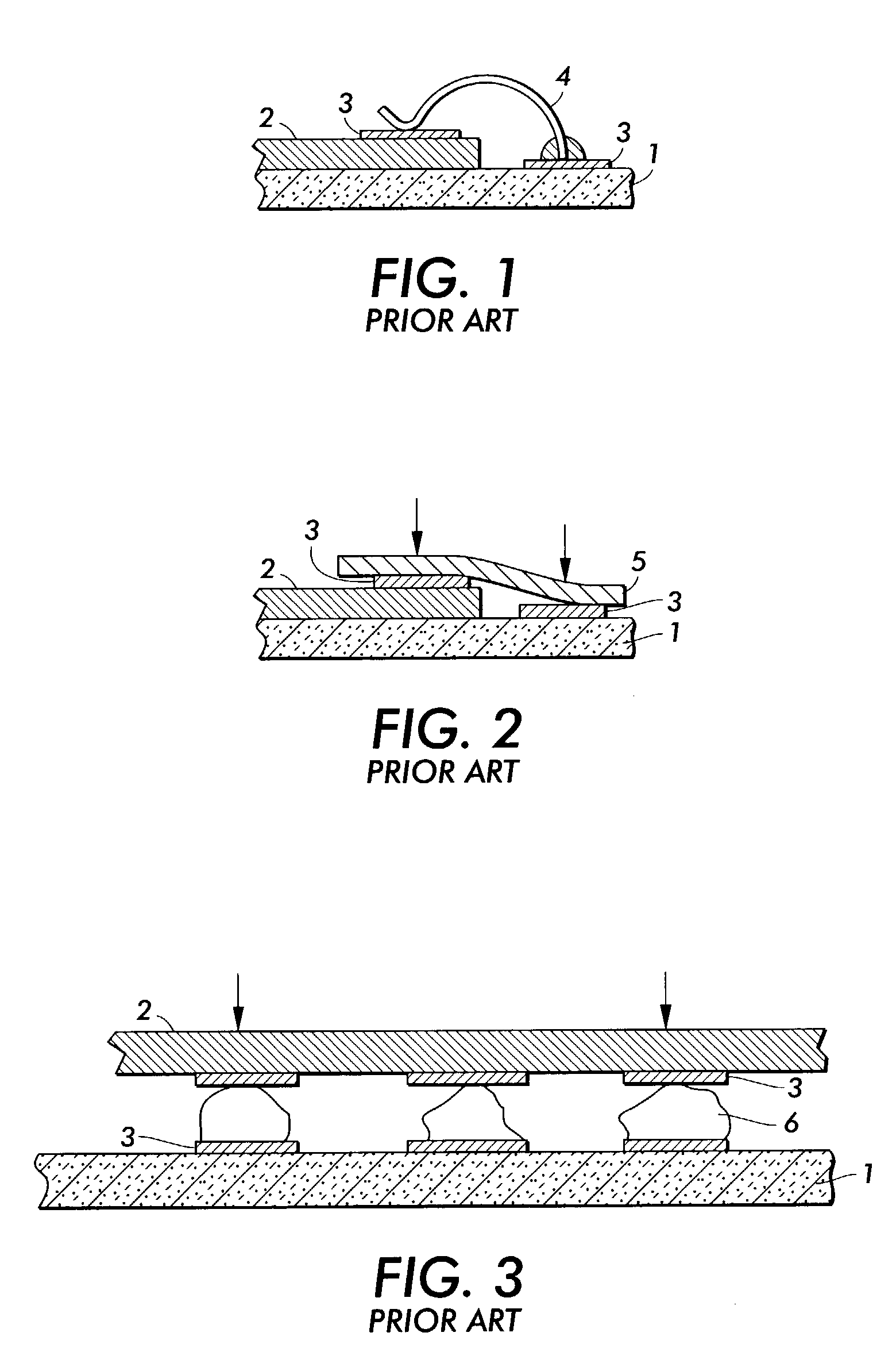
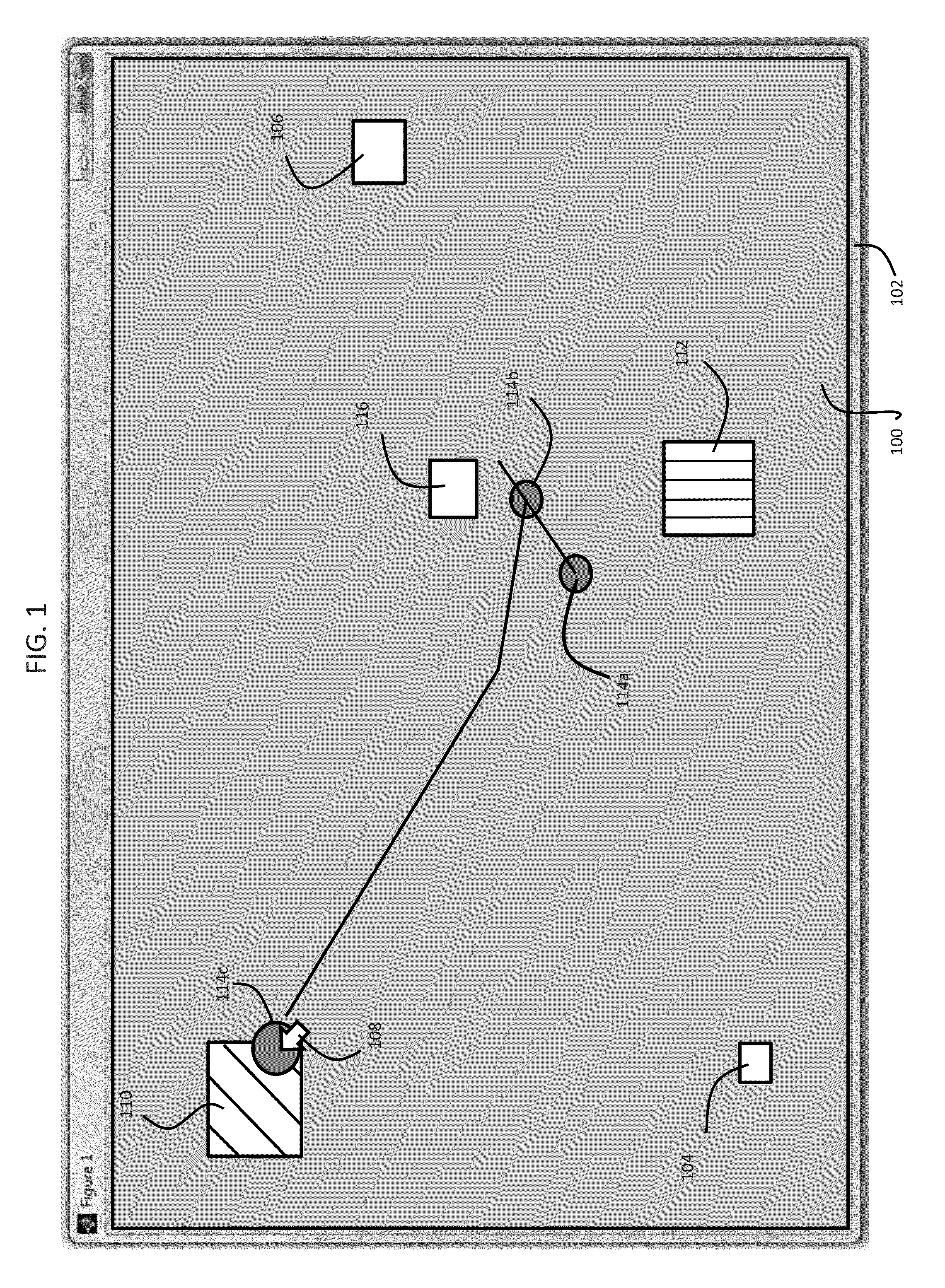
Patents
Literature
116 results about "Stress profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
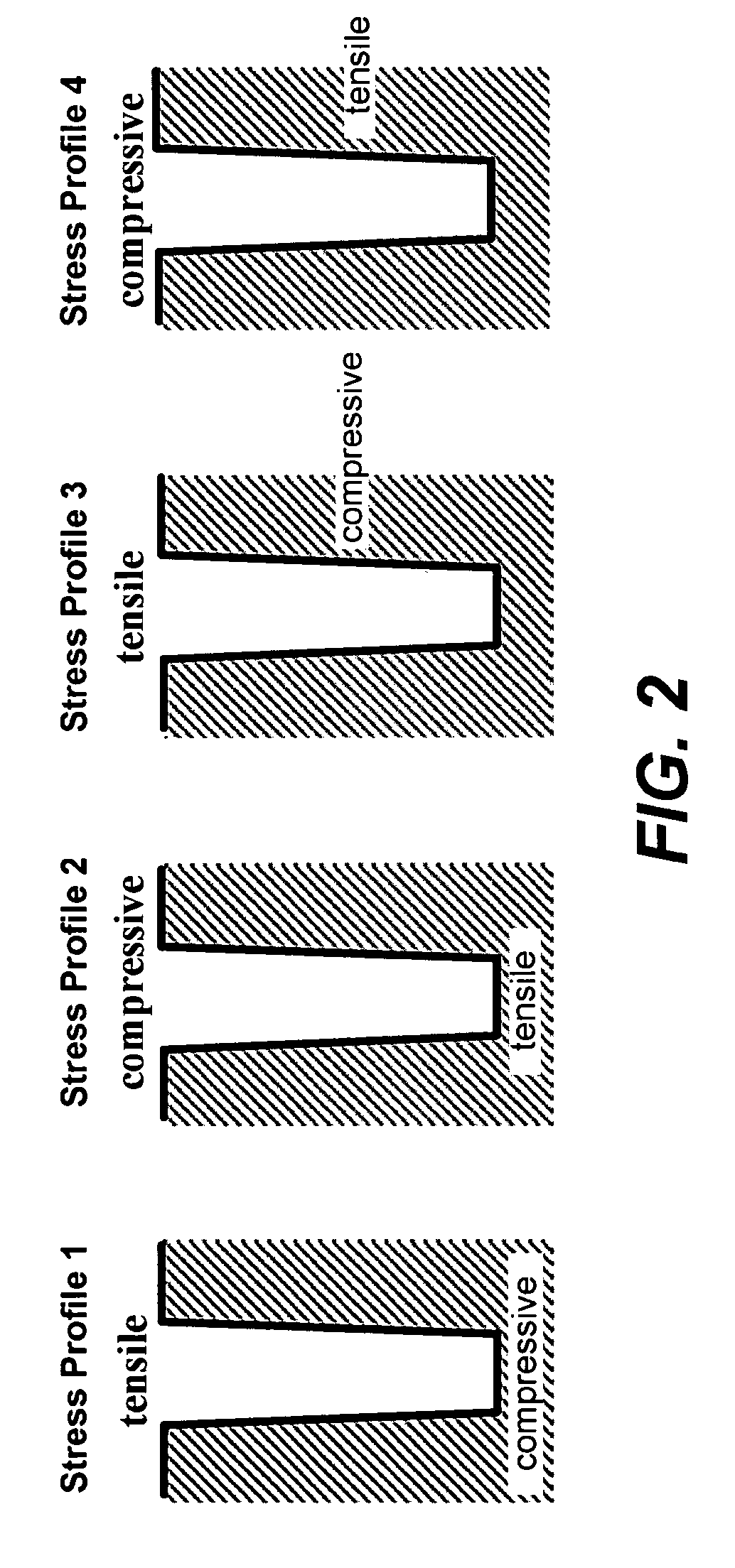
The Stress Profile is a psychosocial instrument for measuring stress in life in general and at work at the levels of the individual, the group and the organization.
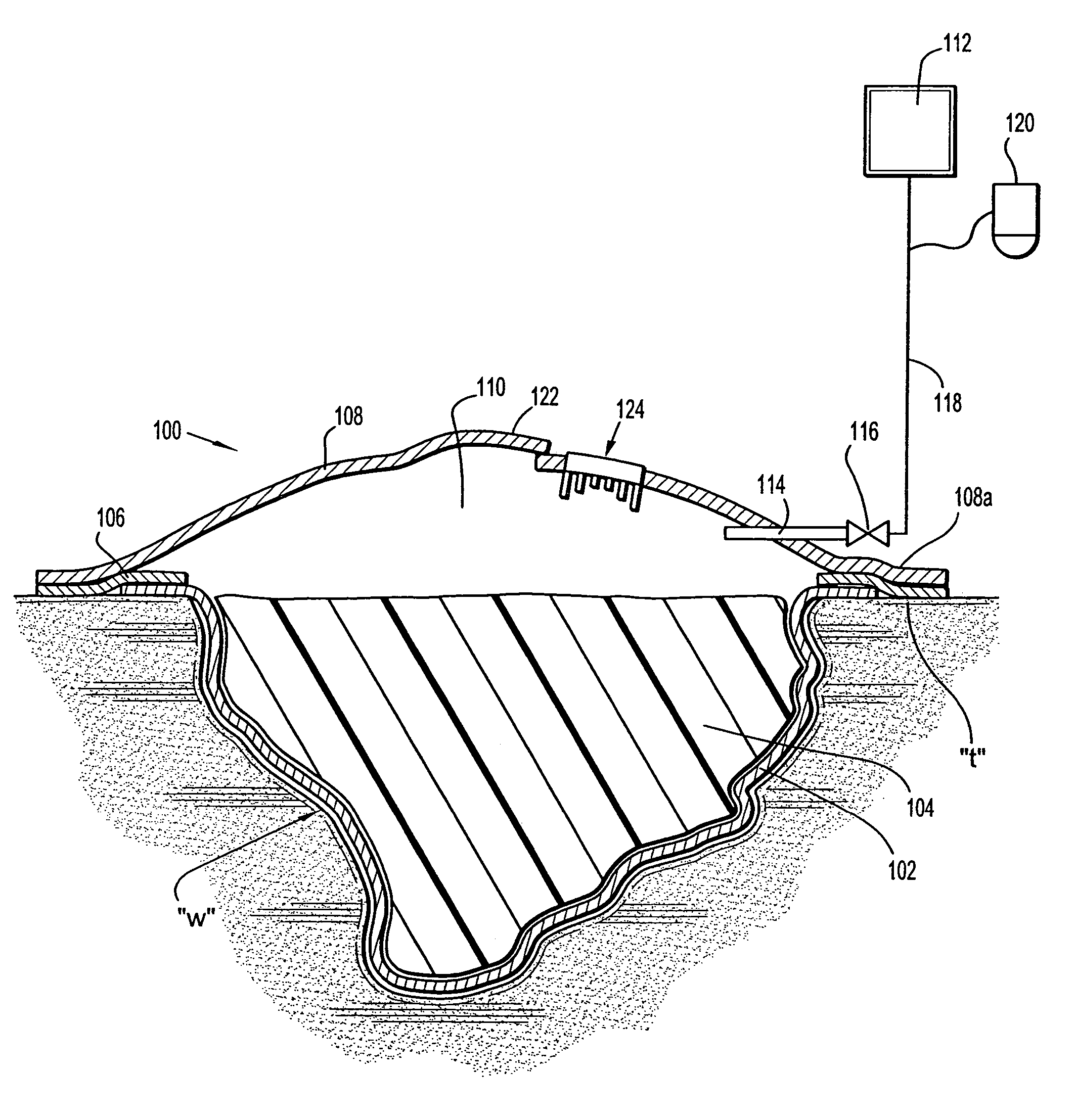
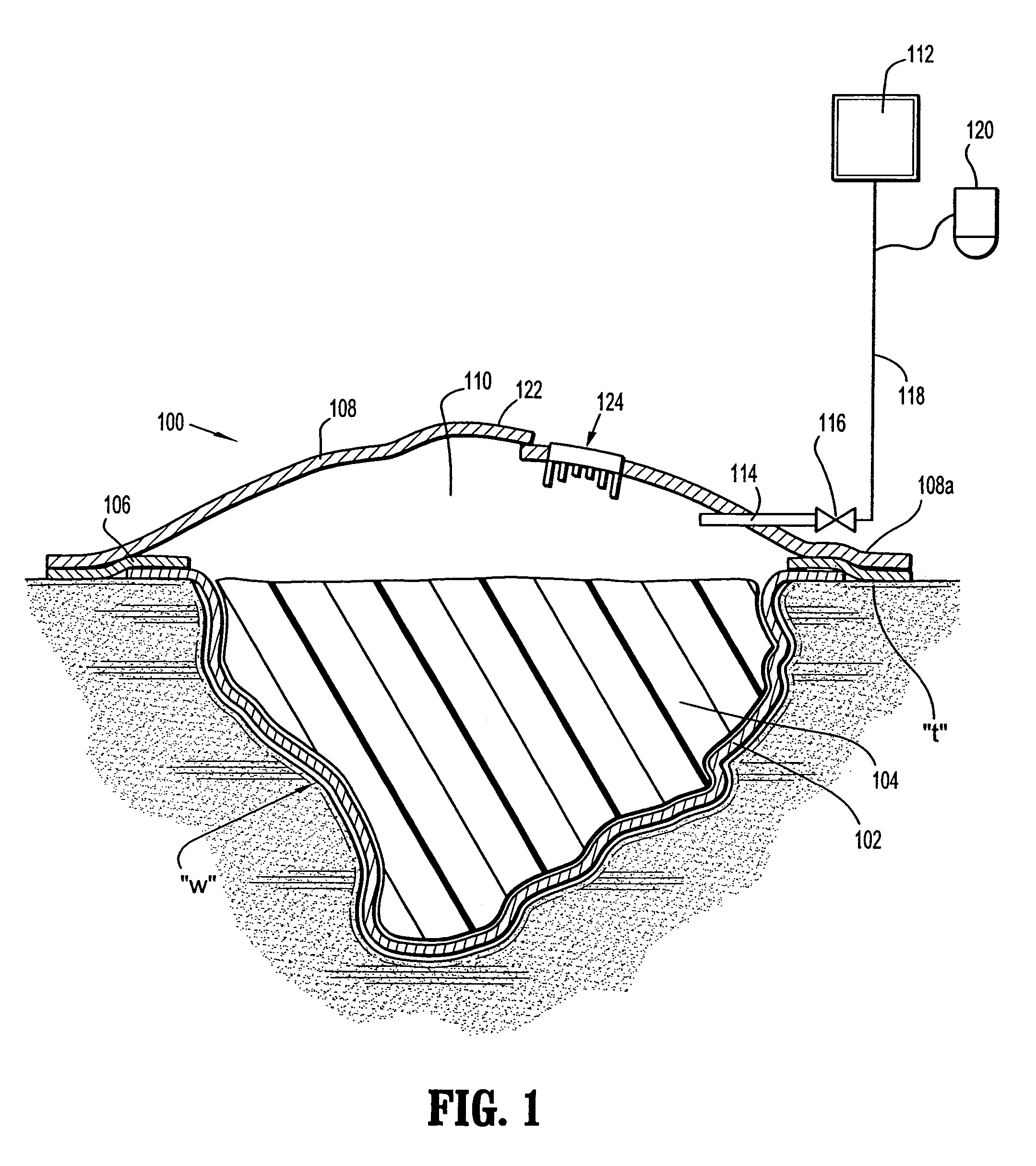
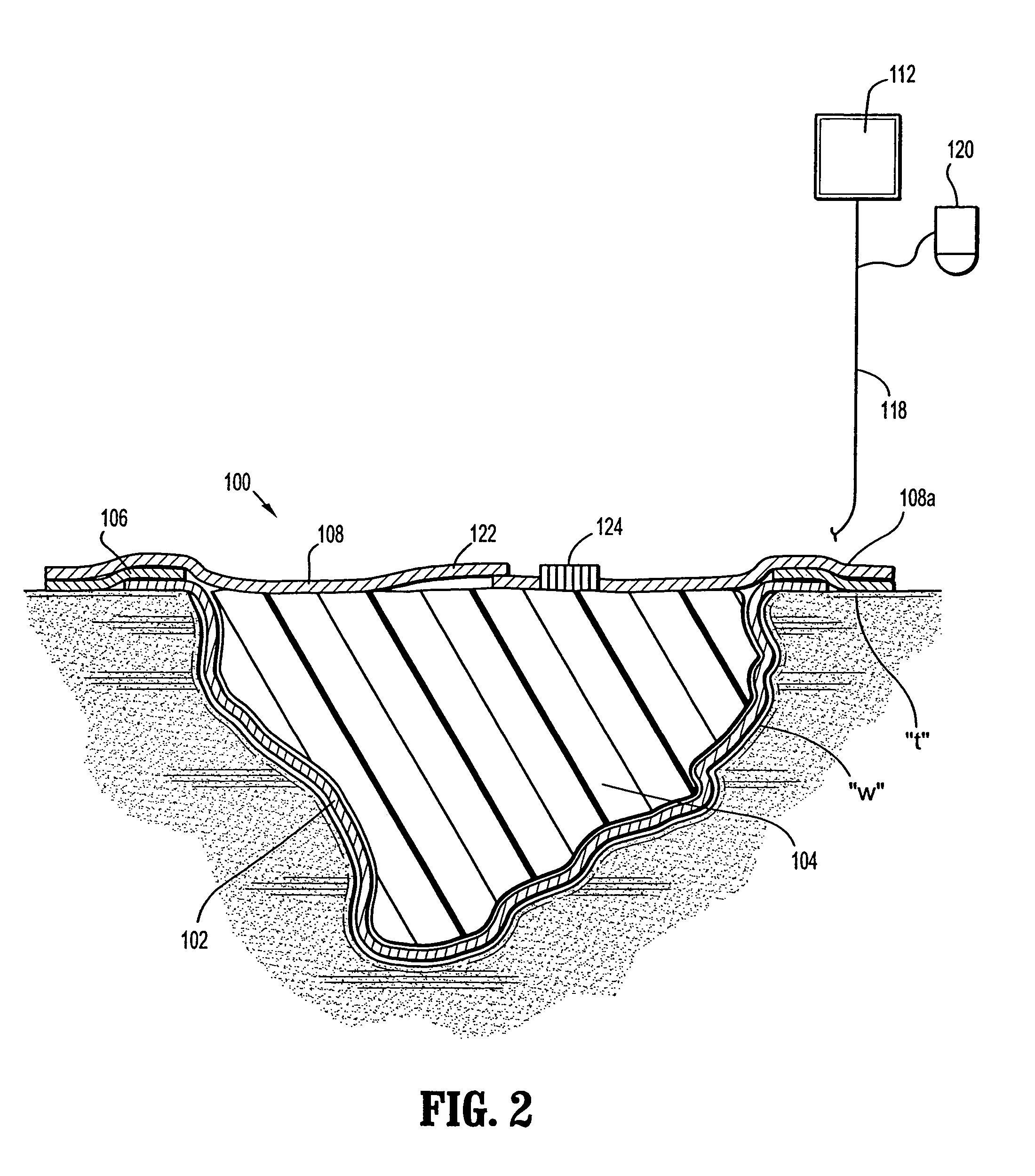
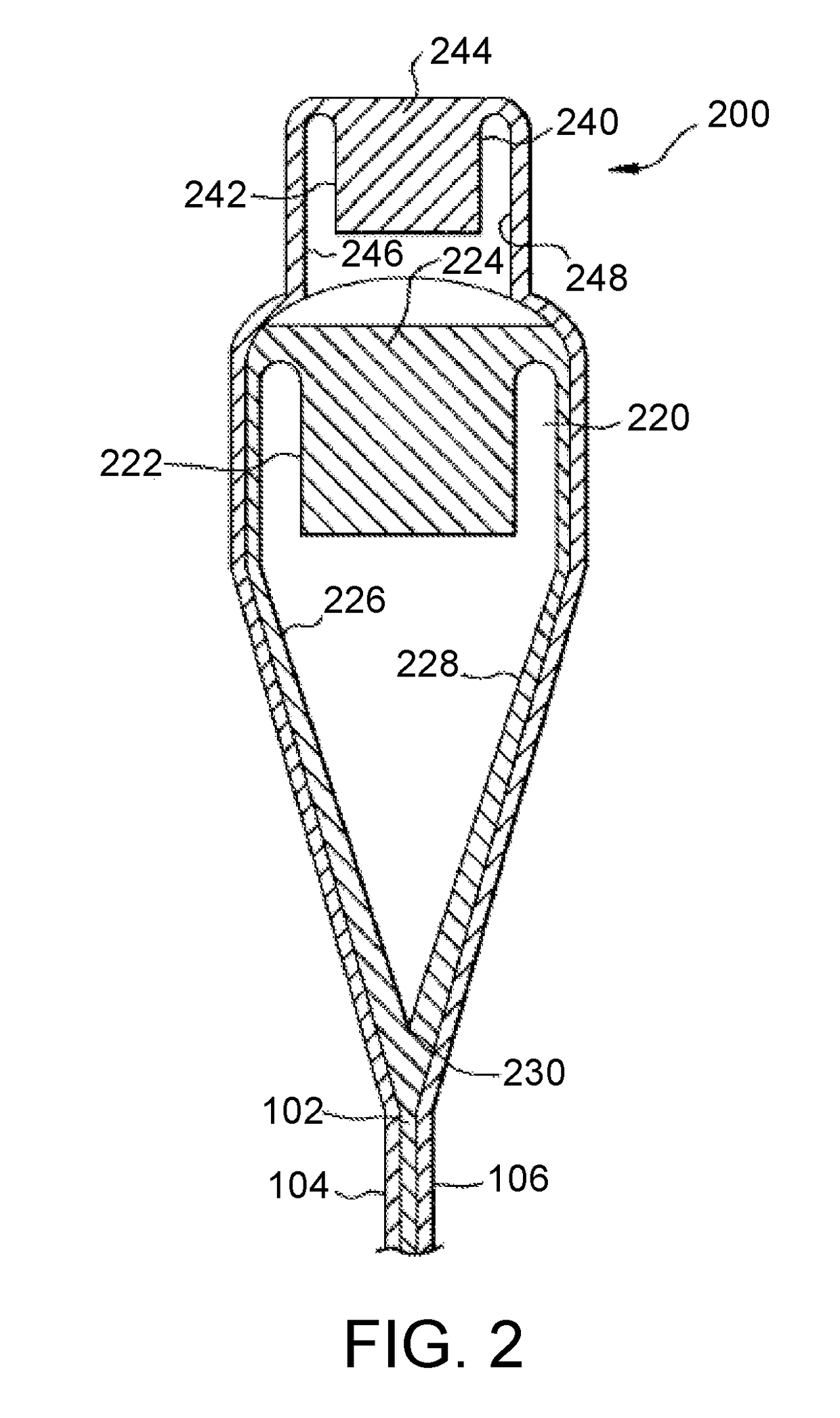
Wound dressing with vacuum reservoir
A wound dressing apparatus includes a wound dressing member dimensioned for positioning relative to a wound bed. The wound dressing member including an internal vacuum reservoir and has a port in communication with the vacuum reservoir for applying subatmospheric pressure to the vacuum reservoir to facilitate removal of fluid from the wound bed. The wound dressing member includes a visual pressure indicator associated therewith for indicating a level of pressure within the vacuum reservoir. The visual pressure indicator includes color indicia having a plurality of colors corresponding to a condition of the pressure within the vacuum reservoir. The wound dressing member includes a lower absorbent member positionable adjacent the wound bed and an upper member which at least partially defines the vacuum reservoir. At least one of the top member and the lower absorbent member has the visual pressure indicator mounted thereto. The preferred visual pressure indicator includes an electronic position sensor. The visual pressure indicator further includes circuit means and visible alarm means. The circuit means is adapted to actuate the visible alarm means when the position sensor detects a relative positioning of the top member of the wound dressing member to provide a visual indication of the condition of the subatmospheric pressure within the vacuum reservoir.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
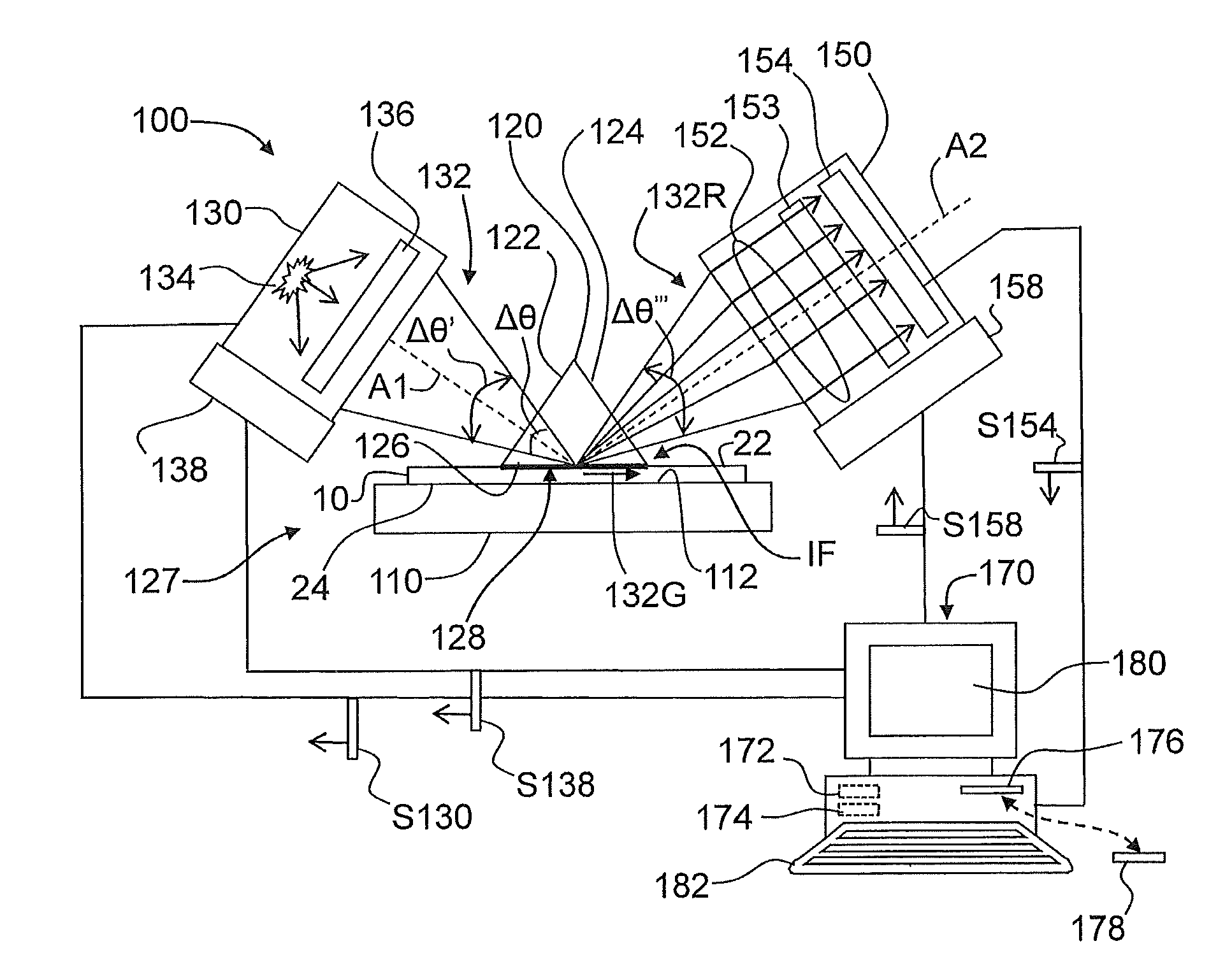
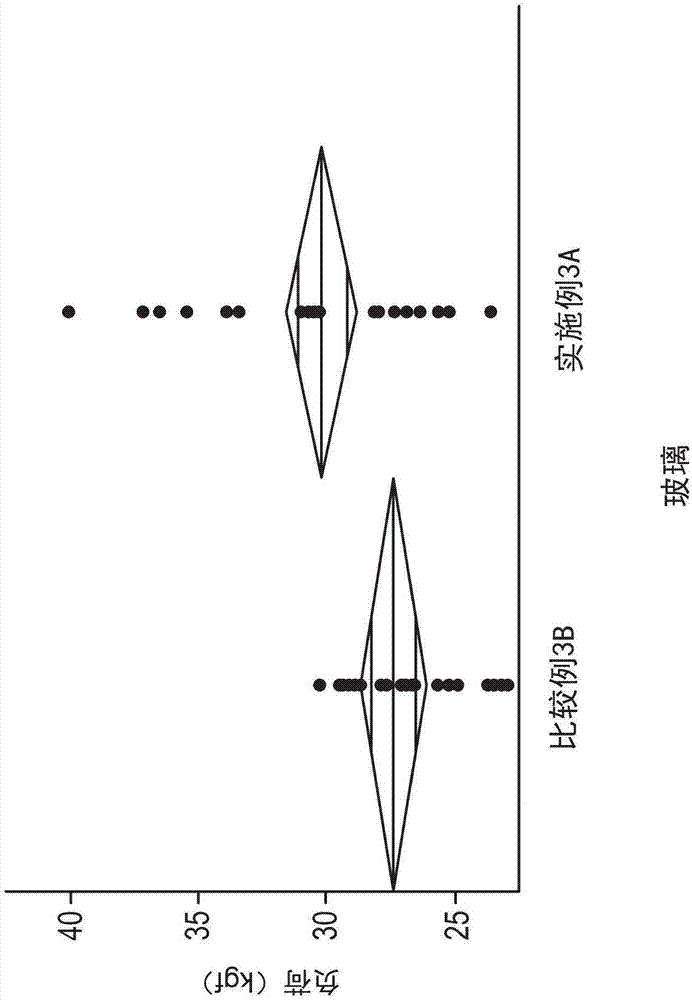
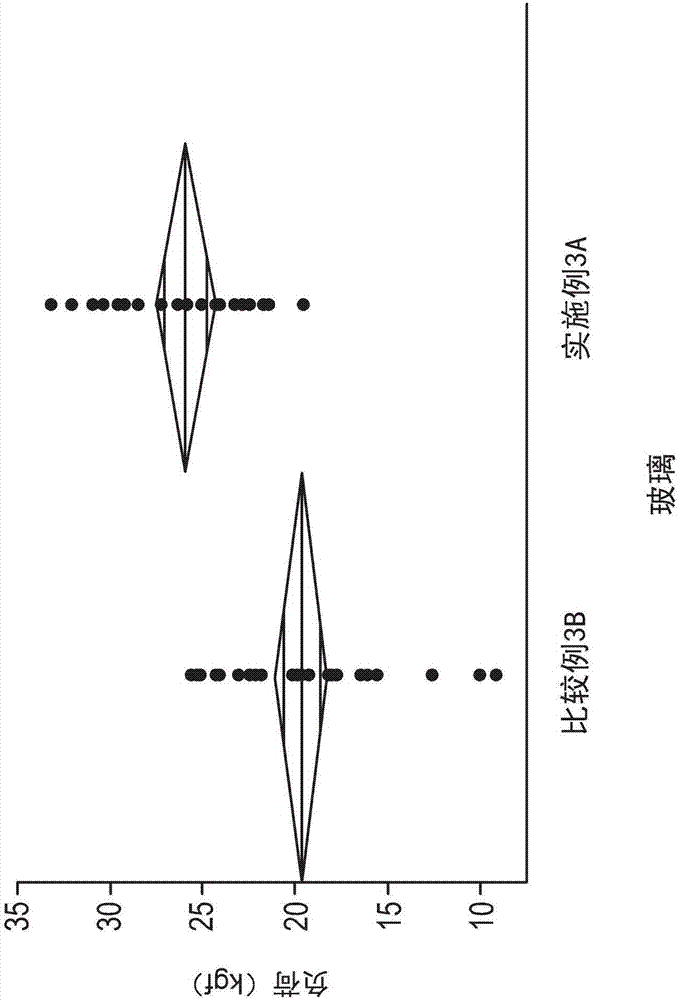
Systems and methods for measuring the stress profile of ion-exchanged glass
