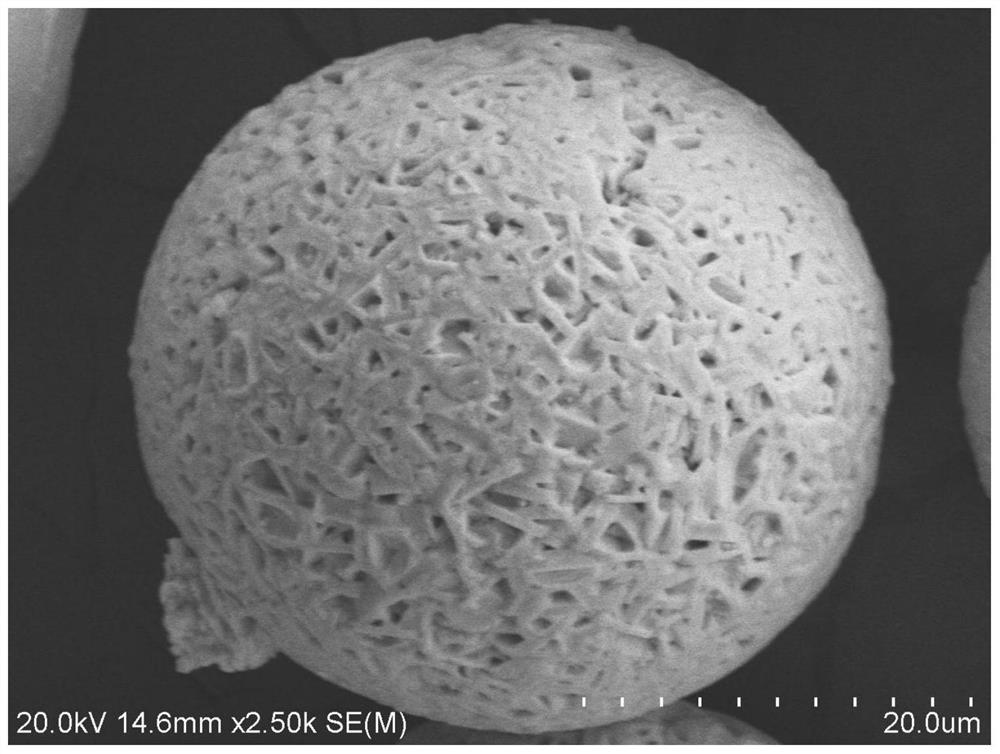
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Hafnium diboride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
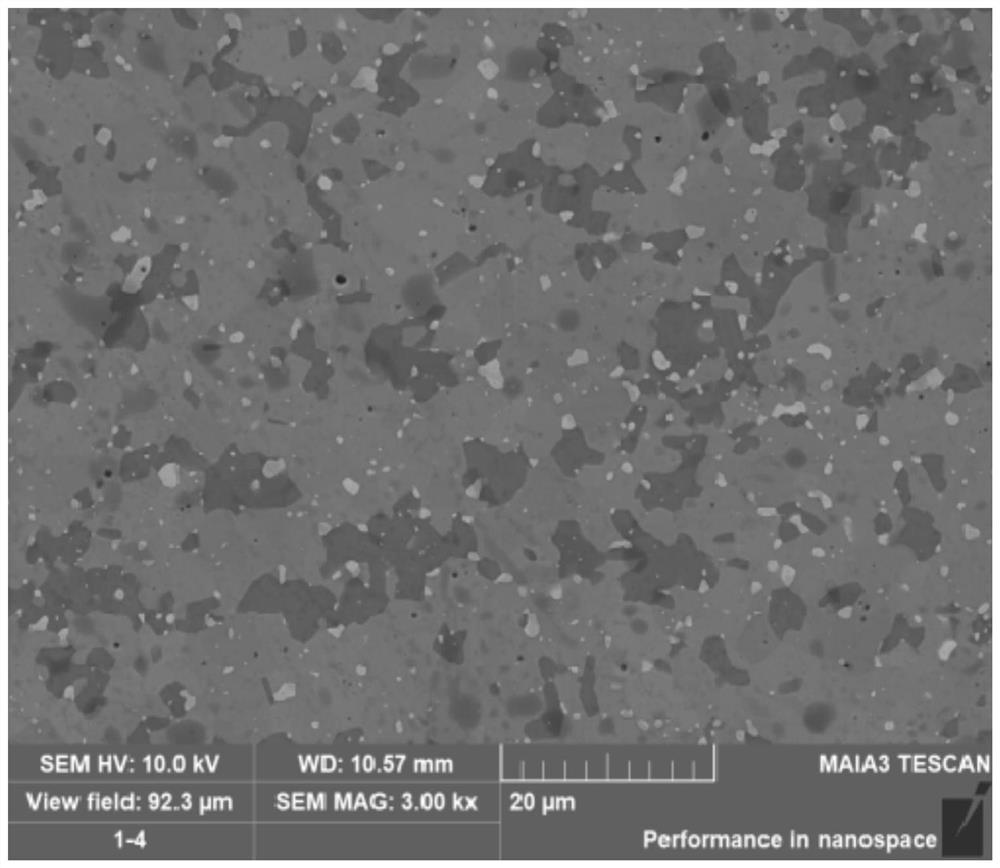
Hafnium diboride belong to the class of Ultra-high-temperature ceramics, a type of ceramic composed of hafnium and boron. It has a melting temperature of about 3250 degrees Celsius. It is an unusual ceramic, having relatively high thermal and electrical conductivities, properties it shares with isostructural titanium diboride and zirconium diboride. It is a grey, metallic looking material. Hafnium diboride has a hexagonal crystal structure, a molar mass of 200.11 grams per mole, and a density of 10.5 grams per cubic centimeter.
Coated pressing surfaces for abrasion resistant laminate and making laminates therefrom
A press plate for producing decorative laminate from resin impregnated paper, with alumina particles on its pressing surface, is coated with diborides selected from the group consisting of hafnium diboride, molybdenum diboride, tantalum diboride, titanium diboride, tungsten diboride, vanadium diboride, or zirconium diboride or mixtures thereof for making the press plate resistant to scratching. The preferred diborides are titanium and zirconium. The most preferred diboride is titanium. The color, gloss and surface appearance of laminate pressed with a titanium diboride coated press plate is substantially the same as laminate pressed with the press plate before coating.
Owner:WILSONART
Zirconium and Hafnium Boride Alloy Templates on Silicon for Nitride Integration Applications
InactiveUS20080164570A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBorideSemiconductor structure
Semiconductor structures are provided comprising a substrate and a epitaxial layer formed over the substrate, wherein the epitaxial layer comprises B; and one or more element selected from the group consisting of Zr, Hf and Al and has a thickness greater than 50 nm. Further, methods for integrating Group III nitrides onto a substrate comprising, forming an epitaxial buffer layer of a diboride of Zr, Hf, Al, or mixtures thereof, over a substrate; and forming a Group III nitride layer over the buffer layer, are provided which serve to thermally decouple the buffer layer from the underlying substrate, thereby greatly reducing the strain induced in the semiconductor structures upon fabrication and / or operation.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Environmentally-friendly cable filling material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103351548AHigh volume resistivityHigh temperature resistantPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsLow-density polyethyleneWear resistant
The invention provides an environmentally-friendly cable filling material and a preparation method thereof. The material is characterized by comprising the following raw materials by weight parts: 55-59 parts of SG-4PVC resin, 21-24 parts of metallocene linear low-density polyethylene, 3-4 parts of Mo2B5, 4-5 parts of hafnium diboride, 12-14 parts of polyphenylene thioether, 4-6 parts of poly-4-methyl-1-pentene, 32-36 parts of bentonite, 12-14 parts of alumina, 21-24 parts of barium sulfate, 2-3 parts of zinc oxide, 1-2 parts of an accelerator TMTM, 2-3 parts of bis-tetradecene alcohol ester, 2-3 parts of a silane coupling agent KH 550, 1-2 parts of a cross-linking agent TAC, 4-6 parts of epoxy tetrahydro dicapryl phthalate, 1-2 parts of tributyl tin chloride, 10-12 parts of carbon black N 660, 14-17 parts of precipitated silica, and 6-8 parts of modified diatomite. The cable filling material provided by the invention is high in volume resistivity, high temperature resistant, good in insulating property, relatively good in electrical property and good in wear-resistant property.
Owner:ANHUI TIANXING OPTICAL FIBER COMM EQUIP
High temperature-resistant resistor ceramic composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106587990AHigh thermal conductivityImprove heat resistanceZirconium hydrideCeramic composite
The invention discloses a high temperature-resistant resistor ceramic composite material. The high temperature-resistant resistor ceramic composite material is prepared from barium titanate, zirconium dioxide, eucryptite, magnesium oxide, zirconium boride, hafnium diboride, lead zirconate, strontium carbonate, molybdenum disulfide, titania, yttrium oxide, calcium carbonate, thallium carbide, hafnium carbide, zirconium carbide, silicon nitride, zirconium oxide, polyvinyl alcohol, copper oxide, niobium pentoxide, tungsten trioxide, lead tetraoxide, alumina, silica and assistants. The invention also provides a preparation method of the high temperature-resistant resistor ceramic composite material. The high temperature-resistant resistor ceramic composite material has excellent high temperature resistance.
