Methods and systems for evaluating tumor mutational burden
A mutation load, tumor technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial assay/examination, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that whole exome sequencing is not widely available, expensive, time-consuming, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0639] In embodiments of the methods described herein, a step or parameter in the method is used to modify a downstream step or parameter in the method.
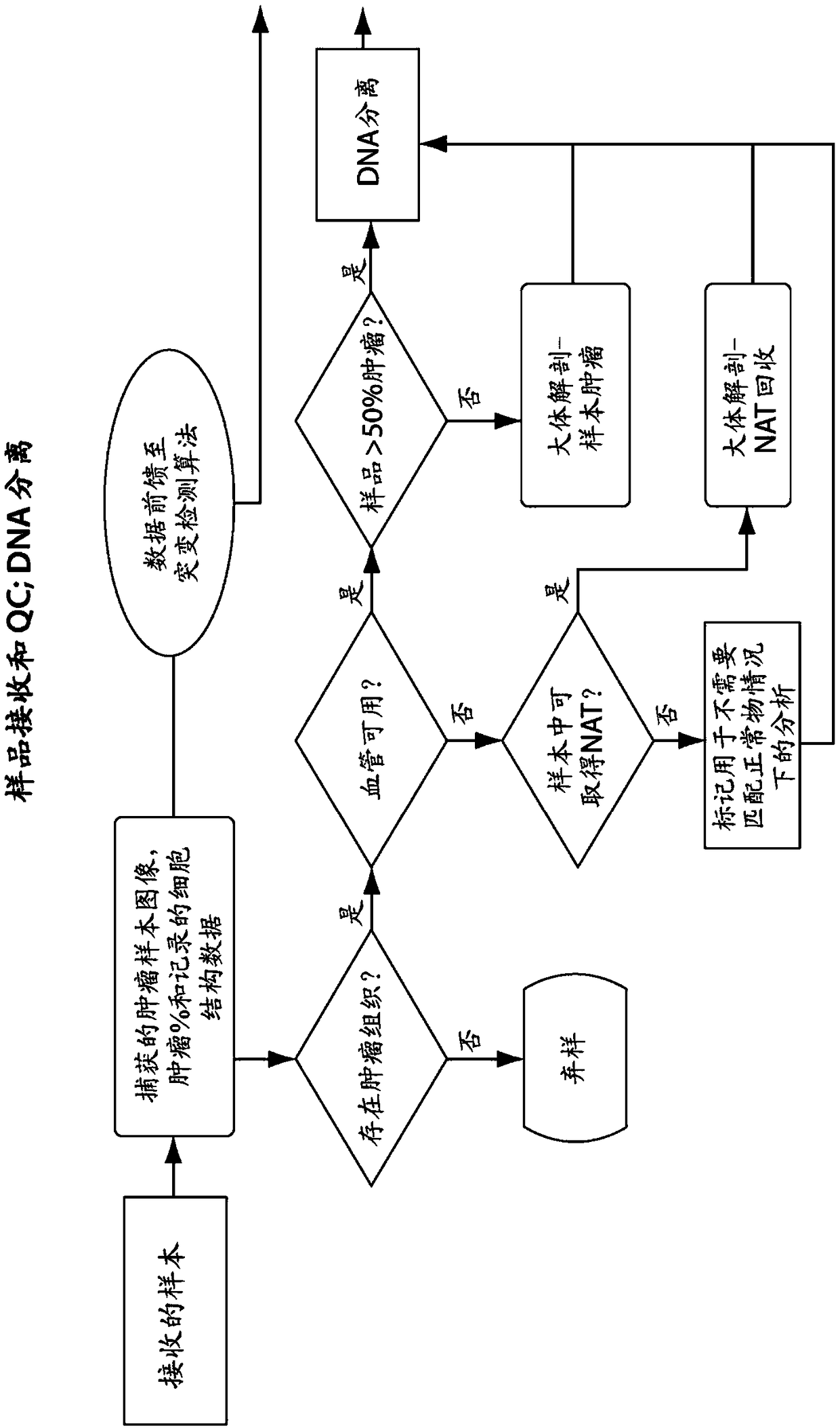
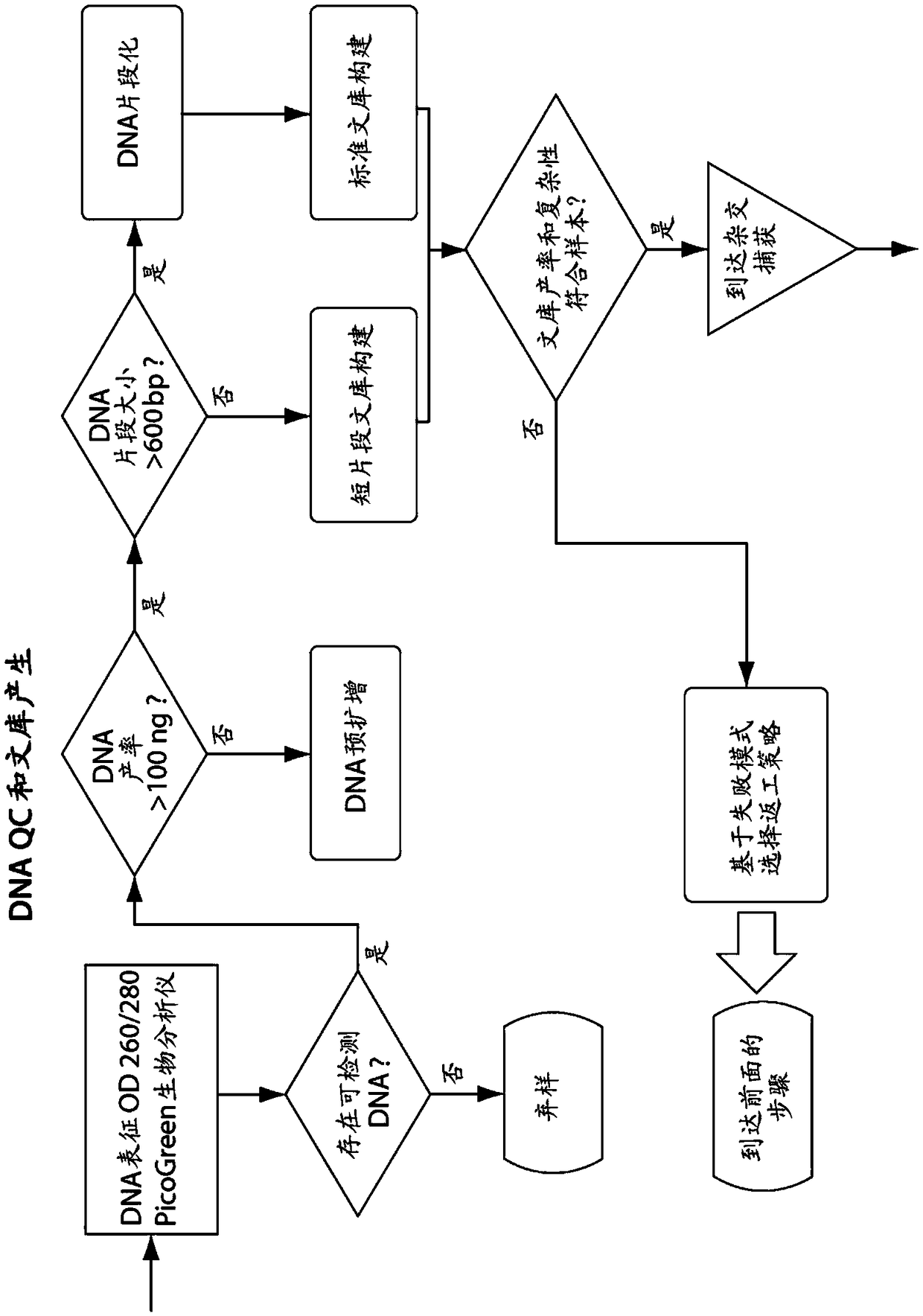
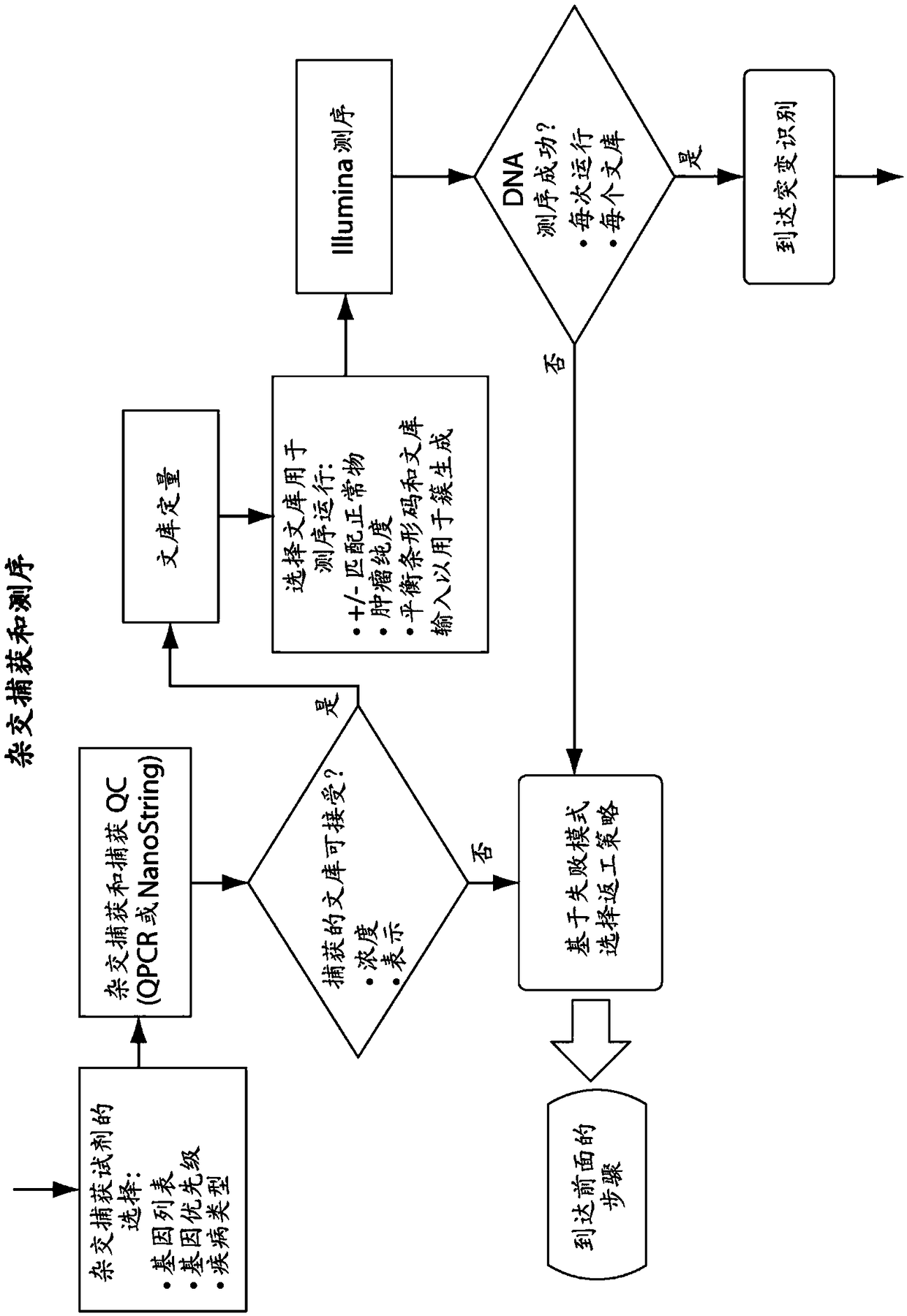
[0640] In one embodiment, the characteristics of the tumor sample are used to modify downstream steps or parameters in one or more or all of: isolation of nucleic acid from said sample; library construction; bait design or selection; hybridization conditions; sequencing; Read mapping; select a mutation calling method; mutation calling; or mutation annotation.
[0641] In one embodiment, the characterization of isolated tumor (or control) nucleic acid is used to modify downstream steps or parameters in one or more or all of: isolation of nucleic acid from said