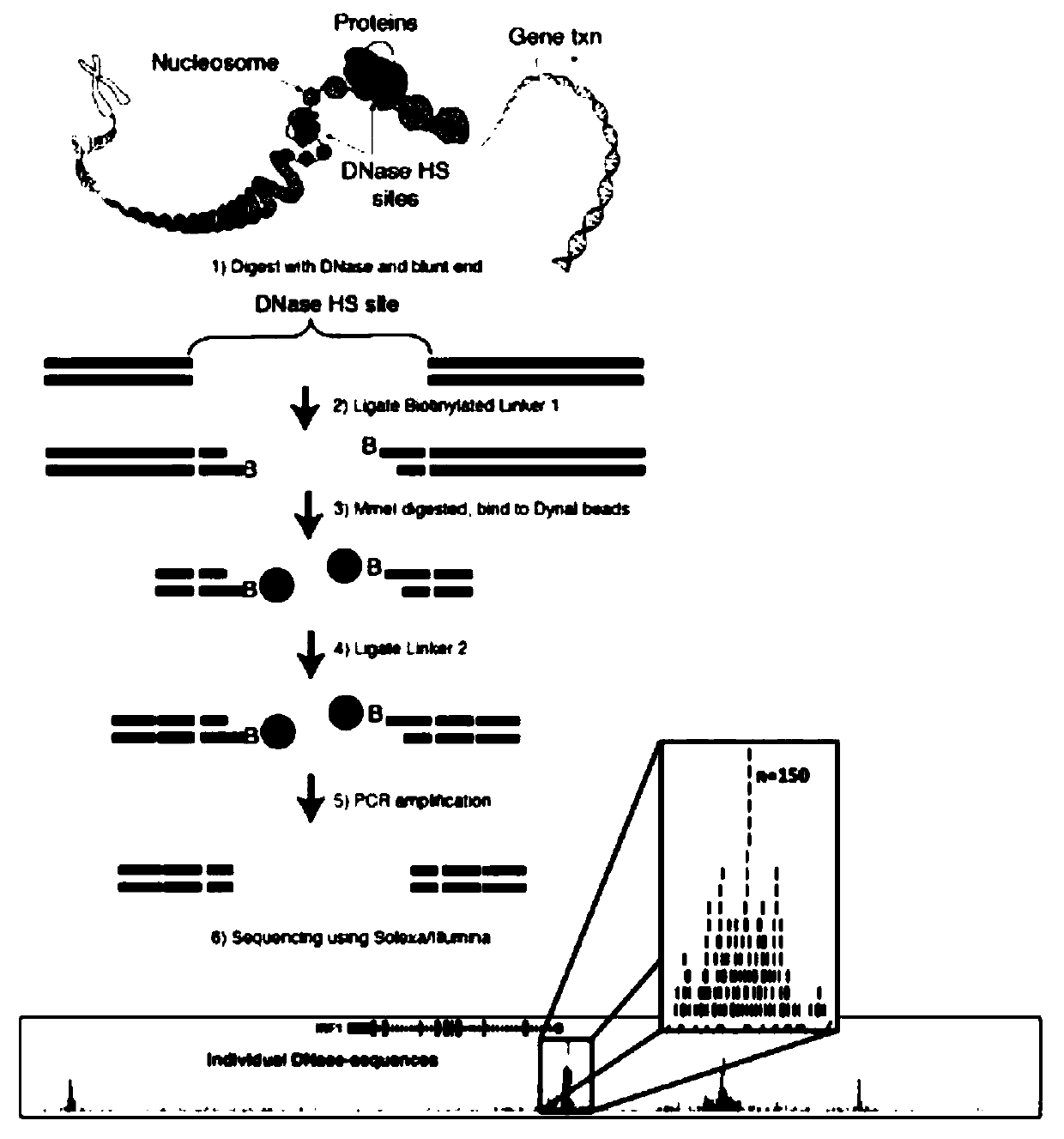
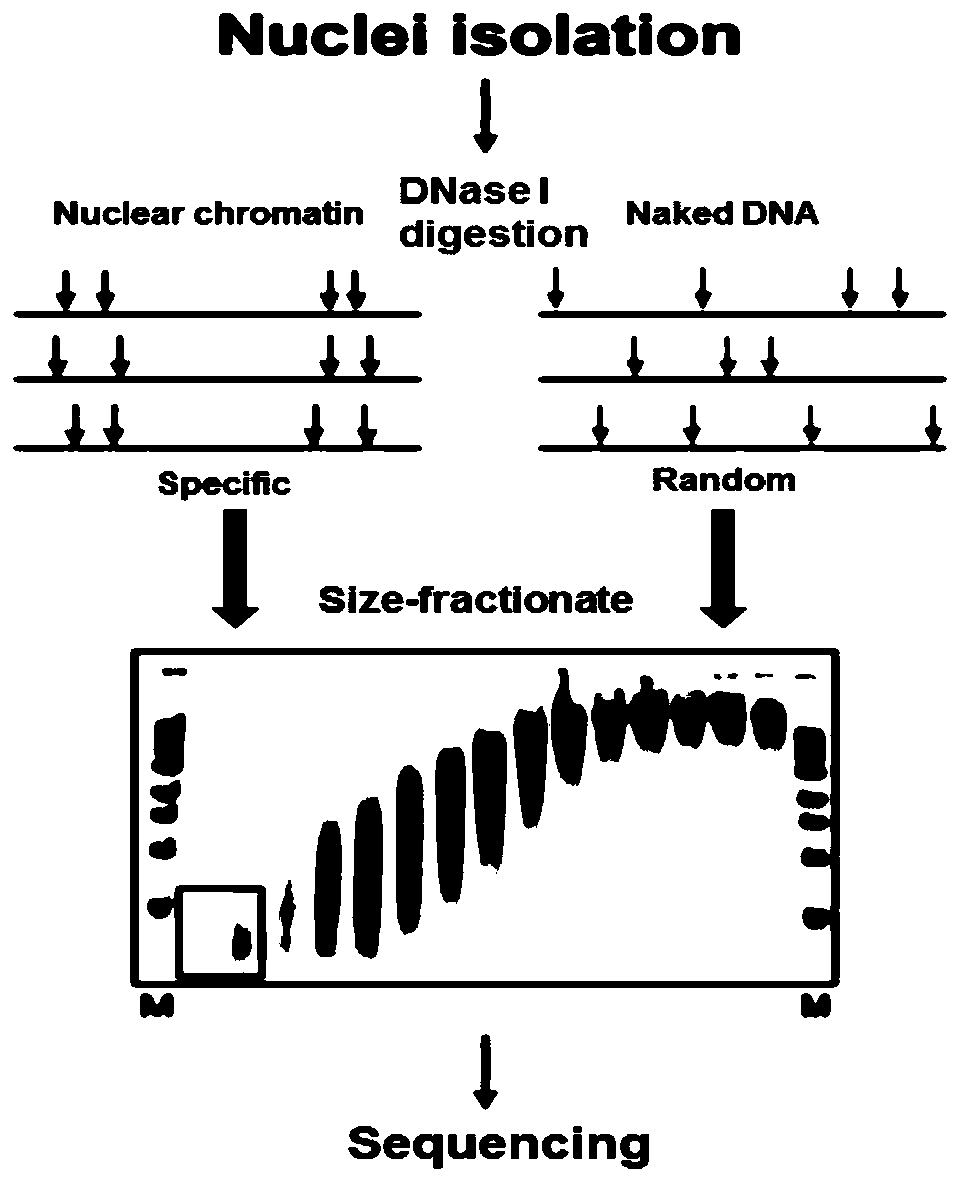
Method for identifying open chromatin sites of plant genomes by using micrococcal nuclease
A technology of micrococcal nuclease and plant genome, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to directly identify the core sequence of functional DNA elements, limited application of plant genome, and increased experimental costs, etc. problem, to achieve strong visualization effect, short time-consuming, and easy-to-repeat effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] (1) Plant material cross-linking:
[0063] Select 2-5g of the experimental material (wheat, corn, rice or Arabidopsis leaves) to be tested, cut into pieces of a certain size, soak in the final concentration of cross-linking fixative, and cross-link at 4°C for 10 minutes under vacuum conditions .
[0064] A 2.5M glycine solution was added to the cross-linking liquid to obtain a final concentration of 125 mM, and vacuum treatment was performed at 4° C. for 5 minutes.
[0065] Discard all the cross-linking solution, rinse three times with sterilized distilled water, place all the leaves on absorbent paper, and dry them in the air for 10 minutes. Wrapped in paper and frozen in liquid nitrogen for 10 minutes, the leaves were taken out and stored in a -80°C refrigerator for later use.
[0066] (2) extracting and purifying the nucleus of the plant material:
[0067] The fixed leaves were ground into powder with liquid nitrogen, and 10 ml of the powder was taken to extract cel...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2 RE-MNase-seq identification of open chromatin loci in wheat genome
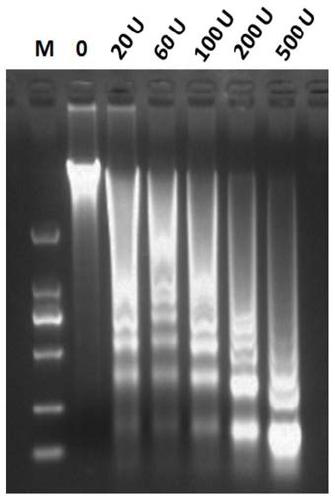
