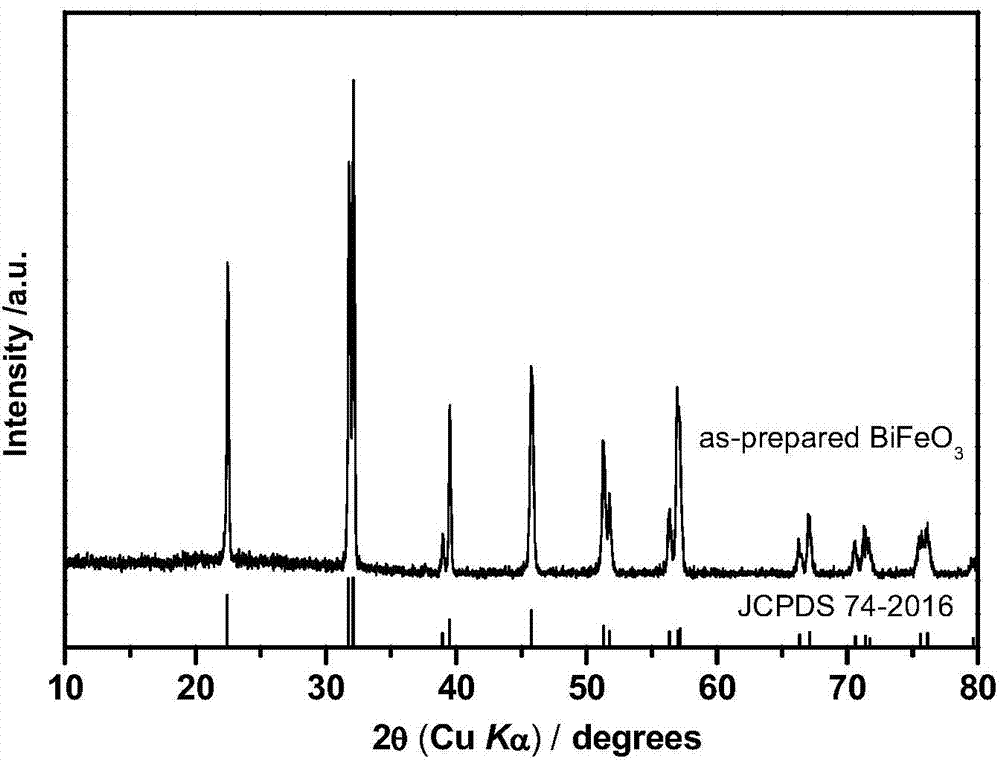
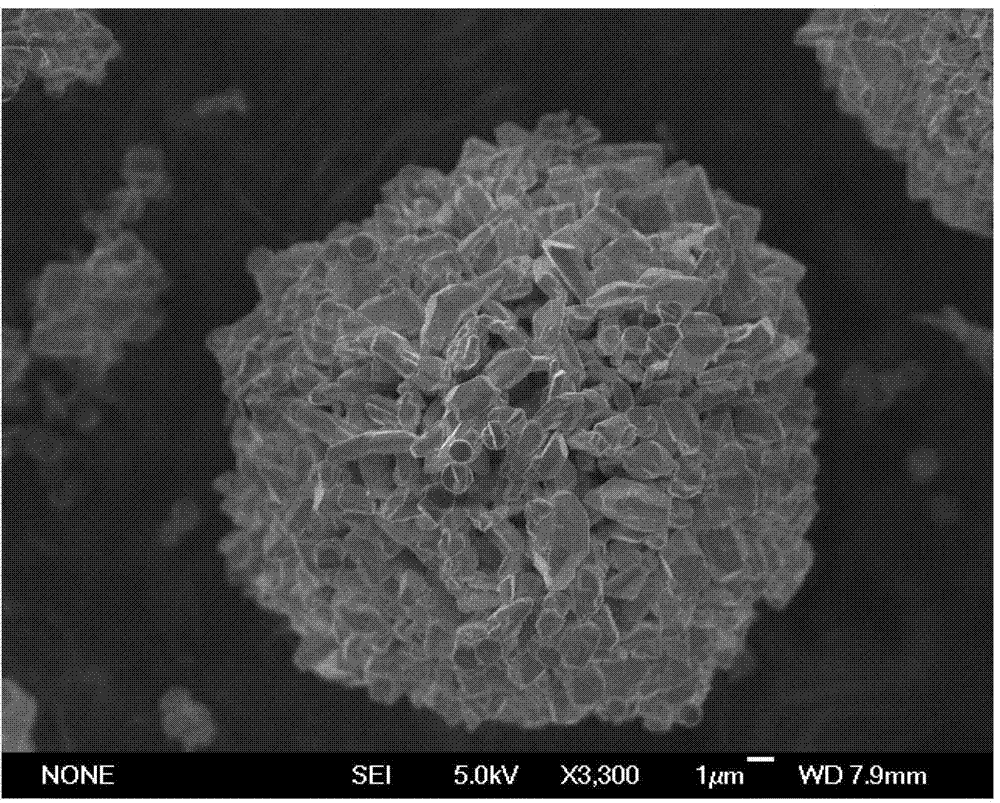
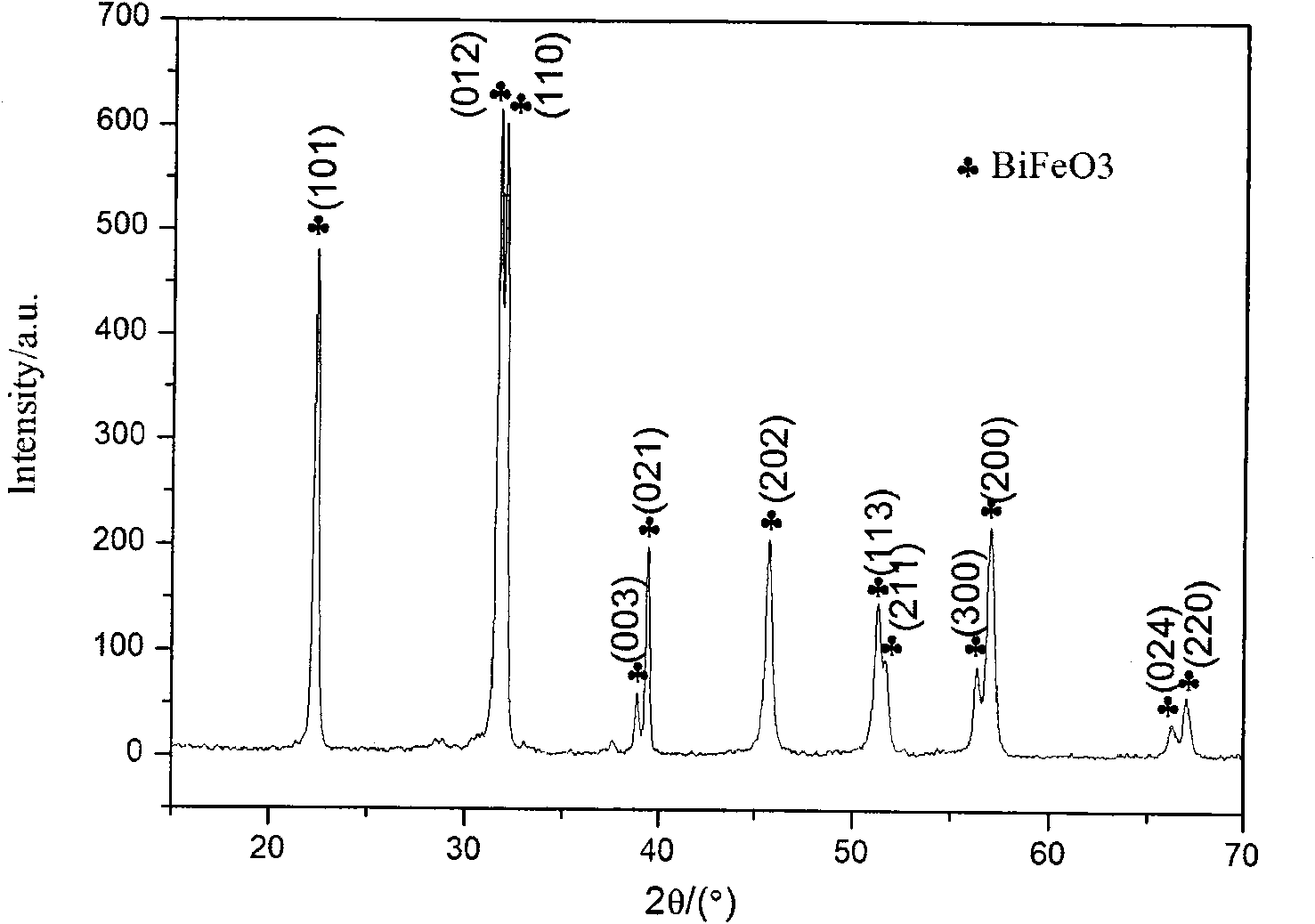
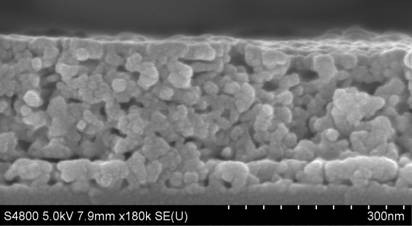
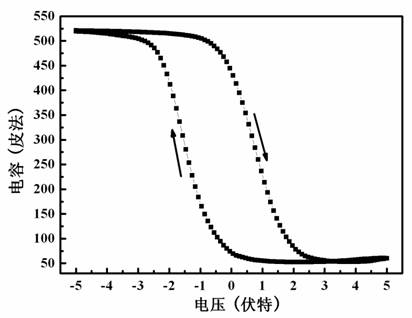
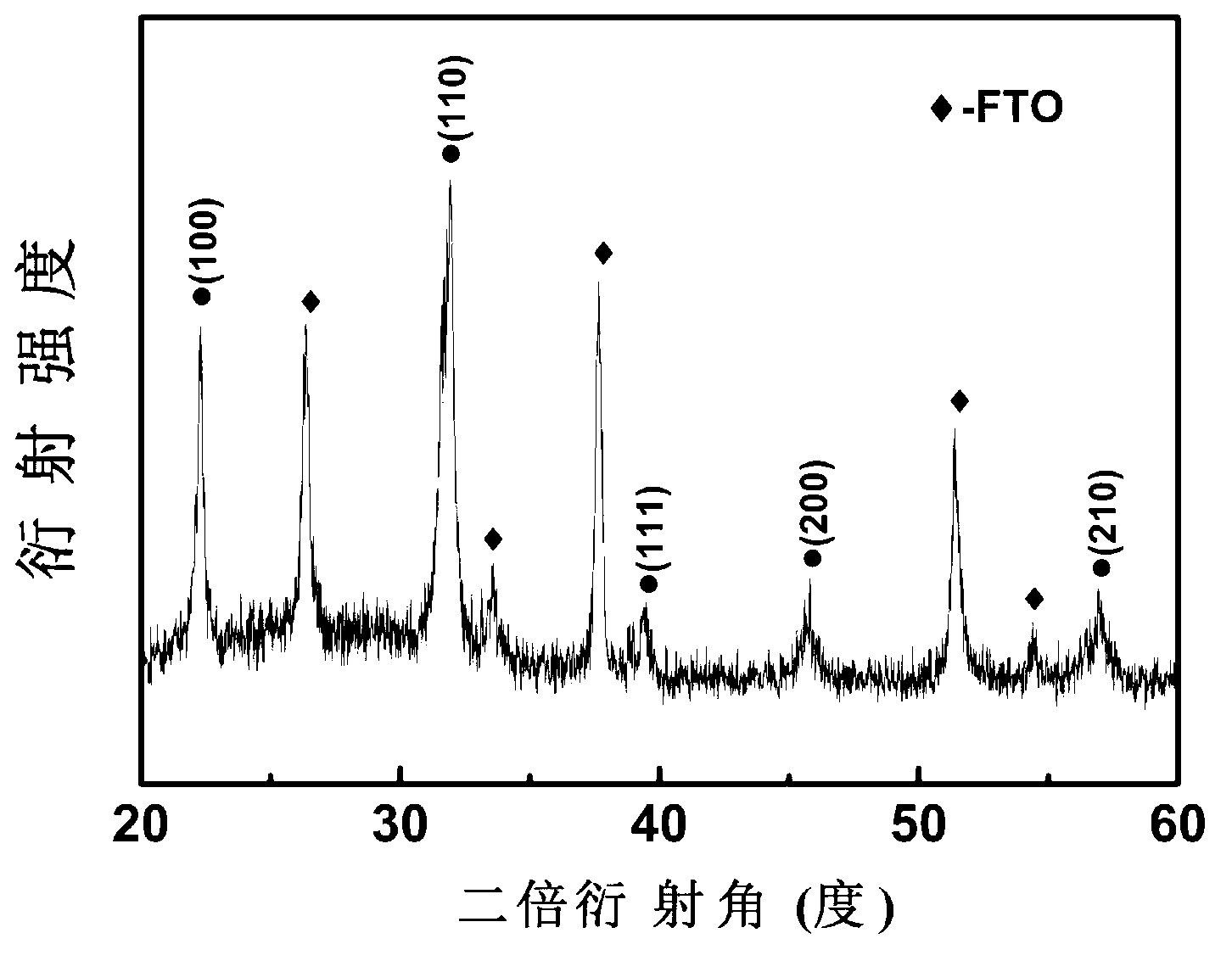
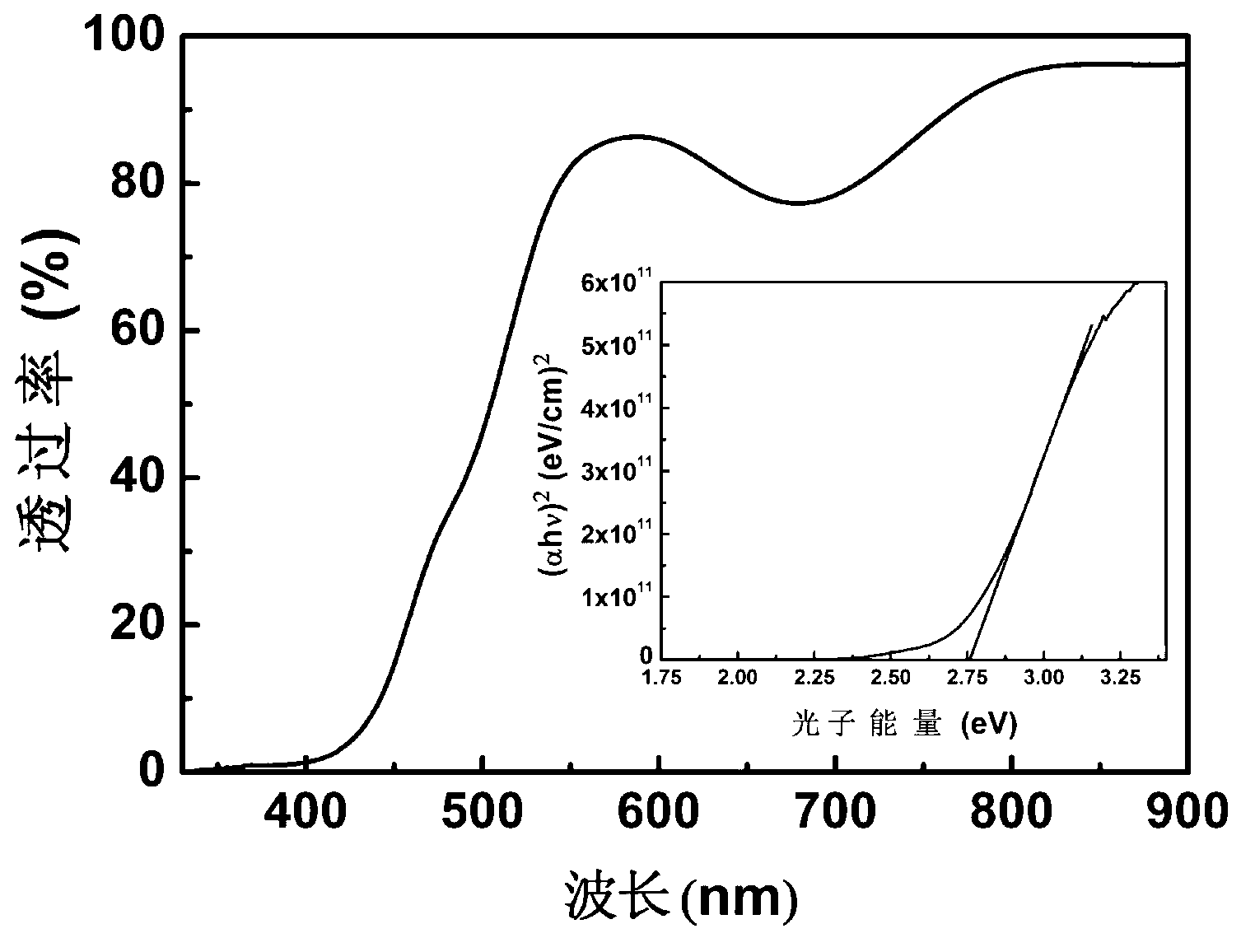
Patents
Literature
479 results about "Bismuth ferrite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
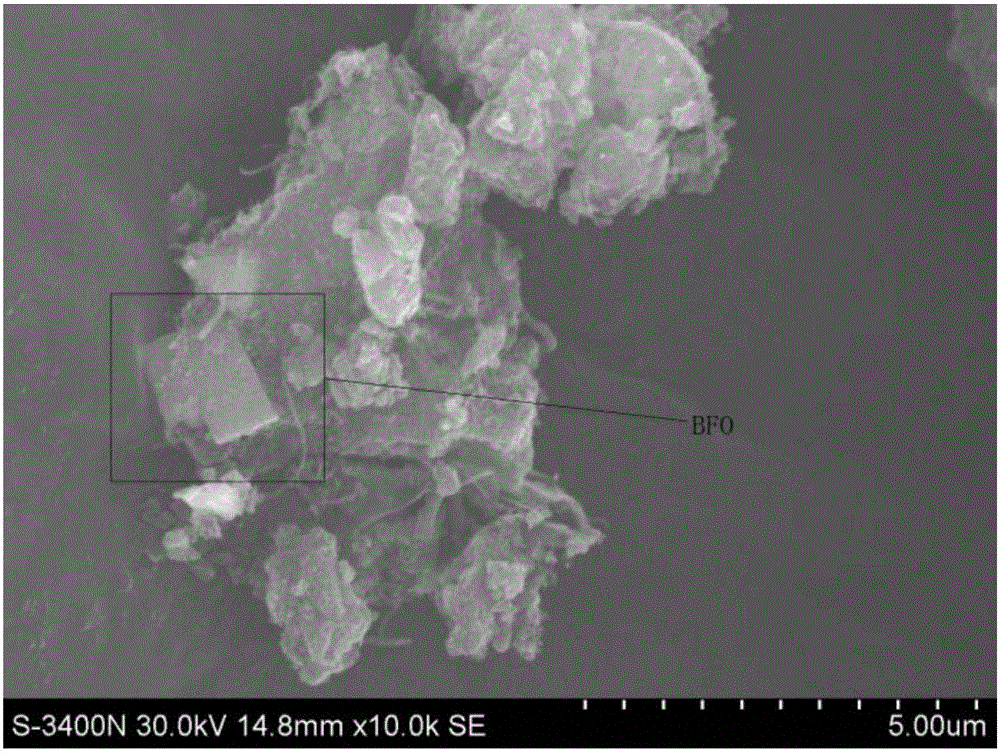
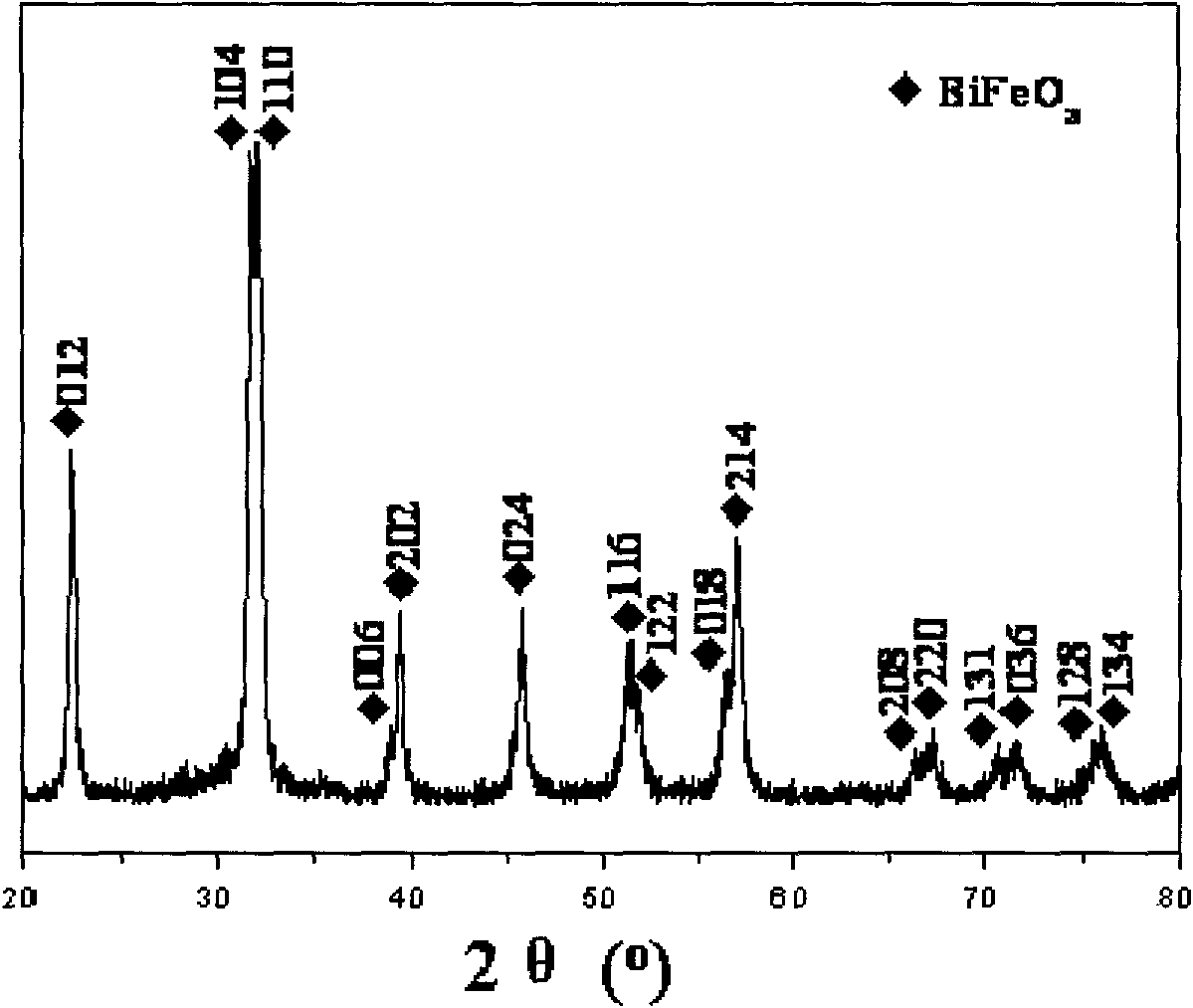
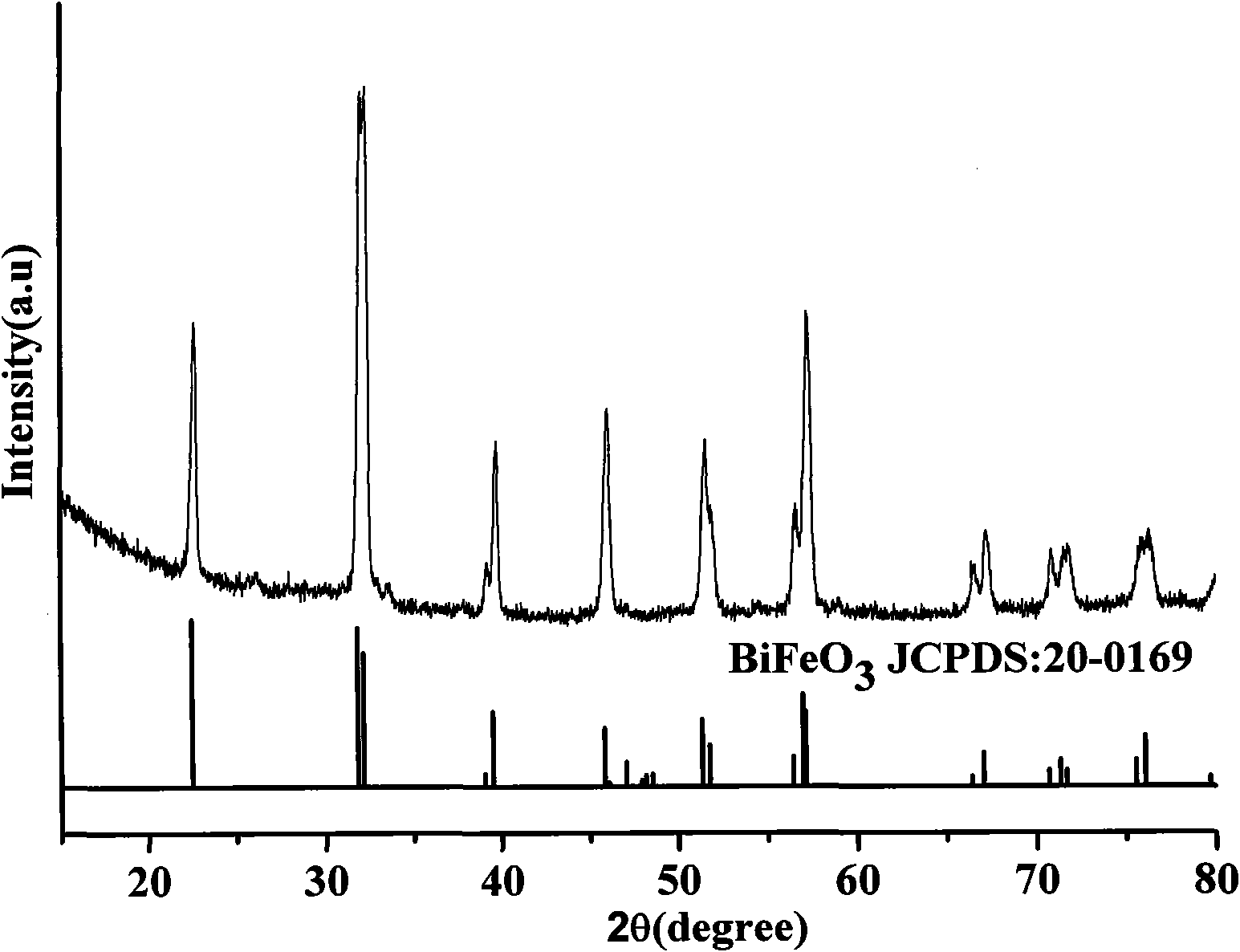
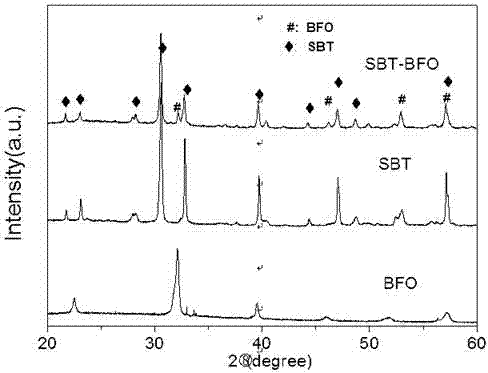
Bismuth ferrite (BiFeO₃, also commonly referred to as BFO in materials science) is an inorganic chemical compound with perovskite structure and one of the most promising multiferroic materials. The room-temperature phase of BiFeO3 is classed as rhombohedral belonging to the space group R3c. It is synthesized in bulk and thin film form and both its antiferromagnetic (G type ordering) Néel temperature (approximately 653 K ) and ferroelectric Curie temperature are well above room temperature (approximately 1100K) .
Resistive random access memory based on bismuth iron thin film system and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101587936AHigh and low resistance state resistance value is stableWith magnetoelectric coupling effectElectrical apparatusDigital storageSputteringStatic random-access memory
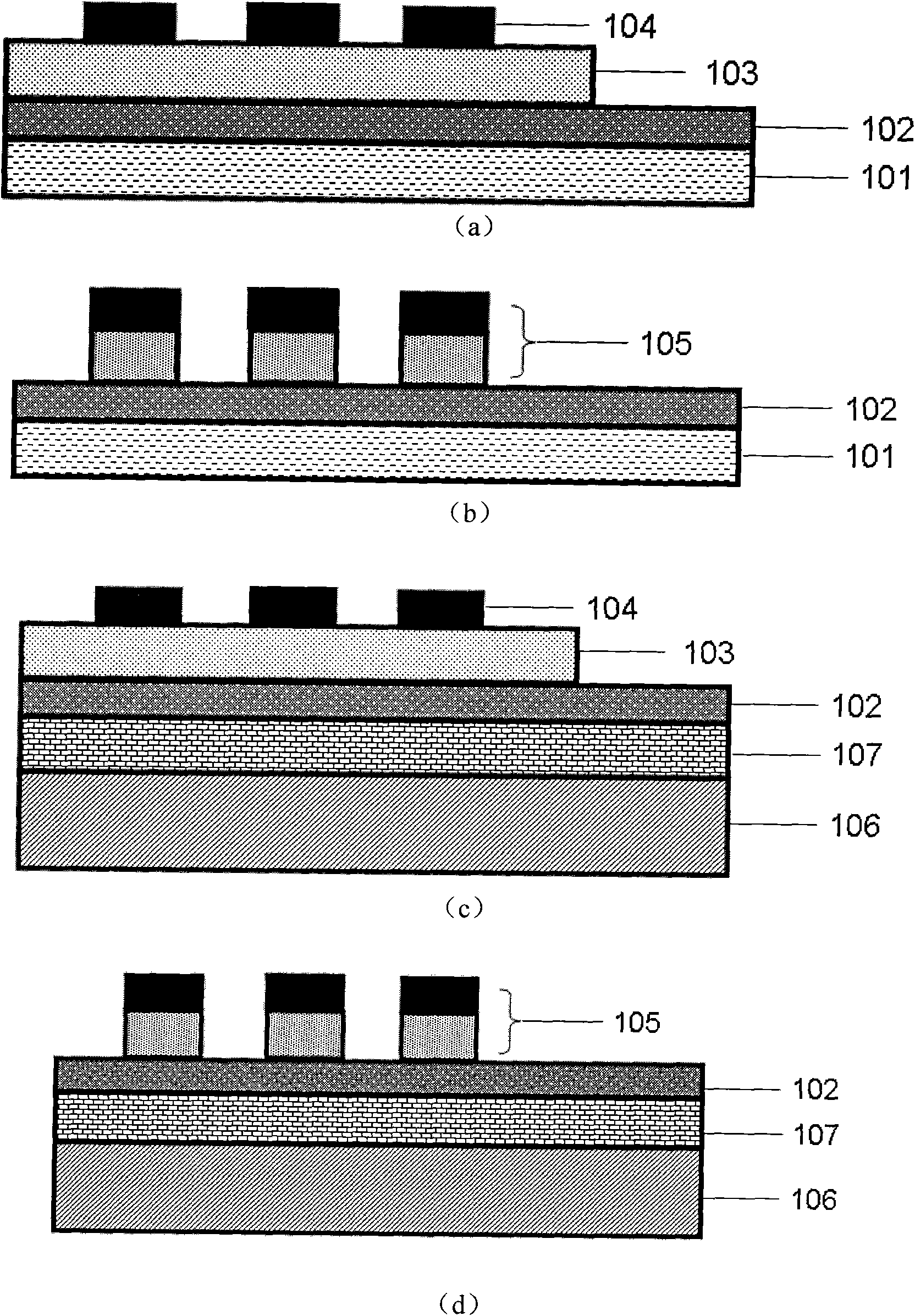
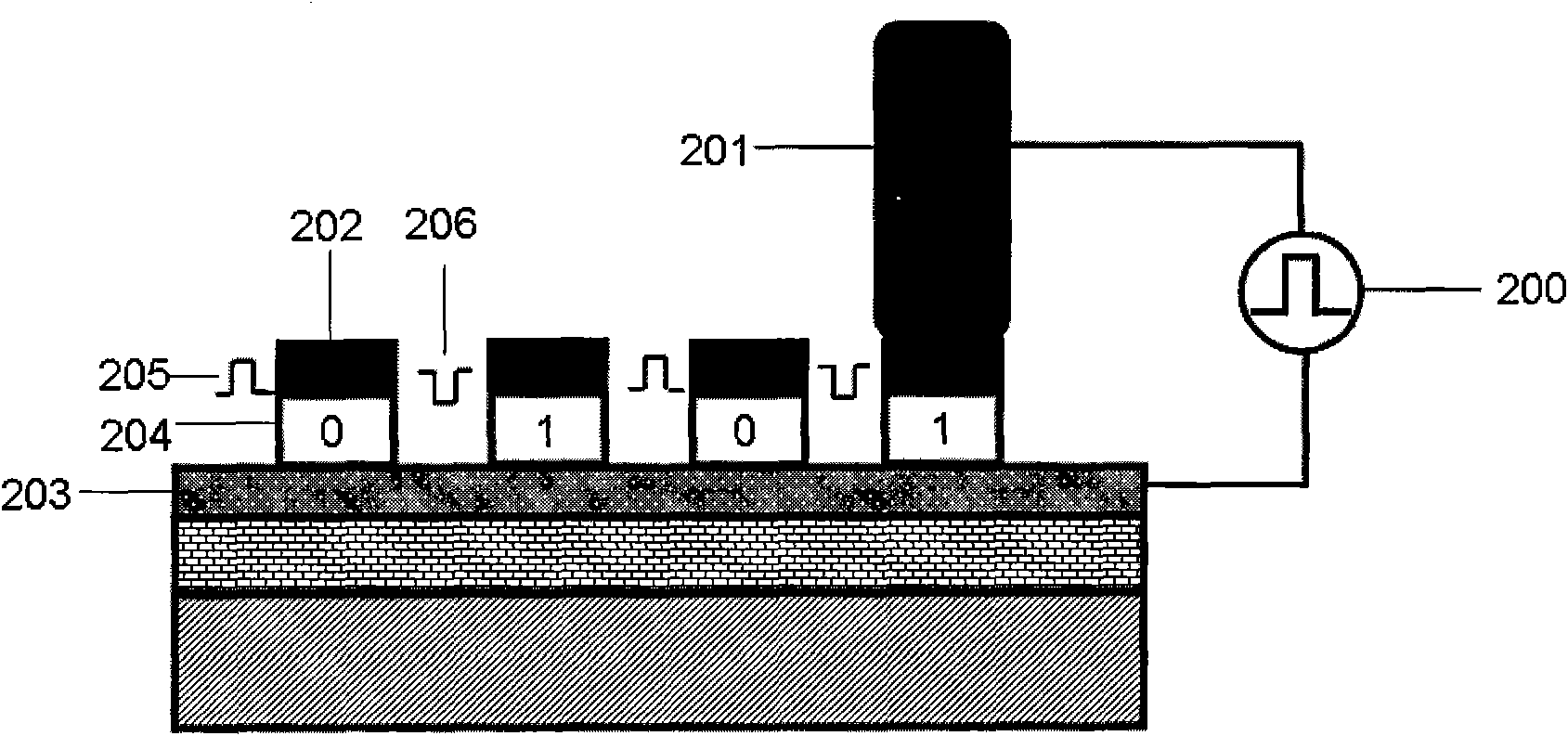
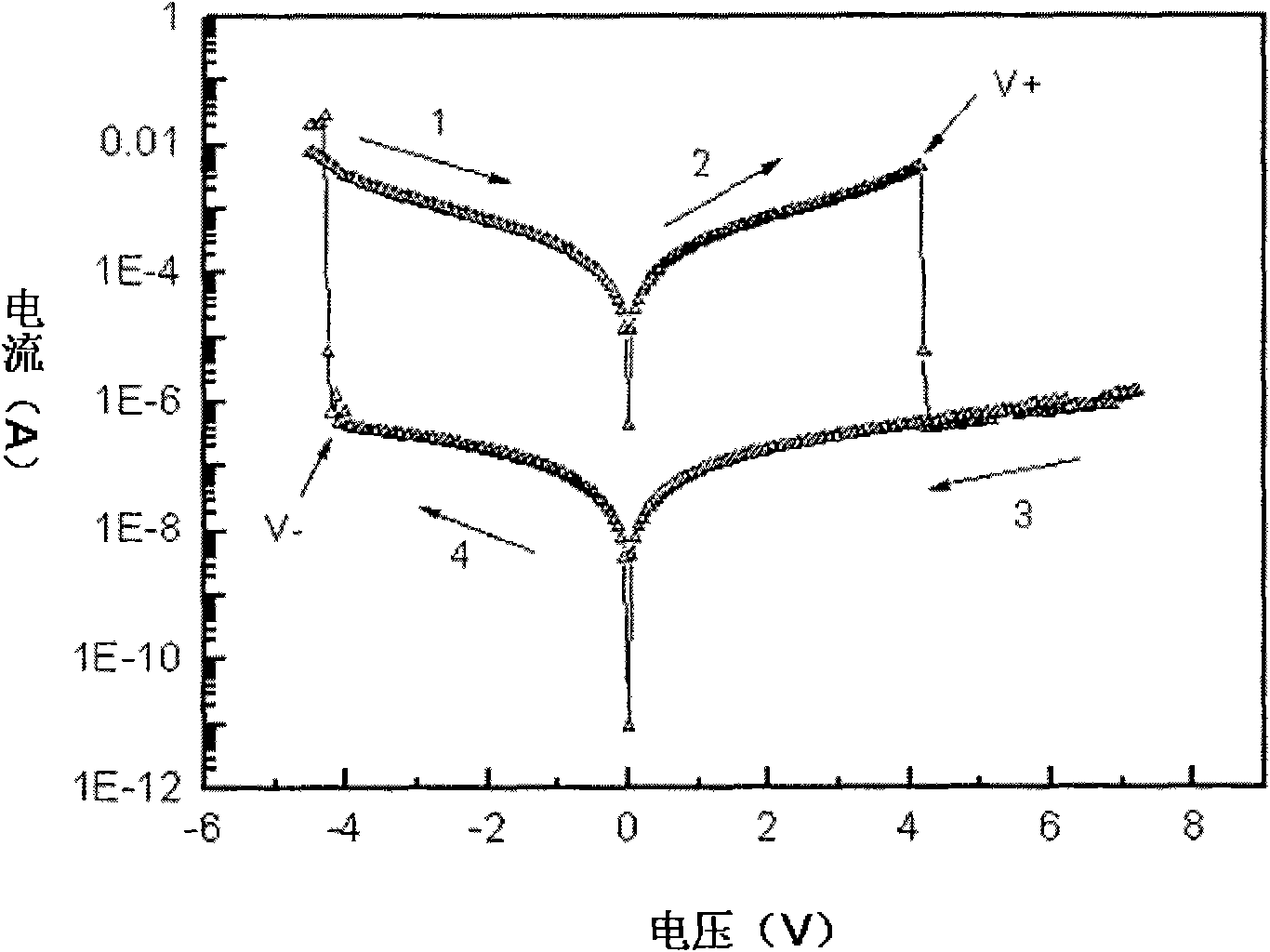
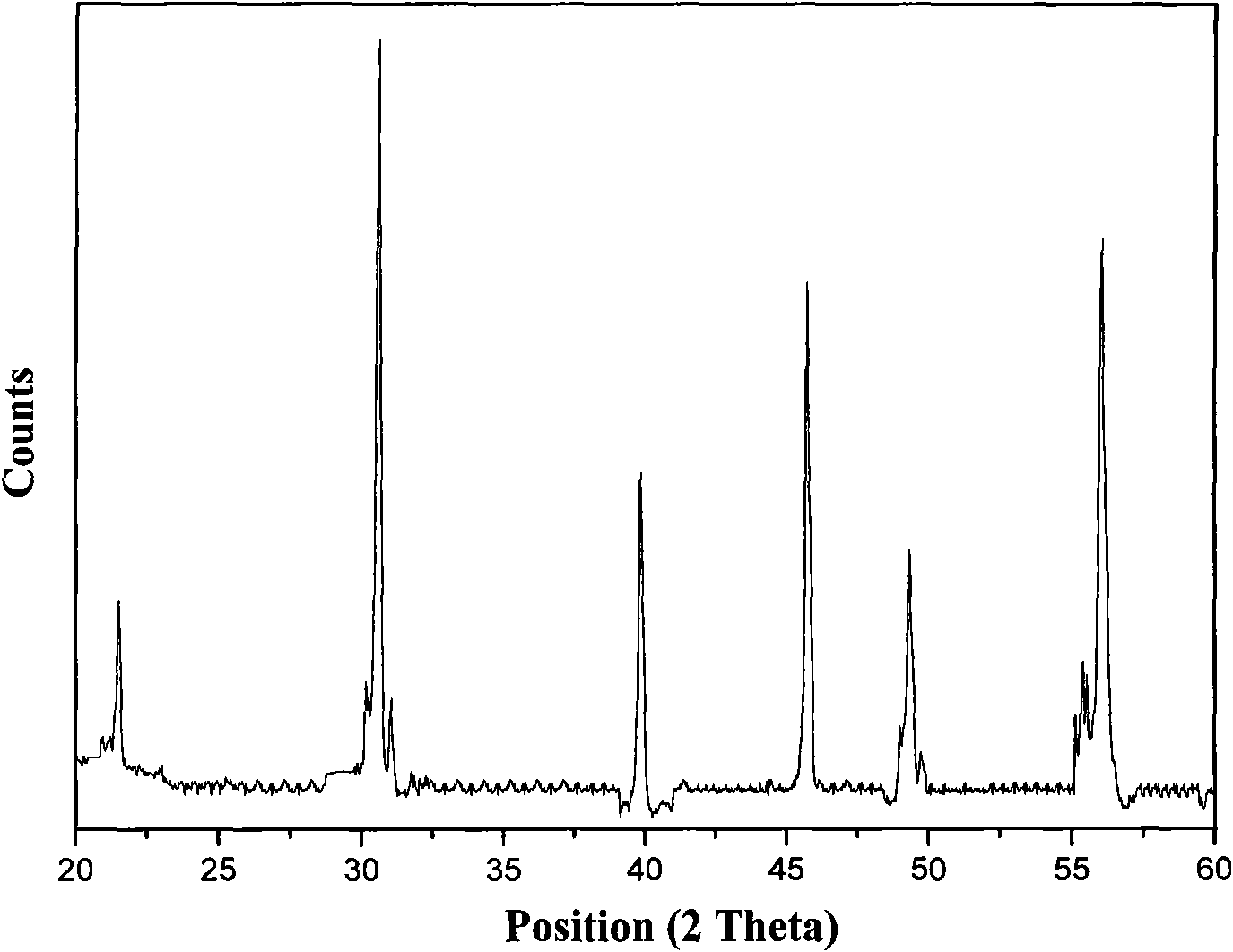
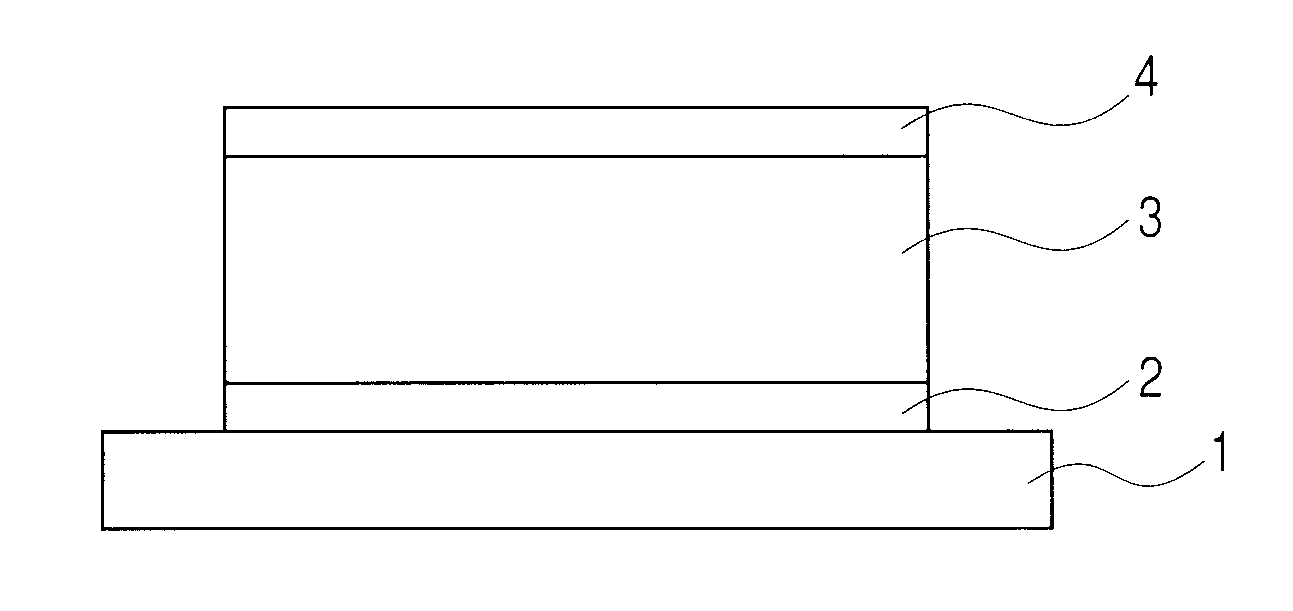
The invention relates to a resistive random access memory based on bismuth iron thin film system and manufacturing method thereof. The memory comprises an insulating substrate (101) layer as the first layer, a lower electrode (102) as the second layer, a bismuth iron thin film (103) as the third layer, an upper electrode (104) as the fourth layer; the manufacturing method utilizes the method thermal evaporation or magnetron sputtering to grow the lower electrode on the insulating substrate layer, utilizes the method of magnetron sputtering, pulsed laser deposition or colloidal sol-gel to grow the bismuth iron thin film on the lower electrode, finally utilizes the method of thermal evaporation or magnetron sputtering to grow the upper electrode on the bismuth iron thin film, and utilizes the method of ultraviolet lithography, electron beam or ion beam etching to obtain the electrode pattern. The memory provided by the invention has excellent electroluminescent resistance effect and good stability, and has simple manufacturing method, low cost and is easy for manufacturing in large scale and commercial process.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing bismuth ferrite photocatalyst
InactiveCN101890354ACause secondary pollutionFully contactedWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsSolventPhotocatalytic degradation
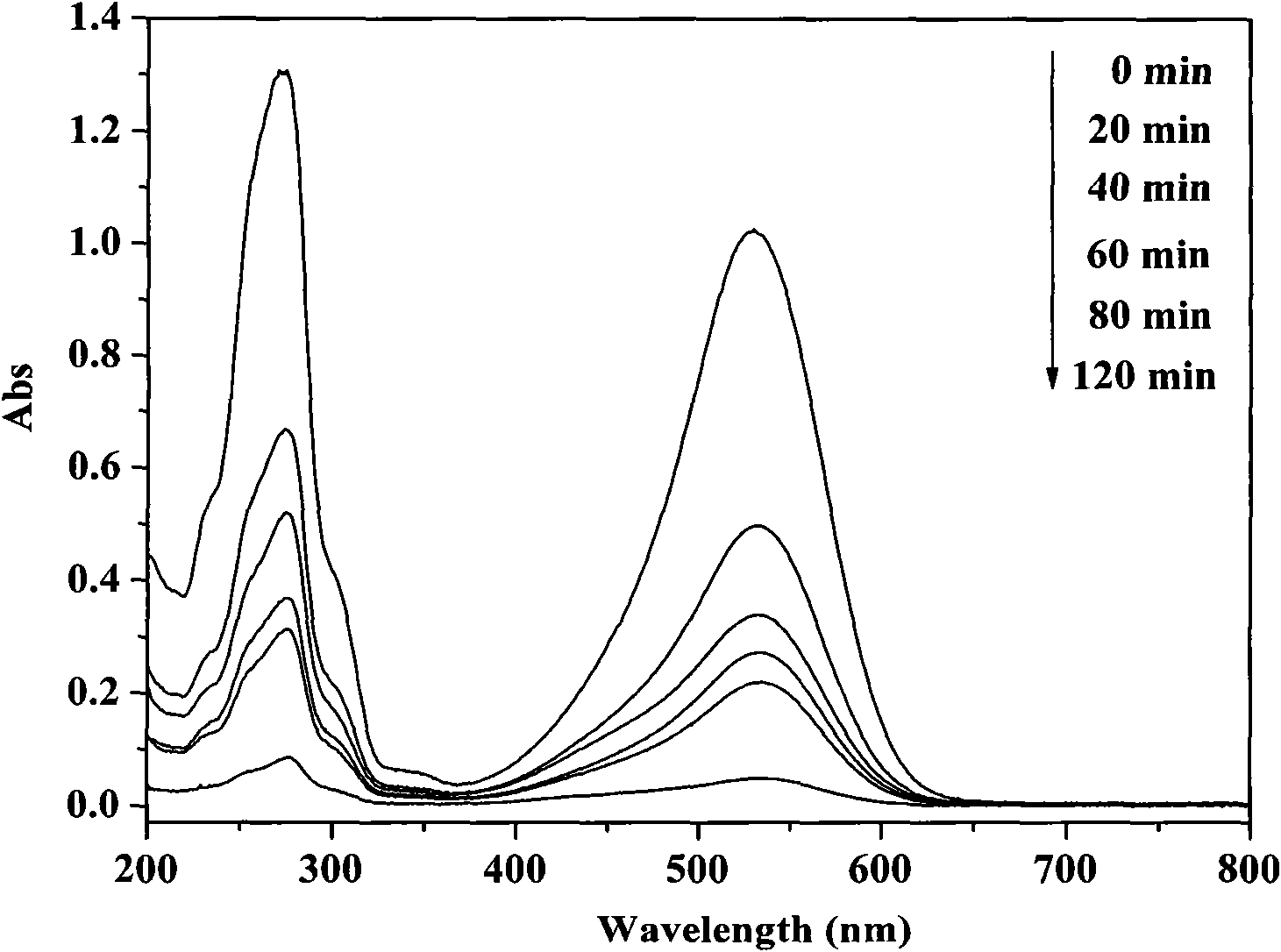
The invention belongs to the fields of environmental science and engineering, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a bismuth ferrite photocatalyst capable of efficiently degrading organic pollutants in water by utilizing photocatalysis technology. The photocatalyst bismuth ferrite is synthesized by a solvent method; and during synthesis, a molar ratio of bismuth nitrate to ferric nitrate is 12:1, a xenon lamp is taken as a light source, and the bismuth ferrite is fully mixed with neural red solutions with different concentrations to photo-catalyze and degrade the neutral red dye in aqueous solution. The invention provides a high-efficiency method for removing the neutral read dye from the water. The method can remove over 70 percent of the neutral red dye (the concentration is 10 to 30 milligrams / liter) from the water in 2 hours; moreover, the photocatalyst has the advantages of simple preparation process, large particle size and easy recycling; and the method has the advantages of easy operation, low cost, high efficiency, time conservation, and good industrial application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
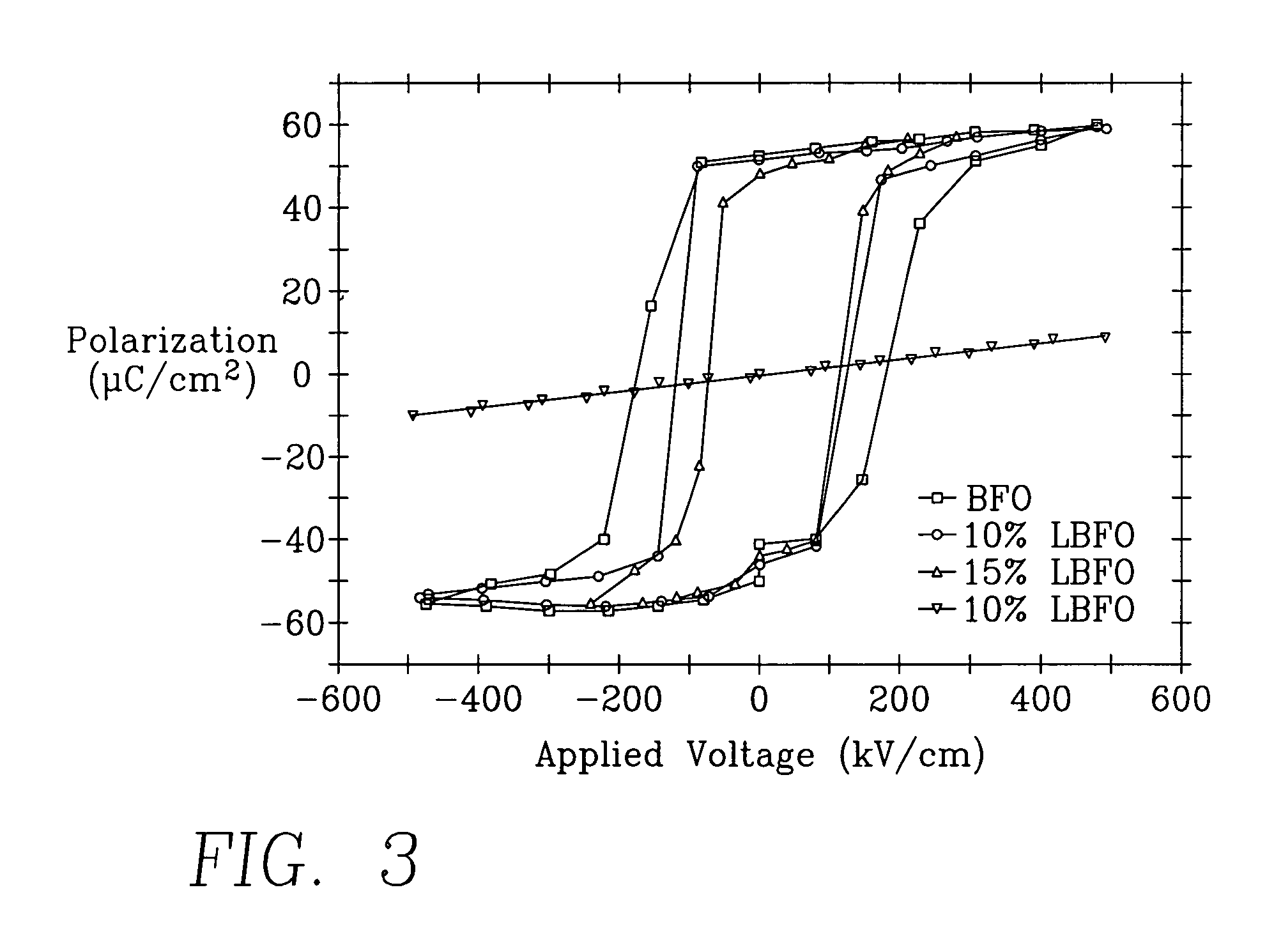
Rare earth/alkaline earth metal and transition metal doped bismuth ferrite nano multiferroic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101734725AImprove magnetic propertiesExcellent magnetic permittivityNanostructure manufactureIron compoundsCapacitanceSolvent
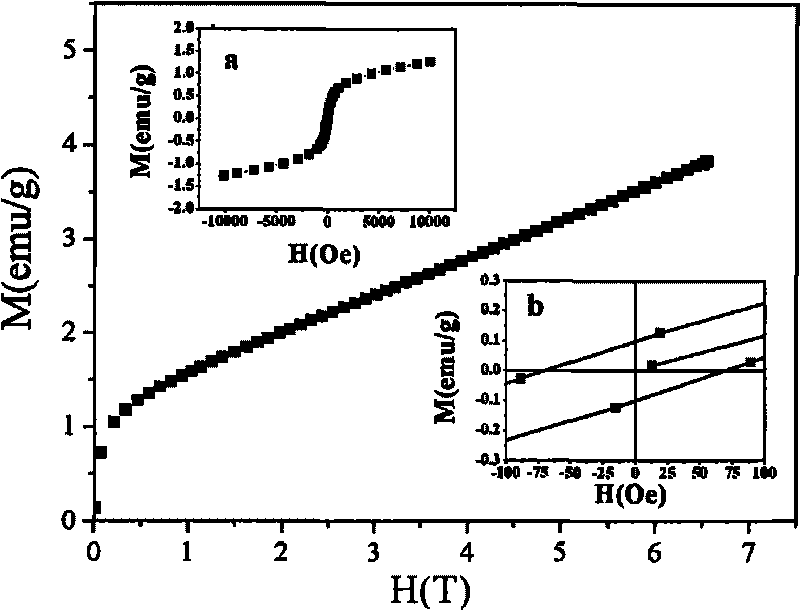
