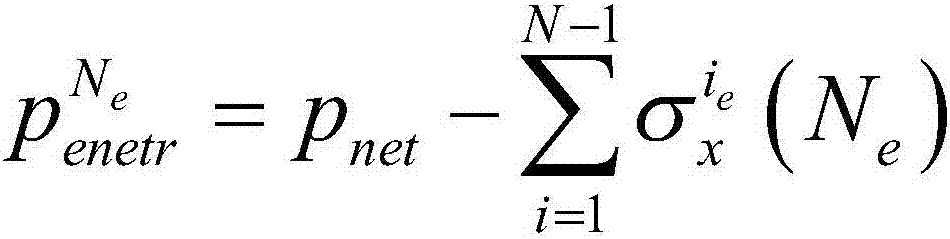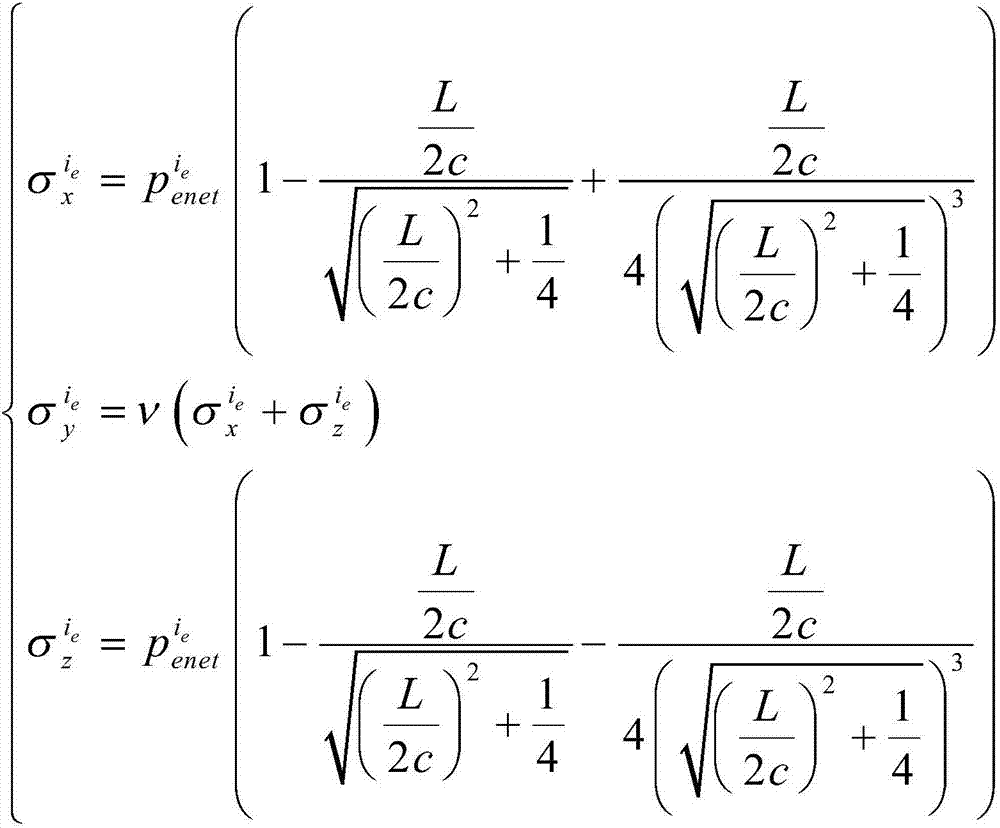Patents
Literature
127 results about "In situ stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In-situ stresses are the stresses which developed due to weight of the overlying materials and also due to the confinement and the past stress history at a point below the rock surface of the undisturbed rock mass. These stresses may vary considerably from one point to other.
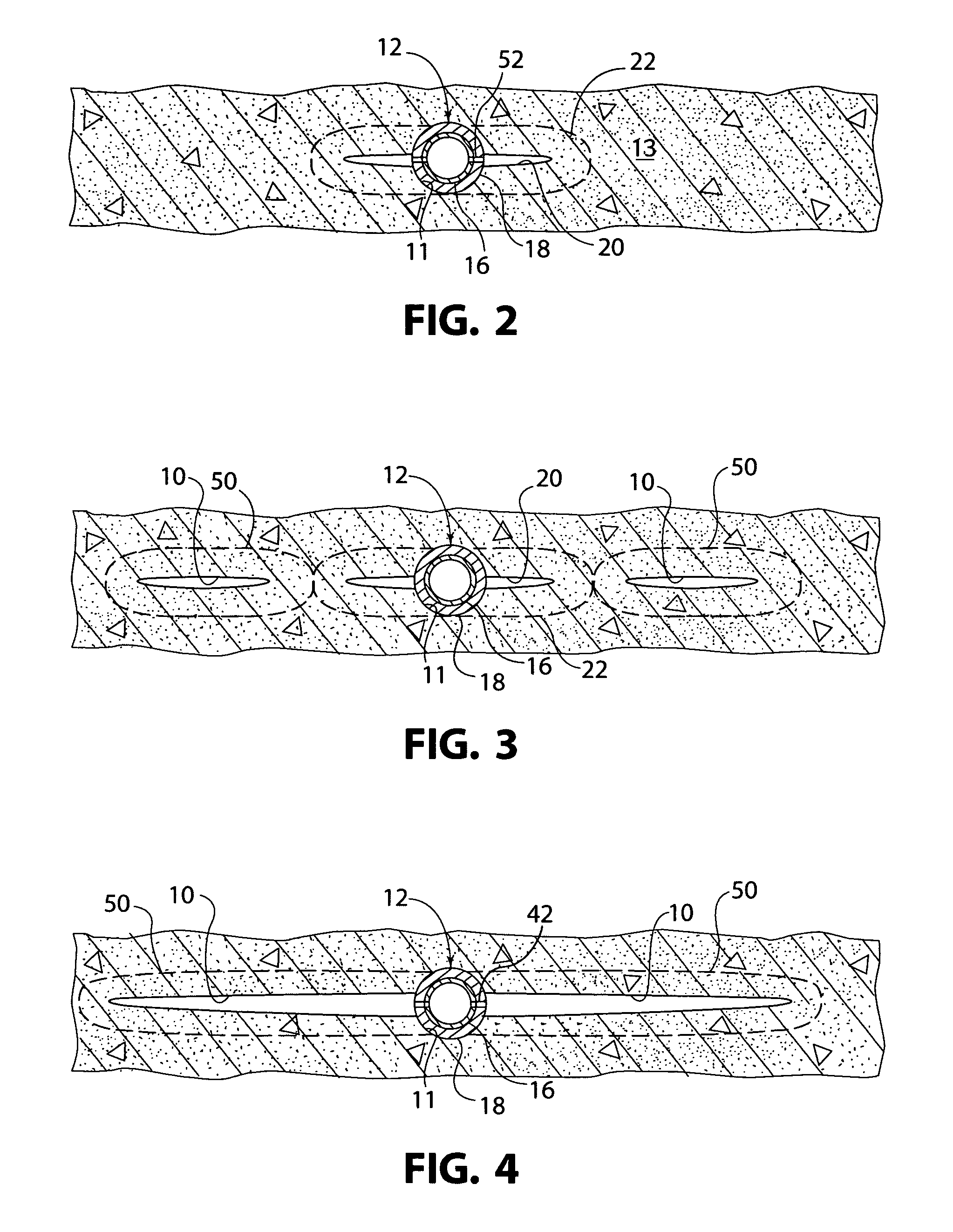
Method of stimulating oil and gas wells using deformable proppants
ActiveUS7322411B2Reduce cloggingMinimize damageFluid removalDrilling compositionFracturing fluidDolomite
A method of fracturing using deformable proppants minimizes proppant pack damage, without compromising the fracturing fluid's proppant transport properties during pumping, by use of deformable proppants. Selection of proppant is dependent upon the mechanical properties of the formation rock. The strength of the deformable proppant is dependent upon the modulus of the formation rock being treated such that the proppant is capable of providing, at the very least, a minimum level of conductivity in in-situ stress environments. The maximum elastic modulus of the deformable proppant is less than the minimum modulus of the formation rock which is being treated. The method is particularly applicable in fracturing operations of subterranean reservoirs such as those comprised primarily of coal, chalk, limestone, dolomite, shale, siltstone, diatomite, etc.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
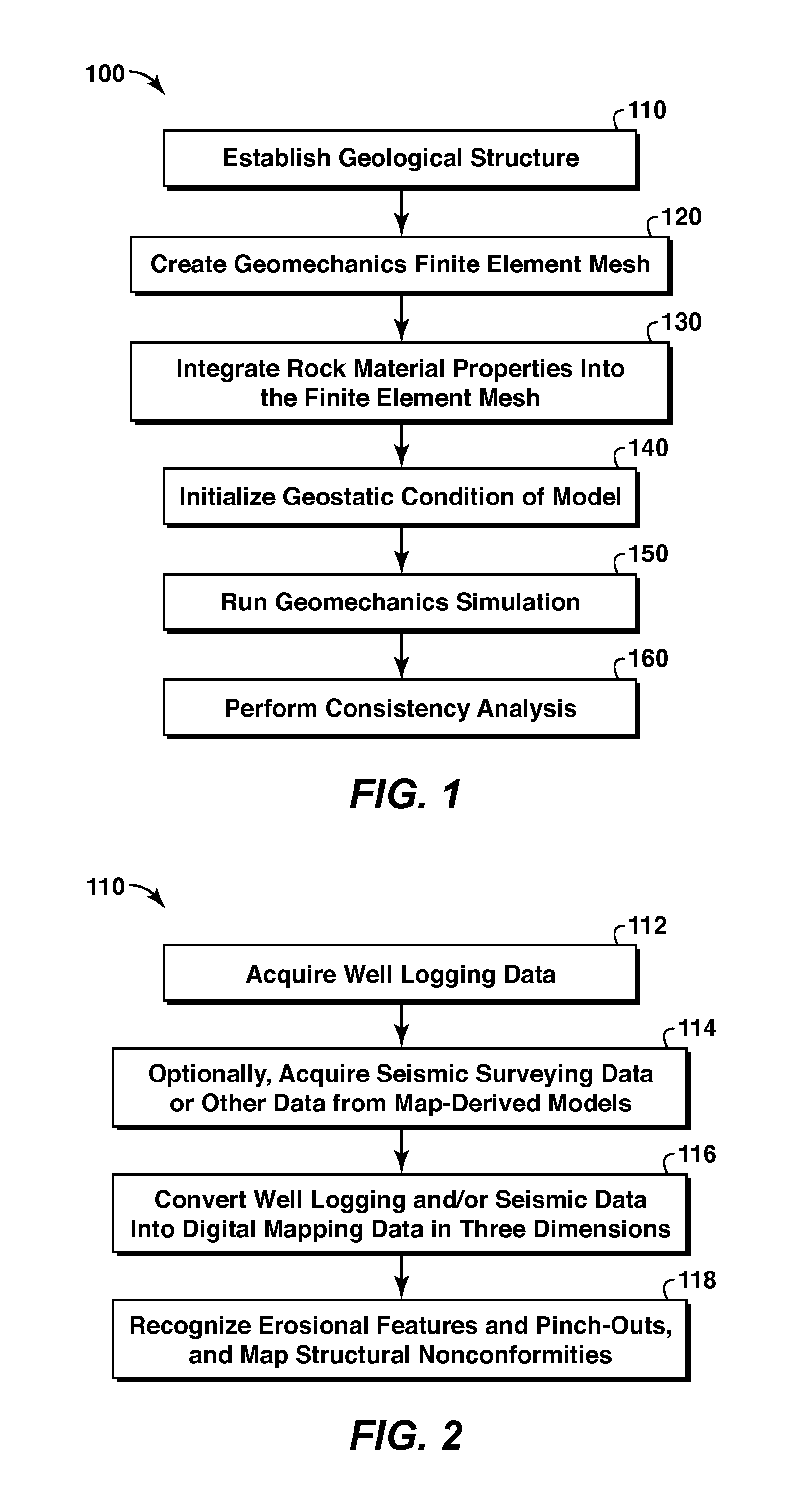
Method For Modeling Deformation In Subsurface Strata
ActiveUS20110166843A1Minimize prospectElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyElement analysisMechanical property
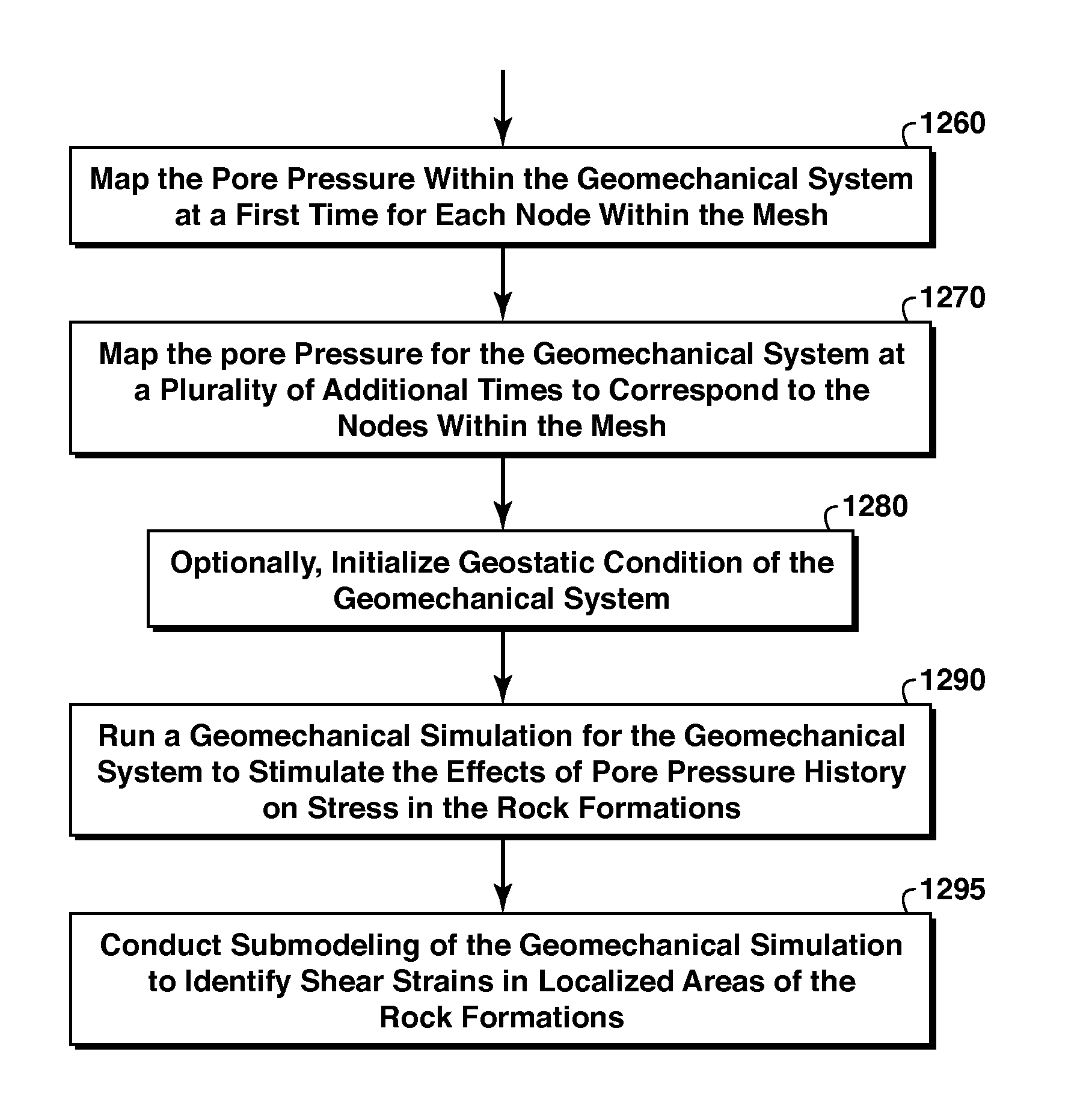
A method for modeling deformation in subsurface strata, including defining physical boundaries for a geomechanical system. The method also includes acquiring one or more mechanical properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries, and acquiring one or more thermal properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries. The method also includes creating a computer-implemented finite element analysis program representing the geomechanical system and defining a plurality of nodes representing points in space, with each node being populated with at least one of each of the mechanical properties and the thermal properties. The program solves for in situ stress at selected nodes within the mesh.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
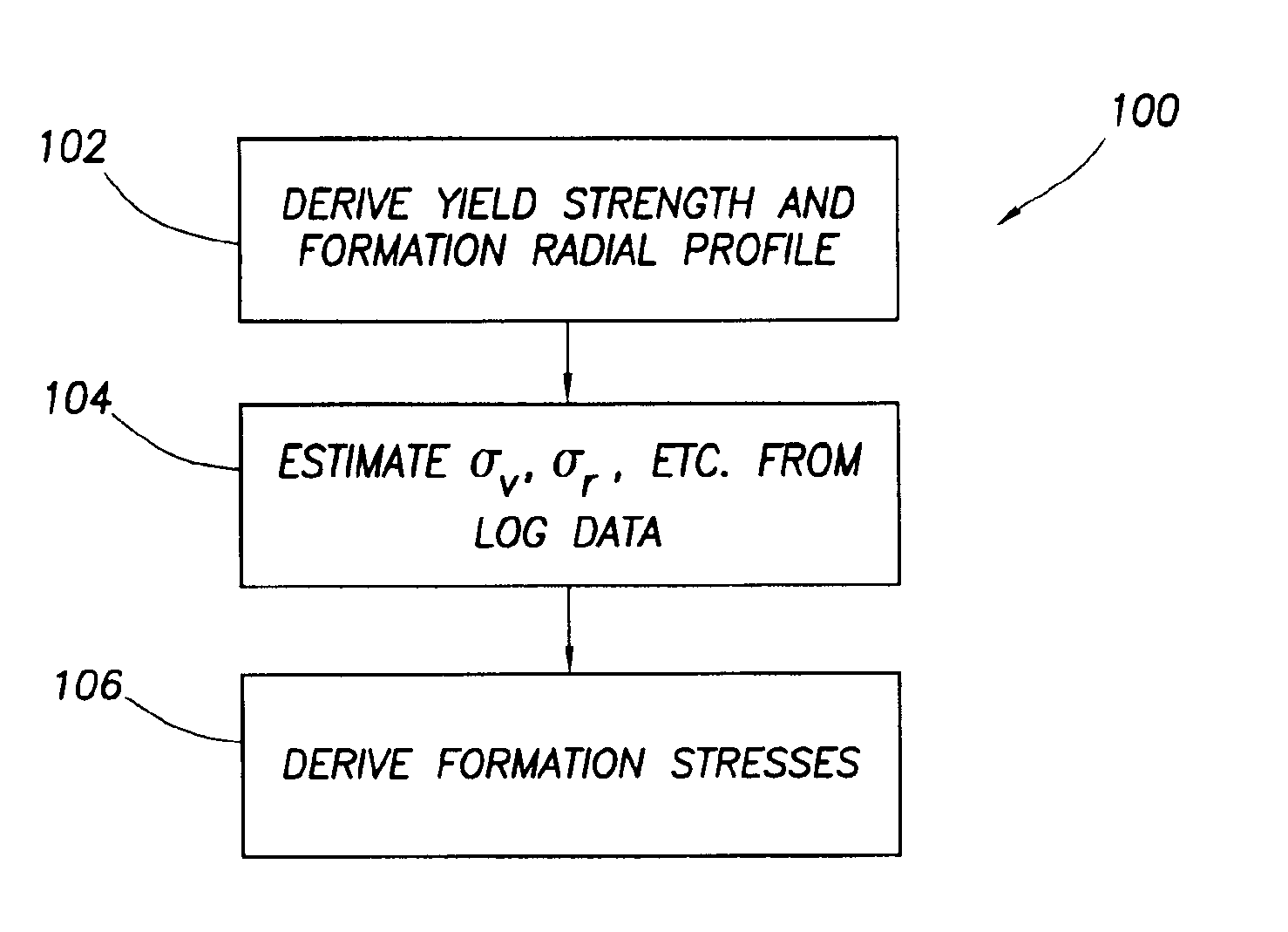
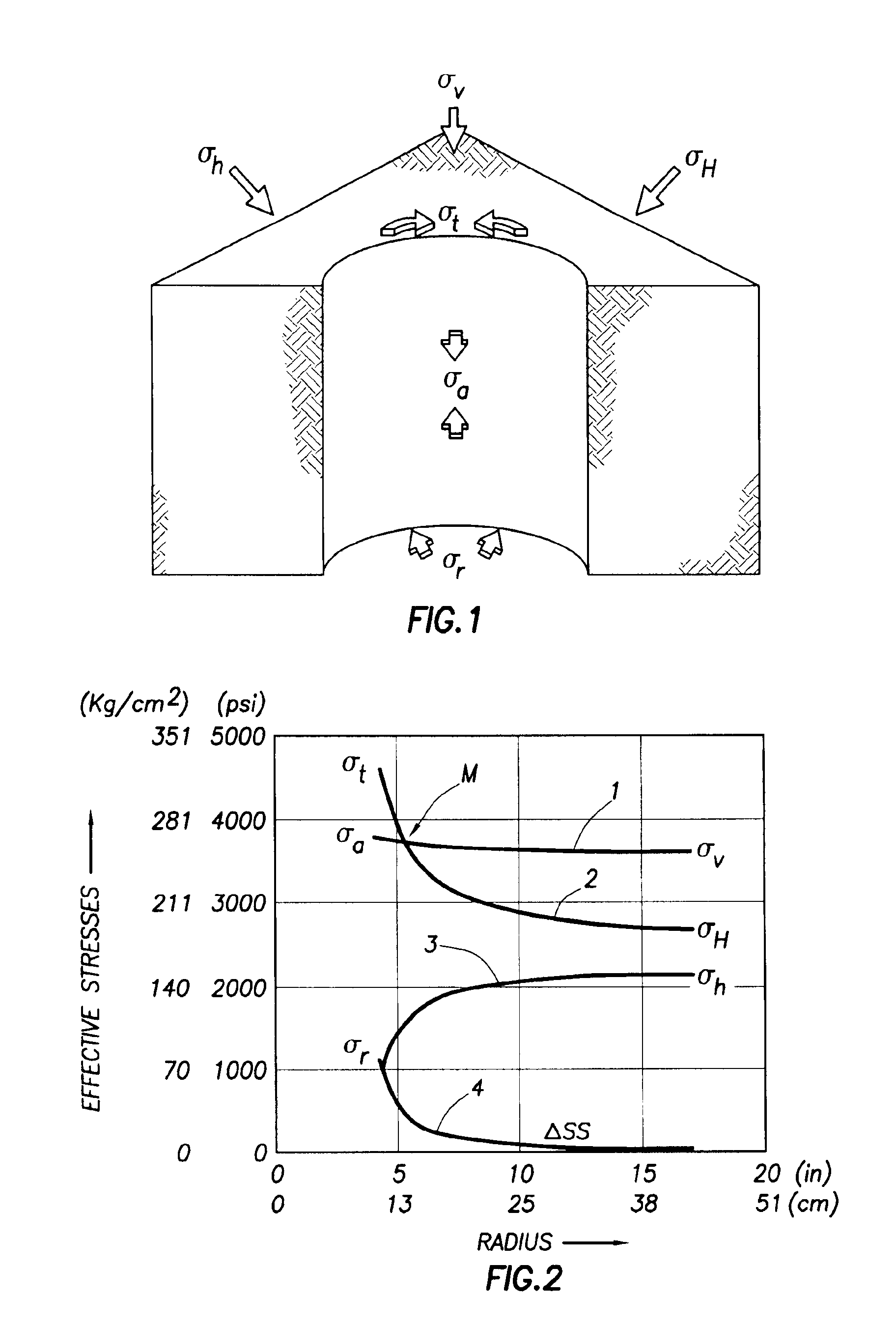
Methods and systems for determining formation properties and in-situ stresses
ActiveUS6904365B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingRadial stressUltimate tensile strength
Systems and methods for determining a formation property related to formation strength and stresses are disclosed. A method for determining a formation strength includes obtaining radial formation property measurements at different wellbore pressures; generating a radial stress profile based on a formation model; generating a radial stress function from the radial stress profile; and comparing the radial formation property measurements with the radial stress function to determine the formation strength. A method for determining a formation stress profile includes deriving formation parameters from a formation radial profiling; obtaining formation log data that comprise formation density data; estimating formation stresses from the formation log data; and deriving a radial stress profile based on a formation model, the derived formation parameters, and the estimated formation stresses.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method of stimulating oil and gas wells using deformable proppants
ActiveUS20060151170A1Minimizing proppant pack damageImproves retained proppant pack permeabilityFluid removalDrilling compositionFracturing fluidUltimate tensile strength
