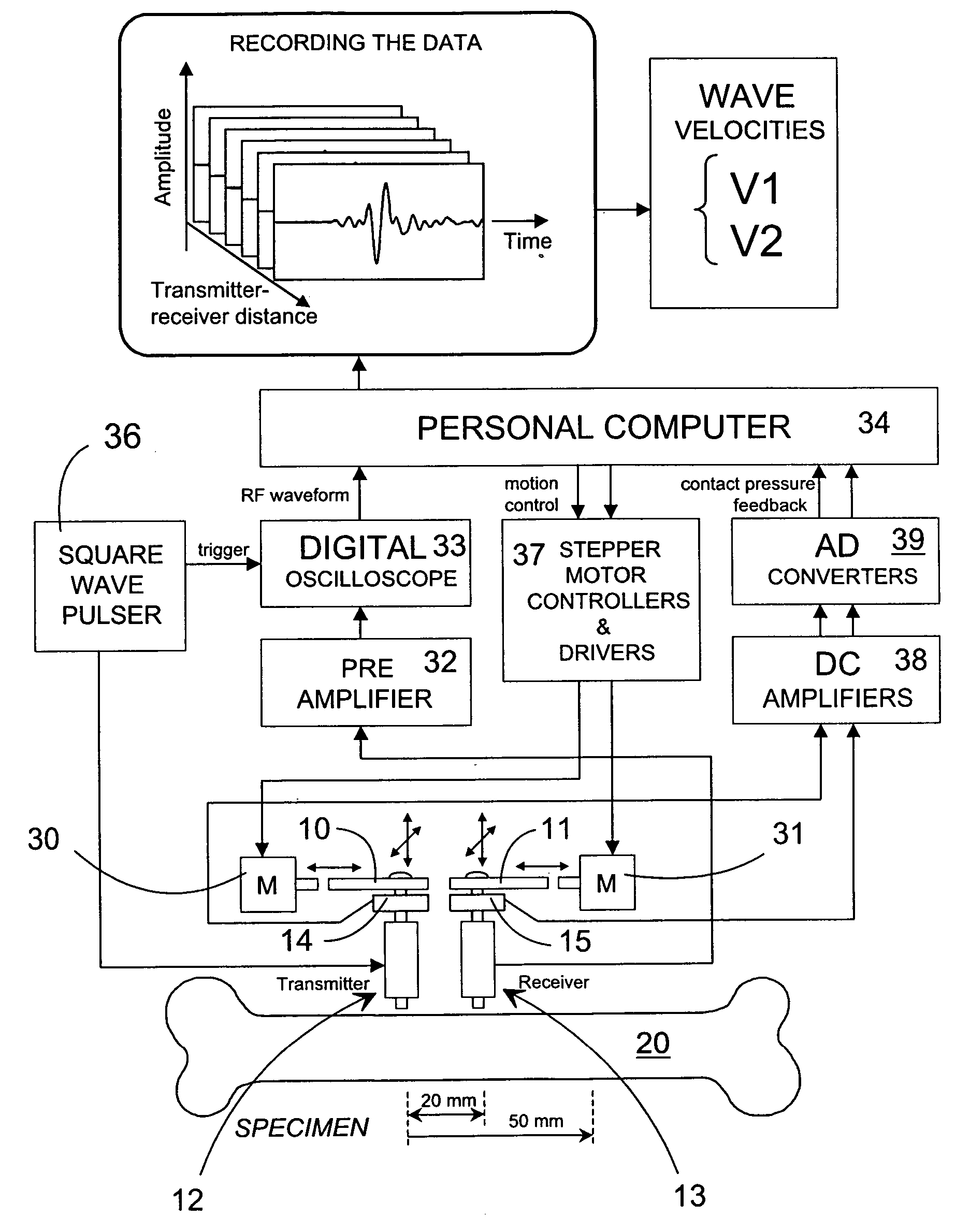
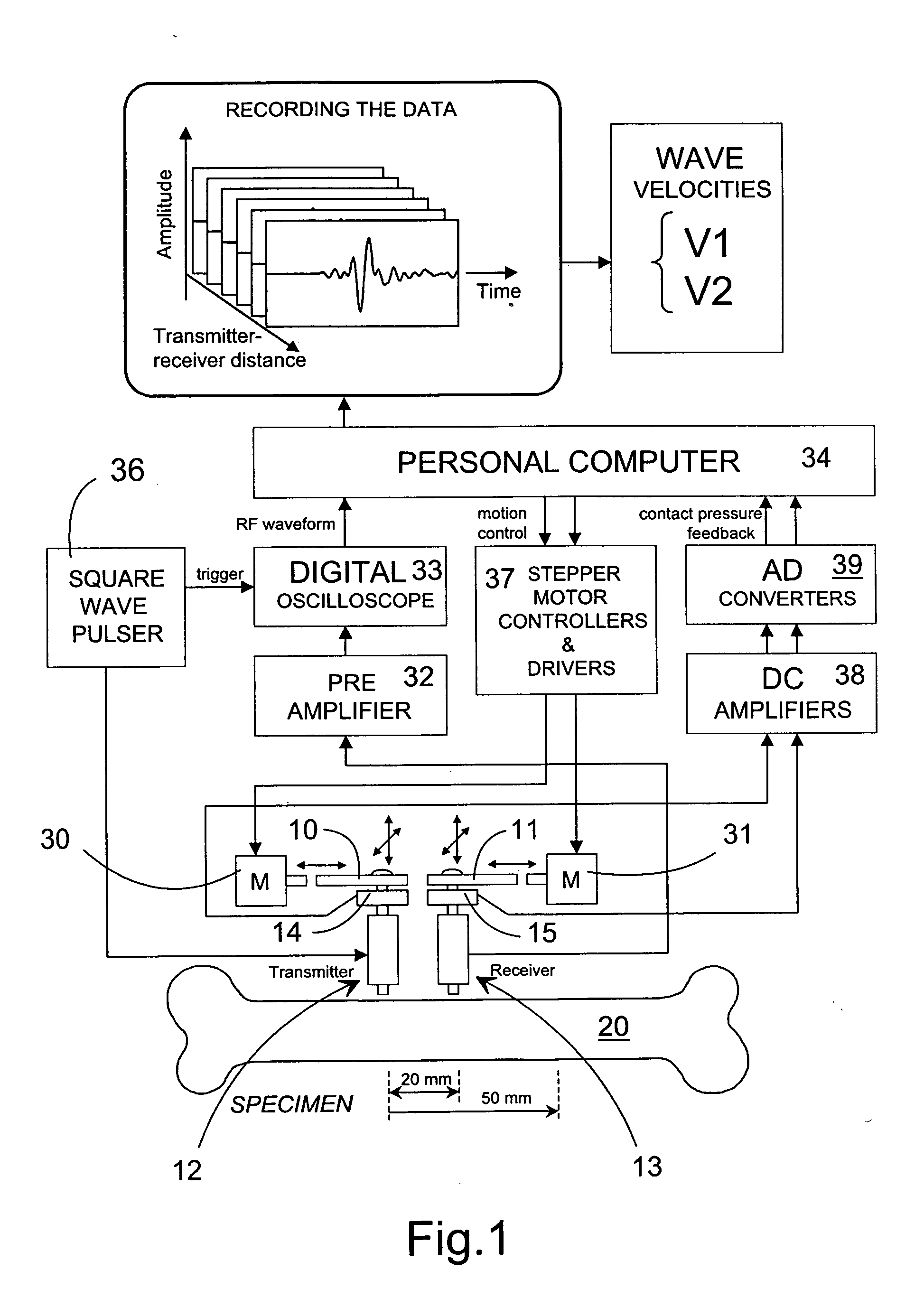
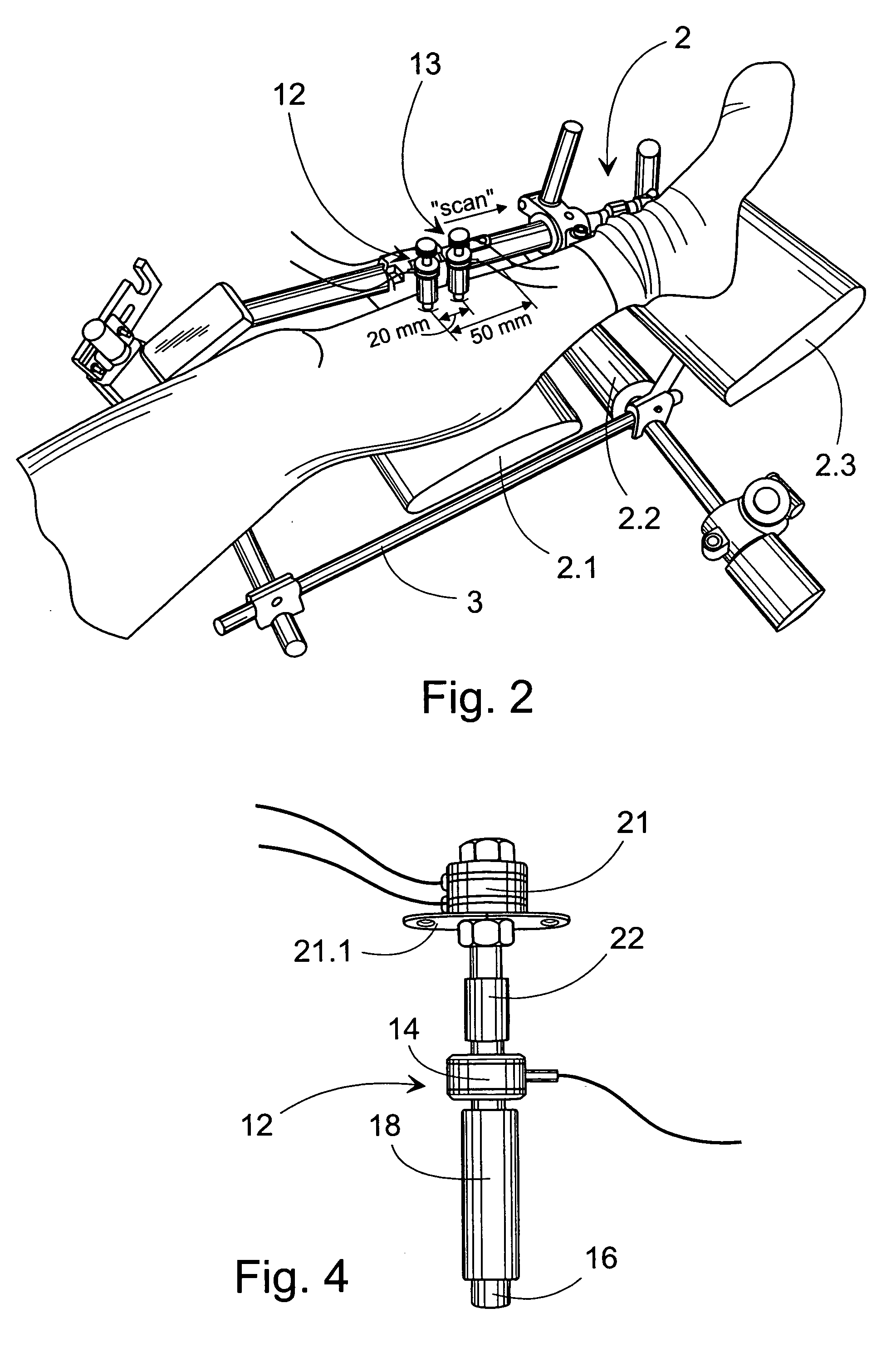
Method and device for the non-invasive assessment of bones
ActiveUS7601120B2Enhanced thickness-dependenceMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidBone densityTransducer
A method for the in vivo non-invasive characterization of the material and architectural properties of a bone in which an ultrasonic wave is introduced into a bone in such way as to produce one or more guided wave modes within the bone, and the signals emerging from the bone are stored and analyzed to determine the propagation characteristics of the guided wave / s. These measured guided wave propagation characteristics are then processed to obtain estimates of desired bone properties such as cortical thickness, bone density and bone elastic constants. The invention also includes an unltrasound arrangement with movable transducers.
Owner:OSCARE MEDICAL
Method and device for the non-invasive assessement of bones
ActiveUS20050004457A1Difficult to observeSmall sizeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidBone densityTransducer
A method for the in vivo non-invasive characterization of the material and architectural properties of a bone in which an ultrasonic wave is introduced into a bone in such way as to produce one or more guided wave modes within the bone, and the signals emerging from the bone are stored and analyzed to determine the propagation characteristics of the guided wave / s. These measured guided wave propagation characteristics are then processed to obtain estimates of desired bone properties such as cortical thickness, bone density and bone elastic constants. The invention also includes an unltrasound arrangement with movable transducers.
Owner:OSCARE MEDICAL
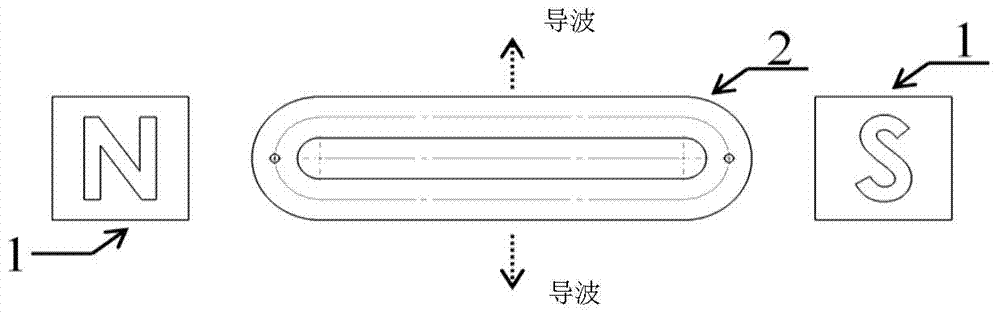
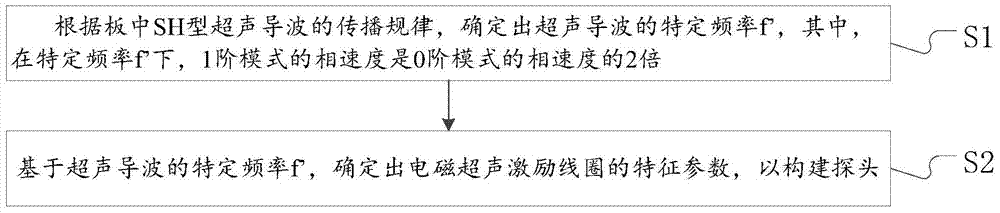
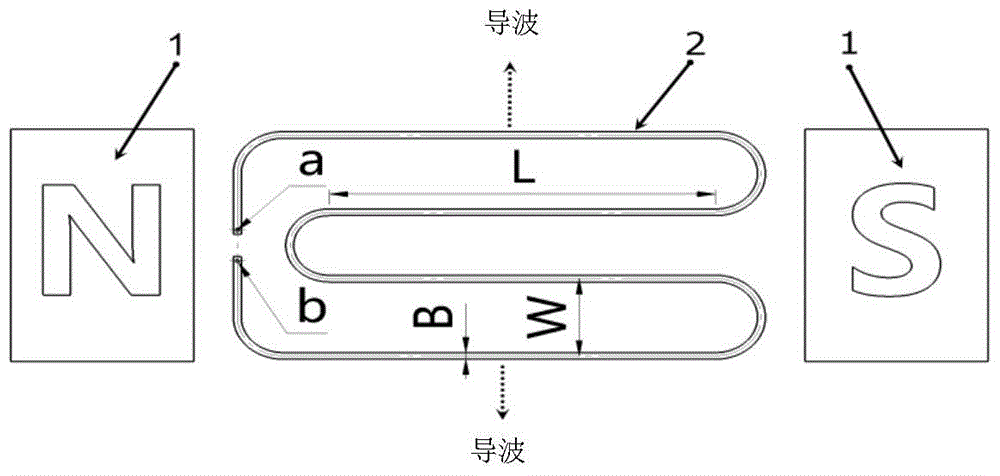
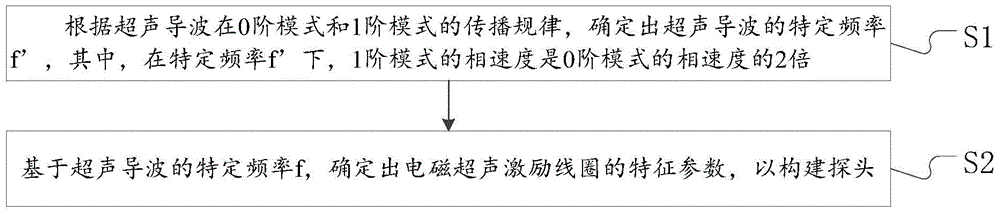
Electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe design method
ActiveCN104330476ASimplifyImprove signal-to-noise ratioUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Guided wave propagation
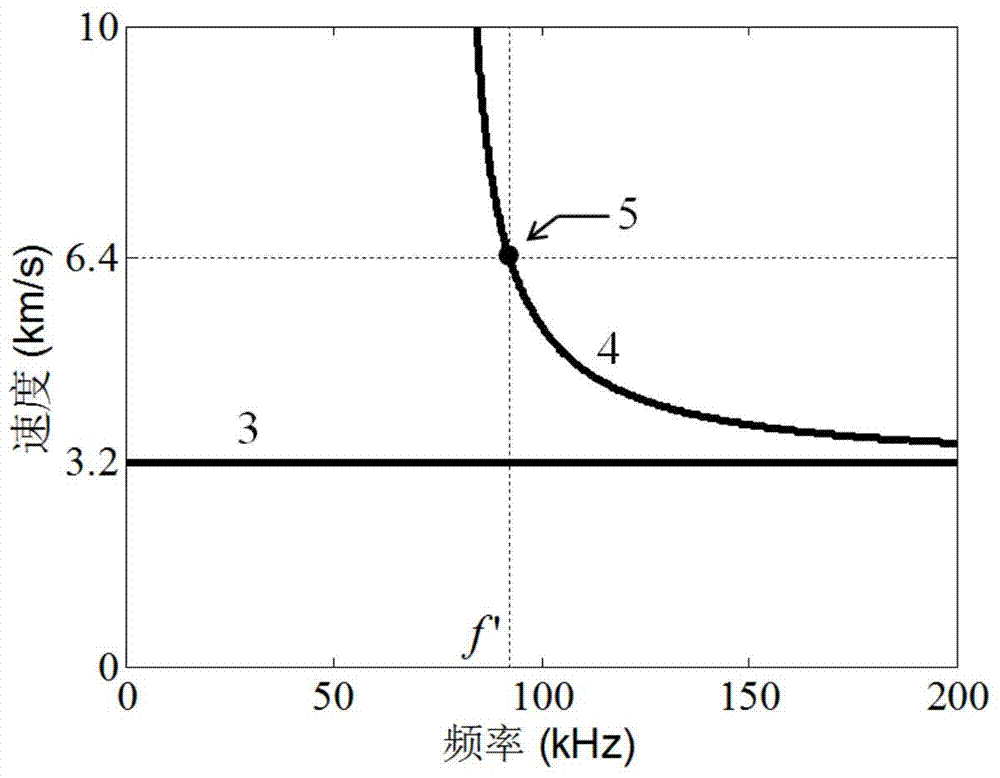
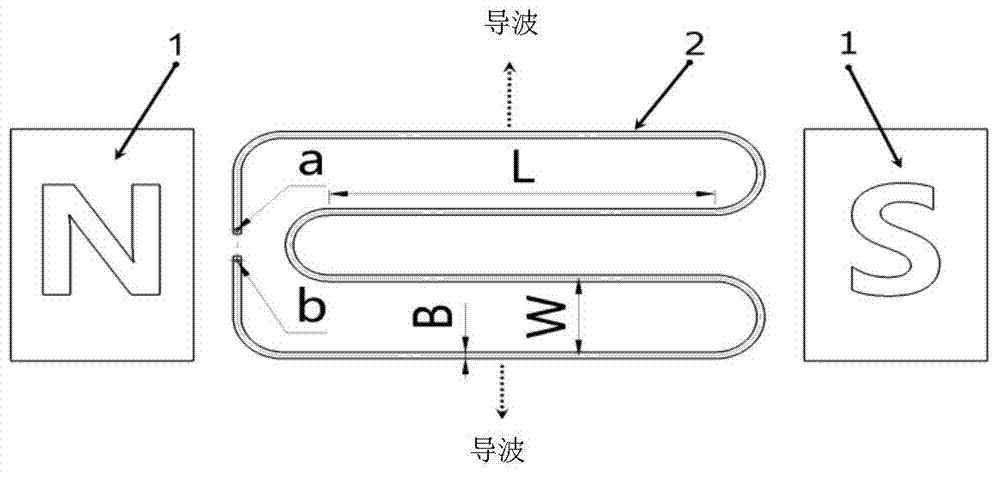
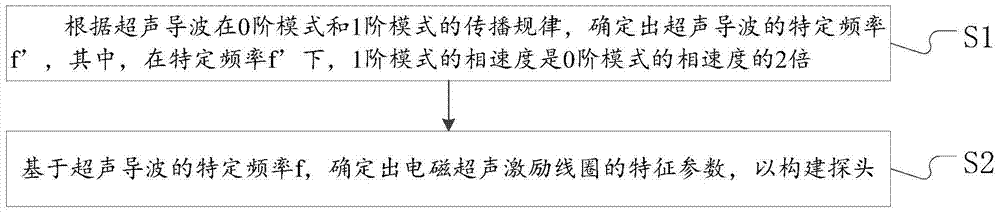
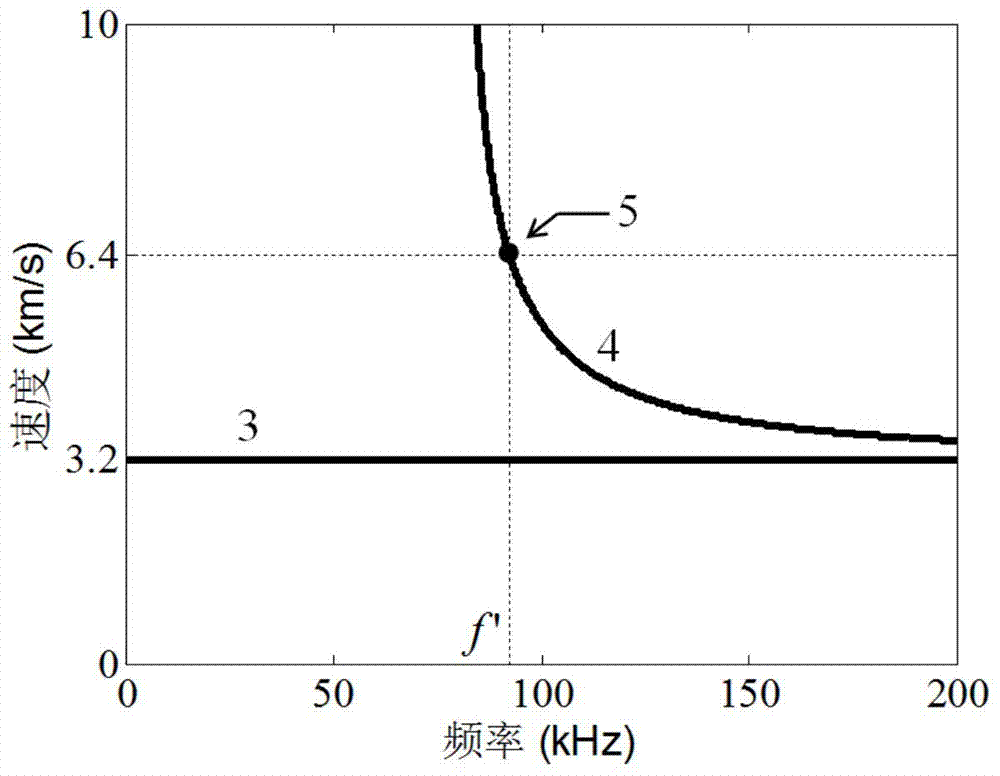
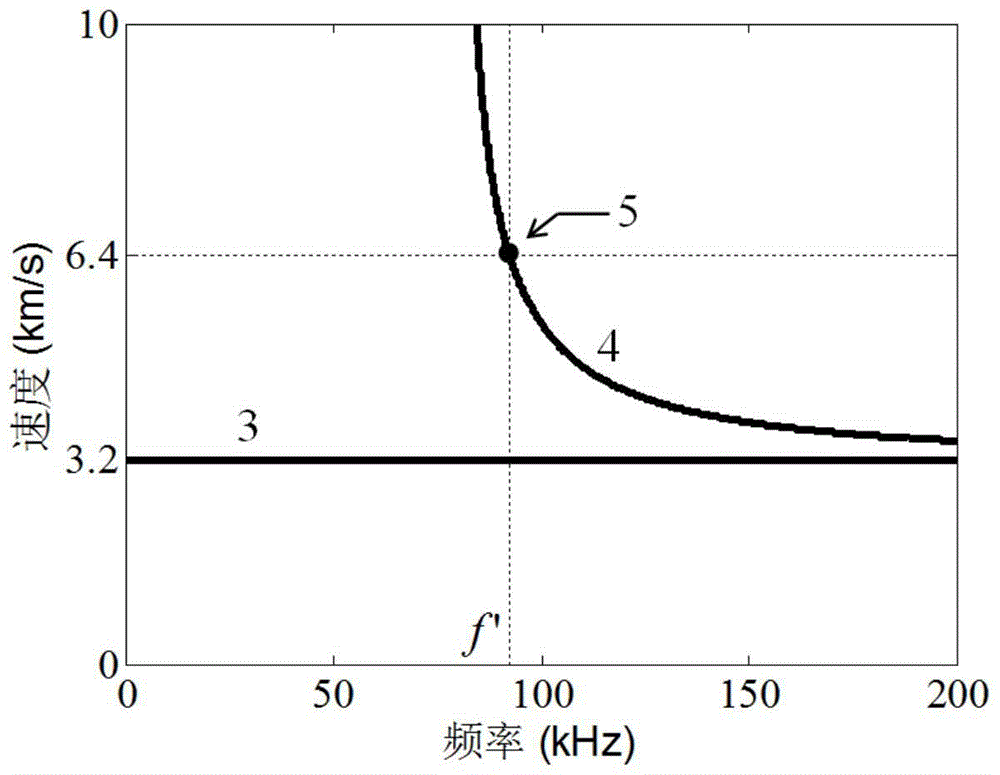
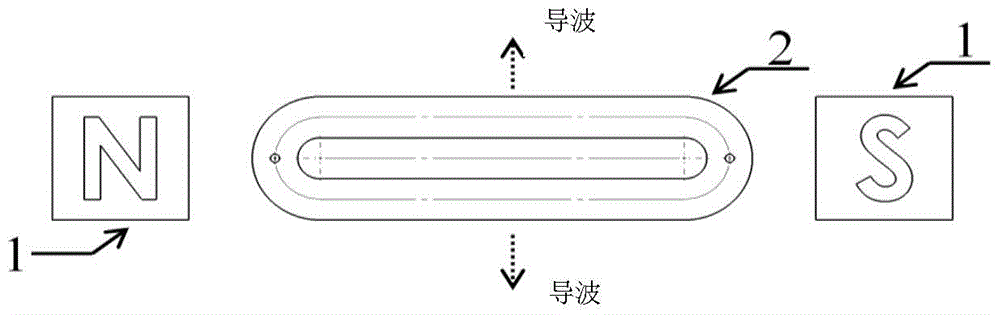
The invention discloses an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe design method, according to the sound propagation principle, namely SH type guided wave propagation rule, in a solid plate, optimum excitation frequency is determined, and according to the frequency, an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe is designed; enhancement of SH type 0 order mode guided wave and inhibition of 1 order mode guided wave in the plate can be realized, simplification of the mode of a guided wave excited in a particular frequency can be realized, the signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and defect detection probability and quantization accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe design method based on magnetic induced shrinkage or elongation effect
ActiveCN104330477ASimplifyGuided wave suppressionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationSonificationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
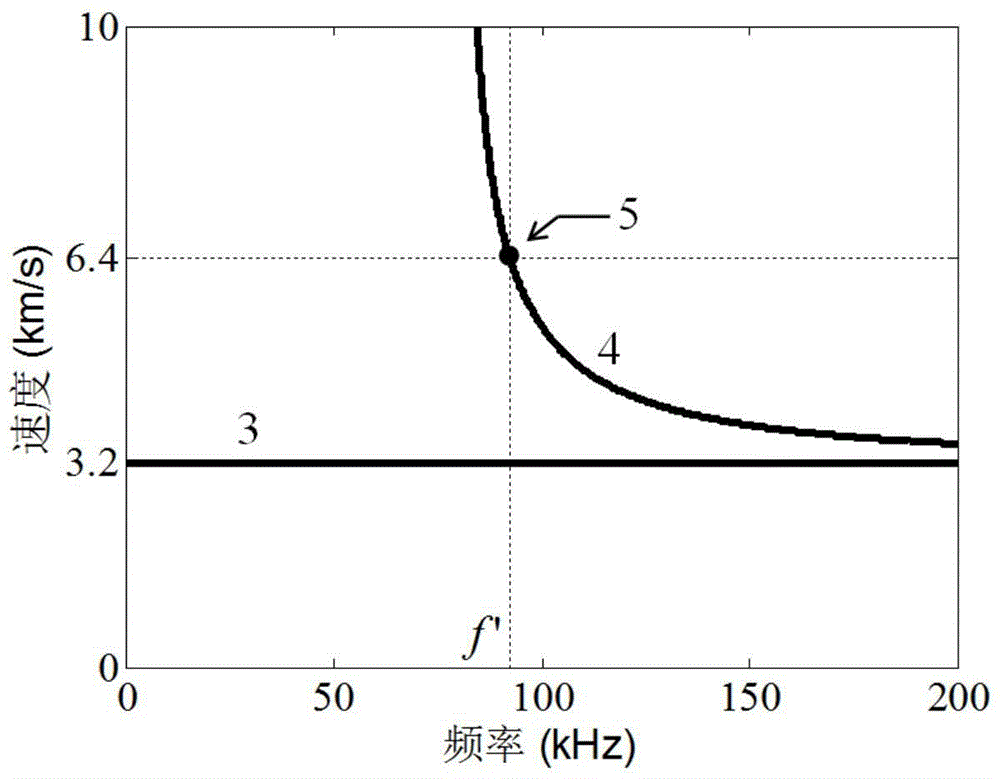
The invention discloses an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe design method based on magnetic induced shrinkage or elongation effect, according to the sound propagation principle, namely SH type guided wave propagation rule, in a solid plate, optimum excitation frequency is determined, and according to the frequency, an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe is designed; the prominent advantage of the proposed design method are that a right excitation frequency f' is selected for enhancement of1 order mode guided wave in the plate and effective inhibition of 0 order mode guided wave, simplification of the mode of a guided wave excited in a particular frequency can be realized, the signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and the defect detection probability and quantization accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Coated Nanofiller/Polymer Composite Sensor Network for Guided-Wave-Based Structural Health Monitoring
ActiveUS20180045588A1Quickly and effectively generatedLiquid surface applicatorsAdditive manufacturing apparatusStructural health monitoringEngineering
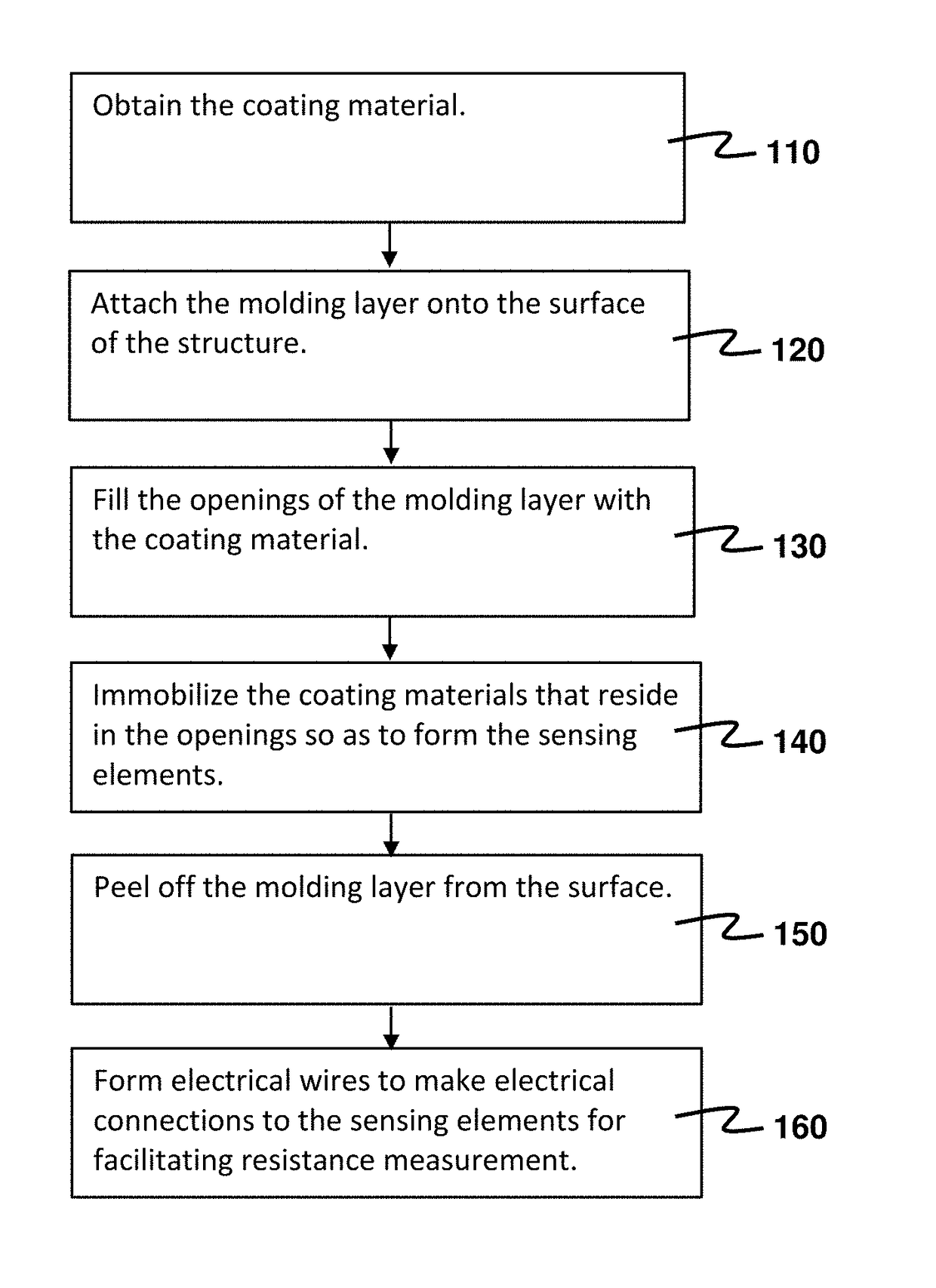
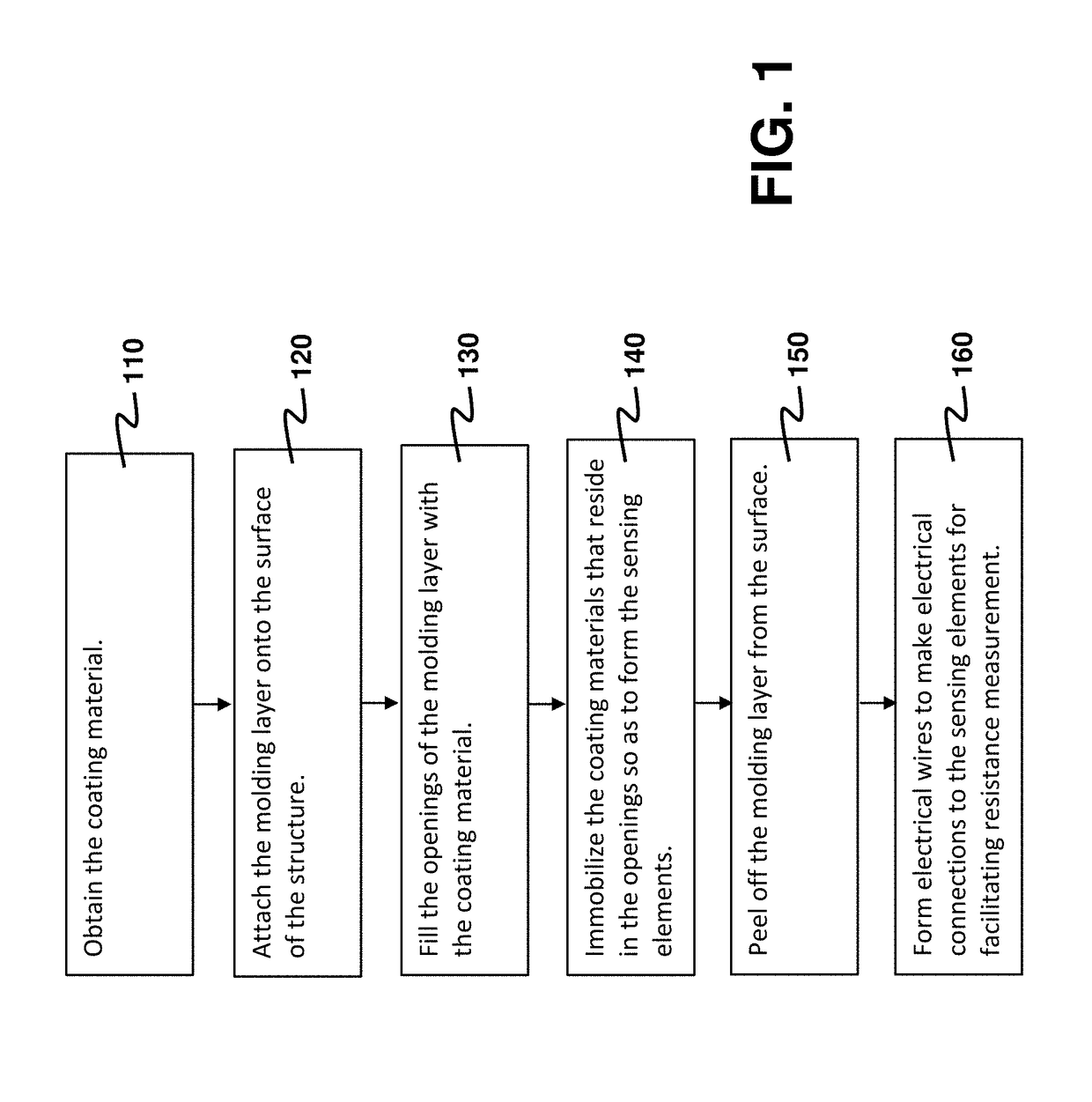
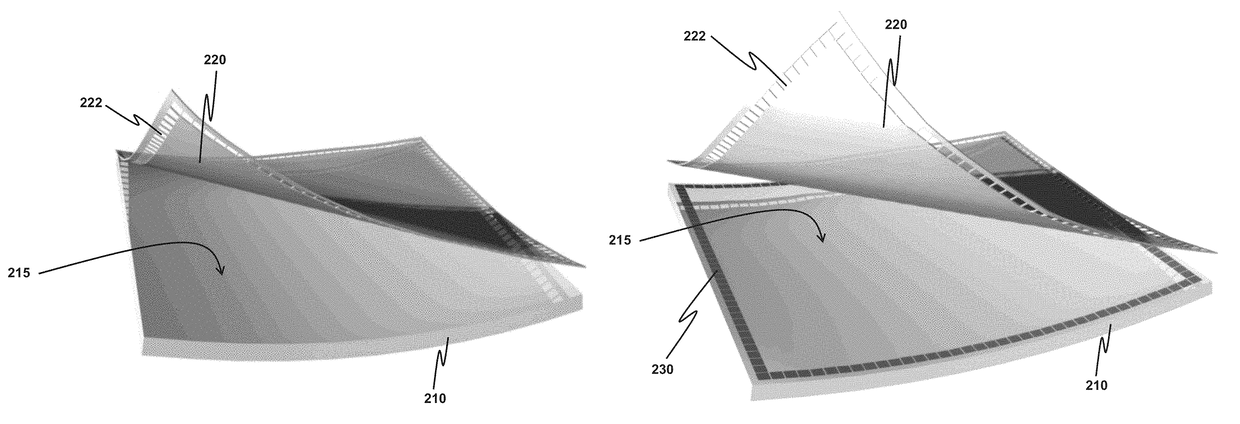
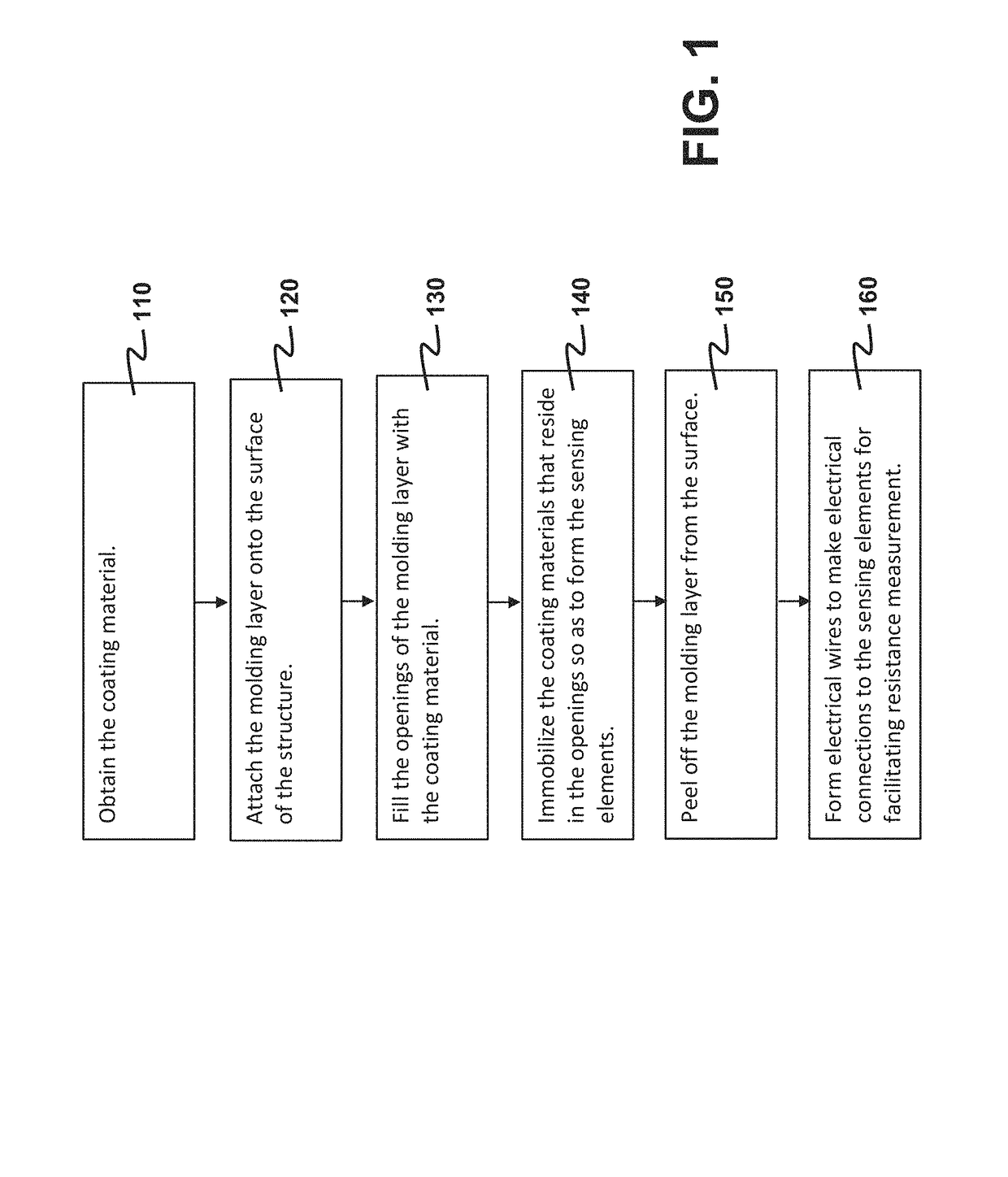
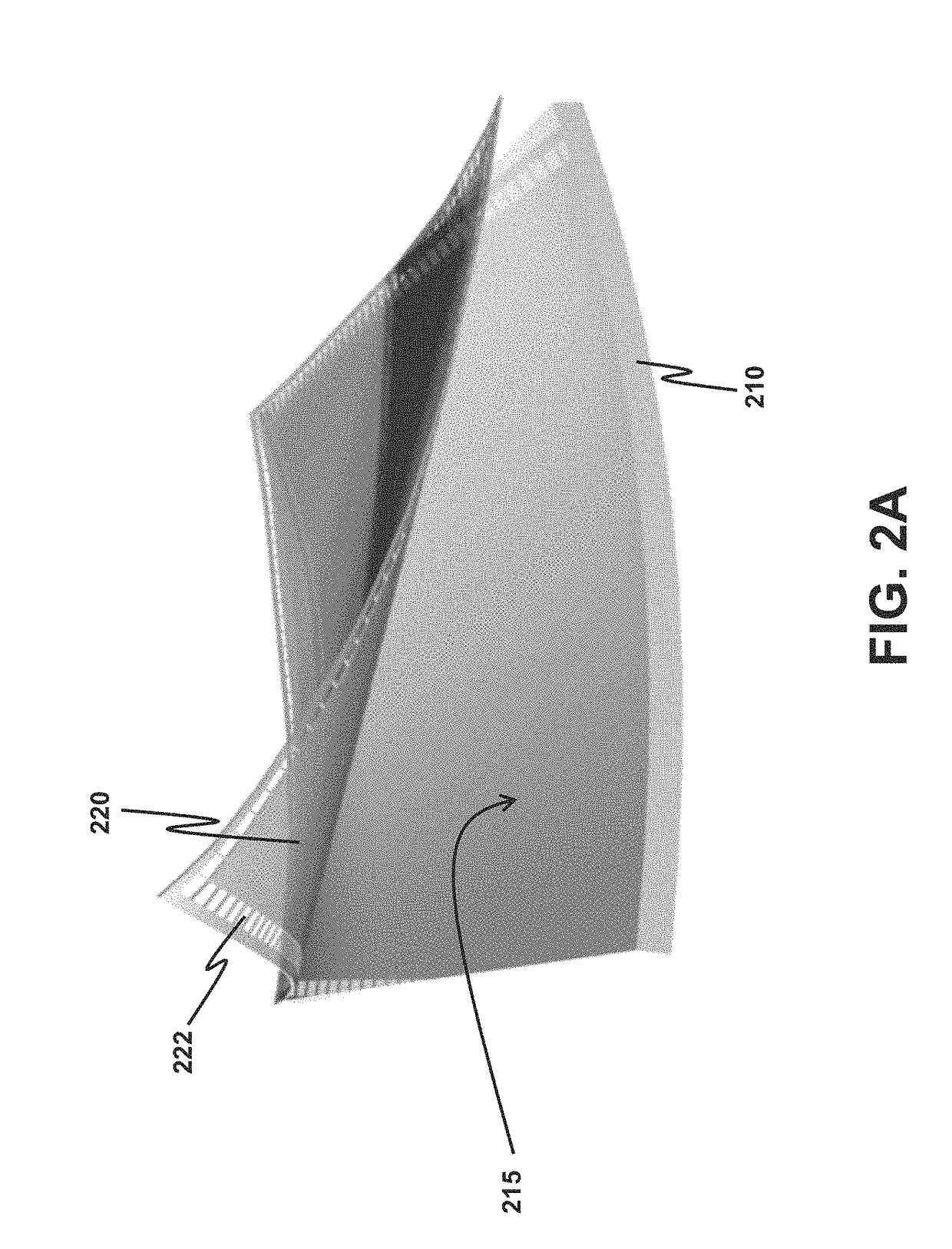
