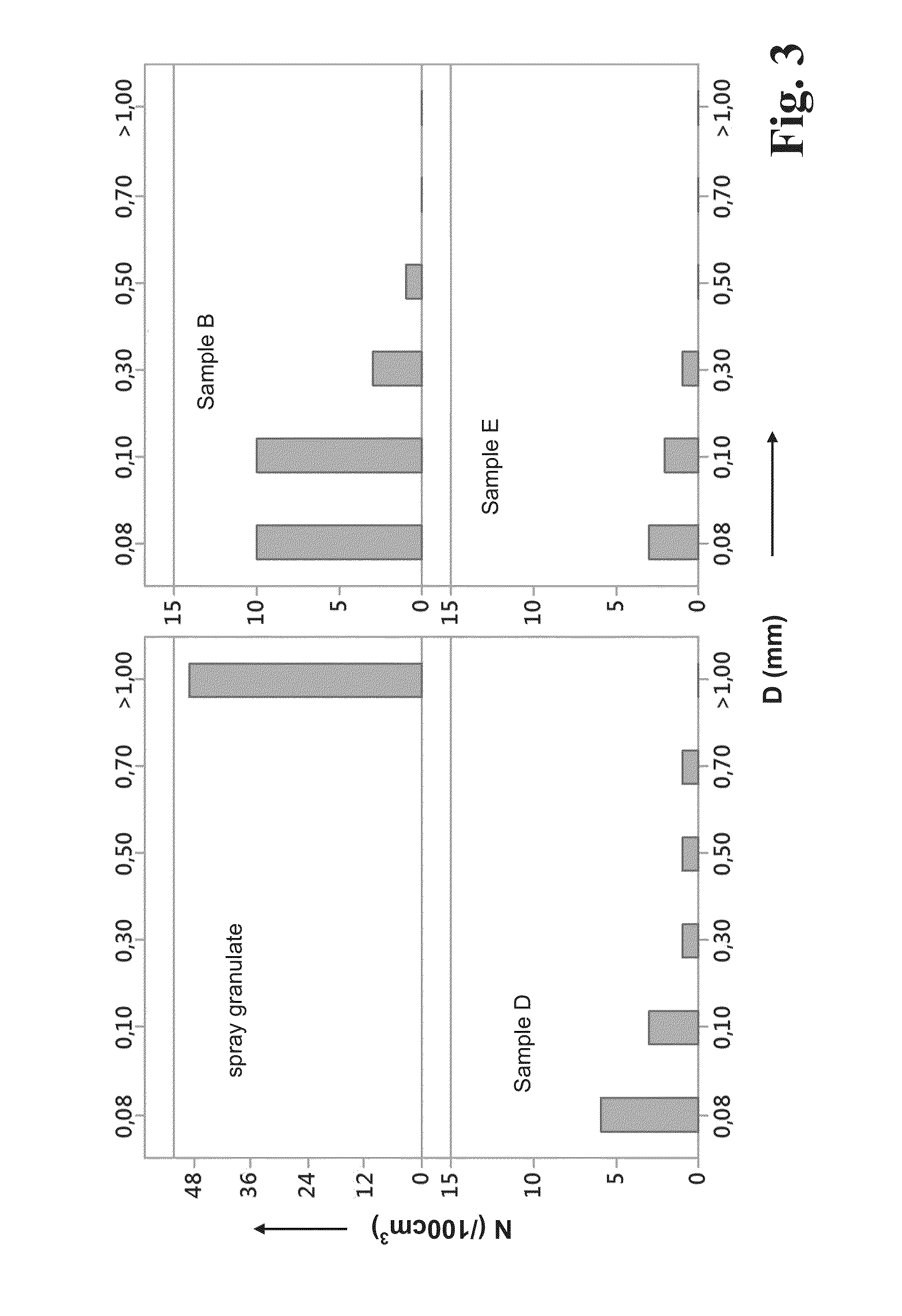
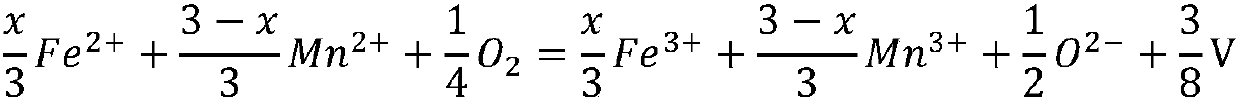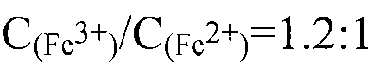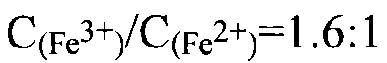Patents
Literature
288 results about "Sintering atmosphere" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Controlled Atmosphere Sintering is the process of forming a solid mass of material by heat and/or pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. The study of sintering in metallurgy powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy. An example of sintering can be observed when ice cubes in a glass of water adhere to each other.
Atmosphere control method for sintering process of high-frequency wide-temperature low-loss MnZn ferrite
ActiveCN107555984AHigh densityIncreased power lossInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureHeat conservationFerrite (magnet)
The invention provides a sintering atmosphere control method in preparation of high-frequency wide-temperature low-loss MnZn ferrite. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out primary heating and heat preservation, carrying out secondary heating and heat preservation, cooling, carrying out heat preservation, and finally cooling. According to the method, corresponding oxygen partial pressure is adjusted at different temperatures and in different temperature changing processes, zinc loss in a sintering process can be reduced, and element valence change and impure phase precipitationat high temperature are inhibited, so that the soft magnetic property of the material is improved; and by adding reasonable heat preservation time, sintering internal stress can be effectively reduced, and the material is prevented from cracking in the sintering process. The method provided by the invention is applicable to preparation of multiple MnZn ferrites, and the wide-temperature low-lossMnZn power ferrite used at the frequency of 0.1-5MHz can be obtained; reasonable technological parameters can improve yield in preparation process, and a product with uniform and stable performance can be beneficially obtained; and the method is simple and practicable and has practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Online self-sharpening metallic bond and super-hard abrasive precision grinding pellet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103009270ALow shrinkageHigh strengthAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesPolyvinyl alcoholDecomposition
The invention provides an online self-sharpening metallic bond and super-hard abrasive precision grinding pellet and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of precision grinding pellets. Raw materials of the precision grinding pellet comprise a super-hard abrasive and a metallic bond, wherein the super-hard abrasive is diamond micro-powder; the diamond concentration falls within a range of 75-100 %; and the metallic bond uses a multicomponent alloy bond whose main components are copper powder, tin powder, aluminum powder, copper-clad ball shaped graphite powder, silicon dioxide and ferroferric oxide powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing and stirring the diamond micro-powder as well as the copper powder, the tin powder and the aluminum powder; adding polyvinyl alcohol to a mixture and mixing the polyvinyl alcohol and the mixture; adding the silicon dioxide, the copper-clad ball shaped graphite powder and the ferroferric oxide powder to an obtained mixture and mixing these materials and the obtained mixture; filling the mixture into a graphite mold; maintaining the pressure of the graphite mold for 5-10 minutes after pressurizing the graphite mold to 100-250 MPa; and carrying out hot pressing sintering on the graphite mold in a sintering furnace, wherein the sintering atmosphere is ammonia decomposition gas. Through the adoption of the online self-sharpening metallic bond and super-hard abrasive precision grinding pellet provided by the invention, online automatic sharpening can be achieved without blockage and offline repairing.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Oxide sintered body, manufacturing method therefor, manufacturing method for transparent conductive film using the same, and resultant transparent conductive film
The present invention relates to the oxide sintered body substantially containing zinc, tin and oxygen, useful as a target, which can be sputtered under charging of high DC power, without generation of arcing or crack, and a manufacturing method for an oxide transparent conductive film formable in high-speed, and the oxide transparent conductive film excellent in chemical resistance. The oxide sintered body substantially containing zinc, tin and oxygen; containing tin at an atomic number ratio, Sn / (Zn+Sn), of 0.23 to 0.50, and being composed mainly of a zinc oxide phase and at least one kind of zinc stannate compound phase, or being composed of at least one kind of zinc stannate compound phase; provided by a method for manufacturing the oxide sintered body by formulating an aqueous solvent to raw material powder containing powder of a zinc stannate compound, or mixed powder of tin oxide powder and zinc oxide powder, and after mixing the resulting slurry for equal to longer than 15 hours, by subjecting the slurry to solid-liquid separation, drying and granulation, and subsequently compacting by charging the granule into a mold, followed by sintering the resultant compact under sintering atmosphere at 1300 to 1500° C. for equal to or longer than 15 hours.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Method of manufacturing powder metallurgy nitrogen/high nitrogen containing stainless steel parts
