Patents
Literature
293 results about "Boriding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Boriding, also called boronizing, is the process by which boron is introduced to a metal or alloy. It is a type of surface hardening. In this process boron atoms are diffused into the surface of a metal component. The resulting surface contains metal borides, such as iron borides, nickel borides, and cobalt borides, As pure materials, these borides have extremely high hardness and wear resistance. Their favorable properties are manifested even when they are a small fraction of the bulk solid. Boronized metal parts are extremely wear resistant and will often last two to five times longer than components treated with conventional heat treatments such as hardening, carburizing, nitriding, nitrocarburizing or induction hardening. Most borided steel surfaces will have iron boride layer hardnesses ranging from 1200-1600 HV. Nickel-based superalloys such as Inconel and Hastalloys will typically have nickel boride layer hardnesses of 1700-2300 HV.
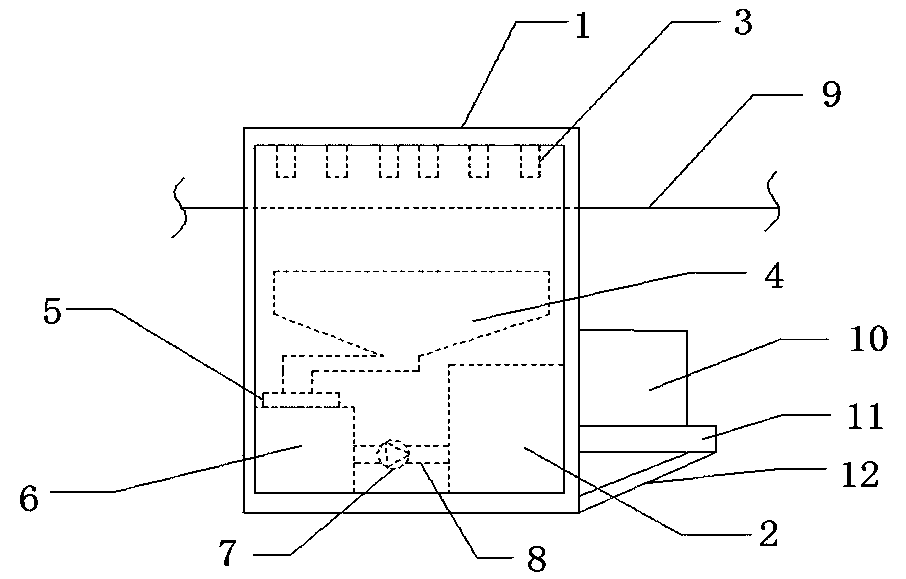
Method for surface boriding of hard alloy
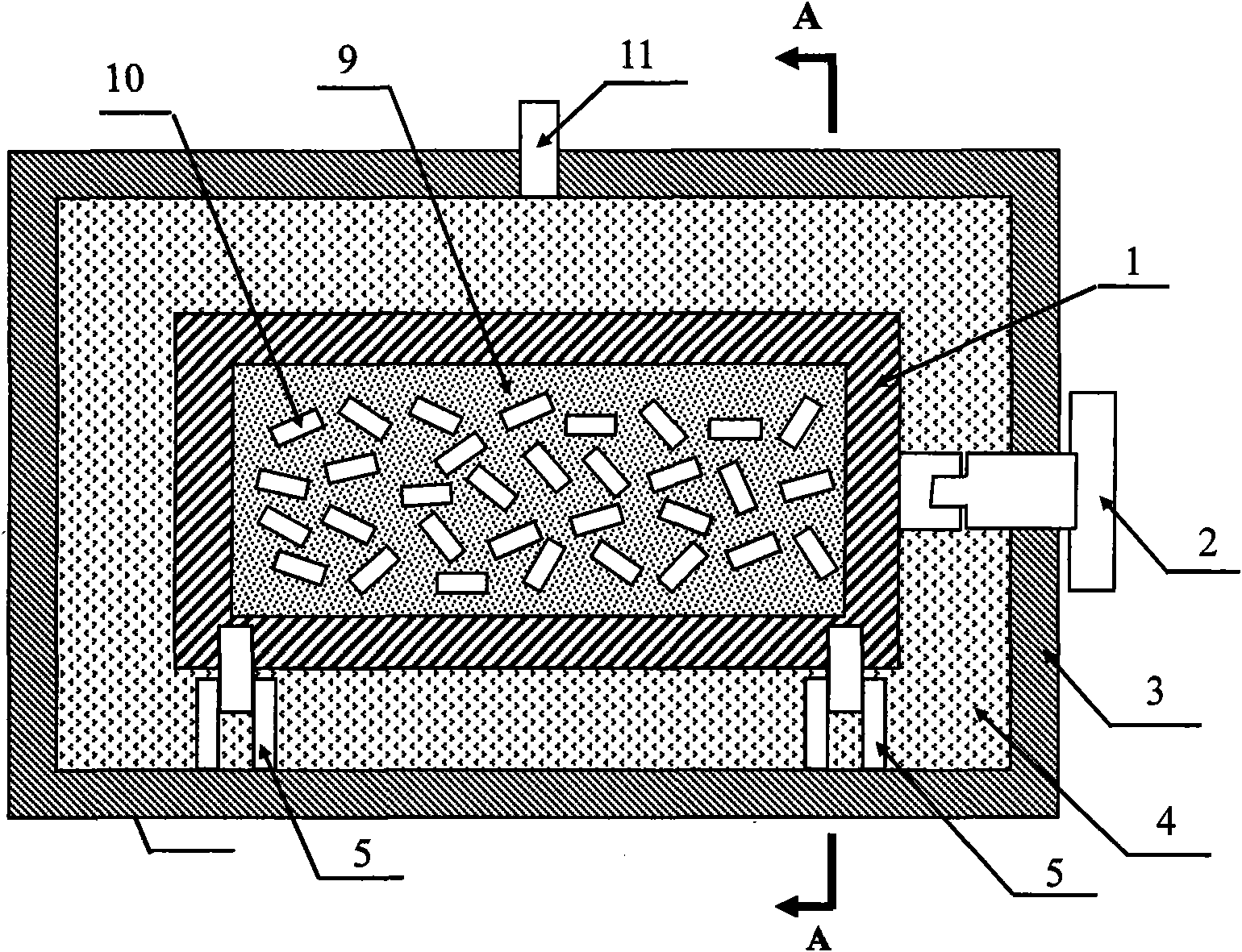
The invention discloses a new method for surface boriding of hard alloy, which sequentially comprises the following steps of: removing an oxidation layer on the surface of the hard alloy; embedding the hard alloy into a solid boriding agent, putting the mixture into a nearly-closed boriding container, and putting the container into an induction heating furnace; vacuumizing the furnace, stopping vacuumizing until the vacuity is over 100 Pa, and filling inert gas or hydrogen; after the gas in the furnace reach the pressure, starting to perform induction heating to reach the boriding temperature of between 800 and 1,300 DEG C, and performing heat preservation for 0.5 to 8 hours to realize gas-solid phase boriding. The solid boriding agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5 to 50 percent of boron supply agent, 2 to 40 percent of activating agent and the balance of fillers, wherein the boron supply agent is one or more of powdered B4C, BN and amorphous boron; the activating agent is two or more of powdered KBF4, NaBF4, NH4BF4, (NH4)2CO3, rare earth oxide and Mg powder, and one of the mixture is an activating agent containing a B element; and the filler consists of graphite powder granules and SiC powder or Al2O3 powder. Through the method, the boriding thickness of sintered hard alloy blank is more than 0.1 millimeter and is close to 1 millimeter, so the surface abrasion resistance of the hard alloy is improved greatly.
