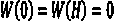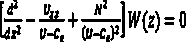Patents
Literature
278 results about "Microwave remote sensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microwave remote sensing pixel element decomposing method based on land and water living beings classifying information
InactiveCN101963664ASolve the problem of low spatial resolutionImprove spatial resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSensing dataBrightness temperature
The invention provides a microwave remote sensing pixel element decomposing method based on land and water living beings classifying information, which comprises the steps of: by using land and water living beings classifying information of spectrum remote sensing data, establishing a microwave mixed pixel element decomposing module, and calculating component brightness temperature in a microwavemixed pixel element by solving an underdetermined equation set. Through obtaining positions and brightness temperature values of different components in the microwave mixing pixel element, the space resolution of the microwave mixing pixel element of water and land boundary is remarkably improved, microwave brightness temperature values and classifying information of the water and land living beings in an observing region are obtained, and the precision of post stage inversion of the microwave remote data is improved. The invention has the important meanings of completing the decomposition ofthe microwave mixing pixel element data of the water and land boundary in a global region, ensuring that the decomposed microwave remote data space resolution is similar to the spectrum remote sensing data space resolution adopted in the classification, solving the problem of low space resolution of the microwave remote sensing data, and broadening the application field of the microwave remote sensing data.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
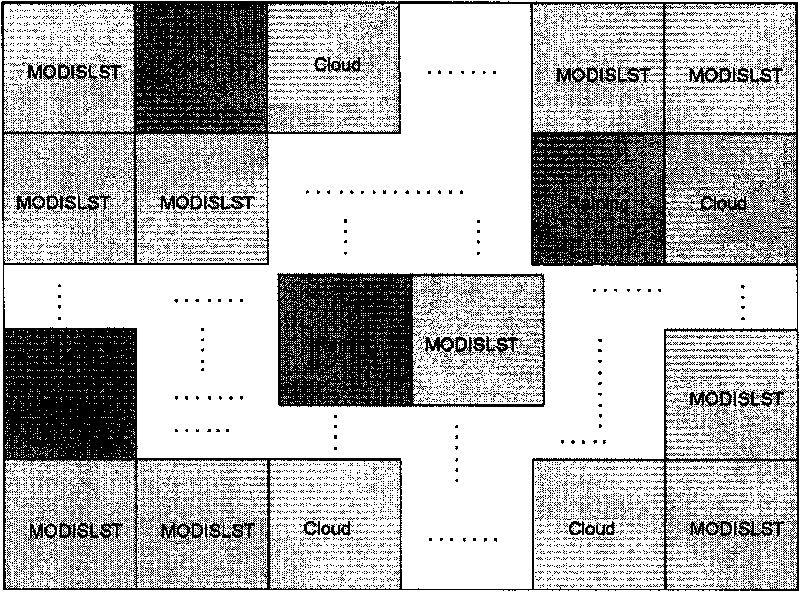
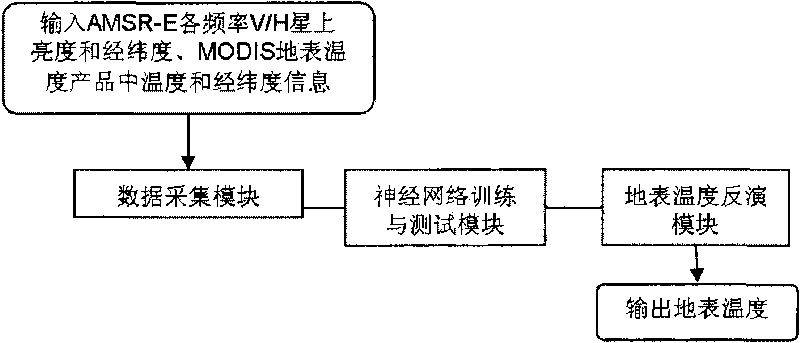
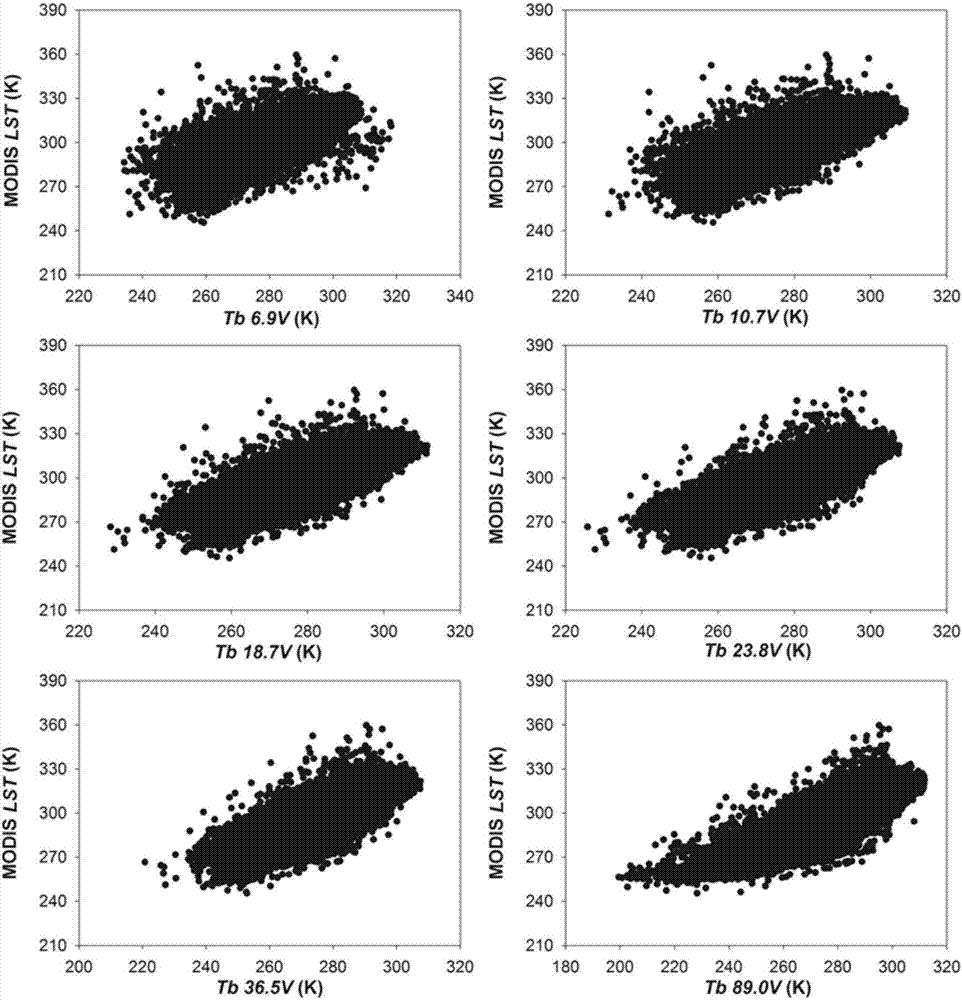
