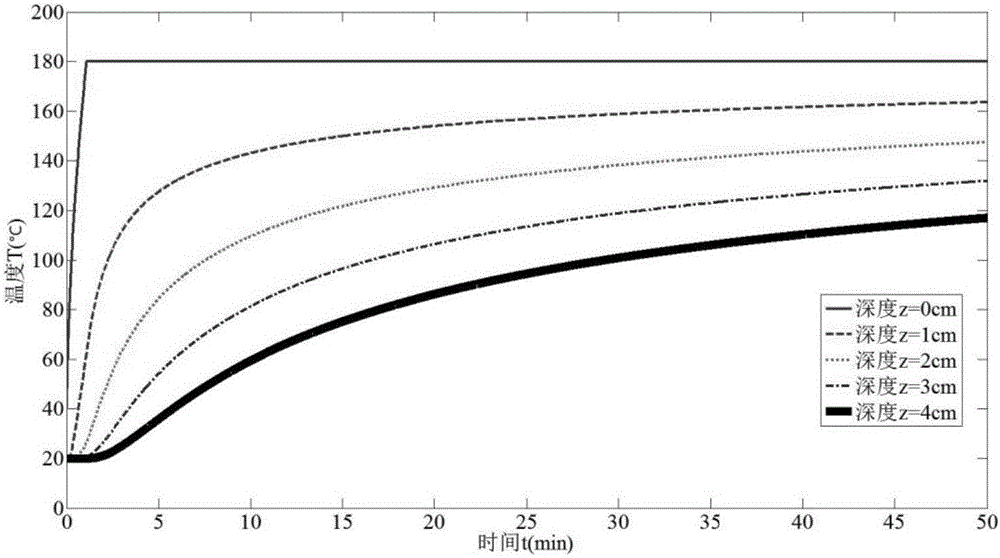
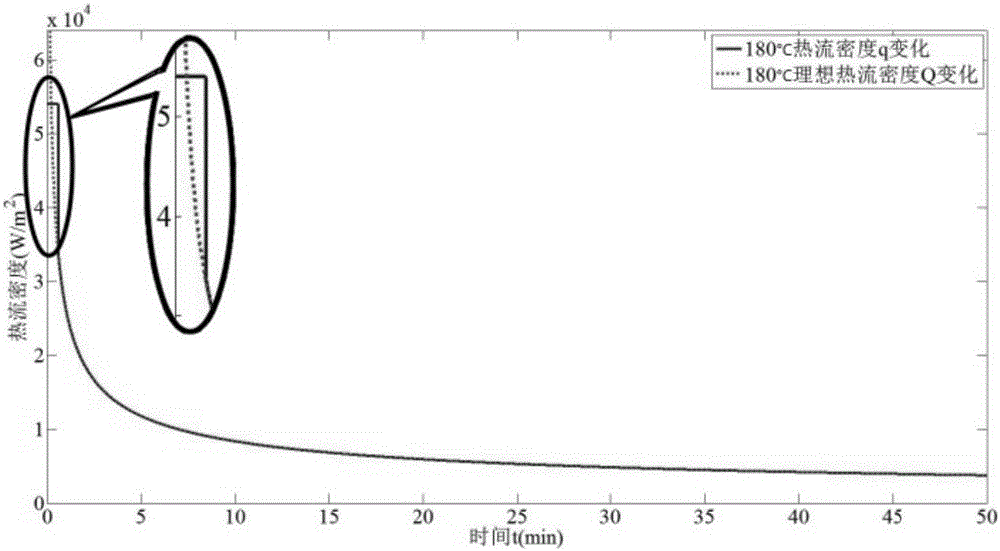
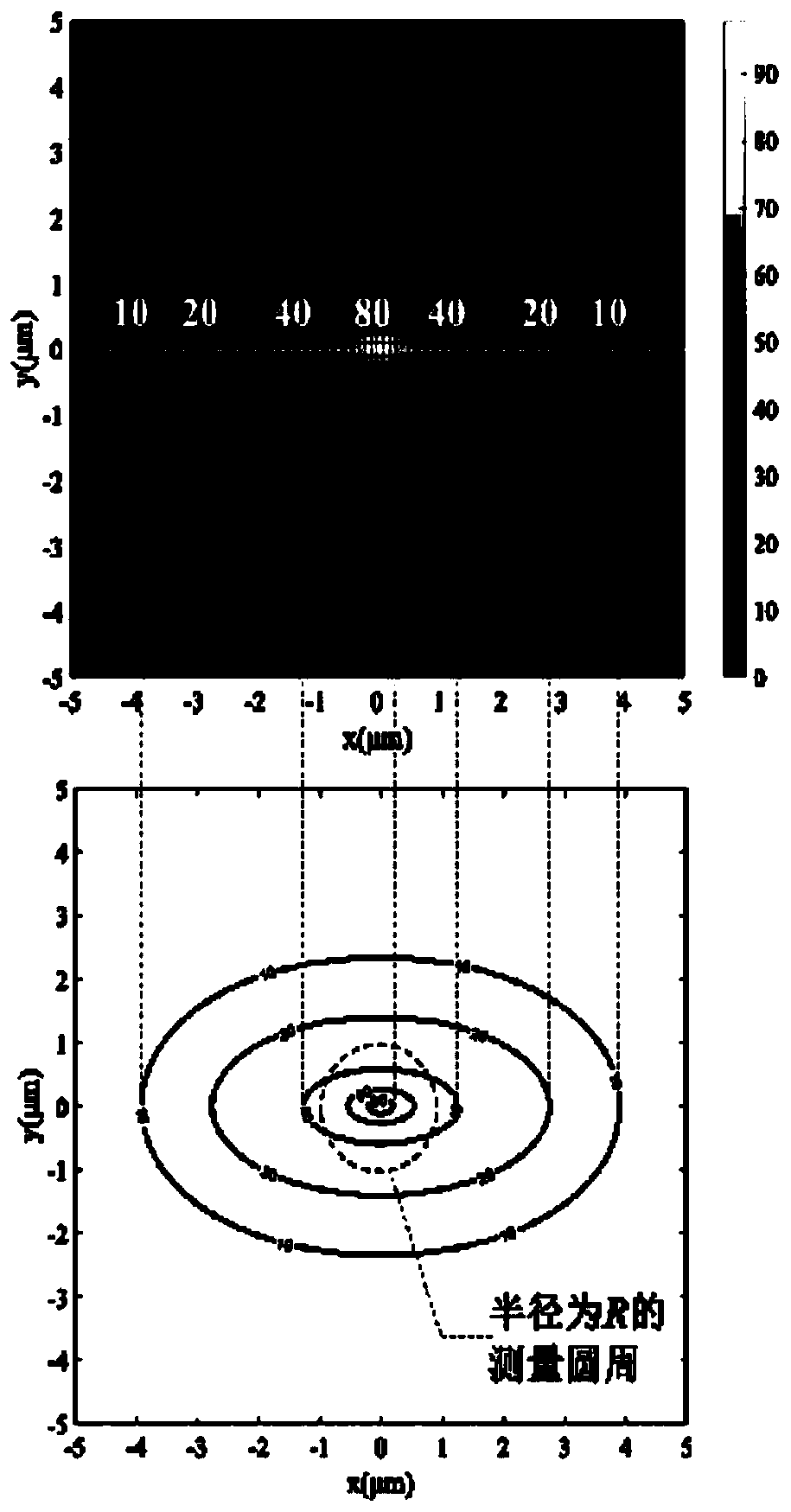
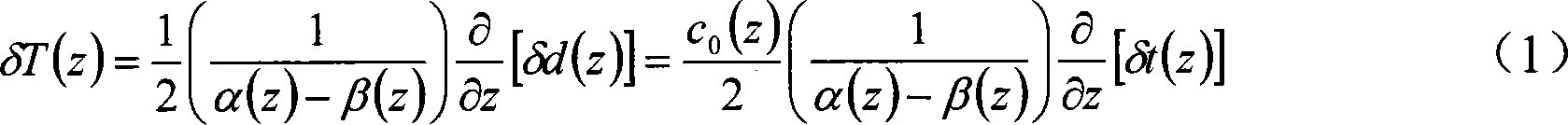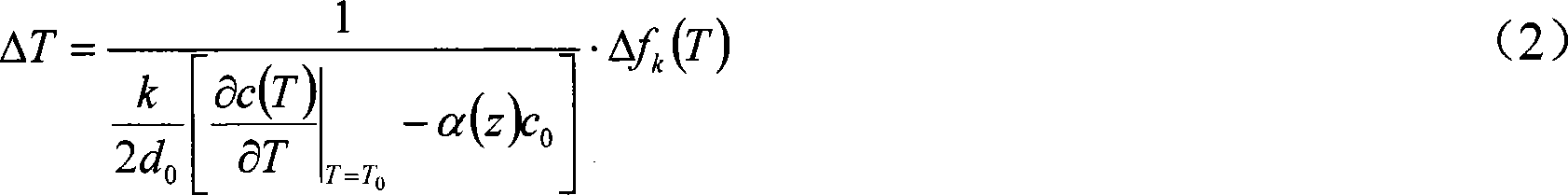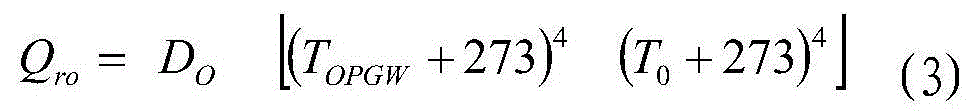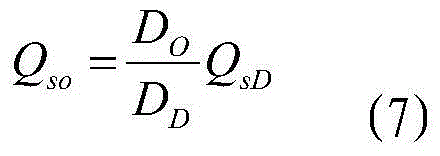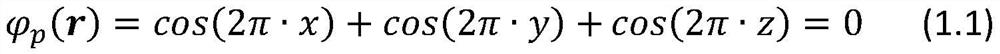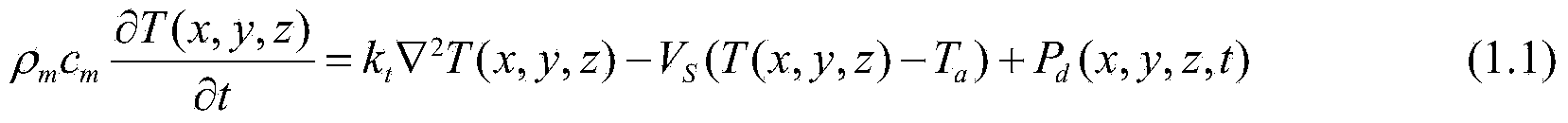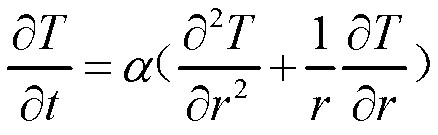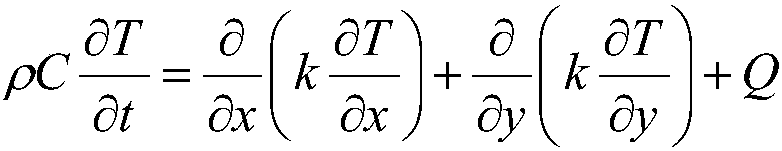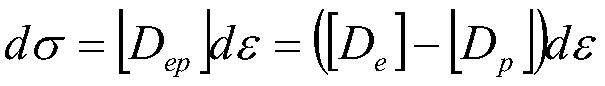Patents
Literature
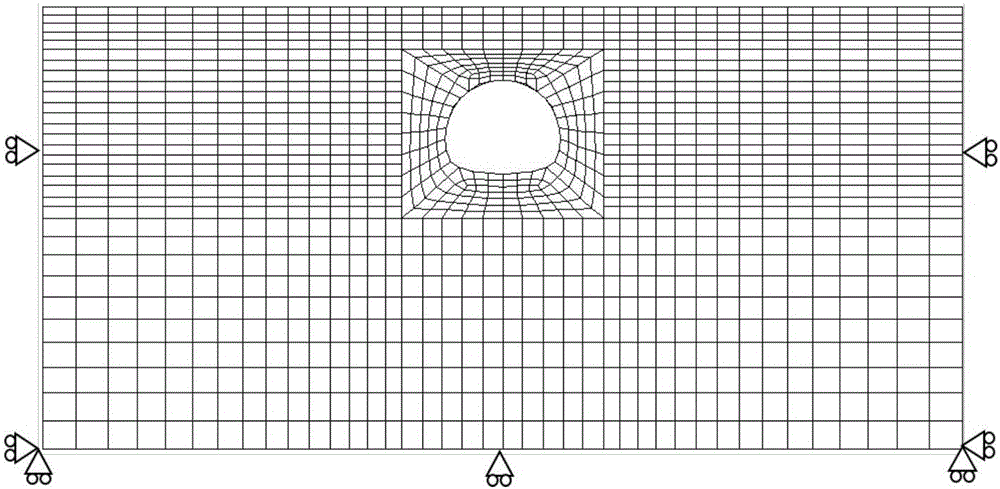
151 results about "Conduction equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The heat conduction equation is a partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or the temperature field) in a given body over time. Detailed knowledge of the temperature field is very important in thermal conduction through materials.
