Patents
Literature
210results about How to "Reduce common mode noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
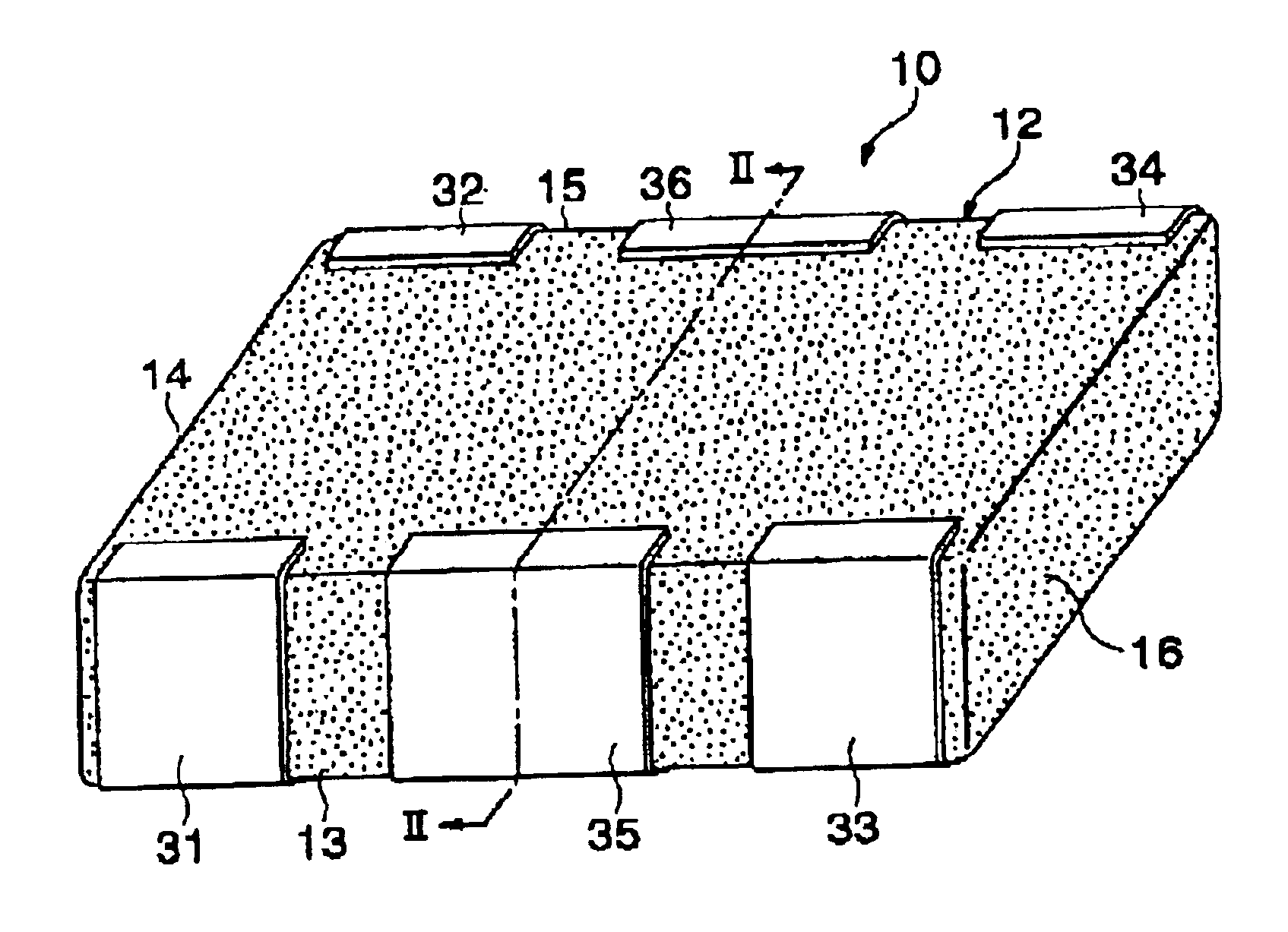
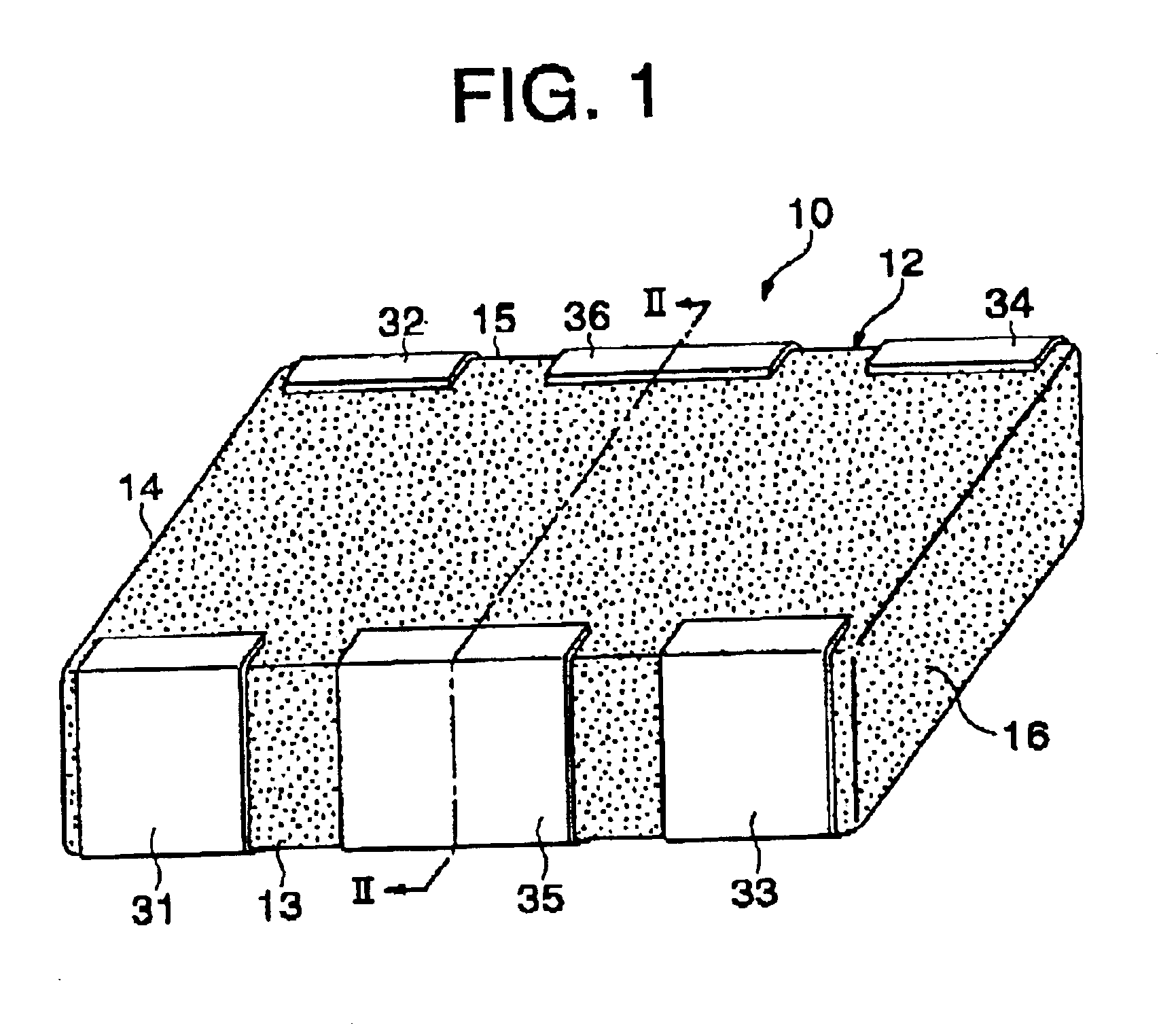
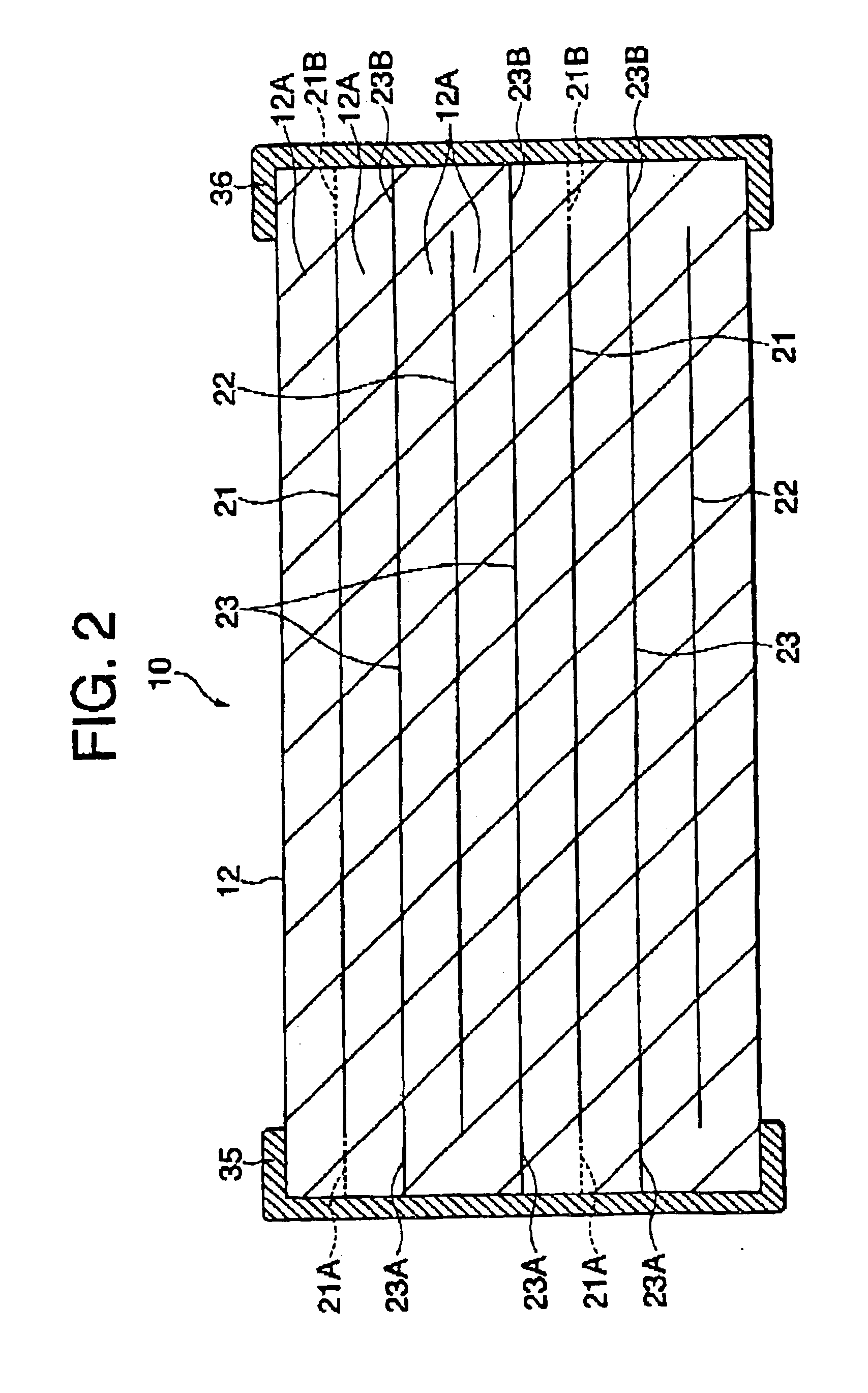
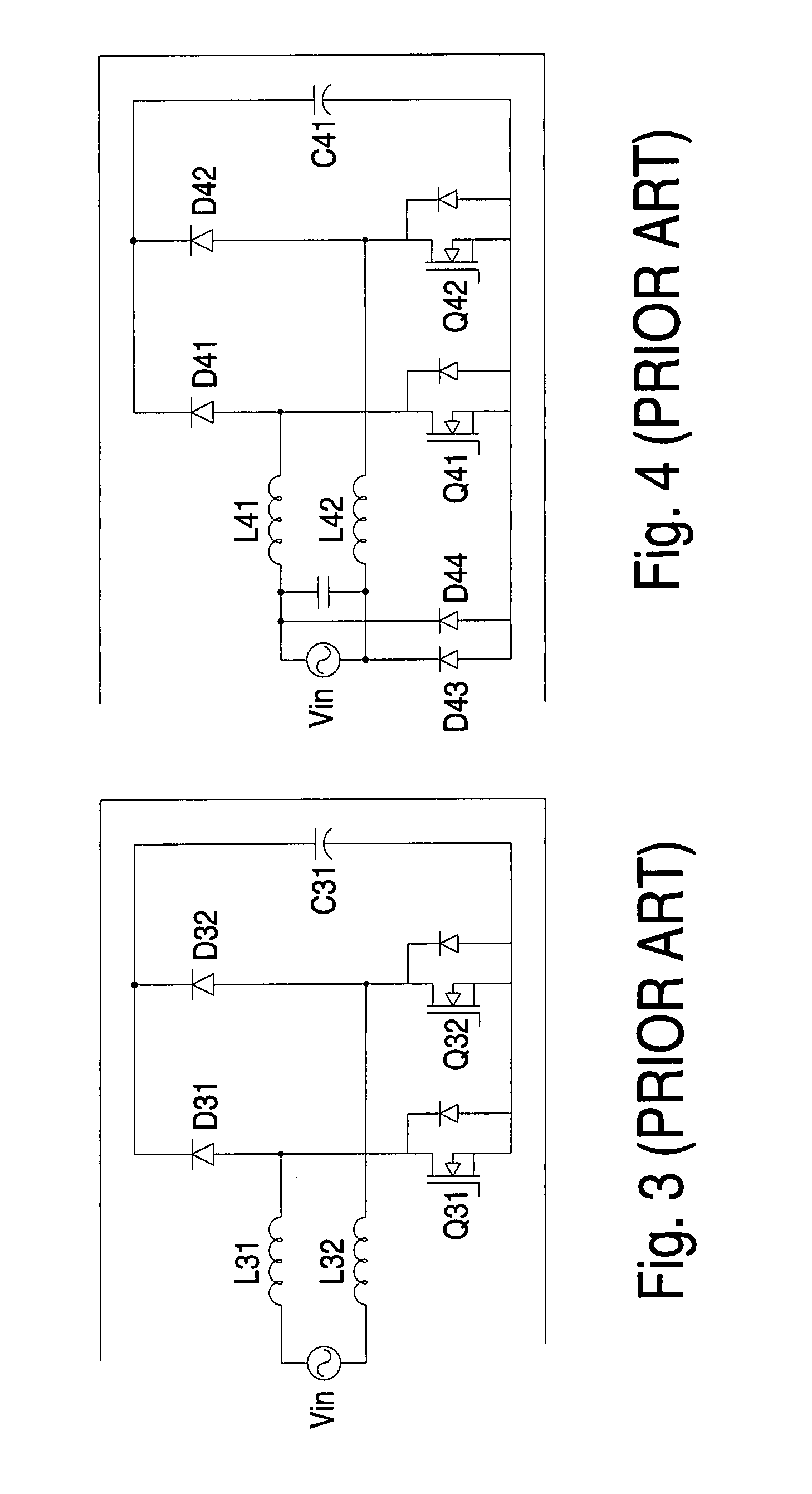
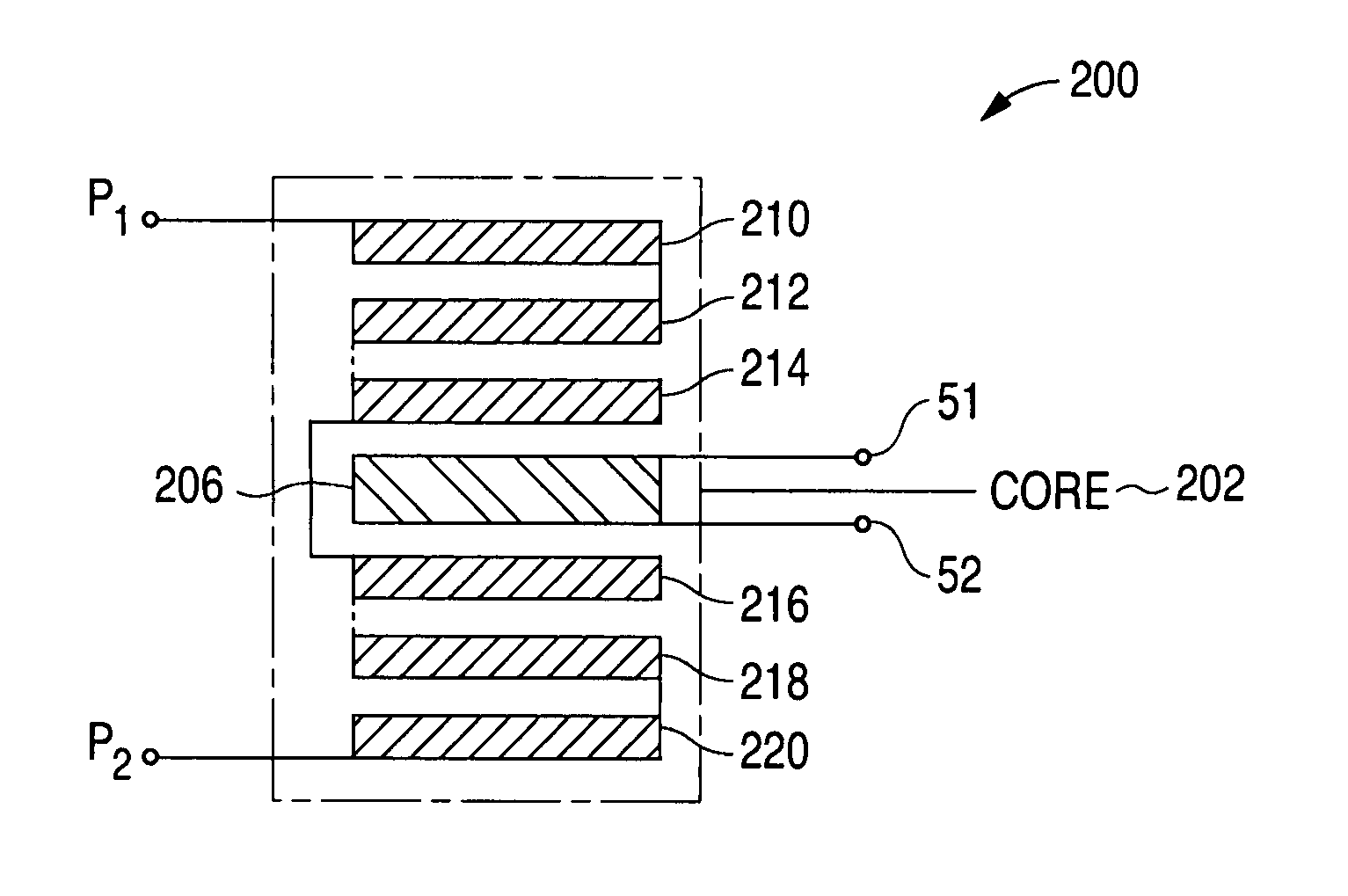
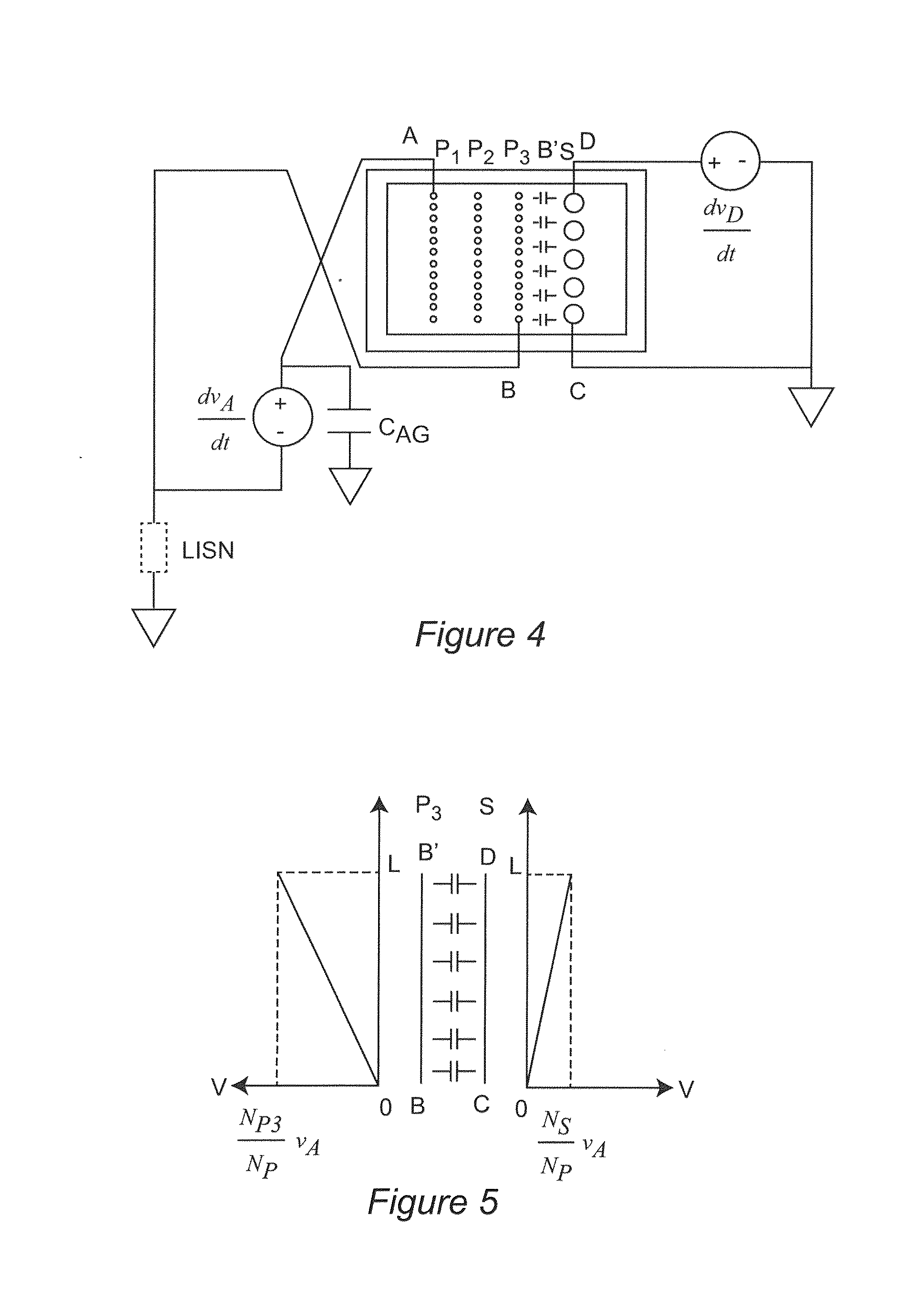
Multilayer feedthrough capacitor
InactiveUS6768630B2Reduce common mode noiseESL is further reducedAnti-noise capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesElectrical conductorEngineering
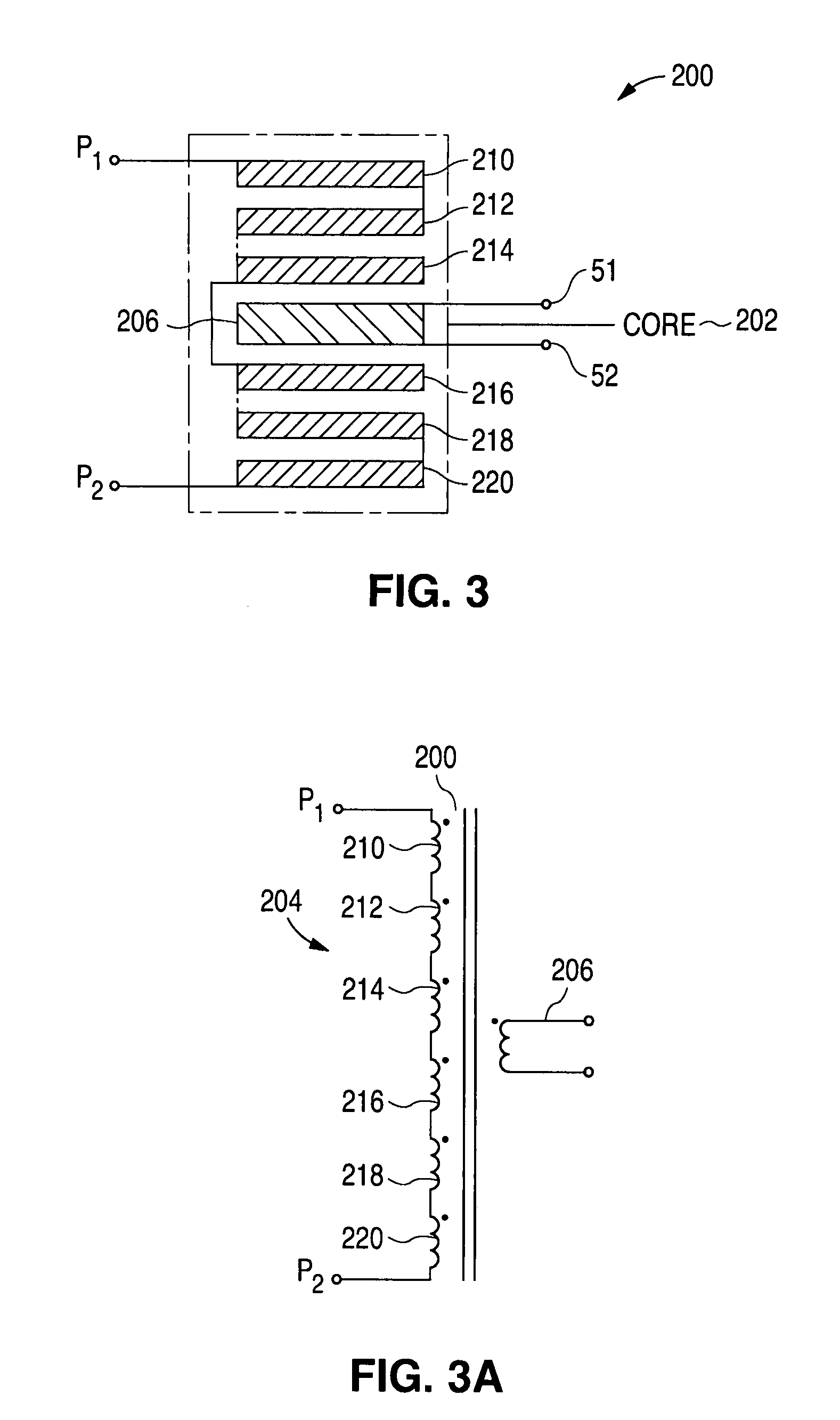
A multilayer feedthrough capacitor having a first internal conductor arranged in a dielectric body, an intermediate internal conductor arranged in the dielectric body and stacked with the first internal conductor via a ceramic layer, a second internal conductor arranged in the dielectric body and stacked with the intermediate internal conductor via a ceramic layer, a first terminal electrode formed at an outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the first internal conductor, a second terminal electrode formed at the outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the second internal conductor, and an intermediate terminal electrode formed at the outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the intermediate internal conductor. The intermediate terminal electrode is connected to the ground, while the first terminal electrode and the second terminal electrode are connected to paths for transmitting signals. The first internal conductor and the second internal conductor have currents flowing through them in opposite directions.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
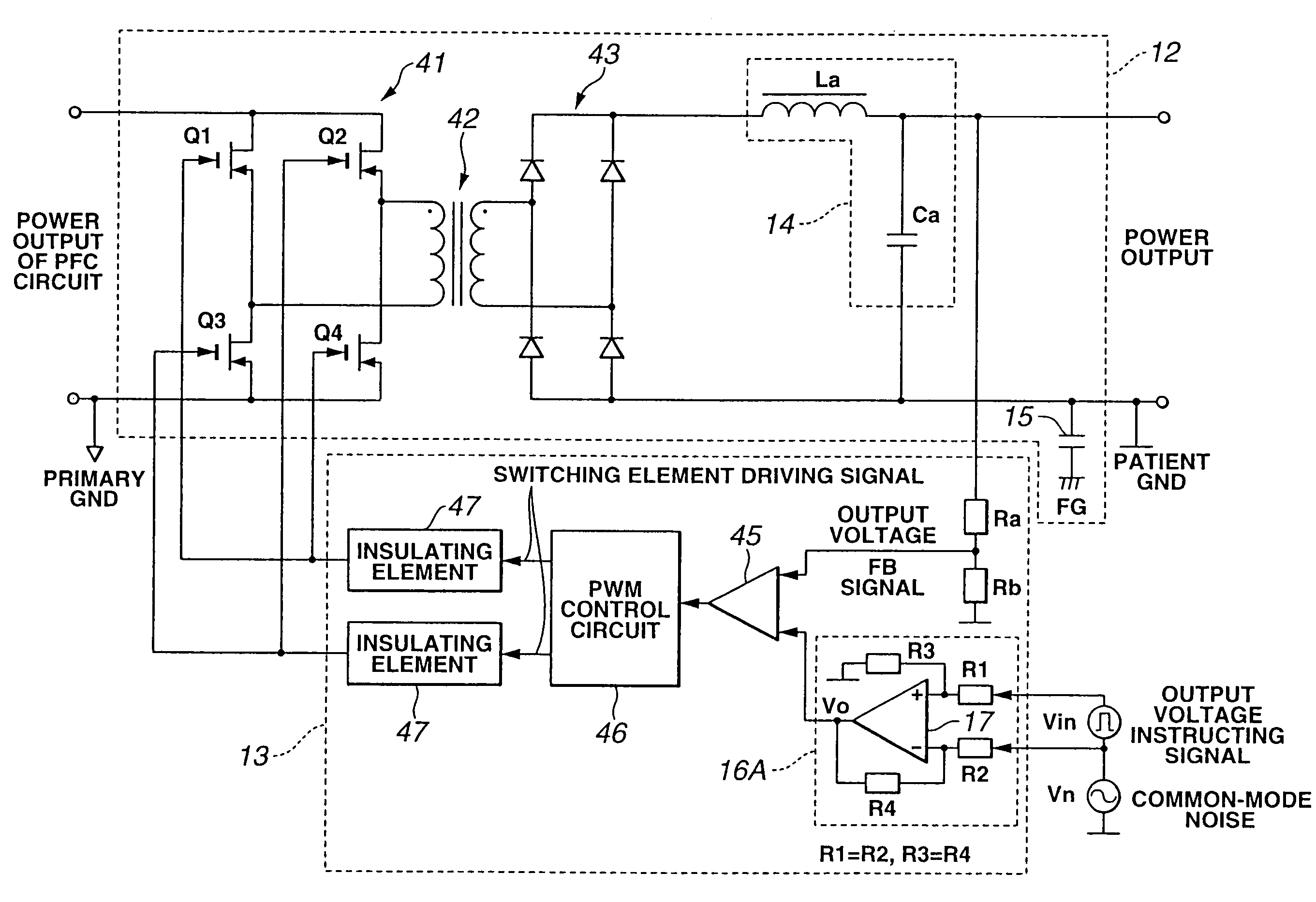
Power supply apparatus for electric operation
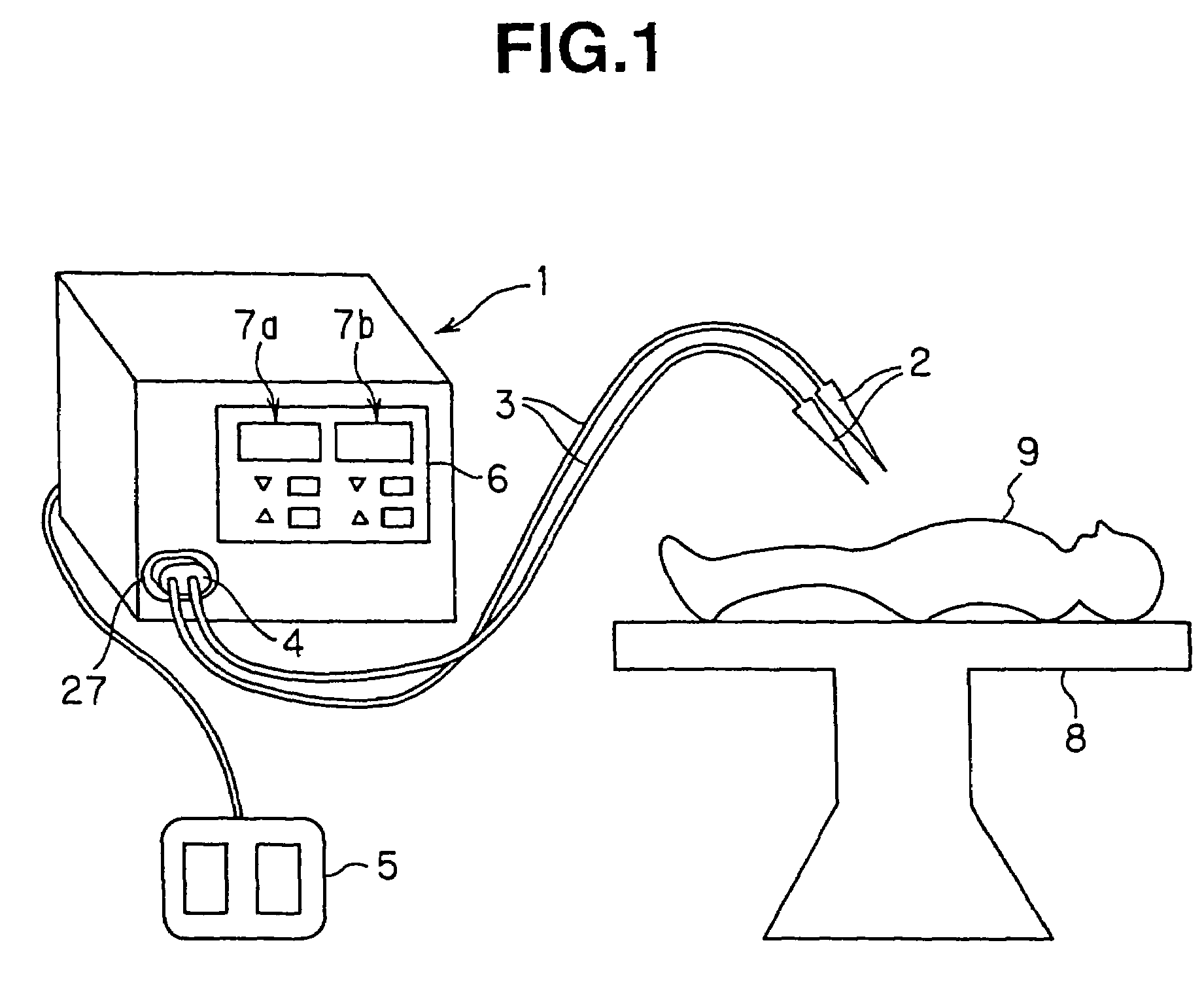
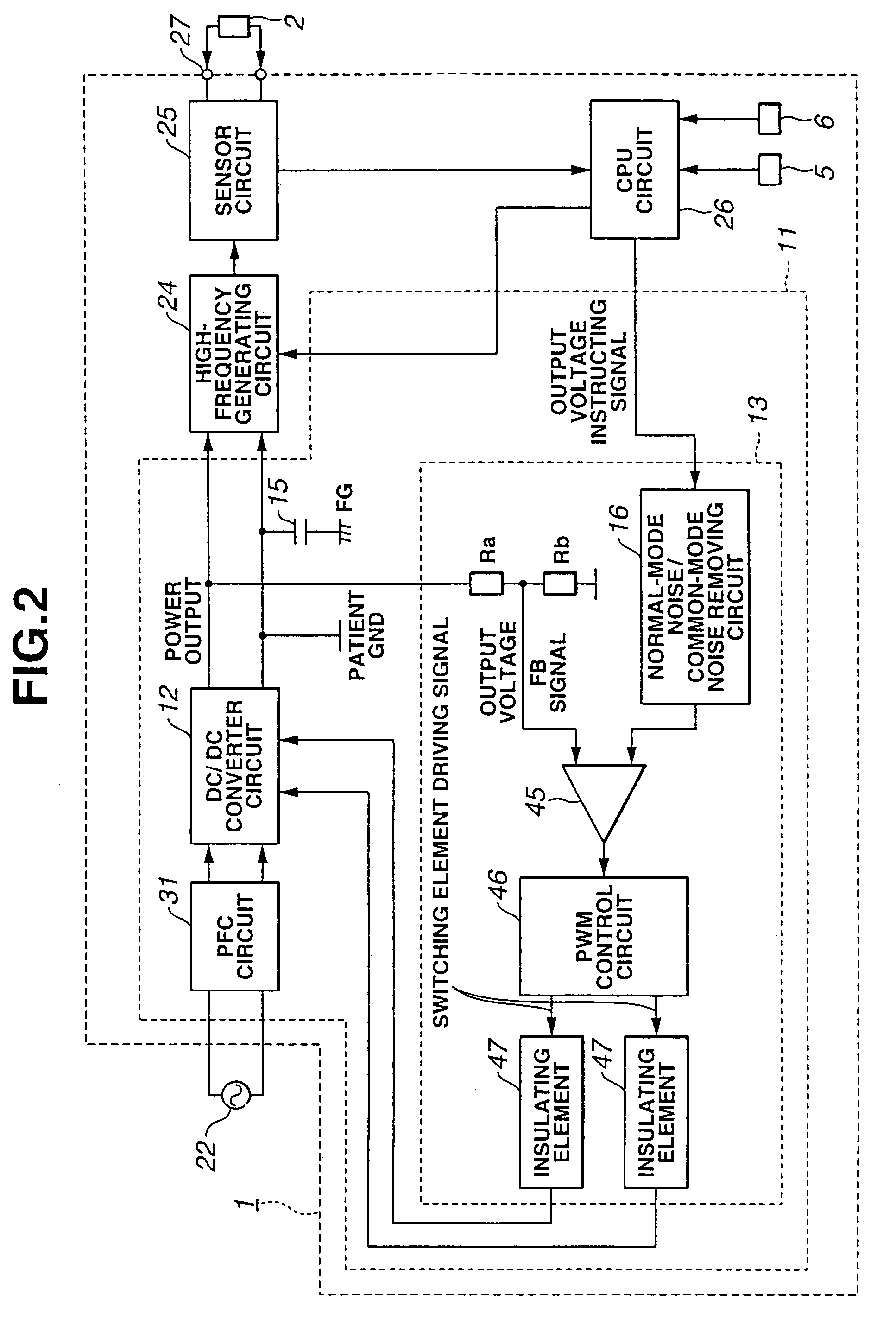
ActiveUS7324357B2High frequencyReduce common mode noiseDc-dc conversionSurgical instruments for heatingNormal modeEngineering
A power supply apparatus for electric operation is provided for an electric operation apparatus, and includes an instructing signal input portion which generates a DC output voltage to a high-frequency generating circuit that generates a high frequency and which receives an instructing signal for controlling the output voltage. The instructing signal input portion includes at least a noise reducing circuit which reduces a normal-mode noise.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
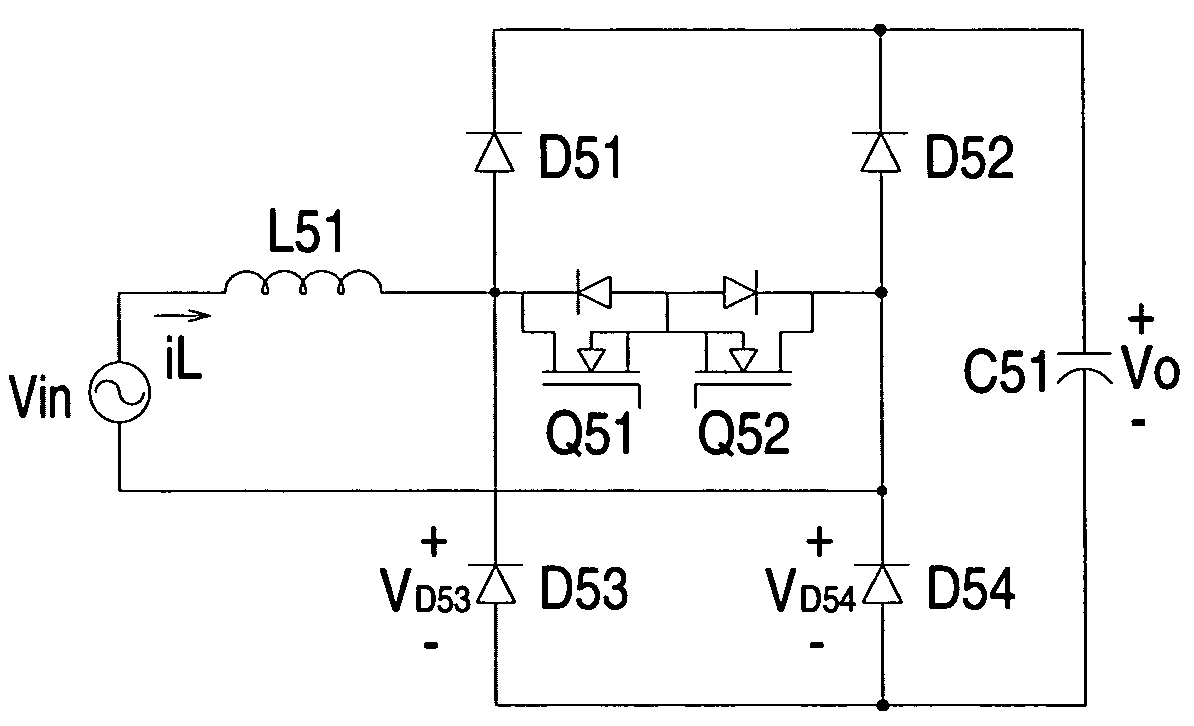
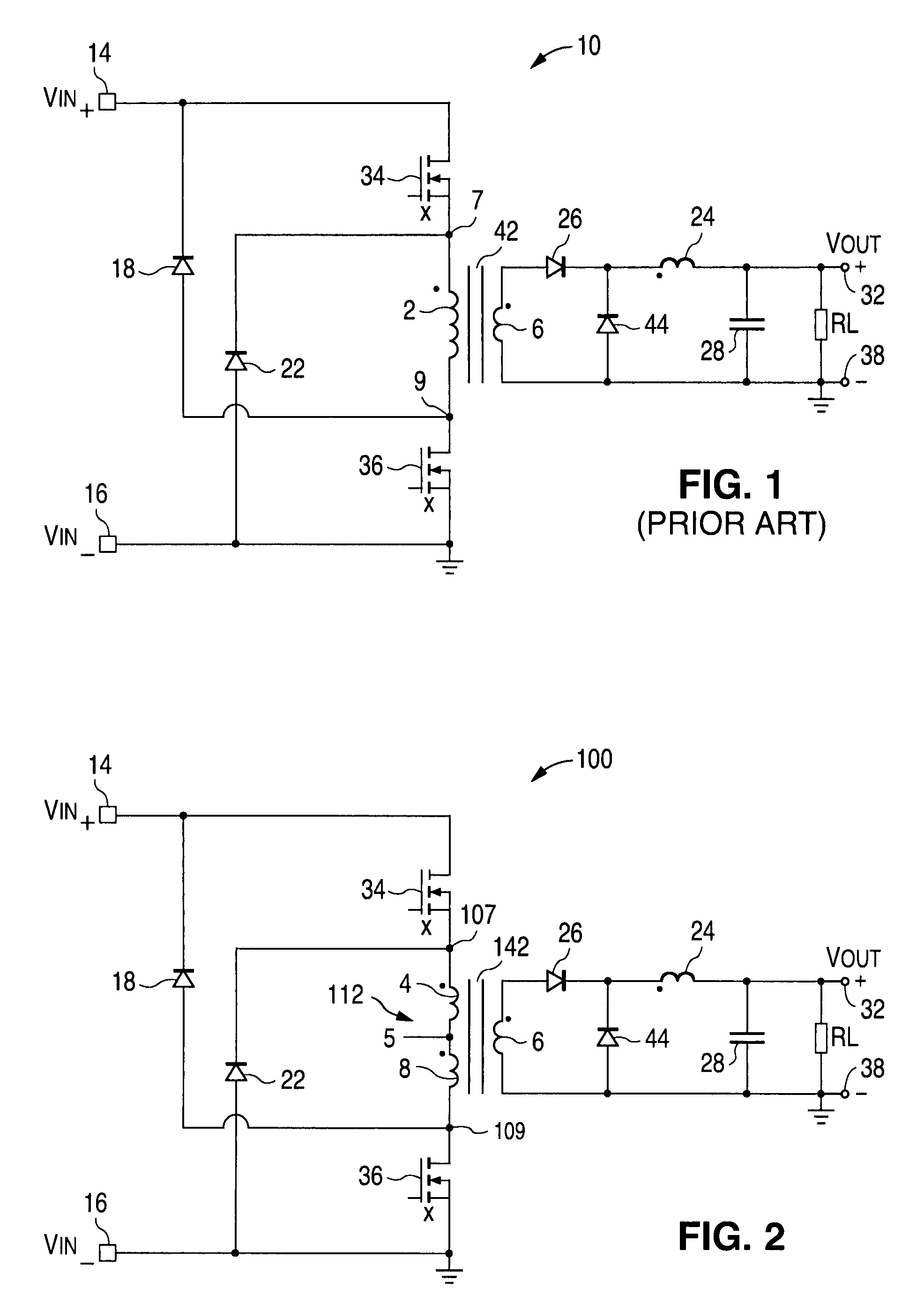
Bridgeless pfc converter with low common-mode noise and high power density
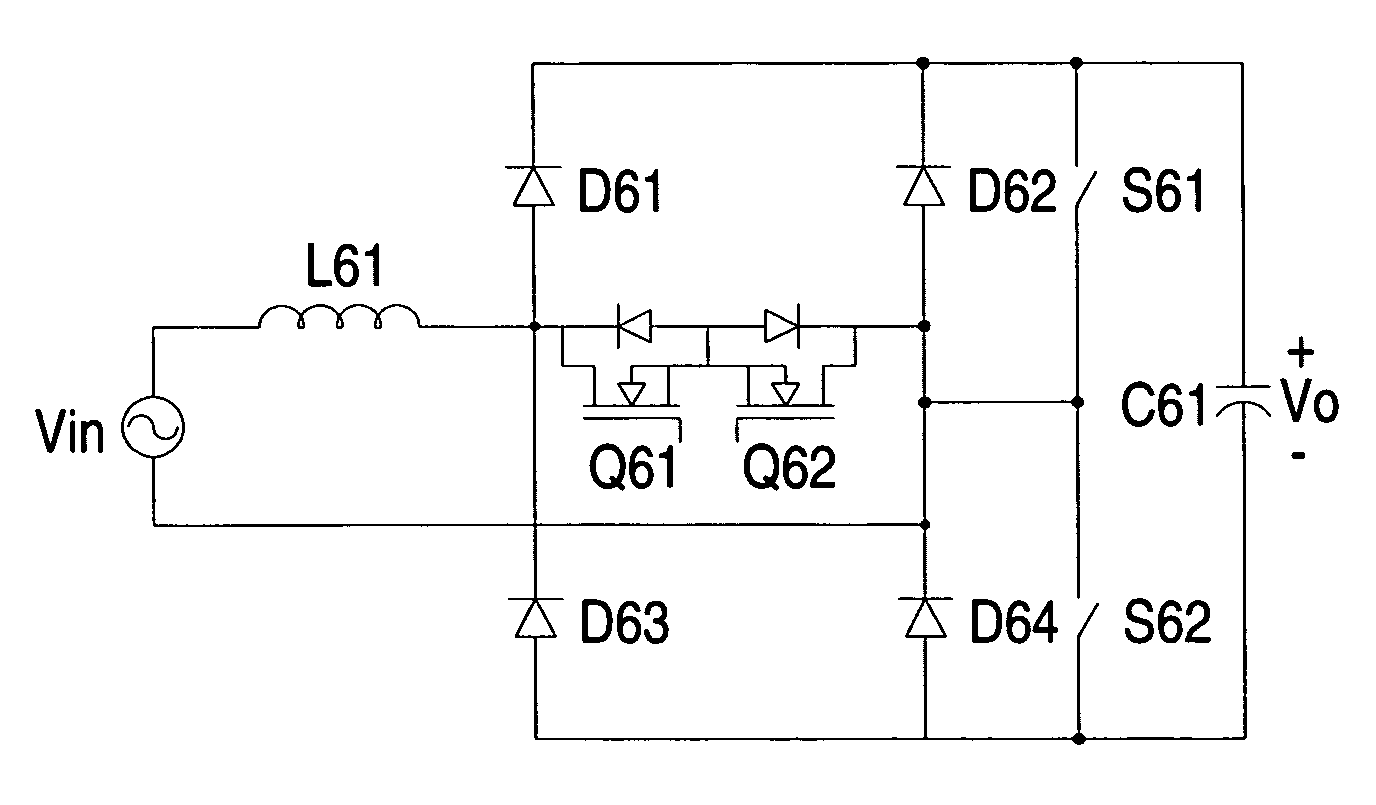
ActiveUS20070279955A1Reduce common mode noiseImprove power densityAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionInductorEngineering
A bridgeless power factor correction converter that can reduce common-mode noise and enhance power density is made up of a boost inductor coupled to an input end, a bidirectional switch connected in series with the boost inductor, a first series rectifying circuit having a junction node connected between the boost inductor and the bi-directional switch, a second series rectifying circuit connected in parallel with the first series rectifying circuit and having a junction node coupled to the bi-directional switch, and an output capacitor connected in parallel with the second series rectifying circuit, in which the second series rectifying circuit is made up of slow-recovery diodes and the first series rectifying circuit is made up of fast-recovery diodes.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Interface Devices, Systems and Methods for Multimodal Probes