Owner:ZHUZHOU HARD ALLOY GRP CO LTD
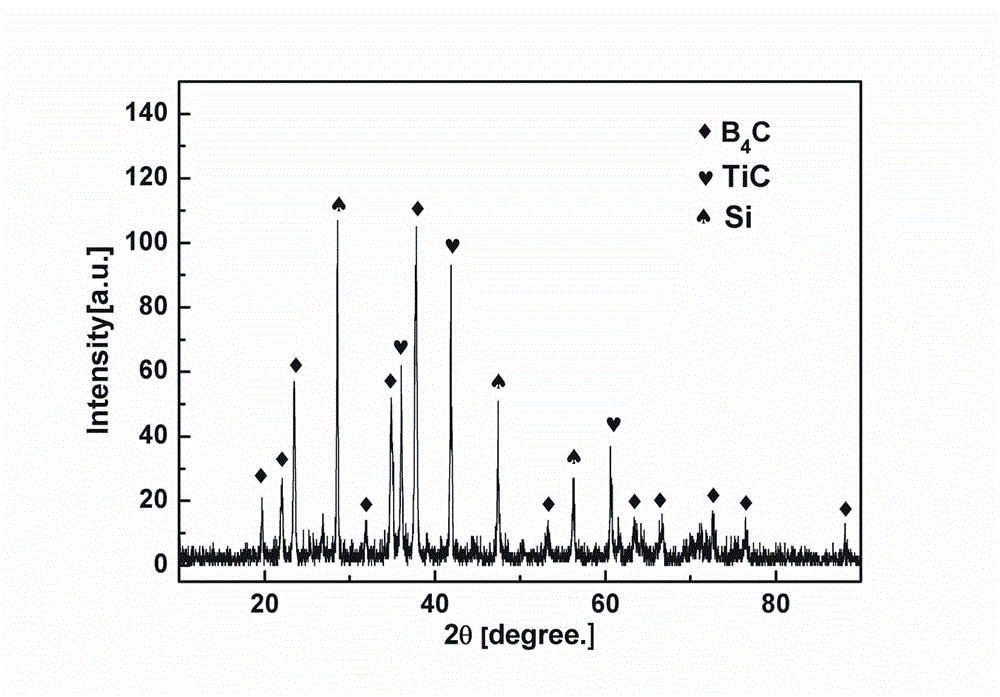
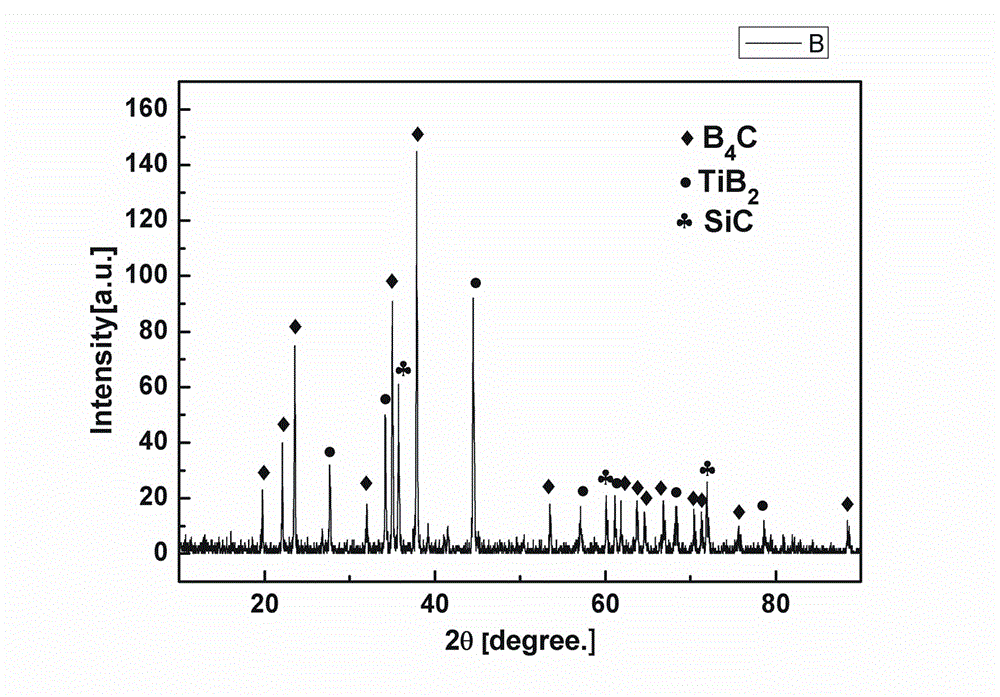
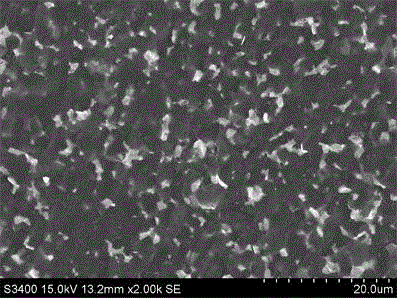
High-hardness ceramic composite material of boron carbide-titanium boride-silicon carbide and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-hardness ceramic composite material of boron carbide-titanium boride-silicon carbide and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a ceramic material. The composite ceramic is prepared from boron carbide, silicon carbide and silicon powder in a hot-pressing sintering manner via reaction. The composite ceramic contains 50-90wt% of boron carbide, 27-5.4wt% of titanium boride and 23-4.6wt% of silicon carbide. The defects of overhigh sintering temperature, and difficulty of improvement of the toughness and the hardness at the same time of the existing boron carbide ceramic are solved; carbon generated by reaction of the boron carbide and the titanium boride is removed by monatomic silicon; and the carbon for reducing the hardness of the base material is converted into hard material silicon carbide which is evenly dispersed, so as to play roles in enhancing the toughness and improving the material hardness. The high-toughness boron carbide composite ceramic can be prepared at low temperature on the premise of not reducing the hardness of a base body.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Boriding agent
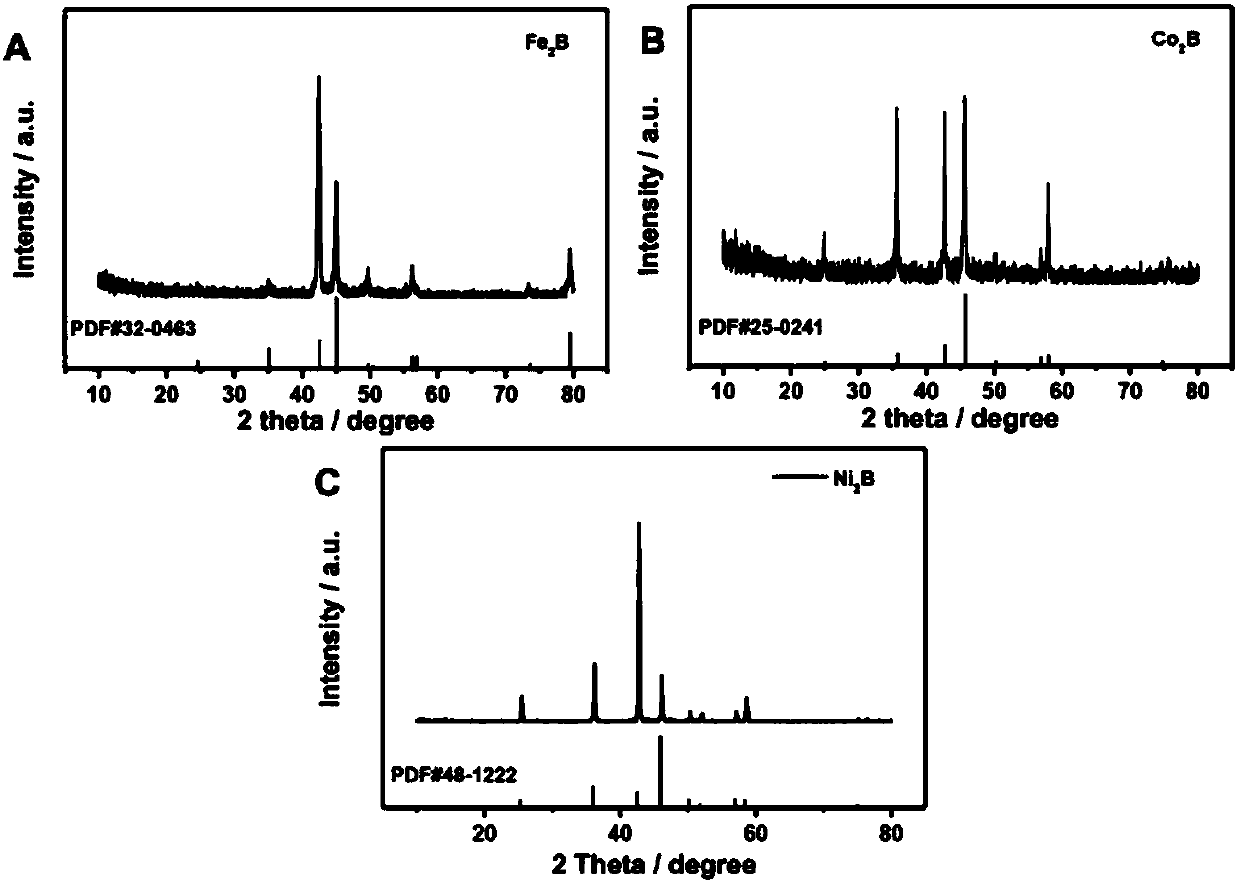
A boriding agent for generating boride layers on metallic workpieces, containing boron-releasing substances, activating substances and, in the remainder, refractory, inert extender. The activating substance is a combination of 1 to 5 wt. % potassium tetrafluoroborate and 5 to 40 wt. % calcium fluoride, relative to the total quantity of the boriding agent. With this boriding agent it is possible for single-phase, Fe2B-containing boride layers to be generated on workpieces made of ferrous materials. The agent results in lower emissions of fluorine and fluoride.
Owner:HOUGHTON DURFERRIT GMBH
Preparation method and device for industrial microwave heating diffusion coating
InactiveCN101565810AClose contactEnables indirect heat treatmentSolid state diffusion coatingChemical treatmentThermal energy
The invention relates to a preparation method and a device for an industrial microwave heating diffusion coating. The method uses microwave to directly heat a sealed metal container that is wrapped with absorptive microwave heating material and constantly rolls, and then to indirectly to heat filled powder seeping agent and embedded metal workpieces in the container, and prepares a heat diffusion coating on the surface of the metal workpieces under the mutual and comprehensive action of microwave heat energy, mechanical friction impact medium and seeping agent. Microwave heating material crucially functions as a volumetric source to directly heat the sealed metal container rolling constantly, and can effectively isolate the interaction of the microwave and the metal container to prevent the metal container from reflecting the microwave and causing an arc phenomenon. The method can complete the processes of sherardizing (Zn), aluminizing (Al), zinc / aluminum (Zn / Al) common impregnation and boriding (B), and can be promoted and applied to other powder embedding technologies, effectively shorten chemical treatment and hot treatment time and reduce hot treatment temperature.