Patents
Literature
48 results about "Baroreceptor function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
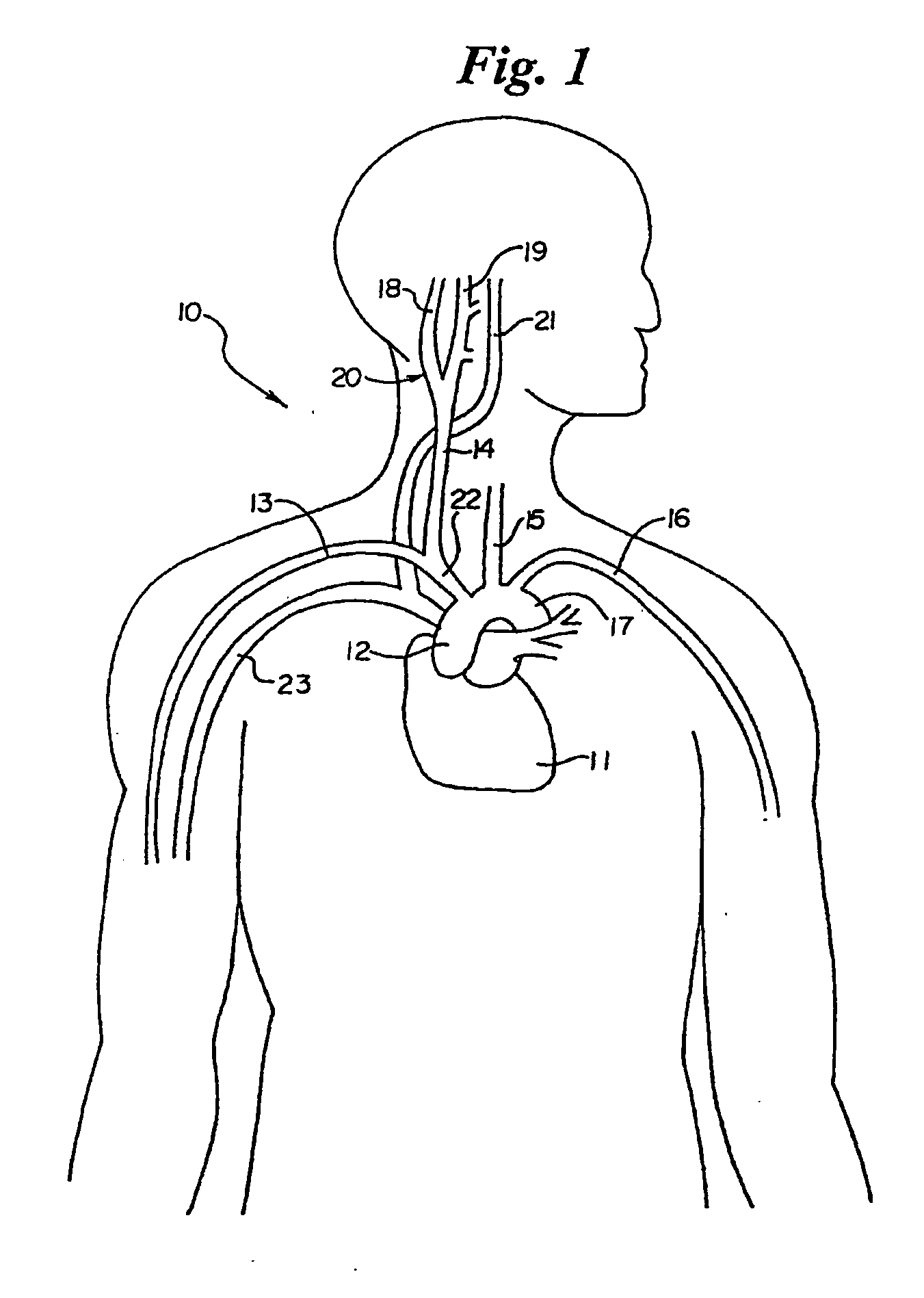
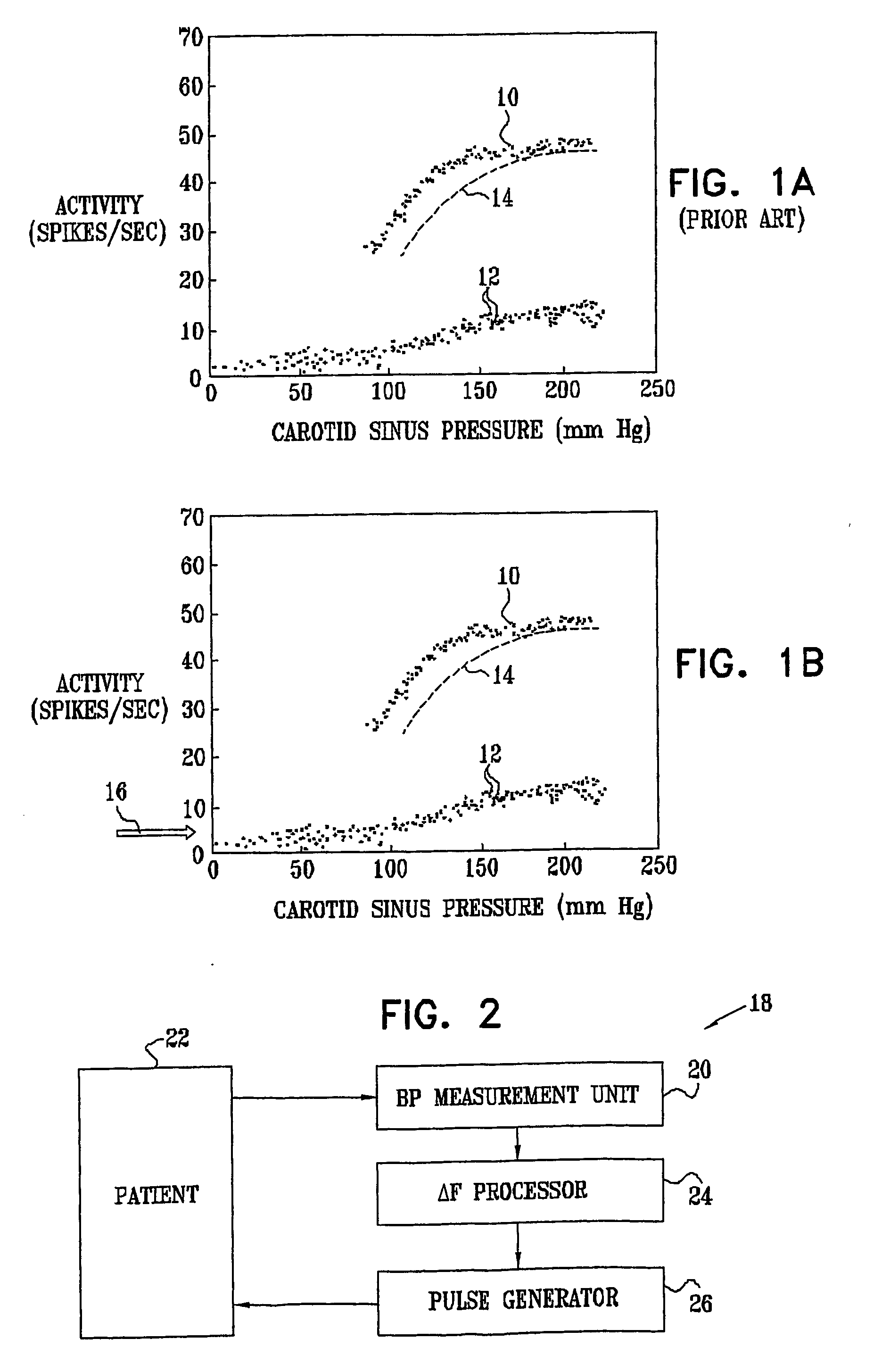
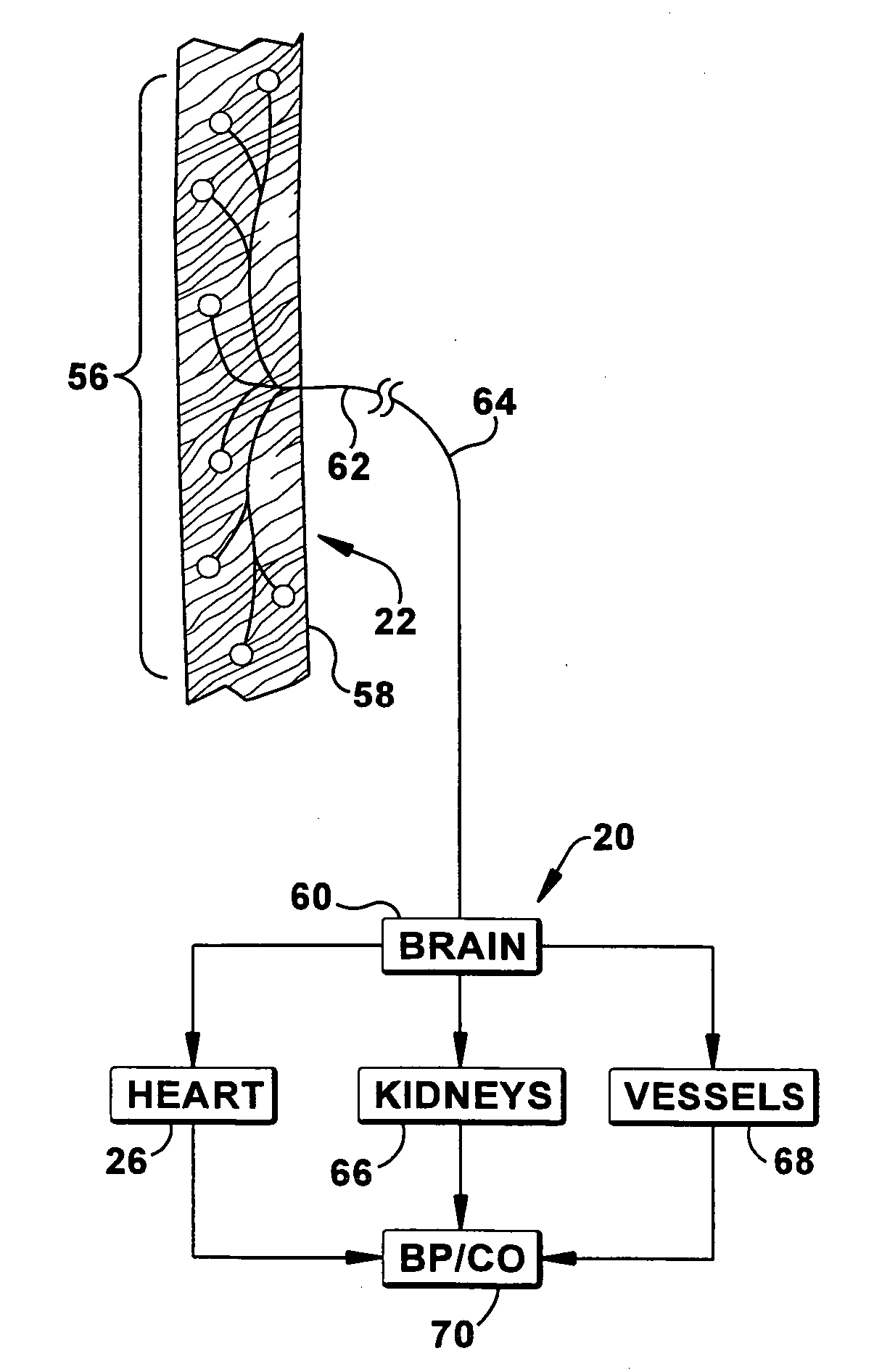
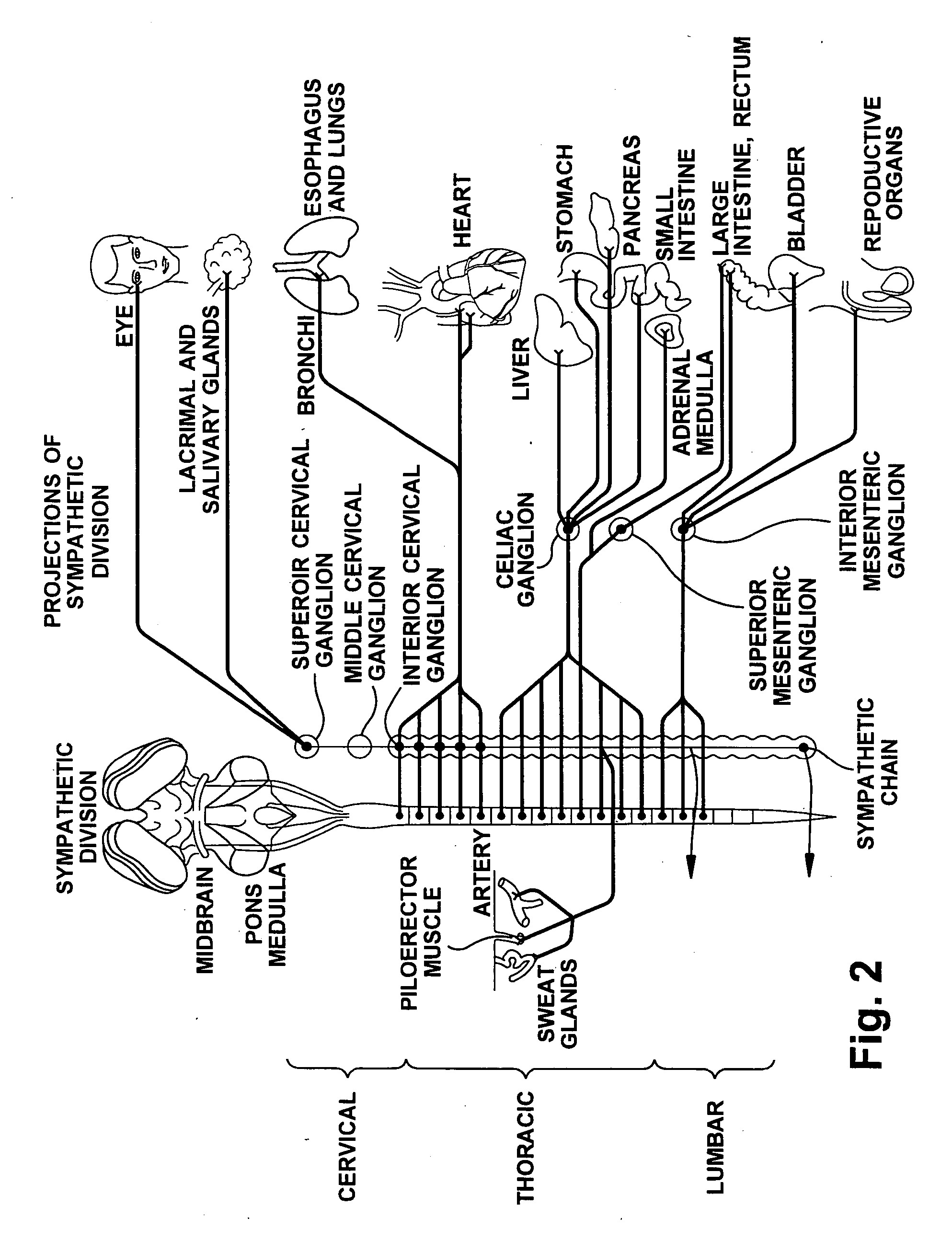
Baroreceptors (or archaically, pressoreceptors) are sensors located in the blood vessels of all vertebrate animals. They sense the blood pressure and relay the information to the brain, so that a proper blood pressure can be maintained. Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptor sensory neuron that are excited by a stretch of the blood vessel.
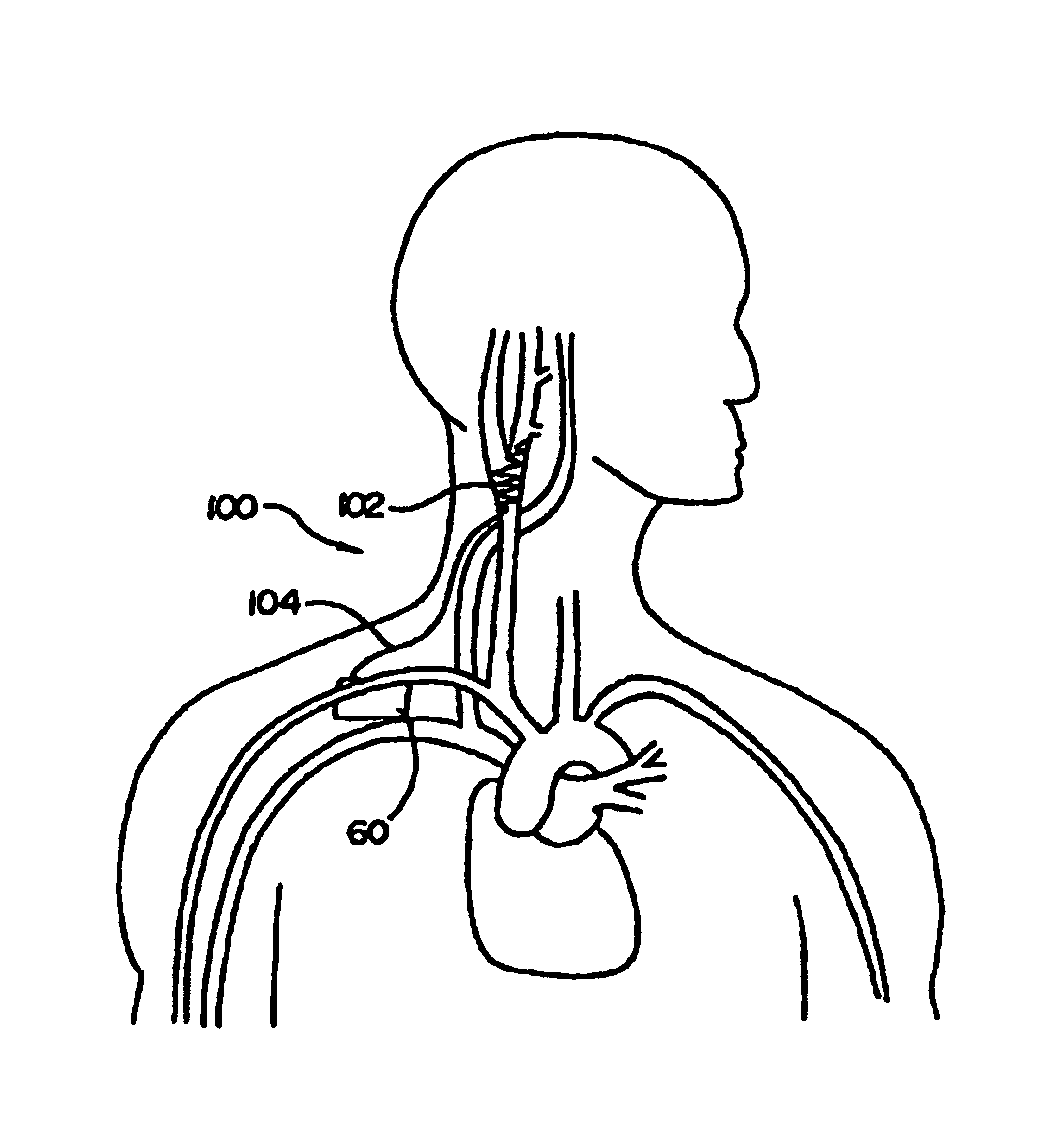
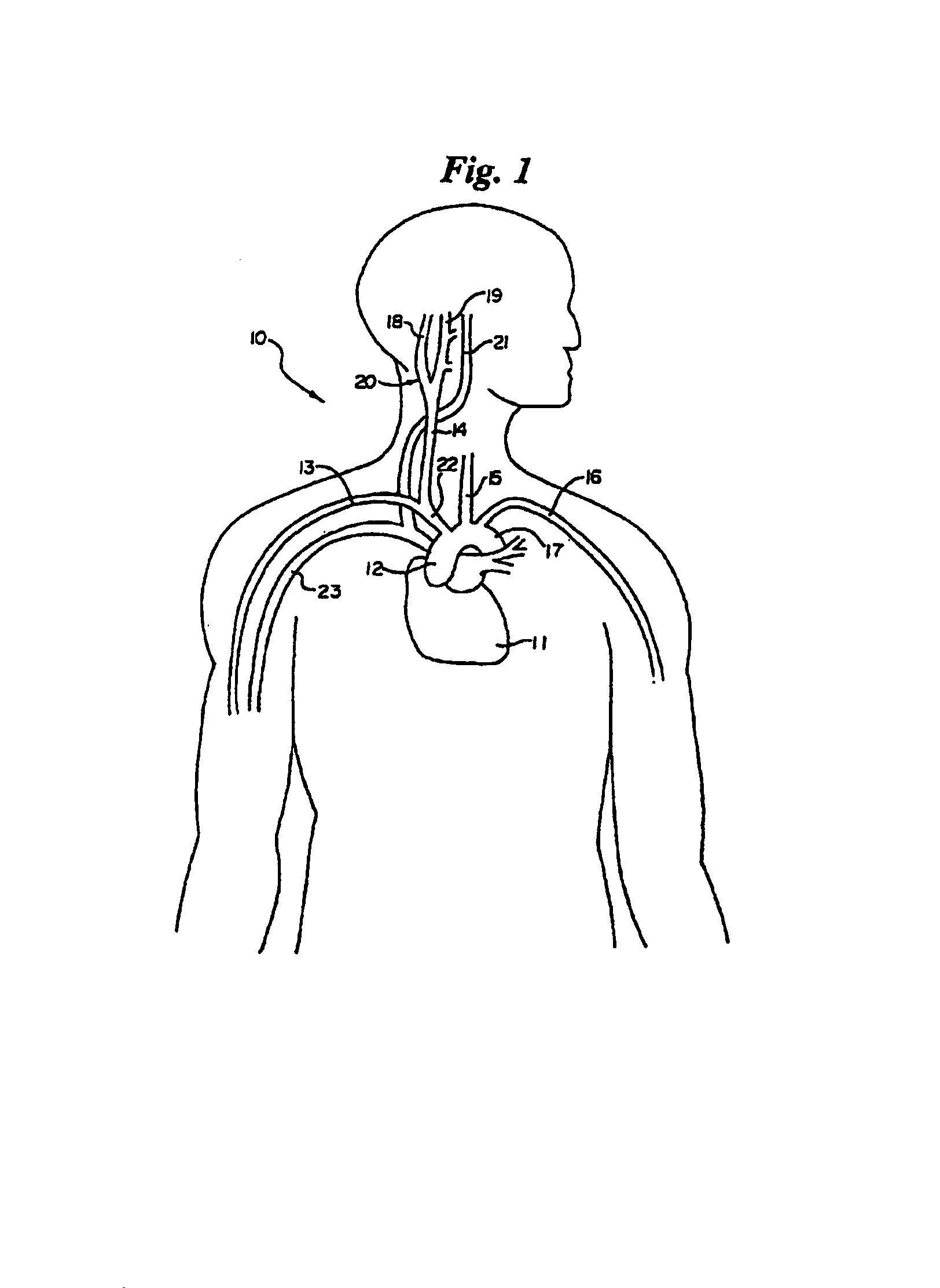
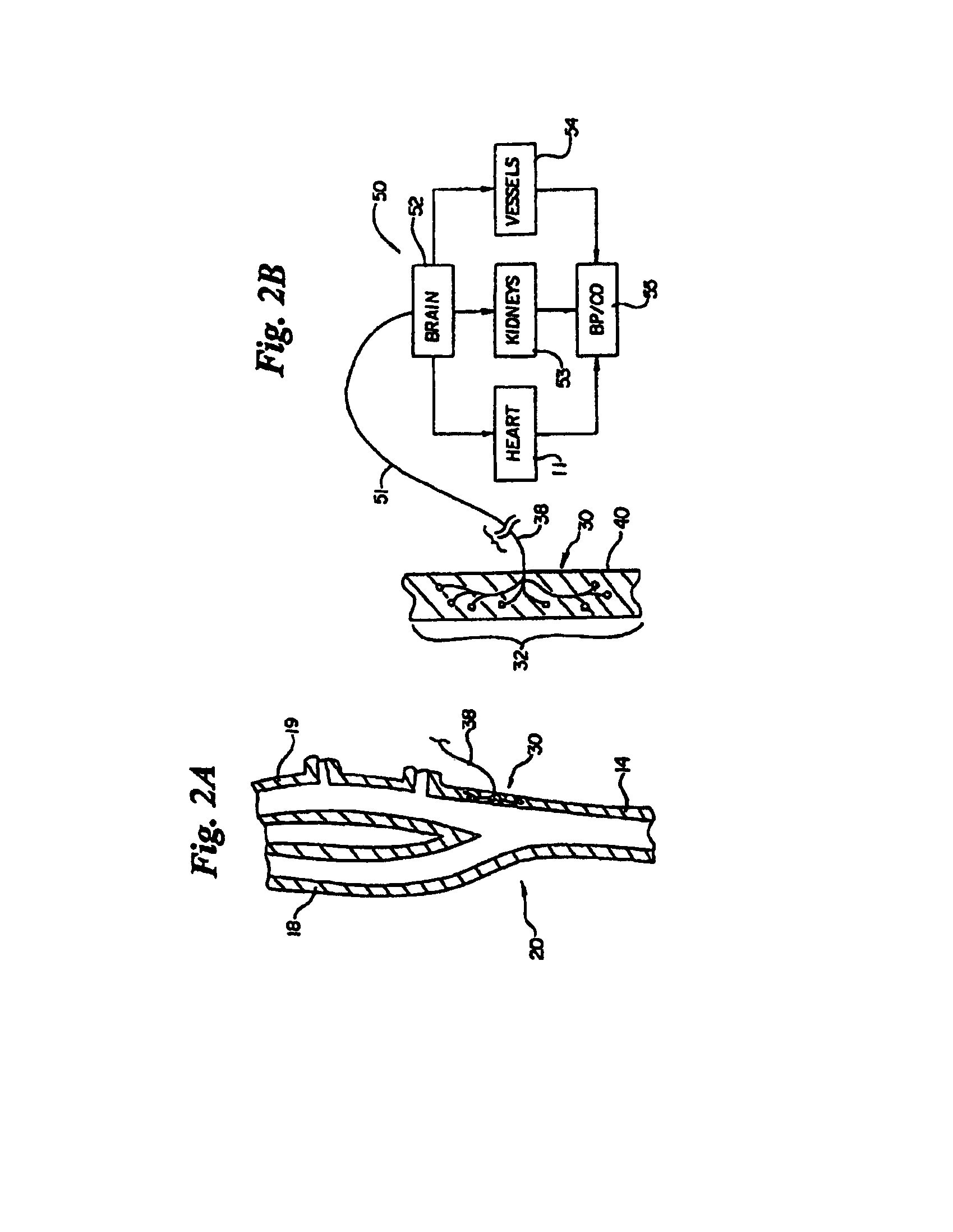
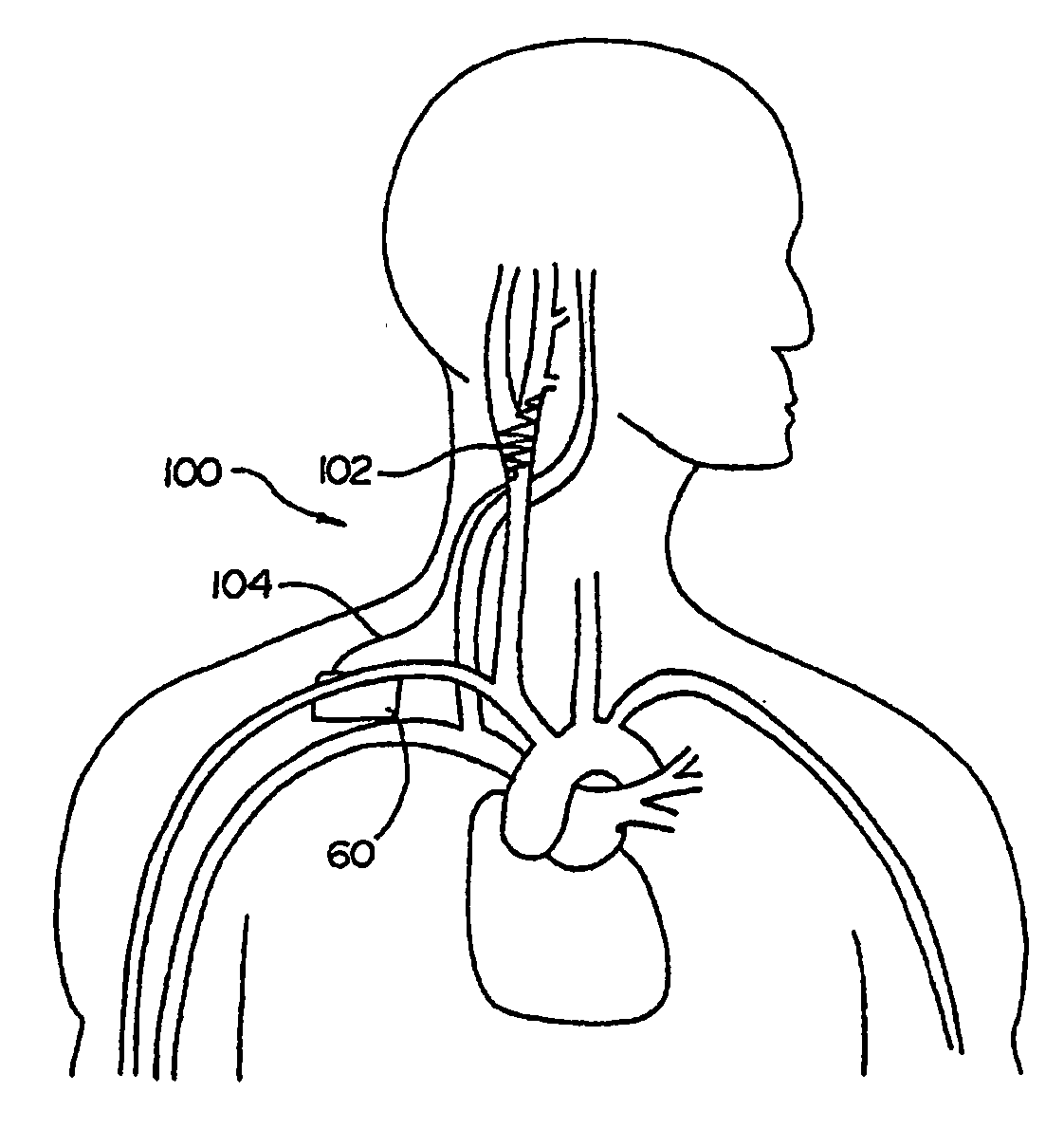
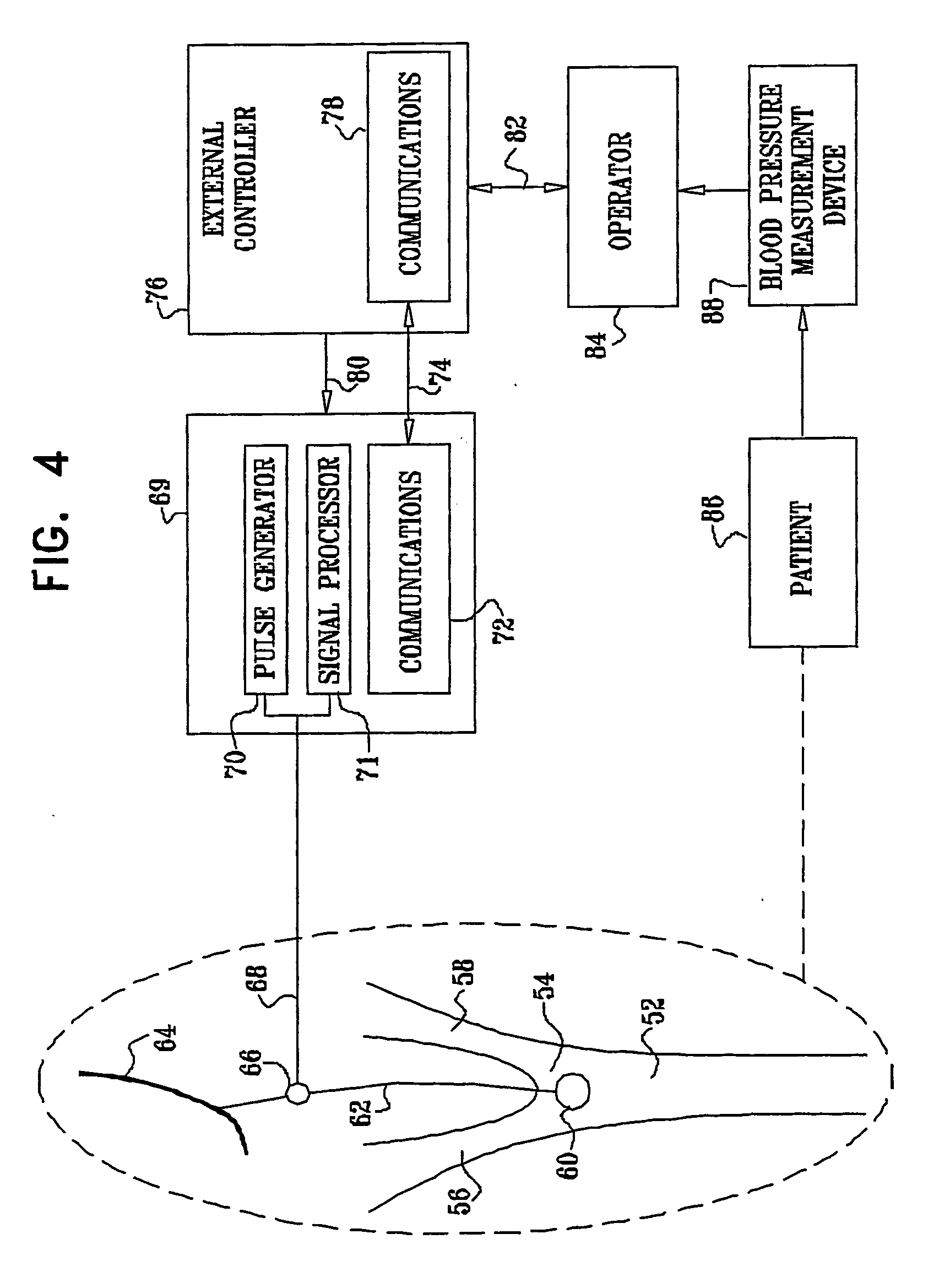
