Patents
Literature
36 results about "Medical genetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics.
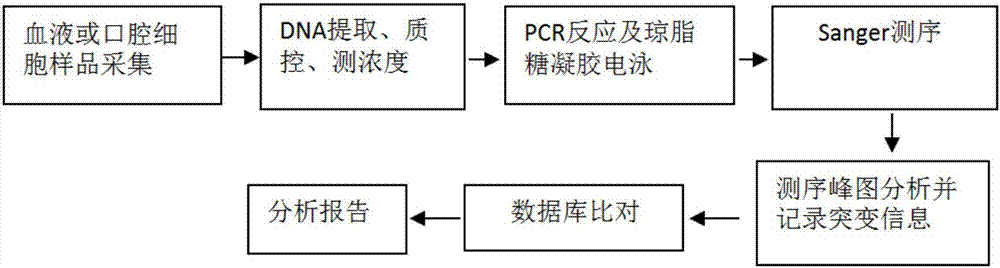
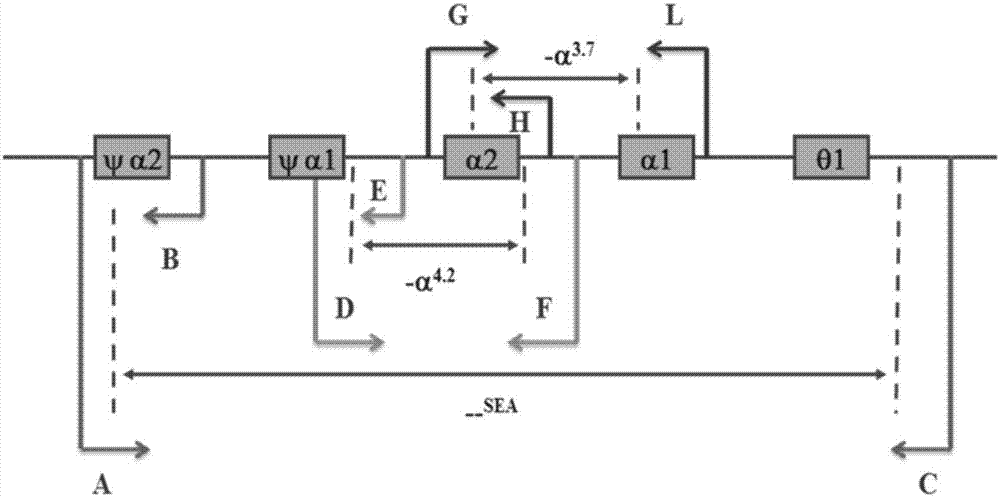
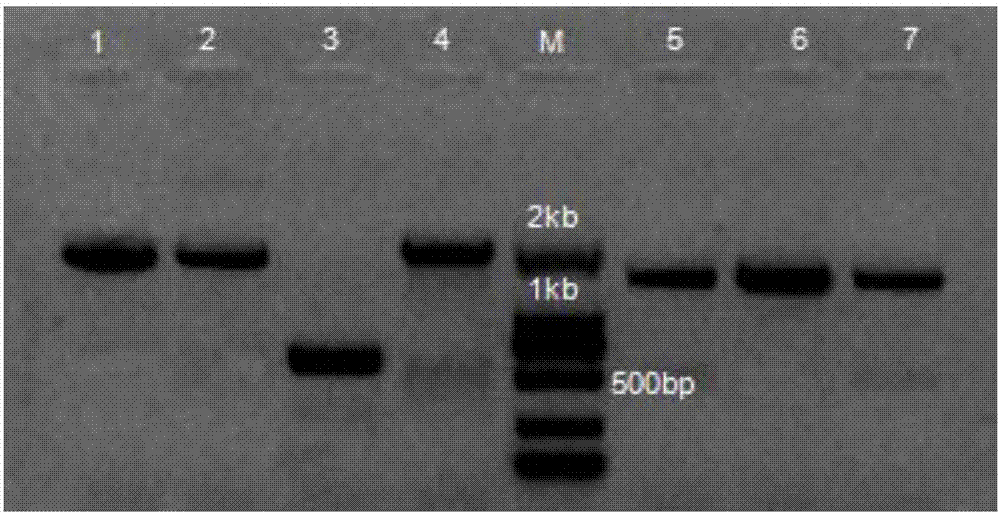
Kit and method for detecting mutation of thalassemia-related gene and use thereof
The invention provides a kit and method for detecting mutation of a thalassemia-related gene and a use thereof and relates to the technical field of medical genetics. The kit for detection is used for detecting many types of patients such as people needing premarital checkup, people in gestation, newborns, people in a zone having high incidence of thalassemia and people having thalassemia family heredity history, can realize accurate, comprehensive, visual and simple detection of mutation of a thalassemia-related gene, has a detection mutation range comprising HBA1, HBA2 and HBB genes in the genome and neighbouring zones and has the characteristics of simpleness, accuracy, good repeatability and promotion and use easiness.
Owner:深圳市龙华区人民医院 +1
Fluorescently-labeled X-InDel locus composite amplification system and application thereof
ActiveCN104131067AHigh sensitivityHigh individual recognition rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceInsertion deletionDNA paternity testing
The invention provides a fluorescently-labeled X-InDel locus composite amplification system. By means of the system, eighteen insertion-deletion genetic polymorphism loci on an X chromosome can be compositely amplified, wherein the eighteen loci are respectively labeled with three fluoresceins FAM, HEX and TAMRA. The composite amplification system is high in sensitivity and individual identification rate, is high in polymorphism, is good in stability and repeatability, is accurate in typing results and can satisfy a practical requirement. A kit can be manufactured on the basis of the composite amplification system, can be used for paternity test, dyad paternity test, grandparent and grandchild test, sibling test and individual identification. New technologies can be provided for the fields such as anthropology, medical genetics and the like.
Owner:ACADEMY OF FORENSIC SCIENCE
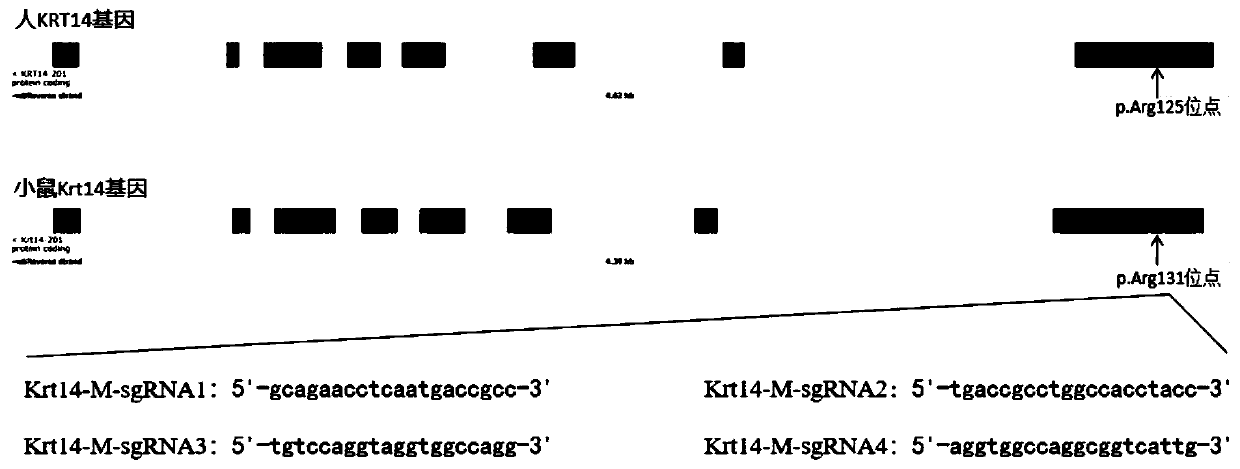
sgRNA targeting sequence specifically targeting mouse Krt14 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110777144AEfficient cuttingEfficient shootingStable introduction of DNAAnimals/human peptidesNucleotide sequencingMedical genetics
The invention discloses a sgRNA targeting sequence specifically targeting a mouse Krt14 gene and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of medical genetics and molecular biology. A nucleotide sequence corresponding to sgRNA is any one of four sequences of SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4. The invention further discloses a method for editing the mouse Krt14 gene by using the sgRNA targeting sequencing specifically targeting the mouse Krt14 gene. The sgRNA targeting sequence can mediate the efficient cleavage of target DNA by Cas9 protein, and then be usedfor editing the mouse Krt14 gene to affect the function of protein encoded by the mouse Krt14 gene. The sgRNA targeting sequence can achieve efficient targeting by a CRISPR / Cas9 system, and the efficiency is 70%, 90%, 65% and 100% separately.
Owner:人科(北京)生物技术有限公司
Acquisition and application of a novel oncolytic adenovirus-thymidine kinase gene construct
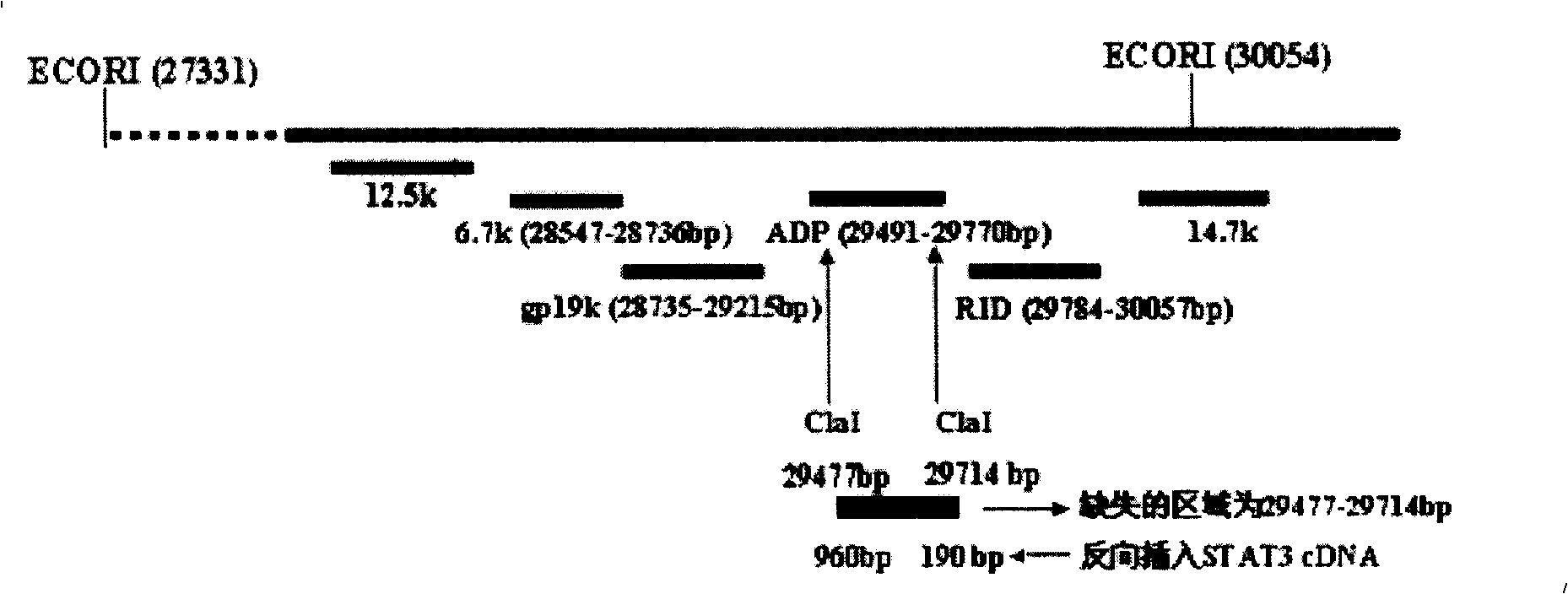
InactiveCN102286433AHas therapeutic effectIncrease productionGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesEnzyme digestionConserved sequence
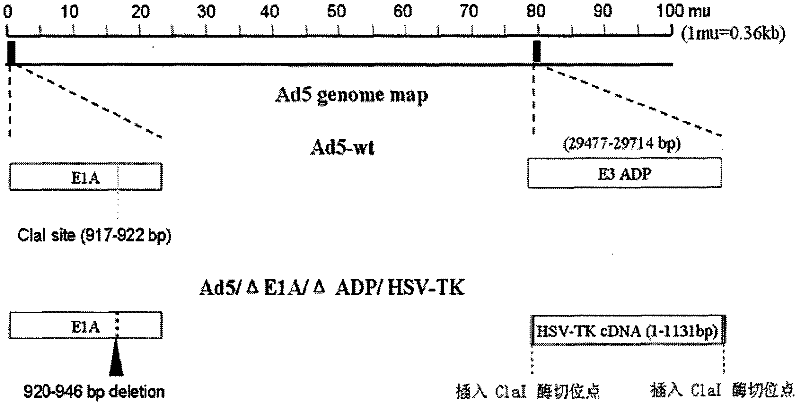
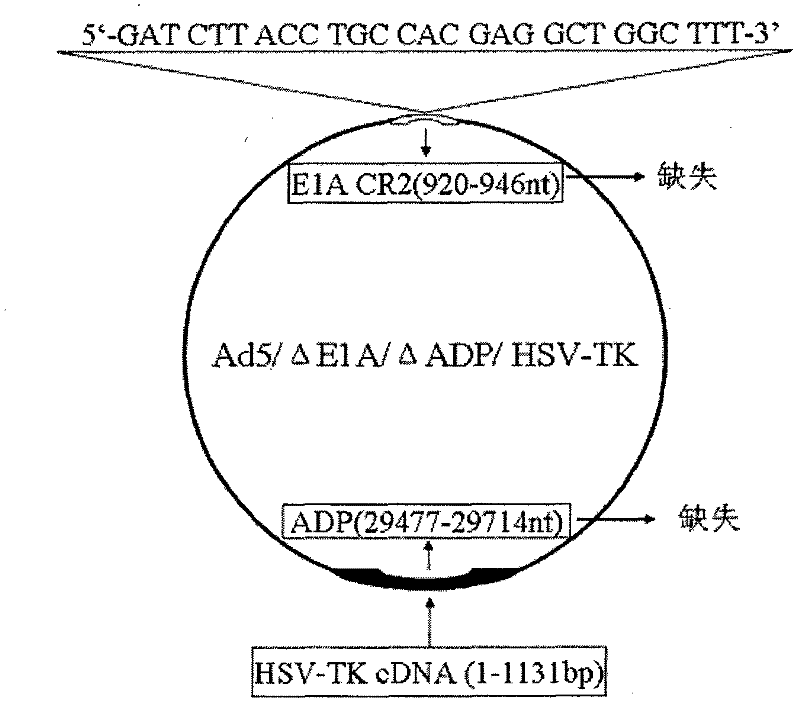
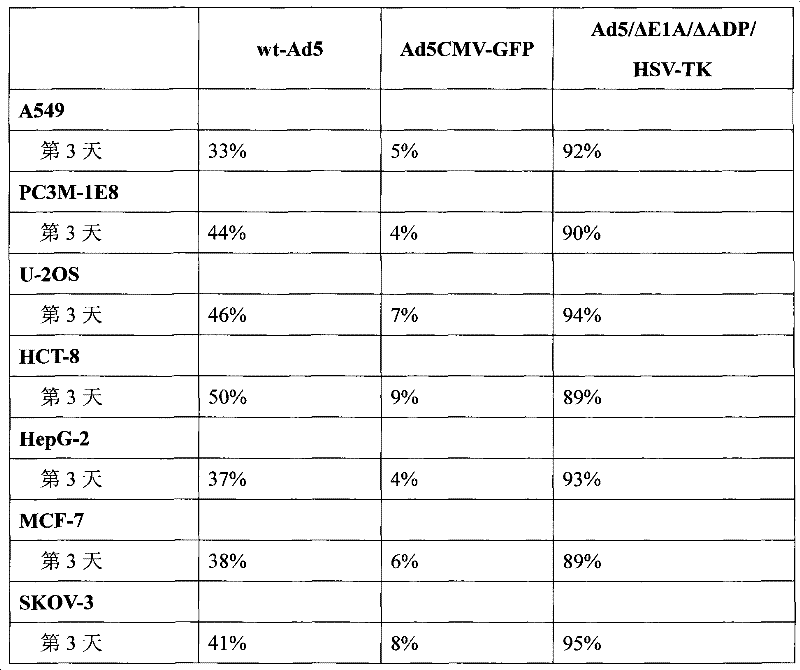
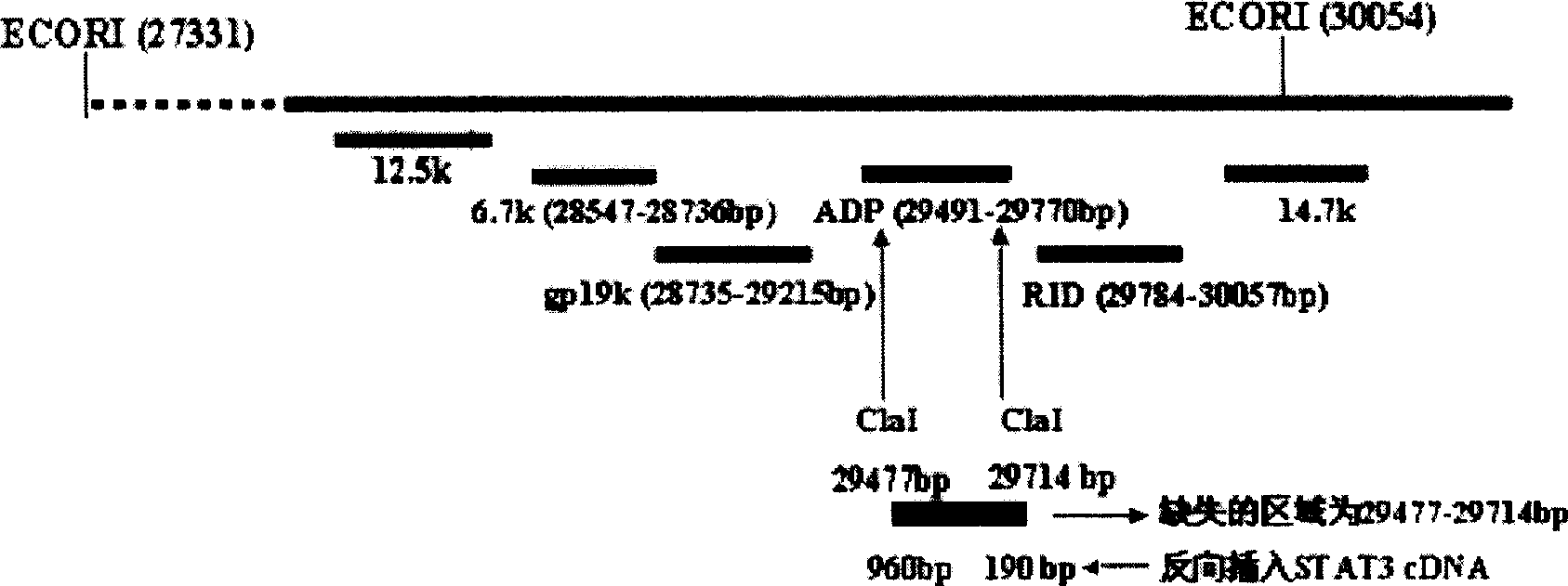
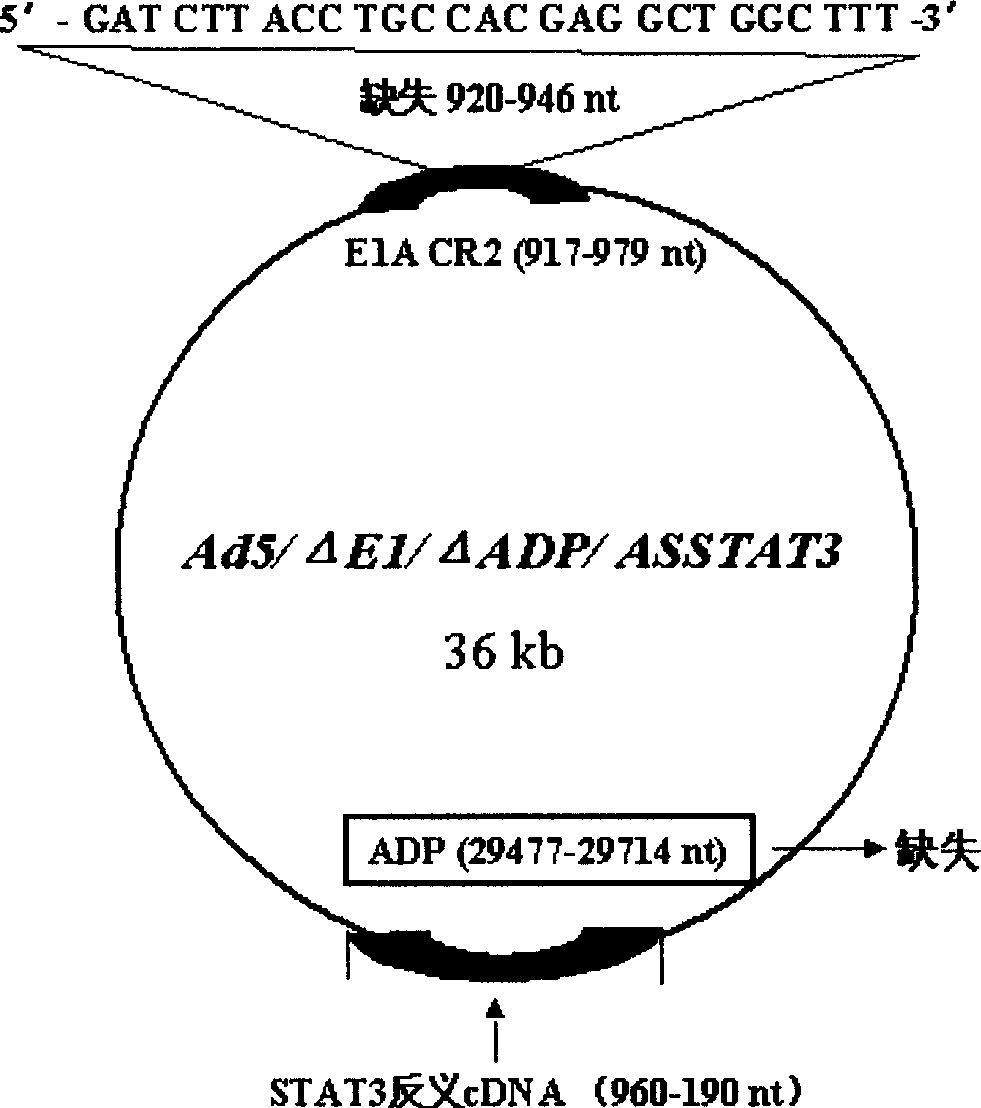
The invention discloses a construction scheme of artificially transforming human type 5 adenovirus (Ad5), and a specific application of a novel oncolytic adenovirus construct obtained by the scheme in tumor treatment, and belongs to the technical field of medical genetic engineering. A recombinant adenovirus construct obtained by PCR amplification site-directed deletion, enzyme digestion, ligation, cloning, homologous recombination, transfection, adenovirus monoclonal purification, etc., its technical characteristics are: Ad5 genome E1A conserved sequence 2 27 bases were deleted in the (CR2) region; 29477-29714nt of the ADP gene in the E3 region was deleted; and the full-length coding sequence (1131bp) of the HSV-TK gene was inserted in the deleted region. This construct is a new type of oncolytic adenoviral vector with higher tumor selective replication ability, which utilizes the suicide gene function of HSV-TK and the double killing effect of oncolytic virus to dissolve tumor cells, and has great potential in the biological treatment of tumors. Unique practical value.