The invention discloses a rare earth / alkaline earth metal and transition metal doped bismuth ferrite nano multiferroic material, and the chemical formula is Bi1-xRxFe1-yMyO3, wherein R is rare earth metal or alkaline earth metal, M is transition metal, x is not less than 0 and not more than 0.30, and y is not less than 0 and not more than 0.02. The preparation method has the steps of taking ferric nitrate, bismuth nitrate, rare earth / alkaline earth metal oxide or nitrate and transition metal nitrate as raw materials, taking ethylene glycol as a solvent, or using a specific additive for matching, mechanically stirring, forming even ethylene glycol solution, then aging at room temperature, evaporating and drying the obtained solution at the temperature of 160-250 DEG C, and carrying out thermal treatment at lower temperature for obtaining rare earth / alkaline earth metal A-site doped, transition metal B-site doped and rare earth / alkaline earth metal A-site and transition metal B-site co-doped bismuth ferrite nanoparticles of 20-100nm. The prepared nano multiferroic material has stable crystal quality, thereby having extensive application prospects in the fields of information storage, magnetic sensors of spin electronic devices, capacitor-inductor integrated devices and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
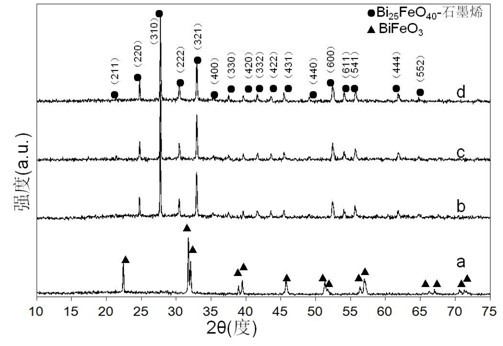
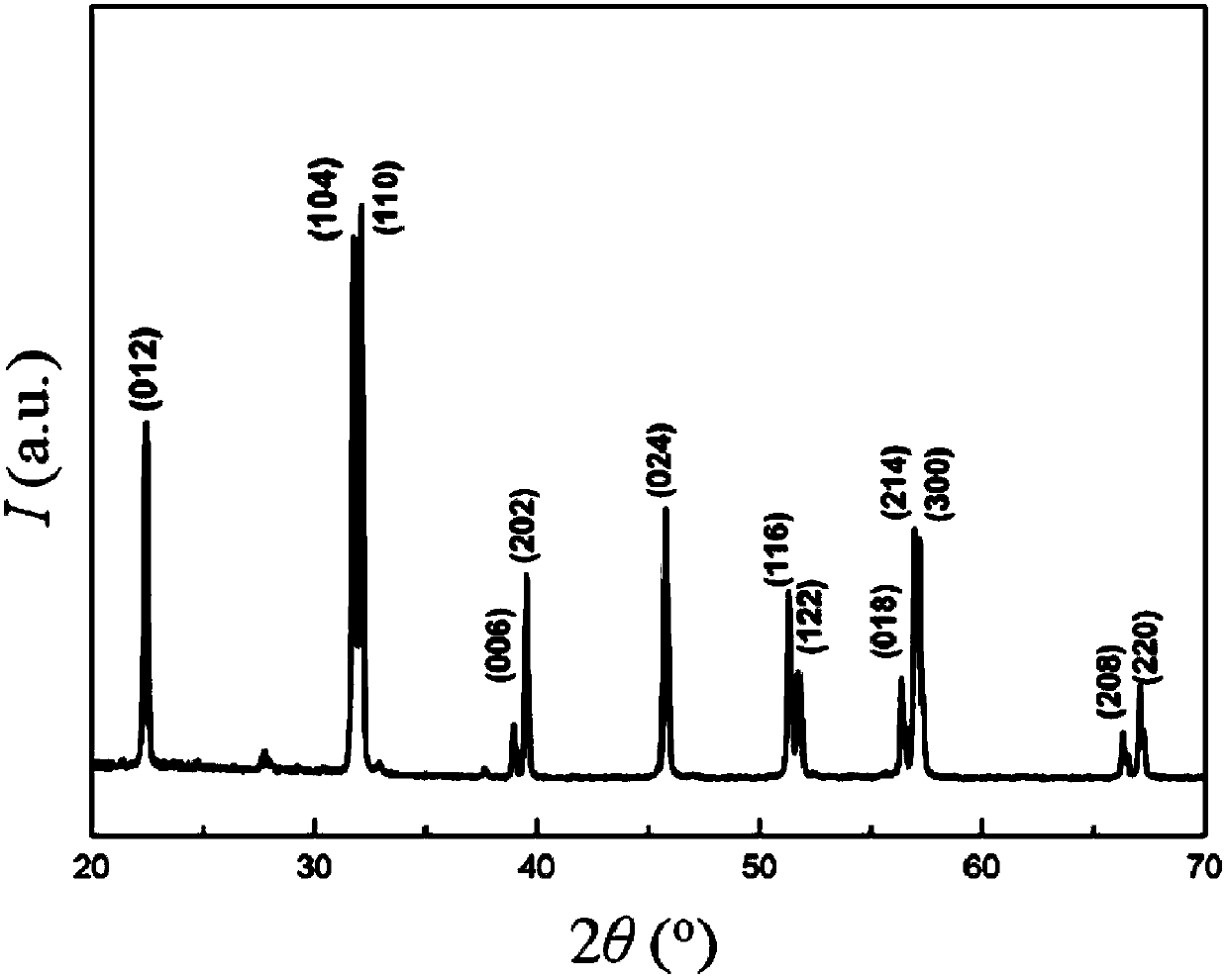
Bismuth ferrite-graphene compounding magnetism visible light catalyst, as well as preparation method and application of same
InactiveCN102626634AHigh catalytic activityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystMeth-
The invention discloses a bismuth ferrite-graphene compounding photochemical catalyst with visible light responds, and a preparation method of the bismuth ferrite-graphene compounding photochemical catalyst. The catalyst prepared by the method comprises the following components according to mass percentage: 60-95% of bismuth ferrite and 5-40% of graphene. The preparation method is characterized in that the reduction of graphite oxide and the compounding of the bismuth ferrite and the graphene are finished by one step, and the catalyst prepared by the method has relatively high magnetism and good visible light responds. When the catalyst prepared by the method is used for treating methylthionine chloride solution by using visible light catalysis, a relatively good degradation effect can be obtained. Therefore, the invention has significance in the development of the visible light catalyst, and the visible light catalyst has a good application prospect when being used for sewage treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bismuth ferrite-based leadless piezoelectric ceramic with high Curie temperature and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a bismuth ferrite-based leadless piezoelectric ceramic with high Curie temperature and a preparation method thereof. The general formula for the piezoelectric ceramic is (1-x-y)(BizM1-z)t(FeuM'1-u)O3-xBaTiO3-yBiMnO3, wherein, M is a trivalent metallic element with large ionic radius, M' is a trivalent metallic element with small ionic radius, and x, y, u, t and z represent mole content in a ceramic system and satisfy the following relations: 0<=x<=1.0, 0<=y<=0.1, 0<z<1, 0.85<t<1.2, 0<u<1 and x+y<1. The piezoelectric ceramic is prepared by a conventional ceramic preparation method through selection of proper technological parameters. The piezoelectric constant d33 of the ceramic can reach 140 pC / N, Curie temperature can reach 490 DEG C, and Kt is more than 0.50. The preparation method has the advantages of a simple and stable process, and obtained leadless piezoelectric ceramic has excellent performance and is suitable for being used under high temperature.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Bismuth ferrite nano fiber material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses bismuth ferrite nano fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the bismuth ferrite nano fiber comprises the following steps: 1) using bismuth nitrate or a hydrate thereof and iron nitrate or a hydrate thereof as raw materials, dissolving the two raw materials in a solvent, adding a complexing agent, stirring to obtain bismuth ferrite sol, then adding a polymer as a spinning aid in the bismuth ferrite sol, and stirring evenly to obtain a precursor solution; 2) performing electrostatic spinning of the precursor solution to obtain bismuth ferrite precursor fiber; and 3) performing heat treatment of the bismuth ferrite precursor fiber to remove the polymer to obtain the bismuth ferrite nano fiber. In the BiFeO3 (bismuth ferrite) nano fiber prepared by the preparation method, crystal grains of the fiber are arranged along the axial direction to form a bamboo-joint-like structure. The bismuth ferrite nano fiber has a narrow forbidden bandwidth (2.1-2.3 eV), a high utilization rate of visible light, a large specific surface area and few crystal boundaries and crystal faces, can effectively improve the separation of photogenerated carriers and reduce the recombination rate of photogenerated electrons and holes, has a high quantum efficiency, and shows more excellent photocatalytic properties than nanoparticles.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
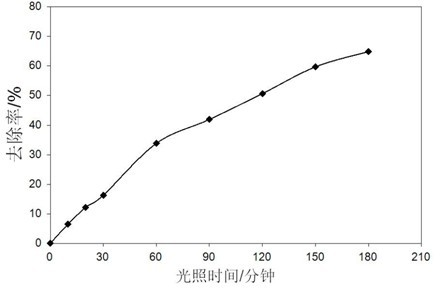
Method for degrading organic waste water by photo-assisted activation of potassium hydrogen persulfate through bismuth ferrite
InactiveCN104743633AEfficient degradationLarge specific surface areaWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPhoto assistedMethyl blue