Method by utilizing passive microwave remote sensing data AMSR-E (Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS ) to invert surface temperature
InactiveCN101738620AAvoid difficultiesReduce unknownsElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationEarth observationData set
The invention relates to a method by utilizing passive microwave remote sensing data AMSR-E to invert surface temperature. The method comprises three steps of: step 1, collecting MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) surface temperature product which is provided by an American Earth Observation Data Center and used as AMSR-E surface temperature data by latitude and longitude control, and establishing a training and testing database; step 2, utilizing a neutral network to perform repetitive training and testing; and step 3, performing inversion calculation on AMSR-E actual image data, and actual surface verification and application analysis. The product obtained by the method has high precision, and overcomes the effect of clouds and partial raining on thermal infrared.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
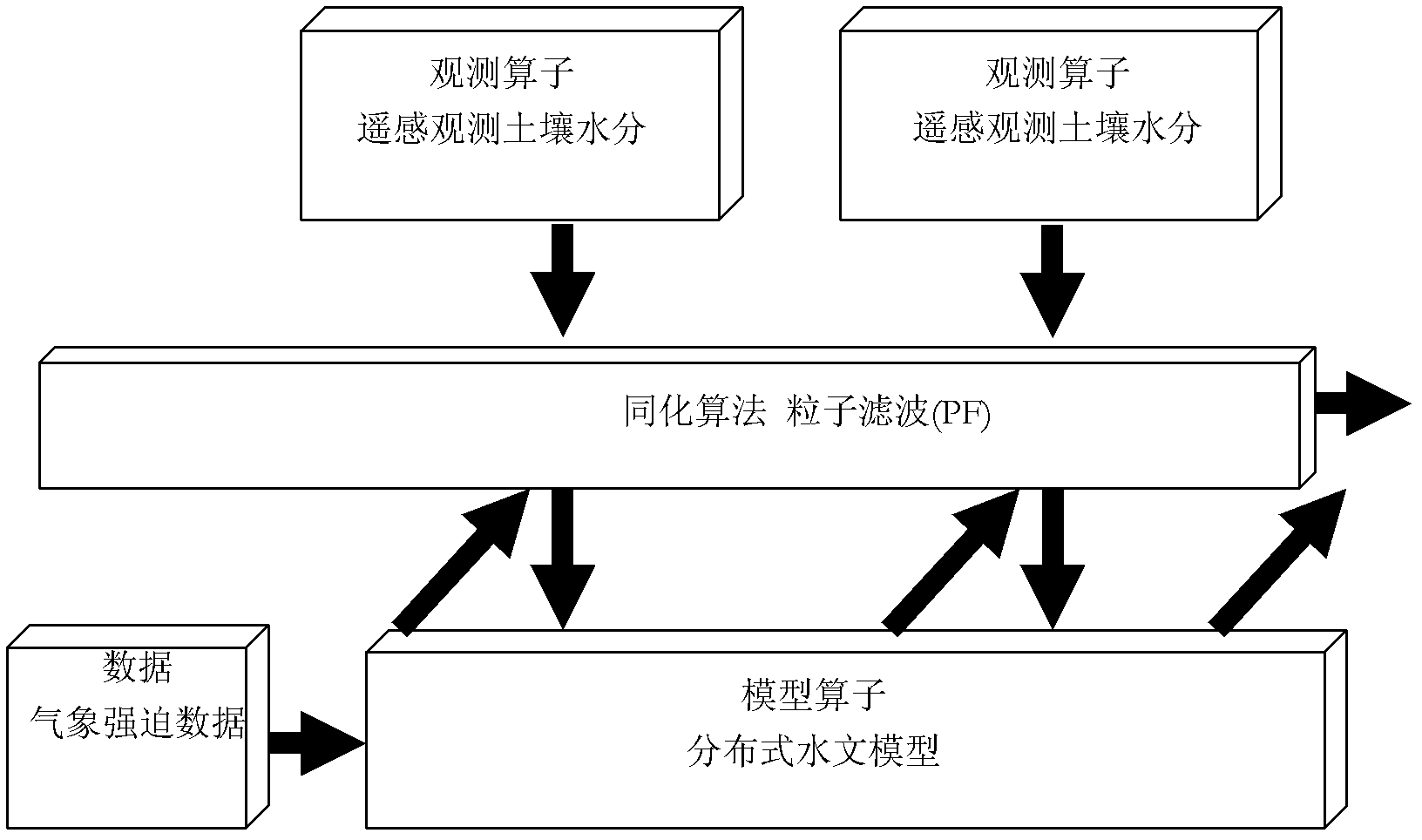
Watershed scale soil moisture remote sensing data assimilation method
InactiveCN102354348AEfficient integrationGood day-to-day runoff simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHydrometryData set
Owner:NANJING UNIV
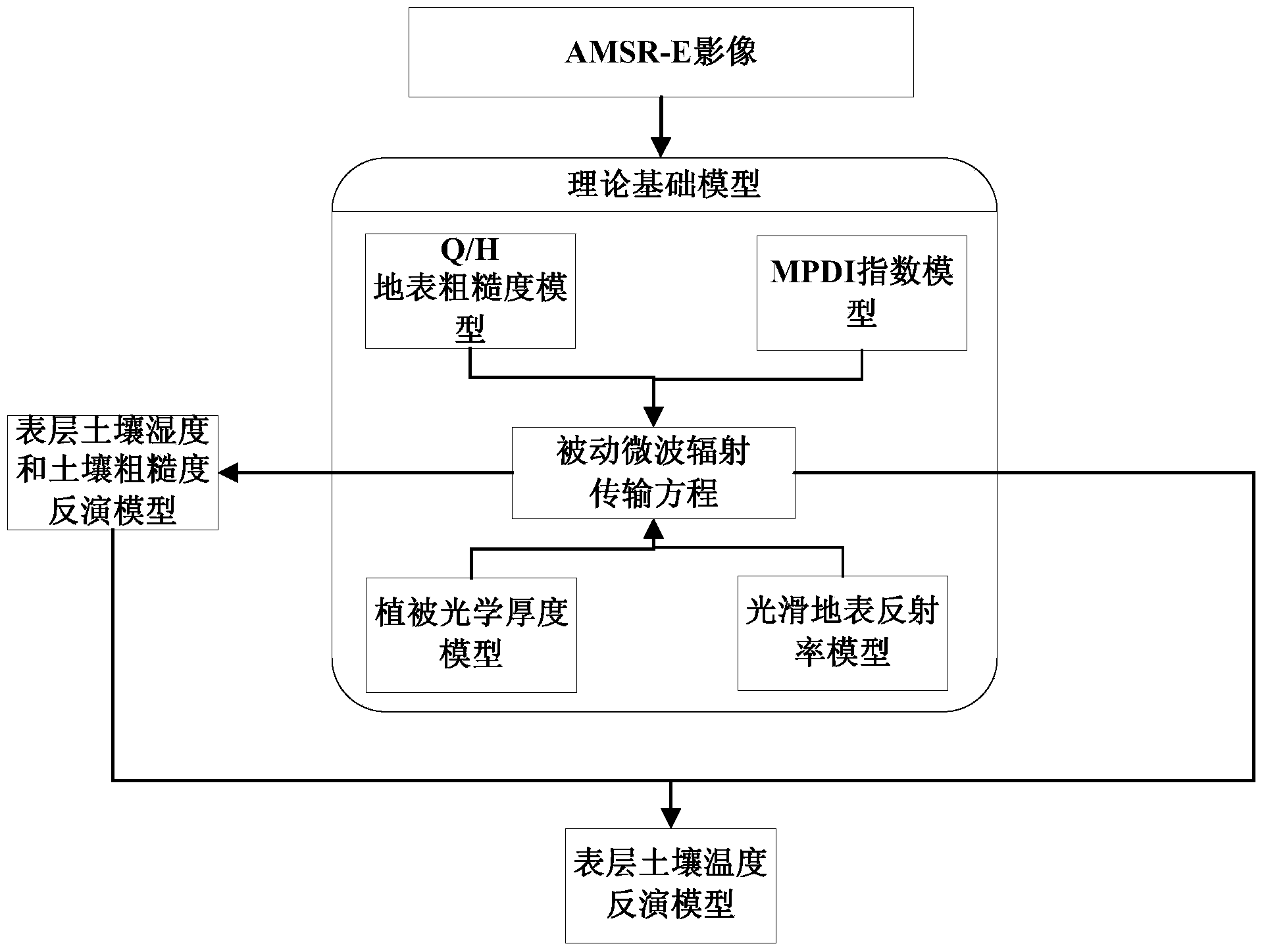
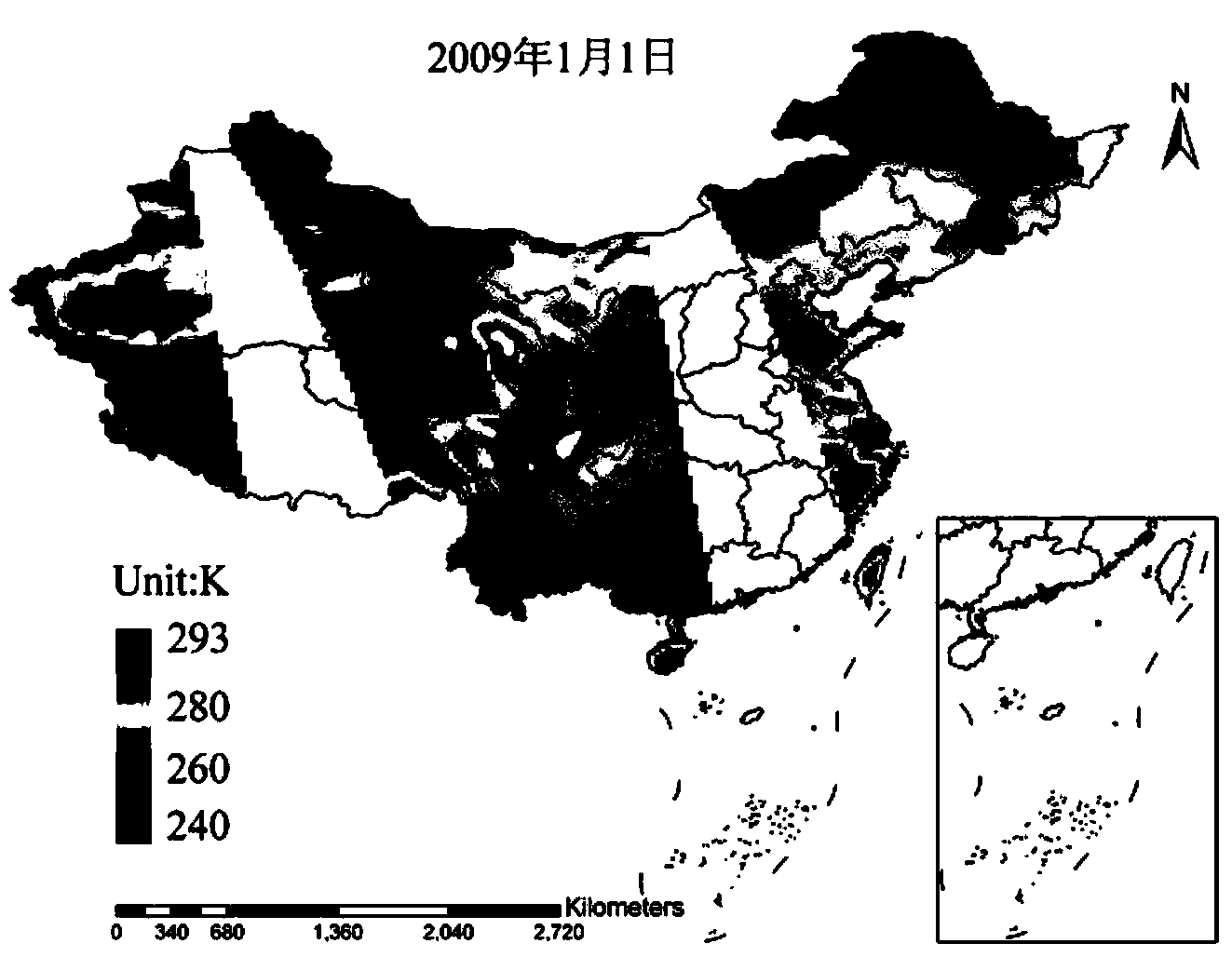
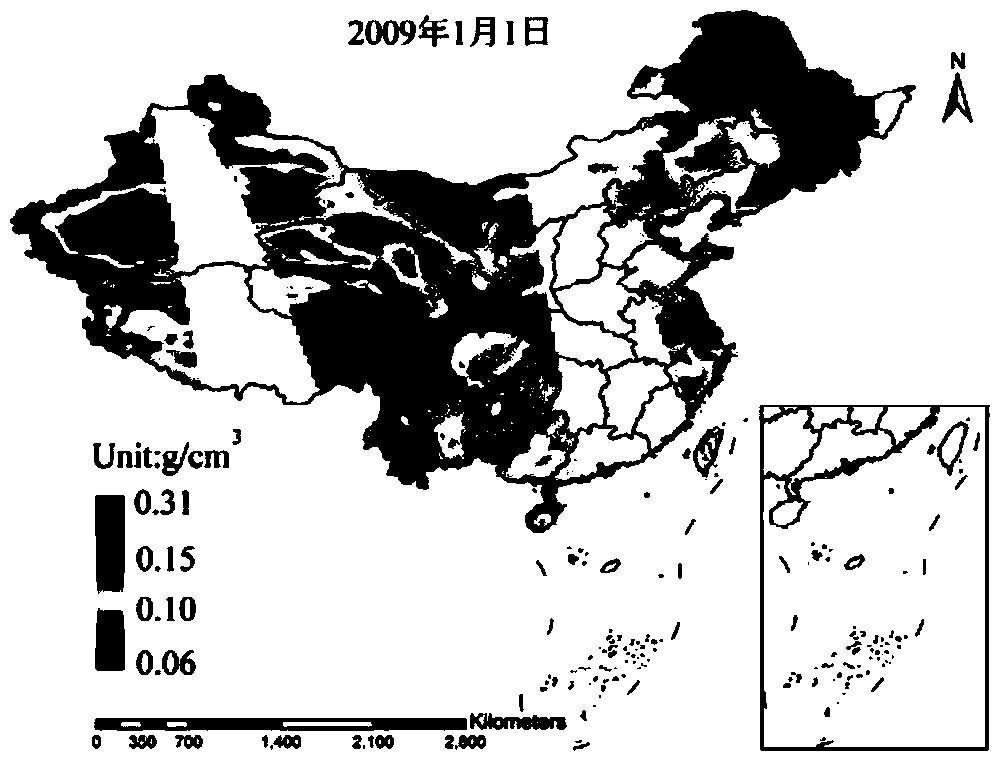
Method for inverting surface soil physical parameters through passive microwave remote sensing
InactiveCN103969268AMaterial analysis using microwave meansRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadiation transferSoil temperature
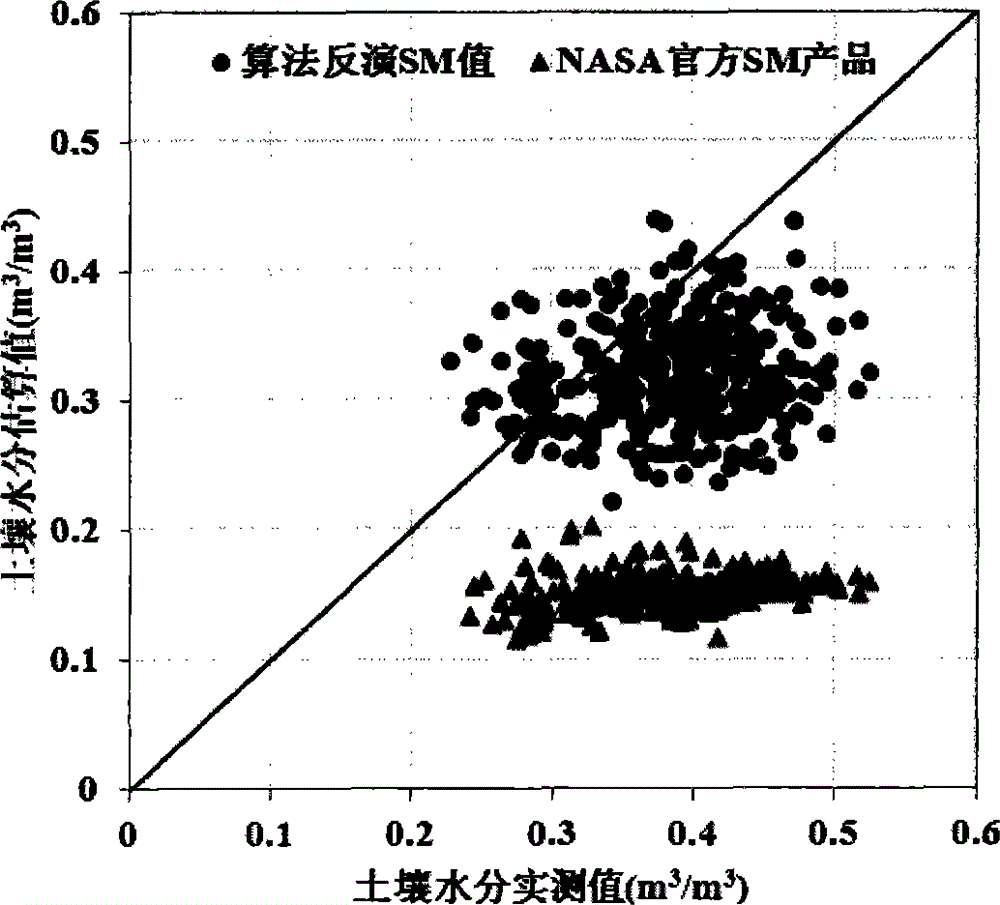
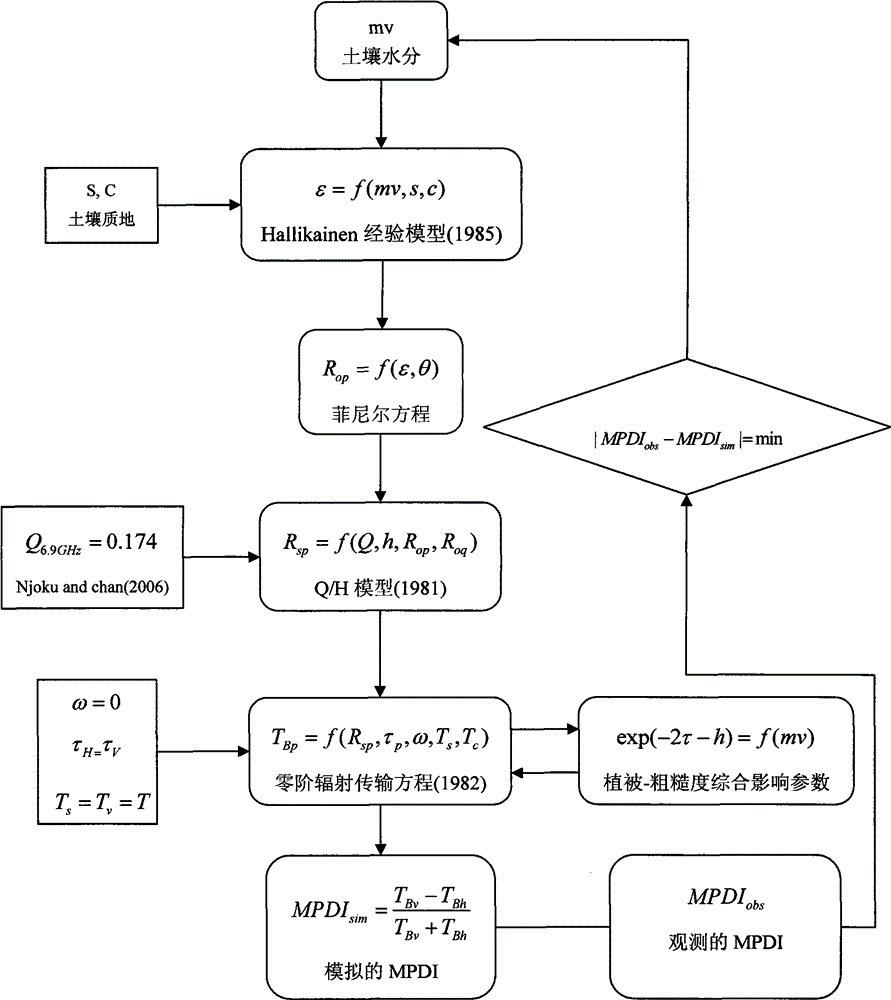
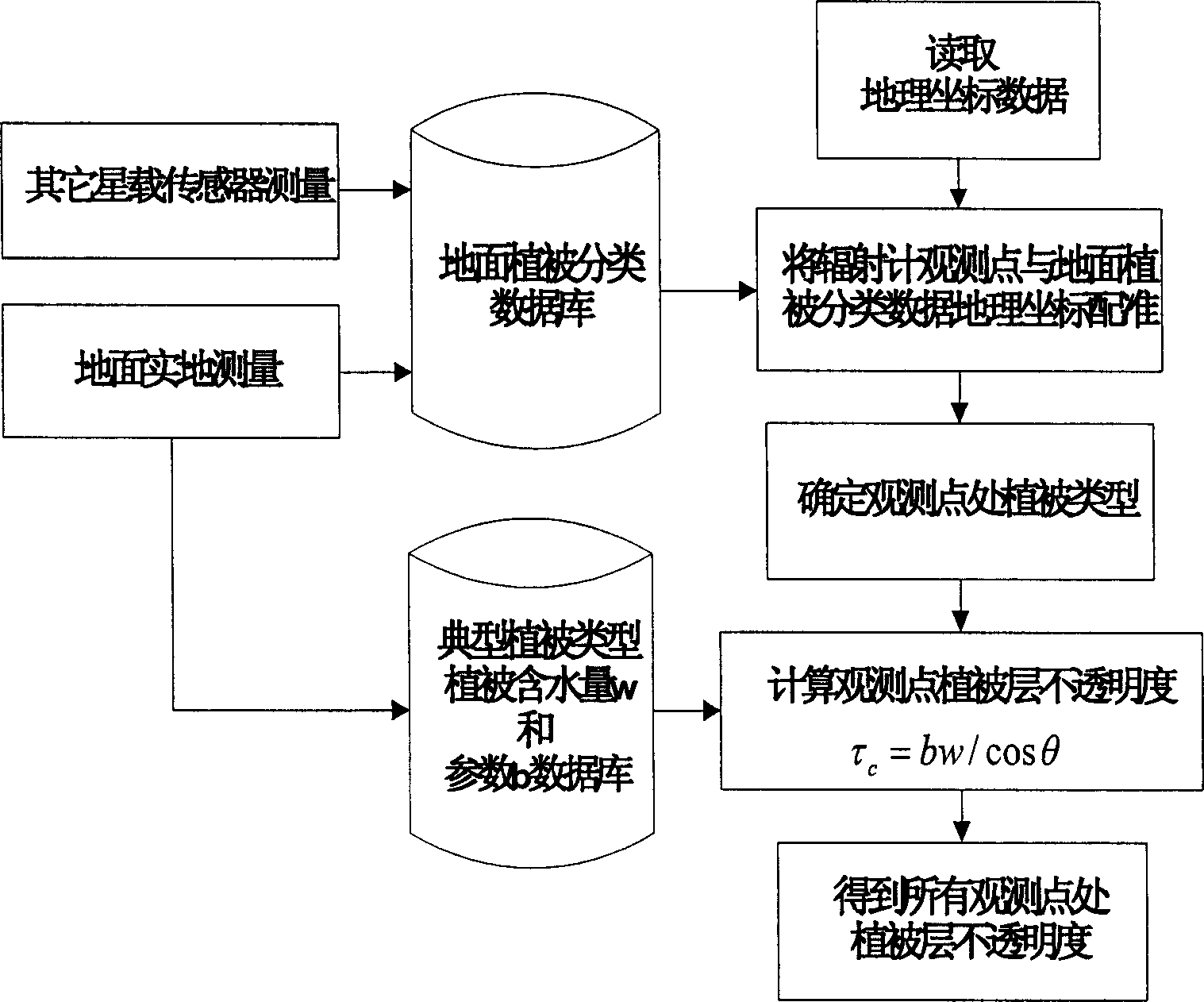
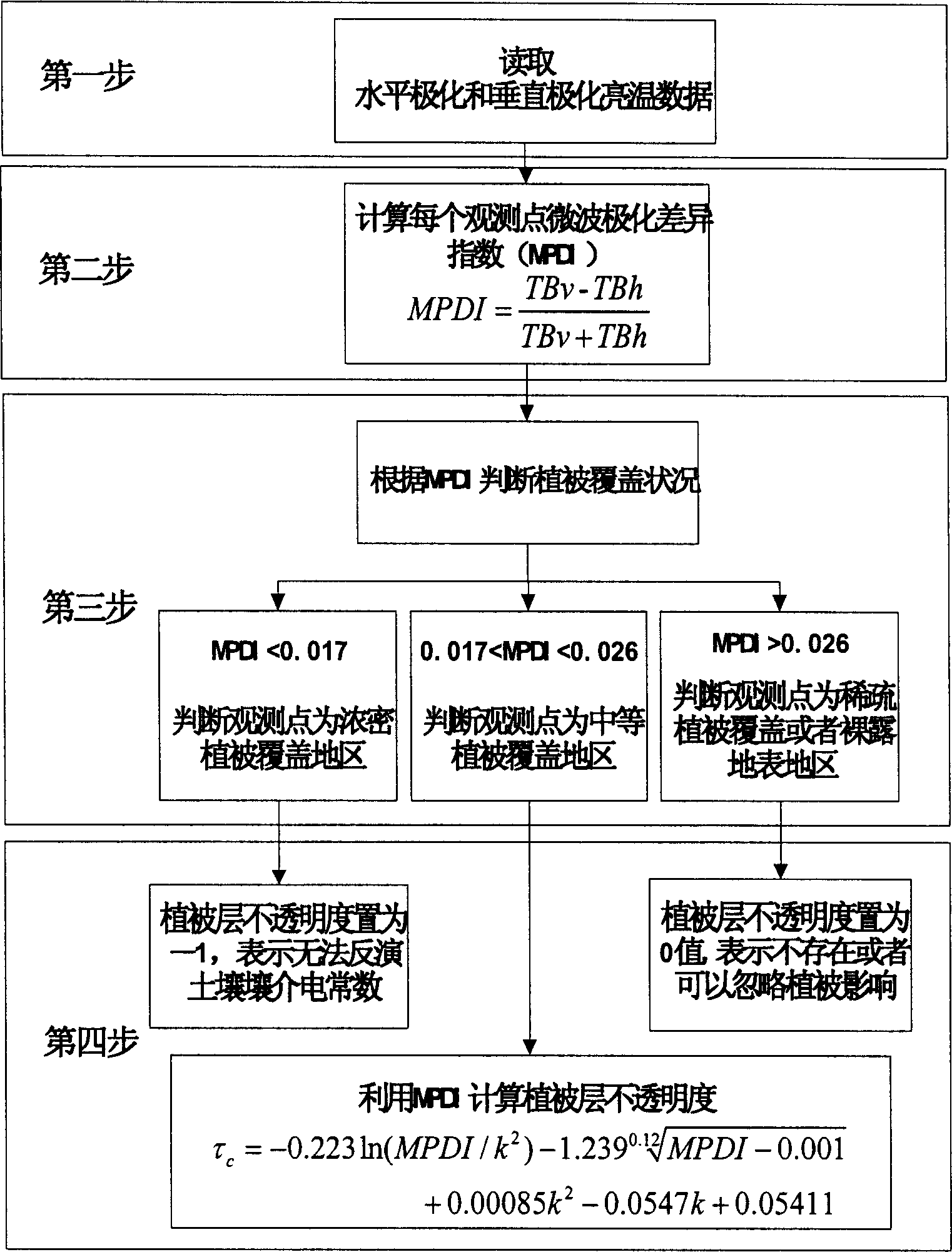
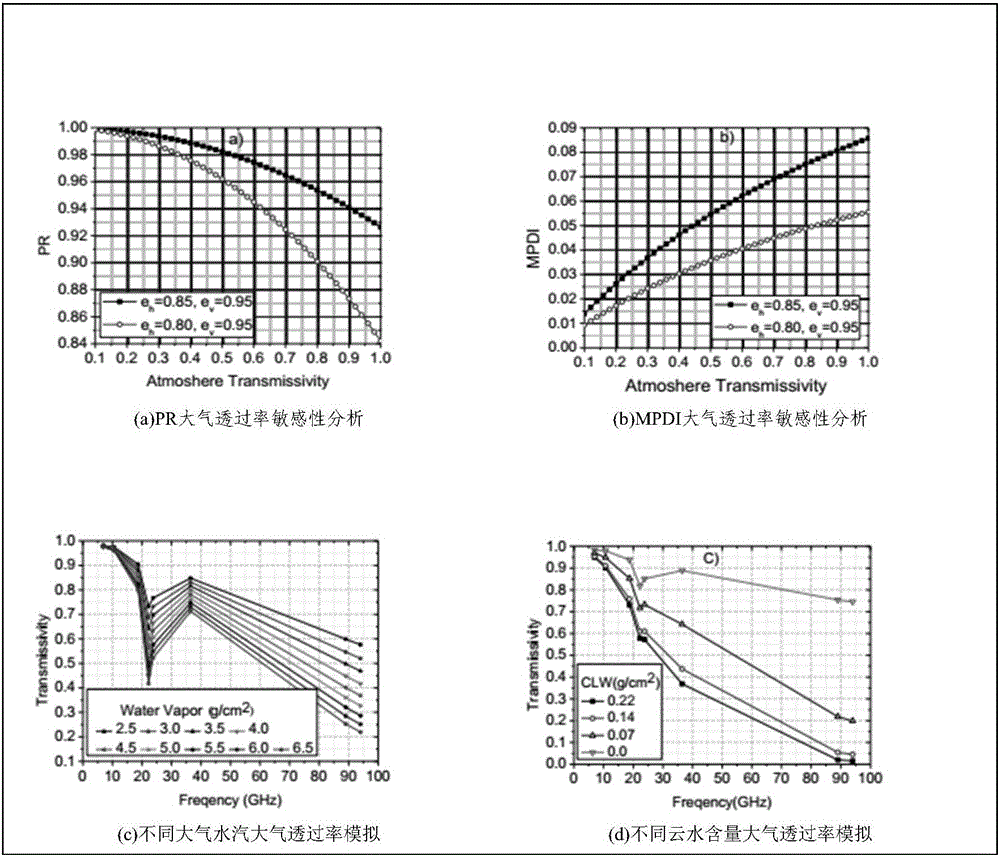