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ultra-fast boriding of metal surfaces for improved properties
InactiveUS20100018611A1Fast boridingDesirable mechanical propertySolid state diffusion coatingMetallurgyUltra fast
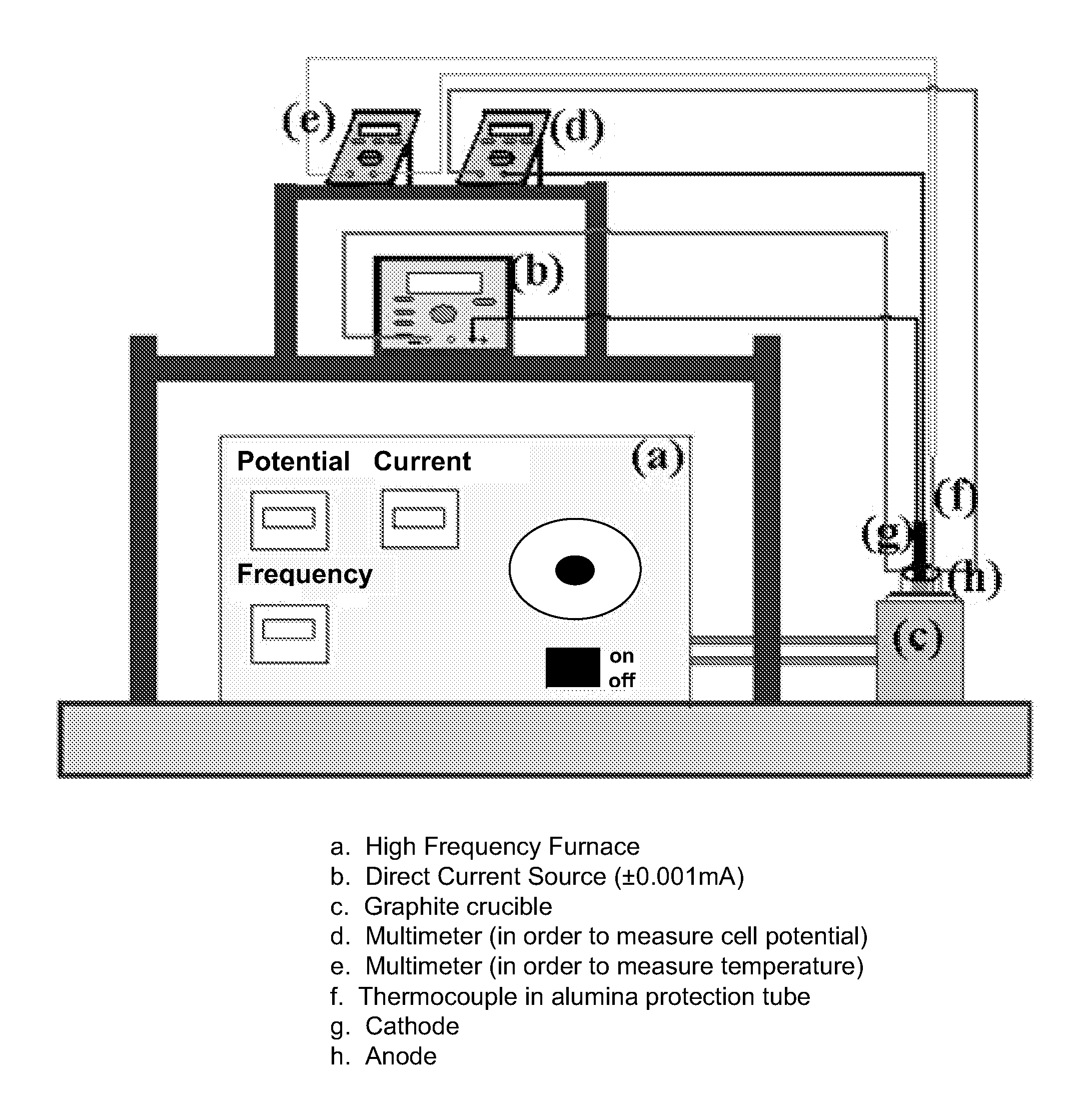
A method of ultra-fast boriding of a metal surface. The method includes the step of providing a metal component, providing a molten electrolyte having boron components therein, providing an electrochemical boriding system including an induction furnace, operating the induction furnace to establish a high temperature for the molten electrolyte, and boriding the metal surface to achieve a boride layer on the metal surface.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Technological process for surface low temperature boriding of low carbon steel
InactiveCN1699617ALower boronizing temperatureImprove boronizing efficiencySolid state diffusion coatingLow temperature plasmaVacuum pump
The present invention relates to a low temperature boriding process on mild steel surface, belonging to the field of surface heat treatment processing technology. The characteristic of the present invention is nanometerizing steel surface and then low temperature plasma boriding. The process includes the following procedures: 1) mechanical grinding of the surface of mild steel for nanometerization treatment before boriding, 2) charging the mild steel sample after nanometerization treatment in a plasma heat treatment furnace, vacuum pumping up to 40 Pa, starting heating by ion glow between electrodes, adding boriding reagent B(OCH3)3 and blowing the mixed gas of Ar and H2. Operation voltage is 800- 1200 V, the pressure of mixed gas is 400 -1000 Pa, plasma boriding temperature is kept at 500- 650 degree C for 4-8 hours. Then the furnace is cooled down to room temperature, resulting in obtaining surface boriding mild steel. The boriding layer mainly contains Fe2B of crystalline phase with hardness of HV 1700 - 2100.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
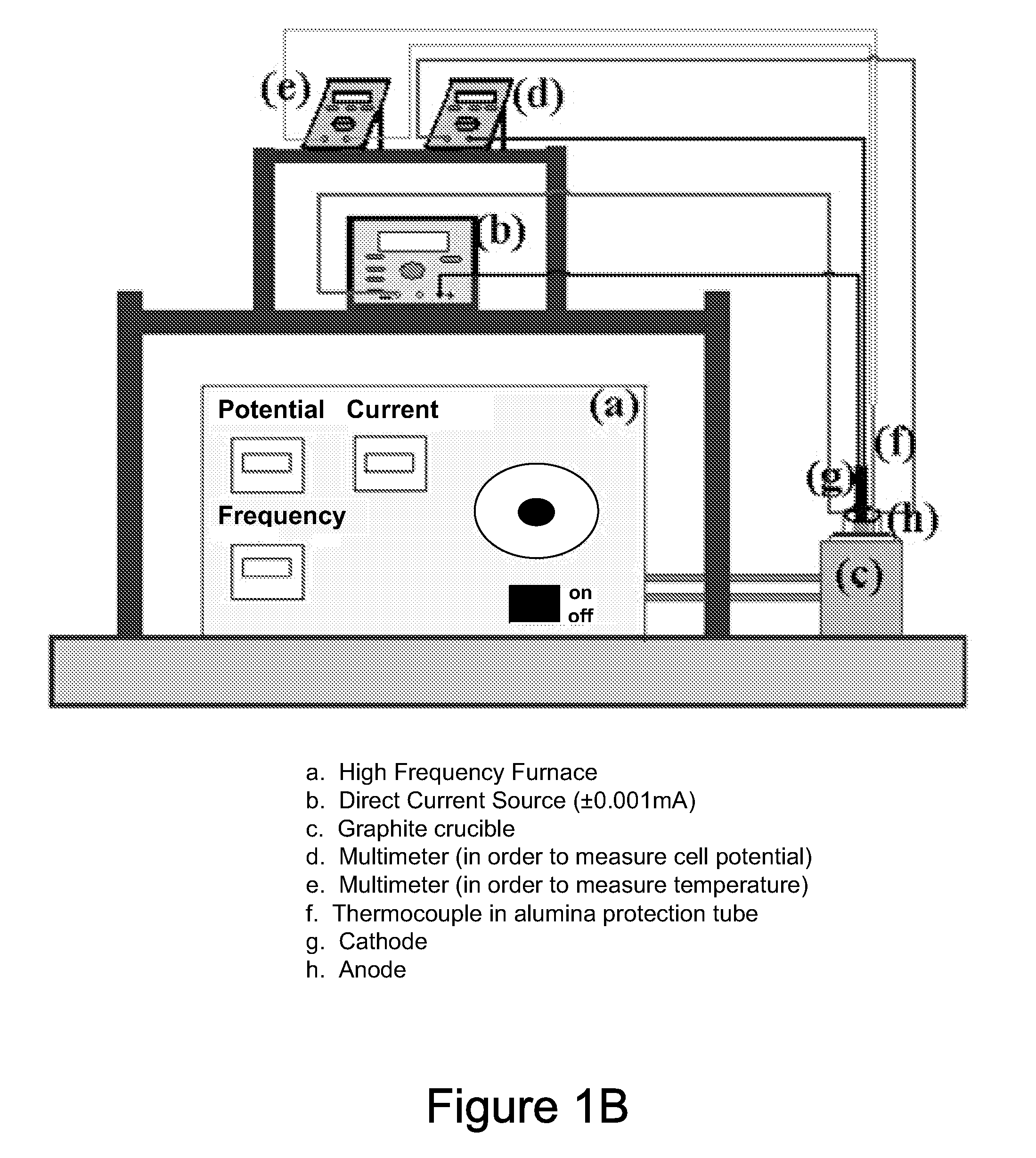
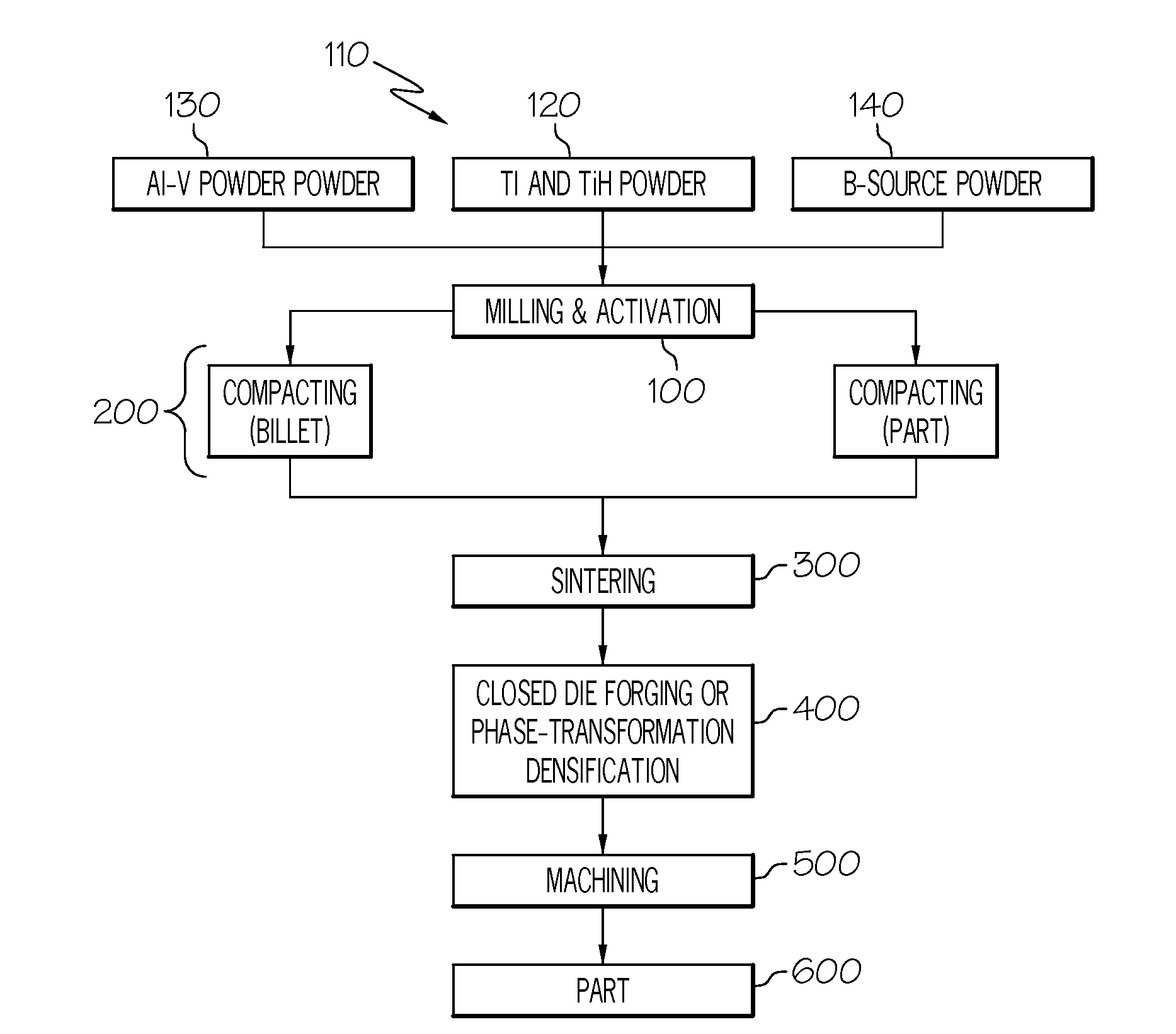
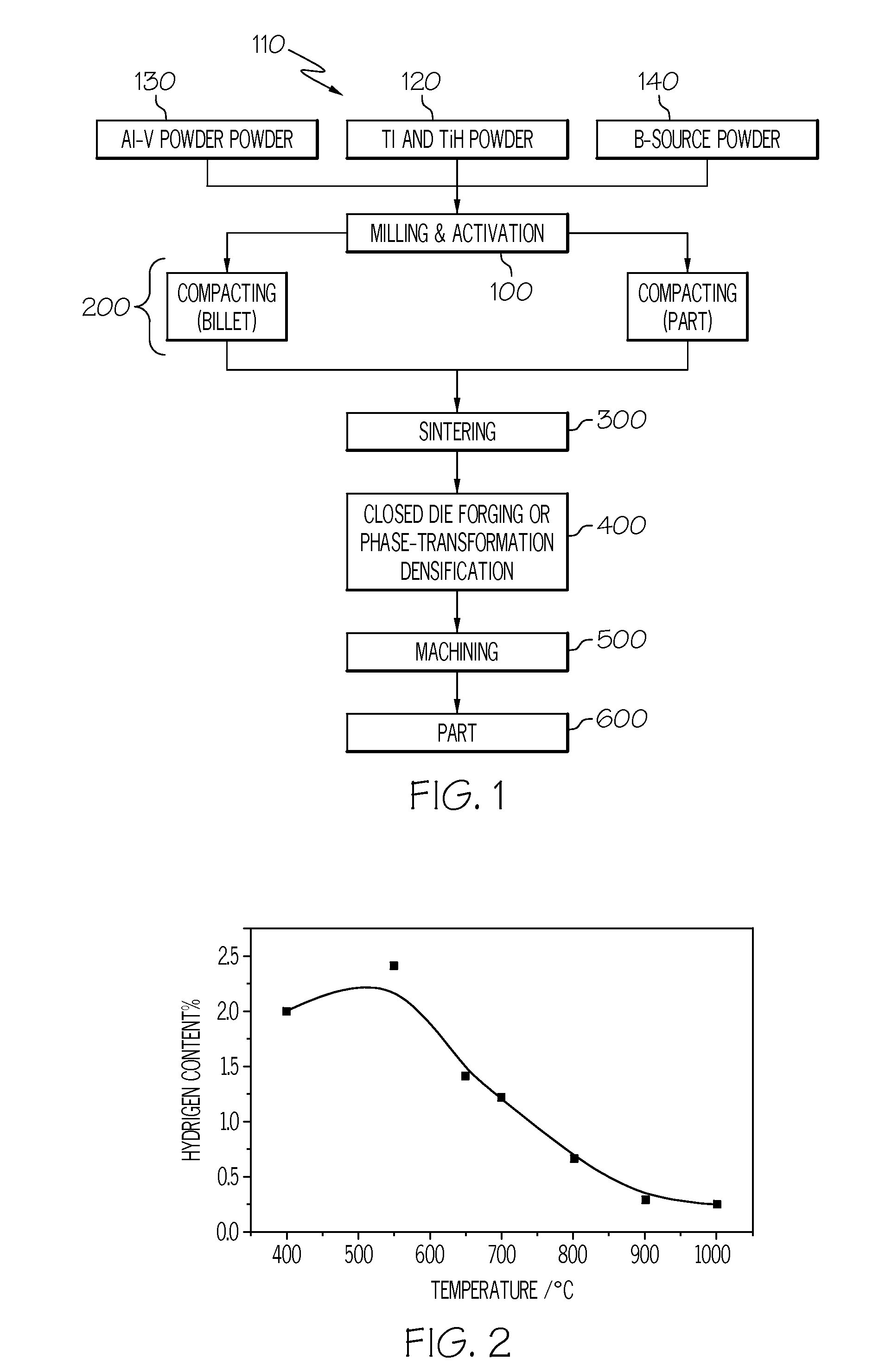
METHOD OF MAKING TITANIUM ALLOY BASED AND TiB REINFORCED COMPOSITE PARTS BY POWDER METALLURGY PROCESS