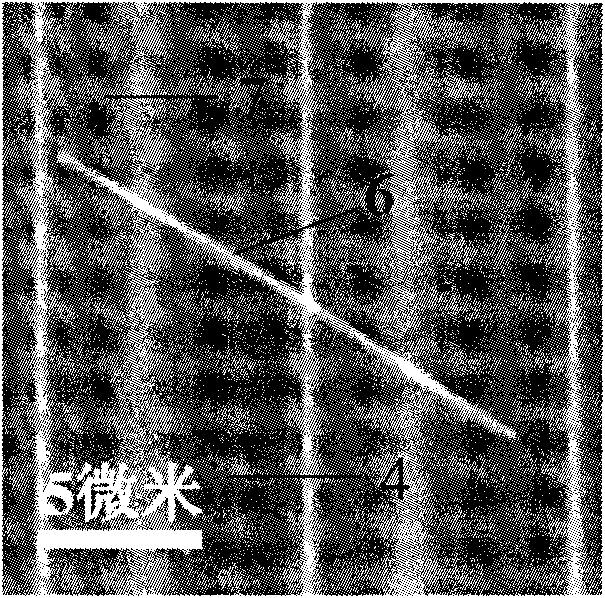
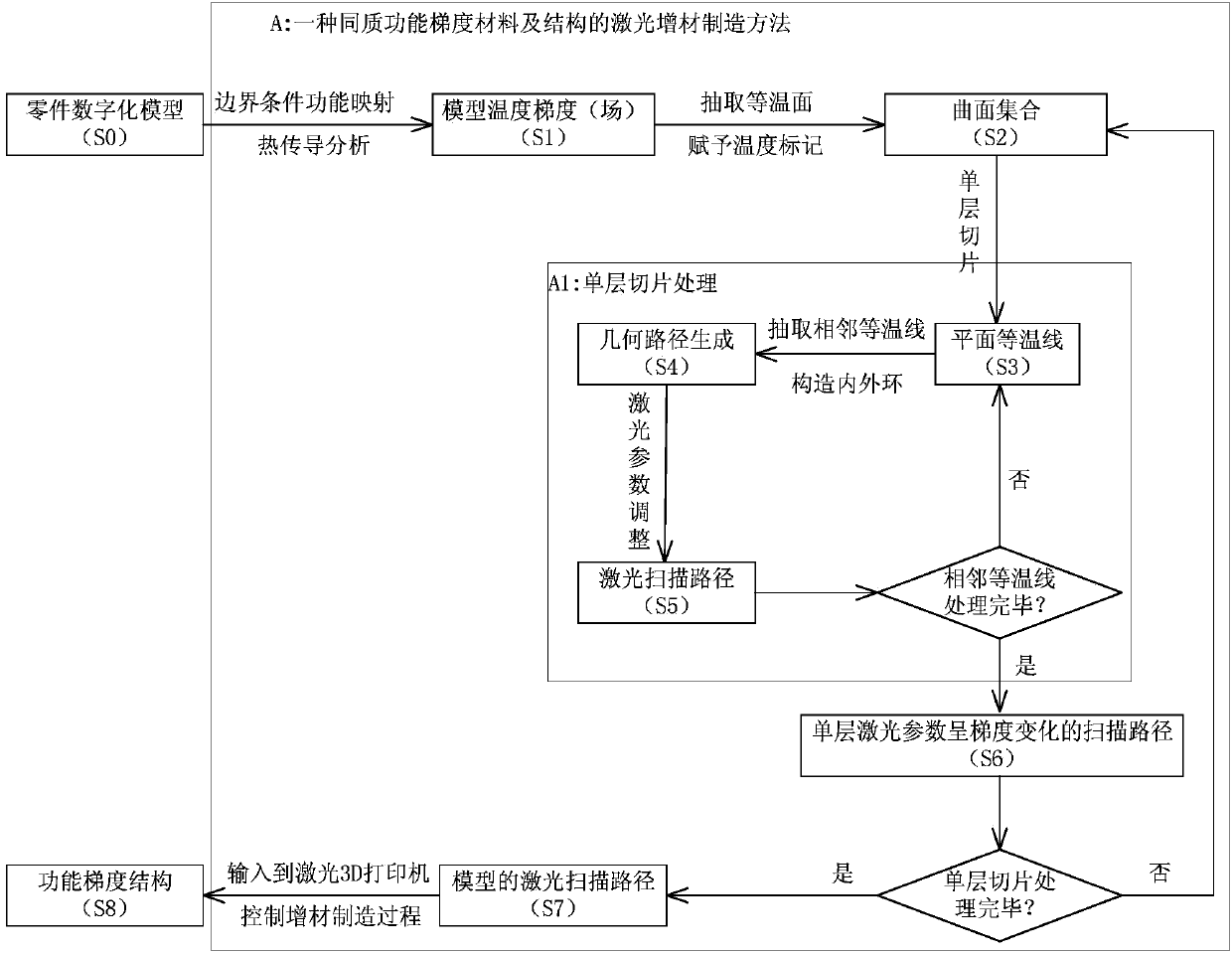
Laser additive manufacturing method for homogeneous functionally graded material and structure
ActiveCN104190930AOvercome functionOvercome structureIncreasing energy efficiencyLaser scanningOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a laser additive manufacturing method for a homogeneous functionally graded material and structure. The method includes the following steps that different functions are mapped into different temperatures which serve as boundary conditions to be exerted on different parts of a three-dimensional model; a three-dimensional finite element method is used for calculating a heat conduction equation of the model, inner temperature graded distribution, namely the temperature field of a model, is obtained, that is a temperature field of the model is obtained; an isothermal surface of the model is extracted, and a curved surface set with different temperature marks is obtained; slicing is conducted on the curved surface set, the intersection outline of each layer and the isothermal surface is obtained, in other words, plane isothermal lines are obtained; slices of each layer are processed, and a scanning route with laser parameters of the single layer in graded variation is obtained; the steps are repeatedly conducted until slicing is completed and a laser scanning route of the model is obtained; the generated laser scanning route is input into a laser 3D printing machine to control the additive manufacturing process, and the homogeneous functionally graded structure is obtained. According to the additive manufacturing method, the fact that the homogeneous functionally graded material and the homogeneous functionally graded structure can be manufactured in an additive mode is achieved, and the fact cannot be achieved through a current laser additive manufacturing method.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
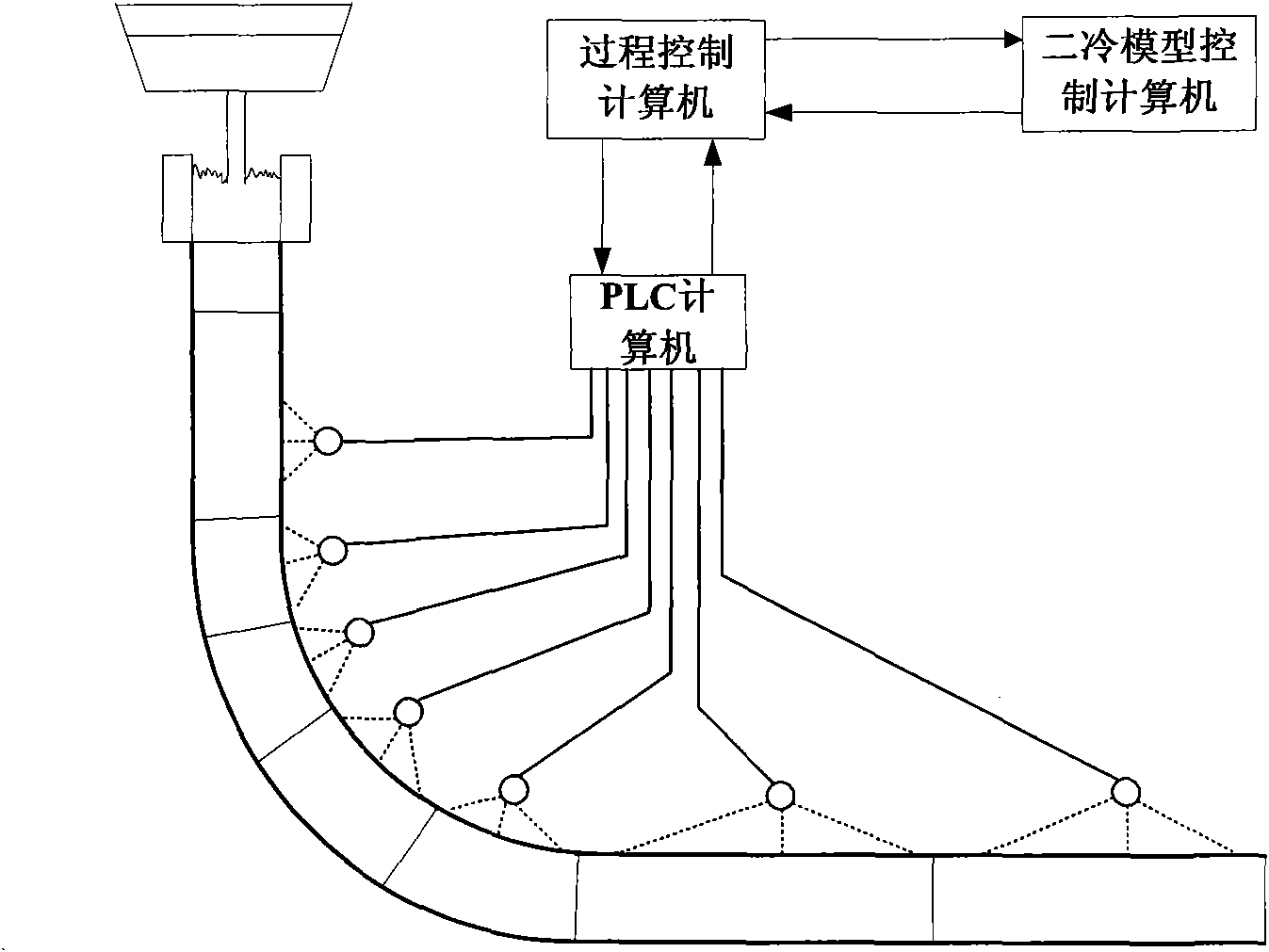
Dynamic secondary cooling control method for slab continuous casting based on double-cooling mode
The present invention discloses a dynamic secondary cooling control method for slab continuous casting based on a double-cooling mode, which comprises the following steps of: collecting casting process data and indexing target cooling temperatures and ABC parameters of each cooling area; dynamically calculating the heat conduction process of a continuously cast slab in the current period according to a heat conduction equation; calculating the temperature tracking error of each cooling area and calculating the water amount of each cooling area in a second cooling mode by taking the temperature tracking error as a regulation factor; respectively calculating the water amount of each cooling area in a first cooling mode based on the ABC parameters and the current casting speed; determining whether the temperature tracking error exceeds a preset threshold and comparing the water amounts in the two modes to determine the cooling mode and the controlled water amount in the current period; and validating the reasonableness of the controlled water amount, and correcting the controlled water amount to be a preset maximum water amount or minimum water amount if the controlled water amount exceeds the preset maximum water amount or minimum water amount. The invention guarantees the quality stability of the cast blank in secondary cooling process.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
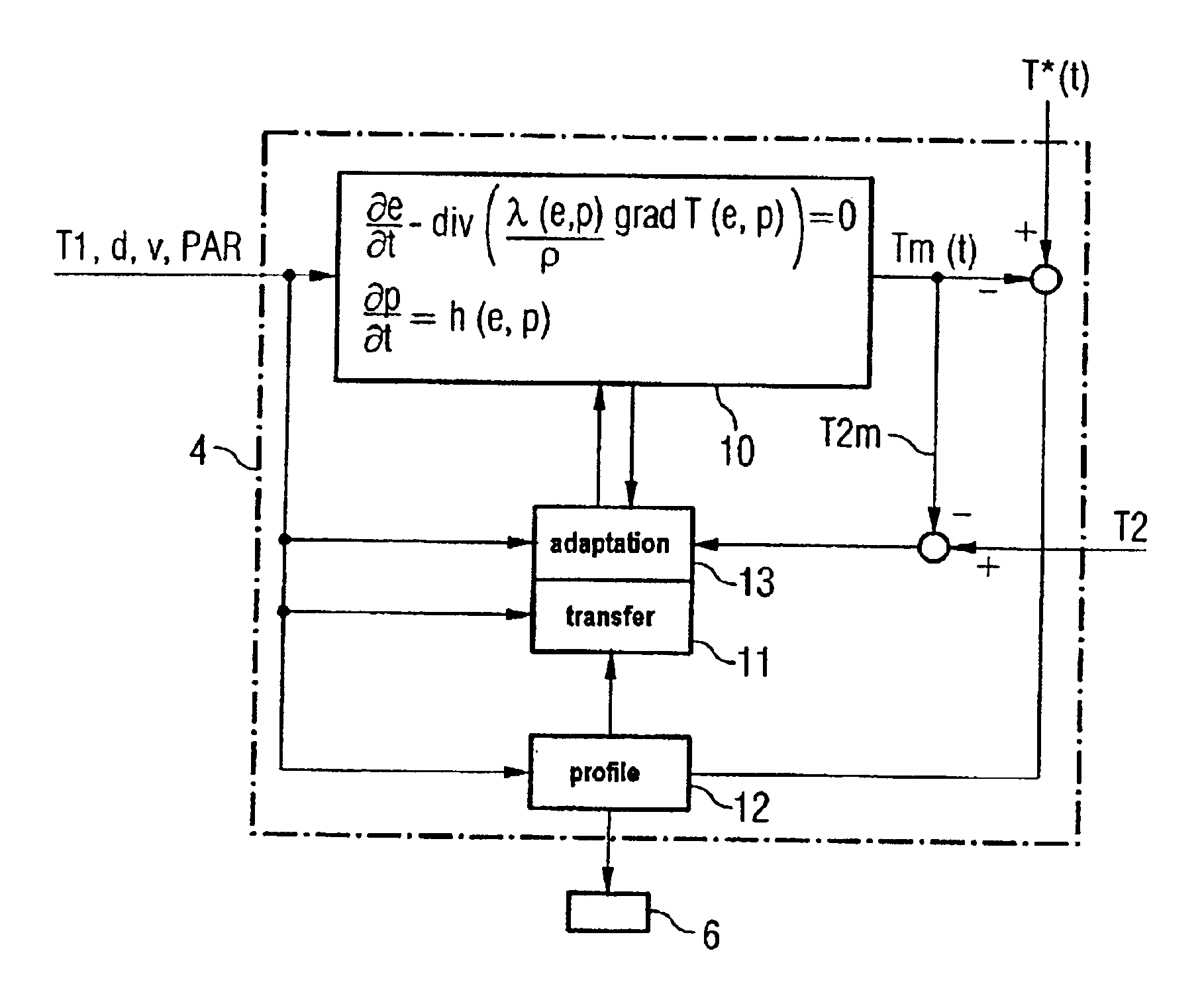
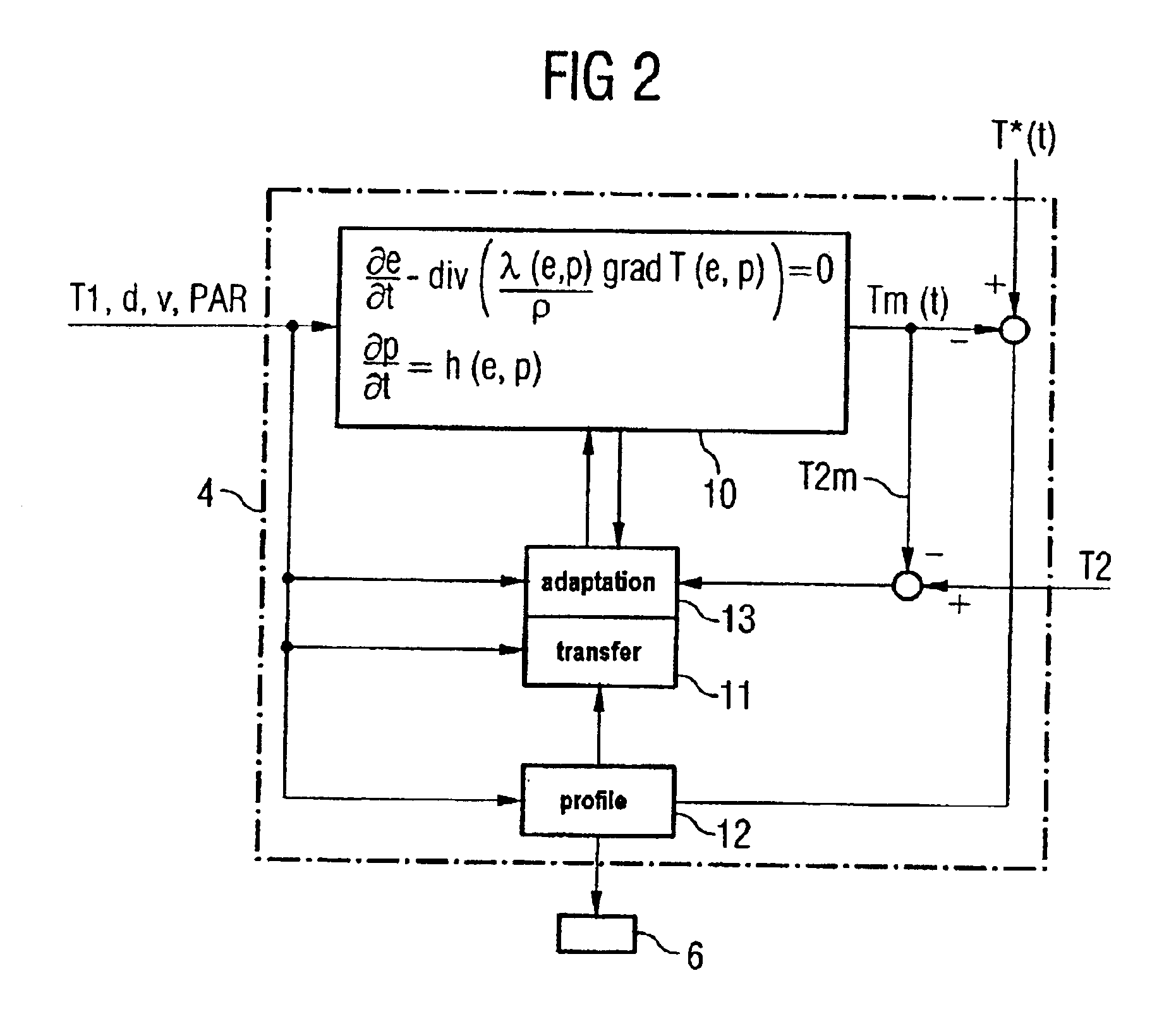
Method for cooling a hot-rolled material and corresponding cooling-line models
InactiveUS6860950B2Temperature control deviceAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesVolumetric Mass DensityLine model
To determine the temperature profile (Tm(t)) of a hot-rolled material (1) in a cooling line (5), a heat conduction equation which takes the following form ∂e∂t-div[λ(e,p)ρ·grad T(e,p)]=0where e is the enthalpy, λ the thermal conductivity, p the degree of phase transformation, ρ the density and T the temperature of the rolled material at the rolled-material location and t is the time, is solved in a cooling-line model (4).
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
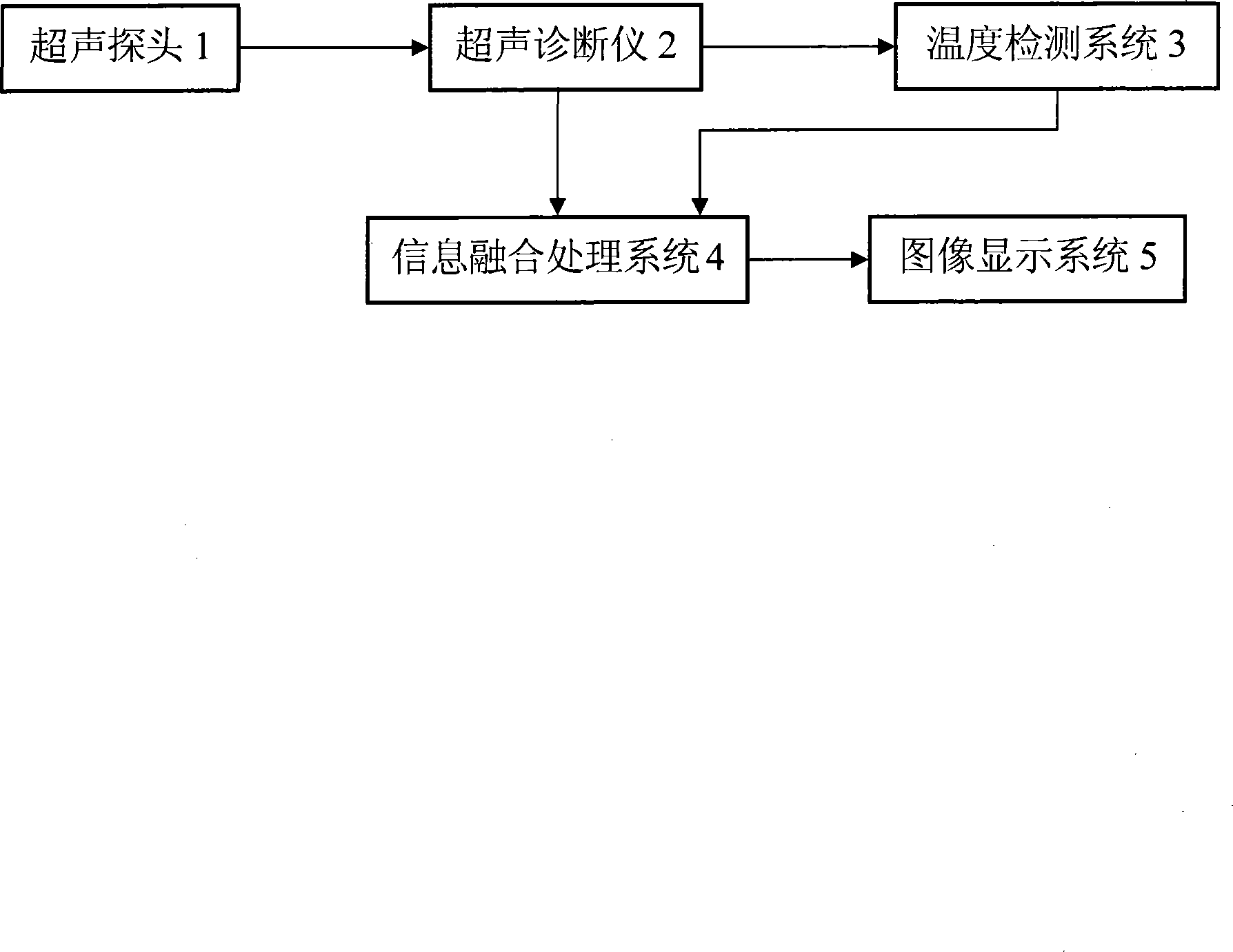
Ultrasonic real time harmless human body temperature-measuring device and temperature-measuring method
InactiveCN101125088ASolve the difficulty of variable temperature characteristic parametersSolve changing difficultiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringRelational modelBody temperature measure
The present invention relates to an ultrasonic real-time nondestructive body temperature measuring device and the temperature measurement method; the present invention establishes a relationship model of the temperature increment and the echo signal in the time domain or the frequency domain based on that the thermal characteristics of the human tissues and the ultrasound beams which pass through the human tissues thereof have better correlation with the temperature increment on the beam path during the slow change, furthermore, the present invention uses the numerical calculation method (such as, finite element / finite difference method) which is based on the nonlinear medical ultrasonic field to carry out the real-time dynamic calibration of the thermal coefficient of the deep tissue by establishing a Pennes biological heat conduction equation (BHTE) in a human structural model, so as to solve the difficulties that the characteristic parameters of the tissue temperature are too changeable ; the present invention uses the combination method of the numerical calculation and the ultrasonic detection to eliminate the problem of the heat-acoustic lens and adopts the fusion imaging method of the temperature information and the tissue structure information to visually display the temperature distribution and the structure distribution in the body.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Probe for electronic clinical thermometer
ActiveUS20060209920A1No slack givenImprove production efficiencyThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHuman bodyHeat flux
Providing a probe for an electronic clinical thermometer, which can measure a surface temperature and a deep body temperature of a human body securely in short time, the probe includes a cylindrical housing, a bottomed metal pipe fitted into a top end of the cylindrical housing, and a substrate having two thin-film heat-sensitive elements arranged perpendicularly on an inner wall of the bottomed metal pipe so as to fix one side edge of the substrate tightly on the inner wall. By measuring heat flux between the two thin-film heat-sensitive elements, the surface and the deep body temperatures of the human body can be predicted by applying the measured values into a heat conduction equation without waiting the sensor to reach in heat balance.