ActiveUS20140142436A1Reduce common mode noiseHigh voltageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcoustic sensorsElectricityEngineering
In one aspect, the invention relates to one or more rotatable elements and one or more stationary element such that the elements are arranged along a common axis of rotation co-linear with or substantially parallel to an optical path. The optical path is a portion of a sample arm of an interferometer. Further, the rotatable and stationary elements are configured to couple electrical signals and optical signals between a data collection probe and an interface unit or other component of an imaging system. In one embodiment, the data collection probe is a combination ultrasound and OCT probe. In one aspect, the invention relates to a rotary joint in which the optical fiber and a fiber optic rotary joint lie in the center of one or more conductive elements of an electrical rotary joint which are annularly disposed around one or both of the optical fiber and optical rotary joint.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Bridgeless PFC converter with low common-mode noise and high power density
ActiveUS7605570B2Improve power densityReduce common mode noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionInductorHigh power density
A bridgeless power factor correction converter that can reduce common-mode noise and enhance power density is made up of a boost inductor coupled to an input end, a bidirectional switch connected in series with the boost inductor, a first series rectifying circuit having a junction node connected between the boost inductor and the bi-directional switch, a second series rectifying circuit connected in parallel with the first series rectifying circuit and having a junction node coupled to the bi-directional switch, and an output capacitor connected in parallel with the second series rectifying circuit, in which the second series rectifying circuit is made up of slow-recovery diodes and the first series rectifying circuit is made up of fast-recovery diodes.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Common Mode Choke Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20130049918A1Reduce common mode noiseReduce noiseTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCores/yokesInductanceElectrical and Electronics engineering
An embodiment integrated common mode choke comprises a magnetic core, a magnetic plate, a first winding coil and a second winding coil. The magnetic plate is inserted within an inner circumference of the magnetic core. The first winding coil and the second winding coil are wound are wound in the same direction through the magnetic core. The integrated common mode choke is equivalent to a common mode choke and a differential mode choke connected in series. The inductance value of the differential mode choke can be changed by adjusting either the gap between the magnetic plate and the magnetic core or the thickness of the magnetic plate.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Three-phase three-level soft-switched pfc rectifiers
