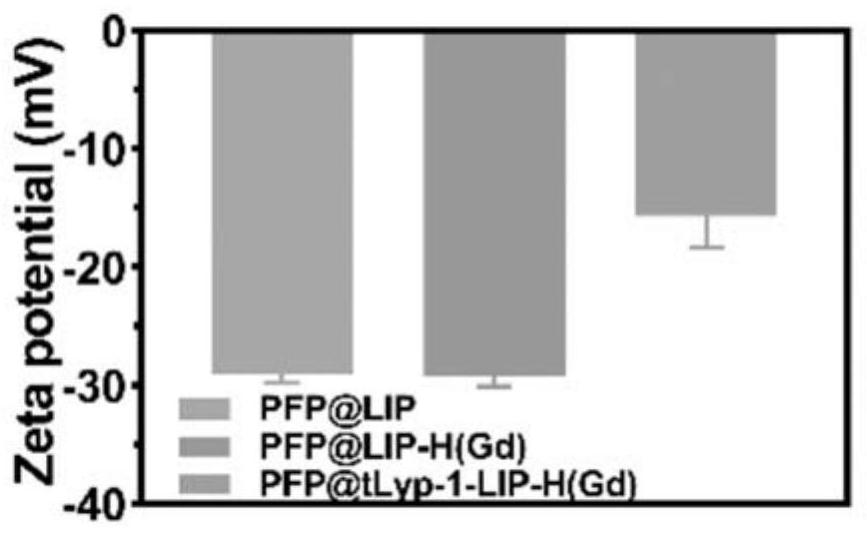
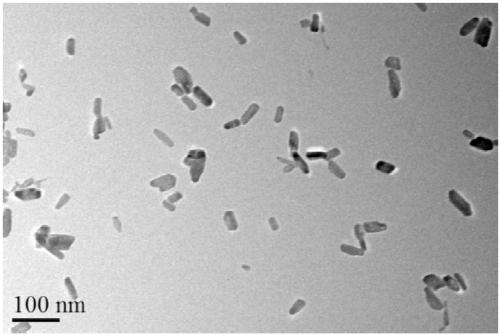
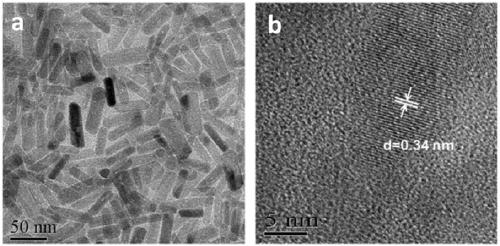
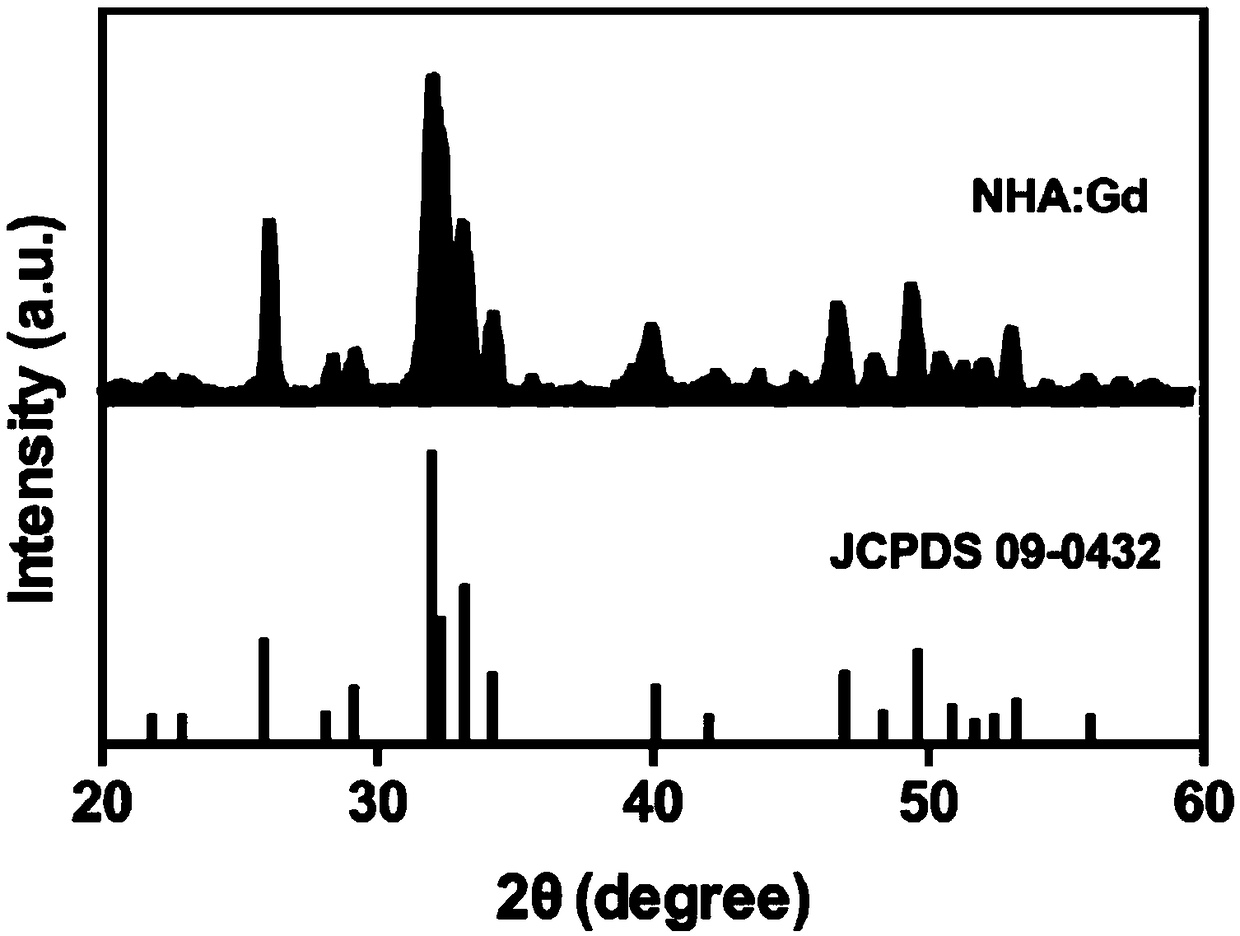
Patents
Literature
56results about How to "Enhanced magnetic resonance imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
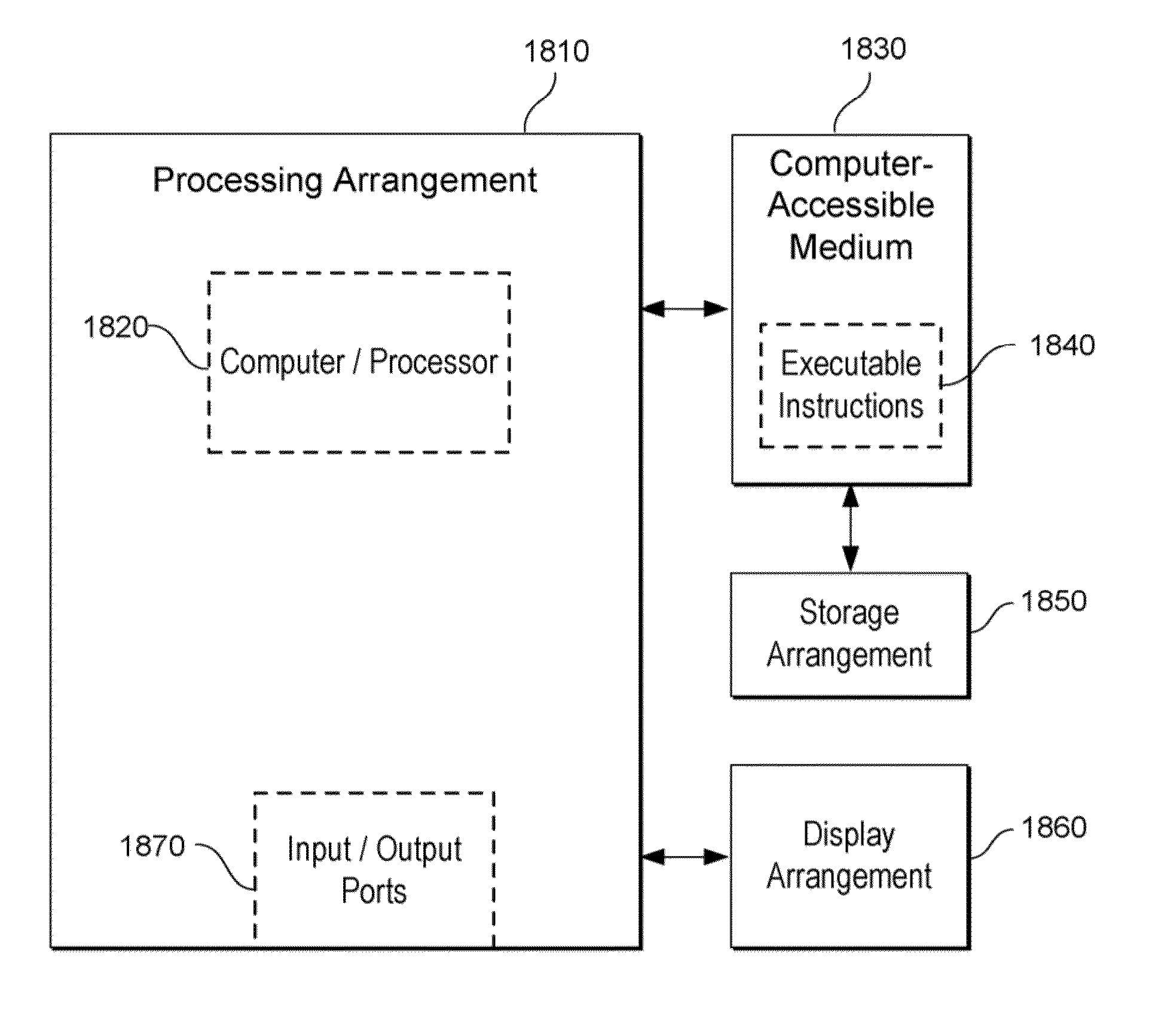
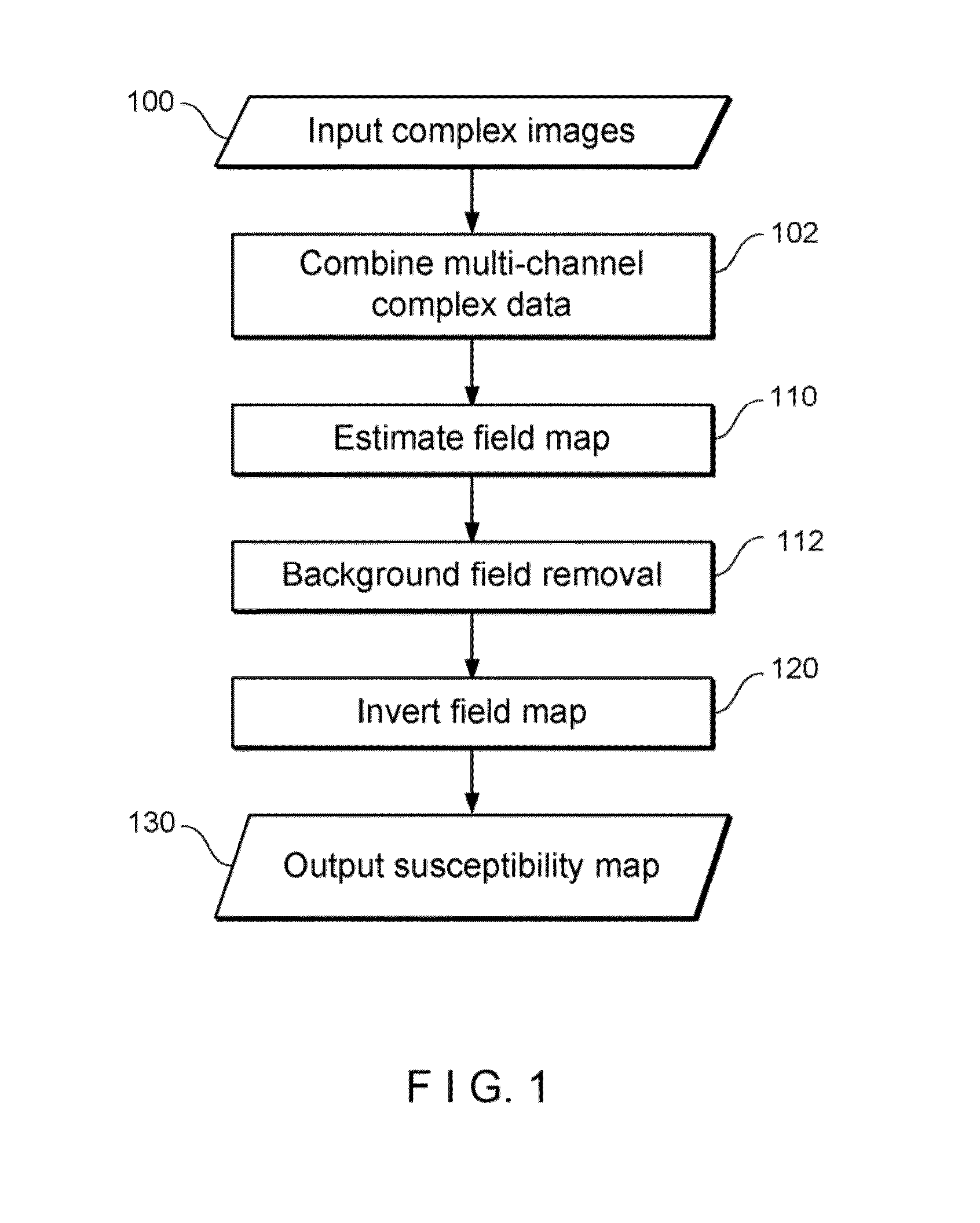
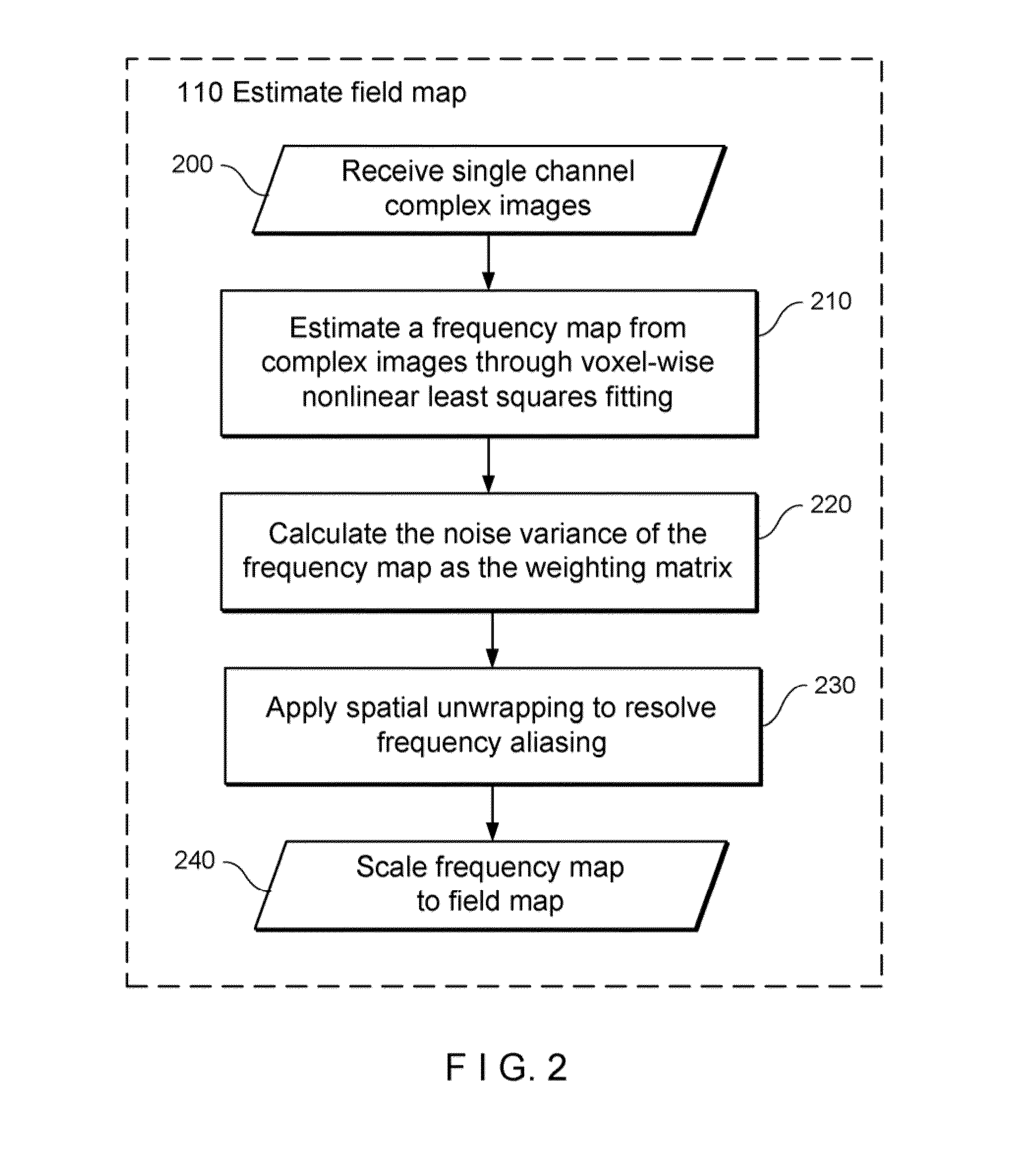
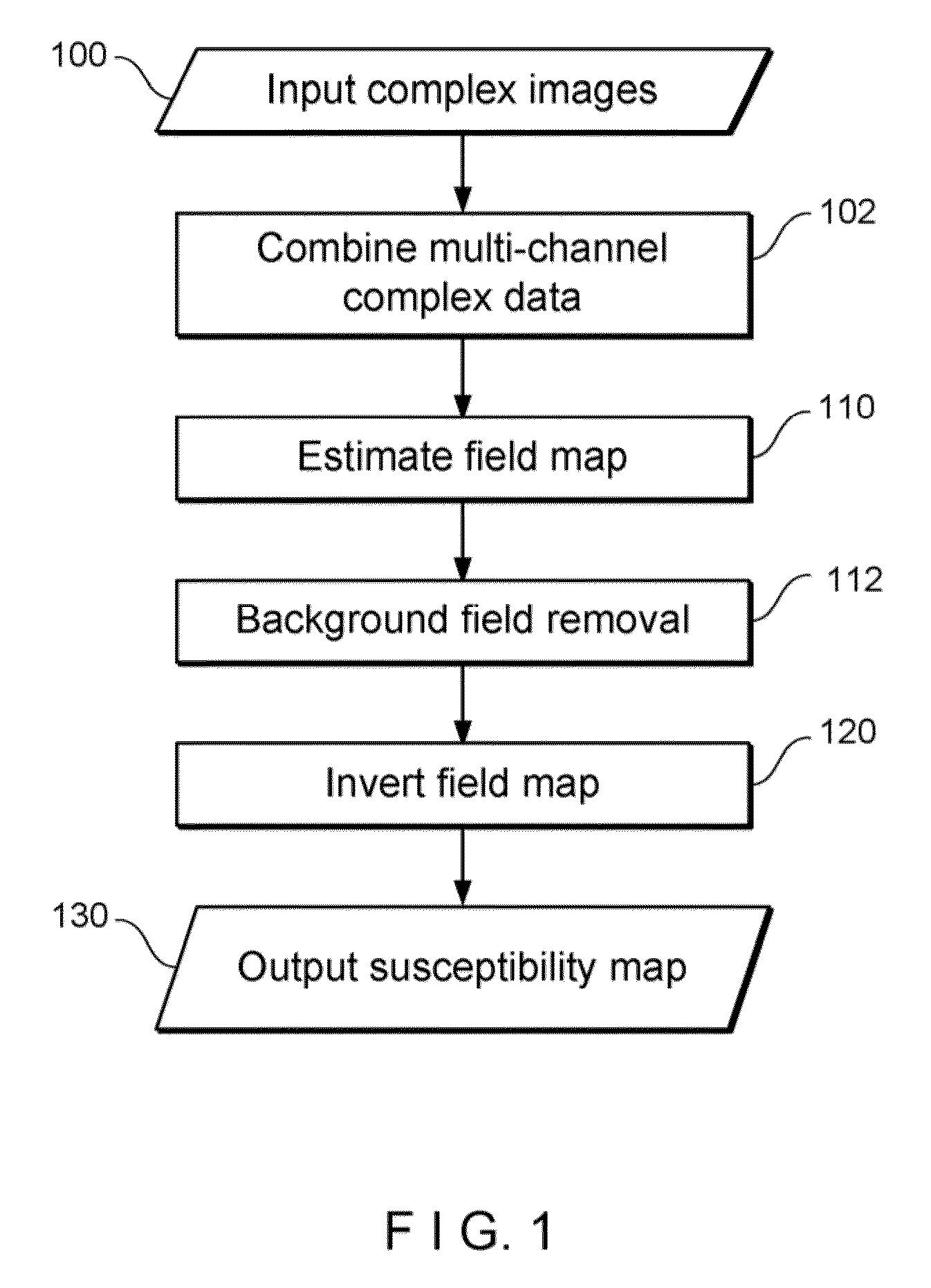
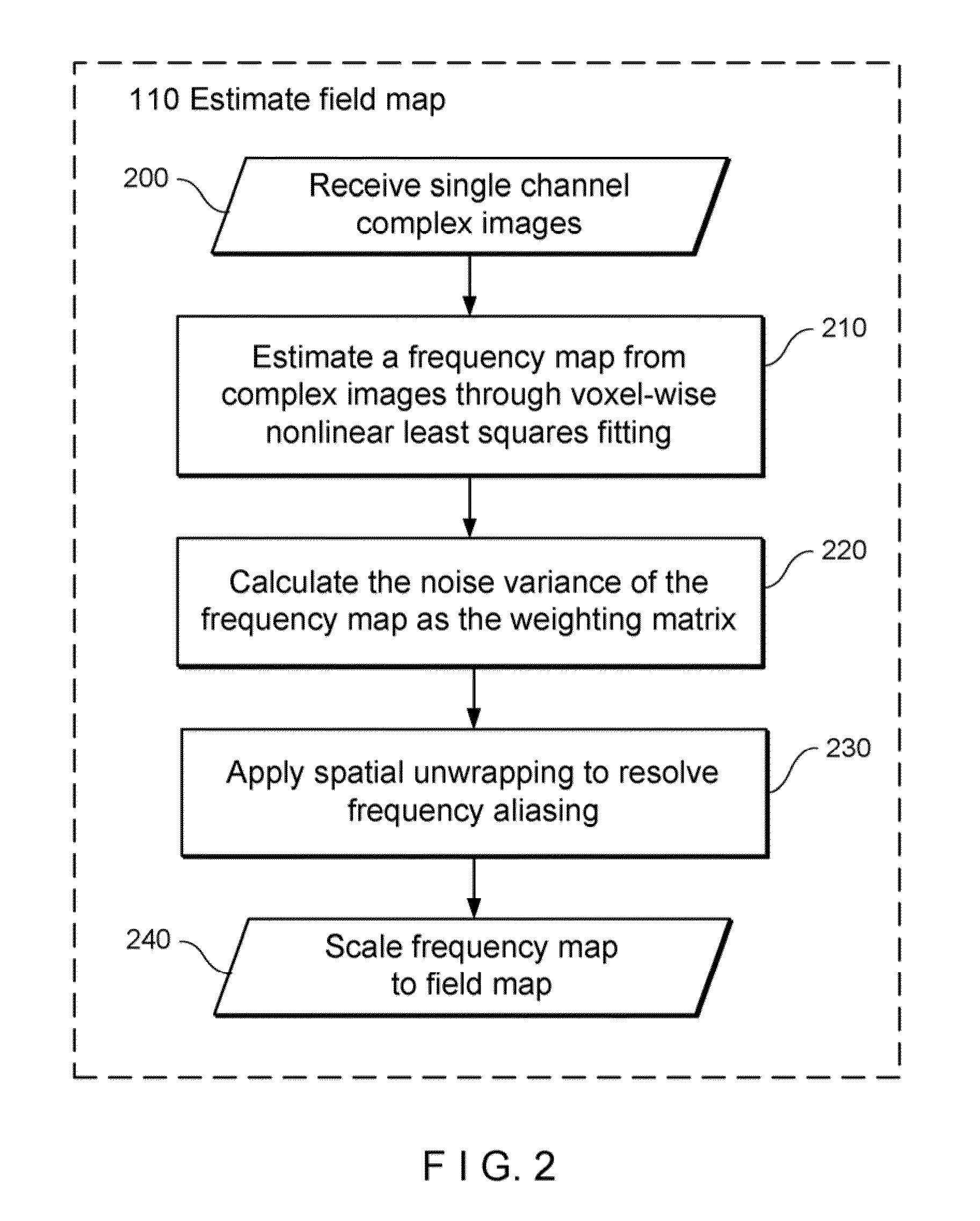
System, Process and Computer-Accessible Medium For Providing Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
ActiveUS20130221961A1Overcome limitationsEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingSensorsElectric/magnetic detectionQuantitative susceptibility mappingComputer science
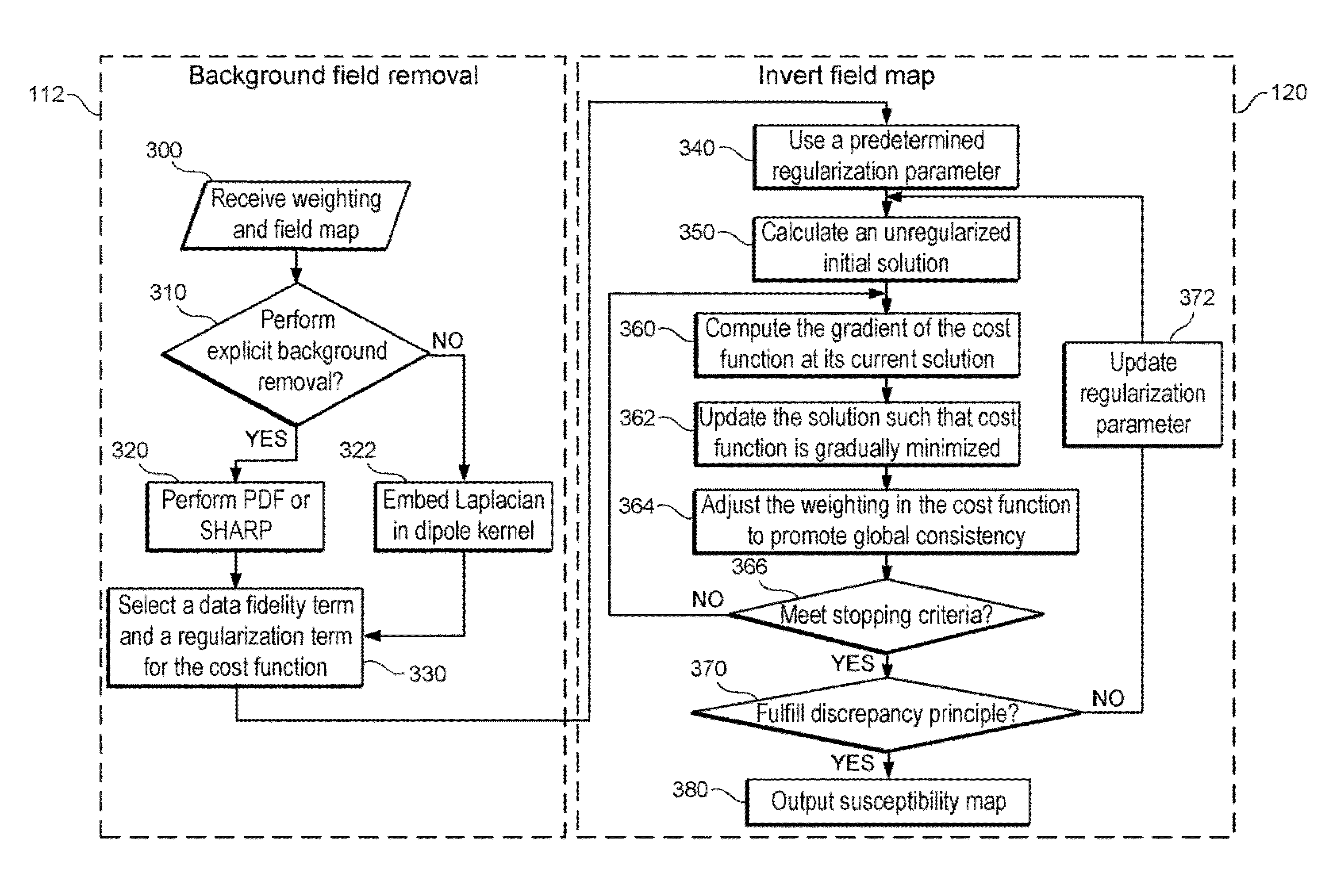
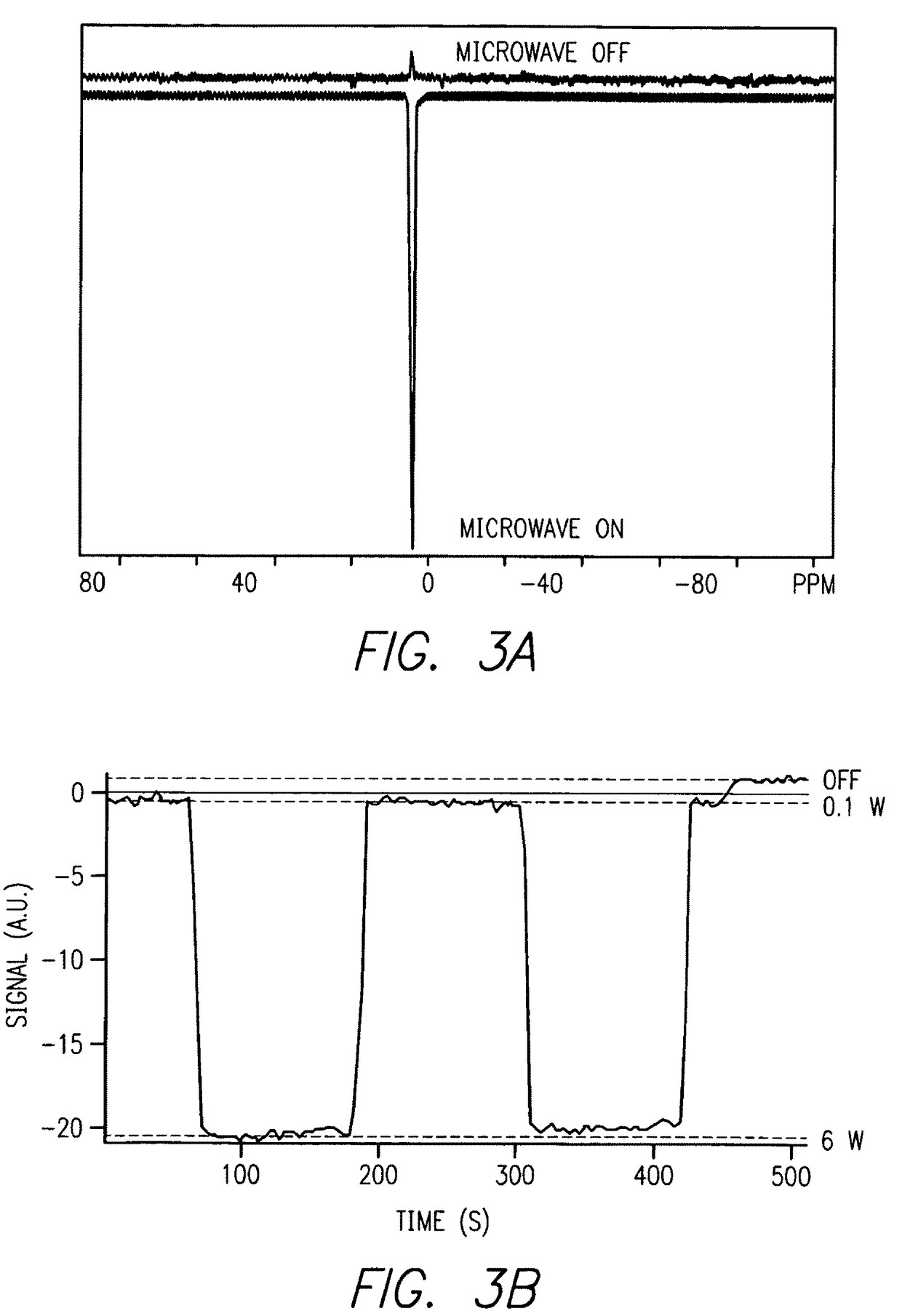
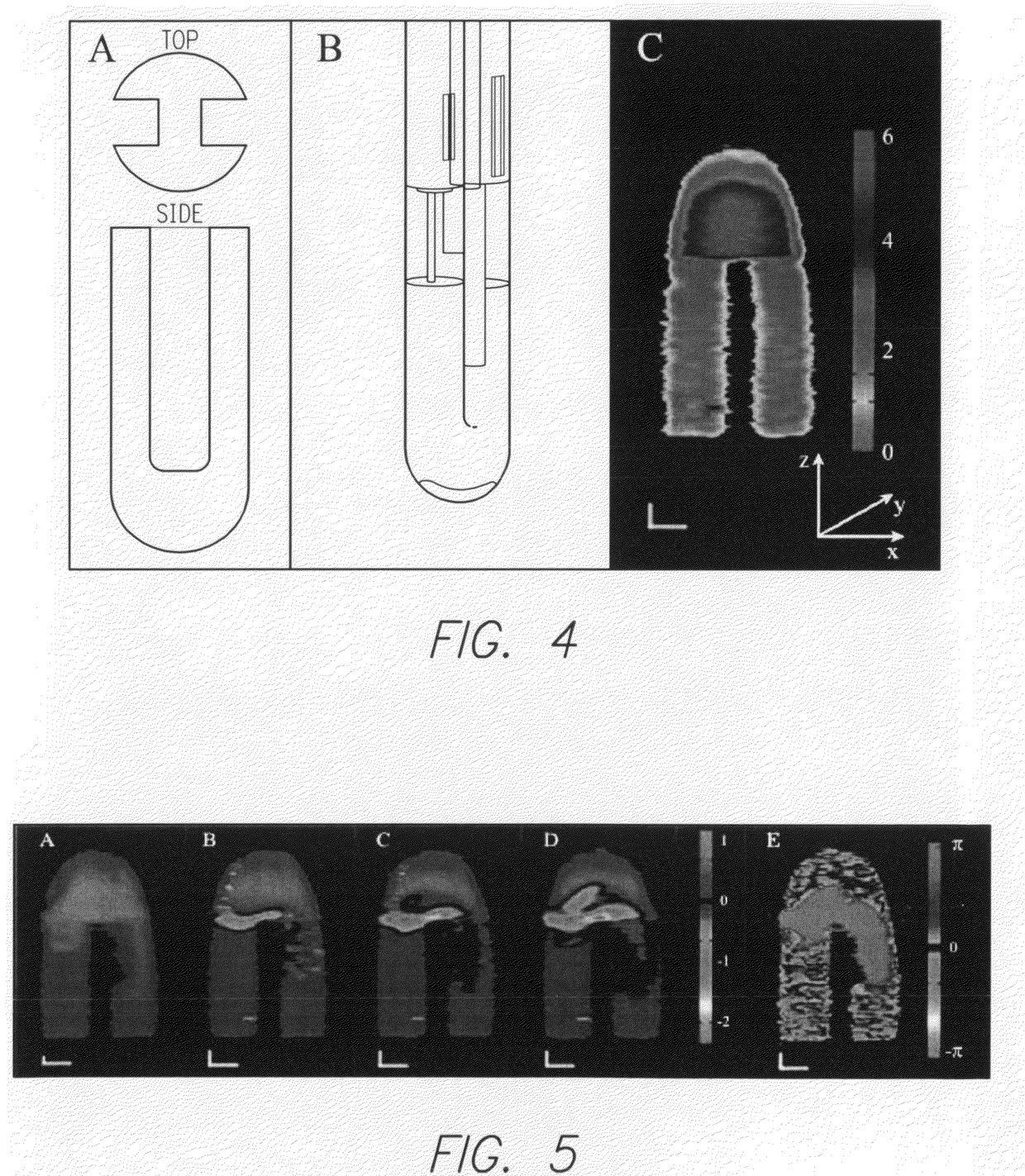
Exemplary quantitative susceptibility mapping methods, systems and computer-accessible medium can be provided to generate images of tissue magnetism property from complex magnetic resonance imaging data using the Bayesian statistical approach. The likelihood is constructed directly using the complex data. A prior is constructed from matching structures or information content in known morphology. The quantitative susceptibility map can be determined by, e.g., maximizing the posterior. Thus, according to the exemplary embodiment, system, method and computer-accessible medium can be provided for determining information associated with at least one structure. Using such exemplary embodiment, it is possible to receive signals associated with the structure(s), where the signals can include complex data that is in the complex domain.
Owner:MEDIMAGEMETRIC
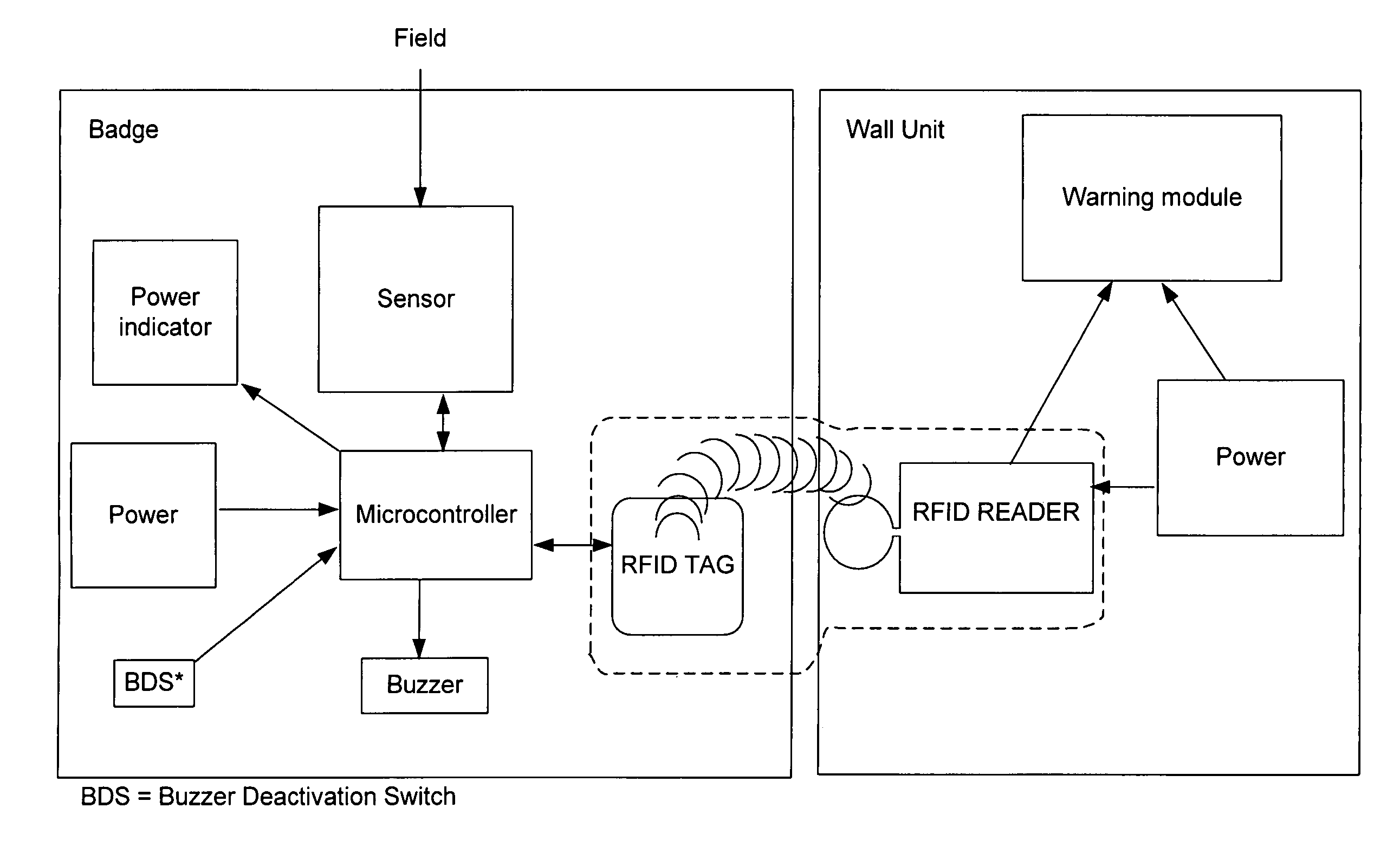
Method and apparatus for ferrous object and/or magnetic field detection for MRI safety
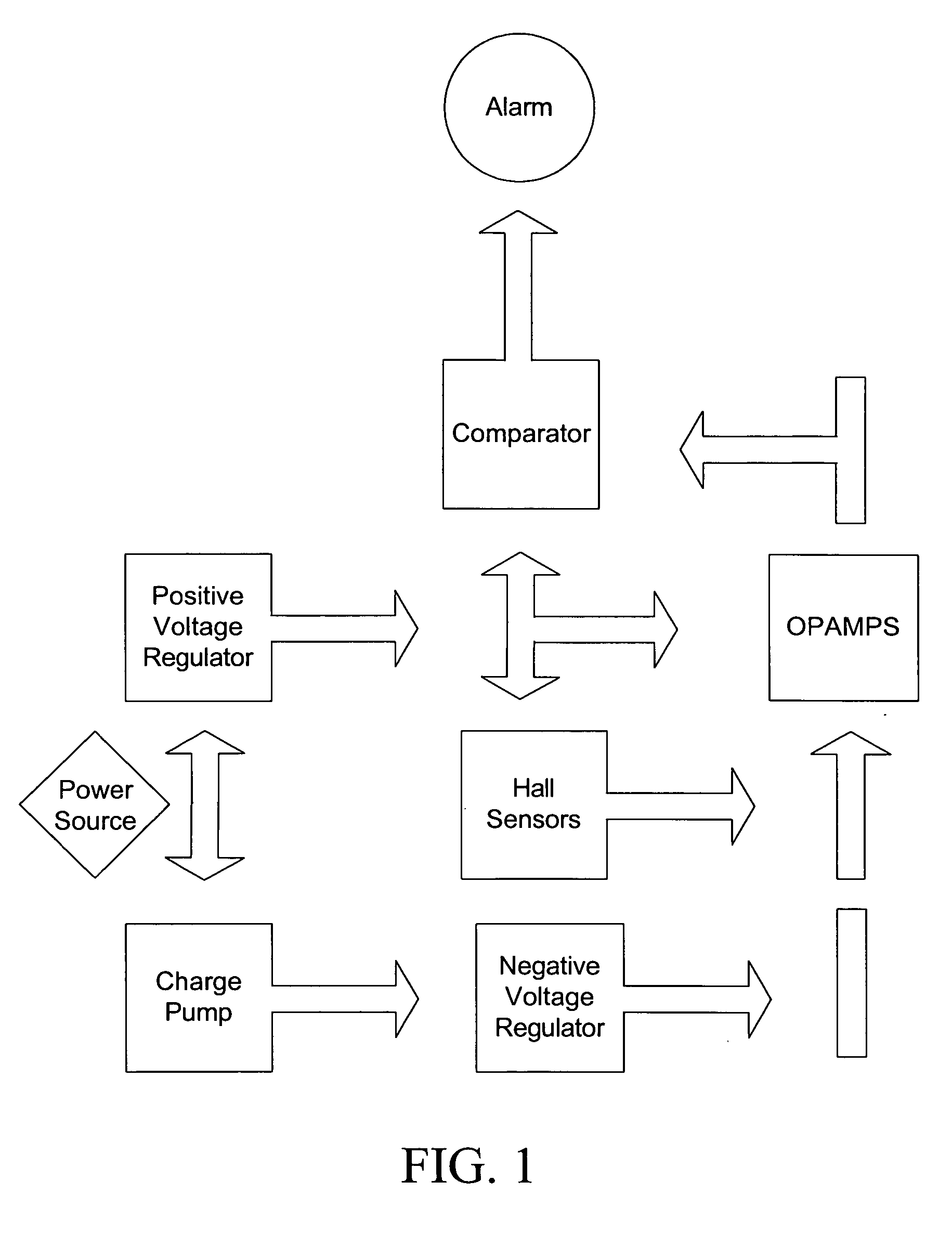
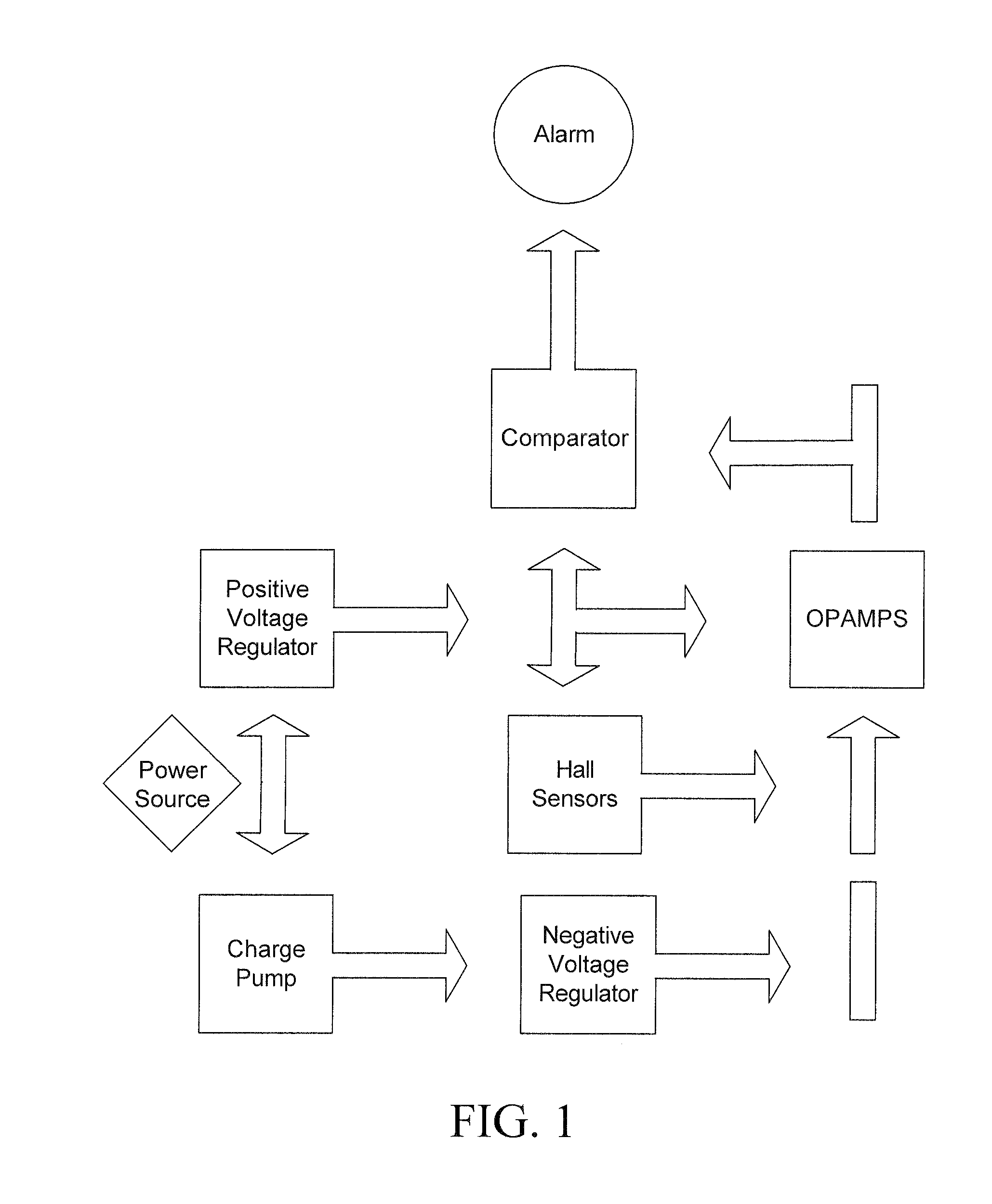
InactiveUS20070132581A1Improve magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) safetyImprove securityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringRechargeable cellEngineering
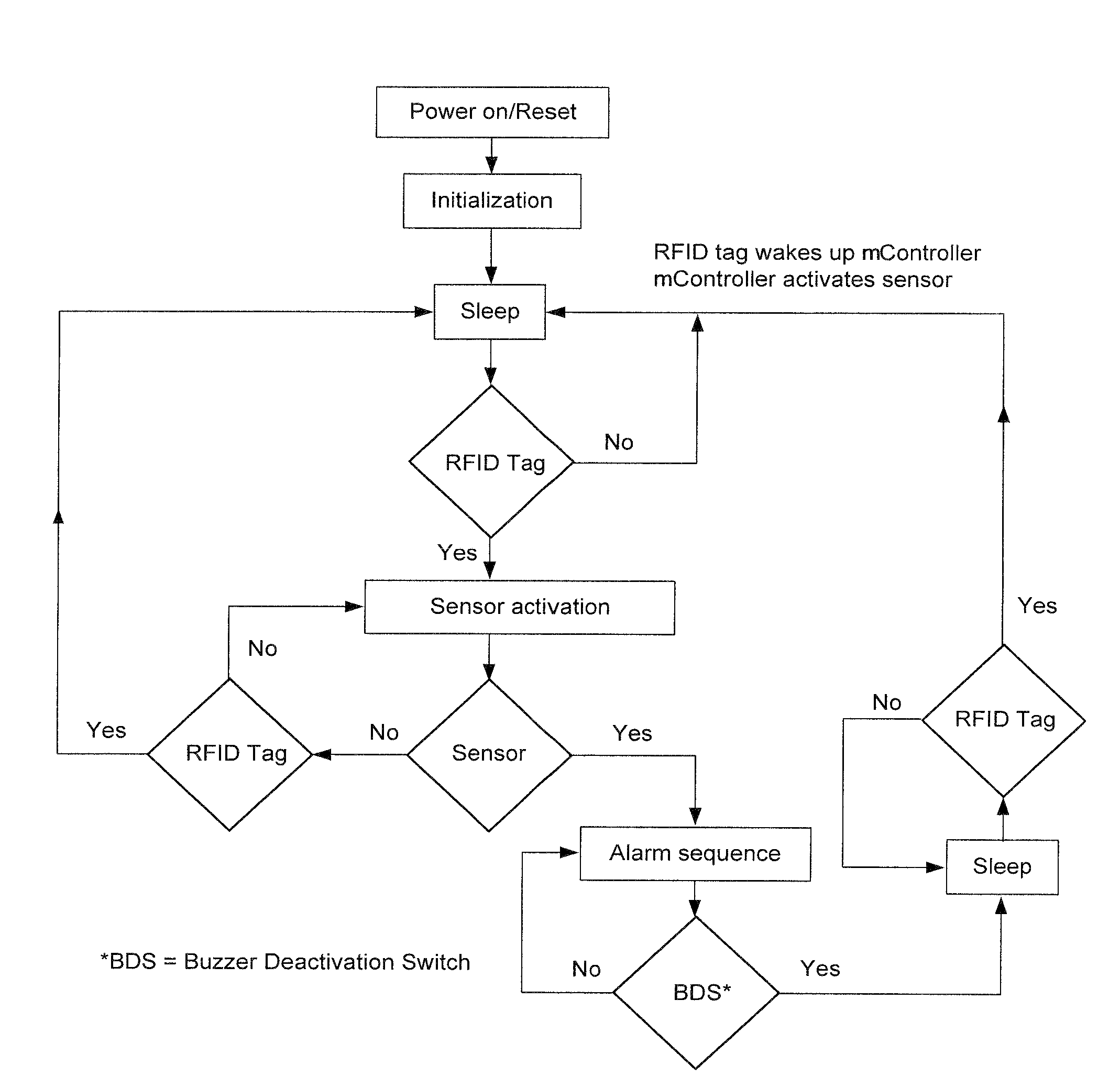
A method and apparatus for ferrous object and / or magnetic field detection are provided. Embodiments can improve magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) safety and increase the safety of MRI facilities. Embodiments can detect a given magnetic field strength around a MRI machine and alert users to the field's presence. In an embodiment, the magnetic field warning system can rely on a single badge that warns its user. In another embodiment, the badge can utilize an RFID system. The RFID system can turn the badge on when it enters the MRI room and off when it leaves the MRI room. In another embodiment, a badge with a rechargeable battery and charger can be utilized with or without an RFID tag. The subject badges or other detection devices can be worn by a person, located on or near a ferrous object, embedded in clothing, or located in other positions convenient to a user.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Wearable magnetic resonator for MRI resolution improvement, and application device including the same
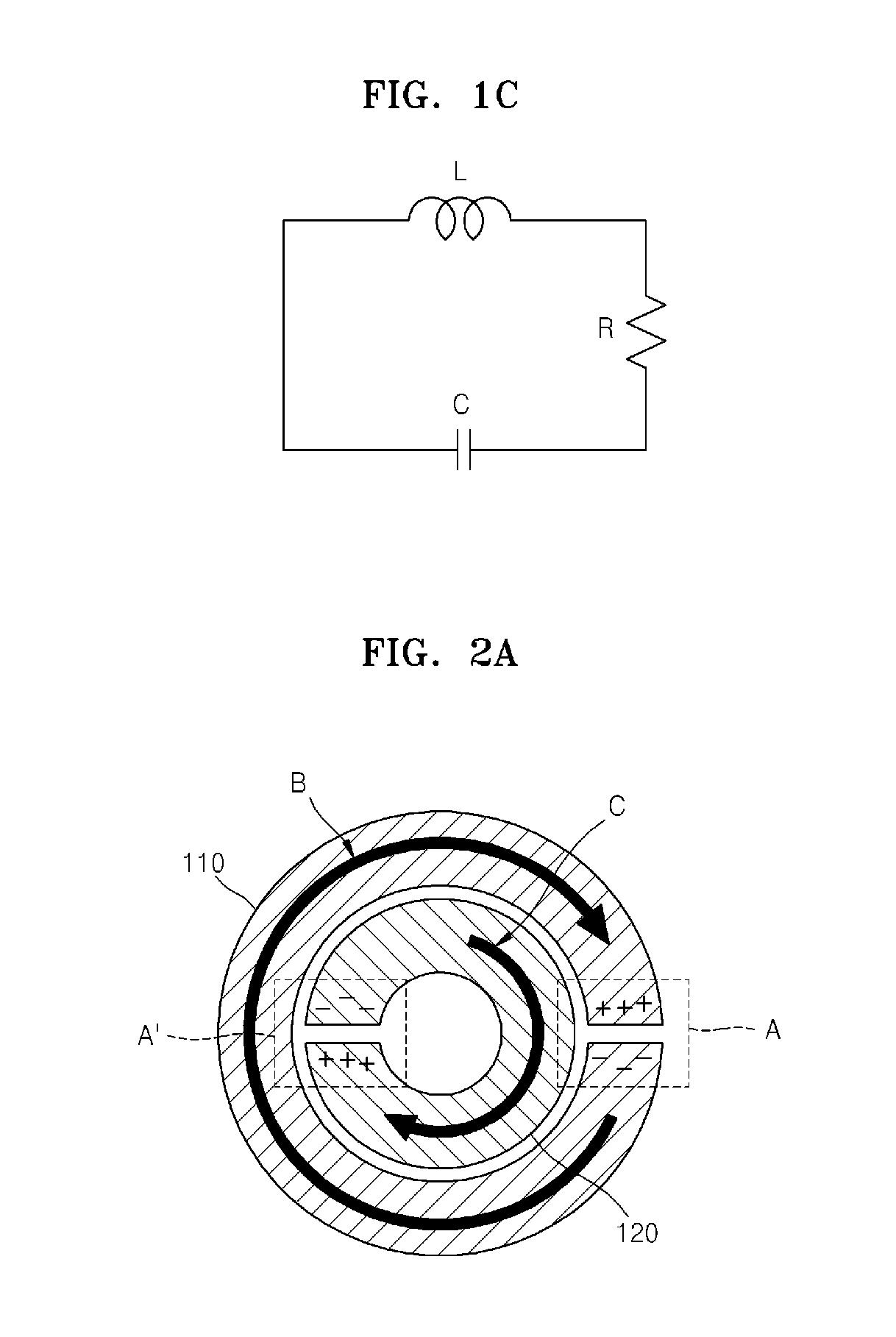
InactiveUS20100127707A1Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingSpeed measurement using accelerationDiagnostic recording/measuringCapacitanceHuman body
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices detect a magnetic field having a particular frequency induced by hydrogen nuclei included in a human body and convert the detected magnetic field into two- or three-dimensional images, thereby visualizing the internal structure of the human body without causing any harm to the human body. The higher the resolution of an MRI technique, the more accurate a diagnosis can be obtained. Thus, various methods are introduced to improve resolutions. For example, a wearable magnetic resonator and an application device including the wearable magnetic resonator are provided. The wearable magnetic resonator is flexible and used to improve MRI resolution by amplifying MR signals while being attached to a human body to amplify MR signals when MRI is performed. The wearable magnetic resonator includes the following: a dielectric thin film that is flexible; and a conductor thin film that is disposed to have a split ring resonator (SRR) structure on the dielectric thin film and is flexible, wherein the wearable magnetic resonator includes an inductance component and a capacitance component, and the wearable magnetic resonator amplifies a magnetic field by resonating at a predetermined frequency, thereby improving a MRI resolution.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
MR-signal emitting coatings
InactiveUS6896874B2Improve visualizationEnhanced signalGenetic material ingredientsGlovesTherapeutic TechniqueMedical device