Owner:ANHUI RUIXIN AUTOMATION INSTR
Near-infrared radiation ceramic coating used for ethylene cracking furnace and preparation method and application of near-infrared radiation ceramic coating
ActiveCN107556885AHigh bonding strengthImprove thermal shock resistanceChemical industryEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyCeramic coating
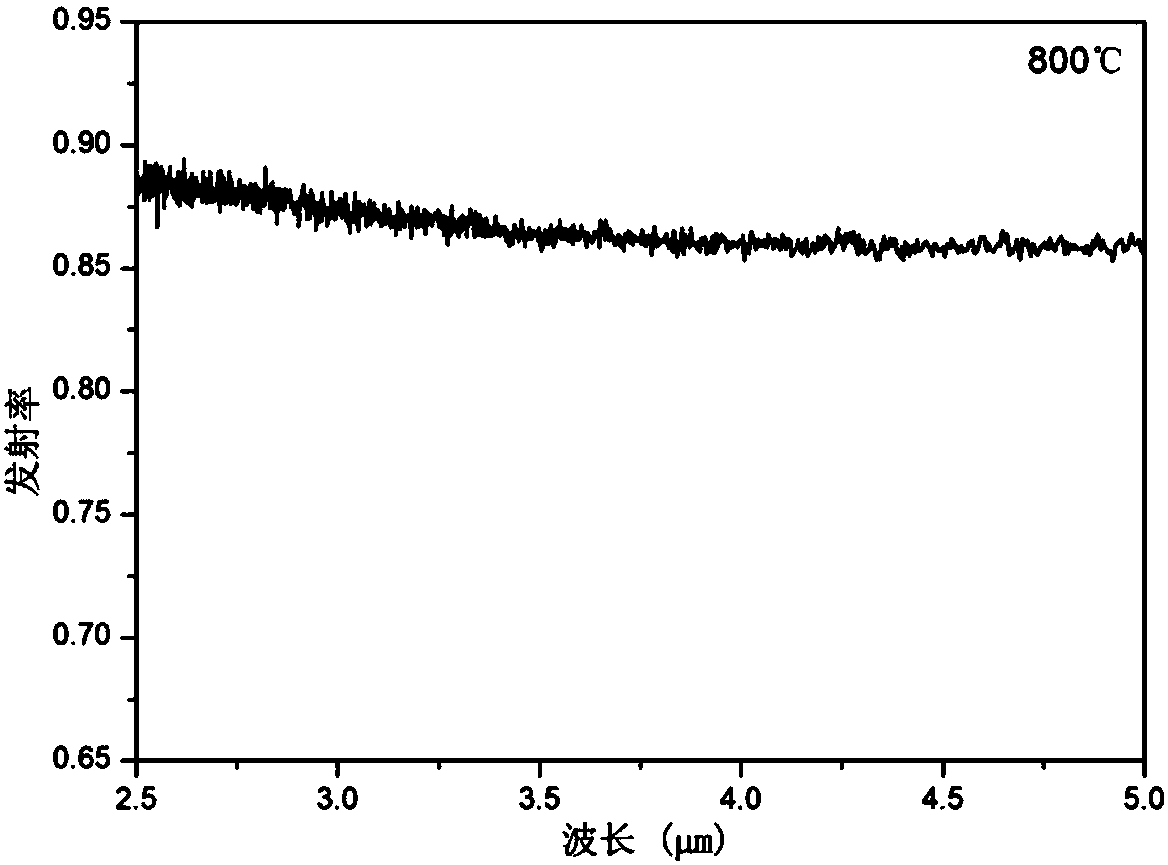
The invention discloses a near-infrared radiation ceramic coating used for an ethylene cracking furnace. The coating includes a component I and a component II in a mass ratio of 20:1. The component Iincludes epoxy resin, borosilicate glass powder, silicon carbide, silica, boron carbide, titanium diboride, hafnium diboride, zirconium diboride, a solvent and a thixotropic agent, and the component II includes a curing agent and ethanol. The bonding strength of the coating and a high-temperature-resistant alloy base at a normal temperature and a high temperature are improved, and the thermal shock resistance of the coating is improved. The obtained coating has adhesive force at a normal temperature and a high temperature more than 5 MPa, can bear an 800-degree high temperature, has the thermal shock resistance more than 500 K / S, and is not prone to crack or peel off. The emissivity of the coating in a near-infrared band is improved, and the radiation energy-saving efficiency is improved.At a high temperature of 800-1000 DEG C, the emissivity of the coating in a near-infrared band in a range of 3-5 micrometer can reach 0.86-0.92.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-purity hafnium diboride micro-powder combustion synthesis method
InactiveCN101112993AHigh purityProcess stabilityMetal boridesRare earth metal compoundsCombustionHigh energy
A combustion synthesis method of high purity diboride hafnium micropowder relates to a synthesis method of diboride hafnium micropowder material. The invention solves the problems of high raw materials cost, high energy consumption, long production period and high processing cost in the existing preparation methods of diboride hafnium micropowder. The invention proportions the basic raw material according to the weight percentage: diboride hafnium: 30 percent-60 percent, boron oxide: 10 percent -40 percent, magnesium powder: 15 percent -50 percent and the weight of added diluent diboride hafnium is 0-3 times of the basic material; being dried and mixed, the material is put into a closed pressure vessel that is cooled with cycling water; the raw material is transformed into products by propagating combustion after being ignited and the diboride hafnium micropowder is obtained after magnesium oxide is removed by acid pickling. The invention can be realized by replacing partial boron oxide and magnesium powder with boron carbide. The invention has the advantages of high reaction speed, short synthesis time, saving a great deal of energy, low cost, high production efficiency and high product purity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Powder metallurgy abrasion-resistant bearing material and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103537693AHigh strengthIncrease bearing pressureTurbinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsPollutionPolytetrafluoroethylene
The invention discloses a powder metallurgy abrasion-resistant bearing material. The powder metallurgy abrasion-resistant bearing material is characterized by being manufactured from, by weight, 2.2-2.3 parts of molybdenum, 2.2-2.3 parts of titanium, 0.3-0.35 part of bismuth, 72-73 parts of steel powder of waste tools, 3.4-3.5 parts of manganese powder, 0.2-0.4 part of Sb, 0.2-0.3 part of Bi, 0.5-0.8 part of Yb, 2-3 parts of zinc stearate, 0.2-0.4 part of hafnium diboride, 1-2 parts of polytetrafluoroethylene and 1-2 parts of auxiliaries. The powder metallurgy abrasion-resistant bearing material is reasonable in formula, the manufactured bearing material is high in strength and bearing capacity, a manufactured bearing is compact in organization, good in microstructure, very few in pore, and excellent in structural rigidity, hardness, fatigue resistance and tensile strength performance. The powder metallurgy abrasion-resistant bearing material is small in pollution to the environment and simple in production step, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:WUHU HONGKUN AUTO PARTS
Preparation method of nano hafnium boride powder
ActiveCN113816379APlay a role in boron fixationExcellent morphologyCarbon compoundsNanotechnologyBorideAcetic acid
