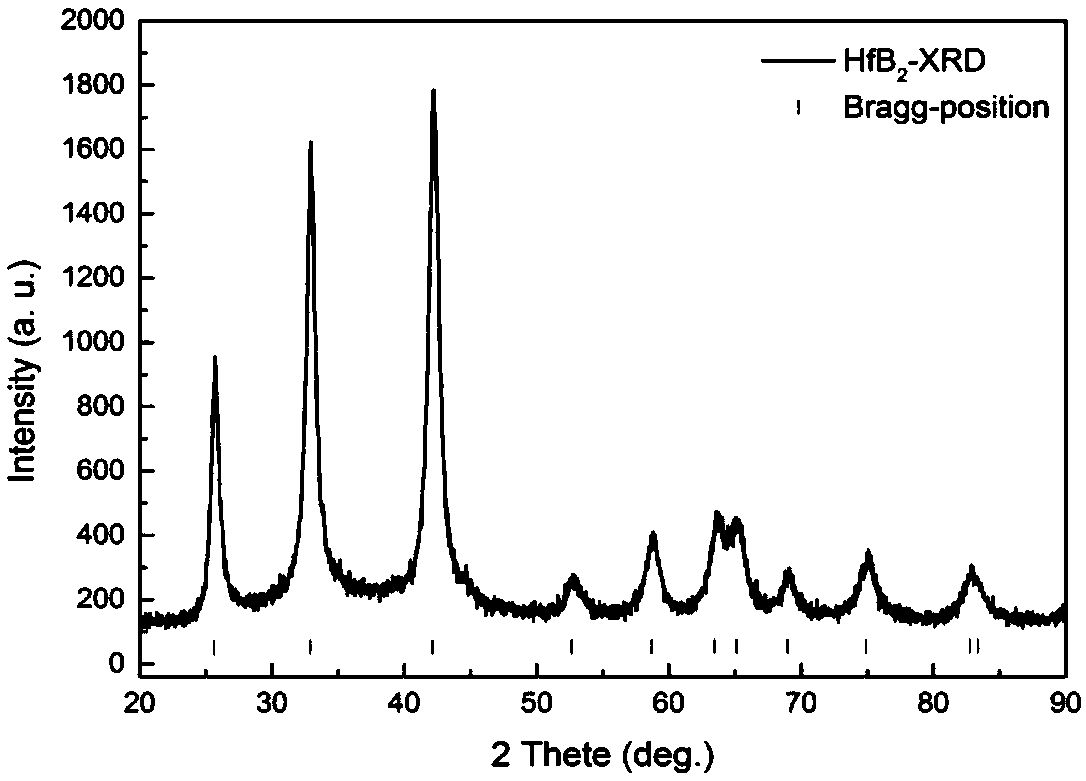
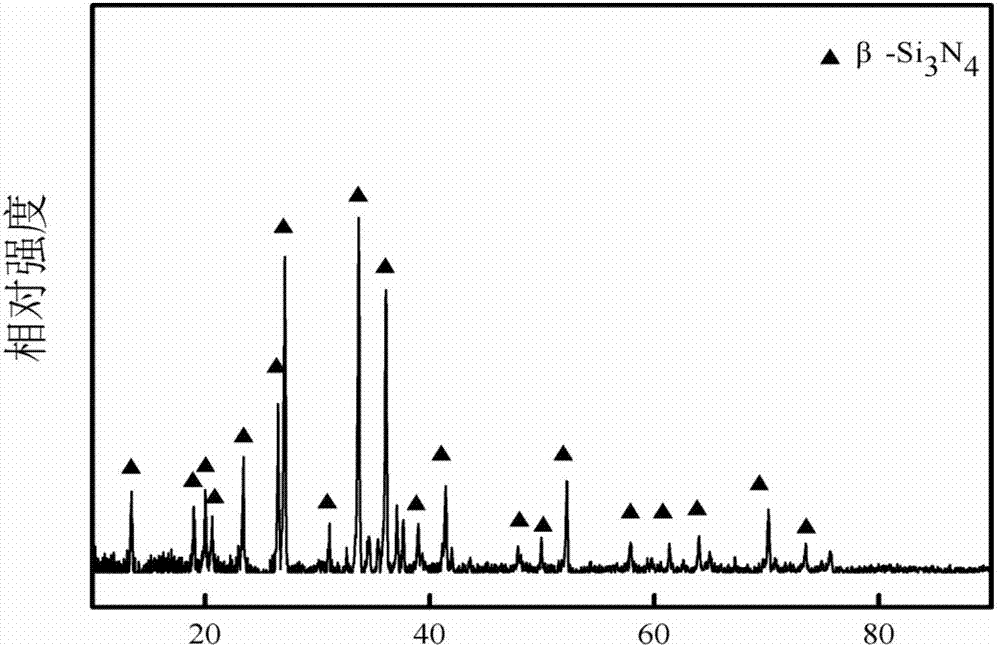
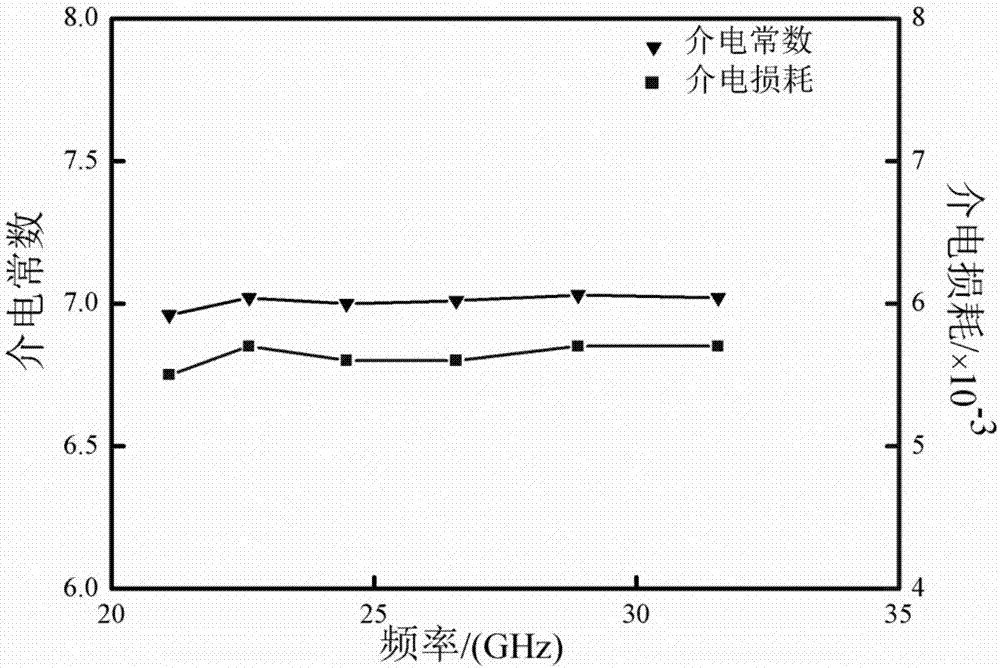
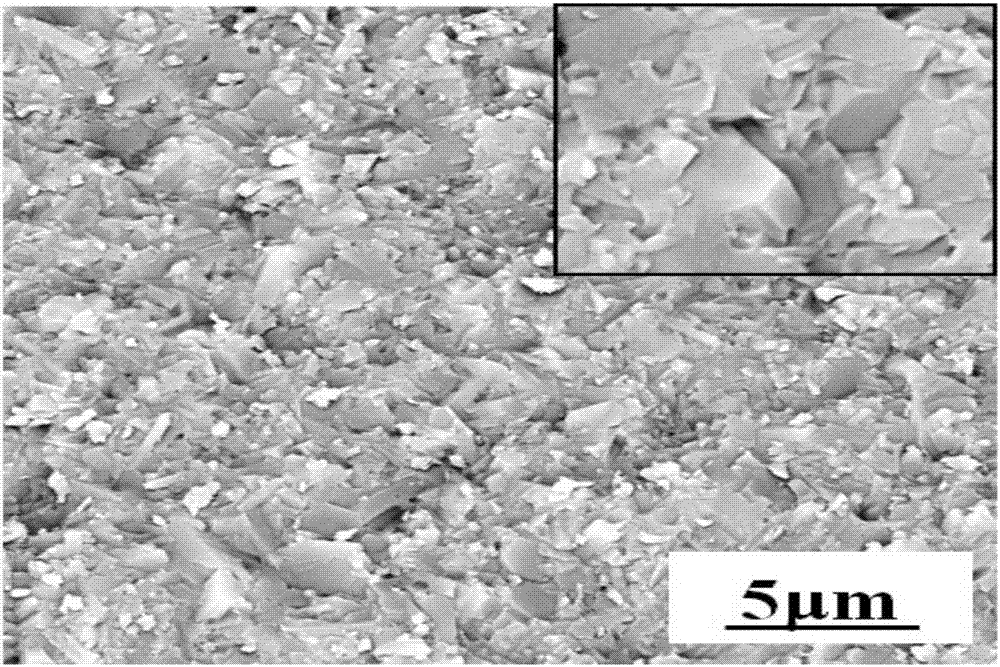
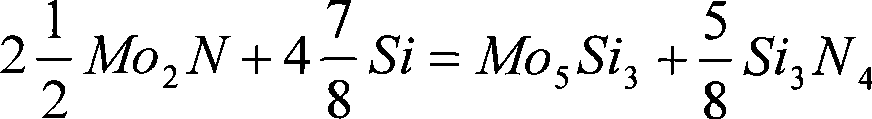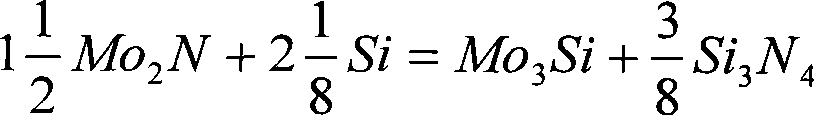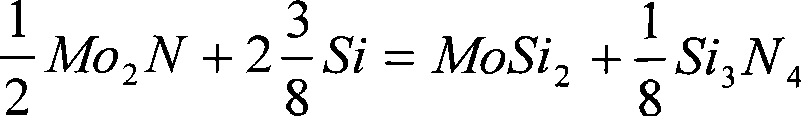Patents
Literature
117results about How to "Sintering process is simple" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
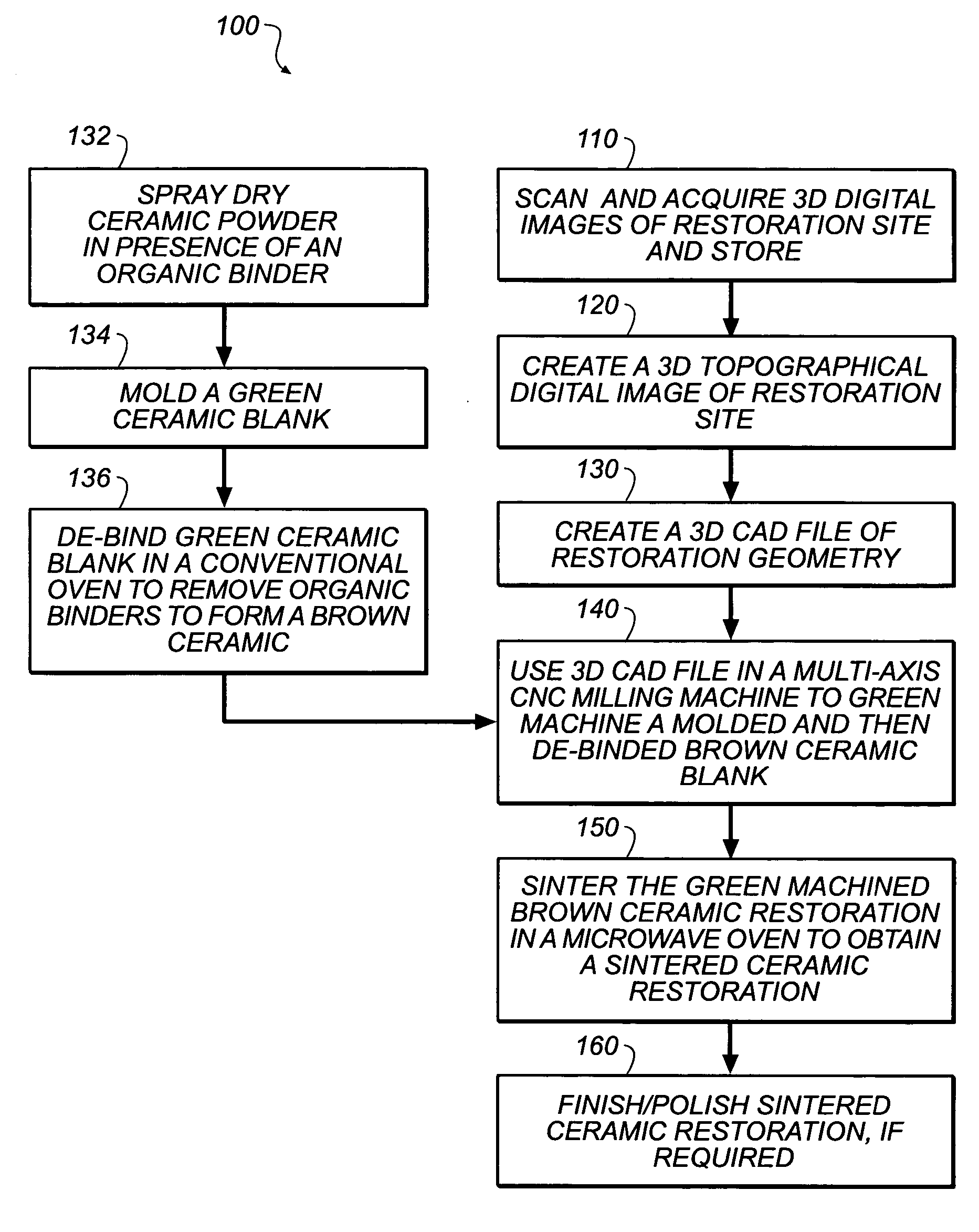
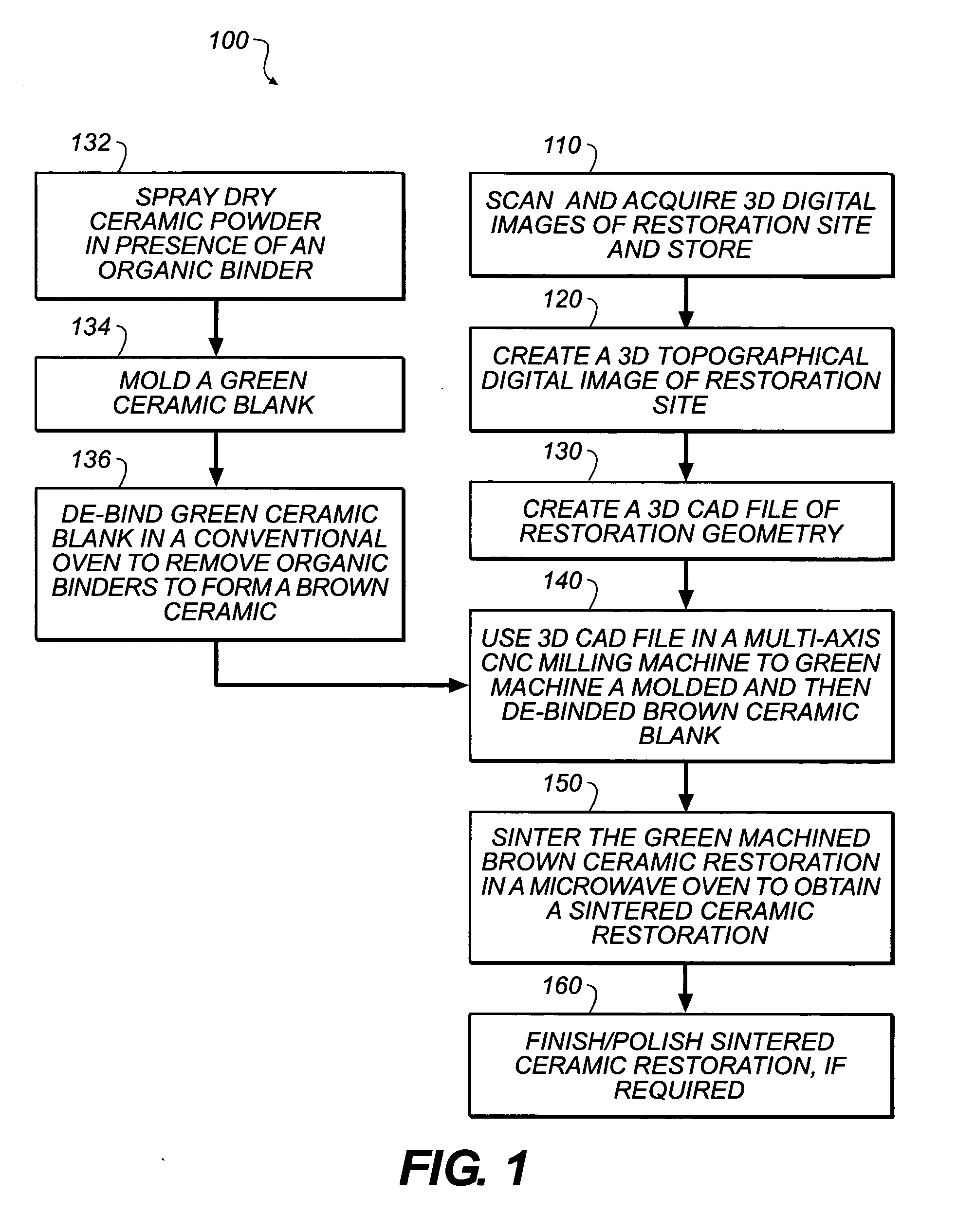
Method of making ceramic dental restorations
InactiveUS20050261795A1Without diminishing easeHigh speedTeeth fillingSpecial data processing applicationsHigh densityDental surgeon
Dental restorations can be made by acquiring a three-dimensional digitized image of a dental restoration site. A ceramic blank from which volatile organic binders have been removed, is then machined according to the three-dimensional digitized image to form a “brown” ceramic restoration. This material is then sintered using microwave energy to provide a high density ceramic dental restoration corresponding to the dental restoration site. This method can be carried out within a few hours thereby saving the patient several dental visits and enabling the dentist to better serve the patient directly in the office.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Bismuth ferrite-based leadless piezoelectric ceramic with high Curie temperature and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a bismuth ferrite-based leadless piezoelectric ceramic with high Curie temperature and a preparation method thereof. The general formula for the piezoelectric ceramic is (1-x-y)(BizM1-z)t(FeuM'1-u)O3-xBaTiO3-yBiMnO3, wherein, M is a trivalent metallic element with large ionic radius, M' is a trivalent metallic element with small ionic radius, and x, y, u, t and z represent mole content in a ceramic system and satisfy the following relations: 0<=x<=1.0, 0<=y<=0.1, 0<z<1, 0.85<t<1.2, 0<u<1 and x+y<1. The piezoelectric ceramic is prepared by a conventional ceramic preparation method through selection of proper technological parameters. The piezoelectric constant d33 of the ceramic can reach 140 pC / N, Curie temperature can reach 490 DEG C, and Kt is more than 0.50. The preparation method has the advantages of a simple and stable process, and obtained leadless piezoelectric ceramic has excellent performance and is suitable for being used under high temperature.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Preparation method for active element sintered ZTA (Zirconia Toughened Alumina) particulate reinforced steel based compound grinding roller and grinding disk
The invention discloses a preparation method for an active element sintered ZTA (Zirconia Toughened Alumina) particulate reinforced steel based compound grinding roller and a grinding disk. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) uniformly mixing multiple active element powder, and then adding a defined amount of binding agents and fully mixing with ZTA particulates so as to uniformly cover the active element powder on the surfaces of the particulates, filling into a graphite mould, pressing, and then drying; 2) sintering, thereby obtaining a porous precast block; 3) fixing the precast block on a specific casting position and pouring molten metal, cooling and de-molding, thereby obtaining the compound grinding roller or grinding disk. According to the preparation method, the shape and size of the ZTA particulate precast block can be controlled through the mould and the technique is simple and has higher production efficiency, yield and practicability. Besides, the active element introduced into the interface can increase the wettability and binding strength of the interface and a compound layer structure with interactive distributed enhanced phase and base can ensure the longer service life of the grinding roller and the grinding disk under high stress effect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Composite high-temperature molybdenum disilicide-base material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101531519AImprove antioxidant capacityAdjust the coefficient of thermal expansionComposite substrateRoom temperature
The invention relates to a composite high-temperature molybdenum disilicide-base material and a preparation method thereof. The method can prepare the composite high-temperature material under lower production cost, which has the highest room temperature toughness equivalent to that of high-temperature alloys, higher high temperature intensity, high temperature creep resistant performance and certain plastic processing performance; the substrate of the composite high-temperature material is a composite substrate composed of MoSi2 and Si3N4, wherein the average crystal grain size of the MoSi2 is smaller than 2 microns, and the average grain diameter of the Si3N4 particulates is smaller than 1 microns. The method adopts the following technical proposal: Mo2N powder or powder of Mo5Si3 or Mo3Si are used as initial powder to obtain composite powder Mo3Si-Mo5Si3-Si3N4 or Mo5Si3-MoSi2-Si3N4 after being processed by siliconization or nitridation-siliconization, the composite powder is further enhanced and mixed with materials such as Si powder, SiC powder and the like, and is pressing molded, and then a blank is sintered under the temperature of 1415 to 1550 DEG C, and finally the sintered blank is plastic deformed, thus obtaining a required dense article of the composite high-temperature material.
Owner:李琎 +1