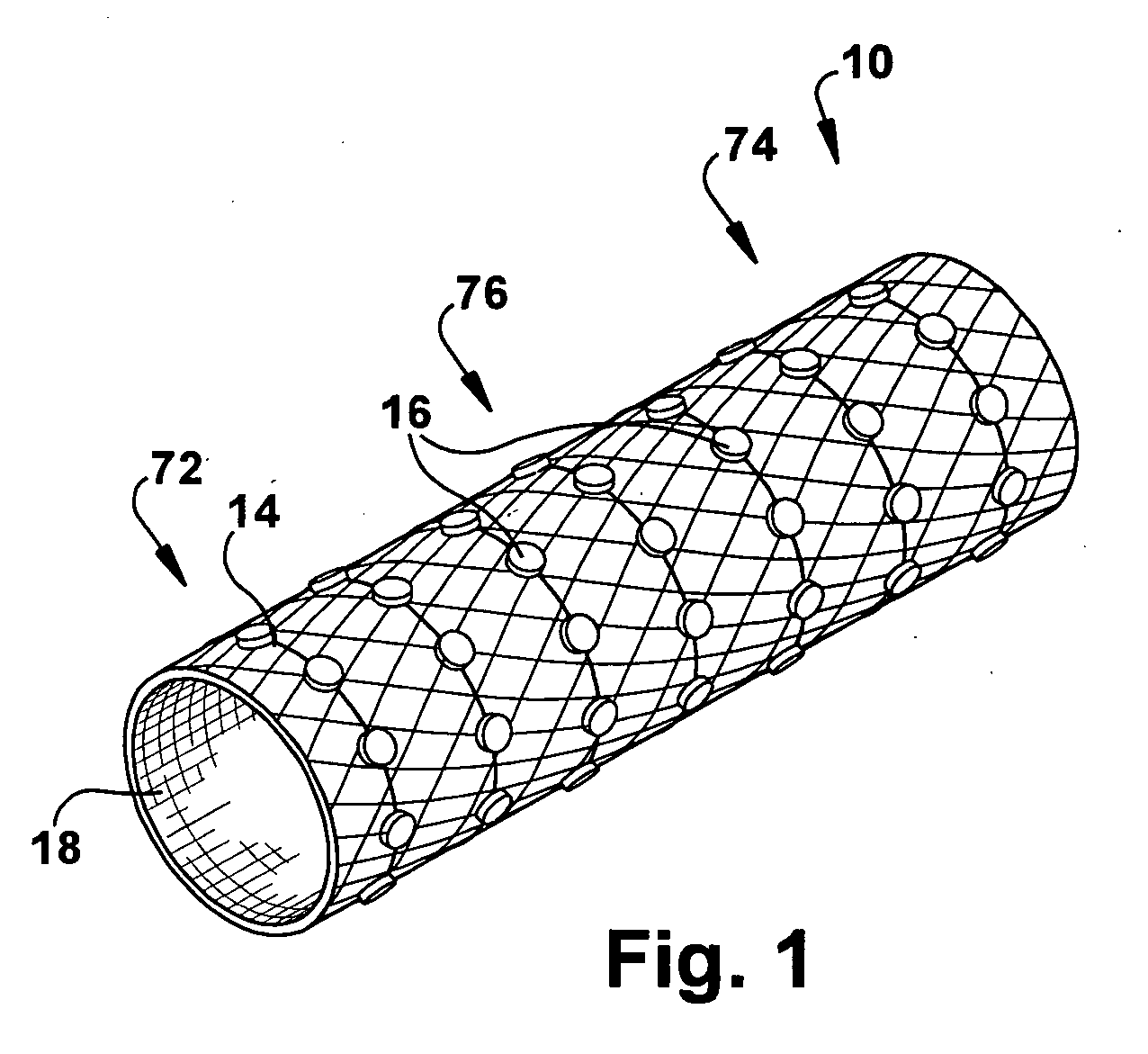
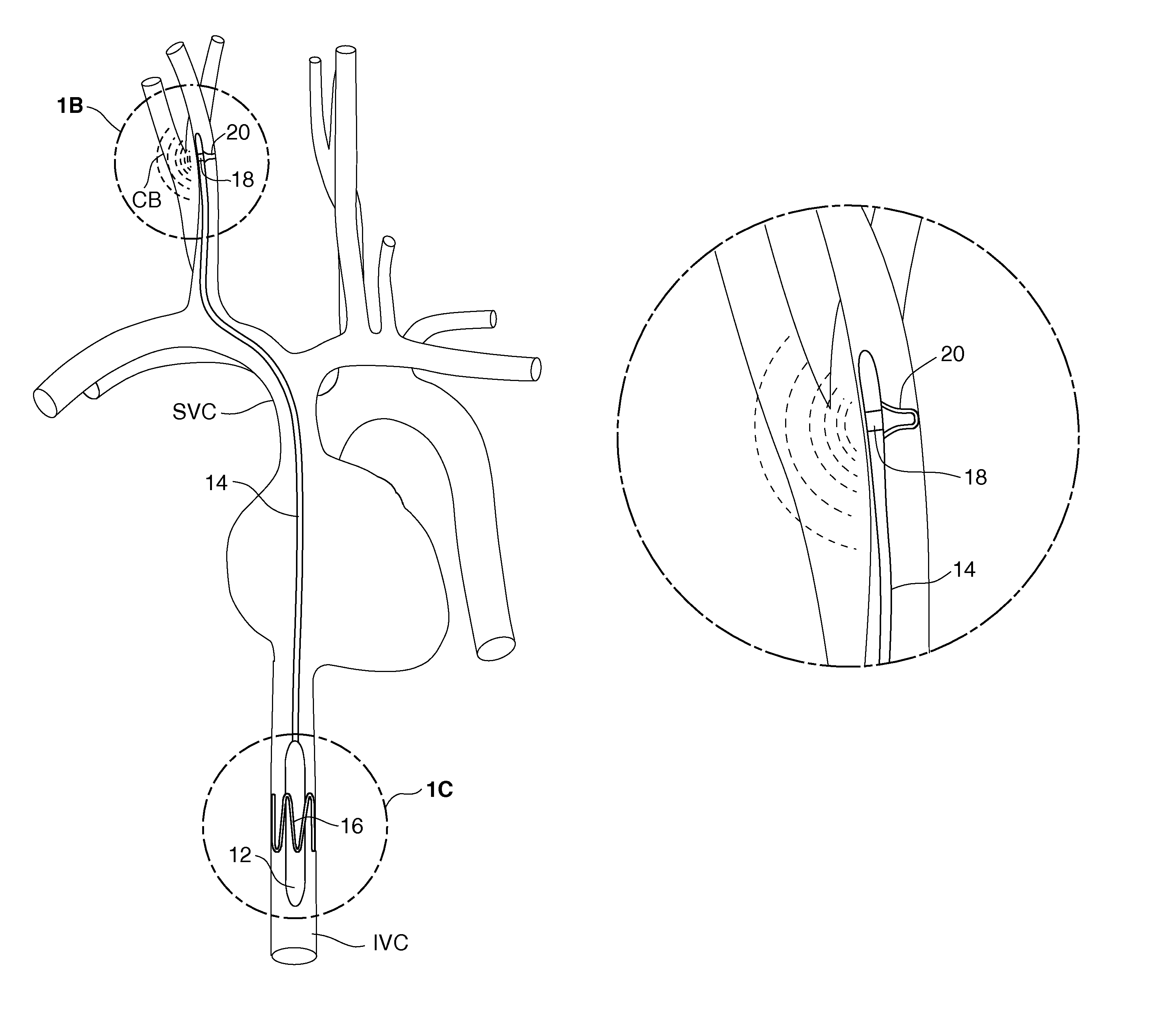
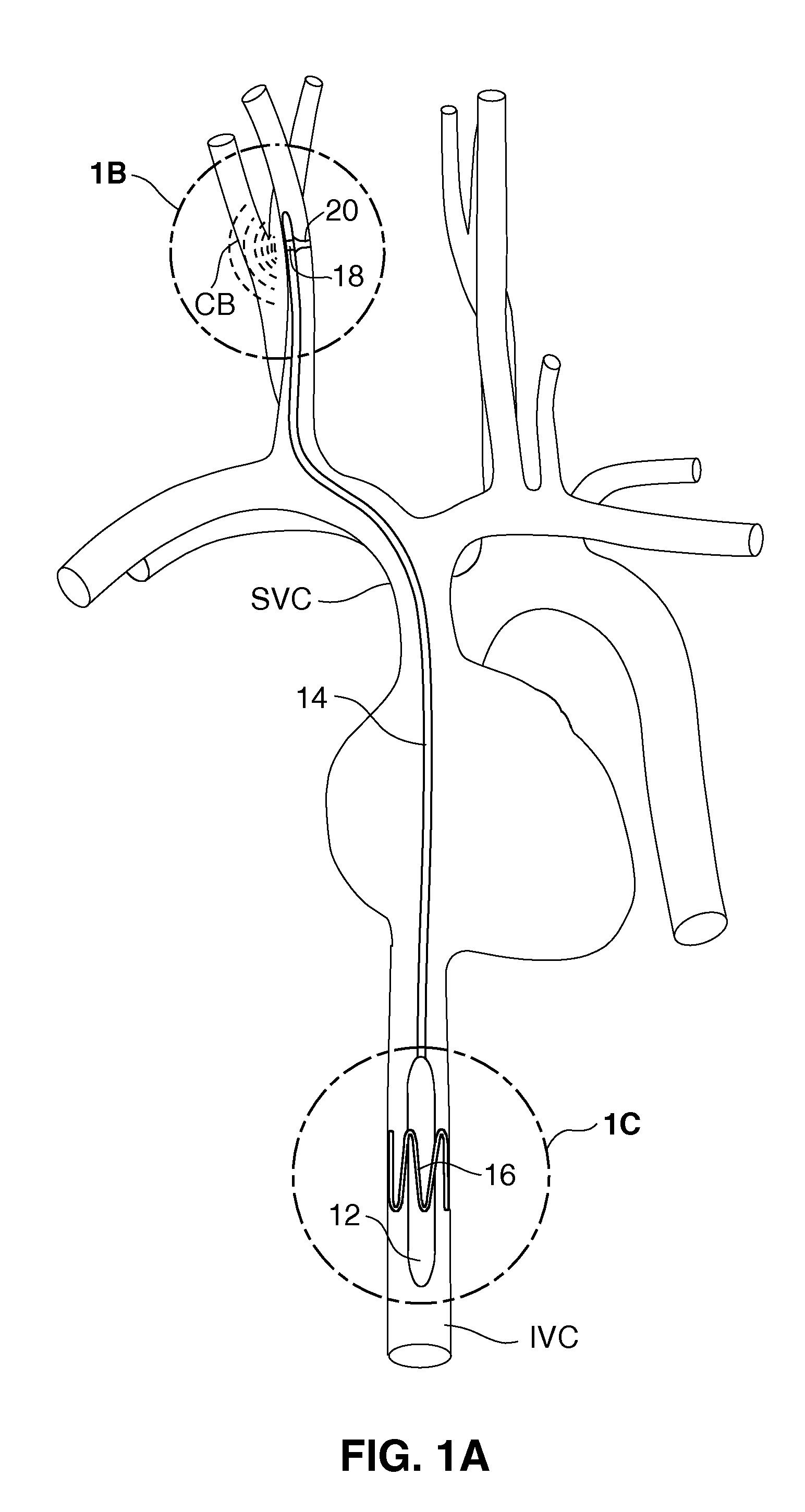
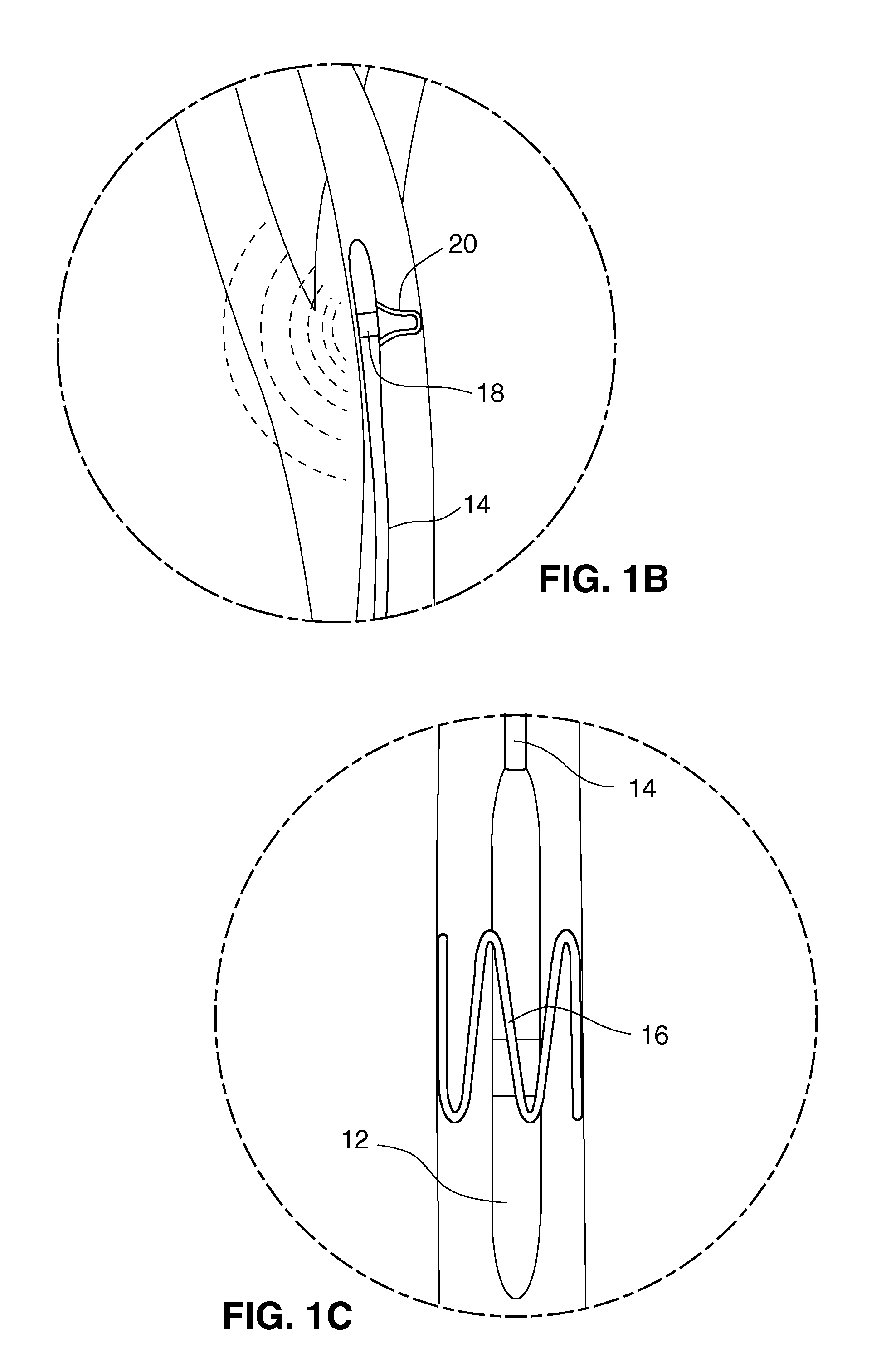
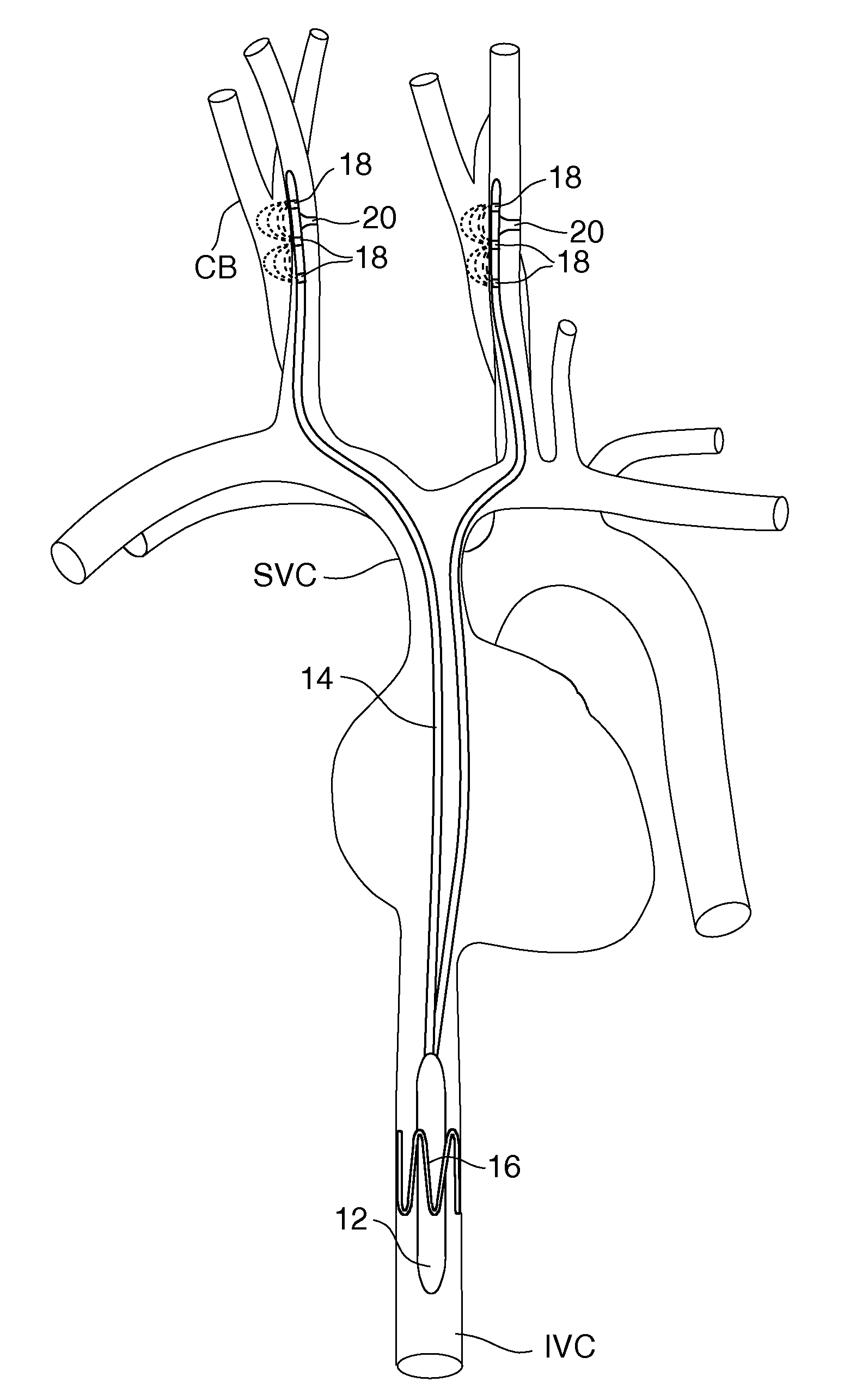
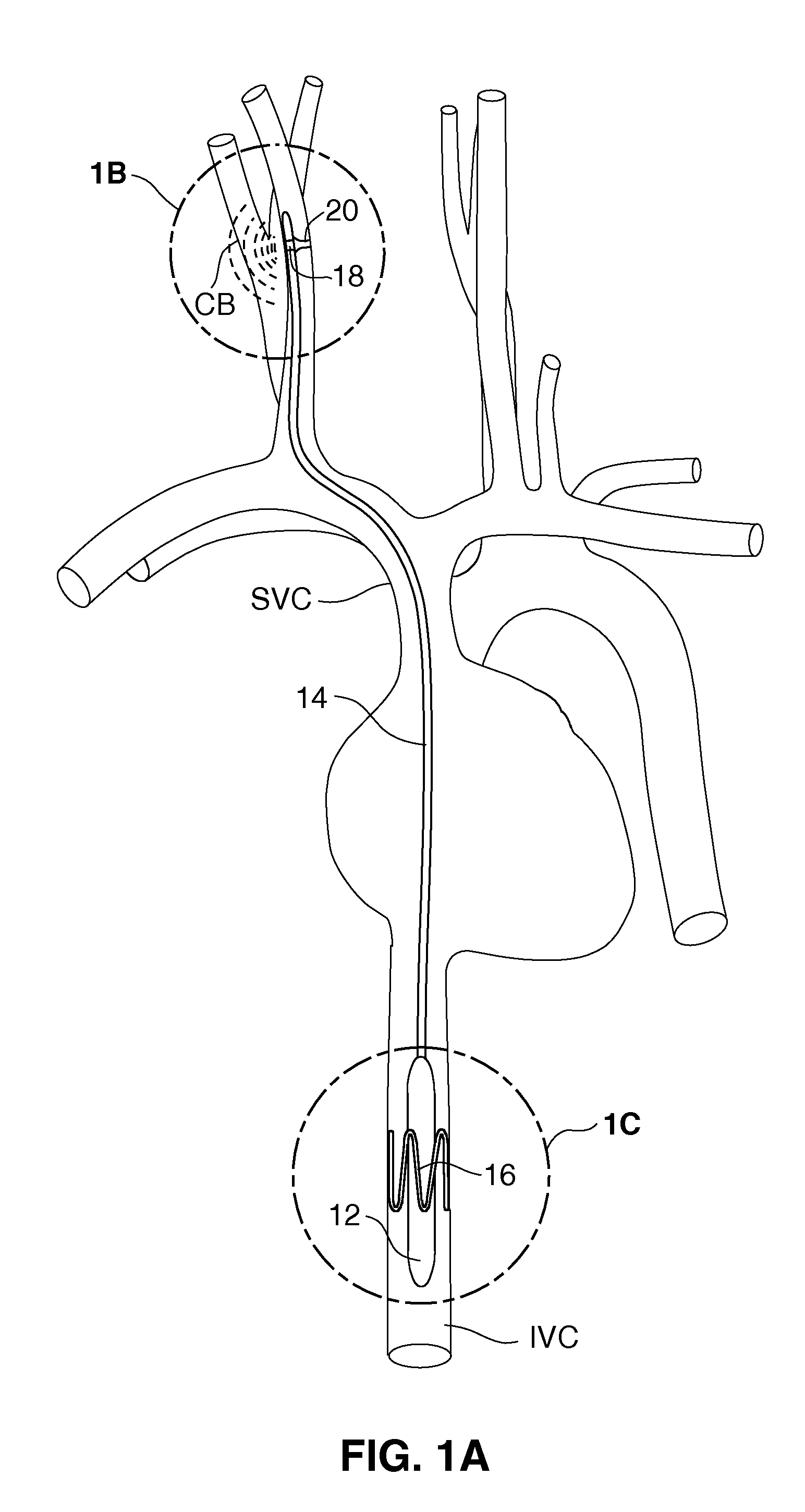
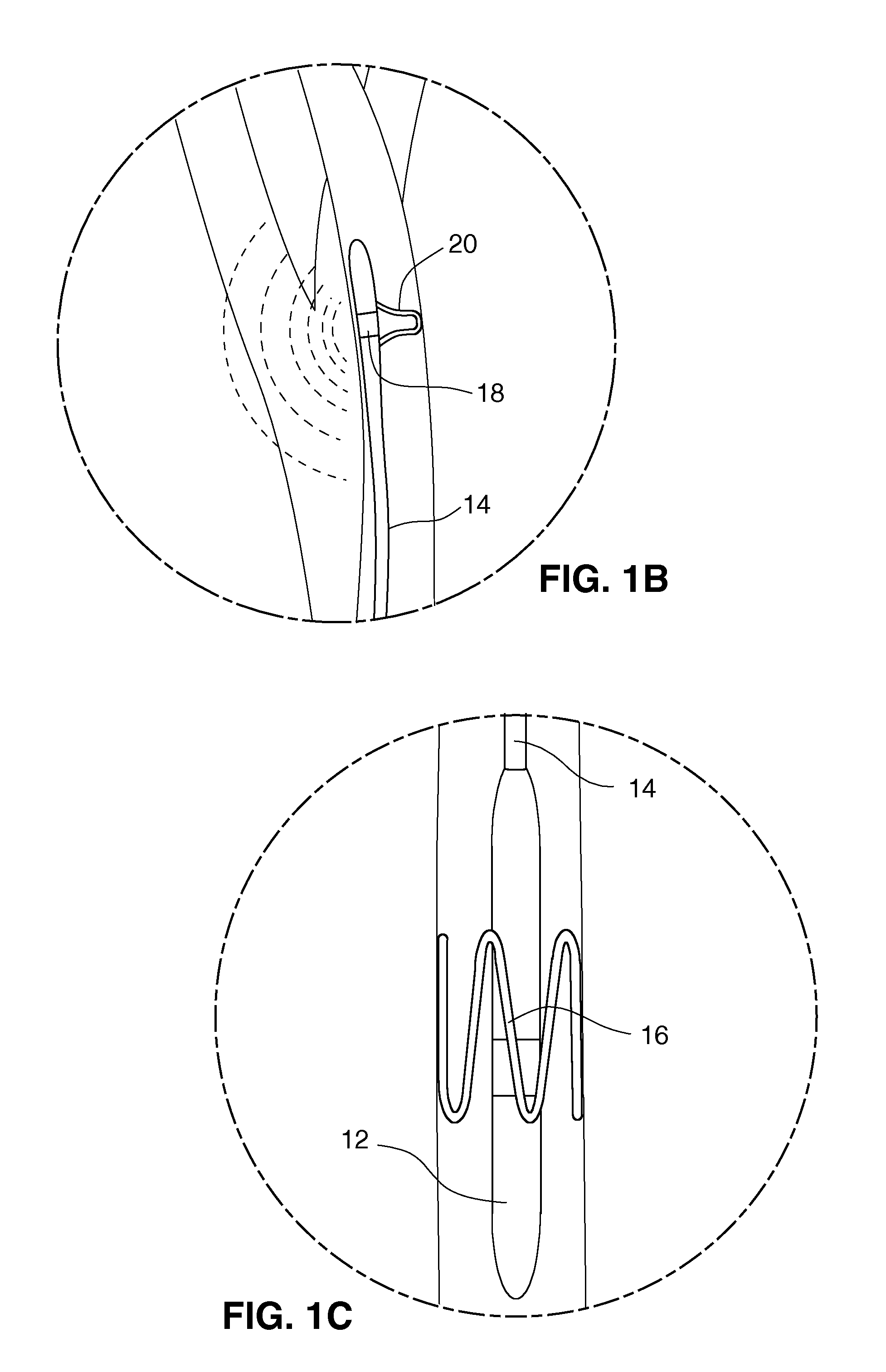
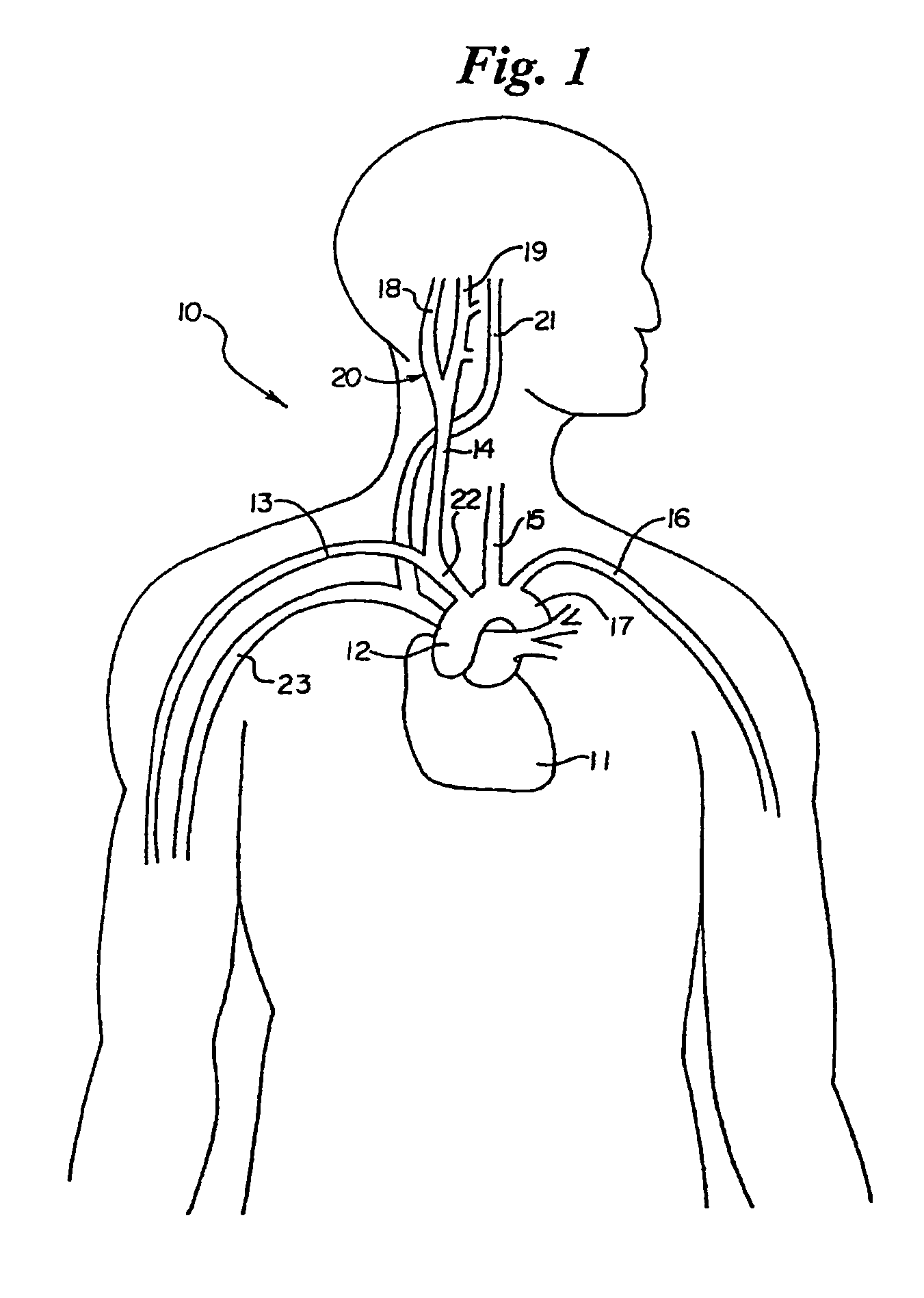
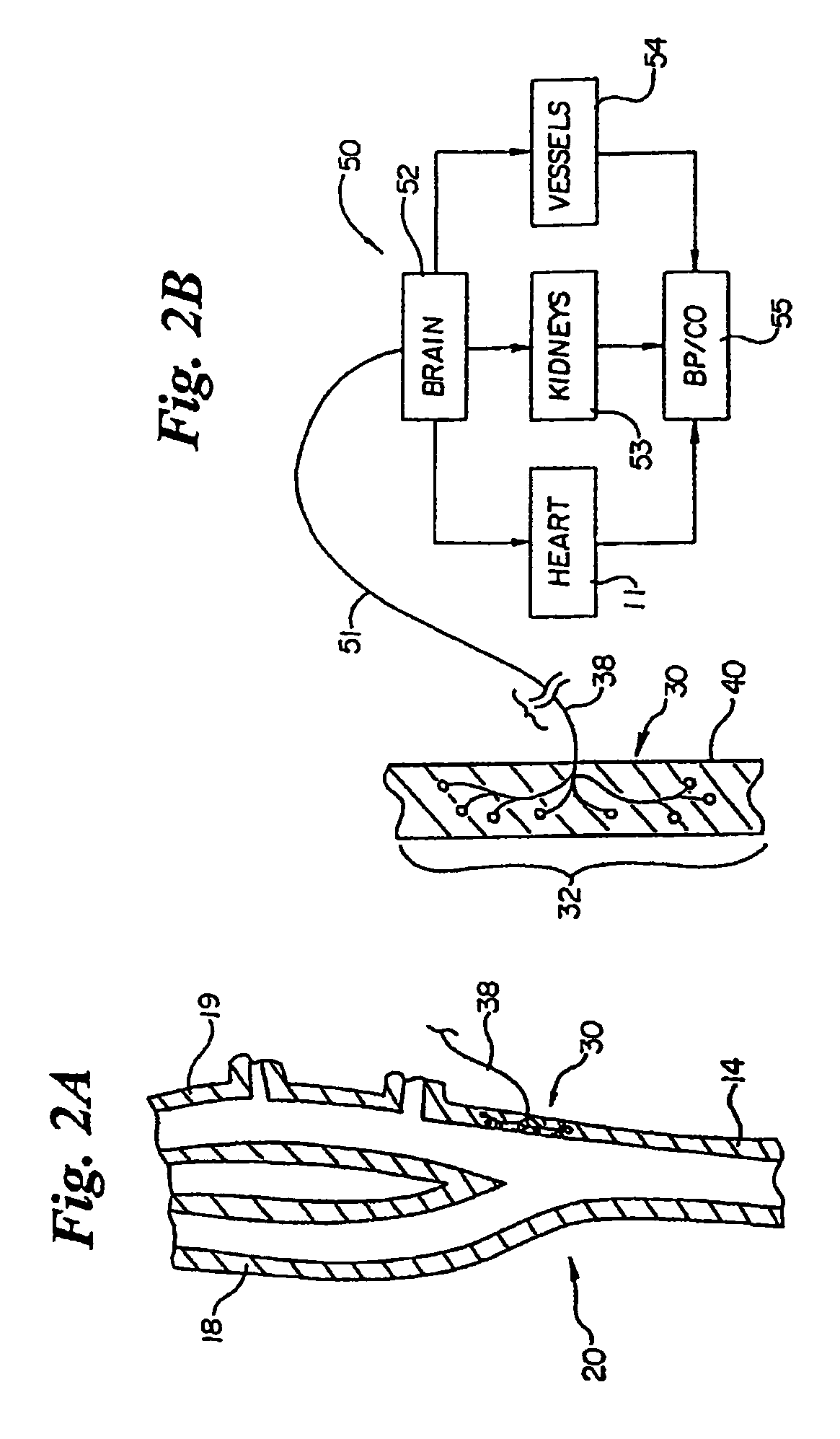
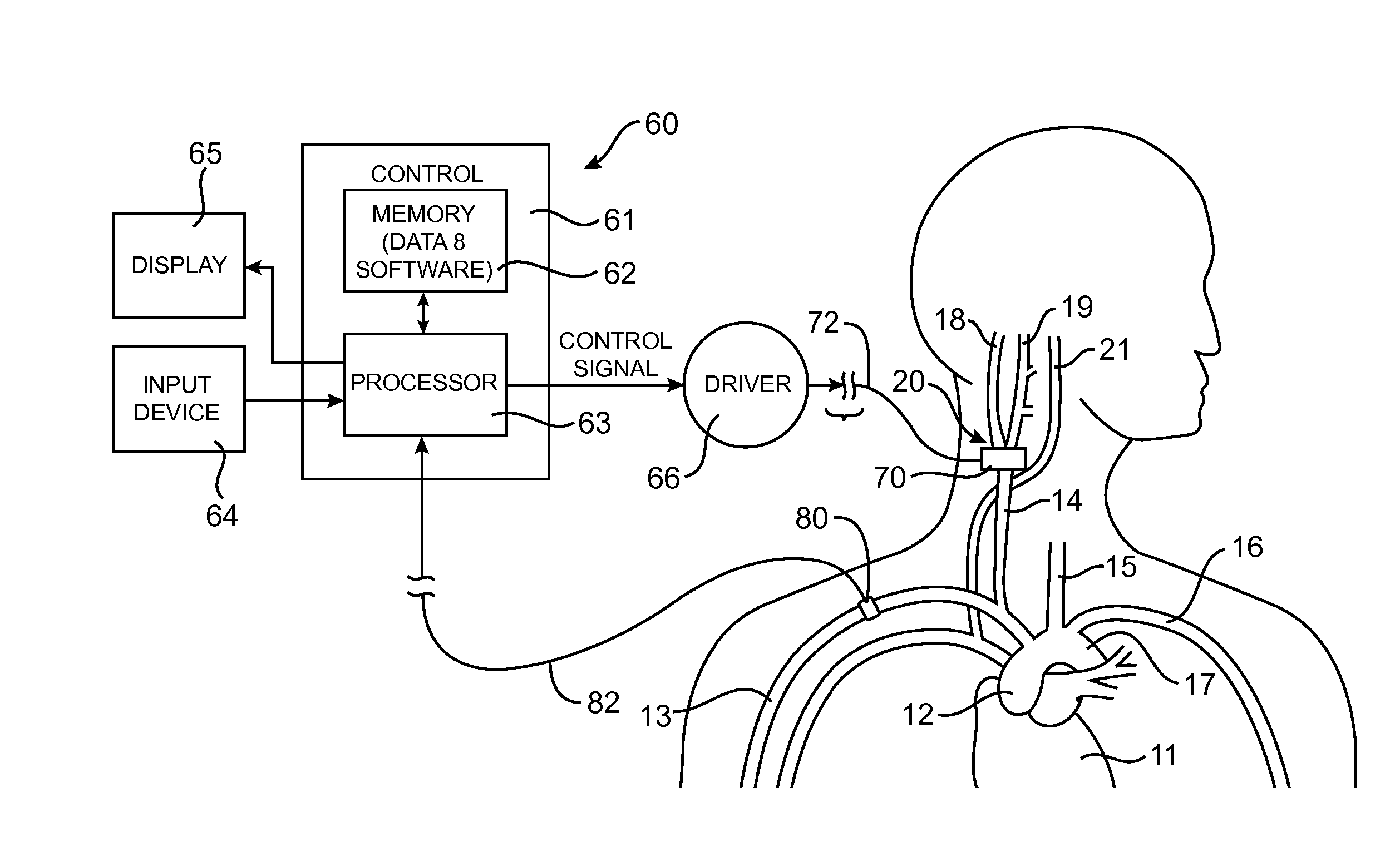
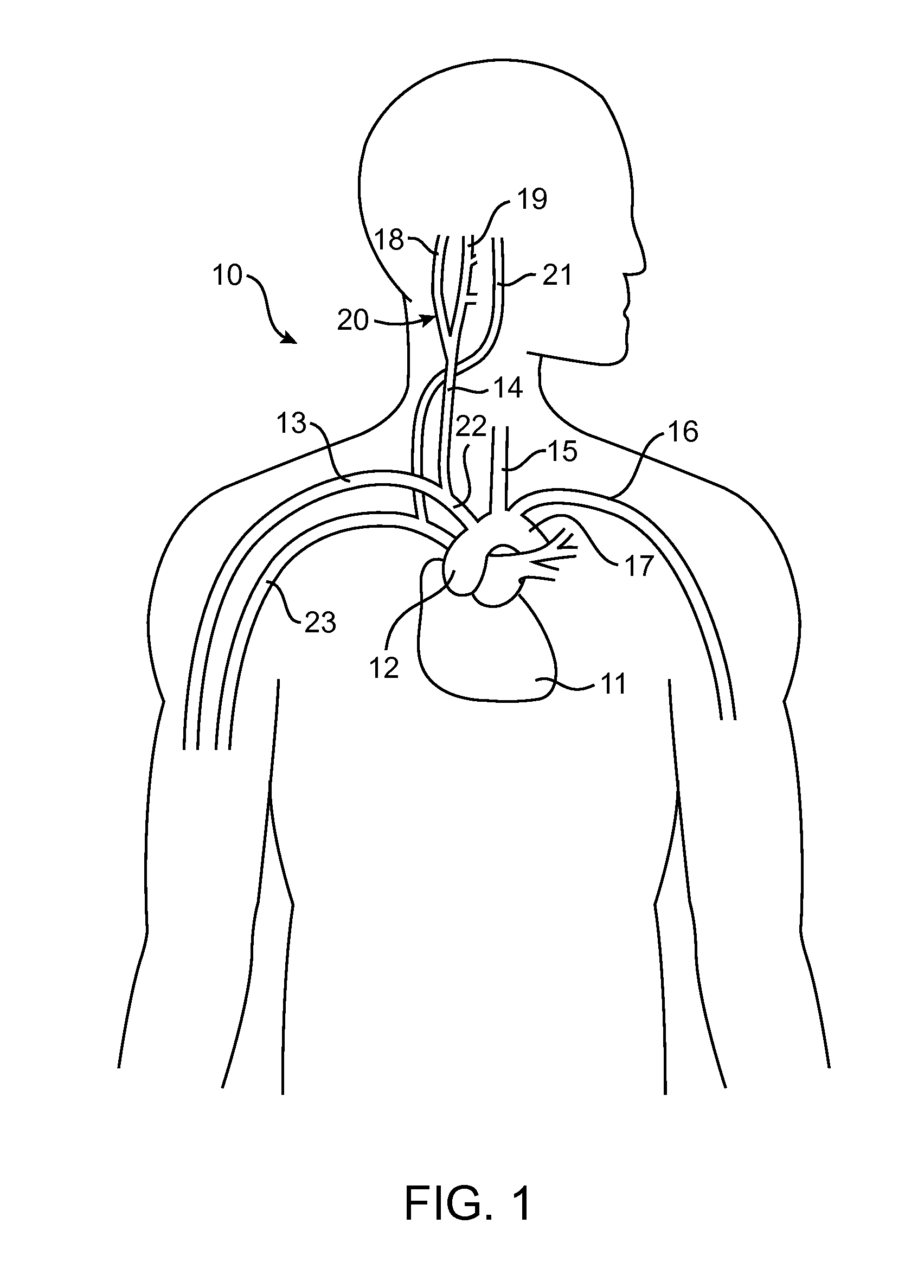
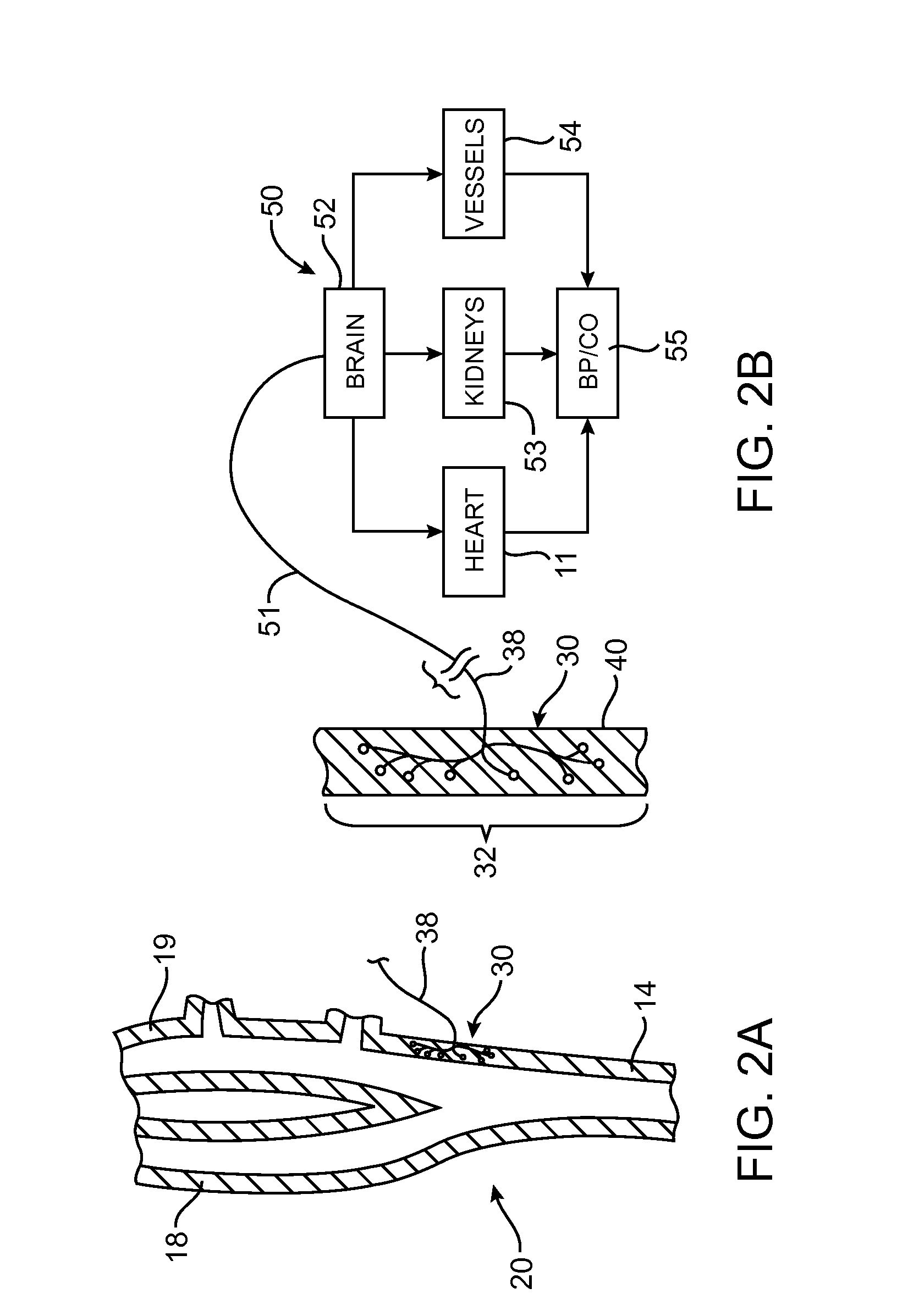
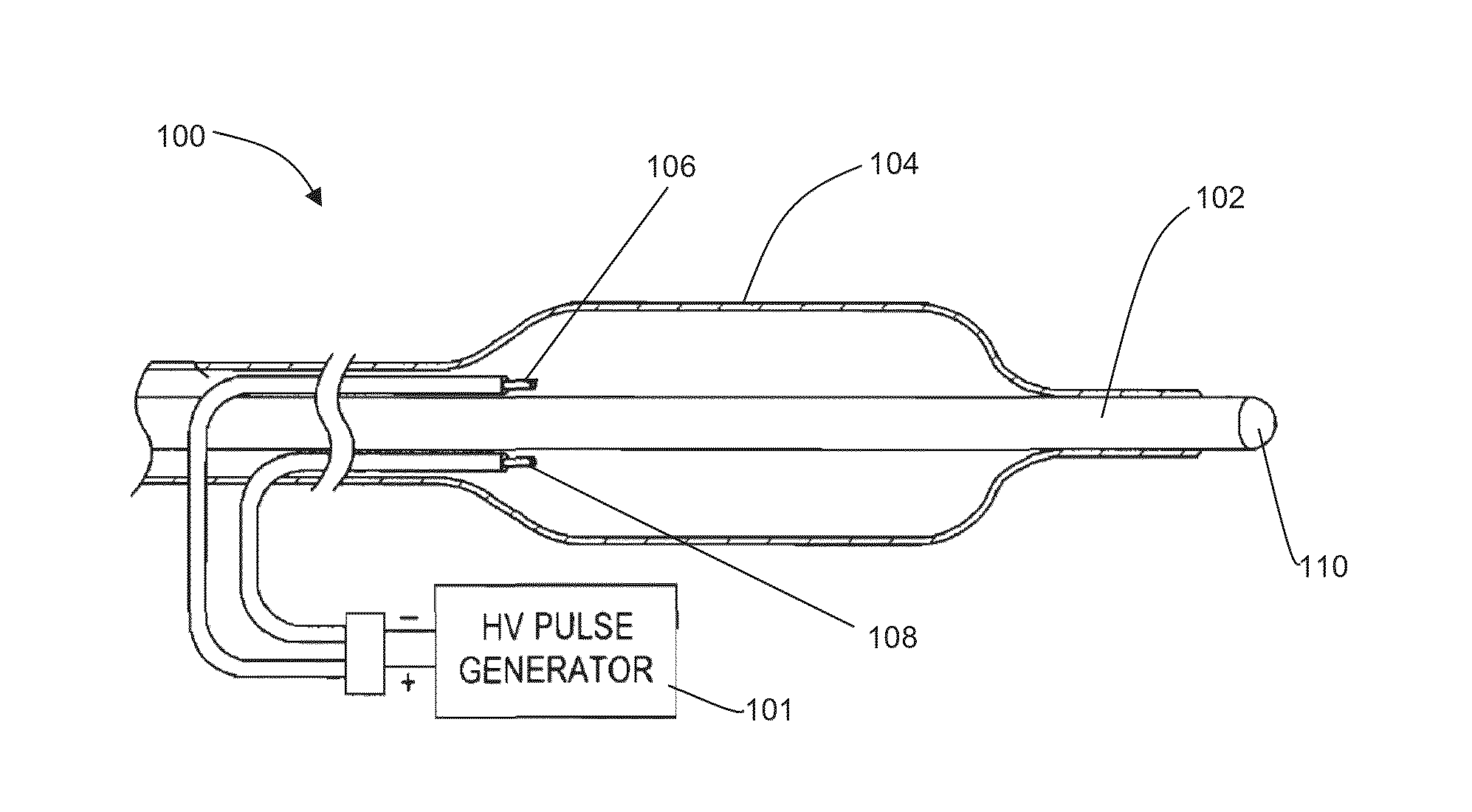
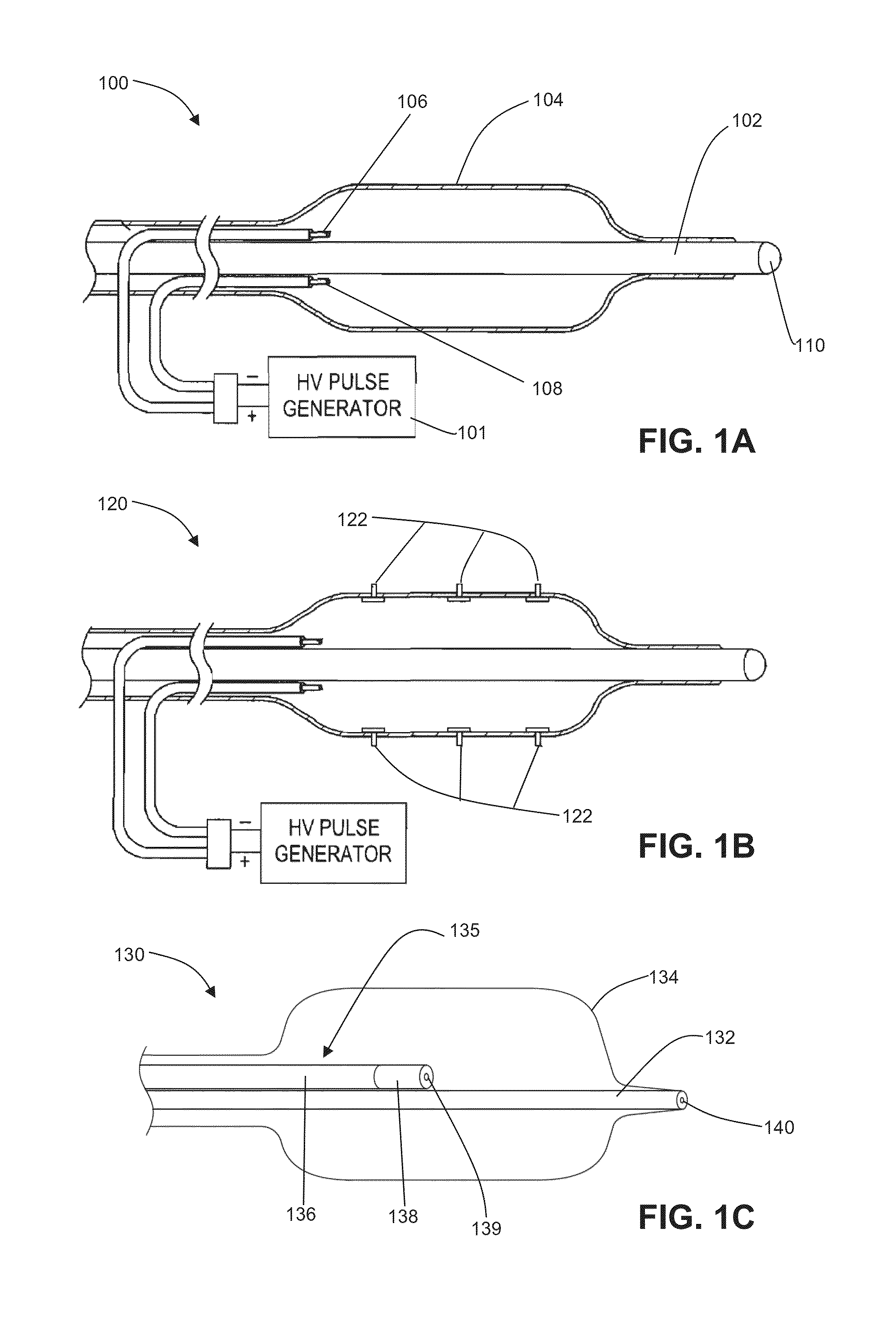
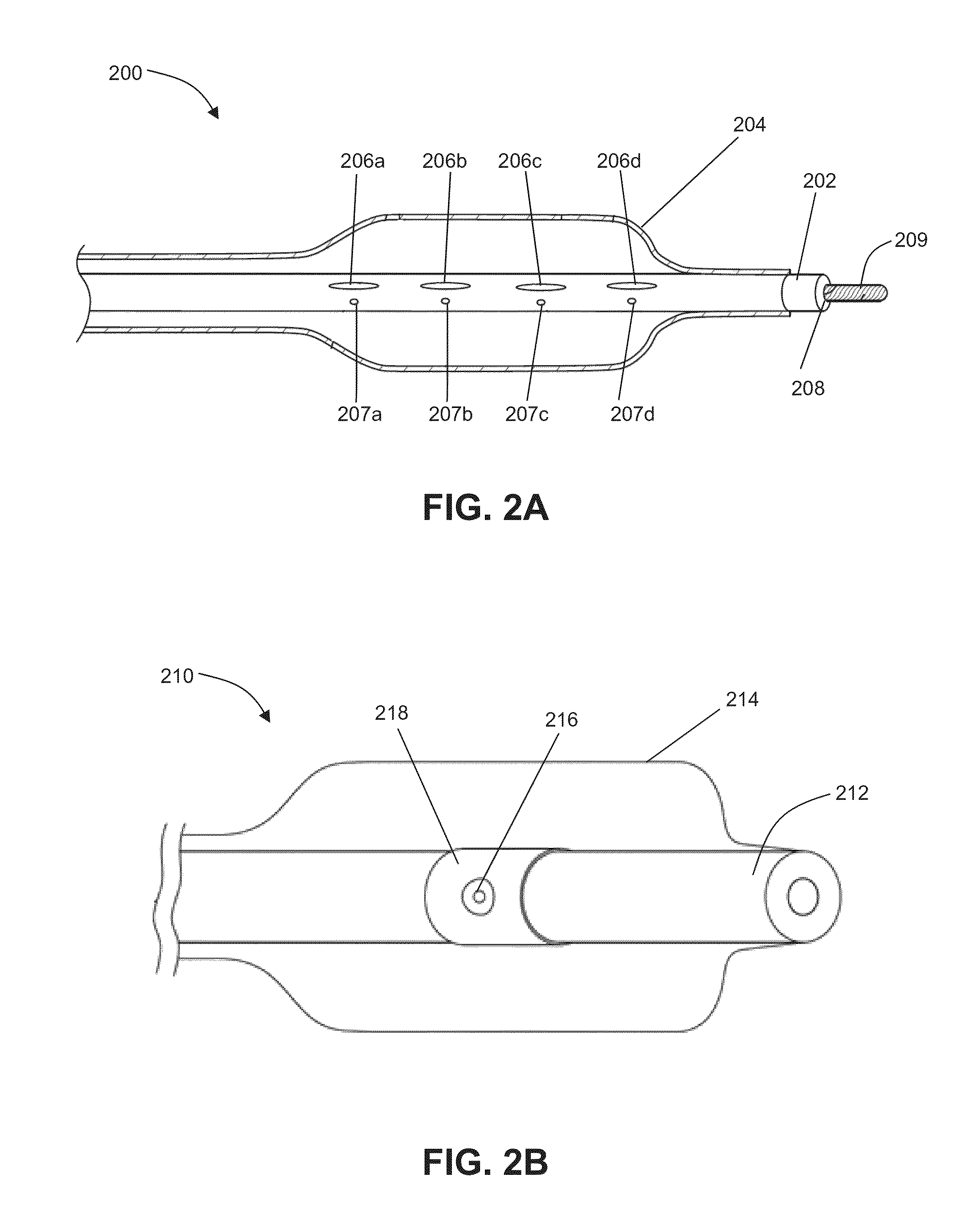
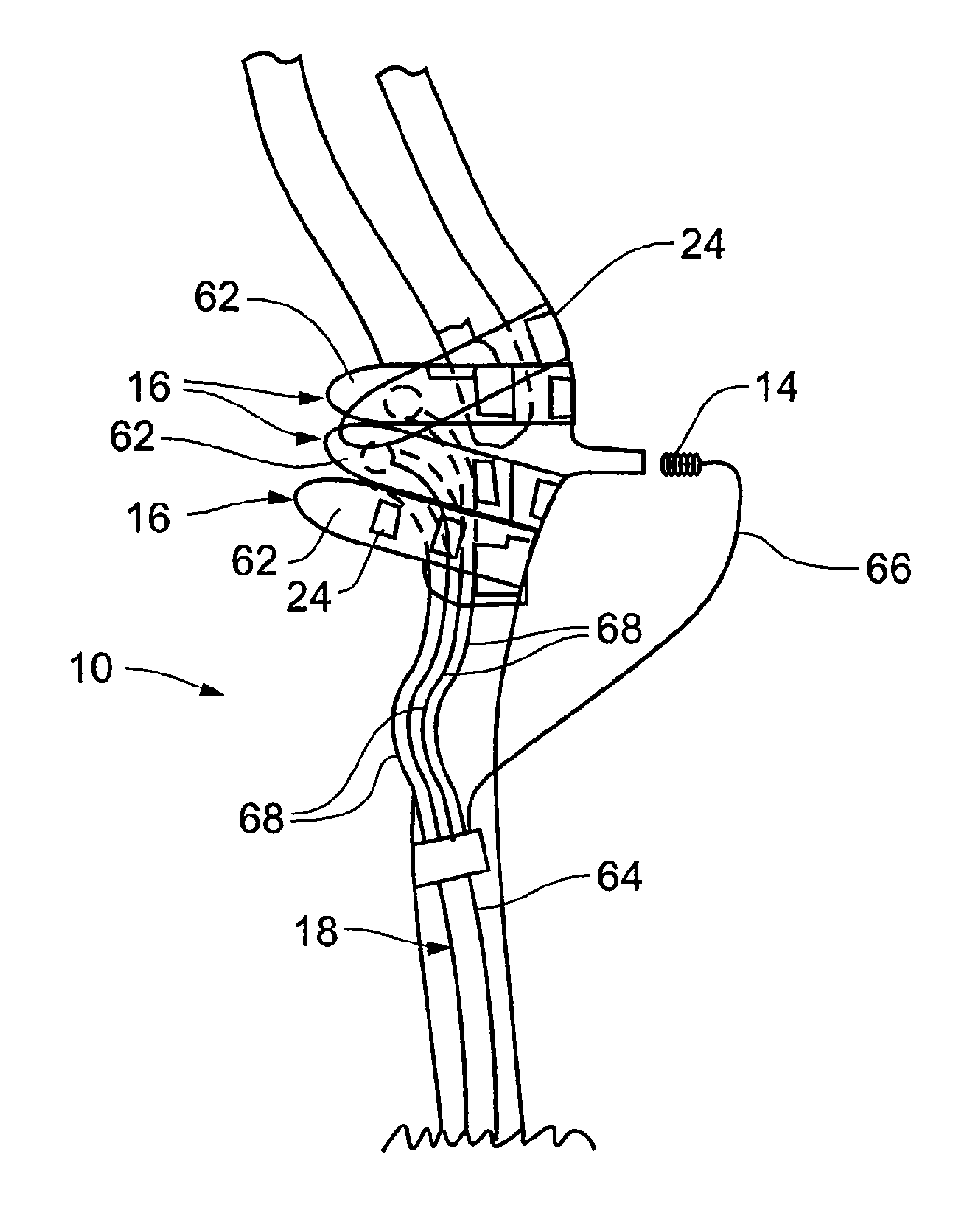
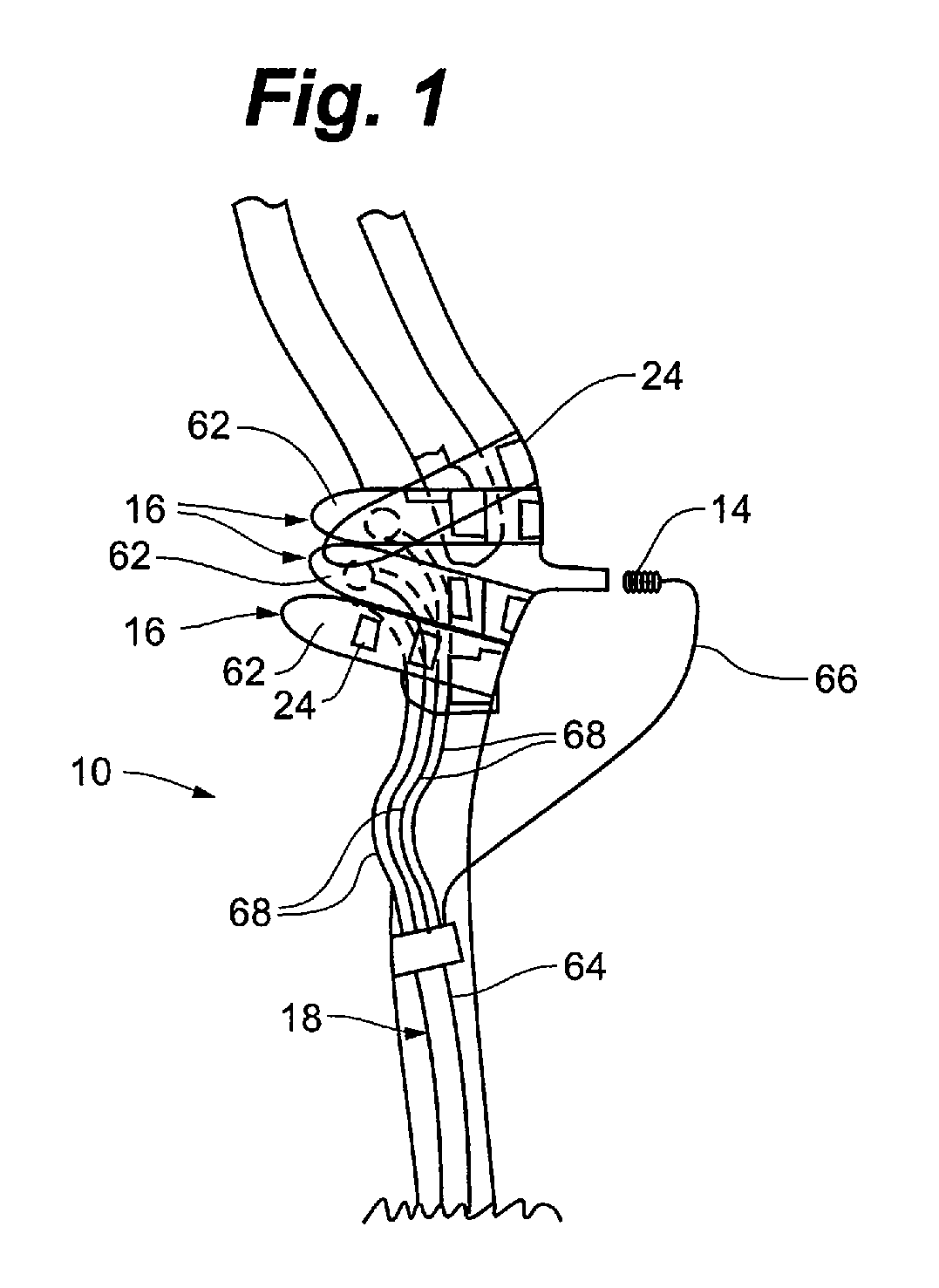
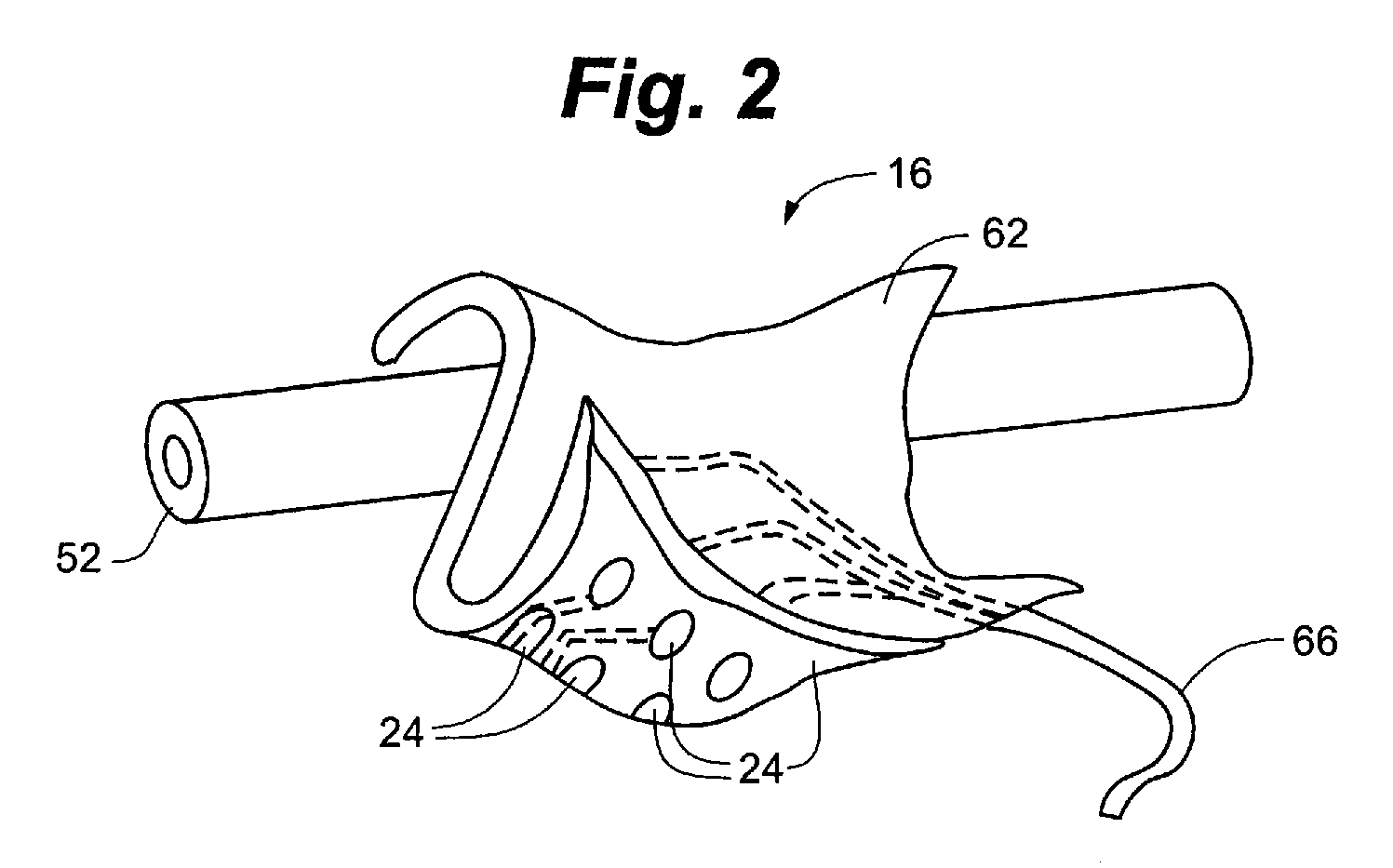
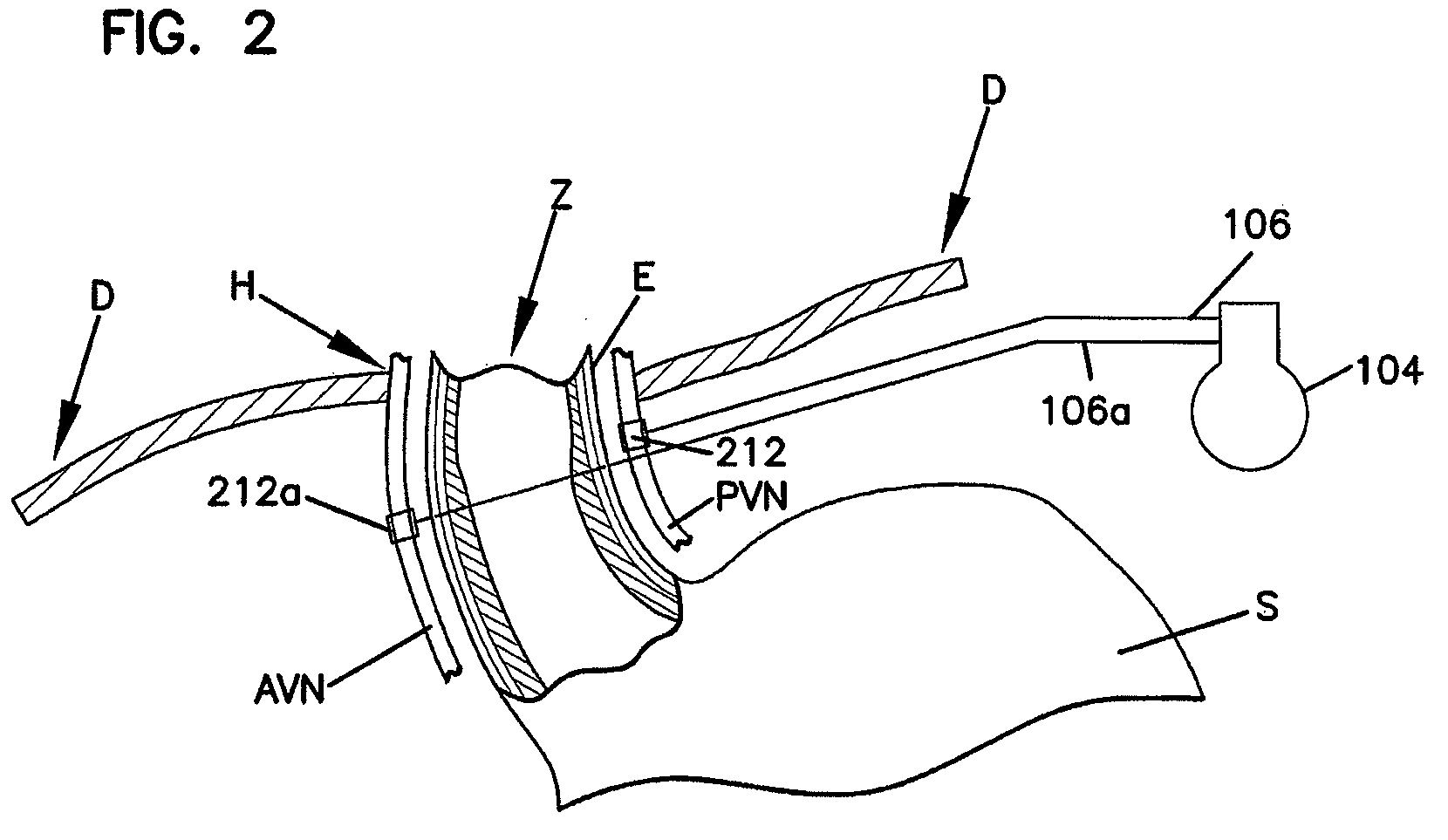
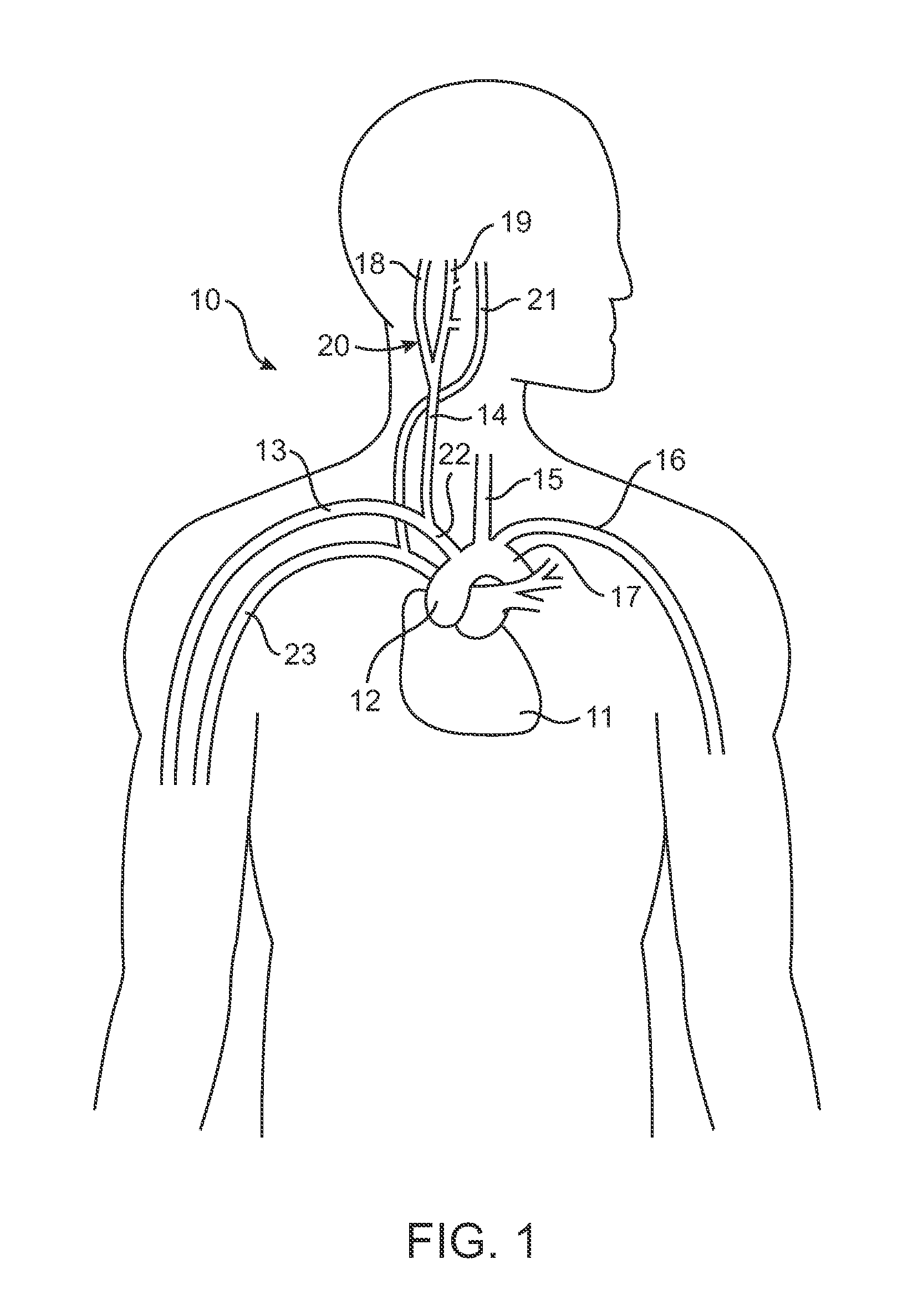
