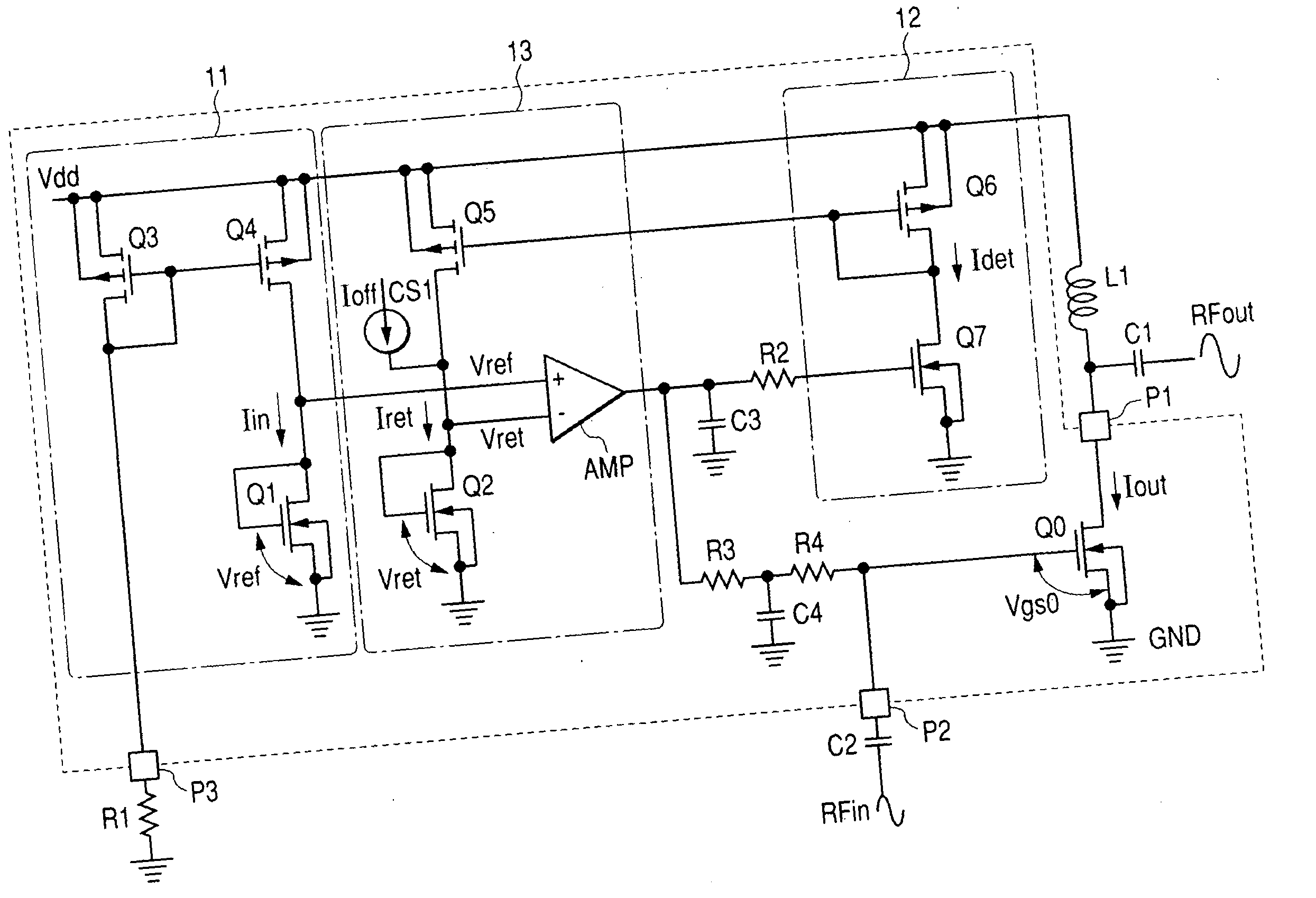
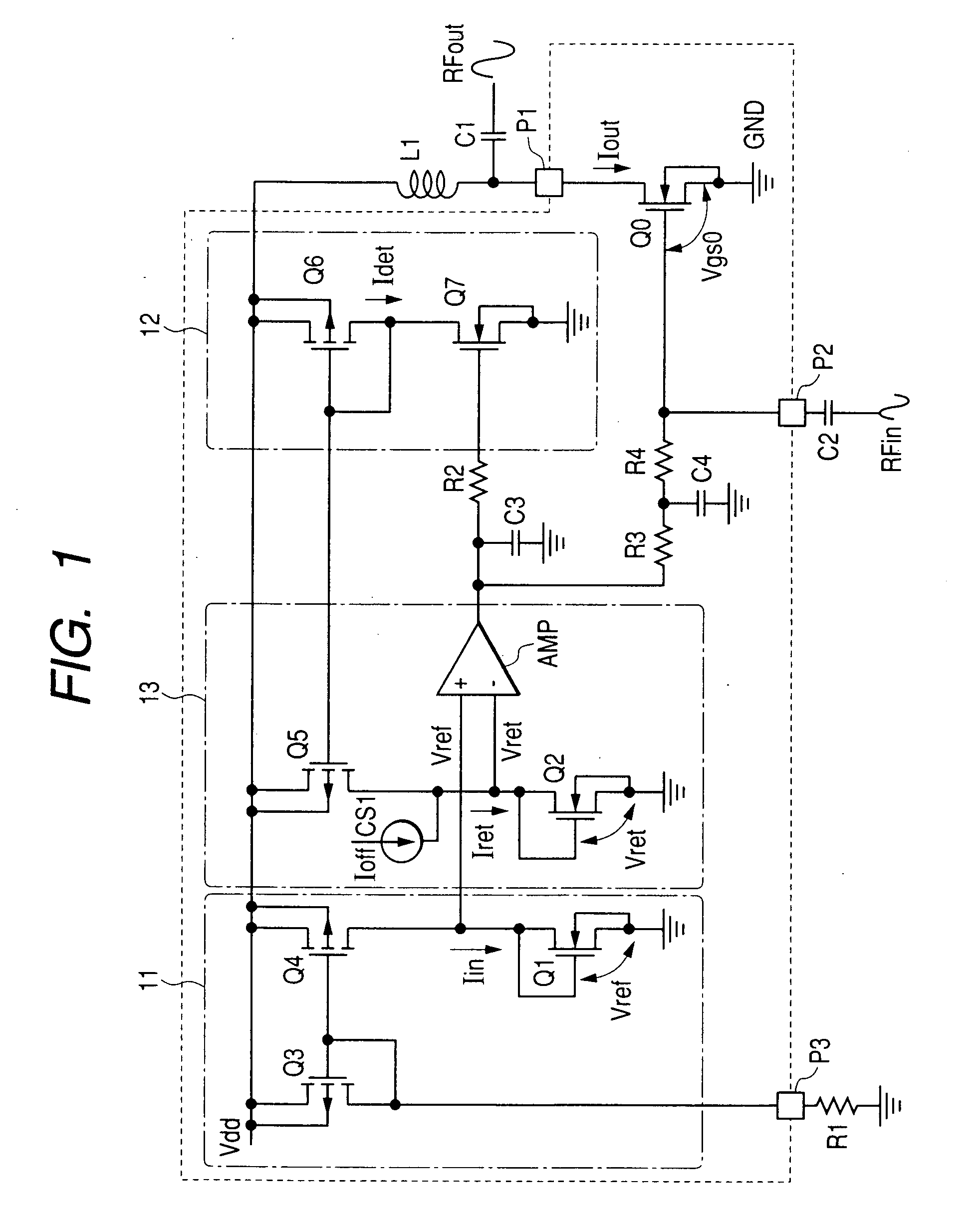
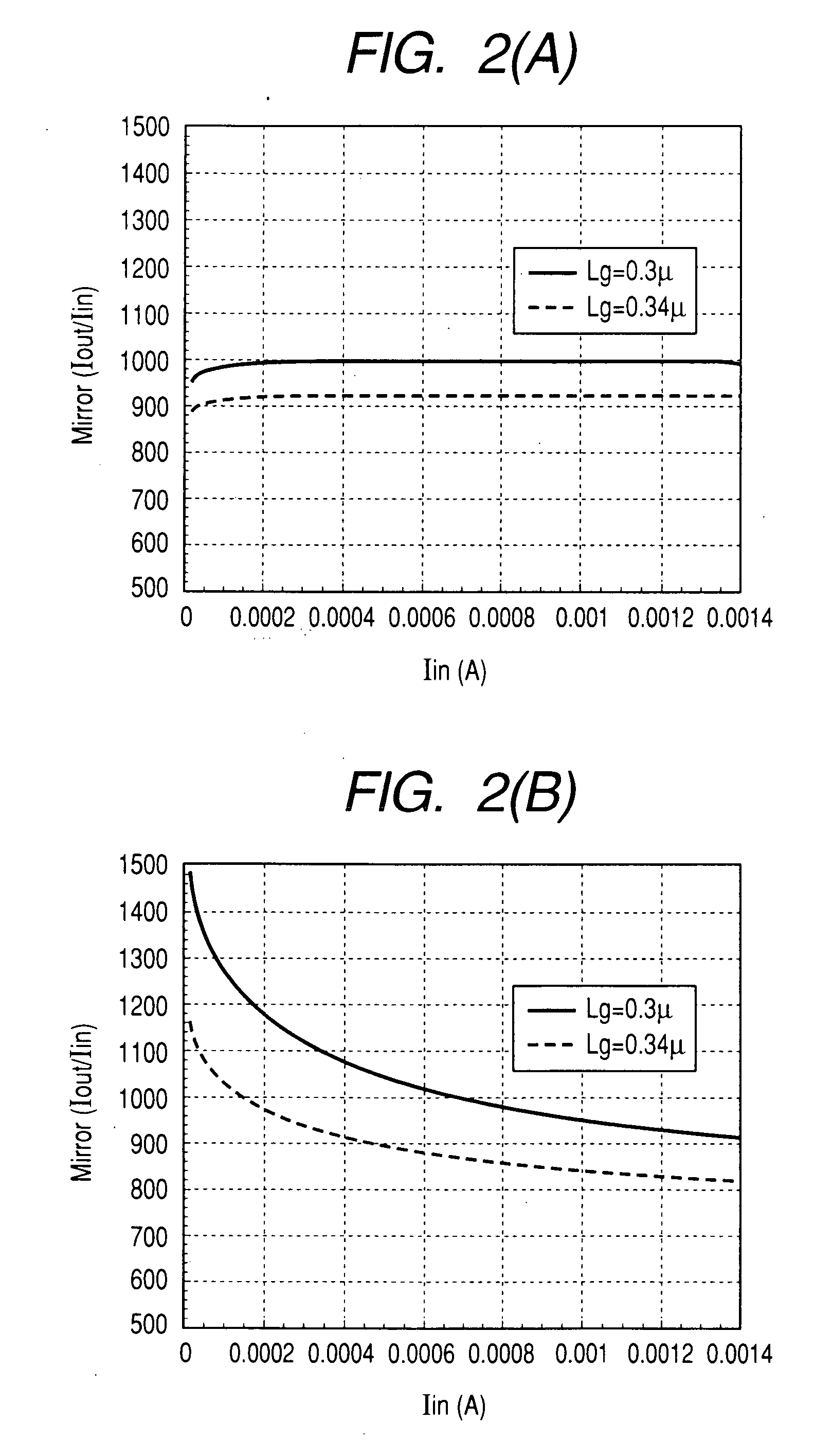
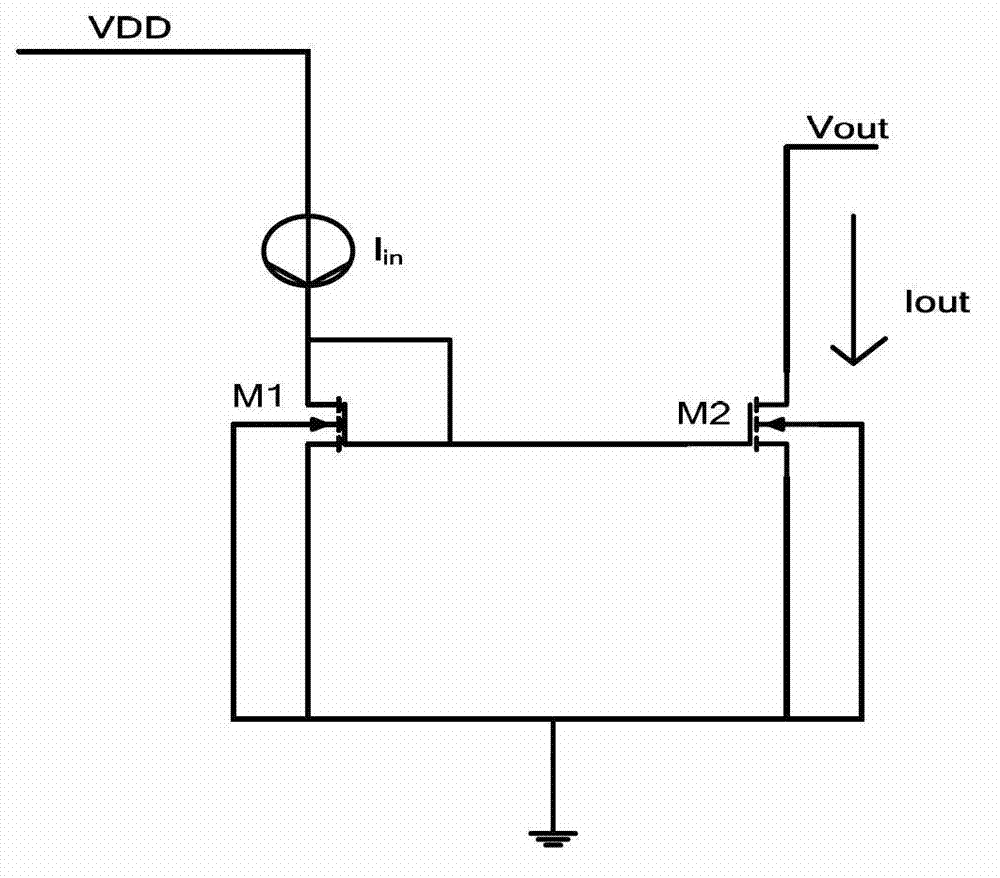
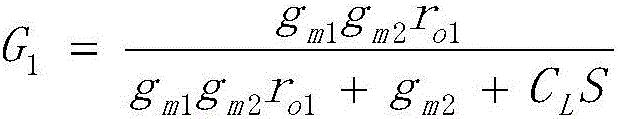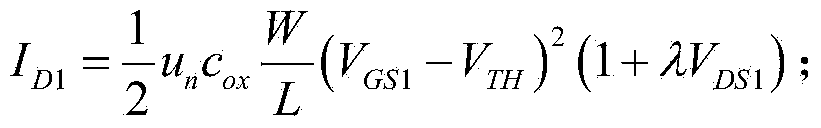Patents
Literature
78 results about "Channel length modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
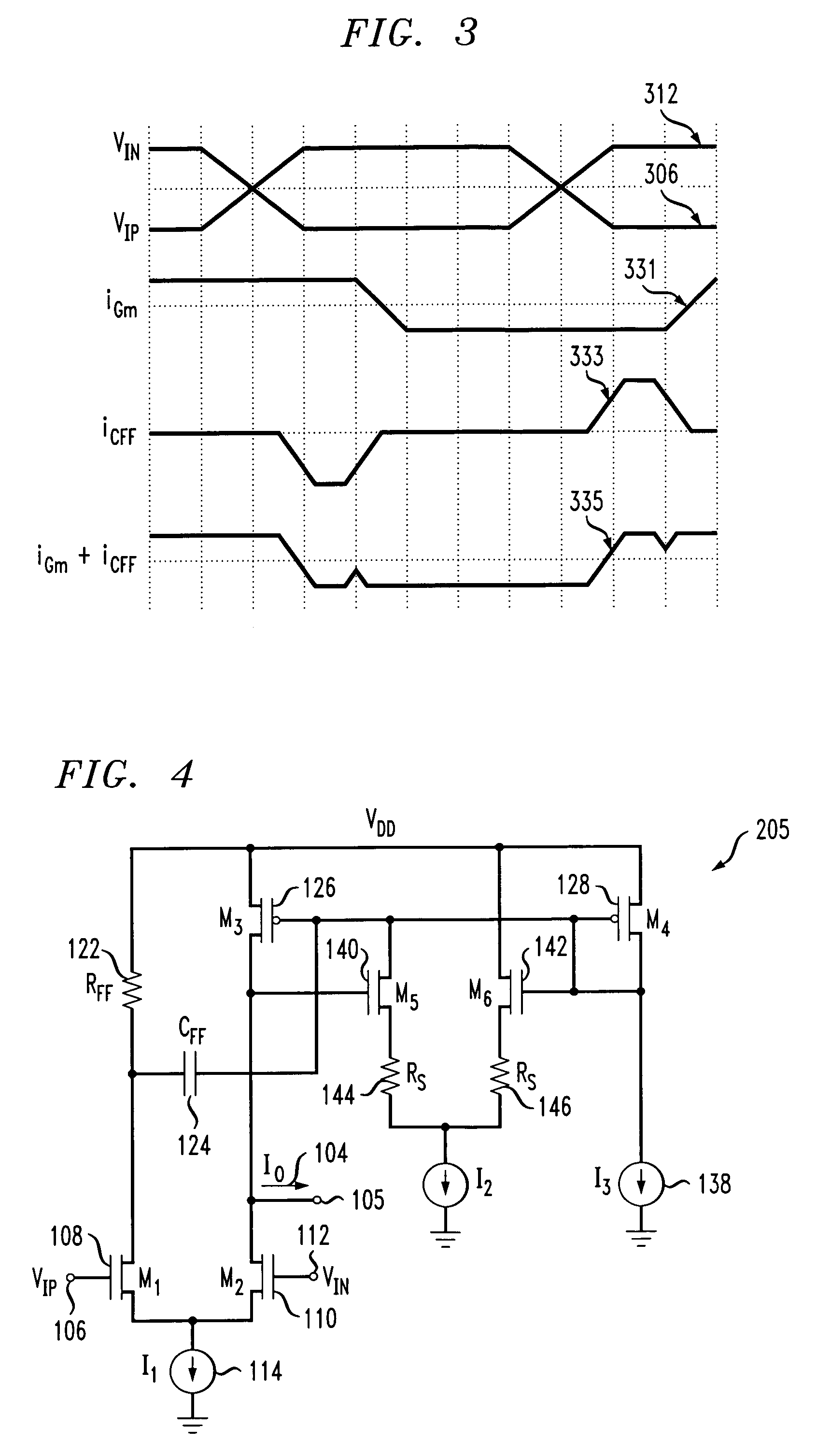
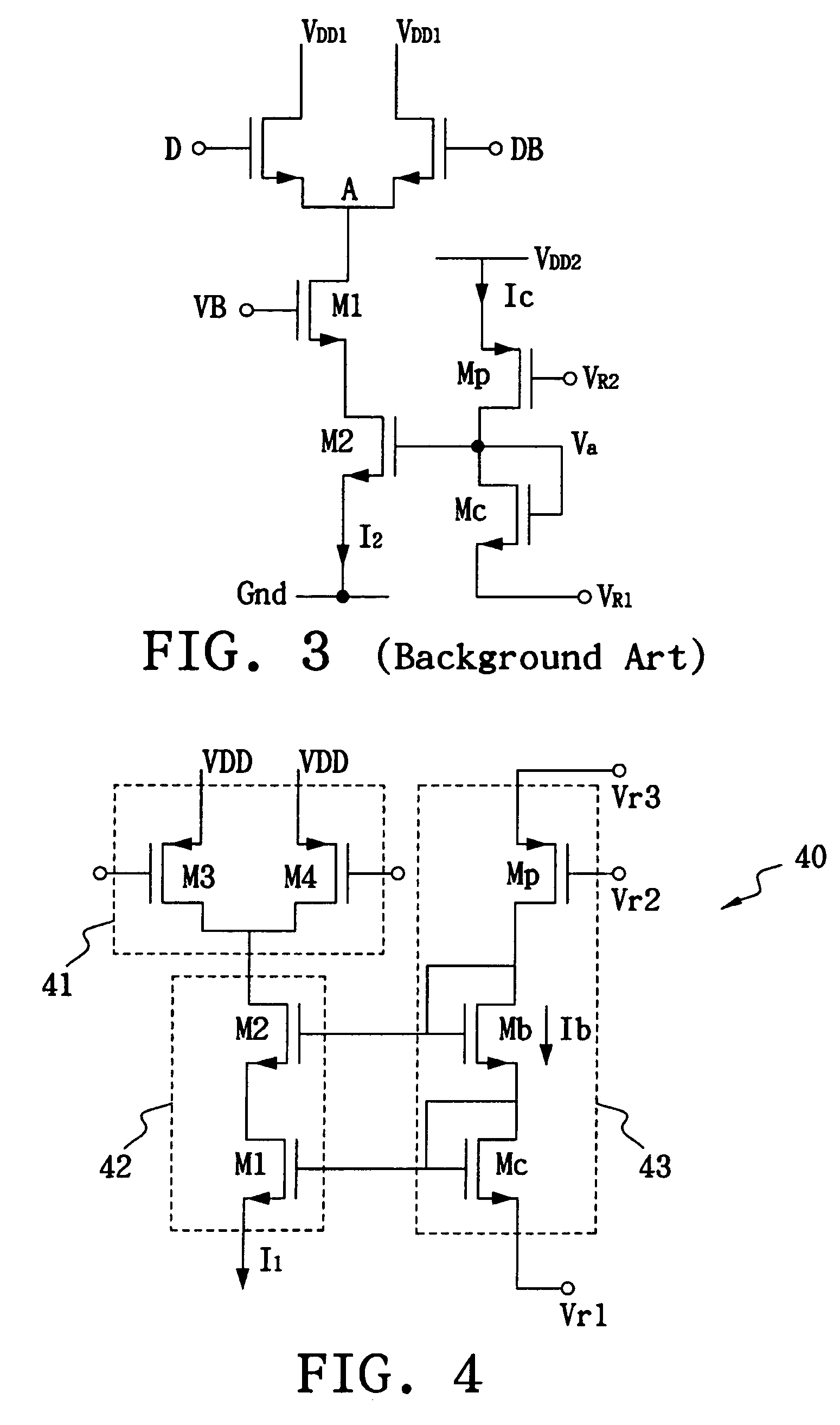
One of several short-channel effects in MOSFET scaling, channel length modulation (CLM) is a shortening of the length of the inverted channel region with increase in drain bias for large drain biases. The result of CLM is an increase in current with drain bias and a reduction of output resistance. Channel length modulation occurs in all field effect transistors, not just MOSFETs.