[0084] Select 60U MNase enzyme-digested wheat cell nuclear DNA, separate by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, and then reclaim all DNA fragments that do not contain 150bp in 50-280bp for construction of Illumina sequencing library ( Figure 7 ), separation and purification of 200-450bp DNA fragments ( Figure 8 ) for 2x150PE sequencing on the Illumina Nova-seq sequencing platform.
[0085] Quality control analysis was performed on the sequencing data, and the results are shown in Table 2. The results of preliminary quality analysis showed that the alignment rate of the whole wheat genome was 97.32%, and that of Q20 was 64%-69%, indicating that the data quality was reliable and could be used for the identification and functional analysis of open chromatin loci in the whole wheat genome. A total of 100,000 sites were initially identified ( Figure 9 ), through correlation analysis with gene ...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3 RE-MNase-seq identifies open chromatin loci in the maize genome.
[0089] Select 60U MNase enzyme-digested corn nuclear DNA, separate it by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, and then recover all DNA fragments excluding 150bp in 50-280bp for construction of Illumina sequencing library, separate and purify 200-450bp DNA fragments for Illumina Nova- The seq sequencing platform performs 2x150PE sequencing.
[0090] Quality control analysis was performed on the sequencing data. The preliminary quality analysis results showed that the comparison rate of the whole maize genome was 94.50%, and the comparison rate of Q20 was 45%, indicating that the data quality is reliable and can be used for the identification of open chromatin sites in the whole maize genome. Identification and functional analysis. A total of 40,000 loci were initially identified ( Figure 13 ), through the association analysis of the relationship with gene expression, it was found that at the gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com