Patents
Literature
191 results about "Common code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for classification of software using characteristics and combinations of such characteristics
ActiveUS20090187992A1Provide capabilityMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionCoding blockSoftware
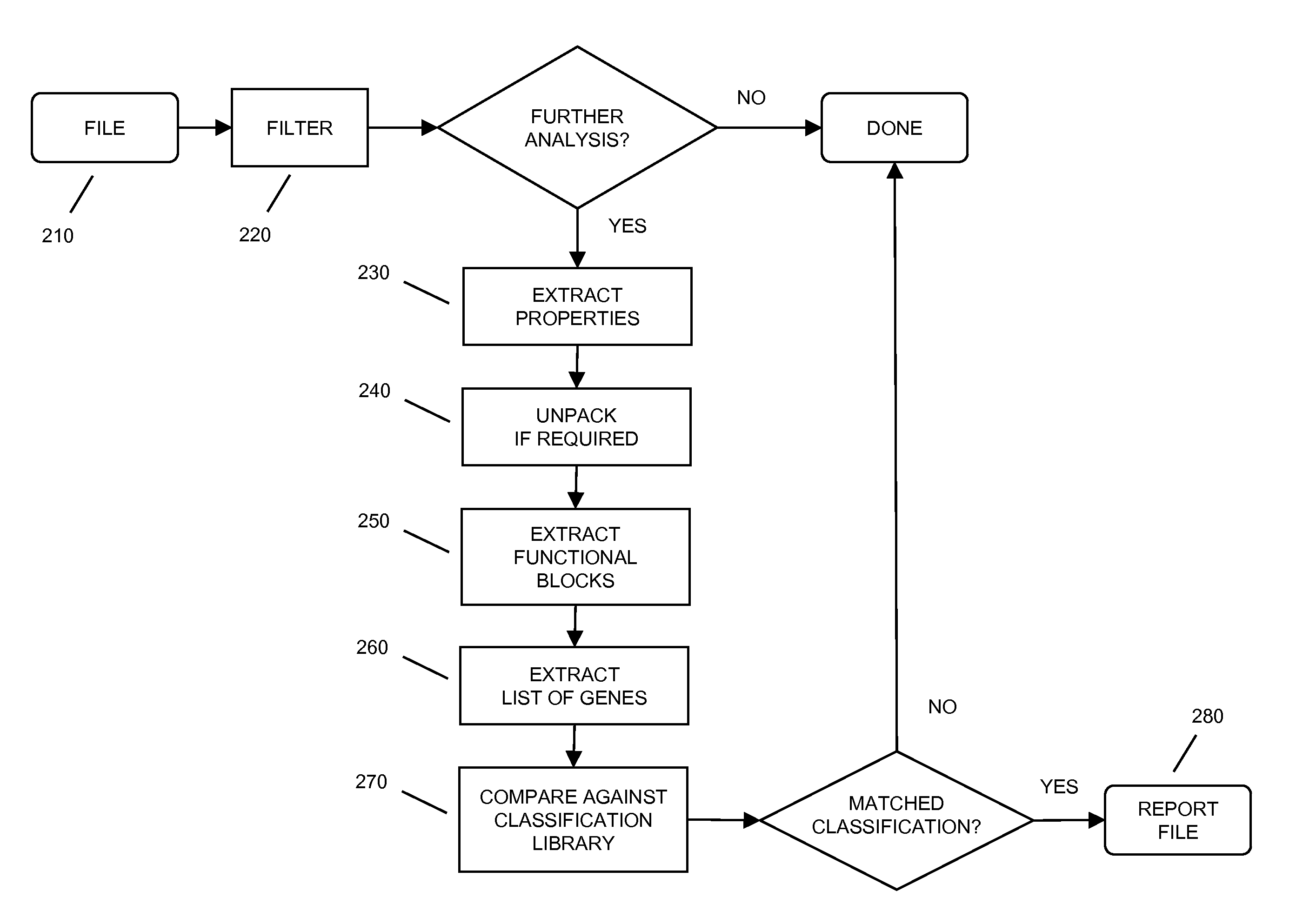
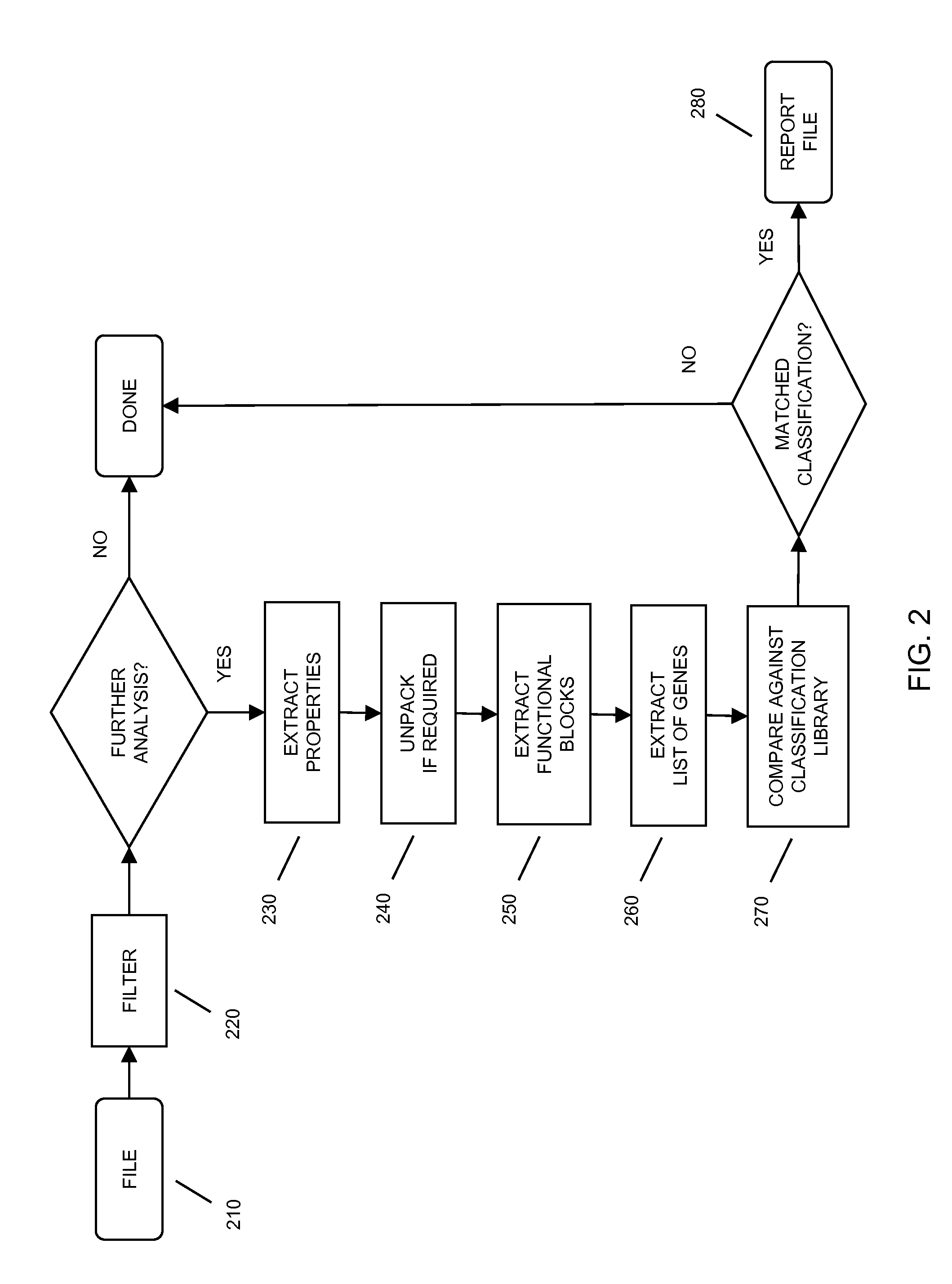
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for the steps of identifying a functional code block that performs a particular function within executable code; transforming the functional code block into a generic code representation of its functionality by tokenizing, refactoring, or the like, the functional code block; comparing the generic code representation with a previously characterized malicious code representation; and in response to a positive correlation from the comparison, identifying the executable code as containing malicious code.
Owner:SOPHOS
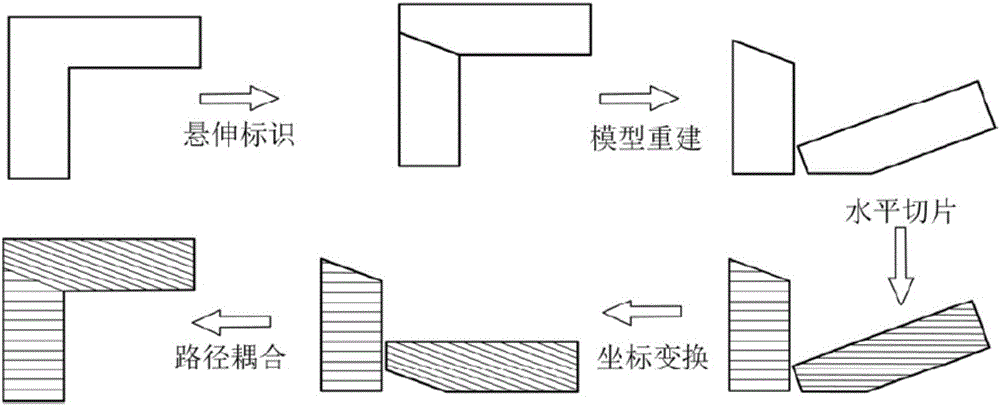
Non-support three-dimensional printing method based on inclined layering
ActiveCN105904729ASave printing raw materialsImprove printing efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusSupport removalCoupling
The invention discloses a non-support three-dimensional printing method based on inclined layering. The method comprises five steps of model surface overhanging area identification, model reestablishment, horizontal slicing, motion code coordinate transformation, and path coupling; a path includes two parts: a horizontal layered path and an inclined layered path. A path track inclined relative to a horizontal plane is formed at an overhanging part; when the region is printed, a new layer of material can be guaranteed to be not only suffered from gravity but also is suffered from an adhesive force in a deposition process due to the presence of a formed printing layer on an upper layer. An additional supporting material is omitted, a printing raw material is saved, the printing efficiency is improved, and a process of subsequent support removal is omitted. The inclined layered three-dimensional printing path provided by the invention has a common code format, can be directly applied in commercial and open-source desktop type three-dimensional printers, has extensive application prospects, and can be extended to the three-dimensional printing technology in biology, chemical engineering, macromolecule and food industries.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
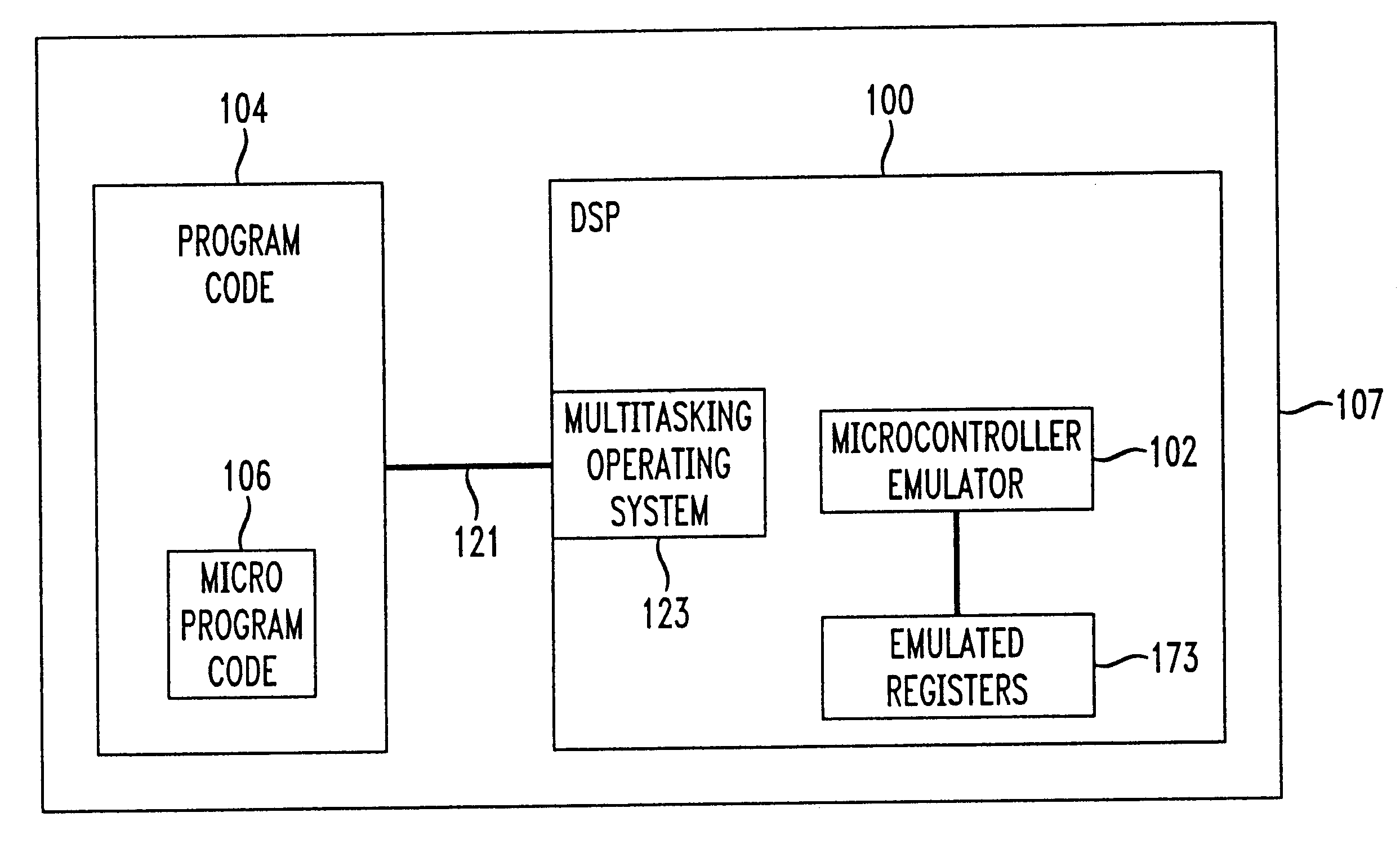
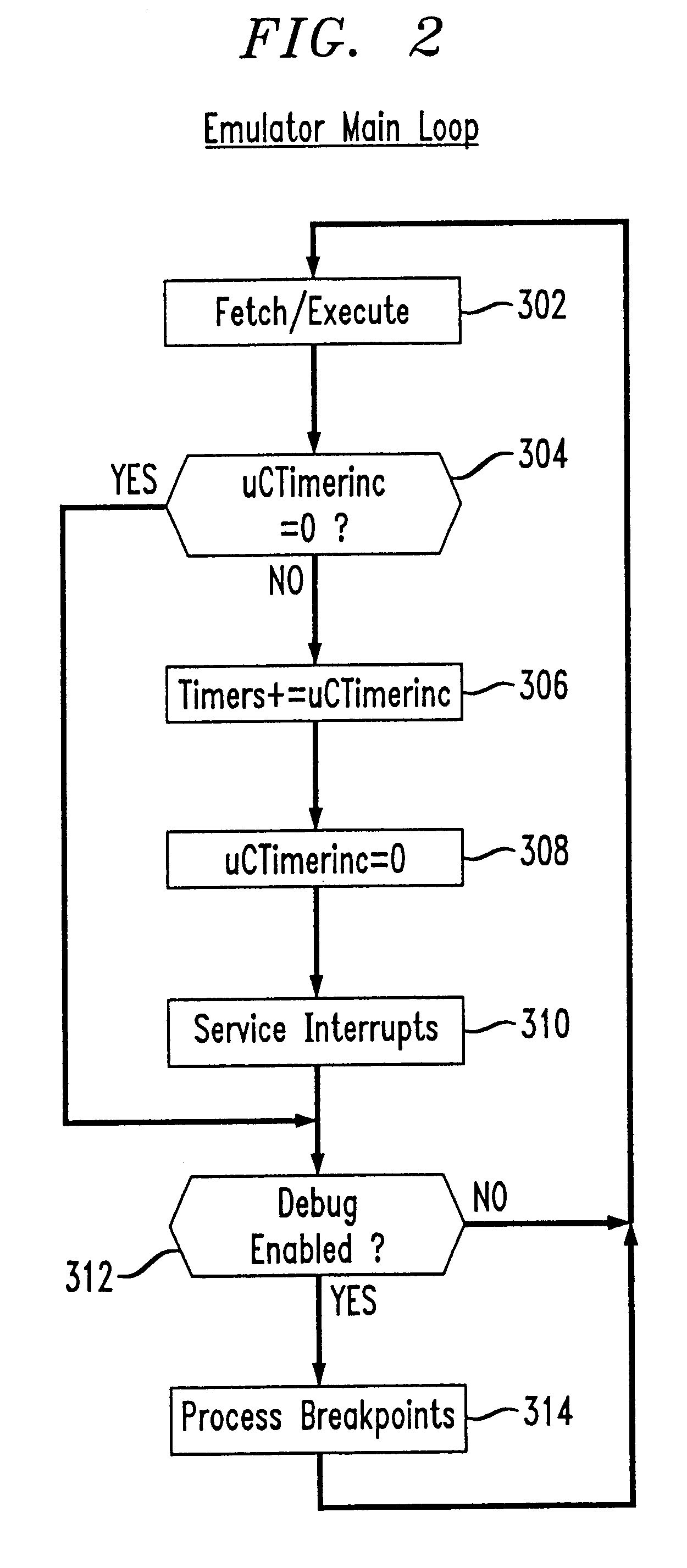
DSP emulating a microcontroller
InactiveUS6564179B1General purpose stored program computerSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMicrocontrollerOperational system
The present invention provides a processor device and technique having the capability of providing a two-processor solution with only one processor. In accordance with the principles of the present invention, a host processor is programmed in its native source and machine code language, and an emulated second processor is programmed in a different native source or machine code language particular to that emulated processor, to allow programming specialists in the different processors to develop common code for use on the same host processor. A multitasking operating system is included to allow time sharing operation between instructions from program code relating to the host processor (e.g., a DSP in the disclosed embodiment), and different program code relating to the emulated processor. The program code relating to the host processor (e.g., DSP) is written in program code which is native to the DSP, while the program code relating to the emulated processor (e.g., microcontroller) is written in program code which is native to the microcontroller. The SoftCore emulation module allows both DSP code and control code written for a microcontroller to execute independently on the same processor by multi-tasking resources in the faster, host processor (e.g., in the DSP), giving equal time slots of processor time to each processor (real and emulated).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
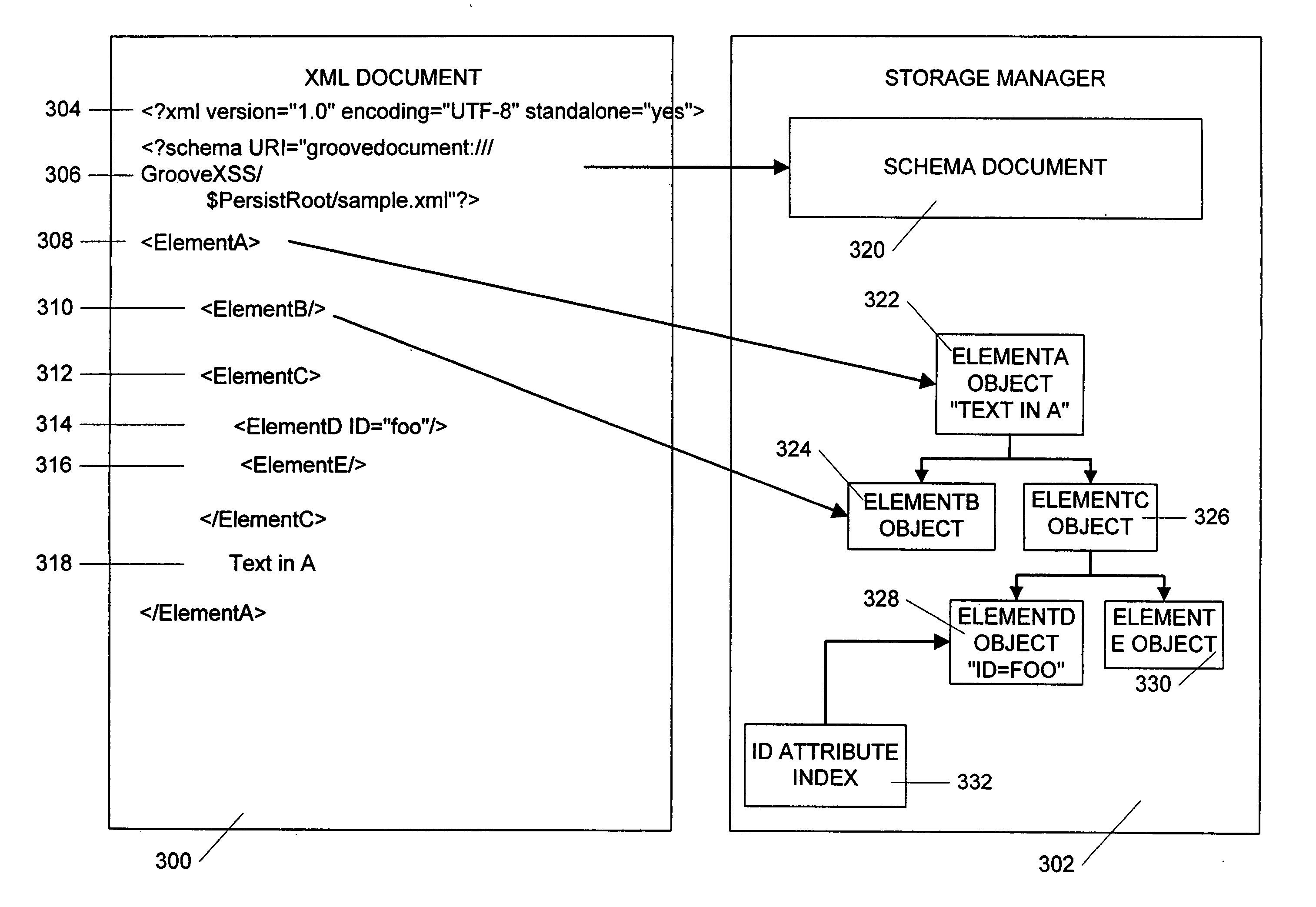
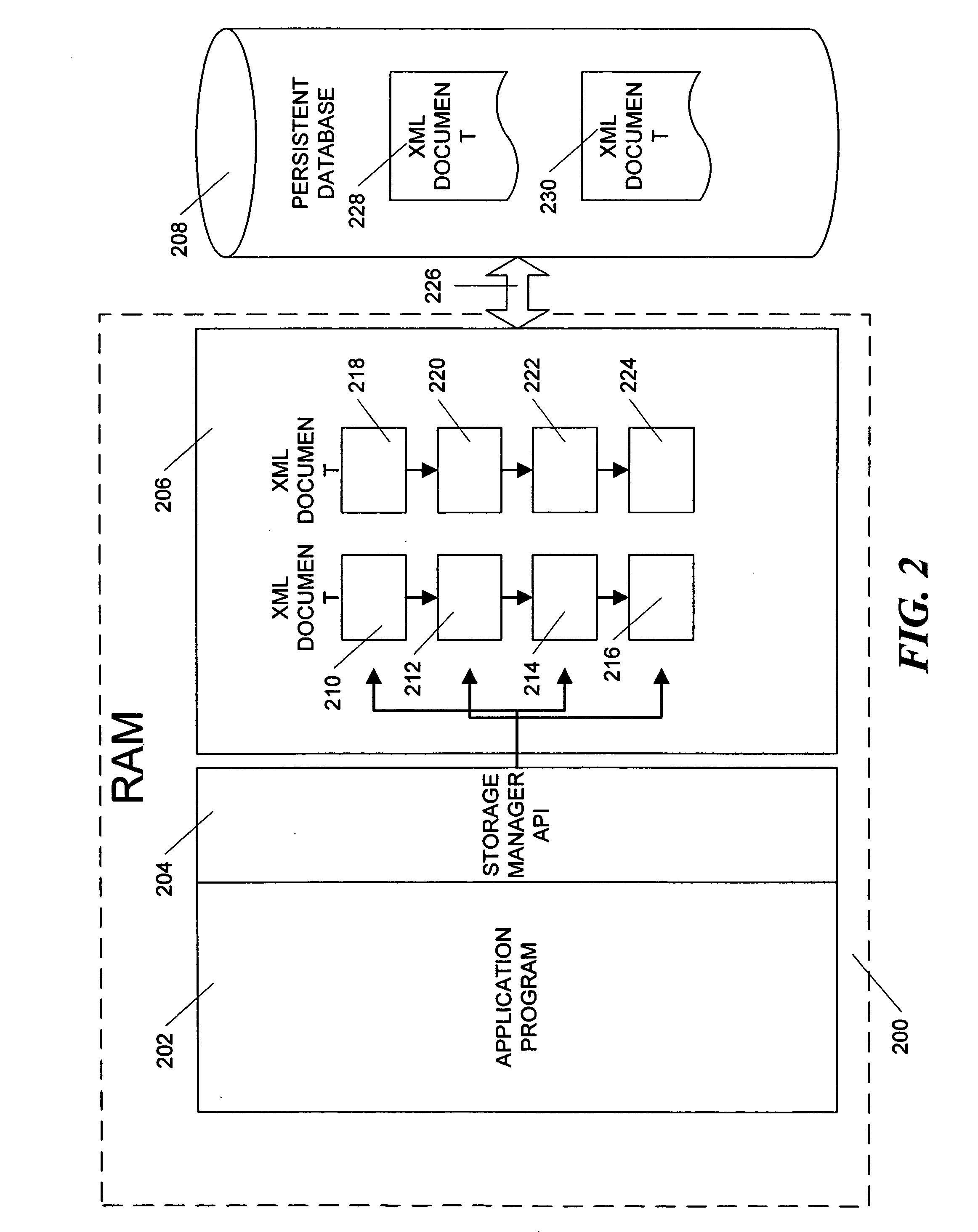
Method and apparatus for efficient management of XML documents
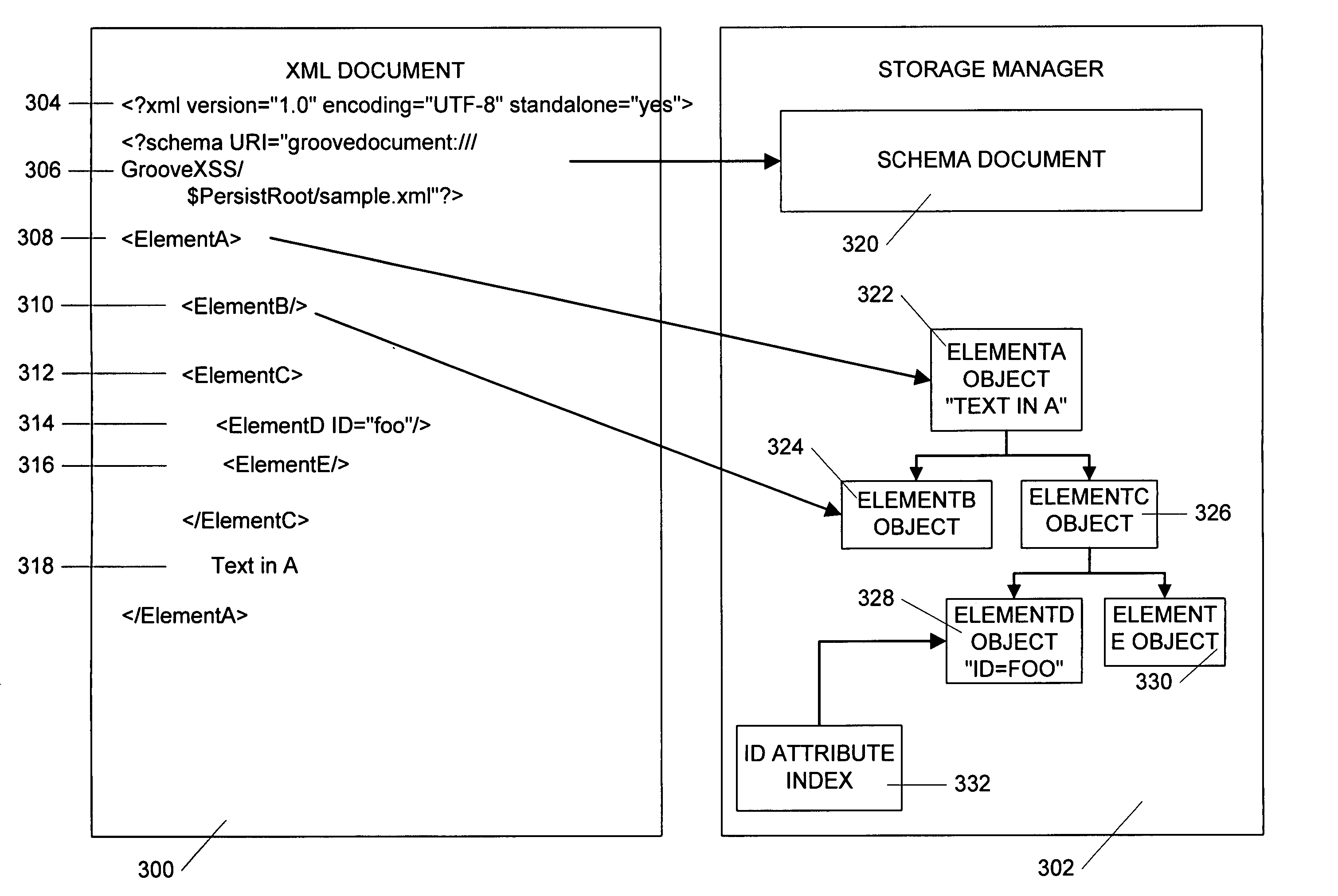
InactiveUS20050171970A1Rapid positioningConsistent interfaceDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingAs elementTerm memory
An in-memory storage manager represents XML-compliant documents as a collection of objects in memory. The collection of objects allows the storage manager to manipulate the document, or parts of the document with a consistent interface and to provide for features that are not available in conventional XML documents, such as element attributes with types other than text and documents that contain binary rather than text information. In addition, in the storage manager, the XML-compliant document is associated with a schema document which defines the arrangement of the document elements and attributes. The schema data associated with a document can contain a mapping between document elements and program code to be associated with each element. The storage manager further has methods for retrieving the code from the element tag. The retrieved code can then be invoked using attributes and content from the associated element and the element then acts like a conventional object. Further, the storage manager allows real-time access by separate process operating in different contexts. The objects that are used to represent the document are constructed from common code found locally in each process. In addition, the data in the objects is also stored in memory local to each process. The local memories are synchronized by means of a distributed memory system that continually equates the data copies of the same element in different processes. Client-specified collections are managed by a separate collection manager. The collection manager maintains a data structure called a “waffle” that represents the XML data structures in tabular form. A record set engine that is driven by user commands propagates a set of updates for a collection to the collection manager. Based on those updates, the collection manager updates index structures and may notify waffle users via the notification system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Workflow Development Platform
InactiveUS20070143736A1Reduce software development costsReduce the cost of trainingDigital computer detailsResourcesThird partyBusiness process
The present invention is a workflow processing system that encapsulates common workflow tasks into independent components which are visually represented in a workflow diagram at design-time. The platform accepts third-party and / or customer provided components easily without disrupting the common code base. This allows a customer to have one platform to capture / accept the different types of information their operations require, define their business processes, and deliver the information to their receiving destination of choice.