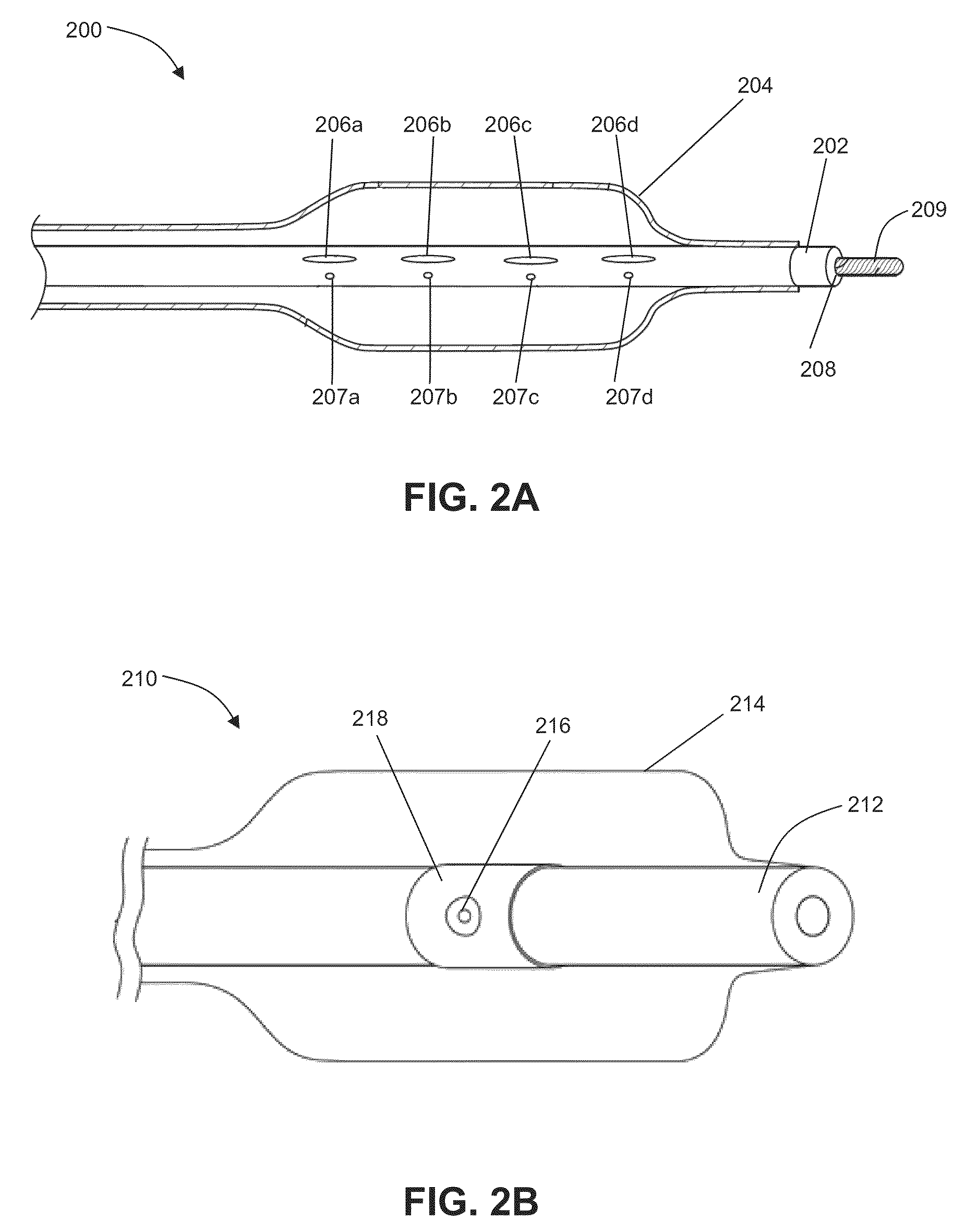
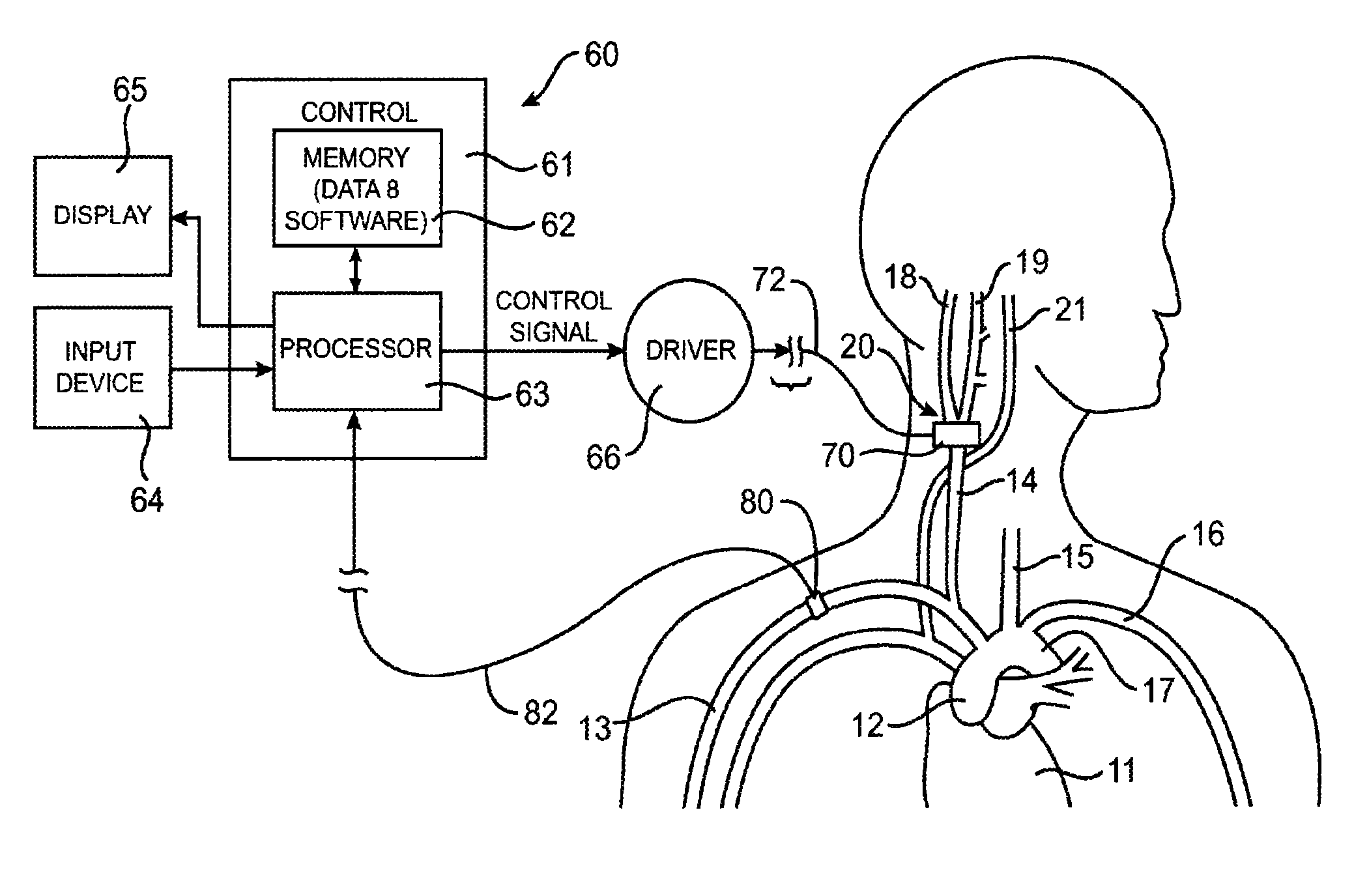
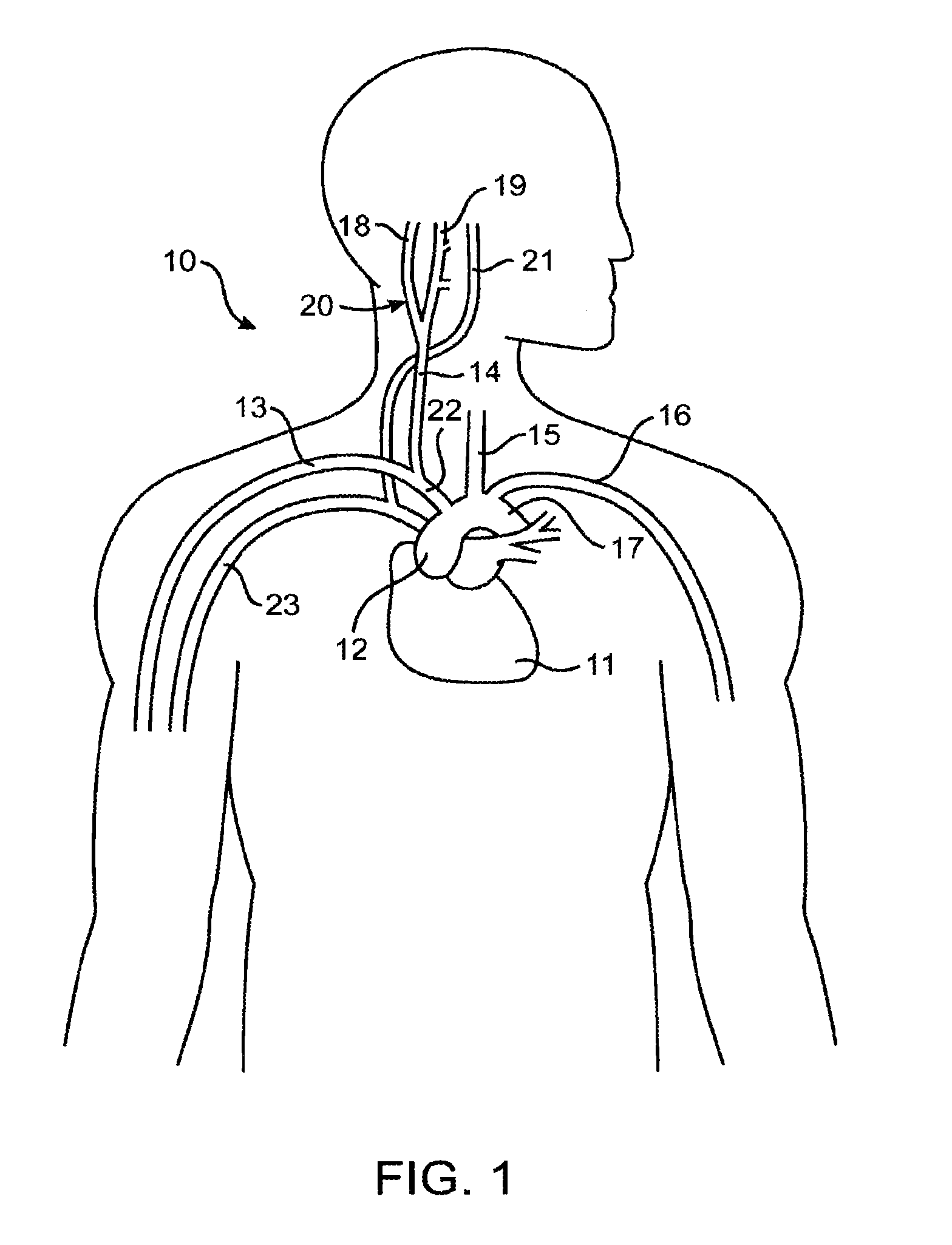
Electrode designs and methods of use for cardiovascular reflex control devices
InactiveUS7158832B2RemissionReduce pressureInternal electrodesExternal electrodesNervous systemBaroreceptor function
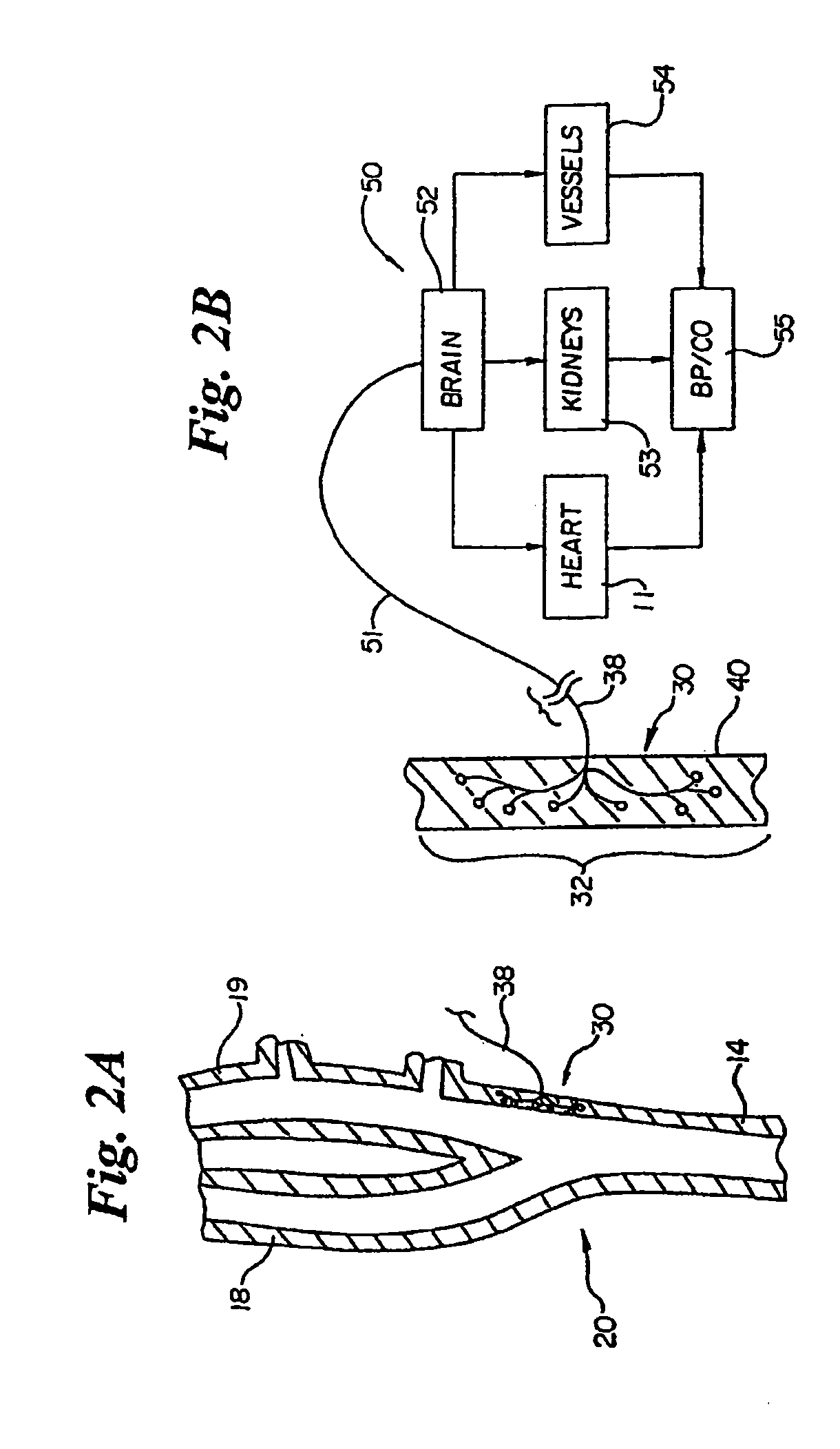
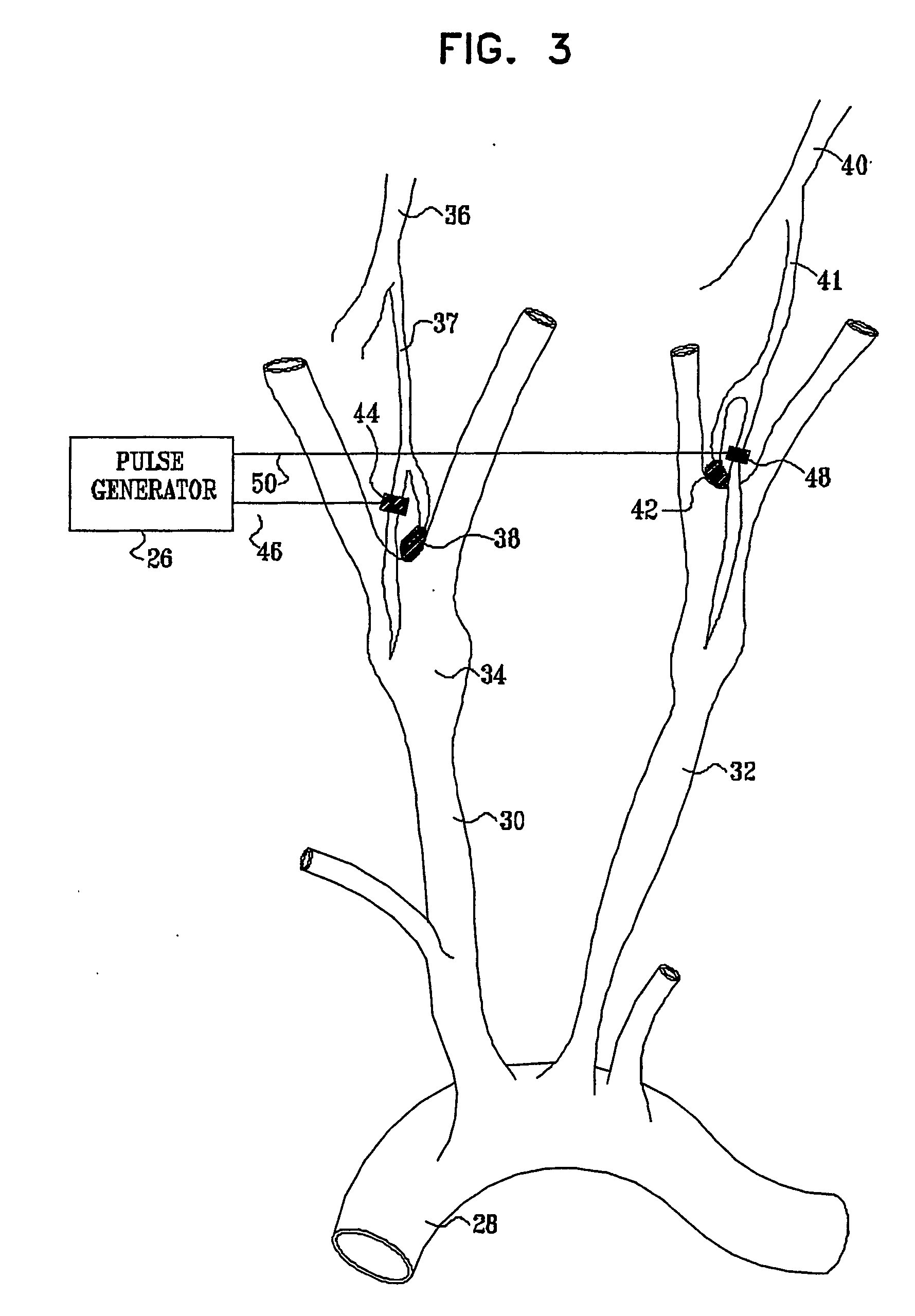
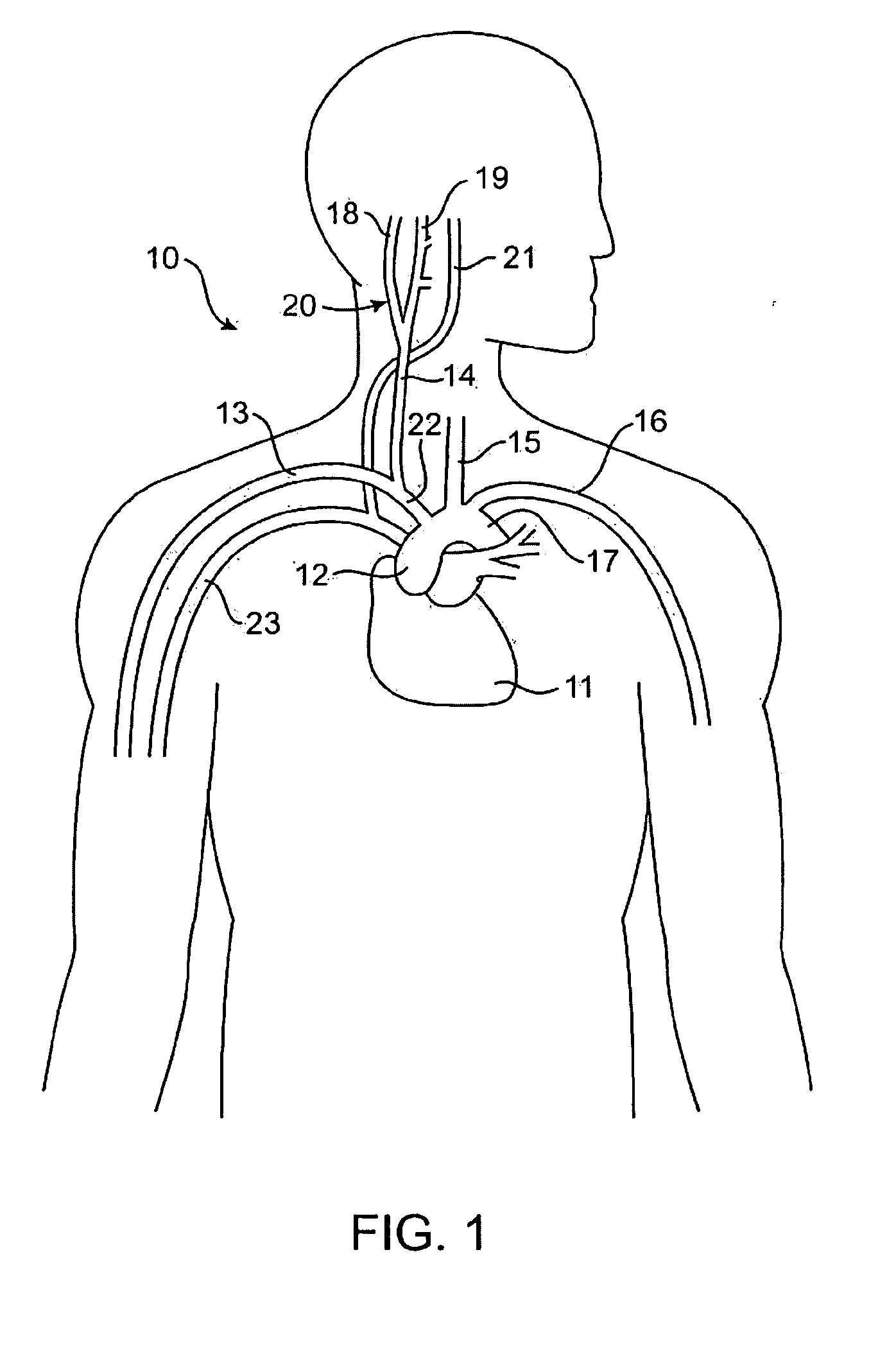
Devices, systems and methods by which the blood pressure, nervous system activity, and neurohornonal activity may be selectively and controllably reduced by activating baroreceptors. A baroreceptor activation device is positioned near a baroreceptor, preferably in the carotid sinus. The baroreceptor activation device may utilize electrodes to activate the baroreceptors. The electrodes may be adapted for connection to the carotid arteries at or near the carotid sinus, and may be designed to minimize extraneous tissue stimulation.
Owner:CVRX
Stimulus regimens for cardiovascular reflex control
ActiveUS20050251212A1Reduces excessive blood pressureDeleterious effectElectrotherapyAngle modulation detailsNervous systemRegimen
Devices, systems and methods by which the blood pressure, nervous system activity, and neurohormonal activity may be selectively and controllably reduced by activating baroreceptors. A baroreceptor activation device is positioned near a baroreceptor, for example a baroreceptor in the carotid sinus. A control system may be used to modulate the baroreceptor activation device. The control system may utilize an algorithm defining a stimulus regimen which promotes long term efficacy and reduces power requirements / consumption.