ActiveUS9140543B1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansOptical coefficientMaterials science
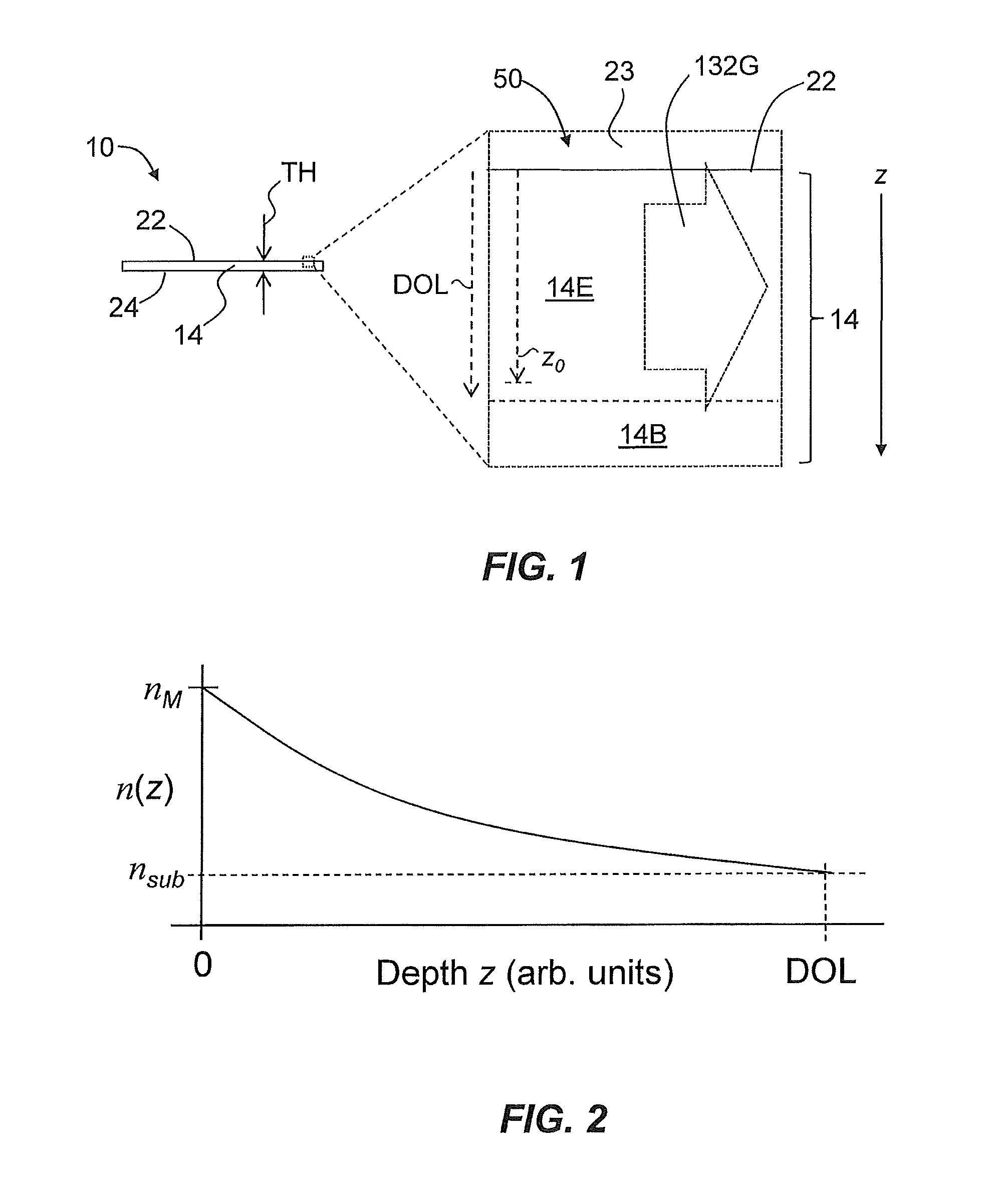
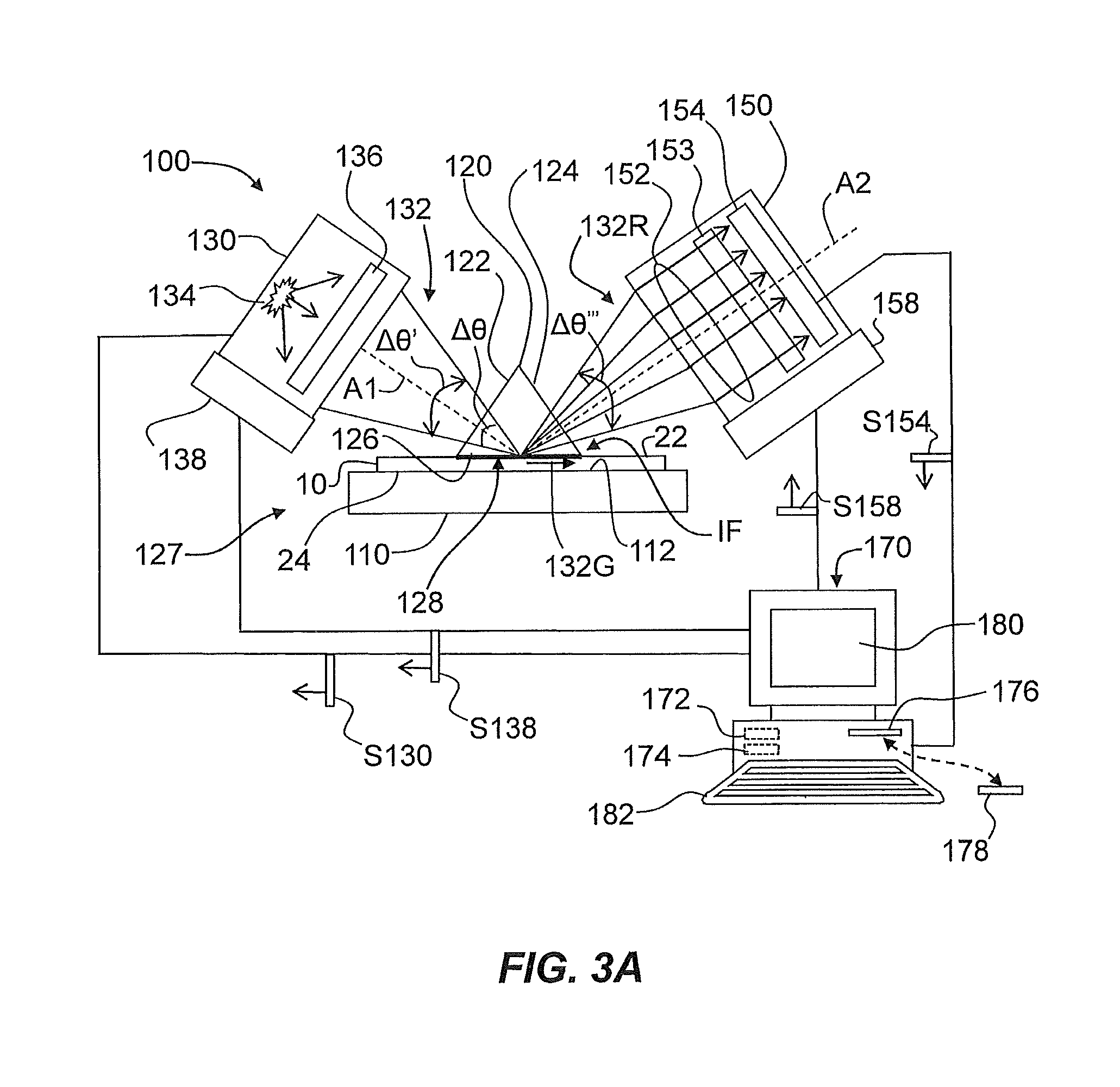
Systems and methods for measuring the stress profile of ion-exchanged glass are disclosed, based on the TM and TE guided mode spectra of the optical waveguide formed in the ion-exchanged glass. The method includes digitally defining from the TM and TE guided mode spectra positions of intensity extrema, and calculating respective TM and TE effective refractive indices from these positions. The method also includes calculating TM and TE refractive index profiles nTM(z) and nTE(z) using either an inverse WKB calculation or a fitting process that employs assumed functions for nTM(z) and nTE(z). The method also includes calculating the stress profile S(z)=[nTM(z)−nTE(z)] / SOC, where SOC is a stress optic coefficient for the glass substrate. Systems for performing the method are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for the production of thin substrates
InactiveUS20070249140A1Improve efficiencyLarge thicknessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolar cellInduced stress
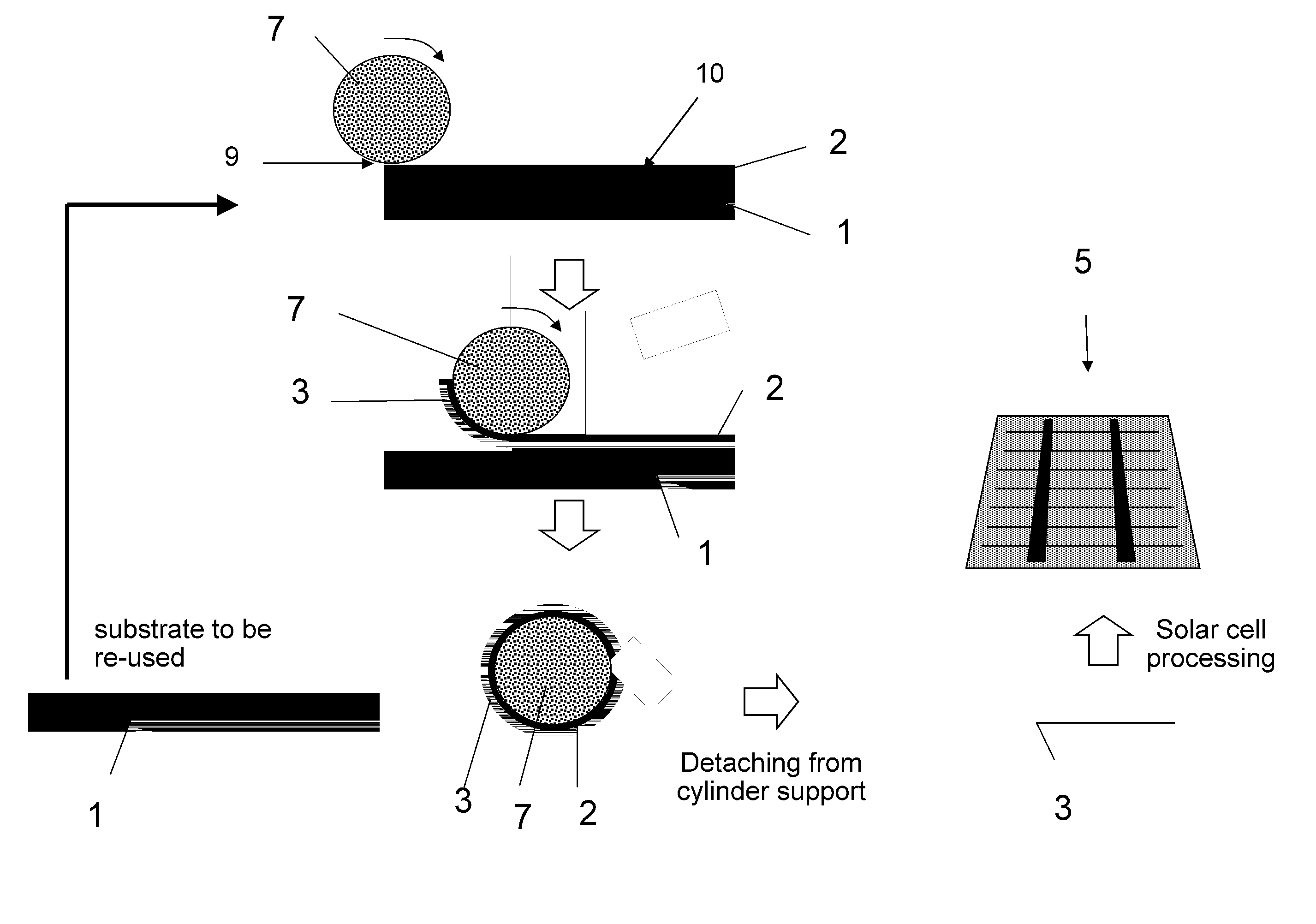
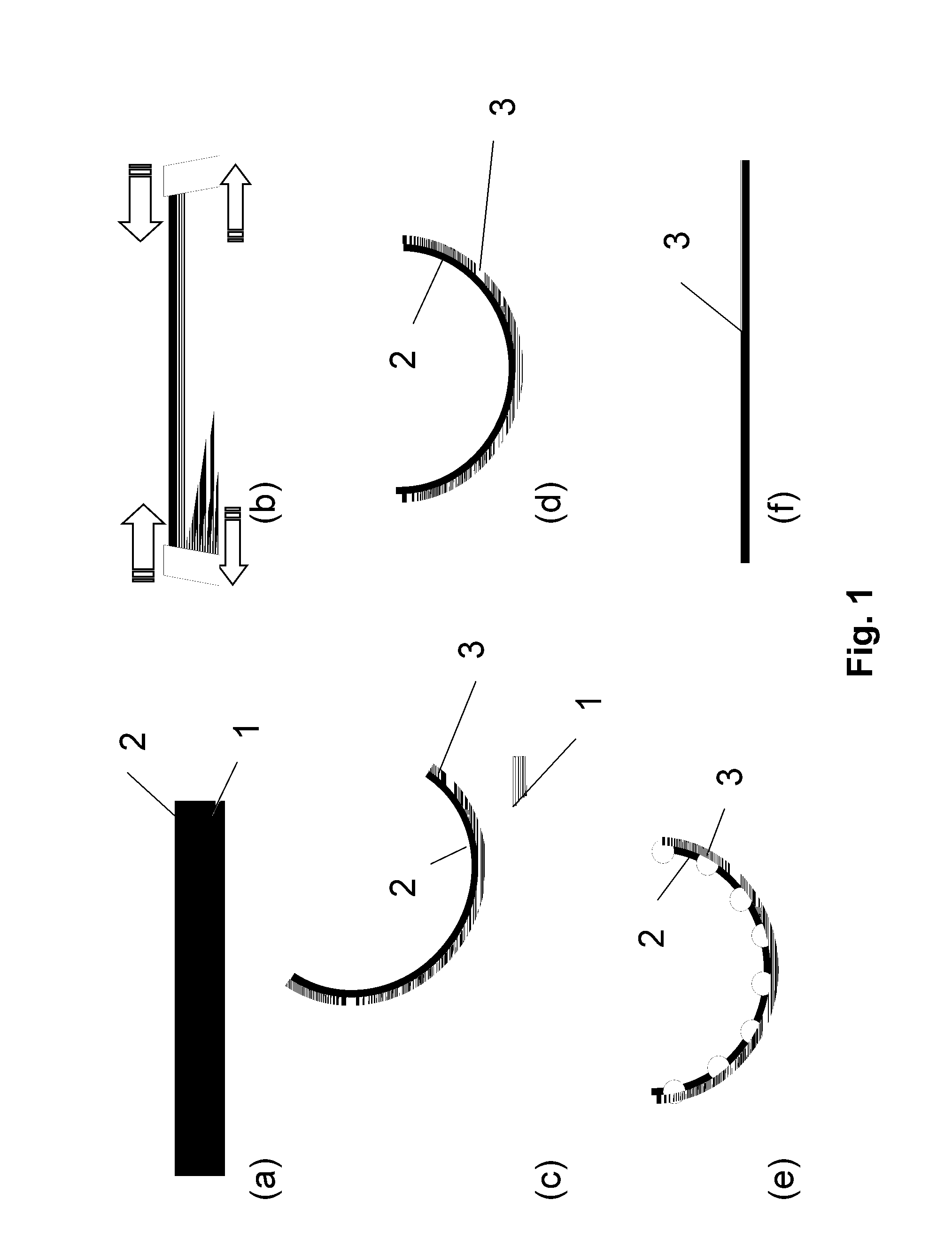
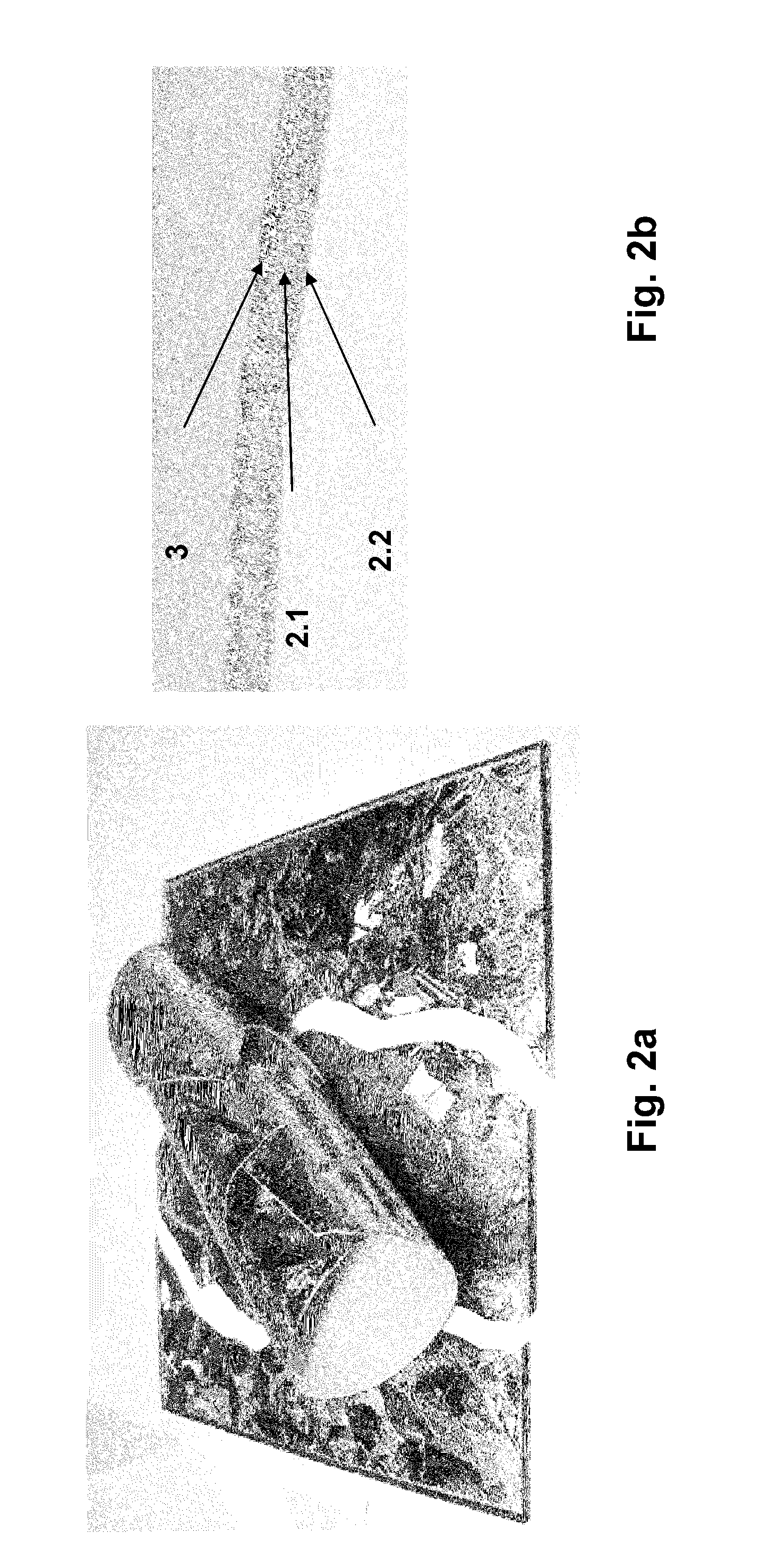
A method is provided for producing a thin substrate with a thickness below 750 microns, comprising providing a mother substrate, the mother substrate having a first main surface and a toughness; inducing a stress with predetermined stress profile in at least a portion of the mother substrate, said portion comprising the thin substrate, the induced stress being locally larger than the toughness of the mother substrate at a first depth under the main surface; such that the thin substrate is released from the mother substrate, wherein the toughness of the mother substrate at the first depth is not lowered prior to inducing the stress. The method can be used in the production of, for example, solar cells.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Methods and systems for determining formation properties and in-situ stresses
ActiveUS6904365B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingRadial stressUltimate tensile strength