Owner:MICROSYST TECH
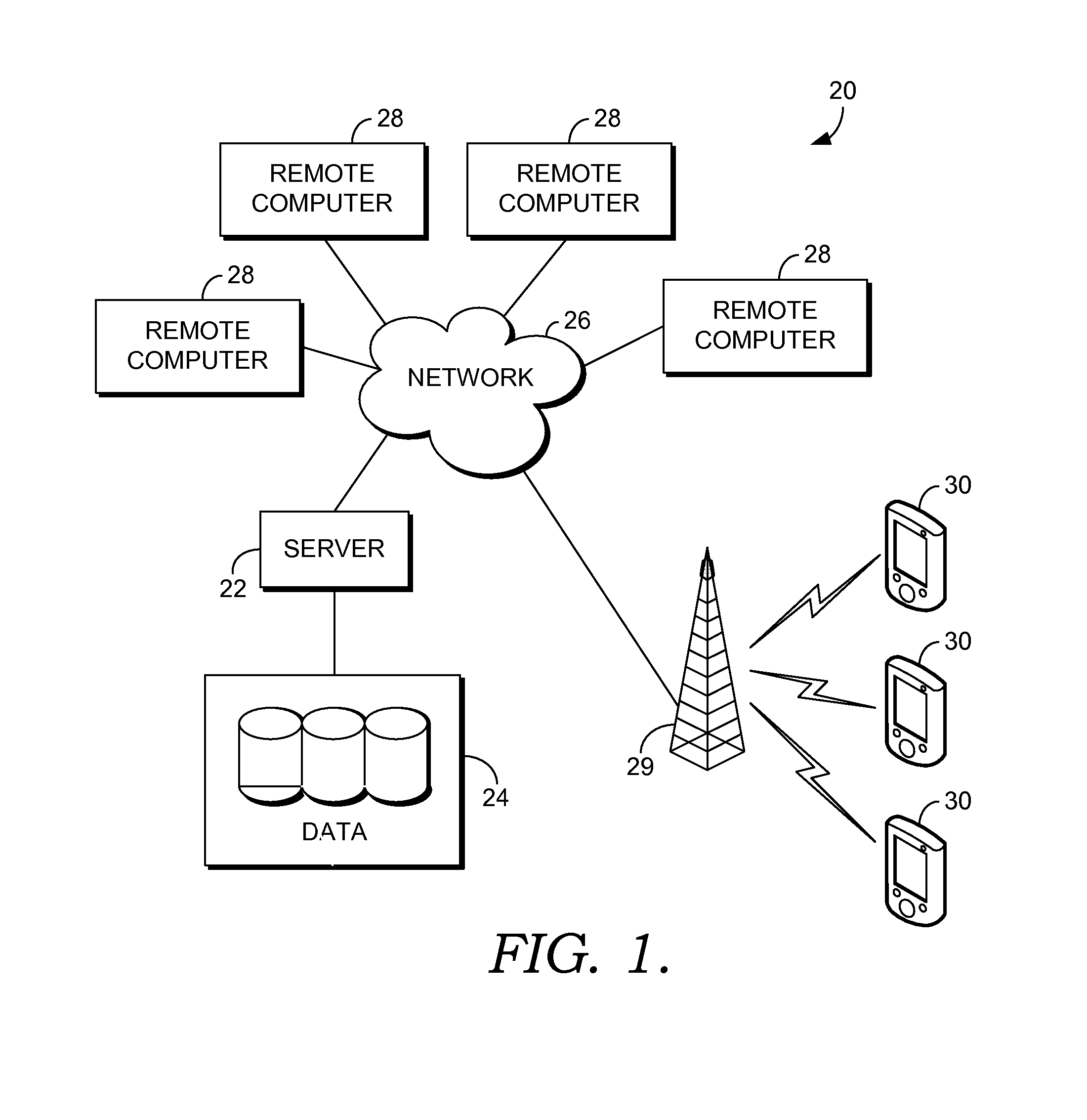
System and method for generating and sending promotional offers via text message
A method for electronically generating and providing promotional offers to a mobile device is provided. Consumer-initiated text messages are directed to a common code. Based on a natural language request from the consumer in the text message, promotional offers matching the consumer request from a group of promotional offers for a number of businesses are identified and sequentially sent in sets to the consumer. Promotional offers are provided based on the location of the consumer.
Owner:INTERACTIVE COUPON EXCHANGE
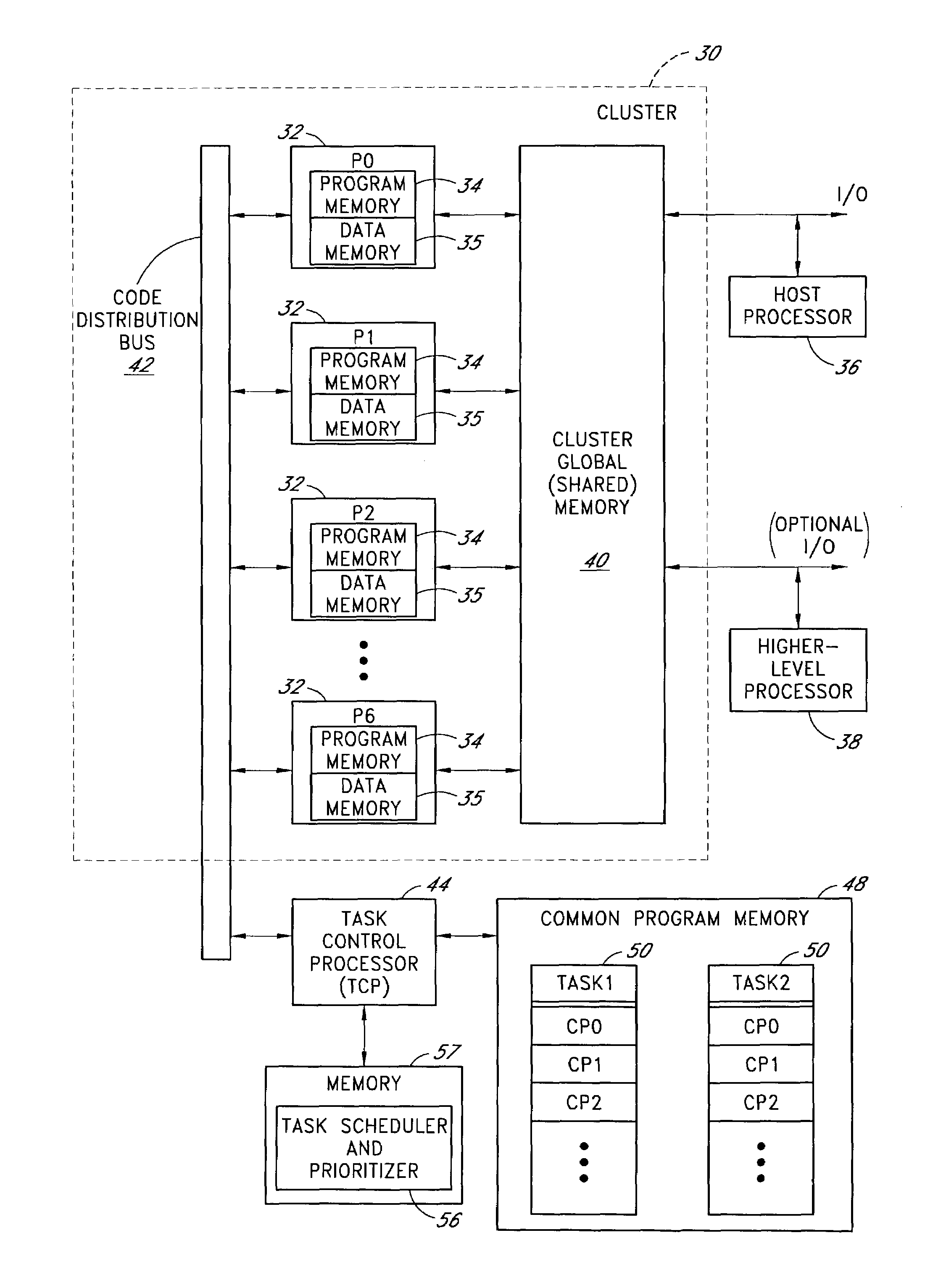
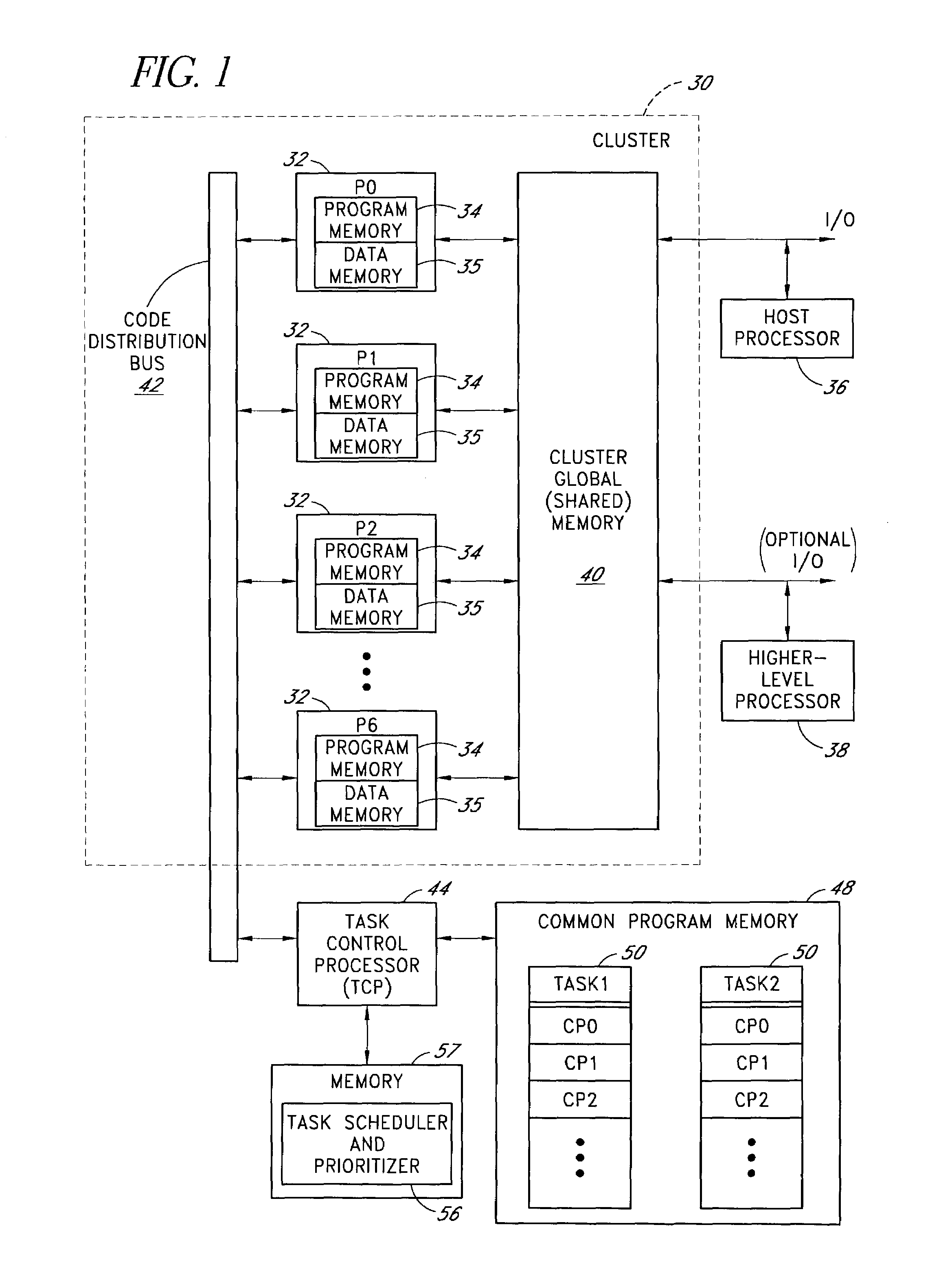
Processor cluster architecture and associated parallel processing methods
ActiveUS6959372B1High level of performanceGeneral purpose stored program computerProgram loading/initiatingCode distributionComputer science
A parallel processing architecture comprising a cluster of embedded processors that share a common code distribution bus. Pages or blocks of code are concurrently loaded into respective program memories of some or all of these processors (typically all processors assigned to a particular task) over the code distribution bus, and are executed in parallel by these processors. A task control processor determines when all of the processors assigned to a particular task have finished executing the current code page, and then loads a new code page (e.g., the next sequential code page within a task) into the program memories of these processors for execution. The processors within the cluster preferably share a common memory (1 per cluster) that is used to receive data inputs from, and to provide data outputs to, a higher level processor. Multiple interconnected clusters may be integrated within a common integrated circuit device.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
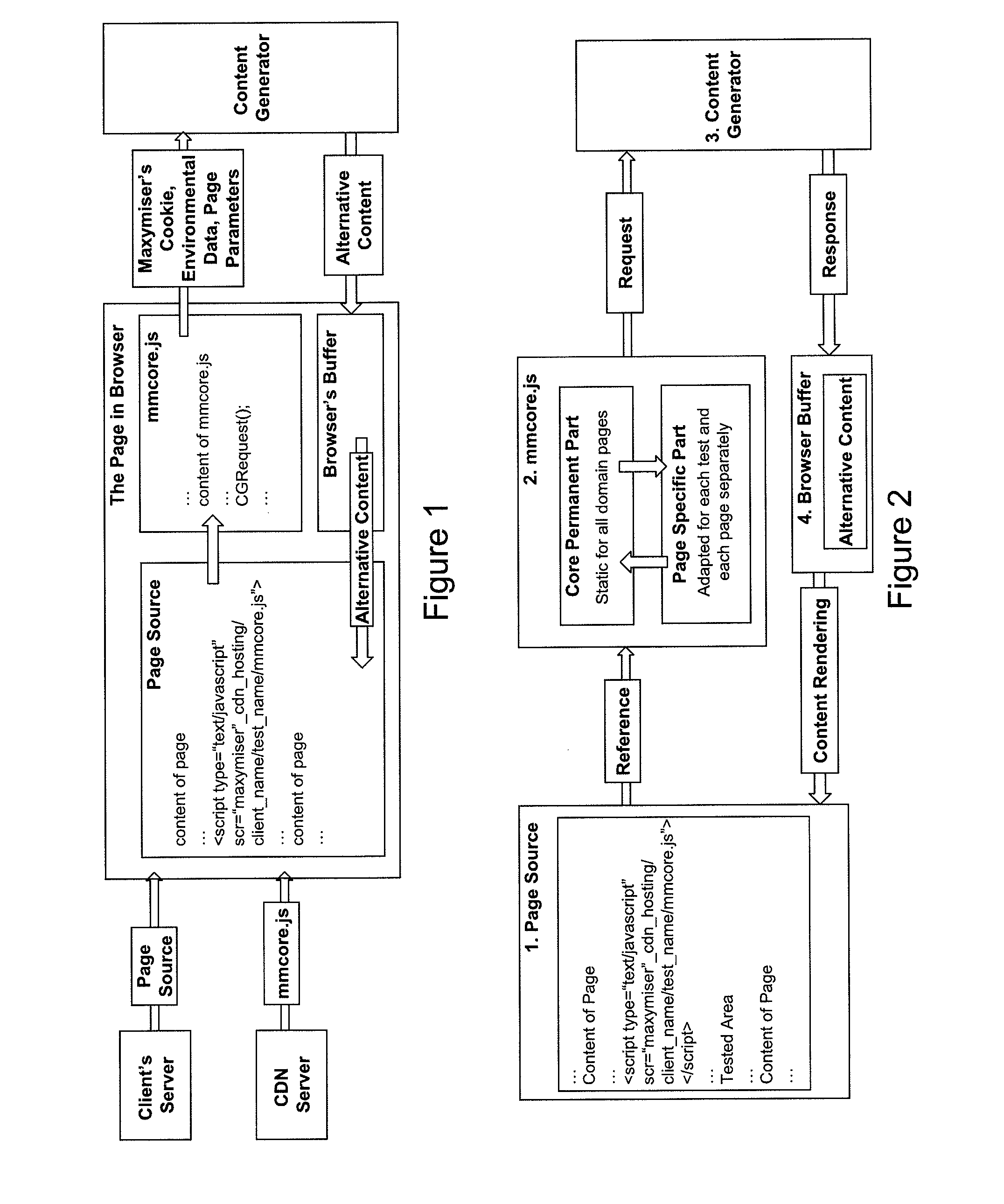
Method of Website Optimisation
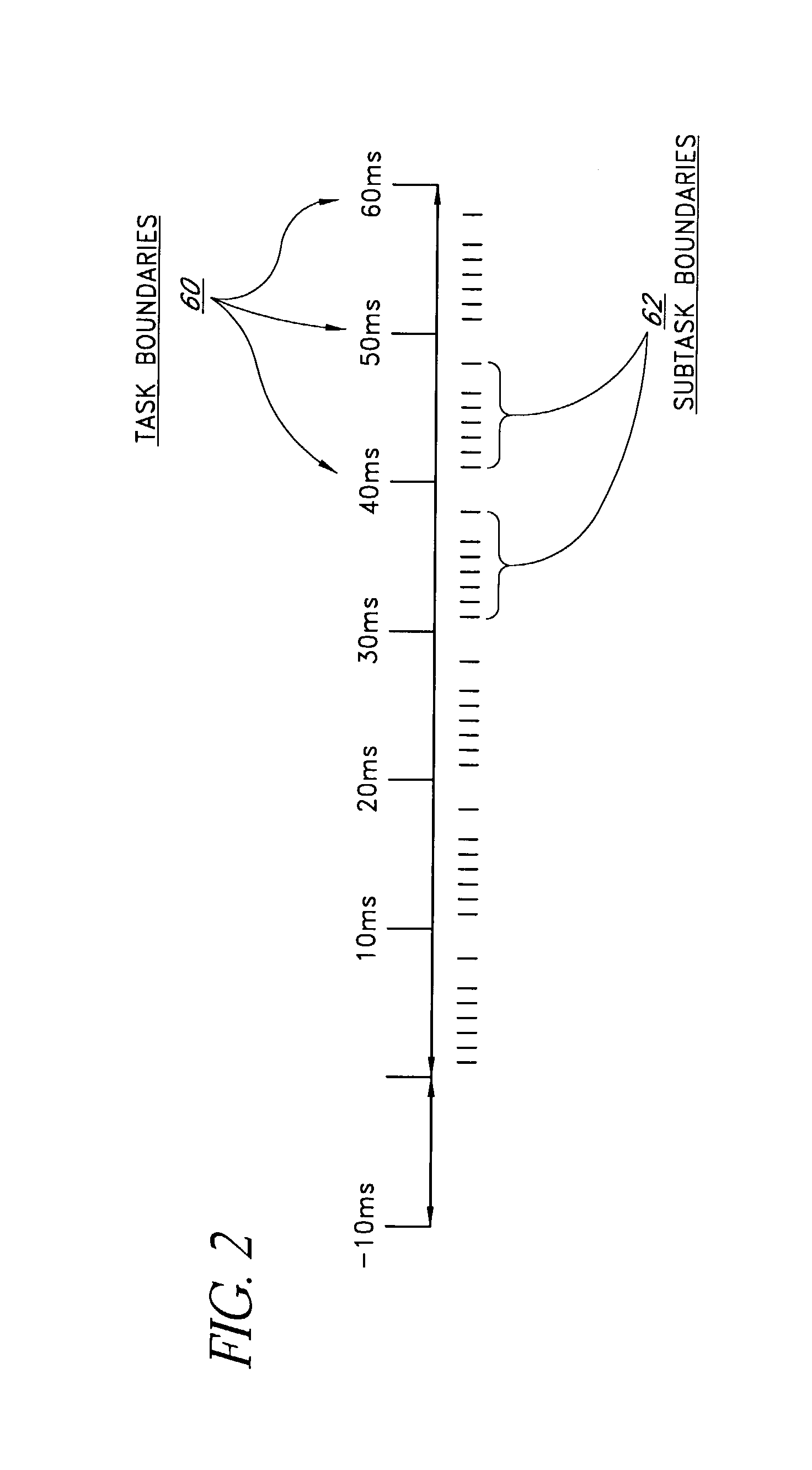
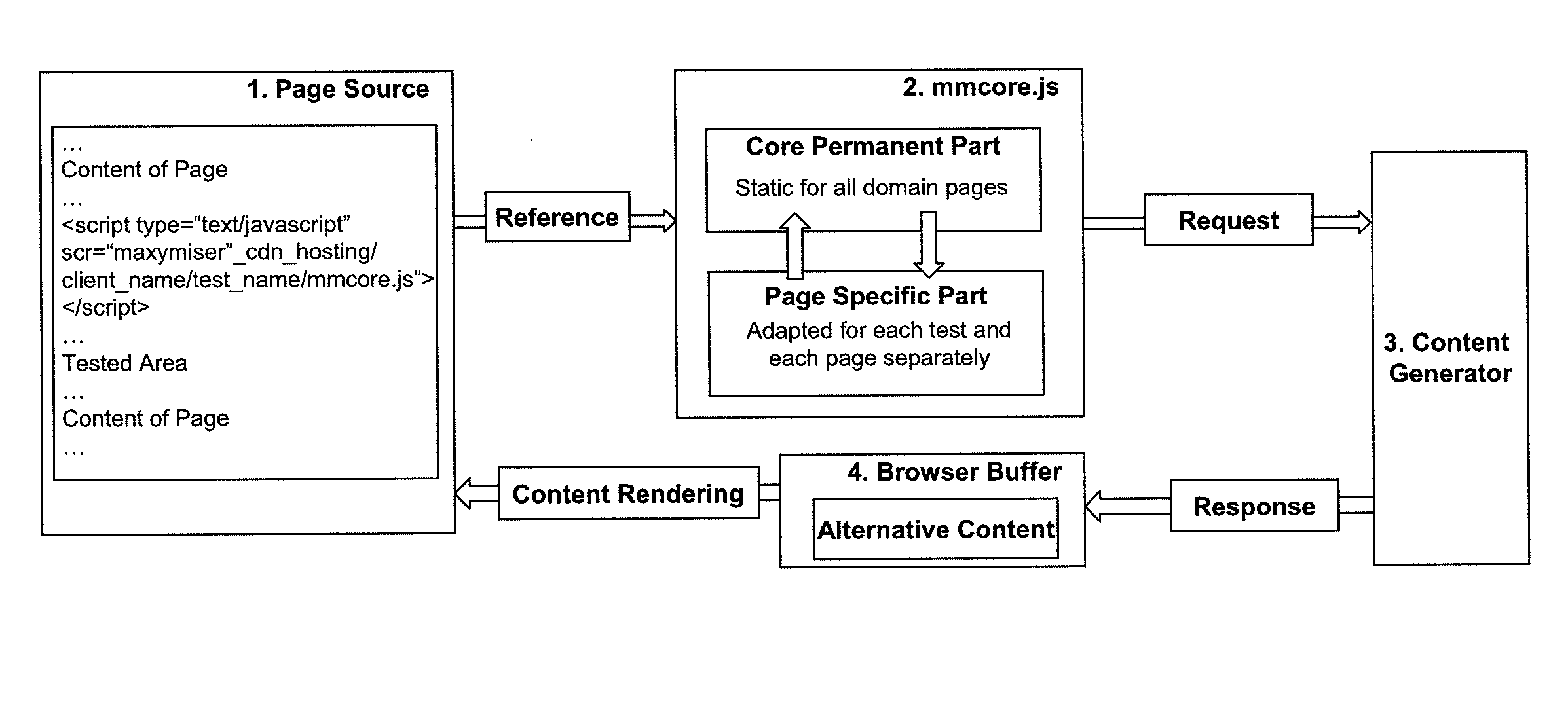
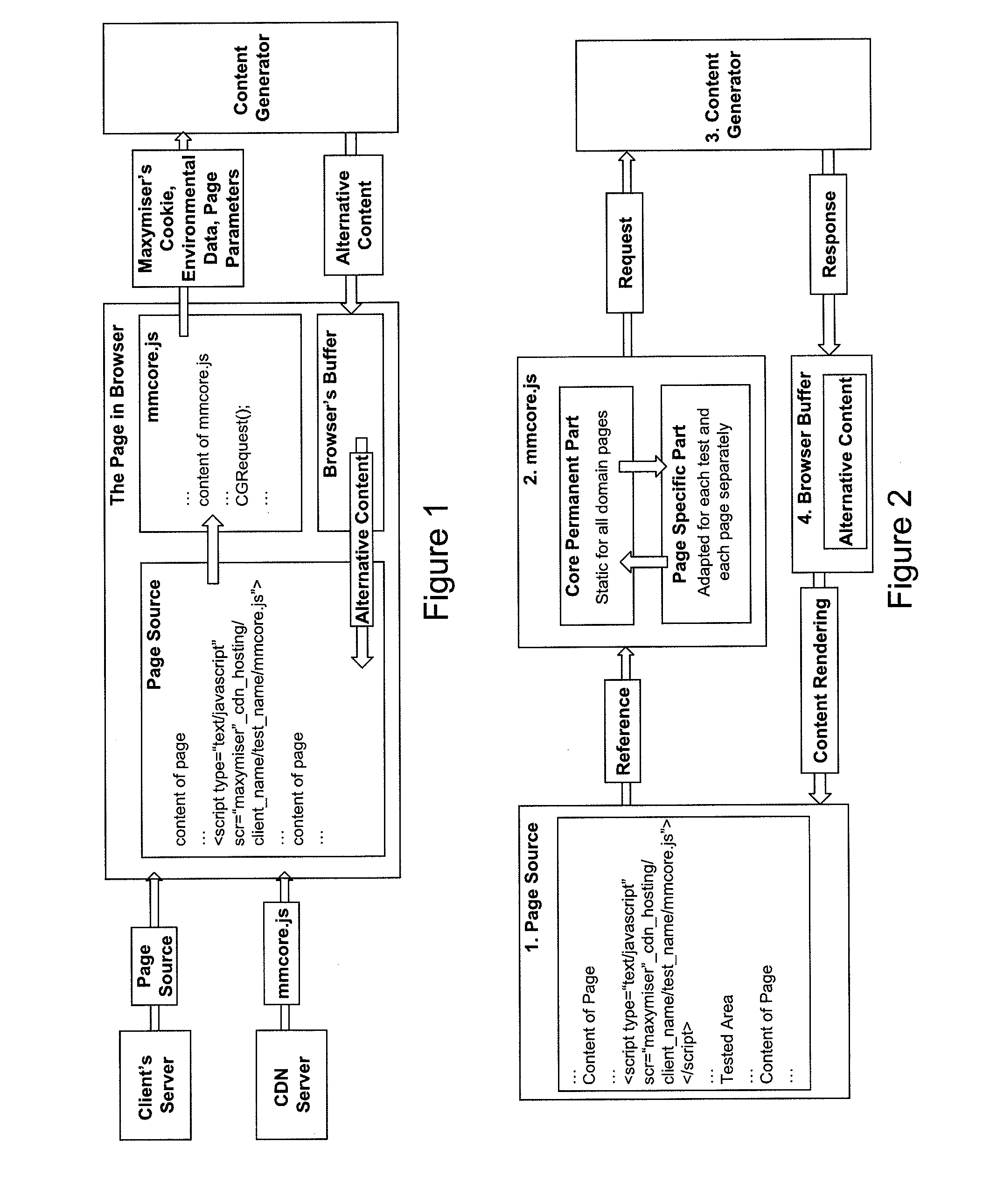
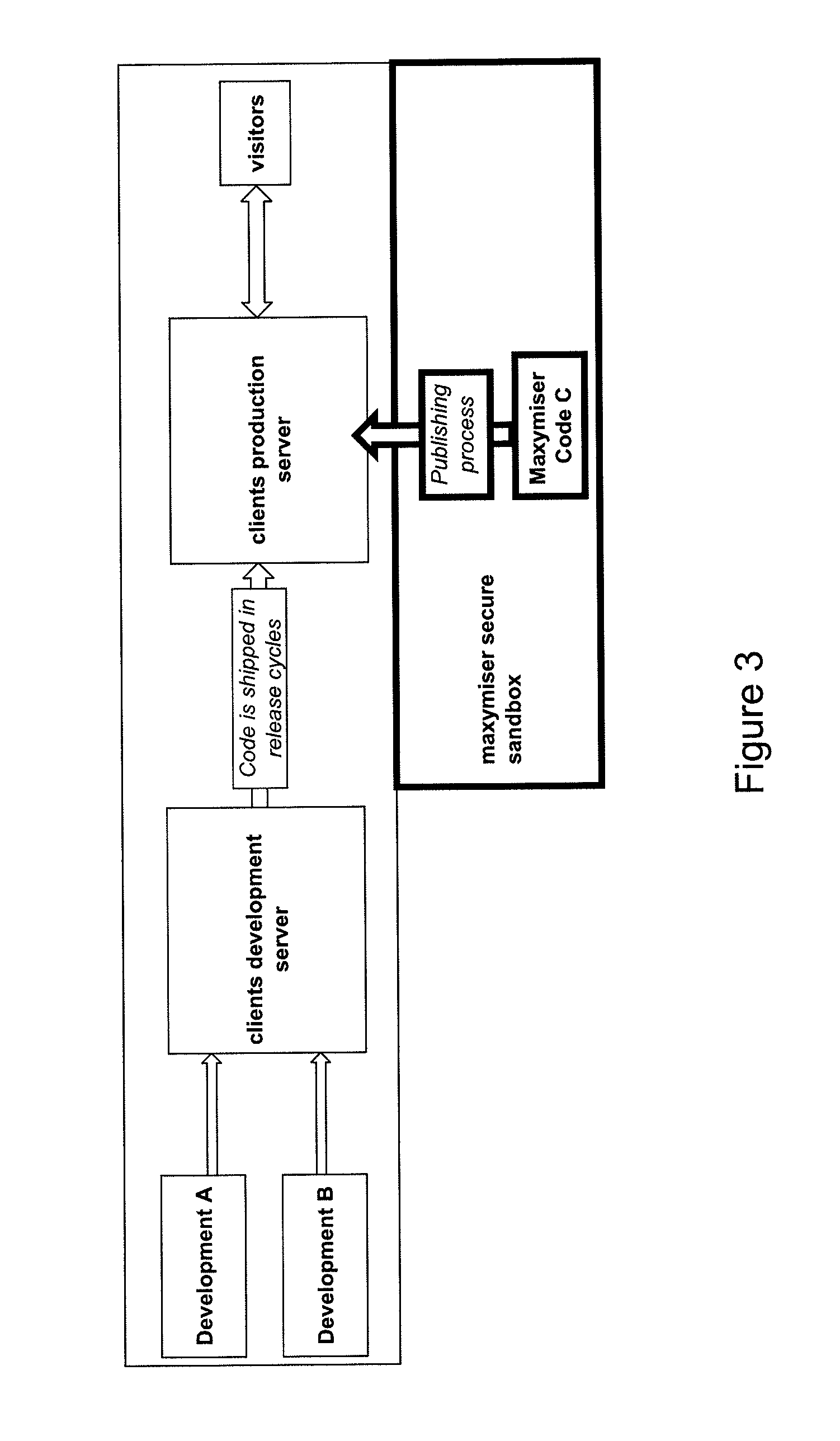
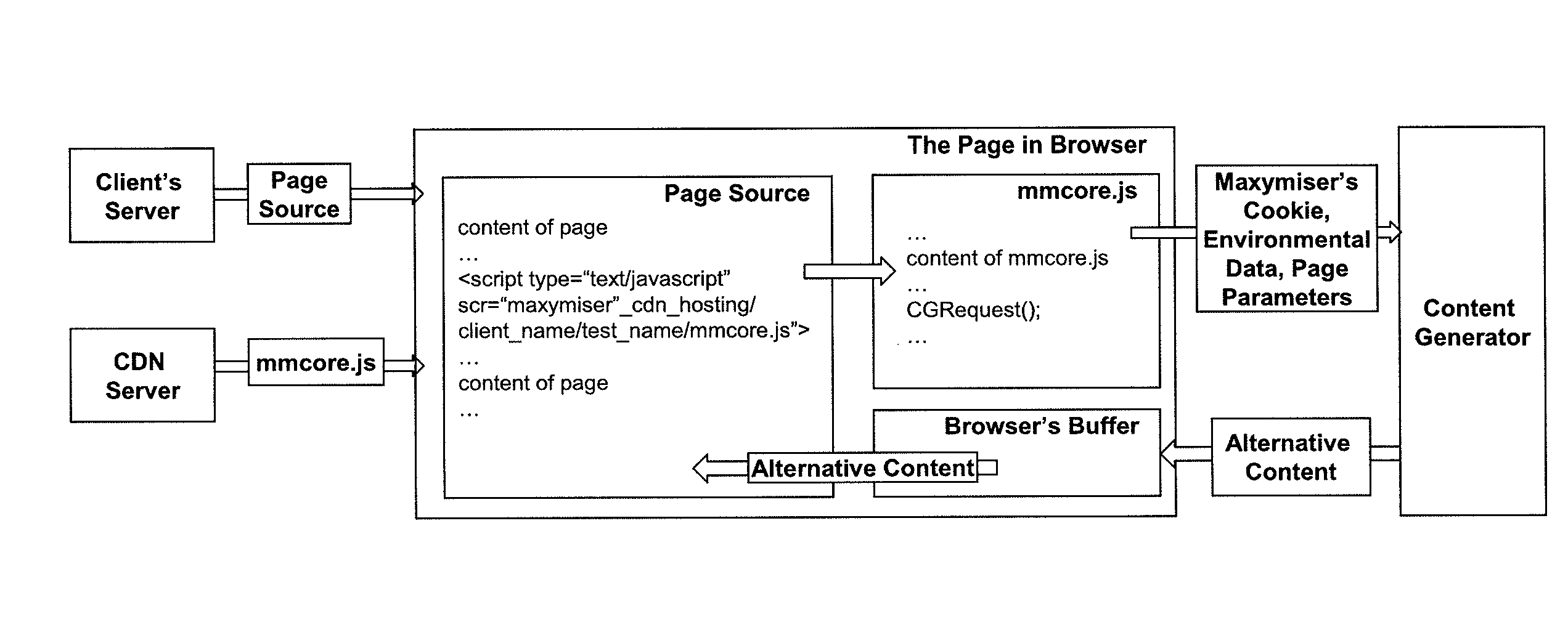
ActiveUS20100313183A1Improve conversion rate performanceLower requirementTransmissionSpecific program execution arrangementsWeb siteWeb page
A website optimisation system is integrated with a website by applying generic code to the website, that being the only code needed to be applied to the native source code of the website to enable the website optimisation system to optimise the website by altering one or more of: the data, functions or content assets of web pages in the website. Integration can be achieved on a one-time basis. The generic code can be placed into a website's page template or global page header, or manually to all pages in a website. The generic code can be just a single line of code, such as JavaScript code. The generic code remains the same irrespective of any differences in the data, functions or content assets of the web pages. The generic code includes code for all commands that enable tracking of the actions that relate to the optimisation objectives.