Owner:CVRX
Technique for blood pressure regulation
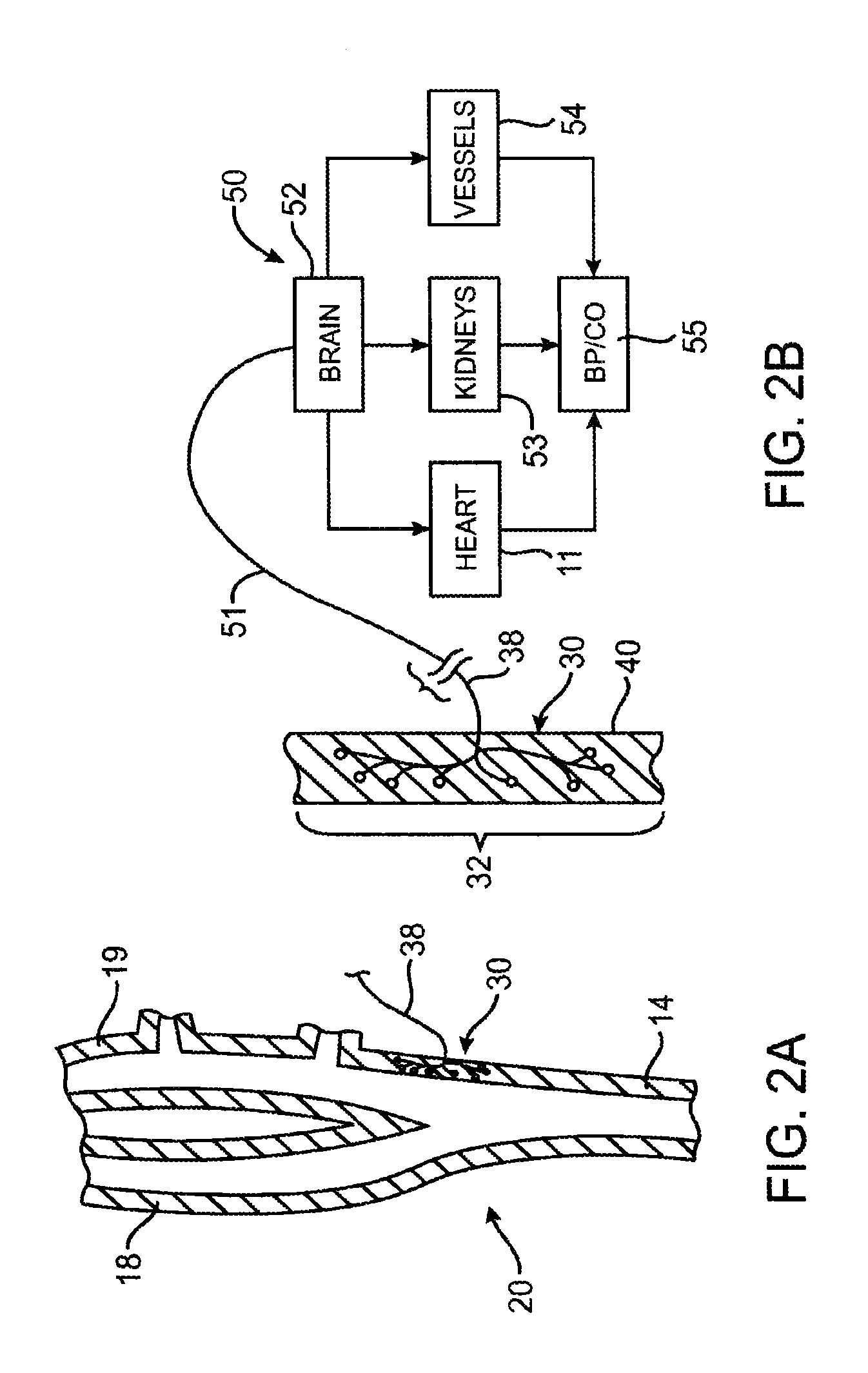
InactiveUS20060089678A1High baroreceptor discharge rateHigh activityInternal electrodesEvaluation of blood vesselsWhole bodyBaroreceptor function
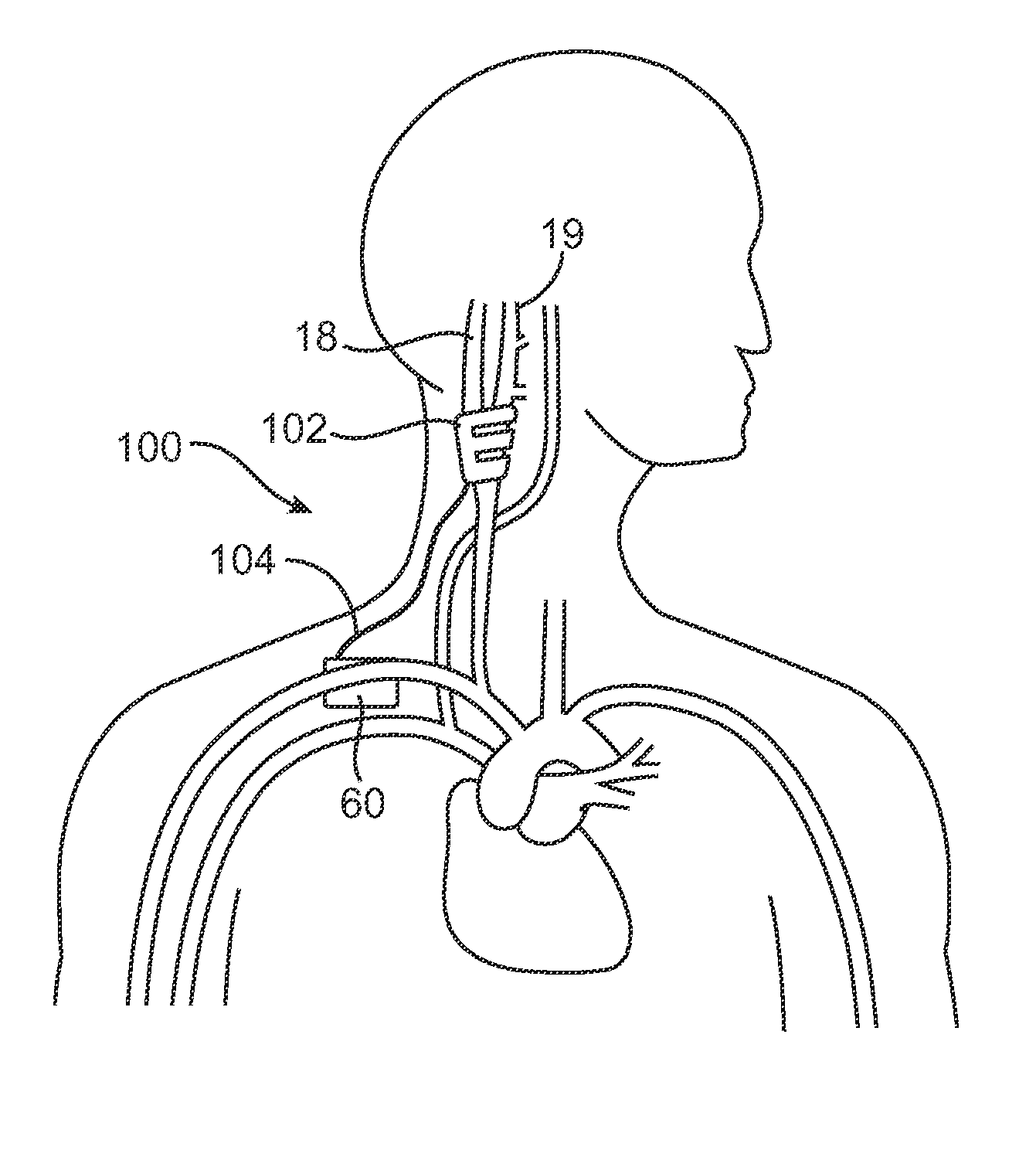
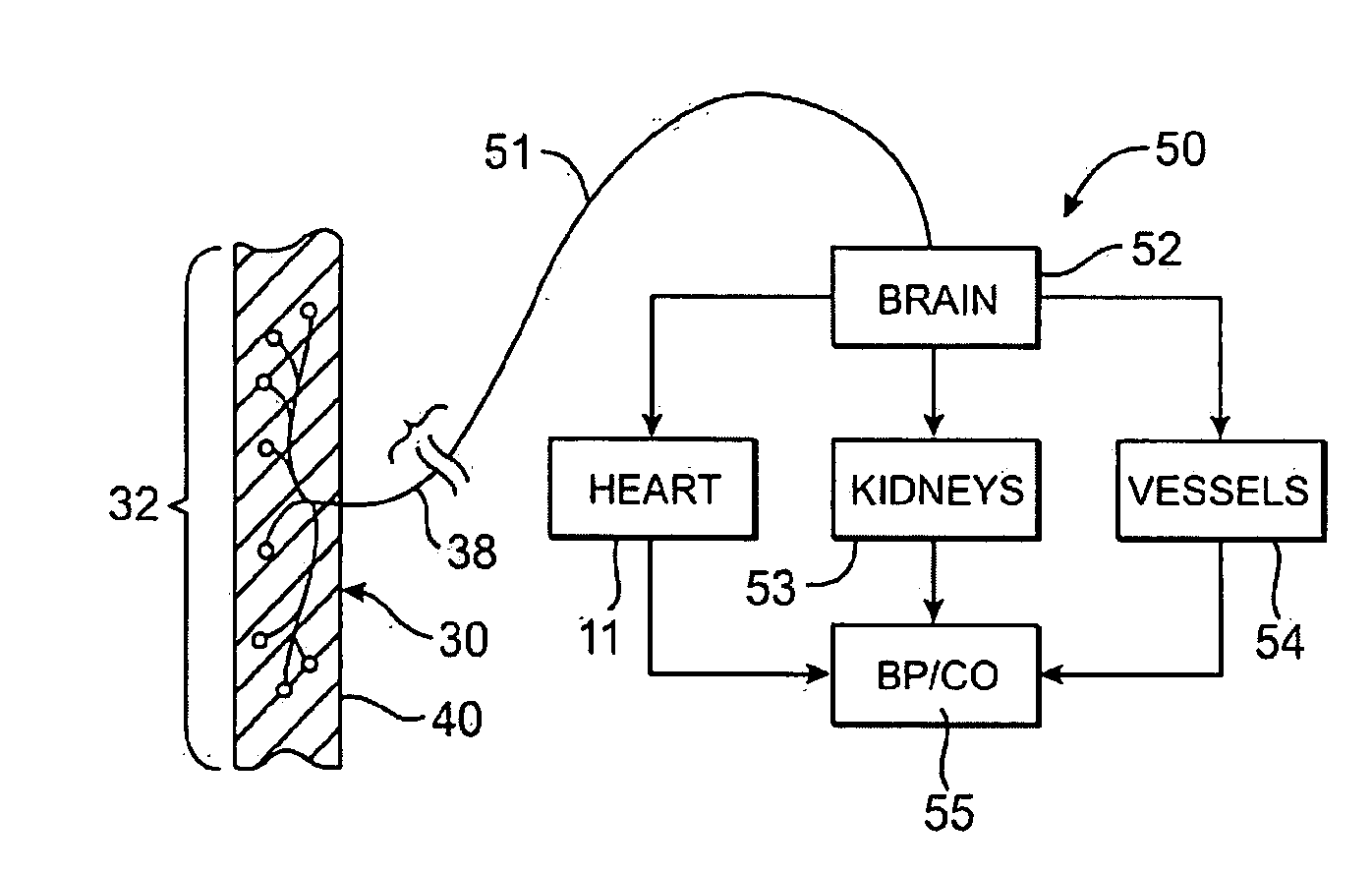
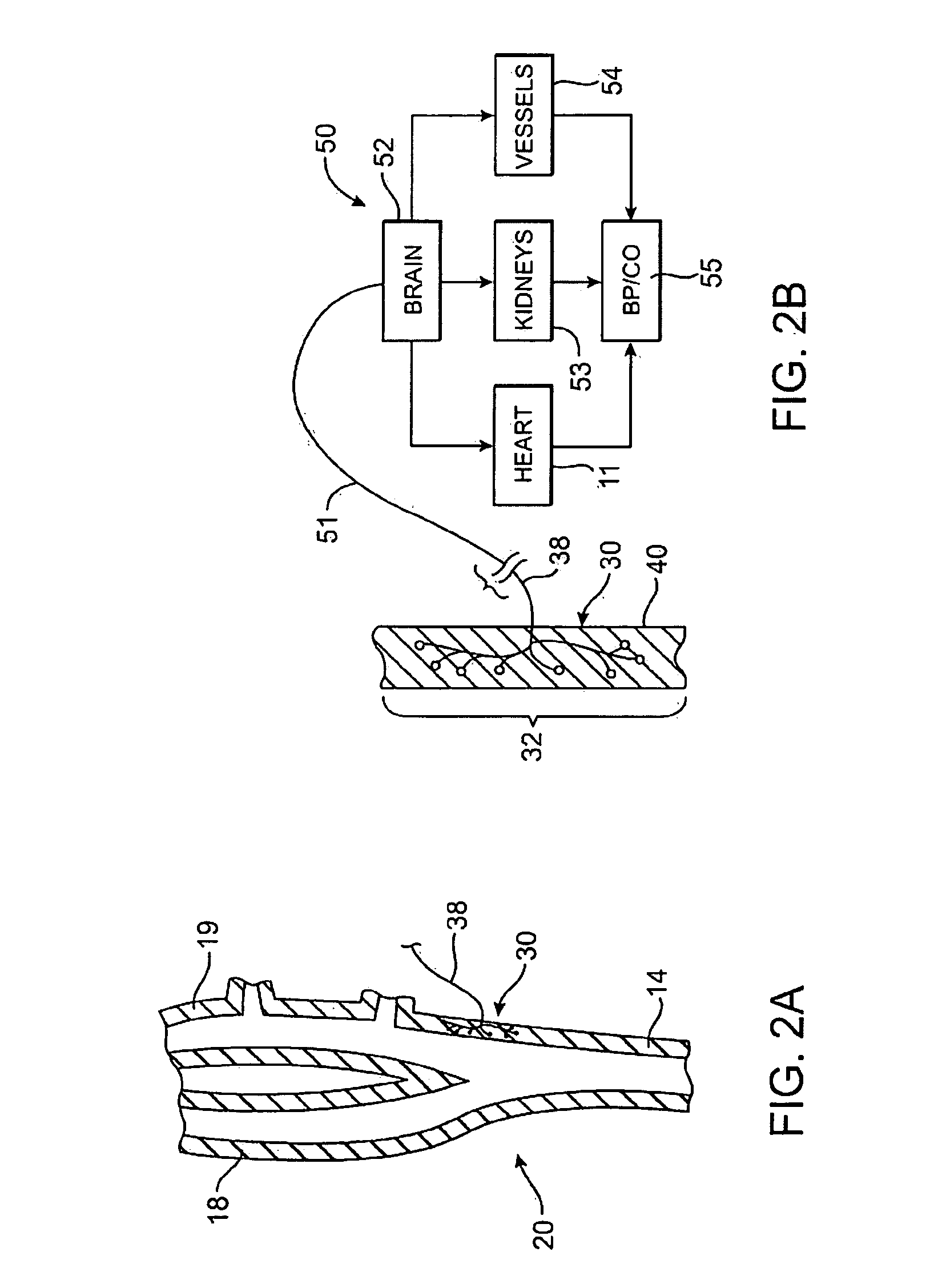
An implantable device (20) uses the carotid baroreflex in order to control systemic blood pressure. The implant includes sampling and pulse stimulation electrodes (44) preferably located on the carotid sinus nerve branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve, adjacent and distal to the carotid sinus baroreceptors. The stimulators have an external control unit, which communicates with the implant for determining appropriate operational parameters, and for retrieving telemetry information from the device's data bank. Typically two internal devices are implanted, one at each side of the patient's neck.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
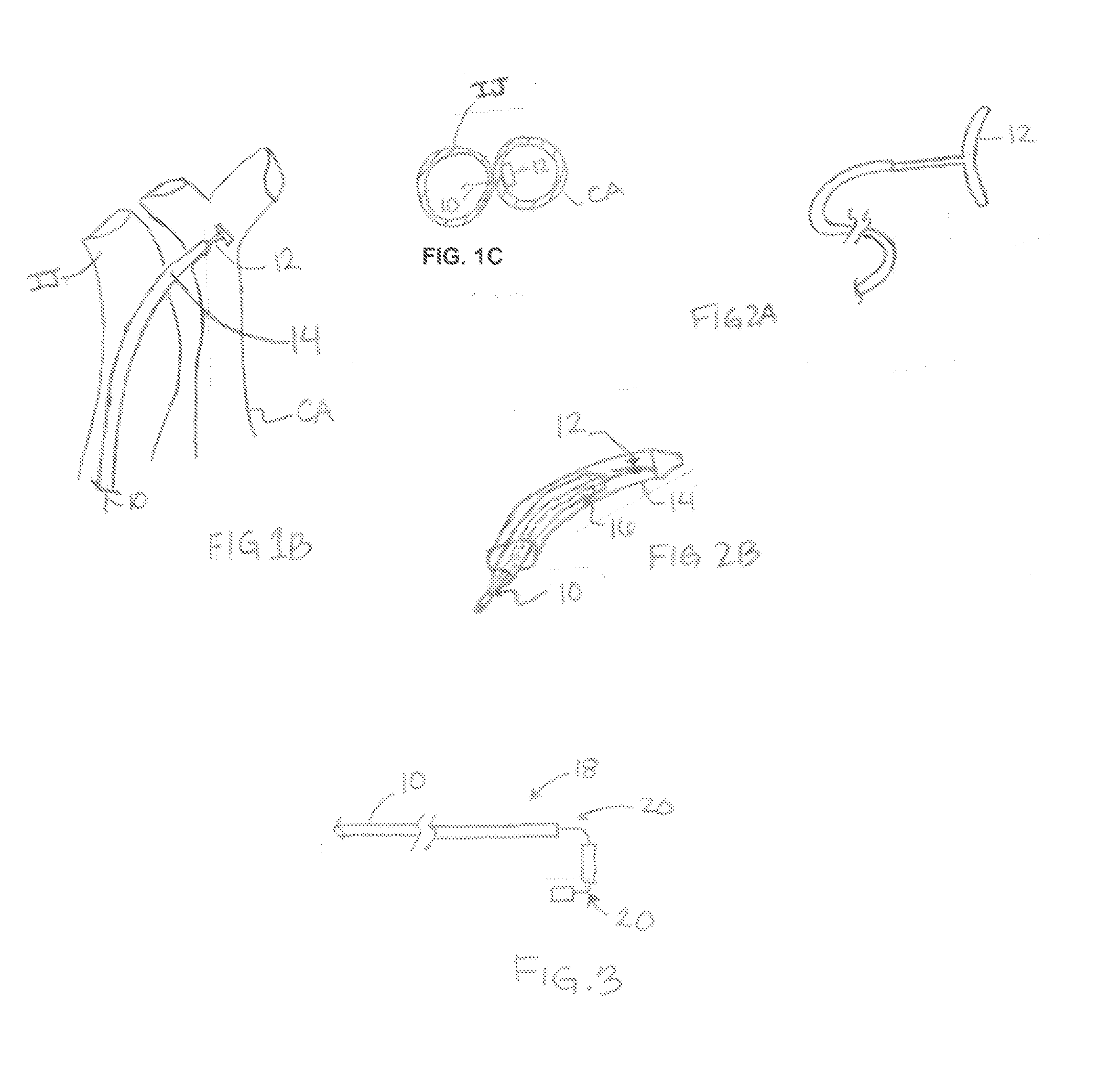
Apparatus and method for modulating the baroreflex system
An apparatus for insertion into a blood vessel and for modulating the baroreflex system of a mammal includes an expandable support member for engaging a wall of a blood vessel at a desired location where baroreceptors are located, and at least one electrode connected with the expandable support member. The at least one electrode is arranged to selectively deliver electric current to modulate the baroreceptors. The apparatus further includes an insulative material attached to at least a portion of the expandable support member for isolating blood flowing through the vessel from the electric current delivered by the at least one electrode.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
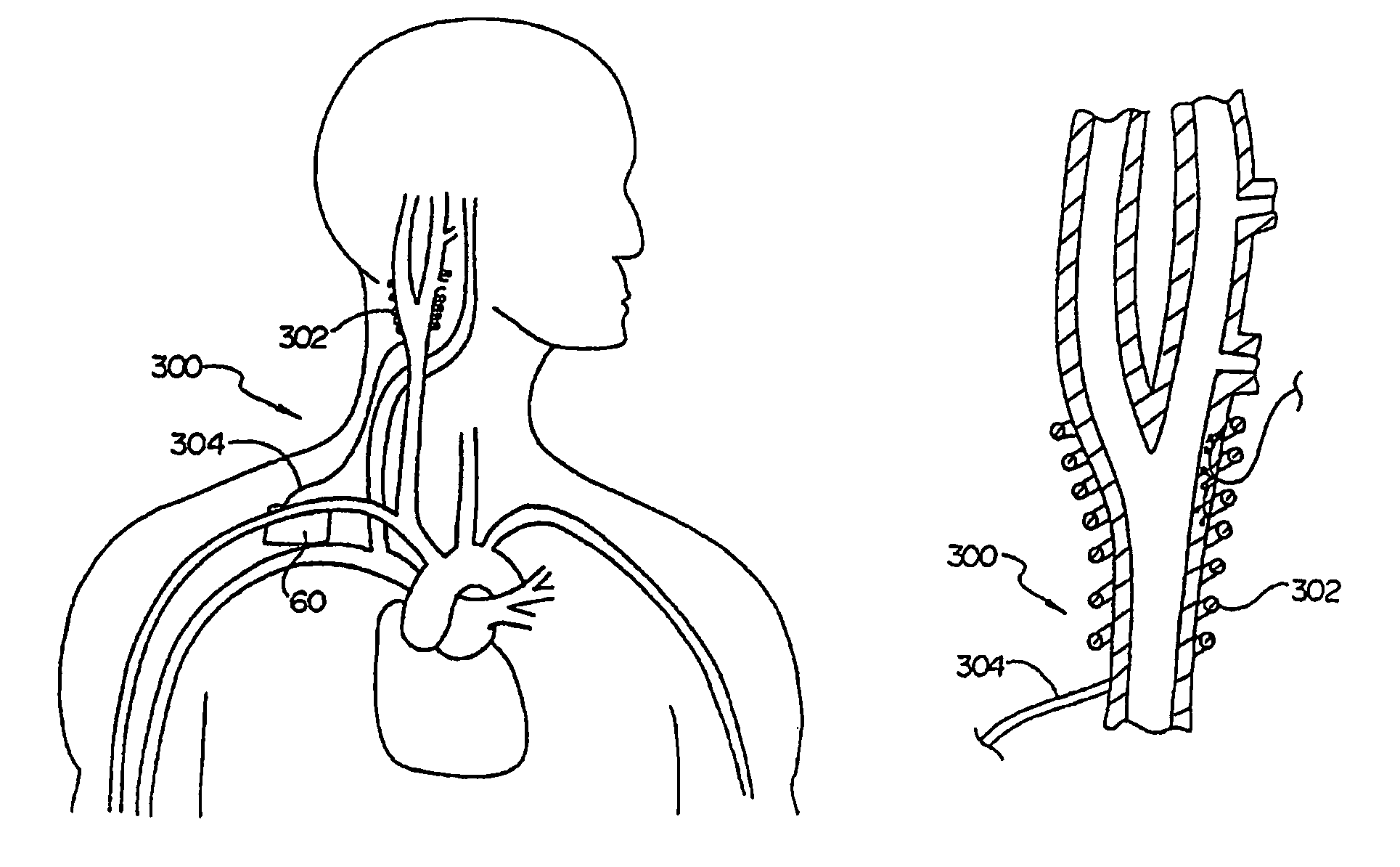
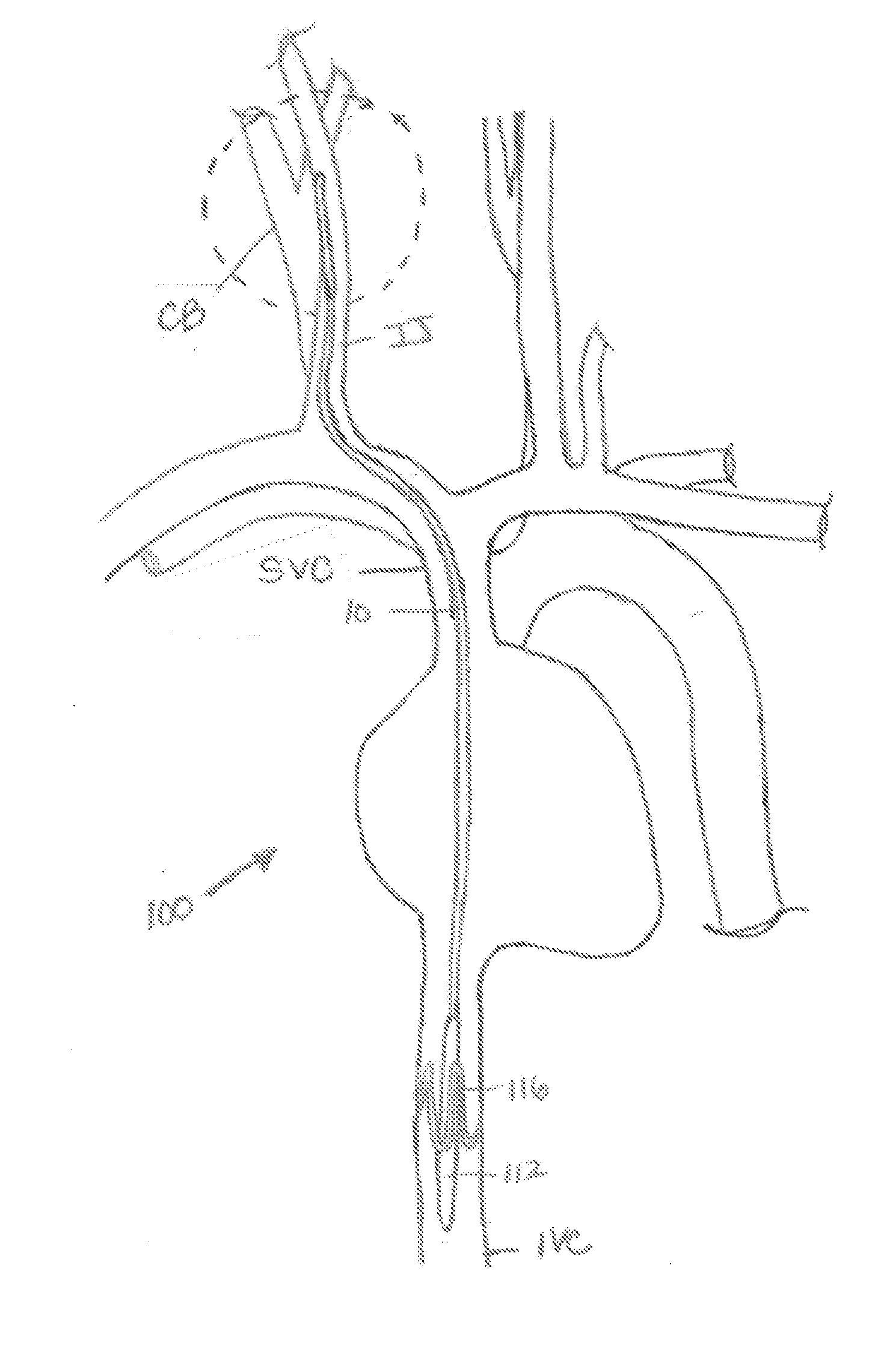
System and method for transvascularly stimulating contents of the carotid sheath
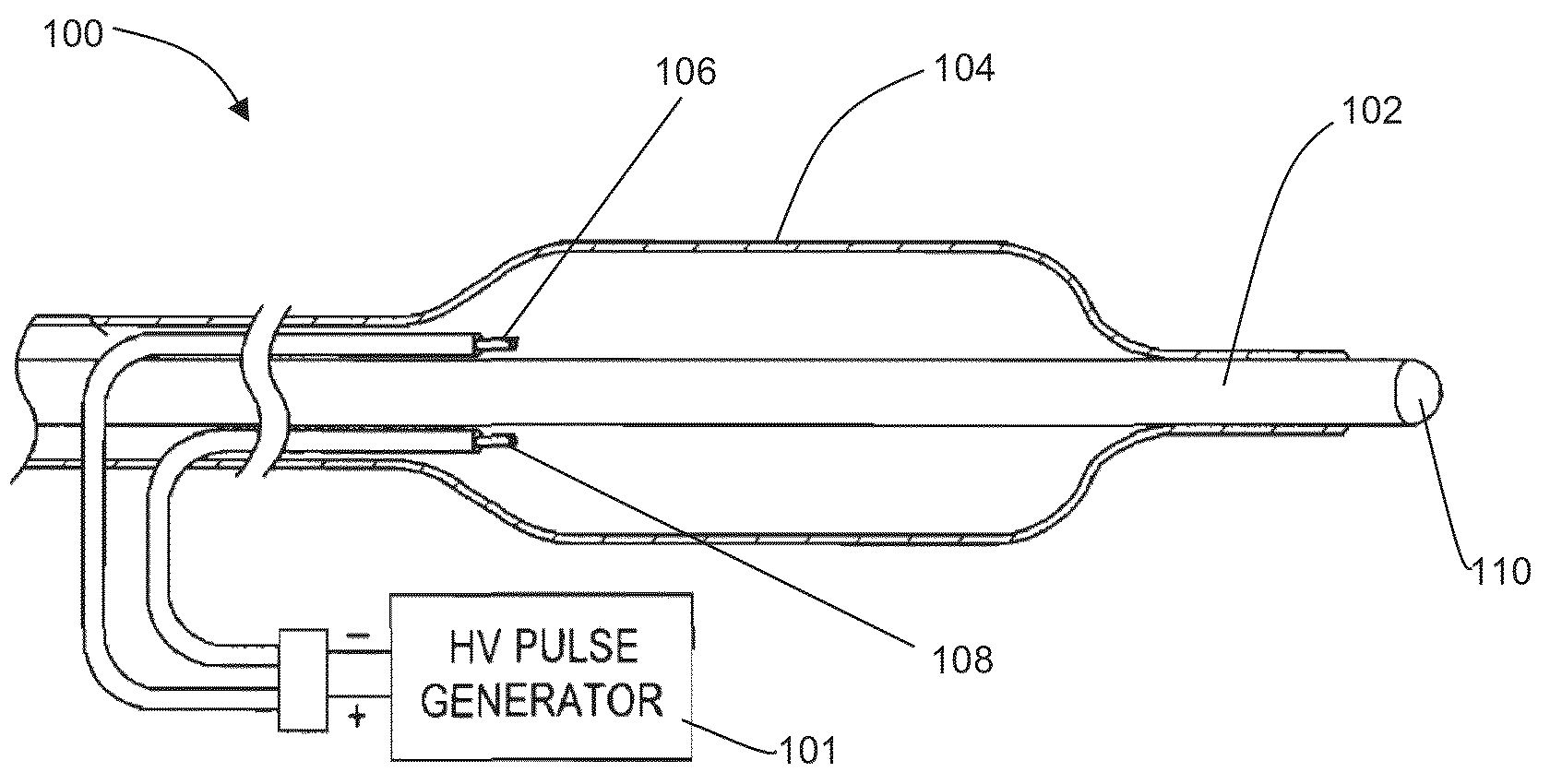
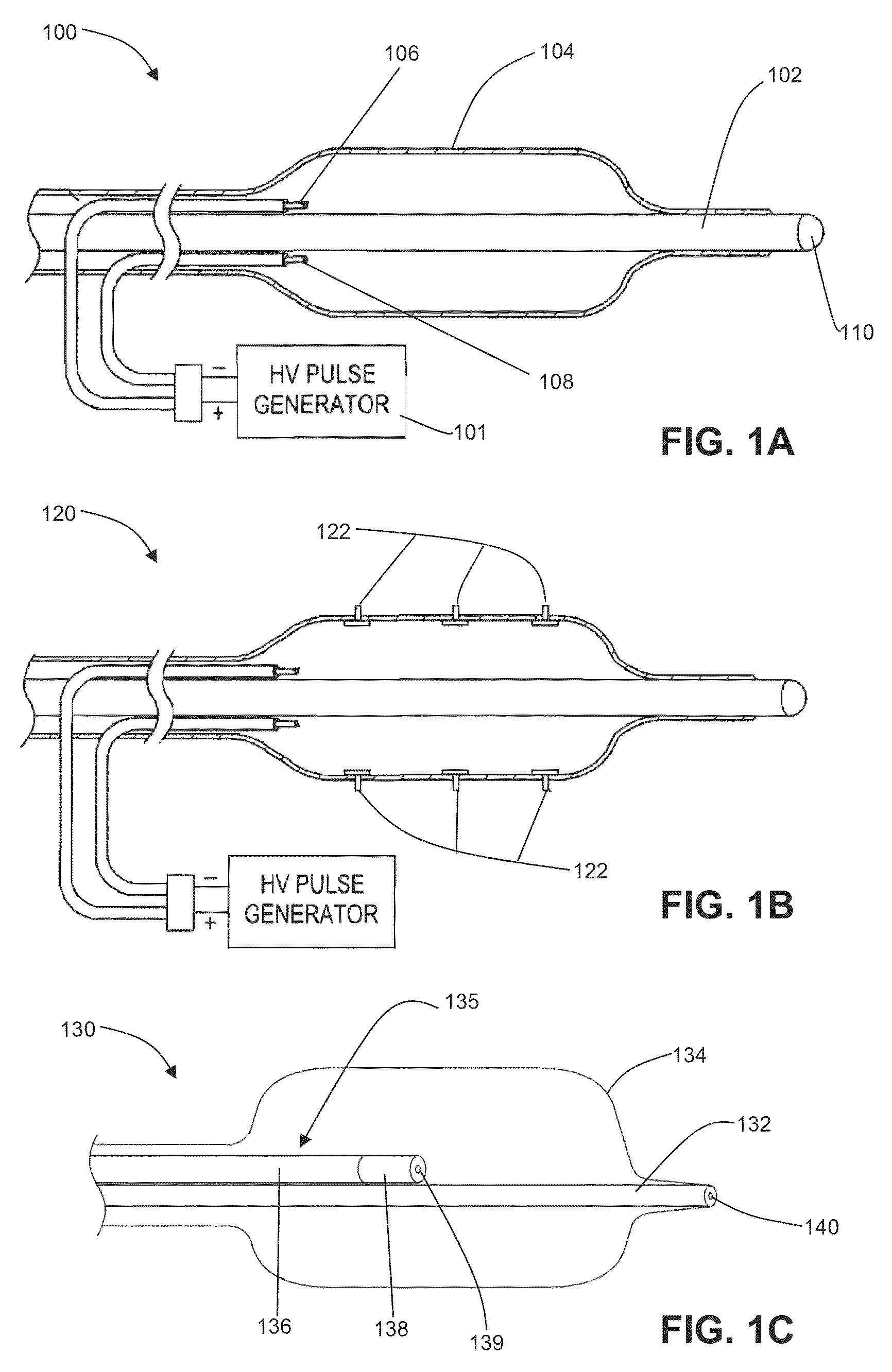
Methods and systems are disclosed for stimulating contents of the carotid sheath using an intravascular pulse generator and lead. The lead carries an energy delivery device such as an electrode, which is anchor within the portion of the internal jugular vein that is disposed within the carotid sheath. The energy delivery device is energized to transvenously direct energy to target contents of the carotid sheath external to the internal jugular vein. Such target contents may include nervous system elements associated with the carotid sinus baroreceptors, the carotid sinus nerve and associated nerve branches, and or the vagus nerve and associated nerve branches. The system may be used to control blood pressure and / or to lower heart rate and may be suitable for treatment of hypertension, heart failure, or other conditions.
Owner:NUXCEL2 LLC
System and method for transvascularly stimulating contents of the carotid sheath
Methods and systems are disclosed for stimulating contents of the carotid sheath using an intravascular pulse generator and lead. The lead carries an energy delivery device such as an electrode, which is anchor within the portion of the internal jugular vein that is disposed within the carotid sheath. The energy delivery device is energized to transvenously direct energy to target contents of the carotid sheath external to the internal jugular vein. Such target contents may include nervous system elements associated with the carotid sinus baroreceptors, the carotid sinus nerve and associated nerve branches, and or the vagus nerve and associated nerve branches. The system may be used to control blood pressure and / or to lower heart rate and may be suitable for treatment of hypertension, heart failure, or other conditions.
Owner:NUXCEL2 LLC
Stimulus regimens for cardiovascular reflex control
InactiveUS7840271B2Reduce pressureDeleterious effectElectrotherapyAngle modulation detailsNervous systemRegimen
Devices, systems and methods by which the blood pressure, nervous system activity, and neurohormonal activity may be selectively and controllably reduced by activating baroreceptors. A baroreceptor activation device is positioned near a baroreceptor, for example a baroreceptor in the carotid sinus. A control system may be used to modulate the baroreceptor activation device. The control system may utilize an algorithm defining a stimulus regimen which promotes long term efficacy and reduces power requirements / consumption.
Owner:CVRX
Baroreflex Therapy for Disordered Breathing
InactiveUS20070021794A1RemissionReduce pressureSpinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesBaroreceptor functionBiological activation
A method is provided for treating respiration conditions of a patient. The method comprises monitoring or measuring a respiration parameter indicative of a need to modify activity of a baroreflex system of the patient, and controlling a baroreceptor activation device to cause or modify activation of a baroreflex response of the patient in response to the monitoring or measuring of the respiration parameter.
Owner:CVRX
Methods and Devices for Treating Hypertension
Devices, systems and methods are described which control blood pressure and nervous system activity by stimulating baroreceptors. By selectively and controllably activating baroreceptors and / or nerves, the present invention reduces blood pressure and alters the sympathetic nervous system; thereby minimizing deleterious effects on the heart, vasculature and other organs and tissues. A baroreceptor activation device or other sensory activation device is positioned near a dermal bone to provide the treatment.
Owner:SYMPARA MEDICAL
Shockwave nerve therapy system and method
ActiveUS20140046229A1Reduce and block activationModulate neural activitySurgeryChiropractic devicesBaroreceptor functionBiological activation
Disclosed herein are intravascular systems and methods for modulating the activation of neural activity using shock wave devices. Such systems and methods may be used to modulate the activity of the renal plexus and / or baroreceptors of the carotid sinus for the treatment of hypertension.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
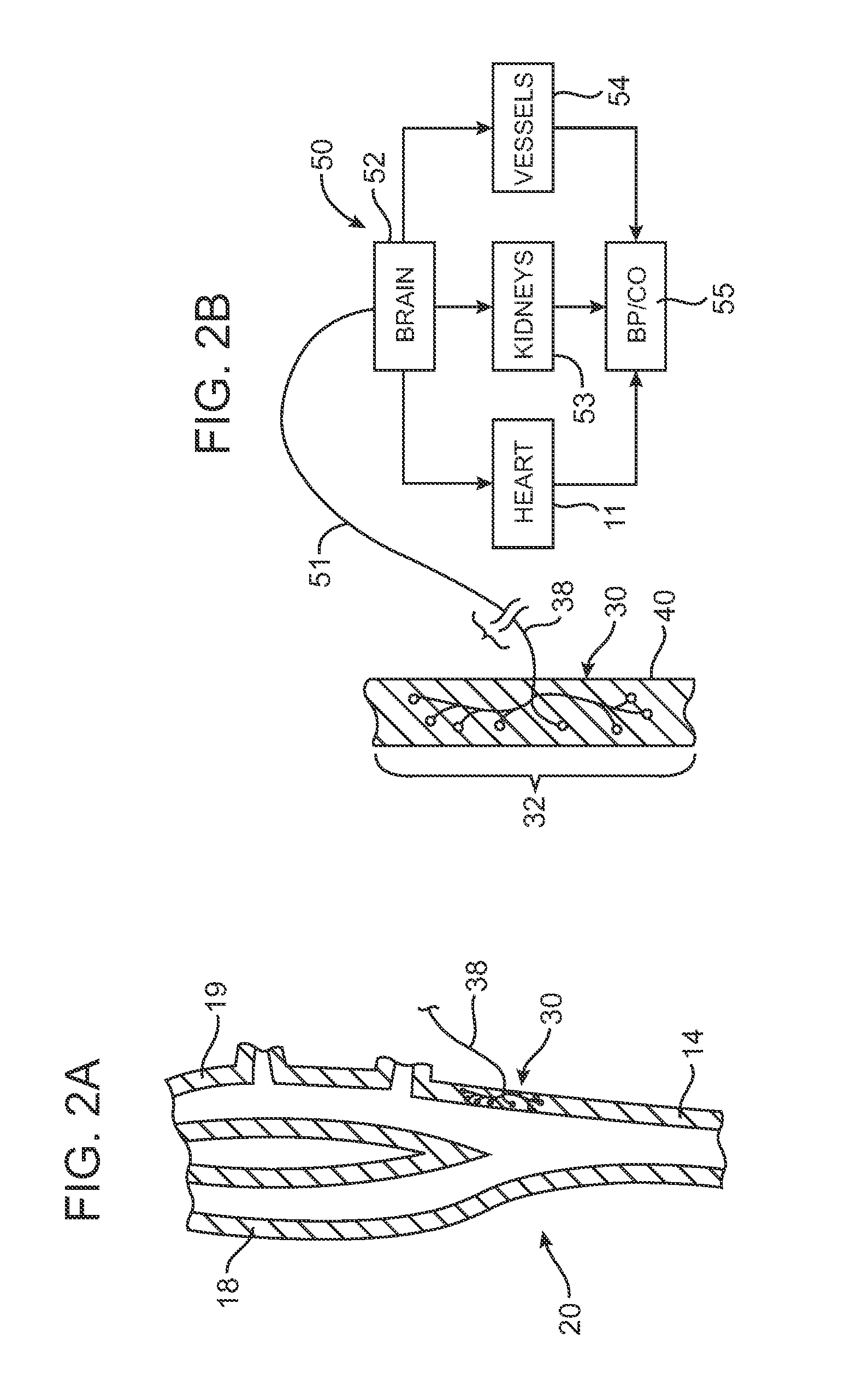
Intravascular system and method for blood pressure control
InactiveUS20100211131A1Spinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesNervous systemBlood vessel
An intravascular lead is used to deliver energy for stimulating nervous system targets using energy delivery elements (e.g. electrodes) that are in direct contact with the nervous system targets. The lead may be positioned within the internal jugular vein and the nervous system targets may include the carotid artery / carotid sinus bulb and / or associated baroreceptor afferents, and / or surrounding nervous system targets in the region of the internal jugular vein, such as the carotid sinus nerve and / or associated nerve branches and / or the vagus nerve and / or associated nerve branches. Stimulation energy travels along a conductive bridge that extends from the intravascular lead to the nervous system target, or is relayed from the intravascular lead to another device disposed within or surrounding the target structure.
