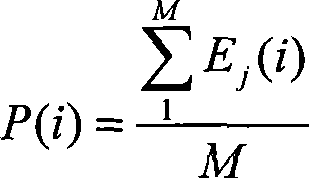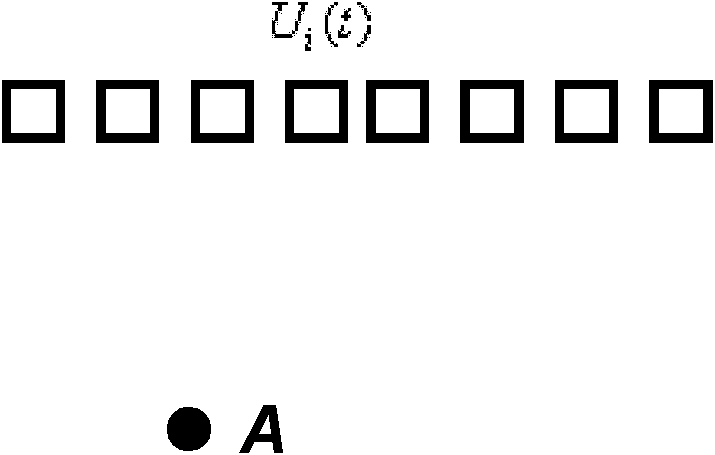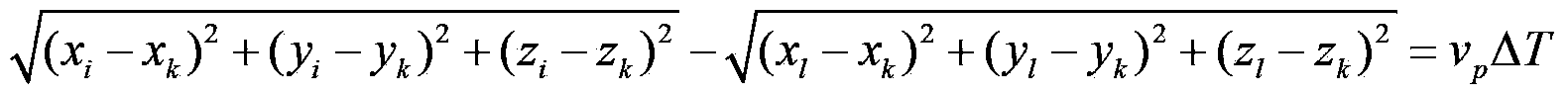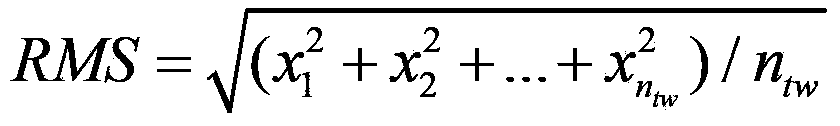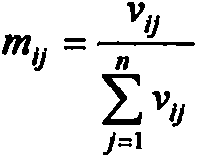Patents
Literature
472 results about "Wave packet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
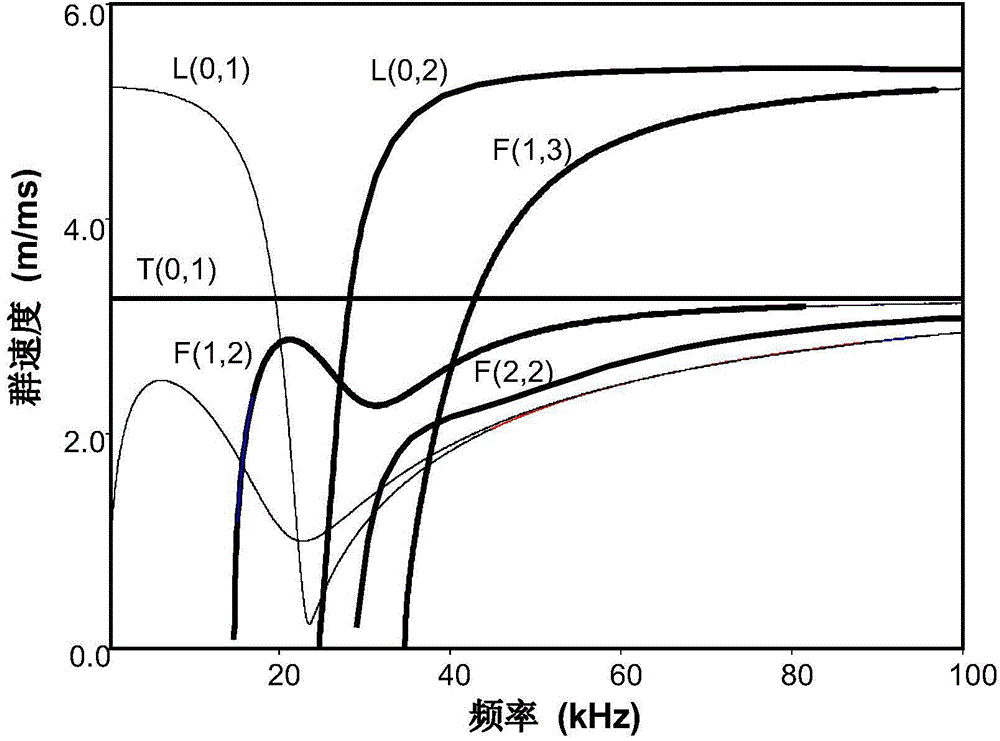
In physics, a wave packet (or wave train) is a short "burst" or "envelope" of localized wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion, see figure) or it may change (dispersion) while propagating.
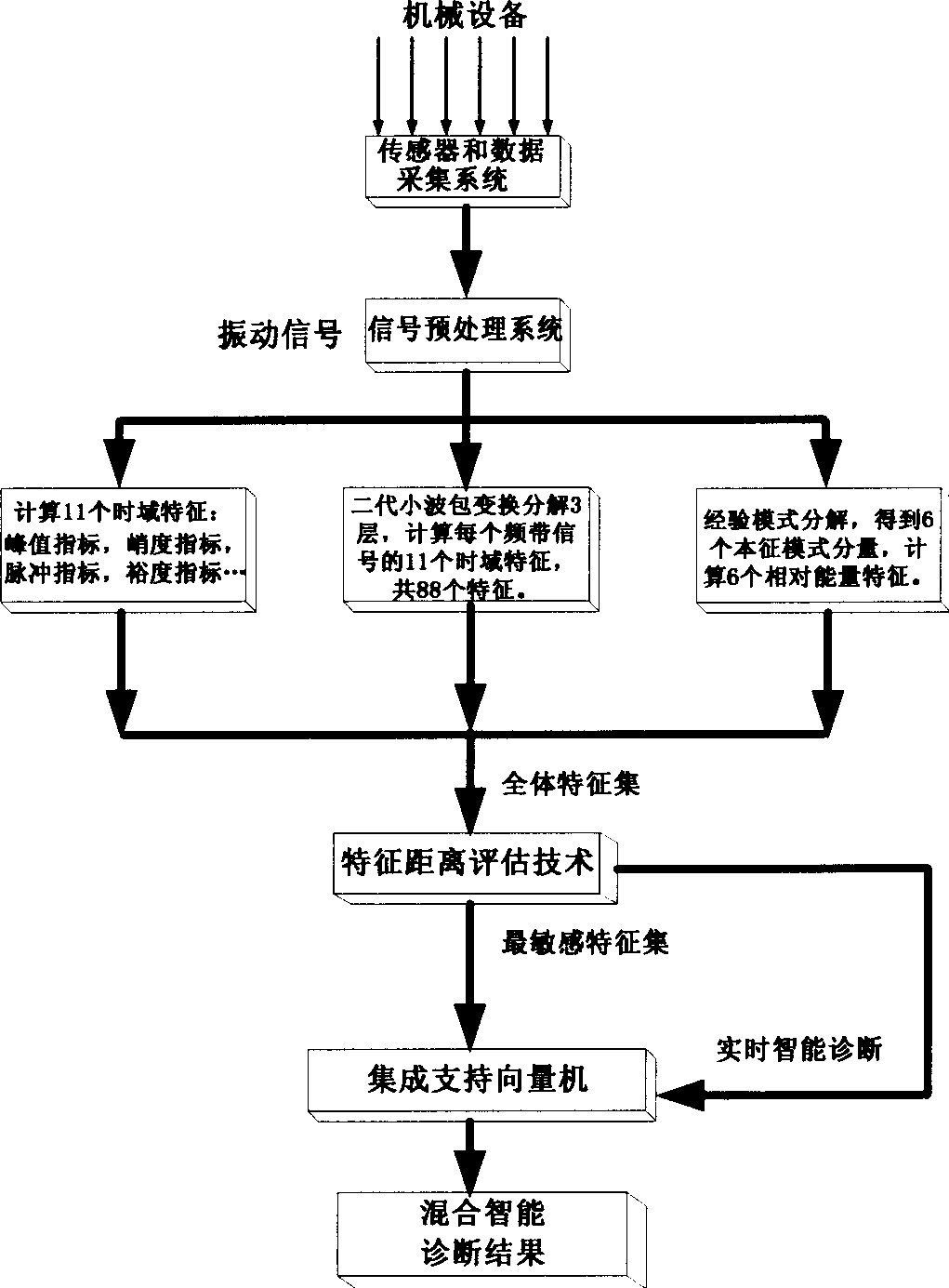
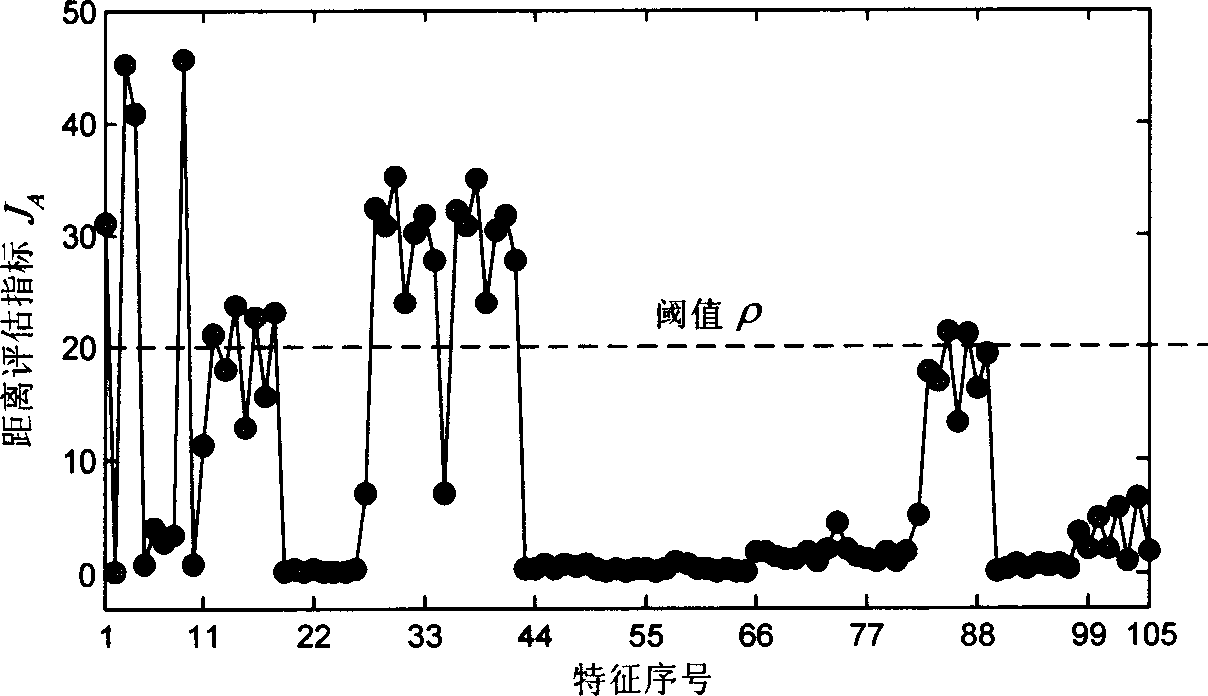
Integrated supporting vector machine mixed intelligent diagnosing method for mechanical fault
InactiveCN1811367ARealize intelligent diagnosisEfficient removalMachine part testingTime domainSupport vector machine
The present invention discloses an integrated support vector machine mixed intelligent diagnosis method of machine failure. Said method includes the following steps: respectively adopting and lifting small wave packet, utilizing frequency band and empirical mode decomposition process to decompose vibration signal according to the eigen mode component and extract time domain statistical character of decomposed signal to form total characteristic set; providing characteristic distance evaluation technique and characteristic evaluation index; utilizing said characteristic evaluation index to select most sensitive characteristic set from the total characteristic set; using said most sensitive characteristic set as diagnosis characteristics and creating integrated support vector machine mixed intelligent diagnosis model so as to implement intelligent diagnosis of machine failure state.
Owner:SHENJI GRP KUNMING MACHINE TOOL
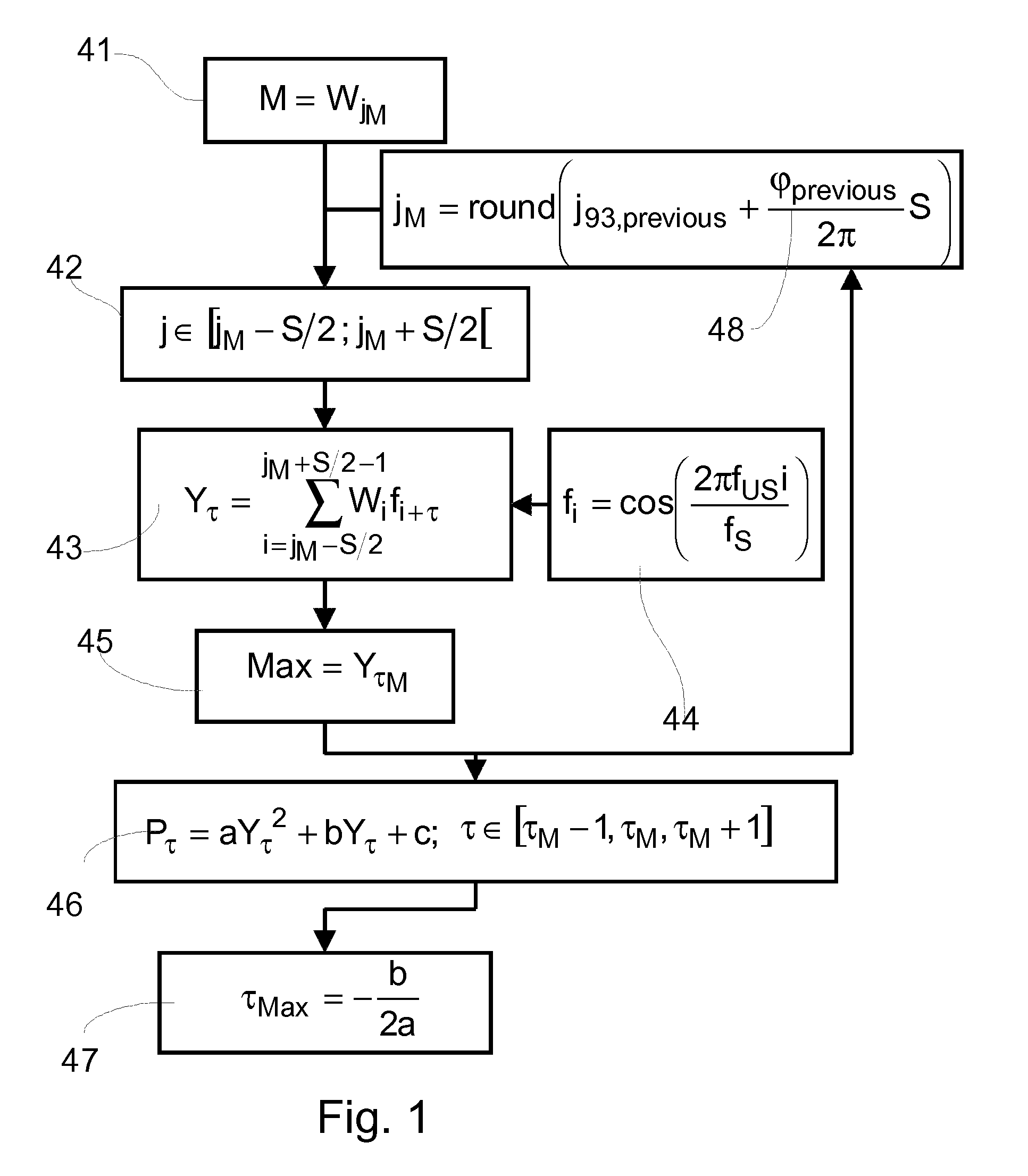
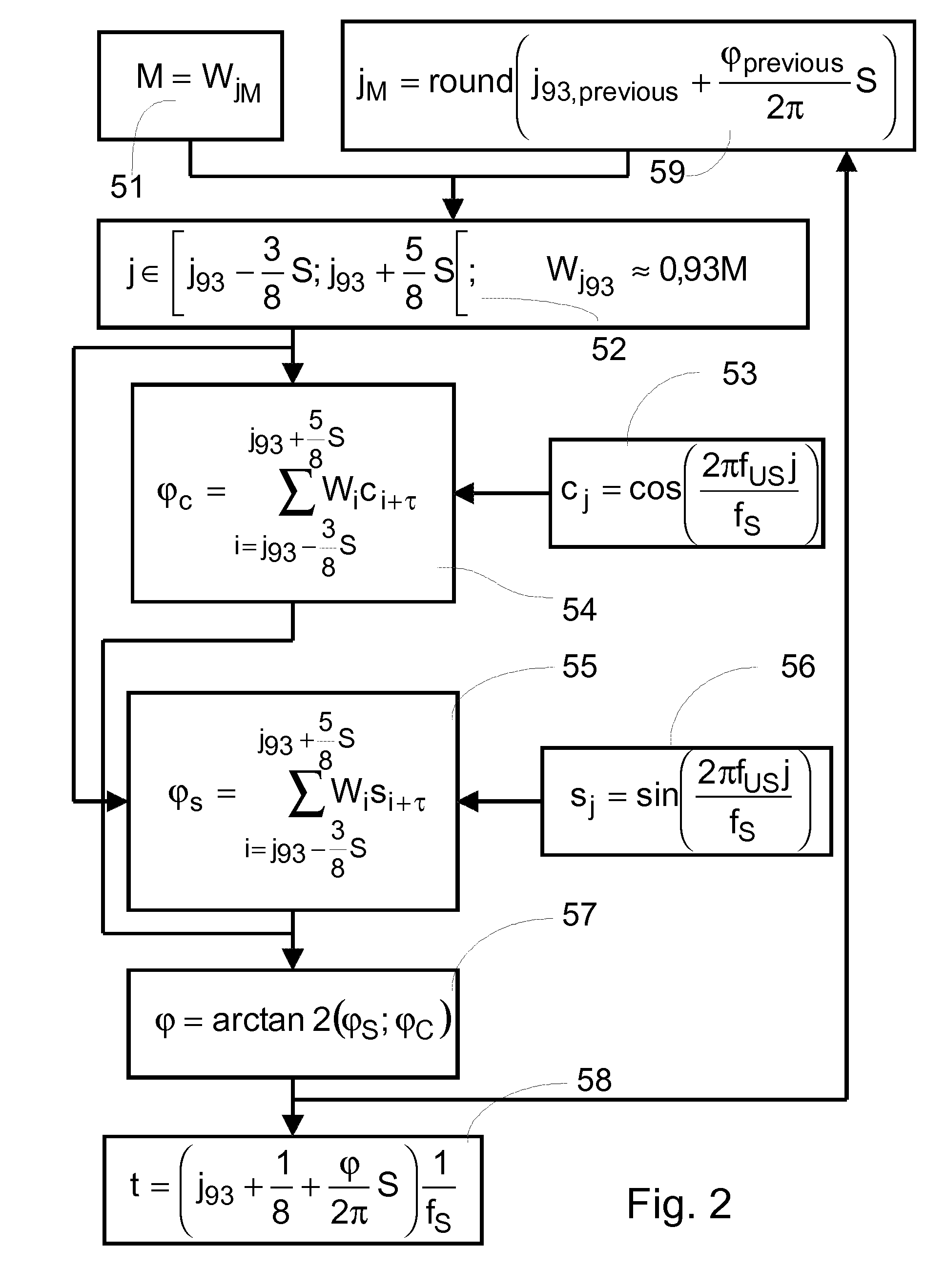
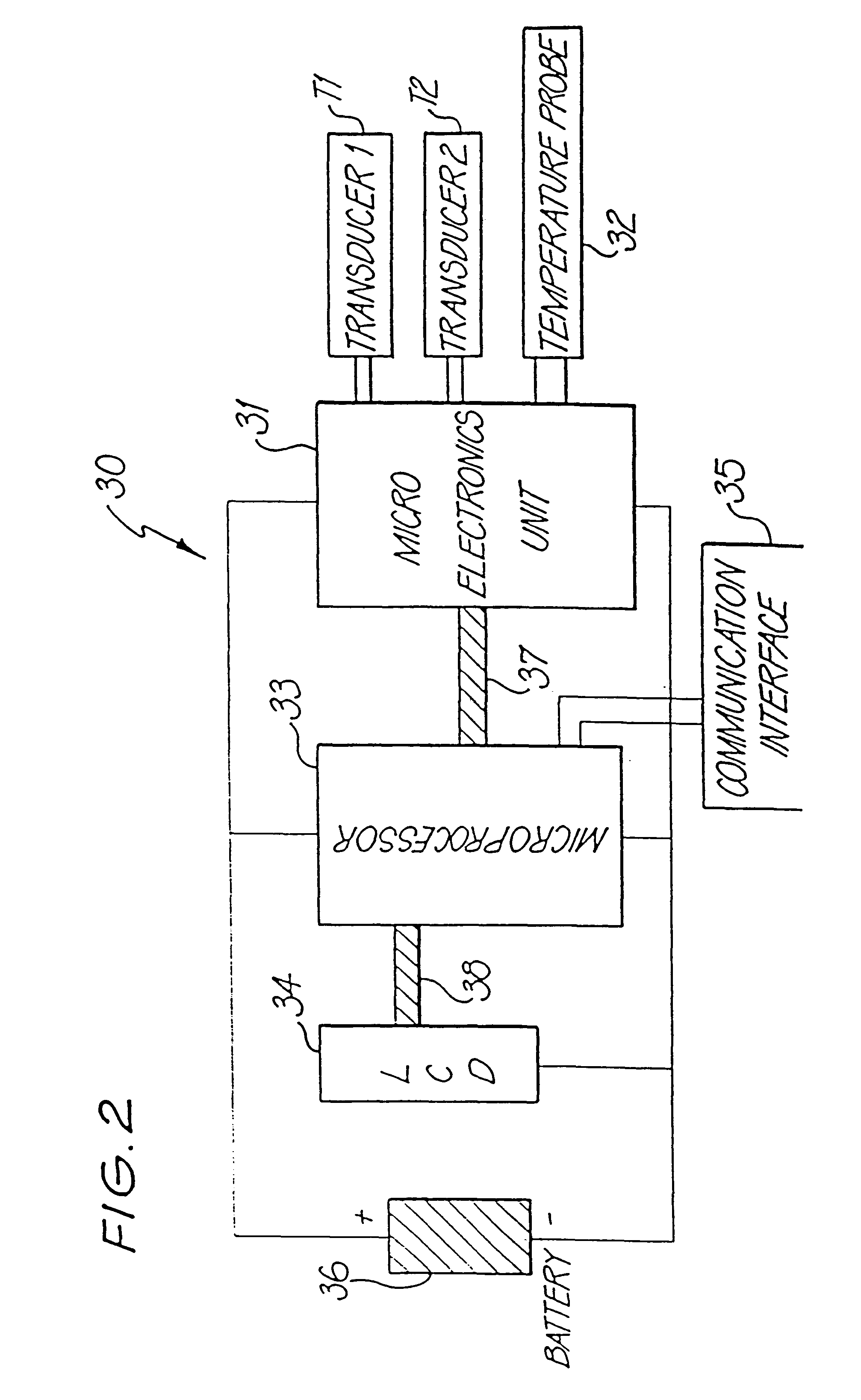
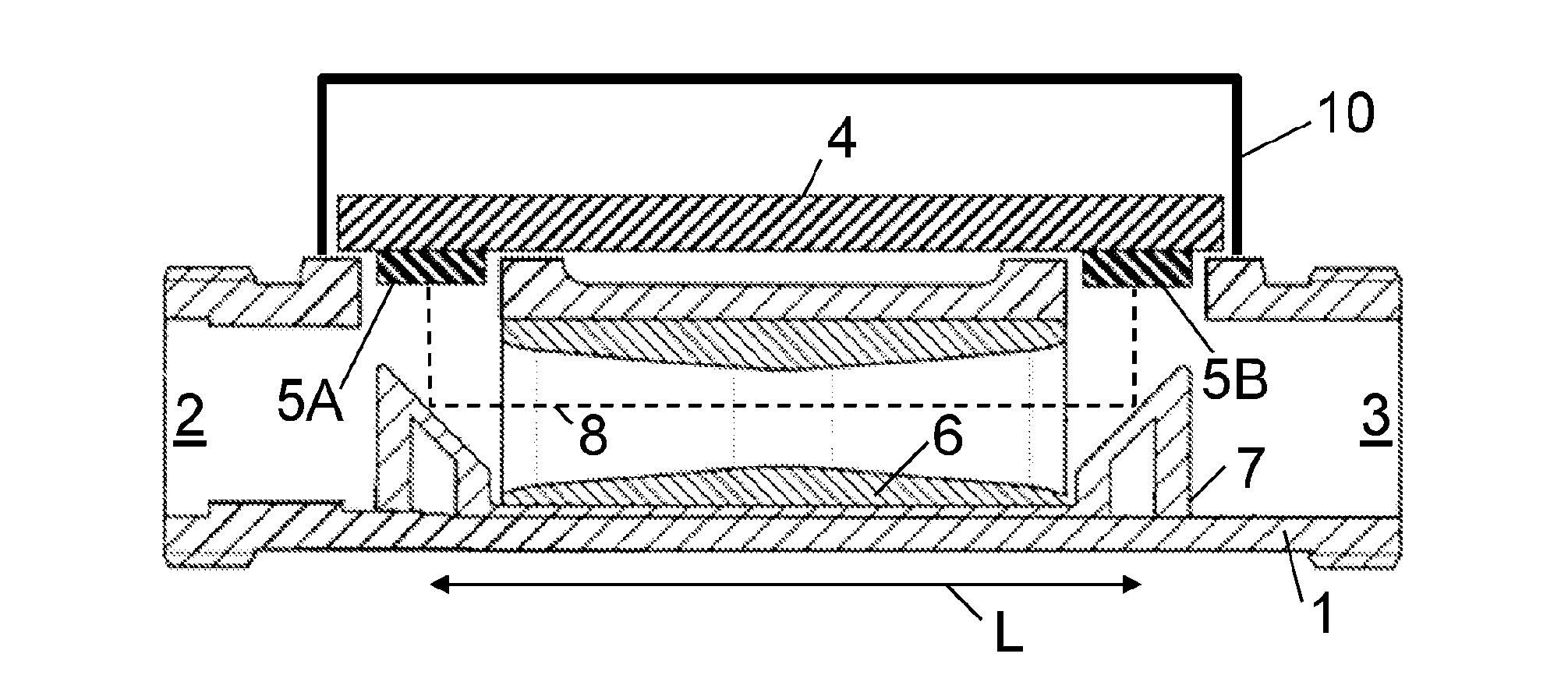
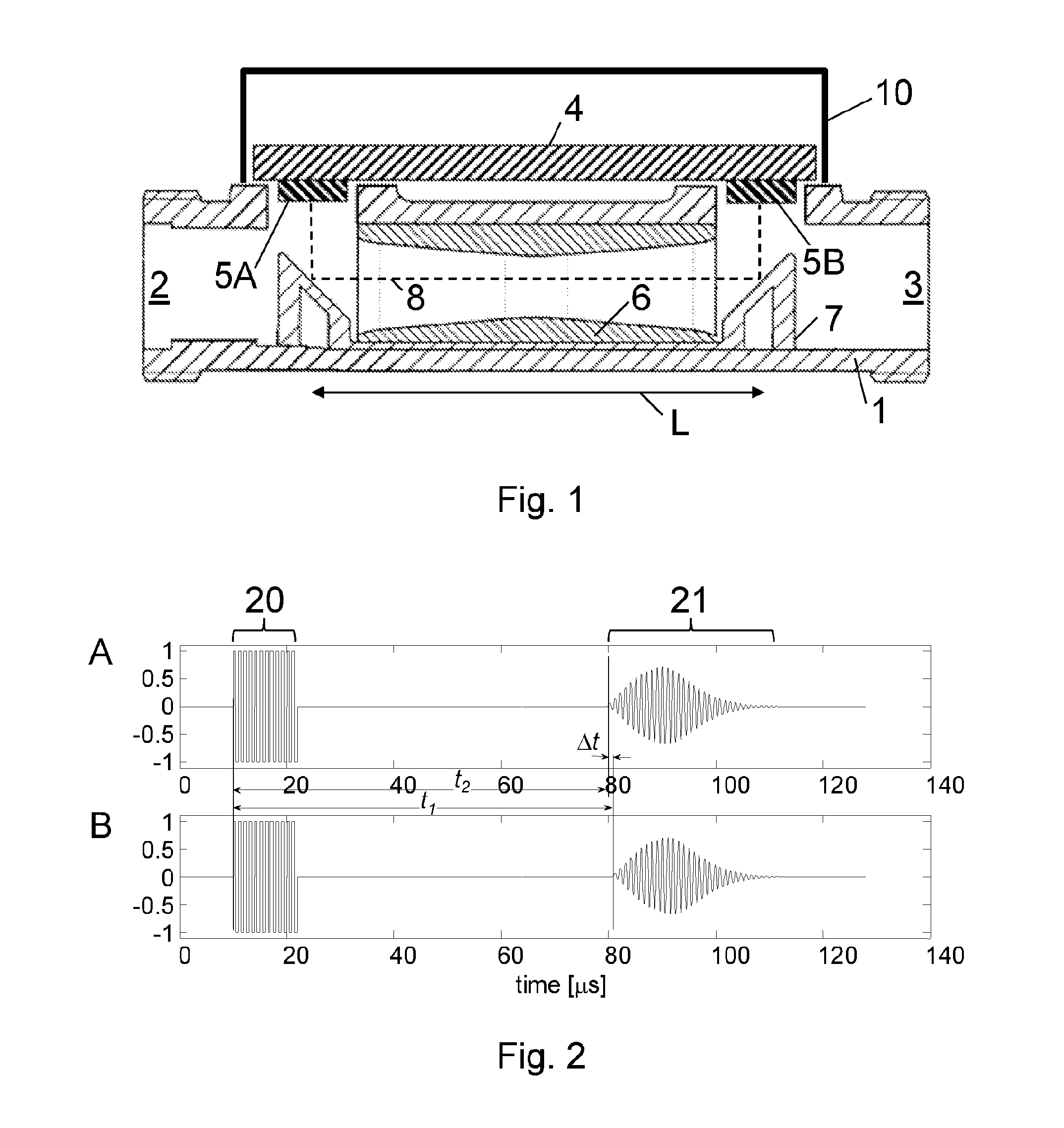
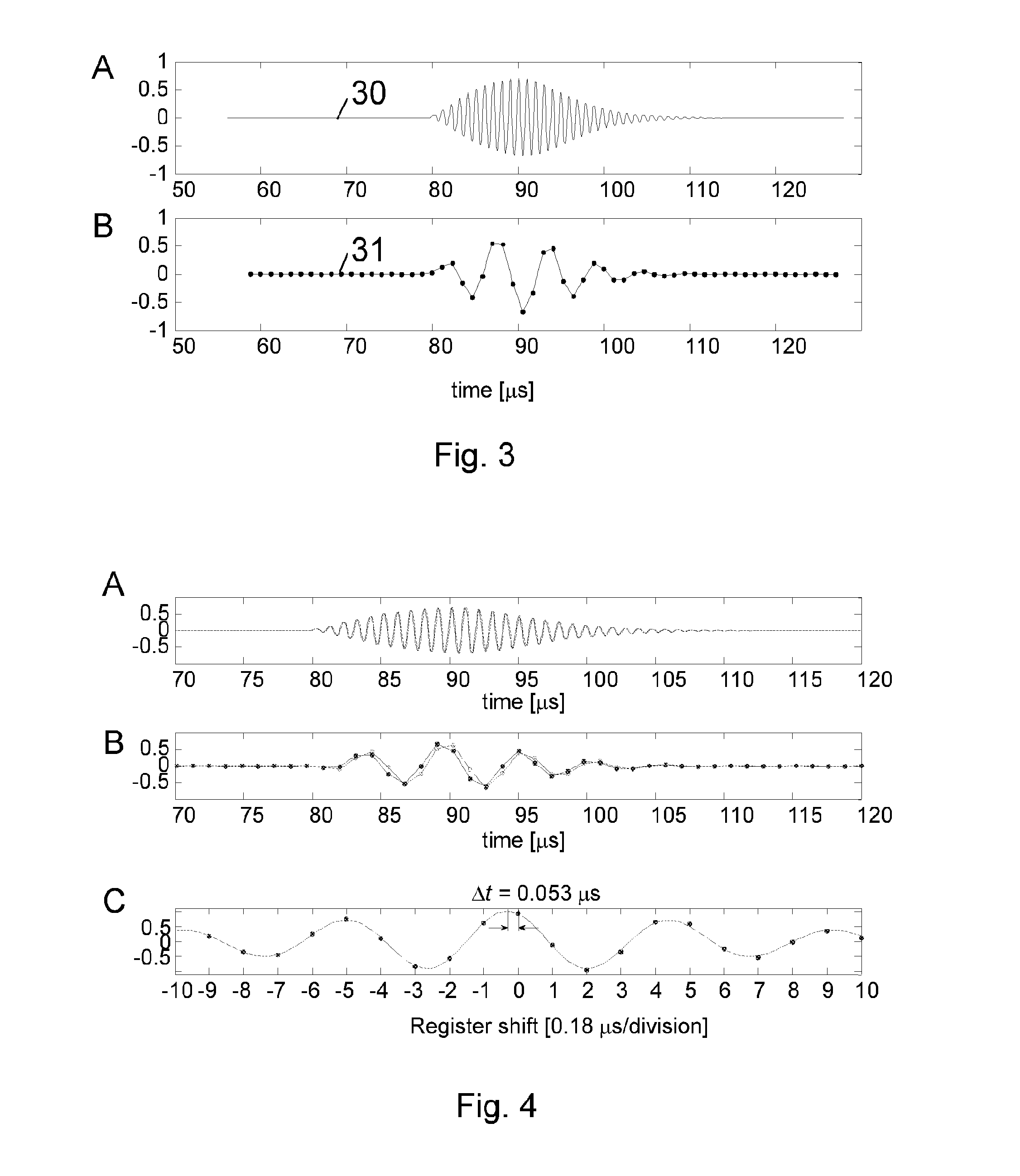
