Genomic DNA extraction method suitable for bacteria and/or fungi
An extraction method and genome technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of prolonged detection time, inaccurate test results, low sensitivity, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing the possibility of errors, shortening the required time, and having a wide range of applications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
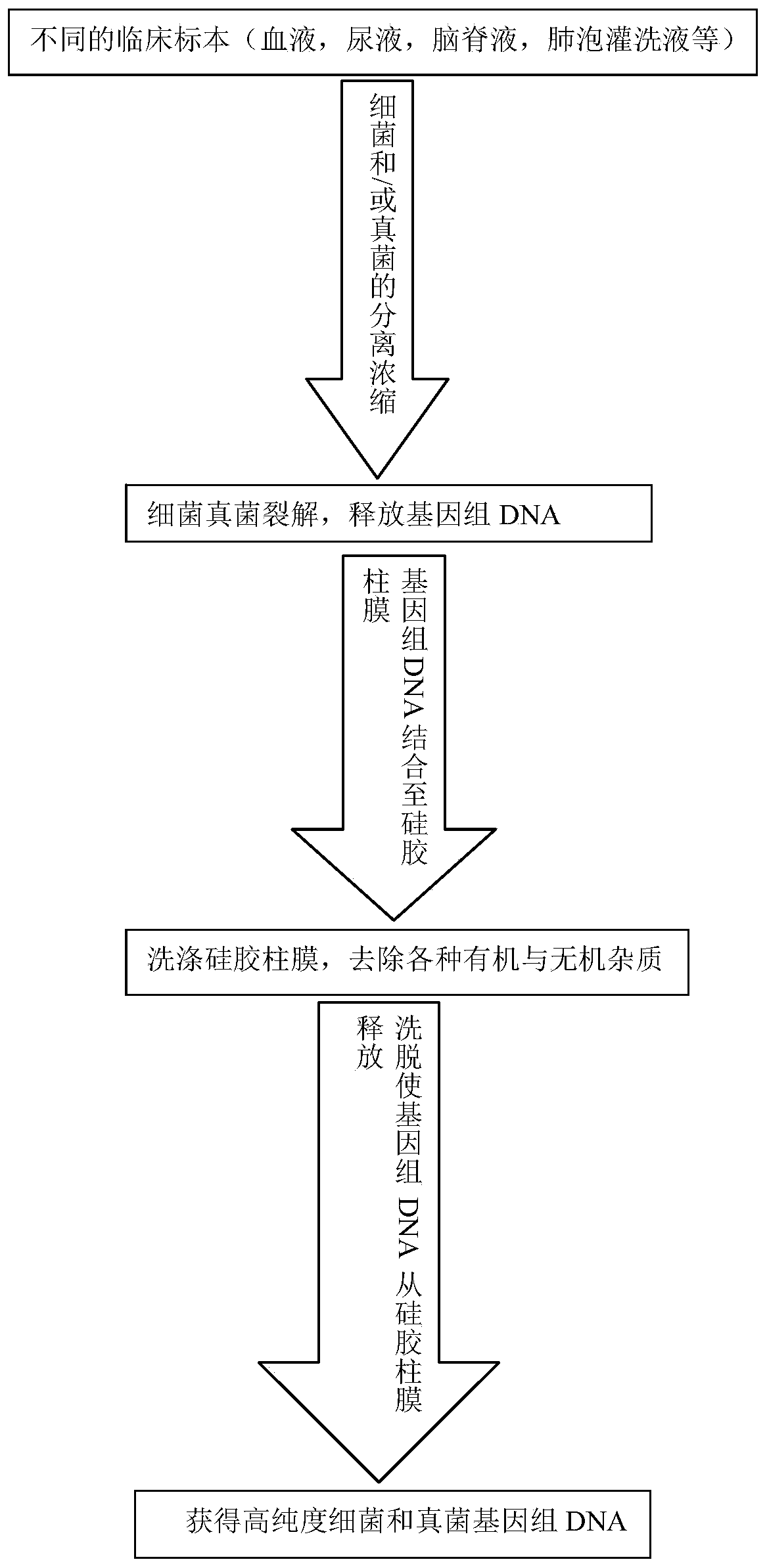
[0045] 1. Process clinical specimens to obtain bacterial and / or fungal pellet concentrates
[0046] By processing different clinical specimens, bacteria and / or fungi can be effectively separated from somatic cells and body fluid components, so that bacteria can be concentrated to increase the unit effective concentration of bacteria and / or fungi. The processing methods for clinical specimens with different characteristics are given below:
[0047] For the whole blood sample, since the sample contains a large number of red blood cells, the heme released after the lysed red blood cells has a certain degree of inhibition on the subsequent DNA analysis, so for the whole blood sample, the operation of the present invention is: take 500 μl of anticoagulated blood, add 450 μl of red blood cells to lyse Solution (the composition of erythrocyte lysate is: 0.15M NH 4 Cl, 10mM KHCO 3 , 0.1mM EDTA, water, pH7.2-8.0) after inverting and mixing, let it stand for 5 minutes to lyse red bloo...
