Acquiring contrast-enhanced, T1-weighted, cine magnetic resonance images
A technology for acquiring images and magnetic resonance imaging, which is applied in the directions of magnetic resonance measurement, material analysis through resonance, and adjustment of magnetic variables. Effects of increasing equipment usage efficiency and patient throughput, increasing simplicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The invention has too many possible implementations to be described here. Some possible implementations which are presently preferred are described below. It is important to emphasize, however, that these are descriptions of implementations of the invention, not of the invention, and that the invention is not limited to the implementations described in detail in this section, but is described in broader terms in the claims.
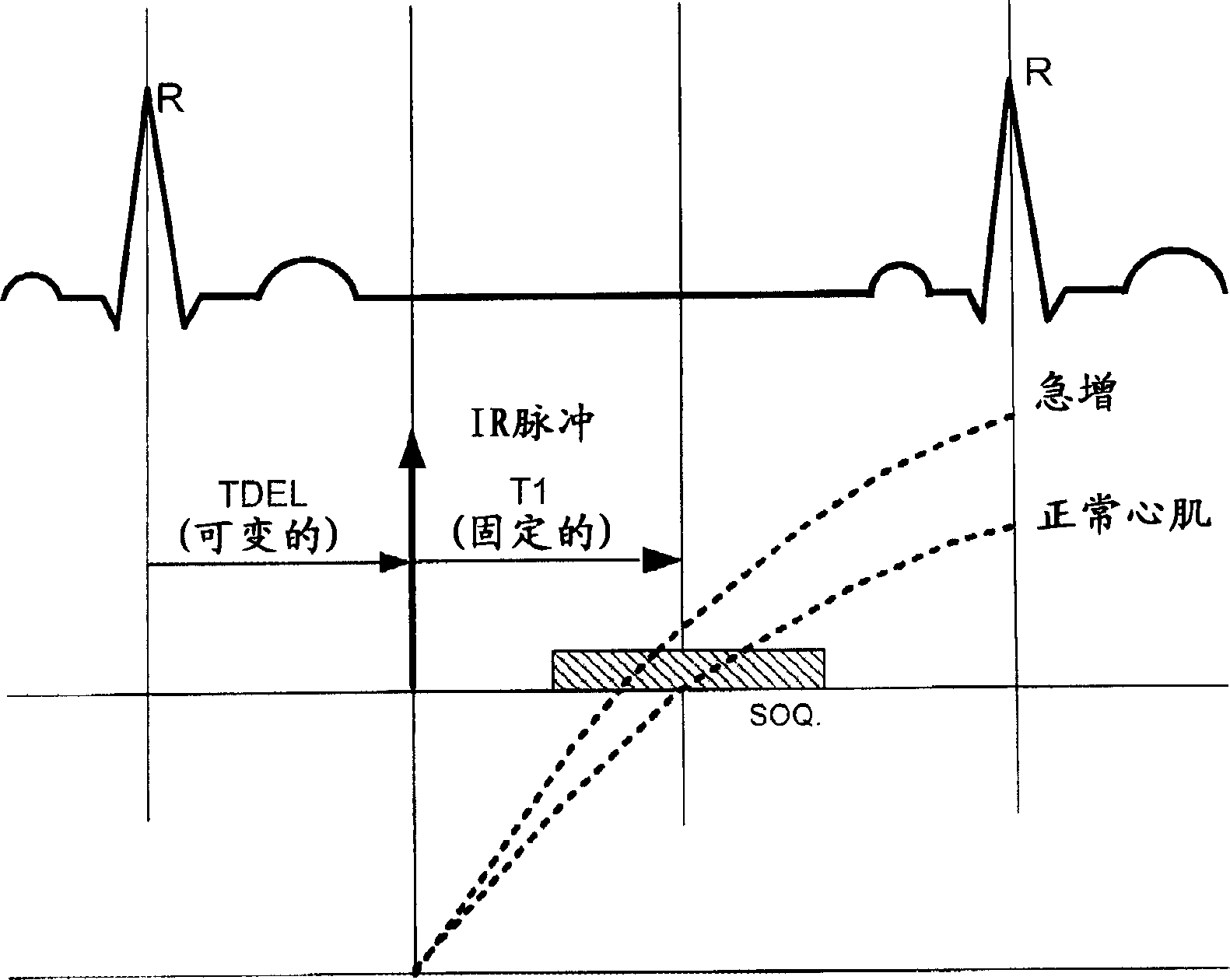
[0030] One implementation includes a class of pulse sequences that includes a combination of aspects of delay-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and cinegraphic magnetic resonance imaging.
[0031] One aspect of delayed-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging is performing an inversion pulse prior to data acquisition. This inverted pulse is used to zero the normal myocardial signal to highlight hyperenhancing myocardial tissue (non-viable myocardium). Data acquisition occurs at a consistent location in the cardiac cycle, usually end-diastole.
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com