Method for determining the temporal position of a wave packet and flow measuring device
ActiveUS8103461B2Improve accuracyLess-expensive componentVolume/mass flow measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringDischarge measurementsComputer science
The invention relates to a method for determining the temporal position of a wave packet (31) in a flow measuring apparatus, and to a flow measuring apparatus. The method includes the sampling of the wave packet at a plurality of points in time, wherein a measured value is created at each point in time. Subsequently, a sum of products (43, 54, 55, 63, 64) is calculated, wherein each product is calculated for a determined point in time from a plurality of points in time and each product is the product of a value of a compare function (44, 53, 56, 61, 62) at the determined point in time and the measured value at the determined point in time. Finally, the temporal position of the wave packet is calculated from the sum of products.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL GMBH
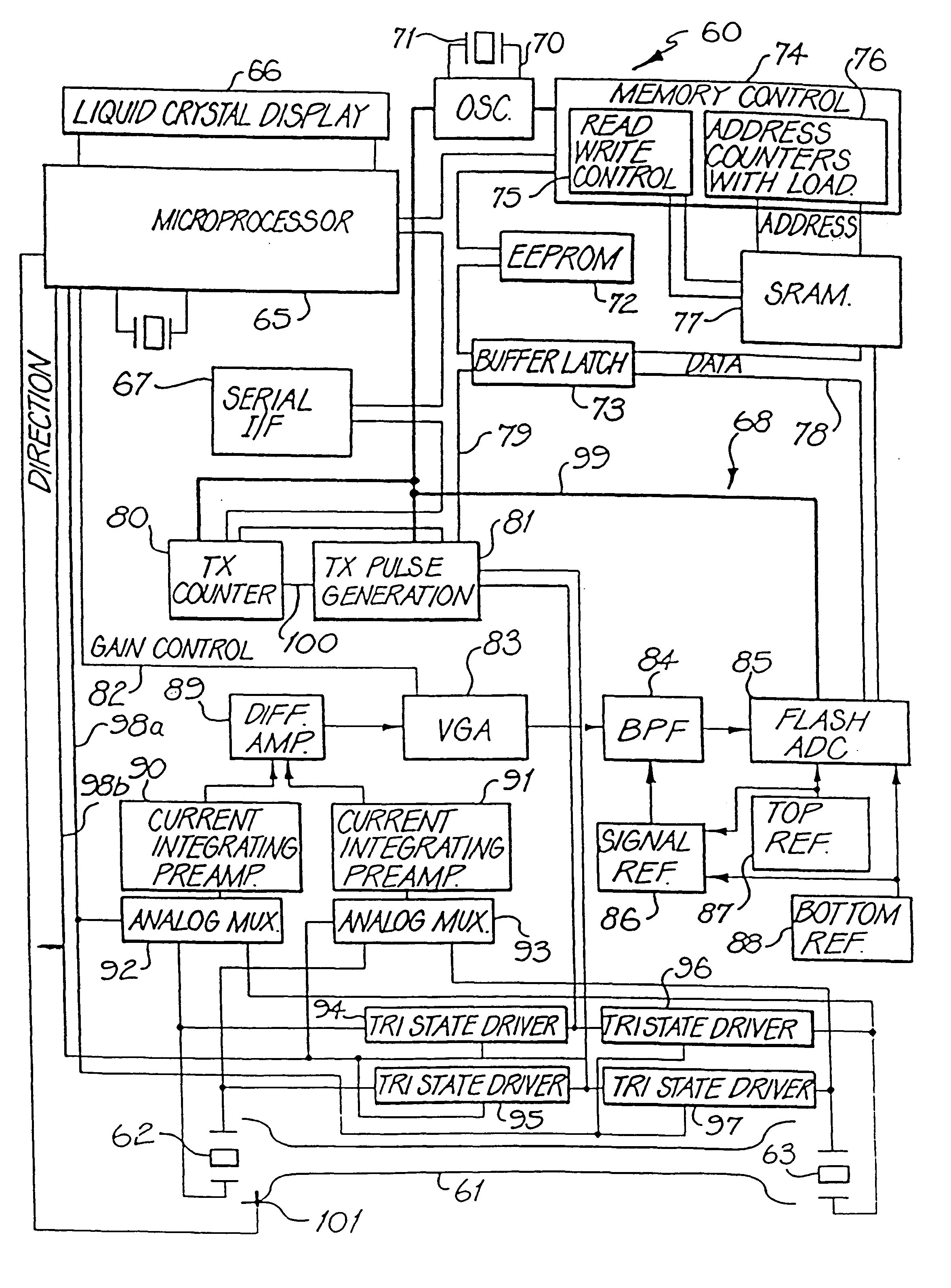
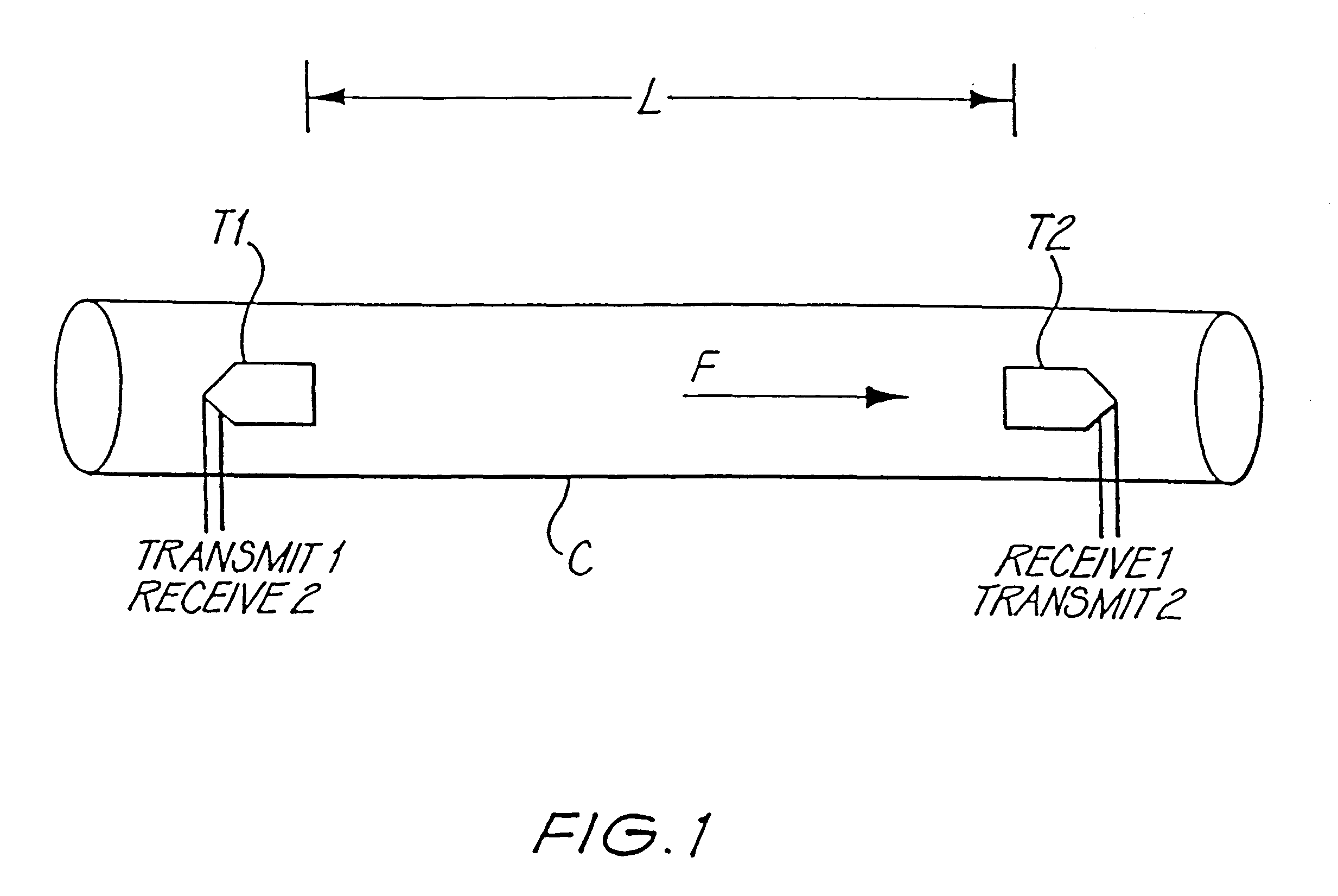
Digital speed determination in ultrasonic flow measurements
InactiveUS6305233B1Wave based measurement systemsVolume/mass flow measurementSonificationUltrasonic sensor
A method and device (60) is described which measures the speed of a flowing fluid (F) by measuring the difference in time taken for an ultrasonic signal to travel first upstream and then downstream in the fluid. In each direction the device (60) calculates the time taken for an ultrasonic wave packet emitted by one ultrasonic transducer (62) to be received by another (63). The method used consists of the digitisation (85) of the received waveform and the subsequent identification of waveform features by comparison with a standard template of the waveform. The position in time of these features is then determined with respect to a high speed clock (70). The results are then used in a weighted computation to determine the time of arrival of the waveform at the transducer (63).