Transition metal diboride high-entropy ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a transition metal diboride high-entropy ceramic and a preparation method thereof, mainly relates to a high-entropy ceramic material with excellent performance, and belongs tothe field of high-temperature ceramics. At least five IVB, VB and VIB groups of transition metal boride powder is mixed according to the same mole ratio, high-energy ball milling and vacuum treatmentof mixture are implemented, the mixture is packaged and pre-pressed by high-melting-point packaging material, and the packaged mixture is sintered at the pressure of 4-10GPa and at the temperature of1000-1800 DEG C to form the diboride high-entropy ceramic. The diboride high-entropy ceramic is firstly prepared by a high-temperature and high-pressure method and has the advantages of high breakingtenacity, compactness and hardness, small grain size, excellent oxidation resistance and the like. the method has the advantages that the method is low in cost, environmentally friendly, simple in sintering process, good in product performance and high in finished product ratio, and raw materials are easily acquired. Industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing gradient cemented carbide with cubic carbide free layer
The invention relates to a process for preparing gradient cemented carbide with a cubic carbide free layer, which is generally used for preparing a coated cemented carbide substrate. The process is characterized in that: an initial component adopts a nitrogen-free cemented carbide raw material, and is prepared into a blade or a sample green compact by a standard cemented carbide preparation process; and a sintering process adopts a one-step sintering method comprising the following steps of: performing sintering by adopting normal dewaxing and deoxidizing processes, introducing micro-pressure nitrogen to react the nitrogen with carbides in the cemented carbide substrate to synthesize a nitrogen-containing cubic phase, evacuating the nitrogen at gradient sintering temperature and switching to sintering in a denitriding atmosphere like vacuum to form a surface layer into a cubic phase-free and cobalt layer-rich structure, namely, the cubic carbide free layer. The process is characterized in that: a nitrogen-containing phase is not added into the cemented carbide raw material, so the increasing of alloy porosity caused by the early decomposition of the nitrogen-containing phase can be avoided; the reaction nitrogen-addition of the cemented carbide substrate is realized by controlling the reaction between the sintering atmosphere and the cemented carbide substrate, so the gradient cemented carbide with the cubic carbide free layer also can be prepared under the condition of not adding the nitrogen-containing phase into the initial component; due to the adoption of the one-step sintering method, the sintering process can be simplified and the production cost can be reduced; and the prepared gradient cemented carbide comprises the cubic carbide free layer with the thickness of 10 to 40 microns, and has high compactness and bending resistance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +2
Preparation method for Ti3AlC2-strenghted Ag-based electrical contact material
The invention provides a preparation method for a Ti3AlC2-strenghted Ag-based electrical contact material. The composite material is composed of Ti3AlC2 and an Ag base body. The mass percent of a Ti3AlC2 strengthening phase is 1%-70%. The Ti3AlC2-strenghted Ag-based electrical contact material is prepared by mixing Ti3AlC2 powder and Ag powder in proportion for 5 min-300 min, conducting cold press molding under the pressure ranging from 100 MPa to 900 MPa, and sintering a green body for 1-24 hours at a temperature ranging from 500 DEG C to 1000 DEG C in protective atmosphere or vacuum. The prepared Ag-based composite material has the beneficial effects of being high in compactness, uniform in structure, moderate in hardness, good in electrical conductivity, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High temperature stable X9R type multilayer ceramic capacitor dielectric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103936414AOvercome the high temperature reduction effectReduce lossBarium titanateCeramic capacitor
The invention discloses a high temperature stable X9R type multilayer ceramic capacitor dielectric material and a preparation method of the high temperature stable X9R type multilayer ceramic capacitor dielectric material. The high temperature stable X9R type multilayer ceramic capacitor dielectric material disclosed by the invention is prepared by the steps of adding a calcium-boron-silicon compound to a barium titanate-sodium bismuth titanate-niobium pentoxide eutectic compound serving as a matrix, compounding one or more of Ce, Nd and La oxides, and compounding one or more of barium-manganese oxide, magnesium oxide and zinc oxide; and the invention provides the preparation method of the high temperature stable X9R type multilayer ceramic capacitor dielectric material. The X9R type multilayer ceramic capacitor dielectric material prepared by using the material and the method provided by the invention has high temperature resistance (above 200 DEG C), and good temperature stability, and enable components and parts such as multilayer ceramic capacitors, tuners and duplexers to be suitable for the application at a high temperature (above 200 DEG C), thus having extremely high industrialization prospect and industrial application value.
