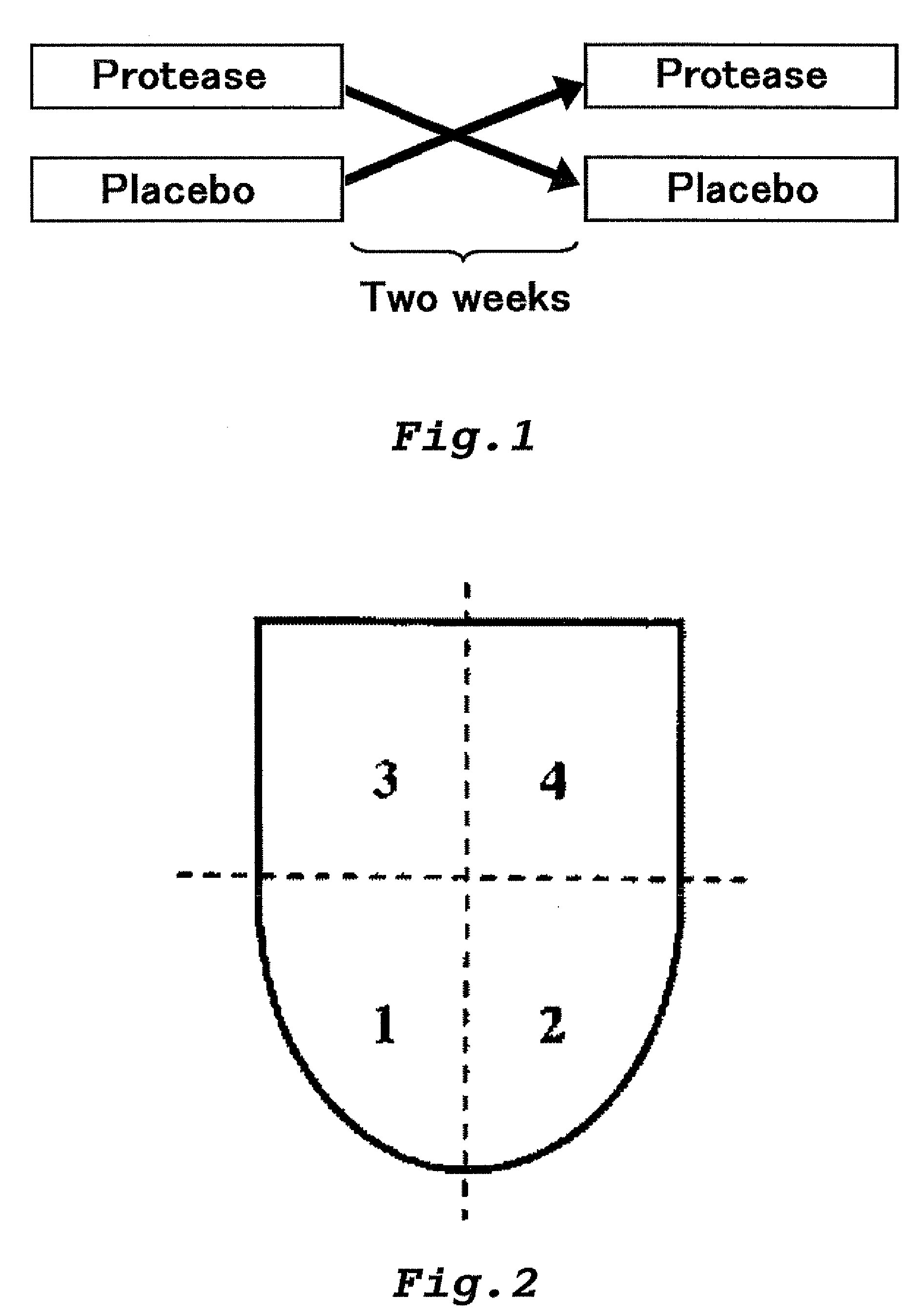
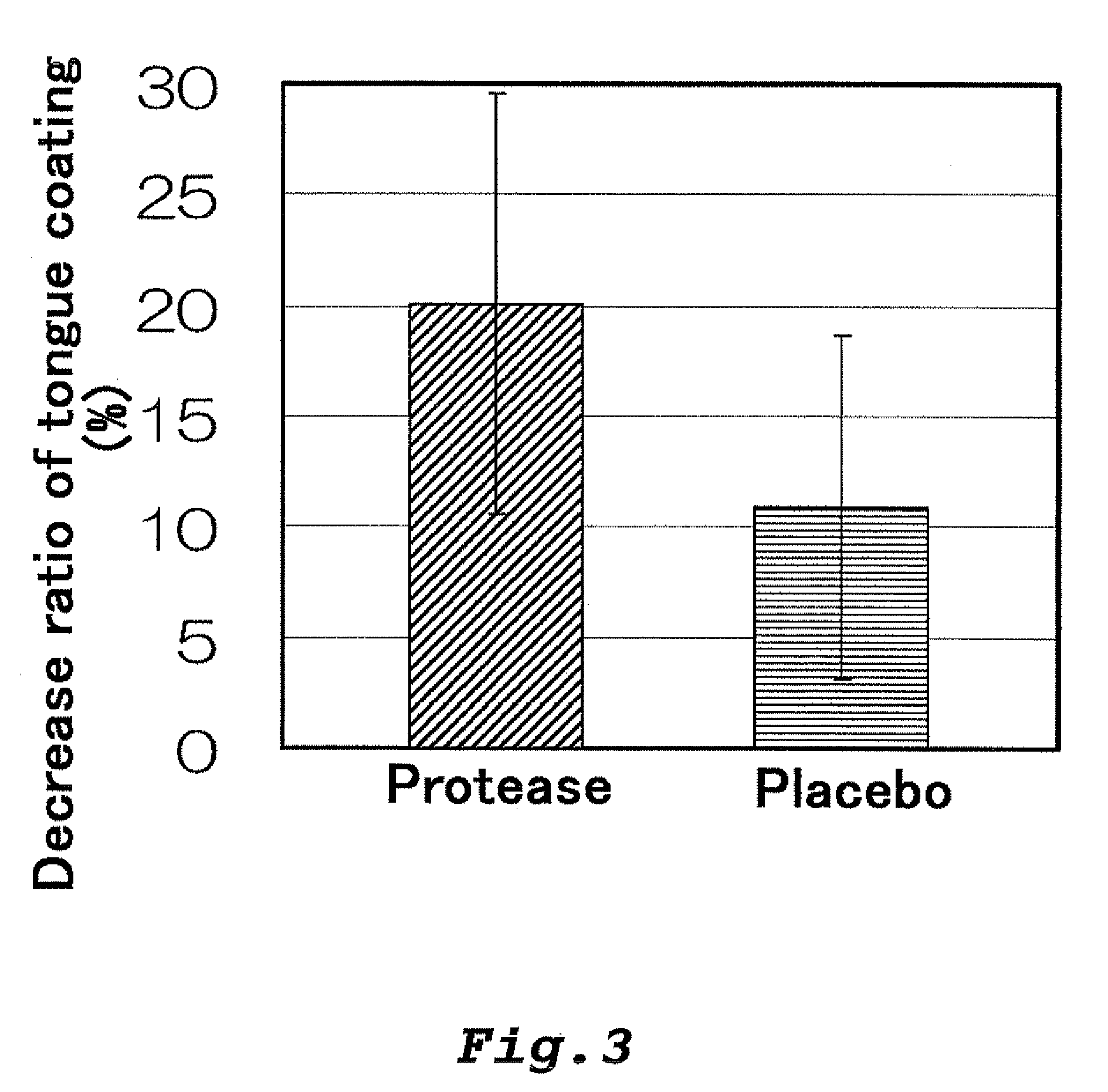
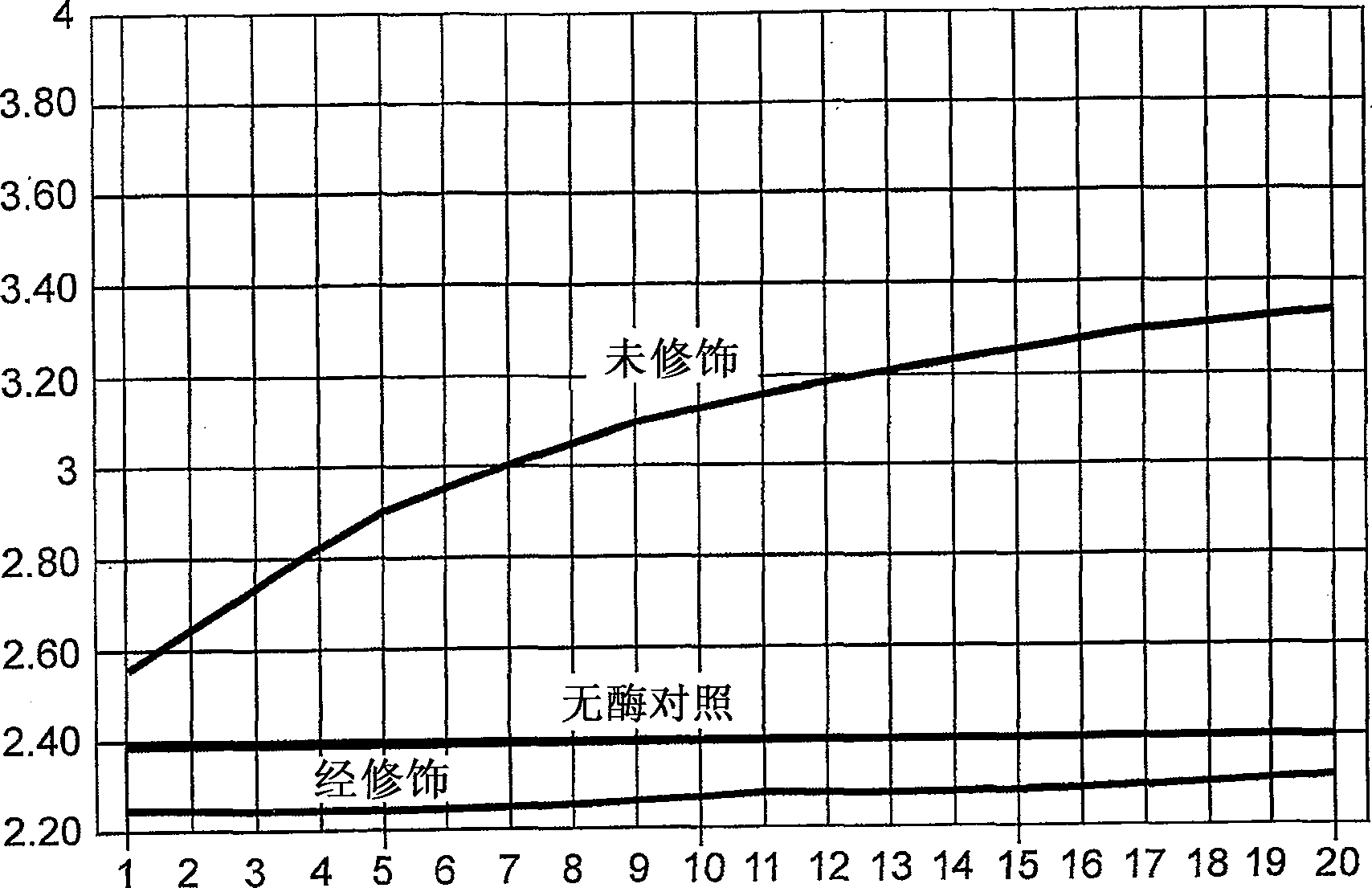
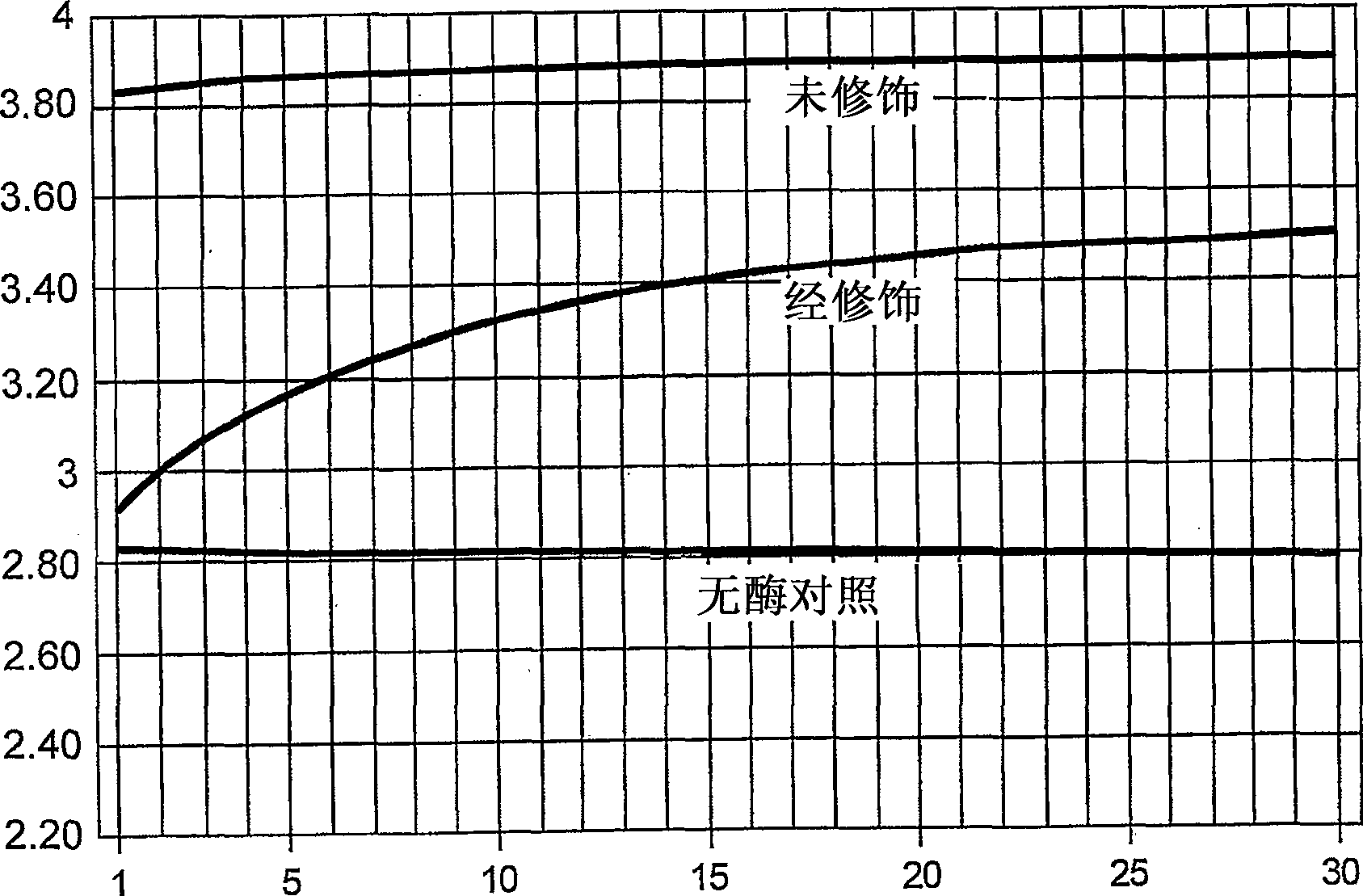
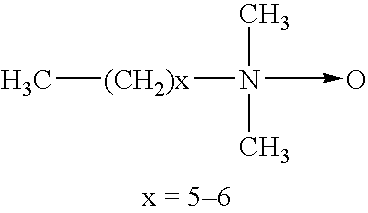Patents
Literature
51 results about "Thermostable enzymes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
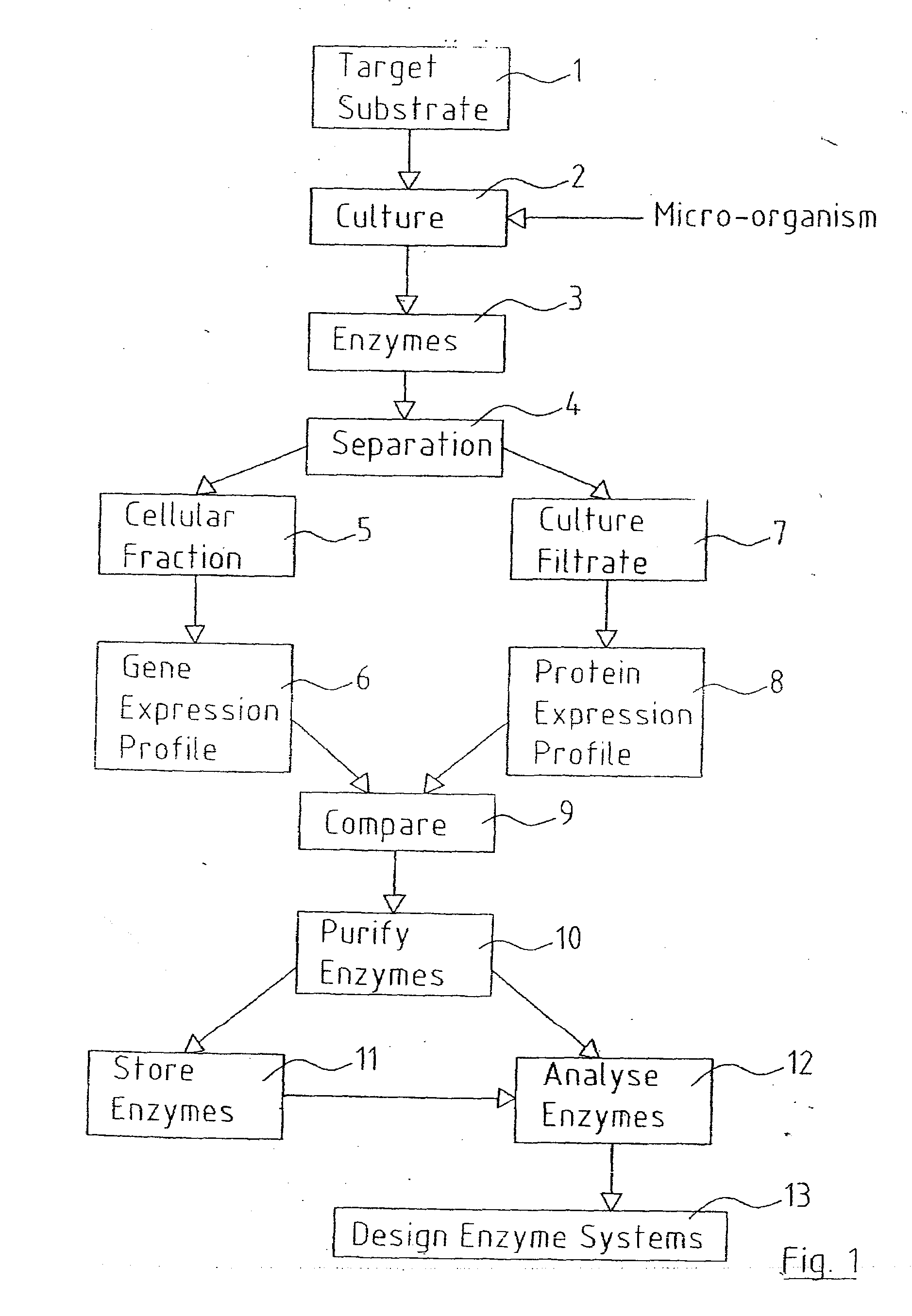
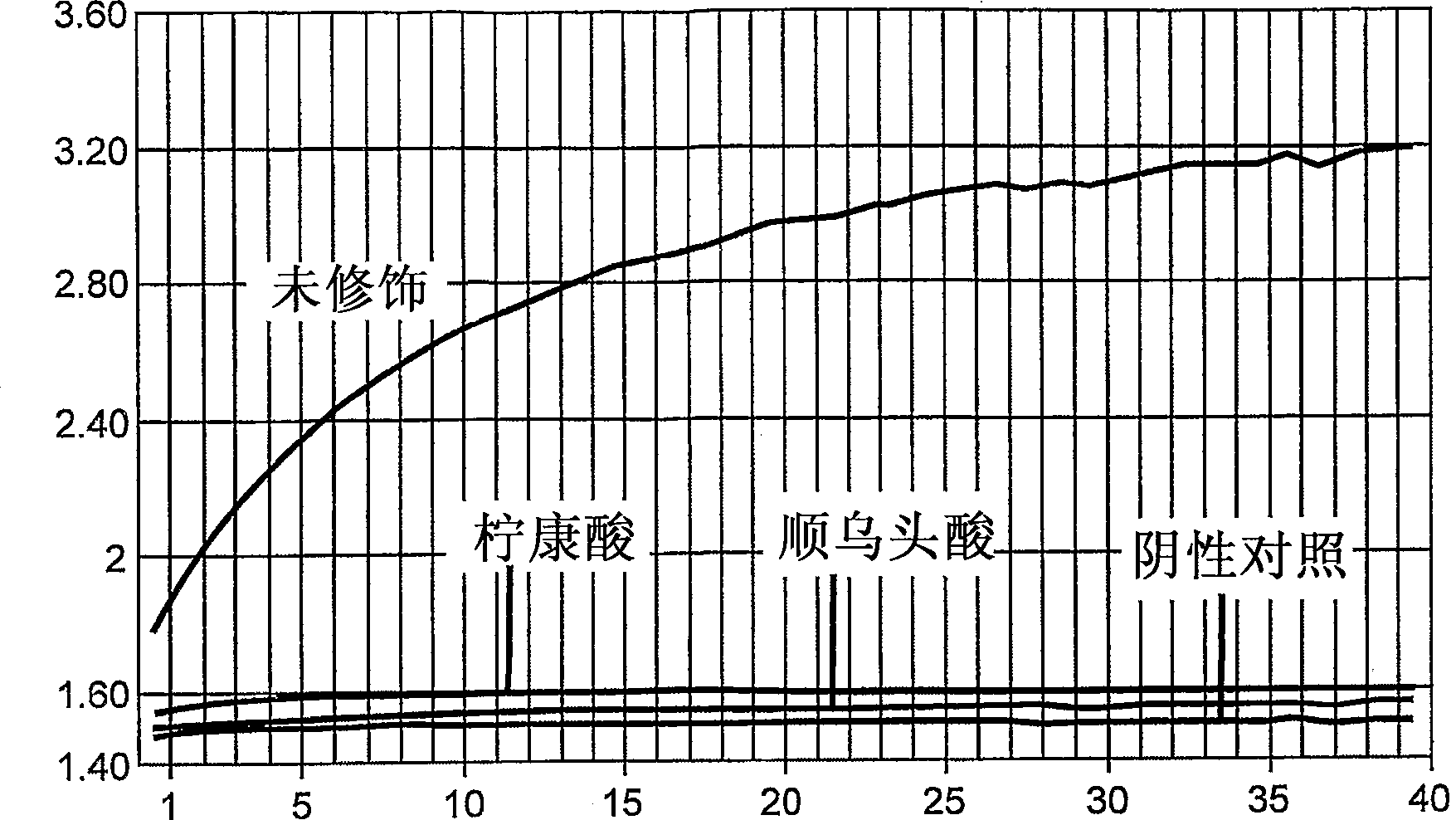
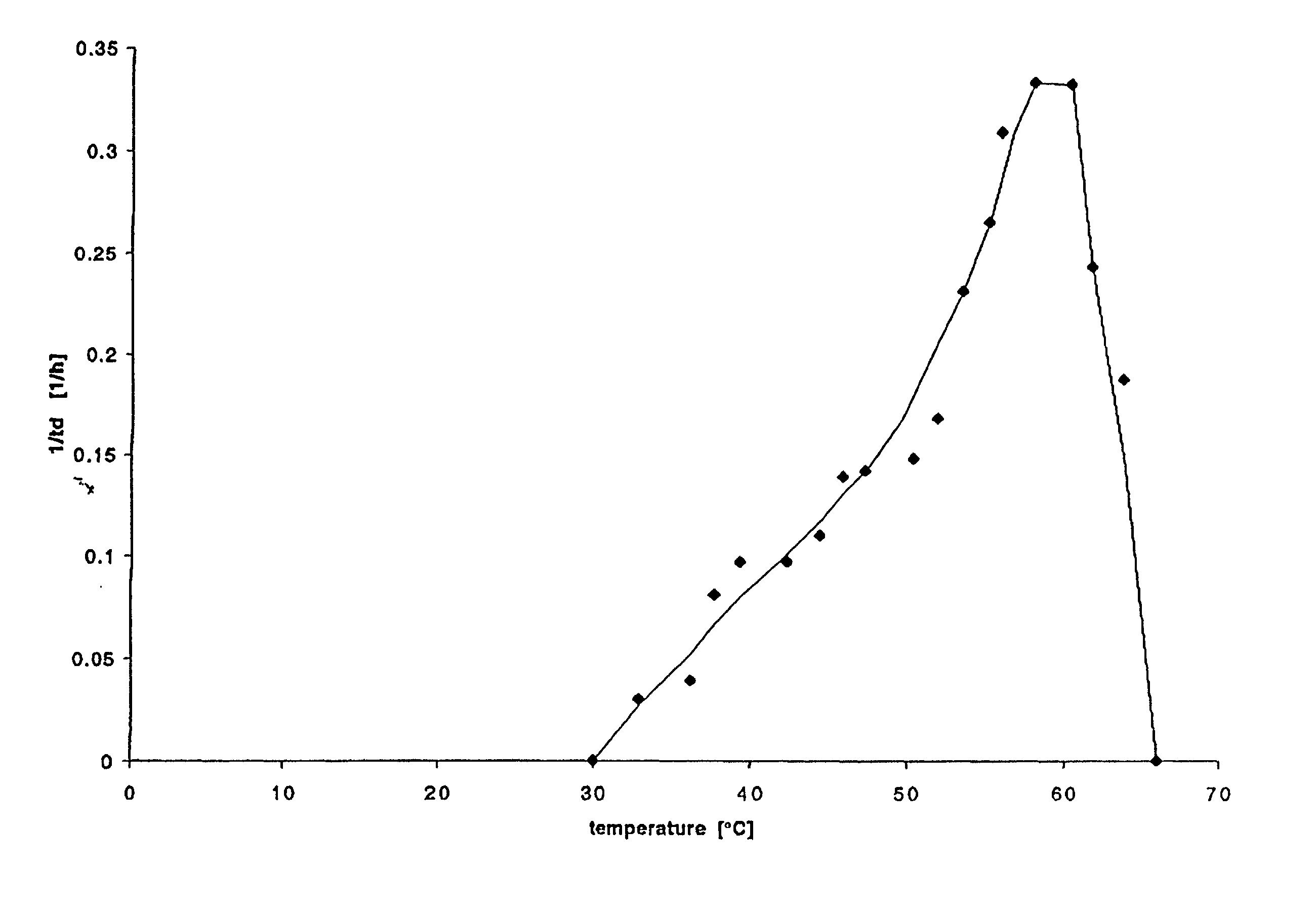
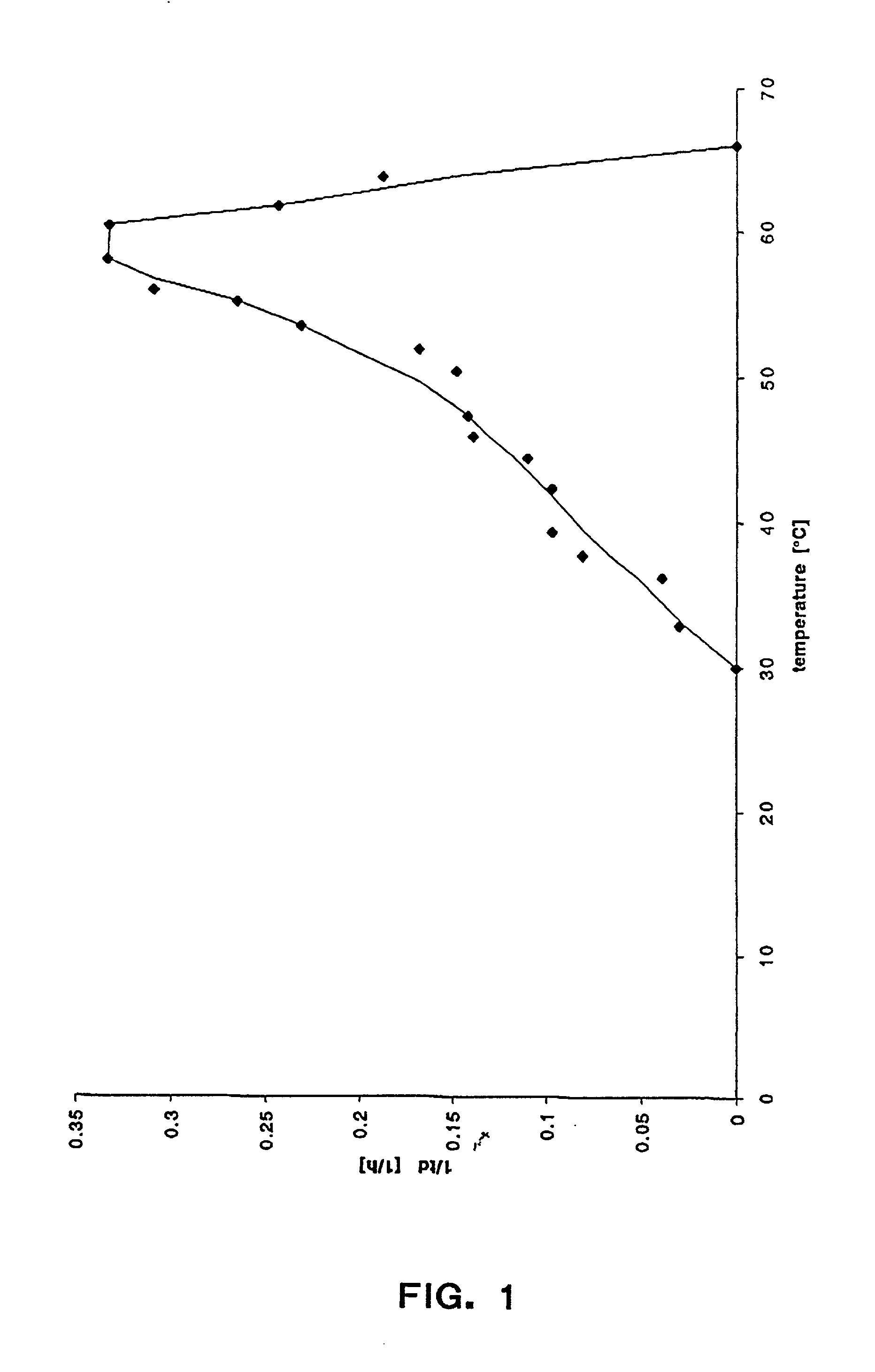
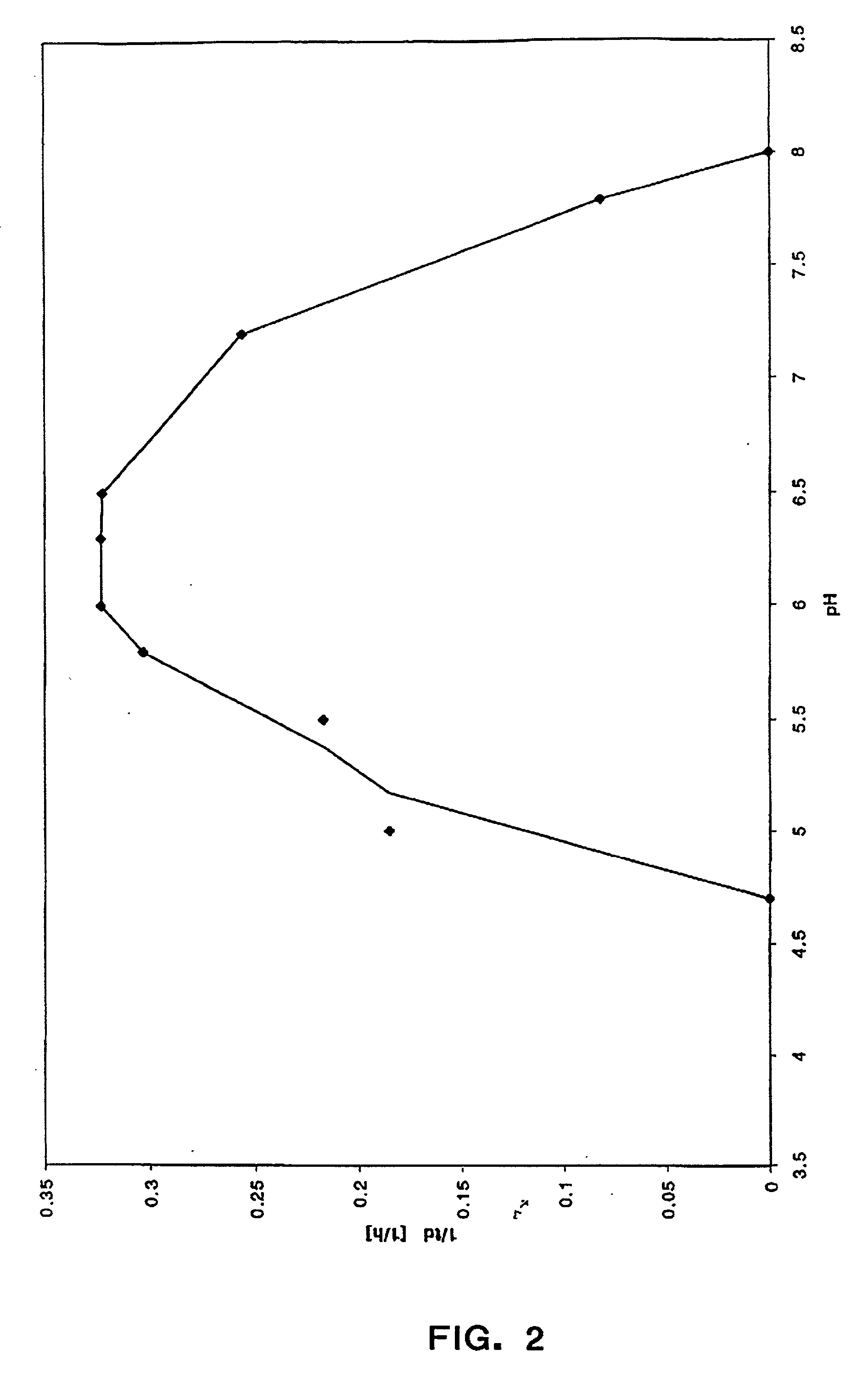
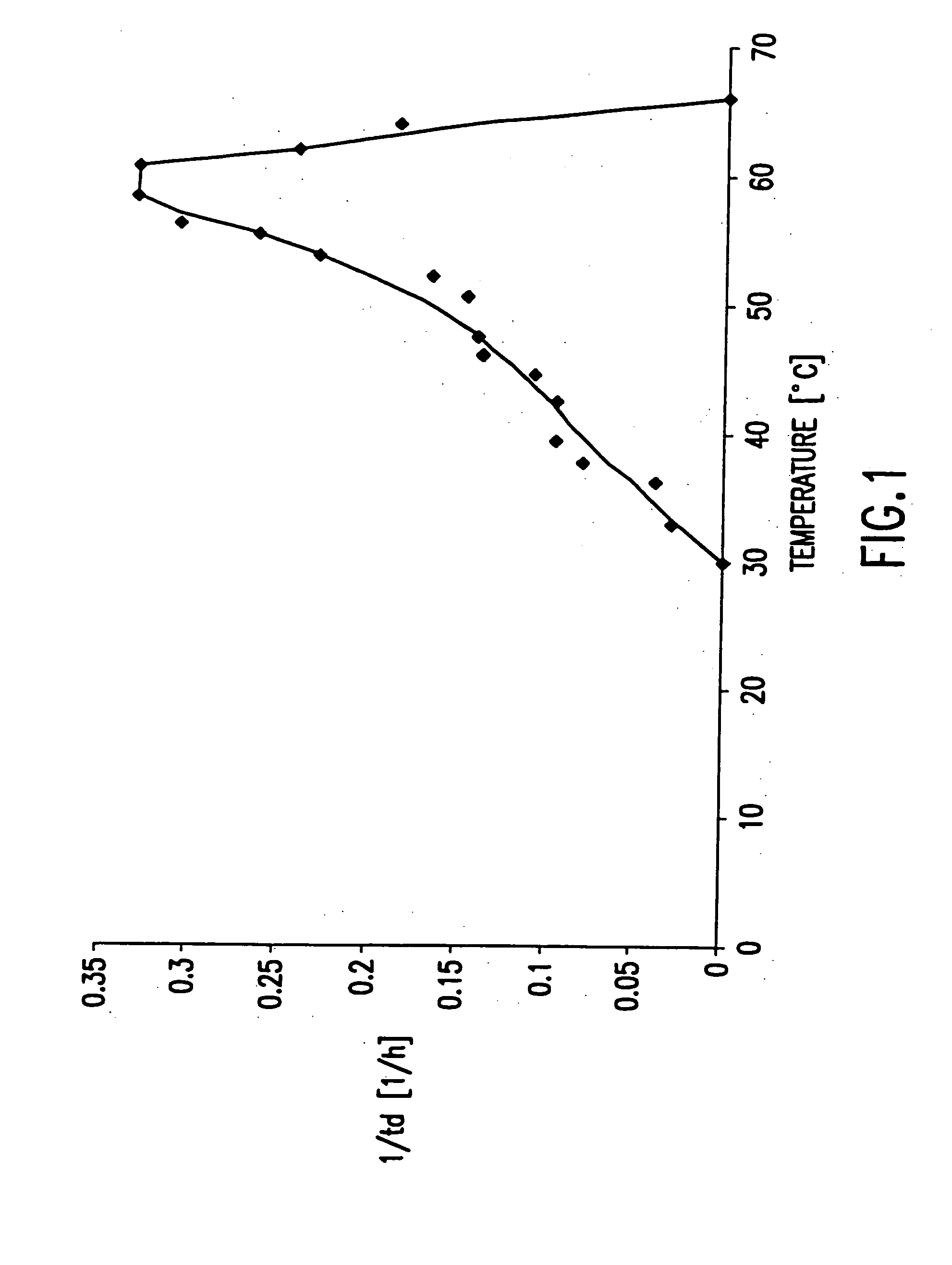
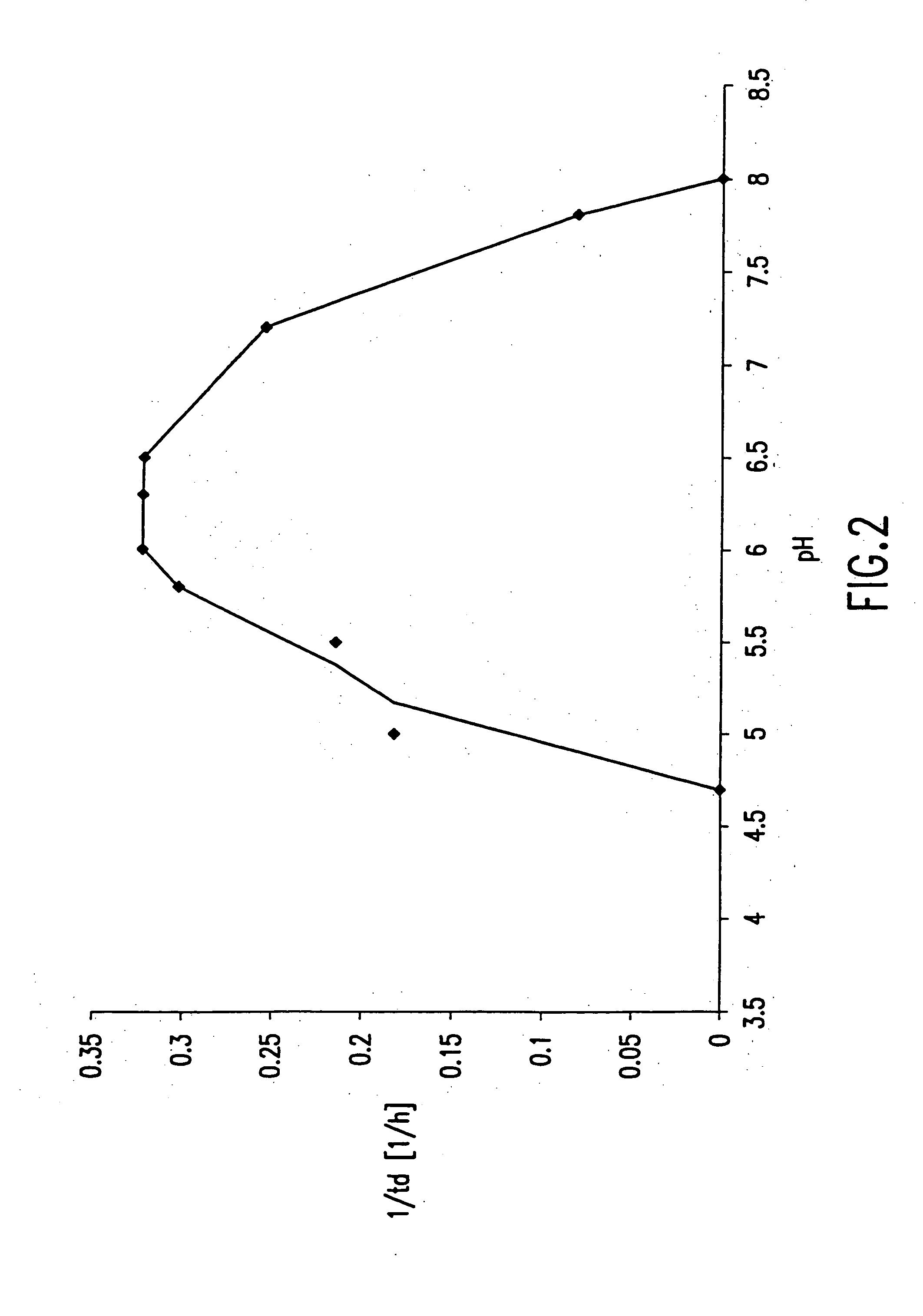
However, the thermostable enzymes obtained from the special microorganisms (hyper-thermophilic microorganisms) alive at high temperature (over 70 ) have unique characteristics of: EHigh reactivity at high temperature (70 - 100 ) ELong-term stability at ambient temperature EHigh purity available
Kits for amplifying and detecting nucleic acid sequences, including a probe
InactiveUS6040166AStrong specificityReduce manpowerNanotechSequential/parallel process reactionsOligonucleotide primersNucleic acid sequencing
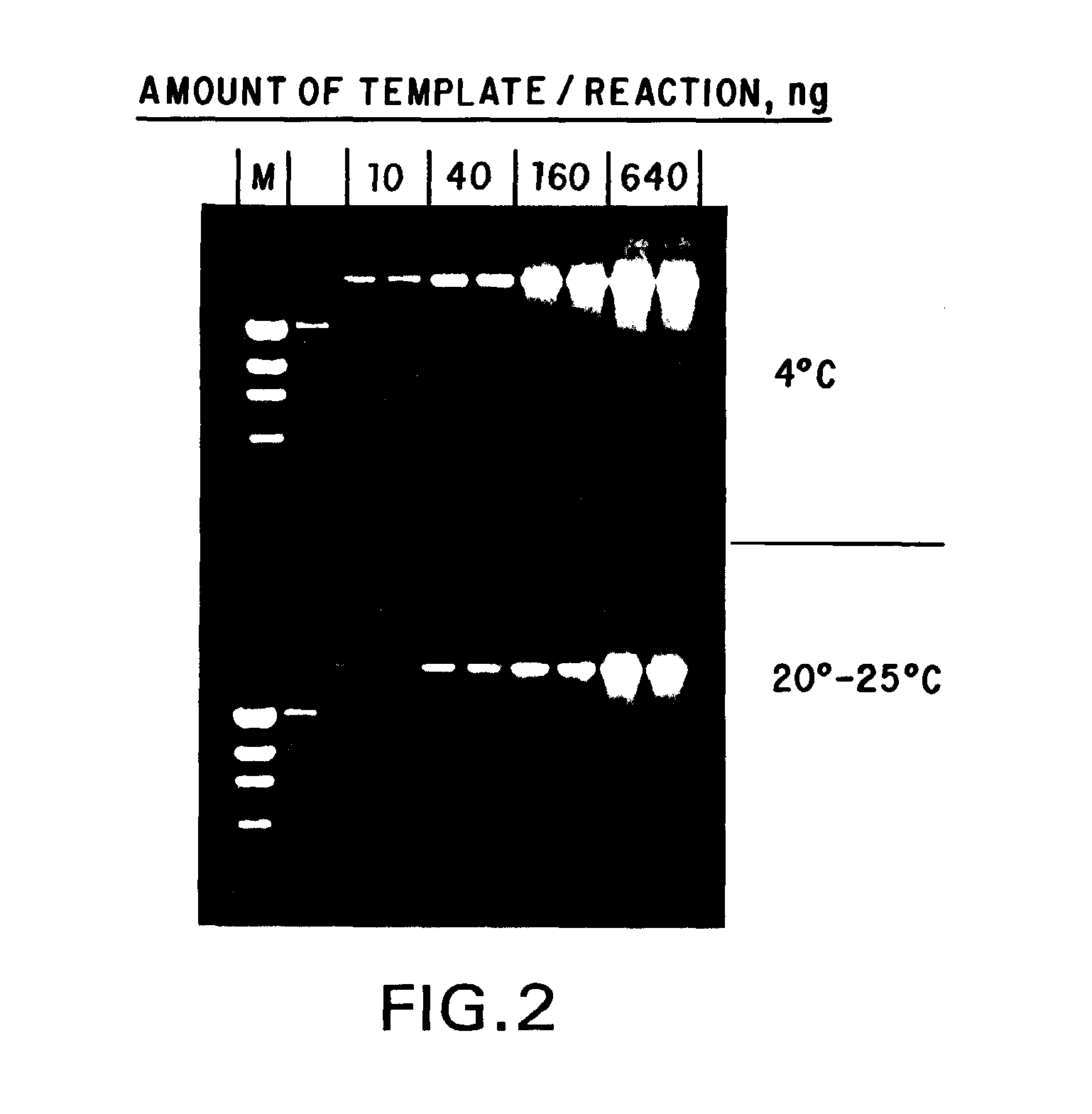
The present invention is directed to a process for amplifying any target nucleic acid sequence contained in a nucleic acid or mixture thereof using a thermostable enzyme. The process comprises treating separate complementary strands of the nucleic acid with a molar excess of two oligonucleotide primers, extending the primers with a thermostable enzyme to form complementary primer extension products which act as templates for synthesizing the desired nucleic acid sequence, and detecting the sequence so amplified. The steps of the reaction can be repeated as often as desired and involve temperature cycling to effect hybridization, promotion of activity of the enzyme, and denaturation of the hybrids formed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Kits for amplifying and detecting nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6514736B1Strong specificityReduce manpowerNanotechSequential/parallel process reactionsOligonucleotide primersNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to a process for amplifying any target nucleic acid sequence contained in a nucleic acid or mixture thereof using a thermostable enzyme. The process comprises treating separate complementary strands of the nucleic acid with a molar excess of two oligonucleotide primers, extending the primers with a thermostable enzyme to form complementary primer extension products which act as templates for synthesizing the desired nucleic acid sequence, and detecting the sequence so amplified. The steps of the reaction can be repeated as often as desired and involve temperature cycling to effect hybridization, promotion of activity of the enzyme, and denaturation of the hybrids formed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
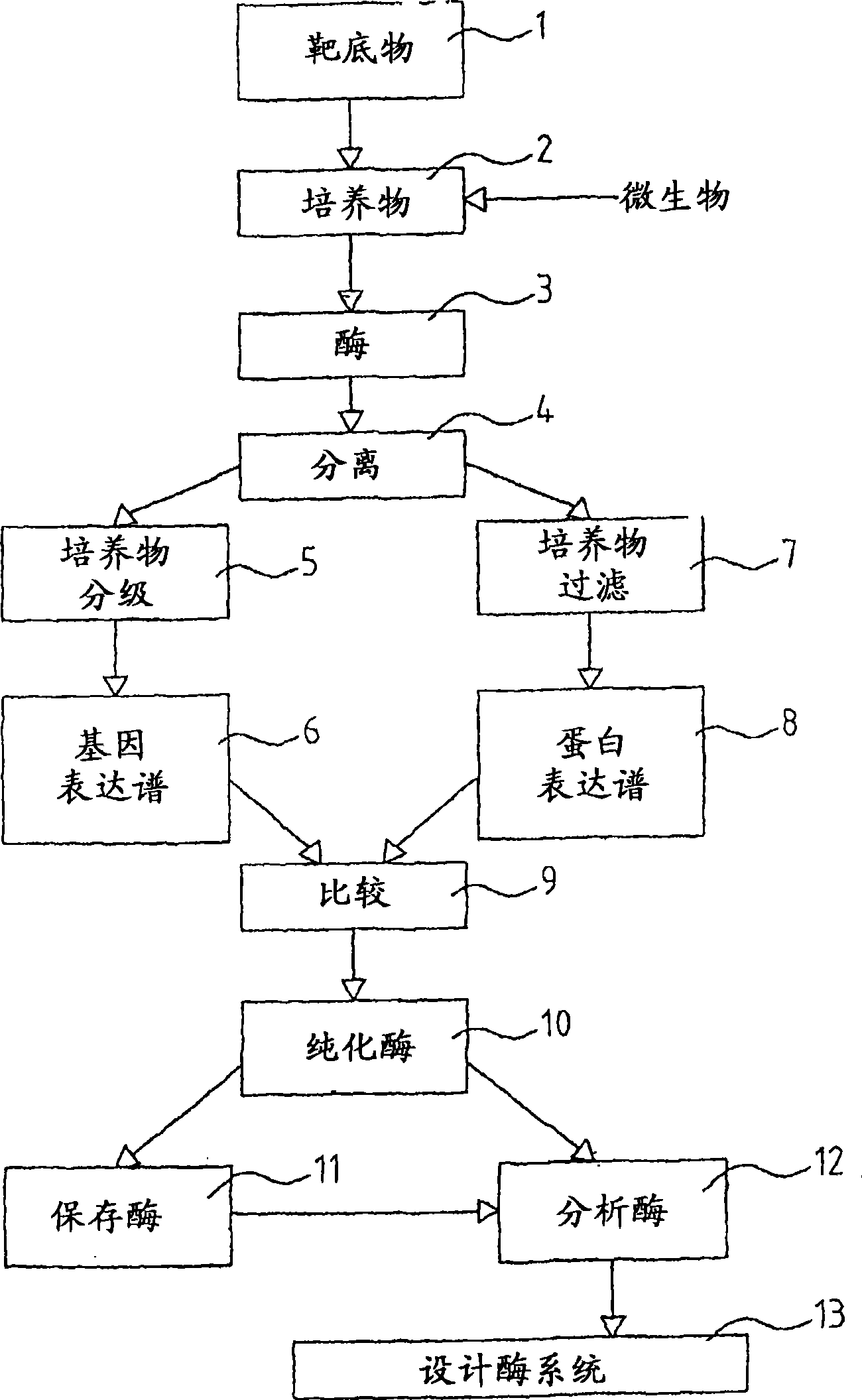