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
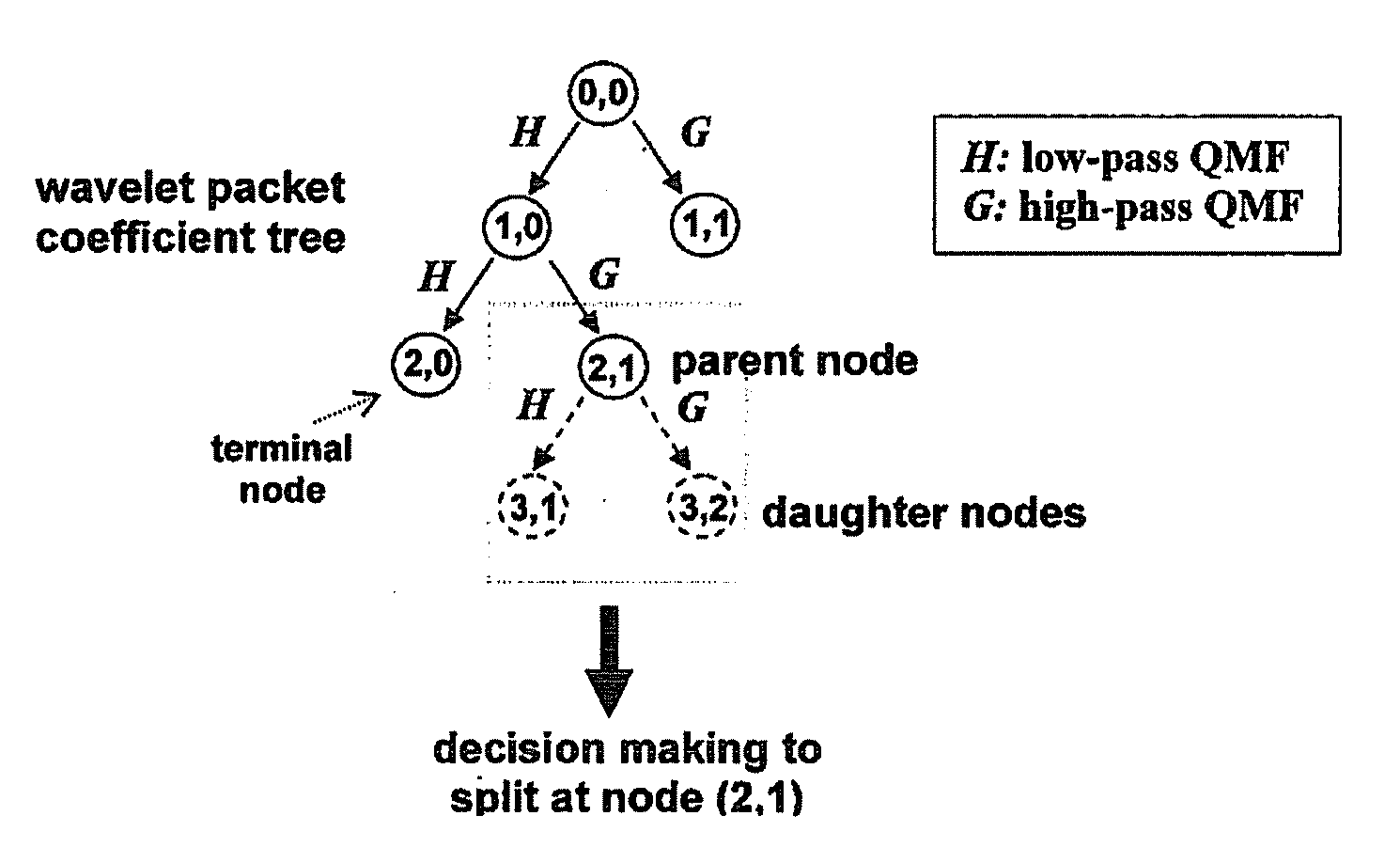
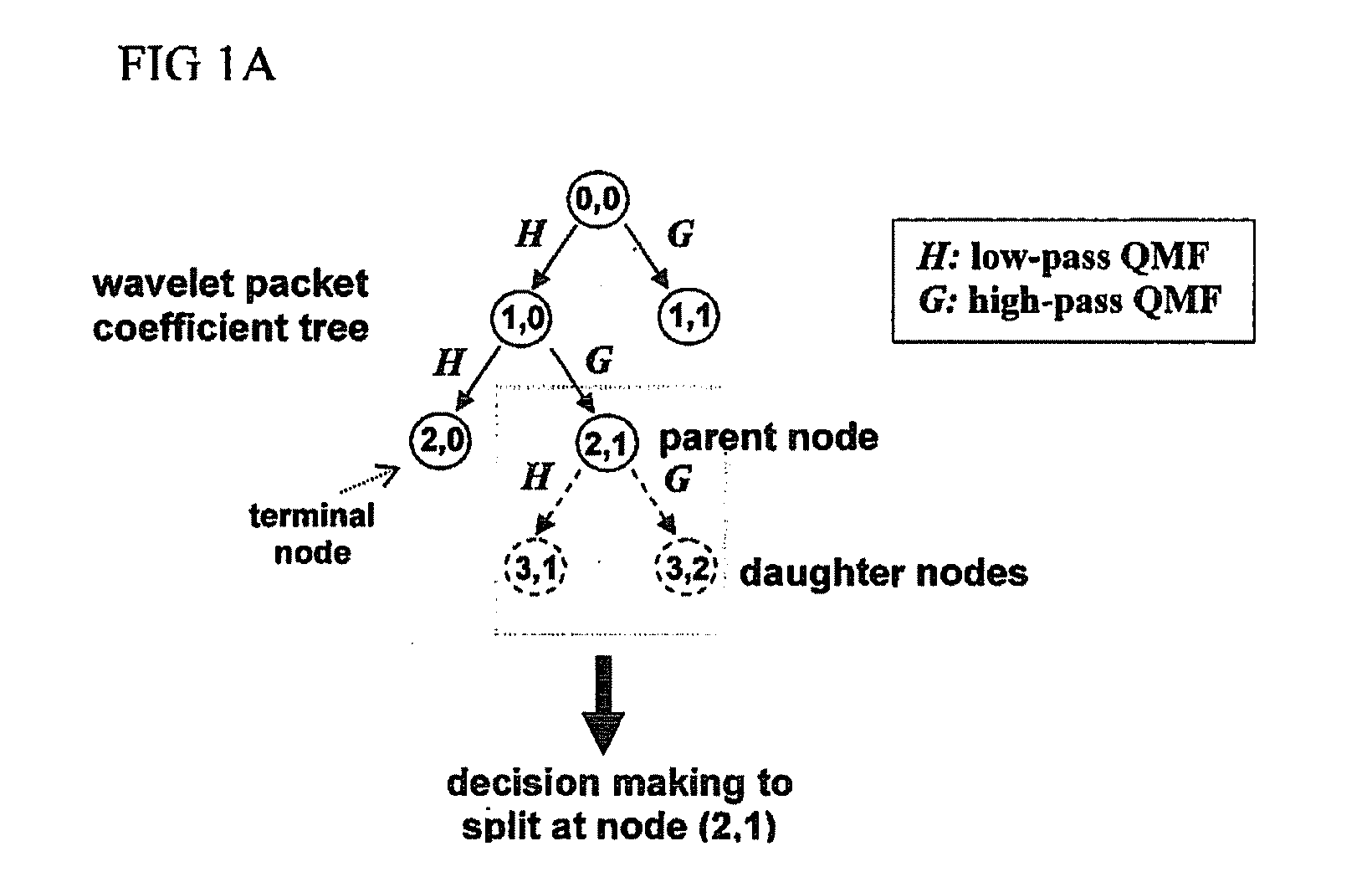
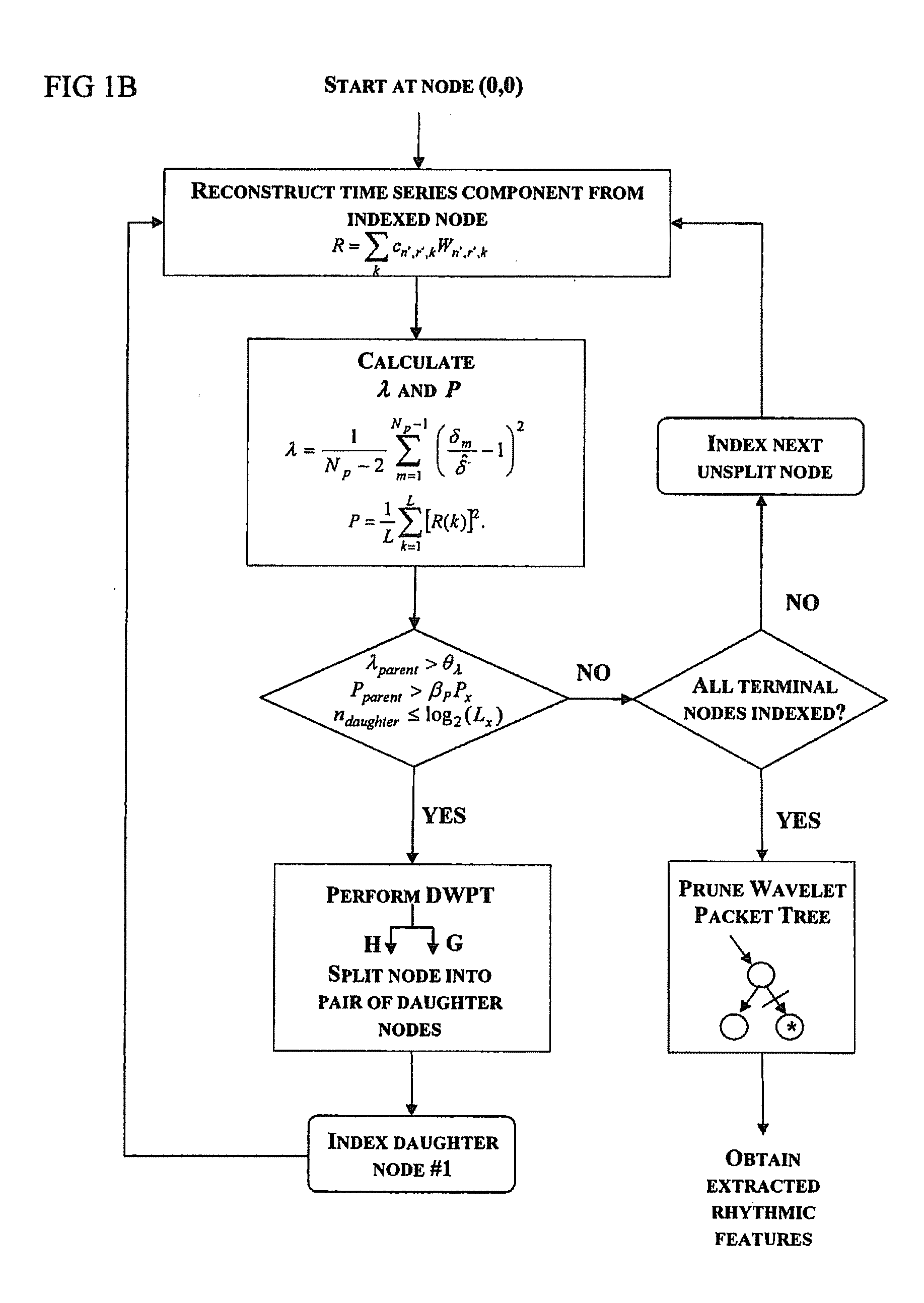
Method and rhythm extractor for detecting and isolating rhythmic signal features from an input signal using the wavelet packet transform
A method of detecting and isolating at least one rhythmic component from a discrete-time input signal, comprises subjecting the input signal to discrete wavelet packet transform multi-resolution analysis; applying wavelet packet basis selection criteria to the result of the analysis to evaluate rhythmic signal features of the input signal; and isolating at least one rhythmic signal component from the input signal based on the evaluation.
Owner:NEUROCHIP CORP
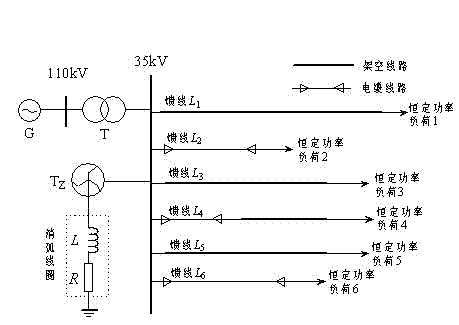
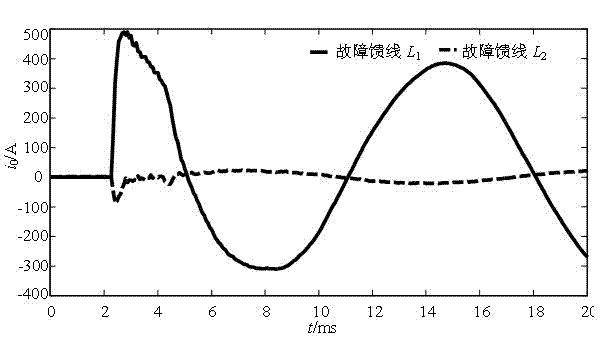
Power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors
ActiveCN103245883AThe principle is simpleImprove timelinessFault locationElectric power systemTransient current
The invention relates to a power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. When a power distribution network runs into a single-phase earth fault via an arc suppression coil grounding system, a transient zero-sequence current component detected by a measuring end is a nonlinear non-stationary signal formed by different frequency components. By taking the fault component as a study object, time-frequency characteristics of a fault transient current of the fault component are analyzed by utilizing the wavelet packet theory, time-frequency distribution regularities among all feeder lines under different fault conditions are described according to similarity of the time-frequency characteristics, and consequently line selection criteria based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristics can be obtained. The method is simple in principle, only utilizes short-time window zero-sequence current data of 5ms after the fault, can identify faulty feeders under the conditions of small fault angle and high resistance ground fault, has excellent timeliness and robustness, is free from influence of an arc fault or a resistance ground fault, requires a low sampling rate for hardware, and is highly practical.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
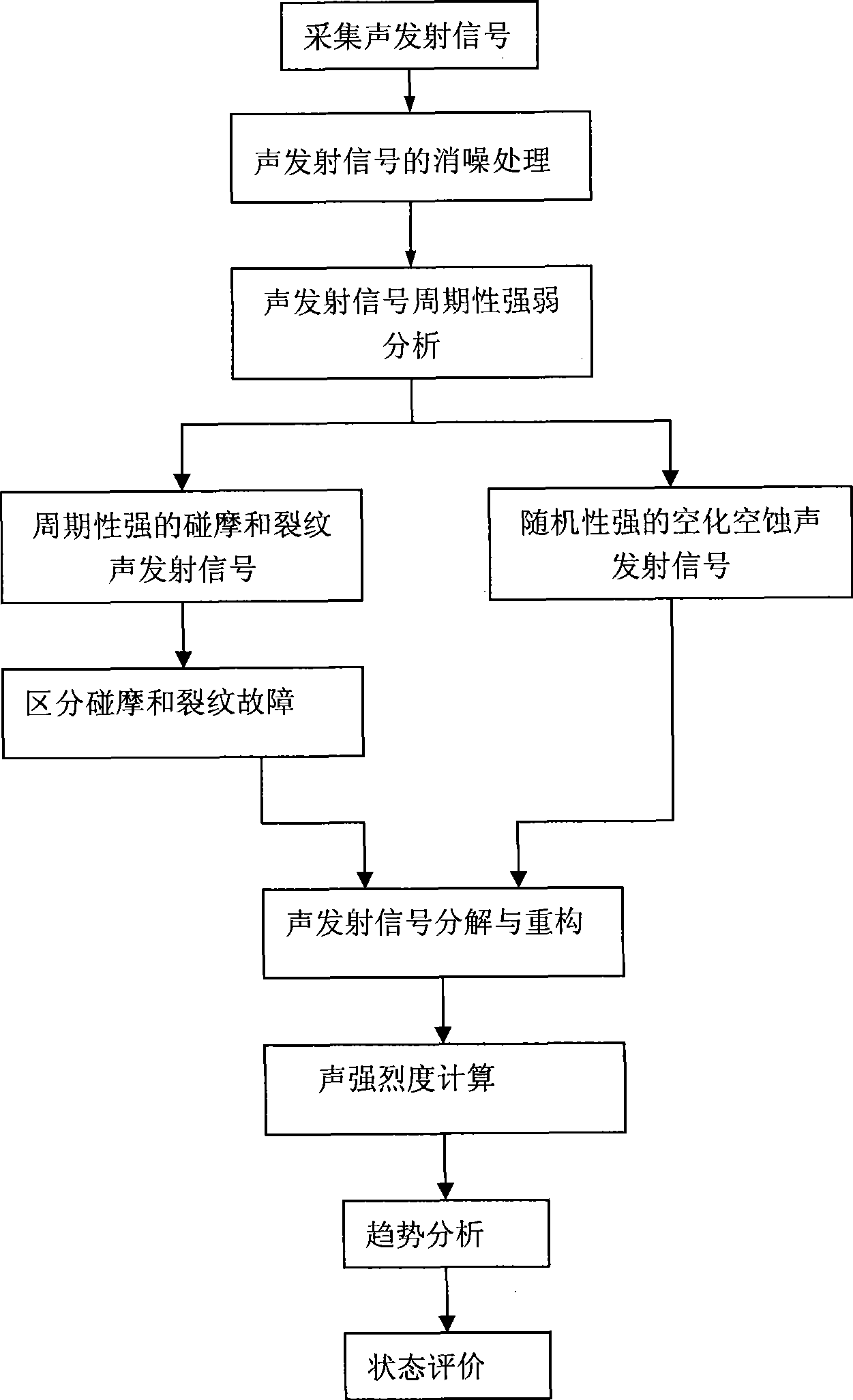
Failure diagnosis method and apparatus of hydroturbine based on acoustic emission technology
InactiveCN101435799AAvoid Low Frequency Noise InterferenceContinuous acquisitionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFrequency spectrumCavitation
The invention discloses a hydroturbine fault diagnosis method and a hydroturbine fault diagnosis device based on acoustic emission technology. The method applies the acoustic emission technology to the fault diagnosis of a hydroturbine set, obtains acoustic emission signals on a hydroturbine draft tube and guide vanes of a watermill chamber through an acoustic emission sensor, eliminates noise by adopting morphological filtering technology, adopts the pulse repetition rate to analyze the intensity of the periodicity of the acoustic emission signals, combines spectrum analysis and waveform nearness analysis to identify common rub impact, cracks as well as cavitation and cavitation erosion states, and applies wavelet packet technology for the decomposition and reconstruction of the signals to calculate the acoustic intensity of acoustic emission and perform the trend analysis of parameters of the acoustic intensity along with the working condition such as active power, water head and guide vane opening, further to comprehensively know the operation state and performances of a hydroturbine generator set and guide the operation of a hydroturbine.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
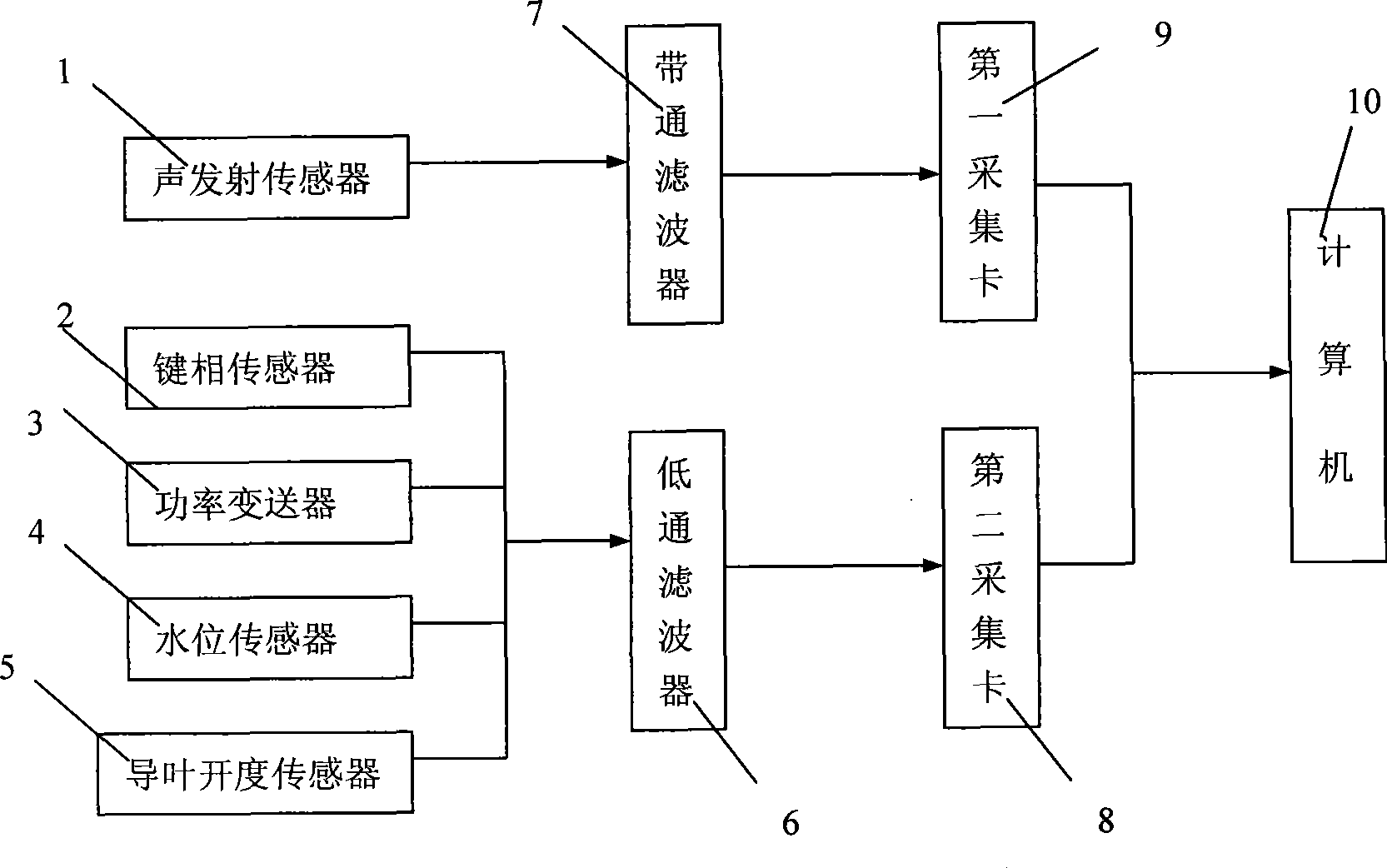
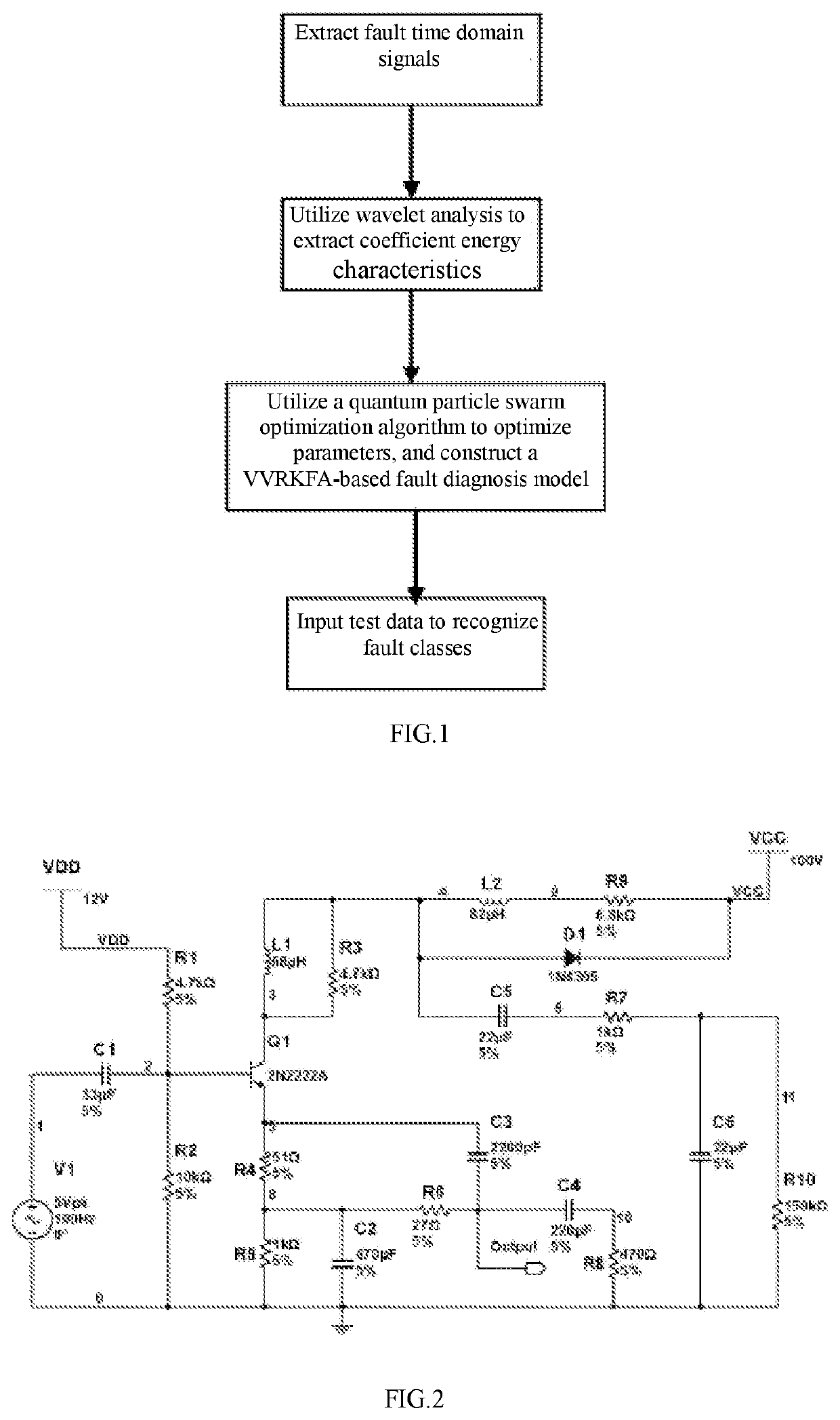
Method for diagnosing analog circuit fault based on vector-valued regularized kernel function approximation
ActiveUS20200271720A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedKernel methodsElectrical testingAlgorithmWavelet packet transformation
A method for diagnosing analog circuit fault based on vector-valued regularized kernel function approximation, includes steps of: step (1) acquiring a fault response voltage signal of an analog circuit; step (2) carrying out wavelet packet transform on the collected signal, and calculating a wavelet packet coefficient energy value as a characteristic parameter; step (3) utilizing a quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm to optimize a regularization parameter and kernel parameter of vector-valued regularized kernel function approximation, and training a fault diagnosis model; and step (4) utilizing the trained diagnosis model to recognize circuit faults.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
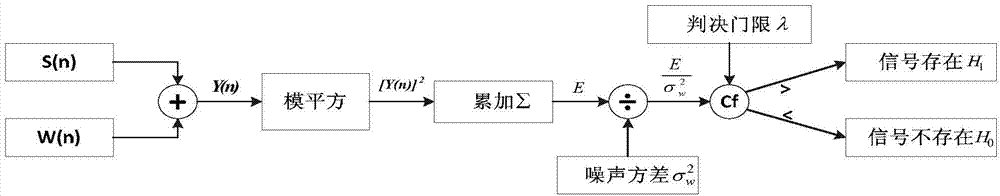
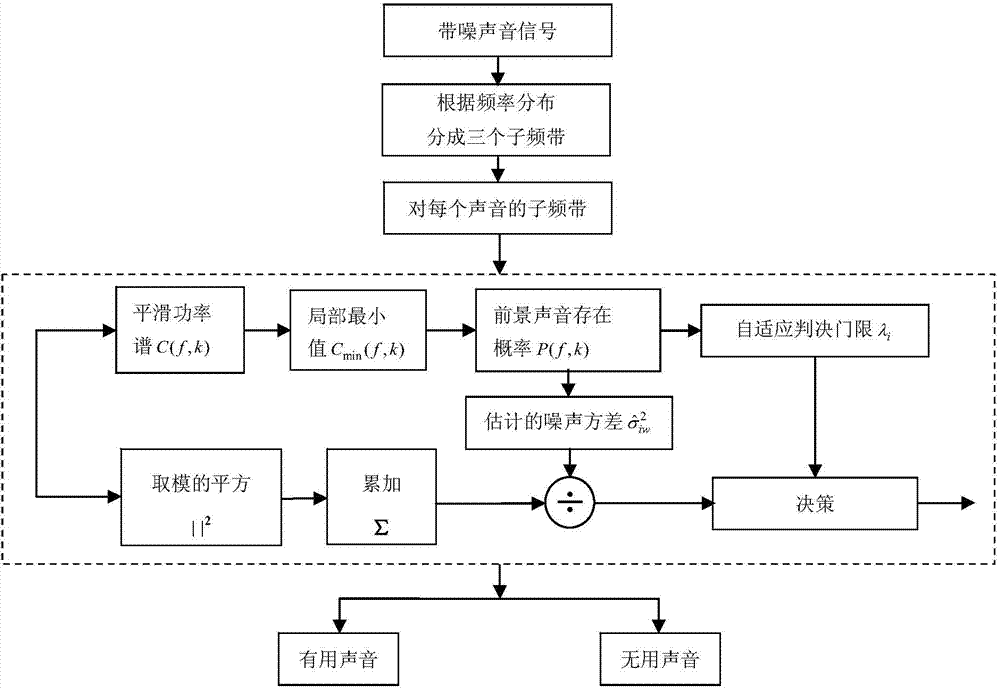
Twitter identification method based on self-adaption energy detection under complex environment
InactiveCN103489446AImprove efficiencyEasy to identifySpeech analysisPattern recognitionNoise power spectrum
The invention relates to a twitter identification method based on self-adaption energy detection under a complex environment. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of firstly, dividing twitter into three frequency bands according to the frequency distribution condition of the twitter; secondly, detecting twitter acoustical signals containing noise through a self-adaption energy detection method based on noise power spectrum estimation and the foreground sound existence probability, and screening out the useful twitter signals; thirdly, extracting Mel-scale WPSCC features from the useful twitter signals according to distribution of the Mel scales; fourthly, conducting modeling, classification and identification on the extracted Mel-scale WPSCC features and extracted Mel-scale MFCC features through an SVM classifier. The WPSCC features extracted through the method have a better anti-noise function and are better in identification performance after undergoing self-adaption energy detection, the method is more suitable for twitter identification under the complex environment and has a good classification and identification effect on the twitter sound containing noise under the complex environment.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
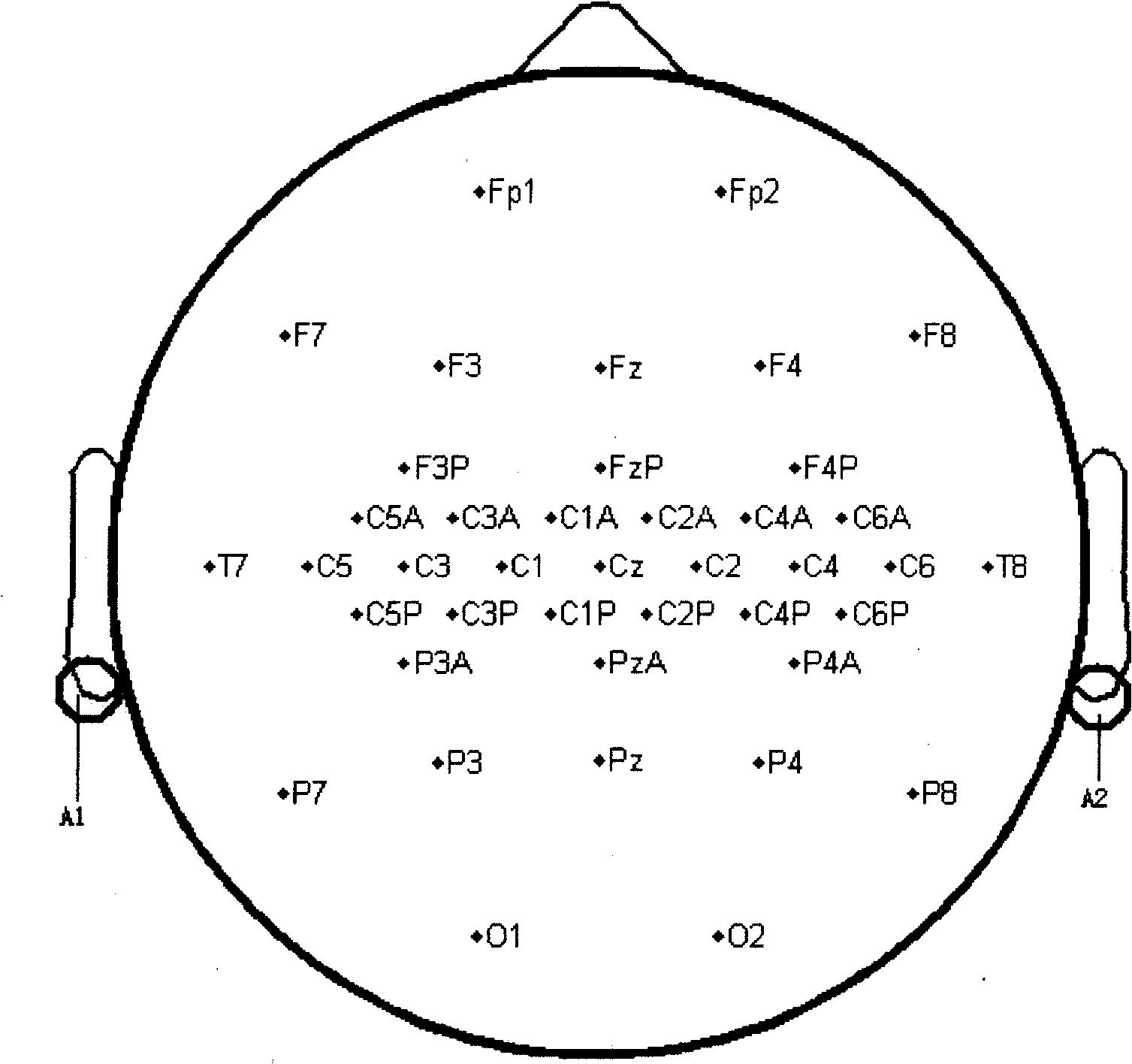
Method for capturing signals and extracting characteristics of stand imagination action brain wave
ActiveCN101352337ASignificant ERD/ERS phenomenonDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFeature extractionIndependent component analysis
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical engineering and computer, and relates to a signal collecting and characteristic extraction method used for standing imagining action electroencephalogram. The method of the invention mainly comprises the steps as follows: (1) collecting and pre-processing of standing imagining action electroencephalogram signals; (2) spatial gaining of characteristic small wave package; (3) independent component analysis of small wave package domain; (4) reconstruction of electroencephalogram signals; (5) signal extracting. The method of the invention solves the problem of exact extraction of the electroencephalogram characteristic in standing imagining electroencephalogram action, thus providing powerful supports for correctly recognising the lower limbs motion mode, effectively converting the mode into the control command applied to a lower limbs auxiliary recovery system and realizing the self-standing of the paraplegia patients.