Owner:FUJIAN TORCH ELECTRON TECH CO LTD
Sintering method for high saturated flux density MnZn ferrite
ActiveCN101090016AHigh saturation flux densityLow costInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyPartial pressure
This invention provides a sintering method for a high-saturated flux density MnZn ferrite including the following steps: a, a first temperature-rising stage, b, a second temperature-rising stage, c, a heat preservation stage, d, temperature-reducing, which can increase the saturated flux density of MnZn ferrite greatly by controlling the temperature and oxygen partial pressure during the sintering process, besides, no expensive asistant components are needed in the preparation process.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Functionally graded material shape and method for producing such a shape
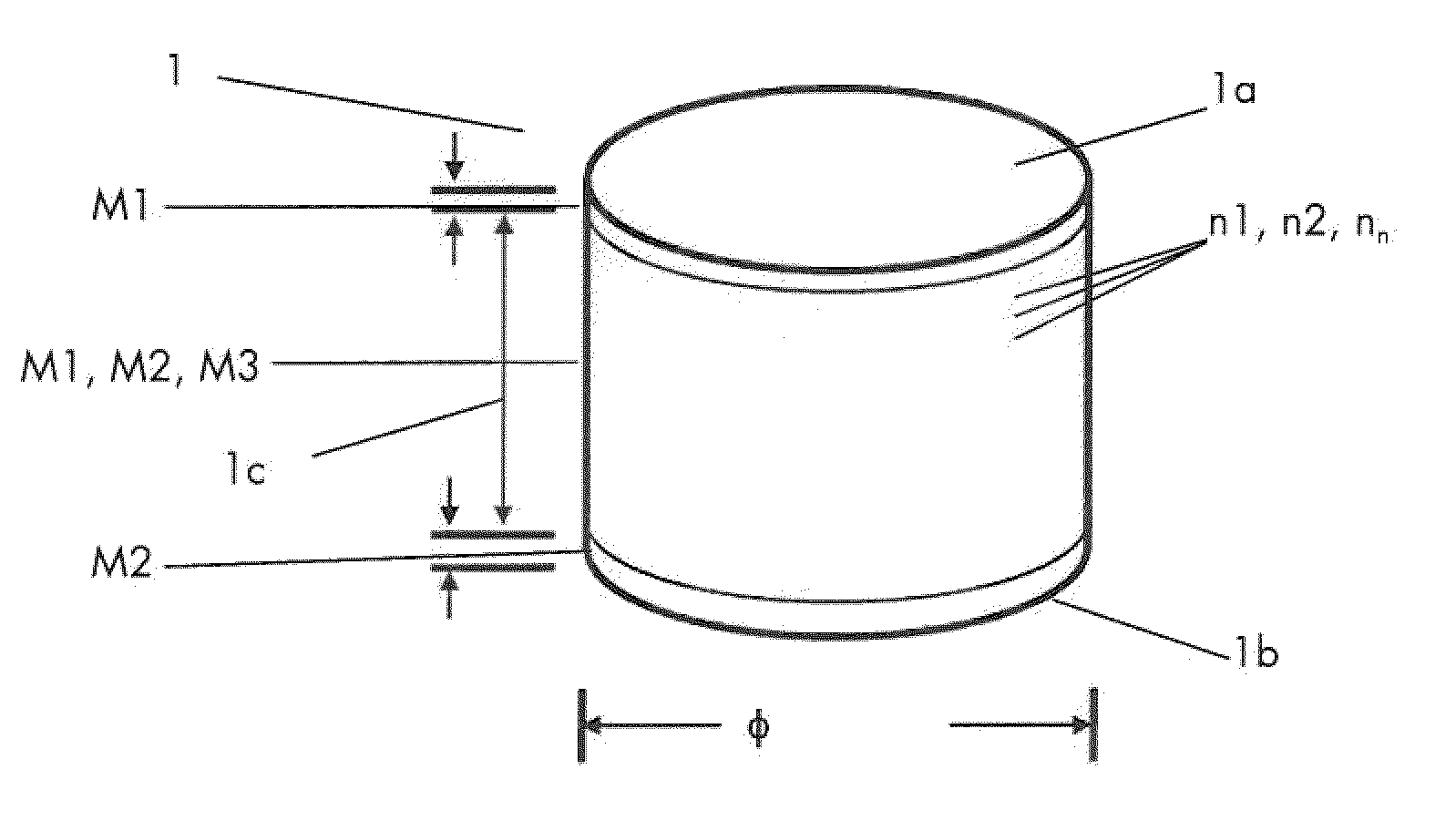
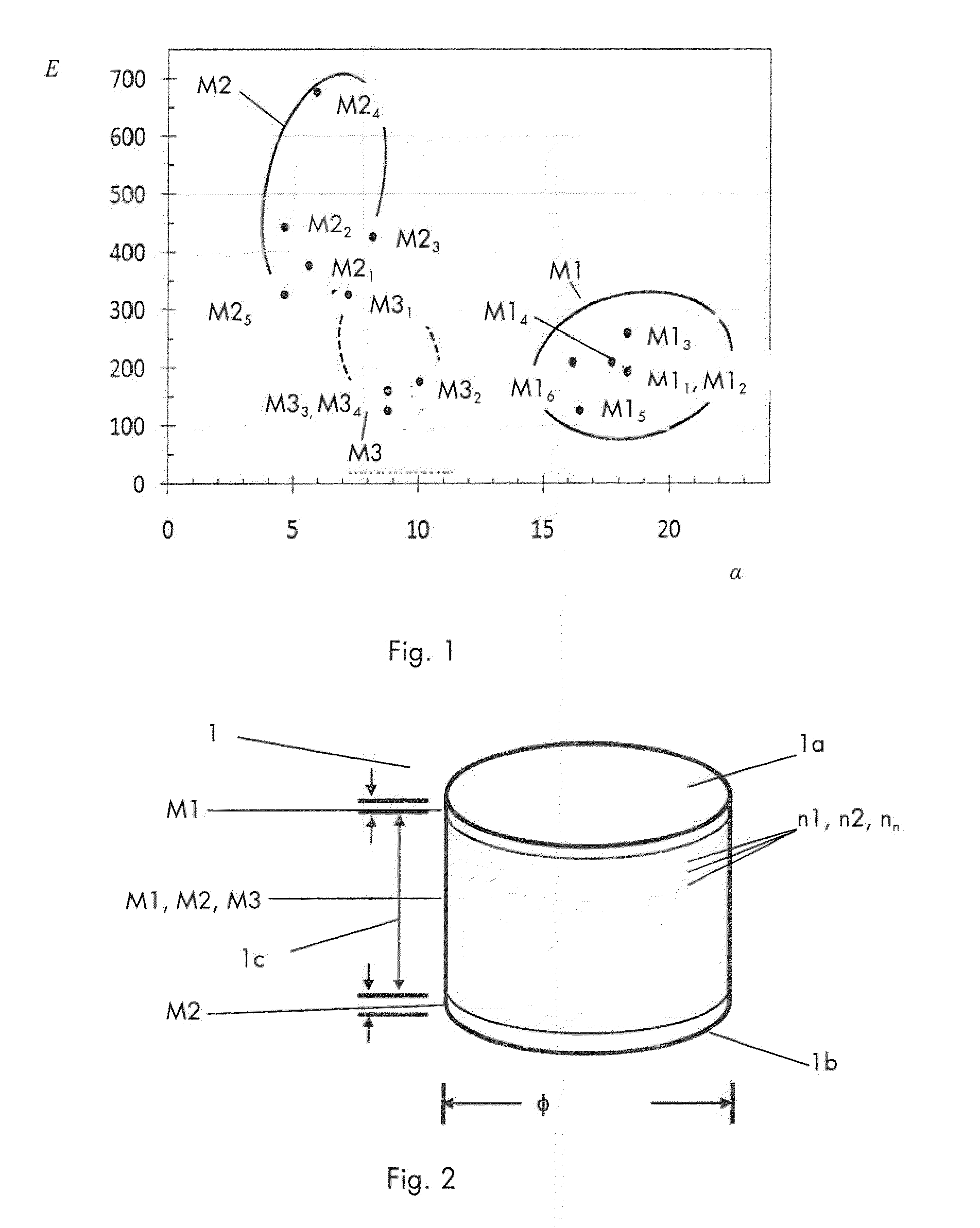
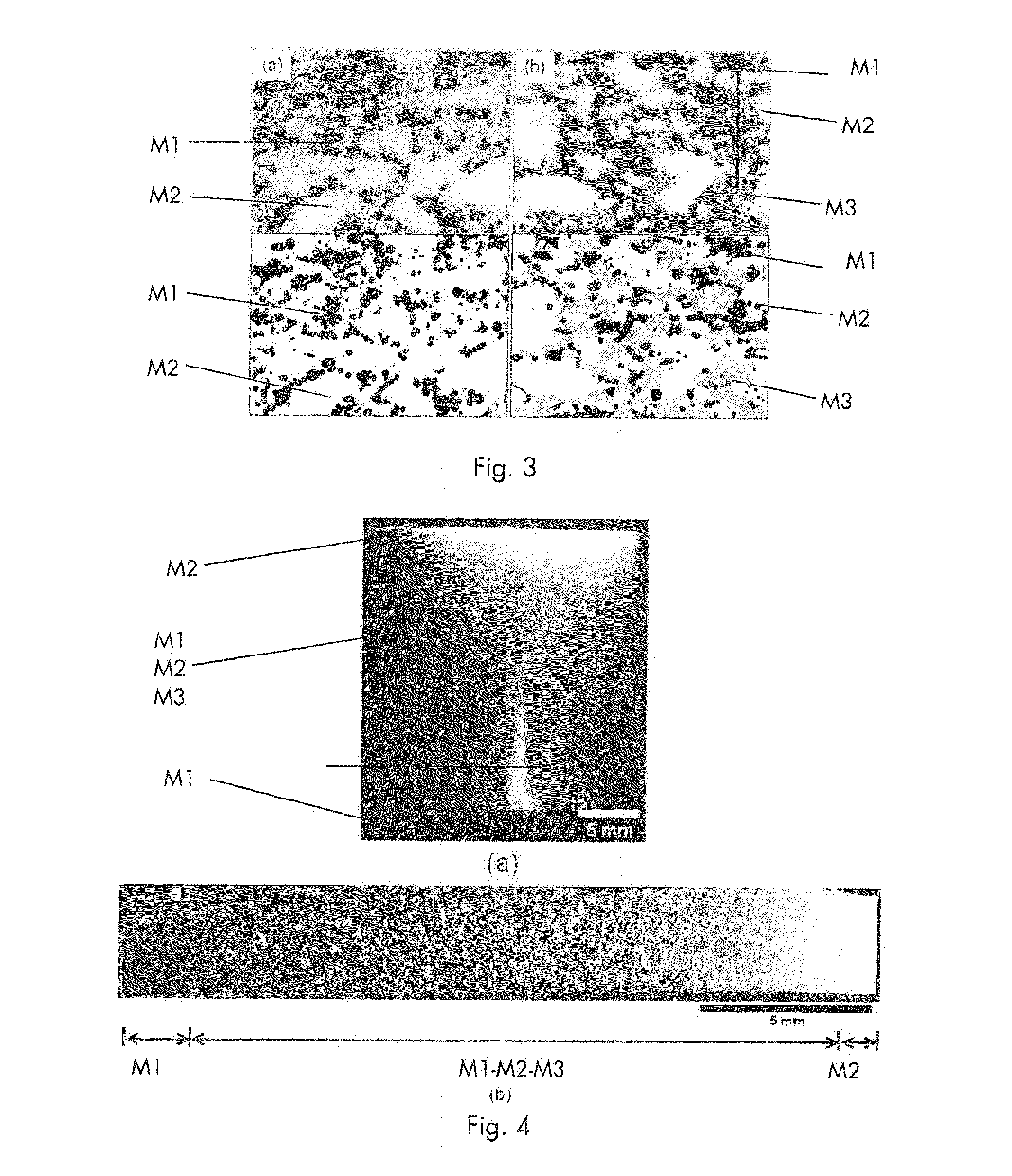
InactiveUS20110236713A1Minimize interfaceWeakening rangeMaterial nanotechnologyThin material handlingFunctionally graded materialMethods of production
The invention relates to a functionally graded material shape (1) where a first material (M1) is fused with a second material (M2) through sintering and a method of production of said functionally graded material shape (1). Said first material (M1) has a first coefficient of thermal expansion (α1) and said second material (M2) has a second coefficient of thermal expansion (α2), differing from the first coefficient of thermal expansion (α1). The invention is characterized in that the shape (1) further comprises a third material (M3) adapted to, together with M1 and M2, create an intermediate composite material phase intermixed between the first and the second materials (M1, M2). Said third material (M3) has a coefficient of thermal expansion (α3) intermediate between the first coefficient of thermal expansion (α1) of the first material (M1) and the second coefficient of thermal expansion (α2) of the second material (M2).
