Patents
Literature
626results about How to "Reliably determined" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
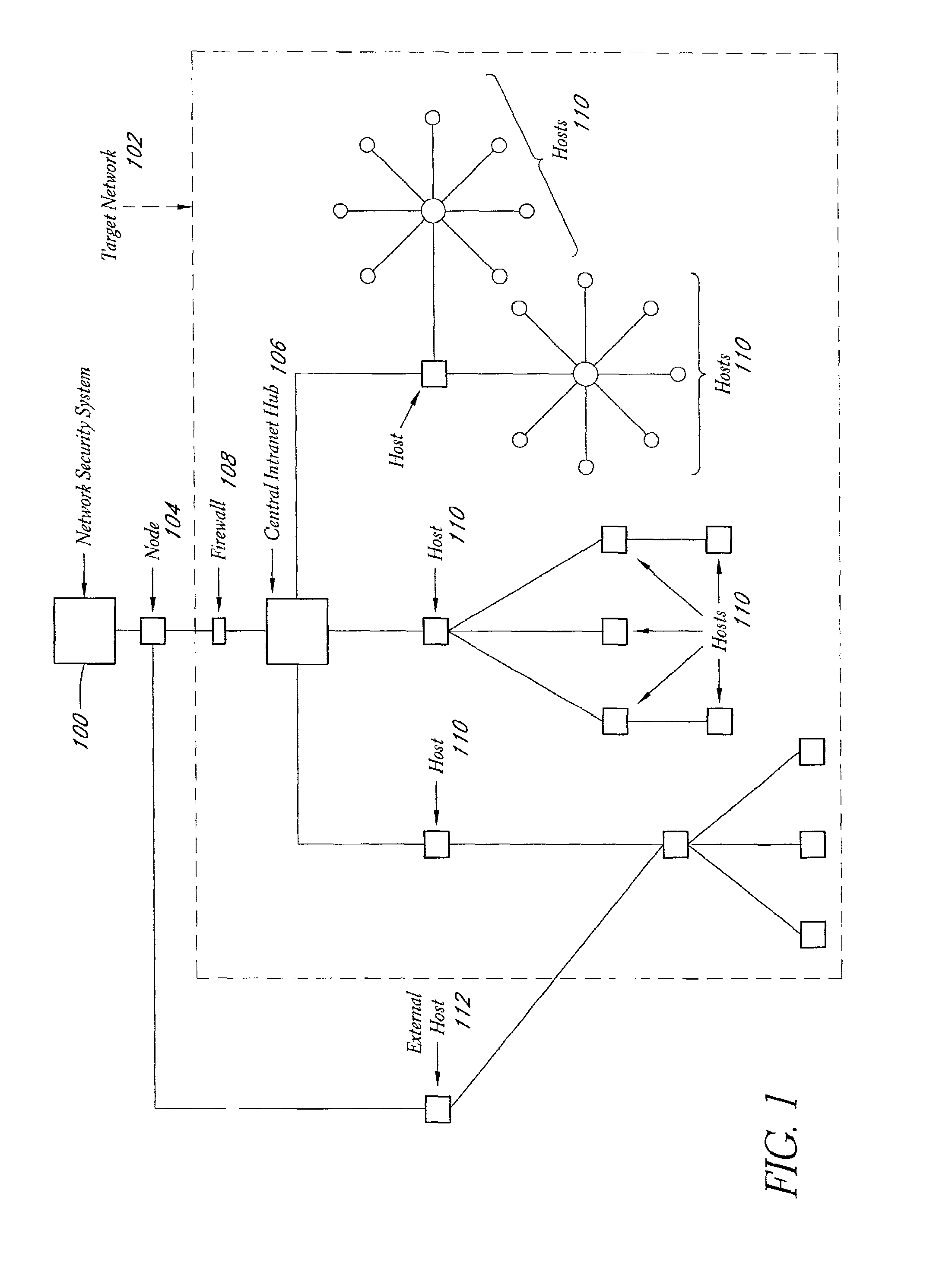
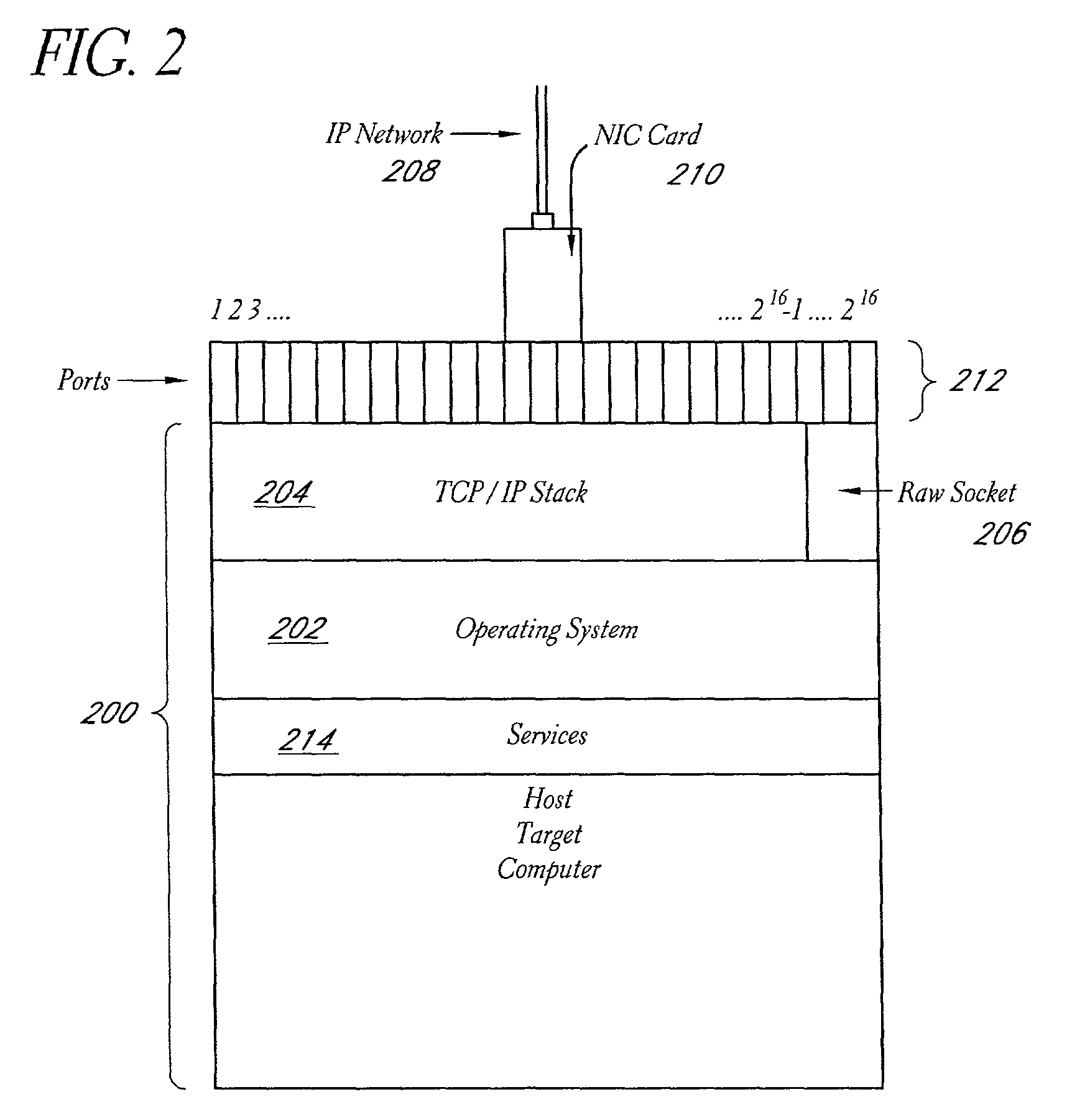
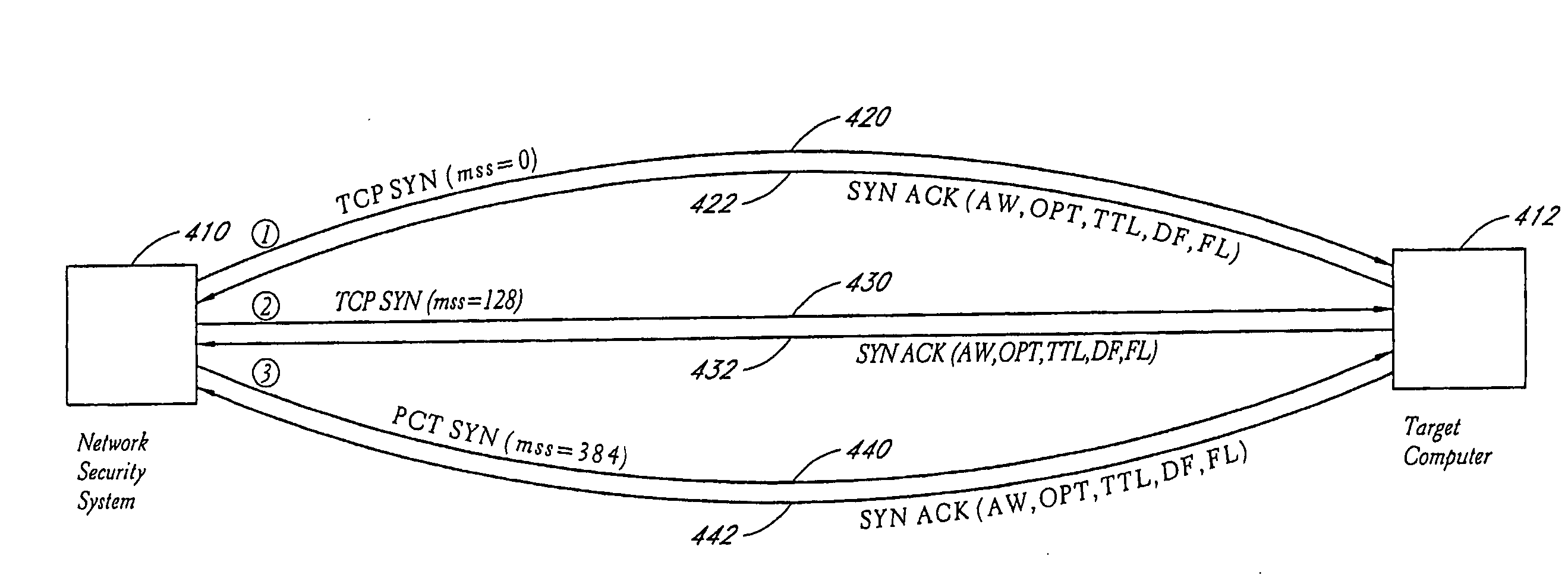
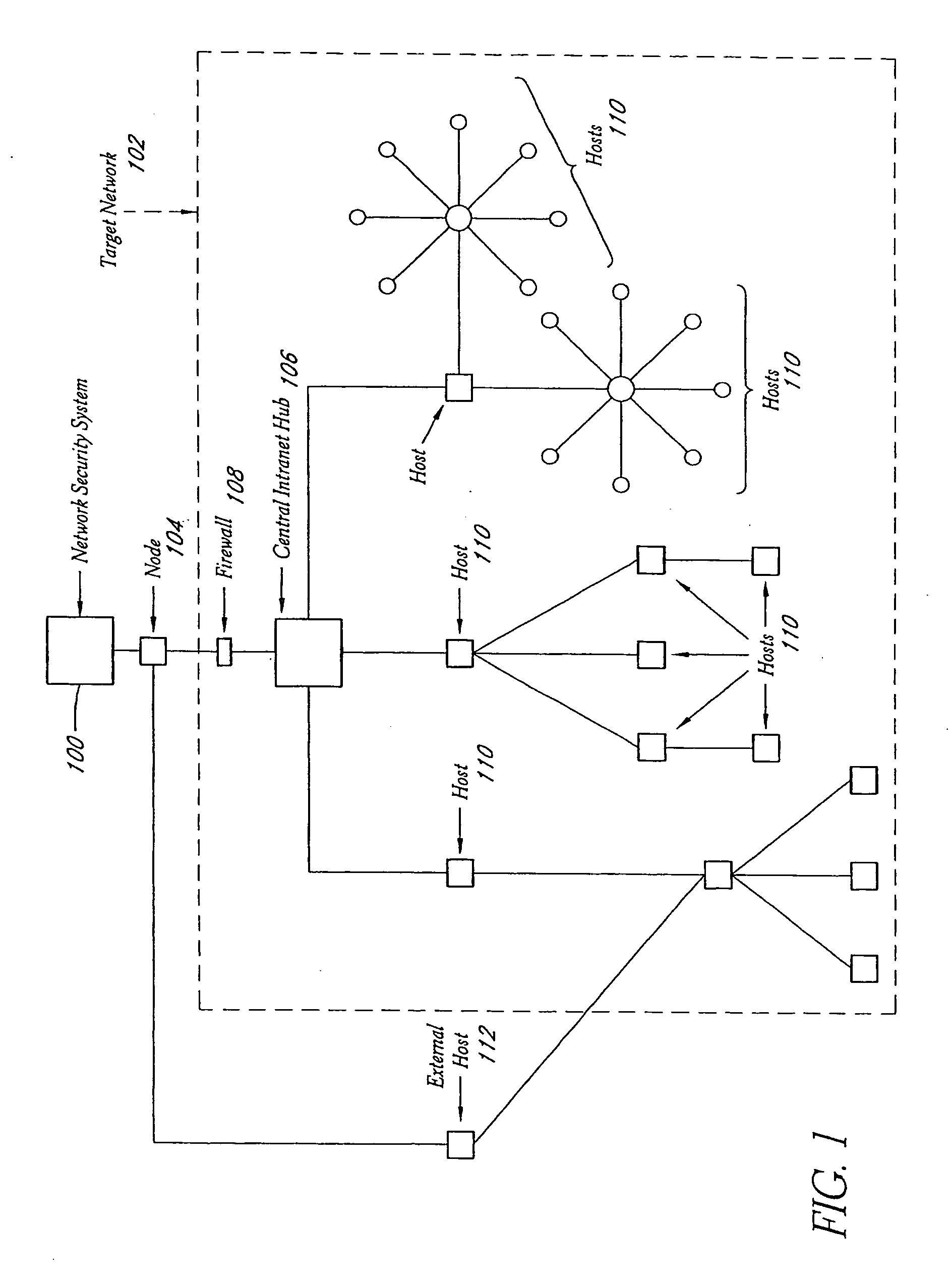
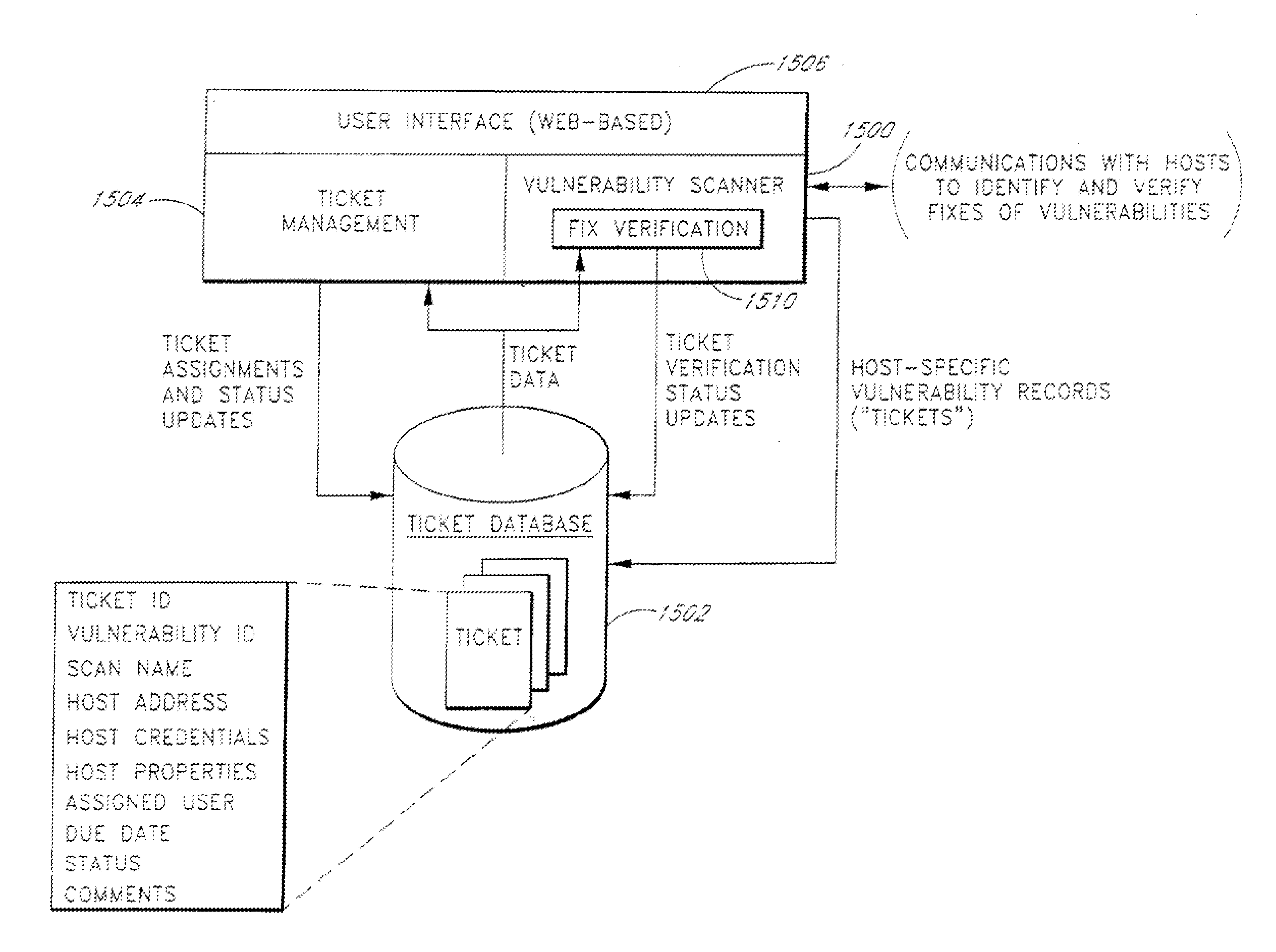
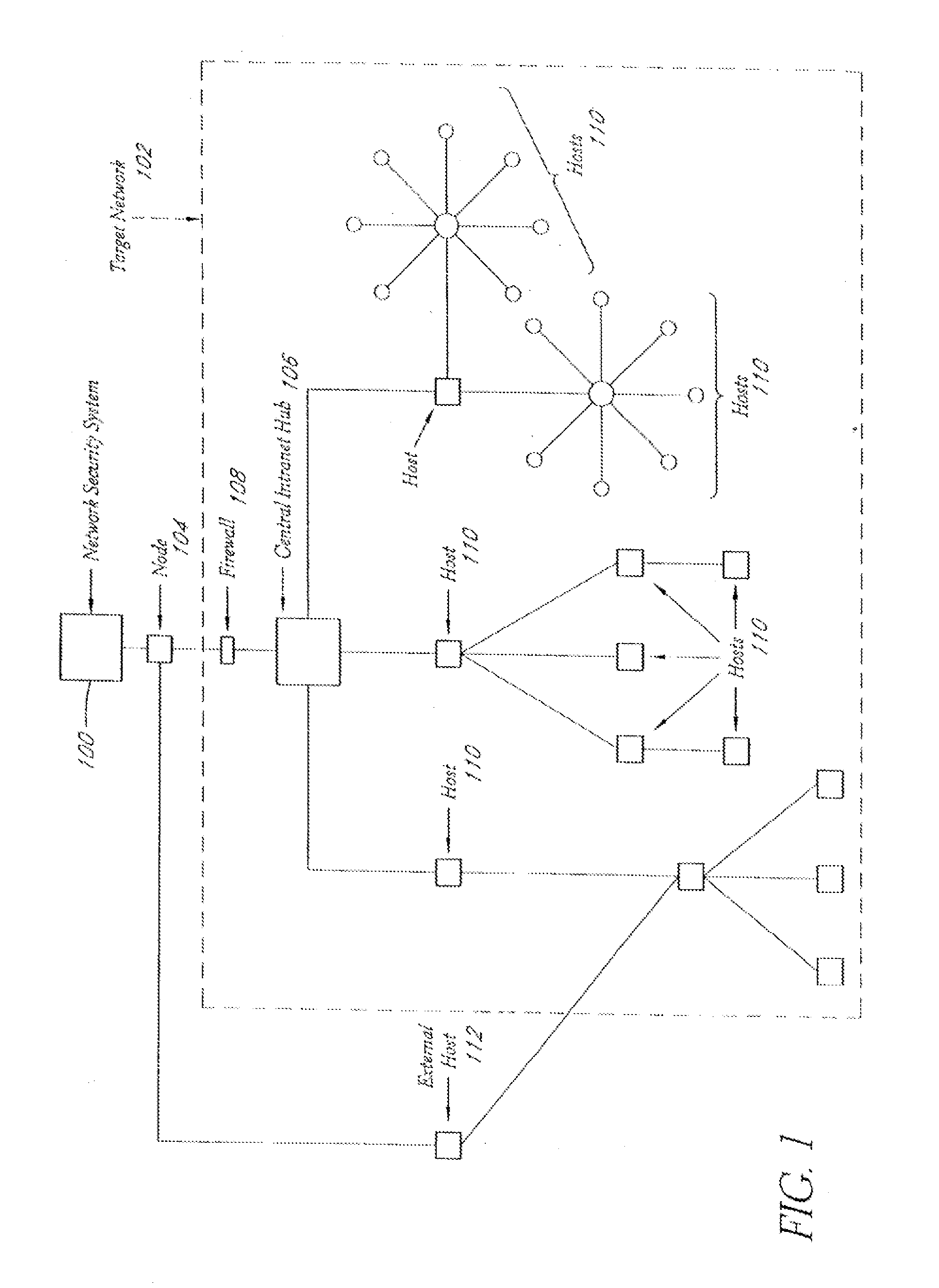
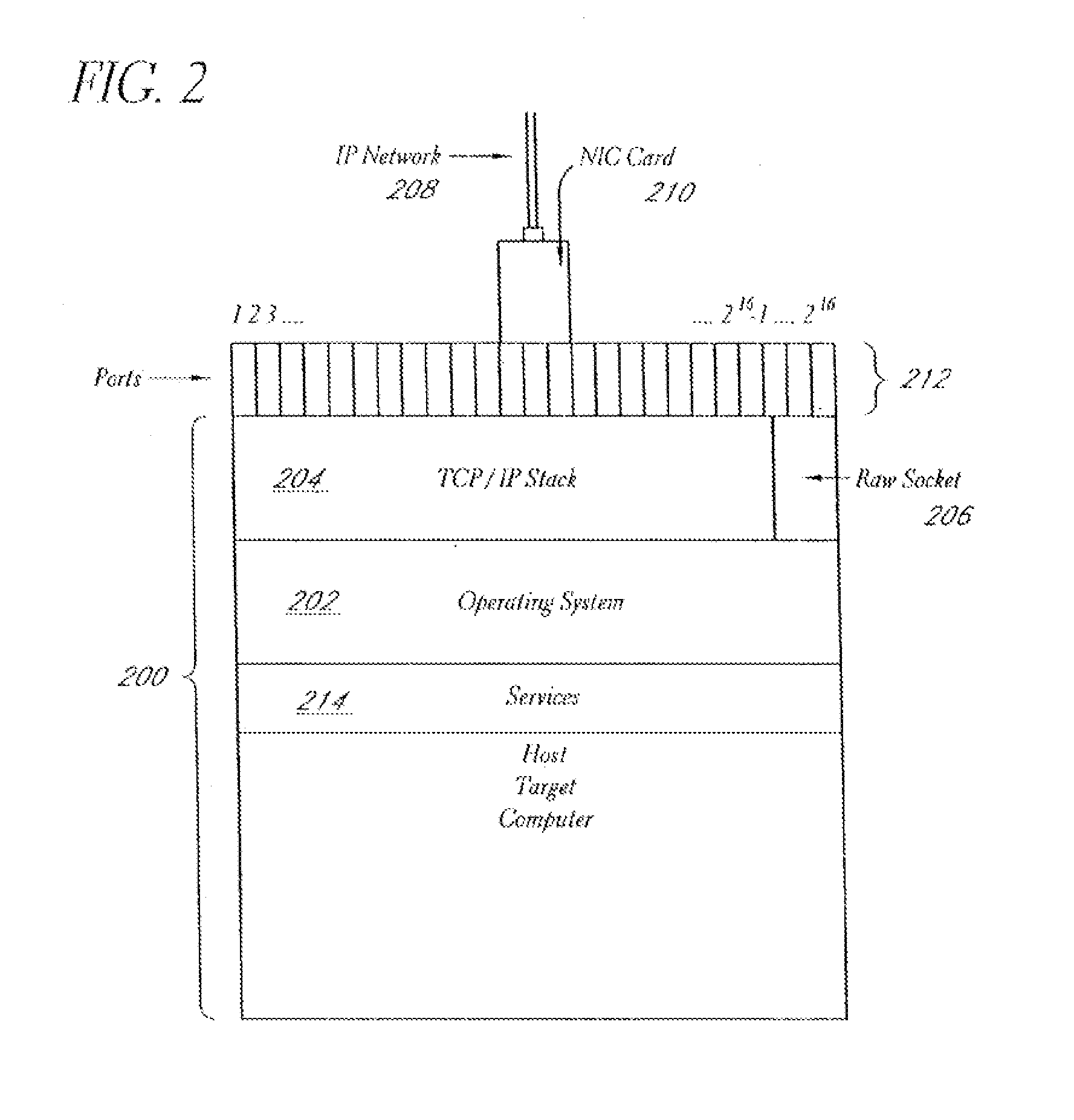
System and method for network vulnerability detection and reporting
ActiveUS7257630B2Reduce the possibilityReliably determinedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionGraphicsOperational system
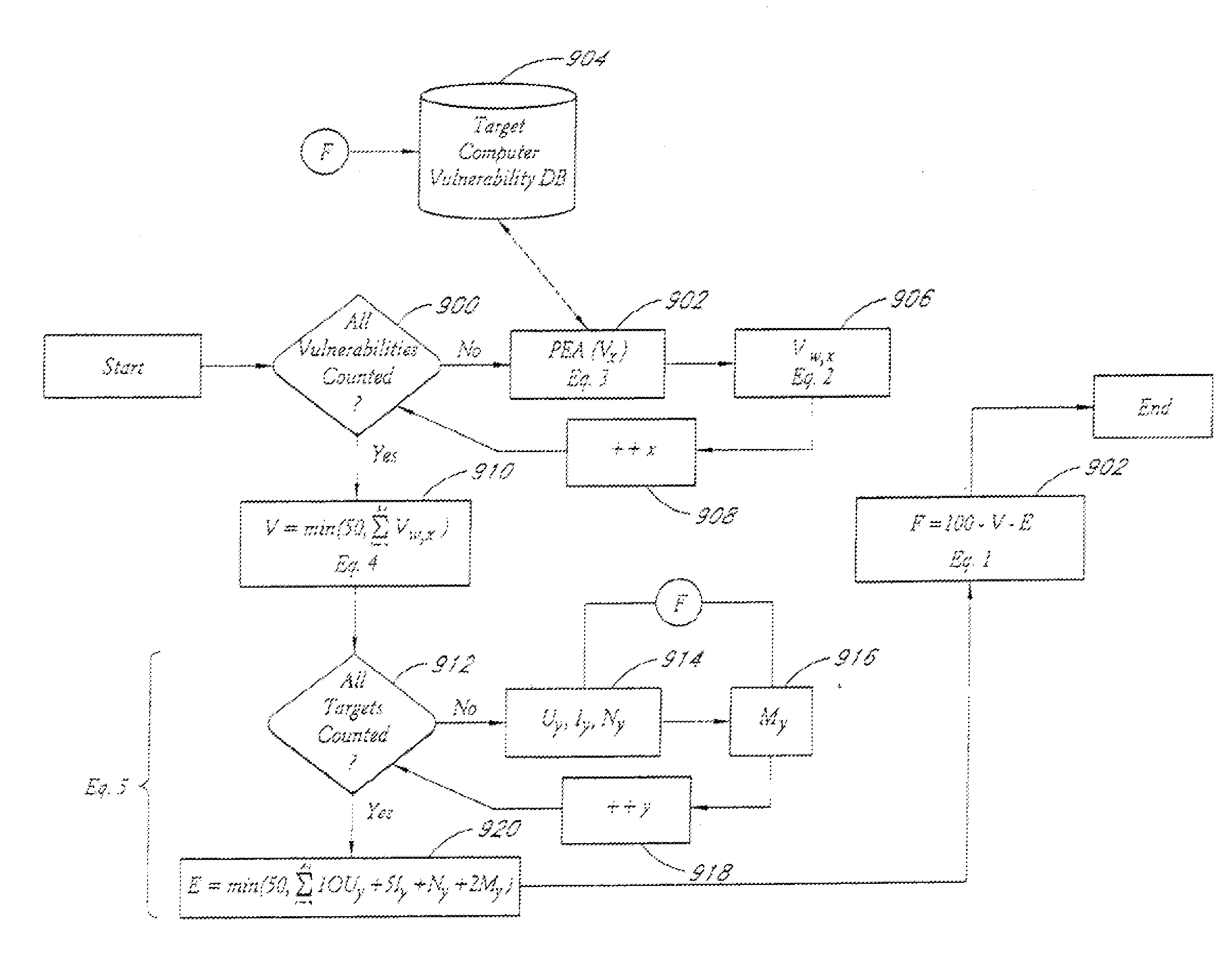
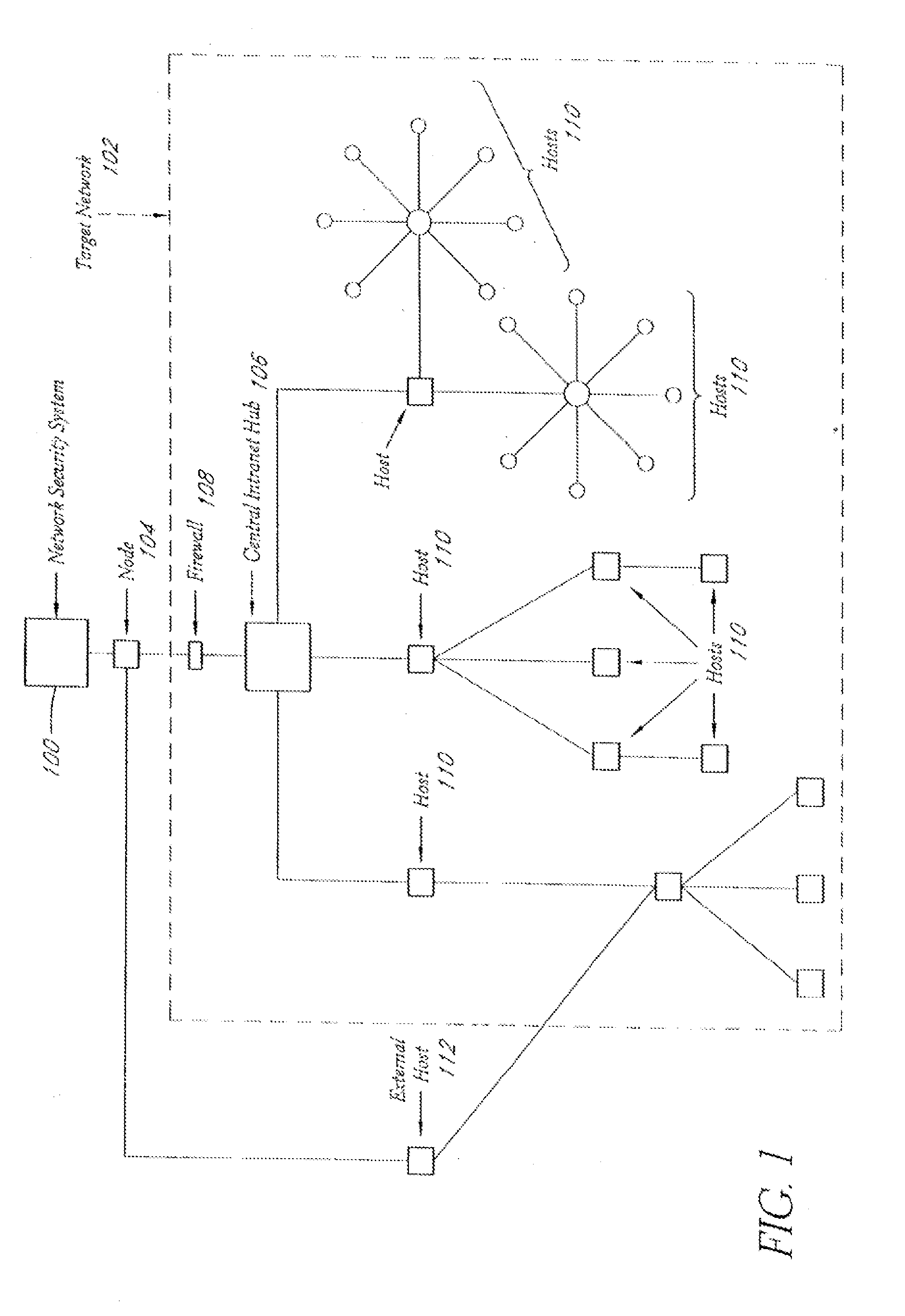
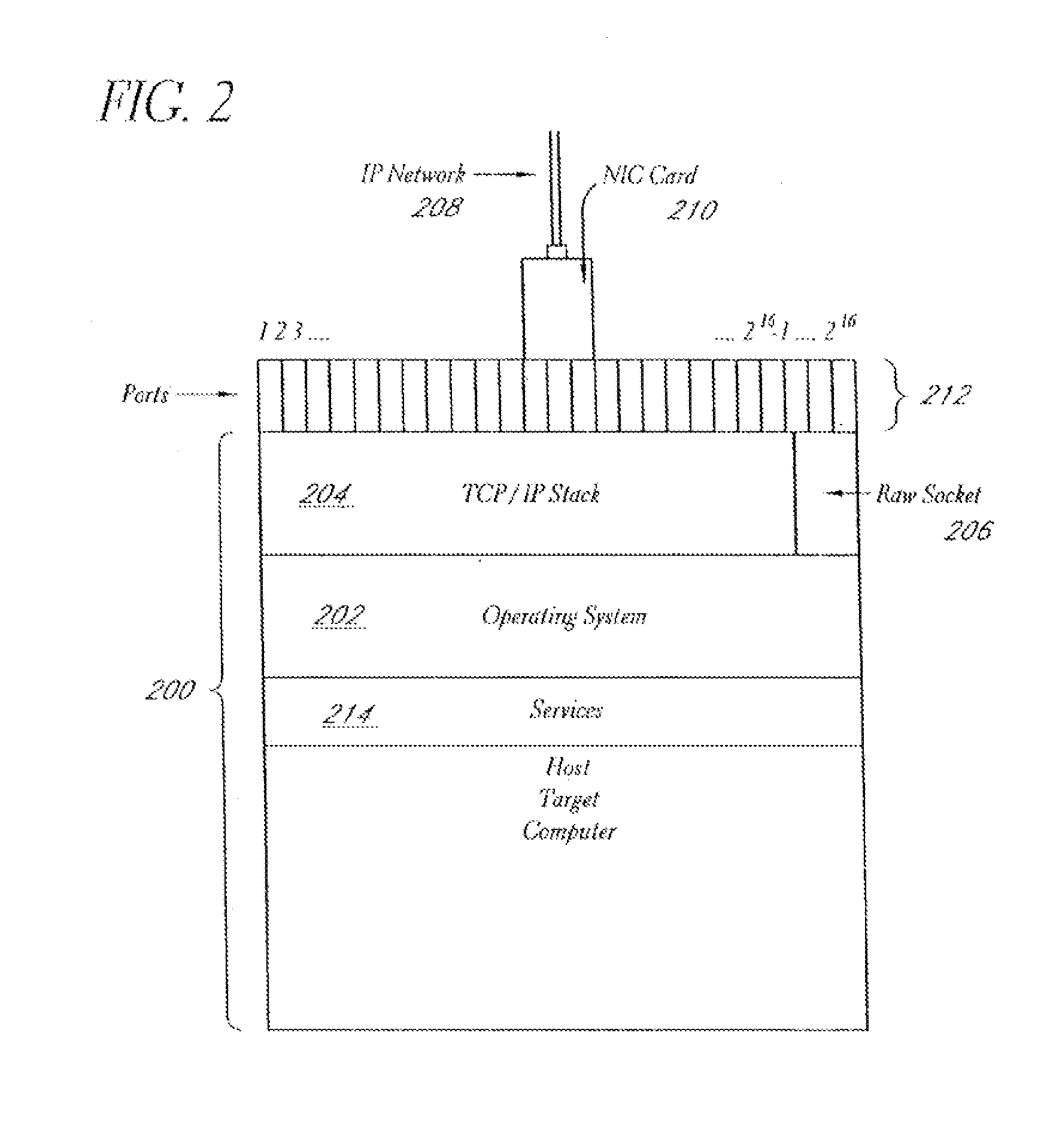
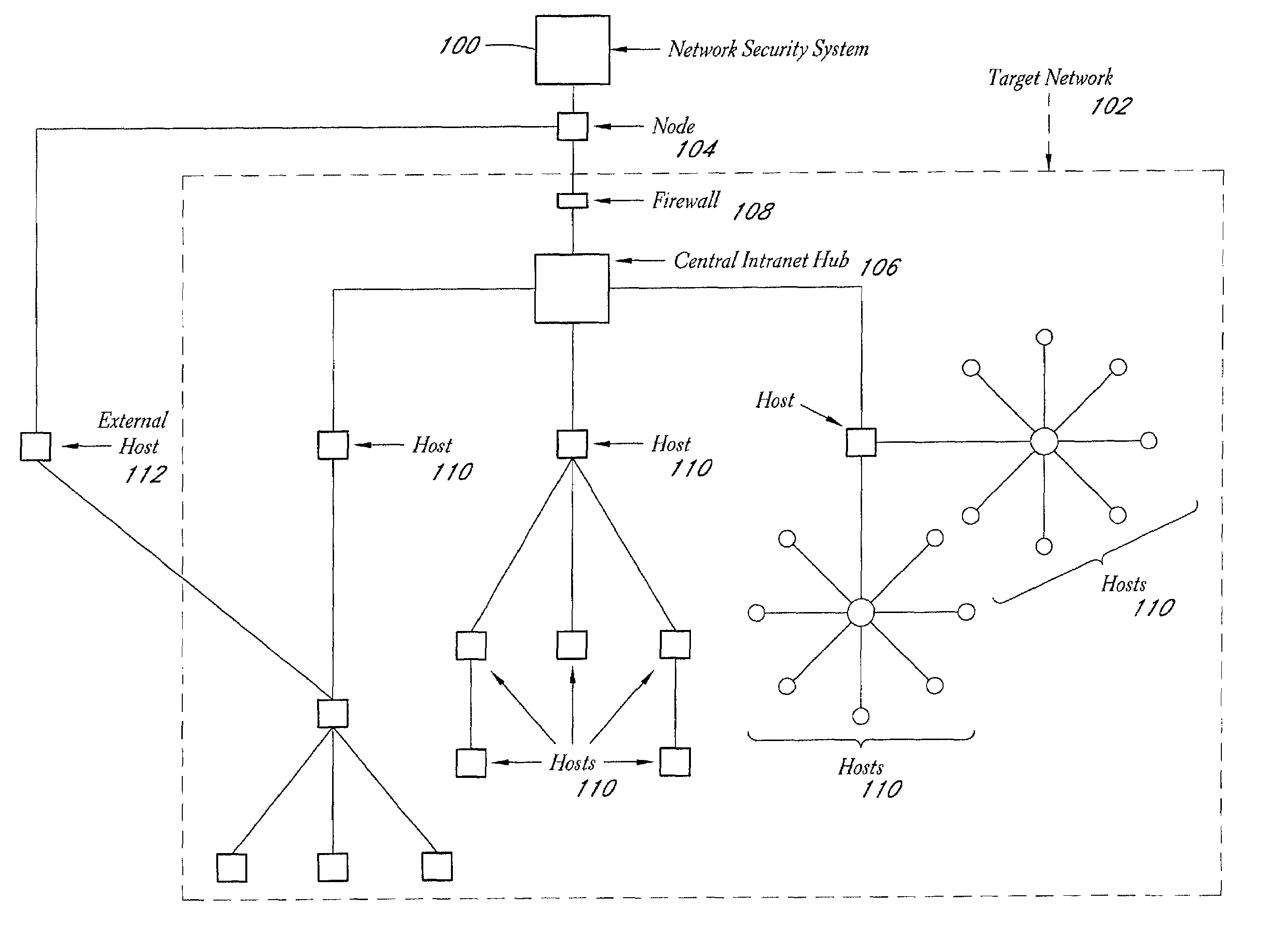
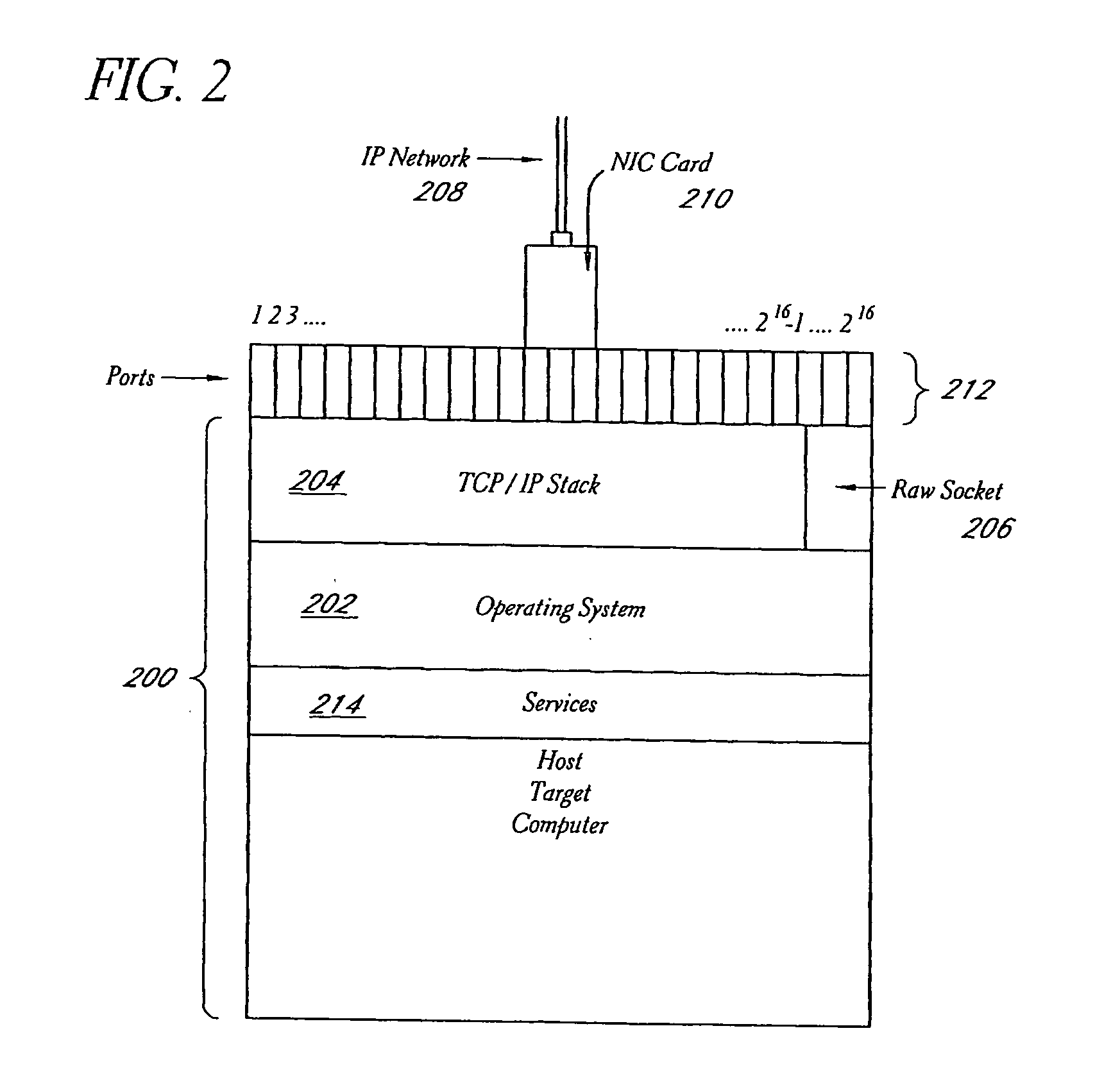
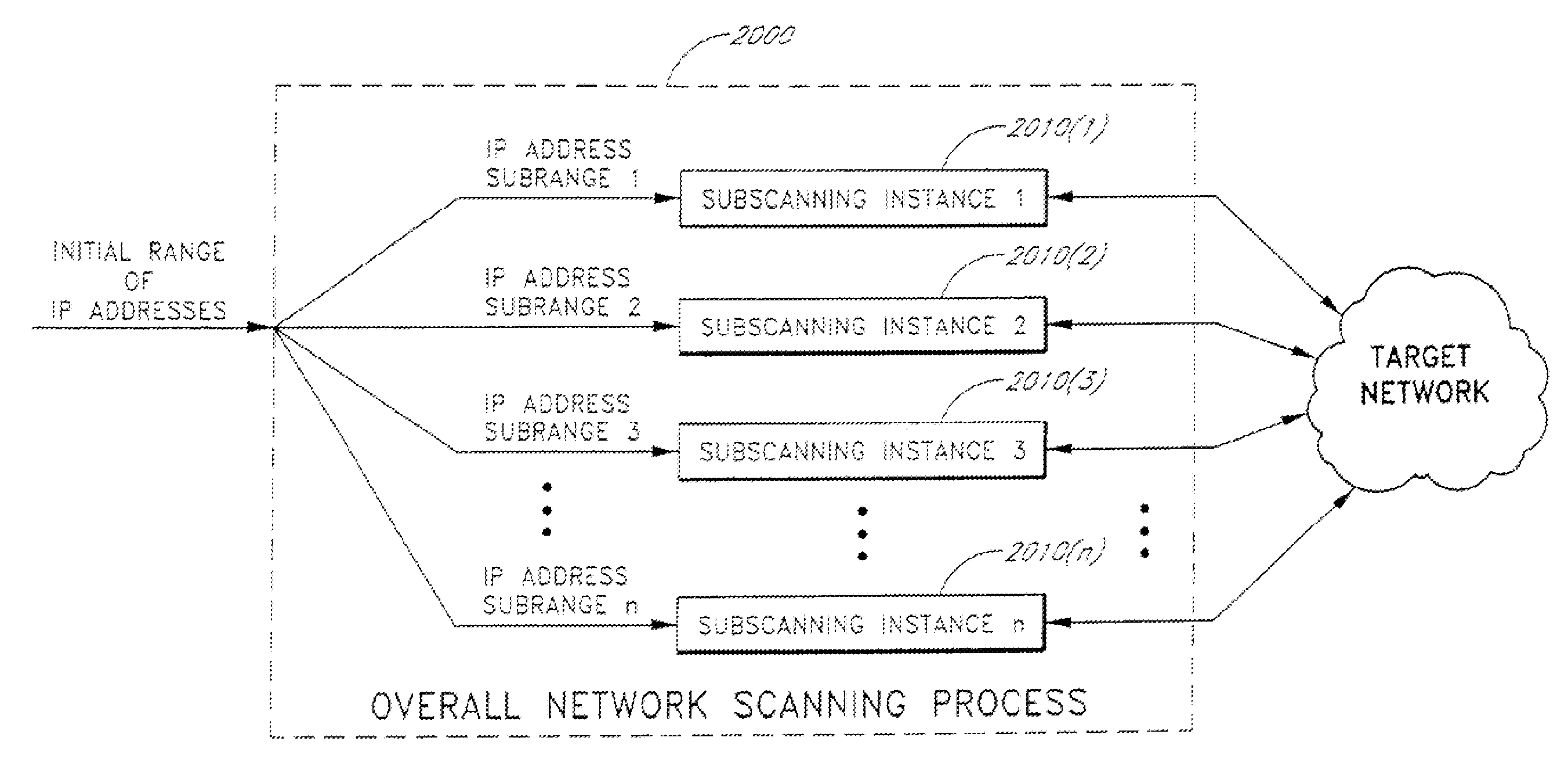
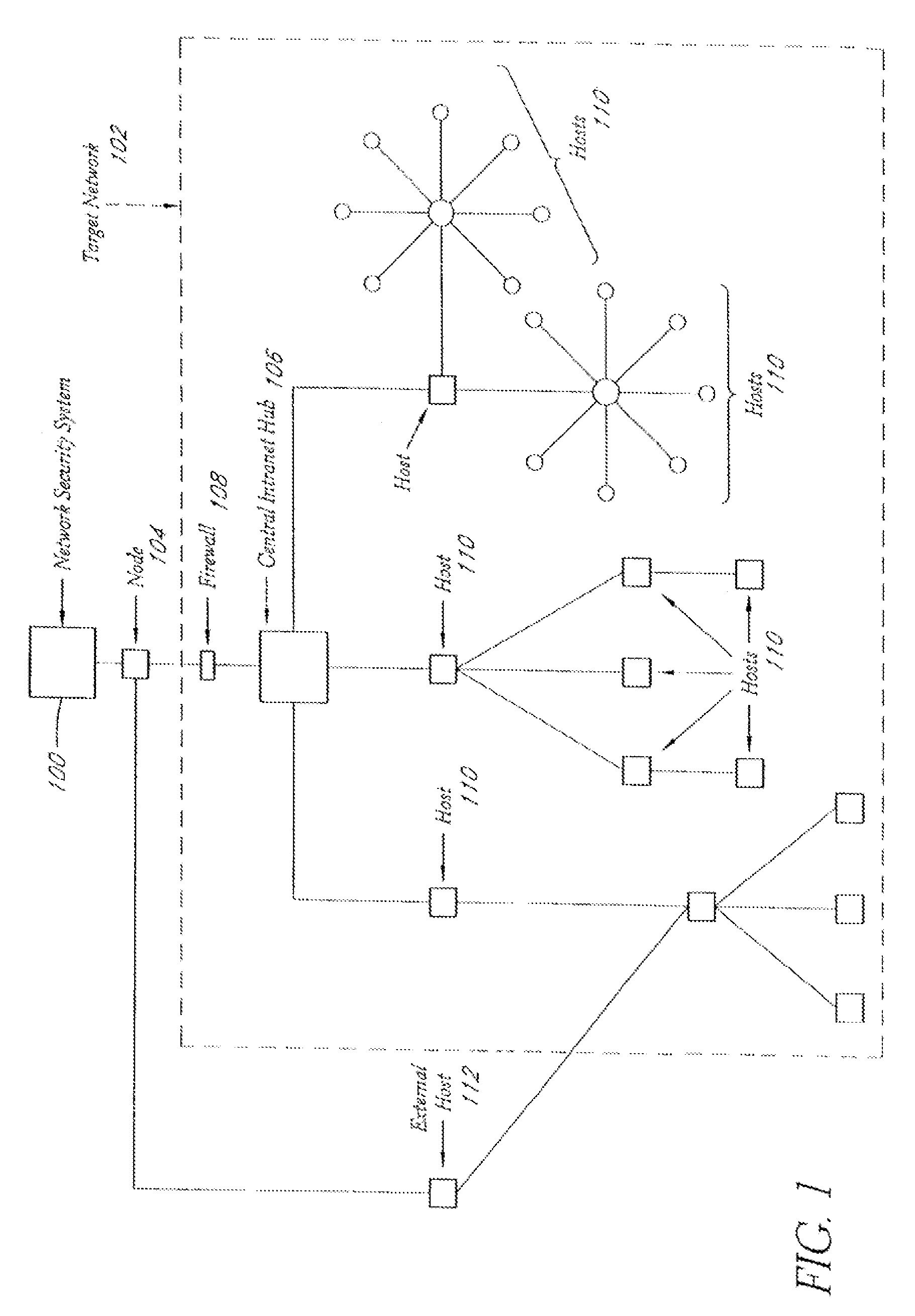
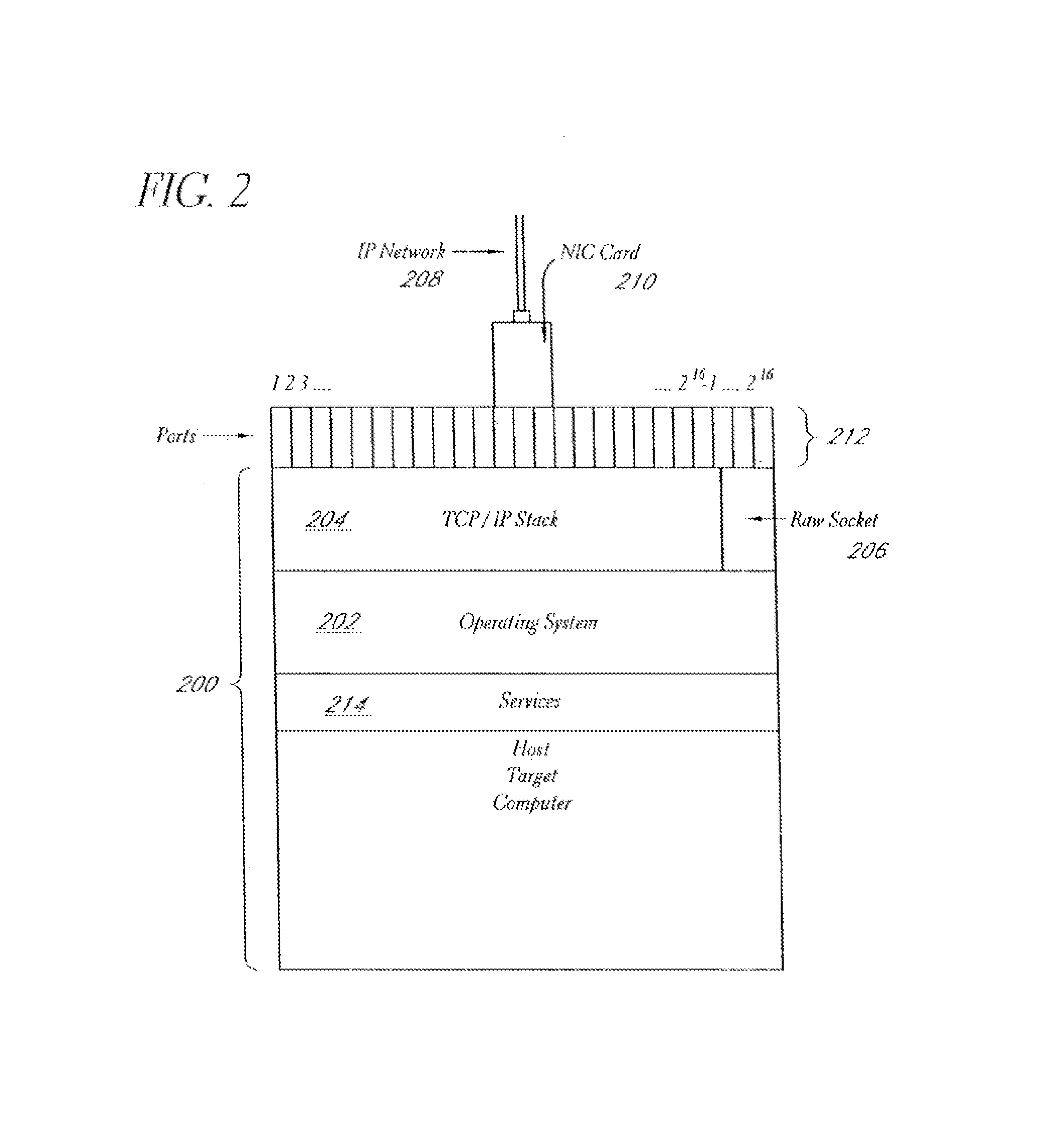
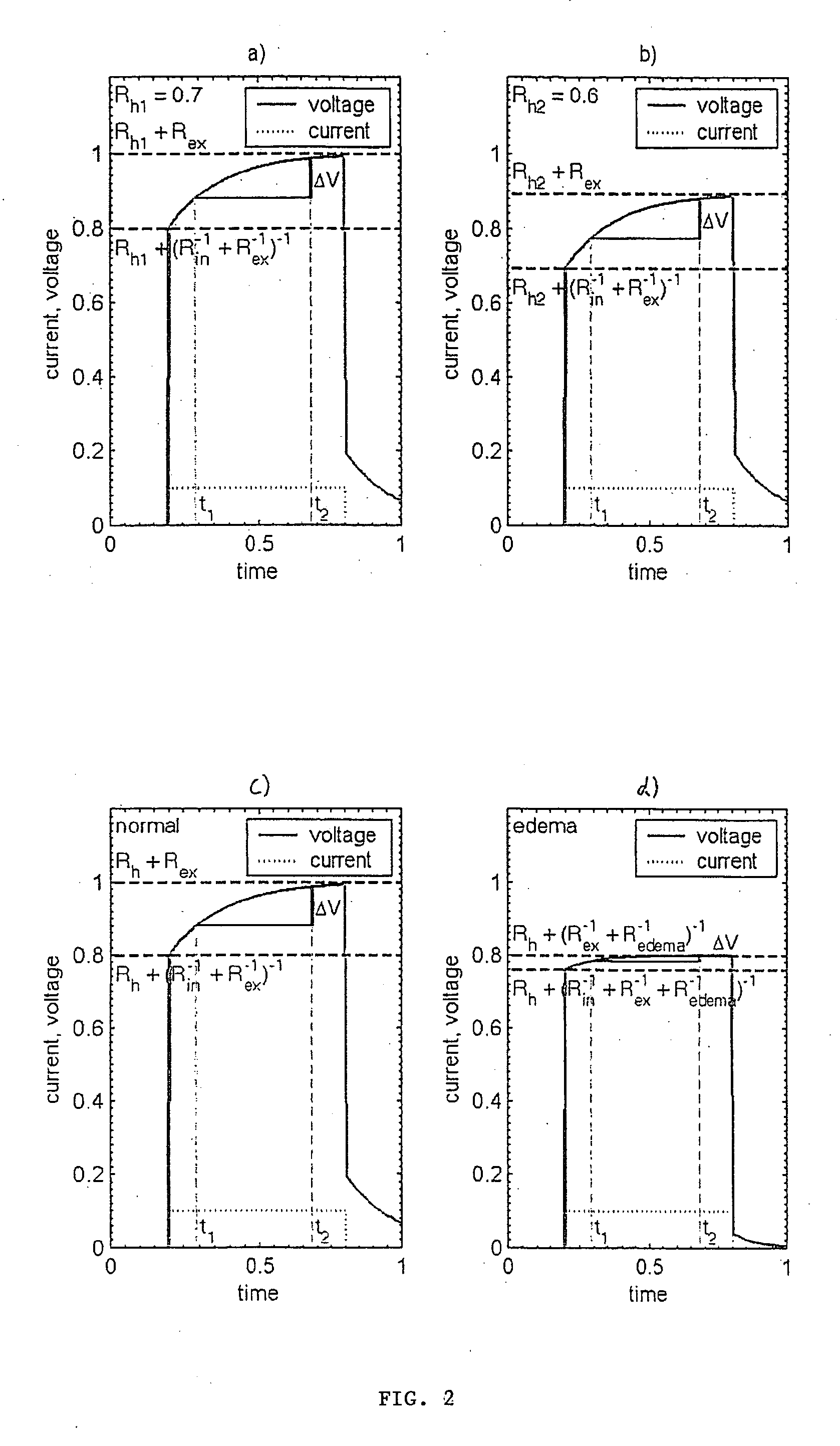
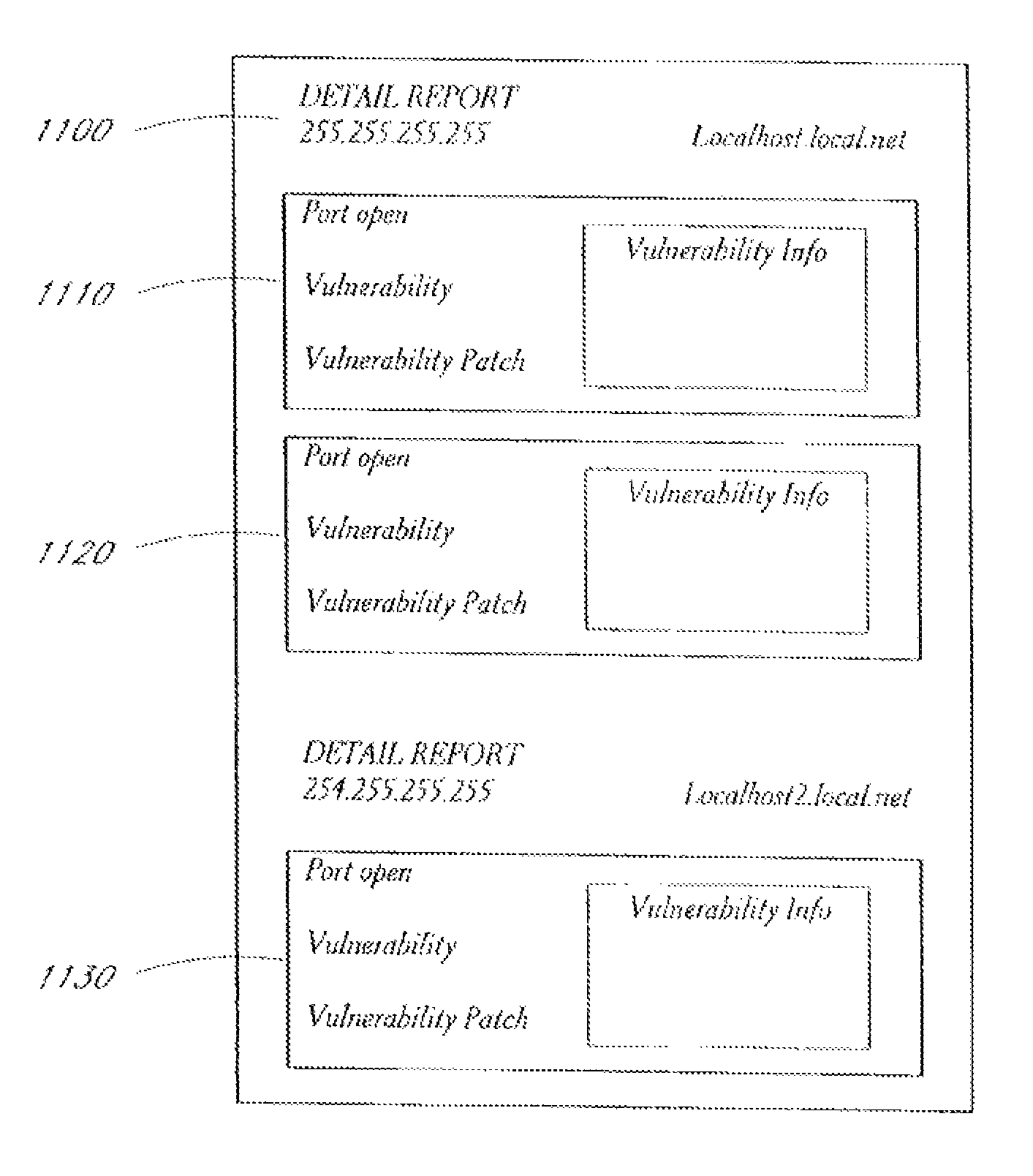
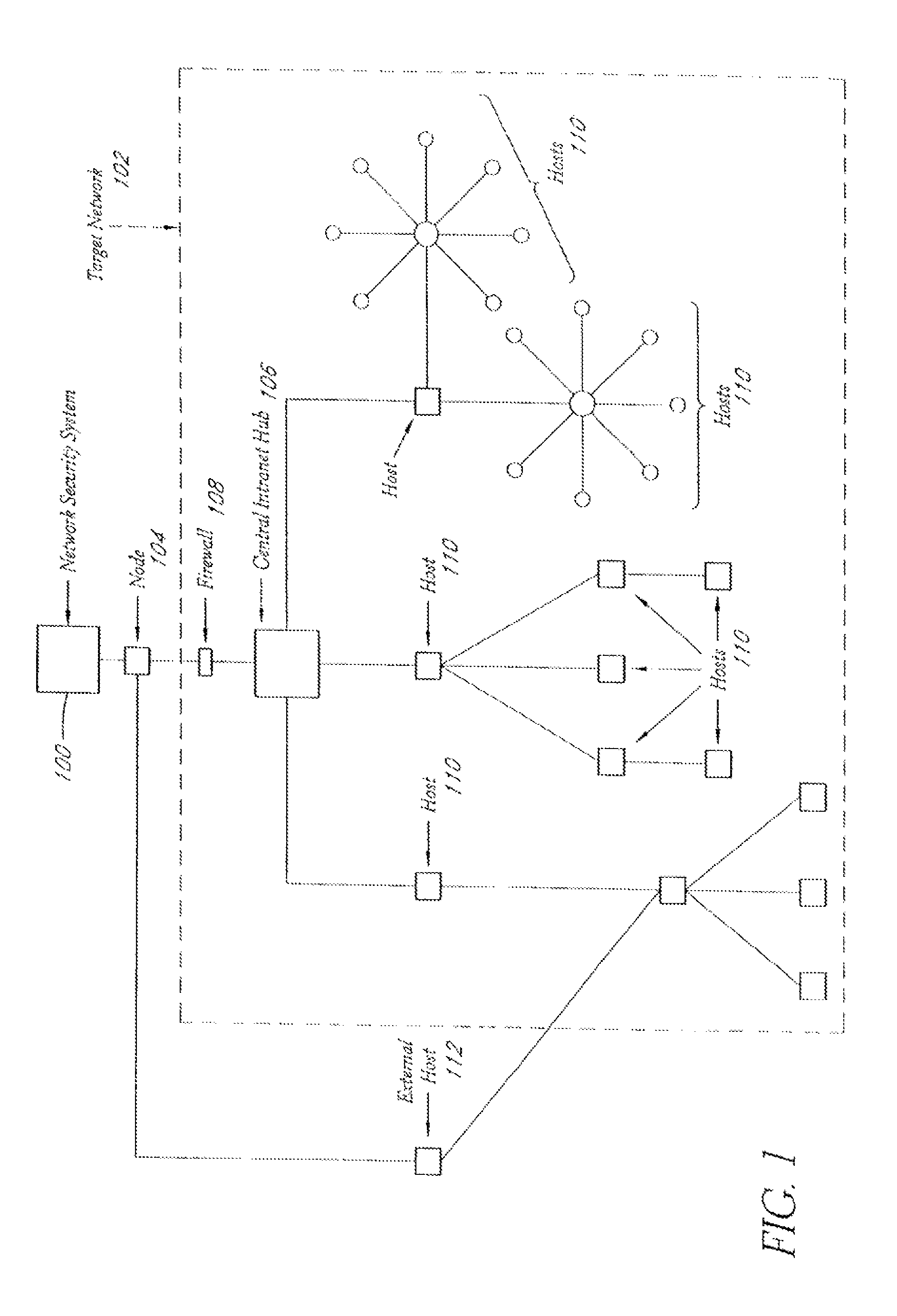
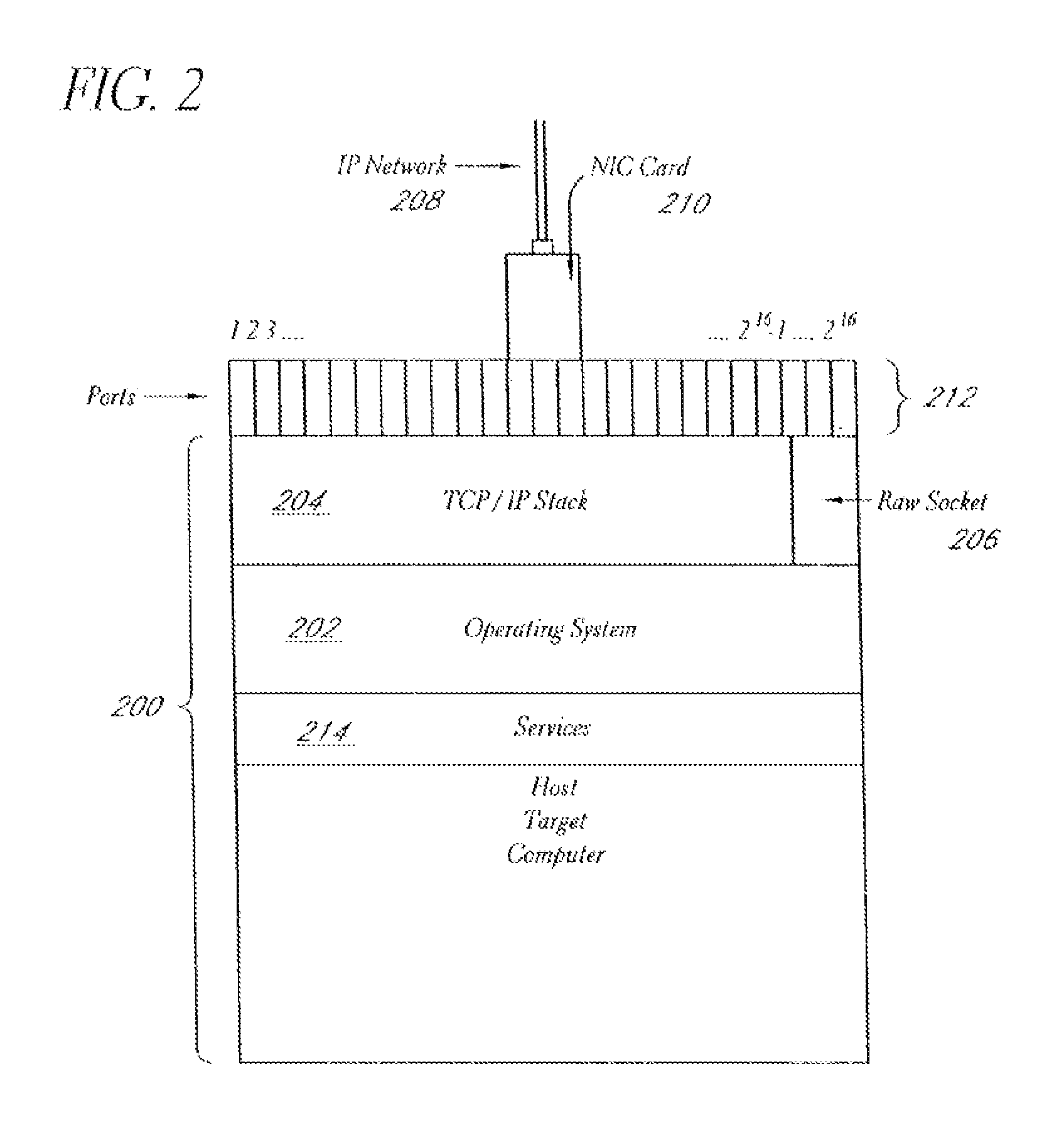
A system and method provide comprehensive and highly automated testing of vulnerabilities to intrusion on a target network, including identification of operating system, identification of target network topology and target computers, identification of open target ports, assessment of vulnerabilities on target ports, active assessment of vulnerabilities based on information acquired from target computers, quantitative assessment of target network security and vulnerability, and hierarchical graphical representation of the target network, target computers, and vulnerabilities in a test report. The system and method employ minimally obtrusive techniques to avoid interference with or damage to the target network during or after testing.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
System and method for network vulnerability detection and reporting
ActiveUS7152105B2Easy to useReliably determinedElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisGraphicsOperational system
A system and method provide comprehensive and highly automated testing of vulnerabilities to intrusion on a target network, including identification of operating system, identification of target network topology and target computers, identification of open target ports, assessment of vulnerabilities on target ports, active assessment of vulnerabilities based on information acquired from target computers, quantitative assessment of target network security and vulnerability, and hierarchical graphical representation of the target network, target computers, and vulnerabilities in a test report. The system and method employ minimally obtrusive techniques to avoid interference with or damage to the target network during or after testing.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