Owner:INTERVENTIONAL AUTONOMICS
Method and system for implantable pressure transducer for regulating blood pressure
ActiveUS7835797B2Facilitate communicationReduce and increase blood pressureSpinal electrodesElectrical conductorElectro stimulation
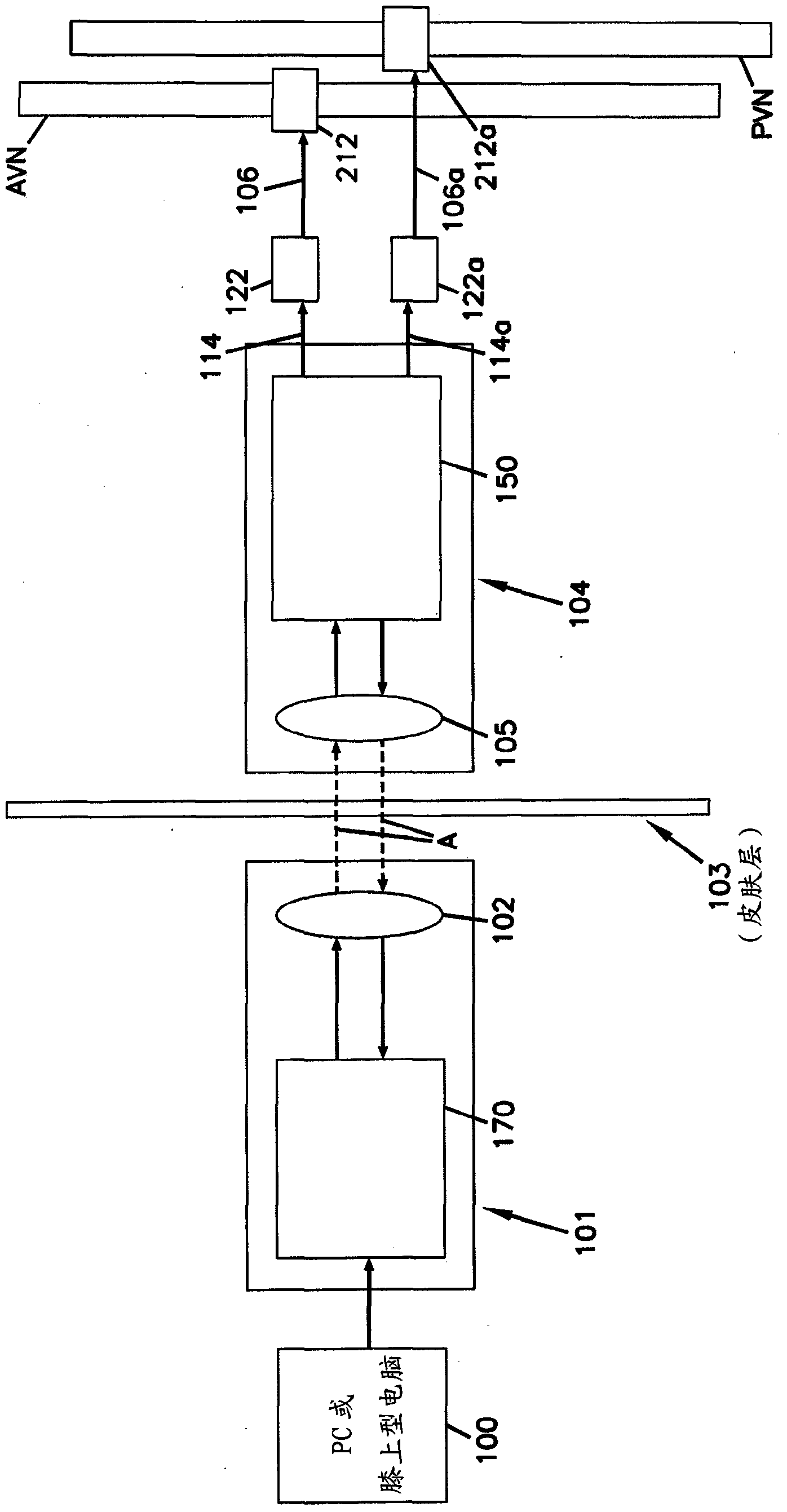
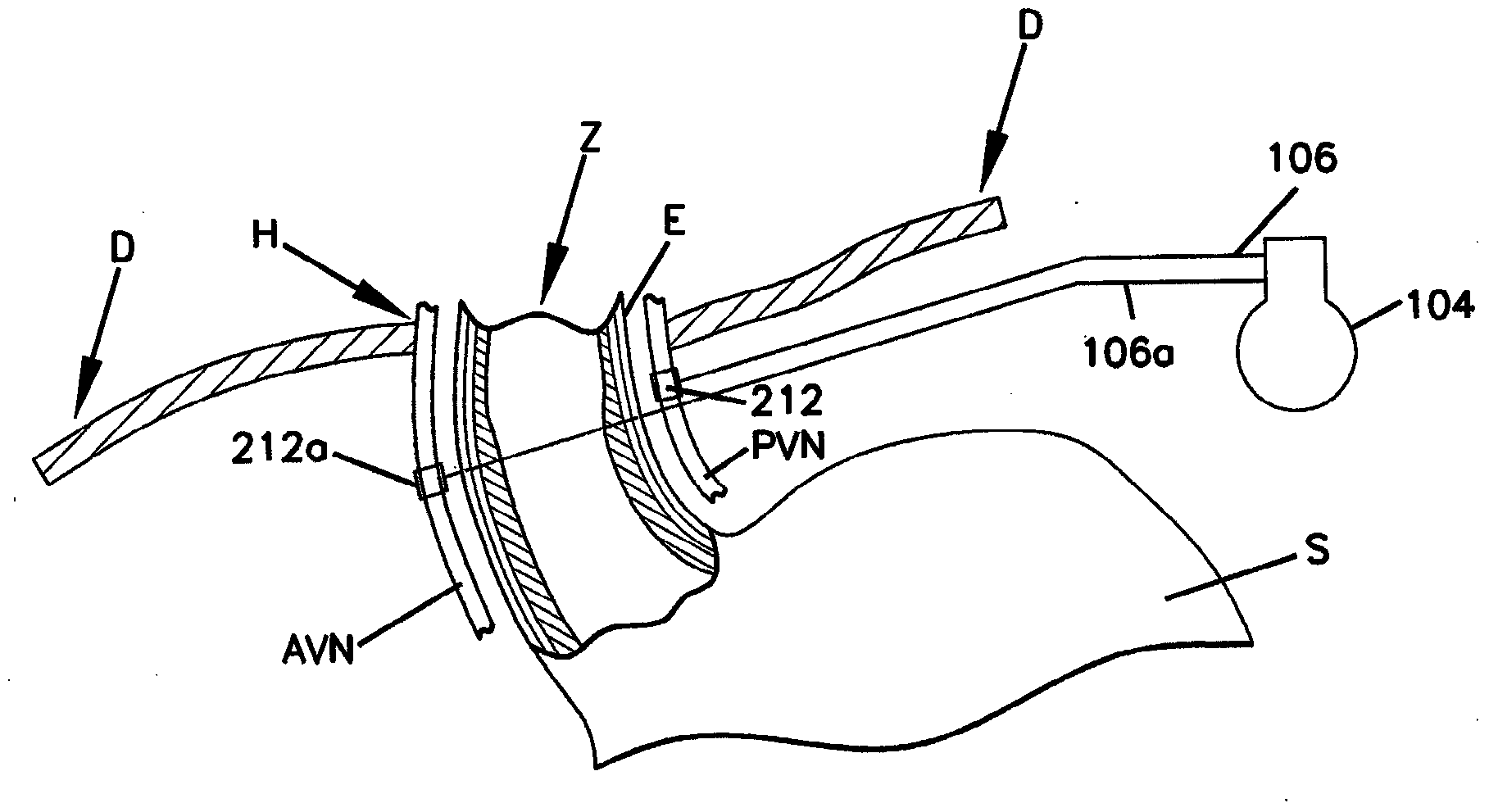
An apparatus and a system can chronically and automatically measure a physiologic parameter associated with the high pressure side of the vasculature and / or regulate blood pressure based upon the measured parameter. The apparatus may be made up of a transducer, a baroreflex activation device having one or more electrodes, and a lead having two or more conductors. The system can measure a physiologic parameter and selectively administer a therapy, such as, for example, electro-stimulation of baroreceptors, based upon the measurement. The transducer for measuring the physiologic parameter can be chronically implanted in the high-pressure side of the vasculature. The implantation method may include intravascularly positioning the transducer in the external carotid artery in such a way that the transducer is first introduced into the arterial vasculature through the superior thyroid artery.
Owner:CVRX
Methods and devices for treating hypertension
InactiveUS20150305974A1Lower blood pressureChiropractic devicesInertial sensorsNervous systemMedicine
Devices, systems and methods are described which control blood pressure and nervous system activity by stimulating baroreceptors. By selectively and controllably activating baroreceptors and / or nerves, the present disclosure, according to some embodiments reduces blood pressure and alters the sympathetic nervous system; thereby minimizing deleterious effects on the heart, vasculature and other organs and tissues. A baroreceptor activation device or other sensory activation device is positioned near a dermal bone to provide the treatment.
Owner:SYMPARA MEDICAL
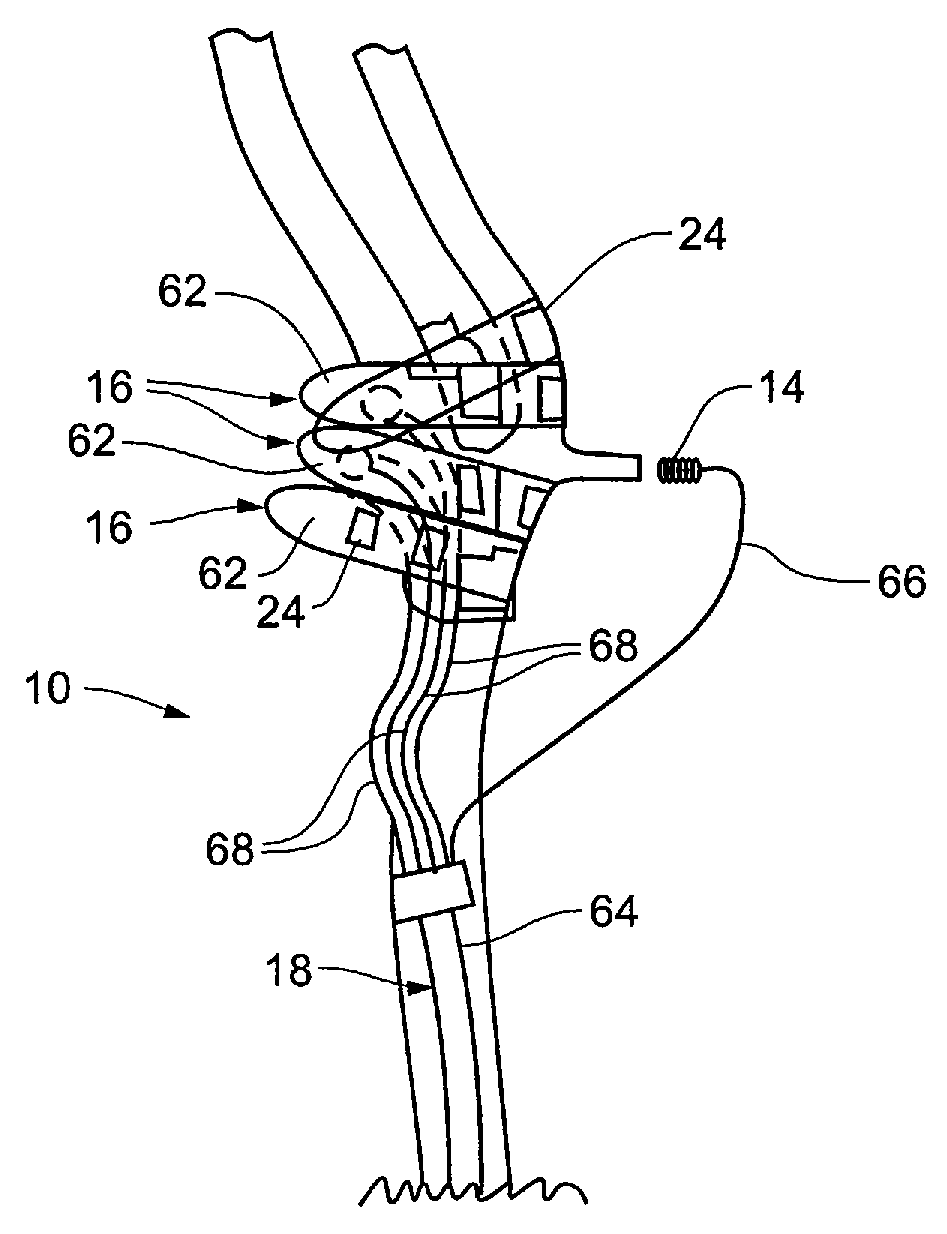
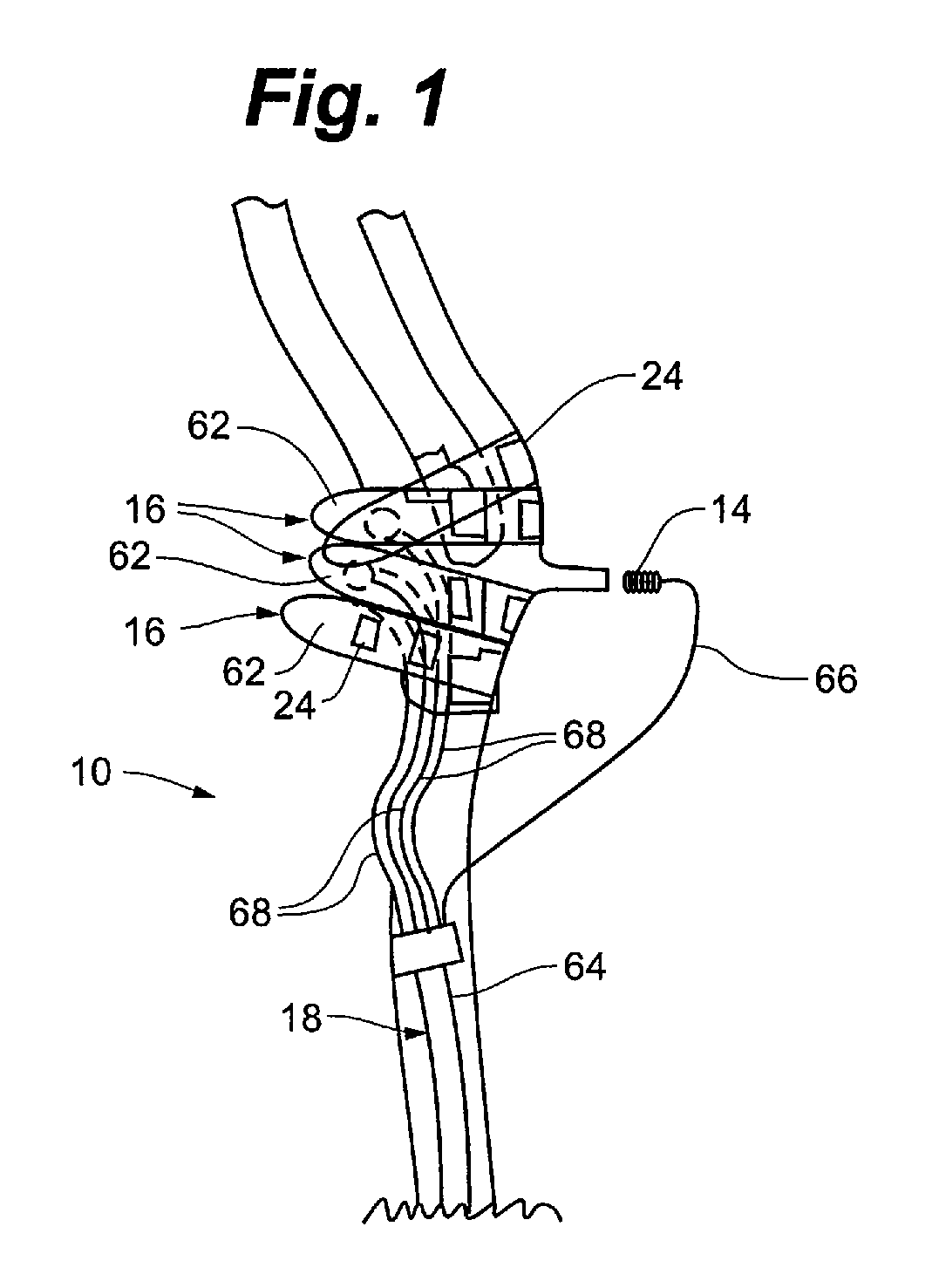
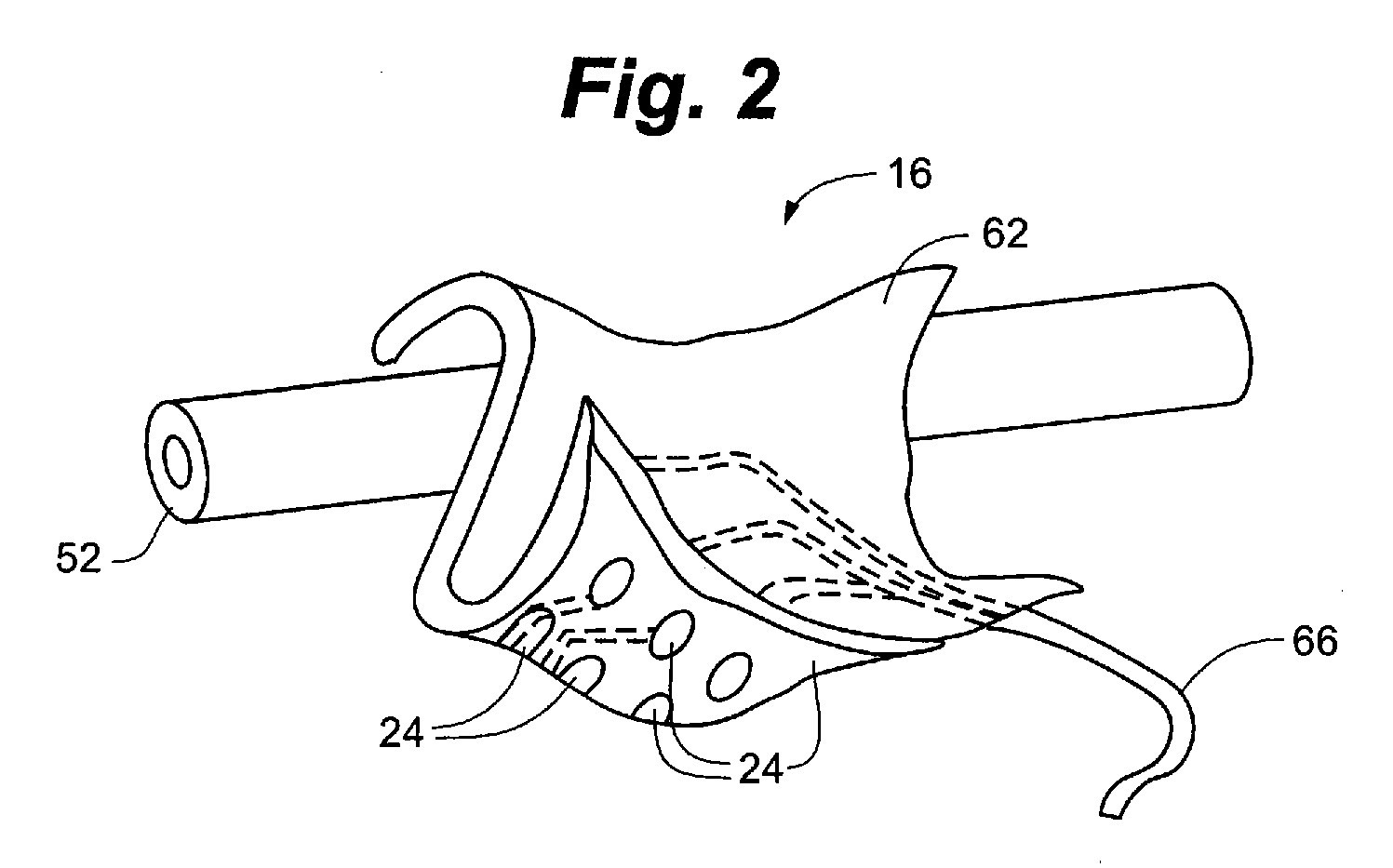
Devices for regulation of blood pressure and heart rate
InactiveUS20130237948A1Downregulate activityImprove efficiencyElectrotherapyWave amplification devicesSplanchnic nervesBlocking nerve
A method and apparatus for treating a condition associated with impaired blood pressure and / or heart rate in a subject comprising applying an electrical treatment signal, wherein the electrical treatment signal is selected to at least partially block nerve impulses, or in some embodiments, to augment nerve impulses. In embodiments, the apparatus provides a first therapy program to provide a downregulating signal to one or more nerves including renal artery, renal nerve, vagus nerve, celiac plexus, a splanchnic nerve, cardiac sympathetic nerves, spinal nerves originating between T10 to L5. In embodiments, the apparatus provides a third therapy program to provide an upregulating signal to one or more nerves including a glossopharyngeal nerve and / or a tissue containing baroreceptors.
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
Method and system for implantable pressure transducer for regulating blood pressure
ActiveUS20090143837A1Facilitate communicationLower blood pressureSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationElectrical conductorElectro stimulation
An apparatus and a system can chronically and automatically measure a physiologic parameter associated with the high pressure side of the vasculature and / or regulate blood pressure based upon the measured parameter. The apparatus may be made up of a transducer, a baroreflex activation device having one or more electrodes, and a lead having two or more conductors. The system can measure a physiologic parameter and selectively administer a therapy, such as, for example, electro-stimulation of baroreceptors, based upon the measurement. The transducer for measuring the physiologic parameter can be chronically implanted in the high-pressure side of the vasculature. The implantation method may include intravascularly positioning the transducer in the external carotid artery in such a way that the transducer is first introduced into the arterial vasculature through the superior thyroid artery.
Owner:CVRX
Methods and Devices for Treating Hypertension
Devices, systems and methods are described which control blood pressure and nervous system activity by stimulating baroreceptors. By selectively and controllably activating baroreceptors and / or nerves, the present invention reduces blood pressure and alters the sympathetic nervous system; thereby minimizing deleterious effects on the heart, vasculature and other organs and tissues. A baroreceptor activation device or other sensory activation device is positioned near a dermal bone to provide the treatment.
Owner:SYMPARA MEDICAL