Embodiment 2
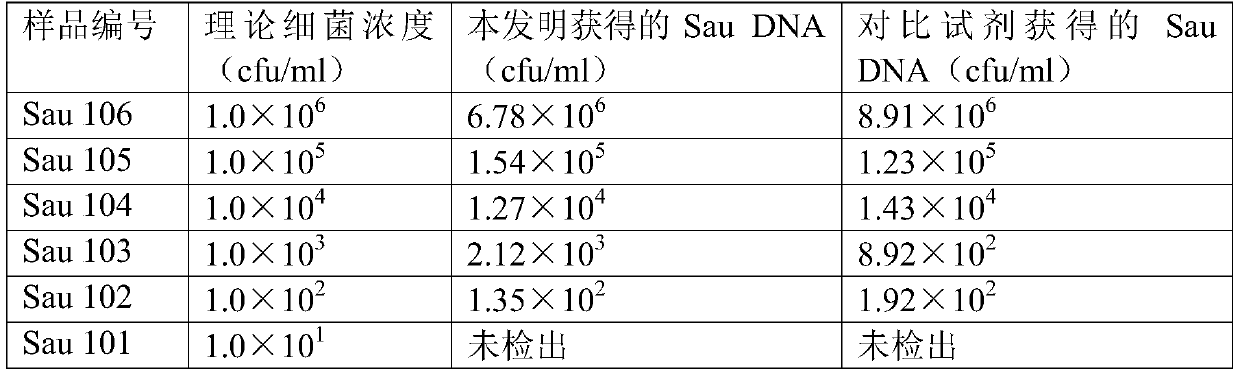
[0065] Example 2: Extraction and detection of Staphylococcus aureus genomic DNA in blood samples
[0066] Staphylococcus aureus belongs to the genus Staphylococcus, is a representative of Gram-positive bacteria, and is a common food-borne pathogenic bacteria.
[0067] A copy was tested positive for Staphylococcus aureus by the automatic biological mass spectrometry detection system Microflex LT / SH, and the bacterial content was determined to be 1.0×10 by DENSICHECK turbidimeter. 8 CFU / ml bacterial solution, use normal EDTA anticoagulated whole blood to dilute the bacterial solution to contain 1.0×10 6 CFU / ml (No. Sau106), 1.0×10 5 CFU / ml (code Sau105), 1.0×10 4 CFU / ml (No. Sau 104), 1.0×10 3 CFU / ml (code Sau103), 1.0×102CFU / ml (code Sau 102), 1.0×10 1 CFU / ml (No. Sau 101) blood samples of Staphylococcus aureus were used as experimental materials for the extraction of bacterial genomic DNA from blood as simulated bacterial infection samples.
[0068] Take more than 500ul s...
Embodiment 3
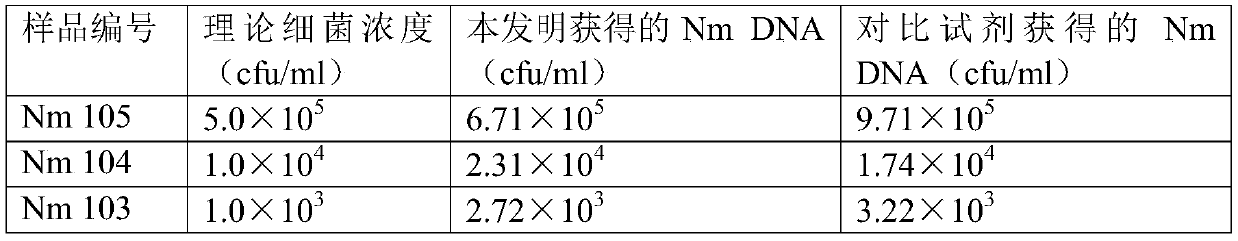
[0079] Example 3: Extraction and detection of Neisseria meningitidis genomic DNA in cerebrospinal fluid samples
[0080] Neisseria meningitidis (N. meningitidis), referred to as meningococcus (meningococcus), is the pathogenic bacteria of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis (referred to as meningitis). Neisseria meningitidis is a Gram-negative diplococcus with a diameter of about 0.8 μm.
[0081] A portion was tested positive for Neisseria meningitidis by the automatic biological mass spectrometry detection system Microflex LT / SH, and the bacterial content measured by the DENSICHECK turbidimeter was 3.0×10 8 CFU / ml bacterial solution, respectively use the non-bacterial infected cerebrospinal fluid to dilute the bacterial solution to contain 5.0×10 5 CFU / ml (No. Nm105), 1.0×10 4 CFU / ml (No. Nm104), 1.0×10 3 CFU / ml (No. Nm 103), 1.0×10 2 CFU / ml (No. Nm 102) Neisseria meningitidis cerebrospinal fluid sample, as a simulated bacterial infection sample for genomic DNA extraction e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com