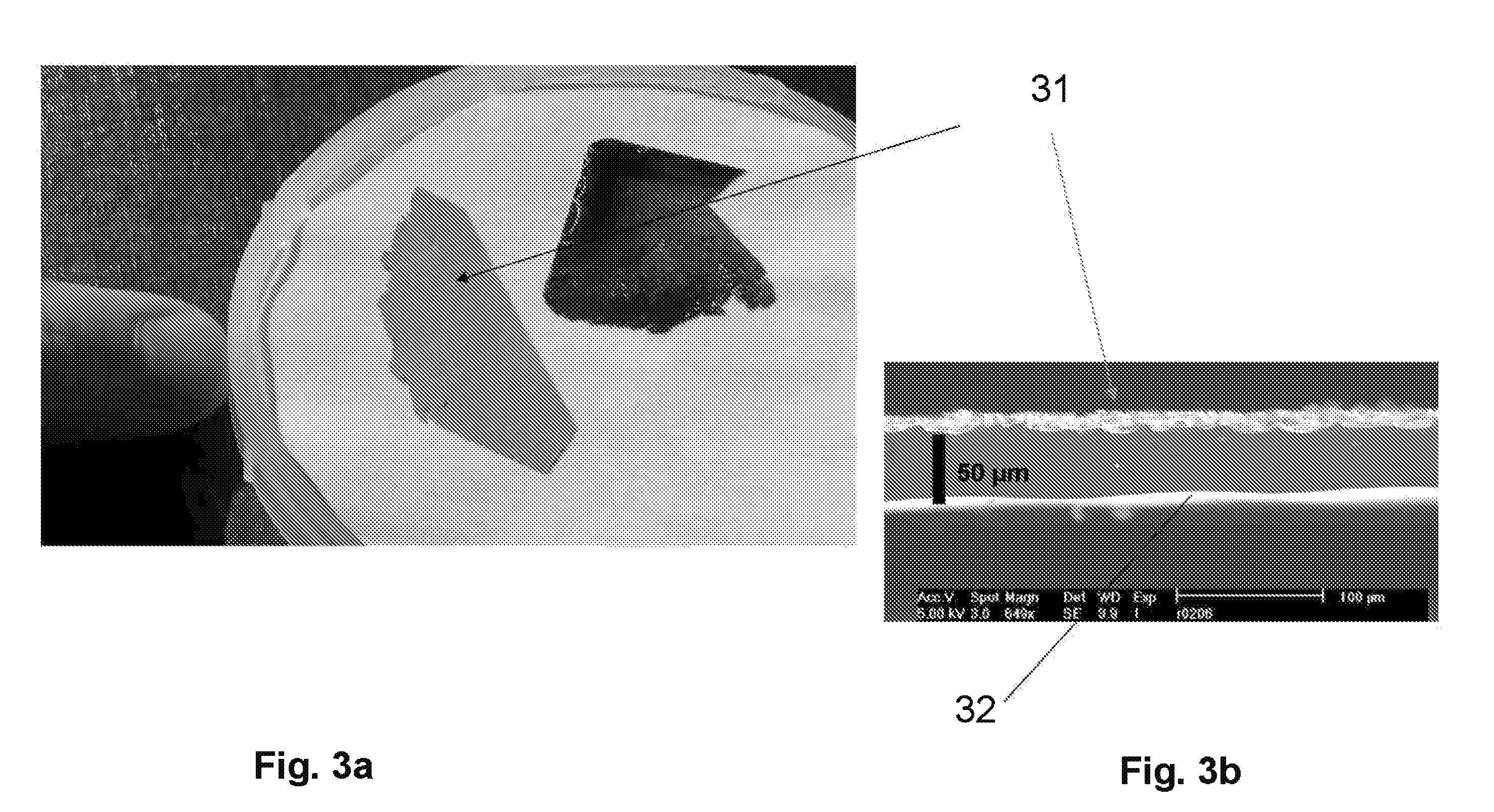
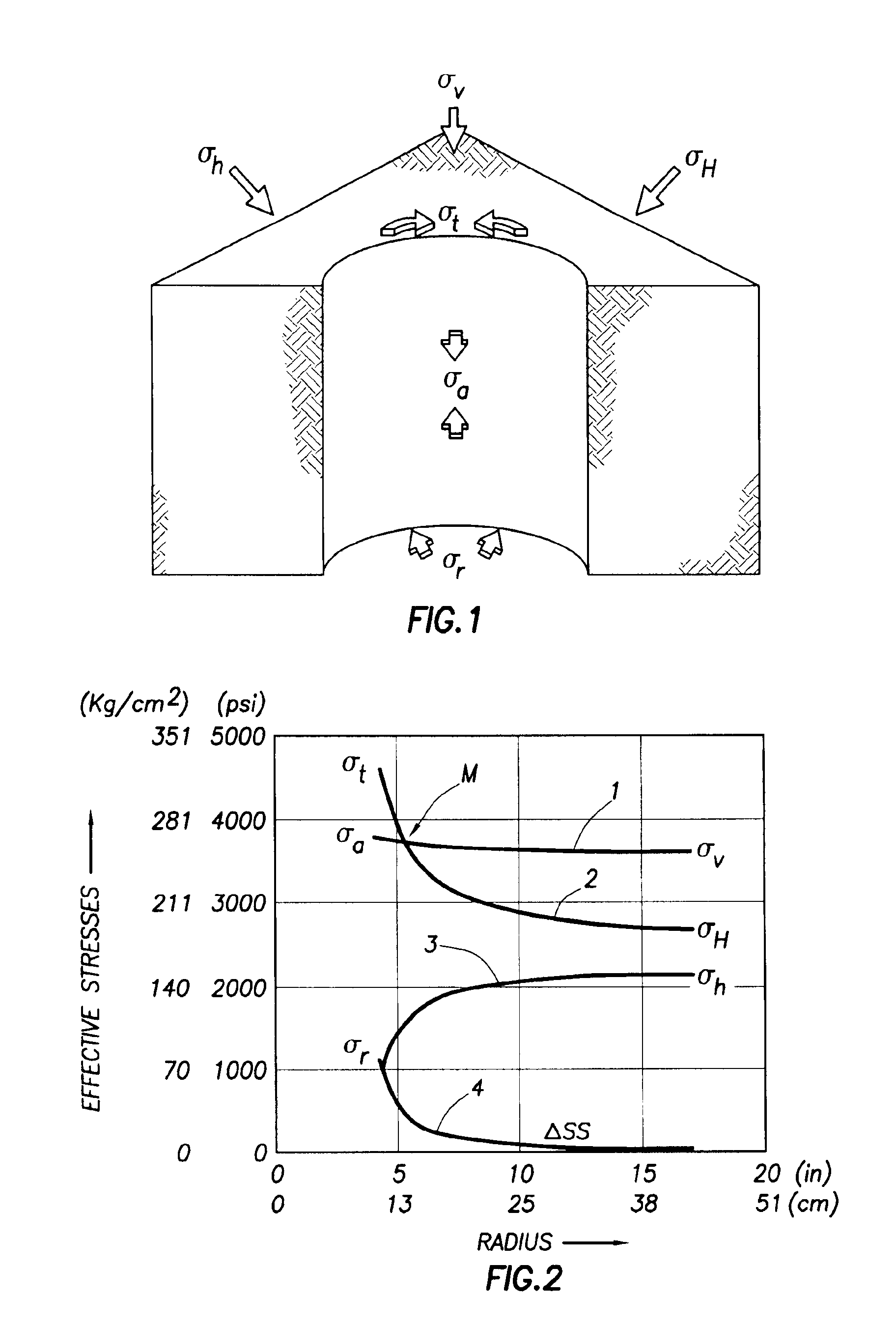
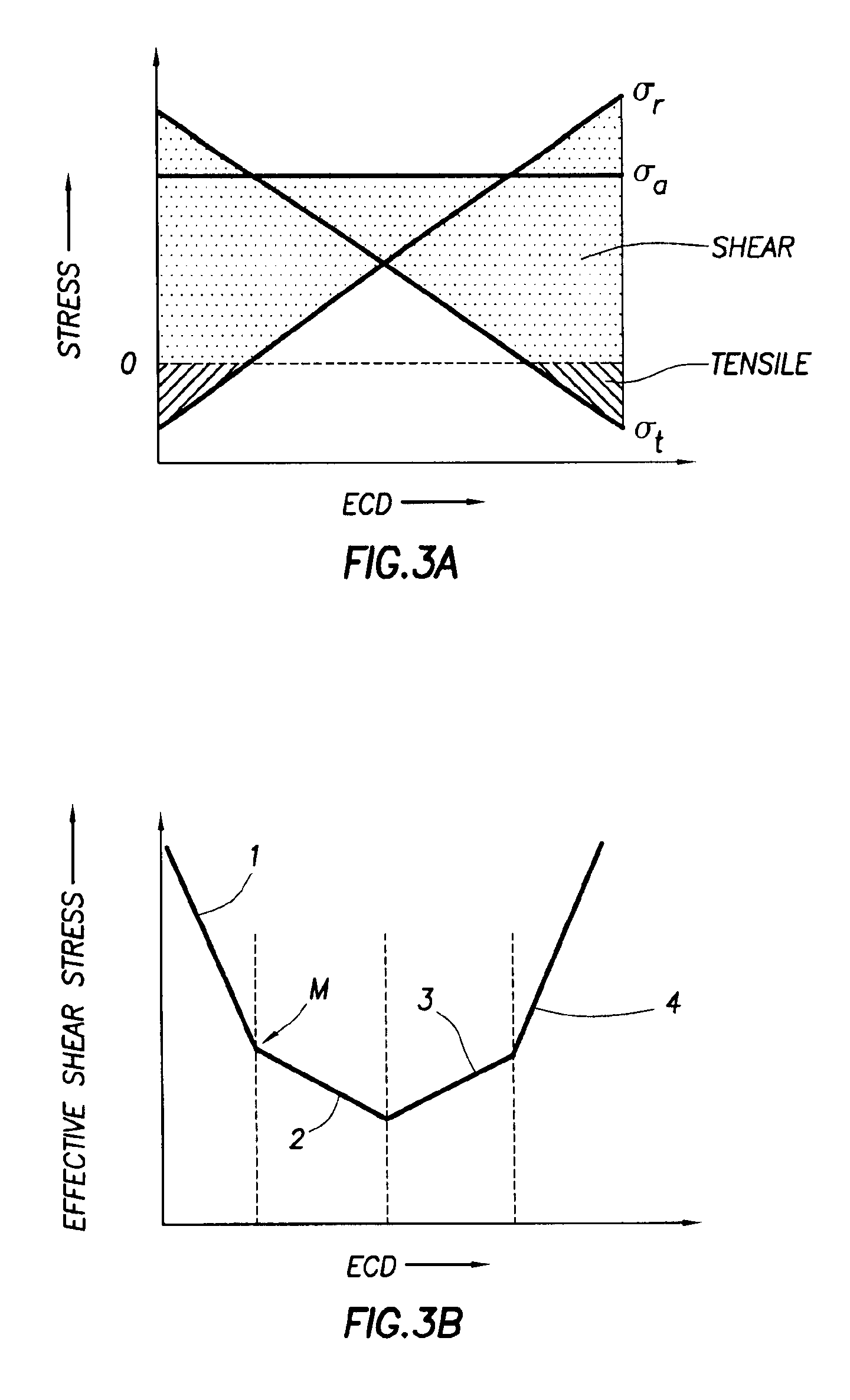
Systems and methods for determining a formation property related to formation strength and stresses are disclosed. A method for determining a formation strength includes obtaining radial formation property measurements at different wellbore pressures; generating a radial stress profile based on a formation model; generating a radial stress function from the radial stress profile; and comparing the radial formation property measurements with the radial stress function to determine the formation strength. A method for determining a formation stress profile includes deriving formation parameters from a formation radial profiling; obtaining formation log data that comprise formation density data; estimating formation stresses from the formation log data; and deriving a radial stress profile based on a formation model, the derived formation parameters, and the estimated formation stresses.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Photolithographically-patterned variable capacitor structures and method of making
InactiveUS6922327B2Speed and easeEliminate needAnti-noise capacitorsMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitanceDielectric layer
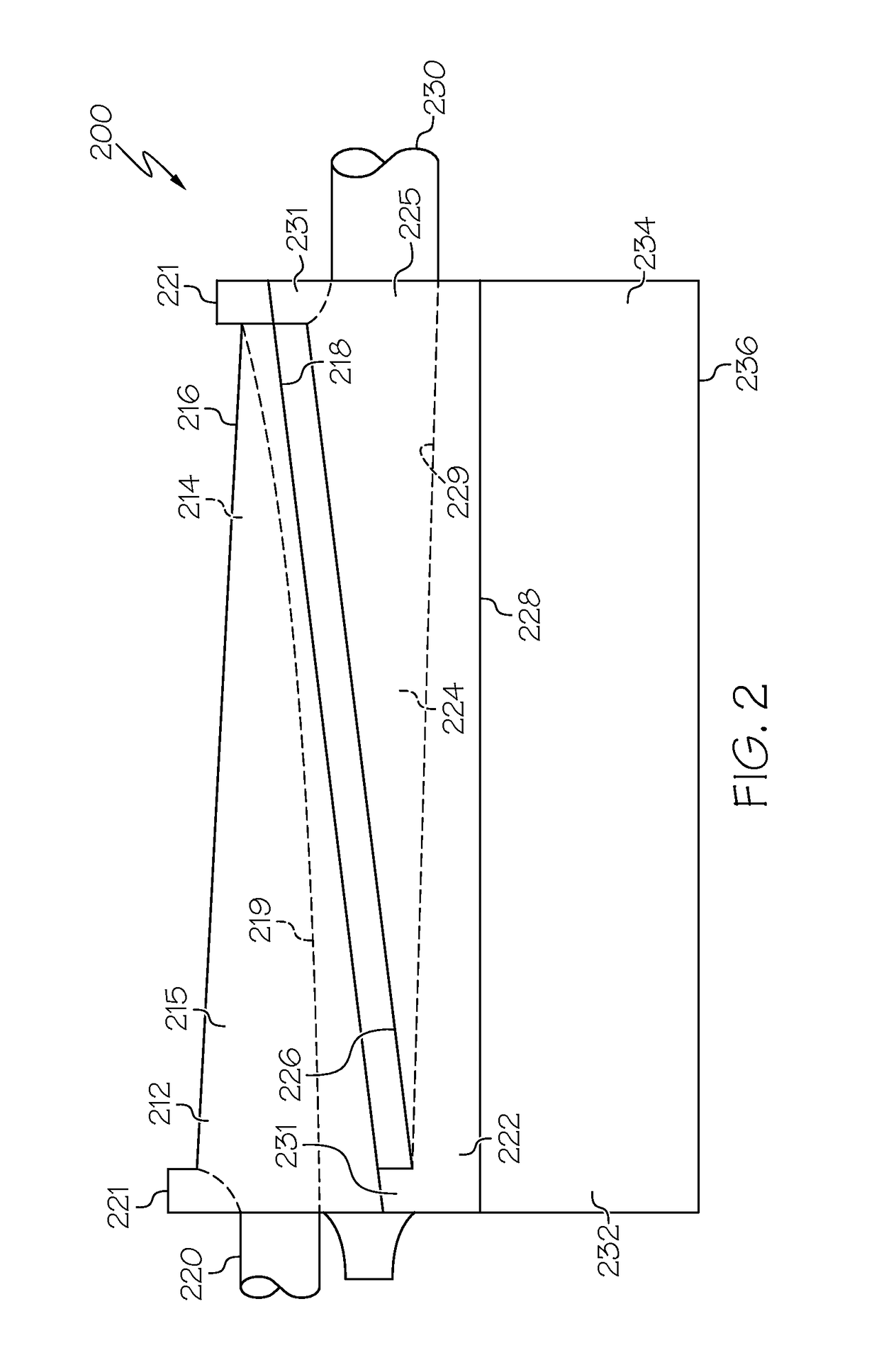
A new type of high-Q variable capacitor includes a substrate, a first electrically conductive layer fixed to the substrate, a dielectric layer fixed to a portion of the electrically conductive layer, and a second electrically conductive layer having an anchor portion and a free portion. The anchor portion is fixed to the dielectric layer and the free portion is initially fixed to the dielectric layer, but is released from the dielectric layer to become separated from the dielectric layer, and wherein an inherent stress profile in the second electrically conductive layer biases the free portion away from the dielectric layer. When a bias voltage is applied between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer, electrostatic forces in the free portion bend the free portion towards the first electrically conductive layer, thereby increasing the capacitance of the capacitor.