Owner:DIAMORPH AB
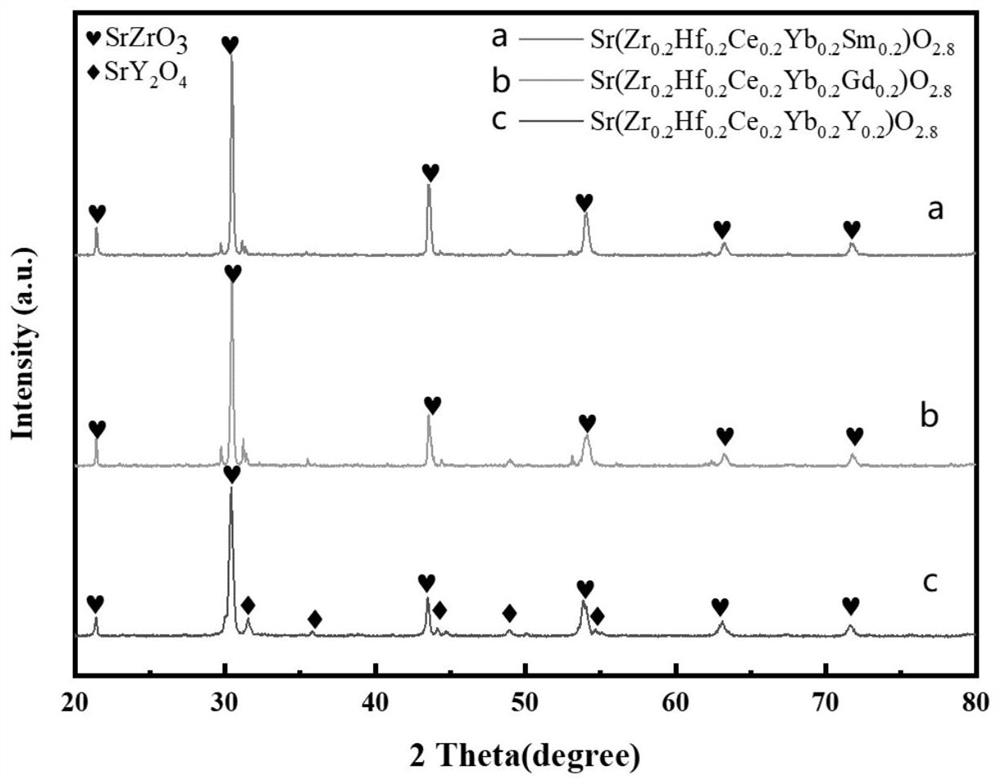
Novel perovskite structure high-entropy ceramic and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112919908AGood phase stability at high temperatureLow thermal conductivityAlcoholPolyvinyl alcohol
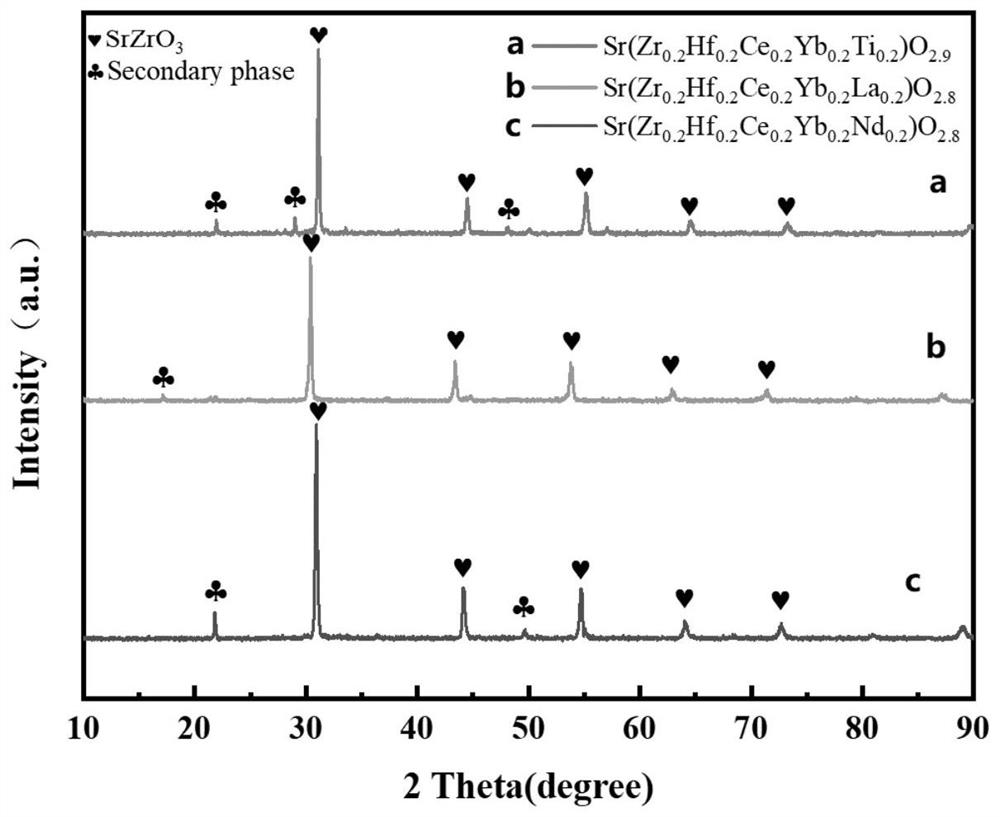
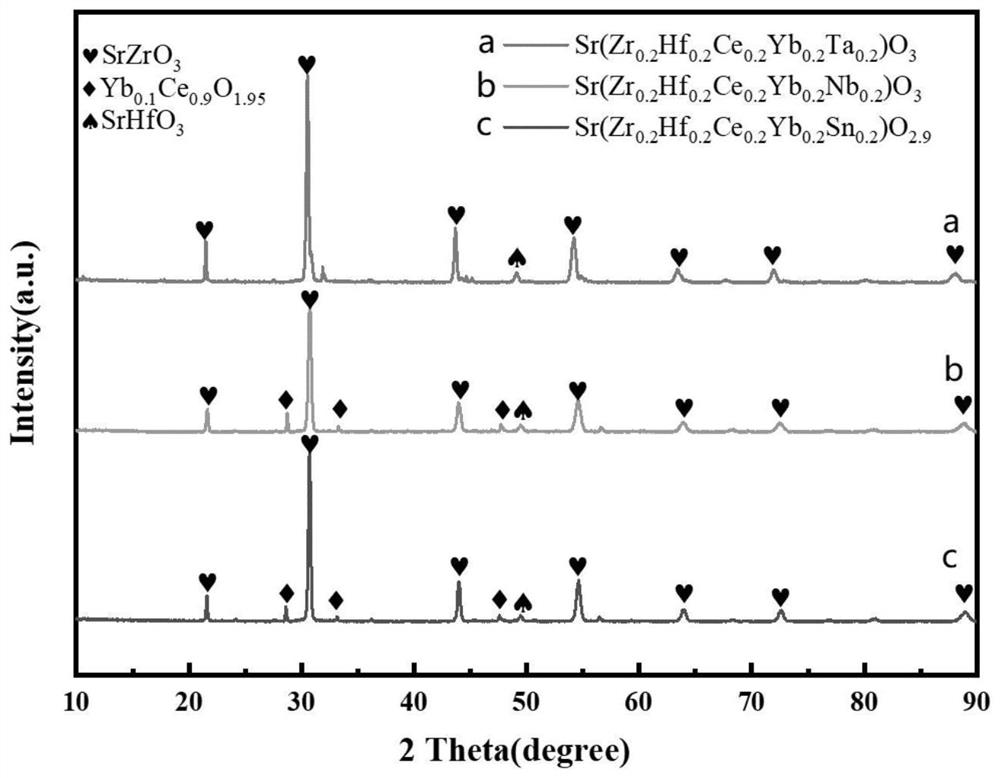
The invention discloses a novel perovskite structure high-entropy ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the ceramic is an ABO3 type perovskite structure, the A-site element is Sr, and the B-site element is Zr, Hf, Ce, Yb and Me which are in an equal molar ratio. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting the components into a mortar, adding absolute ethyl alcohol, and performing grinding; performing drying in a drying oven after the grinding, then transferring dried material into a muffle furnace for pre-calcining, and naturally cooling obtained material to room temperature to obtain a ceramic powder; putting the ceramic powder into the mortar, adding a polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution and absolute ethyl alcohol, performing grinding again, and performing drying and sieving after the grinding is sufficient, adding the sieved ceramic powder into a steel mold of a table type powder tablet press, pre-pressing into a disc-shaped or strip-shaped block material, and then putting the block material into a cold isostatic press for cold isostatic pressing treatment to obtain a ceramic green body; and finally, calcining the ceramic green body in a muffle furnace, and performing cooling in the furnace to obtain the novel perovskite structure high-entropy ceramic. The high-entropy ceramic has the advantages of high stability, low thermal conductivity and relatively high hardness and density.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of lead zirconate titanate nanometer powder
Production for Pb(ZrxTi(1-x)O3) nanometer powder is disclosed. It is carried out by: taking Ti(O-C4H9)4, Zr(NO3)4íñ5H2O, Pb(CH3COO)2íñ3 H2O as raw material, C2H6O2 as solvent, mixing C2H6O2 solution of Zr(NO3)4íñ5H2O with C2H6O2 solution of Ti(O-C4H9)4, back-flowing at temperature 60-70deg.C for 30mins, dripping C2H6O2 solution of Pb(CH3COO)2.3 H2O into system, back-flowing at 60-70deg.C for 3hrs, thermostatic drying for 10hrs in 100deg.C fan drying case, and dried gel powder sintering at temperature 400deg.C and 600deg.C in crucible to obtain yellow nanometer Pb(ZrxTi(1-x)O3) powder. It costs low and is simple.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for preparing titanium dioxide photo-anode of DSSC (Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell)
InactiveCN103700502AEmission reductionSimple production processLight-sensitive devicesCapacitor electrodesAlcoholTetrachloride