A method for forming a structural-strain sensor network on a structure is provided. The sensor network has plural nanocomposite sensing elements having high sensitivity, and can be quickly fabricated. The method comprises attaching a molding layer having openings onto the surface, and filling the openings with a coating material made of nanocomposite hybrid material. After immobilizing the coating material in the openings, the sensing elements are formed and the molding layer is removed. Electrical wires are formed on the surface such that two opposite electrodes are formed on each sensing element. The resistance between the two electrodes indicates a strain experienced. The sensor network finds applications in identifying a damaged location or an impact location on the structure for structural health monitoring. Voltage waveforms measured at the sensing elements are analyzed to estimate the damaged location or the impact location according to a guided-wave propagation model.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Structural guided wave response group velocity frequency dispersion test method
ActiveCN110068613ARealize measurementEasy to implementAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave structureIntermediate frequency
The invention relates to a structural guided wave response group velocity frequency dispersion test method. A single PZT piezoelectric element pair is arranged on a structural part, and PZT piezoelectric elements respectively serve as a signal exciter and a sensor, thus a guided wave signal excitation-sensing measurement channel is formed; according to a test frequency band, designing a group of narrow-band excitation signals, and acquiring structural guided wave response signals under corresponding excitation; performing time interception on all the acquired structural guided wave response signals and respectively performing normalizing processing on the intercepted signals according to maximum peak amplitudes of direct wave signals, then performing synchronous overlap according to an excitation moment benchmark, performing time-frequency processing on an overlapped signal, and calculating according to wave crest distribution in a time-frequency processing result as well as a propagation distance to obtain guided wave propagation frequency dispersion characteristic in a to-be-detected structure. The test method provided by the invention can be based on existing test conditions, simply realizes test and analysis on frequency dispersion characteristic in structures such as a plate, a shell, a pipe and a column and has better supporting effect and application value on health monitoring study and application of a guided wave structure.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECH
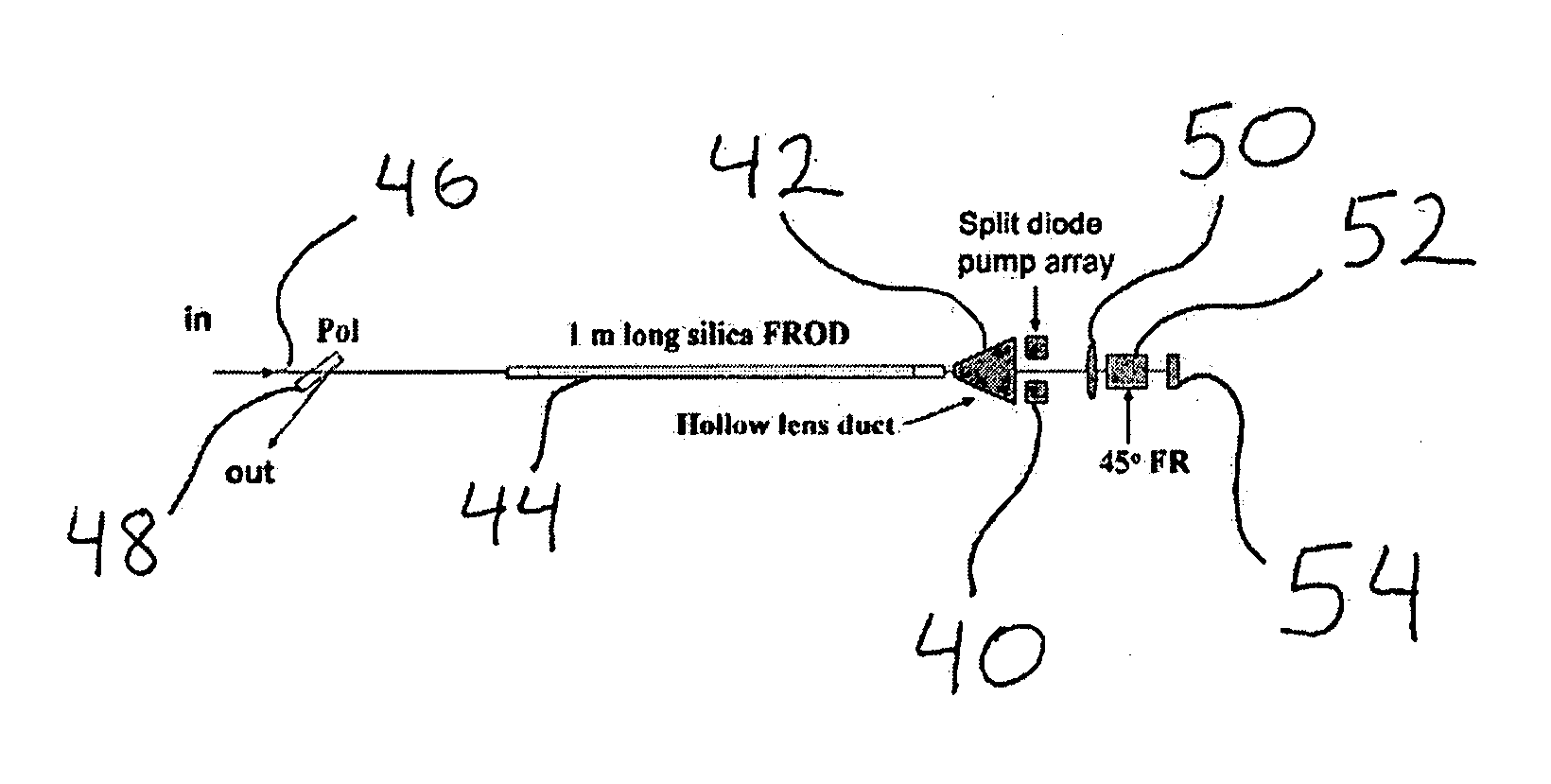
Hybrid fiber-rod laser
ActiveUS20120287951A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingThermal energyFiber
Single, or near single transverse mode waveguide definition is produced using a single homogeneous medium to transport both the pump excitation light and generated laser light. By properly configuring the pump deposition and resulting thermal power generation in the waveguide device, a thermal focusing power is established that supports perturbation-stable guided wave propagation of an appropriately configured single or near single transverse mode laser beam and / or laser pulse.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
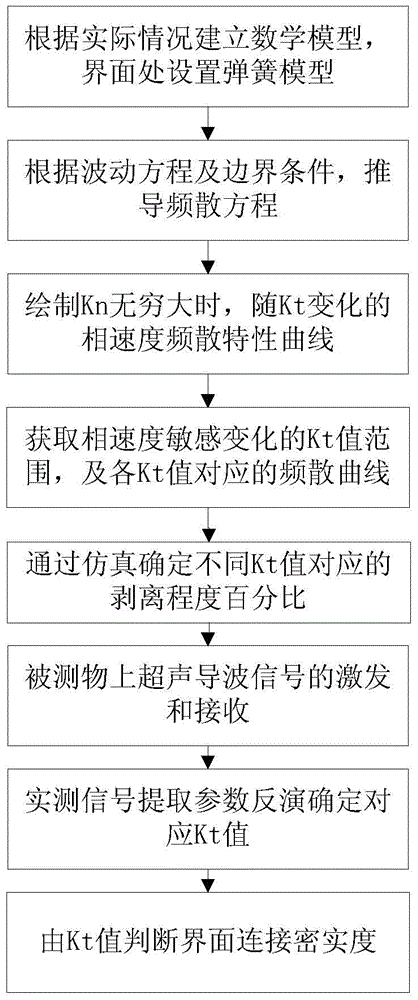
Method for judging connecting compactness of interface by using spring stiffness coefficient
InactiveCN104458570AFew parametersAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing mechanical meansStiffness coefficientSignal on
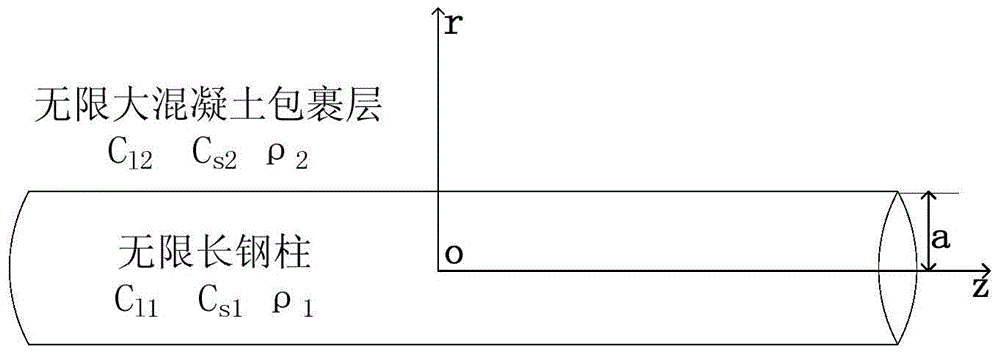
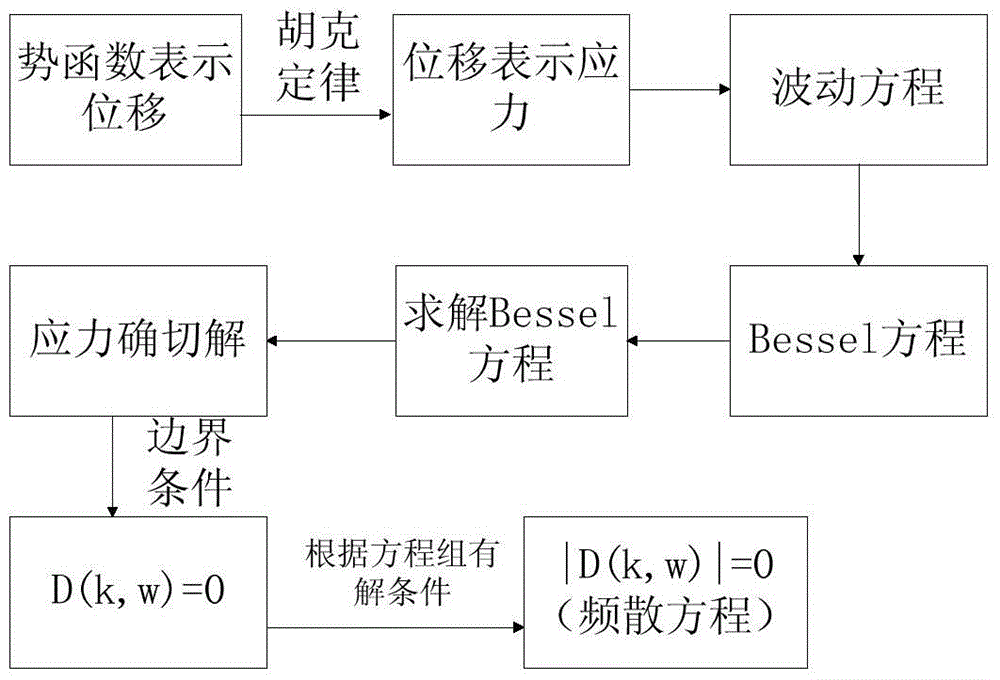
The invention discloses a method for judging the connecting compactness of an interface by using a spring stiffness coefficient. The method is mainly used for ultrasonic nondestructive testing of the interface compactness and comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a corresponding model according to actual conditions, and arranging a spring model at the interface; (2) deducing out a frequency dispersion equation of guided wave propagation according to a wave equation and boundary conditions; (3) drawing out a changing curve of phase velocity along with the tangential stiffness coefficient Kt under the condition that the normal stiffness coefficient Kn is infinitely great so as to obtain a tangential stiffness coefficient value with relatively sensitive phase-velocity change and a corresponding frequency-dispersion characteristic curve; (4) determining peeling-degree percentage values corresponding to different Kt values by simulation; (5) exciting and receiving ultrasonic guided wave signals on a tested object; (6) extracting parameters from actual testing signals to carry out inversion and further determine corresponding Kt values; and (7) judging the compactness degree of the interface by the tangential spring stiffness coefficient value. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the connecting condition of the interface of a bonding part can be relatively well obtained and the quality monitoring and the maintenance can be carried out on the bonding part in a relatively effective manner.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Hybrid fiber-rod laser