Methods for obtaining thermostable enzymes, DNA polymerase I variants from Thermus aquaticus having new catalytic activities, methods for obtaining the same, and applications of the same
The present invention provides a method for obtaining thermostable enzymes. The present invention also provides variants of DNA polymerase I from Thermus aquaticus. The present invention further provides methods of identifying mutant DNA polymerases having enhanced catalytic activity. The present invention also provides polynucleotides, expression systems, and host cells encoding the mutant DNA polymerases. Still further, the present invention provides a method to carry out reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and kits to facilitate the same.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Thermophilic denitrifying bacillocin, screening and use thereof
InactiveCN1614006AImprove propertiesReduce viscosityOrganic detergent compounding agentsBacteriaActive agentThermostable enzymes
This invention relates to selection and application of thermophil denitriding Bacillales,of which conservation number is CGMCC-1228. Initial strain is from water of oil field. The strain is obtained by selection, inoculation, and domestication with good thermal stability. It belongs to soil Bacillales and can be used in fermented industry, which needs thermally stable enzyme. It grows well in the oil field and can degrade paraffin and decrease viscosity to improve liquidity. All of this can increase recovery and carriage efficiently. It can be used to control pollution and prepare surfactant.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Methods for obtaining thermostable enzymes, DNA polymerase I variants from Thermus aquaticus having new catalytic activities, methods for obtaining the same, and applications of the same
The present invention provides a method for obtaining thermostable enzymes. The present invention also provides variants of DNA polymerase I from Thermus aquaticus. The present invention further provides methods of identifying mutant DNA polymerases having enhanced catalytic activity. The present invention also provides polynucleotides, expression systems, and host cells encoding the mutant DNA polymerases. Still further, the present invention provides a method to carry out reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and kits to facilitate the same.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
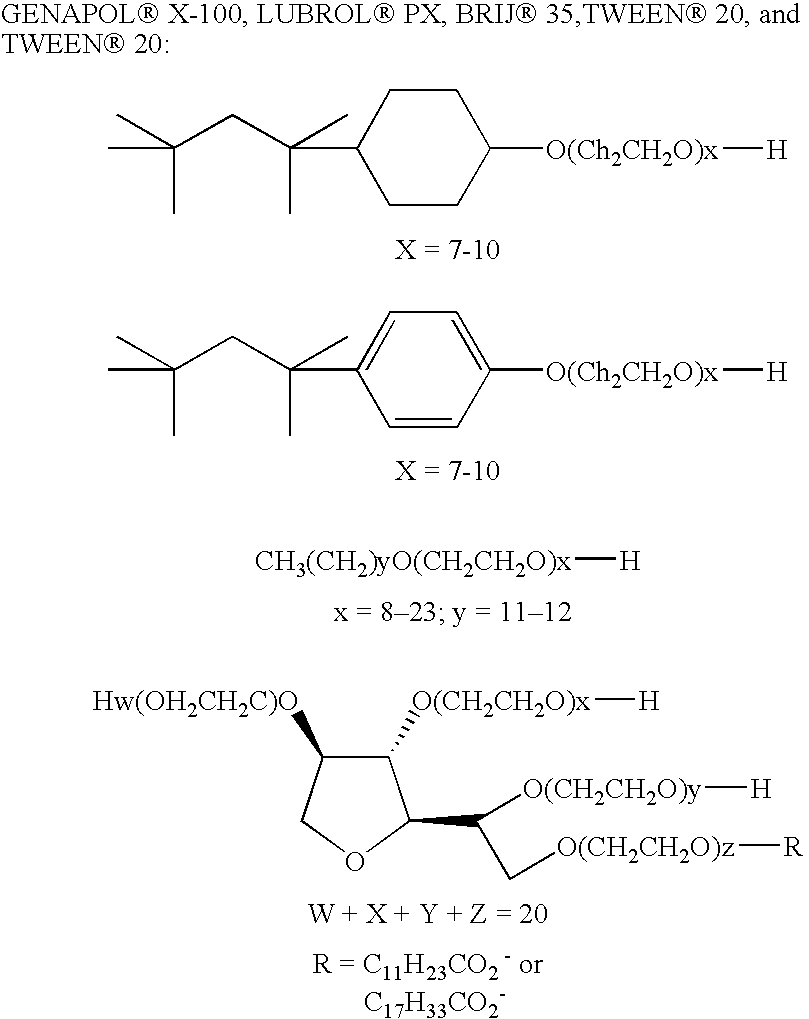
Polymerase stabilization
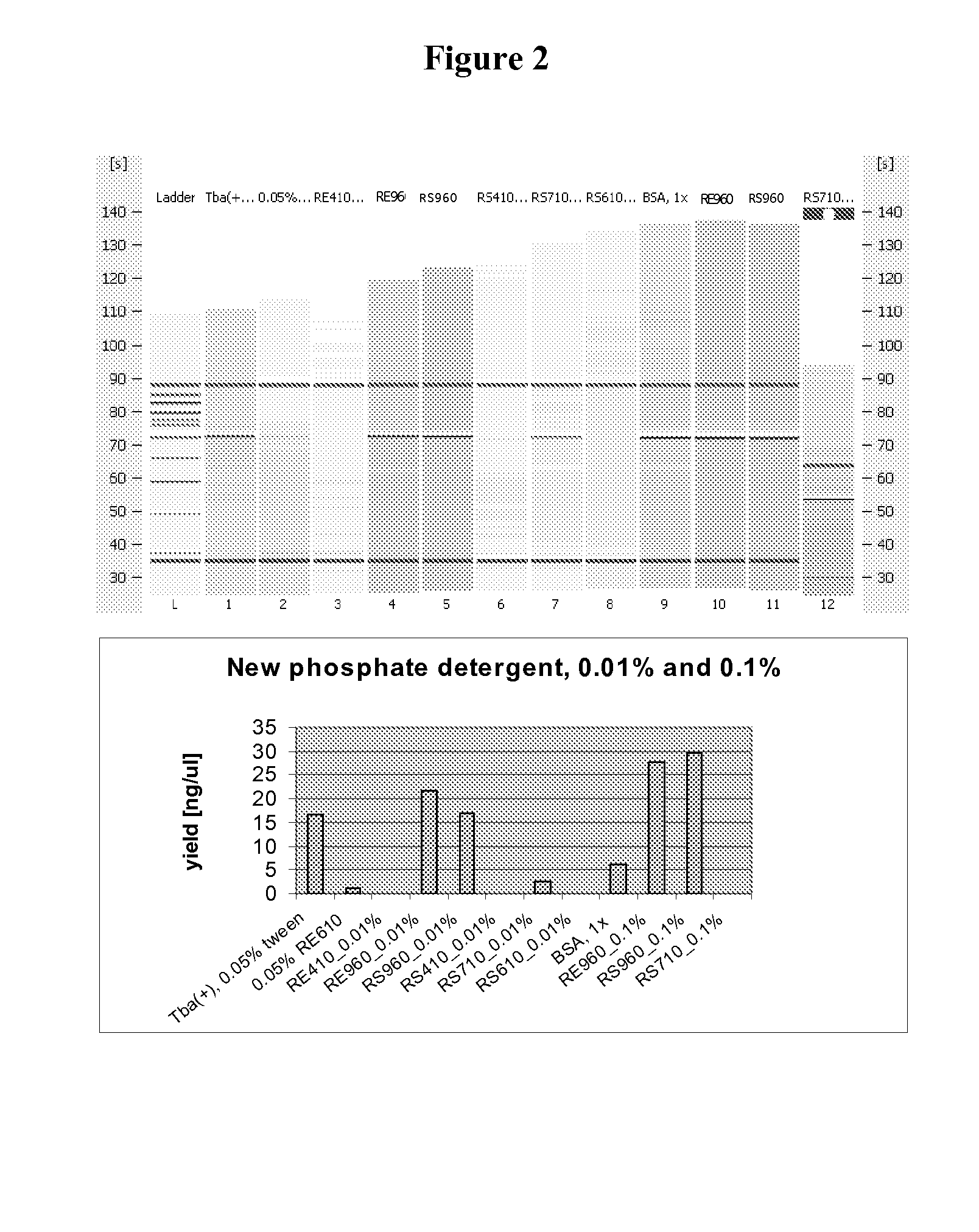
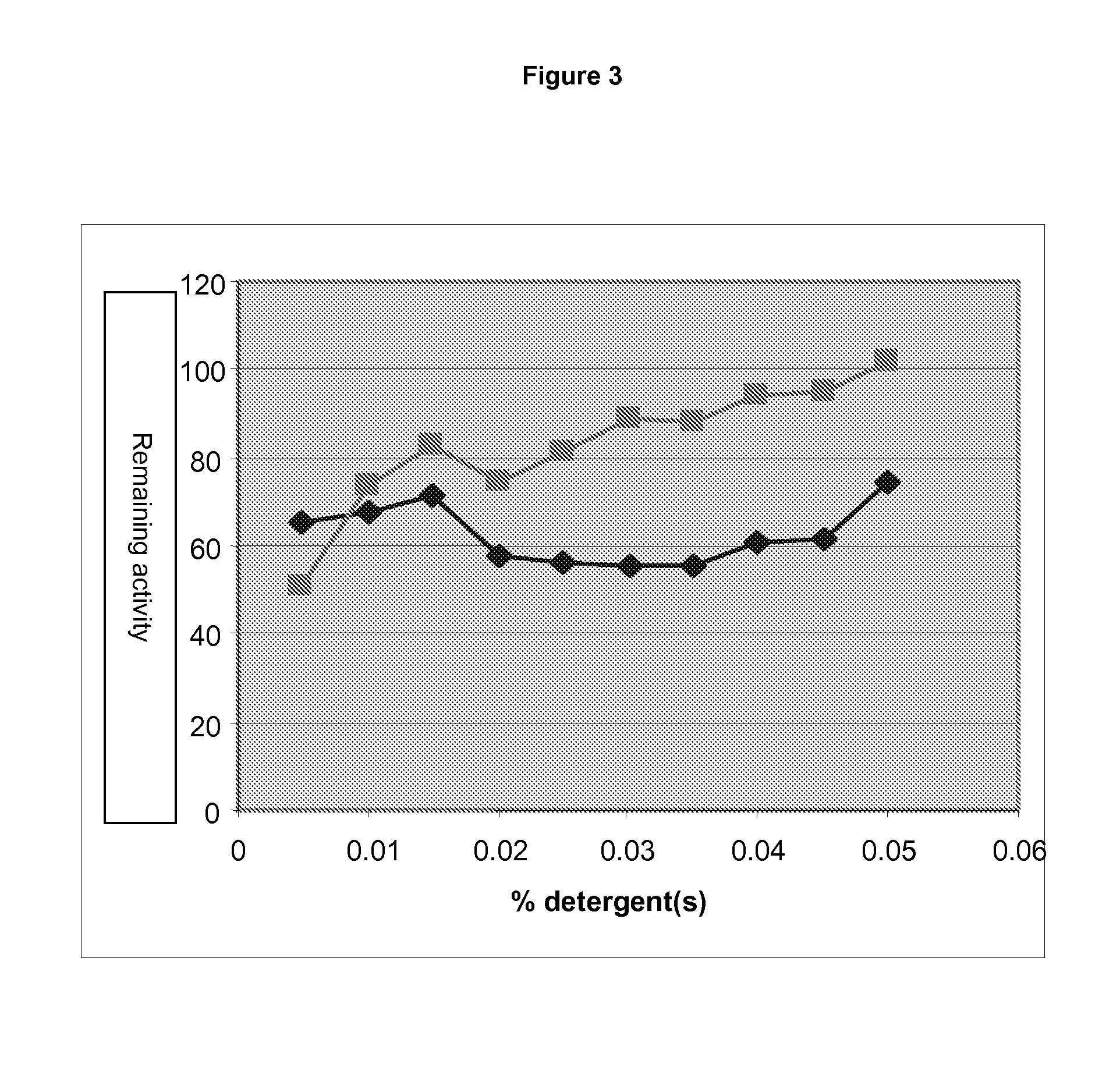