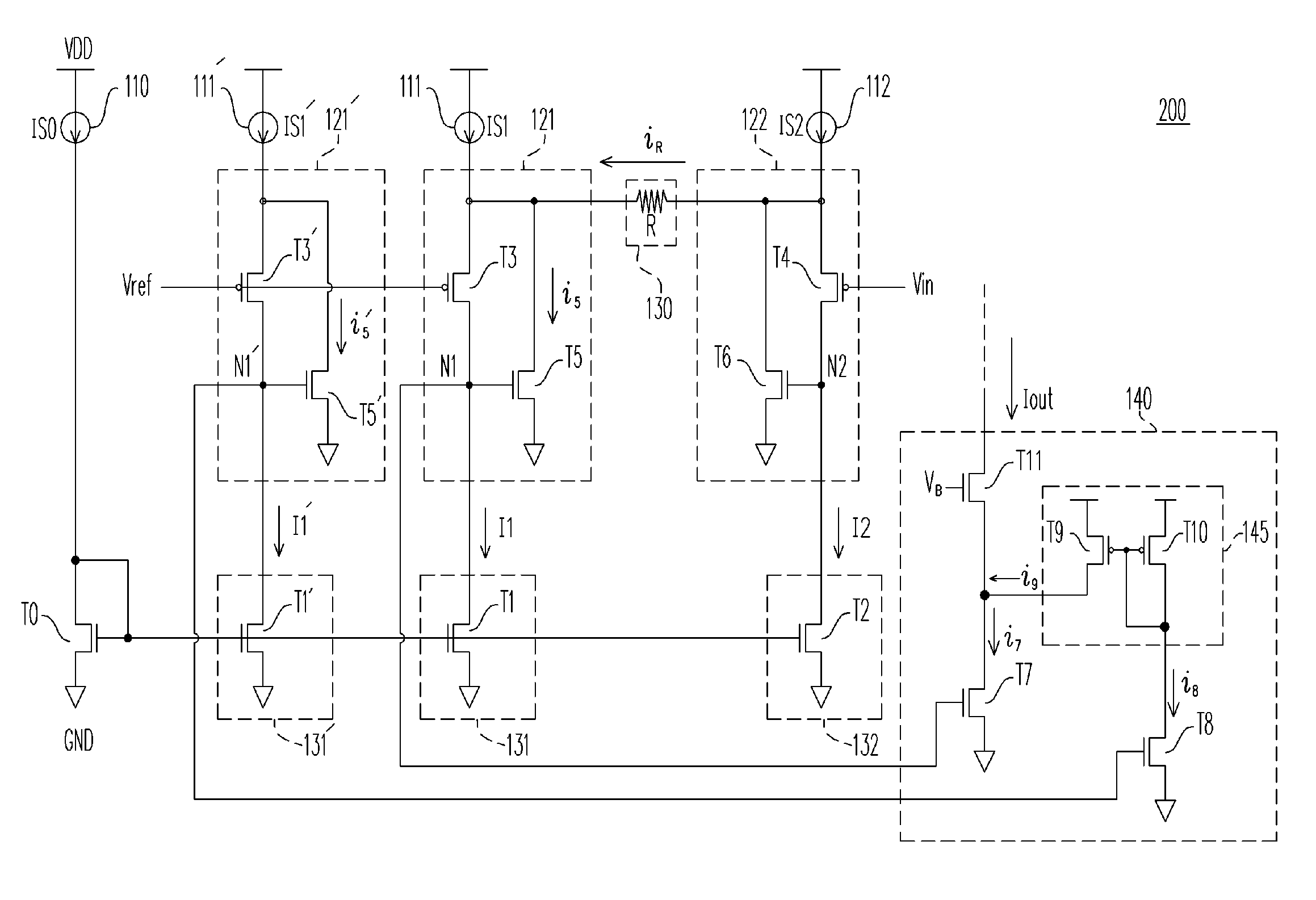
Electroluminescent display compensated drive signal
ActiveUS20100225634A1Increase the aperture ratioIncrease productionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingChannel length modulationDriving current
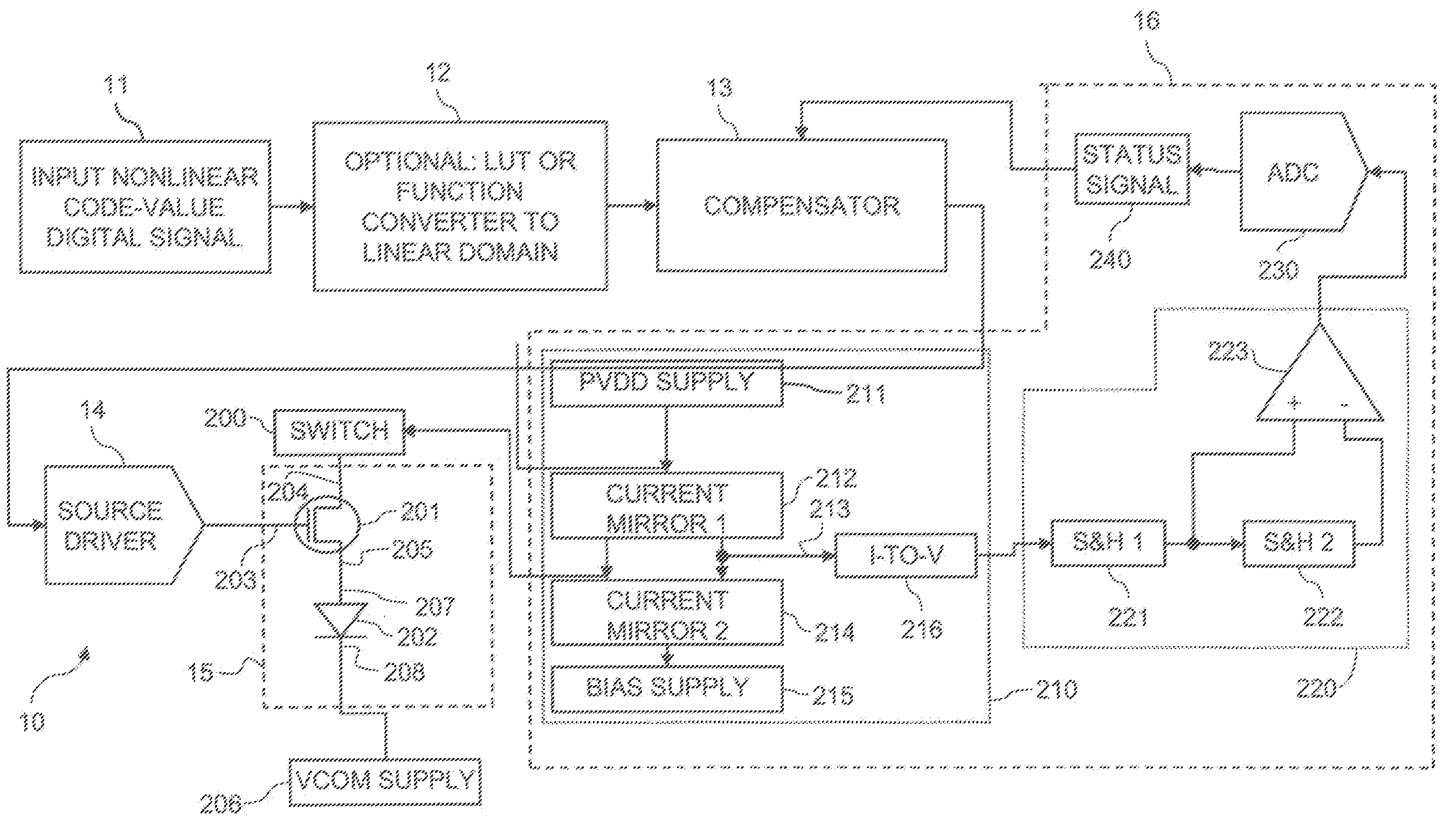
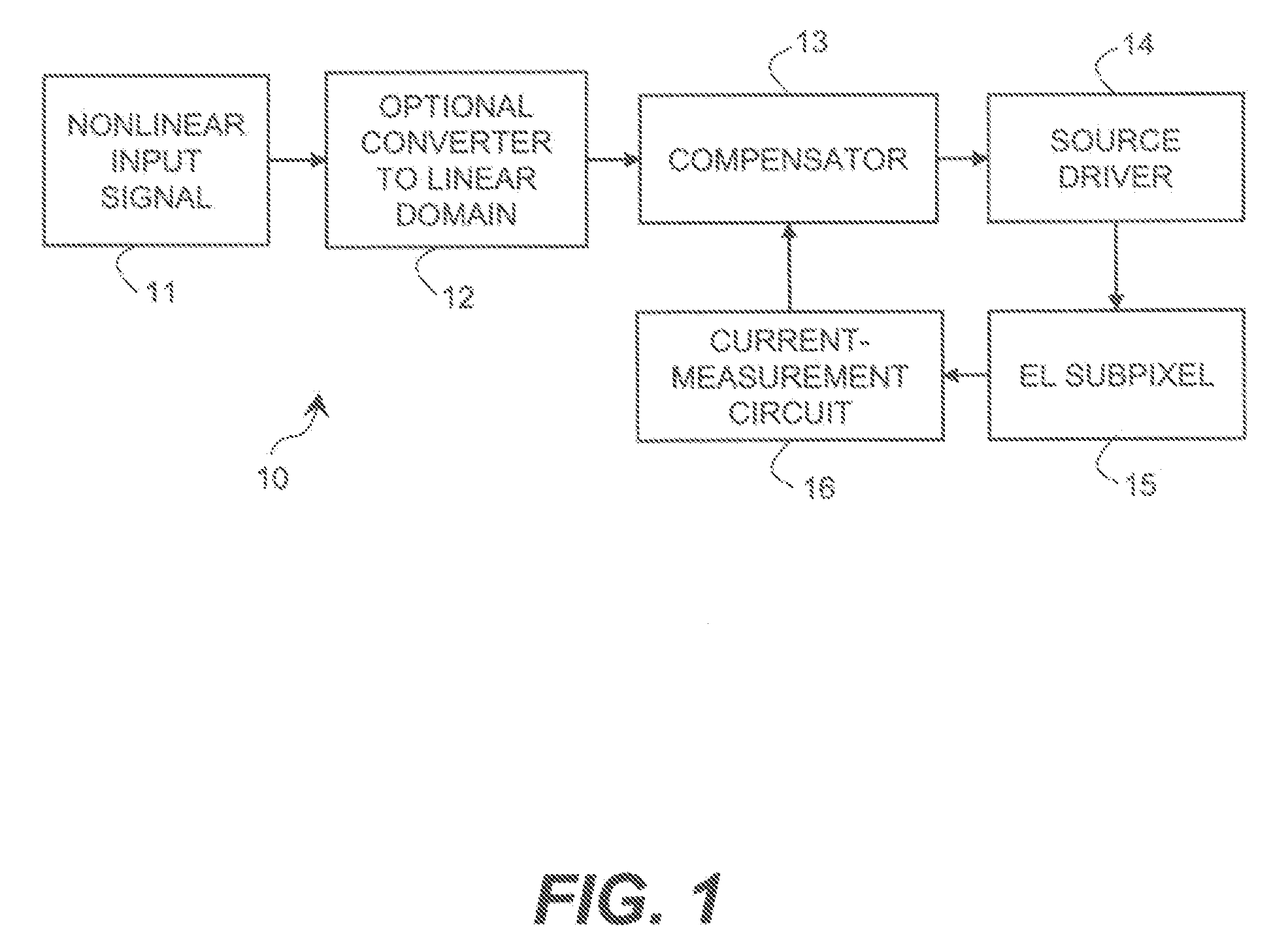
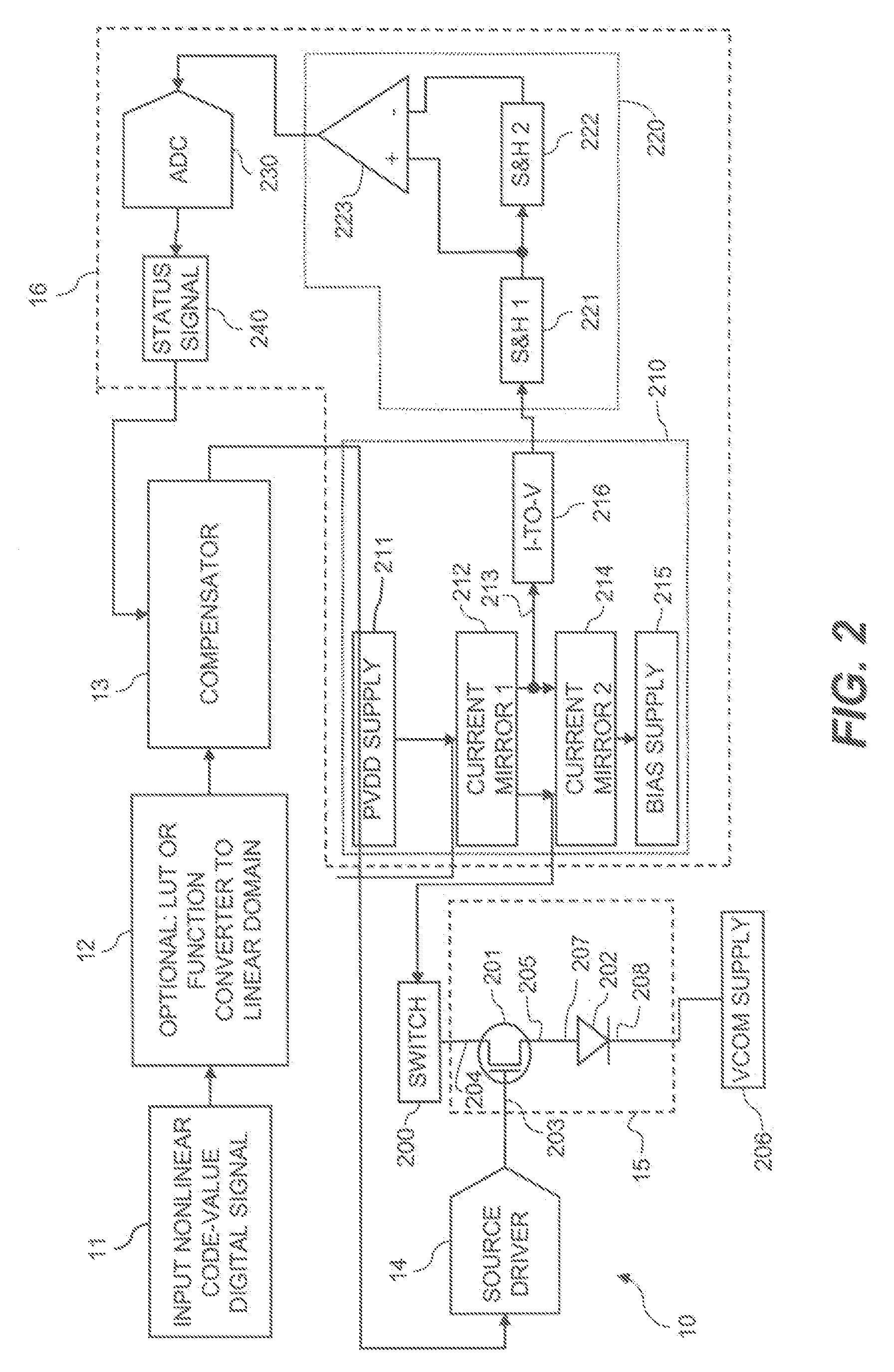
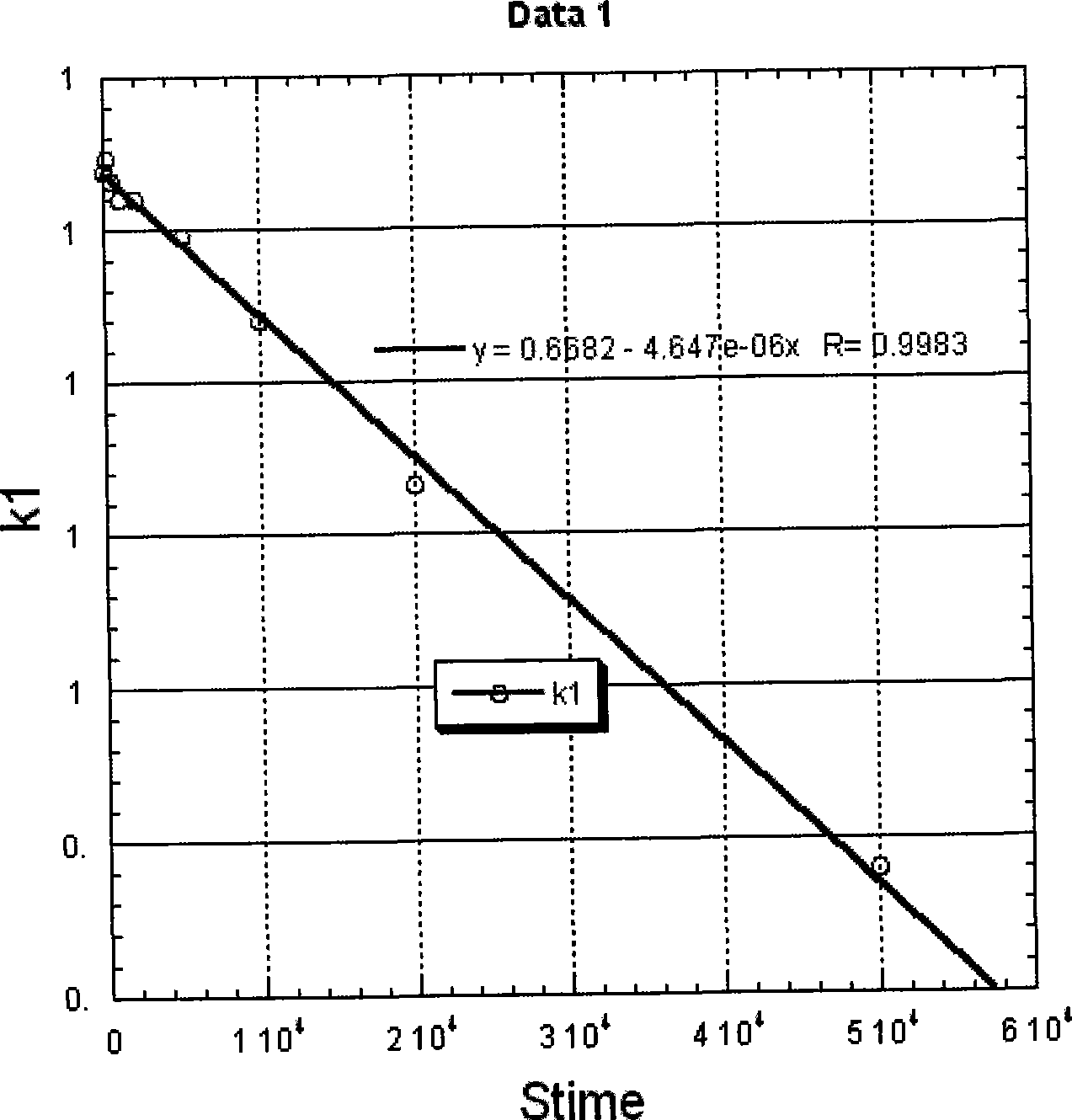
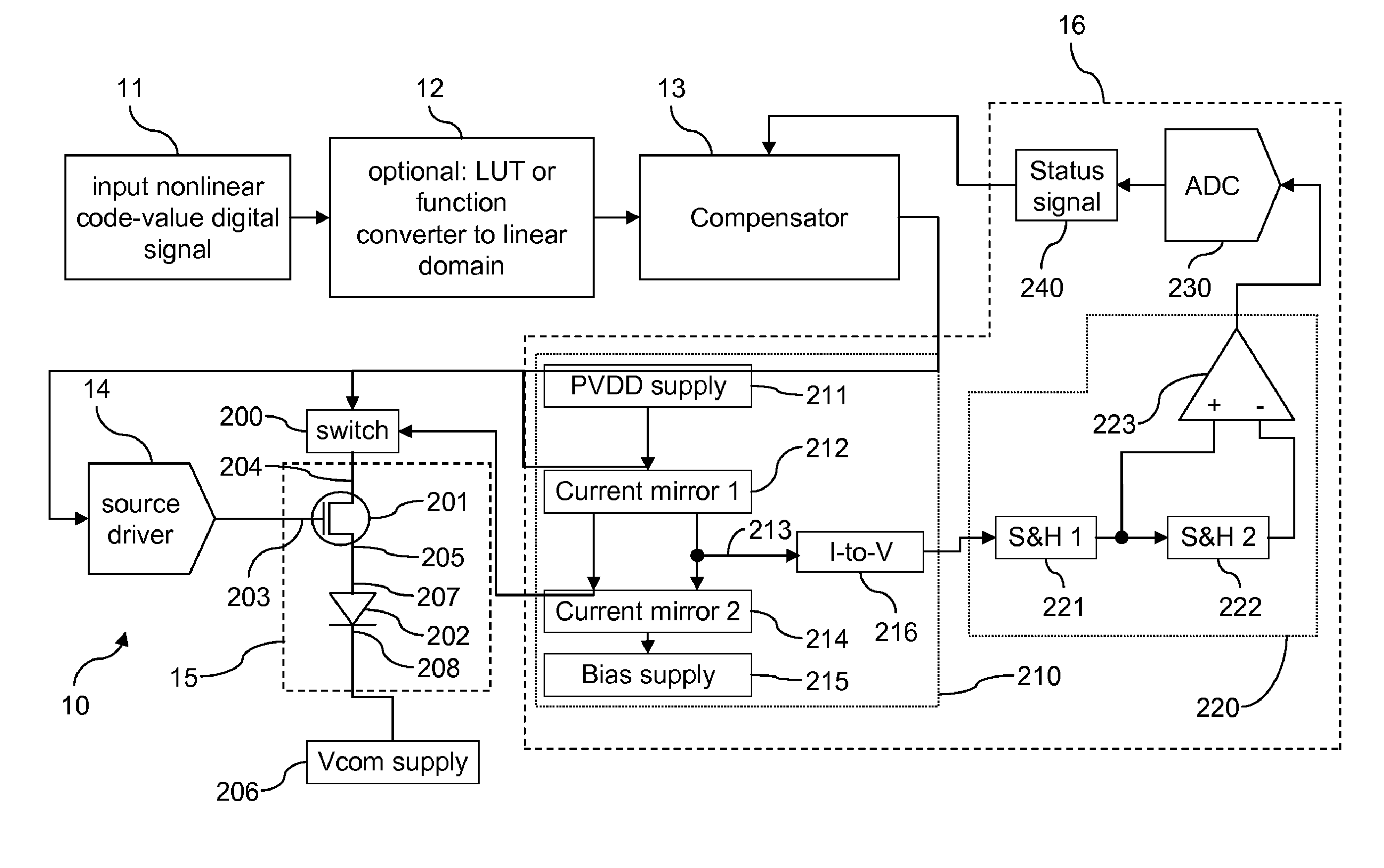
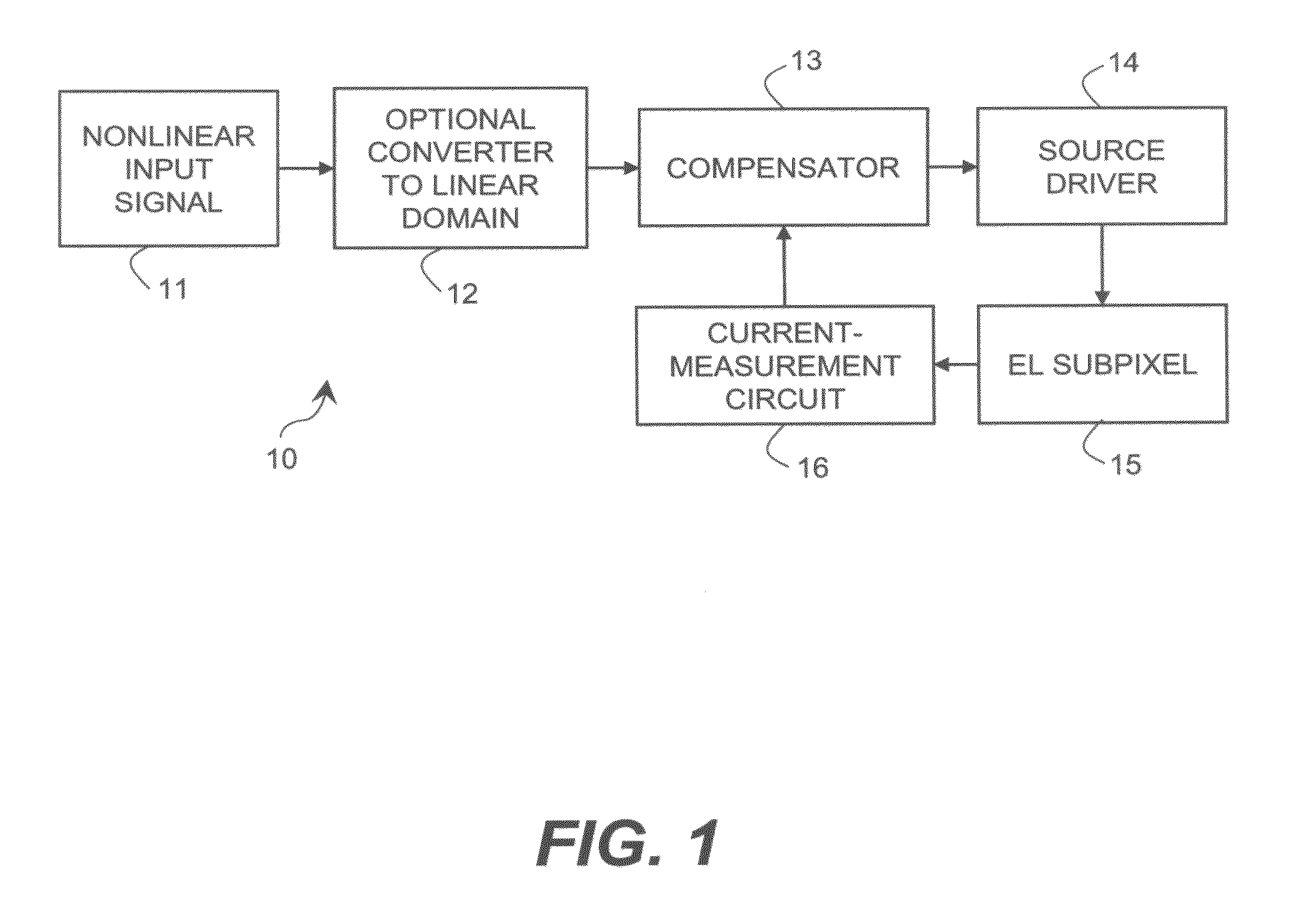
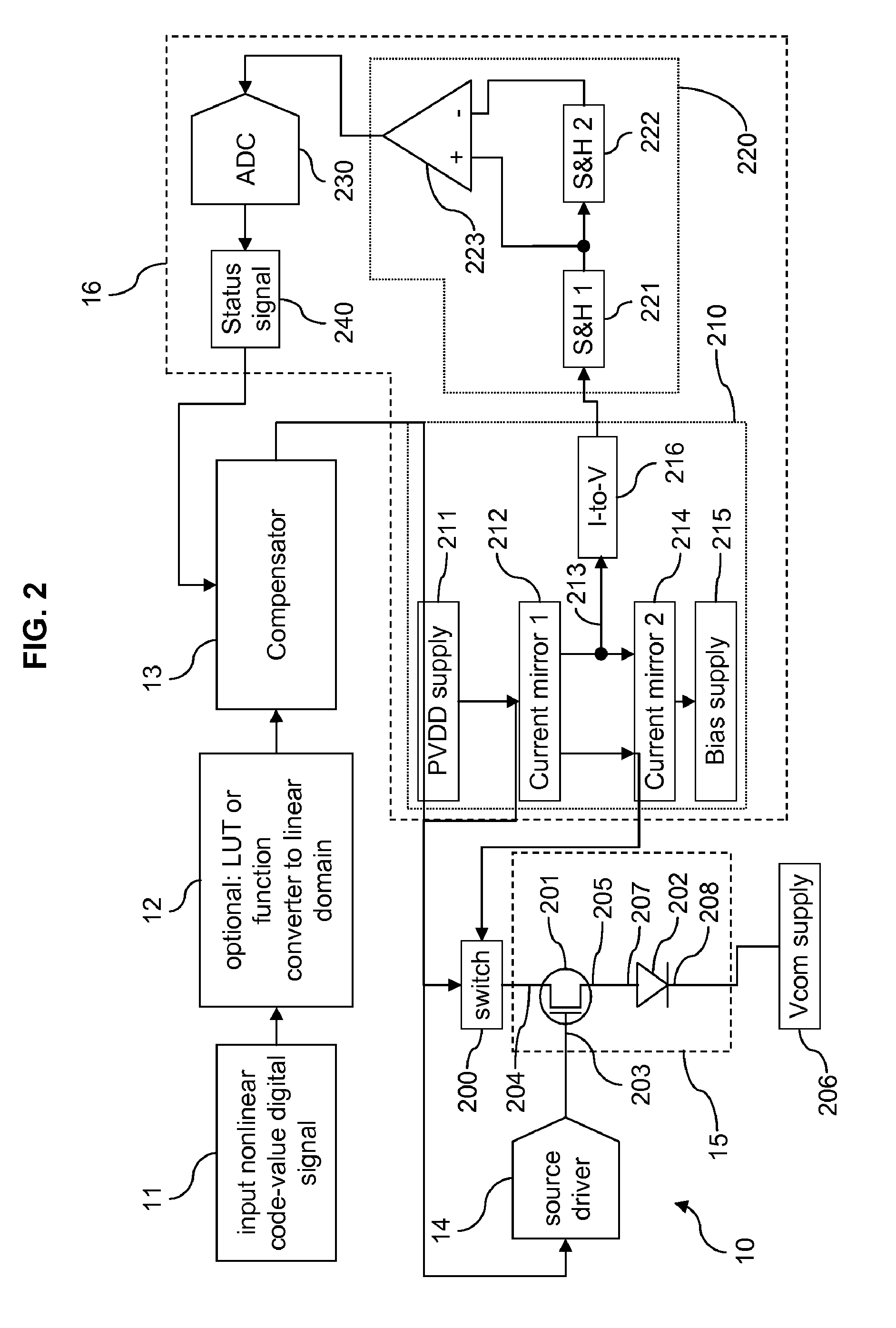
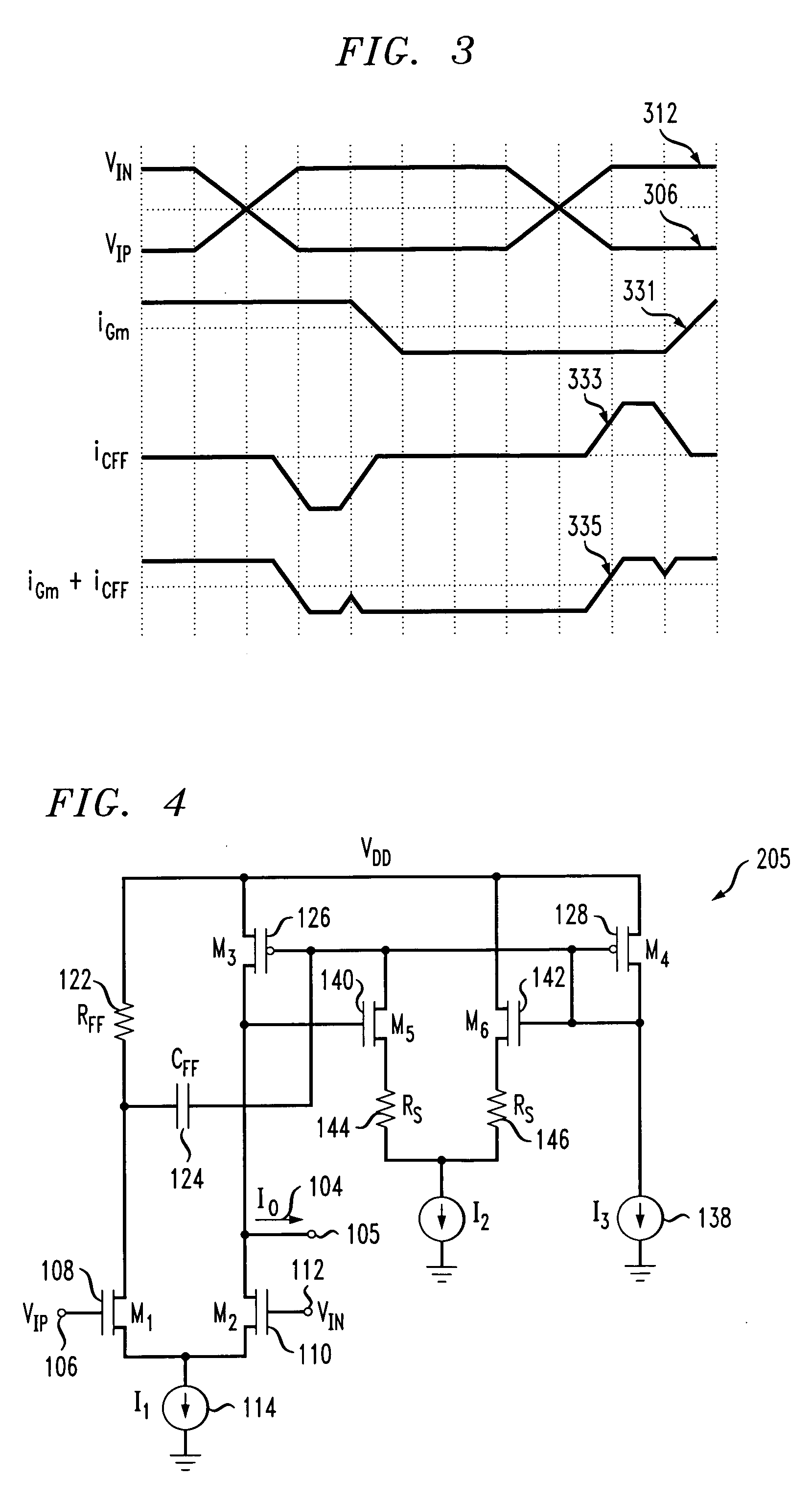
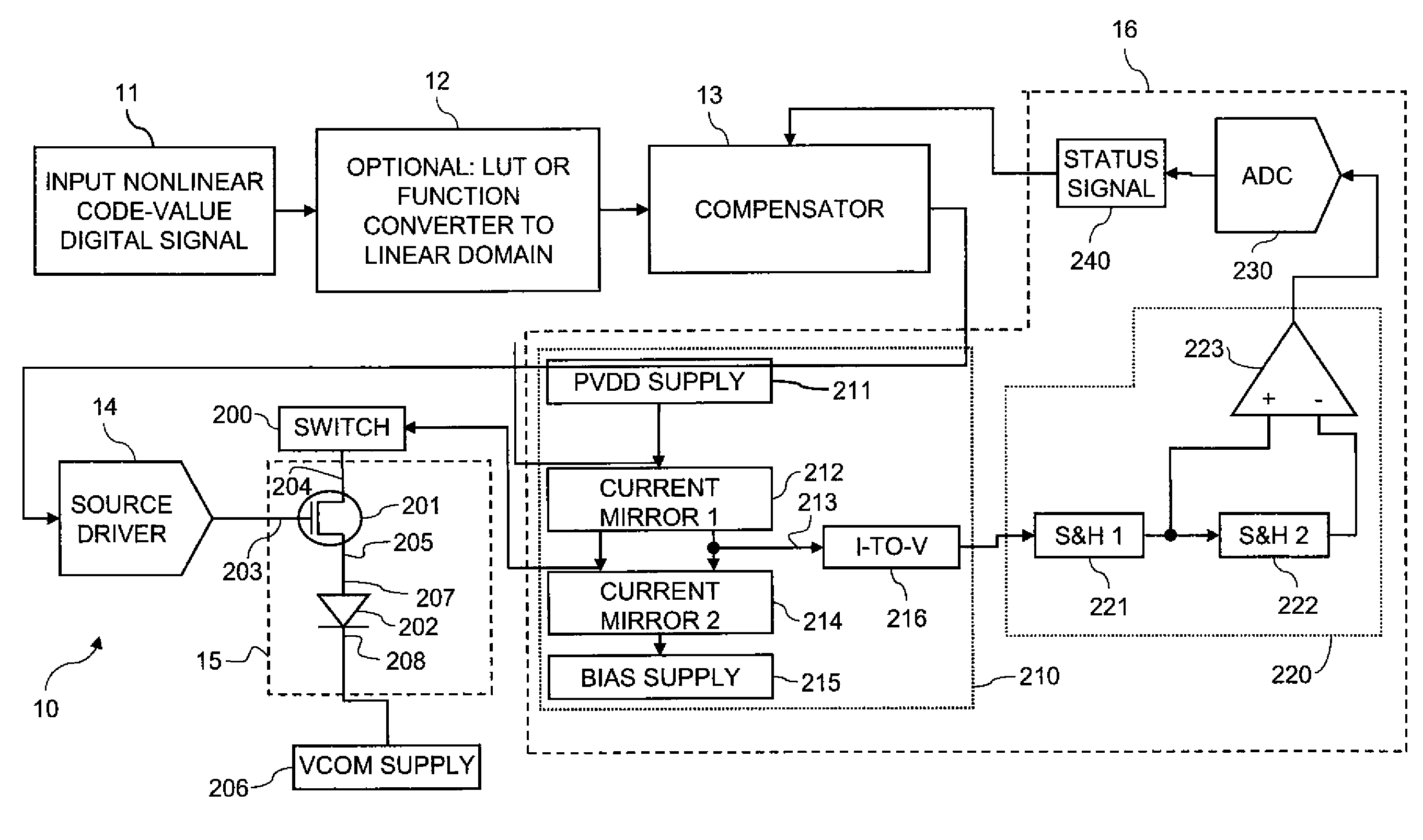
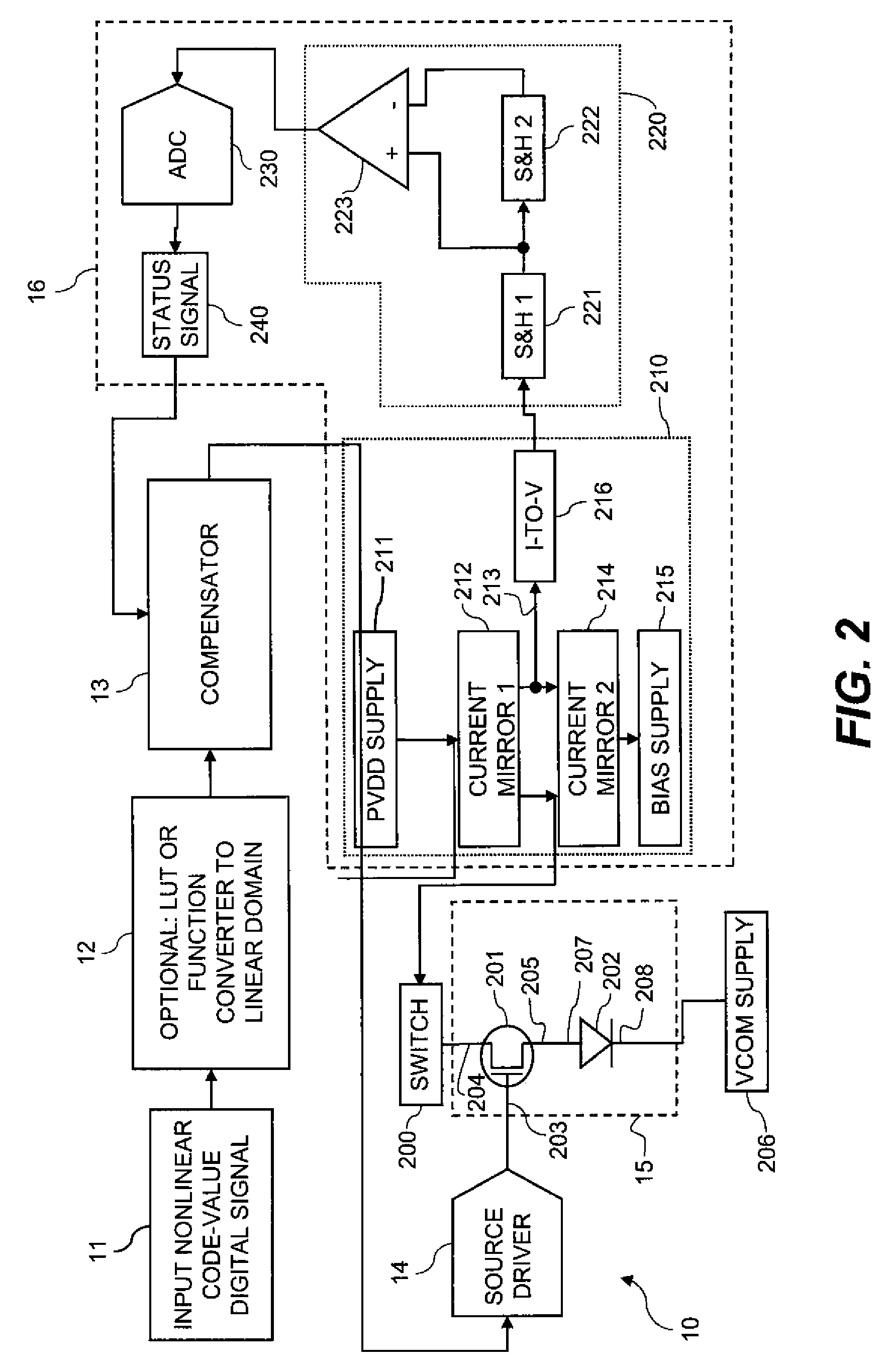
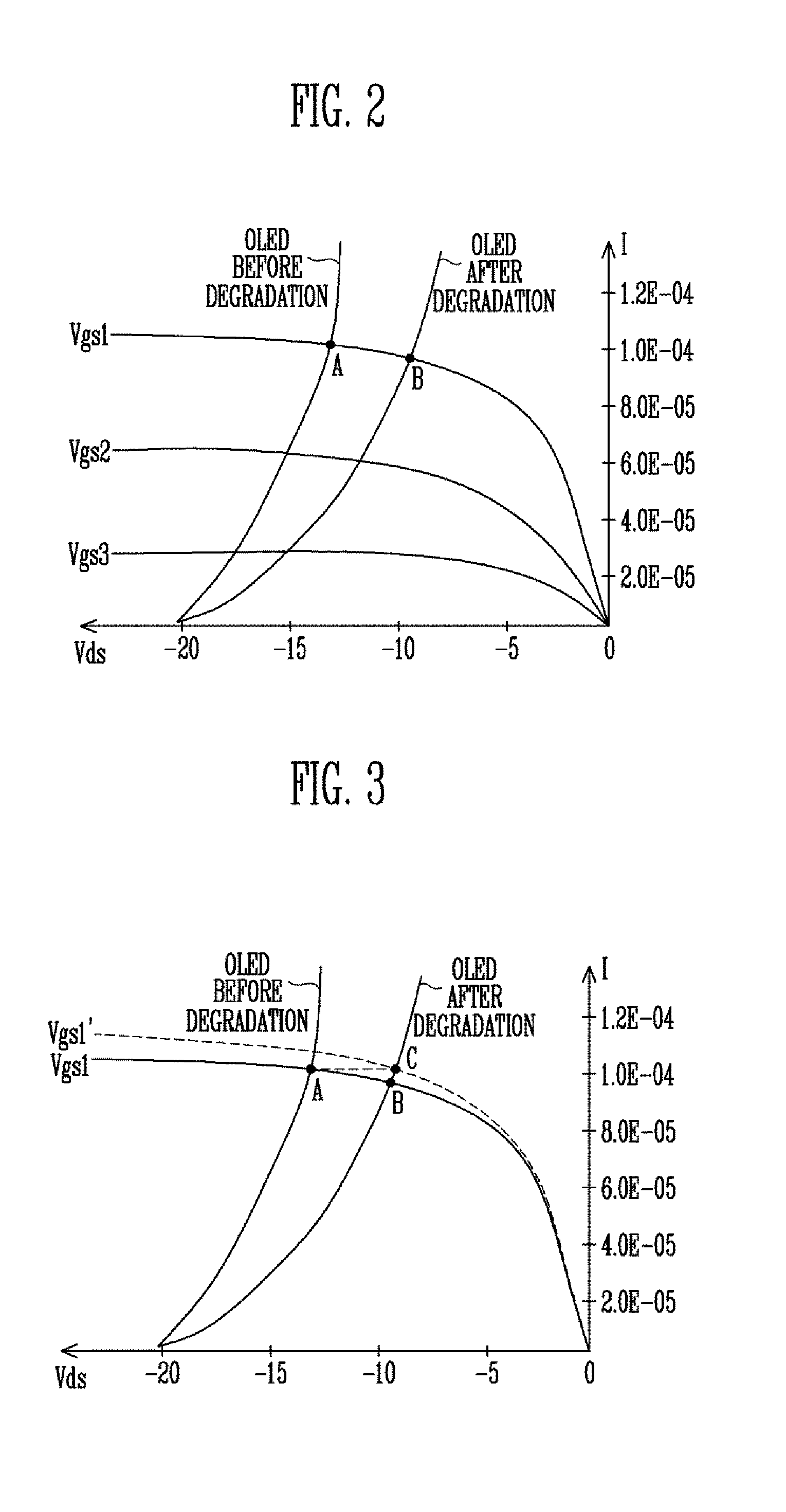
Subpixels on an electroluminescent (EL) display panel, such as an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) panel, are compensated for initial nonuniformity (“mura”) and for aging effects such as threshold voltage Vth shift, EL voltage Voled shift, and OLED efficiency loss. The drive current of each subpixel is measured at one or more measurement reference gate voltages to form status signals representing the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL emitter of those subpixels. Current measurements are taken in the linear region of drive transistor operation to improve signal-to-noise ratio in systems such as modern LTPS PMOS OLED displays, which have relatively small Voled shift over their lifetimes and thus relatively small current change due to channel-length modulation. Various sources of noise are also suppressed to further increase signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
High frequency power amplifier circuit and electronic component for high frequency power amplifier
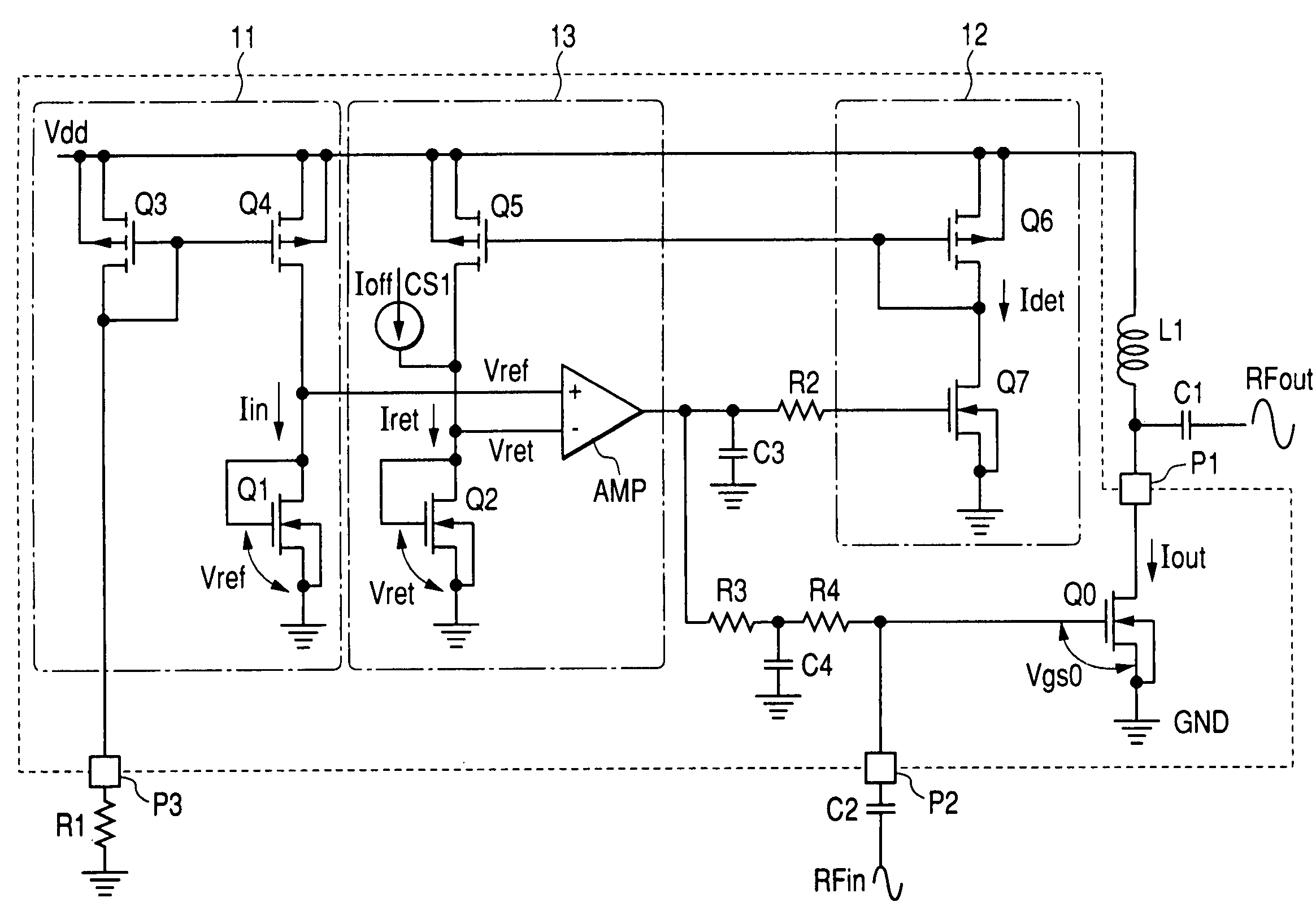
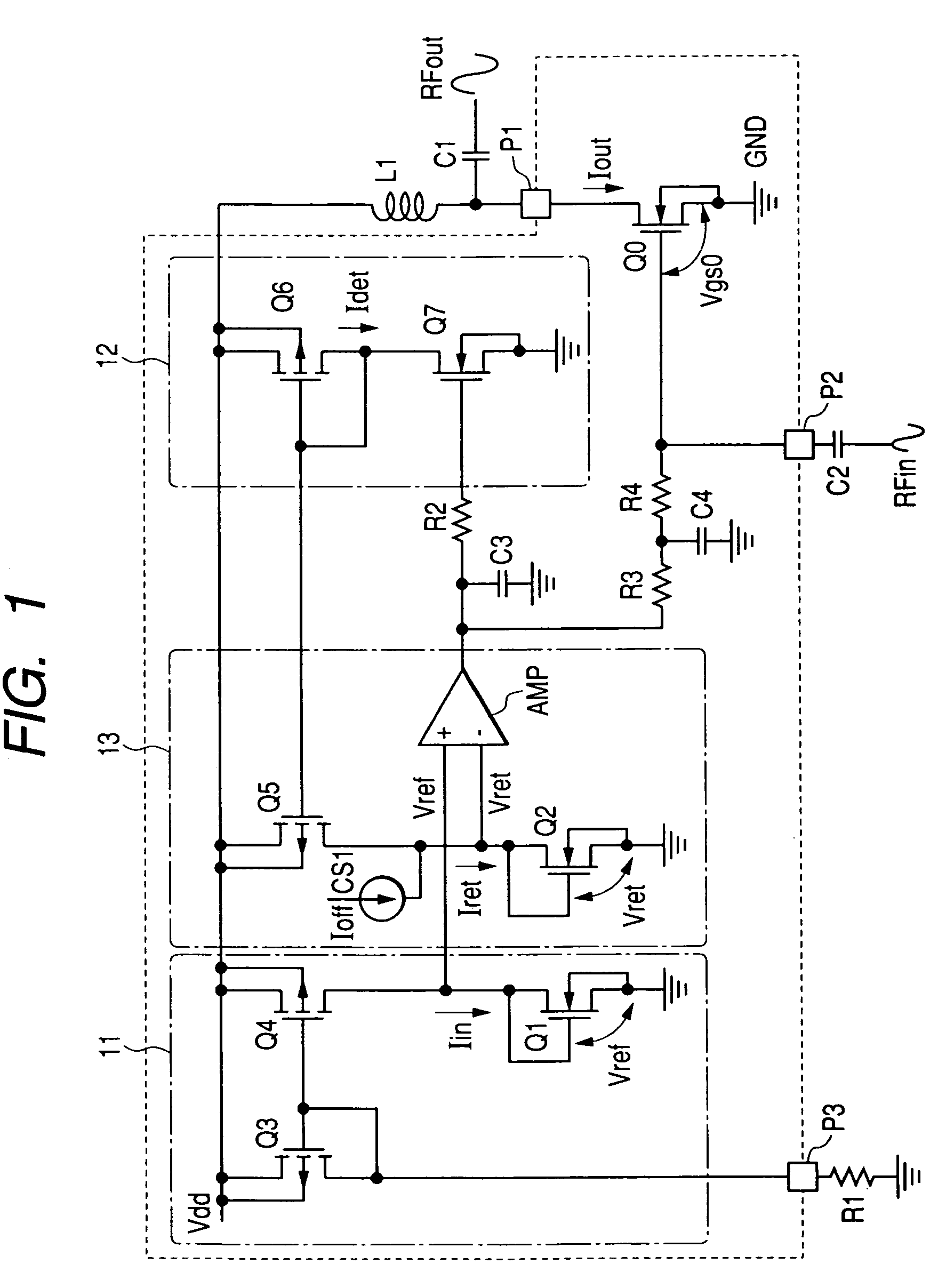
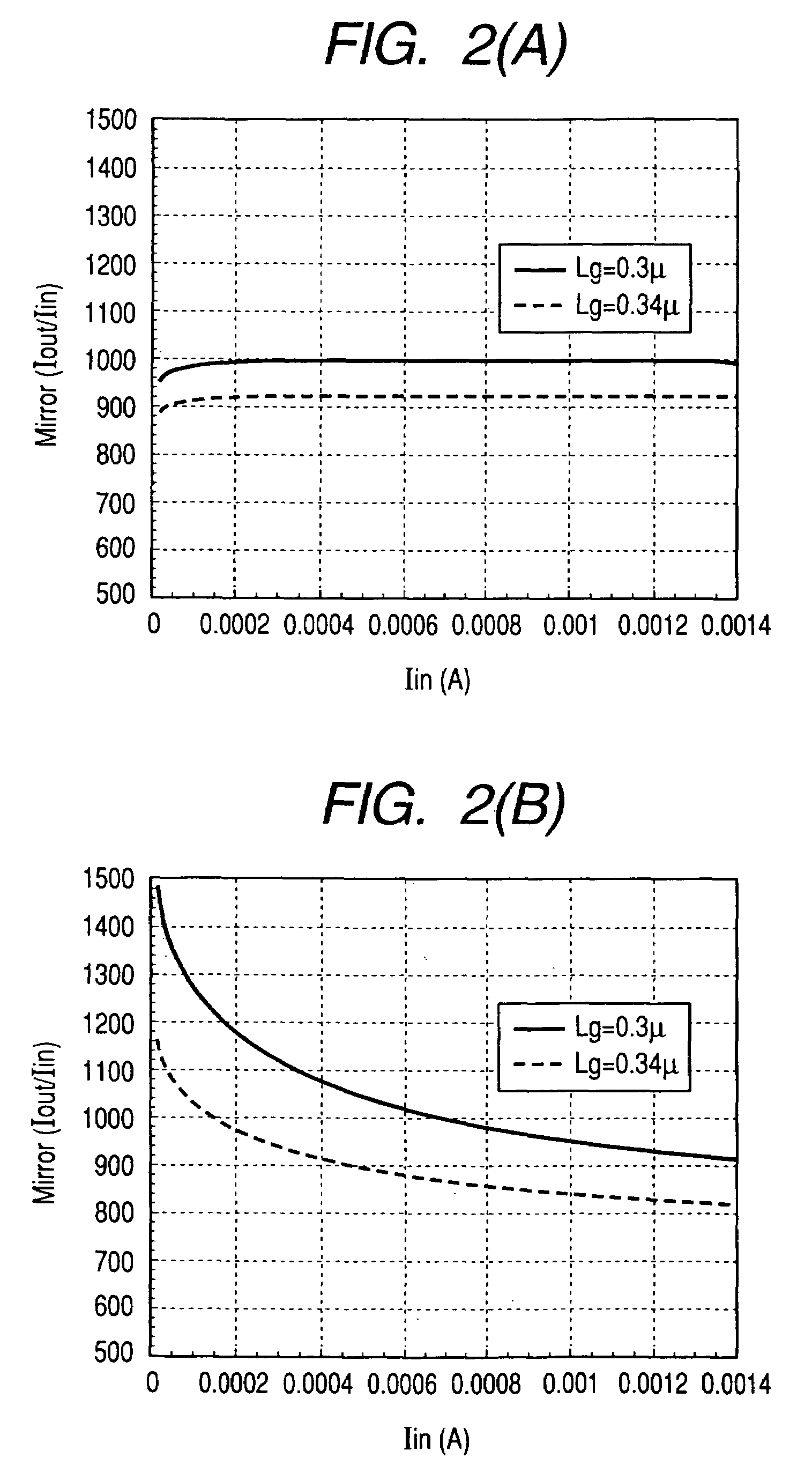
ActiveUS20050083129A1Avoid short channel effectsReduce widthGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationChannel length modulationAudio power amplifier
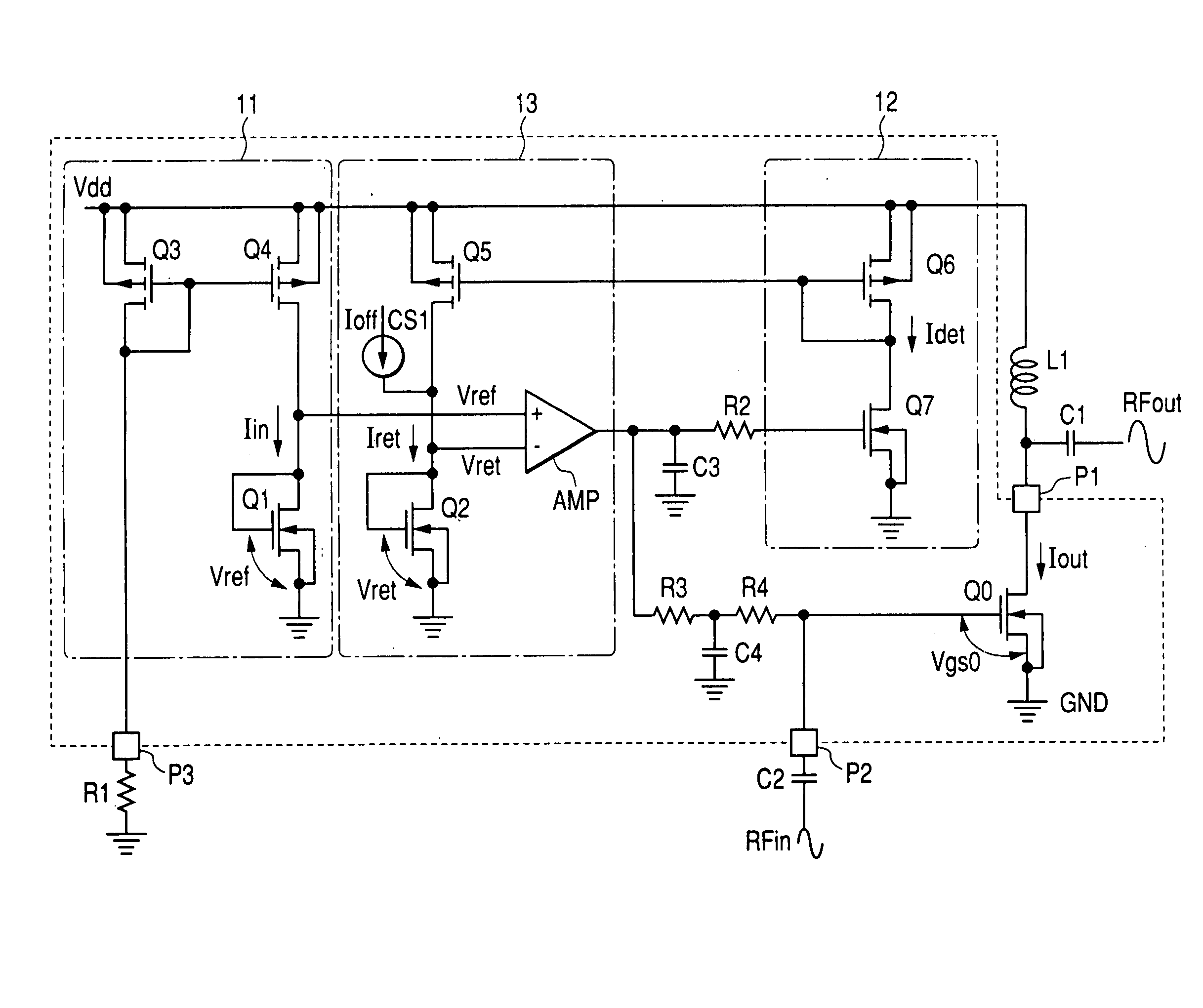
In a high frequency power amplifier circuit that supplies a bias to an amplifying FET by a current mirror method, scattering of a threshold voltage Vth due to the scattering of the channel impurity concentration of the FET, and a shift of a bias point caused by the scattering of the threshold voltage Vth and a channel length modulation coefficient λ due to a short channel effect are corrected automatically. The scattering of a high frequency power amplifying characteristic can be reduced as a result.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
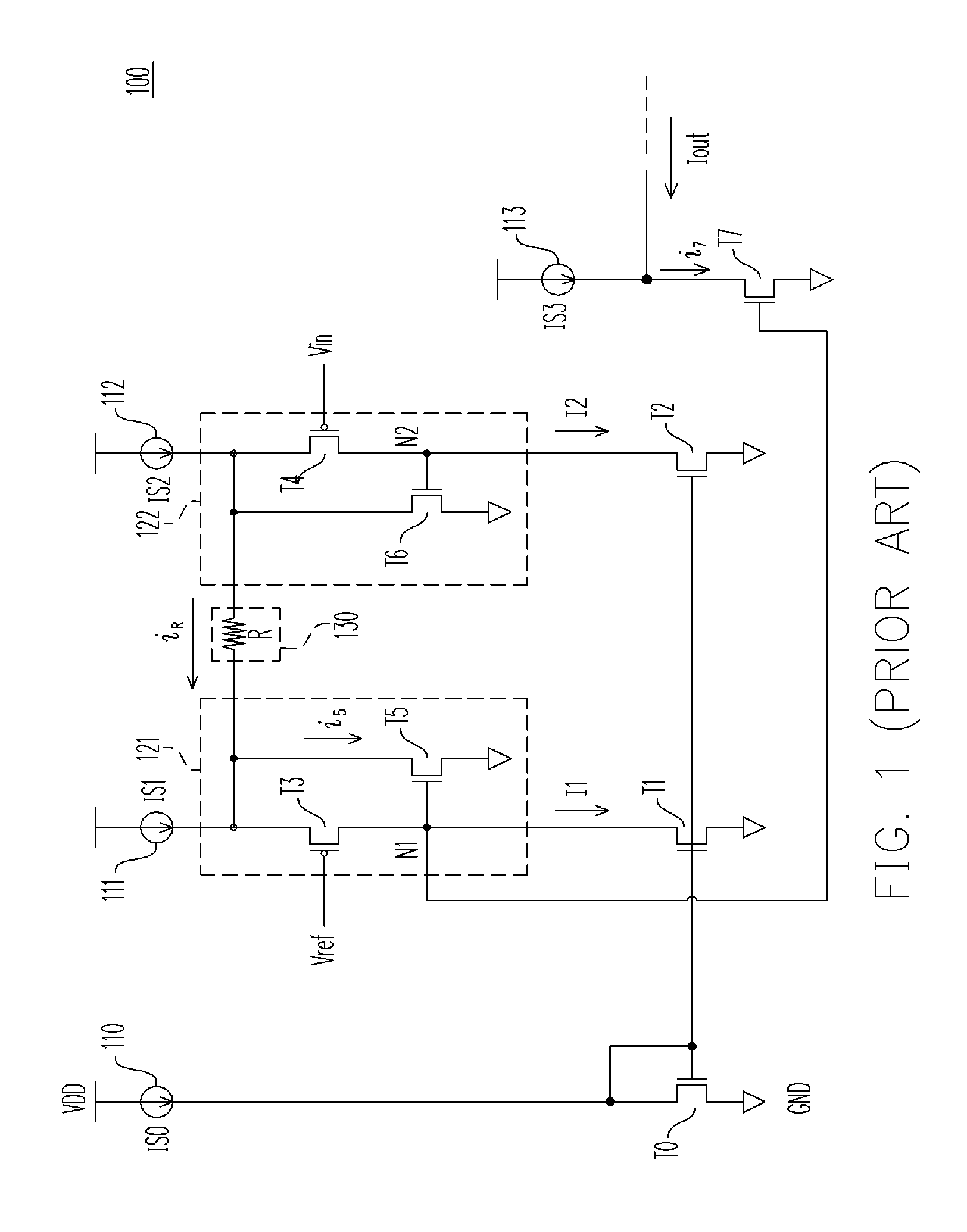
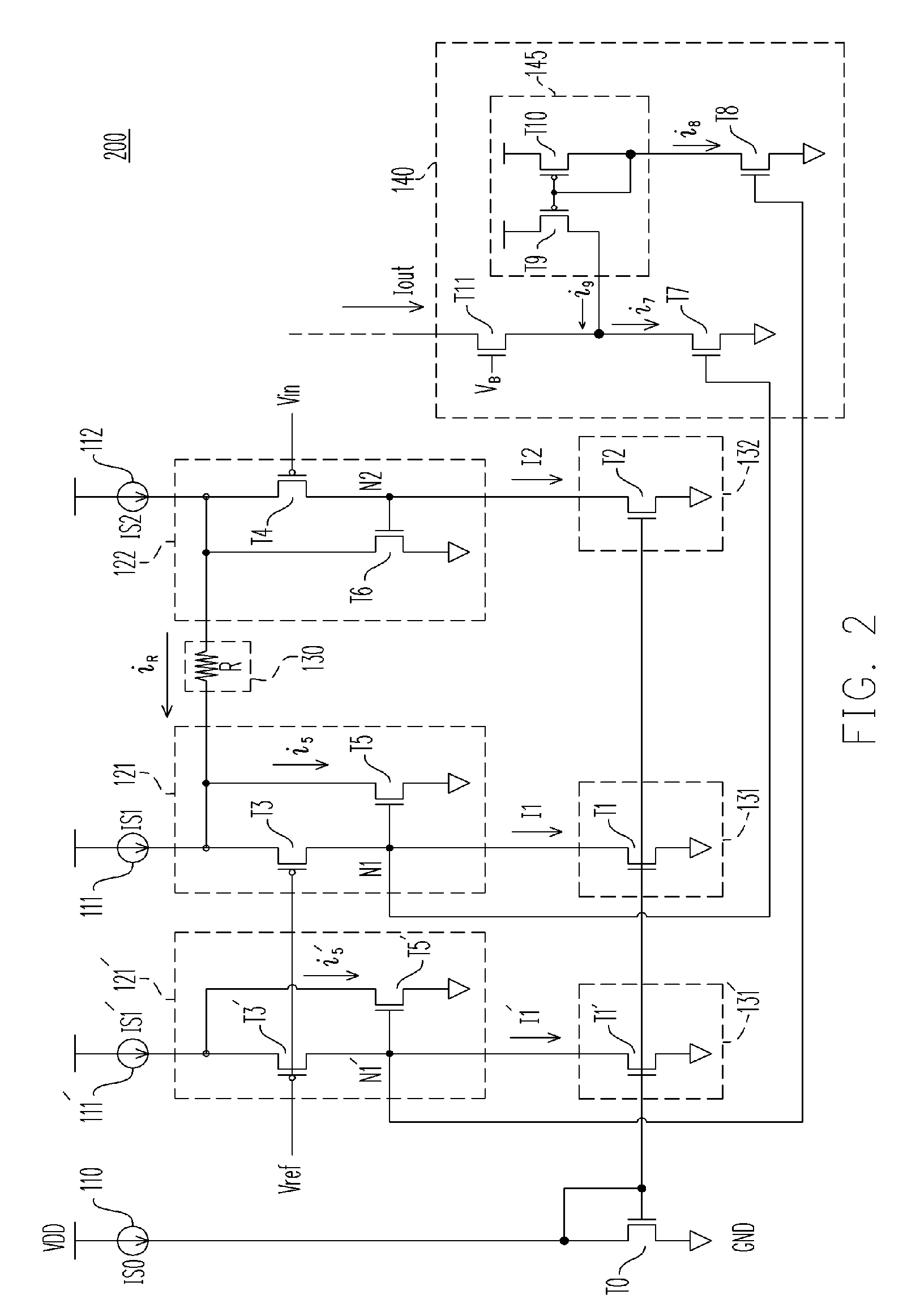
Method and apparatus for providing a modulation current
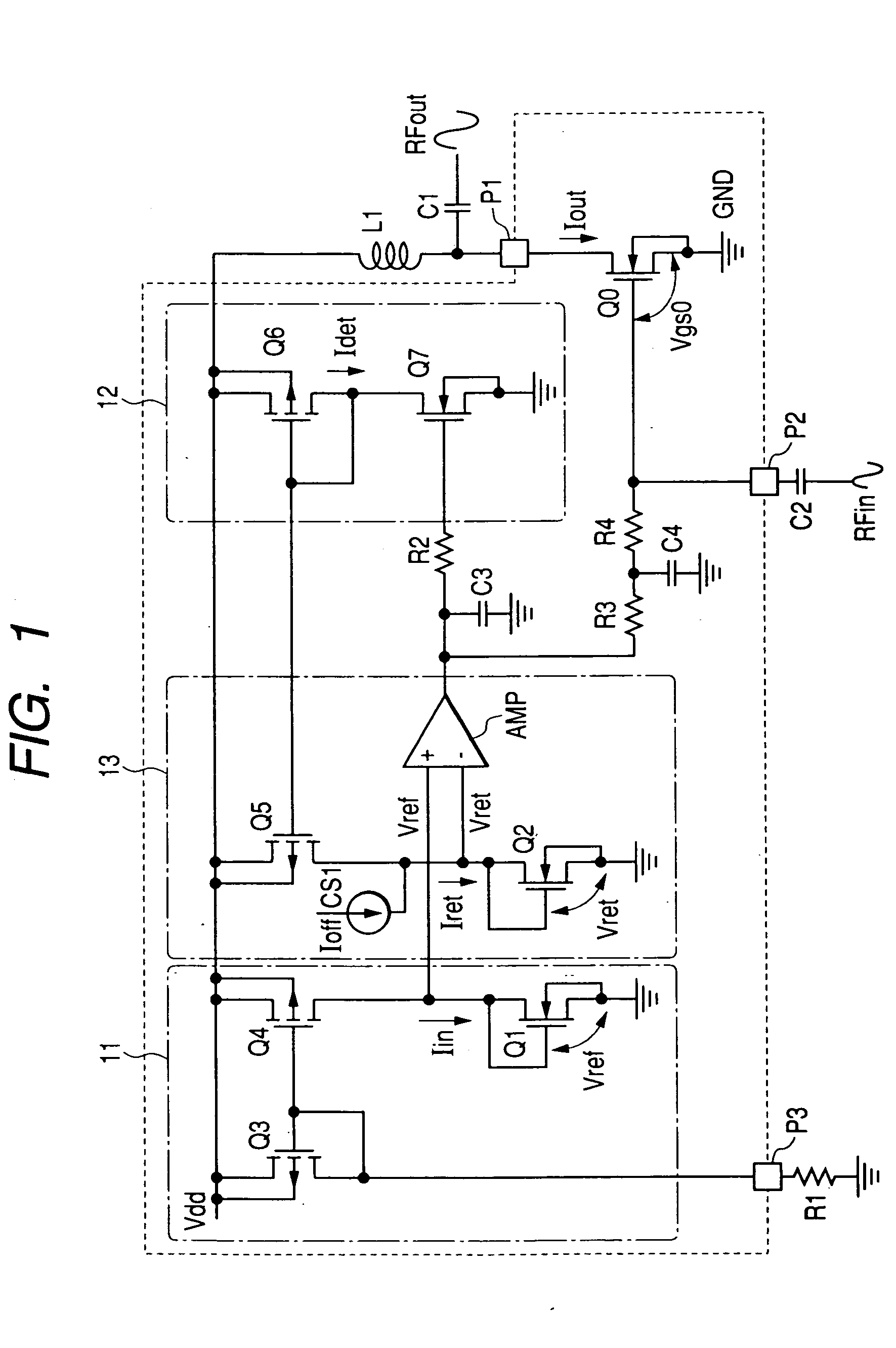
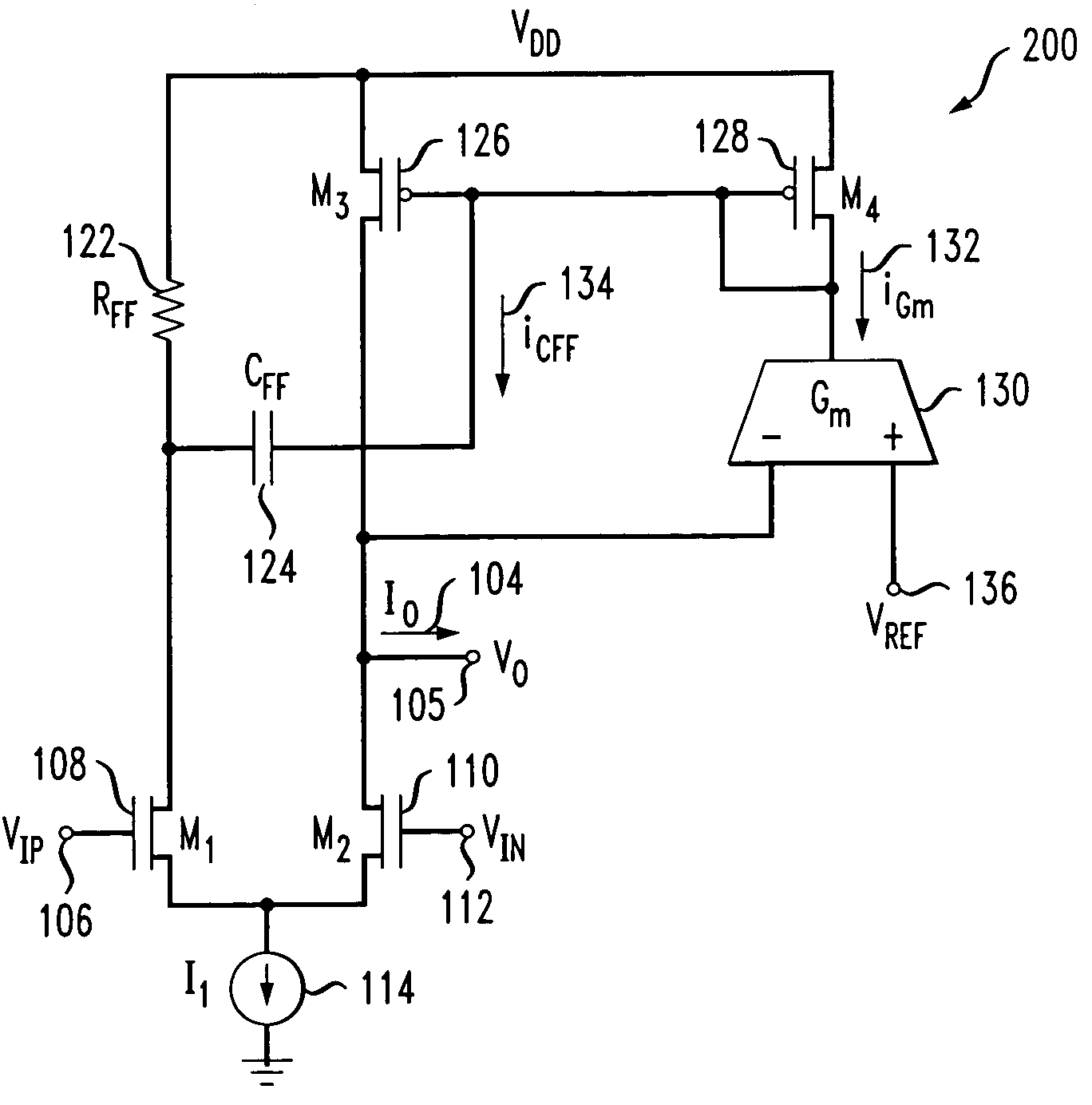
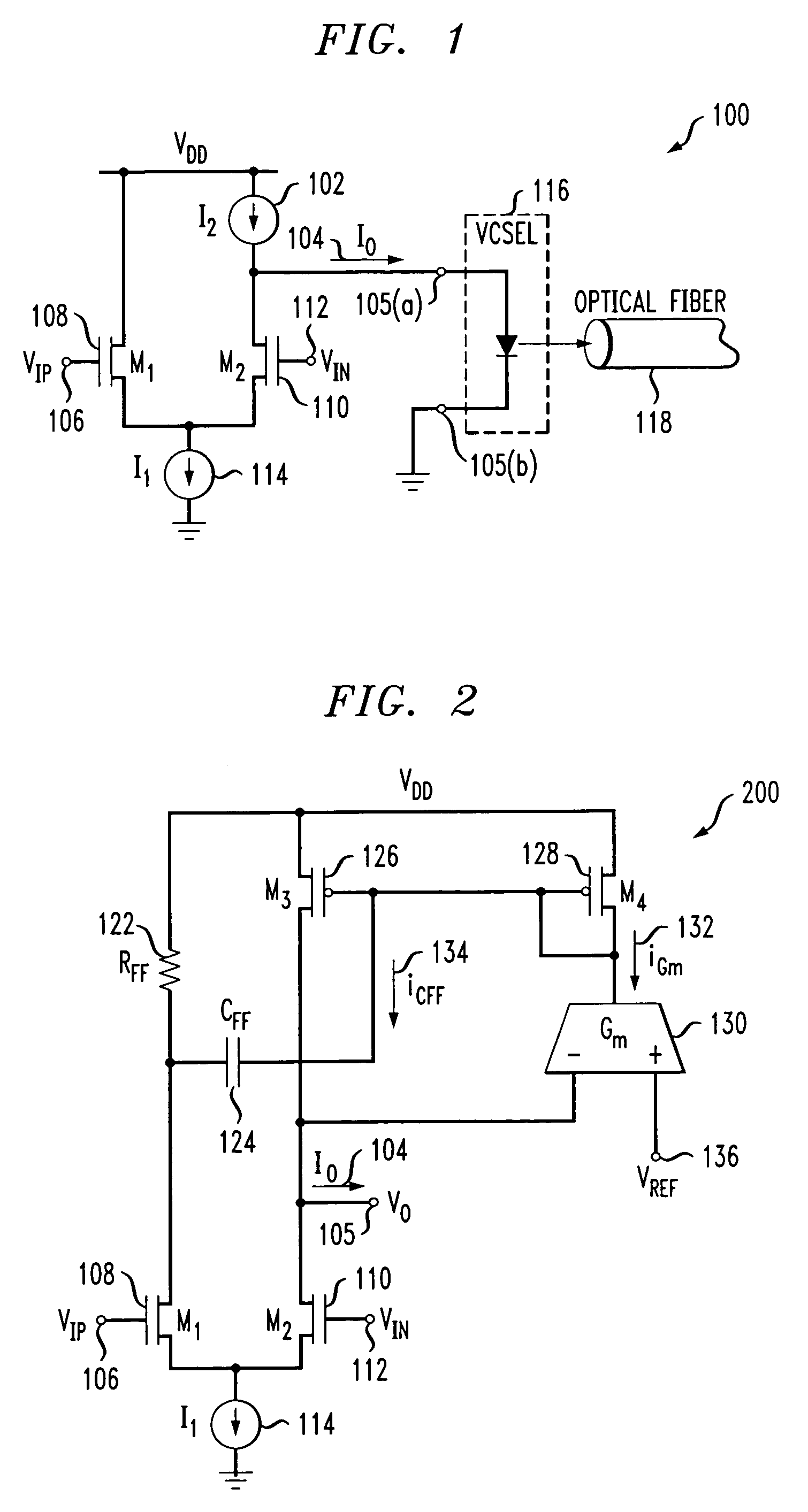
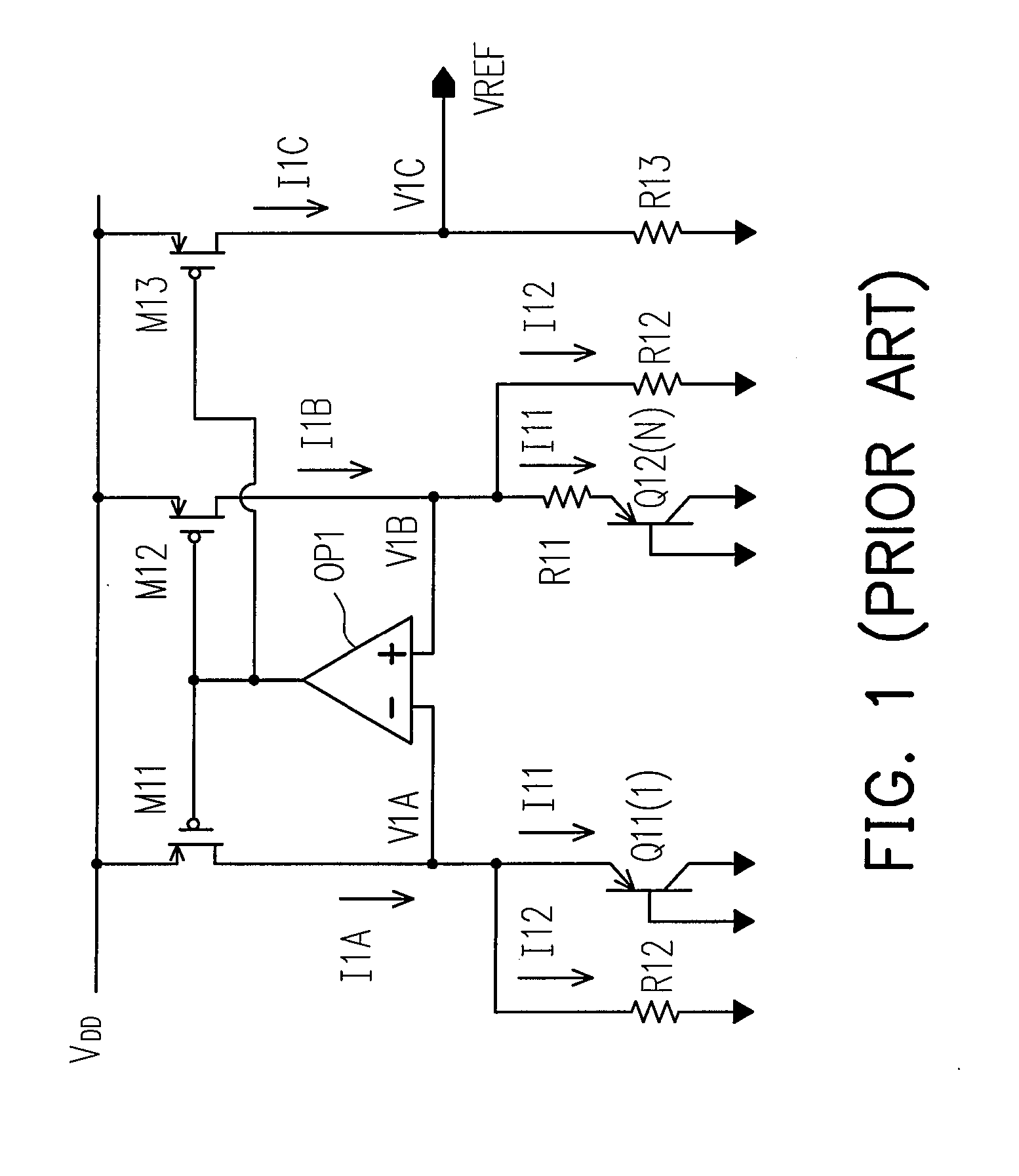
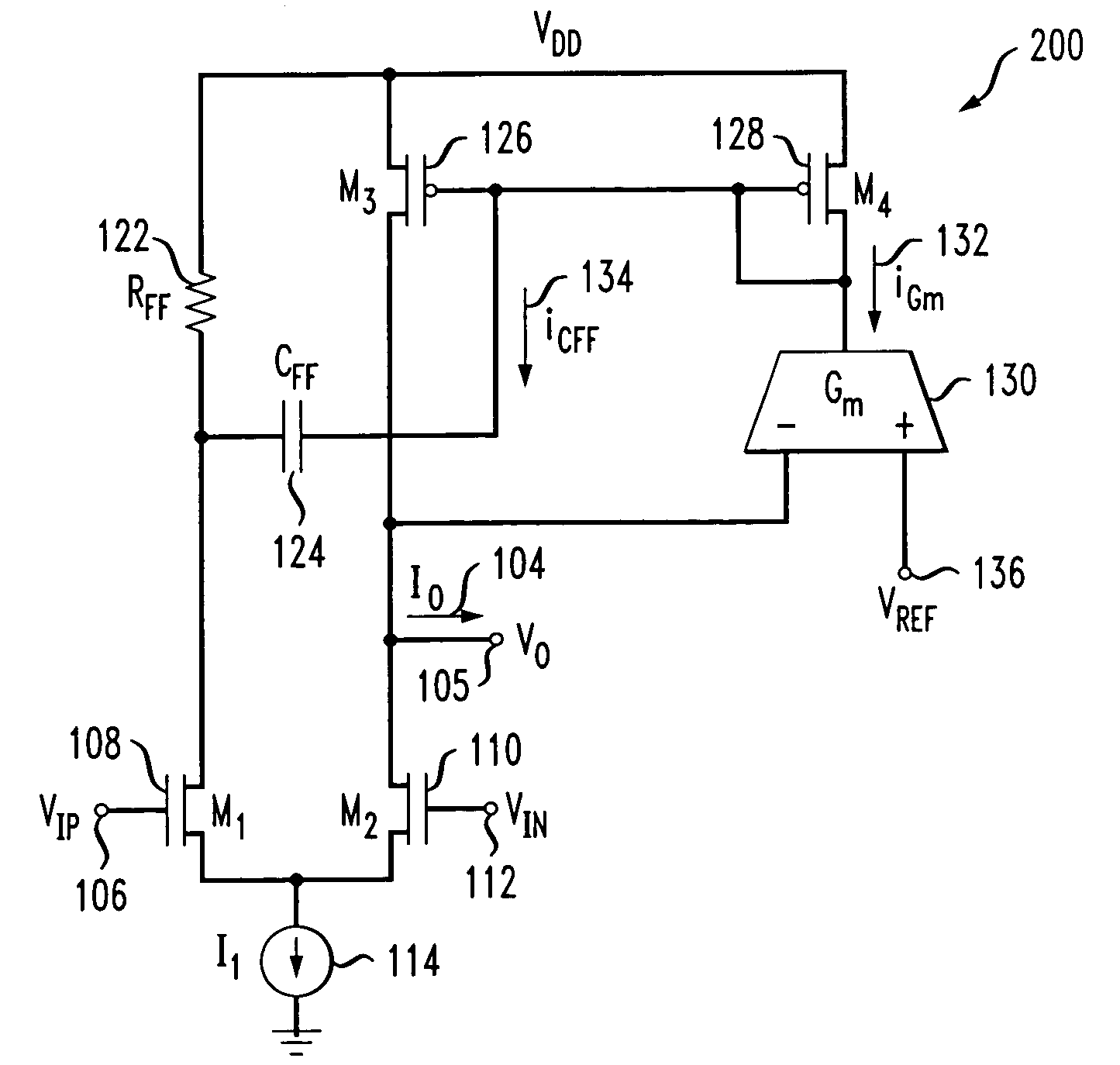
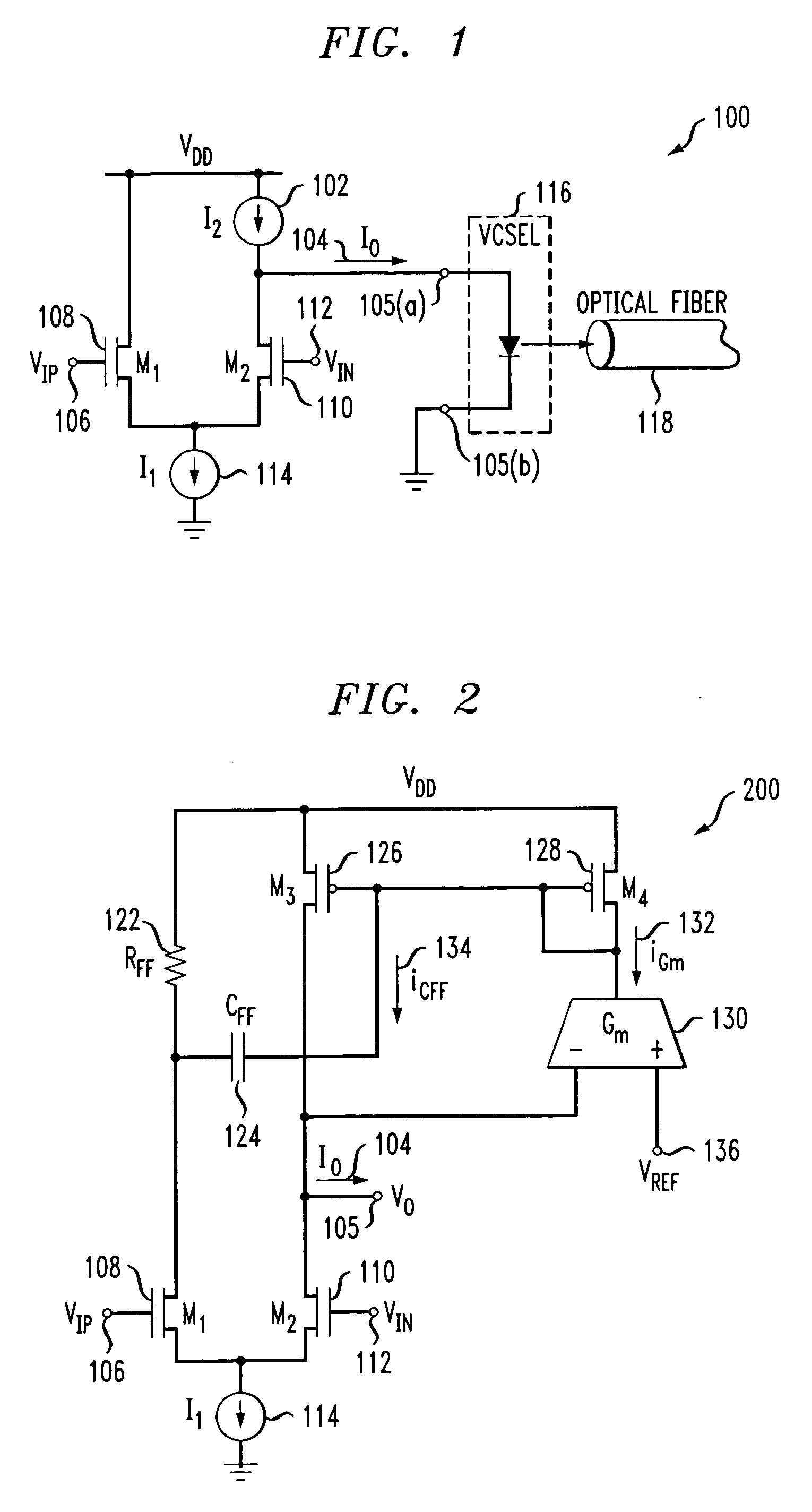
ActiveUS7154923B2Easy to adjustLaser detailsPulse modulationChannel length modulationFeedback circuits
Techniques are disclosed for providing modulation current that includes output impedance compensation with a feed-forward bandwidth enhancement and pre-distortion modulation to control waveform transition symmetry. A feedback circuit senses output node voltage and increases the overdrive voltage of a current source. This offsets the loss of current due to channel length modulation and increases the effective output impedance of the source. A feed-forward circuit enhances the bandwidth of the impedance compensation feedback loop. Waveform transition symmetry is improved by pre-distorting a laser modulation current by introducing an undershoot current on the falling edge of the modulating current.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
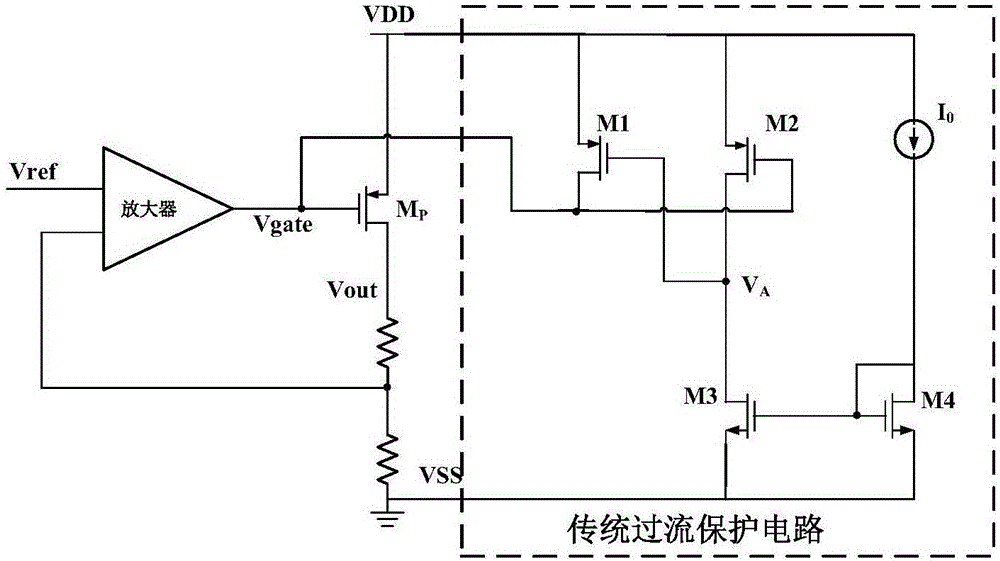
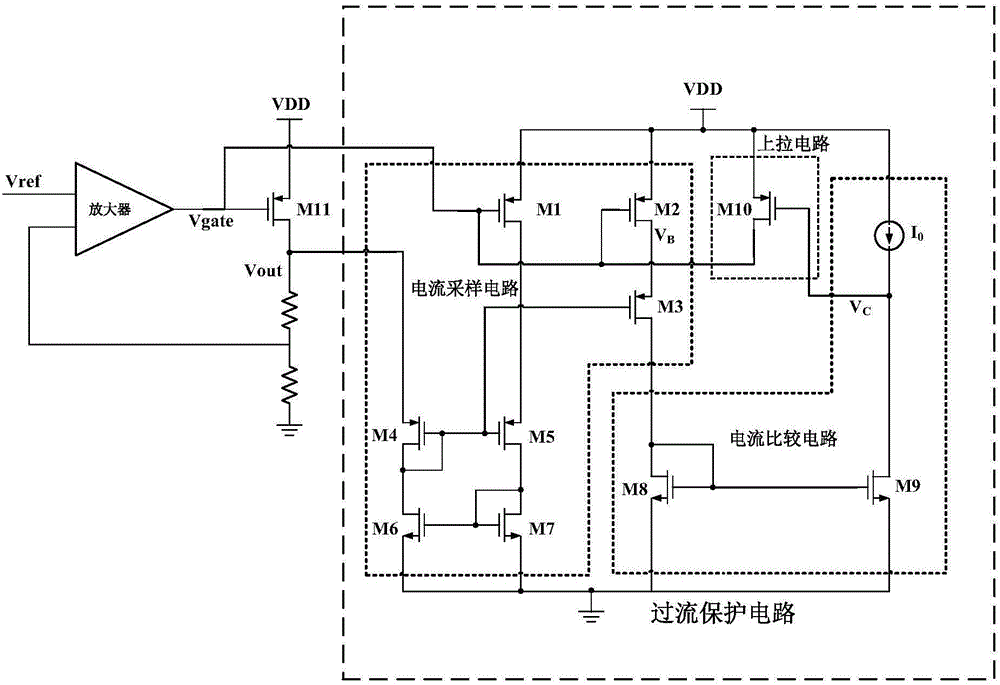
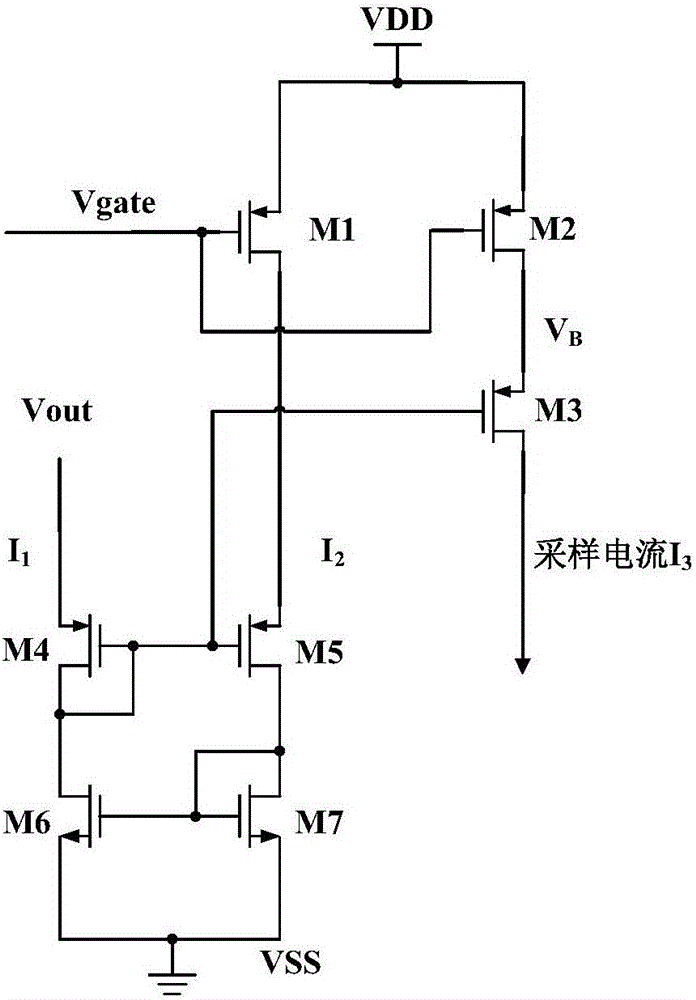
Overcurrent protection circuit for low dropout linear voltage regulator
InactiveCN106774595AReduce currentReduce the problem of excessive deviation from the ideal valueElectric variable regulationChannel length modulationCurrent sample
The invention discloses an overcurrent protection circuit for a low dropout linear voltage regulator. The overcurrent protection circuit for the low dropout linear voltage regulator comprises a current sampling circuit, a current comparison circuit and an upward pull circuit, wherein the current sampling circuit samples gate-drain voltage of a power tube of the low dropout linear voltage regulator, and outputs a sampling current to the current comparison circuit, the current comparison circuit mirrors the sampling current through a current mirror, and then compares the sampling current with a current of a current source, and after output current value of the low dropout linear voltage regulator exceeds current protection threshold value, control voltage output by the current comparison circuit powers on the upward pull circuit, and the upward pull circuit pulls up gate end voltage of the power tube of the low dropout linear voltage regulator, and thereby limits increasing of the output current, and plays a part in overcurrent protection. The overcurrent protection circuit for