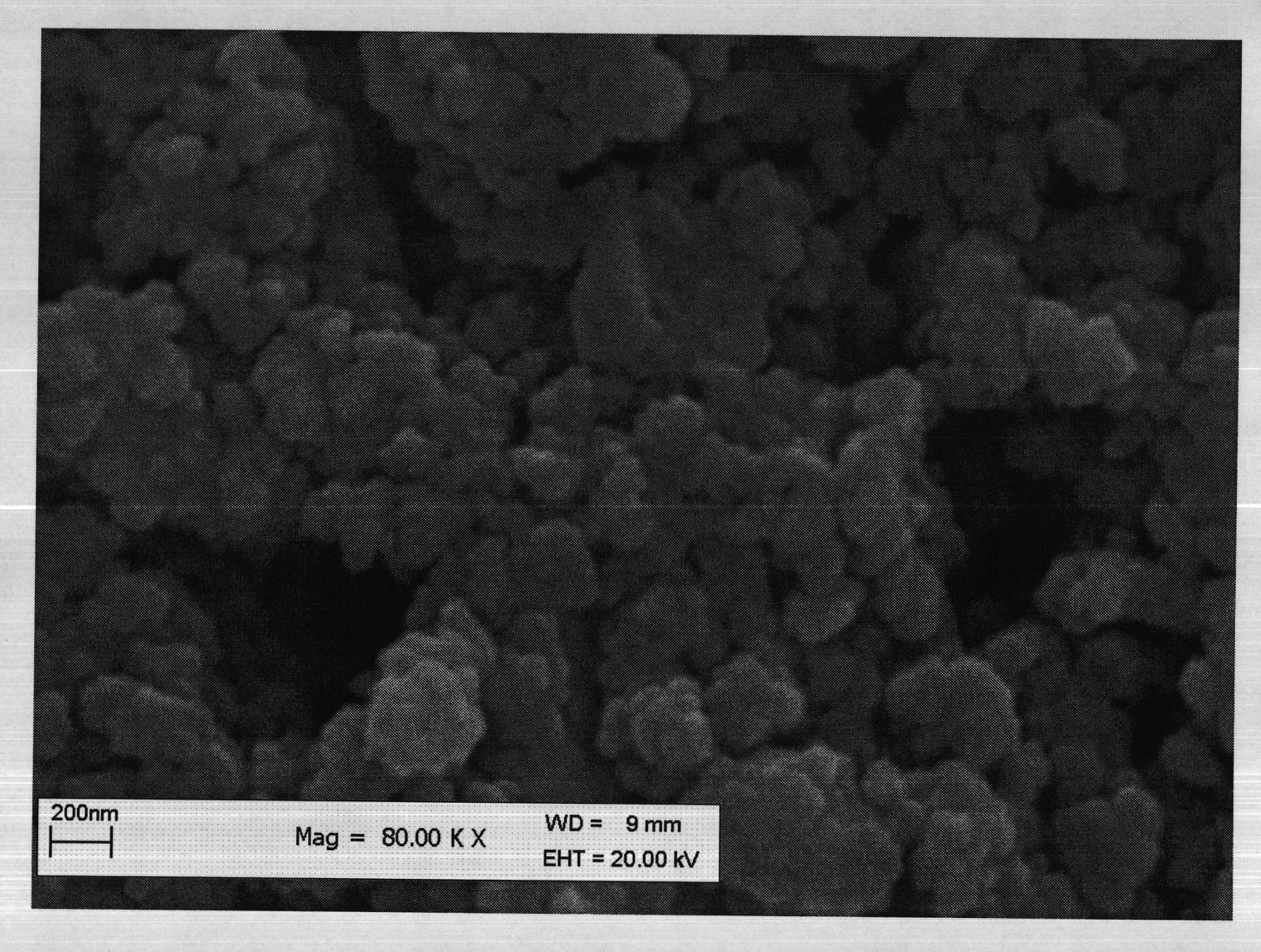
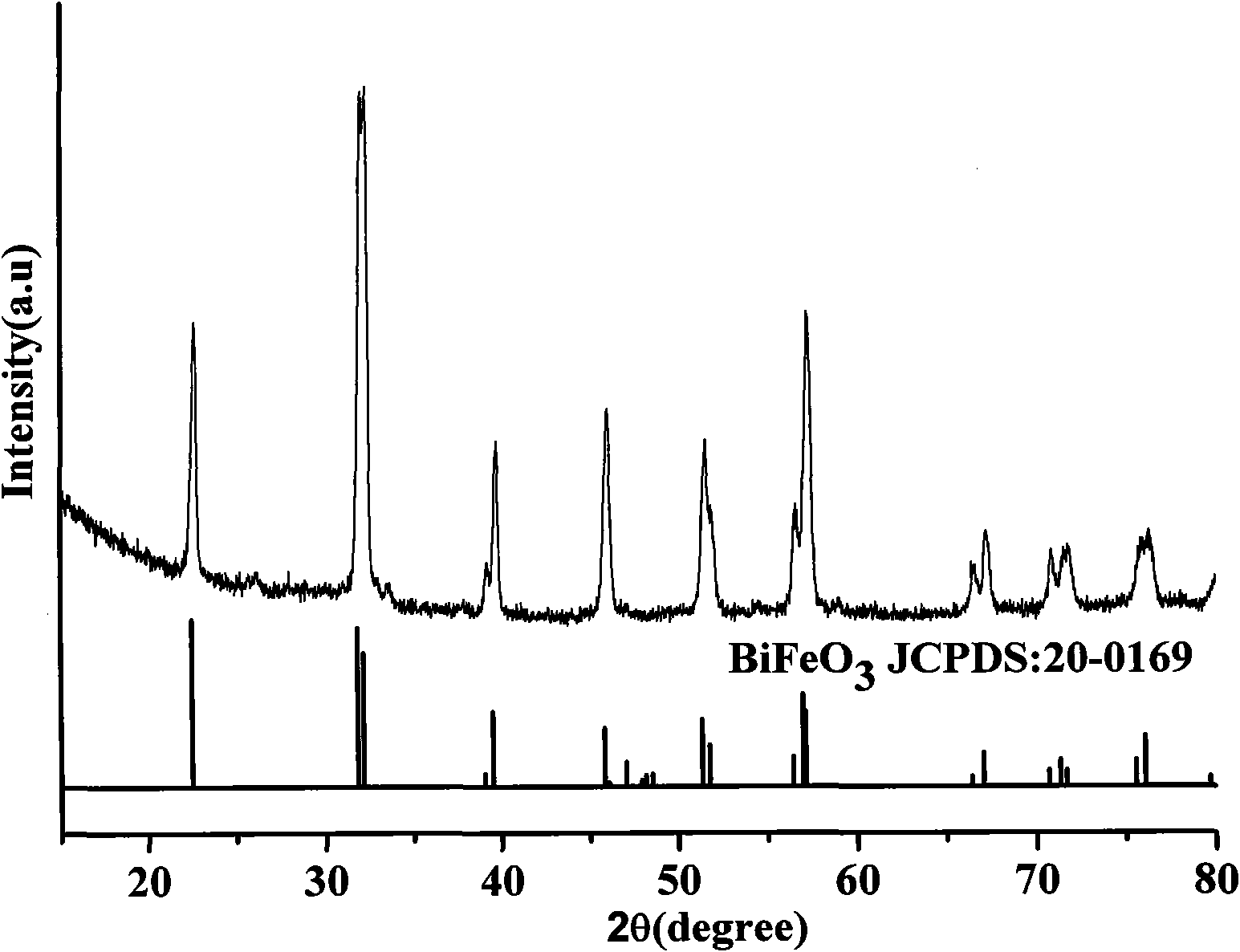
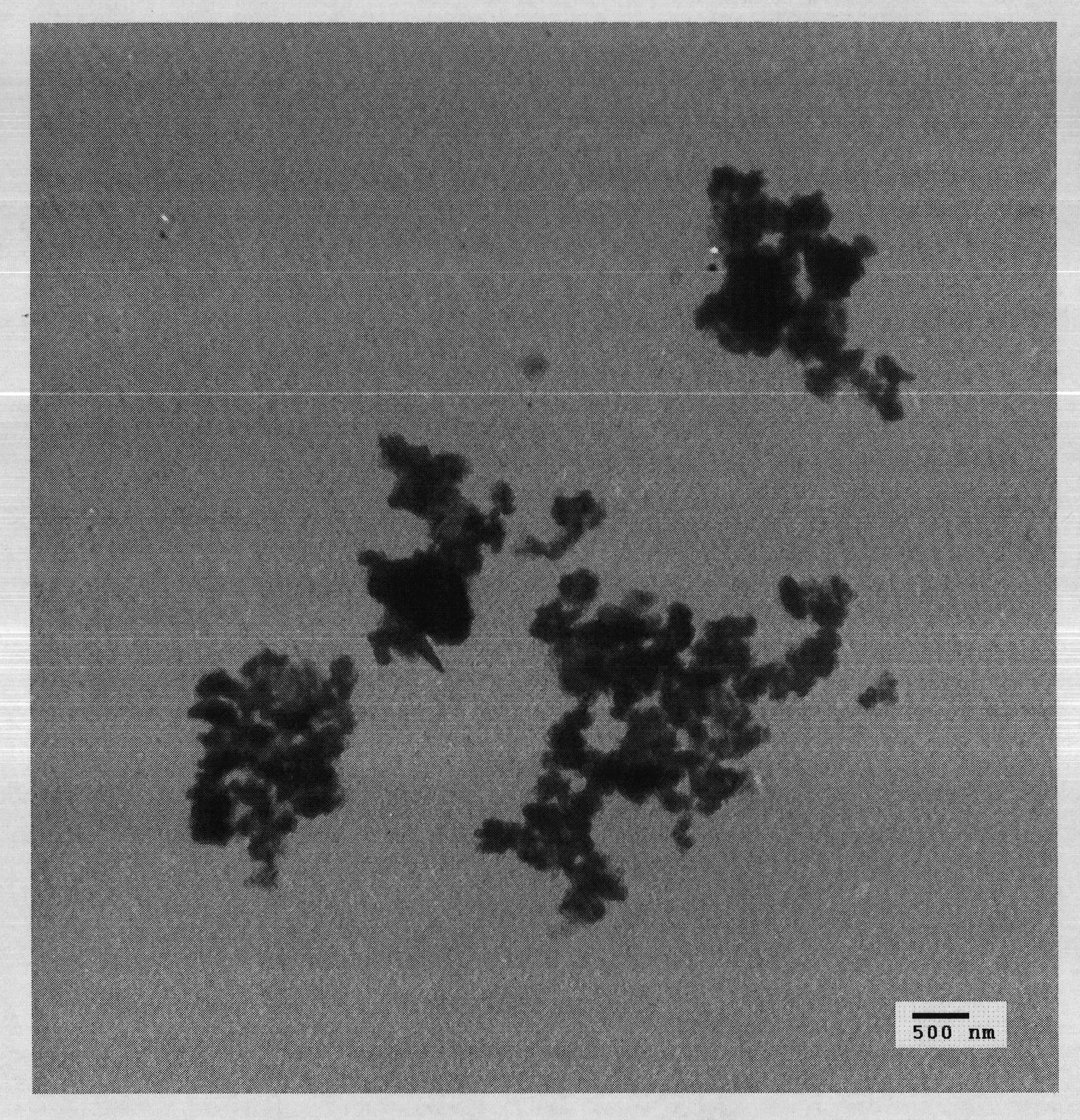
Method for preparing bismuth ferrite material by two-step solid-phase reaction
A technology of solid phase reaction and room temperature solid phase reaction, applied in chemical instruments and methods, iron compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of limited chemical reaction and slow diffusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] According to the molar ratio of Bi:Fe:NaOH=1:1:1, weigh bismuth nitrate, ferric nitrate and sodium hydroxide and mix and grind for 0.5 hours;
[0020] The reactant undergoes a solid-phase reaction at room temperature, changing from a white powder to a yellow-brown porridge paste reactant. After 30 minutes, the reaction is completed and a yellow-brown powder product is obtained;
[0021] After washing the powder with water to remove the by-product sodium nitrate, it is dried and heated at 400°C for 1 hour to obtain part of the desired product bismuth ferrite;