Treatment of peripheral vascular disease by baroreflex activation
InactiveUS20080167690A1Relieve symptomsImprove local vasodilationElectrotherapyDiseaseVascular disease
Peripheral vascular diseases, such as peripheral artery disease, are treated by activating a baroreflex response of a patient suffering from or at risk of these conditions. In the exemplary embodiments, the baroreflex response is activated using an implantable system comprising a controller and a device which activates the baroreceptor or baroreceptor nerve in order to initiate the baroreflex response.
Owner:CVRX
Shockwave nerve therapy system and method
ActiveUS9237984B2Reduce and block activationModulate neural activitySurgeryVibration massageBaroreceptor functionBiological activation
Disclosed herein are intravascular systems and methods for modulating the activation of neural activity using shock wave devices. In one embodiment, the system is used to treat the nerves in the renal plexus. In a second embodiment, the system is used to treat the baroreceptors in the carotid sinus. In a preferred embodiment, the shock wave generator is in the form of electrodes mounted within an inflatable balloon.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Methods and Devices for Treating Hypertension
Devices, systems and methods are described which control blood pressure and nervous system activity by stimulating baroreceptors. By selectively and controllably activating baroreceptors and / or nerves, the present invention reduces blood pressure and alters the sympathetic nervous system; thereby minimizing deleterious effects on the heart, vasculature and other organs and tissues. A baroreceptor activation device or other sensory activation device is positioned near a dermal bone to provide the treatment.
Owner:SYMPARA MEDICAL
Methods and Devices for Treating Hypertension
Devices, systems and methods are described which control blood pressure and nervous system activity by stimulating baroreceptors. By selectively and controllably activating baroreceptors and / or nerves, the present disclosure reduces blood pressure and alters the sympathetic nervous system; thereby minimizing deleterious effects on the heart, vasculature and other organs and tissues. A baroreceptor activation device or other sensory activation device is positioned near a dermal bone to provide the treatment.
Owner:SYMPARA MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for monitoring the baroreceptor reflex of a user
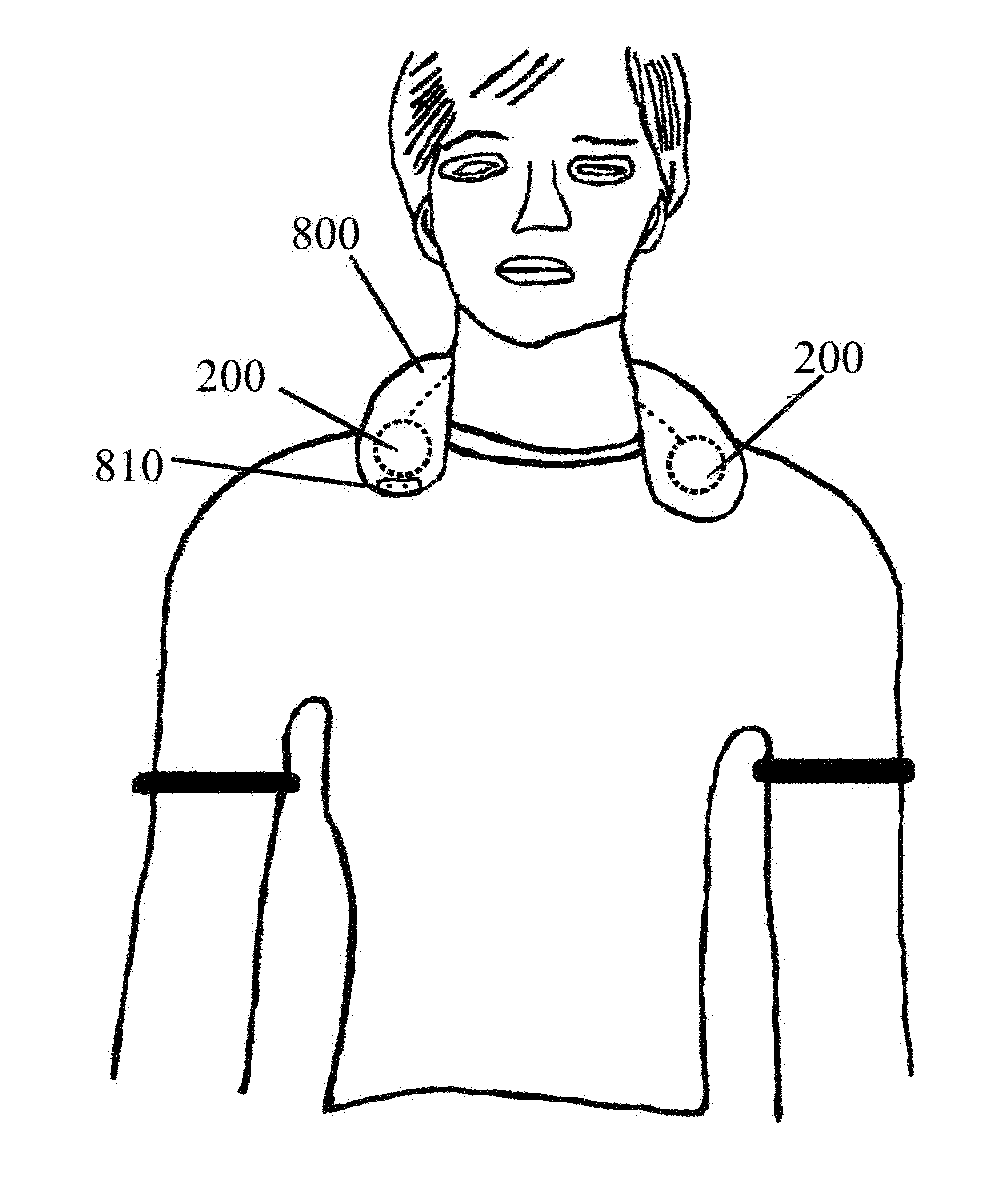
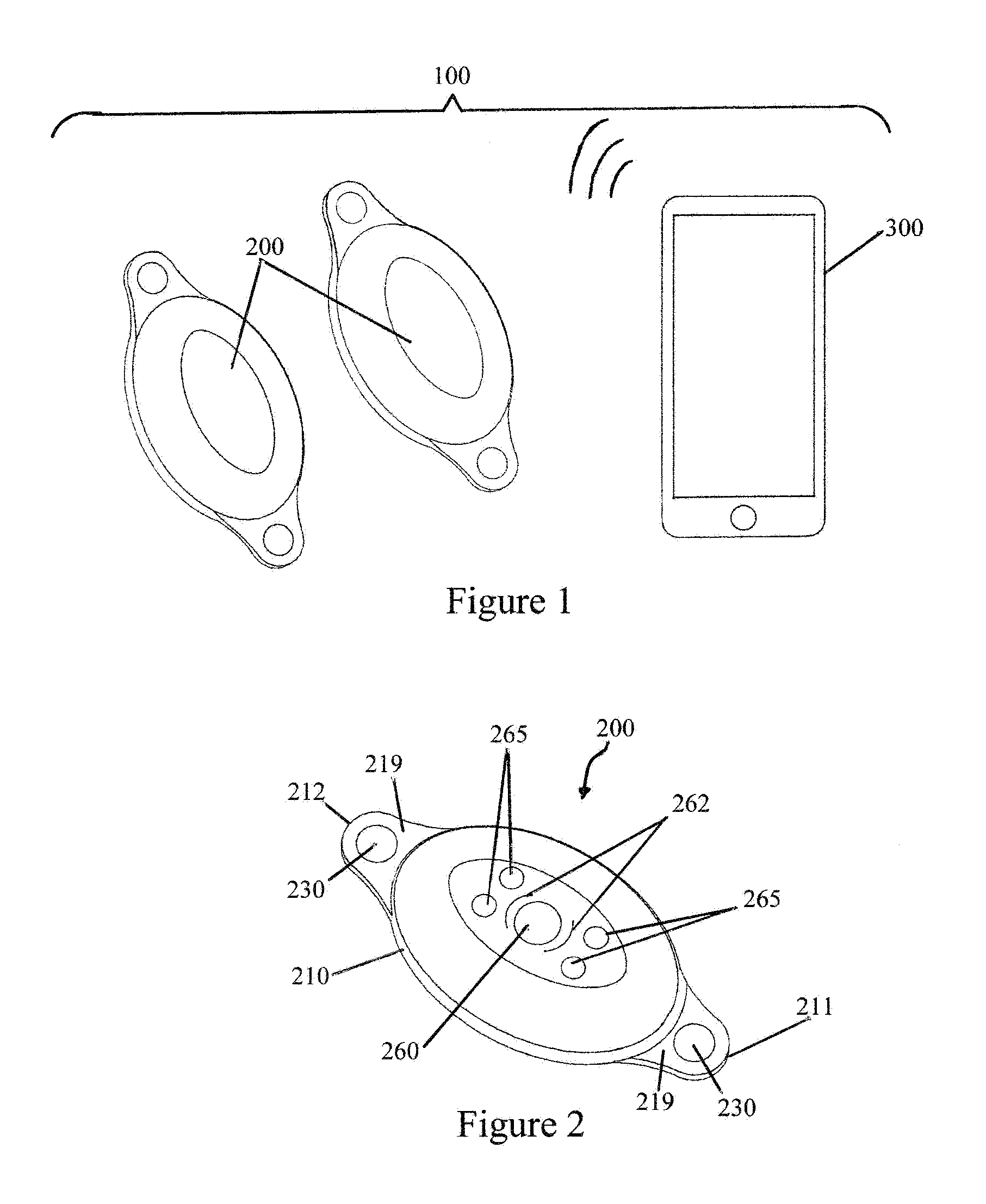
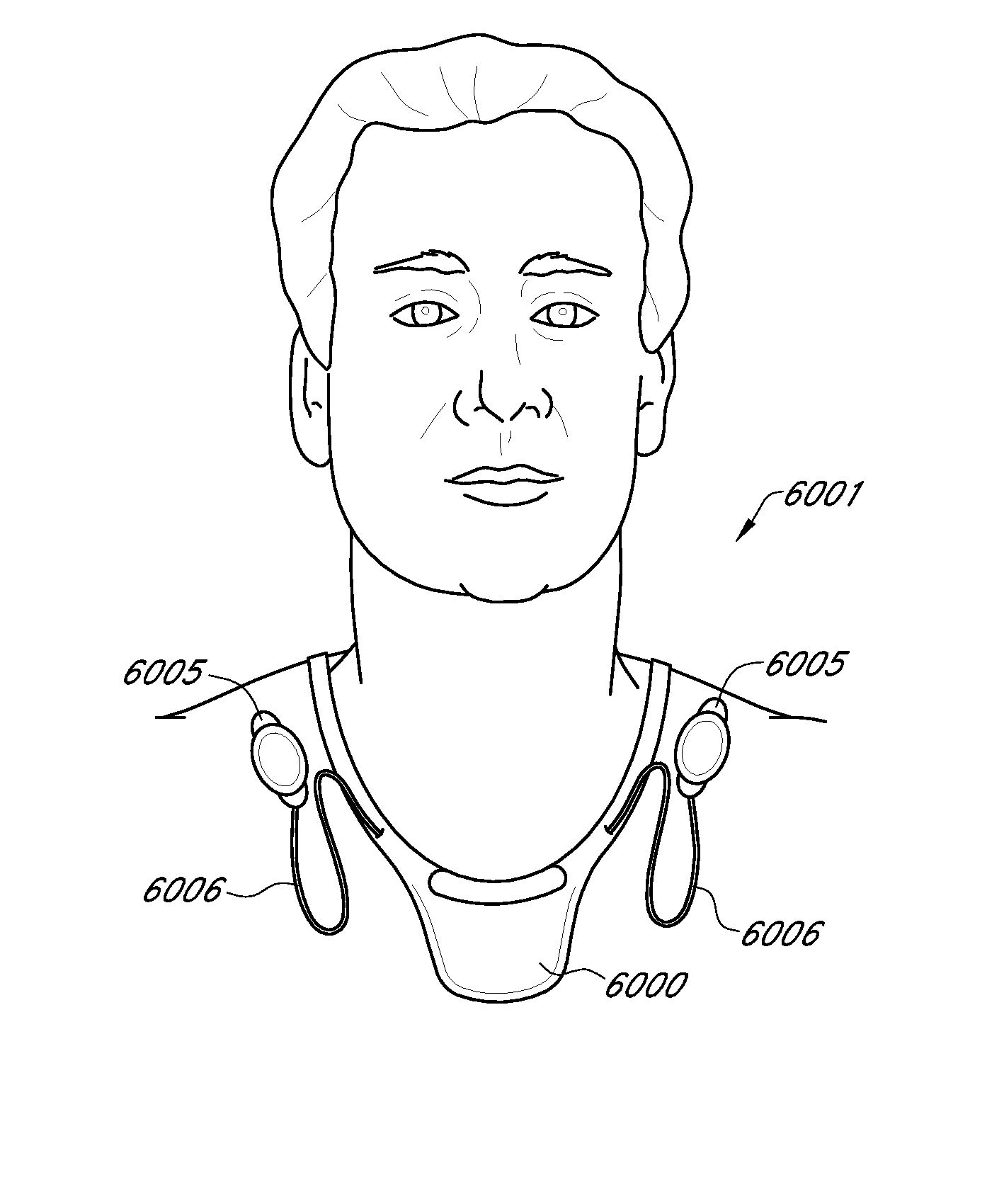
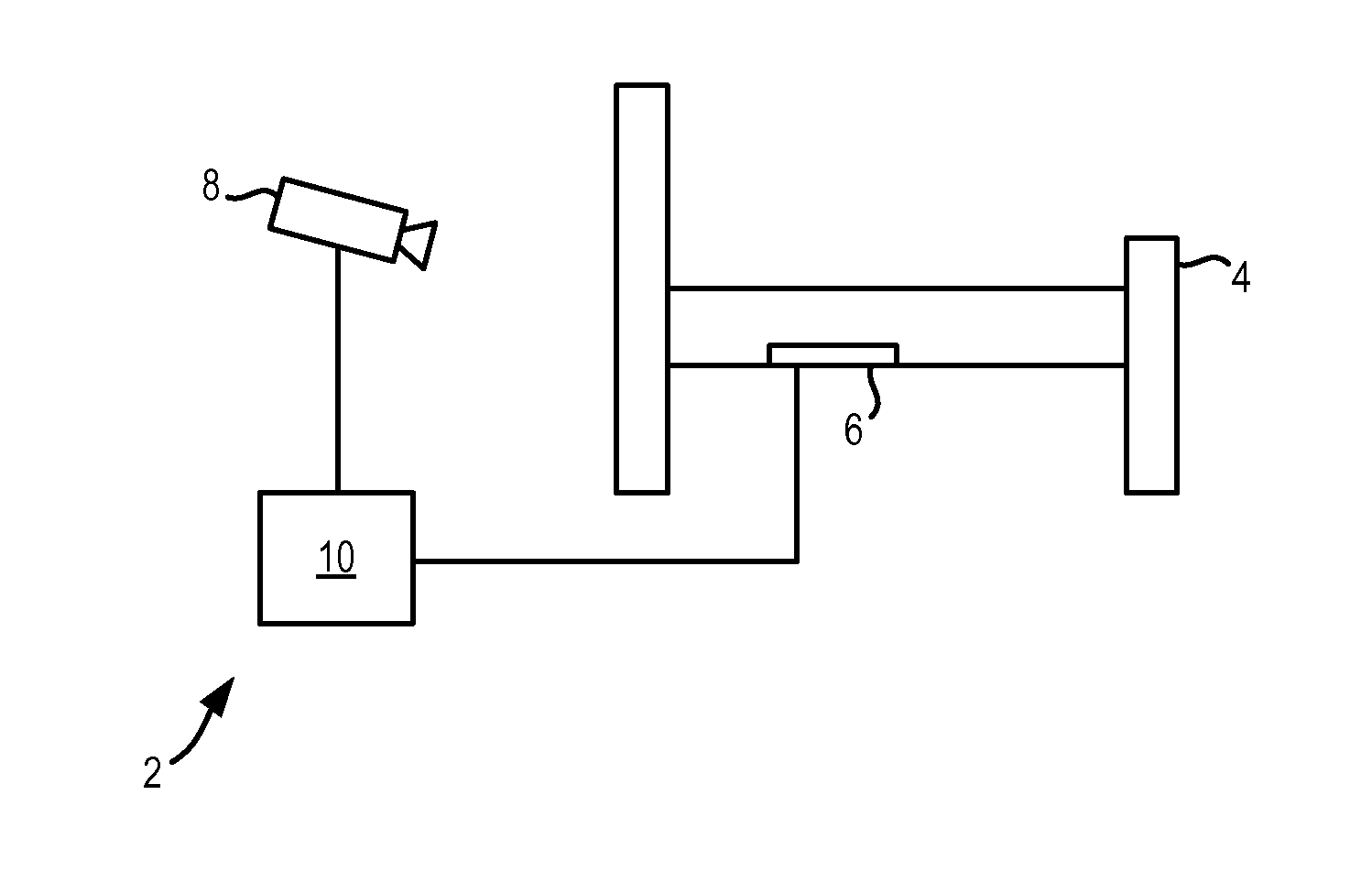
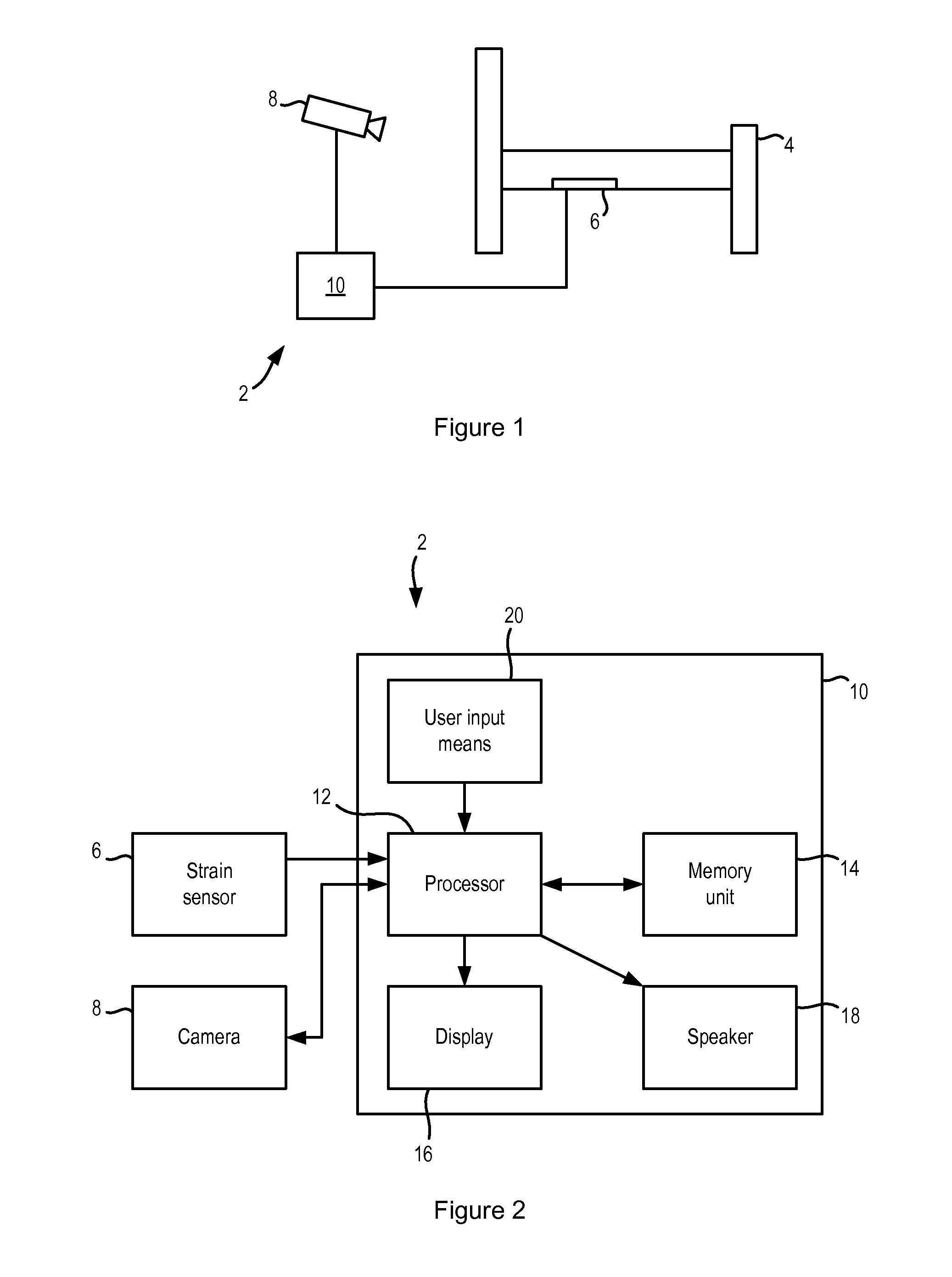
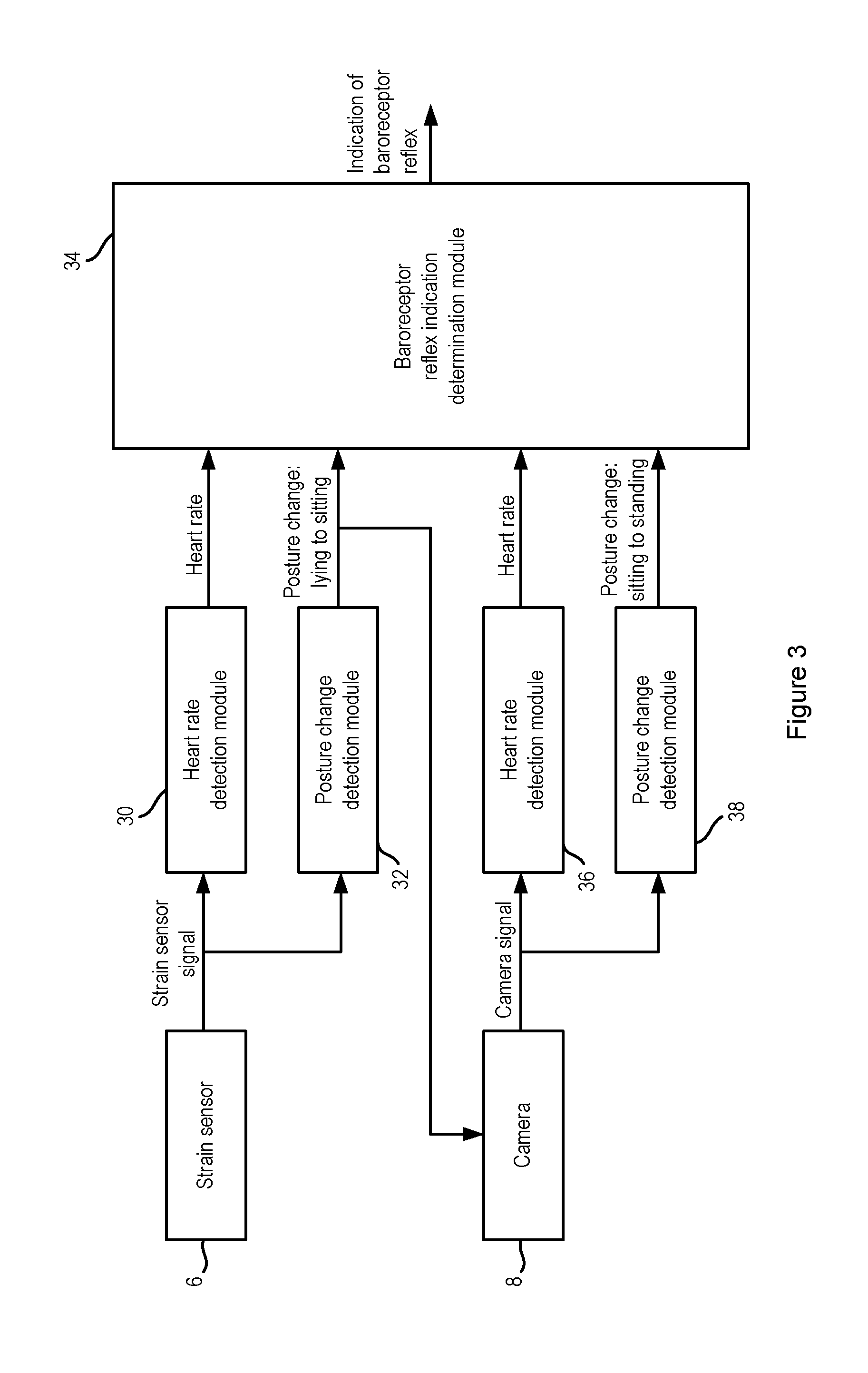
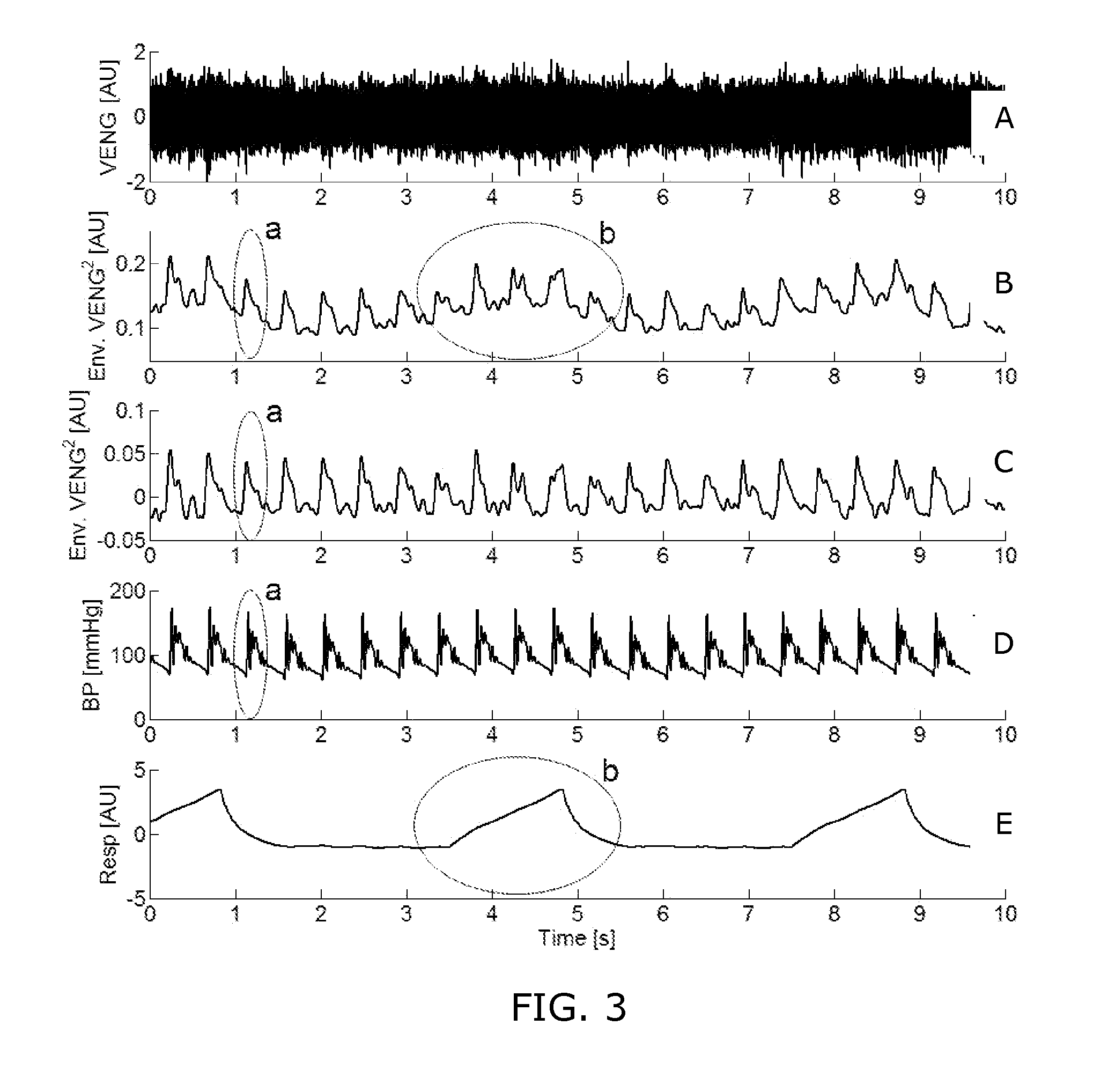
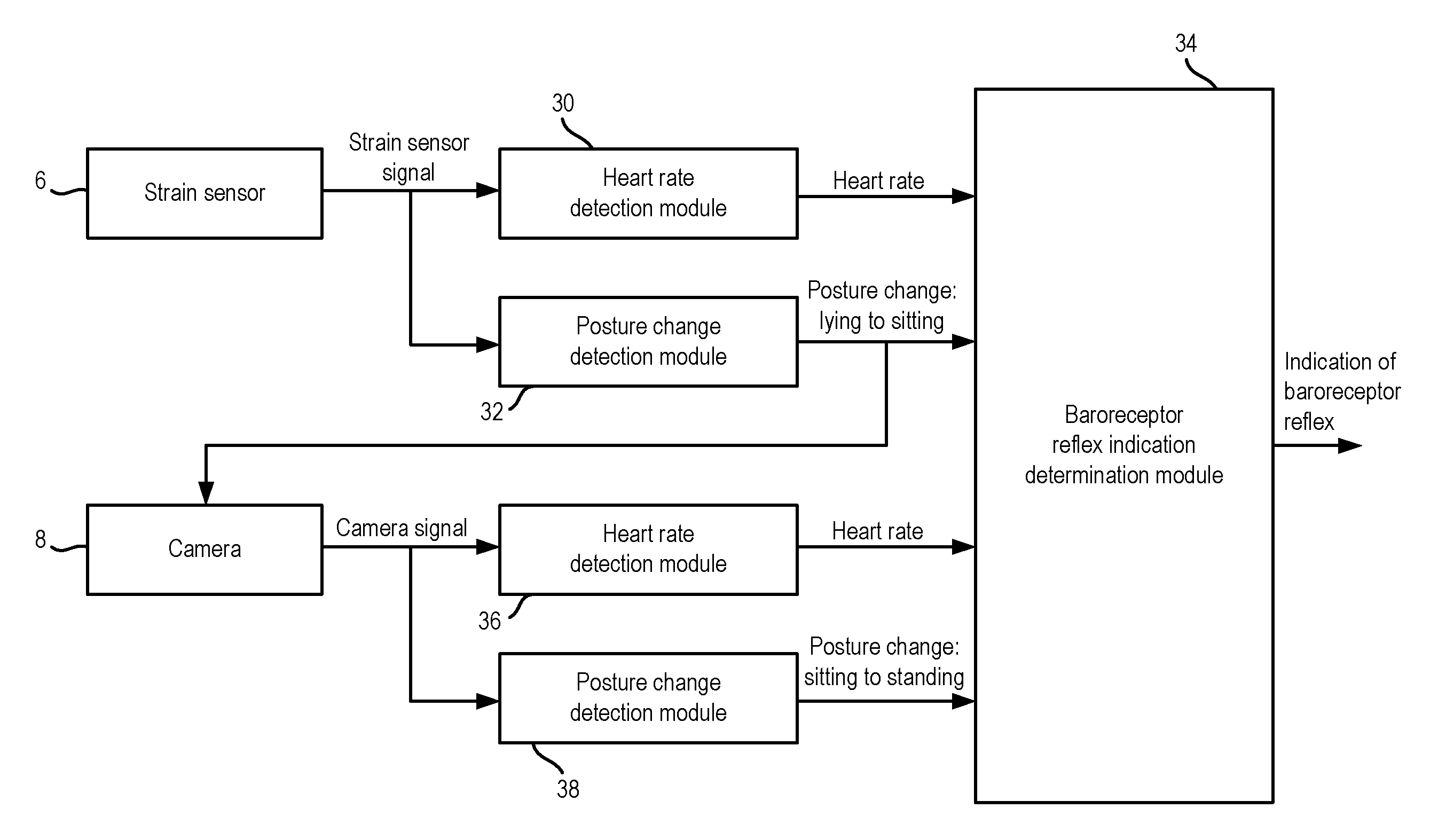
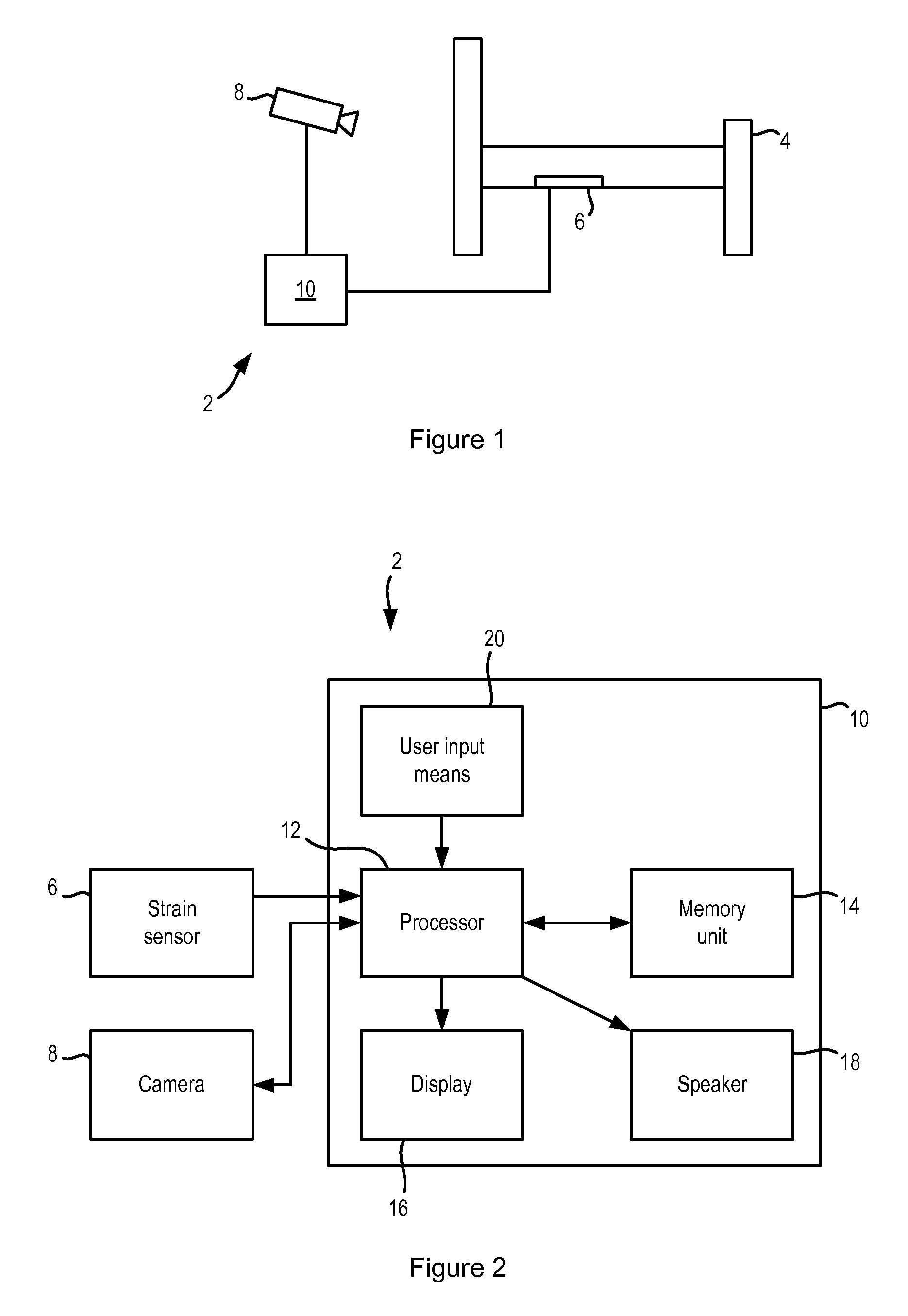
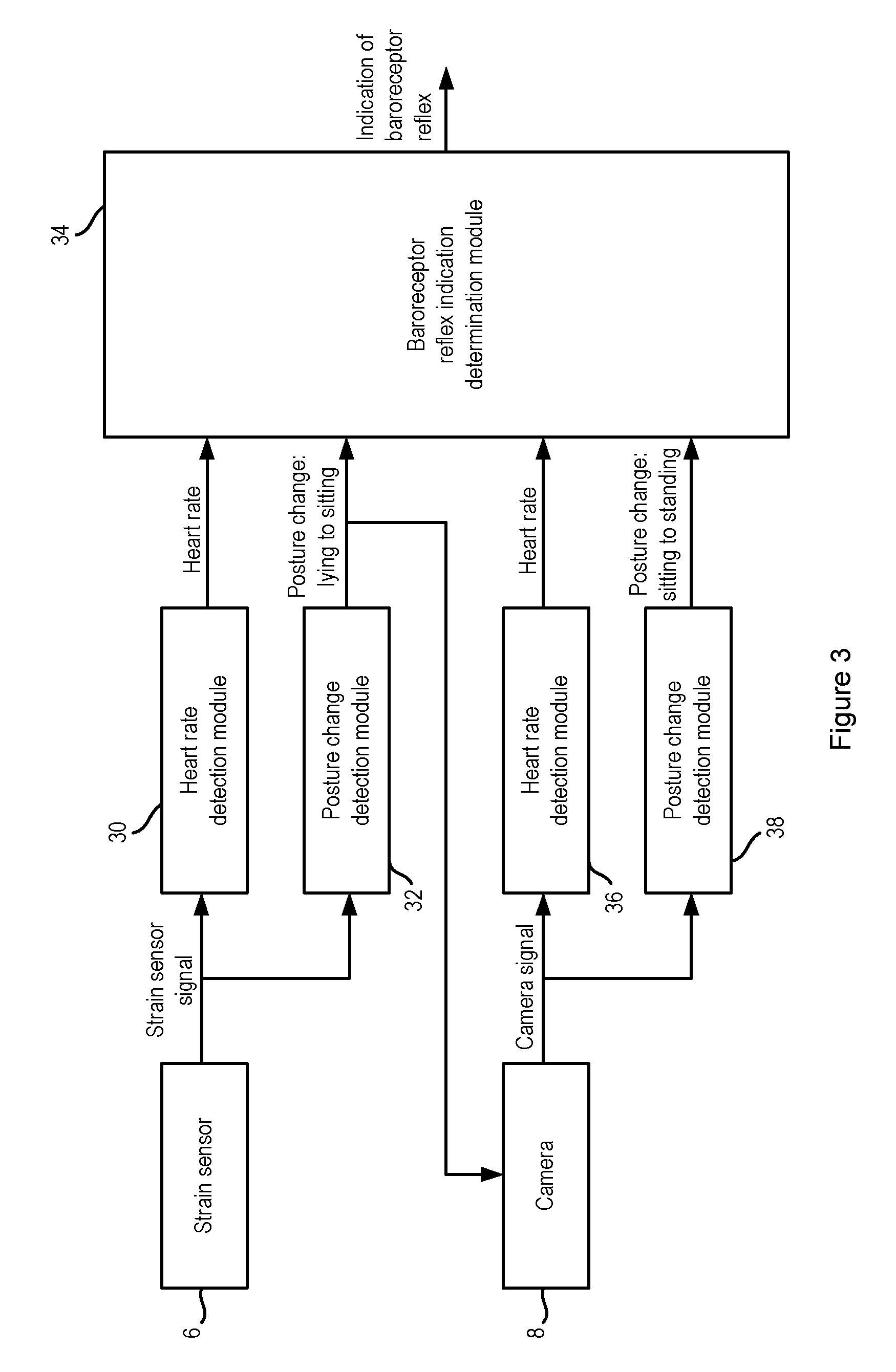
ActiveUS20140358017A1Reduce power consumptionSure easyMedical data miningCatheterReflexBaroreceptor function
There is provided an apparatus for use in monitoring the baroreceptor reflex in a user, the apparatus comprising a processor configured to process a signal output by a first sensor that is attached to or located proximate to a bed to determine when the user moves from a lying position on the bed to a sitting position, and to provide an indication of the baroreceptor reflex of the user by processing the signal to determine the change in the heart rate of the user that occurs as a result of moving from the lying position to the sitting position.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Methods and Devices for Treating Hypertension
Owner:SYMPARA MEDICAL
External Baroreflex Activation
InactiveUS20080288017A1Reducing excessive blood pressureGood effectElectrotherapyArtificial respirationActivation methodMedicine
Methods and systems for external baroreflex activation of a baroreceptor system of a patient from a stimulator external to the patient. The method and devices, enable baroflex therapy on a temporary basis and / or assess the response of a patient to such baroreflex therapy.
Owner:CVRX
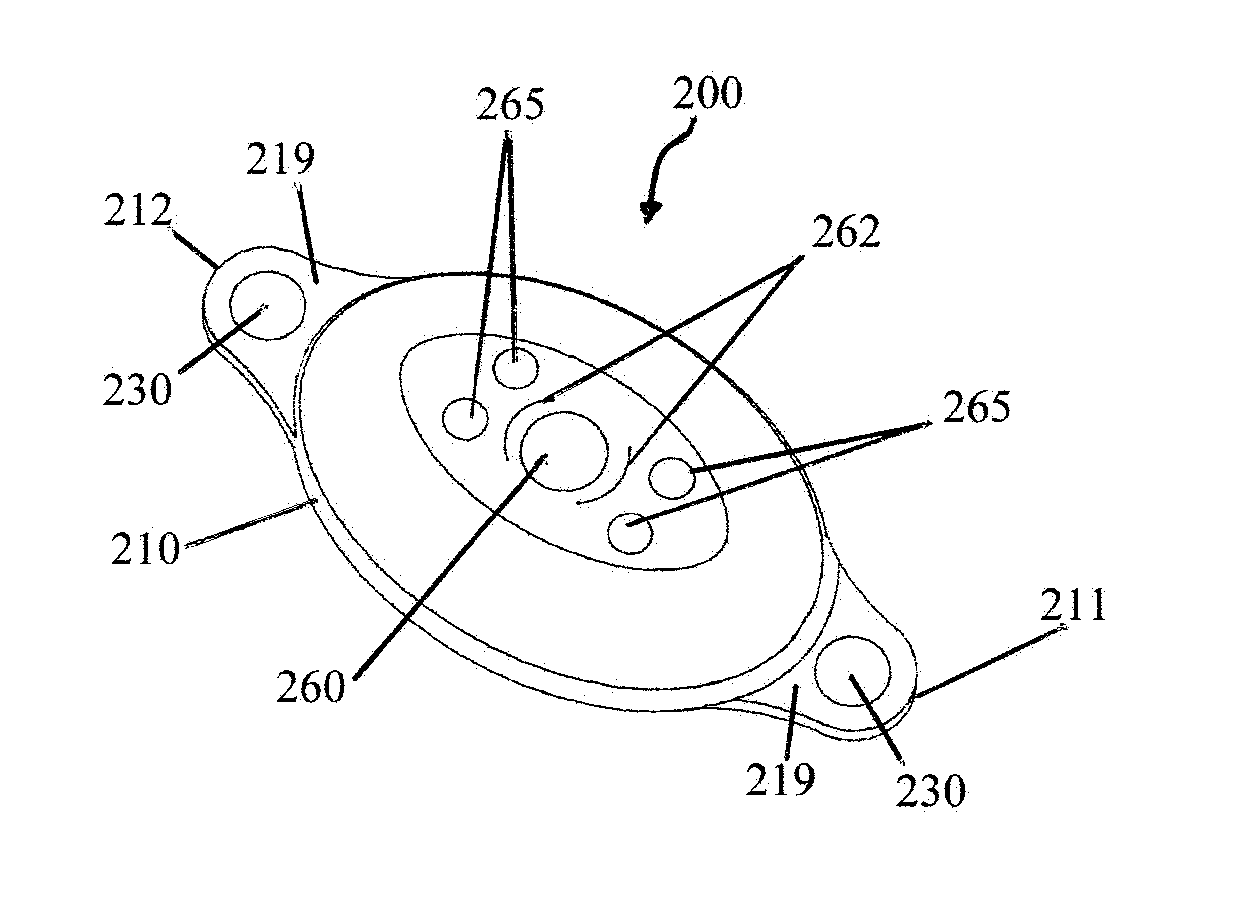
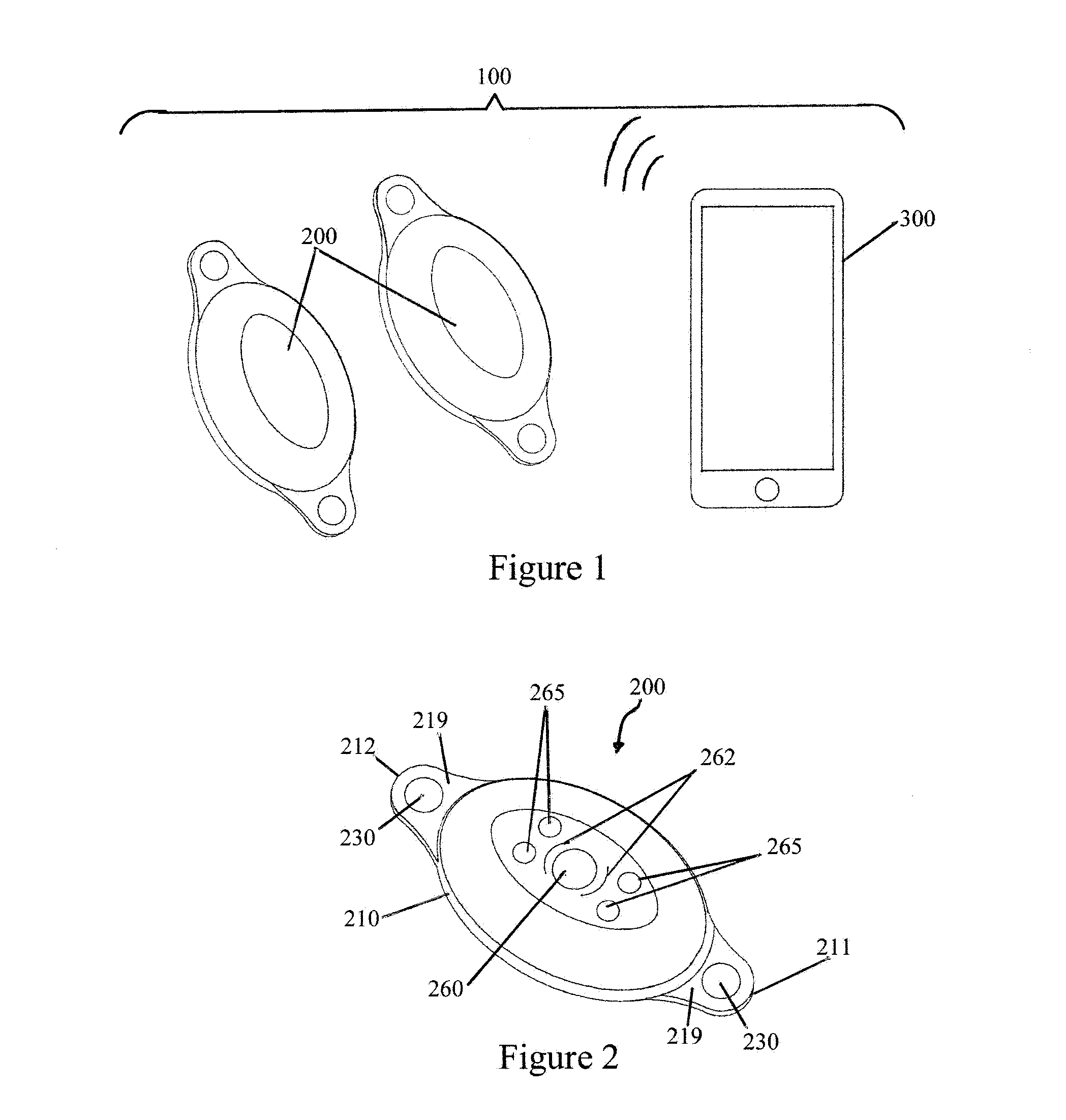
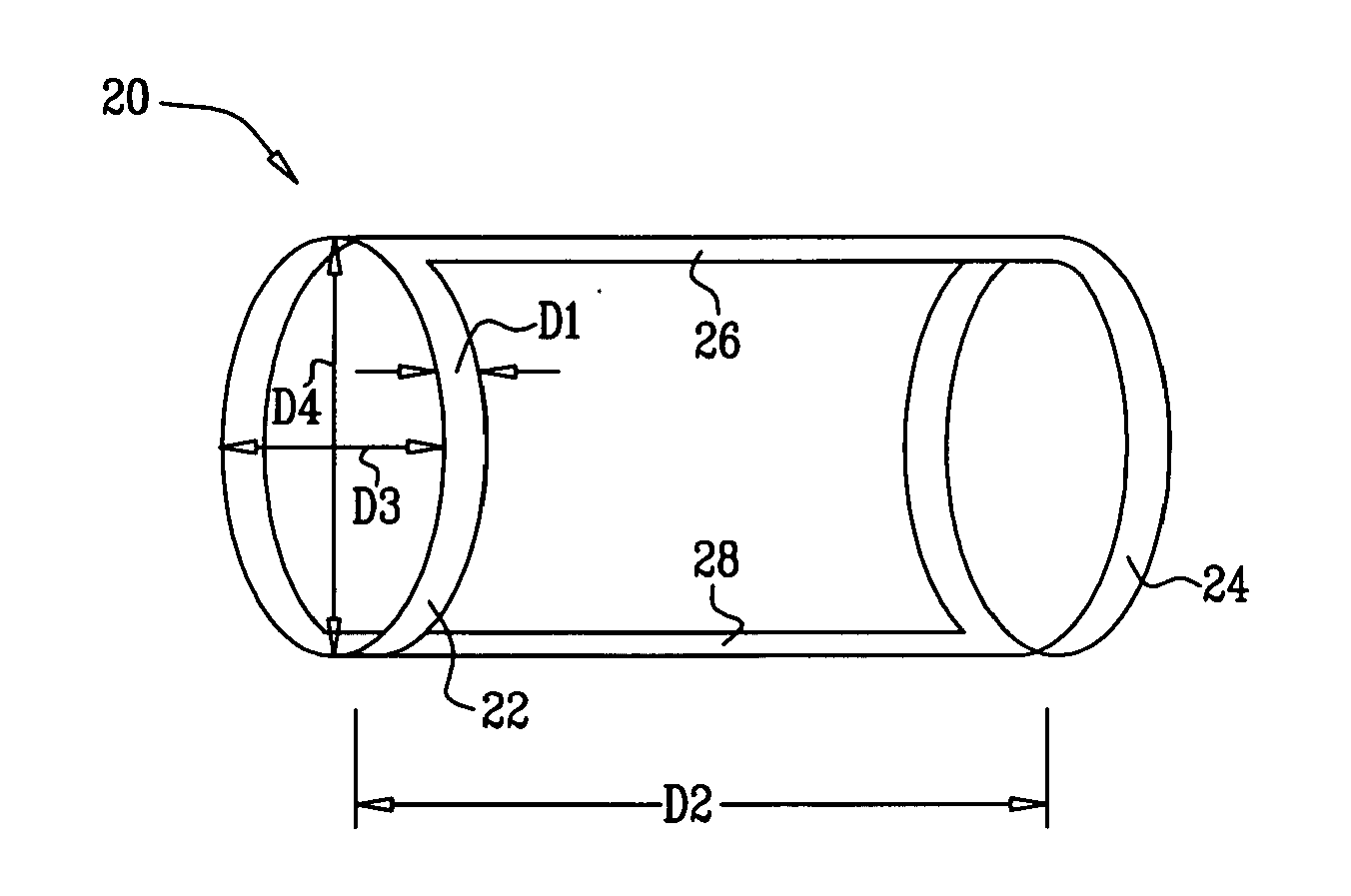
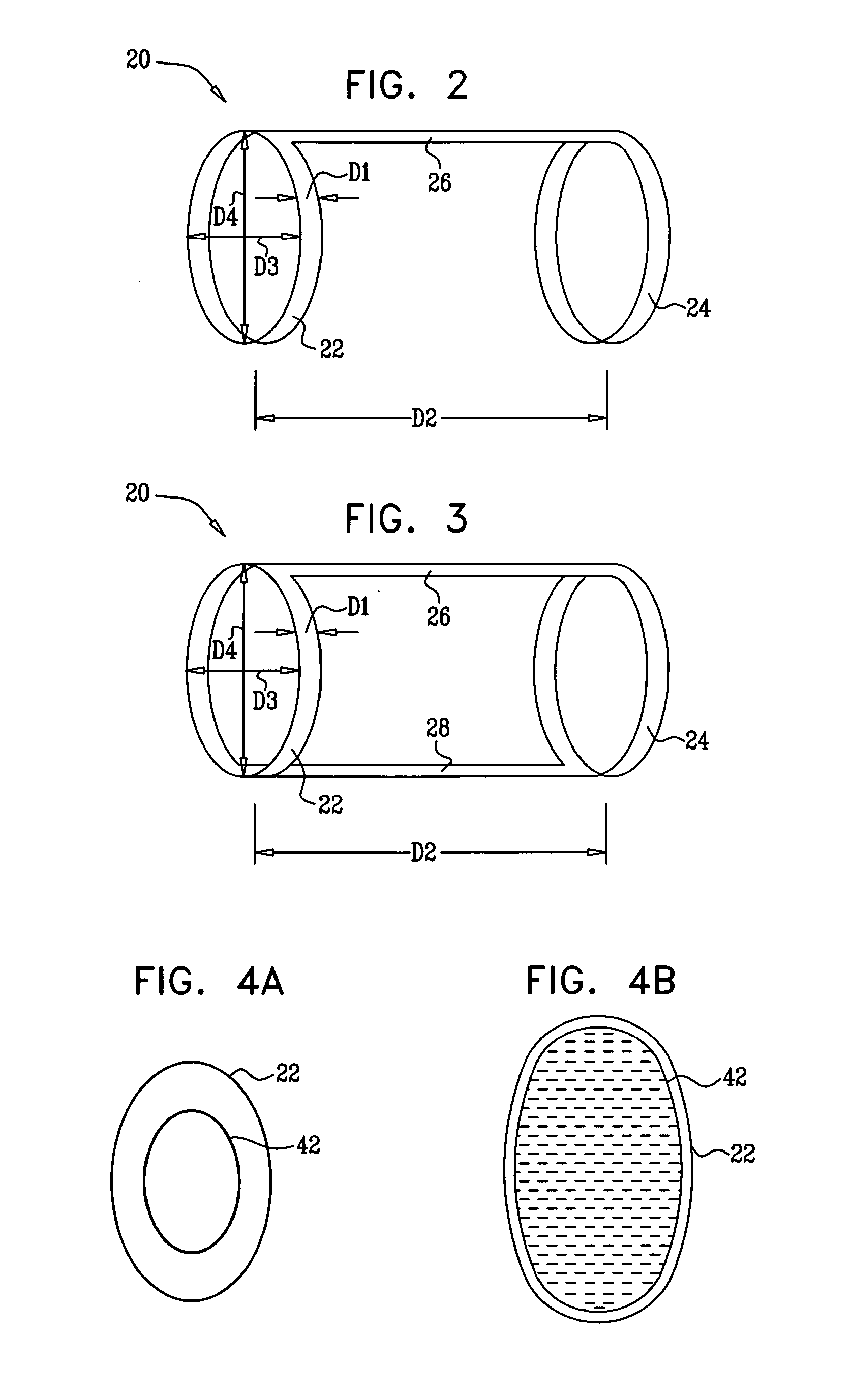
Elliptical element for blood pressure reduction
ActiveUS20110230953A1Reduced responseIncrease pressureStentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesBaroreceptor functionPressure reduction
Apparatus is provided for treating hypertension of a subject. The apparatus includes an implantable element which has a non-circular shape and which is configured to reduce the hypertension by facilitating an assumption of a non-circular shape by a blood vessel in a vicinity of a baroreceptor of the subject, during diastole of the subject. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:VASCULAR DYNAMICS