A method of fracturing using deformable proppants minimizes proppant pack damage, without compromising the fracturing fluid's proppant transport properties during pumping, by use of deformable proppants. Selection of proppant is dependent upon the mechanical properties of the formation rock. The strength of the deformable proppant is dependent upon the modulus of the formation rock being treated such that the proppant is capable of providing, at the very least, a minimum level of conductivity in in-situ stress environments. The maximum elastic modulus of the deformable proppant is less than the minimum modulus of the formation rock which is being treated. The method is particularly applicable in fracturing operations of subterranean reservoirs such as those comprised primarily of coal, chalk, limestone, dolomite, shale, siltstone, diatomite, etc.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
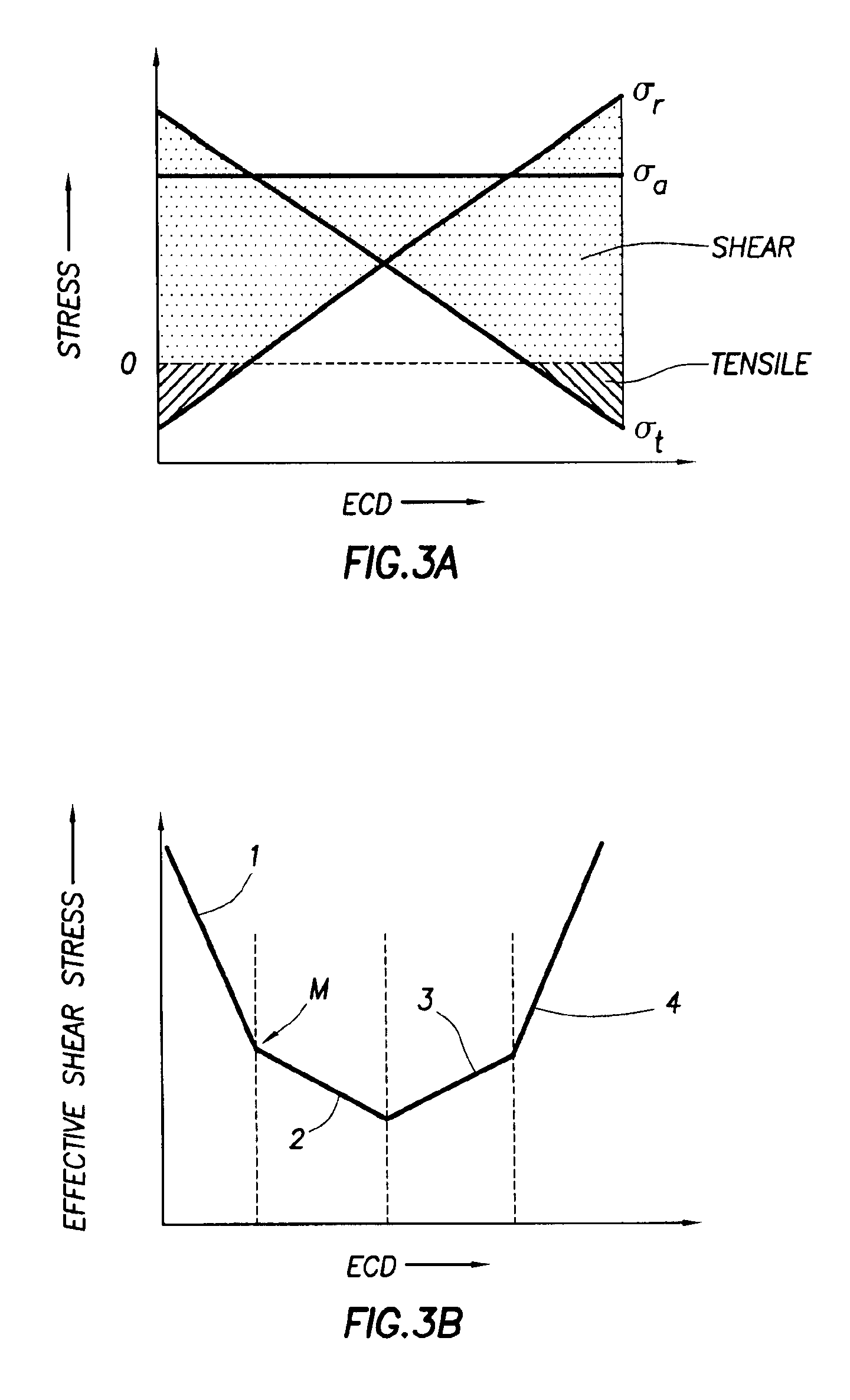
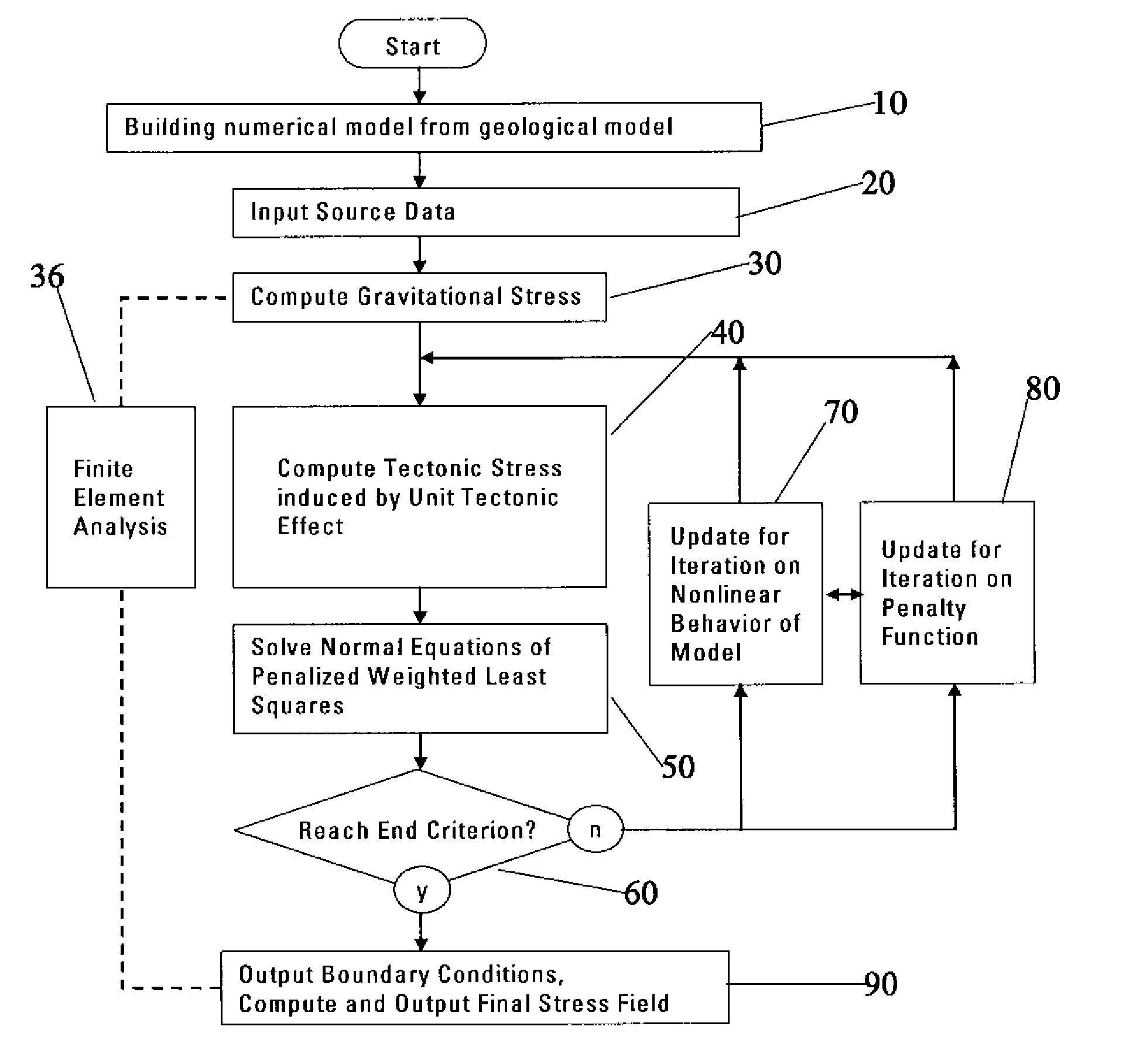
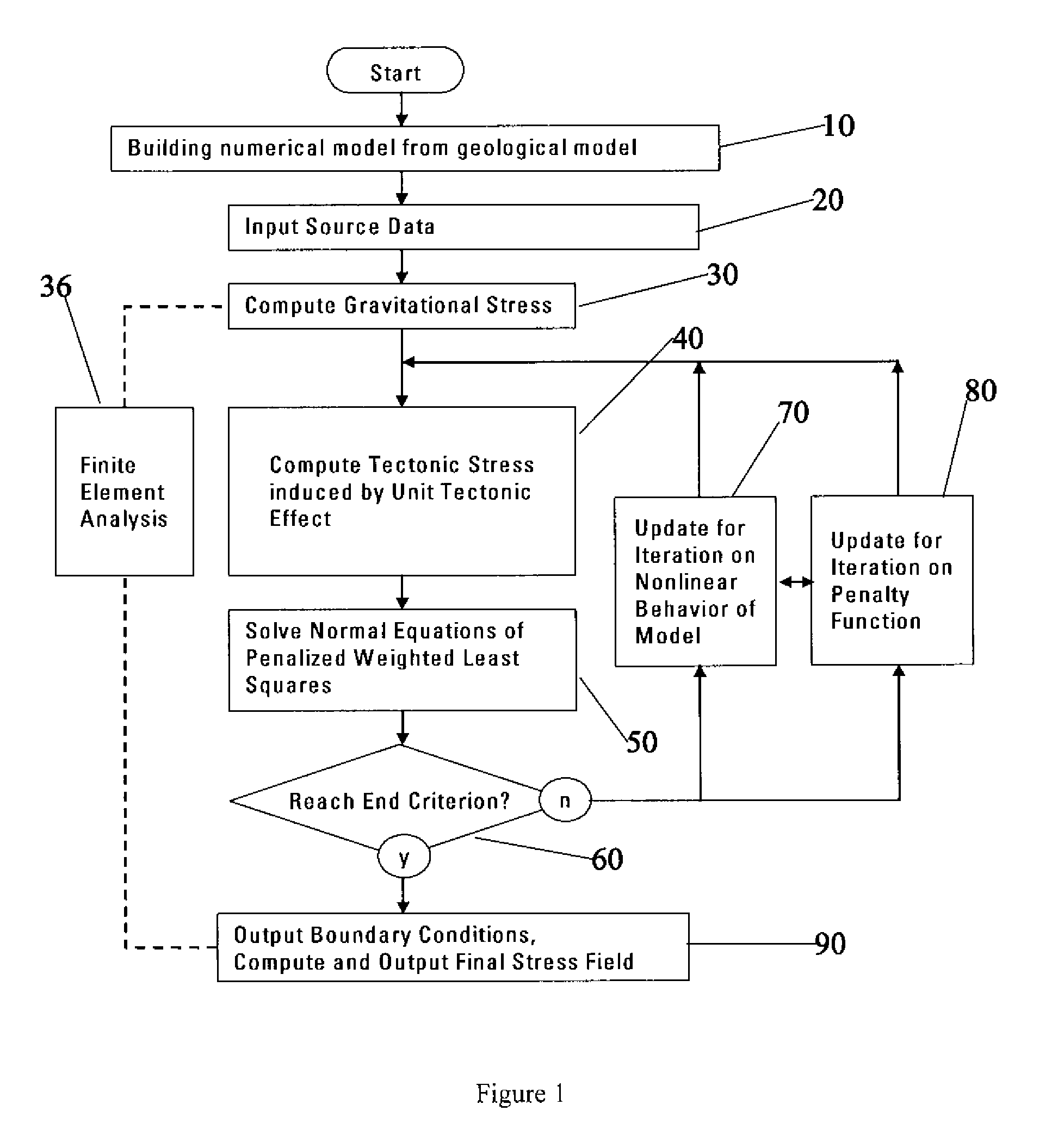
Method and system to invert tectonic boundary or rock mass field in in-situ stress computation
A method, system and computer program product for inverting boundary conditions for rock mass field in-situ stress computation for a geologic structure are disclosed. According to an embodiment, the current invention includes a method for inverting boundary conditions for rock mass field in-situ stress computation for a geologic structure, the method comprising: considering physical constraint of the geological structure; deriving and solving normal equations of penalized weighted least squares, said normal equations of penalized weighted least squares partially representing said physical constraint of the geological structure; and outputting boundary conditions and reproducing the rock mass field in-situ stress based on the result of said solved normal equations of penalized weighted least squares.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
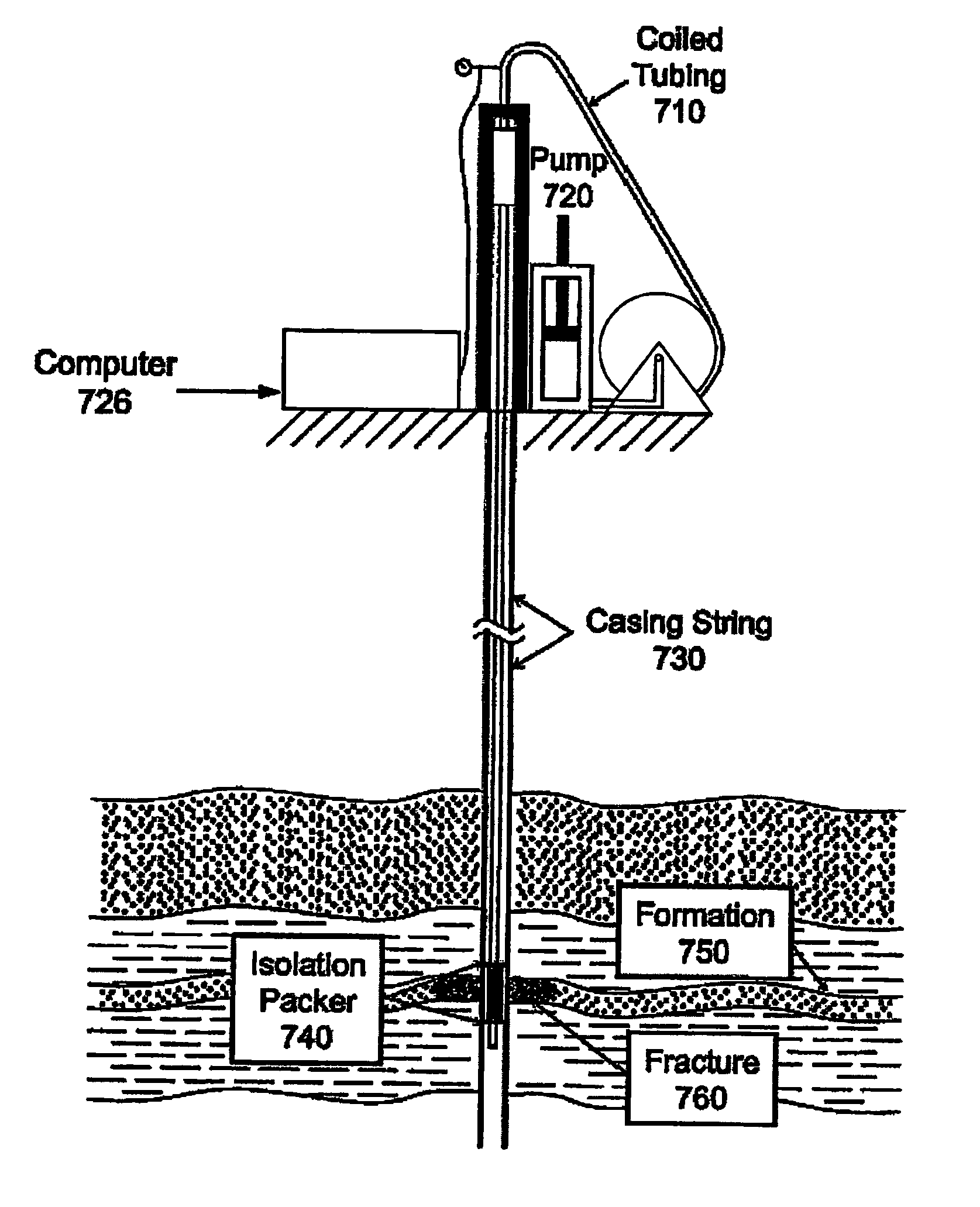
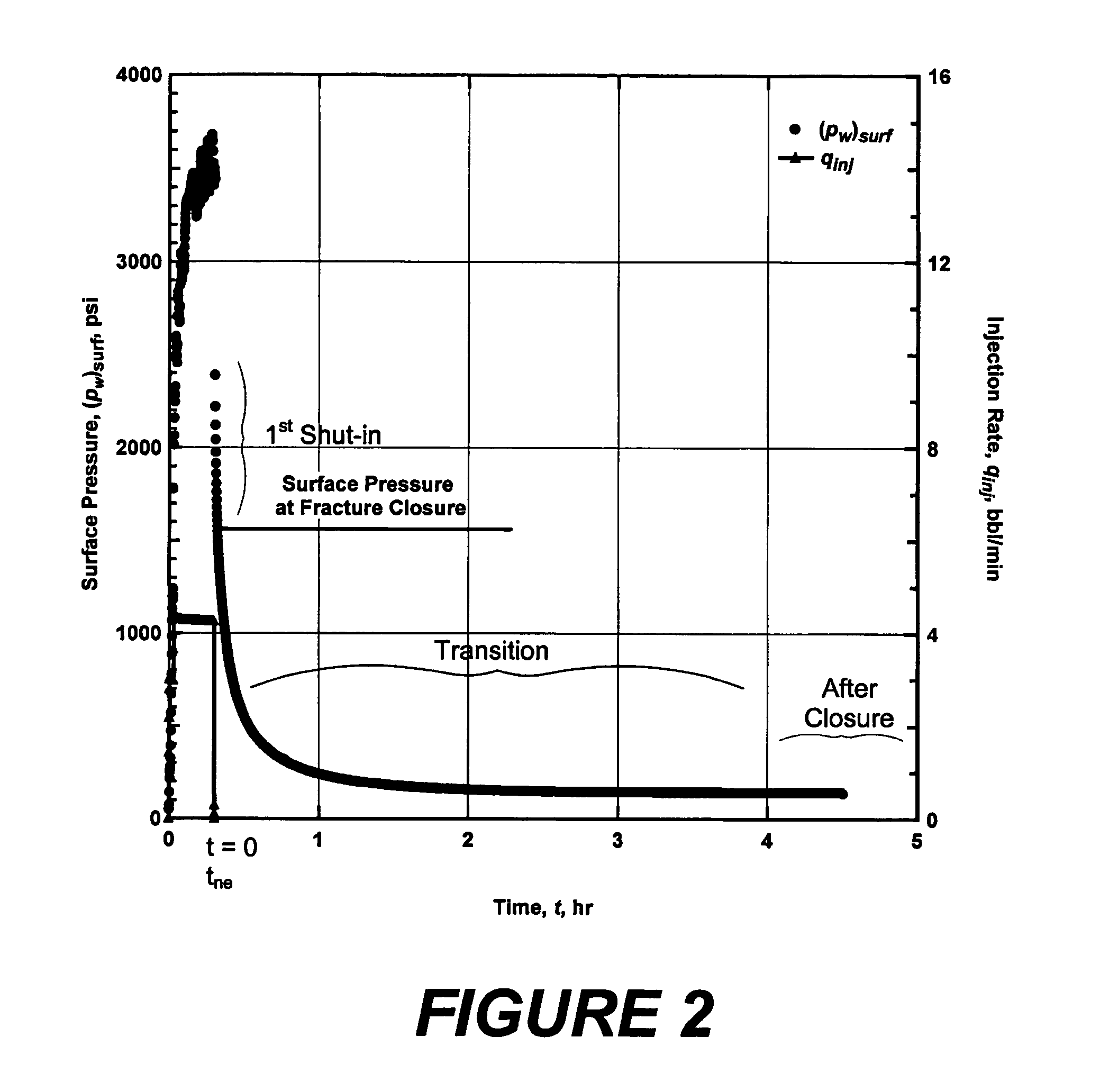
Method and an apparatus for detecting fracture with significant residual width from previous treatments
ActiveUS20050222852A1Rapid determinationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyDual unitMedicine
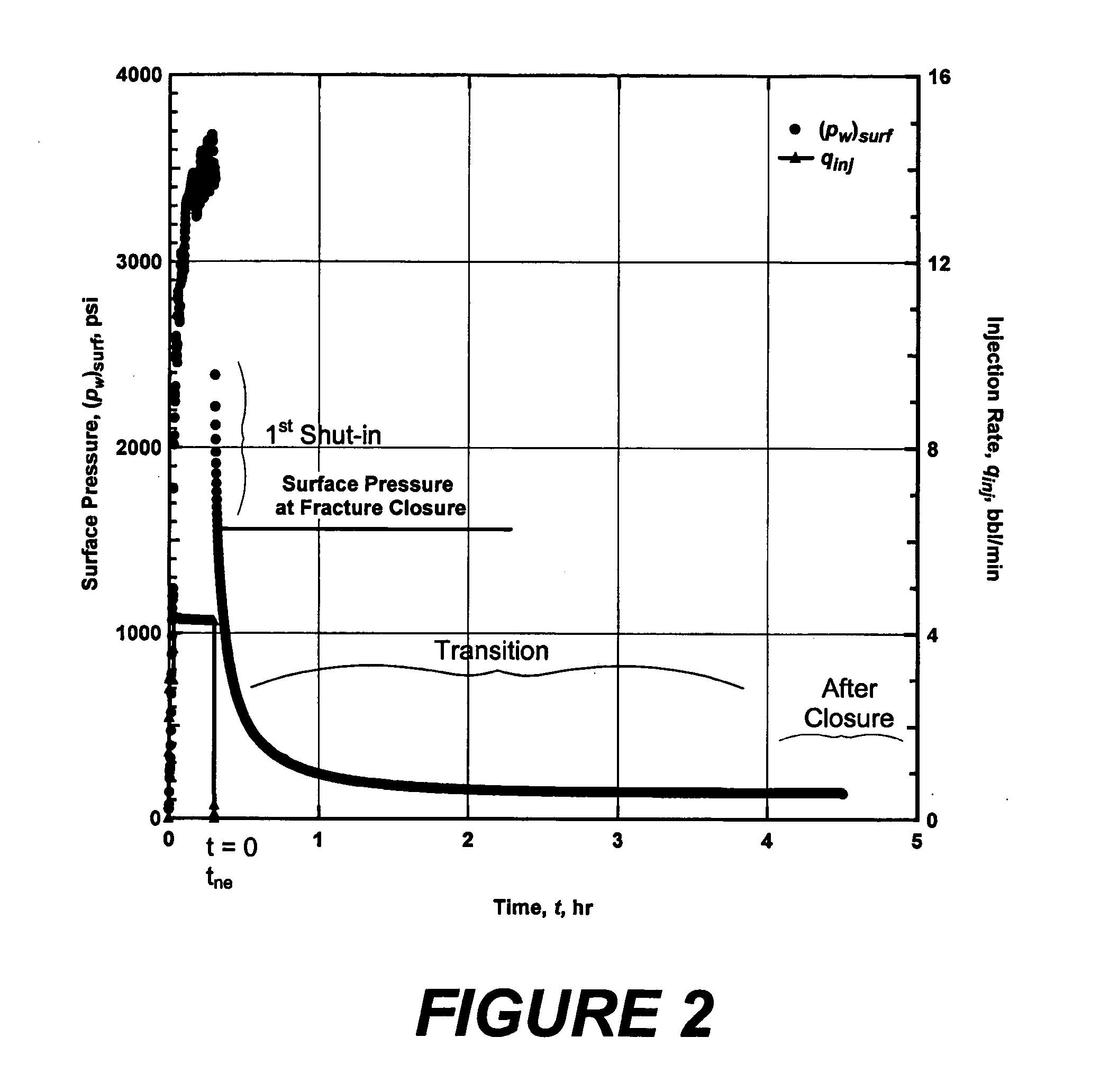
A refracture-candidate diagnostic test is an injection of compressible or slightly compressible fluid such as liquid, gas, or combination at pressures in excess of minimum in-situ stress and formation fracture pressure with pressure decline following injection test recorded to detect a fracture retaining residual width from previous stimulation treatments. The diagnostic consists of small volume injections with injection time being a small fraction of time required for compressible or slightly compressible reservoir fluid to exhibit pseudoradial flow. The fracture-injection portion of a test can be considered as occurring instantaneously, and the results obtained in an open infinite-conductivity hydraulic fracture with pressures above fracture closure stress during before-closure portion of pressure falloff and with pressures less than fracture closure stress during after-closure portion of pressure falloff. Data measurements are transformed into a constant rate equivalent pressure transformation to obtain adjusted pressures or adjusted pseudovariables which are analyzed to identify dual unit-slope before and after closure periods confirming a residual retaining width.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing process
InactiveCN103527163AIncrease success rateSolve the problem of inadequate transformationFluid removalBottom hole pressureWell logging
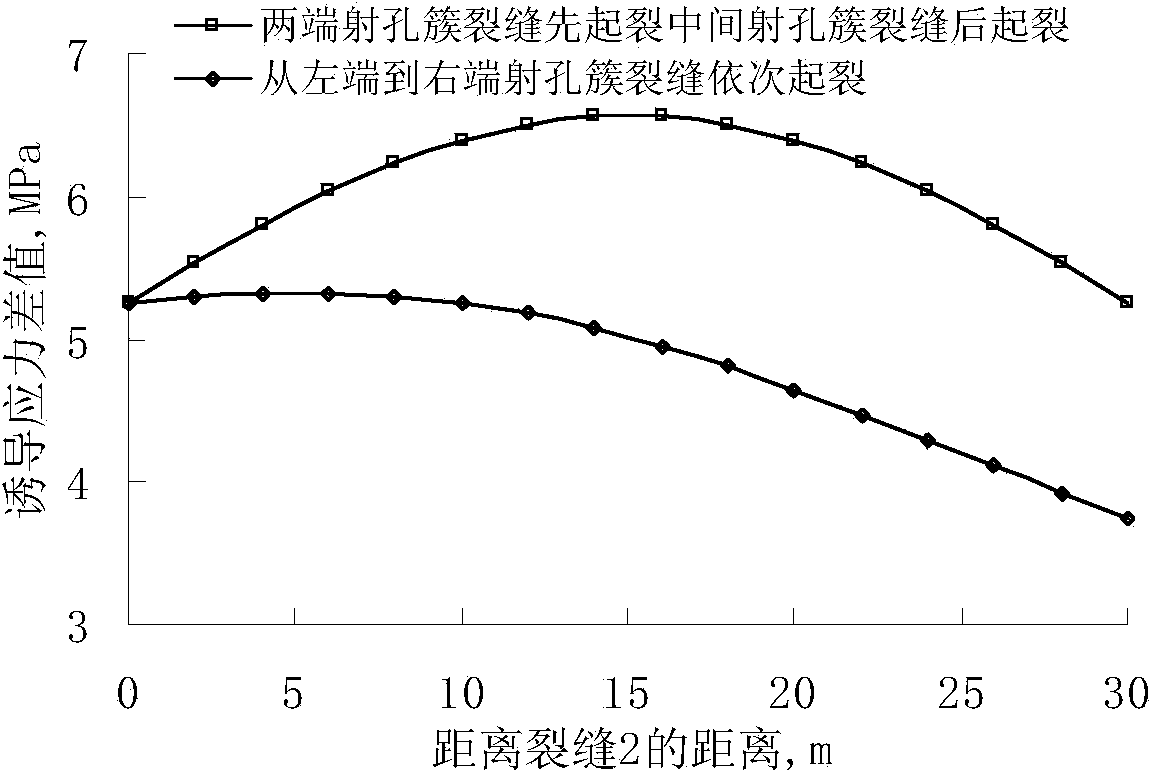
