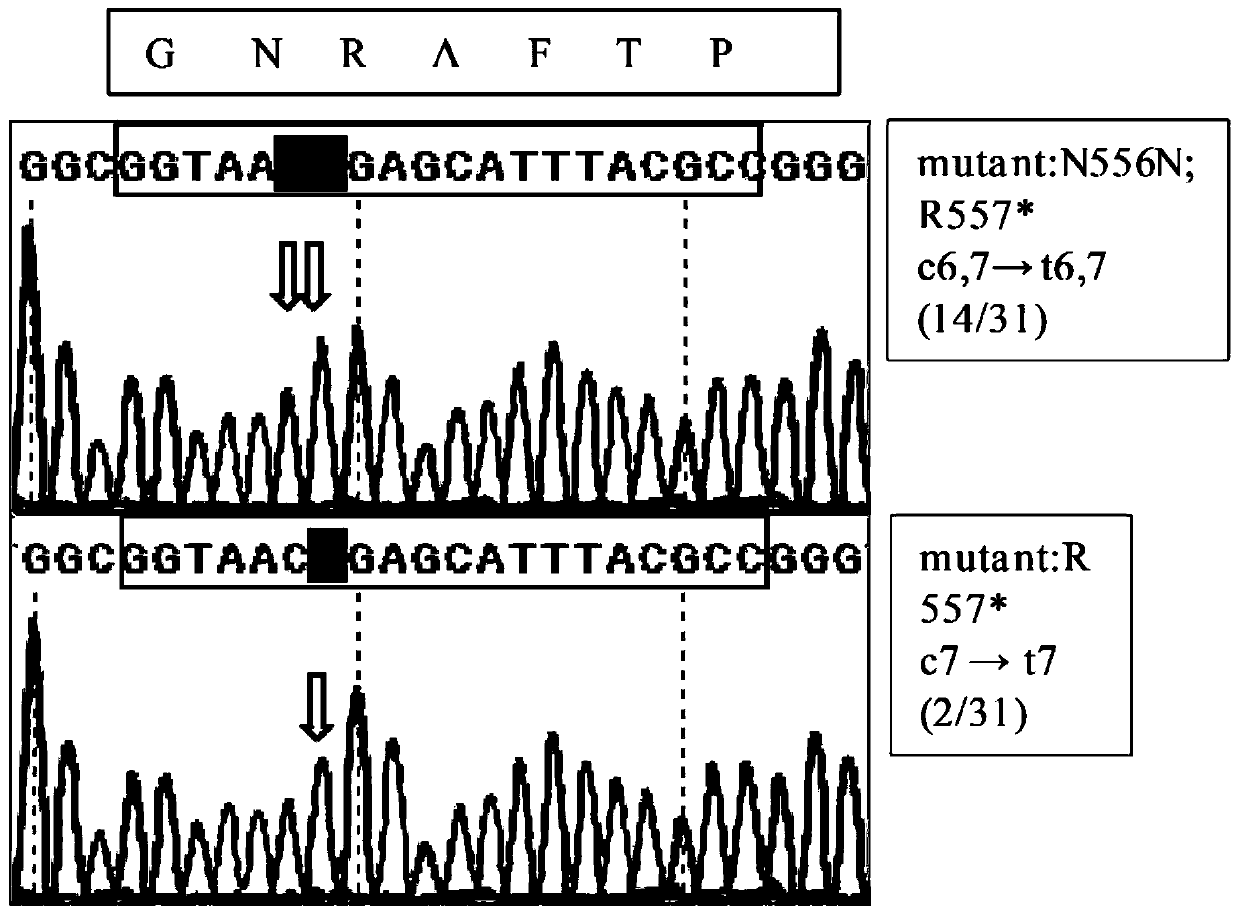
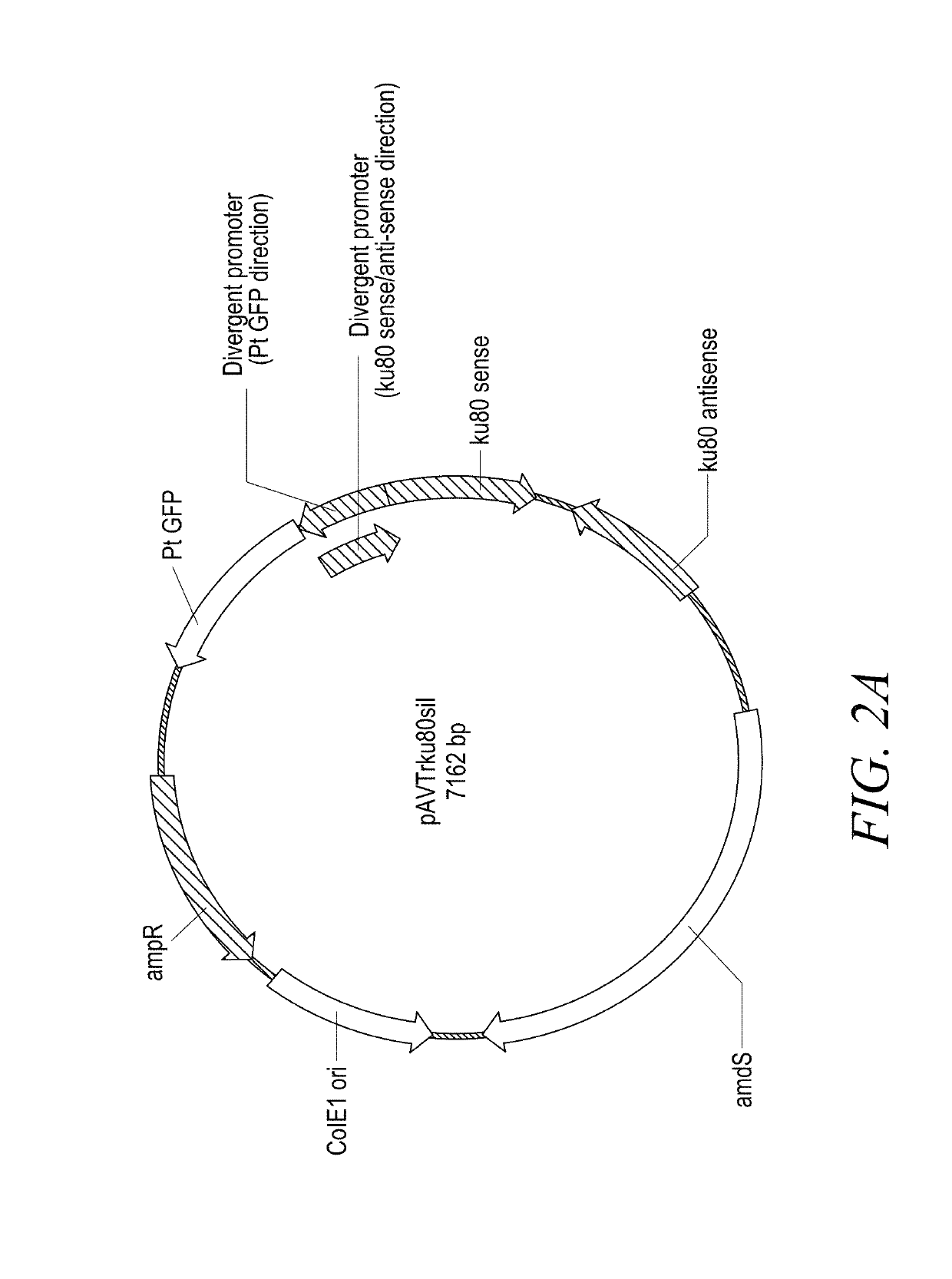
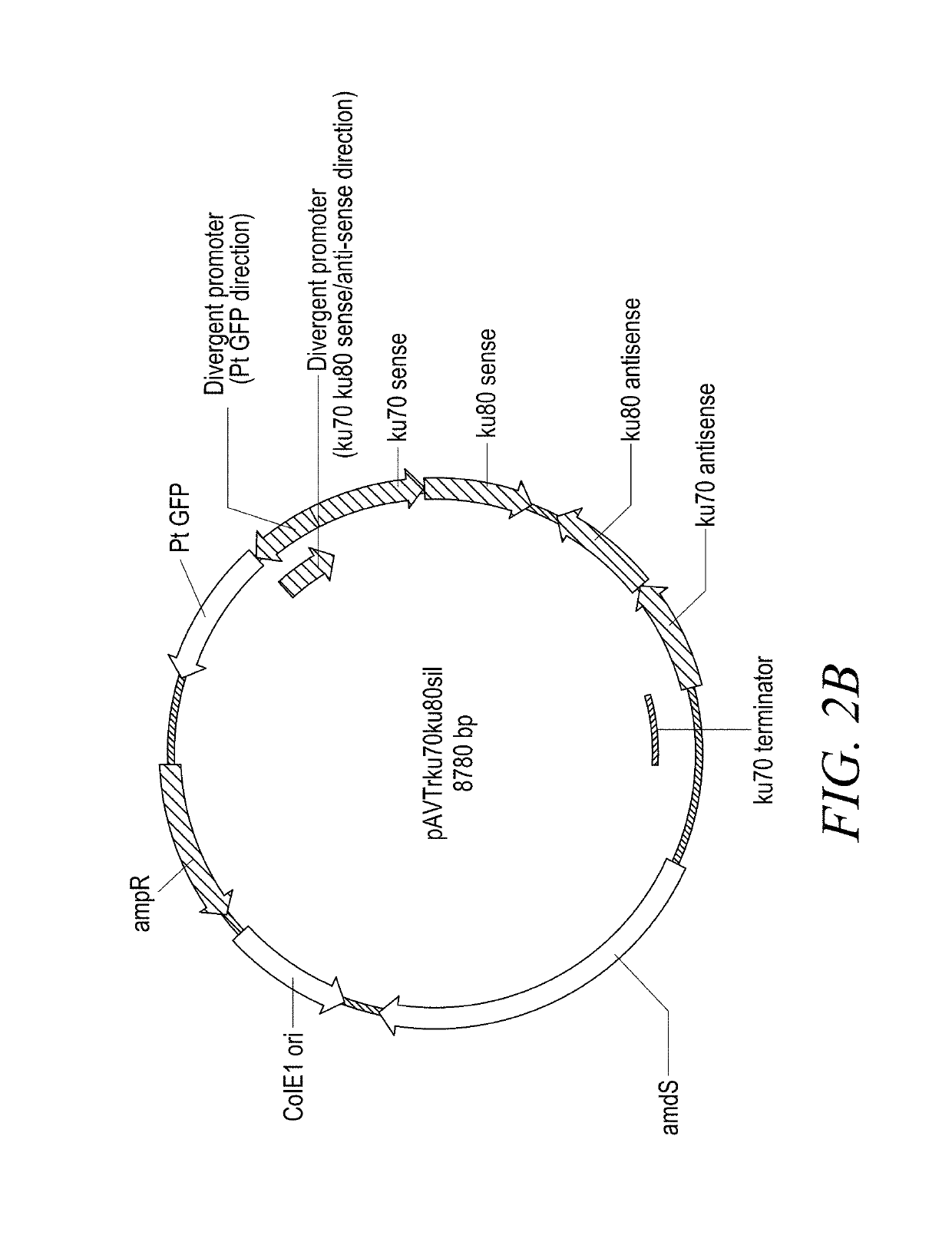
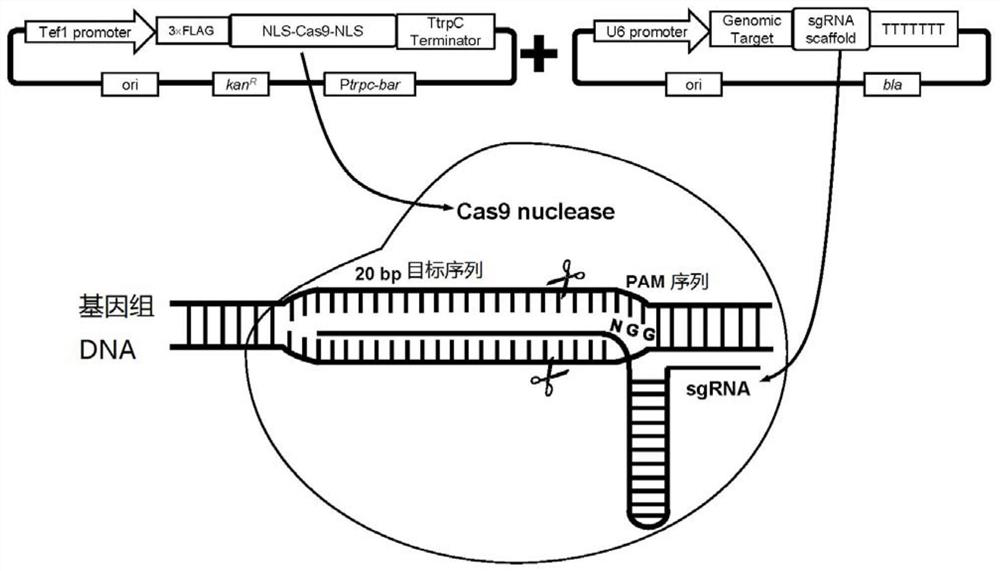
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Fungal genome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fungal Genomics. The Fungal Genomics group at the Broad Institute has sequenced and analyzed a wide diversity of fungal organisms that are important to medicine, agriculture and industry. Over 100 fungi have been sequenced, including human and plant pathogens as well as fungi that serve as basic models for molecular and cellular biology.