The invention belongs to the field of nano material preparation, and particularly relates to a novel method for preparing hafnium boride powder through a coprecipitation method. The specific process comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving HfCl4 in acetic acid to obtain a transparent solution A; dissolving boric acid and D-sorbitol in acetic acid, and stirring until the boric acid and the D-sorbitol are completely dissolved to obtain a transparent solution B; (2) after the solution B is cooled to room temperature, dropwise adding the solution A into the solution and stirring until white floccules are separated out and the solution becomes milk white; (3) drying an obtained sol; (4) fully grinding to obtain a white powdery hafnium boride precursor; and (5) calcining the hafnium boride precursor at a high temperature to obtain the nano hafnium boride powder. The preparation method is easy to operate, conditions are easy to control, and the production period is short; the prepared hafnium boride powder has nano-scale particle size and uniform distribution, and has good morphological characteristics, ultrahigh purity and high yield. And a technical basis is provided for realizing engineering and industrial preparation of high-performance, high-strength and ultrahigh-temperature ceramic materials.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing high-compactness hafnium diboride ceramics
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-compactness hafnium diboride ceramics. According to the method, hafnium diboride powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling, acid washing, vacuum treatment and encapsulation and pre-pressing with high-melting point covering materials, and is then directly sintered into the high-compactness hafnium diboride ceramics under the conditions of 3to 15 GPa and 600 to 2000 DEG C. A high-temperature and high-pressure method is used for preparing a pure phase hafnium diboride block material having a good crystal form and a microstructure for thefirst time; the characteristics of small crystal particle dimension, high crystallinity degree, high compactness degree and stable structure are realized; high hardness and excellent fracturing toughness are realized. The preparation process is simple; the high melting point, high intensity, high hardness, high toughness and high anti-oxidization performance are realized; the material is developedto become the novel high-temperature structure ceramic material, and can be used as a candidate material of an airplane engine high-temperature-resistant component, can also be developed into novel hard alloy, can replace tungsten carbide hard alloy cutters, and can also be applied to the field of mechanical cutting.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
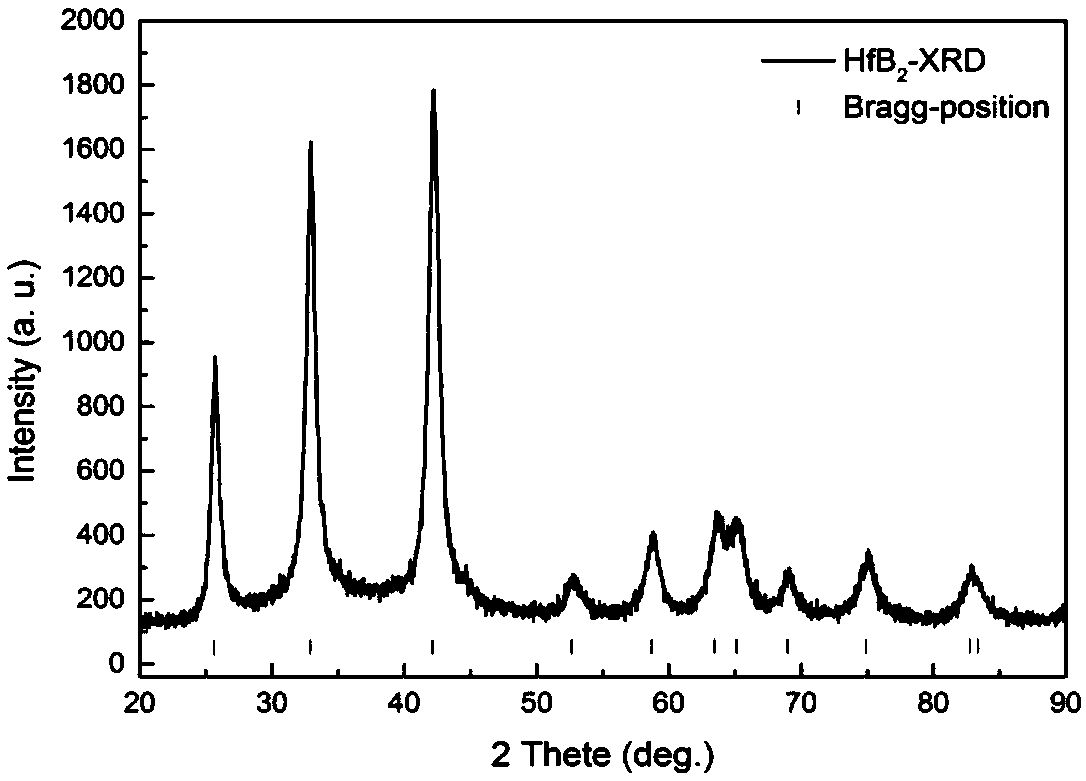
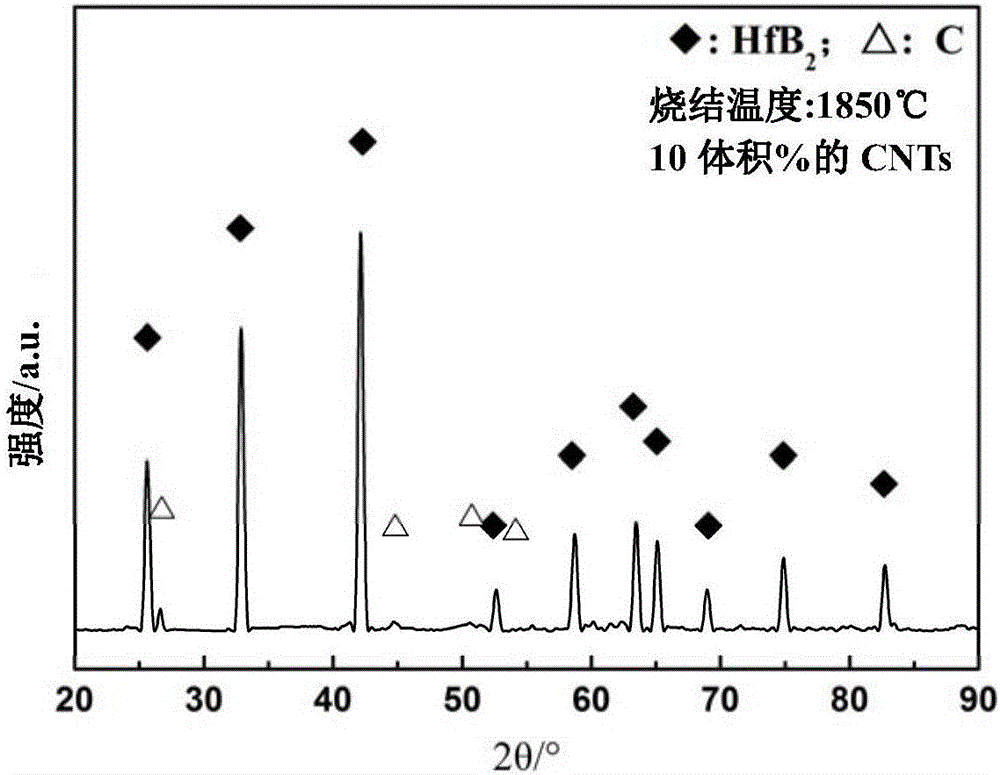
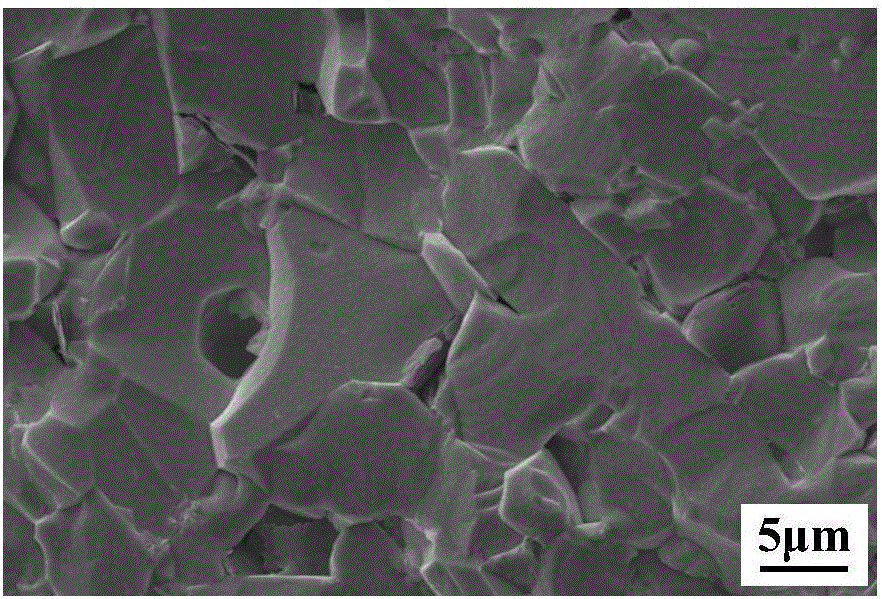
Carbon nanotube toughened hafnium diboride super-high-temperature ceramic composite material and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106518085AImprove fracture toughnessImprove thermal shock resistanceCeramic compositeCarbon nanotube
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
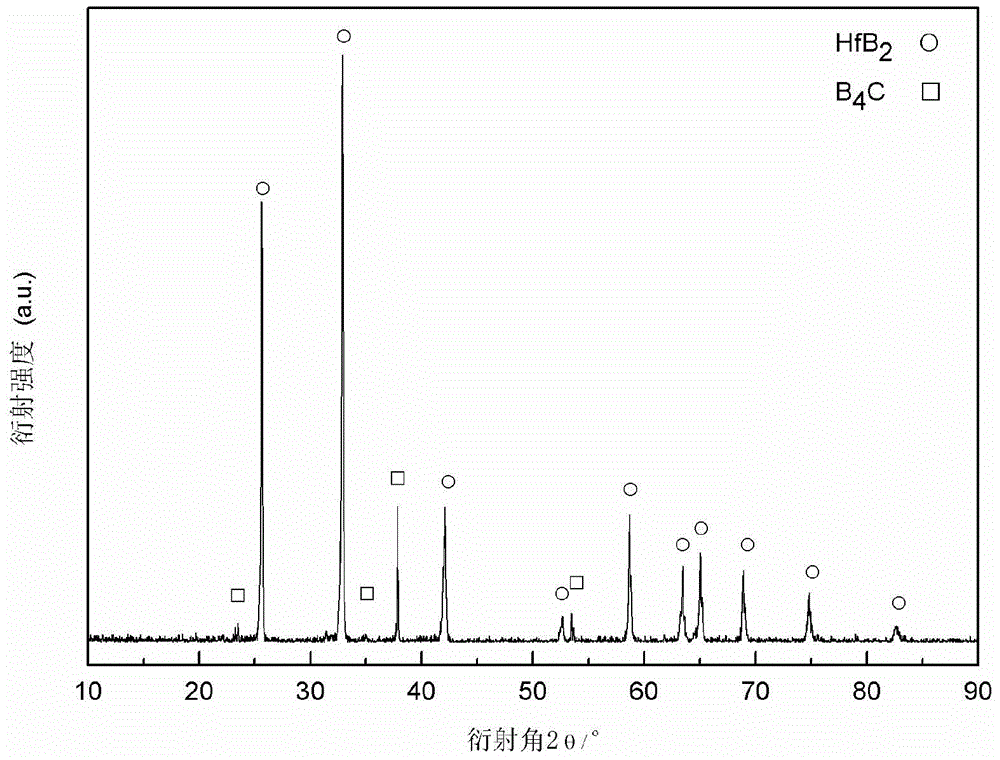
Preparation method for B4C-HfB2 high-temperature eutectic in-situ composite ceramic
The invention discloses a preparation method for B4C-HfB2 high-temperature eutectic in-situ composite ceramic. According to the invention, the proportion of boron carbide and hafnium boride is changed so as to prepare a uniformly distributed eutectic structure, wherein the molar content of hafnium boride is 10% to 50%. The preparation method comprises the following concrete steps: uniformly mixing boron carbide powder and hafnium boride powder, then pressing the mixed powder into a flake with a diameter of 10 mm at room temperature via cold isostatic pressing and preparing a B4C-HfB2 eutectic composite material by using an arc melting method. Compared with a traditional solid phase sintering method, the preparation method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the method is simple, a preparation cycle is short, and the prepared B4C-HfB2 composite ceramic has high density and more excellent high temperature performance. In addition, the composite ceramic has performance advantages of both HfB2 and B4C and can be used as an ultra-high temperature ceramic material.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Special cable material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103351552AIncrease elasticityImprove cold resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsMonoglycerideSilanes
The invention provides a special cable material and a preparation method thereof. The special cable material is characterized by comprising the following raw materials by weight parts: 8-12 parts of cis-1,4-polyisoprene rubber, 32-35 parts of SG-3PVC, 2-3 parts of Mo2B5, 4-5 parts of hafnium diboride, 6-8 parts of polyisobutylene, 3-5 parts of stearic acid monoglyceride, 9-12 parts of polycarbonate, 4-6 parts of poly-1-butene, 5-6 parts of turpentine, 24-28 parts of meerschaum powder, 18-22 parts of vermiculite powder, 2-3 parts of zinc oxide, 1-2 parts of an accelerator DM, 1-2 parts of an accelerator PZ, 3-4 parts of vinyl-tris(beta-methoxyethoxy)silane, 1-2 parts of an anti-oxidant 168, 1-2 parts of an anti-oxidant 1010, 3-4 parts of antimony trioxide and 6-8 parts of modified diatomite. The cable material is good in elasticity and cold resistance, high in tensile strength, anti-oxidation, and relatively good in electrical properties.