The invention relates to a method for preparing a titanium dioxide photo-anode of a DSSC (Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell). The method comprises the steps of immersing cleaned conductive glass into a titanium tetrachloride solution, taking out the conductive glass after being subjected to heat preservation in 25-75 DEG C for 10-90 minutes, leaching and drying the conductive glass, and obtaining the conductive glass which is subjected to once titanium tetrachloride processing, wherein the concentration of the titanium tetrachloride solution is 20-500 mM, and solvents in the titanium tetrachloride solution are water and / or alcohol; drying the obtained conductive glass after coating a titanium dioxide sizing agent on the surface of the obtained conductive glass which is subjected to the once titanium tetrachloride processing, carrying out single sintering by baking the conductive glass in 250-650 DEG C for 0.1-5 hours, and obtaining the titanium dioxide photo-anode of the DSSC. According to the method disclosed by the invention, twice titanium tetrachloride processing in a standard method is reduced into the once titanium tetrachloride processing, not only is the production technology simplified and is the production cost reduced, but also the emission load of the corrosive titanium tetrachloride solution in a production process is reduced, and thus the production process is more environment-friendly.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
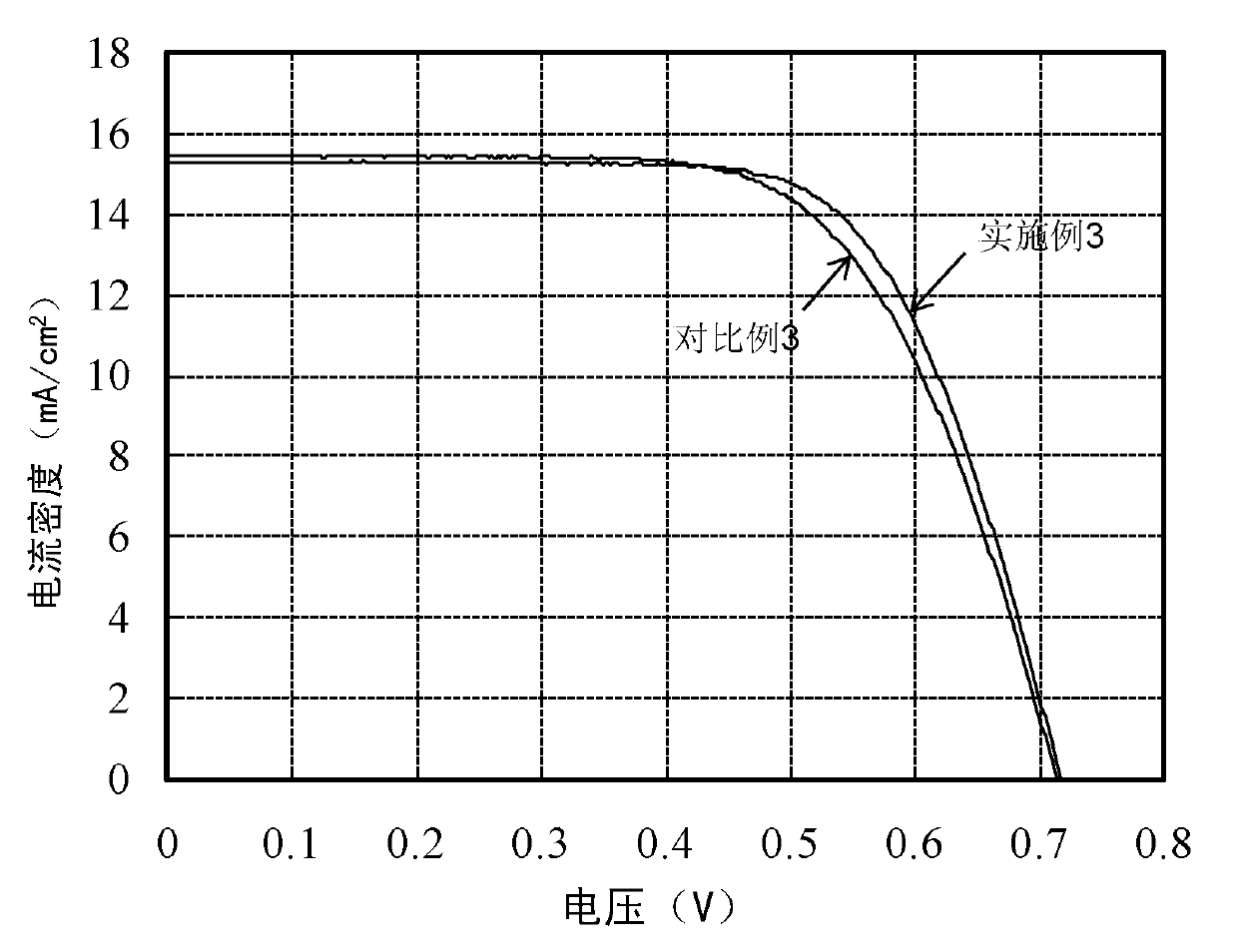
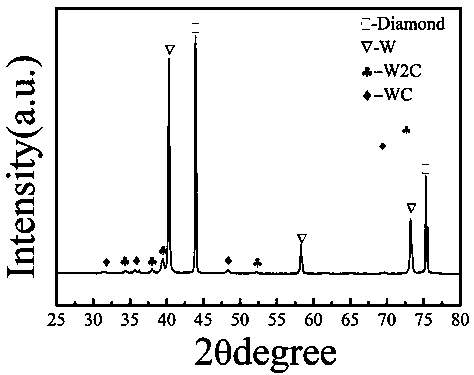
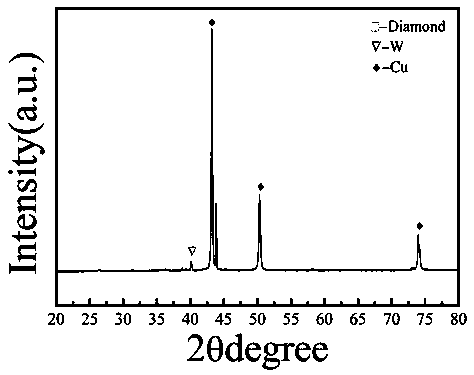
Preparation method of diamond/copper composite high in heat conduction performance
ActiveCN107916356AImprove protectionSimple separation processTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusPowder mixtureRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a diamond / copper composite high in heat conduction performance. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, uniformly mixing diamond obtained after surface of the diamond is subjected to degreasing and roughening treatment with tungsten powder according to the mass ratio of 1: 4.5, heating a powder mixture under the vacuum condition, conducting heat preservation for 2-8 hours at the temperature of 1030 DEG C, and finally, separating out modified tungsten-plated diamond, wherein the vacuum degree is 10<-2>-10<-4> Pa, and the temperature rising rate is 5 DEG C / min; and 2, uniformly mixing the tungsten-plated diamond, with the mean particle size being 125 microns, obtained after surface modification with copper powder with the mean particle size being 45 microns with the total volume content of the tungsten-plated diamond accounting for 55%, sintering an obtained powder mixture, and then cooling the obtained power mixture to the room temperature, so that the diamond / copper composite is obtained, wherein the sintering parameters are that the pressing pressure is 40 MPa, the temperature is 1000 DEG C, the temperature risingrate is 100 DEG C / min, the sintering time is 10 minutes, and the atmosphere is vacuum.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
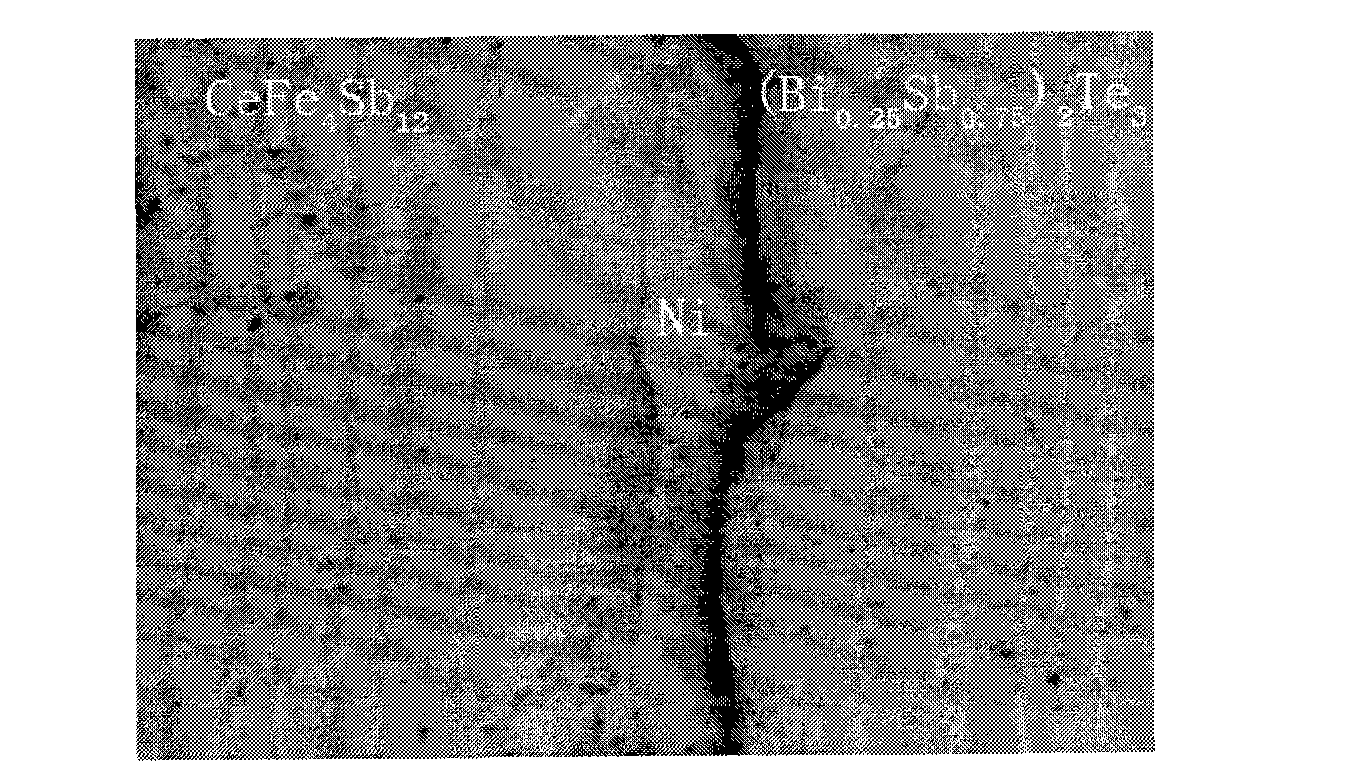
P-type (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3/CeyFe4Sb12(y=0.8-1.2)-based bulk gradient thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101794858AClean interfaceHigh bonding strengthThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsGraphite
