Patents
Literature
277 results about "Adobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adobe (/əˈdoʊbi/ ; [aˈðoβe]) (Arabic: الطوب, romanized: aṭ-ṭūb) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. Adobe is Spanish for mudbrick, but in some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, the term is used to refer to any kind of earth construction. Most adobe buildings are similar in appearance to cob and rammed earth buildings. Adobe is among the earliest building materials, and is used throughout the world.
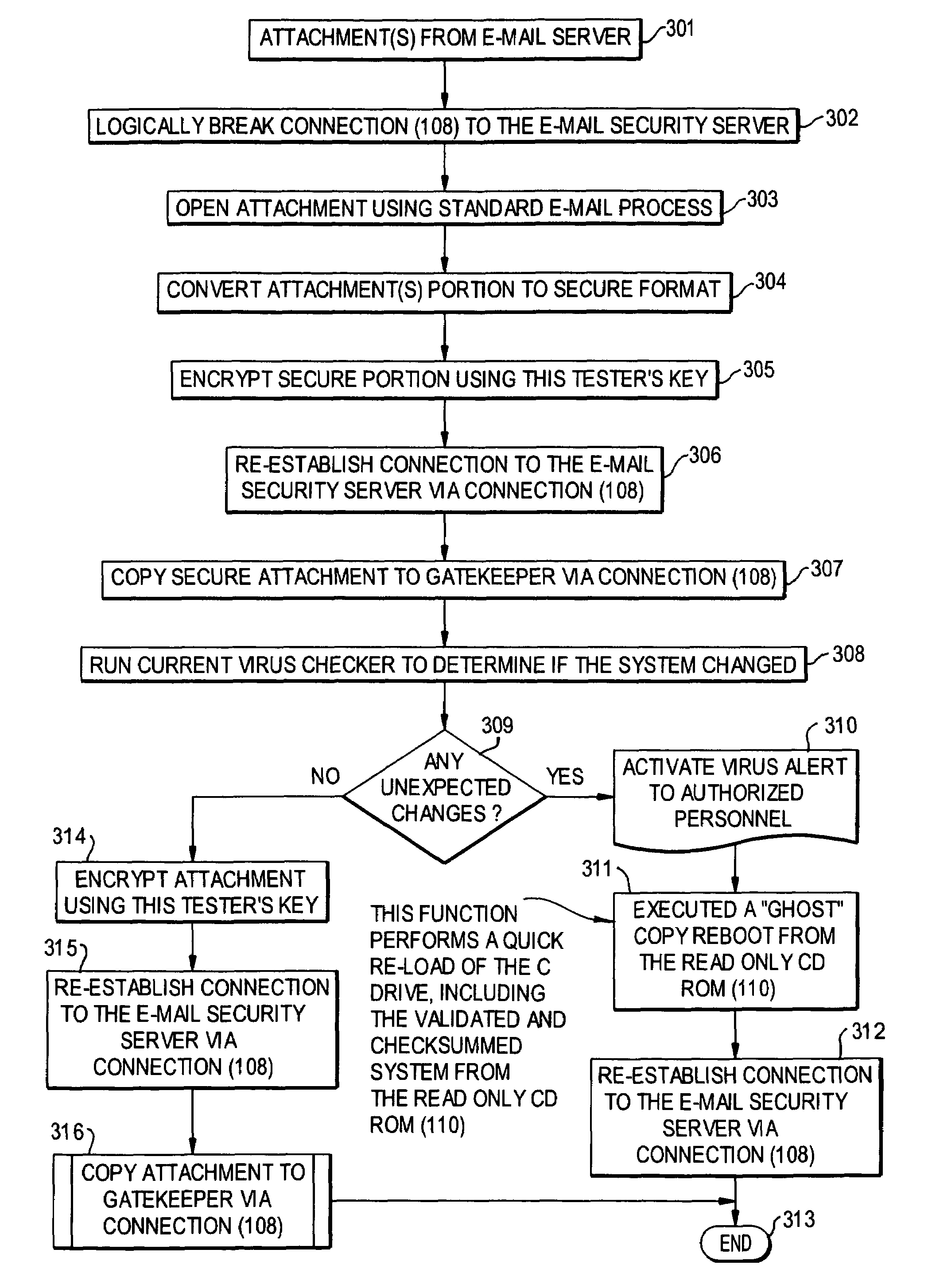
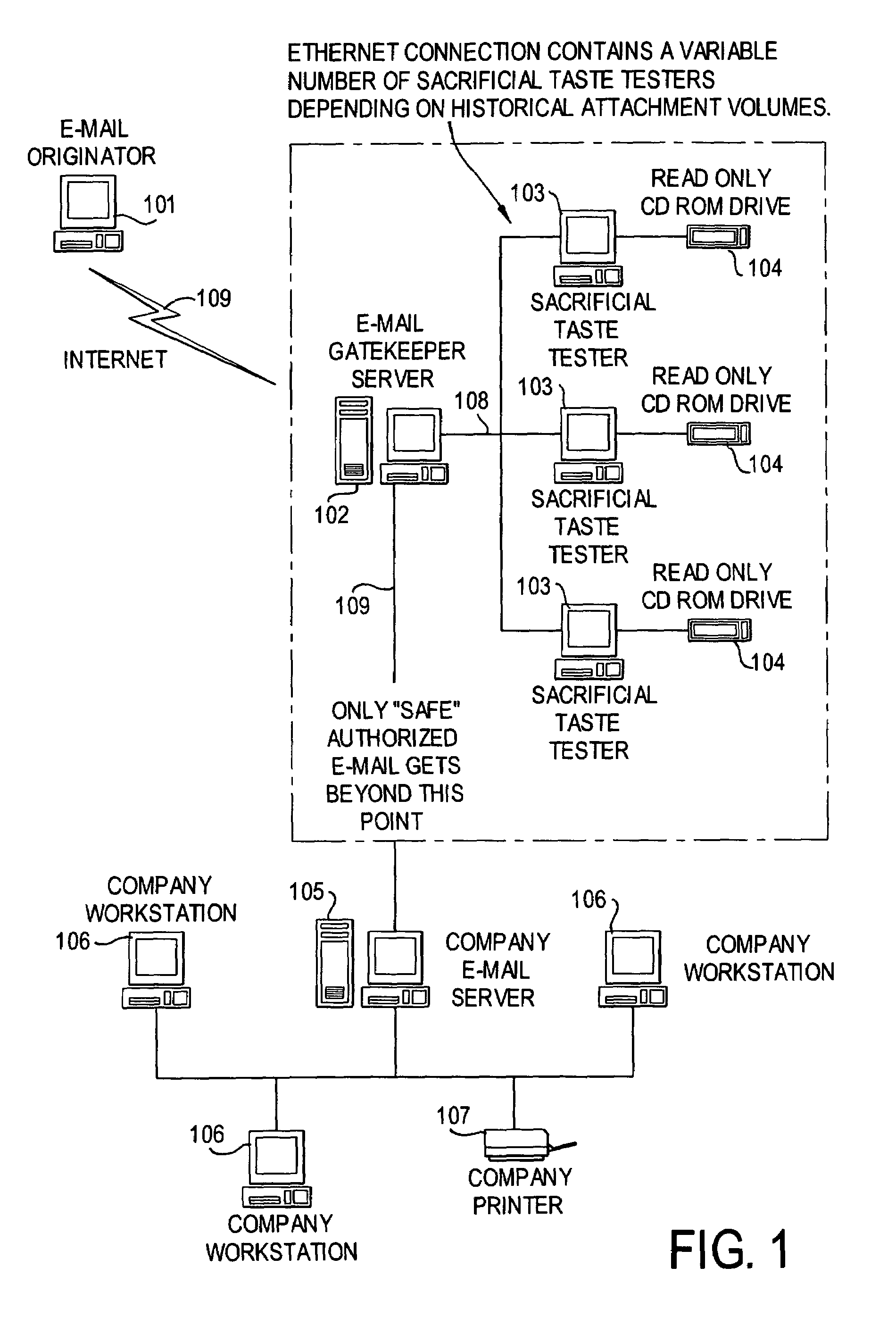
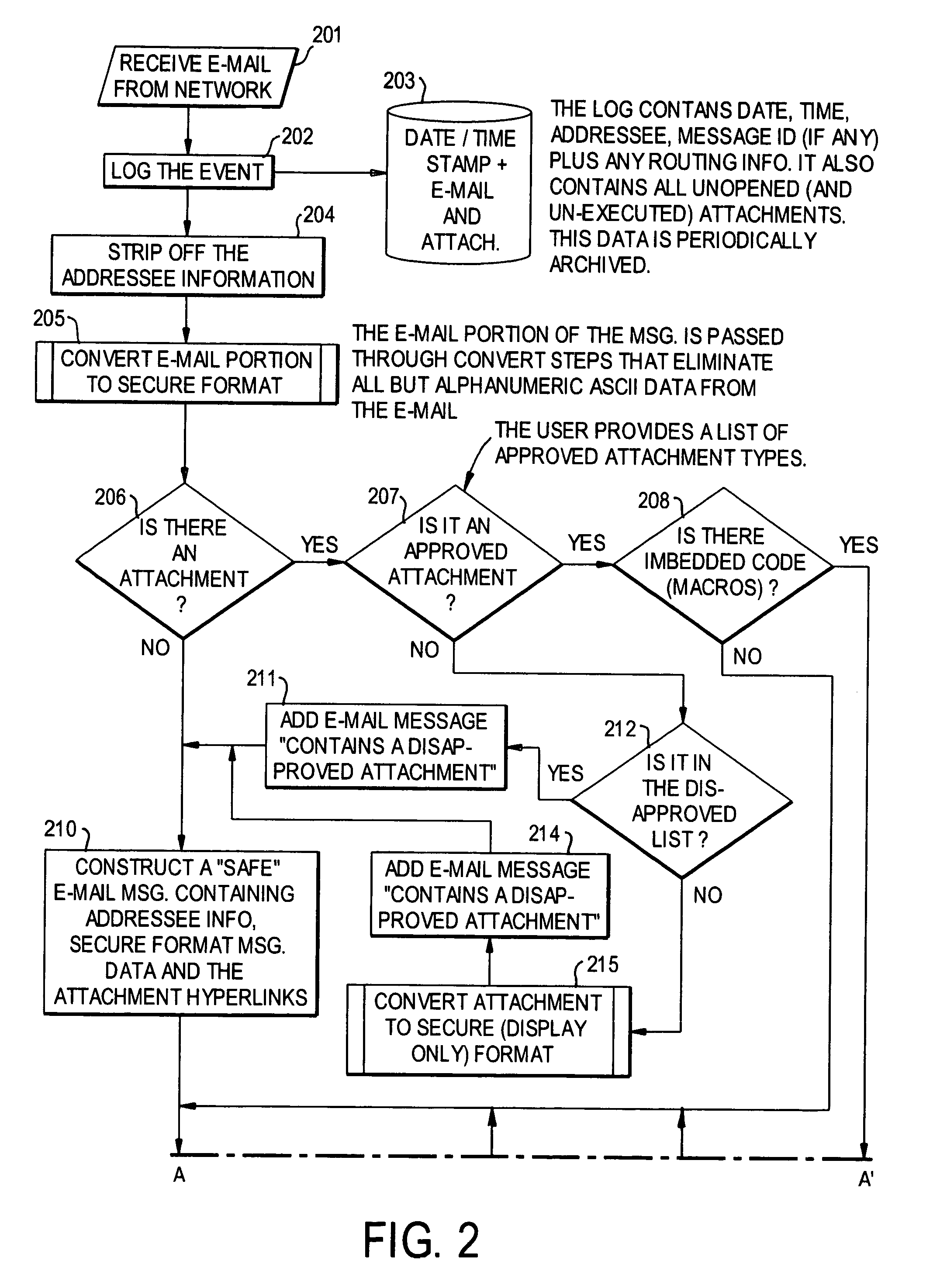
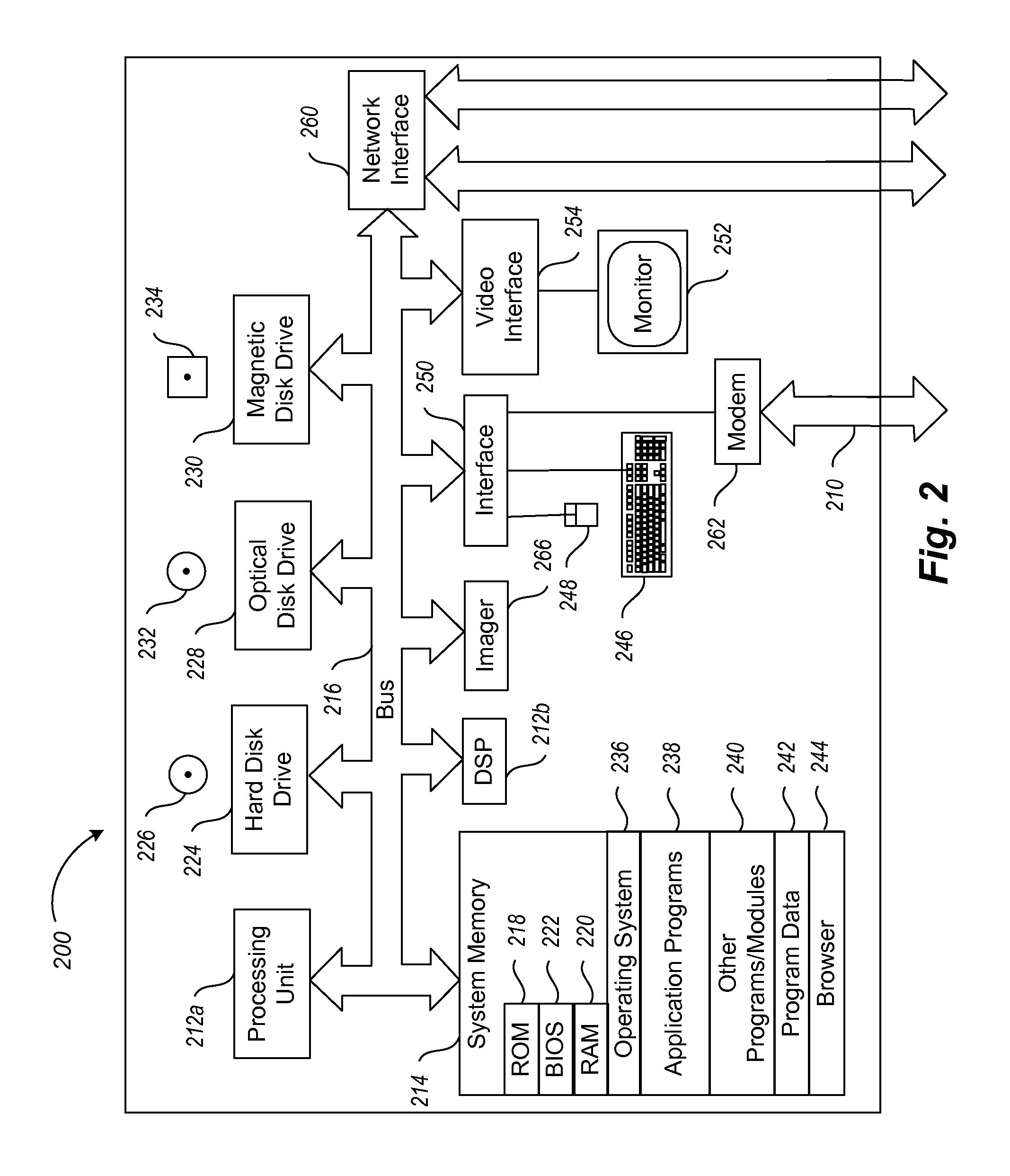
E-mail virus protection system and method
InactiveUS7506155B1Detection securityEnsuring Safe ExecutionHardware monitoringPlatform integrity maintainanceAdobeProtection system
A network is protected from e-mail viruses through the use of a sacrificial server. Any executable programs or other suspicious parts of incoming e-mail messages are forwarded to a sacrificial server, where they are converted to non-executable format such as Adobe Acrobat PDF and sent to the recipient. The sacrificial server is then checked for virus activity. After the execution is completed, the sacrificial server is rebooted.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
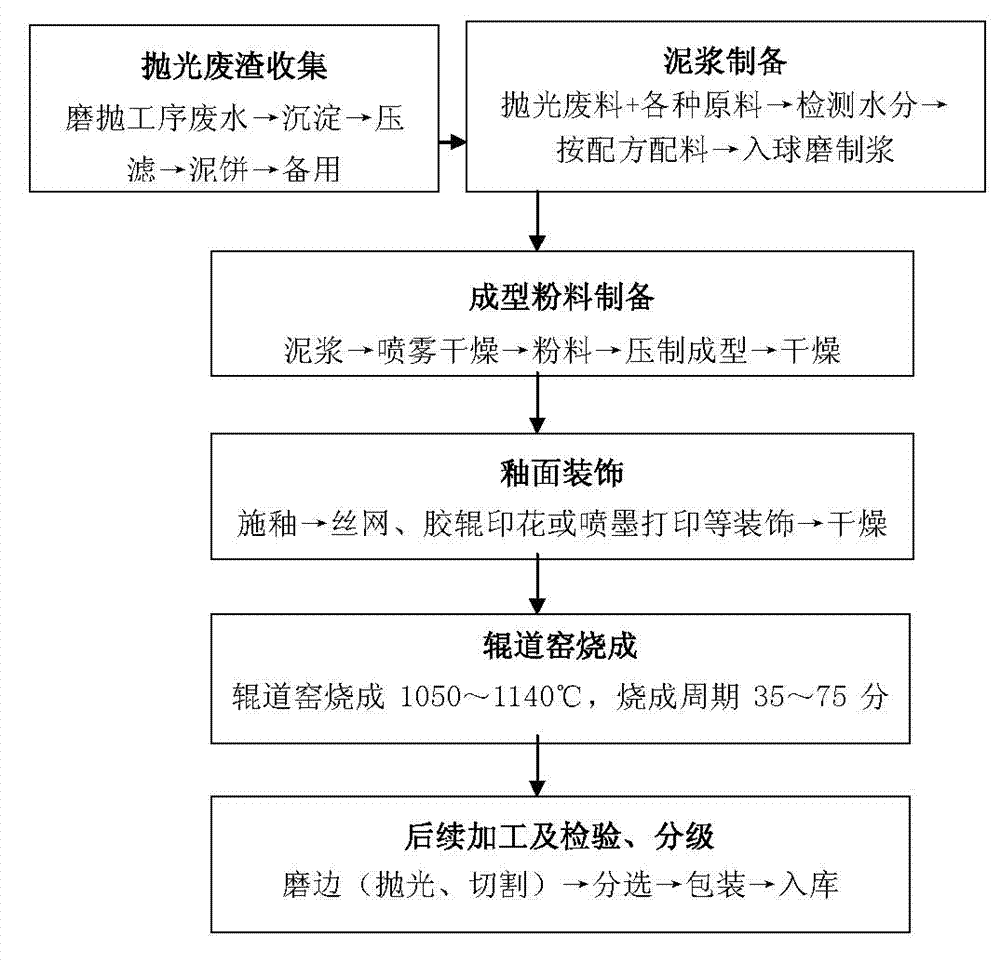
Low-temperature fast-fired ceramic tile and production process thereof
ActiveCN103693942AReduce burning energy consumptionReduce energy consumptionCeramic materials productionClaywaresBrickFiltration
The invention relates to a low-temperature fast-fired ceramic tile and a production process thereof. The blank material of the ceramic tile comprises at least one selected from the group consisting of fine granules produced during grinding and polishing in production of polished tiles, fine granule-containing waste water collected after polishing and a waste polishing material obtained after deposition and press filtration; the blank material of the ceramic tile is composed of, by weight, 48 to 73% of the waste polishing material, 5 to 20% of porcelain sand, 20 to 27% of clay and 2 to 5% of a mineralizer. The production process comprises the following steps: (1) collecting the waste polishing material, carrying out batching according to a formula and then carrying out wet ball milling so as to obtain slurry, wherein the waste polishing material stood for subsequent usage in press filtration and other raw materials are calculated on a dry basis; (2) subjecting the slurry to spray drying so as to obtain powder and carrying out dry-pressing so as to form a ceramic adobe; (3) drying the adobe, glazing the adobe and carrying out surface decoration; and (4) putting a decorated blank into a ceramic roller kiln for firing, wherein fast firing temperature is 1050 to 1140 DEG C, a firing period is 35 to 75 min, and the ceramic tile with a water absorption rate of less than 0.5% is sintered.
Owner:GUANGDONG JIA MEI CERAMIC
Stone powder sludge sintering brick and method for making the same
InactiveCN101081732AHigh strengthImprove performanceCeramic materials productionClaywaresAdobeAdhesive
The present invention discloses one kind of stone powder sludge sintering brick and its production process. The stone powder sludge sintering brick is produced with stone powder sludge from stone material producing process as main material, sludge from river, lake or sea, building waste clay or clay as adhesive, slag, coal slack, fly ash or coal as inner material, and through crushing, stirring, forming adobe, drying, roasting and other steps. The present invention has the features of waste utilization, environment friendship, saving in soil, low power consumption, high compression strength, etc. It may be used in replacing sintered clay brick.
Owner:林建国
Press formed dry glaze for ceramic tile adobe and its prepn process
The present invention discloses one kind of dry glaze for once forming ceramic tile adobe and its preparation process. The dry glaze consists of type-I dry glaze and type-II dry glaze. The type-I dry glaze has the similar composition and sintered surface effect to that of ceramic tile adobe; and the type-II dry glaze consists of mineral materials and has the components including Li2O / Na2O / K2O 1.0-30 weight portions, CaO 1.0-25 weight portions, MgO 0-15 weight portions, ZnO 0-50 weight portions, BaO 0.5-20 weight portions, SiO2 40-80 weight portions, Al2O3 1.5-20 weight portions, ZrO2 0-30 weight portions, TiO2 0-35 weight portions, B2O3 0-30 weight portions, PbO 0-50 weight portions, P2O50-25 weight portions, and ceramic color or coloring oxide or other coloring compound 0-40 weight portions. The dry glaze may be used to obtain ceramic tile products with different surface decoration effects, high wear resistance, anti-fouling performance and other advantages.
Owner:GUANGDONG SANSHUI TANDH GLAZE CO LTD
Three-dimensional high simulation ceramic tile with matte glaze surface and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108727037AExtended service lifeGood three-dimensionalCeramic shaping apparatusAdobeComputer printing
The invention discloses a three-dimensional high simulation ceramic tile with matte glaze surface and a preparation method thereof, the method comprising the following steps: 1) adopting a laser four-dimensional fine carving system to finely carve a digital mold; 2) Positively pressing green body molding; 3) Controlling the water absorption rate of the ceramic tile before glazing at 15%-20% by controlling the drying temperature of the ceramic tile adobe or the biscuiting temperature of the ceramic tile adobe; 4) spraying a small amount of high-titanium impervious ground coat under high pressure; 5) spraying a small amount of matte glaze under high pressure; 6) using a digital ink jet printer to print decorative ink and functional ink; 7) decorating the dry particle frit, and adopting a controllable negative pressure absorbing dry particle frit equipment to absorb excess dry particle frit; 8) sintering to obtain the three-dimensional high imitation ceramic tile with matt glaze surface,the preparation method provided by the invention obtains the three-dimensional high simulation ceramic tile with matte glaze surface with three-dimensional simulation, 2-6 glossy units of glaze surface gloss and lifelike surface decoration effect through the collaborative and innovative preparation including mold sculpture, glaze formula control, high-pressure glaze spraying and effect decoration.