Owner:ANHUI CABLE
Grinding wheel for machining PCD blade
InactiveCN111037479AReduce consumptionFast feedingAbrasion apparatusOther manufacturing equipments/toolsBoridePolycrystalline diamond
The invention discloses a grinding wheel for machining a PCD blade. The grinding wheel comprises a grinding wheel base body, wherein a grinding layer is sequentially arranged on the grinding wheel base body, a wear-resistant layer is arranged on the grinding wheel base body, and the grinding layer comprises components, by weight, 40-45 parts of polycrystalline diamond powder, 7-11 parts of SiC whisker, 2-4 parts of hafnium boride, 3-6 parts of titanium boride, 0.5-1 parts of cobalt boride, 0.5-1 parts of tin oxide, 0.2-0.4 parts of iron oxide, 3-10 parts of pore-forming agent, 4-6 parts of resin. The grinding wheel has the advantages that while the same surface grinding quality is guaranteed, the higher feeding speed can be provided, machining efficiency is improved, when the finishing effect similar to that of an existing grinding wheel is achieved, consumption of a single grinding wheel is smaller than that of a grinding wheel in the prior art, the peripheral grinding wheel is sharper than the grinding wheel in the prior art, and the service life can be prolonged by about 40%.
Owner:无锡市星火金刚石工具有限公司
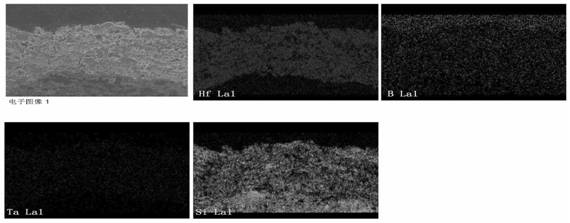
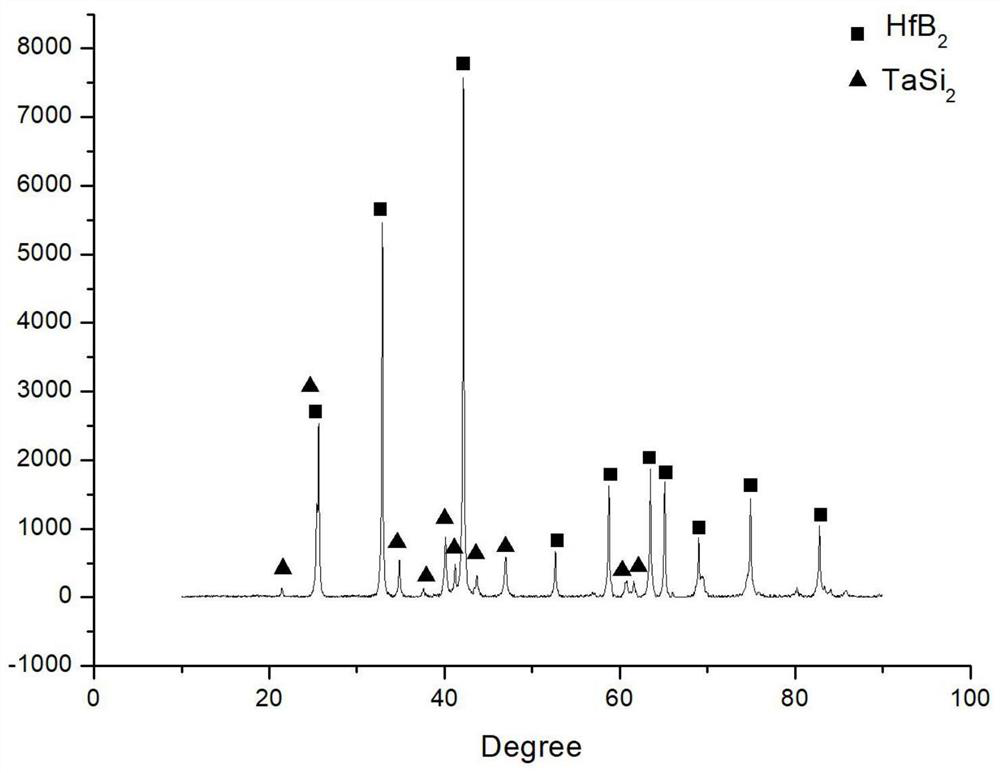
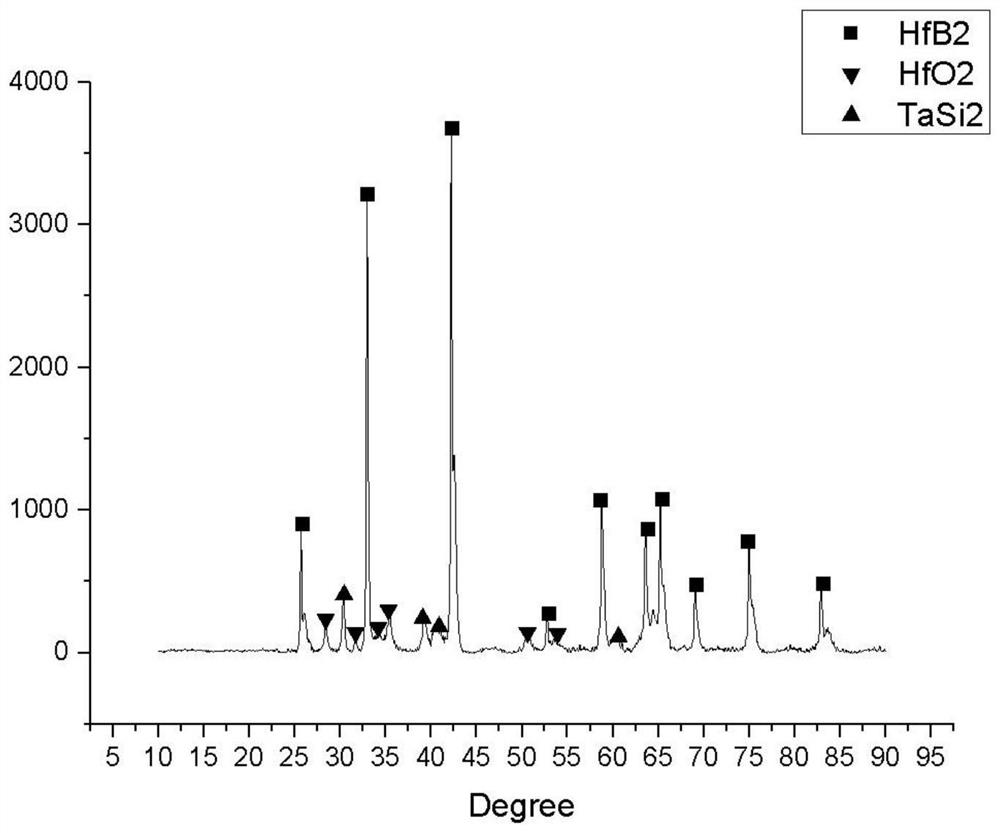
Hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide composite coating and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114000092AReduce porosityImprove high temperature protection abilityMolten spray coatingCeramic coatingUltra-high-temperature ceramics
The invention provides a hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide composite coating and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of composite coatings. According to the invention, hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide composite powder is used as a coating raw material, and tantalum disilicide serves as a modification component of hafnium diboride; on one hand, an oxidation product SiO2 of tantalum disilicide can serve as a good high-temperature sealing and filling phase, and hole defects of the hafnium diboride coating are sealed and filled; and on the other hand, another oxidation product Ta2O5 of tantalum disilicide can undergo a solid solution reaction with HfO2 to form HfTaOx, so the crystal transformation of HfO2 is inhibited to a certain extent, and the high-temperature thermal stability of the coating is improved. The obtained coating is an ultra-high-temperature ceramic coating and has good oxidation resistance at a temperature of 1800 DEG C. The coating is prepared in an atmospheric plasma spraying mode, hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide powder is high in deposition efficiency, and the hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide powder can be fully molten and does not decompose in a spraying process.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optical lens without light loss and its manufacturing process
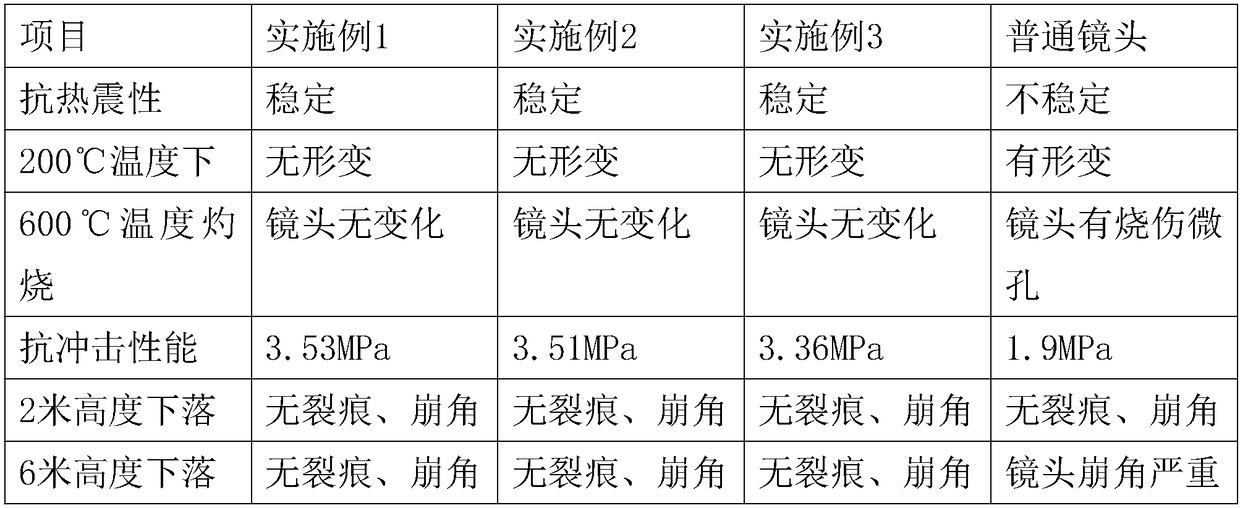
The present invention relates to the optical lens technology field, especially to an optical lens without optical return. The lens is made of the raw materials, parts by weight, consisting of the quartz sand of 52-58 parts, the alum of 4-8 parts, the sodium carbonate of 10-13 parts, the nanometer silicon dioxide of 4-6 parts, the modified graphene of 8-12 parts, the lithium hydrate of 4-6 parts, the hafnium boride of 7.5-8 parts, the potassium chloride of 8-10 parts, the vanadium pentoxide 5-8 parts, the iron carbide of 5-8 parts, the barium silicide of 4-6 parts, the tungsten silicide of 1-2 parts, the cobalt dioxide of 4-5.5 parts and the vitrification fiber of 2.5-3 parts. The lens is good in the diffraction to the ray of light and very low in optical return, is very suitable for the shooting usage in the highlight, and is low in the lens image drifting.