The present invention provides a coating that emits magnetic resonance signals and a method for coating medical devices therewith. The coating includes a paramagnetic metal ion-containing polymer complex that facilitates diagnostic and therapeutic techniques by readily visualizing medical devices coated with the complex. The present invention also provides methods by which pre-existing polymers and medical devices may be made MR-imageable. The invention also provides methods of improving MR-imageability of polymers and medical devices by encapsulating the polymers and medical devices with hydrogels.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Temperature-controlled magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS20090140735A1Improve image qualityEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTemperature controlImaging quality
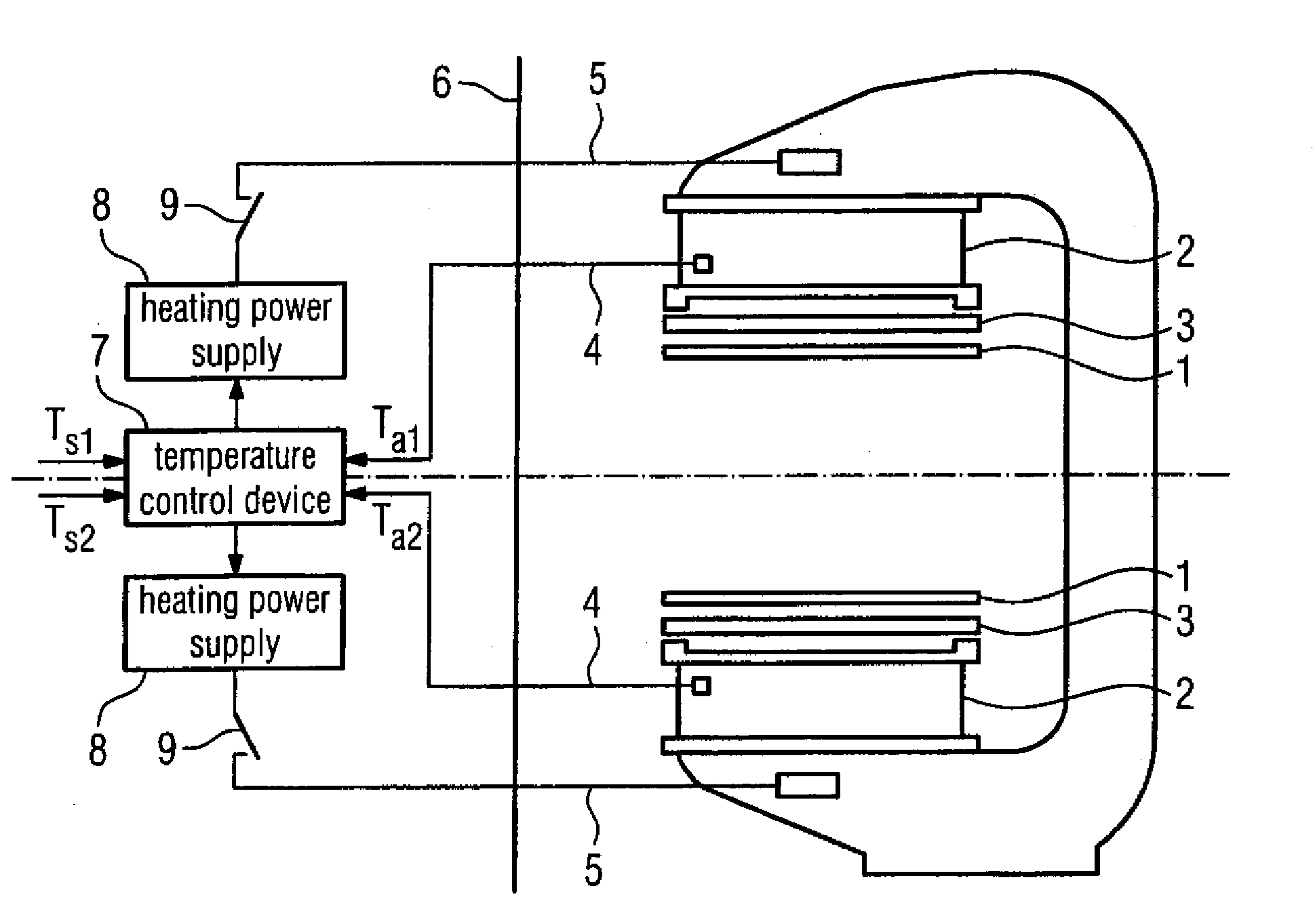
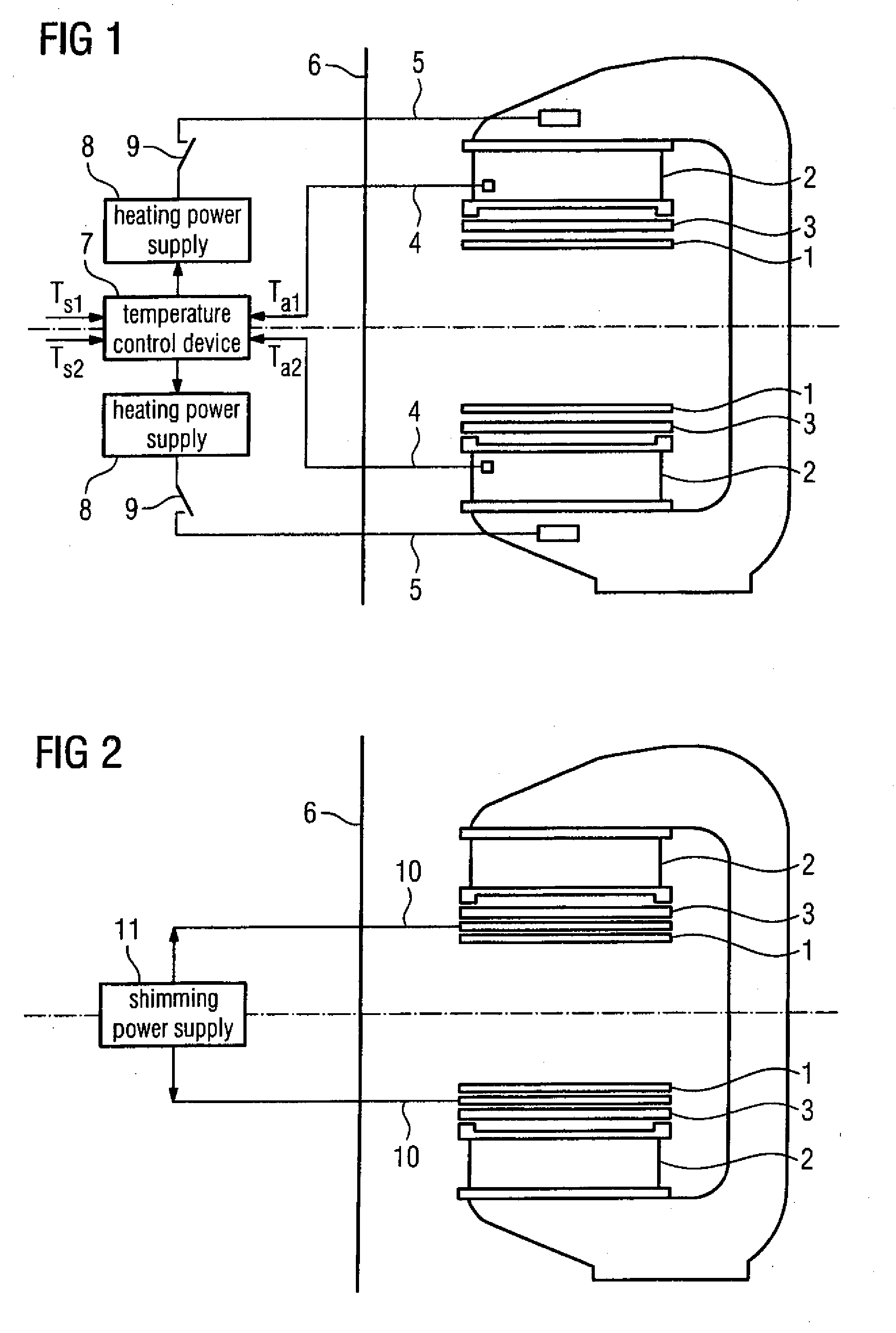
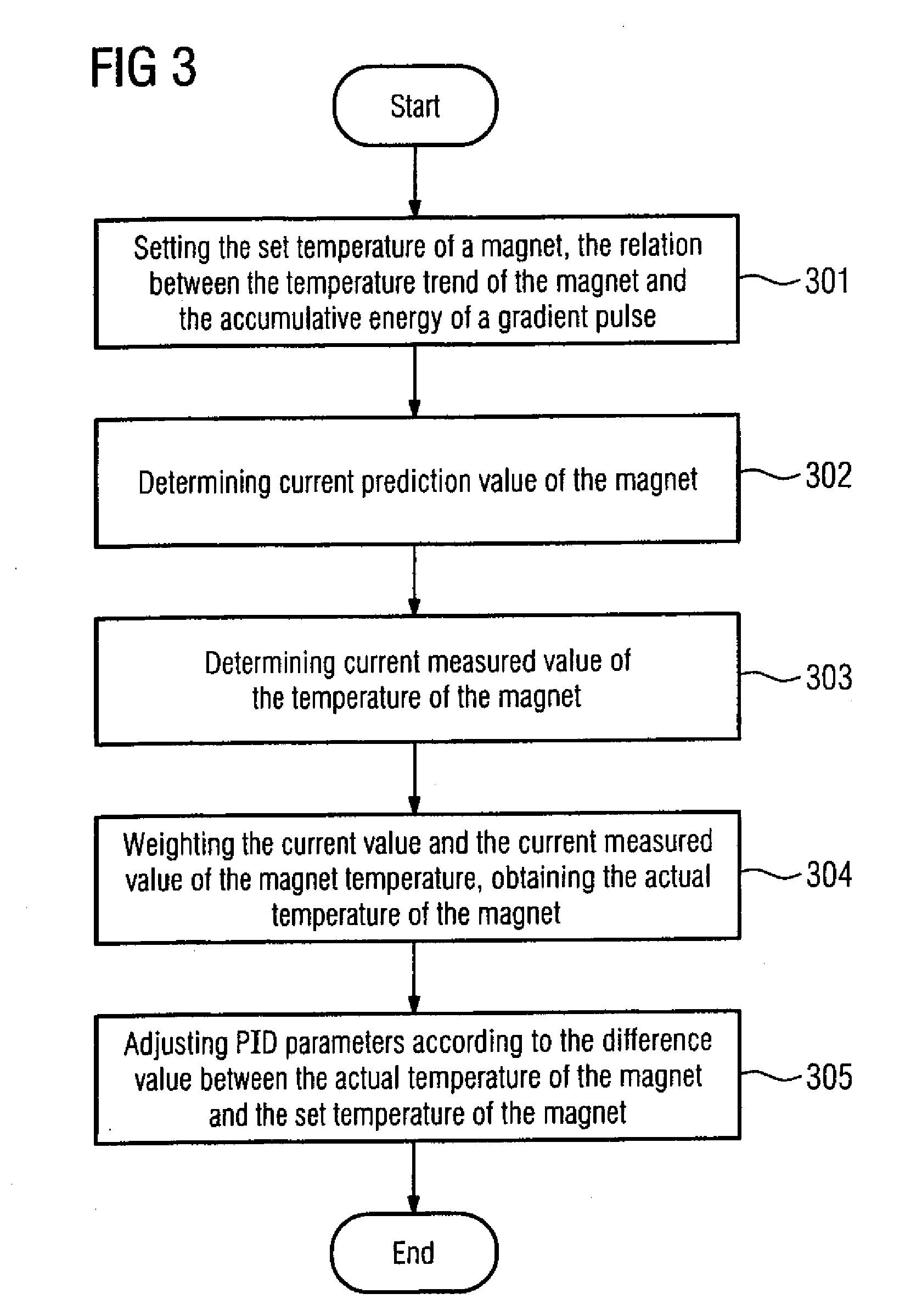
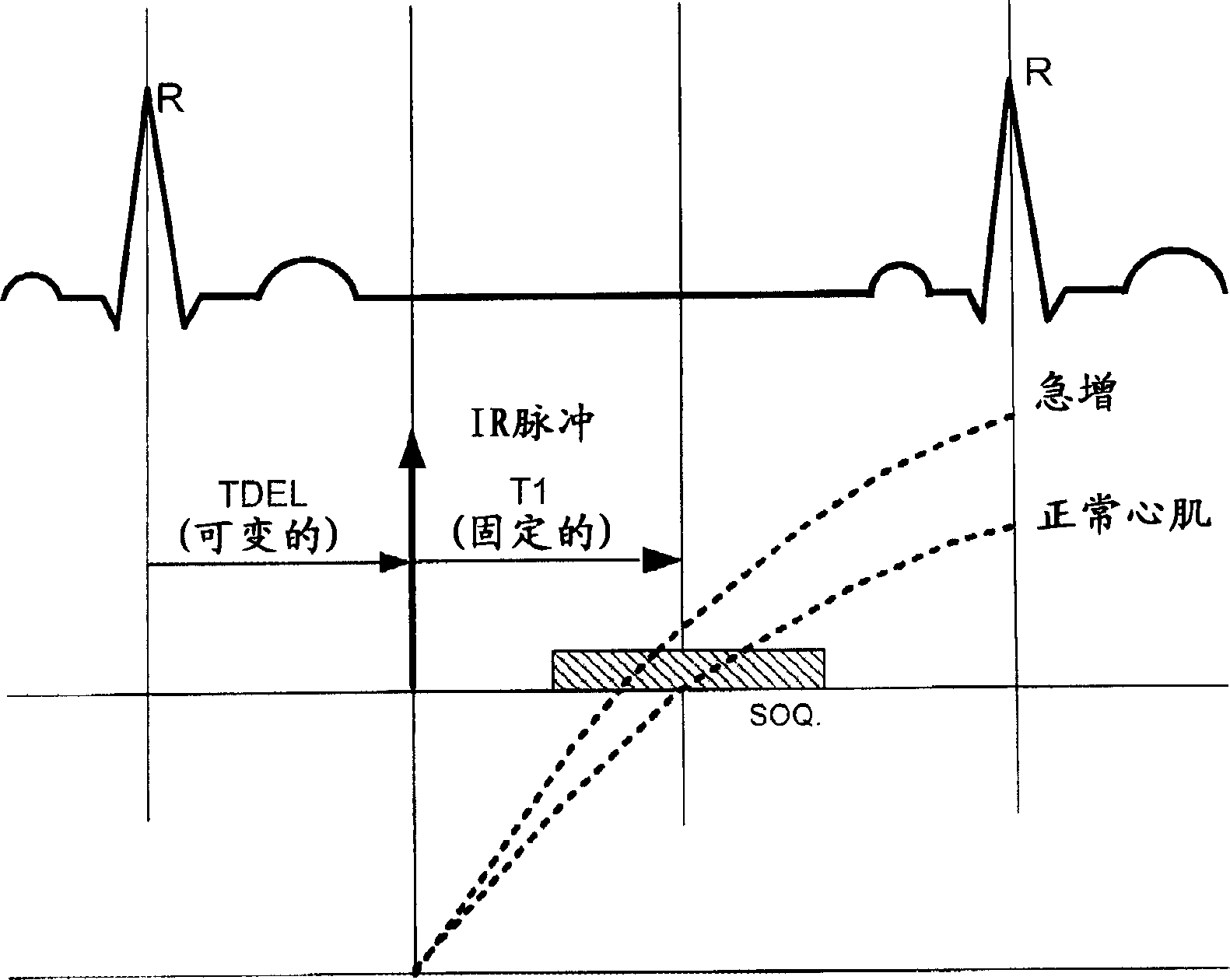
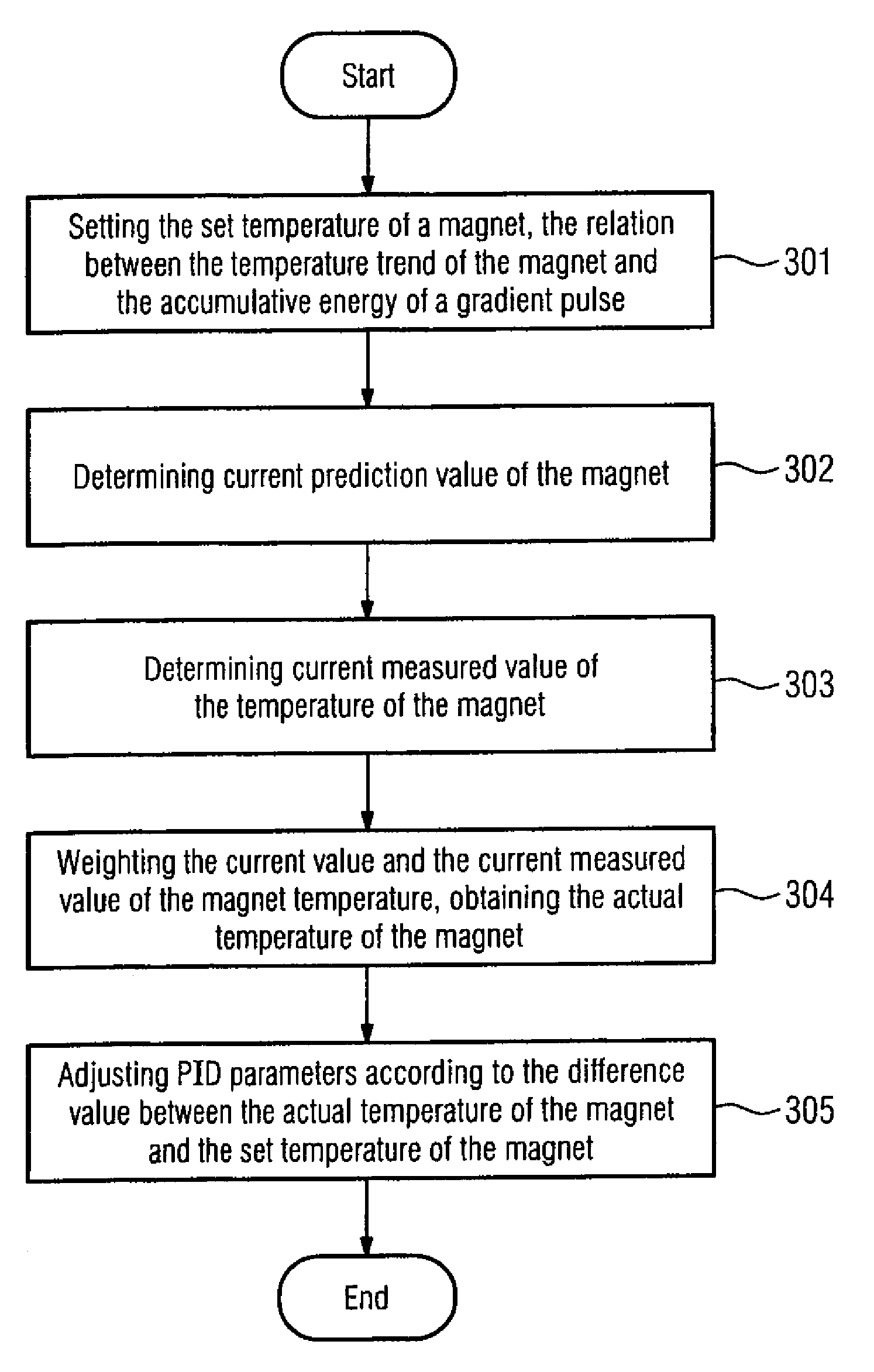
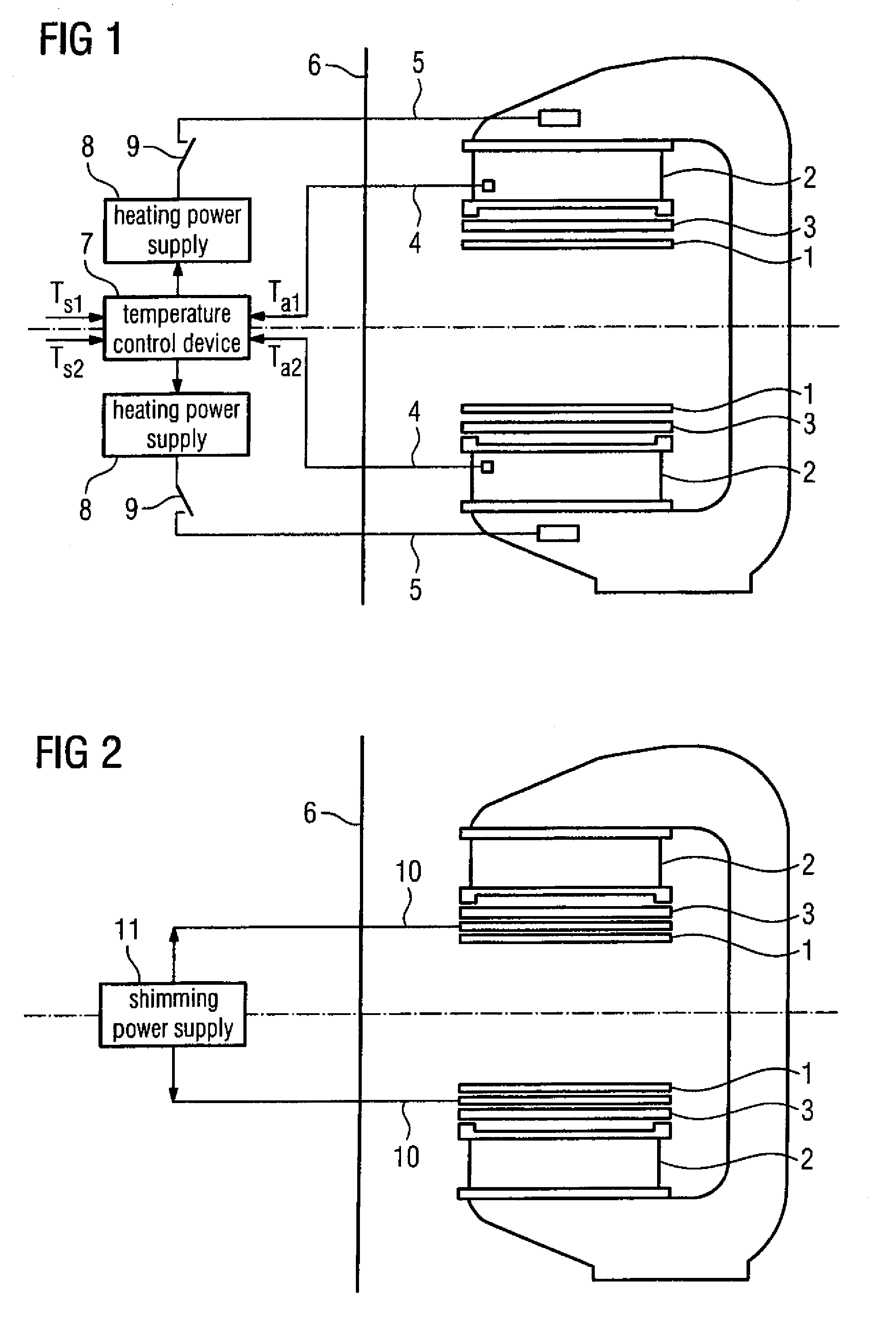
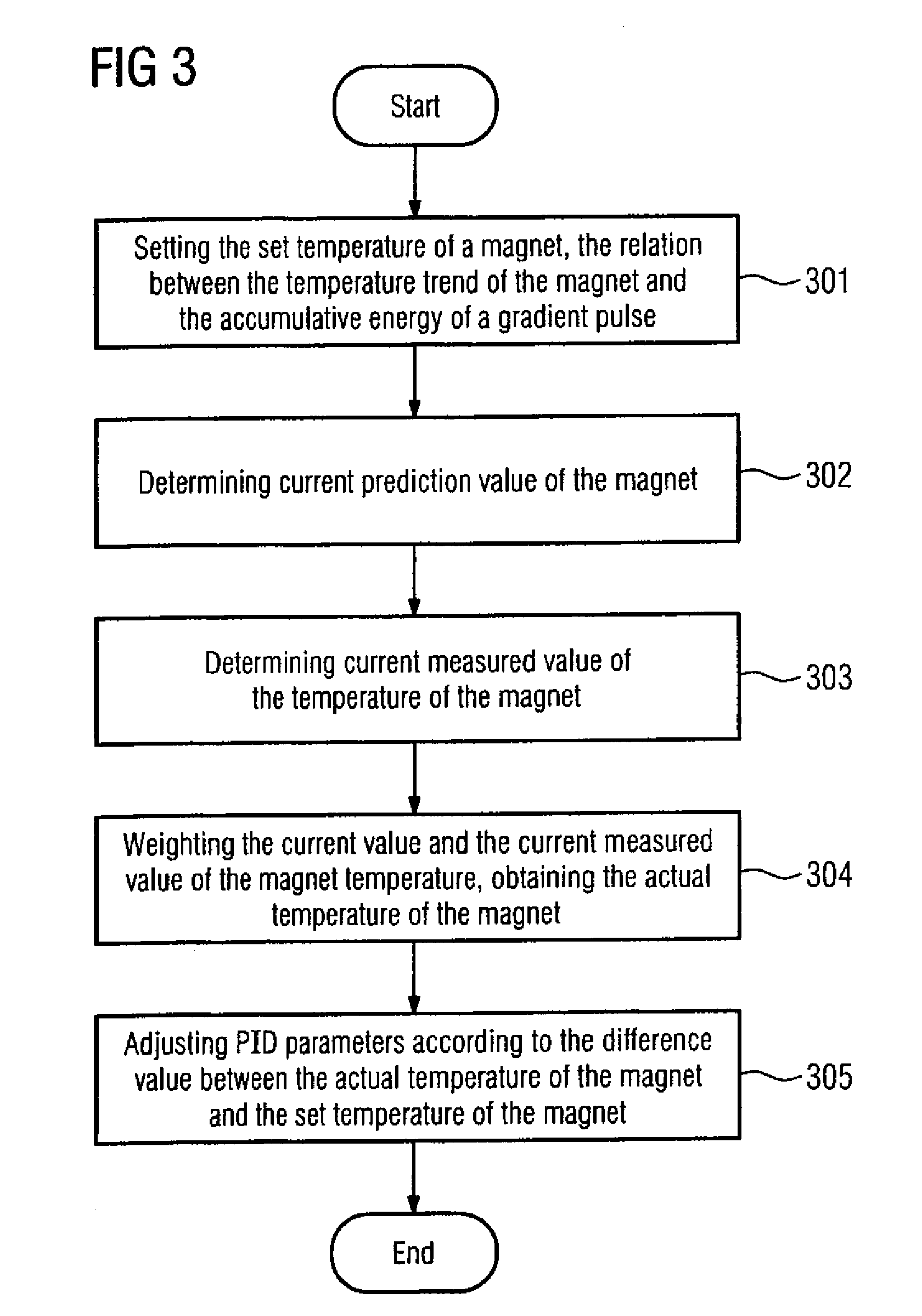
A method for improving the imaging quality of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment and MRI equipment, include obtaining a corresponding relationship between a deterioration factor of imaging quality and the cumulative energy of gradient pulses applied by successive scanning MRI sequences, then determining a predicted value of a current deterioration factor of imaging quality according to the currently applied cumulative energy of the gradient pulses and said corresponding relationship, adopting a corresponding method to carry out dynamic regulation or compensation using the predicted value of said deterioration factor of imaging quality as a reference, so as to cancel the influence produced by the heating effect of the gradient system to the imaging quality, thereby effectively improving the imaging quality of the MRI equipment.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System, process and computer-accessible medium for providing quantitative susceptibility mapping
ActiveUS9213076B2Overcome limitationsEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingSensorsElectric/magnetic detectionQuantitative susceptibility mappingComputer science
Exemplary quantitative susceptibility mapping methods, systems and computer-accessible medium can be provided to generate images of tissue magnetism property from complex magnetic resonance imaging data using the Bayesian statistical approach. The likelihood is constructed directly using the complex data. A prior is constructed from matching structures or information content in known morphology. The quantitative susceptibility map can be determined by, e.g., maximizing the posterior. Thus, according to the exemplary embodiment, system, method and computer-accessible medium can be provided for determining information associated with at least one structure. Using such exemplary embodiment, it is possible to receive signals associated with the structure(s), where the signals can include complex data that is in the complex domain.
Owner:MEDIMAGEMETRIC
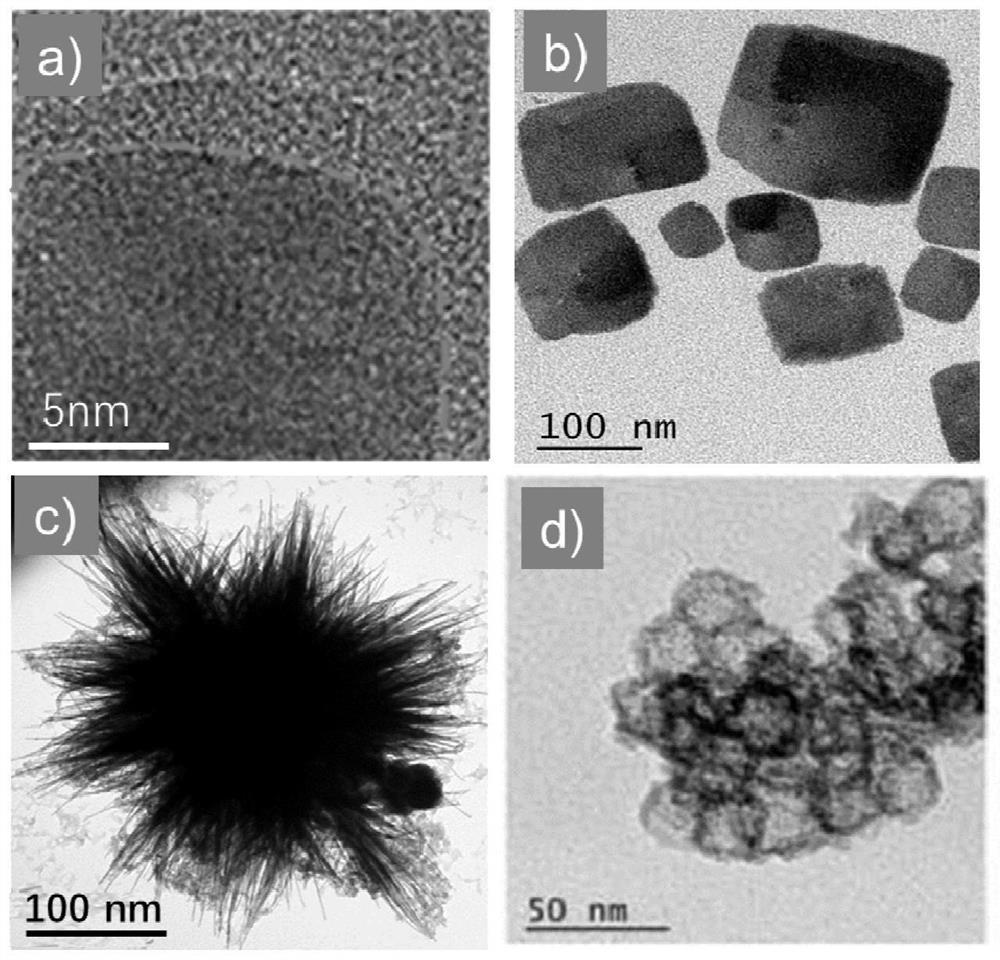
Nickel doped copper sulfide nano material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104548094AEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingFunctionalEnergy modified materialsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsTherapeutic effectCopper sulfide
The invention provides a nickel doped copper sulfide nano material. The chemical general formula of the nickel doped copper sulfide nano material is Cu1-xNixS, wherein CuS refers to a substrate, Ni<2+> refers to doping ions, and the value range of x is that x is larger than 0 and is smaller than or equal to 0.8; the nickel doped copper sulfide nano material provided by the invention is a multifunctional nano material and simultaneously has a magnetic resonance imaging function and a photothermal therapy effect, so that the nickel doped copper sulfide nano material can be used as a magnetic resonance imaging probe and a photothermal therapy reagent and is a nano material integrating detection and therapy. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application of the nickel doped copper sulfide nano material.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Bulk production and usage of hyperpolarized 129Xenon
InactiveUS6125654AEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingHigh sensitivitySolidificationLiquefactionSpin relaxationSpins
