Patents
Literature
459 results about "Arc melting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arc Melting. is used for melting metals– typically to form alloys. Heating is via an electric arc struck between a tungsten electrode and metals placed in a depression (crucible) in the copper hearth.
Low thermal expansion coefficient NaMxAlySiz high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
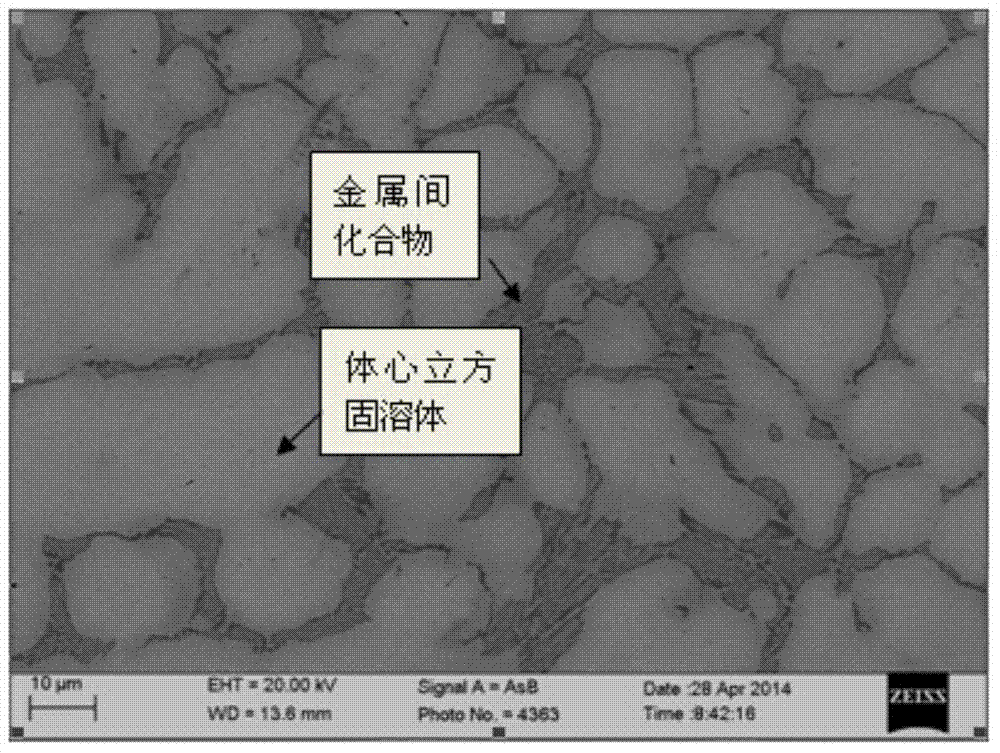
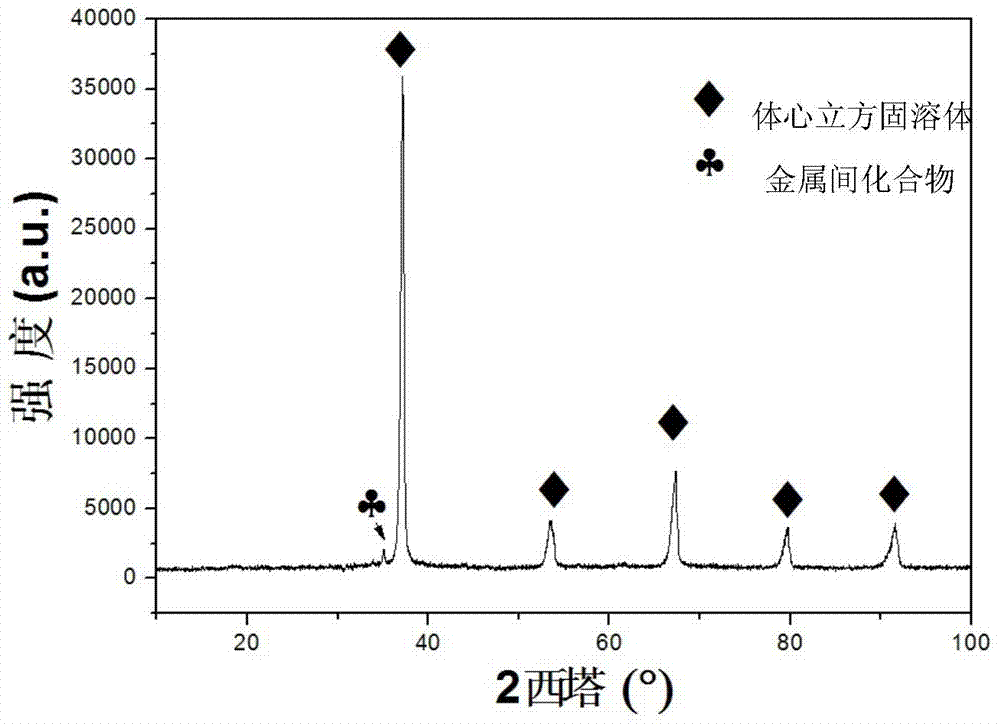
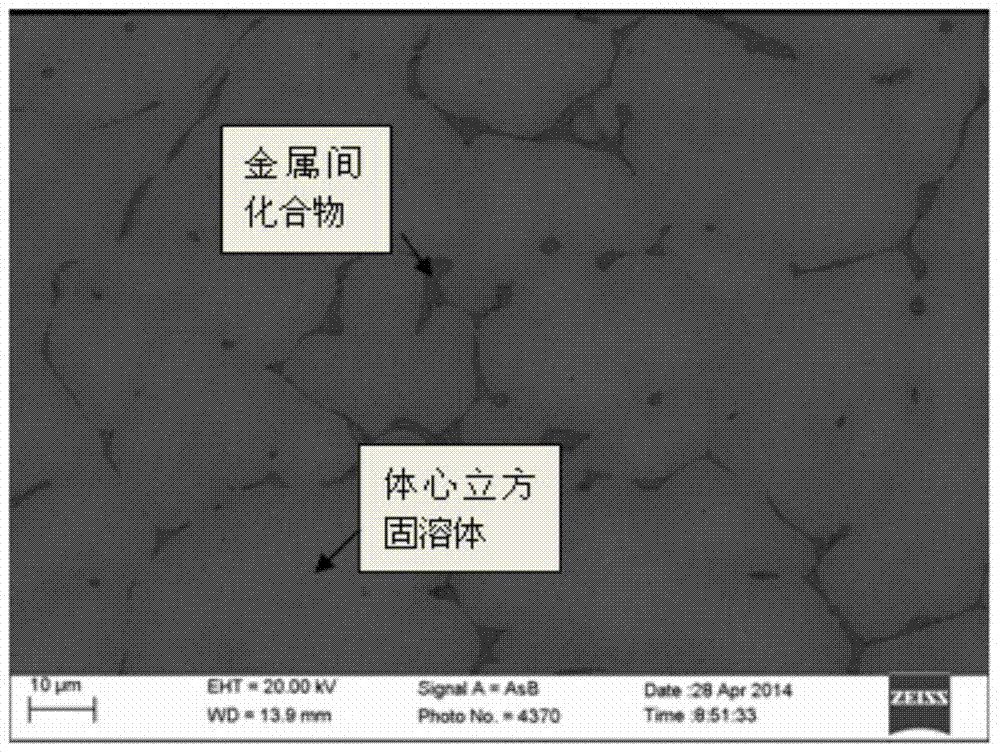
The invention relates to a low thermal expansion coefficient NaMxAlySiz high entropy alloy and a preparation method thereof, the chemical components of the alloy are as follows: 75 <= a <= 100%, 0 <= x <= 10%, 0<= y<= 10%, 0<= z<= 5%, N is arbitrary three or more than three of Ta, Nb, Hf, Zr, Ti, Mo and W, and M is any one or more than one of V, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni and Cr. The alloy phase structure is as follows: a body centered cubic solid solution and an intermetallic compound. The alloy is prepared by arc melting method in three stages. The NaMxAlySiz high entropy alloy has a low thermal expansion coefficient at the temperature in the range of room temperature to 1000 DEG C, the change rate is less than 20%, and the alloy has a broad application prospect in the high temperature industrial field.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
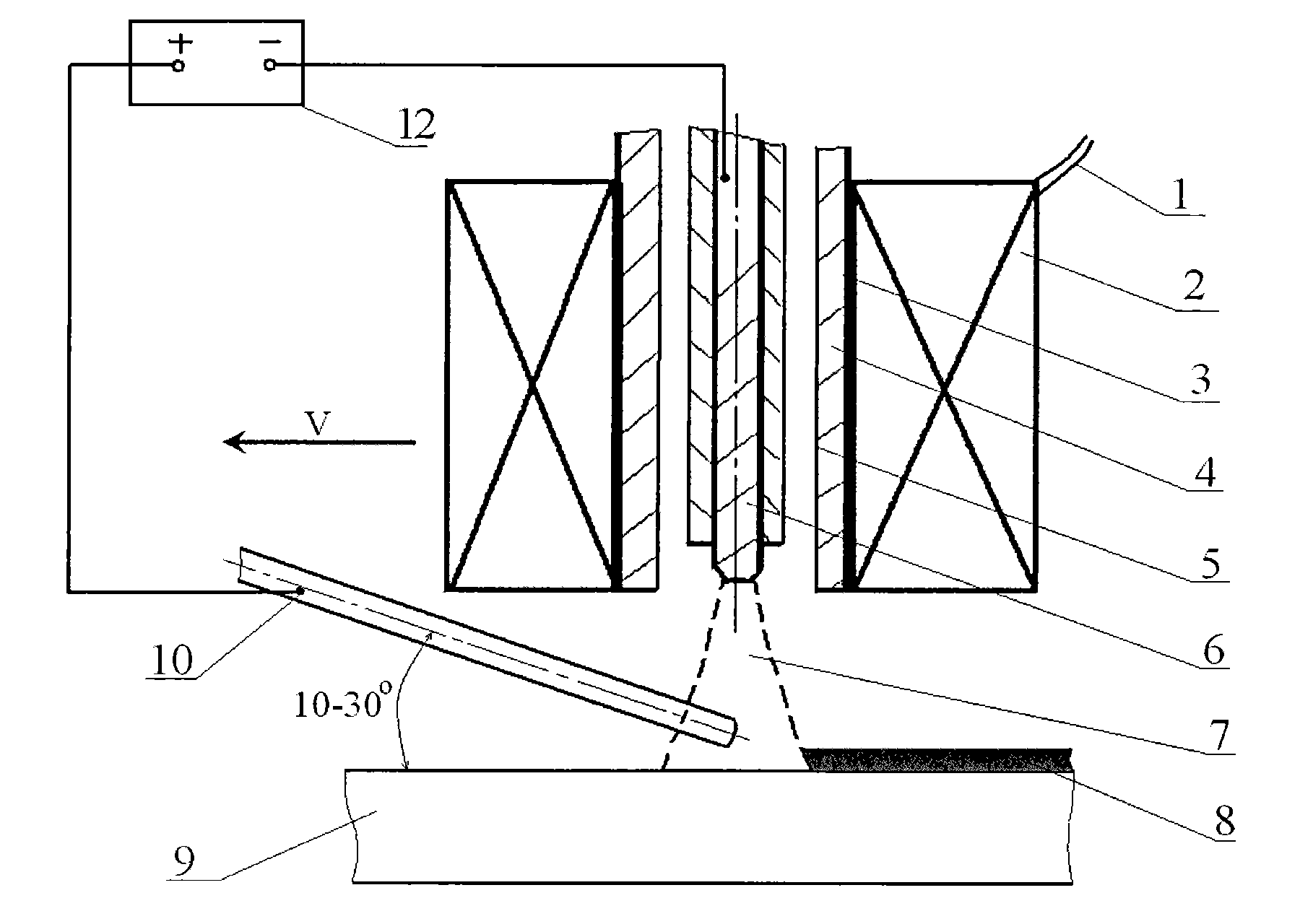
Electromagnetic current coupling field assisted hybrid melting-brazing method for laser-TIG arc and equipment
InactiveCN101862913AImprove connection qualityInhibition formationSoldering apparatusWelding apparatusMetallic materialsWelding defect
The invention discloses an electromagnetic current coupling field assisted hybrid melting-brazing method for a laser-TIG arc and equipment. In addition to the use of the welding zone, an alternating magnetic field is added to control properties of plasma formed through ionization of laser, arc and a raw material metal, thereby improving the laser utilization rate. Under the electric field assisted comprehensive effect, the weld melting depth is increased, and the assistant effect on the melting bath of the liquid-state brazing filler metal for laser-arc melting-brazing is realized through electromagnetic stirring and excitation and enhancement, thereby promoting the orderly flow of the liquid-state brazing filler metal and the rupture, wetting, spreading and proliferation of the liquid-state brazing filler metal on the surface of the high metal material, improving the full mixing of the liquid-state brazing filler metal and the base metal formed by melting the low-melting-point metal material, improving the uniformity of the components of the brazed weld, stabilizing the welding process, reducing welding defects, increasing the welding speed, improving the weld formation, optimizing the structure and performance of the brazed weld, and improving the quality of the brazed joint. Moreover, the equipment has the advantages of simple structure, flexible application, low cost, good effect and easy realization.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Petroleum steel tube capable of anti hydrogen sulfide stress corrosion and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN1948538AExcellent physical and chemical propertiesEasy to useDrilling rodsFurnace typesElectric arc furnaceArc melting
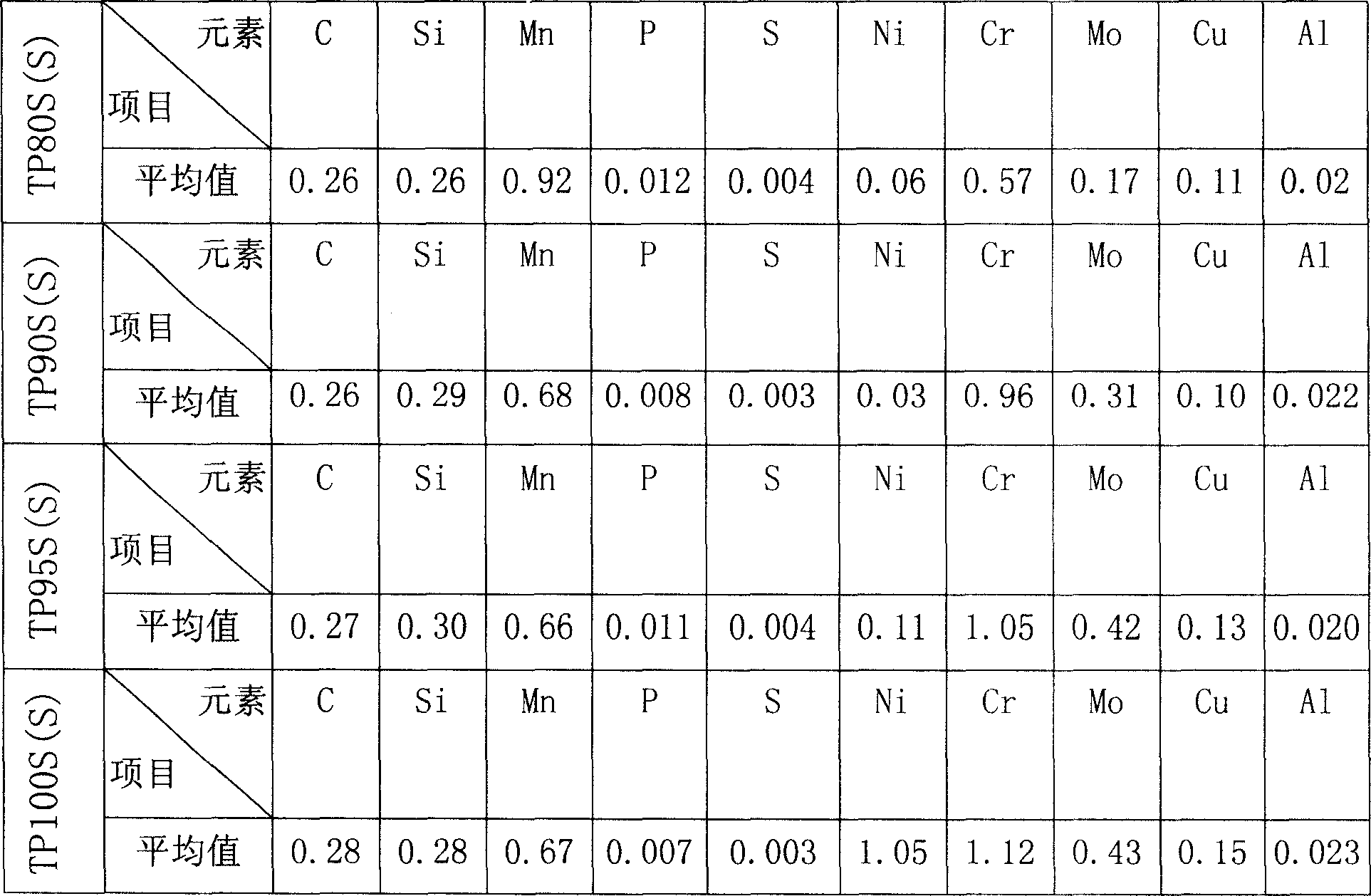
The invention offers oil steel pipes which can resist stress corrosion by hydrogen sulfide. Weight proportion of their compound is: C 0.25-0.32%,Si 0.10-0.40%,Mn 0.60-1.20%, P<=0.020%,S<=0.010%,Ni<=0.25%,Cr 0.55-1.20%,Mo 0.10- 0.50%,Cu<=0.30%,Al 0.010-0.040% and the allowances are Fe. Scrap steel and spongy iron or melted iron is taken as melting materials. After arc melting, external refinement and vacuum deaeration, they are cast continuously to get round billiets. Then, they are hot rolled to seamless steel pipes and finally to bushing and oil pipes by heat processing of quench and temper. The steel pipes have good physicochemical property and their indexes all reach or exceed API standard. Threshold value of resisting stress corrosion by hydrogen sulfide reaches 90%SMYS, which precedes the standard request and can be extensively applied in oil-gas field with hydrogen sulfide.
