Glass-based articles including a stress profile comprising two regions, and methods of making
A stress distribution, glass-based technology, applied in the field of glass and glass-ceramic products, glass-based products, can solve the problem of stress distribution of glass-based products without thermal tempering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0098] As used herein, the term "about" means that quantities, dimensions, formulations, parameters and other quantities and characteristics are not exact or need be exact, but may be approximate and / or larger or smaller as required, such as reflective tolerances, conversions factors, rounding, measurement errors, etc., and others known to those skilled in the art. When the term "about" is used to describe a value or the end of a range, it is to be understood that the disclosure includes the specific value or end to which it refers. Regardless of whether the numerical value or the end value of the range in the description has "about", the numerical value or the end value of the range is intended to include the following two embodiments: one is modified by "about", and the other is not modified by "about". "Retouch. It should also be understood that the endpoints of each range are meaningful in combination with the other endpoints as well as independently of the other endpoint...
Embodiment 1
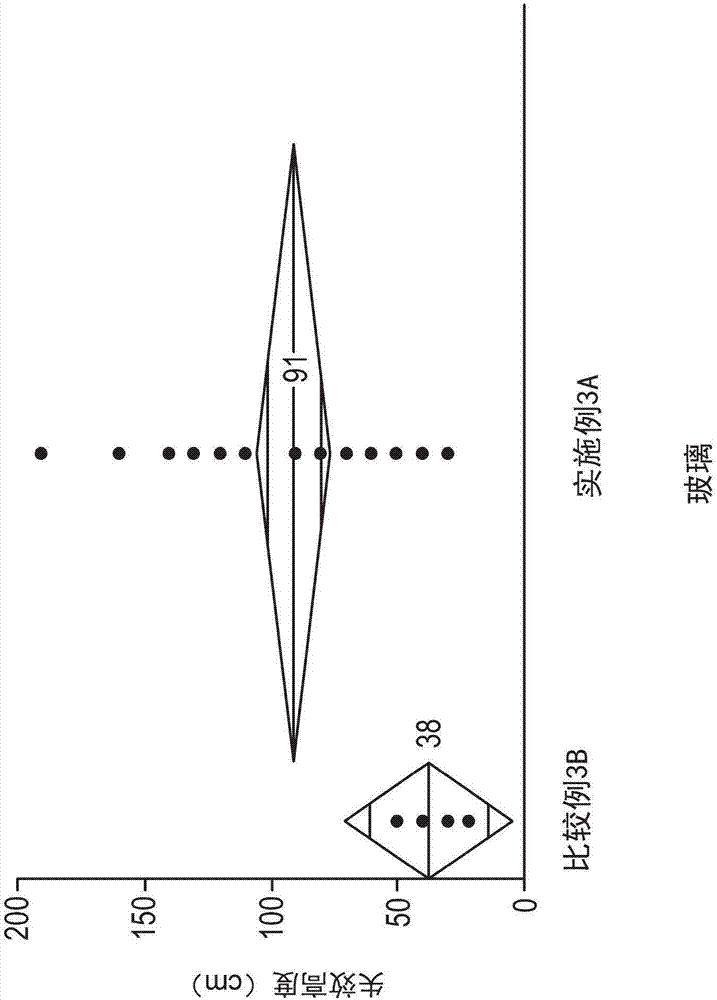
[0341] Examples 1A-1G included glass substrates having the following nominal composition: about 63.46 mole % SiO 2 , 15.71 mol% Al 2 o 3 , 6.37 mol% Li 2 O, 10.69 mol% Na 2 O, 0.06 mol% MgO, 1.15 mol% ZnO, 2.45 mol% P 2 o 5 and 0.04 mol% SnO 2 . The glass substrate has a thickness of 0.8mm. According to the conditions listed in Table 2, the glass substrates of Examples 1A-1G contained 100% NaNO 3 Ion exchange is performed in a molten salt bath with a temperature of about 390°C. The resulting glass-based article has a maximum CT value, which is plotted as a function of ion exchange time in Figure 5 .
[0342] The ion exchange condition of table 2 embodiment 1A-1G
[0343] Example
Immersion time in bath (hours)
Maximum CT
1A
0.5
30
1B
1
42
1C
1.5
52
1D
2
56
1E
3.75
67
1F
8
63
1G
16
55
[0344] The stress distribution of Example 1E was measure...
Embodiment 2
[0348] Example 2A included a glass substrate having the same composition as Example 1 and having a thickness of 0.8 mm. The glass substrate contains 51% KNO 3 and 49% NaNO 3 and ion exchange in a single molten salt bath having a temperature of about 380°C for 3.75 hours. The resulting glass-based articles had stress profiles as described in Table 4.