The invention discloses a method for degrading organic waste water by photo-assisted activation of potassium hydrogen persulfate through bismuth ferrite, belonging to the technical field of waste water treatment. A perovskite structure BiFeO3 in the invention has a spherical morphology and is prepared by adding a certain amount of a surface active agent under hydrothermal conditions; the specific surface area is high; and the prepared BiFeO3 self can degrade organic pollutants by photocatalysis under the irradiation of visible light. According to the method disclosed by the invention, BiFeO3 is applied to degrading the organic pollutants by activating potassium hydrogen persulfate; the methyl orange degradation rate within 15 min is 94%; the methyl blue degradation rate within 40 min is 90%; the rhodamine degradation rate within 40 min is 65%; by means of combined use of BiFeO3 and potassium hydrogen persulfate, the organic pollutants are oxidized and degraded; the organic pollutants can be effectively degraded under better illumination conditions; the organic pollutants can also be effectively oxidized and degraded without light or under poor illumination conditions; and therefore, the method has good application prospect.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing bismuth ferrite powder by microwave hydrothermal method
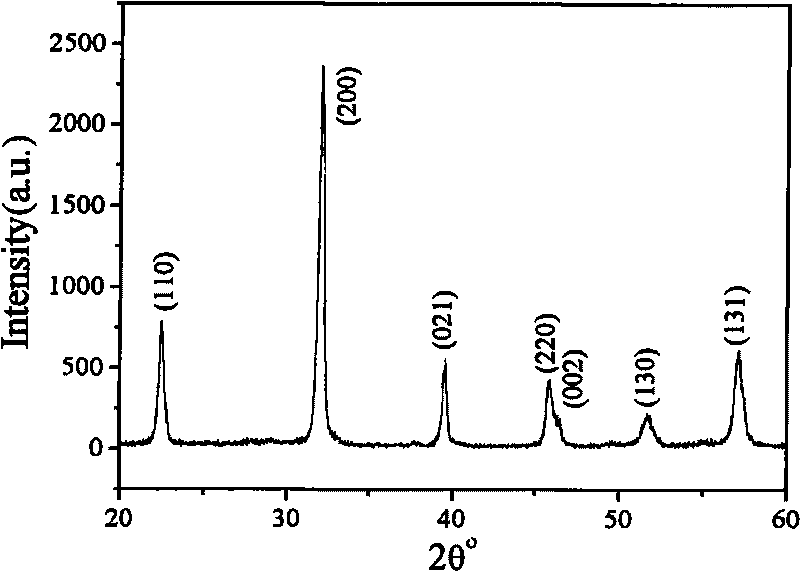
The invention discloses a method for preparing bismuth ferrite powder by microwave hydrothermal method, comprising: (1) dissolving FeCl3.6H2O and Bi(NO3)3.5H2O in proper amount of glycol to prepare into a parent salt solution; (2) dripping the parent salt solution into an aqueous ammonia solution with the concentration being 0.1-0.5mol / l and dripping speed being less than 2ml / min, and after finishing dripping, continuing to stir for 0.4-1h to obtain a deposit; (3) washing the deposit with de-ionized water repeatedly, ageing, and preparing a hydrothermal reaction precursor; and (4) adding the precursor solution into a microwave hydrothermal reaction kettle with the filling ratio being 60-75%, adding a mineralizer into the reaction kettle, placing the reaction kettle into a microwave assistant hydrothermal synthesizer to react for certain period, taking out a product in the reaction kettle, washing with de-ionized water to obtain a neutral product, washing the neutral product with absolute ethanol, and drying at room temperature to obtain the bismuth ferrite powder. The invention has the advantages of complete crystallization of BiFeO3, uniform grain fineness distribution, simple technical control, short technical cycle and energy saving.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
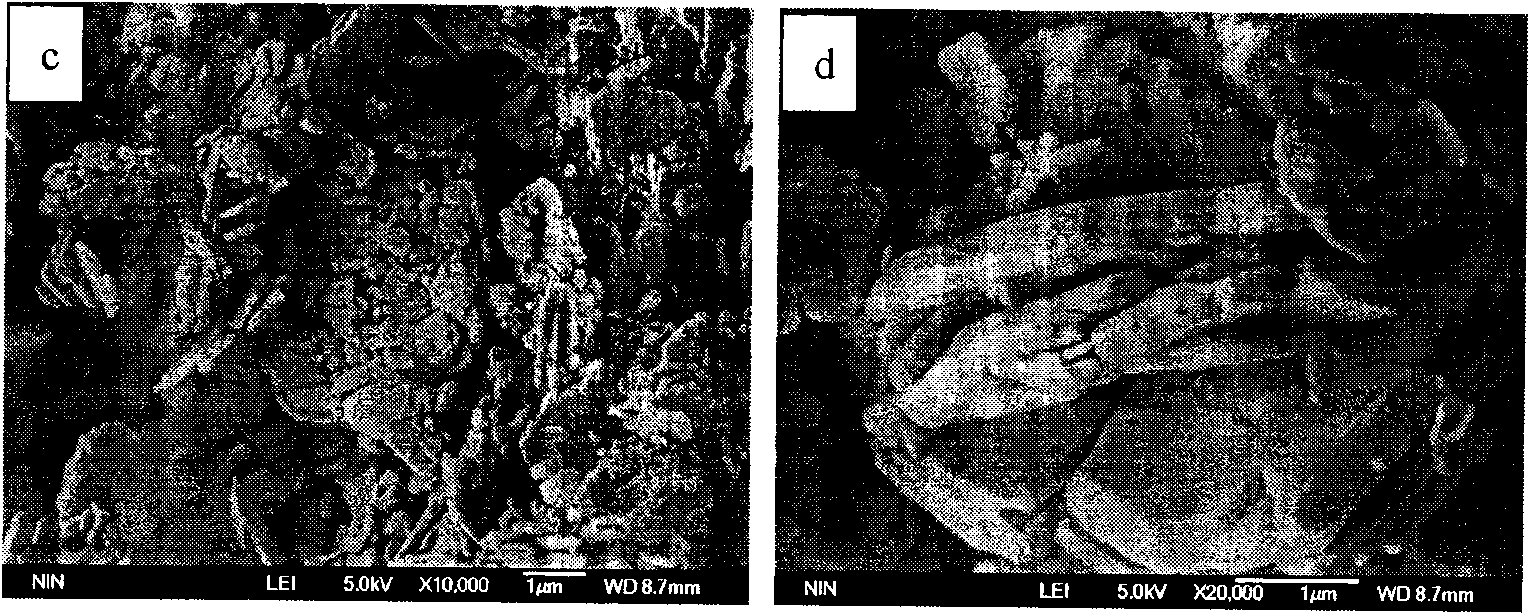
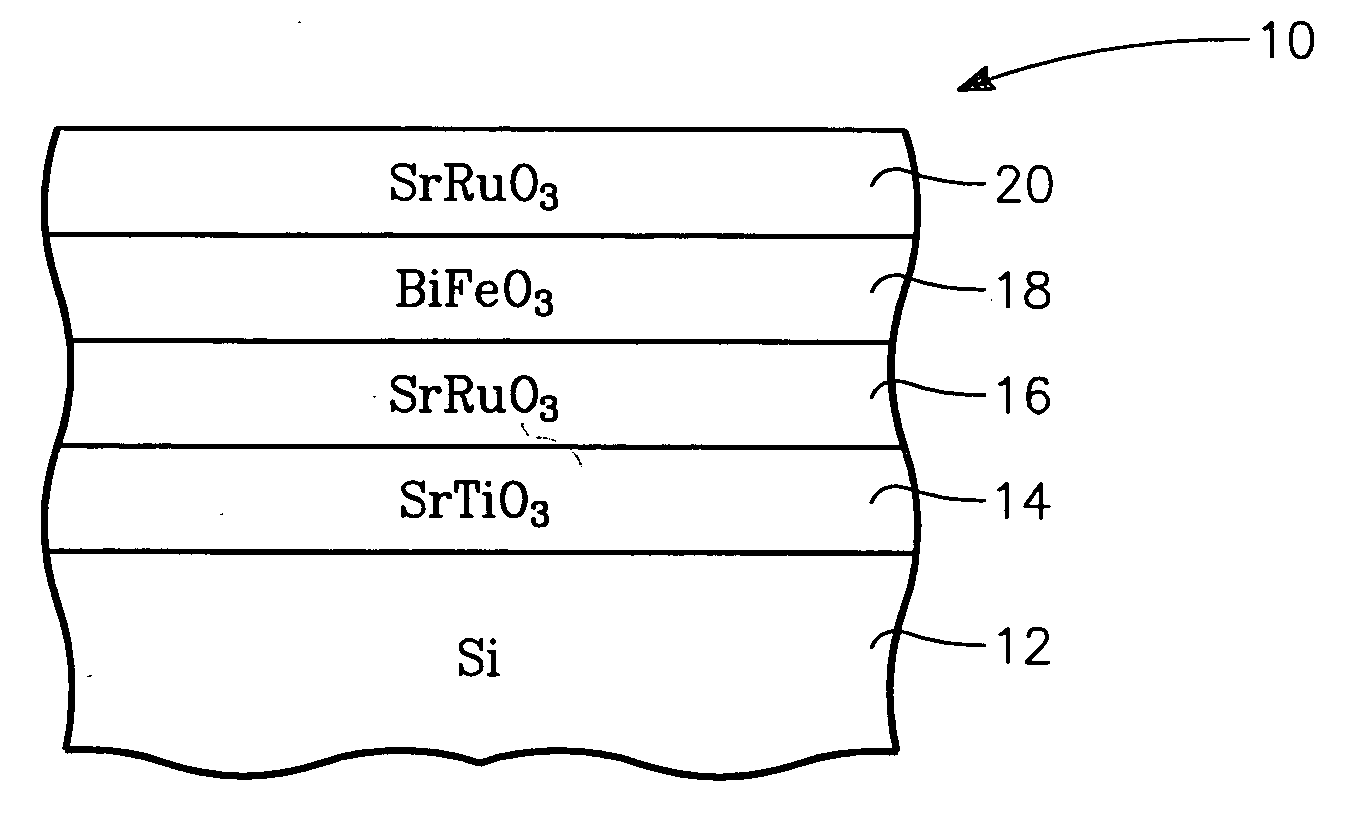
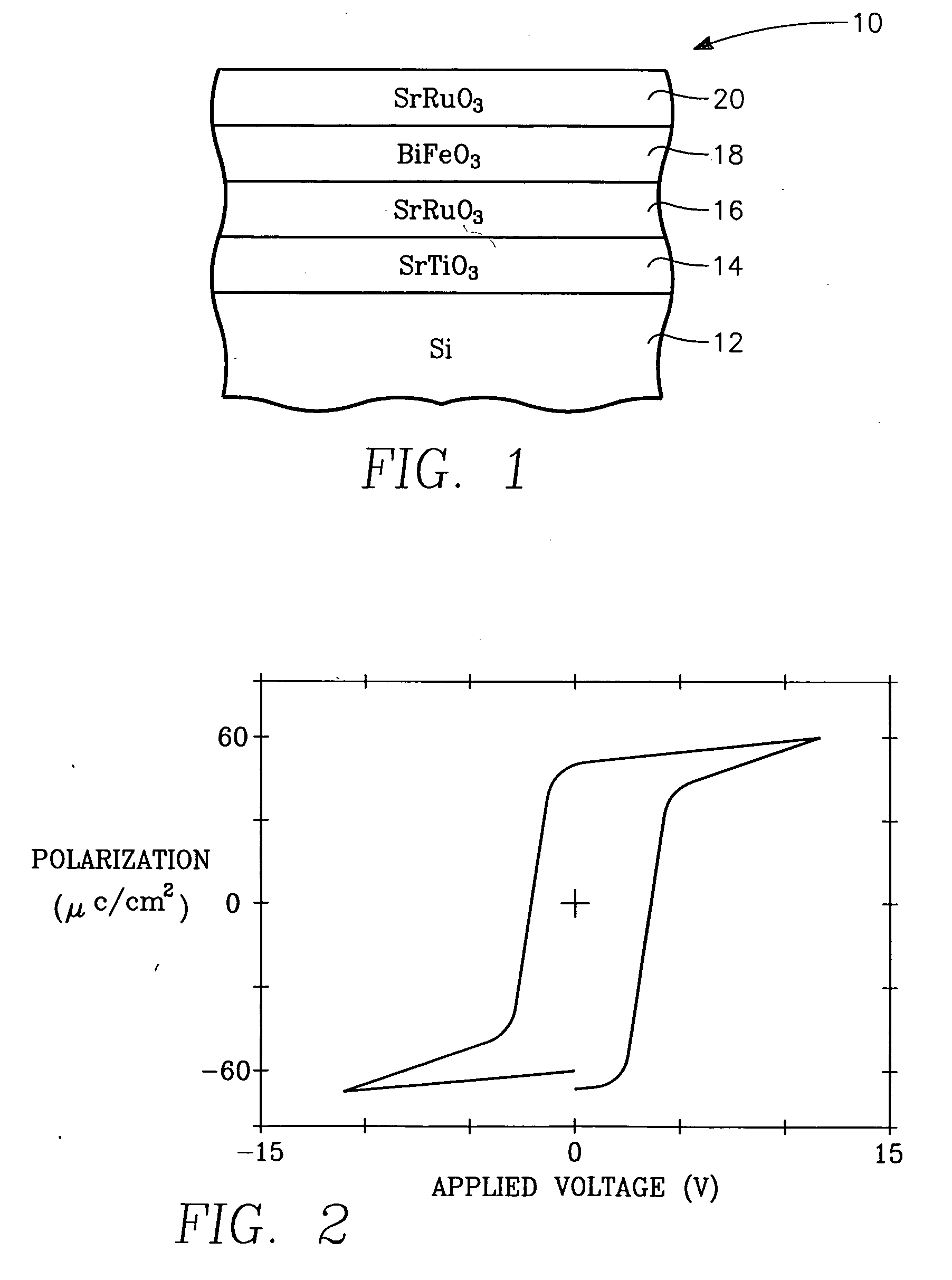
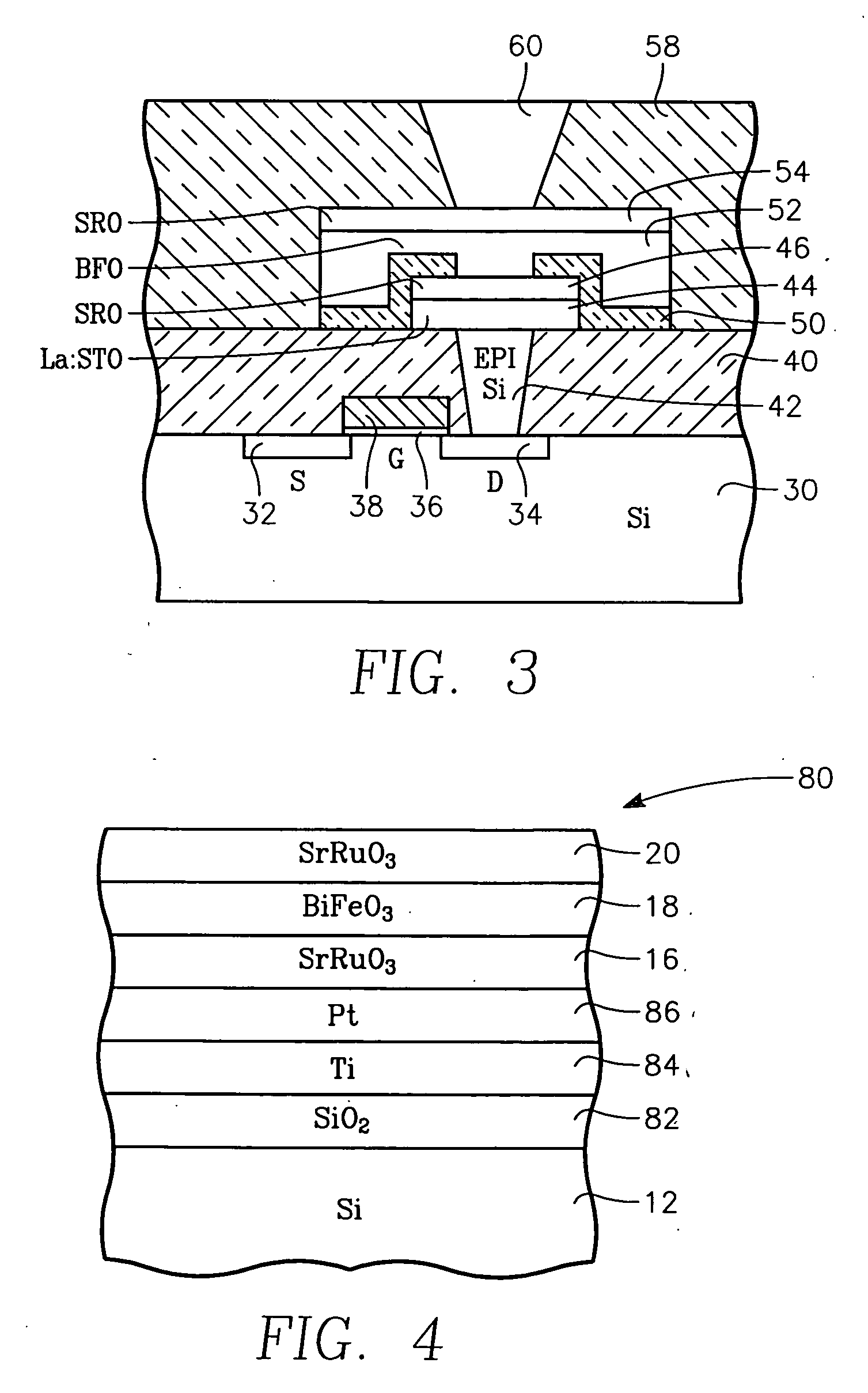
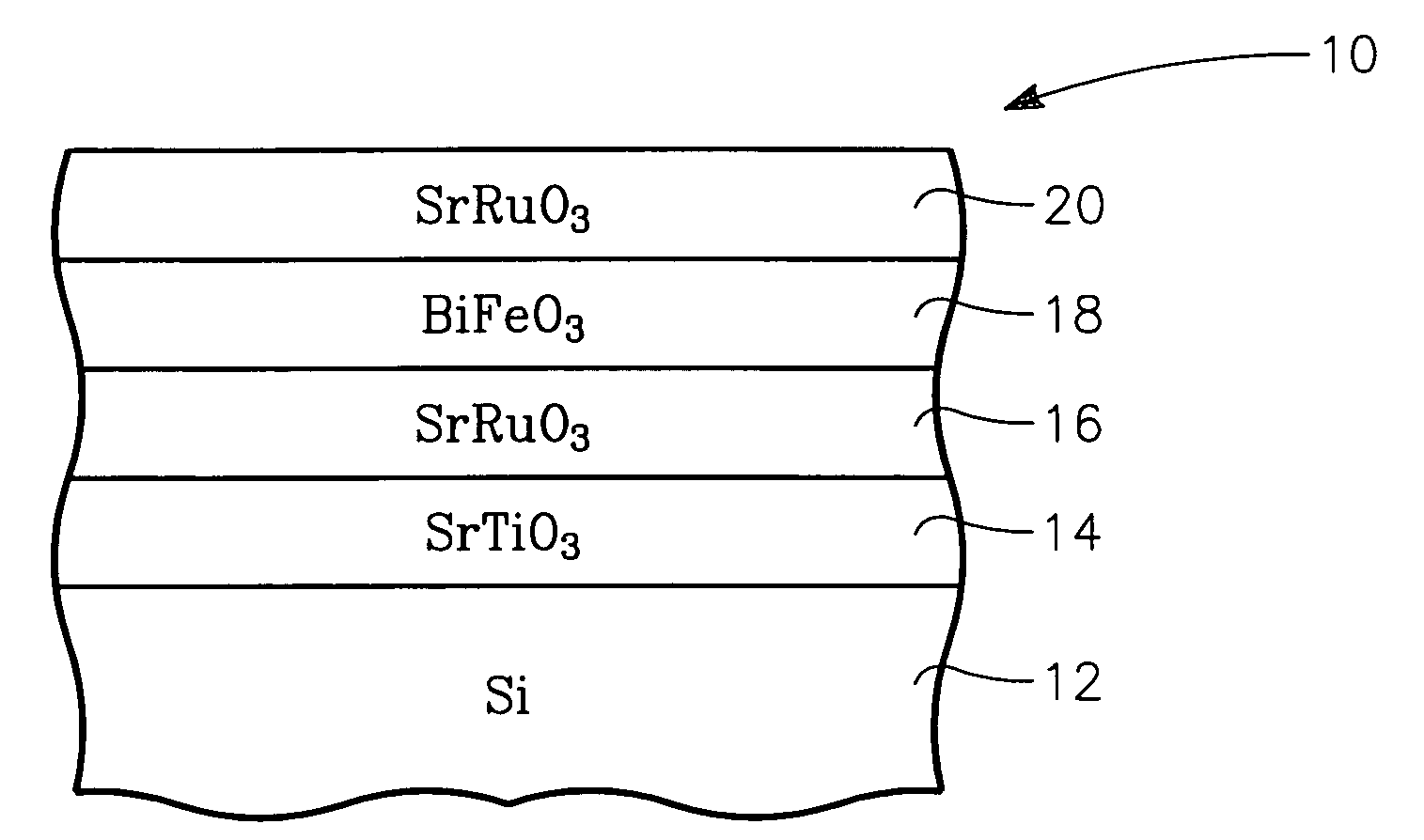
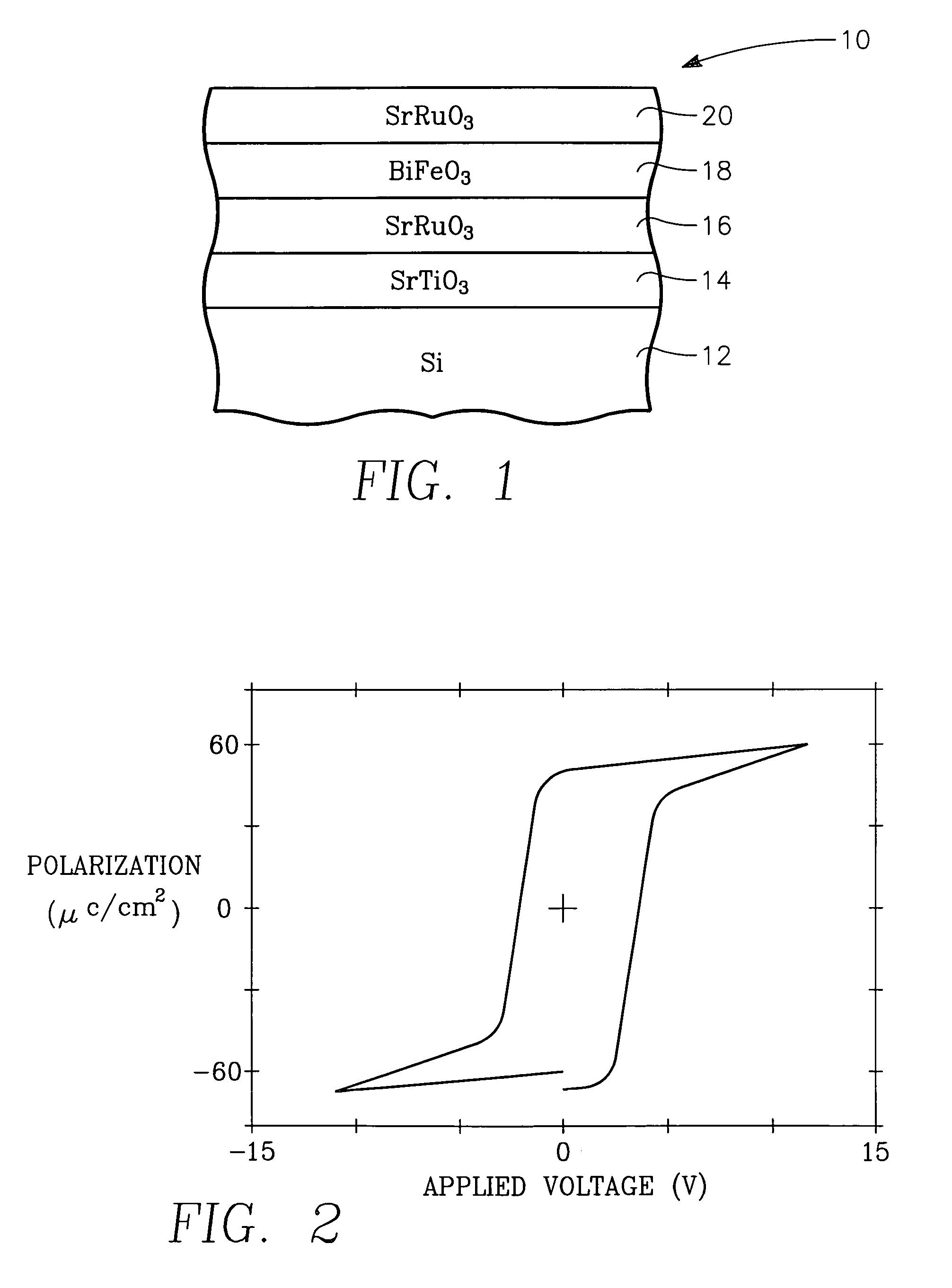
Oriented bismuth ferrite films grown on silicon and devices formed thereby
InactiveUS20070029592A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStrontium titanatePlatinum
A functional perovskite cell formed on a silicon substrate layer and including a functional layer of bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3 or BFO) sandwiched between two electrode layers. An intermediate template layer, for example, of strontium titanate allows the bismuth ferrite layer to be crystallographically aligned with the silicon substrate layer. Other barrier layers of platinum or an intermetallic alloy produce a polycrystalline BFO layer. The cell may be configured as a non-volatile memory cell or a MEMS structure respectively depending upon the ferroelectric and piezoelectric character of BFO. The films may be grown by MOCVD using a heated vaporizer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Multiferroic Nanoscale Thin Film Materials, Method of its Facile Syntheses and Magnetoelectric Coupling at Room Temperature
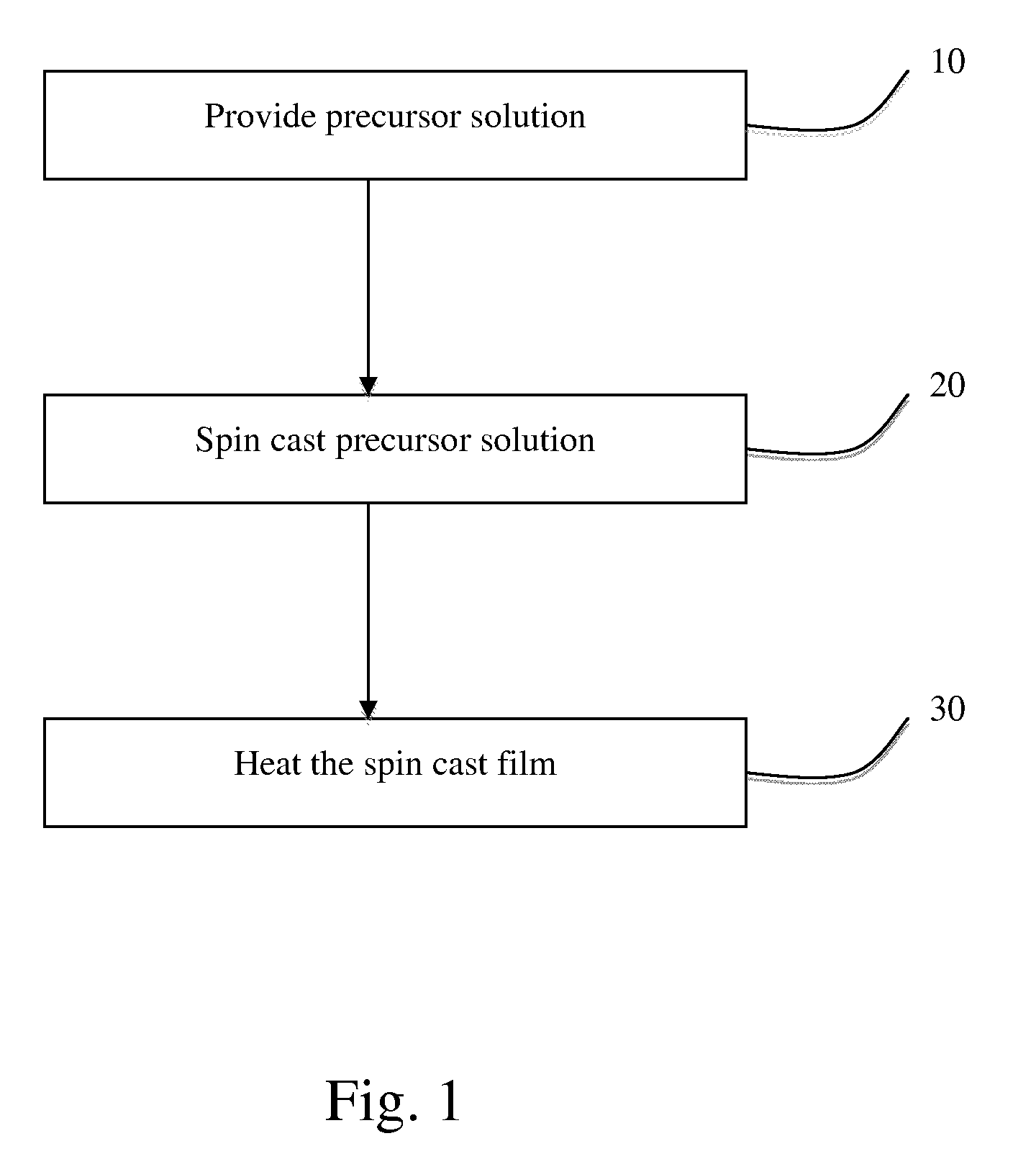
Methods of producing a multiferroic thin film material. The method includes the steps of providing a multiferroic precursor solution, subjecting the precursor solution to spin casting to produce a spin cast film, and heating the spin cast film. The precursor solution may include Bi(NO3)3.5H2O and Fe(NO3)3.9H2O in ethylene glycol to produce a bismuth ferrite film. Further, the thin film may be utilized in varied technological areas, including memory devices for information storage.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
Bismuth ferrite microsphere photocatalyst with hollow structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101791558ANo pollution in the processSimple preparation processMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsThermal ageingAlcohol
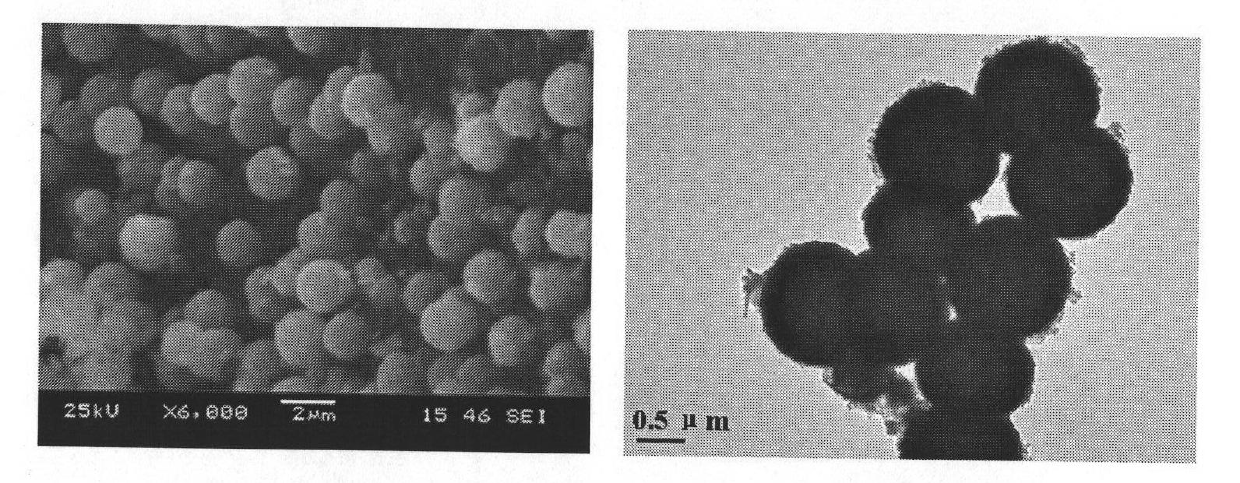