Owner:中电云脑(天津)科技有限公司
Monitoring method for time reversal damage to no-datum Lamb wave of engineering structure
InactiveCN102998370AAchieving focus reconstructionEliminate scalabilityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEllipseEngineering
The invention discloses a monitoring method for time reversal damage to no-datum Lamb wave of an engineering structure. The monitoring method comprises the following steps of: distributing a group of excitation / sensing arrays on a structure to be monitored; building detection channels, and collecting Lamb wave response signals of all excitation / sensing channels; intercepting the response signals, and then conducting time reversal to obtain time reversal structure response signals; loading the time reversal structure response signals onto corresponding excitation, and collecting time reversal focusing structure response signals on the corresponding sensing; and in the time reversal focusing structure response signals of all the detection channels, extracting the occurrence time difference of focusing main wave crest and sidelobe signals, taking the occurrence time difference as a characteristic parameter, calculating to obtain the position and approximate range of the damage by adopting an ellipse positioning method, and analyzing and judging the health condition of the structure to be detected. With the method, the wave packet extension and signal aliasing caused by frequency dispersion can be eliminated, no-datum active positioning and detection to the Lamb wave can be realized, and the healthy monitoring practicalization of the structure can be benefited.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Ultrasonic scanning and detection method based on sonic time reversal method
InactiveCN102621223AImprove the problem of poor focusImprove signal-to-noise ratioAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationSound sources
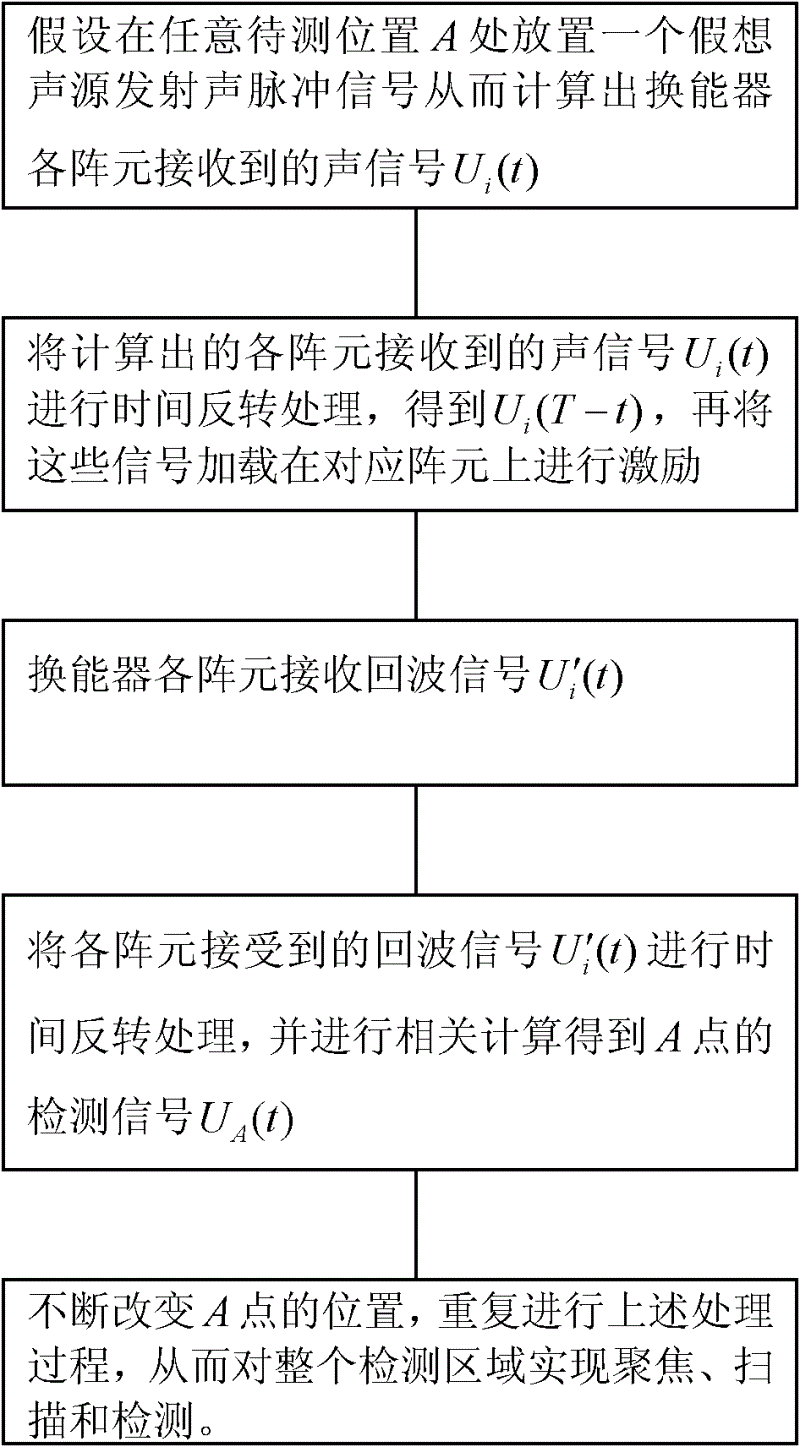
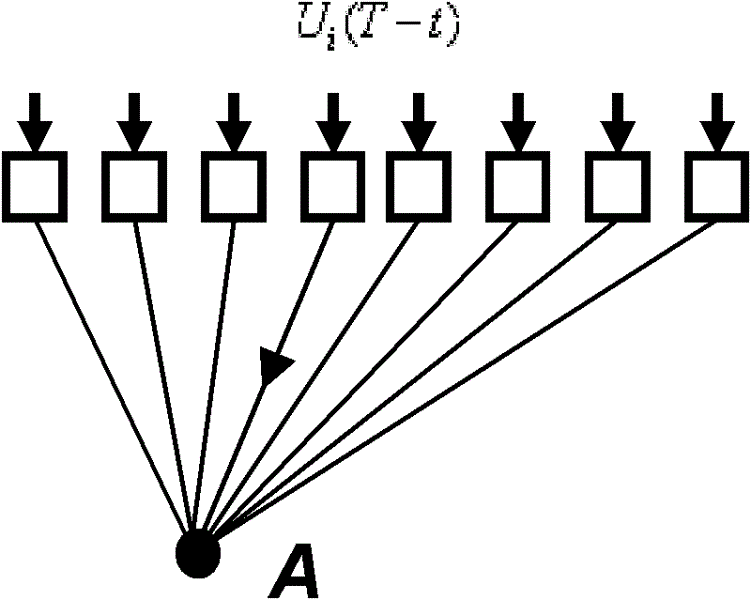
The invention provides an ultrasonic scanning and detection method based on a sonic time reversal method, comprising the following steps: arranging an imaginary sound source at a preset focal point to transmit sound pulses, calculating acoustical signals received by each array element of an energy transducer by a medium structure; carrying out time reversal treatment on the received acoustical signals, and using the acoustical signals as drive pulses to load on the corresponding energy transducer array elements for driving to allow a sound field to focus at the preset focal point; then receiving echo acoustical signals by each array element of the energy transducer, and collecting and storing; carrying out time reversal treatment on the echo acoustical signals, acquiring acoustical signals at the preset focal point by related calculation, using the acoustical signals as detection data to analyze and determine; continuously changing the position of the preset focal point, repeating theabove process, so as to scan and detect the whole detection area. The method utilizes sonic time reversal adaptive focusing and ultrasonic phased array scanning mode to realize ultrasonic scanning and detection of various wave packages which are simultaneously focalized, and high signal to noise ratio and image resolution can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
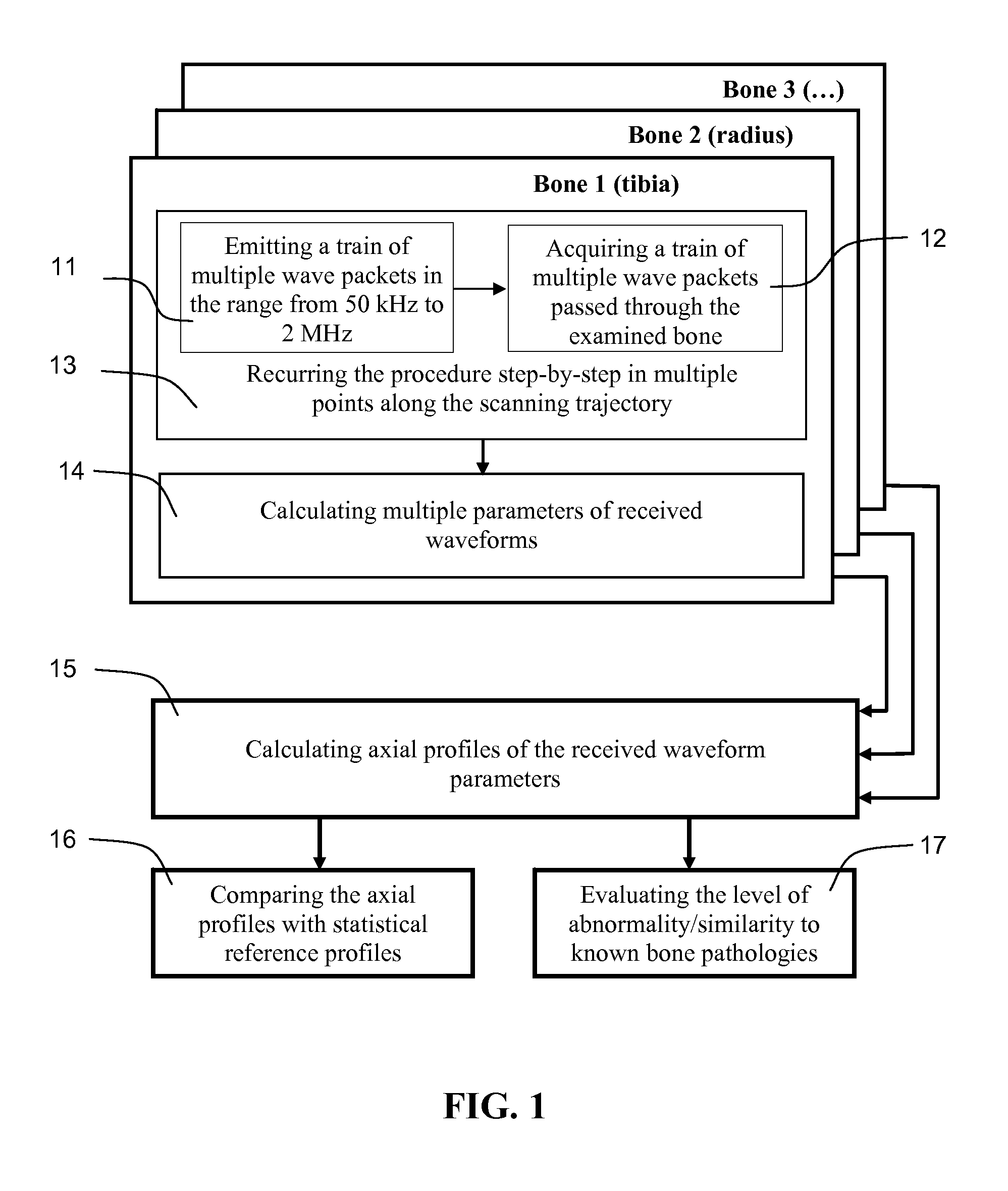
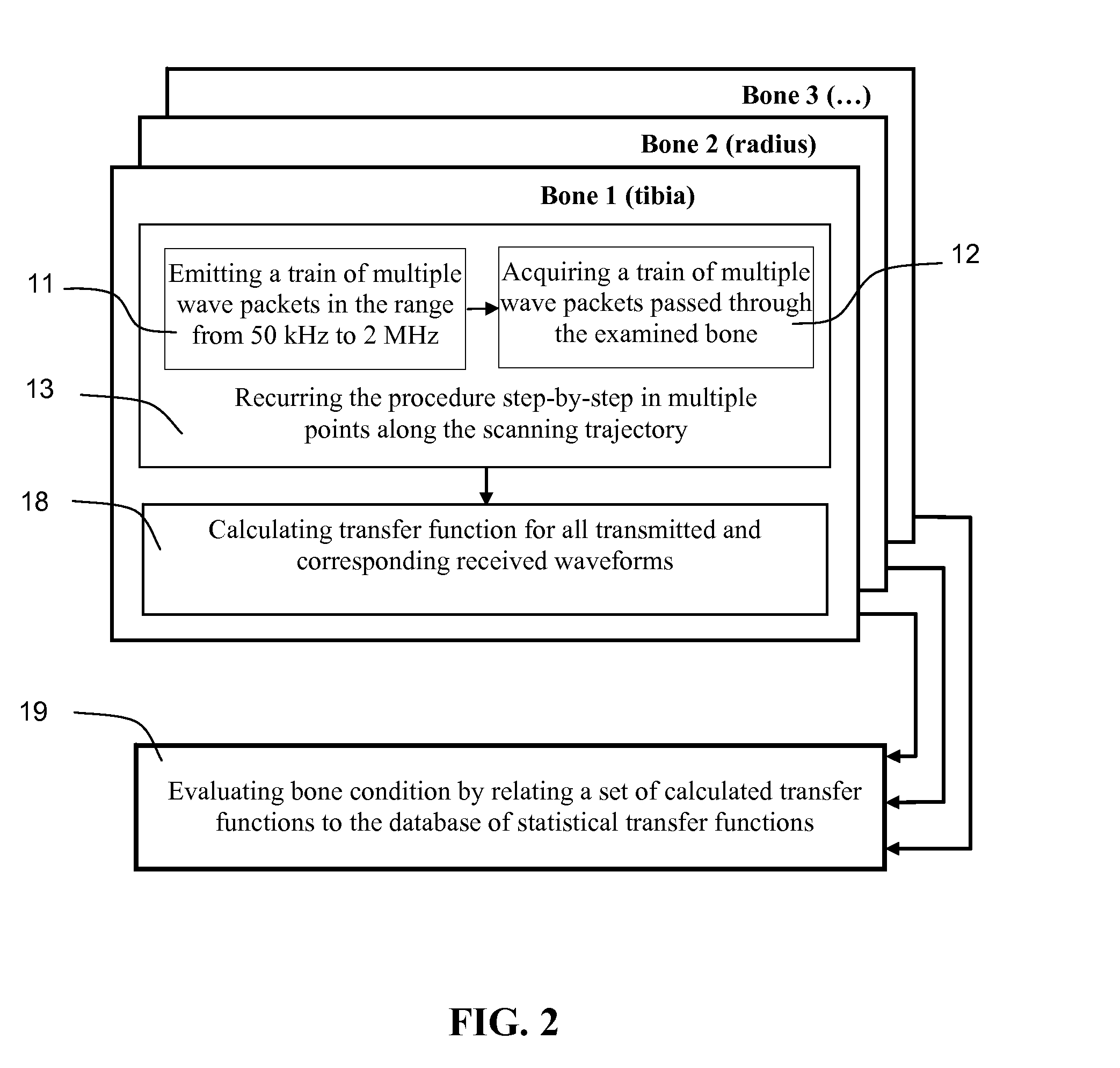
Ultrasonic method and apparatus for assessment of bone
InactiveUS20080097211A1Reliable identificationReduce errorsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationFeature extraction
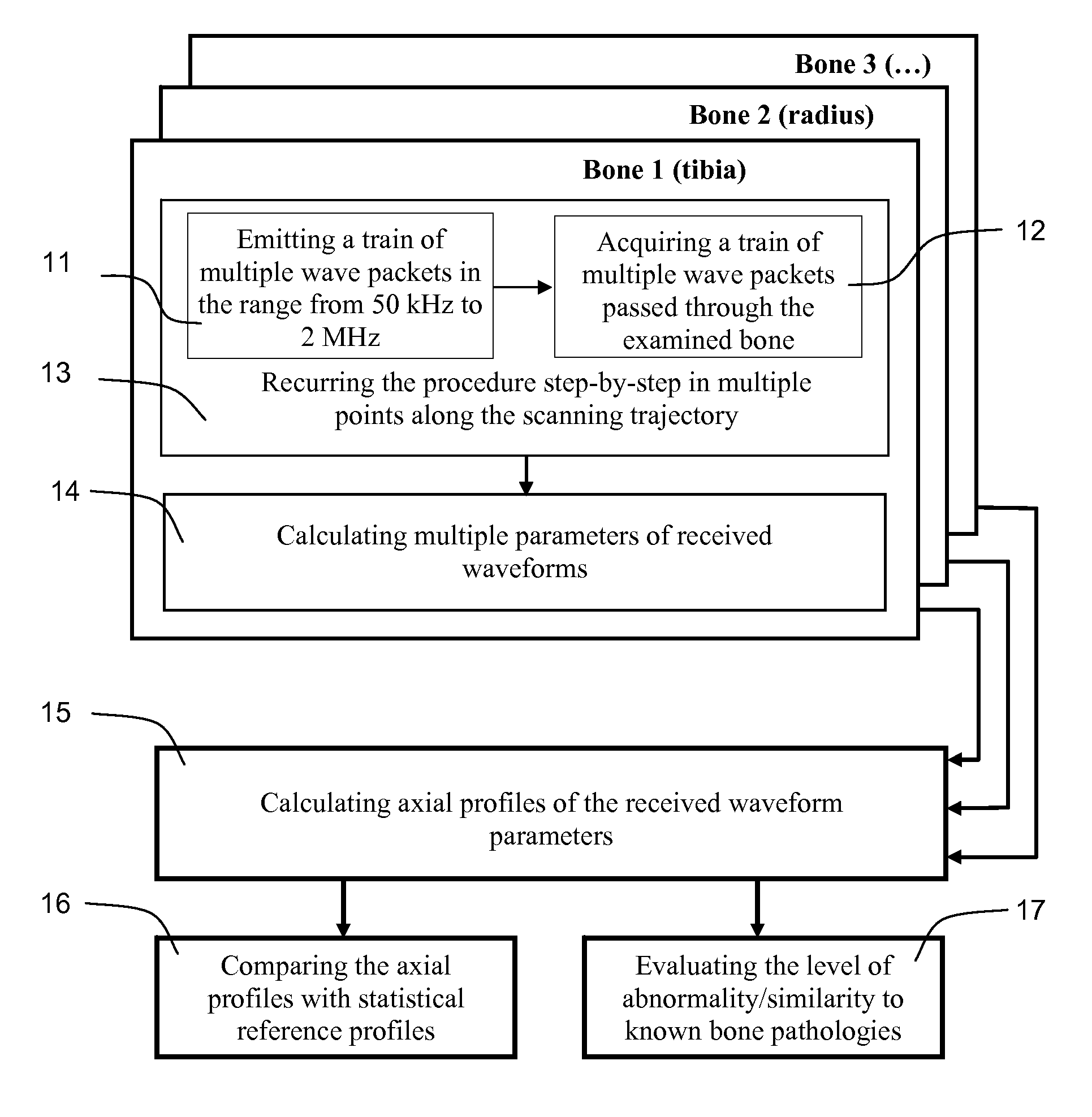
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for non-invasive bone evaluation based on a broadband ultrasonic transducer emitting a train of ultrasonic wave packets of multiple carrier frequencies ranging from about 50 kHz to about 2 MHz. Receiving broadband ultrasonic transducer accepts broadband ultrasonic signal propagated through the bone. Computer processing means provide for data analysis and feature extraction allowing diagnostic evaluation of the bone, including comparing the features of the received signal to a database of known bone conditions.
Owner:ARTANN LAB
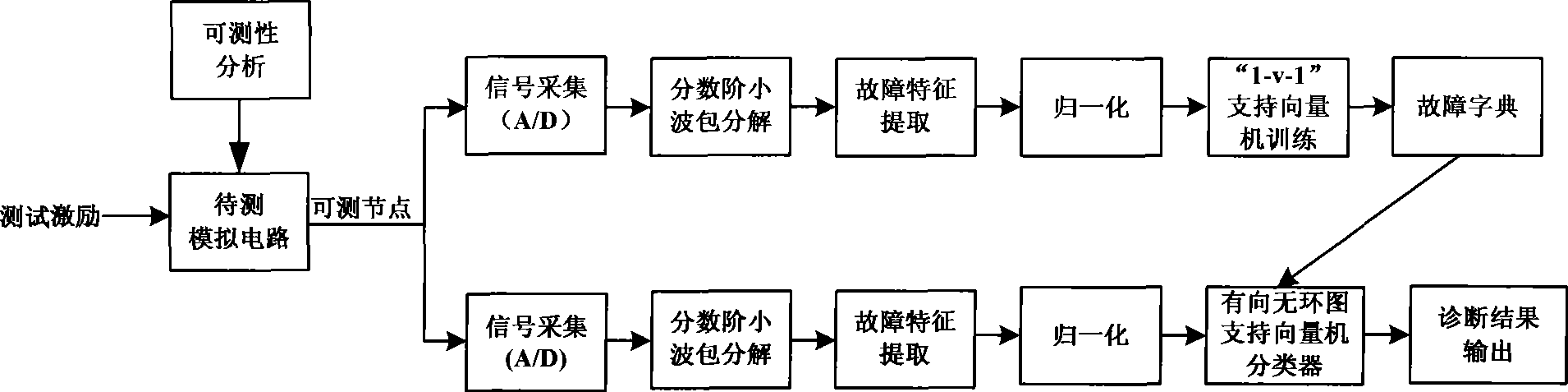
Analog-circuit fault diagnosis method based on DAGSVC
InactiveCN101533068AEfficient extractionSmall scaleAnalog circuit testingTest sampleImage resolution
The invention discloses an analog-circuit fault diagnosis method based on DAGSVC. The method comprises the following steps: applying certain test excitation to a analog circuit to be tested; acquiring circuit output response signals to be tested in a testable node of the circuit; performing multi-order fractional order wavelet packet (FRWPT) transformation on the acquired circuit output response signals and extracting fault characteristics so as to form a test sample; and performing calculation by utilizing fault-dictionary prestored information together with the DAGSVC to classify and position faults. The method has the advantages of global training optimality, fewer needed training samples, high fault-information resolution and the like, and can improve the precision and efficiency of diagnosing the faults of analog circuits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
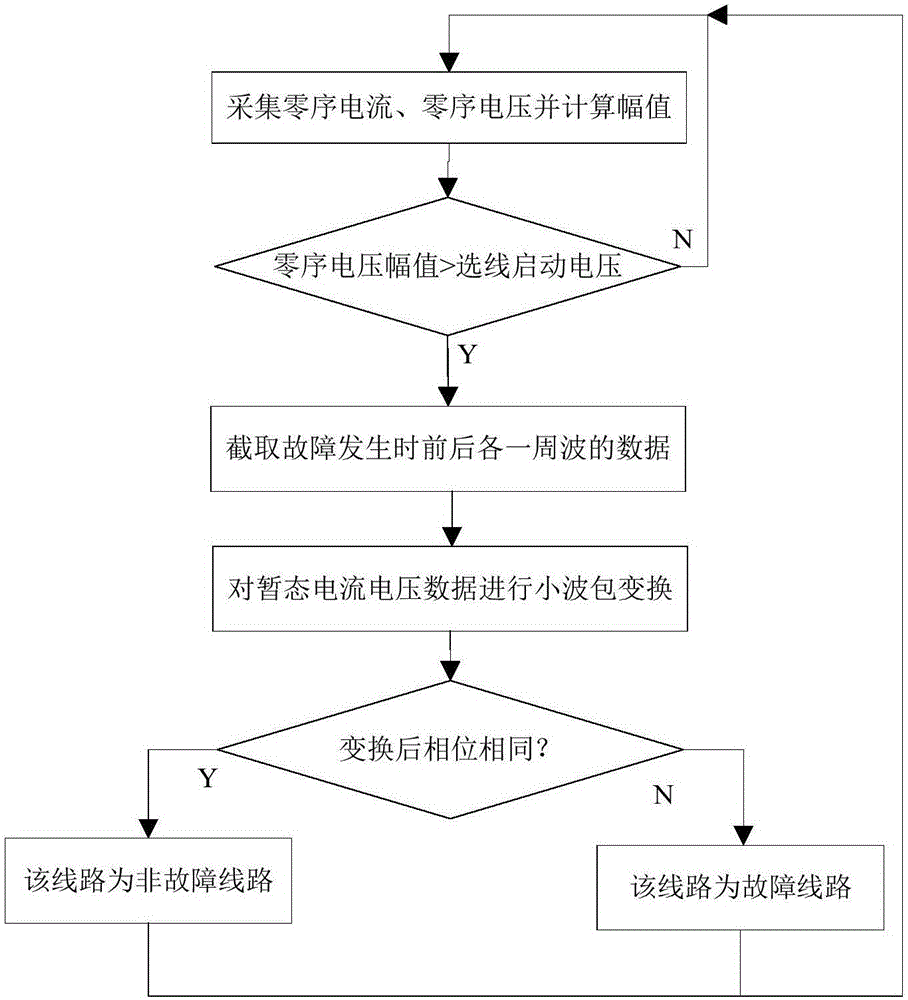
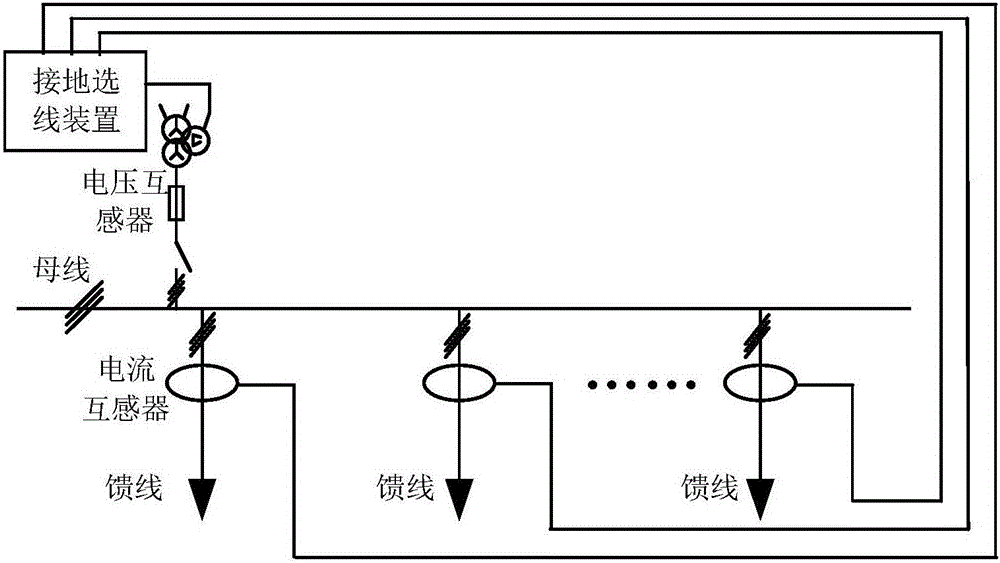
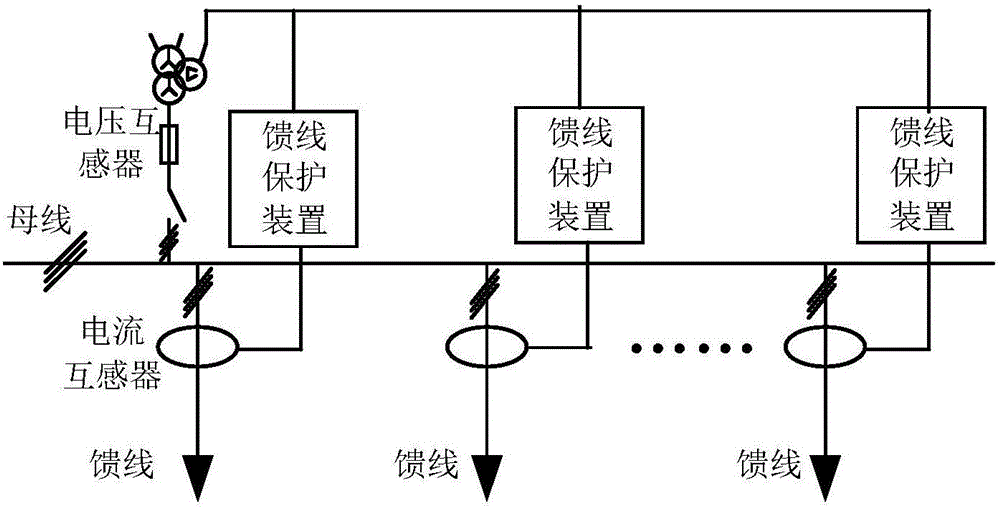
Single-phase grounding line selection method for small-current grounding system
InactiveCN106324432ARich in transient componentsSolve the problem of inaccurate line selectionFault location by conductor typesTransient stateEngineering
The invention discloses a single-phase grounding line selection method for a small-current grounding system, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting the zero sequence voltage of a bus or an outgoing line and the zero sequence current of the outgoing line, and calculating the amplitude of the zero sequence voltage in real time; 2, determining that the bus or the outgoing line has a single-phase grounding fault when the amplitude of the zero sequence voltage is greater than the amplitude of a line selection start voltage, and switching to step 3; 3, extracting the data of zero sequence current and voltage of a cycle before a moment when a fault happens and a cycle after the moment of the fault happens, and carrying out the wavelet packet transformation of the data of transient zero sequence voltage and current; 4, comparing the phases of the transient zero sequence current and voltage after the wavelet packet transformation: determining that a line is not a fault line if the phases are the same, and determining that the line is a fault line if the phases are opposite, thereby completing the grounding line section. The method solves a problem of a higher line selection misjudgment rate caused by that the phases and amplitudes of the zero sequence currents of the fault line and the non-fault line when a conventional arc suppression coil grounding system has a single-phase grounding fault.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Three-phrase pulse-width modulation (PWM) rectifier fault diagnosis method based on wavelet packet analysis and support vector machine