A method of preparing a titanium-based metal matrix composite. In one form, titanium hydride can be added to substantially pure titanium, an alloying material and a source of boron such that a mixture of these materials can be compacted and sintered in a powder metallurgy process to produce a component made up of a titanium boride reinforced titanium alloy. In another form, the substantially pure titanium, alloying material and source of boron could be vigorously mixed (with or without the titanium hydride) to such an extent that oxide films that may have built up on the titanium precursor can be removed to minimize the presence of oxygen in the manufactured component.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Powder material for boiler tube high temperature resistance and wear resistance protecting and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103878363AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceMetallic material coating processesSurface engineeringWear resistant
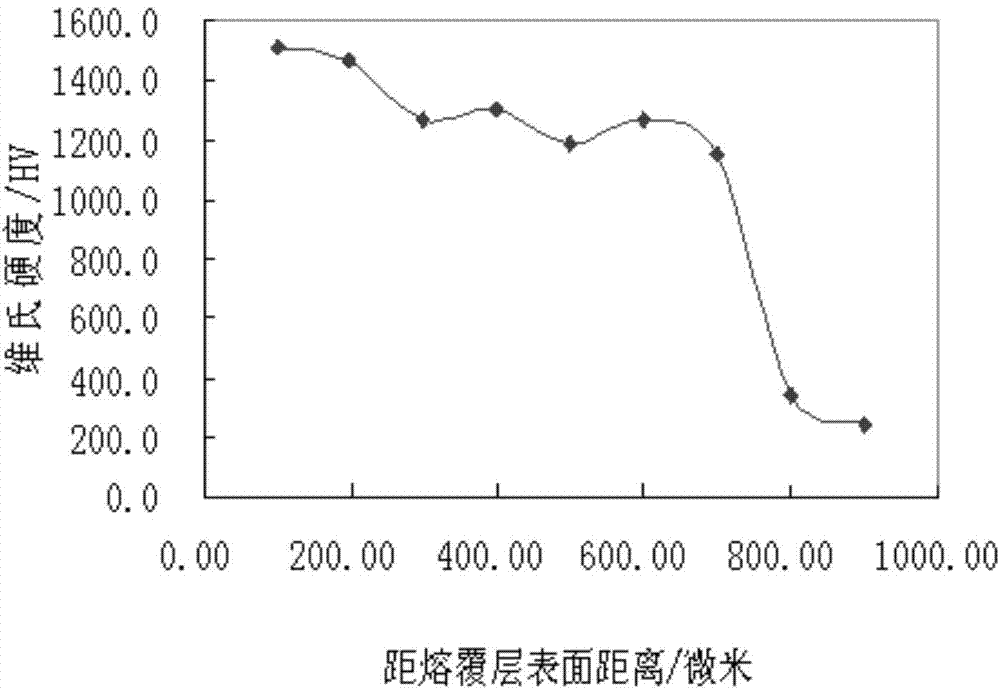
The invention relates to powder material for boiler tube high temperature resistance and wear resistance protecting and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of surface engineering. The power material comprises the following components, by weight percentage, 10-20% of titanium-nickel alloy powder, 1.5-3.5% of graphite powder, 0.5-1% of silica powder, 8-25% of nickel-chromium alloy powder Ni80Cr20, 5-10% of iron boride powder and the balance of tri-chromium dicarbide powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps that power material is prepared, mix powder is formed, liquid-containing binders are prepared, sizing agents are prepared from the mix powder, prilling is completed through spray drying, and finished product powder is prepared from screening the prilling powder and is used for preparing a cladding layer. The metal cladding layer with high wear resistant duplex ceramic is formed through laser cladding, and the hardness ranges from 1100 HV to 1600 HV, so that the powder material for boiler tube high temperature resistance and wear resistance protecting and the preparation method thereof has the advantages that efficiency of the laser cladding is higher, loss of powder spattering is low, grain of the cladding layer is tiny, wear resistance of the cladding layer is high and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
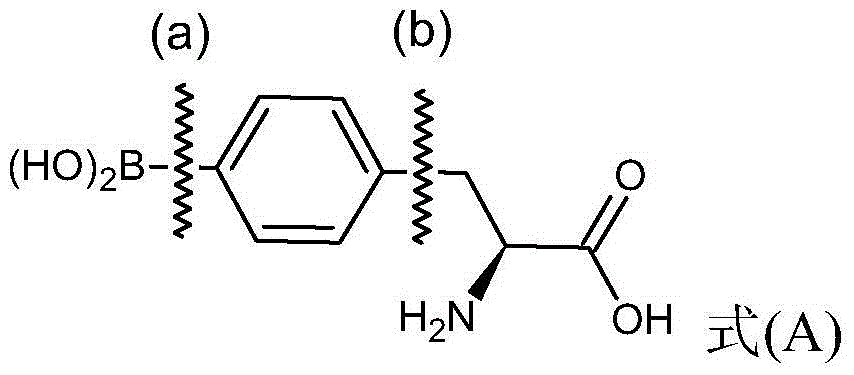
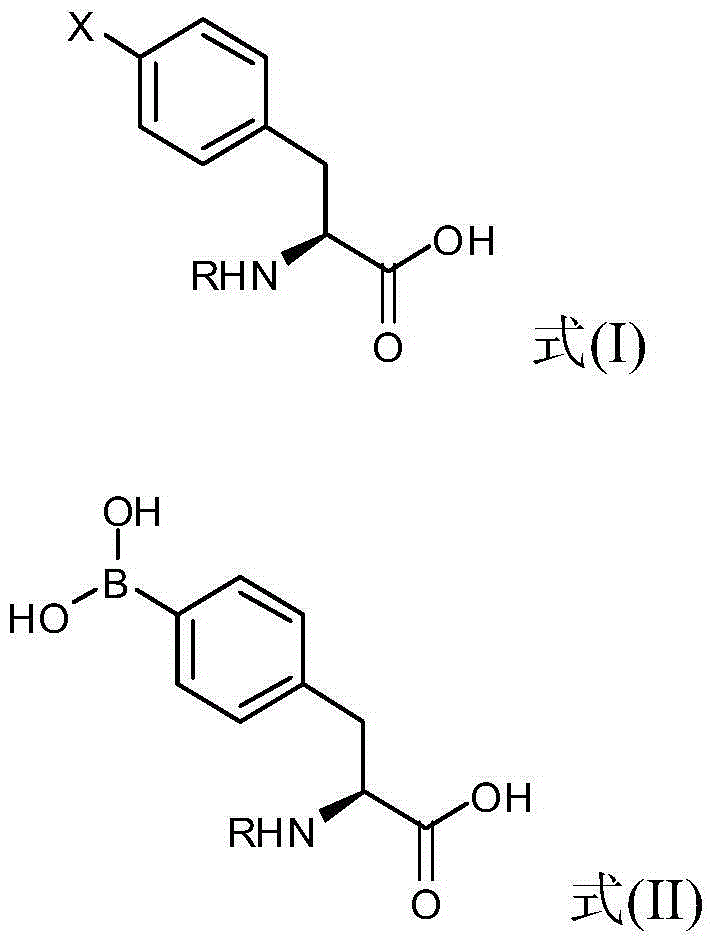
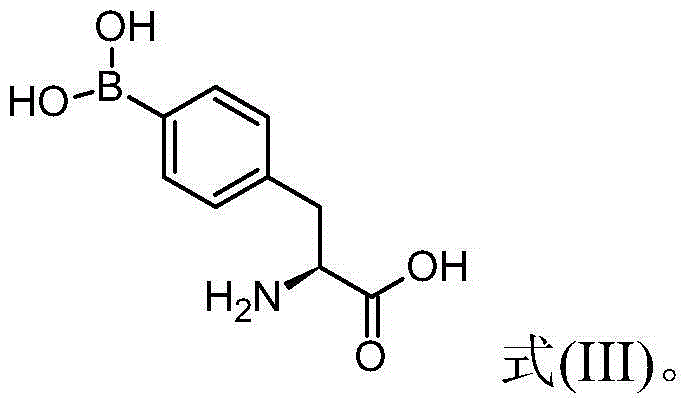
4 - dihydroxy boryl - l-phenylalanine preparation method
InactiveCN104447823AReduce processHigh chemical purityGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBulk chemical production4-dihydroxyborylphenylalanineBoriding
The invention provides a 4 - dihydroxy boryl - L-phenylalanine preparation method which is as follows: reacting amino terminal-protected (S) - 4 -halogeno phenylalanine shown as the formula (I) with a boriding agent and an organic lithium compound to obtain a reaction mixture containing amino terminal-protected (S) - 4 - dihydroxy boryl phenylalanine shown as the formula (II) with R being a protective group; separating the reaction mixture to obtain the amino terminal-protected (S) - 4 - dihydroxy boryl phenylalanine; and de-protecting the amino terminal-protected (S) - 4 - dihydroxy boryl phenylalanine to obtain 4 - dihydroxy boryl - L-phenylalanine.