System and method for network vulnerability detection and reporting
InactiveUS20070011319A1Easy to useReliably determinedDigital computer detailsPolarising elementsGraphicsOperational system
A system and method provide comprehensive and highly automated testing of vulnerabilities to intrusion on a target network, including identification of operating system, identification of target network topology and target computers, identification of open target ports, assessment of vulnerabilities on target ports, active assessment of vulnerabilities based on information acquired from target computers, quantitative assessment of target network security and vulnerability, and hierarchical graphical representation of the target network, target computers, and vulnerabilities in a test report The system and method employ minimally obtrusive techniques to avoid interference with or damage to the target network during or after testing.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
System and method for network vulnerability detection and reporting
ActiveUS7243148B2Reduce likelihoodReliably determinedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionQuantitative assessmentVulnerability detection
A system and method provide comprehensive and highly automated testing of vulnerabilities to intrusion on a target network, including identification of operating system, identification of target network topology and target computers, identification of open target ports, assessment of vulnerabilities on target ports, active assessment of vulnerabilities based on information acquired from target computers, quantitative assessment of target network security and vulnerability, and hierarchical graphical representation of the target network, target computers, and vulnerabilities in a test report. The system and method employ minimally obtrusive techniques to avoid interference with or damage to the target network during or after testing.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Haplotype analysis
InactiveUS7700325B2High analysisReliable determinationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStatistical analysisHaplotype
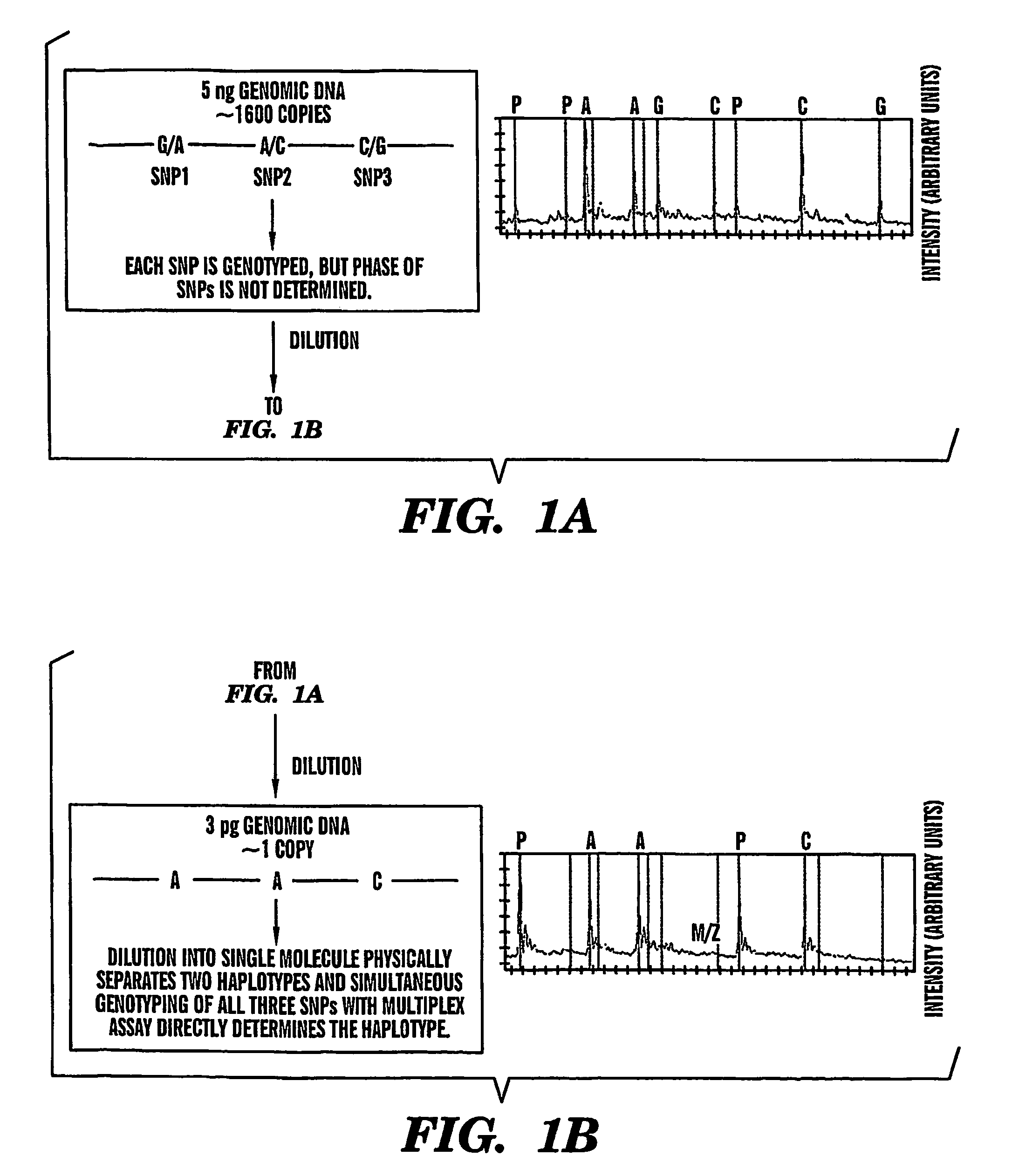
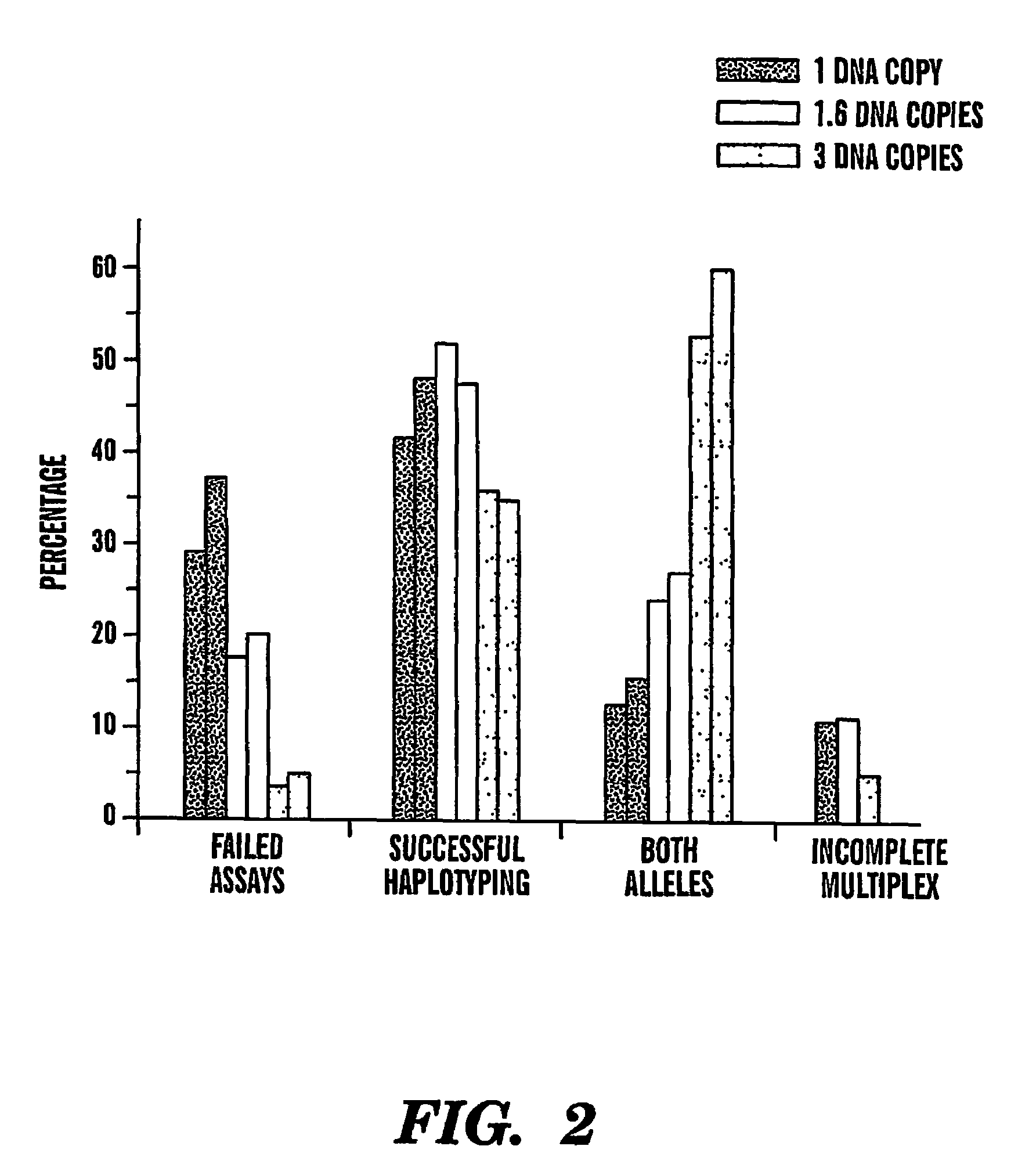
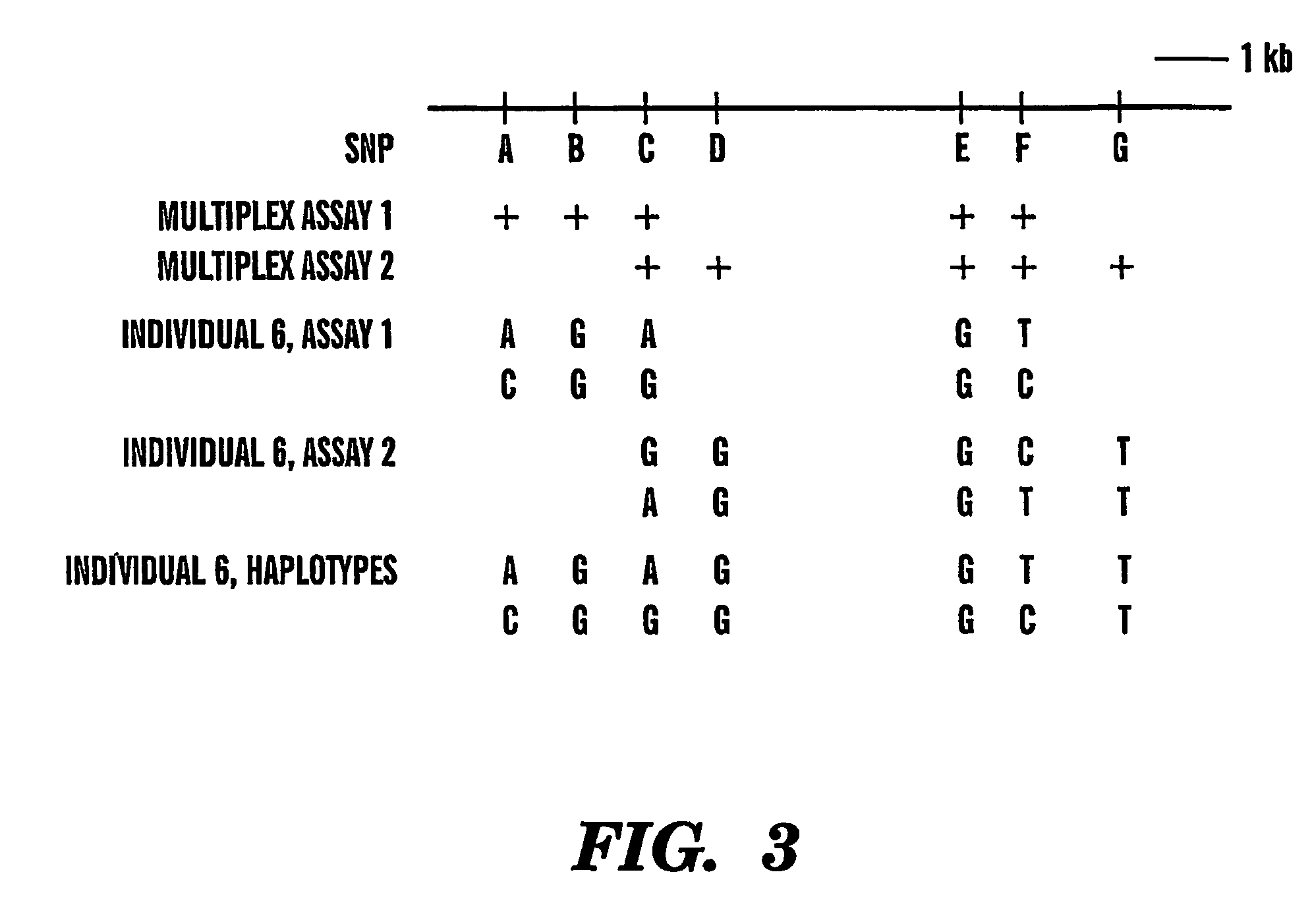
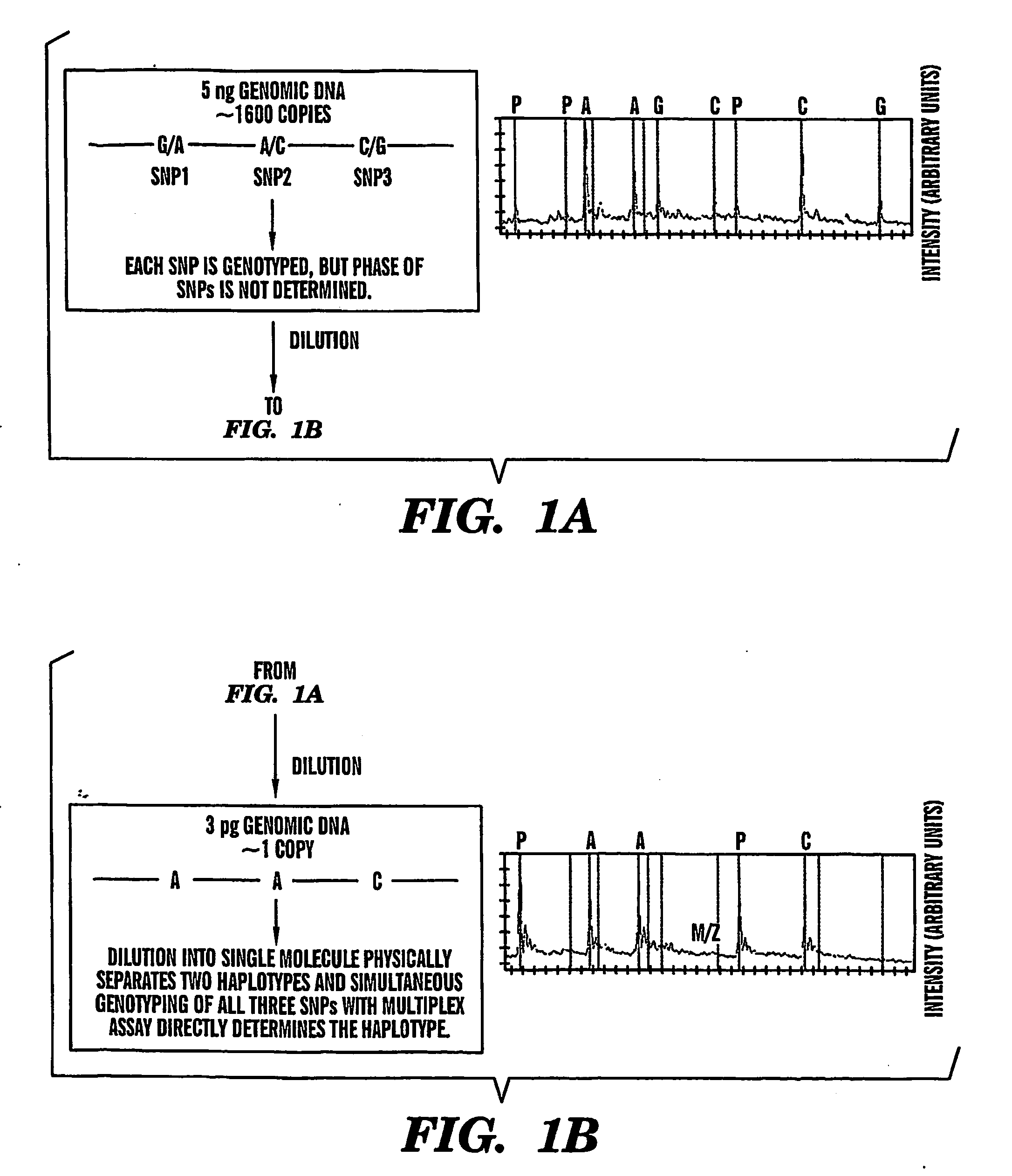
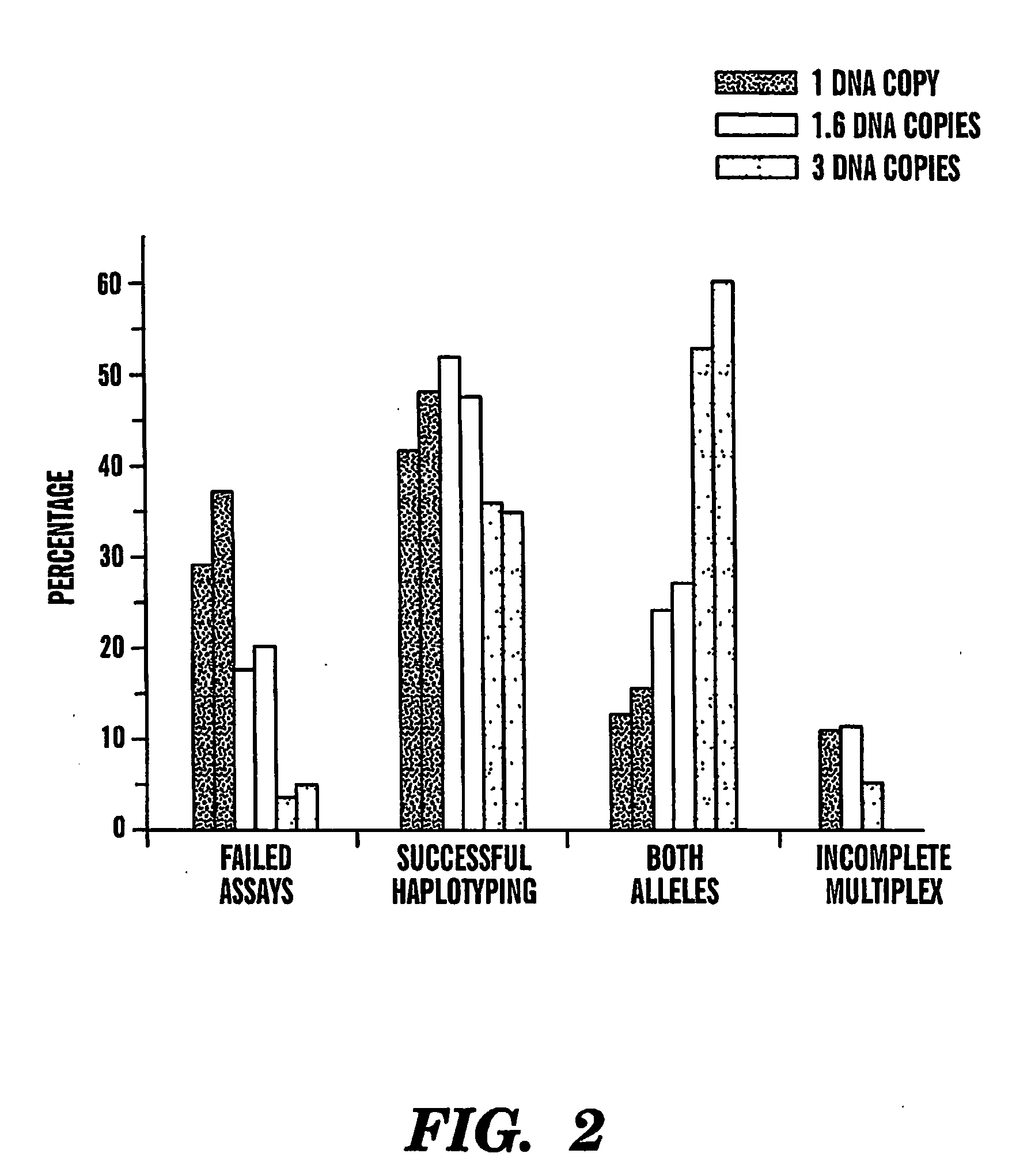
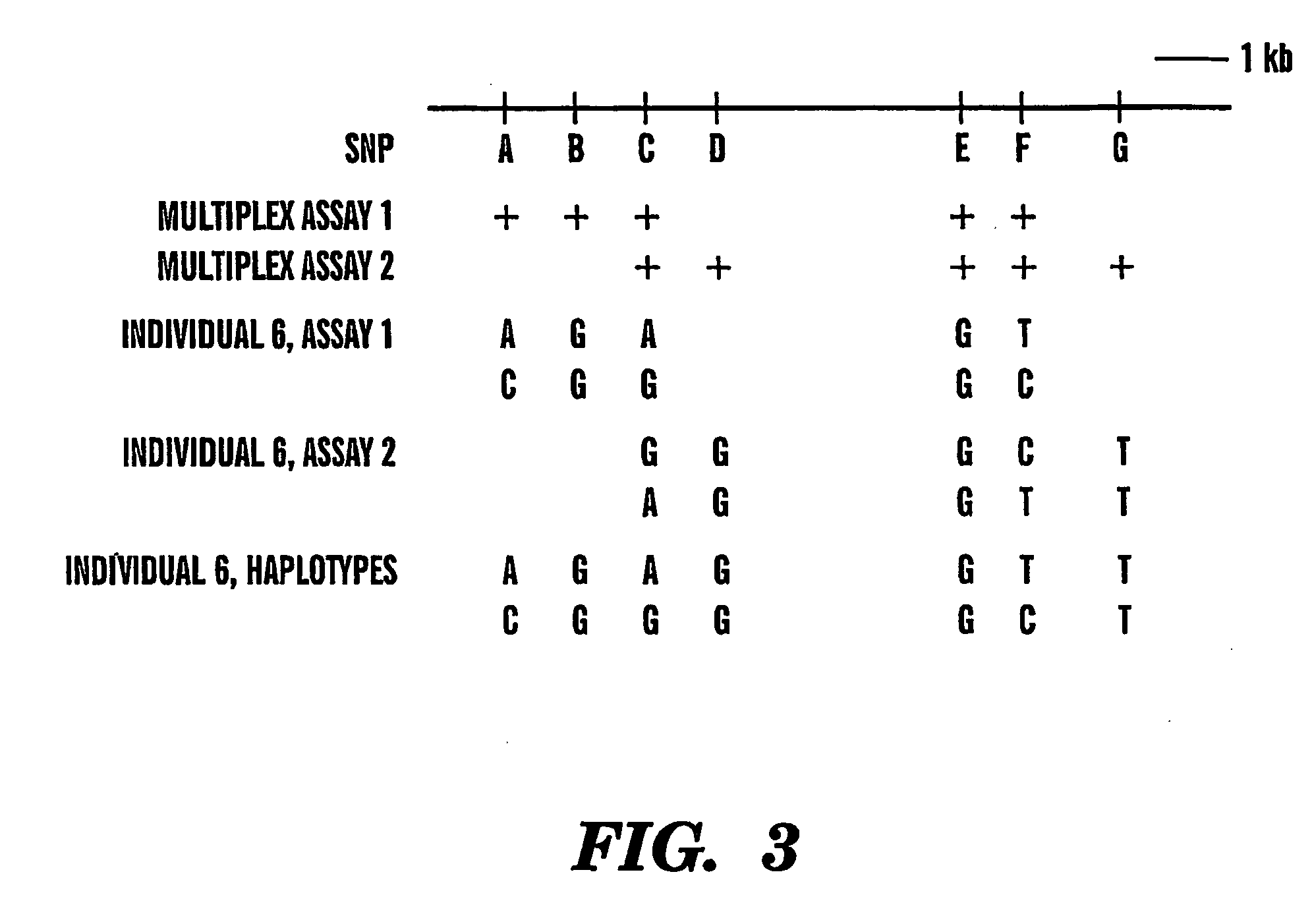
