Wide-temperature-range low-loss ferrite and preparation method thereof
A low loss, ferrite technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of high loss, achieve the effect of reducing magnetic loss, uniform grain growth, and promoting grain growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
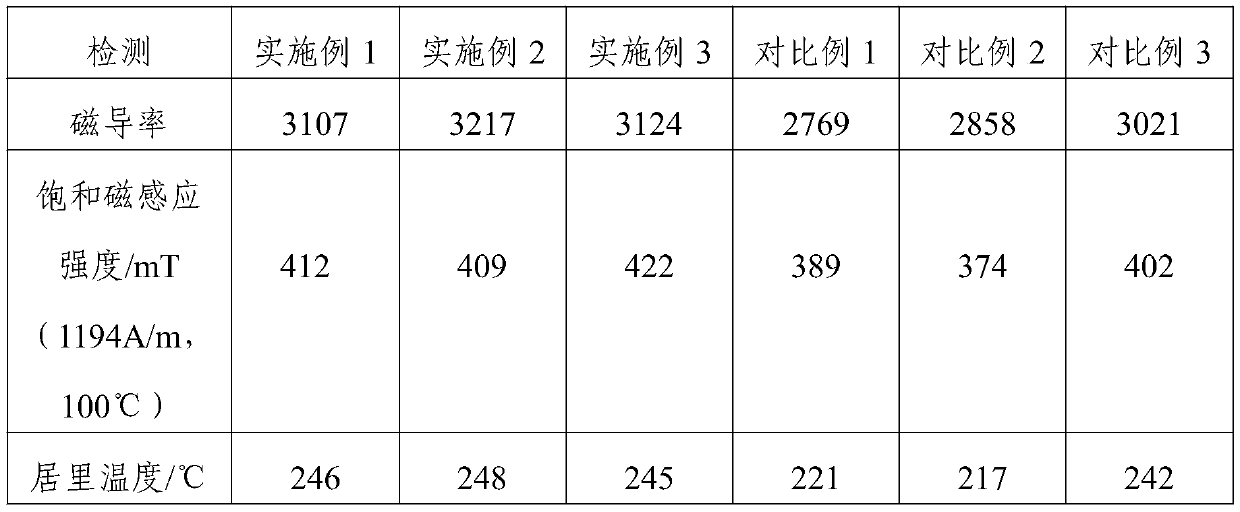
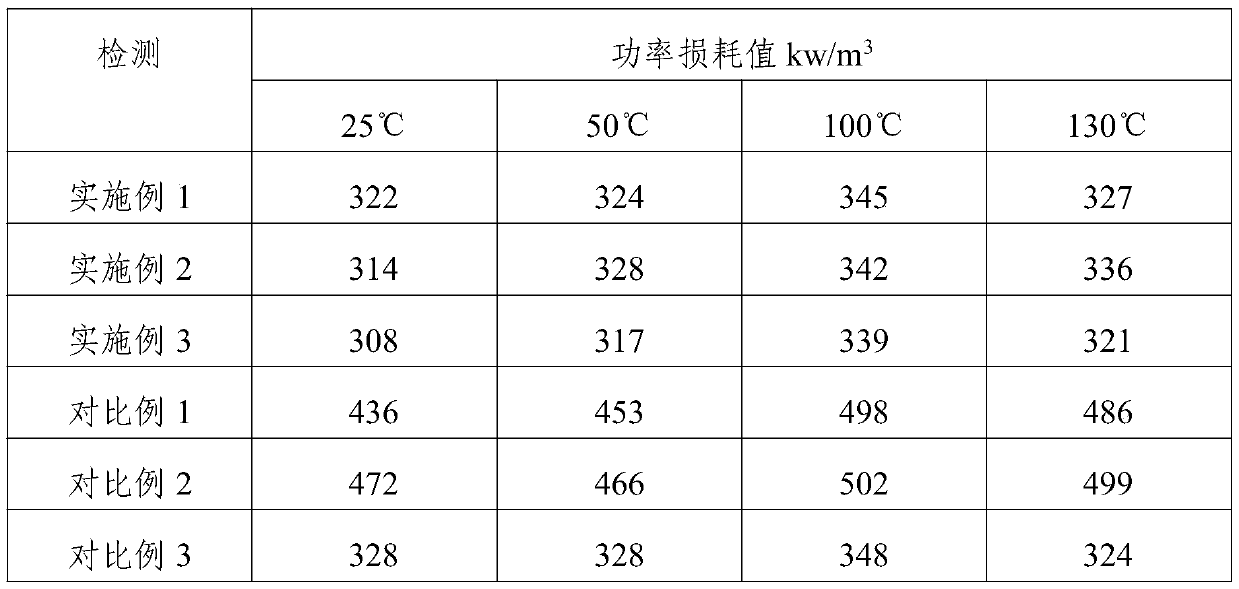
[0031] A wide-temperature low-loss ferrite, which is made of the following parts by weight of raw materials: 90 parts of iron trioxide, 12 parts of nano-titanium dioxide, 18 parts of magnesium oxide, 6 parts of barium oxide, 52 parts of manganese dioxide, 6 parts of the first mixture, 0.8 parts of the second mixture, wherein the first mixture is a mixture of chromium trioxide, tungsten trioxide, copper oxide, and zinc oxide in a mass ratio of 3:1:4:12; The second mixture is a mixture of lanthanum hexaboride, cerium oxide, and ammonium tungstate in a mass ratio of 2:1:1.
[0032] The preparation method of the first mixture includes the following steps:
[0033] (1) Mix chromium trioxide, tungsten trioxide, copper oxide, and zinc oxide at a high temperature of 320-350℃ for 2-3 hours, then take it out, and cool it with supercooled water;
[0034] (2) The above-mentioned cooled material is pulverized and ground to a particle size of 0.2-0.3 μm to obtain the first mixture.
[0035] The pr...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A wide-temperature low-loss ferrite, the wide-temperature low-loss ferrite is made of the following parts by weight of raw materials: 100 parts of ferric oxide, 18 parts of nano titanium dioxide, 22 parts of magnesium oxide, 12 parts of barium oxide, 60 parts of manganese dioxide, 8 parts of the first mixture, 1.2 parts