The present invention relates to a method for preparing powder metallurgic nitrogen-contained / high-nitrogen stainless steel components, and comprises the following steps: raw materials preparation, forming, degreasing treatment, sintering and other static press, wherein, during the static press such as the sintering, the temperature increasing speed is 3 to 10 DEG C per minute; the sintering gas is the pure nitrogen or the mixed gas of the nitrogen, hydrogen and the argon; the pressure / partial pressure of the nitrogen is consistent with the solubility of the nitrogen in the alloy system; the sintering temperature is 1200 to 1450 DEG C, and the heat preservation period is 10 to 20 minutes; after the density is more than 90 to 95 percent, the pressure is increased to 3 to 10 MPa; the partial pressure is maintained the same during the pressure increasing process, and the pressure is distributed on the argon and the hydrogen, and the heat preservation period is 60 to 240 minutes; after the density is more than 99 percent, the pressure is decreased and rapid cooling is performed. The content of the nitrogen of the component that is made with the method hereinabove can be controlled to the highest level; the composition constitution is uniform, the density is high, the flexibility is good, the deformation is less, the precision is high and the corrosion-resistance is good.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Magnetic pearlescent pigment and preparation method thereof
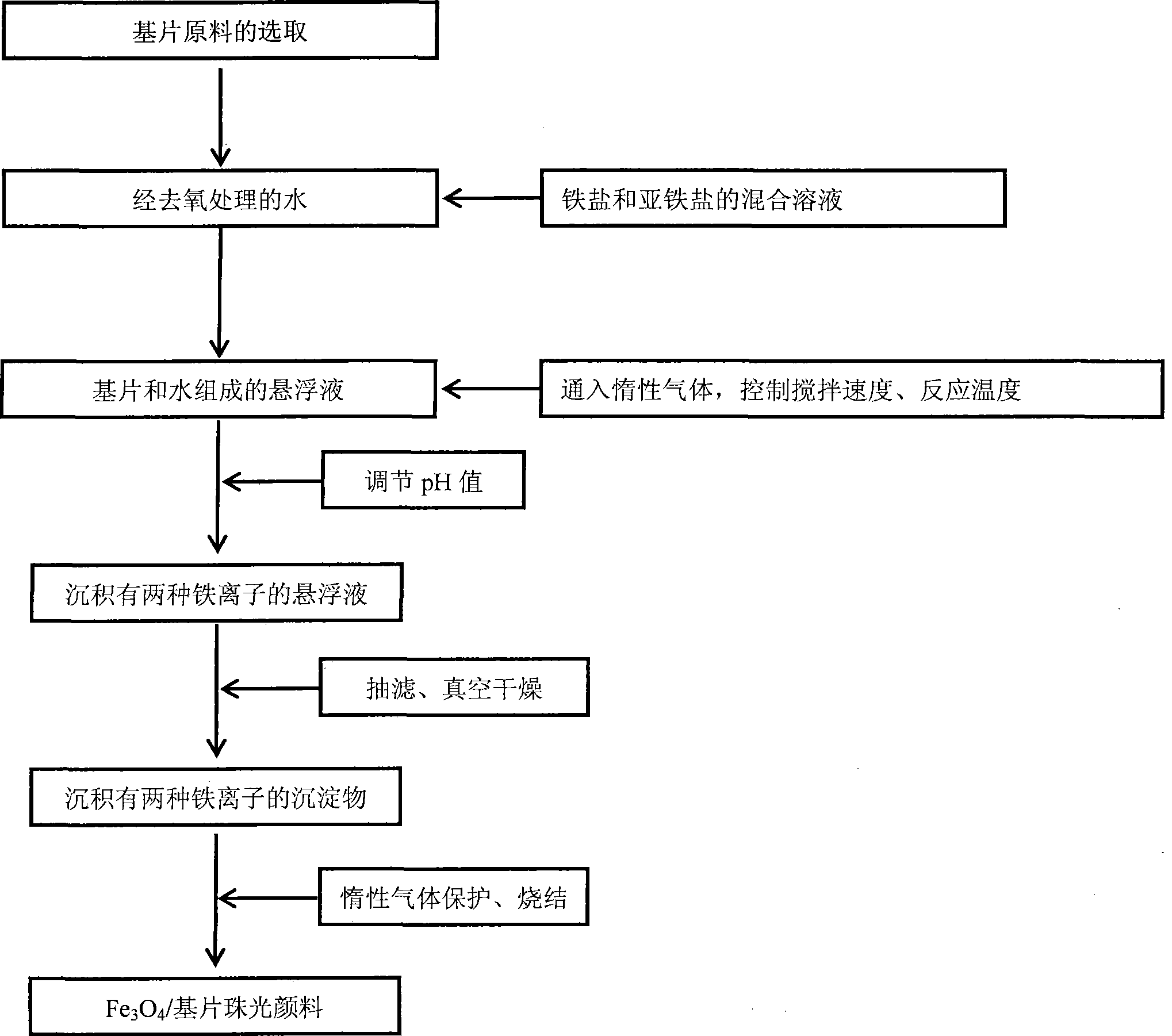
The invention discloses a magnetic pearlescent pigment and a preparation method thereof. The magnetic pearlescent pigment has black luster and takes a substrate with a particle diameter of 10-60mum as a cladding substrate, and the substrate is clad with Fe3O4. The preparation method of the magnetic pearlescent pigment comprises the following steps: dropwise adding ferric iron salt solution and ferrous iron salt solution to mica suspension at a certain temperature; controlling pH value for coprecipitation to deposit the precipitated ferroferric oxide evenly and compactly on the mica under the protection of inert gas; calcining in an inert atmosphere to prepare the magnetic pearlescent pigment. The prepared magnetic pearlescent pigment has a flat and compact deposition surface, high cladding rate and obvious pearlescent effect. The preparation method helps realize coprecipitation of the ferric iron and the ferrous iron and cause the ferroferric oxide to clad a sericite substrate evenly. The preparation method is suitable for the preparation of various pearlescent pigments, and a coprecipitation method and sintering atmosphere control are introduced to provide the possibility of depositing and cladding the oxides with different valences.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY +1
Method of preparing titanium dioxide, stannum dioxide and doping composite fiber material thereof
InactiveCN101033082AGood lookingSimple structureNanostructure manufactureTitanium dioxideTin dioxideNitrogen gas
This invention relates to a method for preparing fiber TiO2, SnO2 and its doped compound material characterizing in utilizing a fiber material as a template, taking TBT, titanium tetrahalide, tin tetrachloride or a mixture as a precursor, which is carried by nitrogen or argon and enters into a reactor with a gas containing ammonia for chemical gaseous phase deposition, in which, the gas flow, deposition temperature and the sinter atmosphere and temperature are controlled, the inert gas is heated to get load-type fiber material to be sintered under the atmosphere of oxidation and reaction to remove the fiber template and form an oxide fiber material, and utilize the active carbon fiber template and ignition process to form porous fiber or tubular fiber material.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Tungsten based composite material with granules of double carbide enhanced
A composite carbide particles reinforced W-base composition is prepared from composite carbide particles (10-60 vol.%) and W-base composition through sintering in H2, argon gas, N2, or vacuum at 1900-2300 deg.C. Said composite carbide may be chosen from 4Tac.Zrc, 4Tac.Hfc, TiC.NbC.TaC.HfC, and ZrC.NbC.TaC.HfC. Its advantages are high mechanical performance, and high resistance to oxidizing and ablation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Porous Thermoelectric Material and Process for Producing the Same
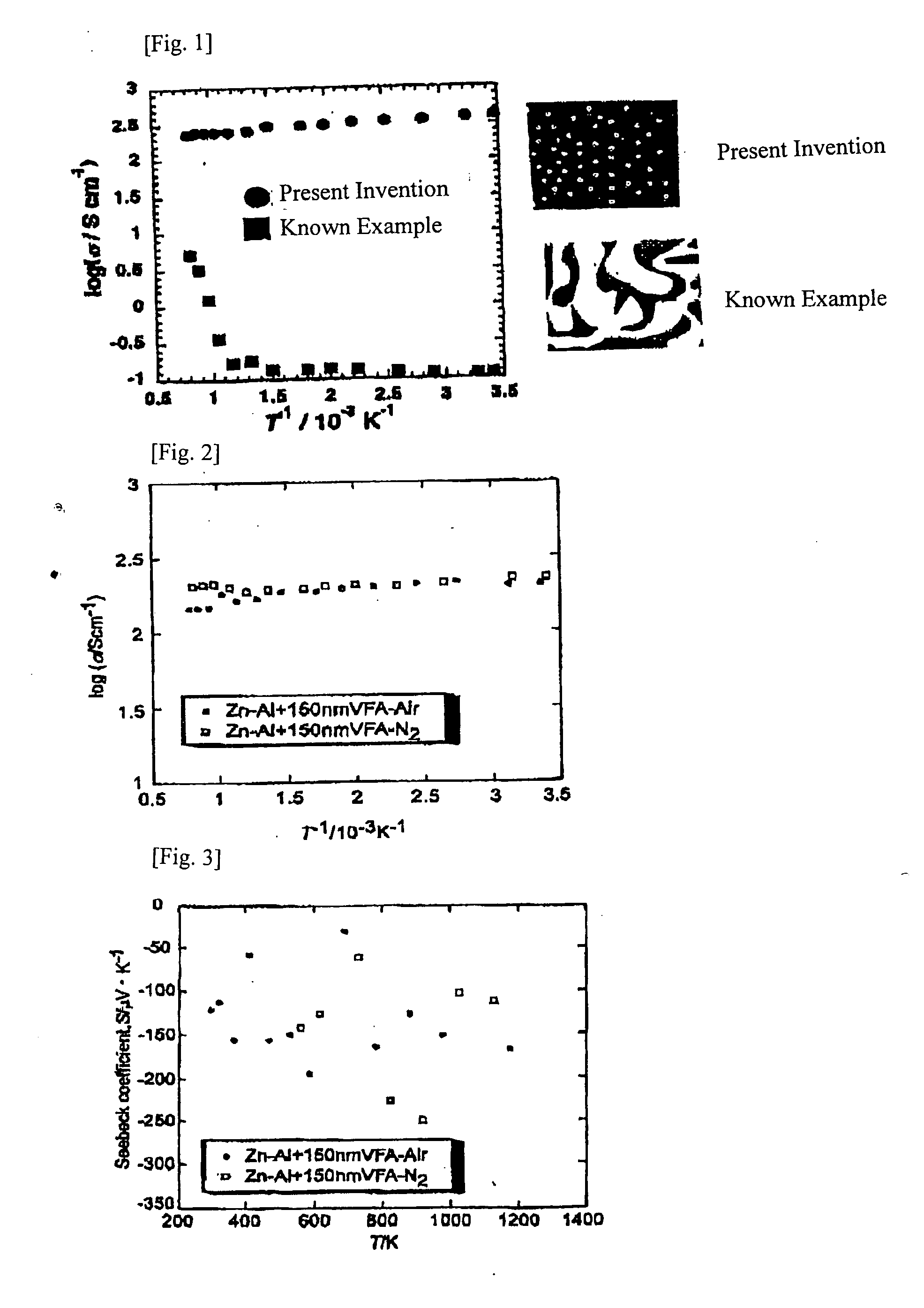