Owner:ISHIZUKI ELECTRONICS
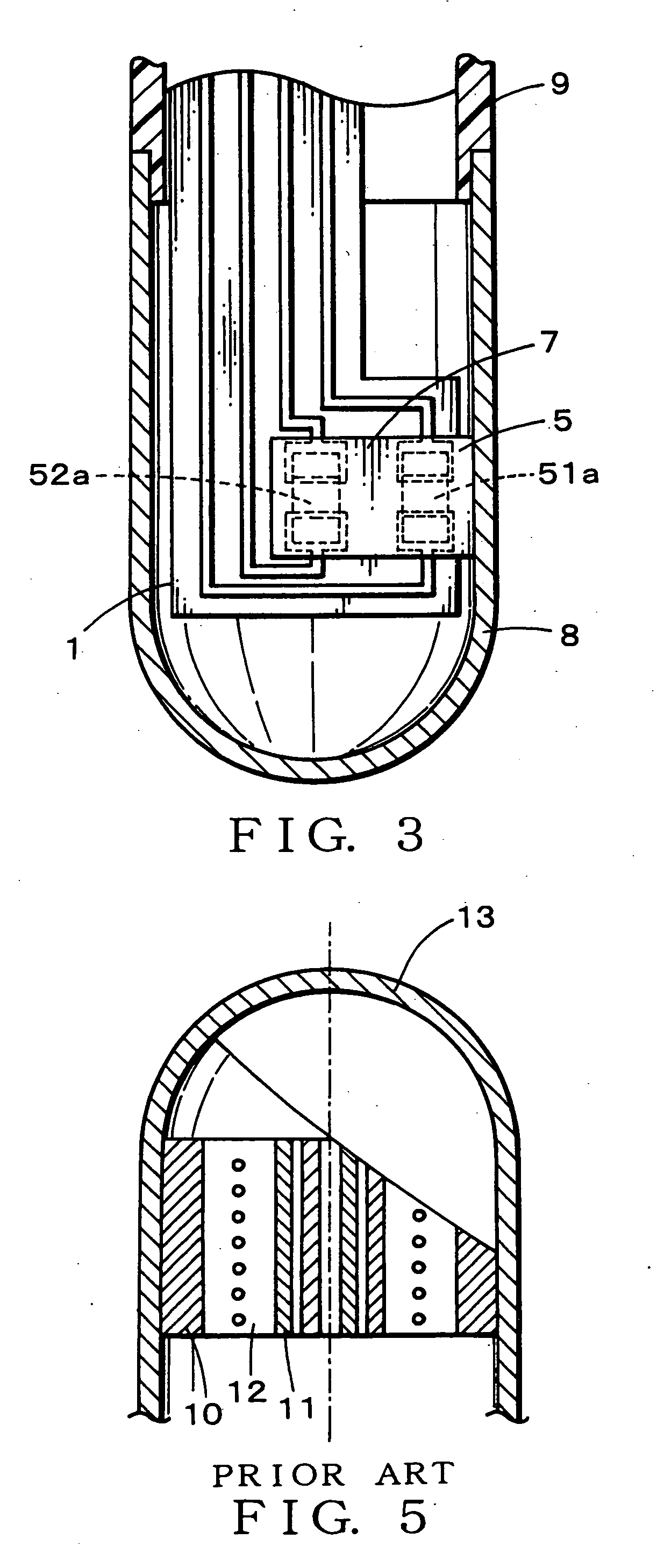
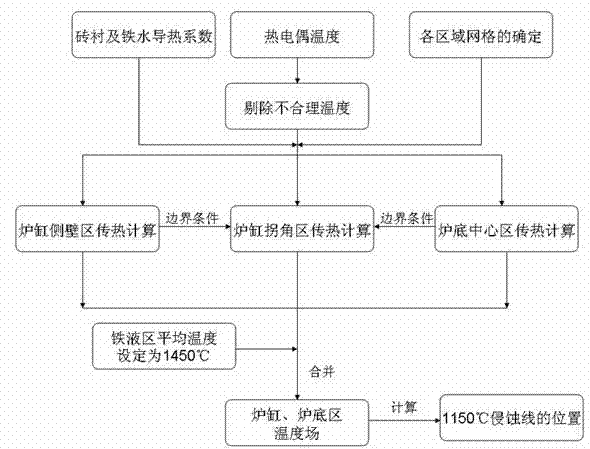
Method for determining position of erosion line of hearth of blast furnace
InactiveCN102876825AMeet various requirements of operationMonitor Hearth ConditionChecking devicesBrickHearth
The invention discloses a method for determining the position of an erosion line of a hearth of a blast furnace and belongs to the technical field of prolonging service life of the blast furnace. Compared with the prior art, the method for determining the erosion line of the hearth of the blast furnace has the advantages that the calculation amount is small, and accuracy is high. According to the method, a temperature field in a brick line of the hearth is directly calculated based on a steady-state heat conduction equation by a method for stabilizing a grid by using finite elements or finite difference; the heat conductivity coefficient of the brick lining is determined according to the temperature of grid nodes in iterative computation; if the temperature is more than 1,450 DEG C, the temperature field in the brick lining of the hearth is calculated and determined by using the effective heat conductivity coefficient of molten iron; the position of the position of the 1,150-DEG C erosion line is determined according to the temperature field; according to the method for determining the position of the erosion line, the temperature field is only needed to be calculated once; and compared with the conventional method, the method has the advantages that the calculation amount is greatly reduced, the calculation cycle is shortened, various requirements of operation of the blast furnace can be met, the calculation stability is greatly improved, and the division temperature of the molten iron and the brick line is set to be 1,450 DEG C, so that the actual requirement of the blast furnace can be met.
Owner:JIANGSU YONGGANG GROUP CO LTD
Swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method under rainfall infiltration condition
ActiveCN106202980AOvercome deficienciesOvercome defectsInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsSoil mechanicsFluid solid coupling
The invention discloses a swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method under the rainfall infiltration condition. The swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method comprises the following steps: adopting a fluid-solid coupling module and compiling a relevant FISH language program, and realizing the relation of change of the non-saturated region matrix suction, the non-saturated permeability coefficient and the soil strength parameter along with the moisture content in the unsaturated seepage process; then based on the 'humidity stress field theory', according to the similarity of a seepage continuity differential equation and a heat conduction equation, deducing the equivalent conversion relation of a thermodynamic parameter and a seepage parameter, and adopting a thermodynamic module to realize swelling soil swelling deformation process under the humidifying condition. According to the swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method, the swelling soil humidifying and swelling whole-process numerical calculation under the rainfall infiltration condition can be effectively and comprehensively realized, so that effective scientific guidance means are provided for engineering design and construction in the high-risk area of the swelling soil engineering disaster, and meanwhile application of the computational soil mechanics to the technical fields of practical engineering construction, geological disaster prevention and control, and the like, is powerfully driven.
Owner:SHANXI PROVINCIAL RES INST OF COMM +1
Modeling method for a metal
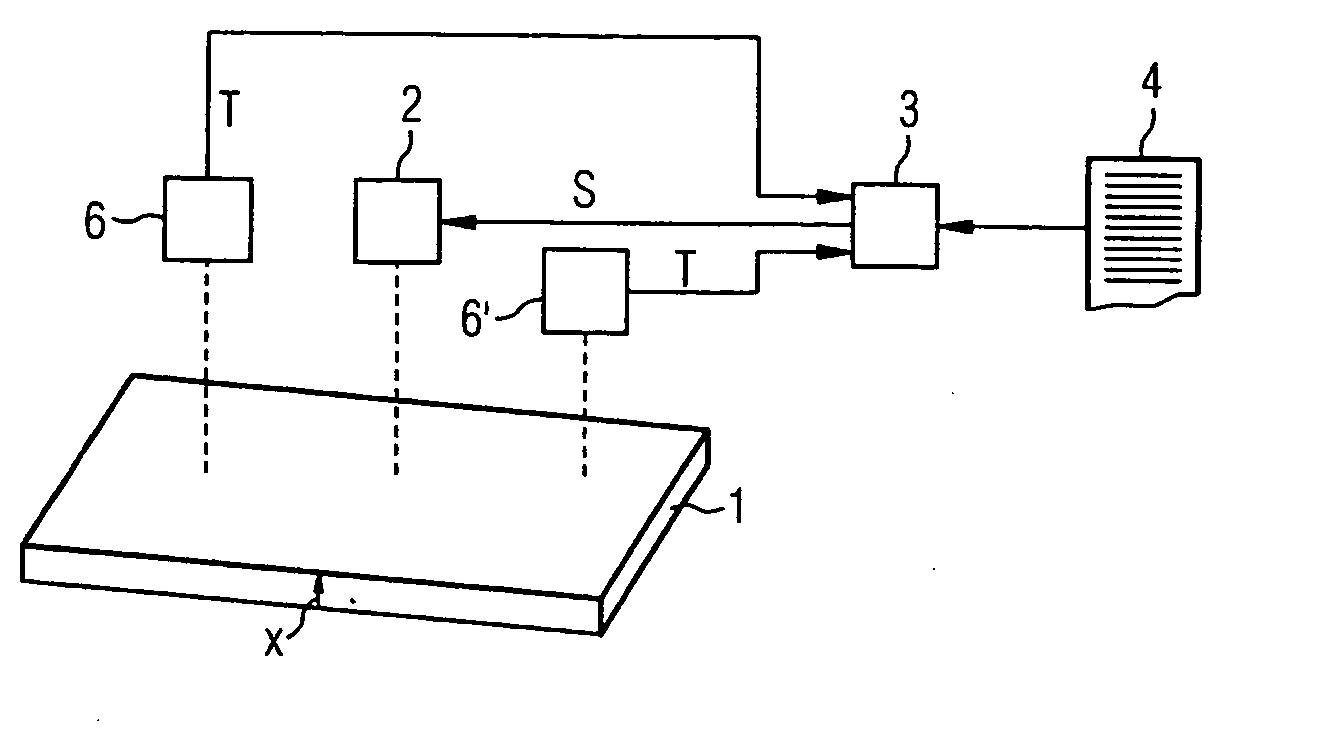
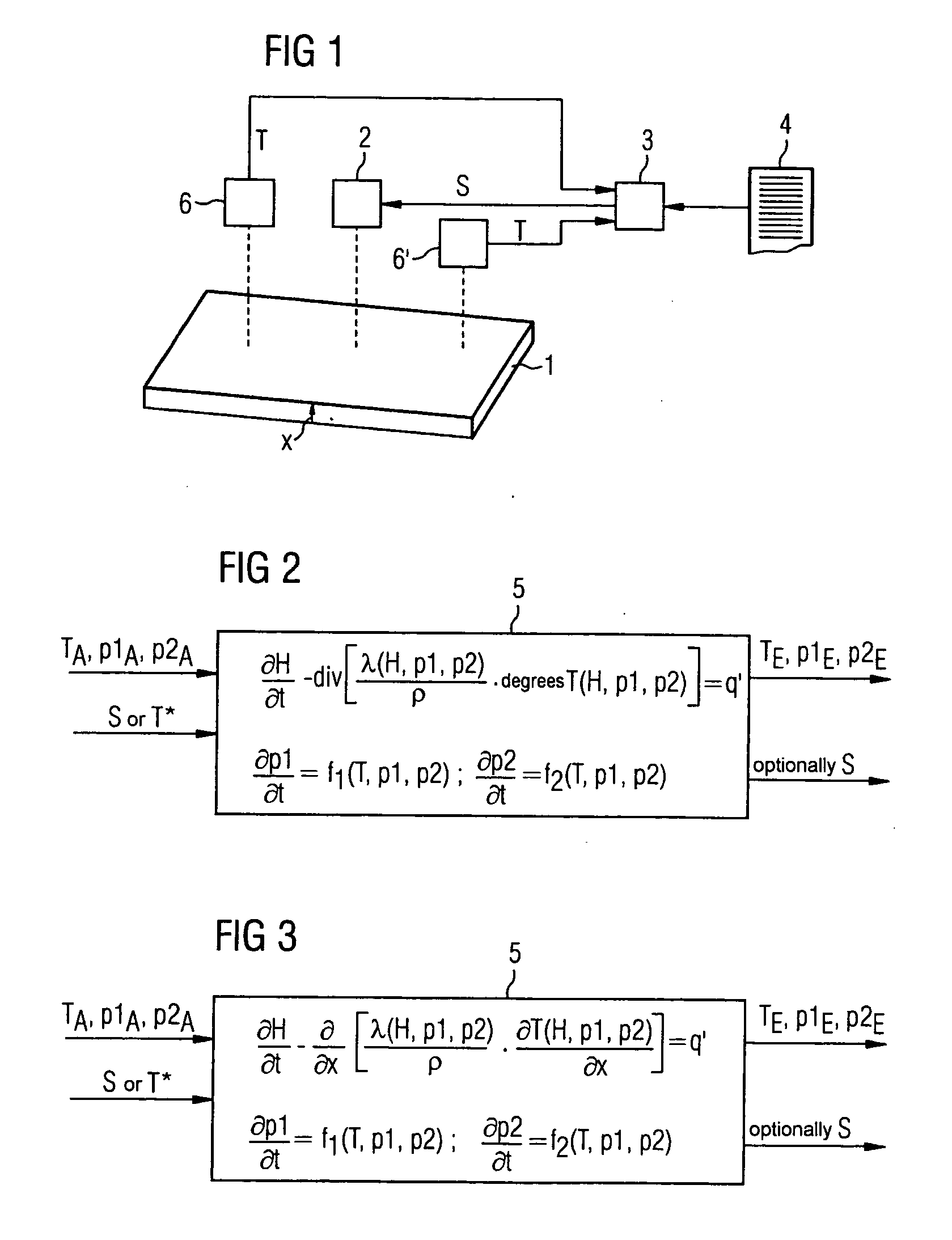
ActiveUS20050016712A1Modeling resultSimulator controlCasting safety devicesModel methodFree energies
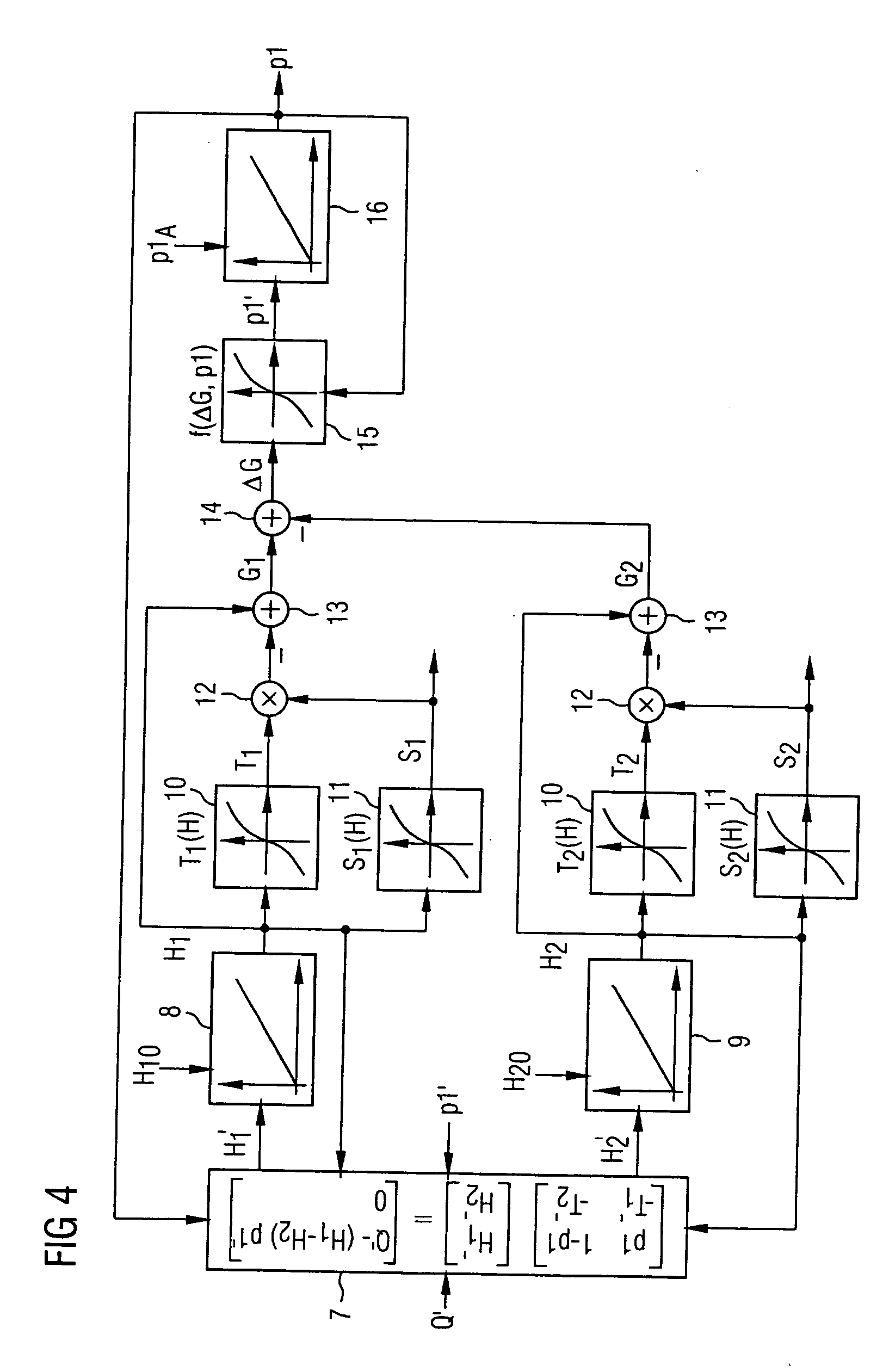
The temperature (T) of a metal (1) can be influenced directly or indirectly by at least one actuator (2) which is actuated in accordance with a control variable (S). The control variable (S) and starting values (TA, p1A, p2A) for a temperature of the metal (1) and phase proportions in which the metal (1) is at least in a first phase or a second phase, respectively, are predetermined for a material model (5). A heat conduction equation and a transformation equation are solved in real time within the material model (5), taking account of these variables (TA, p1A, p2A) , and in this way expected values (TE, p1E, p2E) are determined for these variables. As part of the transformation equation, the Gibbs' free energies (G1, G2) of the phases of the metal (1) are determined, a transformation rate of the metal (1) from the first phase to the second phase is determined therefrom, and the expected proportions (p1E, p2E) are determined from the latter.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
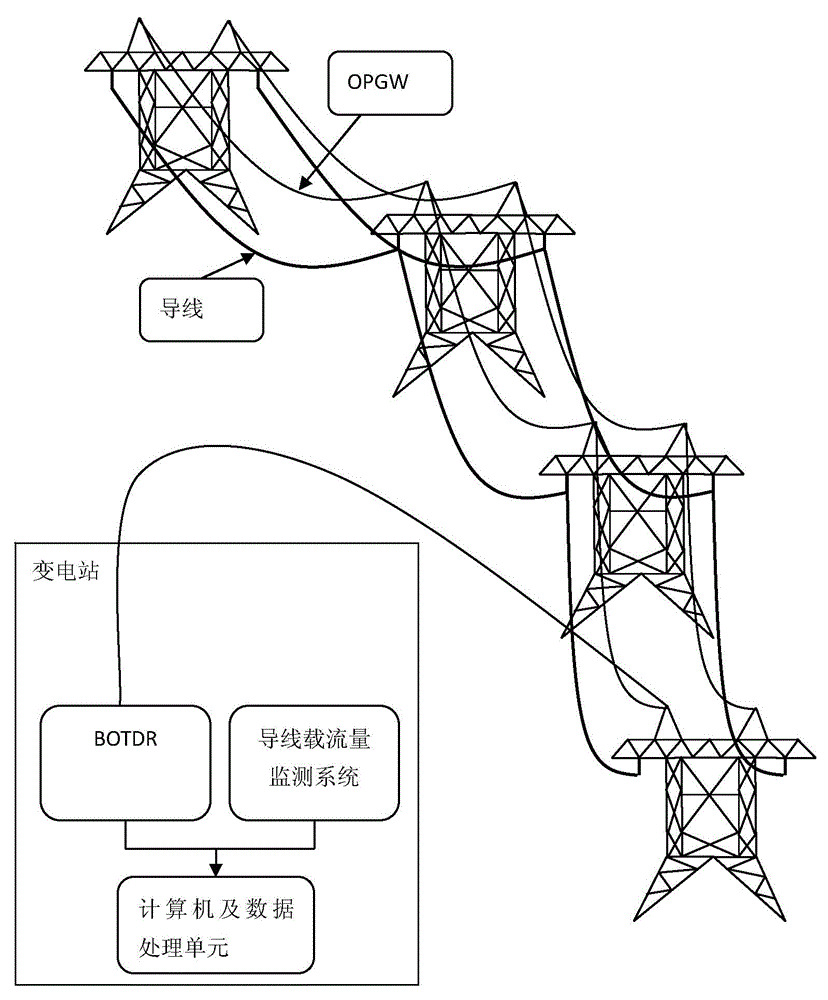
BOTDR-based transmission line wire temperature distributed monitoring device and BOTDR-based transmission line wire temperature distributed monitoring method
InactiveCN104316216ARealize computingRealize monitoringThermometers using physical/chemical changesConvection heatIterative method
The invention relates to a BOTDR-based transmission line wire temperature distributed monitoring device and a BOTDR-based transmission line wire temperature distributed monitoring method. A BOTDR is connected with an optical fiber in an OPGW. Two variables, temperature and stress, of detection points in a transmission line OPGW are separated by a Brillouin scattering frequency shift temperature and stress demodulator; the relationship between OPGW distributed temperature and wire distributed temperature is established according to steady-state heat conduction equations of the transmission line OPGW and a wire; the convection heat radiation coefficient changing with time on the line is calculated according to monitored temperature data of the transmission line OPGW in adjacent periods of time; and the wire temperature distribution of the transmission line is calculated by a Newton iterative method based on material parameters of the transmission line OPGW and the wire and dynamic carrying capacity information of the wire measured by a transmission line wire carrying capacity monitoring system. Distributed temperature monitoring on a transmission line wire is realized. The device and the method of the invention have the beneficial effect that real-time and long-distance online temperature distribution monitoring on an OPGW and a wire of a transmission line can be realized by mounting only one piece of equipment in a substation.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Probe for electronic clinical thermometer