Owner:XEROX CORP
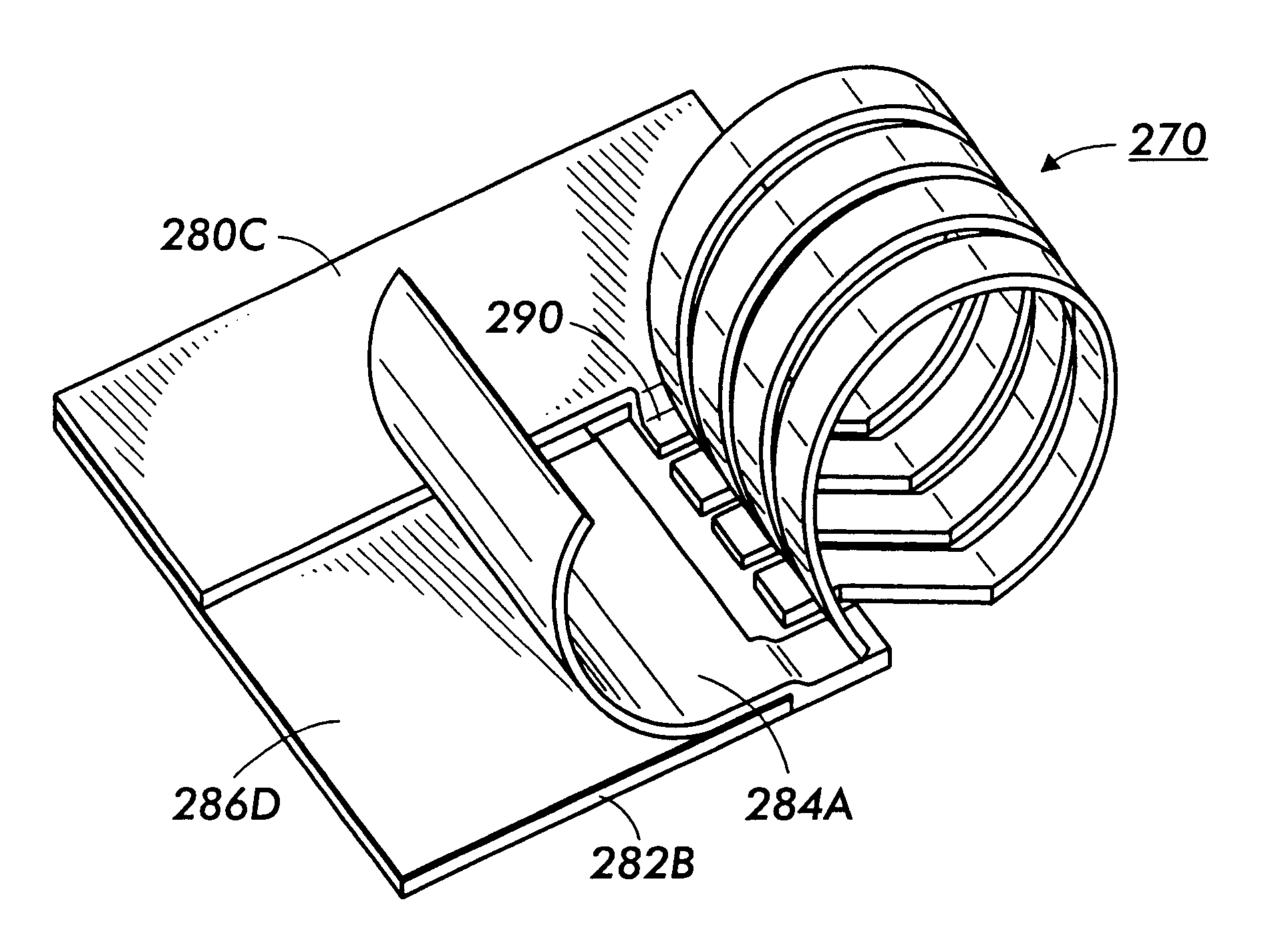
Photolithographically-patterned out-of-plane coil structures and method of making
InactiveUS6856225B1Reduce speedEliminate needSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsMicro structureTransformer
An out-of-plane micro-structure which can be used for on-chip integration of high-Q inductors and transformers places the magnetic field direction parallel to the substrate plane without requiring high aspect ratio processing. The photolithographically patterned coil structure includes an elastic member having an intrinsic stress profile. The intrinsic stress profile biases a free portion away from the substrate forming a loop winding. An anchor portion remains fixed to the substrate. The free portion end becomes a second anchor portion which may be connected to the substrate via soldering or plating. A series of individual coil structures can be joined via their anchor portions to form inductors and transformers.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Glasses and glass ceramics including a metal oxide concentration gradient
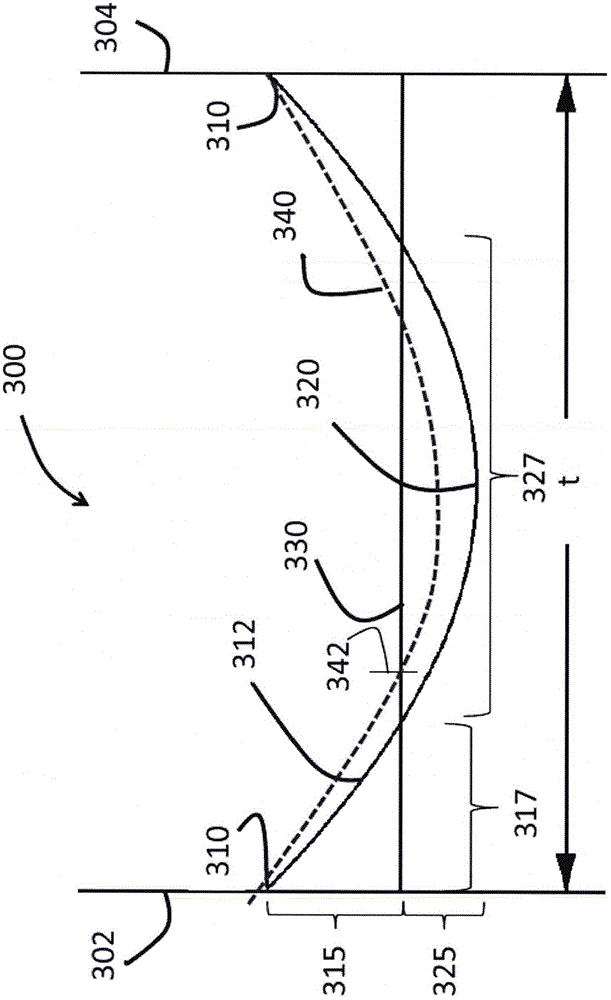
The invention relates to glasses and glass ceramics including a metal oxide concentration gradient. Embodiments of a glass-based article including a first surface and a second surface opposing the first surface defining a thickness (t) of about 3 millimeters or less (e.g., about 1 millimeter or less), and a stress profile, wherein all points of the stress profile between a thickness range from about 0t up to 0.3t and from greater than 0.7t, comprise a tangent that is less than about -0.1 MPa / micrometers or greater than about 0.1 MPa / micrometers, are disclosed. In some embodiments, the glass-based article includes a non-zero metal oxide concentration that varies along at least a portion of the thickness (e.g., 0t to about 0.3t). In some embodiments, the concentration of metal oxide or alkali metal oxide decreases from the first surface to a point between the first surface and the second surface and increases from the point to the second surface. The concentration of the metal oxide may be about 0.05 mol % or greater or about 0.5 mol % or greater throughout the thickness. Methods for forming such glass-based articles are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Photolithographically-patterned out-of-plane coil structures and method of making
InactiveUS6582989B2Capacitor with electrode distance variationSolid-state devicesMicro structureTransformer
An out-of-plane micro-structure which can be used for on-chip integration of high-Q inductors and transformers places the magnetic field direction parallel to the substrate plane without requiring high aspect ratio processing. The photolithographically patterned coil structure includes an elastic member having an intrinsic stress profile. The intrinsic stress profile biases a free portion away from the substrate forming a loop winding. An anchor portion remains fixed to the substrate. The free portion end becomes a second anchor portion which may be connected to the substrate via soldering or plating. Alternately, the loop winding can be formed of two elastic members in which the free ends are joined in mid-air. A series of individual coil structures can be joined via their anchor portions to form inductors and transformers.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Articles having improved residual stress profile characteristics produced by laser shock peening
InactiveUS6752593B2Increase penetration depthControl of depthPropellersReaction enginesOptoelectronicsLaser peening
Articles produced by laser shock processing exhibit various compressive residual stress distribution profiles. A gas turbine engine airfoil includes an asymmetrical stress profile formed through the thickness of its thin section. The articles include plural laser shock peened surfaces and plural regions having deep compressive residual stresses imparted by laser shock peening extending into the article from the laser peened surfaces. One article includes at least one set of simultaneously formed, adjacent non-overlapping laser shock peened surfaces. Another article includes at least one set of opposing laser shock peened surfaces formed at different times at opposite sides of the article. Another article includes at least one set of opposing laser shock peened surfaces formed simultaneously at opposite sides of the article using laser beams having different pulse lengths. Another article includes at least one set of laterally offset laser shock peened surfaces simultaneously formed at opposite sides of the article.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