Owner:广东协进陶瓷有限公司
Alumina-magnesia refractory brick containing light porous aggregate and its making process
The present invention relates to one kind of alumina-magnesia refractory brick containing light porous aggregate and its production process. The technological scheme is that the alumina-silica refractory brick is produced with light porous Al2O3-MgO refractory material 30-70 wt%, compact Al2O3-MgO refractory material 0-35 wt%, fine magnesia powder 5-30 wt%, fine alpha-Al2O3 powder 3-10 wt%, fine corundum powder 0-25 wt% and fine spinel powder 0-25 wt%, and through mixture, adding waste pulp liquid in 3-7 wt% as binding agent, stirring, pressing to form adobe, drying at 100-150 deg.c for 12-48 hr, sintering at 1400-1600 deg.c for 2-5 hr and naturally cooling. The alumina-magnesia refractory brick has high macro porosity, small average pore size, low heat conductivity and high medium erosion resistance, and may be used in the permanent layer or work layer in high temperature kiln, furnace and container.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing construction material by utilizing electrolytic manganese slag
InactiveCN101570037ARemove hidden dangers of pollutionGood environmental benefitsSolid waste managementMixing operation control apparatusElectrolysisSlag
The invention provides a method for preparing a construction material by utilizing electrolytic manganese slag, including the following steps: (1) pretreatment: additive is blended in the electrolyticmanganese slag, water is added for fully stirring, and the raw material reacts in the open air for 1-7 days, wherein the added additive is mixture of lime, plaster and kaolin; (2) cement, sandstonescoarse aggregate, sandstones fine aggregate and component selection air entraining agent are added into the electrolytic manganese slag after the pretreatment, water is added and blended evenly to form a mixture; (3) the mixture is loaded into a mould and formed on a compression forming machine by vibration and pressurizing, and then demoulding is carried out; (4) adobe is naturally cured for 14-28 days, thus obtaining the electrolytic manganese slag construction material product. The technique is simple with high product quality and low production cost and has good social, economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for producing ceramic surface archaizing brick
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of the metallic glaze antique brick, which mainly comprises two steps of manufacturing adobe of the antique brick and glazing on the product brick, wherein the manufacturing adobe of the antique brick consists of material collection, mashing, color matching, drying for product powder, brick pressing and brick body drying while the glazing on the product brick is mainly composed of manufacturing of glaze slurry, glazing and firing the antique brick etc. the invention has advantages of low water absorption rate, high strength, good effect of anti-skid and anti-fouling, durability etc, which can be widely used for wall or floor decoration of the excellent hotels, large-sized arena, airport, residence house etc.
Owner:关锐华
Alumina-silica refractory brick containing light porous aggegate and its making process
The present invention relates to one kind of alumina-silica refractory brick containing light porous aggregate and its production process. The technological scheme is that the alumina-silica refractory brick is produced with light porous Al2O3-SiO2 refractory material 30-70 wt%, compact Al2O3-SiO2 refractory material 0-35 wt%, fine corundum powder 5-25 wt%, fine alpha-Al2O3 powder 3-10 wt%, fine mullite powder 5-15 wt% and fine clay powder 0-10 wt%, and through mixture, adding waste pulp liquid in 3-7 wt% and one or two kinds of silicasol as binding agent, stirring, pressing to form adobe, drying at 100-150 deg.c for 12-48 hr, sintering at 1400-1600 deg.c for 2-5 hr and naturally cooling. The alumina-silica refractory brick has high macro porosity, small average pore size, low heat conductivity and high medium erosion resistance, and may be used in the permanent layer or work layer in high temperature kiln, furnace and container.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Technique for manufacturing ceramic glazed tile with natural stone texture
The invention relates to ceramics imitating marble glaze manufacturing technology and the improvement of its device. Its main processes are that flush lettering type adobes is extruded by the press, dried, burning of brick at low temperature, then decreased under the common temperature, sprinkled with water to humid, flowed casting material, transmitted to the water curtain to disappear along the horizontal direction, dried and burning of brick again, polished the edge of the section, package in stages. The workings of the flow liner pattern material equipment are that two or many color paste with certain viscosity are flowed into one or many flow liner pattern material mixing device by plasticity soft tube with different calibers. The mixing device can be moved left and right along the crossbeam. After mixed or without mixing the color paste is flowed into the paste storing cavity, and flowed casting to the prepared flush lettering type adobes.