The invention discloses a P-type (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3 / CeyFe4Sb12(y=0.8-1.2)-based bulk gradient thermoelectric material, which comprises a material of a low-temperature layer and a material of a medium-temperature layer, wherein the low-temperature layer comprises (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3; the medium-temperature layer comprises CeyFe4Sb12(y=0.8-1.2); and a Ni or Cu transitional layer is arranged between the materials of the two layers. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the thermoelectric material, which comprises: firstly, preparing a CeyFe4Sb12 bulk according to a chemical formula; secondly, preparing (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3 powder; and finally, placing the CeyFe4Sb12 bulk in a graphite mold, flatly spreading the transitional layer of the (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3 powder on the CeyFe4Sb12 bulk and placing the mold in an SPS sintering furnace to sinter the materials. The thermoelectric material of the invention has a clean interface and high bonding strength and can be widely used in the field of low-high temperature waste gas and heat power generation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of Y2O3-MgO nano complex-phase infrared transparent ceramic
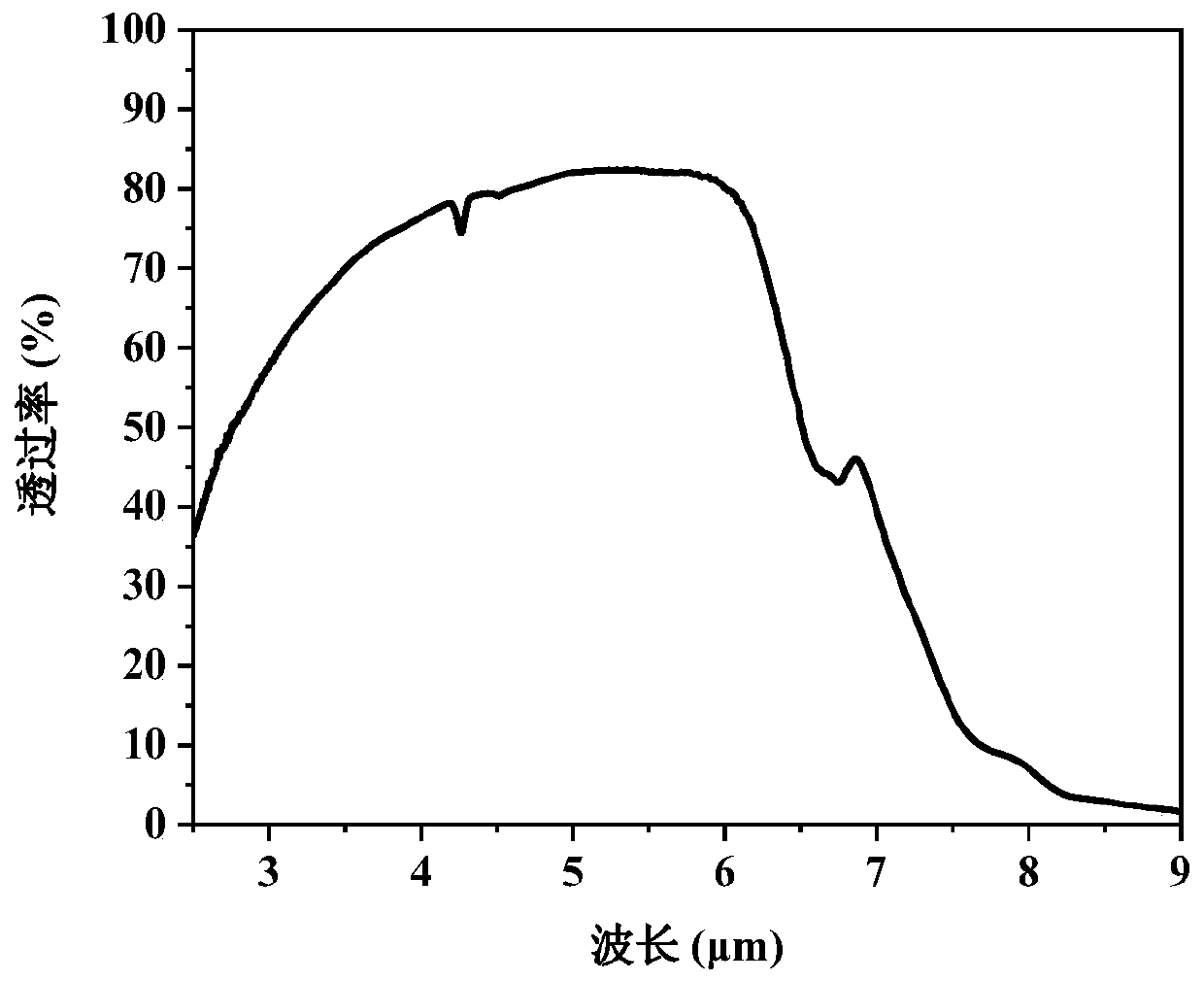
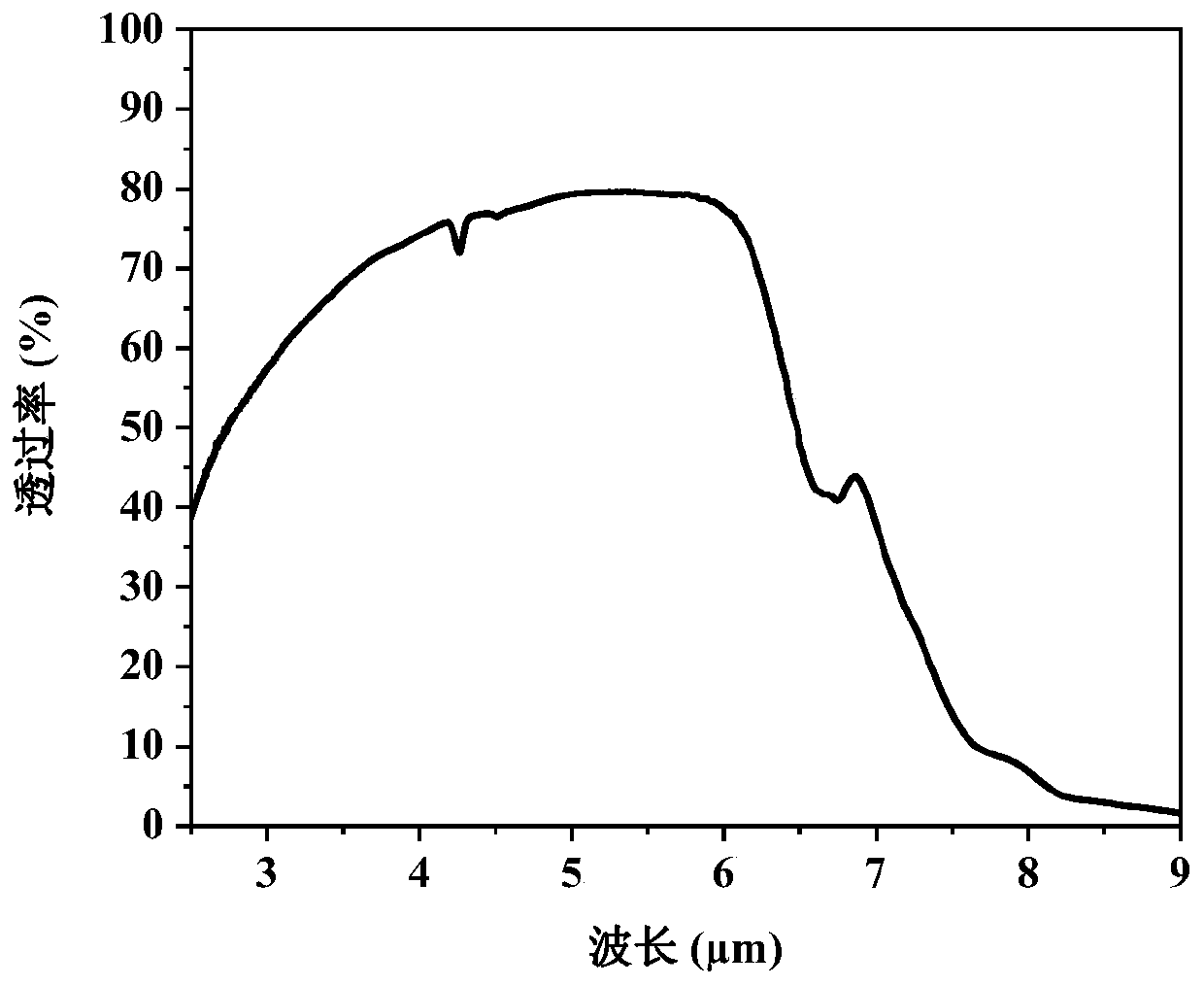
The invention relates to a preparation method of Y2O3-MgO nano complex-phase infrared transparent ceramic. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly pressing Y2O3-MgO complex-phasenano-powder into a biscuit, carrying out a two-step sintering process in a muffle furnace in an air atmosphere to obtain a ceramic blank and then carrying out hot isostatic pressing sintering to obtain the infrared transparent Y2O3-MgO nanovcomplex-phase ceramic. The density is close to the theoretical density, the grain size is small, the average transmittance (thickness is 2.0 mm) of mid-infrared 3-6 microns is greater than 76% so as to be superior to that of a sample prepared through conventional auxiliary hot isostatic pressing sintering after sintering.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
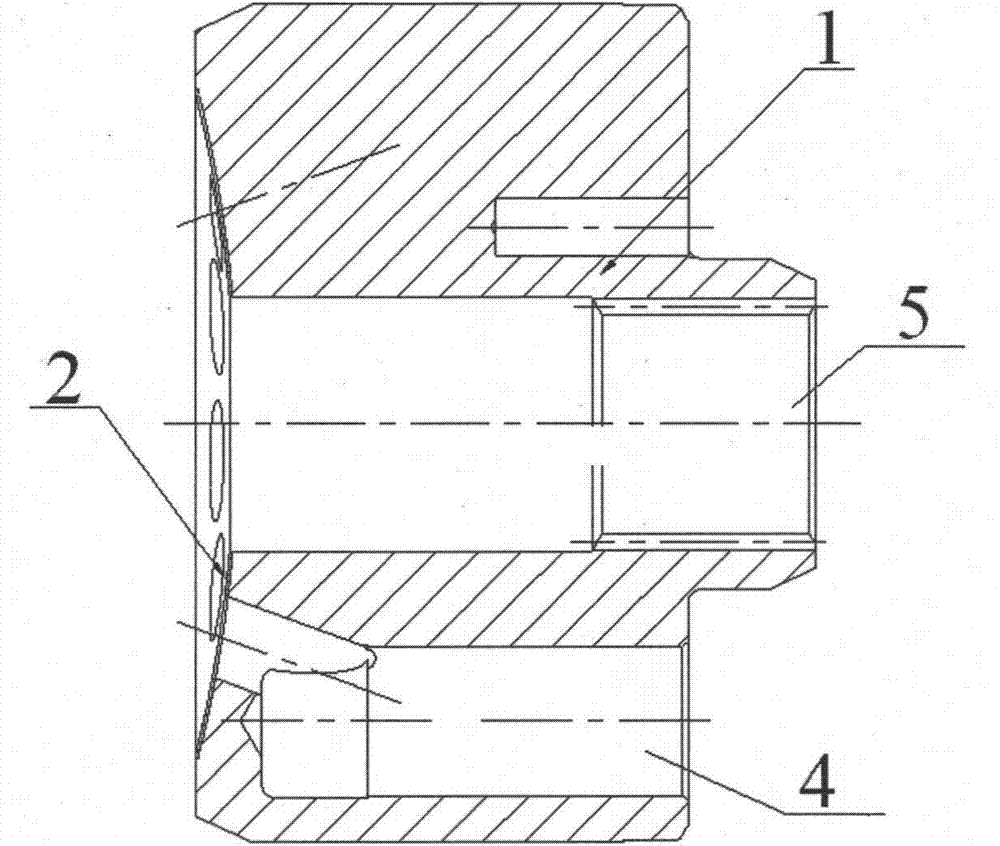
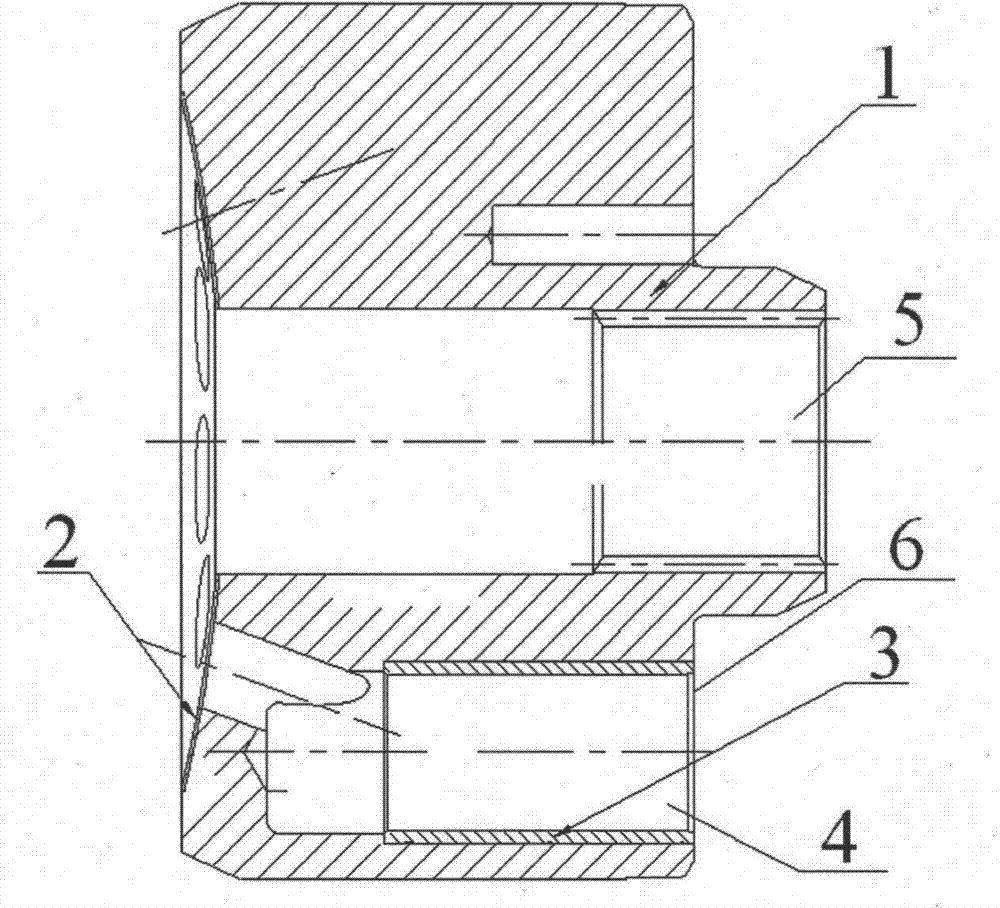
Cylinder block assembly inlaid with copper bush and machining method for same
ActiveCN103697016AMature processing technologyEasy to process and produceFluid-pressure actuatorsEngineeringCopper
The invention discloses a cylinder block assembly inlaid with a copper bush. The cylinder block assembly comprises a cylinder block, wherein a sintered layer is arranged on the matching surface of the cylinder block and a port plate; an axle hole is formed in the middle of the cylinder block; a hole groove is formed in one side of the axle hole in the cylinder block; the copper bush is arranged in the hole groove; and the cylinder block is machined from steel parts. The process route of the cylinder block assembly disclosed by the invention comprises rough turning, sintering, finish turning, spline drawing, copper bush press-fit, radial facing, nitrogen treatment and copper bush fine boring. The cylinder block assembly disclosed by the invention is easy to machine and produce, and capable of decreasing production cost; a sintering process for the cylinder block is simple; and the sintered layer is not liable to fall off.