Owner:ANHUI CHANGGENG OPTICS TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing feeding nozzle for continuous high-purity alumina melting furnace and continuous melting furnace
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
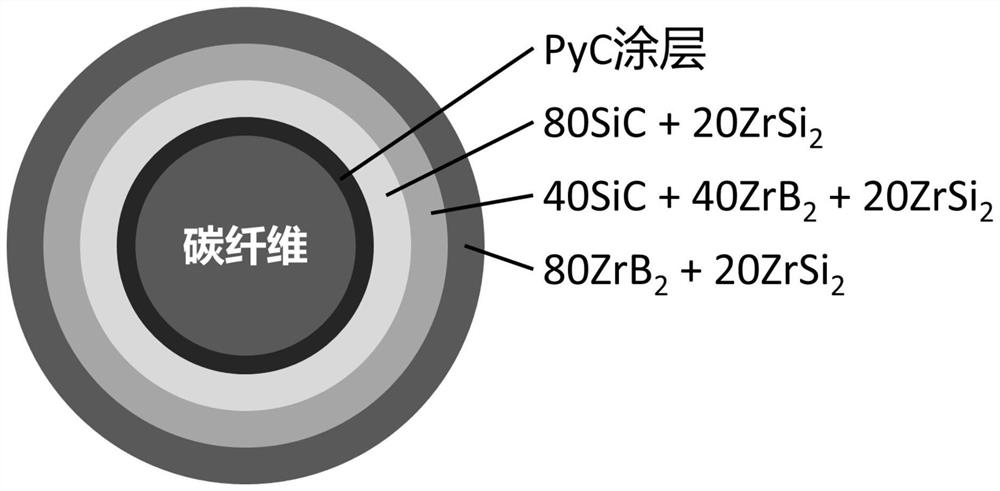
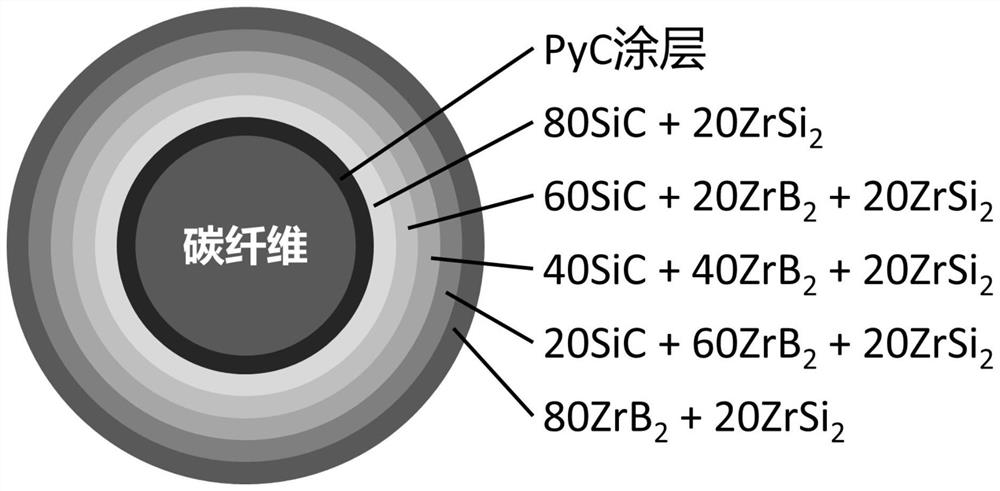
Carbon fiber toughened ultra-high-temperature ceramic matrix composite capable of avoiding thermal mismatching and preparation method of carbon fiber toughened ultra-high-temperature ceramic matrix composite
The invention belongs to the field of ultrahigh-temperature ceramic-based composite materials, and particularly relates to a carbon fiber toughened ultrahigh-temperature ceramic-based composite material capable of avoiding thermal mismatching and a preparation method of the carbon fiber toughened ultrahigh-temperature ceramic-based composite material. In the section direction of the carbon fiber, n layers of gradient ceramic matrixes with thermal expansion coefficients gradually increasing from inside to outside with the carbon fiber as the center are arranged, and the ceramic matrixes are prepared from diboride ultra-high-temperature ceramic, silicon carbide and zirconium disilicide; the diboride superhigh temperature ceramic comprises zirconium diboride or hafnium diboride; the preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out electrophoretic deposition on n layers of radial gradient ceramic coatings on carbon fibers, and then carrying out hot pressed sintering to obtain the composite material. The method has the advantages that the problem of thermal mismatching of the carbon fibers and the matrix is solved, the mechanical performance of the composite material is improved, and the oxidation resistance and ablation resistance of the composite material are prevented from being reduced; due to the designed gradient ceramic matrix, the fracture resistance and the thermal shock resistance of the composite material are improved; the matrix components are optimized, and the ultra-high temperature resistance of the composite material is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
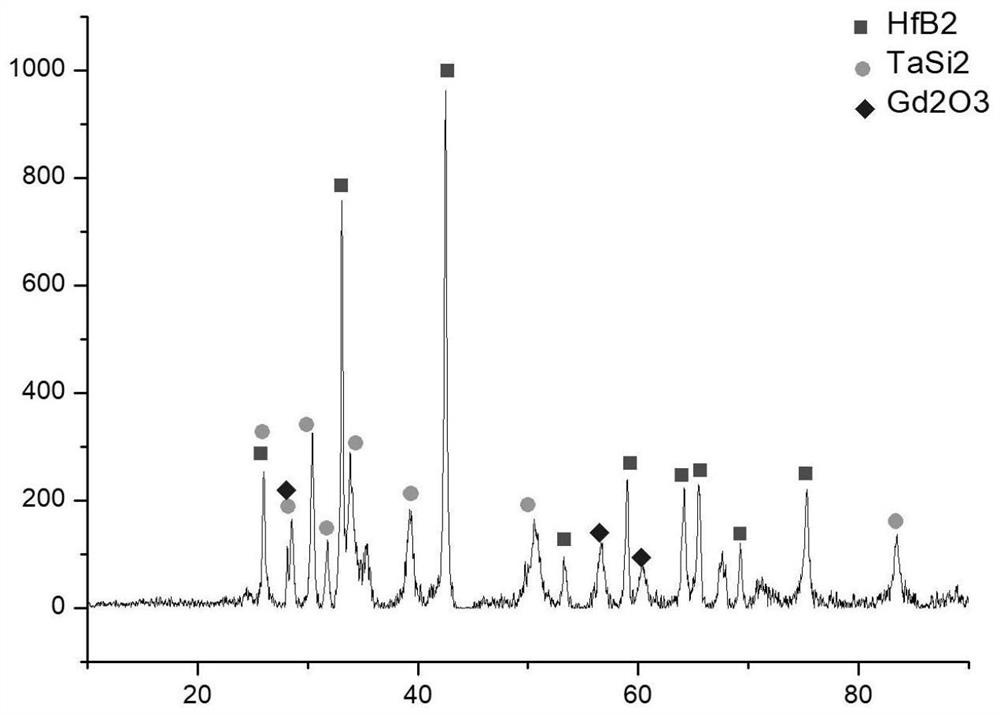
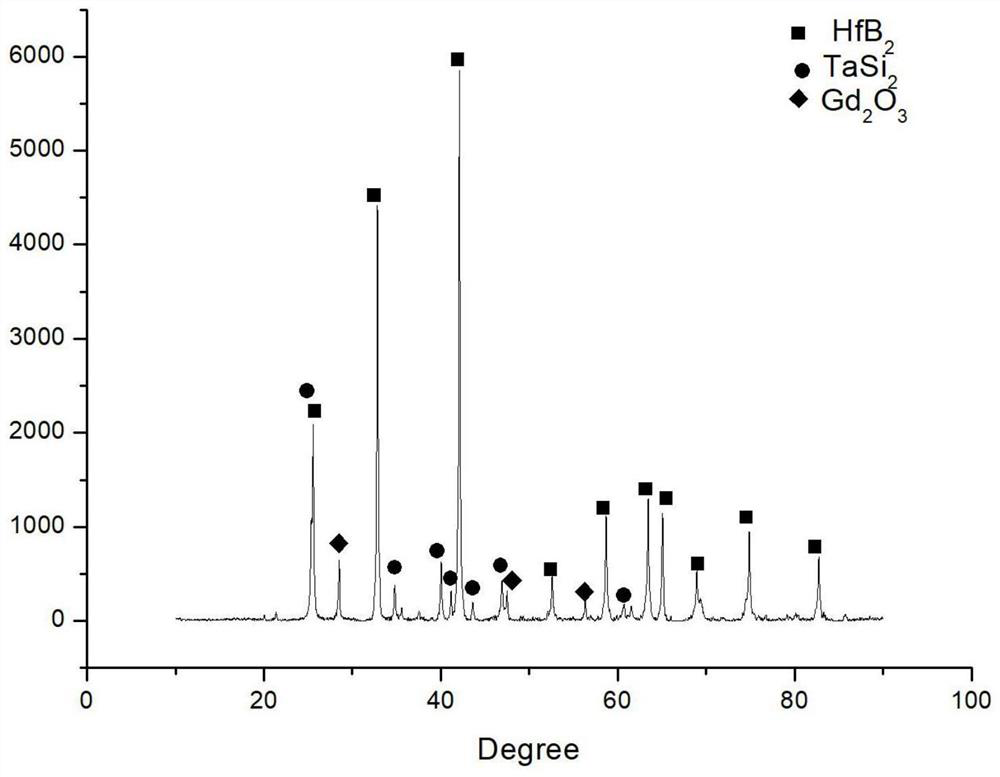
Hafnium diboride-silicon carbide-tantalum disilicide-gadolinium oxide composite coating and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a hafnium diboride-silicon carbide-tantalum disilicide-gadolinium oxide composite coating and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of composite coatings. According to the invention, hafnium diboride-silicon carbide-tantalum disilicide-gadolinium oxide composite powder is used as a raw material of the coating, so that not only is relatively strong high-temperature oxidation resistance of hafnium diboride-silicon carbide of a traditional system maintained, but also crystal transformation of an oxide is stabilized and a glass phase is supplemented by using a tantalum disilicide adding phase; and the gadolinium oxide adding phase is used for improving the overall emissivity of the coating and enhancing the viscosity of the glass phase, so that the high-temperature oxygen corrosion resistance of the coating is further improved. The coating is prepared in an atmospheric plasma spraying mode, the method has the advantages of being simple in process, easy to control, high in production efficiency, low in cost and the like, and meanwhile the characteristics that the thickness of the coating is controllable, the defects of the coating are reduced, the compactness of the coating is improved, and the characteristics of a powder material are reserved to the maximum degree can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
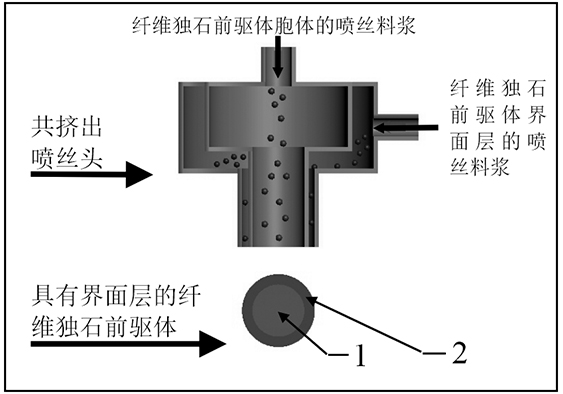
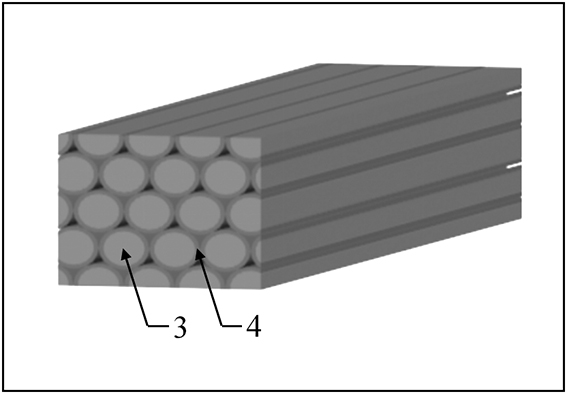
Process for preparing weak interface fiber monolith hafnium boride ceramic by wet spinning and co-extrusion method
InactiveCN111848175AThin diameterImprove plasticityInorganic material artificial filamentsWet spinning methodsFiberBoride