Owner:HANGZHOU NABEL CERAMIC
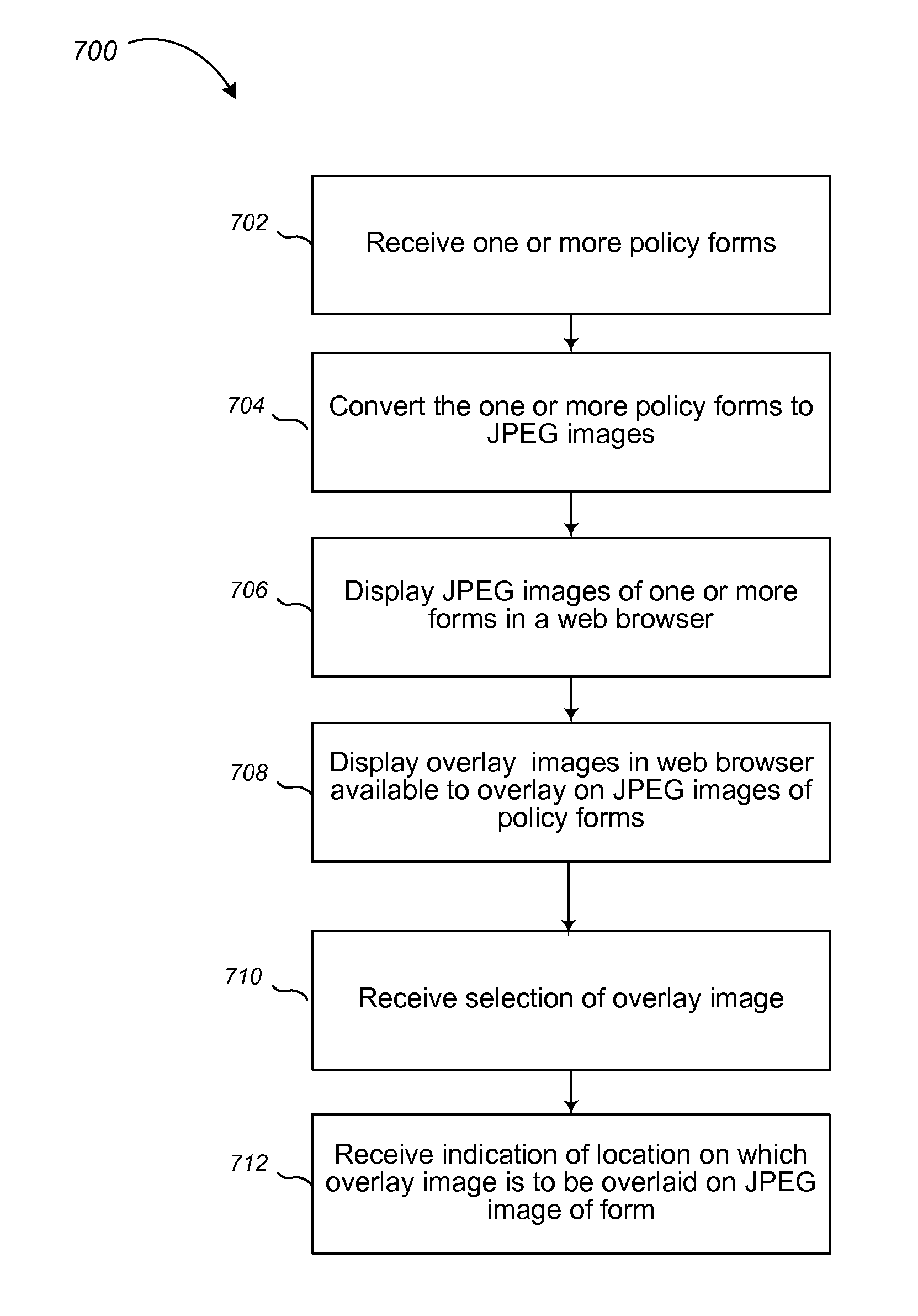
Overlaying images in automated insurance policy form generation
Overlaying images in automated insurance policy form generation includes electronically converting a first form in a first format to a second format to and in response to receiving a Web page request, electronically communicating the second form to be displayed within the Web browser instead of electronically communicating the first form in the first format to be displayed within the Web browser. In the case where the first format is Adobe® portable document format (PDF) and the second format is Joint Picture Expert Group (JPEG) format, this enables the user of the browser to overlay images on the forms within the Web page interface of the browser, while it appears to the user they are overlaying images on the original PDF versions of the forms. The final integrated PDF form is then generated from the data indicating the location of the overlay image on the underlying JPEG form. This process may also apply to insurance policy forms wherein the overlay image is a state specific stamp to be placed on the underlying form.
Owner:VERTAFORE
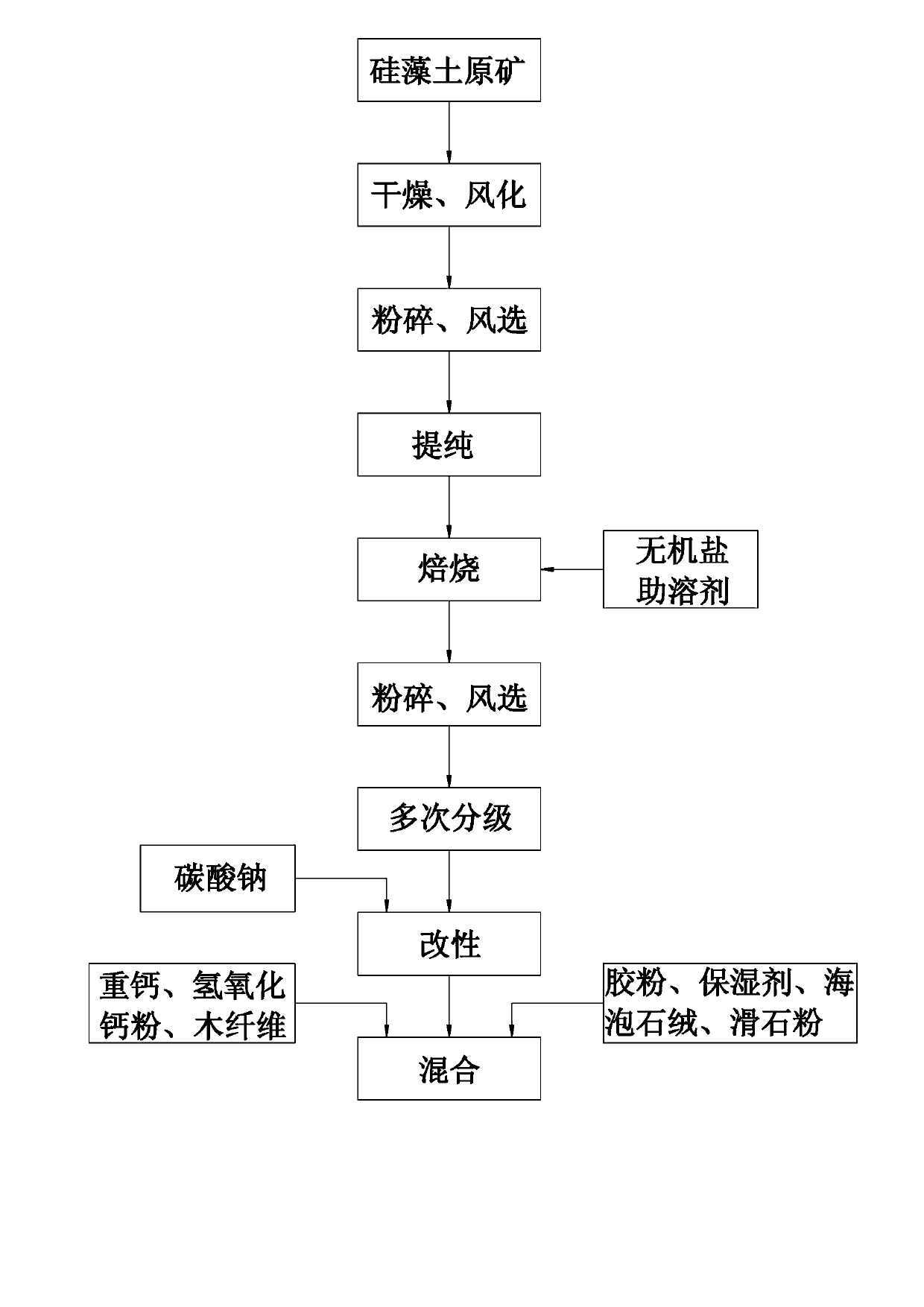
Modified diatom-ooze interior decorative material and production technique thereof
The invention relates to a modified diatom-ooze interior decorative material which is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 30-32% of modified kieselguhr, 22-24% of coarse whiting, 5-8% of calcium hydroxide powder, 4-6% of wood fiber, 3-4% of rubber powder, 1-2% of humectant, 22-23% of meerschaum wool and 8-10% of talcum powder. The production technique comprises the following steps: naturally drying and weathering kieselguhr raw ores, detecting the adobe, grading, and transporting to a processing workshop; pulverizing, carrying out air separation, adding a cosolvent, calcining in a high-temperature calcining kiln to remove water and organic impurities, pulverizing, grading repeatedly, carrying out air separation to remove inorganic impurities, and proportionally mixing with calcium hydroxide, coarse whiting, natural rubber and the like. Compared with the existing diatom-ooze product, the modified diatom-ooze interior decorative material provided by the invention has superstrong adsorption capacity, can not shed powder or fade, can be scrubbed with a wet rag, has the advantages of long service life (more than 20 years), no edge tilting, no shedding, no fading and oxidation resistance, and always looks new.
Owner:吉林省临江天元催化剂有限公司 +1
Super-white polished brick
This invention relates to a ultrawhite polishing brick. According to weight shares the raw materials includes: calcined alumina 5 to 10 shares, burning talcum 10 to 40, ultrawhite ball clay 18 to 25, water washing kaolin 5 to 12, low temperature feldspar 13 to 25, middle and high temperature porcelain sand 10 to 18 shares. The process includes: ball milling, spraying and corning, shaping by quenching, adobe drying and kiln burning. This invention has high whiteness, good thermostability, and avoid zirconium silicate radioactive problem.
Owner:霍镰泉
Static press-forming method of gypsum steam brick adobe
InactiveCN101612757AImprove pass rateIncrease productivitySolid waste managementMixing operation control apparatusAdobeBrick
The invention discloses a static press-forming method of a gypsum steam brick adobe, relating to a production method of a gypsum brick adobe. Dihydrate ardealite, slag, hydraulic cementing material and liquid phase adhesive are used as raw materials. According to the method, the raw materials are proportionally mixed and sent into a mould of a forming machine. When the forming machine is kept in a static condition, the ardealite mixed material is pressed by high pressure to obtain a formed adobe. The application of the method shows that the shapes and the size of the adobe and a finished brick conform to the standards, the volume weight of the finished brick can be thoroughly controlled to be 800-1500 kg / m<3>, and the finished product ratio is over 95 percent. The method not only reduces the energy consumption but also improves the adobe qualification rate and the production efficiency. The method requires simple technical apparatuses, has low production cost, can select corresponding technical apparatus models according to the production scale or the storage amount of the ardealite, and is suitable for enterprises producing gypsum steam bricks.
Owner:GUIZHOU KAILIN GRP CO LTD
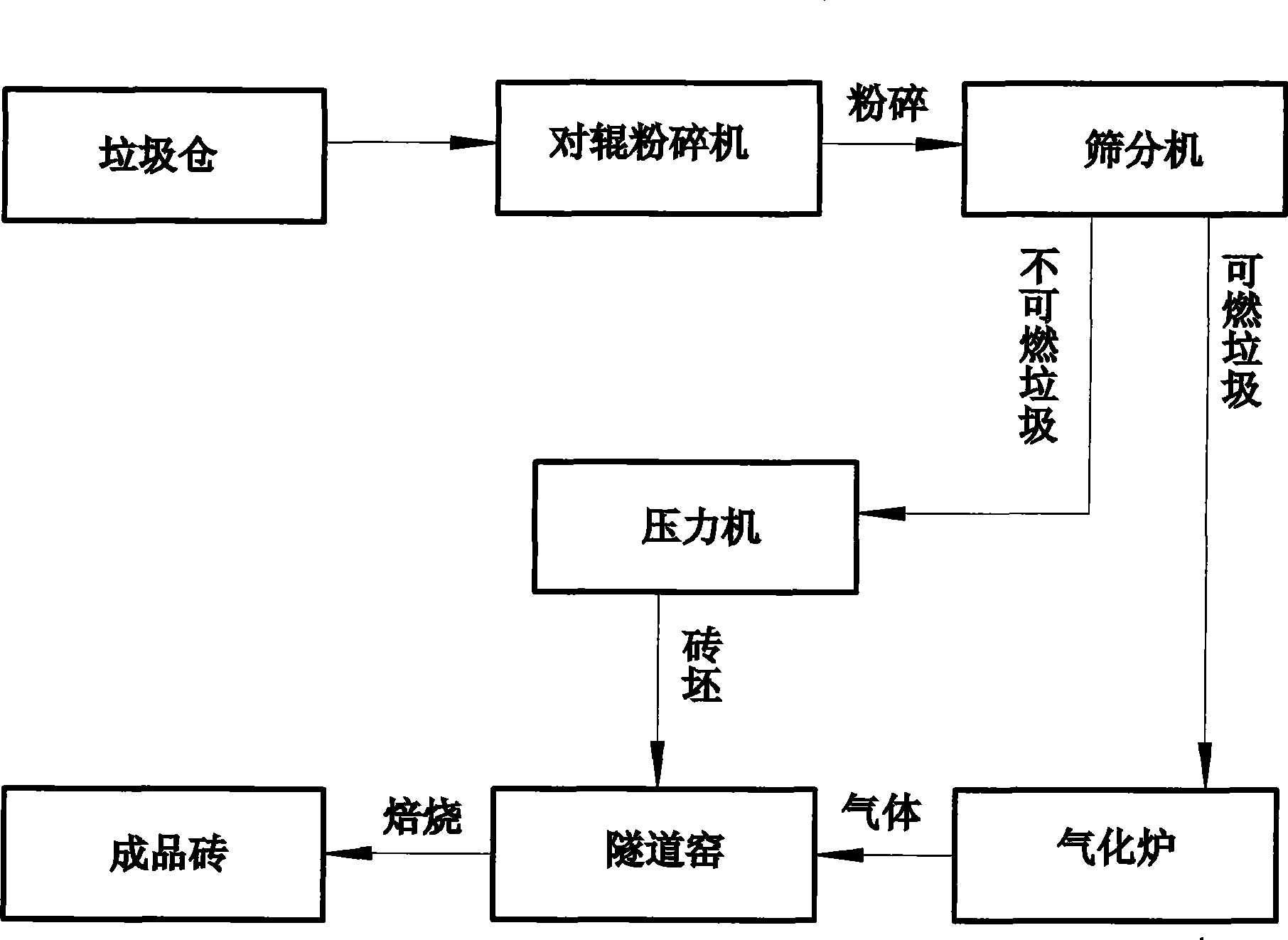
Method for manufacturing bricks by using household garbage
InactiveCN101519300AReduce manufacturing costSolve storage problemsIncinerator apparatusCeramic materials productionTunnel kilnAdobe
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing bricks by using household garbage. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing and mixing 40 portions to 70 portions of non-combustible garbage, 10 portions to 20 portions of coal gangue and 20 portions to 40 portions of clay, adding 20 percent to 30 percent of water into the mixed material, mixing evenly and preparing adobes by dry pressing under the pressure; placing the adobes into a tunnel kiln; introducing the gas generated by the gasified burnable garbage in a gasifying furnace into the tunnel kiln to be as fuel; and obtaining the adobes by roasting at the temperature of 1050 to 1100 DEG C. The method can adopt the gas generated by the burnable garbage after gasification as fuel for high-temperature burning, fully realizes the effective utilization of the household garbage and reduces the production cost of the brick; the material contains the coal gangue which can sinter by self-combustion under high temperature and provide heat; and the method has short production time, simple technique and easy operation, saves energy and is beneficial to environmental protection. By inspection, the pressure resistance of the brick can be up to 8MPa.