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for providing purified thermostable enzymes, particularly thermostable DNA polymerases, that are free of exogenous detergents. The present invention also provides methods for providing such purified thermostable DNA polymerases to assays in an active form by adding one or more detergents. The present invention further provides compositions and kits comprising purified thermostable DNA polymerases for use in a variety of applications, including amplification and sequencing of nucleic acids.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Thermostable enzyme promoting the fidelity of thermostable DNA polymerases-for improvement of nucleic acid synthesis and amplification in vitro
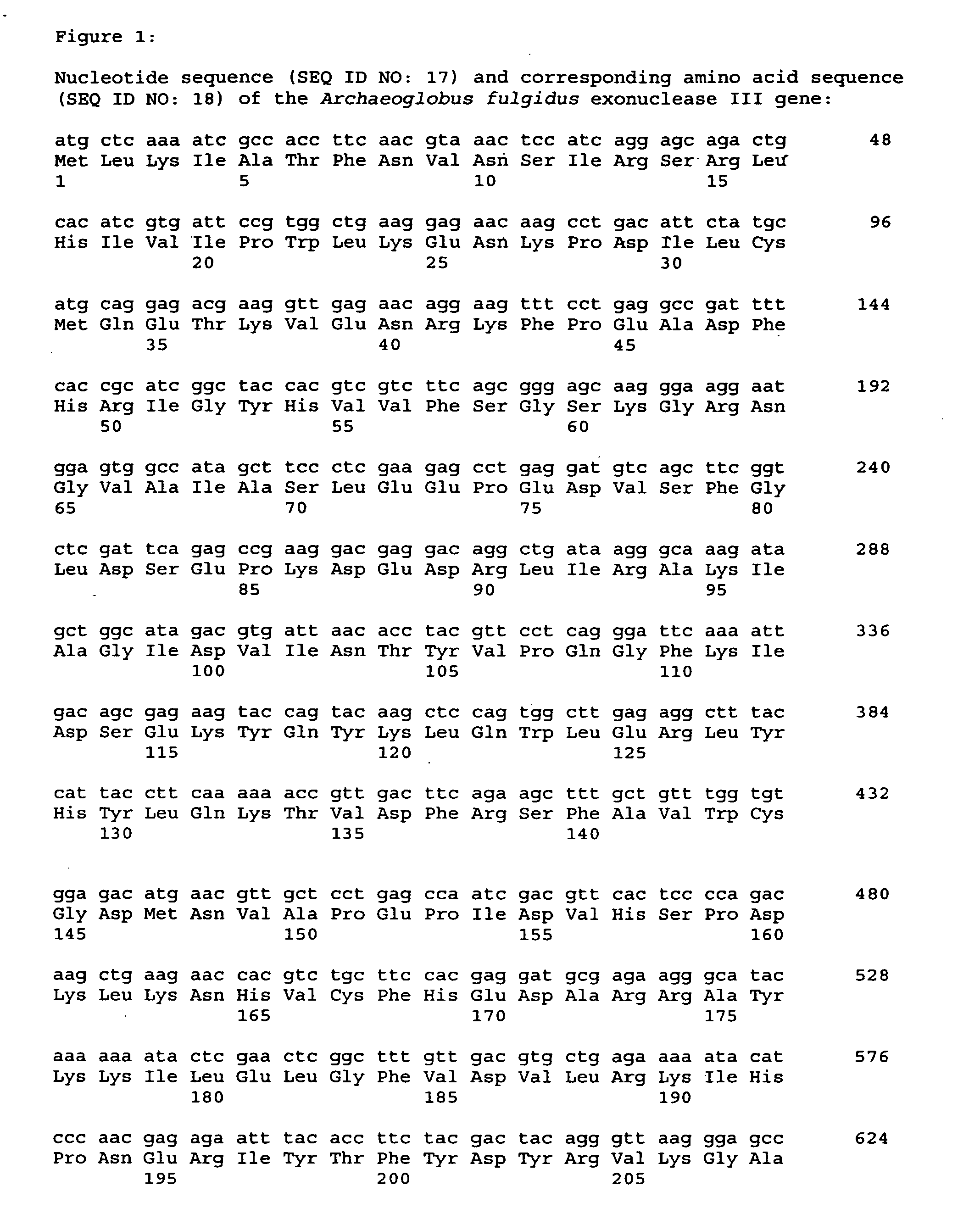
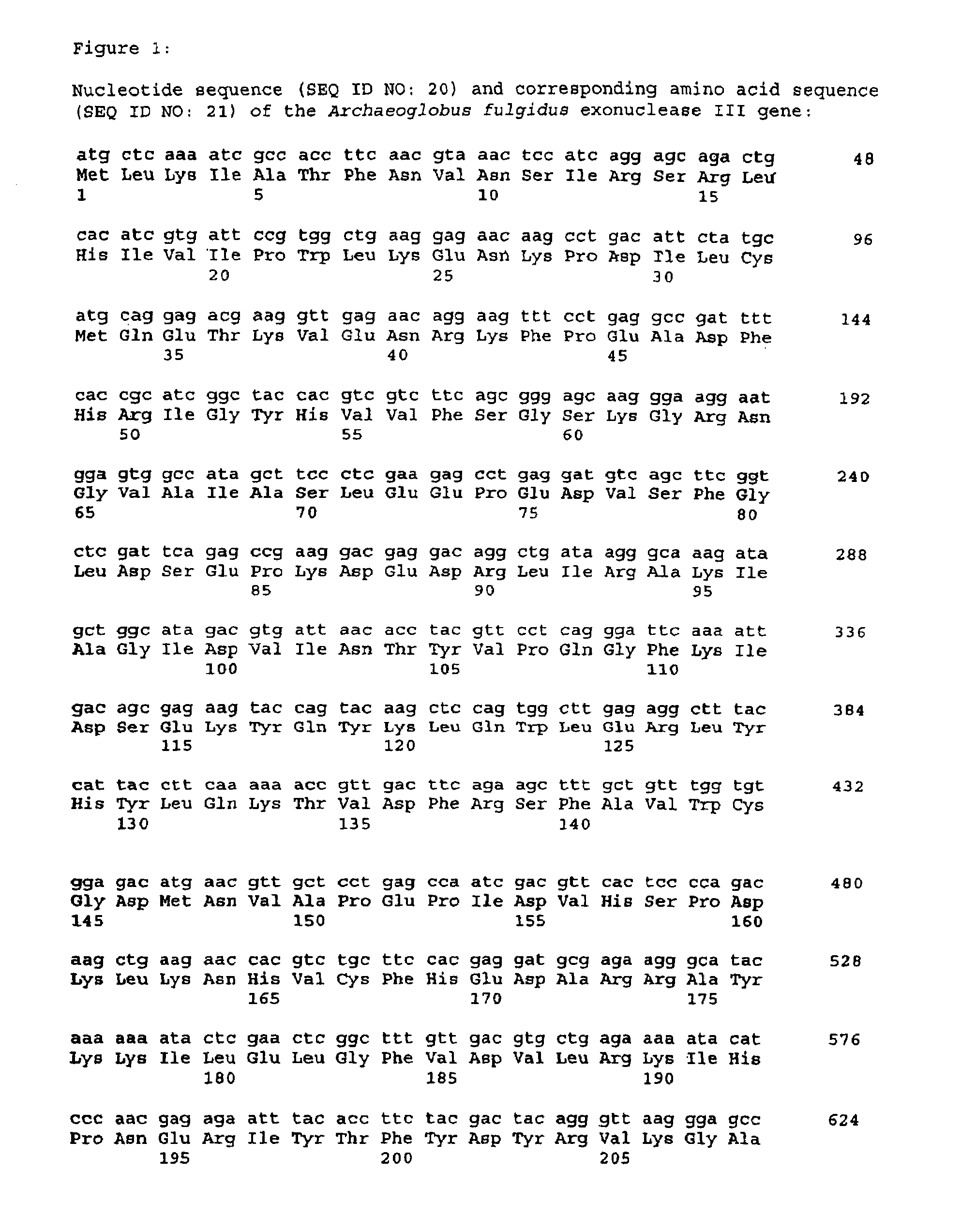
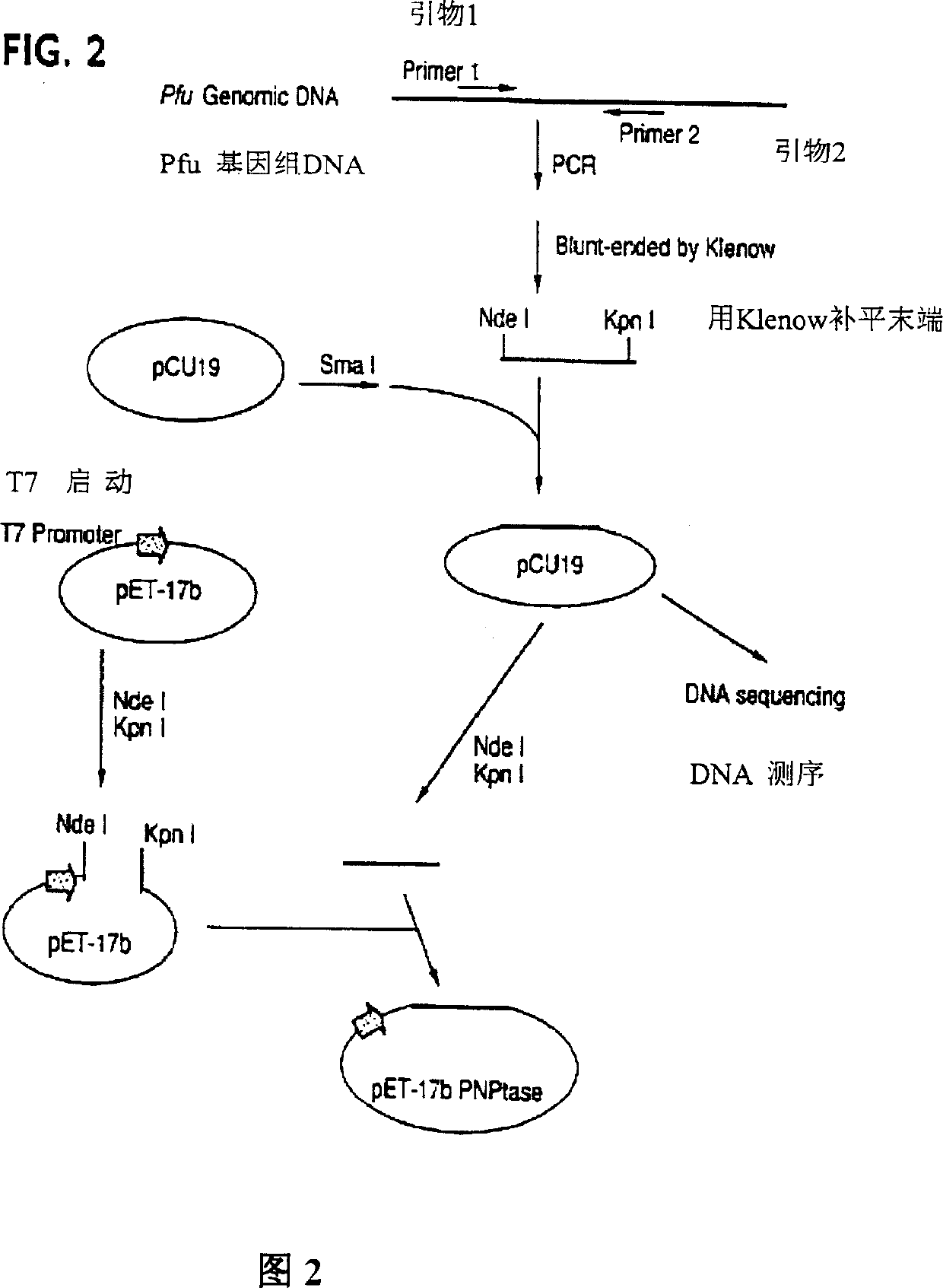
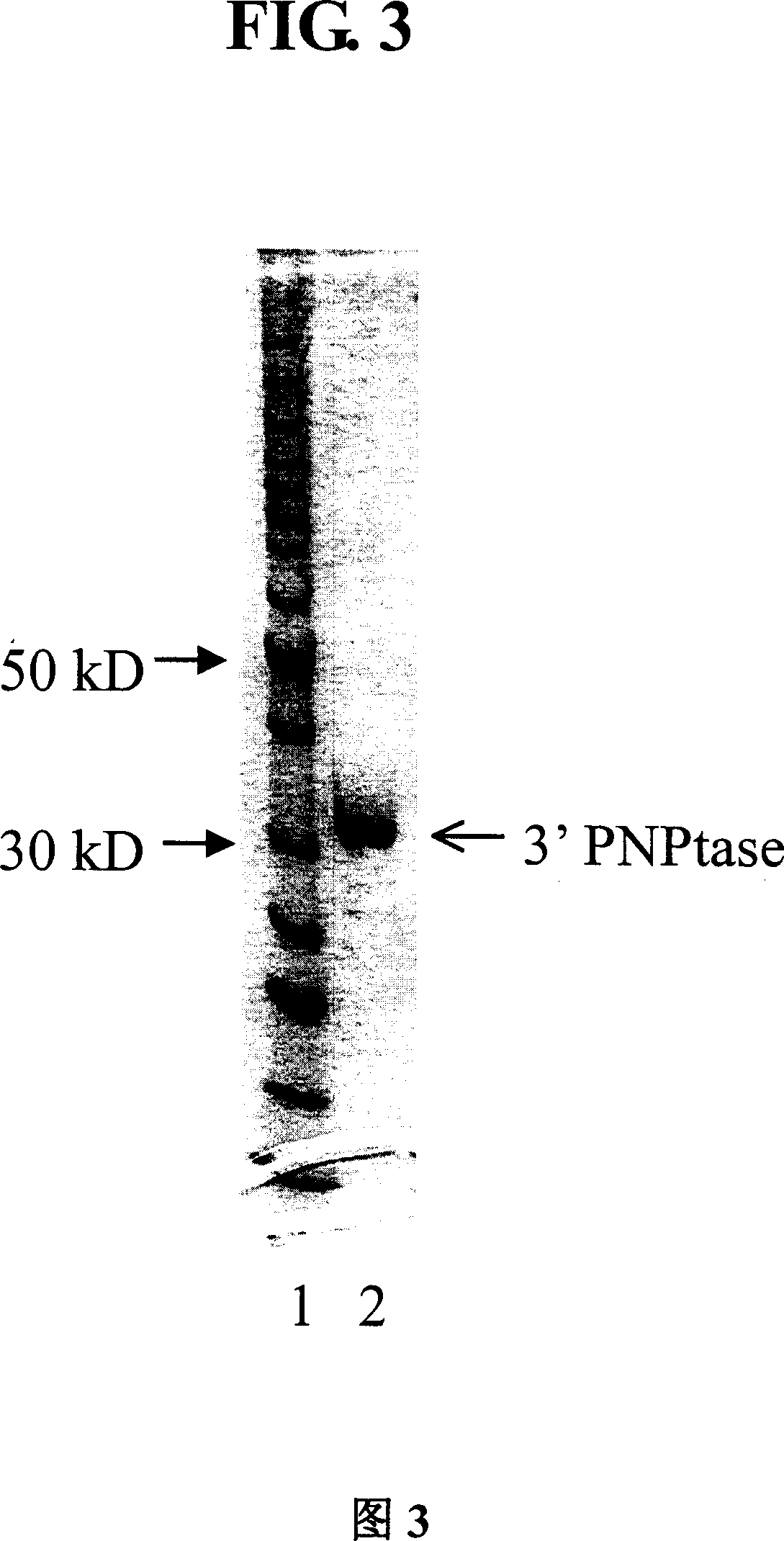
A purified thermostable enzyme is derived form the thermophilic archaebacterium Archaeoglobus fulgidus. The enzyme can be native or recombinant, is stable under PCR conditions and exhibits double strand specific exonuclease activity. It is a 3′-5′ exonuclease and cleaves to produce 5′-mononucleotides. Thermostable exonucleases are useful in many recombinant DNA techniques, in combination with a thermostable DNA polymerase like Taq especially for nucleic acid amplification by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH +1
Thermostable enzyme promoting the fidelity of thermostable DNA polymerases-for improvement of nucleic acid synthesis and amplification in vitro
A purified thermostable enzyme is derived form the thermophilic archaebacterium Archaeoglobus fulgidus. The enzyme can be native or recombinant, is stable under PCR conditions and exhibits double strand specific exonuclease activity. It is a 3′-5′ exonuclease and cleaves to produce 5′-mononucleotides. Thermostable exonucleases are useful in many recombinant DNA techniques, in combination with a thermostable DNA polymerase like Taq especially for nucleic acid amplification by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH +1
Talaromyces emersonii enzyme systems
InactiveUS20100028485A1Easy to adaptCost effectiveBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to strains of Talaromyces emersonii which are thermostable and encode thermostable enzymes. The enzymes retain activity at temperatures above 550 C. These strains and enzymes find use in a variety of processes from waste reduction to the production of novel food ingredients and the production of bio-fuels.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
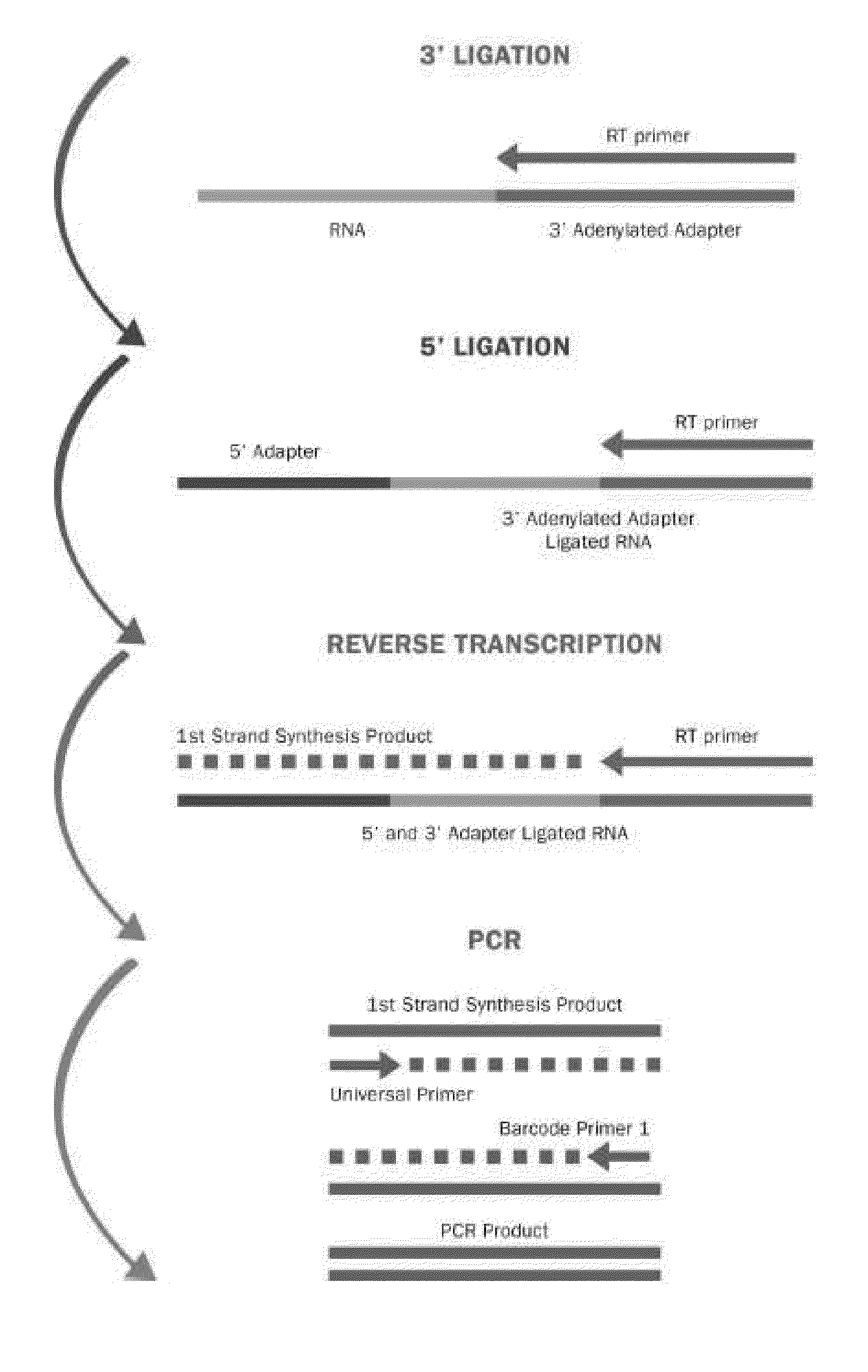
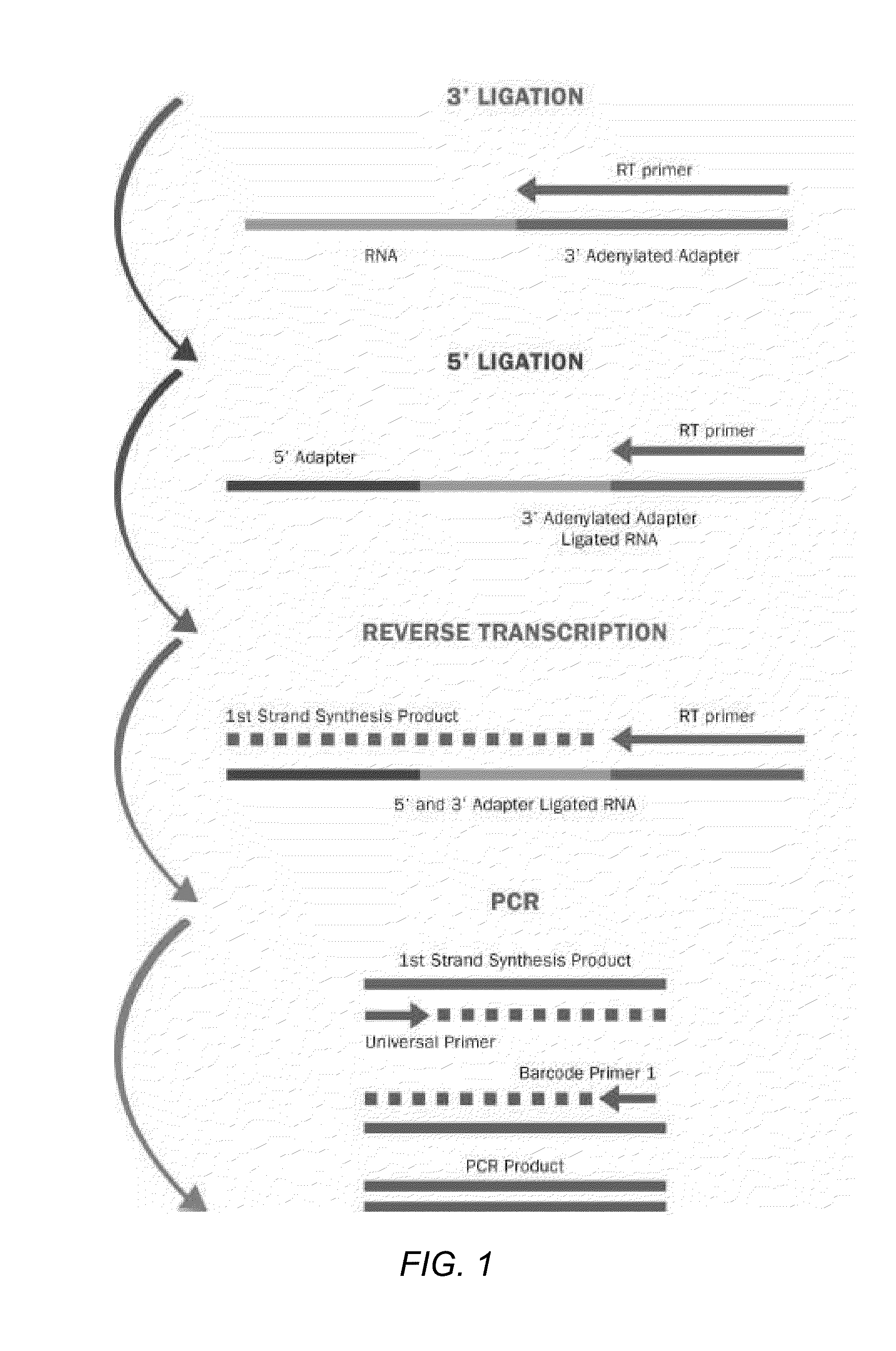
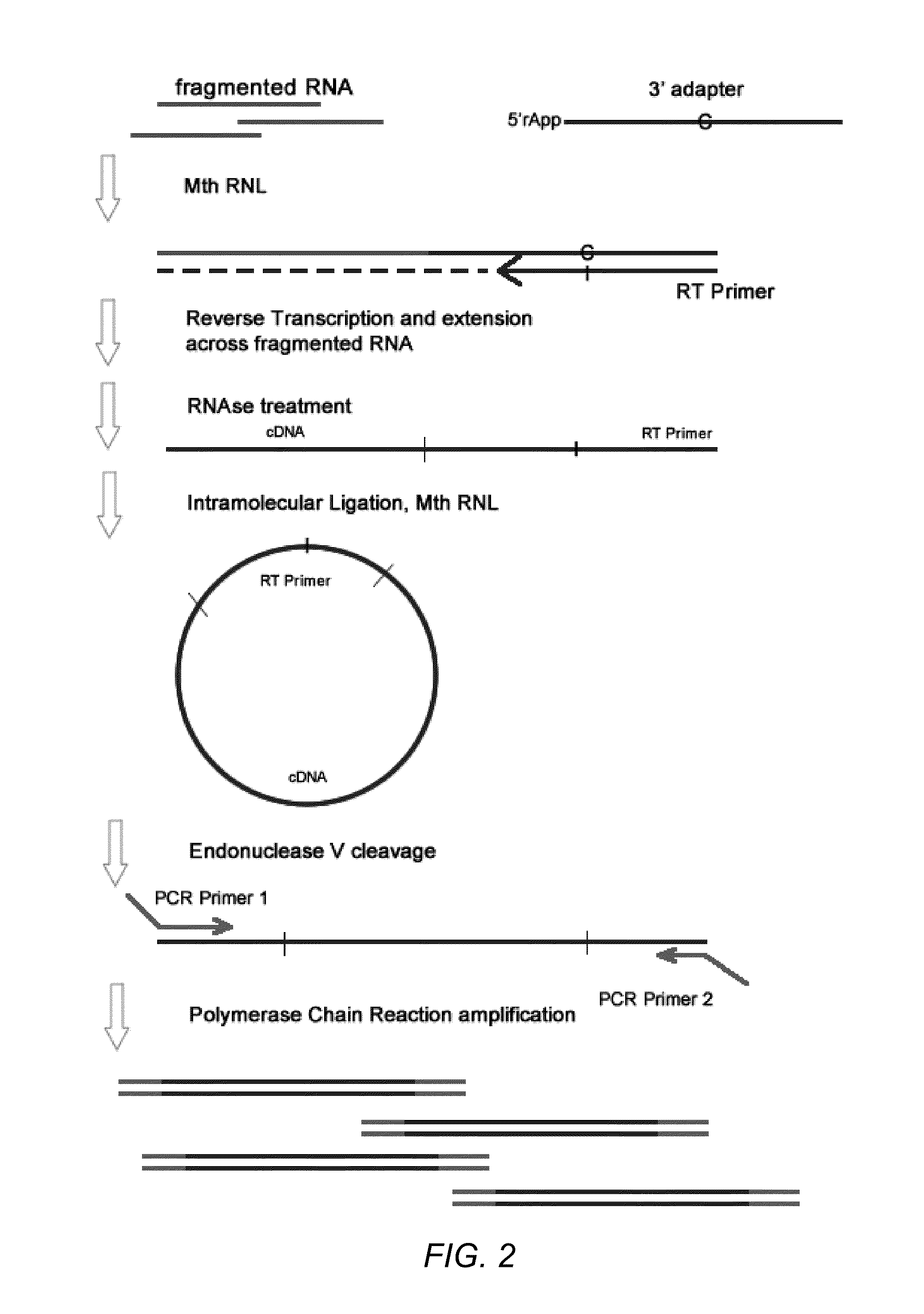
Methods for improving ligation steps to minimize bias during production of libraries for massively parallel sequencing
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
Stable compositions for nucleic acid amplification and sequencing
InactiveUS20090233283A1Maintain activityMaintain enzyme activityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme stabilisationGlycerolSerum albumin