ActiveUS20130235626A1Low rateReduce conduction lossAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionClamp capacitorThree level
A low input-current-harmonic three-phase three-level boost rectifier includes an input stage for receiving a three-phase input voltage in relation to a neutral node and an output stage adapted to couple to at least one load. The rectifier further includes one or more switching converter stages, each having a plurality of serially-connected switches coupled to the neutral node, one of the serially-connected switches operating with a fixed duty cycle while the other of the serially-connected switches operating with a variable duty cycle, the fixed duty cycle being a substantially 50% duty cycle and the variable duty cycle being less than or equal to a substantially 50% duty cycle. The serially-connected switches are coupled to clamping diodes and clamping capacitors. The rectifier further includes one or more controllers adapted to vary the switching frequency and / or duty cycle of the plurality of switches based on at least one of a condition of the at least one load or the input voltage and includes one or more decoupling stages, each including one or more inductive elements adapted to inductively decouple the output stage from at least one of the one or more switching converter stages.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Filterless class D power amplifier
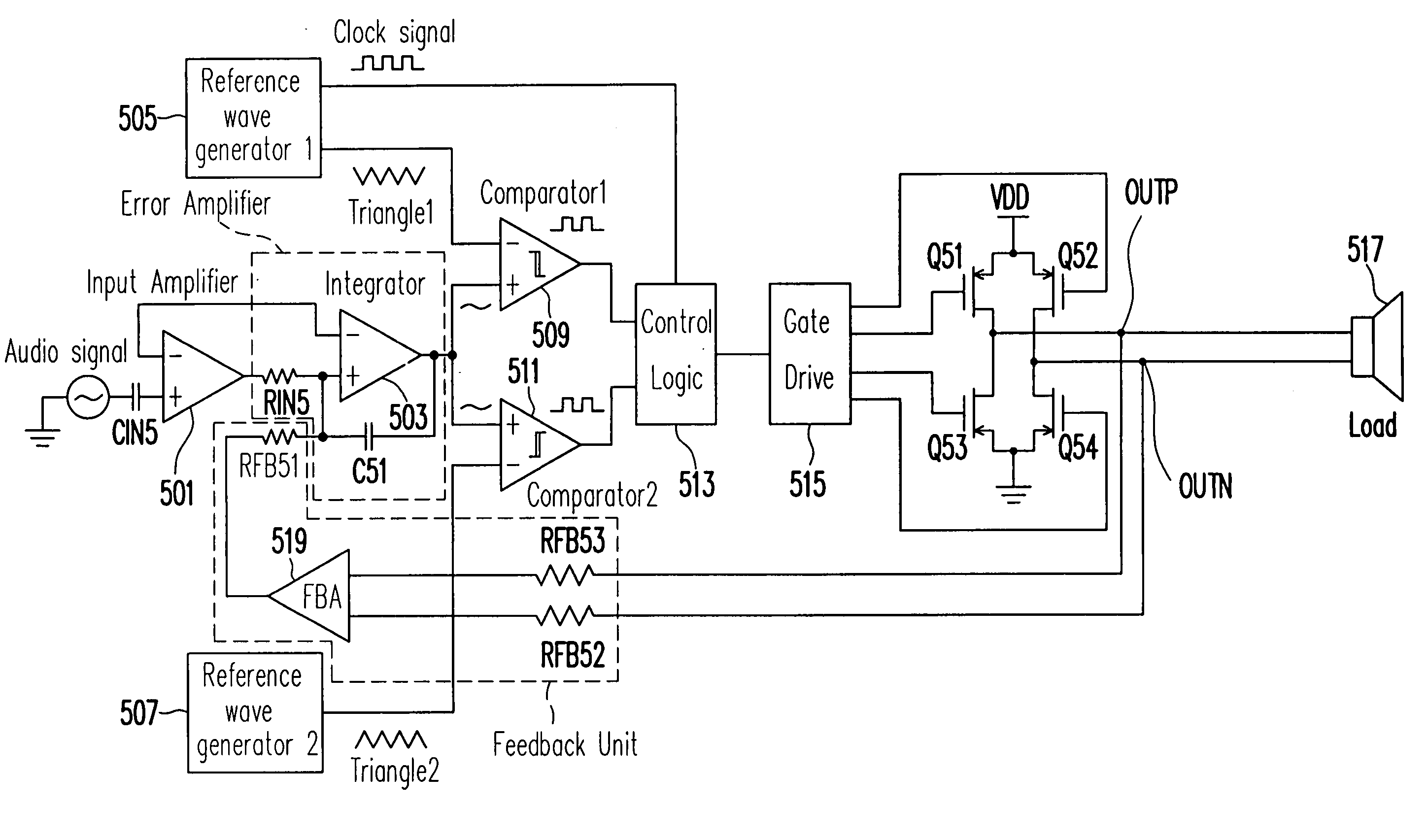
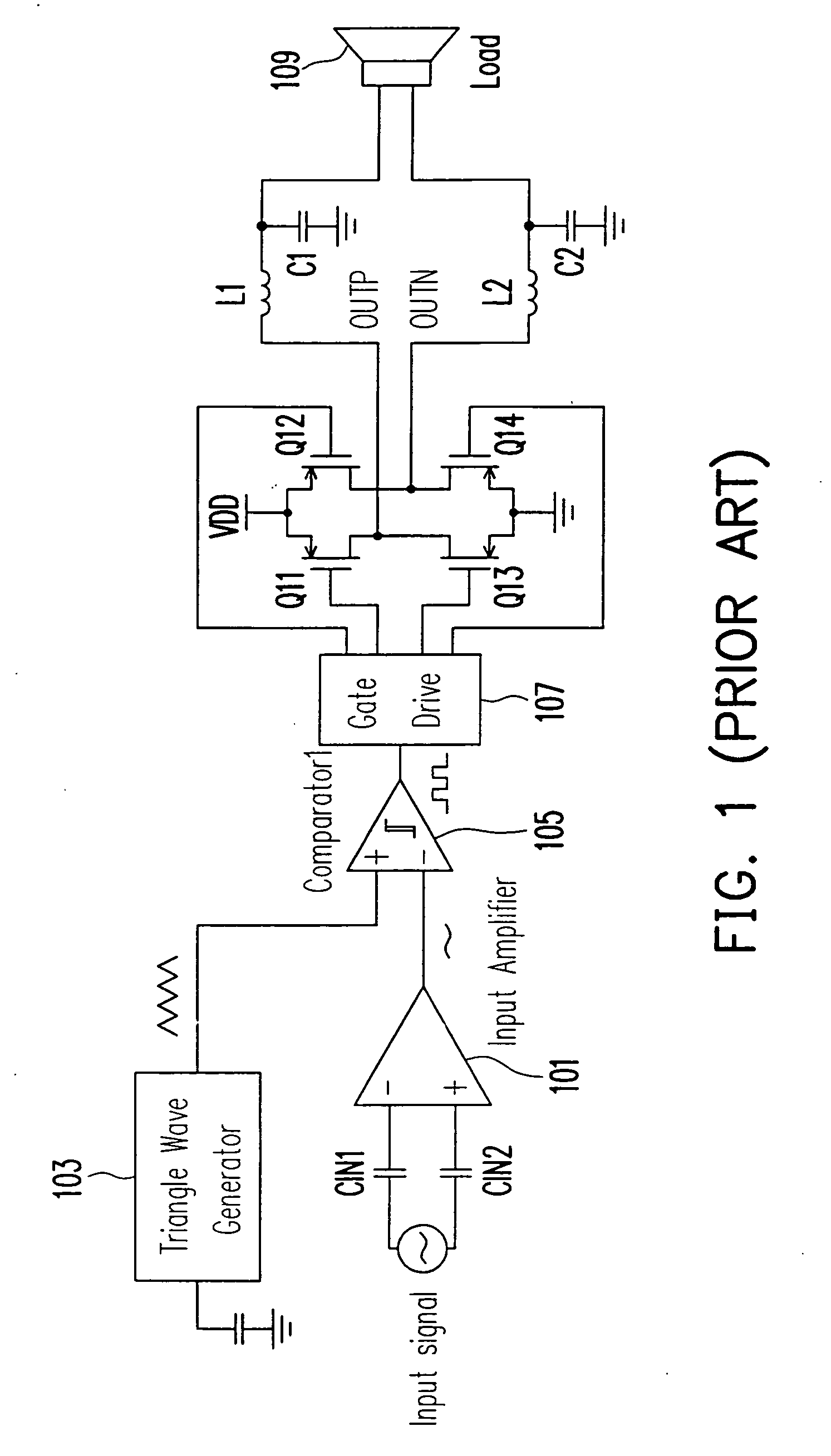
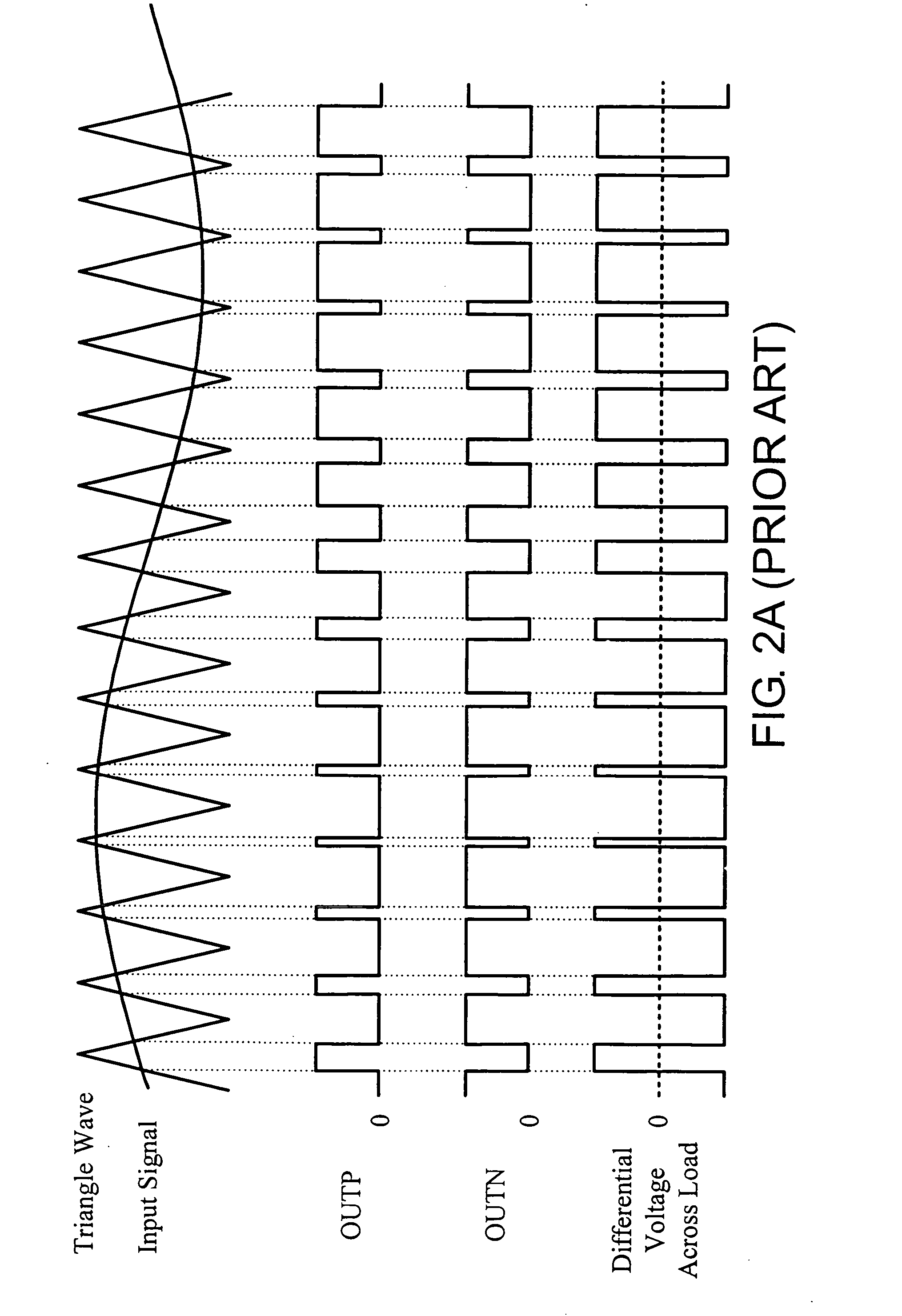
InactiveUS20070146069A1Reduce decreaseEliminate common mode noisePulse duration/width modulationDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorAudio power amplifierEngineering
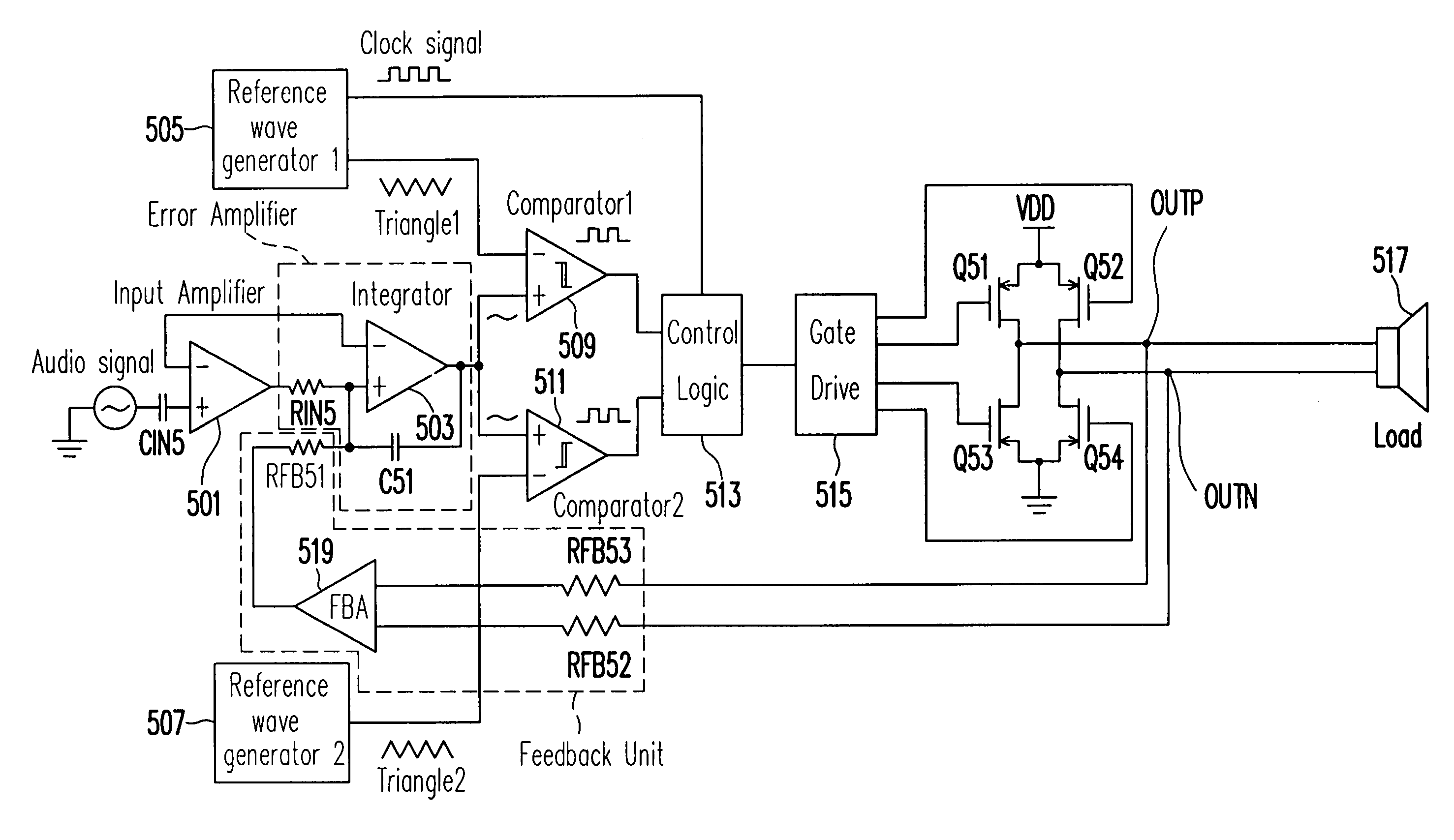
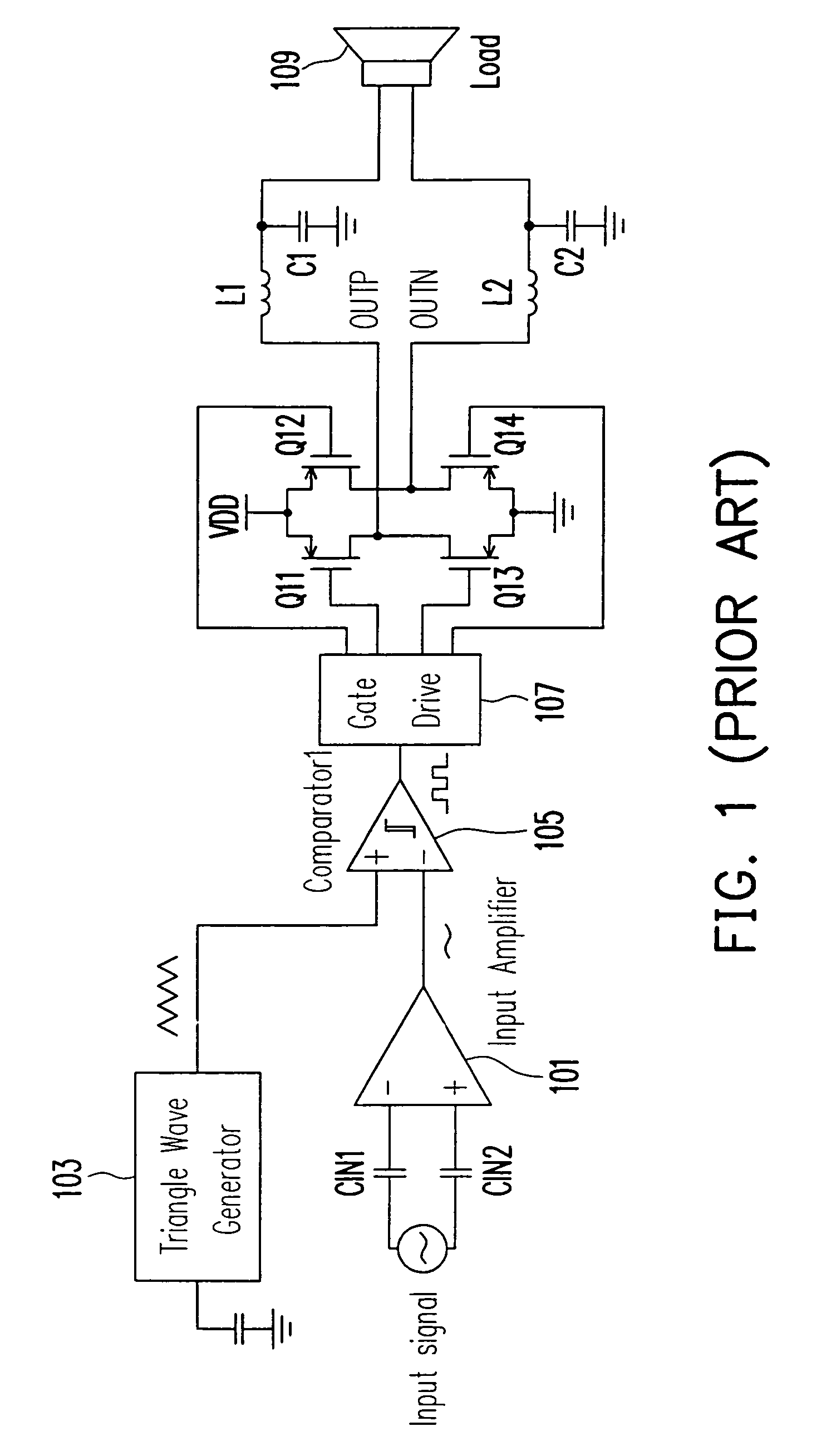
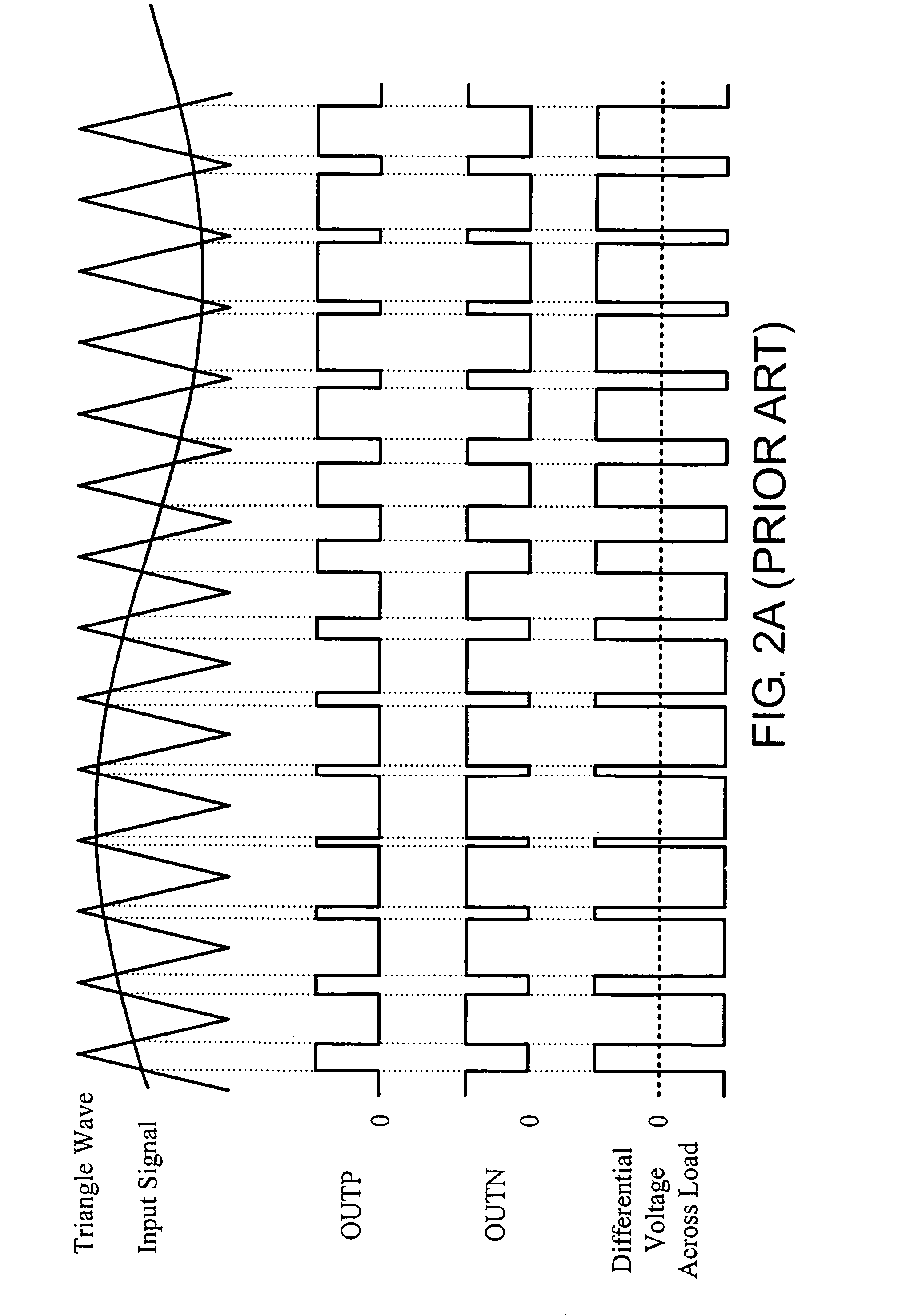
A double reference wave modulation scheme for filterless power amplifiers is disclosed for reducing EMI and common mode voltages. In the filterless power amplifier, differential outputs for driving load impedance are feedback and corrected based on input audio signals. Reference wave generators generate reference waves. A control logic results pulses in the pair of differential outputs in response to a clock signal or a reference voltage and a cross relationship between the input audio signal and the first and second reference waves. Pulses of one of the differential outputs are not overlapped with pulses of the other of the differential outputs for eliminating common mode noises of the power amplifier.
Owner:AMAZION ELECTRONICS NC
Filterless class D power amplifier
InactiveUS7332962B2Improve sound qualityReduce common mode noiseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
A double reference wave modulation scheme for filterless power amplifiers is disclosed for reducing EMI and common mode voltages. In the filterless power amplifier, differential outputs for driving load impedance are feedback and corrected based on input audio signals. Reference wave generators generate reference waves. A control logic results pulses in the pair of differential outputs in response to a clock signal or a reference voltage and a cross relationship between the input audio signal and the first and second reference waves. Pulses of one of the differential outputs are not overlapped with pulses of the other of the differential outputs for eliminating common mode noises of the power amplifier.