Owner:李兴业
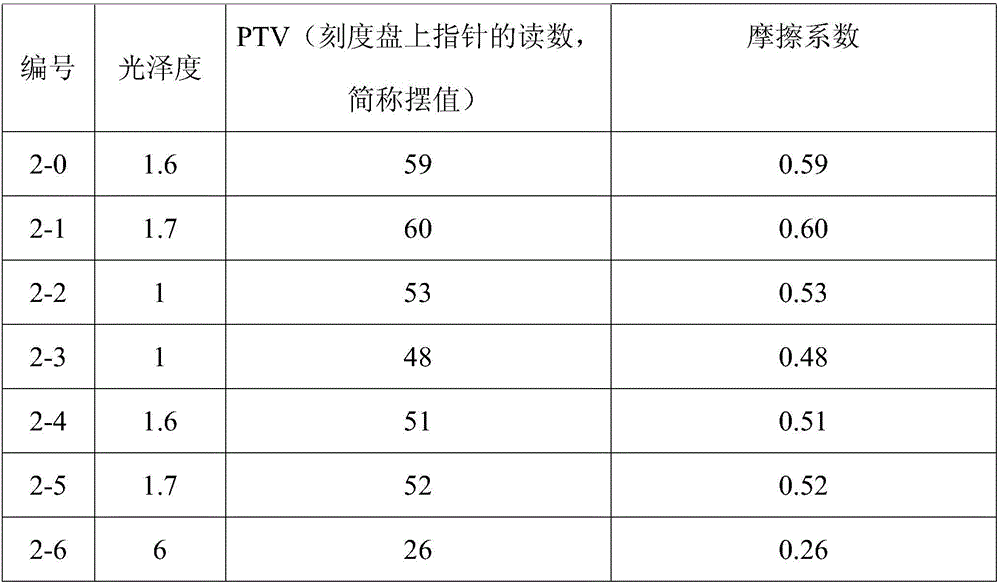
Surface skid resistance enhancing glazed tile adobe and preparation method thereof
A surface skid resistance enhancing glazed tile adobe and preparation method thereof, the preparation method comprises the steps of A, preparing rough glaze: weighing by mass 60-100 parts of bright transparent frit powder, 25-35 parts of kaolin, 1-2 parts of alumina, then the above raw materials being added with water to prepare into glaze pulp with specific weight less than 1.3; B, preparing and sintering the product: spreading antifouling finish on the surface of adobe, then spreading the rough glaze obtained from step A, the glazing amount of the rough glaze being ,<=0.5 kg / m2, sintering ready after drying, and finally obtaining the finished product after polishing treatment. The proposed surface skid resistance enhancing glazed tile adobe and preparation method thereof, carries out improvements from glaze material formula, through the performance combination of two kinds of glaze materials, enabling the coefficients of the product skid resistance to be stabilized on a relatively higher value, and achieving the goal of increasing the performances of skid resistance and ant fouling.
Owner:FOSHAN DONGPENG CERAMIC +2
Method for producing pattern permeating ceramic tile
The present invention relates to a production process of pattern permeating ceramic tile and alters traditional liquid color distributing into solid dry grain distributing in producing plished pattern permeating ceramic tile. The production process features that produced solid grains with different granularity and adsorbed coloring metal ion(s) or crystal grains with coloring metal ion(s) are distributed onto the prefabricated ceramic tile adobe before adding permeation assistant, sintering and polishing. The pattern permeating ceamic tile product has rich color, natural and ever-changing pattern is like natural stone material.
Owner:FOSHAN OCEANO CERAMICS
Workflow integration with adobe™flex™user interface
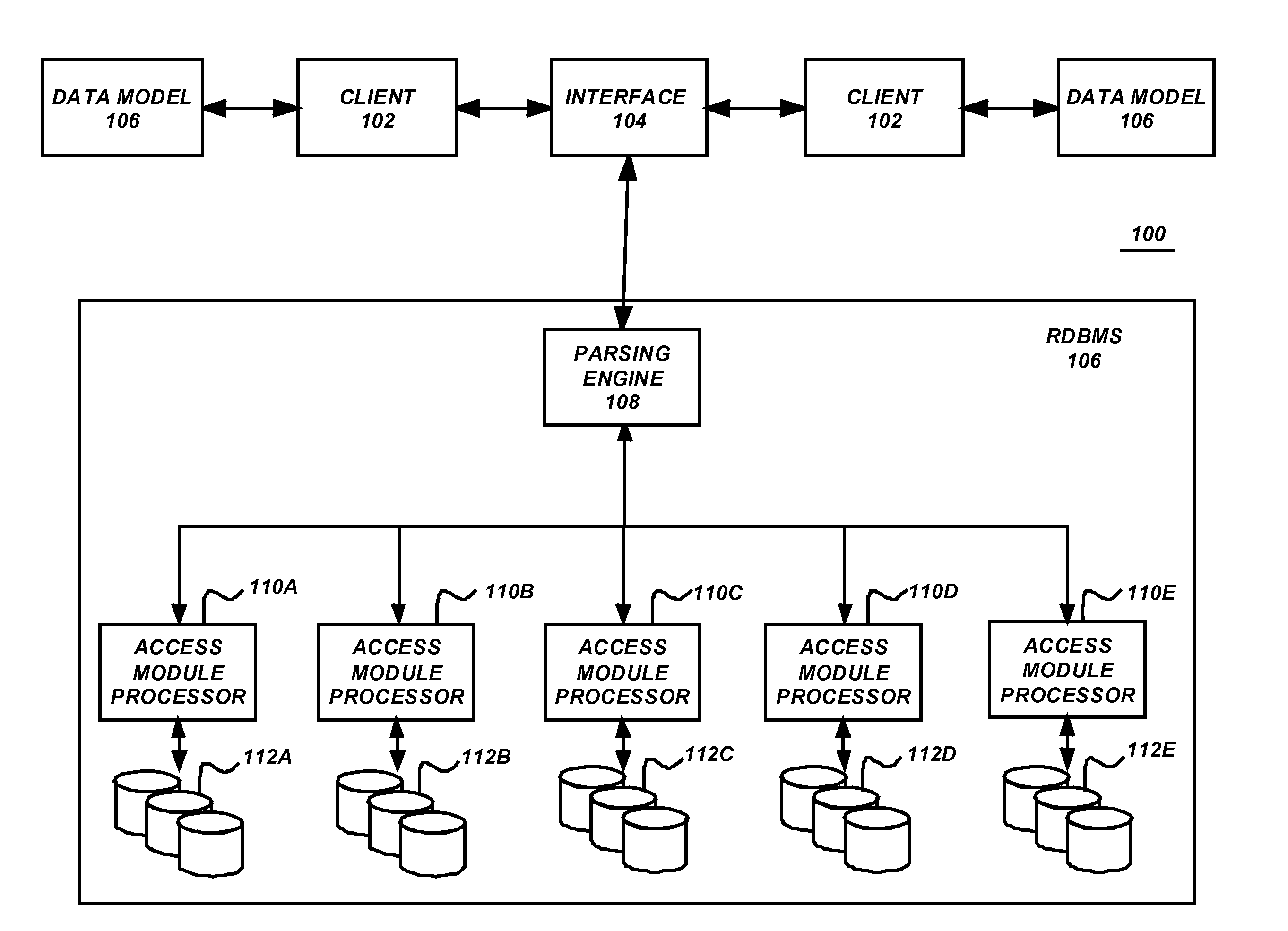
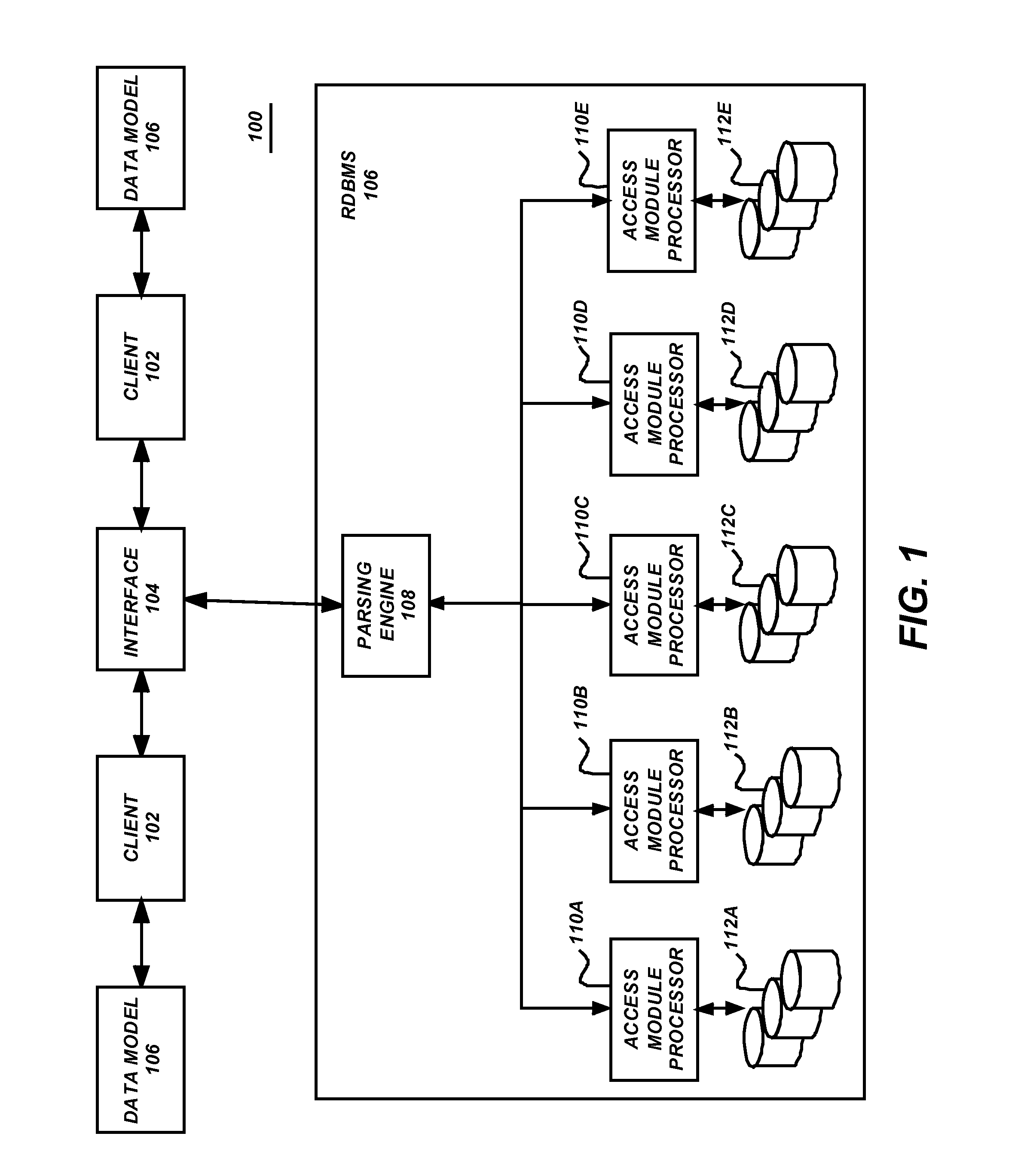
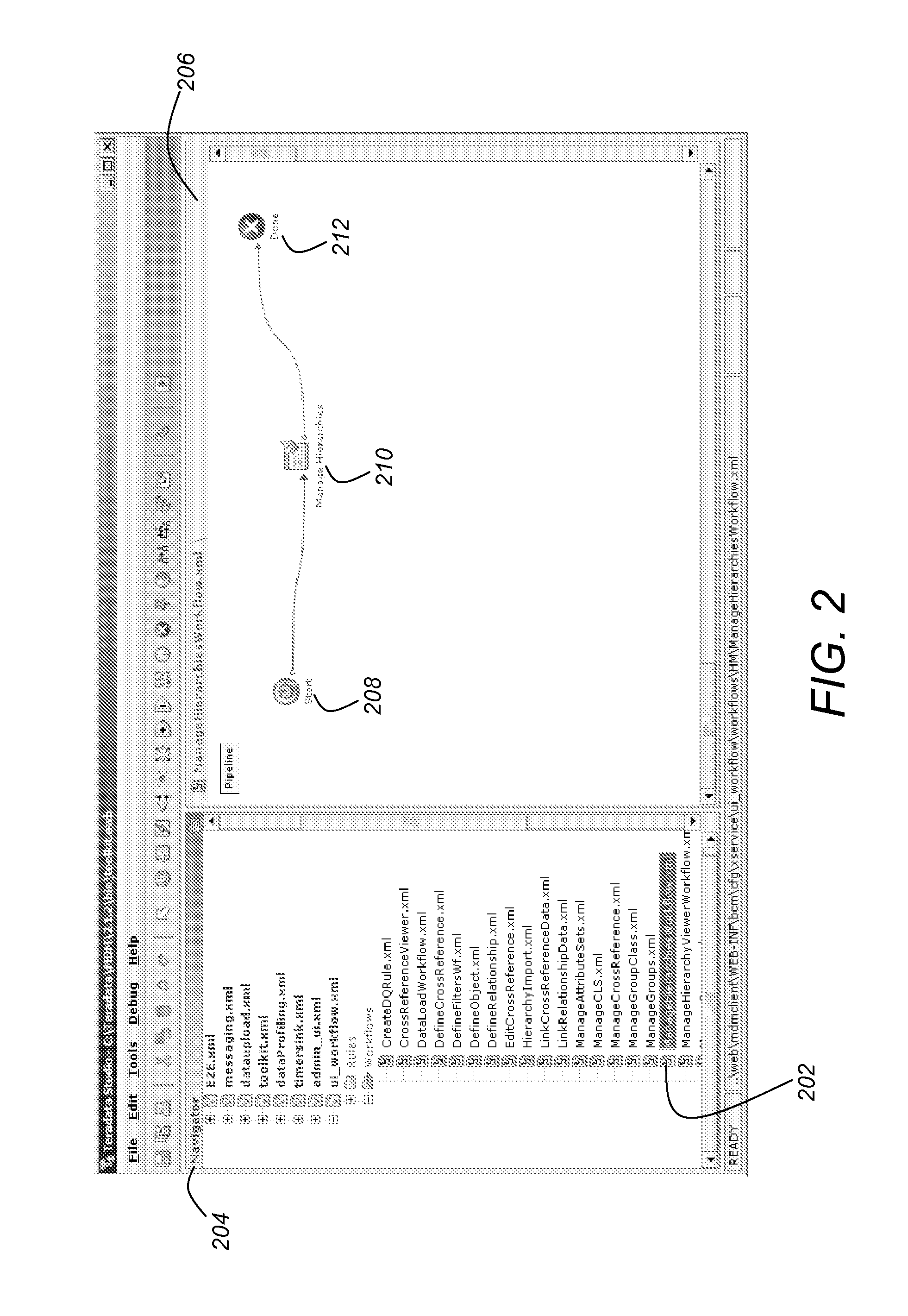
A method, system, apparatus, and article of manufacture provides the ability to visualize master data management (MDM) data as part of a MDM workflow user interface (UI) in a computer system. MDM data resides in one or more tables of a relational database management system. An MDM system maintains, as part of a process and framework, a first process workflow to manage relationship data. The relationship data is data required to manage an association of one piece of MDM data to another piece of MDM data. A first process workflow provides a UI node that contains a link to a file that describes UI components to display when the first process workflow is executed. A first component of the UI component identifies an Adobe™ Flex™ based UI component. The Adobe™ Flex™ based UI component enables the representation and viewing of the MDM data in a hierarchy.