The production and usage of hyperpolarized 129Xenon which comprises providing solid xenon with either an internal (dissolved) or external (imbedded) nuclear spin relaxant, loading and positioning the solid xenon in a low temperature refrigerator operating in the range of 5 mK to 30 mK with a surrounding magnetic field of between about 10 and 20 Tesla enabling high xenon spin polarizations between about 10% and 50% to be obtained in a time of about 1-3 days owing to the properties of the relaxant, separating the xenon from the relaxant or otherwise rendering the relaxant inoperable after polarizing and thereby switching off further relaxation and insuring preservation of the polarization of the xenon in solid, liquid or gaseous form for storage or external use for long times, ranging from weeks to the order of minutes, depending on the usage conditions.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly reconstructing magnetic resonance images on basis of adaptive structure low-rank matrixes
InactiveCN107991636AImprove reconstruction qualityImprove balanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWeight coefficientResonance
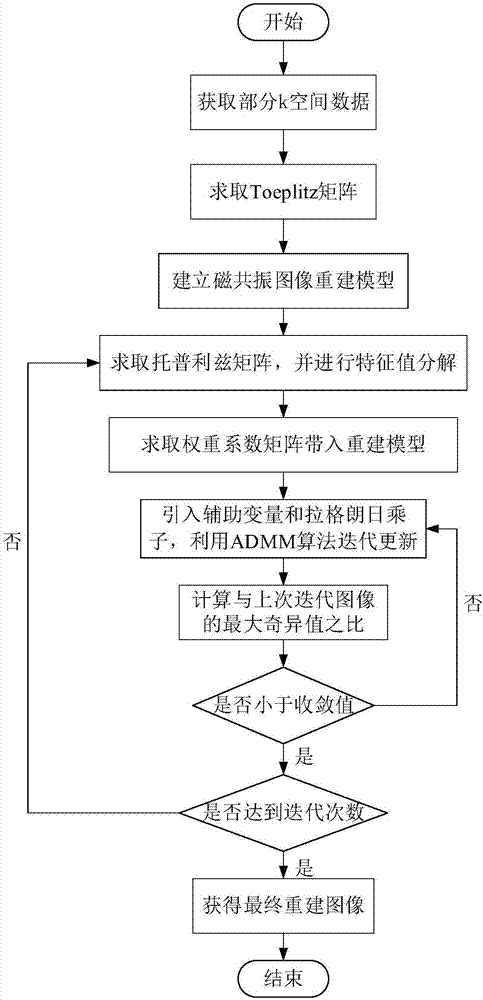
The invention discloses a method for quickly reconstructing magnetic resonance images on the basis of adaptive structure low-rank matrixes, and relates to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging. The quality of reconstructed images can be improved by the aid of the method. The method includes steps of (1), acquiring partial k spatial data; (2), solving partial derivatives and constructing Toeplitz matrixes; (3), building image reconstruction models; (4), deforming the Toeplitz matrixes and decomposing characteristic values; (5), computing weight coefficient matrixes and leading the weight coefficient matrixes into the reconstruction models; (6), introducing auxiliary variables and Lagrange multipliers and carrying out iterative solution by the aid of ADMM (alternating direction method of multipliers) algorithms; (7), judging whether convergence conditions are met by reconstruction results or not; (8), acquiring ultimate magnetic resonance images when iterative times are reached, or updating the Toeplitz matrixes by the current reconstructed images obtained by means of iteration, and returning the step (4) to continue operation. Compared with first-order and second-order structure low-rank and total-variation methods, the method has the advantage that the reconstructed images with high quality can be obtained by the aid of the method under the condition of identical under-sampling multiples.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by radio-frequency pulse
ActiveCN103033784AImprove controllabilityReduced imaging timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData spacePulse sequence
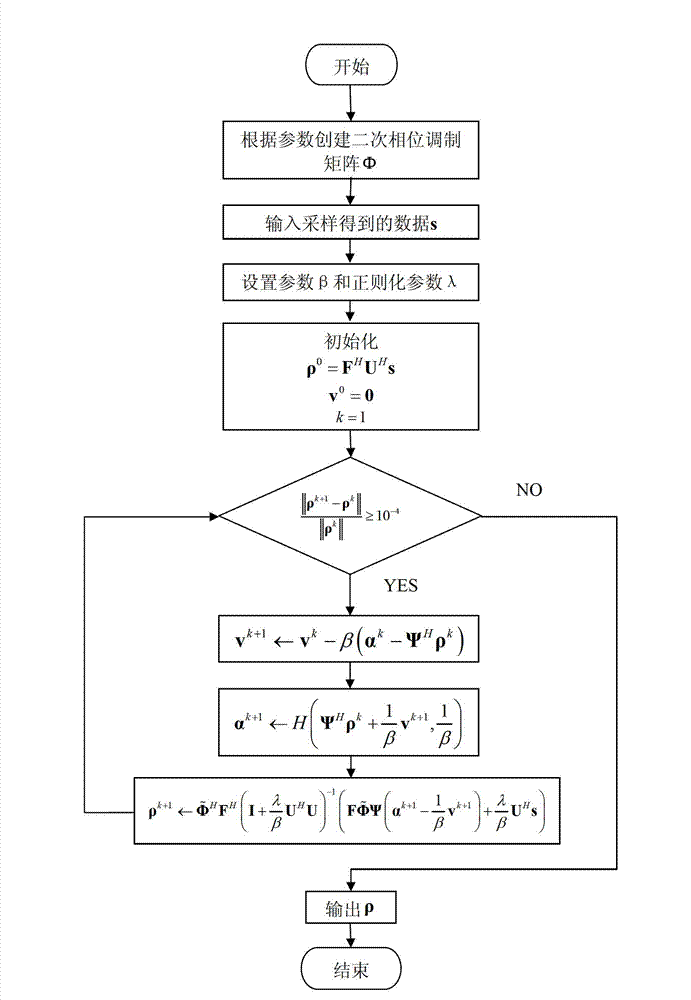
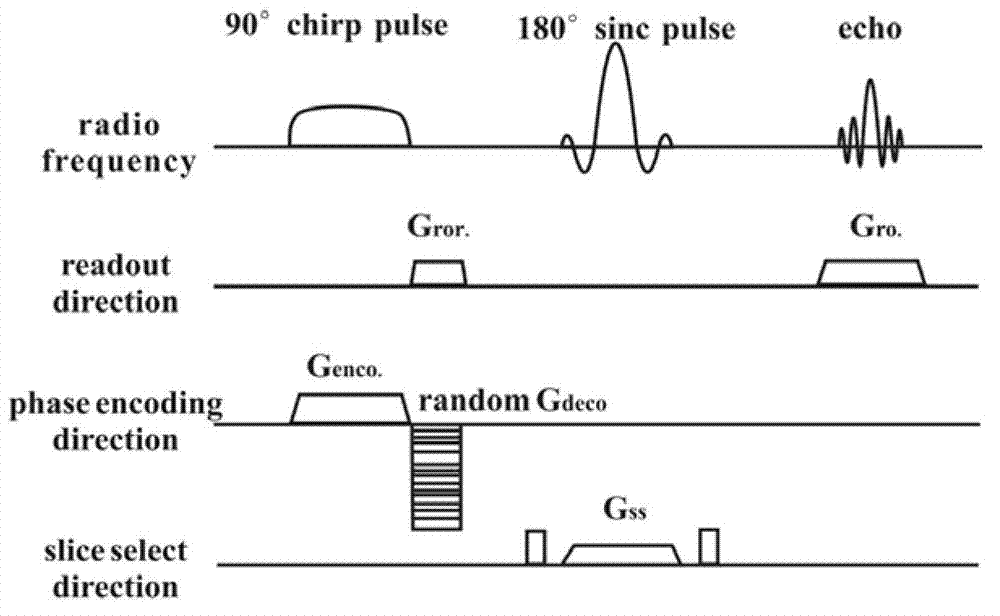
The invention discloses a compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by a radio-frequency pulse, and relates to the magnetic resonance imaging method. The invention provides the compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by the radio-frequency pulse, wherein the compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by the radio-frequency pulse is capable of controlling a space K to spread spectrum easily. The method includes the spectrum spreading to the space K from the radio-frequency pulse, undersampling at random and image reconstruction. In the magnetic resonance imaging, the radio-frequency pulse of linear frequency modulation is exerted along the phase encoding direction to control the energy diffusion of magnetic resonance imaging data space. The undersampling at random is carried out to the imaging data with spread spectrum, and sampling time is reduced. In terms of the undersampling data, suggested fast reconstruction algorithm is adopted to carry out sparse reconstruction to the imaging. Due to the fact that radio-frequency pulse sequence is utilized to carry out the spread spectrum of the space K, compared with space K with a shim coil, the controllable property of the spread spectrum of the space K is good. The purposes of reducing imaging time and accelerating the magnetic resonance imaging are achieved by adopting the methods of undersamping the magnetic resonance signal at random and the image reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method and Apparatus for Ferrous Object and/or Magnetic Field Detection for MRI Safety
InactiveUS20090266887A1Improve securityEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingMagnetic measurementsVerifying markings correctnessEngineeringOpen label
A method and apparatus for ferrous object and / or magnetic field detection are provided. Embodiments can improve magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) safety and increase the safety of MRI facilities. Embodiments can detect a given magnetic field strength around a MRI machine and alert users to the field's presence. In an embodiment, the magnetic field warning system can rely on a single badge that warns its user. In another embodiment, the badge can utilize an RFID system. The RFID system can turn the badge on when it enters the MRI room and off when it leaves the MRI room. In another embodiment, a badge with a rechargeable battery and charger can be utilized with or without an RFID tag. The subject badges or other detection devices can be worn by a person, located on or near a ferrous object, embedded in clothing, or located in other positions convenient to a user.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Charged particle beam therapy and magnetic resonance imaging
