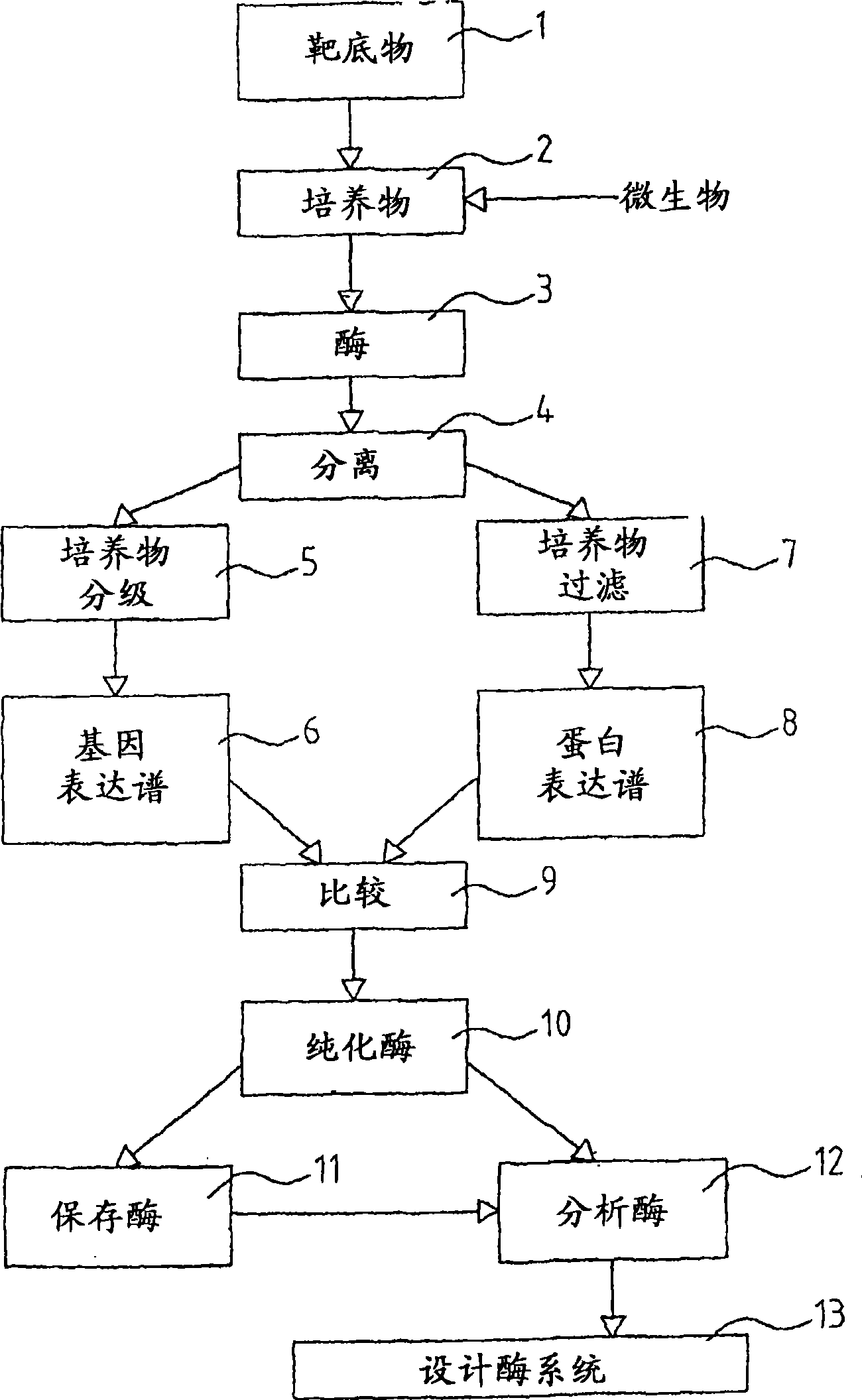
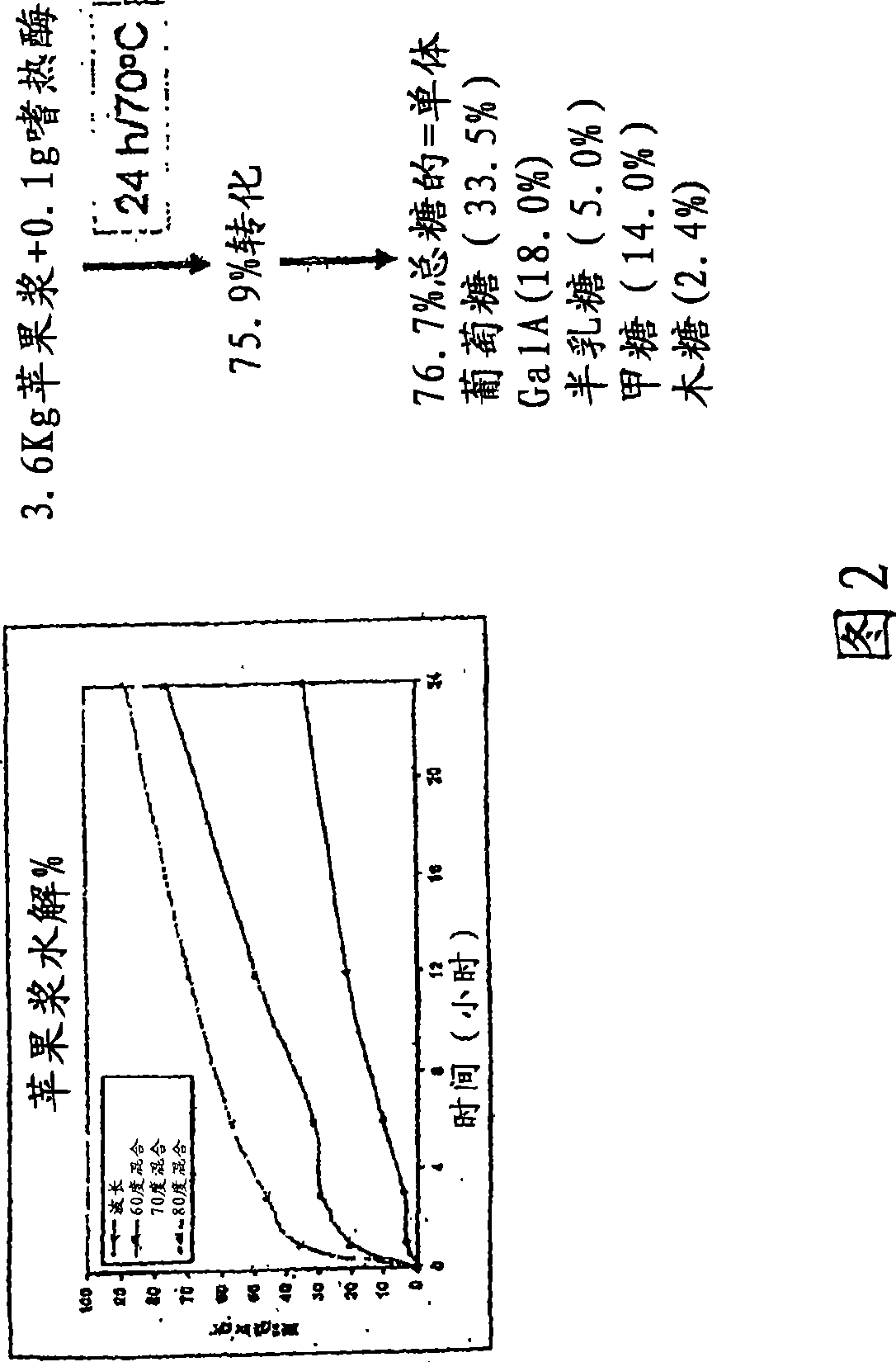
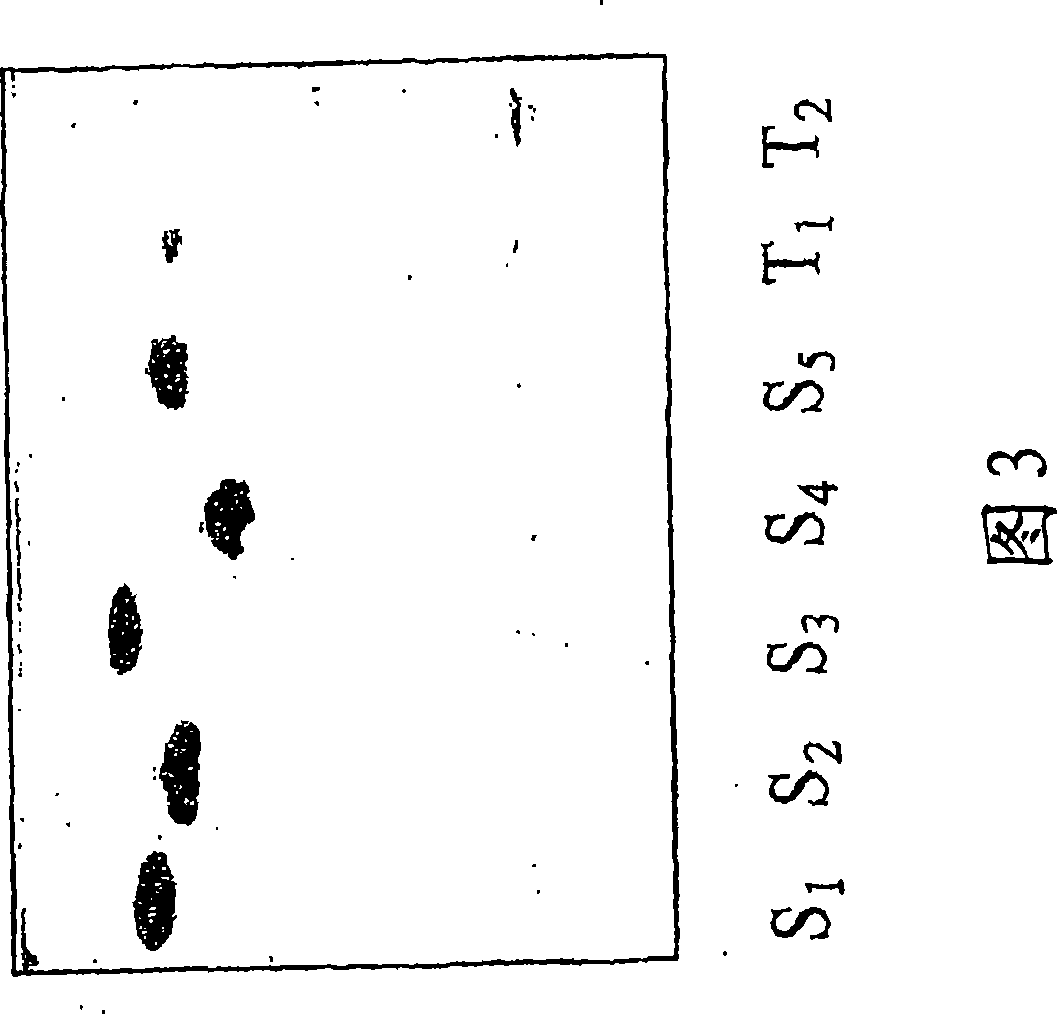
Talaromyces emersonii enzyme systems
A technology of Talaromyces and strains, applied in the directions of enzymes, hydrolases, glycosylases, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the display of multiple activities, excessive consumption of time and cost, waste of processes, etc., and achieve enhanced storage and transportation. Potential, time and cost savings, effect of short reaction times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Embodiment 1T.emersonii IMI393751, separation
[0077] Freshly harvested (approximately 200 g) clean grass (turf) cuttings and other mixed plant biomass were placed in closed containers to simulate a composting environment, and incubated at 65°C for approximately 2 hours in a constant temperature climate chamber (combined pasteurization and equilibration of substrates). Keep the humidity / moisture level at -65-70%. Use a container to provide low pulses of humidified, filtered air at intervals through the line. After 2 hours, a spore