Owner:AMAZION ELECTRONICS NC
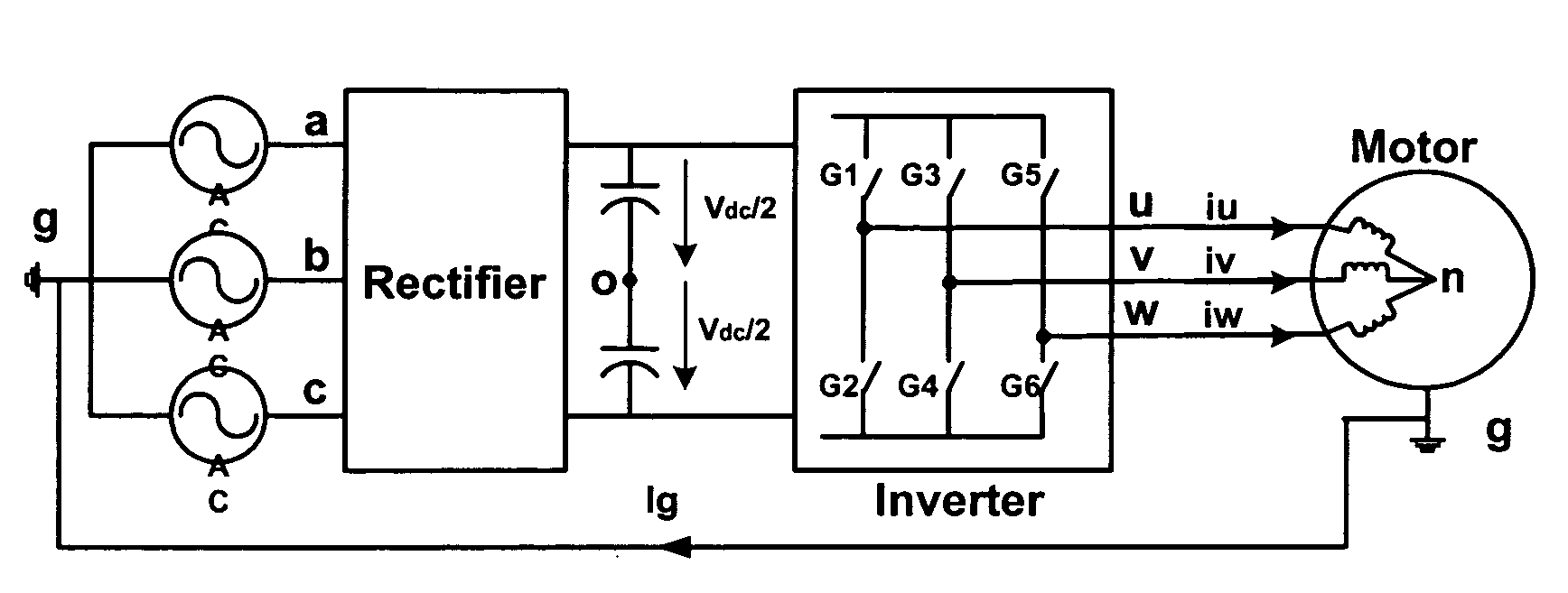
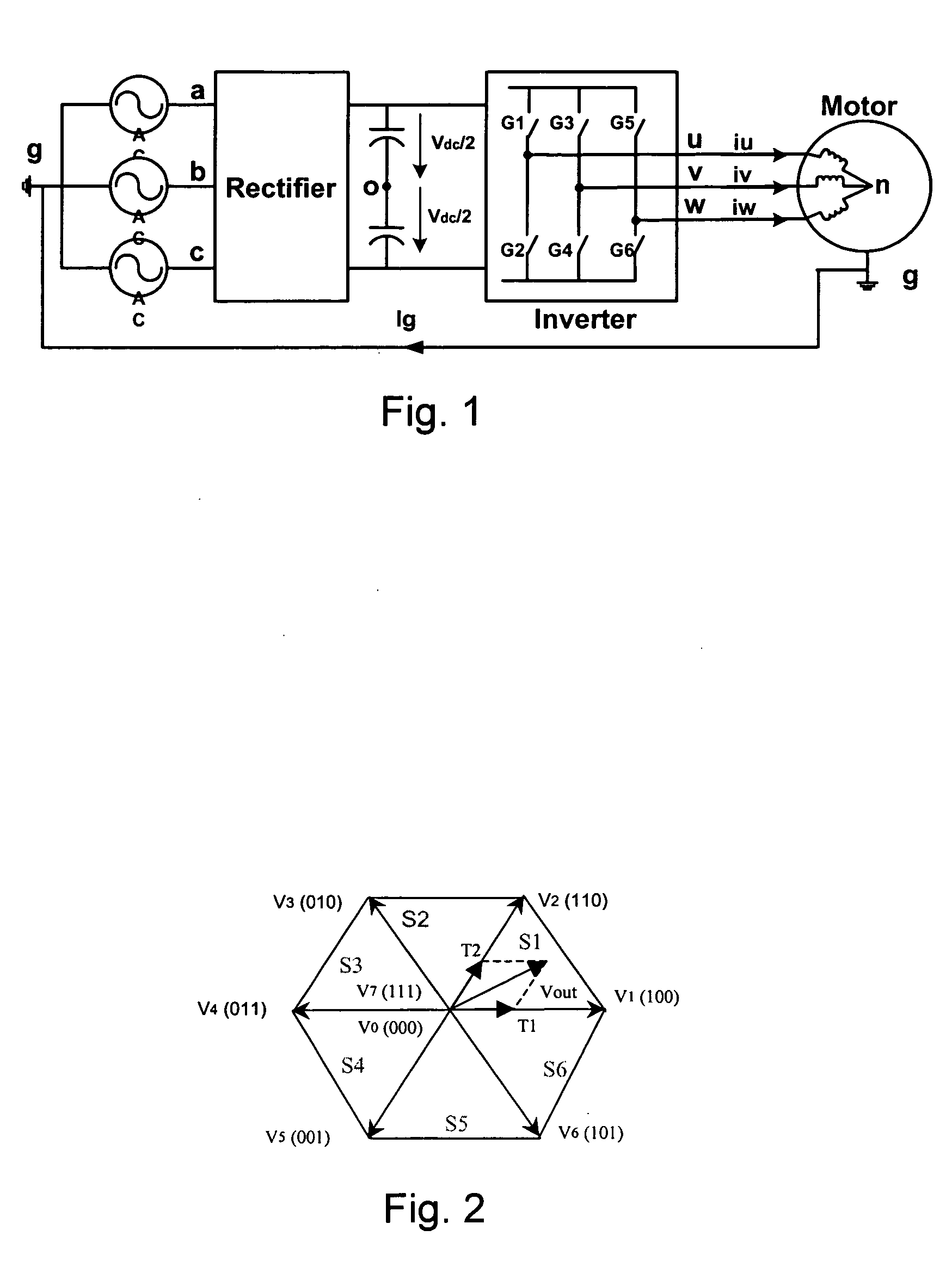
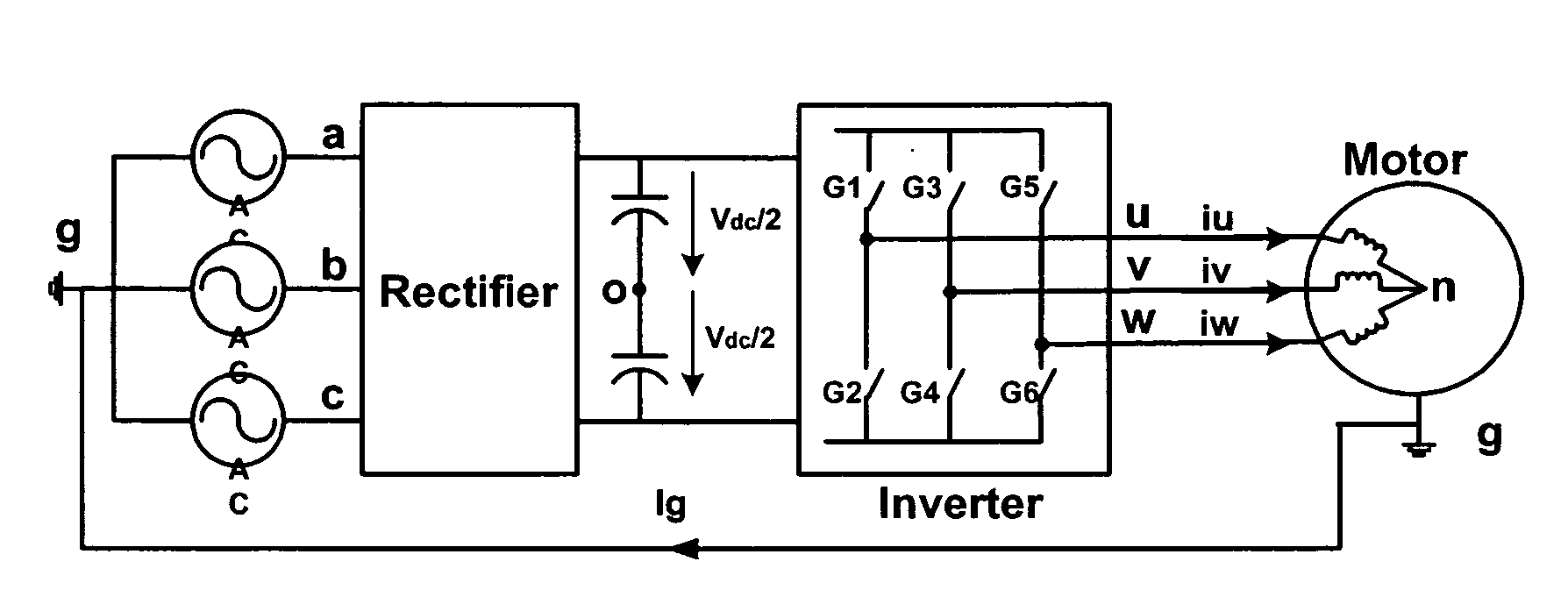
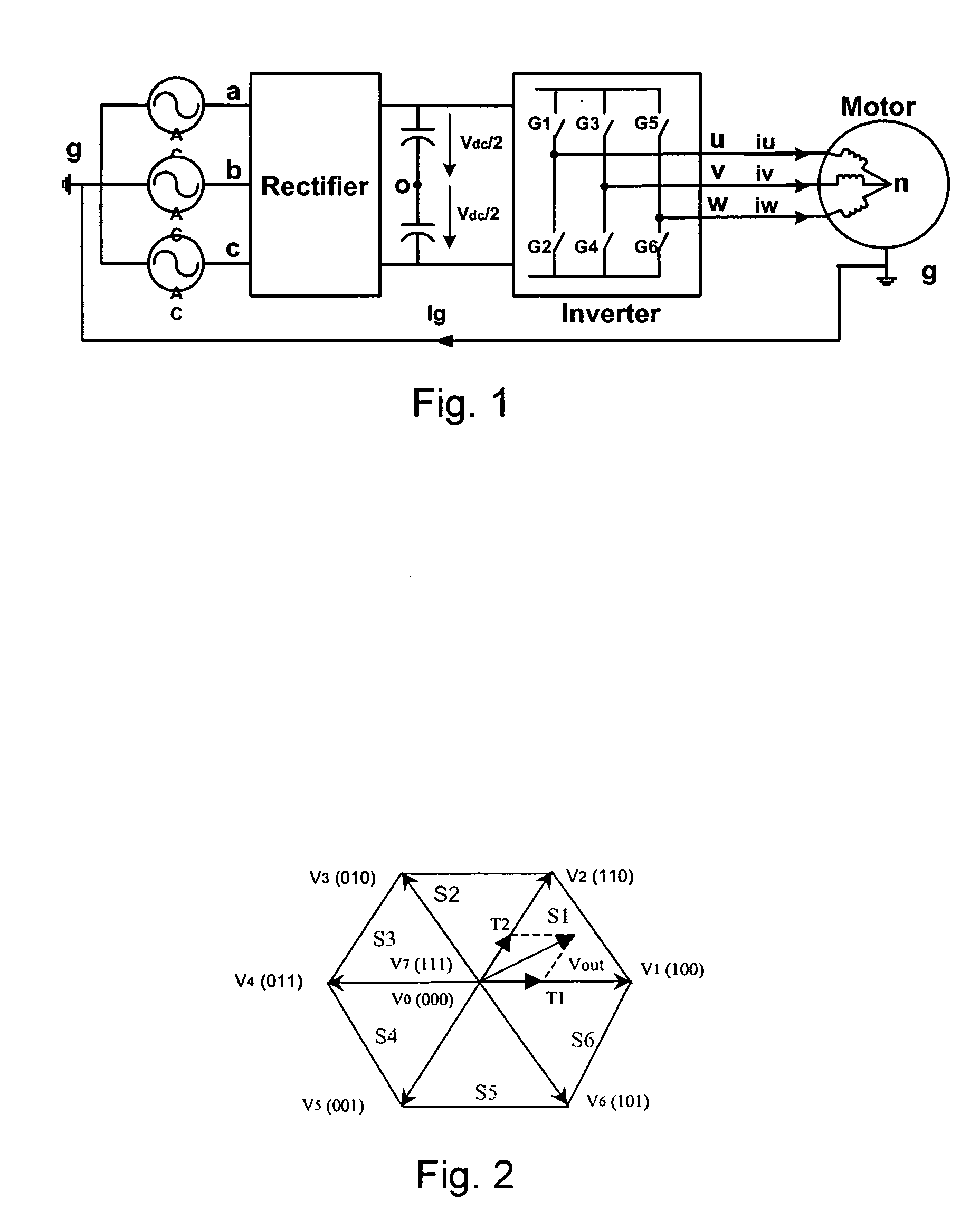
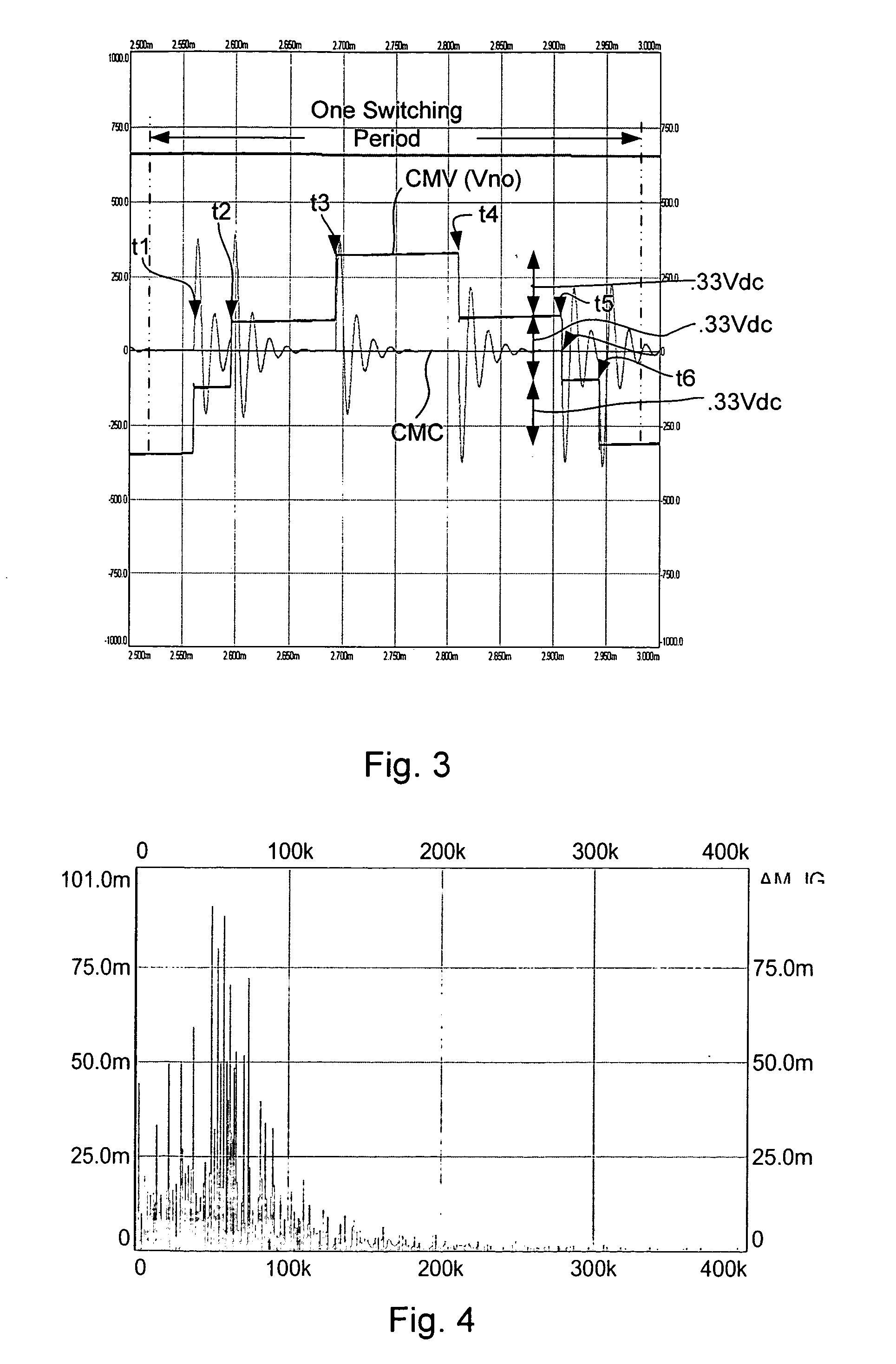
Modulation methods and apparatus for reducing common mode noise
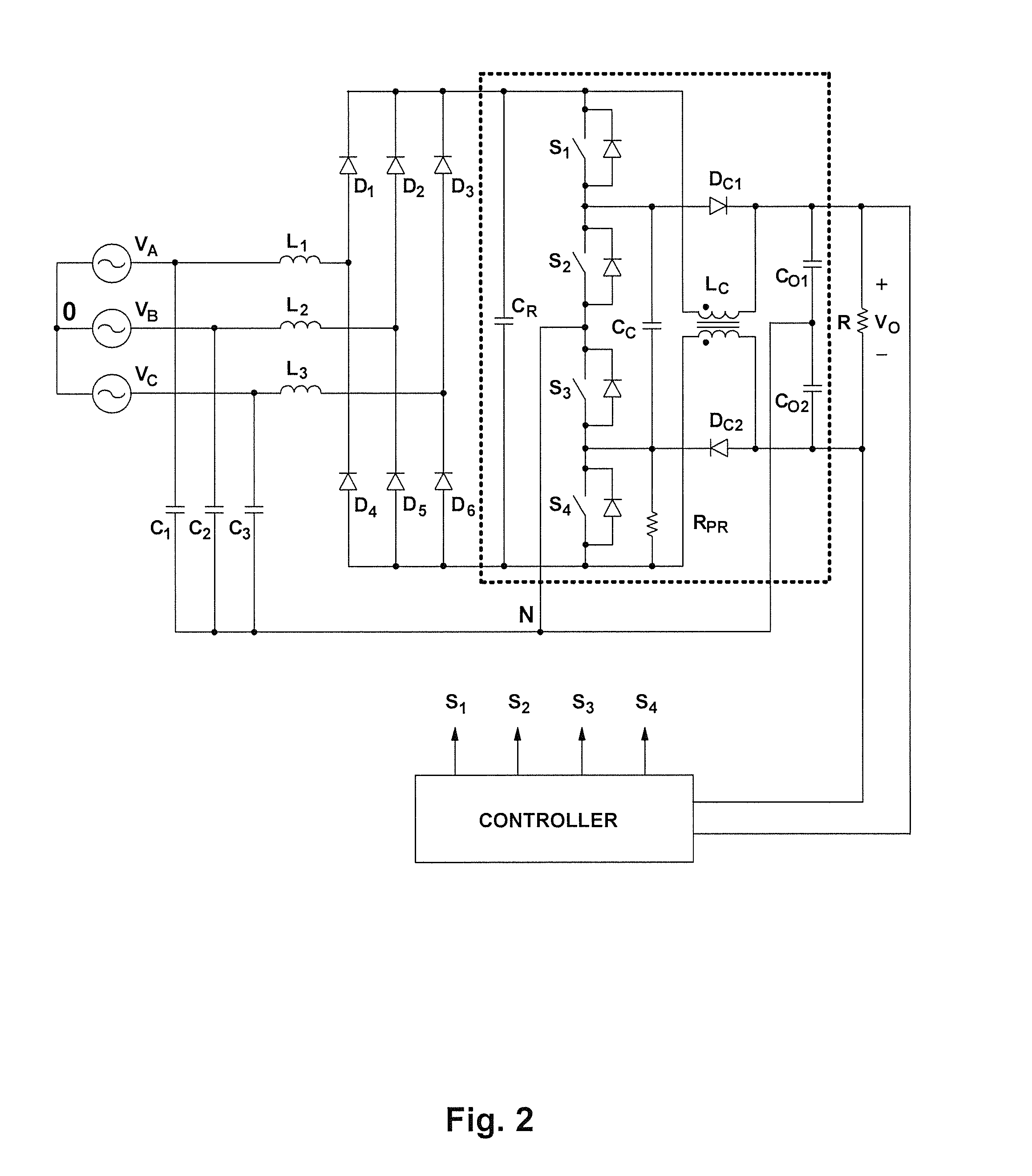
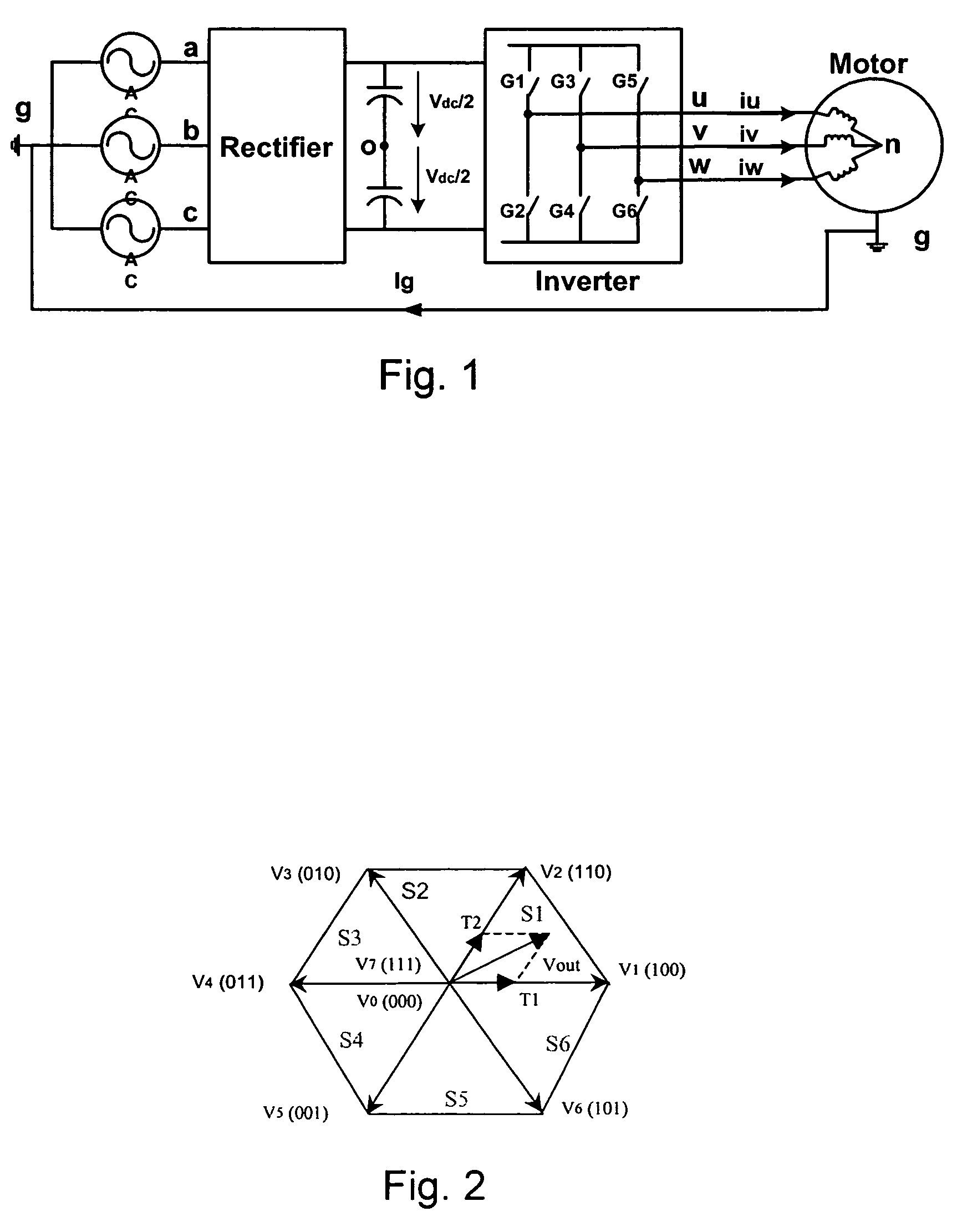
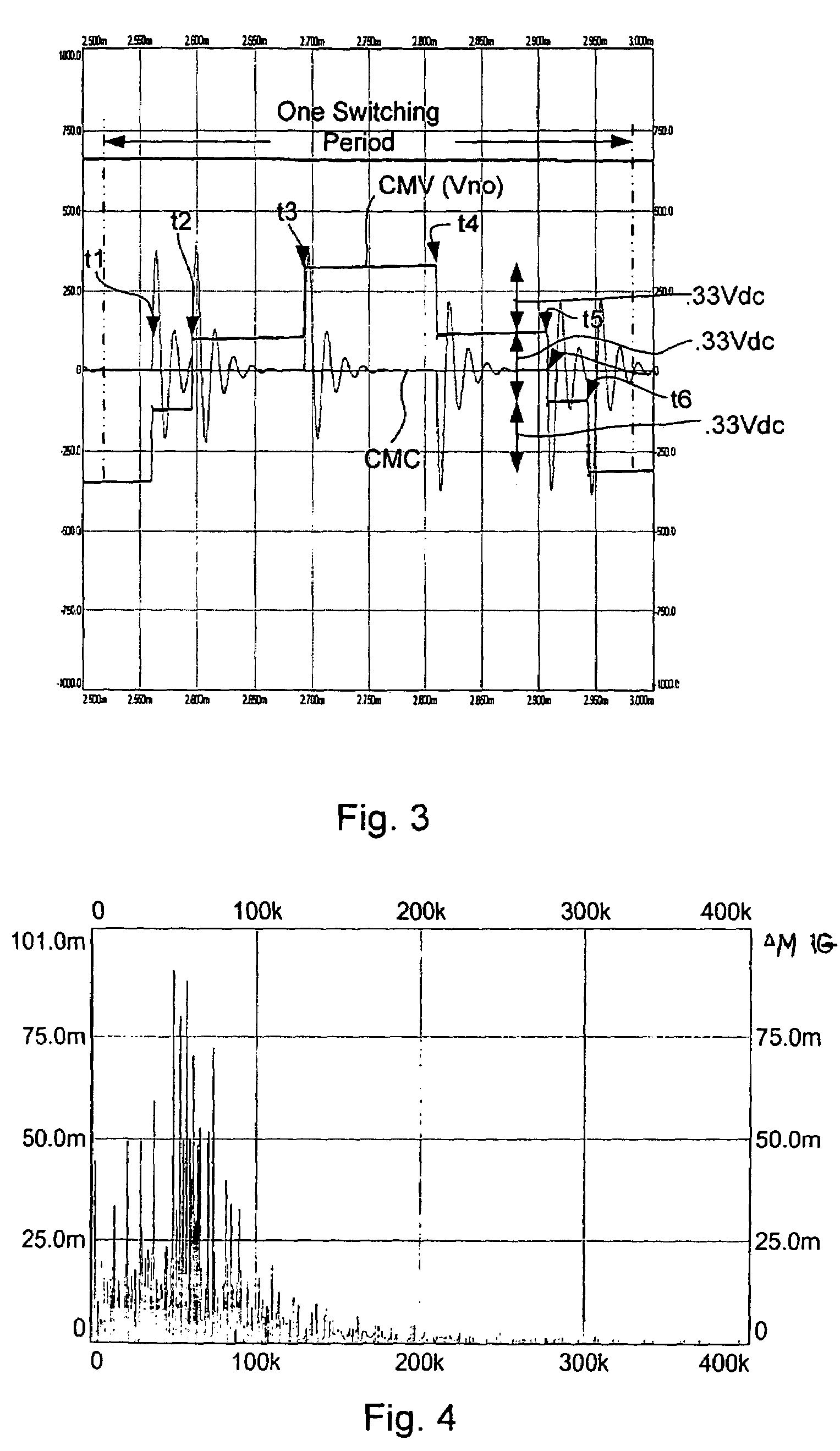
ActiveUS7400518B2Reduce common mode noiseMinimize impactAC motor controlAc-dc conversionWave shapeCarrier signal
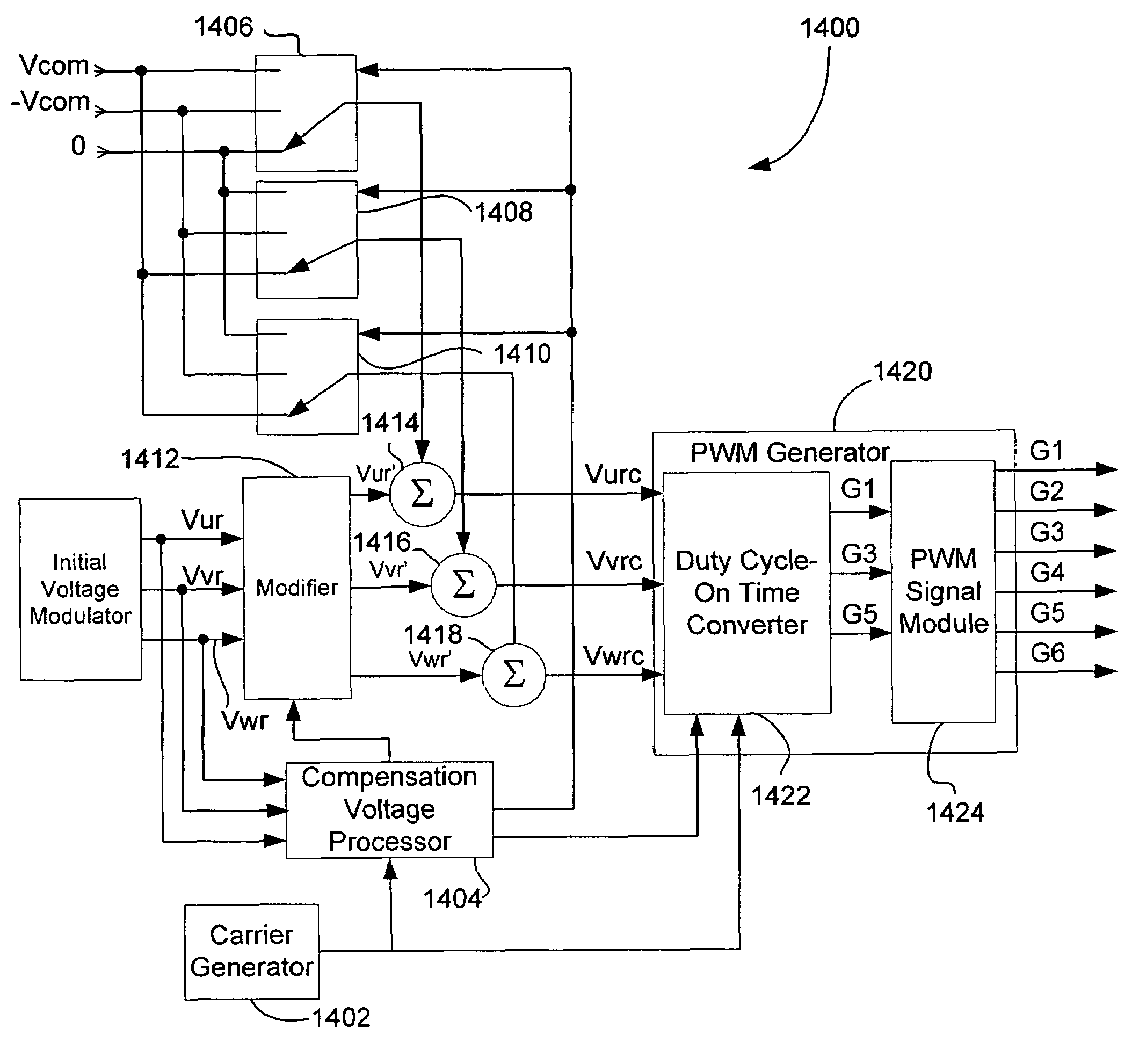
A method and apparatus for reducing common mode noise in a three phase pulse width modulated (PWM) system the method comprising the steps of receiving modulating waveforms, identifying a first of the modulating waveforms that is instantaneously the maximum of the modulating waveforms, identifying a second of the modulating waveforms that is instantaneously the minimum of the modulating waveforms, for a first phase associated with at least one of the first and second identified waveforms, substituting a first substitute waveform for the one of the first and second waveforms, for the first phase, modifying at least one of the first substituted waveform and duty cycle signals generated by comparing the first substituted waveform with the carrier signal as a function of a first rule set to substantially minimize the effects of turn on delays and for at least one of the second and third phases, modifying at least one of the associated modulating waveform and duty cycle signals generated by comparing the modulating waveform with the carrier signal as a function of a second rule set to substantially eliminate the effects of turn on delays where the second rule set is different than the first rule set.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Coupled Inductor for Interleaved Multi-Phase Three-Level DC-DC Converters
ActiveUS20160172976A1Reduces current circulatingTotal current dropAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionThree levelEngineering
Output current ripple is reduced in a three-level DC-DC power converter by connecting a plurality of phase legs in parallel between a source of input power and an output of the power converter and conducting power from the source of input power to the power converter output in an interleaved manner. The large current that results from such interleaved operation is reduced to acceptable levels, potentially less than the output current ripple of the power converter by providing inversely coupled inductors having a mutual inductance preferably greater than the inductor of the power converter in respective phase legs and in series in the circulating current path to avoid any need to increase the power converter inductance due to the circulating current. The inductor and inversely coupled inductors are preferably integrated into a single magnetic element of compact design.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Power factor correcting converter