InactiveCN103116090AOvercoming the large amount of dataThe kernel function is simpleElectrical testingDiagnosis methodsEnergy spectrum
The invention discloses a three-phrase pulse-width modulation (PWM) rectifier fault diagnosis method based on wavelet packet analysis and a support vector machine. The three-phrase PWM rectifier fault diagnosis method based on wavelet packet analysis and the support vector machine includes the steps: first, building a three-phrase PWM rectifier, determining classification principles and utilizing a wavelet packet arithmetic to analyze a direct current side output voltage of the rectifier; then, conducting energy spectrum and power spectrum analysis on a rebuilt small signal, determining a fault characteristic vector and building a data sample; and finally, choosing a support vector machine kernel function and a parameter, and building a multiple-value classifier so as to achieve fault diagnosis of the three-phrase PWM rectifier. The three-phrase PWM motor-generator set fault diagnosis method based on wavelet packet analysis and the support vector machine can improve fault diagnosis rate of the three-phrase PWM motor-generator set, avoid the problems of the data process and optimization of the traditional test method and effectively improve safety of an electric and electronic rectifier device.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for predicating critical instability of brittle material through using energy characteristic value of acoustic emission signal
InactiveCN104965026APredict critical instabilityMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesInstabilityWavelet
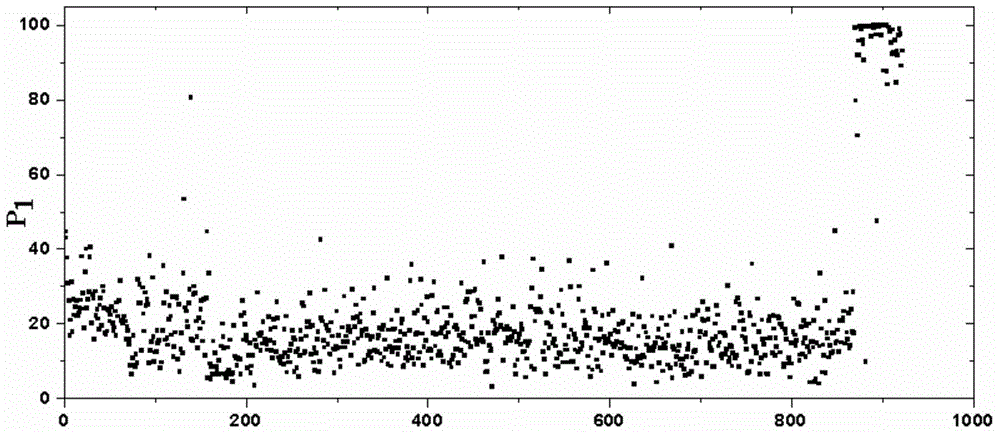
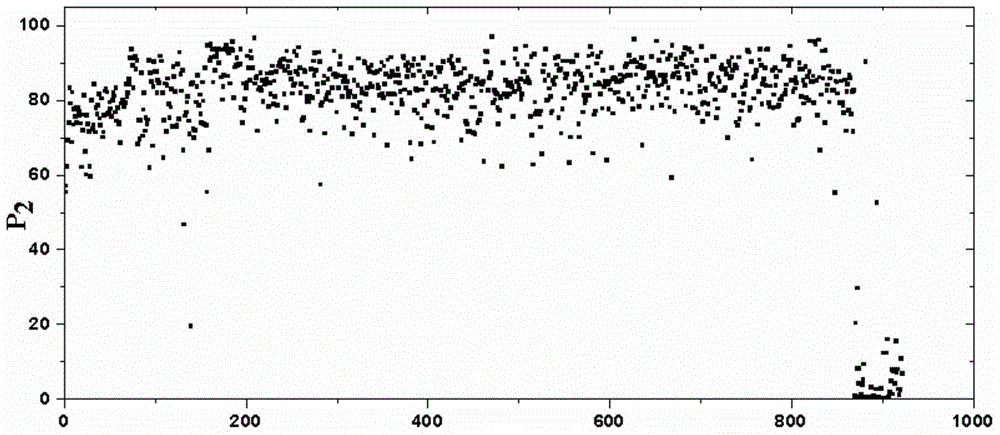
The invention relates to a method for predicating the critical instability of a brittle material through using the energy characteristic value of an acoustic emission signal, and belongs to the technical field of material damage detection. The method comprises the following steps: arranging an acoustic emission sensor on a brittle material to be monitored, and acquiring an acoustic emission signal; 2, selecting a small wavelet base according to the waveform characteristic of the acoustic emission signal; 3, carrying out first grade wavelet packet decomposition on the acoustic emission signal to obtain a low frequency range signal and a high frequency range signal; 4, respectively calculating the energy characteristic values P1 and P2 of the low frequency range signal and the high frequency range signal; 5, respectively drawing the statistical charts of the energy characteristic value P1 of the low frequency range signal and the energy characteristic value P2 of the high frequency range signal; and 6, judging whether the brittle material to be monitored is in a critical instability state or not according to the change state of the P1 and the P2. The method overcomes the disadvantages of an acoustic emission parameter analysis method and a fast Fourier transform analysis method, monitors the destroy process to the material in real time, can visually determines the danger degree before expansion of cracks, and can predict the critical instability state of the material.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Super broad coverage multiple beam bathymetric side scanning sonar device
InactiveCN101149436AImprove surveying and mapping efficiencyHigh measurement accuracyMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsProcess systemsEngineering
This invention provides a kind of over-square overlay multi-wave-packet sound side sonar equipment. It includes the water extension 1, underwater extension 2 and the cable 11 and 12 connects them; the water extension 1 is mainly an embedded integral control machine, combines the signal process system 6, the left signal collection and pre-process system 7, the right signal collection and pre-process system 8 and the left signal conditioning system 9, the right signal conditioning system 10; the underwater extension 2 is composed of the left acoustics warehouse 3 and right acoustics warehouse 4, the left acoustics warehouse 3 is the same with the right acoustics warehouse 4, they are set symmetrically. This invention can gets the over-square overlay underwater land form and physiognomy information , improves the ocean mapping effect and measure precision; it creates the result image such as the digital sound data and side image and so on, to make the system has the detection ability of microtopograghy and small target.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Linear frequency modulation (FM) signal parameter estimation method based on small-wave-packet denoising and power spectral entropy
InactiveCN102508206ASmall amount of calculationReal-time estimateWave based measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Curve fitting
The invention aims at providing a linear frequency modulation (FM) signal parameter estimation method based on small-wave-packet denoising and power spectral entropy, which includes the following steps: denoising signals in a multi-dimension small-wave-packet mode, and determining small-wave-packet function and small-wave-packet decomposition level; calculating power spectral entropy of signals denoised in a small-wave-packet mode, and setting an entropy feature data base of linear FM signals with different FM slope under the condition of different signal to noise ratios; carrying out interpolation operation for obtained discretized entropy features; fitting the curve after interpolation of a cubic spline function with a polynomial function, and obtaining FM slop of linear FM signals under the condition of different signal to noise ratios and relational expression with input entropy features; and estimating FM slop of linear frequency modulation (LFM) signals received by a receiver by utilizing the fit expression. The linear FM signal parameter estimation method based on small-wave-packet denoising and power spectral entropy is small in calculated amount and capable of estimating FM slop of LFM in real time under the premise of meeting the requirement for parameter estimation accuracy.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Ultrasonic flow meter with digitally under-sampled flow measurements
ActiveUS20140318268A1Little developmentMitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or more disadvantages of flow metersVolume/mass flow measurementFluid speed measurementPropagation timeAcoustic wave
The invention relates to a method of operating an ultrasonic flow meter by digitally sampling received signals. Acoustic wave packets are transmitted through a measuring distance in opposite directions, and the received signals are digitized at a sampling frequency being below the Nyquist-limit of two times the signal frequency of the wave packet to generate digitized under-sampled signals 31. From the digitized under-sampled signals, the difference in propagation time along the measuring distance is determined.