Owner:TAIWAN BIOTECH
Molybdenum boride ceramic system hot spray coating material, and preparation method and application of molybdenum boride ceramic system hot spray coating material
InactiveCN106399893AHigh hardnessImprove thermal shock resistanceMolten spray coatingTransportation and packagingSpray coatingSpare part
The invention relates to a molybdenum boride ceramic system hot spray coating material which comprises the following ingredients by mass percentage: 60-80% of MoxBy, 10-30% of Ni or Co, 5-20% of Cr, and 0-5% of WmBn, wherein MoxBy is at least one of MoB or MoB2, and WmBn is at least one of WB or WB2 or W2B5. The molybdenum boride ceramic system hot spray coating material having significant advantages in aspects of thermal erosion resistance, high-temperature skimming wear resistance, molten metal erosion resistance and the like is prepared via unique raw material selection and proportion, as well as corresponding technical steps and parameter limitation, and is particularly applicable to surface hot spraying of spare parts such as sink rolls, stable rolls and shaft sleeves of a garbage incinerator and a hot galvanizing production line.
Owner:LUOYANG GOLDEN EGRET GEOTOOLS
Composite diamond coating hard alloy cutter mold and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109930129AAvoid it happening againImprove stress distributionChemical vapor deposition coatingMicro nanoEtching
The invention discloses a composite diamond coating hard alloy cutter mold and a preparation method thereof. The surface layer of the hard alloy cutter mold is provided with composite coatings composed of boron-doped or non-boron-doped micron-crystal diamonds and nanocrystalline diamonds which are alternately arranged, and a layer of diamond-like coating DLC is deposited on the surface of each composite diamond coating. The preparation method comprises the steps of oil removal and degreasing, chemical micro-etching, plasma activation, plasma enhanced gaseous boronizing, plasma cleaning, diamond slurry ultrasonic grinding, nano-scale and micron-diamond seed crystal planting, and vapor-phase deposition of the diamond composite coatings. According to the method, boron atoms enter diamond crystal lattices by doping boron in the diamond deposition process, the internal stress of the diamond coatings is adjusted, and the generation of a stress sudden change region is avoided, so that the situation that the stress of each layer is not matched is avoided fundamentally, the stress distribution inside the composite coatings is effectively improved, the integrity of the micro-nano composite coatings is further improved, the substrate-film binding force is improved, and the comprehensive mechanical property of the composite coatings is improved.
Owner:HU-NAN NEW FRONTIER SCI & TECH LTD
Boronizing agent and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101135038AImprove performanceReduce distortionSolid state diffusion coatingBoridingRare earth
The present invention relates to one kind of low temperature solid boriding agent and its usage. The solid boriding agent consists of ferroboron 5-50 wt%, urea 3-30 wt%, RE compound 1-20 wt%, KBF4 5-40 wt%, charcoal 5-20 %, and silicon carbide for the rest. The RE compound is compound of La, Ce, Tb or Yt. When the low temperature solid boriding agent is used, is adopted a two-section heating process including the first heating to 500-600 deg.c and maintaining for 1-5 hr, the subsequent heating to 630-750 deg.c and maintaining for 2-8 hr and cooling in the furnace to obtain borided layer. The present invention has low boriding temperature, less deformation in the borided layer, improved borided layer performance and simplified process.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Surface low-temperature boriding process for hot-work die steel
InactiveCN1970825AImprove wear resistanceHigh boronizing temperatureSolid state diffusion coatingBoridingHot work
The invention discloses a low-temperature boronizing method of heat mould steel surface, which comprises the following steps: a. proceeding nanometer disposal for steel mould surface; b. removing dirt on the surface of steel sample; c. boronizing in the vacuum; d. cooling to indoor temperature; coating boronizing agent with thickness at 2-5mm; drying.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Carbon steel boriding medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103014605AReduce usageImprove boronizing effectSolid state diffusion coatingSodium bicarbonateFerrosilicon
The invention relates to a carbon steel boriding medium and a preparation method thereof. The carbon steel boriding medium is composed of the following materials in percentage by weight: 25% of borax, 8% of sodium fluoroborate, 22% of clay, 7% of urea, 6% of ferrosilicon, 4% of ammonium bicarbonate, 1.0% of alumium, 0.002% of titanium dioxide, 0.3% of rare earth fluoride and the balance of graphite and charcoal by weight percentage. According to the technical proposal provided by the invention, the dosage of the rare earth is reduced and the boriding effect is improved.