The invention belongs to a catalyst technology which relates to a bismuth ferrite microsphere photocatalyst with a hollow structure and a preparation method thereof. The defects of large grain diameter of a catalyst, small specific surface area, poor adsorption of the molecules of a pollutant and small photocatalytic activity exist in the prior art. The molecular formula of the bismuth ferrite microsphere photocatalyst with the hollow structure is BiFeO3, the grain diameter is 1.0 to 2.0mum, the thickness of the ball wall is 100 to 200nm, and the specific surface area is 7.2 to 28.1m2 / g. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving bismuth salt and ferric salt into a mixed alcohol solution of absolute ethyl alcohol and glycerol, adding citric acid and mixing evenly; dispersing by ultrasonic sound, putting into a stainless steel hydrothermal kettle and carrying out thermal ageing by a solvent; and drying an ageing product and calcining to prepare the bismuth ferrite microsphere photocatalyst with the hollow structure. The invention has the advantages that raw materials are cheap and are easy to obtain; the preparation process is simple; the bismuth ferrite microsphere photocatalyst has uniform grain diameter and large specific surface area; the photocatalytic activity is enhanced; and the catalyst can be repeatedly used.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing bismuth titanate-barium titanate powder by hydrothermal method
InactiveCN101913853AShort reaction timeReaction is easy to controlBarium titanateParticle-size distribution
The invention provides a method for preparing bismuth titanate-barium titanate powder by hydrothermal method. The method is characterized by belonging to the hydrothermal synthesis technique and the field of functional ceramics. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing KOH and deionized water into mineralizer solution of which the concentration is 4 to 10mol / L; blending Bi(NO3)3.5H2O, Fe(NO3)3.9H2O, BaCl2 and TiCl4, which serve as raw materials, according to the following chemical formula: xBiFeO3-(1-x)BaTiO3 (x is more than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 0.9), addinghydrochloric acid and the deionized water dropwise into the raw materials, and uniformly stirring to completely dissolve the raw materials; slowly adding the mixture into the KOH mineralizer solutiondropwise, and uniformly stirring to obtain fulvous precursor solution; and adding the precursor solution into a reactor, putting the reactor in a 200 DEG C oven for keeping the temperature for 6 to 36 hours, and naturally cooling and filtering to the reactor to obtain the reaction product, namely the bismuth titanate-barium titanate powder. The bismuth titanate-barium titanate powder solid solution powder prepared by the invention has the advantages of good crystallization, uniform grain distribution, simple process flow, short reaction time and energy conservation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Bulk effect solar cell material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102176472AUniform and dense surfaceHigh crystallinityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSolar cellMetal electrodes
The invention provides a bulk effect solar cell material which comprise a metal electrode, BiFeO3 ferroelectrics and a LaNiO3 / Si substrate, wherein the BiFeO3 ferroelectrics grows vertical to the direction of the LaNiO3 / Si substrate. The invention also provides a preparation method of the bulk effect solar cell material. The method comprises the following steps of: with BiFeO3 as structural material, preparing pure phase BiFeO3 film by using a sol-gel method, spin-coating the obtained BiFeO3 film on the LaNiO3 / Si substrate and carrying out stepped annealing at a high temperature, and finally sputtering electrodes to the BiFeO3 film. The BiFeO3 film disclosed by the invention has uniform and dense surface, good crystalline properties and no impurity phase, and can test photovoltaic effect by using a metal electrode-ferroelectric-buffer layer substrate sandwich structure. The test structure is simple and clear and larger open-circuit voltage can be obtained.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Bismuth ferrite-graphene nanometer composite material for the filed of photocatalysis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102941103AIncrease profitStrong absorption capacityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNano compositesGraphene nanocomposites
The invention discloses a bismuth ferrite-graphene nanometer composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is composed of graphene and BiFeO3 nanoparticles coated on the surface of graphene. The BiFeO3 nanoparticles have a diameter of 100-500nm, and the graphene has a diameter of 5-10 mum and thickness of 2-15nm. The preparation method is as follows: first, preparing BiFeO3 precursor nanoparticles by a co-precipitation method; and then mixing the nanoparticles with the graphene for a hydrothermal reaction, so as to prepare the bismuth ferrite-graphene composite material. The bismuth ferrite-graphite composite material provided by the invention has band gap of 1.78-2.15eV, strong visible light absorption, and large specific surface area, and can effectively improve separation of photo-generated carriers, reduce recombination rate of the carriers, and show photocatalytic performance more excellent than that of nanoparticles. Experiments show that the nanometer composite material can degrade more than 80% of target degradation product in 2 h, so as to demonstrate excellent visible photocatalytic activity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