Owner:MAXYMISER
Zone detection locator
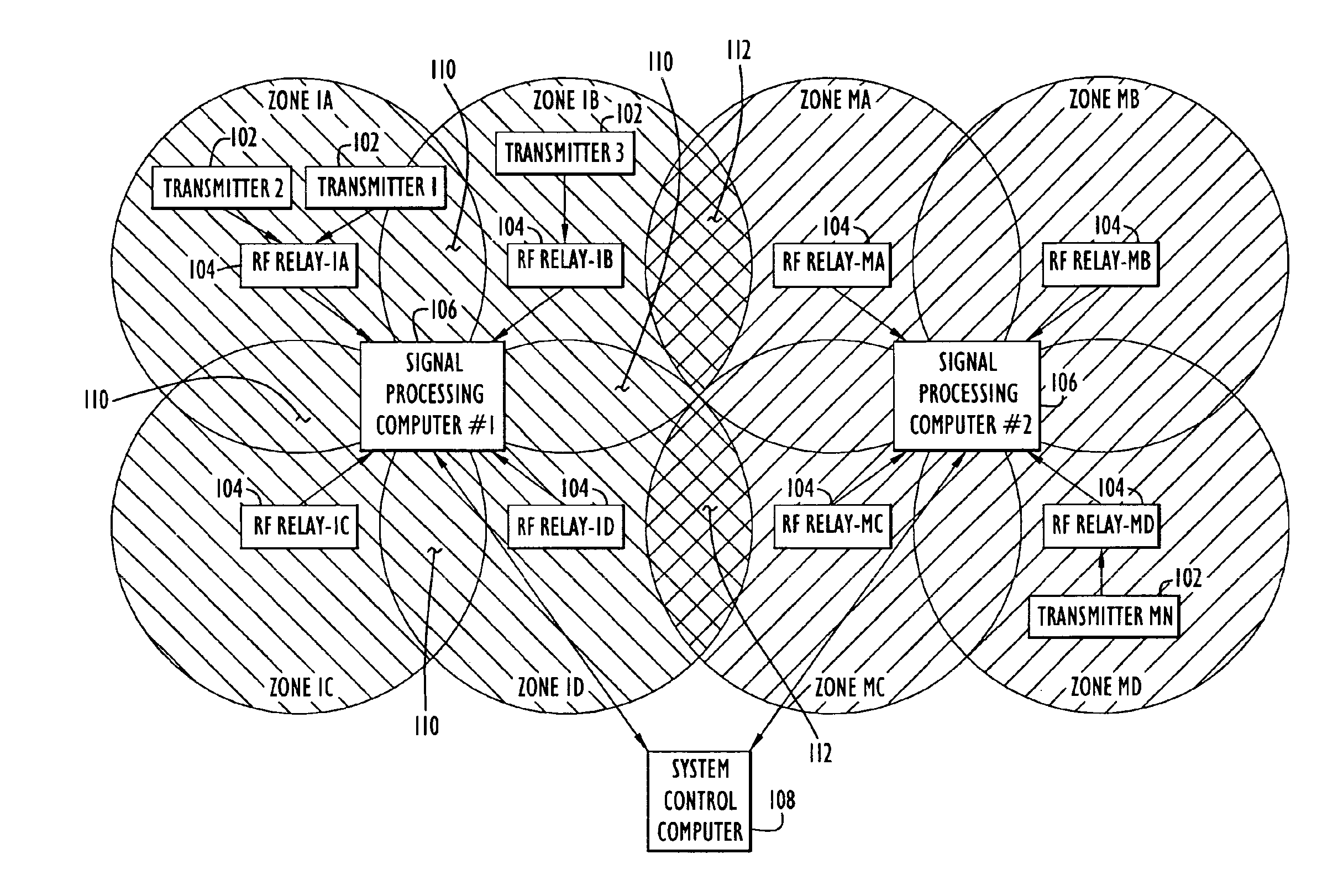
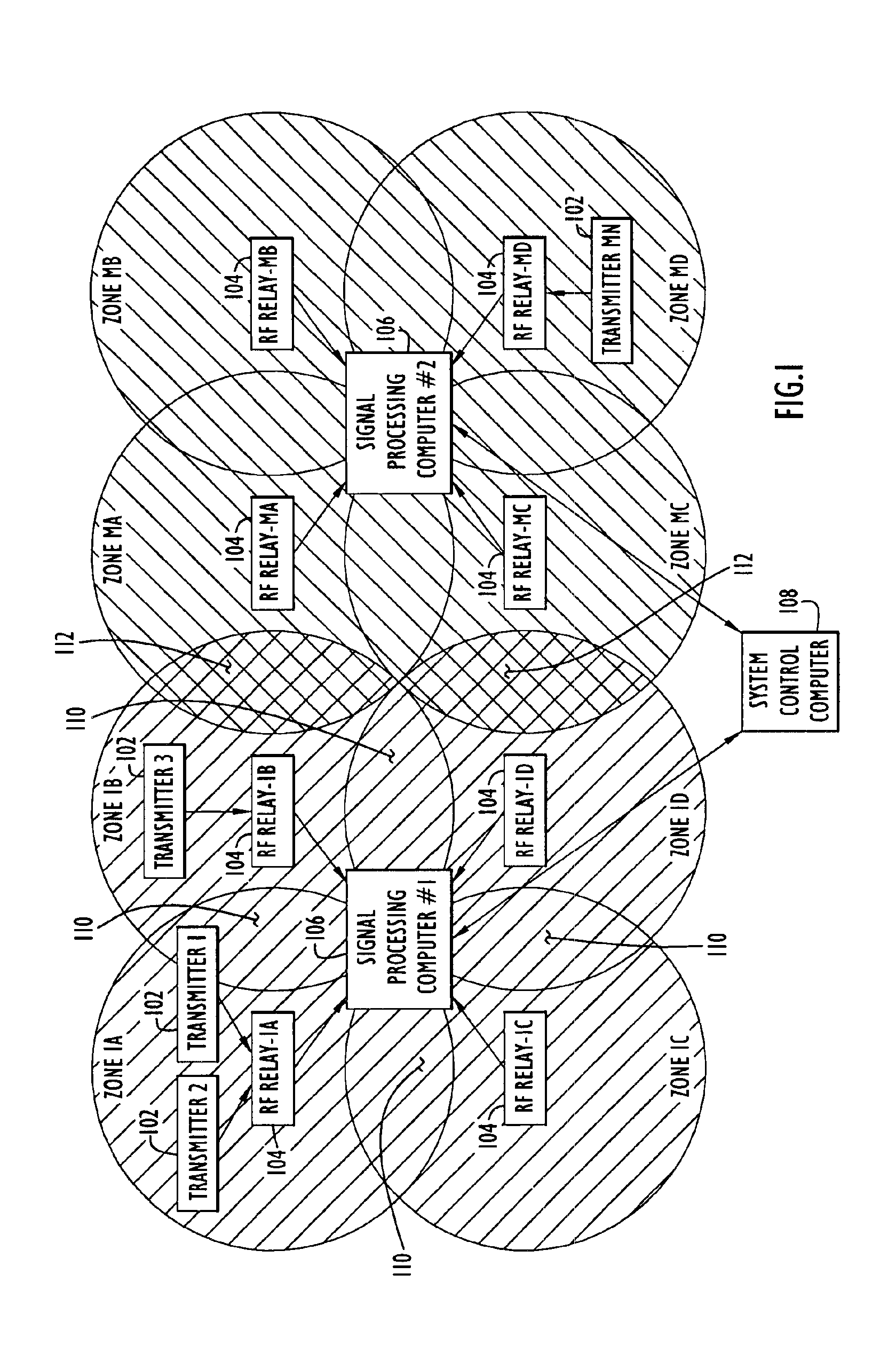
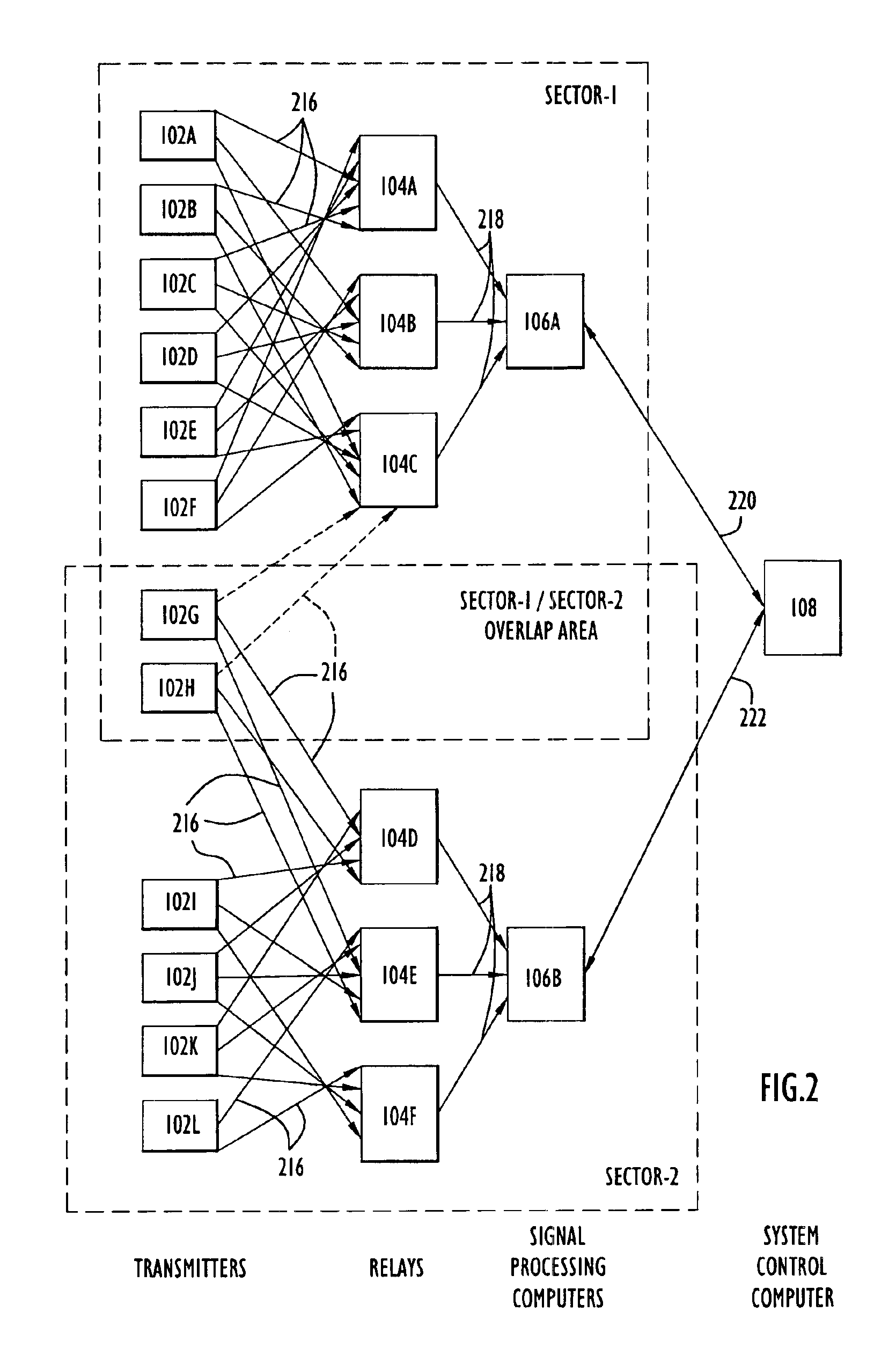
InactiveUS6917290B2Reduced signaling processReduce complexityMemory record carrier reading problemsPosition fixationEngineeringMatched filter
A method and apparatus for a zone detection system in which assets and personnel to be monitored are assigned a transmitter that emits a transmitter signal that includes a common code and a unique code. Processing requirements associated with restricted zone monitoring are reduced by scanning received signals for the single common code or a relatively small number of common codes. Processing requirements associated with locating an individual transmitter are reduced by scanning for a single transmitter signal. Transmitter signals are relayed by sub-sector RF-relays to a centralized sector signal processing computer. One or more signal processing computers interface with a system controller that supports a centralized user interface configurable to manage one or more sectors. CDMA matched filter techniques, power signature maps, and two-dimensional / three-dimensional convolution techniques are used to efficiently detect signals and to refine the estimated location a specific transmitter or a group of transmitters.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
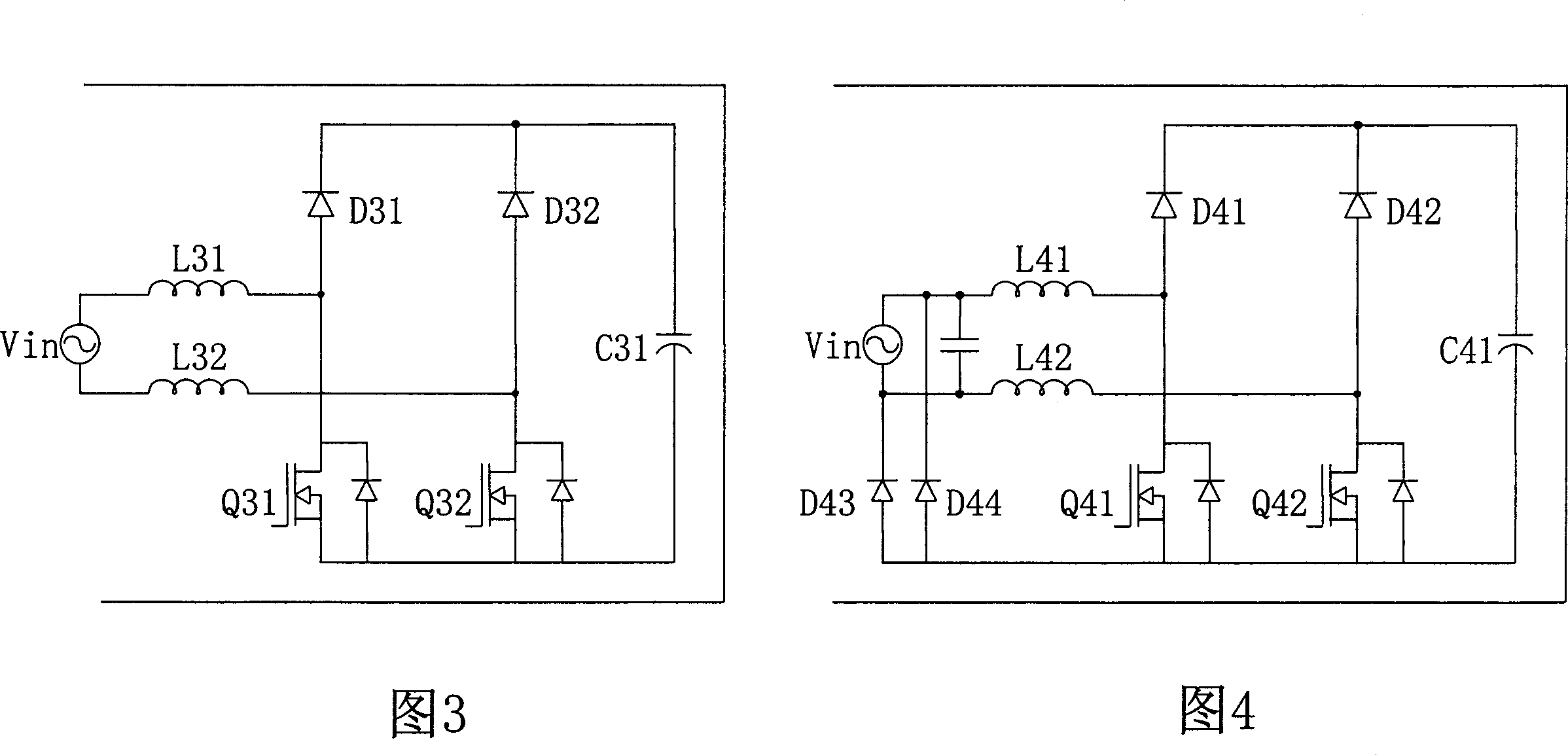
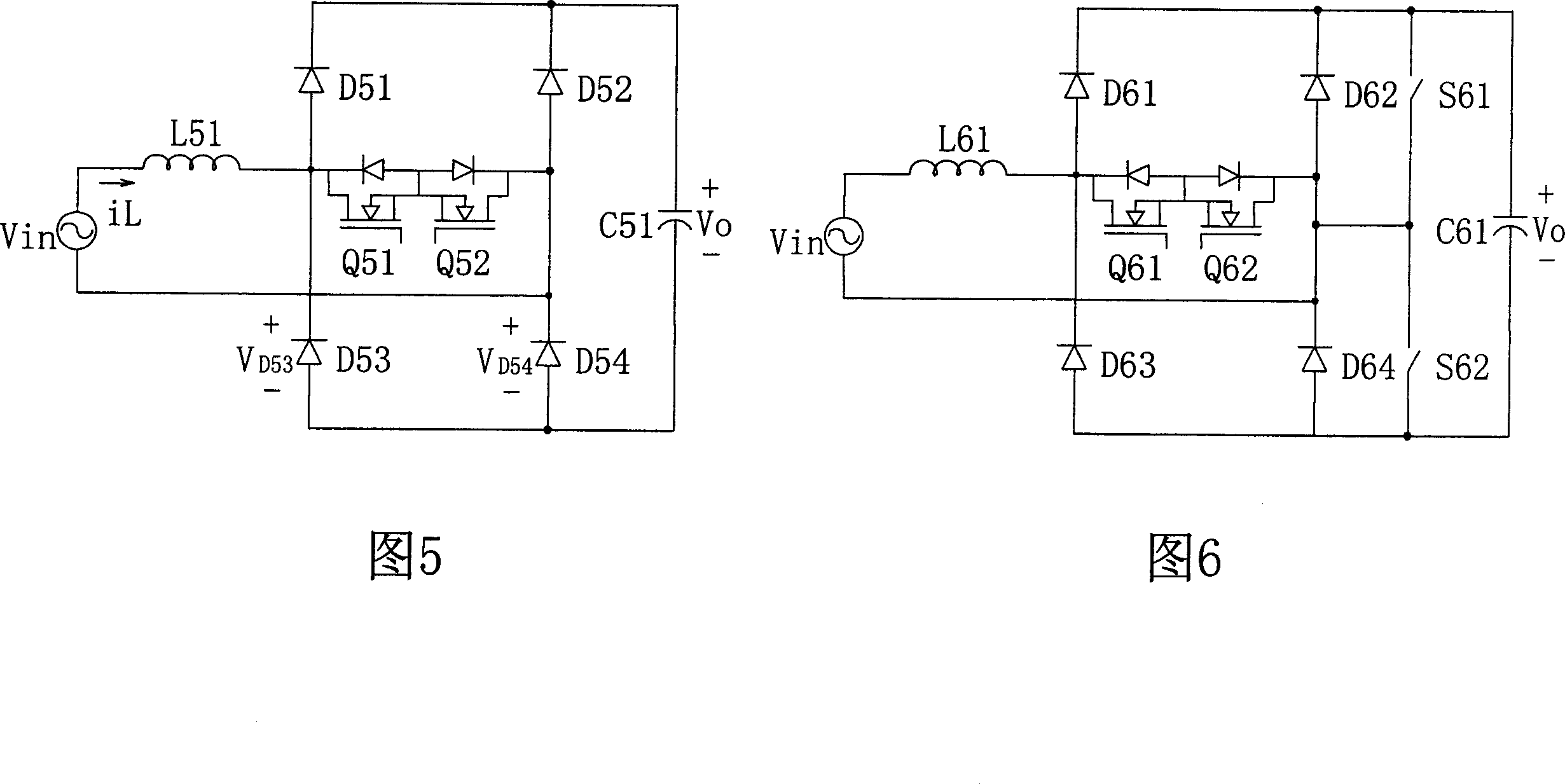
Power factor correcting converter
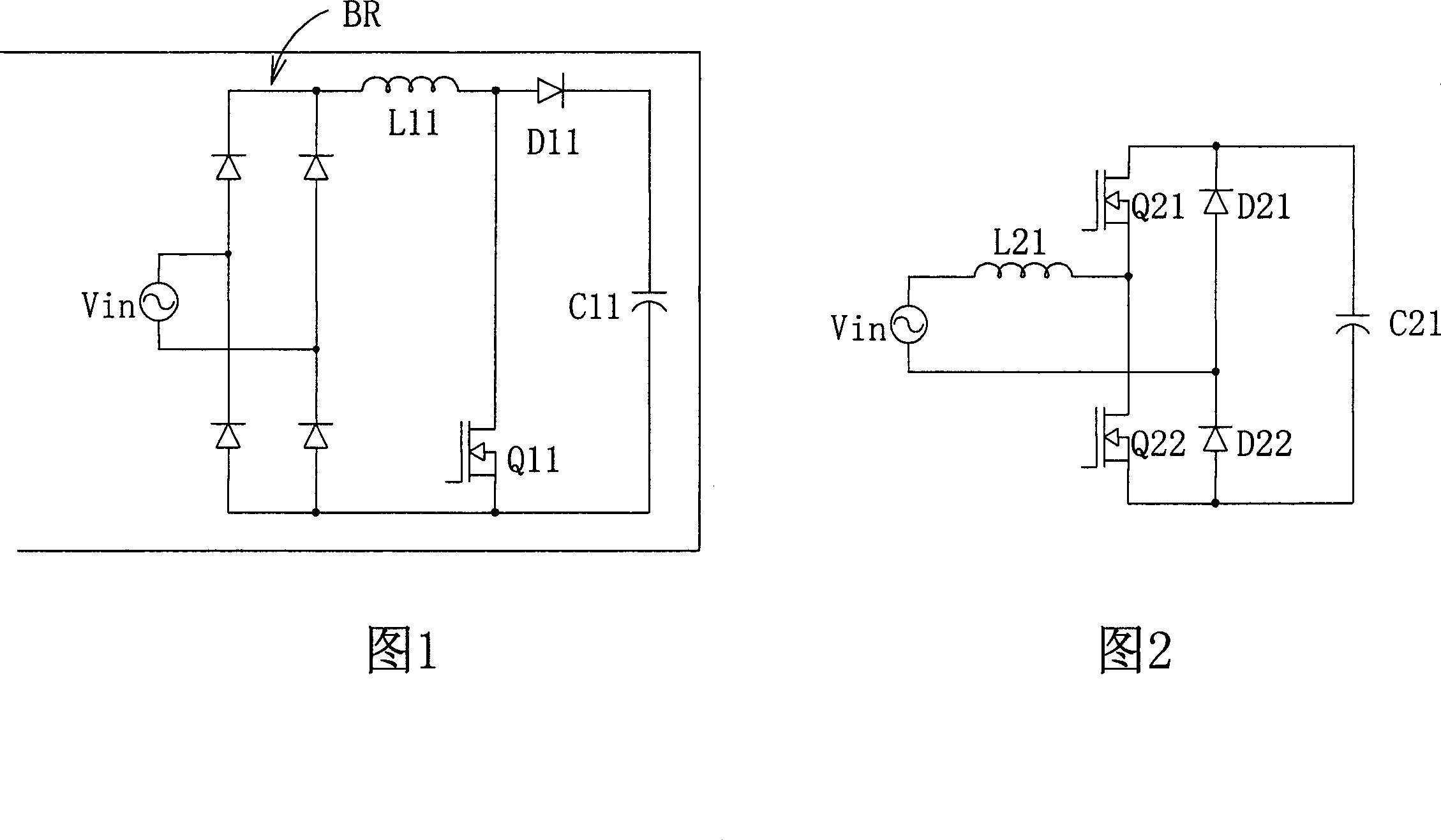
ActiveCN101083398AReduce common mode noiseEliminate jumpingAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitancePower factor
The invention is a bridge-free power factor correction (PFC) converter able to reduce common code noises and increase power density, comprising: boost inductor coupled to input end; two-way switch connected in series with the boost inductor and having junction node coupled between the boost inductor and two-way switch; second series rectifier circuit, having junction node coupled to the two-way switch; and output capacitor connected in parallel with the second series rectifier circuit; where the second series rectifier circuit is composed of slow recovery diode and the first series rectifier circuit is composed of fast recovery diode. Thus, the invention can reduce common mode noises in the converter and increase the power density of the converter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
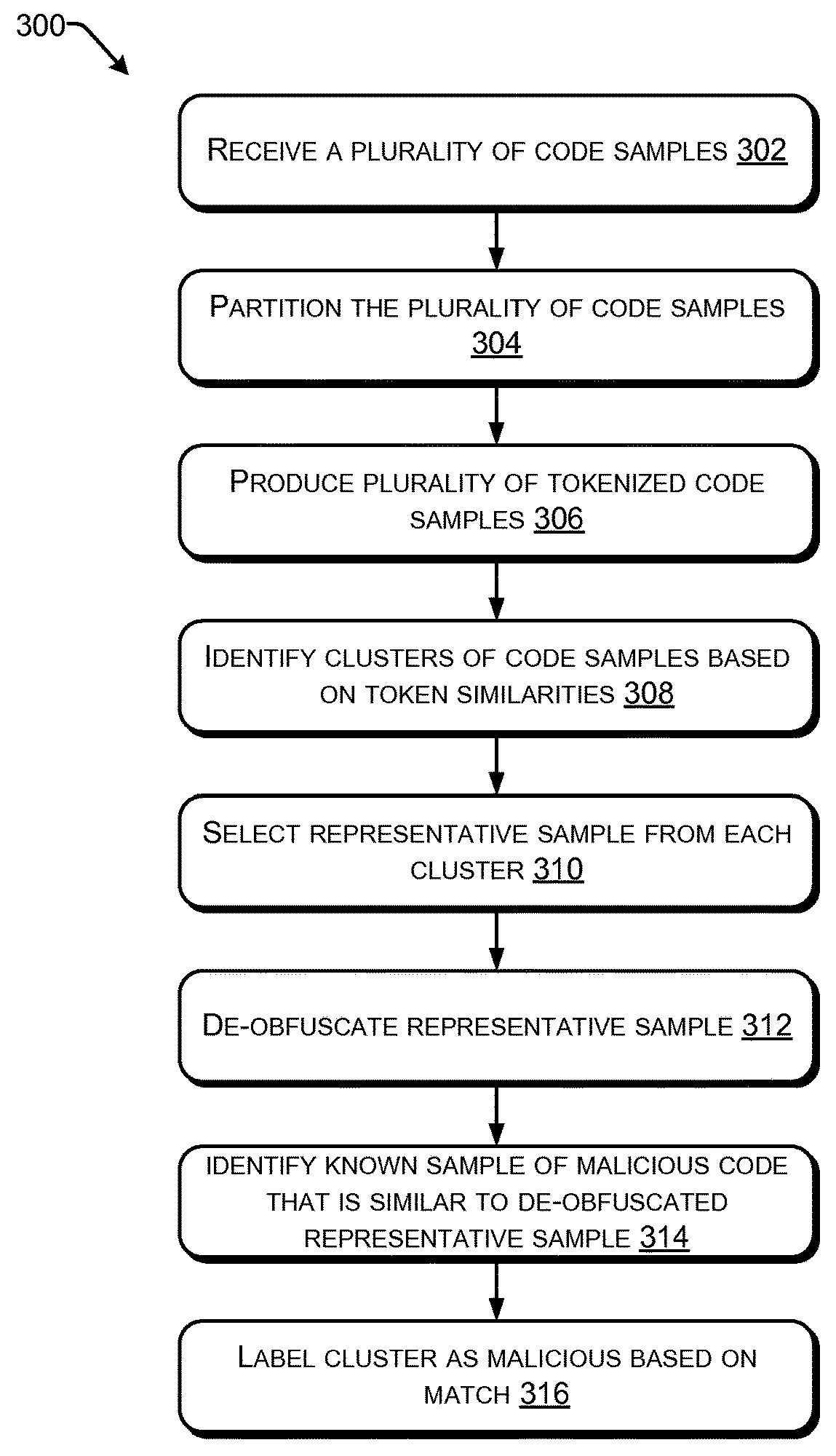
Code labeling based on tokenized code samples
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for efficient management of XML documents
InactiveUS20050165815A1Rapid positioningConsistent interfaceDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsAs elementTerm memory
An in-memory storage manager represents XML-compliant documents as a collection of objects in memory. The collection of objects allows the storage manager to manipulate the document, or parts of the document with a consistent interface and to provide for features that are not available in conventional XML documents, such as element attributes with types other than text and documents that contain binary rather than text information. In addition, in the storage manager, the XML-compliant document is associated with a schema document which defines the arrangement of the document elements and attributes. The schema data associated with a document can contain a mapping between document elements and program code to be associated with each element. The storage manager further has methods for retrieving the code from the element tag. The retrieved code can then be invoked using attributes and content from the associated element and the element then acts like a conventional object. Further, the storage manager allows real-time access by separate process operating in different contexts. The objects that are used to represent the document are constructed from common code found