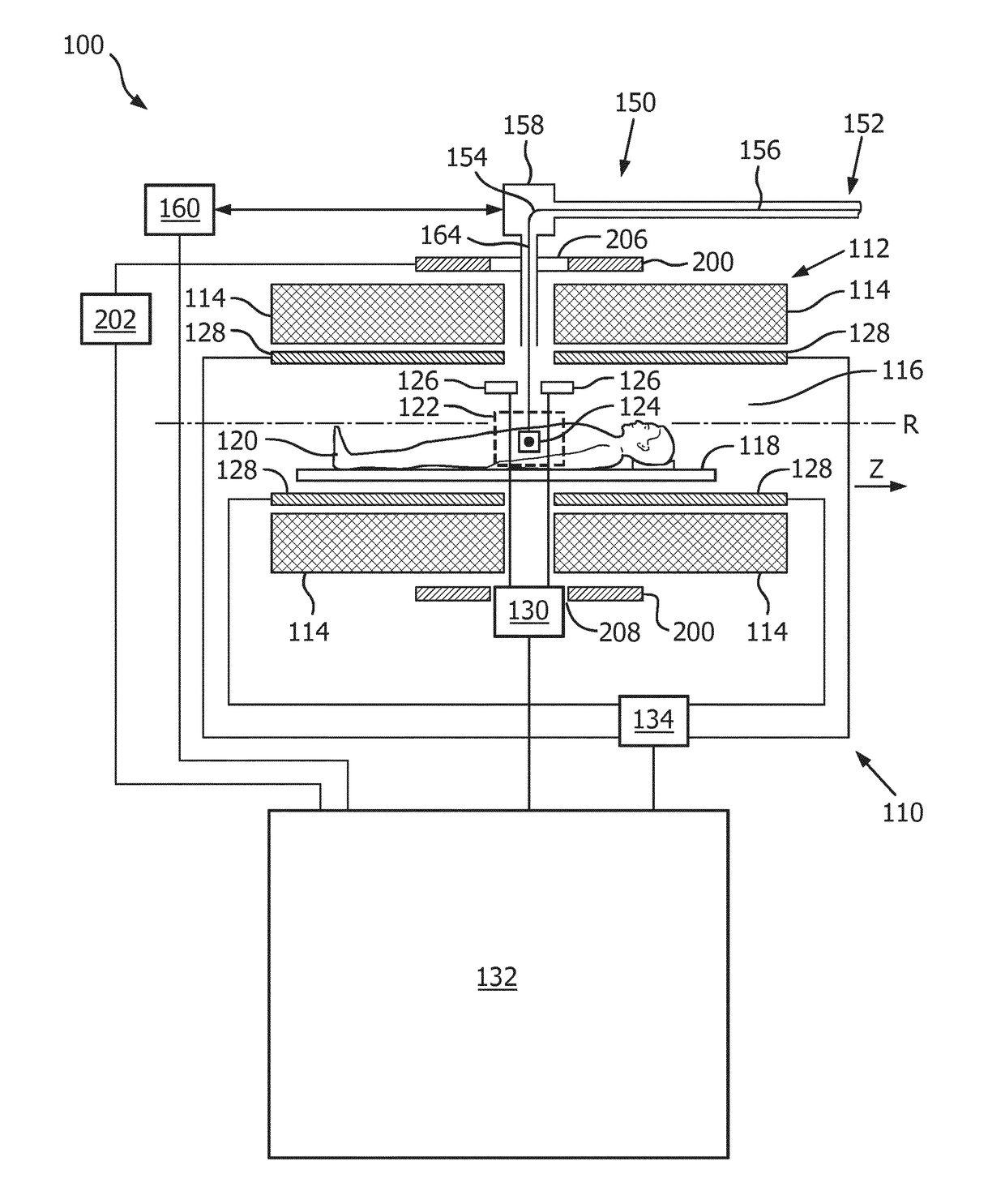
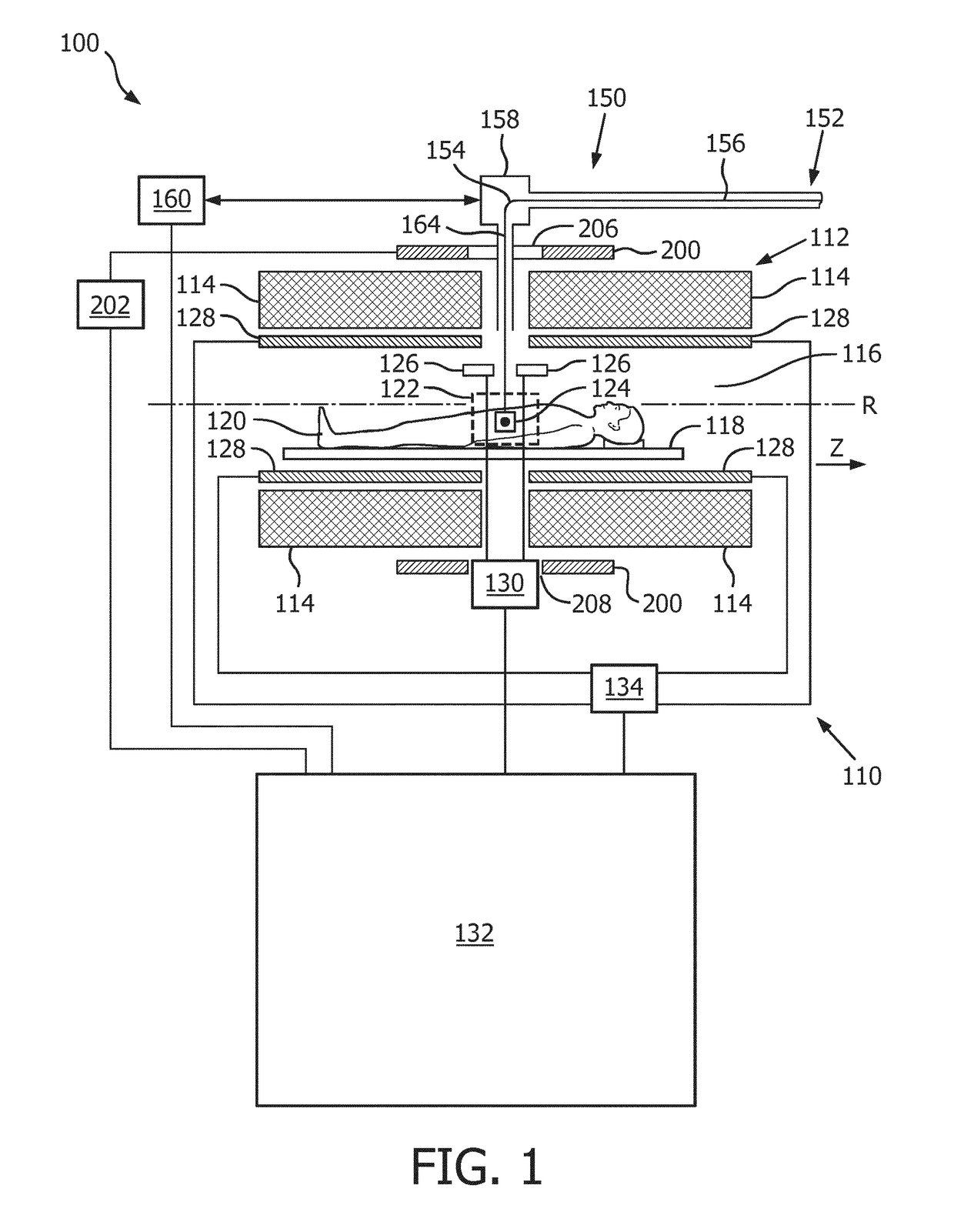
ActiveUS20170120075A1Reliable compensationReliable magnetic resonance imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRotational axisBending magnets
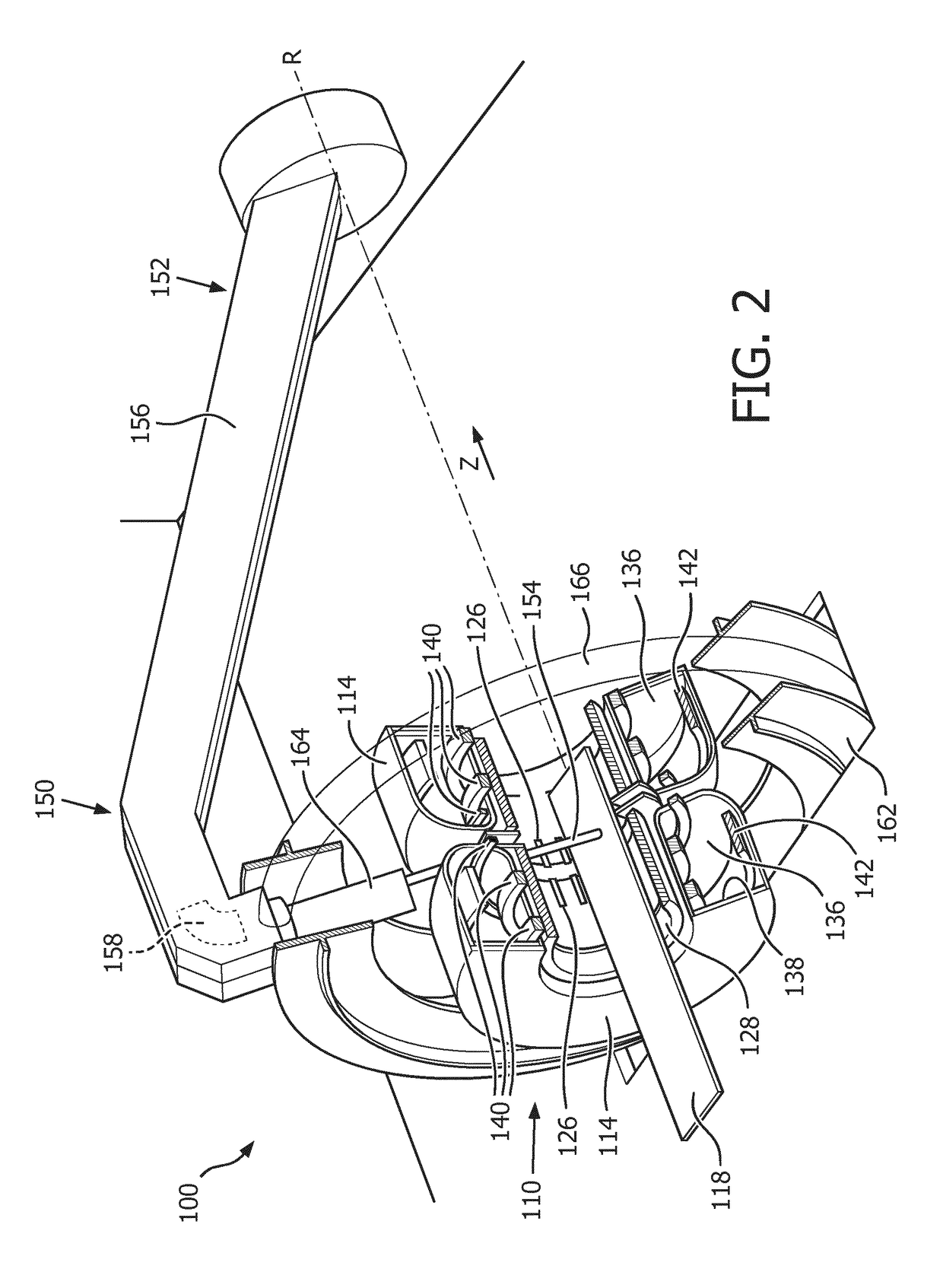
The present invention provides a medical apparatus (100) comprising a magnetic resonance imaging system (110) for acquiring magnetic resonance data from an imaging volume (122) covering at least partially a subject of interest (120), wherein the magnetic resonance imaging system (110) comprises a main magnet (112) for generating a magnetic field within the imaging volume (122), a particle beam apparatus (150) having a particle beam line (152) for a particle beam (154) of charged particles, including a gantry (156) configured for rotating around a rotational axis (R), which is arranged in the longitudinal direction of the main magnet (112), wherein the gantry (156) comprises at least one bending magnet (158) for directing the particle beam (154) to an irradiation volume (124) within the imaging volume (122), an active compensation coil (200), which is arranged to substantially surround at least the imaging volume (122), and a control unit (132) for controlling the active compensation coil (200) for canceling a stray field caused by the at least one bending magnet (158) within the imaging volume (122) at least in the longitudinal direction of the main magnet (112). The present invention also provides a shielding method for use in the above medical apparatus (100).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Magnetic resonance image reconstruction method based on regularized depth image prior method
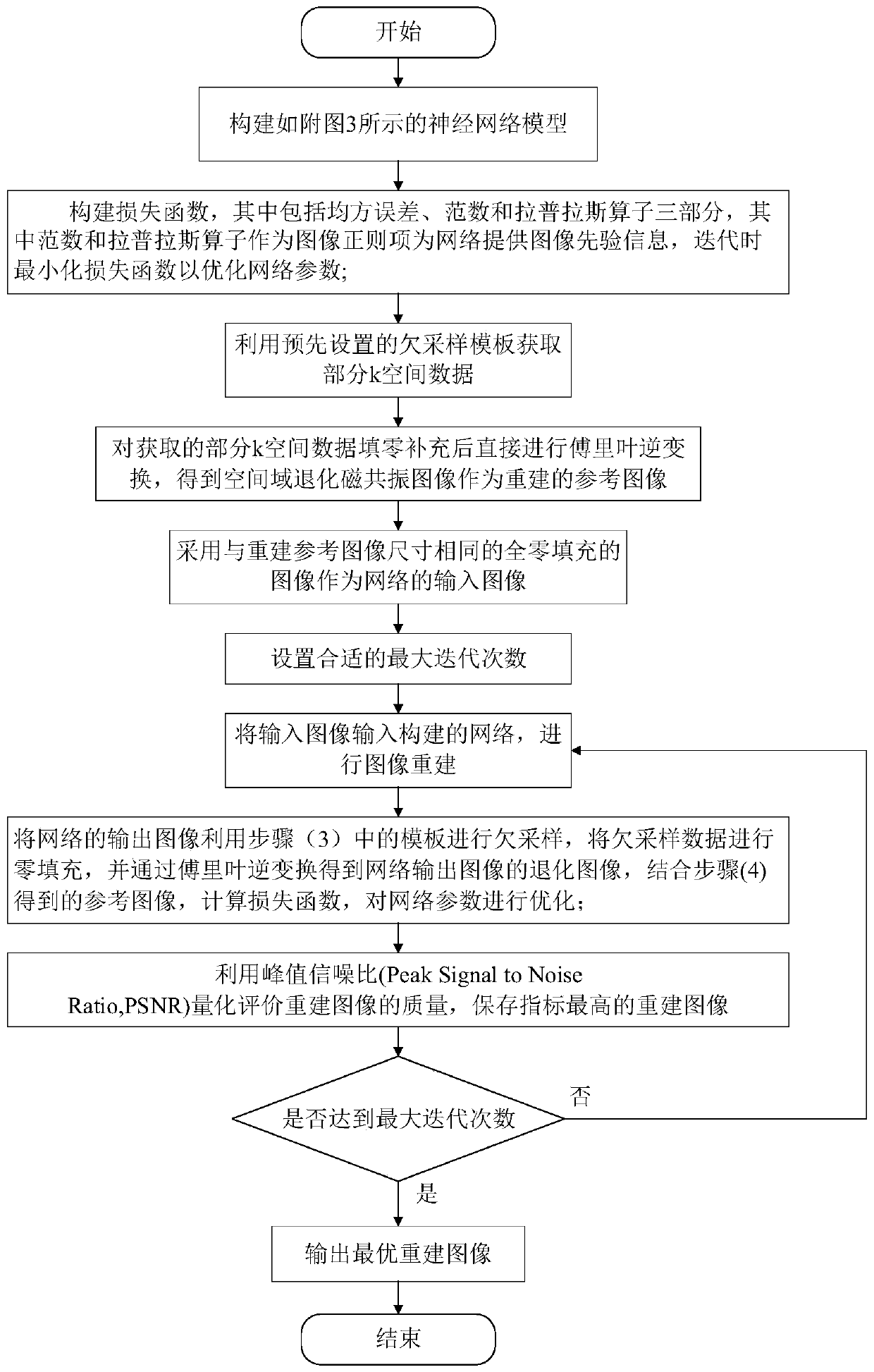
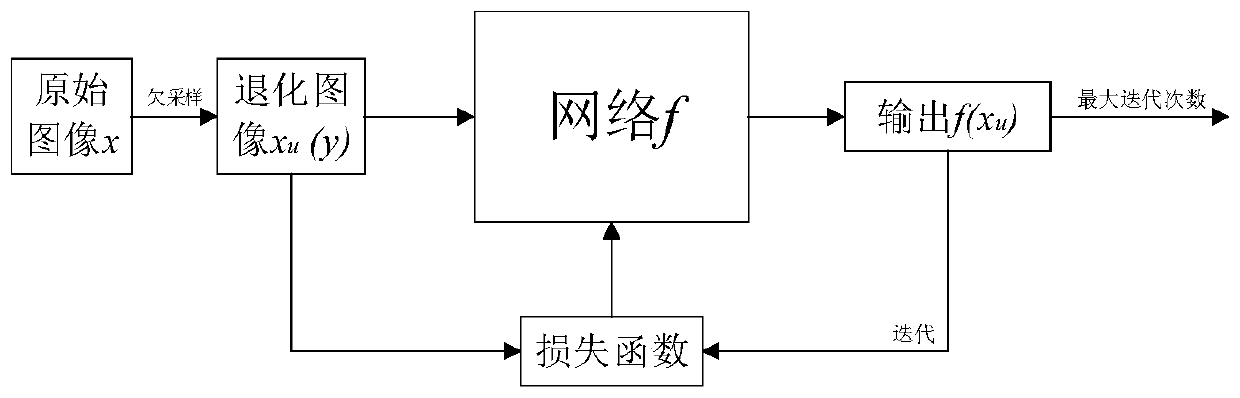
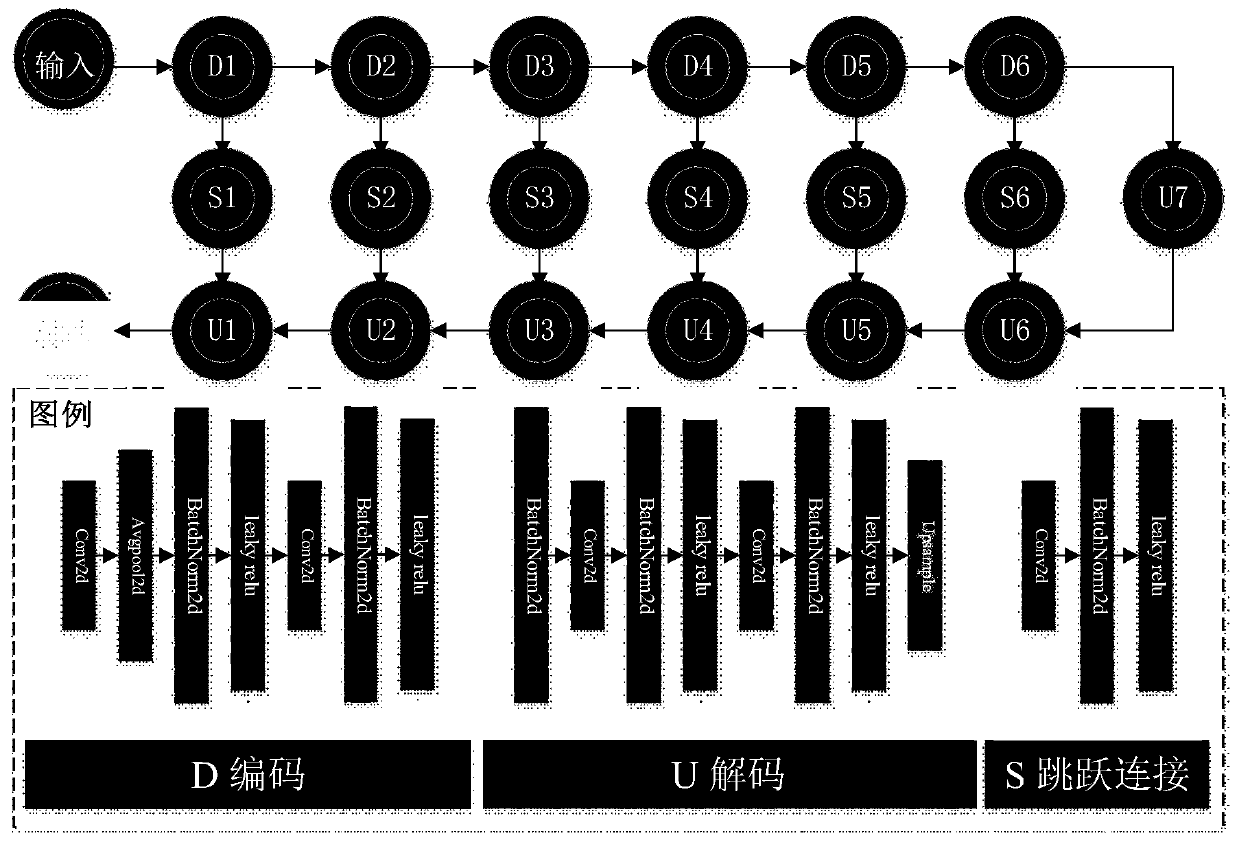
ActiveCN110490832AImprove computing efficiencyImprove accelerationImage enhancementImage analysisImage reconstruction algorithmNetwork model
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance image reconstruction method based on a regularized depth image prior method, and relates to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging. The invention aims to solve the problem of limitation of a conventional magnetic resonance image reconstruction algorithm based on deep learning, and aims to improve the quality of a reconstructed image and shorten the reconstruction time. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a neural network model; (2) constructing a loss function containing a regular term; (3) acquiring partial k spacedata; (4) obtaining a reconstructed reference image; (5) constructing network input; (6) setting the maximum number of iterations; (7) reconstructing an image by using a network; (8) obtaining a degraded image of the network output image, calculating a loss function in combination with the reference image, and optimizing network parameters; (9) storing the output image with the highest index; and(10) judging whether the number of iterations reaches the maximum number of iterations, if so, outputting the optimal reconstructed image, and otherwise, returning to the step (7). Compared with a convolutional neural network, the method has the advantages that the dependence on data is small, a high-quality reconstructed image can be obtained, and the reconstruction speed is increased.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
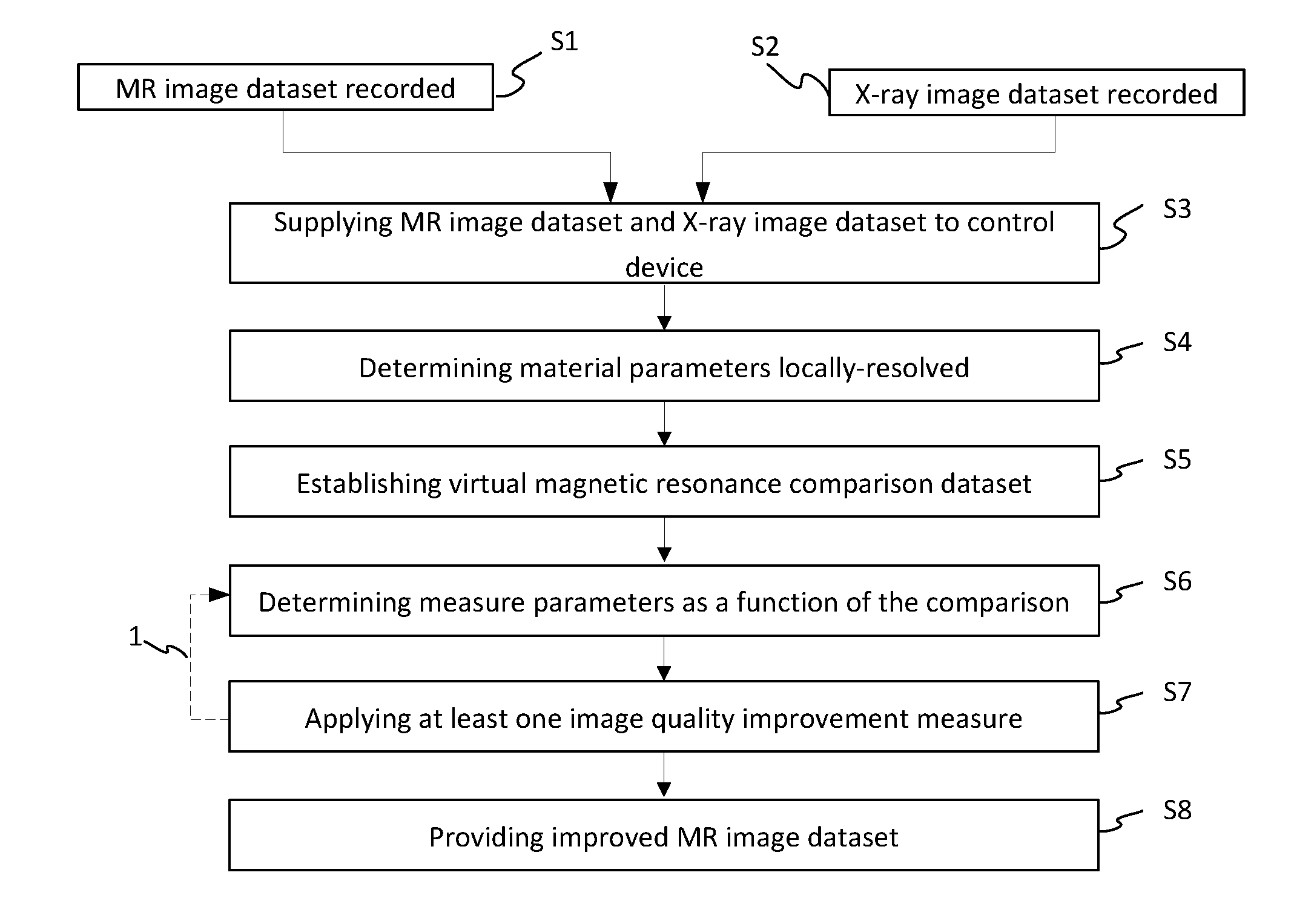
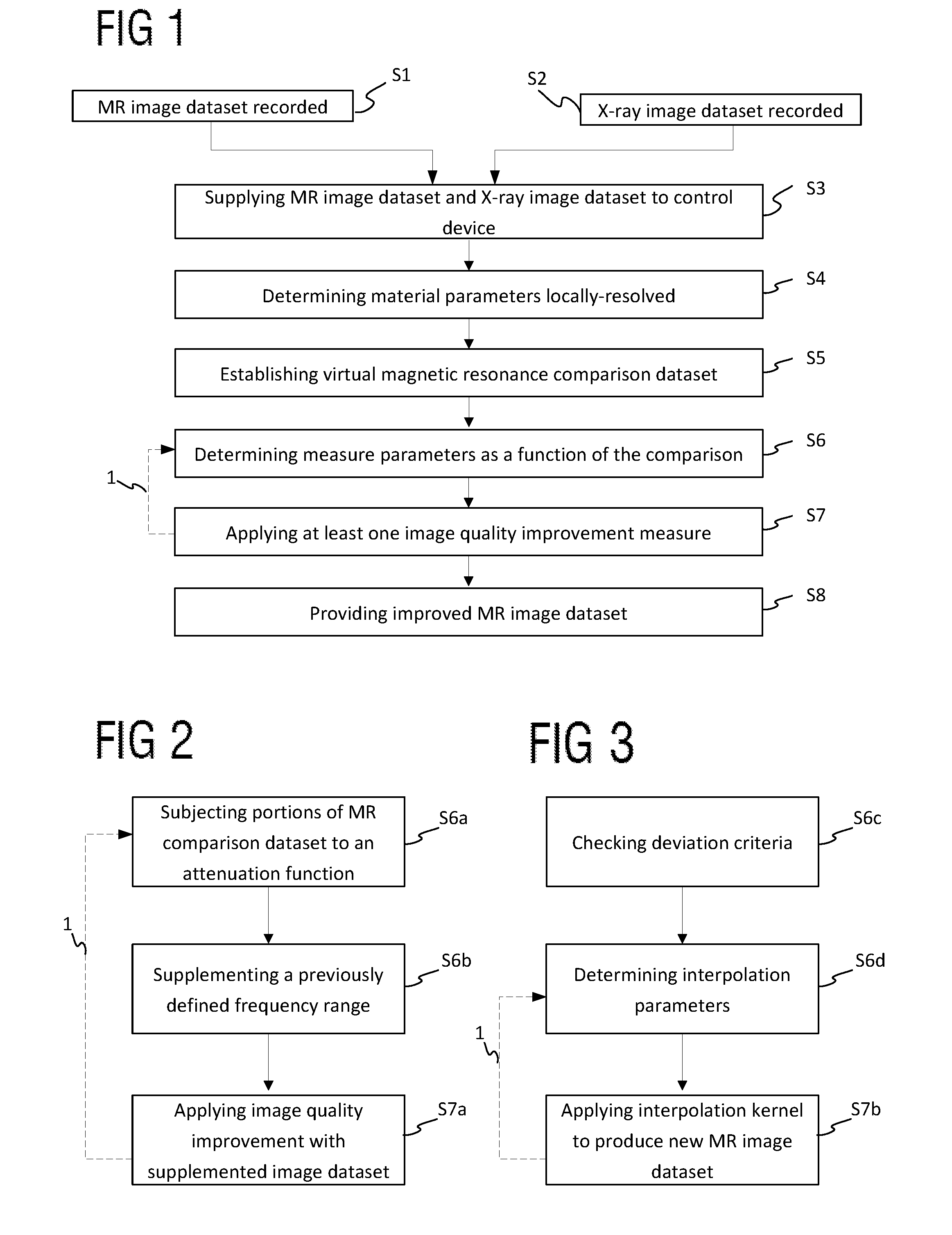
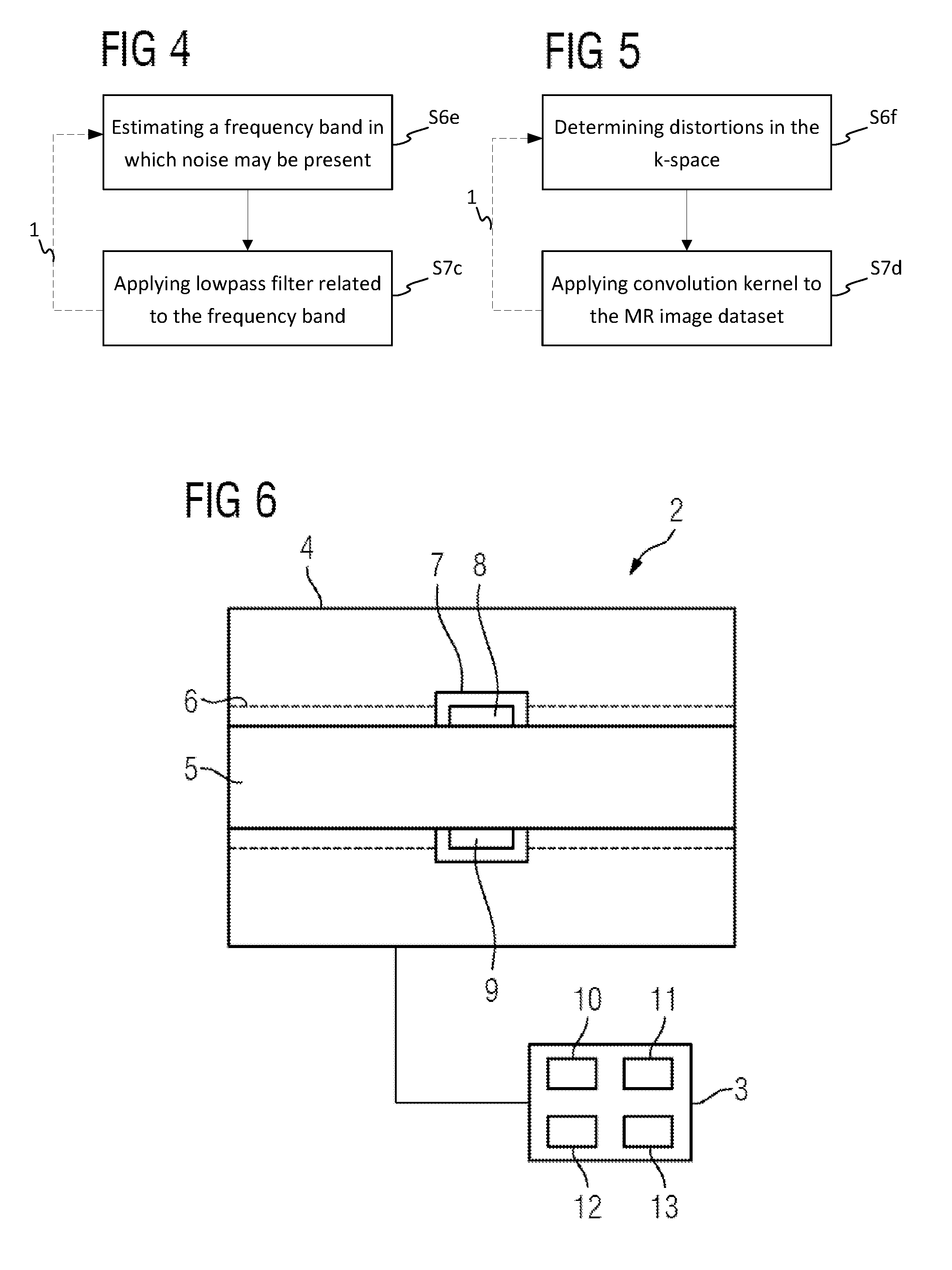
Image quality of a magnetic resonance image dataset
ActiveUS20160217555A1Improve image qualityImprove applicabilityImage enhancementImage analysisX ray imageNuclear magnetic resonance
A method for improving the image quality of a three-dimensional magnetic resonance image dataset recorded with a magnetic resonance device, wherein, from at least one correction image dataset recorded with a modality other than magnetic resonance imaging, registered with the magnetic resonance image dataset, showing at least partly the same recording region as the magnetic resonance image dataset, especially an x-ray image dataset, relevant material parameters are derived locally-resolved for the magnetic resonance imaging, which are used for establishing a virtual magnetic resonance comparison dataset in a simulation wherein, as a function of a comparison between the magnetic resonance image dataset and the magnetic resonance comparison dataset, at least one measure parameter describing an image quality improvement measure to be applied in the k-space is determined and the image quality improvement measure is carried out with the measure parameter relating to the magnetic resonance image dataset.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance of water under ambient conditions