ActiveCN101083398AReduce common mode noiseEliminate jumpingAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitancePower factor
The invention is a bridge-free power factor correction (PFC) converter able to reduce common code noises and increase power density, comprising: boost inductor coupled to input end; two-way switch connected in series with the boost inductor and having junction node coupled between the boost inductor and two-way switch; second series rectifier circuit, having junction node coupled to the two-way switch; and output capacitor connected in parallel with the second series rectifier circuit; where the second series rectifier circuit is composed of slow recovery diode and the first series rectifier circuit is composed of fast recovery diode. Thus, the invention can reduce common mode noises in the converter and increase the power density of the converter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
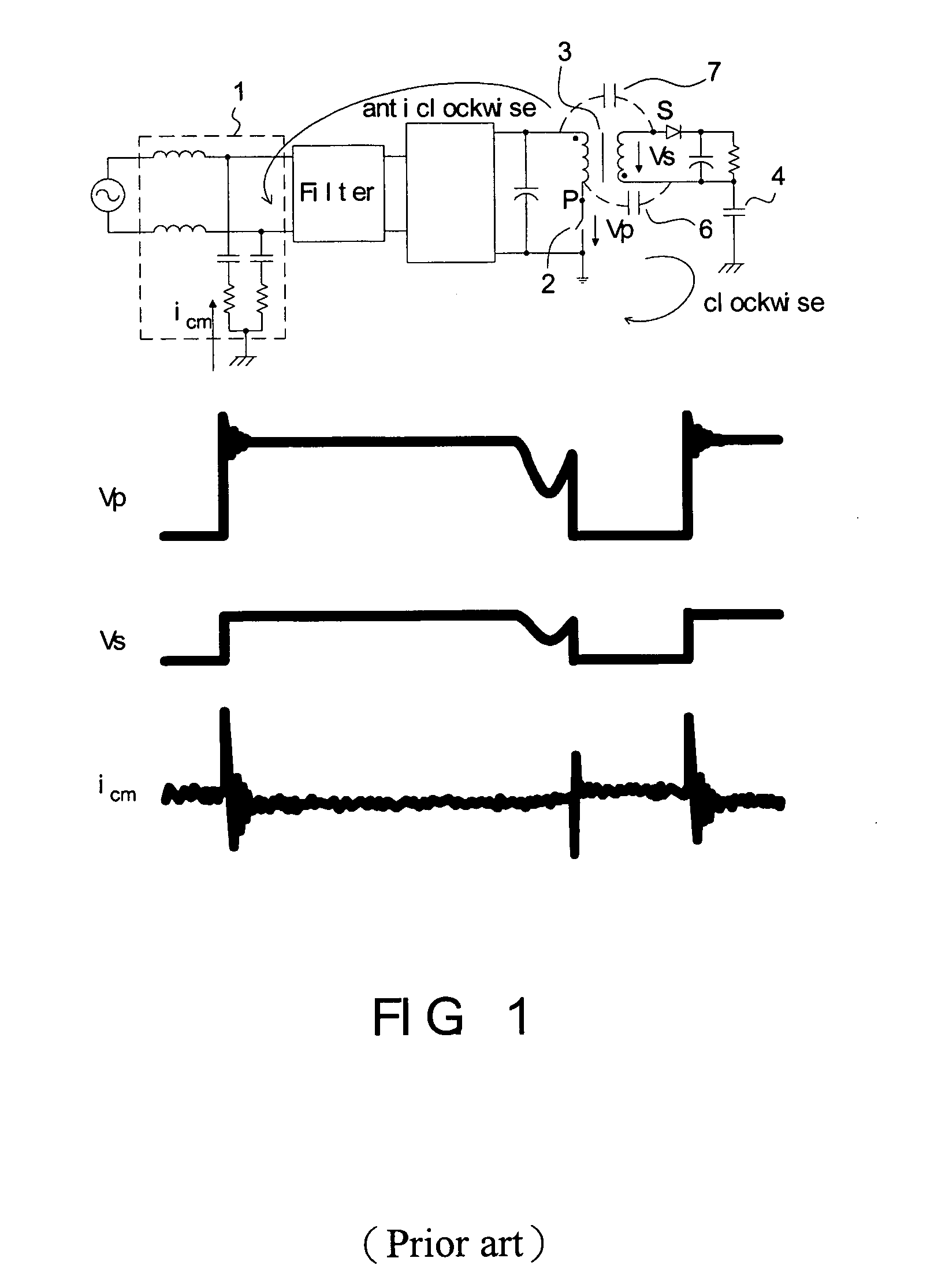
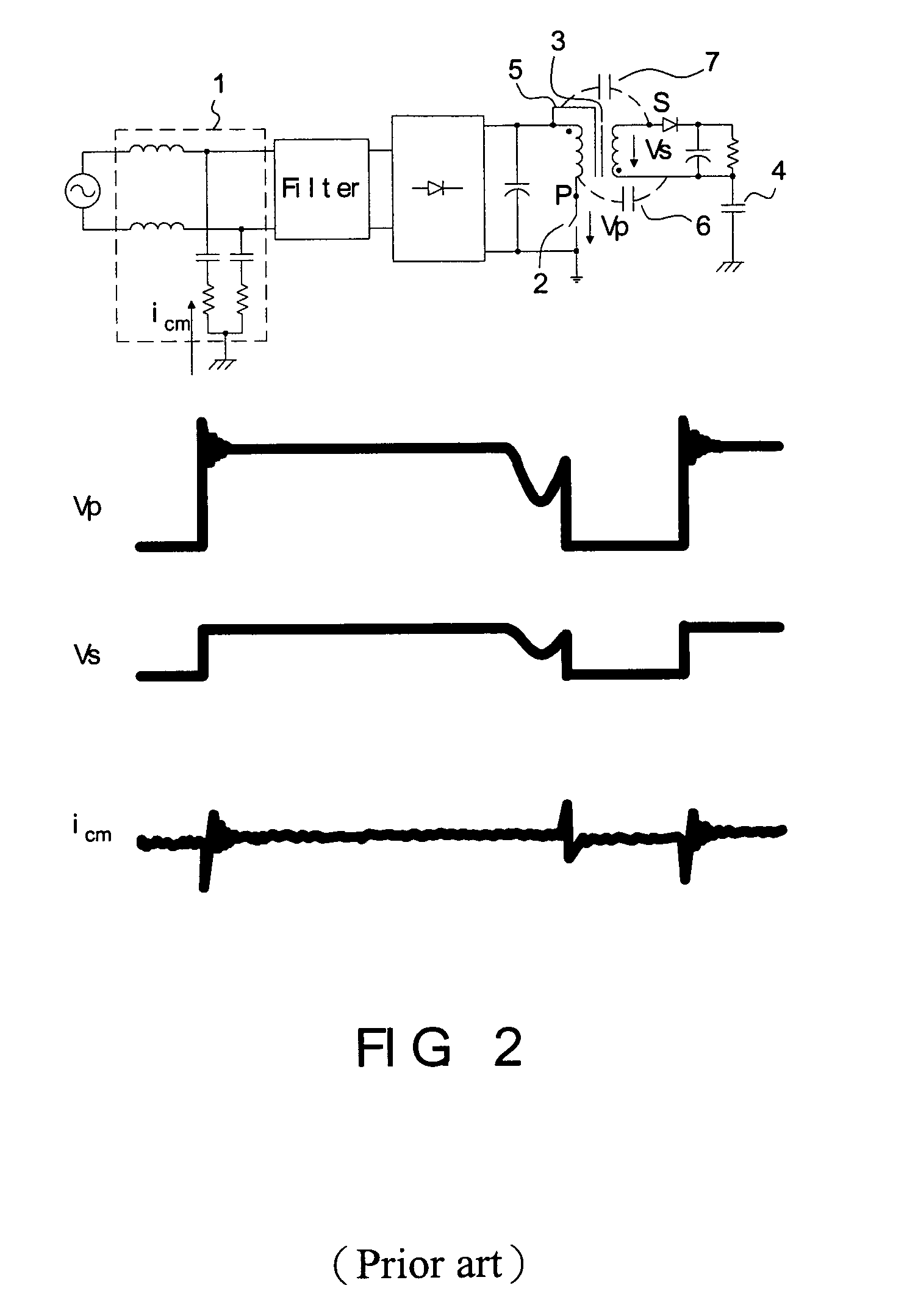
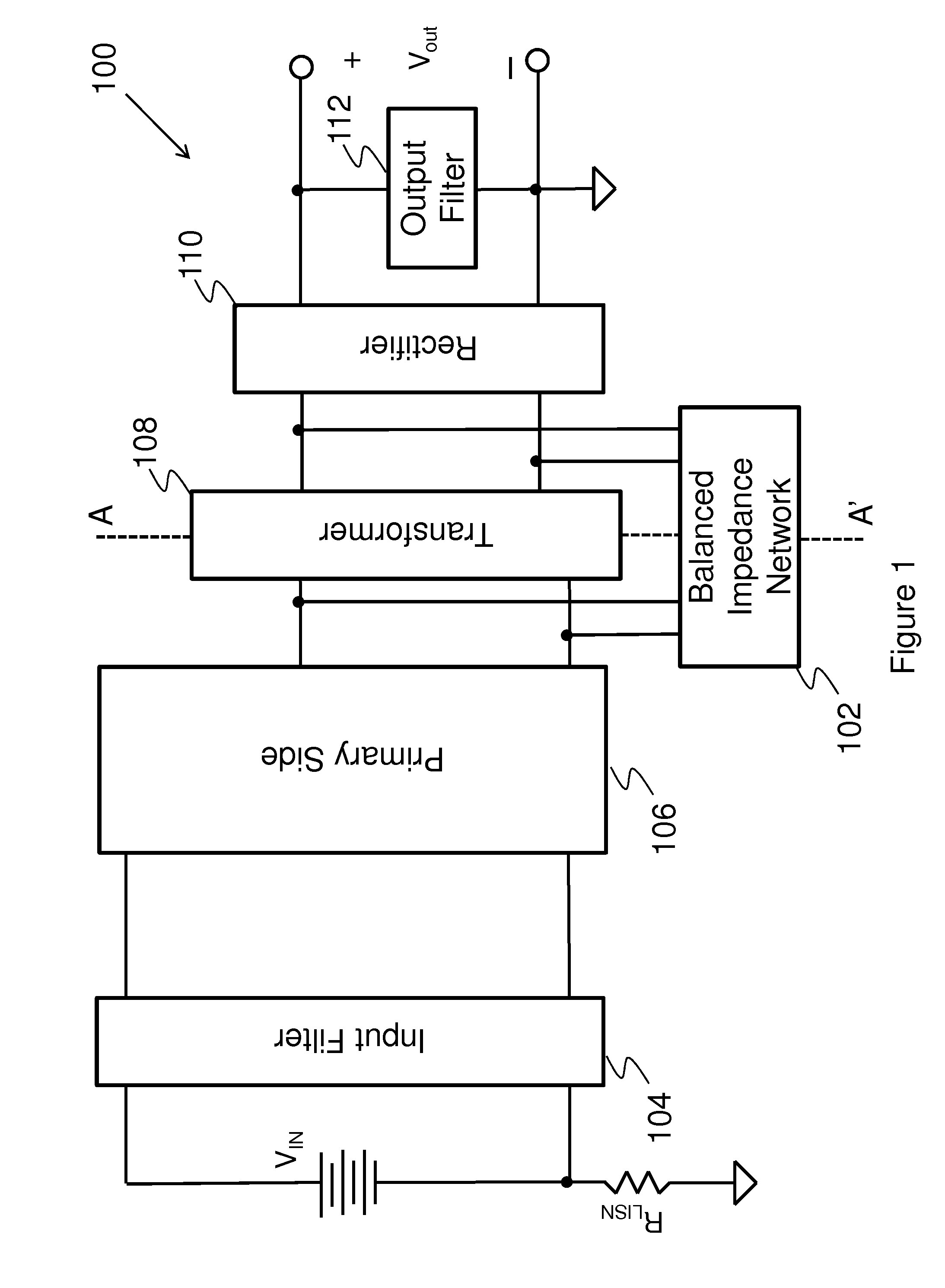
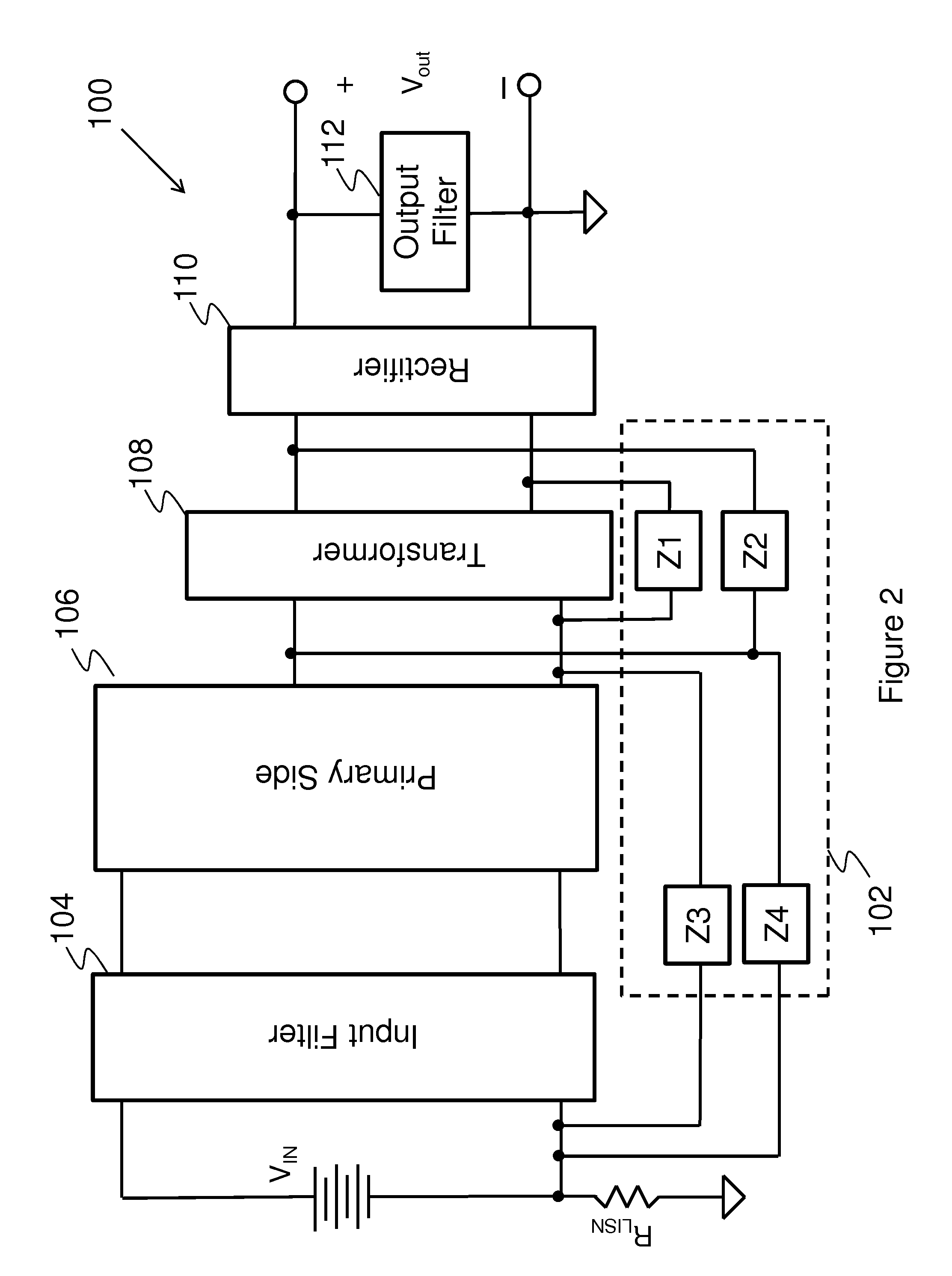
Method for suppressing common mode noise
ActiveUS20070171585A1Reduce common mode noiseImpedence networksEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringElectrical impedance
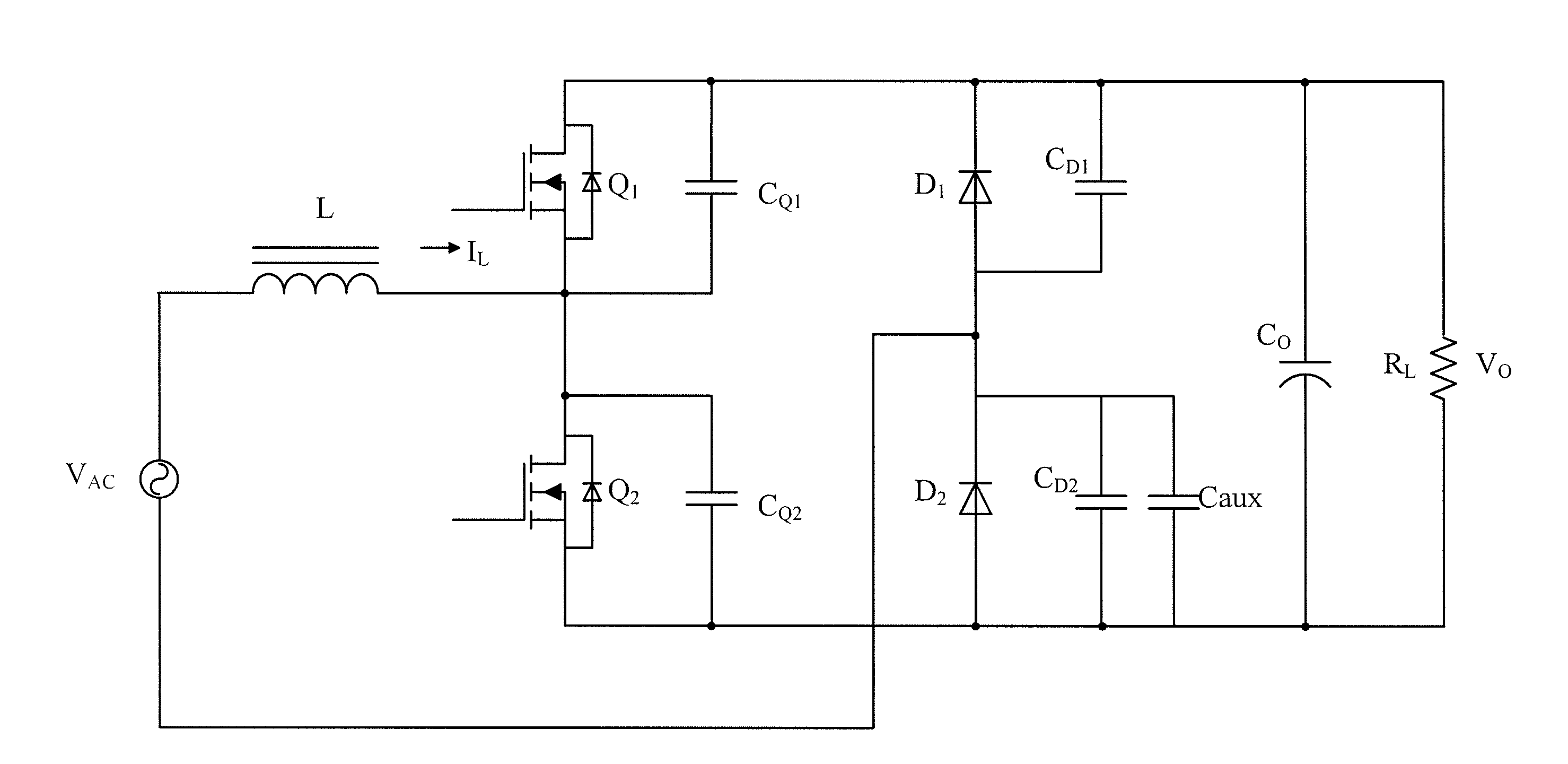
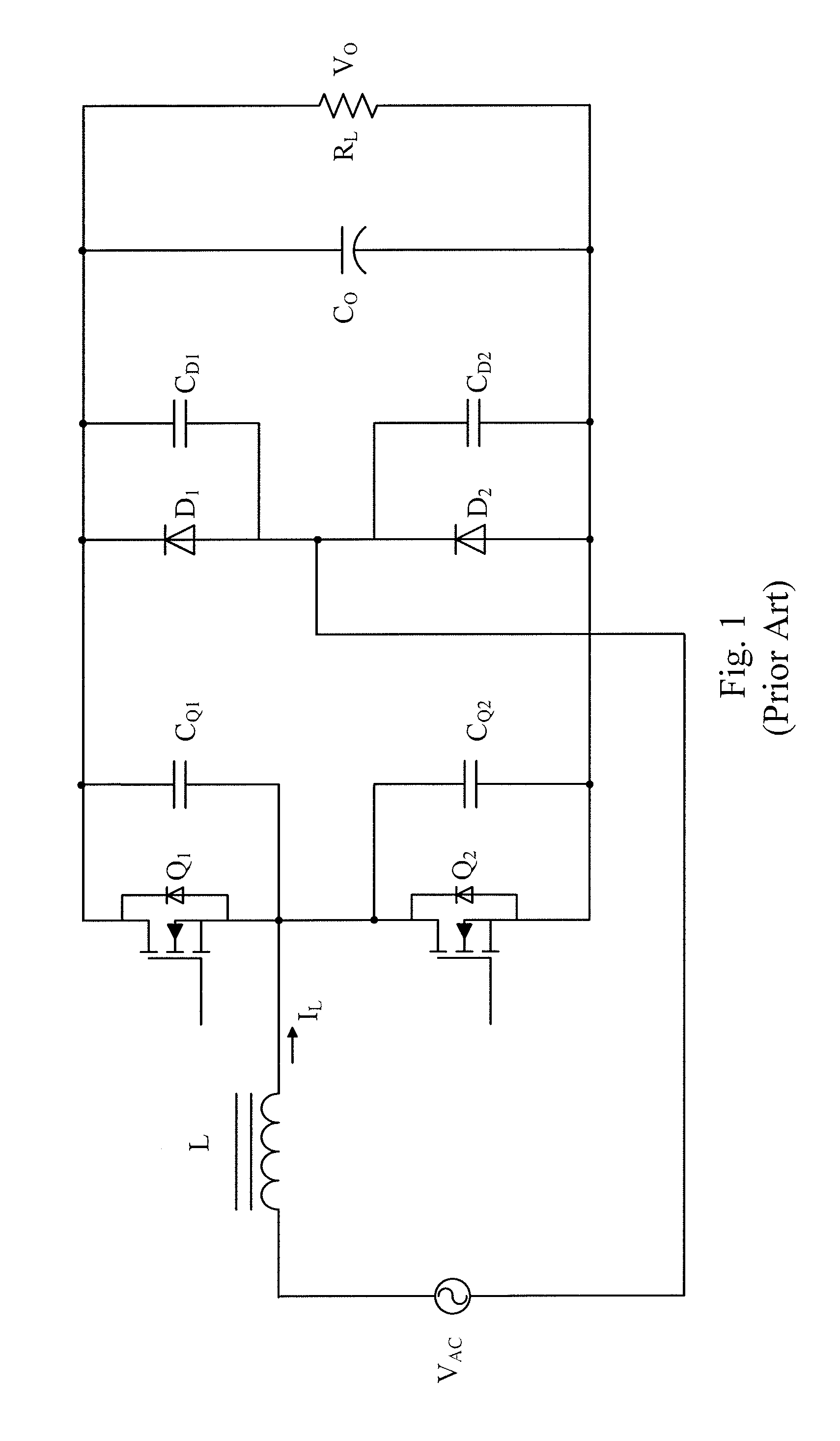
The present invention discloses a power converter with low common mode noise. The power converter having a primary side and a secondary side, comprises a transformer having a primary winding and a secondary winding, and at least one electrostatic shield disposed between the primary winding and the secondary winding, wherein the electrostatic shield is configured with partial first region of the primary winding and partial second region of the secondary winding such that the electrostatic shield partially shields with the primary winding and the secondary winding to reach the purpose of suppressing the common mode noise. In addition, another method can be used to reduce the common mode noise of a power converter having primary side and secondary side, which is adding some additional impedance between the static points and jump points of the primary side and secondary side.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
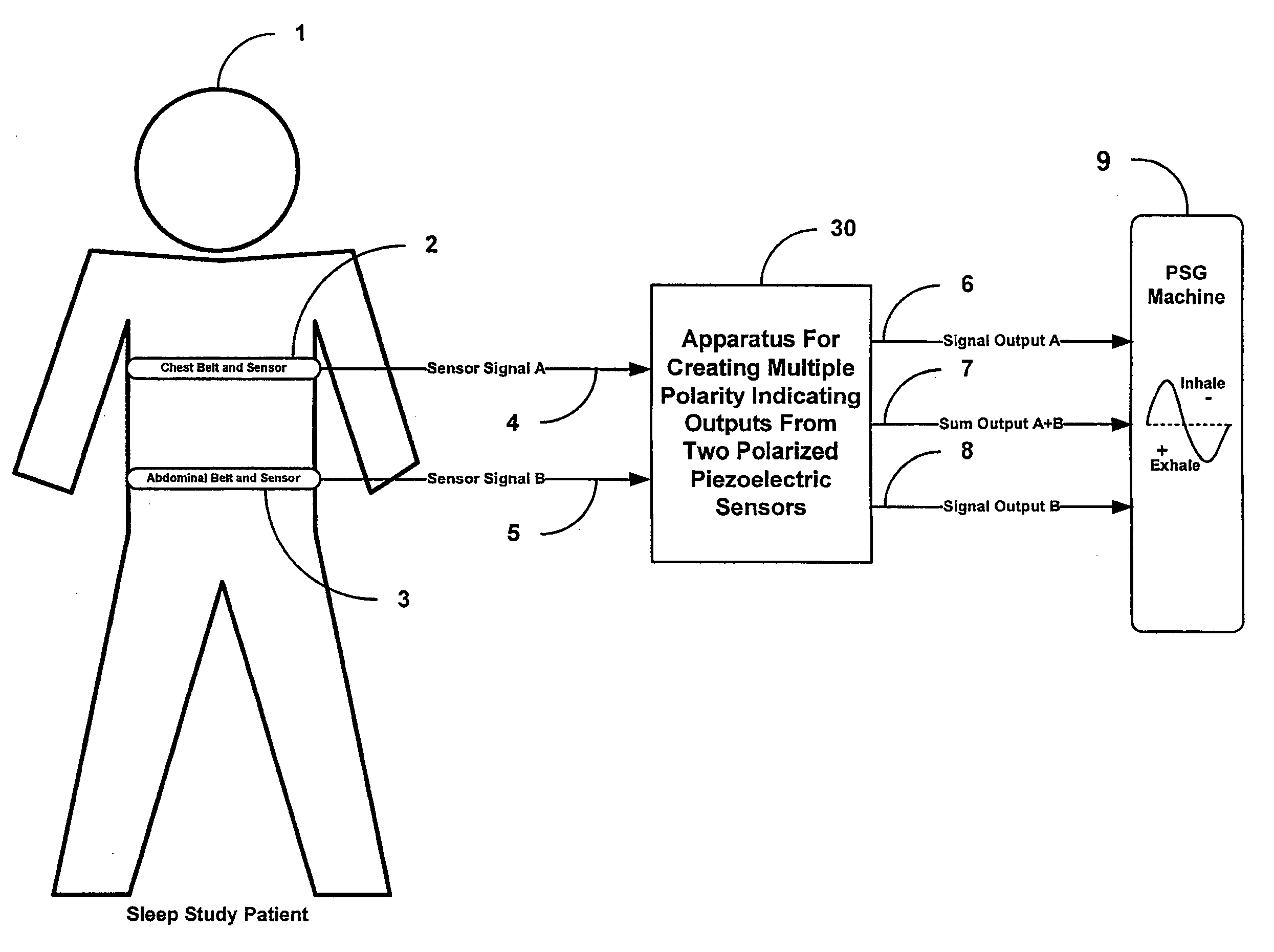
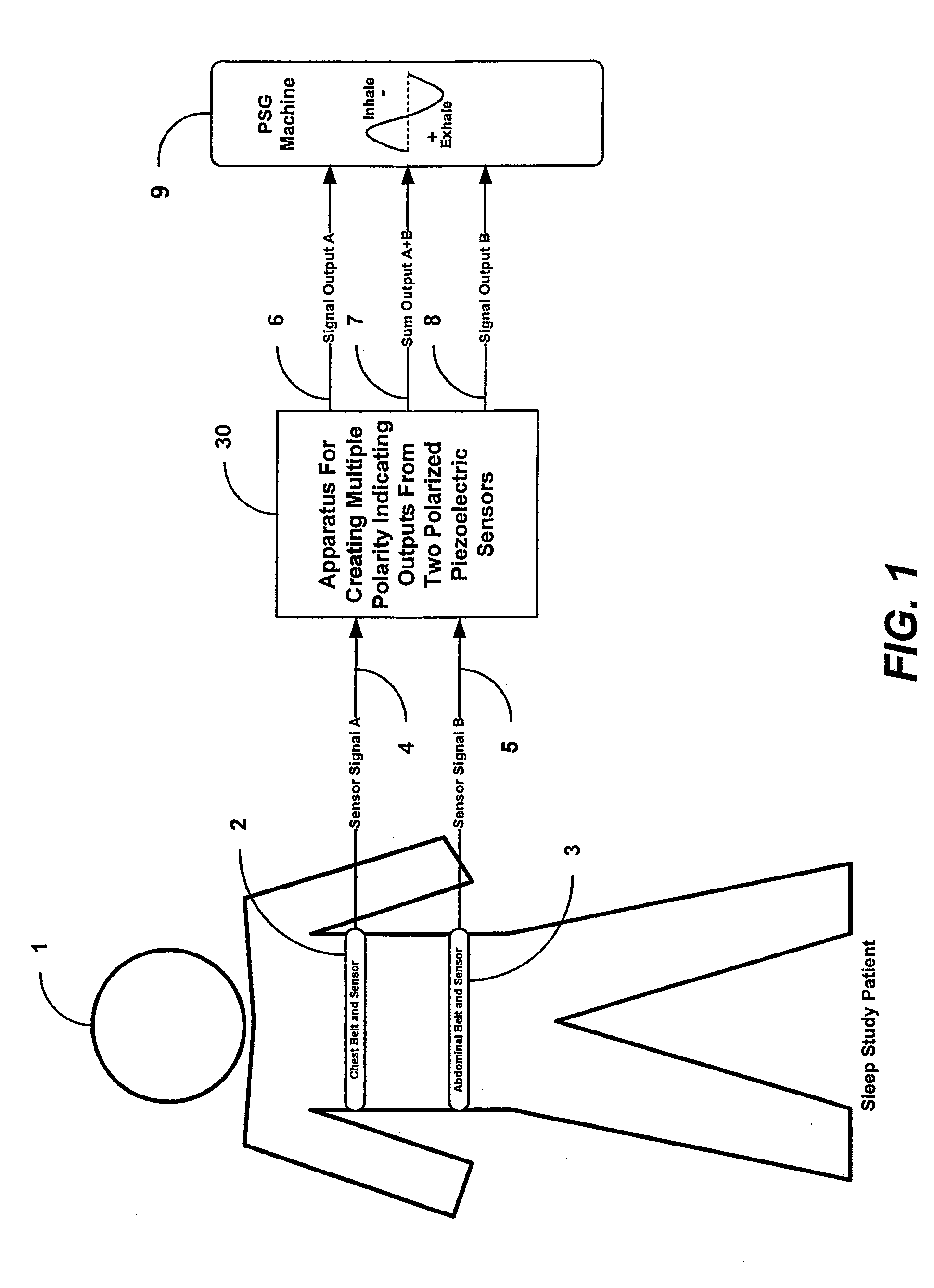
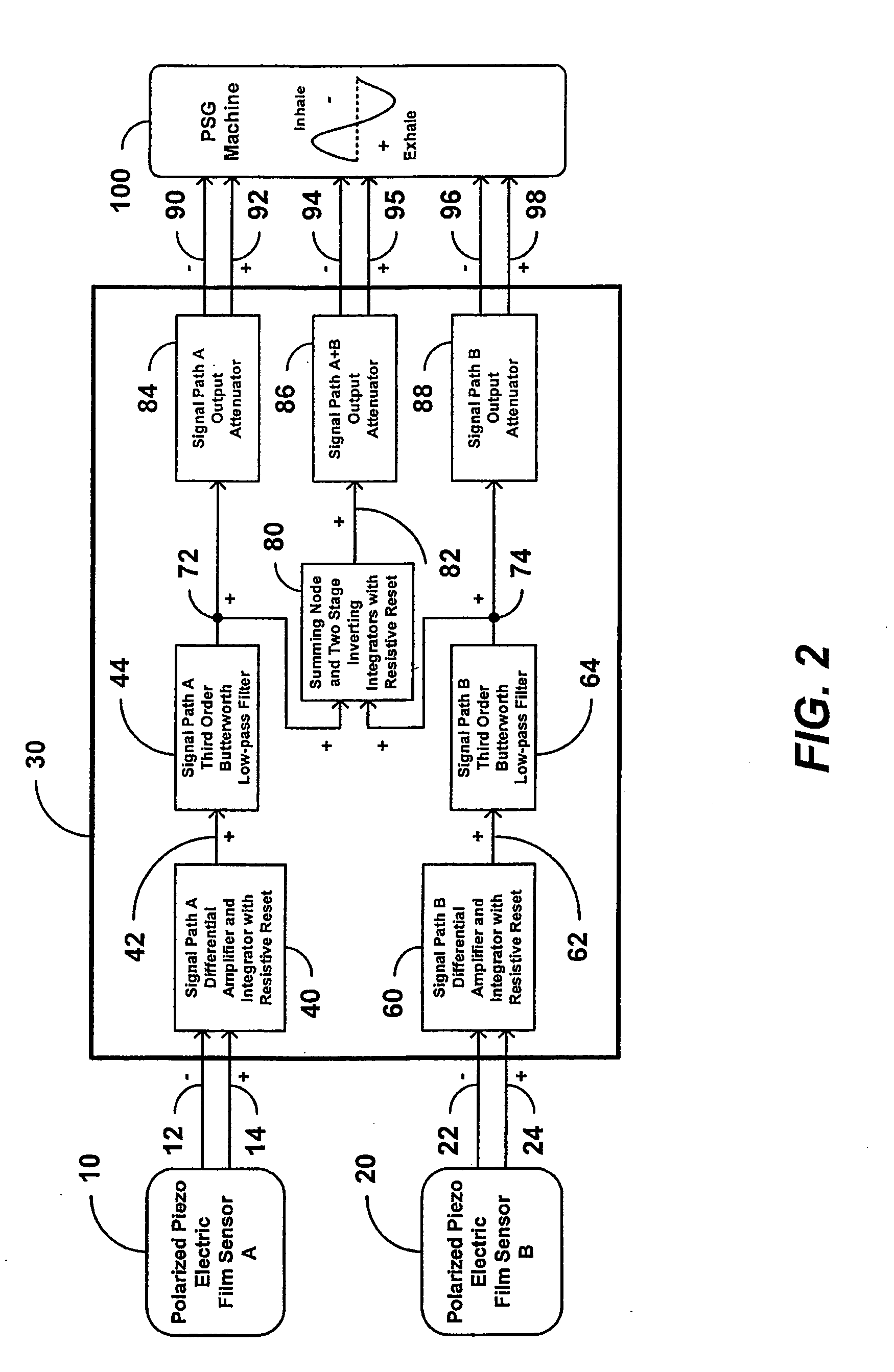
Apparatus and method for creating multiple polarity indicating outputs from two polarized piezoelectric film sensors
InactiveUS20090259135A1Reduce unwanted differential noiseReduce common mode noiseRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