Owner:TERADATA US
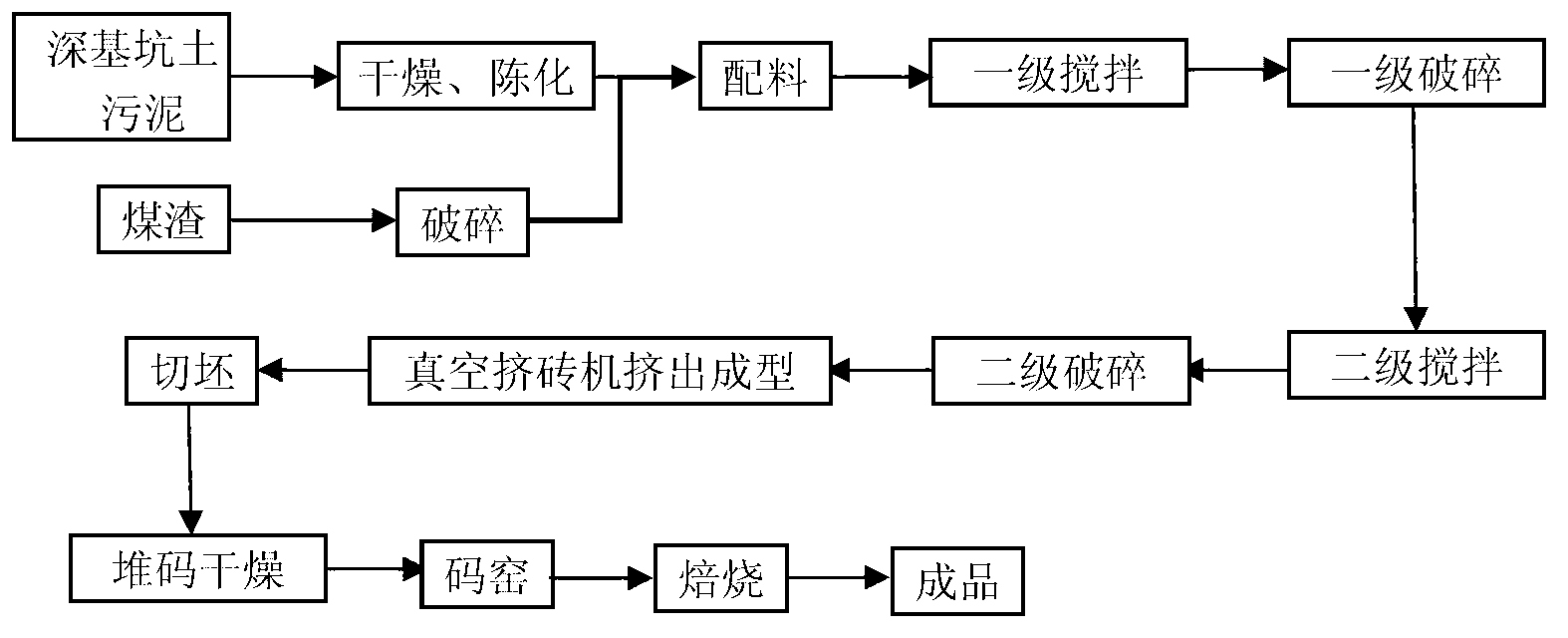
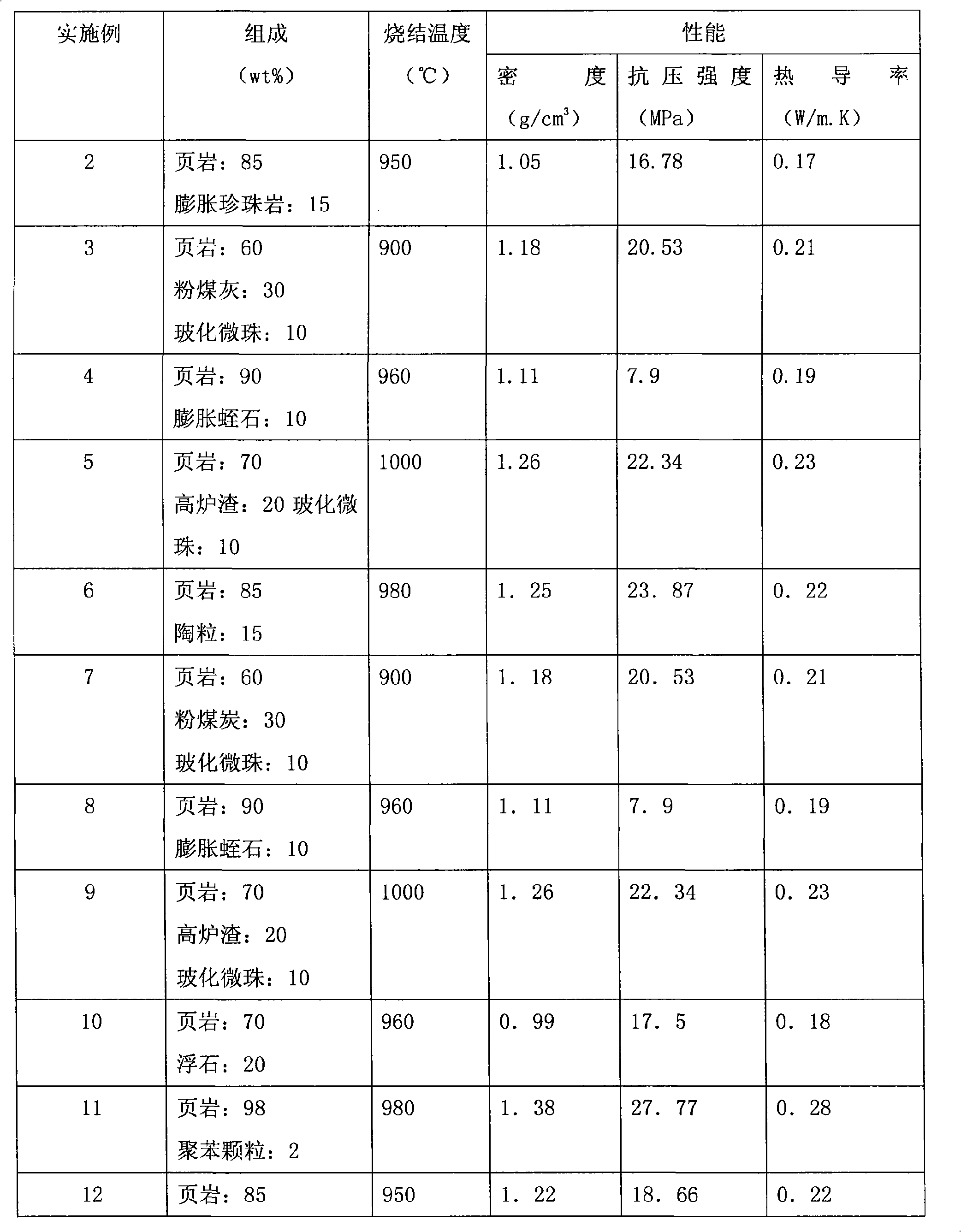
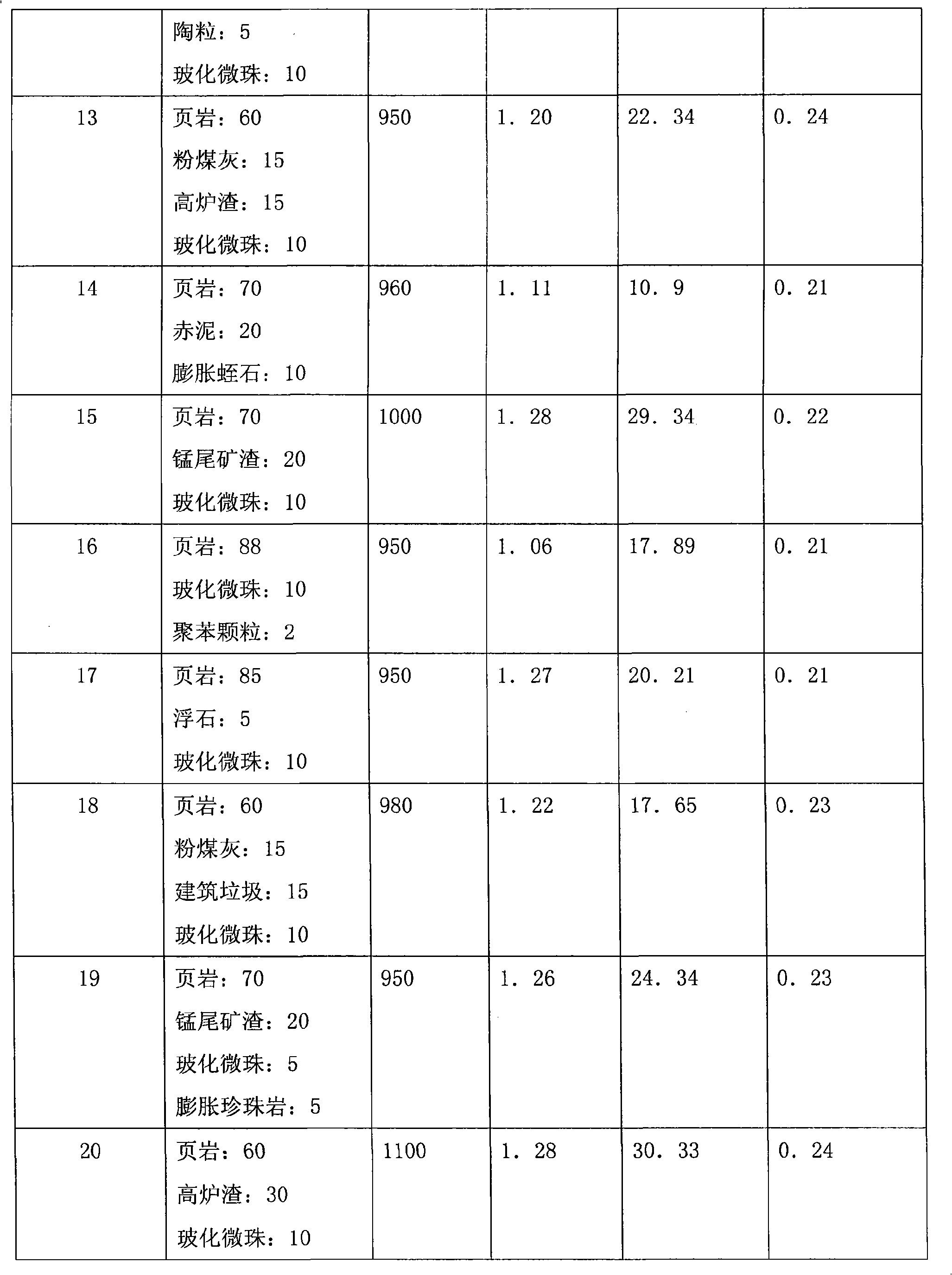
Deep foundation pit soil-sintered porous brick and production method thereof
InactiveCN102795831AGood mechanical propertiesImprove insulation effectCeramicwareBrickThermal insulation
The present invention relates to a building wall material, and discloses a deep foundation pit soil-sintered porous brick and a preparation method thereof. The deep foundation pit soil-sintered porous brick of the present invention is composed by the following raw materials by mass percentage: 30-50% of deep foundation pit soil; 20-40% of deep foundation pit soil dry powder; 20-30% of cinder; and 1-10% of an adobe regulator. The deep foundation pit soil-sintered porous brick of the present invention is good in mechanical properties and thermal insulation properties with strength up to MU20, and can be used as an ordinary load-bearing or non-load-bearing wall material.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Shale composite sintering brick and preparing technique thereof
The invention discloses a shale compound sintered brick. The brick is made from the following raw materials with weight percentages: 30-98% of shale, 0-40% of slag and 2-50% of light aggregate. The production technology comprises the following steps: the shale is crushed, the crushed shale is evenly mixed with the light aggregate, or the crushed shale is evenly mixed with the slag and the light aggregate to obtain a mixture; the mixture obtained in the step two is added with water and evenly mixed to obtain adobe stock, the water accounts for 5-30% of the weight of the mixture; the adobe stock obtained in the step three is made into green brick; the green brick is dried; the dried green brick is piled and sintered in a kiln. The sintered brick leaves a large amount of air holes after the brick body is sintered, the air holes prevent heat bridges from forming, therefore, the brick has good thermal insulation property and the specific weight of the brick body is greatly reduced. The sintered brick can be used for making bearing and non-bearing walls.