locally in each process. In addition, the data in the objects is also stored in memory local to each process. The local memories are synchronized by means of a distributed memory system that continually equates the data copies of the same element in different processes. Client-specified collections are managed by a separate collection manager. The collection manager maintains a data structure called a “waffle” that represents the XML data structures in tabular form. A record set engine that is driven by user commands propagates a set of updates for a collection to the collection manager. Based on those updates, the collection manager updates index structures and may notify waffle users via the notification system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
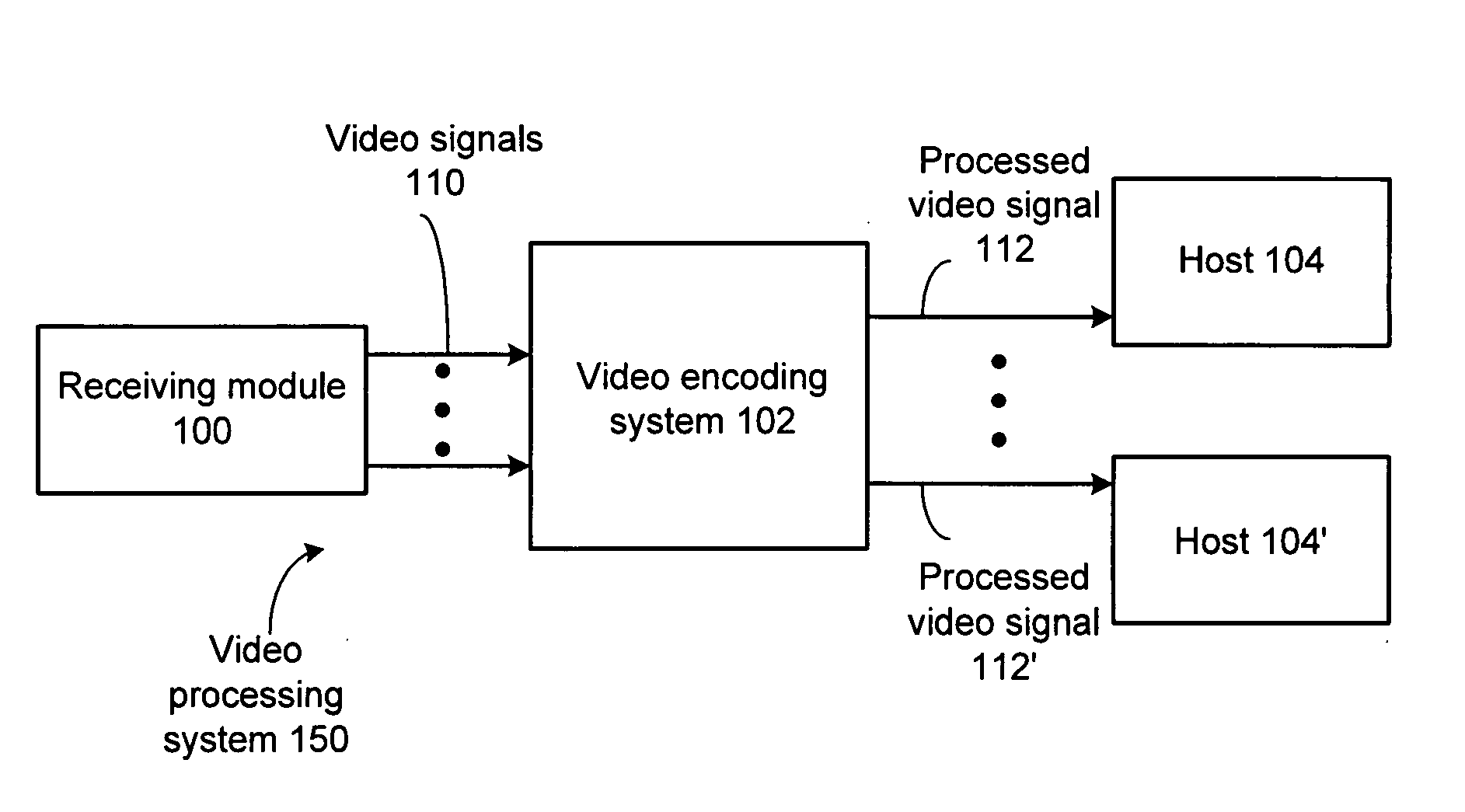
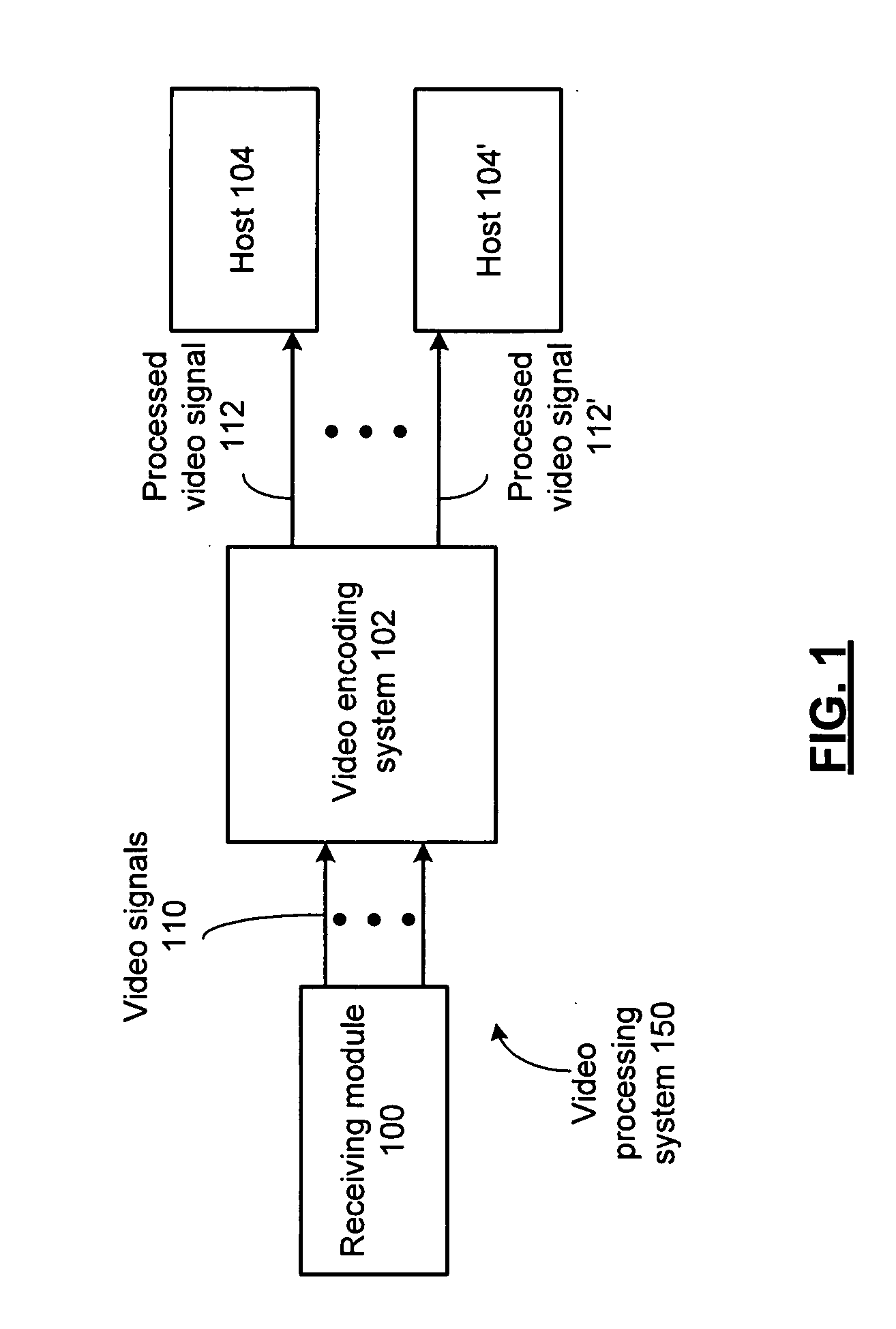
Video encoding system with universal transcoding and method for use therewith
InactiveUS20090147840A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationComputer hardwareVideo encoding
An encoding system includes a first signal interface for receiving a first video signal in a first format. A second signal interface receives a second video signal in a second format. A first encoding module generates a first processed video signal in a third format. A second encoding module generates a second processed video signal in a fourth format, wherein the second processed signal is generated contemporaneously with the first processed video signal and wherein the first format differs from the third format and the second format differs from the fourth format.
Owner:VIXS SYSTEMS INC
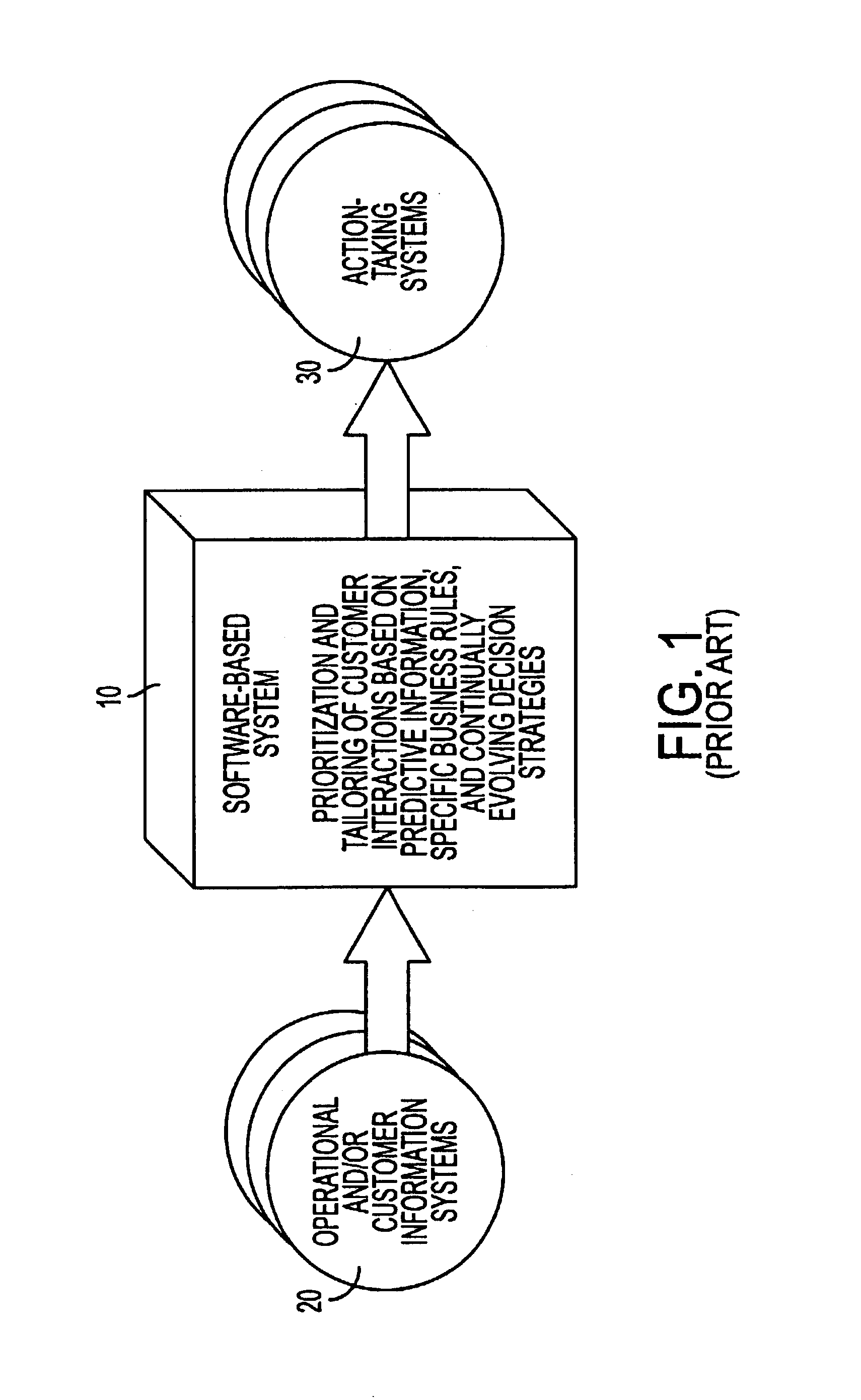
Decision management system which is cross-function, cross-industry and cross-platform
A computer-implemented rules based decision management system which is cross-platform, cross-industry and cross-function. The decision management system has a software architecture which includes a common code layer, a processing platform layer and a data architecture layer. The common code layer includes a common code kernel simultaneously operable on first and second hardware platforms which are different from each other, and provides software processing to interpret and apply the strategies. The processing platform layer includes a first software module supporting a processing mode for the first hardware platform, and a second software module supporting a processing mode for the second hardware platform. The data architecture layer includes a first data module supporting data storage and access by the first software module, and a second data module supporting data storage and access by the second software module.
Owner:CGI TECH & SOLUTIONS
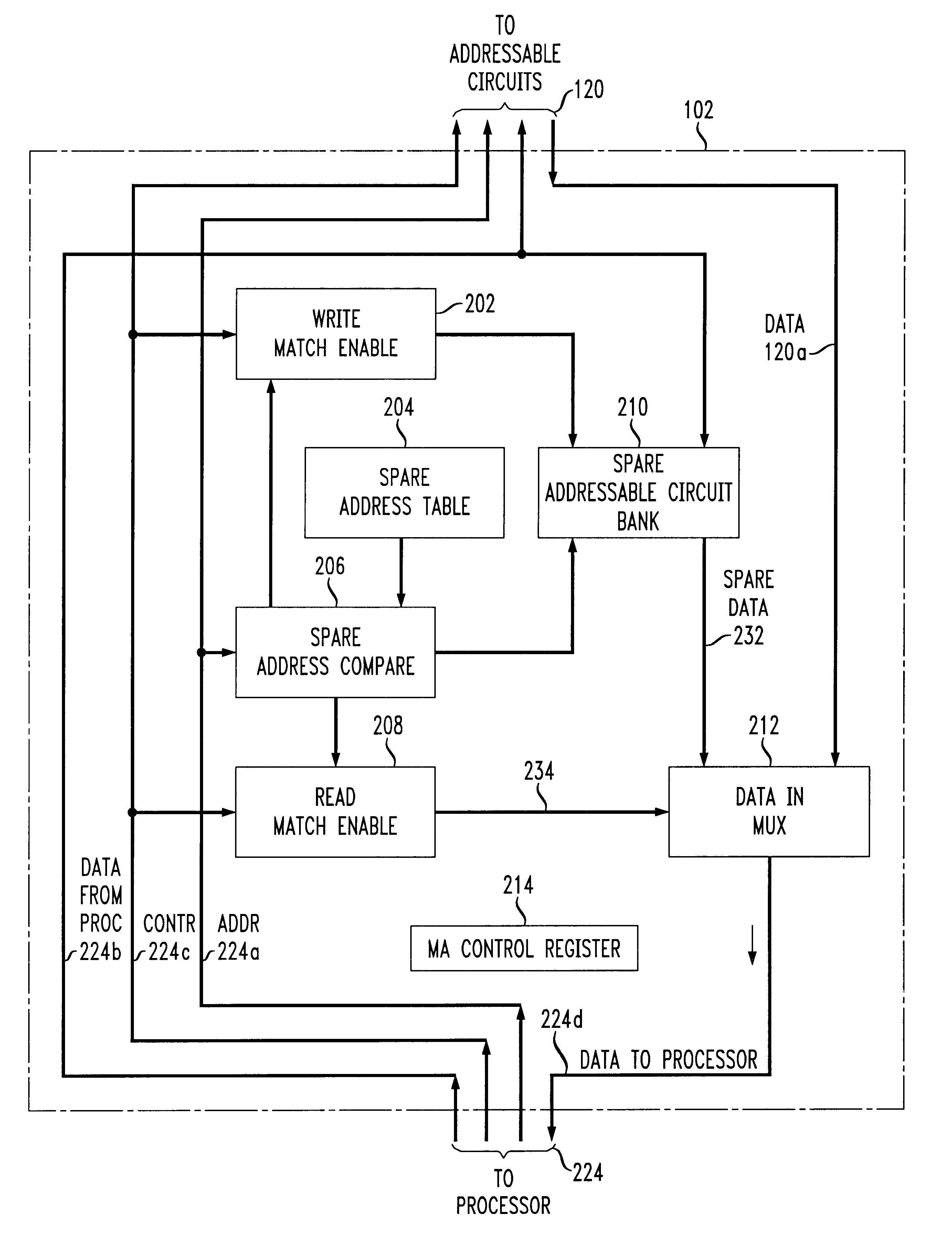
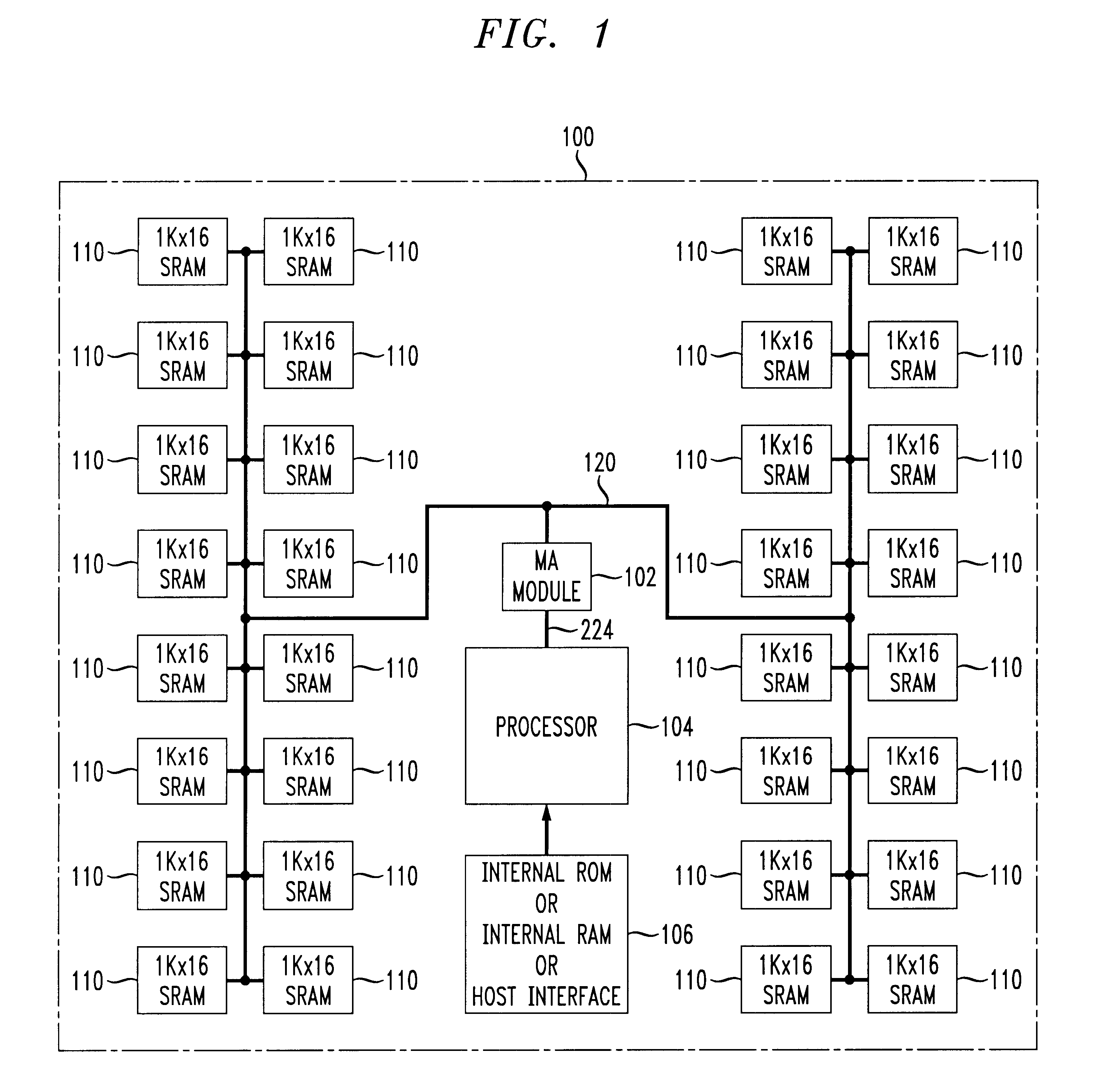
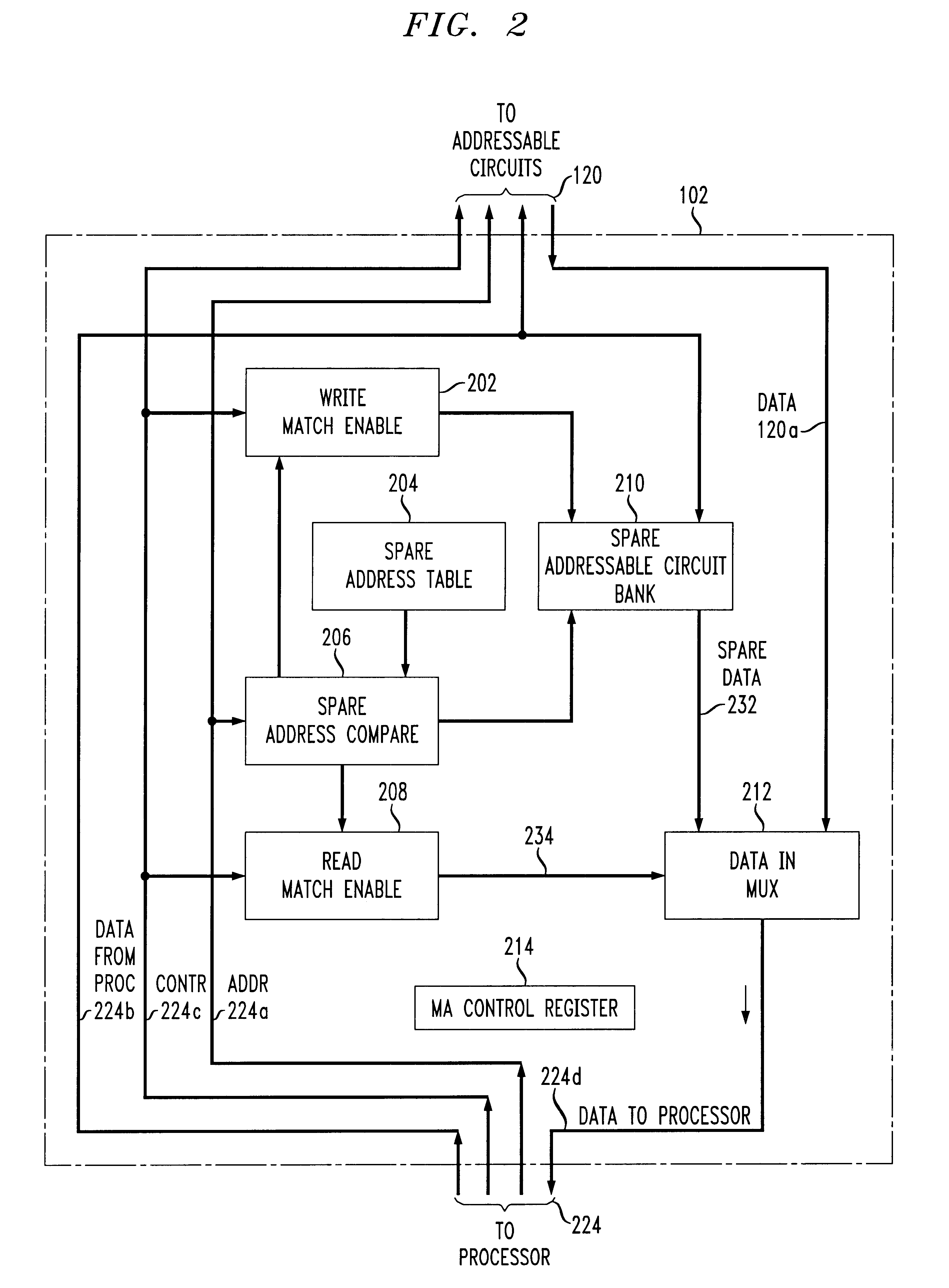
Memory aliasing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6438672B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsOperating systemContext switch
A flexible memory overlaying apparatus and method stores repeatedly referenced information, e.g, common global variables, common code segments, interrupt service routines, and / or any other user or system definable information, in spare addressable circuits accessed by a memory aliasing or overlaying module. The memory aliasing module monitors (or snoops) memory access by a processor to redirect access to certain appropriate addressable circuits to provide faster access to the information than would be available in an access made from main memory. The memory overlaying apparatus and method provides an efficient context switching, e.g., during an interrupt, enables a reduction in the size of instruction code requirements, and helps avoid the occurrences of cache misses, and / or thrashing between cached pages.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Convergence among concurrently executing threads