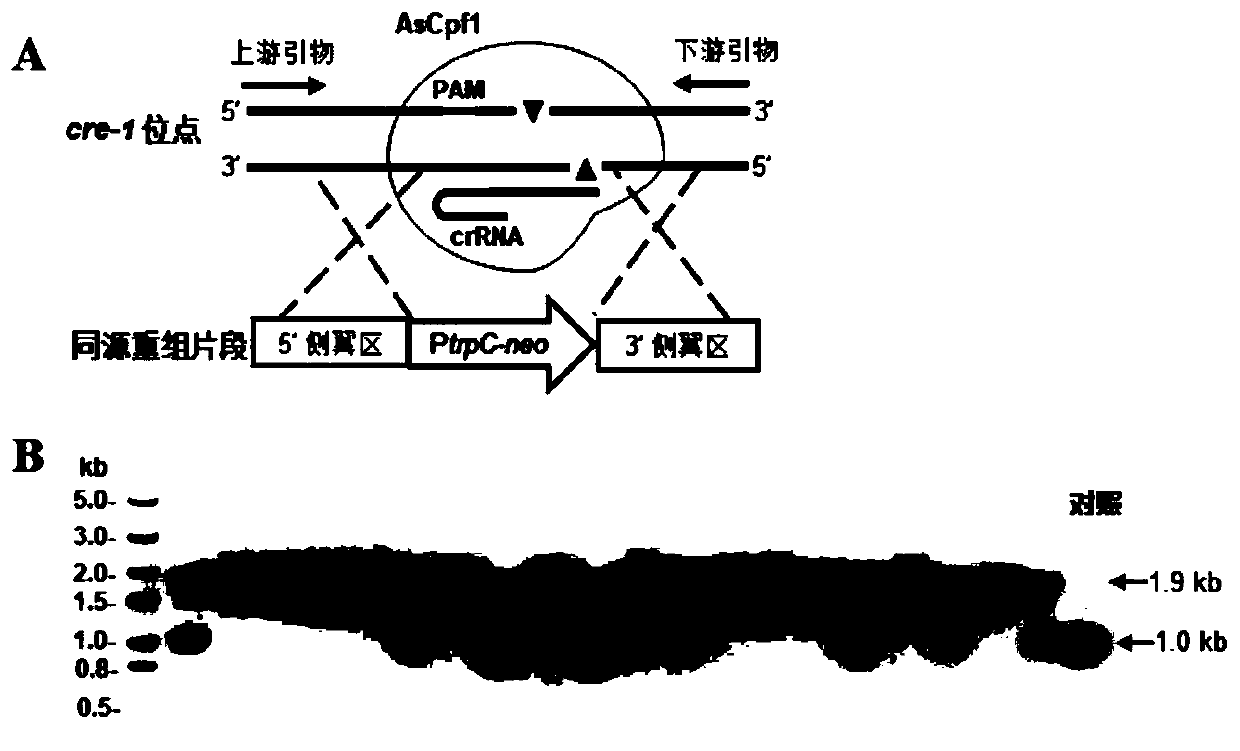
Promoter and expression vector for adjusting and controlling sgRNA transcription, genome editing system and application
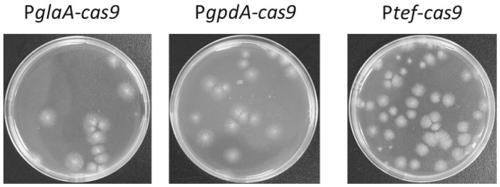
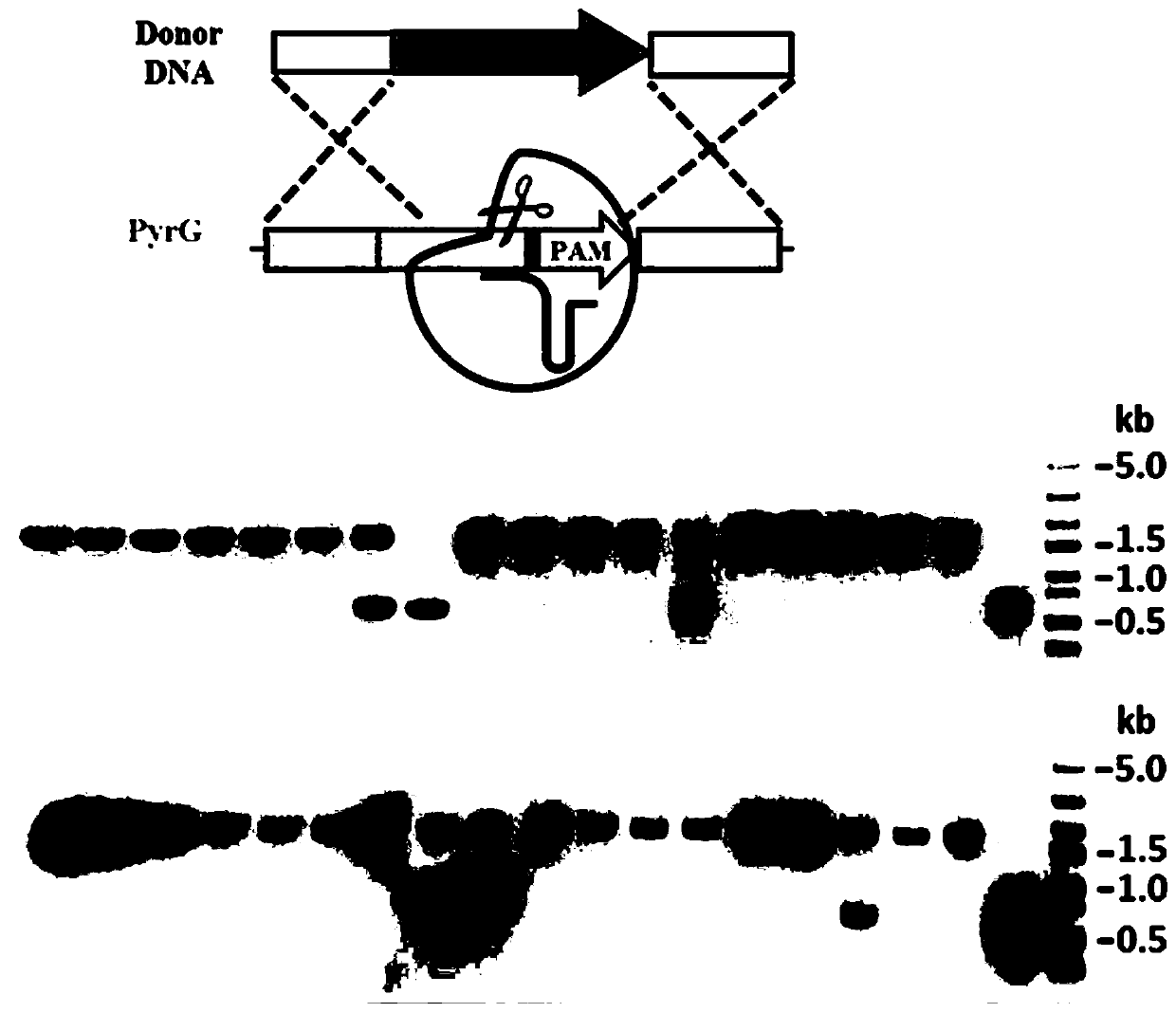
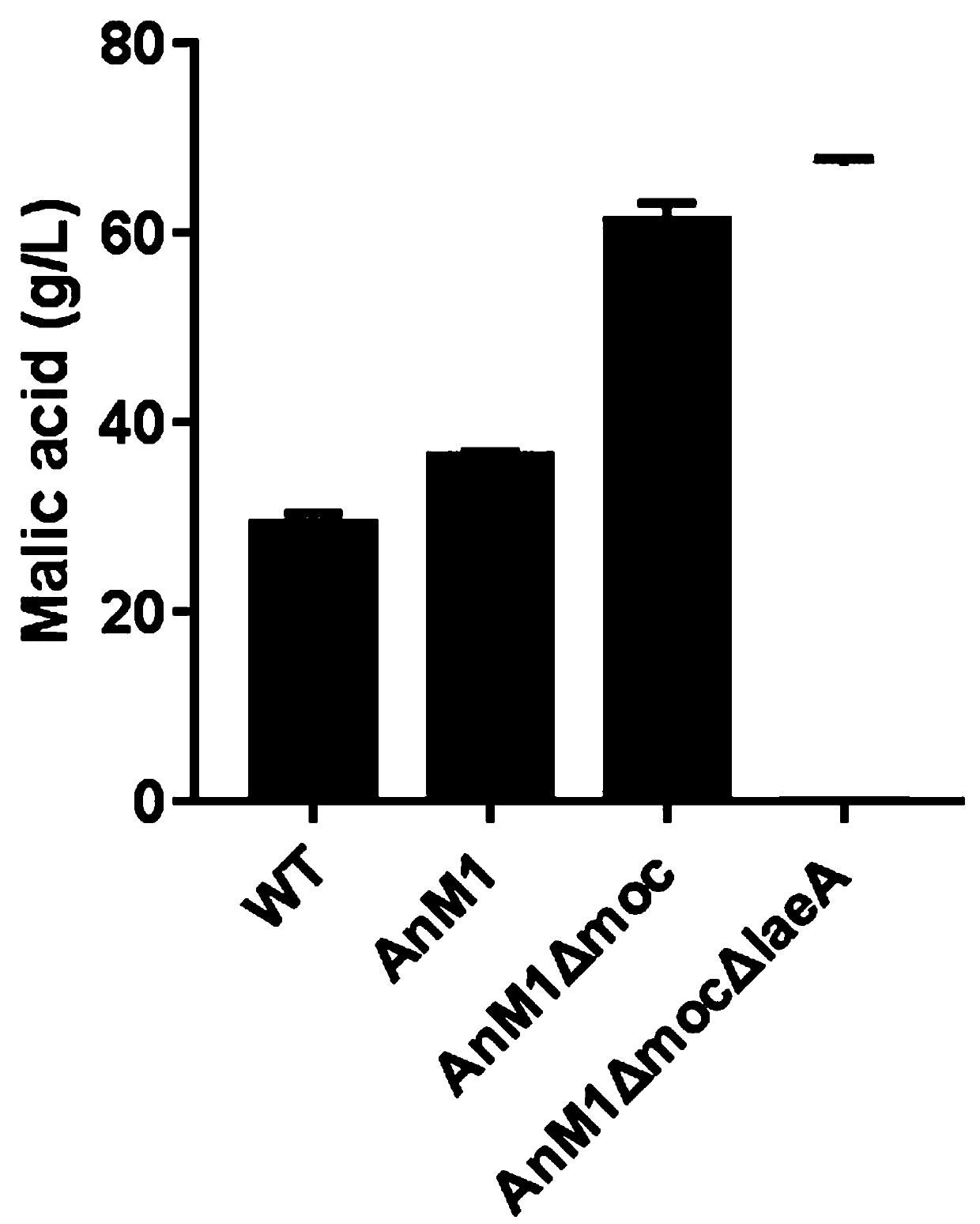
The invention relates to a promoter and expression vector for adjusting and controlling sgRNA transcription, a genome editing system and application. The promoter with the function of adjusting and controlling sgRNA encoding DNA transcription comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the promoter can be used for constructing the expression vector for adjusting and controlling sgRNAencoding DNA transcription and used in the CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing system, and then the genome editing system can be used for significantly improving the editing efficiency of fungal genomes. By utilizing the promoterand expression vector for adjusting and controlling sgRNA transcription, the genome editing system and application, fungi, especially filamentous fungusstrains can be more efficiently transformed, for example, the level of producing malic acid by aspergillusniger is significantly improved, and great application andpromotion value is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for fast extracting AM epiphyte environment DNA in plant rhizosphere soil
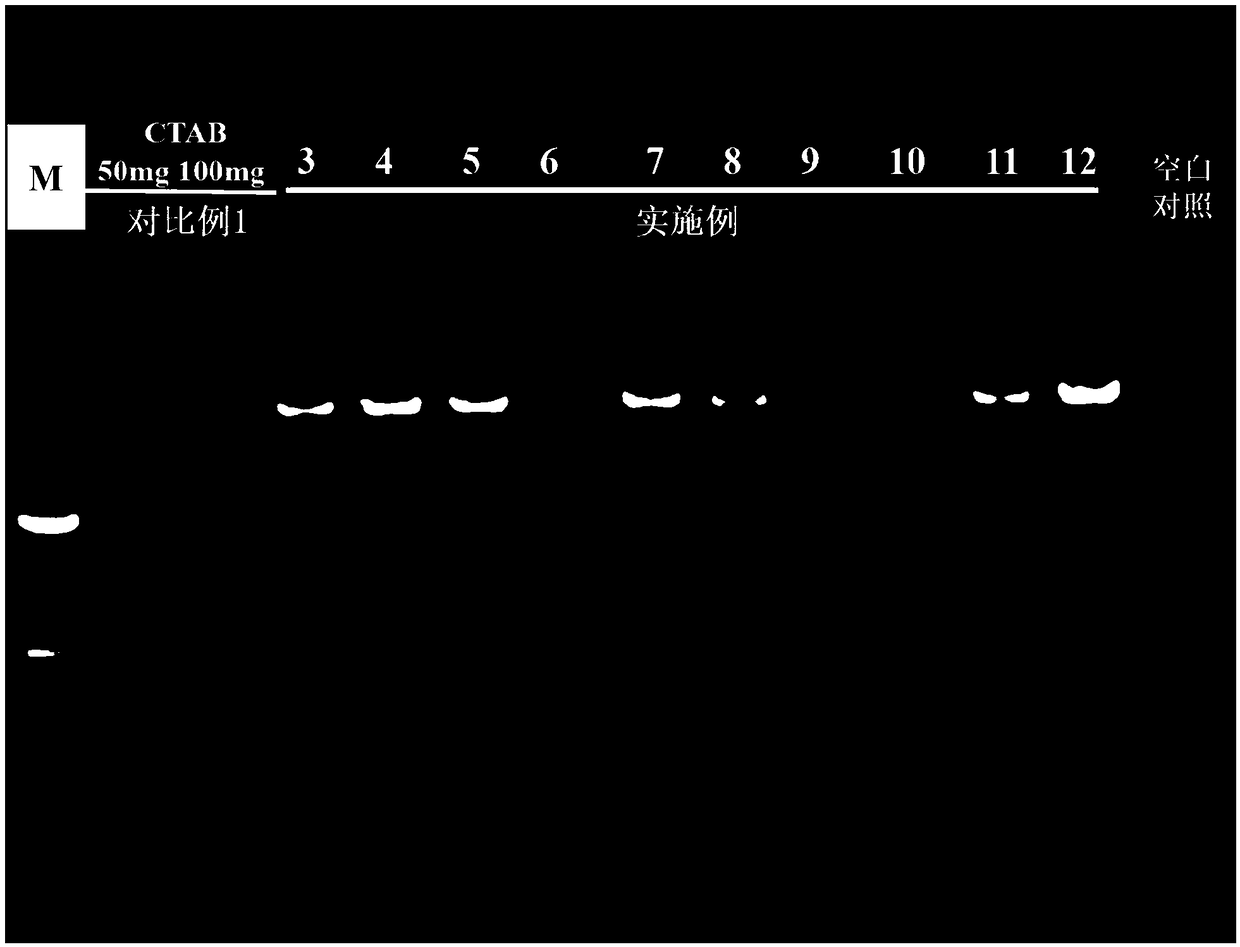
The present invention relates to process of fast extracting AM fungal genome DNA in plant rhizosphere soil environment, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and applied microbiology. The process includes the first wet screening to eliminate great amount of PCR proliferation limiting factors from rhizosphere soil, collecting AM fungal related structures of rhizosphere soil for DNA extraction, mechanically breaking wall and adding CTAB to promote DNA release, and further purifying with Chelex-100 resin. The process is easy, simple and fast, and has great DNA extracting amount, capacity of being concentrated and purified and other advantages. The present invention has excellent application foreground.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
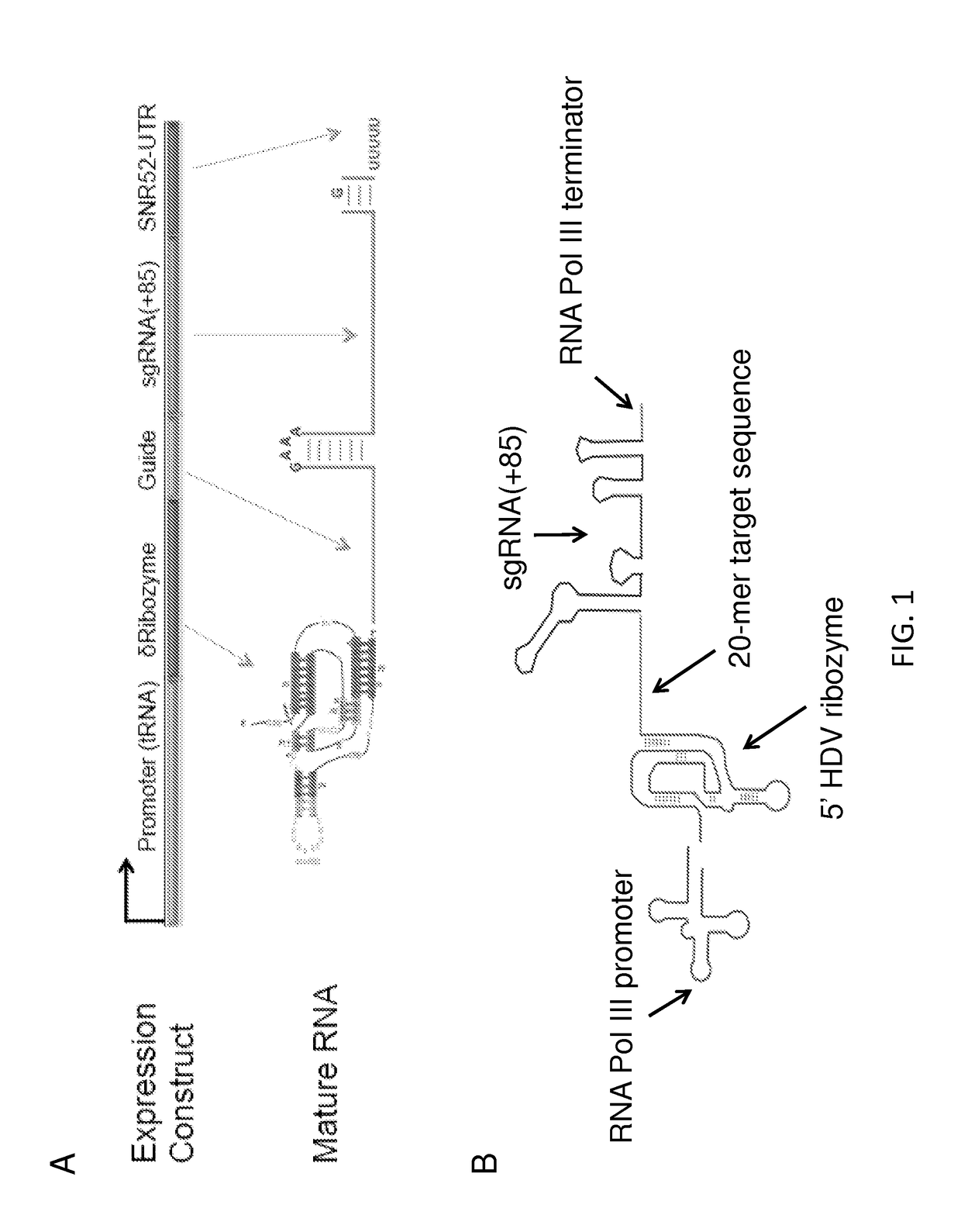
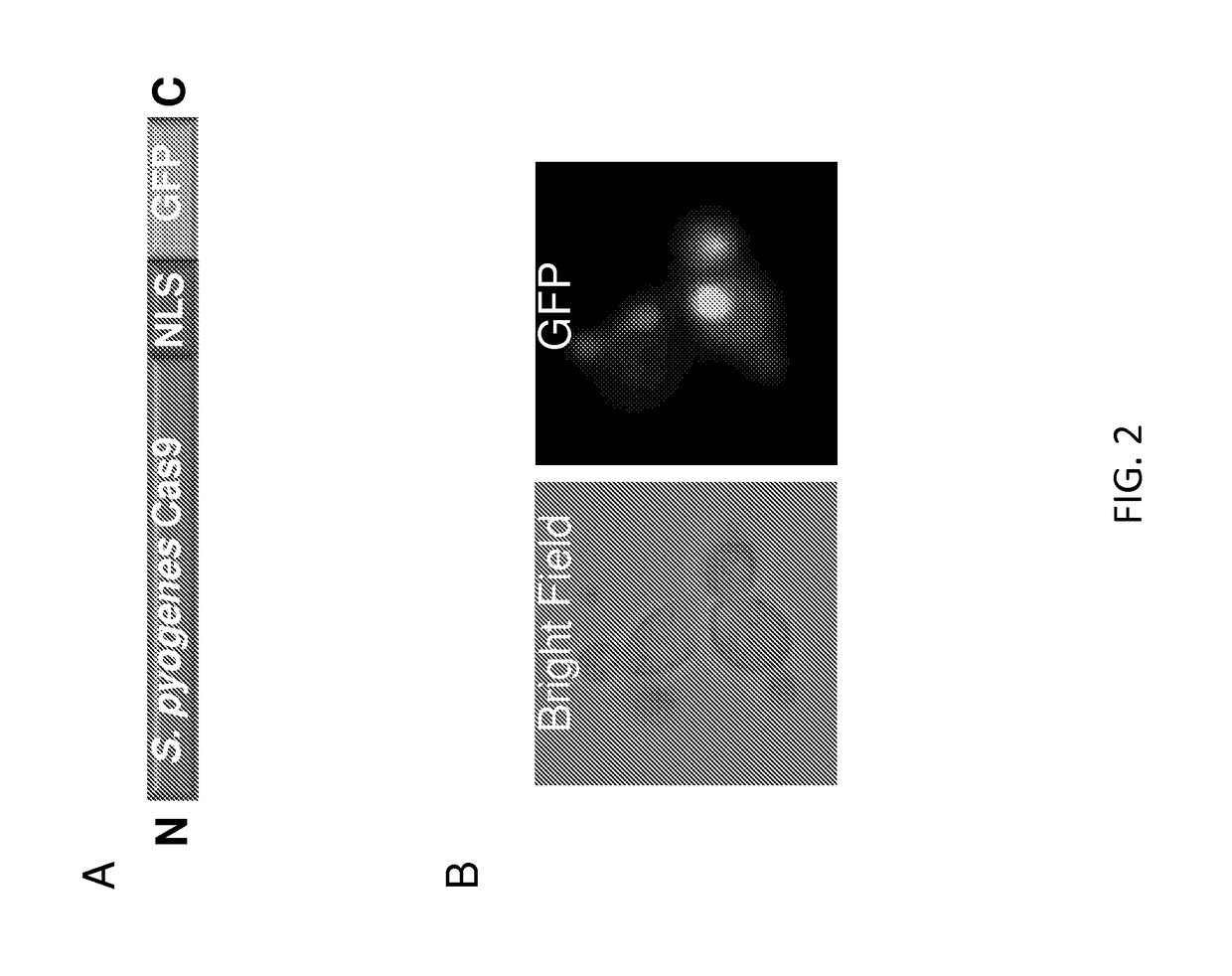
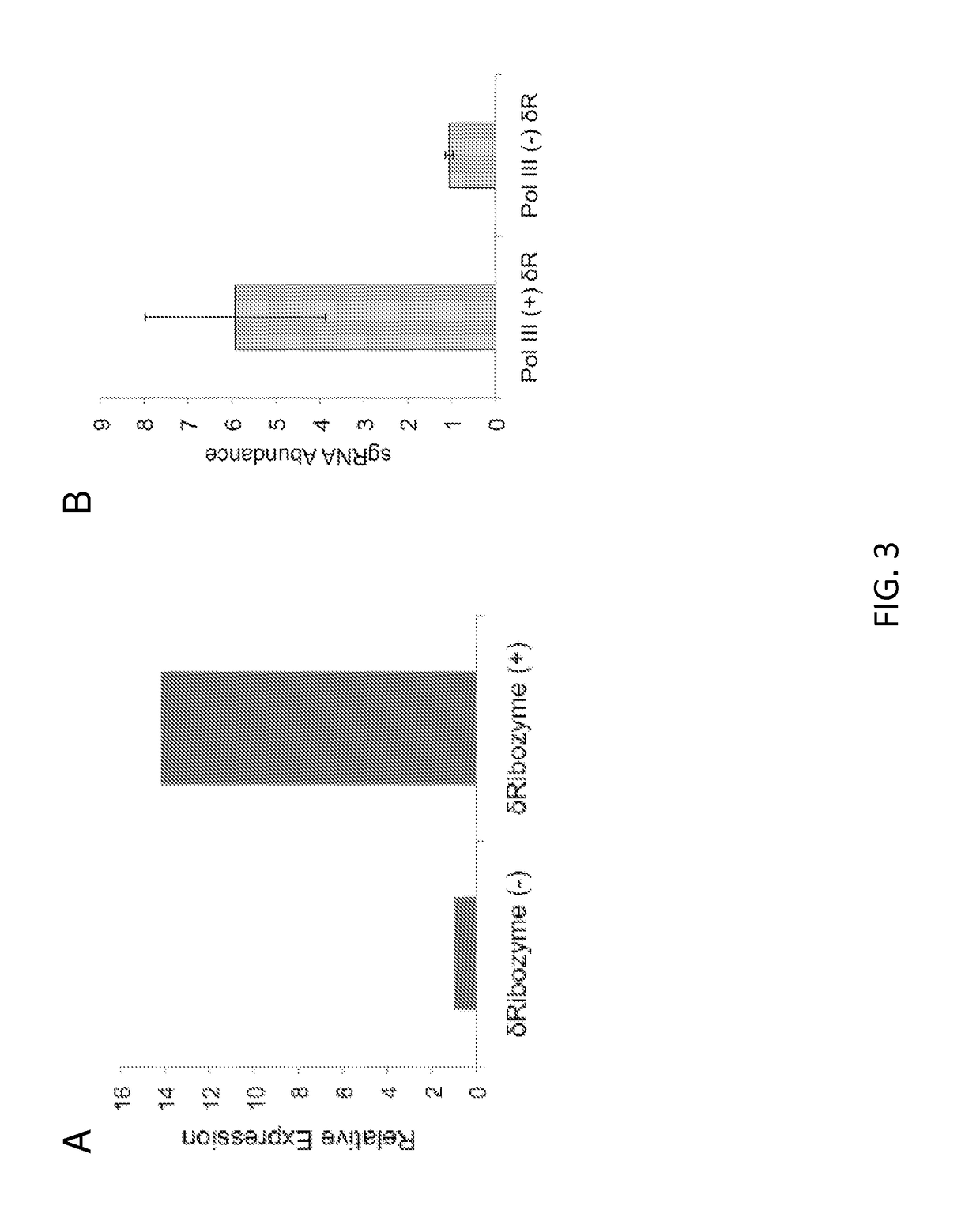
Vectors and methods for fungal genome engineering by crispr-cas9
The present disclosure provides expression vectors containing a nucleic acid encoding an RNA polymerase III promoter, a ribozyme, a CRISPR-Cas9 single guide RNA, and an RNA polymerase III terminator, where the ribozyme is 5′ to the CRISPR-Cas9 single guide RNA, as well as ribonucleic acids encoded thereby. Further provided are fungal cells containing an expression vector described herein, as well as methods of fungal genome engineering through use of an expression vector described herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method for extracting endophytic fungi genomes of wild roses
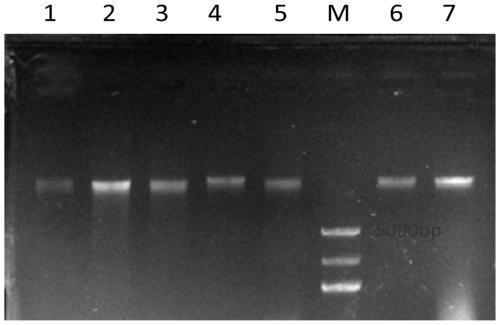
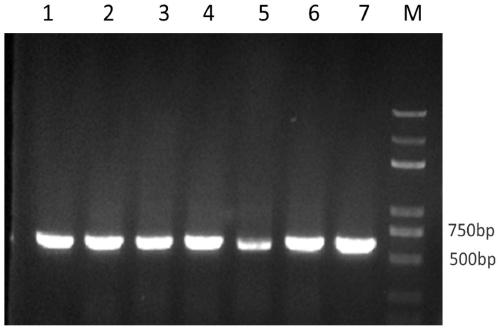
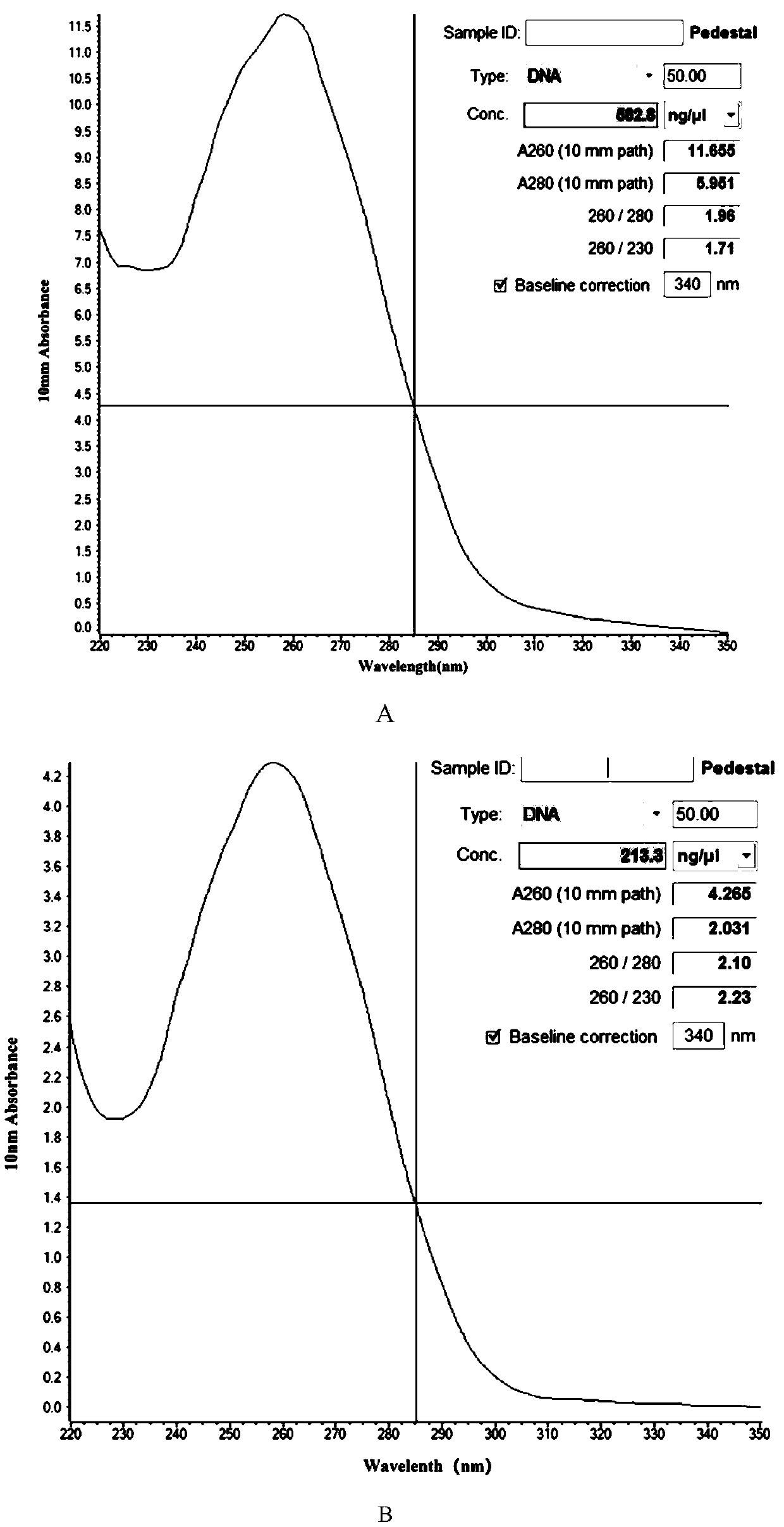
The invention discloses a method for extracting endophytic fungi genomes of wild roses. The method comprises the following steps: disinfecting the surfaces of wild roses and then performing liquid nitrogen treatment, and extracting endophytic fungi genomes by adopting combination of a CTAB mixed solution and a soil microorganism DNA brutal extracting kit. The method is designed aiming at the specificity of wild rose samples, and the adverse influences of quinones substances, phenol substances, polyphenol oxidase contained in wile rose plants, incomplete dilapidated walls, and the like on the extraction efficiency of genomes DNA can be avoided. The method can be applied to extraction of endophytic fungi genomes of all the wild roses, and has the characteristics of being wide in application range and high in extraction rate. The method can achieve a good extraction effect after being applied to extraction of endophytic fungi genomes in Dali purple flowers of wild roses and the endophytic fungi genomes of seven-sister wild roses, and the extracted genomes DNA can be used for various molecules experiments.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for detecting fungal diversity in traditional soybean paste fermentation process