An apparatus or method can be configured to receive first information indicative of respiratory effort of a subject from a first piezoelectric film sensor and second information indicative of respiratory effort of the subject from a second piezoelectric film sensor, and to process the received first and second information to produce an electronic signal output indicative of respiratory effort of the subject, the processing including averaging the received first information using a first differential amplifier and signal integrator with resistive reset to reduce differential noise and to attenuate common-mode noise, and averaging the received second information using a second differential amplifier and signal integrator with resistive reset to reduce differential noise and to attenuate common-mode noise.
Owner:DYMEDIX
Modulation methods and apparatus for reducing common mode noise
ActiveUS20070268051A1Reduce common mode noiseAC motor controlConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPhase correlationPhase shifted
A method and apparatus for reducing common mode noise in a three phase pulse width modulated (PWM) system, the method comprising the steps of receiving the first, second and third modulating waveforms, identifying one of the modulating waveforms that is at least one of instantaneously the maximum and instantaneously the minimum of the modulating waveforms as a first identified waveform, wherein comparison of the first identified waveform to the carrier signal would generate a first on-off pulse sequence associated with a phase corresponding to the first identified waveform, generating switch control signals associated with the phase corresponding to the first identified waveform that cause a modified on-off pulse sequence that is phase shifted from the first pulse sequence, using the second and third modulating waveforms to generate second and third on-off pulse sequences corresponding to the second and third phases and providing the modified pulse sequence and the second and third pulse sequences to the one of the inverter and the converter.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System for crosstalk noise reduction on twisted pair, ethernet, polyphase and shielded wire systems
InactiveUS20050018596A1Reduce crosstalk noiseReduce impedance mismatchFrequency-division multiplex detailsCross-talk reductionDigital signal processingOperating frequency