The invention relates to a tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing process. Data including in-situ stress magnitude and direction, horizontal well azimuth and length, reservoir Young moduli, a Poisson ratio, a well logging interpretation result and the like are collected and used as basic parameters for calculating induced stress needed for generation of complex cracks in tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing; according to reservoir physical characteristics, induced stress difference value variation conditions of three or more perforation clusters in the same fracturing segment according to different crack initiation sequences are contrasted, and preference is given to the perforation cluster crack initiation sequences with the maximal induced stress difference value as the target; preference is given to perforation cluster gaps so that the complex cracks can be formed through fracturing in the same fracturing segment of a horizontal well; in cooperation with perforation parameter optimization and with bottom hole pressure control as the target, the effect that the cracks of the perforation clusters at the two ends are initiated and extended for a certain distance through discharge capacity adjustment and then the discharge capacity is improved to utilize perforation friction for pressing open the cracks of the perforation clusters in the middle is achieved; then, prepad fluid and sand-carrying fluid containing a propping agent are poured into the cracks in sequence to realize transformation of the shape of the complex cracks of the fractured horizontal well.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
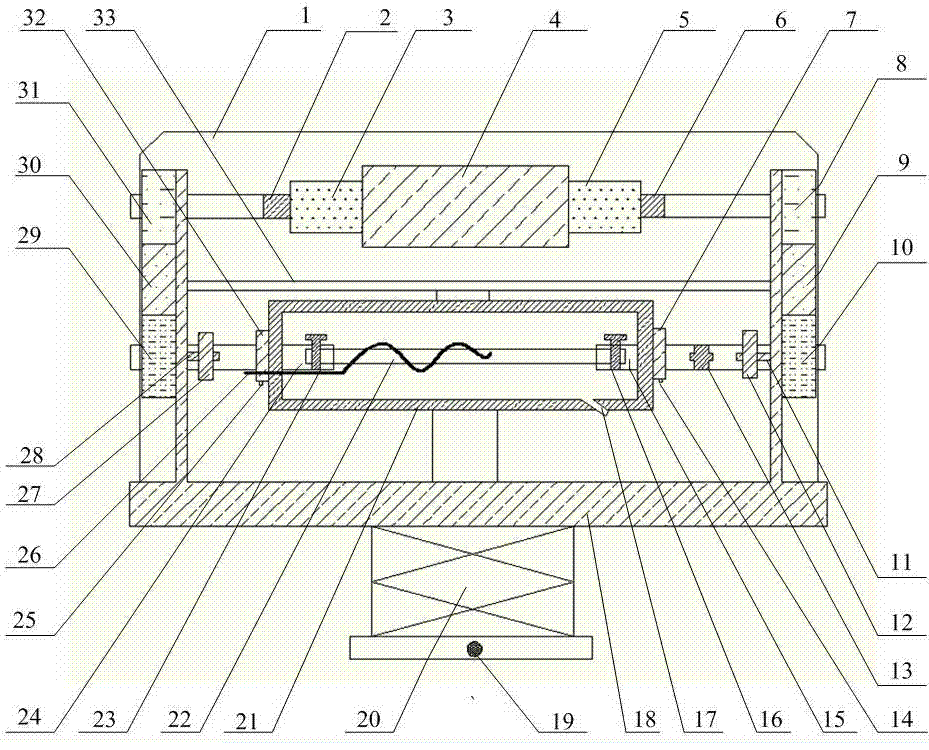
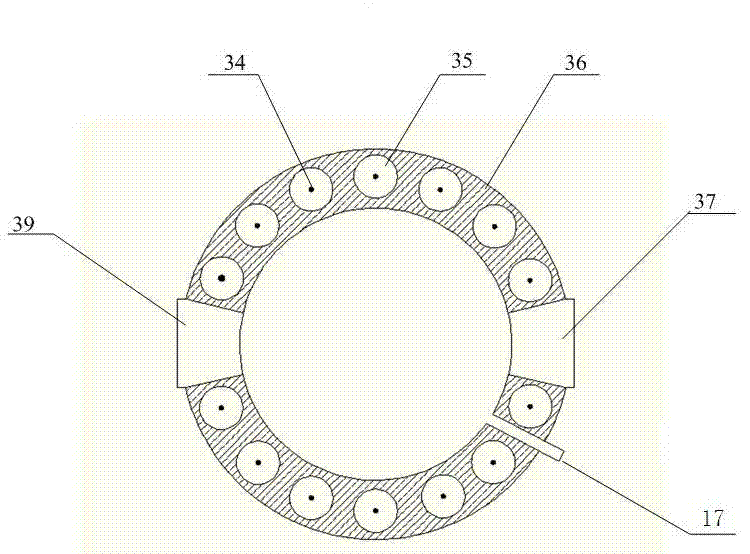
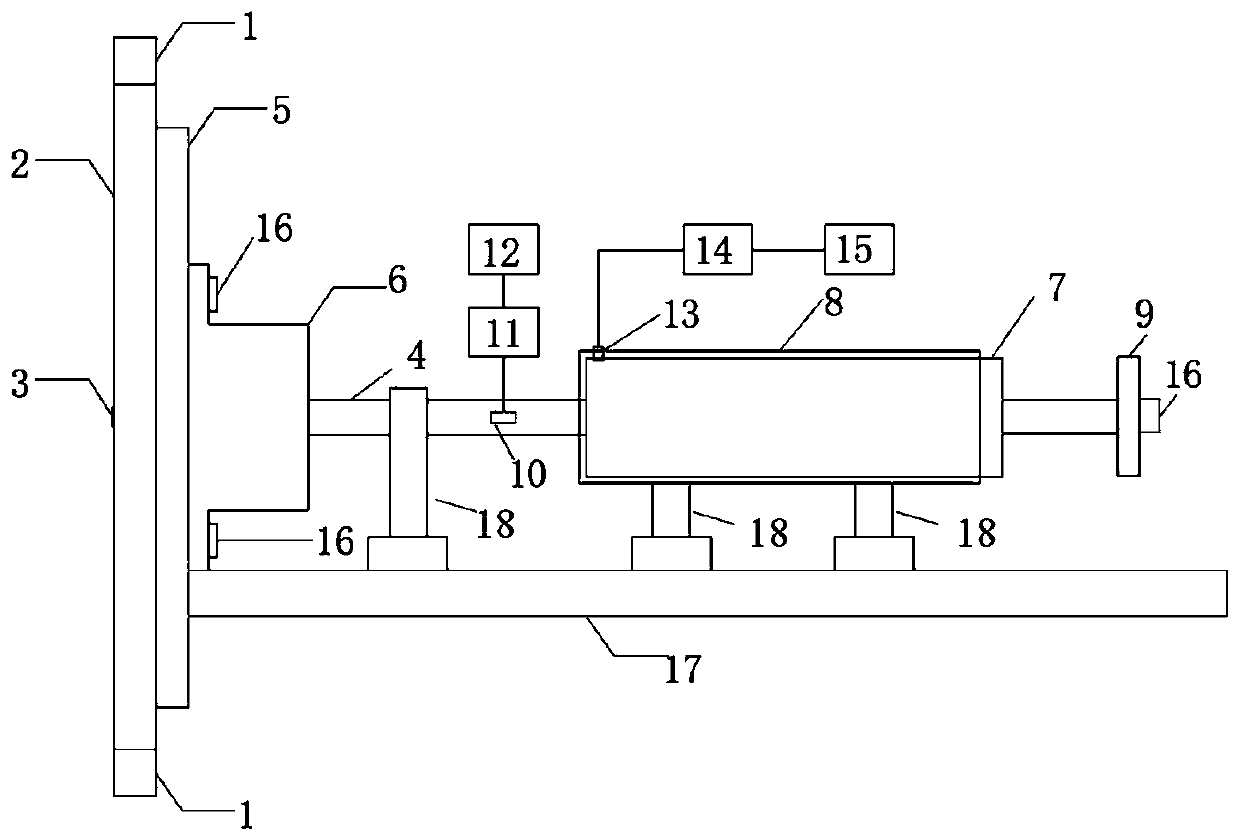
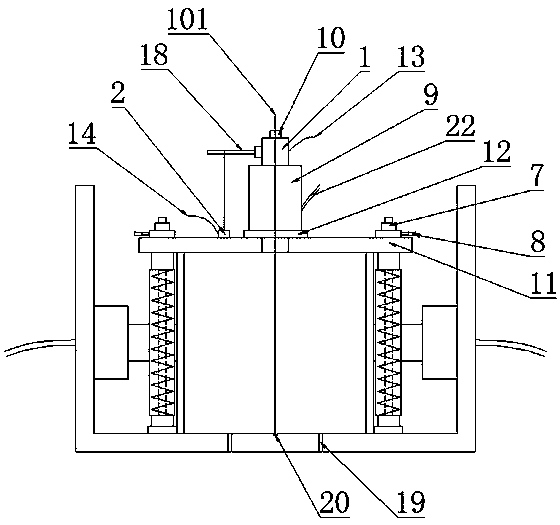
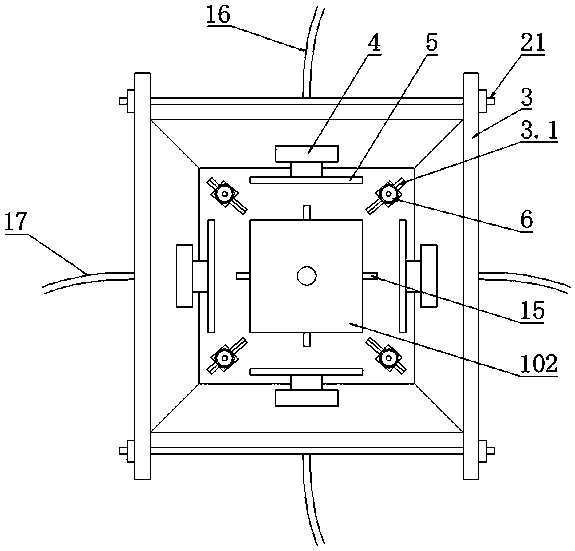
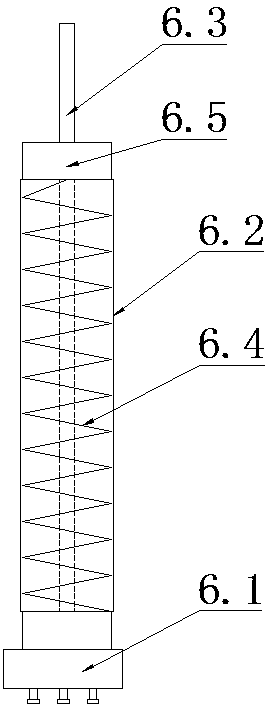
In-situ stress-temperature loading device for neutron diffraction technology
The invention discloses an in-situ stress-temperature loading device for a neutron diffraction technology. A frame in the device is designed into a door frame type structure, a hollow-shaft servomotor is utilized for driving multiple stages of gears with the same specification and the size to rotate via a speed reducer, and the horizontal motion operation of a test sample can be further realized through a guide component and a clamp. By controlling the forward rotation (reverse rotation) of the hollow-shaft servomotor, bidirectional synchronous drawing (compression) of the test sample is realized; and by controlling the rotational speed of the hollow-shaft servomotor, the speed regulation of drawing (compression) of the test sample is realized. A cavity type high-temperature furnace with the design based on a resistance heat radiation structure is matched with the frame to use, a temperature control instrument is used for controlling the temperature in a body cavity of the high-temperature furnace, fan-shaped through holes are respectively formed in the neutron incidence direction and the scattering direction, and quartz glass is further used for sealing. The in-situ stress-temperature loading device for the neutron diffraction technology, disclosed by the invention, can be used on a variety of neutron scattering (diffraction) spectrometers for realizing the neutron scattering (diffraction) in-situ stress-temperature loading testing technology.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Method for predicting vertical well volume fractured reservoir reform volume of low permeable reservoir
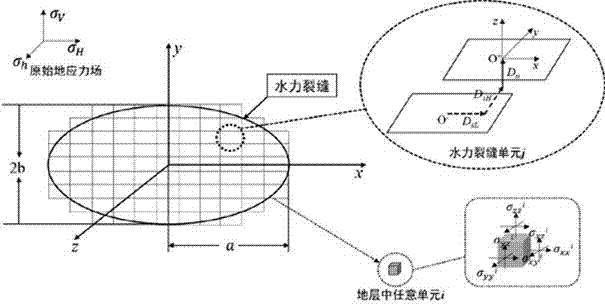
The invention discloses a method for predicting vertical well volume fractured reservoir reform volume of low permeable reservoir. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) calculating the induced stress produced by hydraulic fracture in a three-dimensional space; (2) calculating the formation pore pressure obtained after leak-off of fracturing fluid; (3) calculating the formation pore elastic stress obtained after the leak-off of the fracturing fluid; (4) overlapping the stress fields obtained in the step (1), (2) and (3) with an in-situ stress field to obtain a new crustal stress field, and calculating the magnitude and direction of three-way principal effective stress in the overlapped reservoir space; (5) calculating the open fracture determination coefficient M of a natural fracture in the reservoir space and the shear fracture region determination coefficient S of the natural fracture so as to predict the volume fractured reservoir reform volume. The method is used for predicting the reservoir reform volume after vertical well volume fracturing, is better in operability and accuracy, provides a favorable theoretical basis for effect evaluation and yield prediction after vertical well volume fracturing of the low permeable reservoir, and overcomes the defects of the prior art.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method for increasing fracture penetration into target formation