InactiveCN102586453ARich structural diversityThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to a method for detecting fungal diversity in the traditional soybean paste fermentation process. The invention aims to solve the problems that the traditional method for detecting the fungal diversity in the soybean paste fermentation process is high in workload and detection results are inaccurate. The method comprises the following steps of: weighing a soybean paste sample, adding the soybean paste sample into a phosphate buffer solution, suspending, adding glass beads, oscillating, centrifuging, and collecting a supernatant; washing a precipitate, centrifuging, and collecting a supernatant; centrifuging, abandoning a supernatant, washing a precipitate to obtain thalli, adding the phosphate buffer solution into the thalli, blowing and beating until a suspension is obtained, and oscillating to obtain a pretreated sample; extracting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a fungal genome in the pretreated sample; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification to obtain a product A; diluting the product A, and performing PCR amplification to obtain a product B; and loading the product B serving as a sample, and performing electrophoresis by using a denatured gradient gel electrophoresis device to finish the detection. The method is simple, and high in sensitivity, repeatability and reliability, and comprehensively reflects the diversity of flora structures.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Method for knocking out fungus genes
InactiveCN105331628AImprove stabilityAvoiding SCRaMbLE EffectsMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyFungal genome
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and discloses a method for knocking out fungus genes. The method includes: respectively introducing nucleotide sequences identified by Vika recombinase into the upstream and downstream of target genes in fungus genomes; identifying protein with Vika recombinase activity, shearing the nucleotide sequences identified by the Vika recombinase, and knocking out the target genes to obtain fungi with the target genes being knocked out. The method has the advantages that a Vika-vox recombinase system is successfully applied to fungus gene knocking out, knocking out of the target genes is achieved, a new method is provided for fungus gene knocking out, and function researches and performance optimization of fungus genes are benefited.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for breaking wall for filamentous fungus genomic DNA extraction
The invention discloses a method for breaking walls for filamentous fungus genomic DNA extraction. The walls are broken in a multi-step centrifugation and glass rod extrusion mode; the method specifically comprises the following steps in sequence: culturing fungi, collecting the thallus, adding an extraction liquid in multiple steps, freezing, crushing the filamentous thallus, collecting a genomic DNA solution, and precipitating the genomic DNA. According to the method, an ordinary refrigerator of -20 DEG C and a self-made glass rod are adopted, the experimental equipment is easily available, the dependence on liquid nitrogen in the conventional method is reduced, living contaminants in grinding by using a mortar are reduced, the method is convenient to operate, economic and practical, filamentous fungus genomic DNA can be conveniently and rapidly obtained, and thus the method is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
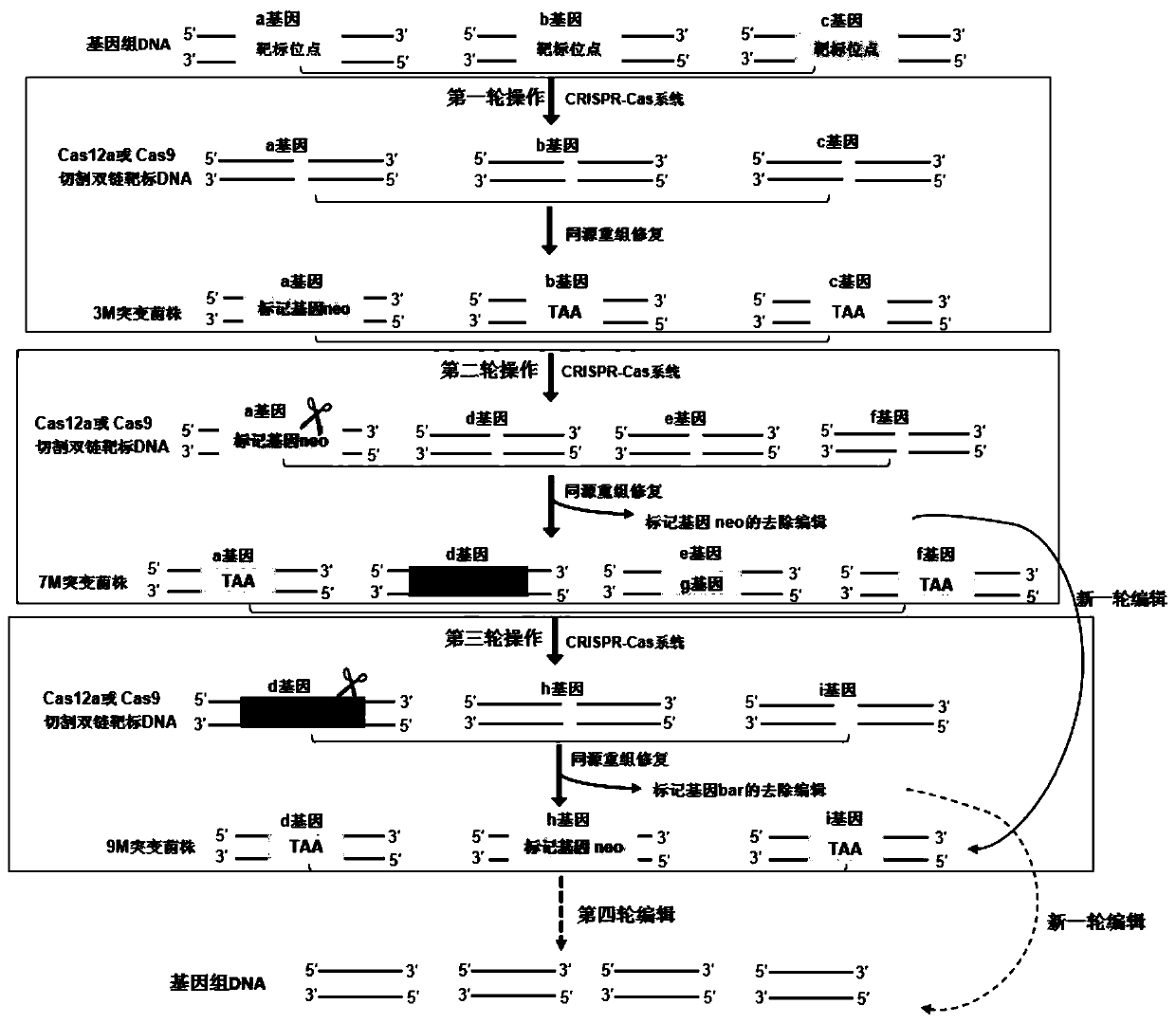
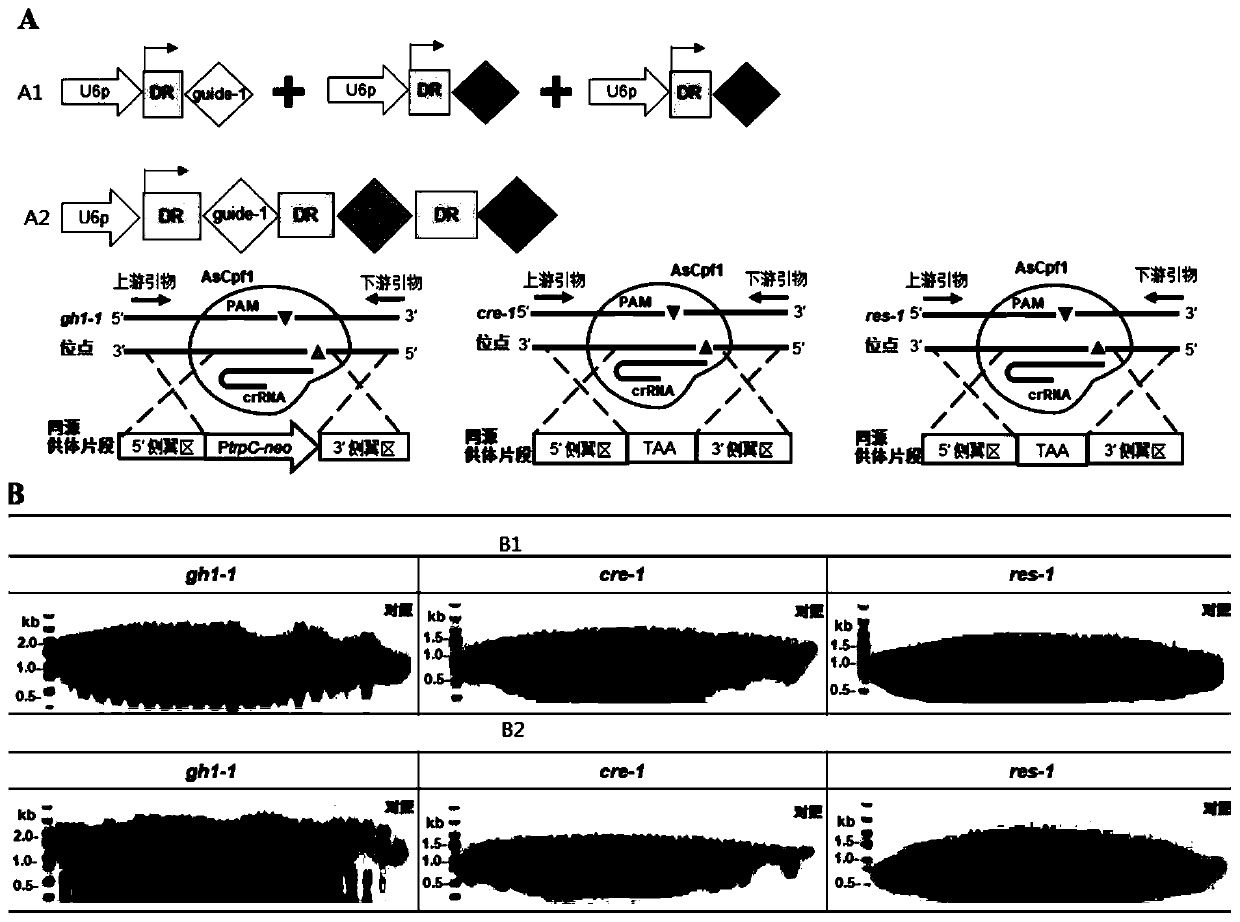
System for multi-round editing of fungal genome by CRISPR system and method thereof
ActiveCN110205334ASolve the problem of not being able to edit multiple timesSolve the bottleneck problem of low editing positive rateHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAFungal genomeGenome editing