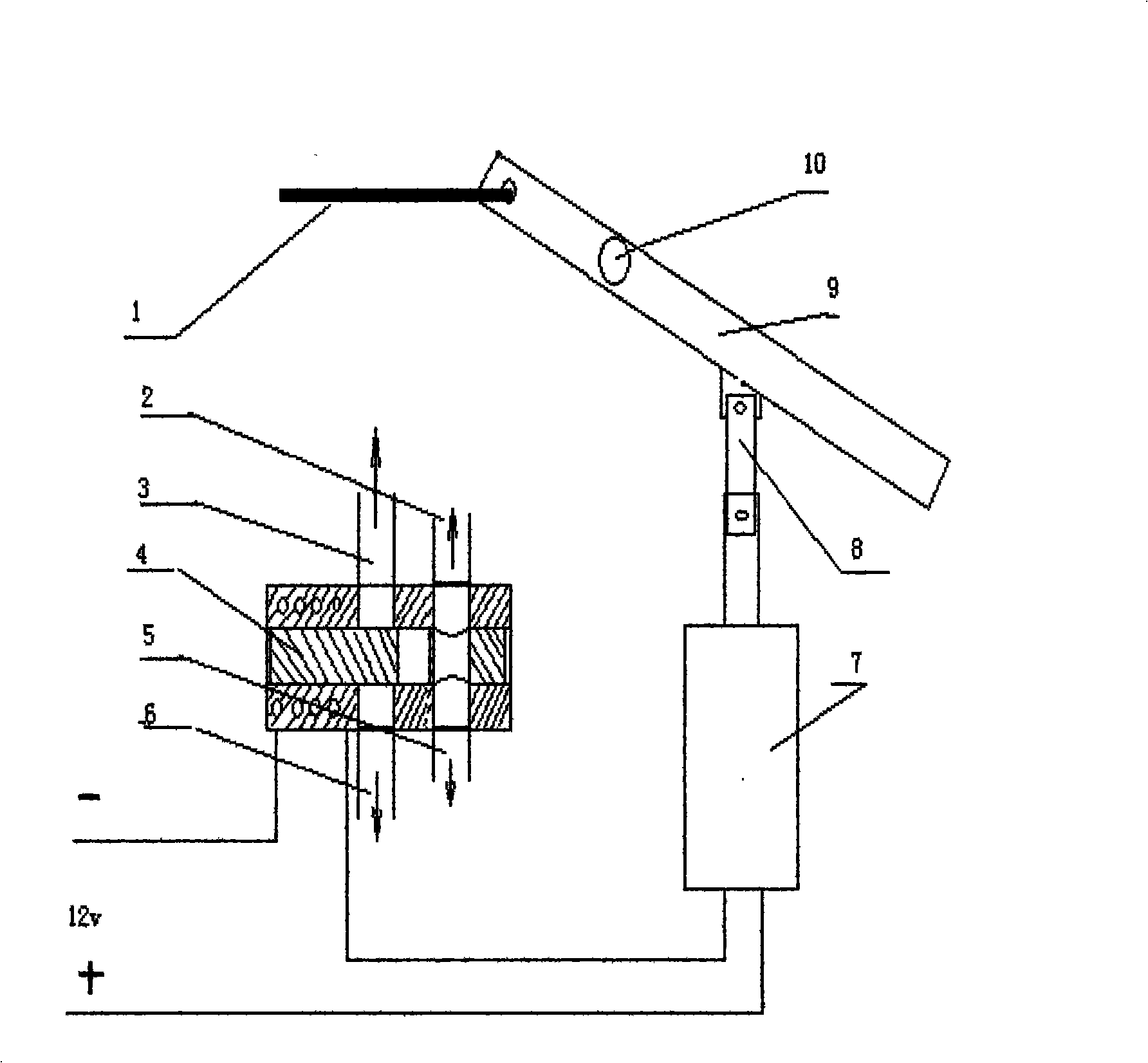
Safety valve of accelerator pedal motor vehicle
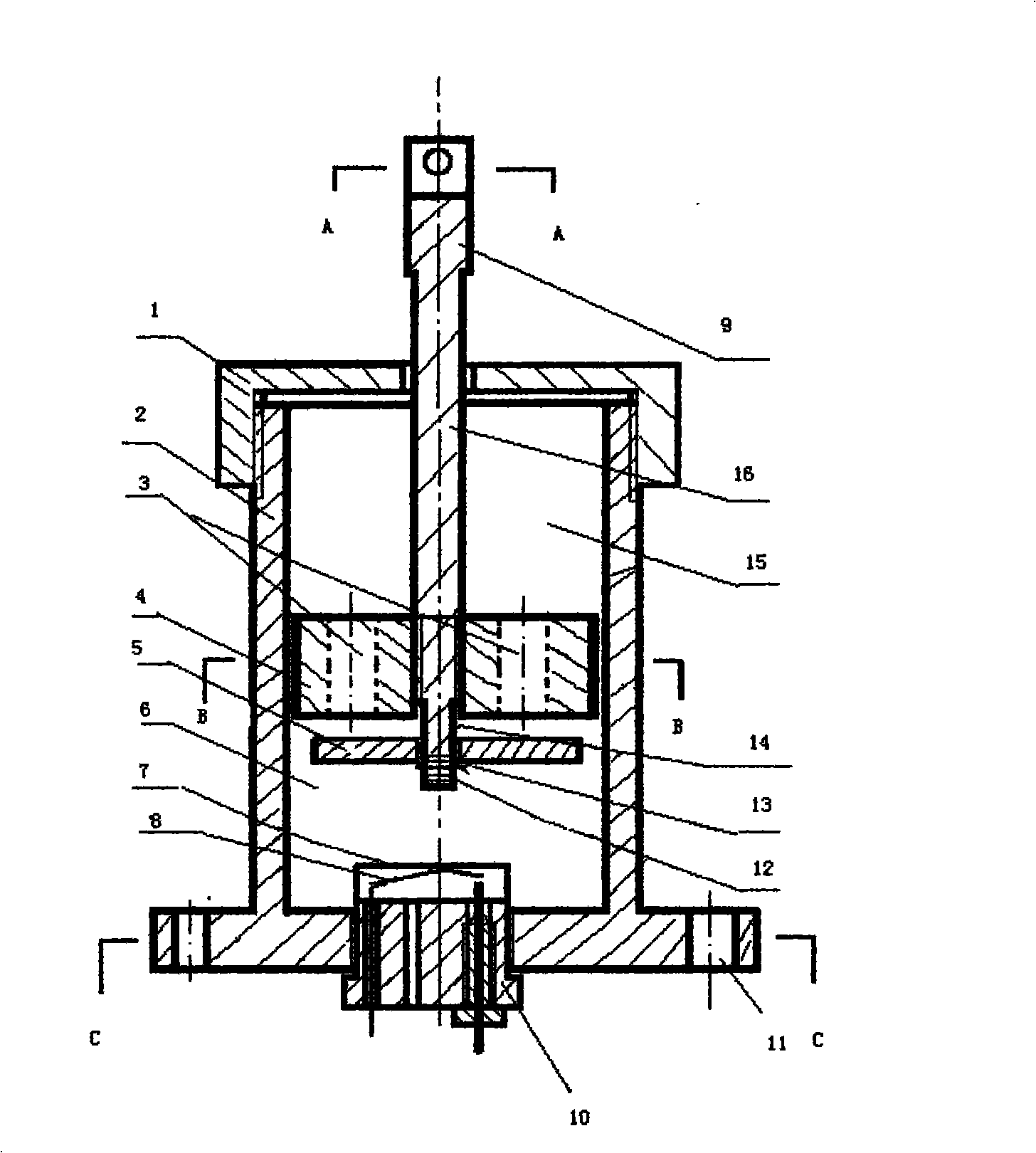
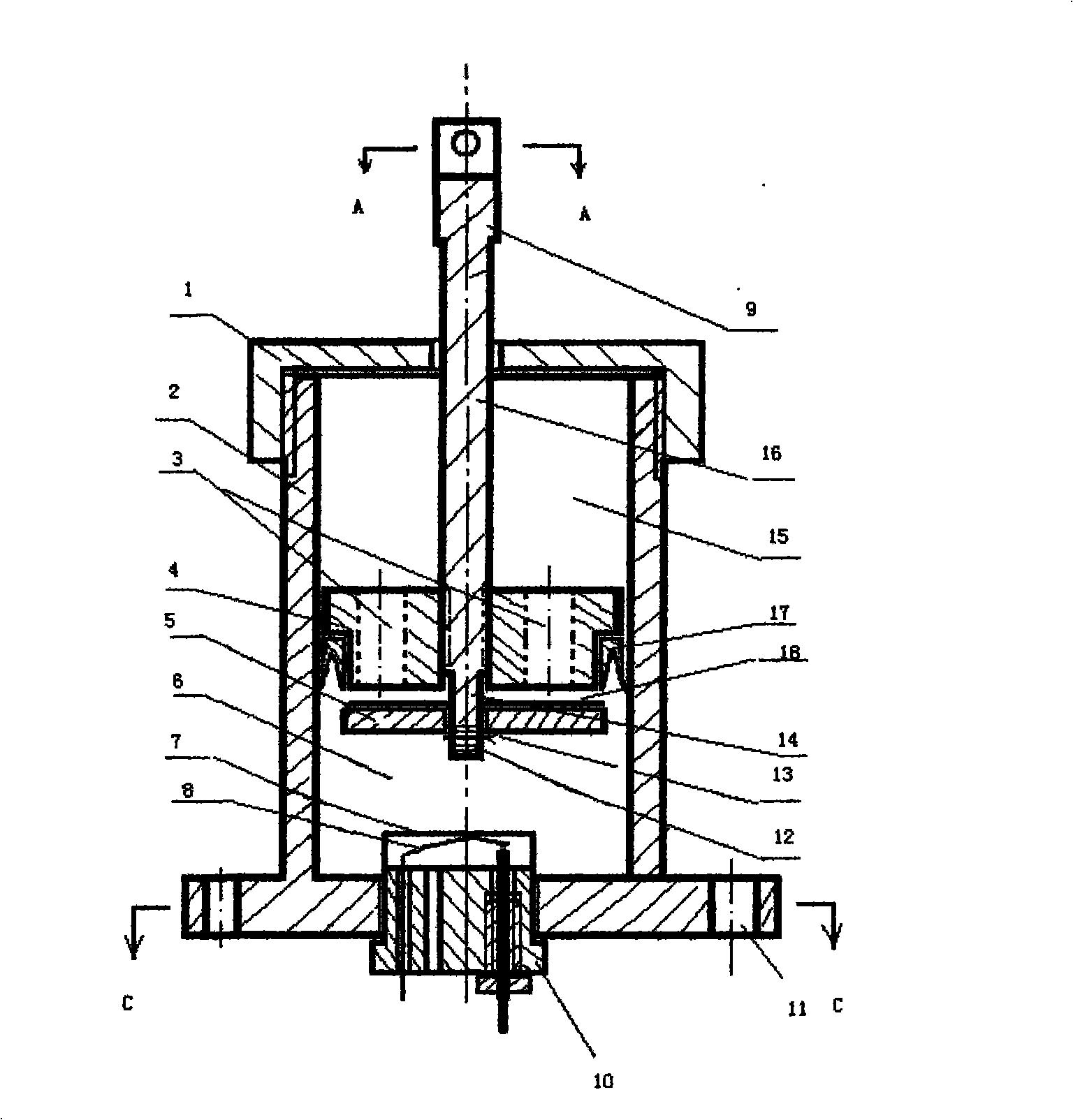
InactiveCN101524964ADo not change operating habitsBrake emergency controlAutomatic initiationsTractorsLiquid mediumBaroreceptor function
The invention relates to a device for emergently and safely braking an accelerator of a motor vehicle. The device is characterized by comprising an accelerator operating rod, an accelerator pedal safety valve, a pressure sensor and an electromagnetic brake; the accelerator pedal safety valve is a columnar cylinder body filled with liquid; a piston and a piston rod can move between two ends of the cylinder body; liquid medium can flow via a through hole in the piston; one end of the through hole is provided with a corresponding valve plate; the piston rod is movably connected with the accelerator operating rod; a baroreceptor is arranged in the accelerator pedal safety valve and when a driver steps the accelerator by mistake in an emergency, the valve can close the through hole in the piston automatically and instantaneously so as to support and fix the accelerator operating rod tightly; and simultaneously the pressure change of the liquid excites an automatic braking system by the baroreceptor so as to achieve the purpose of emergency brake.
Owner:胡义平
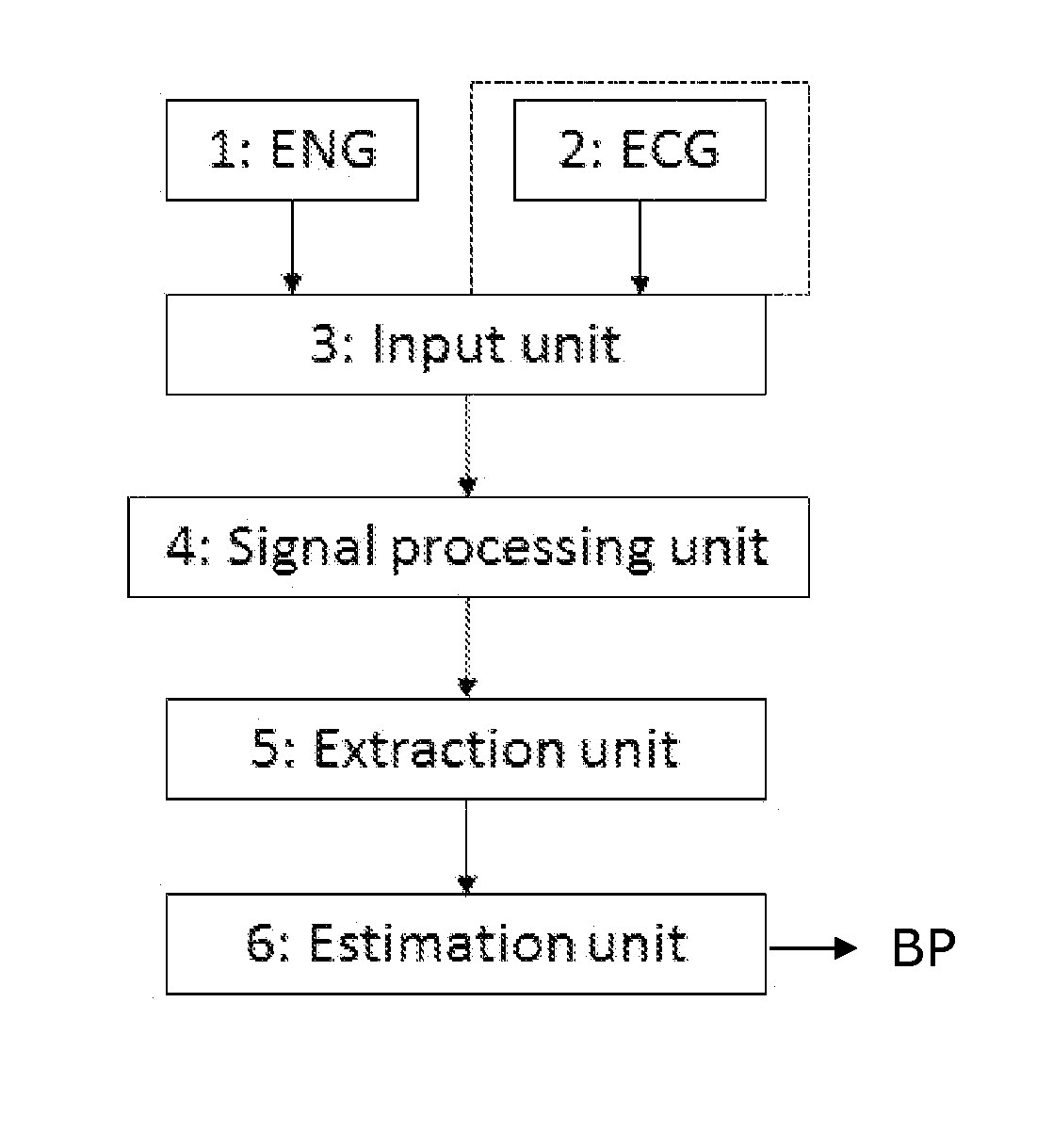
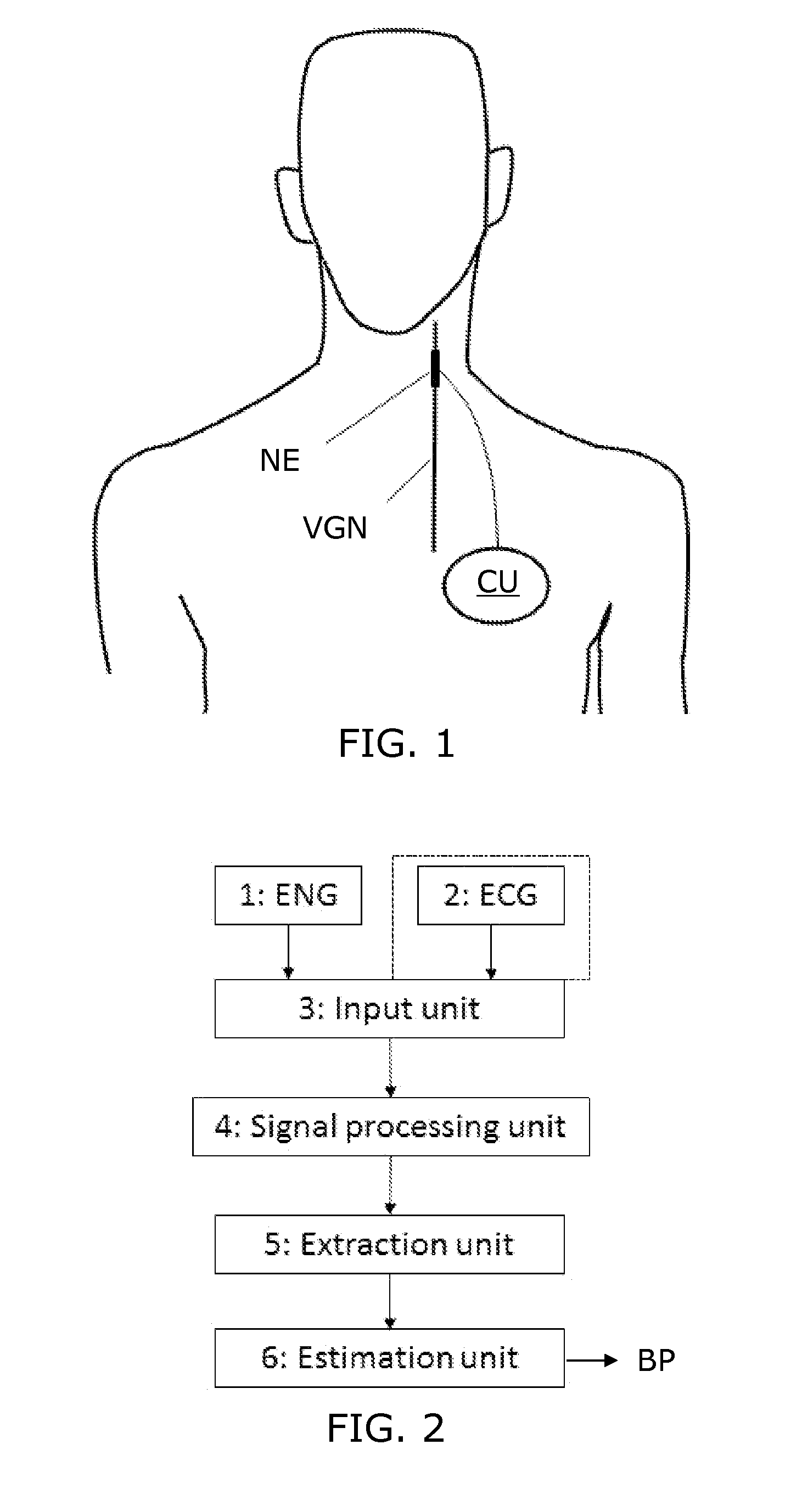
Blood pressure estimation based on neural activity
InactiveUS20150216483A1Reliably determinedHigh activityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalNerve fiber bundle
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
Method and apparatus for monitoring the baroreceptor reflex of a user
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
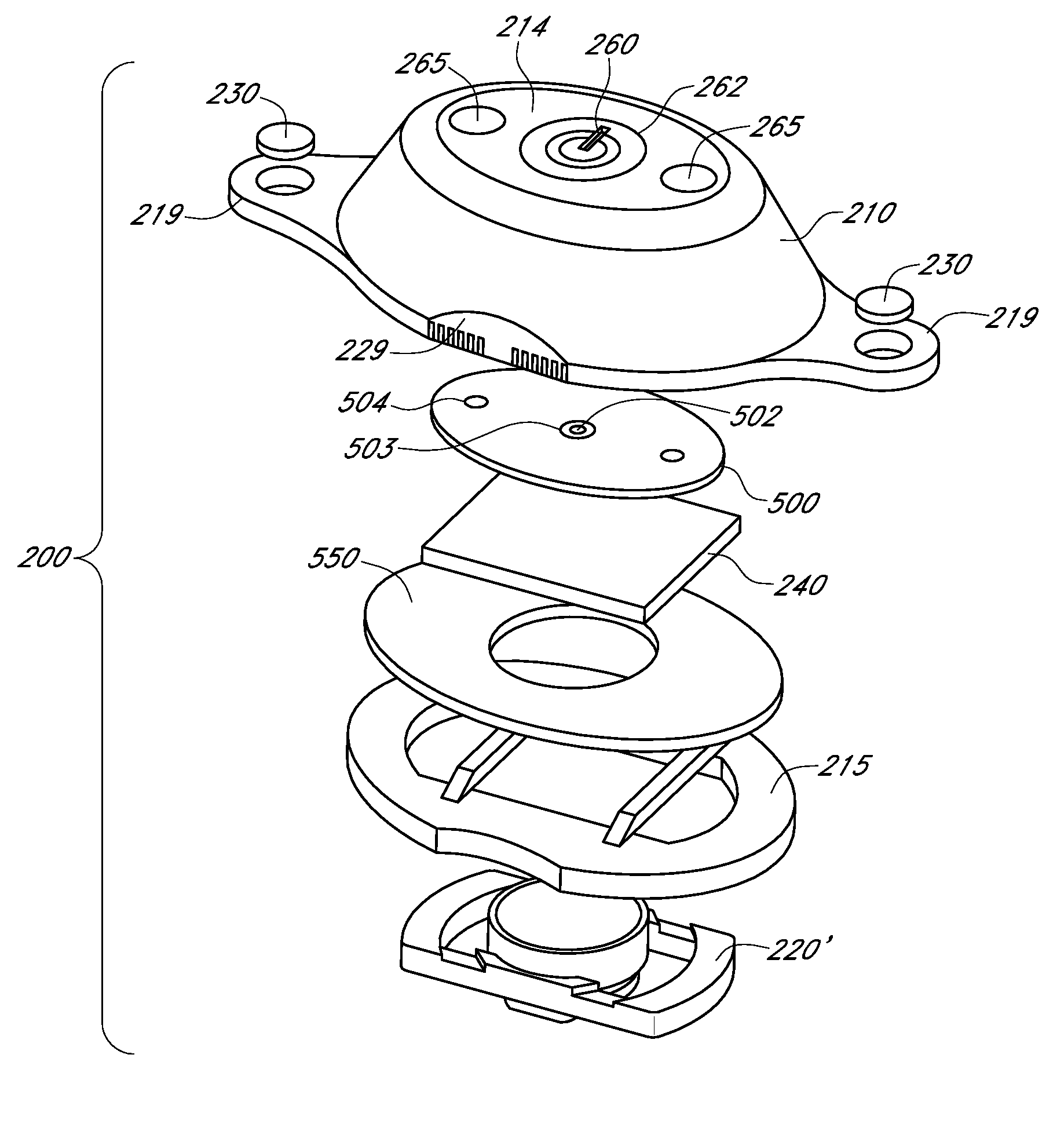
Electrode structures and methods for their use in cardiovascular reflex control
InactiveUS20100222831A1Reduce pressureDeleterious effectSpinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesNervous systemRegimen
Devices, systems and methods are described by which the blood pressure, nervous system activity, and neurohormonal activity may be selectively and controllably reduced by activating baroreceptors. A baroreceptor activation device is positioned near a baroreceptor, preferably a baroreceptor located in the carotid sinus. A control system may be used to modulate the baroreceptor activation device. The control system may utilize an algorithm defining a stimulus regimen which promotes long term efficacy and reduces power requirements / consumption. The baroreceptor activation device may utilize electrodes to activate the baroreceptors. The electrodes may be adapted for connection to the carotid arteries at or near the carotid sinus, and may be designed to minimize extraneous tissue stimulation.
Owner:CVRX
Closed in-vitro ventricular drainage apparatus
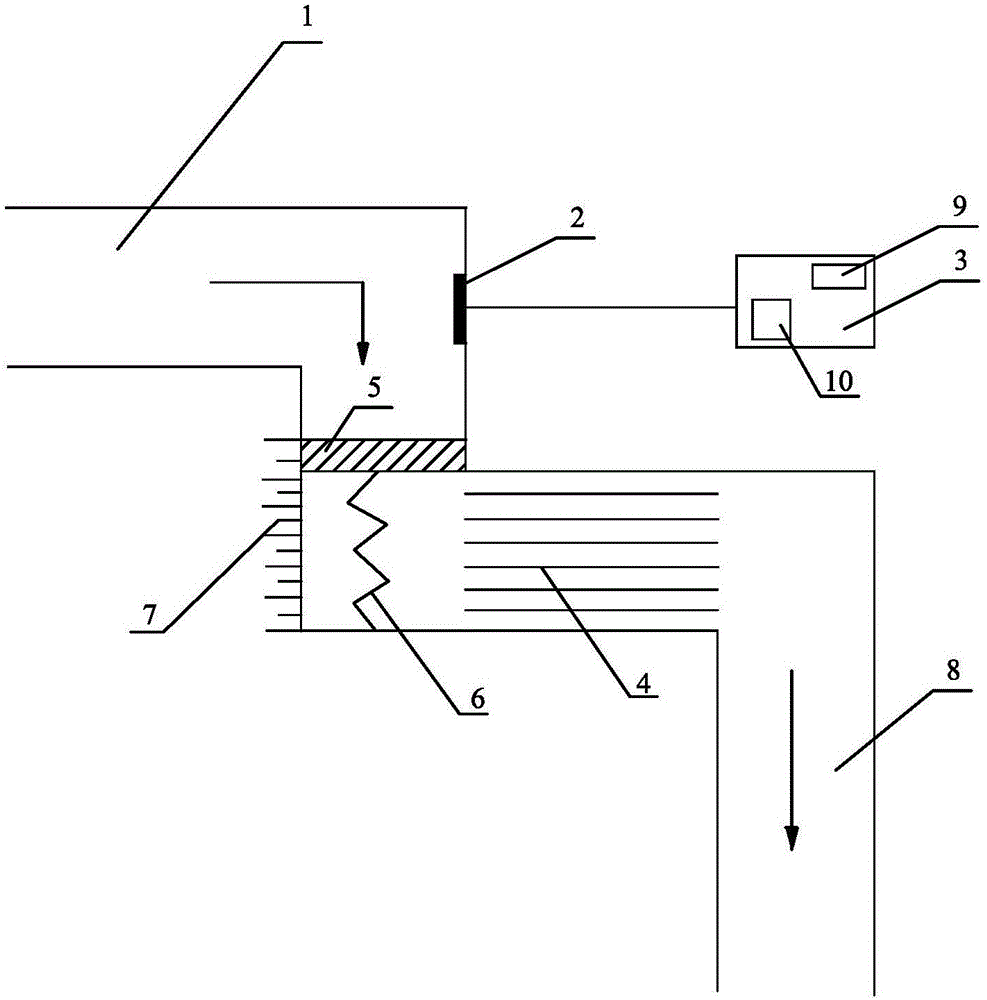
InactiveCN106421940AEfficient detectionReasonable designElectrocardiographyMedical devicesMedicineBaroreceptor function
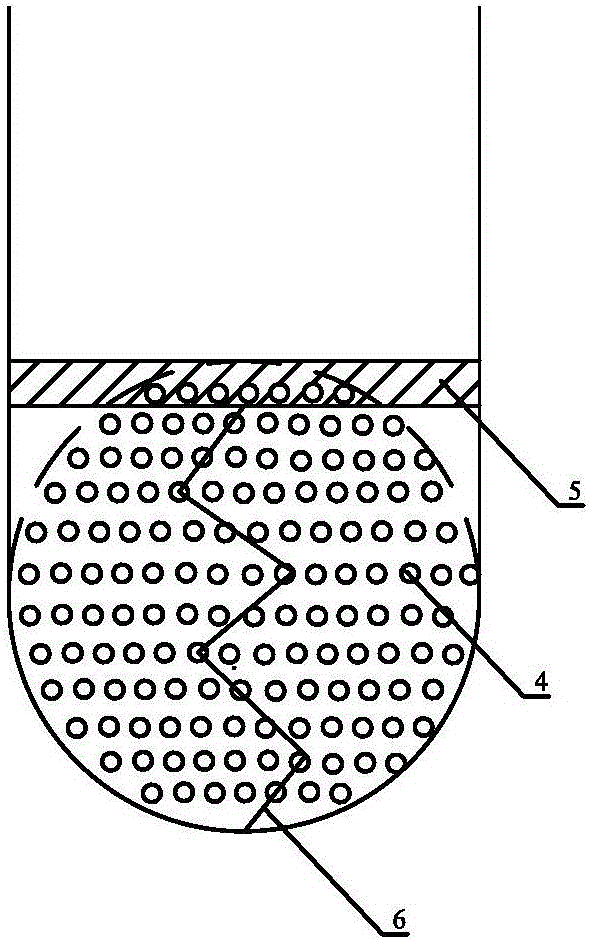
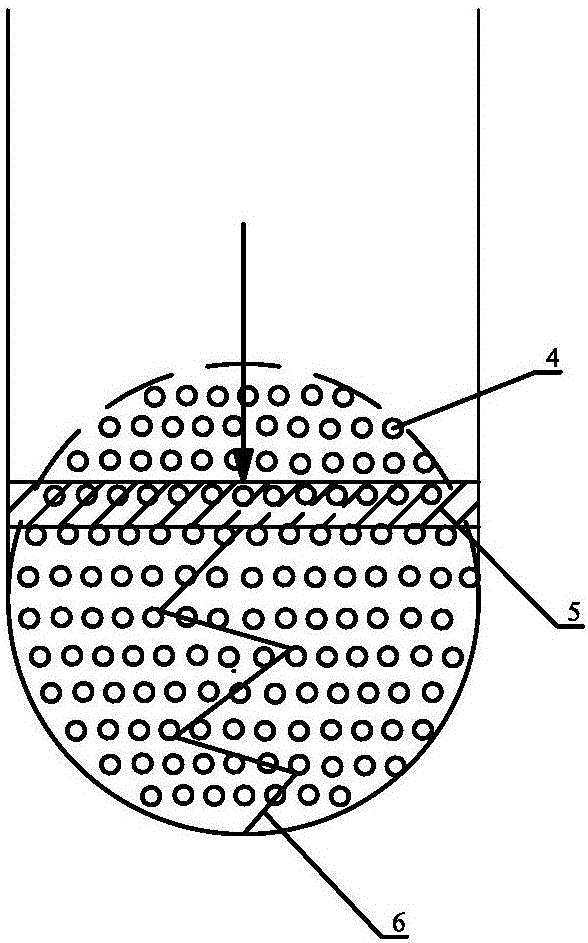
The invention relates to a closed in-vitro ventricular drainage apparatus, which comprises two pipelines which are bent in the form of right angles and an analyzer which is arranged outside the pipelines, wherein the two pipelines, which are bent in the form of the right angles, include a first pipeline and a second pipeline; a horizontal part of the first pipeline is connected to a cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube which is close to a ventricular end; a vertical part of the second pipeline is connected to a drainage bag; a vertical part of the first pipeline communicates with a horizontal part of the second pipeline; a piston is arranged in the vertical part of the first pipeline; a spring is connected to the lower surface of the piston; the tail end of the spring is fixedly connected to the bottom of the vertical part of the first pipeline; a baroreceptor is arranged at the inner side of the pipe wall of the vertical part of the first pipeline; the baroreceptor is connected to the analyzer; and capillaries are arranged on the horizontal part of the second pipeline. The closed in-vitro ventricular drainage apparatus provided by the invention can overcome shortcomings in the prior art which adopts open drainage and fails to accurately monitor change in intracranial pressure, and the drainage apparatus is capable of conducting pressure monitoring and heart rate monitoring in vitro and is strong in intuitivity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Devices for regulation of blood pressure and heart rate
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com