ActiveUS7441950B2No slack givenEasy to insertThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat fluxEngineering
Providing a probe for an electronic clinical thermometer, which can measure a surface temperature and a deep body temperature of a human body securely in short time, the probe includes a cylindrical housing, a bottomed metal pipe fitted into a top end of the cylindrical housing, and a substrate having two thin-film heat-sensitive elements arranged perpendicularly on an inner wall of the bottomed metal pipe so as to fix one side edge of the substrate tightly on the inner wall. By measuring heat flux between the two thin-film heat-sensitive elements, the surface and the deep body temperatures of the human body can be predicted by applying the measured values into a heat conduction equation without waiting the sensor to reach in heat balance.
Owner:ISHIZUKI ELECTRONICS
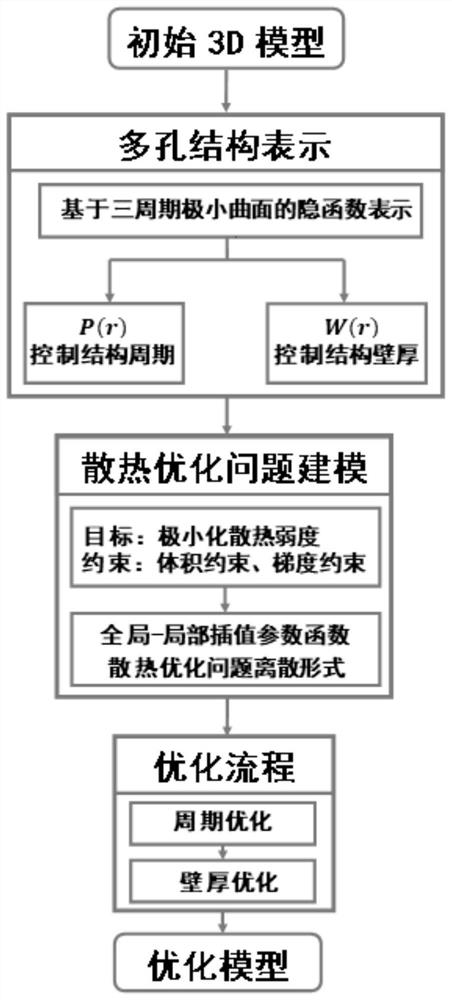
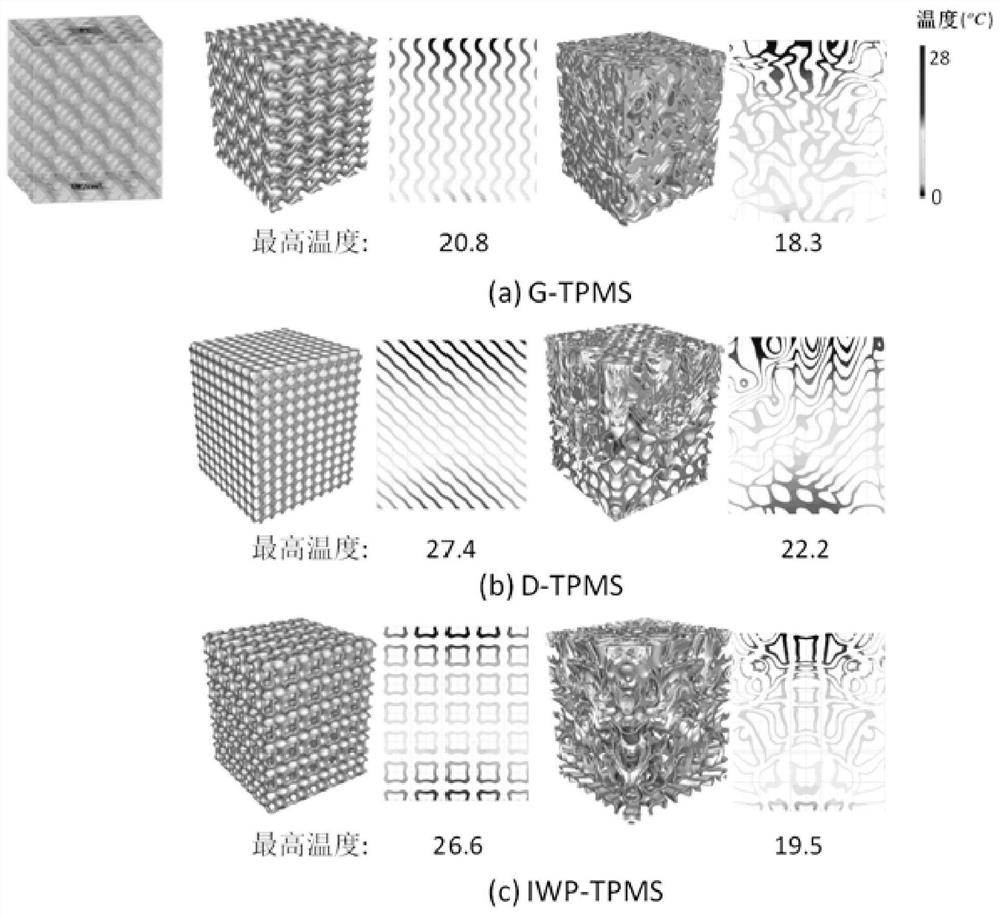
Design and optimization method of three-dimensional porous heat dissipation structure based on three-period minimum curved surface
ActiveCN111737835AHigh surface area to volume ratioHigh full connectivityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputer Aided DesignProcess engineering
The invention discloses a design and optimization method of a three-dimensional porous heat dissipation structure based on a three-period minimum curved surface, and belongs to the field of computer aided design. Firstly, a porous structure is established through implicit function representation of a three-period minimal curved surface; secondly, according to a steady-state heat conduction equation, a heat dissipation problem is converted into a heat dissipation weakness minimization problem under a given constraint condition; then, a parameter function is directly solved by utilizing a global-local interpolation method; finally, period optimization and wall thickness optimization are conducted on the modeling problem, and the optimized porous sheath-shaped structure with the smooth periodand wall thickness changes is obtained. Due to the porous structure, the heat dissipation performance, the heat conduction efficiency and the heat conduction efficiency are greatly improved. The porous structure designed by the invention has the characteristics of smoothness, full connectivity, controllability, quasi-self-supporting property and the like, the applicability and the manufacturability of the structure are ensured due to the characteristics, the porous structure is suitable for a 3D printing manufacturing method, an internal structure in the printing process does not need to be additionally supported, and the printing time and printing materials are saved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for quantitatively evaluating saturation of complex oil and gas reservoir
ActiveCN102979517AFully reflect the conduction mechanismReflect the conduction mechanismBorehole/well accessoriesLithologyComputational model
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively evaluating saturation of a complex oil and gas reservoir. A calculation formula of a rock conductive hole porosity is deduced based on a Maxwell conduction equation; and in combination with a result of the electric petrophysical experiment of 12 rock properties, the relationship among cementation indexes and an effective porosity and a conductive hole porosity difference corresponding to the cementation index can be deduced, so that a high-precision calculation model of the cementation index in an Archie equation can be exactly established. According to the method, the relationship between the effective porosity and the conductive hole porosity is established, so that the calculation model of the cementation index can take the conductive hole porosity as a bridge to deduce a universality expression between the cementation index and the effective porosity in the Archie equation; and the method has strong universality, and can comprehensively reflect conductive mechanisms of the complex reservoir. The invention provides an effective method with high precision and strong universality for quantitatively evaluating the saturation of a complex porosity type reservoir by using the Archie equation; and the method can be widely used for quantitatively evaluating the saturation of various complex porosity type reservoirs.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Method for measuring thermal conductivity of single semiconductor nanowire material
ActiveCN102053101AAvoid damageReduce processing stepsMaterial heat developmentMicro nanoSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to a method for measuring the thermal conductivity of a single semiconductor nanowire material. The method comprises the following steps of: suspending a semiconductor nanowire material to be measured on a substrate etched with a groove; confirming the diameter D1 of the semiconductor nanowire to be measured and the length L of the suspended part of the semiconductor nanowire sample suspended on the groove through an SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope); selecting an excitation light source, observing the remarkable red shift of the peak position of a band-edge fluorescence transmitter peak of the nanowire when laser is focused in the center of the suspended part of the nanowire and the laser strength is changed, measuring the variance relation of the nanowire fluorescence spectrum with temperatures and estimating the local temperature of the suspended nanowire part under the laser illumination so as to acquire the temperature grads of the nanowire under a certain laser power density. According to the calculation of a heat conduction equation of a one-dimensional nanowire sample: K=x*(2L / pai*D12)(beta*lambda / beta*pa)-1, the thermal conductivity of a single nanowire is derived. The method for deriving the local temperature and the thermal conductivity by utilizing the photoluminescent property of the semiconductor material is practically applied to the aspect of non-contact micro-nano thermal property measurement.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Solar radiation temperature effect analysis method and system of civil engineering structure
InactiveCN106092628APhysical concepts are clearEfficient analysisStructural/machines measurementLongitudeDirect radiation