The present invention provides an efficient way for high throughput haplotype analysis. Several polymorphic nucleic acid markers, such as SNPs, can be simultaneously and reliably determined through multiplex PCR of single nucleic acid molecules in several parallel single molecule dilutions and the consequent statistical analysis of the results from these parallel single molecule multiplex PCR reactions results in reliable determination of haplotypes present in the subject. The nucleic acid markers can be of any distance to each other on the chromosome. In addition, an approach wherein overlapping DNA markers are analyzed can be used to link smaller haplotypes into larger haplotypes. Consequently, the invention provides a powerful new tool for diagnostic haplotyping and identifying novel haplotypes.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
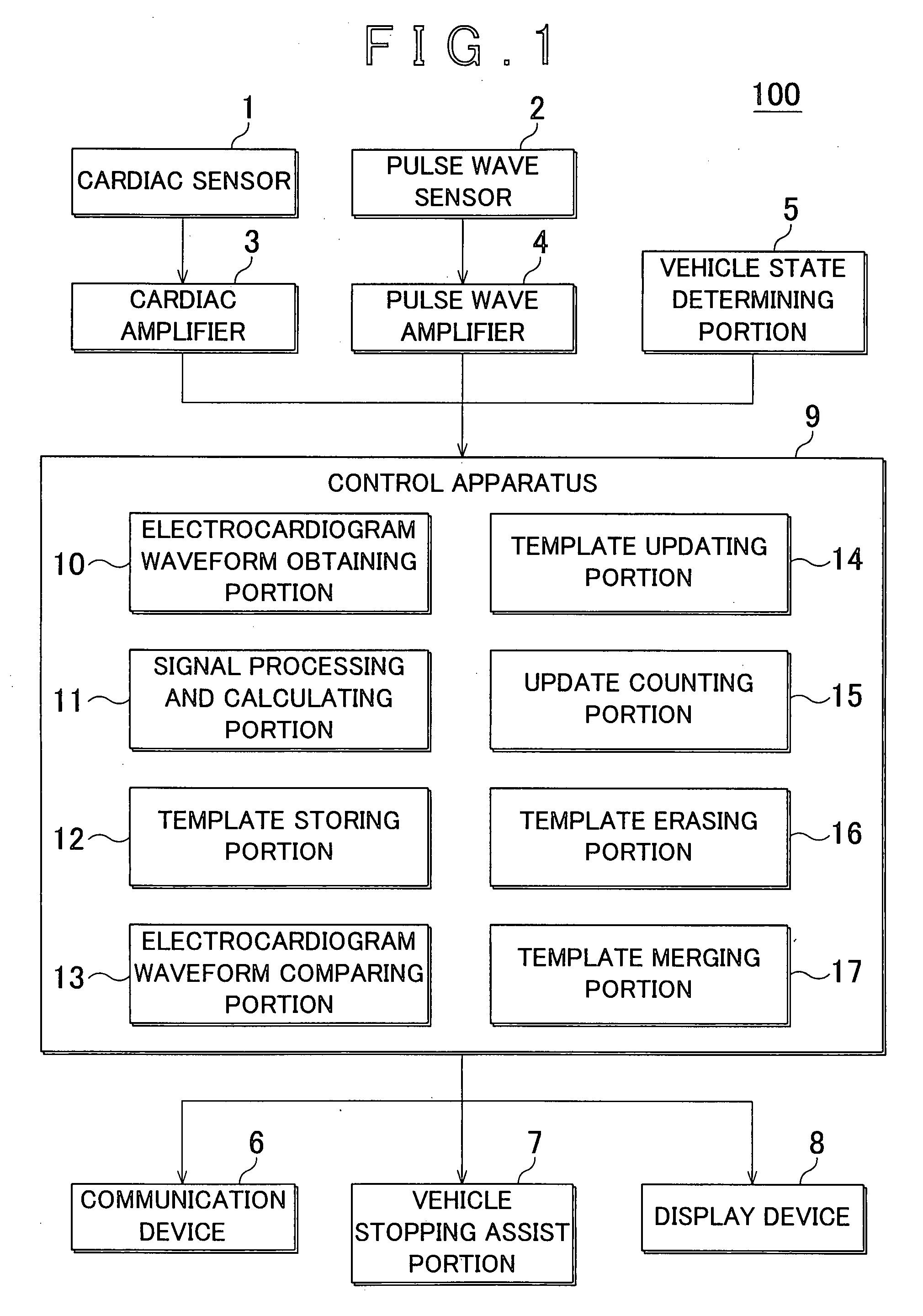
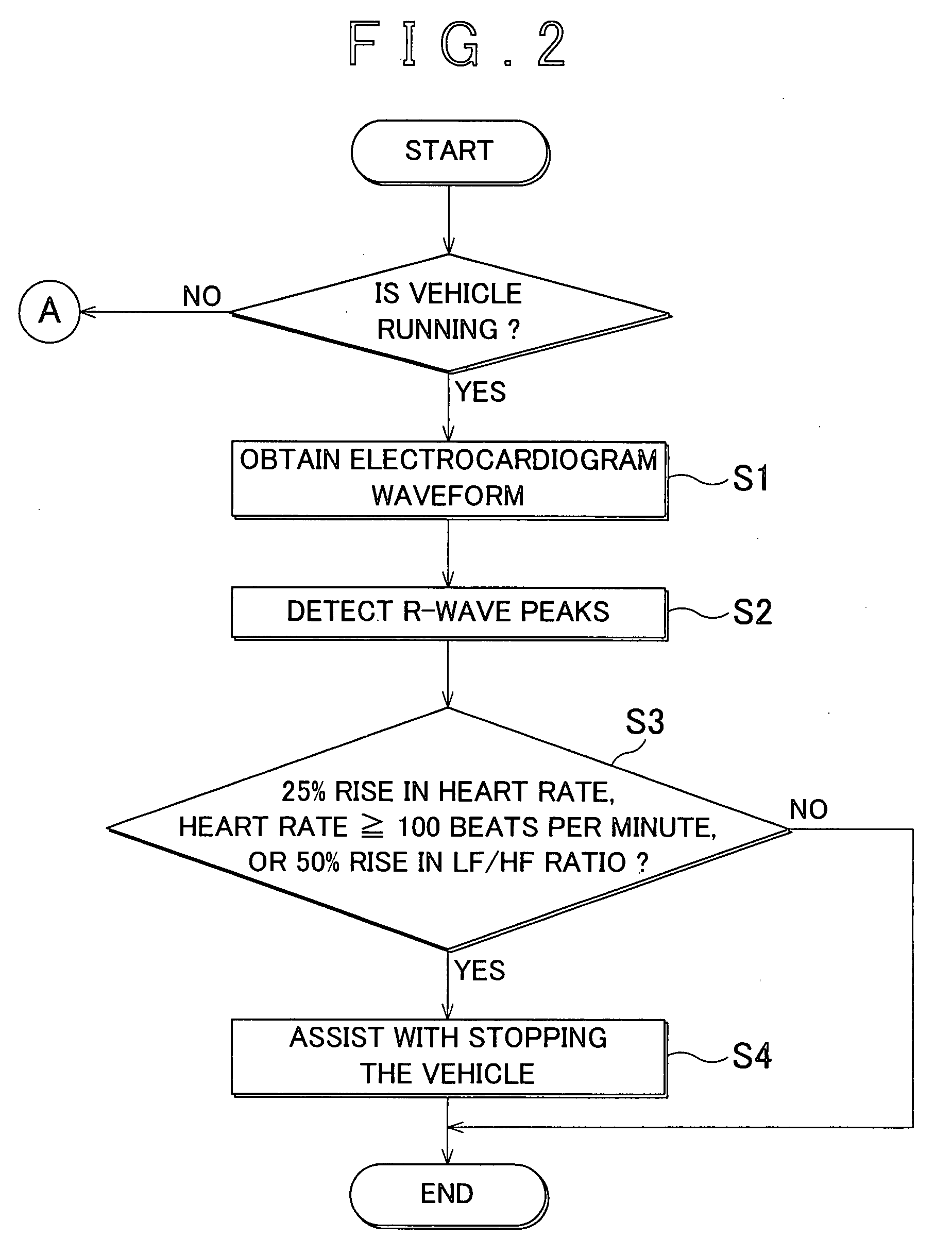
Method and device for monitoring heart rhythm in a vehicle
ActiveUS20070265540A1Reliably determineReliably determinedElectrocardiographySensorsDriver/operatorCardiac rhythm monitoring
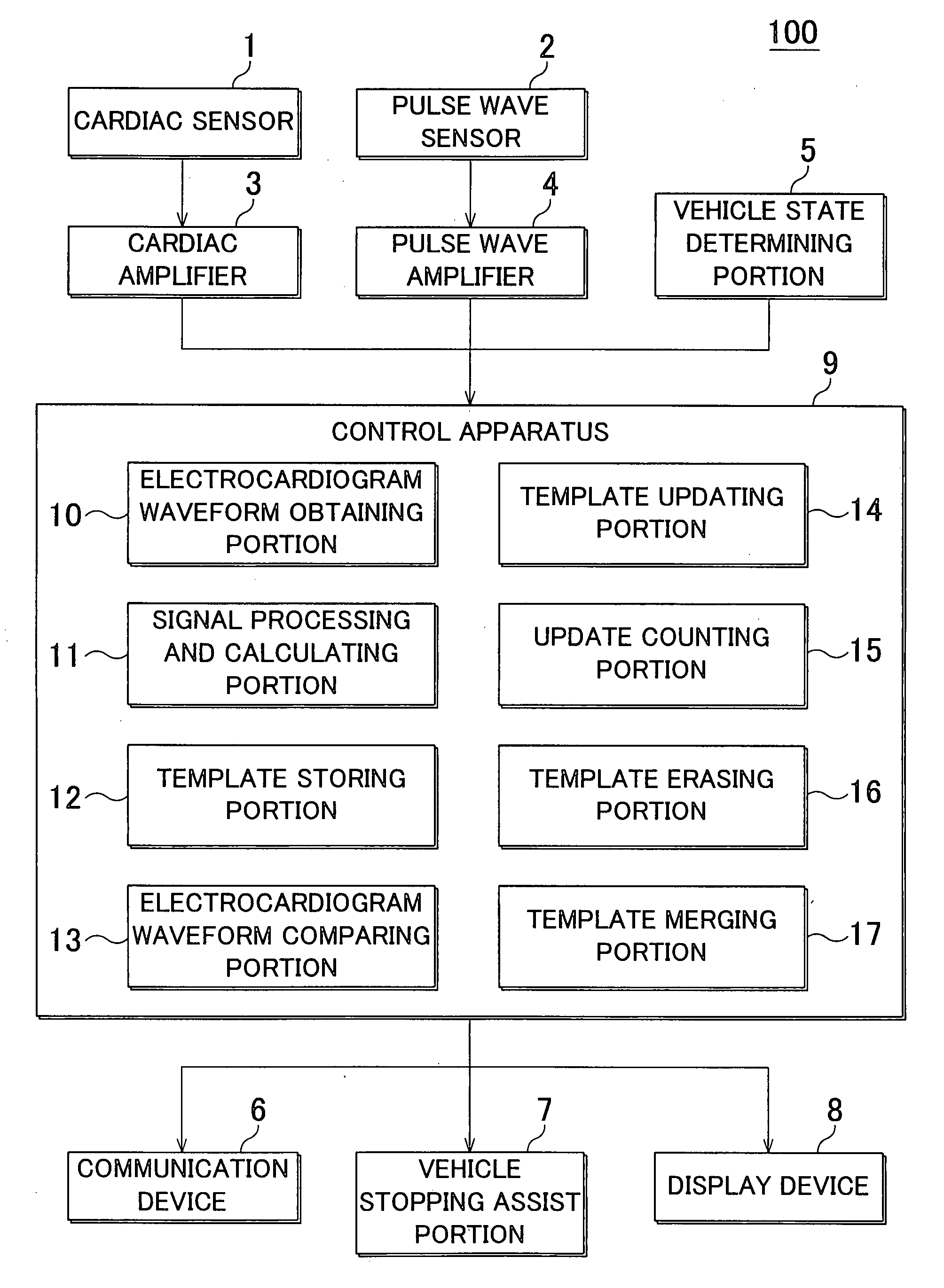
An heart rhythm monitoring device for a vehicle, which determines whether a driver has an arrhythmia includes a vehicle state determining portion that determines whether the vehicle is stopped; an electrode arranged on a steering wheel in a position where the driver grips the steering wheel; an electrocardiogram waveform obtaining portion that obtains a first electrocardiogram waveform from the electrode; and a signal processing and calculating portion that determines whether the heart rhythm of the driver is erratic based on the first electrocardiogram waveform. When the vehicle is in motion, the signal processing and calculating portion determines whether the heart rhythm of the driver is erratic based on the waveform component that is strong with respect to noise in the first electrocardiogram waveform.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +2
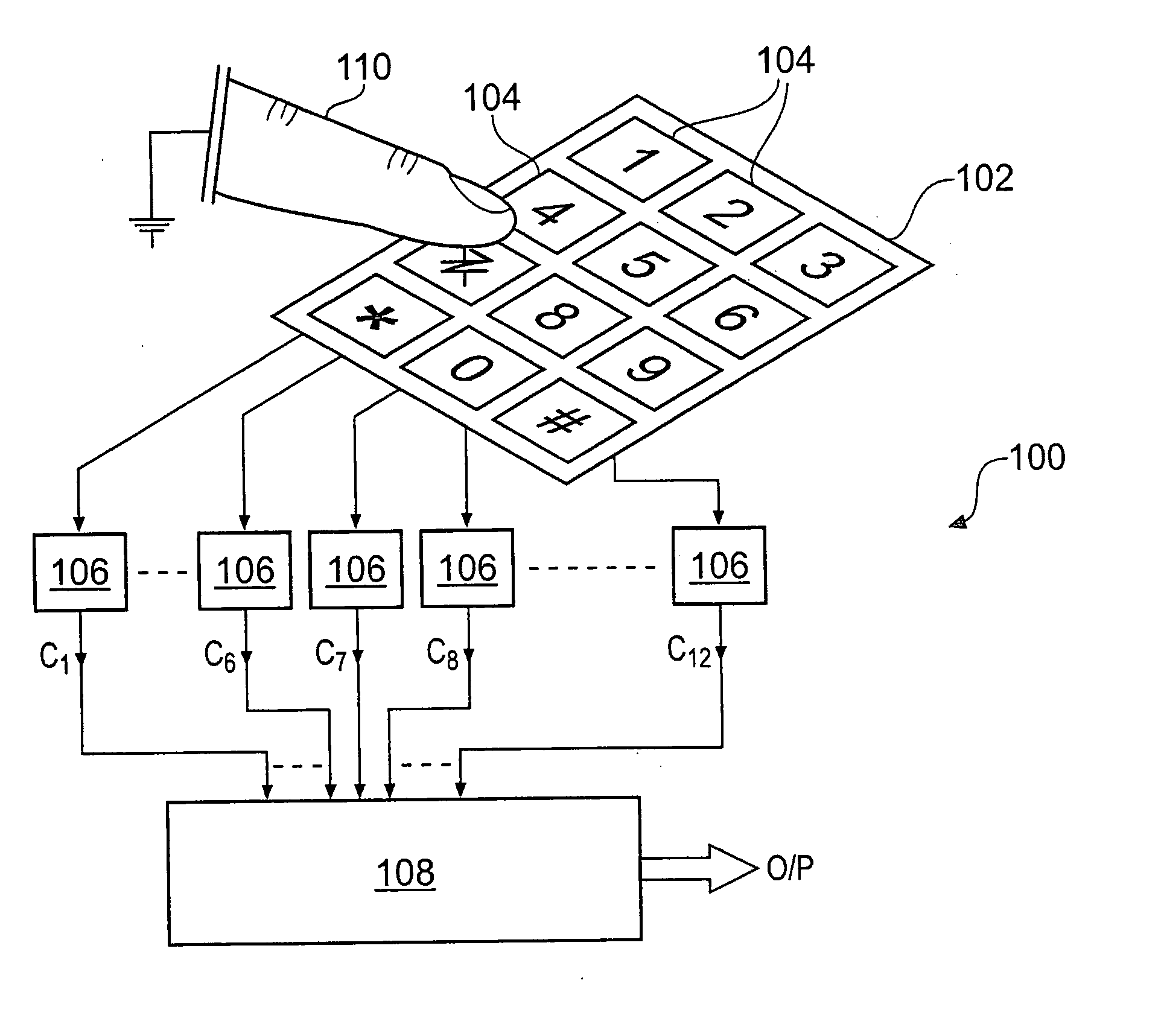
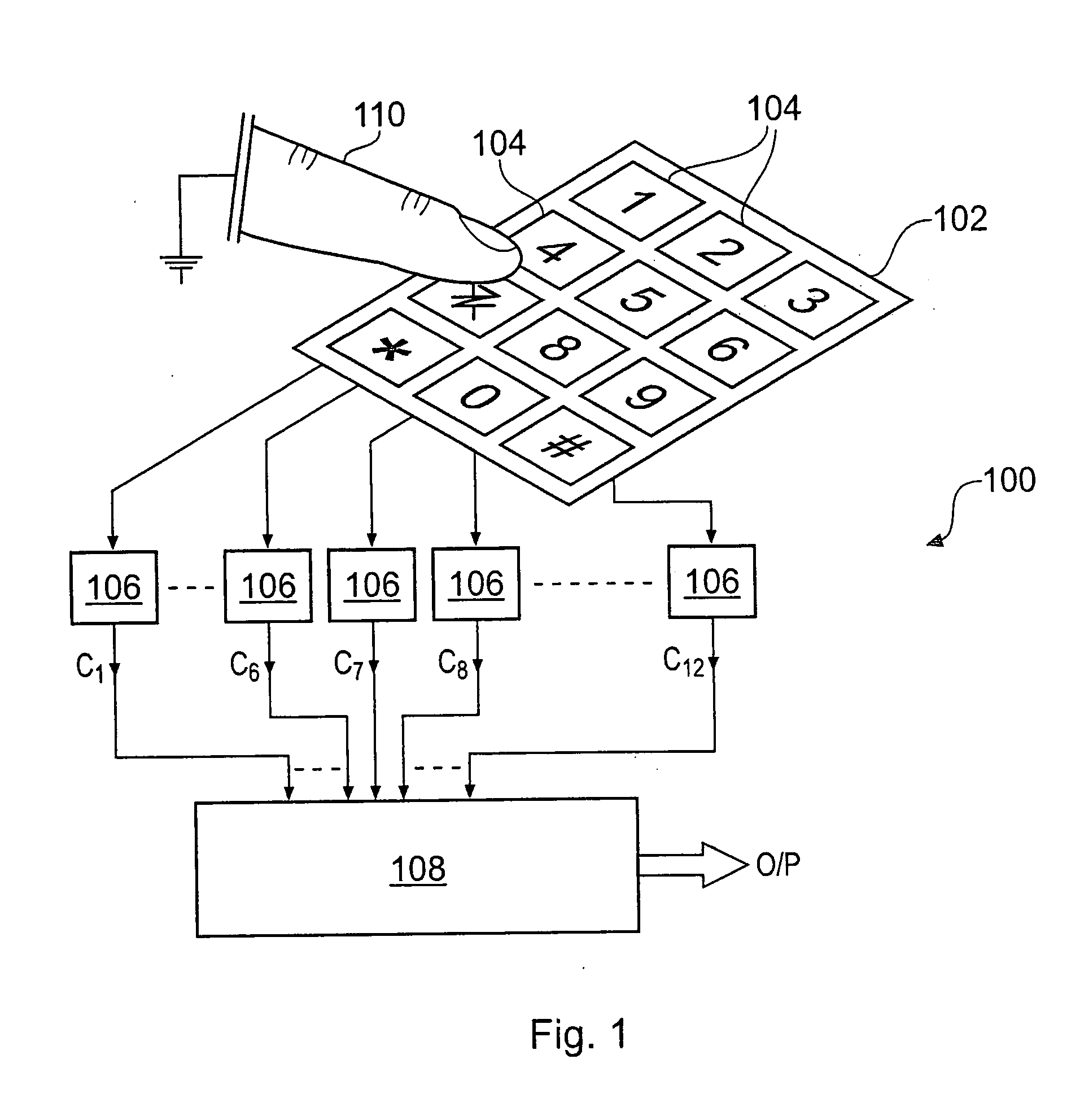
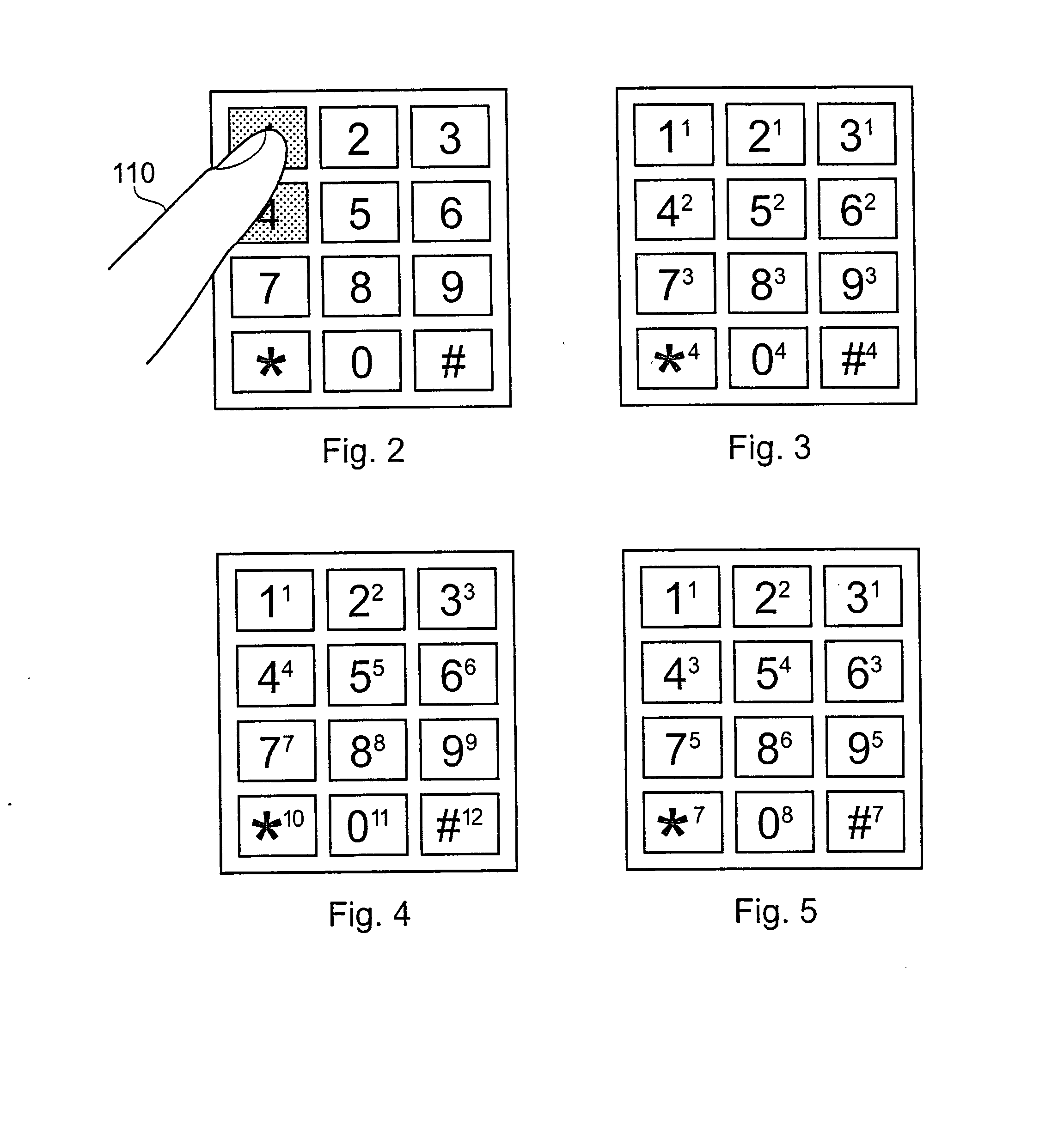
Capacitive Keyboard with Position Dependent Reduced Keying Ambiguity
InactiveUS20070273561A1Reduce ambiguitySignal strength value can be enhancedElectronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingHuman–computer interactionCapacitance transducer
Owner:NEODRON LTD
Haplotype analysis
InactiveUS20070122805A1Reliable determinationHigh analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyNucleic acid molecule
The present invention provides an efficient way for high throughput haplotype analysis. Several polymorphic nucleic add markers, such as SNPs, can be simultaneously and reliably determined through multiplex PCR of single nucleic acid molecules in several parallel single molecule dilutions and the consequent statistical analysis of the results from these parallel single molecule multiplex PCR reactions results in reliable determination of haplotypes present in the subject. The nucleic acid markers can be of any distance to each other on the chromosome. In addition, an approach wherein overlapping DNA markers are analyzed can be used to link smaller haplotypes into larger haplotypes. Consequently, the invention provides a powerful new tool for diagnostic haplotyping and identifying novel haplotypes.