ActiveUS8335420B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberThermal energy
Single, or near single transverse mode waveguide definition is produced using a single homogeneous medium to transport both the pump excitation light and generated laser light. By properly configuring the pump deposition and resulting thermal power generation in the waveguide device, a thermal focusing power is established that supports perturbation-stable guided wave propagation of an appropriately configured single or near single transverse mode laser beam and / or laser pulse.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Ultrasonic guided-wave propagation distance sparse estimation method and detection system thereof
ActiveCN109541042AHigh-resolutionImplement propagation distance estimationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionPattern recognitionSonification
The invention discloses an ultrasonic guided-wave propagation distance sparse estimation method and a detection system thereof. The method comprises the steps of acquiring the frequency-wavenumber curve of a target modal ultrasonic guided wave of a to-be-tested structure, taking unit impulse response signals at different propagation distances as atoms to construct an over-complete dictionary library, acquiring the unit pulse response signal of the to-be-tested structure, adopting the over-complete dictionary database as a signal base to establish the sparse representation model of the unit pulse response signal, and solving a sparse representation model to obtain the distance spectrum of the ultrasonic guided wave propagation. Compared with the prior art, the obtained distance spectrum result has higher range resolution, higher accuracy and better anti-interference effect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ultrasonic guided wave multi-damage identification method based on Bayesian updating and Gibbs sampling
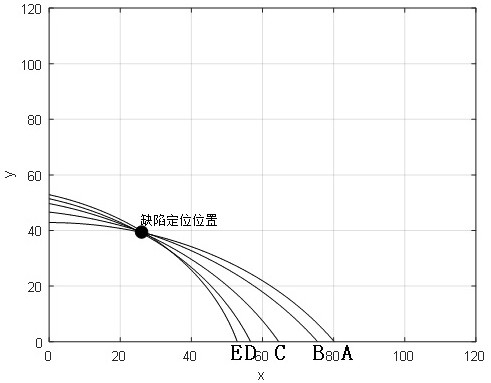
ActiveCN110907540AOvercoming the Difficulty of PositioningReduce mistakesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalAlgorithmPropagation time
The invention provides an ultrasonic guided wave multi-damage identification method based on Bayesian updating and Gibbs sampling. The method comprises: arranging three sensors for ultrasonic guided wave signal acquisition, analyzing each sensor signal to obtain M propagation time ToF of M damage direct scattering, and obtaining M 3 * 1 ToF vectors corresponding to each possible combination mode;performing linearization processing on parameters in the nonlinear damage positioning model based on the guided wave propagation time; solving conditional posterior probability distribution of each parameter by utilizing a Bayesian theorem; using gibbs sampling to sample the conditional posteriori distribution of each parameter, performing Gibbs sampling on a plurality of ToF vector data corresponding to each possible combination mode, and finally, judging the grouping mode with the minimum sample point dispersion degree and reasonable speed parameters to be the finally identified damage position. According to the invention, ultrasonic guided wave multi-damage accurate positioning can be automatically realized based on ToF information of three sensors.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院有限公司
Two-stage damage location recognition method based on guided-wave signal sparse decomposition and damage localization
ActiveCN110542723AReduce the possibilityAchieve lossless denoisingAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalPattern recognitionSonification
A two-stage damage location recognition method based on guided-wave signal sparse decomposition and damage localization relates to the field of ultrasonic non-destructive testing. The present invention aims to resolve a problem that an ultrasonic guided-wave signal analysis result is not accurate enough because a dictionary design method and a signal sparse decomposition algorithm of sparse representation in ultrasonic guided-wave signal overlapping wave packet recognition are not perfect enough. According to the method, a penalty term is used to make coefficient vectors as sparse as possible,a possibility that noise matches dictionary atoms is significantly reduced; a dictionary matrix is designed by using a guided-wave propagation model, wherein problems of guided-wave frequency dispersion, multiplex modes and modal transformation are considered, and an overlapping waveform is recognized in a linear decomposition manner. The method has advantages over a conventional signal processing method. A sparse optimization solution algorithm based on sparse Bayesian learning is used, which has unique advantages in the aspect of handling with under-determined linear problems such as sparserepresentation, and has better robustness for noise.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院有限公司