InactiveUS7906962B2Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingMeasurements using double resonanceDrug compositionsProton NMRRadio frequency
A method and apparatus are provided for treating hydrated material in a fluid that contains water in which a stable nitroxide is attached to the hydrated material. A dynamic nuclear polarization process (DNP) is conducted on the hydrated material whereby to hyperpolarize the water. A polarization cell contains the hydrated material to obtain hyperpolarized water free from the nitroxide. The dynamic nuclear polarization process is conducted using components comprising a tunable, solid state high power X-band driver and an X-band resonator for microwave transmission to the hydrated material. The components can also include a radio-frequency nuclear magnetic resonance probe, a permanent magnet formed to receive the hydrated material, a portable nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and an electron spin resonance detector. The components can be sized to be portable, and include electrical input and output and a lap-size hard-case with access to the electrical input and output.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Application of reduced metal oxide semiconductor nanomaterial in antibacterial material
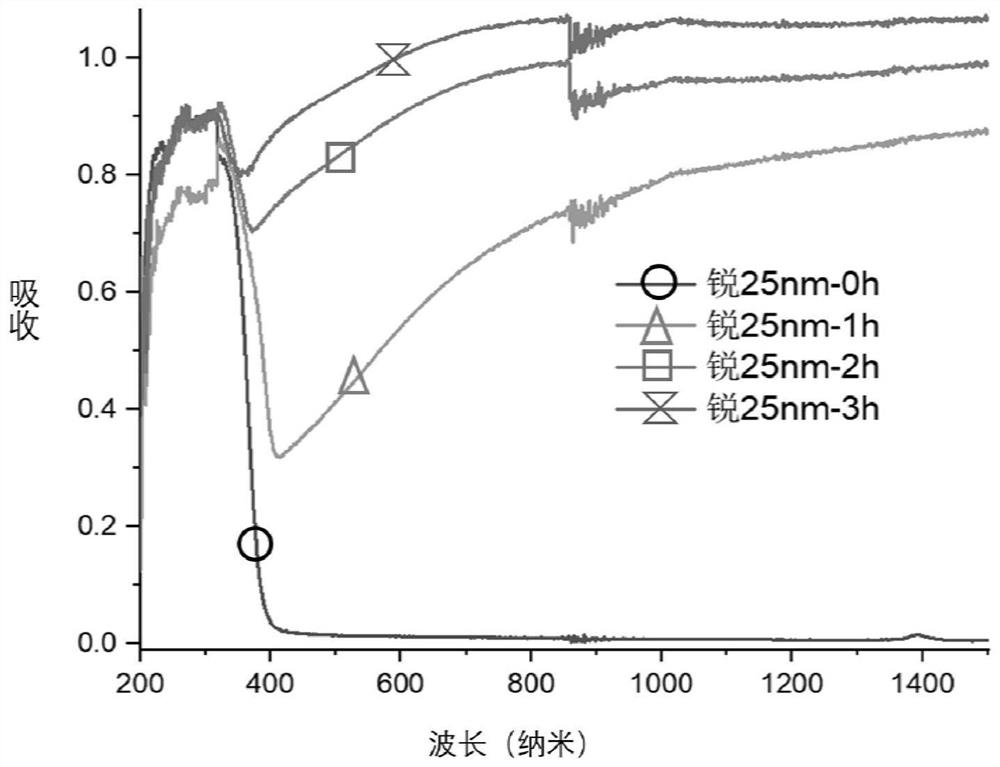
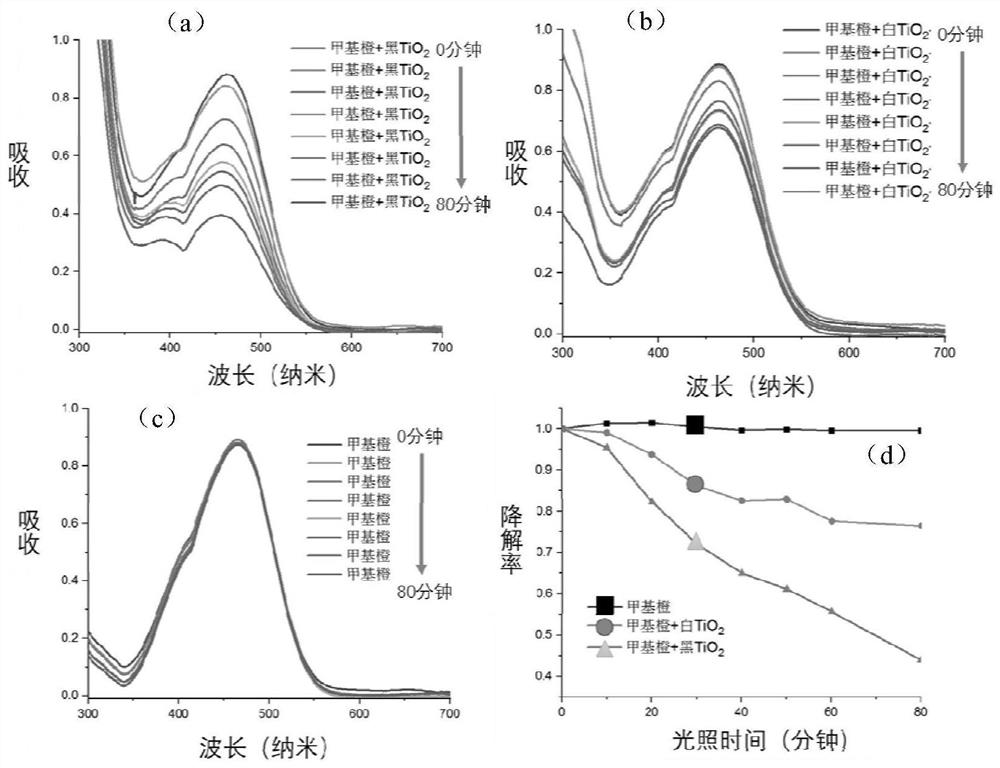
PendingCN113827720AImprove utilizationInhibit synthesisAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryReactive oxygen radicalsUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses an application of a reduced metal oxide semiconductor nanomaterial in an antibacterial material. The antibacterial material can be excited by ultraviolet light, visible light and near-infrared light with the wavelength of 280-1700 nm to generate reactive oxygen free radicals and heat, a killing effect on pathogenic microorganisms is achieved, and compared with white TiO2, the utilization of the excitation light wavelength range is greatly improved. The antibacterial material can generate an inhibition effect on pathogen microproduction through multiple mechanisms. Wide application prospects are realized in the aspects of antibacterial dressings, antibacterial consumables, mask surface antibacterial and self-cleaning coatings and the like.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
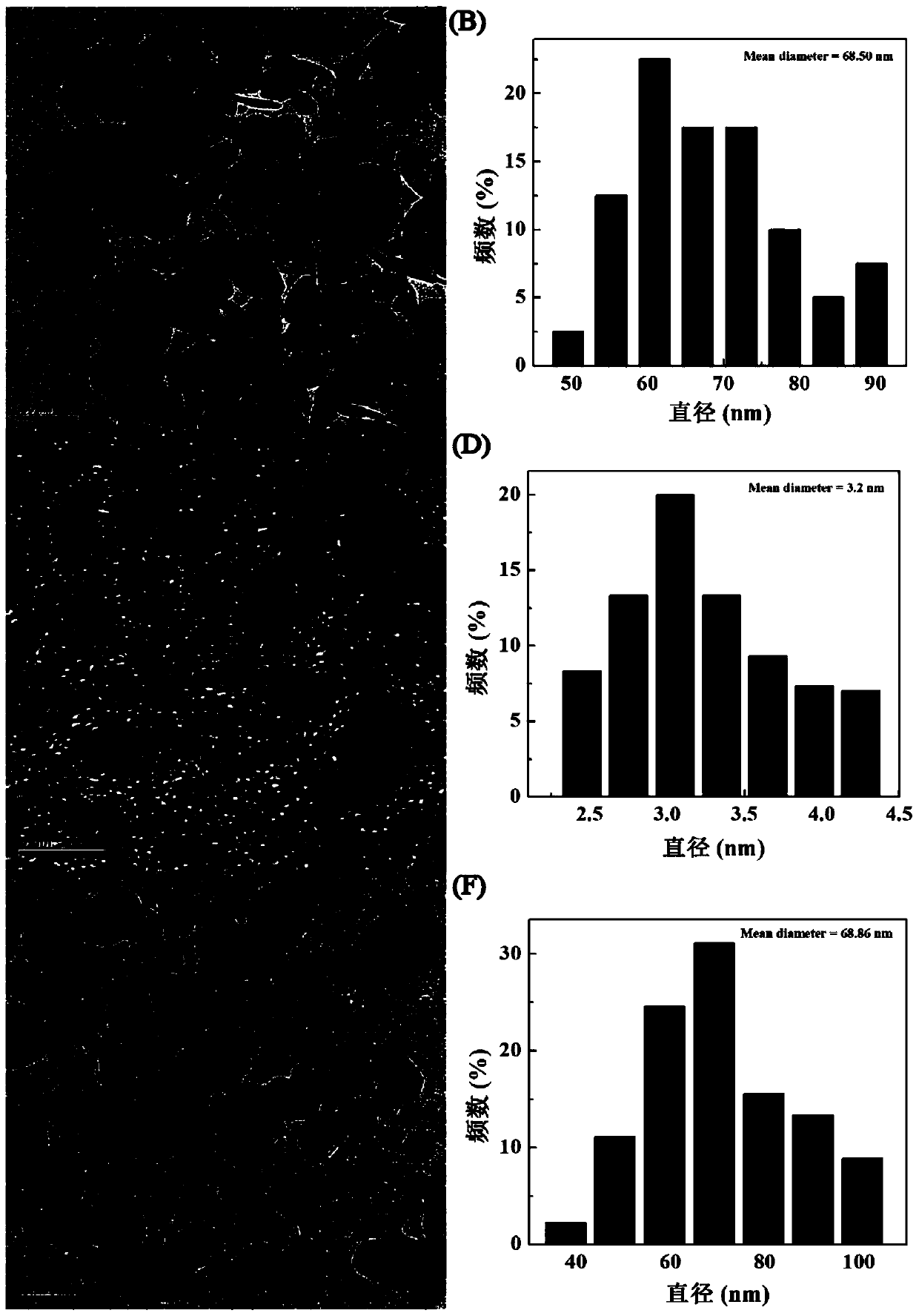
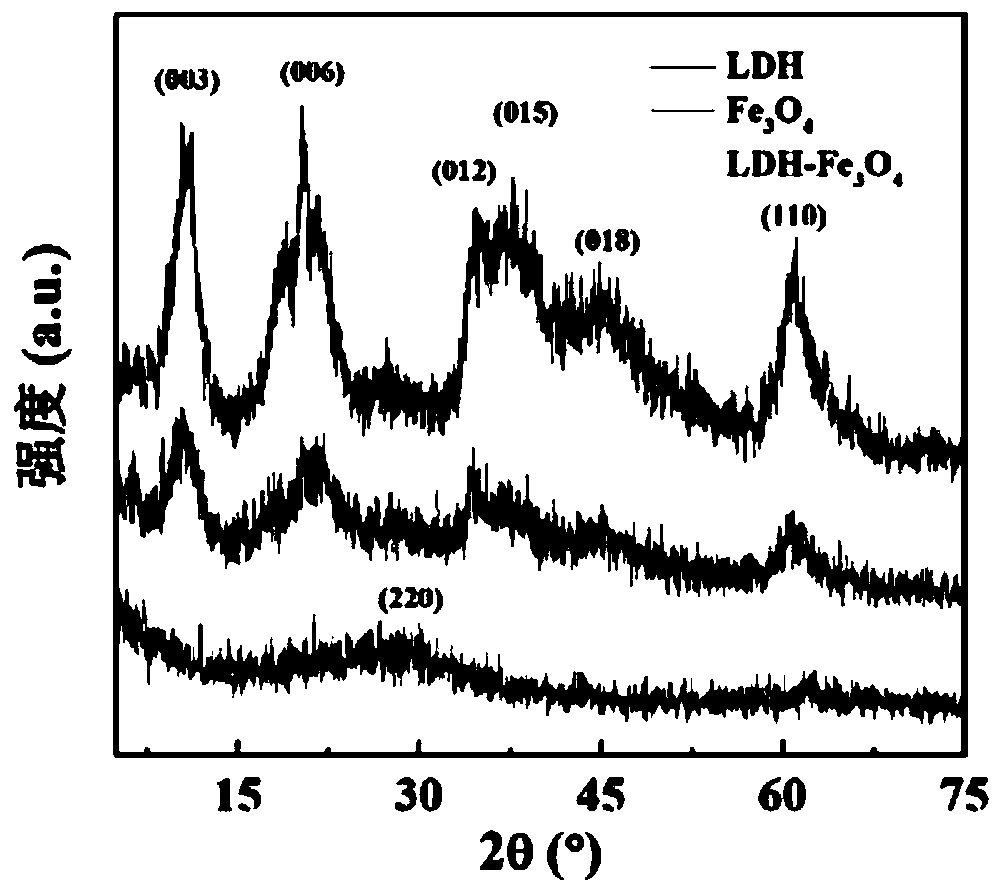
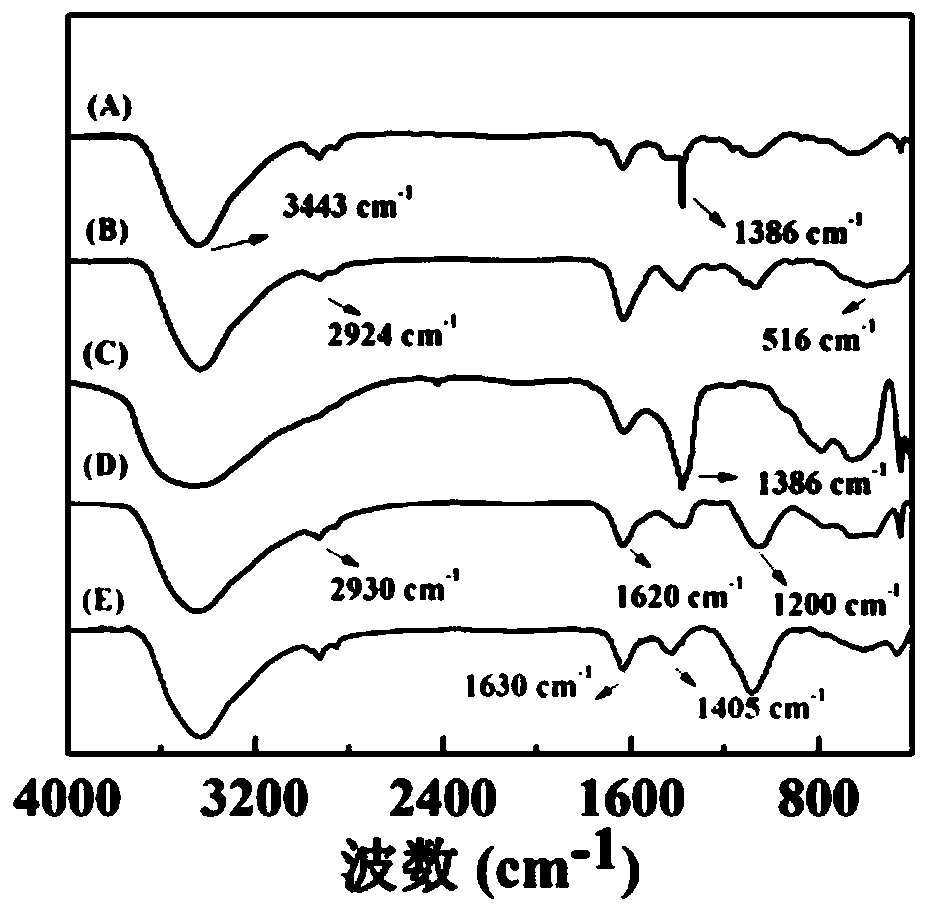
HA-targeted layered doubled hydroxide-ultrafine iron nano material and preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN110013559AWide variety of sourcesSimple processOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDoxorubicinMr imaging
The invention relates to a HA-targeted layered doubled hydroxide-ultrafine iron nano material and preparation and applications thereof. The preparation is as follows: synthesizing an LDH-Fe3O4 nano composite material by a coprecipitation method; covalently bonding activated hyaluronic acid on the surface of an LDH laminate through a silane coupling agent; and finally, carrying out surface loadingof an anticancer drug. The nano-material particles are uniformly distributed, and can enhance the MR imaging effect of the tumor part in an animal body. The LDH-Fe3O4-HA NPs is used as a carrier of ananticancer drug doxorubicin DOX, not only has sensitive pH response and release characteristics, but also can carry out specific recognition on tumor cells expressed by CD44 receptors so as to achieve the idealization effect of efficiently inhibiting tumors.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
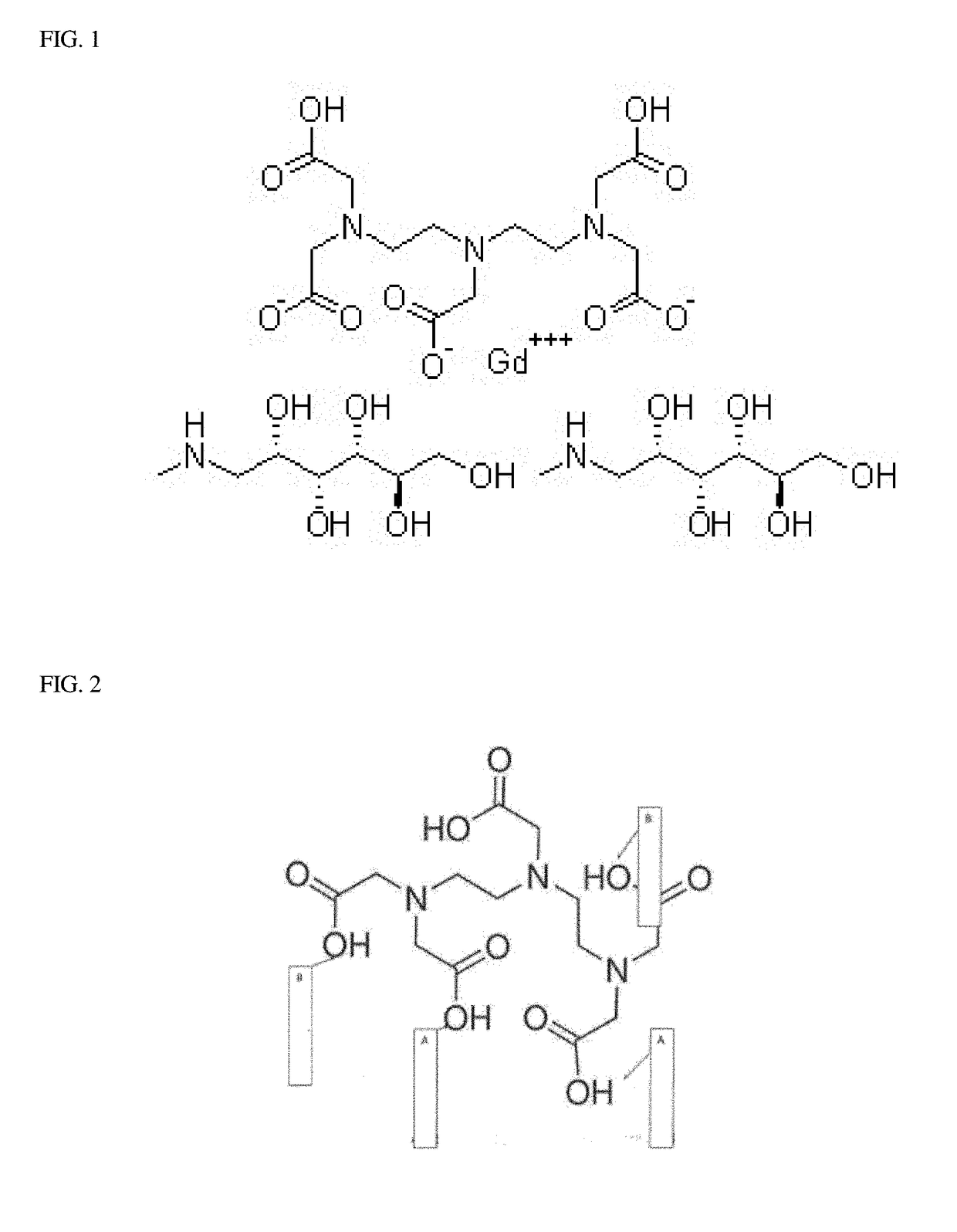
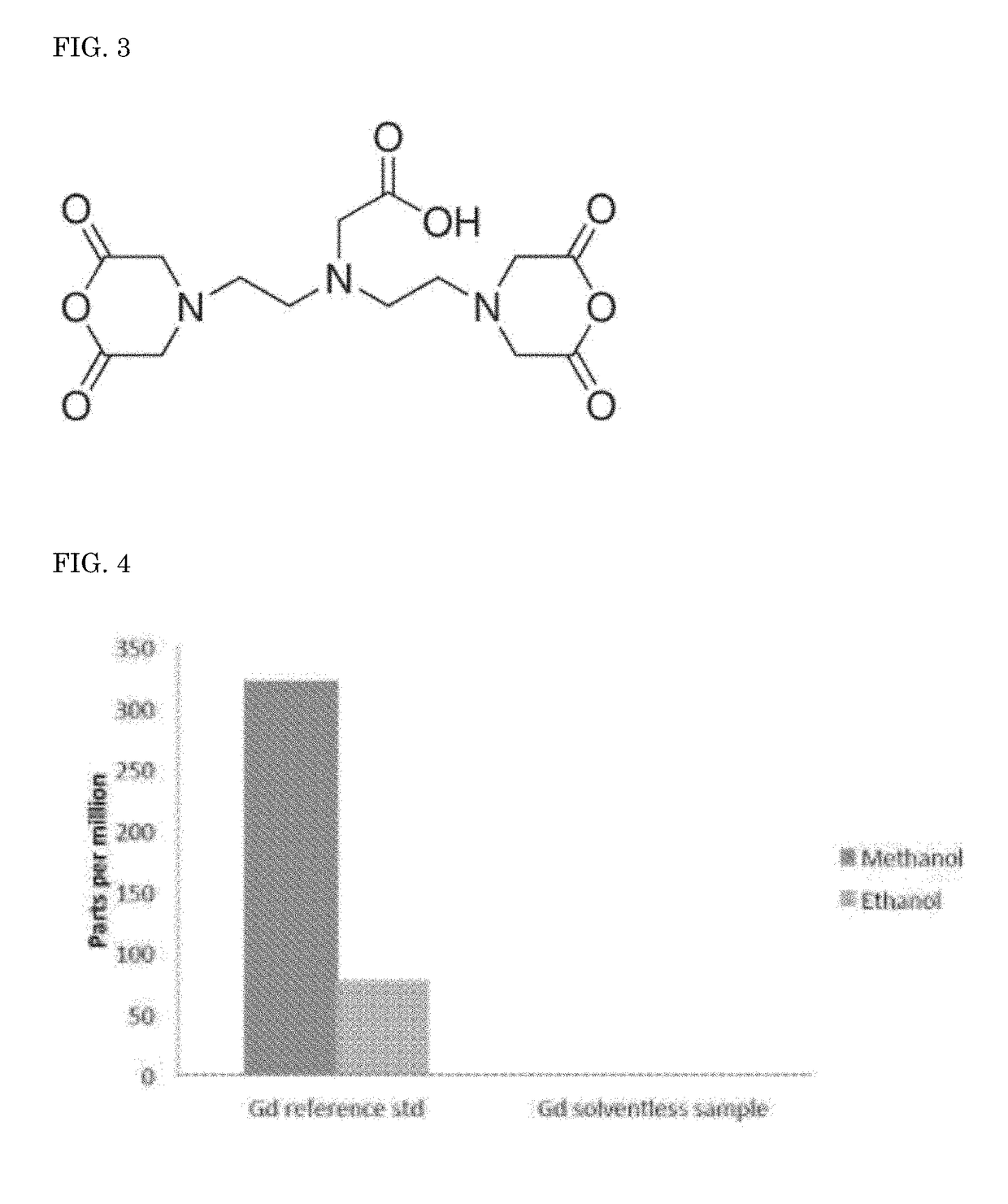
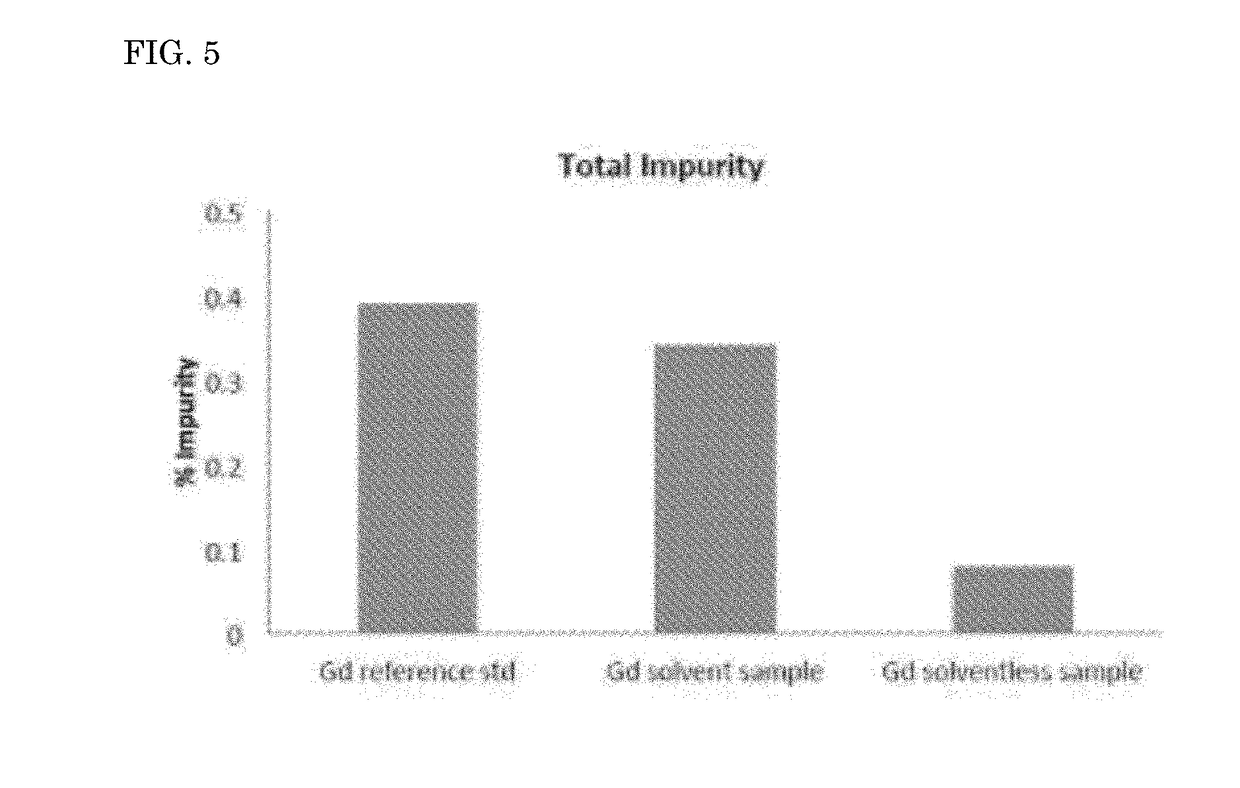
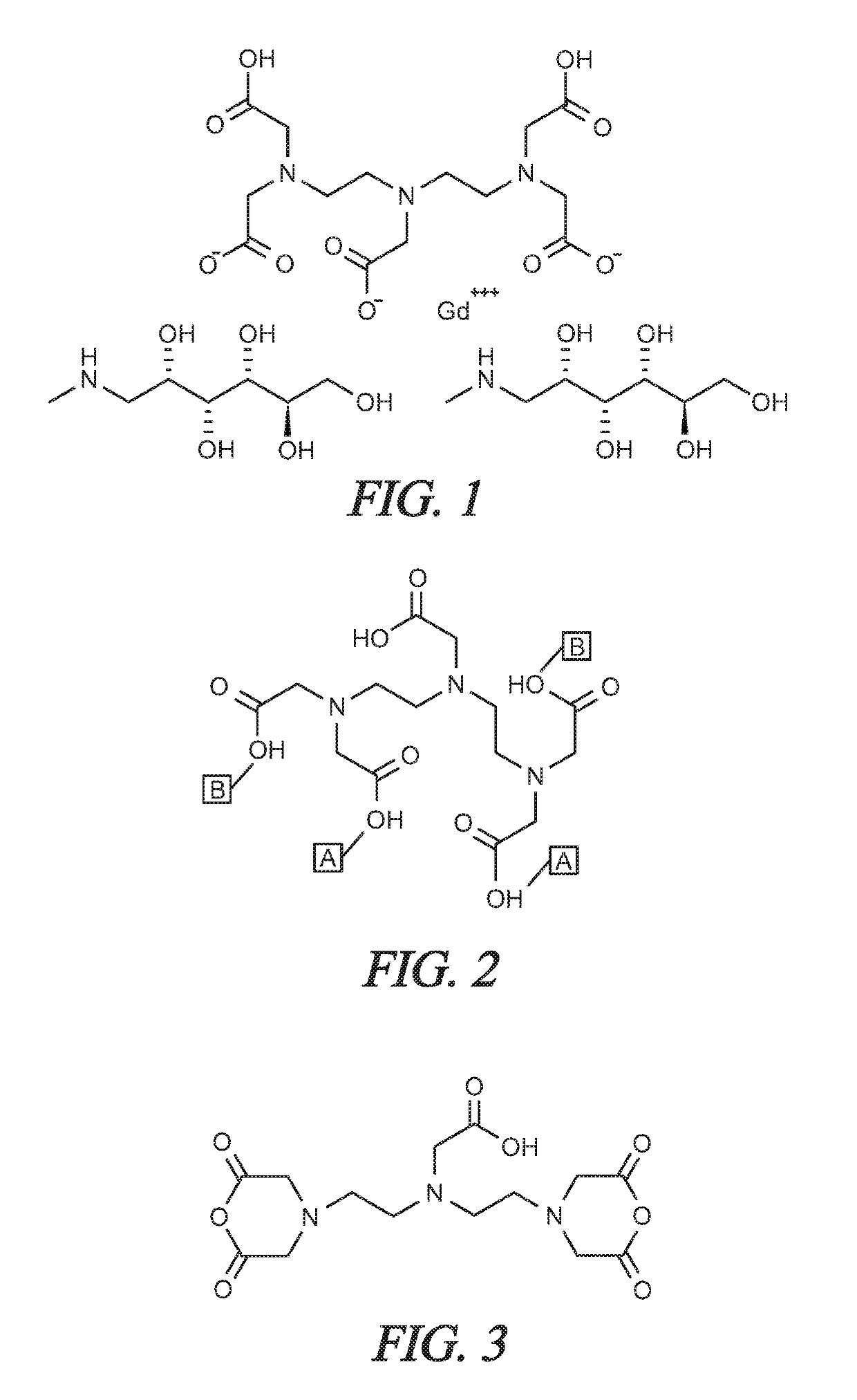
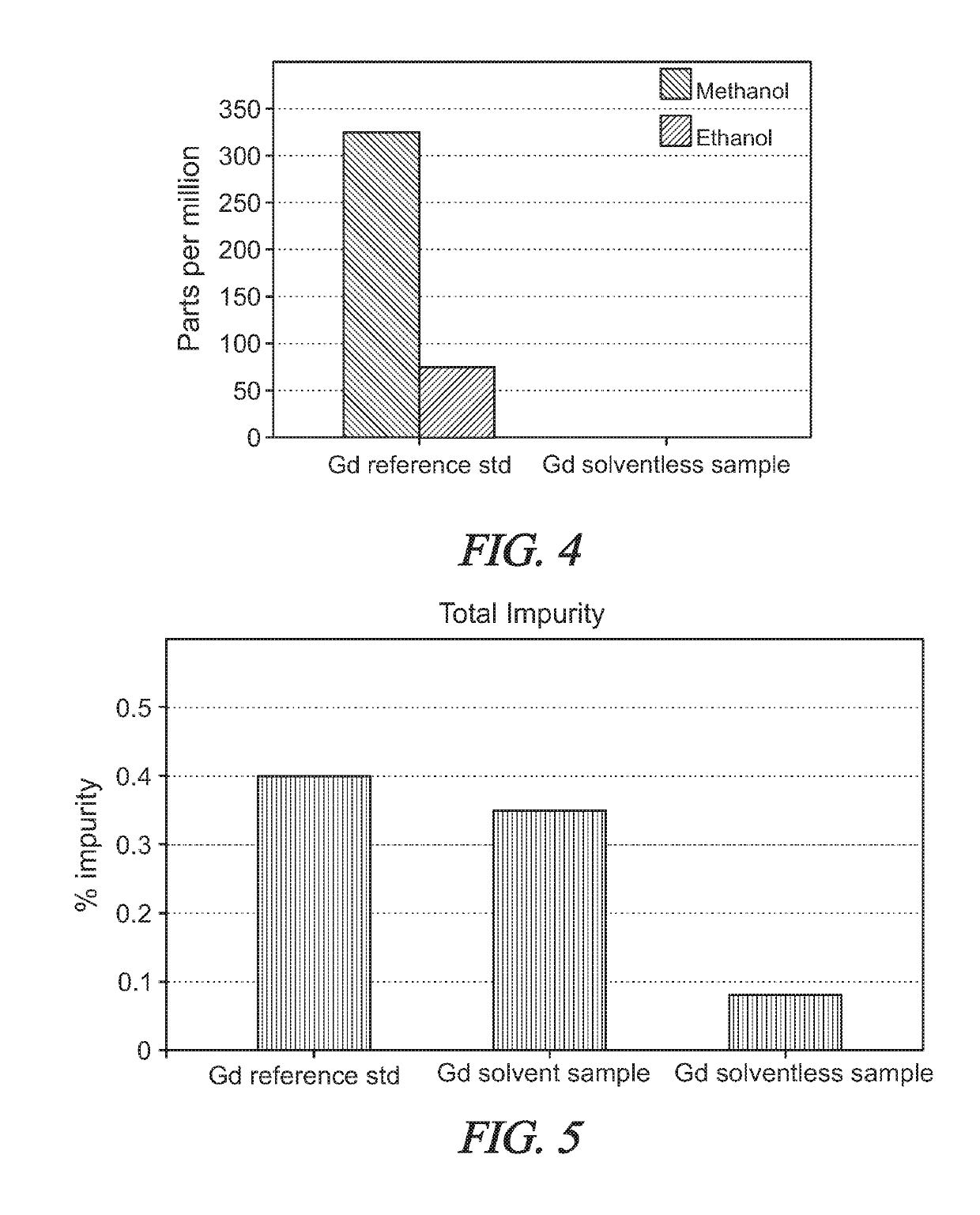
Solvent-Free Gadolinium Contrast Agents
InactiveUS20180185521A1Causes skinReduce the amount requiredDispersion deliveryUrinary disorderGadolinium contrastSolvent free
Disclosed herein are complexes of gadolinium metal, ligand and meglumine that are substantially free of non-aqueous solvents. In particular, solvent-free complexes of 1) gadopentetate dimeglumine and 2) gadoterate meglumine are disclosed and methods of their preparation are disclosed. In addition, methods are disclosed for purifying reactants, monitoring and controlling pH, quantifying the free gadolinium content, quantifying the concentration of gadolinium-ligand complex in aqueous solution, and procedures for producing a drug product in one step. The one step process eliminates the need to dry the gadolinium-ligand complex, which is typically highly hygroscopic. The one step process includes purification steps that do not require the use of non-aqueous solvents.