Owner:马丁
Typing method for multicolor fluorescence composite detection of 20 X-SNP sites
ActiveCN103215360AIncrease success rateSolve the problem of complex genetic relationship identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceTyping methods
The invention discloses a typing method for multicolor fluorescence composite detection of 20 X-SNP sites, belonging to the technical field of medical genetic relationship identification. The typing method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a DNA solution; (2) amplifying; (3) purifying an amplification product; (4) extension reacting; (5) purifying an extension product; and (6) detecting and determining the extension product. By virtue of the invention, the segment range of target DNA to be detected is shortened to 61-99 bp, the success rate of highly degraded DNA typing is improved, and the difficulty of identifying of complicated genetic relationships, for example, ancestral relationship, half-sib relationship and sibship, can be overcome. The typing method has large advantages and potentials on complicated genetic relationship identification and forensic typing of highly degraded material DNA.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Detection method for interpretating nervous system and multiple intelligences from dermatoglyph
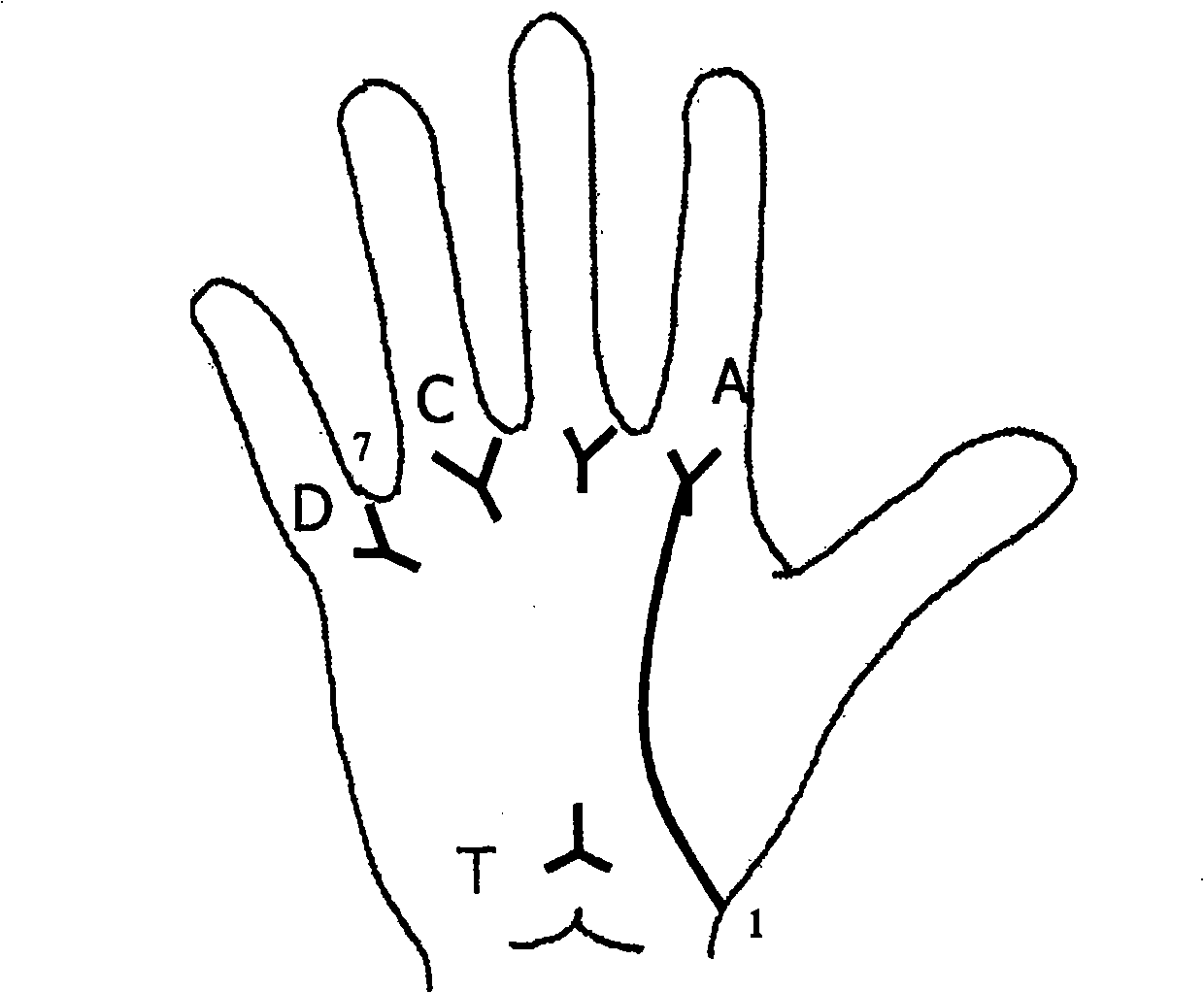
The invention provides a method for detecting a nervous system and multiple intelligences interpretated by dermatoglyphic. The method covers the fields of medical genetic dermatoglyphic, neuroscience and behavior science. Connection between dermatoglyphic and the nervous system is integrated by dermatoglyphic features by different geneogenous patients with neurologic deficit. For example, if a central chief execution weaker is projected by a left thumb by dermatoglyphic detecting, the invention shows the same situations appearing in the fields of autism, sense organ disorder, attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, etc. Weakened moral function causes low stress tolerance and depression trait, which has important reference value for evaluating the possibility of suffering from mental disorder. And the attention deficit disorder also causes learning disability easily. Therefore, the method for detecting the nervous system and multiple intelligences interpretated by dermatoglyphic has higher utility value on the whole use.
Owner:连裕兴
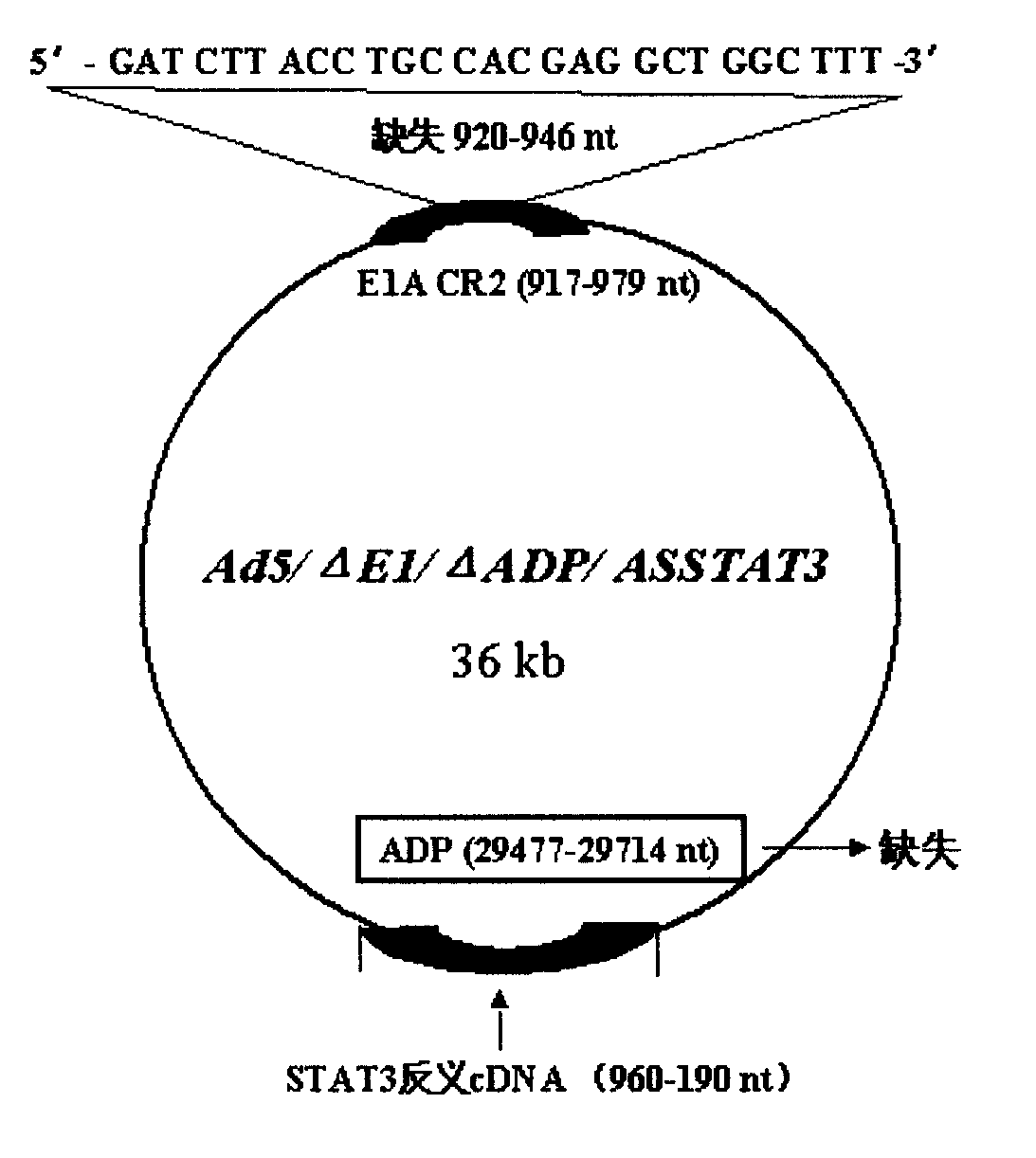
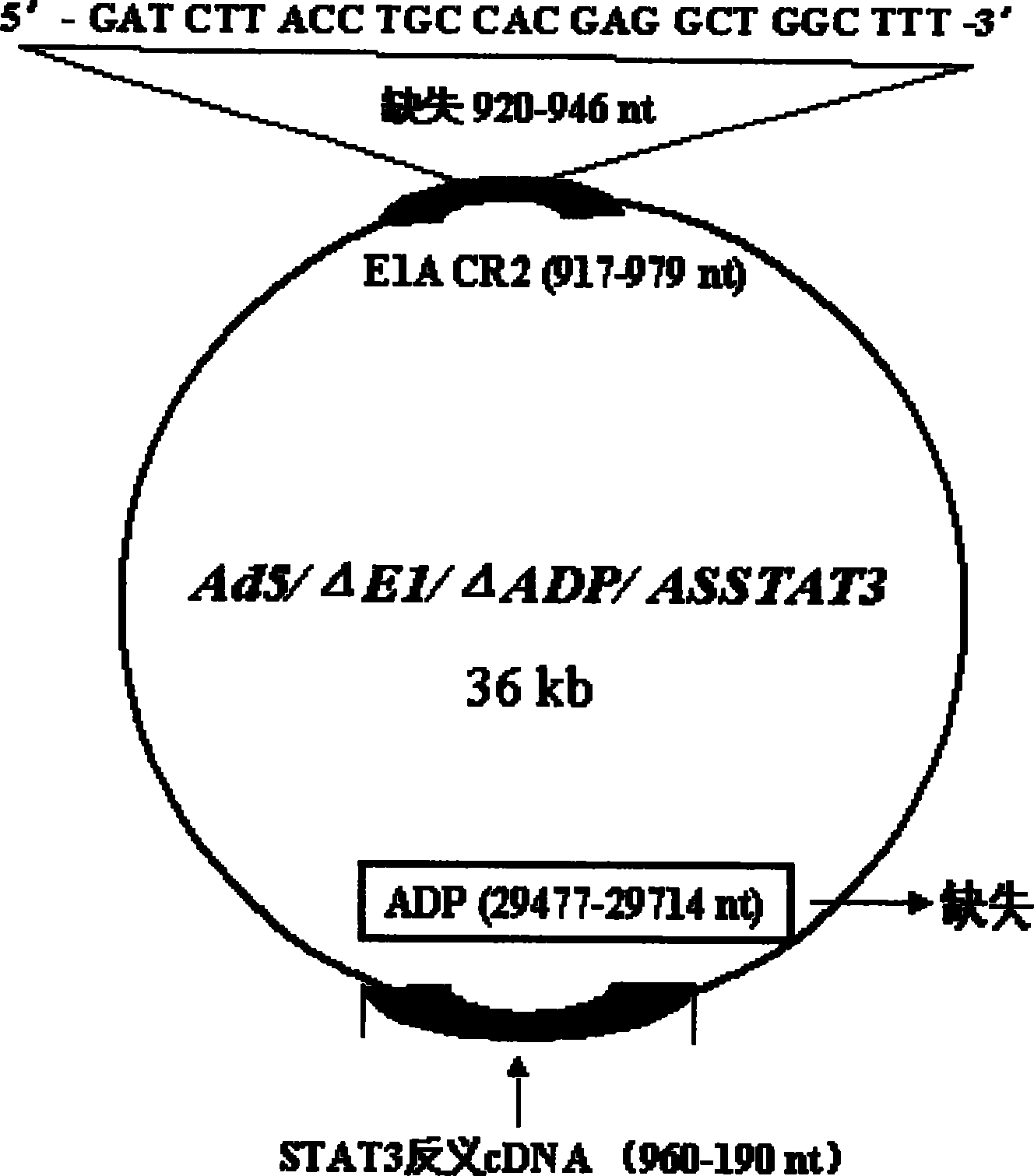
Obtaining method and use of novel oncolytic adenovirus construct with selective tumor blockage STAT3
ActiveCN101440379AIncreased amplificationRetains transcriptional activation propertiesGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsOncolytic adenovirusWilms' tumor
The invention discloses a proposal for constructing novel oncocytic adenovirus of selectively closed tumor STAT3 obtained by manual reconstruction of human 5 type adenovirus (Ad5), and particular application of a recombined adenovirus constructor in tumor treatment, and belongs to the technical field of medical genetic engineering. By techniques of PCR enlarging fixed point deletion, enzyme cutting, connection, cloning, homologous recombination, transfection, single cloning purification of adenovirus and the like, the recombination adenovirus constructor is obtained. The technical characteristics comprise that 27 basic groups are deleted in an E1A conservative sequence 2(CR2) zone of Ad5 genome; 29477 to 29714nt in an E3 zone of ADP gene are deleted; and partial STAT cDNA segments are oppositely inserted in the deletion zones. The constructor is a novel oncocytic adenovirus vector with higher tumor selective copy capability. The constructor has unique practical values in biological treatment of tumor, and also provides a reasonable gene target point specificity treatment mode for the genetic treatment of tumor.