suspension (1 x 10 in 2% sterile water) of T. emersonii (a laboratory stock derived from a 12-year-old isolate of CBS814.70) 8 spores) were used to inoculate the central area of the biomass. The temperature was maintained at 65°C for 2 days and thereafter increased at 2°C intervals every 24 hours until the air temperature inside the climate chamber reached 70°C. The culture was grown for an additional 7 days before aseptically removing ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Example 2: Enzyme system from Talaromyces emersonii for transformation of cellulosic material. The complete hydrolysis of xylose requires the synergistic action of xylanase, β-xylosidase, α-glucuronidase, α-L-arabinofuranosidase and esterase. Table 1. Gives examples of percentages of selected target substrates (including waste / residue) and inducible carbonogens used in this example. Percent induction refers to the weight of carbon source per volume of medium (g / 100ml).
[0086] Table 1: Culture substrates / inducible carbon sources for enzyme production by T. emersonii
[0087]
[0088] ^Included for comparison purposes.
[0089] Based on the results obtained, an enzyme system for the degradation of hemicellulose (xylan) or xylan-rich wood-derived products, residues or wastes was designed using enzymes purified from Talaromyces emersonii. The relative amounts of key enzymes present in the enzyme system are listed in Table 2.
[0090] Table 2: Systems used to degrad...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Example 3: A system from Talaromyces emersonii for the conversion of cereals, sugar beet pulp and other materials rich in arabinoxylan and acetylated hemicellulose, including waste.
[0102] Table 4 presents the Talaromyces emersonii IMI 393751 and two previously identified strains designed for the conversion of cereal cereals, sugar beet pulp, and other materials (including waste) rich in arabinoxylan and acetylated hemicellulose. Relative amounts of different enzyme activities in the designed enzyme systems of the mutant lines.
[0103] Table 4: Enzyme activity of systems used for conversion of arabinoxylan and acetylated hemicellulose rich materials
[0104] enzyme
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com