The invention discloses a method for inverting surface soil physical parameters through passive microwave remote sensing. The method comprises the steps as follows: step one, brightness temperature data and MPDIes (microwave polarization difference indexes) of an AMSR-E passive microwave remote sensing brightness temperature image are acquired by a launched satellite-borne passive microwave remote sensing meter AMSR-E; step two, a relationship of smooth surface reflectance, surface soil roughness parameters, MPDIes and vegetation optical thickness is acquired through deduction; step three, surface soil humidity mv and soil roughness h are calculated; and step four, the surface soil temperature TS is calculated. The method is based on a simplified passive microwave radiation transfer equation and combined with the MPDIes, a Q / H surface soil roughness model, a vegetation optical thickness model, a Fresnel equation and the like, so that a physical inversion model for the surface soil determinant attribute parameters including the soil temperature, the surface soil temperature and the soil roughness is constructed; and the method can be used for inverting the surface soil temperature, soil humidity and surface roughness distribution of China and even the global region and has important scientific significance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method and apparatus for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing
ActiveCN102735697ALarge-scale spatial and temporal distribution informationDynamic spatio-temporal distribution informationMoisture content investigation using microwavesSoil scienceLow frequency band
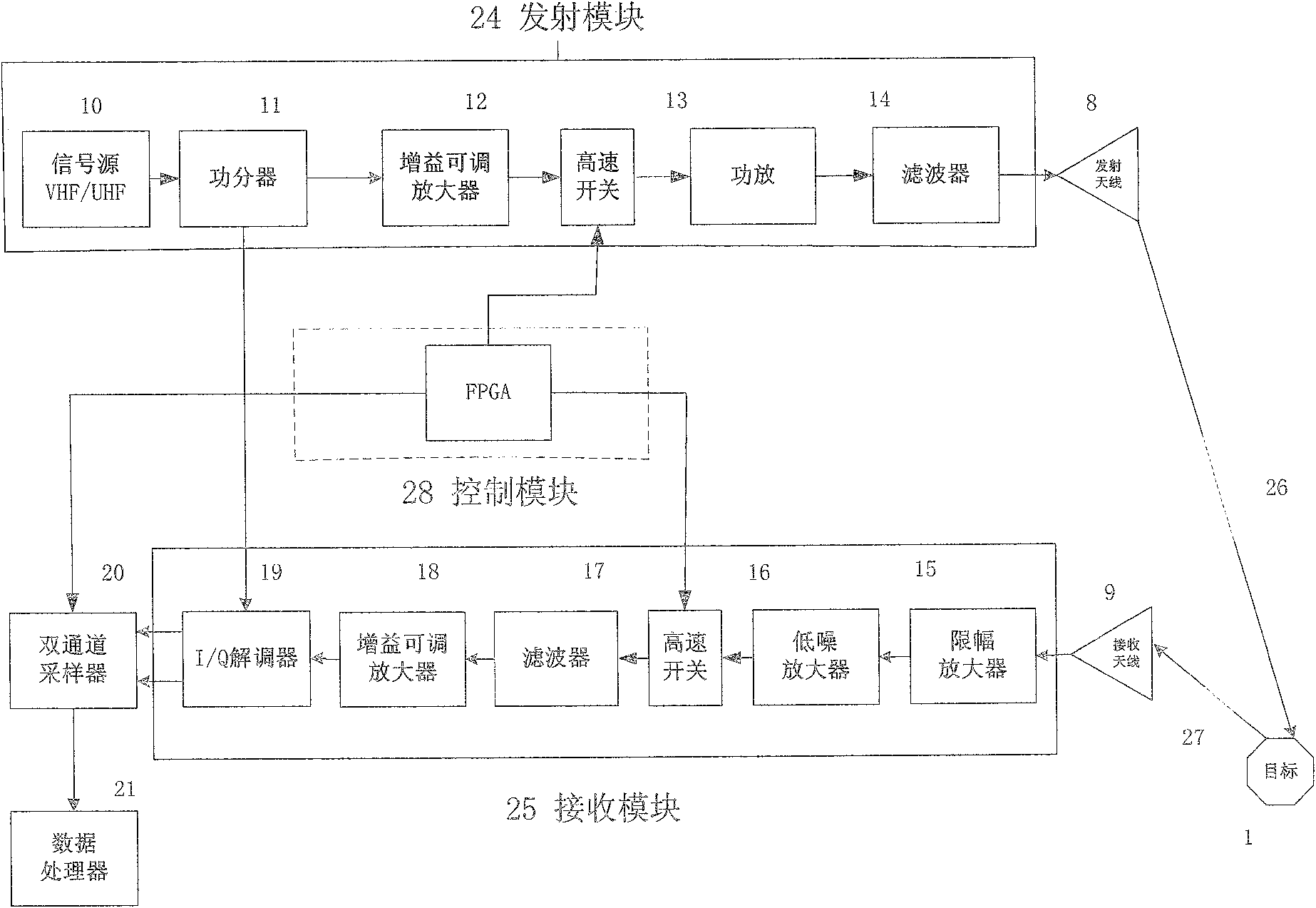
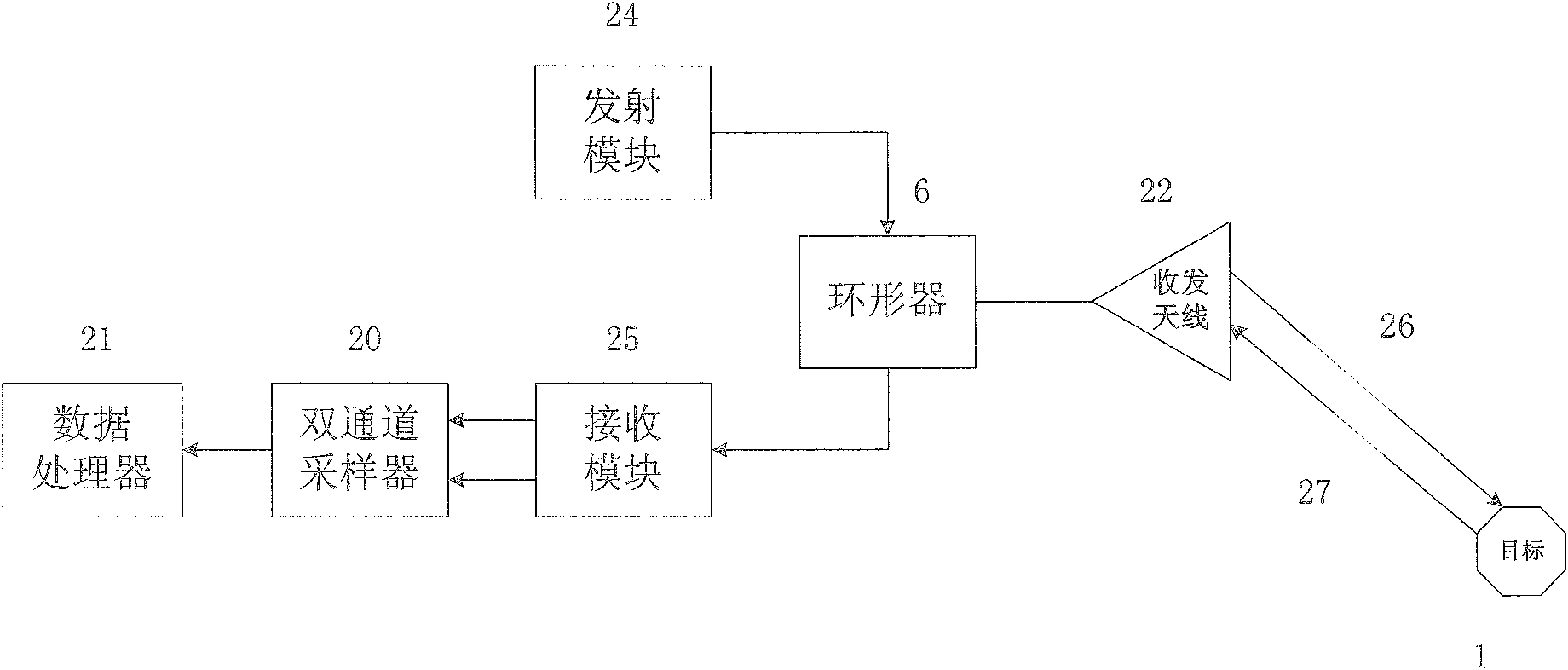
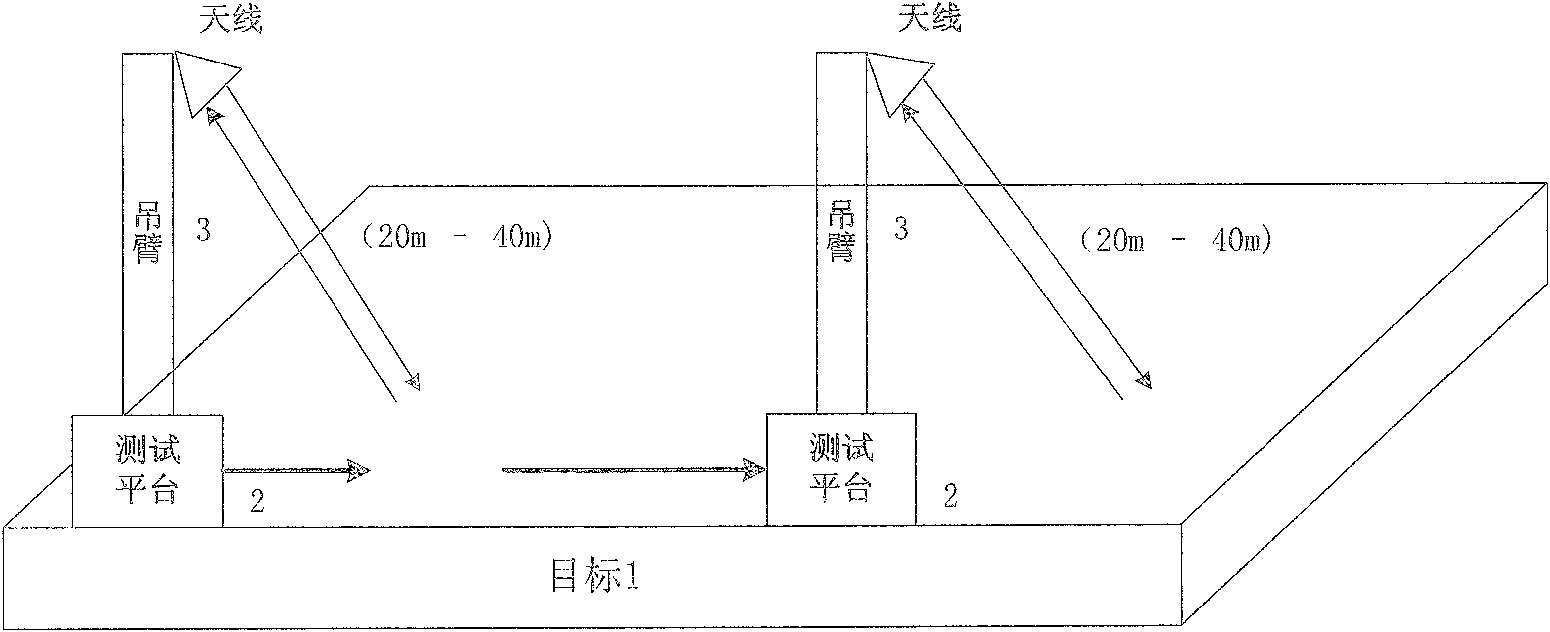
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing, and relates to the technology of microwave remote sensing. The method for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing is provided by utilizing an object-penetrative property of microwave low-frequency bands and also disclosed is the apparatus for detecting deep soil humidity