Method for detecting dissimilar material pipeline sectional area loss based on ultrasonic guided-wave technology
InactiveCN107607629AExpand the scope ofImprove detection efficiencyProcessing detected response signalSonificationWave detection
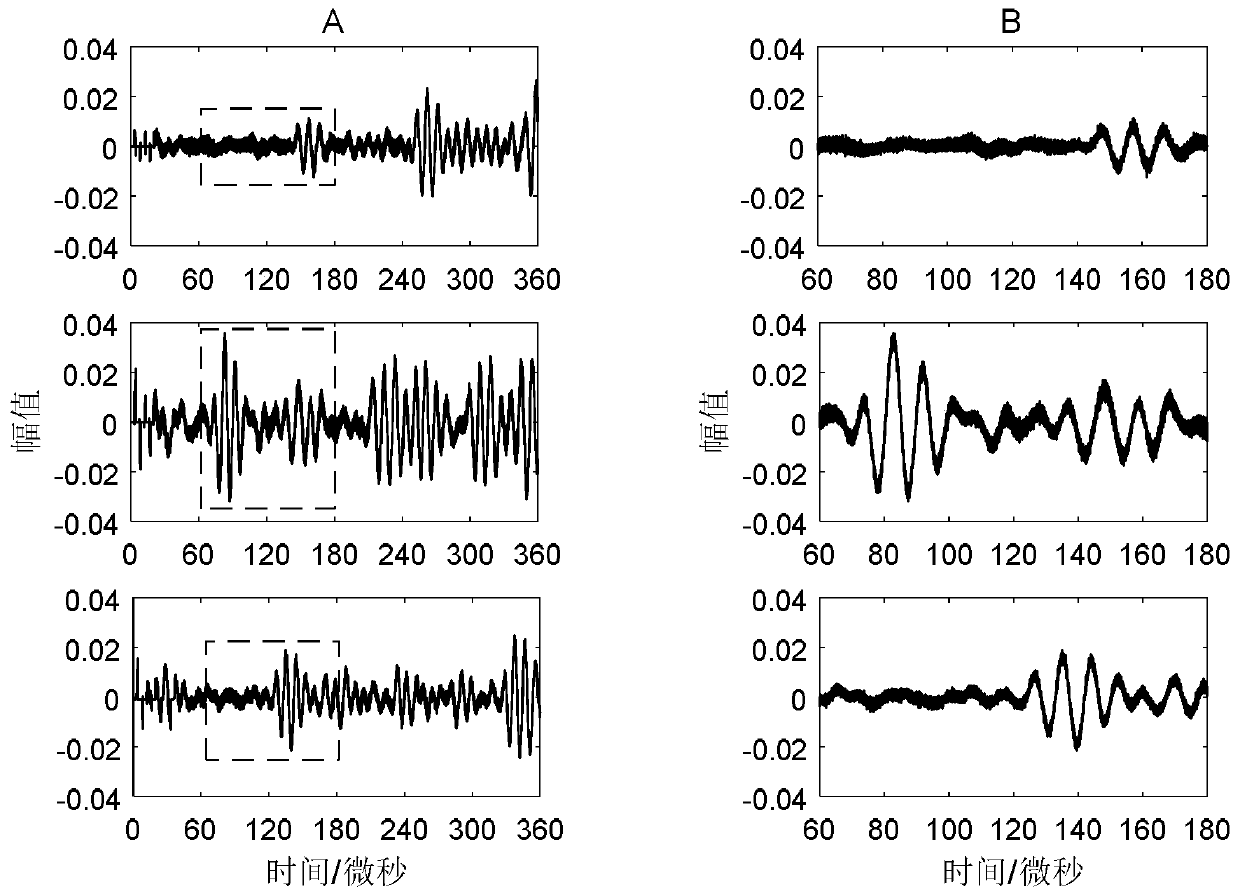
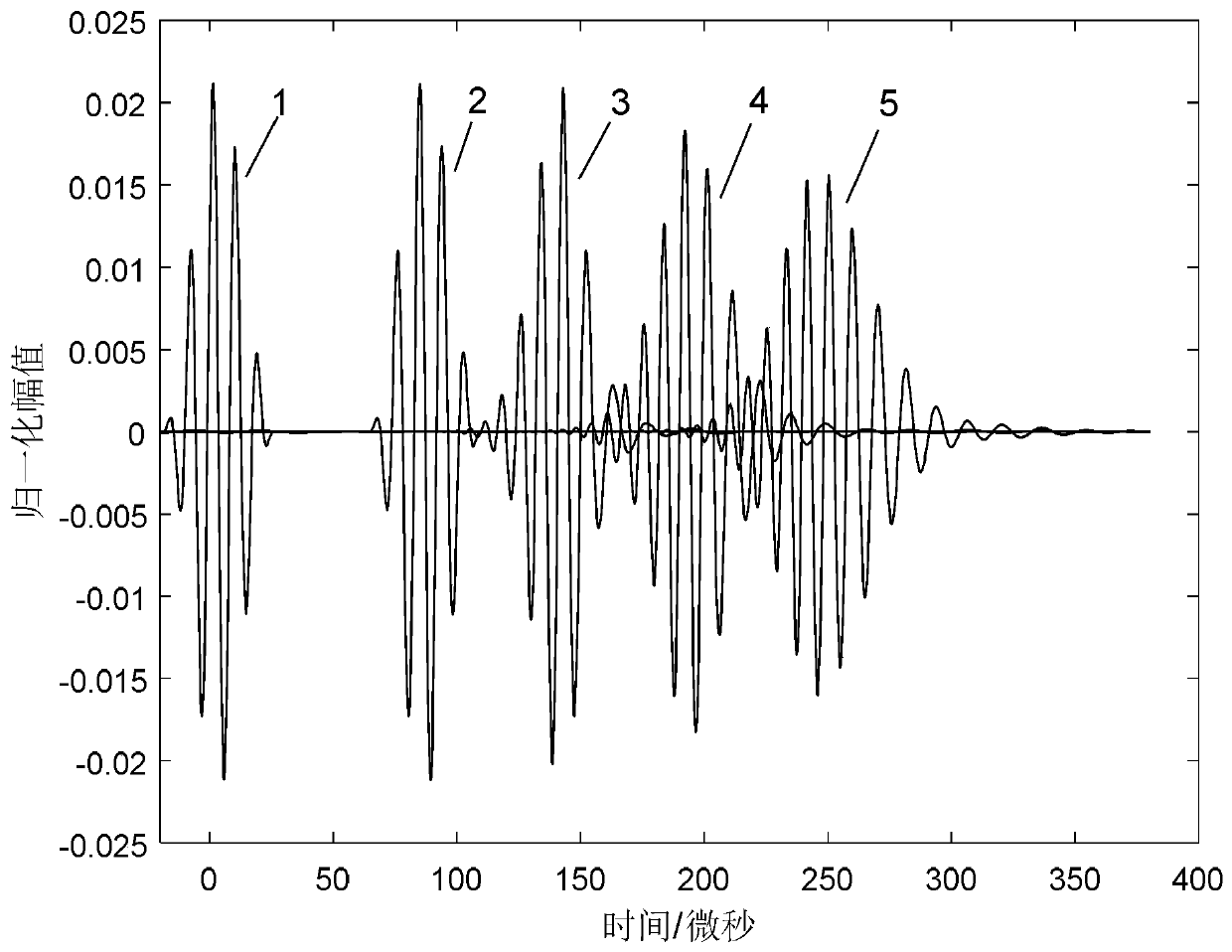
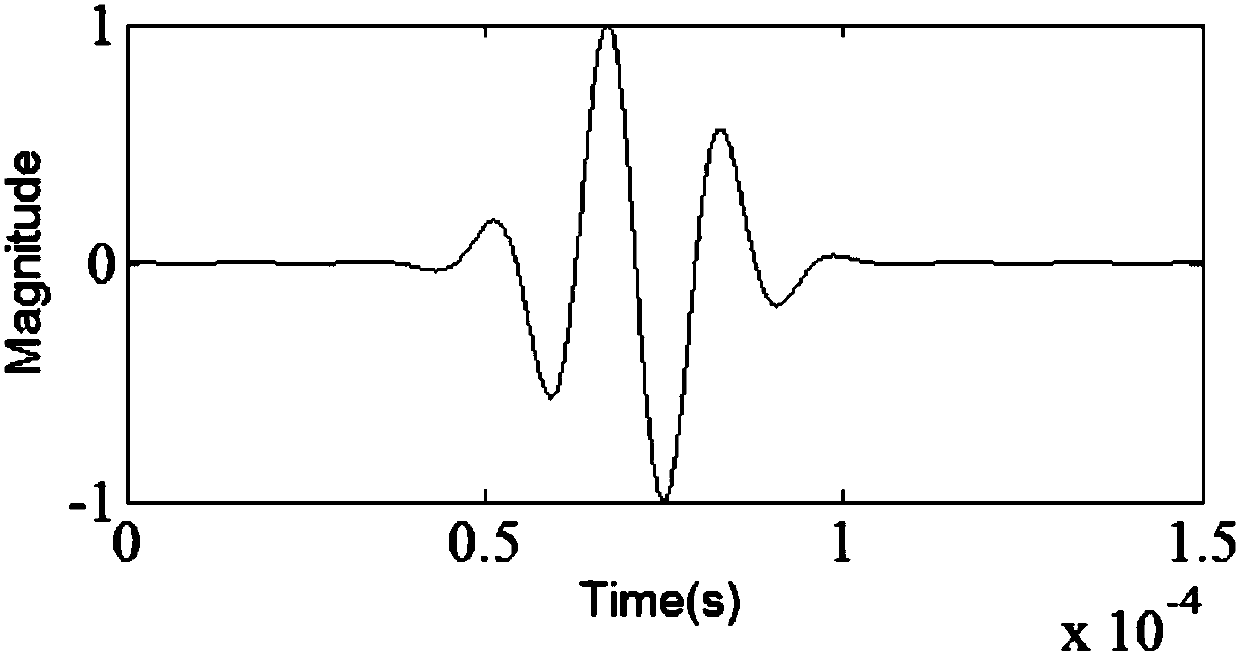
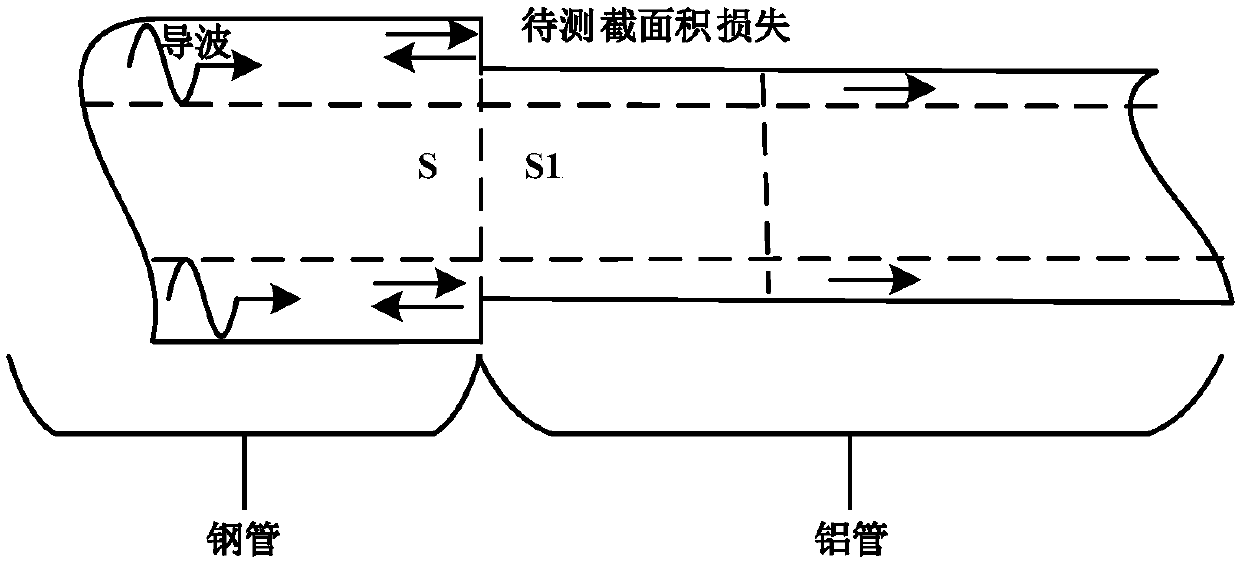
The invention discloses a method for detecting dissimilar material pipeline sectional area loss based on an ultrasonic guided-wave technology, which belongs to the field of nondestructive test of a pipeline. The method is characterized in that an incident signal form is selected, measurement is carried out to obtain a cross-sectional area of the to-be-measured pipeline, and the result is recordedas S0, the cross-sectional area of the dissimilar material pipeline sectional area loss position which is required for being detected in the pipeline is recorded as S1, the density of the pipeline andthe dissimilar material at the to-be-measured sectional area loss position can be recorded as Rho0 and Rho1; the young modulus and Poisson's ratio of the pipeline and the dissimilar material at the sectional area loss position are recorded as E0, v0 and E1 and v1; the guided wave propagation speed of the pipeline and the dissimilar material at the sectional area loss position is obtained and according to the formula shown as the specification, a guided-wave detection device is employed for detecting the to-be-measured pipeline by using appropriate detection frequency, a guided-wave detectionsignal is obtained, an amplitude value Ar and an amplitude value Ai of a reflection signal and the guided-wave incident signal at the sectional area loss position can be obtained, calculation is carried out according to an equation of T=Ar / Ai, and the cross-sectional area of the dissimilar material at the sectional area loss position is obtained according to the formula shown as the specification.The detection method has important engineering value.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Coated nanofiller/polymer composite sensor network for guided-wave-based structural health monitoring
ActiveUS10012553B2Quickly and effectively generatedAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsStructural health monitoringEngineering
A method for forming a structural-strain sensor network on a structure is provided. The sensor network has plural nanocomposite sensing elements having high sensitivity, and can be quickly fabricated. The method comprises attaching a molding layer having openings onto the surface, and filling the openings with a coating material made of nanocomposite hybrid material. After immobilizing the coating material in the openings, the sensing elements are formed and the molding layer is removed. Electrical wires are formed on the surface such that two opposite electrodes are formed on each sensing element. The resistance between the two electrodes indicates a strain experienced. The sensor network finds applications in identifying a damaged location or an impact location on the structure for structural health monitoring. Voltage waveforms measured at the sensing elements are analyzed to estimate the damaged location or the impact location according to a guided-wave propagation model.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
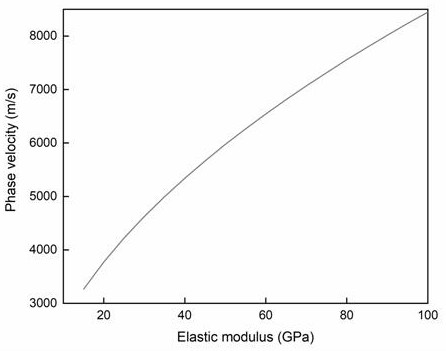
Method for inverting elastic constant of composite material with anisotropic characteristics
PendingCN114428119ATest elastic constantSimple and fast operationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalShear modulusUltrasonic guided wave
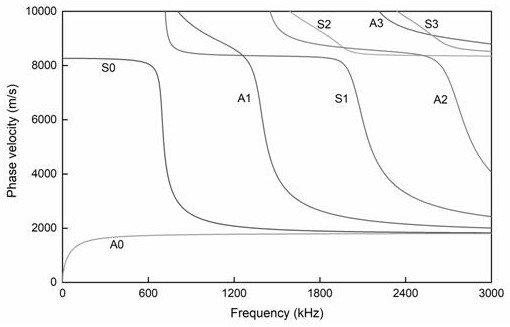
The invention discloses a method for inverting an elastic constant of a composite material with anisotropic characteristics, which comprises the following steps of: 1, solving frequency dispersion equations of a symmetric mode and an antisymmetric mode in an orthotropic plate by adopting a numerical method, and listing frequency dispersion curves of corresponding modes; 2, the excitation frequency of the ultrasonic guided wave test is selected by analyzing the influence of the elastic constant on the frequency dispersion curve; establishing a corresponding relation graph between the elastic constant and the guided wave propagation speed; 3, measuring the propagation speeds of the symmetric mode and the antisymmetric mode in the composite material structure by using an ultrasonic guided wave detection method; and 4, performing inversion by using the relation graph of the elastic constants and the guided wave propagation velocity to obtain the corresponding elastic constants. The method has the technical effects that the anisotropic composite material can be subjected to nondestructive testing, and the elastic modulus and the shear modulus of the composite material component in each main shaft direction can be accurately and quickly obtained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