Owner:姚芙蓉
Surface treatment method for solid carbon-boron complex penetration of low-carbon alloy steel part
InactiveCN105088132AImprove bindingNot easy to fall offSolid state diffusion coatingQuenching agentsSolid carbonRoom temperature
The invention discloses a surface treatment method for solid carbon-boron complex penetration of a low-carbon alloy steel part. The method at least comprises the steps of: (a) carburizing pretreatment and steel part cleaning; (b) carburizing treatment; (c) taking out of a penetration box for carburizing from a resistance furnace, natural cooling to a room temperature, and taking out of a low-carbon alloy steel part after the carburizing treatment; (d) boriding pretreatment and steel part cleaning; (e) boriding treatment; (f) taking out of a penetration box for boriding from the resistance furnace after the boriding treatment in the step (e), natural cooling to the room temperature, and taking out of a low-carbon alloy steel part after the boriding treatment; (g) quenching treatment; and (h) tempering treatment. The method has the following beneficial effects: the carburizing and the boriding are performed in sequence to form a transition layer on the surface of the low-carbon alloy steel, so that a boriding layer and a steel basal body are better in combination and not easy to drop.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Quick formation method of titanium-based composite material having bionic shell structure
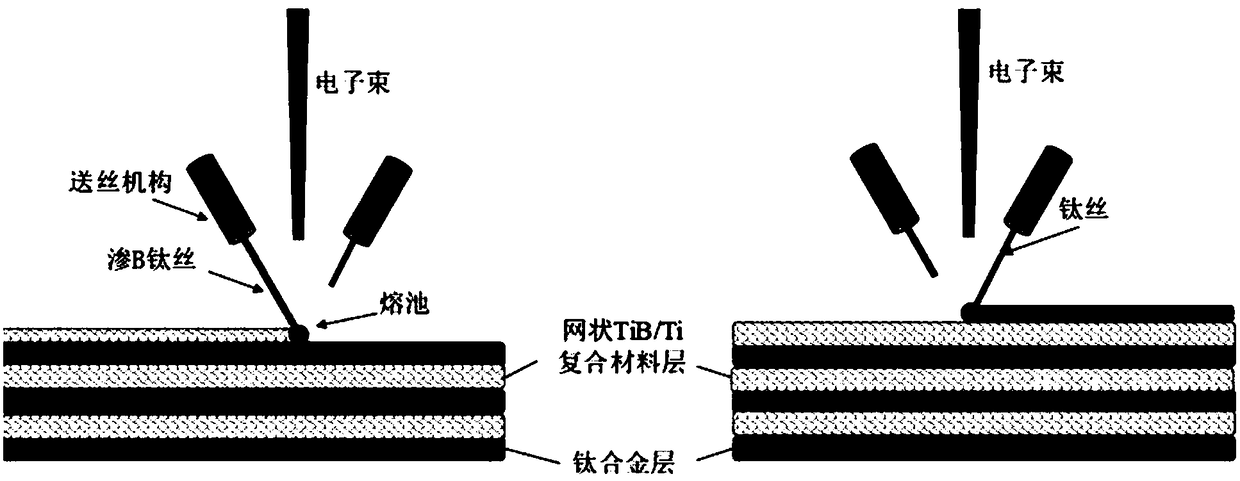
ActiveCN108500263APush effectTight bonding between layersAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyTitanium matrix compositesBoriding
The invention relates to a quick formation method of a titanium-based composite material having a bionic shell structure. By mainly using a titanium wire and a boriding titanium wire as raw materialsand utilizing double wire feeding mechanisms, alternate deposition on the boriding titanium wire and the titanium wire is carried out through an electronic beam fused deposition technology. Accordingto the quick formation method of the titanium-based composite material having the bionic shell structure disclosed by the invention, the titanium-based composite material having the bionic shell structure, prepared by mixing a net structure and a layered structure, can be obtained; and the titanium-based composite material is high in toughness. Moreover, the process has the advantages of strong applicability and short technological processes, and in addition, preparation and application ranges of the titanium-based composite material are greatly widened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
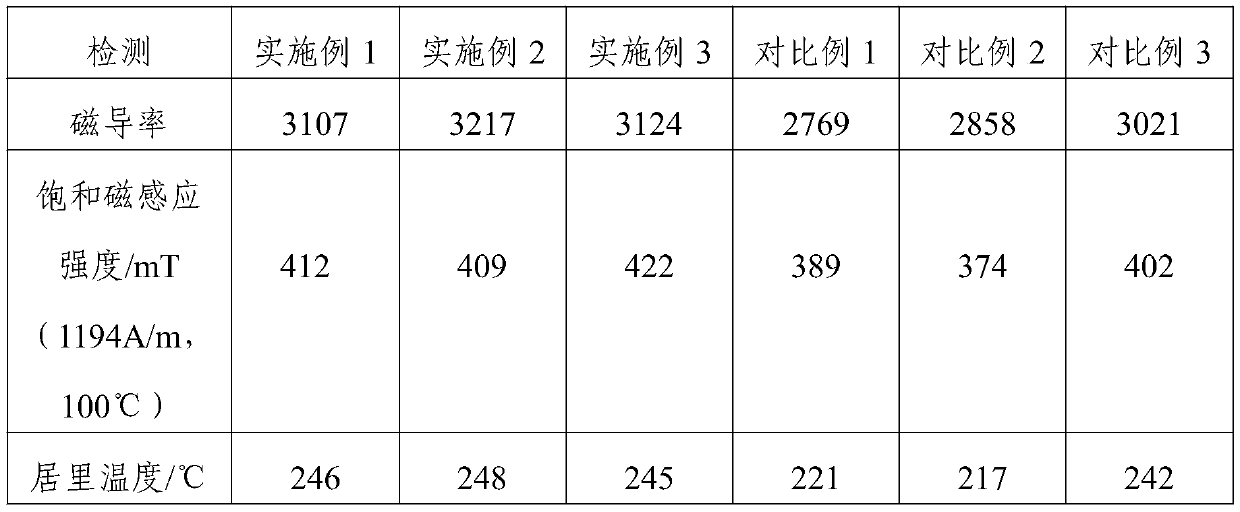
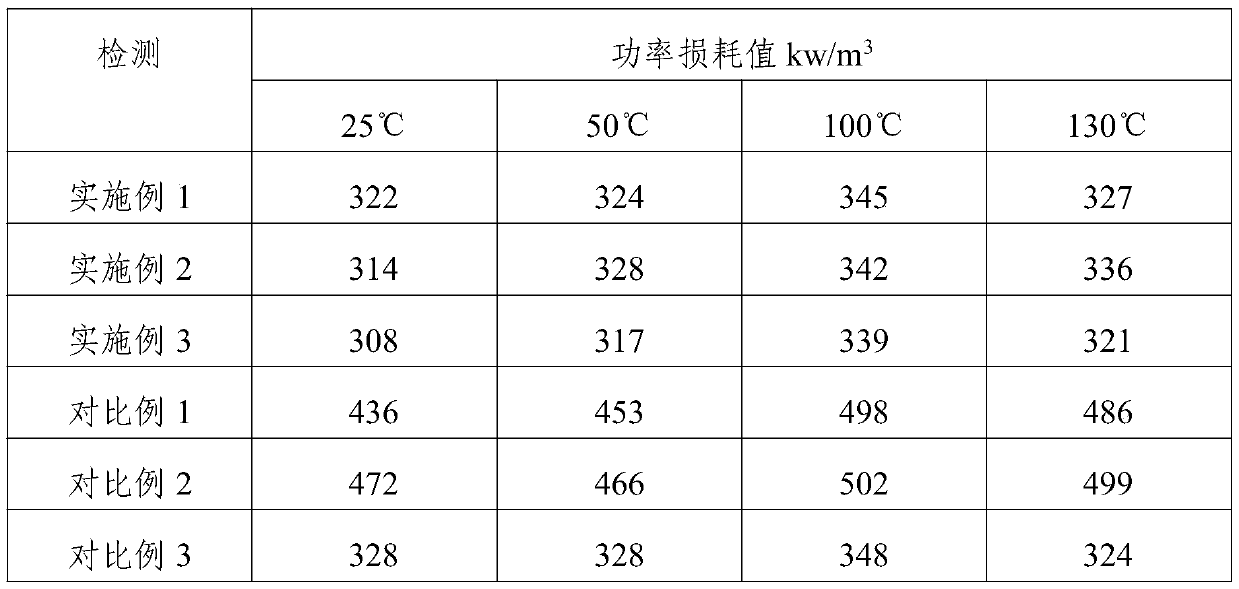
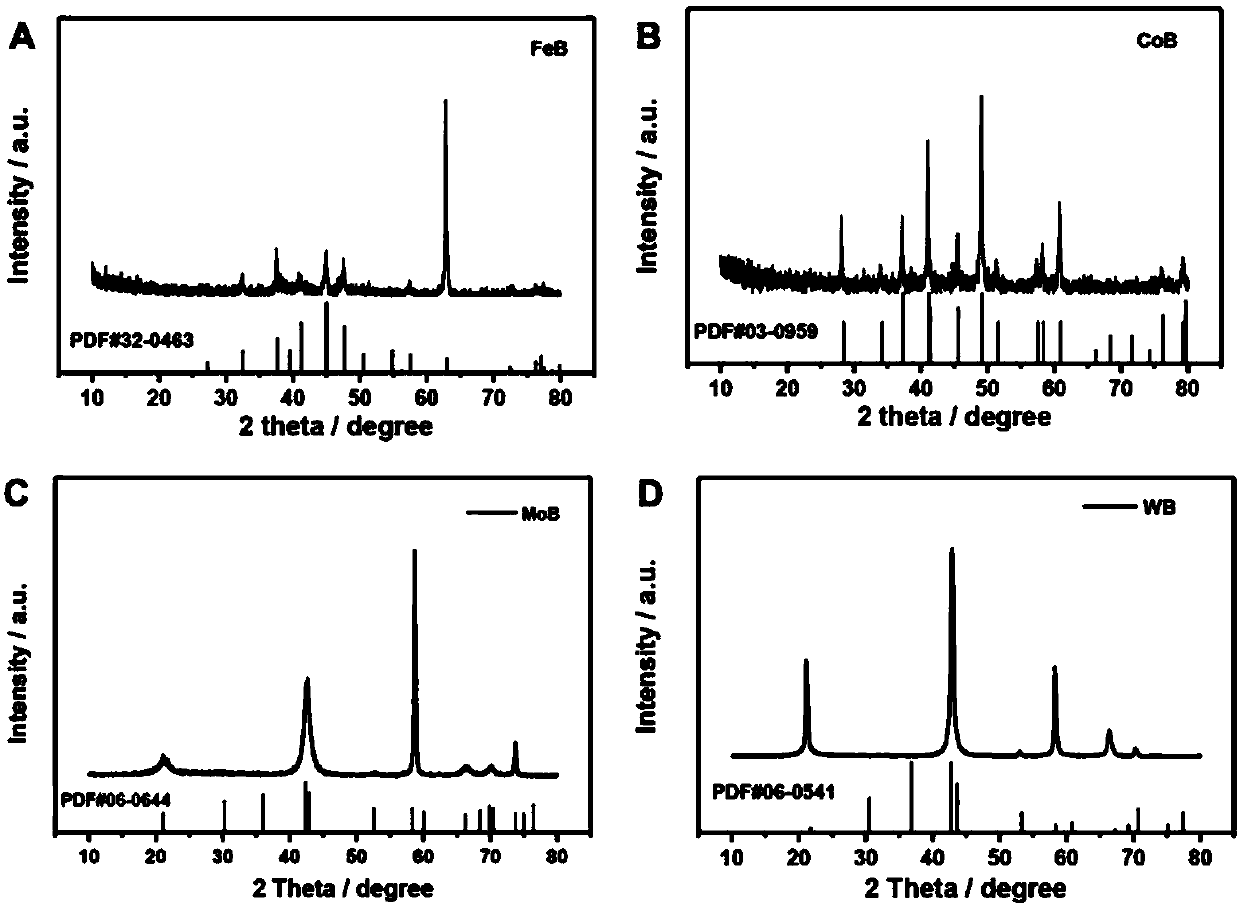
Wide-temperature-range low-loss ferrite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111039667AHigh initial permeabilityReduce magnetic lossInorganic material magnetismTungstateCerium
The invention provides wide-temperature-range low-loss ferrite and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of ferrite processing. The wide-temperature-range low-loss ferrite is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 90-100 parts of ferric oxide, 12-18 parts of nano titanium dioxide, 18-22 parts of magnesium oxide, 6-12 parts of barium oxide, 52-60 parts of manganese dioxide, 6-8 parts of a first mixture and 0.8-1.2 parts of a second mixture, wherein the first mixture is a mixture of chromium sesquioxide, tungsten trioxide, copper oxide and zinc oxide in a mass ratio of 3: 1: 4: 12, and the second mixture is a mixture of lanthanum hexaboride, cerium oxide and ammonium tungstate in a mass ratio of 2: 1: 1. The preparation method overcomes the defects of the prior art, effectively solves the problem of high loss of the traditional ferrite under the conditions of wide temperature and high frequency, effectively saves energy, and is suitable for various environments and fields.
Owner:天长市华磁磁电有限公司
Production method of superfine carbon steel wire
The invention relates to a production method of a superfine carbon steel wire. The production method is characterized in that the production process of the production method comprises the following steps of: coiling raw materials; pickling, and boronizing; carrying out dry type drawing for the first time; carrying out heat treatment; carrying out the dry type drawing for the second time; carrying out the heat treatment; electrogalvanizing; drawing a water tank; and winding a finished product. The production method disclosed by the invention can be used for producing the superfine carbon steel wire which has the advantages of high strength, low stress and good straight-through property in a batched way.