The invention provides a process for preparing weak interface fiber monolith hafnium boride ceramic by a wet spinning and co-extrusion method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) adding a curing agent and a plasticizer into an organic solvent, stirring for dissolving the curing agent and the plasticizer, respectively adding ceramic powder of a fibrous monolith precursor cell and ceramic powder of a fibrous monolith precursor interfacial layer, uniformly stirring to form two spinneret slurries with different components, spraying the spinneret slurries into a gel tank filled with water through a co-extrusion spinneret under mechanical pressure, and carrying out solidification molding to obtain a fibrous monolith precursor with an interfacial layer; (2) carrying out warm-pressing molding; (3) carrying out vacuum degreasing; and (4) carrying out hot-pressing sintering to obtain the weak interface fiber monolith hafnium boride ceramic, the fracture toughness of which can reach 9 MPa.m<1 / 2> or above. The process for forming the fibrous monolith precursor through the wet spinning co-extrusion method is simplified, mechanical arrangement is facilitated, the microstructure of the obtained fibrous monolith hafnium boride super-high-temperature ceramic is accurately controlled, the fracture mode is non-brittle fracture, and the performance is excellent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing hafnium boride powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing hafnium boride powder. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a hafnium source compound in a first solvent to form a first solution; dissolving a boron source compound and a carbon source compound in a second solvent, and adding polyethylene glycol to form a second solution; adding the first solution into the second solution, and collecting the generated precipitate; and drying the collected precipitate, grinding the dried precipitate into powder, and carrying out high-temperature calcination to prepare the hafnium boride powder. The preparation process is simple, the reaction process is easy to control, the production period is short, the cost is low, the prepared hafnium boride powder has high purity, small particle size, narrow particle size distribution and good microstructure, and the mechanical property and sintering driving force of a sintered body can be enhanced in the subsequent forming process.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide composite powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113880586AEasy to operateEasy to achieve industrial mass productionOxidation resistantSolid solution
The invention provides hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide composite powder and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of composite powder materials. The hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide composite powder provided by the invention is in a molten eutectic state and comprises hafnium diboride and tantalum disilicide at mass ratio of (2-11): 1. Tantalum disilicide is used as a modification component of hafnium diboride. On one hand, a high-temperature oxidation product SiO2 of tantalum disilicide can be used as a good high-temperature sealing and filling phase to fill holes of a hafnium diboride coating. On the other hand, another high-temperature oxidation product Ta2O5 of tantalum disilicide can be subjected to a solid solution reaction with HfO2 to form HfTaOx, so that the crystal transformation of HfO2 is inhibited to a certain extent, and the high-temperature thermal stability of the powder is improved. Therefore, the hafnium diboride-tantalum disilicide composite powder provided by the invention has good high-temperature oxidation and ablation resistance.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Heat-resistant electric-conductive glue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106047259AImprove heat resistanceImprove conductivityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesTurpentineTert butyl
The invention discloses heat-resistant electric-conductive glue and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of electric-conductive glue. The heat-resistant electric-conductive glue is mainly prepared from: organic-titanium-modified epoxy resin, polypyrrole, calcium zincate, titanium dioxide, p-tert-butyl pyrocatechol, adipic hydrazide, amino-terminated liquid nitrile rubber, polyacetylene, barium stearate, epoxy soybean oil, dipentyl phthalate, silver-coated copper powder, triethylene diamine, nano hafnium diboride, malonic acid, isoamyl p-methoxycinnamate, acetone and turpentine. The organic-titanium-modified epoxy resin is compounded with the polyacetylene and the polypyrrole, so that the heat resistance and electric conductivity of the glue are improved greatly. Through combination of the dipentyl phthalate, the epoxy soybean oil and other plasticizers, the thermal stability of the electric-conductive glue is improved. The fillers, such as the silver-coated copper powder, calcium zincate and nano hafnium diboride, further improves the electric conductivity of the glue. The electric-conductive glue has good electric conductivity, high strength and good heat resistance.