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Method for synchronizing a base station with a mobile station, a base station and a mobile station
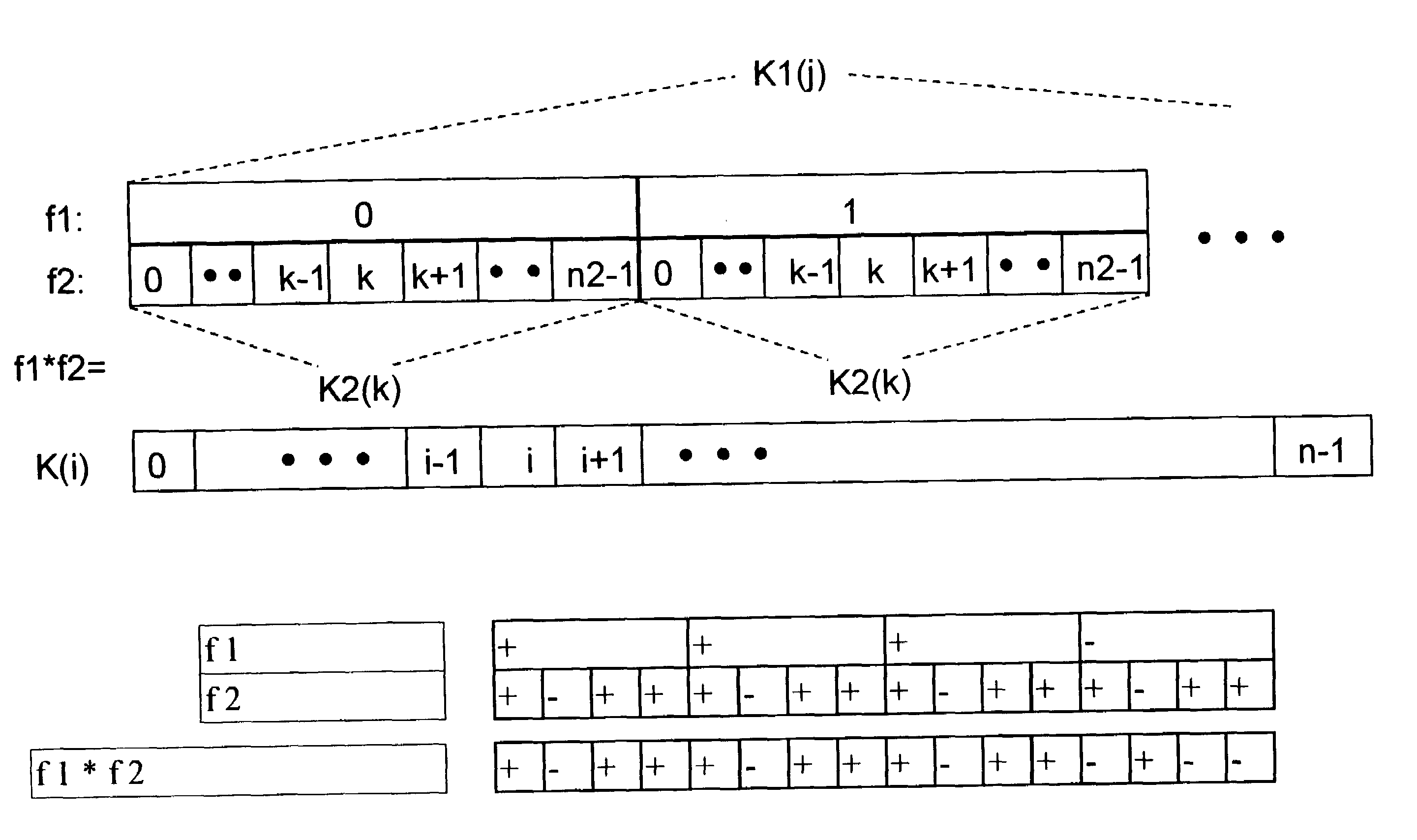
InactiveUS7062002B1Sure easyEasy to useCode division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlMobile stationComputer science
Method for forming and determining a signal sequence, a synchronization method, a transmitting unit and a receiving unit, including the formation of signal sequences that are based on partial signal sequences, the second partial signal sequence being repeated and modulated in the process by the first partial signal sequence, and at least one of the signal sequences being a Golay sequence, and use of these partial signal sequences for the purpose of simplified calculation of correlation sums in a two-stage calculation method, with one partial correlation sum sequence being calculated first.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
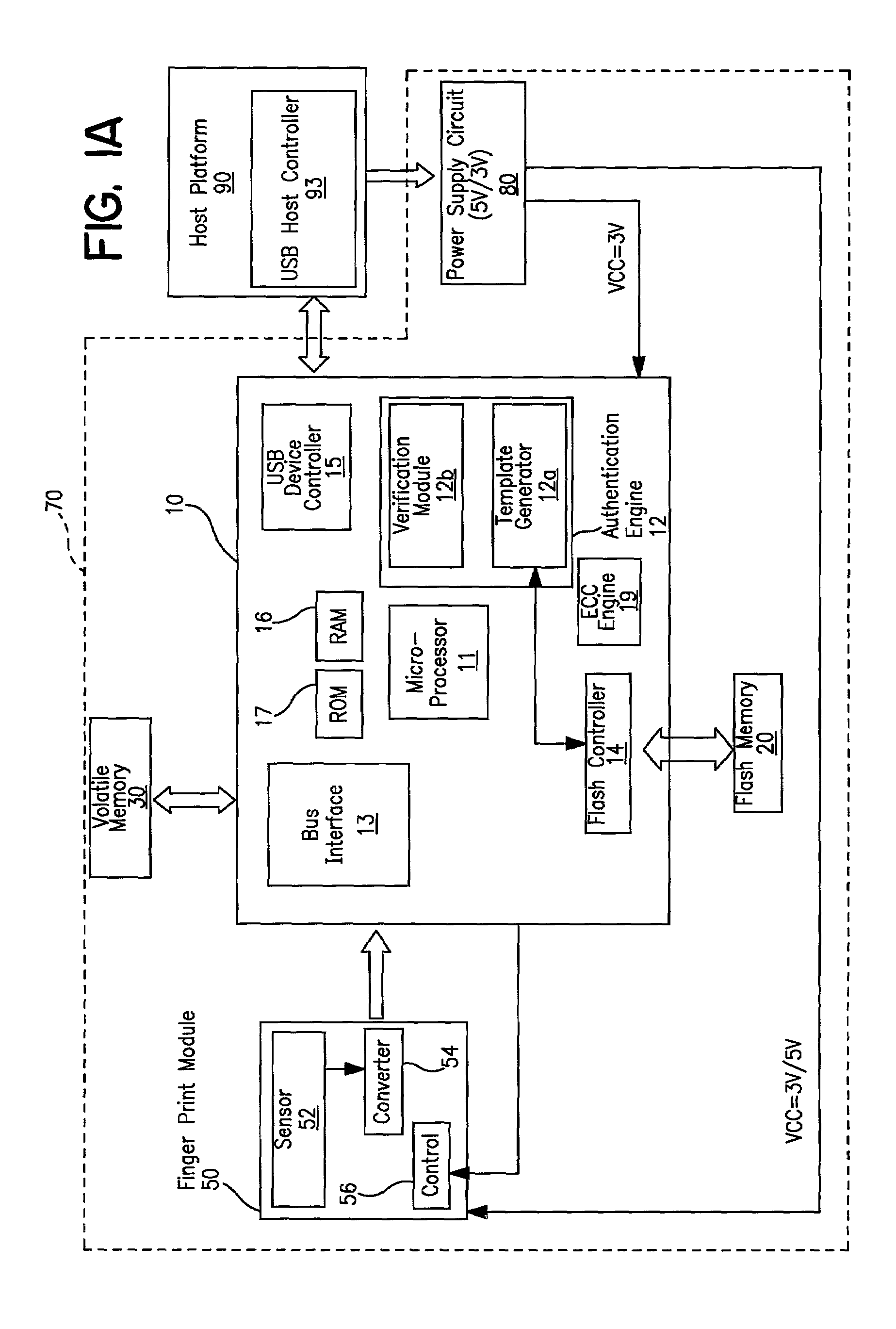
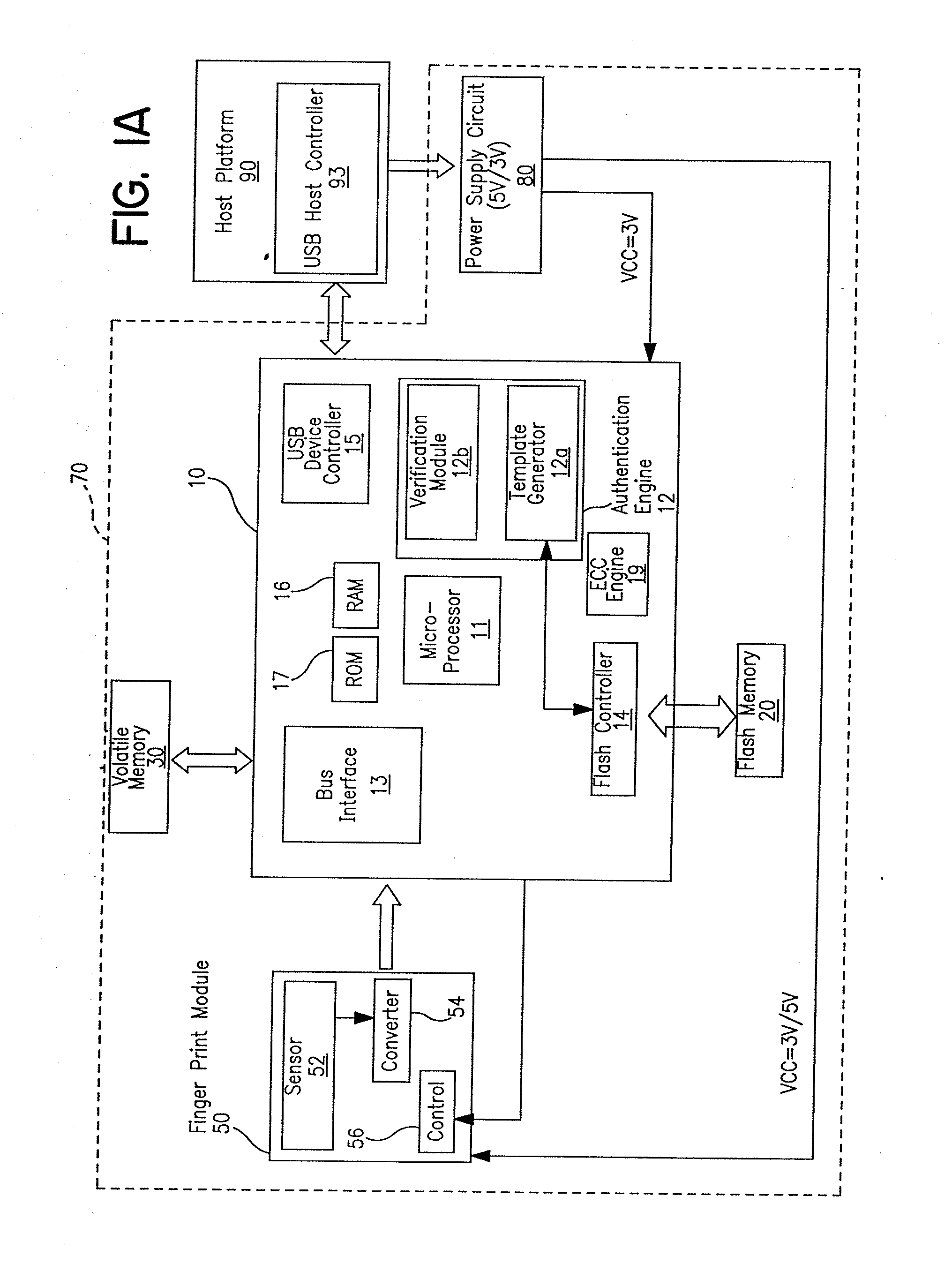
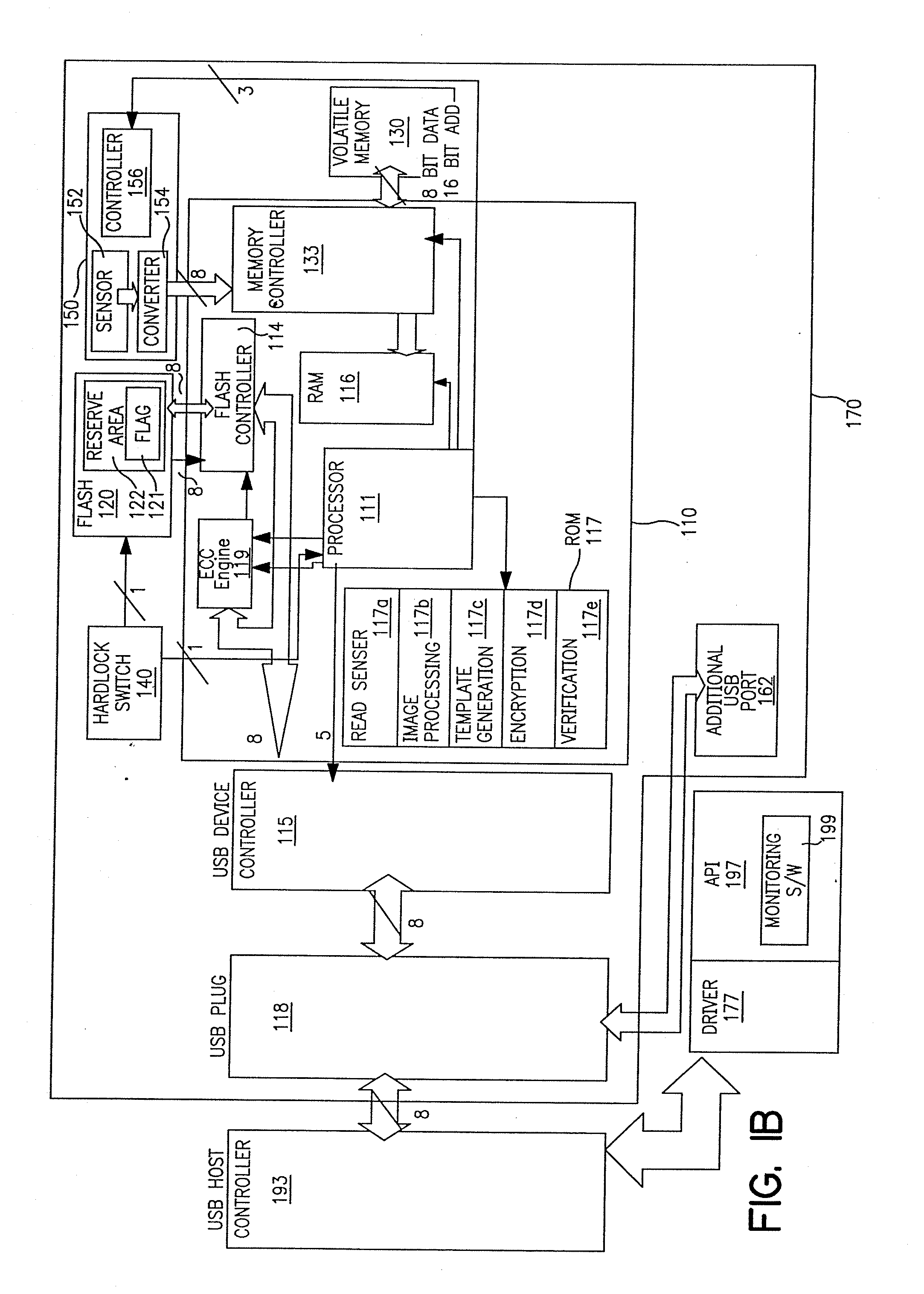
Portable device having biometrics-based authentication capabilities
InactiveUS7549161B2Highly convenient, secured and reliableImpossible to alter, duplicate, or crackDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordUser authentication
Apparatus and method for implementing biometrics-based access control to a restricted resource. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention is realized using a portable device. Specifically, in one embodiment, the portable device includes a microprocessor, a non-volatile memory coupled thereto, and a biometrics-based authentication module controlled by the microprocessor. Preferably, the biometrics technology used is fingerprint authentication technology. The authentication module is capable of registering a fingerprint upon first use of the portable device, storing an encoded version of the fingerprint in the non-volatile memory. Subsequently, the authentication module can read a person's fingerprint and reliably determine whether the fingerprint matches the registered fingerprint stored in the non-volatile memory. If a match is found, access to the restricted resource is granted to that person; otherwise, access is denied. Embodiments of the present invention thus provide a highly convenient, secured and reliable method and system for user authentication and access control which was not achievable in prior art password-based authentication approaches.