Owner:JIANGYIN FASTEN WIRE PRODUCTS CO LTD
Preparation process of rod-like ZrB2 toughened ZrB2-SiC ultrahigh-temperature ceramic
InactiveCN104230364AGood resistance to oxidation and ablationGood for crack deflectionRotary evaporatorFracture toughness
The invention provides a preparation process of a rod-like ZrB2 toughened ZrB2-SiC ultrahigh-temperature ceramic. The preparation process is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) adding zirconium boride ceramic powder into a solvent, uniformly stirring, adding a bonder and a plasticizer, and stirring for the second time to form uniform ceramic suspension, wherein the zirconium boride ceramic powder is formed by mixing rod-like zirconium boride powder with silicon carbide powder according to a volume percent ratio of (70%-90%) to (10%-30%); (2) drying the ceramic suspension in vacuum by adopting a rotary evaporator to form mixed powder; (3) degreasing the mixed powder in vacuum in a graphite grinding tool, and during degreasing, heating to 600-700 DEG C at the speed of 1-3 DEG C / min and preserving heat for 0.5-1 hour; and (4) performing hot pressed sintering in an argon gas atmosphere at 1,900-2,000 DEG C under the pressure of 20-40MPa for 0.5-2 hours to obtain the rod-like ZrB2 toughened ZrB2-SiC ultrahigh-temperature ceramic. The preparation process is simple; the obtained ceramic material is relatively good in oxidative ablation resistance, remarkably improved in fracture toughness and good in processability.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Metal boride water-splitting catalyst, preparation method and application of catalyst in electro-catalytic water splitting
ActiveCN108212157ARich reservesLow priceMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesOxygenOxygen evolution
The invention discloses a metal boride water-splitting catalyst, a preparation method and an application of the catalyst in electro-catalytic water splitting and belongs to the technical field of preparation of an electrocatalyst. The metal boride water-splitting catalyst is prepared with a solid-phase boriding method, transition metal is coated with a solid boriding agent, and boriding treatmentis performed through temperature programming heating. The boriding agent is prepared from a necessary boriding medium and an unnecessary filling agent. Compared with liquid boriding, a solid boridingmethod has the advantages that the surface clearing difficulty is low after boriding, requirements for equipment are low, and the method is applicable to boriding treatment of various transition metals. The catalyst has very good intrinsic catalysis activity and stability performance under the alkaline condition, and the required potential is 300-400 mV when the current density is 10 mA cm<-2>; the electro-catalytic water splitting oxygen evolution stability can be as long as at least 100 h while the performance is not attenuated, and the catalyst can replace noble metals to promote commercialapplication of electro-catalytic water splitting.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Ultra-fast boriding of metal surfaces for improved properties
ActiveUS20130056363A1Fast boridingDesirable mechanical propertySolid state diffusion coatingBoridingUltra fast
A method of ultra-fast boriding of a metal surface. The method includes the step of providing a metal component, providing a molten electrolyte having boron components therein, providing an electrochemical boriding system including an induction furnace, operating the induction furnace to establish a high temperature for the molten electrolyte, and boriding the metal surface to achieve a boride layer on the metal surface.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Oil well tubing coupling and sucker rod joint integrated boriding method
InactiveCN101487110AEasy to stretchGood anti-corrosion and wear-resistant effectSolid state diffusion coatingCouplingBoriding
The invention relates to a boronizing method of integration of a pumping tube coupling and a pumping rod collar, which is characterized in that the tube coupling is used as a container for containing a boronizing agent, the rod collar is used as a mandrel for reducing heat capacity and increasing cooling rate during the cooling process, the rod collar is placed in the middle of the boronizing agent inside the tube coupling and heated by high temperature. The ingenious conception of the method can ensure that the tube coupling can reach higher tensile properties, the effects of anticorrosion and wear-resistance are much better than the rod collar and tube coupling made by common heat treating method, and the same amount of boronizing rod collars can be produced when the boronizing tube couplings are being made, thus increasing the production efficiency significantly, reducing the amount of boronizing agent used and decreasing the cost greatly. The hardness of the inner surface of the tube coupling and the outer surface of the rod collar obtained through the methods is HV 1100 to 1600, the thickness of the boronizing layer is 50 Mum to 90 Mum, the yield strength of the tube coupling is more than 552 MPa, the tensile strength is more than 689 MPa, and the elongation is more than 16 percent.
Owner:吉林省大多天盛金属陶瓷技术有限公司
High-thermal-conductivity die-casting aluminum alloy material produced from secondary aluminum and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of aluminum alloys, and discloses a high-thermal-conductivity die-casting aluminum alloy material produced from secondary aluminum and a preparation method thereof. The high-thermal-conductivity die-casting aluminum alloy material is characterized in that (1) used materials are mainly reclaimed materials; (2) main components of an aluminum alloy comprise Si, Mg, Fe, Sr, B and Al, and the aluminum alloy comprises the following components including, by mass, 7.0%-11.0% of the Si, 0.3%-1.0% of the Mg, 0.6%-0.90% of the Fe, 0.02%-0.06% of the Sr, less than or equal to 0.03% of the B and the balance of the Al; (3) a smelting furnace is provided with double gates; and (4) in the production process, boronizing treatment is adopted, the standing time is prolonged, elements influencing the heat conductivity are settled to the bottom of the furnace in a boride form, and molten aluminum purification is achieved.
Owner:HUAJIN NEW MATERIALS RES INST GUANGZHOU CO LTD +1
Magnesium-rare earth-boron alloy with high heat resistance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103849802AReduce typesAvoid pollutionSolid state diffusion coatingRare-earth elementHigh resistance
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
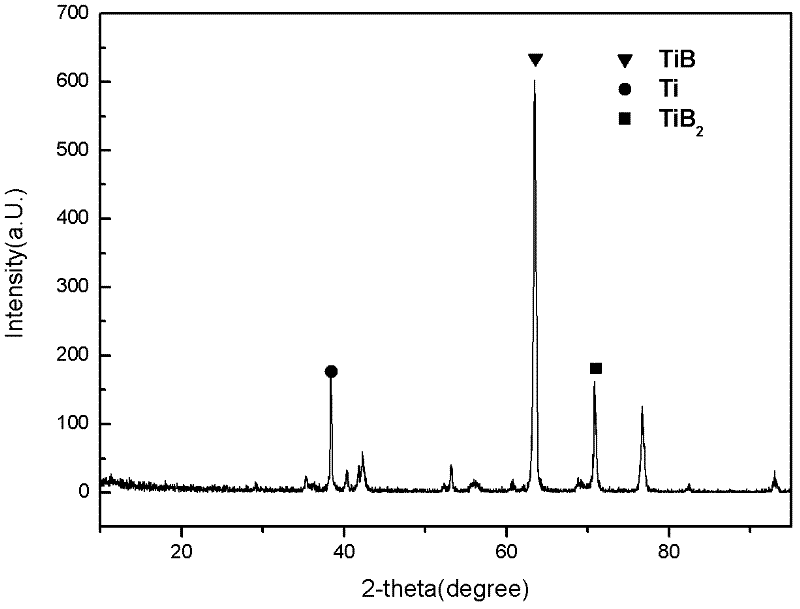
Nanostructured titanium monoboride monolithic material and associated methods
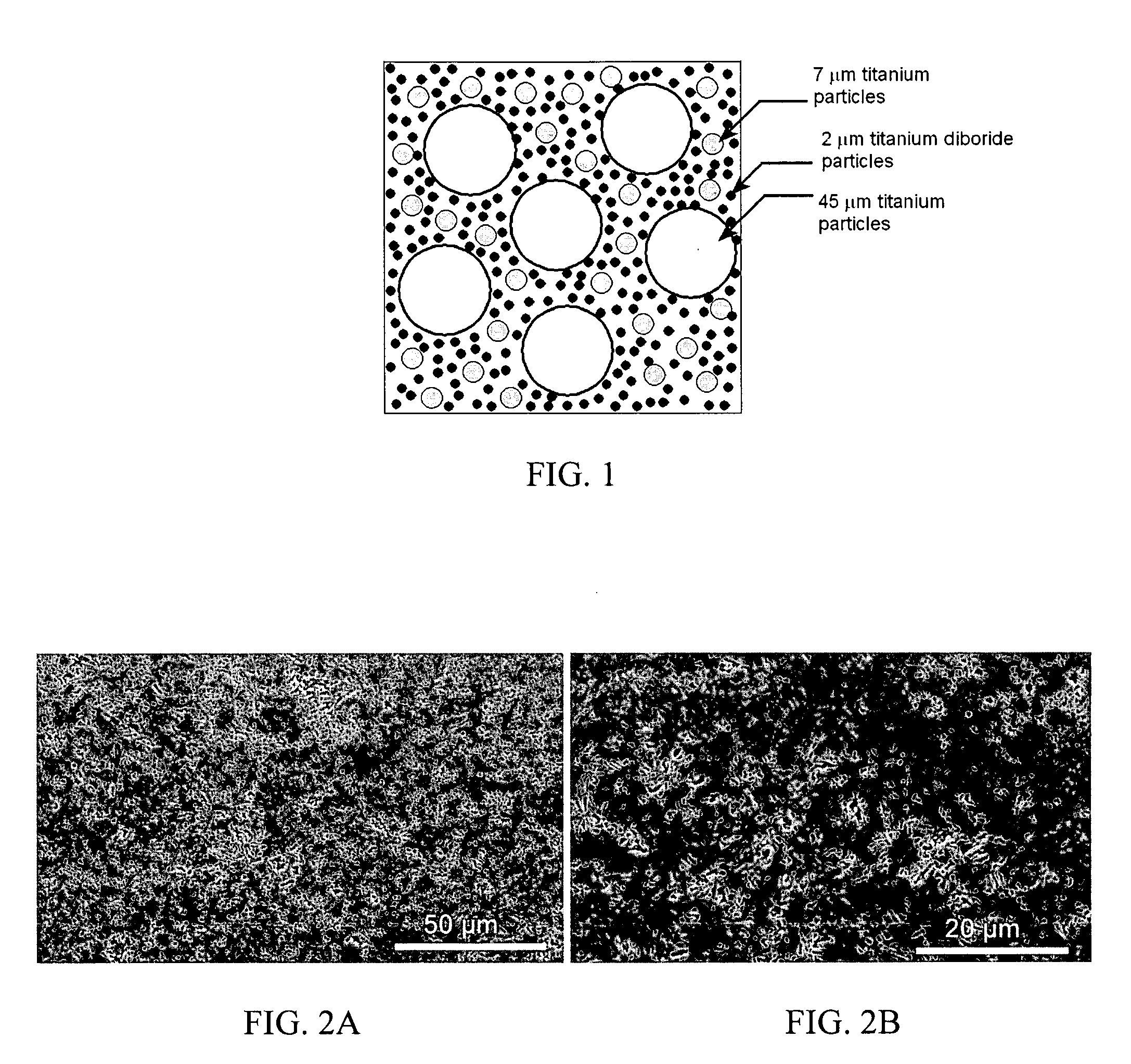
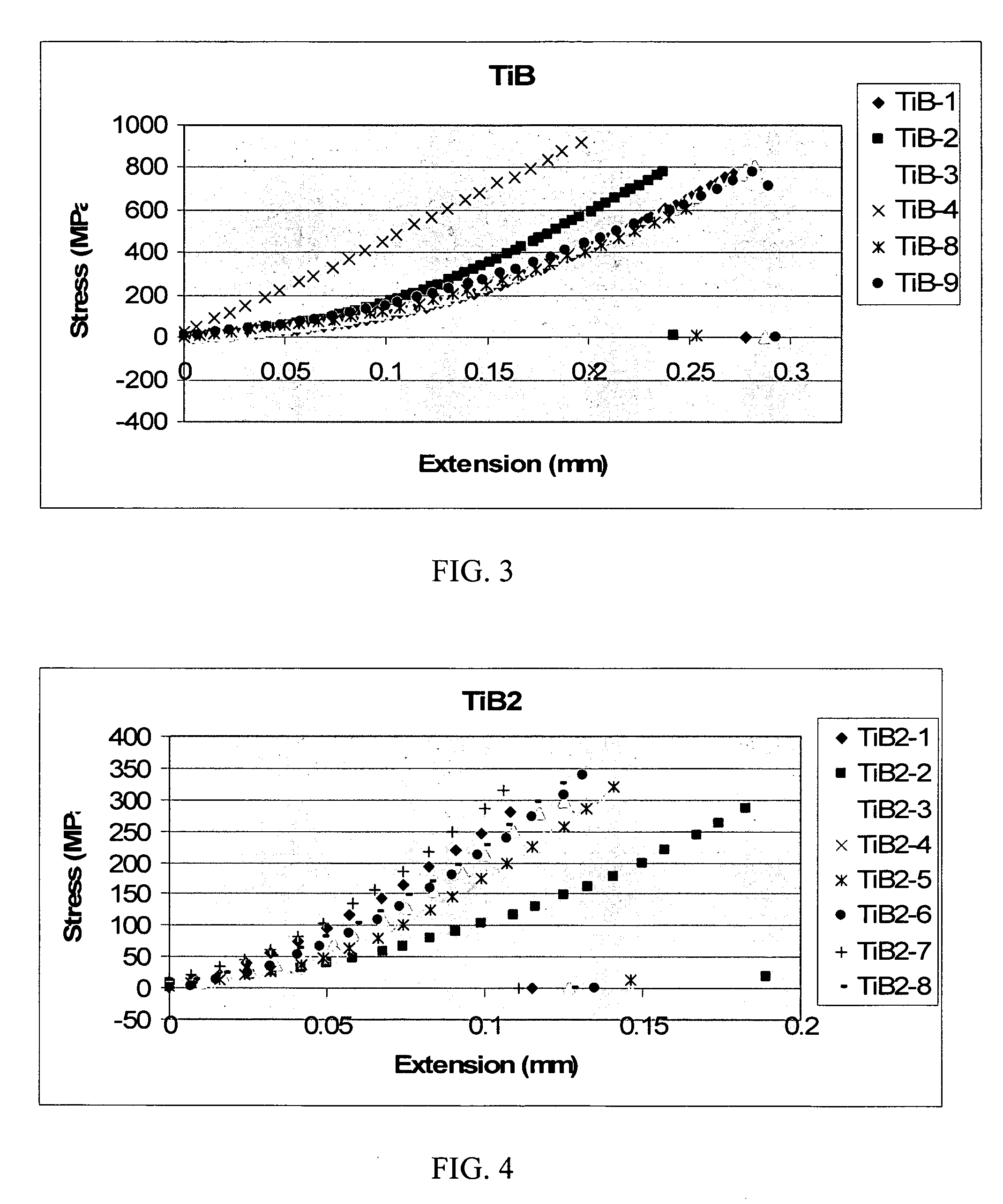
InactiveUS20070018139A1Machinability easeManufacturing EasePolycrystalline material growthConductive materialBorideWear resistant