Owner:南京江北新区生物医药公共服务平台有限公司
Method for correcting human genome damage through micro nutrient substances according to genetic background
InactiveCN105200125ALower levelMaintain stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenomicsHuman DNA sequencing
The invention relates to a method for correcting human genome damage through micro nutrient substances according to the genetic background and belongs to the technical field of nutrition genomics and medical genetics application. The method comprises the steps that peripheral blood of an individual is sampled, the levels of folate of the blood, serum VB12 and serum Hcy are detected, nuclear DNA is extracted, the MTHFR C677T and A1298C genetypes and the genome damage condition of the individual are combined, and micro nutrient substance intervention suggestions are given to the individual with the high genome damage according to reference values (the folate of erythrocyte is higher than 700 nM, the serum folate is higher than 34 nM, the serum VB12 is higher than 300 pM, and the serum Hcy is lower than 8 micrometers) at which various blood micro nutrient substances maintain the stability of genomes, so that the heredity damage of the individual is corrected, and the stability of the genomes is maintained. The strategy is beneficial to preventing cardiovascular diseases and reducing the risk factor of genome damage related diseases.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
SiRNA (small interfering ribose nucleic acid) for inhibiting homosapiens chromosome2open reading frame 3(C2 or f3) (GCF) gene expression, carrier of SiRNA for inhibiting GCF gene expression and application
InactiveCN102994503AHigh interference efficiencyStrong specificityGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBase JGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a SiRNA (small interfering ribose nucleic acid) for inhibiting homosapiens chromosome 2 open reading frame 3(C2 or f3) (GCF) gene expression, which belongs to the field of medical genetic engineering. Deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) for an encoding SiRNA is selected from arbitrary group of (a), (b) and (c): (a) a base sequence of a positive-sense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the base sequence of an antisense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.2; (b) the base sequence of the positive-sense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.3, and the base sequence of the antisense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.4; and (c) the base sequence of the positive-sense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.5, and the base sequence of the antisense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.6. The invention further discloses a recombinant plasmid which comprises the DNA of the encoding SiRNA and a GCF-shRNA-HeLaCGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center) No.5821, and a cell line has high RNA interfering efficiency, strong specificity and no toxic and side effects and can effectively inhibit GCF gene expression. The SiRNA for inhibiting GCF gene expression, the recombinant plasmid and the GCF-shRNA-HeLa monoclonal cell can also be used for preparing medicines for treating cervical cancer.
Owner:NAT INST FOR RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION & NUCLEAR SAFETY CHINESE CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION +2
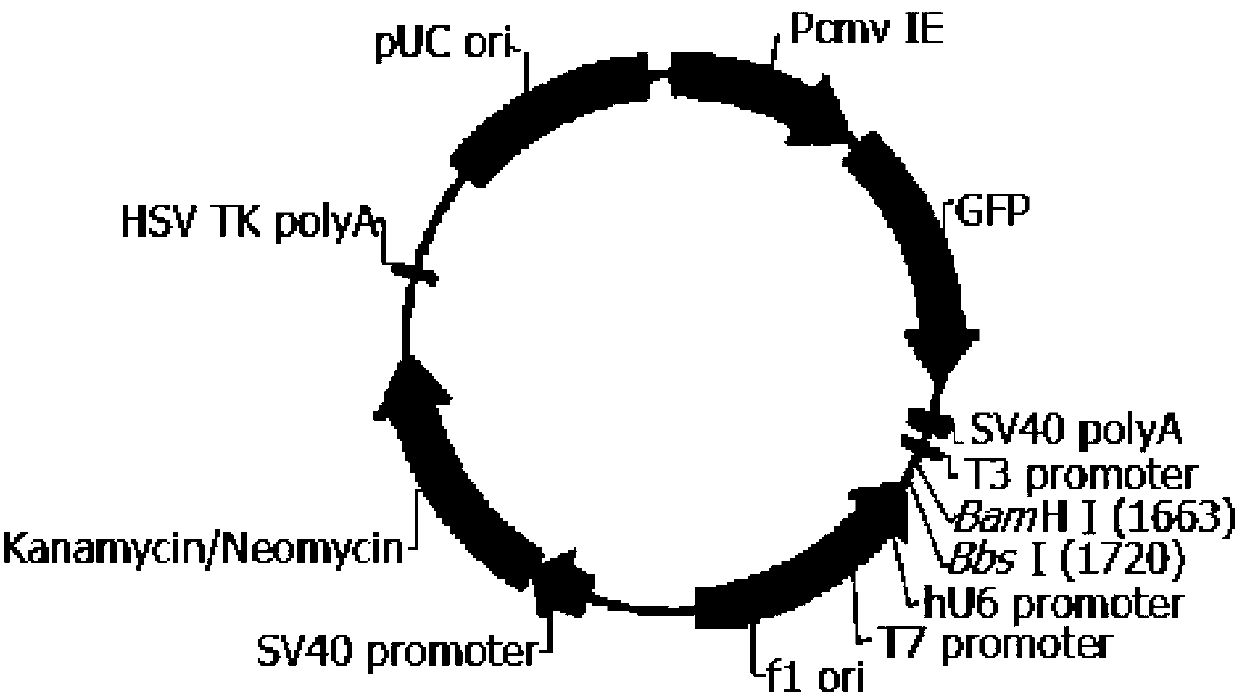
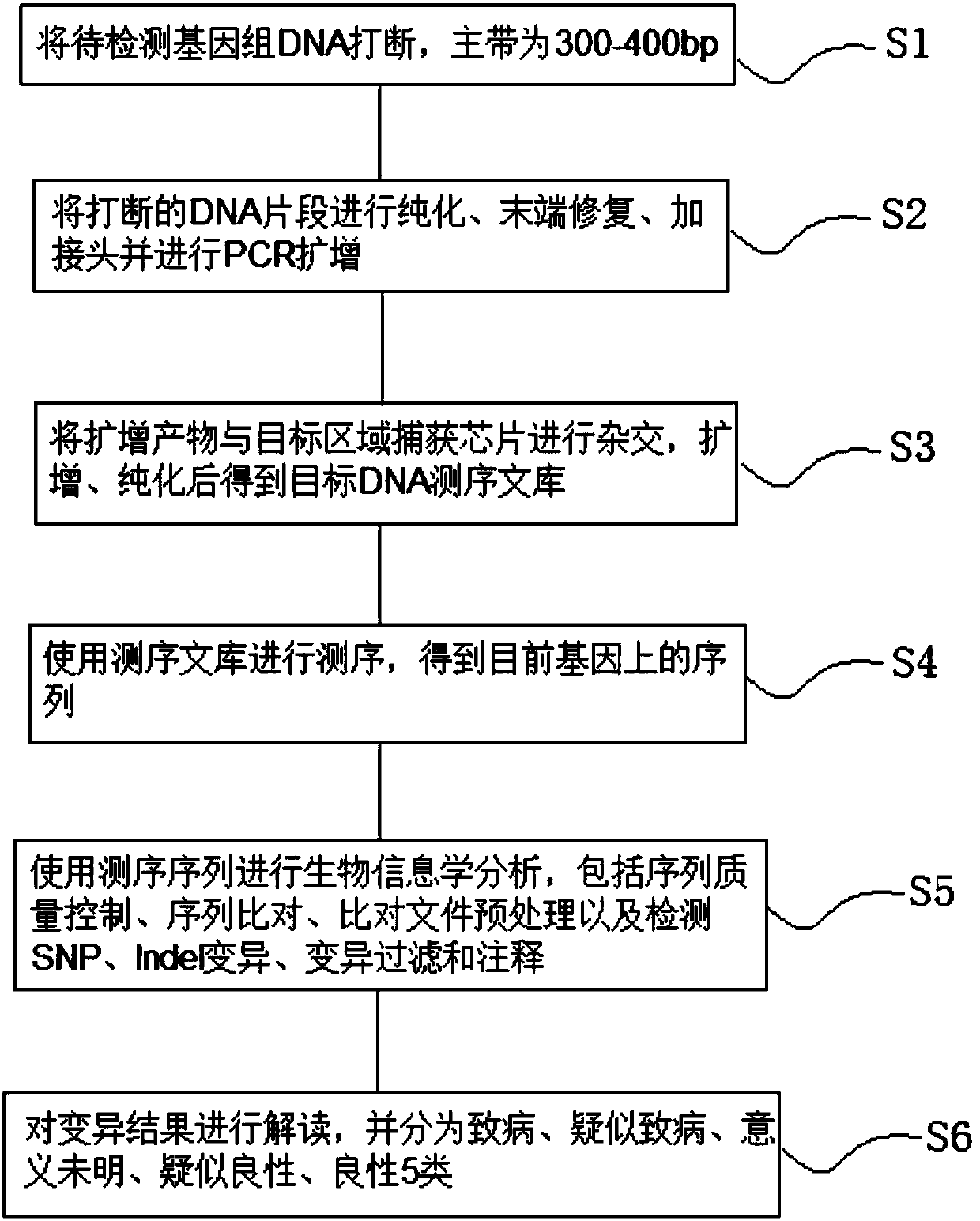
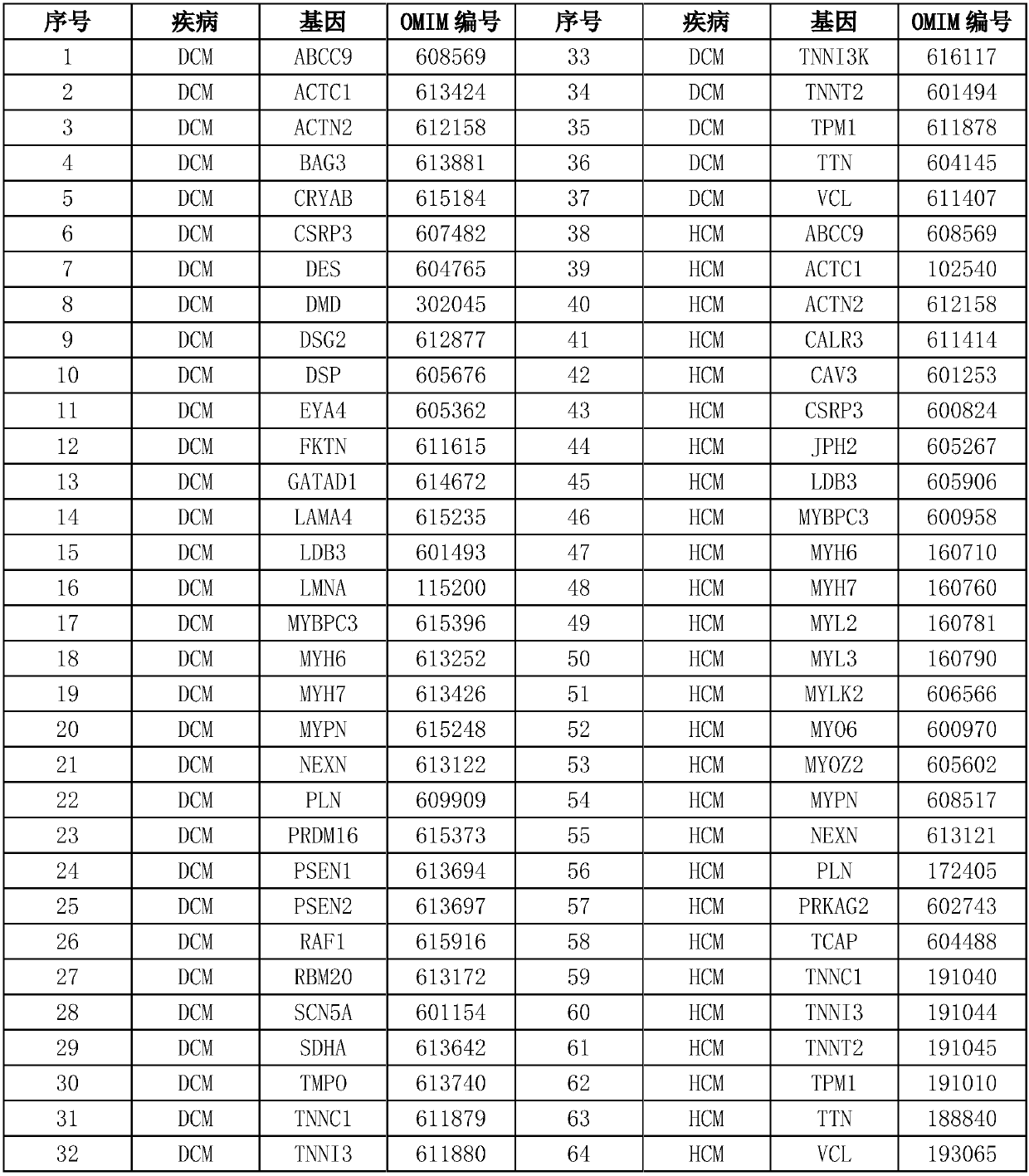
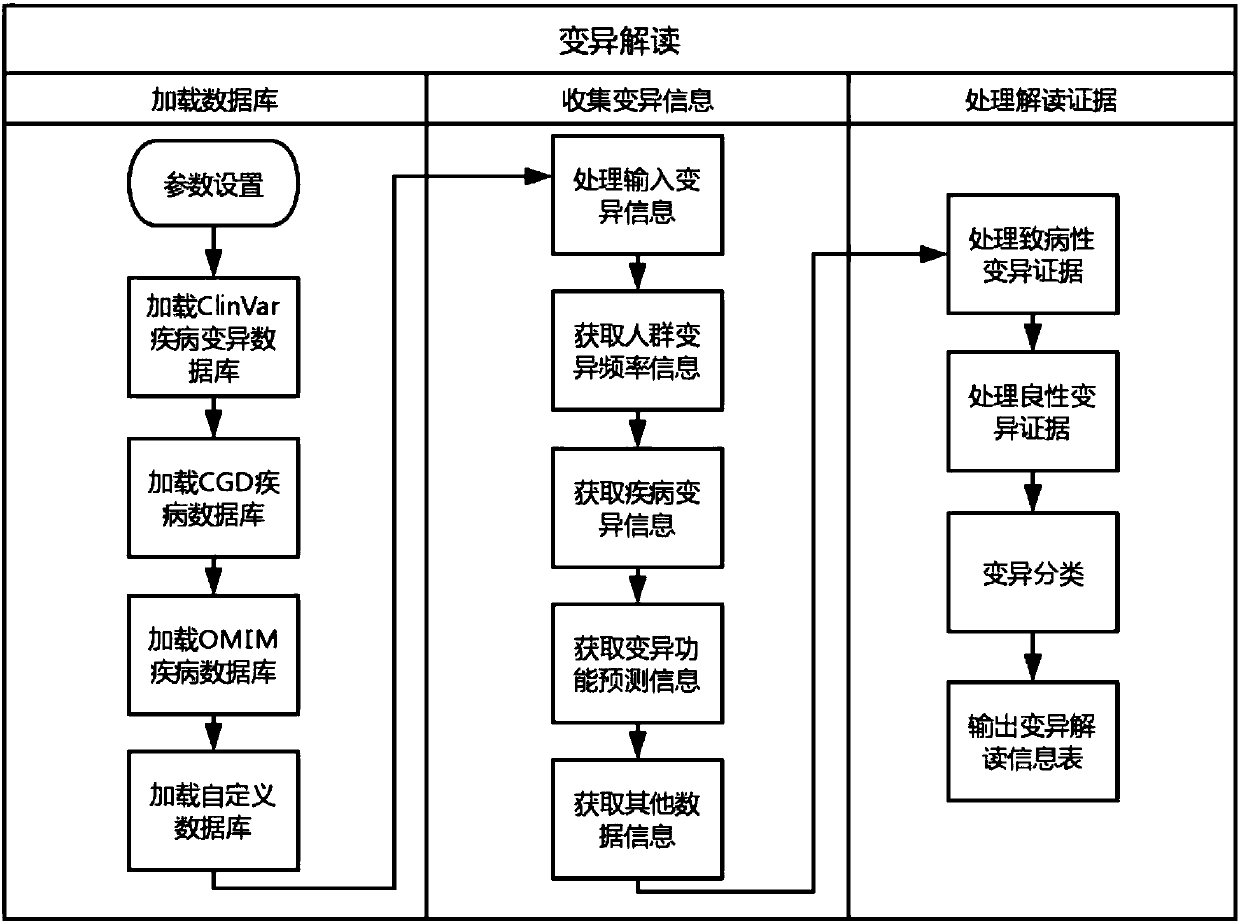
Detection method and chip for susceptibility gene of dilatant and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
InactiveCN109762879AShort processStrong targetingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGuidelineHypertrophic cardiomyopathy
The invention relates to a detection method and chip for a susceptibility gene of dilatant and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Based on a target region capture high-throughput sequencing technology, a group of specific and effective gene set associated with DCM / HCM cardiovascular disease is selected and is subjected to high-throughput capture and sequencing analysis by a self-developed probe library-building capture process and analysis software, so as to find out variation conditions of genetic level cardiovascular disease-related genes, especially DCM / HCM genes and the like, by gene means to screen the susceptibility gene. The screening result refers to the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) and the Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP) to interpret variations. Compared with conventional high-throughput sequencing, a kit has the advantages of high pertinence, low cost, fast flow and the like.