Owner:TIANJIN PIPE GROUP CORP
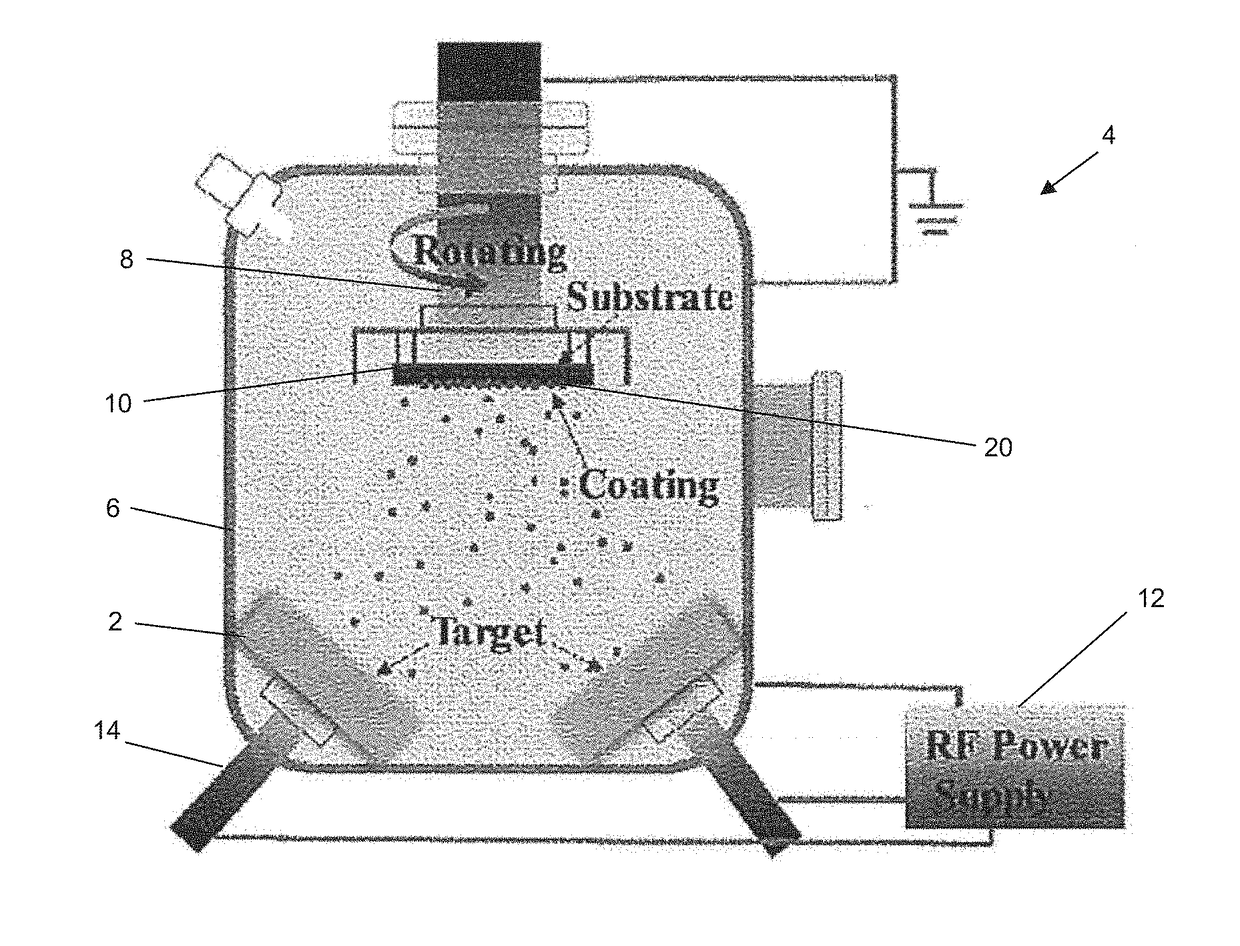
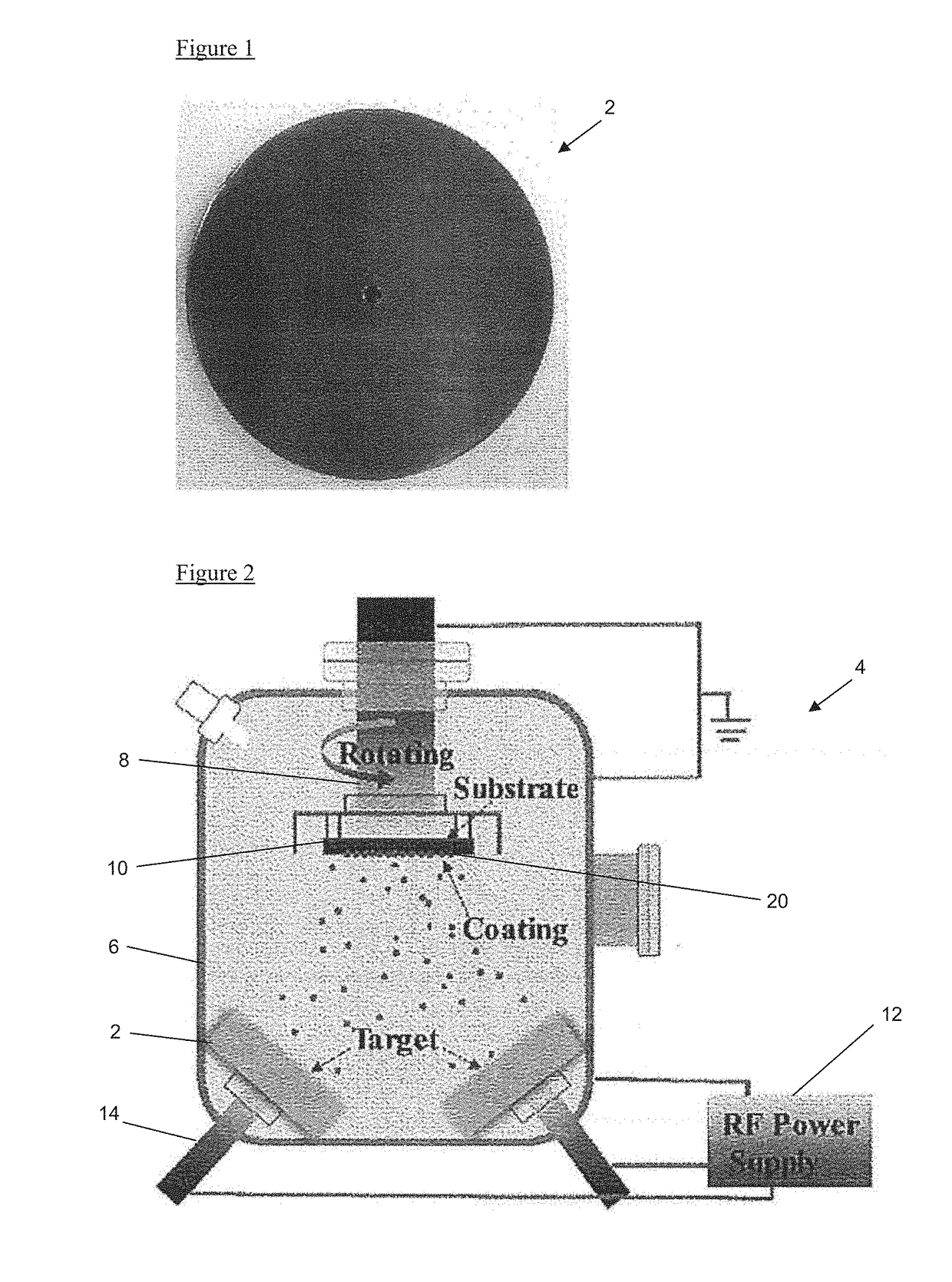
High entropy alloy thin film coating and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20180223417A1High hardnessImprove wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh entropy alloysRadio frequency sputtering
A method for preparing a high entropy alloy thin film coating includes preparing a melt alloy by arc melting raw materials including five or more elements, casting the melt alloy into a mold to form a target, placing the target inside a vacuum chamber of a magnetron sputtering system, and rotatably fixing a substrate inside the vacuum chamber, spaced apart from the target. A high entropy alloy thin film is deposited on the substrate by high vacuum radio frequency sputtering inside the vacuum chamber.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for preparing CuCr25 electrical contact
The invention discloses a method for preparing CuCr25 electrical contact by utilizing the vacuum self-consuming arc-melting technology. The method comprises the steps that 1, qualified Cu powder and Cr powder are selected according to composition proportion of CuCr25 electrical contact materials and mixed; 2, cold isostatic pressing is conducted on the evenly mixed powder; 3, sintering is conducted on a self-consuming electrode which is subject to cold isostatic pressing; 4, self-consuming smelting is conducted on the electrode which is subject to sintering. By means of the method for preparing the CuCr25 electrical contact by utilizing the vacuum self-consuming arc-melting technology, the inclusion problem caused by scaling-off of a crucible in the preparation process of the electrical contact materials through the smelting and casting technology is solved, microstructures of the CuCr25 electrical contact materials in the casting state are refined, the gas content in a casting ingot is reduced, and the alloy casting ingot is purified.
Owner:SHAANXI SIRUI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Two-stage plasma gasifying, melting and cracking method and device of waste containing organic matters
ActiveCN102000691ANo emissionsComplete gasificationSolid waste disposalGlass furnace apparatusGeneration rateHigh energy
The invention relates to a treatment method of waste containing organic matters, in particular to two-stage plasma gasifying, melting and cracking method and device of the waste containing organic matters, belonging to the field of gasifying, melting and cracking techniques. In the invention, the serious defects of high energy consumption of the waste containing organic matters and more flying ash during the plasma arc melting and cracking are solved, thereby thoroughly utilizing the energy of the organic matters and maximizing the treating efficiency, thoroughly cracking the tar, reducing the generation rate of Dioxin, obtaining synthesis gas with high quality and high heat value as much as possible, providing guarantee for the subsequent gasification power generation, the hydrogen energy recovery or the production of green liquid fuel, simultaneously finishing one-step recovery of noble metals and direct utilization of glass bodies in the field of building materials, laying foundation for the large-scale commercial development and application of the energy of the waste containing organic matters, and thoroughly solving the possible pollutant discharging problem in the gasifying process of the organic matters, particularly the dangerous waste.
Owner:HOOTECH
Material of negative electrode for lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20170338482A1Avoid destructionExtended service lifeSecondary cellsNegative electrodesHigh entropy alloysMetallurgy
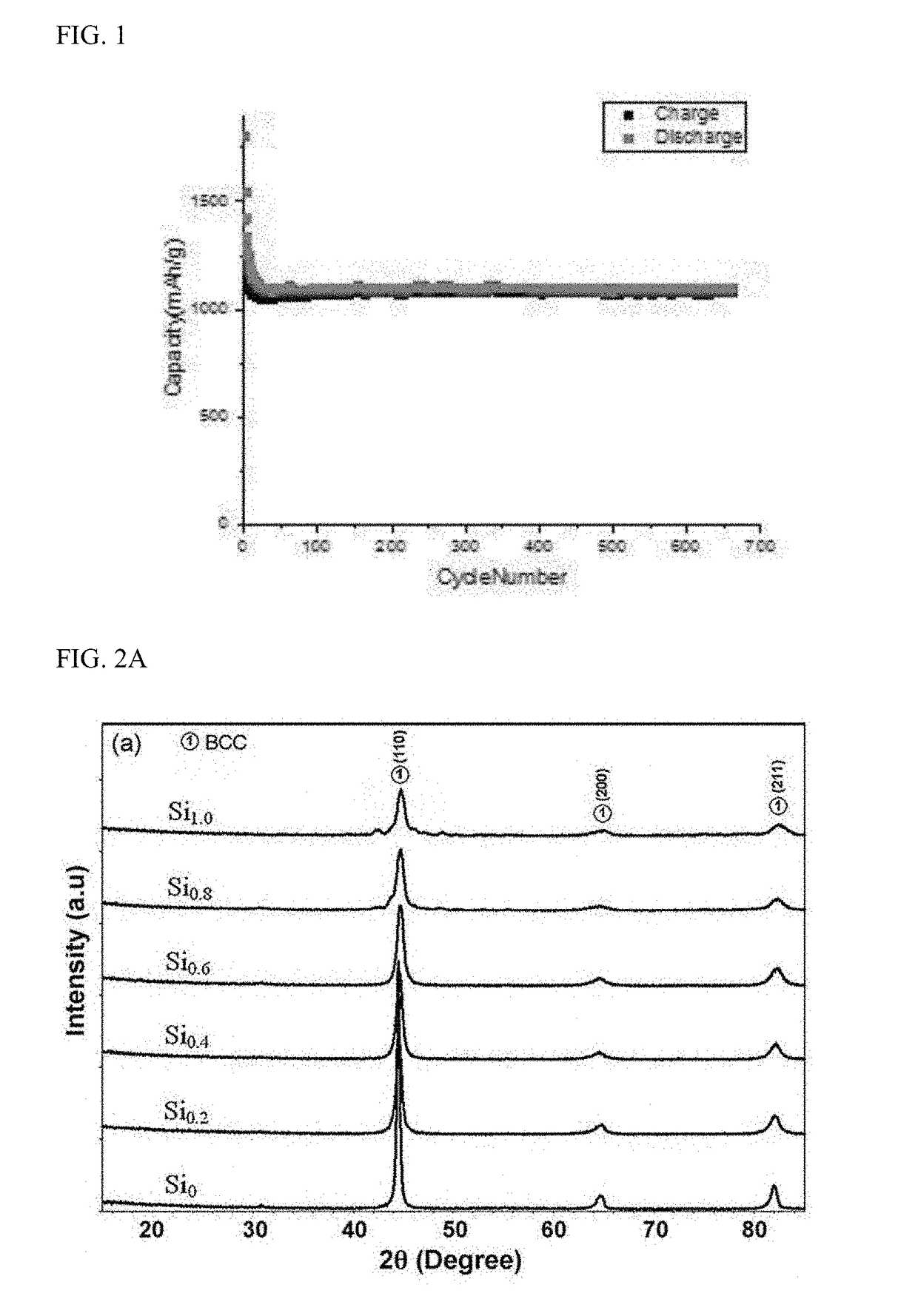
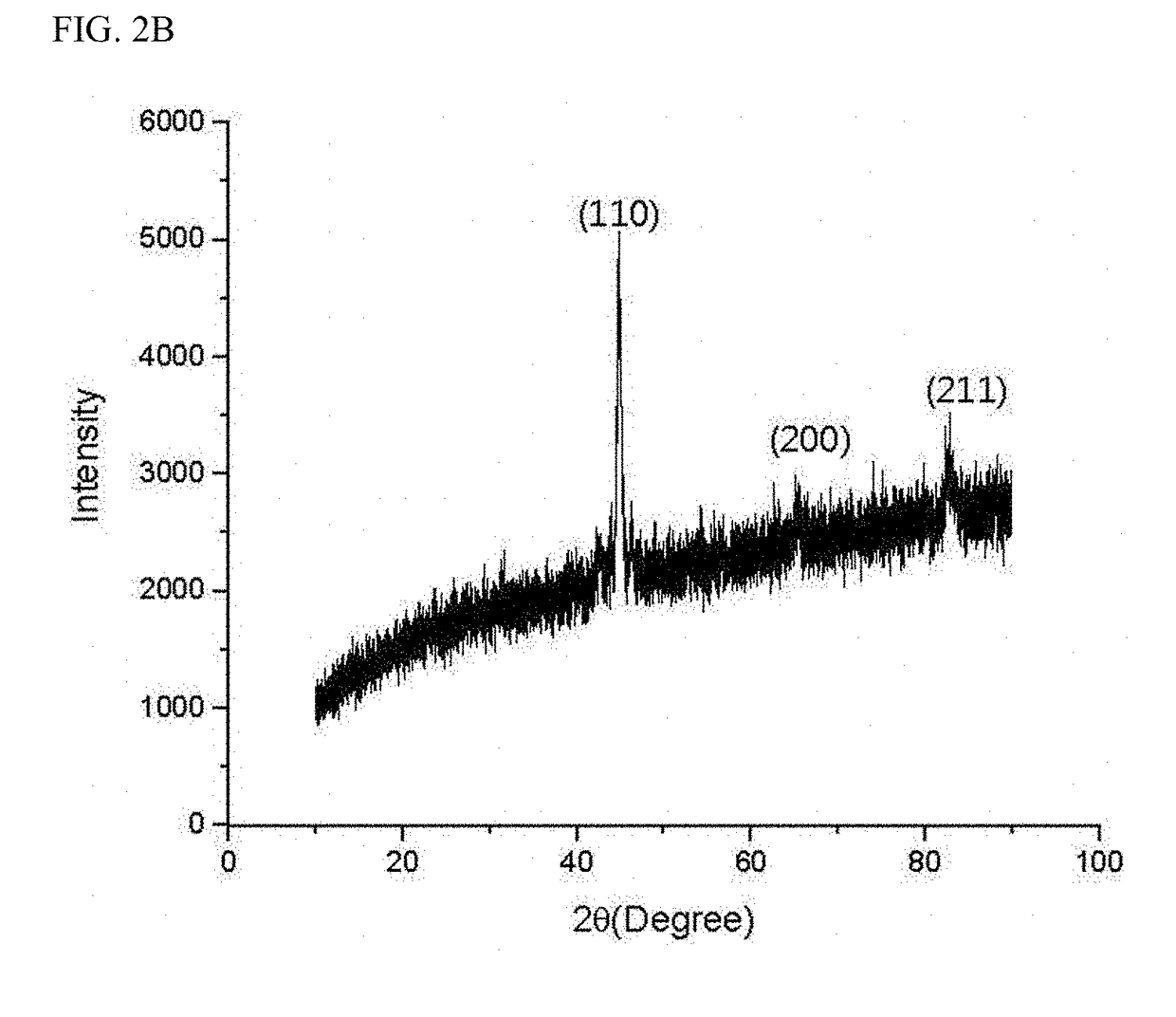
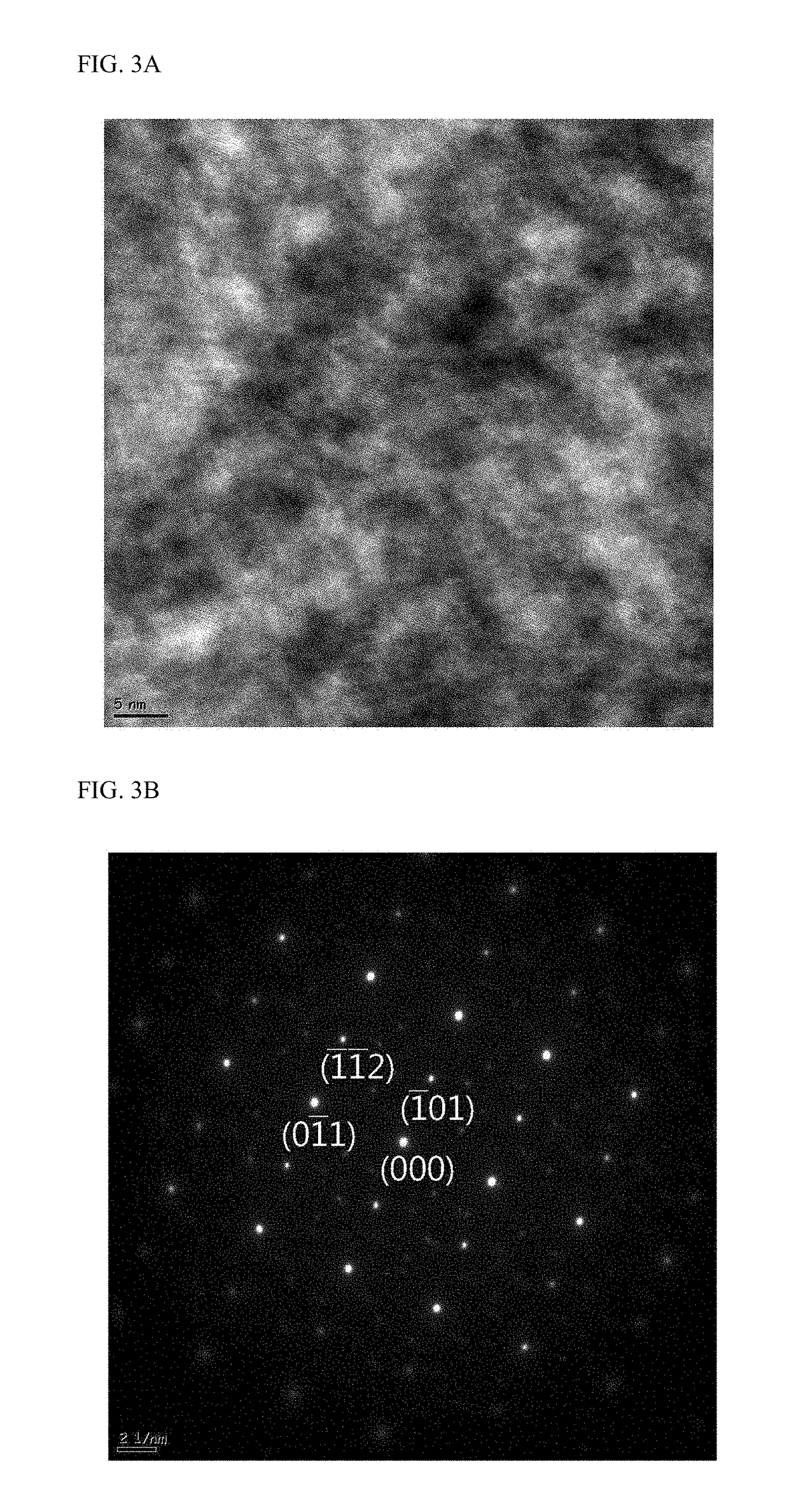
The present invention is related to a material of negative electrode for a lithium secondary battery manufactured by alloying a material which does not form silicon and intermetallic compounds with silicon through the arc melting alloying. More particularly, the present disclosure is related to a material of negative electrode for lithium secondary battery wherein the capacity and life expectancy have been improved by mixing silicon and five or more kinds of metals which do not form an intermetallic compound with silicon to have almost the same atomic ratio in order to improve the volume expansion problem and initial efficiency characteristics of silicon when using silicon as the anode active material of a lithium secondary battery and by applying a buffering action to the volume expansion of the silicon in the charging and discharging process of the electrode through the use of high entropy alloy manufactured by alloying through arc melting.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Preparation method of short-process titanium alloy Ti-Ni-Nb