Owner:KAMSTRUP
A multichannel speech enhancement method using postfilter
InactiveCN1523573AEfficient removalImprove speech enhancement performanceSpeech analysisTime domainTime delays
The invention discloses a kind of voice enhancing method which uses postposition filter, it includes following steps: 1) calculates the time delay of voice signal in each channel; 2) aligns each channel in time domain through delay compensation; 3) carries on wave-packet formation to signal in each channel with wave-packet producer; 4) estimates the self power spectrum and noise including signal self power spectrum of purified voice signal, gets the frequency response function of Wiener filter; it obtains the self power spectrum estimation through eliminating the noise self power spectrum estimation from noise including signal cross-power spectrum; 5) uses the postposition Wiener filter to carry on filter to wave-packet producer, realizes the enhancement of voice. The invention considers the correlation of each channel noise, this accords the reality condition, especially it can eliminate the noise in low frequency , enhances the effect of voice enhancing.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wave packet superposition microseism ground location method
ActiveCN103399300AHigh precisionSolving Polarity Reversal IssuesPosition fixationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
The invention relates to a wave packet superposition microseism ground location method. The method comprises the following steps of (a) dividing a model into a plurality of grids, and giving a threshold value for a number of iteration and an external enveloping superposition value; (b) selecting a detector, calculating a time for a microseism event in a designated grid to reach each designated detector, and correcting the time difference; (c) getting a root-mean-square amplitude of the corrected signal of the detector, solving external envelop, and adding the external envelops together to get an external enveloping superposition channel; (d) changing the grid, calculating the external enveloping superposition channel of the detector in a novel designated grid, traversing all grids to get the external enveloping superposition channel set; (e) picking up the microseism event on the external enveloping superposition channel set, and determining a position of the microseism; (f) calculating a signal-to-noise ratio of the picked microseism event; (g) repeating the steps of (b) to (f) until meeting the number of the iteration to obtain multiple microseism event positions, and counting the percentage of the times on each position in the total times; and (h) determining the microseism event exceeding the threshold value as a microseism valid event.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
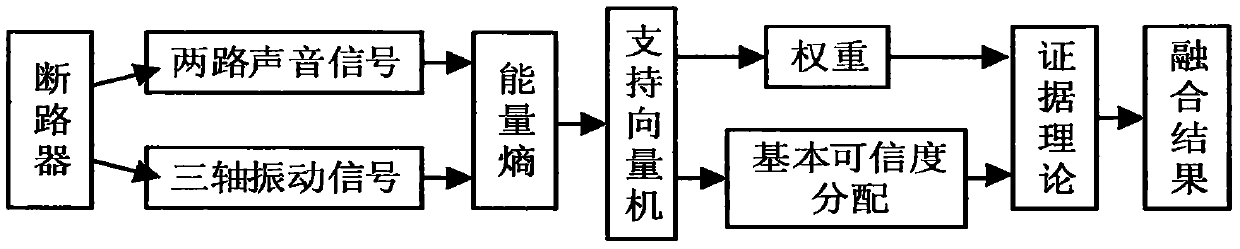
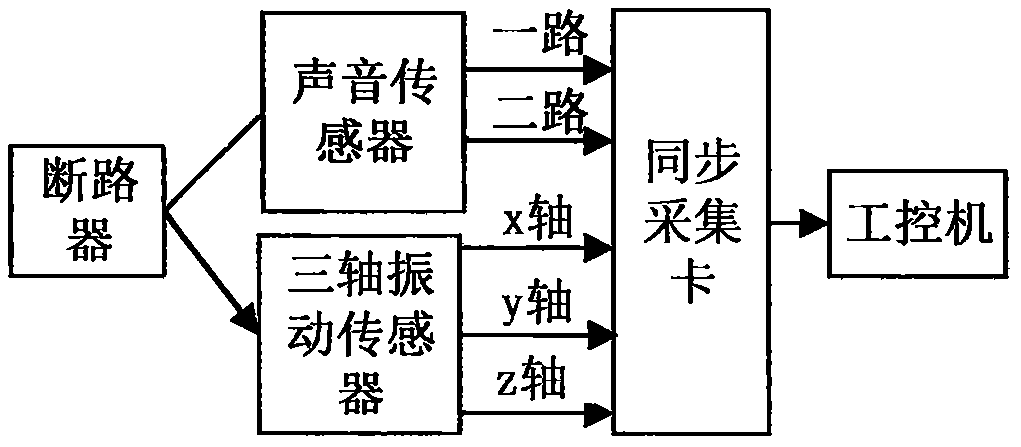
Circuit breaker fault diagnosis method for sound and vibration signal fusion processing
The invention discloses a circuit breaker fault diagnosis method for identifying a circuit breaker fault diagnosis based on sound and vibration signal fusion processing. There are four states: stuck fault, base loose fault, and refusal to move fault. (2) Step 2, use the db3 wavelet base to decompose the acoustic and vibration signals into three layers, and reconstruct the signals on the eight nodes in the third layer; perform the Hilbert transform on the reconstructed signals of the eight nodes , to obtain the modulus envelope. (3) The envelope signal is divided into 3 sections according to the principle of before opening, during opening and after opening. According to the principle of equal energy, it is divided into 3 sections before opening, 9 sections during opening, and after opening It is divided into 3 sections, and the energy entropy of the wavelet packet square difference of each state of the circuit breaker is extracted. (4) Input the feature vector matrix of each signal into the support vector machine and use the "one vs one" voting strategy to obtain the basic probability distribution. (5) Using improved evidence theory to fuse multi-sensor information to identify circuit breaker fault types.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
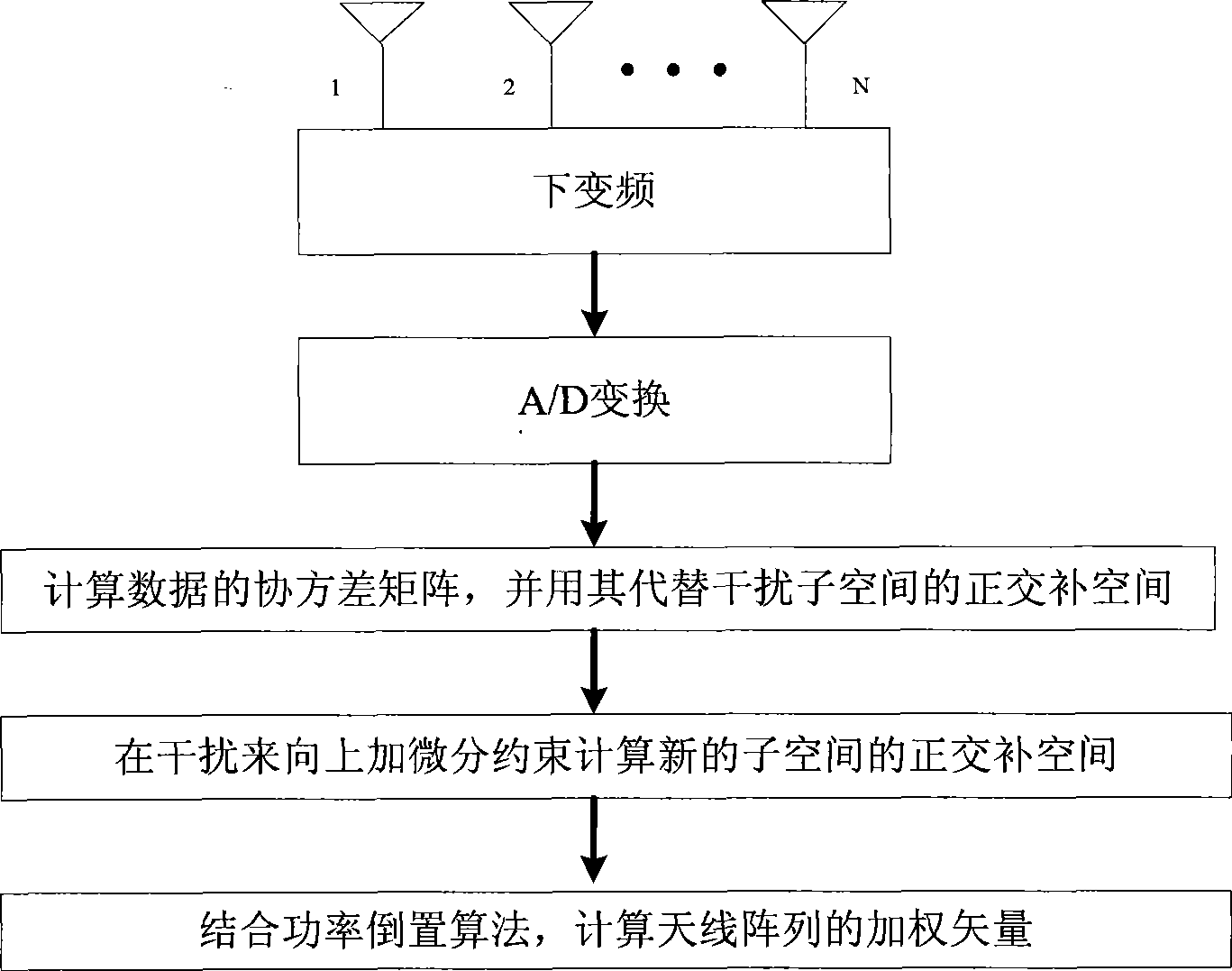
Trough widened interference suppression method of high-dynamic satellite navigation system
InactiveCN101482605AIncreased output signal stemIncreased output signal-to-interference ratioBeacon systems using radio wavesIntermediate frequencyArray element
The invention discloses a high dynamic satellite navigation system interference suppression method widening zero defect, the method comprises: respectively down-frequency conversing N ways of radio frequency signals received by the N (N>2) element aerial array into IF signals; respectively performing the A / D conversion for the IF signals in the N ways obtained by the down-frequency conversion; obtaining the orthogonal complement space of the interference subspace based on the relation between the interference power and the satellite signal and the noise power, by using the N ways IF digital signals obtained in the step 2; calculating the new orthogonal complement space of the subspace relating to the differentiation order, the array element position and the interference subspace based on the differential constraint principle; combining the new orthogonal complement space of the subspace and the power invert algorithm to calculate the weighting vector of the aerial array based on the wave packet zero defect width setting proportionality coefficient to be reached by using the obtained new orthogonal complement space of the subspace in the step4. The invention can enable the output signal inference ratio of the satellite navigation receiver under high dynamic environment to be obviously increased, and can reduce the mis-capturing rate of the satellite signal by the satellite navigation receiver under high dynamic environment.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