Owner:葛均波 +2
EBV transfected chimera quality-control cell for birth defect antenatal diagnosis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104059884AEasy to set upIncrease the difficultyMicrobiological testing/measurementForeign genetic material cellsCulture fluidBiology
The invention relates to an EBV transfected chimera quality-control cell for antenatal diagnosis and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to medical genetics. The invention is mainly characterized in that the preparation method comprises: taking residual living cells which are used for chromosomal disease diagnosis as needed by clinical diagnosis and treatment and are definitely diagnosed to have common numerical abnormalities of chromosomes, separating lymphocytes, culturing in an RPMI-1640 culture solution containing cyclosporin A and EBV under a condition of 37 DEG C and 5% CO2, allowing B lymphocytes to form immortalized lymphoblast lines with infinite reproduction capability, performing subculture amplification to reach a desired amount, then cryopreserving the cell lines, mixing the cell lines according to a required ratio for quality control when in use so as to prepare each original cell line with only one type of numerical abnormalities of chromosomes into a chimera quality-control cell line which has a specific ratio and multiple combinations of numerical abnormalities of chromosomes, is universal for various testings, and is more difficult for differential diagnosis. Original cells are easily available, and waste excessive cells are prepared artificially into practical and effective quality-control cells which can be amplified as needed.
Owner:翁炳焕
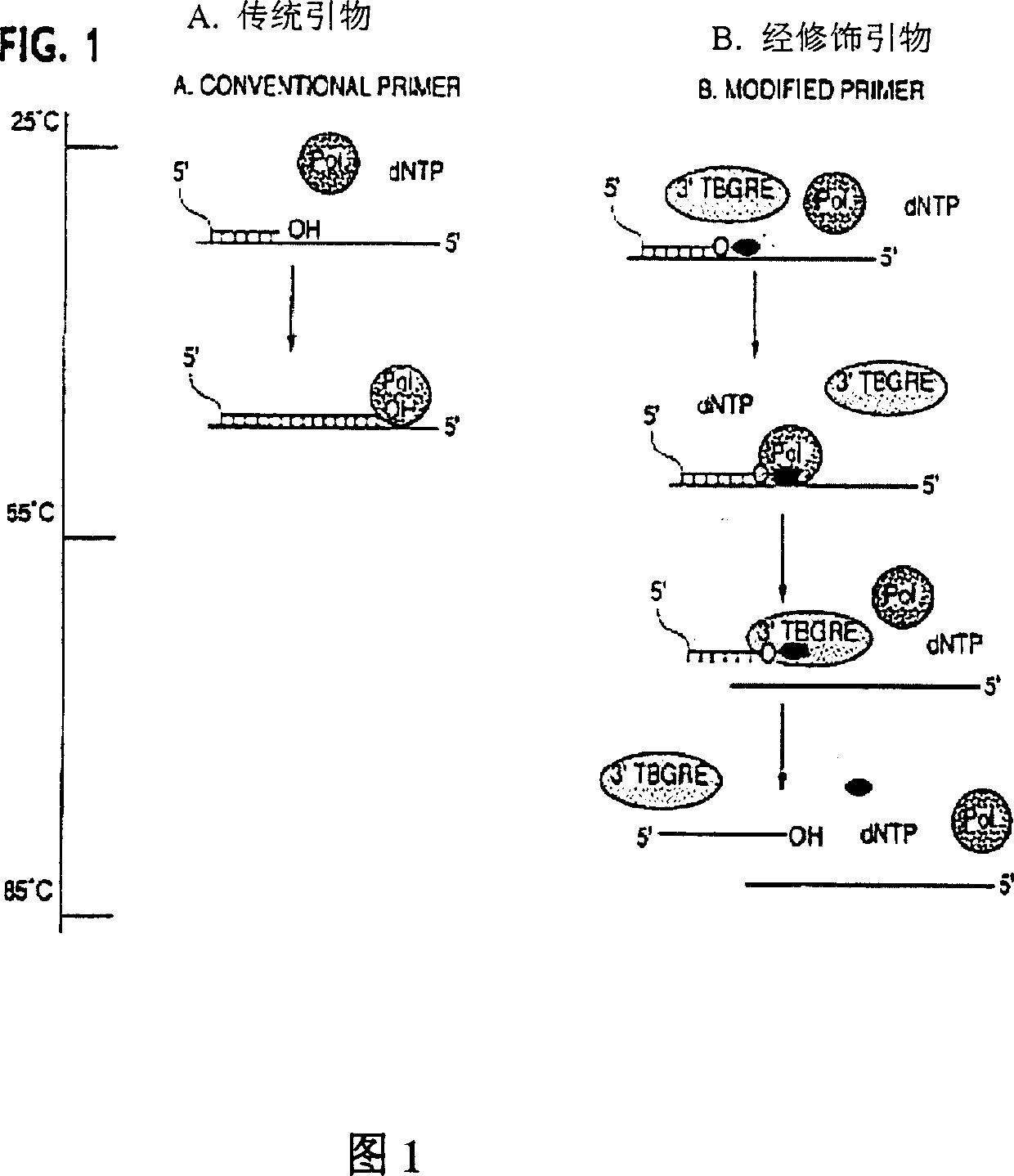
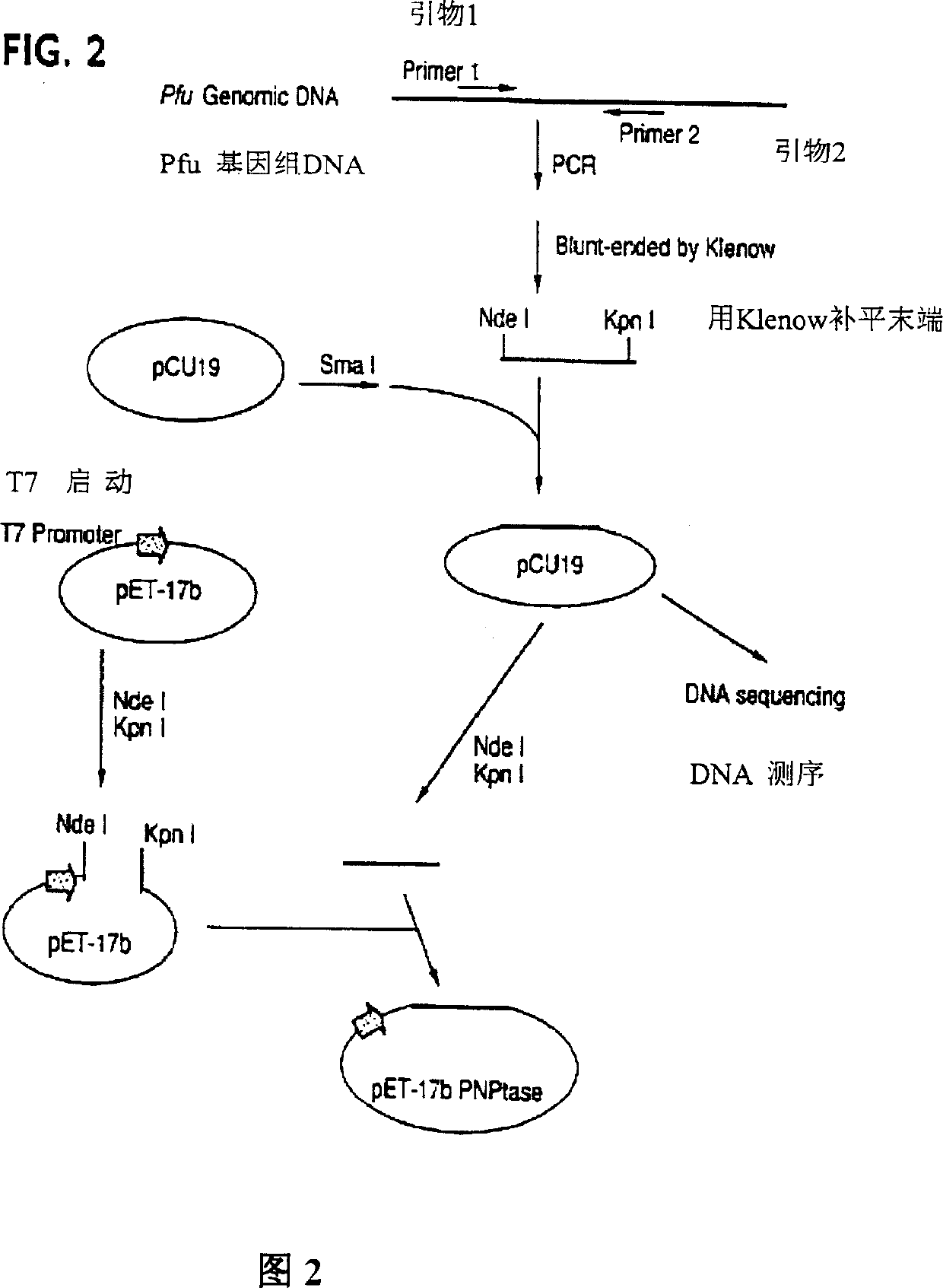
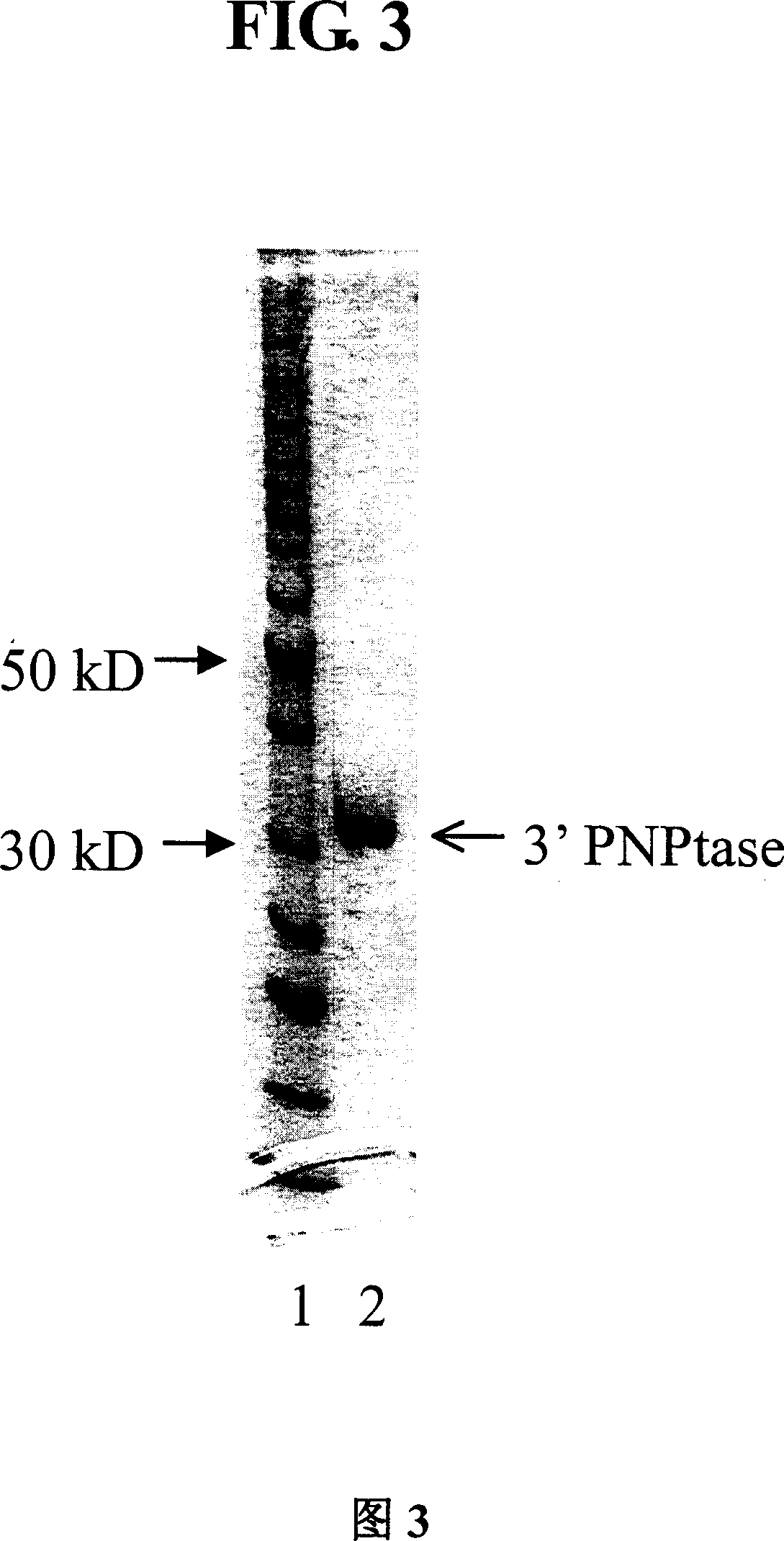
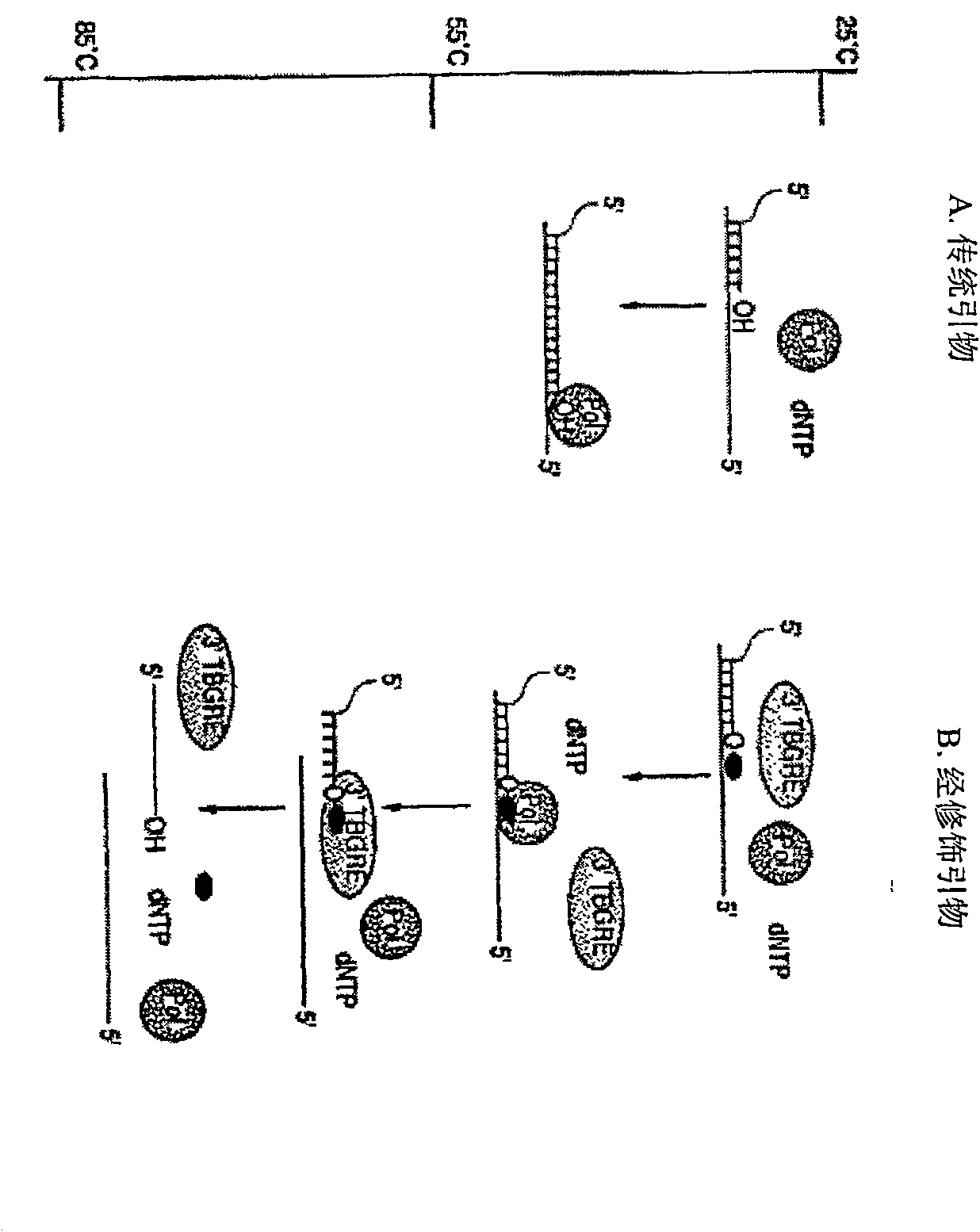
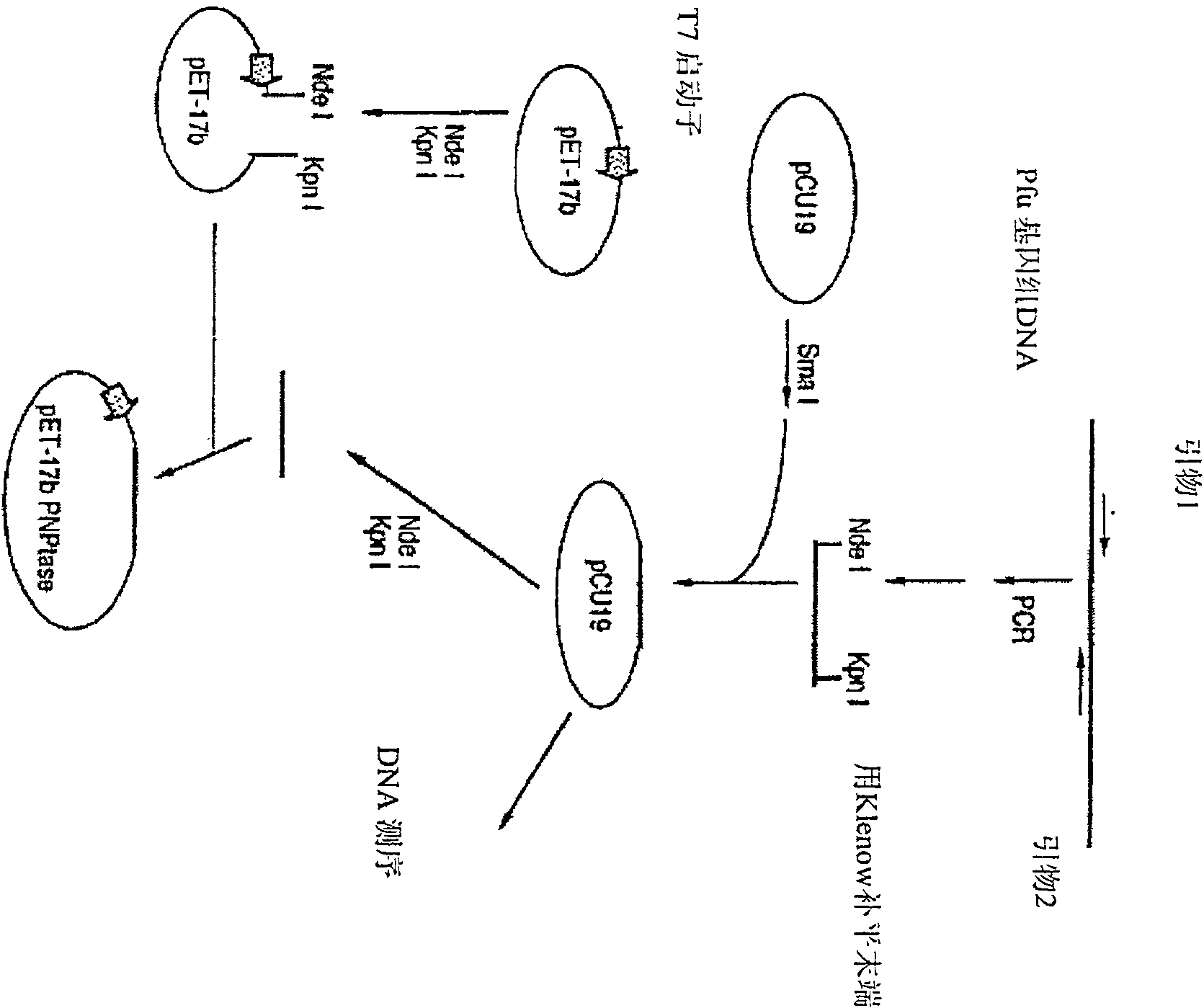
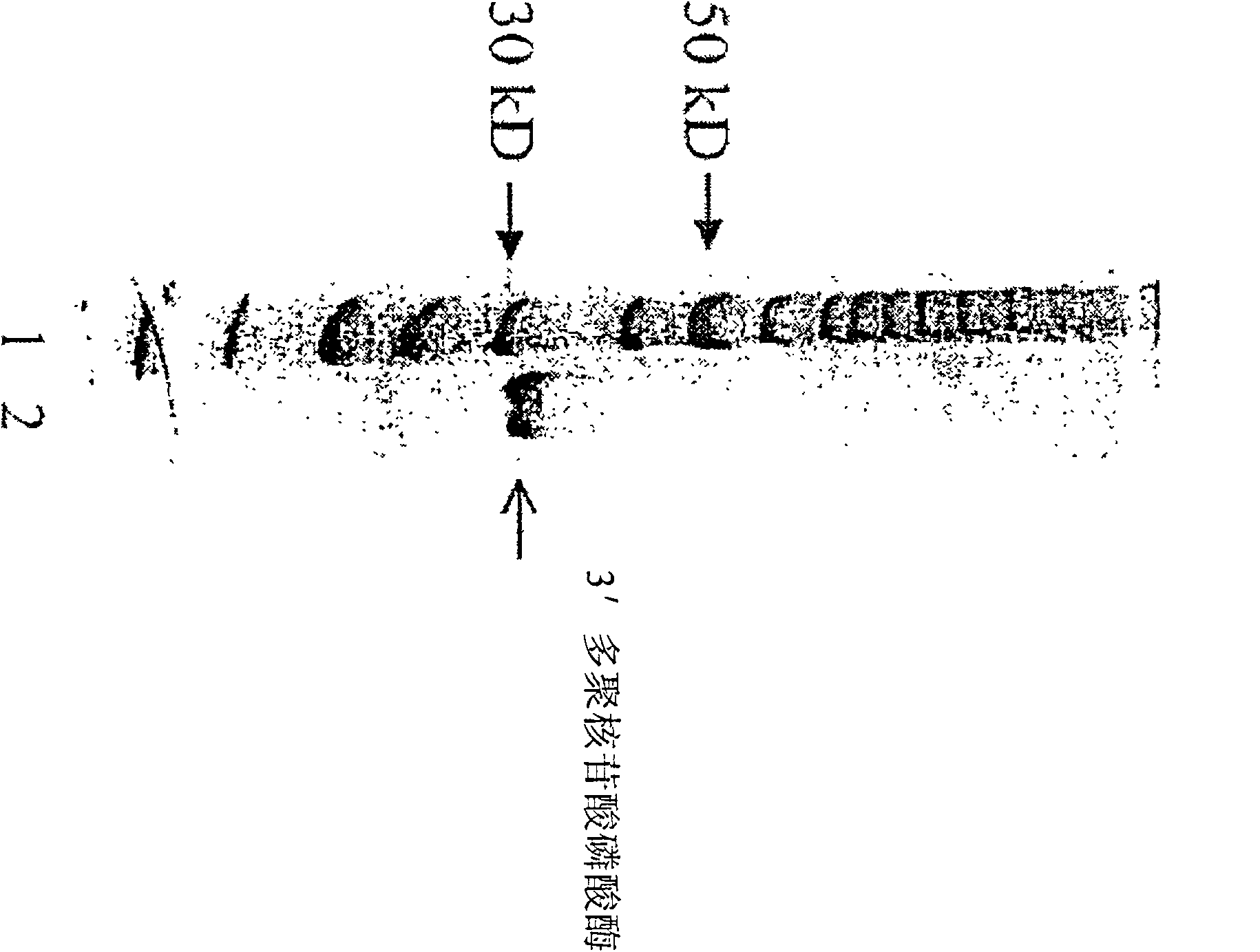
Method and compositions for improved polynucleotide synthesis
The sensitivity and specificity of polynucleotide synthesis is increased by protecting the 3'-end of an oligonucleotide used as a primer in the synthesis of the polynucleotide. Protection of the 3'-end of an oligonucleotide prevents non-specific chain elongation. Removal of blocking group an elevated temperature, using a thermostable enzyme, permits template-specific polynucleotide synthesis. The present invention also provides oligonucleotides with a 3' end protected by a blocking group and a thermostable enzyme capable of removing the blocking group at an elevated temperature. The compositions and methods of the invention are very useful in a variety of techniques for DNA / RNA amplification and analysis, including medical genetics research and diagnosis, pathogen detection, forensic, and animal and plant genetics applications, among others.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FULENGEN
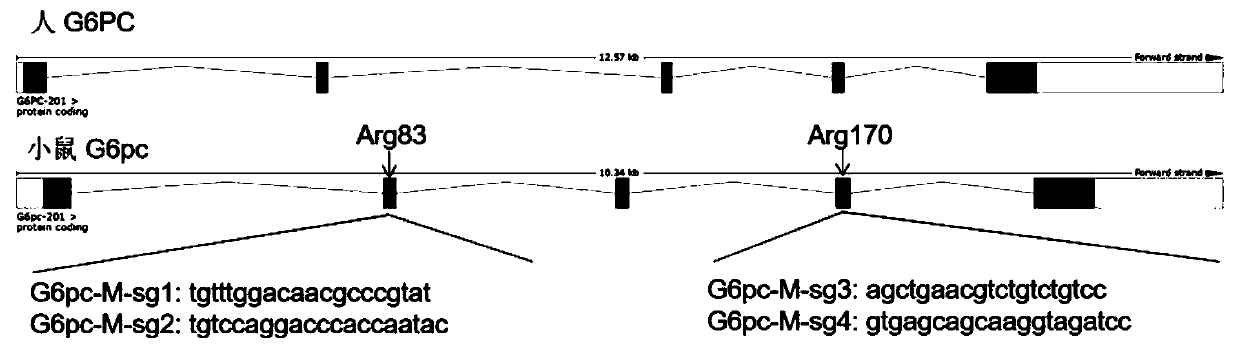