Owner:覃树强
Dispersion-strengthened high-entropy dodecaboride-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a dispersion-strengthened high-entropy dodecaboride-based composite material and a preparation method thereof. The dispersion-strengthened high-entropy dodecaboride-based composite material is prepared from high-entropy ceramic and hafnium diboride. The Hf element is added into the system, so that the hardness value of the material system is greatly improved, and the problem of insufficient hardness of high-entropy ceramic in the prior art is solved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Special filler for high-dispersity capacitor film and preparation method of special filler
The invention discloses special filler for a high-dispersity capacitor film. The special filler is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-3 parts of dimolybdenum pentaboride, 2-4 parts of hafnium diboride, 2-2.5 parts of gas-phase aluminum oxide, 2-3 parts of polyisobutene, 1-2 parts of polystyrene microsphere, 0.3-0.4 part of sodium oleate, 0.5-0.8 part of chlorinated paraffin, 2-3 parts of lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, 2-2.4 parts of sulfonamide, 60-65 parts of municipal sludge, a proper amount of 5%-7% hydrochloric acid, a proper amount of water and 15-20 parts of an assistant. According to the filler, gas-phase aluminum oxide is added, so that the dispersity and flowability of the filler are improved, and the film is uniform, smooth, high in strength and toughness, good in dielectricity and high in finished capacitor rate; due to the municipal sludge, the cost is reduced, the fineness is high, and the reinforcement performance is good; due to the assistant, the dispersity and reinforcement performance of the filler and the strength and impact toughness resistance of the film can be improved.
Owner:ANHUI ZHUANGYUANLANG ELECTRONICS TECH
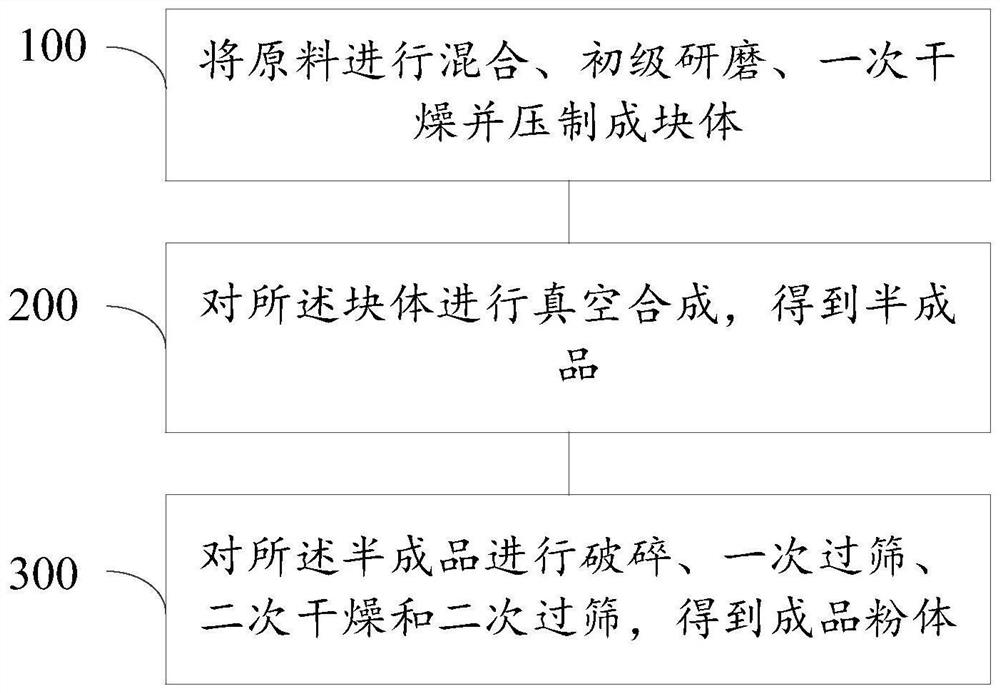
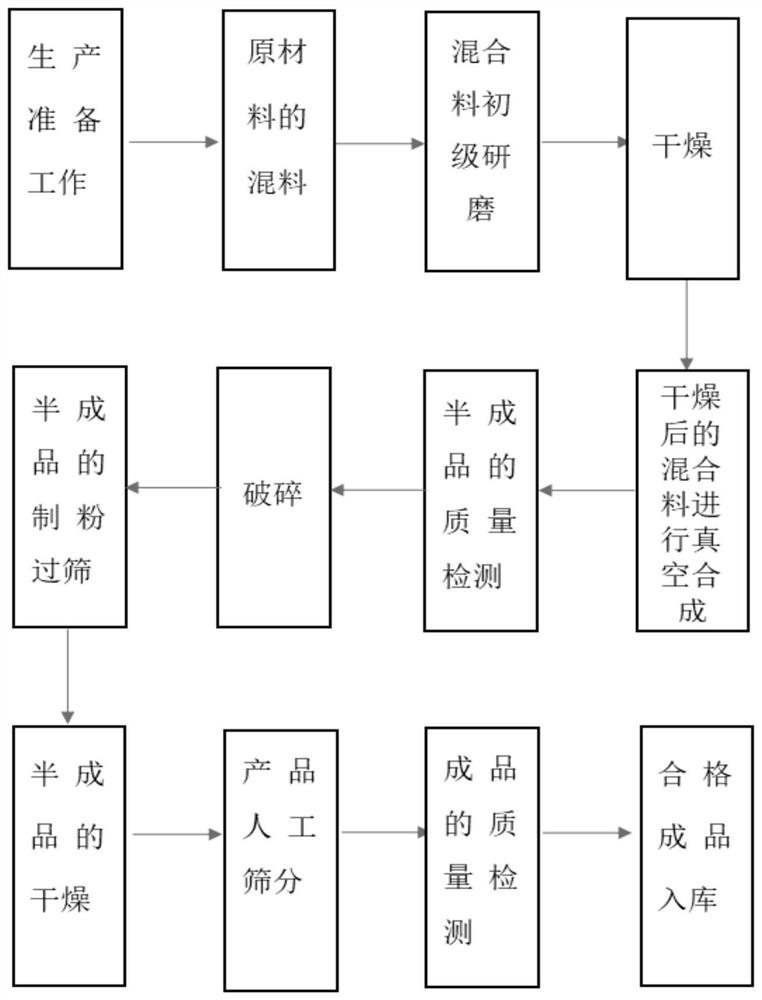
Preparation method of hafnium boride powder
The invention relates to a preparation method of hafnium boride powder, which comprises the following steps: sequentially mixing hafnium oxide, boron carbide and carbon black as raw materials, and conducting primary grinding, primary drying, vacuum synthesis, crushing, primary sieving, secondary drying and secondary sieving, thereby obtaining the hafnium boride powder with high purity and ultrafine granularity. The invention discloses two drying processes and two sieving processes, in the primary drying process, the product is dried into blocks after being mixed and ground, so that raw material loss caused by vacuumizing is prevented, in the secondary sieving process, the ball milling time of the synthesized powder is adjusted according to the required particle size condition, so that products with different particle sizes are produced, and the fineness of the granularity is also ensured. According to the method, the purity of the prepared hafnium boride powder can be improved, and the fineness of the granularity of the prepared hafnium boride powder can also be improved.
Owner:北京华威锐科化工有限公司
Low smoke zero halogen flame retardant polyphenyl ether elastomer cable material and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN103351523AImprove bindingImprove mechanical propertiesPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsAluminium hydroxideTG - Triglyceride
Provided is a low smoke zero halogen flame retardant polyphenyl ether elastomer cable material and a preparation method therefor. The cable material is characterized by comprising, by weight, 25-28 parts of polyphenyl ether, 30-34 parts of ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymers (EMA1126AC), 5-7 parts of tantalum boride, 2-3 parts of hafnium diboride, 1-2 parts of boric acid, 4-6 parts of glycerol monostearate, 2-3 parts of zine stearate, 1-2 parts of zinc oxide, 4-5 parts of colza oil, 12-15 parts of aluminium hydroxide powder, 26-29 parts of bauxite, 3-4 parts of glycerol triglyceride, 2-3 parts of methyltrimethoxysilane, 1-2 parts of accelerant DM and 6-8 parts of modified diatomite. The cable material can pass the VW-1 vertical burning test, and is advantaged by excellent flame retardance, good mechanical property, good hydrolytic resistance, good electrical insulating property and high and low temperature resistance.