The invention discloses a system for multi-round genome editing in fungal cell by a CRISPR system, and a method for multi-round genome editing in fungal cells. The system for multi-round genome editing performs multi-round editing operations on the target fungal genome, wherein the homologous donor DNA in each round of editing operations contains one or more corresponding homologous donor DNA sequences for editing by aiming at different genes, only one donor homologous donor DNA contains a marker gene, and the marker genes of two adjacent rounds are different. The system successfully realizesconvenient, high-efficiency, multi-round (unrestricted) editing of the filamentous fungal genome, and has important significance for genome-directed editing and metabolic engineering of filamentous fungi.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Kit for extracting fungal genome DNA
InactiveCN104975006AQuick extractionSuitable for commercial productionDNA preparationFungal genomeFungal gene
The invention relates to a kit for extracting fungal genome DNA and belongs to the technical field of biology. The kit for extracting the fungal genome DNA comprises the specific steps of crushing fungal cells, dissociating DNA and removing impure proteins, adsorbing DNA by using a DNA adsorbing column, removing impurities and eluting DNA, finally, so as to obtain a liquid which is the fungal genome DNA which is subjected to electrophoresis detection in 1% sepharose gel. The conventional steps for extracting the fungal genome DNA are tedious, consume a long time, and can extract the fungal genome DNA in about 18 hours generally. The method provided by the invention, compared with the conventional fungal genome extraction method, only needs about 7 hours to extract the fungal genome DNA, so that a lot of extraction time is saved, and the fungal genome DNA can be extracted more effectively, quickly and economically. Meanwhile, the kit is suitable for commercial production and has a certain economic value.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Molecular detection method of tea white scab leaves
PendingCN106591454ATimely and accurate preventionEffectively improve quality and efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMolecular identificationFungal genome
Owner:湖南省茶叶研究所
Method for extracting fungal genome on surface of aged tobacco
PendingCN106148329AFully lysedImprove extraction efficiencyDNA preparationFungal genomeGradient centrifugation
The invention relates a method for extracting a fungal genome on the surface of aged tobacco. The method includes the two main steps of aged tobacco surface fungus enrichment and genome DNA extraction. Fungi are enriched through buffering solution soaking and gradient centrifugation, grinding and cell disruption are conducted by means of liquid nitrogen, and the DNA of the genome of fungi is extracted by means of a kit shown in the description. By means of liquid nitrogen grinding, fungal cell walls can be fully split, extraction efficiency of the DNA of the fungi is improved, the DNA isolation kit in the description includes the innovation patent inhibitor removal technology, and the yield of the genome can be effectively increased. The method can be used for efficiently and quickly extracting the DNA of the fungal genome on the surface of aged tobacco.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
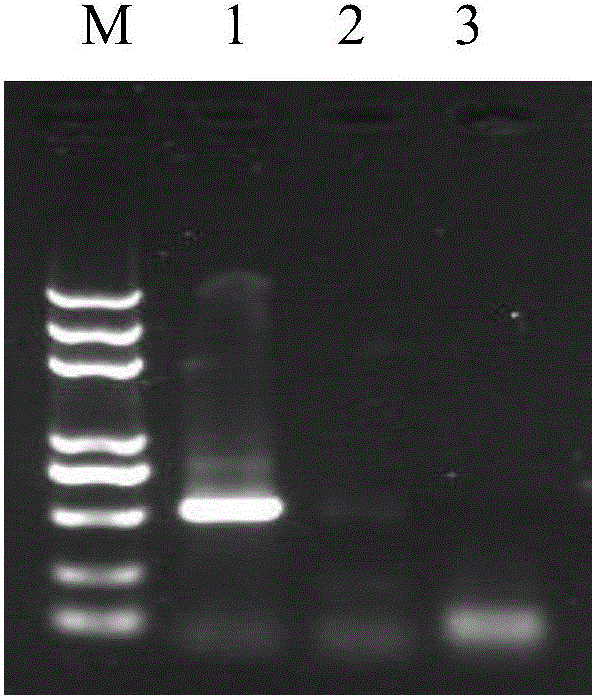
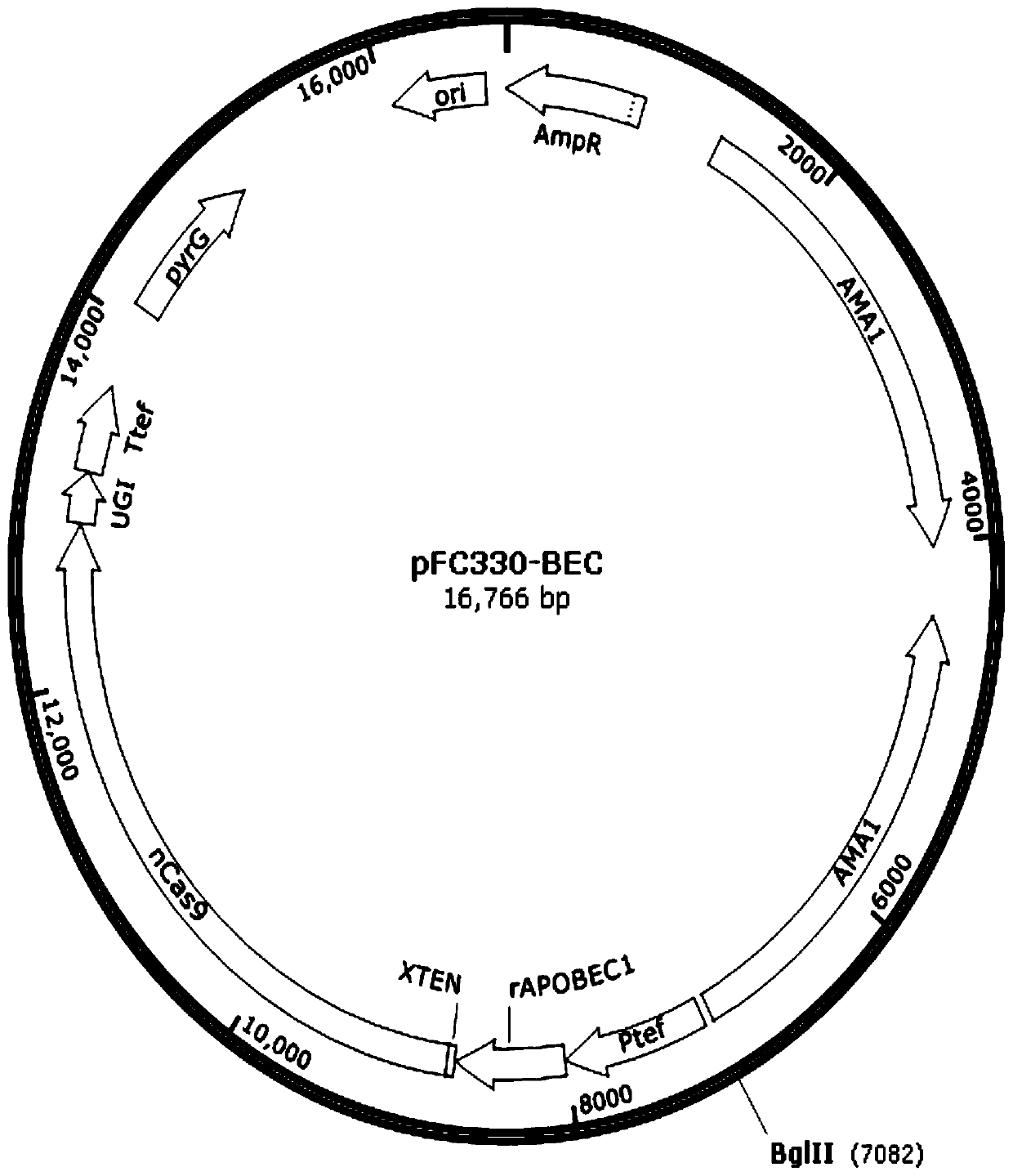
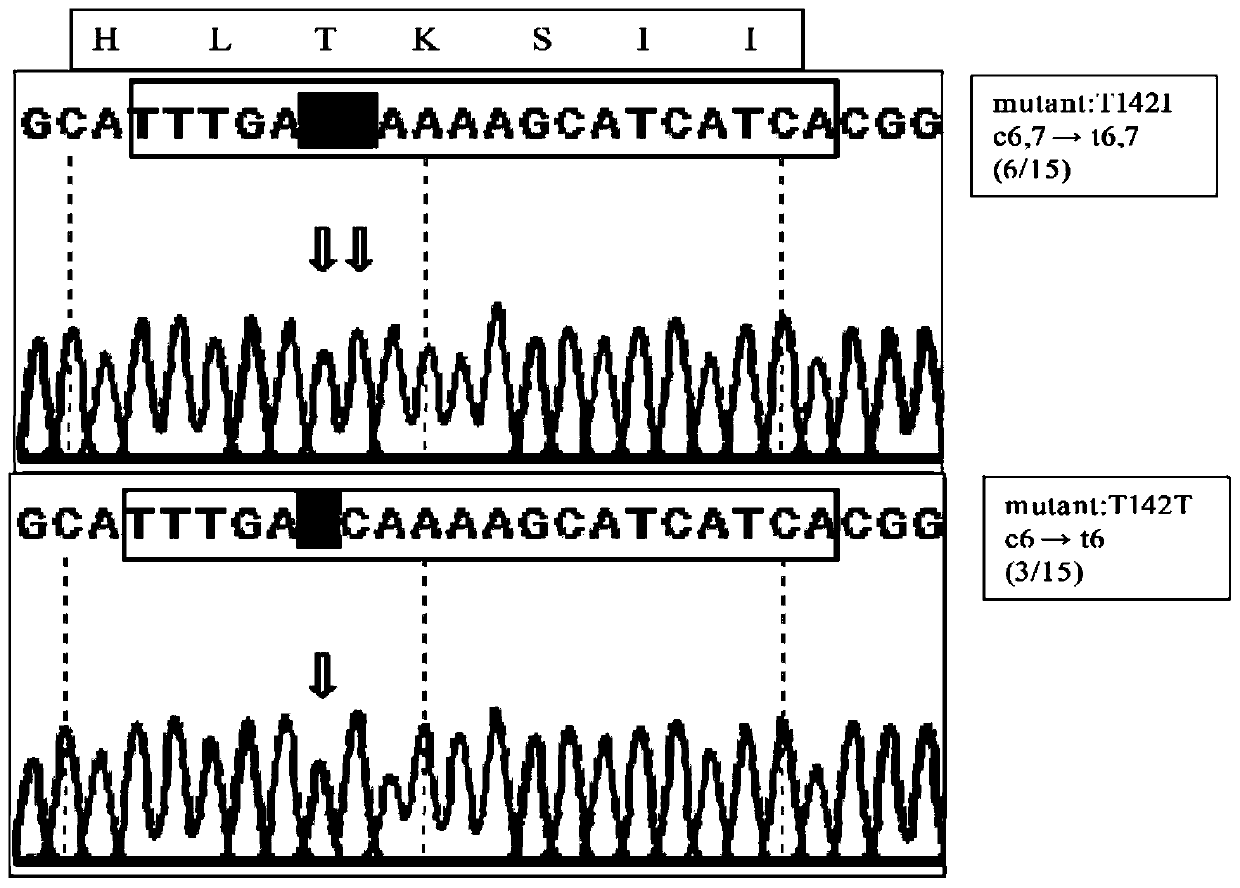
pFC330-BEC plasmid capable of achieving base precise point mutation and application thereof
The invention discloses a pFC330-BEC plasmid capable of achieving base precise point mutation and an application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the pFC330-BEC plasmid is shown as SEQ ID NO: 3, which comprises a rAPOBEC1-XTEN-nCas9-UGI fusion gene fragment that can be expressed in aspergillus niger, an escherichia coli resistance gene fragment AmpR, a pyrG selection marker, a filamentous fungusautonomously replicating sequence AMA1, a promoter Ptef, and a plasmid replication origin ori. The plasmid can efficiently and rapidly mutate cytosine at any position on a filamentous fungal genome into thymine, and can achieve mutation of amino acid or inactivation of a gene. The plasmid has broad application prospects in molecular breeding, physiological characteristics, metabolites, host transformation and industrial production of filamentous fungi, and can provide a new technical platform for genetic engineering modification of the filamentous fungi.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for rapidly extracting fungal genome DNA