The present invention is directed to compositions comprising mixtures of reagents, including thermostable enzymes (e.g., thermostable DNA polymerases), buffers, cofactors and other components, suitable for immediate use in nucleic acid amplification or sequencing techniques without dilution or addition of further components. The compositions contain no stabilizing agents (e.g., glycerol or serum albumin) and unexpectedly maintain activity for extended periods of time upon storage at temperatures above freezing. These compositions are useful, alone or in the form of kits, for nucleic acid amplification (e.g., by the Polymerase Chain Reaction) and sequencing (e.g., by dideoxy or “Sanger” sequencing), or for any procedure utilizing thermostable DNA polymerases in a variety of medical, forensic and agricultural applications. In particular, the compositions and methods are useful for amplifying and sequencing nucleic acid molecules that are larger than about 7 kilobases in size.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Thermostable DNA polymerases and methods of making same
InactiveUS20060035360A1Enhanced DNA polymerase activityFacilitating chemical disruptionBacteriaHydrolasesThermostable enzymesDNA
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for providing purified thermostable enzymes, particularly thermostable DNA polymerases, that are free of exogenous detergents. The present invention also provides methods for providing such purified thermostable DNA polymerases to assays in an active form by adding one or more detergents. The present invention further provides compositions and kits comprising purified thermostable DNA polymerases for use in a variety of applications, including amplification and sequencing of nucleic acids.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Talaromyces emersonii enzyme systems
The invention relates to strains of Talaromyces emersonii which are thermostable and encode thermostable enzymes. The enzymes retain activity at temperatures above 550C. These strains and enzymes find use in a variety of processes from waste reduction to the production of novel food ingredients and the production of bio-fuels.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY
Nucleic acid-free thermostable enzymes and methods of production thereof
The present invention provides thermostable enzymes, such as DNA polymerases and restriction endonucleases, that are substantially free from contamination with nucleic acids. The invention also provides methods for the production of these enzymes, and kits comprising these enzymes which may be used in amplifying or sequencing nucleic acid molecules, including through use of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Thermostable C. BESCII enzymes