Owner:ANHUI CABLE
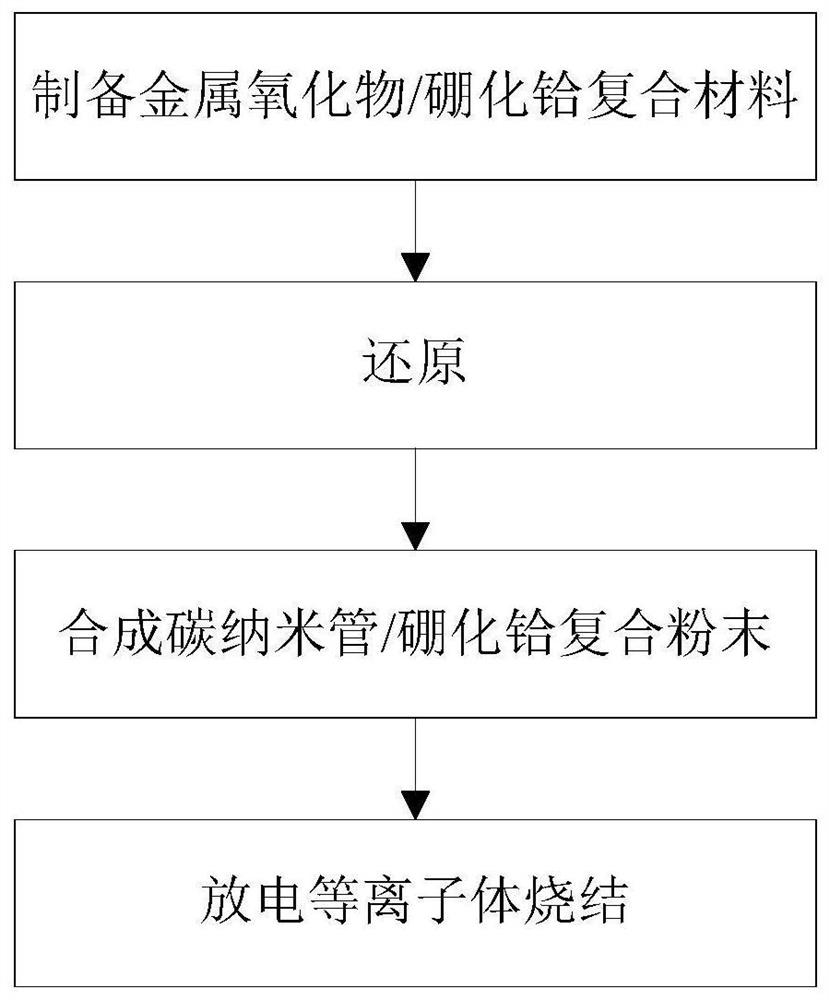
An in-situ synthesized carbon nanotube/hafnium boride nanocomposite material and its preparation method
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A 1500~1700°C anti-oxidation coating on the surface of a carbon/carbon composite material and its preparation method
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
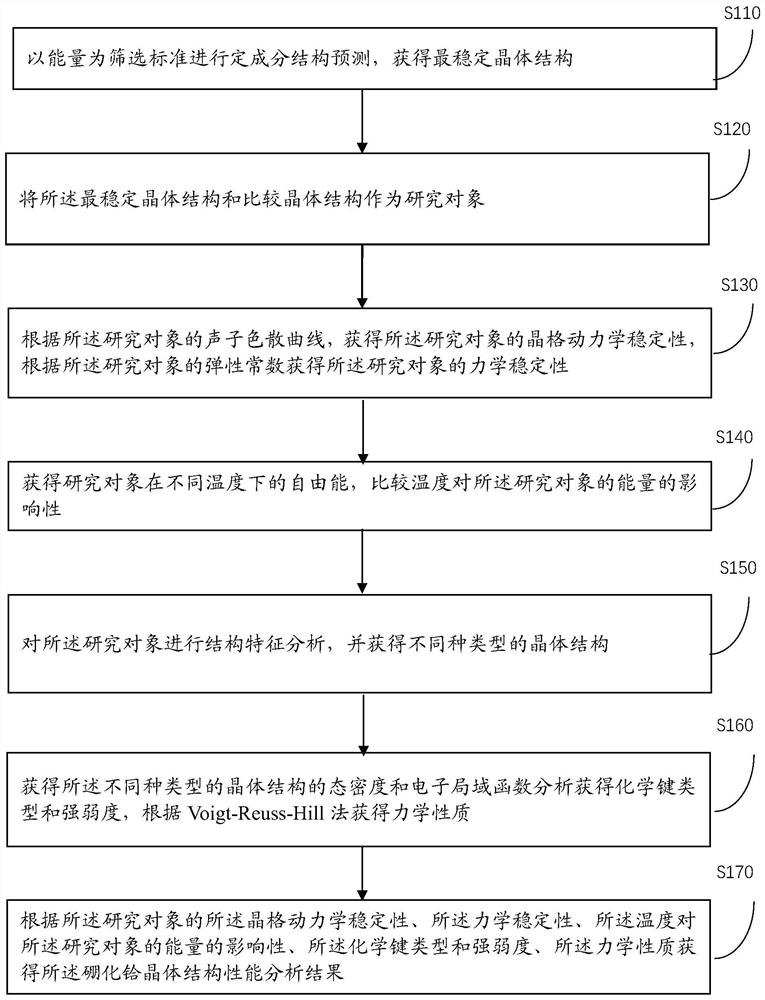
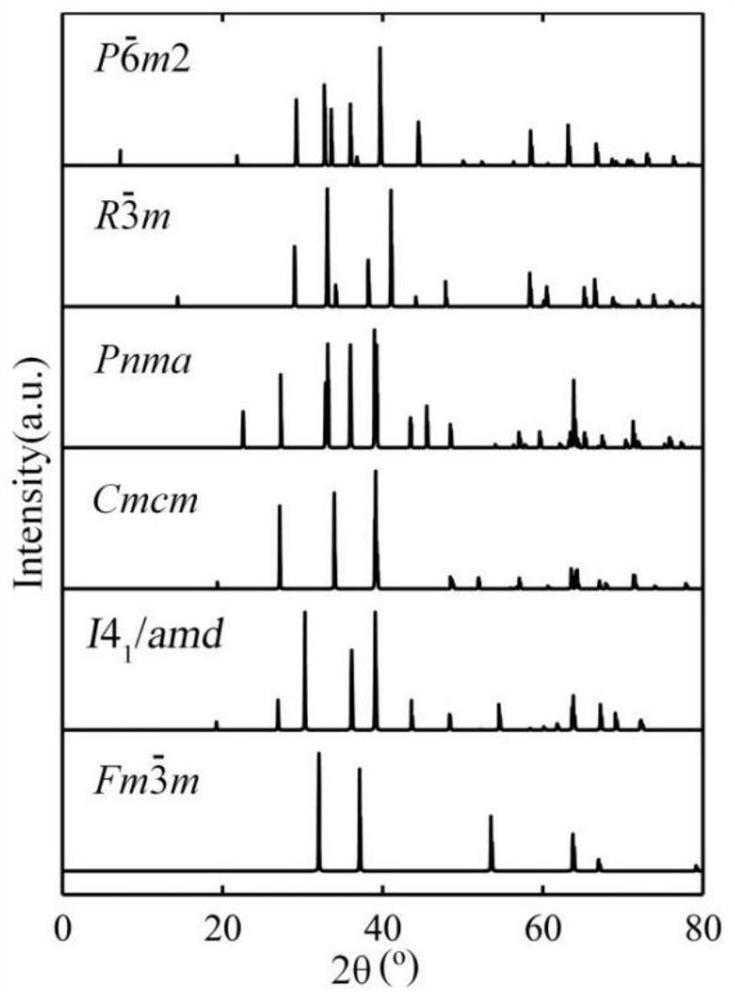
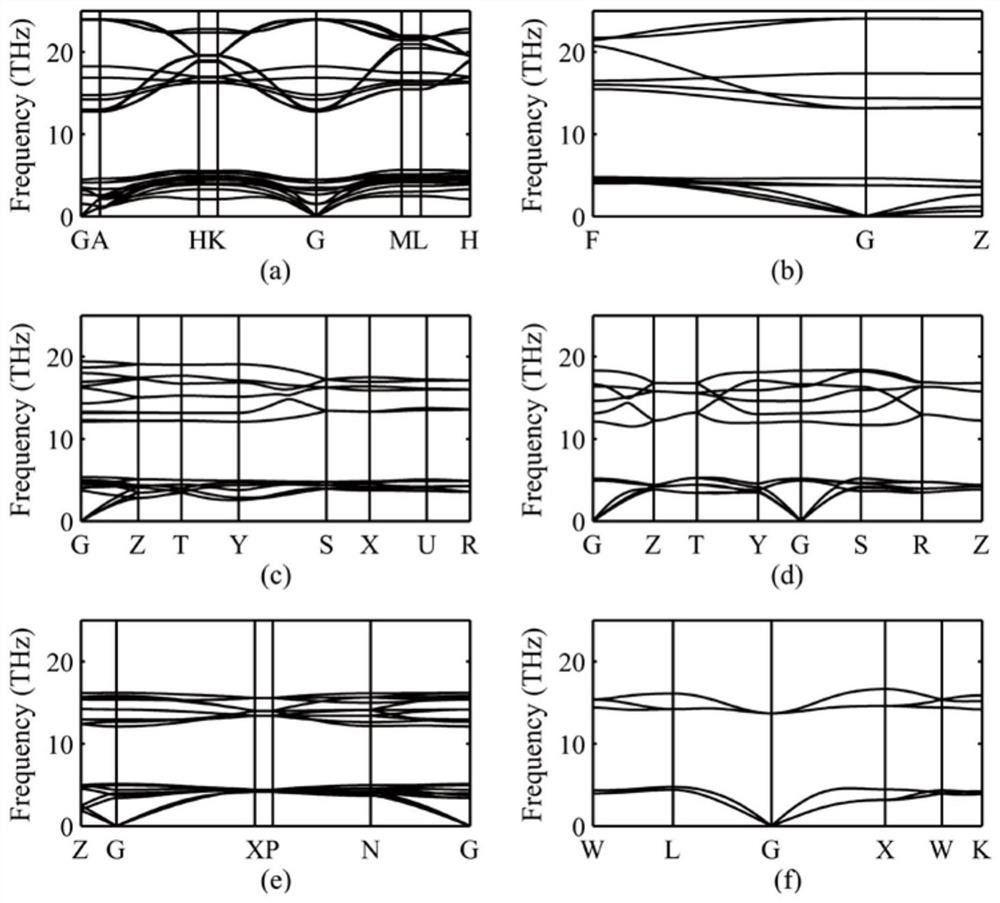
A method for predicting crystal structure
ActiveCN108229090BStrong reliabilitySimple structureChemical property predictionMolecular entity identificationBorideLattice dynamics
A crystal structure prediction method provided by the present application relates to the technical field of material structure, and the method includes: obtaining the most stable crystal structure; taking the most stable crystal structure and the comparative crystal structure as research objects; obtaining the research object Lattice dynamics stability, obtaining the mechanical stability of the research object; obtaining the free energy of the research object at different temperatures, comparing the influence of temperature on the energy of the research object; analyzing the structural characteristics of the research object , and obtain different types of crystal structures; according to the lattice dynamics stability of the research object, the mechanical stability, the influence of the temperature on the energy of the research object, the chemical bond type and The strength and the mechanical properties are obtained from the hafnium boride crystal structure performance analysis results. It has achieved the technical effects of comprehensive prediction of crystal structure, high accuracy and strong reliability of prediction results.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com