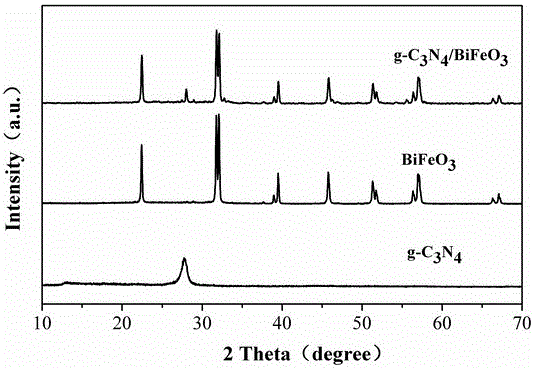
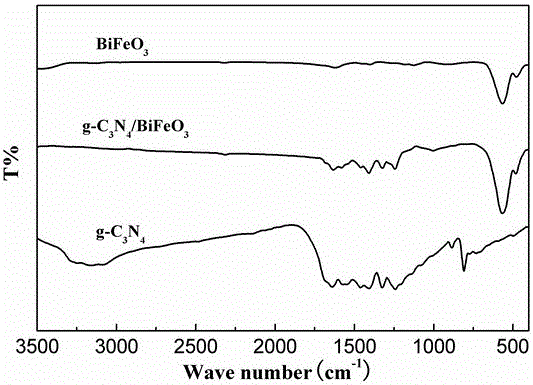
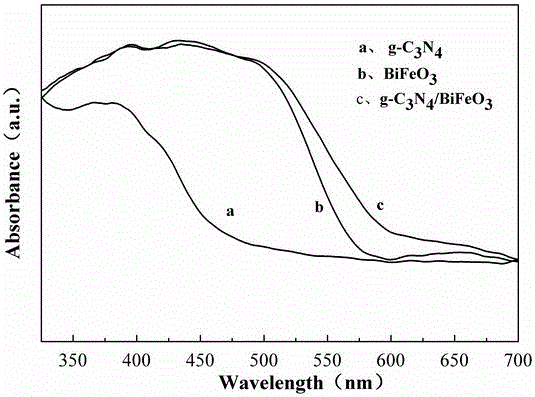
Preparation and application of composite photocatalyst g-C3N4-BiFeO3 for efficiently removing persistent organic pollutants
ActiveCN105056981AHigh specific surface areaEasy to separatePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPersistent organic pollutantSewage
The invention discloses preparation and an application of a composite photocatalyst g-C3N4-BiFeO3 for efficiently removing persistent organic pollutants. The method adopts a sol-gel method for synthesis, and the g-C3N4-BiFeO3 composite photocatalyst is synthesized by one step with the sol-gel method. A xenon lamp is taken as a light source, BPA which is the persistent organic pollutant in the environment is taken as a photodegradation model, and a composite material and a BPA solution are mixed sufficiently for photocatalytic degradation and simulation of the BPA persistent organic pollutant in the water environment. The invention provides a method for efficiently removing the BPA in the water environment, more than 90% of the BPA in the water environment is removed within 2 hours with the method, the concentration is 10 mg / L, the performance is stable, the g-C3N4-BiFeO3 composite photocatalyst is synthesized successfully by one step for the first time, and the preparation and the application has great significance and development prospects in sewage treatment.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
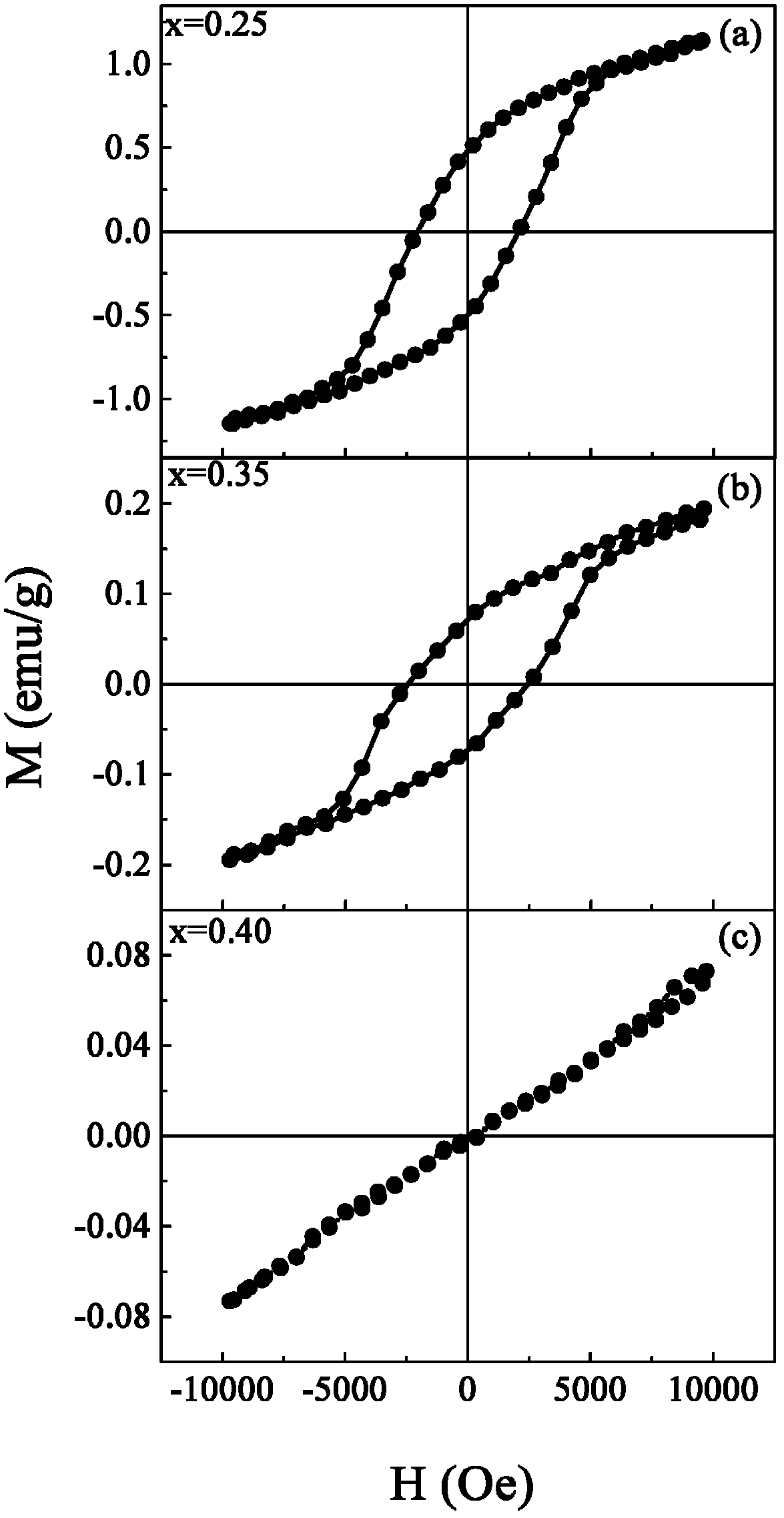
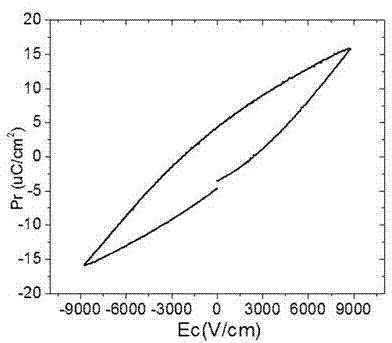
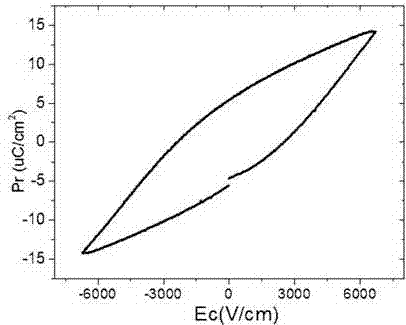
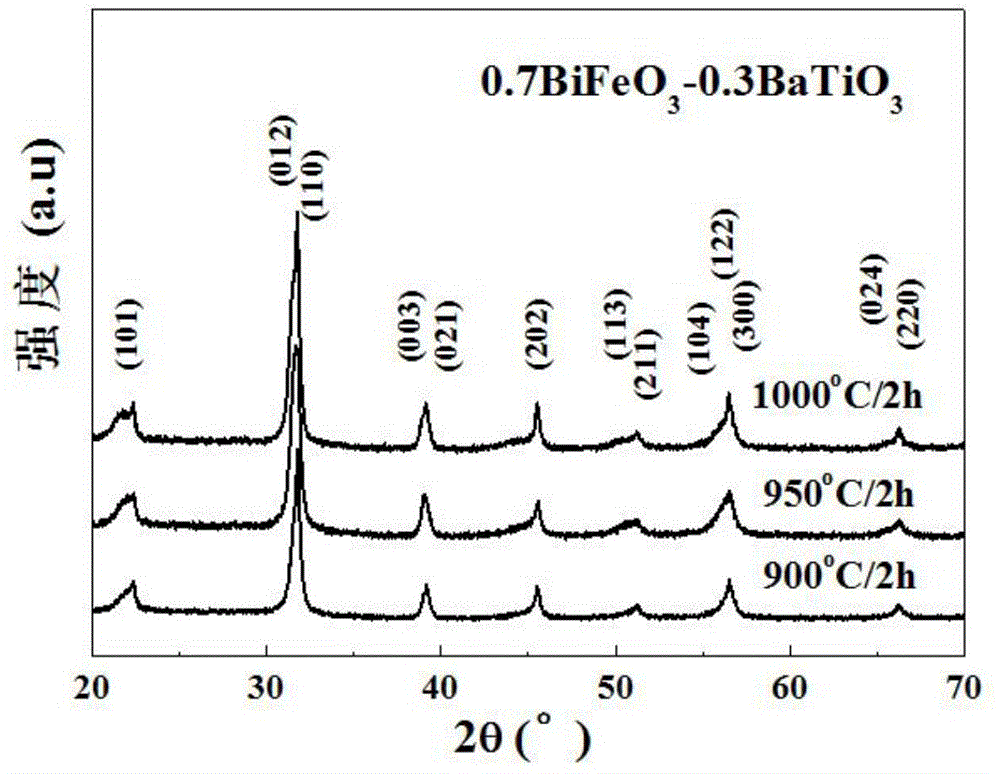
Preparation method for high resistivity bismuth ferric-barium titanate solid solution magnetoelectricity ceramic material
The present invention discloses a preparation method for a high resistivity bismuth ferric-barium titanate solid solution magnetoelectricity ceramic material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) based on a general formula of a ceramic material, weighing raw materials according to a stoichiometric ratio, placing the raw materials in a ball mill to carry out wet milling and mixing, and drying; 2) placing the mixed powder in a box type high temperature electric furnace to carry out pre-synthesis; 3) carrying out coarse crushing, wet milling, and fine crushing for the pre-synthesized material, then drying, carrying out mixing and pelletizing for the dried powder and a binder, then carrying out pressing to prepare a thin disc biscuit; 4) carrying out heat preservation and binder removing for the biscuit; 5) carrying out sintering and heat preservation for the binder-removed biscuit to obtain the bismuth ferric-barium titanate solid solution magnetoelectricity ceramic material. According to the present invention, the bismuth ferric-barium titanate solid solution magnetoelectricity ceramic material of the present invention has characteristics of a complete perovskite structure and excellent electrical insulation property, the Curie temperature of the ferroelectricity material is more than 350 DEG C, the Curie temperature of the ferromagnetic material (the anti-ferromagnetic material) is more than 350 DEG C, the room temperature remanent polarization Pr is more than 18 muC / cm<2>, the remanent magnetization Mr is 0.49 emu / g, such that the multiferroic material with the high magnetoelectric coupling coefficient has the application and development value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
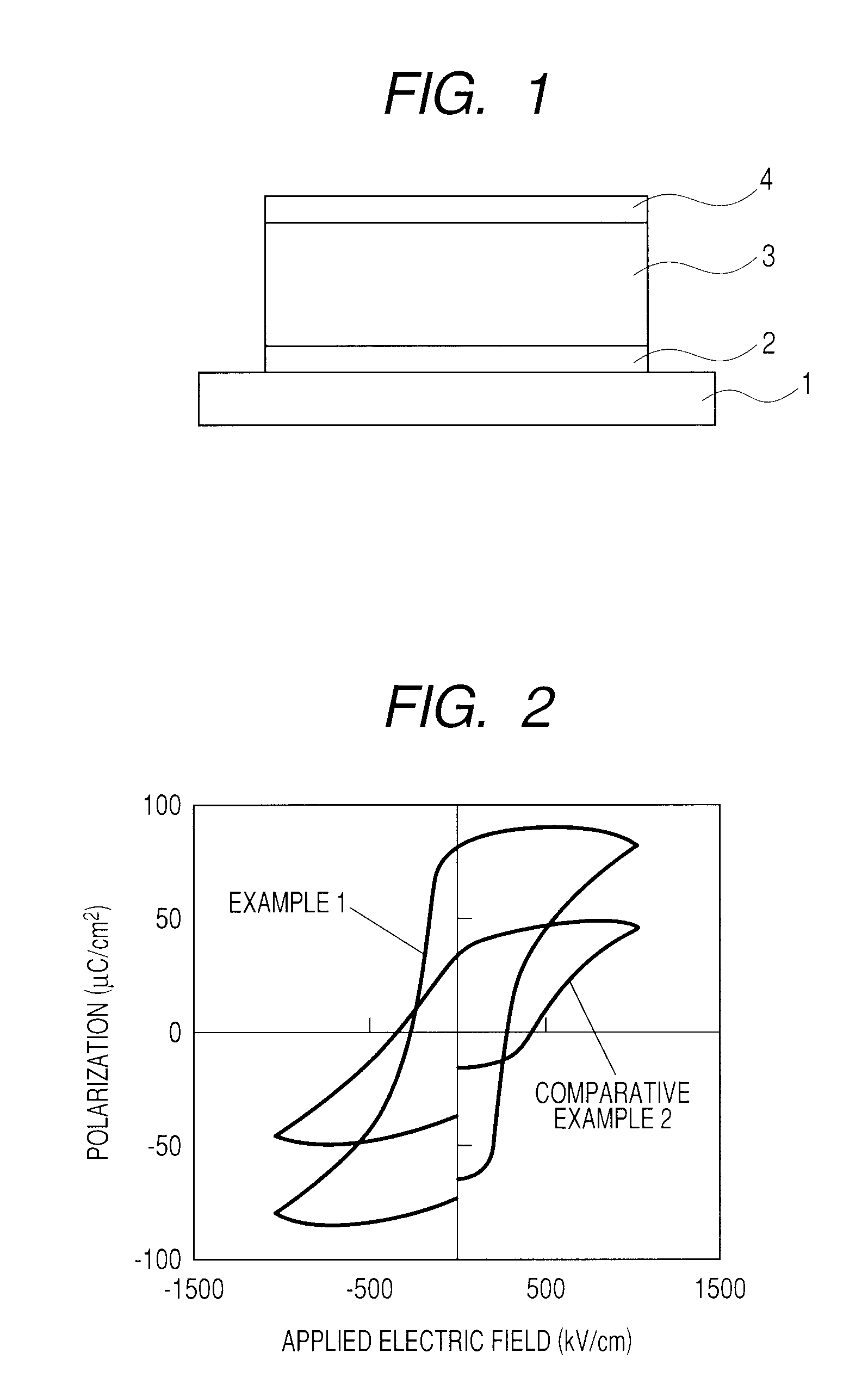
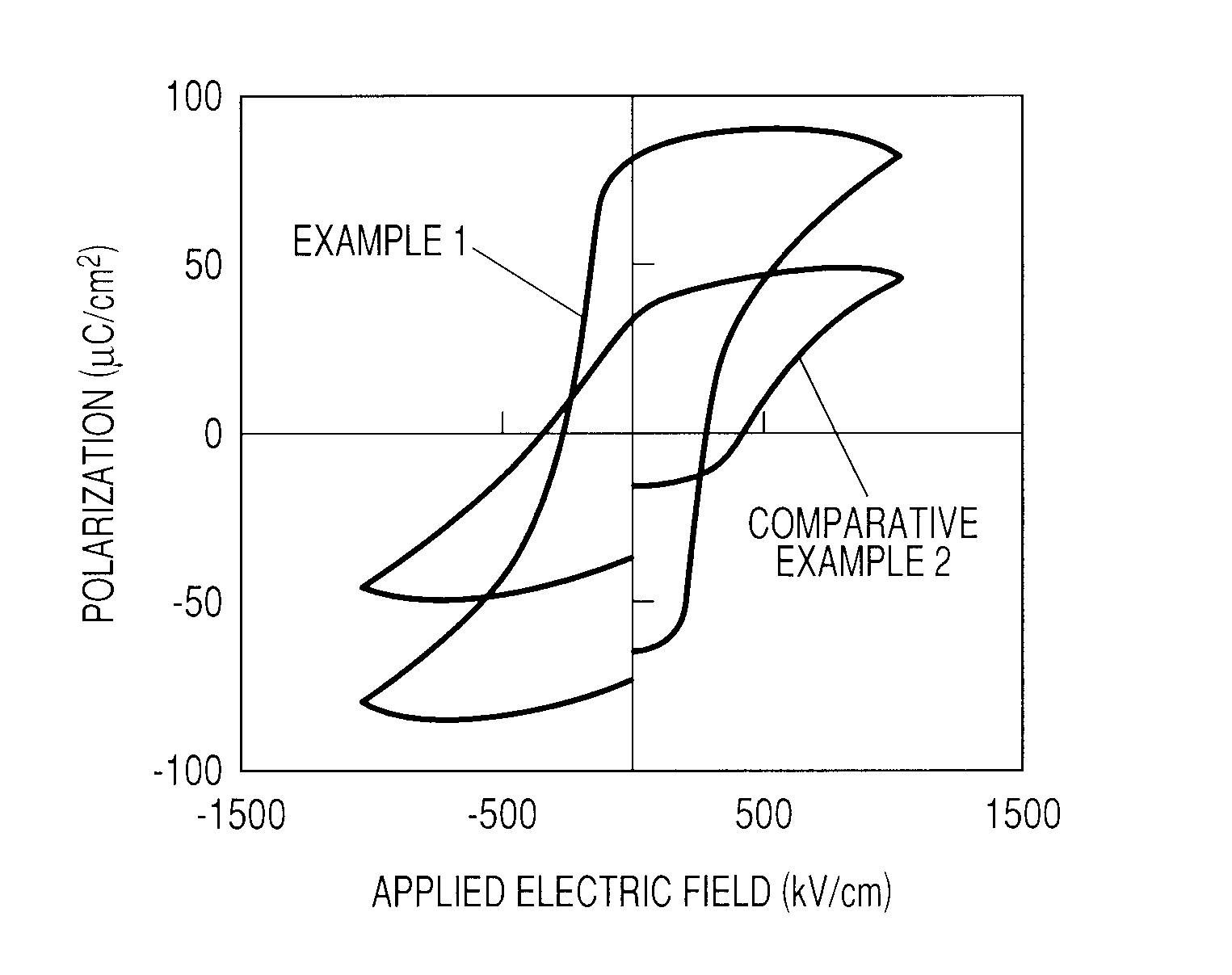
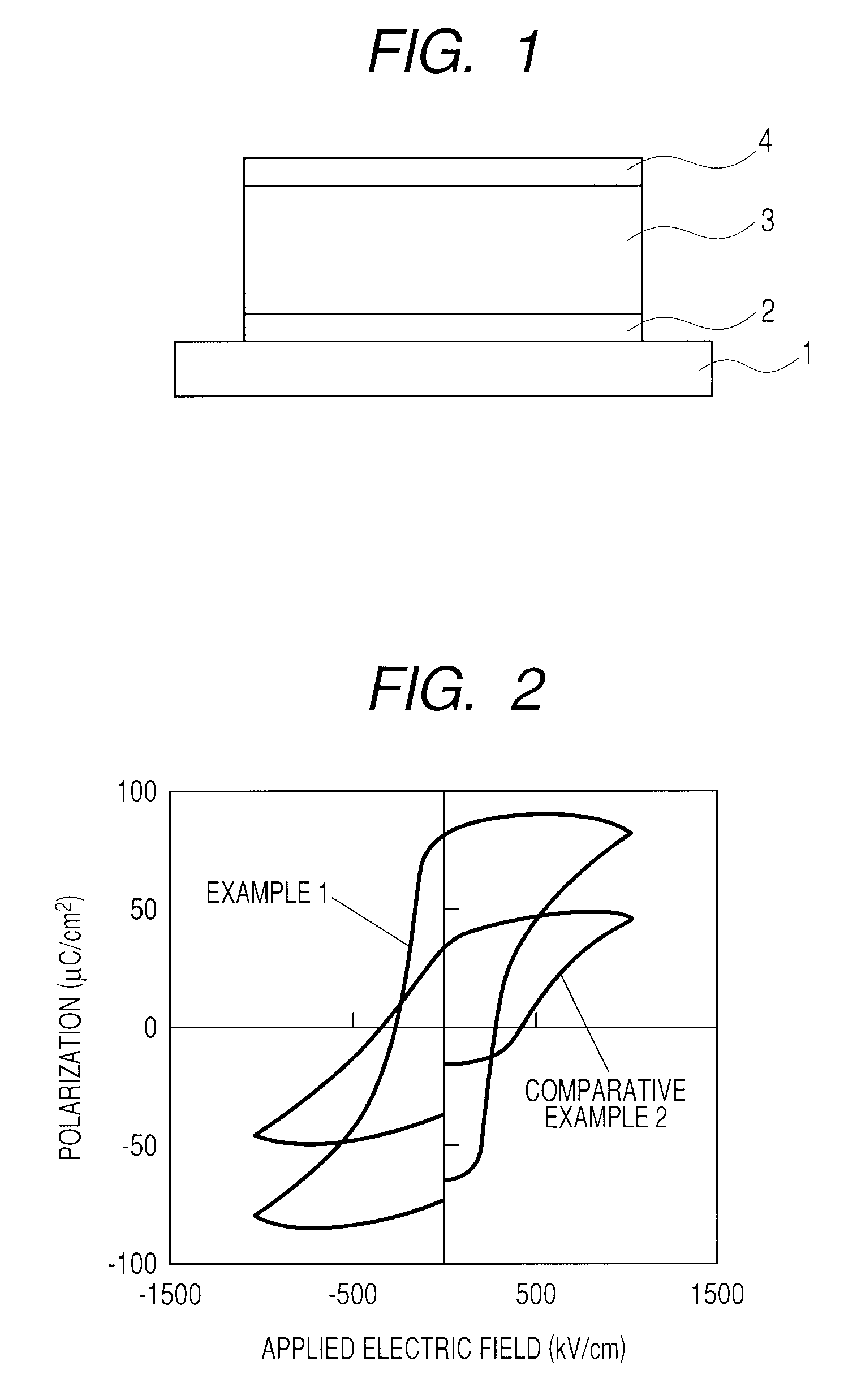
Ferroelectric material, method of producing ferroelectric material, and ferroelectric device
ActiveUS20100208412A1Improve ferroelectric propertiesImprove insulation performanceMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsManganeseCrystal structure
Provided are a ferroelectric material having good ferroelectricity and good insulation property, and a ferroelectric device using the ferroelectric material. In the present invention, the ferroelectric material includes a metal oxide having a perovskite-type crystal structure, in which: the metal oxide contains bismuth ferrite whose iron is substituted by manganese, and at least one of a copper oxide and a nickel oxide; the bismuth ferrite is substituted by manganese at a substitution ratio of 0.5 at. % or more to 20 at. % or less with respect to a total amount of iron and manganese; and at least one of the copper oxide and the nickel oxide is added in an amount of 0.5 mol % or more to 20 mol % or less with respect to the bismuth ferrite whose iron is substituted by manganese.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Bismuth ferric/bismuth titanate laminated construction electric capacity and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN101136404AMaximum polarizationGood anti-fatigue propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceFerroelectric capacitor