[0349] The stress distribution of table 4 embodiment 2A
[0350] surface compressive stress
500MPa
layer depth for potassium
12 microns
Stress at the DOL of potassium
161 MPa
Maximum CT
70MPa
DOC
150 microns
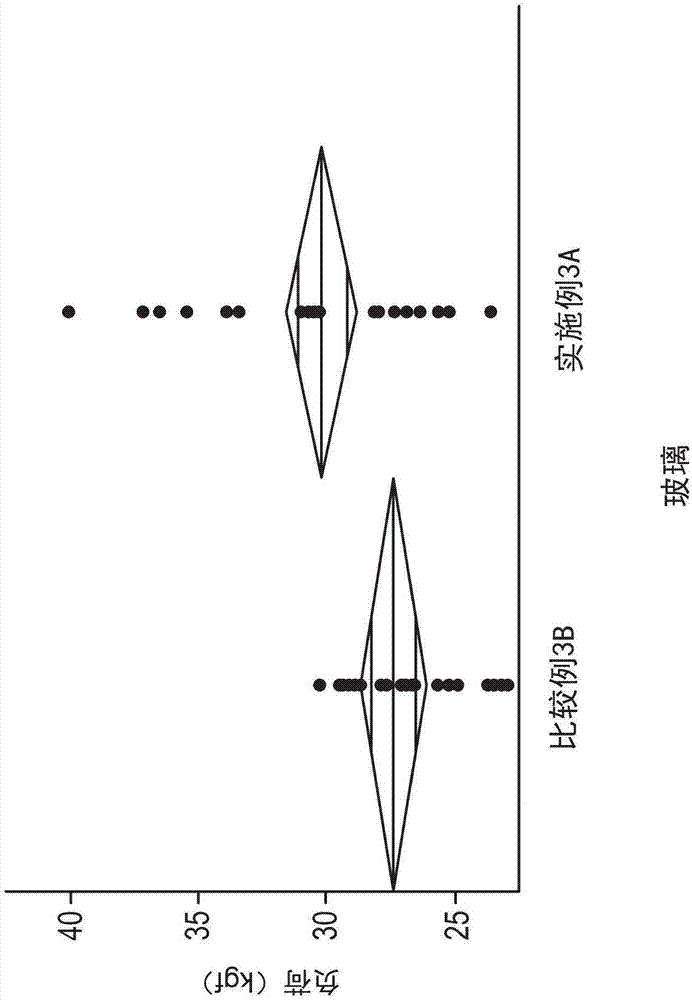
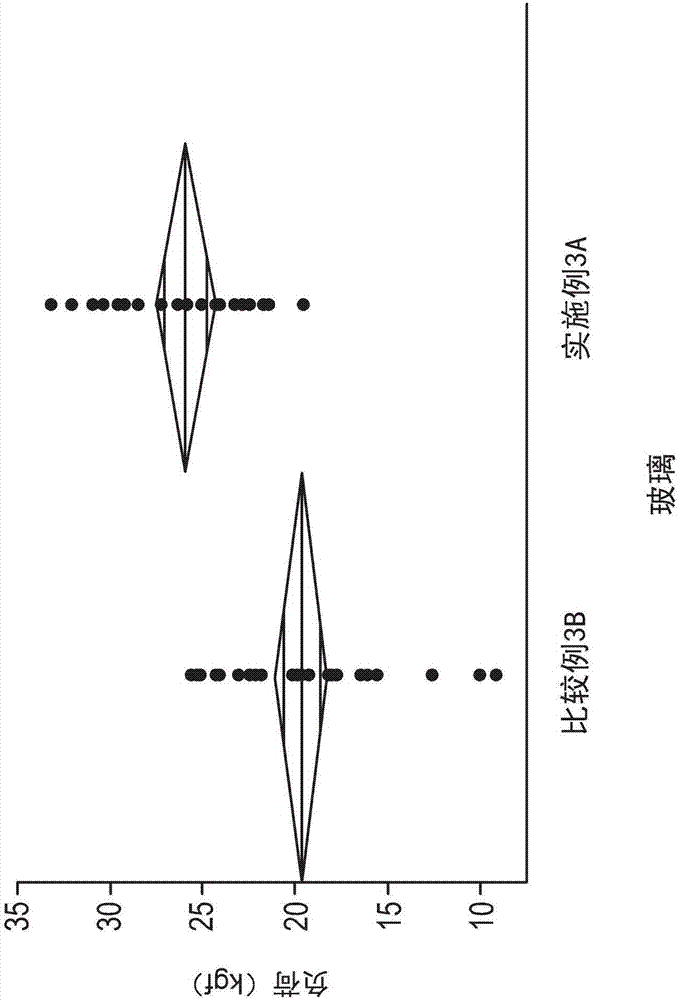
[0351] The AROR test as described herein was performed on the glass-based article of Example 2A. One set of glass-based articles was abraded with a load or pressure of 5 psi, a second set of glass-based articles was abraded with a load or pressure of 25 psi, and a third set of glass-based articles was abraded with a load or pressure of 45 psi. Figure 7 AROR...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| draft ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com