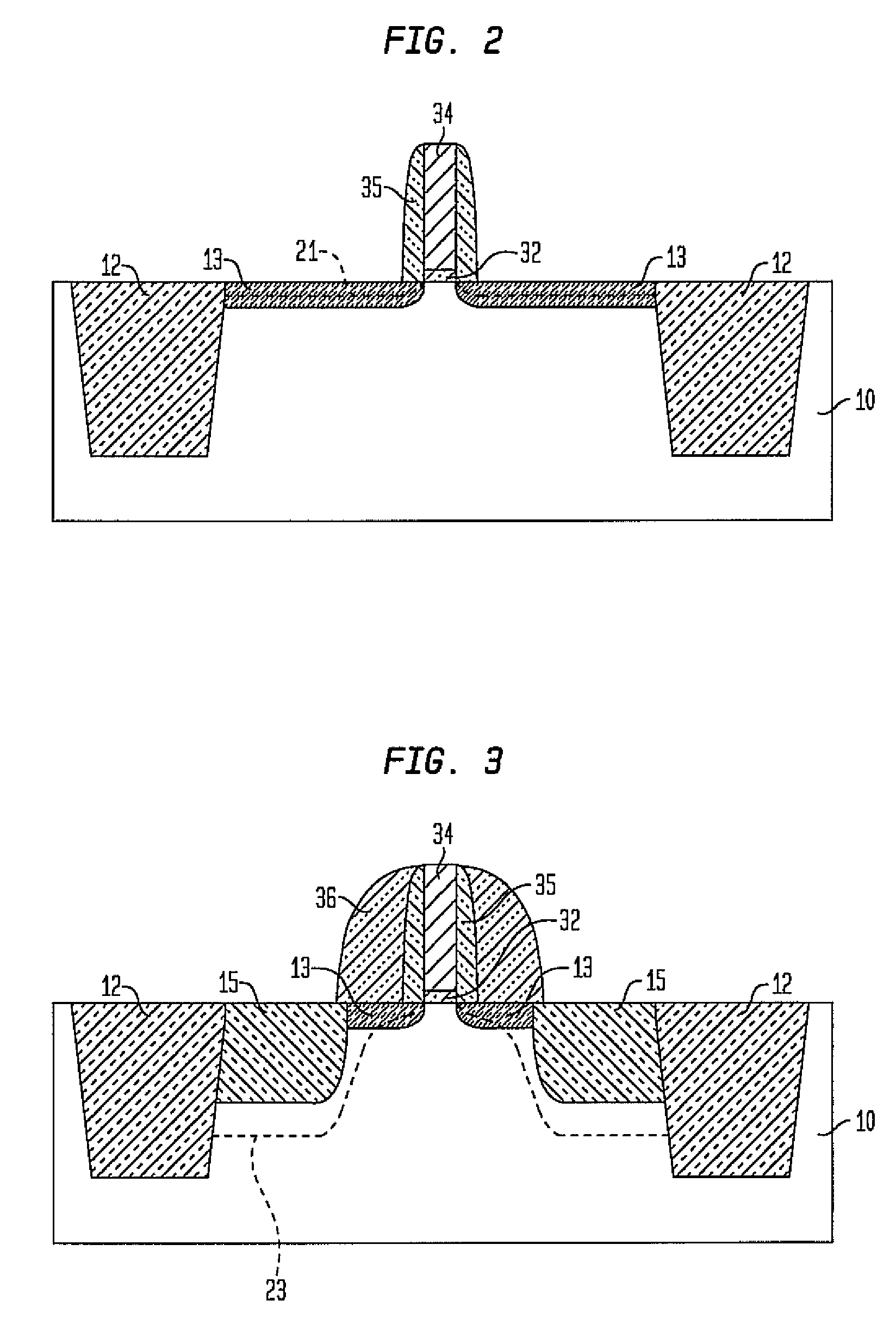
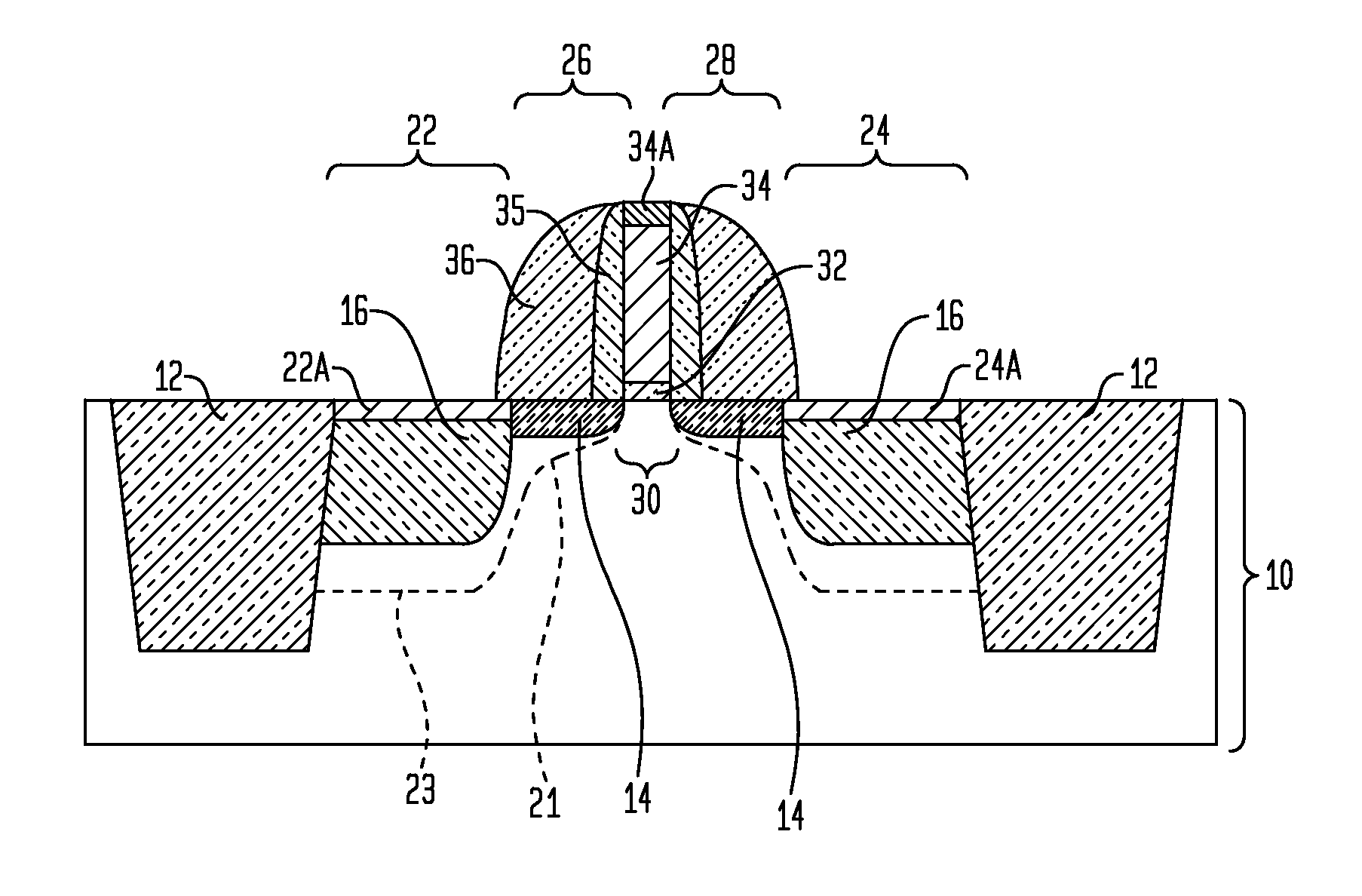
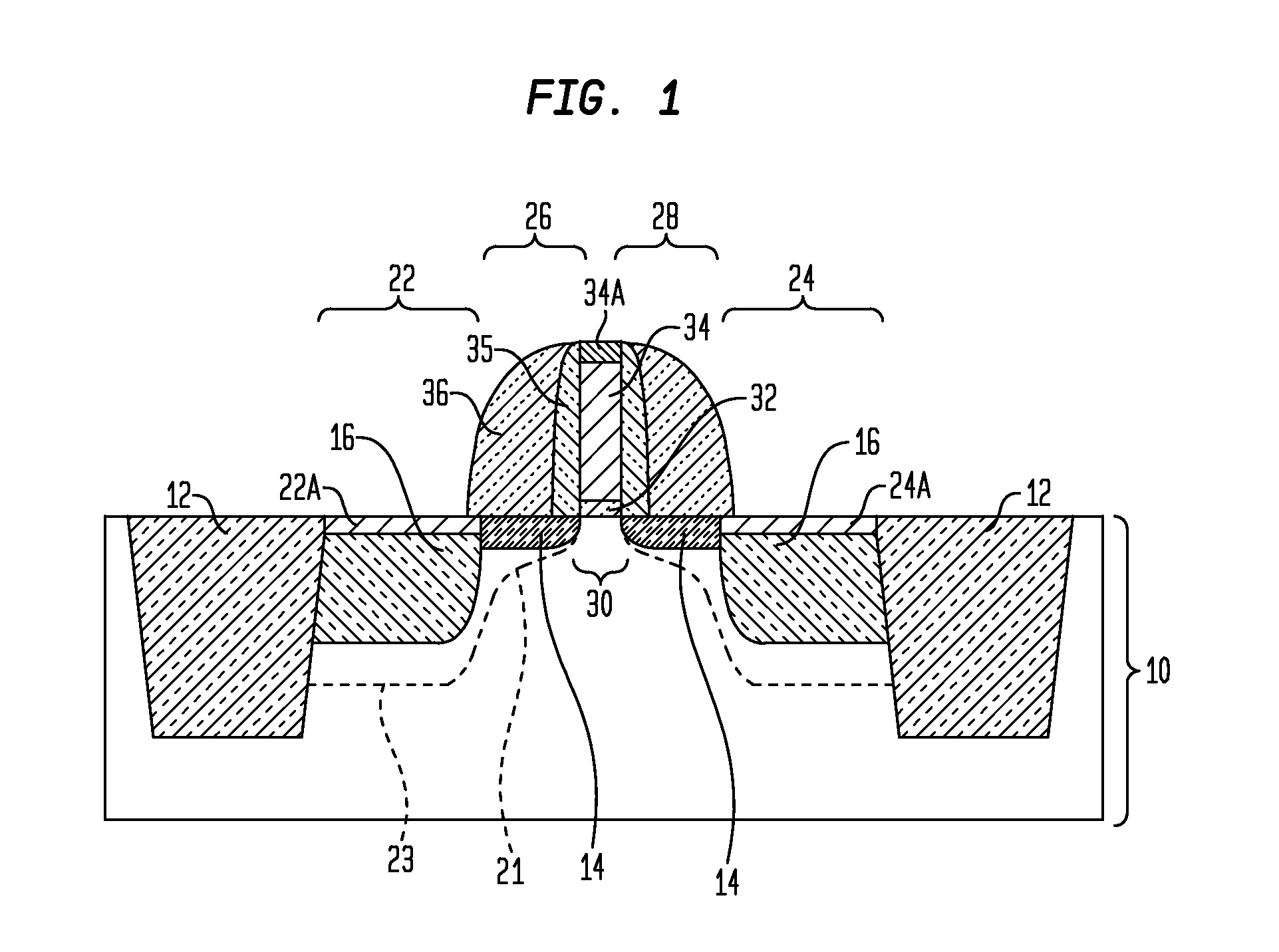
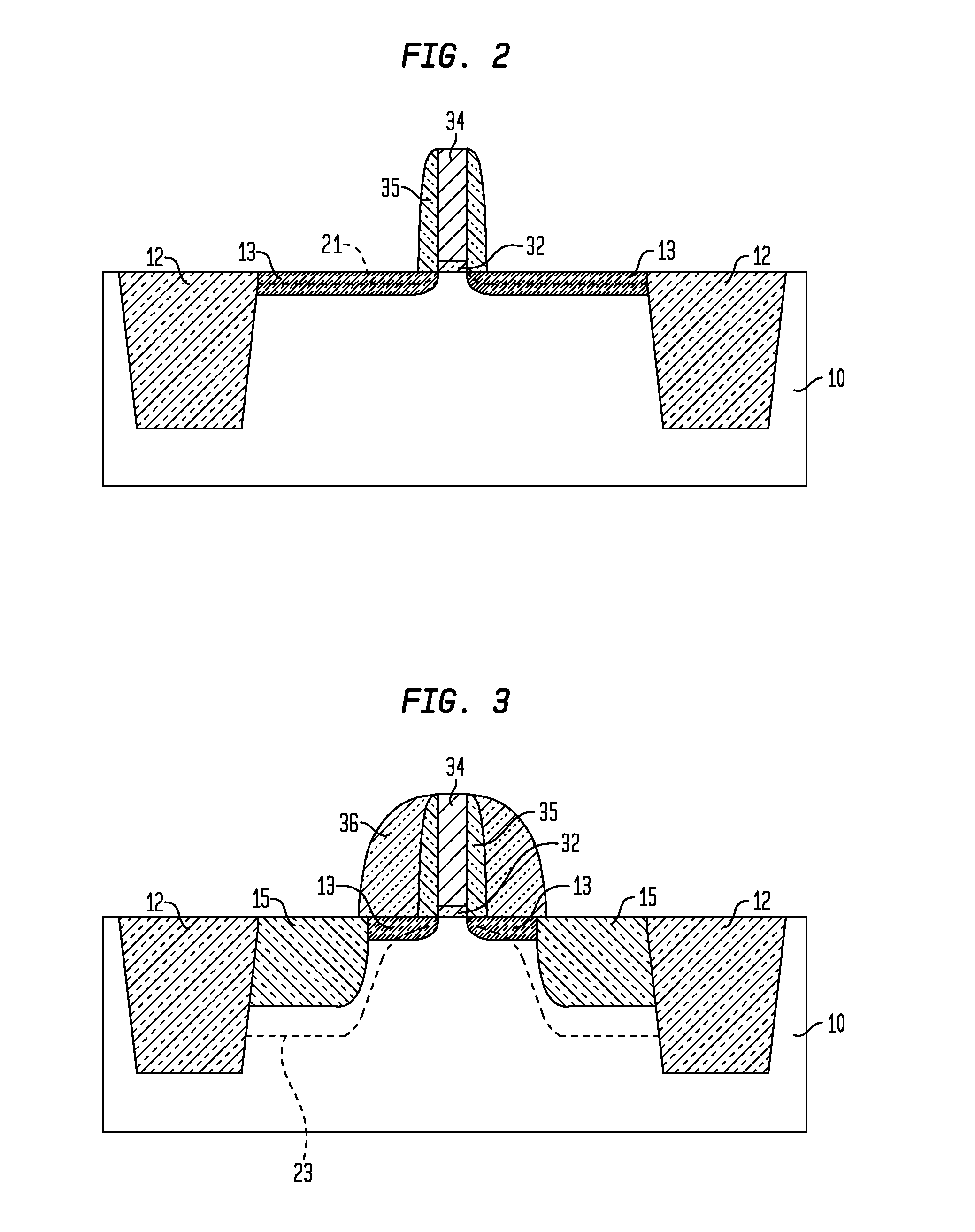
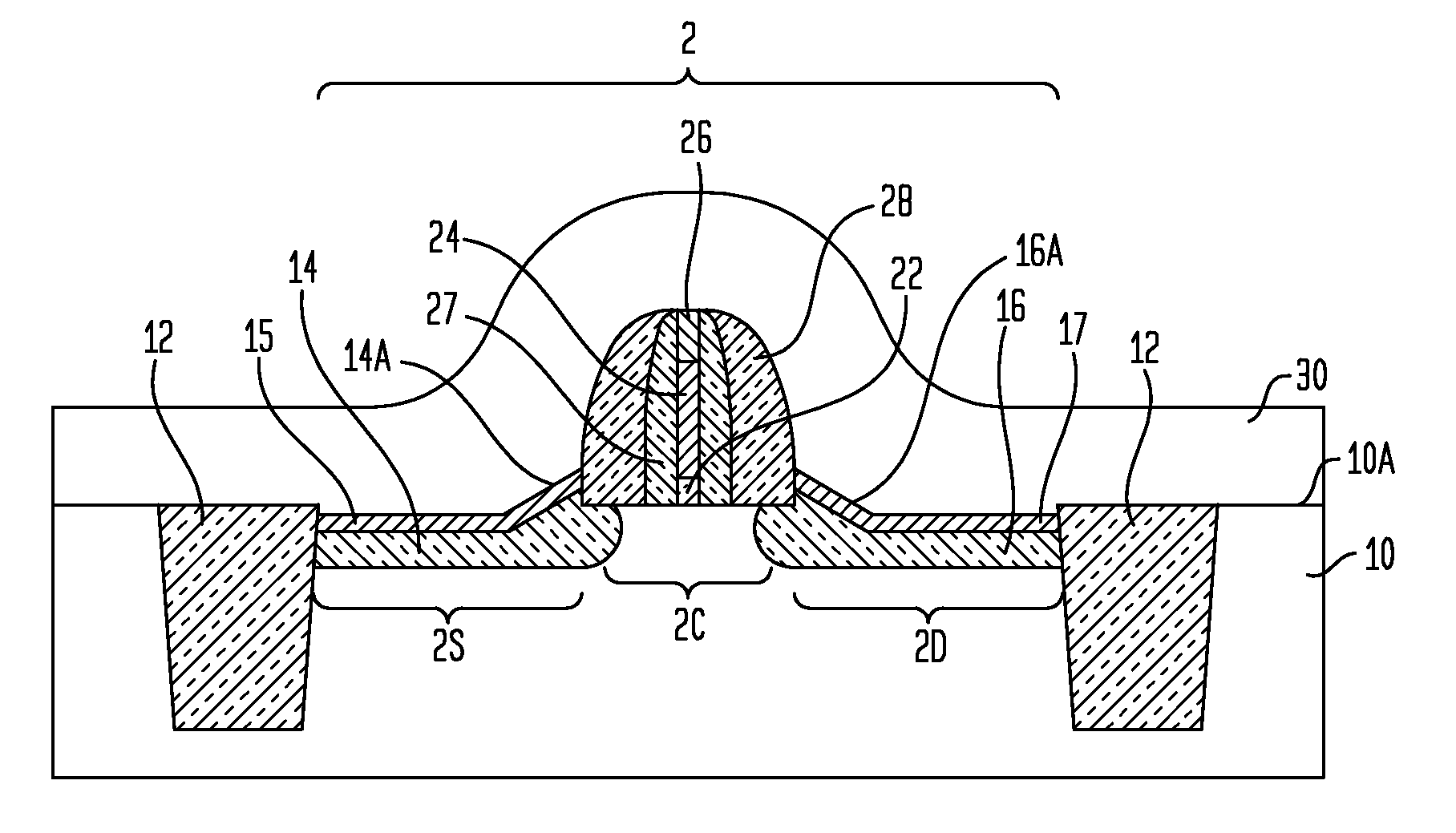
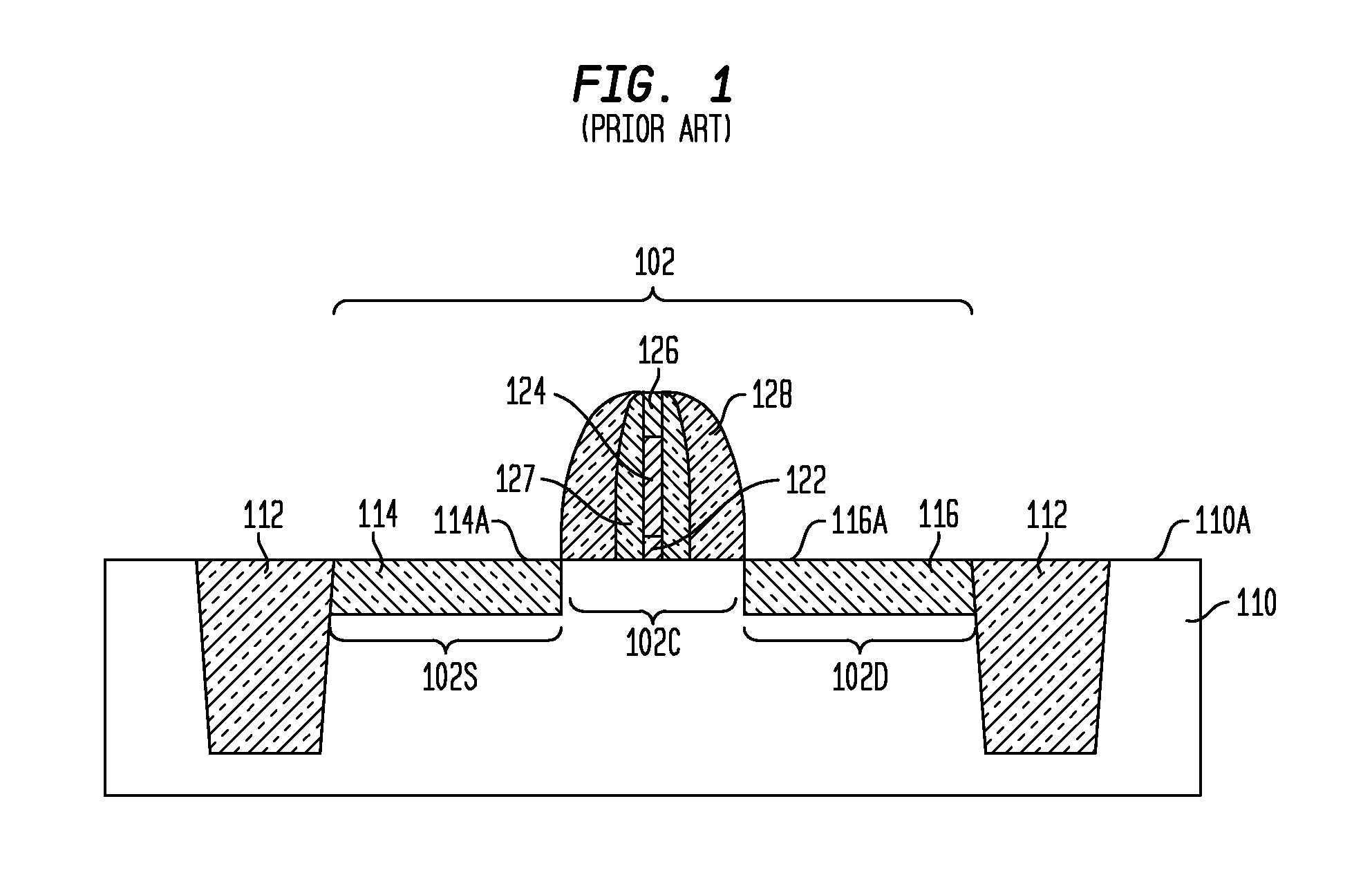
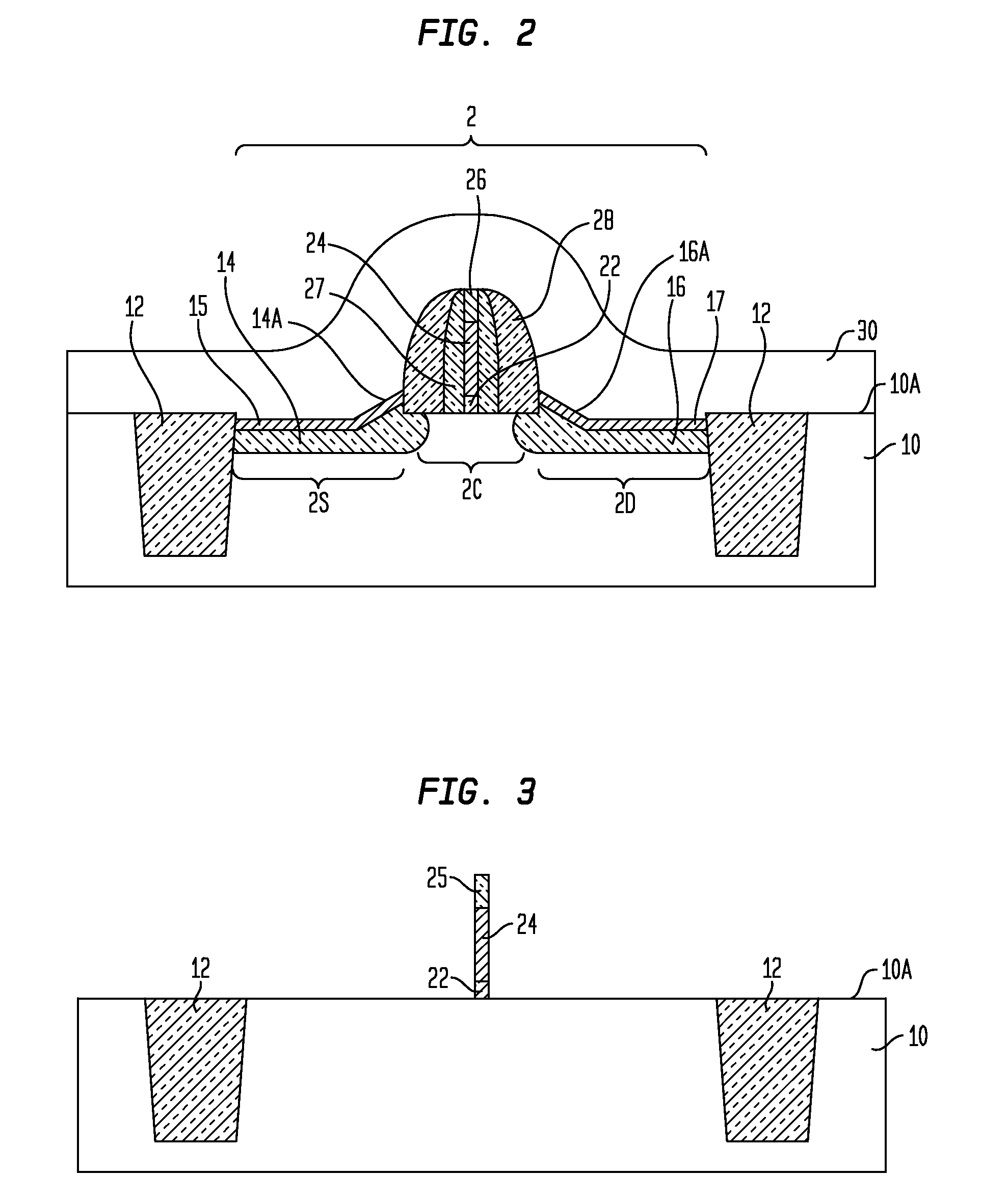
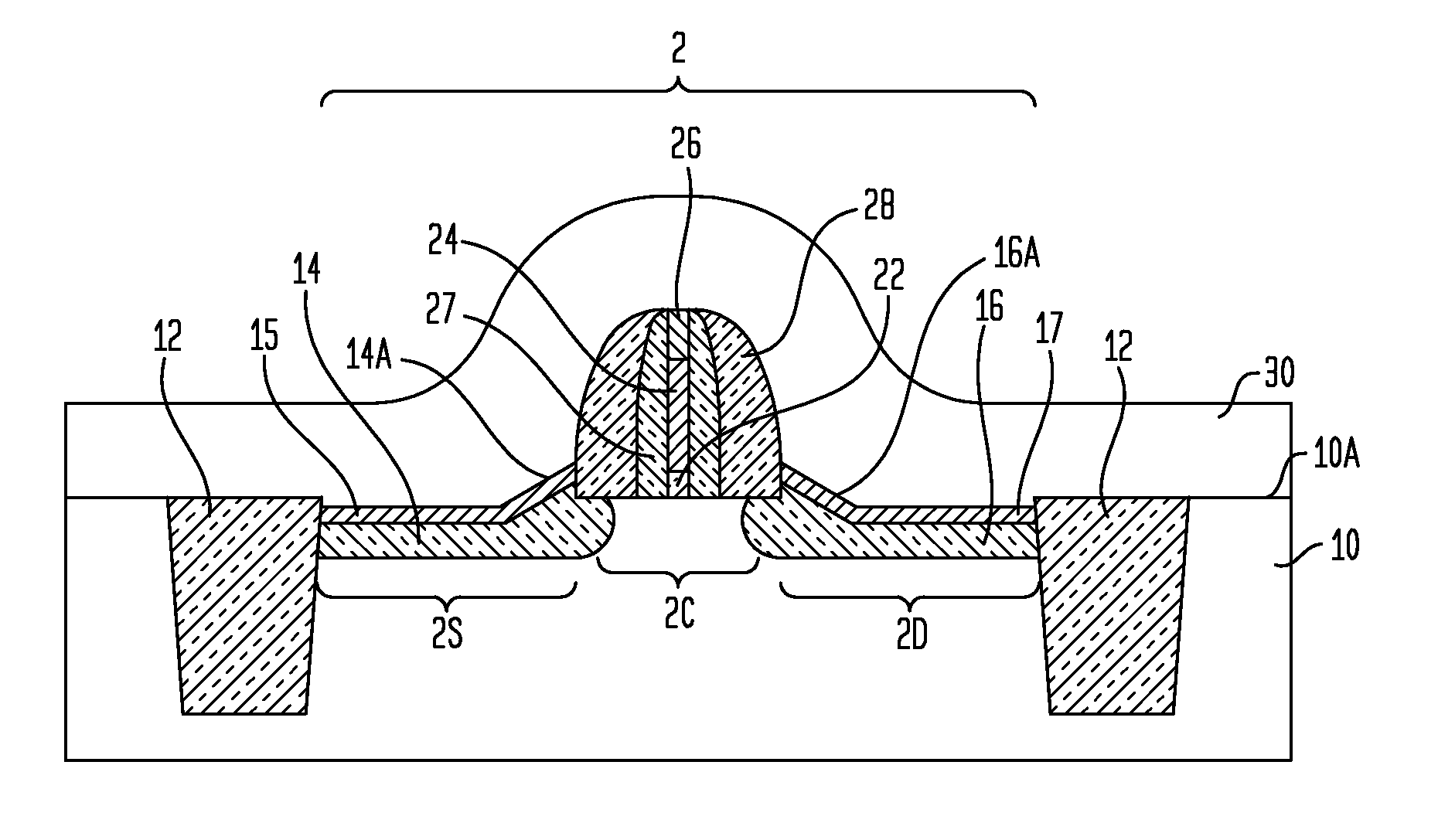
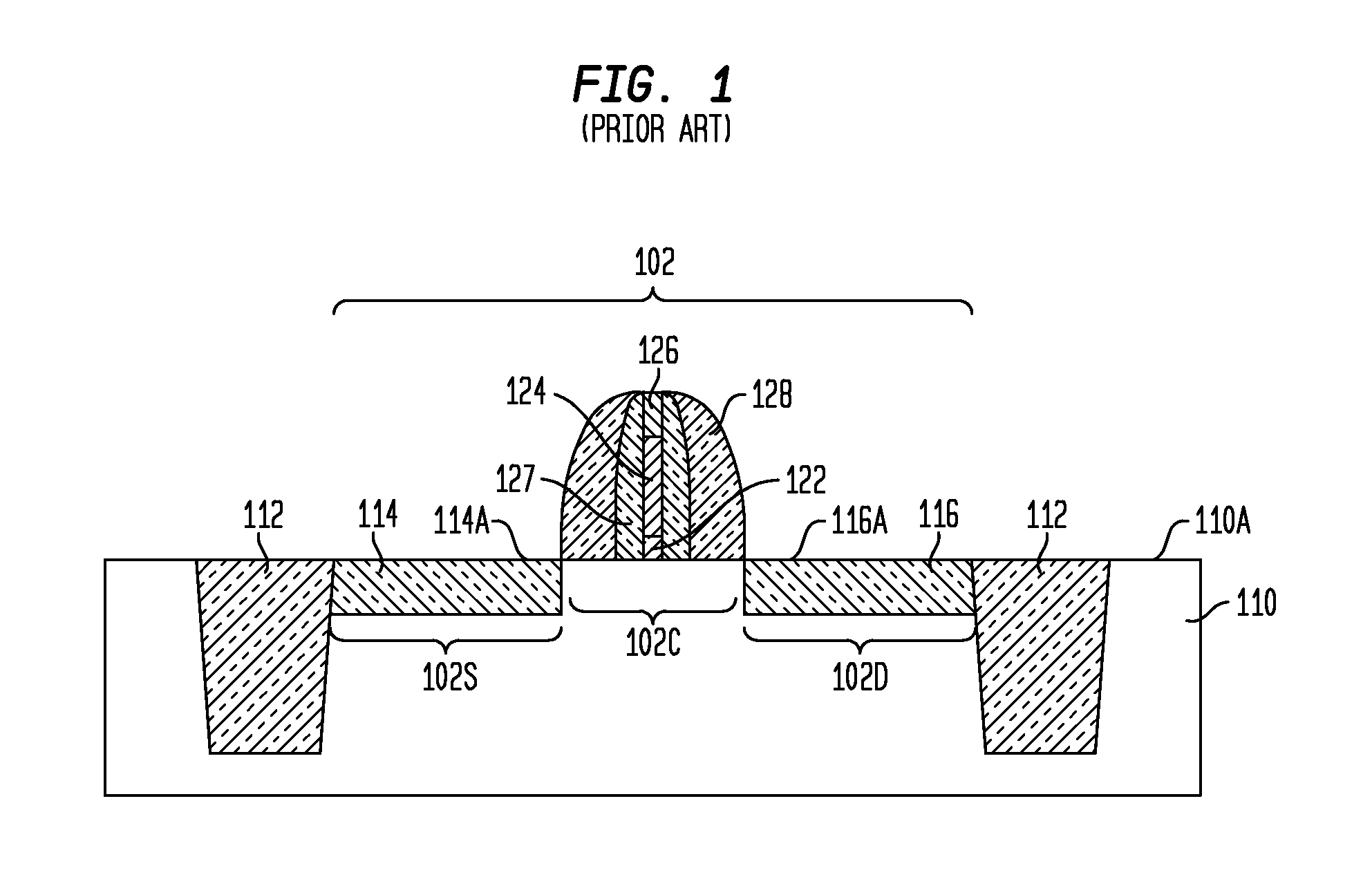
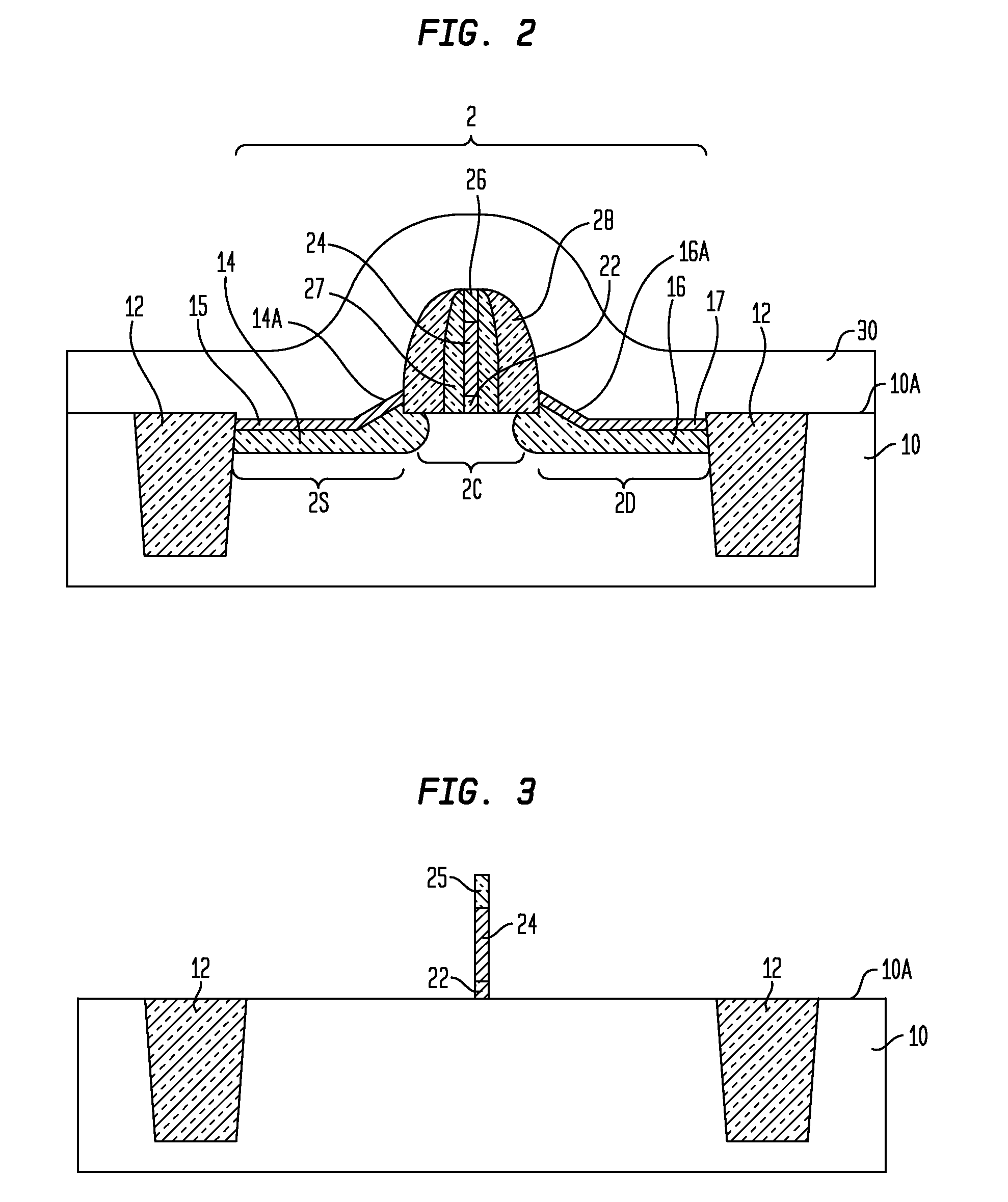
N-channel MOSFETs comprising dual stressors, and methods for forming the same
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device including at least one n-channel field effect transistor (n-FET). Specifically, the n-FET includes first and second patterned stressor layers that both contain a carbon-substituted and tensilely stressed single crystal semiconductor. The first patterned stressor layer has a first carbon concentration and is located in source and drain (S / D) extension regions of the n-FET at a first depth. The second patterned stressor layer has a second, higher carbon concentration and is located in S / D regions of the n-FET at a second, deeper depth. Such an n-FET with the first and second patterned stressor layers of different carbon concentration and different depths provide improved stress profile for enhancing electron mobility in the channel region of the n-FET.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
System for laser shock processing objects to produce enhanced stress distribution profiles
InactiveUS6759626B2Increase penetration depthLaser beam welding apparatusStress distributionShock hardening
Various laser shock processing systems are provided to establish selective compressive residual stress distribution profiles within a workpiece. An asymmetrical stress profile may be formed through the thickness of a thin section of a gas turbine engine airfoil. One system is configured to simultaneously irradiate a workpiece with a set of laser beams to form a corresponding set of adjacent non-overlapping laser shock peened surfaces, enabling the shockwaves to encounter one another. Another system irradiates opposite sides of the workpiece at different times to form opposing laser shock peened surfaces, enabling the shockwaves to meet at a location apart from the mid-plane. Another system simultaneously irradiates opposite sides of the workpiece using laser beams having different pulse lengths to form opposing laser shock peened surfaces. Another system simultaneously irradiates opposite sides of the workpiece to form a set of laterally offset laser shock peened surfaces.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
N-channel mosfets comprising dual stressors, and methods for forming the same
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device comprising at least one n-channel field effect transistor (n-FET). Specifically, the n-FET comprises first and second patterned stressor layers that both contain a carbon-substituted and tensilely stressed single crystal semiconductor. The first patterned stressor layer has a first carbon concentration and is located in source and drain (S / D) extension regions of the n-FET at a first depth. The second patterned stressor layer has a second, higher carbon concentration and is located in S / D regions of the n-FET at a second, deeper depth. Such an n-FET with the first and second patterned stressor layers of different carbon concentration and different depths provide improved stress profile for enhancing electron mobility in the channel region of the n-FET.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
Method of making photolithographically-patterned out-of-plane coil structures
InactiveUS20030179064A1Contact member manufacturingContact member assembly/disassemblyMicro structureTransformer
An out-of-plane micro-structure which can be used for on-chip integration of high-Q inductors and transformers places the magnetic field direction parallel to the substrate plane without requiring high aspect ratio processing. The photolithographically patterned coil structure includes an elastic member having an intrinsic stress profile. The intrinsic stress profile biases a free portion away from the substrate forming a loop winding. An anchor portion remains fixed to the substrate. The free portion end becomes a second anchor portion which may be connected to the substrate via soldering or plating. A series of individual coil structures can be joined via their anchor portions to form inductors and transformers.