InactiveCN104946622AQuality improvementShorten the timeDNA preparationSodium acetateBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly extracting fungal genome DNA. The method comprises the following steps: adding lysate into hyphae or sporocarp which is grinded with liquid nitrogen, adding PCA, and centrifuging; adding 3M of sodium acetate into the upper-layer water phase, further adding precooled absolute ethyl alcohol, and leaving to stand for 5-10 minutes at -20 DEG C; centrifuging, abandoning the supernate, bleaching and precipitating with 75% alcohol, centrifuging, and abandoning the supernate; adding ddH2O and RNase to dissolve the components, and preserving at -20 DEG C. Compared with other methods, the method for rapidly extracting fungal genome DNA is simple to operate, high in feasibility, small in DNA extraction material, high in DNA extraction efficiency, good in integrity and stability, relatively low in impurity content, and can be directly applied to further research such as ITS sequencing. DNA of sporocarp can be also extracted, so that the hypha activation and culture time can be shortened, and an efficient and feasible molecular technical method for macro fungus molecular biological research is provided.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
PCR primer and quantitative detection method for rapidly detecting strawberry colletotrichum gloeosporioides
InactiveCN111893208ARapid implementation of identification workHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyFragaria
The invention relates to a PCR primer and quantitative detection method for rapidly detecting strawberry colletotrichum gloeosporioides. The PCR primer is designed according to a cutinase gene consensus sequence of colletotrichum gloeosporioides physiological races and comprises two primers Cfcut1 and Cfcut2 and an amplification product 115bp; by utilizing the PCR primer and the quantitative detection method, fungal genome DNA or field sample DNA can be subjected to PCR detection without separation and culture of pathogenic bacteria, the amplification efficiency is high, the specificity is good, the amplification efficiency of the primer is 99.47%, and colletotrichum gloeosporioides compound species causing strawberry anthracnose can be rapidly detected and identified; and through real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR, absolute quantitative detection can be carried out on the biomass of the colletotrichum gloeosporioides in a sample, the occurrence period and the prevalence intensityof the anthracnose are predicted timely and accurately, the anthracnose is prevented and treated and even avoided, negative influences caused by use of pesticide can be reduced, and a basis is provided for comprehensive prevention and treatment of the anthracnose.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
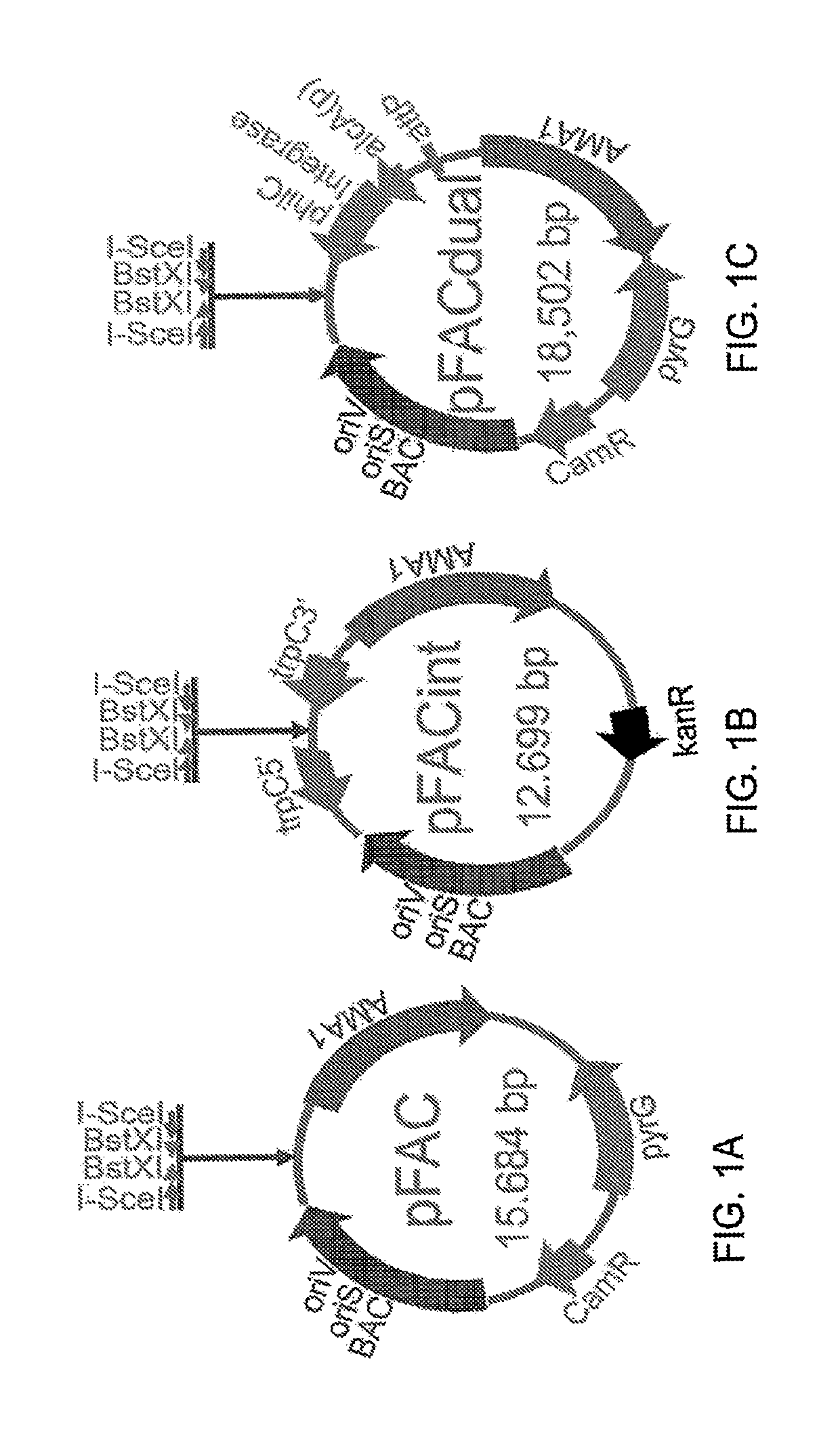
Fungal artificial chromosomes, compositions, methods and uses therfor
ActiveUS20170211077A1Reduced expression levelAlter protein structureMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorOrigin of replicationBiotechnology
Fungal artificial chromosome (FAC) vectors are disclosed. A vector can be replicated in a bacterial or a fungal host, and can comprise an insert of heterologous DNA up to about 500 kilobases. A vector can be used for cloning and expressing a secondary metabolite (SM) gene cluster. An insert sequence can be modified by homologous recombination. A vector can be a plasmid comprising bacterial and fungal origins of replication, as well as bacterial and fungal selection marker genes. Also disclosed are vectors that can be integrated into a fungal genome, and dual function vectors which can be replicated in a bacterial or a fungal host and can also be integrated into a fungal genome. Also disclosed are methods of generating plasmid libraries including vectors comprising intact SM gene clusters.