The disclosure provides thermostable enzymes isolated from Caldicellulosiruptor bescii and fragments thereof useful for the degradation of cellulose and / or hemicellulose, including thermostable cellulases and hemicellulases. The disclosure further provides nucleic acids encoding the thermostable enzymes of the disclosure. The disclosure also provides methods for the conversion of cellulose and hemicellulose into fermentable sugars using thermostable enzymes of the disclosure. The disclosure also provides enzyme cocktails containing multiple enzymes disclosed herein. The enzymes can be used to release sugars present in cellulose or hemicellulose for subsequent fermentation to produce value-added products.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
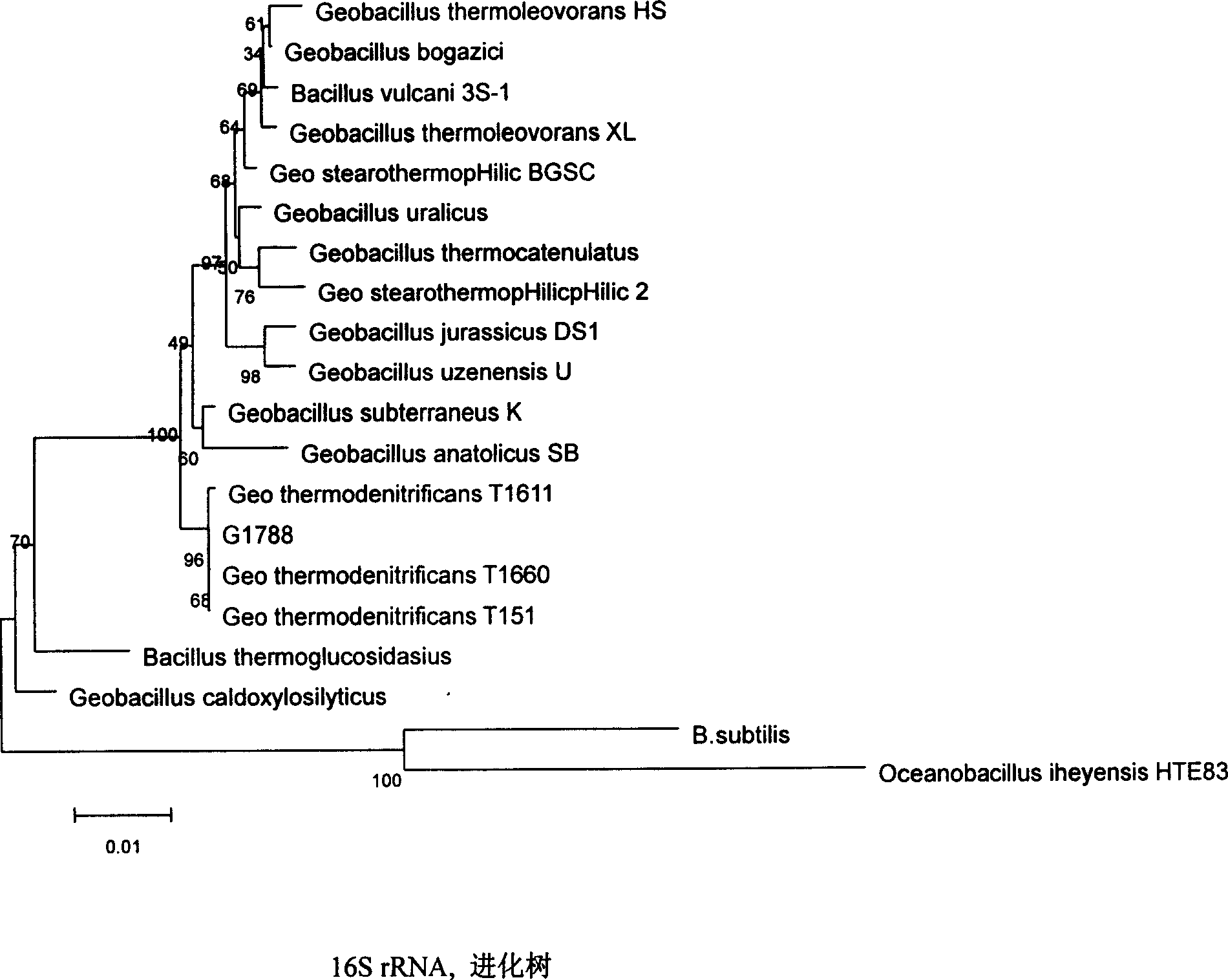
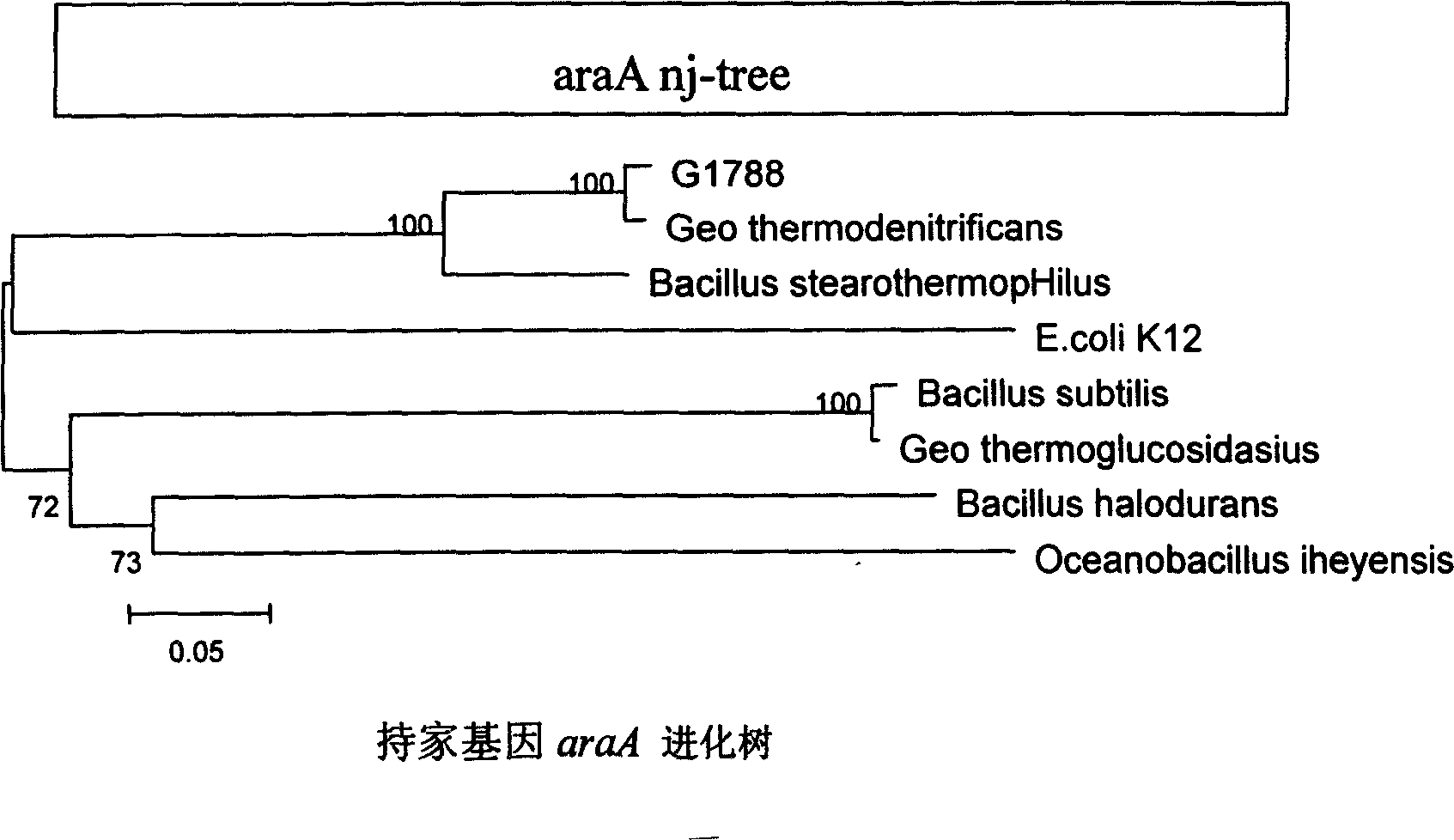
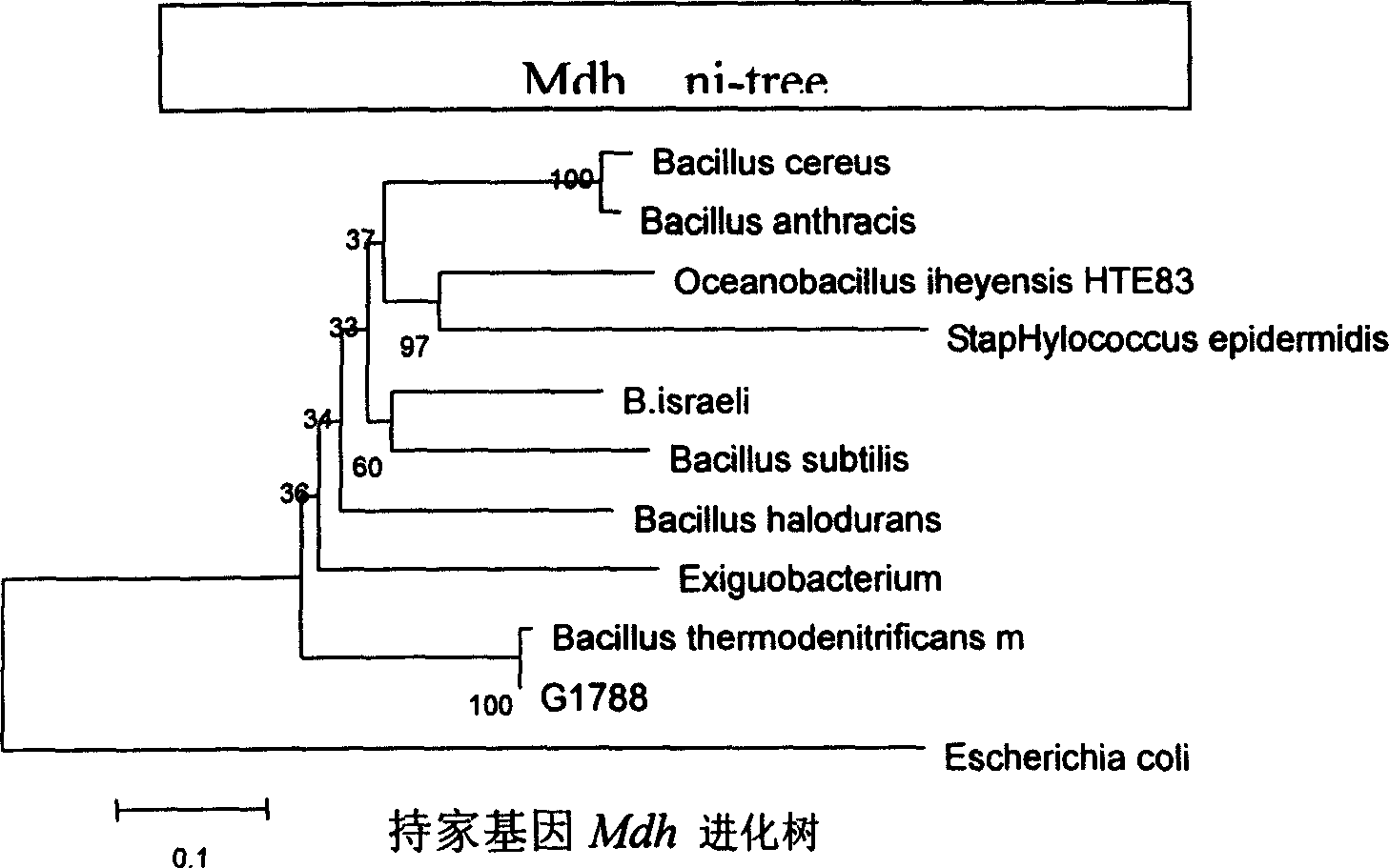
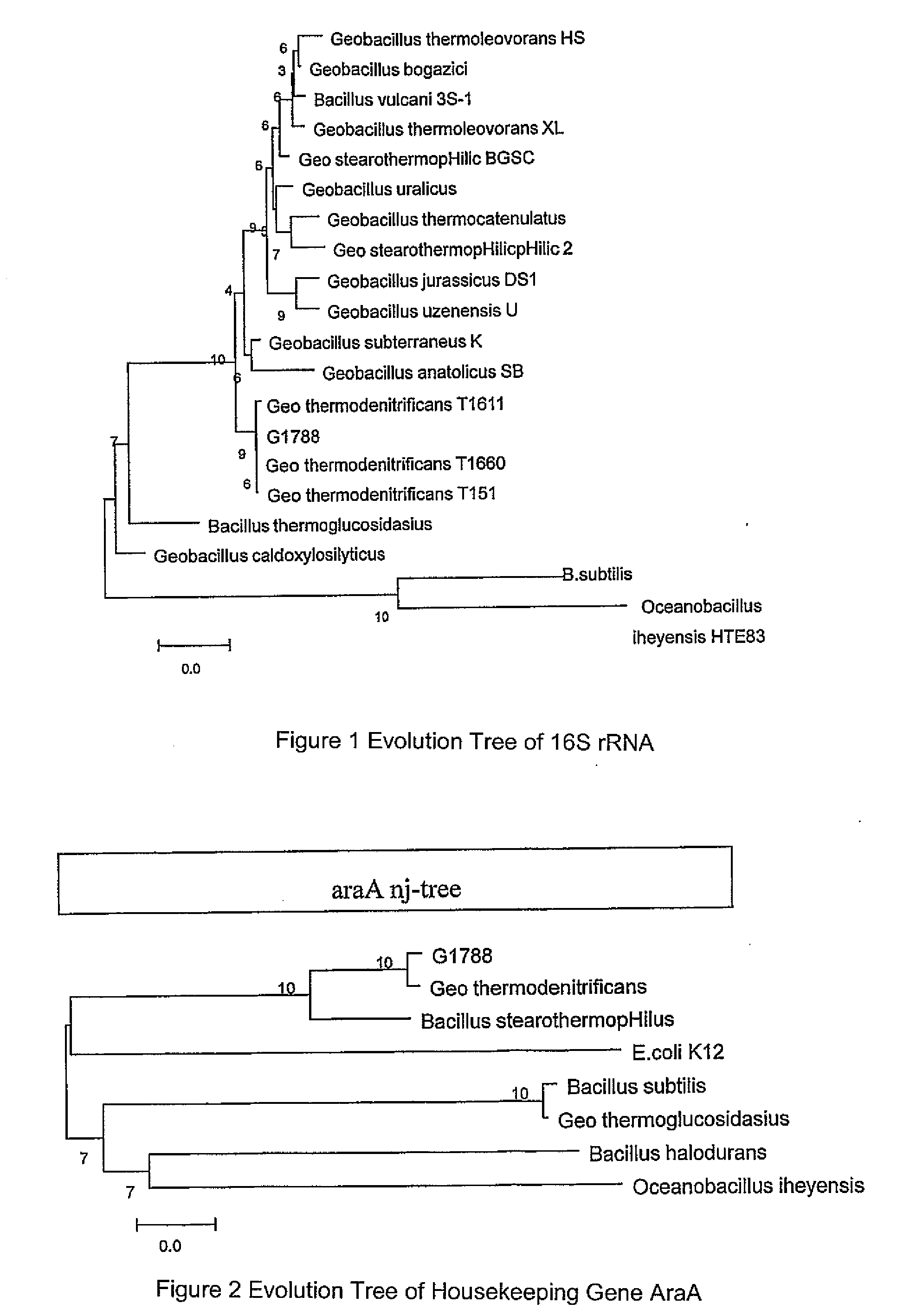
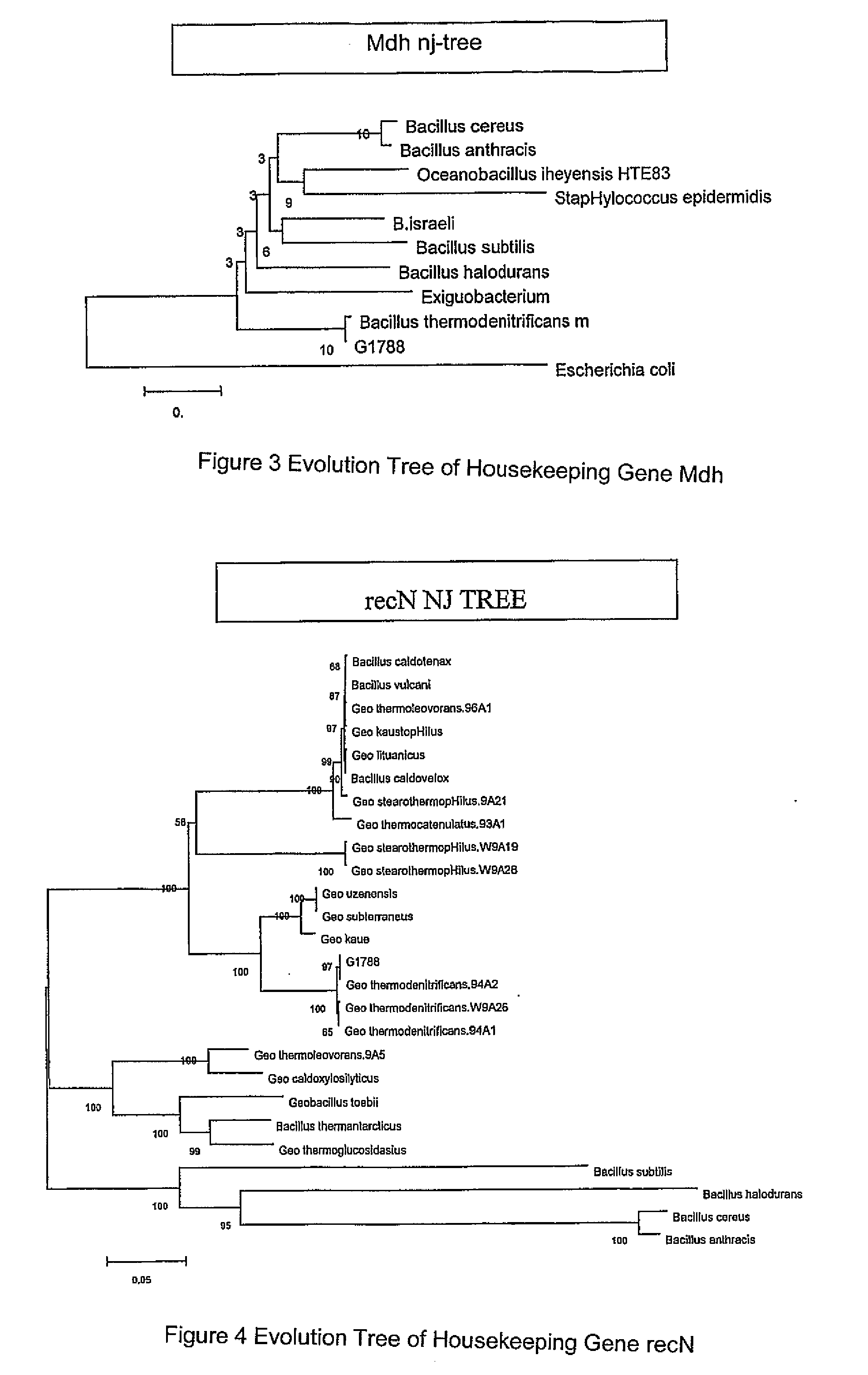
Geobacillus thermodenitrificans as well as the screening method and the uses thereof
InactiveUS20090148881A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove featuresOrganic detergent compounding agentsBacteriaAlkaneScreening method
The invention provides a strain of Geobacillus thermodenitrificans as well as the screening method and the uses thereof. The strain was deposited as the number CGMCC-1228 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of the China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms. The strain was obtained by primary screening, re-screening, inoculation, domestication and propagation using the bacteria in the aqueous samples from the strata of oil field as the original screening strain. The strain screened in the invention belongs to the genus Geobacillus, which can tolerate a high temperature, and has good thermostability, which can be applied to the industrial production which need the condition of thermostable enzymes, such as fermentation, etc. With its ability of growing well in the oil-reservoir environment, degrading alkanes, decreasing viscosity and increasing fluidity of crude oil, the strain is able to remarkably enhance the yield of oil and improve the transporting efficiency of oil. Additionally, with its good ability of degrading oil, it can be developed for the treatment and clearing of the material such as the oil contaminated water, etc., so it can be useful in protection of the environment. This strain also has the ability of decreasing the surface tension of substances, which can be applied to the industry of biosurfactants preparation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Inactivation method
ActiveUS20070224611A1Reduce enzyme activityInhibition formationBiocideOrganic chemistryThermostable enzymesChemical modification
The present invention relates to the field of thermostable enzymes, methods for their inactivation, and related uses, kits and reagents. In particular, the invention relates to a method for reversible inactivation of thermophilic enzymes by chemical modification under aqueous or non-aqueous conditions.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BALTICS UAB
Endoglucanases