SgRNA targeting sequence specifically targeting mouse G6pc gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110878301AFully activatedRaise the ratioHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAMedical geneticsDNA
The invention discloses a sgRNA targeting sequence specifically targeting the mouse G6pc gene and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medical genetics and molecular biology. Thenucleotide sequence corresponding to the sgRNA contains the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also discloses a method for editing the mouse G6pc gene by using the above sgRNA targetingsequence specifically targeting the mouse G6pc gene. The sgRNA targeting sequence of the invention can mediate the Cas9 protein and efficiently cut target DNA, and further can be used for editing themouse G6pc gene to affect the function of mouse G6pc gene encoding protein. The sgRNA targeting sequence can efficiently realize targeting by a CRISPR / Cas9 system with an efficiency of 100%.
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Fluorescence in situ hybridization hTERT transfected external quality assessment cell line and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104059882ALive foreverMeet quality control requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceDigestion
The invention relates to a fluorescence in situ hybridization hTERT transfected external quality assessment cell line for diagnosis quality control in medical genetics, and a preparation method thereof. The invention is mainly characterized in that the preparation method comprises: performing double digestion of plasmid pCIneo-hTERT and a carrier pLXSNneo by endonucleases of EcoR I and Xho I, connecting the digestion products of hTERT and pLXSNneo by Ligation Mix, constructing a pLXSNneo-hTERT recon, transfecting, by liposome, residual adherent living cells which are in logarithmic growth and are definitely diagnosed to have common numerical abnormalities of chromosomes as needed by clinical diagnosis and treatment, screening cell lines integrated with the recons by G418, performing subculture amplification and cryopreservation, then taking the cell lines, mixing the cell lines according to a required ratio for quality control so as to convert each original cell line with only one numerical abnormality of chromosomes into a chimera quality-control cell line with a certain ratio of common numerical abnormalities of chromosomes. Therefore, the difficulty for differential diagnosis and chimera diagnosis is increased; original cells are easily available; waste residual cells are converted into effective immortalized quality-control cells; external quality assessment is carried out by the difficult quality-control cells; and the cell line of the invention has important significance on in-time discovery and solution of quality problems, and diagnostic level improvement.