InactiveUS7032671B2Reliable and goodReliable methodSurveyFluid removalFracturing fluidVertical growth
A method of propagating a fracture farther from a well-bore into an oil and / or gas-bearing zone of a target formation while inhibiting growth of the fracture into an adjacent water-bearing zone under or over the oil and / or gas-bearing zone, comprises creating a zone of increased in-situ stress a vertical distance adjacent a target interval and then creating a main fracture in the target interval by, for example, fracturing the target interval with enough fracture fluid and pressure to propagate the main fracture, inter alia, vertically to the zone of increased in-situ stress. When vertical growth of the main fracture reaches the limit set by the zone of increased stress, additional fracture fluid pumped into the target interval tends not to propagate the main fracture vertically beyond that limit and, instead, tends to propagate the main fracture more laterally and farther from the well. Such zone(s) of increased in-situ stress can be created above, below, or both above and below the target interval.
Owner:NEW IPT INC
Method and an apparatus for detecting fracture with significant residual width from previous treatments
ActiveUS7774140B2Rapid determinationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyDual unitReservoir fluid
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Soft rock multi-measuring-point ground stress testing method by using connecting rod
InactiveCN103528718AEnables continuous monitoringUniform mediumForce measurement by measuring frquency variationsMechanical modelsEngineering
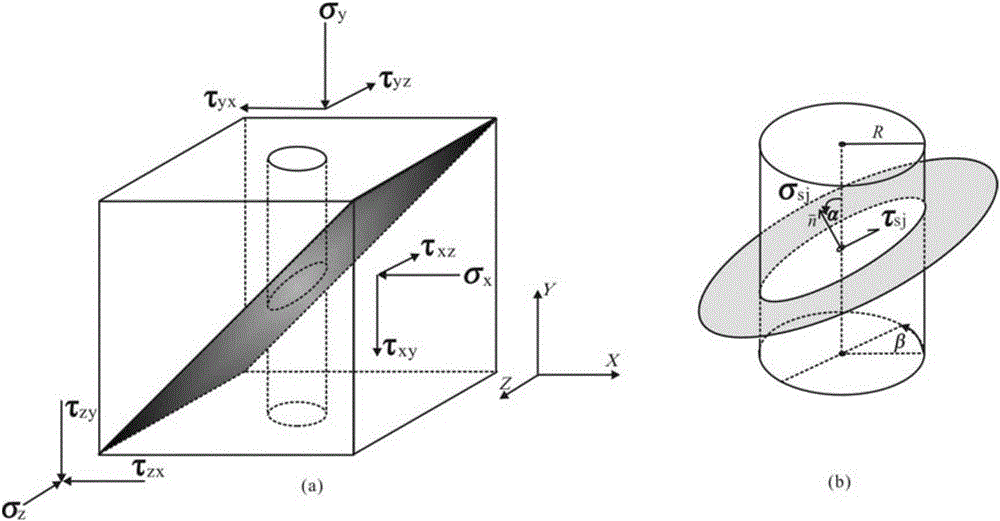
The invention discloses a soft rock multi-measuring-point ground stress testing method by using a connecting rod. During working, a plurality of groups of three-way pressure boxes (each group has two pressure boxes) are closely fixed on the connecting rod by using locking screws and multiple connecting rod sections are sequentially installed and operated till all measuring point three-way pressure boxes are pushed to a design position; the connecting rod is also used as a grouting pipe, full-hole grouting is performed, the stress to the three-way pressure boxes is measured and resolved to obtain stress components Sigma'(x), Sigma'(y), Sigma'(z), Tau'(xy), Tau'(yz) and Tau'(zx) of each pair of three-way pressure boxes at positions in a hole under a drill hole local coordinate system, then a cylindrical double-medium mechanical model is established, and stress components Sigma (x), Sigma (y), Sigma (z), Tau (xy), Tau (yz) and Tau (zx) of an in-situ stress field of the position of the drill hole are obtained by adopting a numerical simulation method through iterative convergence. Since the connecting rod used in the method is also used as the grouting pipe, uniform grouting is realized, grout mediums in the hole are uniform and the calculation is simpler and more convenient to perform; the ground stress values of multiple measuring points in deep soft rock can be directly measured and the continuous monitoring of the ground stress is realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and device for predicting rock burst in tunnel, and storage medium and system
InactiveCN107748103AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUltimate tensile strengthRock mass strength