Owner:S COM SYST S
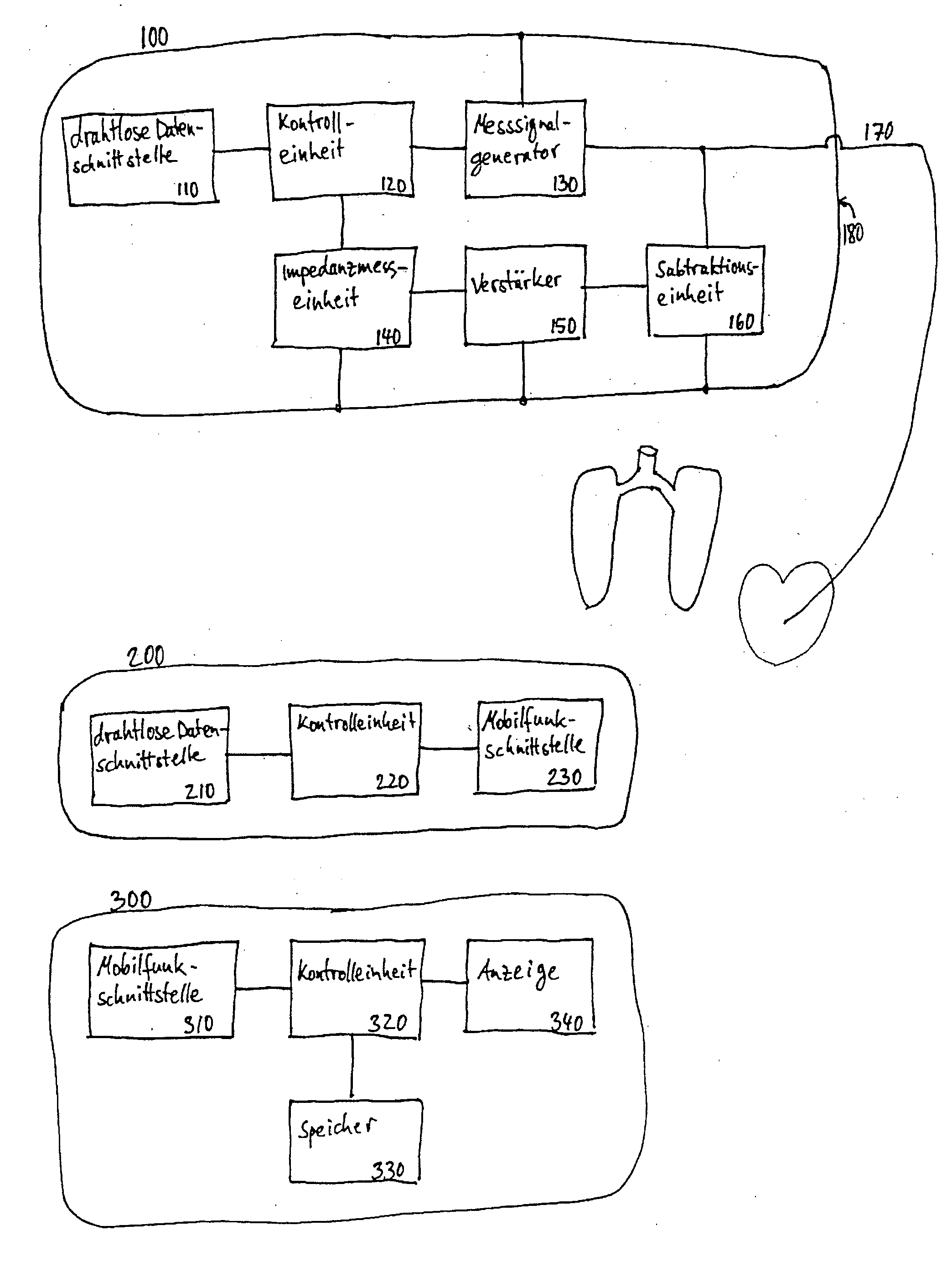
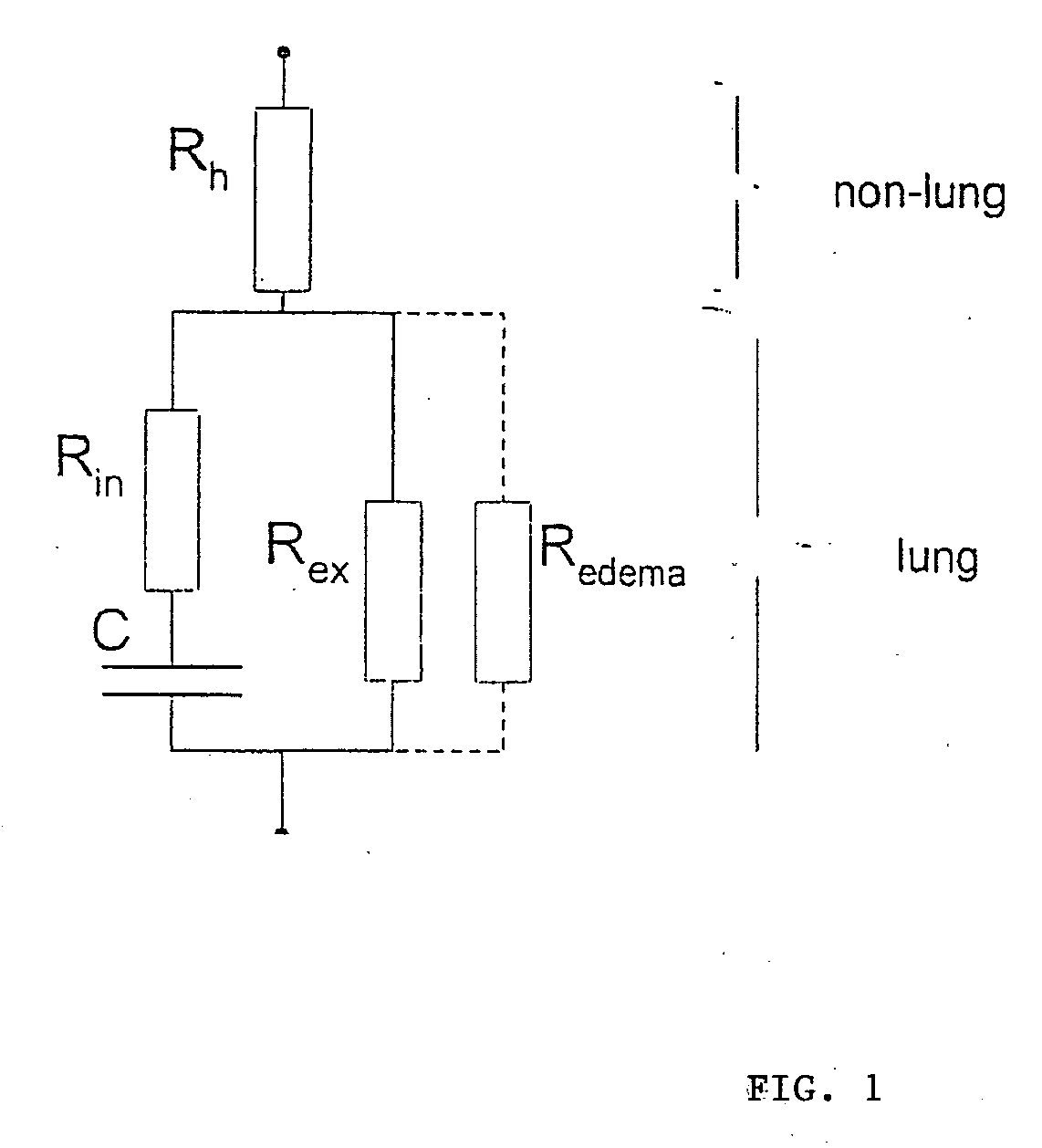
Device for determining thoracic impedance
ActiveUS20060135886A1Reliably determinedResistance/reactance/impedenceHeart stimulatorsPower flowSignal generator
An electromedical implant includes a measuring signal generator, an impedance measuring unit to determine the impedance of human or animal tissue, a control unit which, for controlling the measuring signal generator and the impedance measuring unit, is at least indirectly connected to the measuring signal generator and to the impedance measuring unit, as well as an electrode arrangement comprising at least two electrodes which can be directly or indirectly connected or at least temporarily connected to the measuring signal generator and to the impedance measuring unit, or to a connection for such an electrode arrangement. The measuring signal generator is designed to generate and emit a current pulse or a series of current pulses, and the control unit is designed at a specific point in time to cause the measuring signal generator (to generate and emit a current pulse, and to cause the impedance measuring unit to measure the voltage that is present between the electrodes connected to the measuring signal generator and the impedance measuring unit after the passing of at least two time periods of different length that start with commencement of the current pulse being emitted and end before the end of emitting the current pulse, and to issue a voltage value which in each case represents the measured voltage.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
System and method for network vulnerability detection and reporting
ActiveUS7664845B2Reduce the possibilityReliably determinedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionGraphicsOperational system
A system and method provide comprehensive and highly automated testing of vulnerabilities to intrusion on a target network, including identification of operating system, identification of target network topology and target computers, identification of open target ports, assessment of vulnerabilities on target ports, active assessment of vulnerabilities based on information acquired from target computers, quantitative assessment of target network security and vulnerability, and hierarchical graphical representation of the target network, target computers, and vulnerabilities in a test report. The system and method employ minimally obtrusive techniques to avoid interference with or damage to the target network during or after testing.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
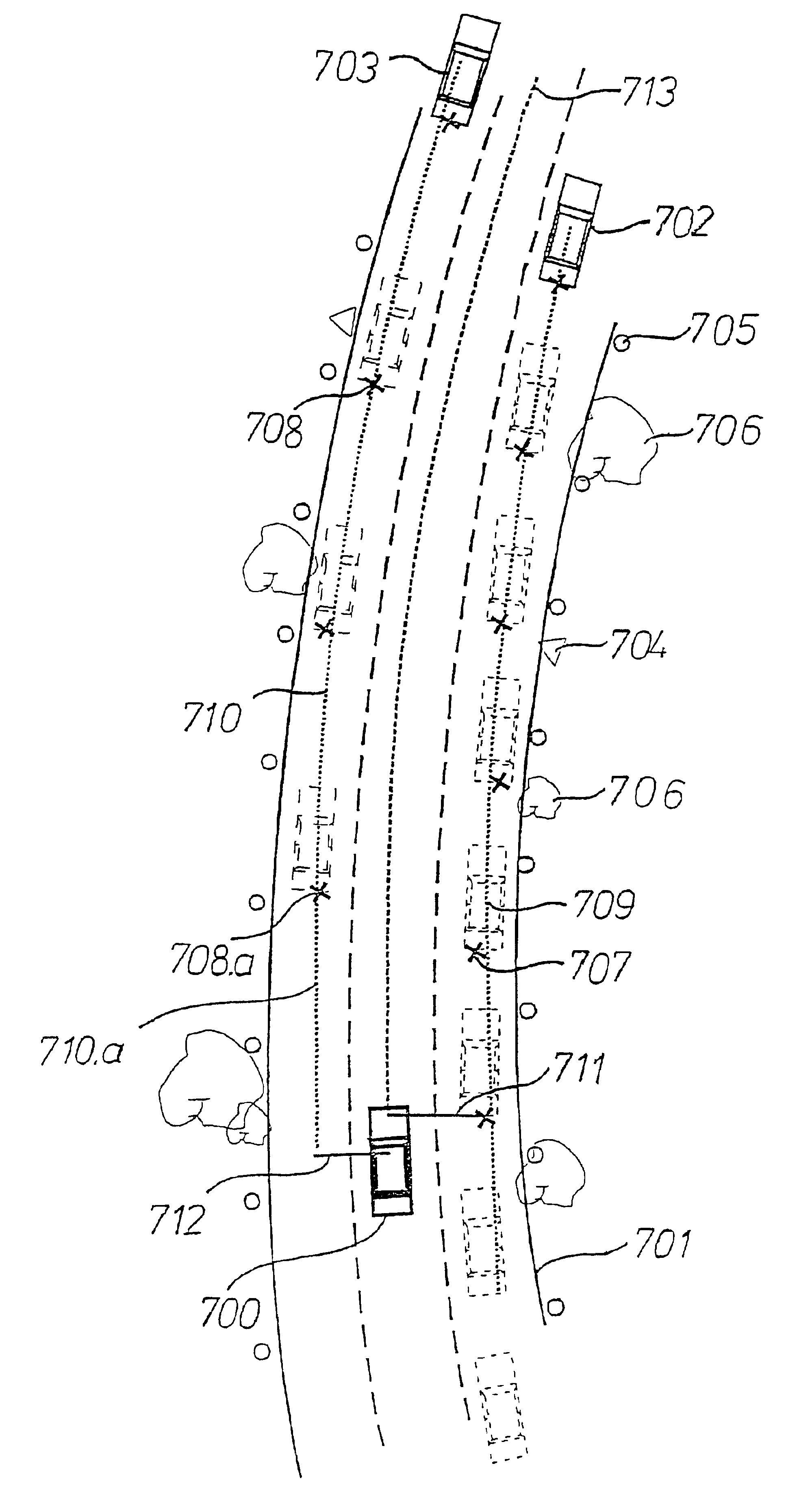
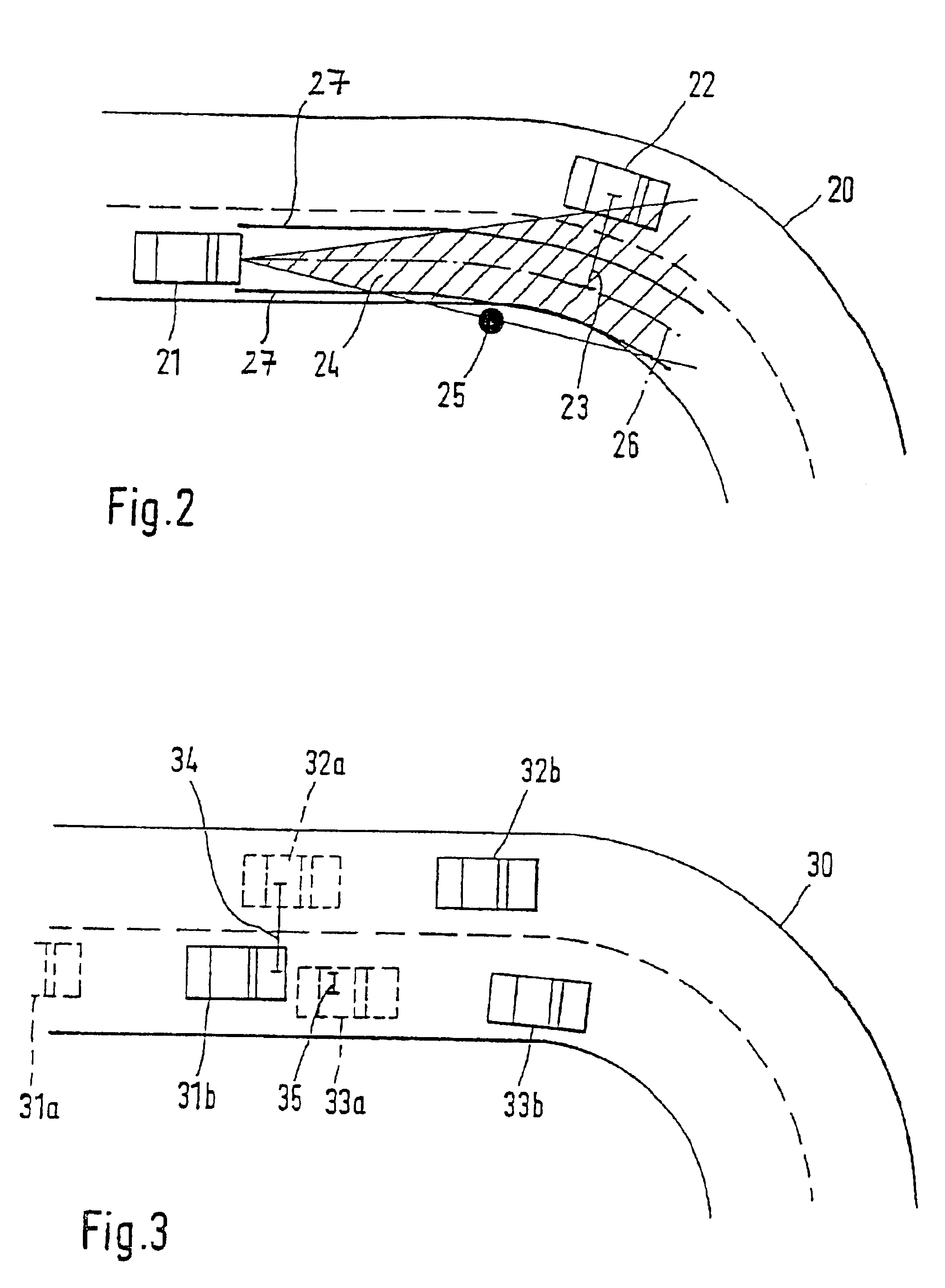
Method and device for determining a future travel-path area of a vehicle
InactiveUS6853906B1Reliably determinedReduce error rateInstruments for road network navigationVehicle fittingsDistance sensorsEngineering
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
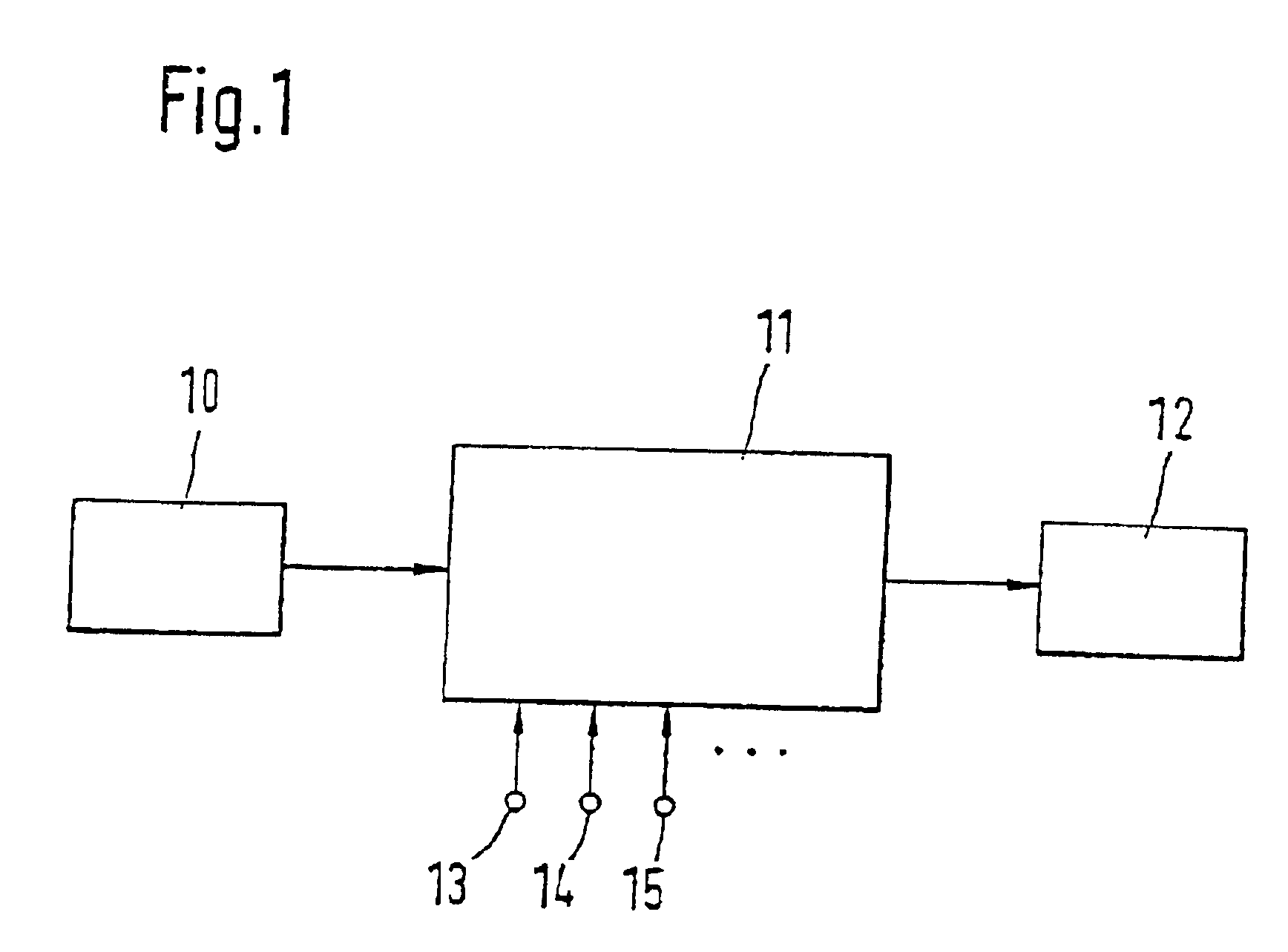
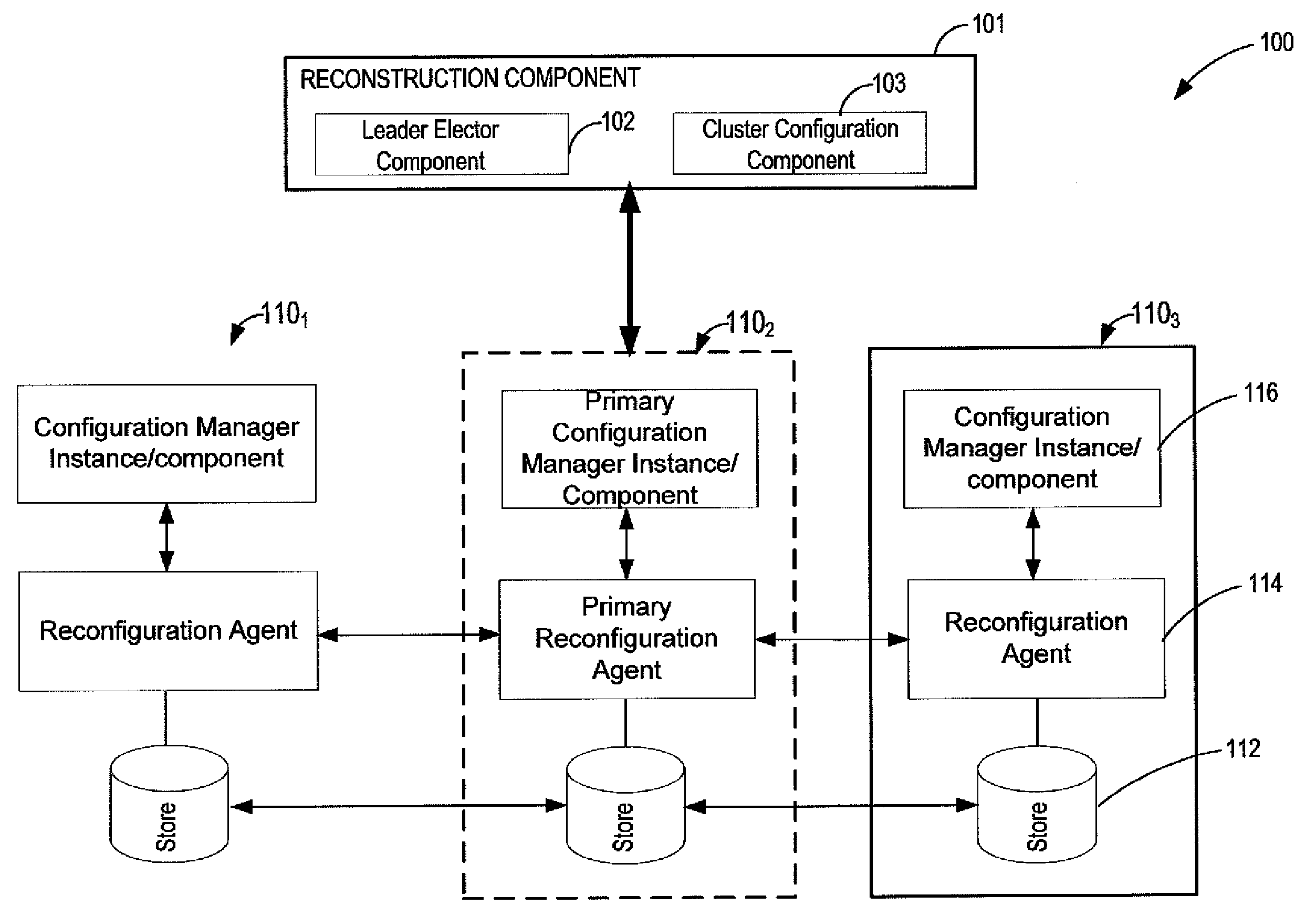
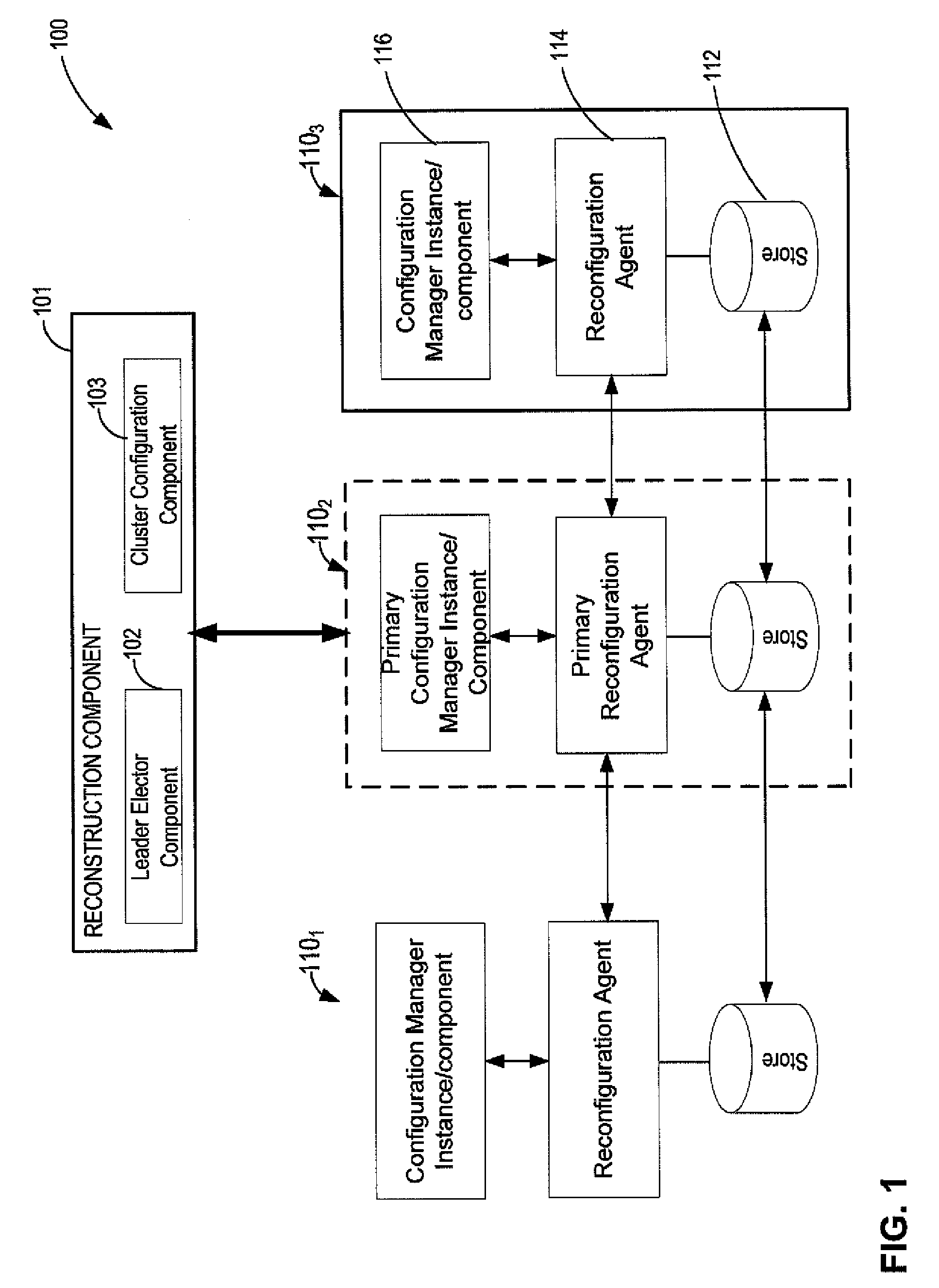
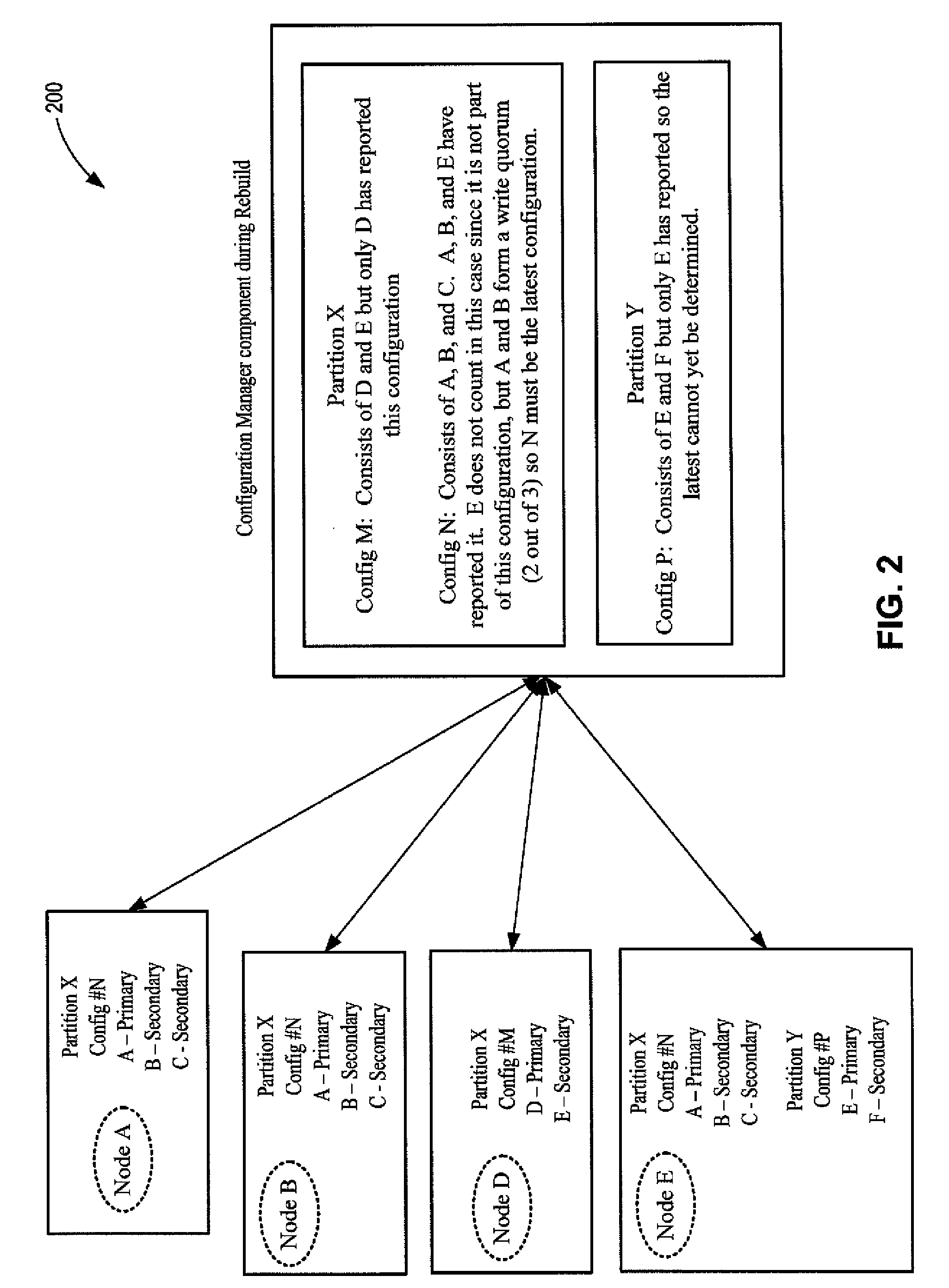
Configuration management in distributed data systems
InactiveUS20100114826A1Reliably determinedError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsConfiguration management databaseDistributed computing
Systems and methods for managing configurations of data nodes in a distributed environment A configuration manager is implemented as a set of distributed master nodes that may use quorum-based processing to enable reliable identification of master nodes storing current configuration information, even if some of the master nodes fail. If a quorum of master nodes cannot be achieved or some other event occurs that precludes identification of current configuration information, the configuration manager may be rebuilt by analyzing reports from read / write quorums of nodes associated with a configuration, allowing automatic recovery of data partitions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for network vulnerability detection and reporting
InactiveUS7543056B2Reliably determinedSimple methodMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionGraphicsOperational system
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Personal Identification Device and Personal Identification Method
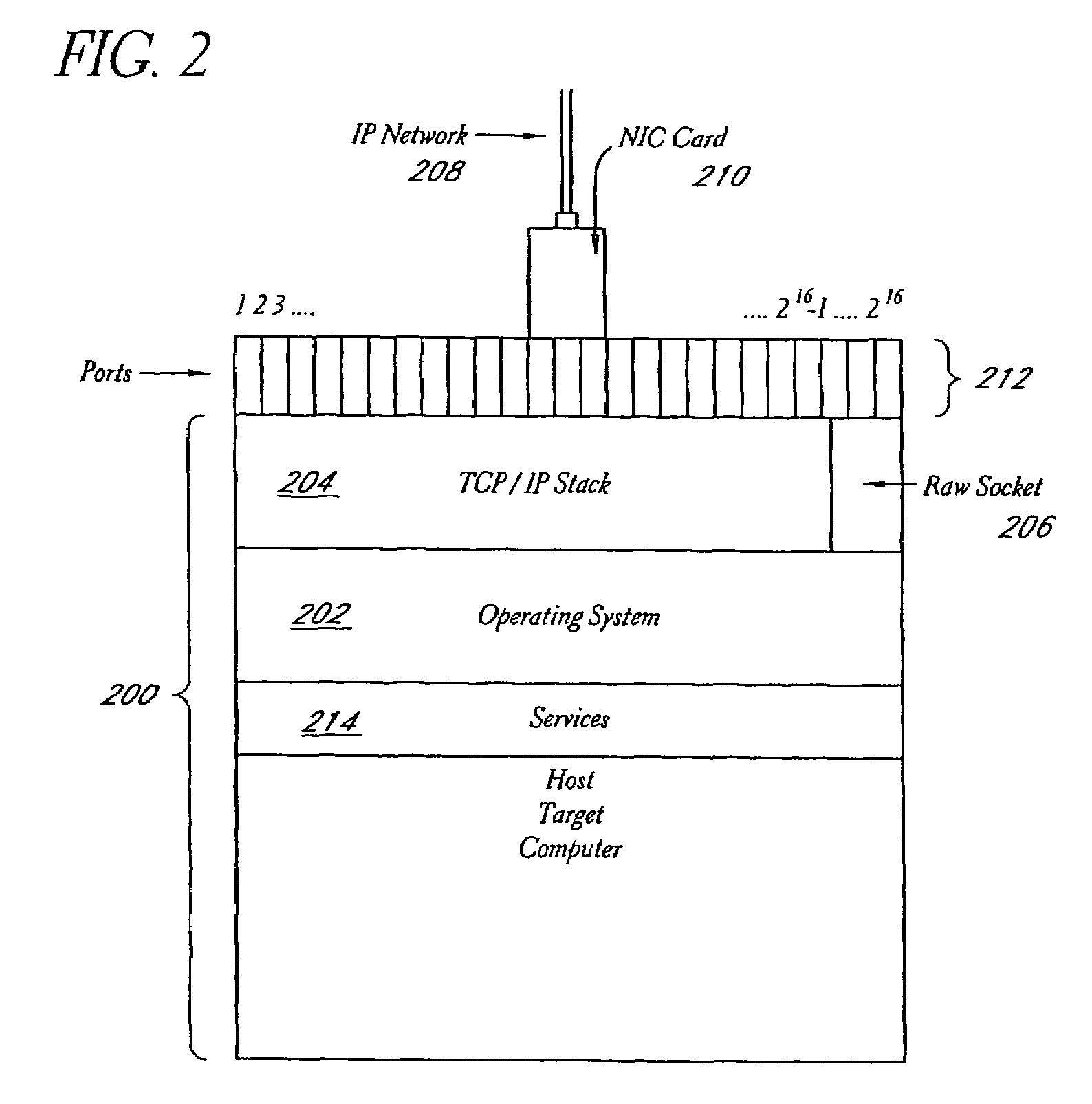
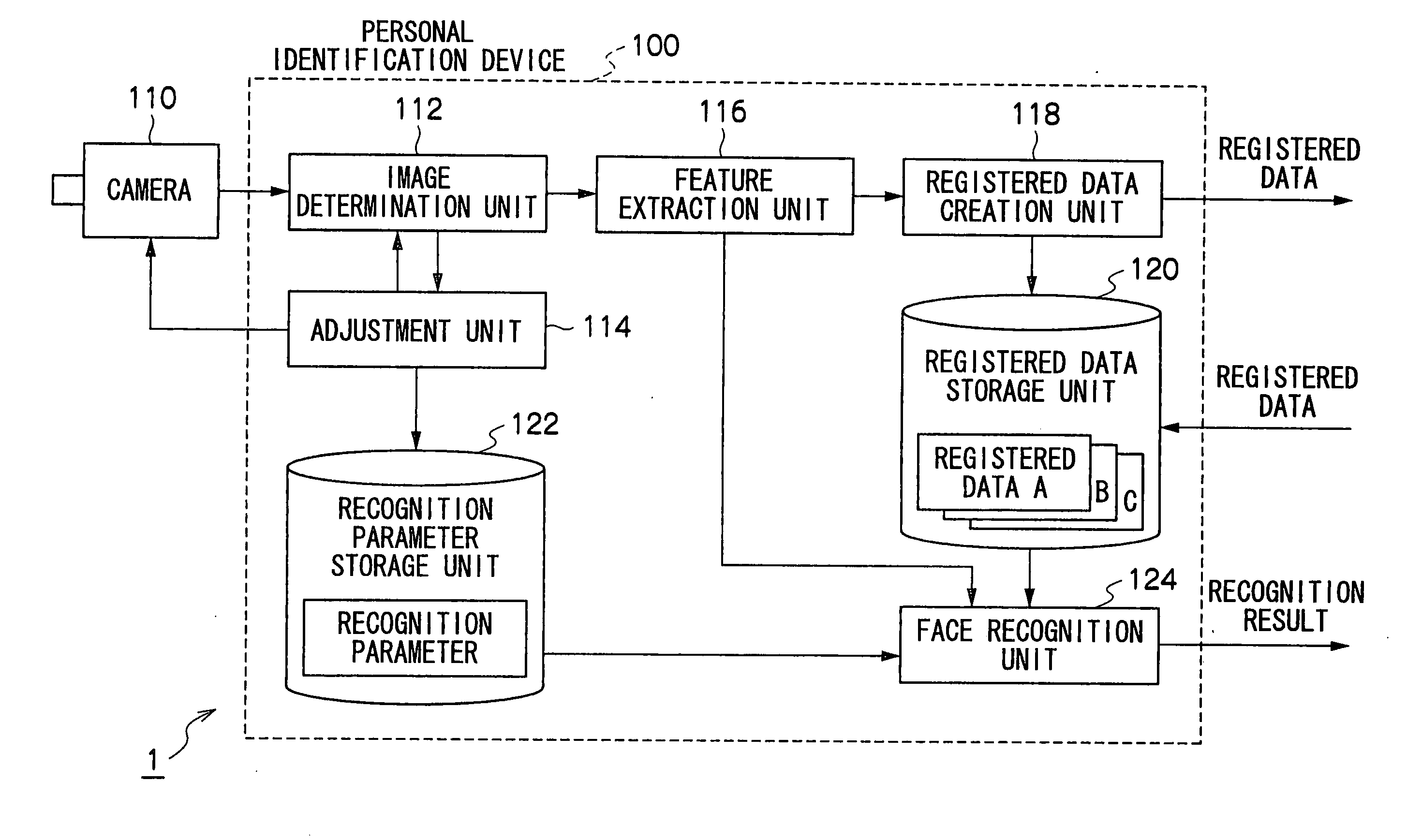
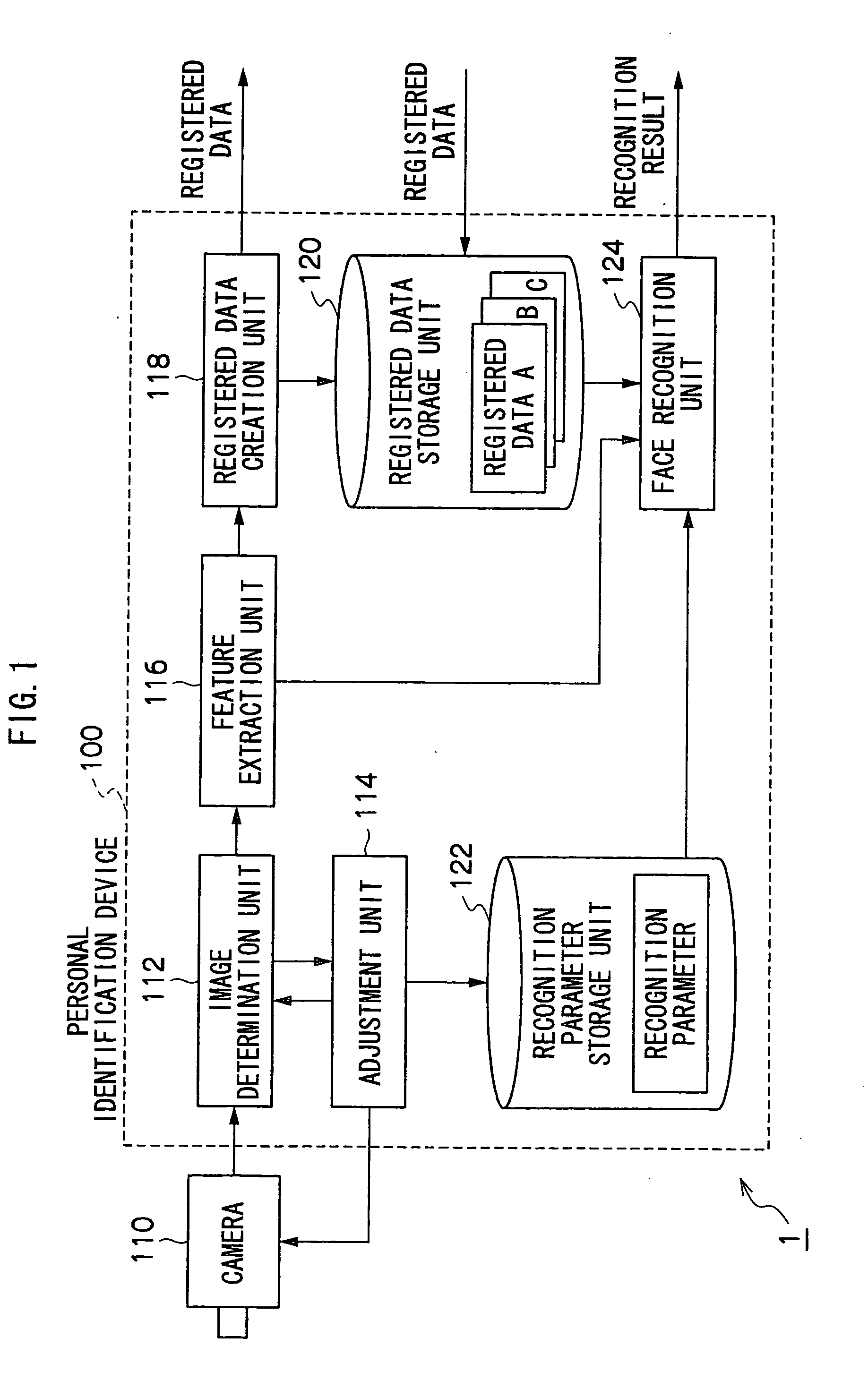
InactiveUS20090060293A1Improve performanceImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage extractionFeature extraction