the low dropout linear voltage regulator can effectively restrain channel length modulation effects of a current sampling tube in the current sampling circuit, decreases occurrence rate of the problem that deviation between value of the current sampled by the current sampling circuit and ideal value is overlarge, improves current sampling accuracy of the overcurrent protection circuit, and obtains accurate starting threshold value of the overcurrent protection circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High frequency power amplifier circuit and electronic component for high frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS7304539B2Avoid short channel effectsReduce widthGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationChannel length modulationHigh frequency power
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
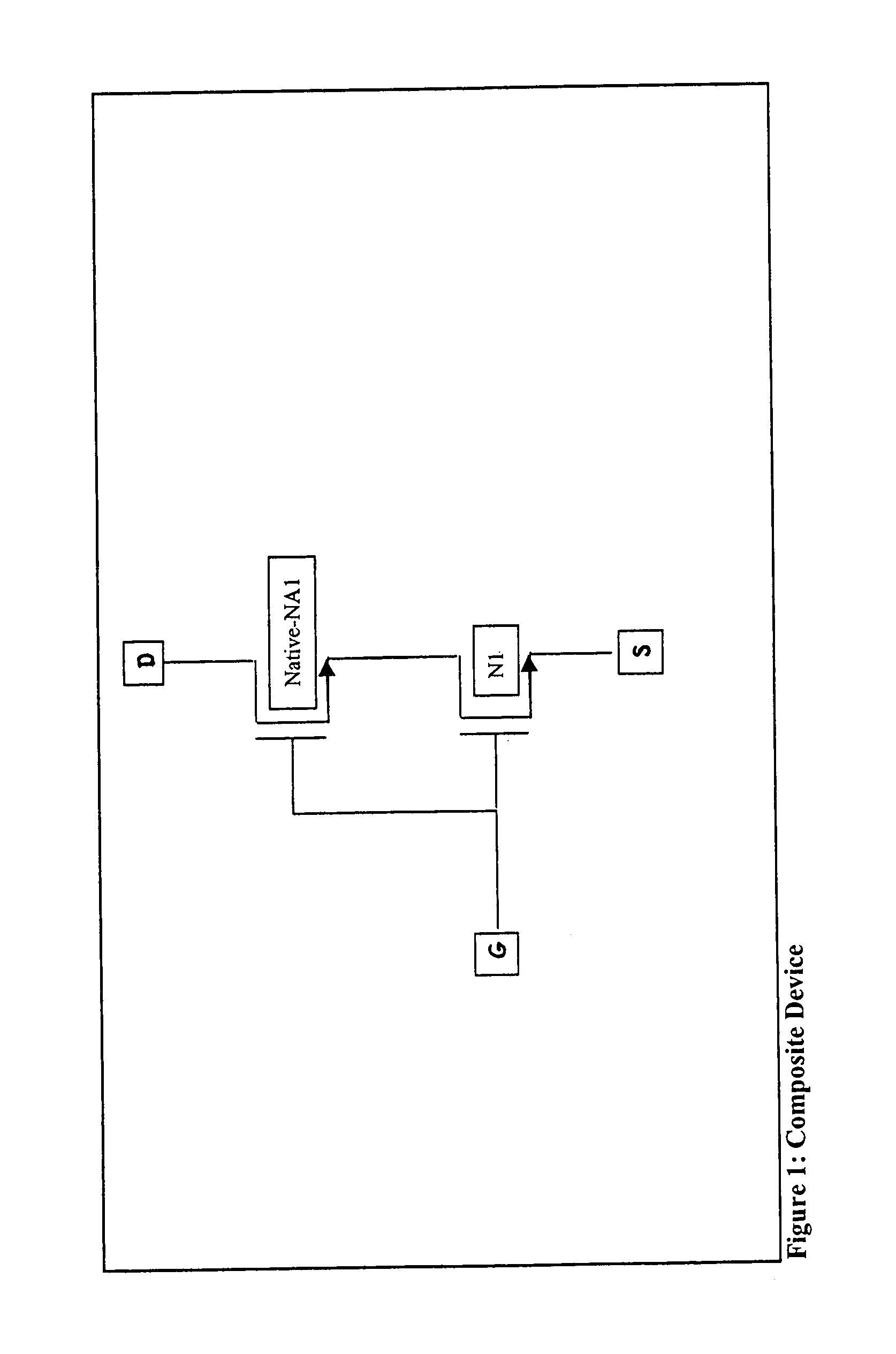
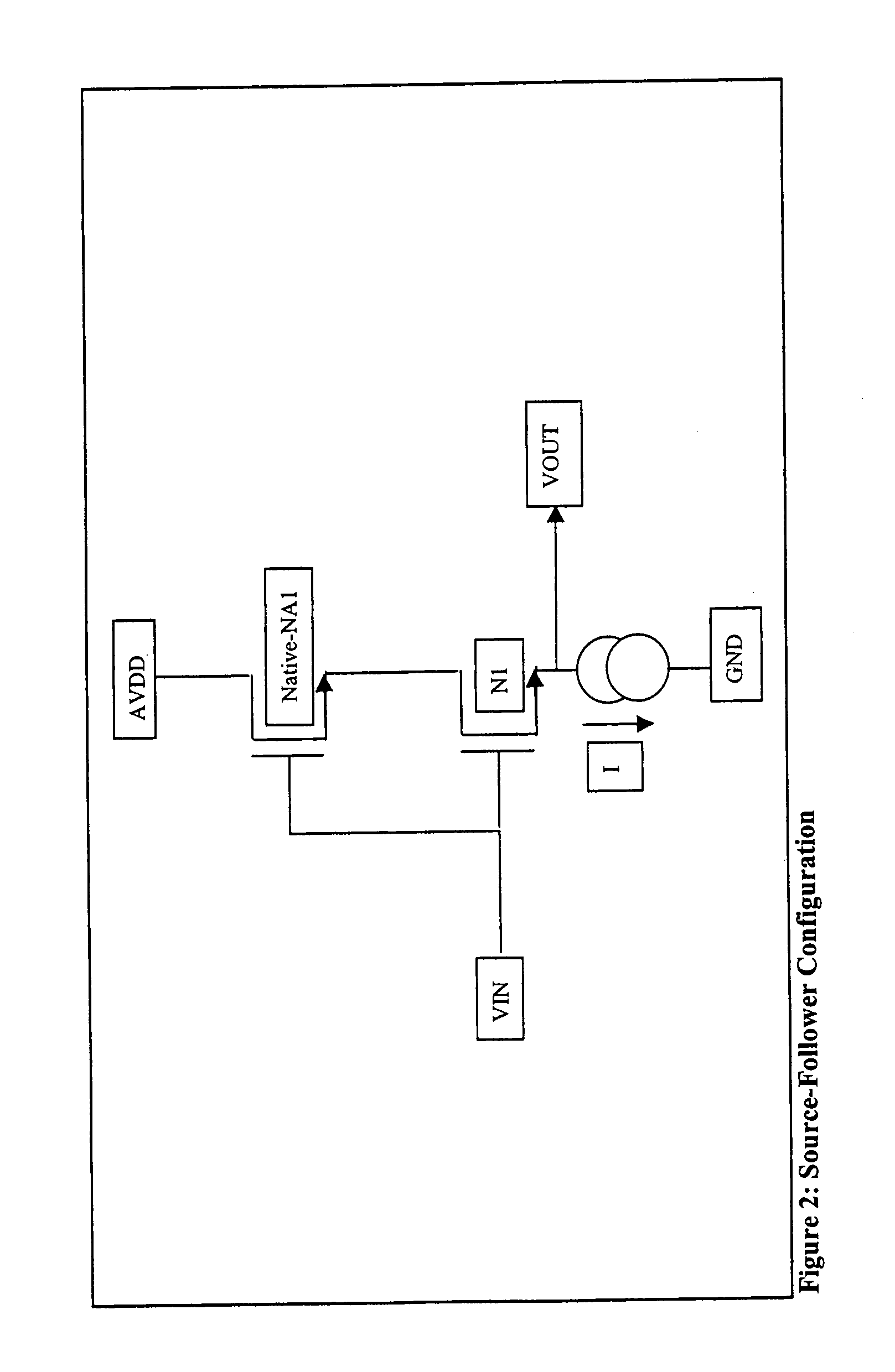
NMOS composite device Vds bootstrappers
ActiveUS7019580B1Eliminate the effects ofMitigate of modulationAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectronic switchingChannel length modulationLinearity
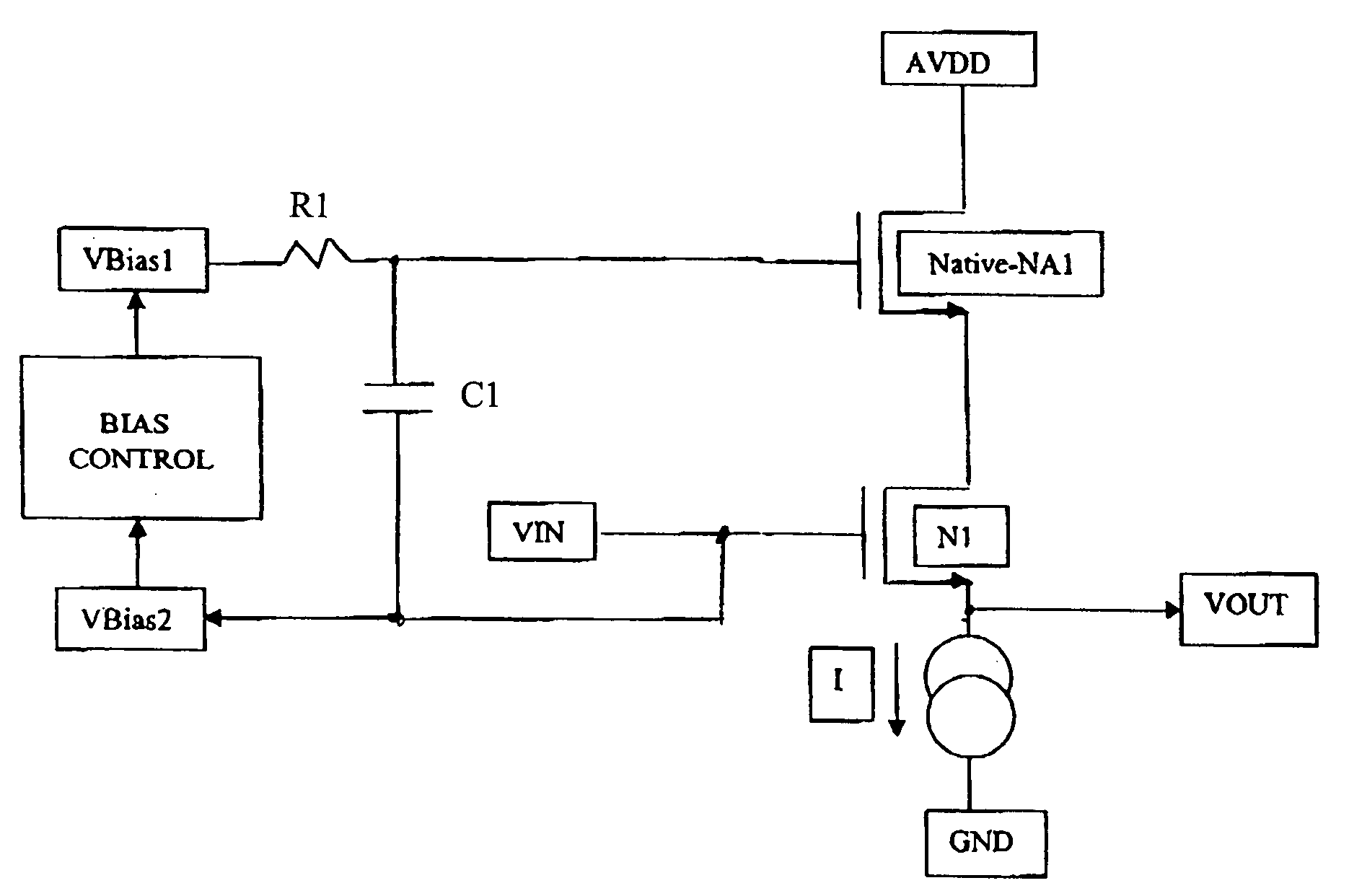
NMOS composite device Vds bootstrappers that mitigate the effects of decreased power supply rejection and increased channel length modulation in minimum or short channel length devices. The NMOS composite devices have a native or at least a low threshold device over a short channel device, with the gate of the native or low threshold device being controlled responsive to the input or output of the short channel device to clamp the drain—source voltage of the short channel device while holding the short channel device in saturation. In one embodiment, a native device is used, with the gate or the native device being connected to the gate of the short channel device. Other embodiments, including embodiments in the form of source followers having enhanced linearity are disclosed.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
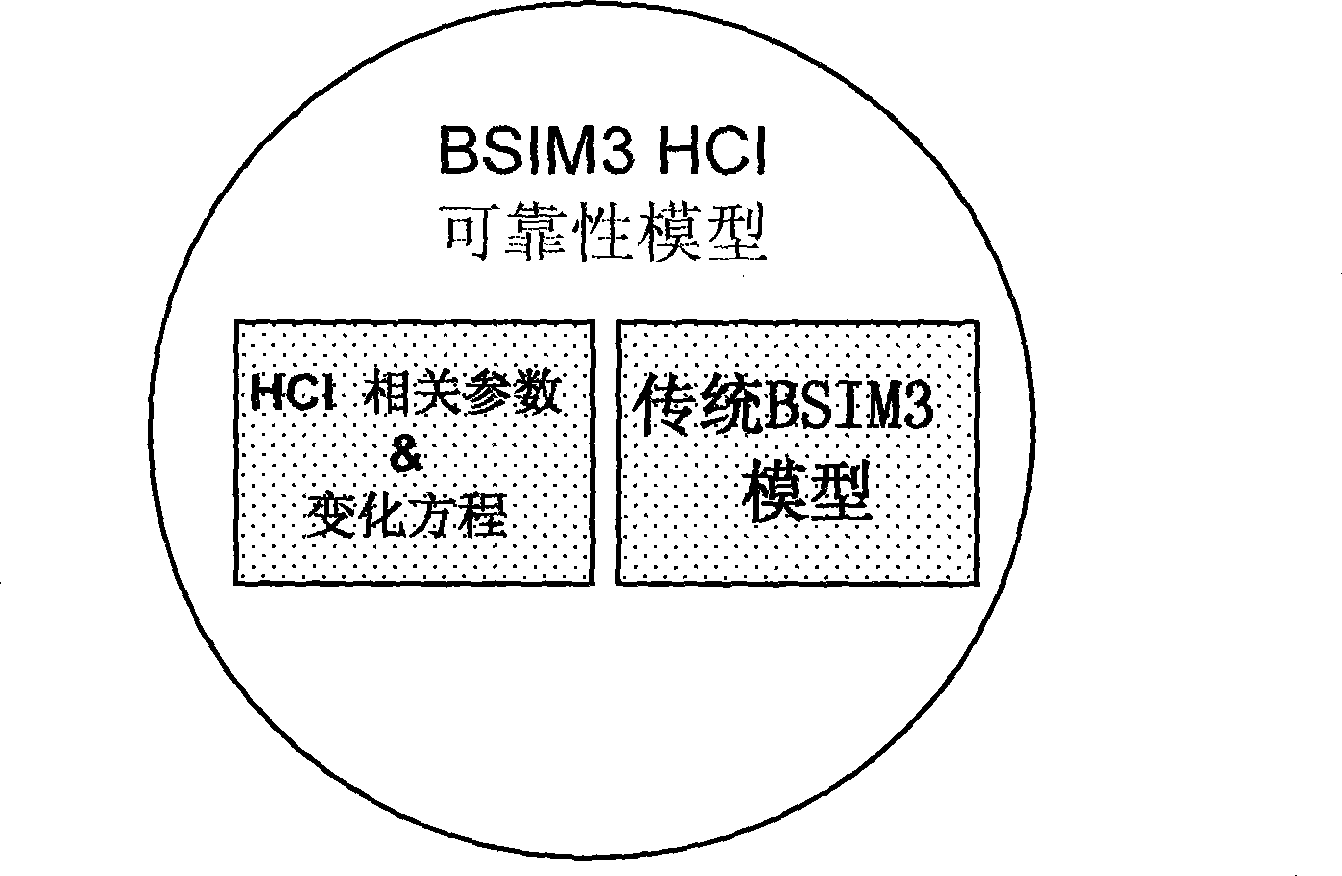
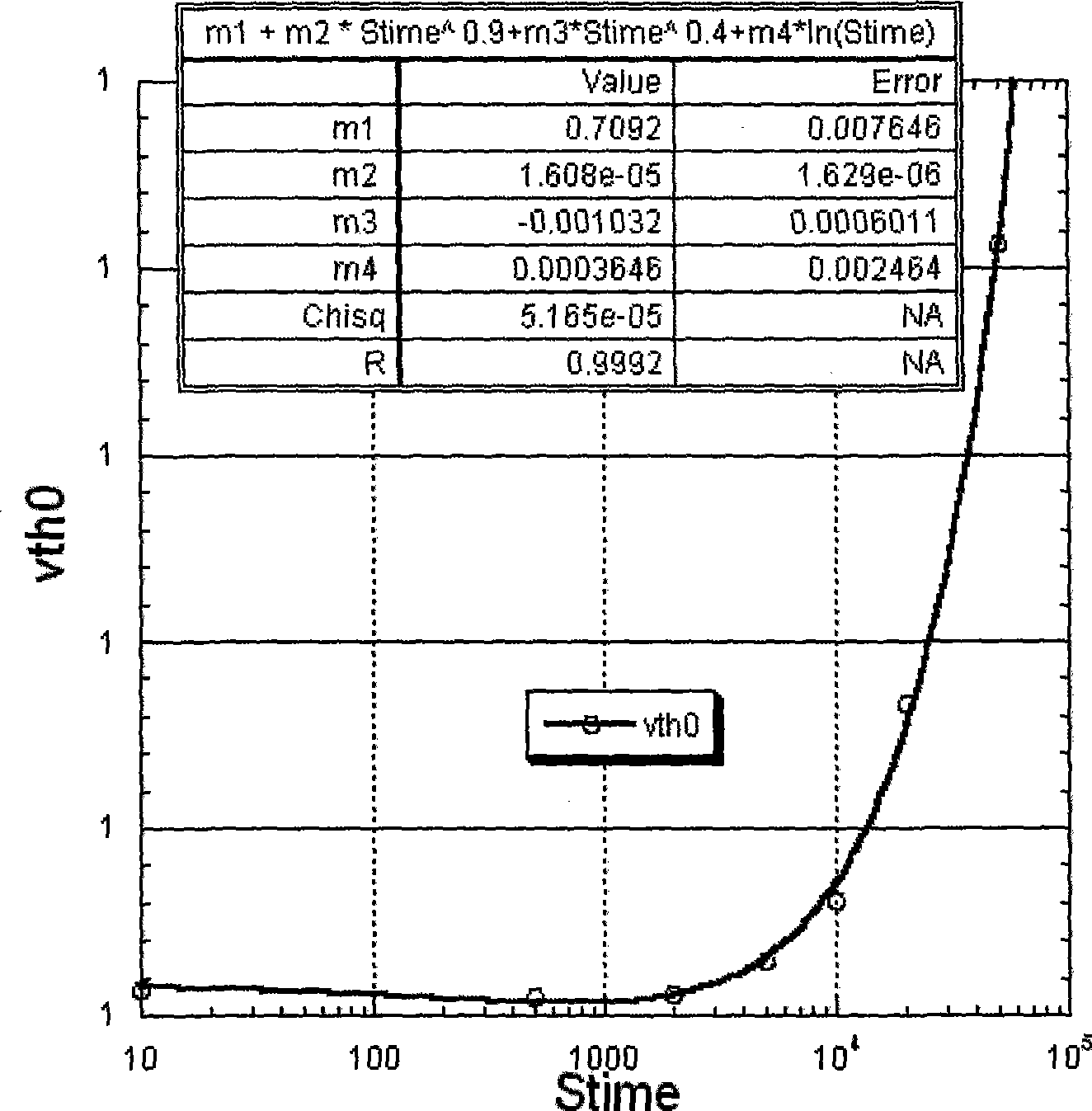
BSIM3 HCI reliability model used in MOSFET electrical simulation
InactiveCN101464919AReduce riskLow costSpecial data processing applicationsChannel length modulationEffect factor
The invention provides a BSIM3 HCI reliability model which is applied to MOSFET electrical simulation. The model provides a method for calculating output characteristics after the degradation of a transistor impacted by HCI effect according to bias voltage exerting time of MOSFET in a bias voltage condition. The method comprises the following steps: Conditions of the transistor impacted by hot carrier degradation effect and the occurred variation on bias voltage exerting time are considered on the basis of standard BSIM3 model, and meanwhile, parameters of seven standard BSIM3 model are redefined as follows: a long channel threshold voltage Vth0 under a condition of zero Vbs, first-order body effect factor of threshold voltage K1, the mobility ratio under zero offset electric field Mu0, mobility ratio decay effector Muc, channel length modulation parameter of silicon charge effect A0, grid-bias voltage modulation parameter of silicon charge effect Ags and silicon bias voltage modulation parameter Keta of silicon charge effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
Electroluminescent display compensated drive signal
ActiveUS8194063B2Raise the ratioIncrease productionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingChannel length modulationDriving current
Subpixels on an electroluminescent (EL) display panel, such as an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) panel, are compensated for initial nonuniformity (“mura”) and for aging effects such as threshold voltage Vth shift, EL voltage Voled shift, and OLED efficiency loss. The drive current of each subpixel is measured at one or more measurement reference gate voltages to form status signals representing the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL emitter of those subpixels. Current measurements are taken in the linear region of drive transistor operation to improve signal-to-noise ratio in systems such as modern LTPS PMOS OLED displays, which have relatively small Voled shift over their lifetimes and thus relatively small current change due to channel-length modulation. Various sources of noise are also suppressed to further increase signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
High frequency power amplifier circuit and electronic component for high frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS20080068086A1Avoid short channel effectsReduce widthGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationChannel length modulationHigh frequency power
In a high frequency power amplifier circuit that supplies a bias to an amplifying FET by a current mirror method, scattering of a threshold voltage Vth due to the scattering of the channel impurity concentration of the FET, and a shift of a bias point caused by the scattering of the threshold voltage Vth and a channel length modulation coefficient λ due to a short channel effect are corrected automatically. The scattering of a high frequency power amplifying characteristic can be reduced as a result.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Low voltage current mirror