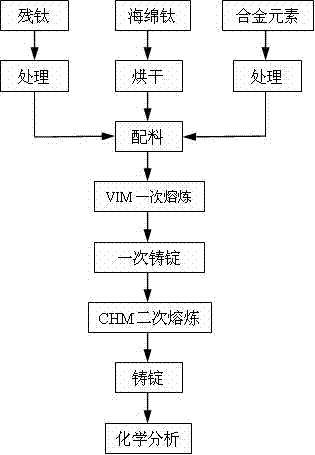
The invention relates to an energy-saving high-efficiency short-procedure process for preparing a high-quality titanium alloy Ti-Ni-Nb. The energy-saving high-efficiency short-procedure process comprises a crucible vacuum induction melting (VIM) technology of titanium and a titanium alloy and a cold hearth melting (CHM) technology of titanium and the titanium alloy. The VIM technology is used for preparing a primarily cast ingot of titanium and the titanium alloy, and replacing vacuum consumable-electrode arc melting (VAR) electrode preparation of an alloy in the traditional preparation process and one-time smelting of the alloy, and the CHM technology is used for carrying out secondary refining of the primarily cast ingot of titanium and the titanium alloy and preparing the cast ingot of titanium and the titanium alloy, in a required shape. According to the energy-saving high-efficiency short-procedure process for preparing the high-quality titanium alloy Ti-Ni-Nb, the preparation procedure of the alloy can be simplified, and high-quality alloy cast ingots of multiple shapes are produced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
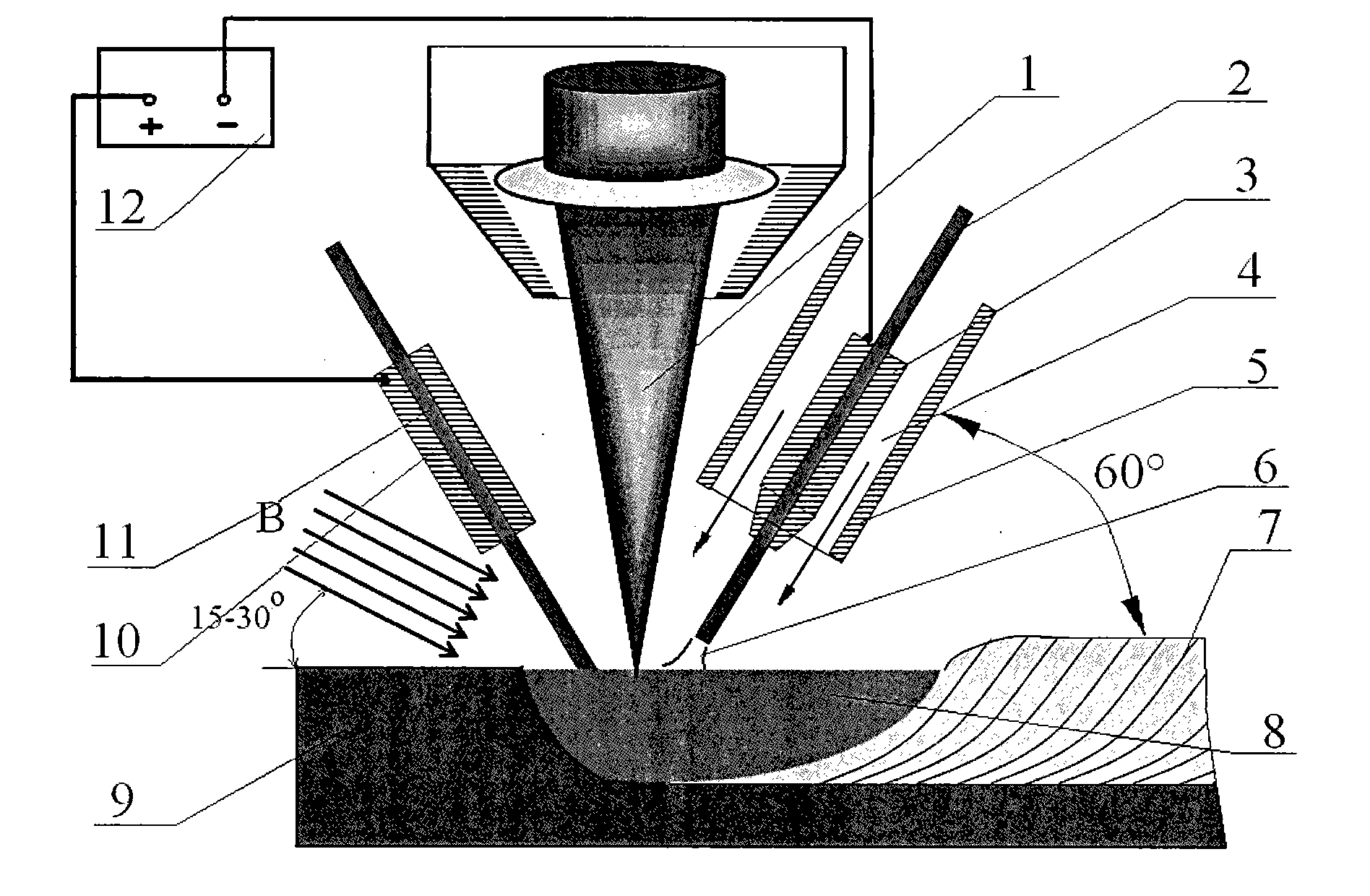
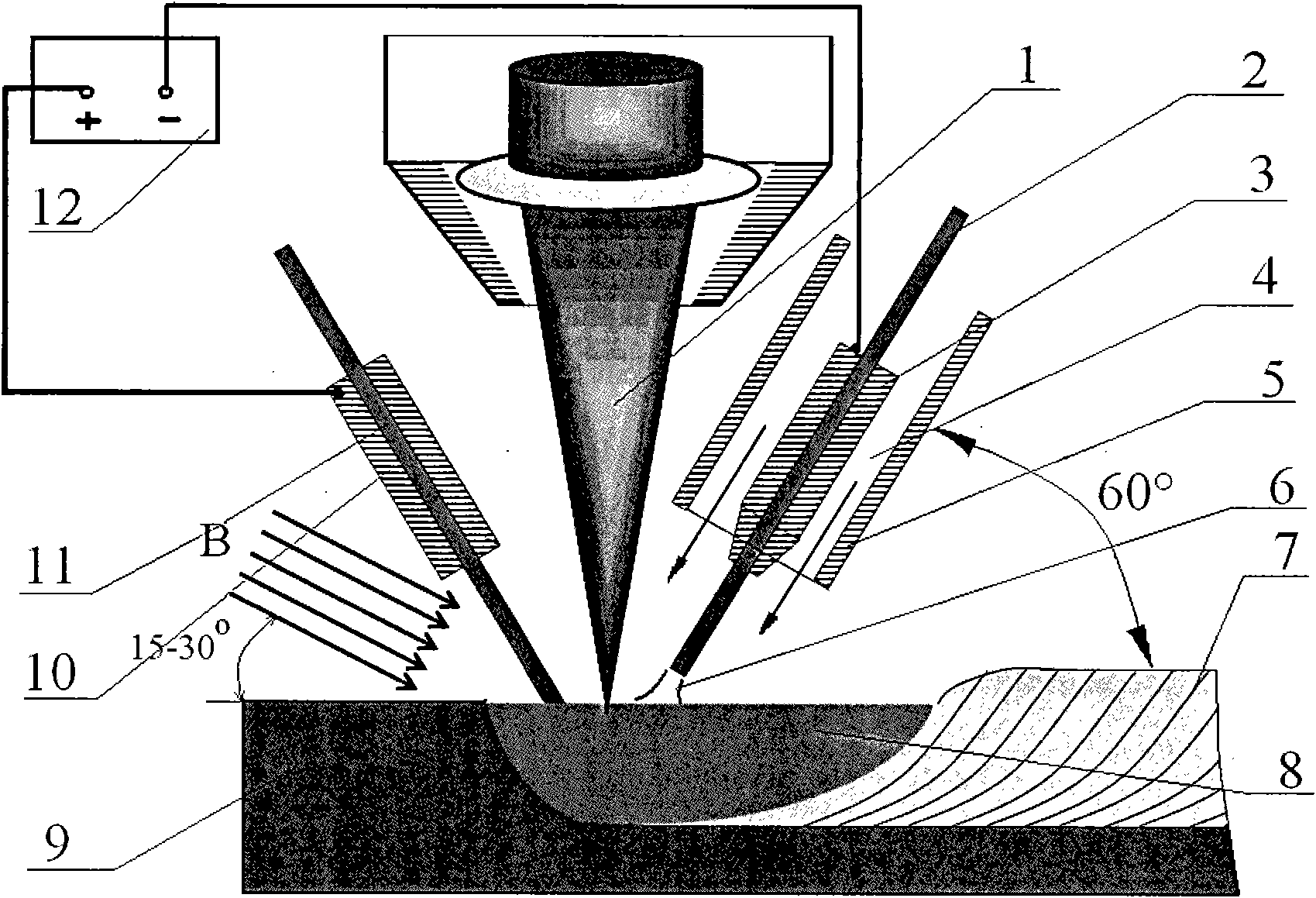
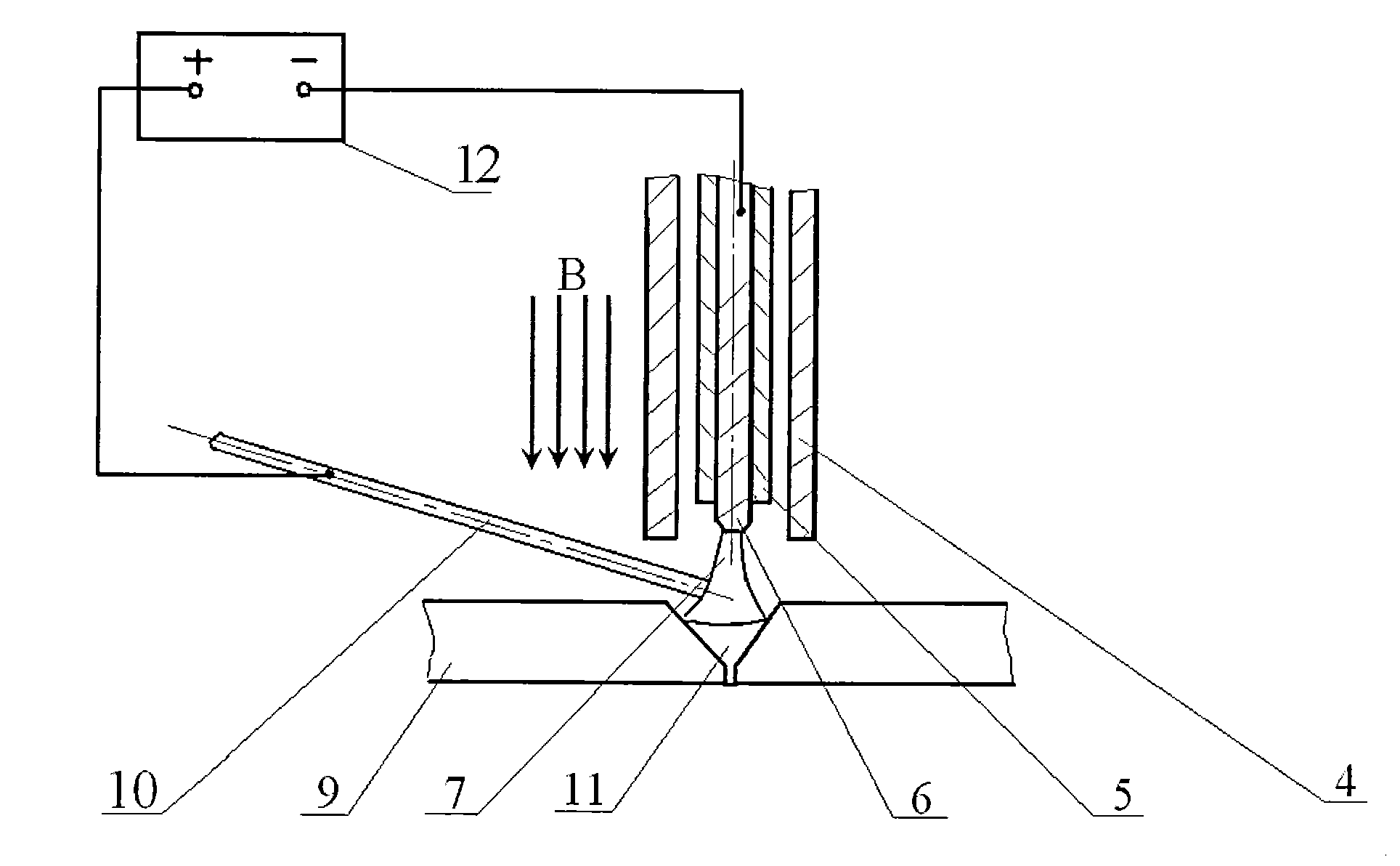
Perforated TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) arc melting brazing method of dissimilar metal
InactiveCN102615398AEvenly distributedReduce temperature gradientArc welding apparatusMelting tankLiquid metal
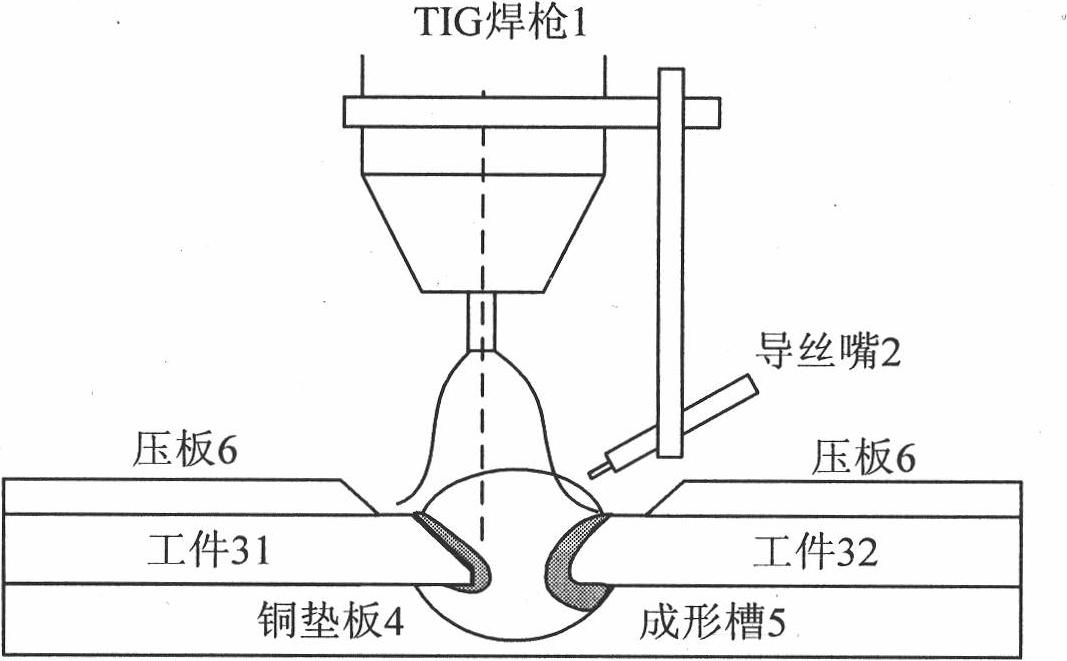
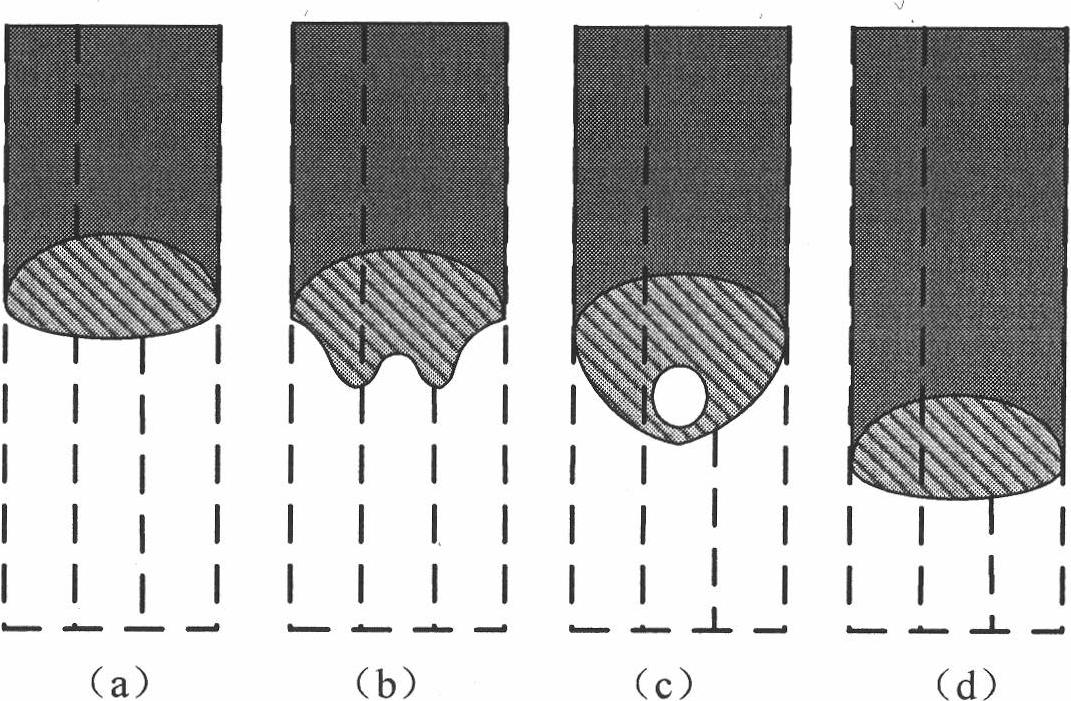
The invention provides a perforated TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) arc melting brazing method of a dissimilar metal. The perforated TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) arc melting brazing method of the dissimilar metal comprises the following steps that: a steel / aluminum or titanium / aluminum plate is clamped by a rigid clamp and a copper base plate to be assembled into butt joints, and the matching between a gap and the size of a molding groove is ensured; a guidewire mouth of a wire feeder and a welding gun are assembled into a whole, the wire feeding angle is 30 to 45 degrees, the wire is fed at a low-melting-point metal side, and the distance between a tungsten electrode and a workpiece is controlled in a range of 2-3mm; after small perforated holes obviously grow up, welding wires are sent to the small perforated holes along the low-melting-point metal side in an inching wire feeding mode, and continuously flow along a groove until a molten pool is spread at the front and back of the groove, and the inching wire filing is continuously carried out after the obvious small perforated holes are formed; and the steps are repeated until the melting brazing process is finished. The plasma pressure in the perforated holes promotes the spreading of liquid metal to the back of a high-melting-point metal to realize one-side welding with back formation. Complex equipment and structure do not exist, the operation is simple, the cost is low, and the process stability is good.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of producing electrode for titanium alloy vacuum consumable smelting directly added with high melting metal
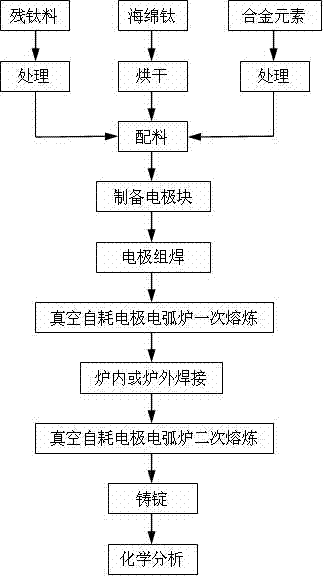
This invented electrode is joint-welded by a directly pressed electrode block with a groove and a high melting point metal bar suitable for the shape of the groove of the electrode block on the basis of conventional preparation of electrodes with Ti alloy vacuum self-cost arc melting.
Owner:西安赛特金属材料开发有限公司
Zirconium based amorphous alloy and manufacture method thereof