A nanostructured monolithic titanium boride (TiB) material and methods of forming such a material are disclosed and described. This material has a room-temperature four-point flexural strength about three times that of commercially available titanium diboride (TiB2). The achievement of nanostructured internal microstructural arrangement having a network of interconnected titanium monoboride whiskers affords a very high strength to this material above some of the best ceramic materials available in the market. The material contains a small amount of titanium, but it is largely made of TiB phase with substantially no TiB2. The nanostructured monolithic titanium boride material can be formed by high temperature processing of a powder precursor having carefully selected weight and size distributions of titanium and titanium diboride powders. Potential applications of this material can include wear resistant components such as die inserts for extrusion dies, nozzles, armor, electrodes for metal refining etc. An important advantage of TiB over other hard ceramics is that TiB can be cut by electro-discharge machining (EDM) without difficulty, unlike most ceramics.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Heat treatment process of aluminum alloy extrusion die
InactiveCN109402332AImprove stabilityHigh hardnessSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesRoom temperatureBoriding
The invention relates to a heat treatment process of an aluminum alloy extrusion die. The heat treatment process comprises the steps of machining, boriding, quenching, tempering, cleaning and tufftriding, specifically, firstly, an aluminum alloy extrusion die material is machined firstly; then the surface of the aluminum alloy extrusion die is decontaminated, after decontamination treatment, the aluminum alloy extrusion die is placed into a stainless steel container with a cover, the space between the inner side of the stainless steel container and the outer side of the aluminum alloy extrusion die is filled with boriding powder, the space between a cover body of the stainless steel container and a stainless steel container body is sealed through refractory mortar, finally the stainless steel container is placed into a furnace to be heated to 900 DEG C for heat preservation for 2-4 h, then furnace cooling is conducted to the room temperature, and the die is taken out; then the die issubjected to heat treatment, namely vacuum quenching and three-time tempering, and then oil contamination cleaning is conducted; and finally, the cleaned aluminum alloy extrusion die is placed into anitriding furnace to be tufftrided. According to the heat treatment process, the performance such as hot melt loss resistance and adhesion resistance of the aluminum alloy extrusion die is improved.
Owner:河南精诚汽车零部件有限公司
Wire rod metal surface pretreatment method, wire rod rust removal method and sand blasting device
PendingCN108747610AReduce generationAvoid secondary damageAbrasive machine appurtenancesAbrasive blasting machinesWire rodPretreatment method
The invention provides a wire rod metal surface pretreatment method. The wire rod metal surface pretreatment method comprises following step that bending rust removal, steel brush rust removal, abrasive belt rust removal, sand blasting rust removal, ultrasonic washing and pressure water flushing are sequentially carried out so as to achieve wire rod surface mechanical rust removal. The invention further discloses a wire rod rust removal method. The wire rod rust removal method comprises the following steps of S1, mechanical rust removal, S2, washing, S3, boronizing, S4, drawing and S5 windingup. The invention further provides a sand blasting device. The device comprises a shell, a sand box is arranged on the bottom of the shell, multiple inlets and multiple outlets allowing multiple wirerods to enter in and out are symmetrically formed in the two sides of the shell, multiple sand blasting heads are arranged at the upper end of the interior of the shell, and the sand blasting heads communicate with a sand box for sand blasting. According to the wire rod metal surface pretreatment method, the mechanical rust removal method is adopted, acid pickling and phosphorization processes arereduced, environment friendliness and high efficiency are achieved, in the mechanical rust removal process, surface rust is removed, boronizing is carried out to form a boronizing film, friction in the drawing process is reduced, and the secondary damage on the surface of a wire rod is avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU JULI WIRE ROPE
Boriding agent for boriding on metallic titanium surface and boriding technique
The invention discloses a boriding agent for boriding on a metallic titanium surface and a preparation method thereof. The boriding agent comprises the following ingredients in mass percent: 20-35% of Na2B4O7, 10-20% of H3BO3, 10-20% of B4C, 15-25% of KCl, 15-25% of NaCl, and 1-5% of KBF4. The boriding technique of the invention comprises the steps of: firstly putting a metallic titanium sample in a boriding agent fused mass with special ingredients, maintaining the temperature for a period to form a boriding layer on the surface of the metallic titanium sample; and then, performing a quenching treatment to cure the boriding layer so as to obtain a thick and uniform boriding layer with high hardness and good bonding force on the surface of the metallic titanium sample, and the fused salt on the surface of the metallic titanium sample is easy to treat. The boriding technique of the invention has the advantages of simple and easy control operation, little boriding agent loss, short operation duration and low energy consumption, so that the boriding technique is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:江苏奇纳新材料科技有限公司
Method for preparing superfine zirconium boride powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing superfine zirconium boride powder, belonging to the technical field of ceramic materials. The method is as follows: burdening raw materials at a certain mole ratio, namely, the mole ratio of ZrO2 to B2O3 to B4C to C12H2O11 is 3: (2-4): (1-3):1; adding alcohol in the burdened raw materials for abundantly grinding; drying; pressing the mixed materials to a green body; placing the green body in a graphite or corundum crucible, embedding analytical pure activate carbon at the periphery of the green body, and putting in a high-temperature electric resistance furnace; reacting and synthesizing under the protection of flow high-pure argon, wherein the synthesis temperature is 1450-1550 DEG C and kept for 1-6 hours; and after cooling along with the furnace, taking the green body out, and fully grinding the green body to the superfine powder. In the invention, the cost of the used raw material is low, and a device and an operation flow process are simple; and by analysis of X-ray diffraction (XRD), only zirconium boride exists in the superfine powder, the average crystallite dimension of the zirconium boride is less than 100nm, and a result obtained by observation of scanning electron microscope (SEM) indicates that the average particle dimension is less than 500nm.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method for anticorrosion steel used for water-cooling spray nozzle
ActiveCN106119724AImprove impact resistanceReduced diffusion rateSolid state diffusion coatingMolten stateBoriding
The invention discloses a preparation method for anticorrosion steel used for a water-cooling spray nozzle. The method comprises the following steps that raw materials are heated into a molten state to obtain a liquid alloy, wherein the liquid alloy comprises, by weight, 0.1-0.25% of C, 1.2-1.5% of Cr, 0.3-0.6% of Al, 1.2-1.6% of Mg, 0.2-0.3% of Zr, 0.4-0.6% of Ni, 1.2-1.3% of Mn, 0.08-0.12% of Mo, 0.1-0.13% of V, 0.03-0.06% of Co, 0.02-0.05% of Ga, 1.5-1.6% of T, 0.6-0.8% of Si and the balance Fe; a steel billet is obtained through casting; heat treatment is conducted; boriding is conducted; and the steel billet subjected to heat treatment and boriding is coated with a conversion film.
Owner:滁州帝邦科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com