A personal identification device of the present invention is provided with a registered data storage unit for storing registered data containing facial feature data for a registered user, a recognition parameter storage unit for storing recognition parameters, a image determination unit for determining whether or not the image quality of a user facial image input from an imaging device is appropriate, an adjustment unit for adjusting the settings of the imaging device or modifying the recognition parameters, in accordance with the result of determination carried out in the image determination unit, a feature extraction unit for extracting user facial feature data from a facial image, and a face recognition unit for comparing the extracted feature data with the registered data to determine whether or not the user is a registered user based on the result of comparison and the recognition parameters.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Reduction of vertical segregation in a discharge lamp
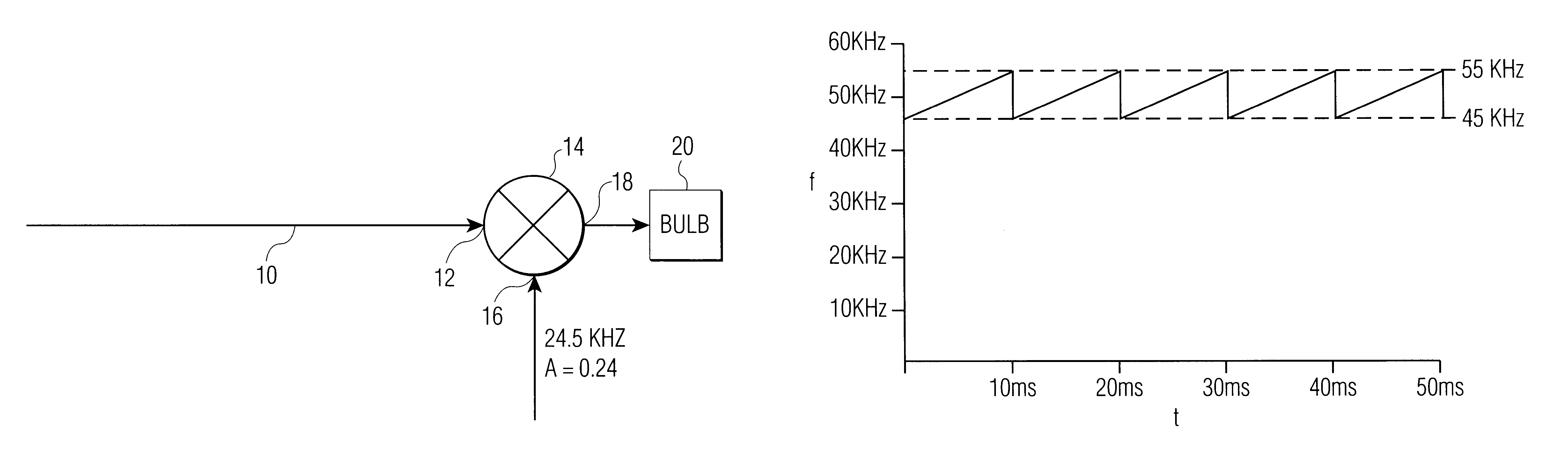
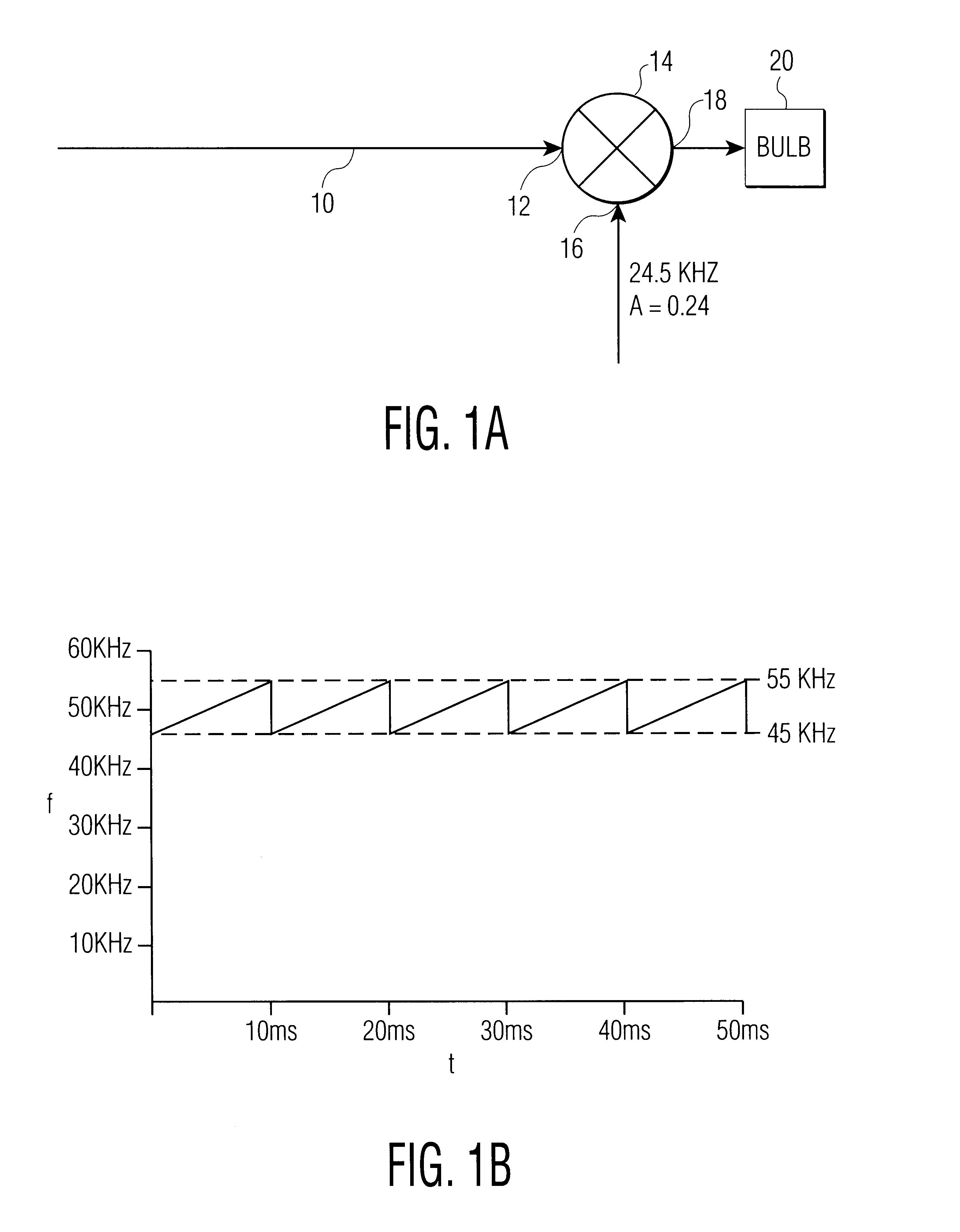
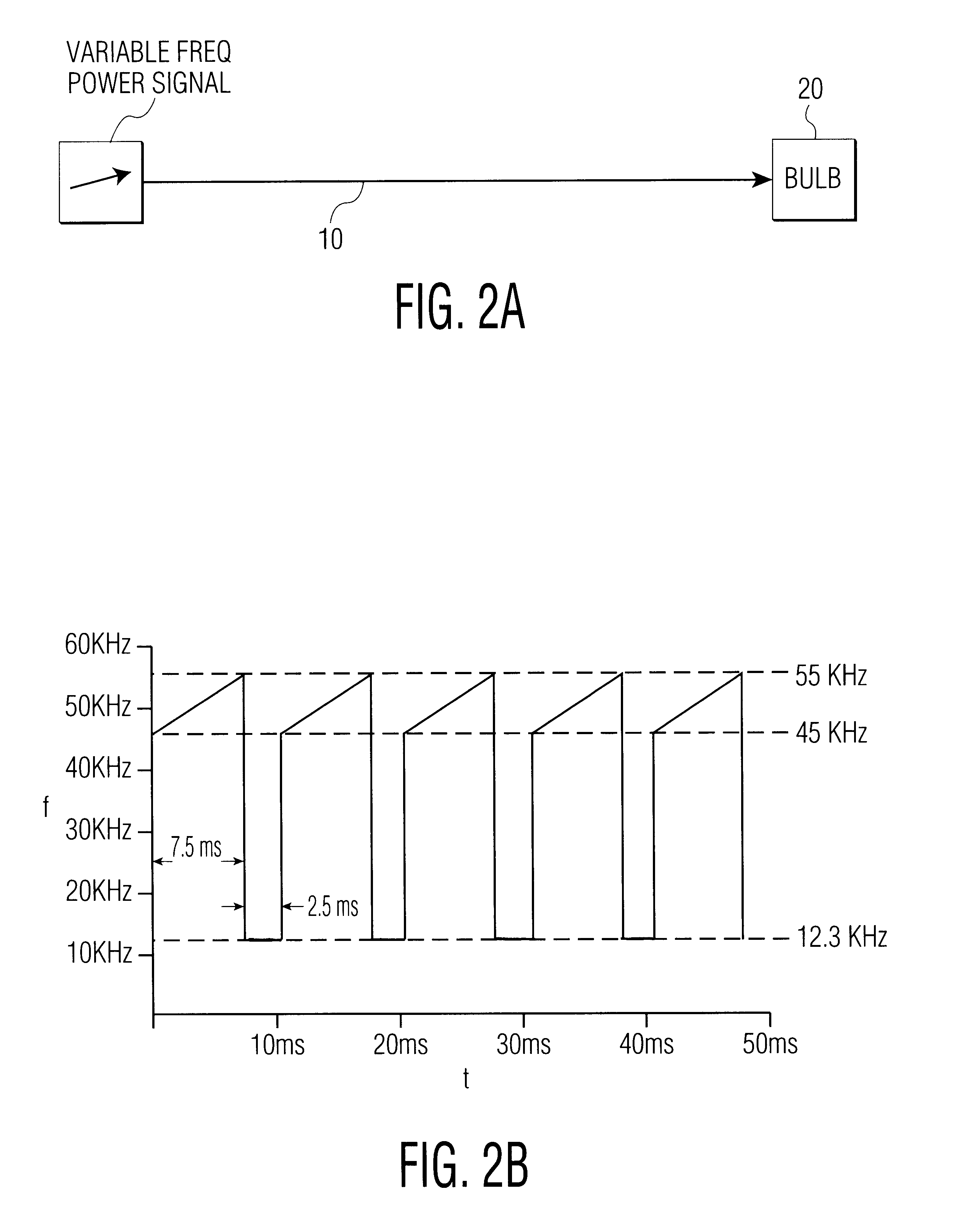
InactiveUS6184633B1Promote degradationIncrease temperatureElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementGas-discharge lampConstant frequency
An apparatus for reducing vertical segregation of a discharge lamp. A current / voltage input sweeps through a frequency range between the first azimuthal acoustic resonance mode and a first radial acoustic resonance mode of the discharge lamp. The current / voltage input is subsequently amplitude modulated. Alternatively, without amplitude modulation, the current / voltage input sweeps through the frequency range for a first portion of the period, and then for a second portion of the period drops to a relatively constant frequency.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
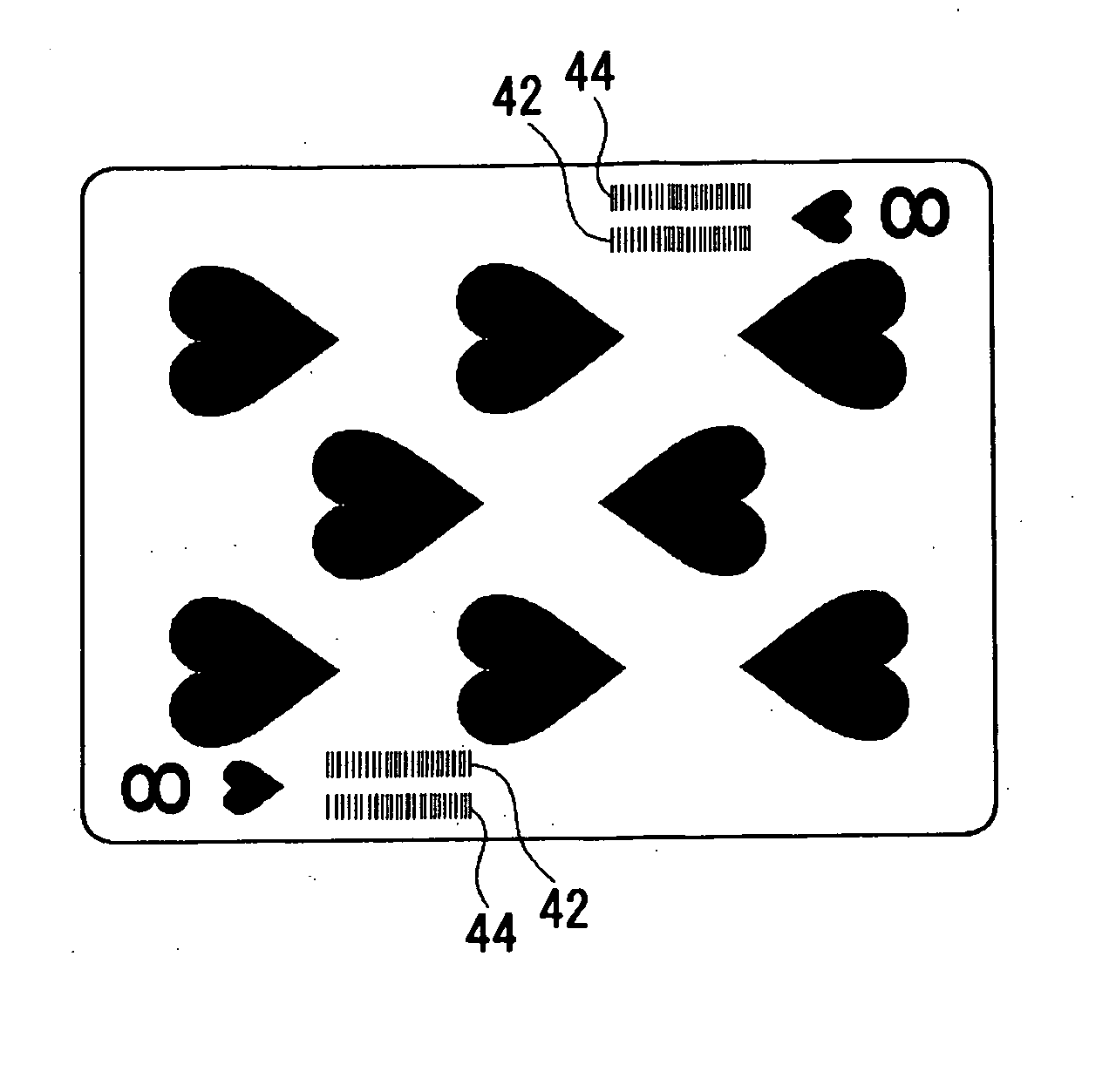
Card game cheat detector
InactiveUS20060247036A1Reliable readSimple and inexpensive configurationCard gamesVideo gamesComputer hardwareGame play
Owner:ANGEL GRP CO LTD
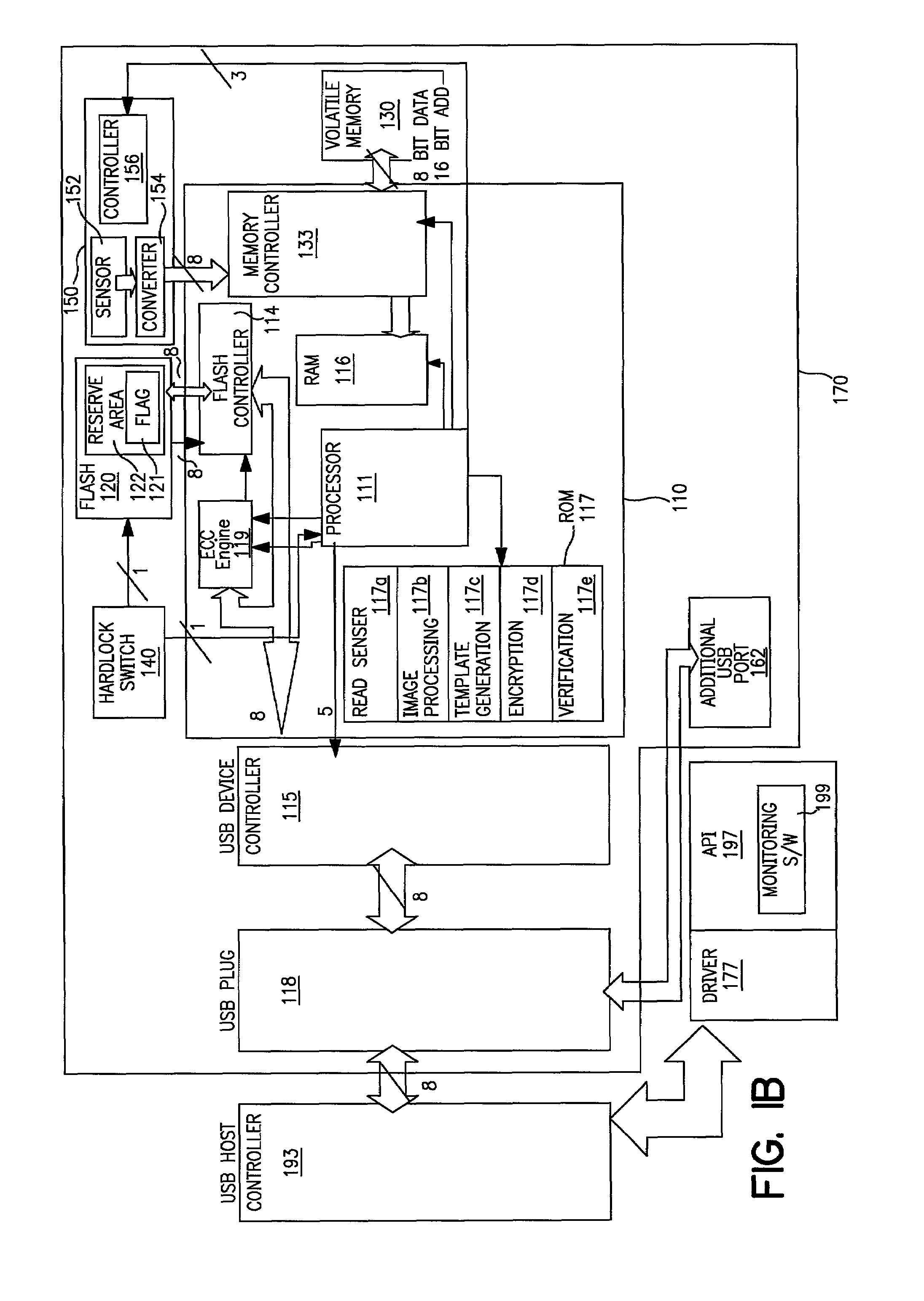
Portable device having biometrics-based authentication capabilities
InactiveUS20080049984A1Access is deniedReliably determinedInput/output to record carriersImage analysisUser authenticationBiometric trait
Apparatus and method for implementing biometrics-based authentication. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention is embodied in a portable device. Specifically, in one embodiment, the portable device includes a microprocessor, a non-volatile memory coupled thereto, and a biometrics-based authentication module controlled by the microprocessor. Preferably, the biometrics technology used is fingerprint authentication technology. The authentication module is capable of registering a fingerprint upon first use of the portable device, storing an encoded version of the fingerprint in the non-volatile memory. Subsequently, the authentication module can read a person's fingerprint and reliably determine whether the fingerprint matches the registered fingerprint stored in the non-volatile memory. If a match is found, access to information in the non-volatile memory is granted to that person; otherwise, access is denied. Embodiments of the present invention thus provide a highly convenient, secured and reliable method and system for user authentication and access control which was not achievable in prior art password-based authentication approaches.
Owner:TREK 2000 INT
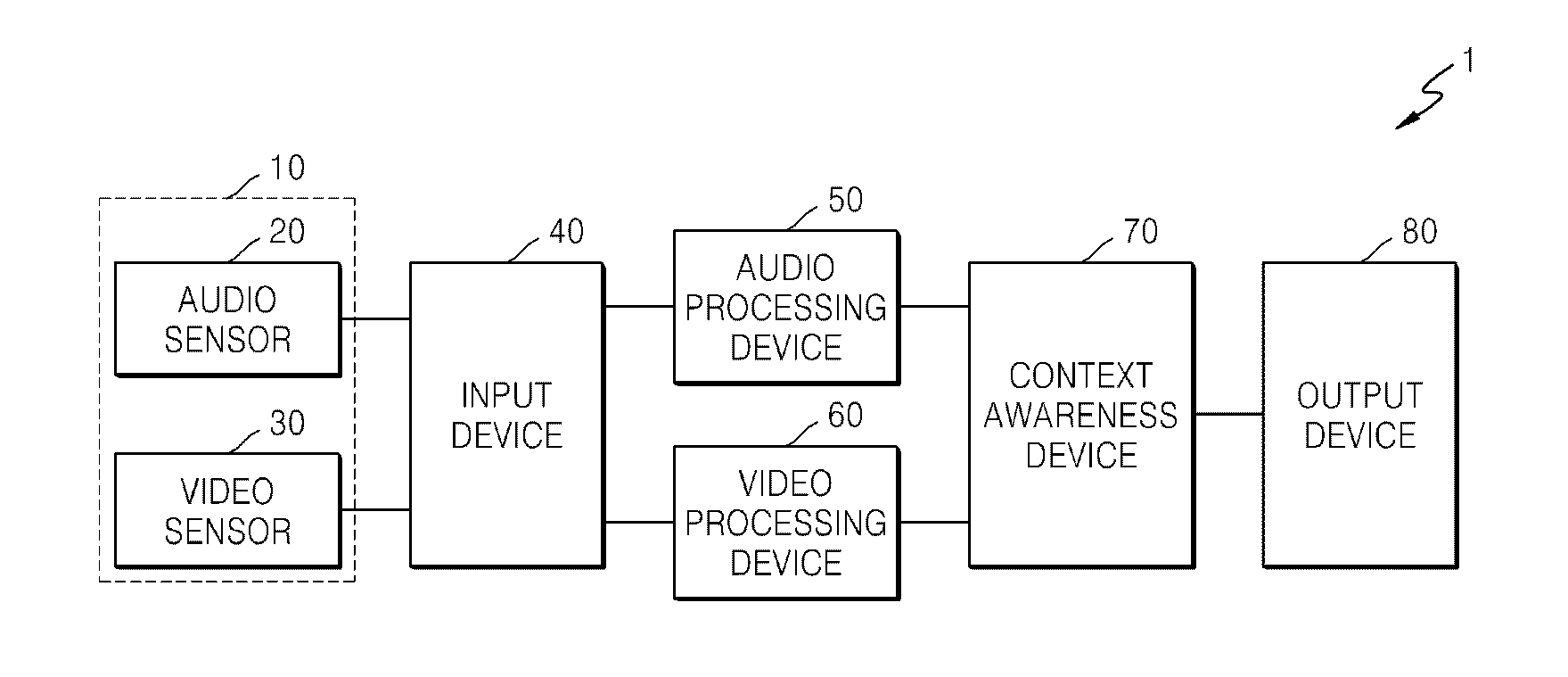
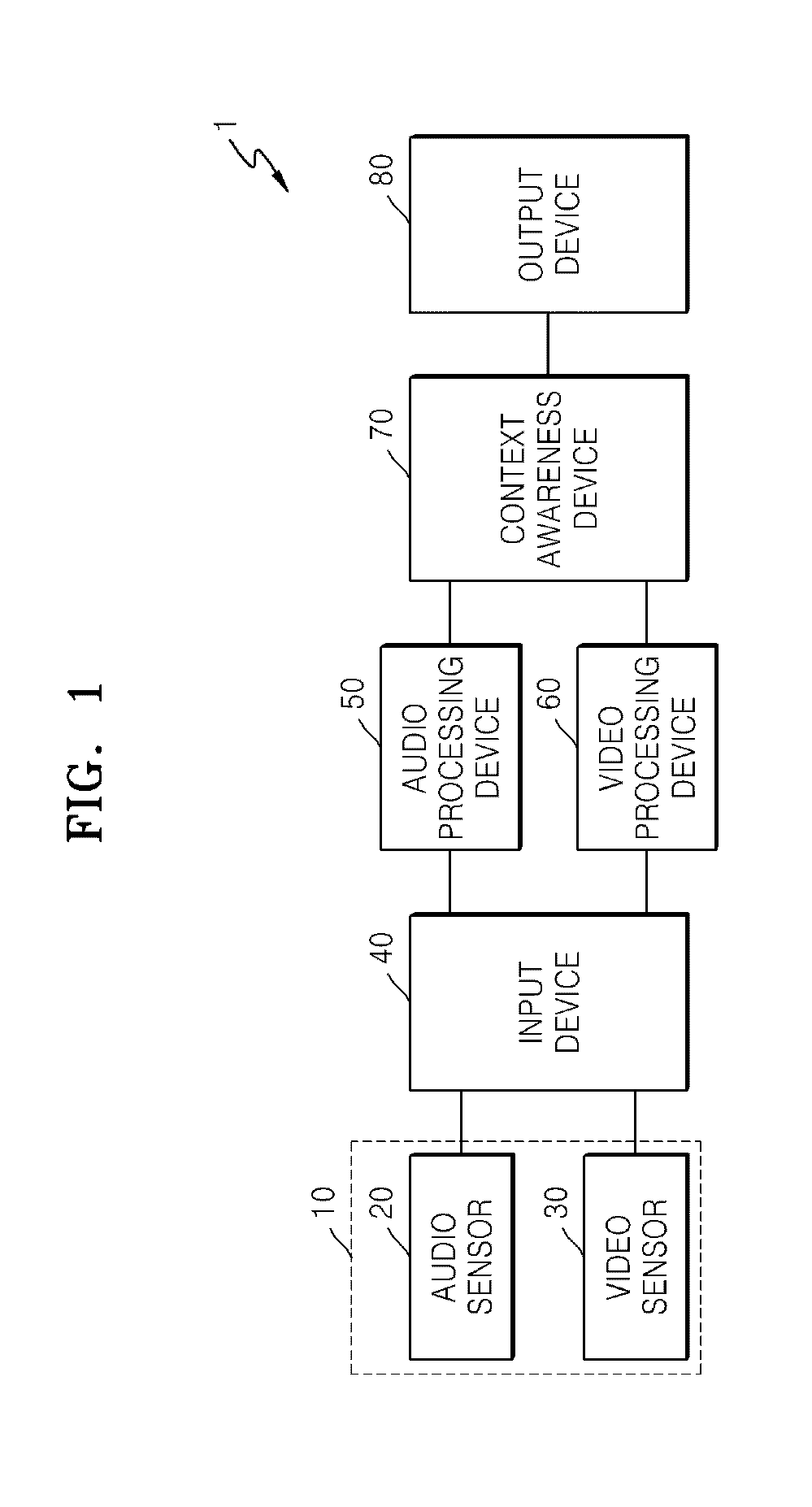
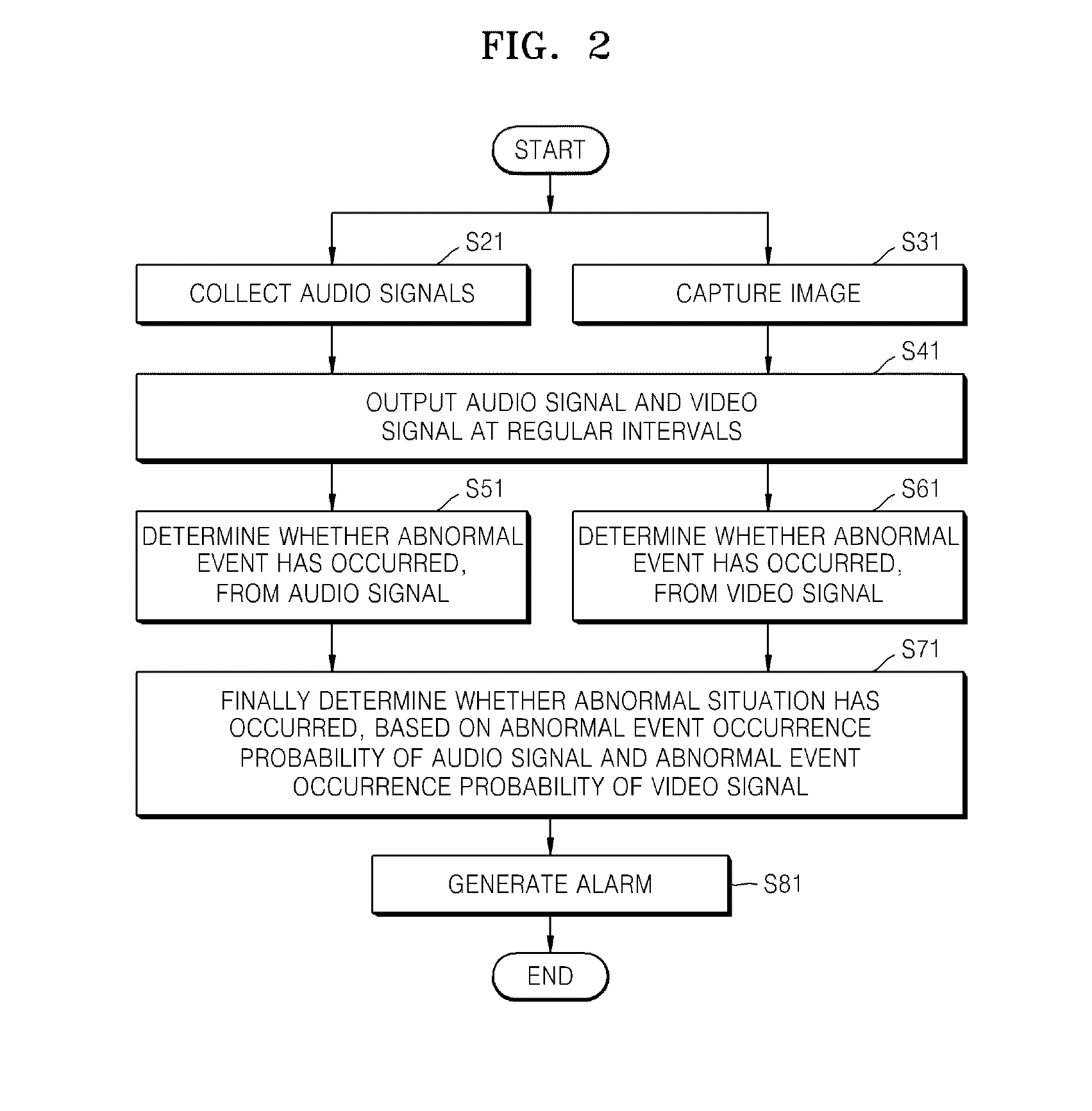
Indoor surveillance system and indoor surveillance method
ActiveUS20140055610A1Stable and efficientReliably determinedImage enhancementImage analysisSurveillance MethodsAudio signal
A surveillance system and method are provided. The surveillance system includes an audio processing device which extracts an audio feature of an audio signal, and determines whether an abnormal event has occurred in a monitoring region, based on the audio feature; a video processing device which extracts a foreground region from a video signal, and determines whether an abnormal event has occurred in the monitoring region, based on motion information of the foreground region; and a context awareness device which calculates an audio abnormal probability and a video abnormal probability by respectively accumulating results of abnormal event occurrence / non-occurrence determinations performed on audio signals and results of abnormal event occurrence / non-occurrence determinations performed on video signals for a certain period of time, and finally determines whether an abnormal situation has occurred in the monitoring region, by using respective combined probability distribution models for a normal situation and the abnormal situation.