Owner:翁炳焕
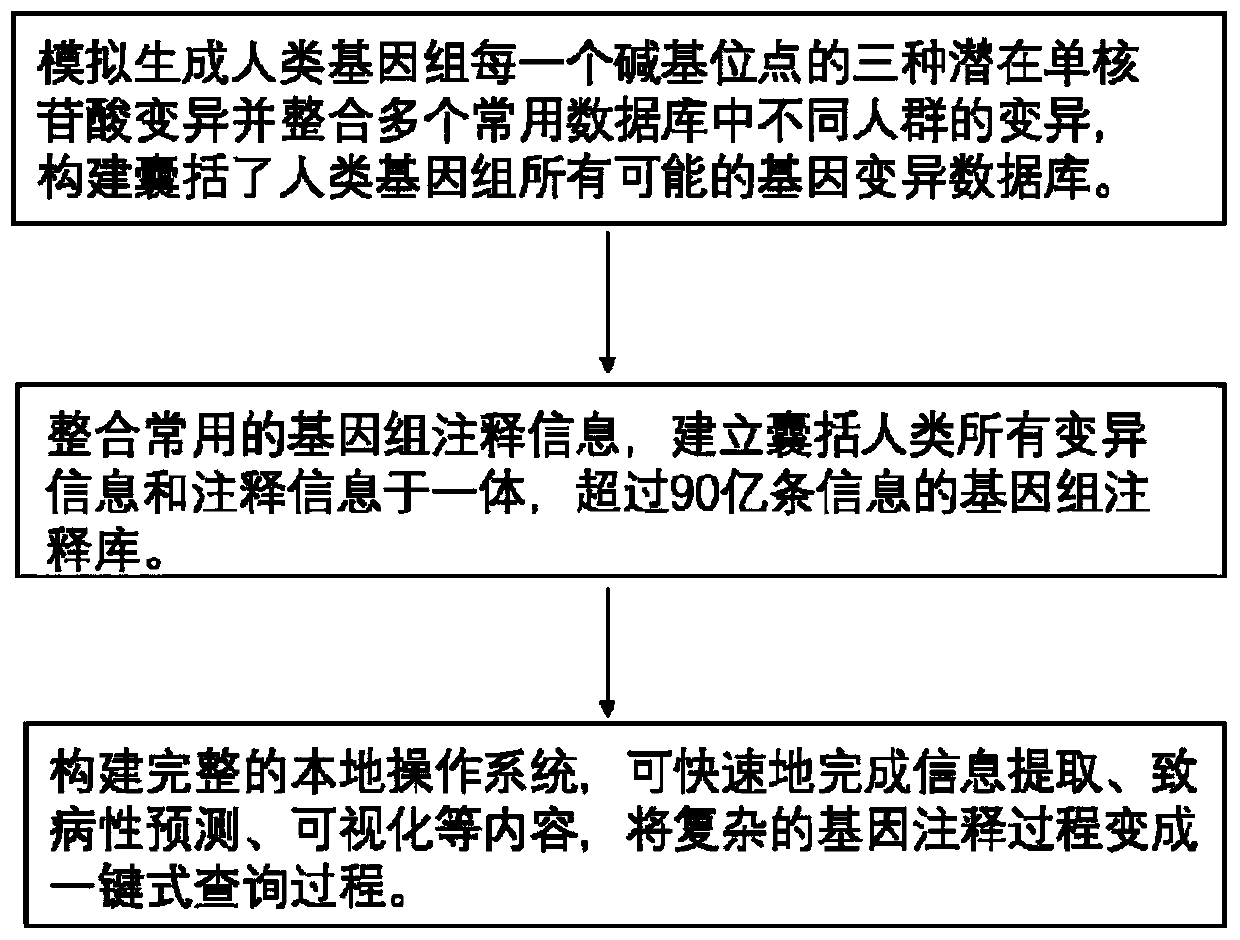
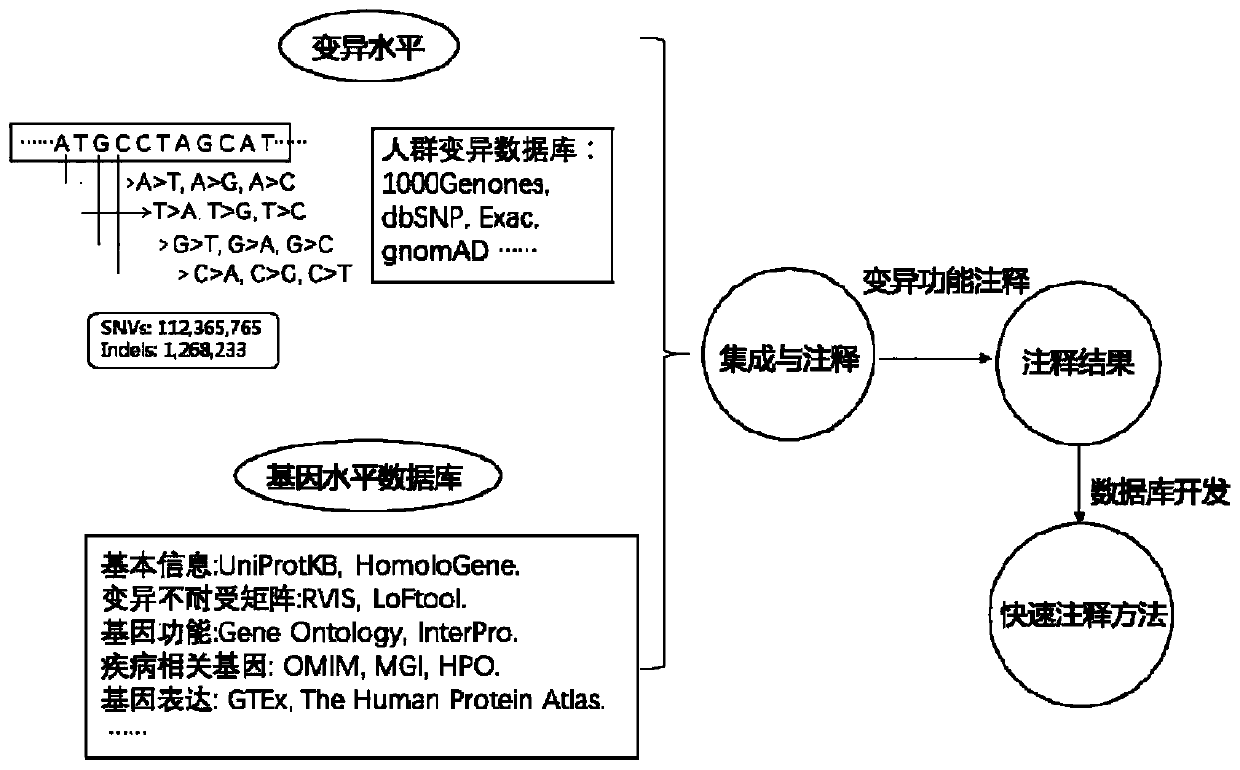
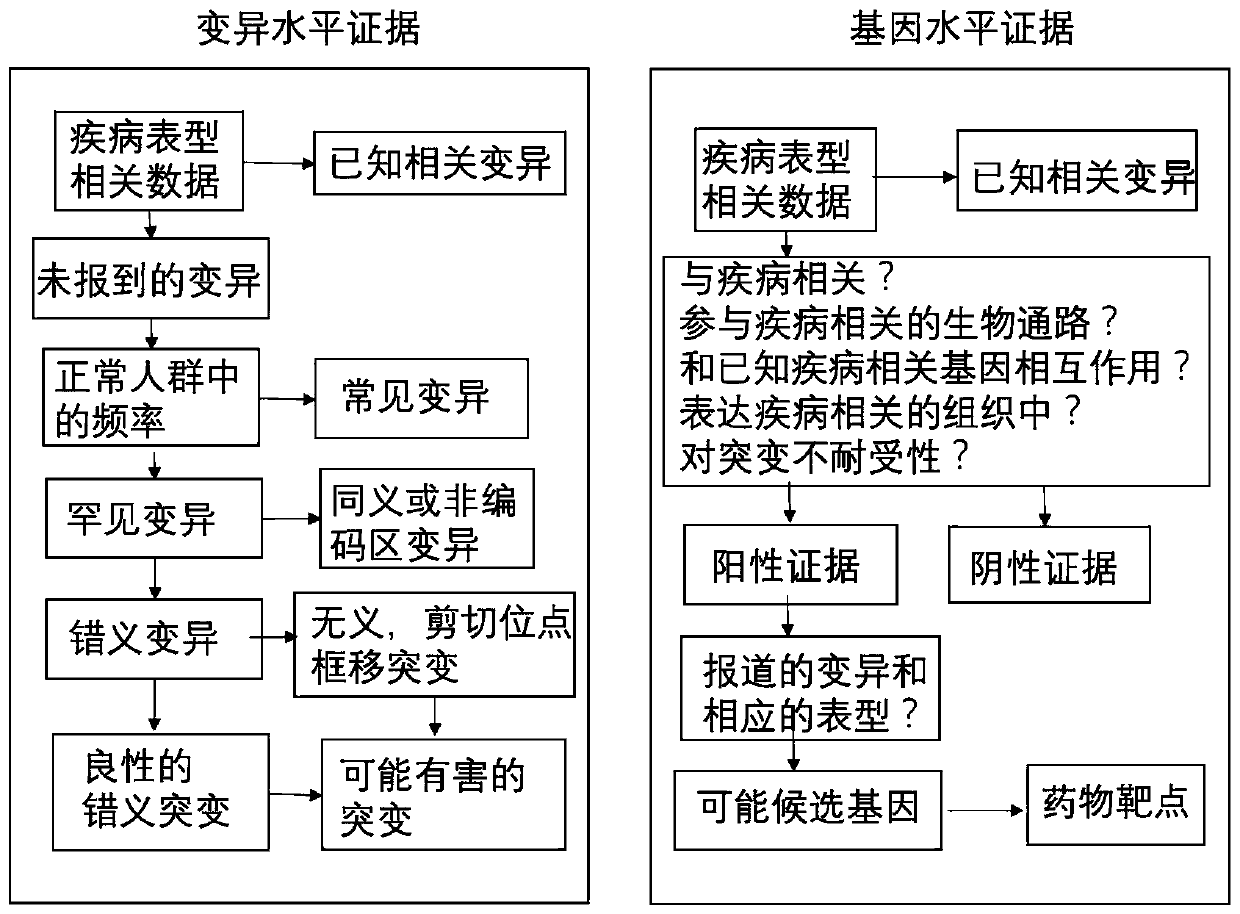
Method for quickly annotating gene mutations of human beings
The invention is applicable to the technical field of medical genetics, and provides a novel method for quickly annotating genes and mutations by constructing an information query database with complete annotations. The method comprises the following steps: (1) simulating to generate three potential mononucleotide variations of each base site of a human genome, and integrating the variations of different populations in a plurality of common databases to construct a database including all possible gene variations of the human genome; (2) further integrating common genome annotation informationon the basis, and establishing a genome annotation library including all variation information and annotation information of human beings into a whole and more than 9 billion pieces of information; and (3) quickly completing information extraction, pathogenicity prediction, visualization and other content in a query mode according to the database. According to the method, a complex gene annotationprocess is changed into a one-stop query process, so that the problems of non-uniform formats, complicated operation and low efficiency caused by matching different gene variations in multiple databases one by one are avoided.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
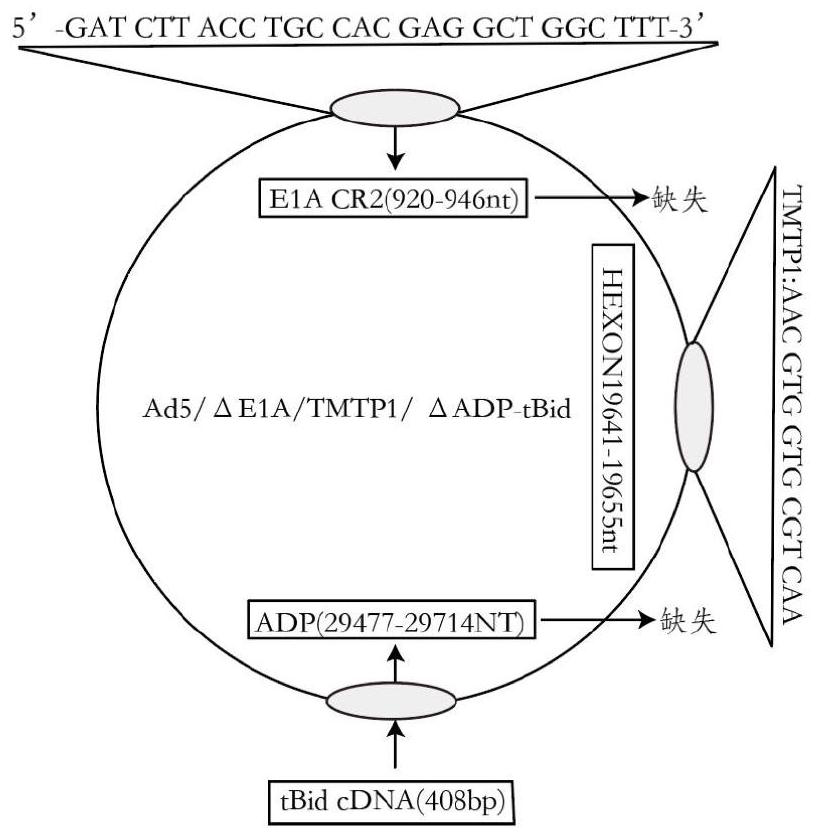
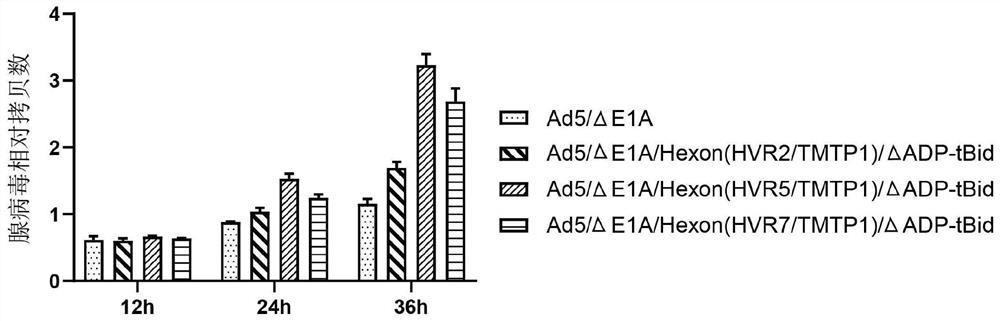
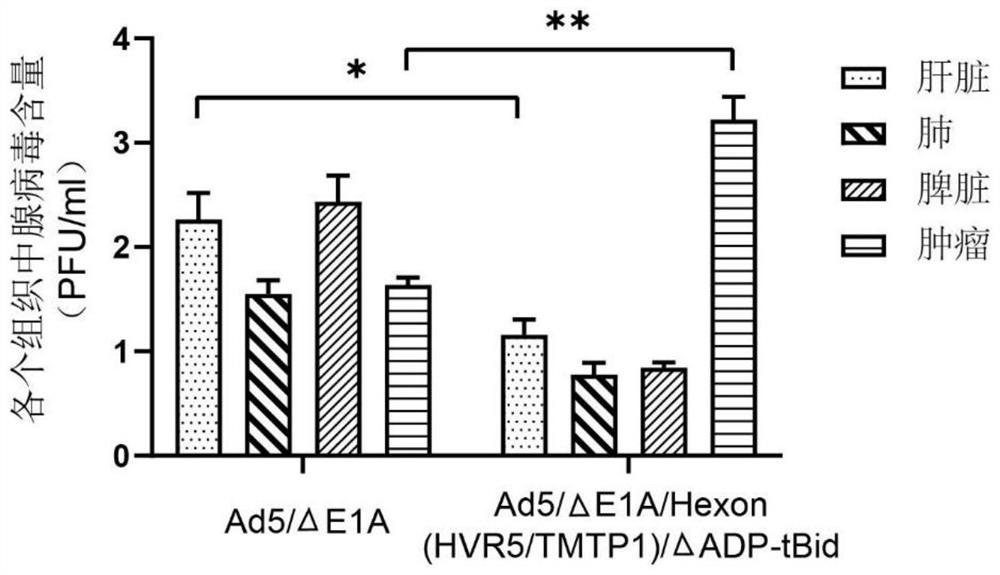
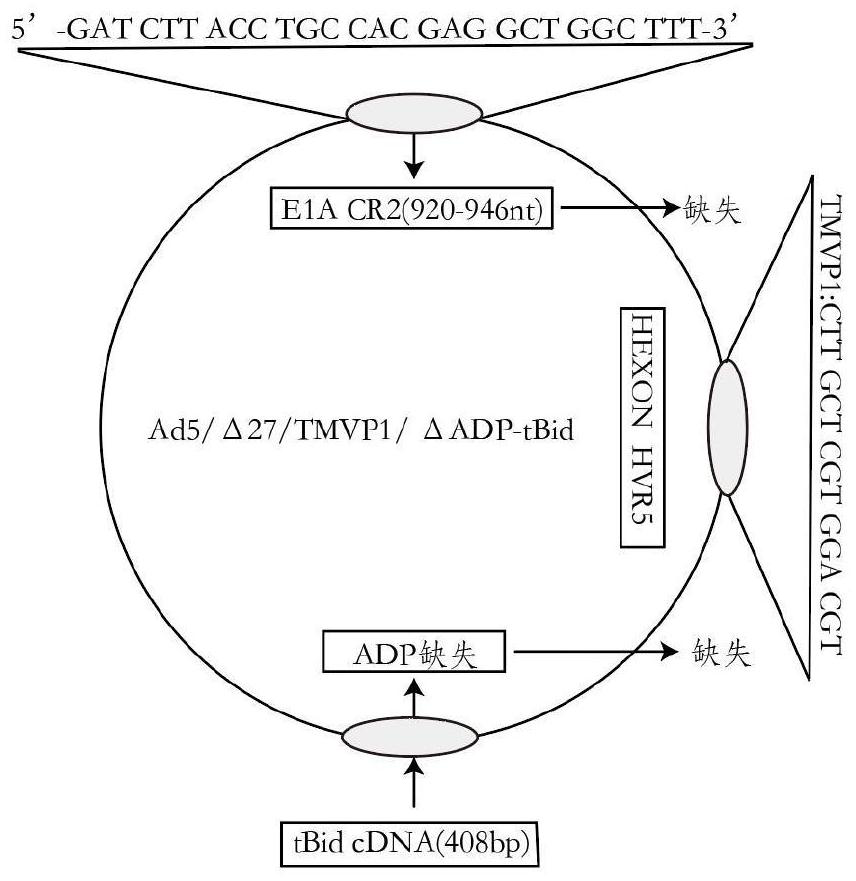
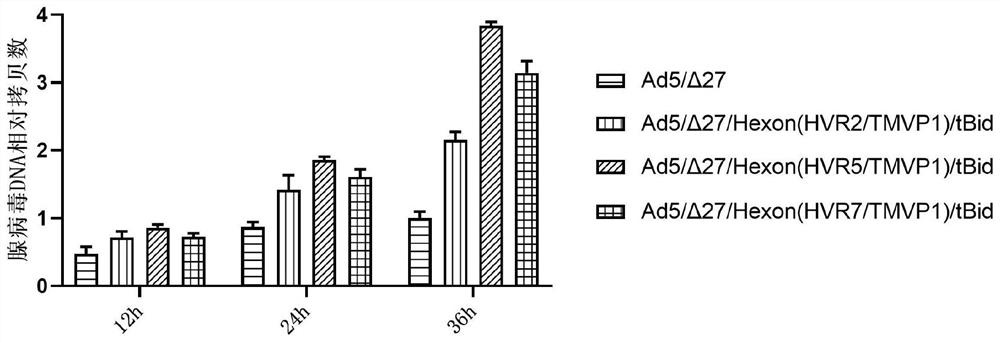
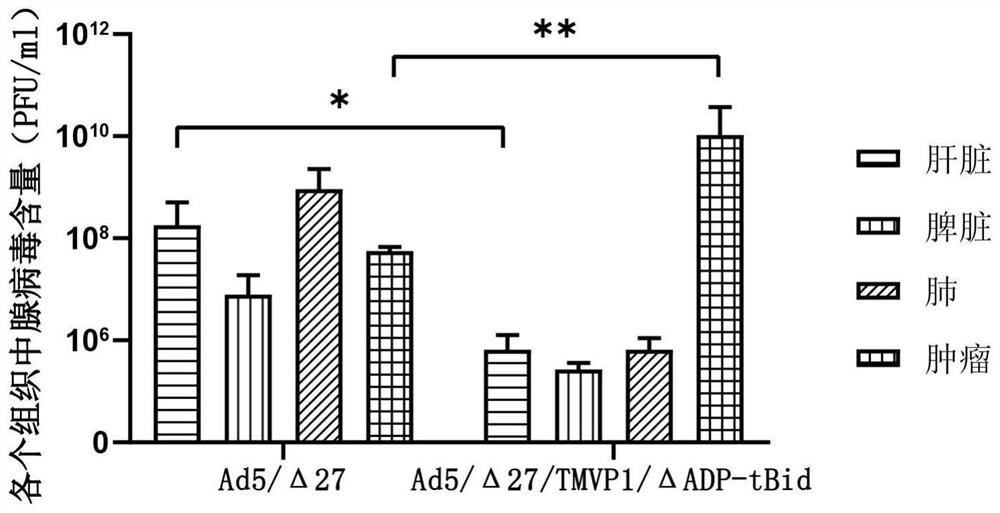
Oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying TMTP1 and tBid as well as construction method and application of oncolytic adenovirus recombinant
PendingCN114317463AExploitationPositive pharmaceutical valuePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTumor targetConserved sequence
The invention discloses an oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying TMTP1 and tBid as well as a construction method and application of the oncolytic adenovirus recombinant, and belongs to the technical field of medical genetic engineering. According to the invention, 27 basic groups in a 920nt-946nt region are deleted in a second region of an E1A conserved sequence of a human type 5 adenovirus gene, a gene sequence for coding a tumor targeting peptide TMTP1 is inserted in a 19641nt-19655nt region of a Hexon hypervariable region 5, an E3 region is deleted in a 29477nt-29714nt region of an ADP gene to form a deletion region, a gene sequence of a mitochondrial apoptosis peptide tBid is inserted in the deletion region, and a Cla1 enzyme cutting site is introduced. The invention also discloses a construction method and application of the oncolytic adenovirus recombinant. The oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying the TMTP1 and the tBid disclosed by the invention has an ideal targeting effect and a strong killing effect.