The application provides a method and a device for predicting rock burst in a tunnel, and a storage medium and a system. The method includes the steps of: acquiring Hoek-Brown rock mass strength of surrounding rocks at a to-be-tested depth and the maximum ground stress of an in-situ stress field in the direction being vertical to tunnel axis; calculating a predicted index of rock burst, wherein the threshold value of the predicted index of rock burst is the ratio of the Hoek-Brown rock mass strength to the maximum ground stress of the in-situ stress field in the direction being vertical to tunnel axis; and predicting rock burst level according to the threshold value of the predicted index of the rock burst.
Owner:INST OF ROCK & SOIL MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Uniaxial tension sample holder capable of testing in-situ stress and electrical property for transmission electron microscope
InactiveCN102353580AIn situ mechanicsRealize electrical comprehensive performance testStrength propertiesMicroscope slideConventional transmission electron microscope
A uniaxial tension sample holder capable of testing in-situ stress and electrical property for a transmission electron microscope belongs to the researching fields of transmission electron microscope fitting and nano-material in-situ measurement. A prior art can realize stress signal reading during material deformation, but has strict requirements on a sample and only suits for a none-dimensionalnano-material like a nano wire or a nanotube, or a sample prepared by focused ion beam cutting; besides the prior art can not realize electrical property measurement under a stress state. The sample holder comprises a self-design transmission electron microscope sample holder, a deformation microscope slide, a sample head and compressing tablets. The deformation microscope slide is fixed on the sample head through the compressing tablets; a circuit used for measuring cantilever beam minimal deformation and a circuit used for measuring sample electrical signals of the deformation microscope slide are connected to electrodes on two sides of the sample head and connected to external testing equipment through a lead in the sample holder, so as to realize real time monitoring on the stress and the electrical signals.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
In-situ stress testing method of method for relieving stress in original hole site for multiple times
ActiveCN103075150AImprove scienceIncrease authenticityBorehole/well accessoriesStress distributionLithology
The invention discloses an in-situ stress testing method of a method for relieving stress in an original hole site for multiple times, and the method belongs to the field of in-situ stress testing. First, a location which has complete lithology and is suitable for in-situ stress testing is selected; a guide hole with the diameter being 127mm is drilled at the selected in-situ stress testing location, and the bottom of the hole is abraded; then a small hole with the diameter being 37mm is drilled, and the depth of the small hole is 300mm to 500mm; and a hollow inclusion is arranged in the small hole to relieve the stress and measure the in-situ stress for the first time; second, based on the measurement of the in-situ stress for the first time, an original drill bit continues to drill and core toward a deeper part along the original hole site, the in-situ stress is measured for multiple times continuously, and the multiple times of stress relieving depth intervals is 2m to 3m; and third, multiple times of in-situ stress testing results are compared and analyzed, the stress distribution area of in-situ rock is determined according to the change rules of the stress, and the distribution rules of the stress field of the in-situ rock are analyzed. The in-situ stress testing method of the method for relieving stress in the original hole site for multiple times has the advantages that the scientificalness and the truth of testing data are improved by measuring the in-situ stress values of the same hole site at different depths repeatedly for multiple times, so that re-drilling is prevented, and a complicated construction process is reduced.