Owner:XEROX CORP
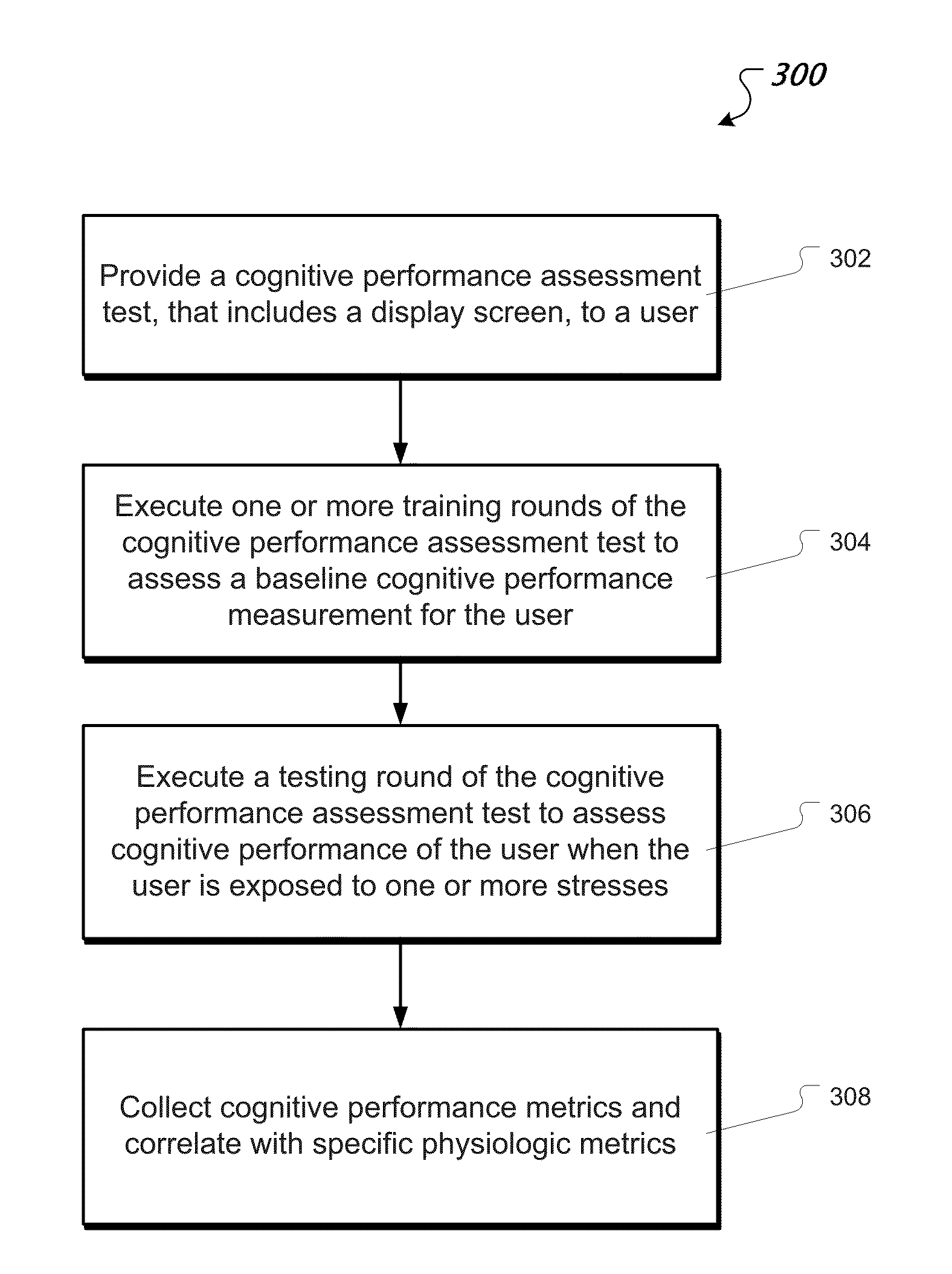
Cognitive performance assessment test
InactiveUS20150164418A1Lower performance requirementsAccurate identificationSensorsPsychotechnic devicesOxygen deprivationStress conditions
This document provides systems and methods for testing and assessing cognitive performance of a user over a period of time in order to test environmental effects and other factors on the performance of the user. For example, cognitive performance over a period of time can be assessed for users experiencing stress conditions including hypoxia (oxygen deprivation), hypothermia, sleep deprivation, fatigue or other factors that may cause degradation in cognitive performance. Furthermore, the systems and methods described herein can be used to identify when hypoxia has manifested in the cerebral circulation of an individual rather than merely in the extremities of an individual.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Mosfets comprising source/drain regions with slanted upper surfaces, and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080006854A1High strengthIncrease overall stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETEtching
The present invention relates to improved metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) devices comprising source and drain (S / D) regions having slanted upper surfaces with respect to a substrate surface. Such S / D regions may comprise semiconductor structures that are epitaxially grown in surface recesses in a semiconductor substrate. The surface recesses preferable each has a bottom surface that is parallel to the substrate surface, which is oriented along one of a first set of equivalent crystal planes, and one or more sidewall surfaces that are oriented along a second, different set of equivalent crystal planes. The slanted upper surfaces of the S / D regions function to improve the stress profile in the channel region as well as to reduce contact resistance of the MOSFET. Such S / D regions with slanted upper surfaces can be readily formed by crystallographic etching of the semiconductor substrate, followed by epitaxial growth of a semiconductor material.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Method for the production of thin substrates
InactiveUS20100323472A1Easy to controlLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolar cellInduced stress
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Glass-based articles including a stress profile comprising two regions, and methods of making
PendingCN107265884ACasings with display/control unitsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsMechanical engineeringMaterials science
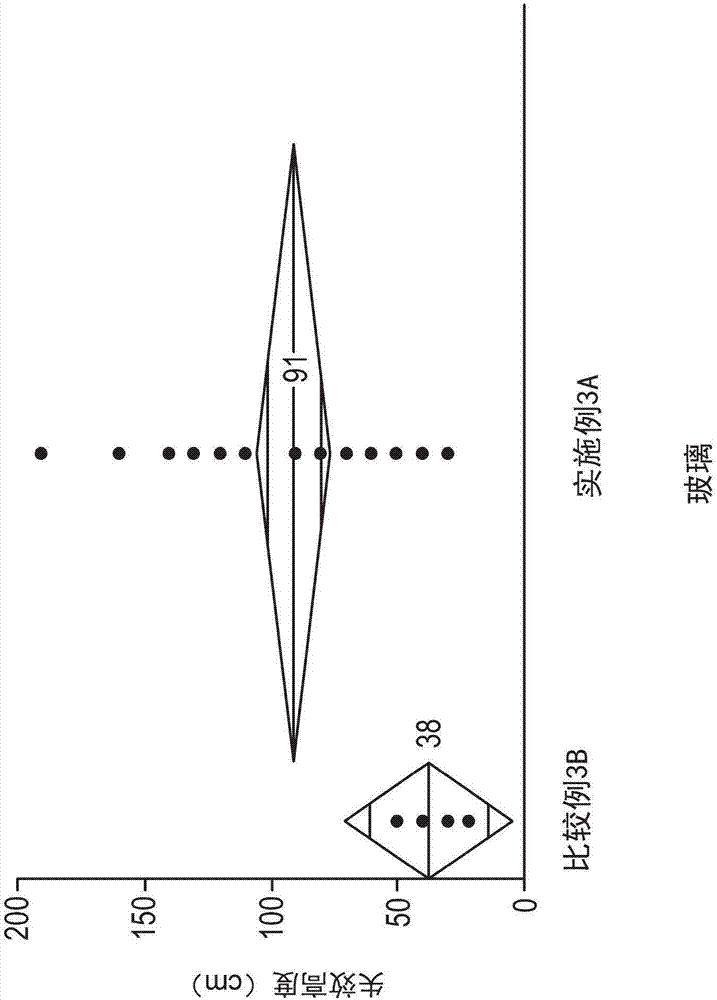
The invention provides glass-based articles including a stress profile comprising two regions and methods of making. The glass-based article includes a first surface and a second surface opposing the first surface defining a thickness (t) in a range of 0.1-2mm, and a stress profile extending along the thickness (t), wherein at last one point in the stress profile in a first thickness range of about 0.t to 0.020.t and greater than 0.98.t has a tangent line which has a slope from about -200MPa / [mu]m to -25MPa / [mu]m or from 25MPa / [mu]m to 200 MPa / [mu]m, and all points in the stress profile in a second thickness range of from about 0.035.t to less than 0.965.t have tangent lines which have a slope from about -15MPa / [mu]m to 15MPa / [mu]m. The stress profile contains surface CS about 200-100MPa, wherein the stress profile contains the DOC in the range of about 0.1.t to 0.25.t.
Owner:CORNING INC
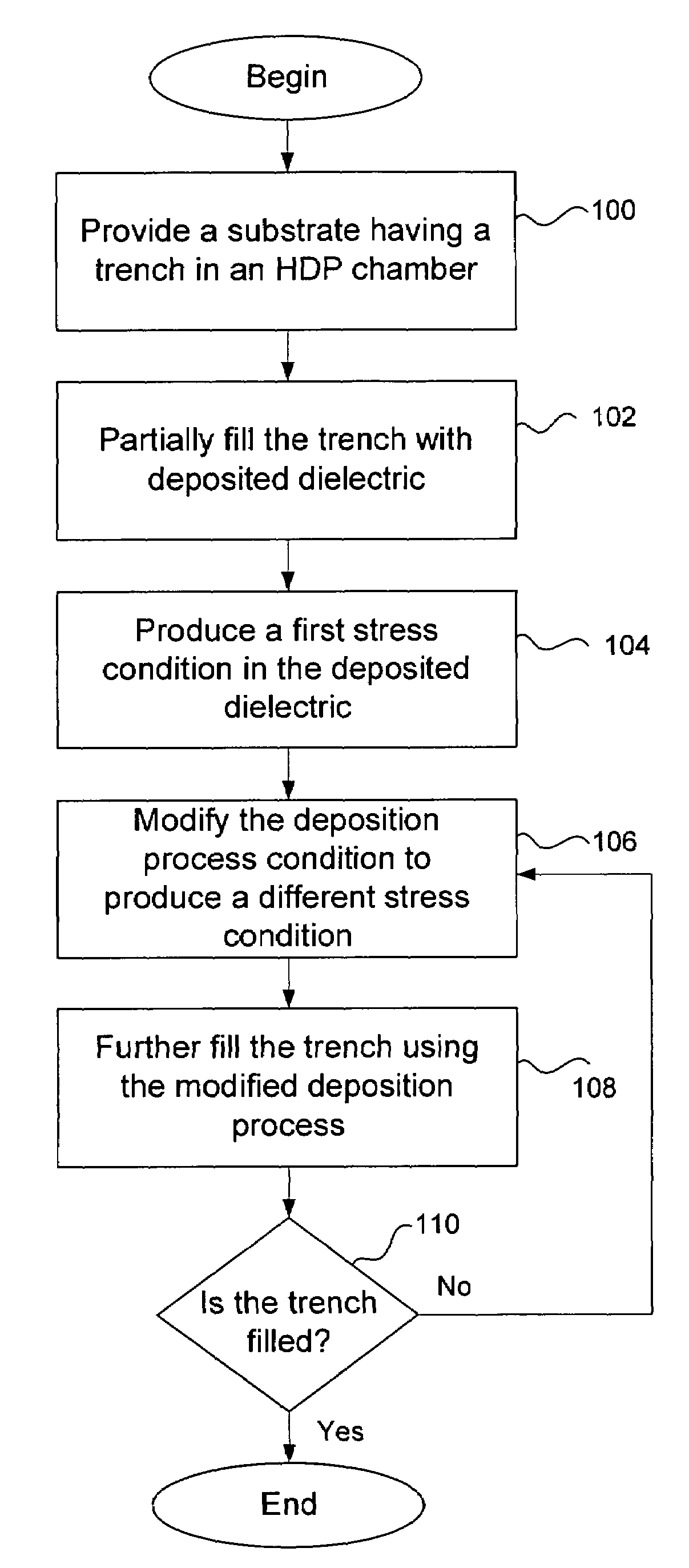
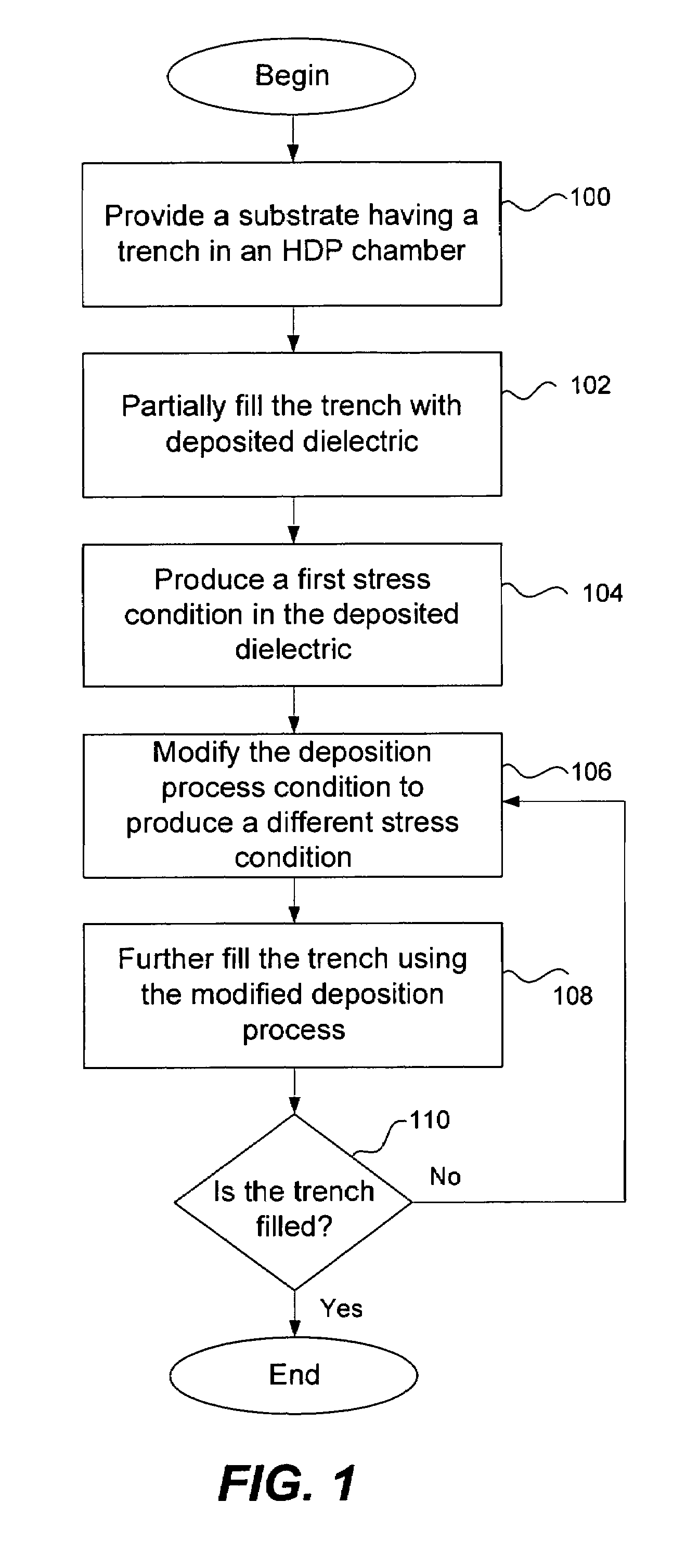
Stress profile modulation in STI gap fill
InactiveUS7482245B1Without adversely impacting efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricHigh density
High density plasma (HDP) techniques form silicon oxide films having sequentially modulated stress profiles. The HDP techniques use low enough temperatures to deposit silicon oxide films in transistor architectures and fabrication processes effective for generating channel strain without adversely impacting transistor integrity. Methods involve partially filling a trench on a substrate with a portion of deposited dielectric using a high density plasma chemical vapor deposition process. The conditions of the process are configured to produce a first stress condition in the first portion of the deposited dielectric. The deposition process condition may then be modified to produce a different stress condition in deposited dielectric. The partially-filled trench may be further filled using the modified deposition process to produce additional dielectric and can be repeated until the trench is filled. Transistor strain can be generated in NMOS or PMOS devices using stress profile modulation in STI gap fill.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
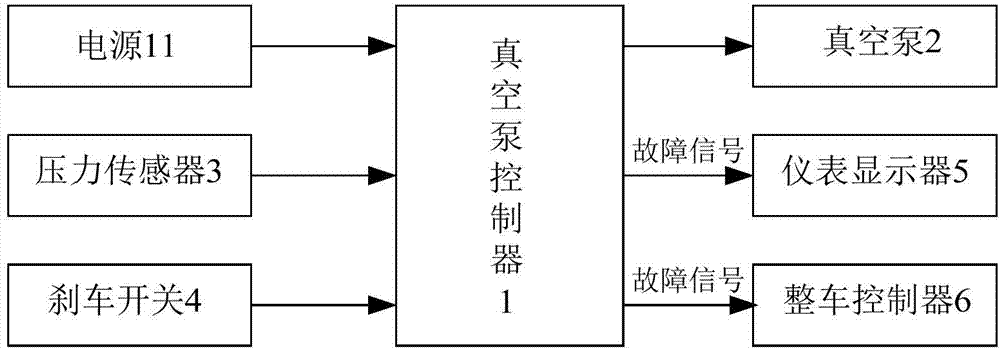
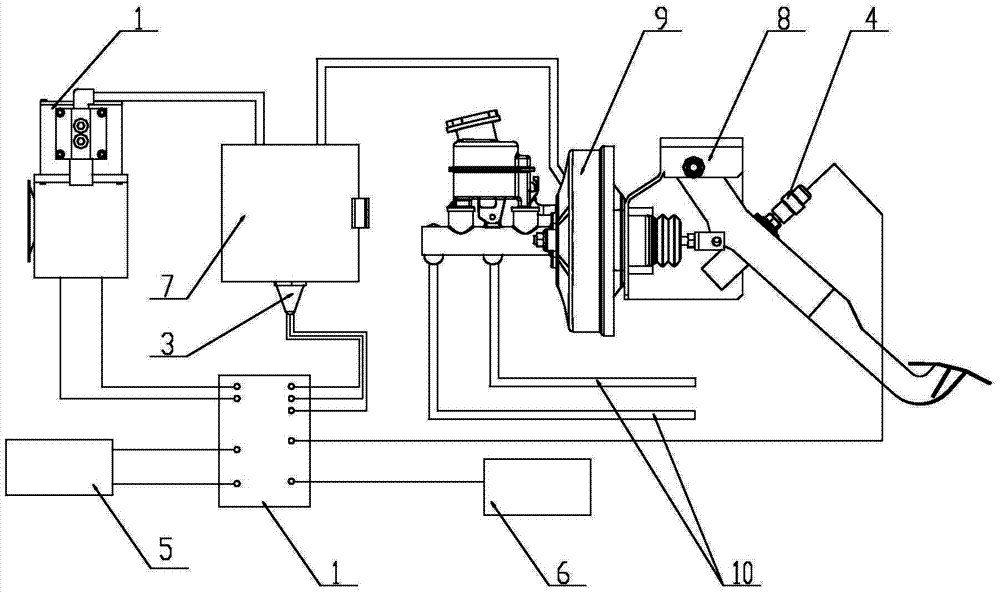
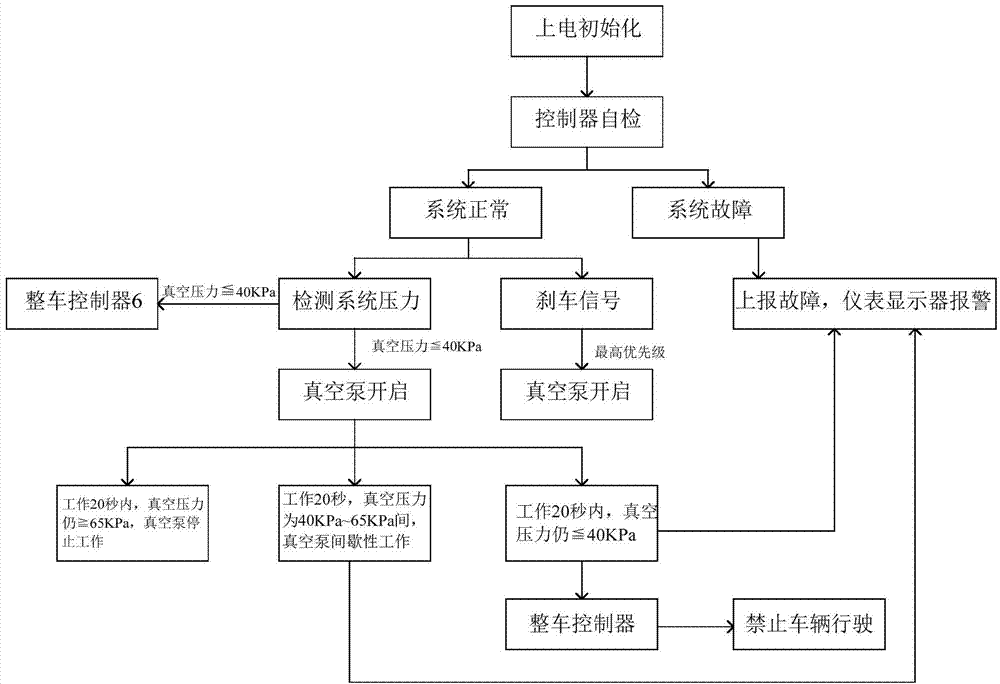
Vacuum pump control system and control method for electric automobile
InactiveCN103863291AImprove self-check securityGuarantee the level of automationBraking action transmissionElectricityControl system
The invention provides a vacuum pump control system for an electric automobile. The vacuum pump control system comprises a vacuum pump controller, and a vacuum pump, a pressure sensor, a brake switch, an instrument display and a vehicle control unit which are electrically connected with the vacuum pump controller respectively, wherein the pressure sensor is arranged at an air outlet of a vacuum air tank and is used for detecting air pressure in the vacuum air tank; the brake switch is connected with a brake pedal, and is switched on to transmit a brake signal to the vacuum pump controller; the instrument display is used for outputting a fault signal transmitted by the vacuum pump controller; the vehicle control unit is used for regulating the running condition of the electric automobile according to the pressure condition of the vacuum pump under the control of the vacuum pump controller. The invention also provides a vacuum pump control method for an electric automobile.
Owner:SHENZHEN GREENWHEEL ELECTRIC VEHICLE CO LTD
MOSFETs comprising source/drain regions with slanted upper surfaces, and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS7485524B2High strengthIncrease overall stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETEtching
The present invention relates to improved metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) devices comprising source and drain (S / D) regions having slanted upper surfaces with respect to a substrate surface. Such S / D regions may comprise semiconductor structures that are epitaxially grown in surface recesses in a semiconductor substrate. The surface recesses preferable each has a bottom surface that is parallel to the substrate surface, which is oriented along one of a first set of equivalent crystal planes, and one or more sidewall surfaces that are oriented along a second, different set of equivalent crystal planes. The slanted upper surfaces of the S / D regions function to improve the stress profile in the channel region as well as to reduce contact resistance of the MOSFET. Such S / D regions with slanted upper surfaces can be readily formed by crystallographic etching of the semiconductor substrate, followed by epitaxial growth of a semiconductor material.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
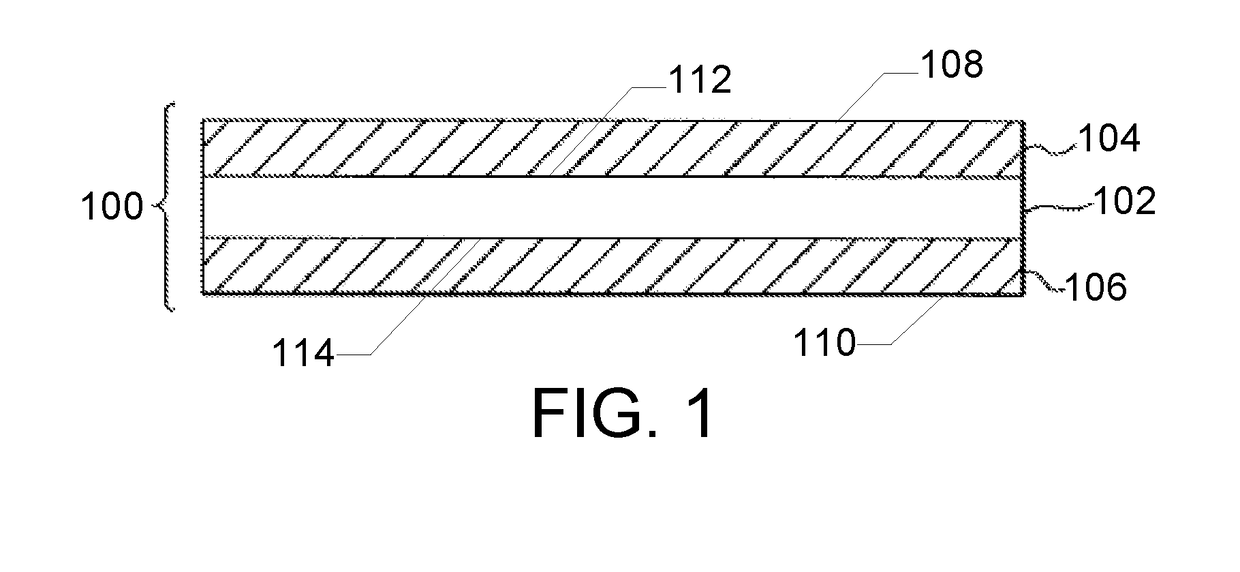
Laminated glass article with determined stress profile and method for forming the same
A glass laminate includes a glass core layer having a core coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and a glass cladding layer adjacent to the core layer and having a cladding CTE that is less than the core CTE such that the core layer is in tension and the cladding layer is in compression. A stress profile of the glass laminate includes a compressive peak disposed between an outer surface of the cladding layer and an inner surface of the cladding layer.