This invention relates to a BFO / BXT laminated capacitor and its preparing method, in which, the capacitor includes: a substrate made of silicon and orderly combined with an oxidation layer, a lower electrode metal layer, a BFO film and an upper metal layer, in which, a BXT induction film is set between the lower electrode metal layer and the BFO film. The method includes: preparation of sol of RFO and BXT precursors and preparation of the capacitor of its laminated structure and the ferroelectric capacitor prepared with this method includes excellent property of anti-fatigue, high residual polarized intensity, low operational voltage and better dielectric property.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing bismuth ferrite material by two-step solid-phase reaction
InactiveCN102010012ASmall specific surface areaUniform particlesIron compoundsSolid reactionRoom temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing a bismuth ferrite material by a two-step solid-phase reaction, in particular to a method for preparing uniform bismuth ferrite particles at a relatively low temperature. The method comprises the following steps of: performing a solid-phase reaction on raw materials at room temperature so as to obtain a reactant with a large specific surface area, high reaction activity and small particle size; and heating the reactant at a relatively low temperature so as to obtain a bismuth ferrite product. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that: the method has relatively low synthesis temperature, simple process and high efficiency, is low in cost, is easy to control and expand, and the like. The bismuth ferrite product obtained by the method has high purity, small particle size and uniform particles.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
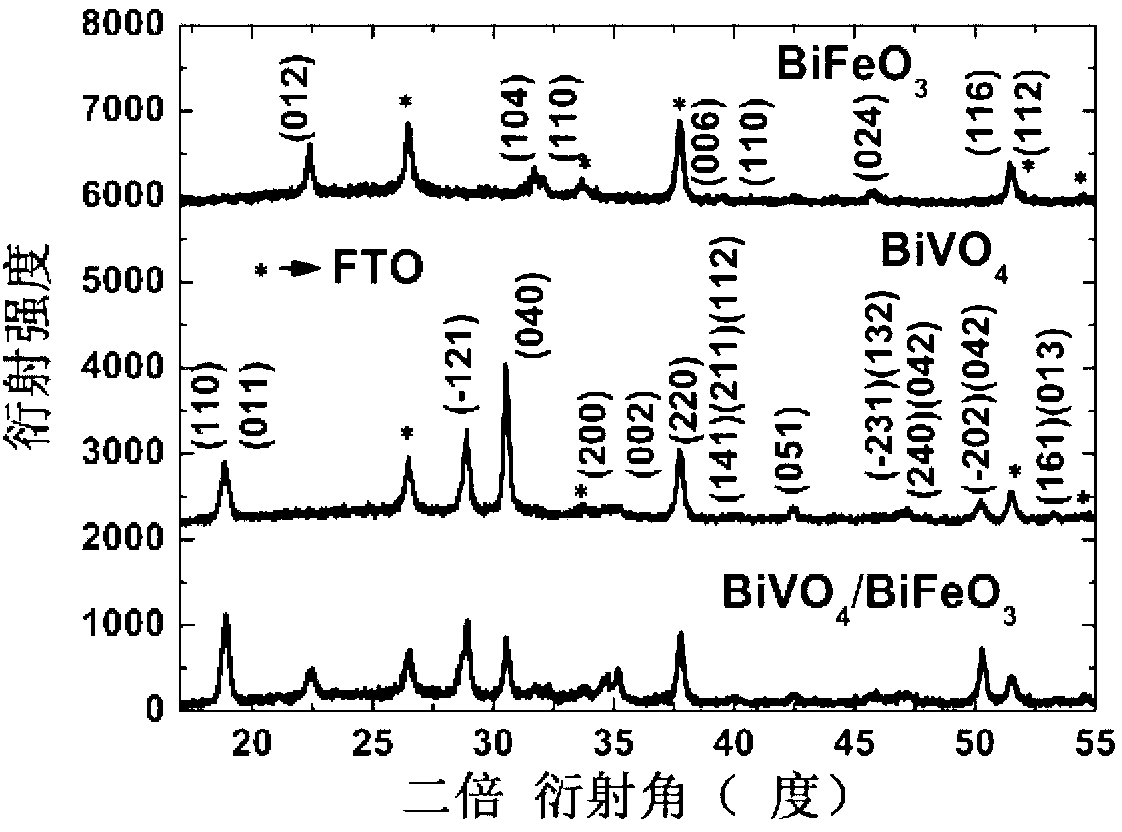
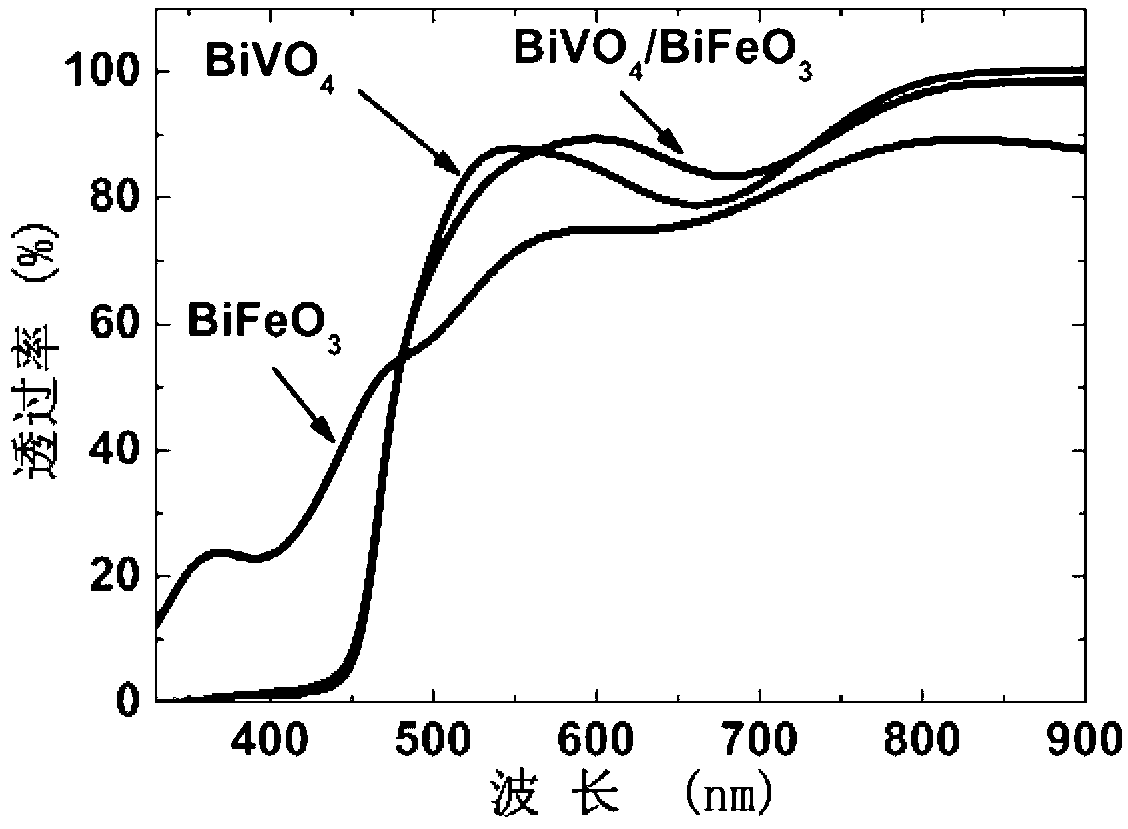
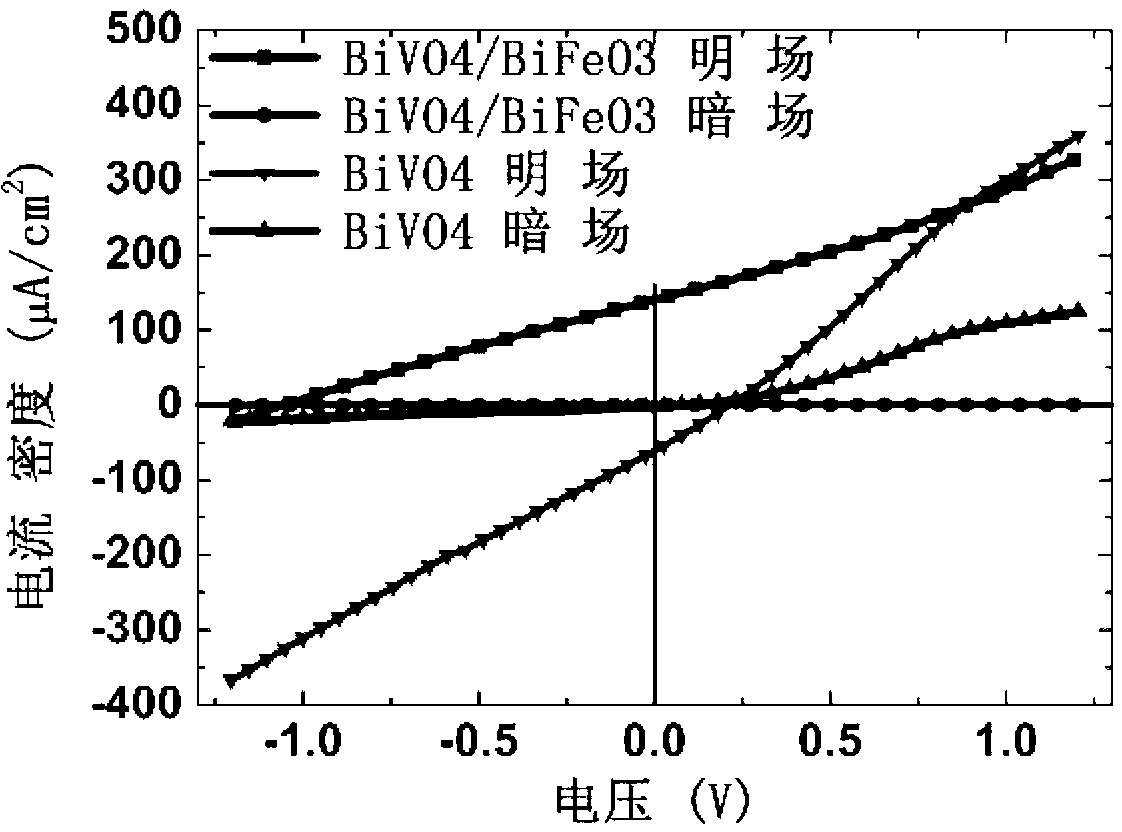
Method for preparing bismuth vanadate/bismuth ferrite heterojunction film solar cells
InactiveCN103078013ANo impurityReduce manufacturing costRenewable energy productsSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionBismuth vanadate
The invention relates to a method for preparing bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction film solar cells on a glass substrate. The method comprises the following steps: selecting FTO (Fluorinedoped Tin Oxide) conductive glass as a base, preparing a perovskite-structure bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction film with a chemical solution deposition method, and then preparing a top electrode on the film with a physical sputtering method to obtain the solar cells. The photovoltaic effect of the bismuth vanadate film can be increased and is reversed by utilizing an ultra-thin bismuth ferrite layer. The method can prepare the bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction film with high consistency and good repeatability on the glass substrate with a low cost. The prepared heterojunction film has good photovoltaic properties, the diode direction of the heterojunction film is opposite to the diode direction of a pure bismuth vanadate film, and ultra-thin bismuth ferrite ferroelectric films and similar bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction films have a wide application prospect in the fields of solar cells and photoelectric devices due to the good properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Ferroelectric material, method of producing ferroelectric material, and ferroelectric device
ActiveUS8216858B2Improve ferroelectric propertiesImprove insulation performanceMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesCrystal structureManganese
Provided are a ferroelectric material having good ferroelectricity and good insulation property, and a ferroelectric device using the ferroelectric material. In the present invention, the ferroelectric material includes a metal oxide having a perovskite-type crystal structure, in which: the metal oxide contains bismuth ferrite whose iron is substituted by manganese, and at least one of a copper oxide and a nickel oxide; the bismuth ferrite is substituted by manganese at a substitution ratio of 0.5 at. % or more to 20 at. % or less with respect to a total amount of iron and manganese; and at least one of the copper oxide and the nickel oxide is added in an amount of 0.5 mol % or more to 20 mol % or less with respect to the bismuth ferrite whose iron is substituted by manganese.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Bismuth ferrite base film layer stacked structure capacitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102222672AGood lattice matchingImprove insulation performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBarium strontium titanateLanthanide