Owner:徐州大屯工程咨询有限公司
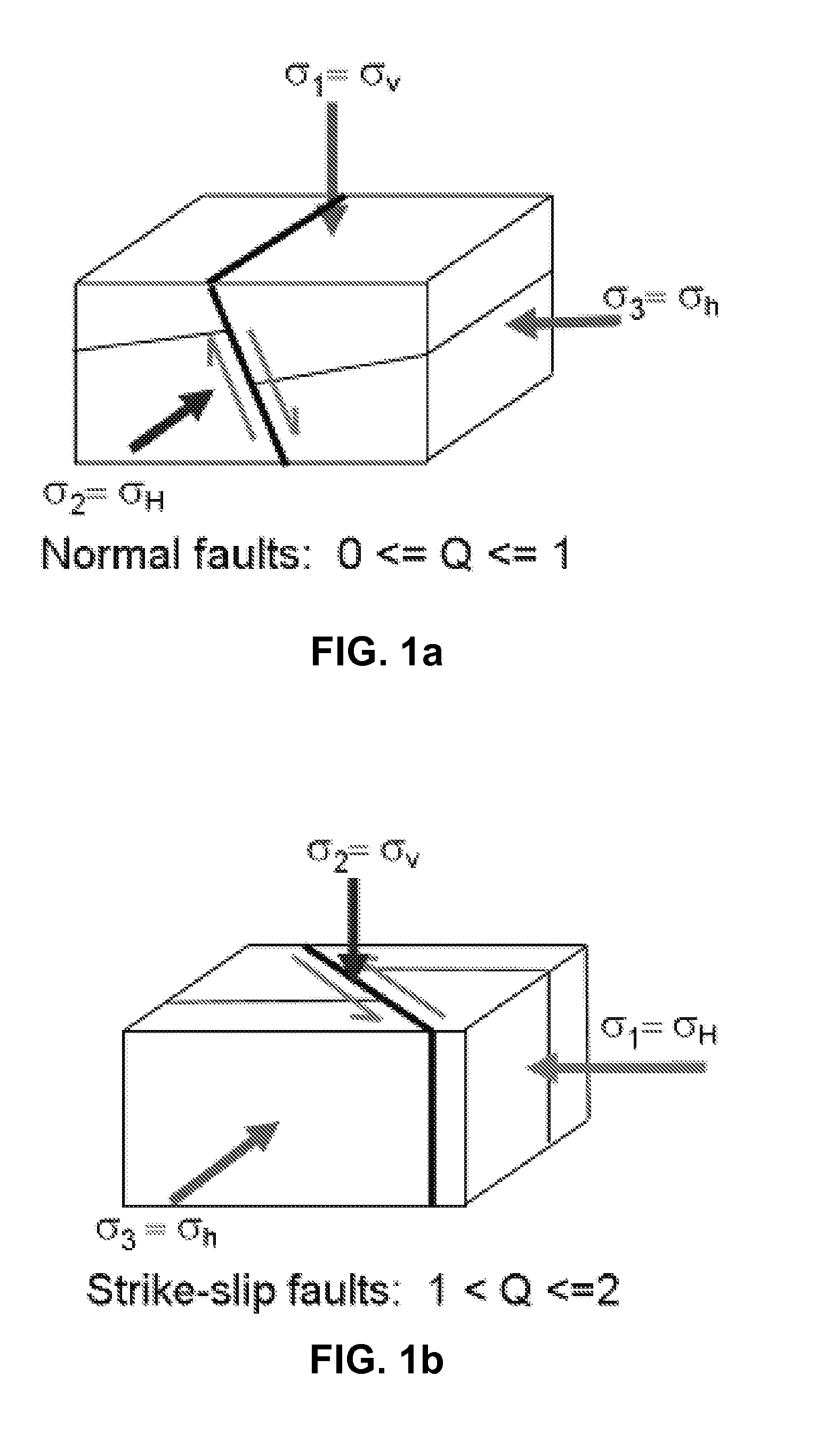
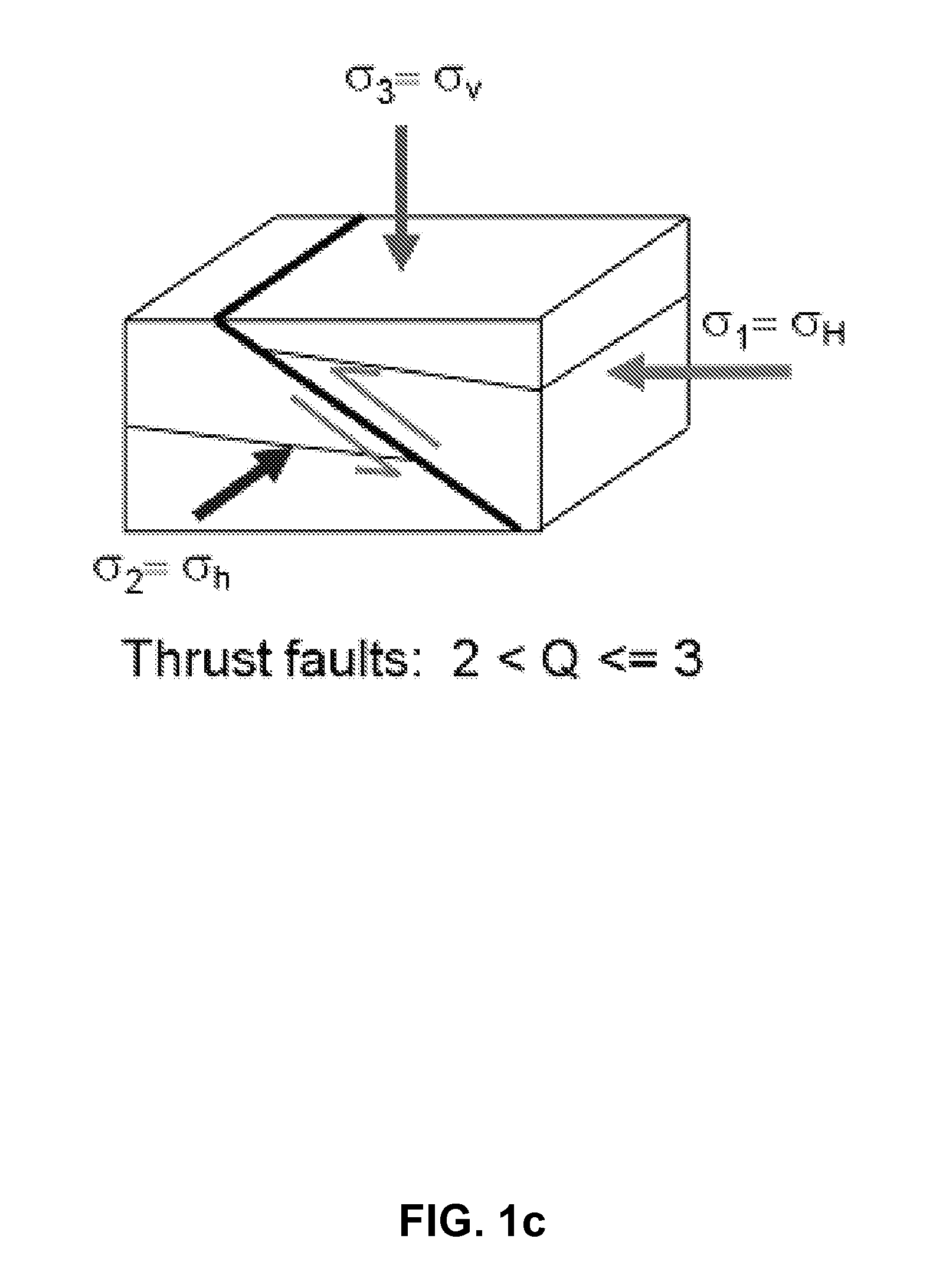
Method and system to determine the geo-stresses regime factor q from borehole sonic measurement modeling
Methods and systems for analyzing subterranean formations in-situ stress are disclosed. A method for extracting geological horizon on-demand from a 3D seismic data set, comprises receiving sonic log data; computing the anisotropic shear moduli C44, C55 and C66; determining in-situ stress type and selecting an in-situ stress expression corresponding to the in-situ stress type; computing stress regime factor Q of the formation interval; and computing and outputting the maximum stress σH by using the stress regime factor Q, Vertical stress σv and Minimum horizontal stress σh.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
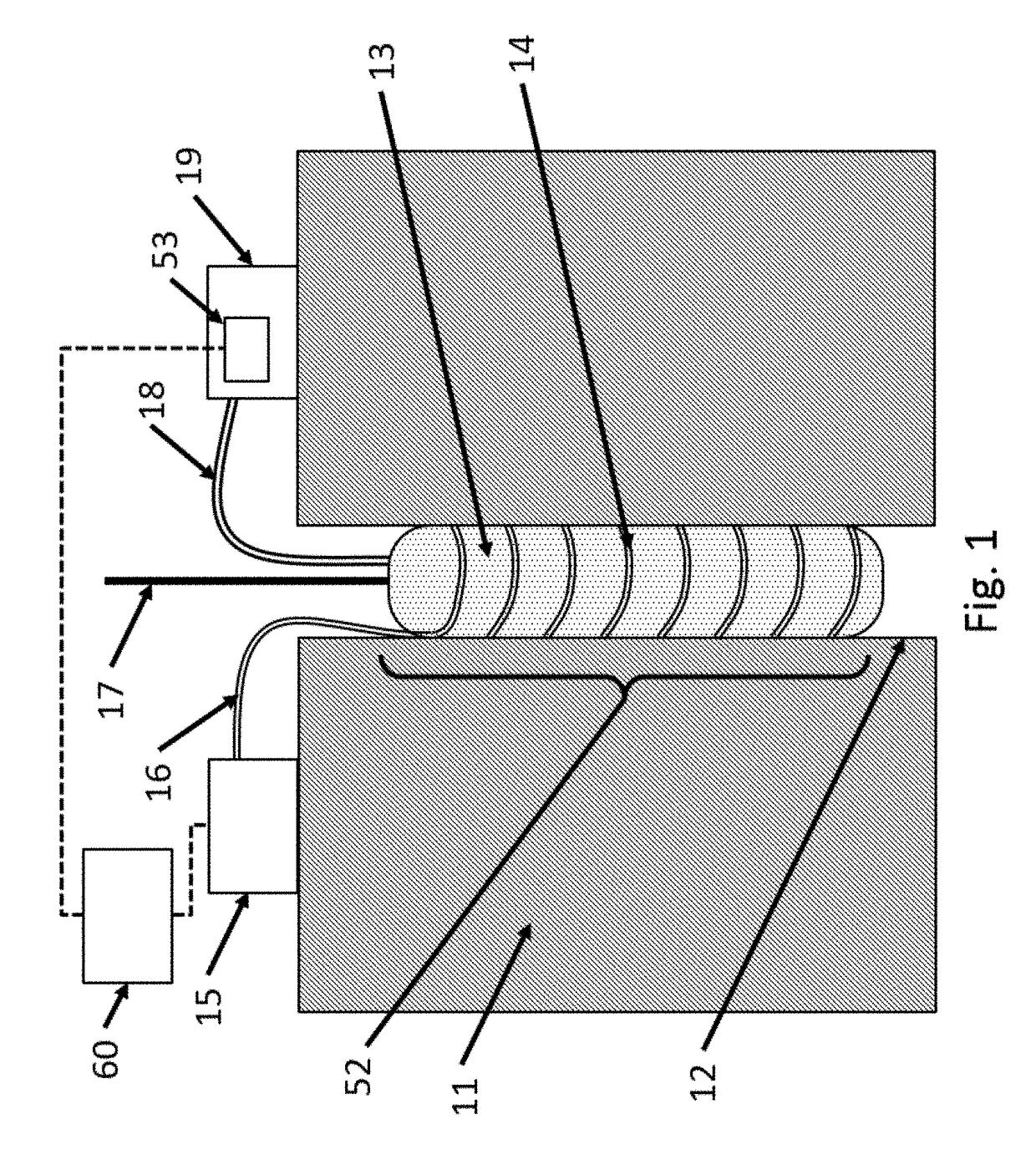
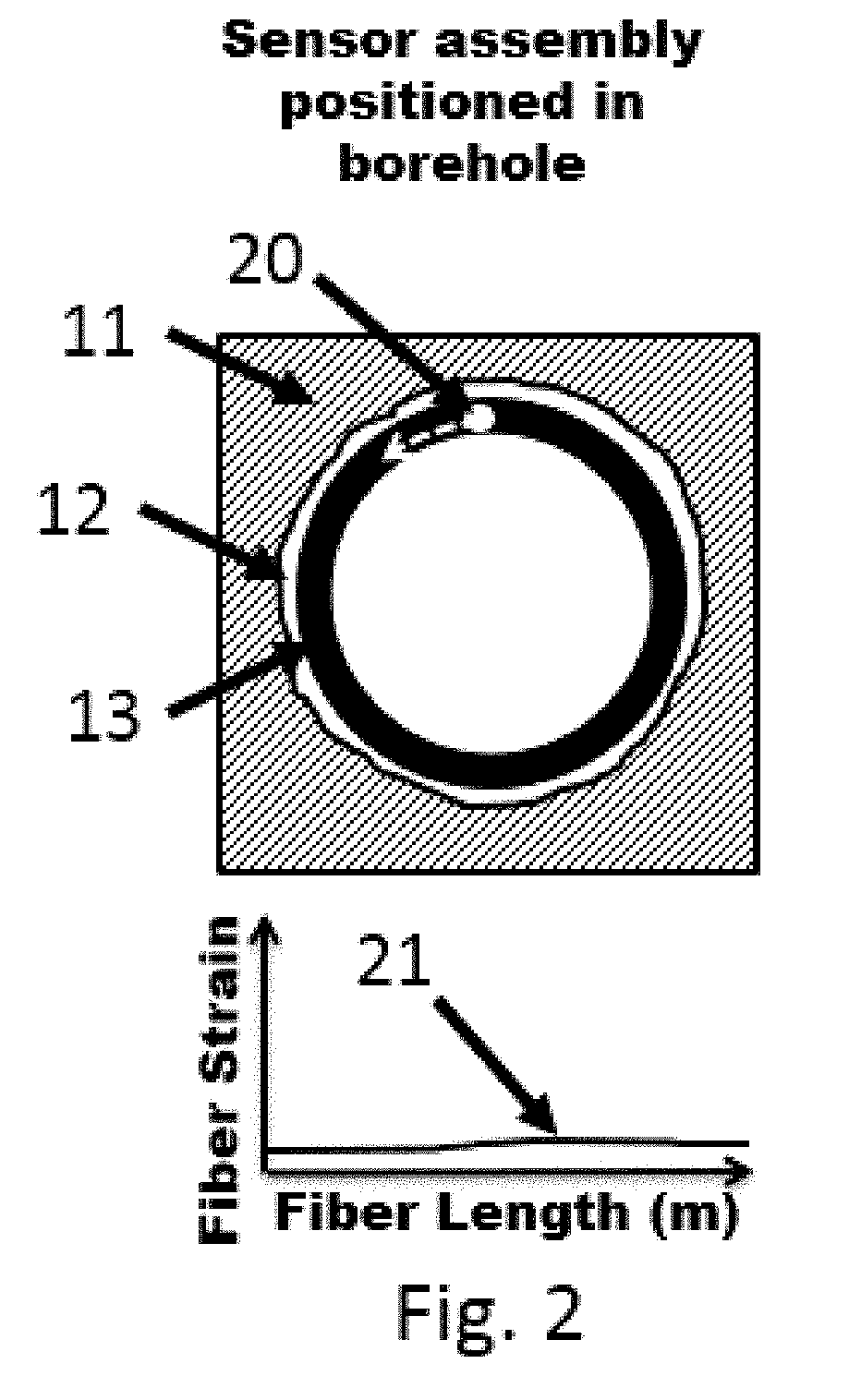
Distributed measurement of minimum and maximum in-situ stress in substrates
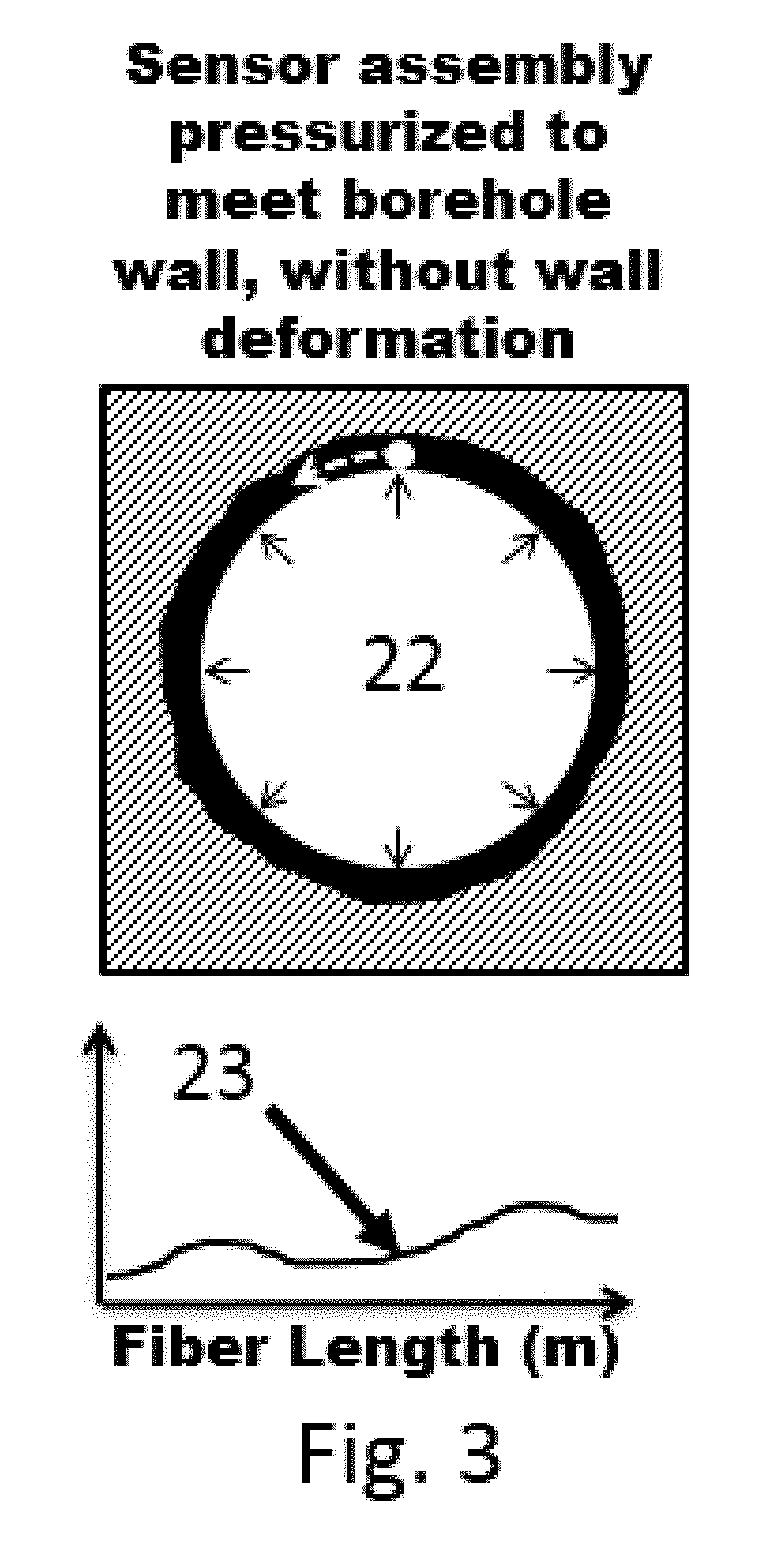
A system for performing distributed measurements of in-situ stress includes an expandable element with at least one fiber optic sensor. The expandable element can be positioned at various depths in a hole in a substrate. A pressurizing device expands (and contracts) the expandable element when the expandable element is inserted in the hole in the substrate to exert pressure on the hole wall. A pressure sensor provides a sensor output indicative of a pressure applied to the hole wall by the expandable element. The fiber optic sensor and an optical interrogator measure strain along a length of the sensor in a continuous, high spatial resolution manner Based on the measured strain and pressure sensor output, the system determines various properties of the substrate such as, minimum principal stress, maximum principal stress, and / or principal stress direction associated with one or more fractures in the substrate, as well as substrate modulus.