The invention discloses a zirconium based amorphous alloy. The amorphous alloy consists of ZraTMbTicBed, wherein a is more than or equal to 20 and is less than or equal to 75; b is more than or equal to 10 and is less than or equal to 50; c is more than or equal to 1 and is less than or equal to 30; d is more than or equal to 10 and is less than or equal to 40; and the sum of a, b, c and d is 100; and TM is two or more than two selected from Cu, Ni, Co, Zn, Nb and Mn. Under protection of inert gas, proportioned alloys are sufficiently alloyed in an arc-melting furnace or an induction melting furnace; and the sufficiently alloyed molten metal is cast or cast by suction in a mould for cooling molding. The invention also provides the zirconium based amorphous alloy and a preparation method thereof. Compared with the prior zirconium based amorphous alloy, bending strength and impact resistance of the zirconium based amorphous alloy provided by the invention are obviously improved (the bending strength of 3,027.50MPa, and impact ductility of 620.578KJ / m<2>), and the zirconium based amorphous alloy has lower requirement on the performance of casting equipment, for example, cooling speed is 10-10<5>k / s, and environment absolute vacuum degree is absolute pressure of vacuum environment of 10<-2>-100Pa, while the hardness of the zirconium based amorphous alloy can reach corresponding requirement.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Processing method of fine-grain superplastic TA15 titanium alloy medium-thickness plate
The invention discloses a processing method of a fine-grain superplastic TA15 titanium alloy medium-thickness plate. The processing method comprises the following steps that 1, vacuum consumable arc melting is carried out to obtain a TA15 titanium alloy cast ingot; 2, after heat preservation, a primary forging stock is obtained through upsetting, drawing, cogging and forging; 3, after heat preservation, a second-stage forging stock is obtained through beta-phase region upsetting and drawing forging; 4, upsetting and drawing forging in an alpha + beta two-phase region is carried out to obtain afourth-stage forging stock; 5, a forge piece is obtained through upsetting, drawing and finish forging; 6, after heat preservation, a first-fire rolled plate blank is obtained through first-fire rolling; 7, after heat preservation, a second-fire rolled plate blank is obtained through second-fire rolling; and 8, the TA15 titanium alloy medium-thickness plate is obtained through annealing treatment. According to the processing method of the fine-grain superplastic TA15 titanium alloy medium-thickness plate, the corresponding deformation temperature is selected and combined with multi-heating-number large-deformation upsetting and drawing forging, so that the TA15 titanium alloy cast ingot with a coarse structure is crushed under the large deformation, driving force is provided for recrystallization, the grain refinement and homogenization degree is improved, and the fine-grain superplasticity TA15 titanium alloy medium-thickness plate is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
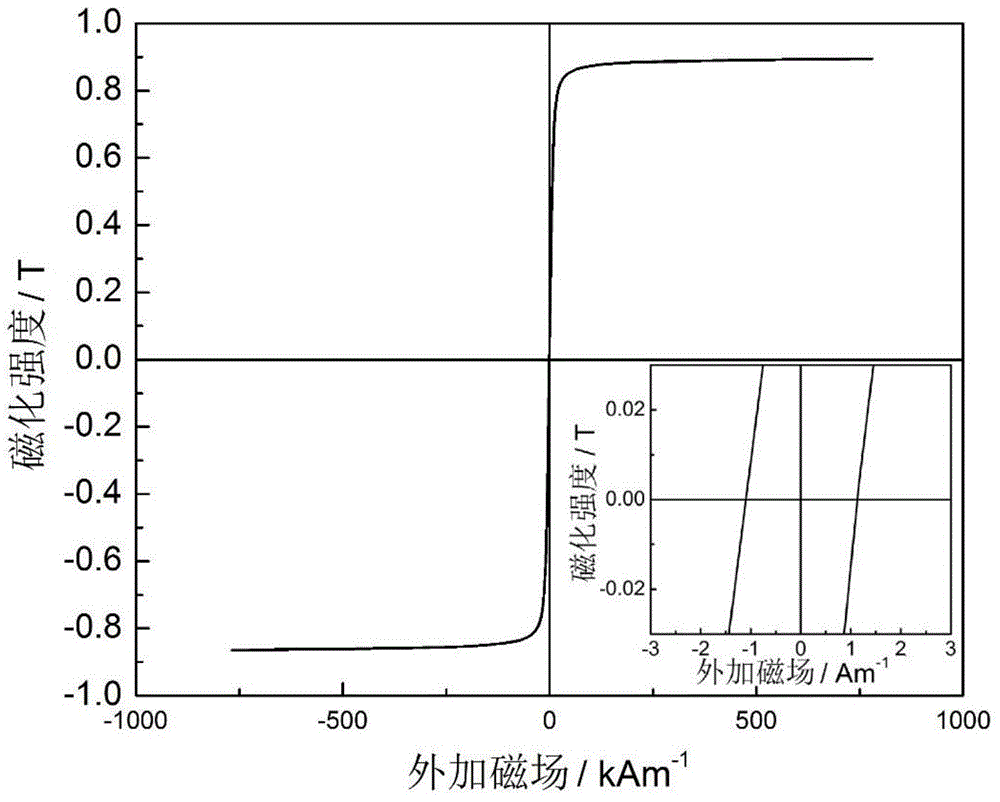
Soft-magnetic high-entropy block amorphous alloy FeCoNiMB and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104878324AEnhanced Amorphous Formation AbilityImprove thermal stabilityMagnetic materialsMagnetizationIngot
The invention provides a soft-magnetic high-entropy block amorphous alloy FeCoNiMB. M represents at least one of P, C and Si elements, and typical compositions include Fe25Co25Ni25Si7.5B17.5, Fe25Co25Ni25Si10B15, Fe25Co25Ni25P5C4Si6B10, Fe25Co25Ni25P12C8B5 and Fe25Co25Ni25P10C10B5. The saturation magnetization of the alloy is 0.80-0.87T, coercivity is 1.1-3.4A / m, and effective magnetic conductivity under 1kHz is 12500-19800. The invention further provides a preparation method of the soft-magnetic high-entropy block amorphous alloy. The preparation method includes preparing a master alloy ingot through arc melting or induction melting, and preparing an amorphous band and an amorphous bar by single-roll melt-spinning and copper-mold casting respectively. The technical blank in preparation of the soft-magnetic high-entropy block amorphous alloy is filled up, and the provided alloy has an application prospect of serving as a soft-magnetic functional device.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
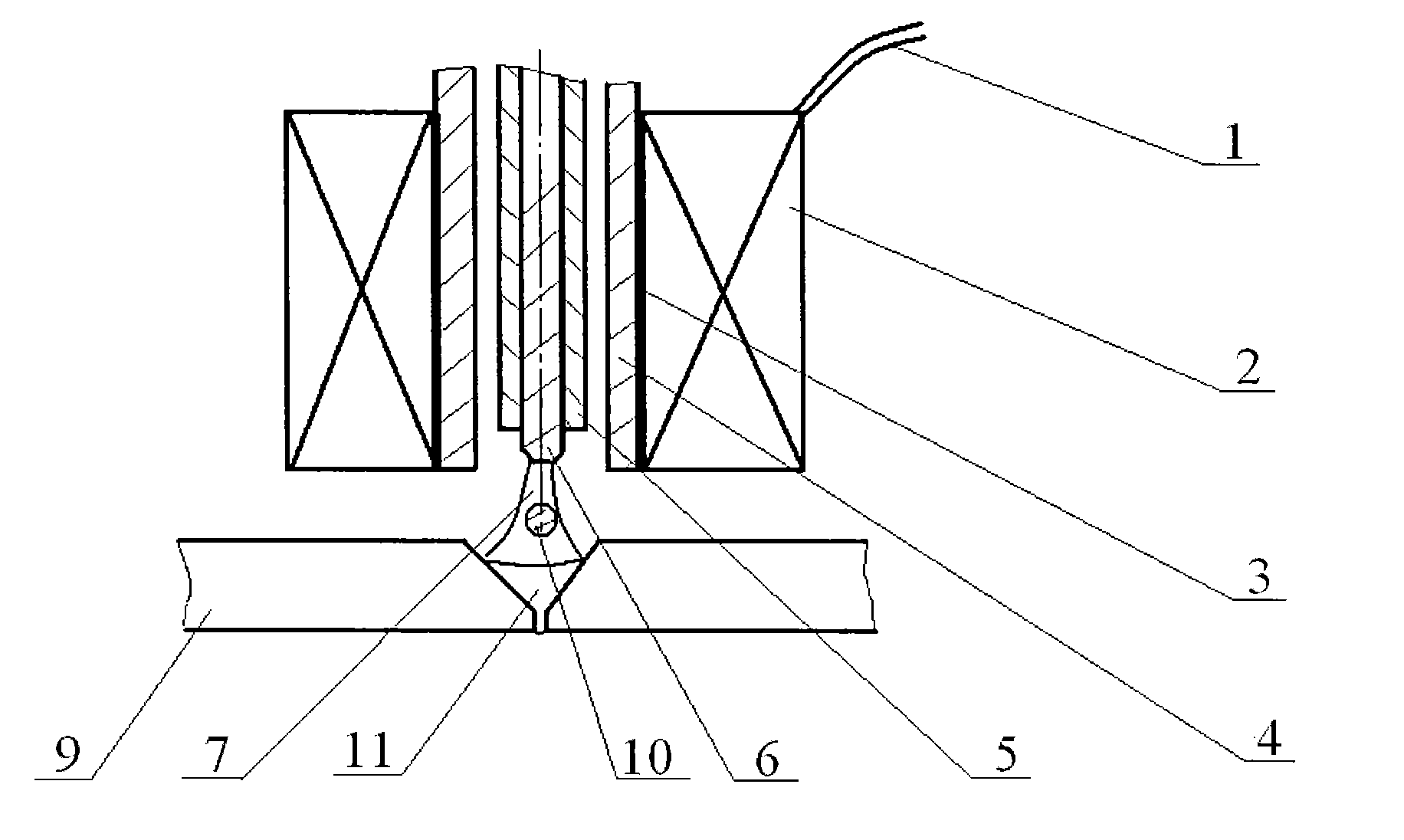
Electromagnetic excited TIG arc melting-brazing hybrid welding method and equipment
InactiveCN101862873AAvoid severe burnsLow heat inputSoldering apparatusMetal working apparatusMetallic materialsWelding defect