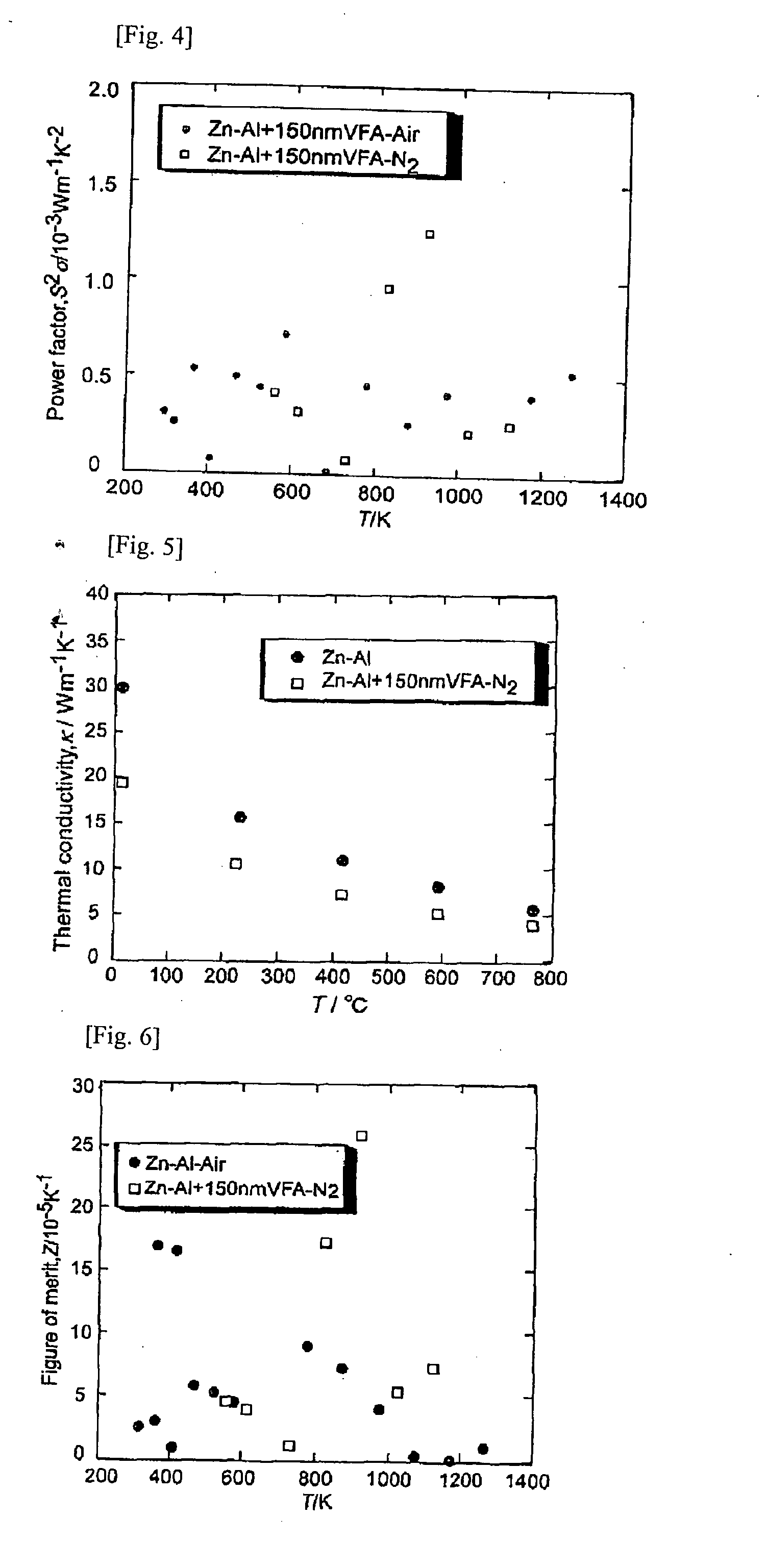
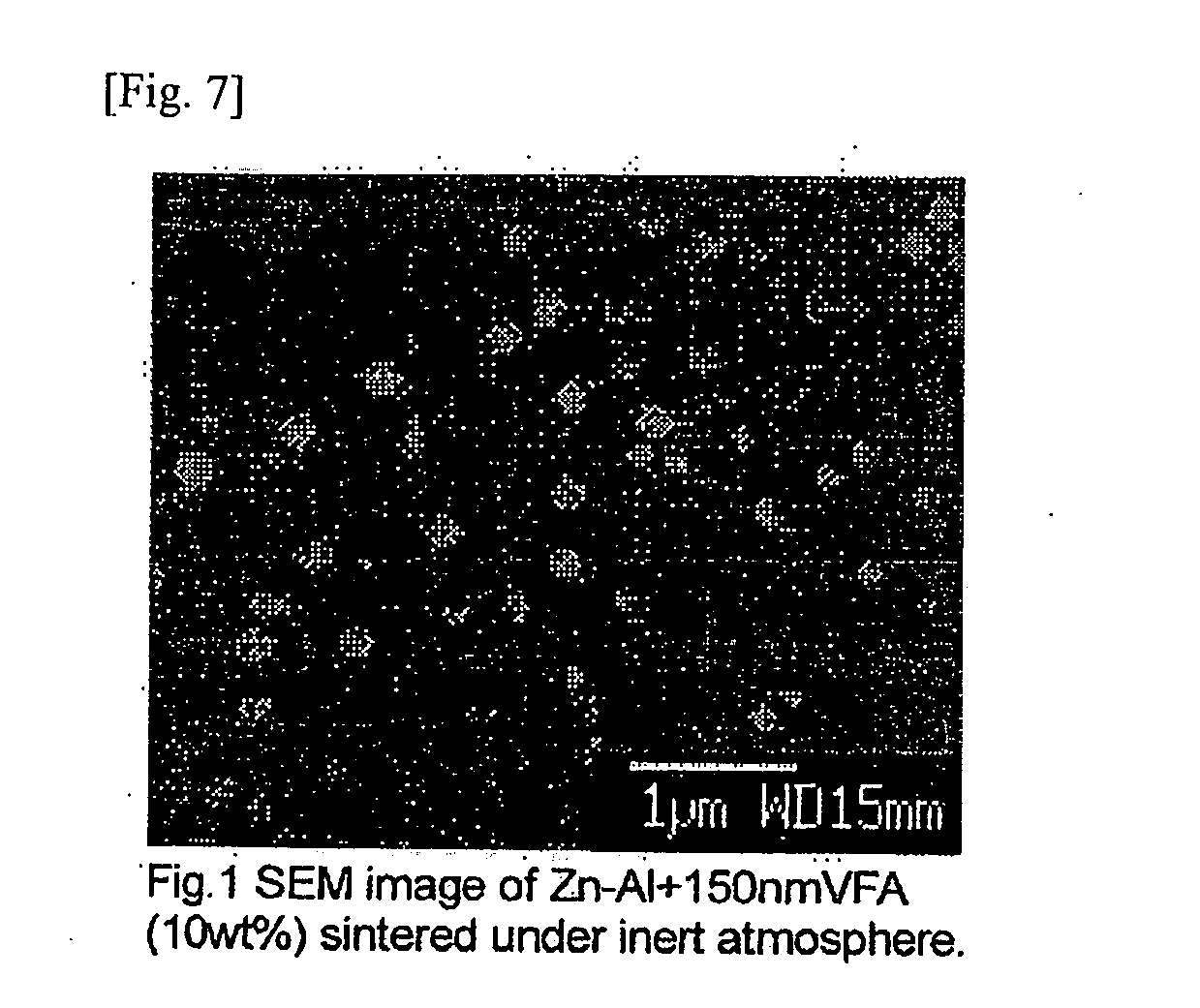
InactiveUS20070240749A1Improve energy efficiencyReduce carbon dioxide emissionsThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsMetallurgy
In a thermoelectric conversion material composed of a porous material, continuous electrical conduction paths are provided by forming voids in the form of independent closed pores or independent closed air tubes inside the material. For example, in producing a sintered body of a thermoelectric material, microparticles having a particle diameter of 1 μm or less serving as a void-forming agent are mixed in a base powder, and in sintering, the sintering atmosphere or sintering temperature is controlled so that after the densification of a solid part formed by sintering the base powder proceeds, the microparticles of the void-forming agent are gasified, thereby producing a porous thermoelectric material having a structure in which minute independent closed pores having an average pore diameter of 1 μm or less are dispersed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Porous cubic boron nitride based material suitable for subsequent production of cutting tools and method for its production
The presently claimed invention relates to a method of making a PcBN cutting tool insert. The method includes the following steps: mixing raw material powders, (e.g., cBN, hBN, TiC, TiN, Ti(C,N), WC, W, C, Co, Co2Al9, Al AlN, Al2O3) with a liquid (e.g., ethanol) and an agent (e.g., polyethylene glycol, PEG) to form a homogeneous slurry with the desired composition; forming spherical powder agglomerates, typically 100 mum in diameter, preferably by spray drying; pressing said agglomerates to form a body of desired dimensions and density using conventional tool pressing technology; removing the agent from the powder at a suitable temperature and atmosphere; raising the temperature to 1000-1350° C. in vacuum; solid state sintering the body at 1000-1350° C. in vacuum, for 1-90 minutes to form a body with 35-55 vol % porosity; optionally, adding 0.5-1000 mbar of nitrogen to the sintering atmosphere at the hold time or during cooling; and HP / HT treating the porous body to form a dense body of desired shape and dimension.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Energy-saving ceramic tunnel kiln
ActiveCN101762154AStable temperatureUniform temperatureFurnace typesCeramic materials productionTunnel kilnElectricity
The invention provides an energy-saving ceramic tunnel furnace. A kiln body is provided with a peheating zone, a clinkering zone and a cooling zone, wherein the clinkering zone is vertically provided with two baffle walls at two ends of a high-temperature zone of between 1,300 and 1,380 DEG C, and the baffle walls are fixed on a kiln top by using a metal hanging piece; the upper part of the high-temperature zone is isolated from the upper parts of other temperature zones, so that the temperature of the high-temperature zone is relatively stable, the temperature of the upper and lower parts is more uniform, and thus the tunnel kiln is favorable for sintering products and saving fuel gas. A combustion system is controlled by adopting full-automatic air / fuel ratios, the fuel gas and combustion air enter a fuel gas burner through precise control and mixing to be combusted in the kiln completely, so that the highest heat value is obtained, surplus air is prevented from entering the kiln, and fuel is saved. A smoke exhaust fan and a combustion fan are controlled by adopting frequency control of motor speed, so that the stability of kiln pressure, the pressure of the combustion air and sintering atmosphere is maintained, the quality of the products is improved and electricity is saved.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHUNXIANG PORCELAIN
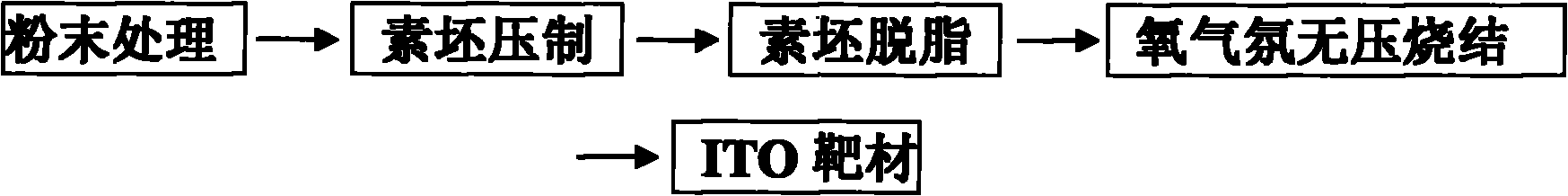
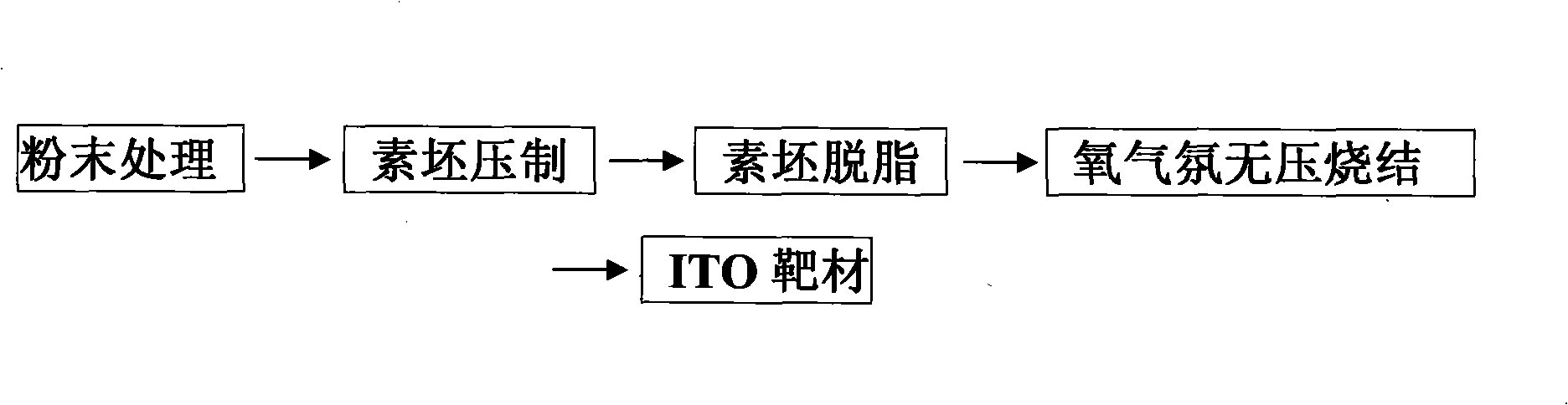
Method of preparing ITO target material by oxygen atmosphere pressureless sintering process
The invention discloses an innovative method of sintering ITO target material, and aims to realize pressureless oxygen atmosphere sintering by optimizing sintering process, and finally to obtain target material having high density and high performance. With sintering method as the basis and according to sintering characteristics of the ITO target material, the method adopts segmented sintering process, and controls oxygen partial pressure of the sintering atmosphere by controlling oxygen flow entering into a hearth to inhibit decomposition of the target material, and to finally obtain the high conductive performance target material, the density of which is more than 99.3%. The oxygen atmosphere pressureless sintering method is a novel ceramic sintering method, and is mainly applied to thesintering of oxide ceramics easy to decompose. Equipment for the method is simple, and products to be sintered are not restricted by size, so large-size ceramics can be produced. It is the first timeto produce the ITO target material by the method, and the ITO target material produced by the method is better than that produced by the commonly used sintering process with hot pressing, sintering process with hot isostatic pressing or common normal pressure sintering process.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of making a fine grained cemented carbide