InactiveCN102809982AImprove mirroring accuracyLarge output resistanceElectric variable regulationLow voltageCascode current mirror
The invention discloses a low voltage current mirror, and aims to solve the problem that output voltage swing is reduced because threshold voltage is wasted by the voltage redundancy of the conventional cascode current mirror. The low voltage current mirror comprises an input current source, a first P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) tube, a second PMOS tube, a third PMOS tube, a first N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tube, a second NMOS tube, a third NMOS tube, a fourth NMOS tube and a fifth NMOS tube. The low voltage current mirror has a cascode output structure, output resistance is very high, and the influence of a load on output current is relatively small, so that the mirror image precision of the current mirror is very high; and a channel length modulation effect is rationally used by the structure, so that compared with the cascode current mirror, the current mirror has the advantages that the redundancy of the threshold voltage is reduced, and the output voltage swing is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Thin film transistor
InactiveUS20070241336A1Reduce the impactReduce impactSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesChannel length modulationElectric field
In first and second gate electrodes constituting a gate electrode, the gate length of the second gate electrode is set shorter than the gate length of the first gate electrode and short enough to produce the short channel effect. The threshold voltage of a second transistor corresponding to the second gate electrode can thereby be made lower than the threshold voltage of a first transistor corresponding to the first gate electrode. When the same voltage is applied to the first and second gate electrodes, an electric field concentration at the channel edge on the drain side is reduced. This in result reduces the channel length modulation effect.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Sub-threshold reference source compensated by adopting electric resistance temperature
InactiveCN101697086AReduce the temperatureReduce power consumptionElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage source
The invention discloses a sub-threshold reference source compensated by adopting electric resistance temperature, which belongs to a range of power supply temperature compensating circuits. The sub-threshold reference source adopts positive temperature coefficient compensating circuit and temperature compensating reference voltage source technology of electric resistance, and consists of three parts comprising a peak current mirror, a negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit and a reference voltage output circuit. A sub-threshold reference circuit for generating constant reference voltage output by using the positive temperature coefficient of the electric resistance and the negative temperature coefficient of the current on a resistor can overcome the influence that the output voltage brought by channel length modulation effect is changed by the fluctuation of power supply voltage to a certain degree; and the sub-threshold reference source has a simple structure and low power consumption, can be applied to an analog integrated circuit with low-power consumption design, and can be broadly applied to a reference voltage source circuit required by a low-power consumption analog and digital-analog mixed circuit for generating low temperature coefficients.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Band-gap reference source with low offset voltage and high PSRR (power supply rejection ratio)
ActiveCN105320205AReduces the impact of channel length modulation effectsLower Offset VoltageElectric variable regulationChannel length modulationEngineering
The invention discloses a band-gap reference source with low offset voltage and a high PSRR (power supply rejection ratio). The band-gap reference source comprises a first P-channel field-effect transistor, a second P-channel field-effect transistor, a third P-channel field-effect transistor, a fourth P-channel field-effect transistor, a first resistor, a second resistor, a third resistor, a first bipolar transistor, a second bipolar transistor and a voltage feedback circuit. According to the band-gap reference source with the low offset voltage and the high PSRR, with the adoption of a double-layer current mirror structure and addition of biasing resistors, influence of channel length modulation effects of current mirrors is reduced, the accuracy of current multiplication coefficients is guaranteed, and maladjustment of output voltage is reduced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
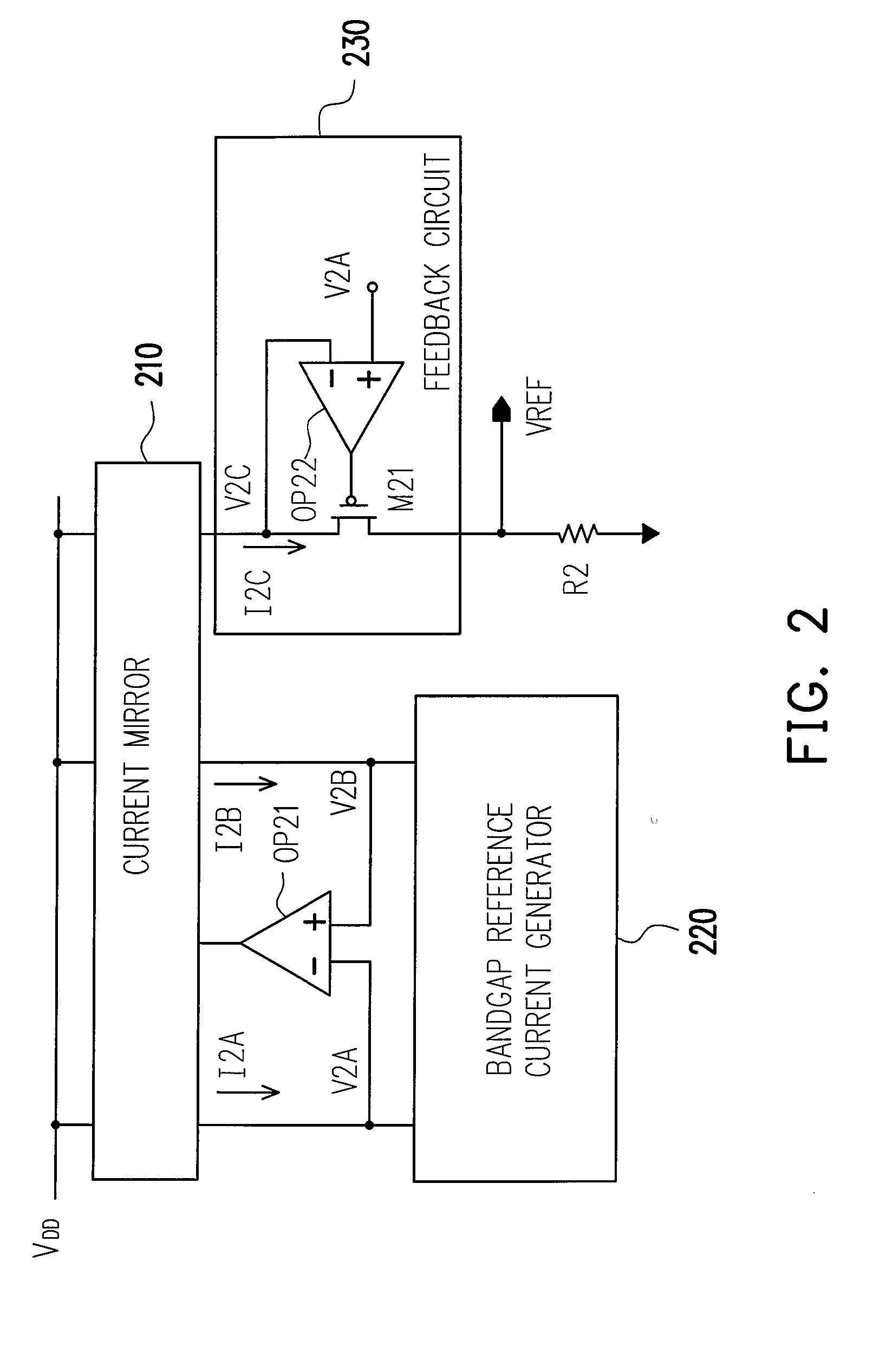
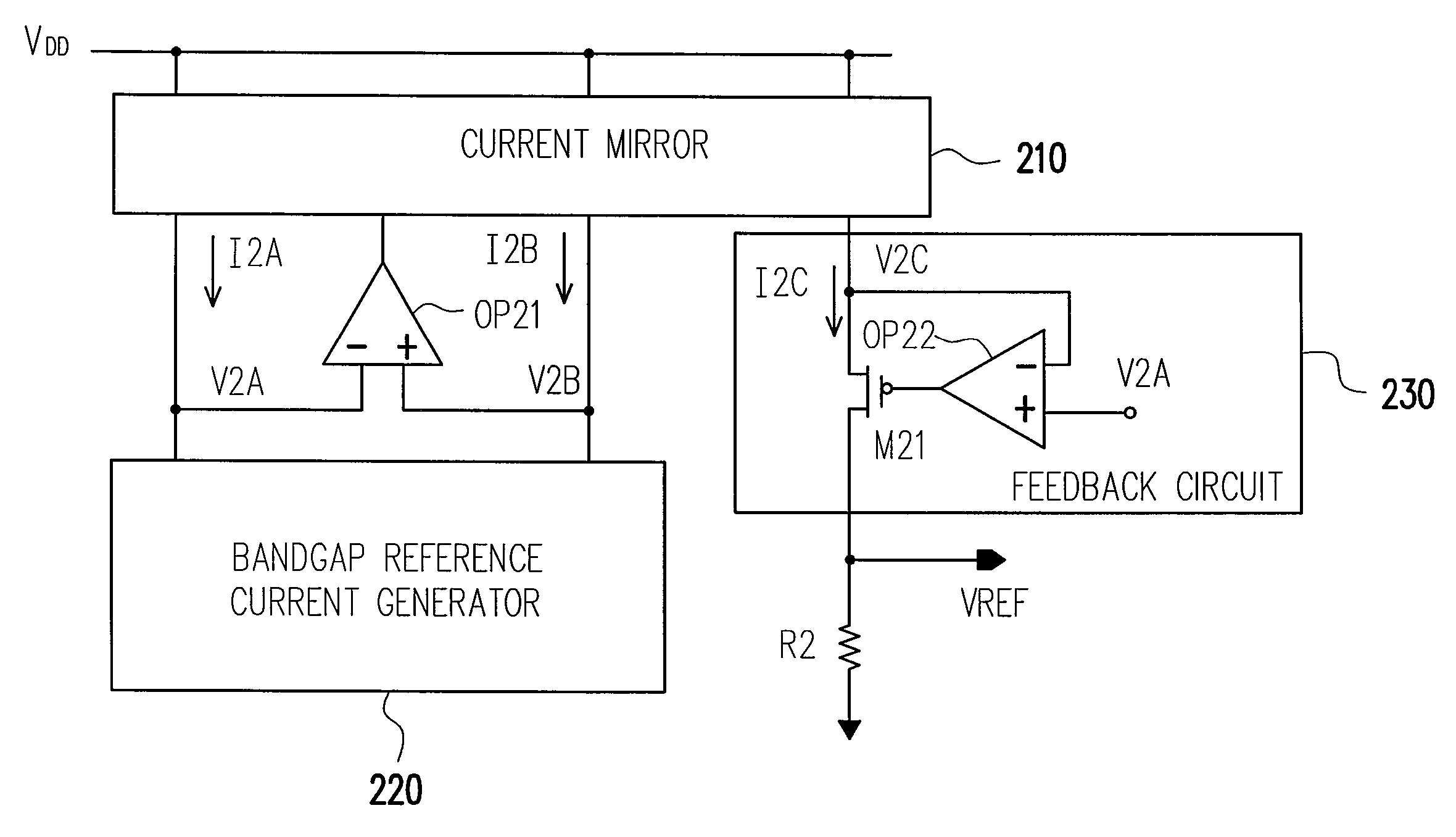
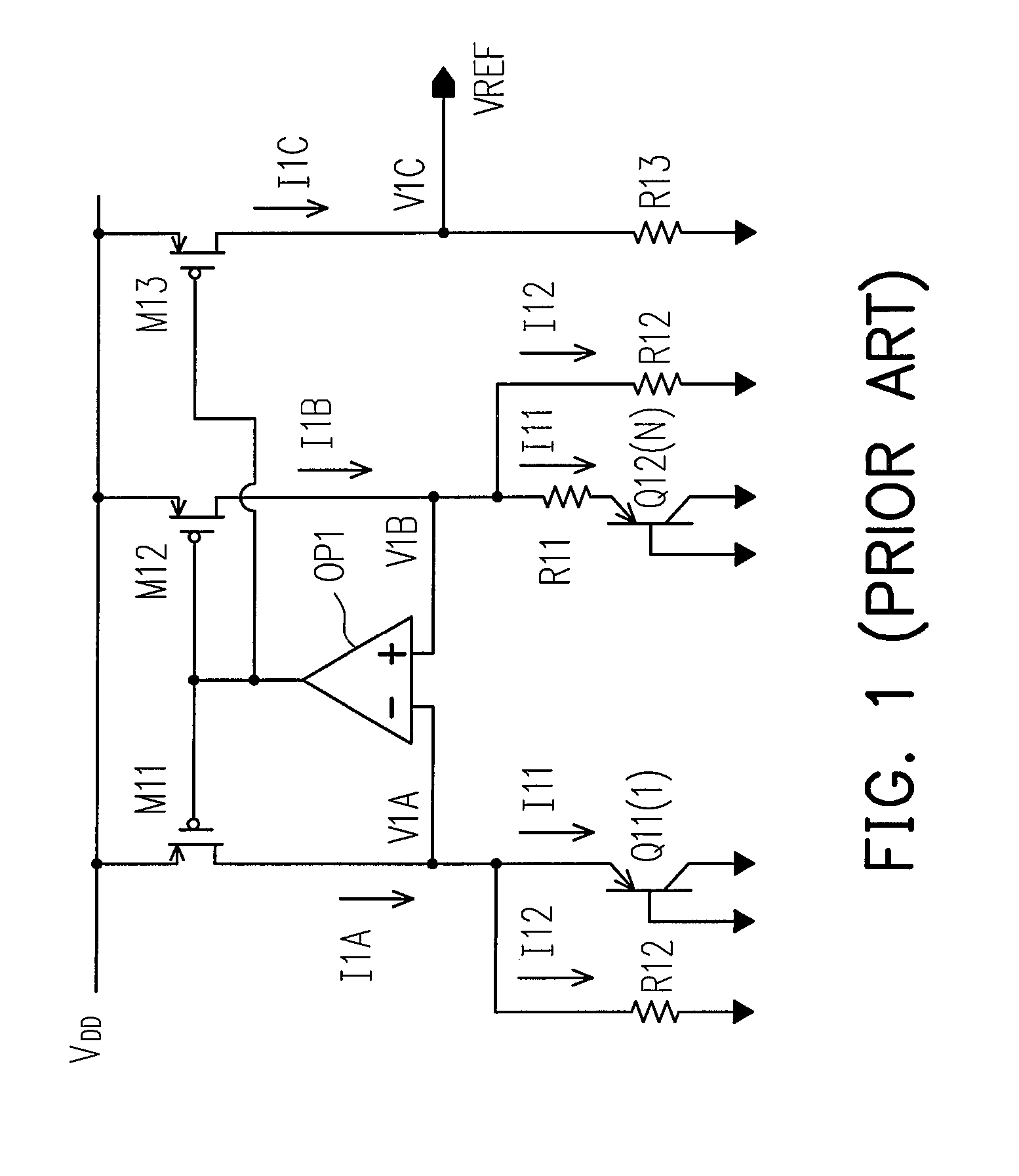
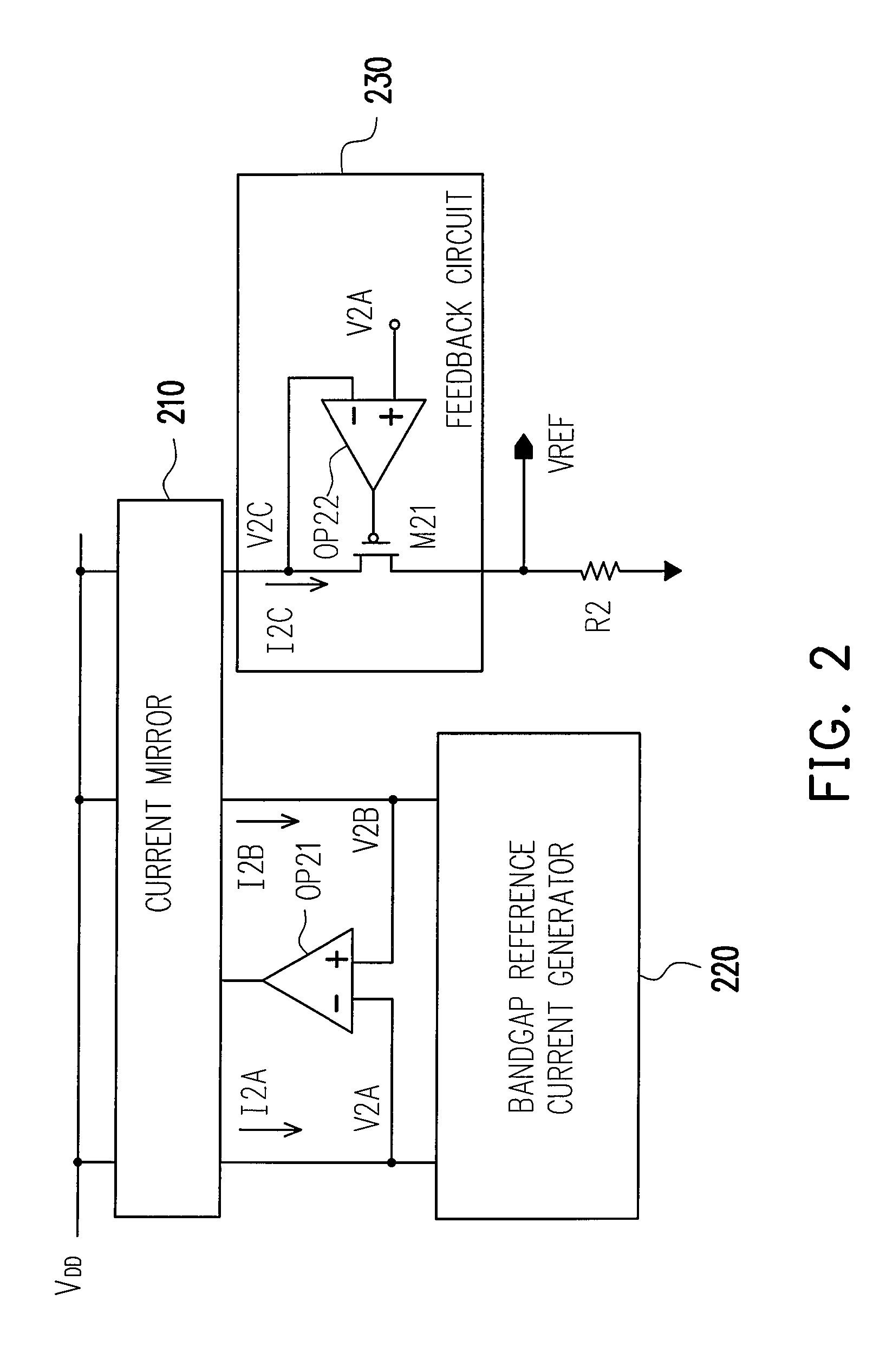
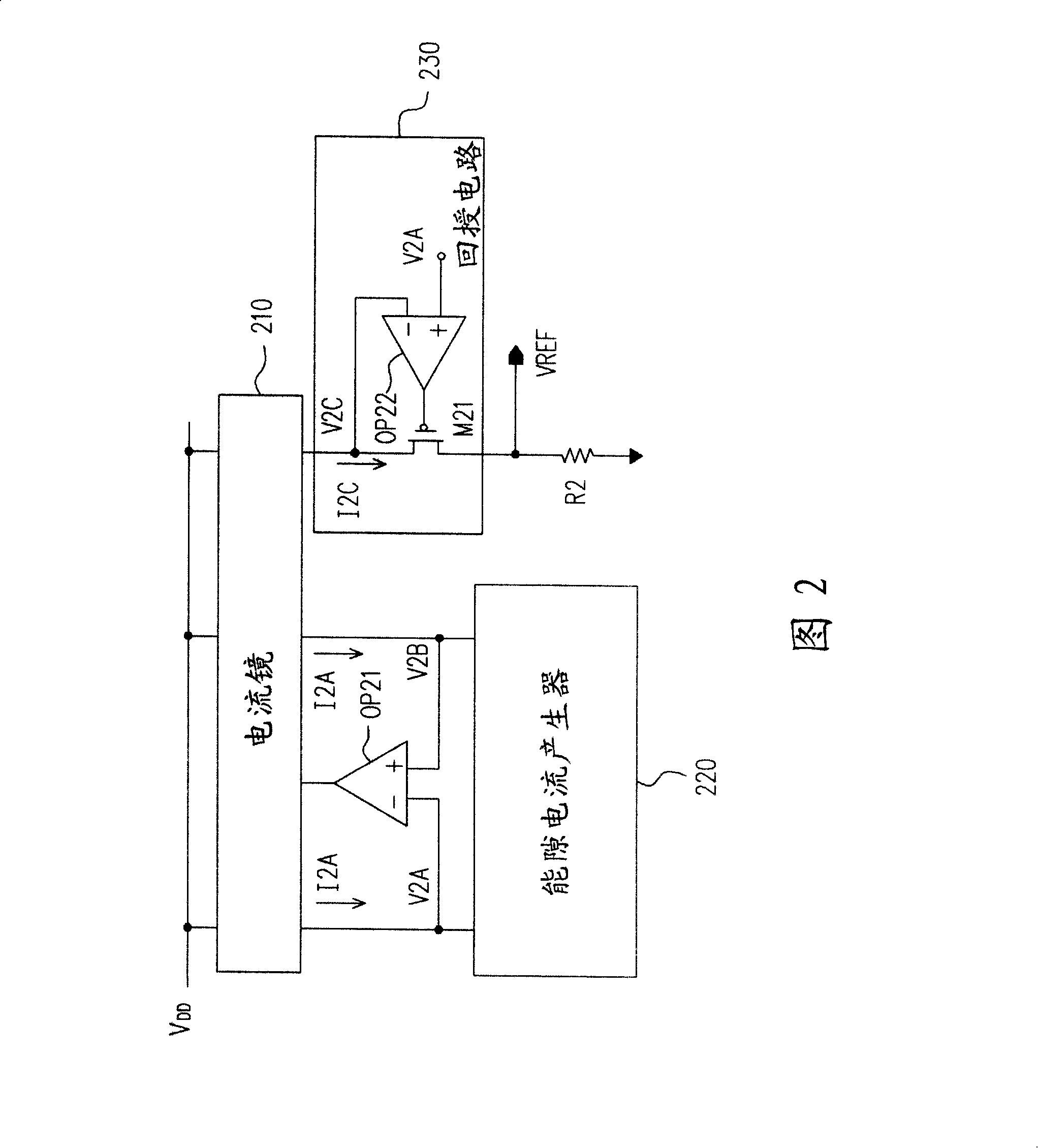
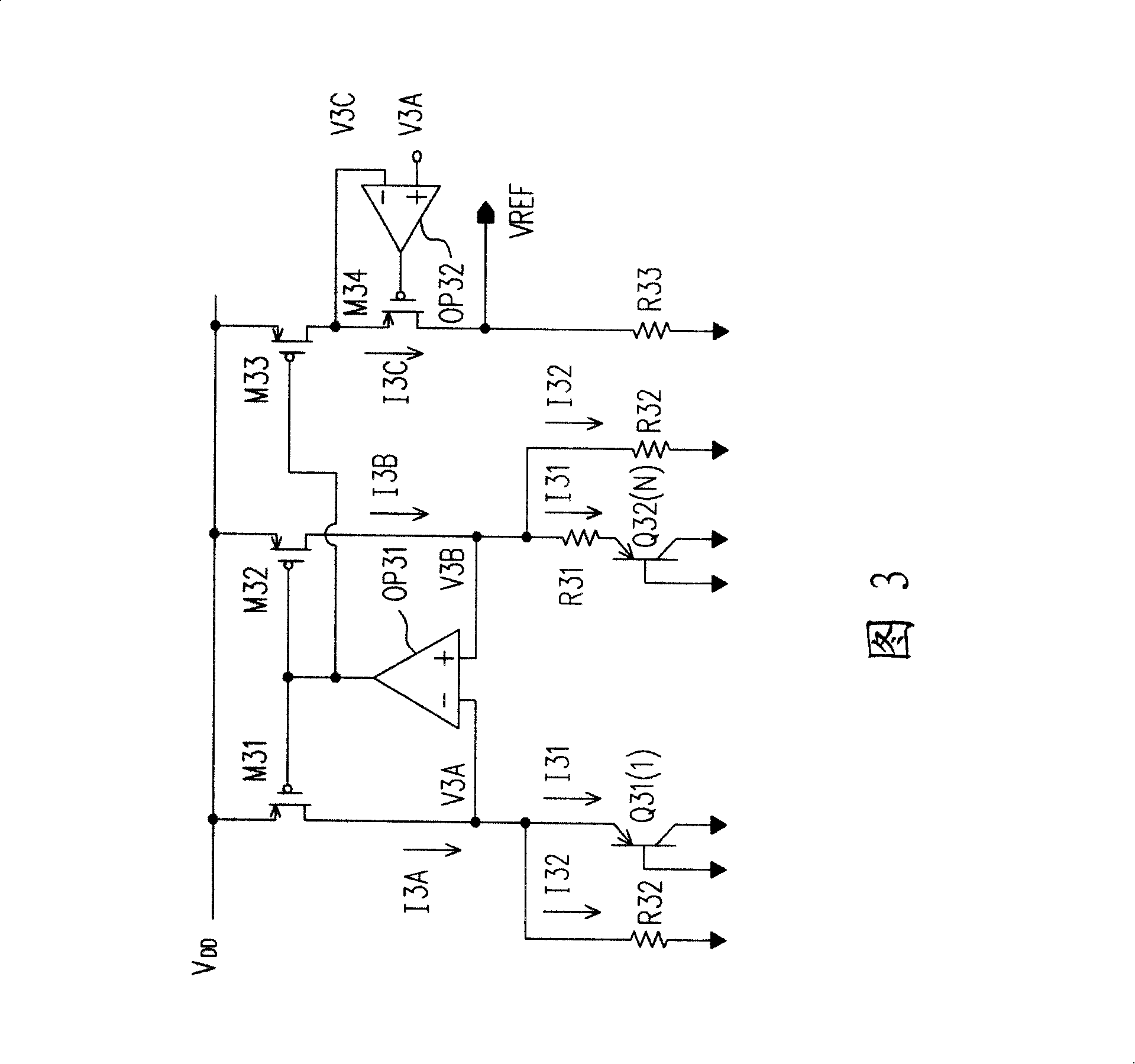
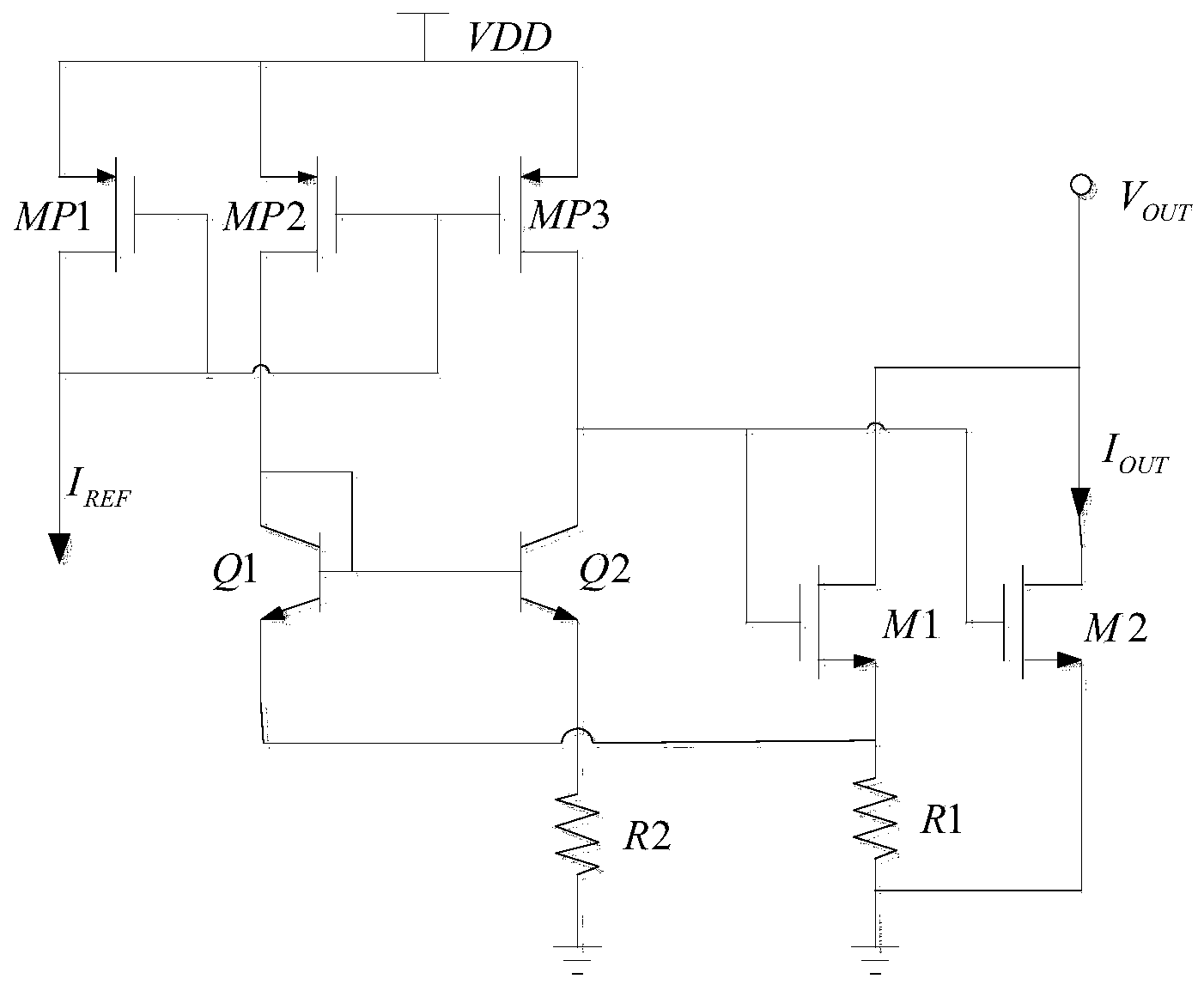
Bandgap reference circuit
ActiveUS20080297131A1Good coefficientImprove featuresElectric variable regulationChannel length modulationAudio power amplifier