The invention discloses an electromagnetic excited TIG arc melting-brazing hybrid welding method and equipment. In addition to the use of the welding zone, an alternating magnetic field is added to control properties of a welding arc, and the assistant effect on the melting bath of the liquid-state brazing filler metal for arc melting-brazing is realized through electromagnetic stirring and excitation and enhancement, thereby promoting the orderly flow of the liquid-state brazing filler metal and the rupture, wetting, spreading and proliferation of the liquid-state brazing filler metal on the surface of the high metal material, improving the full mixing of the liquid-state brazing filler metal and the base metal formed by melting the low-melting-point metal material, improving the uniformity of the components of the brazed weld, reducing welding defects, increasing the welding speed, improving the weld formation, optimizing the structure and performance of the brazed weld, and improving the quality of the brazed joint. Moreover, the equipment has the advantages of simple structure, flexible application, low cost, good effect and easy realization.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for preparing CuCr contact materials by means of vacuum self-consuming arc melting
The invention relates to a method for preparing CuCr contact materials by means of vacuum self-consuming arc melting. The method includes selecting qualified Cu powder and Cr powder, proportionally mixing the Cu powder and the Cr powder with each other to obtain mixtures, compressing the mixtures by the aid of cold isostatic pressures to obtain bars, sintering the bars and carrying out self-consuming melting on the bars to obtain alloy cast ingots; quickly and uniformly melting self-consuming electrodes in a layered manner under the effect of high-temperature arc, dripping the self-consuming electrodes to the bottoms of water-cooled crystallizers, solidifying the CuCr (25%-40%) alloy cast ingots under the matching effects of the molten and dripped self-consuming electrodes and the high cooling speeds of the peripheries of the water-cooled crystallizers so as to obtain uniform and small CuCr alloy structures. The method has the advantages that the CuCr electric contact materials with the Cr content of 25%-40% can be prepared by the aid of vacuum self-consuming arc melting processes and are free of air holes, looseness, inclusion and macroscopic and microscopic defects such as Cu and Cr enrichment, and Cu and Cr microscopic structures are smaller than 30 mu m.
Owner:SHAANXI SIRUI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
CrMoNbTiZr high-entropy alloy material and preparation method thereof
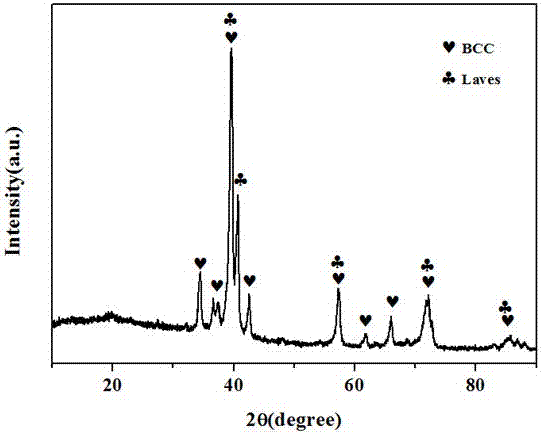
The invention relates to a CrMoNbTiZr high-entropy alloy material and a preparation method of the CrMoNbTiZr high-entropy alloy material. The high-entropy alloy material comprises Cr, Mo, Nb, Ti and Zr, wherein the molar ratio of Cr to Mo to Nb to Ti to Zr is 1:1:1:1:1. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1, powder is prepared, and particularly metal powder is prepared according to the equal molar ratio; 2, powder mixing is carried out, and particularly the prepared powder is mixed to be uniform in a V-shaped powder mixing machine; 3, pressing and block forming are carried out, and particularly the mixed powder is subjected to cold pressing under a pressing machine to form blocks; and alloy is molten, and particularly a vacuum non-consumable arc melting furnace is used for melting the samples which are obtained after the powder is pressed to be blocks. The CrMoNbTiZr high-entropy alloy material mainly comprises a BCC solid solution phase and a small amount of Laves phase, meanwhile has the advantages of being high in hardness, high in corrosion resistance and the like, and has the good application prospect in the field of wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
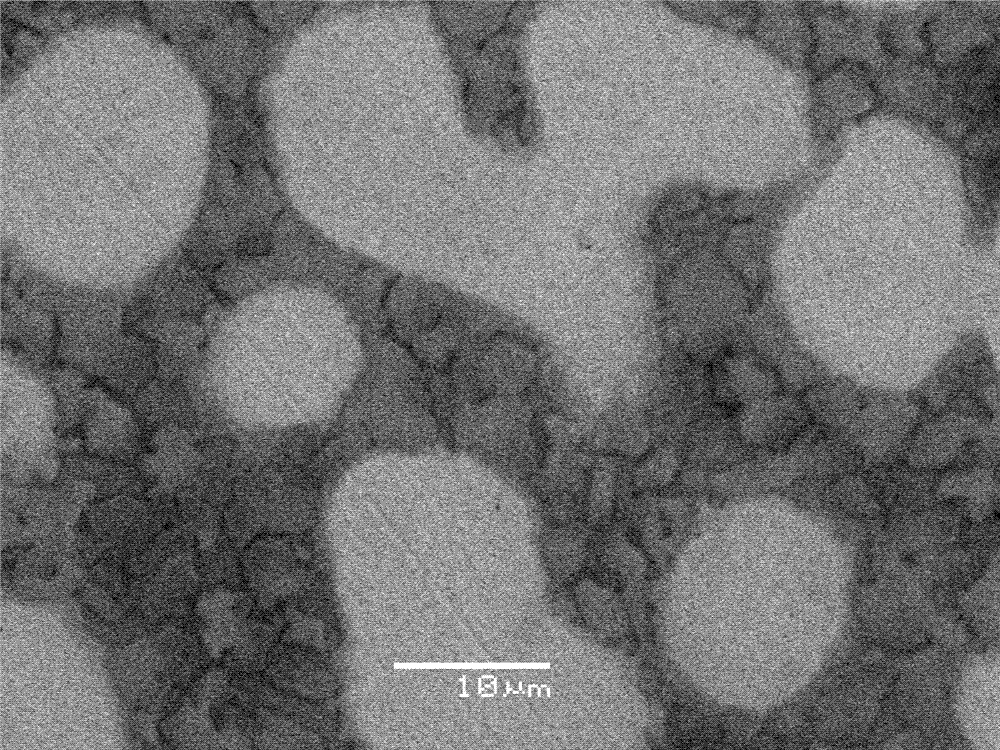
High purity silica crucible by electrolytic refining, and its production method and pulling method
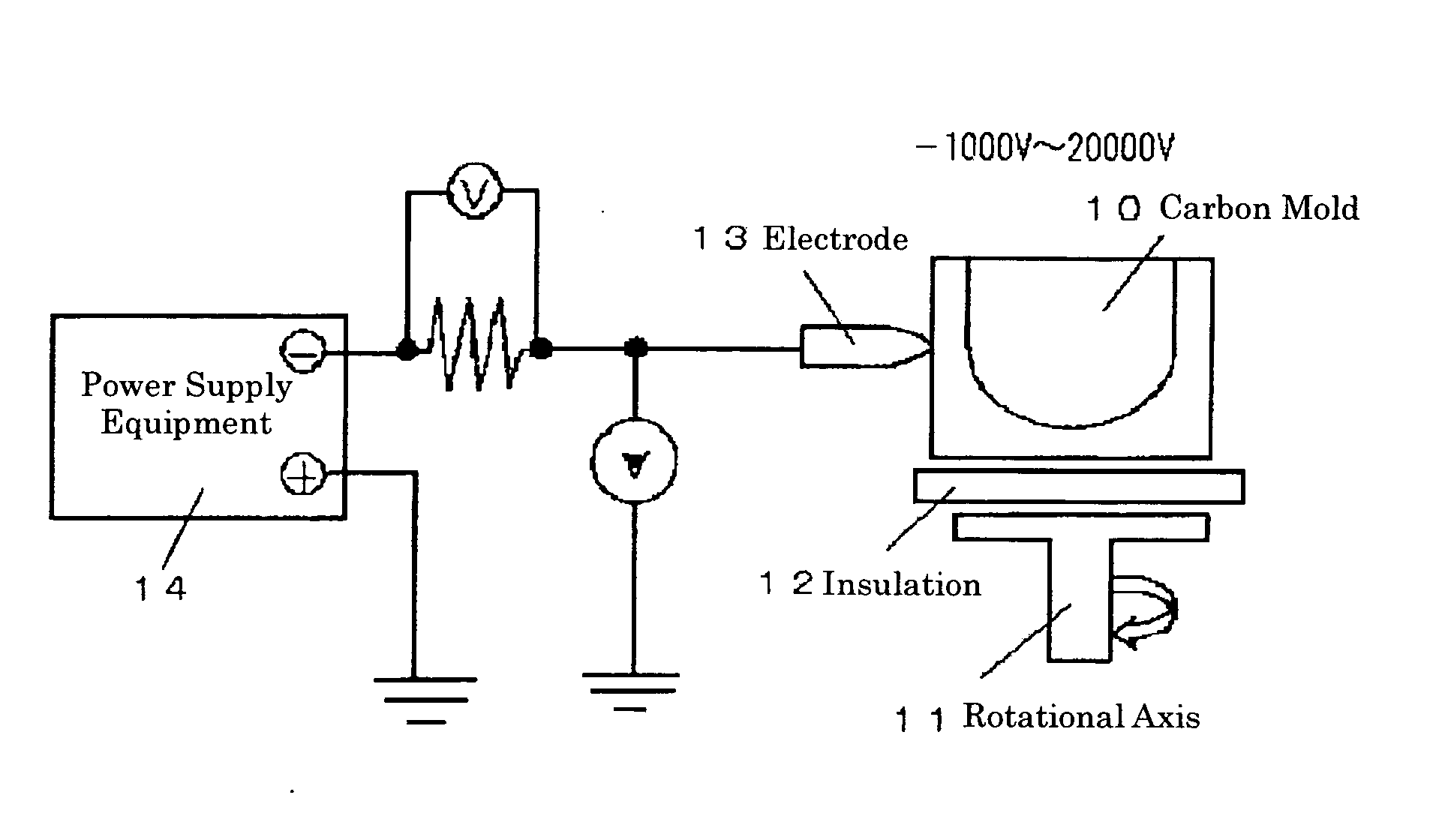
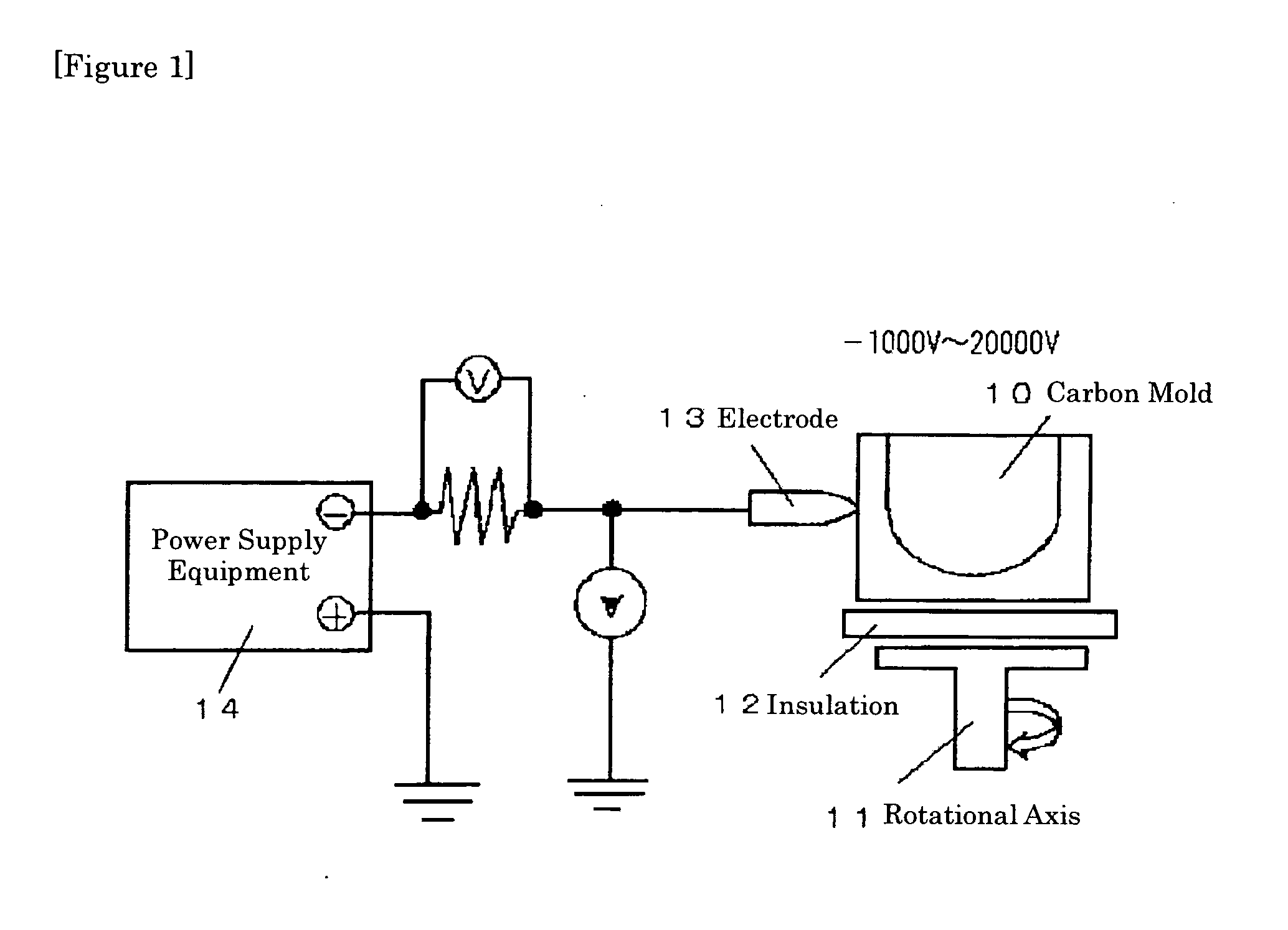
This invention provides a high purity silica crucible having low impurity concentration in its inner portion, and its production method. The crucible, in which at least each content of Na and Li being contained in the depth of 1 mm from the inside surface is less than 0.05 ppm, is given by a production method of a high purity silica glass crucible, wherein a purity of the melted silica powder layer is increased by applying a voltage between a mold and an arc electrode to move impurity metals being contained in the melted silica glass layer to the outside, when the silica crucible is produced by arc plasma heating a raw material powder of silica in an inside surface of a hollow rotary mold. The method comprises, keeping an arc electrode potential of within ±500 V during an arc melting, applying a voltage of from −1000 V to −20000 V to a mold being insulated to the ground, and applying a high voltage to the un-melted silica powder layer of the outside.