According to the present invention there is provided a method of making a finegrained tungsten carbide—cobalt cemented carbide comprising mixing, milling according to standard practice followed by sintering. By introducing nitrogen at a pressure of more than 0.5 atm into the sintering atmosphere after dewaxing but before pore closure a grain refinement including reduced grain size and less abnormal grains can be obtained.
Owner:SANDVIK AB
Alumina titanate ceramica lift tube preparation method
The invention relates to a preparation method of ceramic materials; the raw materials used in the method comprises alumina powder, titanium oxide powder, synthetic material of aluminium titanate and stabilizing agents, wherein, the stabilizing agents comprise magnesium oxide, silica dioxide, ferric oxide, chromium dioxide and zirconium oxide. The conditions of the preparation process are as follows: firstly, the raw material and water carry out ball milling and pulping by a wet method; secondly, the slurry is granulated and dried into powder with the water content to be less than 2 percent; thirdly, isostatic pressing molding is carried out; fourthly, the powder is sintered into a lift tube of aluminium titanate ceramics under the conditions that the sintering temperature is 1,480 to 1,550 DEG C, the sintering time is 20 to 30 hours and the sintering atmosphere is oxidizing atmosphere; wherein, alumina powder, titanium oxide powder, stabilizing agents and water carry out ball milling and pulping by the wet method and granulation to prepare particle size, then the synthetic material of aluminium titanate is prepared by sintering. The product prepared by the method is characterized by low price, non-infiltration of alumina melt, no reaction, high intensity, strong thermal shock resistant capability, no slag during the using process, long service life, etc.
Owner:DONGYING XINKEXINTETAO
Preparation method of micro-nano particle reinforced aluminium matrix composite
The invention provides a preparation method of a micro-nano particle reinforced aluminium matrix composite and belongs to the field of an aluminium matrix composite preparation technology. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out high-energy ball milling on powdery aluminium base alloy and reinforcement powder; carrying out vacuum drying on the prepared composite powder after the end of ball milling and sieving; and carrying out supersonic vibration on the dried and sieved composite powder and carrying out pressureless sintering on the dispersible powder by controlling sintering atmosphere so as to prepare a fully-densified powder metallurgy aluminum matrix composite blank, and carrying out hot working such as extrusion, rolling, die forging and the like on the blank so as to obtain the required aluminium matrix composite. By a brand-new activated sintering densification technology, the composite powder directly undergoes supersonic vibration and densification sintering under atmosphere protection without pressing so as to prepare the fully-densified micro-nano particle reinforced aluminium matrix composite blank. The prepared aluminium matrix composite has uniform reinforcement phase distribution and excellent product performance. The method has no limit in size and shape of the product, is low-cost and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:天津海力特新材料有限公司
Porous cubic boron nitride based material suitable for subsequent production of cutting tools and method for its production
InactiveUS6676893B2Electrically conductive connectionsRelieving strain on wire connectionPorosityDense body
The presently claimed invention relates to a method of making a PcBN cutting tool insert. The method includes the following steps:mixing raw material powders, (e.g., cBN, hBN, TiC, TiN, Ti(C,N), WC, W, C, Co, Co2Al9, Al AlN, Al2O3) with a liquid (e.g., ethanol) and an agent (e.g., polyethylene glycol, PEG) to form a homogeneous slurry with the desired composition;forming spherical powder agglomerates, typically 100 mum in diameter, preferably by spray drying;pressing said agglomerates to form a body of desired dimensions and density using conventional tool pressing technology;removing the agent from the powder at a suitable temperature and atmosphere;raising the temperature to 1000-1350° C. in vacuum;solid state sintering the body at 1000-1350° C. in vacuum, for 1-90 minutes to form a body with 35-55 vol % porosity;optionally, adding 0.5-1000 mbar of nitrogen to the sintering atmosphere at the hold time or during cooling; andHP / HT treating the porous body to form a dense body of desired shape and dimension.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Ceramic dielectrics for base-metal-electrode multilayered ceramic capacitors and the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20070203015A1Low production costPrevent oxidationFixed capacitor electrodesStacked capacitorsBarium titanateCeramic capacitor