Owner:TENNESSEE TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY +1
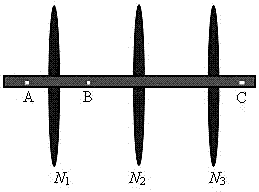
Calculating method for fracturing pressure of each perforation cluster of horizontal well sectioned multi-cluster fracturing
ActiveCN106979000AEnsuring simultaneous crack initiation and propagationAccurate calculationSurveyFluid removalMulti clusterBarrier effect
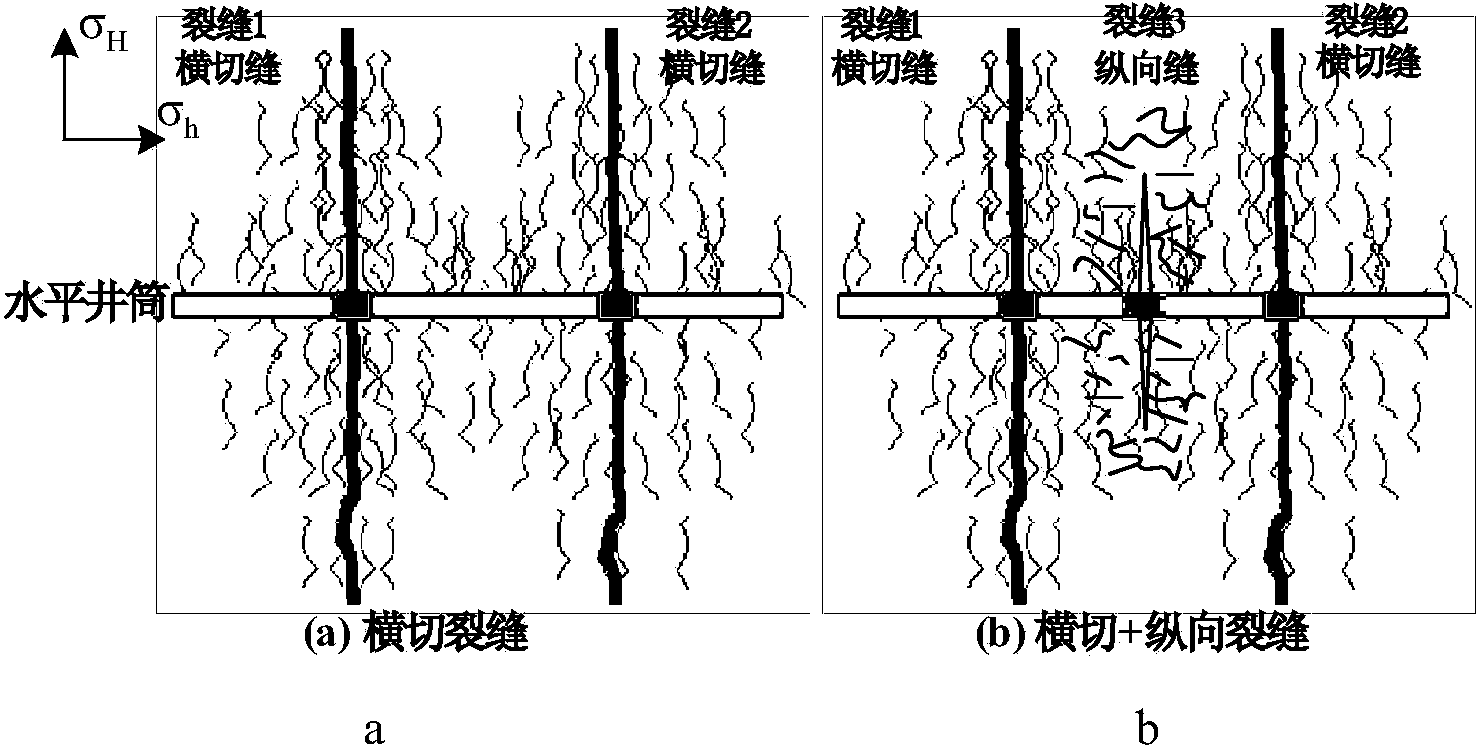
The invention relates to a calculating method for fracturing pressure of each perforation cluster of horizontal well sectioned multi-cluster fracturing. The calculating method comprises the steps that firstly, needed basic parameters comprising the Poisson ratio, in-situ stress, crack height, original net pressure and the like are calculated and collected; secondly, the effective net pressure of the last perforation cluster crack of a N fracturing section relative to a (N+1) fracturing section stratum is calculated; thirdly, the total induced stress borne by the (N+1) fracturing section stratum is calculated; and fourthly, the fracturing pressure of each perforation cluster of a (N+1) fracturing section is calculated, specifically, when the perforation orientation is along the vertical ground stress, the fracturing pressure of each perforation cluster is calculated, when the perforation orientation is along the maximum horizontal ground stress, the fracturing pressure of each perforation cluster is calculated, and the fracturing pressure of each perforation cluster of the (N+1) fracturing section is the minimum value between the two fracturing pressure values. The stress barrier effect and the stress interference effect between cracks when the multiple cracks in horizontal well sectioned multi-cluster fracturing sections are synchronously expanded are considered, and the calculating method more accords with the actual working condition of sectioned multi-cluster fracturing.
Owner:来安县永阳知识产权运营有限公司
Model test device and test method for measuring soil body displacement under action of in-situ stress filed
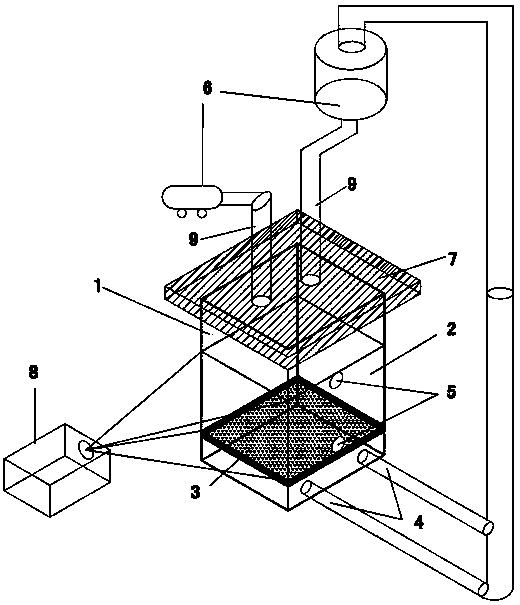
InactiveCN103558041ASimple structureEasy to operateStructural/machines measurementUsing optical meansEngineeringModel test
The invention provides a model test device and test method for measuring soil body displacement under the action of an in-situ stress field. The model test device comprises a transparent model box, a permeable layer, a pore pressure measuring device, a pressure water providing device and a sealing cover plate. The opening position is sealed by the sealing cover plate, a water draining hole is formed in a water draining cavity, a pressure measuring hole is formed in the lateral wall of a soil sample containing cavity, the pore pressure measuring device is arranged in the pressure measuring hole, the pore pressure measuring is in liquid sealing fit with the pressure measuring hole, the sealing cover plate is provided with a water inlet pipe, the pressure water providing device is connected with the water inlet pipe for communicating with the soil sample containing cavity, and the pressure water providing device is communicated with the water draining hole to form a water circulating system. The model test device for measuring the soil body displacement under the action of the in-situ stress field has the advantages of being simple in structure, convenient to operate and low in equipment cost.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Corrective natural fracture hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress measurement method
ActiveCN105716780AReduce application difficultyReduce the number of primary cracksMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFluid pressure measurementShear stressMechanical equation
The invention discloses a corrective natural fracture hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress measurement method. According to the method, a mechanical equation is established for shear stress widely existing in a natural fracture surface, and an in-situ stress tensor is obtained through inversion by searching for a natural fracture surface friction coefficient by use of a least square method and a computer program trial and error method. Through the method provided by the invention, the number of natural fractures needed by a conventional natural fracture hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress measurement method is substantially reduced, many hypothesis conditions set for an in-situ stress field during application of the natural fracture hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress measurement method are eliminated, the application difficulty of the natural fracture hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress measurement method is lowered, and the accuracy of the method is improved.
Owner:NAT INST OF NATURAL HAZARDS MINISTRY OF EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF CHINA
Apparatus for providing externally applied in-situ stress in thin film electrical property measurement and measuring method thereof
This invention discloses an apparatus and its measurement method to provide additional home position mechanical stress in the measurement of thin film electrical property, which comprises micrometer screw gage, rack and metal knife edge, wherein, there is located with an opening in the rack and the micrometer screw gage is fixed on the rack and is located on one side of the edge; the other edge side of the opening is located with a clamper to fix the film and underlay; the metal edge is fixed on the movable bar of the micrometer screw gage. When in measurement, It fixes one end of the film and underlay on the clamper of the apparatus and exposes the other end of the electrode on the metal edge and exerts different expansion and pressing stress on the thin film through adjusting the screw nut of the micrometer screw gage. This invention can be widely used in the study of impact of different thin film on electric property.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for modeling deformation in subsurface strata
A method for modeling deformation in subsurface strata, including defining physical boundaries for a geomechanical system. The method also includes acquiring one or more mechanical properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries, and acquiring one or more thermal properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries. The method also includes creating a computer-implemented finite element analysis program representing the geomechanical system and defining a plurality of nodes representing points in space, with each node being populated with at least one of each of the mechanical properties and the thermal properties. The program solves for in situ stress at selected nodes within the mesh.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
In-situ stress-free resurfacing welding repair process of abrasion of large-sized rotor journal
InactiveCN101704152AGood restorativeReduce lossesArc welding apparatusAcute angleUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to an in-situ stress-free resurfacing welding repair process of the abrasion of a large-sized rotor journal. The process comprises the following steps of: (1), carrying out the preparation work of resurfacing welding, filing and shaping burrs, acute angles and the like at the abraded positions of the large-sized rotor journal, cleaning oil spots and rusty scales chemically, then removing repaired positions and covering fatigue layers; (2), carrying out stress-free resurfacing welding, melting a welding wire coldly by adopting a stress-free resurfacing welding machine, carrying out resurfacing welding without temperature rise on the abraded positions of the journal and remaining a processing redundancy; (3), carrying out rough grinding, then carrying out resurfacing welding on defects after rough grinding and afterwards carrying out polishing and fine grinding; and (4), finally, polishing to reach the required size of the rotor journal. The invention adopts a stress-free resurfacing welding technique, has high strength, good quality, high efficiency, short construction period and low cost, enables the in-situ high-quality repair of the abrasion of the large-sized rotor journal to become actual and provides powerful guarantee for the long-term safe running of a generator set; and a resurfacing welding layer and a rotor basal body are in metallurgical bonding.