Owner:CORNING INC
Glass strengthening by ion exchange and lamination
A laminated glass article having a core layer made from a glass that is not ion-exchangeable, and a clad layer made from a glass that is ion-exchangeable. The laminated glass article has a maximum compressive stress in the clad layer from about 0.05 GPa to about 0.7 GPa, and a compressive stress at an inner surface of the clad layer directly adjacent to the core layer from about 20% to about 45% of a compressive stress at an outer surface of the clad layer. A slope of a stress profile in the clad layer is substantially linear. Methods for manufactured such a laminated glass article also are disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Full-roadway full-process full-cross-section surface deformation monitoring device and method
ActiveUS20180371907A1Simple structureEasy to useMining devicesUsing optical meansDigital imagingDeformation monitoring
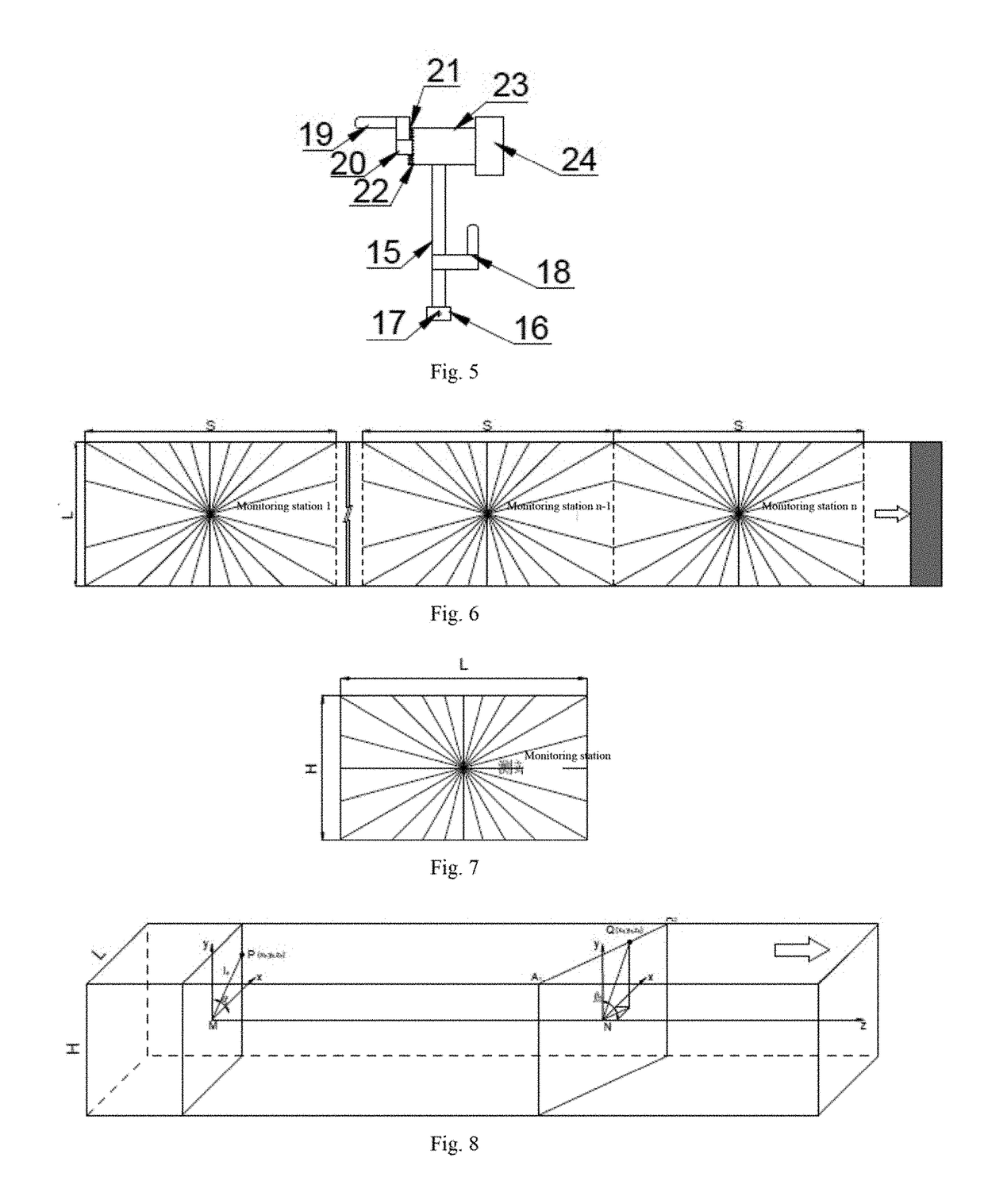
The present invention provides a full-roadway full-process full-cross-section deformation monitoring device and a monitoring method thereof, which are applicable to the field of roadway surface deformation monitoring. A monitoring station is deployed utilizing an anchor rope, a supporting frame and a rotary laser measuring device are connected via a threaded sleeve at the tail end of the anchor rope, the rotary laser measuring device can rotate and drive a laser range finder to rotate, the data of a plurality of cross sections can be measured at the same time with one monitoring station, the data is processed by computer programming, so that the measurement data is converted into coordinates in a three-dimensional coordinate system, and thereby full-roadway full-process full-cross-section digital imaging is realized. The monitoring method attains high measuring accuracy, involves very low artificial error, supports intuitive observation of dynamic roadway deformation condition, can provide accurate warning for roof pressure condition, and provides a technical guarantee for safety of the downhole workers.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
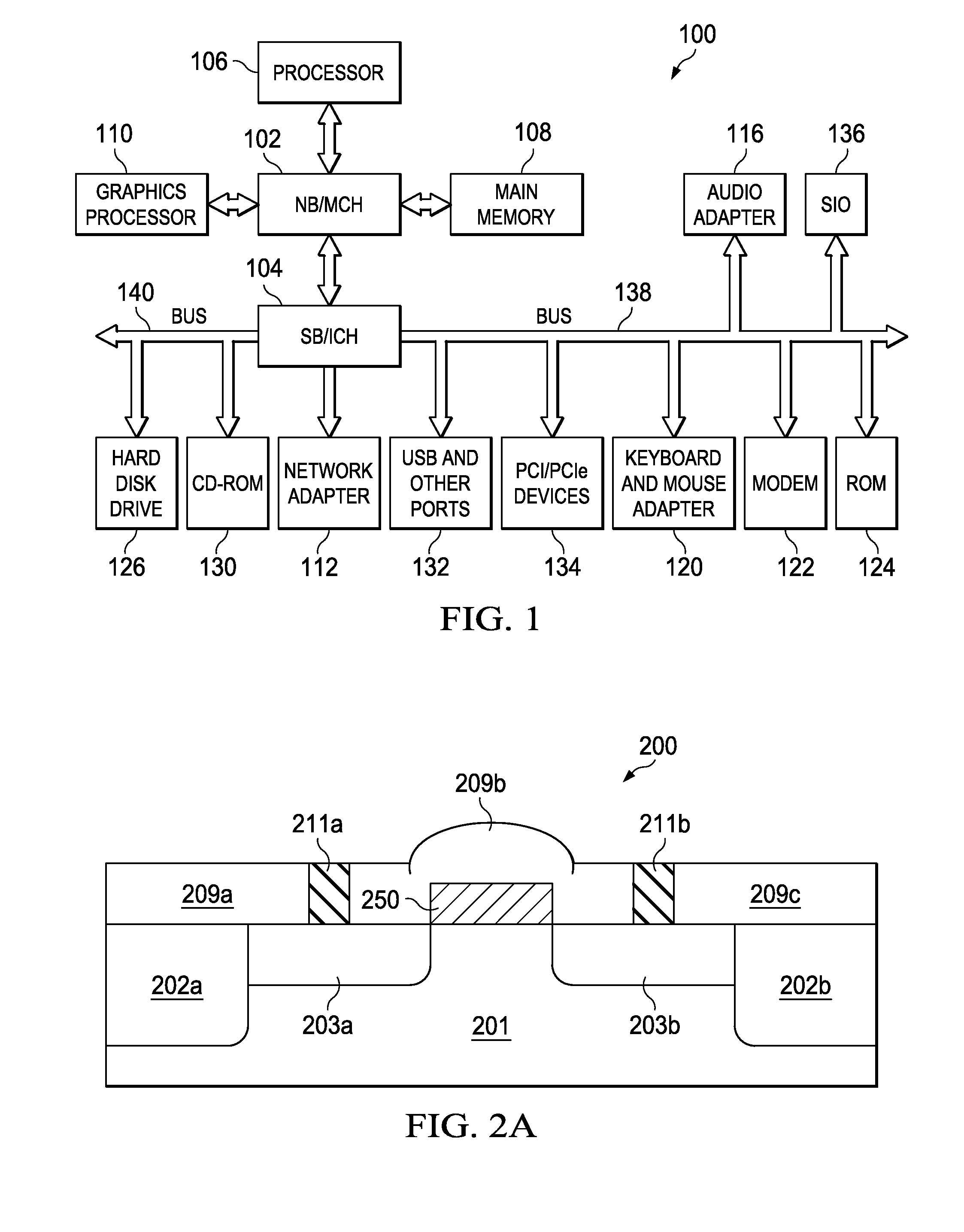
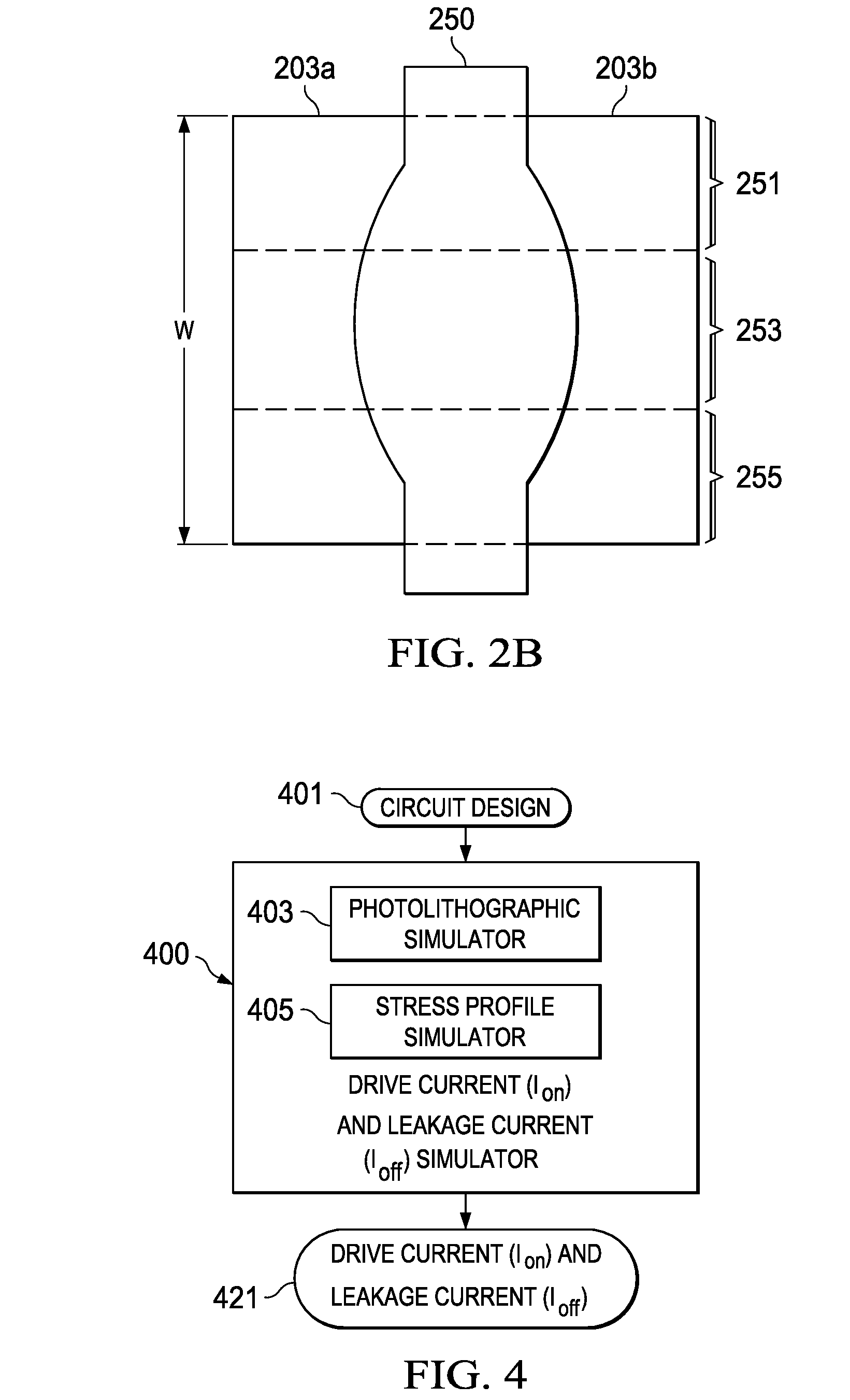
Effective gate length circuit modeling based on concurrent length and mobility analysis
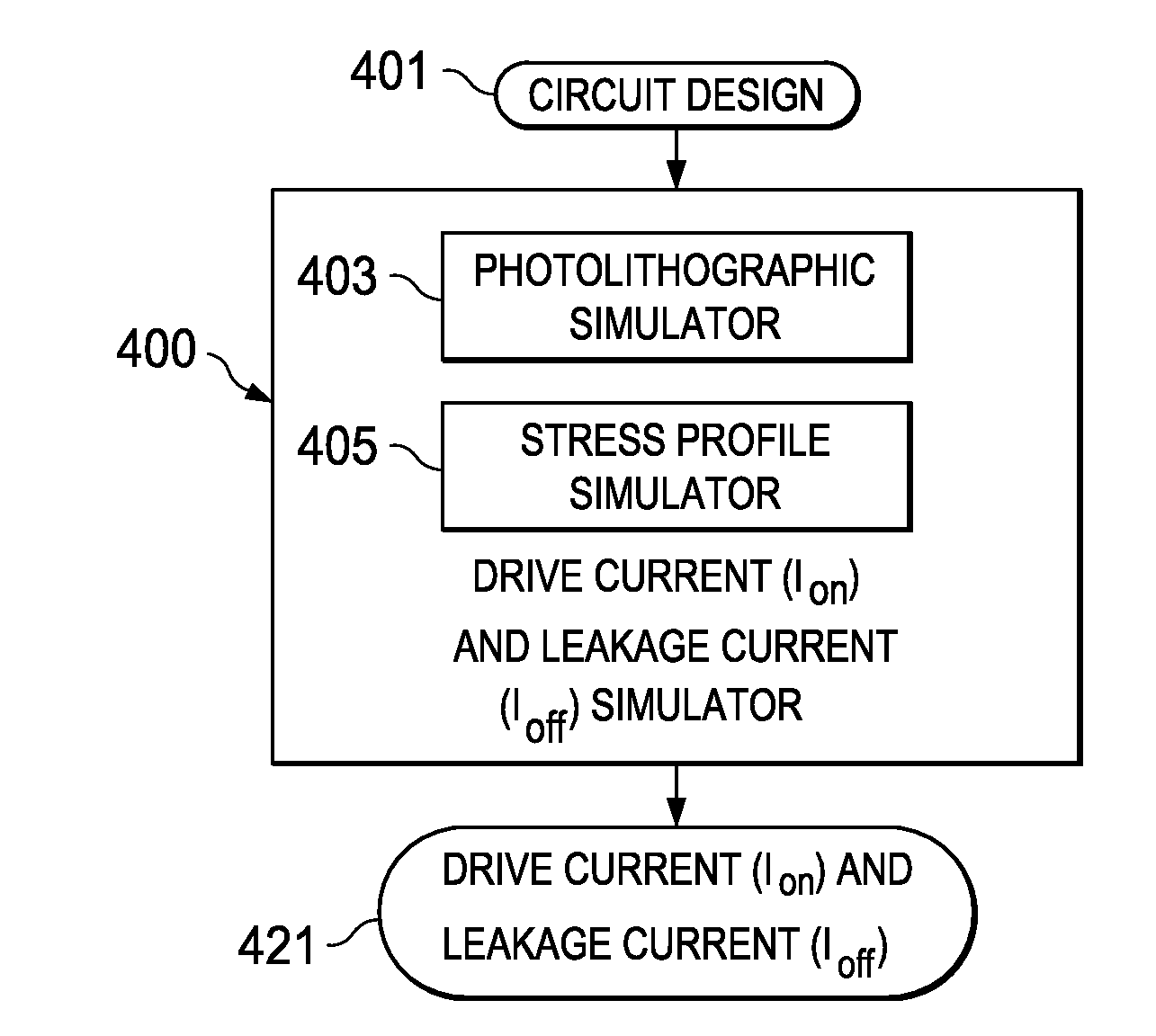
ActiveUS20100257493A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designStress distributionCircuit modeling
Disclosed is a computer implemented method and computer program product to determine metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) gate functional limitations. A simulator obtains a plurality of slices of a MOS gate, the slices each comprising at least one parameter, the parameter comprising a slice gate width and a slice gate length. The simulator determines a current for each slice based on a slice gate length of the slice to form a length-based current for each slice. The simulator determines a length-based current for the MOS gate by summing the length-based current for each slice. The simulator calculates a stress profile for each slice. The simulator determines a slice carrier mobility for each slice based on the stress profile of each slice. The simulator determines a carrier mobility-based current for each slice, based on each slice carrier mobility. The simulator determines a carrier mobility for the MOS gate based on the carrier mobility-based current for each slice. The simulator determines an effective length for the MOS gate based on the length-based current.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Glass with improved drop performance
ActiveUS20190369672A1Casings/cabinets/drawers detailsDetails for portable computersMechanical engineeringStress profile
Glass-based articles are provided that exhibit improved drop performance. The relationship between properties attributable to the glass composition and stress profile of the glass-based articles are provided that indicate improved drop performance.
Owner:CORNING INC