Owner:INTACT GENOMICS INC
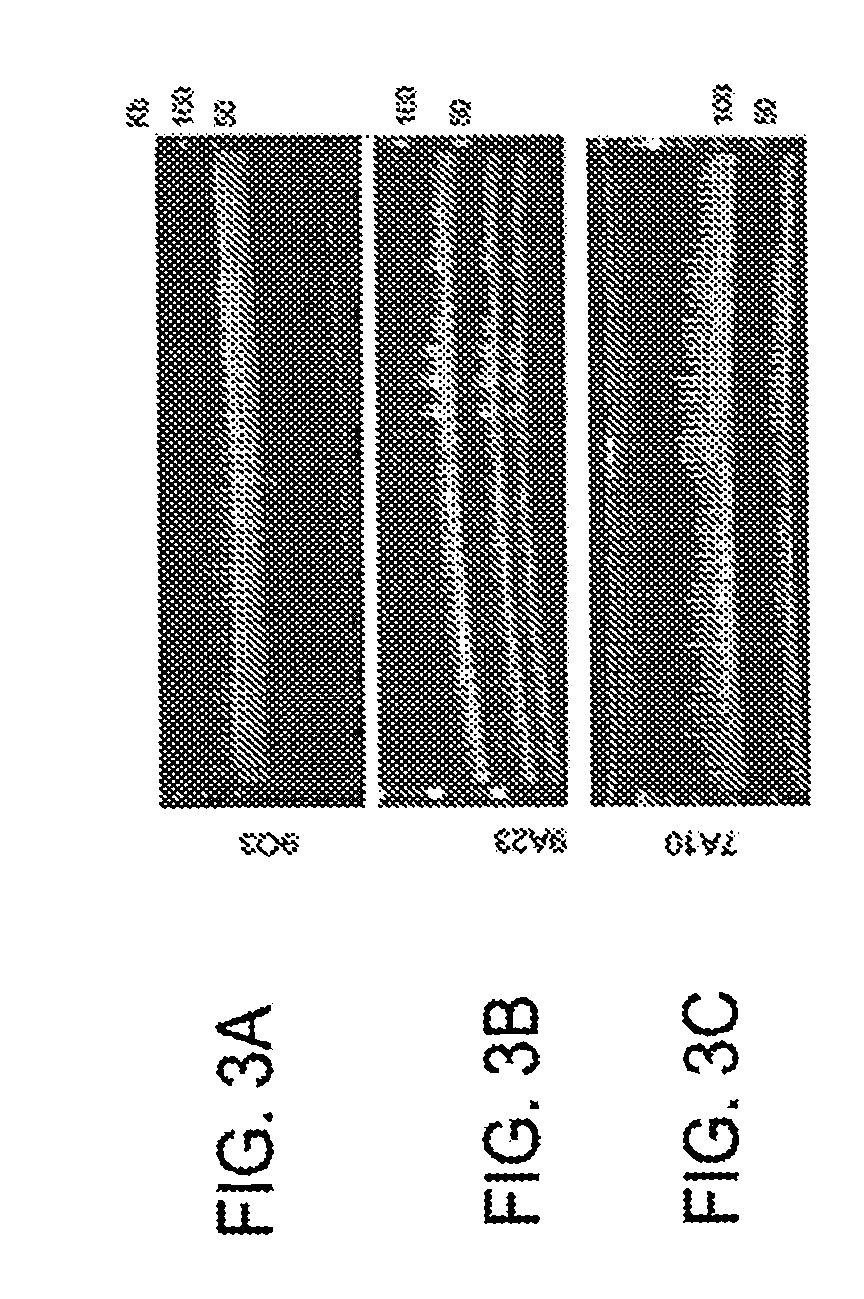
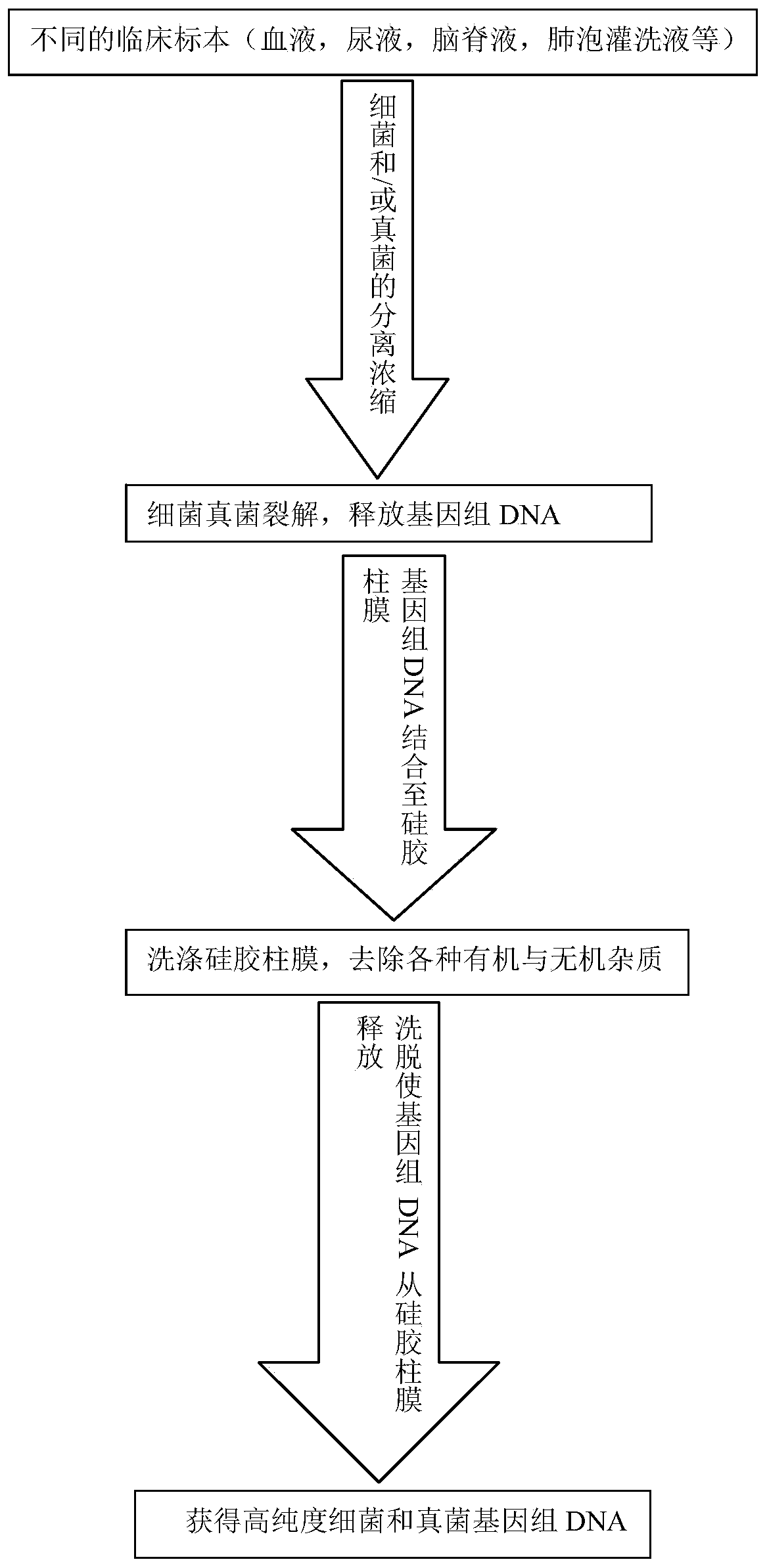
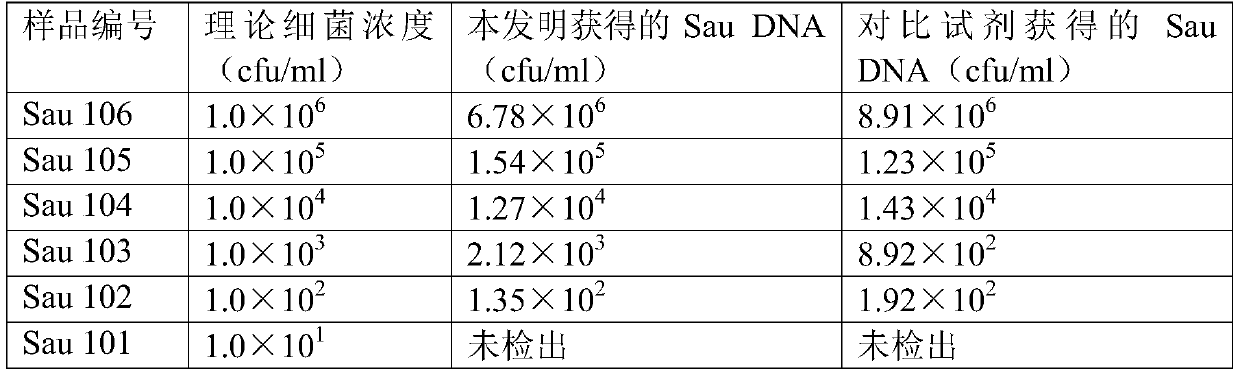
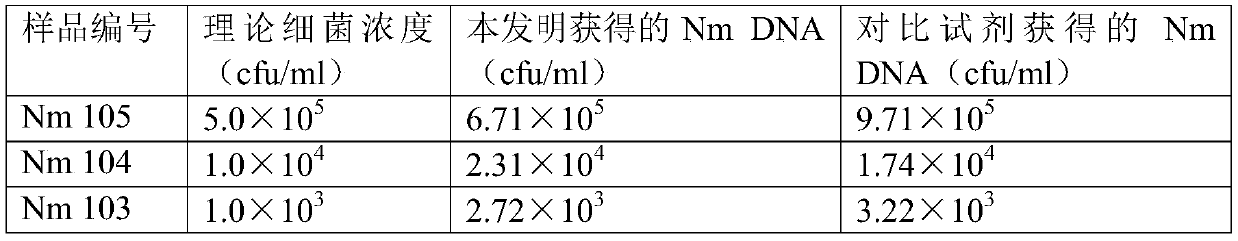
Genomic DNA extraction method suitable for bacteria and/or fungi
InactiveCN110804611AExtraction does not affectReduce the possibility of errorMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenomic DNA
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a genomic DNA extraction method suitable for bacteria and / or fungi. The method comprises the following steps: removing a liquid part in a clinical specimen to obtain a concentrate of fungi and / or bacteria; in the obtained concentrate, adding an appropriate amount of lysozyme, lywallzyme and glass beads, performing mixing, and performing lysis on cellwalls of fungal and / or bacterial cells contained in the concentrate to obtain a cell fluid; and denaturing and degrading protein components in the cell fluid to release genomic DNA to obtain a mixed solution. The method is applicable to both the bacteria and the fungi, the lywallzyme added for lysing the fungal cell walls does not affect the extraction of the bacterial genomic DNA, and the lywallzyme added for lysing the bacterial cell walls does not affect the extraction of the fungus genomic DNA; and when a laboratory technician needs to extract genomic DNA from a strain in the clinical sample, the laboratory technician does not need to distinguish whether the strain is bacteria or fungi.
Owner:BEIJING BEIER BIOENG
A method for extracting the genome of wild rose endophytic fungi
The invention discloses a method for extracting endophytic fungi genomes of wild roses. The method comprises the following steps: disinfecting the surfaces of wild roses and then performing liquid nitrogen treatment, and extracting endophytic fungi genomes by adopting combination of a CTAB mixed solution and a soil microorganism DNA brutal extracting kit. The method is designed aiming at the specificity of wild rose samples, and the adverse influences of quinones substances, phenol substances, polyphenol oxidase contained in wile rose plants, incomplete dilapidated walls, and the like on the extraction efficiency of genomes DNA can be avoided. The method can be applied to extraction of endophytic fungi genomes of all the wild roses, and has the characteristics of being wide in application range and high in extraction rate. The method can achieve a good extraction effect after being applied to extraction of endophytic fungi genomes in Dali purple flowers of wild roses and the endophytic fungi genomes of seven-sister wild roses, and the extracted genomes DNA can be used for various molecules experiments.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of thermomyces PCR template
InactiveCN108642136AReduce incubation timeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFungal genomeTE buffer
The invention provides a preparation method of a thermomyces PCR template. The method comprises the following steps that 1, hyphae of thermomyces is suspended in a TE buffer solution, and a thallus suspension is obtained; 2, the thallus suspension is heated under the temperature of 90 DEG C or above for at least 10 min, and an obtained cracked thallus suspension is adopted as the PCR template. Themethod for obtaining a thermomyces genome can be used for PCR identification of thermomyces genetic converters, the method adopts a small number of thalli, the cultivation time of the converters canbe shortened, converter detection can be performed at the early cultivation period, operation is easy, convenient and rapid, time and labor are saved, the method is economical, free of toxin and environmentally friendly, the follow-up PCR sensitivity is high, specificity is high, it becomes possible that converters can be screened out in a large-scale and high-throughput mode, and the method for rapidly identifying the thermomyces converter has important scientific significance and value.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for fast extracting AM epiphyte environment DNA in plant rhizosphere soil
The present invention relates to process of fast extracting AM fungal genome DNA in plant rhizosphere soil environment, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and applied microbiology. The process includes the first wet screening to eliminate great amount of PCR proliferation limiting factors from rhizosphere soil, collecting AM fungal related structures of rhizosphere soil for DNA extraction, mechanically breaking wall and adding CTAB to promote DNA release, and further purifying with Chelex-100 resin. The process is easy, simple and fast, and has great DNA extracting amount, capacityof being concentrated and purified and other advantages. The present invention has excellent application foreground.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Reagent and method capable of simply and effectively extracting plant pathogenic fungus genomic DNA
ActiveCN110205319AEasy extractionEfficient extractionDNA preparationGenomic sequencingBiological studies