Owner:WUHAN KDWS BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
SiRNA (small interfering ribose nucleic acid) for inhibiting homosapiens chromosome2open reading frame 3(C2 or f3) (GCF) gene expression, carrier of SiRNA for inhibiting GCF gene expression and application
InactiveCN102994503BInhibit expressionHigh interference efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBase JGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a SiRNA (small interfering ribose nucleic acid) for inhibiting homosapiens chromosome 2 open reading frame 3(C2 or f3) (GCF) gene expression, which belongs to the field of medical genetic engineering. Deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) for an encoding SiRNA is selected from arbitrary group of (a), (b) and (c): (a) a base sequence of a positive-sense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the base sequence of an antisense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.2; (b) the base sequence of the positive-sense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.3, and the base sequence of the antisense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.4; and (c) the base sequence of the positive-sense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.5, and the base sequence of the antisense strand is shown as SEQ ID No.6. The invention further discloses a recombinant plasmid which comprises the DNA of the encoding SiRNA and a GCF-shRNA-HeLaCGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center) No.5821, and a cell line has high RNA interfering efficiency, strong specificity and no toxic and side effects and can effectively inhibit GCF gene expression. The SiRNA for inhibiting GCF gene expression, the recombinant plasmid and the GCF-shRNA-HeLa monoclonal cell can also be used for preparing medicines for treating cervical cancer.
Owner:NAT INST FOR RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION & NUCLEAR SAFETY CHINESE CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION +2
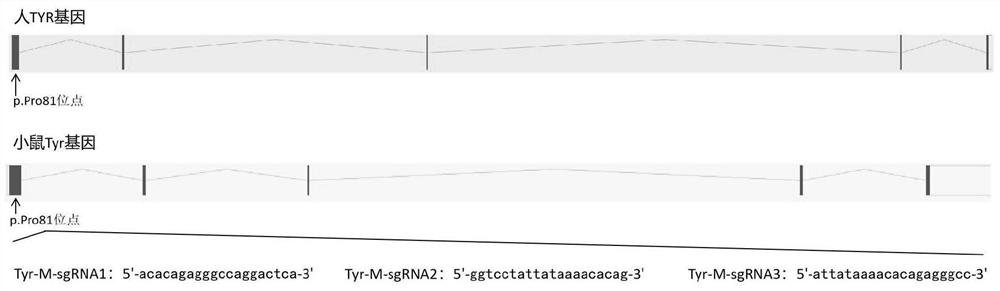
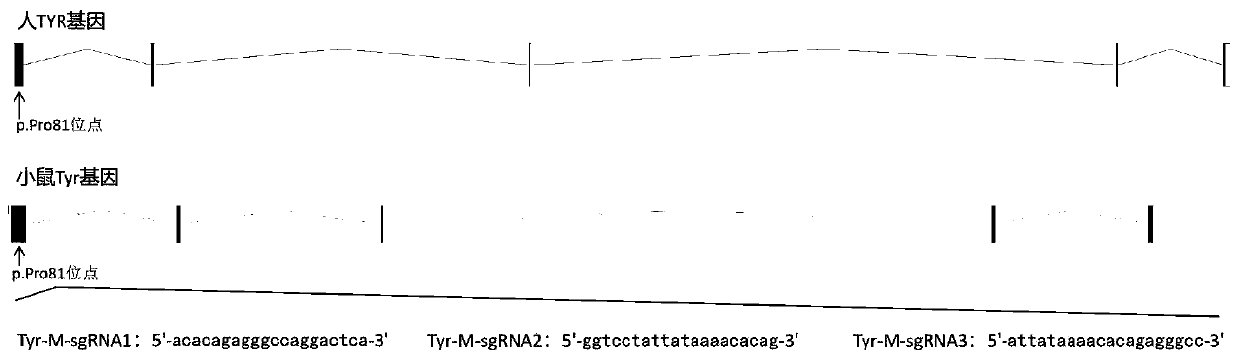
A kind of sgRNA guide sequence and its application of specific targeting mouse tyr gene
ActiveCN110862984BEfficient shootingEnables genotype analysisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotide sequencingMedical genetics
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
SMN gene main transition region DNA amplification method
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical genetics, and relates to a SMN gene main transition region DNA amplification method. The technical problem to be solved is conventional DNA of amain transition region of a SMN gene and the DNA amplification method containing methylation information. The technical scheme is characterized in that a DNA amplification primer is designed, and a 3' end of the primer does not contain nucleotide C in a corresponding genome, so that PCR amplification can be prevented from being affected by potential methylation at the end of the corresponding transition region. The stable and optimized PCR reaction conditions can be found. The main purpose of the method comprises screening for polymorphic sites of the molecular background of gene conversion in the main transition region of the SMN gene, and providing a basis for the methylation of CpG site potentially associated with DNA hypomethylation and SMN gene transformation. The method provides a prerequisite for the study of mechanisms that can relatively reduce the condition of SMA, and can be applied to find gene therapy targets.
Owner:刘维亮 +3
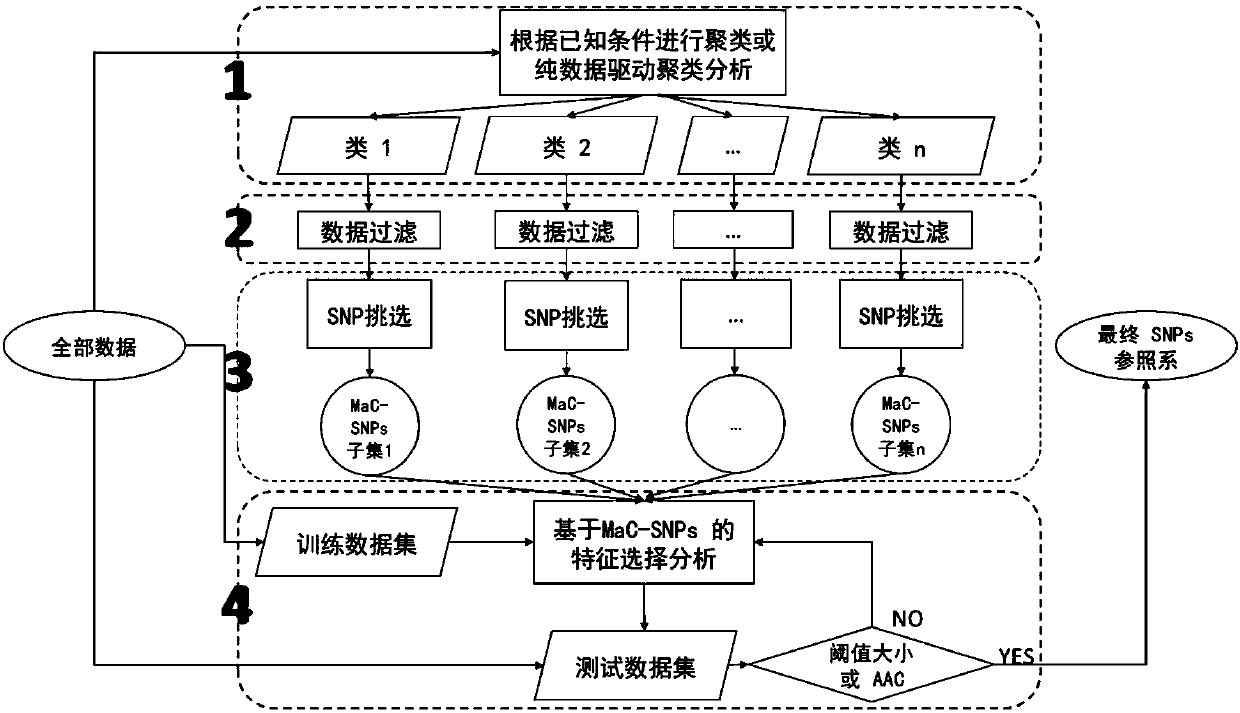
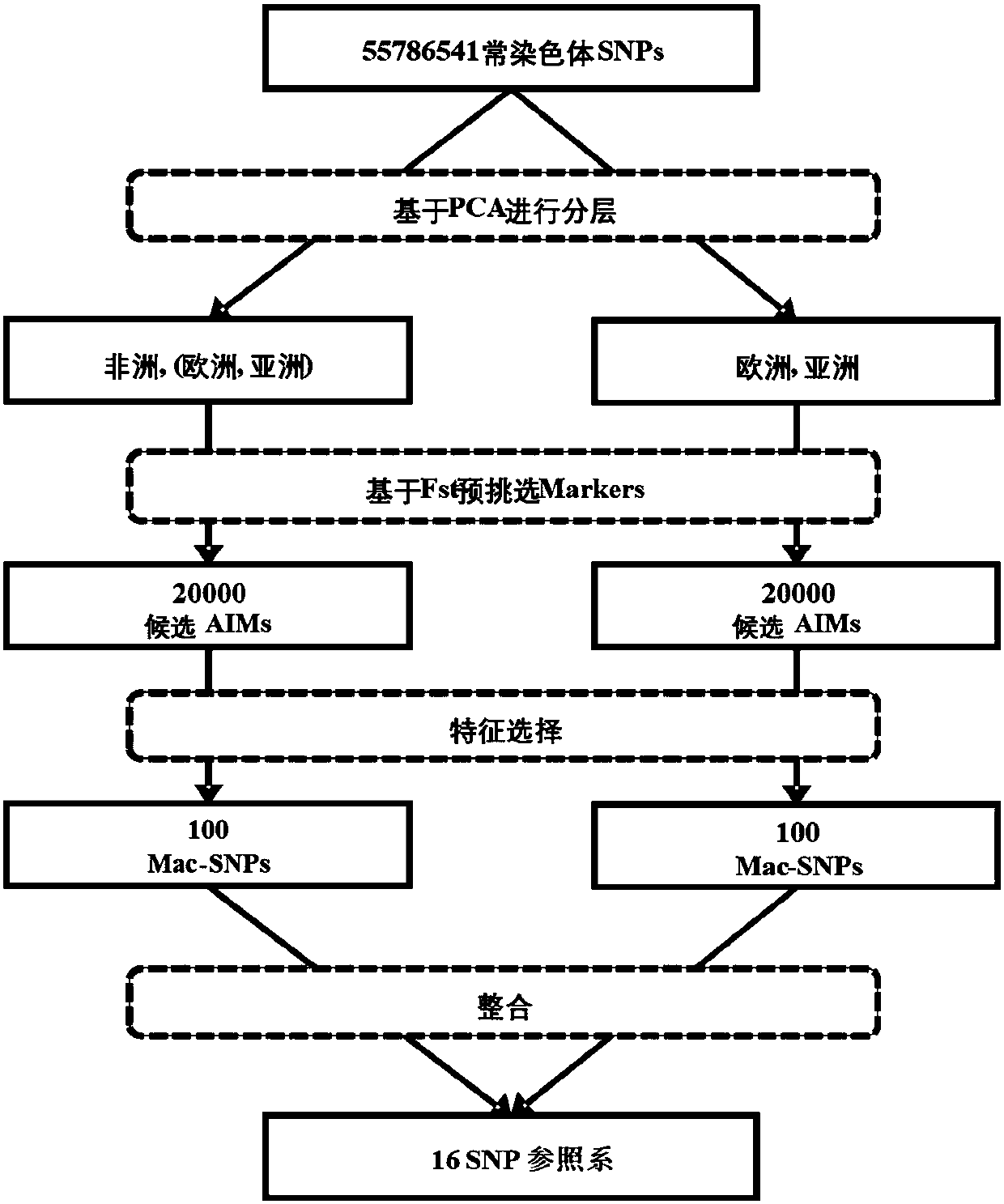
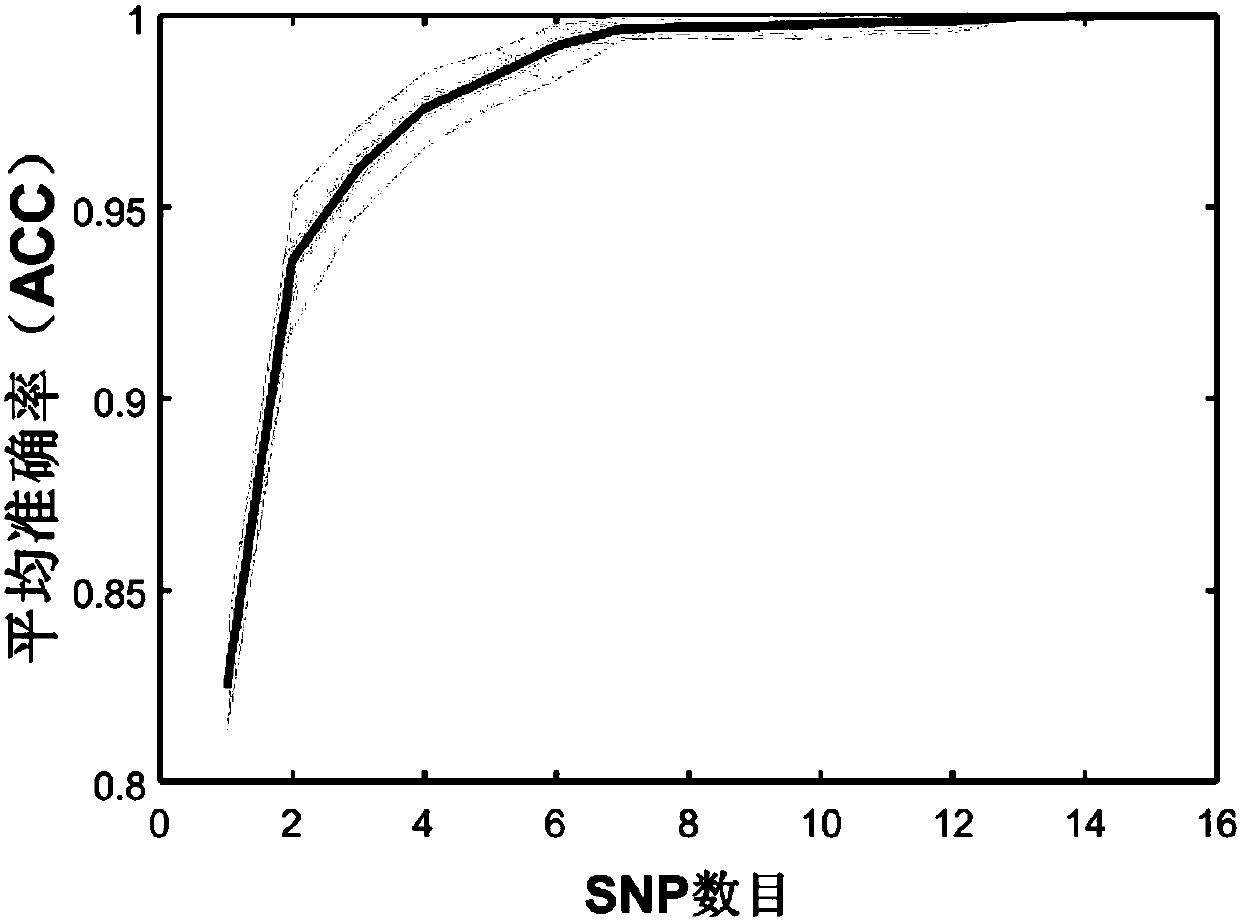
Constructing method of genetic marker reference system for group differentiating and identification, and genetic marker reference system
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and genetics, and particularly discloses a constructing method of a genetic marker reference system for group differentiating and identification, and a genetic marker reference system. The constructing method comprises the steps of performing data segmentation on genetic marker data, performing genetic marker selection, or filtering the segmented data according to the condition, or performing integration optimization on the selected genetic marker. The method according to the invention can successfully reduce computing complexity from O(2n) to O(n2). In combination with some simple pre-screening strategies, the method according to the invention can process the whole genome data of thousands of persons to ten thousands of person, and selects the genetic marker reference system. In actual application, the method can be used for selecting the reference system which has preset accuracy (such as 95% or 99%) and comprises relatively small number of genetic markers according to the actual requirement. The characteristics have an important application value in legal examiner or medical genetic researching.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying TMVP1 and tBid as well as construction method and application of oncolytic adenovirus recombinant
PendingCN114317462AExploitationPositive pharmaceutical valuePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTumor targetConserved sequence
The invention discloses an oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying TMVP1 and tBid as well as a construction method and application of the oncolytic adenovirus recombinant, and belongs to the technical field of medical genetic engineering. According to the invention, 27 basic groups in a 920nt-946nt region are deleted in a second region of an E1A conserved sequence of a human type 5 adenovirus gene, a gene sequence for coding a tumor targeting peptide TMVP1 is inserted in a 19641nt-19655nt region of a Hexon hypervariable region 5, an E3 region is deleted in a 29477nt-29714nt region of an ADP gene to form a deletion region, a gene sequence of a mitochondrial apoptosis peptide tBid is inserted in the deletion region, and a Cla1 enzyme cutting site is introduced. The invention also discloses a construction method and application of the oncolytic adenovirus recombinant. The oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying the TMVP1 and the tBid disclosed by the invention has an ideal targeting effect and a strong killing effect.