The present invention is an electronic circuit that reduces crosstalk in communications systems employing twisted pair, Ethernet, polyphase or shielded wire transmission media. The present invention includes three stages of crosstalk noise reduction. Stage 1 filters common mode noise from the transmission media and balances the resistive and reactive parasitic electrical characteristics of the transmission media that couple each line to the local ground over the operating frequency band. The second Stage performs differential crosstalk noise reduction in real time using multiple feedback loops. It can dynamically locate and set optimal system operating conditions for minimal differential crosstalk coupling for the specific environmental and interfering channel utilization conditions. The third Stage utilizes digital signal processing techniques to further reduce any residual crosstalk after analog-to-digital conversion. The third Stage also functions as a digital controller for the entire system as well as portions of subsystems including the feedback loops of Stage 2.
Owner:MASHHOON HAMID R
High efficiency bridgeless PFC converter and method
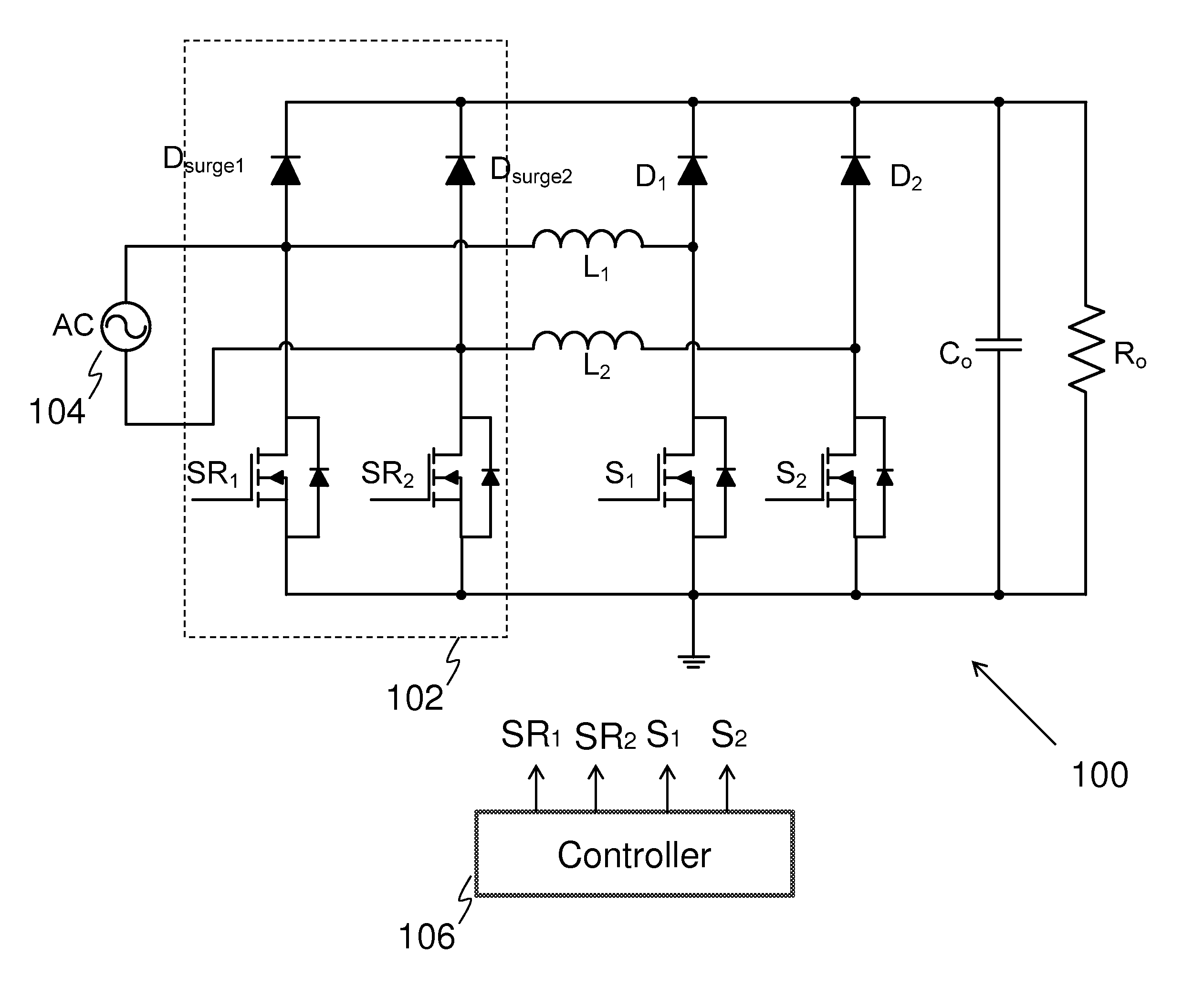
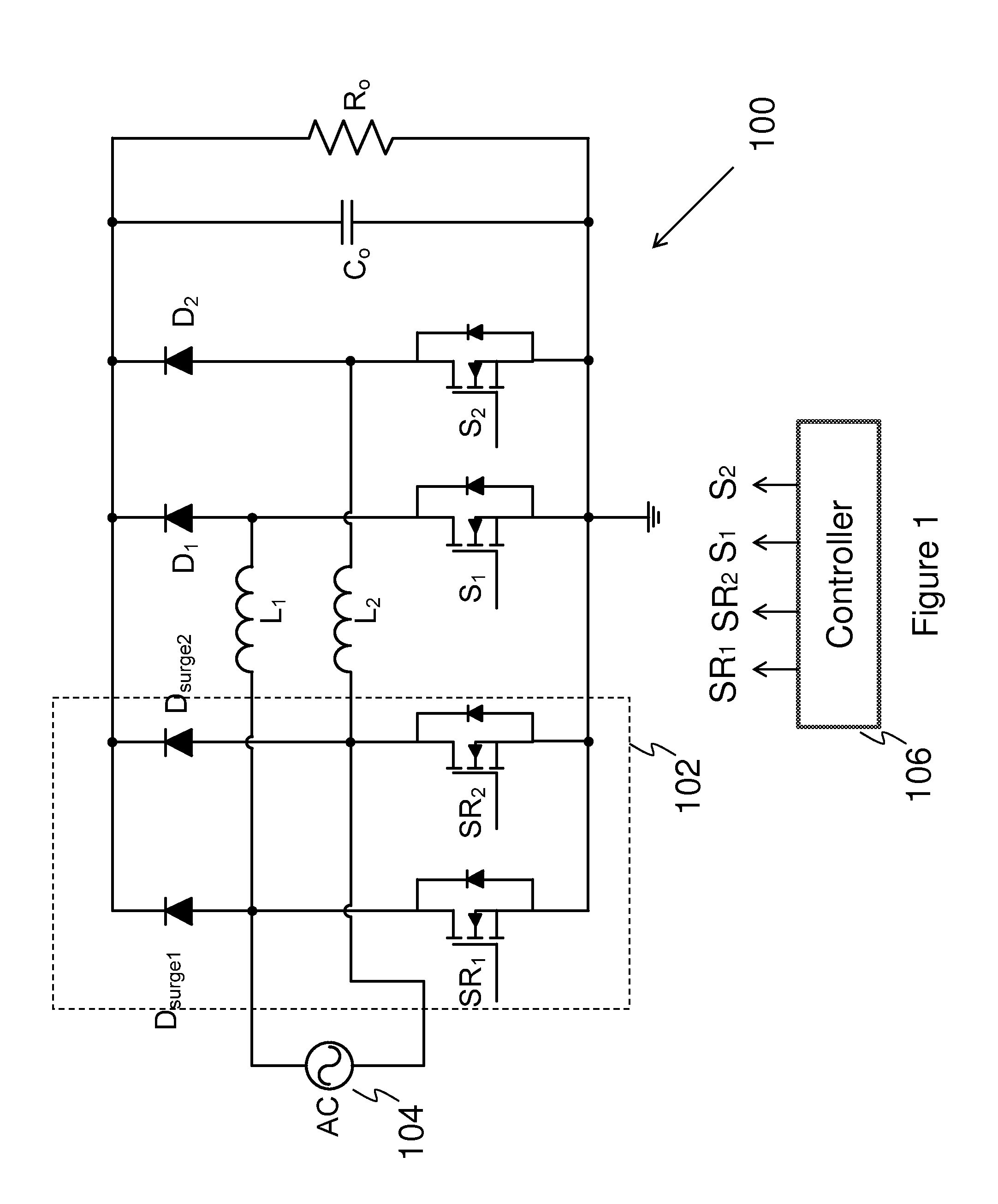
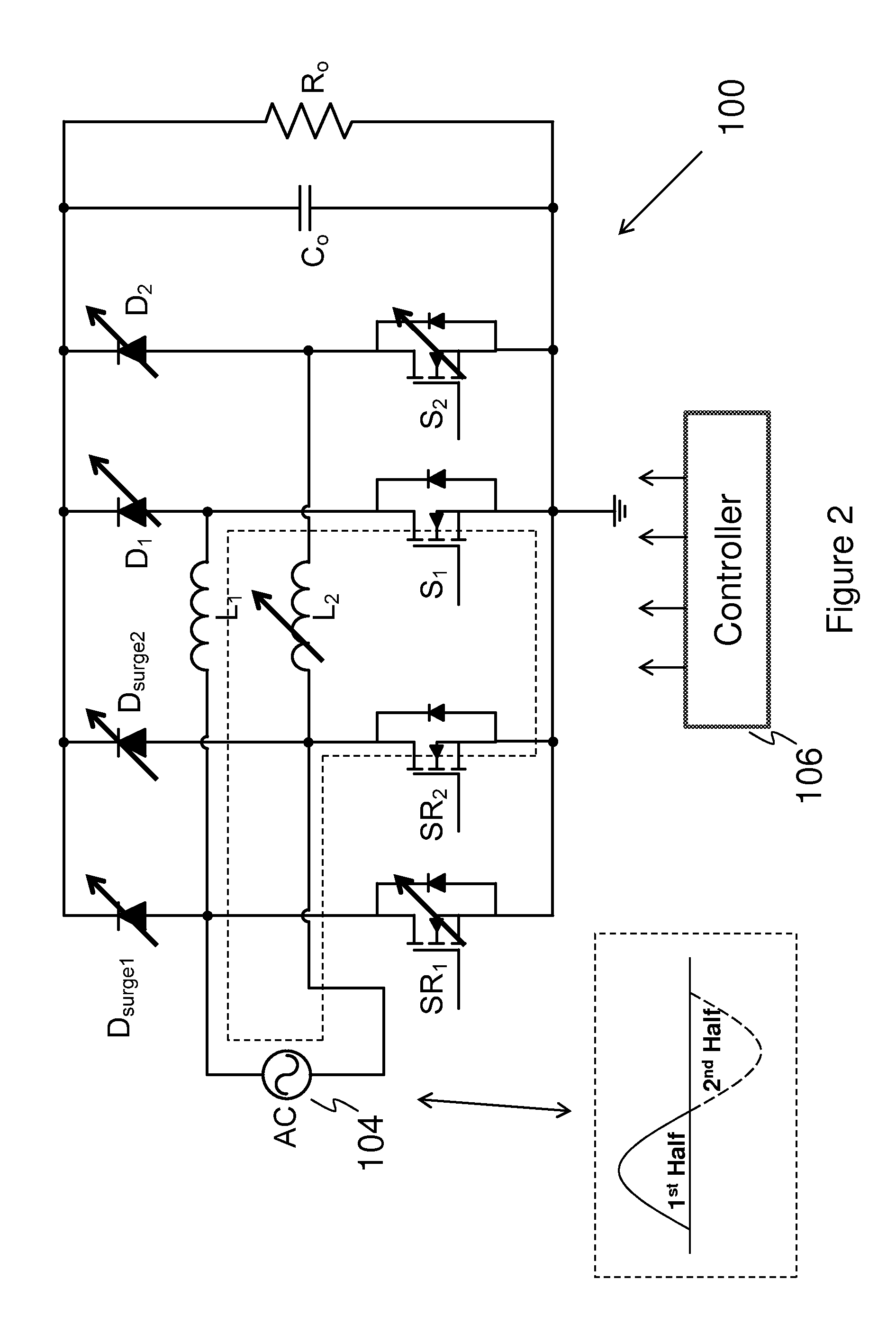
ActiveUS8385032B1Reduce common mode noiseReduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentEngineeringPower factor correction circuits
An embodiment bridgeless power factor correction circuit comprises a first boost converter and a second boost converter connected in parallel. A first switch is coupled between the input of the first boost converter and ground. A second switch is coupled between the input of the second boost converter and ground. Both the first switch and the second switch help to reduce the common mode noise of the bridgeless power factor correction circuit. The bridgeless power factor correction circuit further comprises two surge protection diodes coupled between the inputs of two boost converters and the output of the bridgeless power factor correction circuit.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL POWER TECH CO LTD
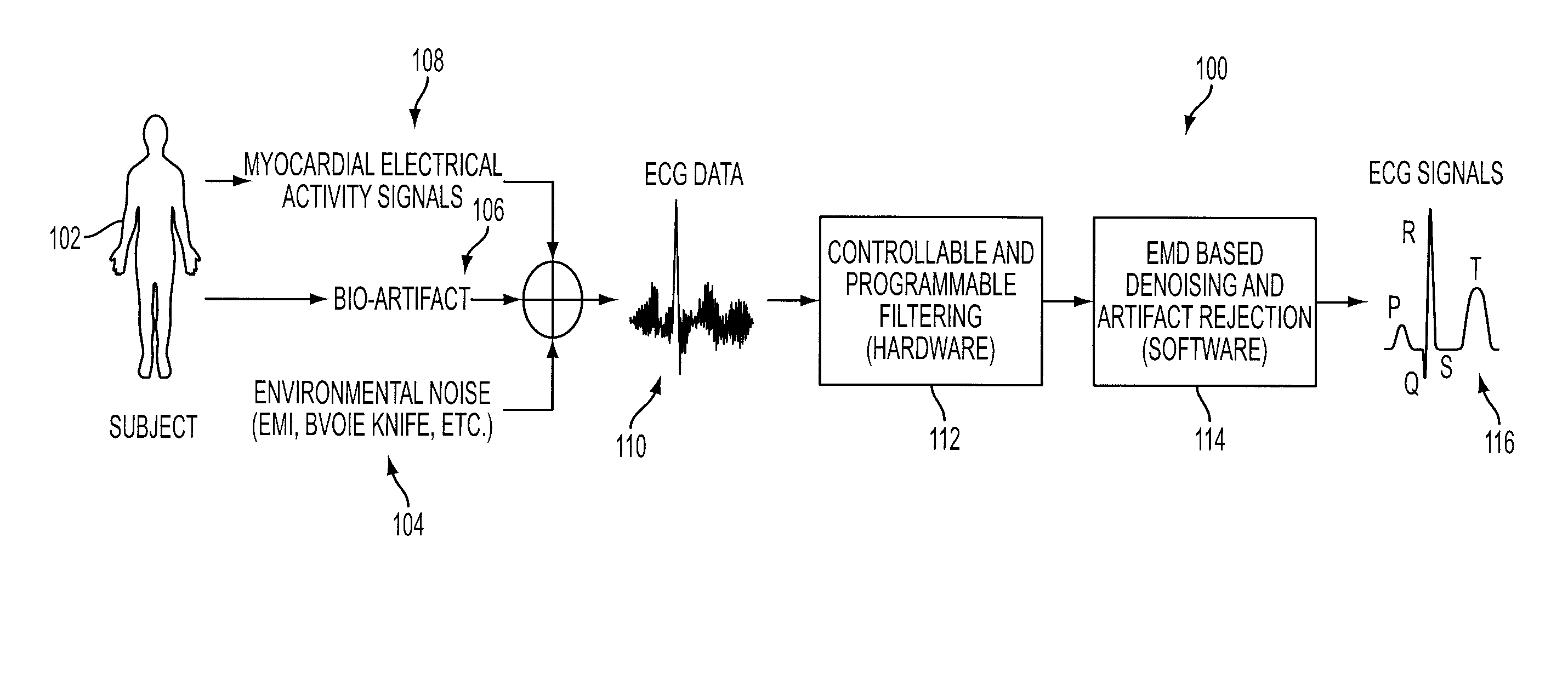
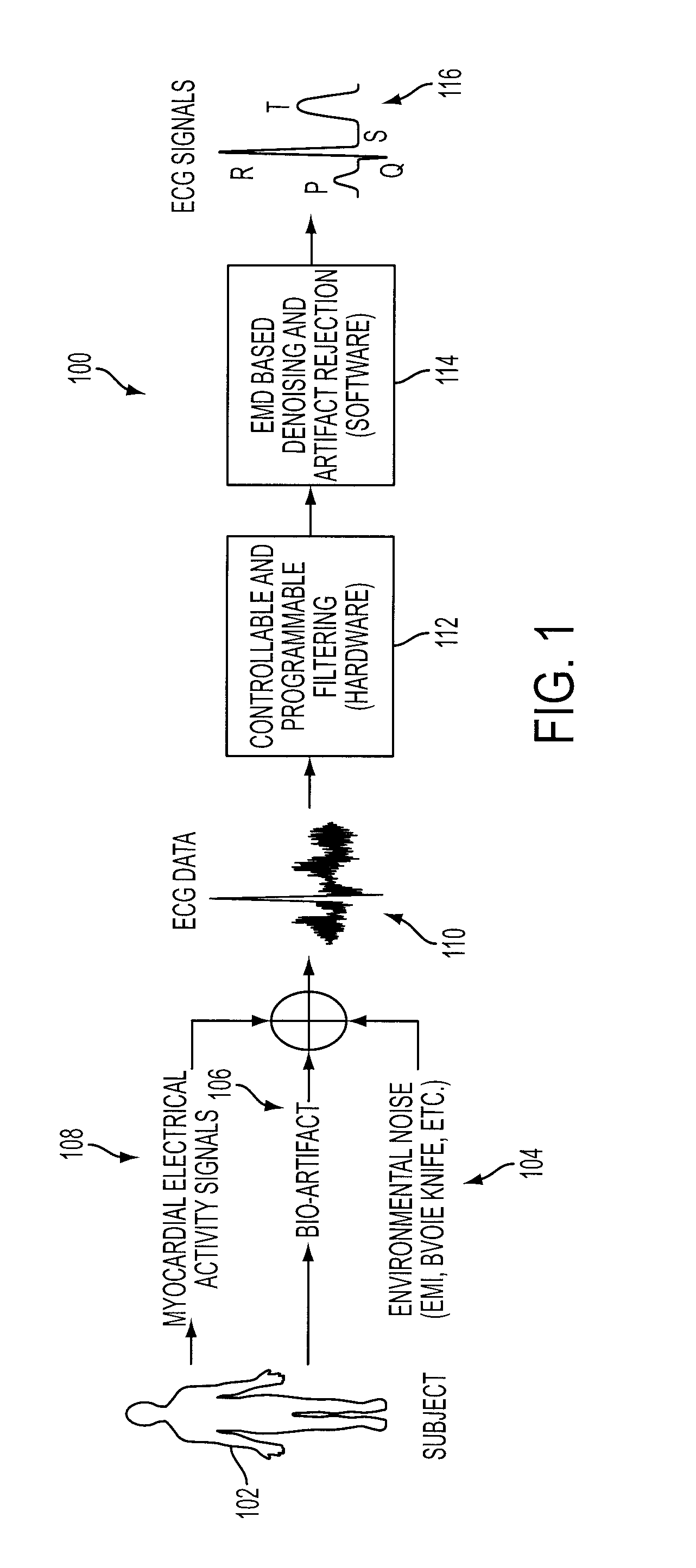
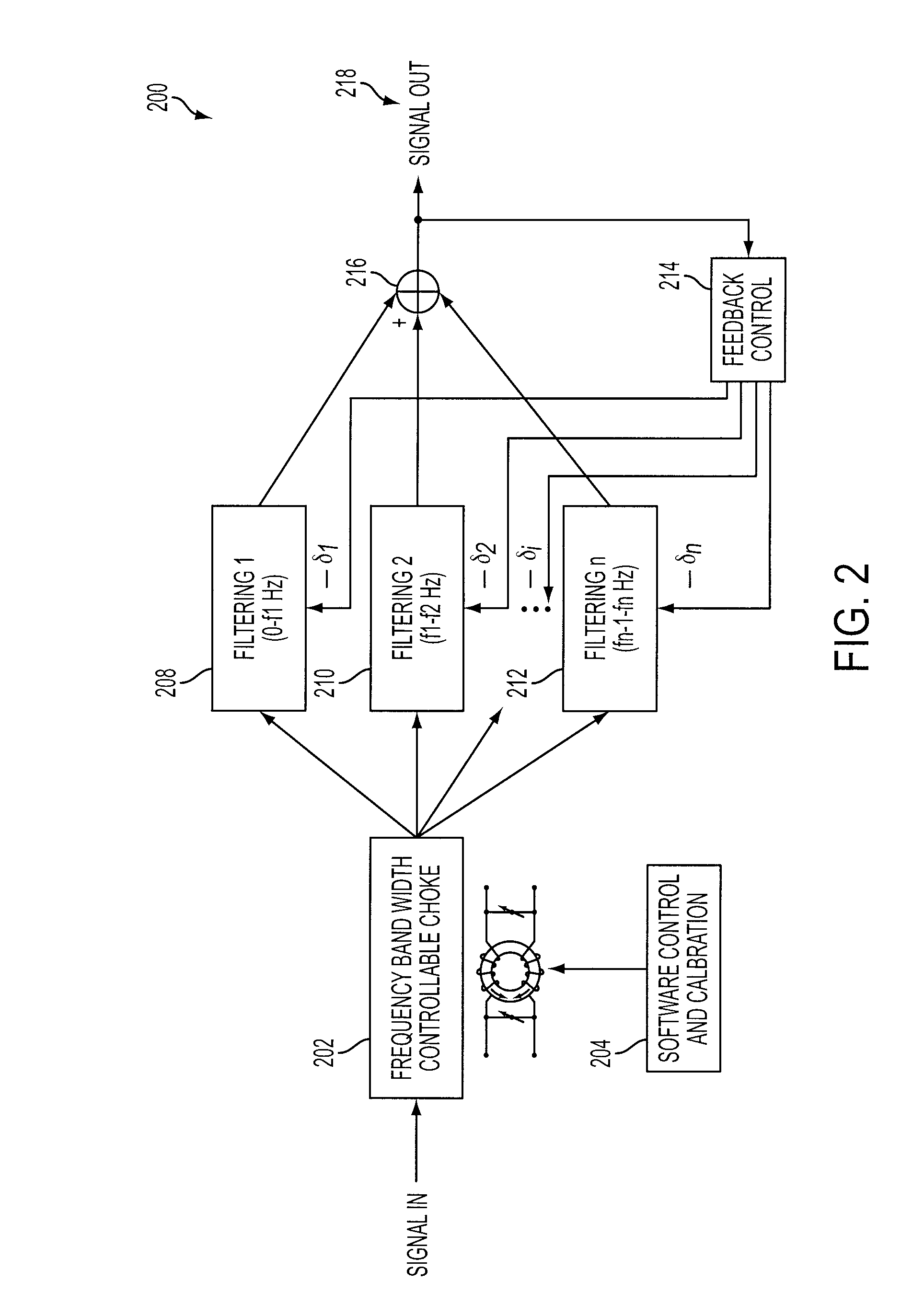
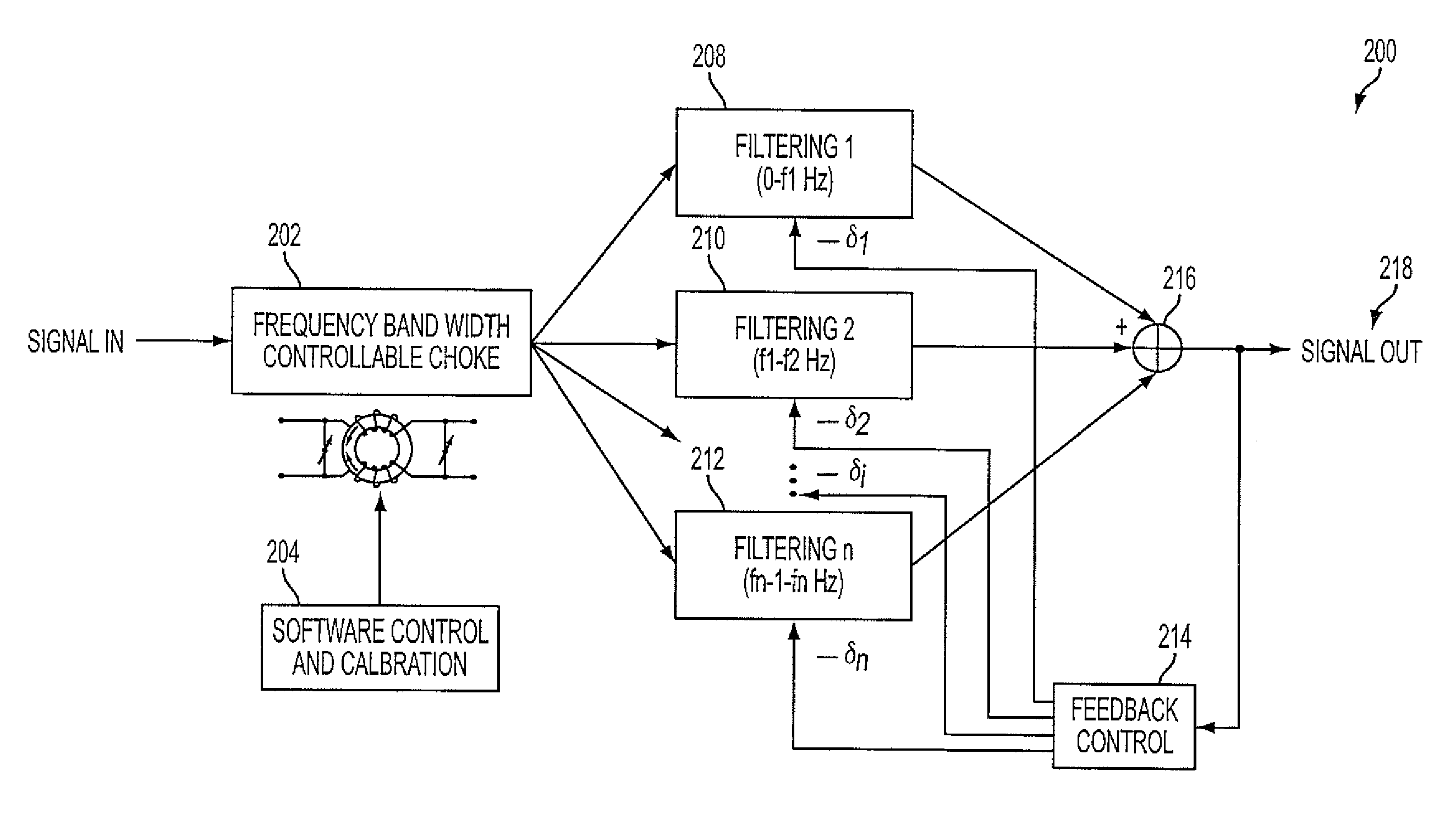
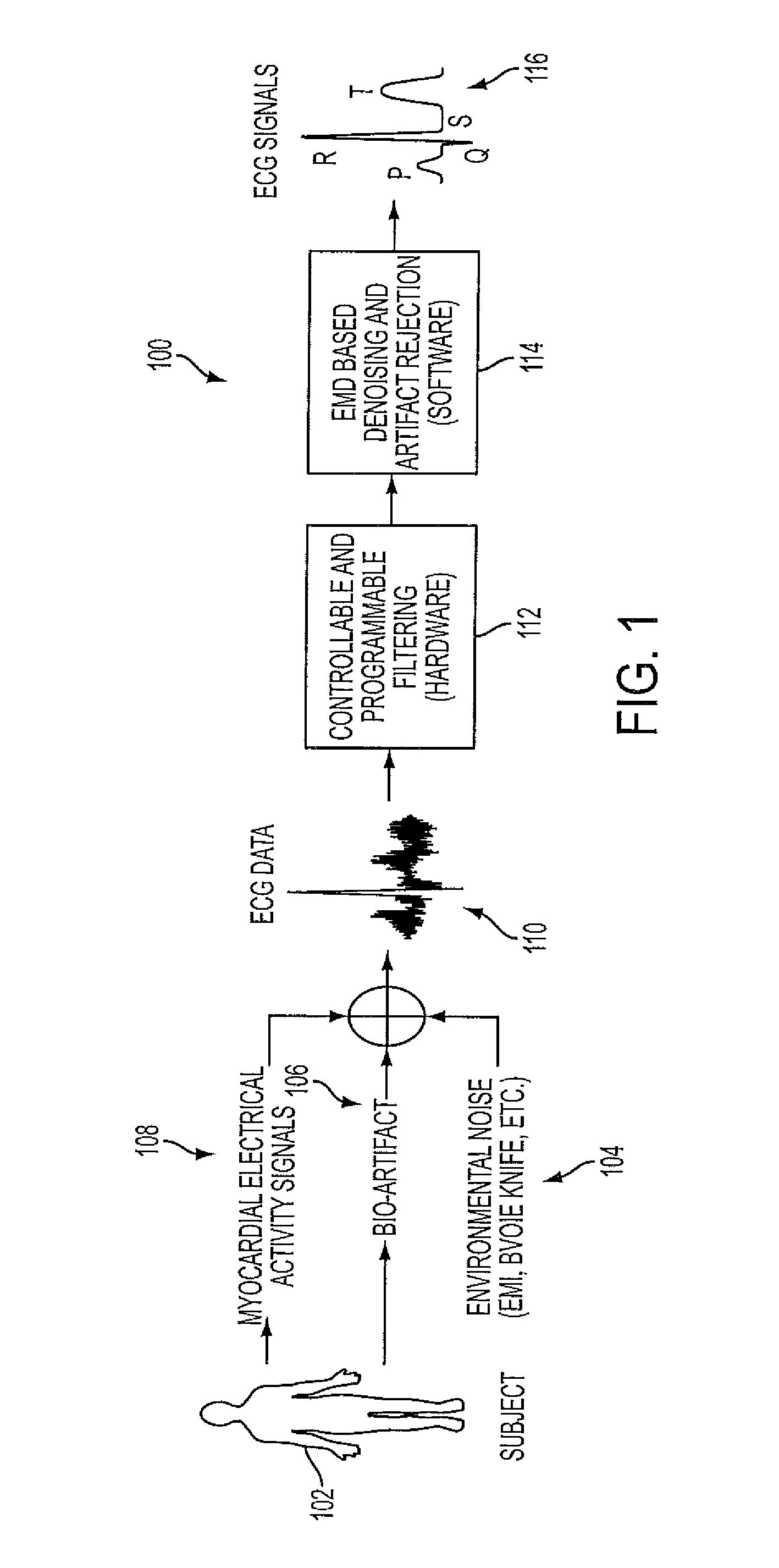
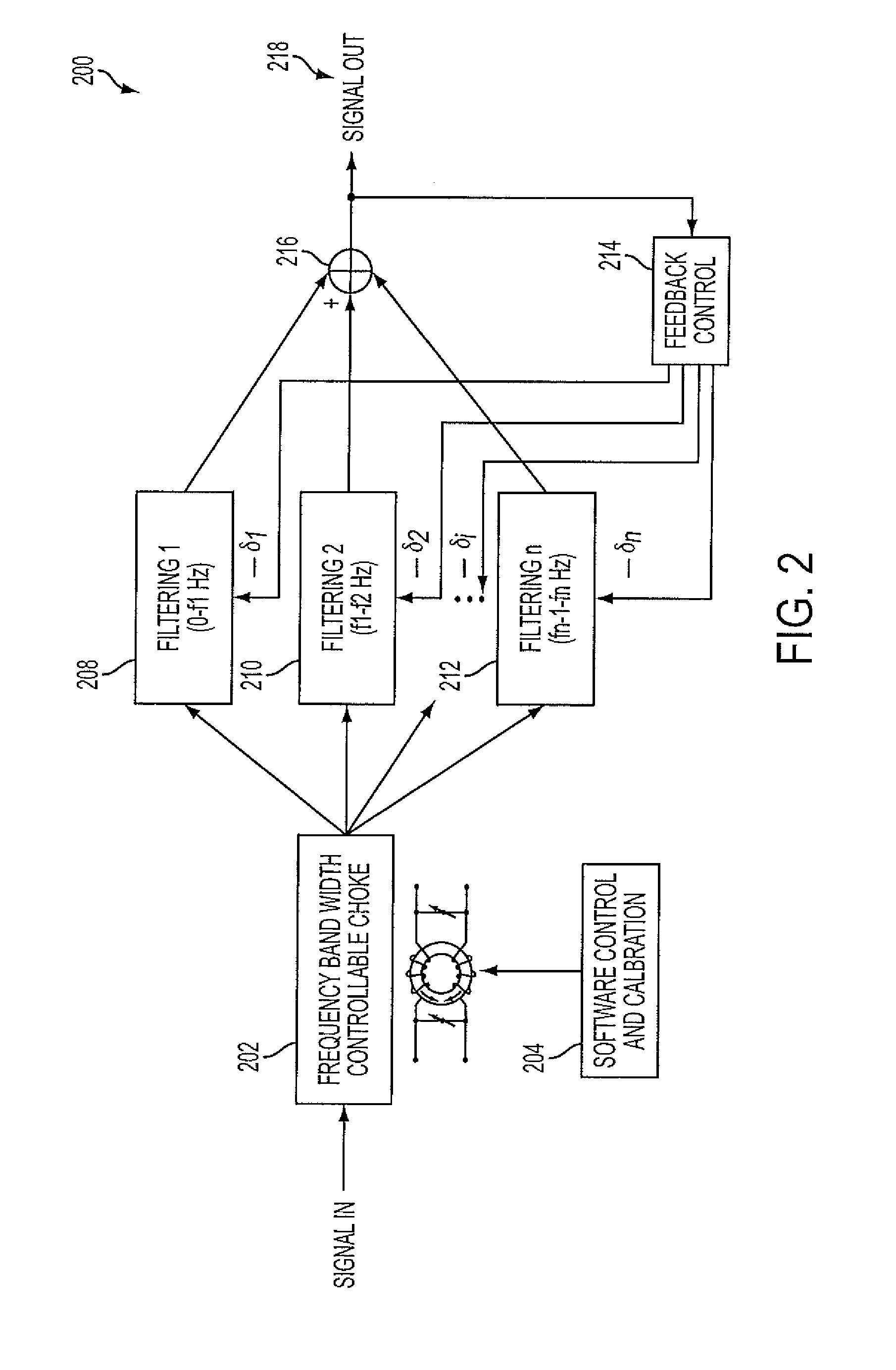
Denoising and Artifact Rejection for Cardiac Signal in a Sensis System
InactiveUS20080269628A1Effectively track cancelReduce common mode noiseElectrocardiographySensorsEngineeringFeedback control
A method and apparatus for denoising and rejecting artifacts from cardiac signals, having the steps of accepting a cardiac signal from a patient, subjecting the cardiac signal from the patient to a frequency band width controllable choke to separate the cardiac signal into predefined frequencies, filtering each of the predefined frequencies to remove dynamic common noise, joining each of the predefined frequencies into a cardiac signal without the dynamic common noise, and providing a feedback control to the filtering of each of the predefined frequencies.