Owner:INVENTURE LLC
Peptide functionalized metal-loaded porphyrin phase-change nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111671923ASolve the technical problem that it is difficult to break through the tumor tissue barrier and penetrate deep into the tumor tissueSolve technical problems deep inside tumor tissueDispersion deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsPorphyrinLiposome
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, relates to a nanoparticle and a preparation method and application thereof, and in particular relates to a peptide functionalized metal-loaded porphyrin phase-change nanoparticle and a preparation method and application thereof. The nanoparticle comprises a shell membrane formed by liposome, and liquid fluorocarbon encapsulated in the shell membrane, wherein a tumor homing cell-penetrating peptide is covalently attached to the shell membrane, and the inside of the lipid bilayer of the liposome is encapsulated with a contrast agent. The nanoparticle has the function of penetrating the tumor blood vessel barrier and the tumor interstitial barrier, can penetrate deep into tumor tissues, and more effectively realizes the diagnosis and treatment of tumors. The nanoparticle of the scheme can be applied in the development and preparation of drugs for tumor diagnosis or treatment.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Magnetic rod-shaped nano-hydroxyapatite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109437139AUniform sizeGood dispersionNanotechnologyPhosphorus compoundsVacuum dryingOleylamine
The invention discloses a magnetic rod-shaped nano-hydroxyapatite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises steps of uniformly mixing sodium oleate, ethanol, and oleylamine so as to obtain a mixed solution A, then adding a calcium chloride aqueous solution, reacting for 30 minutes whilestirring so as to obtain a mixed solution B, then adding a phosphate aqueous solution, continuing reacting for 30 minutes while stirring so as to obtain a mixed solution C, transferring the mixed solution C to a sealed reaction kettle, and reacting for 8 hours at 160 DEG C; cooling a reactant to room temperature, separating precipitates through centrifuging, washing to remove organic impurities, and finally vacuum drying to obtain the magnetic rod-shaped nano-hydroxyapatitematerial. The reaction process is mild, the size of the synthesized rod-shaped nano-hydroxyapatite is controlled through amount of doped gadolinium, and the prepared magnetic rod-shaped nano-hydroxyapatite is uniform in size and has high dispersibility. Compared with commercial Gd-DTPA contrast agent, the magnetic rod-shaped nano-hydroxyapatite material has better magnetic resonance imaging performance and is non-toxic, thereby having a bright application prospect in the biomedical field.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Method and apparatus for correcting the uniformity of a magnetic field
ActiveUS20110163750A1Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingMeet the requirementsElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRPower flowResonance
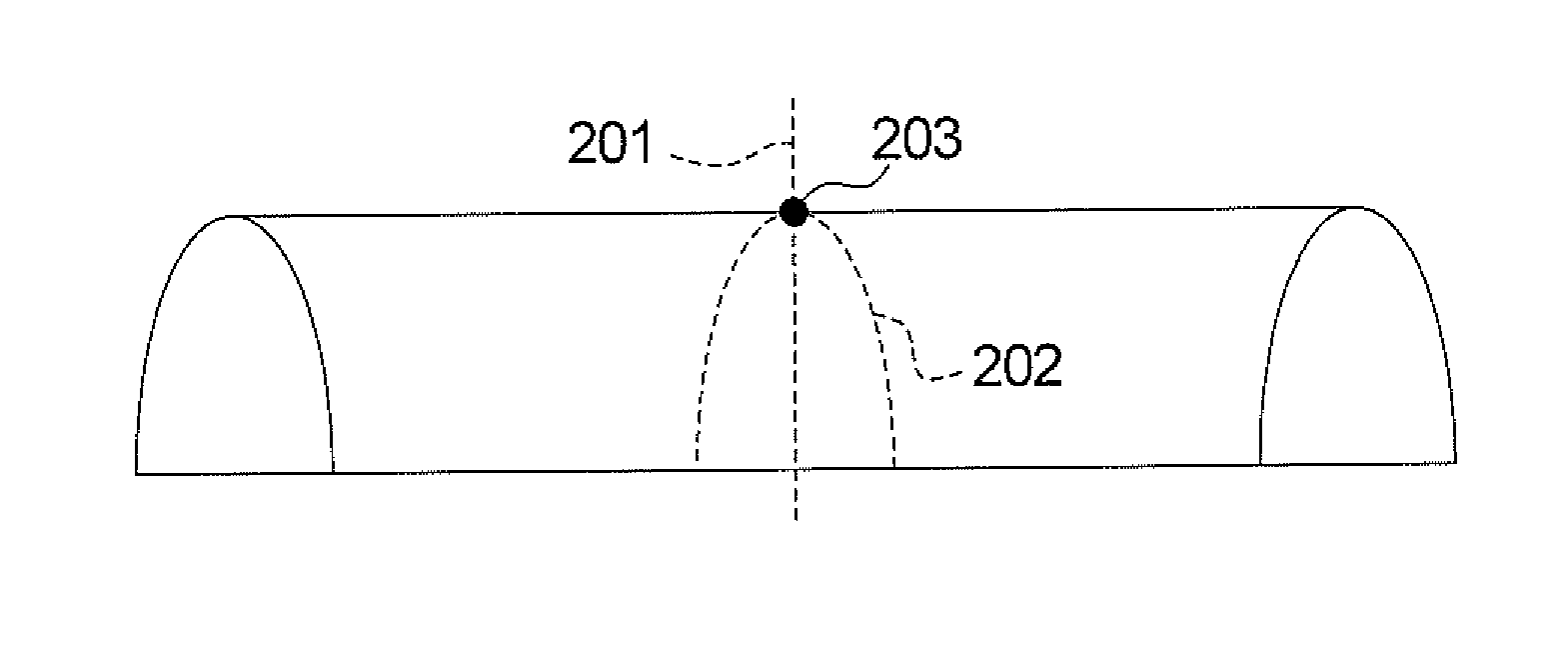
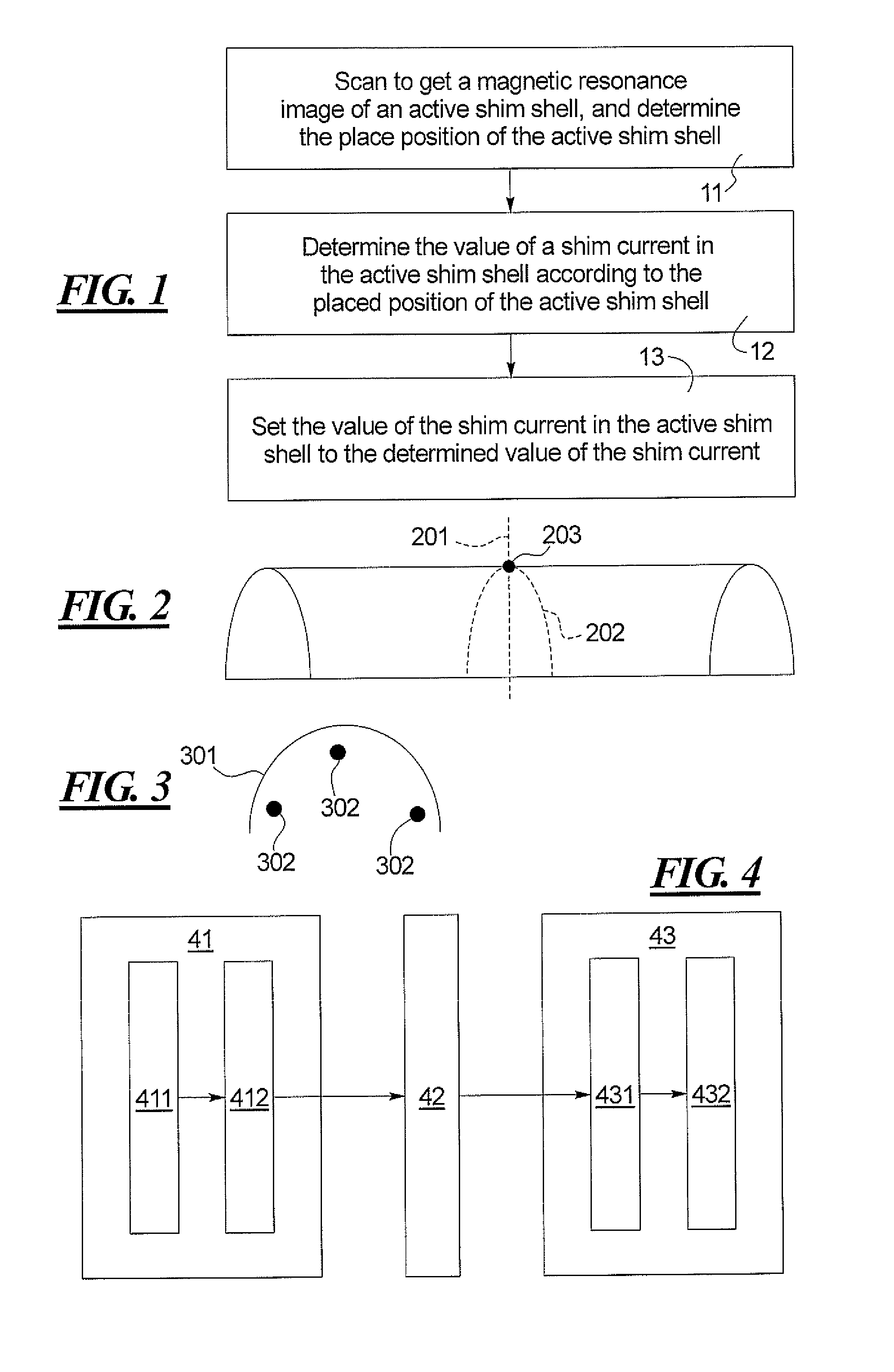
In a method and apparatus for correcting the uniformity of a magnetic field, an active shim shell is placed in the magnetic field, a magnetic resonance image of the active shim shell obtained, and the placement position of the active shim shell is determined by analyzing the magnetic resonance image. The value of a shim current in the active shim shell is determined so as to meet the uniformity requirements of the magnetic field according to the placement position. The value of the shim current in said active shim shell is set to the determined value of the shim current.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
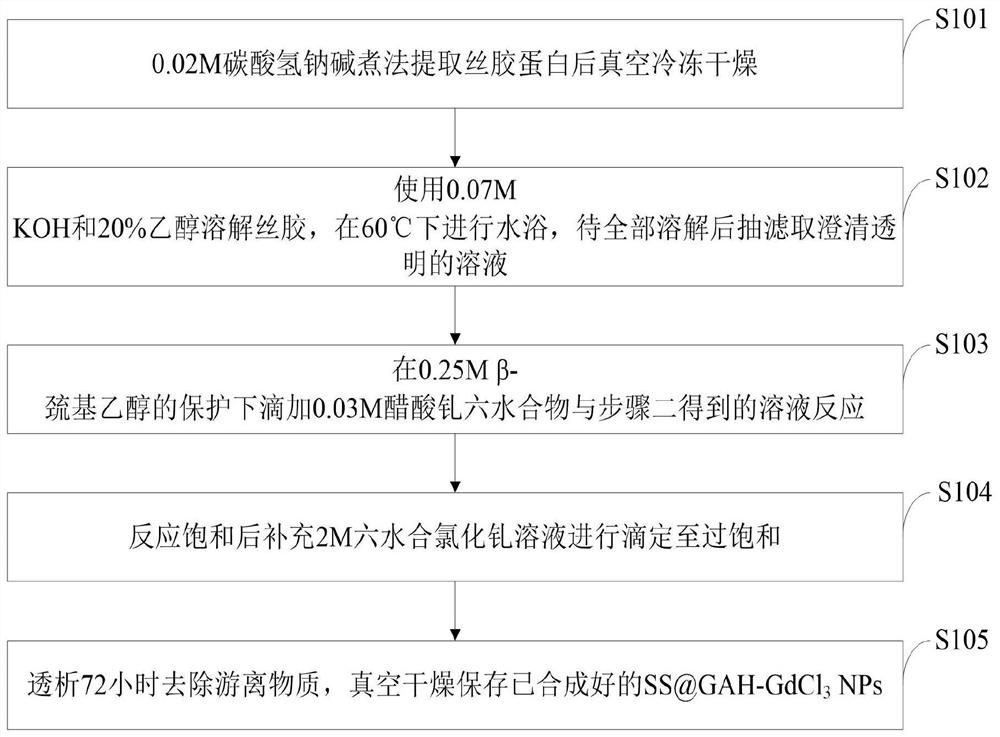
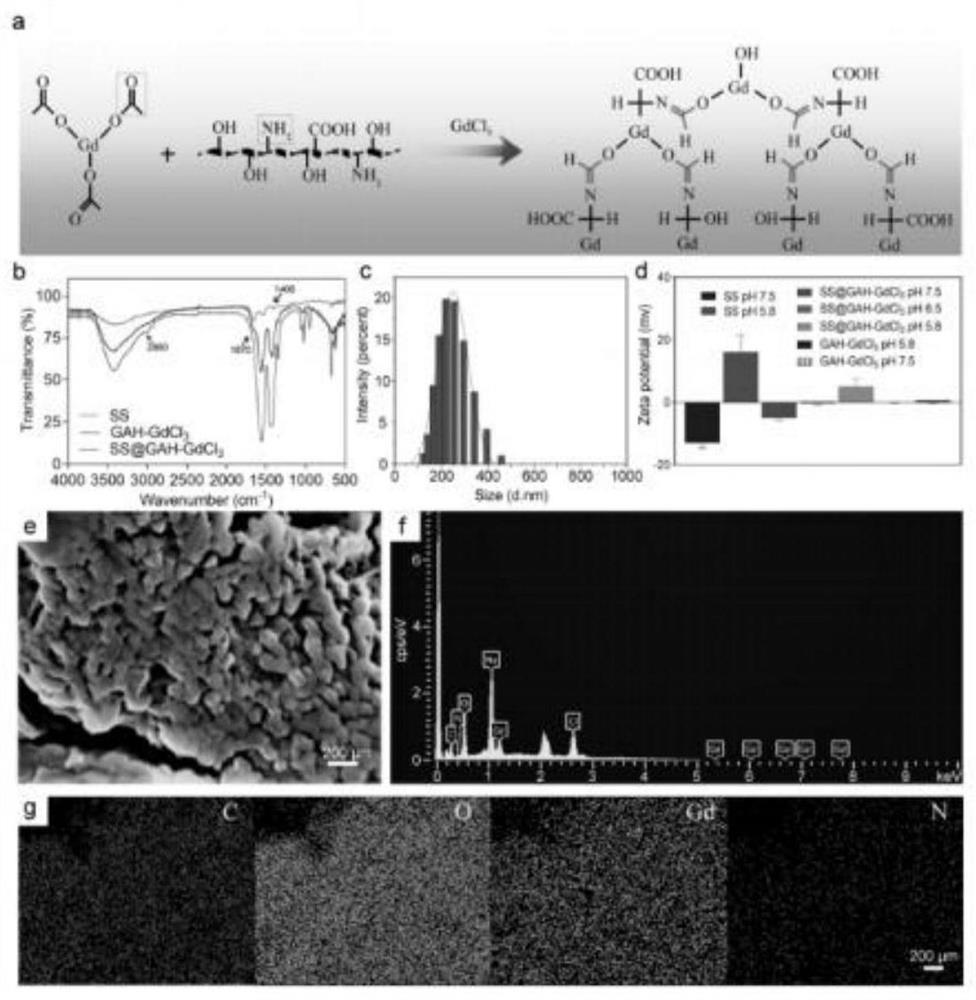
Preparation method of sericin-gadolinium pH responsive targeting tumor nuclear magnetic resonance contrast agent
ActiveCN111632155AImprove securityImprove imaging effectIn-vivo testing preparationsNuclear chemistryContrast medium
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents, and discloses a preparation method of a sericin-gadolinium pH responsive targeting tumor nuclear magnetic resonance contrast agent. The contrast agent is used for enhancing MRI research of tumor tissues, sericin, gadolinium acetate hexahydrate and gadolinium chloride hexahydrate are adopted as raw materials, and the nano contrast agent SS@GAH-GdCl3 is synthesized through a Schiff base reaction. Amino groups of the sericin and aldehyde groups of the gadolinium acetate hexahydrate are subjected to aone-step reaction by a two-step method to form Schiff base, and gadolinium ions are supplemented through electrostatic adsorption of the gadolinium chloride hexahydrate. The contrast agent prepared by the method can smoothly pass through normal tissues and blood vessels, and the surface potential of the contrast agent can be automatically reversed at a tumor part to enter tumor tissues, so that the uptake of tumor cells is increased, and the precise MRI contrast of solid tumors is realized; and the metabolism time of the nano contrast agent is remarkably prolonged by 30-60 min, and is far longer than the pharmacokinetic time of a commercial gadodiamide injection.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Magnetic Resonance Signal Correction