The present invention discloses a new dielectric material can be used as the dielectric for base-metal electrode multilayer ceramic capacitors. In the present invention, a small amount of fine metallic particles are added into barium titanate based powder. The metallic particles can absorb oxygen to prevent the oxidation of the internal electrode. The metal is then oxidized to result in an oxide that can dissolve into the dielectric. The dielectric material of the present invention can be co-fired with nickel or copper internal electrode in a sintering atmosphere of commercial nitrogen or even of air. After sintering, no post-sintering heat treatment is needed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
High temperature sintering resistance furnace
InactiveCN102798286AImprove uniformityGuaranteed uniformityLighting and heating apparatusInsulation layerEconomic benefits
A high temperature sintering resistance furnace comprises a hearth with an insulation layer, wherein the lower part of the hearth is supported by a base, kiln furniture is arranged in the hearth, and an in-furnace hot air circulation system and a rotating device for bearing a workpiece are arranged in the hearth. The uniformity of temperatures at different parts of the high temperature sintering resistance furnace is well guaranteed, particularly when a large batch of workpieces are loaded, the thermotechnical effect deviation in the traditional furnace is eliminated through force convection and kiln furniture rotation, and meanwhile, the sintering atmosphere in the furnace is effectively regulated and improved andthe sintering quality of the workpiece is improved; and the temperature uniformity is excellent, the furnace volume can be sufficiently used, the yield of single furnace can be substantially improved, the energy consumption of single product is reduced, and the economic benefit and the practical value are very high.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST FOR ABRASIVES & GRINDING CO LTD +1
Preparation method of TiB nano-reinforced titanium-based composite material
The invention relates to a preparation method of a TiB nano-reinforced titanium-based composite material, and belongs to the field of metal-based composite materials. According to the method, the composite material is prepared through ball milling, spark plasma sintering and hot rolling. The original powder is prepared through ball milling, the advantages that the sintering efficiency of the discharge plasma is high, and the external pressure and the sintering atmosphere can be controlled are utilized, so that under the low sintering temperature and the high pressure, and on the premise that the TiB2 particles and the surrounding titanium or titanium alloy matrix do not generate in-situ reaction, a sintering block body with high compactness is prepared; and finally, the TiB2 particles in the sintered block body are subjected to in-situ reaction with the surrounding titanium or titanium alloy matrix through hot rolling to form whiskers, and meanwhile, the crystal grains of the matrix are deformed, the porosity in the structure is reduced, and the strength and the plasticity of the composite material are improved. The TiB nano crystal whisker generated in situ in the method is cleanin surface and is uniformly distributed in a matrix and free of agglomeration, has good interface bonding and lattice relationship with the titanium matrix, and can effectively refine matrix crystal grains.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for preparing gradient cemented carbide with cubic carbide free layer
The invention relates to a process for preparing gradient cemented carbide with a cubic carbide free layer, which is generally used for preparing a coated cemented carbide substrate. The process is characterized in that: an initial component adopts a nitrogen-free cemented carbide raw material, and is prepared into a blade or a sample green compact by a standard cemented carbide preparation process; and a sintering process adopts a one-step sintering method comprising the following steps of: performing sintering by adopting normal dewaxing and deoxidizing processes, introducing micro-pressure nitrogen to react the nitrogen with carbides in the cemented carbide substrate to synthesize a nitrogen-containing cubic phase, evacuating the nitrogen at gradient sintering temperature and switching to sintering in a denitriding atmosphere like vacuum to form a surface layer into a cubic phase-free and cobalt layer-rich structure, namely, the cubic carbide free layer. The process is characterized in that: a nitrogen-containing phase is not added into the cemented carbide raw material, so the increasing of alloy porosity caused by the early decomposition of the nitrogen-containing phase can be avoided; the reaction nitrogen-addition of the cemented carbide substrate is realized by controlling the reaction between the sintering atmosphere and the cemented carbide substrate, so the gradient cemented carbide with the cubic carbide free layer also can be prepared under the condition of not adding the nitrogen-containing phase into the initial component; due to the adoption of the one-step sintering method, the sintering process can be simplified and the production cost can be reduced; and the prepared gradient cemented carbide comprises the cubic carbide free layer with the thickness of 10 to 40 microns, and has high compactness and bending resistance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +2