ActiveUS20200081748A1Execution efficiency is improvedPromoting thread convergenceProgram initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationComputer architectureThread scheduling
Convergence of threads executing common code sections is facilitated using instructions inserted at strategic locations in computer code sections. The inserted instructions enable the threads in a warp or other group to cooperate with a thread scheduler to promote thread convergence.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
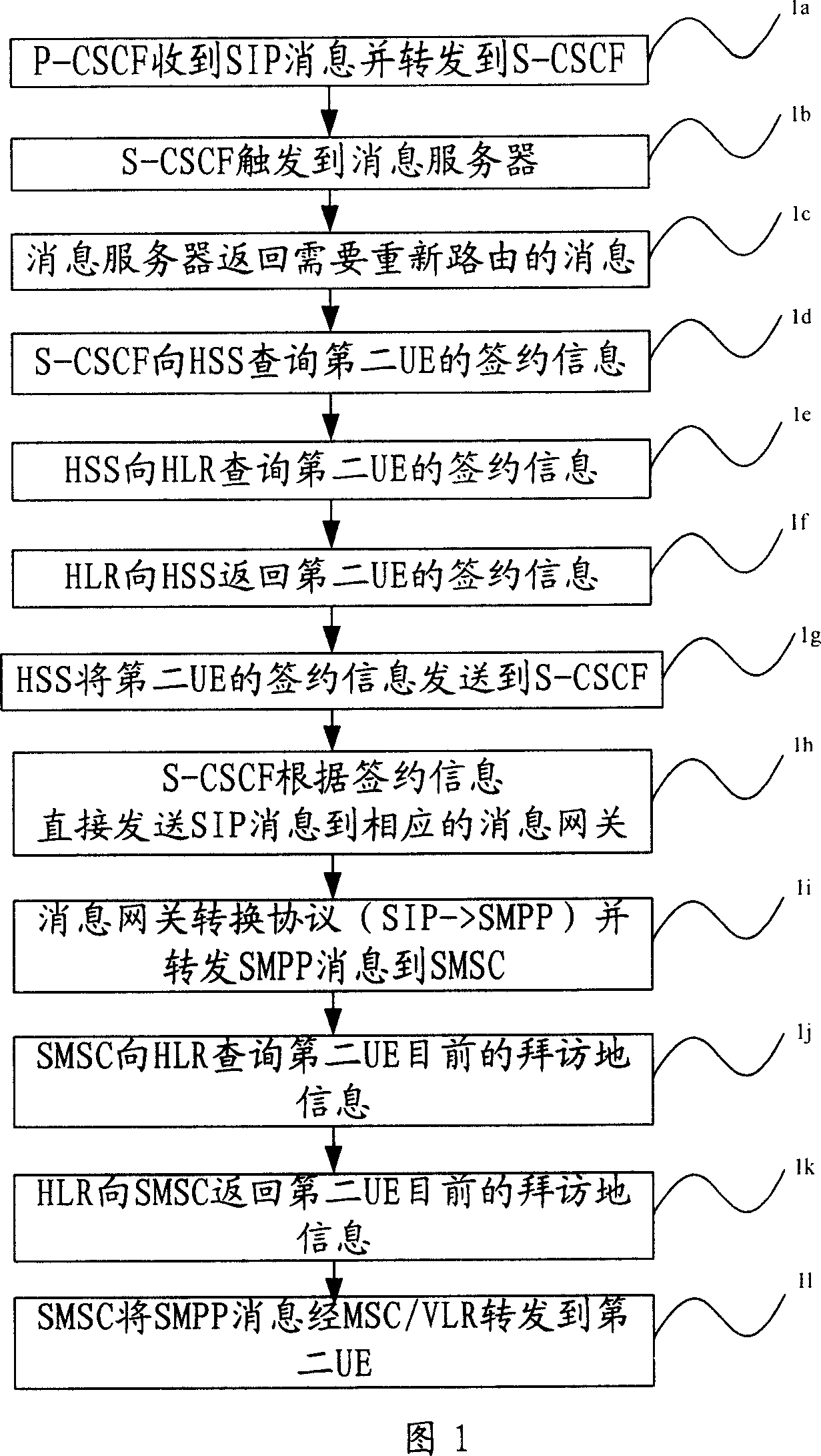
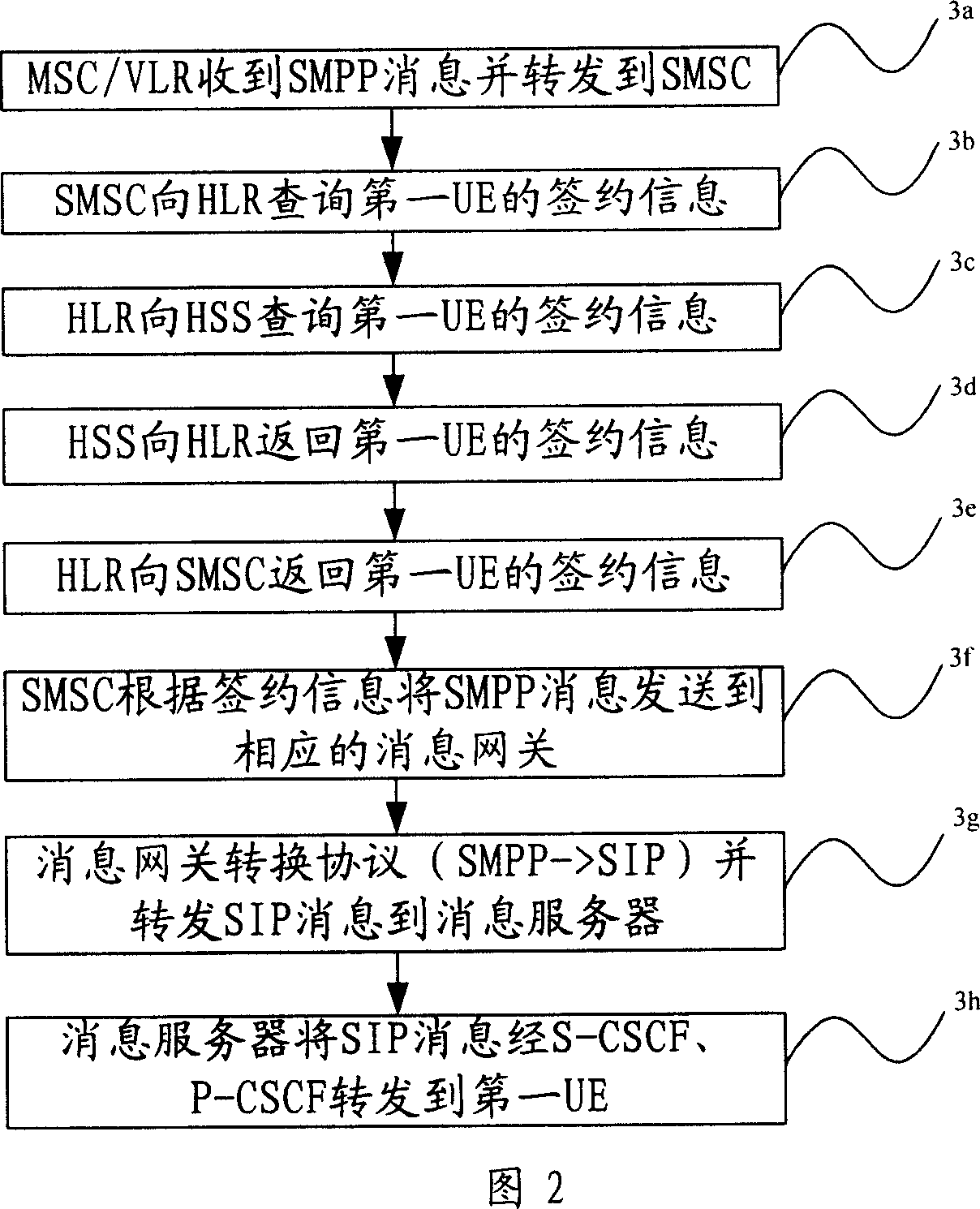
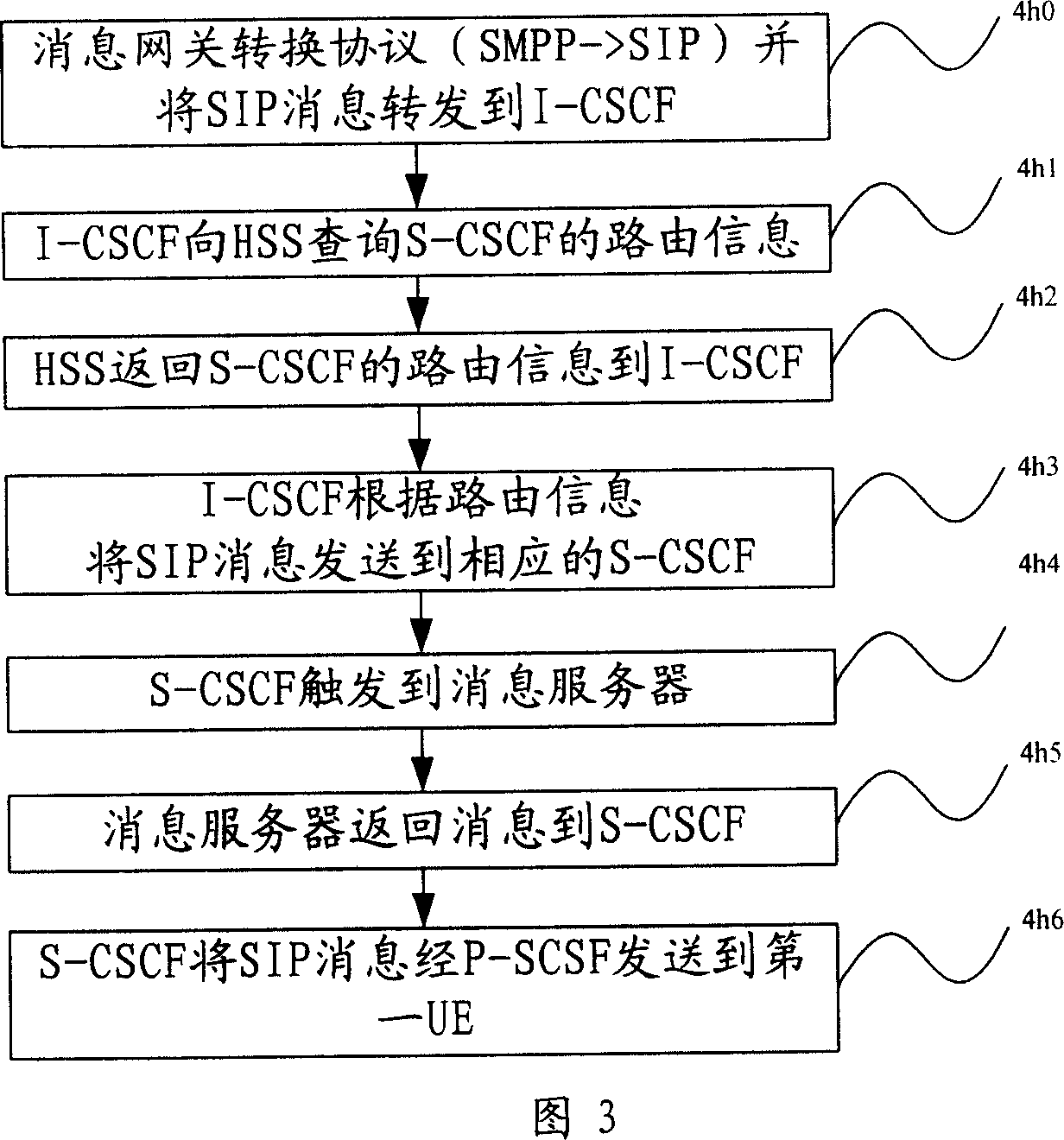
Method for message intercommunication of IMS domain and CS domain
ActiveCN1929434AAchieve interactionNetworks interconnectionNetwork connectionsComputer hardwareCommon code
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
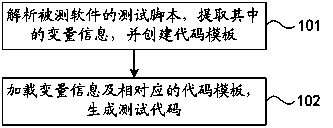
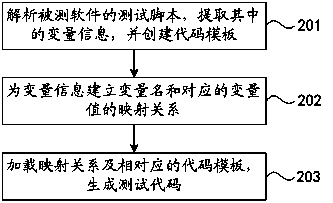
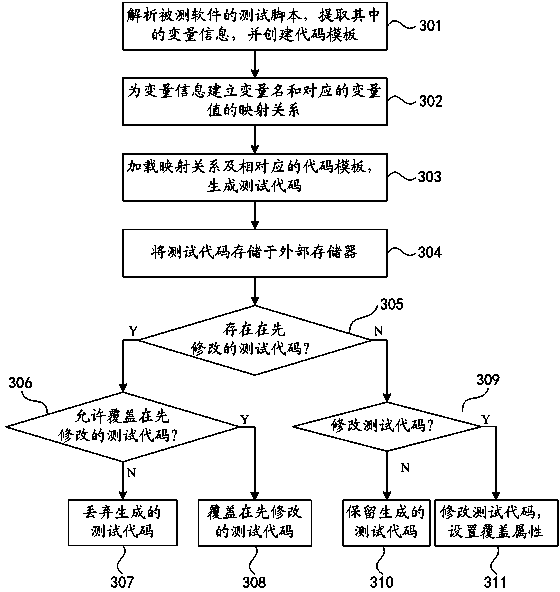
Method and device for generating testing codes
InactiveCN104035873AEase of useFlexibleSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware engineeringUsability
The invention discloses a method and device for generating testing codes. The method comprises the steps that a testing script of tested software is analyzed, and variable information included in the testing script is extracted; original testing codes are classified according to the testing type of the tested software and the programming language of the original testing codes, a differential code portion in each kind of the original testing codes is extracted and marked, and code templates of the original testing codes are formed by the differential code portions and common code portions in the original testing codes; the variable information of the testing script and the corresponding code templates are loaded, the differential code portions marked in the code templates are replaced with the variable information according to set rules, and the testing codes are generated. According to the method and device, the problem that the flexibility of the programming language and the usability of an automatic test framework cannot be obtained at the same time in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
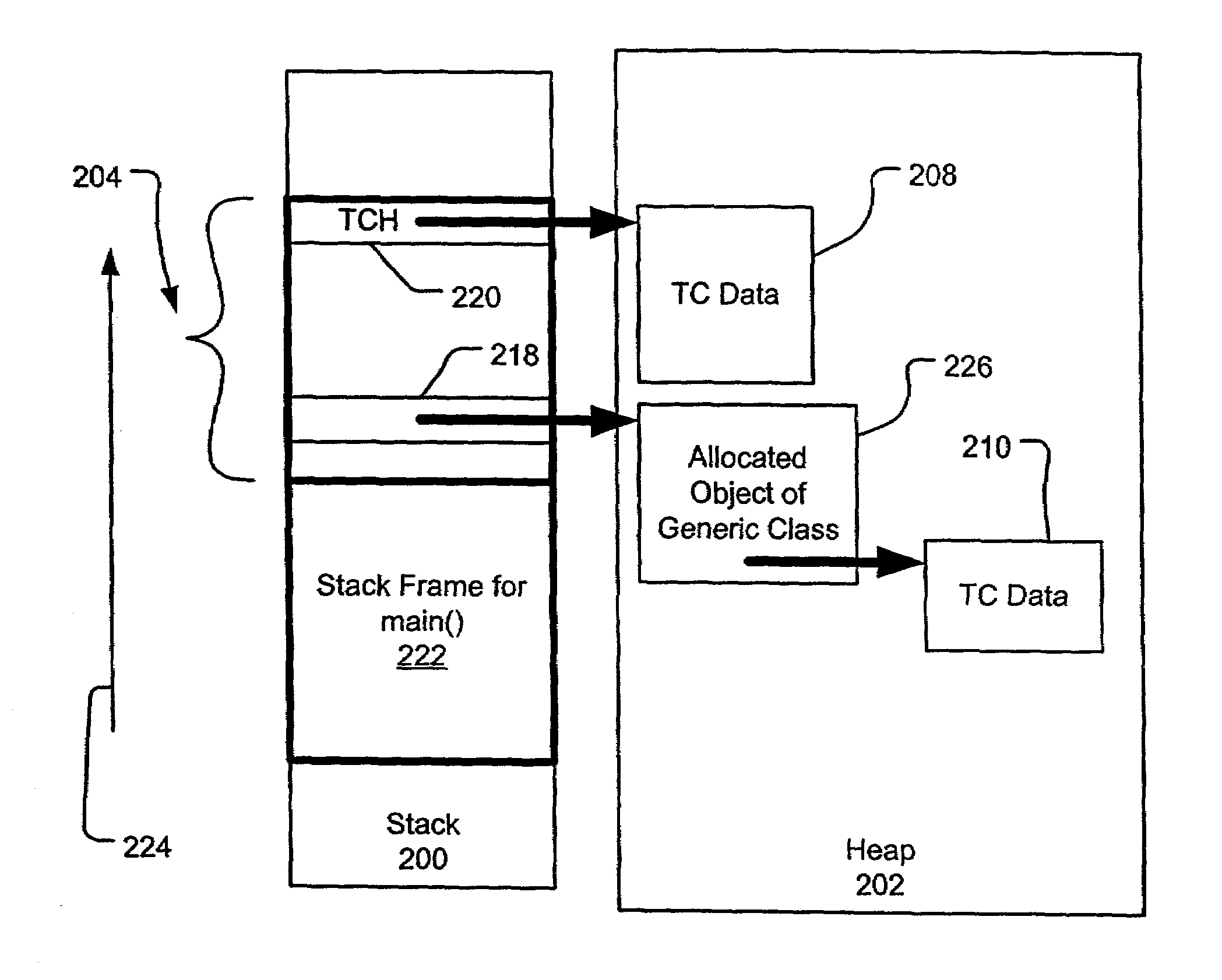
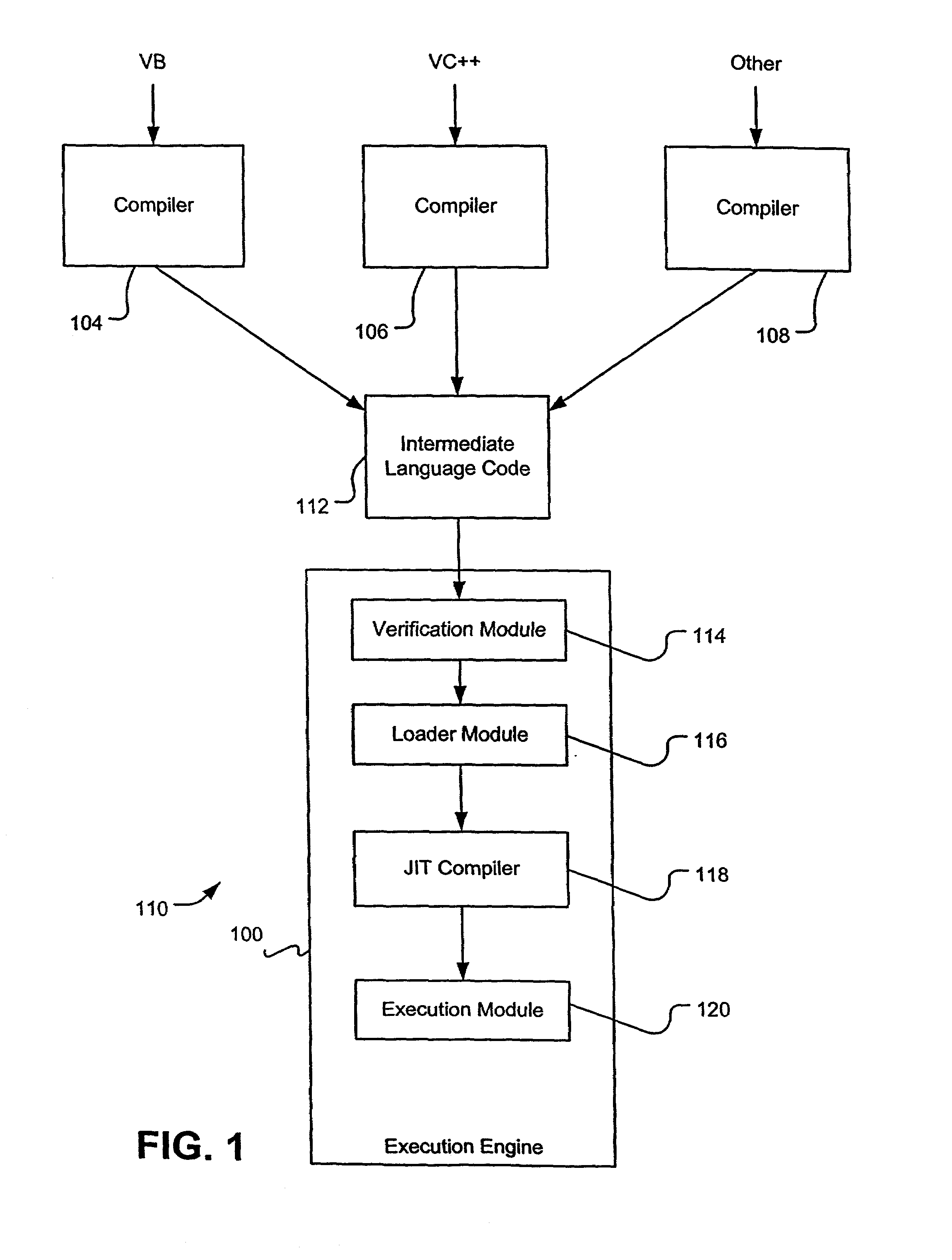
Efficient generic code in a dynamic execution environment
Efficient and flexible support for parametric polymorphism in a dynamic execution environment is provided. The addition of efficient parametric polymorphism in a dynamic execution environment expands the support of features of various source languages in intermediate language code. Dynamic allocation of typing context data and support tables at runtime optimizes memory requirements and performance in a dynamic execution environment. As typing-context-relevant-code-points are executed within the program, indices are assigned to these code points and indexed slots in appropriate typing context data structures are allocated. As a typing-context-relevant-code-point is executed within a typing context, the indexed slot within the associated typing context data structure is filled in with typing context data. Such populated slots may be reused in subsequent execution of the code point within the same typing context to avoid re-computing the typing context data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
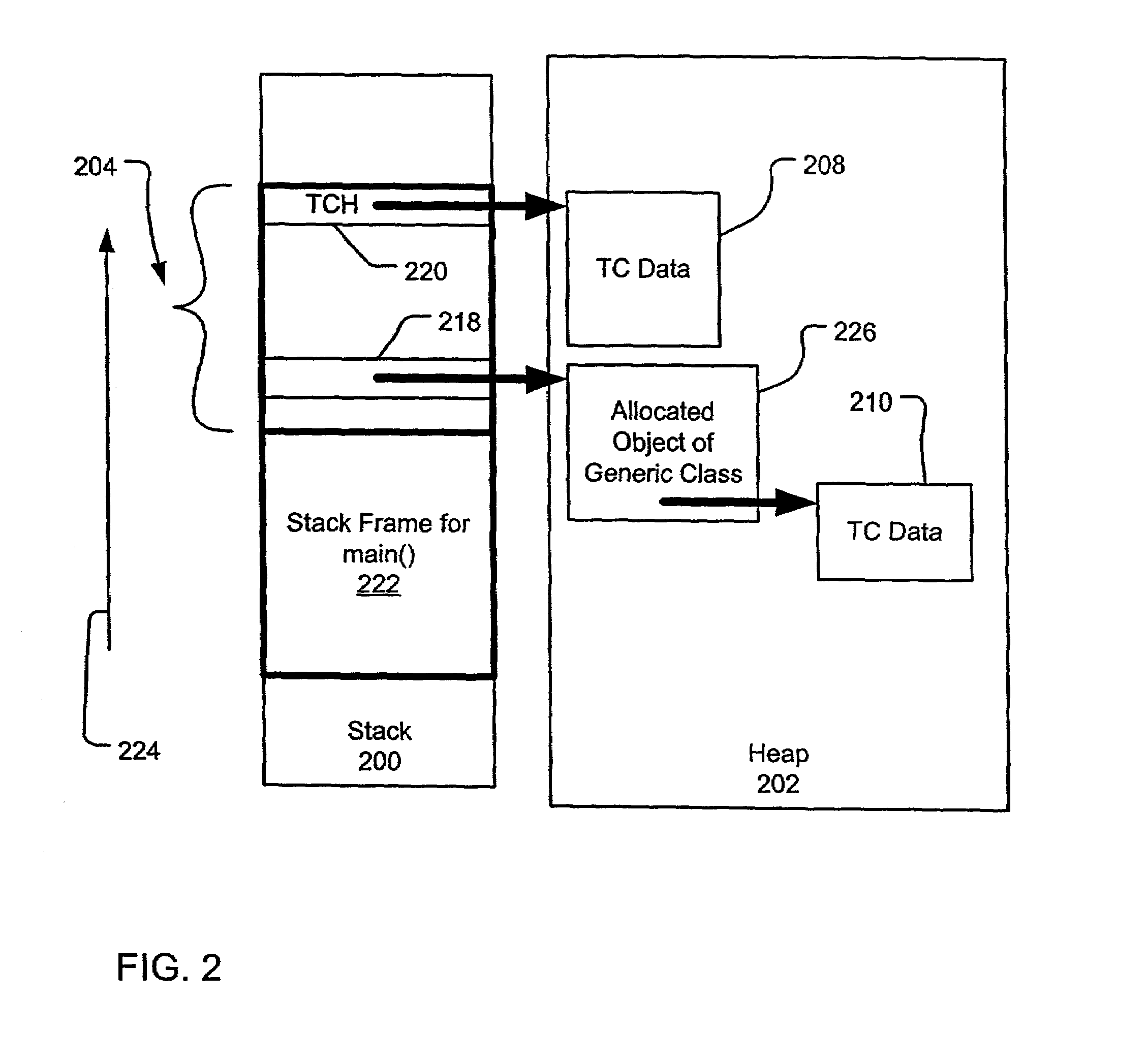
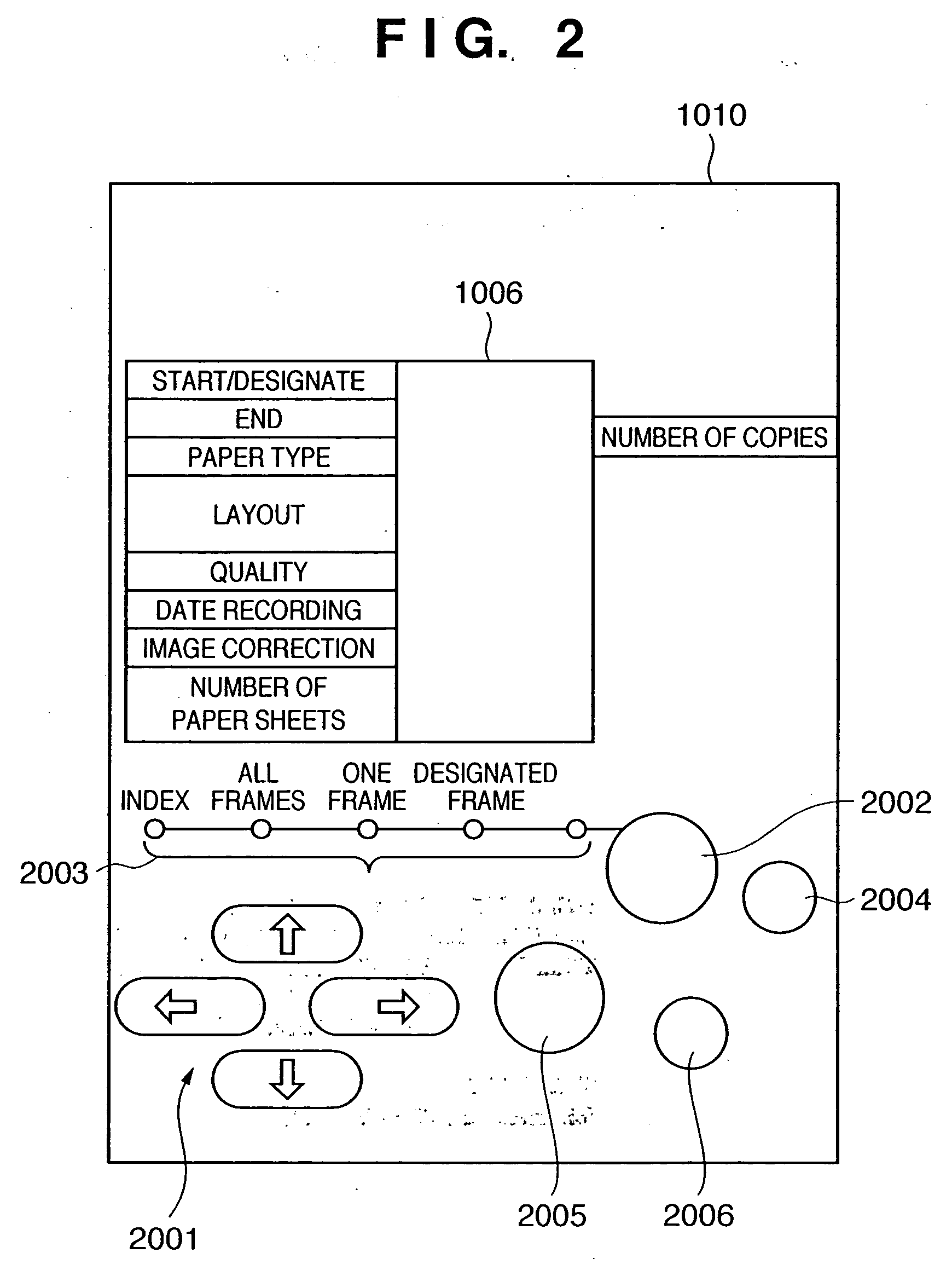
Recording device, recording system, and recording control method thereof
InactiveUS20050052676A1Increase valueDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer scienceDatabase
A print command has a hierarchical structure including a vendor common code, and a vendor unique code, an index print mode or date print mode is designated using the common code, and a detailed print format of each image or the number of index images per sheet in the index print mode can be designated using the unique code.