The invention discloses a reagent and method capable of simply and effectively extracting plant pathogenic fungus genomic DNA. The extracting reagent comprises a solution A and a solution B, wherein the solution A comprises 200mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 250mM NaCl, 25mM EDTA, 0.5wt% of SDS, 1wt% of beta-mercaptoethanol, and 8 microliter of RNA enzyme; the solution B is potassium acetate with the concentration being 5M. When the reagent is used for extraction, high-purity and good-stability genomes can be extracted fast and effectively, the extracted genomes can be directly used for gene cloning andgenome sequencing, and an efficient and feasible molecular detection approach is provided for pathogenic fungus molecular biology study.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
A method for breaking the wall of filamentous fungal genome dna extraction
A wall-breaking method for extracting filamentous fungal genome DNA, which uses multi-step centrifugation and glass rod extrusion to break the wall, and specifically cultures the fungus in sequence, collects the bacteria, adds the extract in multiple steps, freezes, and breaks the filamentous bacteria. A method for collecting genomic DNA solution and precipitating genomic DNA. This method uses a -20°C ordinary refrigerator and self-made glass rods, and the experimental equipment is easy to obtain, which reduces the dependence on liquid nitrogen in the traditional method and the contamination of bacteria during mortar grinding. The filamentous fungus genome DNA can be obtained conveniently and quickly, and can be popularized and used.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Methods for in vivo diversification of single genes
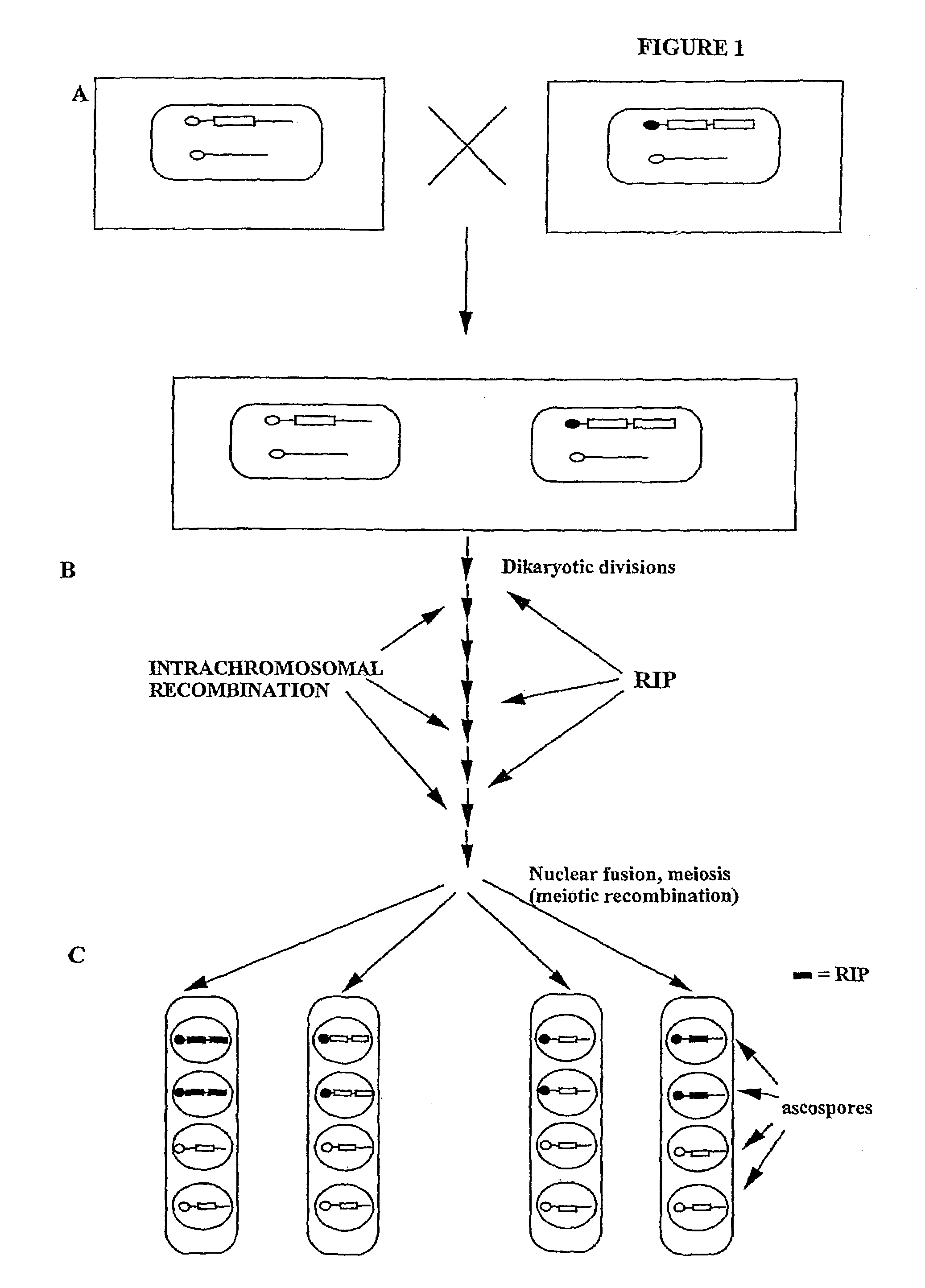
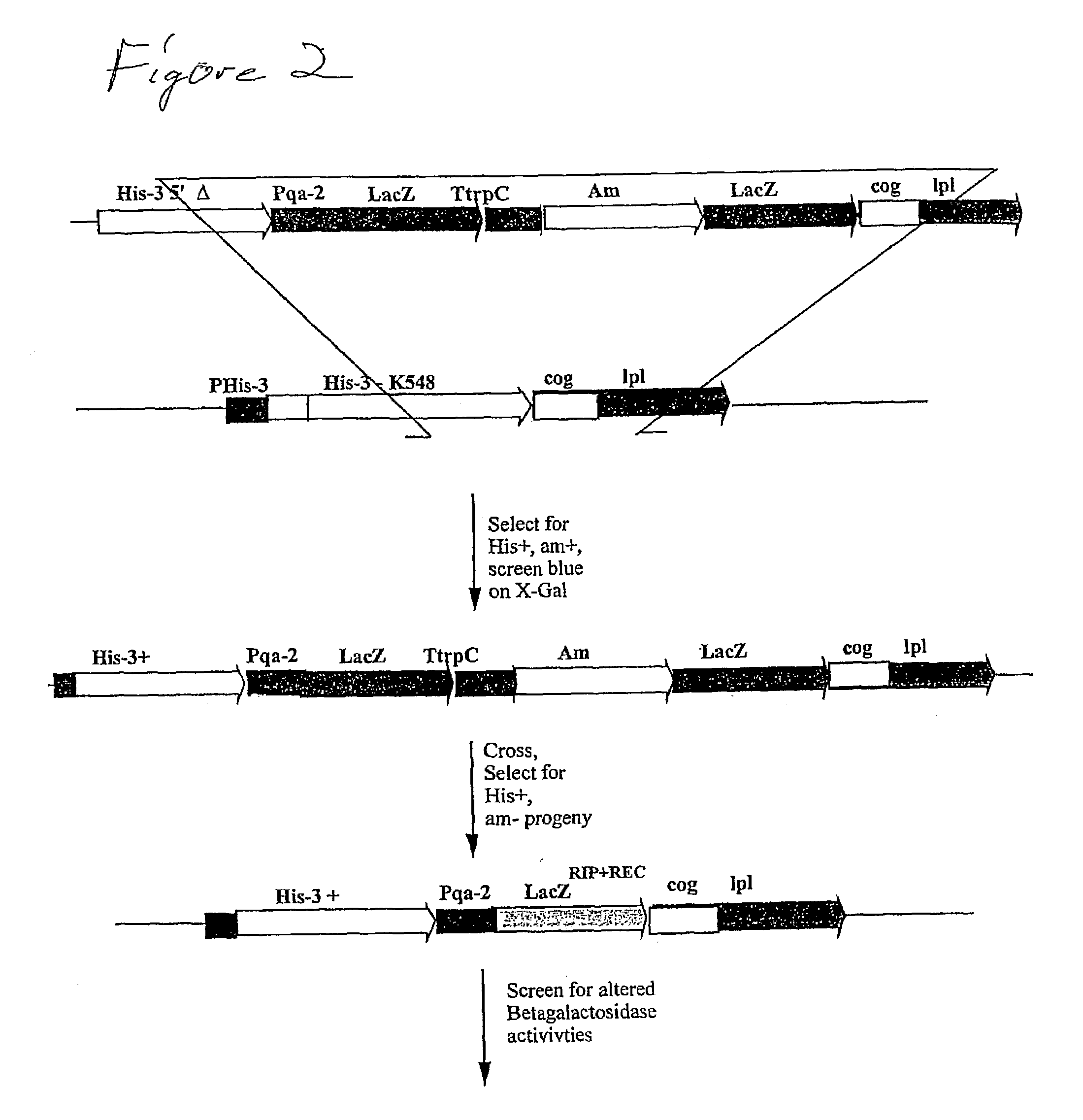
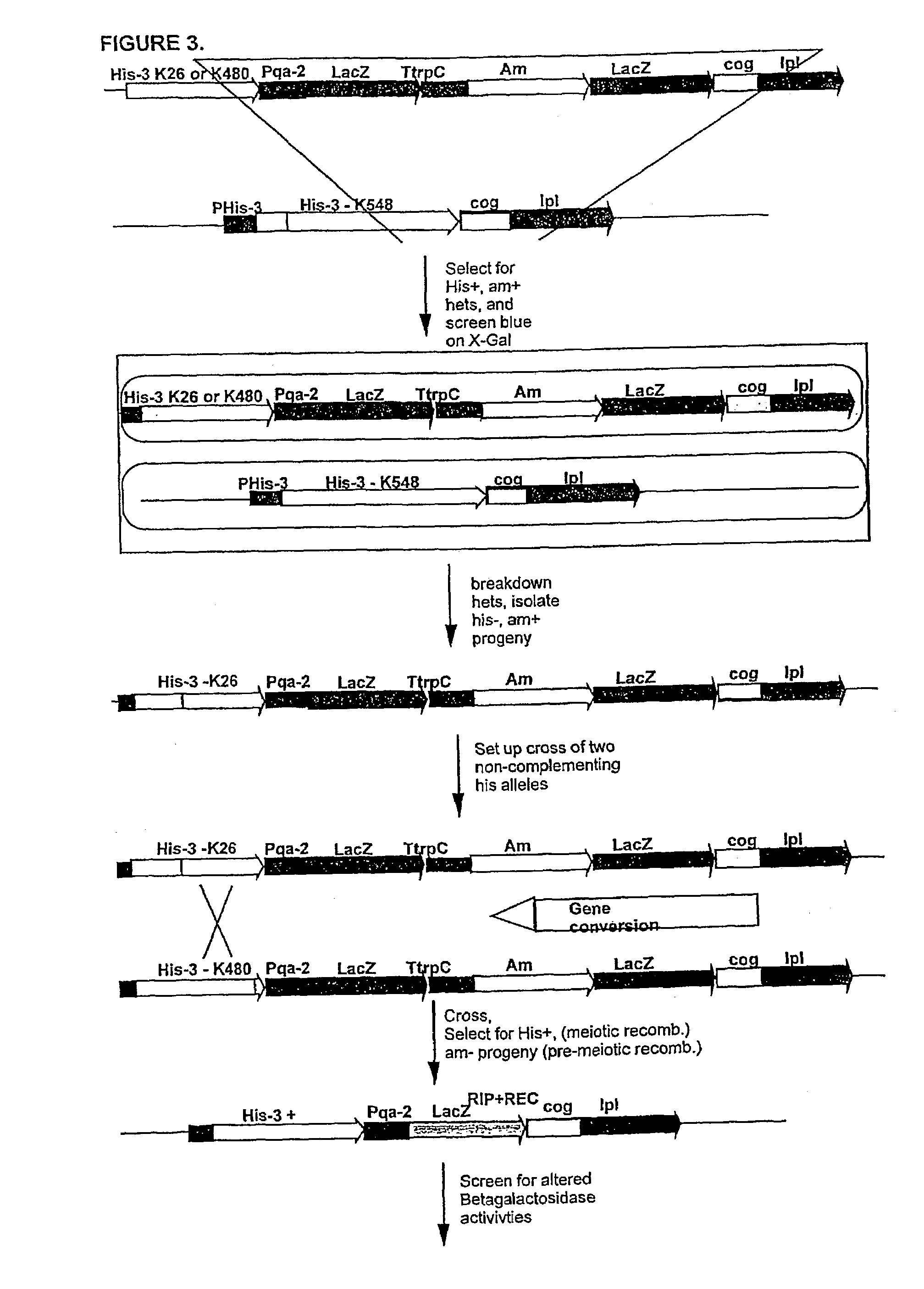
Methods and compositions are provided for the efficient in vivo diversification of gene-products in filamentous fungi, starting from (but not limited to) two or more copies of a single gene constituent. The diversification involve use of the Repeat-Induced Point mutation (RIP) process in N. crassa, and other fungi that have analogous mutational processes. The invention takes advantage of the induction of G:C to A:T transition mutations specific to duplicated DNA sequences during the premeiotic dikaryon phase of the life cycle of the fungus. The methods and compositions of the invention can be utilized to generate diversity in target genes, and are proposed for the purpose of altering and generating novel forms and activities of gene-products thus encoded. Duplicated genes may be introduced into the organism and are present either in tandem, or at separate ectopic locations within the genome of the fungus. After crossing the resulting transformant(s), sexual progeny can then be selected which contain the mutated gene, and subsequently screened for a desired product.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
A genome editing vector, its composed genome editing system and application
ActiveCN108148853BRealize simultaneous editingIncrease production capacityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesGenes mutationFungal gene
The present invention relates to a genome editing carrier, its composed genome editing system and its application, in particular to a thermophilic fungal genome editing carrier, its composed genome editing system CRISPR / Cas9 and its editing method and application, the genome editing carrier Including the promoter that starts the transcription of the coding DNA of the sgRNA, the promoter is the RNA polymerase III type U6 type promoter, and the application of the genome editing system can significantly improve the genome editing efficiency of Myceliophthora strains M.thermophile and M.heterothallica, Simultaneous editing of multiple sites in the Myceliophthora genome can be realized, and then multi-gene mutant strains can be obtained. This series of mutant strains can significantly improve the production capacity of cellulase, and can be used for the genetic engineering of thermophilic fungi with high cellulase production; The genome editing system can also promote the research on the function of the Myceliophthora thermophila gene, and at the same time, it is of great significance to the genome-directed editing and metabolic engineering transformation of the thermophilic industrial cellulase production strain.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
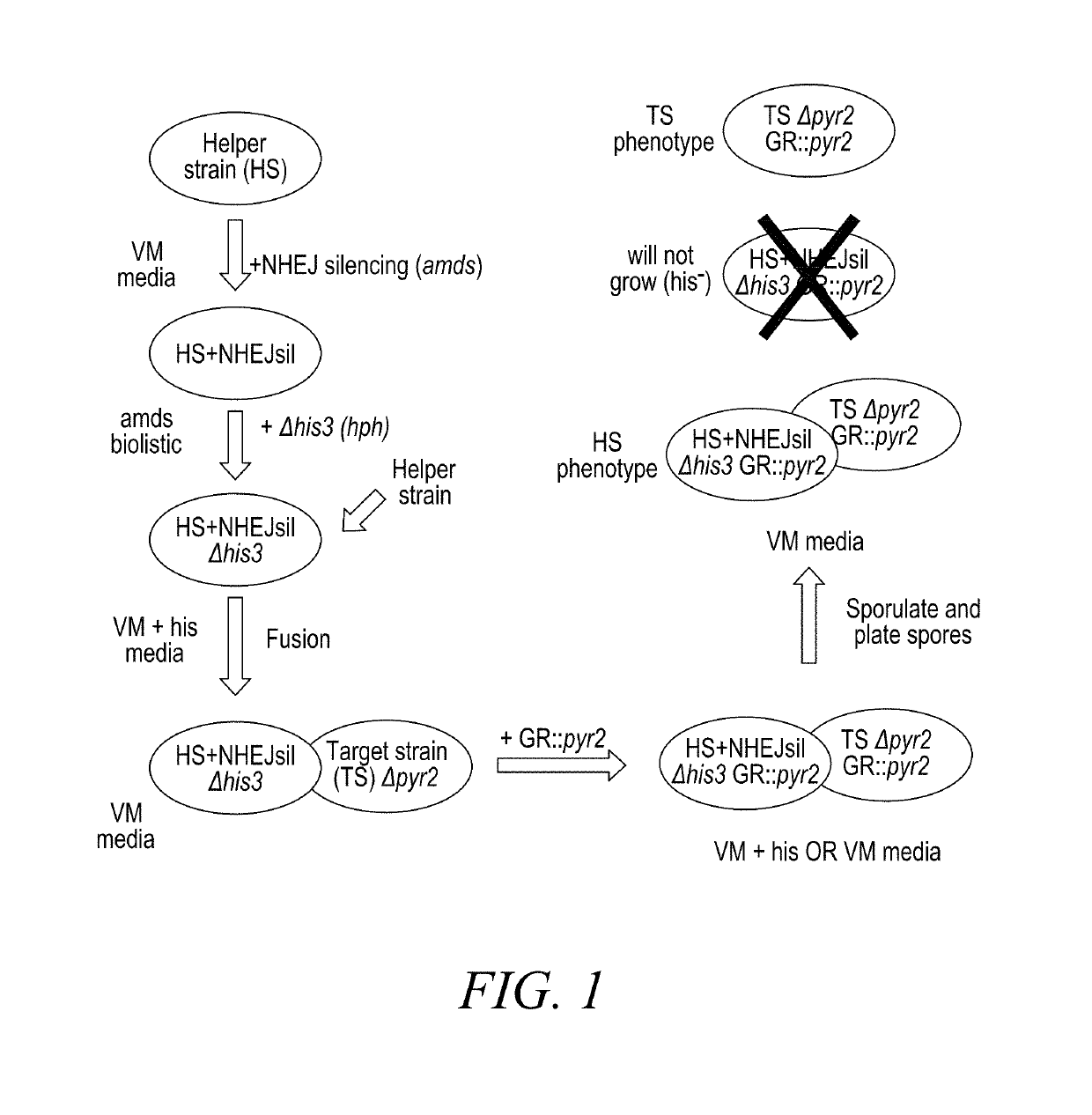
Method for editing filamentous fungal genome through direct introduction of genome-editing protein
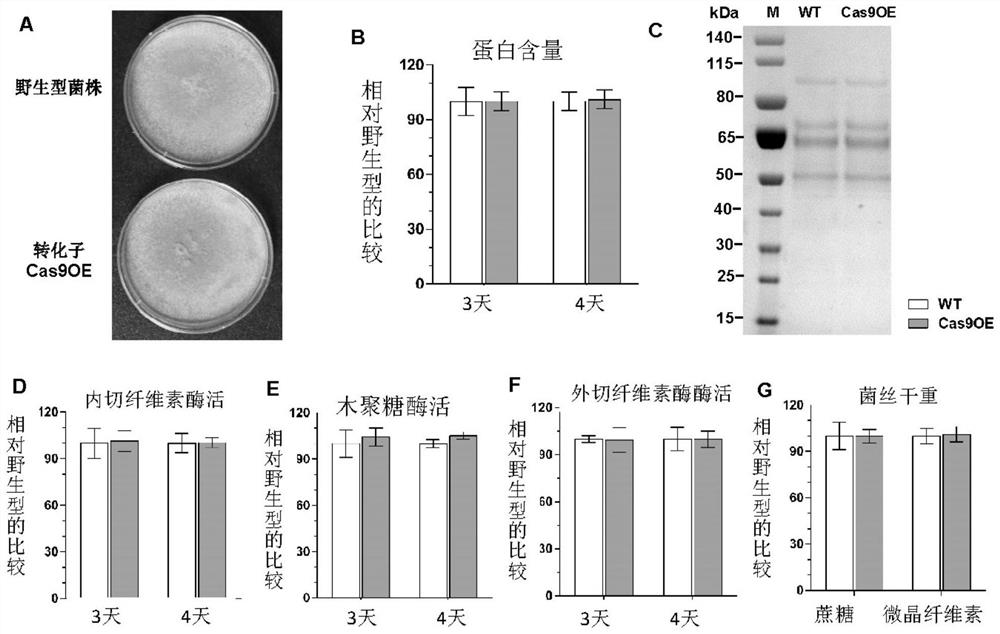
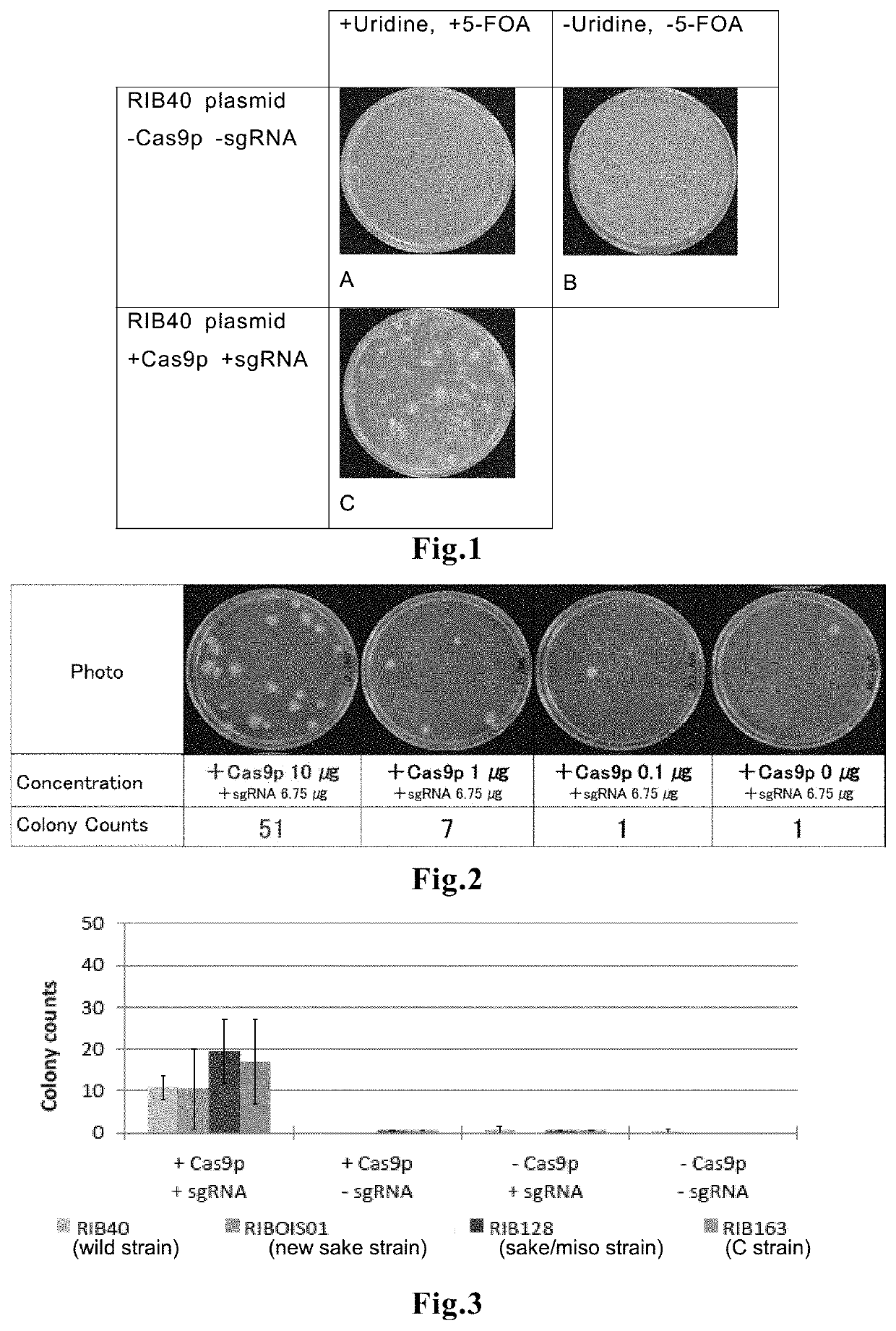
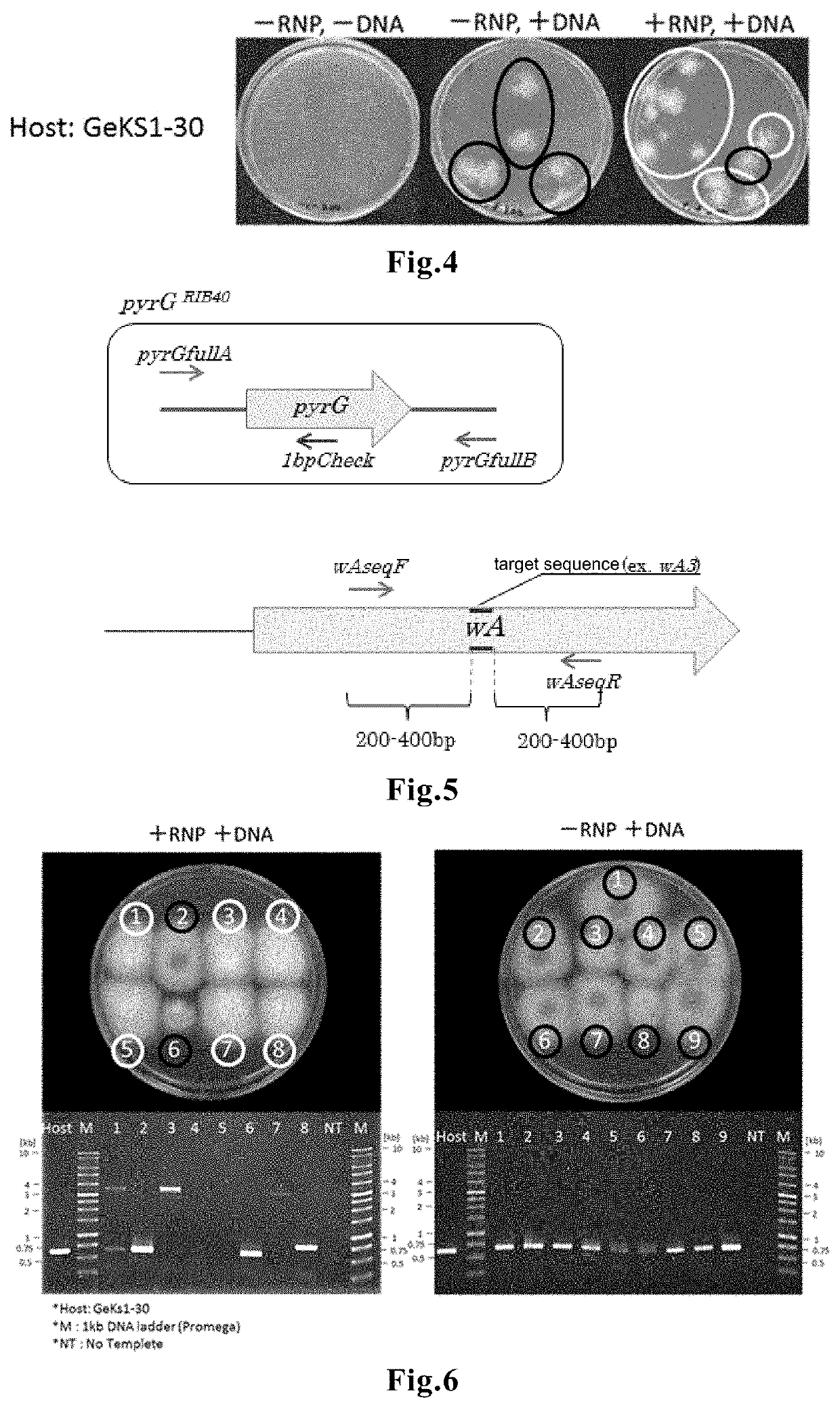
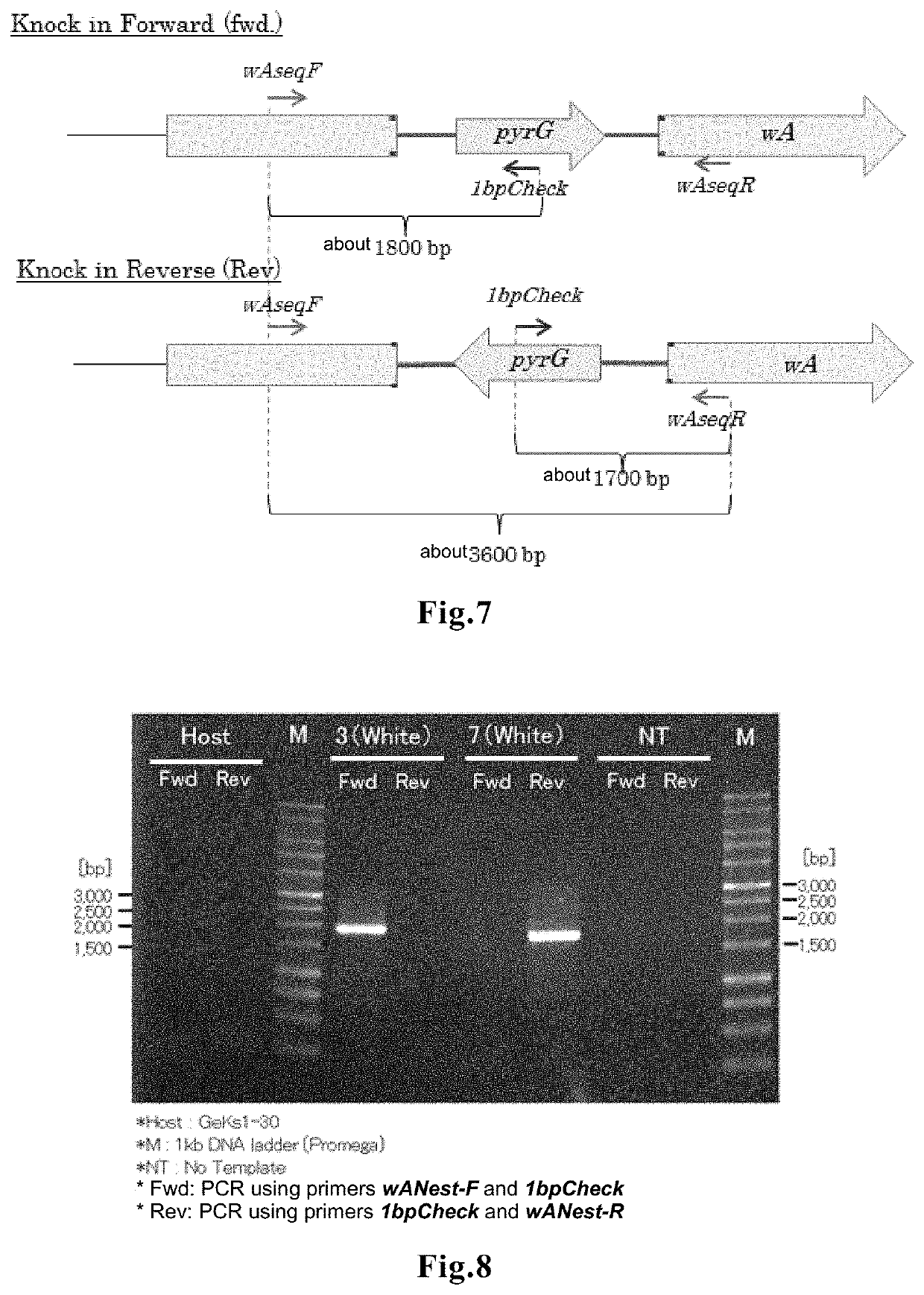
The present invention relates to a method of editing a filamentous fungal genome by direct introduction of a genome editing protein molecule or complex. The method includes three modes. In the first mode, a genome editing protein molecule or complex for a target gene is directly introduced into a cell of an Aspergillus fungus, to edit a gene in the Aspergillus fungal genome. In the second mode, a genome editing protein molecule or complex for a target region in a filamentous fungal genome, and a desired DNA fragment, are directly introduced into a filamentous fungal cell, to knock-in the DNA fragment to a desired target site in the filamentous fungal genome. In the third mode, genome editing protein molecules or complexes for plural target genes are directly introduced into a filamentous fungal cell, to carry out simultaneous editing of the plural genes in the filamentous fungal genome.