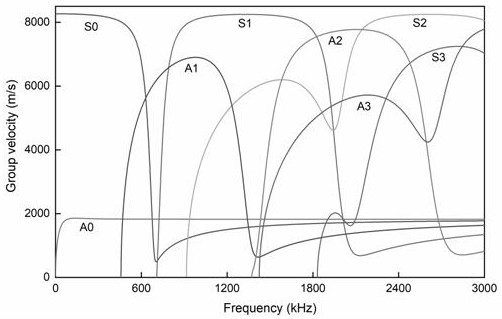
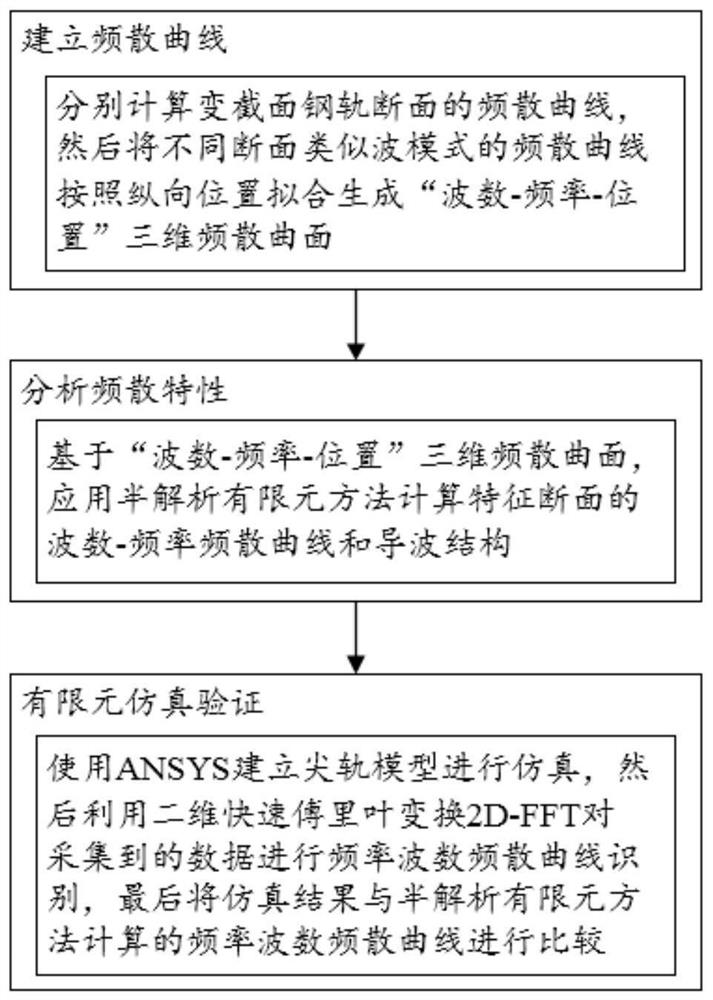
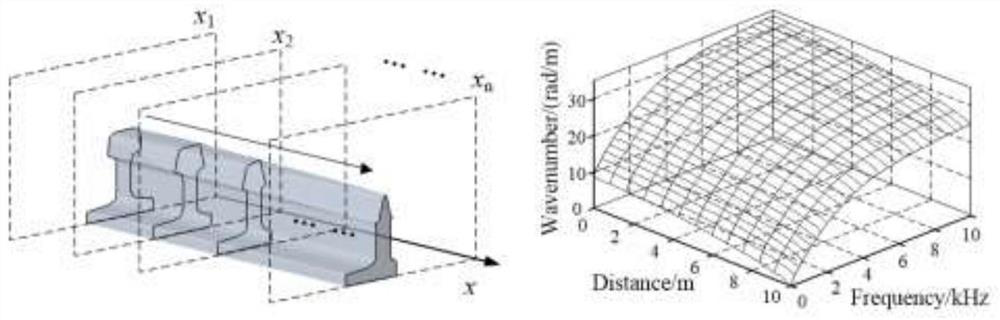
Turnout variable cross-section steel rail guided wave propagation characteristic determination method
ActiveCN112464524AReduce computing timeEffective theoretical guidanceAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDesign optimisation/simulationWave structureFast Fourier transform
The invention relates to the technical field of steel rail turnouts, in particular to a turnout variable cross-section steel rail guided wave propagation characteristic determination method which comprises the following steps: 1, establishing frequency dispersion curves: respectively calculating the frequency dispersion curves of variable cross-section steel rail sections, fitting the frequency dispersion curves with different sections and similar wave modes according to longitudinal positions to generate a'wave number-frequency-position 'three-dimensional frequency dispersion curved surface;2, analyzing frequency dispersion characteristics: calculating a wave number-frequency dispersion curve and a guided wave structure of a characteristic section by applying a semi-analytic finite element method based on the wave number-frequency-position three-dimensional frequency dispersion curved surface; and 3, carrying out finite element simulation verification: establishing a switch rail model for simulation, then performing frequency wavenumber dispersion curve identification on the acquired data by utilizing two-dimensional fast Fourier transform 2D-FFT, and finally comparing a simulation result with a frequency wavenumber dispersion curve calculated by a semi-analytic finite element method. According to the method, the guided wave propagation characteristics of the turnout variablecross-section steel rail can be well determined.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Woven composite material plate damage shape identification method based on ultrasonic guided waves
PendingCN114235971AEasy accessAccurate acquisitionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalComposite materialGuided wave propagation
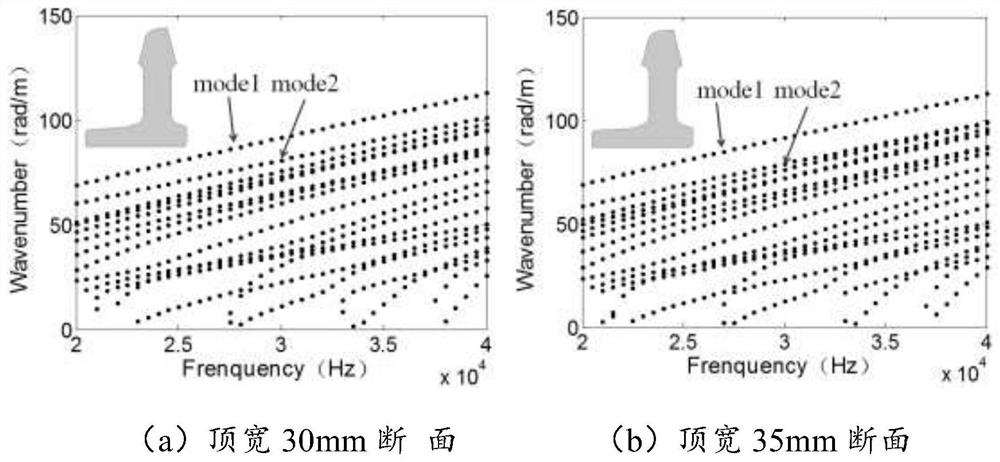
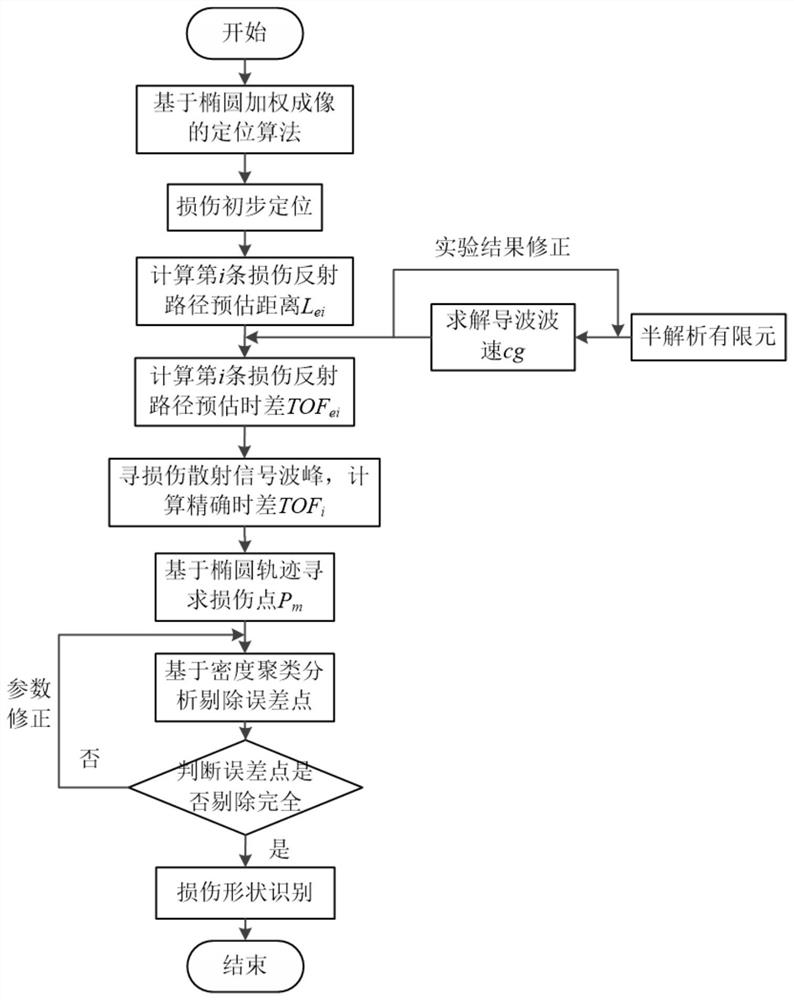
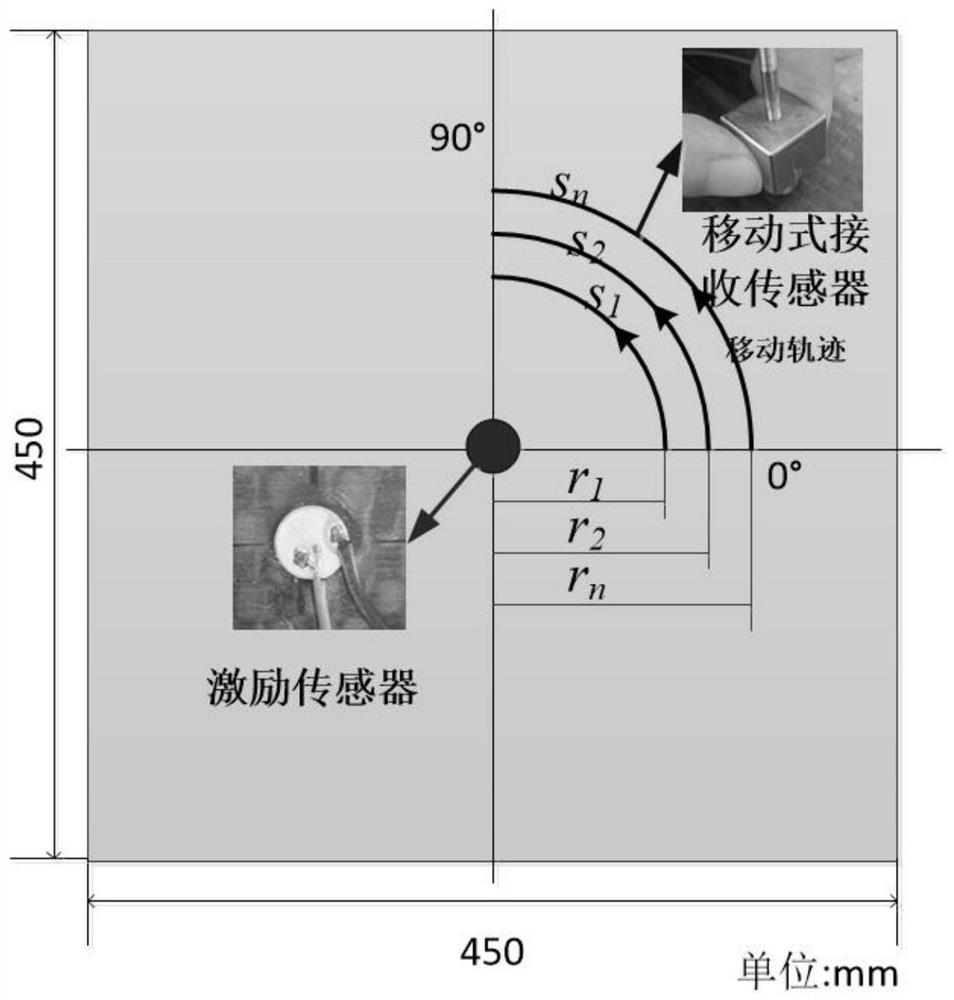
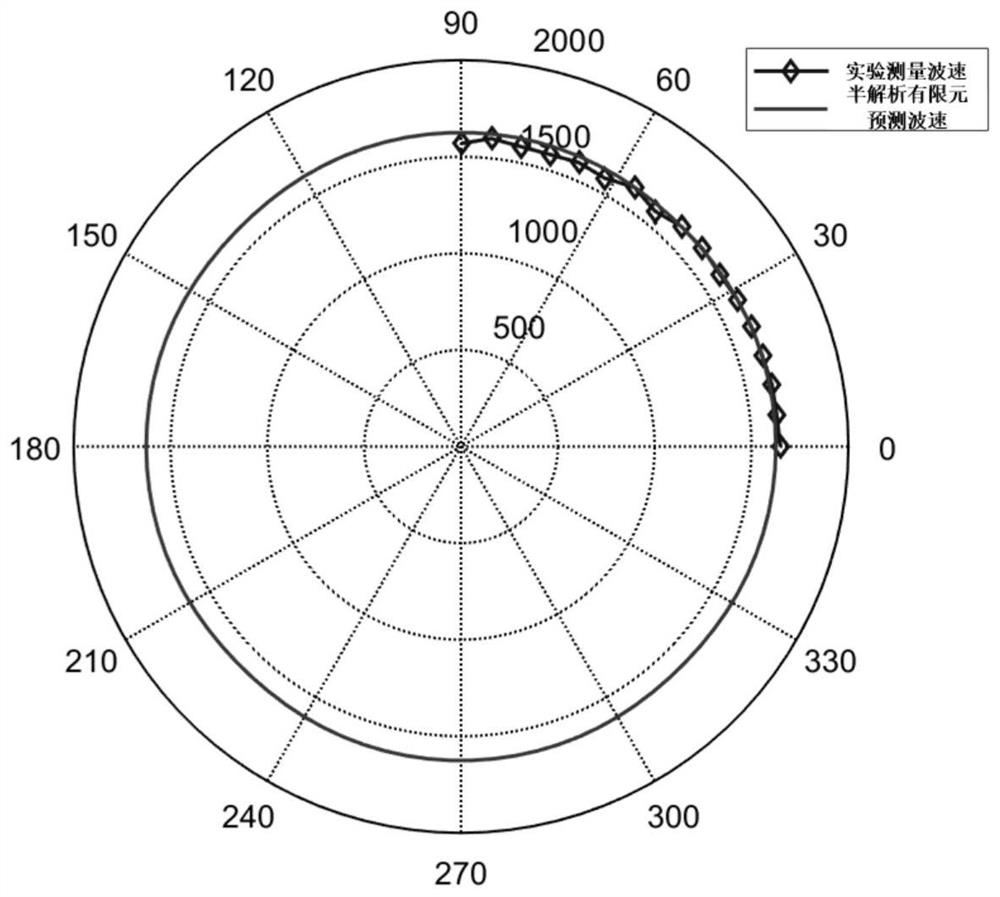
The invention discloses a method for identifying a damage shape of a braided composite material plate based on ultrasonic guided waves. The method comprises the following specific steps: S1, analyzing by a semi-analytical finite element method to obtain a guided wave propagation wave velocity on the braided composite material plate; s2, the guided wave propagation wave velocity on the woven composite material plate is measured through an omni-directional wave velocity measurement method, the semi-analytical finite element model is corrected, and a guided wave mode and frequency suitable for monitoring are selected; s3, a guided wave sensor network is arranged on the woven composite material plate, a sensor is pasted on the surface of the structure, and a propagation path is set for damage monitoring; s4, acquiring guided wave signals of different propagation paths in a lossless state and a lossless state, obtaining damage scattering signals of different paths, and determining a damage center point by using an ellipse weighted imaging method; s5, extracting a real damage reflection time difference; s6, estimating damage boundary points based on the elliptical trajectory, and removing noise points; and S7, predicting the damage area and shape according to the damage boundary points.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY +3
A Design Method of Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Excitation Probe Based on Magnetostrictive Effect
ActiveCN104330477BSimplifyGuided wave suppressionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationSonificationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe design method based on magnetic induced shrinkage or elongation effect, according to the sound propagation principle, namely SH type guided wave propagation rule, in a solid plate, optimum excitation frequency is determined, and according to the frequency, an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe is designed; the prominent advantage of the proposed design method are that a right excitation frequency f' is selected for enhancement of1 order mode guided wave in the plate and effective inhibition of 0 order mode guided wave, simplification of the mode of a guided wave excited in a particular frequency can be realized, the signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and the defect detection probability and quantization accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