Preparation method of yttrium-containing lithium titanate serving as cathode material of lithium ion secondary battery
The invention provides a preparation method for improving the electrical conductivity, charging and discharging performance and circulating performance of lithium titanate serving as the cathode material of a lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a complexing agent into a soluble compound of Li which serves as a lithium source and a soluble compound of Ti which serves as a titanium source; doping yttrium ions by a sol-gel method; and controlling a sintering atmosphere so as to prepare yttrium-containing lithium titanate nanocrystalline and a lithium titanate / C composite material, wherein the lithium titanate composite cathode material has high magnification performance. Through the method, nanocrystalline with high dispersibility and pyrolytic carbon which is uniformly dispersed around or on the surfaces of particles can be prepared and the electrical conductivity of a product is improved remarkably. The yttrium-containing lithium titanate cathode material prepared by the method has high magnification performance and is suitable for power batteries.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Inorganic binder, preparation method and its application in preparation of porous ceramics
The invention relates to an inorganic bond, a preparation method thereof and an application for the preparation of a porous ceramic thereof. The bond consists of alumina and / or aluminum hydroxide, phosphoric acid and boric acid, wherein, the weight percentage content of the alumina and / or the aluminum hydroxide is 70 percent to 99.5 percent, the weight percentage content of the phosphoric acid is 30 percent to 0.5 percent, and additionally the weight percentage content of the boric acid is 0 percent to 15 percent. The weight percentage content of the aluminum hydroxide is converted into Al2O3. The mol ratio of phosphor and aluminum is less than one. When the bond is used for preparing for the porous ceramic, firstly the granular diameter of the alumina or the aluminum hydroxide used for preparing for the bond is confirmed, and the granular diameter of the alumina or the aluminum hydroxide for using is 0.01 time to 0.5 time of the granular diameter of ceramic powder material; non-oxide ceramic powder material is mixed uniformly and mixed uniformly with pore-forming agent or vesicant to be molded and sintered, the sintering temperature is between 900 DEG C to 1600 DEG C. The sintering atmosphere is processed in air or under the inert atmosphere.
Owner:江西高环陶瓷科技股份有限公司
Method for sintering and blending nickel laterite ore
The invention discloses a method for sintering and blending nickel laterite ores. The method comprises the following steps: blending multiple nickel laterite ores of the same components but different mass proportions, wherein the mass ratios of the components are as follows: the ratio of MgO to Al2O3 is 0.2 to 0.6, the ratio of MgO to Al2O3 is 2 to 5, and the ratio of Al2O3 to SiO2 is 0.1 to 0.5; adding an alkali flux and solid fuel to regulate the chemical components, so as to adjust the quaternary alkalinity, the sintering temperature and the sintering atmosphere of a sintered mixed material. The quaternary alkalinity, the sintering temperature and the sintering atmosphere are matched with one another, an appropriate pasting phase is generated in the sintering process of the nickel laterite ores, and the liquid phase generation in the sintering process is improved, so that the ore sintering quality and the metallurgical performance are improved, the sintering energy consumption is reduced, the quality of a blast furnace material is improved, the cost for producing ferronickel by using a smelting method is greatly lowered, and high-quality raw materials are provided for later ferronickel production through smelting in a submerged arc furnace.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Manganese-zinc ferrite magnetic core mfg. method
InactiveCN1402265AReduce lossHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureManganese oxideNitrogen gas
A MnZn ferrite core is prepared from high-Si iron oxide (52.6-54 mol%), zinc oxide (8-12 mol%), manganese oxide (35.4-38 mol%) and calcium oxide (0.02-0.12 wt.%) through sintering in the oxygen partial pressure controlled nitrogen gas or vacuum atmosphere. Its advantages are low cost, low magnetic loss, high saturated magnetic flux density, and short sinter time (20 hr).