Owner:翁履谦
Method for preparing high stone powder mixing quantity porous baked brick
The invention belongs to the field of building material, and relates to a method for preparing a high stone powder mixing quantity porous baked brick which comprises the raw materials by weight percent: 80-95% of stone powder, 3-5% of sintering auxiliary agent and 0-17% of additive. The raw materials are simultaneously added pore for forming a medium with the weight accounting for 3-10% of the total weight of the powder, and the solvent is water solution containing 1-5% of binding agent. The preparation method comprises the steps such as weighing the raw materials, mixing, molding, drying, sintering, cooling and the like. As the organic binding agent and the sintering auxiliary are added, the bonding force among stone powder particles can be enhanced, and the formability and the sinteringperformance of adobe can be improved. By adding the pore for forming the medium, the density of the baked brick can be reduced. The invention has simple technique, low cost, high stone powder demand,energy conservation, environmental protection as well as high strength and low density of the baked brick. The invention can increase the stone powder mixing quantity in the baked brick and simultaneously reduce the density of the baked brick, thus being beneficial to expanding the application field of the baked brick and improving the using performance thereof.
Owner:周立忠 +1
Fully polished glazed ceramic tile with a real stone effect and production process thereof
The invention discloses a fully polished glazed ceramic tile with a real stone effect and a production process thereof. The production process includes the following steps: (A) by means of feed modules, pigments and base adobe powder are mixed into a variety of needed colored adobe powders by a dry mixing method according to needed proportions; (B) by means of a distribution module and a press mechanism, the colored adobe powders are pressed into a fully colored adobe; (C) the fully colored adobe is dried under 120DEG C to 180DEG C for 50 to 100 minutes; (D) the surface of the fully colored adobe is decorated, so that a semifinished product is obtained; (E) the semifinished product is fired once under 1100DEG C to 1250DEG C for 40 to 90 minutes; (F) after the fired product is processed polishing, edging, waxing and filming steps, the finished product is obtained. The invention realizes the representation of the changing colors and texture of natural stone on the ceramic tile, the fully colored adobe can more embody the unique stereoscopic impression of stone, and by means of post-processing processes, such as chamfering and groove broaching, the fully polished glazed ceramic tile can show a full real stone decoration effect.
Owner:DONGGUAN CITY WONDERFUL CERAMICS IND PARK +1
System and Method for Generating Three-Dimensional Figures
InactiveUS20080036762A1Easy to viewComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsAdobe
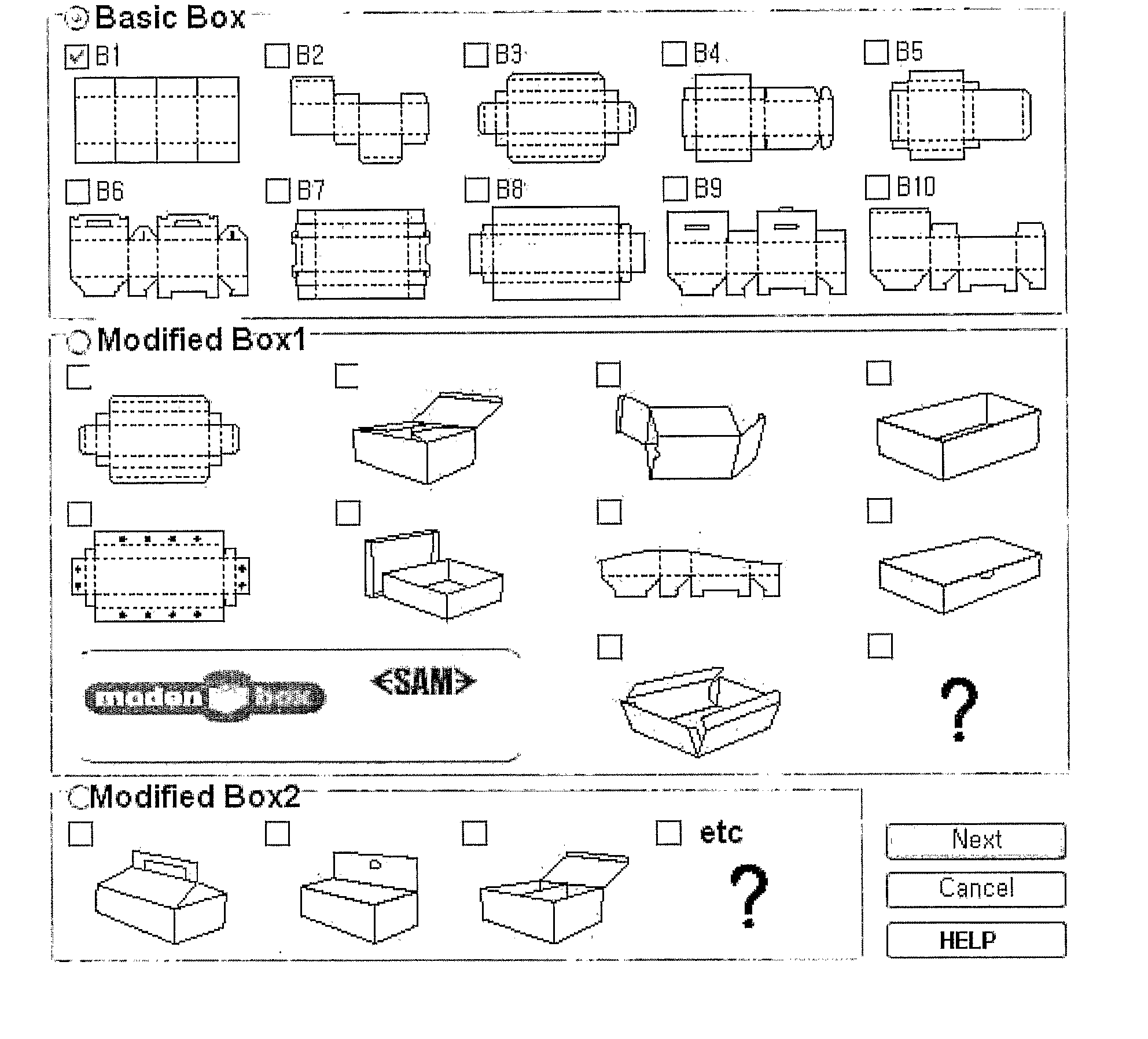
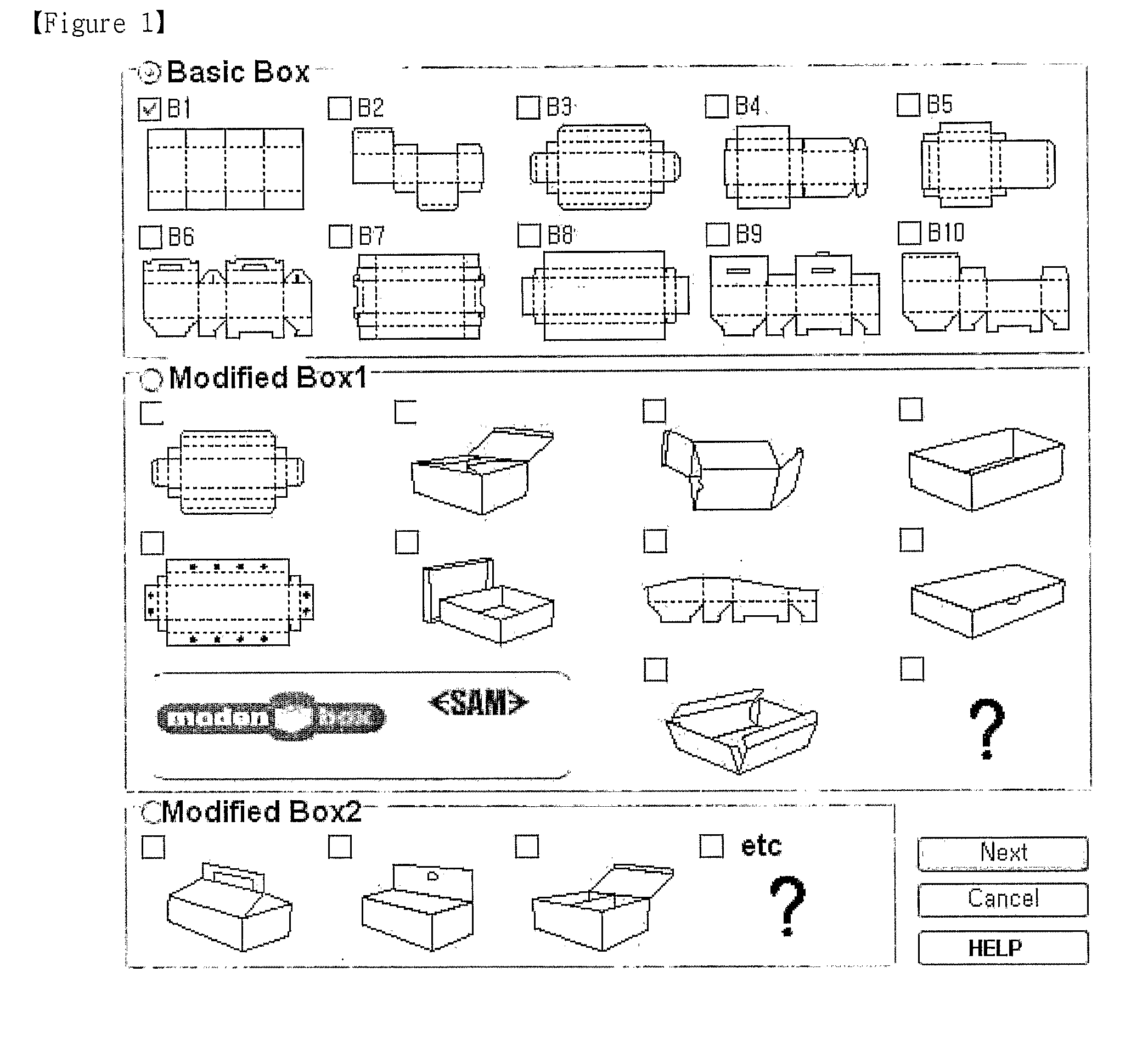
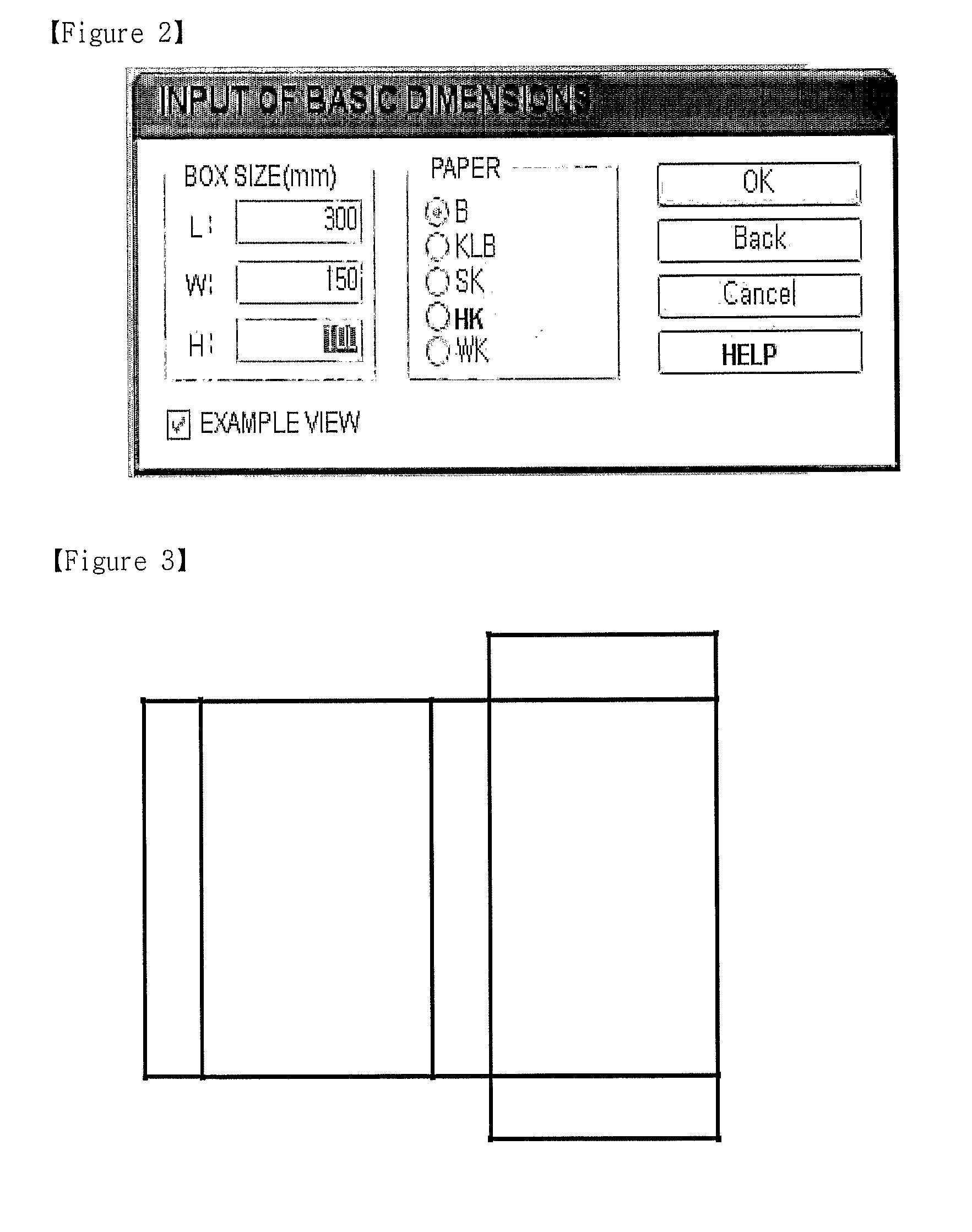
The present invention relates to a system and method, which establish a plug-in relationship with a graphic program, such as Adobe Illustrator, and are adapted to reconstruct each face in three dimensions to include content designed in a two-dimensional development figure, thus converting a two-dimensional object into a three-dimensional object. In the three-dimensional design method, shapes of basic boxes are presented to a user. Dimensions corresponding to a box shape selected by the user are received. Coordinate values of a development figure are changed depending on the dimensions received from the user. A development figure suitable for the changed coordinate values is presented to the user. The design made by the user is partitioned to correspond to faces of the development figure. Three-dimensional coordinate values are set based on input coordinate values. The partitioned design is arranged on the three-dimensional coordinate values, thus generating three-dimensional data.