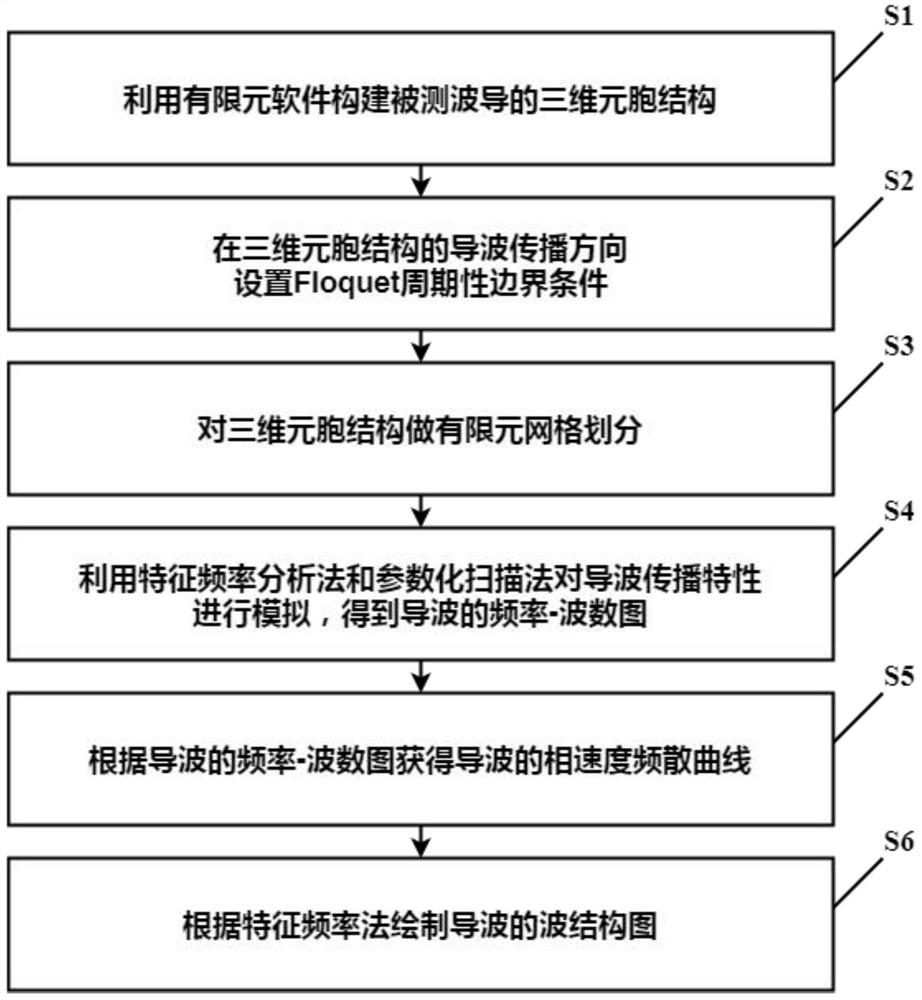
A guided wave propagation characteristic solving method and system
PendingCN112949121AUniversalSimplify the analysis processDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWave structureFrequency wave
The invention relates to a guided wave propagation characteristic solving method and system, and belongs to the field of nondestructive testing. The method specifically comprises the following steps: constructing a three-dimensional cellular structure of a waveguide to be tested by utilizing finite element software; setting floquet periodic boundary conditions in the guided wave propagation direction of the three-dimensional cellular structure; performing finite element grid division on the three-dimensional cellular structure; utilizing a characteristic frequency analysis method and a parameterized scanning method to simulate guided wave propagation characteristics, and importing output data of finite element software into MATLAB for data processing to obtain a frequency-wave number diagram of guided waves; obtaining a frequency dispersion curve of the guided wave according to the frequency-wave number diagram of the guided wave; and drawing a wave structure chart of the guided wave according to a characteristic frequency analysis method. According to the method and the system, the solving process of the guided wave propagation characteristics can be simplified, and the method and the system are suitable for solving the pilot frequency propagation characteristics of any waveguide structure made of different materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
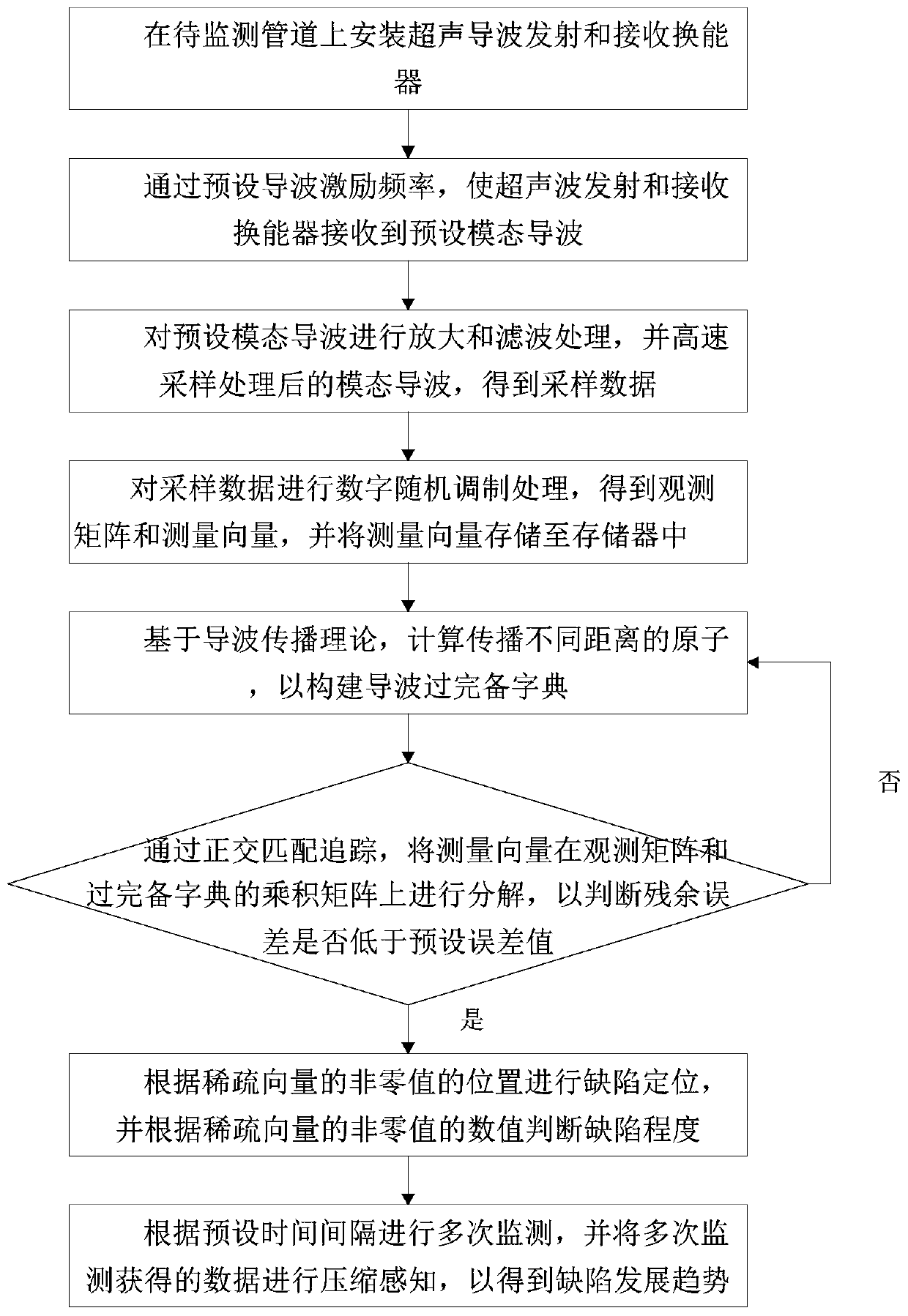
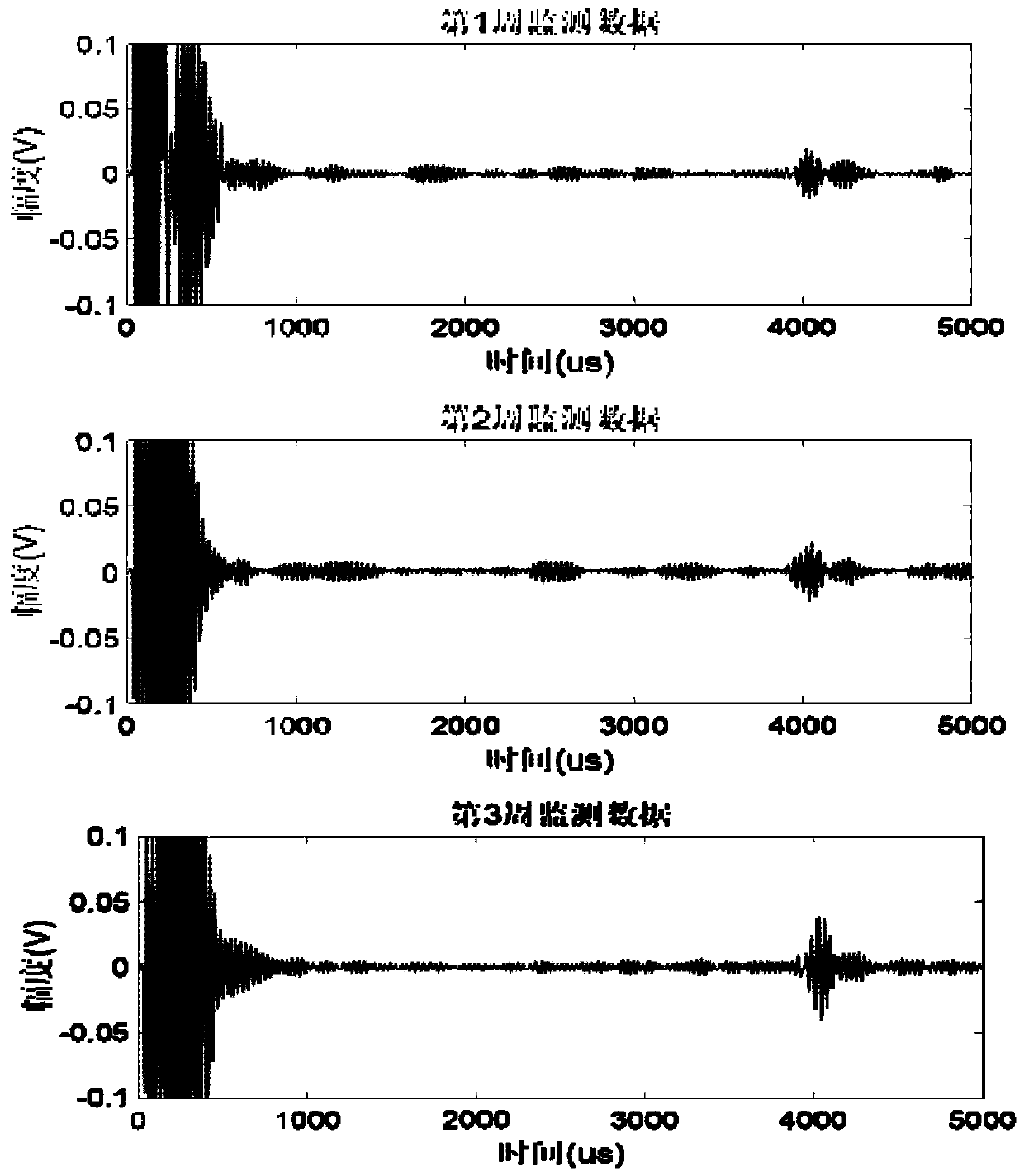
Ultrasonic guided wave compressed sensing health monitoring method for pipeline
The invention discloses an ultrasonic guided wave compressed sensing health monitoring method for a pipeline. The method comprises the steps of installing an ultrasonic guided wave emitting and receiving transducer on the pipeline, wherein the emitting end of the ultrasonic guided wave emitting and receiving transducer excites required modal guided waves, and the receiving end of the ultrasonic guided wave emitting and receiving transducer receives the corresponding modal guided waves; conducting discrete sampling on the guided waves to obtain guided wave monitoring data, conducting digital random modulation on the data to obtain an observation and measurement matrix and measurement vectors, and storing the measurement vectors into a corresponding storage; calculating atoms with differentpropagation distances according to a guided wave propagation theory to construct a guided wave over-complete dictionary; utilizing orthogonal matching pursuit for decomposing the measurement vectors on the observation and measurement matrix and a product matrix of the dictionary to obtain sparse vectors; conducting defect location according to positions of nonzero values of the sparse vectors, andjudging the defect degree according to numerical values of the nonzero values; conducting monitoring multiple times according to a preset time, conducting compressed sensing on monitoring data obtained multiple times to obtain a defect development tendency. By means of the method, the data memory space is reduced, and meanwhile, the defect monitoring precision is guaranteed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Anisotropy compensation MUSIC damage imaging method based on excitation focusing scanning
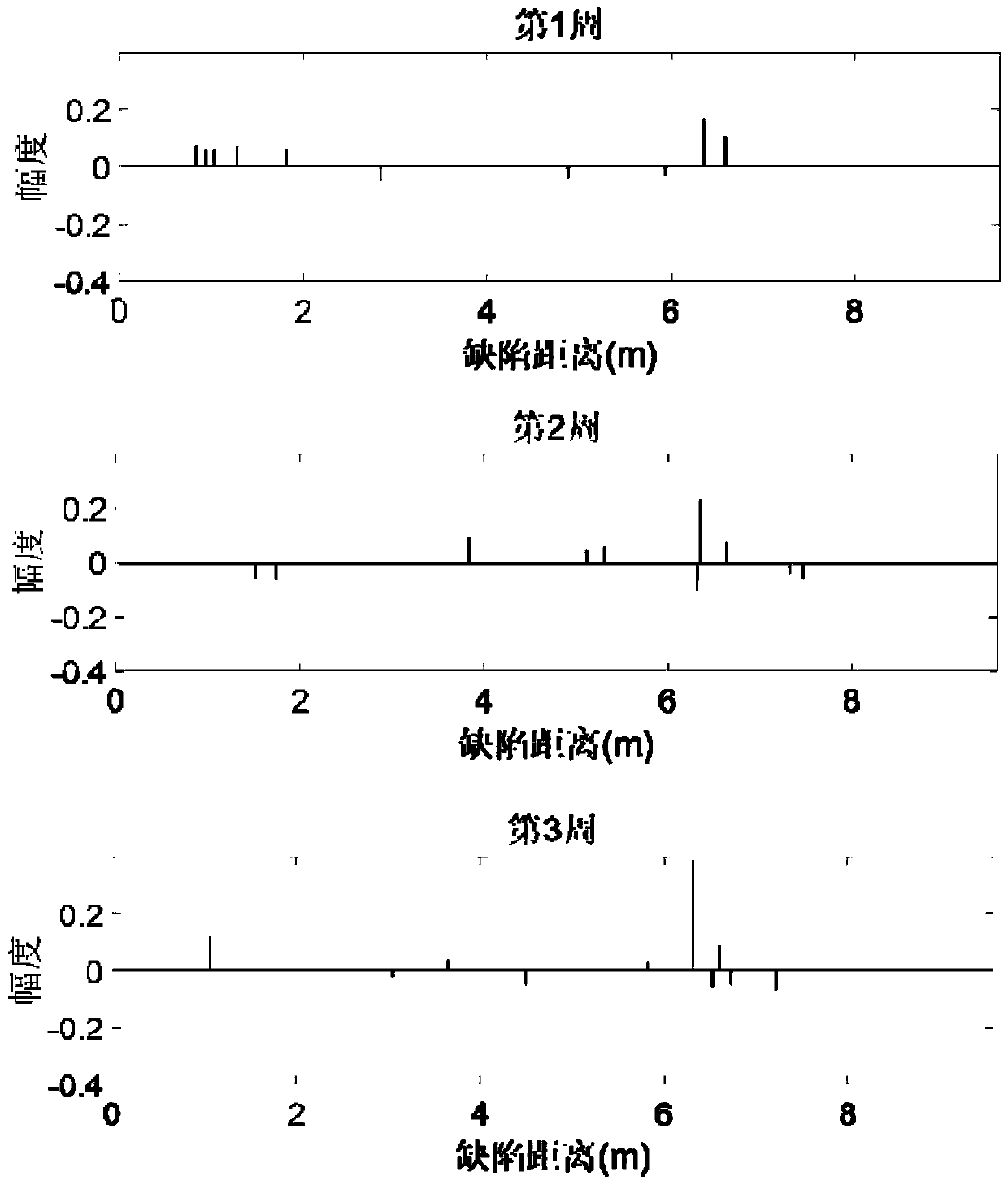
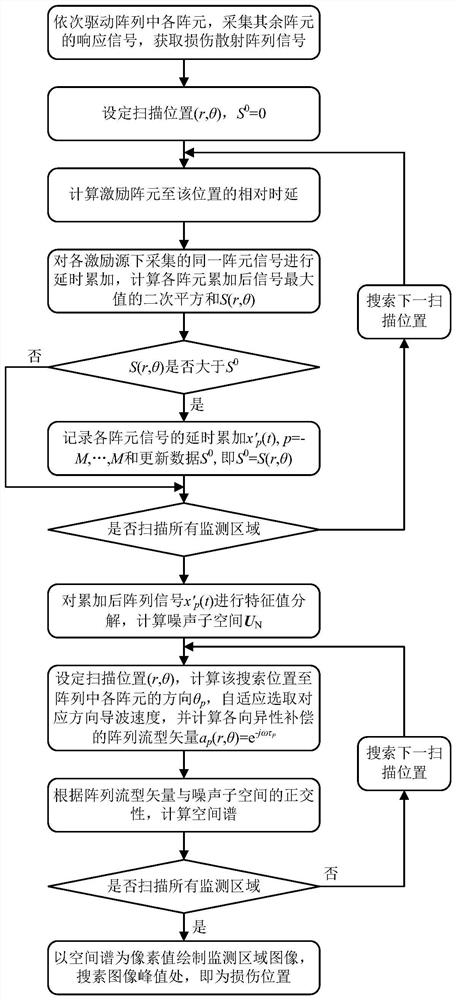
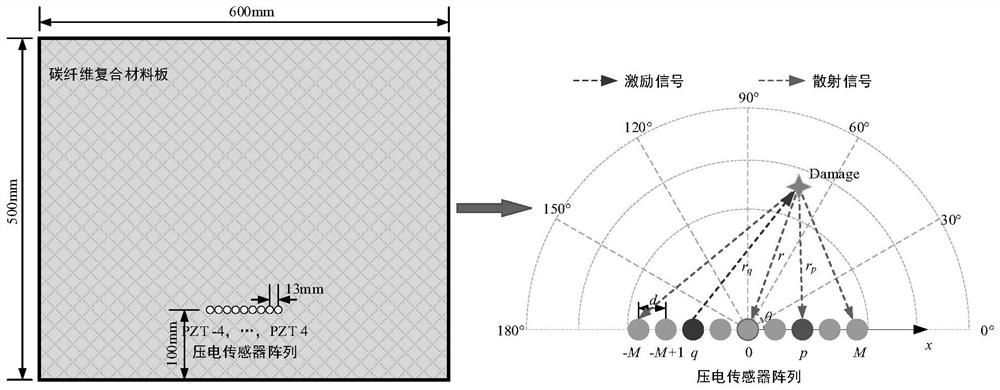
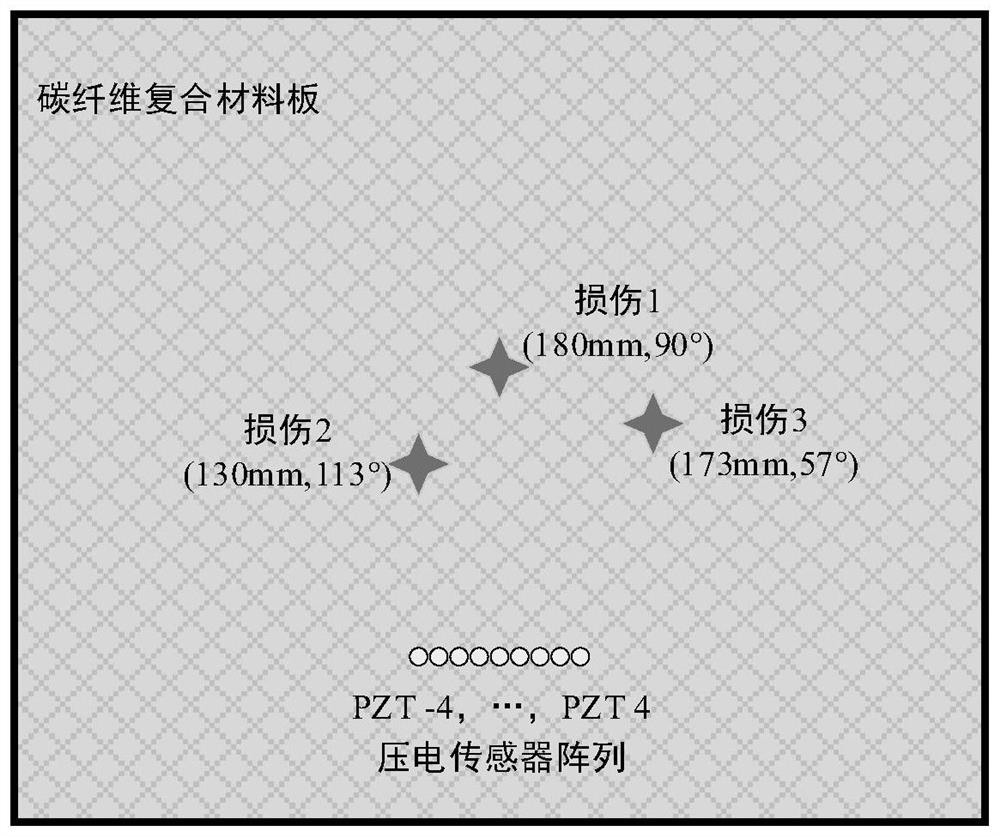
PendingCN114813956AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh positioning accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMultiple signal classificationNoise