ActiveUS20150185307A1Reducing non-linear featureImprove image qualityElectric/magnetic detectionMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsRadio frequencyCorrection method
A magnetic resonance signal correction method, apparatus and system are provided. The method includes receiving a magnetic resonance signal through a radio frequency receiving channel, and correcting the magnetic resonance signal with a signal mapping relationship of the radio frequency receiving channel.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Acquiring contrast-enhanced, T1-weighted, cine magnetic resonance images
InactiveCN1692880ADecrease in the number of closed interestShorten the timeOther printing matterMagnetic property measurementsInversion recoveryCardiac cycle
A method of magnetic resonance imaging of an anatomical site subject to a motion cycle (e.g., the heart during a cardiac cycle), comprising: administering a magnetic resonance contrast agent; waiting for a period of time until the contrast agent is effective to cause a selected portion of the anatomical site (e.g., dead heart tissue) has a different T1 recovery rate than other parts (normal heart tissue); give multiple time-spaced inversion recovery pulses; follow inversion recovery pulses in time spaced by known time intervals Acquire image data at data acquisition time; vary the time at which an inversion recovery pulse is given within a motion cycle so that the relevant data acquisition time is at multiple phases of the motion cycle; process image data acquired at a certain phase of the motion cycle to produce an at least a portion of the image frames of the phase; and performing the processing on a plurality of phases of the motion cycle to generate a plurality of image frames corresponding to the plurality of phases.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +2
Temperature-controlled magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS8013604B2Improve image qualityEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTemperature controlPower flow
A method for improving the imaging quality of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment and MRI equipment, include obtaining a corresponding relationship between a deterioration factor of imaging quality and the cumulative energy of gradient pulses applied by successive scanning MRI sequences, then determining a predicted value of a current deterioration factor of imaging quality according to the currently applied cumulative energy of the gradient pulses and said corresponding relationship, adopting a corresponding method to carry out dynamic regulation or compensation using the predicted value of said deterioration factor of imaging quality as a reference, so as to cancel the influence produced by the heating effect of the gradient system to the imaging quality, thereby effectively improving the imaging quality of the MRI equipment.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance imaging method and magnetic resonance imaging system
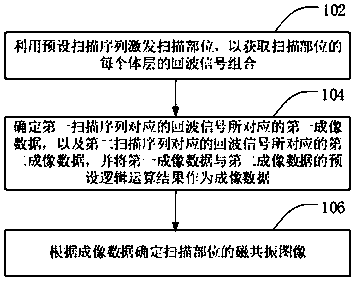
ActiveCN110215209AEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingSolve the problem of large minimum TEDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysicsRegion of interest
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method and a magnetic resonance imaging system. The method includes the following steps: a scanning portion is activated by utilizing a preset scanning sequence to obtain an echo signal combination of each of body layers of the scanning portion, wherein the preset scanning sequence includes a first scanning sequence and a second scanning sequence appearing in a preset combination, the first scanning sequence is a spin echo sequence, the second scanning sequence is a combination of an inversion recovery pulse and the spin echo sequence, and the inversion recovery pulse is used for selection of the body layers; first imaging data corresponding to an echo signal corresponding to the first scanning sequence, and second imaging data corresponding to the echo signal corresponding to the second scanning sequence are determined, and preset logical operation results of the first imaging data and the second imaging data are utilized as imagingdata; and a magnetic resonance image of the scanning portion is determined according to the imaging data. The problem that the signal-to-noise ratio of a region of interest of the scanning portion islow and minimum TE is large is solved in the prior art.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Solvent-free gadolinium contrast agents