Owner:龙工(上海)精工液压有限公司
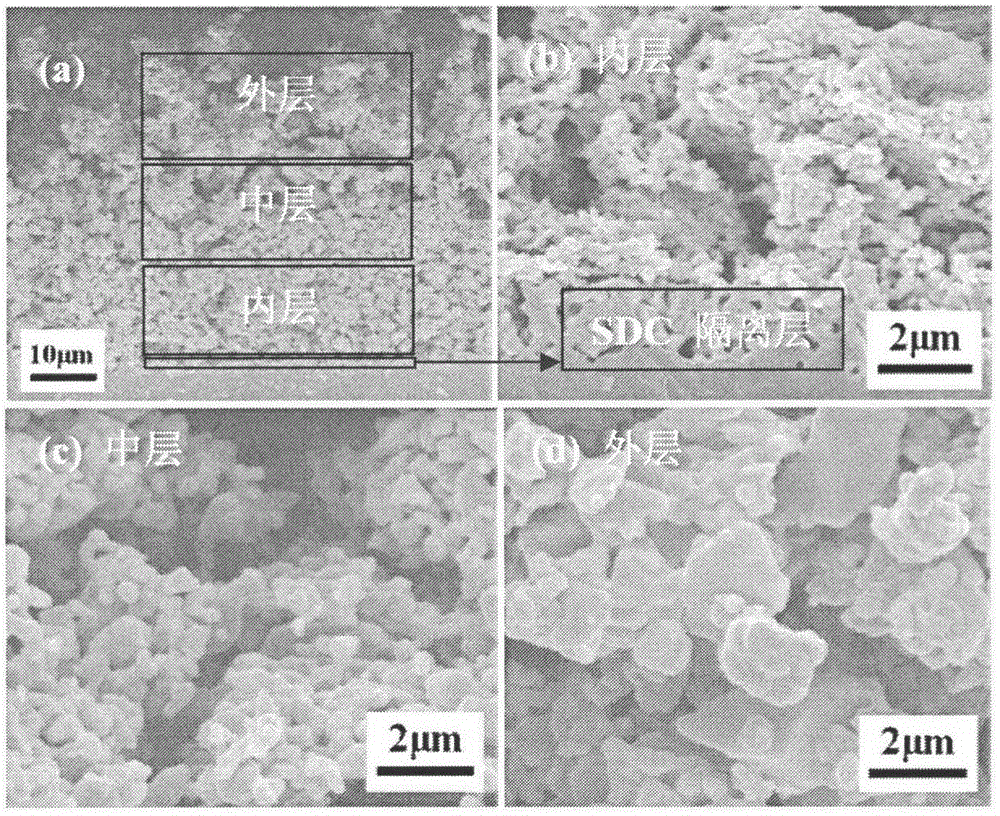
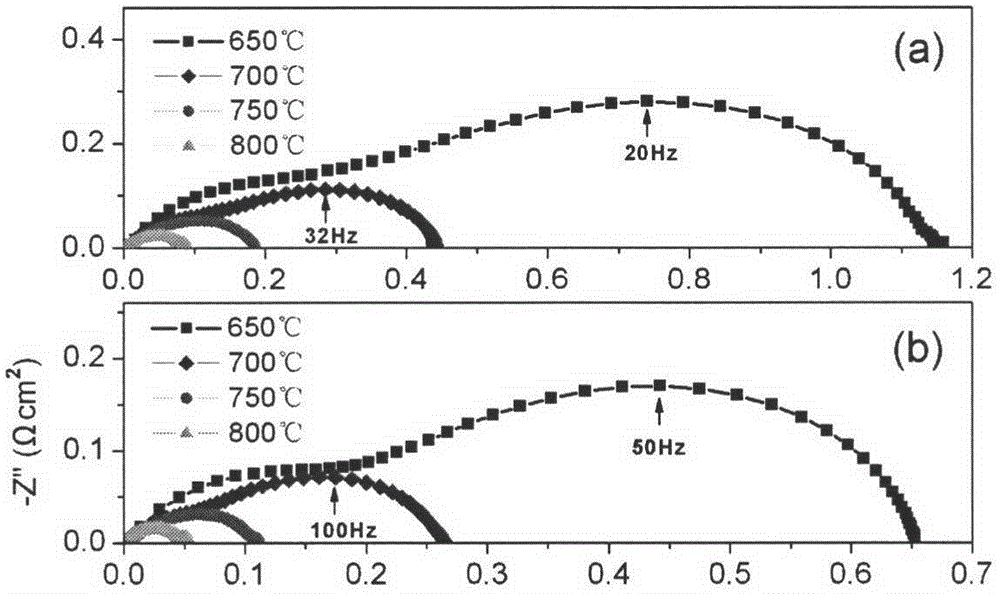
Preparation method of solid oxide fuel cell gradient structure cathode film
InactiveCN104577142AReduce interface impedanceIncrease contactCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPorosityFuel cells
The invention discloses a preparation method of a solid oxide fuel cell gradient porous structure cathode film and belongs to the technical field of electrode design and preparation. A solid oxide fuel cell cathode is subjected to a gradient design and is divided into an inner layer, a middle layer and an outer layer; and the cathode film with the gradient-changeable grain diameter, gradient-changeable air pore size and gradient-changeable porosity is prepared by adopting a laminating tape casting process. The preparation method is simple and low in cost; and a prepared single cell has a good electrochemical performance and is expected to be applied and developed in commercialized production in middle-temperature and low-temperature flat plate type solid oxide fuel cells.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Resin-coated ferrite carrier for electrophotographic developer, its production method, and electrophotographic developer using the resin-coated ferrite carrier
A spherical resin-coated ferrite carrier for an electrophotographic developer which can maintain a stable resistance and chargeability, a favorable charge rising property because of an excellent fluidity, and has a suitable durability, its production method which is excellent in economic efficiency and production stability, and an electrophotographic developer using the resin-coated ferrite carrier, are provided. A resin-coated ferrite carrier for an electrophotographic developer which is a spherical resin-coated ferrite carrier, wherein a carrier core material thereof has an irregular surface to improve the adhesive strength to a resin coat, and wherein the irregularity of the surface takes a finely streaked wrinkle pattern, its production method, and an electrophotographic developer using the resin-coated ferrite carrier, are employed.
Owner:POWDERTECH
Method for preparing high-flatness tungsten-nickel-iron alloy plate
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high-flatness tungsten-nickel-iron alloy plate. The method comprises the following steps of pressing granulated and dried tungsten-nickel-iron alloy powder, and rolling the tungsten-nickel-iron alloy powder to obtain a tungsten-nickel-iron alloy green body with a thickness of 0.5 to 1.8mm and uniform density; placing the obtained tungsten-nickel-iron alloy green body into a sintering furnace, sintering the tungsten-nickel-iron alloy green body under the protection of hydrogen, and cold-rolling the sintered tungsten-nickel-iron alloy green body until the deformation reaches 40 percent; re-sintering the cold-rolled tungsten-nickel-iron alloy green body for 1 to 3 hours at the re-sintering temperature of 1,100 to 1,300 DEG C under the protection of hydrogen; repeating the former two steps until the thickness of the green body is smaller than 0.4mm; overlaying two tungsten-nickel-iron alloy plates with the thickness of 0.15mm, and rolling-milling the tungsten-nickel-iron alloy plates for about 25 times under the pressure of about 15T until the thickness of a single plate is less than 0.1mm. According to the method, a production process is simplified, the energy consumption is lowered, the production cost is reduced, and green production is ensured.
Owner:上海六晶科技股份有限公司
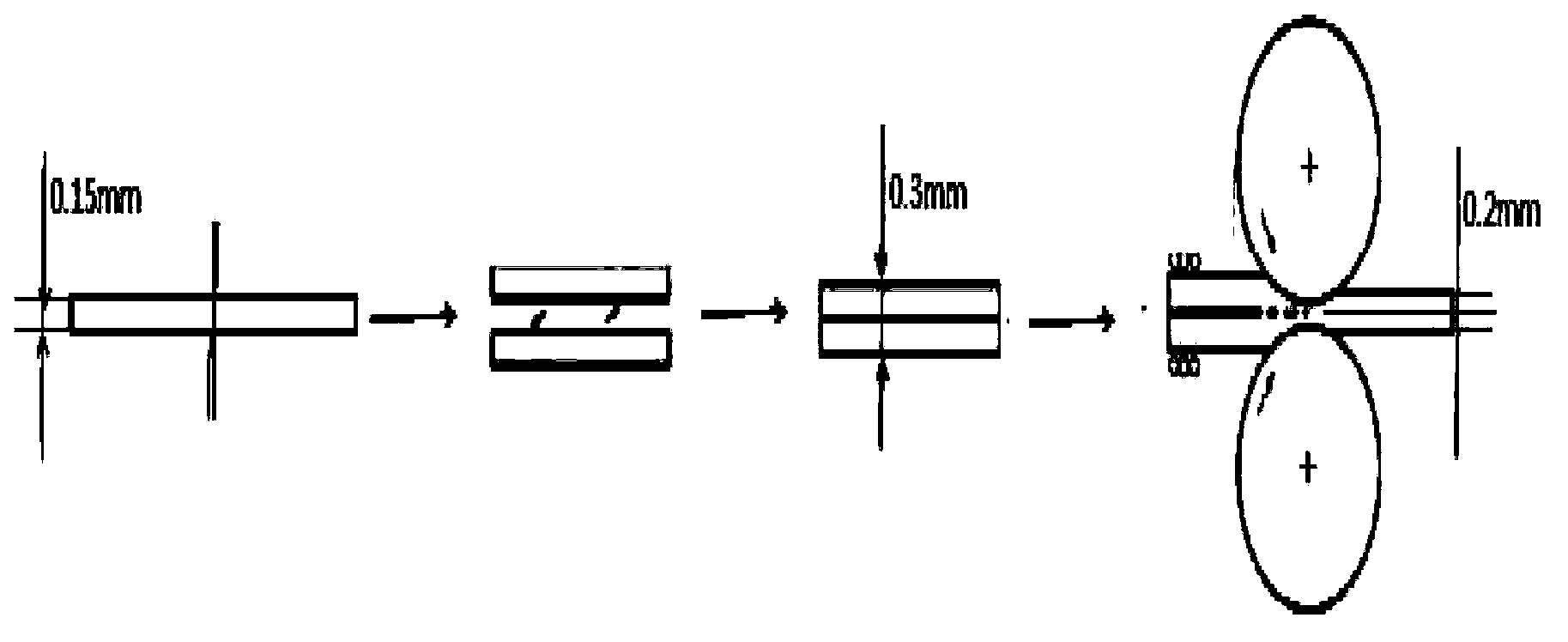
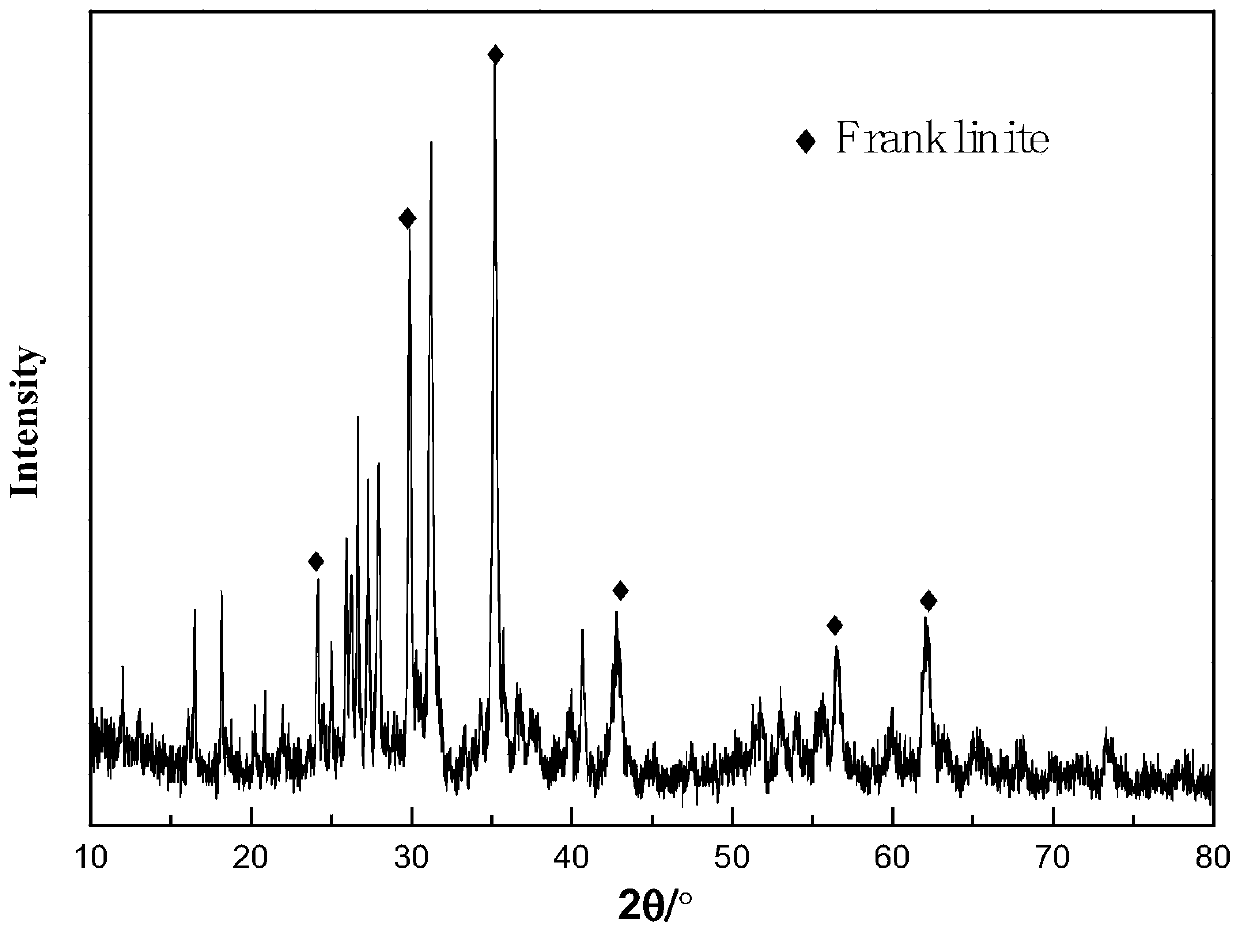
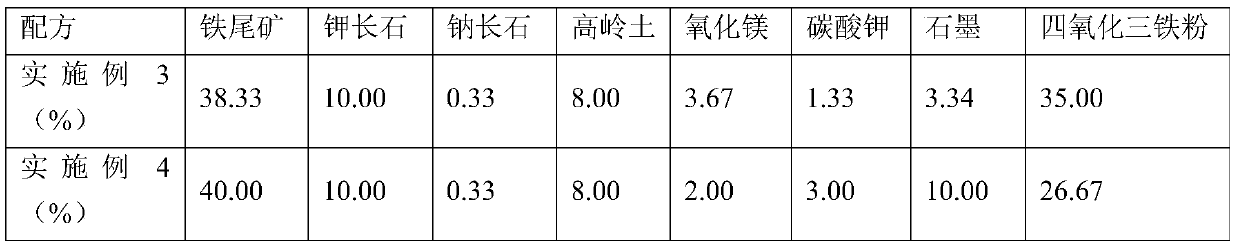
Iron tailing heat-adsorption ceramic material, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110194653AReduce manufacturing costReduce dependenceCeramic materials productionClaywaresKaolin clayThermal coefficient
The invention discloses an iron tailing heat-adsorption ceramic material, and a preparation method thereof. 100% of iron tailing heat-adsorption ceramic material comprises, by mass, 37-42% of iron tailings, 6-10% of kaolin, 1-13.33% of graphite, 5-12% of potassium feldspar, 0.2-0.5% of albite, 1-3% of potassium carbonate, 1 to 4% of magnesium oxide, and 26-35% of ferriferrous oxide. The infrared emission rate of the ceramic material is 0.75 or higher, the 300 DEG C heat conductivity coefficient is 1.70W / (m.K) or higher, the compressive strength is 70MPa or higher, after 25 times of thermal shock resistance tests, no surface cracking is caused (from room temperature to 400 DEG C), and the ceramic material is black. According to the preparation method, the novel heat-adsorbing function ceramic is prepared from iron tailings, adsorption on solar energy is realized, and waste is turned into valuables.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Novel nickel-aluminum-base self-repairing composite material and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a novel nickel-aluminum-base self-repairing composite material. The novel nickel-aluminum-base self-repairing composite material is prepared with nickel powder, aluminum powder, serpentine powder and titanium carbide powder as raw materials. By mass percent, the nickel powder accounts for 57.8%-63.1%, the aluminum powder accounts for 31.2%-33.9%, the serpentine powder accounts for 2%-8%, and the titanium carbide powder accounts for 1%-3%. The invention further discloses a preparing method of the novel nickel-aluminum-base self-repairing composite material. The above raw materials are placed in a high-frequency vibration material mixer with the vibration force being 9,000 N, vibration and material mixing are conducted for 15 min, sintered ingredients evenly mixed are obtained and are placed in a graphite grinding tool, spark plasma sintering is adopted for preparing, and the novel nickel-aluminum-base self-repairing composite material is obtained. The novel nickel-aluminum-base self-repairing composite material prepared through the method has good abrasion resistance, friction reduction and self-repairing performance, the preparing technology is simple, parameters are easy to control, cost is low, and the novel nickel-aluminum-base self-repairing composite material is suitable for batched production and popularization.
Owner:WUHAN MARINE ELECTRIC PROPULSION RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP NO 712 INST
Method for preparing high-compactness hafnium diboride ceramics
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-compactness hafnium diboride ceramics. According to the method, hafnium diboride powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling, acid washing, vacuum treatment and encapsulation and pre-pressing with high-melting point covering materials, and is then directly sintered into the high-compactness hafnium diboride ceramics under the conditions of 3to 15 GPa and 600 to 2000 DEG C. A high-temperature and high-pressure method is used for preparing a pure phase hafnium diboride block material having a good crystal form and a microstructure for thefirst time; the characteristics of small crystal particle dimension, high crystallinity degree, high compactness degree and stable structure are realized; high hardness and excellent fracturing toughness are realized. The preparation process is simple; the high melting point, high intensity, high hardness, high toughness and high anti-oxidization performance are realized; the material is developedto become the novel high-temperature structure ceramic material, and can be used as a candidate material of an airplane engine high-temperature-resistant component, can also be developed into novel hard alloy, can replace tungsten carbide hard alloy cutters, and can also be applied to the field of mechanical cutting.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Si3N4-BN-MAS ceramic composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a Si3N4-BN-MAS ceramic composite material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of silicon nitride-based ceramic composite materials. The objective of the invention is to overcome the technical problems of high cost and low efficiency caused by too high sintering temperature, too great sintering pressure and poor machining properties during production of conventional silicon nitride-based ceramic composite materials. The Si3N4-BN-MAS ceramic composite material provided by the invention is prepared from MgO powder, Al2O3 powder, amorphous SiO2 powder, alpha-Si3N4 powder and hexagonal BN powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, mixing 1.0 to 1.5% of MgO powder, 3.2 to 3.8% of Al2O3 powder, 5.0 to 5.5% of SiO2 powder, 0.01 to 50% of BN powder and alpha-Si3N4 (being the balance), adding a medium and then carrying out ball milling; step 2, then carrying out drying, grinding and sieving successively; step 3, filing a mold with a substance obtained after sieving and carrying out pre-press molding; step 4, carrying out sintering under the protection of an inert gas so as to obtain the Si3N4-BN-MAS ceramic composite material. The preparation method is applied to the field of preparation of Si3N4-BN-MAS ceramic composite materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Carbide-based ceramic material and preparation technology thereof