The invention discloses an anisotropic compensation MUSIC damage imaging method based on excitation focusing scanning, and the method comprises the steps: employing a self-excitation self-sensing piezoelectric sensor array to carry out the focusing scanning of an array excitation signal, and improving the signal-to-noise ratio of a damage scattering signal, aiming at the problem of low imaging precision of a strong attenuation anisotropic structure; the method comprises the following steps of: adaptively correcting an array direction vector in a MUSIC scanning process by utilizing a pre-measured guided wave propagation speed in each direction and adopting a dual anisotropic compensation mechanism of a scanning direction and an array element direction; excitation focusing scanning and a MUSIC algorithm are combined, and final damage imaging positioning is achieved. The method improves the signal-to-noise ratio of damage scattering array signals, compensates array errors caused by structural anisotropy, and has a wide application prospect in damage imaging positioning of a strong-attenuation anisotropic structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A Multiple Damage Identification Method Based on Bayesian Update and Gibbs Sampling
ActiveCN110907540BOvercoming the Difficulty of PositioningReduce mistakesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalAlgorithmPropagation time
The invention provides an ultrasonic guided wave multi-damage identification method based on Bayesian updating and Gibbs sampling. The method comprises: arranging three sensors for ultrasonic guided wave signal acquisition, analyzing each sensor signal to obtain M propagation time ToF of M damage direct scattering, and obtaining M 3 * 1 ToF vectors corresponding to each possible combination mode;performing linearization processing on parameters in the nonlinear damage positioning model based on the guided wave propagation time; solving conditional posterior probability distribution of each parameter by utilizing a Bayesian theorem; using gibbs sampling to sample the conditional posteriori distribution of each parameter, performing Gibbs sampling on a plurality of ToF vector data corresponding to each possible combination mode, and finally, judging the grouping mode with the minimum sample point dispersion degree and reasonable speed parameters to be the finally identified damage position. According to the invention, ultrasonic guided wave multi-damage accurate positioning can be automatically realized based on ToF information of three sensors.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院有限公司
A sparse estimation method of ultrasonic guided wave propagation distance and its detection system
ActiveCN109541042BHigh-resolutionImplement propagation distance estimationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionFrequency waveInterference resistance
The invention discloses an ultrasonic guided-wave propagation distance sparse estimation method and a detection system thereof. The method comprises the steps of acquiring the frequency-wavenumber curve of a target modal ultrasonic guided wave of a to-be-tested structure, taking unit impulse response signals at different propagation distances as atoms to construct an over-complete dictionary library, acquiring the unit pulse response signal of the to-be-tested structure, adopting the over-complete dictionary database as a signal base to establish the sparse representation model of the unit pulse response signal, and solving a sparse representation model to obtain the distance spectrum of the ultrasonic guided wave propagation. Compared with the prior art, the obtained distance spectrum result has higher range resolution, higher accuracy and better anti-interference effect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
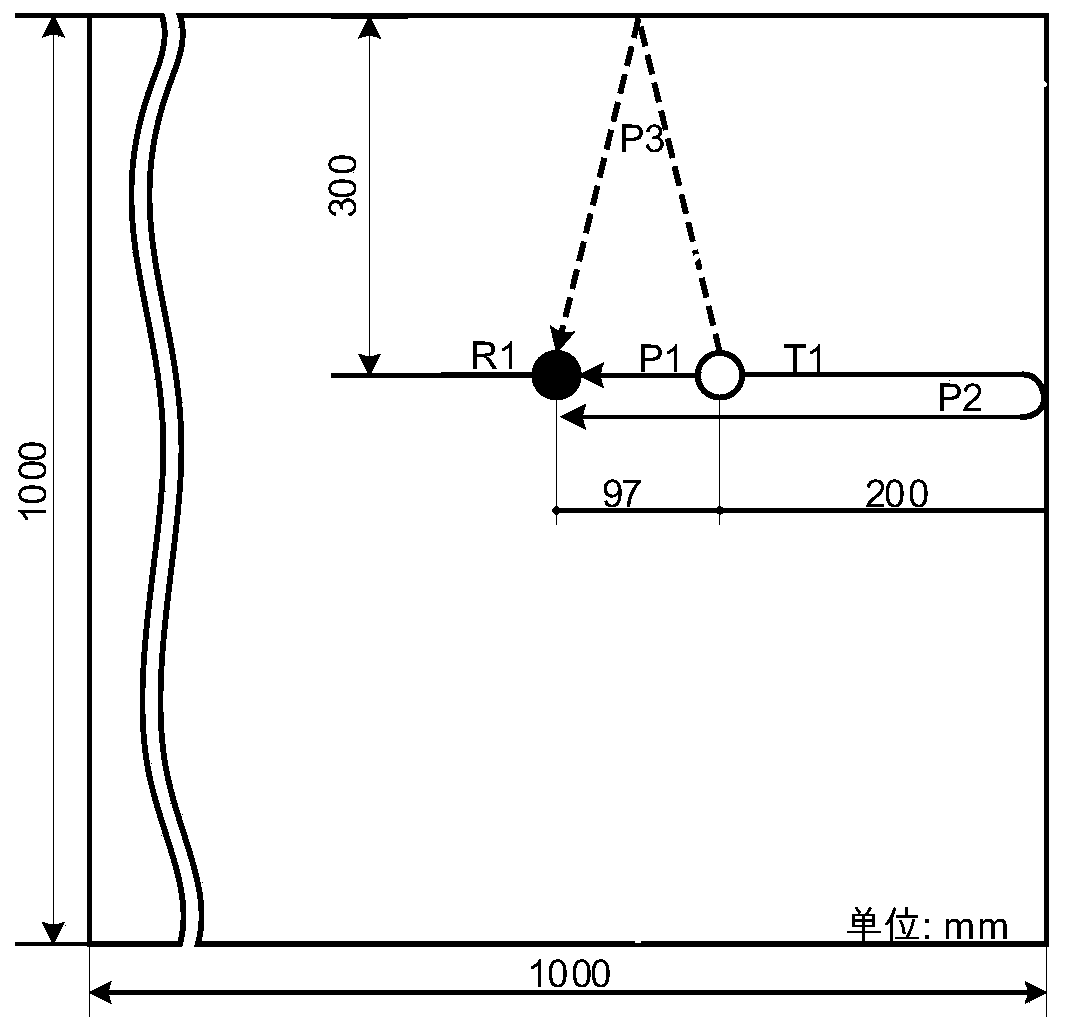
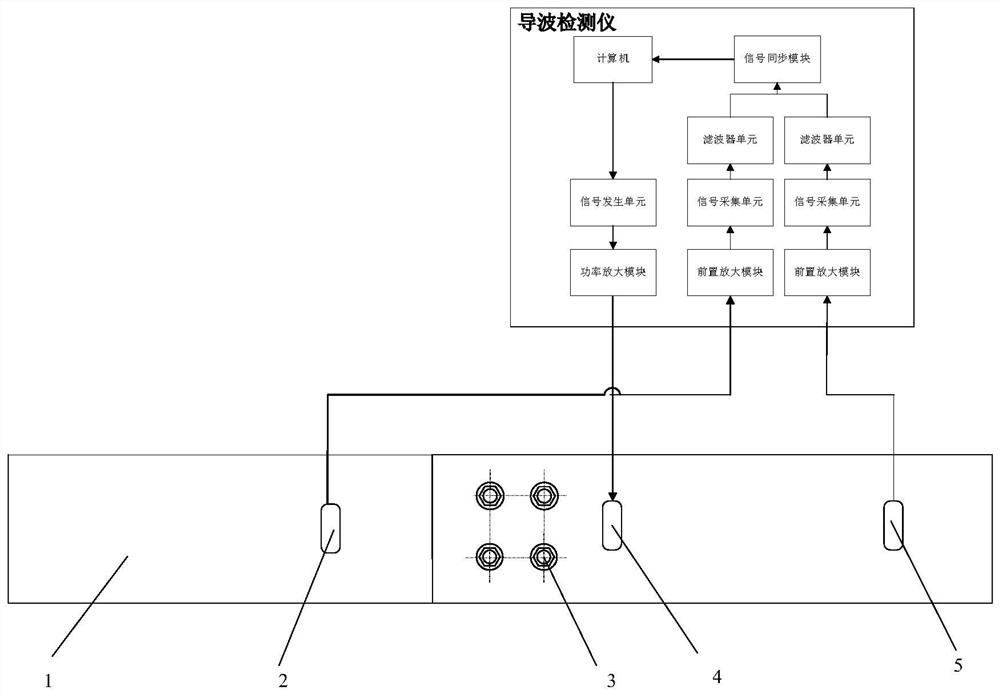
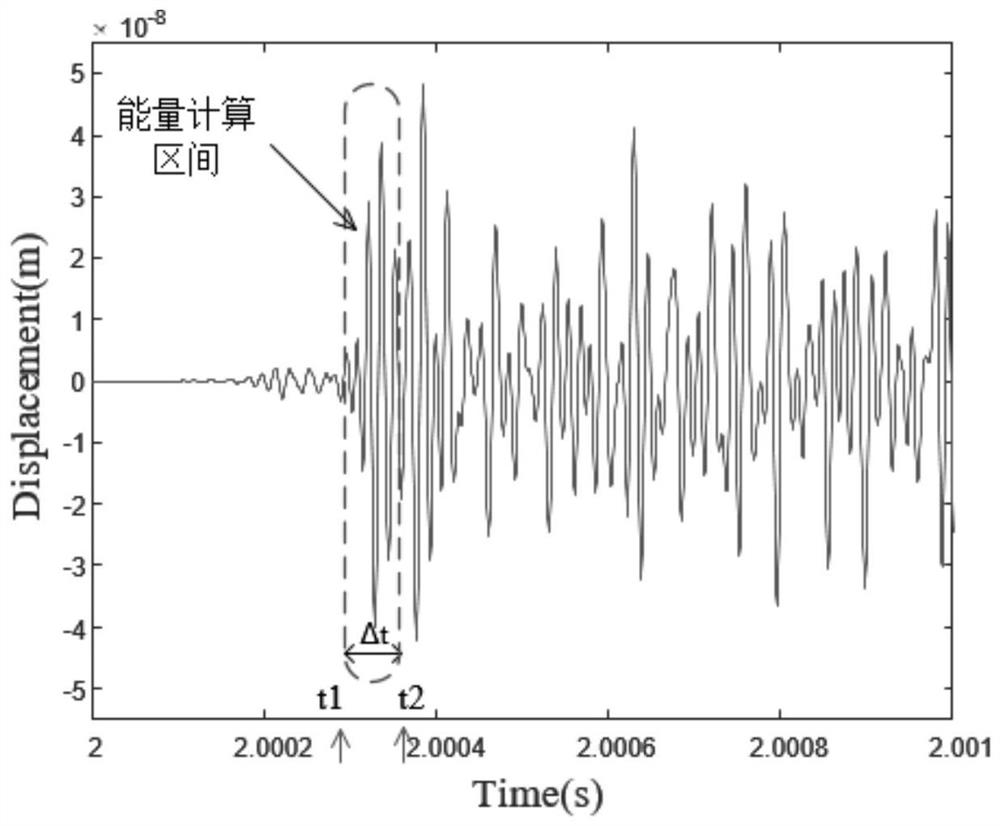
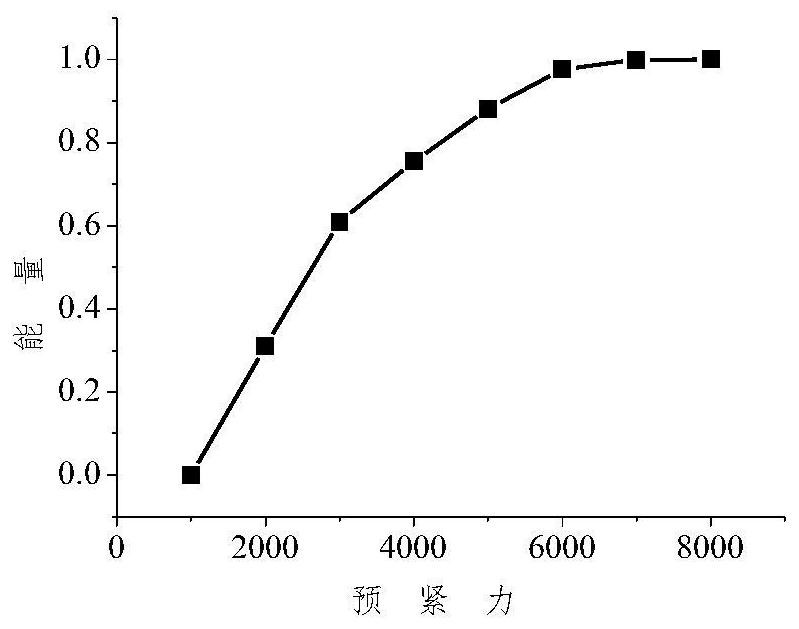
SH guided wave detection method and device for bolt looseness detection
The invention discloses an SH guided wave detection method and device for bolt looseness detection. Processing is performed to obtain the guided wave frequency dispersion characteristic of the flat plate. The surface of the flat plate connected with the bolt group is coupled with three transducers, one transducer excites two guided waves, the two transducers receive guided wave signals, the distance between transmitting and receiving is calculated, the guided wave propagation time is obtained according to the distance and the wave velocity, and the energy calculation time interval is set in combination with the time interval; an energy characteristic value in a calculation time interval is calculated, a quantitative value of looseness of the bolt group is calculated, the quantitative value is compared with a quantitative value under initial bolt group connection to obtain a percentage parameter, and looseness is detected according to the percentage parameter. According to the invention, rapid detection and long-time monitoring of the connecting piece are realized, the device is suitable for detection of the connection condition of bolt groups with different bolt numbers, the transducer is not only simple but also reasonable in design, long-time bolt looseness monitoring can be realized, and monitoring of the flat plate connecting piece which is provided with a surface coating and works for a long time is also very effective.