Owner:JAPAN SUPER QUARTZ CORP
Plasma arc melting enrichment method and plasma arc melting enrichment device for recycling metal elements of platinum group
InactiveCN102649999AHigh recovery rateFast smelting reductionProcess efficiency improvementSolid carbonMelting tank
The invention relates to a method and a device for recycling metal elements, in particular to a plasma arc melting enrichment method and a plasma arc melting enrichment device for recycling metal elements of a platinum group. The method comprises the steps of: mixing and grinding substances containing metal elements of the platinum group, ferric oxide, solid carbon reducer and fluxing agent in a dry method to be placed into a powder spraying tank, utilizing inert gases and / or reducing gases as carrier gases to convey materials in a suspension way so as to pass through an axial central hole of a graphite electrode of a plasma arc melting furnace adopting a close negative-pressure melting way, directly sending the materials into plasma arc to be reduced and melted and to enter a melting pool, utilizing iron collecting agent to collect and carry the elements of the platinum group so as to pass through a melted slag layer to enter a valuable iron melting layer, discharging glass-status melting slag and valuable iron out of a furnace body after standing, carrying out water quenching and granulating on the melting slag discharged from the furnace body, selecting the valuable iron particles or fine grains of the valuable iron to enter a wet metallurgic procedure together with the discharged valuable iron melting body, and continuously separating and purifying the metal elements of the platinum group.
Owner:HOOTECH
High-temperature-resistant high-entropy alloy material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105112759AHigh temperature fatigue resistanceHas the ability to resist high temperature softeningStatic compressionHigh entropy alloys
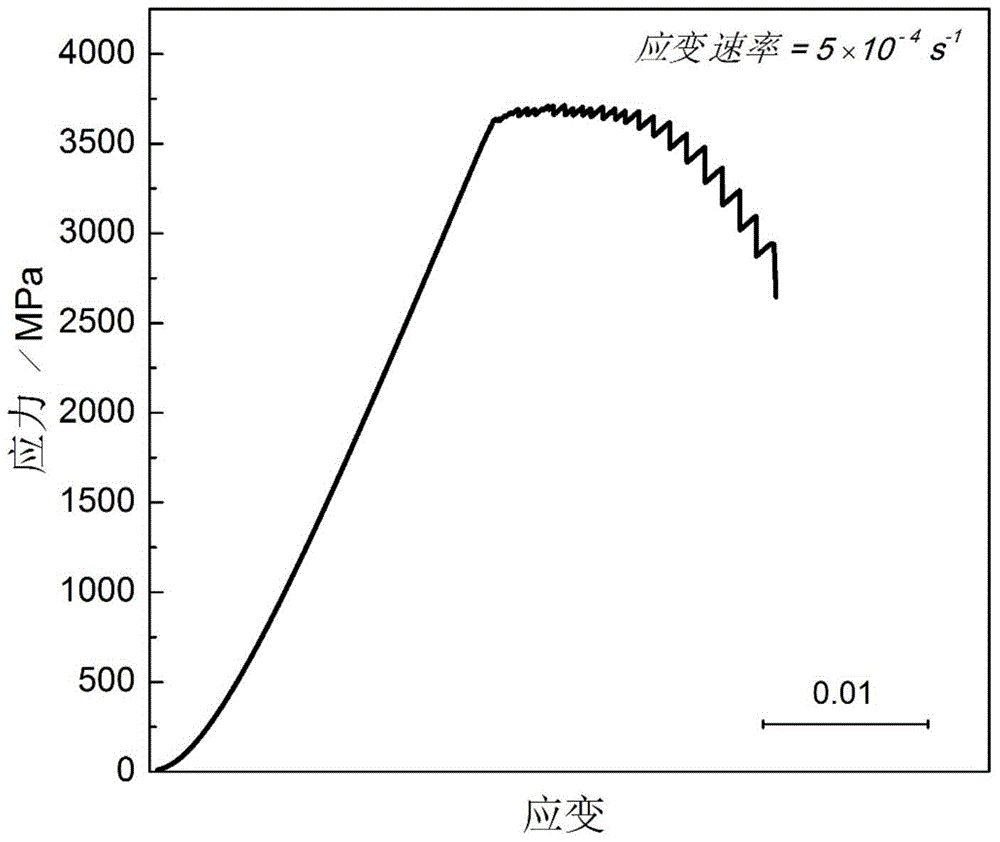
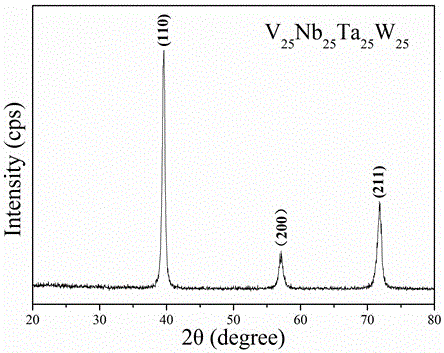
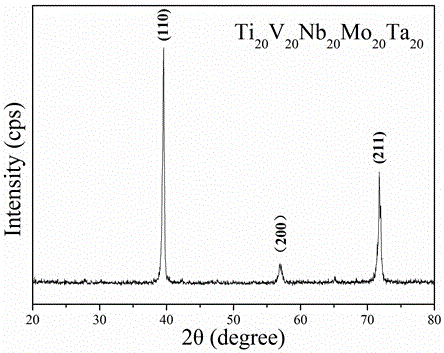
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant high-entropy alloy material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of the alloy materials. The preparation method comprises the steps that four of Ti, V, Nb, Mo, Ta and W are adopted as raw materials; the raw materials are smelted into mother alloy button ingots by a high-vacuum nonconsumable arc melting furnace under high-purity argon shielding; the four button ingots are mounted to be samples in the sizes of phi 20mmx10mm by a metallurgical phase mounting press; the surfaces of the samples are smoothed by 100#, 240#, 400#, 600#, 800#, 1000#, 1200# and 1500# metallurgical phase abrasive paper; then the samples are subjected to mechanical polishing; a crystal structure is determined by an X-ray diffractometer; a scanning electron microscope is used to observe the morphology of a microstructure; a room temperature quasi-static compression performance test is carried out; and the obtained four alloys have higher yield strength and work hardening capacity.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for shaping amorphous alloy thin-wall slim pipe
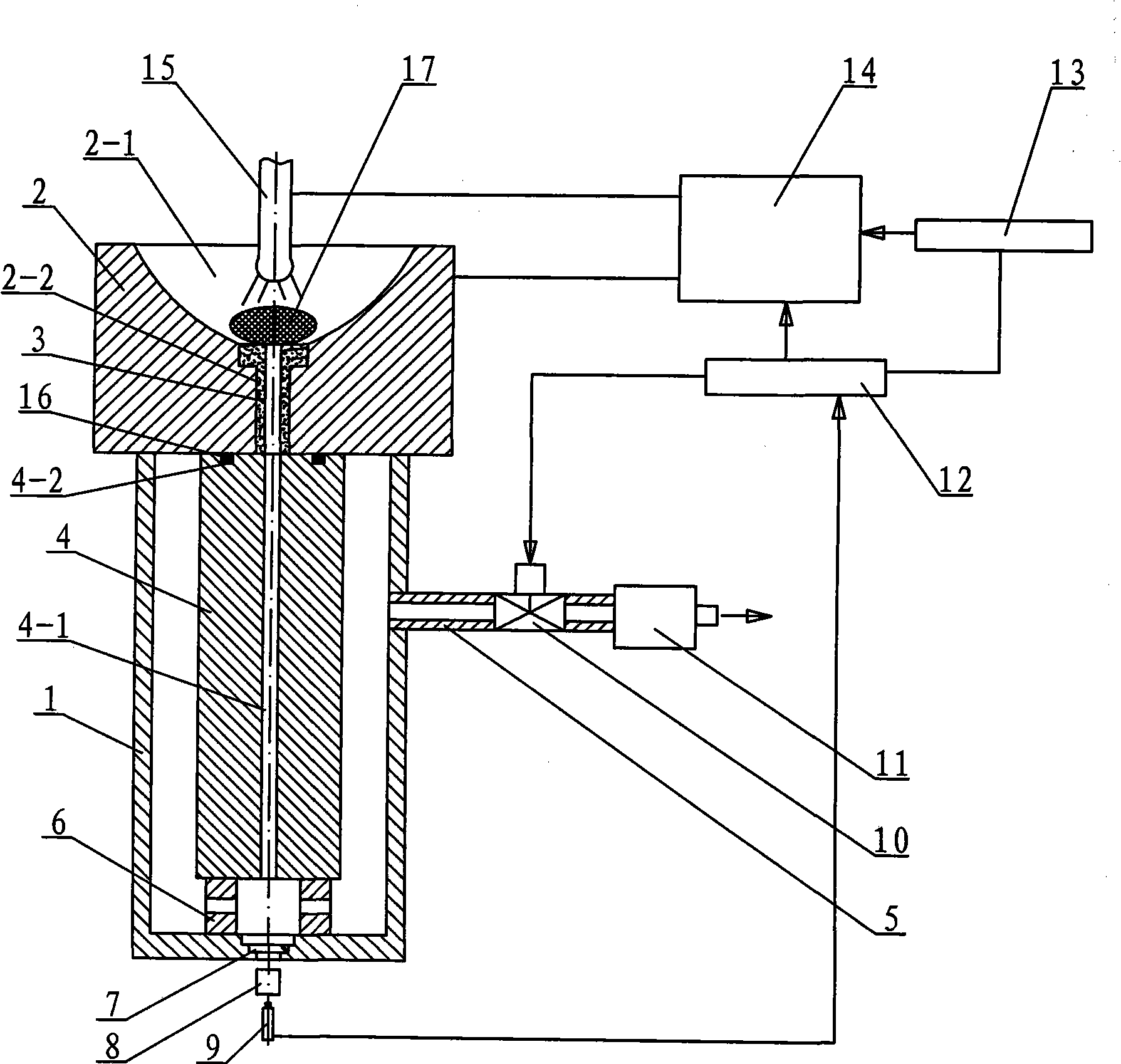
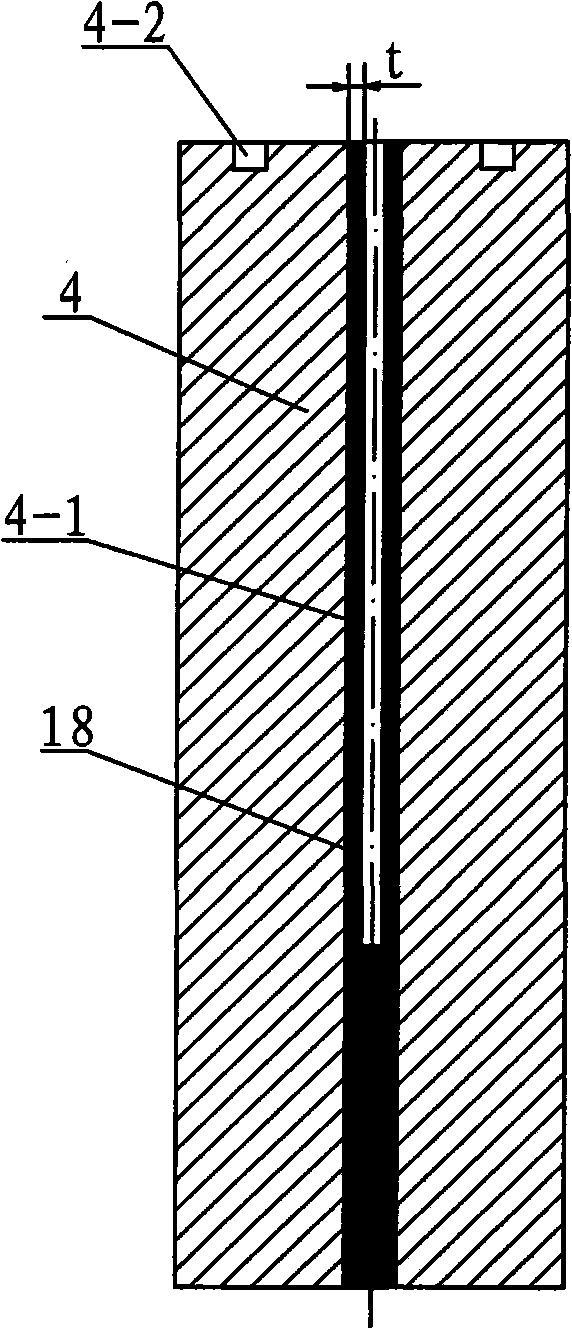
The invention provides a device and a method for shaping an amorphous alloy thin-wall slim pipe, and relates to a device and a method for shaping an amorphous alloy pipe. The invention aims at solving the problems that the thin-wall positions of the prior prepared amorphous alloy pipe can not fill and an inductive crucible easily reacts with the amorphous alloy. The device is a shaping device with a mold cavity, which is formed by the assembly of an arc-melting furnace, a copper crucible, a temperature measuring device, a suction casting valve, a mechanical pump, a tungsten electrode, a metal mold, a suction casting controller and a melting current controller. The method comprises the following steps: an alloy ingot is input; the vacuum degree is 5.0*10<-3>-6.0*10<-3>Pa; the melting current is 250-400A; and when the bottom temperature of the alloy ingot is more than the liquid-phase temperature, the suction casting controller opens the suction casting valve, the mechanical pump draws the air out of the inner cavity of the arc-melting furnace, the alloy liquid flows into the mold cavity, the alloy liquid in contact with the side wall forms a very thin metal scull on the side wall of the mold cavity, and the unsolidified alloy liquid in the center is drawn out of the mold. The invention is used for shaping of the slim alloy pipe.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
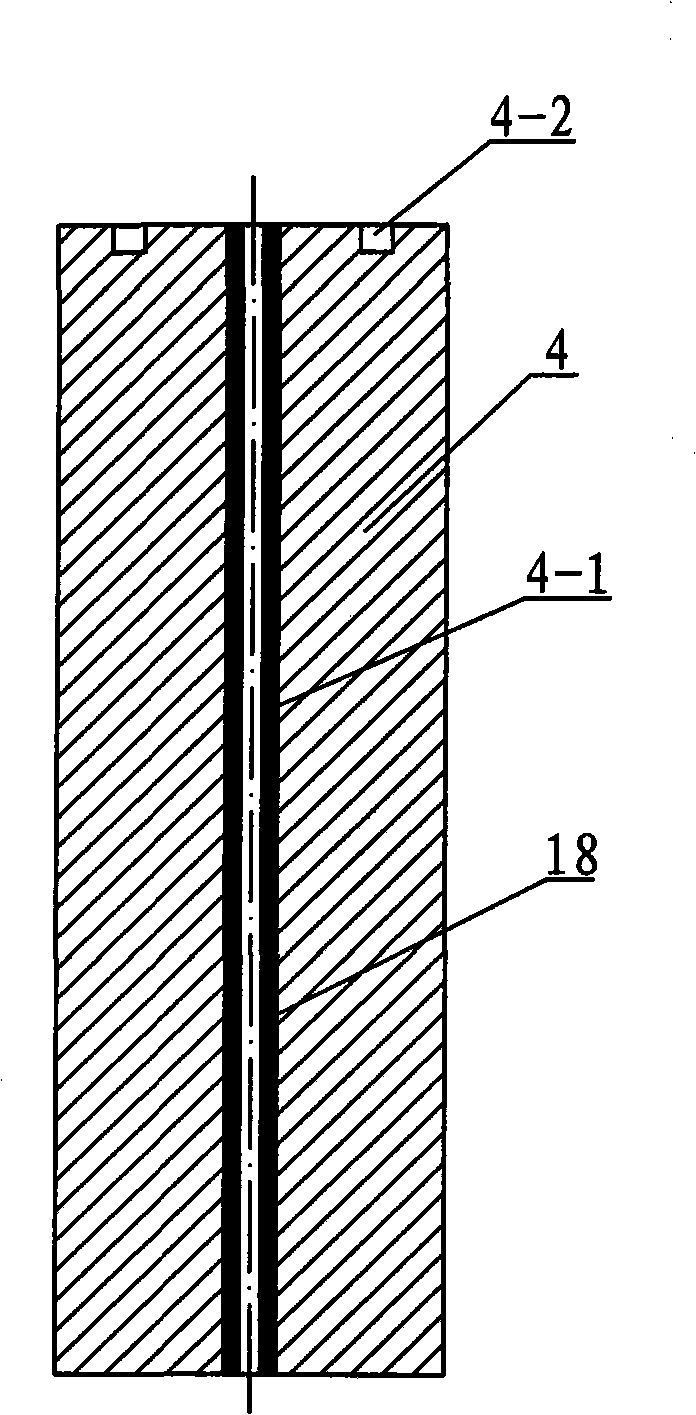
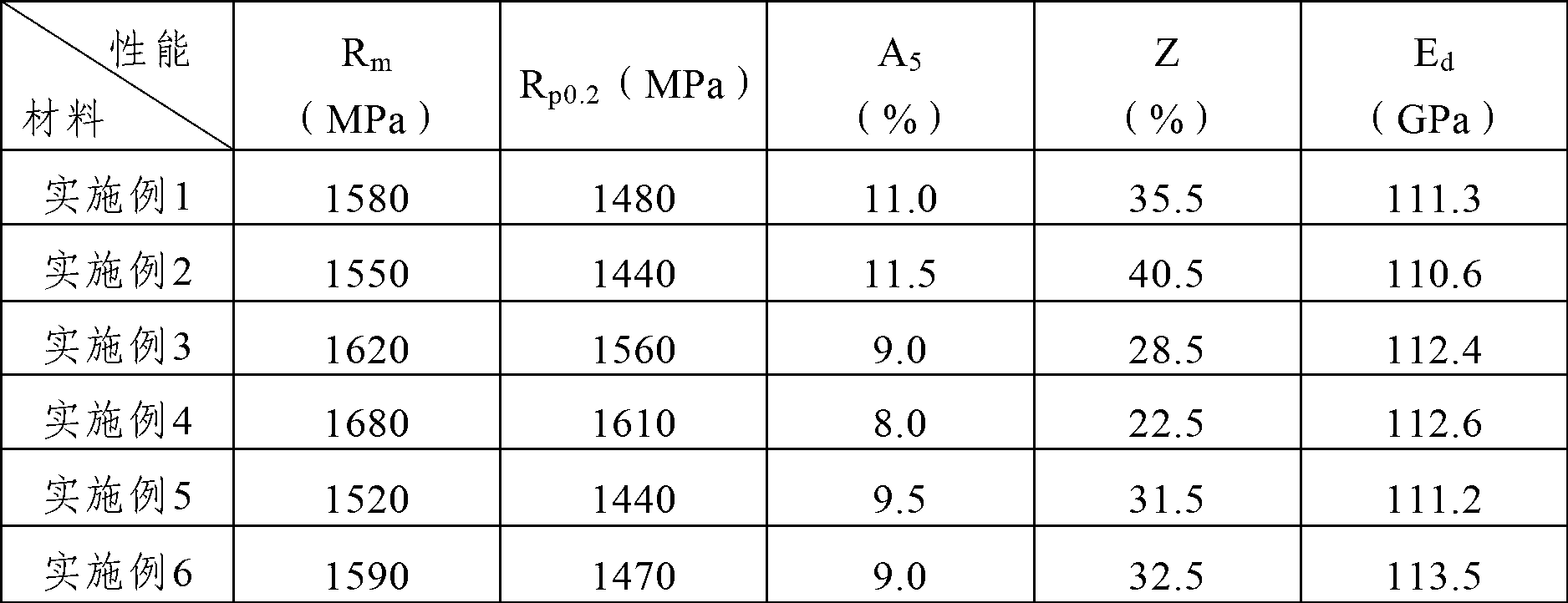
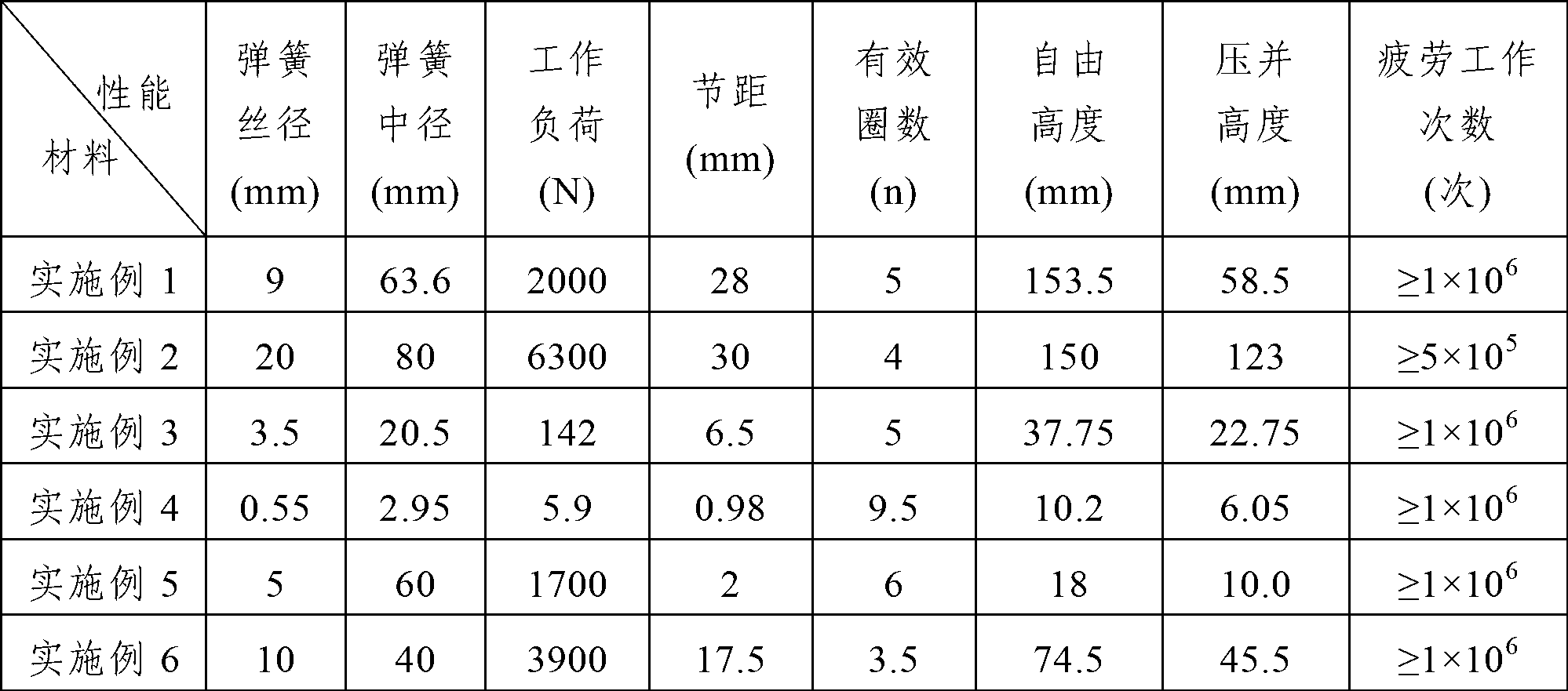
Titanium alloy for spring parts and preparation method of alloy
The invention provides a titanium alloy for spring parts. The titanium alloy comprises the following components in mass ratio: 2.0-4.0% of aluminum, 2.0-4.0% of molybdenum, 2.0-4.0% of vanadium, 2.0-4.0% of chromium, 2.5-4.0% of ferrum and the balance being titanium and unavoidable impurities. The invention also provides a preparation method of the titanium alloy. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing raw materials according to mass ratio and pressing the raw materials into a consumable electrode, and carrying out vacuum consumable arc melting for three times to obtain an ingot, (2) carrying out cogging forging on the ingot and carrying out forming forging or forming processing to obtain a bar billet, and (3) carrying out solid solution and aging treatment on the bar billet to obtain the titanium alloy for spring parts. The titanium alloy for spring parts is simple, practicable, low in cost and suitable for large-scale industrial production, and has excellent mechanical properties; and the prepared spring parts have fatigue life greater than or equal to 5*105 times and are stable in performance, and the industrial production is easy to realize.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
