Optical lens without light loss and its manufacturing process
An optical lens and lens technology, applied in the field of optical lenses, can solve problems such as large light loss, and achieve the effects of low light loss, low lens image drift, and good diffraction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
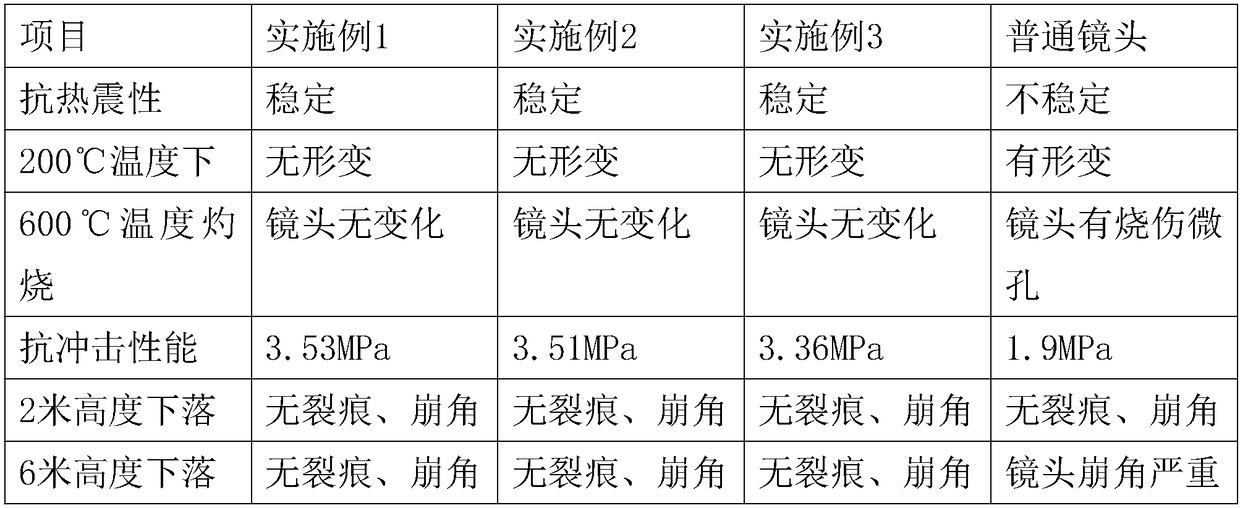
Embodiment 1
[0015] No optical loss optical lens, the lens is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0016] 58 parts of quartz sand, 8 parts of alum, 13 parts of soda ash, 6 parts of nano-silicon dioxide, 12 parts of modified graphene, 6 parts of lithium hydroxide, 8 parts of hafnium boride, 10 parts of potassium chloride, and 8 parts of vanadium pentoxide 8 parts of iron carbide, 6 parts of barium silicide, 2 parts of tungsten silicide, 5.5 parts of cobalt dioxide, and 3 parts of vitrified fiber.
[0017] The preparation method of the modified graphene is to pressurize the graphene with high-temperature nitrogen gas at 240-300°C for 30 minutes, and the pressure is 1.2-1.8MPa, then irradiate the graphene with 32.5nm ultraviolet rays, and then use 40-60MHz ultrasonic waves to Treat for 10 minutes, then calcinate the graphene at a temperature of 300-350° C. for 30 minutes, and wait for the graphene to cool naturally to room temperature to obtain the modified graphene.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0022] No optical loss optical lens, the lens is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0023] 55 parts of quartz sand, 6 parts of alum, 11 parts of soda ash, 5 parts of nano-silicon dioxide, 10 parts of modified graphene, 5 parts of lithium hydroxide, 7.8 parts of hafnium boride, 9 parts of potassium chloride, and 7 parts of vanadium pentoxide parts, 7 parts of iron carbide, 5 parts of barium silicide, 1.5 parts of tungsten silicide, 5 parts of cobalt dioxide, and 2.8 parts of vitrified fiber.
[0024] The preparation method of the modified graphene is to pressurize the graphene with high-temperature nitrogen gas at 240-300°C for 30 minutes, and the pressure is 1.2-1.8MPa, then irradiate the graphene with 32.5nm ultraviolet rays, and then use 40-60MHz ultrasonic waves to Treat for 10 minutes, then calcinate the graphene at a temperature of 300-350° C. for 30 minutes, and wait for the graphene to cool naturally to room temperature to obtain the modified grap...
Embodiment 3
[0029] No optical loss optical lens, the lens is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0030] 52 parts of quartz sand, 4 parts of alum, 10 parts of soda ash, 4 parts of nano-silicon dioxide, 8 parts of modified graphene, 4 parts of lithium hydroxide, 7.5 parts of hafnium boride, 8 parts of potassium chloride, and 5 parts of vanadium pentoxide parts, 5 parts of iron carbide, 4 parts of barium silicide, 1 part of tungsten silicide, 4 parts of cobalt dioxide, and 2.5 parts of vitrified fiber.
[0031] The preparation method of the modified graphene is to pressurize the graphene with high-temperature nitrogen gas at 240-300°C for 30 minutes, and the pressure is 1.2-1.8MPa, then irradiate the graphene with 32.5nm ultraviolet rays, and then use 40-60MHz ultrasonic waves to Treat for 10 minutes, then calcinate the graphene at a temperature of 300-350° C. for 30 minutes, and wait for the graphene to cool naturally to room temperature to obtain the modified graphene...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com