Owner:LANZHOU REMAKE ELECTRIC POWER SCI & TECH
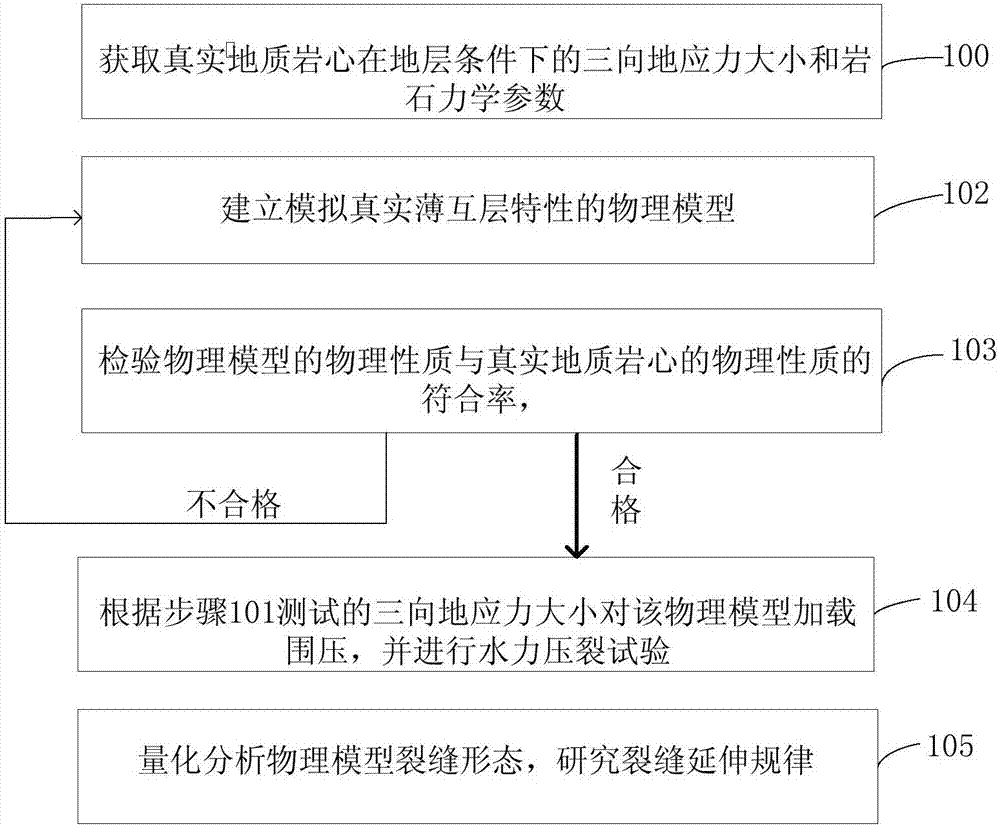
Device and method for quantitatively simulating seam width dynamic change during temporary blocking in seam
The invention provides a device and method for quantitatively simulating the seam width dynamic change during temporary blocking in a seam. The device comprises a first chamber, a second chamber, a first piston, a second piston, a first 3D printing crack surface, a second 3D printing crack surface, a monitoring processing system, a liquid injection system and a liquid collection system. Accordingto the method, fracturing liquid and / or a temporary blocking agent is injected into a crack channel through the liquid injection system, the pressure in a mixed phase chamber is monitored in real time, and the seam width dynamic change in the process of temporary blocking in the seam is monitored in real time through the monitoring processing system. By adopting the device and the method, the typeand proportion of mixed phases in the mixed phase chamber can be designed according to reservoir rock mechanical properties and in-situ stress parameters, fine simulation of reservoir rock mechanicsand stress characteristics is achieved, then temporary blocking in the seam under the reservoir condition reappears, and the seam width dynamic change in the process of temporary blocking in the seamis quantitatively simulated and monitored in real time.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
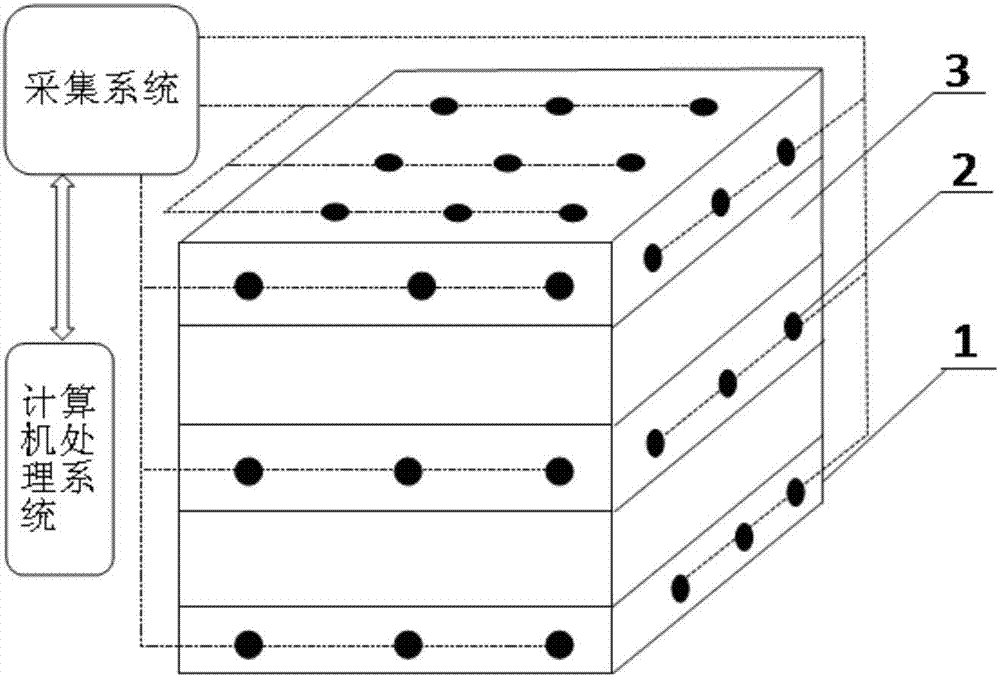
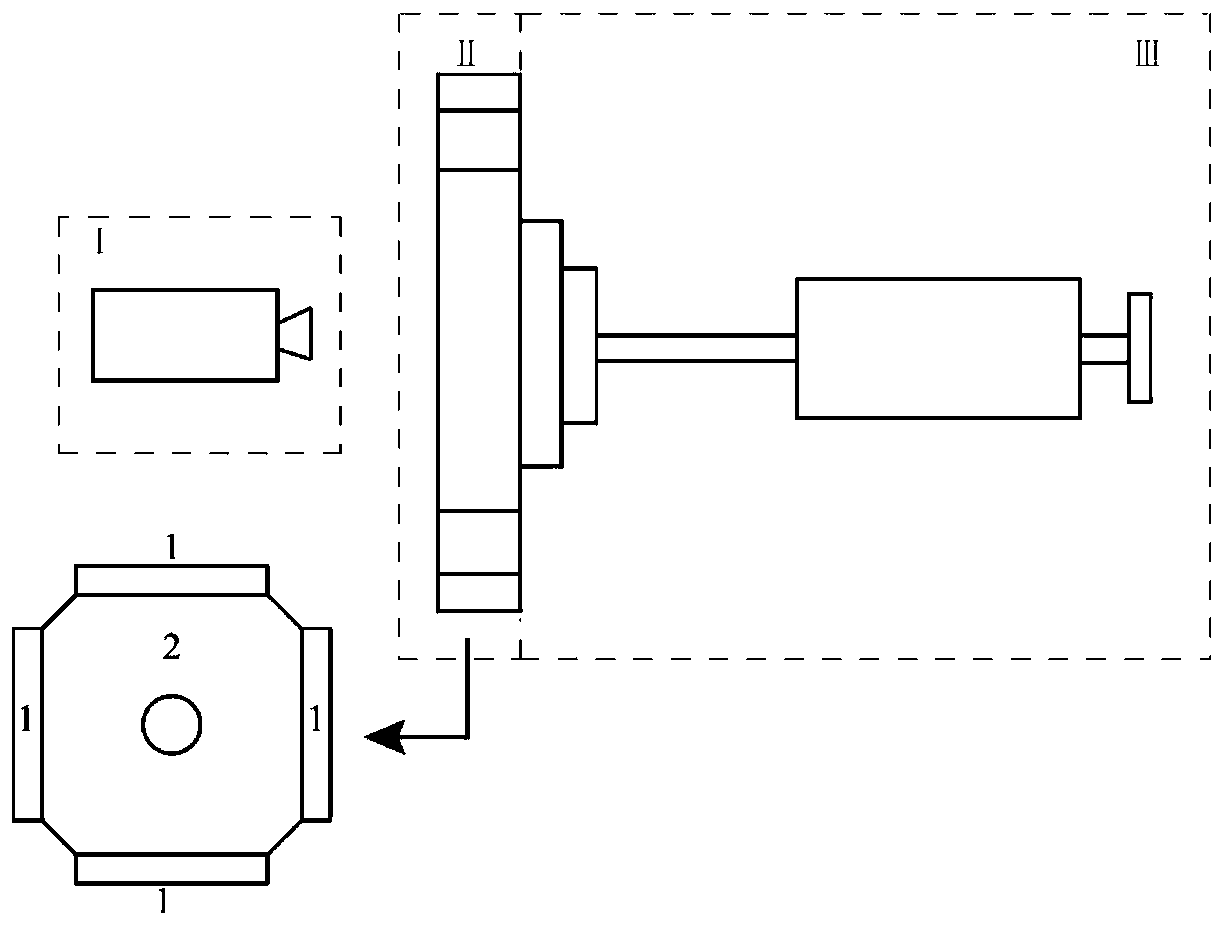
Large true tri-axial physical model test method for researching thin interbed fracturing fracture extension principle
The invention relates to the technical field of oil and gas well production increment, in particular to a large true tri-axial physical model test method for researching a thin interbed fracturing fracture extension principle. The method comprises five steps that the three dimensional in-situ stress size and rock mechanical parameters of a true geological core are obtained; a physical model for simulating a true thin interbed is built; the physical model is tested; the confining pressure is loaded on the physical model, and a hydraulic fracturing test is conducted; and the fracture shape of the physical model is subjected to quantitative analysis, and the fracture extension principle is researched. All test factors of the method approximate the true geological conditions, the thin interbed oil reservoir hydraulic fracturing fracture extension principle can be mastered through the method, thin interbedded reservoir transformation is guided, and the developmental effect of an oil reservoir is greatly improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Test system for simulating transient unloading of excavation of chamber face under different geostress conditions
ActiveCN109932248ASolve the problem that the displacement cannot be measuredSolve the unmeasurableMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringDrilling and blasting
The invention relates to a test system for simulating transient unloading of excavation of a chamber face under different geostress conditions. The test system is capable of simulating a transient unloading process of excavation of the diverticulum face to complete transient unloading of surrounding rocks with different excavation surface shapes under different geostress conditions and different unloading rates, and can record the whole process of the overall displacement variation of the surrounding rocks of a chamber. The test system comprises an in-situ stress simulation device, a transientunloading device and a surrounding rock overall displacement monitoring device. The in-situ stress simulation device is composed of a ground stress loading device and a chamber surrounding rock model. Four loading surfaces in the chamber surrounding rock model directly contact four hydraulic heads of the ground stress loading device. The ground stress loading device and the chamber surrounding rock model are used together and placed on the same plane perpendicular to a horizontal plane. The transient unloading device and the surrounding rock overall displacement monitoring device are placed in the front and rear directions of the plane respectively. The test can indirectly solve the problem that the displacement of surrounding rocks cannot be measured at the moment of excavation and unloading of drilling and blasting in actual engineering.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Drawing test device and method for simulating full-length anchoring quality detection of roadway surrounding rock
InactiveCN109253926AAchieving preload applicationConvenient guidancePreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesComputerized systemEngineering
The invention provides a drawing test device and method for simulating full-length anchoring quality detection of a roadway surrounding rock, and belongs to the technical field of mining engineering.The drawing test device comprises a simulation test box, a drawing system, a pressure sensor for monitoring a drawing force in an anchor rod drawing process, a displacement sensor for monitoring the displacement in the anchor rod drawing process, and a computer system connected with the pressure sensor and the displacement sensor respectively through data transmission conducting wires; the simulation test box comprises a box body, a hydraulic oil cylinder arranged on an inner wall of the box body and under electrohydraulic control, a confining pressure plate arranged on a movable end head of the hydraulic oil cylinder, and a telescopic spring tube; and the drawing system comprises a hollow jack under the electrohydraulic control, an anchor rod anchorage device matching the hollow jack, and a bearing plate and a saucer provided with center holes. The device can realistically realize the simulation of an in-situ stress field of an anchoring body and the pre-tightening force applicationin an anchor rod mounting process so as to restore the site as much as possible.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Coal bed pulsation hydraulic fracturing amplitude and frequency design method
ActiveCN108829993AIncrease the volume of fracturing stimulationIncrease the areaFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelHydraulic fracturing
The invention relates to a coal bed pulsation hydraulic fracturing amplitude and frequency design method. The method comprises the specific steps that 1, basic mechanical parameters, in-situ stress data and pore pressure data of coal are acquired, and a coal strength theoretical model under a pulsation load is obtained; 2, a coal bed pulsation hydraulic fracturing finite element model is established; 3, pulsation pressure is applied to a fracturing well, a stress field of a coal bed is subjected to simulating computation under a certain pulsation frequency and amplitude construction parameter,and distribution of a disturbed stress field of coal bed pulsation hydraulic fracturing is determined; 4, the area of the coal bed of an effective damaged area formed by pulsation hydraulic fracturing transformation is determined, wherein coal for generating damage is coal with formed cracks, and the area of a crack network formed by pulsation hydraulic fracturing transformation is determined; 5,the third and fourth steps are repeated, the area of the crack network generated under different pulsation hydraulic fracturing amplitudes and frequencies is calculated, and a properest pulsation hydraulic fracturing amplitude and frequency parameter combination is calculated, analyzed and selected. According to the method, the coal bed fracturing transformation volume is increased to the greatest extent, and the productivity of a coal-bed gas well is effectively improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Method of Stimulating Oil and Gas Wells Using Deformable Proppants
ActiveUS20080110623A1Minimize damageImprove permeabilityFluid removalDrilling compositionFracturing fluidDolomite
A method of fracturing using deformable proppants minimizes proppant pack damage, without compromising the fracturing fluid's proppant transport properties during pumping, by use of deformable proppants. Selection of proppant is dependent upon the mechanical properties of the formation rock. The strength of the deformable proppant is dependent upon the modulus of the formation rock being treated such that the proppant is capable of providing, at the very least, a minimum level of conductivity in in-situ stress environments. The maximum elastic modulus of the deformable proppant is less than the minimum modulus of the formation rock which is being treated. The method is particularly applicable in fracturing operations of subterranean reservoirs such as those comprised primarily of coal, chalk, limestone, dolomite, shale, siltstone, diatomite, etc.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Mobile test system and methods for in situ characterization of stress and deflection dependent stiffness and bearing capacity of soils and geo-materials
ActiveUS20130283925A1Maximize imparted reaction loadWith balanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessSoil scienceIn situ stress
An integrated mobile test system and methods for characterizing in situ stress or strain / deflection—dependent stiffness and bearing capacity enables the testing of engineering properties of natural, compacted, stabilized, and reinforced soils and geo-materials. The mobile test system and associated methods (1) prepare the ground for testing and (2) apply static or cyclic loading to one or more bearing plates of various geometries positioned at the ground surface or below the ground surface to determine both stress and deflection dependent stiffness relationships and the bearing capacity of the soil or geo-material. Optionally, the mobile test system and associated methods (3) apply ground confining stress conditions independent of the bearing plate loading.
Owner:INGIOS GEOTECHNICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com