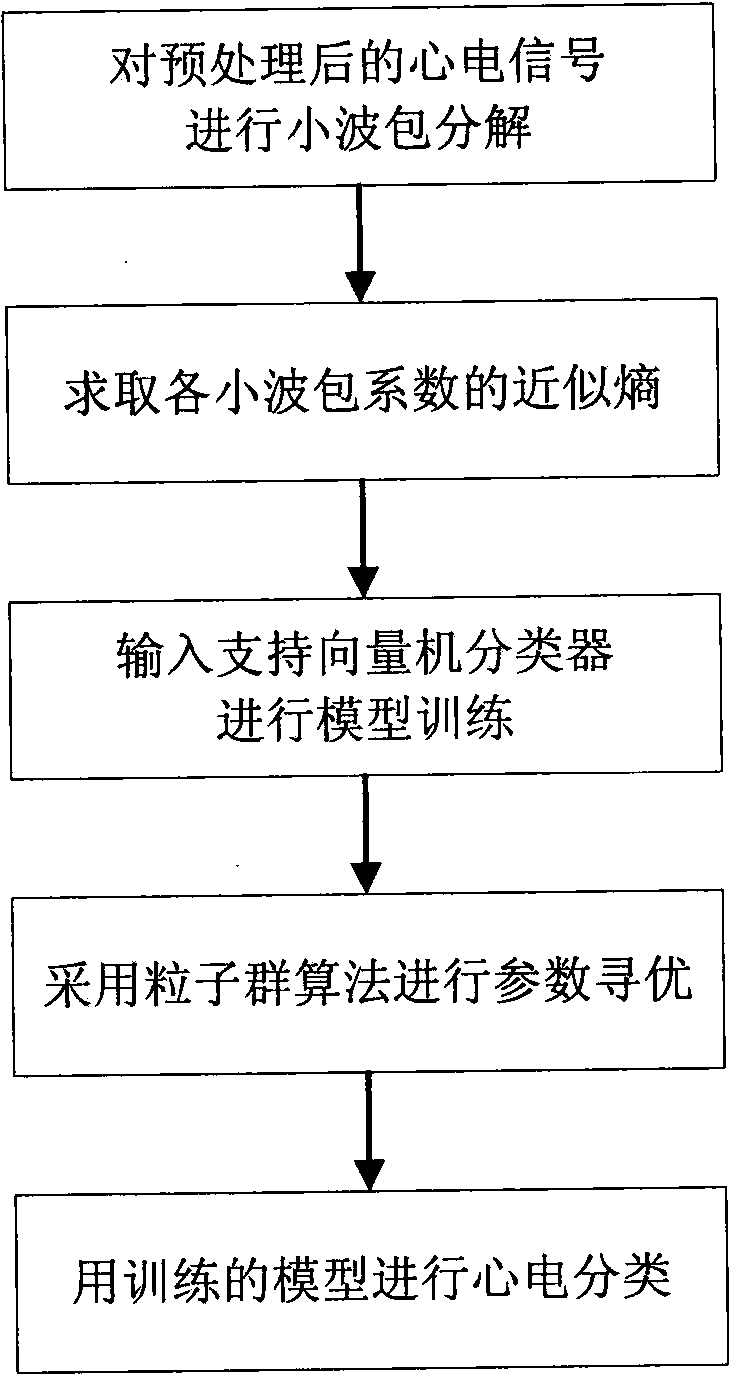
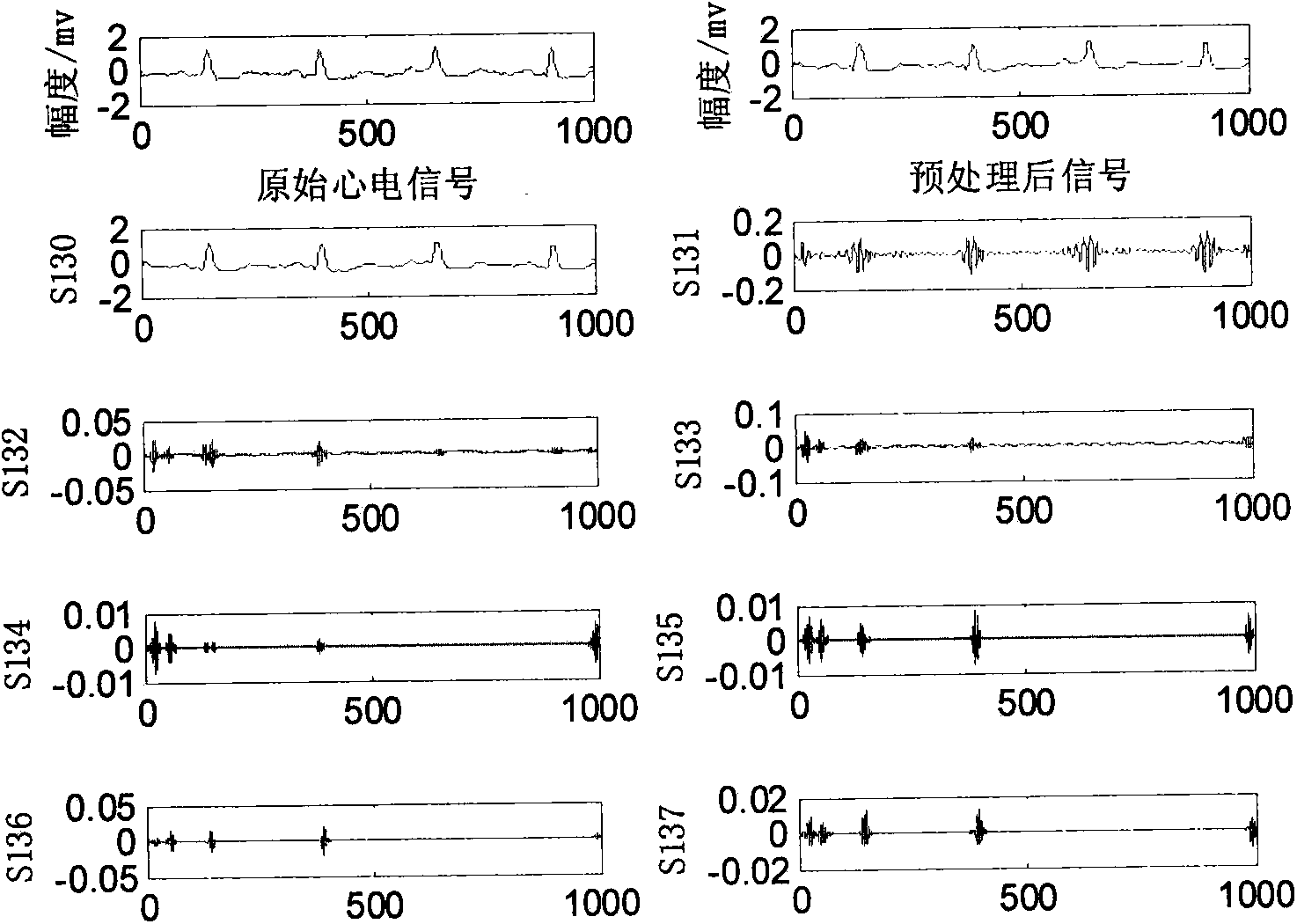
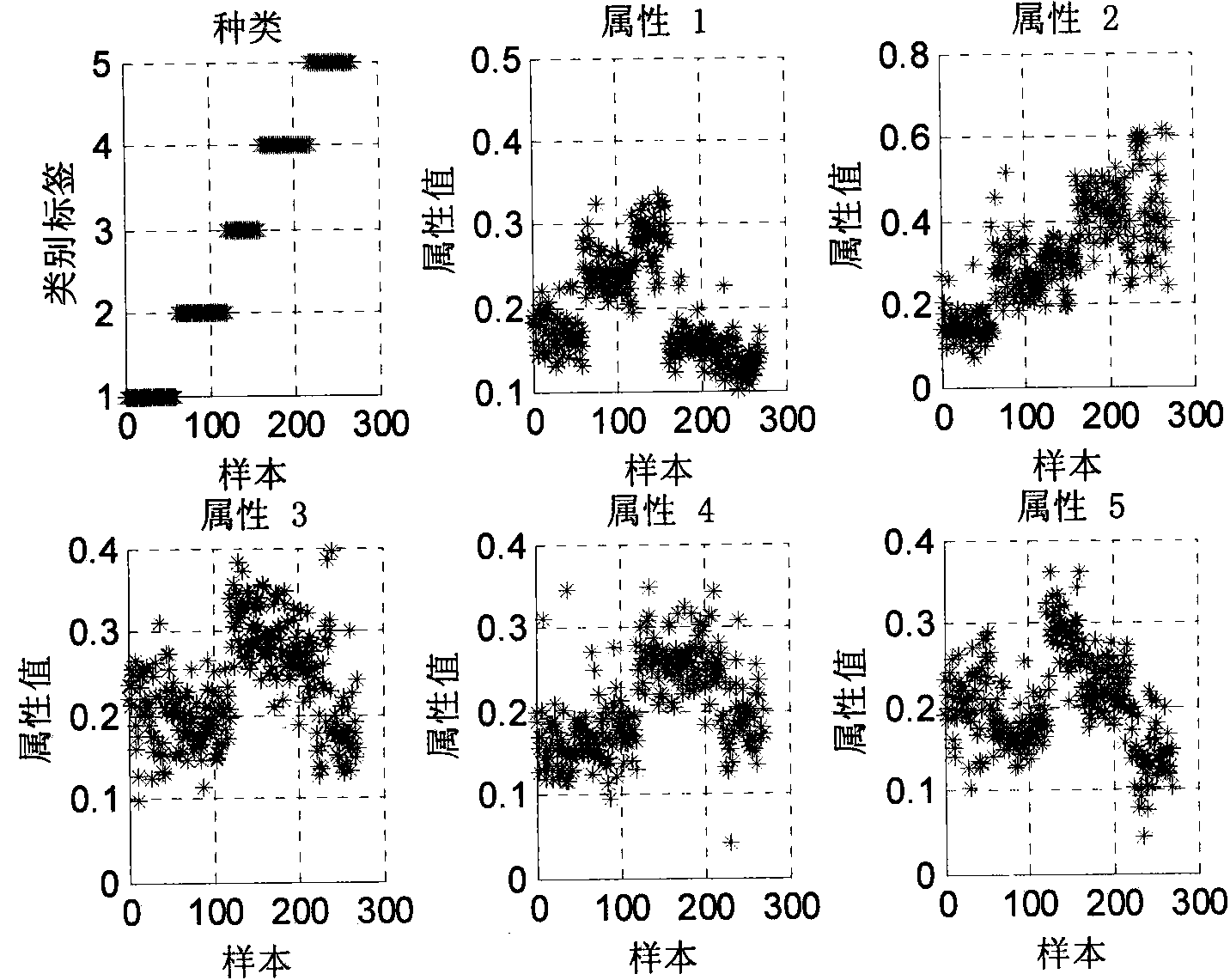
ECG signal classifying method based on wavelet packet and approximate entropy
InactiveCN103927556AImprove efficiencyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionEcg signalFeature vector
The invention discloses an ECG signal classifying method based on a wavelet packet and approximate entropy. The method comprises the steps that wavelet packet decomposition is conducted on preprocessed ECG signals, the wavelet packet coefficients of all nodes are extracted, and then the approximate entropy of all the wavelet packet coefficients is calculated; the obtained approximate entropy is used as a feature vector to be input into a support vector machine classifier, a particle swarm algorithm is used for seeking the optimal parameter of the support vector machine classifier, and various ECG signals are classified. Wavelet packet decomposition is an effective method for analyzing non-stationary signals. The approximate entropy can be used for obtaining stable estimation values only by a small amount of data, good noise-proof and anti-interference capacity is achieved, and the approximate entropy can both be used no mater what the signals are, stochastic or deterministic. According to the ECG signal classifying method, an algorithm for extracting feature vectors is simple, dimensionality reduction in a traditional method is of no need, the speed is high, consumed time is small, the classifying accuracy is high, and the ECG signal classifying method is suitable for an ECG automatic analysis auxiliary diagnosis system.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
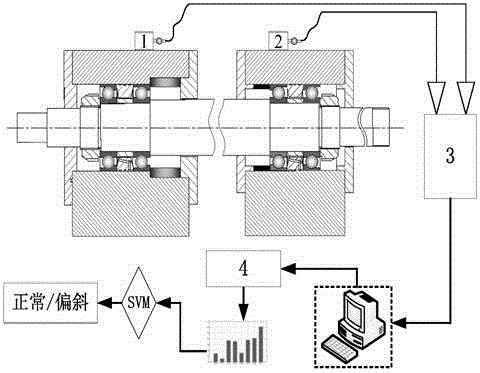
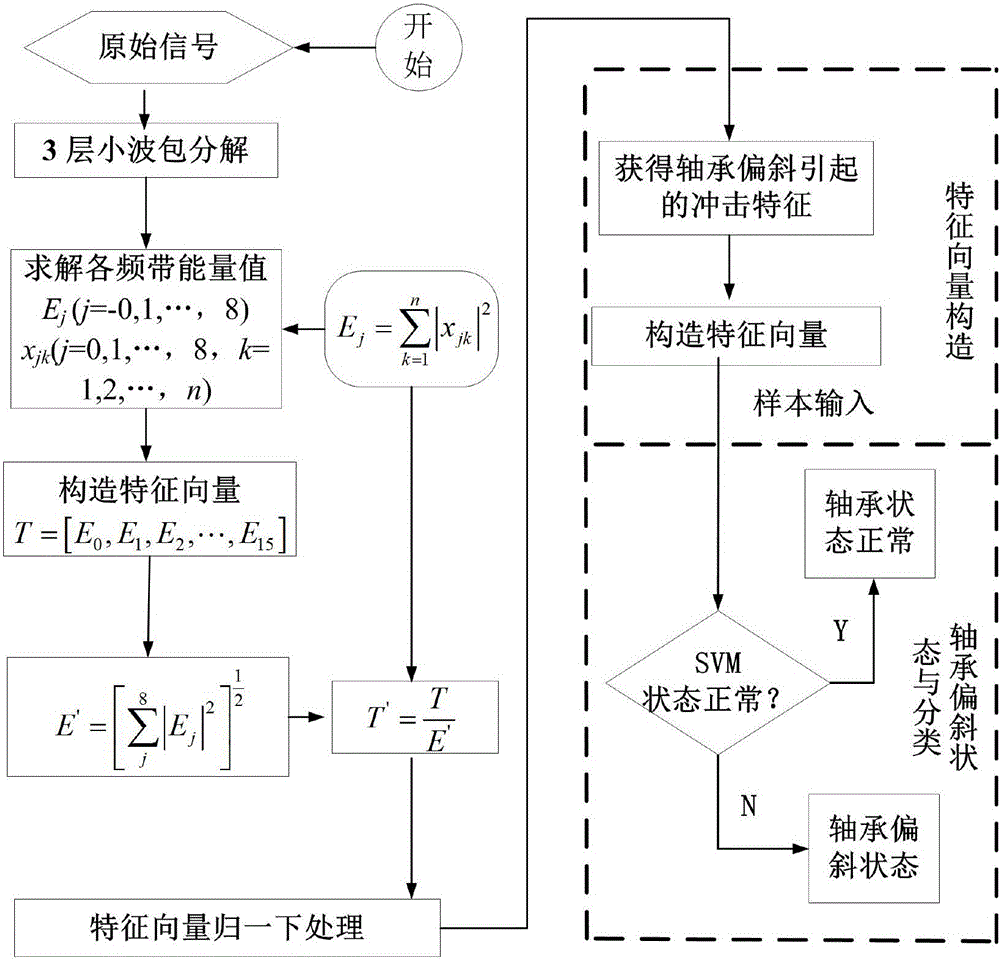
Wavelet-packet-and-support-vector-machine-based on-line detection method for assembling state of main shaft bearing of machine tool
InactiveCN106092578AAccurate identificationMachine bearings testingFeature vectorSupport vector machine
The invention relates to a wavelet-packet-and-support-vector-machine-based on-line detection method for an assembling state of a main shaft bearing of a machine tool. The method comprises: step 1, a vibration acceleration sensor is used for collecting vibration signals of a rolling bearing in a normal operation state and a non-normal operation state; step 2, noise elimination processing is carried out on the collected vibration signal and signal wavelet packet reconstruction is carried out on the vibration signals after noise elimination; step 3, m-layer wavelet packet decomposition is carried out on the reconstructed vibration signals, wherein a decomposition signal in each frequency band represents vibration information of the reconstructed signal in a frequency range; step 4, normalization processing is carried out on feature vectors corresponding to all frequency band energy values and a new feature vector is constructed; and step 5, on the basis of the new feature vector, the new feature vector serving as a sample is inputted into a classifier established by using a support vector machine to carry out training, thereby obtaining a trained SVM diagnosis model. Therefore, on-line detection and diagnosis are carried out on an assembling state of a main shaft bearing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ultrasonic guided-wave based calculation method for separating flexural mode reflected signal
ActiveCN104833729AGet reflection coefficientSave human effortProcessing detected response signalWave structureSonification
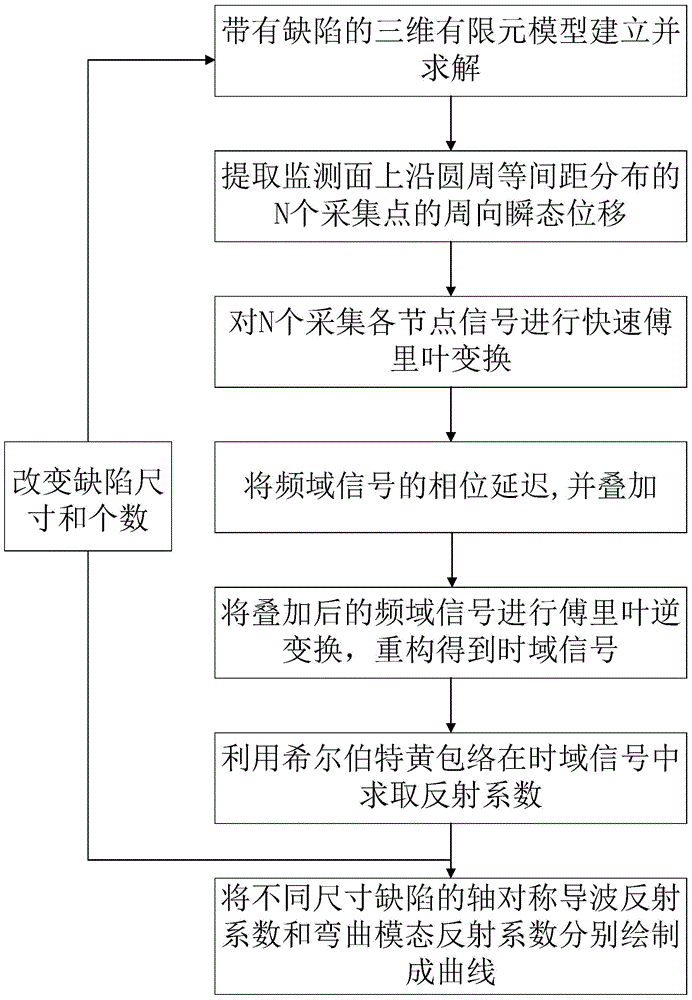
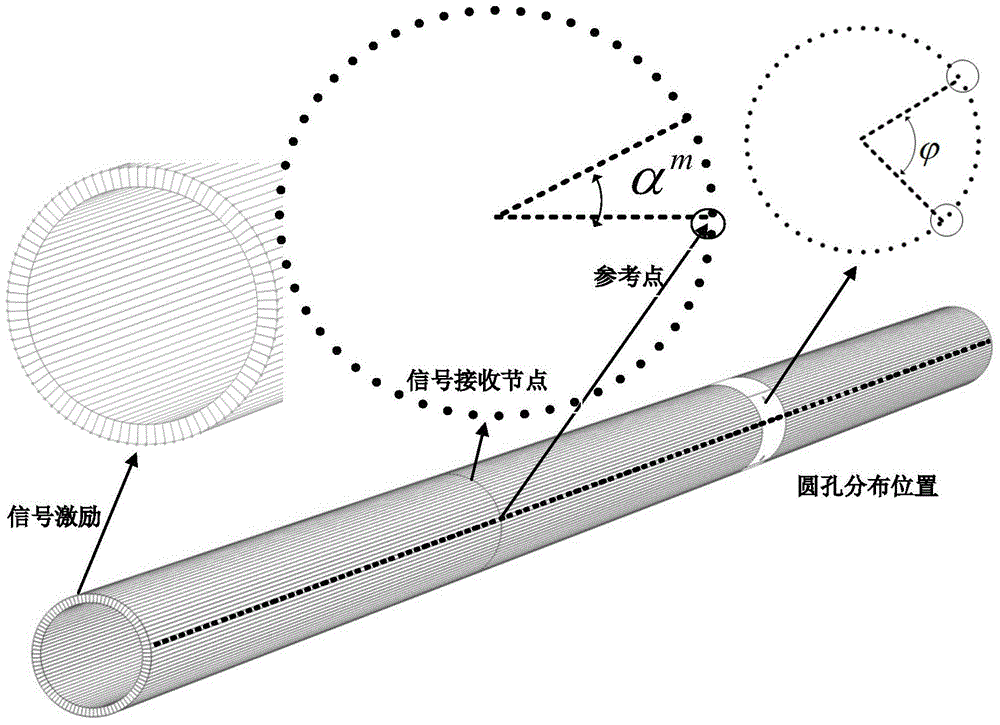
The present invention discloses a calculation method for separating symmetric and flexural mode wave packet and extracting weak signal of the bending mode. Based on the wave structure characteristic theory of axisymmetric mode and bending mode, the method uses finite element software to establish correlative model, extracts transient displacement signal of signal acquisition nodes of a guided-wave monitoring surface, and conducts delay superimposing on the collected signals on the frequency domain in accordance with relative formula; then the superimposed frequency domain signal is subjected to the inverse Fourier transform to obtain guided-wave mode wave packet of each order after separation; and Hilbert-Huang envelope is employed to calculate reflection coefficient for each mode. The method uses secondary development function of finite element software to compile the secondary development program, quantitatively analyze the influence degree of the parameters such as characteristics of defect size, location distribution, the number of defects and the center excitation frequency on the amplitude value of the flexural mode reflection echo generated from the defect locations through modal conversion, thereby integrally utilize reflection coefficients of axisymmetric mode and bending mode to evaluate the distribution of defect locations.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for quantitatively identifying rolling bearing damage