The invention provides a carbide-based ceramic material and relates to the technical field of ceramic preparation. The carbide-based ceramic material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-50 parts of silicon carbide, 5-15 parts of titanium carbide, 3-9 parts of molybdenum carbide, 0.5-11 parts of tungsten carbide, 0.1-0.5 part of vanadium carbide, 0.1-0.5 part of hafnium carbide, 3-10 parts of aluminum oxide, 2-6 parts of boron nitride, 2-8 parts of magnesium zirconate, 11-15 parts of paraffin, 0.3-1.1 part of cerium oxide, 3-7 parts of potassium oxide, 5-15 parts of polyethylene glycol and 1.5-3 parts of additives. The carbide-based ceramic material prepared according to the invention has ultrahigh hardness and excellent chemical stability; the problem of high brittleness of the present carbide-based ceramic is solved; the preparation technology provided by the invention is simple; a high-density ceramic material can be acquired through sintering under normal pressure.
Owner:FOSHAN LANTU TECH CO LTD
Low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics and sintering method thereof
The invention relates to low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics comprising 97 to 99.5 percent of La2Zr2O7 and 0.5 to 3 percent of CuO-TiO2 by percent weight. A preparation method of the low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics comprises three steps of proportioning / mixing, pressing and sintering. According to the low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics and the preparation method of the low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics, La2Zr2O7 ceramics is obtained by using common normal-pressure sintering through introducing a binary sintering adjuvant of the CuO-TiO2 into the La2Zr2O7; a liquid phase is formed at low temperature by utilizing the CuO-TiO2 through regulating the content of the CuO-TiO2 and controlling a sintering process, so that an La2Zr2O7 sintering mechanism is converted from solid-phase sintering to liquid-phase sintering; therefore, the sintering temperature is greatly lowered; and a compact La2Zr2O7 ceramic block body is obtained at about 1100 DEG C, the prepared ceramics has smaller crystal grains, the mechanical property is good, and the energy consumption is low. According to the low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics and the preparation method of the low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics, the components are reasonable, the preparation process is simple, the sintering temperature is low, and the La2Zr2O7 crystal grains prepared by sintering are fine and compact; and the preparation of a ceramic material of an La2Zr2O7 thermal barrier coating or an La2Zr2O7 block body at low temperature can be realized. The low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics and the preparation method of the low-temperature liquid-phase sintered La2Zr2O7 ceramics are suitable for industrialized application.
Owner:江苏兴云新能源有限公司
Preparation method for Ti2SnC reinforced Ag-based electrical contact materials
The invention relates to a preparation method for Ti2SnC reinforced Ag-based electrical contact materials. The composite materials are composed of Ti2SnC and an Ag base body, wherein the mass percentage of the Ti2SnC reinforcement phase is 1-50%. The Ti2SnC powder and Ag powder are mixed for 5-240 min at a ratio, and then subjected to cold press molding under the pressure of 100-800 MPa. A green body is sintered for 1-12 h at 600-1000 DEG C in a protection atmosphere or vacuum, and then the Ti2SnC reinforced Ag-based composite electrical contact materials are obtained. The Ag / Ti2SnC composite electrical contact materials prepared through the method have the advantages of being high in density, uniform in structure, moderate in hardness, good in electrical conductivity and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Resin-coated ferrite carrier for electrophotographic developer, its production method, and electrophotographic developer using the resin-coated ferrite carrier
ActiveUS7824833B2Improve joint strengthImprove maintainabilityDevelopersEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A spherical resin-coated ferrite carrier for an electrophotographic developer which can maintain a stable resistance and chargeability, a favorable charge rising property because of an excellent fluidity, and has a suitable durability, its production method which is excellent in economic efficiency and production stability, and an electrophotographic developer using the resin-coated ferrite carrier, are provided. A resin-coated ferrite carrier for an electrophotographic developer which is a spherical resin-coated ferrite carrier, wherein a carrier core material thereof has an irregular surface to improve the adhesive strength to a resin coat, and wherein the irregularity of the surface takes a finely streaked wrinkle pattern, its production method, and an electrophotographic developer using the resin-coated ferrite carrier, are employed.
Owner:POWDERTECH
Sintering method for high saturated flux density MnZn ferrite
ActiveCN100466114CHigh saturation flux densityLow costInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyPartial pressure
This invention provides a sintering method for a high-saturated flux density MnZn ferrite including the following steps: a, a first temperature-rising stage, b, a second temperature-rising stage, c, a heat preservation stage, d, temperature-reducing, which can increase the saturated flux density of MnZn ferrite greatly by controlling the temperature and oxygen partial pressure during the sintering process, besides, no expensive asistant components are needed in the preparation process.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Method used for preparing AgSbTe2 thermoelectric material
InactiveCN104961107AHigh densityGood repeatabilityBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsHigh energyVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to a method used for preparing a AgSbTe2 thermoelectric material. The method comprises following steps: 1) material preparation, wherein silver telluride and antimony telluride are taken as main raw materials, trace elemental tellurium is taken as a thermoelectric performance regulating composition, and silver telluride, antimony telluride, and elemental tellurium are weighed at a molar ratio of (0.9-1.1)(0.9-1.1):x as reaction raw materials, and x ranges from 0 to 0.04; 2) high energy ball milling, wherein the raw materials disclosed in step 1) are subjected to high energy ball milling in inert gas protection atmosphere so as to obtain single-phase AgSbTe2 powder; and 3) spark plasma sintering, wherein the single-phase AgSbTe2 powder is subjected to spark plasma sintering so as to obtain the compact AgSbTe2 thermoelectric material. The raw materials are stable in the air; oxidation is not easily caused; the whole technology is simple and controllable; preparation cost is low; repeatability is high; density of the prepared AgSbTe2 block material is high; phase is pure; and thermoelectric performance is excellent.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com