Owner:CANON KK
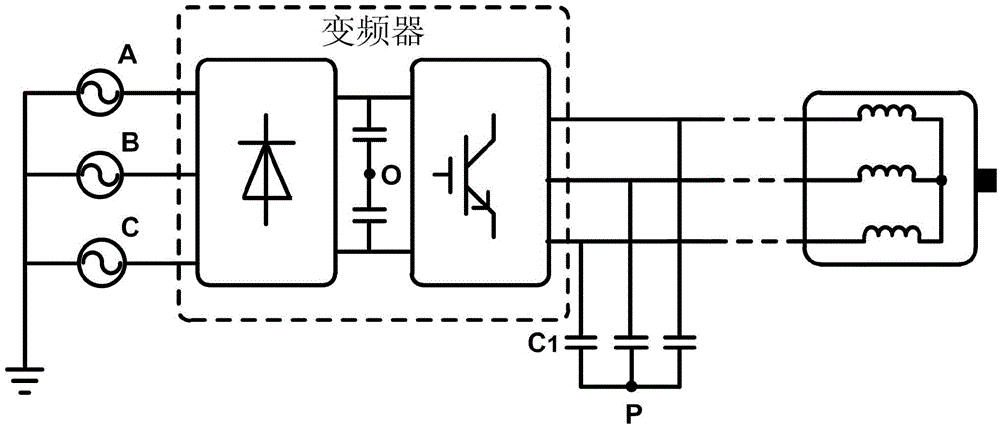
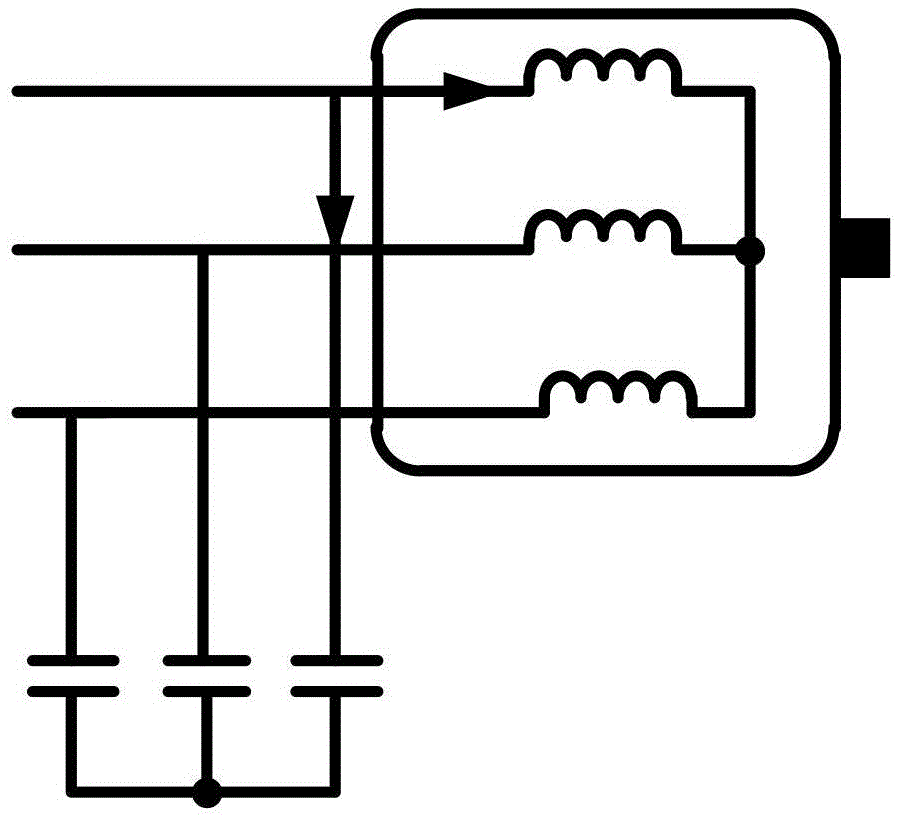
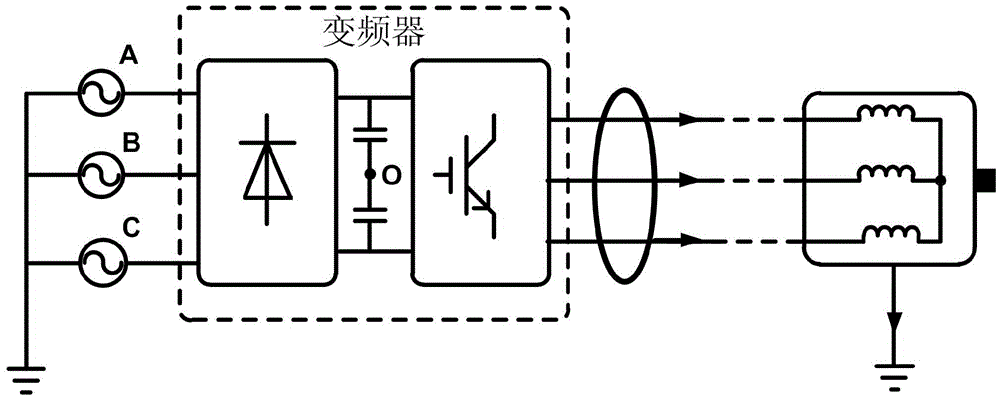
Frequency conversion transmission system motor side common code impedance extraction method
ActiveCN105606899AThe process is simple and convenientEasy to implementResistance/reactance/impedenceFrequency spectrumFrequency conversion
The invention discloses a frequency conversion transmission system motor side common code impedance extraction method. Through measuring time domain waveforms of a common mode voltage and a common mode voltage of a frequency conversion transmission system motor side and through subsequent mathematical calculation, a frequency spectrum characteristic of a frequency conversion transmission system motor side common code impedance is acquired. Compared to a traditional method of extracting an impedance parameter through an electromagnetic numerical calculation method and a network impedance analyzer, in the method of the invention, a complex motor or cable model does not need to be established and a process is simple and is easy to realize. During an impedance extraction process of the traditional method, a port impedance of a motor which does not work is extracted. And in the common code impedance extraction method of the invention, an influence of motor operation on the port impedance is considered so that a common mode current of a motor side can be accurately predicted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
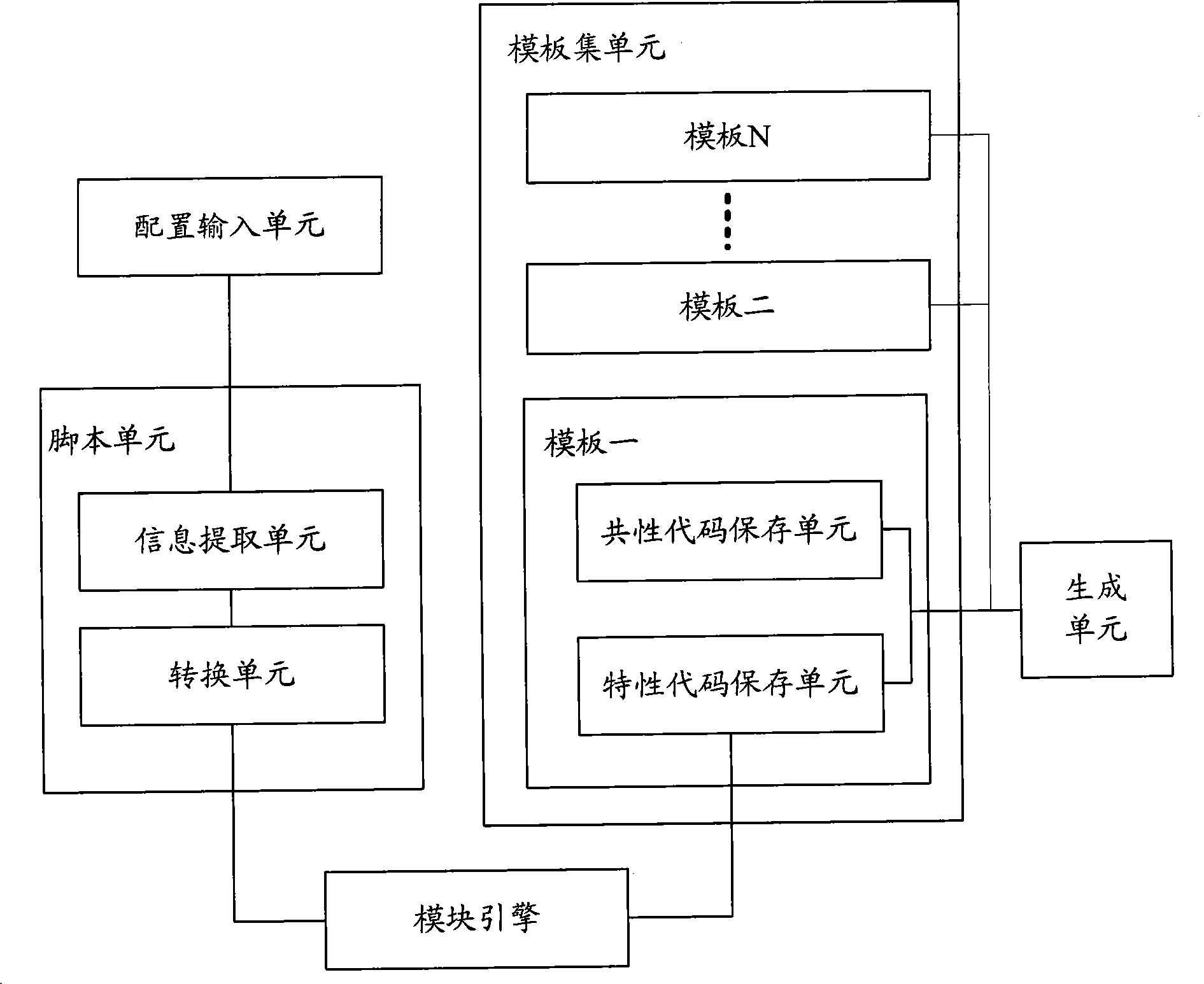
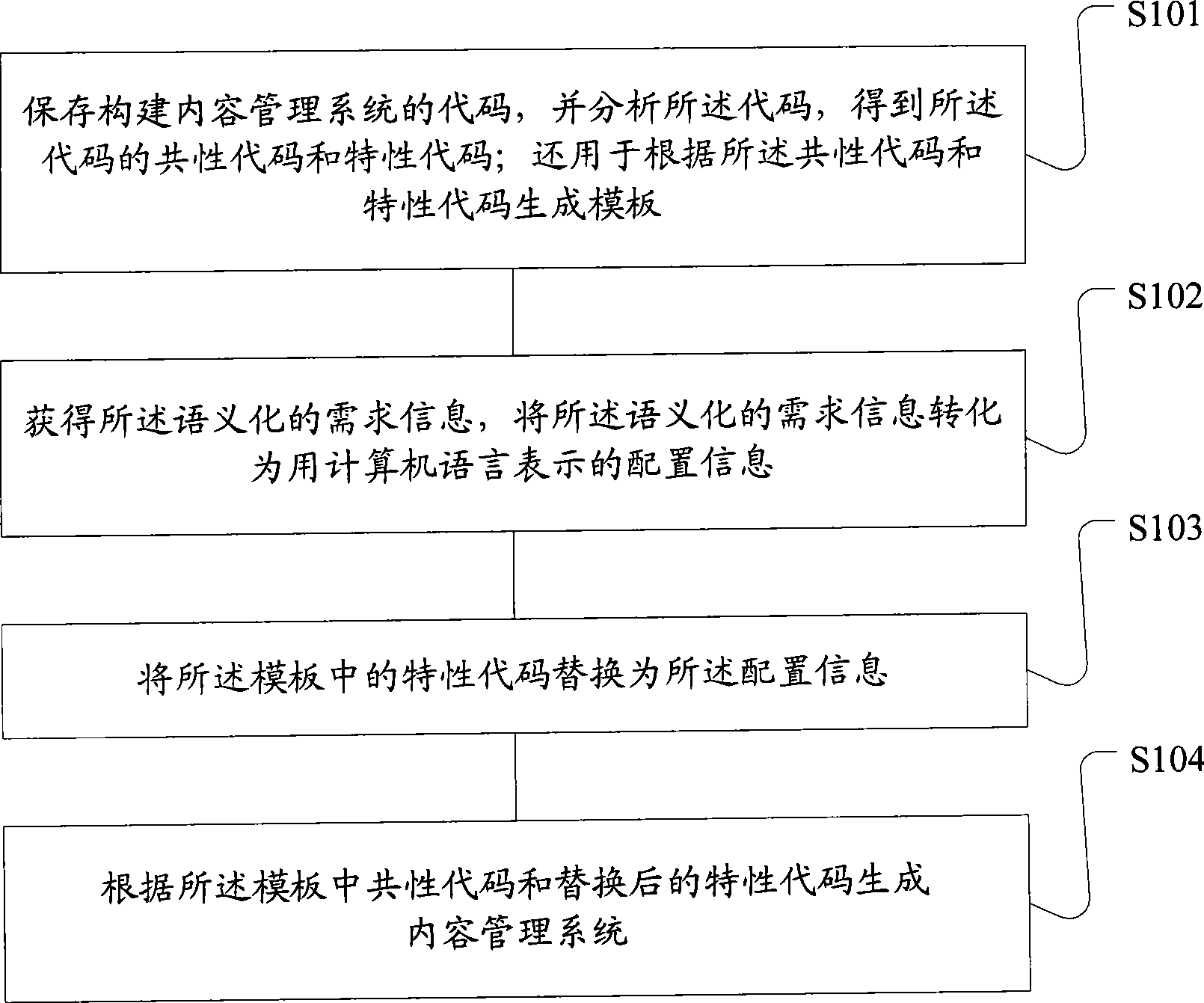
Method for building content management system and device thereof
ActiveCN101446971ABuild fastReduce manpowerSpecial data processing applicationsContent managementContent management system
The invention discloses a method for building a content management system and a device thereof. The device comprises a configuration input unit for inputting semantic demand information; a script unit for acquiring the semantic demand information and converting the semantic demand information into configuration information which is expressed by a computer language; a template set unit for storing a code which is used for building the content management system, analyzing the code to obtain a common code and a characteristic code of the code, and generating the template according to the common code and the characteristic code; a template engine for replacing the characteristic code in the template with the configuration information; and a generation unit for generating the content management system according to the common codes and the replaced characteristic code in the templates. The method and the device can help generate corresponding content management system according to the input configuration information and the template, enhance work efficiency, and reduce cost and error probability.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHI JI GUANG SU INFORMATION TECH
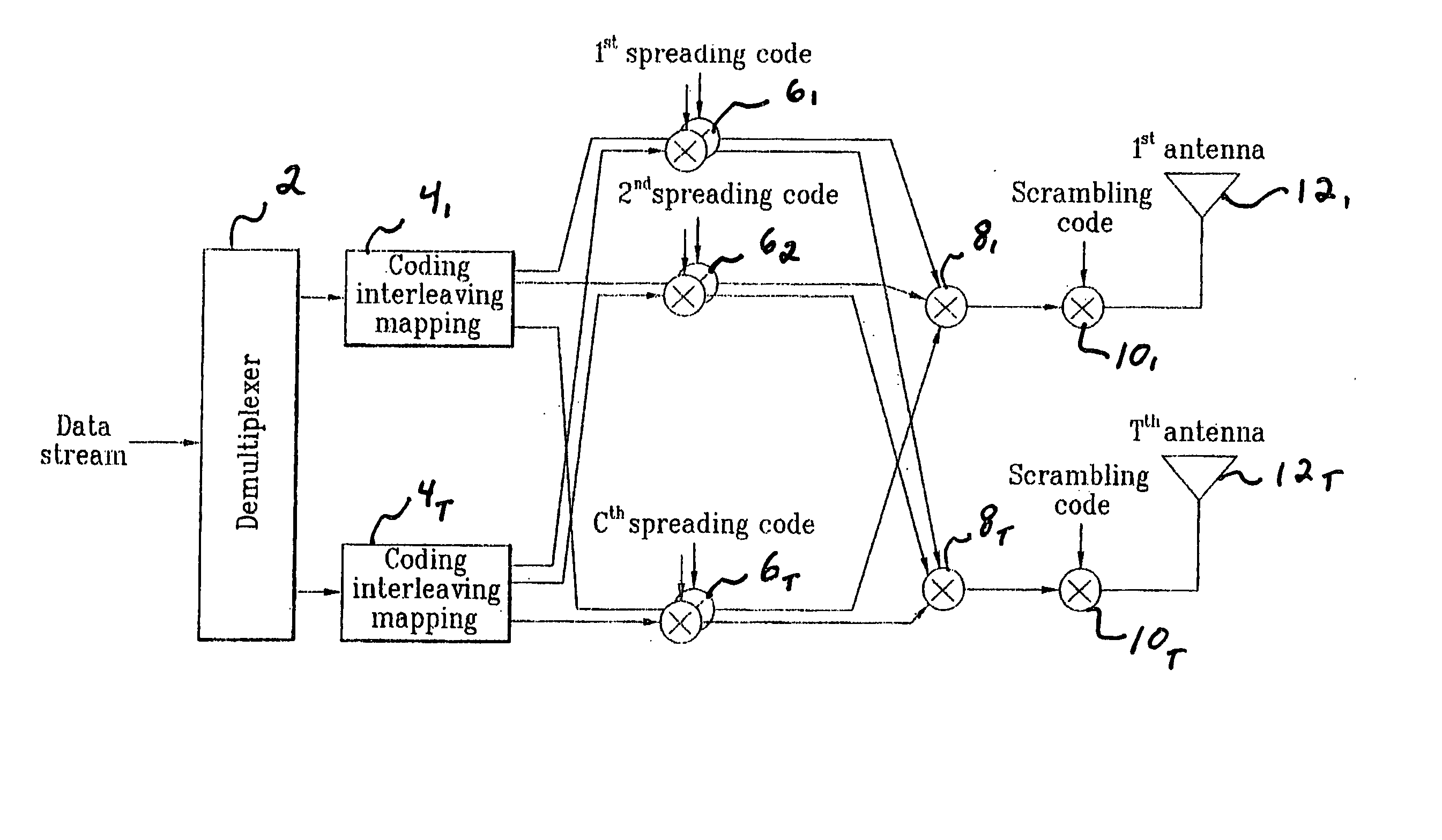
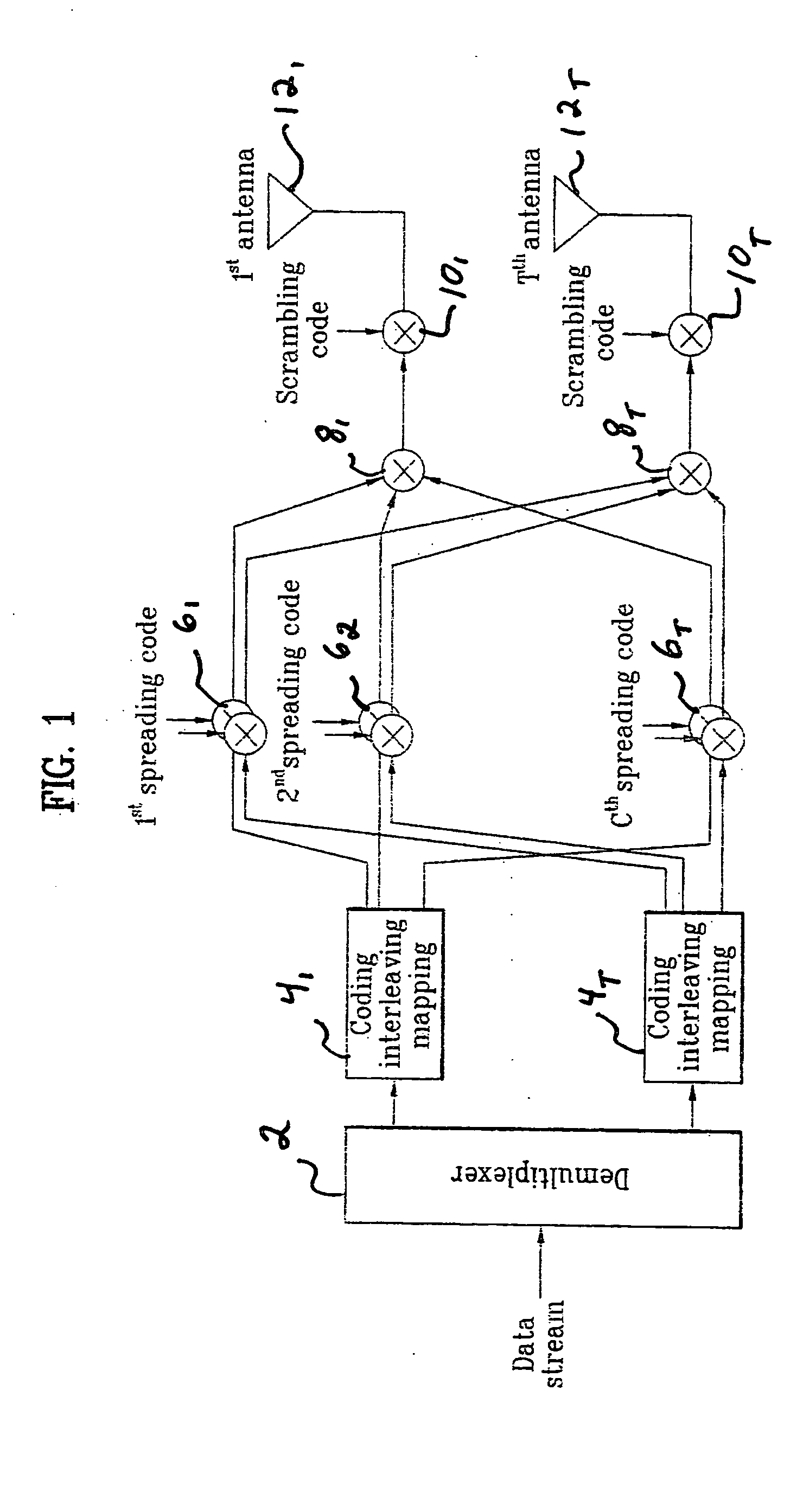
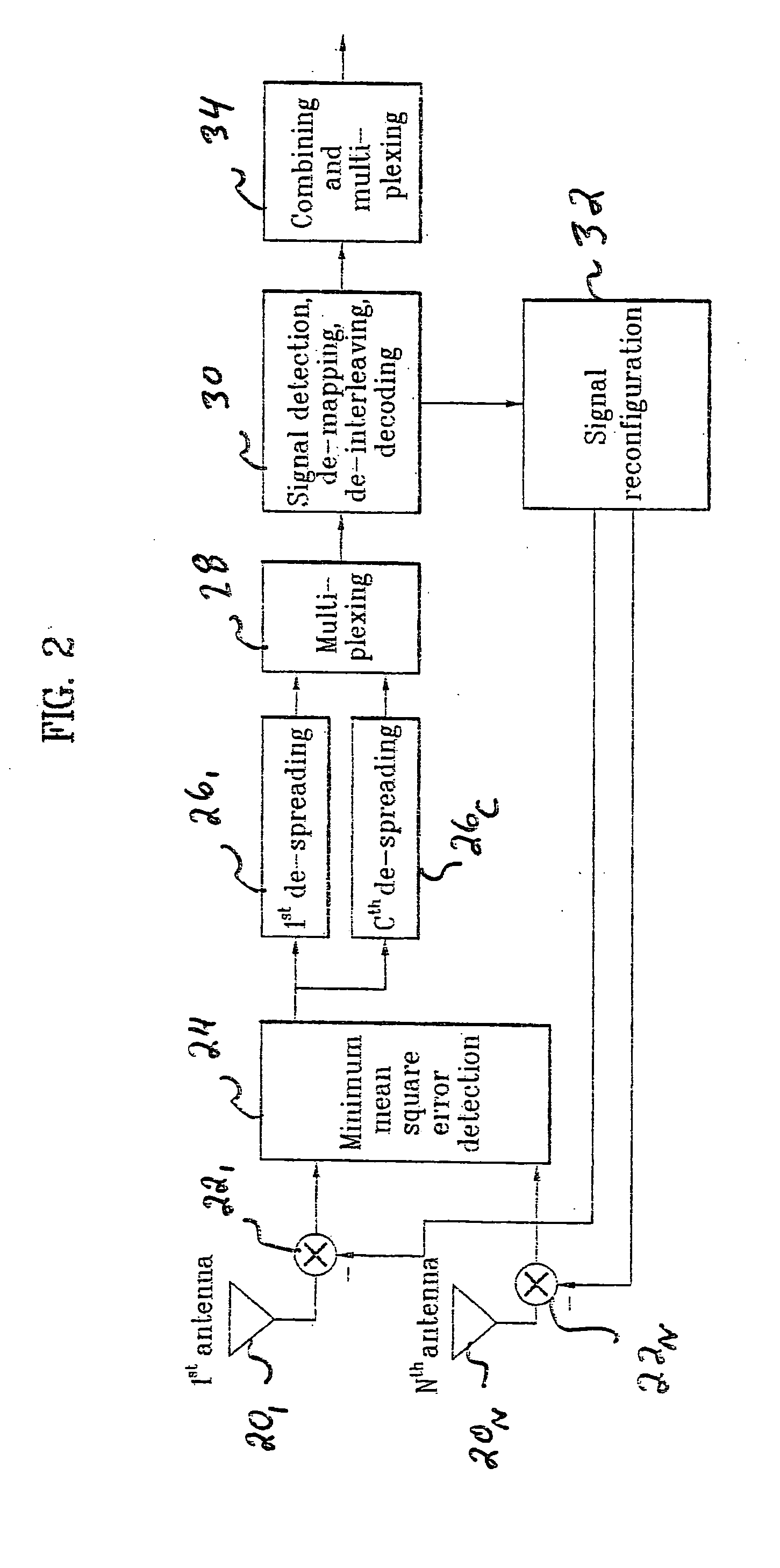
Method of controlling data modulation and coding applied to Multi-Input/Multi-Output system in mobile communications
InactiveUS20050074072A1Reduce load requirementsSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsMulti inputChannel state information
A novel method of communicating in a Multi-Input / Multi-Output communication system. The method includes receiving channel status information corresponding to each transmitting data stream in the MIMO system, and determining a common modulation scheme to use for all of the transmitting data streams based on the received channel status information. A common coding scheme, common modulation scheme, or a common modulation and coding set may also be selected based on the received channel status information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication
InactiveCN106295246ASimple processSimple methodBiostatisticsProteomicsDifferential codingPredictive marker
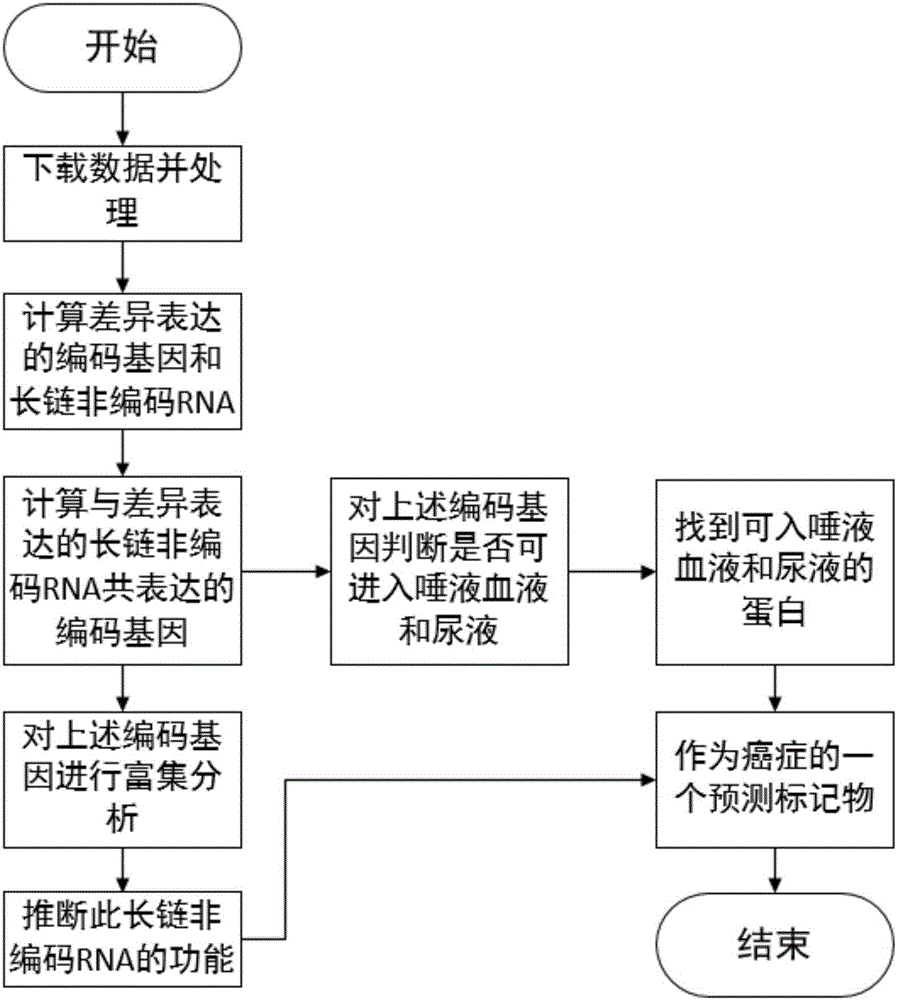
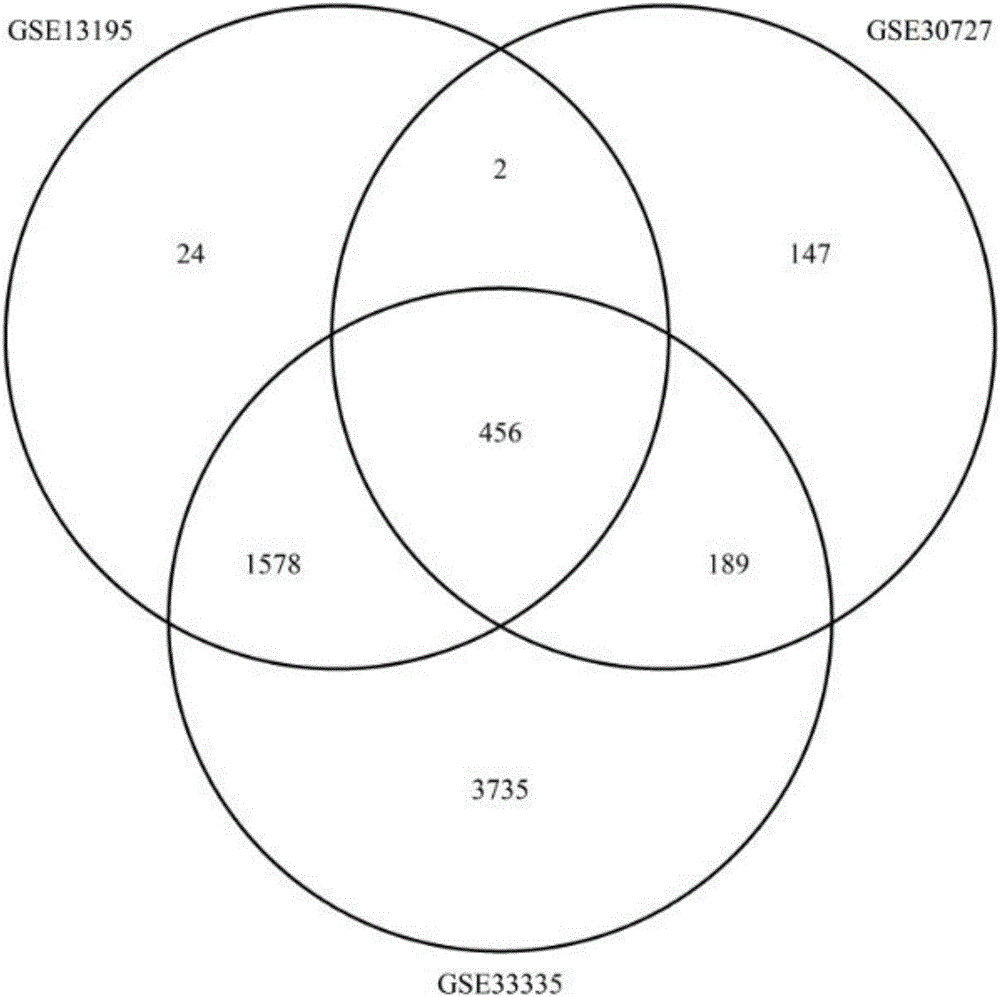
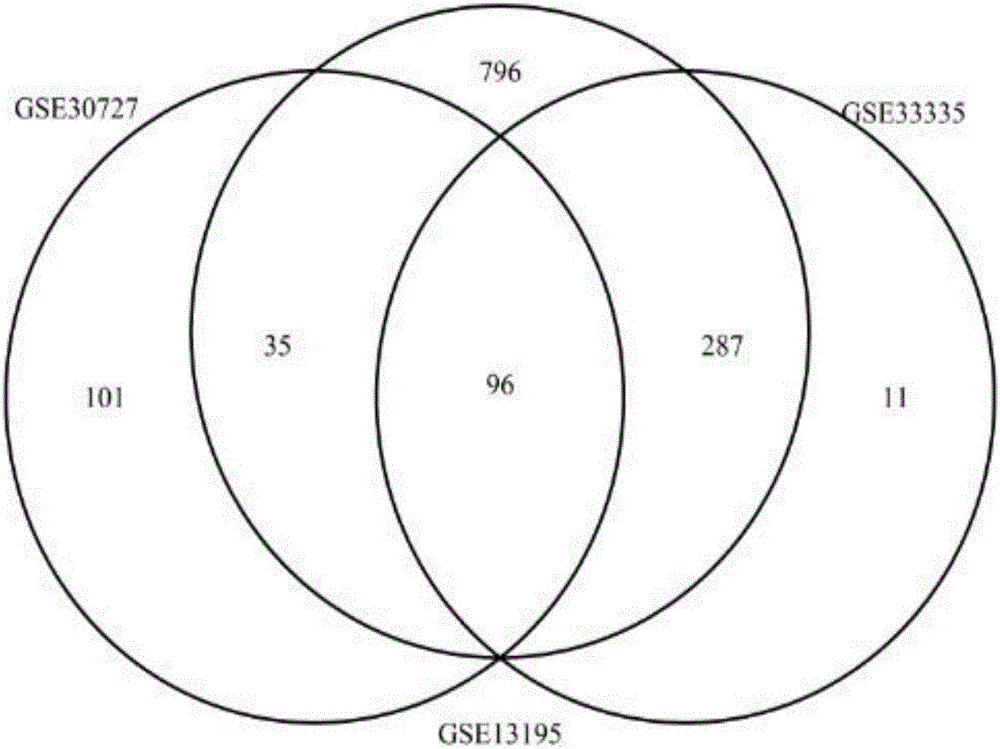
The invention relates to tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication. By taking differential expression of IncRNA in tumors as diagnosis references, a process for finding a relation between IncRNA and tumors includes: step one, downloading data from GEO database, processing the data to obtain expression data of part of IncRNA and exons; step two, subjecting the processed expression data to differential expression analysis; step three, analyzing co-expression and differential coding genes and IncRNA for IncRNA in differential expression; step four, subjecting the coding genes to probe platform annotation; step five, further screening the IncRNA in differential expression to select out most obviously differential IncRNA; step six, performing enrichment analysis to obtain a GOBP process and pathyway, and speculating IncRNA functions through coding gene related biological processes; step seven, analyzing whether common coding genes obtained at the step six can enter blood, saliva and urine or not, analyzing genes which are allowed to enter, and taking the genes and IncRNA as potential predication marks of cancers.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method of website optimisation
A website optimisation system is integrated with a website by applying generic code to the website, that being the only code needed to be applied to the native source code of the website to enable the website optimisation system to optimise the website by altering one or more of: the data, functions or content assets of web pages in the website. Integration can be achieved on a one-time basis. The generic code can be placed into a website's page template or global page header, or manually to all pages in a website. The generic code can be just a single line of code, such as JAVASCRIPT code. The generic code remains the same irrespective of any differences in the data, functions or content assets of the web pages. The generic code includes code for all commands that enable tracking of the actions that relate to the optimisation objectives.