The invention discloses a solar radiation temperature effect analysis method and system of a civil engineering structure. The method comprises the following steps: a geographical longitude and a latitude of a position where the structure is disposed are determined, and through installing a sensing apparatus on the structure, an ambient air temperature and a surface wind speed of the structure are measured. By use of a structure solar radiation model, direct radiation intensity, scattering intensity and reflection intensity acting on the surface of the structure are calculated and determined. According to solar radiation intensity of the structure surface, dynamic temperature boundary conditions are established, by use of a finite-element method, a three-dimensional thermal conduction equation of the structure is solved, and a dynamic temperature effect of any one point at the surface of the civil engineering structure or inside the structure can be determined. The method and system are applied to temperature effect analysis and evaluation of various different types of civil engineering structures under a solar radiation effect, and are particularly applied to analysis evaluation of a temperature effect of a structure with a quite small geometric dimension and a structure with complex shielding around.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Microwave passive circuit electromagnetic heat integral analysis method based on time domain spectrum element method
ActiveCN104050307AGood mannersQuickly obtain temperature distributionSpecial data processing applicationsMaxwell's equationsEngineering
The invention discloses a microwave passive circuit electromagnetic heat integral analysis method based on a spectrum element method. According to the method, firstly, a time domain spectrum element method is adopted for solving maxwell's equations, the instantaneous electric field and magnetic field distribution of a circuit under the effect of high-power pulses is worked out, and the electromagnetic loss at the current moment is obtained. If all of the electromagnetic loss inside a mold is converted into heat energy, the obtained heat energy is substituted into a heat conduction equation, and the temperature distribution conditions of each point at the current moment are obtained. Electricity characteristic parameters of materials at a next moment are obtained by utilizing a relational expression of dielectric parameters along with the temperature change, an electromagnetic field equation is calculated again, and the electromagnetic loss is obtained. The operation is repeatedly cycled in such a way until the preset heating time is completed. Through the electromagnetic heat integral analysis, the distribution condition of the temperature inside the mold along the time change when a filter receives the effect of different pulses can be clearly obtained, the modeling is flexible, the subdivision is convenient, formed matrixes have good sparsity, and the solving efficiency is higher.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
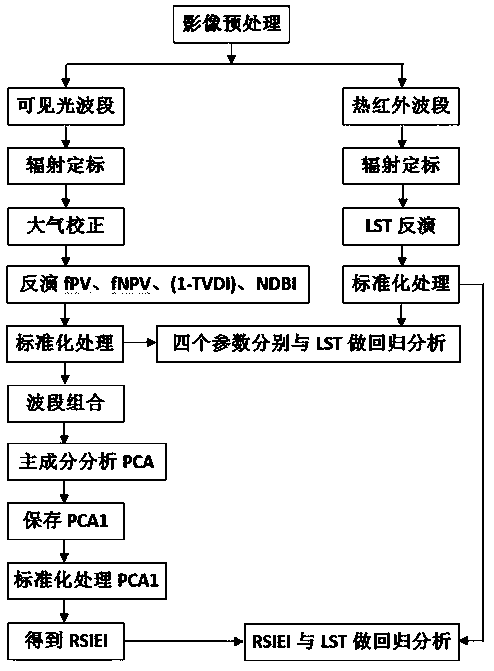
Construction method and application of remote sensing comprehensive ecological model RSIEI for evaluating ground surface thermal environment differentiation effect of mining development dense area
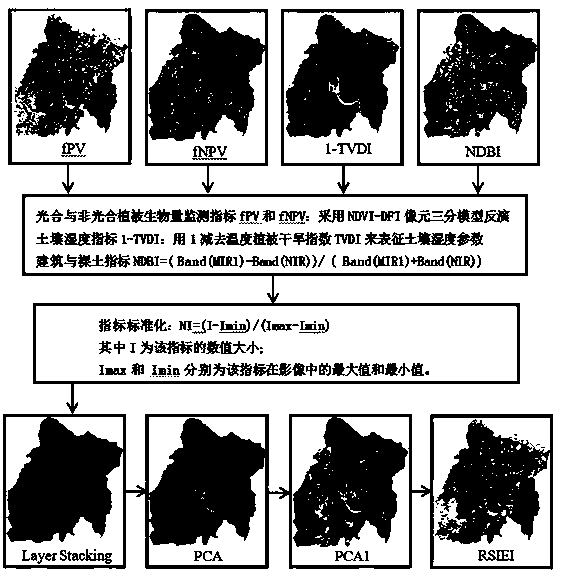
ActiveCN110472357AThe method of determining the index weight is objective and reasonableComplex mathematical operationsBuilding densitySoil science
The invention relates to a construction method and application of a remote sensing comprehensive ecological model RSIEI for evaluating a ground surface thermal environment differentiation effect of amining development dense area. The construction method comprises the following steps: inverting the surface temperature of a research area by using a radiation conduction equation method; representingthe earth surface vegetation biomass by using the photosynthetic vegetation coverage parameter and the non-photosynthetic vegetation coverage parameter; characterizing the soil moisture content by using the soil humidity index parameters; representing the bare soil and building density by using bare soil and building index parameters; and integrating the four basic ecological parameters based ona principal component analysis method to construct RSIEI. The application comprises the step of quantitatively analyzing the contribution of four ecological parameters to the ground surface thermal environment differentiation effect of the mining industry development dense region by means of a statistical method. The method is suitable for evaluating the thermal environment differentiation effectof mining development dense cities, and evaluating the surface thermal environment differentiation effect of small-scale mining development dense villages and towns with administrative boundaries as boundaries is also feasible.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for converting microwave remote sensing surface temperature to thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature
ActiveCN105204024AWork around limited usageHigh precisionICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSensing dataThermal infrared remote sensing
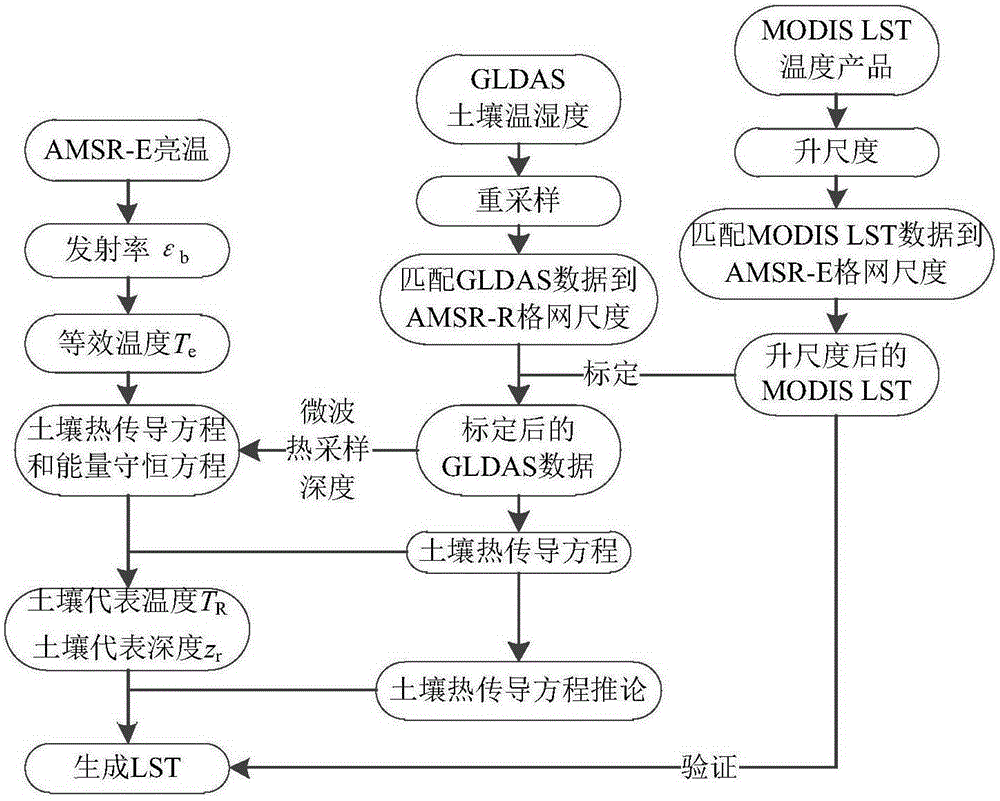
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing application, and particularly relates to a method for converting microwave remote sensing surface temperature to thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature. A physical method suitable for a bare-ground area is provided based on a soil heat conduction equation. The method comprises the steps of data preprocessing; GLDAS data calibration; equivalent temperature generation; conversion from microwave remote sensing surface temperature to thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature, wherein land surface temperature which has the same physical significance as thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature is generated through passive microwave remote sensing data. The method can be universally applied to existing passive microwave remote sensing inversion land surface temperature algorithms. By the adoption of the method, the precision of the algorithms in inversion of bare-ground area surface temperature is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for analytically obtaining closed form expressions for subsurface temperature dept distribution along with its error bounds
ActiveUS7130758B2Efficiently obtainedThermometer detailsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeodynamicsErrors and residuals
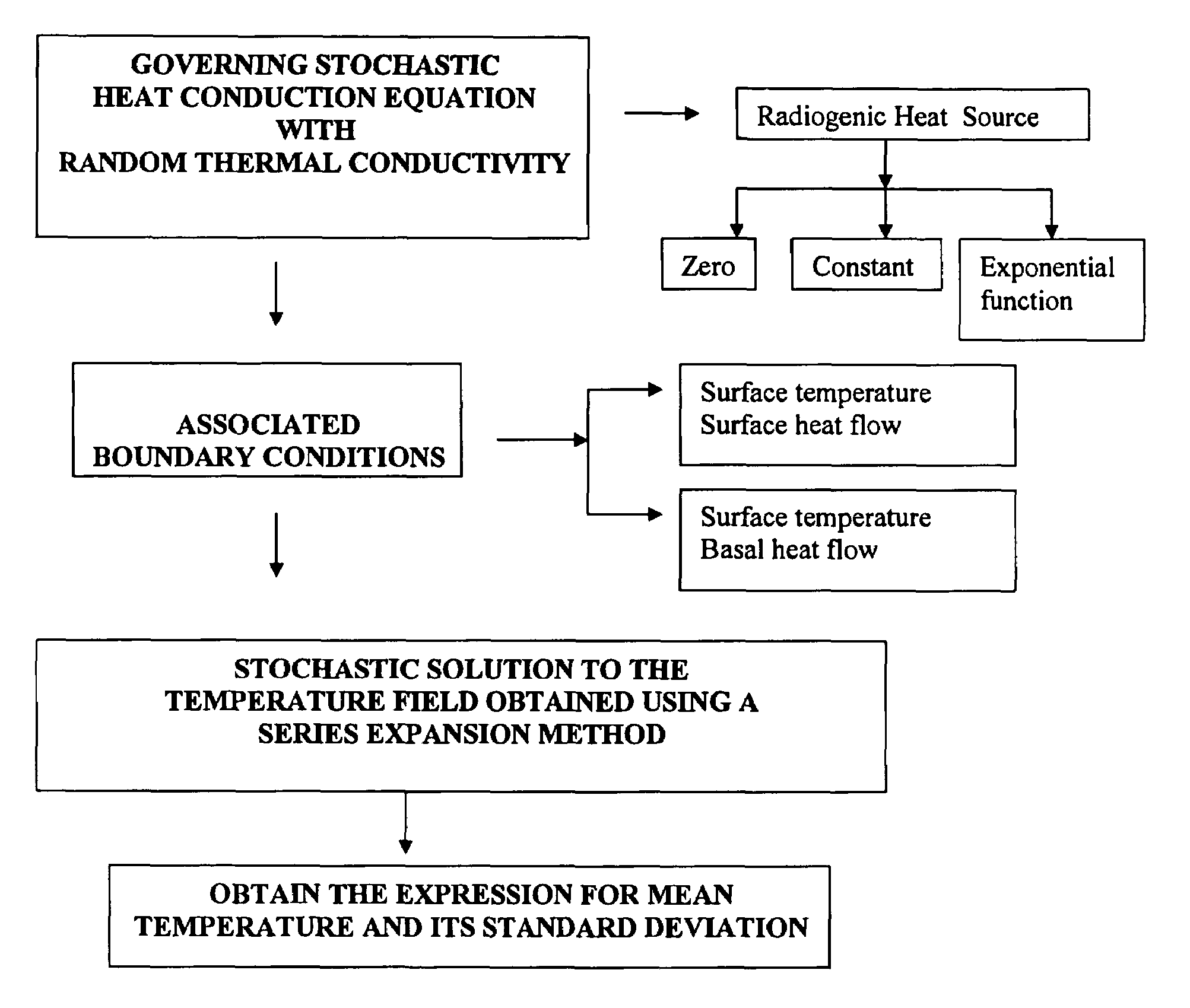
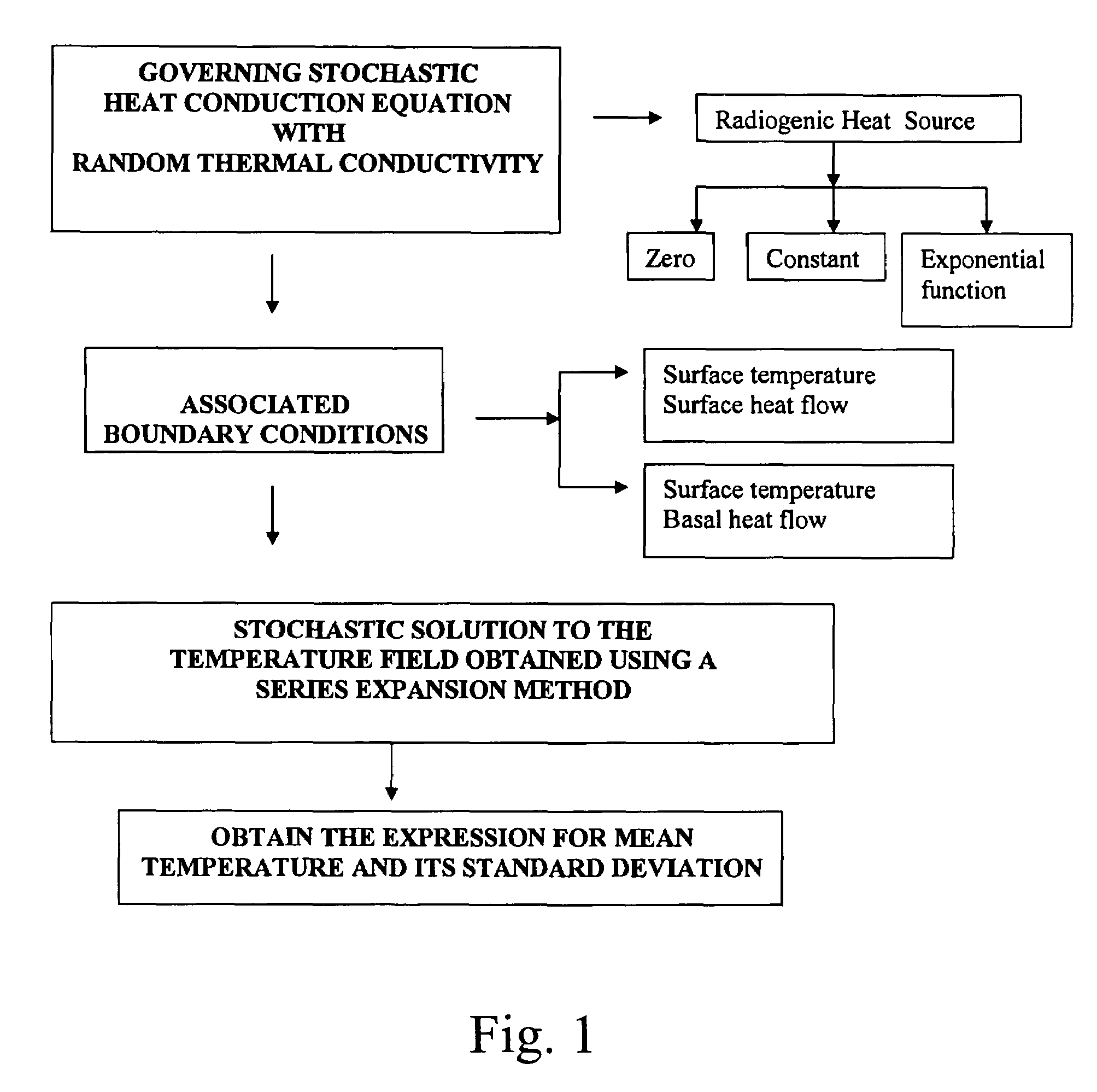
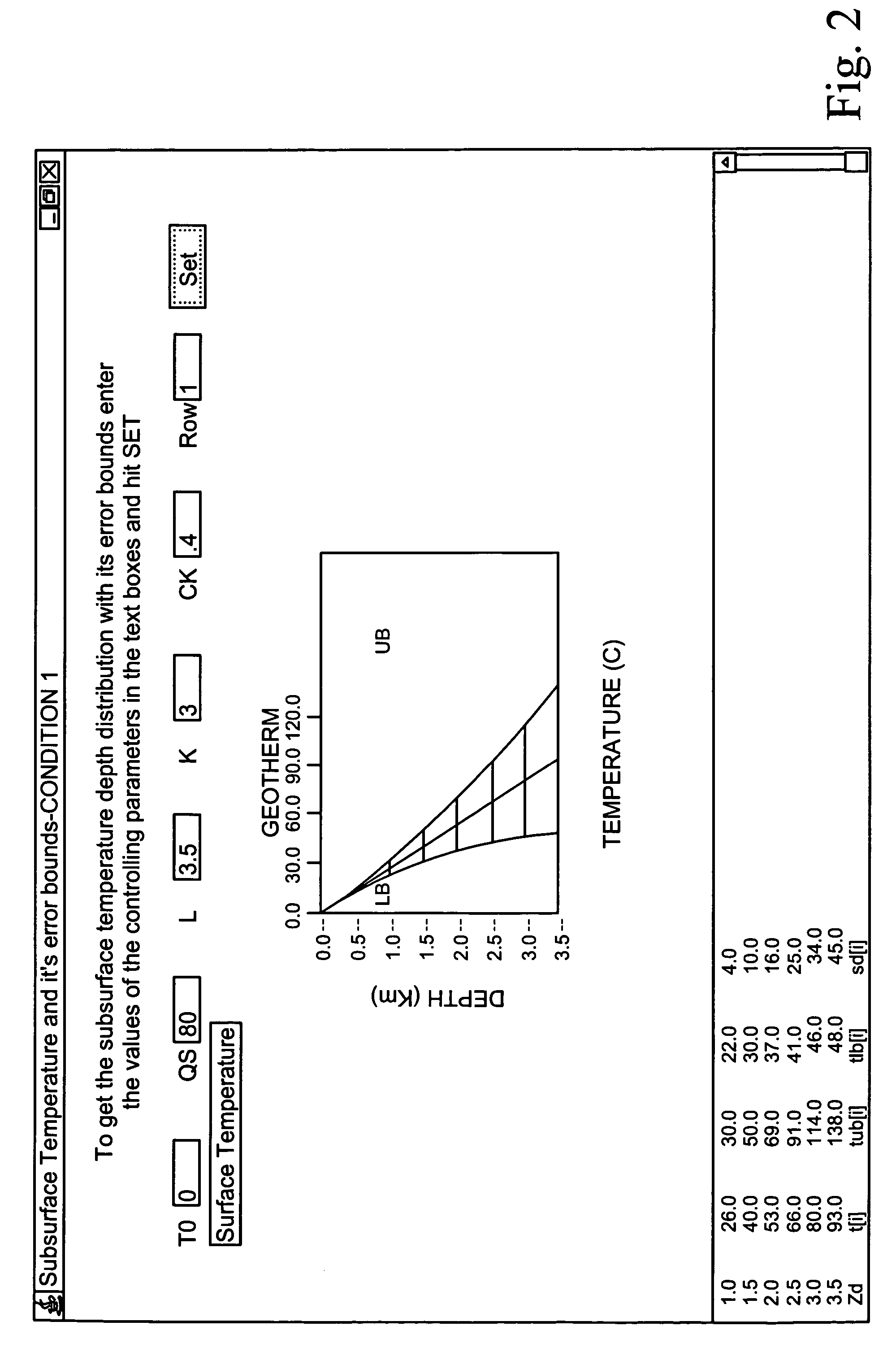