InactiveCN1811377AEffectively match fault signaturesImproving the accuracy of early damage identificationUsing mechanical meansSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionBearing vibration
The present invention discloses a method for quantitatively identifying rolling bearing damage. Said method includes the following steps: making rolling bearing vibration signal undergo the process of second generation small wave packet decomposition; then respectively reconstructing decomposed signal of every frequency band; utilizing Hilbert conversion and demodulation to analyze every frequency band signal to obtain envelope spectrum correspondent to frequency band signal; calculating decibel value of envelope spectrum magnitude correspondent to rolling bearing failure characteristic frequency in every frequency band, extracting maximum value of decibel value correspondent to failure characteristic frequency in every frequency band, then quantitatively identifying rolling bearing early damage condition.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
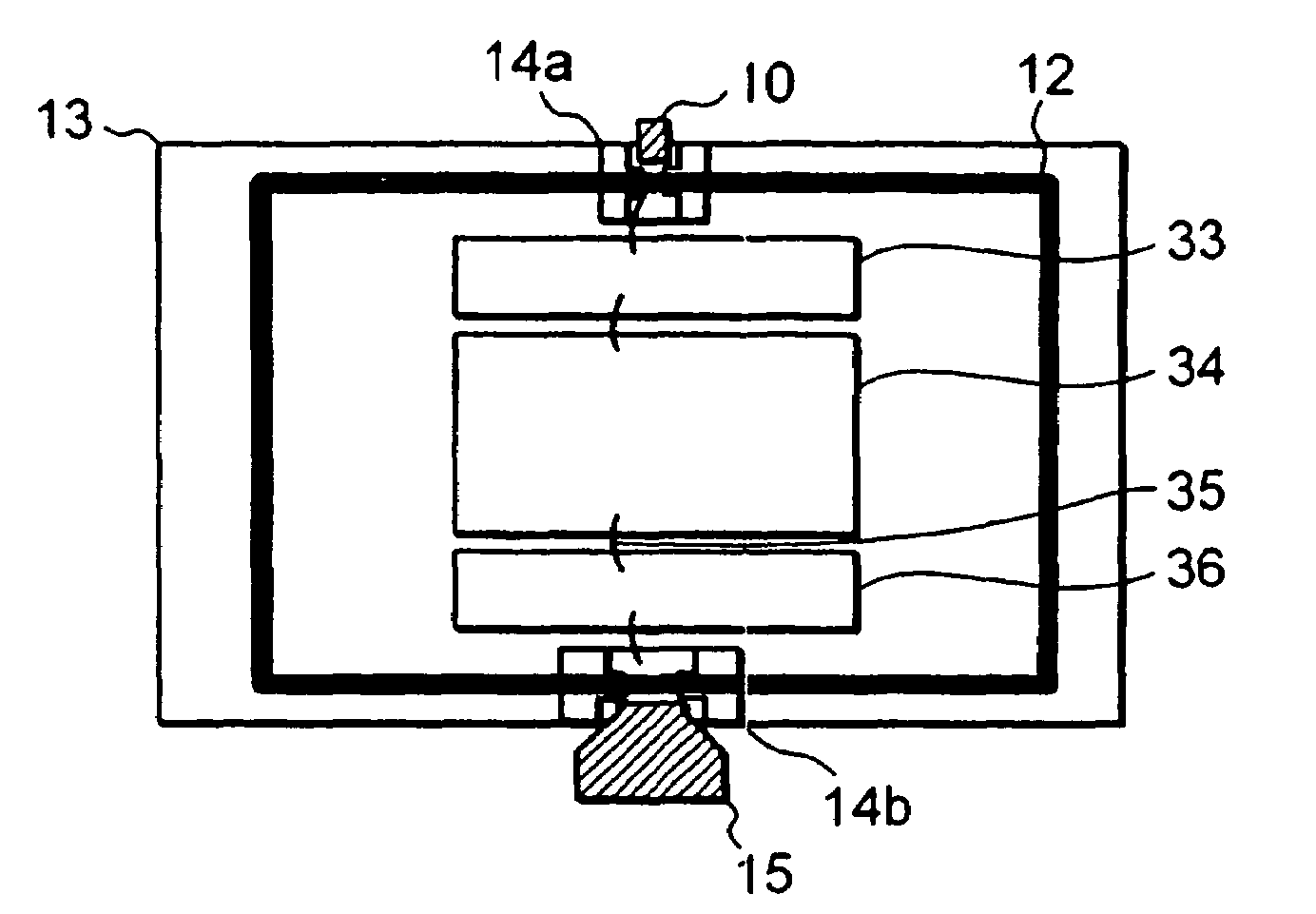
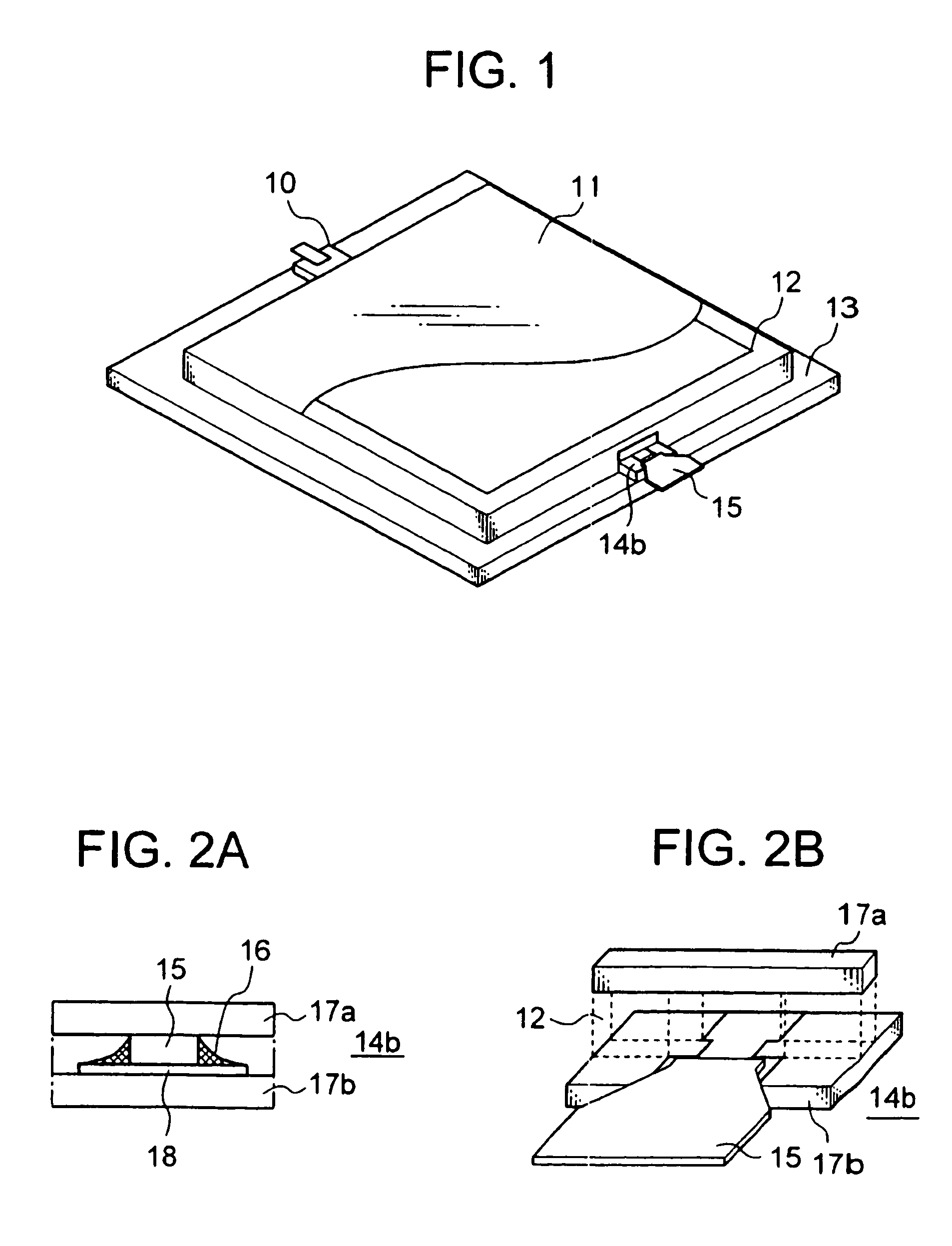
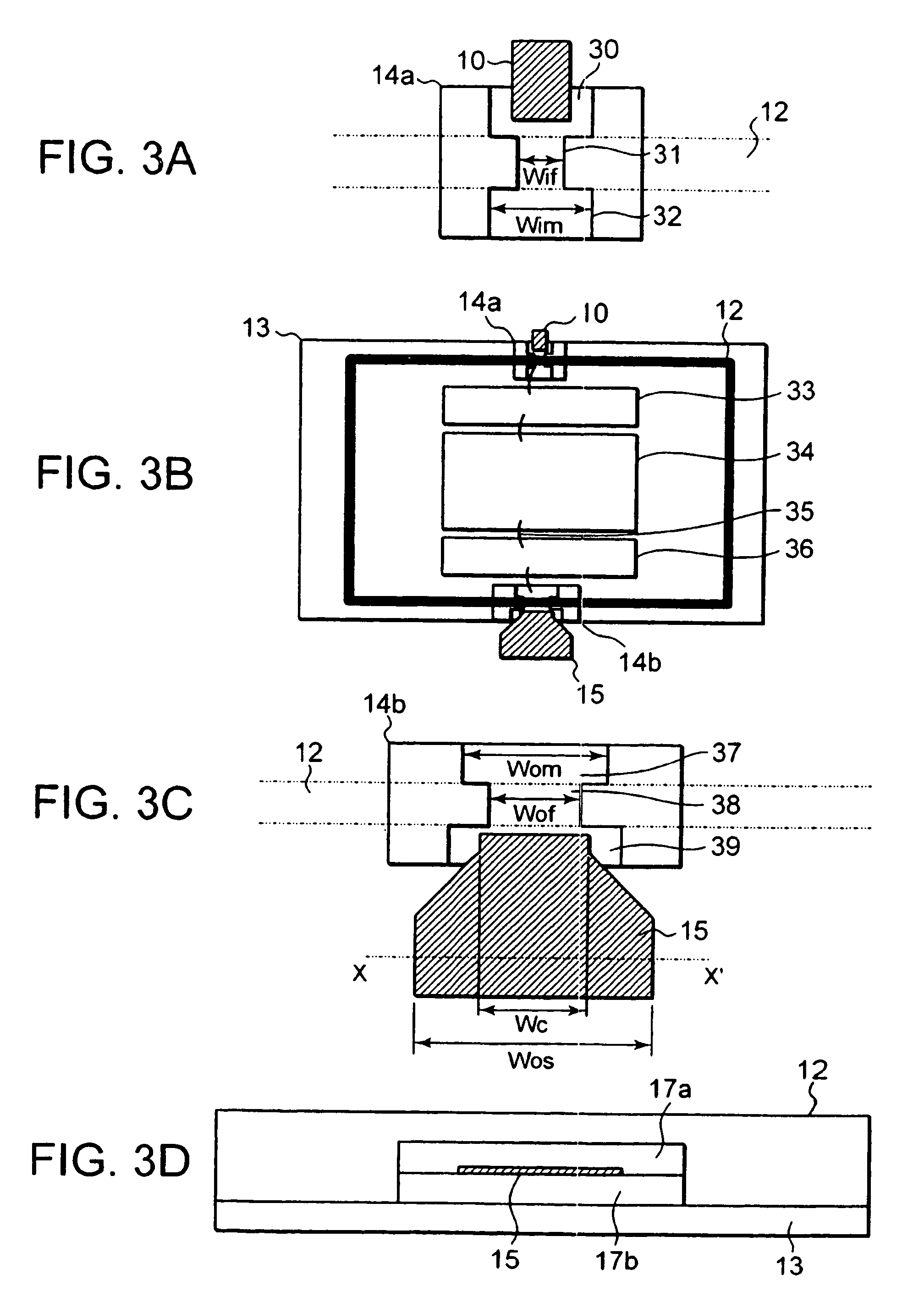
Package for high frequency waves containing high frequency electronic circuit
ActiveUS7486157B2Increase capacityMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
In an embodiment of the invention, a package for high frequency waves mounted by a high frequency electronic circuit comprises an hermetic box-shaped high frequency package containing a high frequency electronic circuit in the inside and shielded by a conductor, an input terminal and an output terminal partly led out to the outside of the high frequency package, an input side feed-through section having one of its opposite ends connected to the input terminal and the other end connected to the high frequency electronic circuit and having a predetermined characteristic impedance; and an output side feed-through section having one of its opposite ends connected to the output terminal and the other end connected to the high frequency electronic circuit and having a characteristic impedance lower than the characteristic impedance of the input side feed-through section as viewed from the output terminal side.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
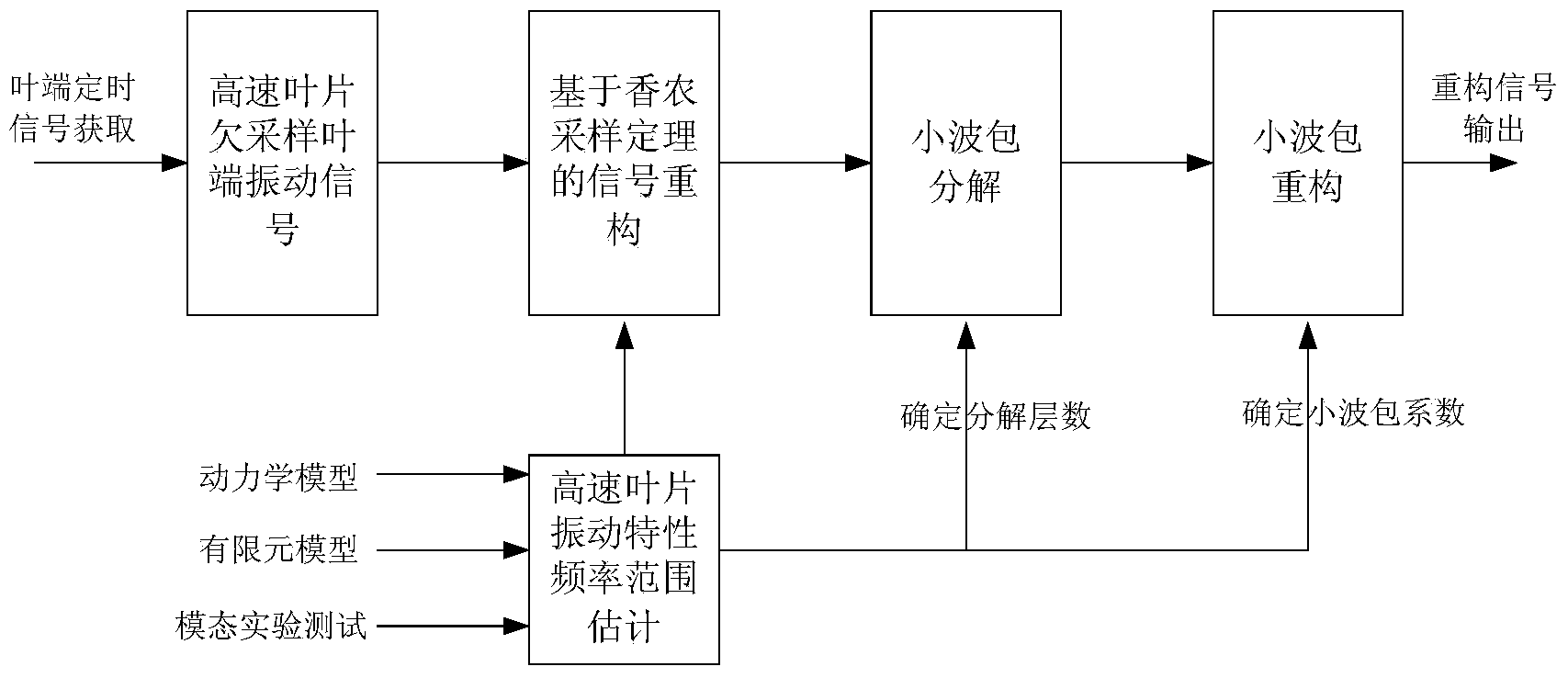
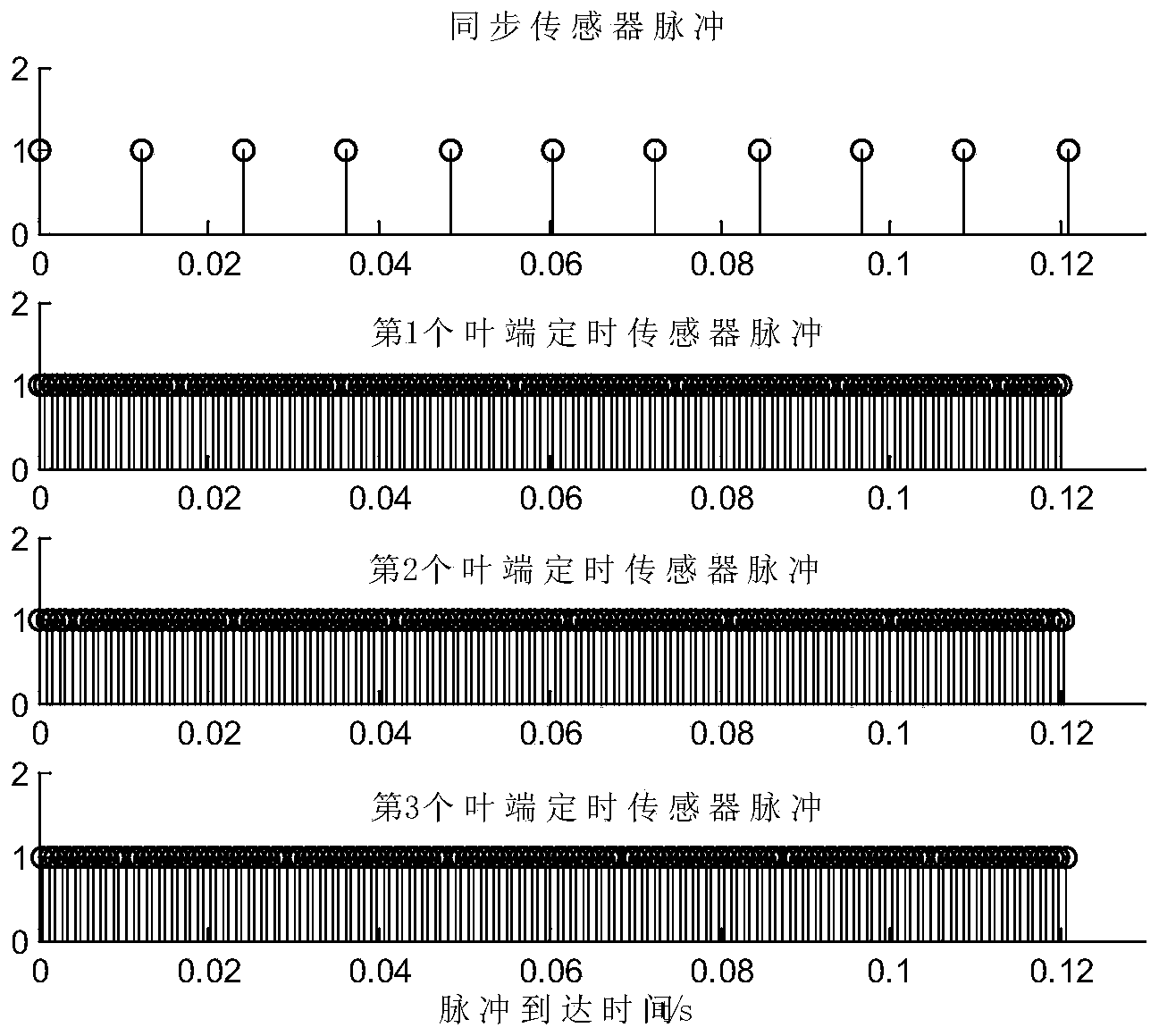
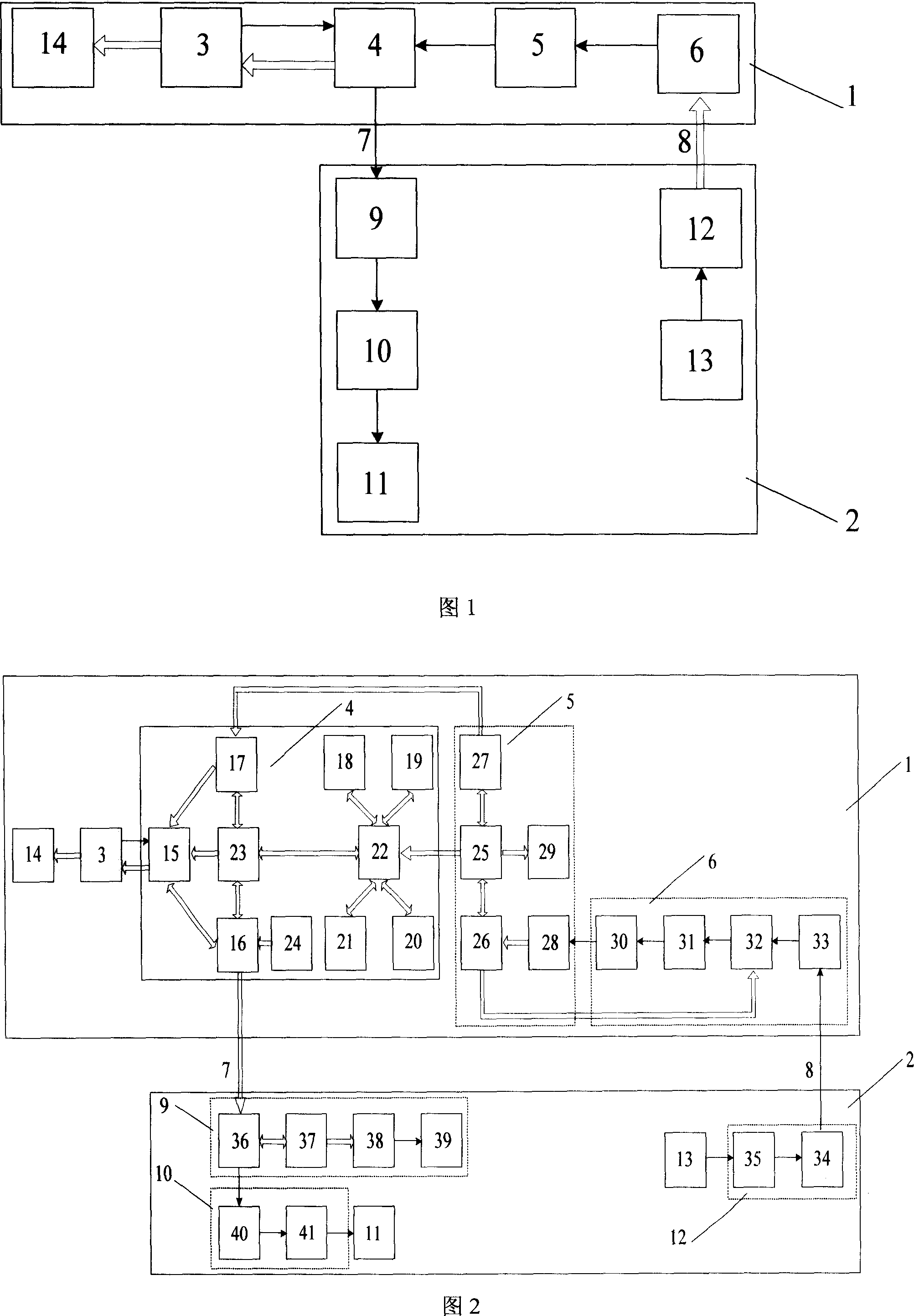
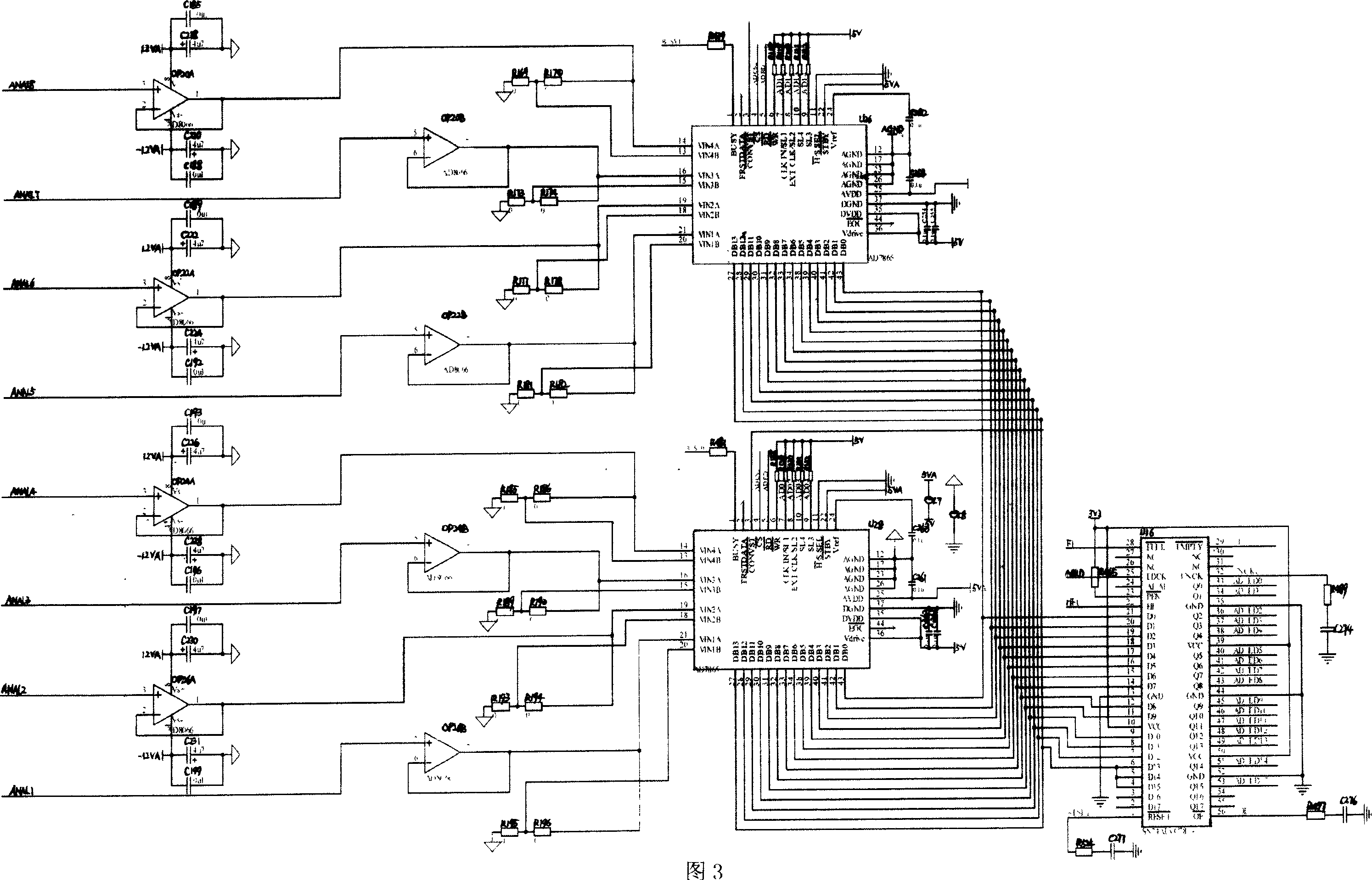
Non-aliasing reconstruction method of high-speed leaf undersampled leaf apex vibration signals
ActiveCN103471703ANo biasNo aliasingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansReconstruction methodReconstruction algorithm
The invention discloses a non-aliasing reconstruction method of high-speed leaf undersampled leaf apex vibration signals. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a leaf apex timing signal acquisition system is used for obtaining undersampled leaf apex vibration signals, (2) the frequency band range of high-speed leaf vibration performance is determined, (3) leaf apex vibration signals are reconstructed for the first time based on the Shannon sampling theorem, (4) proper wavelet packet decomposition layer numbers are determined to enable the assigned frequency band range is consistent with one frequency band after wavelet packet decomposition, (5) signals in the assigned frequency band range are reconstructed again from the reconstructed signals hat(z)[n] at the first time using wavelet packets, (6) the coefficients of wavelet packets except for the Rth wavelet packet are all set to be zero, and the traditional wavelet packet reconstruction algorithm is utilized for reconstructing signals in the frequency band range of [f0-B0 / 2, f0+B0 / 2]. The non-aliasing reconstruction method is simple in process and easy to realize, reconstructed signals are not deflected and not in aliasing, and real and reliable high-speed leaf vibration signals can be provided.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Multi-beam wide covering sea floor relief and geomorphy surveying device
InactiveCN101000242AHigh resolution receptionAccurate acquisitionElectric signal transmission systemsOpen water surveyOcean bottomEngineering
The invention relates to multi-wave packet wide cover undersea topography landform detecting device. It includes above and under water extensions, cable. The above water extension is made up of embedding type integration industrial personal computer, signal processing, collecting, pre-processing, and adjusting devices, storage. The under water extension is made up of signal generating and emitting devices, multi channel emitting and receiving transducer arrays, signal amplifying device. The invention adopts multi channel emitting and receiving transducer array and advanced signal processing technique to gain wide cover undersea topography and landform information to increase marine charting efficiency and precision. Thus it can be widely used in water traffic transportation safety guard, laying submarine cable, and sinks salvaging etc.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com