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified thermostable enzyme derived from the archael bacterium AEPII 1a. In one aspect, the enzyme has a molecular weight of about 60.9 kilodaltons and has a cellulase activity. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells, and can be used to aid in the digestion of cellulose. The invention also provides polypeptides having endoglucanase activity having homology to SEQ ID NO:2.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
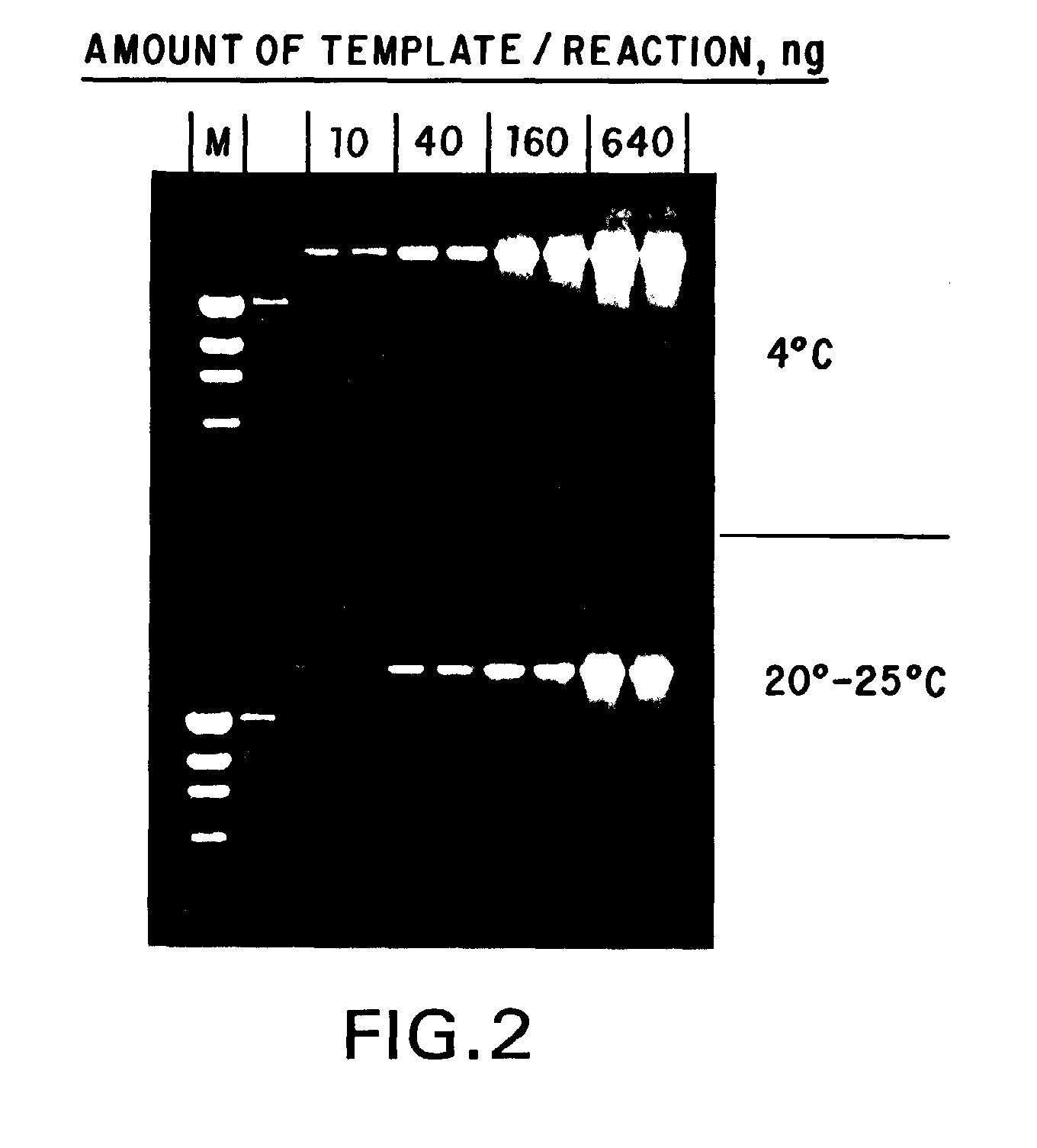
Process for preparation of thermostable enzyme
InactiveUS7267971B2Preparing sample for investigationPretreated surfacesPhosphateThermostable enzymes
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
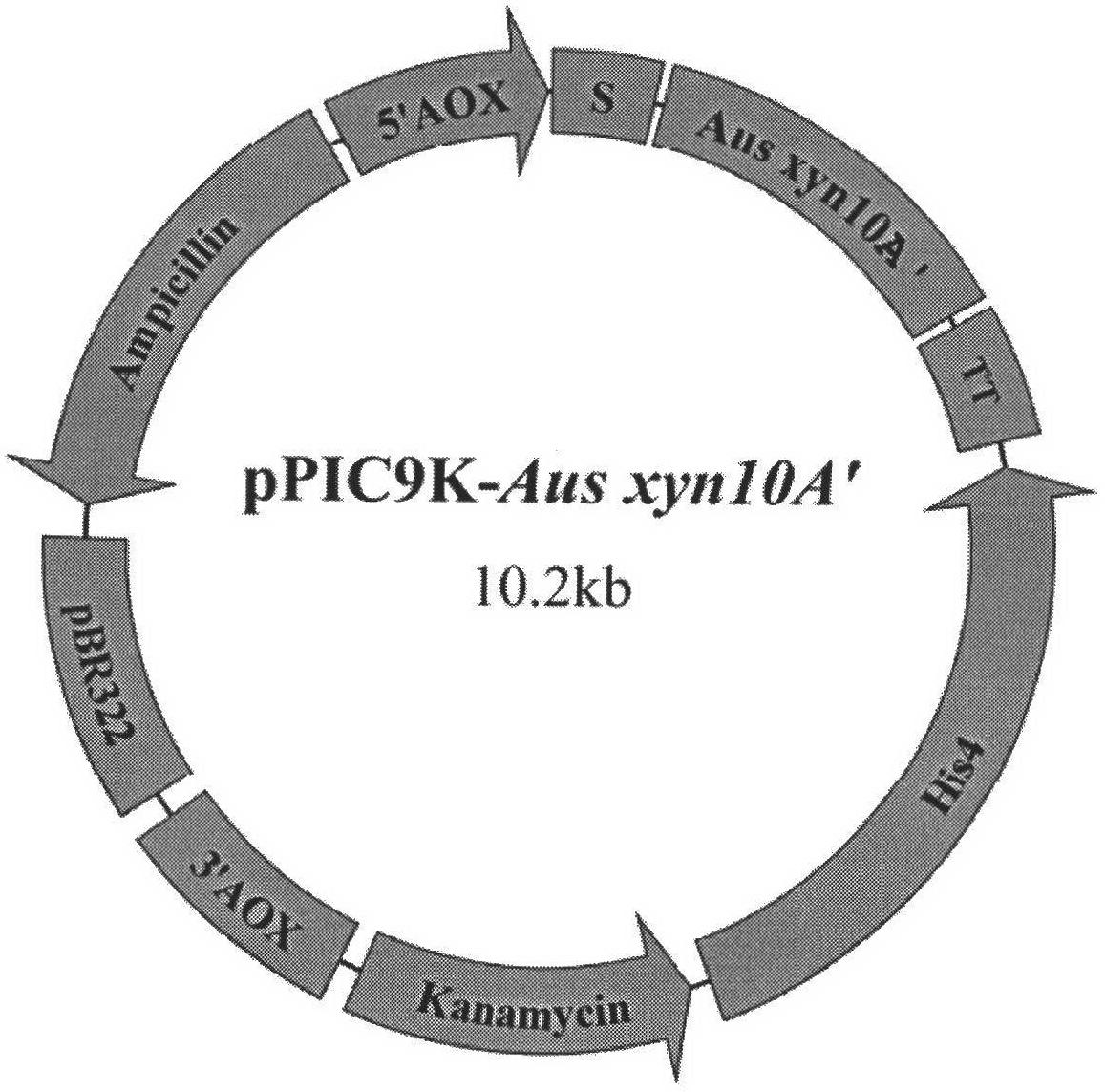
Method for improving optimum temperature of family-10 xylanase
The invention aims to provide a high-efficiency expression and purification method for family-10 xylanase Aus Xyn10A thermostability modified and reconstructed mutant enzyme. According to a comparison result of protein sequences of the Aus Xyn10A (derived from Aspergillus usamii E001) and thermostable xylanase (derived from Thermotoga maritima), the C terminal repeat of thermostable enzyme is used to the C terminal of the Aus Xyn10A by a gene engineering method, and the obtained mutant enzyme is named Aus Xyn10A'. Experimental results prove that the optimum temperature of the mutant enzyme is obviously improved, and the thermostable enzyme serving as a thermostable enzyme preparation has high industrial production potential and economic value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for amplifying and detecting of target nucleic acid sequence using thermostable enzyme
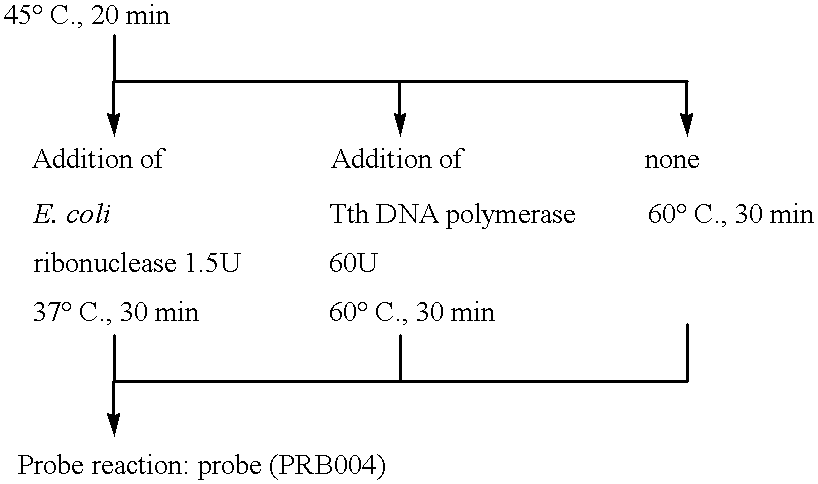
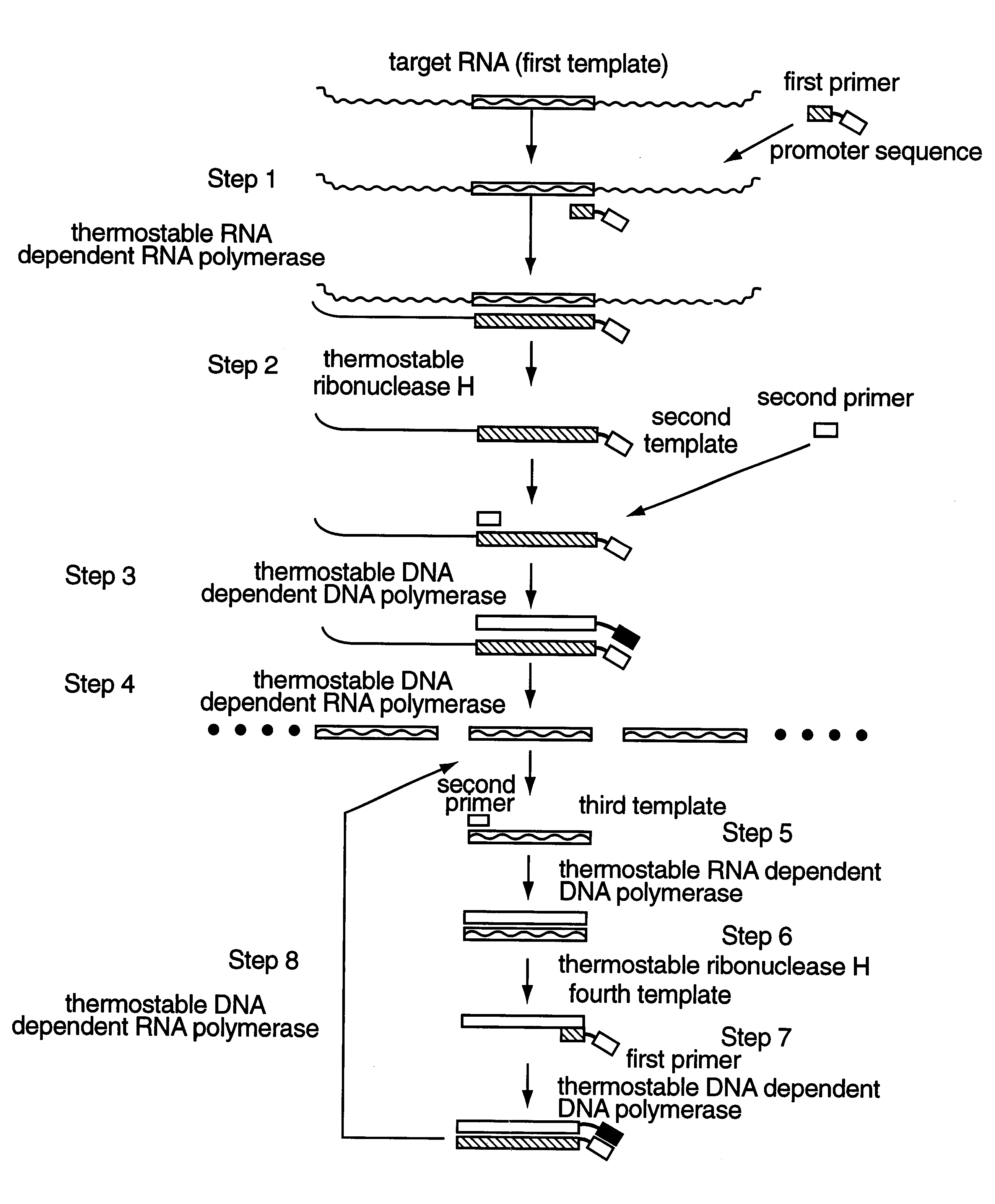
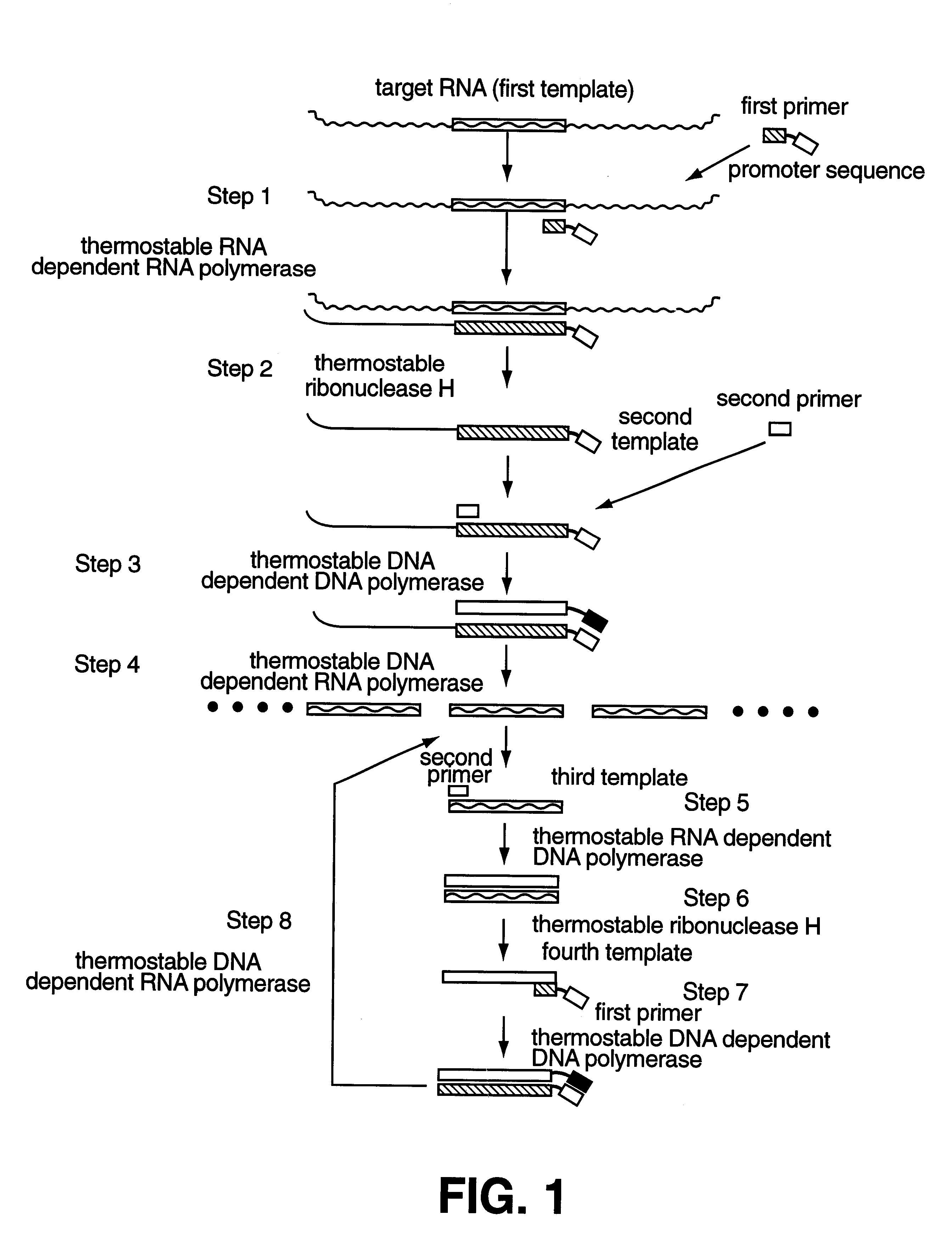
In a method for amplifying the specific nucleic acid sequence, a highly specific amplification which has low possibility of non-specific hybridization can be carried out. Highly stable reagents, the activities of which do not decrease in case of supply and storage, are also provided. Thermostable enzymes are used as RNA dependent DNA polymerase, DNA dependent DNA polymerase, DNA dependent RNA polymerase and ribonuclease H, which are required for the amplification system based on replicated RNA. Especially, it is preferable that a thermostable enzyme derived from Thermus thermophilus which has RNA dependent DNA polymerase activity, DNA dependent DNA polymerase activity and ribonuclease H activity, and thermostable DNA dependent RNA polymerase are used together. By this method, inactivation of enzymes are prevented by using thermostable enzymes, and the amplification can be carried out without sequential addition of enzymes.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Method for treating cellulosic grey fabric, products obtained by this process and their use