Owner:HANWHA TECHWIN CO LTD +1
Sensor device and method with at surface object sensing and away from surface object sensing
ActiveUS20100090712A1Improve usabilityFunction increaseResistance/reactance/impedenceDigital data processing detailsSensor arrayUser input
Methods, systems and devices are described for determining positional information for objects using a sensing device. The various embodiments provide improved user interface functionality by facilitating user input with both objects that are at the surfaced and objects that are away from the surface. The sensor device includes a processing system and a sensor array of sensing electrodes adapted to capacitively sense objects in a sensing region. First, the processing system is configured to determine positional information for objects at the surface in a first portion of the sensing region. Secondly, the processing system is configured to determine positional information for objects that are away from the surface and in a second portion of the sensing region, where the first portion of the sensing region is between the surface and the second portion of the sensing region.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
System And Method For Network Vulnerability Detection And Reporting
ActiveUS20070283441A1Reliably determinedSimple methodMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionGraphicsOperational system
A system and method provide comprehensive and highly automated testing of vulnerabilities to intrusion on a target network, including identification of operating system, identification of target network topology and target computers, identification of open target ports, assessment of vulnerabilities on target ports, active assessment of vulnerabilities based on information acquired from target computers, quantitative assessment of target network security and vulnerability, and hierarchical graphical representation of the target network, target computers, and vulnerabilities in a test report. The system and method employ minimally obtrusive techniques to avoid interference with or damage to the target network during or after testing.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
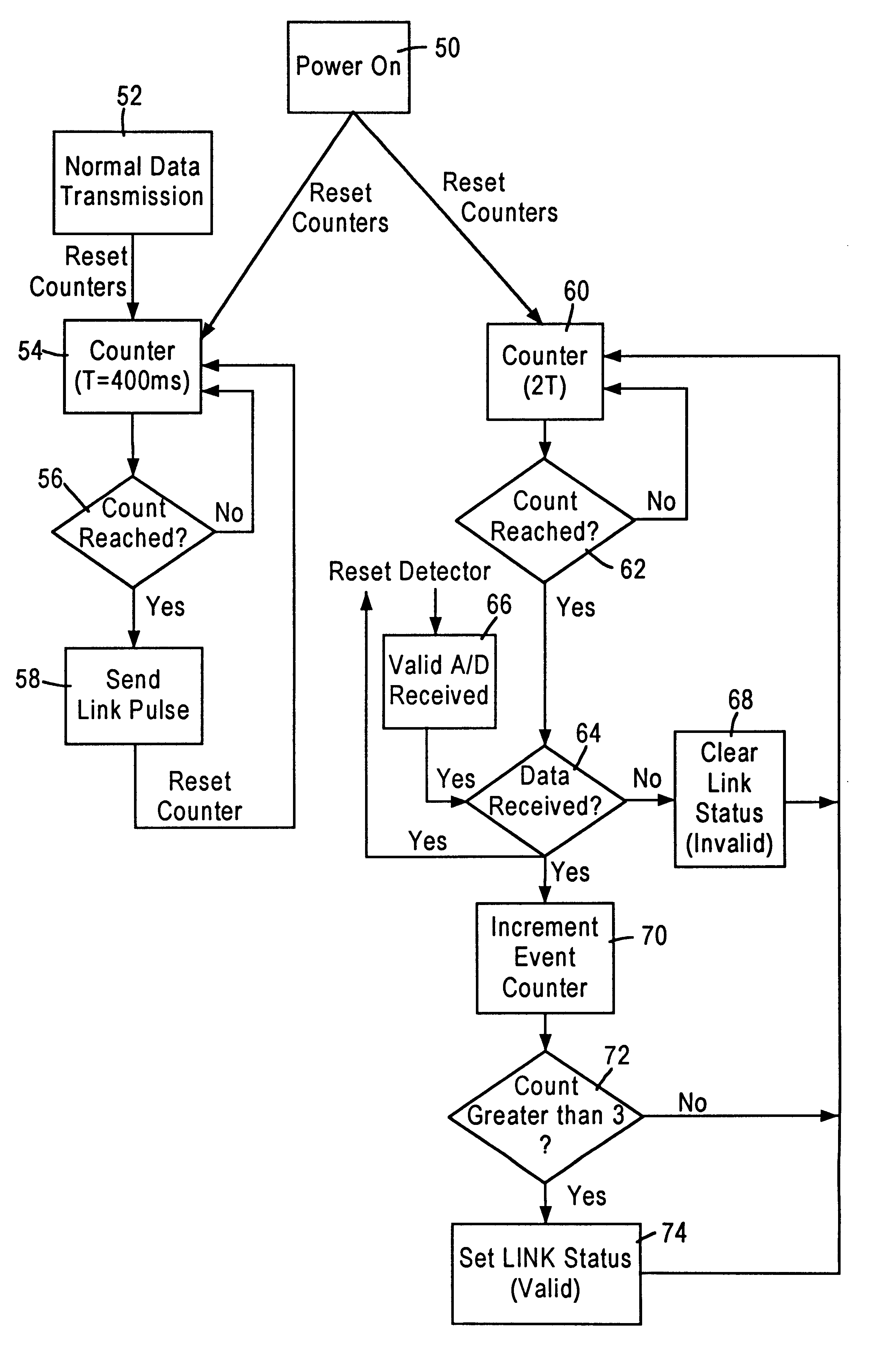
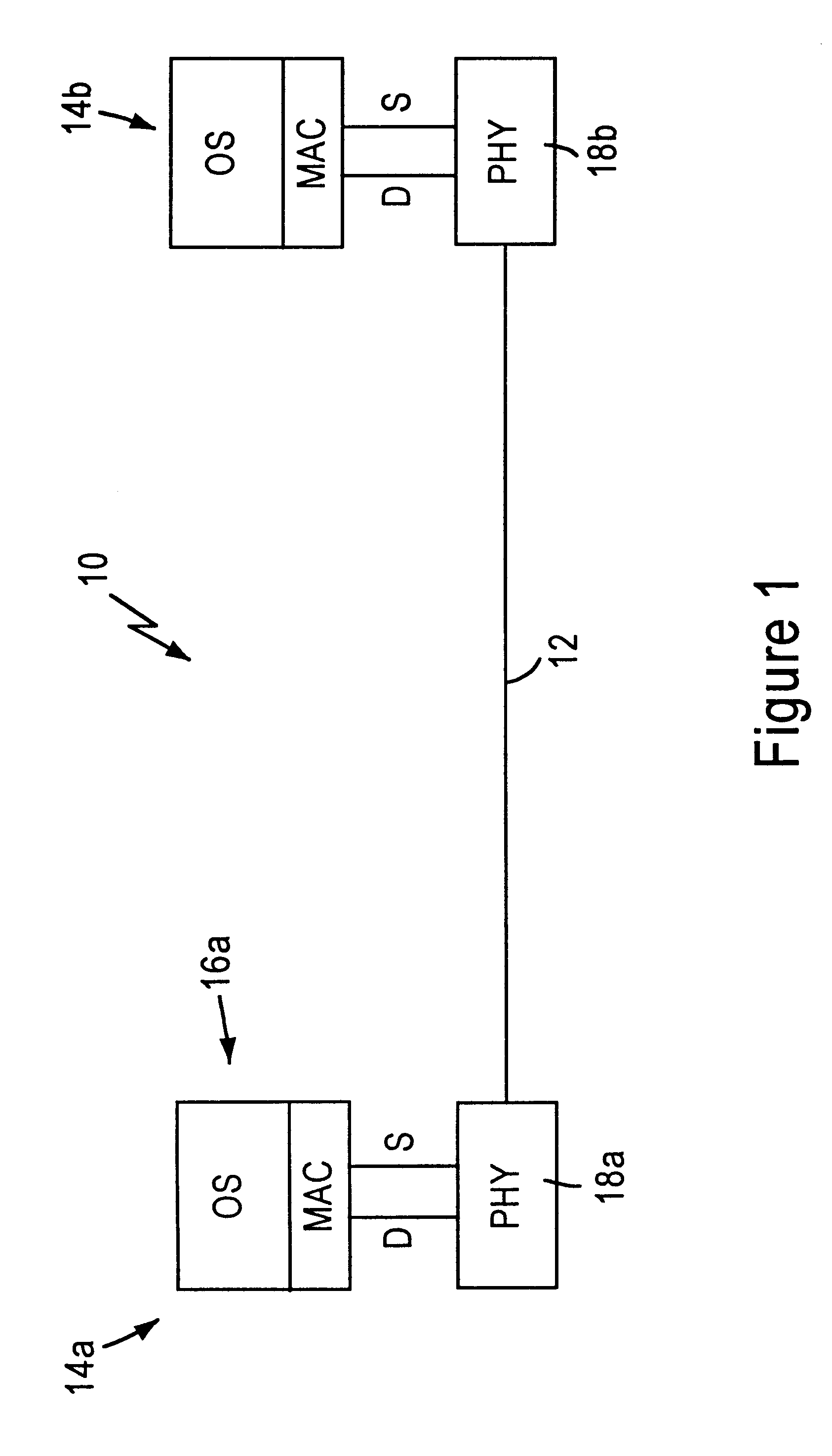
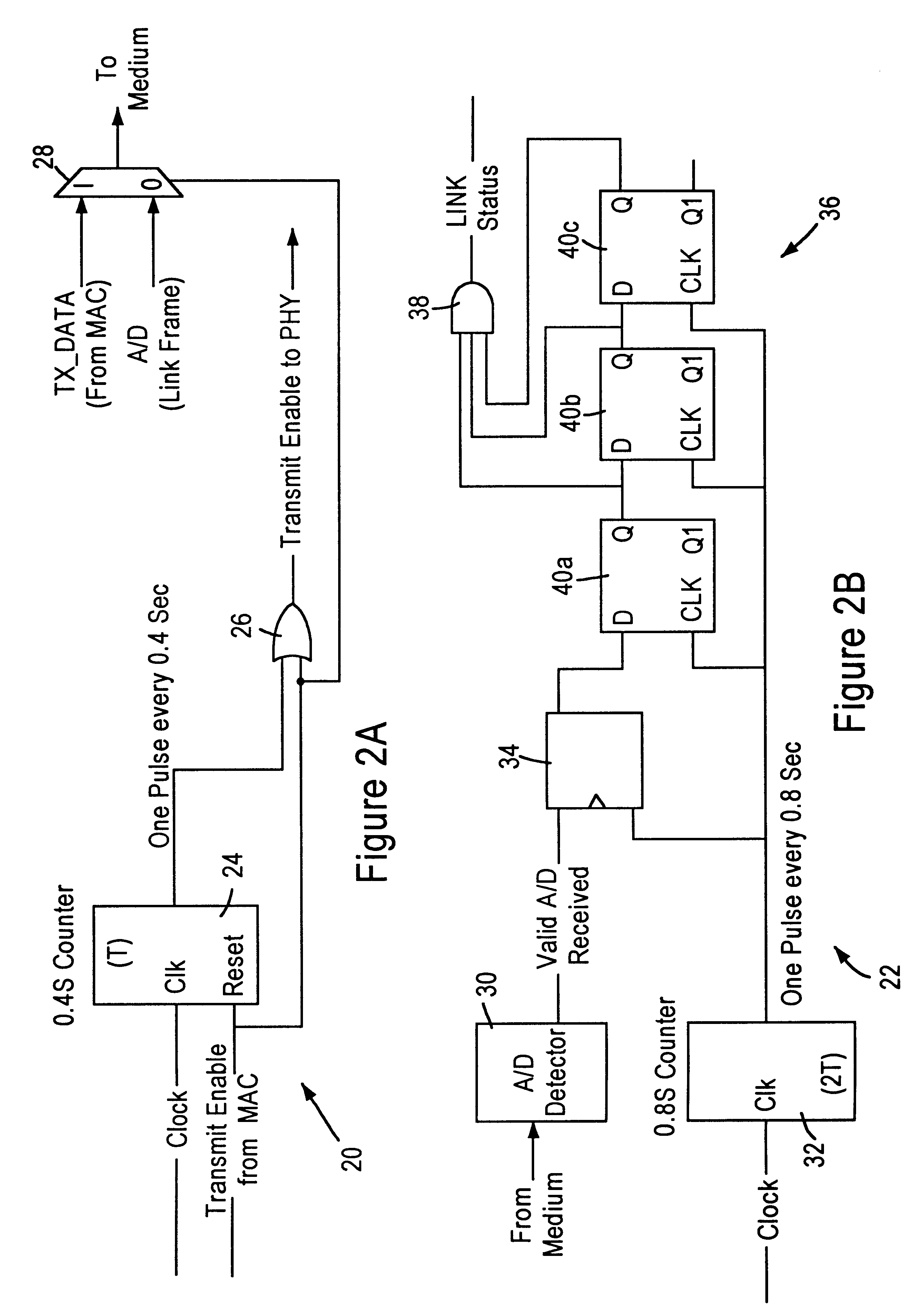
Apparatus and method of determining a link status between network stations connected to a telephone line medium
InactiveUS6292467B1Reliably determinedMinimal disruptionError preventionTransmission systemsPreambleMedia access control
A local area network having a telephone line medium in a home network environment includes physical layer transceivers having transmit and receive state machines enabling each network station to determine a link status on the telephone line medium. The transmit state machine is configured for transmitting a link packet within a prescribed interval (T), less than a minimum packet length of a data packet, and having a preamble and a sufficient number of bytes to allow for transmission. Hence, the link packet will be detected by the other stations on the network, but will not be processed, since it is classified as a runt packet by the media access control layers. The receive state machine monitors the telephone line medium, and if after a prescribed interval (2T) the station has not detected a valid preamble from a data packet or a link packet, then the link status indicator for that station is set to an invalid condition, and subsequently supplied to the station operating system.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
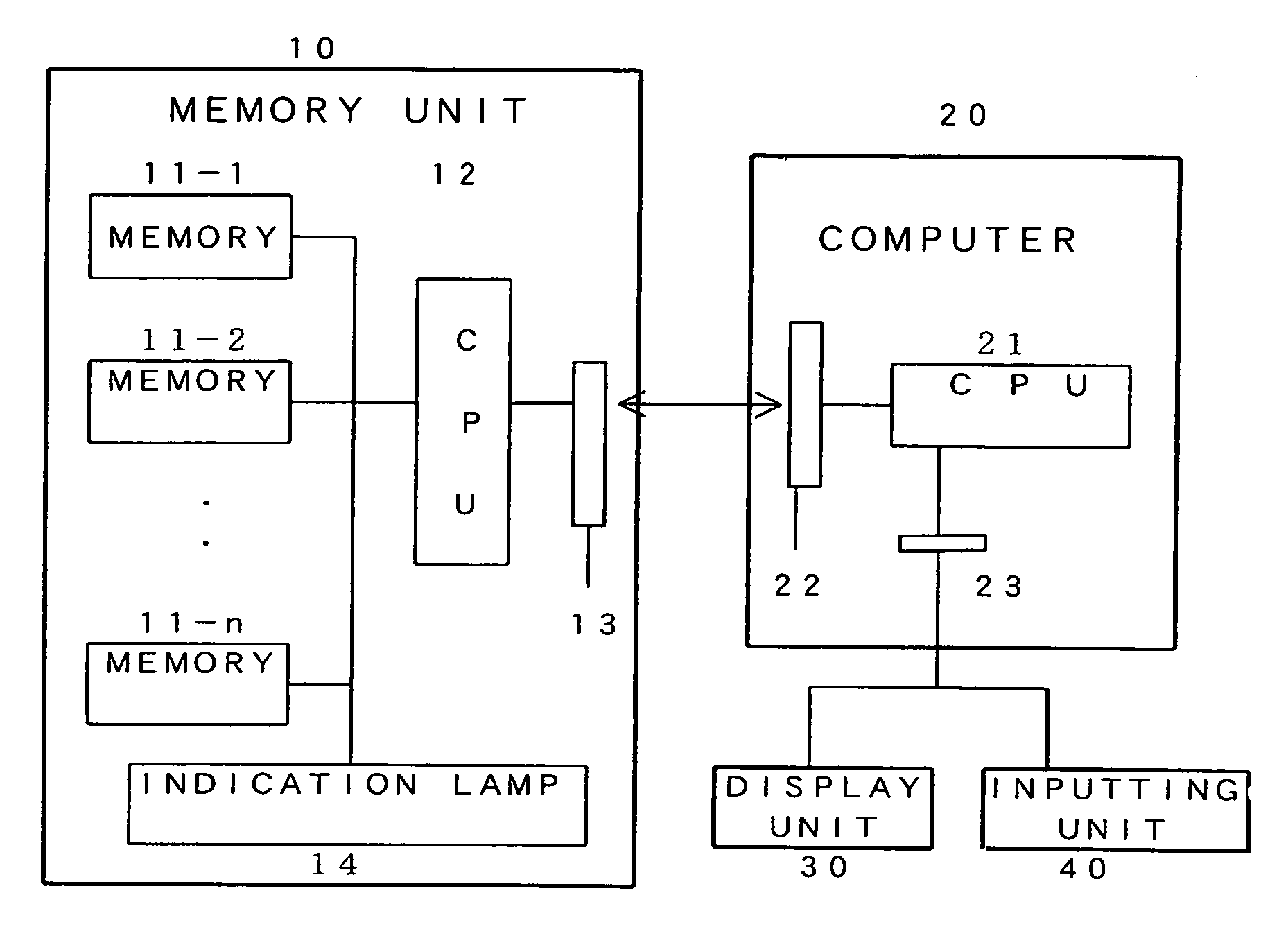
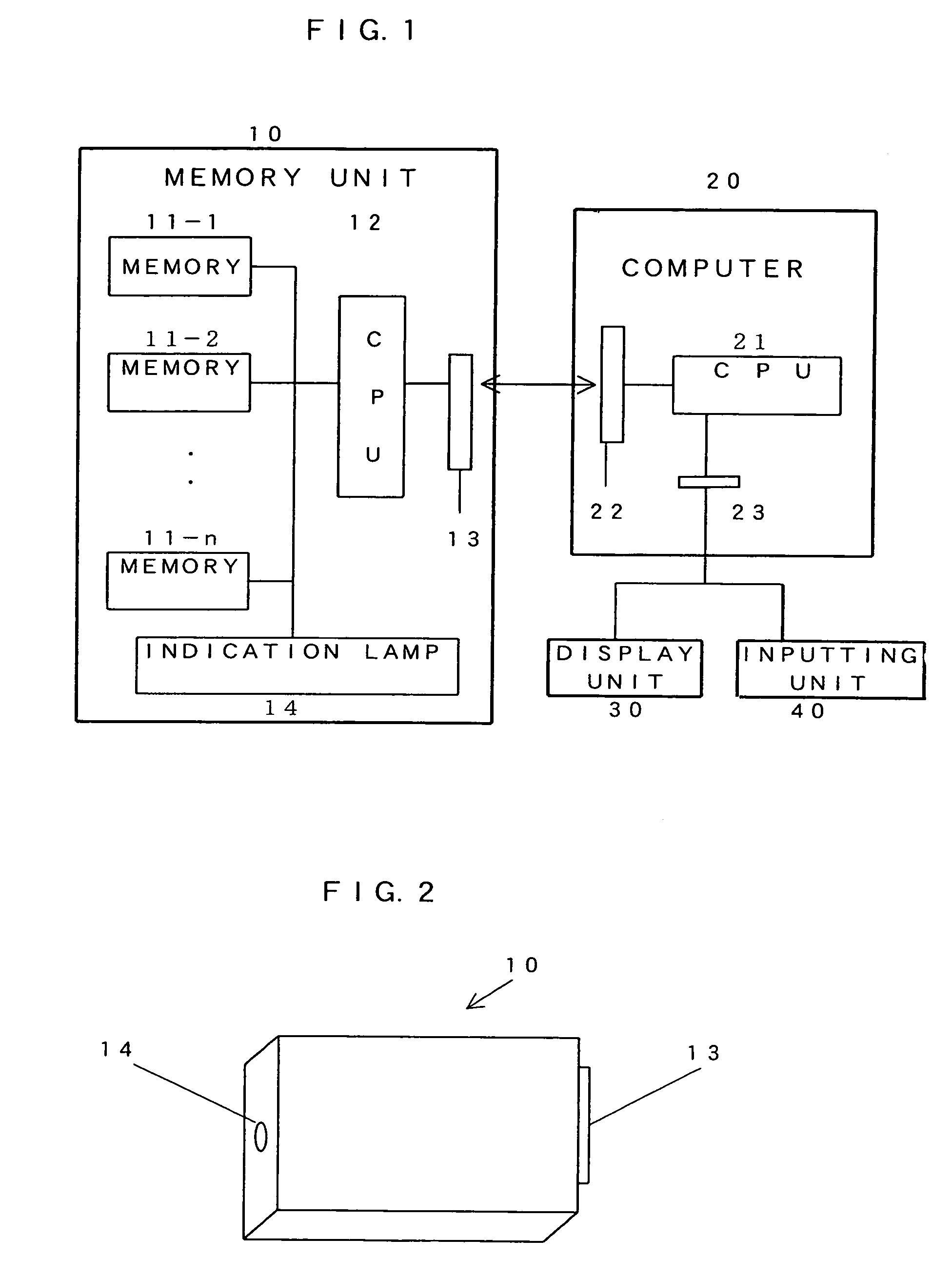
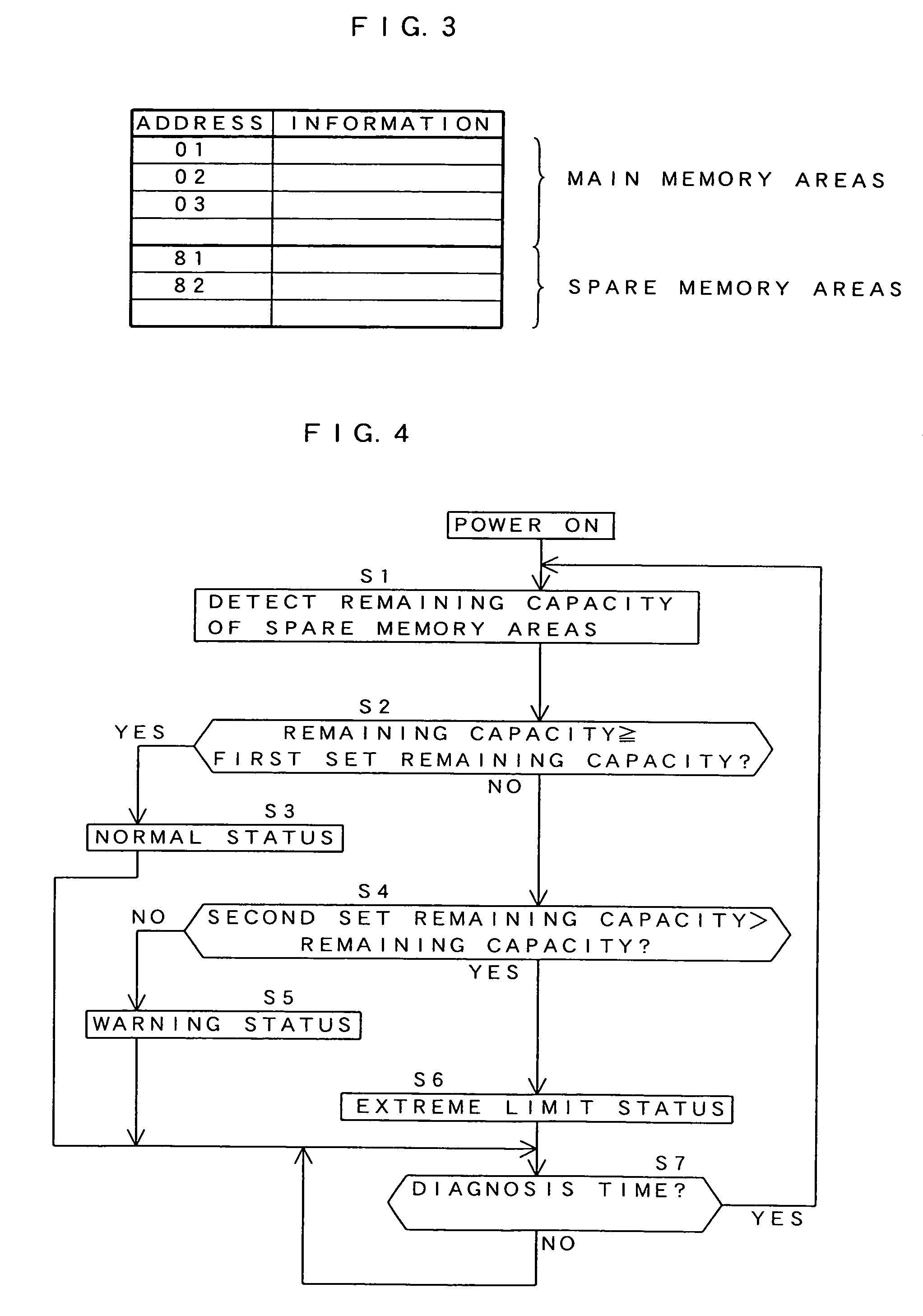
Memory unit having memory status indicator
InactiveUS6993690B1Perform efficiently and appropriatelyReliably determinedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionMemory processingCentral processing unit
A processing unit 12 that is provided in a memory unit 10 can transfer information that is stored in a corresponding address to a spare memory area and prohibit writing of information into the corresponding address when the number write operations to the respective addresses of flash memories 11-1 through 11-3 reaches a set number or when the error frequency in the information stored in the respective addresses reaches a set frequency. When the remaining capacity of a spare memory area reaches a set capacity, an indication lamp 14 may lit or a memory status signal may be transmitted to a processing unit 21 of a computer 20 and displayed on a display unit 30. The memory processing unit 12 may lit the indication lamp 14 when the number write operations to the respective addresses of flash memories 11-1 through 11-3 reaches a set number or when the error frequency in the information stored in the respective addresses reaches a set frequency.
Owner:HAGIWARA SYS COM
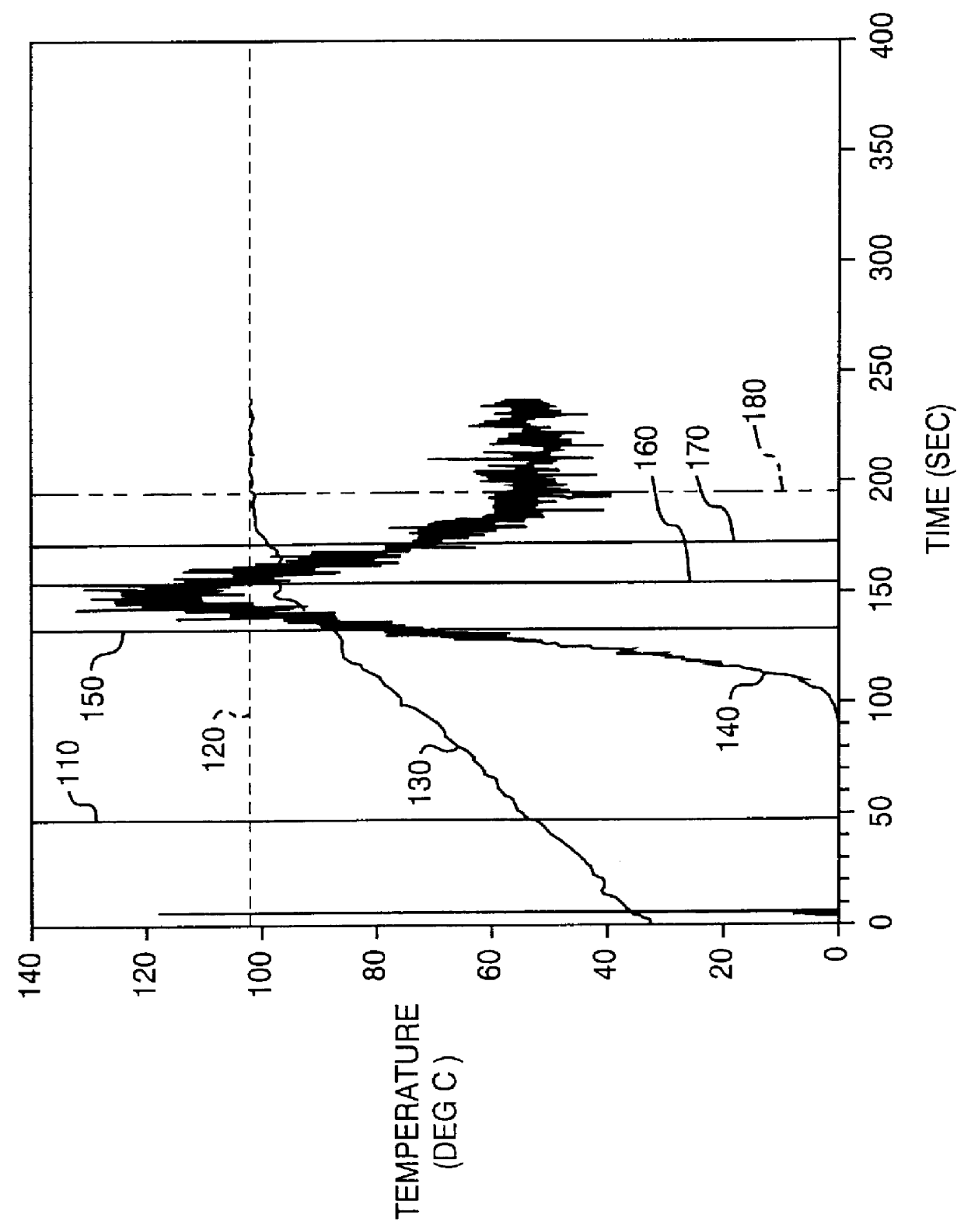
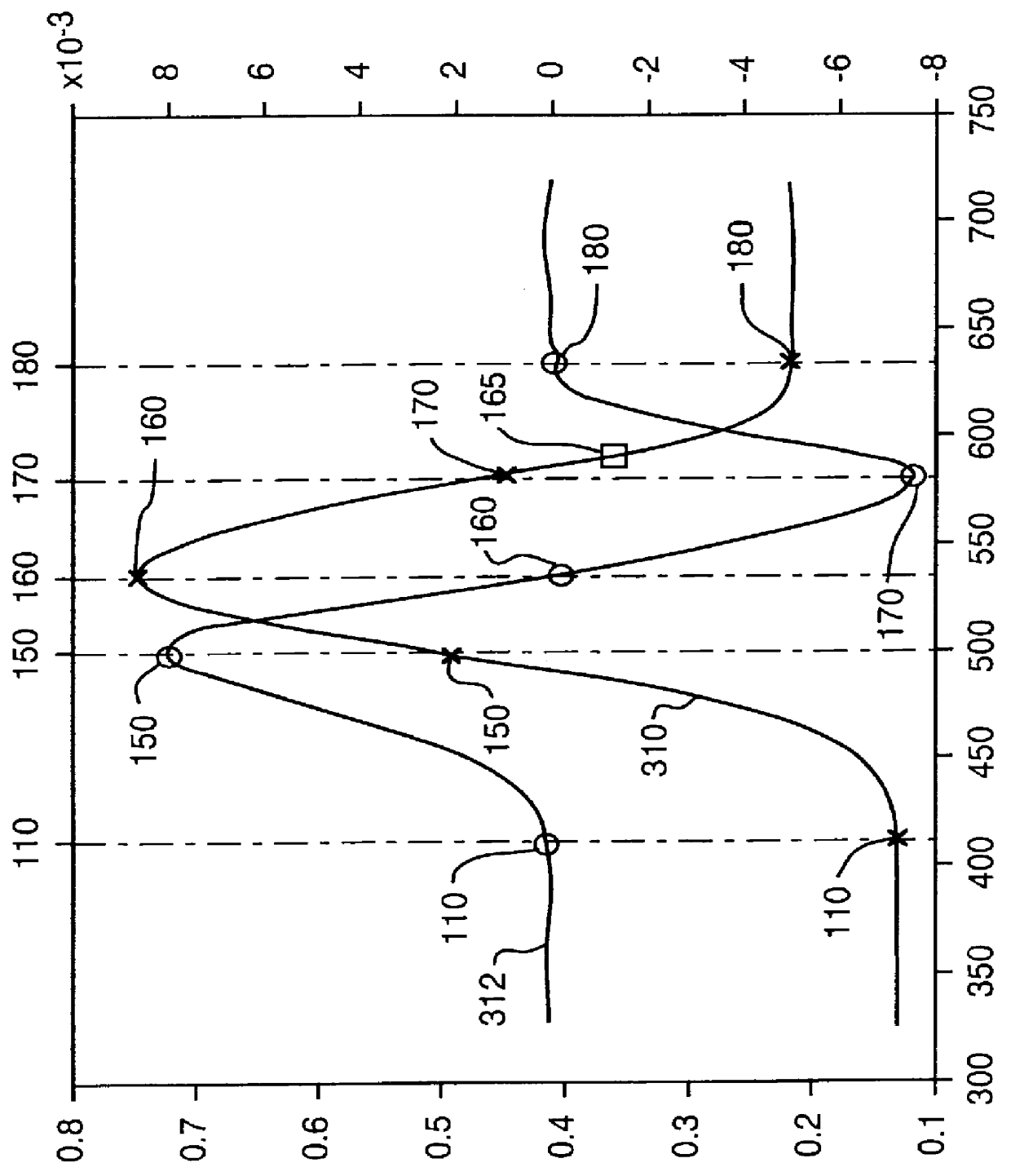
Method and apparatus for boil state detection based on acoustic signal features
InactiveUS6118104AEffective controlReliably determinedVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic sensorSignal frequency
The present invention provides a method of determining the boil states of a liquid as measured by an acoustic sensor which measures the acoustic signal generated by the liquid as it is heated. The acoustic signal is smoothed and a first derivative of the acoustic signal is calculated. Also the frequency of the acoustic signal is measured. Derivative inflection points, zero slope points, and acoustic signal frequencies are utilized to determine the pre-simmer, simmer, pre-boil, boil, boil dry, and boil over states of the liquid.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