High-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108642362AImprove high temperature strengthSolve bad plasticityHigh entropy alloysRoom temperature
The invention discloses a high-entropy alloy. The high-entropy alloy comprises Cr, Fe, Co, Ni and Ta at the non-equal atomic ratio. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the high-entropy alloy. The preparation method comprises the steps of weighing Ta blocks, Co blocks, Cr blocks, Ni blocks and Fe blocks according to the stoichiometric ratio of the alloy elements; then, smeltingthe weighed raw materials in an arc-melting furnace, and obtaining the high-entropy alloy upon completion of smelting. The high-entropy alloy has excellent compression performance at high temperature,and higher plasticity at room temperature as well as excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, and meets the requirement of application to aerospace materials.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Single crystal anatase titanium dioxide nano-tube array and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103225104AGood electron transport propertiesPromote absorptionFrom normal temperature solutionsNanotechnologyUltraviolet lightsSingle crystal
The present invention discloses a single crystal anatase titanium dioxide nano-tube array and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises: adopting an electrical arc melting method to prepare a TiNbZr alloy; carrying out burnishing, washing and drying on the matrix alloy; adopting the dried matrix alloy as an anode, adopting a Pt sheet as a cathode, and carrying out anode oxidation for 0.5-20 h at a room temperature, wherein a voltage is 10-100 V; placing the prepared nanometer titanium dioxide nano-tube array and the matrix alloy in a muffle furnace to carry out a heat treatment in air; and finally adopting hydrofluoric acid steam to remove an amorphous layer and the matrix alloy to obtain the single crystal anatase titanium dioxide nano-tube array. The single crystal anatase titanium dioxide nano-tube array has good cell compatibility and a visible ultraviolet light absorption performance. The preparation method has characteristics of strong controllability, high efficiency and simple operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing quartz glass crucible
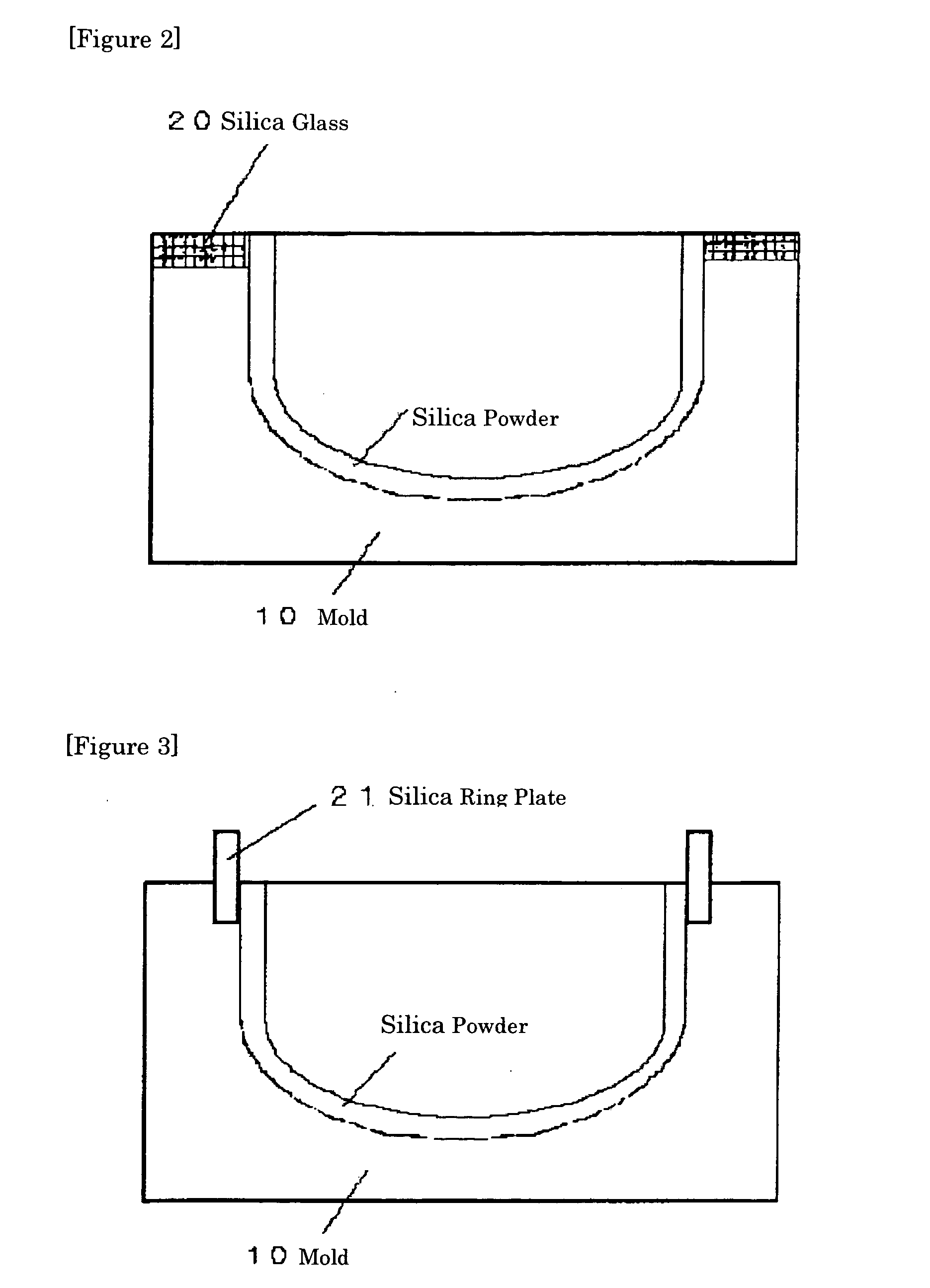
ActiveUS20100005836A1Uniformly formedIncrease vacuumAfter-treatment apparatusBy pulling from meltCrucibleSingle crystal
A method of producing a quartz glass crucible by arc melting a quartz powder molded product loaded on the inner side of a mold while performing vacuum suction, includes initiating the melting of quartz powder from the rim edge of a quartz powder molded product, subsequently lowering the arc electrode or raising the mold to heat and melt the sections on the downside of the rim edge. The method is preferably carried out such that the inner surface of the crucible is sealed within a time corresponding to 10% of the total arc time starting from the initiation of arc melting, and the seal thickness is 3 mm or less. The quartz glass crucible thus produced is useful for the pulling up of silicon single crystals and has a uniform glass layer with fewer internal bubbles.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Method for preparing CuWCr composite material in consumable electrode arc-melting furnace
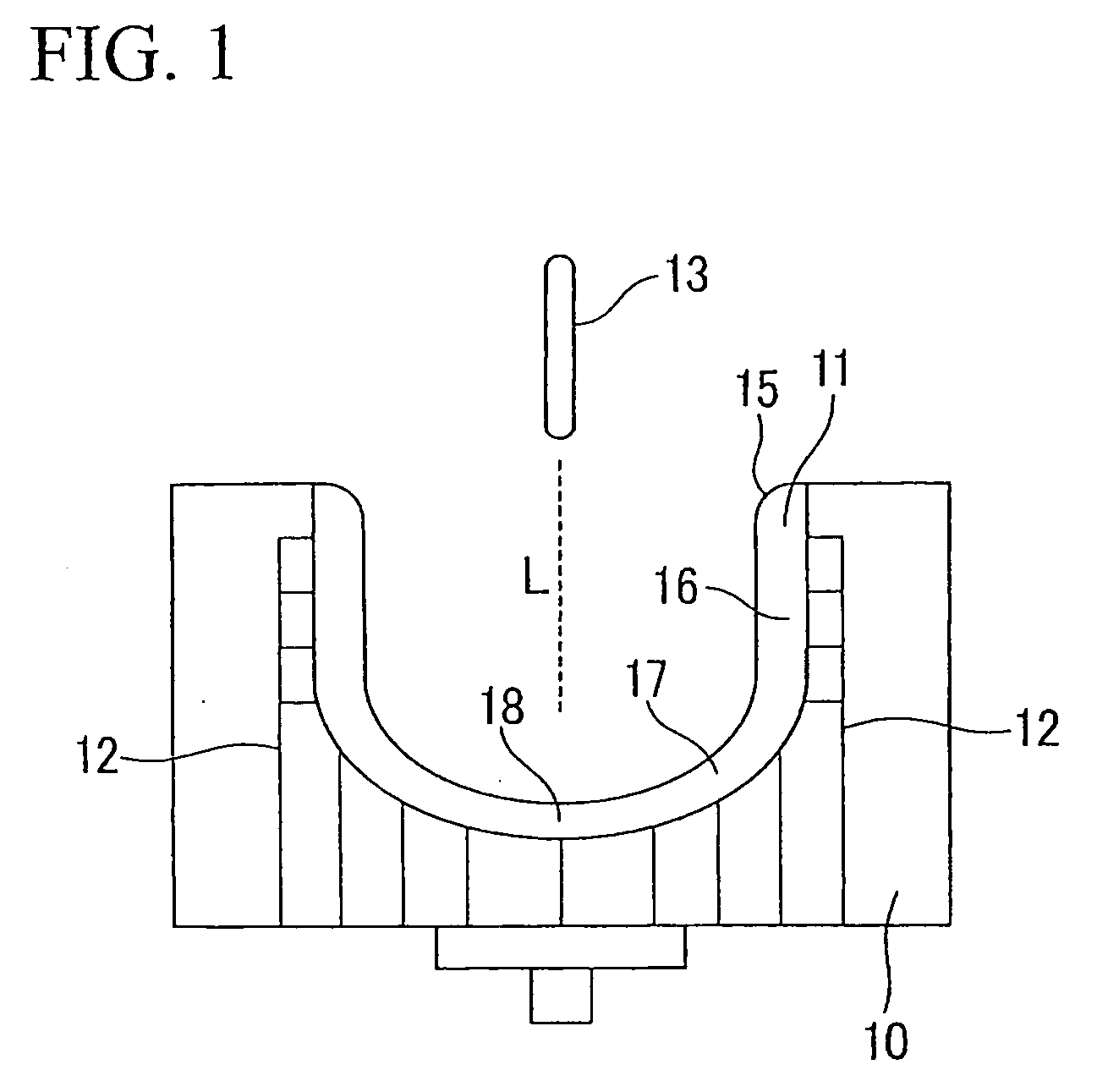
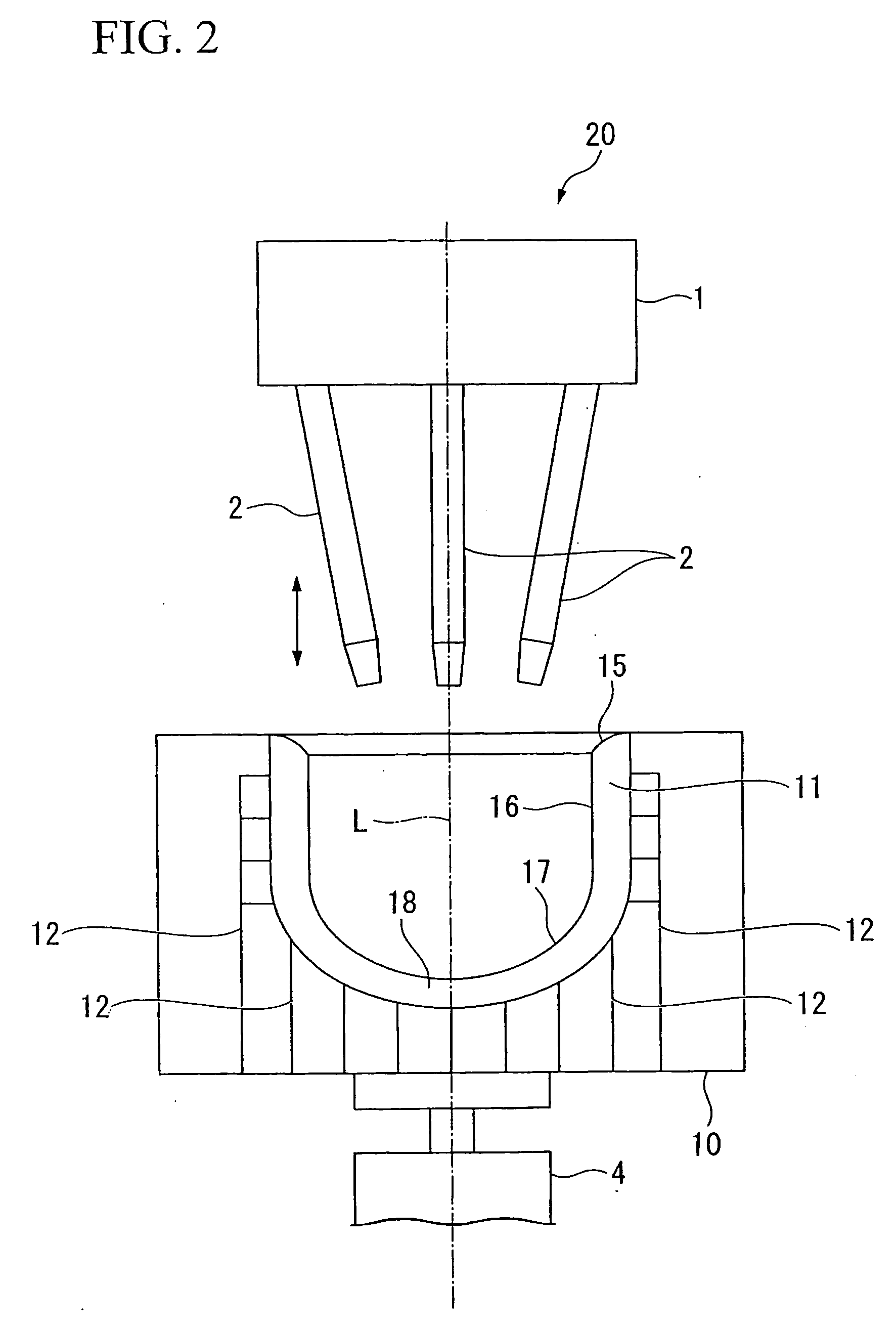
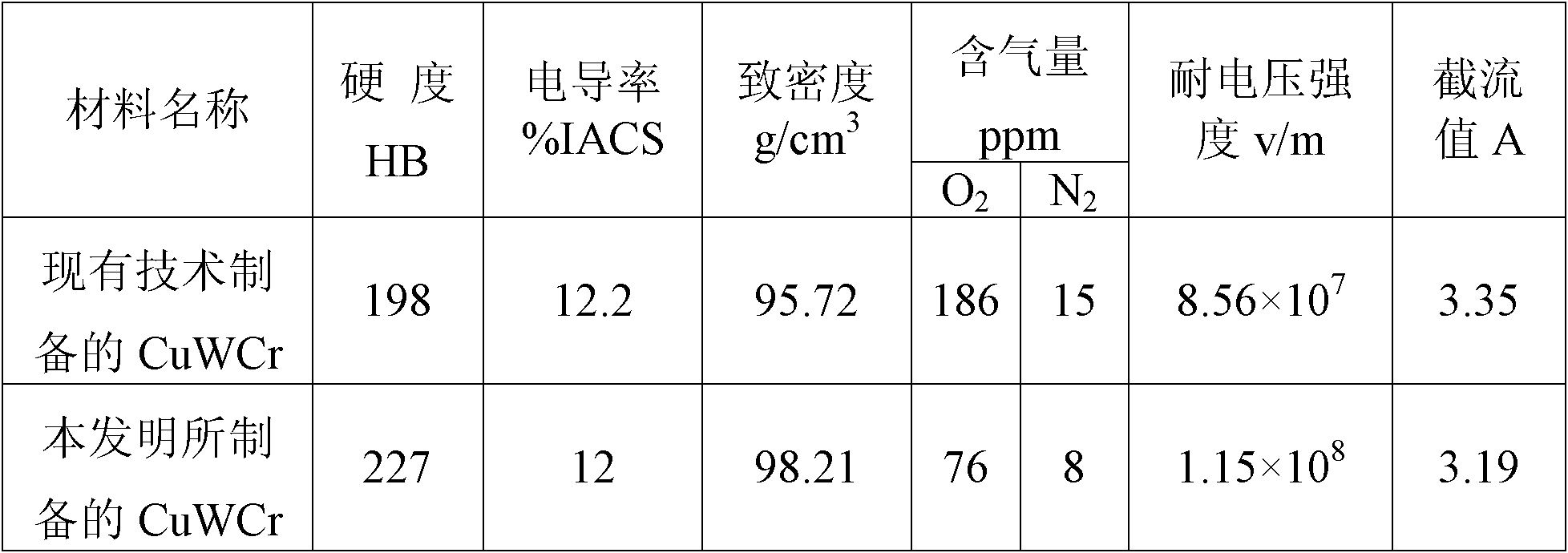
The invention discloses a method for preparing a CuWCr composite material in a consumable electrode arc-melting furnace, which comprises the following steps: mixing Cu powder, W powder and Cr powder in mass percents in a mixer, and carrying out die pressing or cold isostatic pressing on the mixed powder; putting the pressed blank in a vacuum sintering furnace, and heating to 950-1050 DEG C to sinter the pressed blank in a vacuum environment of which the vacuum degree is higher than 10<-2>Pa, thereby obtaining a CuWCr sintered blank; and finally, putting the CuWCr sintered blank in a vacuum consumable electrode arc-melting furnace, melting in a vacuum environment until the CuWCr blank is melted to drop in a water-cooled copper crucible, and taking out the CuWCr composite material after cooling. The invention combines melting and directional solidification to prepare the CuWCr composite material which has uniform and fine structure, high voltage strength resistance, high density, low gas content, fewer impurities and other comprehensive properties.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Low-elastic-modulus high-strength titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a low-elastic-modulus high-strength titanium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy comprises 18 at% of niobium, 0-9 at% of zirconium, 0-9 at% of hafnium and the balance of titanium, wherein the sum of the zirconium and hafnium is 0-9 at%. The preparation method comprises the following steps: smelting in a vacuum consumable / non-consumable arc-melting furnace to obtain a Ti-Nb-Zr(Hf) cast ingot, carrying out homogenizing treatment on the cast ingot, cogging, forging, carrying out intermediate forging, gradually cooling to 900 DEG C from 1000 DEG C to obtain an intermediate plate blank, carrying out solution treatment on the plate blank, and cooling to obtain a structure with orthorhombic martensite phase and residual beta-phase in a certain ratio; and carrying out cold-rolling until the amount of deformation is greater than 60%, thereby obtaining the low-elastic-modulus high-strength titanium alloy plate, of which the elastic modulus is 50-60 GPa, the rolling-direction tensile strength at room temperature exceeds 850 MPa and the elongation percentage is 6-15%. The alloy disclosed by the invention can be widely used in spectacle frames, sports equipment and biomedical devices.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
AlCoCrFeMn high-entropy alloy with non-equal atomic ratio and preparation method of AlCoCrFeMn high-entropy alloy
ActiveCN111235454AHigh strengthGood thermal stability at high temperatureHigh entropy alloysAl element