Owner:MODENBOX +4
Manufacturing method of soft-polished glazed tiles
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of soft-polished glazed tiles. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing adobe; (2) applying ground glaze; (3) applying glossy glaze; (4) performing low-gloss ink spray printing through an inkjet printer; (5) firing glaze at the high temperature to obtain the soft-polished glazed tiles. The manufacturing method is simple and convenient, requires low labor intensity and has low technical requirement; low-gloss ink and the glossy glaze are fused, and accordingly, the soft-polished glazed tiles with a low gloss effect can be manufactured.
Owner:FOSHAN SANSHUI NEW PEARL CONSTR CERAMICS IND +1
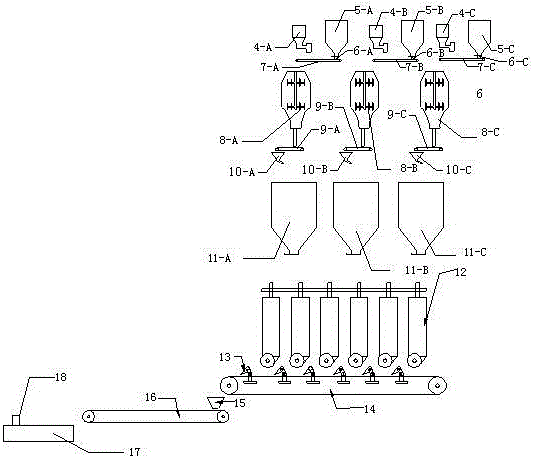
Following adobe cutting and distributing machine
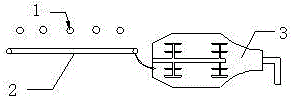
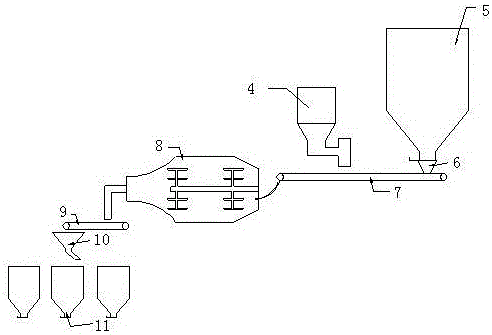
A following adobe cutting and distributing machine is applicable to the brick sintering industry and is assembled behind an extruder and before a setting machine. The following adobe cutting and distributing machine can advance along with continuously-extruded mud stripes automatically, clamp the mud stripes close to the outlet direction of the extruder, ensure that a clamping cutter assembly moves forwards along with the mud stripes at the same speed reliably, then cut the mud stripes away from the outlet direction of the extruder into brick adobes, and then reset to achieve a next circulation of mud strip cutting and brick adobe forming; immediately, the brick adobes enter a adobe distributing mechanism, one or more pairs of powered vertical cylinders of the adobe distributing mechanism transmit both end surfaces of every brick adobe to send the brick adobe into a conveyor belt for conveying. Without a stripe cutter or steel wire cutting, the adobe cutter and the adobe distributing machine are integrated together, so that the production cost is saved, automated operation can be achieved, and adobe necessary conditions for manual or mechanical adobe setting are obtained.
Owner:冉春晖
Method for manufacturing low-temperature red clay colour-painted and glazed ecological ceramic product
The invention relates to the technical field of ceramic technology, in particular to a method for manufacturing a low-temperature red clay colour-painted and glazed ecological ceramic product. The method comprises the following steps of: adobe manufacture, pigment preparation, colour painting operation, glaze water preparation, product glazing, burning and the like. When the method is compared with the prior art, colour painting and glazing can be performed after burning for the first time; the surface is not decorated; the burning temperature is not higher than 1,090 DEG C; and the whole manufacture process only needs burning for two times. Therefore, the manufacturing process is simple; the burning temperature is relatively low; and the effects of energy conservation and environmental friendliness are achieved.
Owner:福建省德化县艺顺陶瓷有限公司
Sintered building brick with high flyash mixing amount and its production process
InactiveCN1398813AIncrease profitShorten the production cycleSolid waste managementClaywaresPulverised fuel ashAir pollution
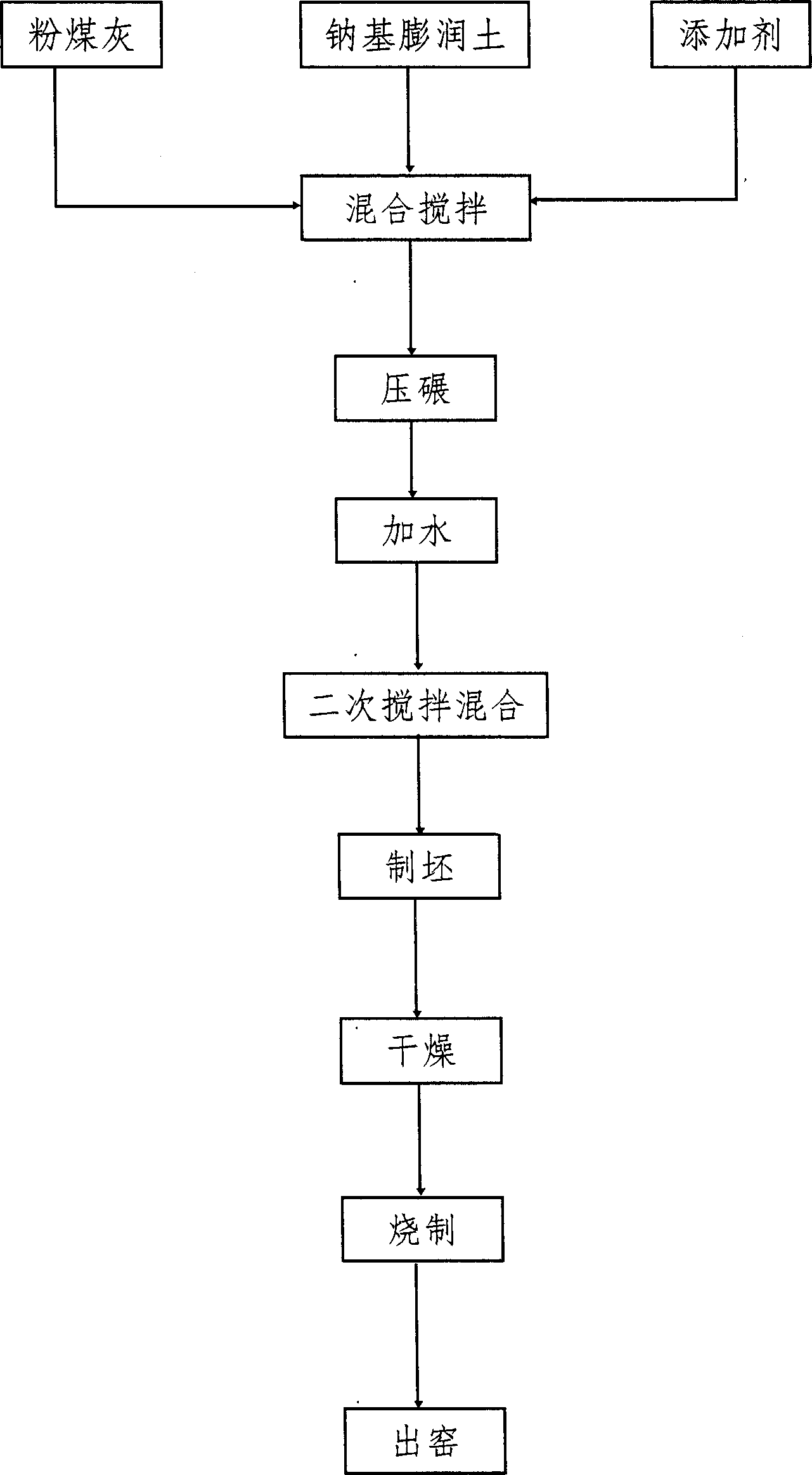
A flyash brick consists of flyash 85-95 weight portions, sodium-base bentonite 5-15 weight portions and additive 3-10 weight portions. Its produced process includes mixing the said components by stirring and rolling, adding water in 18-22 weight portions before stirring for the second time, producing adobe, stoving adobe in drying channel with kiln afterheat, and baking in kiln. The flyash brick has high flyash content and simple production process, and the production has reduced air pollution and high production efficiency.
Owner:韦保行 +1
Ceramic tile powder distribution method
ActiveCN105058566ARich and varied blocky texture effectsEfficient mixingFeeding arrangmentsBrickPrill
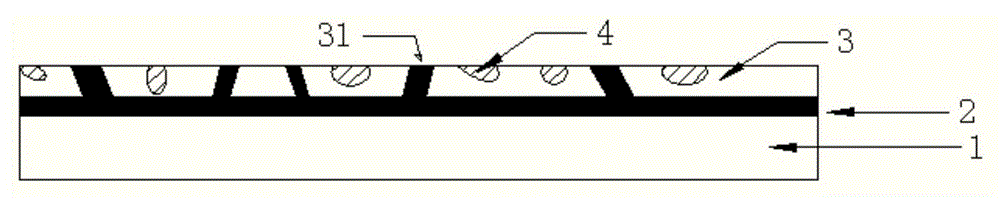
The invention provides a ceramic tile powder distribution method. The ceramic tile powder distribution method comprises that step 1. widely-known ceramic tile surface materials are sprinkled on a distribution belt to form a surface material band, a conveying belt is arranged on the distribution belt, the blanking opening of the conveying belt is arranged above the distribution belt, granular powder is arranged on the distribution belt, and then is rolled to form a granular powder cake, then the granular powder is broken into blocky materials, finally the lump materials are arranged on the surface material band; step 2. widely-known ceramic tile backing materials are sprinkled, then powder is conveyed to a pressing machine through grids in a high-fidelity manner, and is stamped to form an adobe, and the whole distribution flow is completed. Compared with the prior art, blocky materials with blocky textures and other surface material components are mixed well, and the problems that the blocky materials and the surface materials are clustered, in the subsequent stamping process, the exhausting is difficult, a layered phenomenon occurs and the like are avoided. According to the invention, the blocky texture forming process is simplified, the preparation of the blocky materials and the distribution process are carried out at the same time and can be controlled easily.
Owner:FOSHAN DONGPENG CERAMIC +3
Stable low-noise adobe tamping equipment for constructional engineering
PendingCN109778830AReduce noiseAvoid damageUsing liquid separation agentSoil preservationAdobeLow noise
The invention discloses stable low-noise adobe compaction equipment for constructional engineering, and belongs to the technical field of constructional engineering machinery. The equipment comprisesan equipment body; a crankshaft is arranged between the left inner wall and the right inner wall of the equipment body; the outer wall of the crankshaft is movably sleeved with two groups of movable sleeves; a rotating pull rod is hinged to the outer wall of the movable sleeves; a limiting sleeve is arranged at the bottom of an inner cavity of the equipment body; a movable rod is arranged at the top of the limiting sleeve; the top of the movable rod is hinged with the bottom of a rotary pull rod; a driving motor is arranged at the top of the mounting plate through the top of a damping device;a driving gear is arranged on an output shaft of the driving motor; and a driven gear is arranged on the left side of the outer wall of the crankshaft; the driving gear and the driven gear are connected through a chain; rolling wheels are arranged at the bottom of the machine body through a mounting base. The tamping equipment is simple in structure, high in compaction efficiency on the adobe, capable of effectively reducing noise and capable of improving the stability of the compaction equipment.