Analytical solutions to error bounds on the temperature depth distribution have been given in this invention. Solving the one dimensional steady state heat conduction equation for different sets of boundary conditions and radiogenic heat generation and incorporating Gaussian randomness in the thermal conductivity analytical closed form solutions to the mean and variance in the temperature depth distribution have been obtained. These closed form analytical solutions of mean and variance for the temperature field for different conditions have been used to compute and display the plot and results of the temperature depth profiles along with its error bounds. Quantifying the error statistics in the system output due to errors in the system input is very essential for a better evaluation of the system behavior. Earth Scientists involved in understanding the subsurface thermal structure relevant to geodynamical studies will benefit using these findings.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
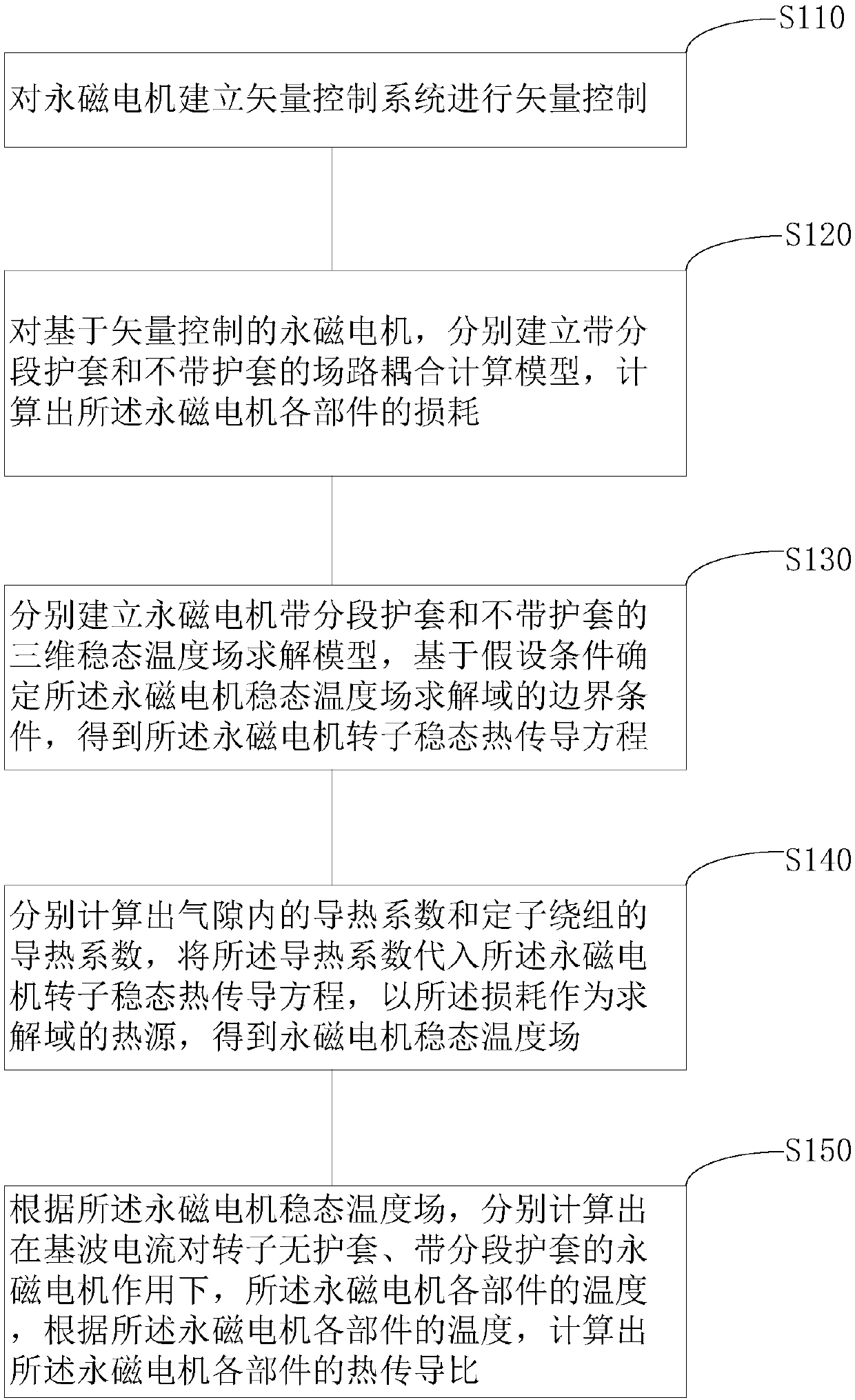
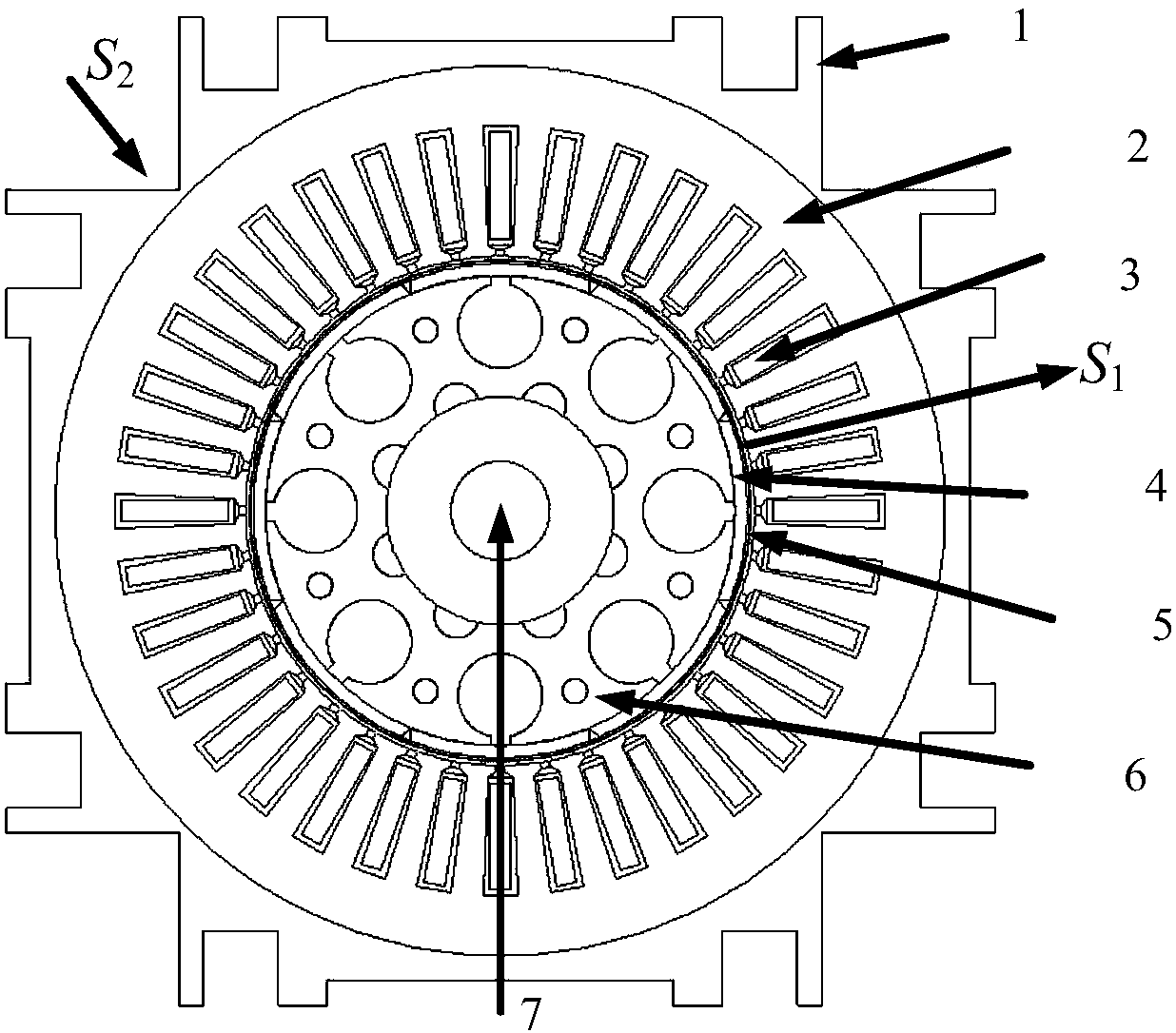
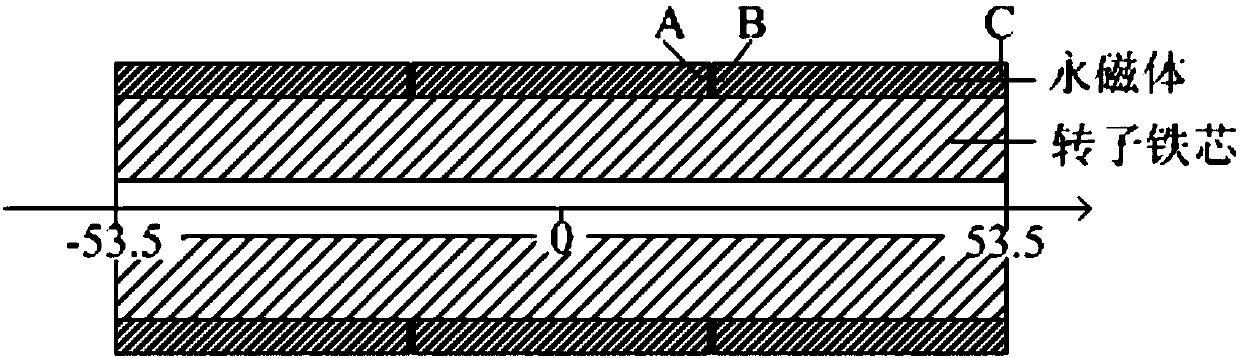
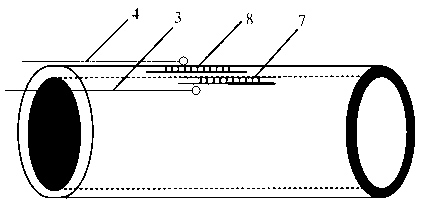
Method for calculating heat transfer ratio based on eddy current loss of rotor segmented sheath of permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN108111079AElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsSteady state temperatureControl vector
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for calculating a heat transfer ratio based on the eddy current loss of a rotor segmented sheath of a permanent magnet motor. The method comprises thefollowing steps: separately establishing a field circuit coupling calculation model with a segmented sheath and a field circuit coupling calculation model without sheath for the permanent magnet motor based on vector control, and calculating the loss of each component; then, separately establishing a three-dimensional steady state temperature field solution model with a segmented sheath and a three-dimensional steady state temperature field solution model without sheath for the permanent magnet motor, determining a boundary condition based on an assumed condition, and obtaining a rotor steadystate heat conduction equation; separately calculating a heat conductivity coefficient in an air gap and the heat conductivity coefficient of a stator winding, substituting the heat conductivity coefficients in the rotor steady state heat conduction equation, and using the loss as the heat source of a solution domain to obtain a steady state temperature field of the permanent magnet motor; and separately calculating the temperature of each component under the action on basic wave current on the permanent magnet motor in which the rotor has no sheath and the permanent magnet motor in which therotor has the segmented sheath, and calculating the heat transfer ratio of each component according to the temperature of each component. The method provided by the invention provides important theoretical basis for the design of an electromagnetic structure of the permanent magnet motor.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Fiber bragg grating measurement system and method for cylindrical structure thermal diffusivity
ActiveCN103217454AHigh measurement sensitivityImprove performanceMaterial heat developmentFiberGrating
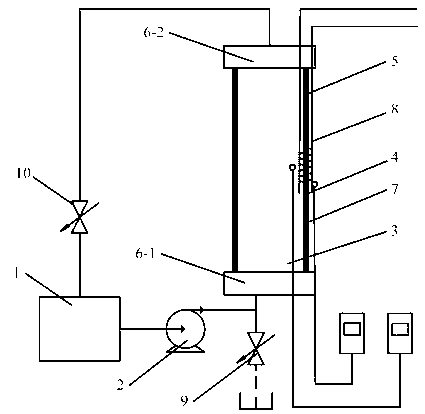
Belonging to the technical field of measurement, the invention relates to a fiber bragg grating measurement system and a method for cylindrical structure thermal diffusivity. The measurement system comprises a heating water tank (1), a water pump (2), a to-be-measured cylinder (5), a control valve (10), an inner wall thermocouple (3), an outer wall thermocouple (4), an inner wall fiber bragg grating sensor (7), and an outer wall fiber bragg grating sensor (8). The measurement method needs: first measuring the change of a central wavelength of the fiber bragg grating sticked on a structure surface along with temperature, and calculating the functional relationship between temperature and the grating central wavelength; second, heating the cylindrical structure by flowing hot water, and measuring the fiber bragg grating central wavelength change along with time so as to obtain the functional relationship of time and the fiber bragg grating central wavelength; then according to a Fourier's second law and boundary conditions, conducting calculation to obtain a temperature-time function; and finally according to a Fourier's one-dimensional heat conduction equation, calculating the thermal diffusivity of the material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Heat distribution analysis method for chip structures
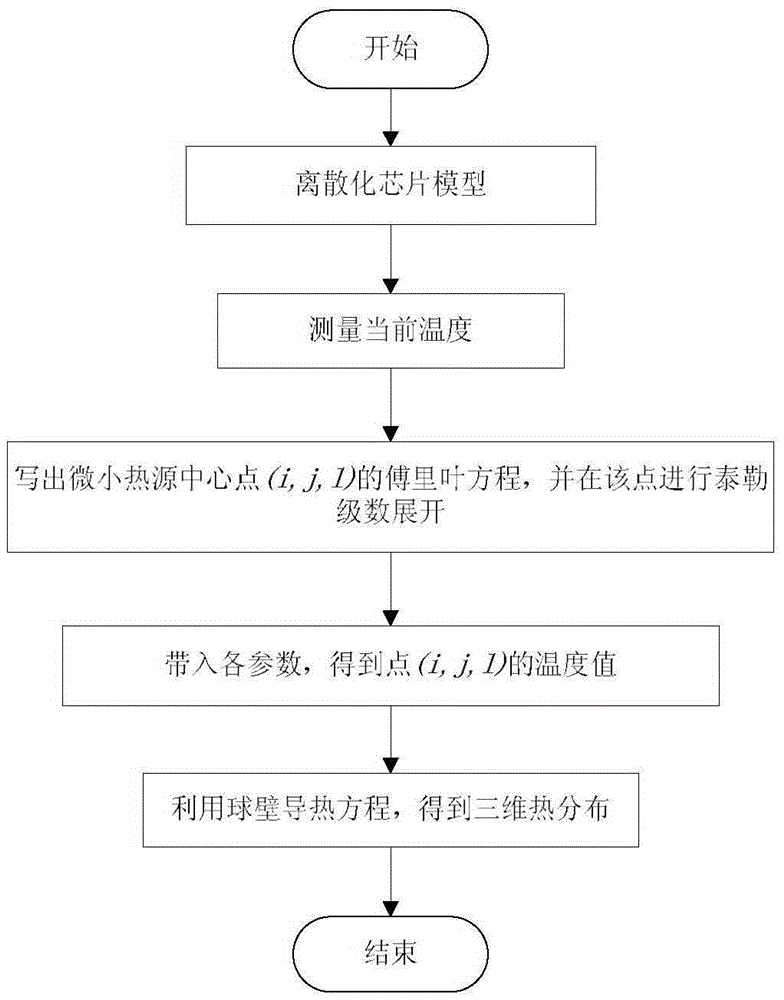
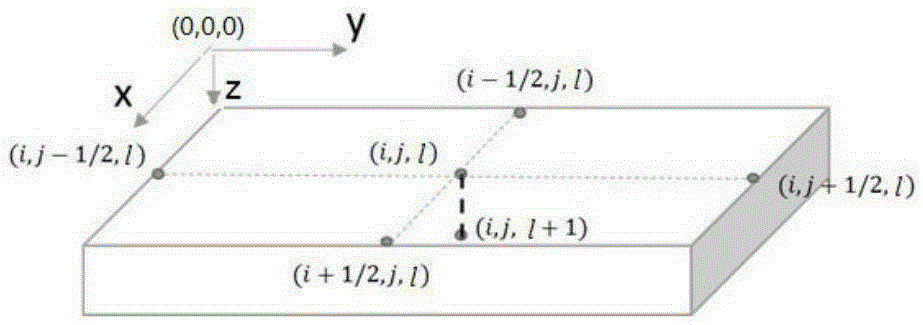
ActiveCN105302964AGuaranteed calculation accuracySmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsEstimation methodsEngineering
The invention discloses a heat distribution analysis method for chip structures, and aims at providing a three-dimensional structure heat distribution estimation method which is high in sped, high in efficiency and low in error. According to the method, two steps are adopted to process the heat distribution of the three-dimensional structure, so that a heat distribution analysis model with low error under different heat generation rates is obtained. On one hand, a lumped circuit model is used for analyzing the temperature value at the highest temperature point of the tiny heat source on the surface of the three-dimensional structure; and on the other hand, a spherical coordinates-based spherical wall heat conduction equation is utilized to obtain the heat distribution of the whole three-dimensional structure by taking the temperature value at the highest temperature point as a boundary condition. According to the three-dimensional structure-based heat distribution analysis model algorithm, the calculation accuracy is ensured, the calculation amount for analyzing the heat distribution of the three-dimensional structure is greatly decreased, the analysis efficiency is improved and the calculation speed is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
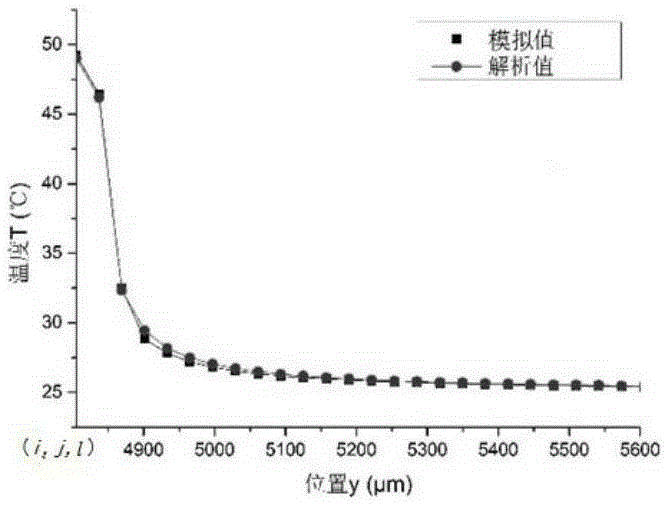
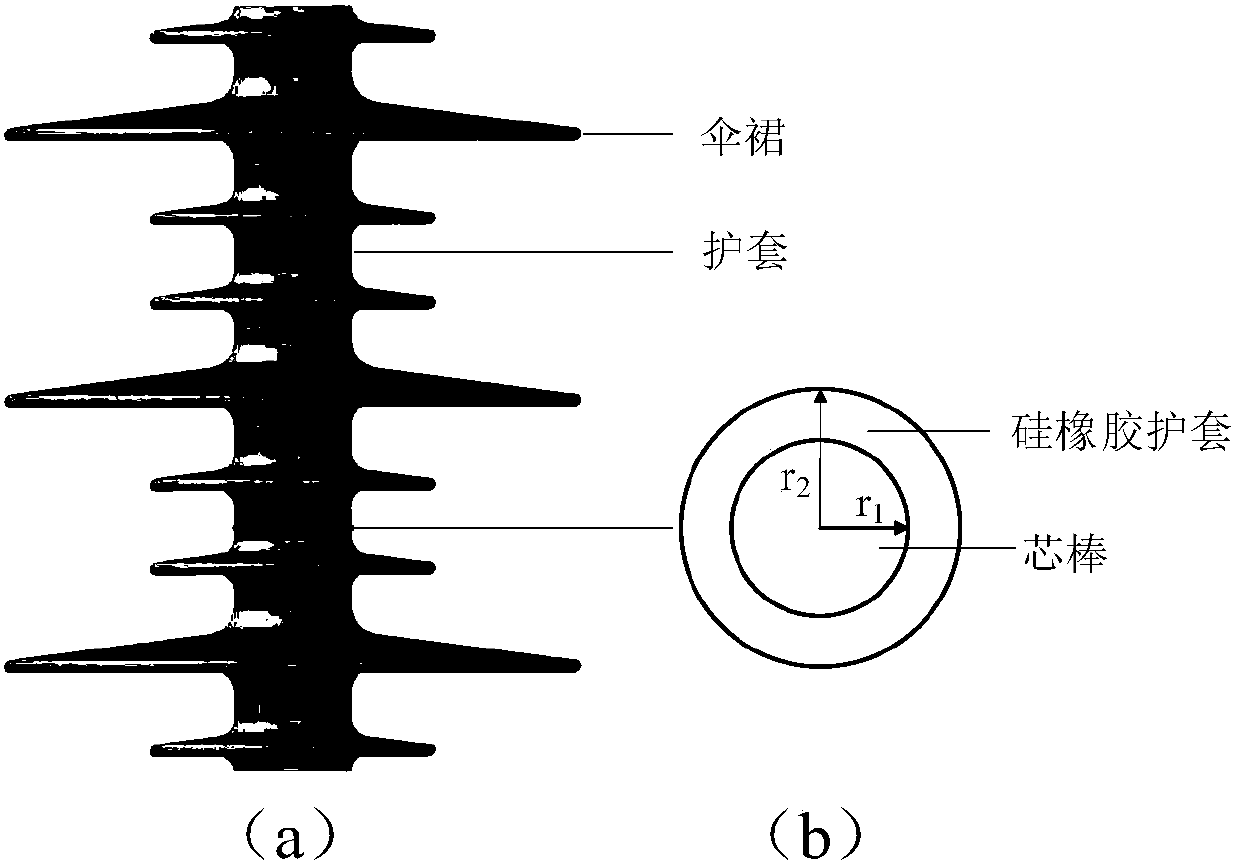
Method and system for insulator temperature rise diagnosis
ActiveCN108363829AImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringDiagnostic methods