The invention discloses an AlCoCrFeMn high-entropy alloy with a non-equal atomic ratio and a preparation method of the AlCoCrFeMn high-entropy alloy. The atomic ratio of all elements of Al to Co to Crto Fe to Mn in the high-entropy alloy is equal to (0.3-0.7): to 2 to 1 to 1 to 1. The preparation method comprises the following steps that (1) a raw material is taken in proportion, and cleaning anddrying are conducted; (2) the raw material is put into a non-consumable arc melting furnace, vacuumizing is conducted and protective gas is added; (3) Ti which is arranged in the furnace in advance is firstly smelted, then the raw material is smelted, and suction casting is conducted by using a copper mold to form an alloy ingot; (4) the alloy ingot is subjected to solid solution, water quenchingand rolling deformation; and (5) the deformed alloy ingot is annealed to obtain the AlCoCrFeMn high-entropy alloy with the unequal atomic ratio. According to the AlCoCrFeMn high-entropy alloy with the non-equal atomic ratio and the preparation method of the AlCoCrFeMn high-entropy alloy, by adding a certain amount of Co element, the strength of the high-entropy alloy is improved, the content of the Co element is increased, and the alloy has good thermal stability; and the plasticity of the high-entropy alloy is adjusted by adding a certain amount of Al element, and the prepared high-entropy alloy has good strength and plasticity.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing copper and chromium 50 electric contact material by utilizing vacuum arc remelting furnace
ActiveCN108441670ASmall particle sizeEvenly distributedTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusVacuum arc remeltingImpurity
The invention relates to a method for preparing a copper and chromium 50 electric contact material by utilizing a vacuum arc remelting furnace. Copper powder with particle diameter ranging from 0.01 micron to 1 micro, and chromium powder with particle diameter ranging from 0.01 micron to 1 micro are prepared with a new method, and are smaller in particle diameter compared with the copper powder and the chromium powder used in the prior art. The prepared copper powder and chromium powder are chosen to be mixed according to certain proportion, the mixer is pressed into material bars by using cold isostatic pressing, and the material bars carry out consumable electrode arc melting after being sintered to form alloy ingots. Under the action of a high-temperature electric arc, a consumable electrode carries out layered melting quickly and evenly and drops to the bottom of a water cooling crystallizer, and because of the large cooling rate on the periphery of the crystallizer furthermore, itis realized that Cu and Cr alloy ingots solidify, and then uniform and fine Cu and Cr alloy structures are obtained, wherein the content of Cr in Cu and Cr alloy ranges from 45% to 55%. According tothe method for preparing the copper chromium 50 electric contact material by utilizing the vacuum arc remelting furnace, a vacuum consumable electrode arc melting method is used for preparing a Cu andCr electric contact material with the content of Cr ranging from 45% to 55% (wt), the material is free of pores, loose, less in impurities, free of macro and micro defects such as Cu and Cr enrichment, and both the microstructure of Cu and the microstructure of Cr are smaller than 20 micrometers.
Owner:SHAANXI SIRUI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method of nuclear-grade zirconium alloy cast ingot
ActiveCN107686902AExcellent compositional uniformity controlImprove processing economyIncreasing energy efficiencyNuclear gradeIngot
The invention belongs to the technical field of zirconium alloy preparation and particularly relates to a preparation method of a nuclear-grade zirconium alloy cast ingot. The preparation method comprises the following steps that (1) the alloy component and the total mass of the finished cast ingot are determined; (2) an intermediate alloy and an alloy cladding are prepared; (3) material mixing isconducted; (4) electrode pressing is conducted; (5) N electrodes are welded into one electrode; (6) vacuum self-consuming arc melting is conducted; and (7) surface machining and dead head cutting areconducted. According to a technology suitable for industrial scale production and used for preparation of the Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe / Cr zirconium alloy cast ingot, the technological economical efficiency can beobviously improved, meanwhile component evenness control over the cast ingot is superior to that of a traditional technology, and the preparation method can be used for industrial scale production ofthe nuclear-grade zirconium alloy cast ingot accordingly.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Preparation method of TiCu50 master alloy material by vacuum consumable arc melting
The invention discloses a preparation method of a TiCu50 master alloy material by vacuum consumable arc melting, which mainly comprises the following steps: (1) mixing raw materials: according to theweight percentage content, the percentage contents of raw material are: Cu 50%, and TiO 50%, the required raw materials are weighted according to the proportion, and the raw materials are mixed in a mixer; (2) pressing: the mixed powder is loaded into a rubber sleeve and is subjected to mechanical vibration, rolling and reverse material mounding, and then the cold isostatic pressing method is adopted to press the mixed powder, and then the pressure-keeping treatment is carried out; (3) sintering: the pressed consumable electrode is loaded into a vacuum sintering furnace for sintering, and thesintering temperature, the holding time and the vacuum degree are controlled; Step (4) smelting: the sintered consumable electrode is charged into a vacuum consumable arc smelting furnace for smelting. The TiCu50 master alloy material prepared by the invention has low gas content and less impurities, and is uniform in composition, and has no macroscopic and microscopic defects such as enrichment of Cu and Ti.
Owner:SHAANXI SIRUI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com