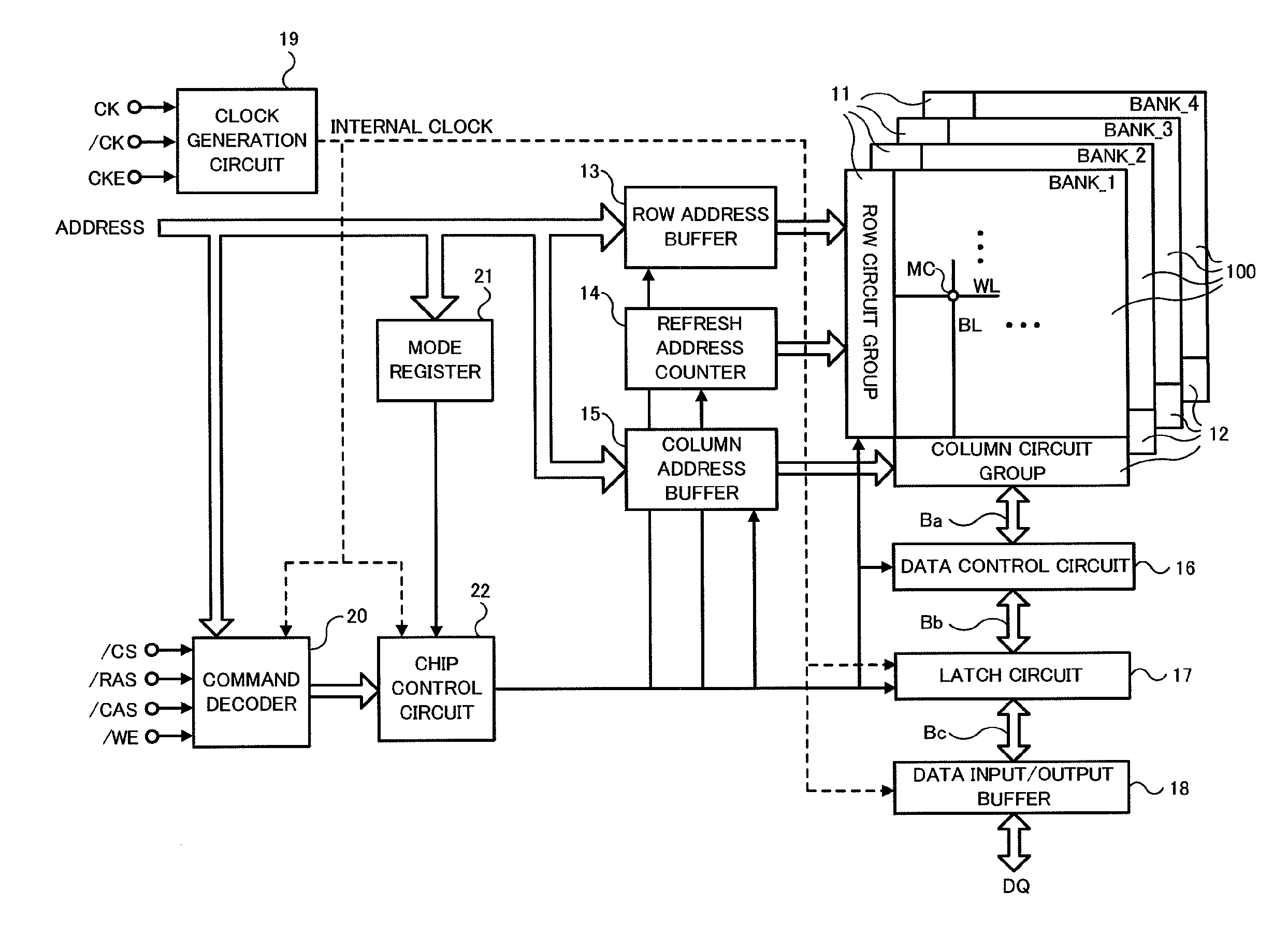
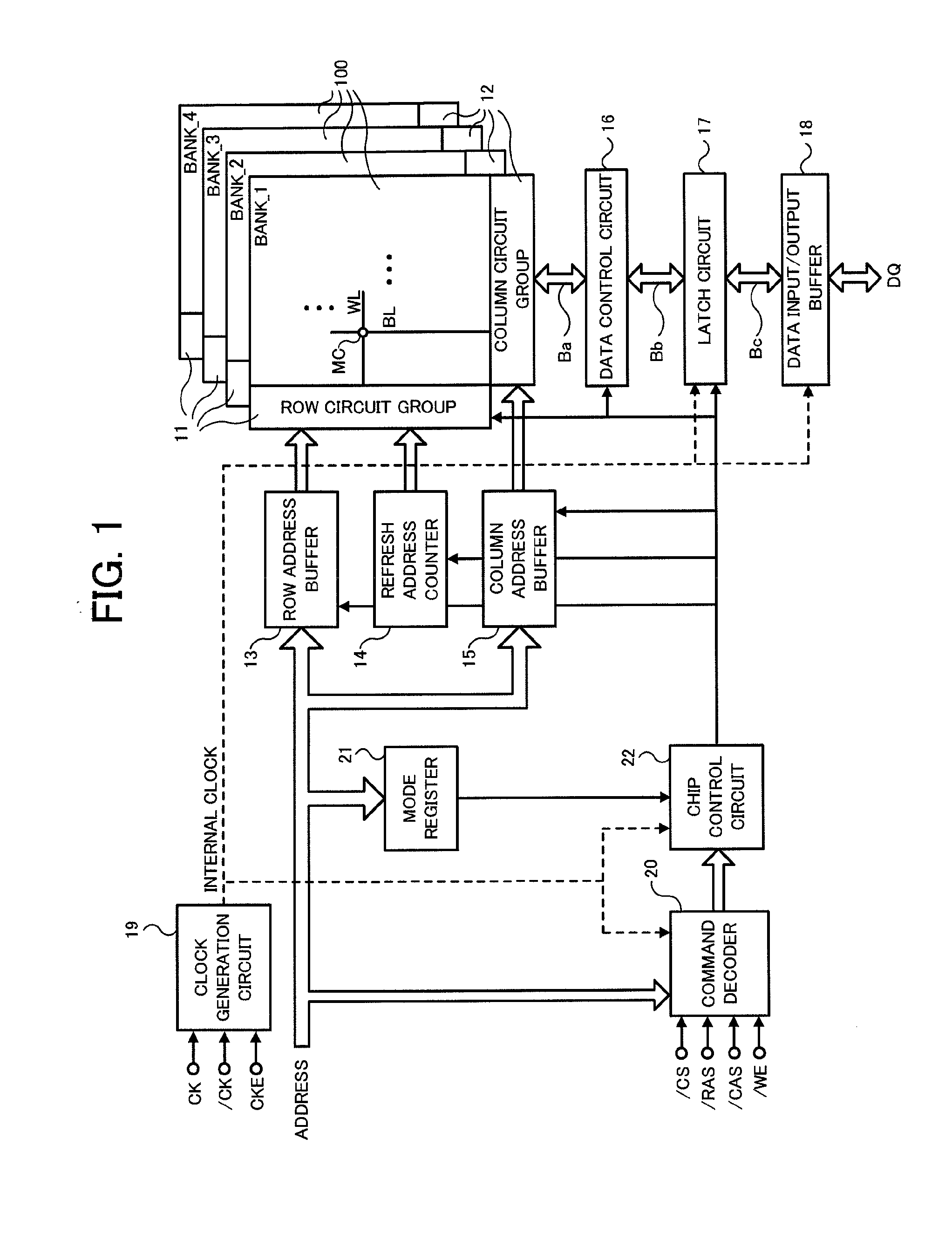
Semiconductor device, refresh control method thereof and computer system
InactiveUS20110225355A1Promote quick completionGrowth inhibitionDigital storageMemory systemsBit lineProcessor register
A semiconductor device comprises a first memory cell array, a register storing information of whether or not one of the word lines in an active state exists in a unit area and storing address information, and a control circuit controlling a refresh operation for a refresh word line based on the information in the register when receiving a refresh request. When the one of the word lines in an active state does not exist, memory cells connected to the refresh word line are refreshed. When the one of the word lines in an active state exists, the one of the word lines in an active state is set into an inactive state temporarily and the memory cells connected to the refresh word line are refreshed after precharging bit lines of the memory cells.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
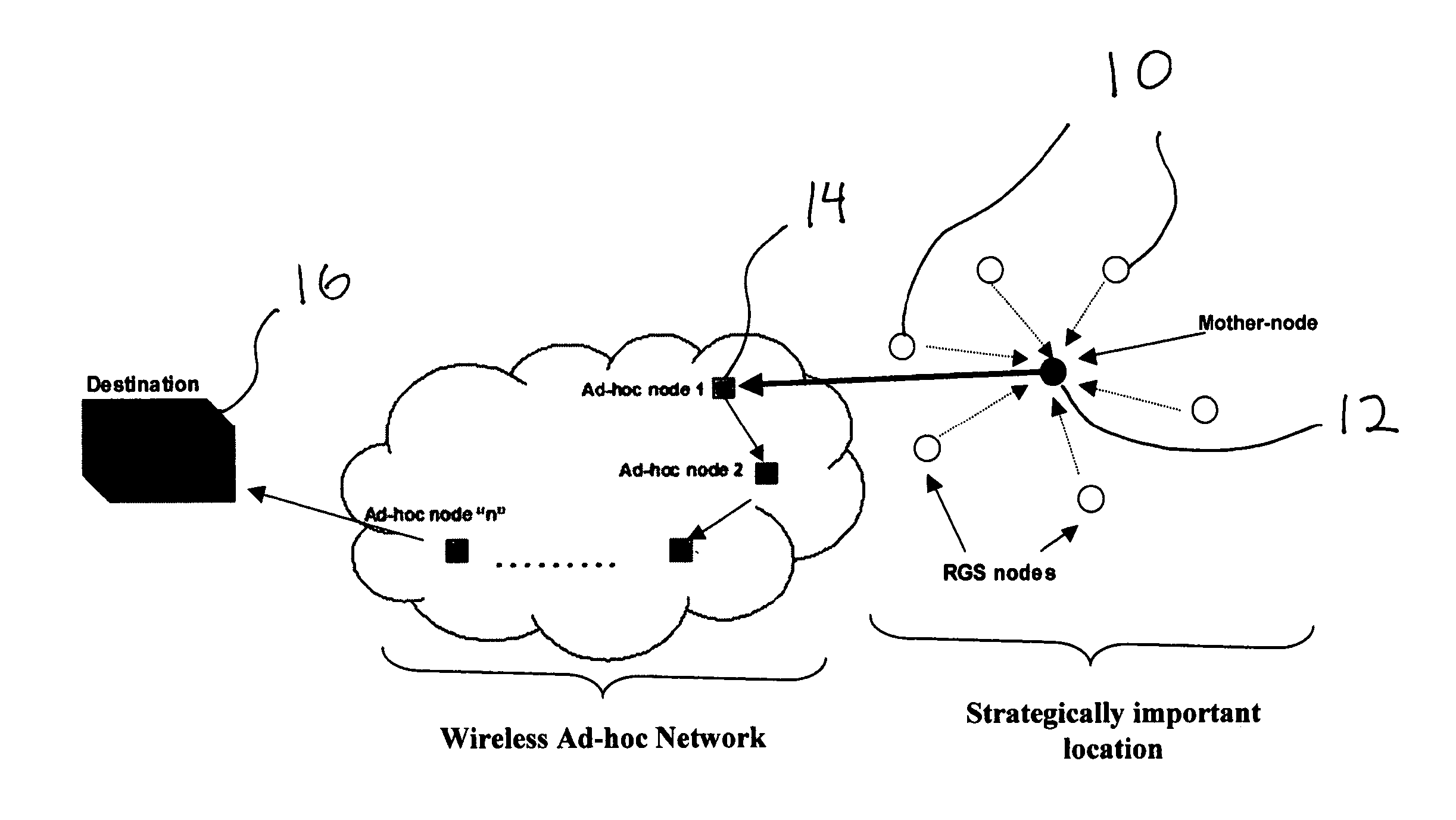
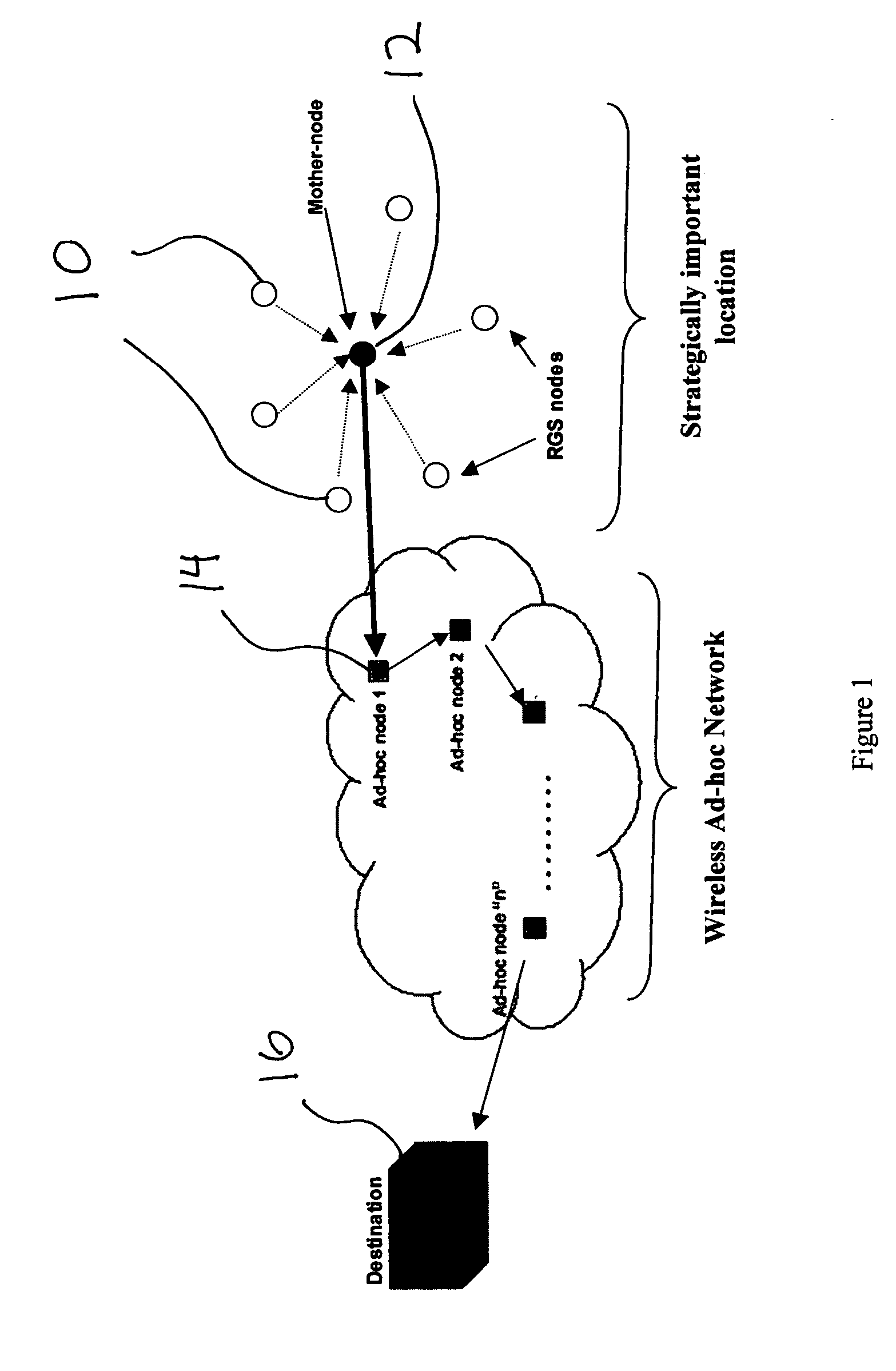
Ultra-wideband radar sensors and networks
InactiveUS20080007445A1Long monitoring capabilityContinuous and reliable operationLoop antennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra wideband radarWireless ad hoc network
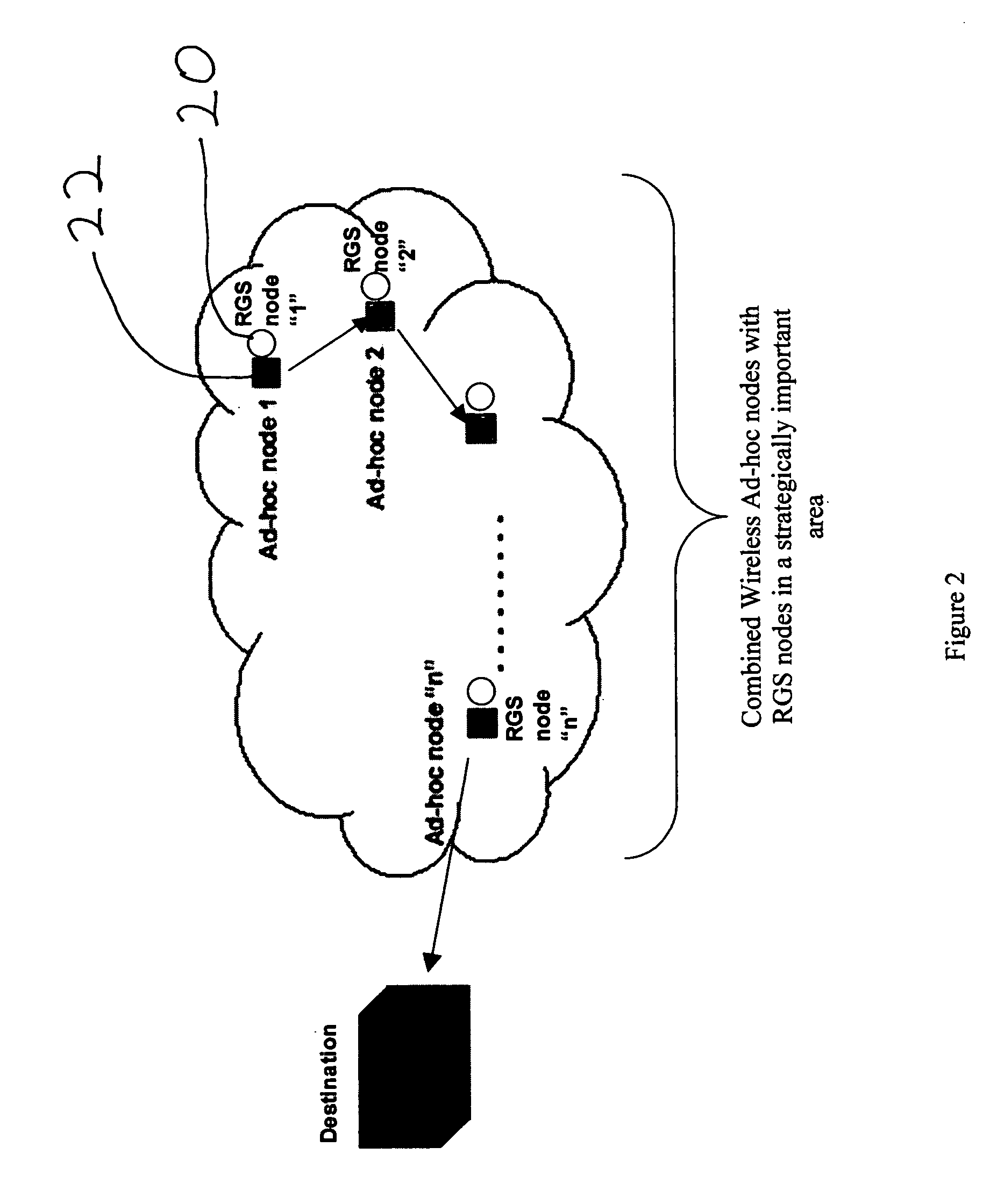
Ultra wideband radar motion sensors strategically placed in an area of interest communicate with a wireless ad hoc network to provide remote area surveillance. Swept range impulse radar and a heart and respiration monitor combined with the motion sensor further improves discrimination.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Data center equipment location and monitoring system
InactiveUS20110084839A1Quickly and easily identifyReliable identificationMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesOperator interfaceData center
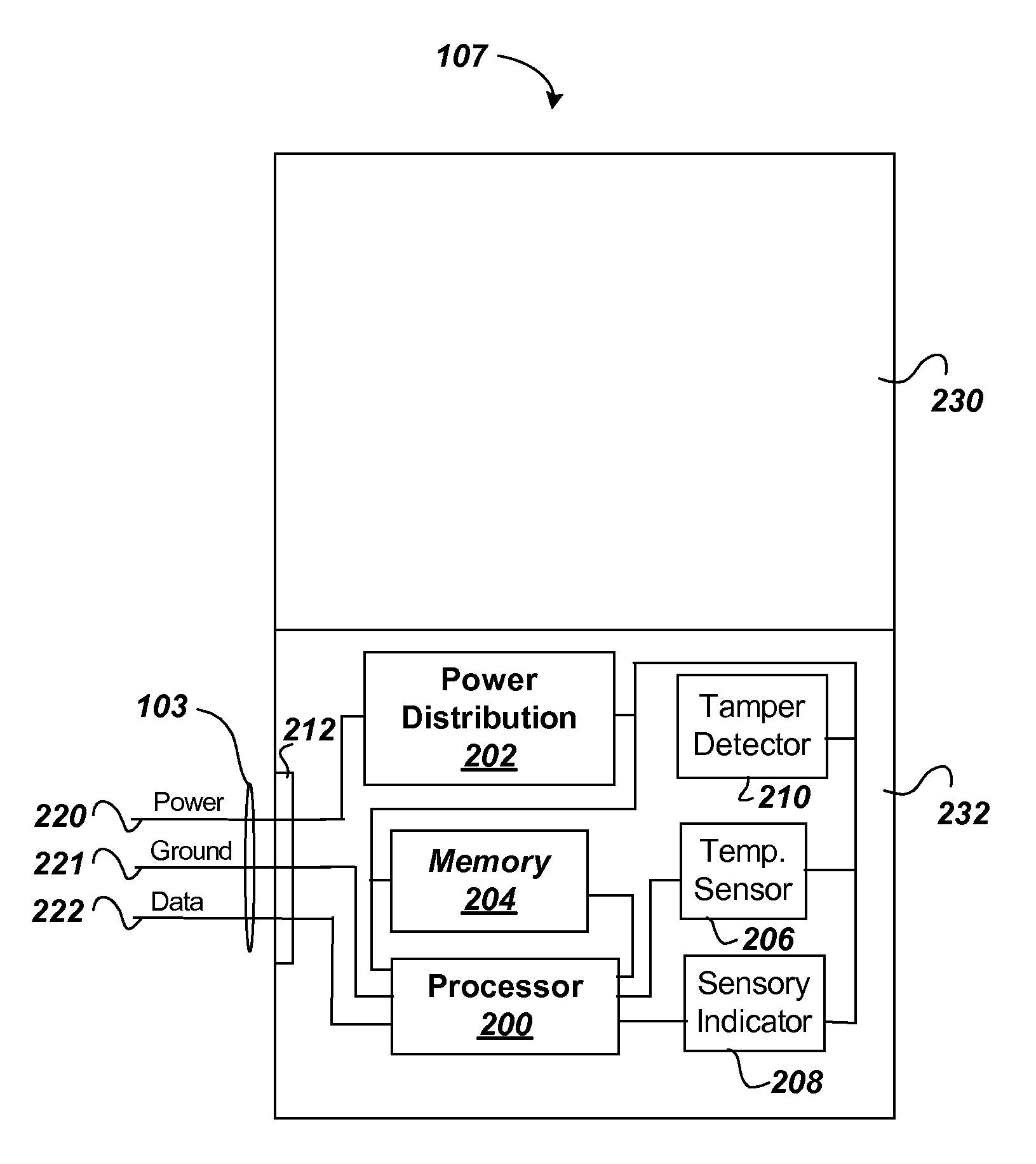
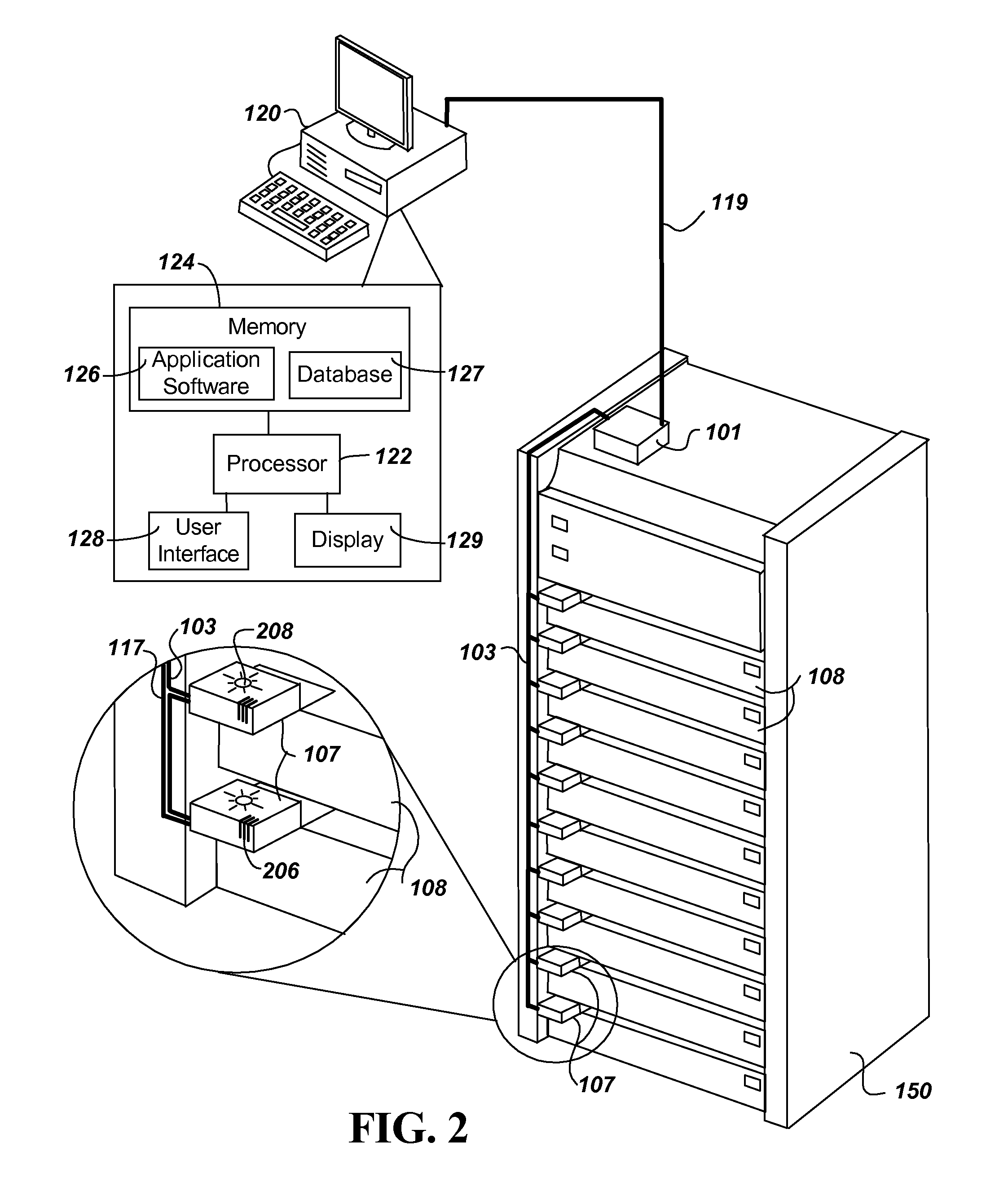
A data center equipment location system includes both hardware and software to provide for location, monitoring, security and identification of servers and other equipment in equipment racks. The system provides a wired alternative to the wireless RFID tag system by using electronic ID tags connected to each piece of equipment, each electronic ID tag connected directly by wires to a equipment rack controller on the equipment rack. The equipment rack controllers then link over a local area network to a central control computer. The central control computer provides an operator interface, and runs a software application program that communicates with the equipment rack controllers. The software application program of the central control computer stores IDs of the equipment rack controllers and each of its connected electronic ID tags in a database. The software application program in operation receives information from the electronic ID tags in real time enabling the central control computer to monitor the status, such as temperature and movement or tampering of each piece of equipment through its connected electronic ID tag. Further, the software application program can send a signal to an individual electronic ID tag to activate a sensory indicator to enable a technician(s) to locate a piece of equipment that is in need of repair or replacement.
Owner:ATTEND SYST
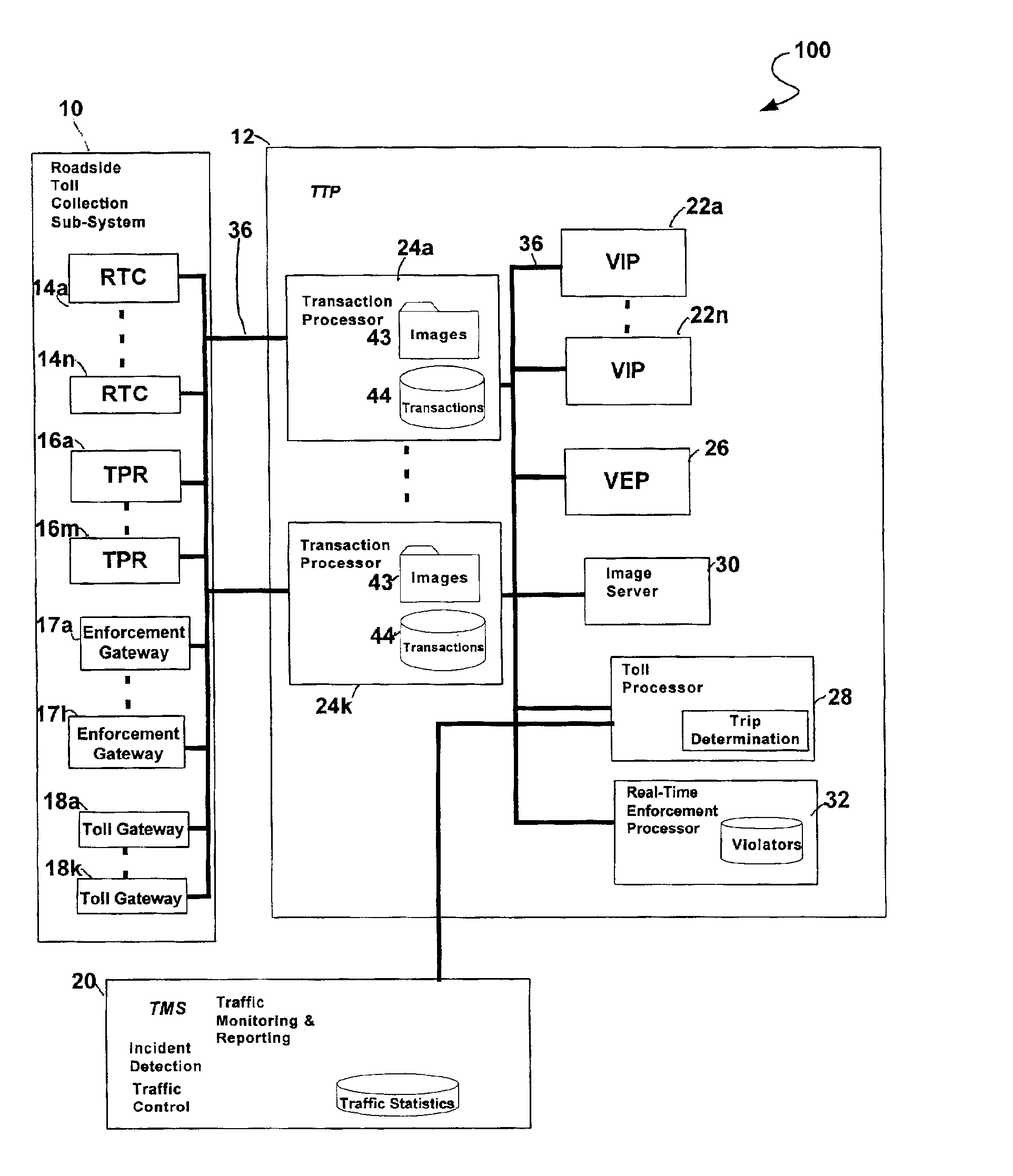
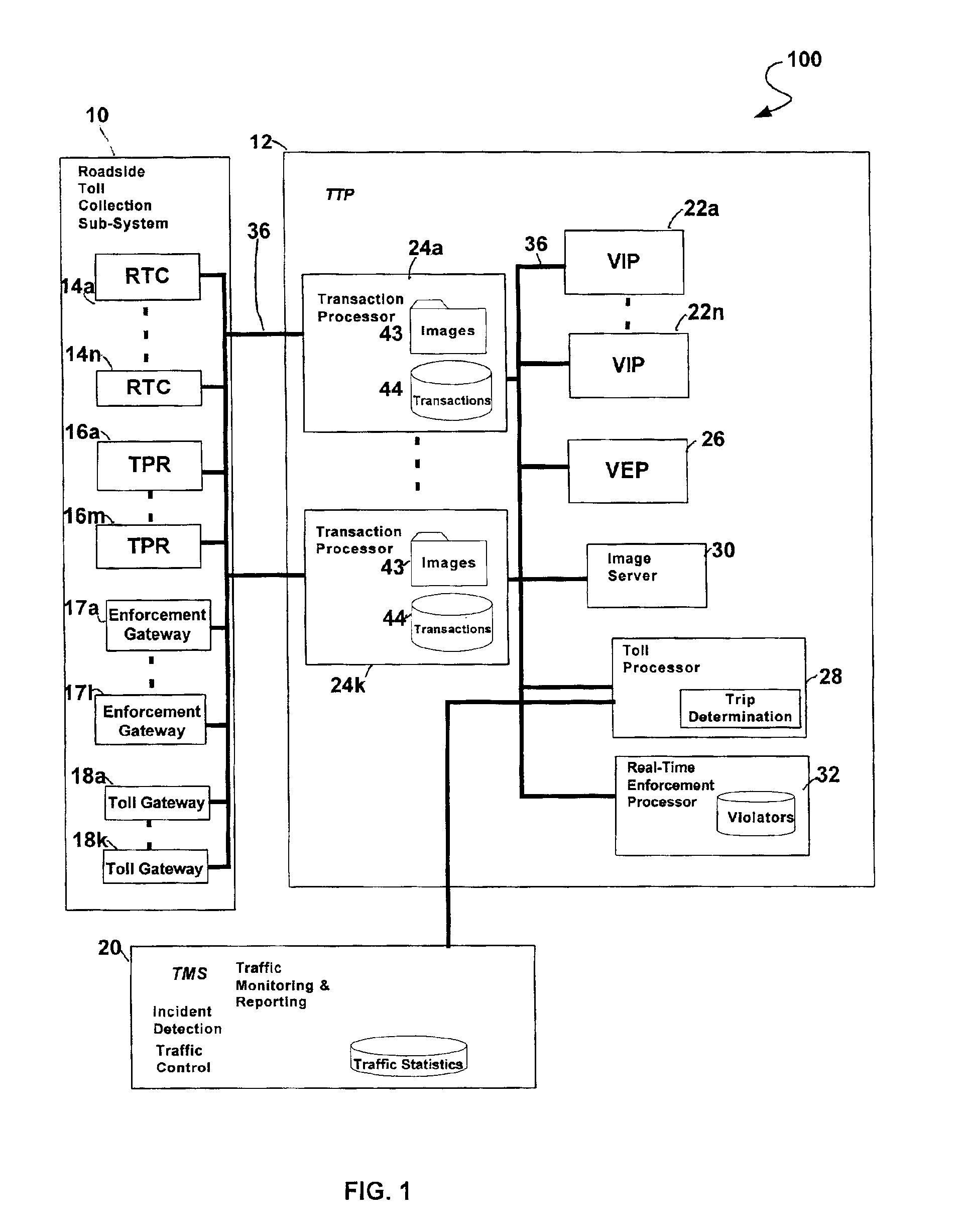
Vehicle trip determination system and method
InactiveUS6922156B2Reduce in quantitySmall error probabilityControlling traffic signalsTicket-issuing apparatusEngineeringVehicle detection
A method for determining a vehicle trip on a roadway includes providing a plurality of vehicle detections from a plurality of gateways, determining a maximum travel time between corresponding pairs of the plurality of gateways, correlating corresponding pairs of the plurality of vehicle detections by determining that a travel time between each of the gateways of each of the corresponding pairs of detections is less than a corresponding maximum travel time, determining a plurality of chainable detections, and determining the boundaries of the trip.
Owner:VERTEX AEROSPACE LLC
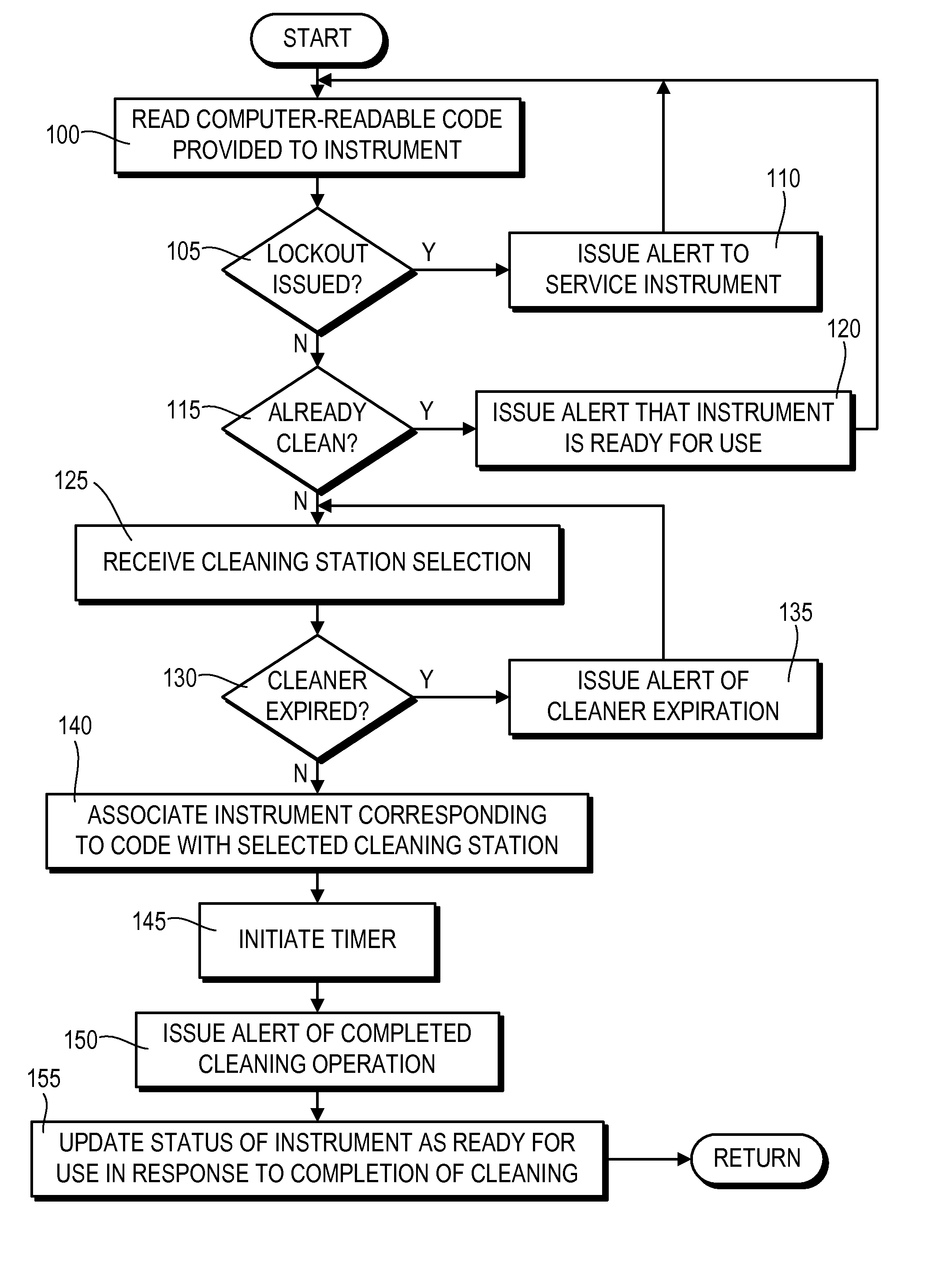
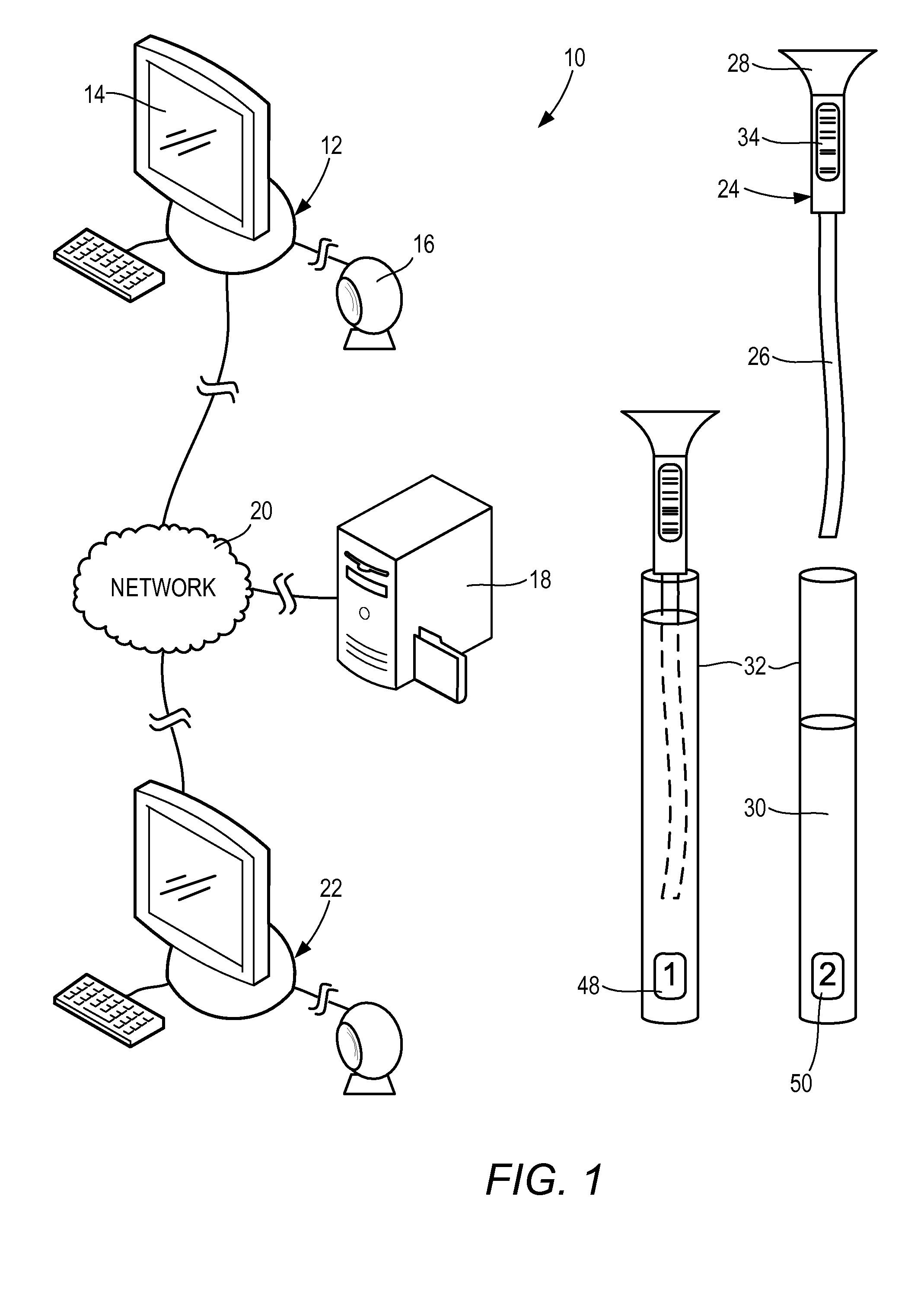
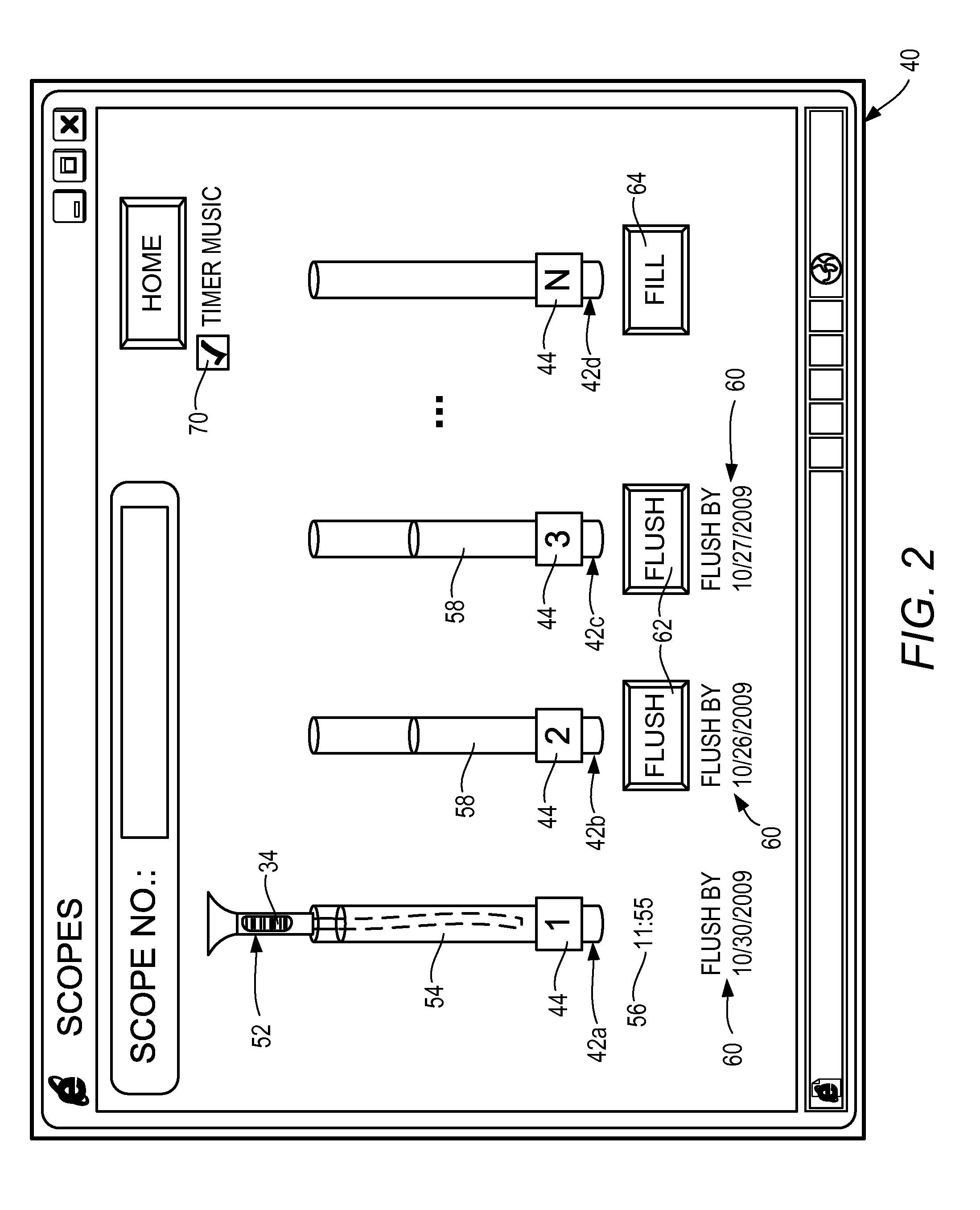
Medical instrument cleaning system and method
InactiveUS20110084835A1Minimize manual inputReliably determinedEndoscopesAlarmsElectronic recordsEngineering
A system and method for monitoring a status of a medical instrument is provided. Using an input peripheral associated with a computer terminal, a code associated with the medical instrument to be subjected to a cleaning operation after a previous use of the medical instrument is received. A timer for monitoring a duration of the cleaning operation is initiated. In response to completion of the cleaning operation determined based on the timer, a status of the medical instrument in an electronic record associated with the medial instrument stored in a non-transitory computer-readable medium is updated to indicate that the medical instrument has been cleaned. An indication that the cleaning operation being performed on the medical instrument is complete is then issued.
Owner:AUGUSTA E N T P C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com