InactiveUS20190269805A1Improve securityLow variabilityDispersion deliveryEmulsion deliveryPharmaceutical drugSolvent free
Disclosed herein are complexes of gadolinium metal, ligand and meglumine that are substantially free of non-aqueous solvents. In particular, solvent-free complexes of 1) gadopentetate dimeglumine and 2) gadoterate meglumine are disclosed and methods of their preparation are disclosed. In addition, methods are disclosed for purifying reactants, monitoring and controlling pH, quantifying the free gadolinium content, quantifying the concentration of gadolinium-ligand complex in aqueous solution, and procedures for producing a drug product in one step. The one step process eliminates the need to dry the gadolinium-ligand complex, which is typically highly hygroscopic. The one step process includes purification steps that do not require the use of non-aqueous solvents.
Owner:INVENTURE LLC
System for accelerated magnetic resonance imaging using parallel coils
ActiveUS9594141B2Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingReduce in quantityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPattern recognitionData set
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
Automatic artifact detection and pulse sequence modification in magnetic resonance imaging
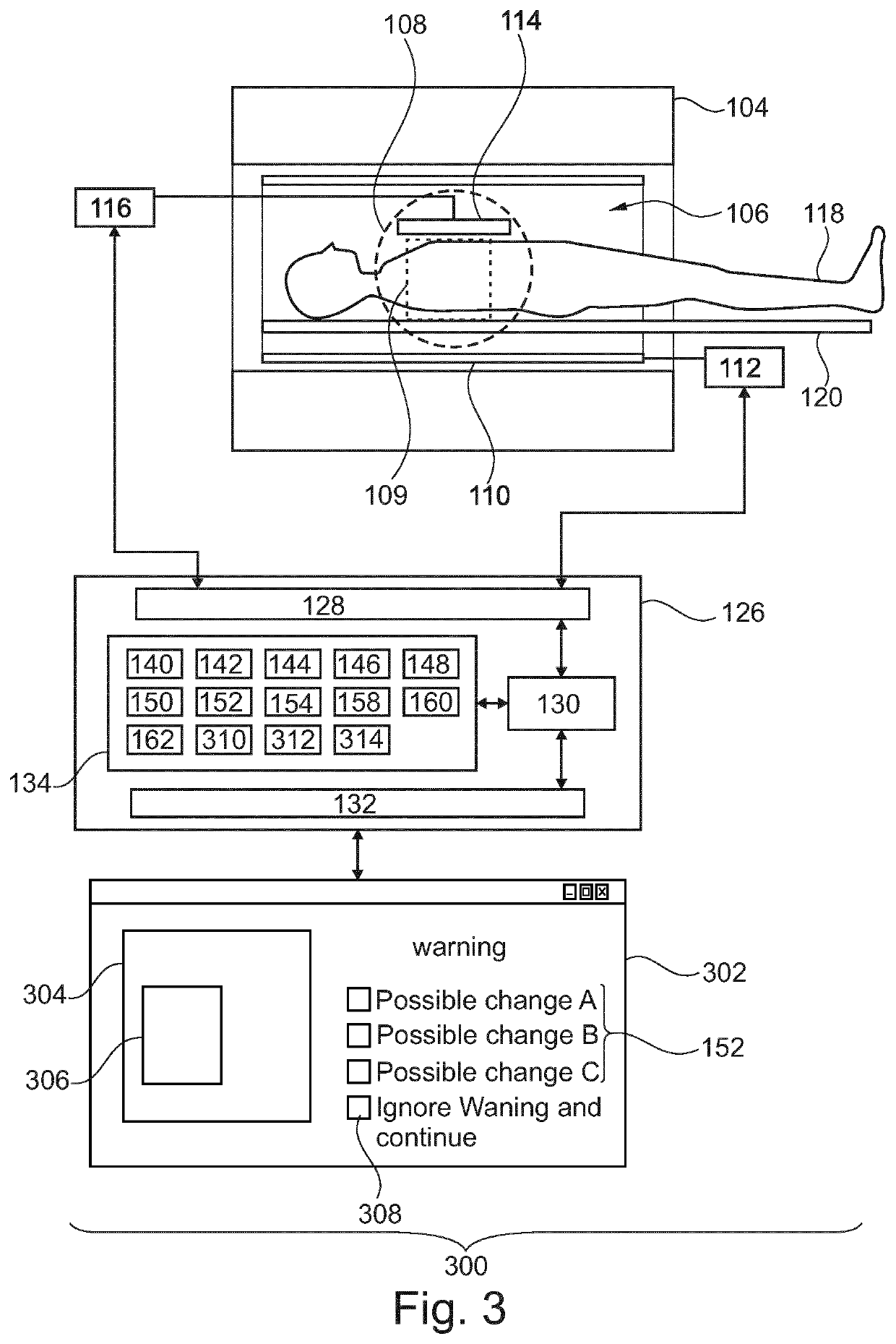
ActiveUS20210156940A1Reduce artifactsQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMri imagePulse sequence
The invention provides for a magnetic resonance imaging system (100, 300). The execution of machine executable instructions causes a processor (130) controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system to control (200) the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire the magnetic resonance imaging data (144) using pulse sequence commands (142) and reconstruct (202) a magnetic resonance image (148). Execution of the machine executable instructions causes the processor to receive (204) a list of suggested pulse sequence command changes (152) by inputting the magnetic resonance image and image metadata (150) into an MRI artifact detection module (146, 146′, 146″). The MRI artifact detection module comprises at least one neural network, which has been trained using images from failed magnetic resonance imaging protocols and / or magnetic resonance data extracted from the magnetic resonance imaging protocols labeled as failed accessed from a log file (312) which logs the execution of previous magnetic resonance imaging protocols. Execution of the machine executable instructions further causes the processor to receive (206) a selection of a chosen pulse sequence command change (158) from the list of suggested pulse sequence command changes. Execution of the machine executable instructions further causes the processor to modify (208) the pulse sequence commands using the chosen pulse sequence command change.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
2-nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent taking 2, 3-biquinoxaline as connecting body and preparation method thereof
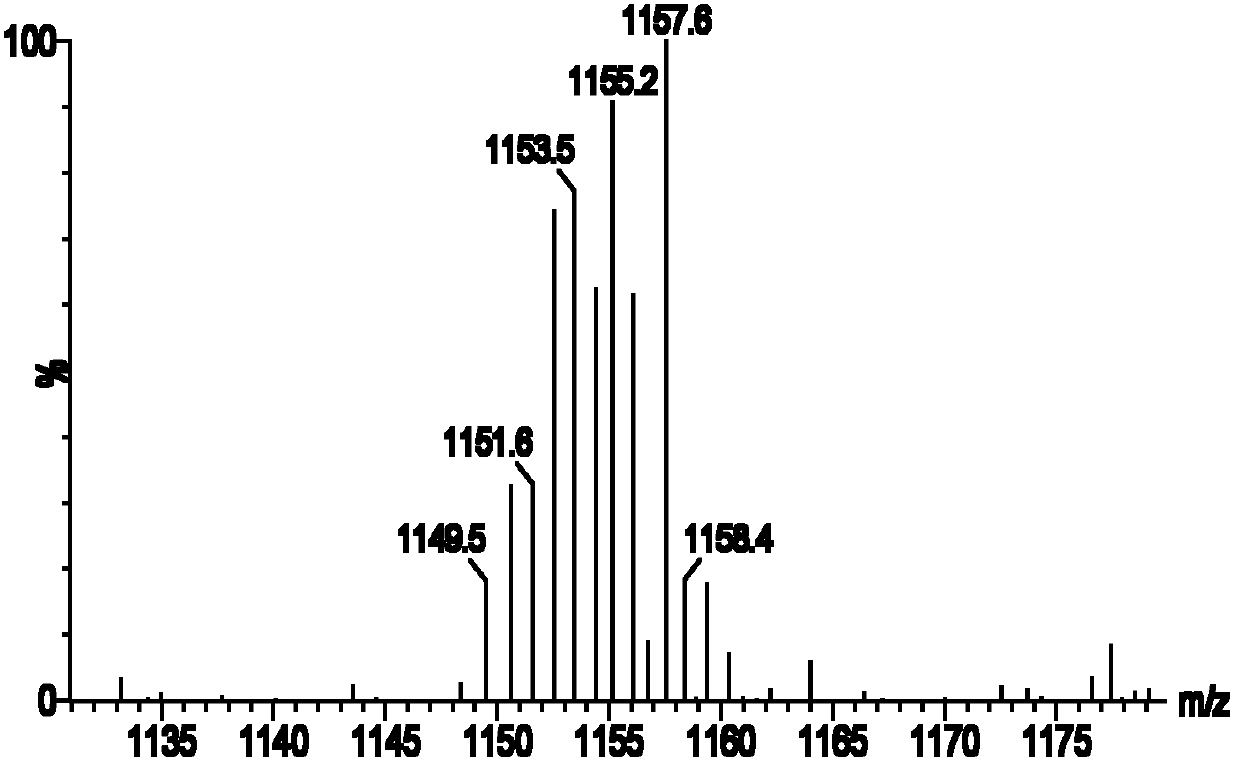
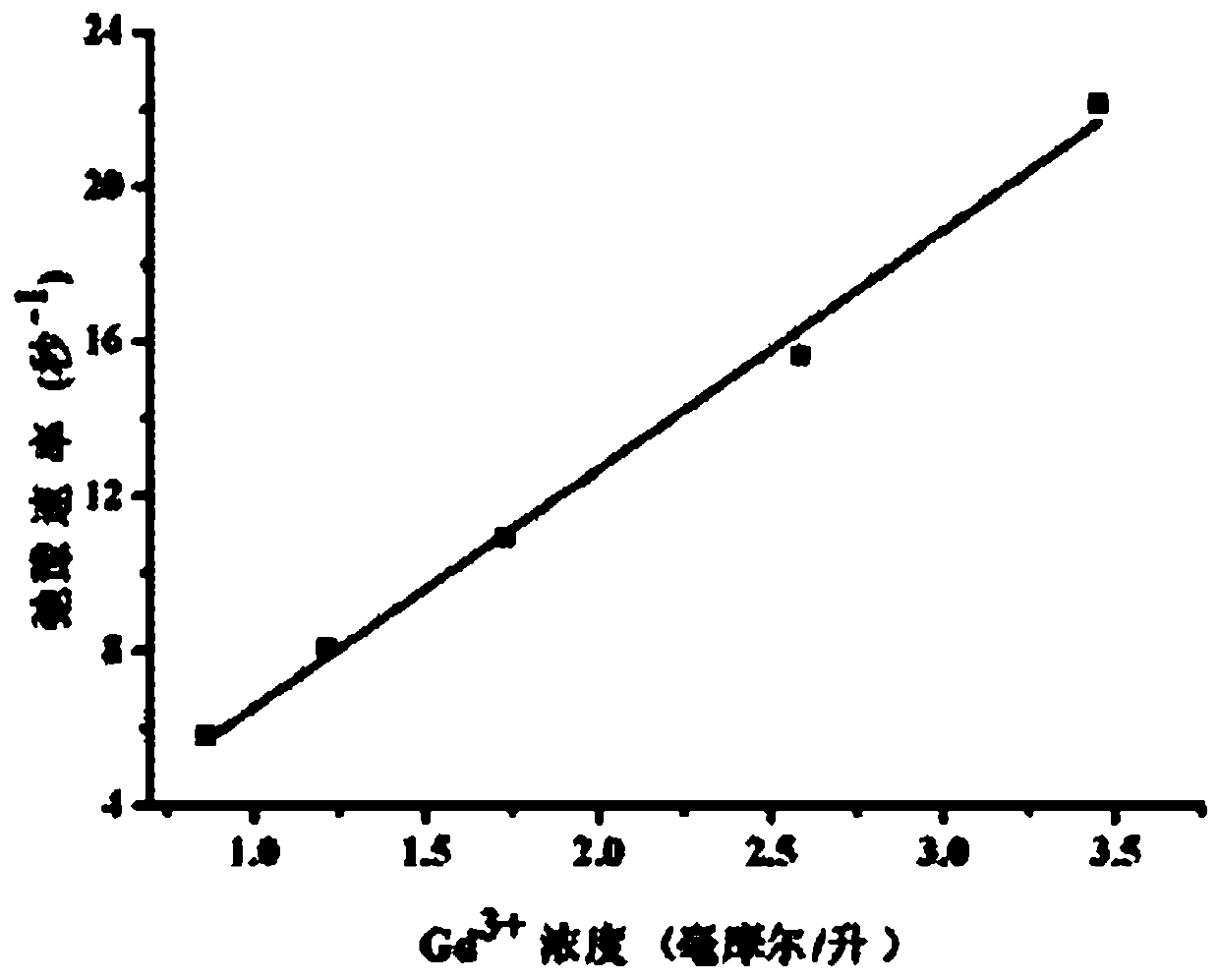
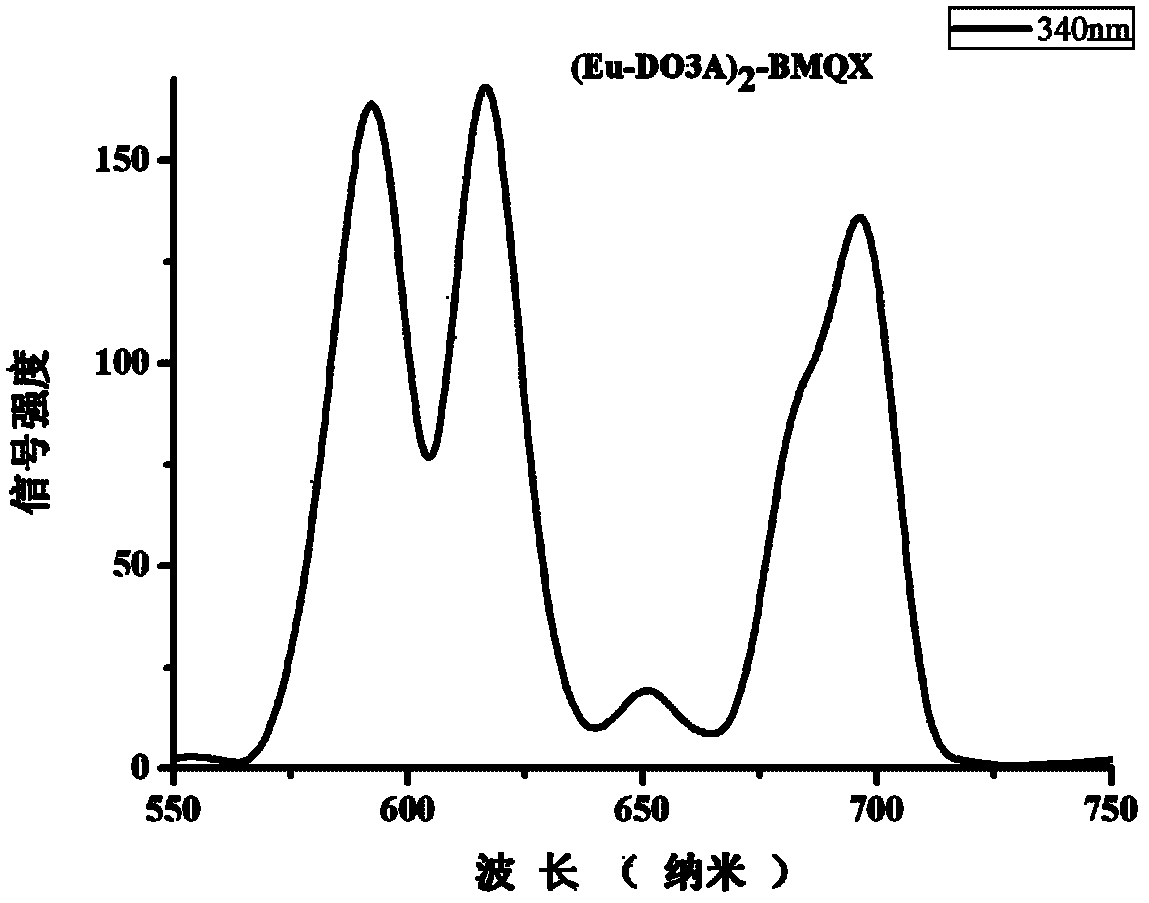
ActiveCN102584869AGood water solubilityEasy to storeGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsIn-vivo testing preparationsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMedicine
The invention discloses a 2-nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent taking 2, 3-biquinoxaline as a connecting body and a preparation method of the 2-nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent, relating to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. The 2-nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent taking the 2, 3-biquinoxaline as the connecting body solves the problems that the relaxation efficiency is low and the thermodynamic stability is poor as the contrast agent adopts a flexible chain to connect a group in the prior art. According to the contrast agent, two DO3A groups are in covalent connection on the rigid-connection group 2, 3-biquinoxaline, and then the rigid-connection group 2, 3-biquinoxaline is chelated with paramagnetism metal ion Gd3<+> to obtain the 2-nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. The invention also provides the preparation method of the 2-nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent taking the 2, 3-biquinoxaline as the connecting body. The relaxation efficiency of the contrast agent (Gd-Do3A)-BMQX can achieve 6.2mM<-1>s<-1>, and the 2-nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent has good stability and is low in toxicity.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com