A bandgap reference circuit includes a reference current generator for respectively generating a first reference current on a first current path and a second reference current on a second current path, a current mirror for generating a third reference current on a third current path based on the first and second reference currents, an operation amplifier for rendering the first reference current substantially identical to the second reference current and a feedback circuit for rendering a node voltage on the first current path substantially identical to another node voltage on the third current path, so as to eliminate possible errors caused by a channel length modulation effect in the current mirror.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for providing a modulation current
ActiveUS20060044072A1Easy to adjustPulse modulationElectric pulse generatorChannel length modulationEngineering
Techniques are disclosed for providing modulation current that includes output impedance compensation with a feed-forward bandwidth enhancement and pre-distortion modulation to control waveform transition symmetry. A feedback circuit senses output node voltage and increases the overdrive voltage of a current source. This offsets the loss of current due to channel length modulation and increases the effective output impedance of the source. A feed-forward circuit enhances the bandwidth of the impedance compensation feedback loop. Waveform transition symmetry is improved by pre-distorting a laser modulation current by introducing an undershoot current on the falling edge of the modulating current.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electroluminescent subpixel compensated drive signal
ActiveUS8217928B2Raise the ratioSimple control signalCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringGate voltage
An electroluminescent (EL) subpixel, such as an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) subpixel, is compensated for aging effects such as threshold voltage Vth shift, EL voltage Voled shift, and OLED efficiency loss. The drive current of the subpixel is measured at one or more measurement reference gate voltages to form a status signal representing the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL emitter of the subpixel. Current measurements are taken in the linear region of drive transistor operation to improve signal-to-noise ratio in systems such as modern LTPS PMOS OLED displays, which have relatively small Voled shift over their lifetimes and thus relatively small current change due to channel-length modulation. Various sources of noise are also suppressed to further increase signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Operational transconductance amplifier
InactiveUS7323934B2Keep required bandwidthPrecise processingDifferential amplifiersAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyChannel length modulationAudio power amplifier
An operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) includes a first, a second and a third differential units, a voltage-to-current converting unit and a current subtraction device. The first and the second differential units receive a differential input voltage and the voltage-to-current converting unit converts it into an output current. The OTA adopts a replica scheme, that is, by copying the first differential unit to generate a third differential unit and then performs a subtraction between the first output current from the first differential unit and the second output current from the third differential unit in order to eliminate the static current component in the output current. In addition, since the first and the third differential units have the same layout, the output current will not vary with the channel length modulation of transistors, and the static current component in the output current can be eliminated completely.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Bandgap reference circuit
ActiveUS7834610B2Good coefficientImprove featuresElectric variable regulationChannel length modulationAudio power amplifier
A bandgap reference circuit includes a reference current generator for respectively generating a first reference current on a first current path and a second reference current on a second current path, a current mirror for generating a third reference current on a third current path based on the first and second reference currents, an operation amplifier for rendering the first reference current substantially identical to the second reference current and a feedback circuit for rendering a node voltage on the first current path substantially identical to another node voltage on the third current path, so as to eliminate possible errors caused by a channel length modulation effect in the current mirror.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
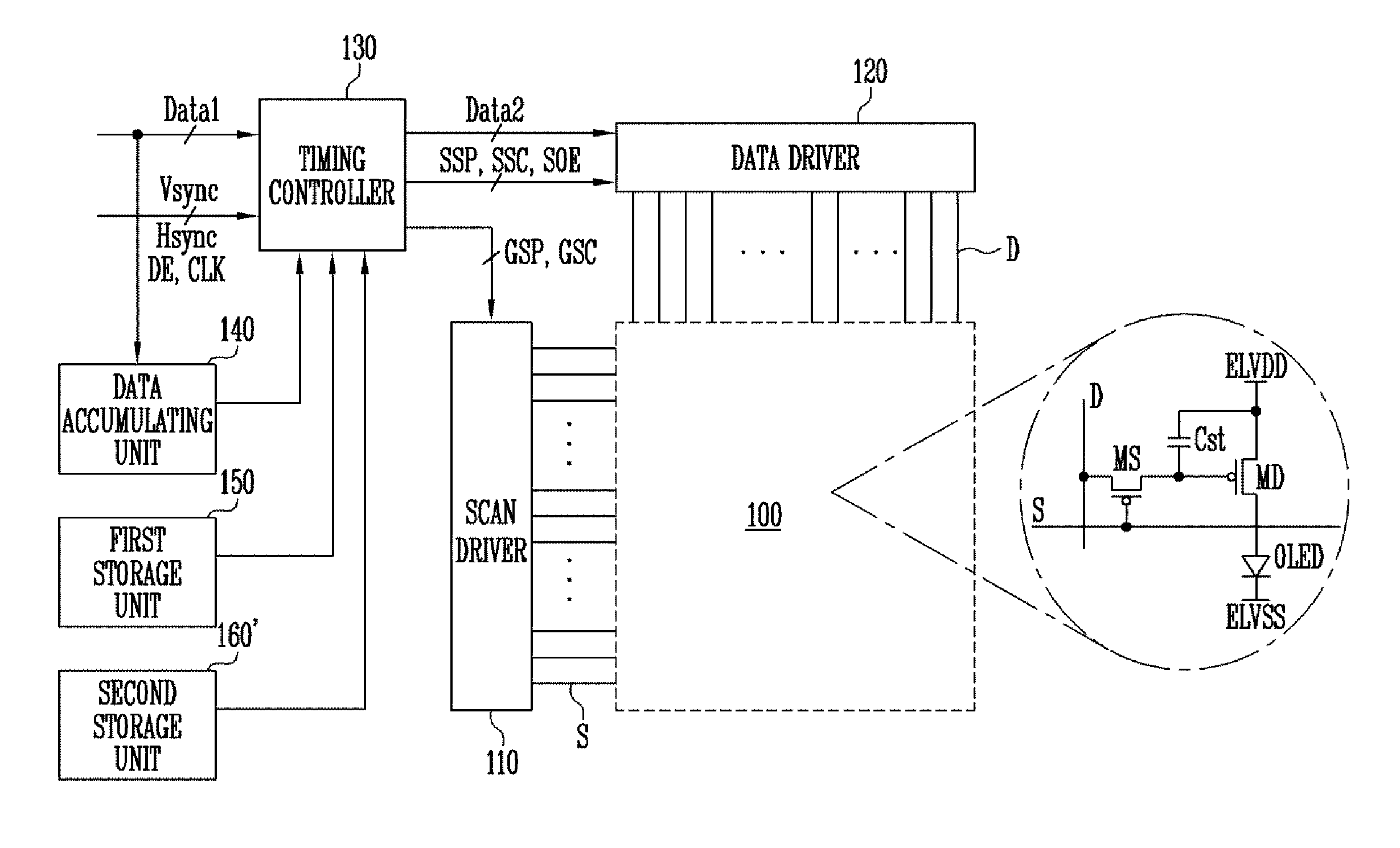
Organic light emitting display device and driving method therefor
ActiveUS20170032743A1Accurate compensationStatic indicating devicesChannel length modulationScan line