Owner:FASMAC CO LTD +1
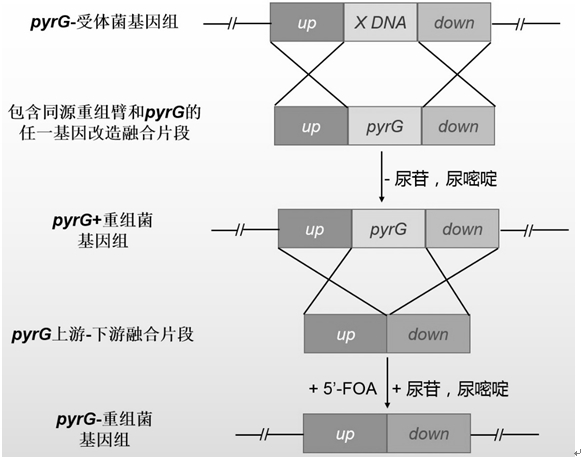
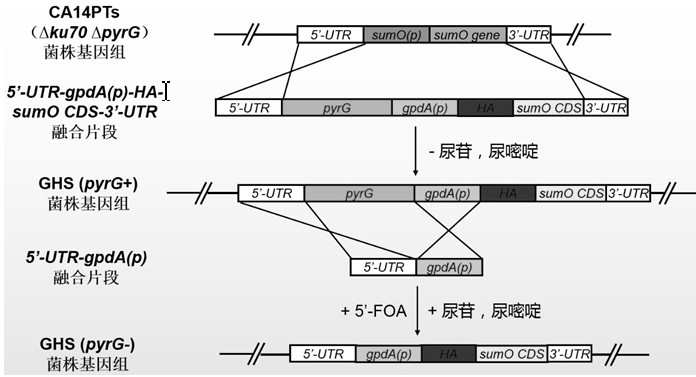
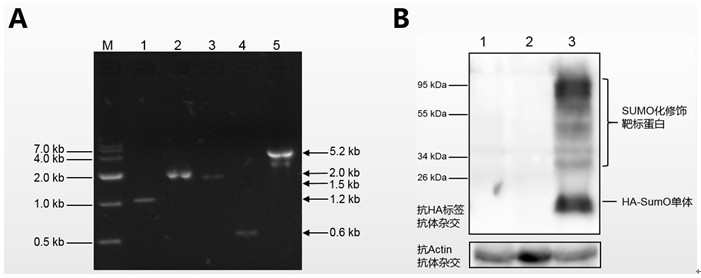
PyrG screening marker recycling method and application
ActiveCN112111415ASolve limitedResolving Differences in Different Genetic Screening Markers for Fungal Genetic BackgroundsFungiMicroorganism based processesRepetitive SequencesOrganism
The invention discloses a novel PyrG screening marker recycling method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the method, the pyrG screening marker can beremoved from a fungal genome without depending on homodromous repetitive sequences at the two ends of the pyrG, redundant repetitive sequence fragments cannot be left on the genome, recombinant bacteria without the pyrG can be used as starting strains again for genetic transformation by using the pyrG, and cyclic utilization of the pyrG screening marker is realized. The pyrG cyclic utilization method disclosed by the invention is suitable for fungi taking the whey glycoside-5'-phosphate decarboxylase coding gene URA3 / pyrG expression element as a genetic selection marker, is simple and easy tooperate, does not influence the genetic background and character of the strain, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Quantitative fungus detection method based on metagenome sequencing
PendingCN112501347ADestruction of permeabilityRaise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingFungal genome
The invention provides a quantitative fungus detection method based on metagenome sequencing. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) sequentially adding saponin and endonuclease into a sample, and removing a host genome; (2) performing wall breaking treatment on the sample without the host genome, and extracting nucleic acid to obtain a fungus genome; (3) performing library constructionand high-throughput sequencing on the fungus genome to obtain original sequencing data; and (4) comparing the original sequencing data with a fungus database, and performing fungus identification andabundance detection. According to the method, host DNA in the sample is removed by adopting the saponin and the endonuclease before high-throughput sequencing, so that the proportion of a human genomeand the interference to the accuracy of a sequencing result are remarkably reduced; and the wall breaking treatment operation is matched, so that the proportion of the fungus genome is increased, thesequencing cost is reduced, and the method has important significance in the field of fungus detection.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Filamentous fungus replicon
The invention discloses a filamentous fungus replicon. The nucleotide sequence of the replicon is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The replicon is obtained by using 19 fungal genomes as templates to construct a metagenome library and transforming aspergillus niger spores for screening, and is from a rhizopus chlamydosporum endophyte burkholderia HKI454 genome. The replicon provided by the invention can play a replication function in an aspergillus niger expression system, can provide stability higher than that of an AMA1 replicon, is a replicon found in fungi except aspergillus nidulans for the first time, enriches a replicon element library, and expands selection diversity of filamentous fungi utilizing the replicon.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Fungal artificial chromosomes, compositions, methods and uses therefor
ActiveUS10337019B2Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorOrigin of replicationBiotechnology
Fungal artificial chromosome (FAC) vectors are disclosed. A vector can be replicated in a bacterial or a fungal host, and can comprise an insert of heterologous DNA up to about 500 kilobases. A vector can be used for cloning and expressing a secondary metabolite (SM) gene cluster. An insert sequence can be modified by homologous recombination. A vector can be a plasmid comprising bacterial and fungal origins of replication, as well as bacterial and fungal selection marker genes. Also disclosed are vectors that can be integrated into a fungal genome, and dual function vectors which can be replicated in a bacterial or a fungal host and can also be integrated into a fungal genome. Also disclosed are methods of generating plasmid libraries including vectors comprising intact SM gene clusters.
Owner:INTACT GENOMICS INC
A simple and effective reagent and method for extracting genomic DNA of plant pathogenic fungi
The invention discloses a reagent and method capable of simply and effectively extracting plant pathogenic fungus genomic DNA. The extracting reagent comprises a solution A and a solution B, wherein the solution A comprises 200mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 250mM NaCl, 25mM EDTA, 0.5wt% of SDS, 1wt% of beta-mercaptoethanol, and 8 microliter of RNA enzyme; the solution B is potassium acetate with the concentration being 5M. When the reagent is used for extraction, high-purity and good-stability genomes can be extracted fast and effectively, the extracted genomes can be directly used for gene cloning andgenome sequencing, and an efficient and feasible molecular detection approach is provided for pathogenic fungus molecular biology study.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com