The invention relates to a method and a system for insulator temperature rise diagnosis. The method comprises the following steps: according to a heat conduction equation of an insulator and a boundary condition corresponding to the insulator, establishing a radial temperature calculation model of the insulator, wherein the radial direction is the direction vertical to a center axis of the insulator; obtaining outer surface temperature of the insulator, insulator parameters, and environment parameters corresponding to the environment where the insulator is in; according to the outer surface temperature, the insulator parameters, the environment parameters, and the radial temperature calculation model, obtaining internal heat source temperature of the insulator; according to the internal heat source temperature, diagnosing temperature rise degree of the insulator. The insulator temperature rise diagnosis method can improve accuracy of insulator temperature rise diagnosis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU POWER SUPPLY BUREAU GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
Method for calculating bituminous pavement heating power control in hot in place recycling process
InactiveCN105912802AShorten regeneration heating timeExtend heating timeDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsHeating timeRoad surface
The invention discloses a method for calculating bituminous pavement heating power control in a hot in place recycling process, and aims at providing reliable basis for the bituminous pavement heating power control in the hot in place recycling process through researching the influences, on the bituminous pavement temperature fields, of heating power. An adopted technical scheme is that the method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a bituminous pavement unsteady state heat conduction model; 2) establishing and simplifying a bituminous pavement unsteady state heat conduction equation; 3) solving the bituminous pavement unsteady state heat conduction equation; 4) simulating bituminous pavement unsteady state heat conduction. According to the method, the relationship between the heating power and the temperature rising characteristics, heating times and thermal power of bituminous mixtures in the bituminous pavement heating link of a bituminous pavement hot in place recycling process is deeply researched on the basis of a heat transfer theory, so as to provide references for the bituminous pavement heating power control.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Thermal diffusivity measurement method for two-dimensional anisotropy nanometer material
The invention discloses a thermal diffusivity measurement method for a two-dimensional anisotropy nanometer material. The method comprises the following steps that: using continuous heating laser to heat the surface of a sample, using continuous detection laser of which the light spot center position is adjustable to detect the steady state plane temperature distribution of the surface of the sample, and obtaining two characteristic directions of the thermal diffusivity of the sample; using heating pulse laser to heat the surface temperature of the sample, enabling the temperature to periodically change, and using detection pulse laser of which the light spot center position is adjustable to obtain the temperature rise and reduction curves of different position points in two characteristicdirections; and according to the temperature rise and reduction curves of different position points, establishing a non-steady-state heat conduction equation set to fit, or utilizing a phase lock principle to carry out data processing to obtain the thermal diffusivity of the sample. The method is a non-contact nondestructive measurement method, the thermal diffusivities of two characteristic directions can be simultaneously obtained, and the direct measurement of the thermal diffusivities of nonmetal two-dimensional anisotropy nanometer materials of which the thickness is from a single atom to hundreds of nm is realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
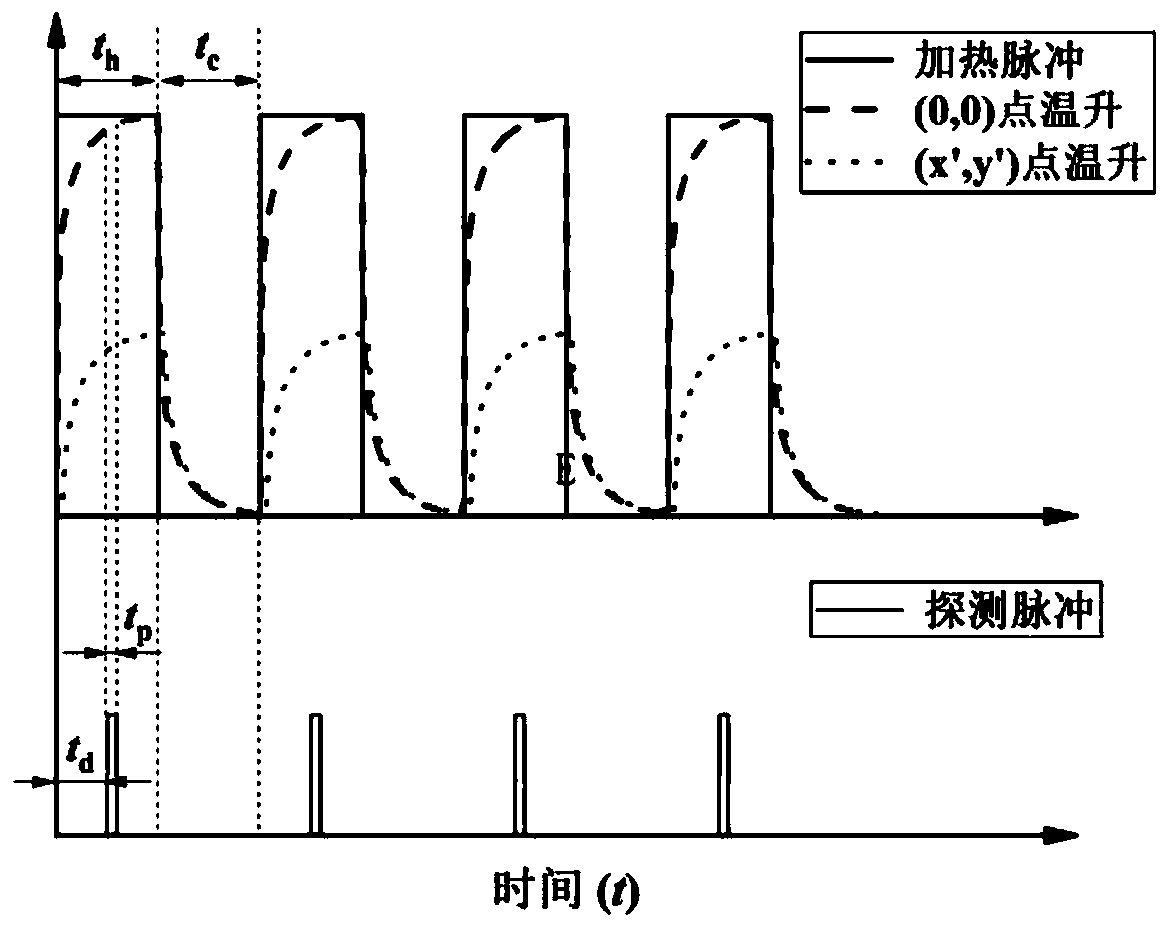
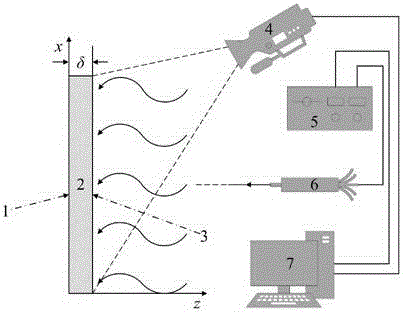
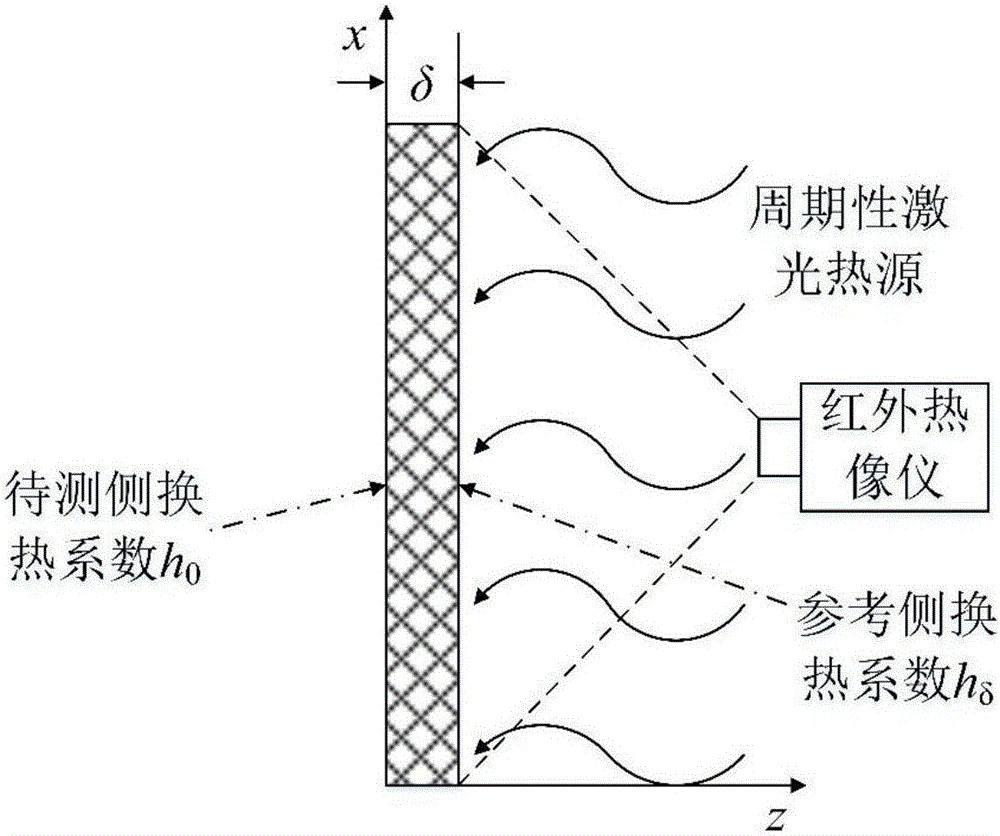
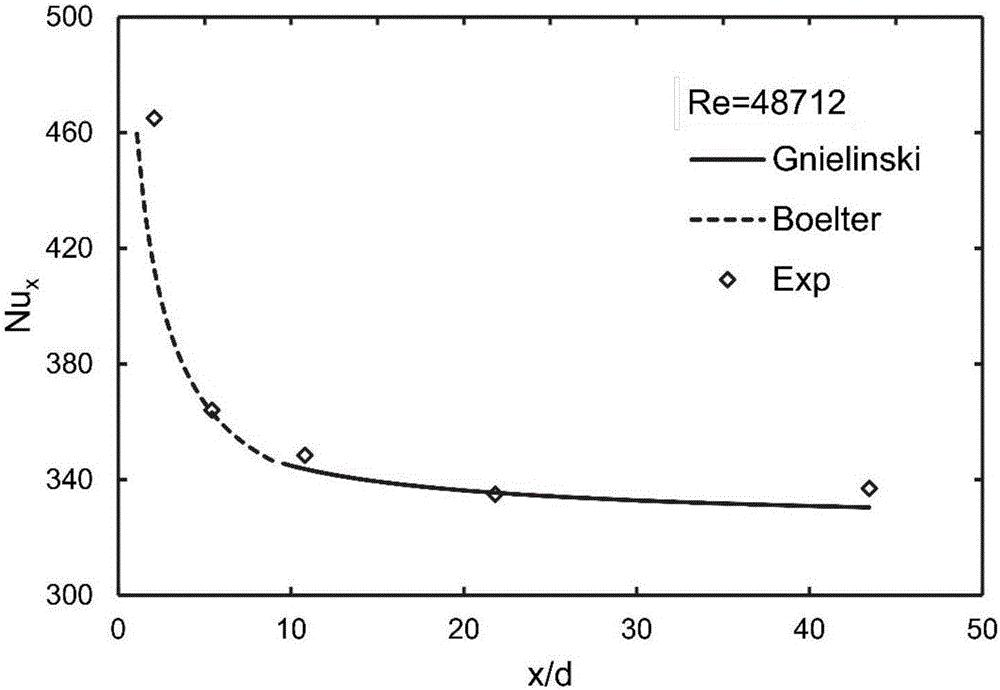
Thin-wall local heat transfer coefficient measuring method based on thermal fluctuation coupling infrared imaging
The invention discloses a thin-wall local heat transfer coefficient measuring method based on thermal fluctuation coupling infrared imaging, and the method obtains a steady local heat transfer coefficient of the other side (a to-be-measured side) of a thin wall through an analytic solution of a one-dimensional unsteady state heat conduction equation under the condition that one side (a reference side with a known heat transfer coefficient) is under the periodic heat flow boundary condition, wherein the other side is in univalent function relation with a phase different between the reference side wall temperature and an applied heat flow fluctuation signal. According to the invention, the method is not affected by the temperature measurement precision of an infrared imager, and can achieve the non-contact quick measurement of the surface local heat transfer coefficient of the features of the thin wall through the collection of the thermal fluctuation of the reference side and a surface temperature signal of the thin wall based on infrared imaging.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV +2
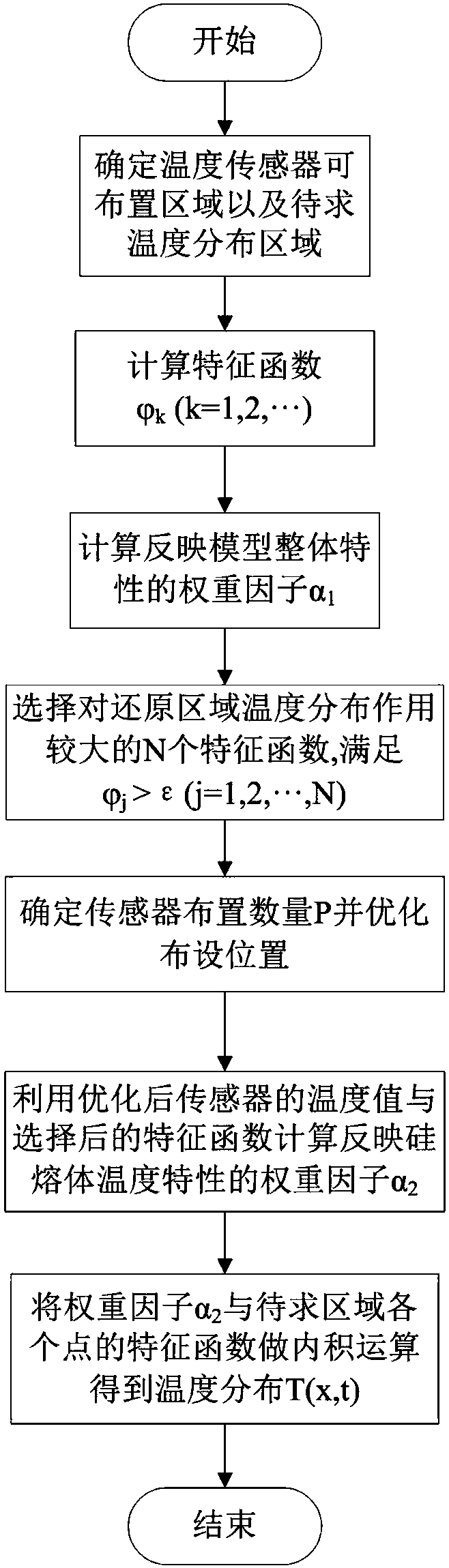
Silicon melt temperature field reconstruction method based on free liquid level temperature measurement value and feature function interpolation
ActiveCN107391789AHigh precisionPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltReconstruction methodSingle crystal
The invention discloses a silicon melt temperature field reconstruction method based on a free liquid level temperature measurement value and a feature function interpolation. The feature value problem of a heat conduction equation is used for analyzing the silicon melt model of the equal-diameter stage of the two-dimensional axial symmetry crystal growth process of a single crystal furnace, and a feature value and a corresponding feature function are obtained by calculation; a threshold scalar function is used for calculating the function of each feature function for an area to be reduced; a scalar value is set as a measuring standard for selecting the feature function; on the basis of a multi-population genetic algorithm, the arrangement position of a temperature sensor measuring point is optimized; finally, the group of temperature measurement values combined on an optimization position and the selected feature function are used for carrying out calculation to obtain a weight factor which reflects he characteristics of a silicon melt area; and an inner product operation is carried out with the feature function of each point in the silicon melt to obtain the temperature distribution of the silicon melt. By use of the method, the influence of a complex structure for an arrangement temperature sensor is reduced, the method is free from a heat conduction physical problem, and expansibility is good.