An organic light emitting display device includes: pixels including driving transistors positioned in regions divided by scan lines and data lines; a data accumulating unit arranged to accumulate first data; a first storage unit storing current and voltage change information corresponding to a degradation of an organic light emitting diode (OLED); a second storage unit storing a compensation value corresponding at least partially to channel length modulation of the driving transistors; and a timing controller programmed to carry out an altering of first data corresponding to an ith pixel so as to generate second data to be supplied to the ith pixel, the altering carried out according to: accumulation stress information for the ith pixel, the accumulation stress information corresponding to the accumulated first data and being stored in the data accumulating unit, the current and voltage change information, and a compensation value corresponding to the ith pixel.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Source electrode follower buffer circuit
ActiveCN106788434ASmall distortionEliminate Signal ErrorsPhysical parameters compensation/preventionChannel length modulationAudio power amplifier
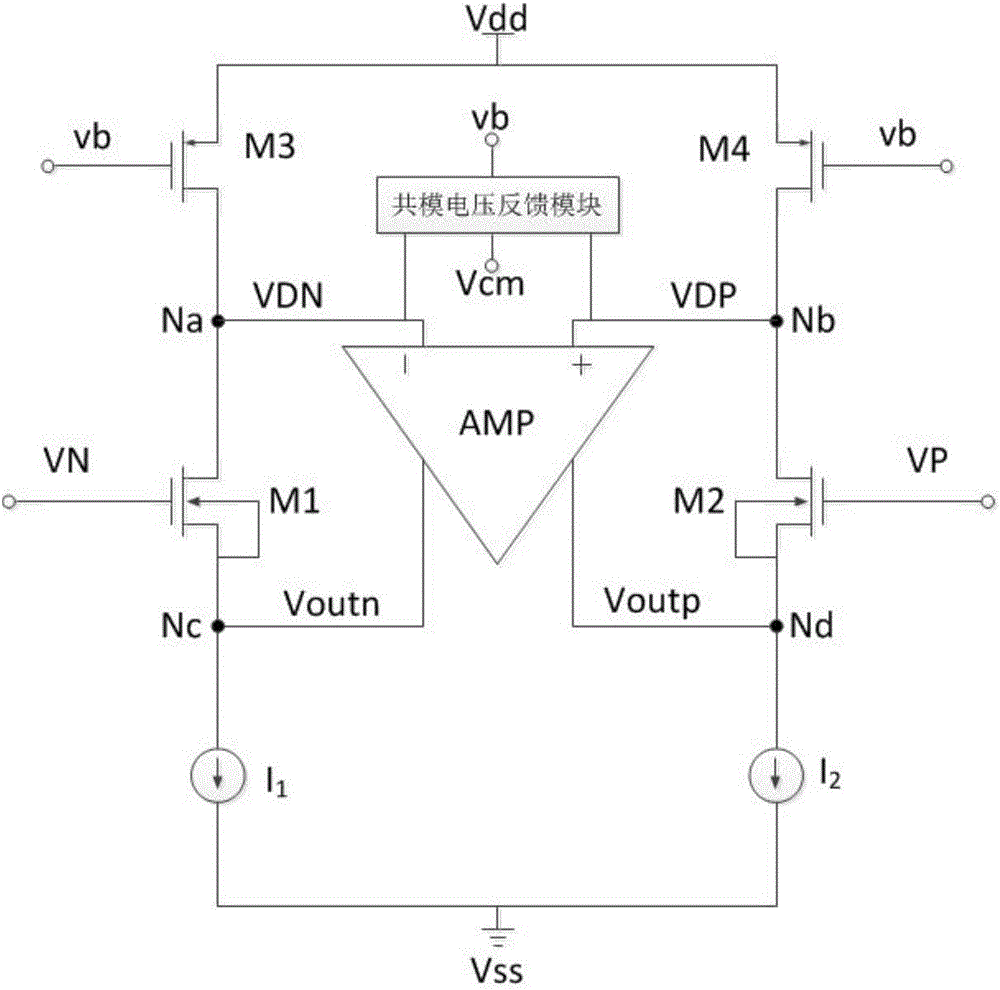
The invention belongs to the technical field of analog-digital converter, and in particular relates to a source electrode follower buffer circuit. The circuit comprises a first NMOS transistor M1, a second NMOS transistor M2, a first PMOS transistor M3, a second PMOS transistor M4, a first current source I1, a second current source I2, a fully differential operational amplifier and a common-mode voltage feedback module, wherein the M1, M2, M3 and M4 always work in a saturation area, source electrode voltages of the M1 and M2 follow the change of VN and VP, an input pair transistor substrate is in short circuit with the source electrode and thus the bulk effect of the transistors is eliminated, a feedback loop formed by the fully differential operational amplifier under a large-swing input signal provides stable static working points for the M1 and M2, when a load is connected with the output end, the feedback loop help the transistors M1 and M2 charge and discharge, current change of the transistors M1 and M2 is reduced, and the linearity of the follower is improved. According to the circuit provided by the invention, the bulk effect and the channel length modulation effect are avoided, current change in the transistor in the follower is greatly reduced, and the circuit has the advantage of high linearity.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for building AlGaN/GaN HEMT device direct current model
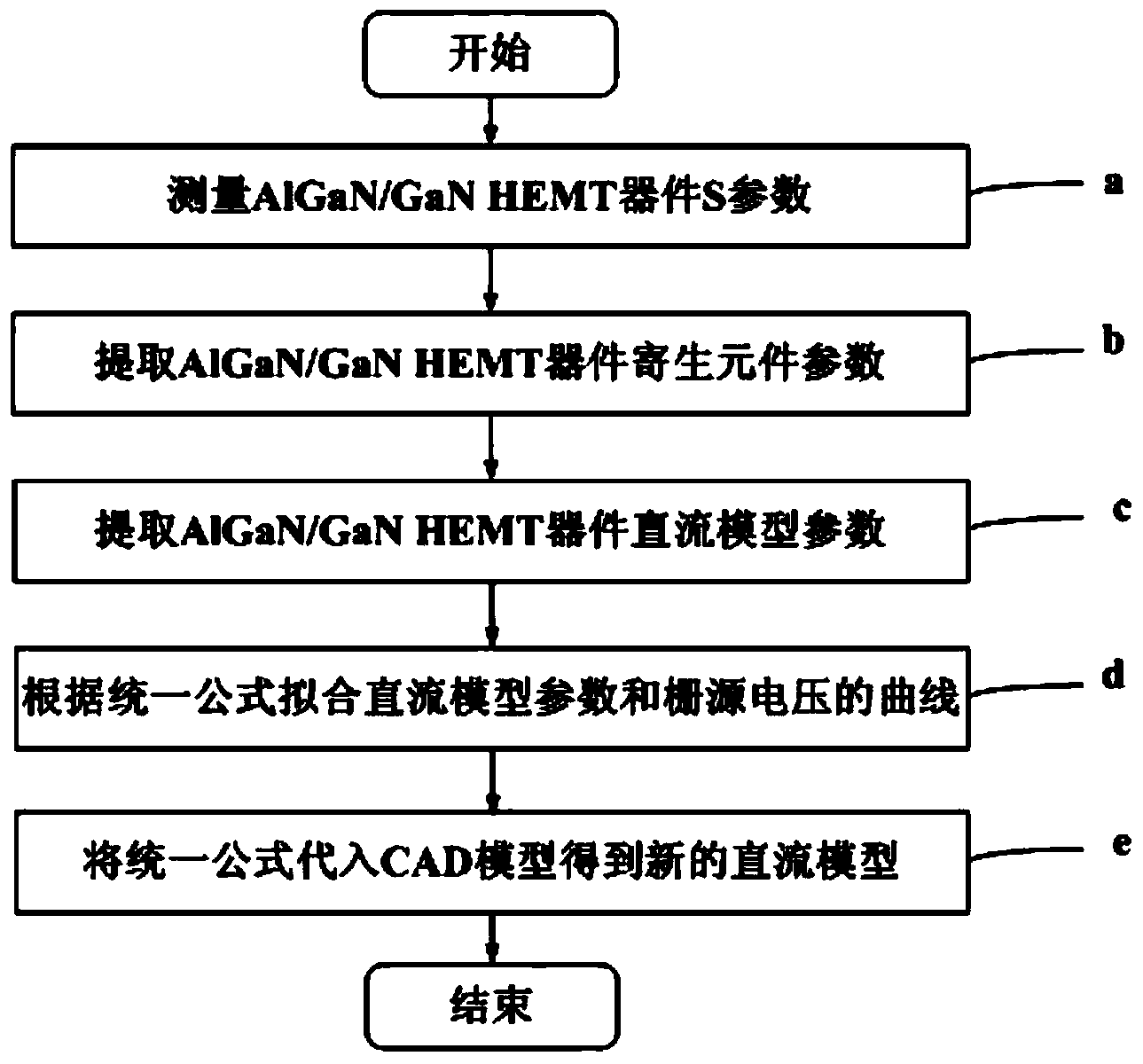
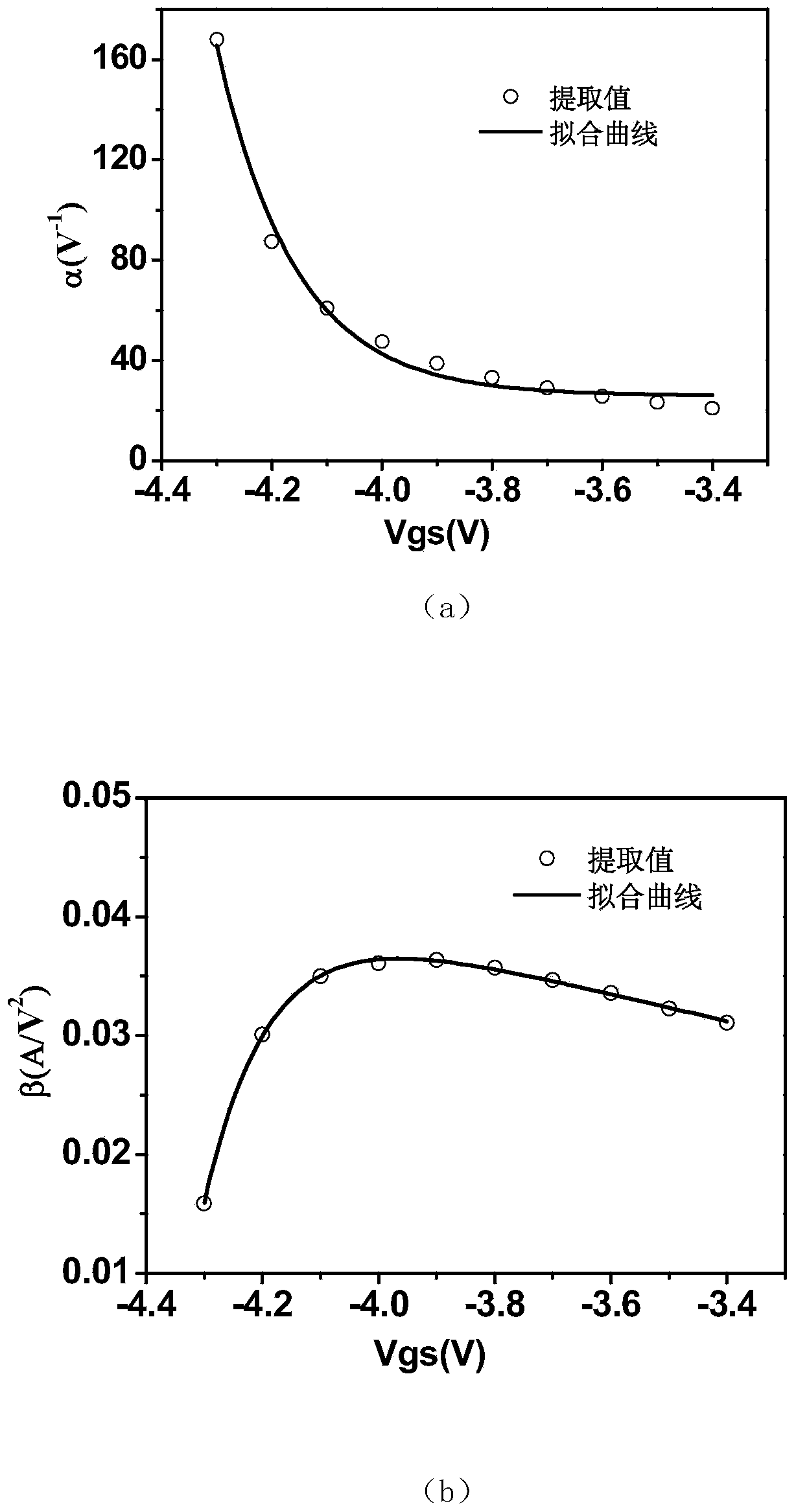
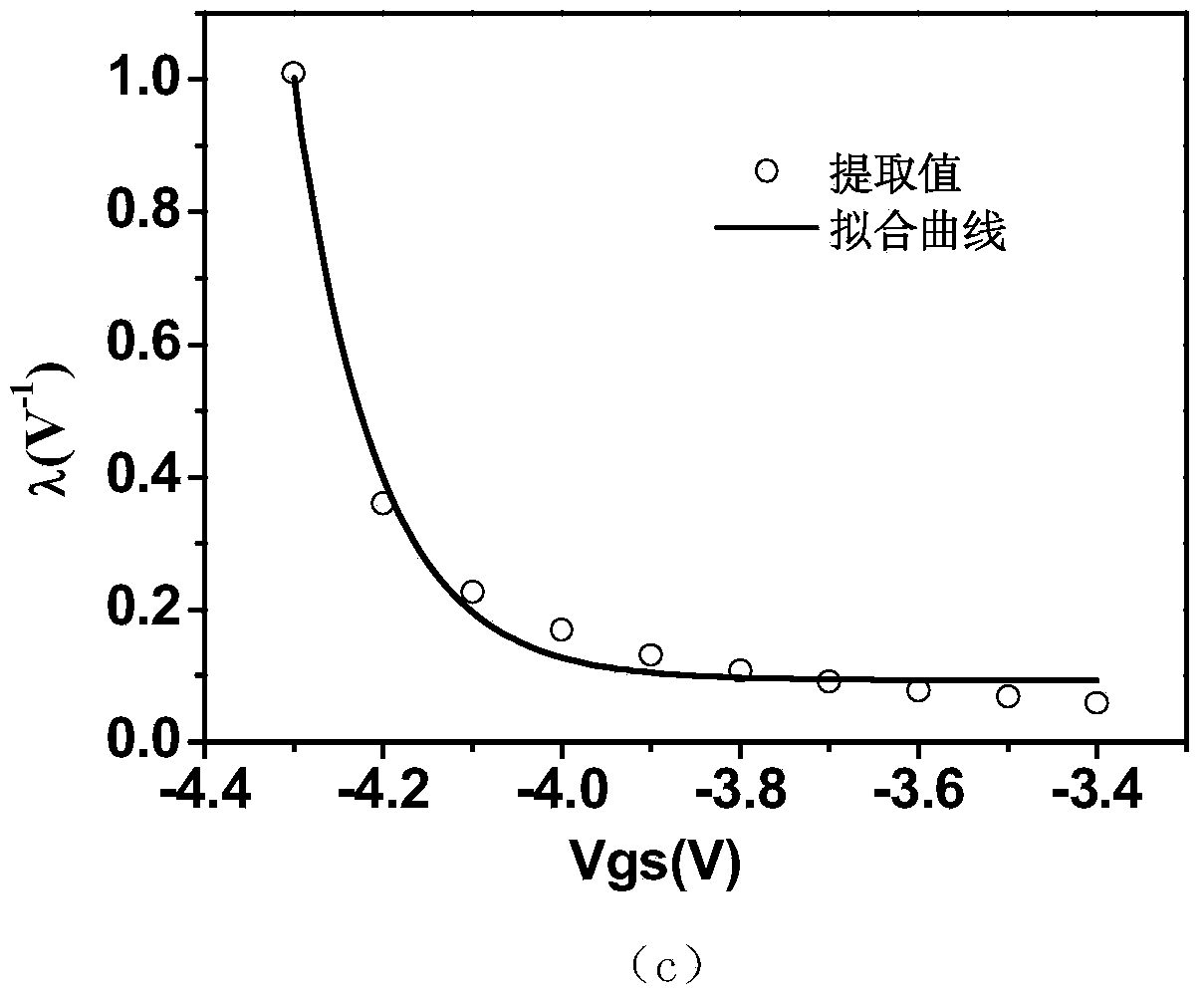
InactiveCN104376161AHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsChannel length modulationLinear relationship
The invention discloses a method for building an AlGaN / GaN HEMT device direct current model. The method includes the steps of a, measuring parameters of an AlGaN / GaN HEMT device S; b, extracting parasitic antenna parameters of the AlGaN / GaN HEMT device and removing influences of parasitic antenna values; c, extracting values of device transconductance parameters beta, voltage saturation parameters alpha and channel length modulation factors gamma; d, fitting beta, alpha and gamma curves changed along with gate-to-source voltage Vgs and obtaining unified expressions, changed along with Vgs, of the parameters beta, alpha and gamma; e, substituting beta, alpha and gamma expressions into a Curtice model, and obtaining the new direct current model. By means of the method, the method of building a direct current parameter and gate-to-source voltage non-linear relationship is adopted for building the new AlGaN / GaN HEMT device direct current model, the model has the gate-to-source voltage bias correlated characteristics, and the accuracy of the direct current model is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Internal voltage generator for semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060103452A1Preventing channel length modulationAvoid lengthLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectric pulse generatorChannel length modulationVoltage generator
Disclosed is an internal voltage generator capable of outputting a constant voltage regardless of change of a supply voltage. The internal voltage generator includes a current mirror unit, drivers and a voltage divider and prevents a channel length modulation phenomenon by changing the structure of the current mirror unit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Linear source follower
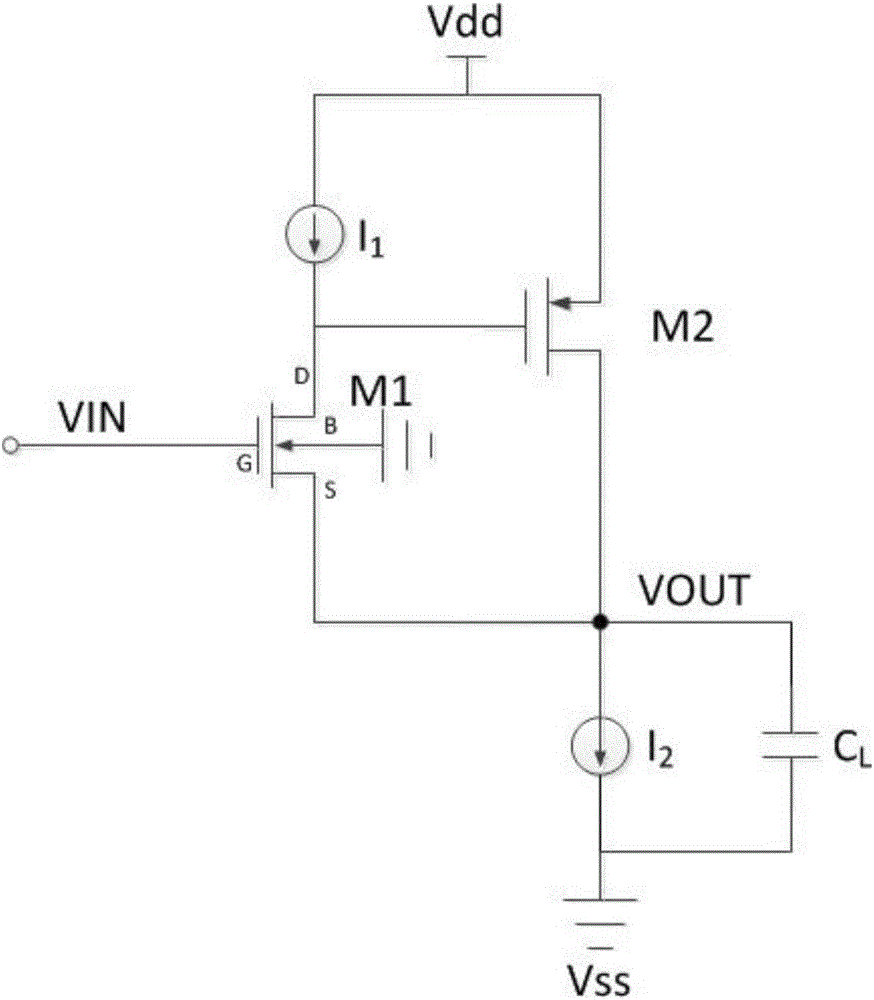
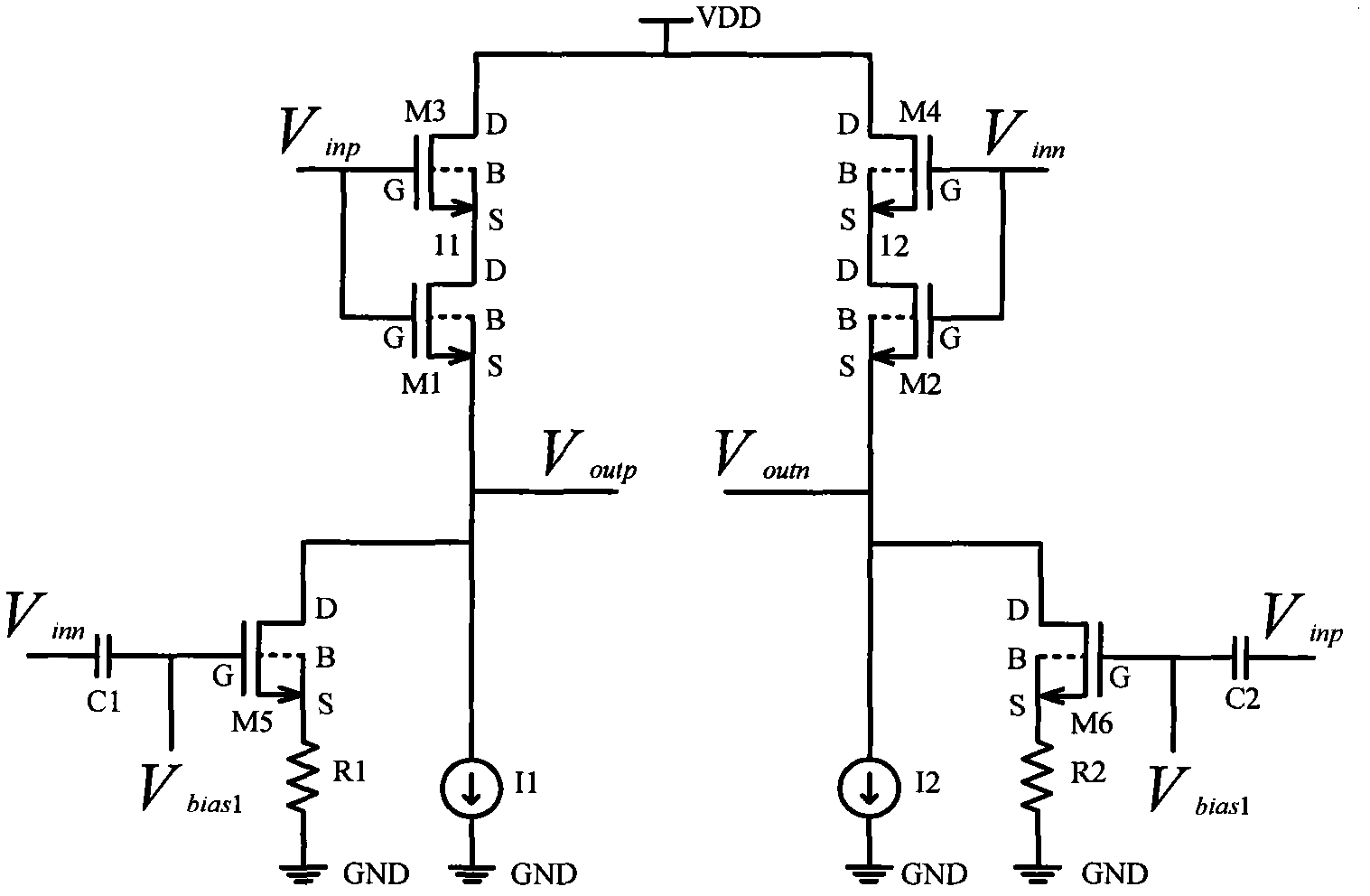
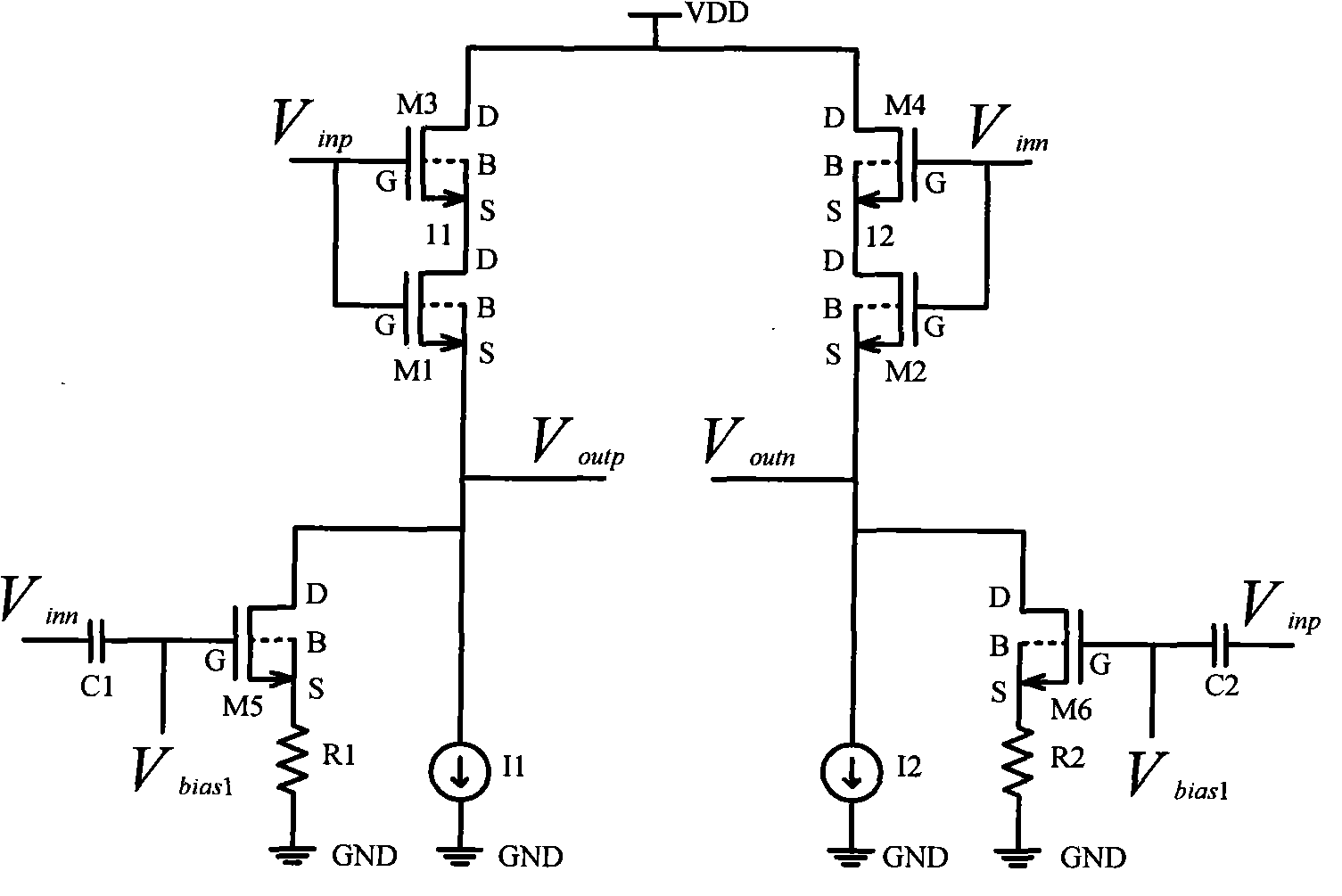