Owner:MAXYMISER
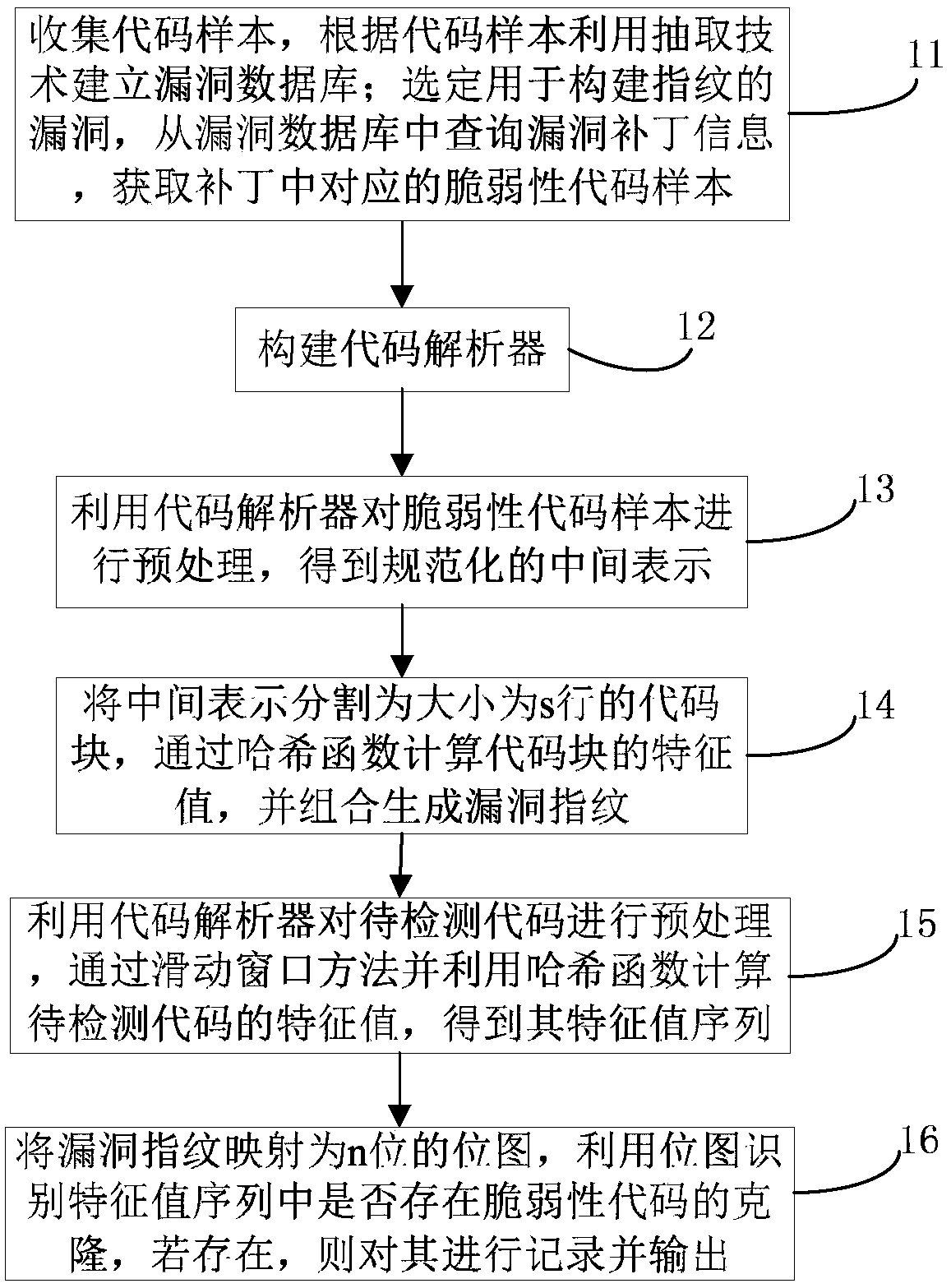
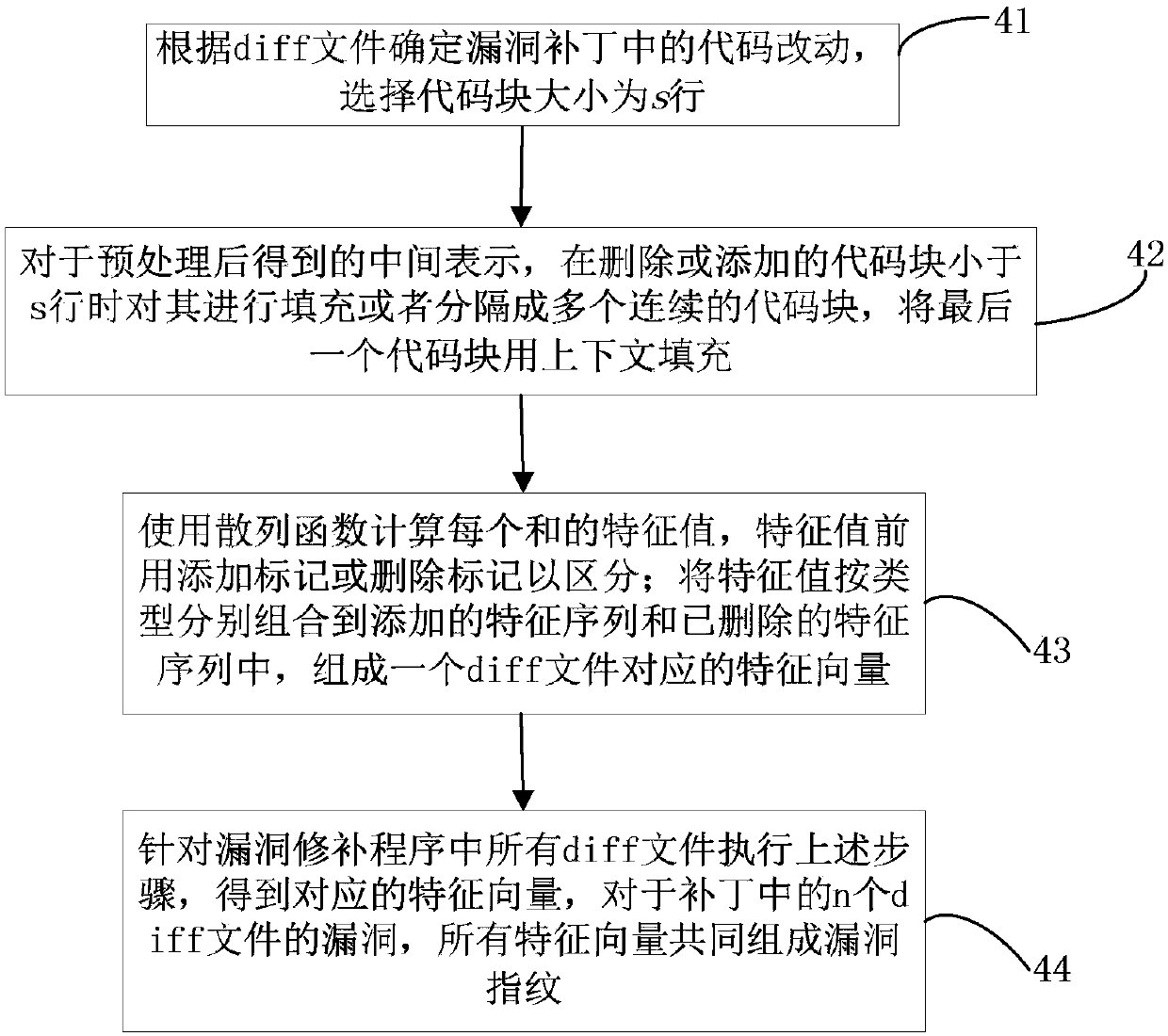
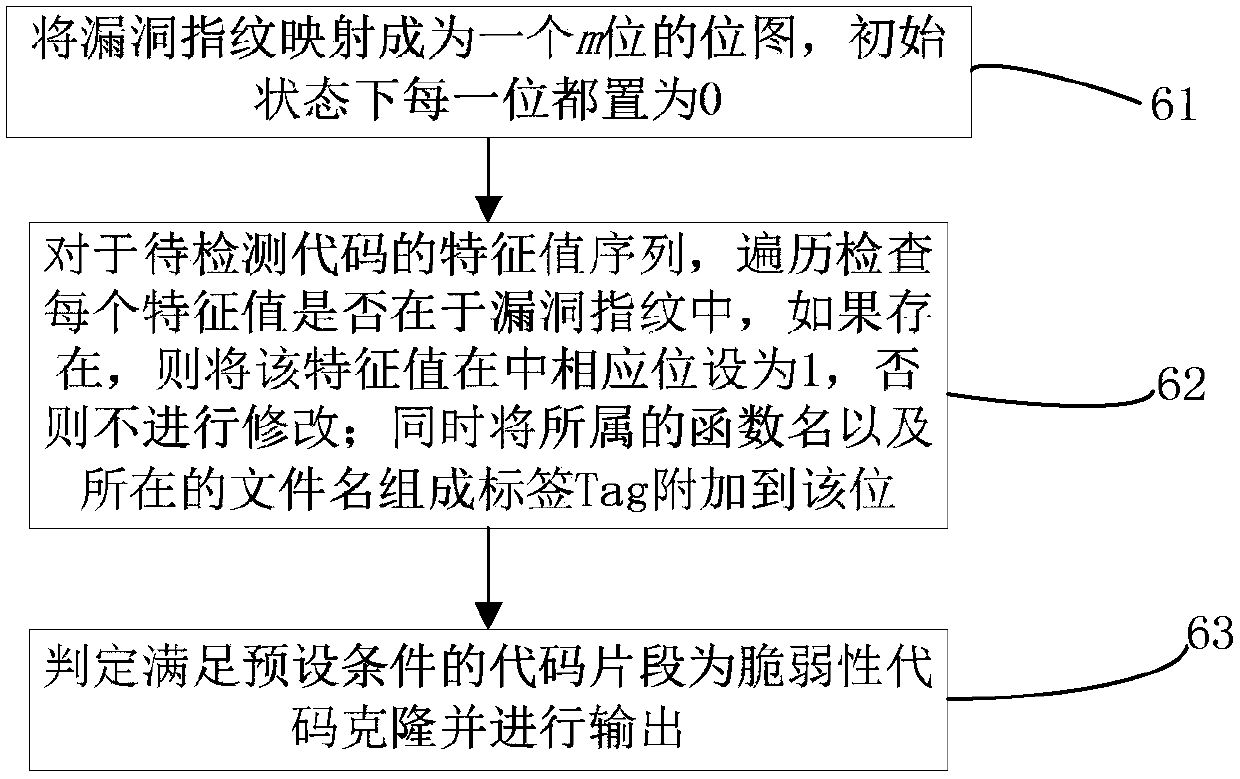
Loophole fingerprint based vulnerability code clone detecting method and device
ActiveCN107688748AEfficient detectionEffective multiplexingPlatform integrity maintainanceCoding blockHash function
The invention relates to a loophole fingerprint based vulnerability code clone detecting method and device. The method includes steps of collecting a code sample, and building a loophole database; selecting the loophole and searching the loophole patch information, and acquiring a vulnerability code sample; structuring a code analyzer; pretreating the vulnerability code sample by means of the codeanalyzer to obtain a standard middle expression; dividing the middle expression to be a code block with size of s line; calculating a characteristic value of the code block through a hash function, and combining to generate the loophole fingerprint; pretreating the code to be detected by means of the code analyzer and acquiring a characteristic value sequence of the code to be detected; mapping the loophole fingerprint to n bit of bit drawing; identifying if the characteristic value sequence is existed with vulnerability code clone by means of the bit drawing and outputting it. The method anddevice can effectively deal with the common code modifying method in the code cloning, well balance the relationship between the detecting efficiency and the detecting accuracy, and effectively detect the large-scale objects while keeping good accuracy.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
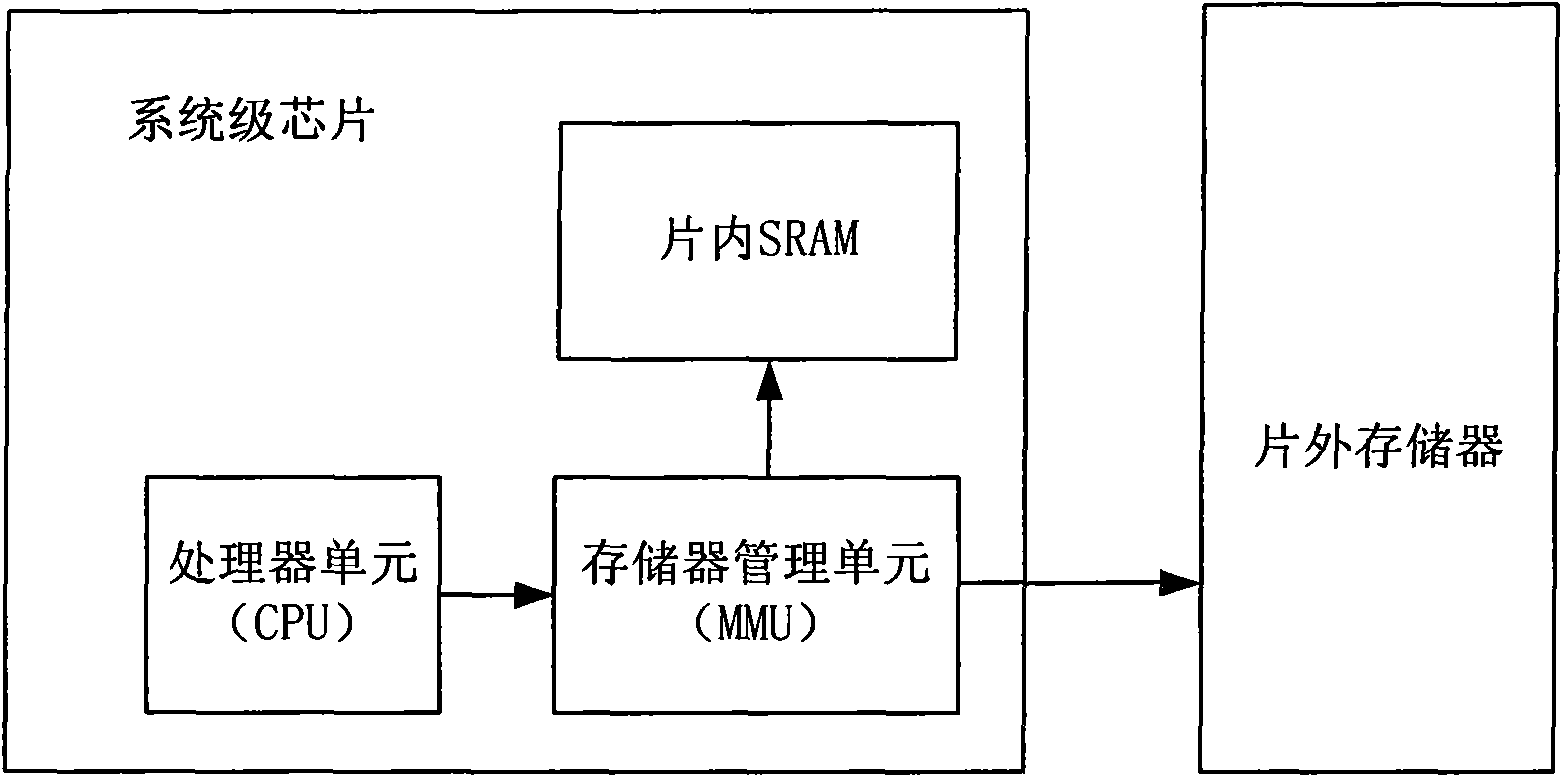
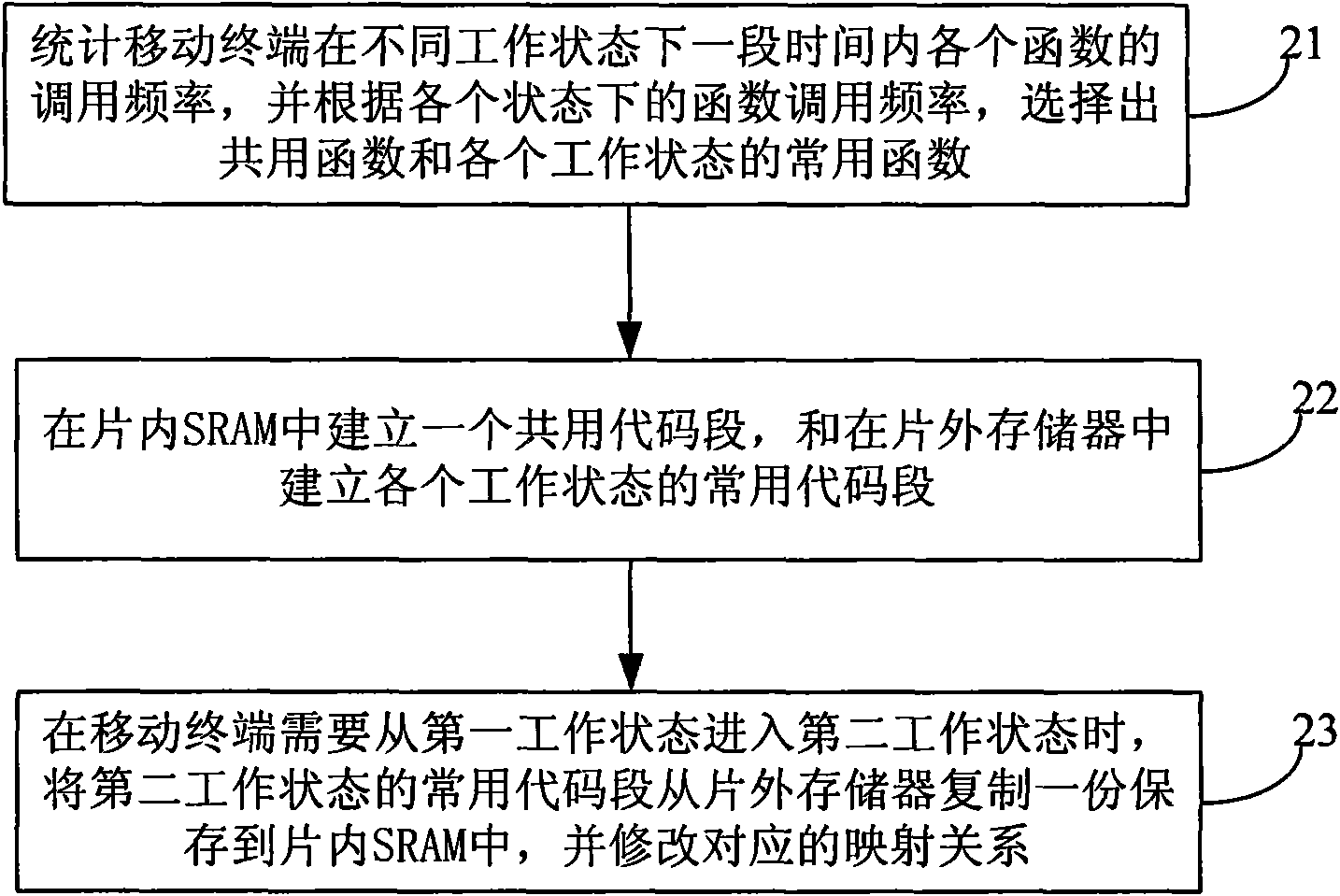
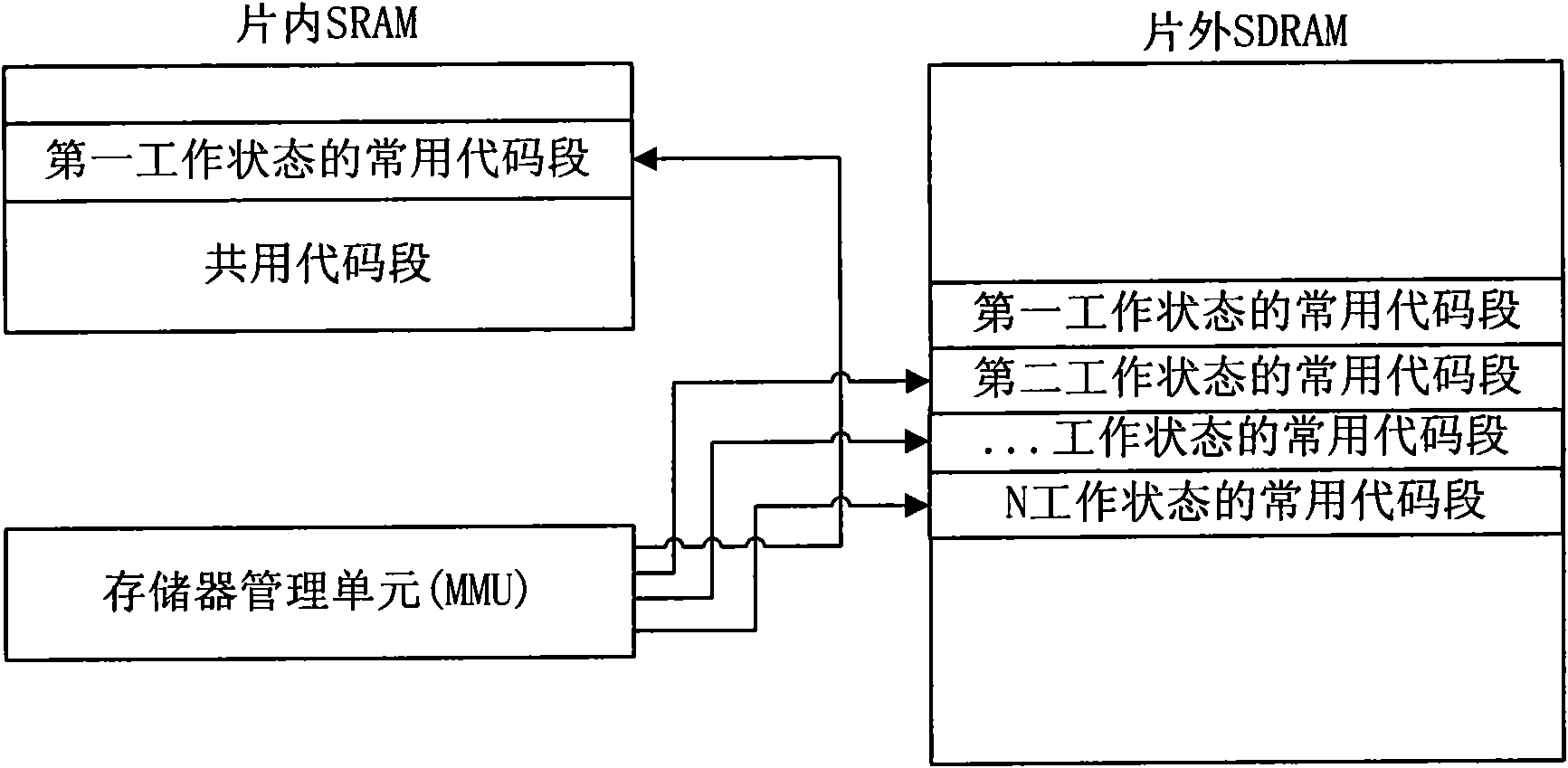
A method to reduce the power consumption of mobile terminals and the mobile terminals
InactiveCN101552840AReduce power consumptionExtended working hoursCurrent supply arrangementsSubstation equipmentWork performanceCode segment
The present invention provides a method to reduce the power consumption of mobile terminals and the mobile terminals. When the mobile terminal in the first working state needs to switch to the second working state, this method will copy the common code segment of the second working state saved in the off-chip memory to in-chip SRAM, modify the mapping relationship in MMU, modify the address of the common code segment of the second working state mapped to the off-chip memory into the common code segment of the second working state mapped to the in-chip memory, and then enter the second working state. The present invention may reduce the power consumption of mobile terminals and enhance the working performance of mobile terminals.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
Path diversity equalization CDMA downlink receiver
InactiveUS7193983B2Multiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityCode division multiple accessMobile station
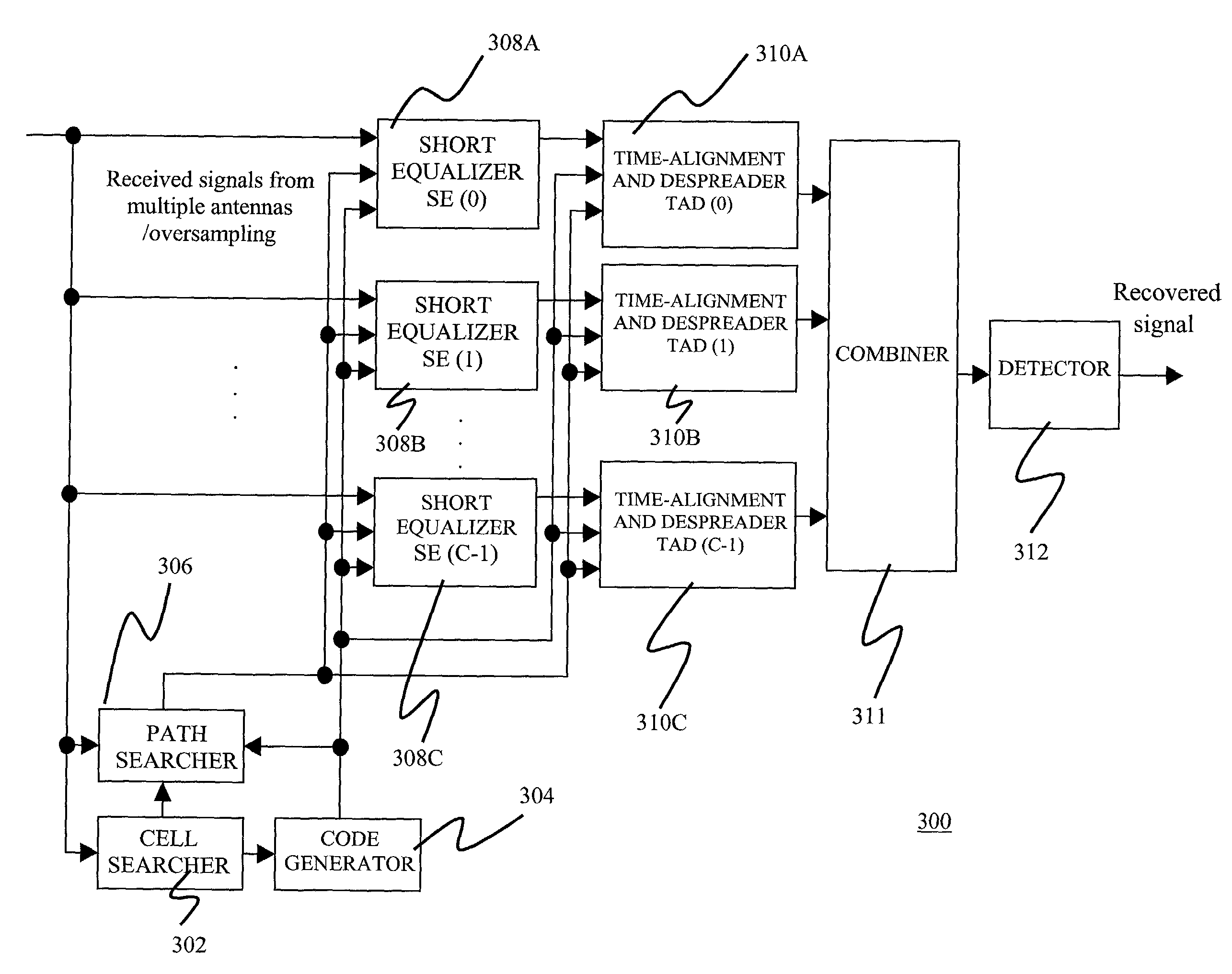
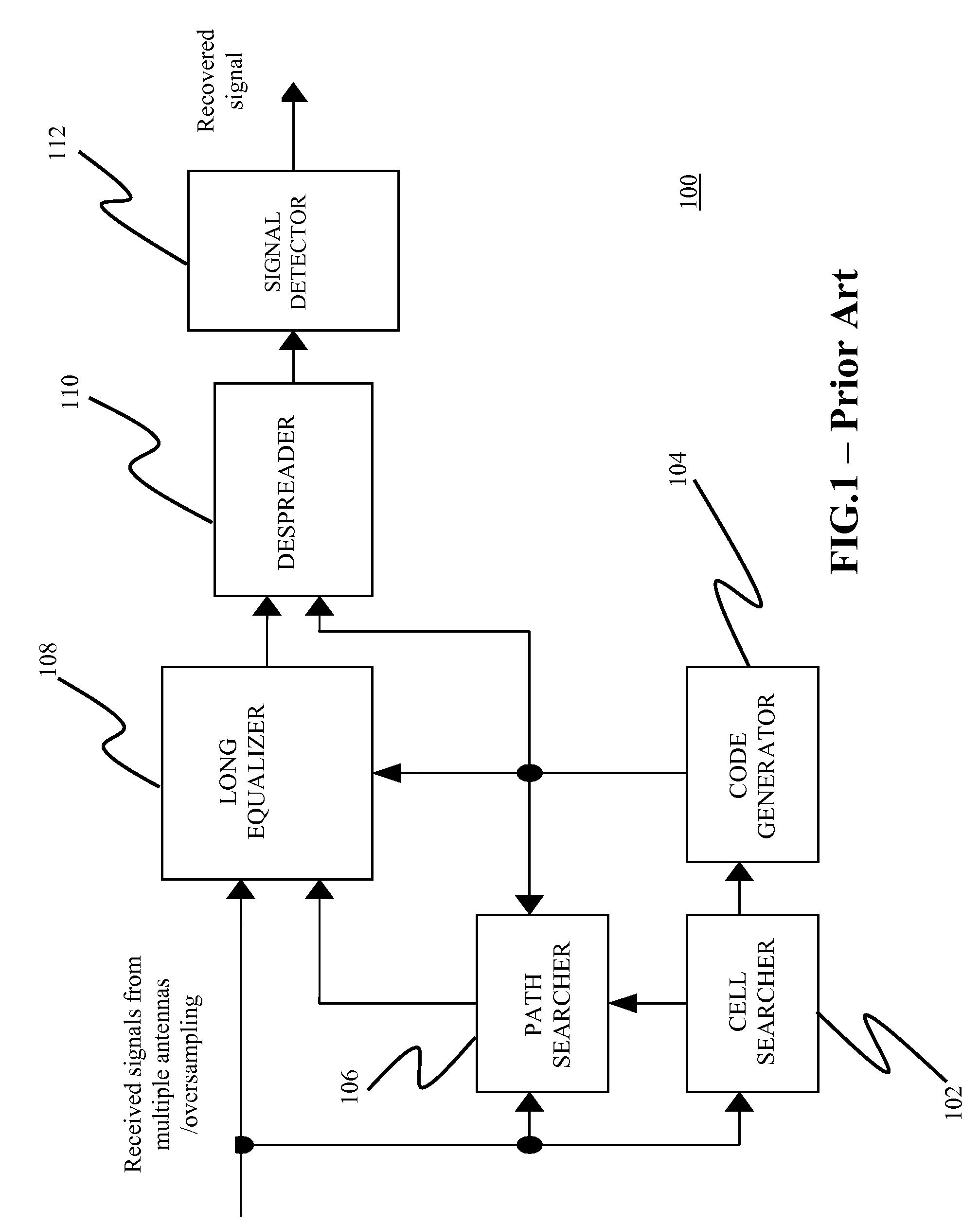
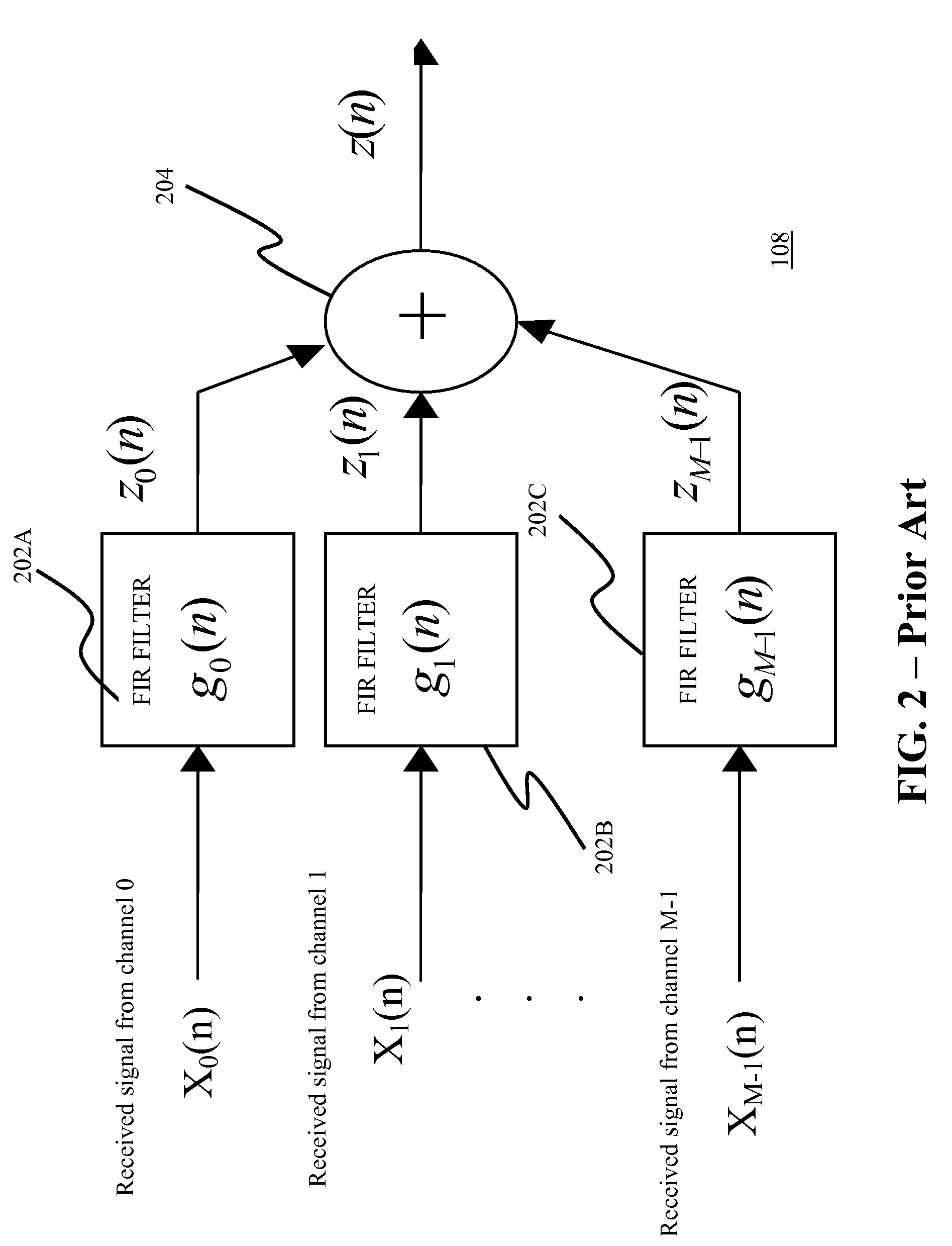