The invention relates to a method for treating a cellulosic grey fabric comprising the following steps: (a) a pretreatment step in which, in the presence of water, at a temperature of 60-100 DEG C, the fabric is contacted with a thermostable enzyme which degrades starch; and (b) an integrated desizing and scouring step in which, in the presence of water, at a temperature of 70 DEG C at the most, the fabric as obtained in step (a) is contacted with an enzyme which degrades a polymeric component of the primary cell wall of cotton and an enzyme which degrades starch. The invention also relates to the use of fabric as obtained using the method of the invention for manufacturing textile products. The invention also provides fabric manufactured using the method of the invention. The invention further relates to textile products manufactured from fabric treated using the method of the invention.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Enzyme-containing candy
InactiveUS20090074678A1Low costCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsAdditive ingredientMaltitol
It is intended to improve a method of adding a non-thermostable enzyme to a candy base material. In the method of the invention, a non-thermostable enzyme is added to a candy base material, and the material is stirred so that a substantially uniform mixed dough-like mixture is obtained within 5 minutes from the addition to obtain the mixed dough-like mixture. Then, the mixed dough-like mixture is cooled on a cooling plate and the mixed dough-like mixture is shaped. Preferably, a main component of the candy base material is selected from the group consisting of reduced palatinose, maltitol, reduced starch syrup, and xylitol.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
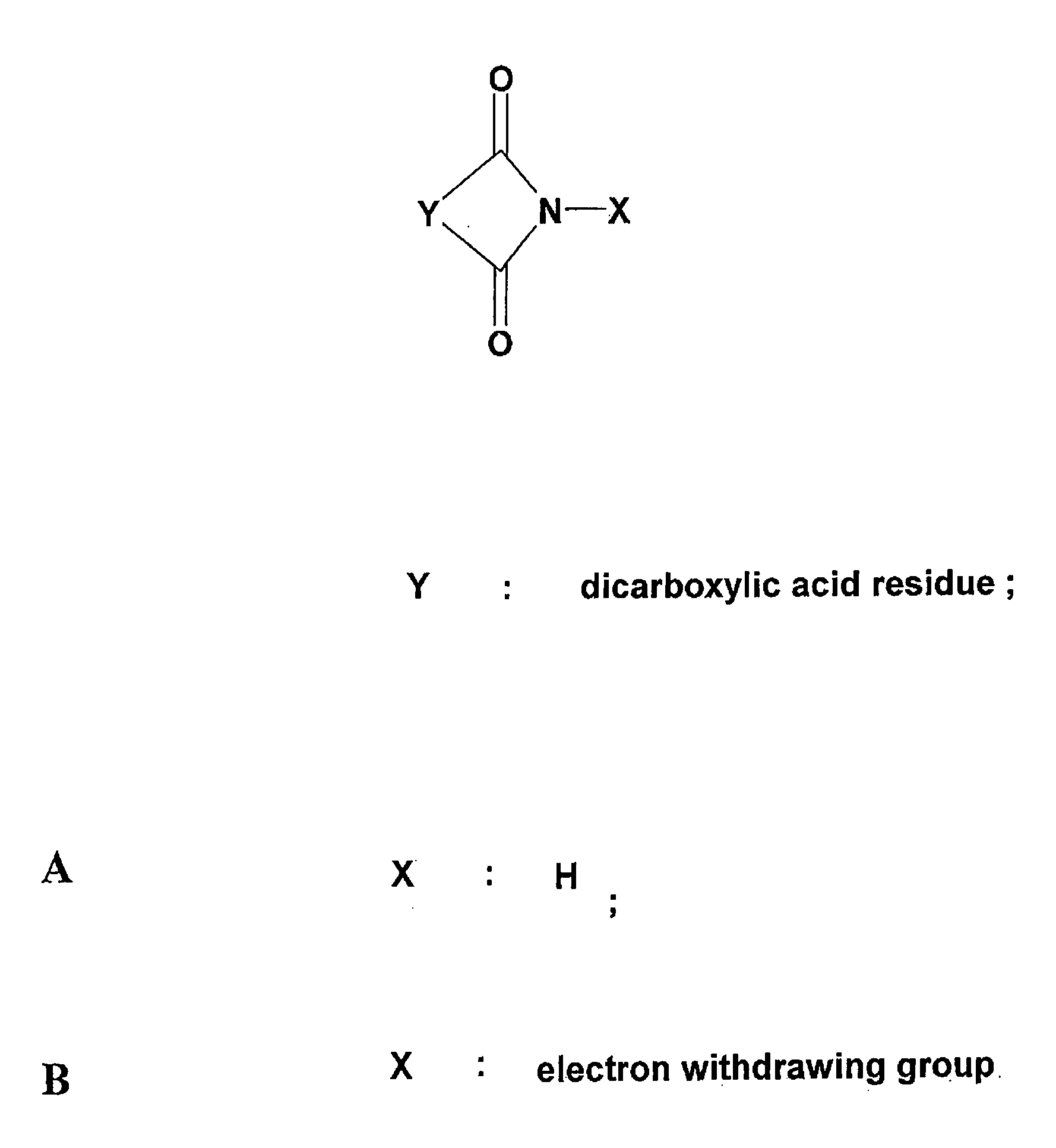
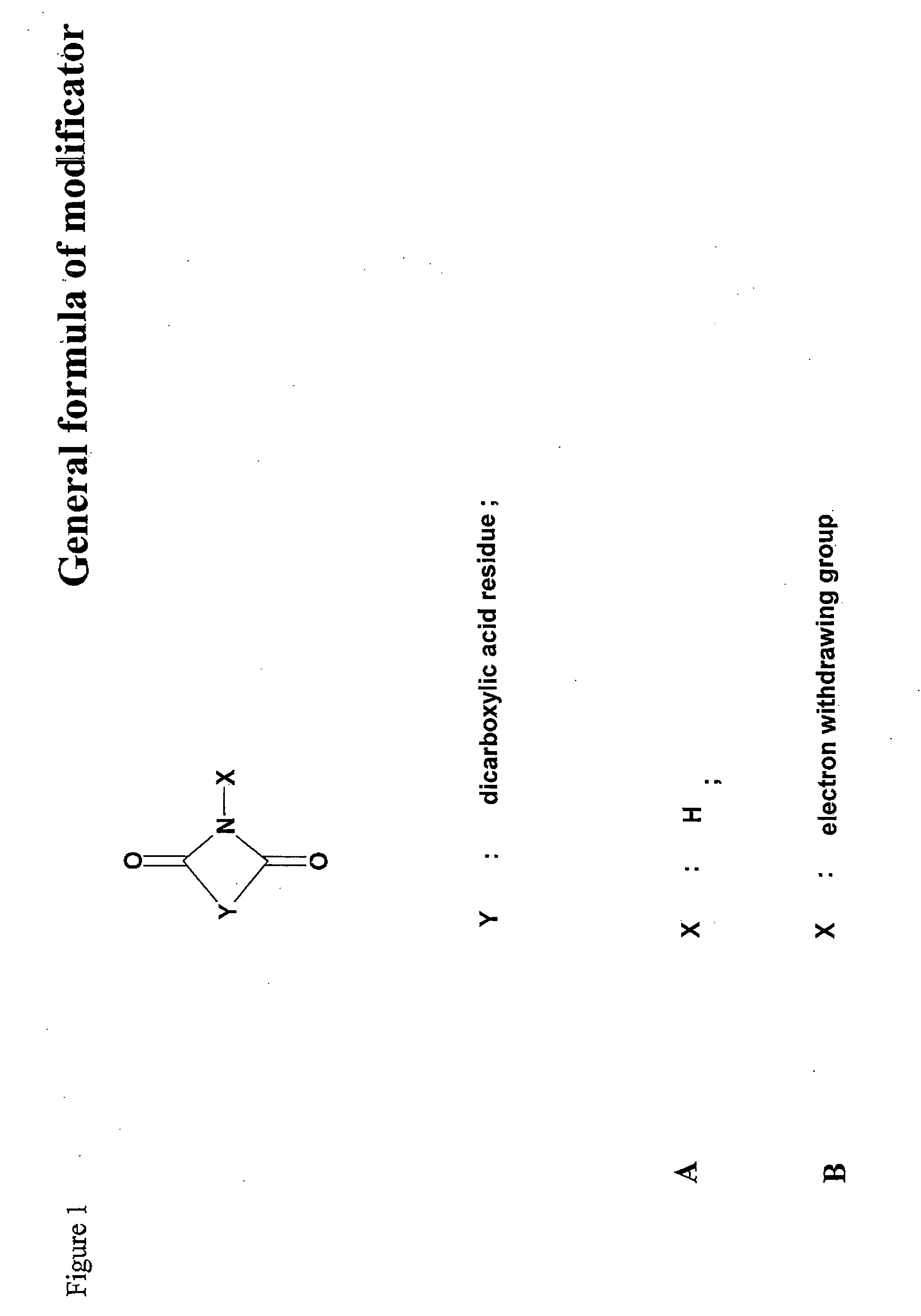
Reversibly modified thermostable enzyme compositions and methods of making and using the same
The present invention provides reversibly modified thermostable enzyme compositions and methods for making the same. The present invention also provides methods of using the reversibly modified thermostable enzyme compositions, as well as kits and systems comprising the reversibly modified thermostable enzymes.
Owner:SUZHOU NUHIGH BIOTECH
Methods of synthesizing polynucleotides using thermostable enzymes
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Novel enzymes which dehydrate glycerol
InactiveUS20020132311A1Simple methodBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyNucleotide
The present invention relates to improved methods and reagents for the production of 1,3-propanediol. In particular, the present invention provides novel thermophilic organisms and thermostable enzymes capable of catalyzing the fermentation of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol. The present invention also relates to methods of isolating such thermophilic organisms, methods of cloning polynucleotides that encode such enzymes, polynucleotides encoding such enzymes, and methods of using such enzymes and organisms for the production of 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Method and compositions for improved polynucleotide synthesis