The invention discloses a linear source follower, which belongs to the technical field of voltage followers and is characterized in that: transistors M1 and M3 are arranged in a cascade mode, and the grids of the transistors M1 and M3 are both connected with an input Vinp; transistors M2 and M4 are connected in a cascade mode, and the grids of the transistors M2 and M4 are both connected with aninput Vinn; the transistors M3 and M4 are both low-threshold transistors; and the transistors M1 and M2 are both high-threshold transistors. The sources S of the transistors M1, M2, M3 and M4 are allconnected with a substrate B. The grid of a transistor M5 is connected with a bias voltage Vbias1 and is connected with the input signal Vinn through a capacitor C1, the drain of the transistor M5 isconnected with an output Voutp, and the source of the transistor M5 is grounded through a resistor R1. The grid of a transistor M6 is connected with the bias voltage Vbias1 and is connected with an input signal Vinp through a capacitor C2, the drain of the transistor M6 is connected with an output Voutn, and the source of the transistor M6 is grounded through a resistor R2. In the invention, a channel length modulation effect and a bulk effect are eliminated, the change of a bias current is lowered, and the linear source follower has the advantages of high linearity under a high-speed input signal.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High-linearity neuromorphic calculation circuit realized by passive voltage stabilizing circuit
ActiveCN113157034AGuaranteed stabilitySolve technical problems with poor linearityEnergy efficient computingElectric variable regulationSequence controlCapacitor voltage
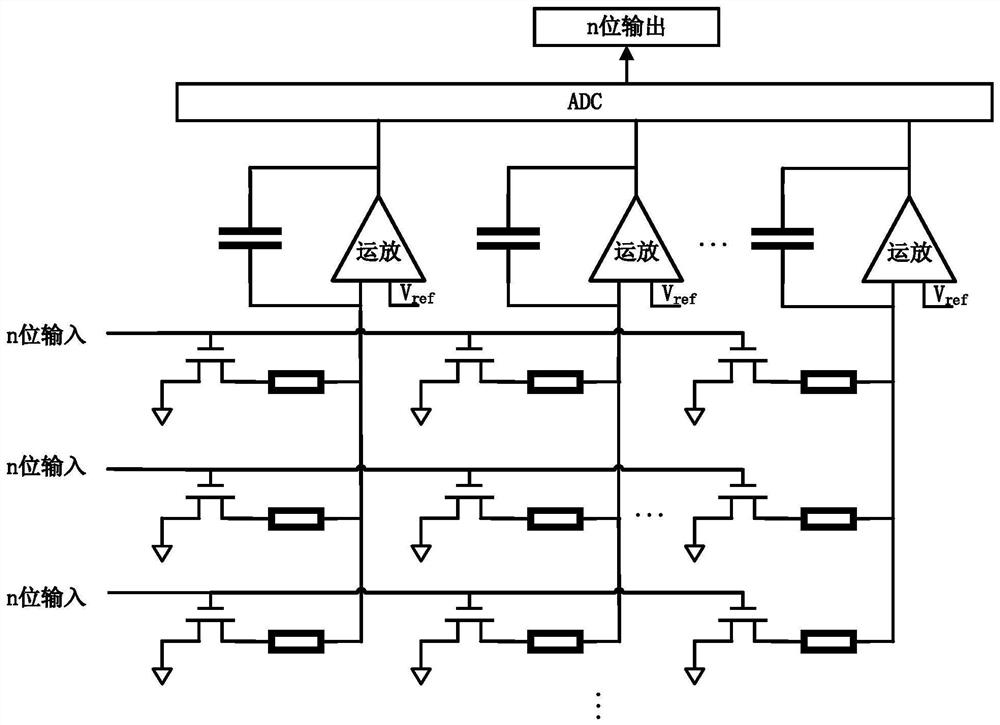
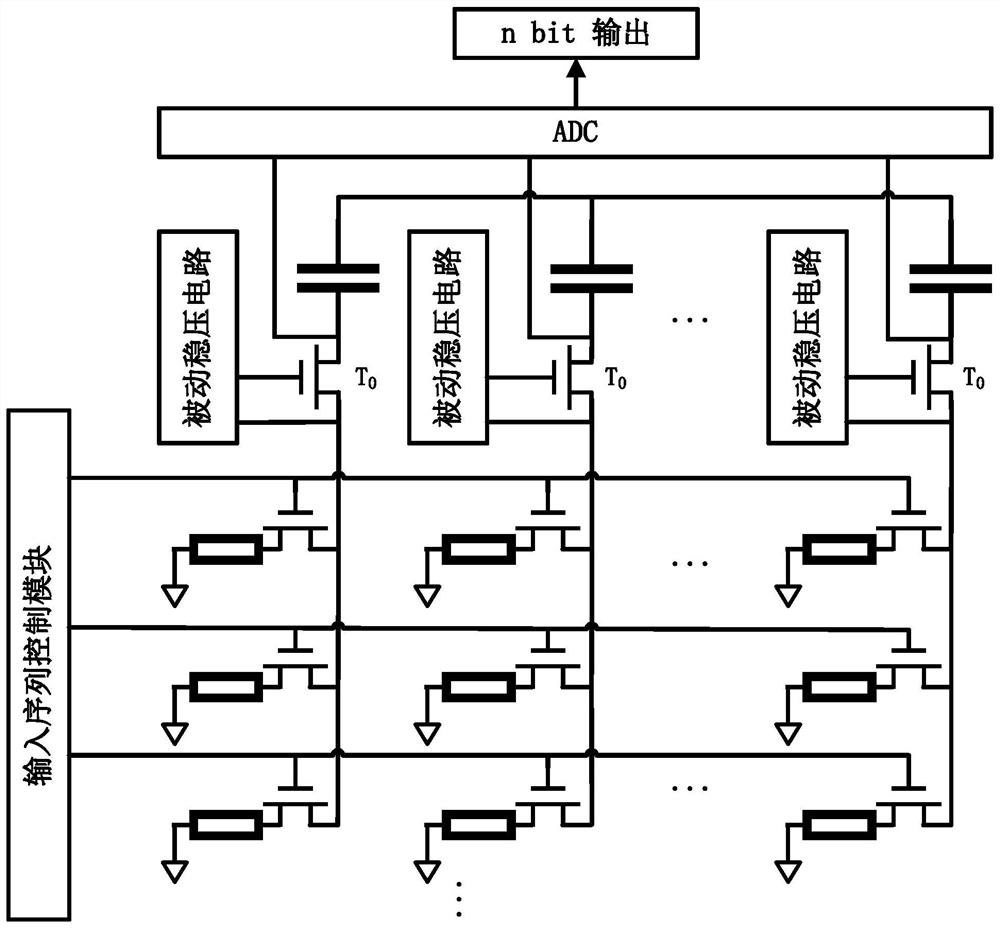
The invention discloses a high-linearity neuromorphic calculation circuit realized by a passive voltage stabilizing circuit. A 1R1T binary storage unit array is connected with an input sequence control switch and a plurality of bit line capacitor voltage isolation transistors, and the input sequence control switch receives input data of a neural network. Each bit line capacitor voltage isolation transistor is connected with a biasing circuit through a respective passive voltage stabilizing circuit, the plurality of bit line capacitor voltage isolation transistors are jointly connected to an analog-to-digital conversion circuit, and a calculation result is output through the analog-to-digital conversion circuit ADC. According to the invention, the influence of the channel length modulation effect caused by the drop of the capacitor voltage in the integration process can be effectively eliminated, so that the integration current is more stable; and meanwhile, the stability of the source voltage of the T0 under different loads can be ensured, and the technical problem that the linearity of the weight value of the circuit is poor due to the fact that the load change is affected is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
High-voltage linear voltage regulator
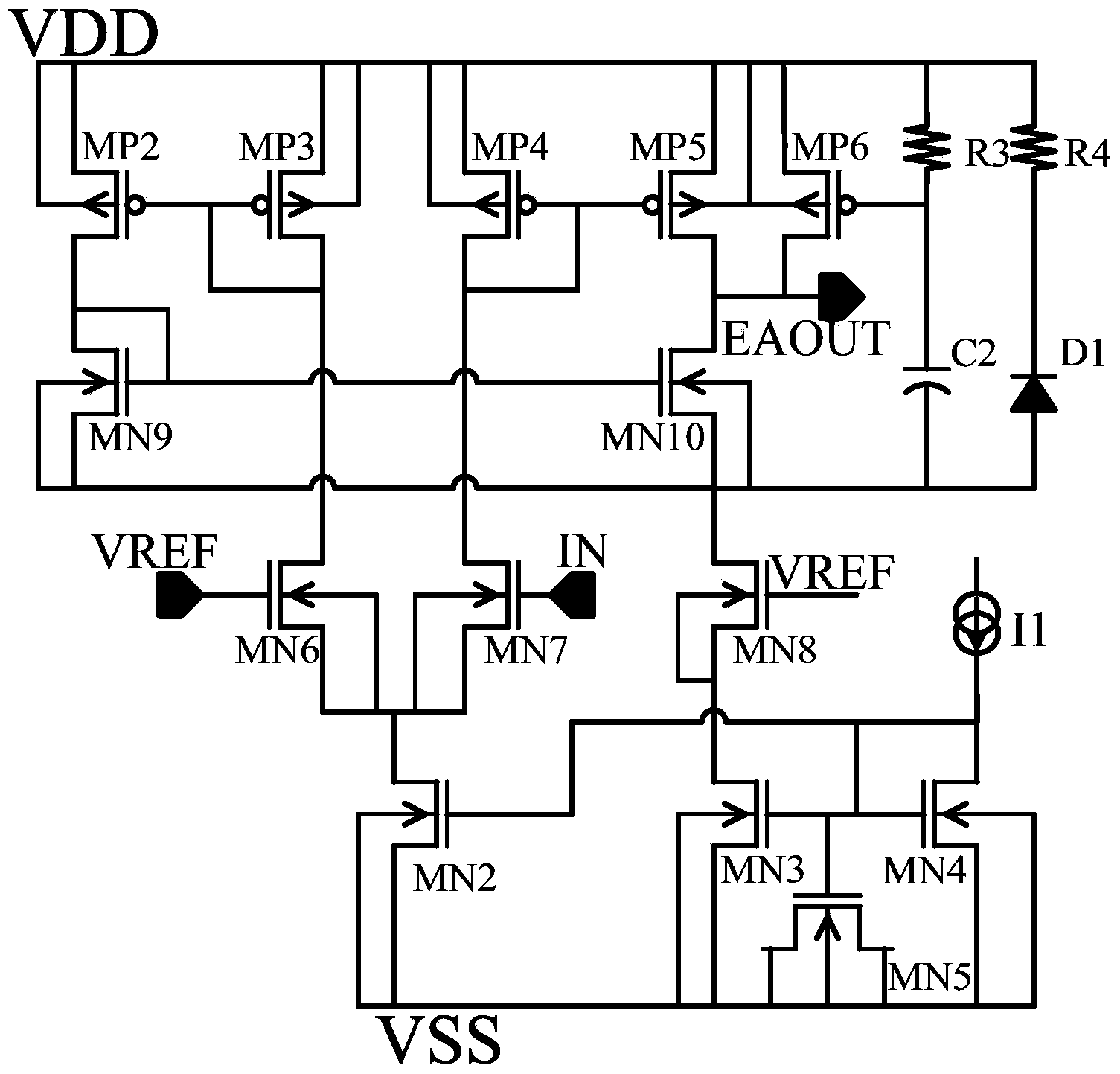
InactiveCN103955251AReduce areaSuppression of channel length modulation effectsElectric variable regulationZener diodeEngineering
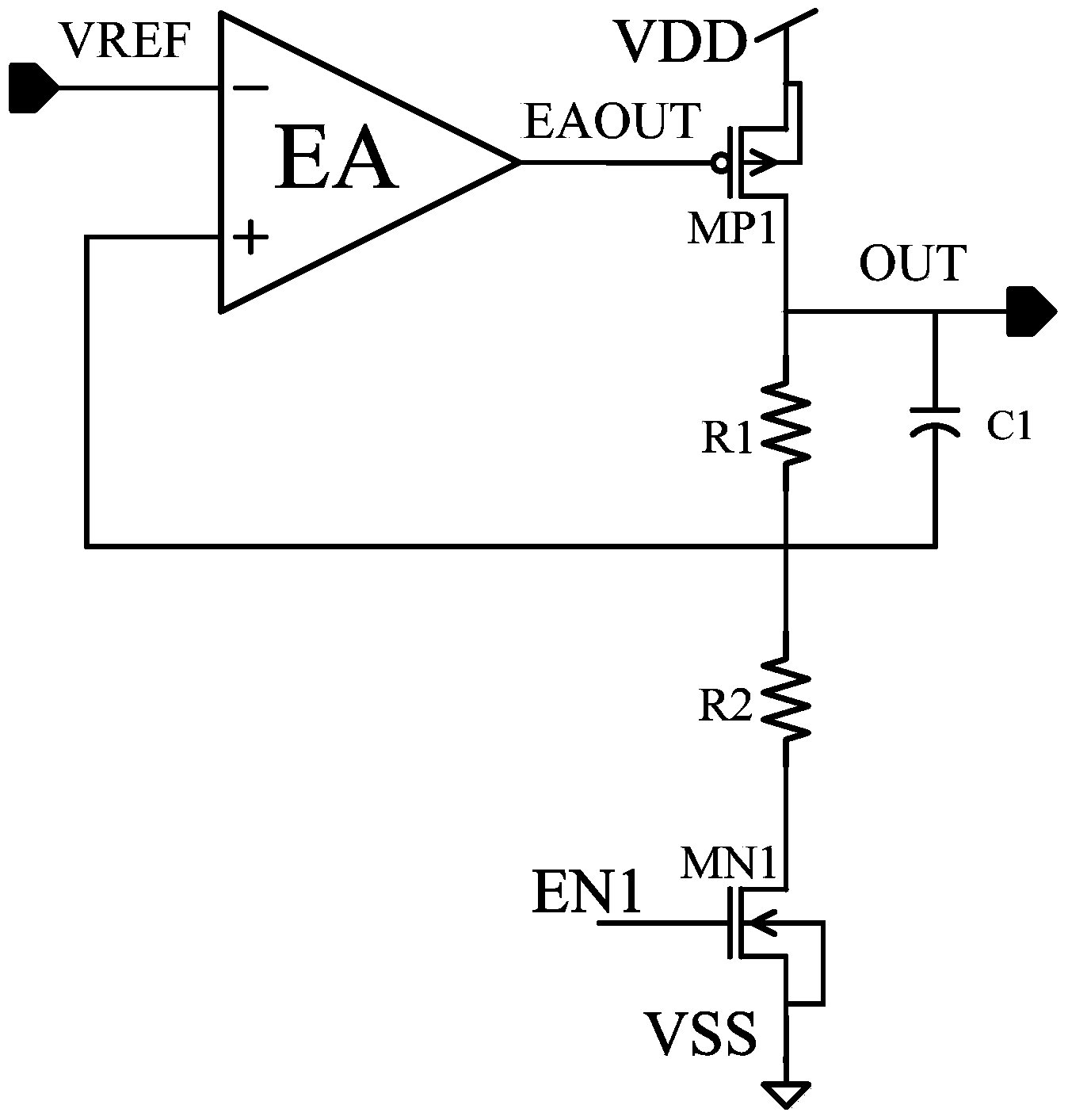
The invention relates to the technique of electronic circuits and particularly relates to a high-voltage linear voltage regulator. According to the high-voltage linear voltage regulator, a circuit structure to the ground is introduced, and a branch formed by connecting a resistor R4 with a Zener diode D1 in series is connected in parallel with a circuit branch formed by connecting a PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube MP5 and an NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube MN10 in series. The breakdown voltage of the Zener diode adopted by the invention is 6V, so that source electrodes of NMOS tubes including MN10 and MN9 namely the point potentials connected with the diode D1 are clamped to high-voltage -6V under the high voltage condition, and the higher voltage effectively protects a grid electrode of a regulating tube. Compared with an existing LDO (Low Dropout Regulator), the grid electrode of the regulating tube is protected and the channel length modulation effect of an MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) in an error amplifier is inhibited under the high voltage condition in the starting process and in the transient response process, so that the use of a high voltage device is reduced, the area of the LDO is reduced, and the performance of the high-voltage LDO is improved. The invention is particularly suitable for the high-voltage linear voltage regulator.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Energy-gap reference circuit
The invention discloses an energy gap reference circuit comprising: a reference current generation circuit generating a first and second reference currents on a first and second current paths; a current mirror generating a third reference current on the third current path based on the first and second reference currents; an operational amplifier to make the first reference current equal to the second reference current; and a feedback circuit to make a mode voltage on the first current path equal to a node voltage on the third current path, to eliminate error caused by probable channel length modulation effect of the current mirror.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Zero-cross detection circuit
InactiveCN105406444AReduced short lifeHigh gainCurrent/voltage measurementEmergency protective circuit arrangementsChannel length modulationHemt circuits