Owner:无锡晶石磁性电子器件有限公司
Method for producing synthetic quartz glass of sio2 granulate and sio2 granulate suited therefor
ActiveUS20160090319A1Cheap productionInexpensive productionSilicaGlass shaping apparatusLength waveInfrared transmission
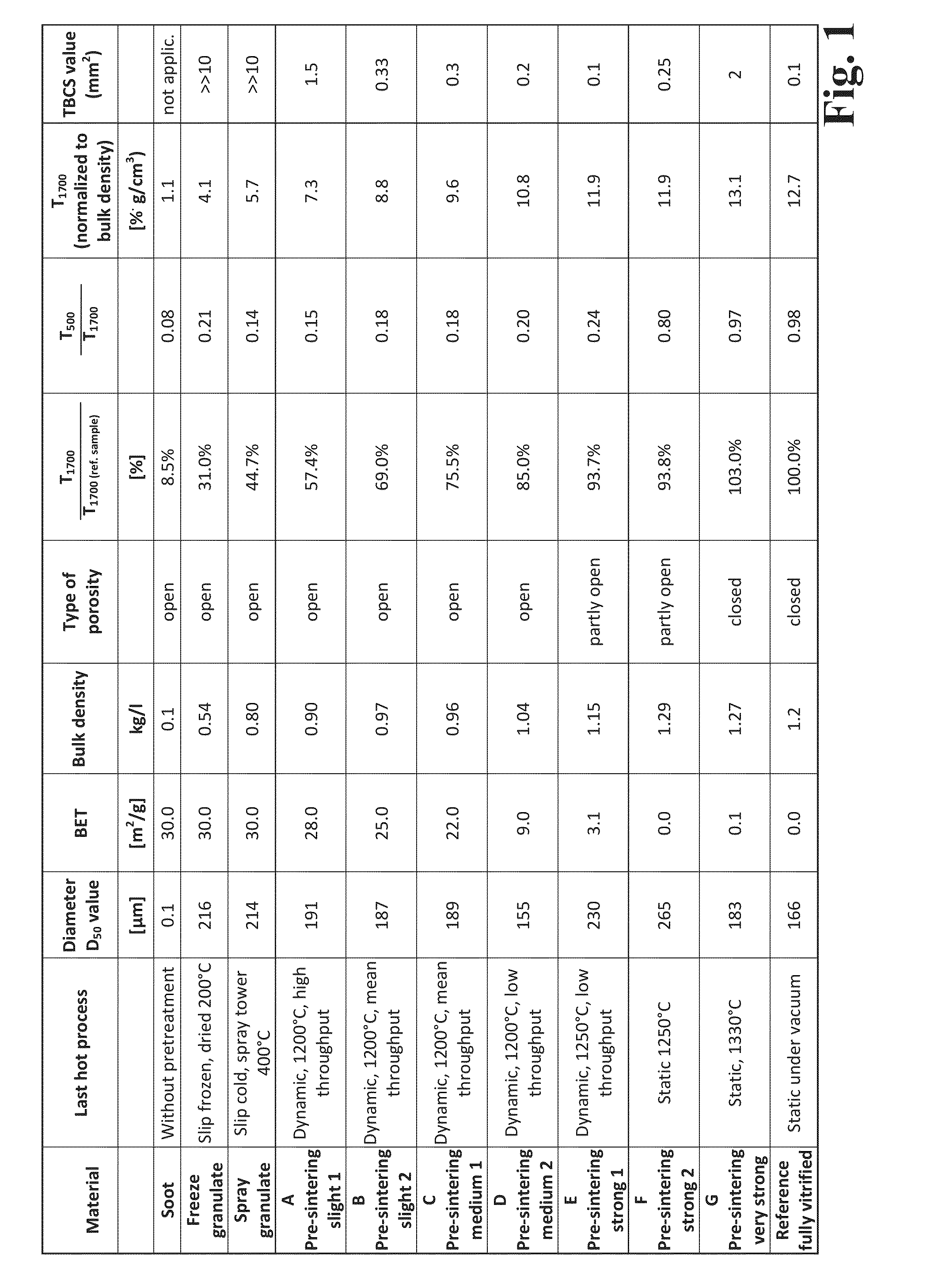
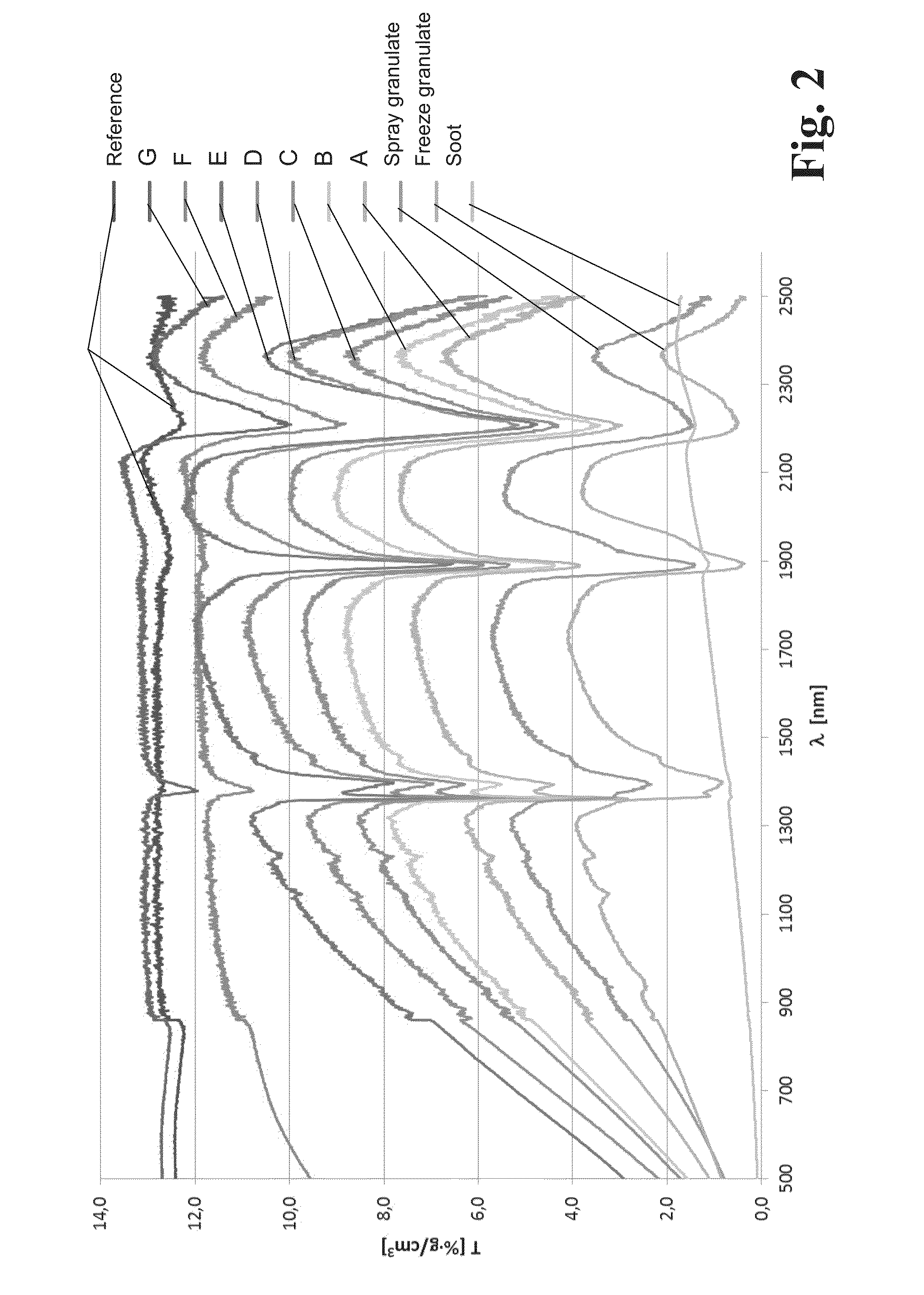
A method for producing synthetic quartz glass by fusion of SiO2 granulate involves synthesizing amorphous SiO2 primary particles, granulating the amorphous SiO2 primary particles to form an open-pore SiO2 granulate, sintering the open-pore SiO2 granulate by heating in a sintering atmosphere at a sintering temperature and for a sintering period to form a densified SiO2 granulate, and melting the densified SiO2 granulate at a melting temperature to form the synthetic quartz glass. To provide an inexpensive production of low-bubble transparent components of quartz glass despite the use of still open-pore SiO2 granulate, the sintering atmosphere, sintering temperature and sintering duration are adjusted such that the densified SiO2 granulate still comprises open pores but manifests a material-specific infrared transmission T1700 at a wavelength of 1700 nm. This transmission is in the range of 50-95% of the infrared transmission T1700 of quartz glass granules of the same material.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Method for preparing ferro-aluminum alloy porous material
The invention relates to a method for preparing a ferro-aluminum alloy porous material, which is directly used for producing the porous material or a filtering element based on a ferro-aluminum inter-metallic compound. The method comprises the following steps: adopting powder containing ferro-aluminum components, and mixing the powder according to the designed weight component ratio; preparing themixture into flaky or formed blanks by adopting die forming, and controlling the pressure between 50 and 300 MPa, or preparing the mixture into tubular parisons by adopting isostatic cool pressing, and controlling the isostatic pressure between 50 and 200 MPa; and adopting a pressureless sintering process at a temperature of between 950 and 1,250 DEG C in a sintering atmosphere of hydrogen gas orcracked ammonia, or adopting vacuum sintering, wherein the key improvements are that the powder containing the ferro-aluminum components comprises Fe powder with the particle size of between 300 and1 mum and FexAly powder with the particle size of between 300 and 1 mum, and the Fe accounts for 76.6 to 3.5 percent and the FexAly accounts for 23.4 to 96.2 percent in percentage by weight.