Owner:朱雪玉
Method for integrating sludge drying by using brickkiln fume afterheat and brick making by using sludge
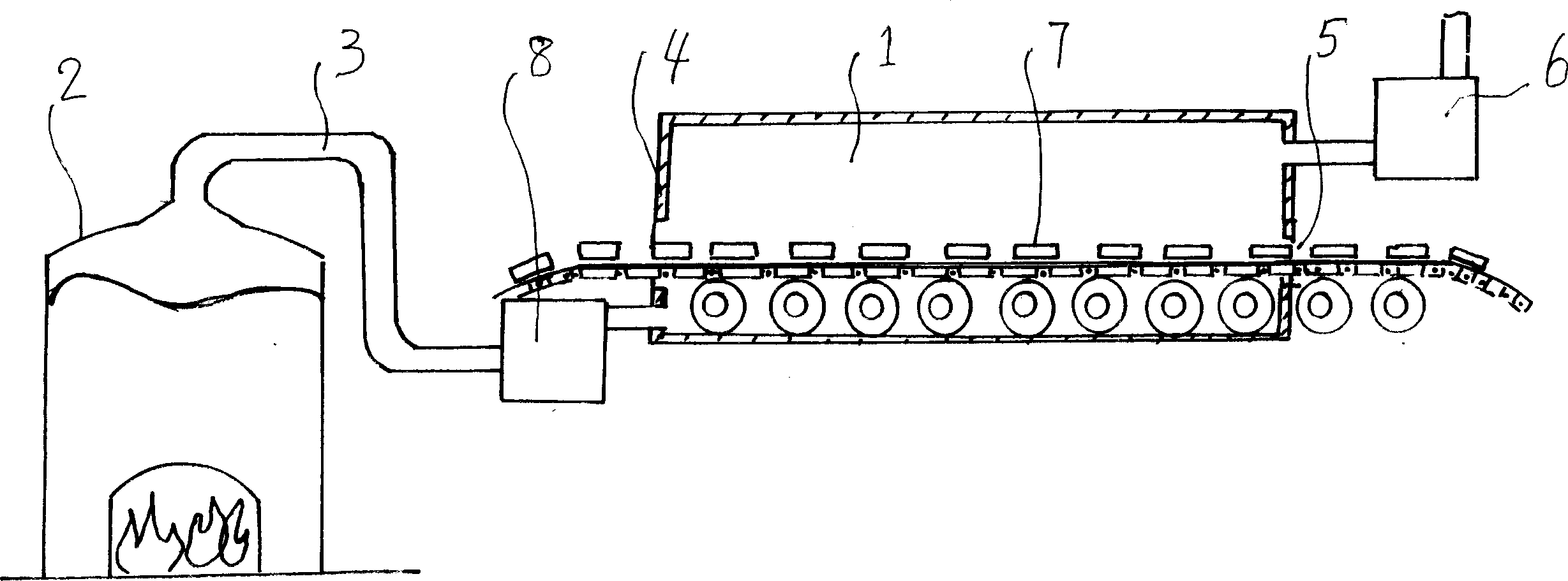
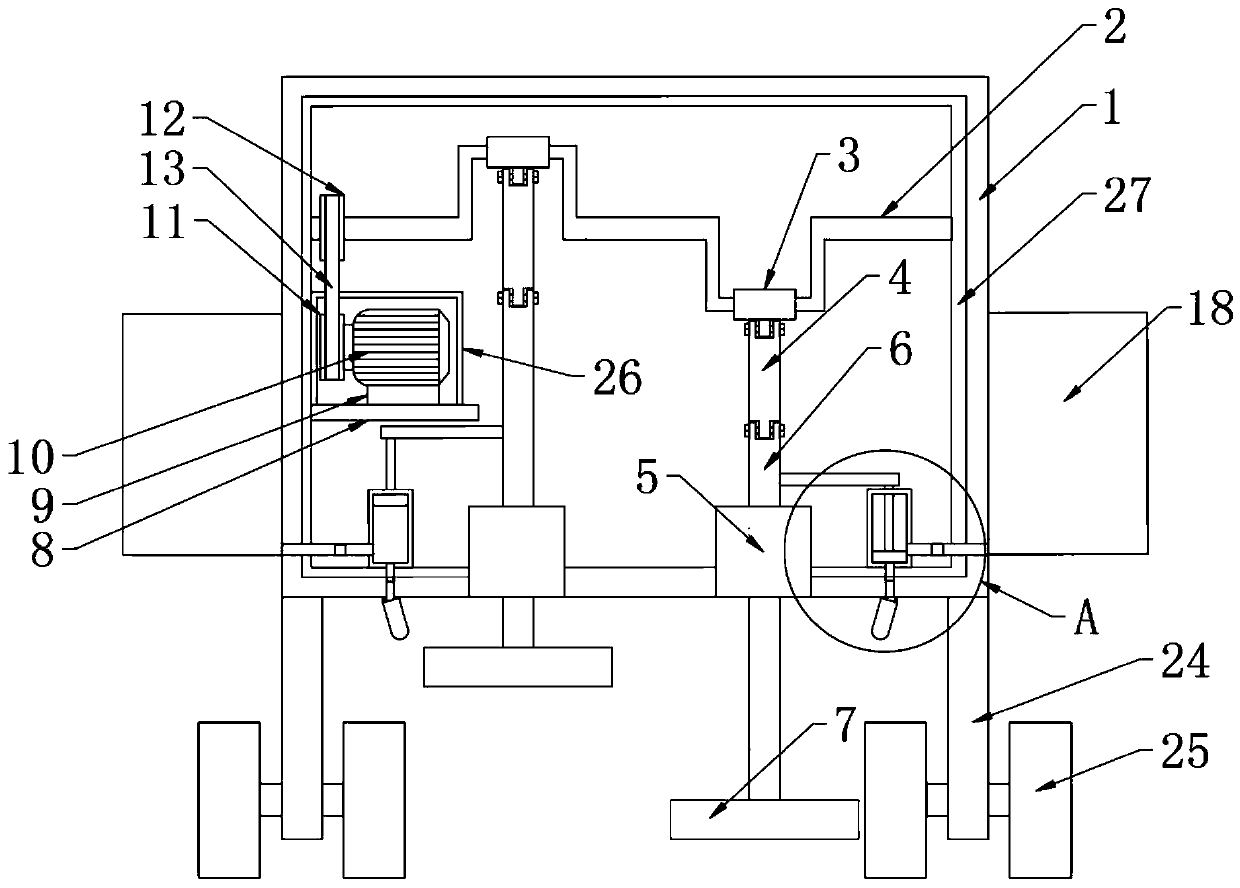
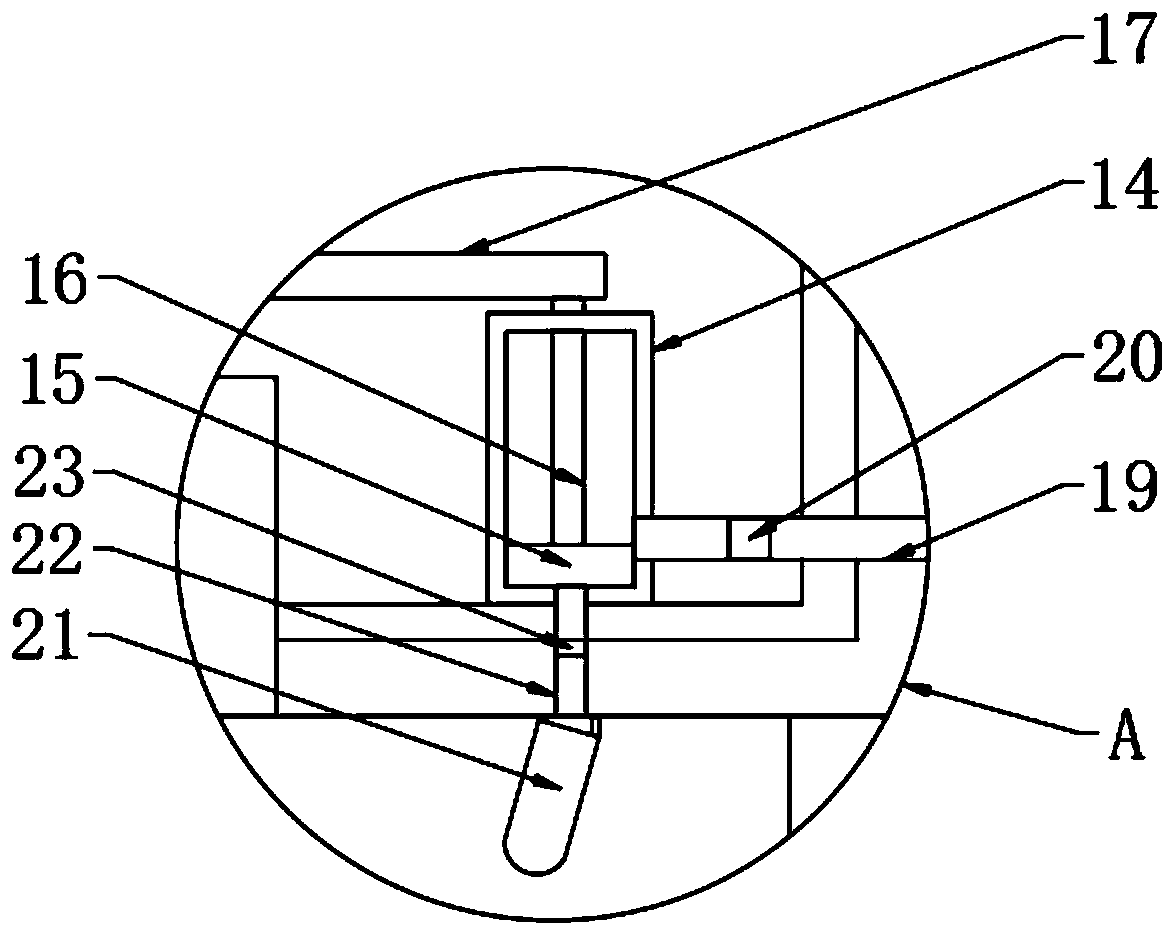
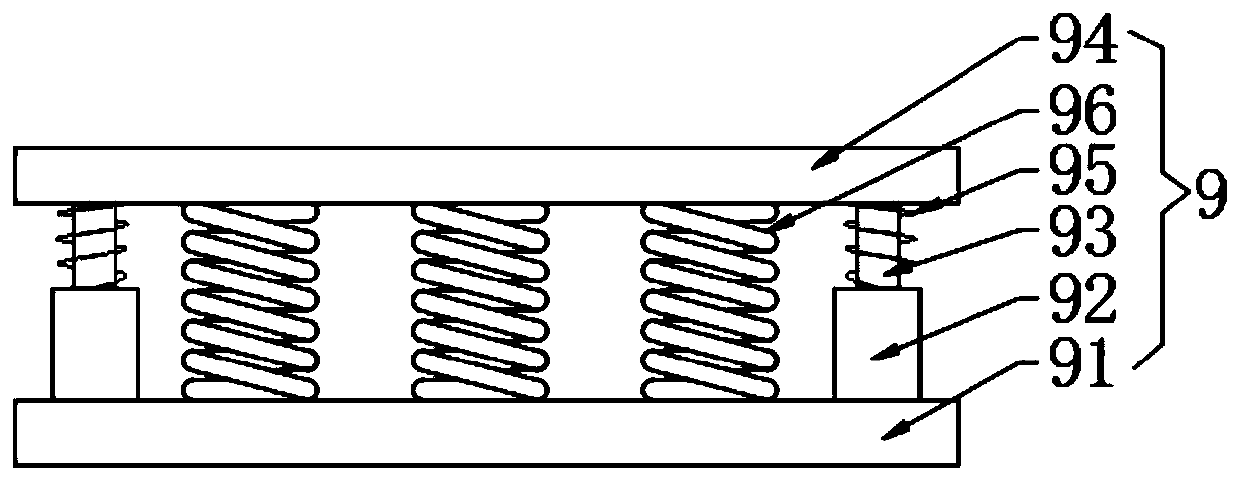
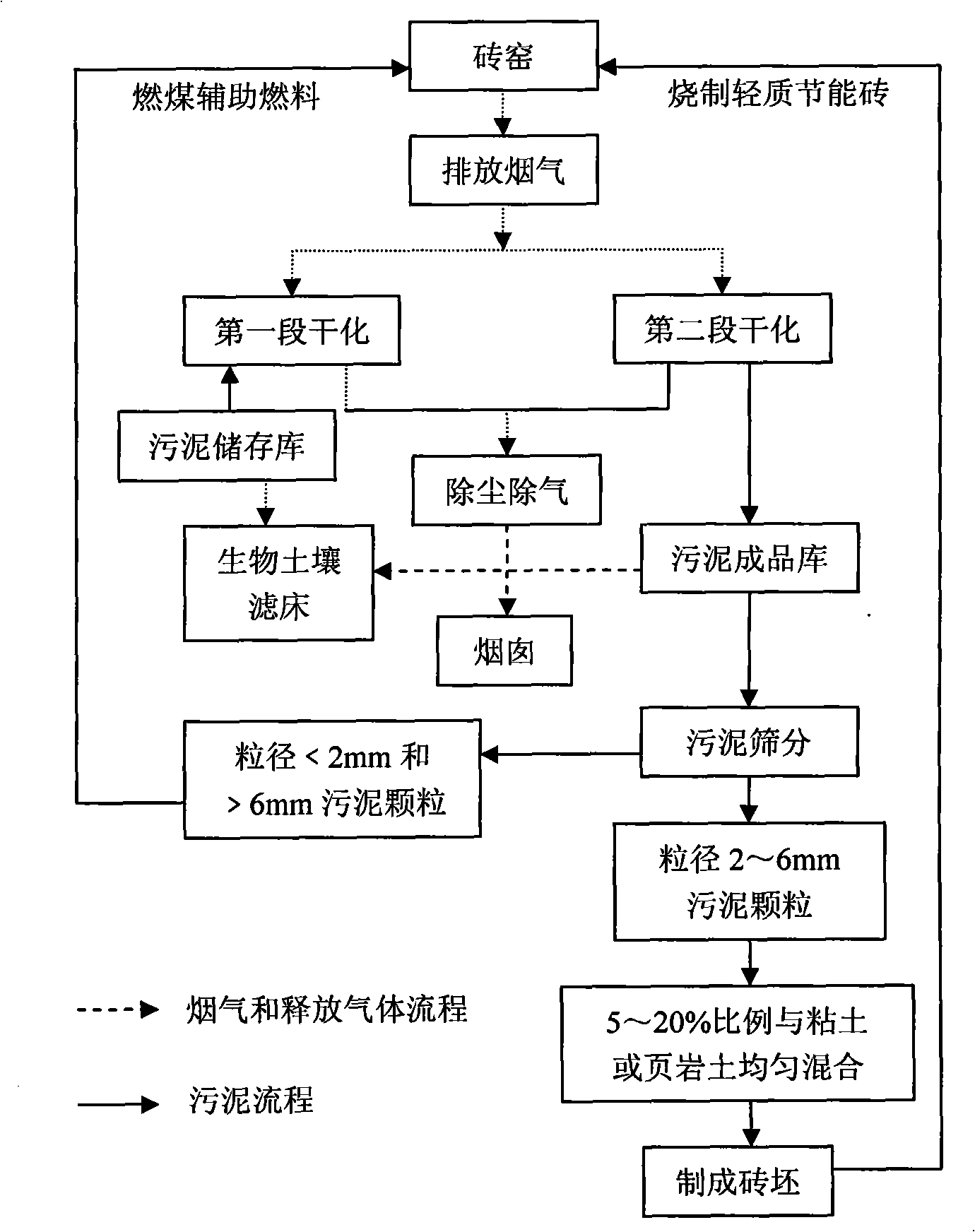
InactiveCN101643305AReduce moisture contentTake advantage ofSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSolid waste disposalAdobeBrick
The invention discloses a method for integrating sludge drying by using brickkiln fume afterheat and brick making by using sludge. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) using an induced draught fan to send hot fume discharged from a brickkiln respectively to a first sludge drying and granulating device and a second sludge drying and granulating device, for purpose of two-stage sludge drying; 2) stacking urban sludge in a sludge storage warehouse and carrying out pretreatment prior to the drying; 3) using a component-type feeder to send the pretreated sludge into the first sludge drying and granulating device, for purpose of first-stage sludge drying; 4) using a conveyor to send the sludge after the first-stage sludge drying into the second sludge drying and granulating device, for purpose of second-stage sludge drying; and 5) granulating the sludge after the second-stage sludge drying; before the entrance into a sludge finished product warehouse, using a screening and separating device to uniformly mix sludge grains with brick-making clay or shale soil; and making adobes and sintering the adobes into light and energy-saving bricks. In the method, waster materials are usedfor treating waster materials, so that the urban sludge is harmlessly treated and recycled, and remarkable social and economic effects can be generated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com