The invention discloses a zero-cross detection circuit. Voltage-withstanding tubes of a sampling circuit are a PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube and an NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube, so that the problem of short service life due to high voltage damage can be solved. The zero-cross detection circuit also comprises a current bias module; the phenomenon of great errors caused by the influence of channel length modulation effect on the mirror current can be reduced; a current comparator is set into a two-stage current comparator; a cascade device is inserted in a first stage circuit; the gain can be improved, and meanwhile, great oscillation amplitude can be realized; the lead of the zero-cross detection circuit is 48 to 50mA; the stability and the identification sensitivity of a system can be improved; the work efficiency can be improved; and the application value is very high.
Owner:WUHU RUIXIN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
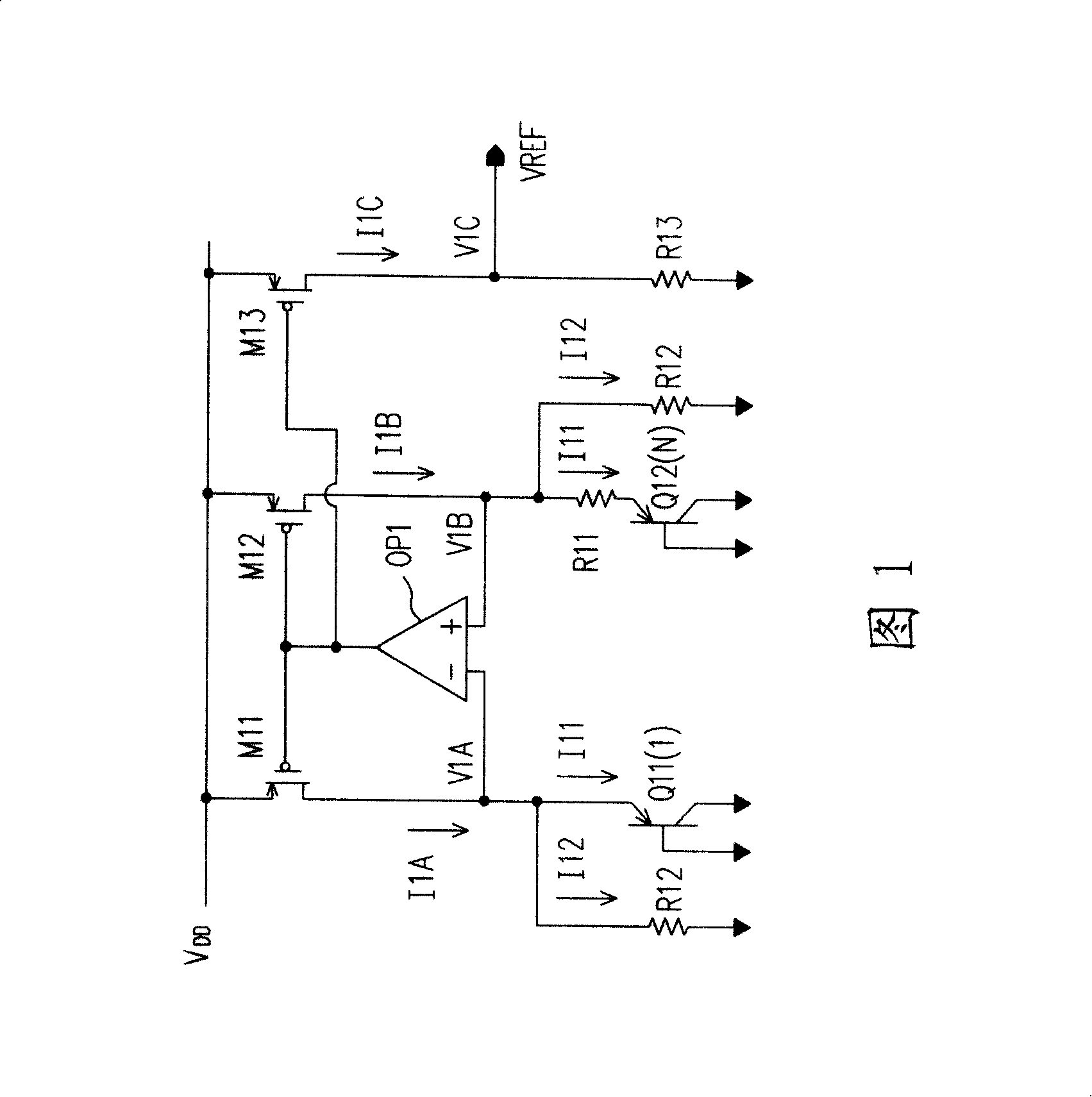
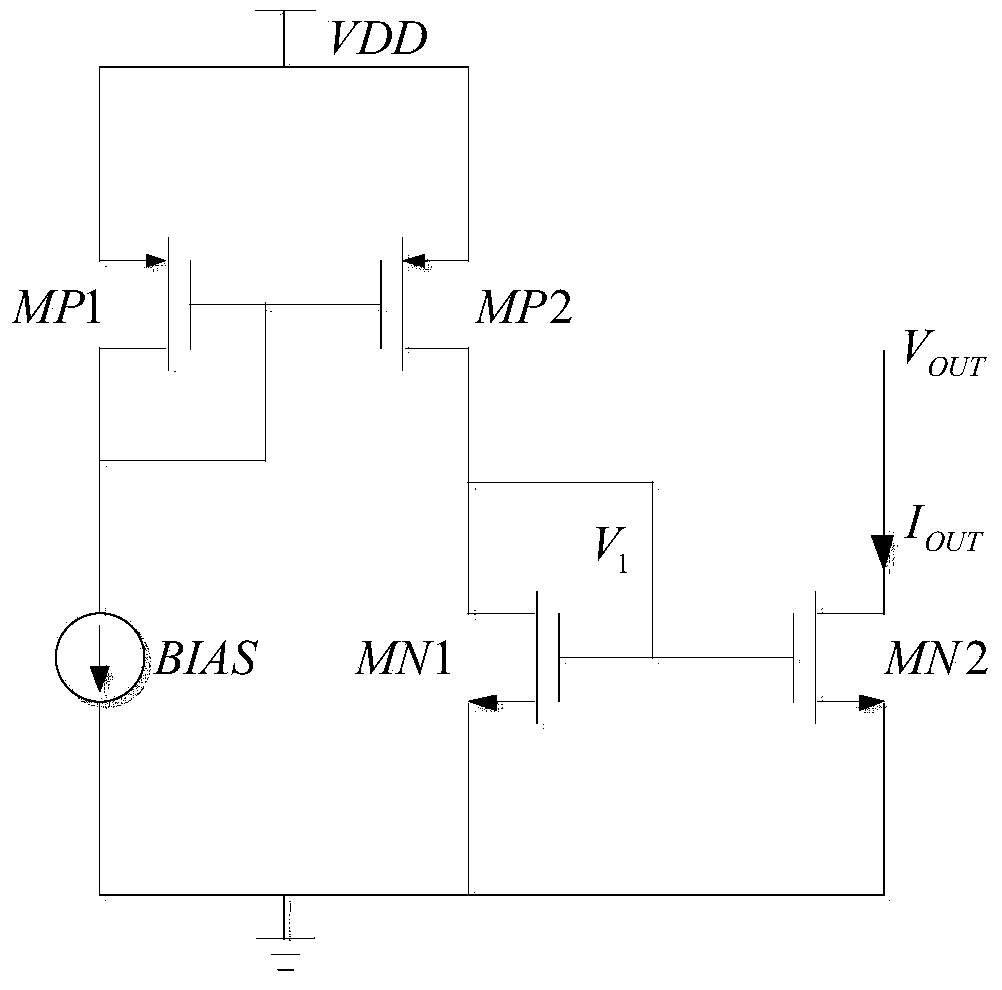
Constant current source with threshold voltage and channel length modulation compensation
InactiveUS7015846B2Good PSRRImprove performanceMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectric signal transmission systemsChannel length modulationElectricity
A constant current source with threshold voltage and channel length modulation comprises a set of cascade transistors and a compensation circuit electrically connected to the set of cascade transistors so as to form a feedback circuit, in which the set of cascade transistors including a first MOS transistor and a second MOS transistor, and the compensation circuit comprises a third MOS transistor, a fourth MOS transistor, a sixth MOS transistor and a seventh MOS transistor. The gate terminal of the third MOS transistor is connected to the gate terminal of the second MOS transistor. The fourth MOS transistor is connected to the third MOS transistor in serial, and the gate terminal of the fourth MOS transistor is connected to the gate terminal of the first MOS transistor, and the second terminal of the fourth MOS transistor is connected to a current-supplying circuit. The gate terminals of the sixth and seventh MOS transistors are electrically connected to the current-supplying circuit, and a current is generated by mirroring flows through the third MOS transistor.
Owner:SPIROX INC
High-voltage high-current control circuit applied to high-voltage power MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) circuit
ActiveCN103645765AEasy to controlElectric variable regulationNegative feedbackChannel length modulation
A high-voltage high-current control circuit applied to a high-voltage power MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) circuit comprises a PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) tube MP1, a PMOS tube MP2, a PMOS tube MP3, a triode Q1, a triode Q2, an MOSFET tube M1, an MOSFET tube M2, a resistor R1 and a resistor R2, wherein the MP1, the MP2 and the MP3 share a grid electrode; the source electrodes of the MP1, the MP2 and the MP3 are connected with a VDD; the drain electrodes of the MP2 and the MP3 are connected with the collector electrodes of the Q1 and the Q2 respectively; the base electrodes of the Q1 and the Q2 are connected with each other; the emitting electrodes of the Q1 and the Q2 are connected with the R1 and the R2 respectively; the M1 and the M2 share a grid electrode and share a drain electrode; the source electrode of the M1 is connected with the R1; the source electrode of the M2, the R1 and the R2 are grounded; the Q1 is matched with the Q2; the R1 and the R2 are resistors matched with each other according to a proportional relation; the width-to-length ratio of the M1 is proportional to that of the M2. The high-voltage high-current control circuit does not consider a channel length modulation effect of a transistor, introduces a negative feedback by the R1 and converts high current into a current comparison signal, thus achieving precise control over the current in a high-voltage high-current mode.
Owner:JIAXING ZHONGRUN MICROELECTRONICS
CMOS input signal buffer applied to front end of high-speed ADC
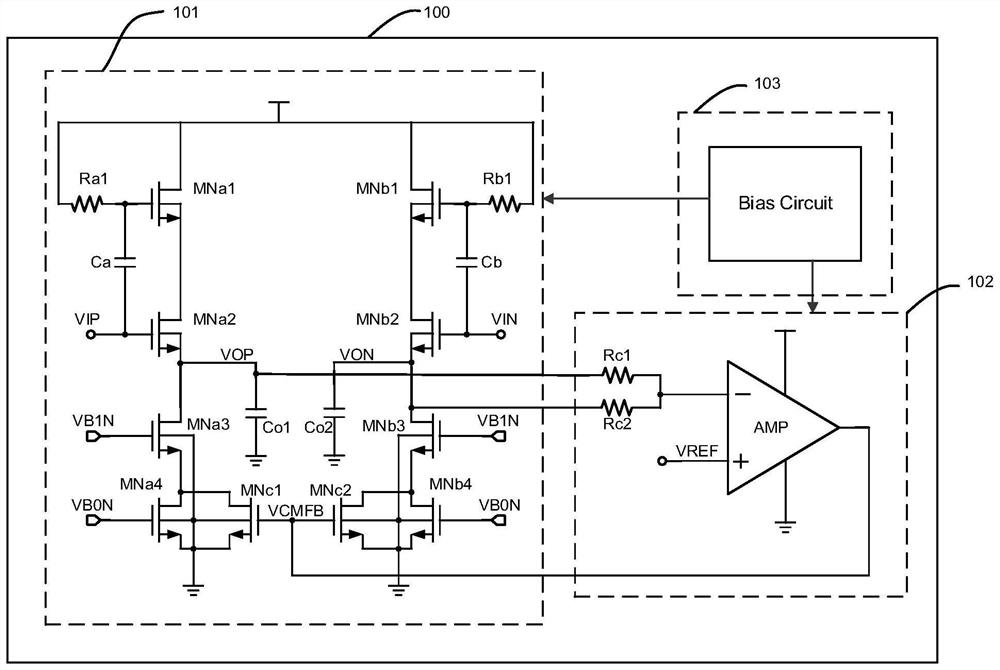
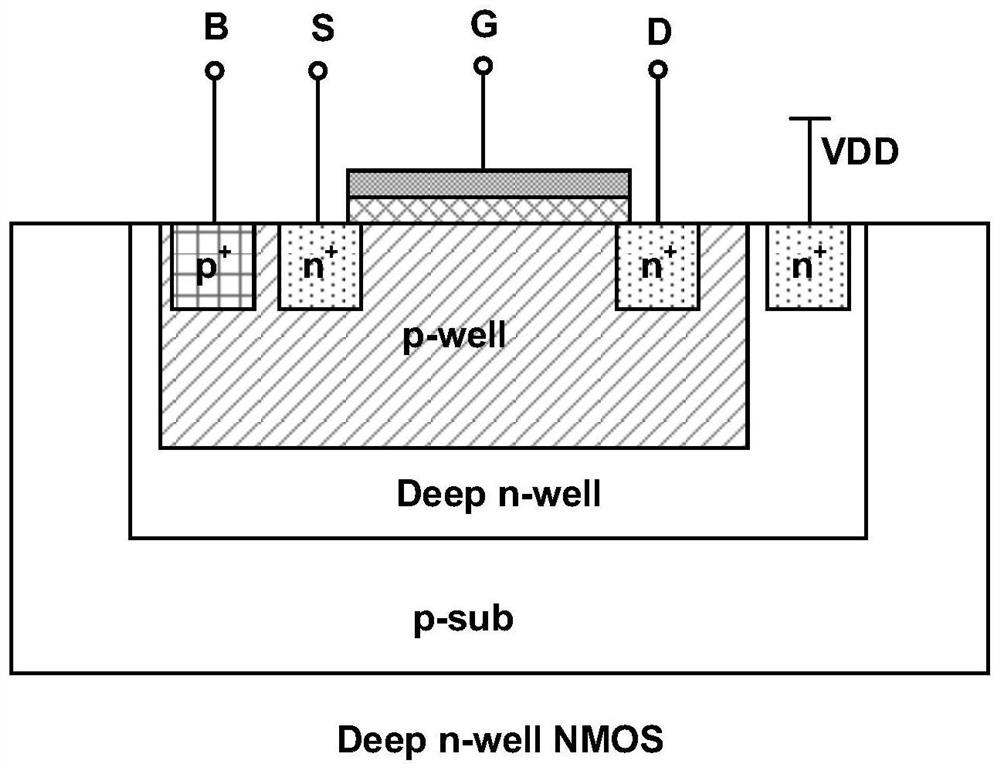
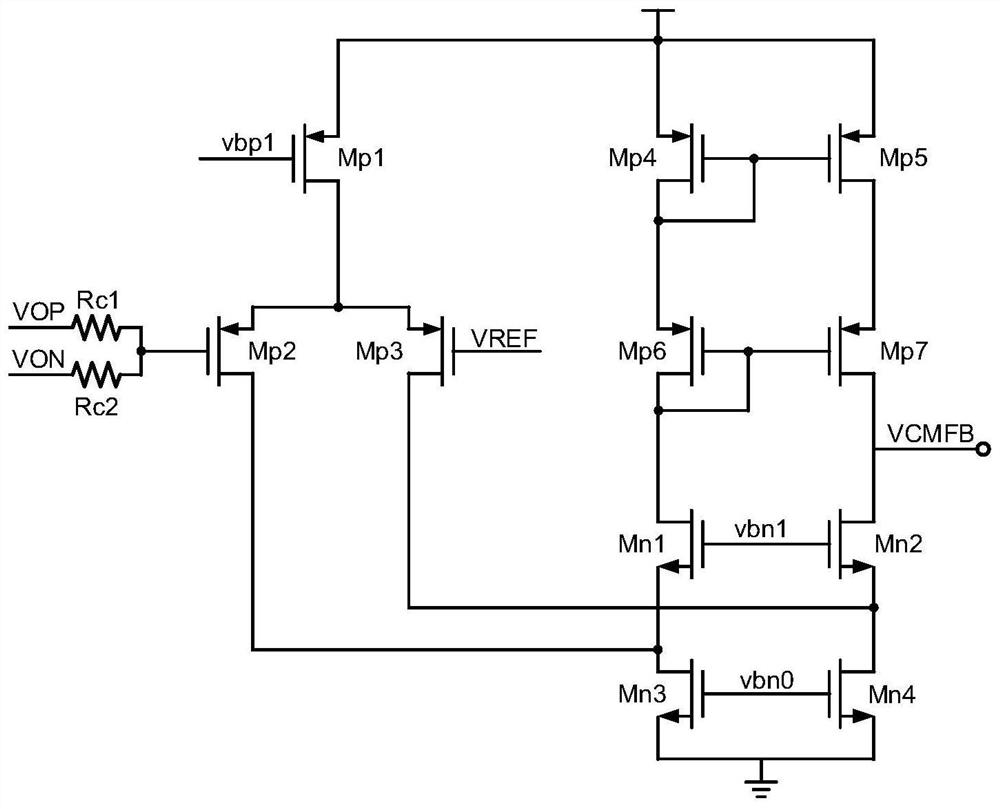
PendingCN111756366AImprove linearitySolve driftLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsAnalogue-digital convertersSoftware engineeringCascode
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits, and particularly relates to a CMOS input signal buffer applied to the front end of a high-speed ADC. The circuit structure comprises an input buffer with two differential source following structures, a common-mode feedback circuit module and a bias circuit module. According to the invention, stable common-mode output of a sourcefollower can be ensured; a channel length modulation effect under a deep submicron CMOS process is avoided; a N-type transistor adopts a deep N-well device to eliminate the substrate bias modulation effect. A cascode current source with large output impedance is used for providing bias current for an input transistor so as to relieve output signal nonlinearity caused by input signal changes. The buffer is used in an ADC circuit, can play a role in improving linearity and isolating an input signal from a post-stage circuit, has good linearity even when an input signal with higher frequency is input, and is particularly suitable for a front-end buffer circuit of a high-speed ADC.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com