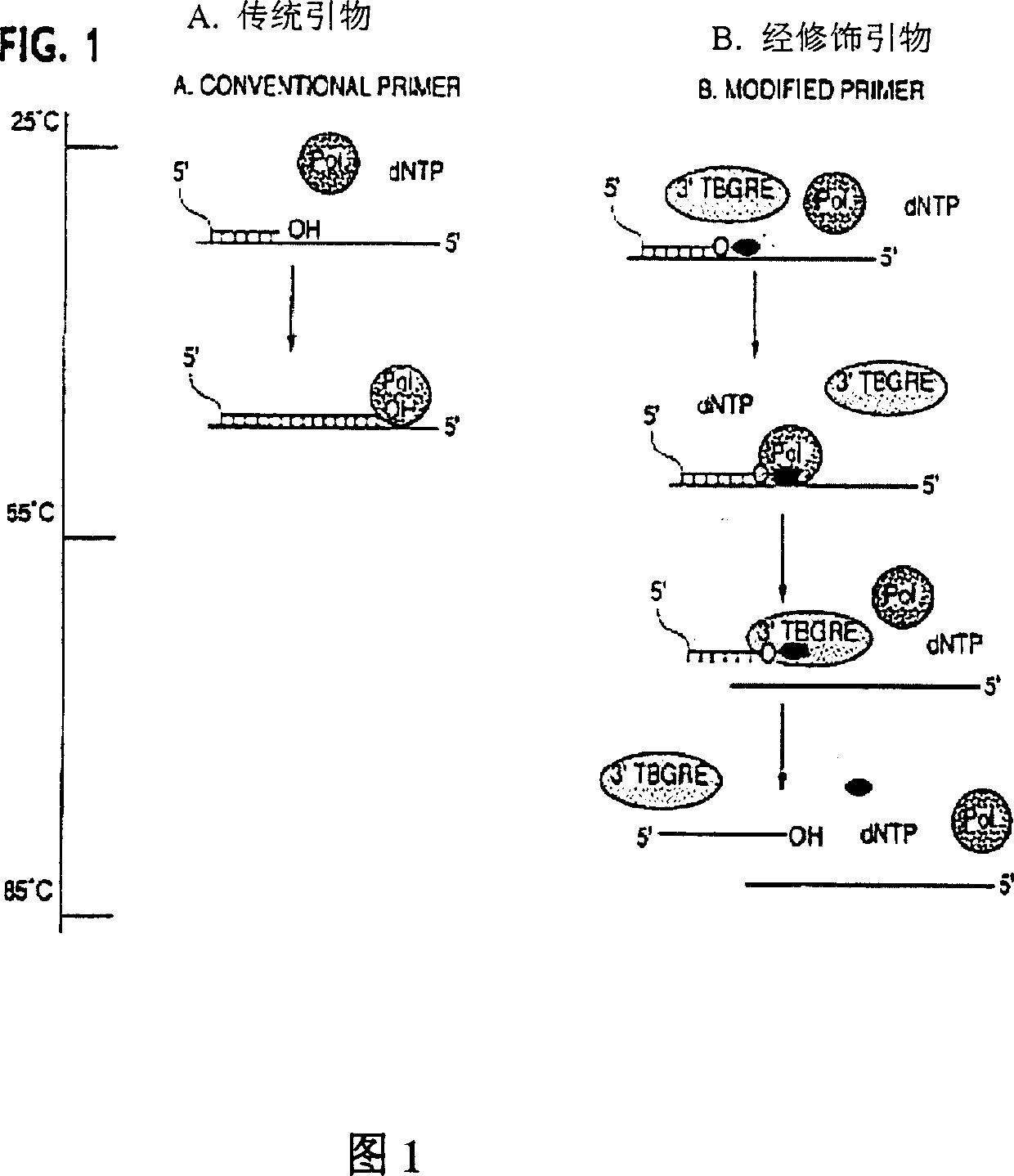
The sensitivity and specificity of polynucleotide synthesis is increased by protecting the 3'-end of an oligonucleotide used as a primer in the synthesis of the polynucleotide. Protection of the 3'-end of an oligonucleotide prevents non-specific chain elongation. Removal of blocking group an elevated temperature, using a thermostable enzyme, permits template-specific polynucleotide synthesis. The present invention also provides oligonucleotides with a 3' end protected by a blocking group and a thermostable enzyme capable of removing the blocking group at an elevated temperature. The compositions and methods of the invention are very useful in a variety of techniques for DNA / RNA amplification and analysis, including medical genetics research and diagnosis, pathogen detection, forensic, and animal and plant genetics applications, among others.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FULENGEN
Stable compositions for nucleic acid amplification and sequencing
The present invention is directed to compositions comprising mixtures of reagents, including thermostable enzymes (e.g., thermostable DNA polymerases), buffers, cofactors and other components, suitable for immediate use in nucleic acid amplification or sequencing techniques without dilution or addition of further components. The compositions contain no stablizing agents (e.g., glycerol or serum albumin) and unexpectedly maintain activity for extended periods of time upon storage at temperatures above freezing. These compositions are useful, alone or in the form of kits, for nucleic acid amplification (e.g., by the Polymerase Chain Reaction) and sequencing (e.g., by dideoxy or “Sanger” sequencing), or for any procedure utilizing thermostable DNA polymerases in a variety of medical, forensic and agricultural applications. In particular, the compositions and methods are useful for amplifying and sequencing nucleic acid molecules that are larger than about 7 kilobases in size.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Novel enzymes which dehydrate glycerol
Owner:SEYFRIED MARKUS +2
Heat-stable enzyme compositions
InactiveUS8399230B2Improve thermal stabilityHigh activityEnzyme stabilisationOn/in organic carrierProduct formationSpray dried
The thermal stability of enzymes is improved by incorporating the enzyme in a matrix of a non-reducing sugar, such as trehalose. Heat-stable compositions of enzymes and sugar are formed by adding the enzymes to a sugar syrup and drying the mixture either by spreading it on a carrier or by spray drying. The enzyme compositions retain higher levels of activity after being subjected to heat in product-forming processes, such as steam pelleting of animal feed supplemented with the enzyme compositions.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com