The invention discloses a bismuth ferrite base film layer stacked structure capacitor and a preparation method thereof, wherein the capacitor comprises a bottom electrode, a substrate, a buffer layer, a ferroelectric film layer and a metal point electrode in sequence from the bottom to top; the buffer layer is a manganese-doped barium strontium titanate film, the chemical formula is Ba0.6Sr0.4Ti(1-x)MnxO3, x is the mole equivalent of element manganese, and x is equal to 0.005-0.05; and the ferroelectric film layer is a bismuth ferrite base film, the chemical formula is Bi(1-y)LnyFeO3, wherein Ln is one of lanthanide, y is the mole equivalent of lanthanide, and y is equal to 0.01-0.2. The preparation method is simple, and the obtained capacitor is a storage cell of a ferro-electric field effect transistor; and the capacitor overcomes the defects that the bismuth ferrite base film capacitor on ordinary silicon substrate has the defects of poor interface performance and high working voltage, and has good energy storage performance.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method of solar battery with bismuth ferrite/sodium bismuth titanate-barium titanate heterostructure ferroelectric film
InactiveCN103078014AUniform grainReduce manufacturing costRenewable energy productsSemiconductor devicesBarium titanateSolar battery
The invention relates to a preparation method of a solar battery with a bismuth ferrite / sodium bismuth titanate-barium titanate heterostructure ferroelectric film. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting SnO2 transparent conducting glass doped with fluorine (FTO for short) as a substrate, preparing the (Na0.5Bi0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 and BiFeO3 ferroelectric film by a chemical solution deposition method, then preparing an electrode on the surface of the film by a physical sputtering method. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages that the ferroelectric photoelectric film with high consistency and good repeatability is prepared on the FTO substrate by low cost. The prepared heterostructure film has more excellent photovoltaic performance than that of the pure BiFeO3, and can be applied in the fields of photoelectric batteries and photoelectronic devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing manganese, nickel codoped bismuth ferrite film by sol-gel process
The invention discloses a method for preparing manganese, nickel codoped bismuth ferrite film by a sol-gel process. The method comprises the steps of weighing material ferric nitrate, bismuth nitrate, manganese acetate and nickel acetate according to a general formula BiFe(1-2x)MnxNixO3 (x is smaller than or equal to 0.05 and greater than or equal to 0.0125); adding glacial acetic acid to agitate for 30 minutes at 80 DEG C; and adding ethylene glycol monomethyl ether to agitate for 180 minutes at room temperature to prepare into a liquid precursor of which the concentration is 0.1-0.2mol / L. The final sample is obtained by preparing a wet film on indium tin oxide / glass or a platinum substrate by a spin-coating method, pre-annealing, finally annealing the film, and repeating the pre-annealing and film annealing processes for 10-20 times. The method has the characteristics that the impurity phase in bismuth ferrite can be effectively restrained; the grain size and the root-mean-square roughness of the film surface are reduced; the insulating property, ferroelectric properties, the ferromagnetic property and the optical property of the sample are improved; and the method is simple in production technology, good in reproducibility, and low in cost.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Bismuth ferrite-strontium bismuth titanatemultiferroic composite film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103496747AControl UniformityLow preparation temperatureIron compoundsBismuth compoundsLeakage current densityNitrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic ceramics, and specifically relates to a bismuth ferrite-strontium bismuth titanatemultiferroic composite film and a preparation method thereof. The bismuth ferrite-strontium bismuth titanatemultiferroic composite film comprises the following raw materials: ferric nitrate, bismuth nitrate, tetrabutyltitanate and strontium acetate. The bismuth ferrite-strontium bismuth titanatemultiferroic composite film has stable structure, and is substantially reduced in leakage current density and strengthened in ferroelectric performance.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Bismuth ferrite films and devices grown on silicon