Owner:XIAN ESWIN MATERIAL TECH CO LTD +1
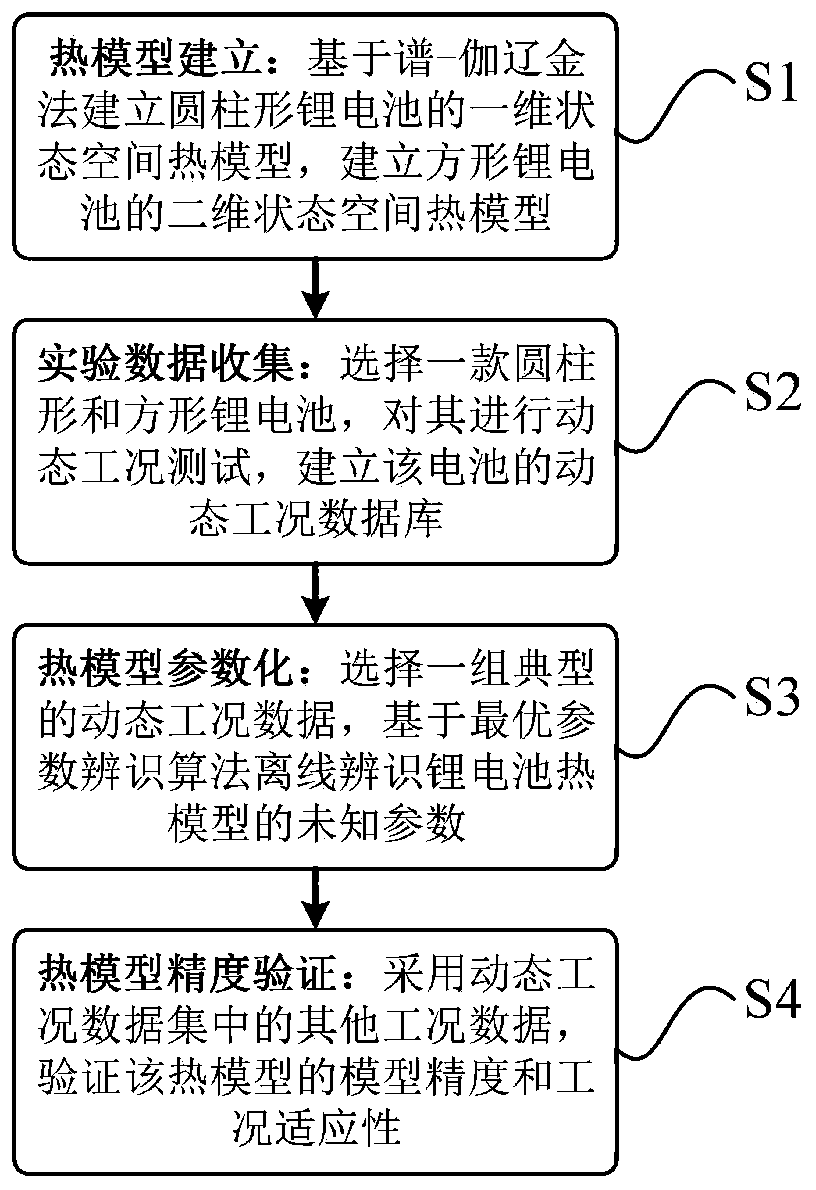
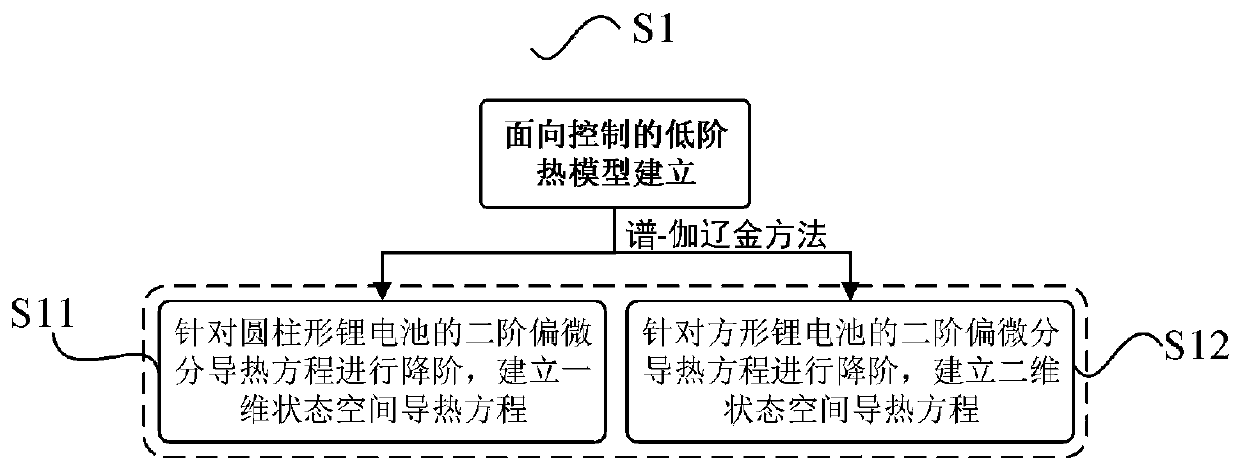
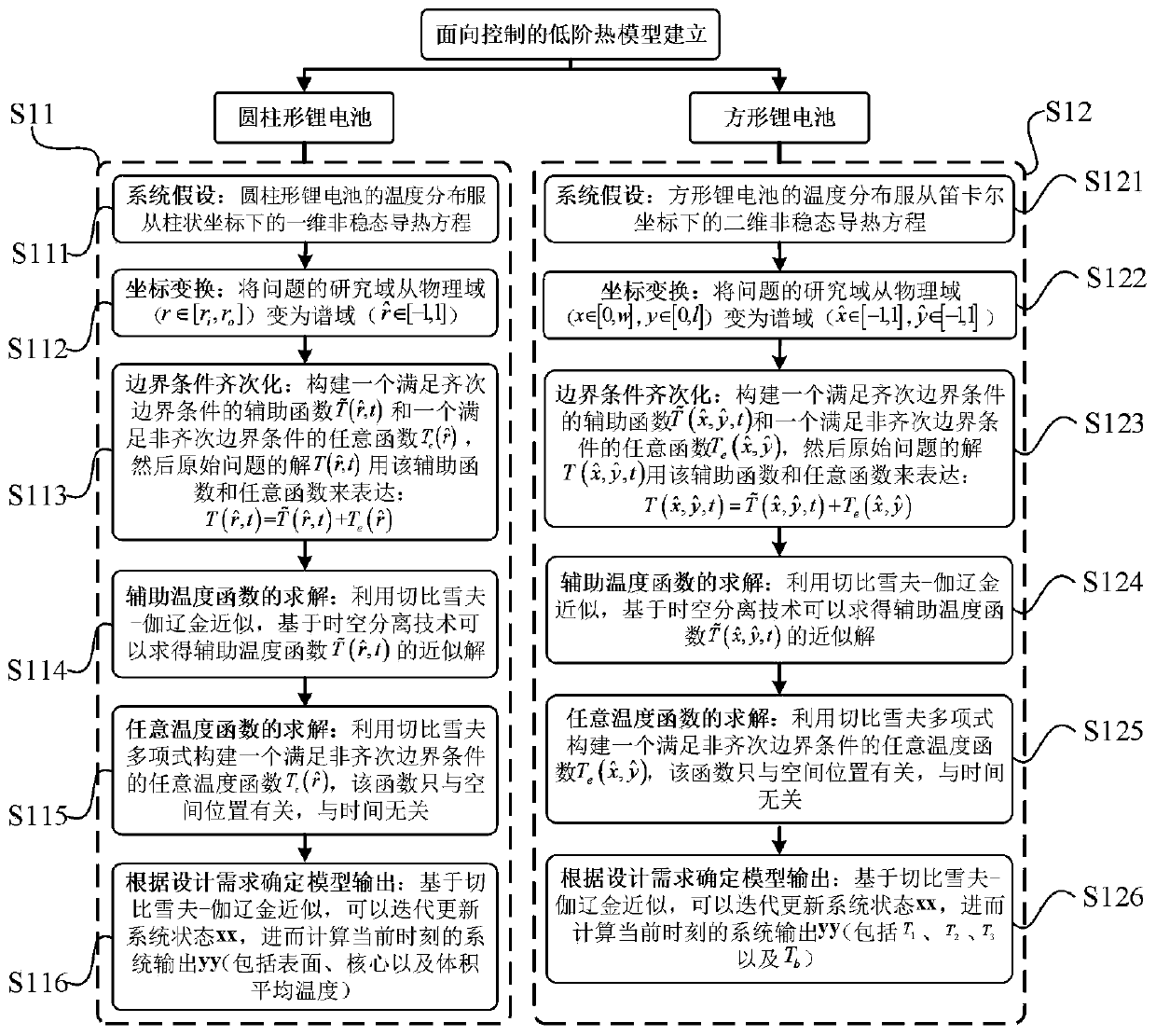
Control-oriented lithium battery thermal model establishing method
ActiveCN111143974AComputationally efficientGlobal optimizationElectrical testingDesign optimisation/simulationControl orientedElectrical battery
The invention relates to a control-oriented lithium battery thermal model establishing method, and belongs to the technical field of battery management. The method comprises the following steps of S1,performing order reduction on second-order partial differential heat conduction equations of cylindrical and square lithium batteries based on a spectrum-Galerkin method, and establishing control-oriented thermal models of the cylindrical and square lithium batteries; S2, selecting a cylindrical lithium battery and a square lithium battery, performing dynamic working condition test on the cylindrical lithium battery and the square lithium battery, and establishing a dynamic working condition data set of the batteries; S3, selecting a group of typical dynamic working condition data, and identifying unknown parameters of the lithium battery thermal model offline based on an optimal parameter identification algorithm; and S4, verifying the model precision and the working condition adaptability of the thermal model by adopting other working condition data in the dynamic working condition data set. Compared with the prior art, the modeling technology has the advantages that the modeling technology is not limited by the geometrical shape of the battery, the established thermal model is efficient in calculation and globally optimal, and detailed temperature information in the battery canbe extracted.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Cable load measurement device and measurement method
ActiveCN108535570ARealize online real-time monitoringEasy to operateElectrical testingElectrical conductorMeasurement device
The invention discloses a cable load measurement device, and relates to the technical field of cable load measurement equipment. The cable load measurement device comprises a temperature probe I, a temperature probe II, a temperature probe III, a controller and an alarm, wherein the temperature probe I is fixed on the surface of an insulating layer; the temperature probe II penetrates through theinsulating layer and is in contact with the surface of a conductor; the temperature probe III is exposed to the air; and the controller is used for computing the temperature and load of the conductor.The invention further discloses a measurement method of the cable load measurement device. The device has the advantages that a relational expression among the working current of the conductor of a cable, the conductor temperature, the temperature of the outer surface of the insulating layer and environment temperature is derived according to the joule law and a heat conduction equation, furtherthe conductor temperature of the cable, the temperature of the outer surface of the insulating layer and the environment temperature are measured, the online real-time measurement of cable load is realized, and the device is convenient to operate, very safe and reliable, simple and efficient.
Owner:陕西协成测试技术有限公司
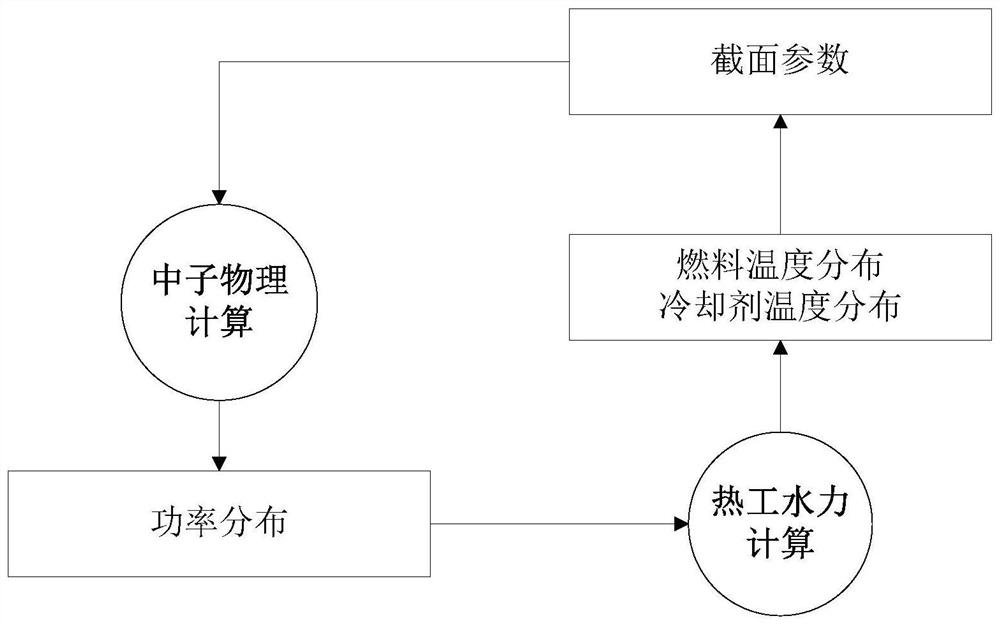
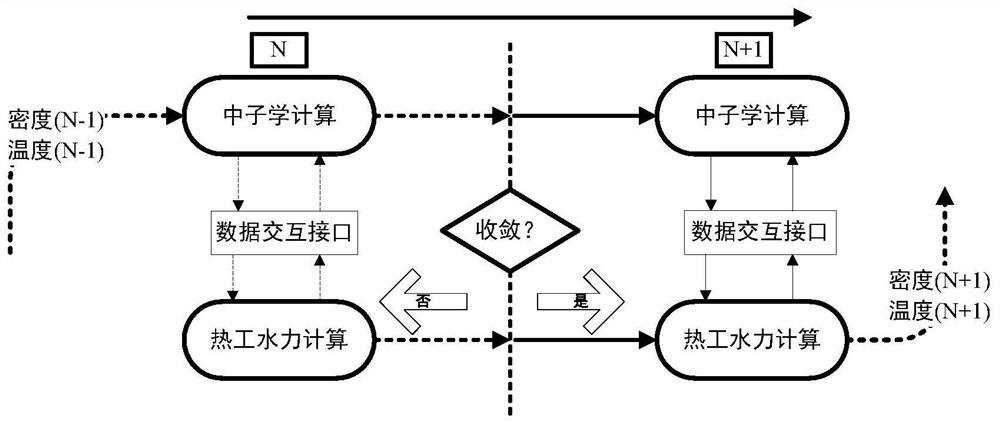
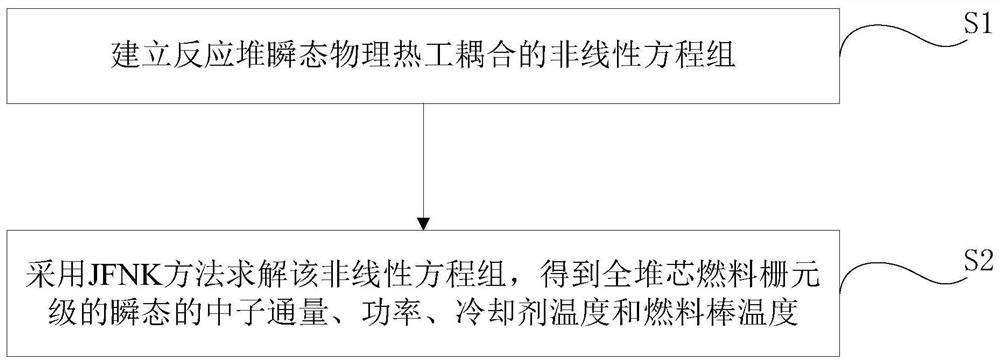
Reactor transient physical and thermal full-coupling fine numerical simulation method and system
ActiveCN112906271AImprove computing efficiencyIncrease the level of detailDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingCoolant flowNonlinear systems of equations
The invention discloses a reactor transient physical and thermal full-coupling fine numerical simulation method and system. The method comprises the steps: S1, establishing a nonlinear equation set of reactor transient physical and thermal coupling ; and S2, solving the nonlinear equation set by adopting a JFNK method to obtain the full-core fuel lattice cell level transient neutron flux, delayed neutron precursor concentration, power, coolant temperature and fuel temperature. According to the method, a neutron physical diffusion equation is dispersed by adopting a fine net difference method, a coolant flow heat transfer equation is simulated by adopting a single-channel model, a cylindrical heat conduction equation is dispersed by adopting a finite volume method, a nonlinear equation set for simulating physical and thermal specialty of a reactor is established, and the nonlinear equation set is solved by adopting a JFNK method; and the three-dimensional transient physical and thermal parameters of the full-core fuel lattice cell level are obtained, and the physical and thermal coupling calculation precision of the reactor is improved.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Welding reverse deformation calculation method
InactiveCN108804725AGuaranteed accuracySmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNonlinear finite element analysisFinite element analyse
The invention discloses a welding reverse deformation calculation method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing two-dimensional geometric models of a temperature field and a deformation field of a to-be-welded workpiece according to a preset reverse deformation and a welding condition; establishing a heat conduction equation and a thermal elastoplastic control equation on the basis of the two-dimensional geometric models, physical performance and mechanical performance of the to-be-welded workpiece and a welding heat source; solving the solid-state heat conduction equationand the thermal elastoplastic equation on the basis of nonlinear finite element analysis software so as to obtain a temperature field and a welding angle deformation in the welding process; and finally determining a welding reverse deformation of the to-be-welded workpiece according to a preset reverse deformation, the welding angle deformation and a deformation target value. Compared with the traditional manners of carrying out analysis by utilizing three-dimensional models, the welding reverse deformation calculation method is capable of reducing the computational complexity of systems and ensuring the correctness of calculation results while obtaining welding reverse deformations of to-be-welded workpieces in an efficient and low-cost manner.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com