Owner:ICE CAP SERIES 106 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I +1
Low noise planar transformer
ActiveUS7292126B2Improve EMI performanceReduce common mode noiseTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsUnwanted magnetic/electric effect reduction/preventionLow noiseCapacitance
An apparatus and method for reducing common mode noise capacitive coupling from a primary winding to a secondary winding in a transformer. In an embodiment, the primary winding has two terminals and a plurality of coil turns therebetween formed by a plurality of PCB layers sandwiched together, each having at least one of the coil turns formed thereon. The coils turns are connected in a predetermined way to form the primary winding. One terminal of the primary winding is connected to a coil turn on a first one of the PCB layers, and the other terminal is connected to a coil turn on a second one of the PCB layers. The PCB layers are stacked to form the primary winding. The secondary winding or windings are positioned adjacent to a selected one of the stacked PCB layers that is in a position between the first and second PCB layers.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
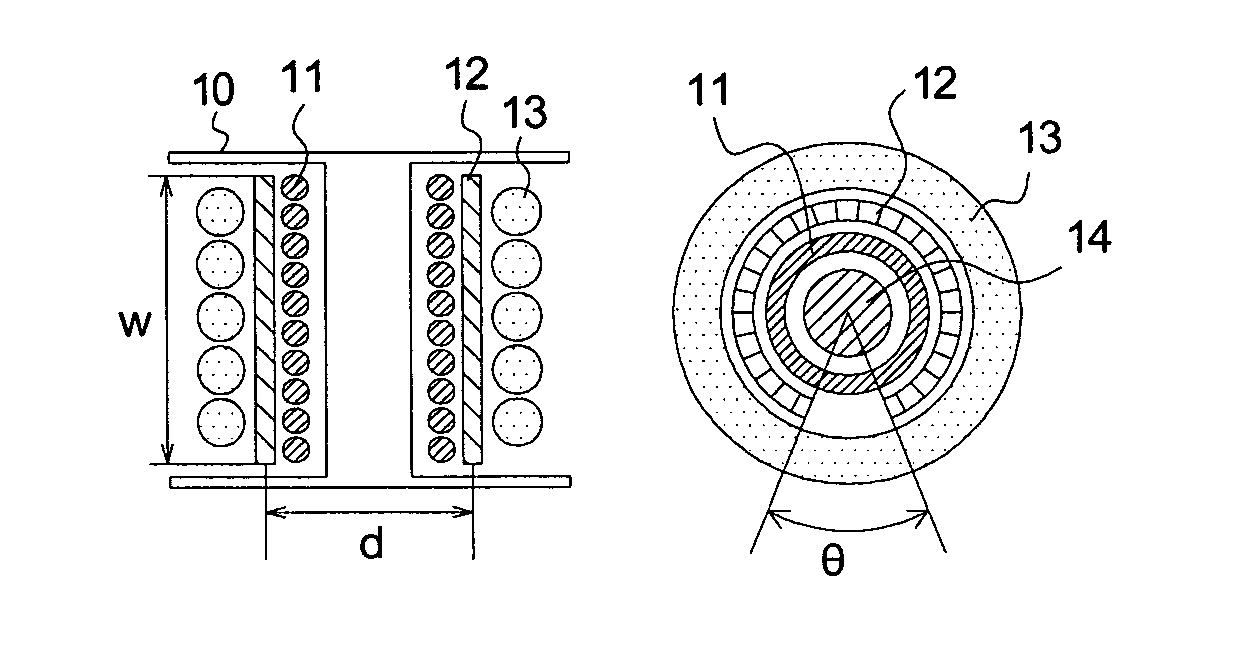
Multilayer feedthrough capacitor
InactiveUS20030227738A1Reduce common mode noiseGood effectAnti-noise capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesElectrical conductorCapacitor
A multilayer feedthrough capacitor having a first internal conductor arranged in a dielectric body, an intermediate internal conductor arranged in the dielectric body and stacked with the first internal conductor via a ceramic layer, a second internal conductor arranged in the dielectric body and stacked with the intermediate internal conductor via a ceramic layer, a first terminal electrode formed at an outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the first internal conductor, a second terminal electrode formed at the outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the second internal conductor, and an intermediate terminal electrode formed at the outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the intermediate internal conductor. The intermediate terminal electrode is connected to the ground, while the first terminal electrode and the second terminal electrode are connected to paths for transmitting signals. The first internal conductor and the second internal conductor have currents flowing through them in opposite directions.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Power factor correction circuit
InactiveUS20130257392A1Reducing common mode noiseReduce noiseEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionPower factor correction circuitsCapacitor
The present disclosure provides a power factor correction circuit. The power factor correction circuit includes an AC power, a first bridge arm, a second bridge arm and at least one auxiliary capacitor. The AC power has first and second ends. The first bridge arm includes first and second switches connected in series with each other. A second terminal of the first switch is connected to a first terminal of the second switch, and is coupled to the first end of the AC power via a first inductor. The second bridge arm is connected in parallel with the first bridge arm, and includes third and fourth switches connected in series with each other. A second terminal of the third switch is connected to a first terminal of the fourth switch and the second end of the AC power. The auxiliary capacitor is connected to the third or fourth switch in parallel.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
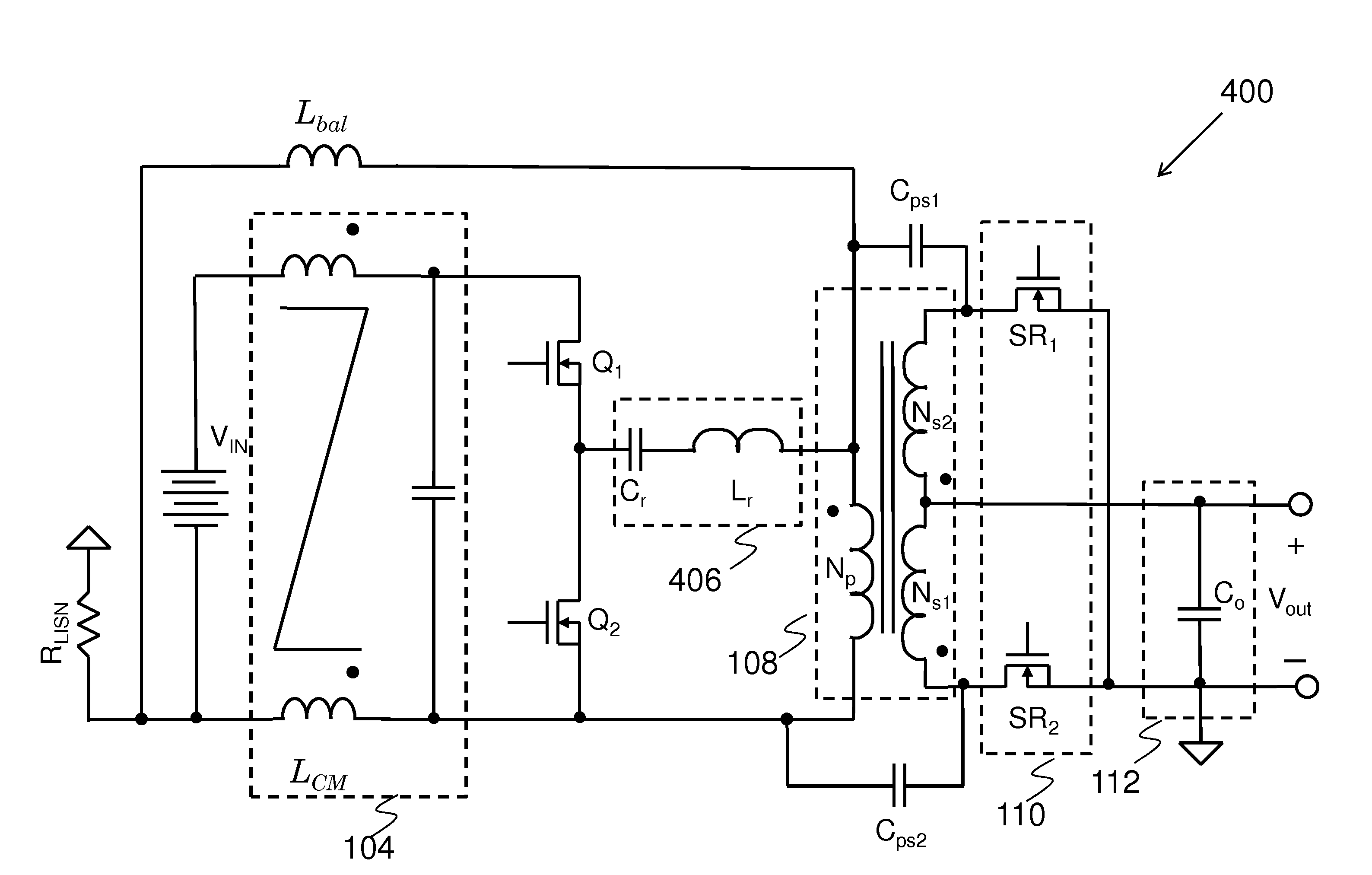
Common Mode Noise Reduction Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20120063173A1Reduce common mode noiseImprove efficiency and reliability and costElectronic circuit testingApparatus with intermediate ac conversionInductorEngineering
An embodiment common mode noise reduction apparatus comprises a common mode choke, a balance inductor, a first capacitor and a second capacitor. The common mode choke is placed between an input dc source and a primary side network of an isolated power converter. The balance inductor is coupled between an upper terminal of a primary winding of the isolated power converter and a negative terminal of the input dc source. The first capacitor is coupled between the upper terminal of a primary side of a transformer and an upper terminal of a secondary side of the transformer of the isolated power converter. The second capacitor is coupled between a lower terminal of the primary side of the transformer and a lower terminal of the secondary side of the transformer of the isolated power converter.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL POWER TECH CO LTD
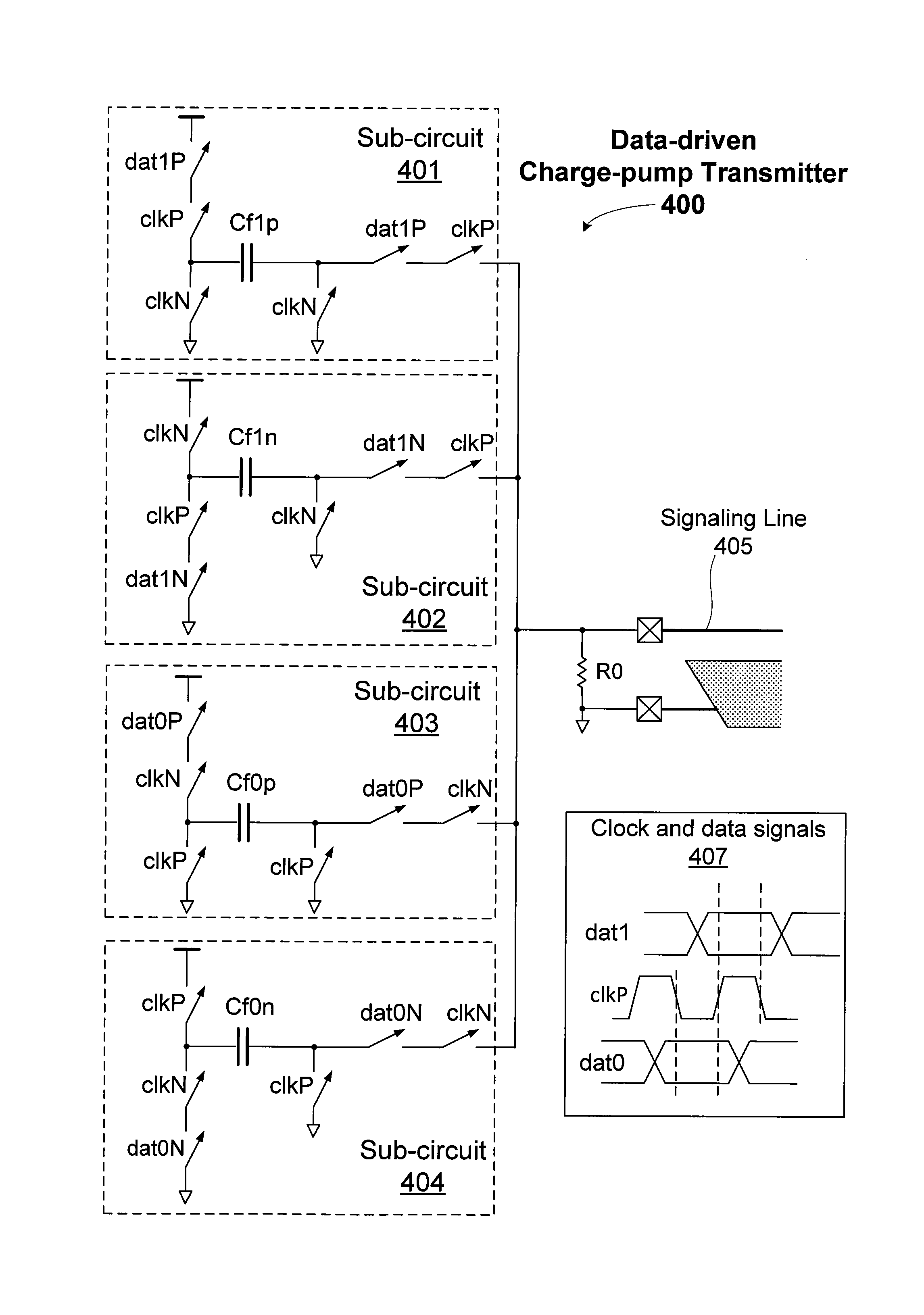
Data-driven charge-pump transmitter for differential signaling
ActiveUS20130194031A1Reduce common mode noiseMinimize generation of noiseSolid-state devicesBaseband systemsDifferential signalingMultiplexer
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a mechanism for transmitting and receiving differential signals. A transmitter combines a direct current (DC) to DC converter including a capacitor with a 2:1 multiplexer to drive a pair of differential signaling lines. The transmitter drives a pair of voltages that are symmetric about the ground power supply level. Signaling currents are returned to the ground plane to minimize the generation of noise that is a source of crosstalk between different differential signaling pairs. Noise introduced through the power supply is correlated with the switching rate of the data and may be reduced using an equalizer circuit.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Active common mode EMI filters
InactiveUS6842069B2Efficient actionReduce common mode noiseAc-ac conversionOscillations generatorsCurrent sensorEngineering
An active EMI filter for reducing common mode noise current in a circuits, comprising: a transistor stage having two transistors coupled in series, a current sensor for sensing the common mode noise current, the current sensor having an output driving the transistor stage, whereby each of the transistors is driven in response to the common mode noise current, a capacitor coupling the transistor stage and the ground return line, the capacitor providing a cancellation current to cancel the common mode noise current, the current sensor comprising a current transformer having a primary coupled with the circuit having the common mode noise. The current sensor and the transistor stage may be coupled in a feed forward arrangement wherein the transistor stage and the current sensor have an amplitude gain of approximately unity; or in a feedback arrangement wherein the transistor stage and current sensor provide high gain.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
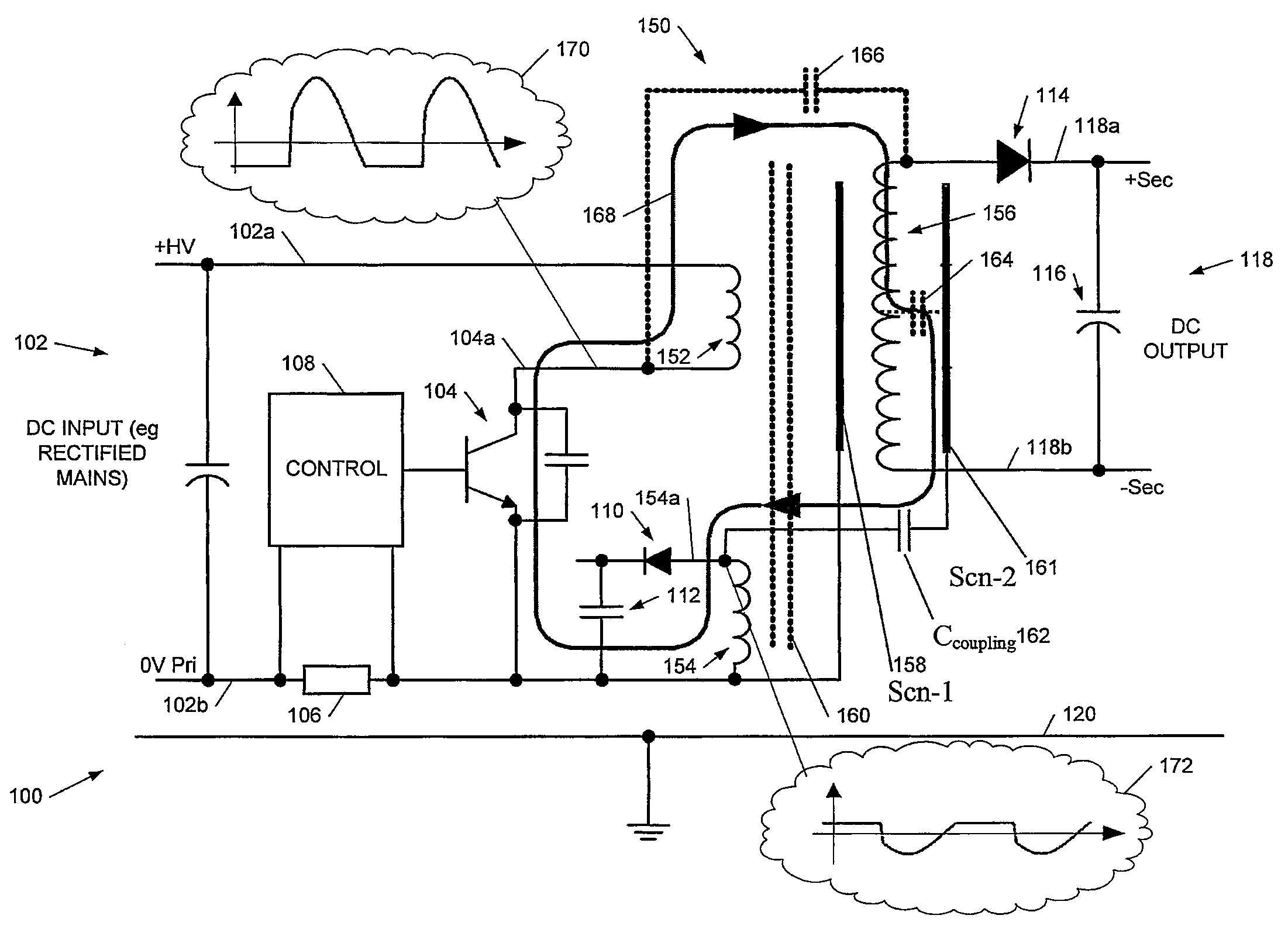
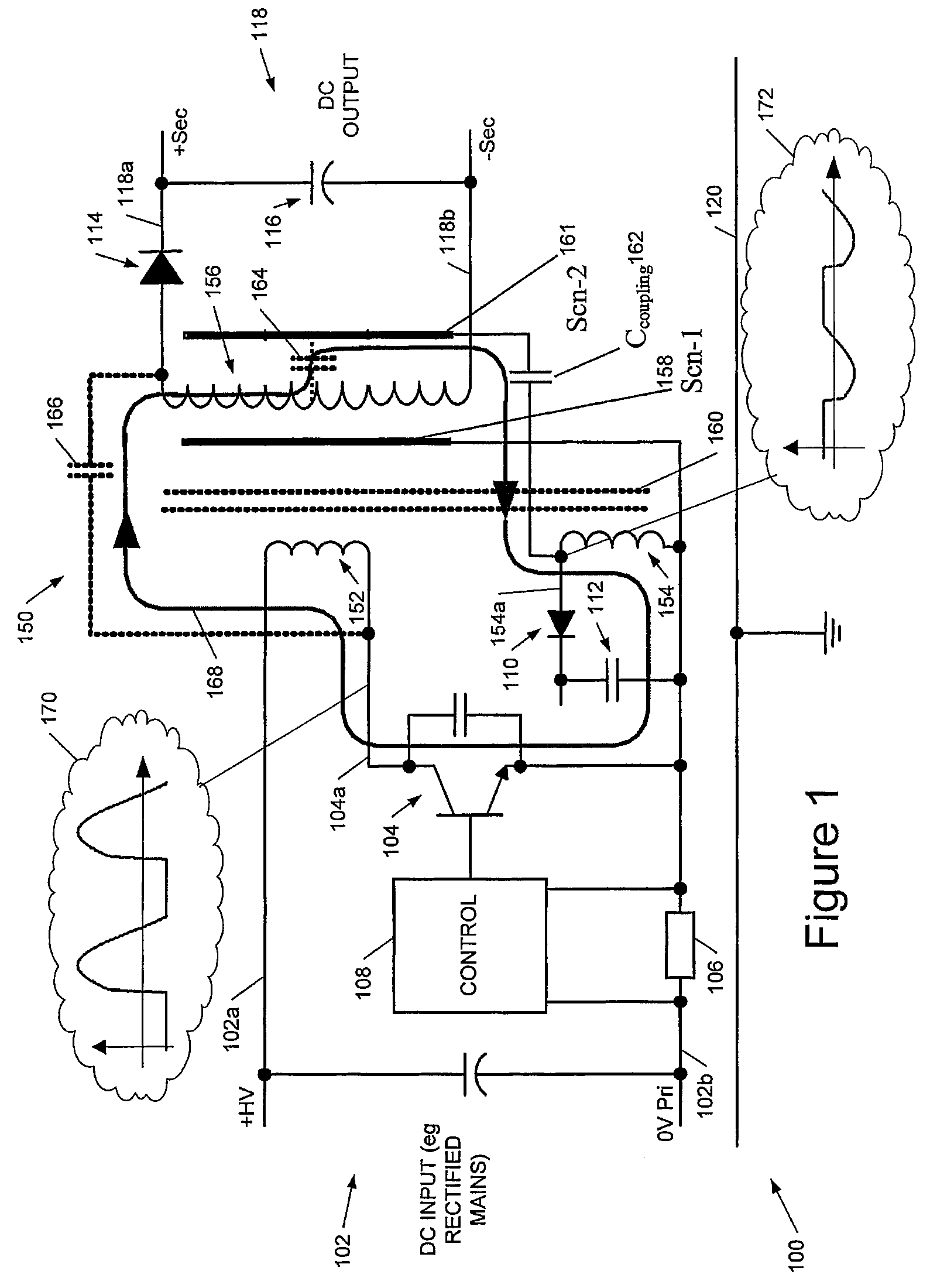
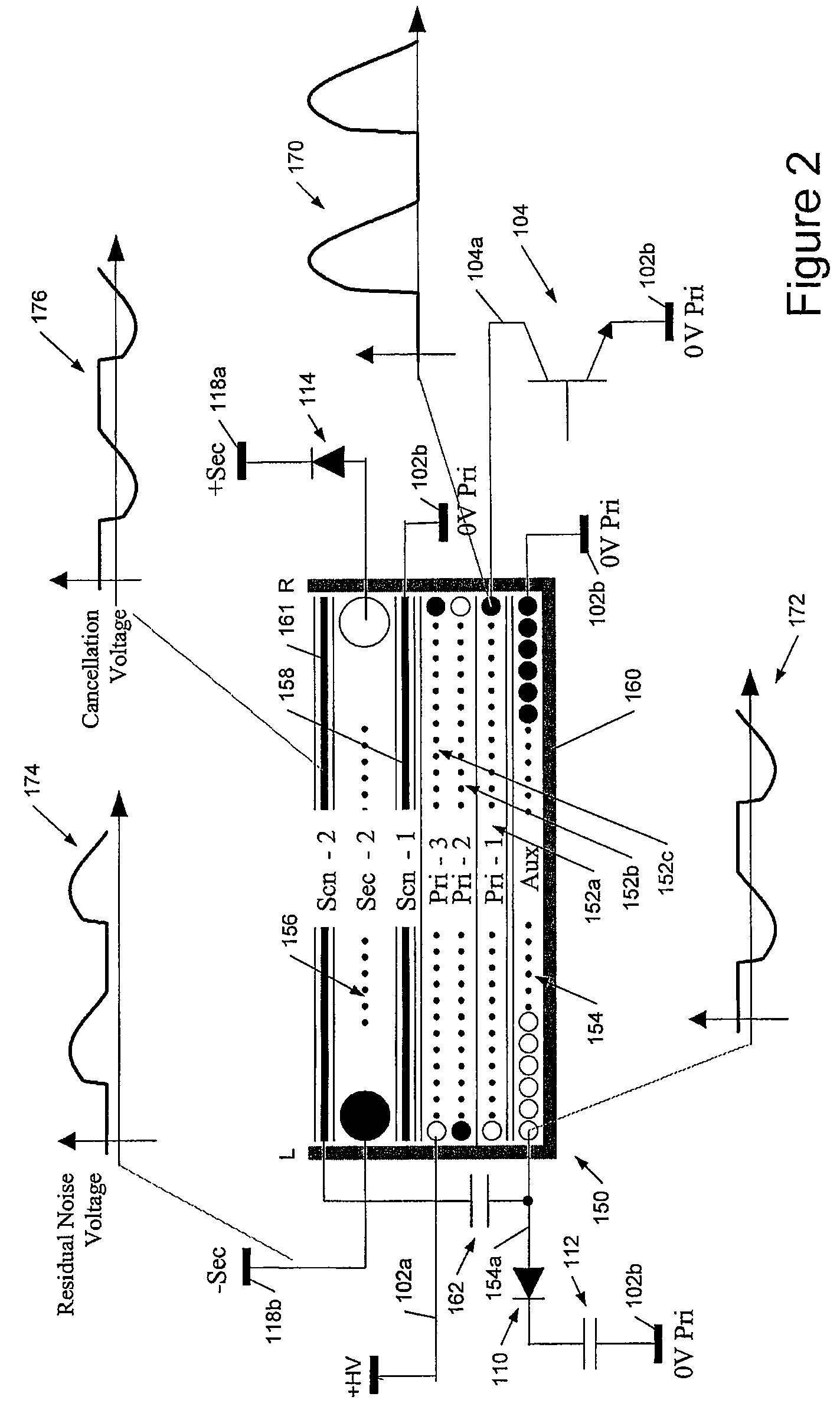
Noise reduction systems and methods for unshielded coupling of switch mode power supply
InactiveUS8023294B2Reduce common mode noiseMaximize separationDc network circuit arrangementsConversion constructional detailsCapacitanceTransformer
We describe a switch mode power supply having a power input, a switch, a transformer, and a power output. The transformer has a primary winding coupled to said power input via said switch, and a secondary winding coupled to said power output. The transformer further comprises an auxiliary winding and a coupling structure capacitatively coupled to said secondary winding of said transformer; wherein said coupling structure does not comprise a shield or screen between said primary and secondary windings. The switch mode power supply further comprises a coupling capacitor connected between said coupling structure and said auxiliary winding to provide a noise suppression voltage from said auxiliary winding to said secondary winding to at least partially cancel a common mode noise voltage on said secondary winding from unshielded coupling from said primary winding.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
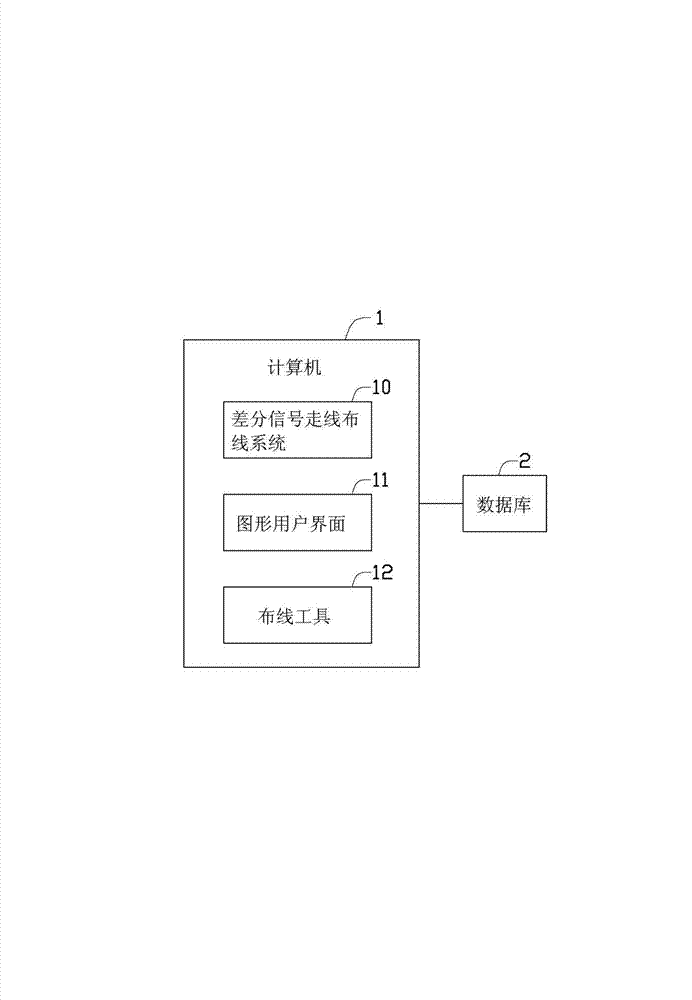
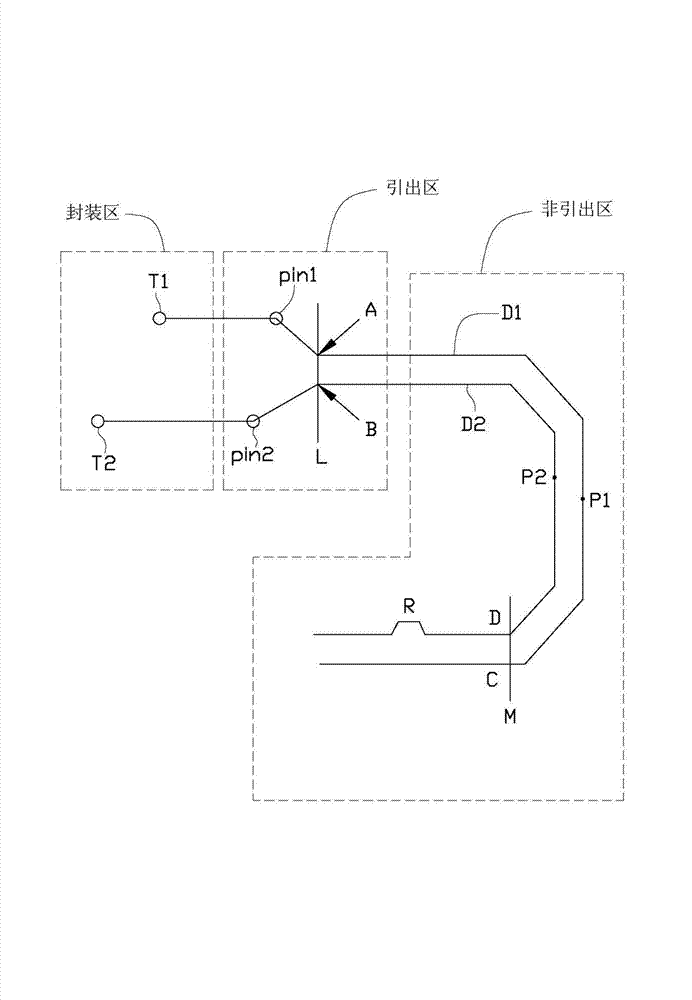
Differential signal routing line distributing system and differential signal routing line distributing method
InactiveCN103366023AReduce common mode noiseComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsDifferential lineSignal routing
A layout method for the creation of a differential pair for the transmission of signals generates a differential pair between a differential signal sender and a differential signal receiver in a layout of a PCB. Differential signals are transmitted via two wires. A plurality of vertical lines are created on the differential pair. Junctions of the vertical lines and the two wires are defined as pairs of points. A first length between one terminal of the differential signal sender and one point of each pair of points and a second length between the other terminal of the differential signal sender and the other point of each pair of points are calculated. If any difference between the first length and the second length does not fall within an allowable range, the lengths of the two wires are adjusted.
Owner:DONGYING POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +2
Transformer Shielding for Common Mode Noise Reduction in Isolated Converters
ActiveUS20140334198A1Reduce and fully eliminate propagationReducing and avoiding transmissionTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDc-dc conversionParasitic capacitanceConductor Coil
At least one shield member interposed between primary and secondary windings of a transformer and connected to the primary and / or secondary windings forms a distributed parasitic capacitance between the shield member and either the winding to which it is not connected or another shield member connected to that winding. Connections are made to the respective transformer windings such that the voltage distributions thus developed cause complementary common mode noise to be conducted in opposite directions in respective portions of the parasitic capacitance such that net common mode current can be made arbitrarily small without requiring that both sides of the distributed parasitic capacitance have complementary or equal voltage distributions. Such complementary common mode currents can be achieved by dividing opposing shield members or developing a voltage distribution in a single shield member in accordance with Faraday's Law.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Modulation methods and apparatus for reducing common mode noise
ActiveUS20070268052A1Reduce common mode noiseMinimize impactAC motor controlAc-dc conversionCarrier signalEngineering
A method and apparatus for reducing common mode noise in a three phase pulse width modulated (PWM) system the method comprising the steps of receiving modulating waveforms, identifying a first of the modulating waveforms that is instantaneously the maximum of the modulating waveforms, identifying a second of the modulating waveforms that is instantaneously the minimum of the modulating waveforms, for a first phase associated with at least one of the first and second identified waveforms, substituting a first substitute waveform for the one of the first and second waveforms, for the first phase, modifying at least one of the first substituted waveform and duty cycle signals generated by comparing the first substituted waveform with the carrier signal as a function of a first rule set to substantially minimize the effects of turn on delays and for at least one of the second and third phases, modifying at least one of the associated modulating waveform and duty cycle signals generated by comparing the modulating waveform with the carrier signal as a function of a second rule set to substantially eliminate the effects of turn on delays where the second rule set is different than the first rule set.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Common mode noise mitigation for integrated touch screens
ActiveUS20200103993A1Reduce noiseEliminating and reducing common mode noiseNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceDisplay device
Some touch screens can be formed by at least partially integrating touch sensing circuitry into a display pixel stackup. In some examples, noise can be introduced into touch sensor panel measurements, for example, from display data lines of a display device proximate to the touch sensor panel. In some examples, rows or columns of touch electrodes can be split and a first portion of the touch sensor panel can be stimulated to measure capacitance and noise and a second portion of the touch sensor panel can be unstimulated and measure noise. In some examples, both the first and the second portions of the touch sensor panel can be stimulated using orthogonal stimulation codes. In some examples, measurements from the first and / or second portions of the touch sensor panel can be subtracted from measurements from the other portion of the touch sensor panel to eliminate or reduce common mode noise.
Owner:APPLE INC
Denoising and Artifact Rejection For Cardiac Signal in a Sensis System
ActiveUS20110015532A1Effectively track cancelReduce common mode noiseElectrocardiographySensorsEngineeringFeedback control
A system denoises and rejects artifacts from cardiac signals, by accepting a cardiac signal from a patient, processing the cardiac signal from the patient using a frequency band width controllable choke to separate the cardiac signal into predefined frequencies, filtering each of the predefined frequencies to remove dynamic common noise, joining each of the predefined frequencies into a cardiac signal without the dynamic common noise, and providing feedback control of the filtering of each of the predefined frequencies.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com