Owner:PIPECHINA SOUTH CHINA CO +1
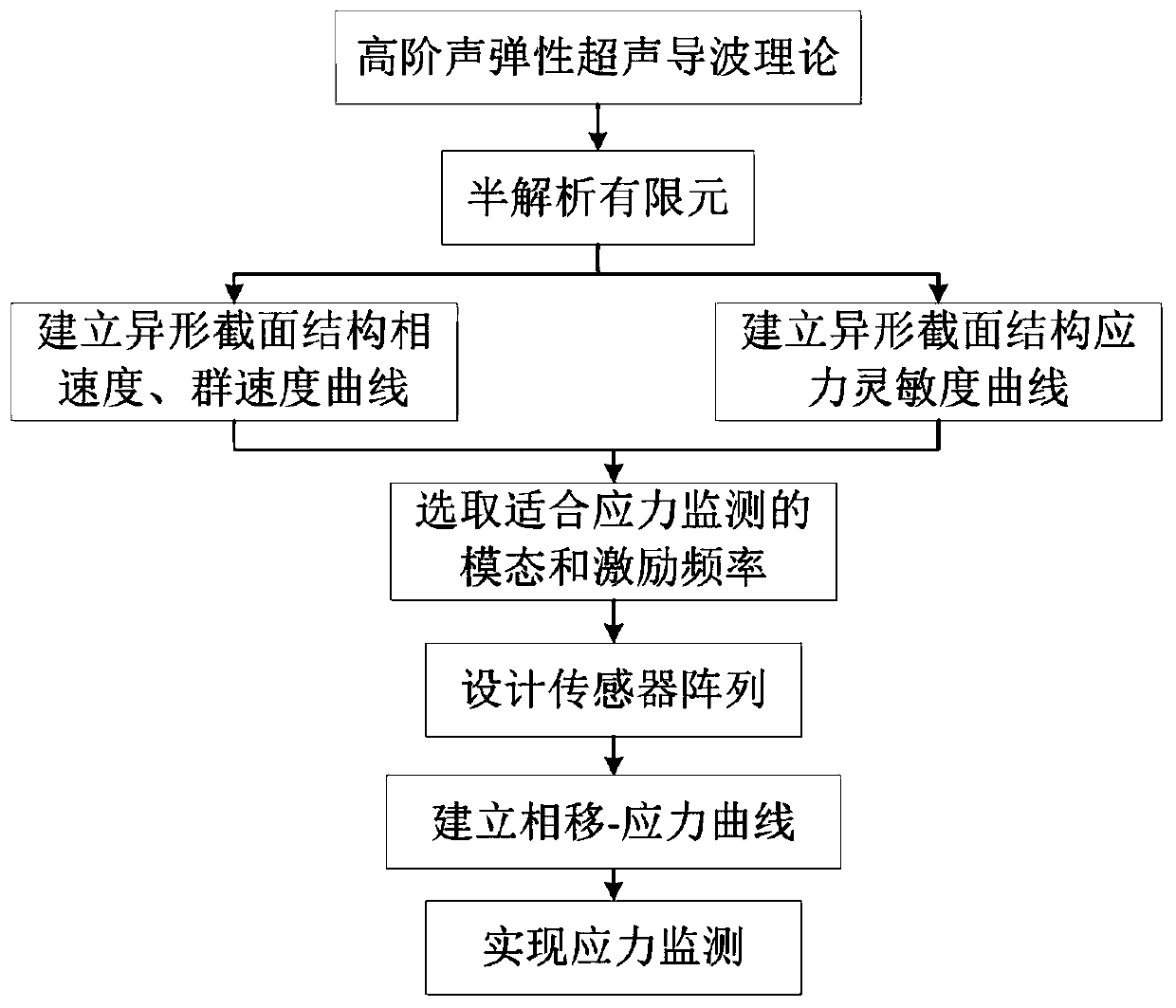
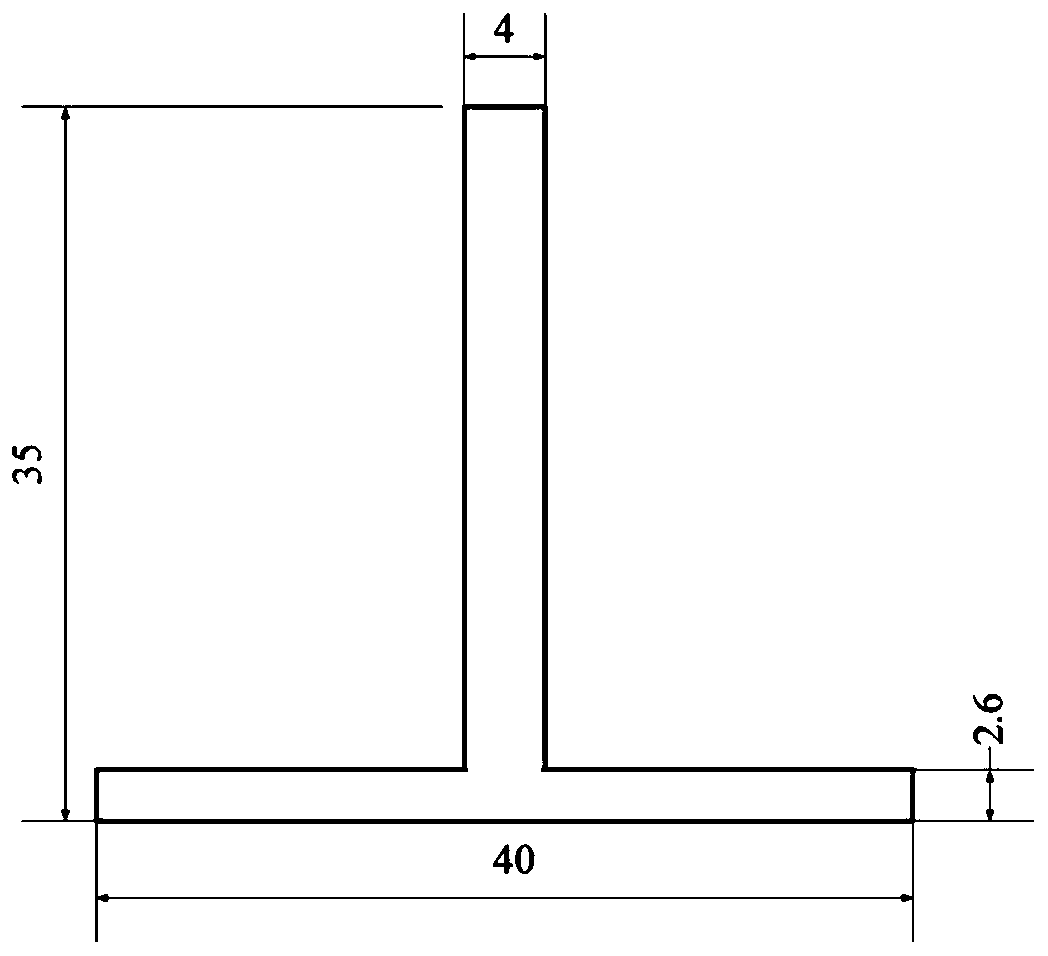
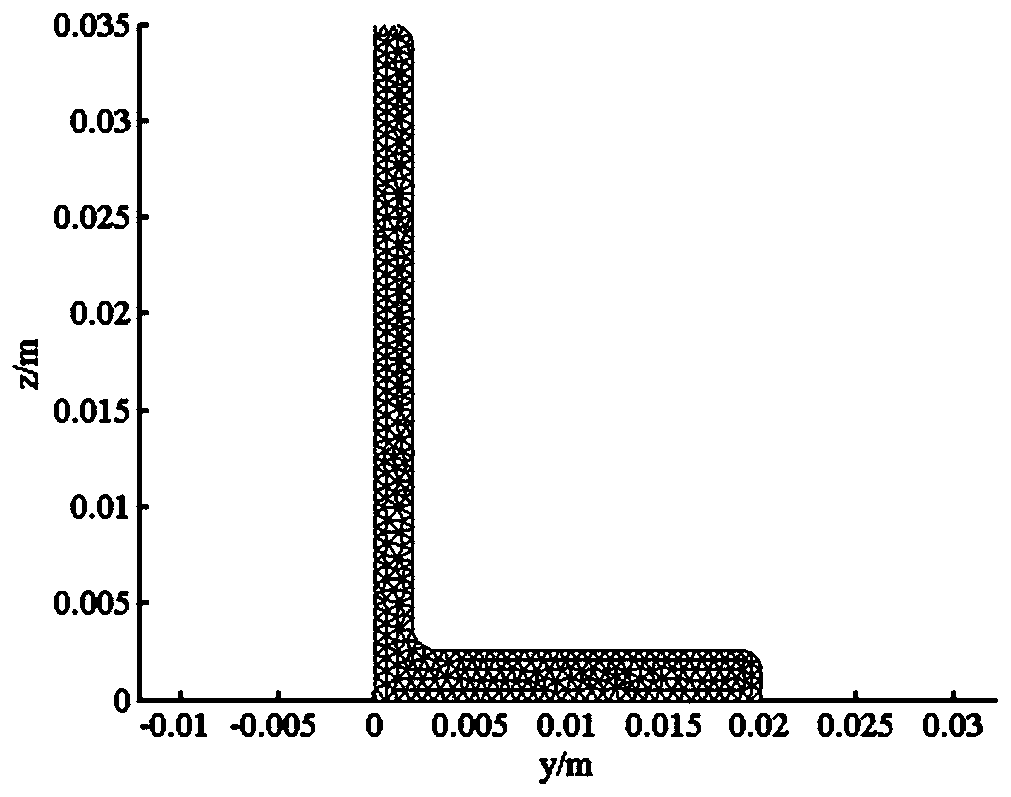
Axial stress monitoring method for stringers with symmetrical cross-section based on high-order acoustoelastic ultrasonic guided waves
The invention discloses a supersonic guide wave axial stress monitoring method for a symmetrical cross-section stringer based on high-order acoustic elasticity. A semi-analytical finite element is combined with a higher-order acoustic elasticity based theory to research influence of the axial stress on guide wave spreading of the symmetrical cross-section stringer, the speed and speed change of the guide wave with / without a stress are solved, proper stress monitoring mode and excitation frequency are selected according to solving results, a sensor array is designed according to spreading characteristics of the mode, and integral stress monitoring is completed. The method fills the blank in supersonic guide wave stress monitoring of the symmetrical cross-section stringer, and general idealsand method are provided for stress monitoring for the supersonic guide wave of the symmetrical cross-section stringer.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Defect location method for sheet metal based on active sweep frequency acoustic excitation
ActiveCN108802184BImprove accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionThin metalEngineering
The present invention proposes a metal sheet defect location method based on active sweep frequency acoustic excitation, said method includes four steps: device layout, signal acquisition, signal processing, and defect location; the method can obtain defect position curves through time delay information , and then determine the defect position according to the intersection point of the defect position curve; the beneficial technical effect of the present invention is: a metal sheet defect location method based on active sweep frequency acoustic excitation is proposed, which can be realized without knowing the propagation velocity of the guided wave in advance Defect location, the positioning accuracy is high.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
A Design Method of Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Excitation Probe
ActiveCN104330476BSimplifyImprove signal-to-noise ratioUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationSonificationGuided wave propagation
The invention discloses an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe design method, according to the sound propagation principle, namely SH type guided wave propagation rule, in a solid plate, optimum excitation frequency is determined, and according to the frequency, an electromagnetic ultrasonic excitation probe is designed; enhancement of SH type 0 order mode guided wave and inhibition of 1 order mode guided wave in the plate can be realized, simplification of the mode of a guided wave excited in a particular frequency can be realized, the signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and defect detection probability and quantization accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
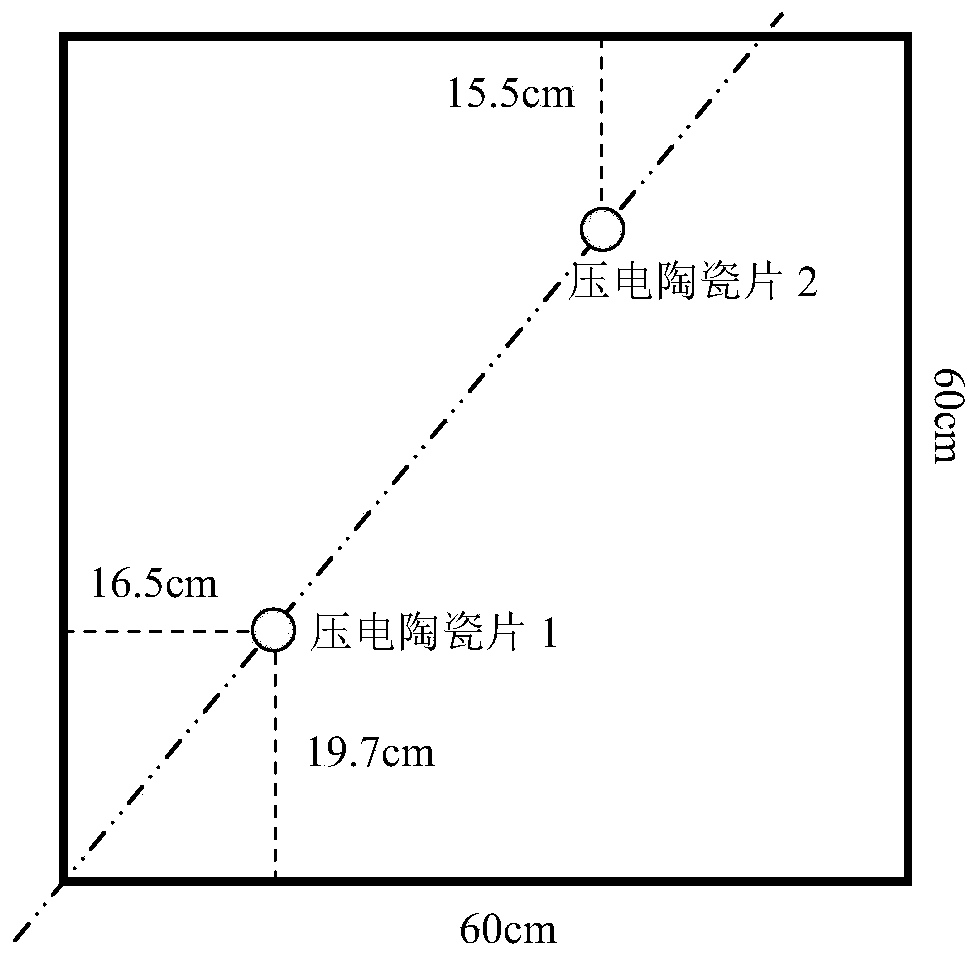
A Method for Testing the Group Velocity Dispersion of Structural Guided Wave Response
ActiveCN110068613BRealize measurementEasy to implementAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave structureEngineering
A method for testing structural guided wave response group velocity dispersion, in which a single group of PZT piezoelectric element pairs are arranged on a structural member as a signal exciter and a sensor respectively to form a guided wave signal excitation-sensing measurement channel; a design is made according to the test frequency band Group narrow-band excitation signals, and collect the structural guided wave response signals under the corresponding excitation; perform time interception on all collected structural guided wave response signals, and normalize the intercepted signals according to the maximum peak amplitude of the direct wave signal, Then perform synchronous superposition according to the excitation time reference, perform time-frequency processing on the superimposed signal, and calculate the propagation dispersion characteristics of the guided wave in the structure to be tested according to the peak distribution and propagation distance in the time-frequency processing results. The method of the invention can easily realize the test and analysis of dispersion characteristics in structures such as plates, shells, pipes, columns, etc. based on the existing test conditions, and has good support and application value for the research and application of guided wave structure health monitoring.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECH
Modeling analysis method for a pipeline heterogeneous interface ultrasonic guided wave propagation rule
PendingCN109829218AImprove applicabilityImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsSustainable transportationComputational scienceWave shape
The invention provides a pipeline heterogeneous interface ultrasonic guided wave propagation rule modeling analysis method, a pipeline comprises a straight pipe and a heterogeneous interface, and themethod comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a pipeline heterogeneous interface dynamic display finite element simulation model; and step 2, obtaining a reflection characteristic waveform of the ultrasonic guided wave at the heterogeneous interface so as to remove the influence of the reflection characteristic waveform on the pipeline damage characteristic waveform. According to theanalysis method, a finite element simulation model of the pipeline heterogeneous interface is established, a dispersion equation and a mode conversion relation of ultrasonic guided waves propagating in the pipeline heterogeneous interface are derived, and a reflection characteristic waveform of the ultrasonic guided waves at the heterogeneous interface is obtained, so that the influence of the reflection characteristic waveform on the pipeline damage characteristic waveform is removed.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ASTRONAUTICAL SYST ENG +1
A method for judging the compactness of interface connection by spring stiffness coefficient
InactiveCN104458570BFew parametersAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing mechanical meansStiffness coefficientSignal on
The invention discloses a method for judging the connecting compactness of an interface by using a spring stiffness coefficient. The method is mainly used for ultrasonic nondestructive testing of the interface compactness and comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a corresponding model according to actual conditions, and arranging a spring model at the interface; (2) deducing out a frequency dispersion equation of guided wave propagation according to a wave equation and boundary conditions; (3) drawing out a changing curve of phase velocity along with the tangential stiffness coefficient Kt under the condition that the normal stiffness coefficient Kn is infinitely great so as to obtain a tangential stiffness coefficient value with relatively sensitive phase-velocity change and a corresponding frequency-dispersion characteristic curve; (4) determining peeling-degree percentage values corresponding to different Kt values by simulation; (5) exciting and receiving ultrasonic guided wave signals on a tested object; (6) extracting parameters from actual testing signals to carry out inversion and further determine corresponding Kt values; and (7) judging the compactness degree of the interface by the tangential spring stiffness coefficient value. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the connecting condition of the interface of a bonding part can be relatively well obtained and the quality monitoring and the maintenance can be carried out on the bonding part in a relatively effective manner.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com