Electroactive apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20020153807A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesMechanical energyEngineering
High performance electromechanical devices suitable for a wide range of applications are described. The electroactive devices are capable of operating in a manner that offers enhanced mechanical displacement responses and increased load-bearing capabilities. In one embodiment, the device is capable of providing a significantly increased level of free displacement. The electroactive devices include an electroactive composite which includes at least one electroactive material that may comprise an electrostrictive or a piezoelectric material and a tensioning device which is adapted for inducing a mechanical pre-load to the electroactive composite structure. The tensioning device exerts a mechanical pre-load upon the electroactive material which alters stress profile, increases mechanical energy and increases stored elastic energy of the electroactive devices.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIVERSITY
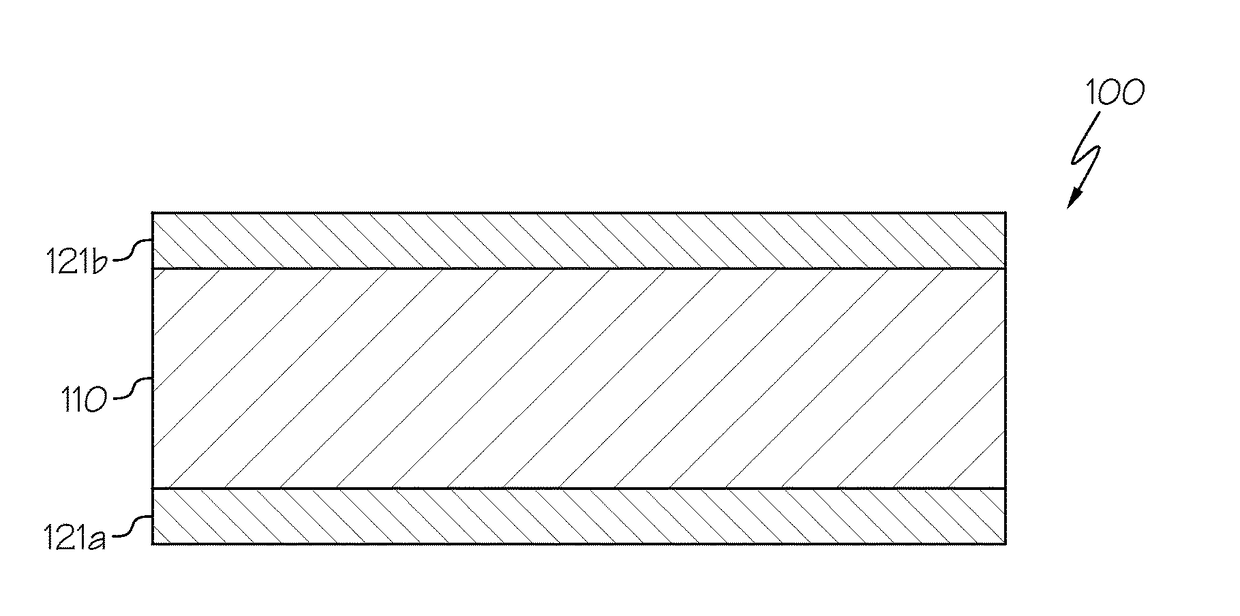
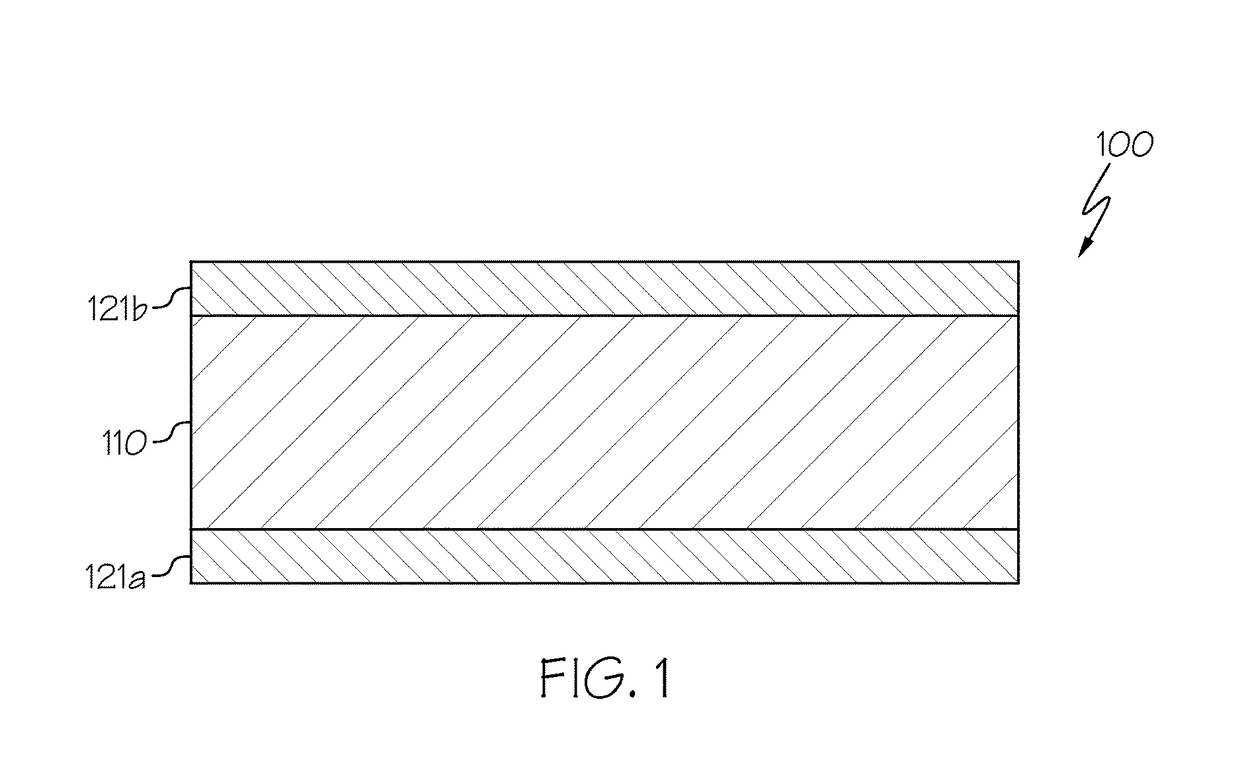
Glass article with determined stress profile and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20170297308A1Glass forming apparatusGlass/slag layered productsThermal expansionOptoelectronics
A laminated glass article includes a core layer and a clad layer directly adjacent to the core layer. The core layer is formed from a core glass composition. The clad layer is formed from a clad glass composition. An average clad coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is less than an average core CTE such that the clad layer is in compression and the core layer is in tension. A compressive stress of the clad layer decreases with increasing distance from an outer surface of the clad layer within an outer portion of the clad layer and remains substantially constant with increasing distance from the outer surface of the clad layer within an intermediate portion of the clad layer disposed between the outer portion and the core layer. A thickness of the intermediate portion of the clad layer is at least about 82% of a thickness of the clad layer,
Owner:CORNING INC
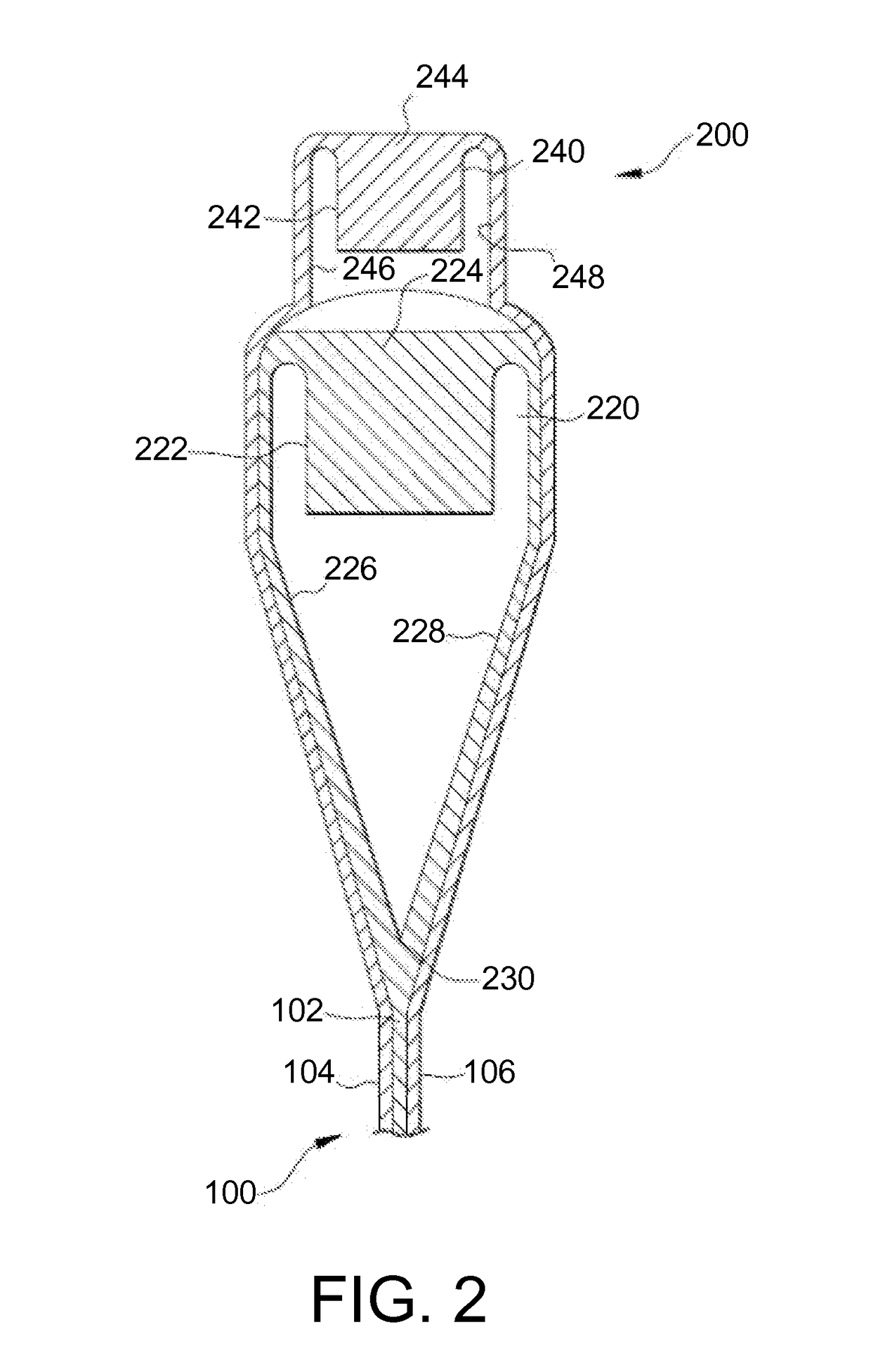
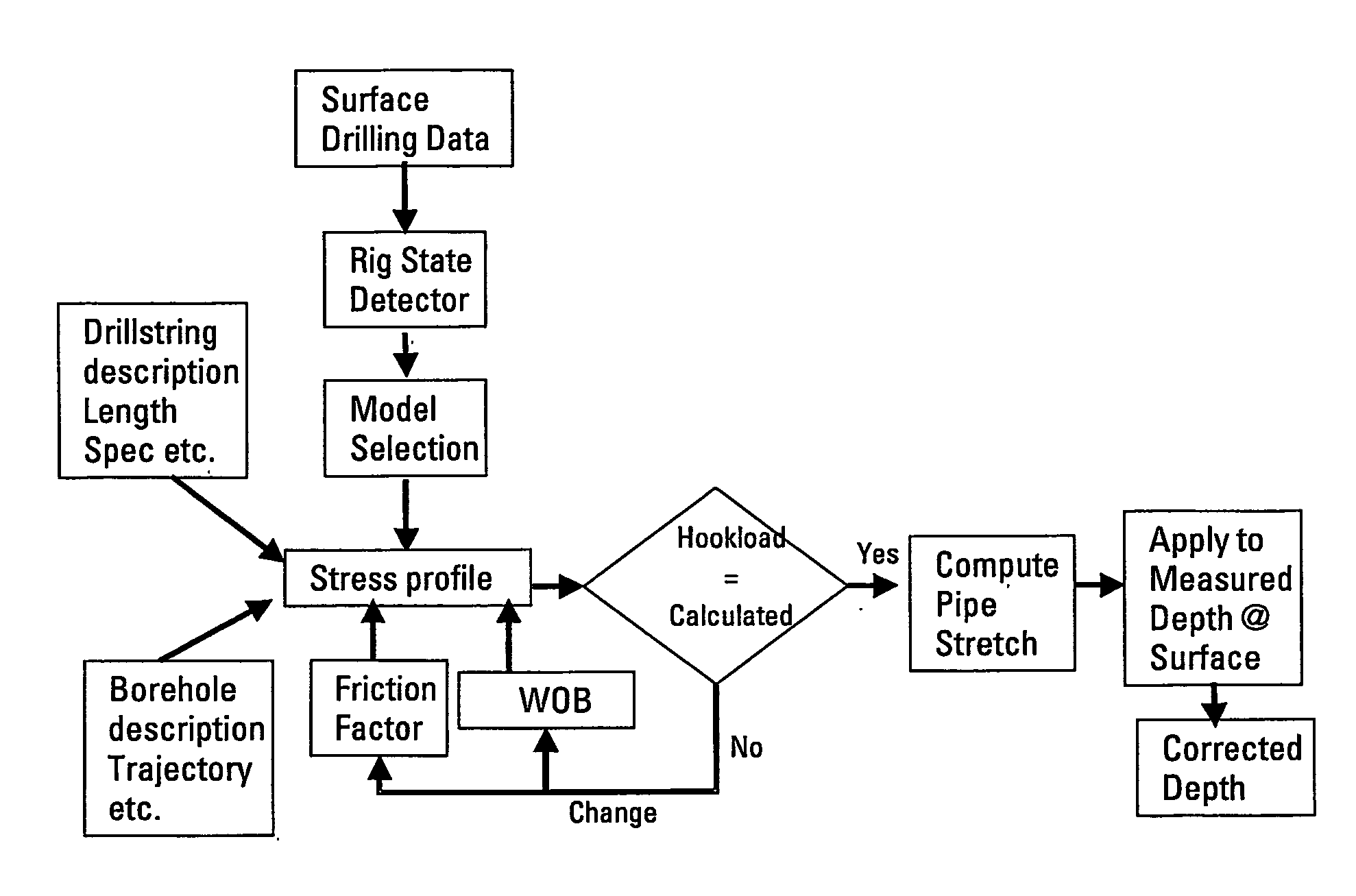
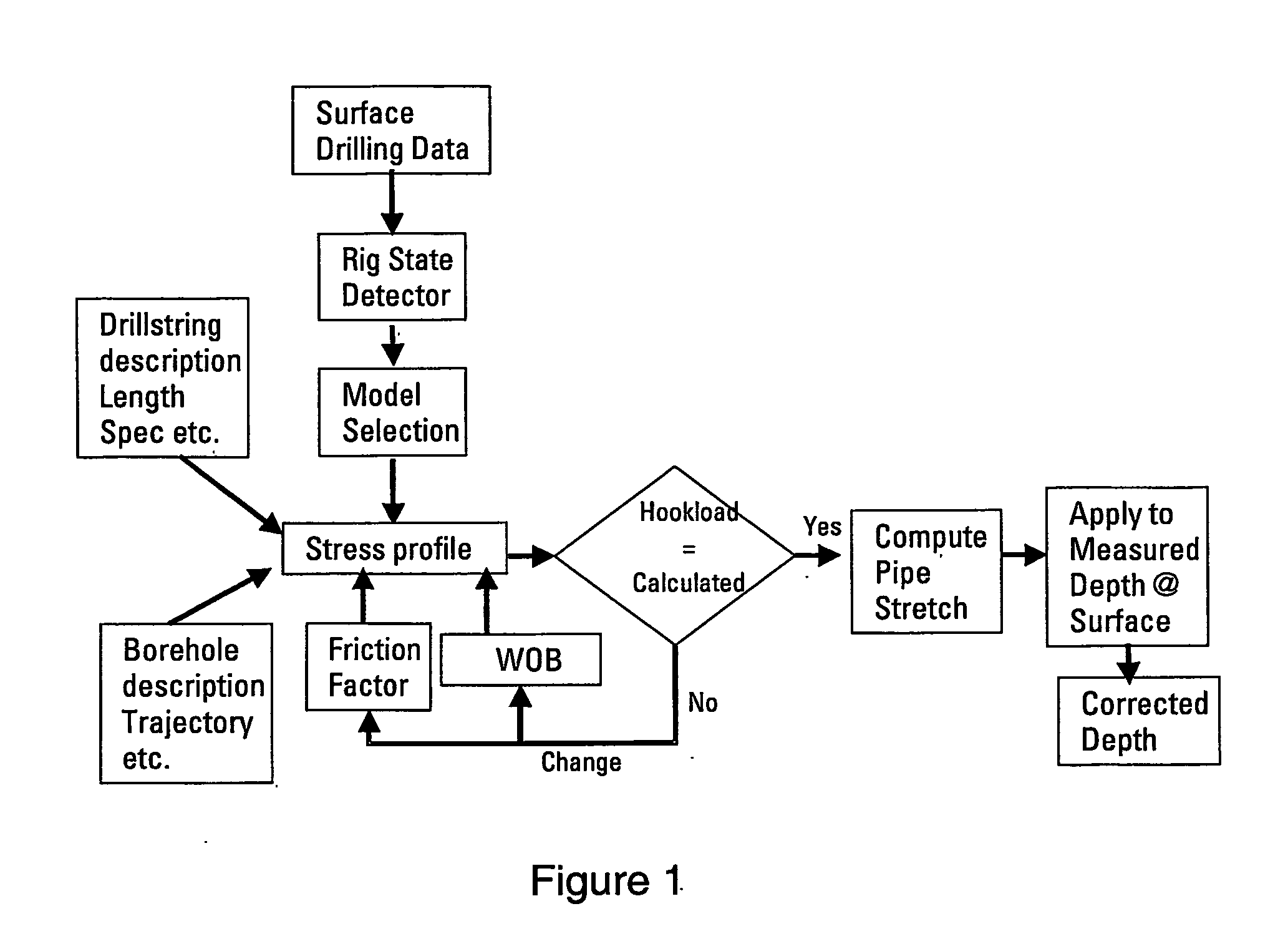
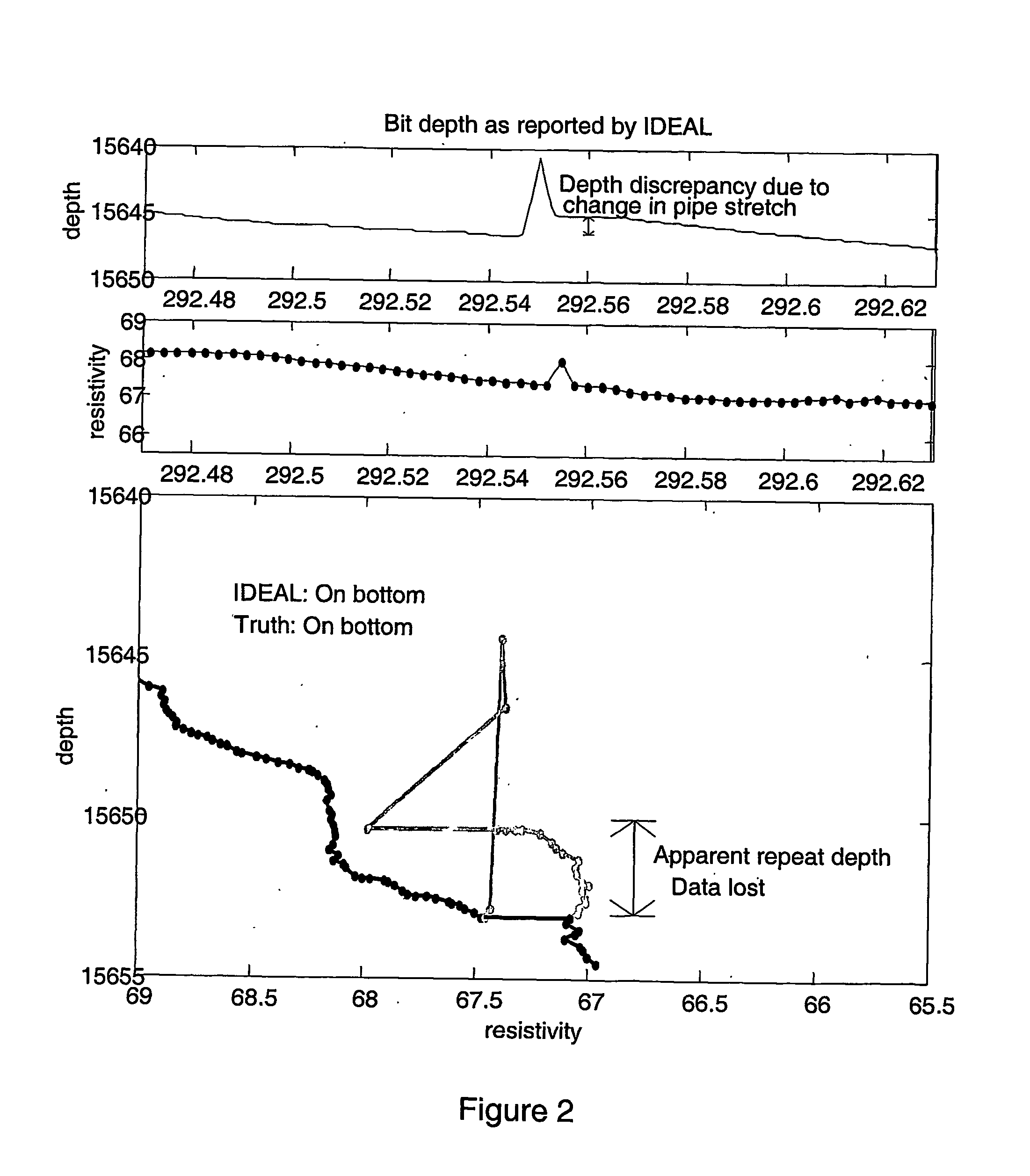
System and method for correcting errors in depth for measurments made while drilling
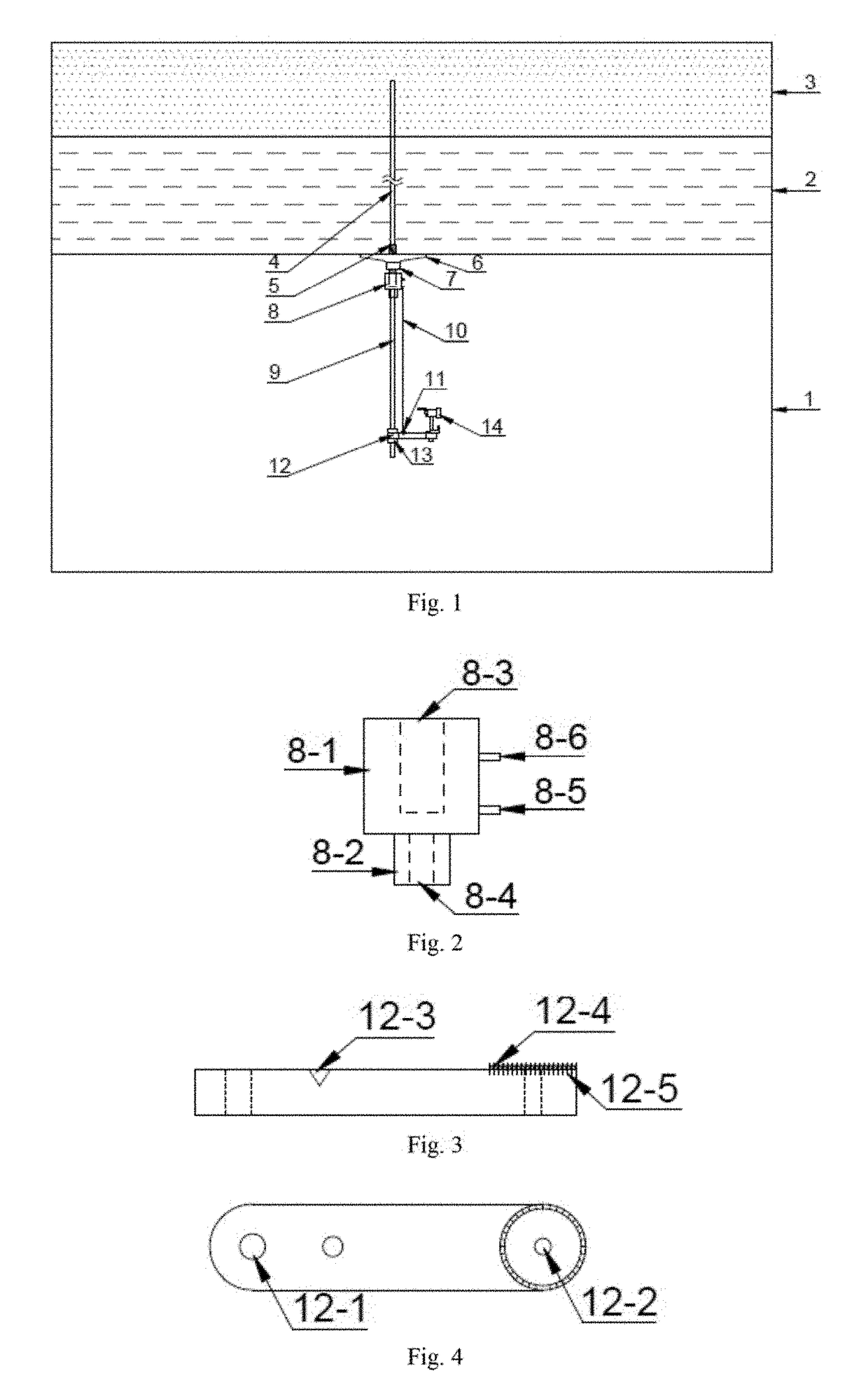
A method and system is disclosed for automatically correcting for depth errors in measurements taken from a drill-string during the drilling phase of the construction of a hydrocarbon wellbore. The correction is based on a stress profile which in turn is based on the states of the drilling rig, drill string description length spec, borehole description trajectory, friction factor and weight on bit.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
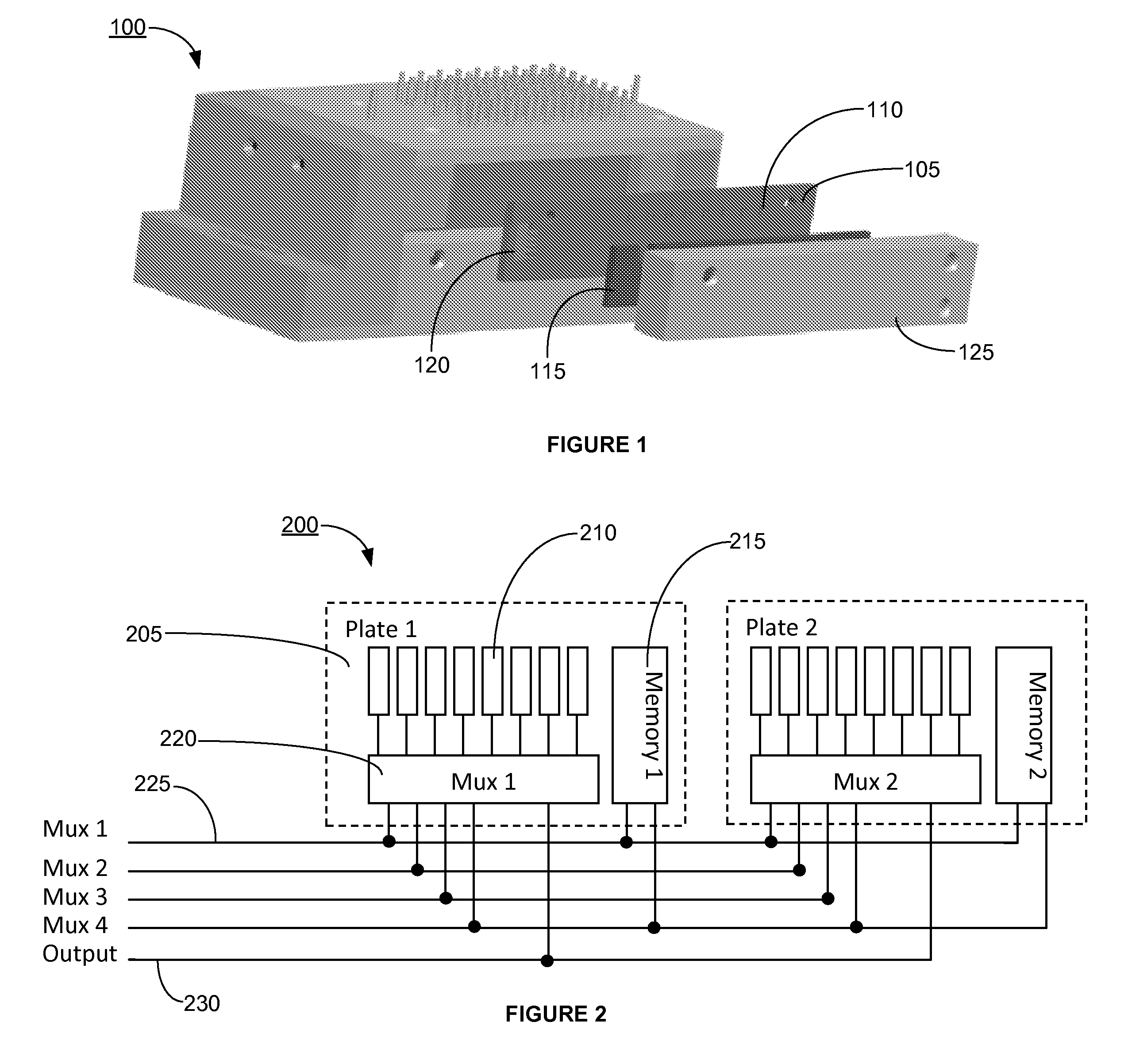
Pressure scanner assemblies having replaceable sensor plates
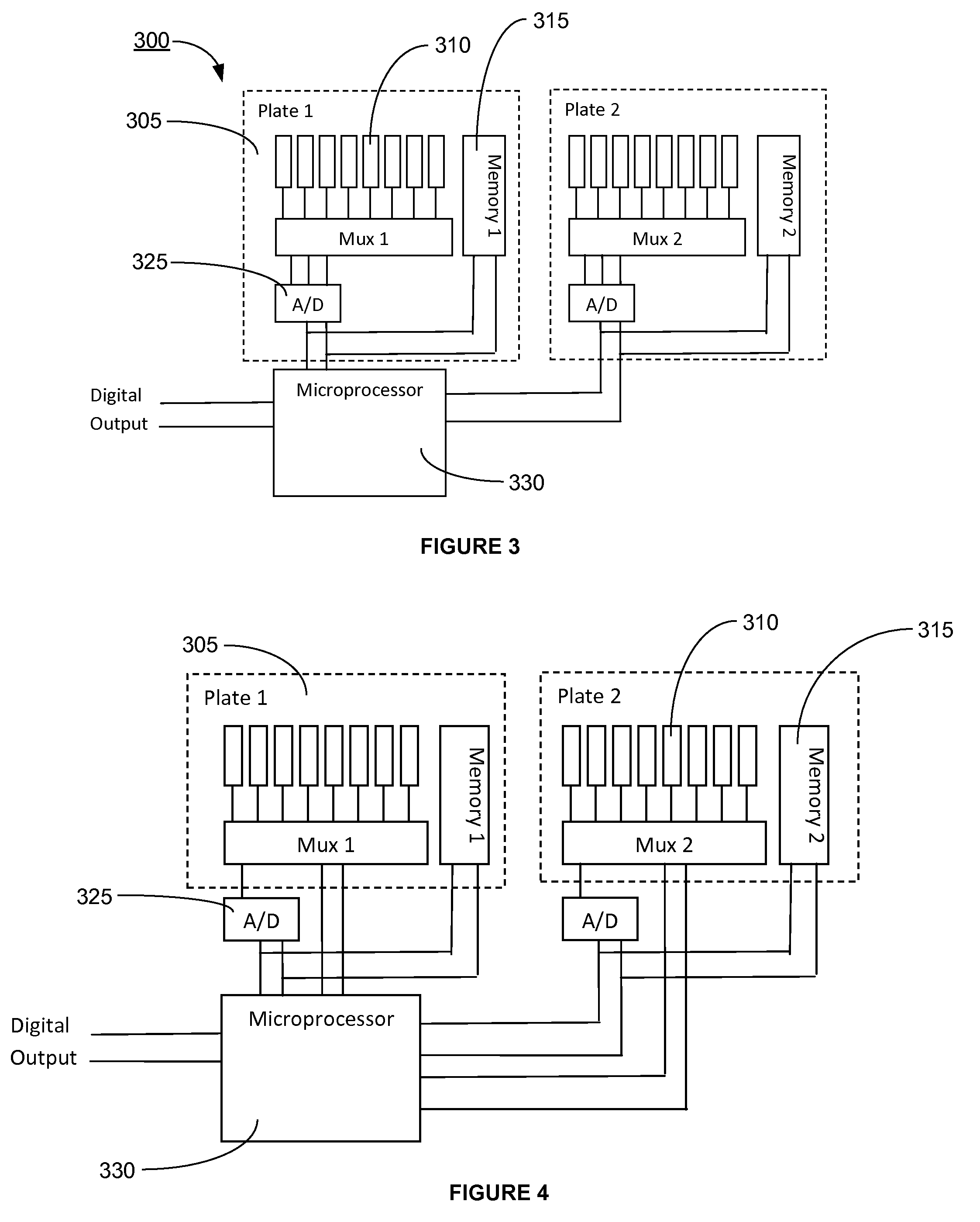
ActiveUS20120016603A1Flow propertiesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsMultiplexingMemory chip
A pressure scanner assembly having at least one replaceable sensor plate, wherein each of the replaceable sensor plates has at least one pressure sensor adapted to transmit a signal substantially indicative of a sensed pressure condition. A memory chip, which stores correction coefficients for each of the pressure sensor to compensate for thermal errors, may be installed on each of the replaceable sensor plates. The signals from the pressure sensors are multiplexed and may be outputted in analog or digital form. The pressure scanner assemblies described herein have sensor plates that can be interchanged with other sensor plates of the same or different pressure range without disrupting the electronic configuration of the pressure scanner assembly or having to recalibrate and / or update the memory chip installed thereon.
Owner:KULITE SEMICON PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com