A functional perovskite cell formed on a silicon substrate layer and including a functional layer of bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3 or BFO) sandwiched between two electrode layers. An optional intermediate template layer, for example, of strontium titanate allows the bismuth ferrite layer to be crystallographically aligned with the silicon substrate layer. Other barrier layers of platinum or an intermetallic alloy produce a polycrystalline BFO layer. The cell may be configured as a non-volatile memory cell or a MEMS structure respectively depending upon the ferroelectric and piezoelectric character of BFO. Lanthanum substitution in the BFO increases ferroelectric performance. The films may be grown by MOCVD using a heated vaporizer.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
High-voltage-withstanding, low-electric-leakage and high-polarization strength bismuth ferrite thin film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103839928AHigh rectangularityHigh polarizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMagnetizationSingle crystal
The invention relates to a high-voltage-withstanding, low-electric-leakage and high-polarization strength bismuth ferrite thin film and a preparation method thereof. The high-voltage-withstanding, low-electric-leakage and high-polarization strength bismuth ferrite thin film comprises a base body, a bottom electrode, a bismuth ferrite dielectric layer and a top electrode, a mono-crystal oxide semiconductor substrate with lattice constant close to that of the bismuth ferrite is used as the base body, the bottom electrode is a conductive oxide thin film, and the top electrode is a metal thin film point electrode. The bottom electrode is deposited on the base body in a coaxial sputtering mode, then the bismuth ferrite dielectric layer is deposited on the bottom electrode in an off-axis sputtering mode, and at last the top electrode is deposited on the bismuth ferrite dielectric layer so that the thin film can be prepared. The prepared BiFeO3 thin film is in a rhombohedral shape and achieves height orientation, a ferroelectric hysteresis loop with good rectangularity is achieved under the room temperature, the intensity of polarization is high, the intensity of magnetization can reach 100 -110 micro coulombs / cm<2>, the voltage withstanding performance is good, and the maximum withstand voltage can achieve 50 v.
Owner:欧阳俊
Ferroelectric photovoltaic device and preparation method of ferroelectric photovoltaic device
InactiveCN102832266AImprove performanceLower Schottky Barrier HeightFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationLead zirconate titanateUltraviolet lights
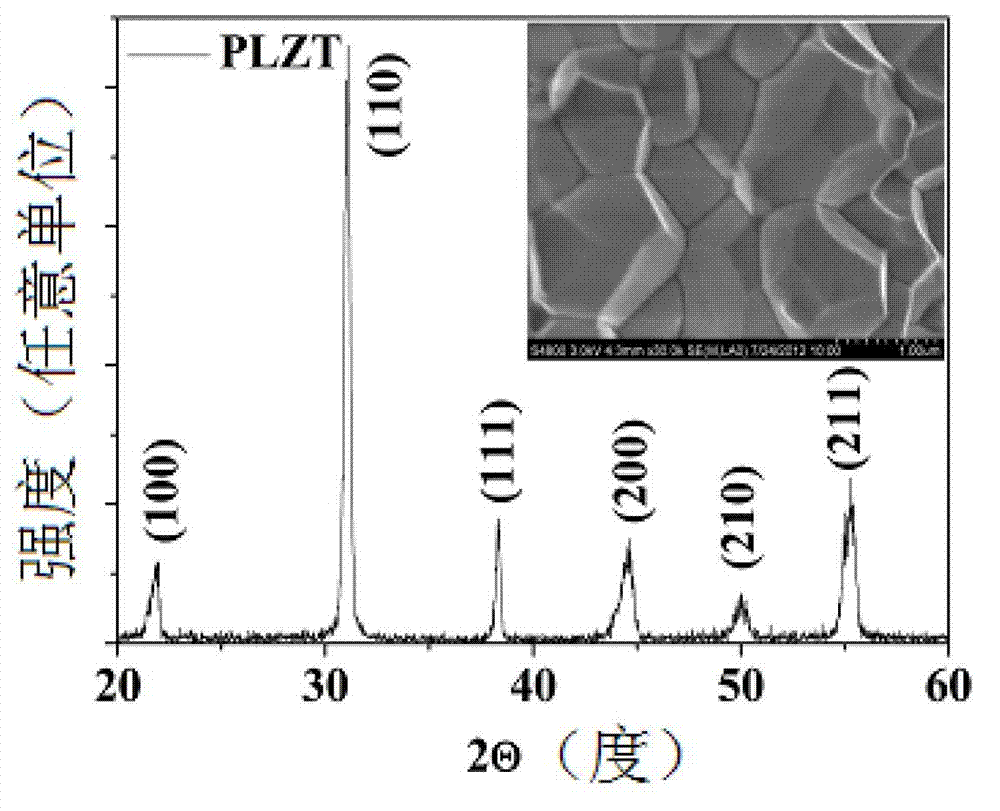
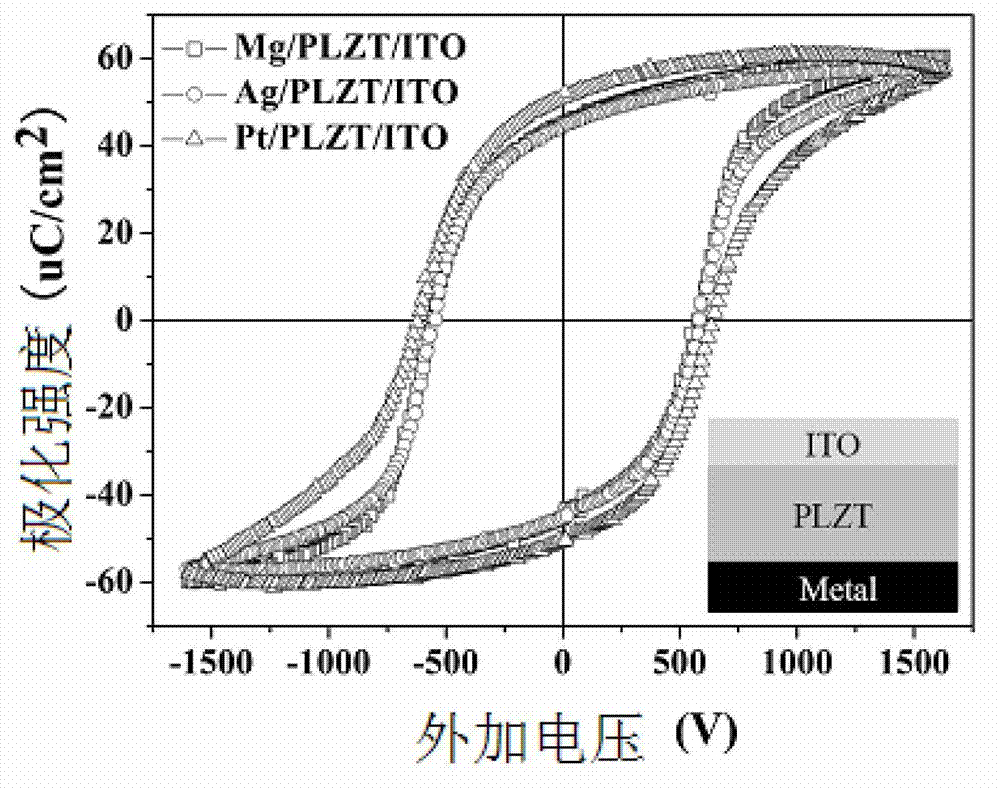
The invention discloses a ferroelectric photovoltaic device which comprises an upper electrode, a lower metal electrode and a ferroelectric material between the two electrodes. The ferroelectric material is lead lanthanum zirconate titanate (PLZT), lead zirconate titanate (PZT), barium titanate (BTO) or bismuth ferrite oxide (BFO), etc., the upper electrode is made of a transparent electrode material such as indium tin oxide (ITO) or aluminum doped zinc oxide (AZO), and the lower metal electrode is made of the metal with a low work unction such as Ag, Al or Mg. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the ferroelectric photovoltaic device. According to the invention, the photovoltaic characteristic of this kind of ferroelectric photovoltaic device can be improved through material design and energy band engineering based on the photoelectric effect of the metal with the low work function and the photovoltaic effect of the ferroelectric material; the light response wavelength of the traditional broad-band gap ferroelectric photovoltaic device can be extended from the range of ultraviolet light to the range of visible light; and the application field of the ferroelectric photovoltaic device can be enlarged.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of bismuth-ferrite-based multiferroic ceramic
InactiveCN104387058APure and single structureThe grain shape is regularly arranged closely and orderlyLaboratory devicePollution
The invention relates to a preparation method of bismuth-ferrite-based multiferroic ceramic. According to the preparation method, such steps in the conventional solid-phase method as pre-sintering and secondary fine grinding are eliminated, raw materials are uniformly mixed, are subjected to direct dry pressing to obtain disc-shaped ceramic with a desired size and then are directly sintered to obtain ceramic. By reasonably controlling experimental parameters such as the ratio and the sintering temperature, the excellent-property multiferroic ceramic having pure and single structure, no impurity phases, regular grain shape and compact and orderly arrangement can be obtained. The method disclosed by the invention is simpler than the conventional solid-phase method and easy to control, has the advantages of low requirement on laboratory device, no pollution and low cost and is easy for realization of industrial production.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com