sample; library construction; bait design or selection ; hybridization conditions; sequencing; read mapping; selection of mutation calling methods; mutation calling; or mutation annotation.
[0642] In one embodiment, the characteristics of the library are used to modi...
Embodiment 1
[0801] Example 1: Comparison of Genome-Wide Mutation Burden with Mutation Burden Measured by Targeted Genes
[0802] In this example, it was determined whether TMB measured by comprehensive genome profiling (CGP) testing targeting 315 genes (1.1 Mb of the coding genome) could provide an accurate assessment of exome-wide TMB. Accurate measurements of TMB obtained by a targeted comprehensive genome profiling test are demonstrated.
[0803] method
[0804] Analyzing TCGA data
[0805] TCGA data were obtained from public repositories (Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network et al. Nat Genet 2013;45:1113-20). For this analysis, so-called somatic variants identified by TCGA were used as raw mutation counts. 38Mb was used as an estimate of exome size. For downsampling analyses, using fractions ranging from 0-10 Mb per fraction for the exome at whole exome TMB = 100 mutations / Mb, 20 mutations / Mb, and 10 mutations / Mb A binomial distribution was used to simulate the observed number of...
Embodiment 2
[0813] Example 2: Mutational Burden Landscape by Cancer Type
[0814] In this example, the distribution of TMB across different cohorts of > 100,000 cancer samples is described and the association between somatic alterations and TMB in over 100 tumor types is tested. A subset of patients was found to exhibit high TMB in virtually all cancer disease types, including many rare tumor types. TMB was found to increase significantly with age, showing a 2.4-fold difference between 10 and 90 years. Using a CGP assay targeting the approximately 1.1 Mb coding genome, it was found that there are many disease types in which a significant proportion of patients with high TMB could benefit from immunotherapy.
[0815] This study provides a better understanding of the TMB landscape across human cancers, based on data from comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP) of >100,000 patient tumors of different types. The analysis described in this example expands significantly on existing data quantif...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com