A code division multiple access downlink receiver for providing wireless communication via a wireless channel between a base station and a mobile station in which the receiver is implemented. The receiver comprises a plurality of subchannels of which each conveys at least one signal received from the base station, and a cell searcher for receiving signals in the plurality of subchannels and retrieving therefrom a common code relating to a cell. The receiver also comprises a code generator for generating a set of common and dedicated codes relating to at least one communication channel using the output of the cell searcher, and a plurality of equalizers for receiving the code generator output and equalizing the received signals in the plurality of subchannels, in which each of the plurality of equalizers includes a plurality of filters in which each of the plurality of filters corresponds to each of the plurality of subchannels, in which the length of each of the plurality of filters is lesser than the length of each of the plurality of subchannels.
Owner:SINGAPORE THE NAT UNIV OF +1
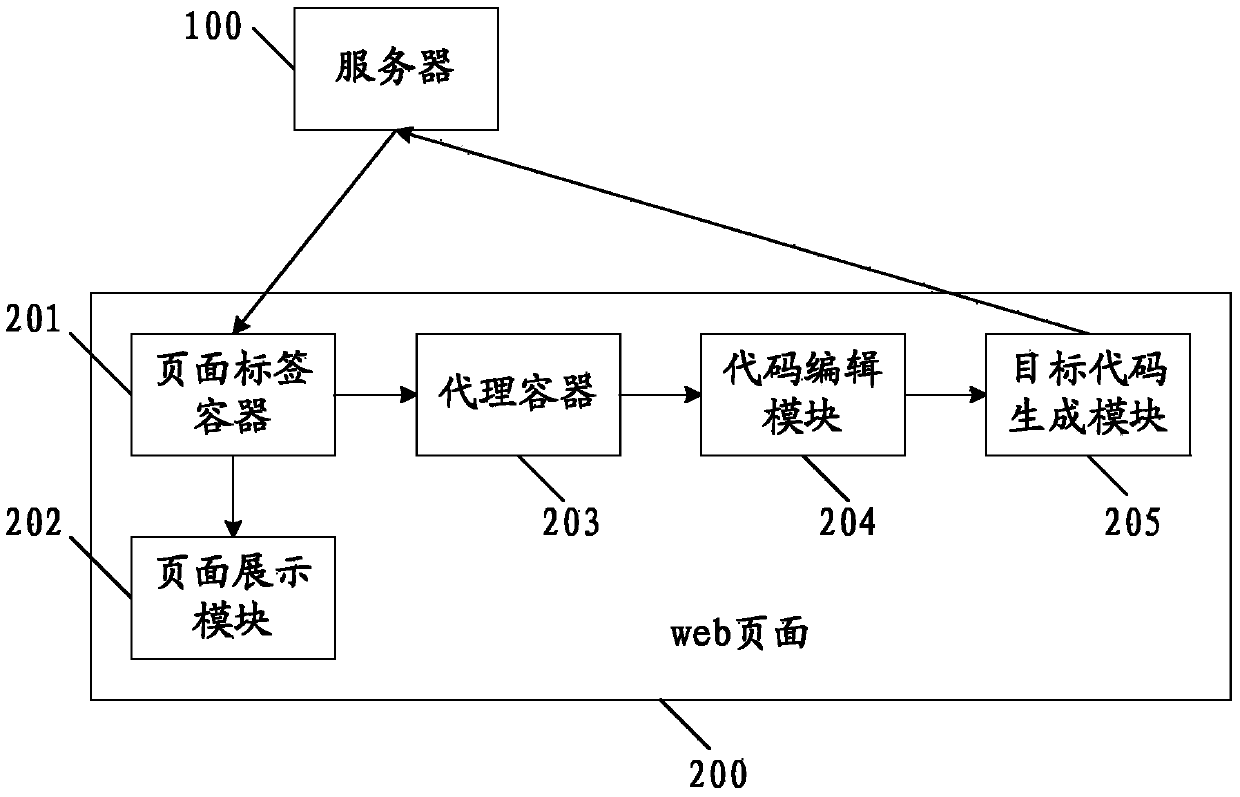
Method and system for achieving visualized edition and combination of codes
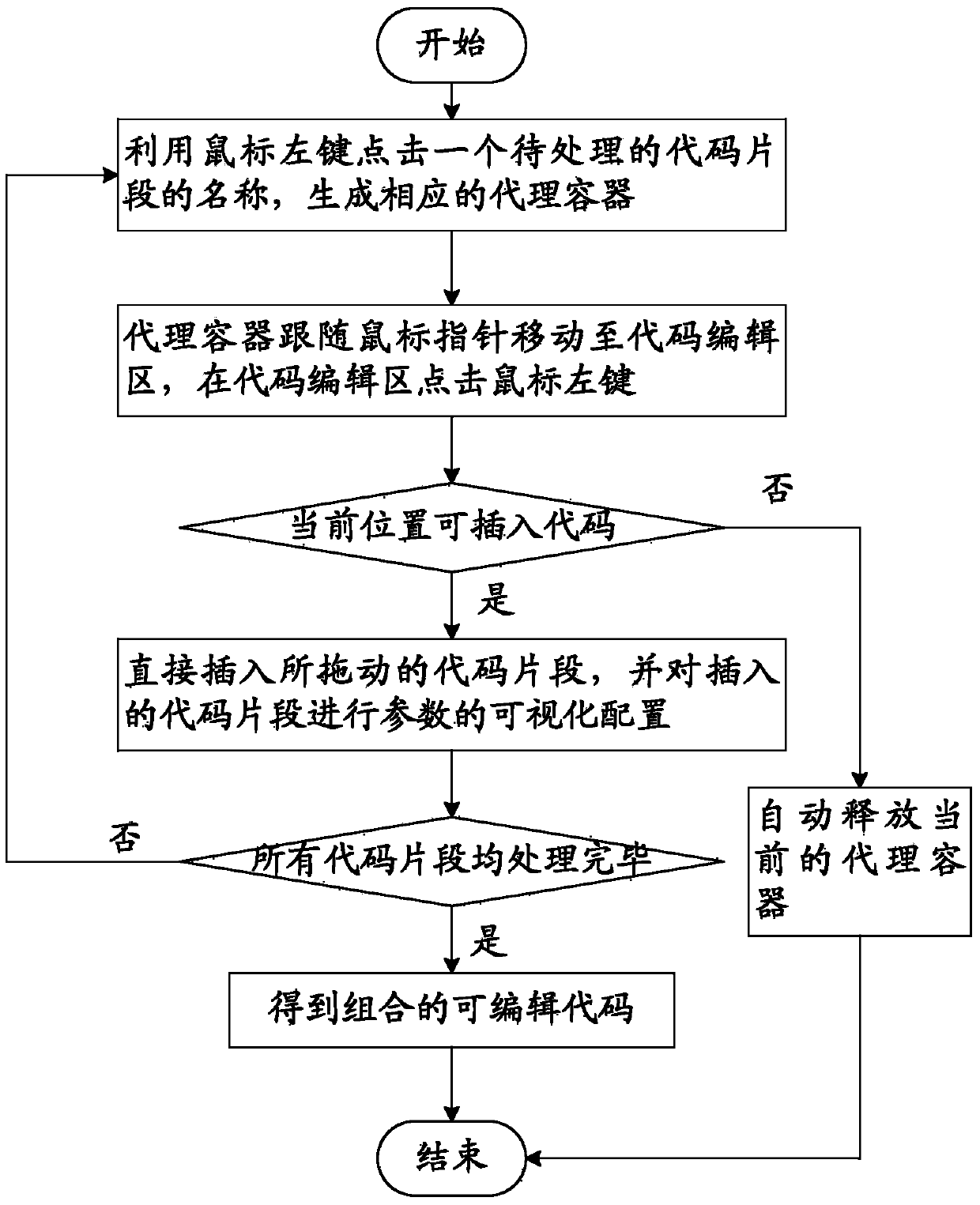
ActiveCN104049978AImprove production efficiencyImprove output efficiencySpecific program execution arrangementsCode snippetObject code
The invention relates to a method and system for achieving visualized edition and combination of codes. The method comprises the steps that a server transmits one or more code snippets to a web page in an escaping mode; the web page loads the escaped code snippets into different web page label containers, and each web page label container is bound to a dragging incident; the web page displays the name, and the web page displays the incoming parameter and outgoing parameter formats corresponding to the code snippets in the web page according to the content of each web page label container; the code snippets to be processed are dragged into a code edition area in sequence for visualized edition and combination, and a combined editable code is generated; the combined editable code is escaped to obtain a target code, and the combined editable code and the target code are both transmitted to the server and stored in the server. The method and system for achieving visualized edition and combination of codes largely improve the multiplex rate of common codes, achieve visualization of code parameter configuration, mark a revisable area and a non-revisable area, and largely improve code generation and output efficiency.
Owner:北京思特奇信息技术股份有限公司
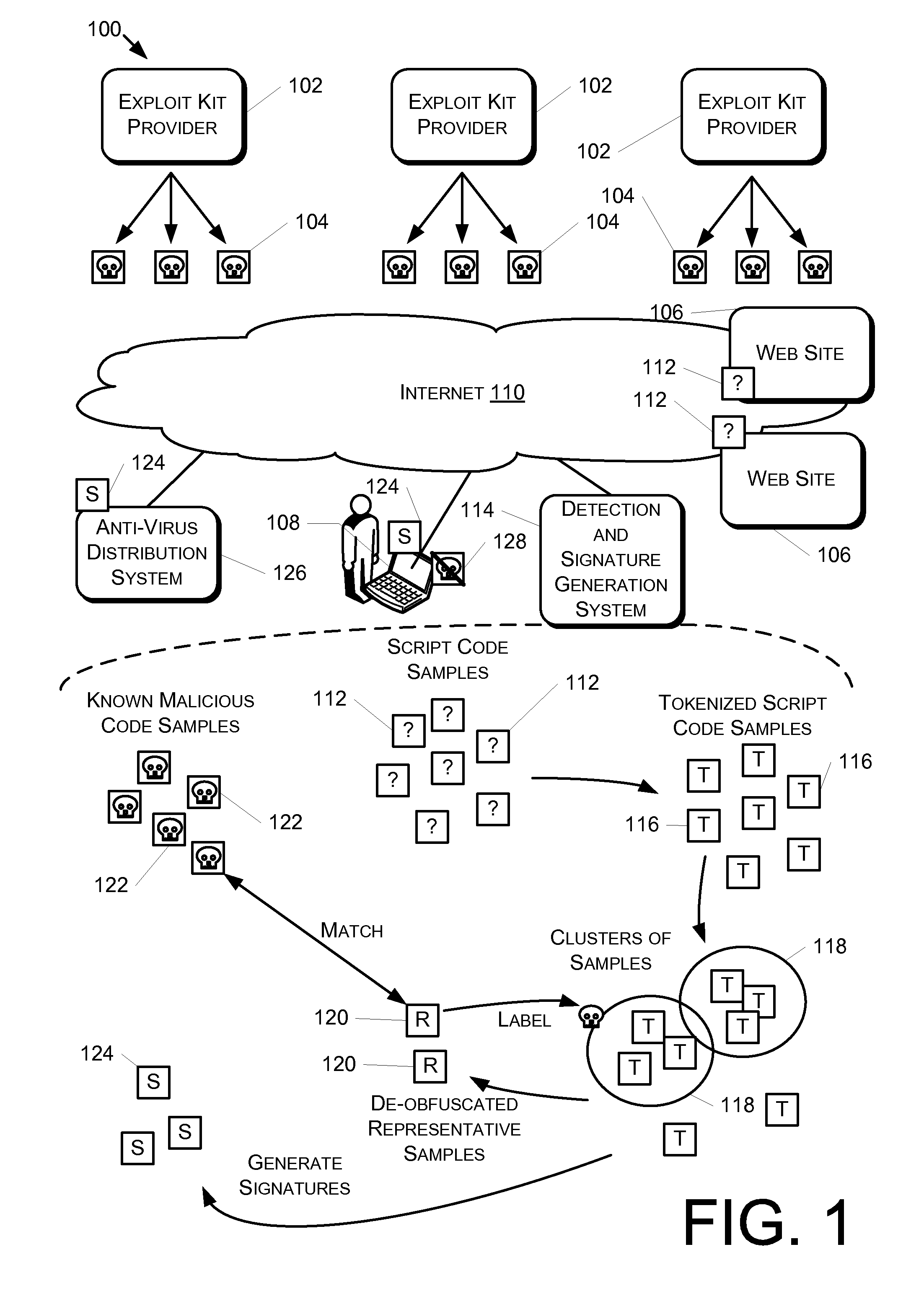
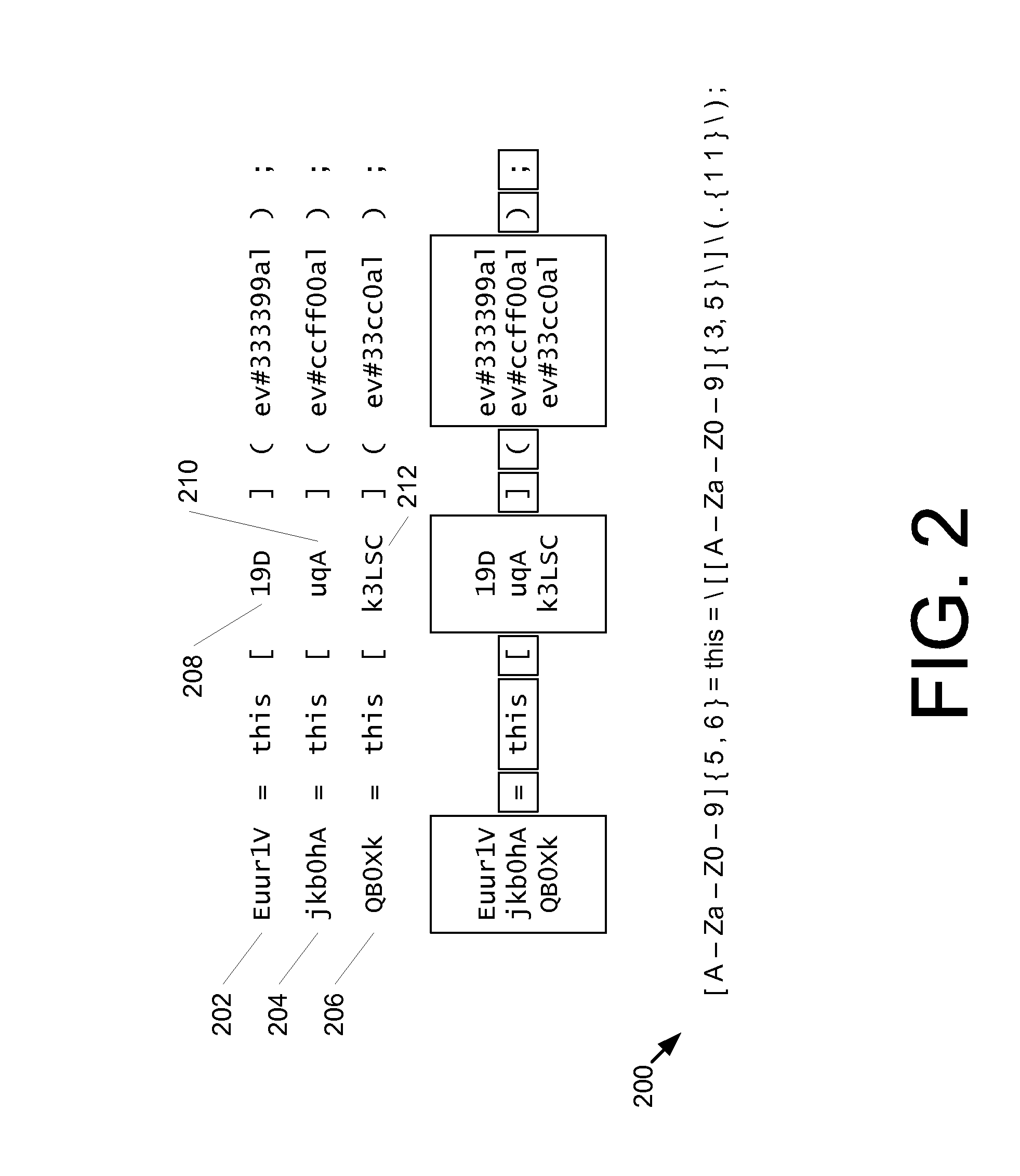
Code Labeling Based on Tokenized Code Samples
ActiveUS20160212153A1Simple conceptMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionPattern recognitionMalware
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for detecting script code malware and generating signatures. A plurality of script code samples are received and transformed into a plurality of tokenized samples. The tokenized samples are based on syntactical elements of the plurality of script code samples. One or more clusters of samples are determined based on similarities in different ones of the plurality of tokenized samples, and known malicious code having a threshold similarity to a representative sample of the cluster of samples is identified. Based on the identifying, the cluster of samples is identified as malicious. Based at least on respective ones of the plurality of tokenized samples associated with the cluster of samples, a generalized code signature usable to identify the script code samples in the cluster of samples is generated.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com