[0022] Then use concentrated nitric acid to dissolve unreacted raw materials in the product at a volume ratio of 1:1, wash with water, and dry to obtain the final product with a yield of 55.2%.
Embodiment 2
[0024] According to the molar ratio Bi:Fe:NaOH=2.5:1:5, weigh bismuth nitrate, ferric nitrate and sodium hydroxide and mix and grind for 1 hour;
[0025] The reactant undergoes a solid-phase reaction at room temperature, changing from a white powder to a yellow-brown porridge paste reactant. After 30 minutes, the reaction is completed and a yellow-brown powder product is obtained;
[0026] Wash the powder with water to remove the by-product sodium nitrate, dry it, and heat it at a temperature of 550°C for 3 hours to obtain part of the desired product bismuth ferrite;
[0027] Then use concentrated nitric acid to dissolve the unreacted raw materials in the product at a volume ratio of 1:1, wash with water, and dry to obtain all the final products, with a yield of 62.1%.
Embodiment 3
[0029] According to the molar ratio of Bi:Fe:NaOH=4:1:10, weigh bismuth nitrate, ferric nitrate and sodium hydroxide and mix and grind for 2 hours;
[0030] The reactant undergoes a solid-phase reaction at room temperature, changing from a white powder to a yellow-brown porridge paste reactant. After 30 minutes, the reaction is completed and a yellow-brown powder product is obtained;
[0031] The powder is washed with water to remove the by-product sodium nitrate, then dried, and heated at 700°C for 6 hours to obtain part of the desired product bismuth ferrite;
[0032] Then use concentrated nitric acid to dissolve unreacted raw materials in the product at a volume ratio of 1:1, wash with water, and dry to obtain all the final product bismuth ferrite, with a yield of 66.8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com