of the second mixture, wherein the first mixture is a mixture of chromium trioxide, tungsten trioxide, copper oxide, and zinc oxide in a mass ratio of 3:1:4:12; The second mixture is a mixture of lanthanum hexaboride, cerium oxide, and ammonium tungstate in a mass ratio of 2:1:1.
[0047] The preparation method of the first mixture includes the following steps:
[0048] (1) Mix chromium trioxide, tungsten trioxide, copper oxide, and zinc oxide at a high temperature of 320-350℃ for 2-3 hours, then take it out, and cool it with supercooled water;
[0049] (2) The above-mentioned cooled material is pulverized and ground to a particle size of 0.2-0.3 μm to obtain ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A wide-temperature low-loss ferrite, which is made of the following parts by weight of raw materials: 95 parts of ferric oxide, 15 parts of nano-titanium dioxide, 20 parts of magnesium oxide, 9 parts of barium oxide, 56 parts of manganese dioxide, 7 parts of the first mixture, 1 part of the second mixture, wherein the first mixture is a mixture of chromium trioxide, tungsten trioxide, copper oxide, and zinc oxide in a mass ratio of 3:1:4:12; The second mixture is a mixture of lanthanum hexaboride, cerium oxide, and ammonium tungstate in a mass ratio of 2:1:1.
[0062] The preparation method of the first mixture includes the following steps:
[0063] (1) Mix chromium trioxide, tungsten trioxide, copper oxide, and zinc oxide at a high temperature of 320-350℃ for 2-3 hours, then take it out, and cool it with supercooled water;
[0064] (2) The above-mentioned cooled material is pulverized and ground to a particle size of 0.2-0.3 μm to obtain the first mixture.
[0065] The prepar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com