Owner:WUHAN KDWS BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
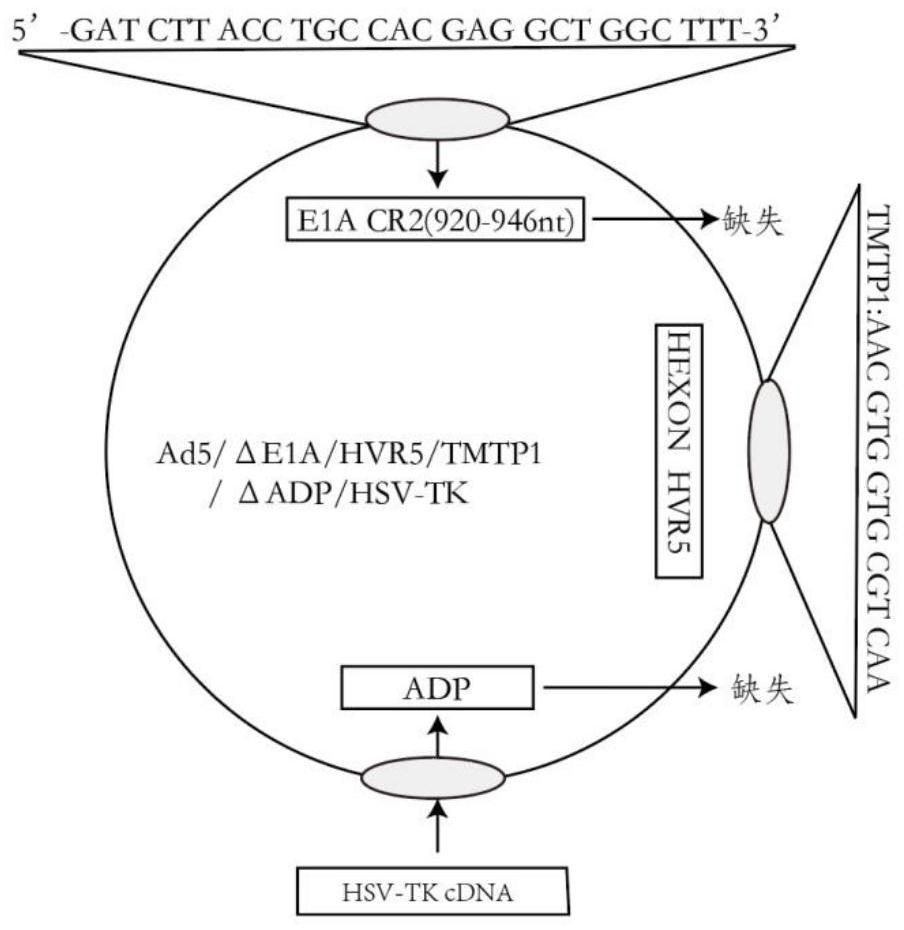
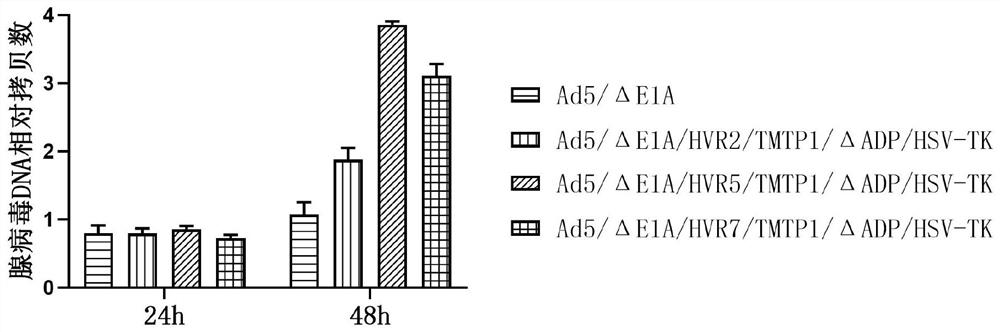
Oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying TMTP1 and HSV-TK as well as construction method and application of oncolytic adenovirus recombinant
PendingCN114231504AExploitationPositive pharmaceutical valuePeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesTumor targetConserved sequence
The invention discloses an oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying TMTP1 and HSV-TK as well as a construction method and application of the oncolytic adenovirus recombinant, and belongs to the technical field of medical genetic engineering. According to the invention, 27 basic groups in a 920-946nt region are deleted in a second region of an E1A conserved sequence of a human type 5 adenovirus gene, a gene sequence for coding a tumor targeting peptide TMTP1 is inserted in a 19641-19655nt region of a Hexon hypervariable region 5, an E3 region is deleted in a 29477th-29714nt region of an ADP gene to form a deletion region, a full-length coding sequence for coding an HSV-TK gene is inserted in the deletion region, and a Cla1 enzyme cutting site is introduced. The invention also discloses a construction method and application of the oncolytic adenovirus recombinant. The oncolytic adenovirus recombinant carrying the TMTP1 and the HSV-TK disclosed by the invention has an ideal targeting effect and a strong killing effect.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
A fluorescently labeled x-indel site compound amplification system and its application
ActiveCN104131067BHigh sensitivityHigh individual recognition rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceInsertion deletionMultiplexing
The invention provides a fluorescently-labeled X-InDel locus composite amplification system. By means of the system, eighteen insertion-deletion genetic polymorphism loci on an X chromosome can be compositely amplified, wherein the eighteen loci are respectively labeled with three fluoresceins FAM, HEX and TAMRA. The composite amplification system is high in sensitivity and individual identification rate, is high in polymorphism, is good in stability and repeatability, is accurate in typing results and can satisfy a practical requirement. A kit can be manufactured on the basis of the composite amplification system, can be used for paternity test, dyad paternity test, grandparent and grandchild test, sibling test and individual identification. New technologies can be provided for the fields such as anthropology, medical genetics and the like.
Owner:ACADEMY OF FORENSIC SCIENCE
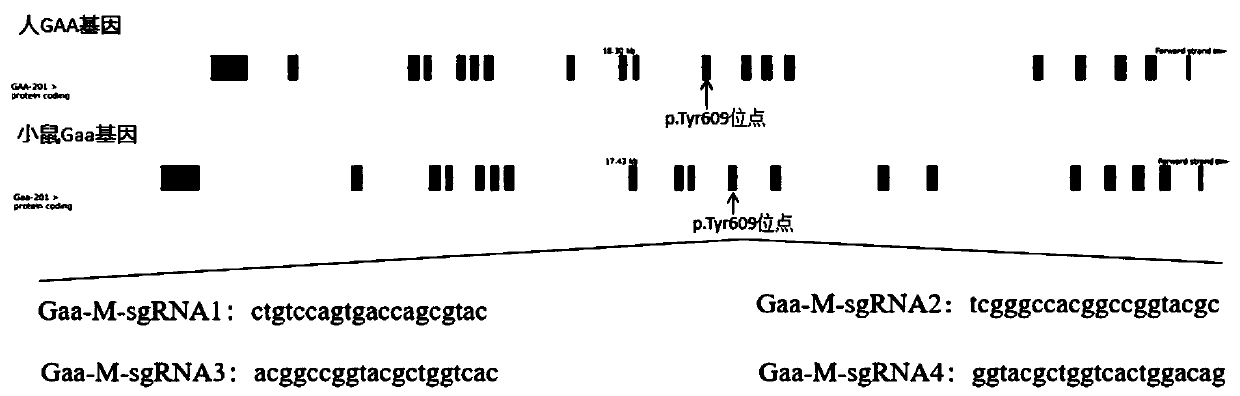
sgRNA guide sequence of specific targeting mouse Gaa gene and application of thereof
ActiveCN110862982AFully activatedRaise the ratioCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotide sequencingMedical genetics
The invention discloses an sgRNA guide sequence of a specific targeting mouse Gaa gene and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of medical genetics and molecular biology. A nucleotide sequence corresponding to the sgRNA is any one of SEQ ID NO. 1, SEQ ID NO. 2 and SEQ ID NO. 3. The invention also discloses a method for editing the mouse Gaa gene by using the sgRNA guide sequence of the specific targeting mouse Gaa gene. The sgRNA guide sequence disclosed by the invention can mediate Cas9 protein to efficiently cut target DNA, so that the sgRNA guide sequence is used forediting the mouse Gaa gene to influence the function of encoding protein of the mouse Gaa gene. According to the sgRNA guide sequence, efficient targeting can be achieved through a CRISPR / Cas9 system,and the efficiency is 100%.
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
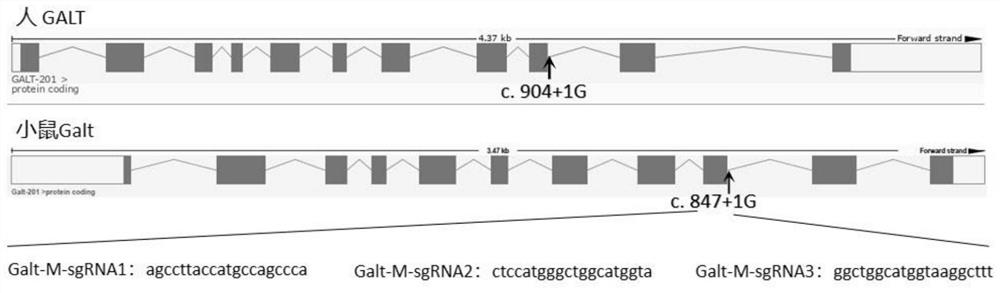
A kind of sgRNA guide sequence specifically targeting mouse galt gene and its application
ActiveCN110777145BEfficient cuttingSpecific cleavageStable introduction of DNAAnimals/human peptidesNucleotide sequencingMedical genetics
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Typing method for multicolor fluorescence composite detection of 20 X-SNP sites
ActiveCN103215360BIncrease success rateSolve the problem of complex genetic relationship identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceTyping methods
The invention discloses a typing method for multicolor fluorescence composite detection of 20 X-SNP sites, belonging to the technical field of medical genetic relationship identification. The typing method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a DNA solution; (2) amplifying; (3) purifying an amplification product; (4) extension reacting; (5) purifying an extension product; and (6) detecting and determining the extension product. By virtue of the invention, the segment range of target DNA to be detected is shortened to 61-99 bp, the success rate of highly degraded DNA typing is improved, and the difficulty of identifying of complicated genetic relationships, for example, ancestral relationship, half-sib relationship and sibship, can be overcome. The typing method has large advantages and potentials on complicated genetic relationship identification and forensic typing of highly degraded material DNA.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
sgRNA guide sequence of specific targeting mouse Tyr gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110862984AEfficient shootingEnables genotype analysisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses an sgRNA guide sequence of a specific targeting mouse Tyr gene and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of medical genetics and molecular biology. A nucleotide sequence corresponding to the sgRNA is any one of SEQ ID NO. 1, SEQ ID NO. 2 and SEQ ID NO. 3. The invention also discloses a method for editing the mouse Tyr gene by utilizing the sgRNA guidesequence of the specific targeting mouse Tyr gene. The sgRNA guide sequence disclosed by the invention can mediate Cas9 protein to efficiently cut target DNA, so that the sgRNA guide sequence is usedfor editing the Tyr gene of a mouse to influence the function of the Tyr gene encoding protein of the mouse. According to the sgRNA guide sequence, efficient targeting can be achieved through a CRISPR / Cas9 system, and the efficiency is 100%.
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Obtaining method and use of novel oncolytic adenovirus construct with selective tumor blockage STAT3
ActiveCN101440379BIncreased amplificationHigh activityGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsOncolytic adenovirusWilms' tumor
The invention discloses a proposal for constructing novel oncocytic adenovirus of selectively closed tumor STAT3 obtained by manual reconstruction of human 5 type adenovirus (Ad5), and particular application of a recombined adenovirus constructor in tumor treatment, and belongs to the technical field of medical genetic engineering. By techniques of PCR enlarging fixed point deletion, enzyme cutting, connection, cloning, homologous recombination, transfection, single cloning purification of adenovirus and the like, the recombination adenovirus constructor is obtained. The technical characteristics comprise that 27 basic groups are deleted in an E1A conservative sequence 2(CR2) zone of Ad5 genome; 29477 to 29714nt in an E3 zone of ADP gene are deleted; and partial STAT cDNA segments are oppositely inserted in the deletion zones. The constructor is a novel oncocytic adenovirus vector with higher tumor selective copy capability. The constructor has unique practical values in biological treatment of tumor, and also provides a reasonable gene target point specificity treatment mode for the genetic treatment of tumor.
Owner:南京江北新区生物医药公共服务平台有限公司
A method for determining the grading of genetic tumor mutation sites
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Method and compositions for improved polynucleotide synthesis
Owner:GUANGZHOU FULENGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com