Owner:李玉清
Method for manufacturing powder metallurgy supporting seat
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a powder metallurgy supporting seat, which sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) pressing a supporting seat base body (1), and arranging a structure for placing a transition block (2) on the supporting seat base body (1); (2) processing the transition block (2); (3) arranging the transition block on the structure for placing a transition block (2) on the supporting seat base body (1), positioning soldering flux between the supporting seat base body (1) and the transition block (2), and then putting the supporting seat base body (1) assembled with the transition block (2) in to a sintering furnace at the temperature of 1000-1300 DEG C under the condition of vacuum or filling with assistant welding gas sintering atmosphere for sintering for 5-50min; (4) after welding, measuring the size and accuracy to determine whether machining and adjusting are needed for correcting the position of the transition block (2) on the supporting seat base body (1); and (5) carrying out steam treatment on the supporting seat base body (1) welded with the transition block (2); therefore, the manufacturing process of powder metallurgy supporting seat can be completed. Compared with the prior art, as the transition block is welded with the supporting seat base body by a powder metallurgy sintering and soldering method, the supporting seat base body has high position, accurate locating accuracy and good connecting strength; and the whole welding process is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:NBTM NEW MATERIALS GRP
Microwave-assisted dynamic continuous calcining device and method for lithium-ion battery material
PendingCN108759459AExcellent consistency of propertiesImprove production efficiencyRotary drum furnacesCharge treatment typeMicrowave powerLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to microwave-assisted dynamic continuous calcining device and method for a lithium-ion battery material. The device comprises a rotary kiln body, a transmission device and a power device, wherein the power device is connected with the rotary kiln body through the transmission device; the rotary kiln body comprises a rotary kiln tube body; independent microwave emitters are continuously arranged on a rotary kiln body shell; waveguide tubes are connected onto the microwave emitters and are connected with the rotary kiln tube body; the temperatures of different temperature areas of the rotary kiln body are controlled through adjusting microwave powers of the microwave emitters; a discharging device is arranged on a kiln head of the rotary kiln body; a feeder is arrangedon a kiln tail of the rotary kiln body; an air supply gun is arranged on the kiln head of the rotary kiln body and communicates with the rotary kiln tube body; an air discharge flue is arranged on thekiln tail of the rotary kiln body; and a sintering atmosphere in the rotary kiln body is controlled through the air supply gun on the kiln head. The microwave-assisted dynamic continuous calcining device and the method for the lithium-ion battery material provided by the invention have high heat utilization ratio, and is particularly good for preparing a nanometer material; continuous feeding anddischarging can be realized, so that the preparation efficiency of the lithium-ion battery material is greatly improved; and the generated greenhouse gas is less so as to have low effect on the environment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of manufacturing gradual-change bore diameter stainless steel antipriming pipe
ActiveCN101428346AImprove breathabilityGuaranteed filtration accuracyFiltration separationPolyvinyl alcoholSS - Stainless steel
The invention provides a preparation method for a stainless steel perforated pipe with gradually-varied aperture, the invention adopts the preparation process that stainless steel powder is mixed with a certain polyvinyl alcohol solution to prepare stainless steel powder suspension, and getter is added into the suspension and poured into a two-piece-type opening and closing rigid pipe die made of stainless steel after even stirring, which centrifugally takes shape on a centrifuge, thereby preparing a green body of the stainless steel perforated pipe with gradually-varied aperture grads; the green body is dried in a blast-type baking oven, and then the demoulding is performed; the green body of the stainless steel perforated pipe after drying is sintered in a vacuum stove, the sintering atmosphere adopts vacuum, and the stainless steel perforated pipe with gradually-varied aperture grads is prepared after cooling. The invention has the advantages that the demoulding attainment rate of the green body of the stainless steel perforated pipe with gradually-varied aperture is greatly enhanced, and the filtering precision of the perforated pipe is ensured; meanwhile, the air transmission coefficient of the stainless steel perforated pipe with gradually-varied aperture is enhanced, and the preparation method solves the phenomenon of the reciprocal relationship between the filtering precision of the stainless steel perforated pipe and the transmission performance in the filtration, separation and application process.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Method of making a fine grained cemented carbide
According to the present invention there is provided a method of making a finegrained tungsten carbide—cobalt cemented carbide comprising mixing, milling according to standard practice followed by sintering. By introducing nitrogen at a pressure of more than 0.5 atm into the sintering atmosphere after dewaxing but before pore closure a grain refinement including reduced grain size and less abnormal grains can be obtained.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Method of manufacturing FeAl intermetallic compound filter material
InactiveCN101108291AStrong acid and alkali corrosion resistanceExcellent anti-vulcanization performanceFiltration separationAl powderHydrogen
The invention discloses the preparation method of a FeAl IMC filtering material.A. Select the Fe powder and Al powder with grain diameter of 100 to 1Mu m, the component match is 75 to 25at per cent Fe and 25 to 75at per cent Al; B. Adopt press forming to prepare platy forming adobe, the press forming pressure is controlled between 100 to 300 Mpa, or adopt isostatic cool pressing to prepare tubular forming adobe, the isostatic pressure is controlled between 50 to 200Mpa; C. the reaction forming adopts non pressure sintering technics, firstly keep heat for 30 to 60 minutes under the temperature of 120 to 150 DEG C., then rises to 1000 to 1200 DEG C. at the rate of 1 to 10 DEG C. and keep heat for 30 to 60 minutes; the sintering atmosphere is hydrogen and cracked ammonium, or adopts vacuum sintering, the vacuum degree is 1 multiply 10 minus 1 to 1 multiply 10 to 3Pa; the cooling stage, the control cooling rate is 10 to 50 DEG C. / min. With adopting the element powder reaction forming technics to prepare filtering material, which is beneficial for controlling the pore structure performance of the filtering material, the prepare process doesn't need adding pore former and lowers energy consumption almost without pollution.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com