through microwave remote sensing. Backscattering coefficients of soils are tested. Soil humidity of different depth is obtained through inverting a deep soil scattering model and a soil dielectric model. A three dimensional image of the distribution of soil humidity in a tested area is formed. The working frequency of the apparatus is in the VHF / UHF band. Soil dielectric constants and humidity parameters of different types of soils in a depth of 0.1-10 m can be detected in a contactless and lossless manner.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave/infrared remote sensing image combined soil moisture inversion method
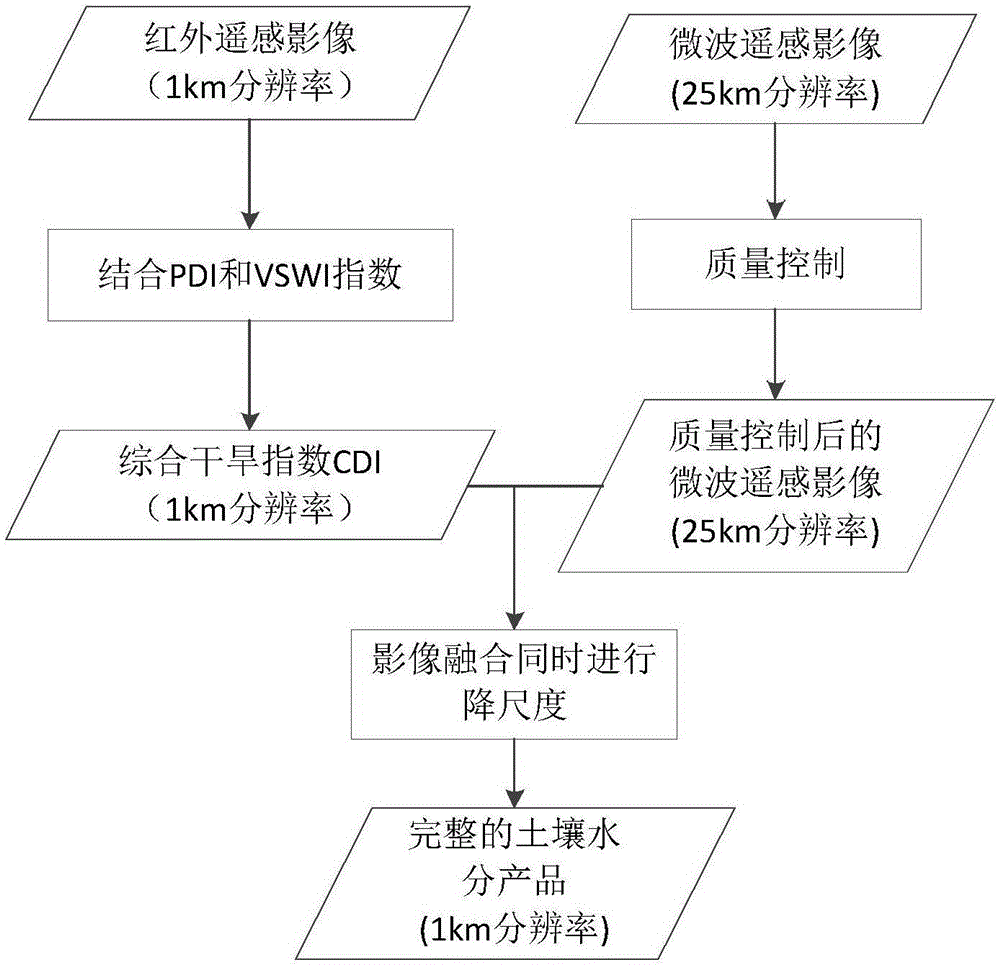
ActiveCN106226260AImproving the Accuracy of Moisture Remote Sensing RetrievalMake up for the shortcomings of low resolutionColor/spectral properties measurementsMoisture content investigation using microwavesSensing dataCorrelation coefficient
The invention relates to a microwave / infrared remote sensing image combined soil moisture inversion method. By combining the applicability characteristics of PDI (precipitation distance index) and VSWI (vegetation supply water index), a remote sensing monitoring model based on CDI (composite drought index) is established according to different ground surface vegetation coverages. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the CDI result by using infrared remote sensing data, calculating the correlation coefficient between the CDI inversion result and microwave remote sensing data by combining the microwave remote sensing data, establishing a regression equation, carrying out image fusion while downscaling the microwave data, converting the CDI result reversed from the infrared data into true soil moisture value, and filling the infrared data null region with the microwave remote sensing data, thereby obtaining the complete high-resolution soil moisture product. The method is simple and practical, and enhances the wide-range soil moisture inversion efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
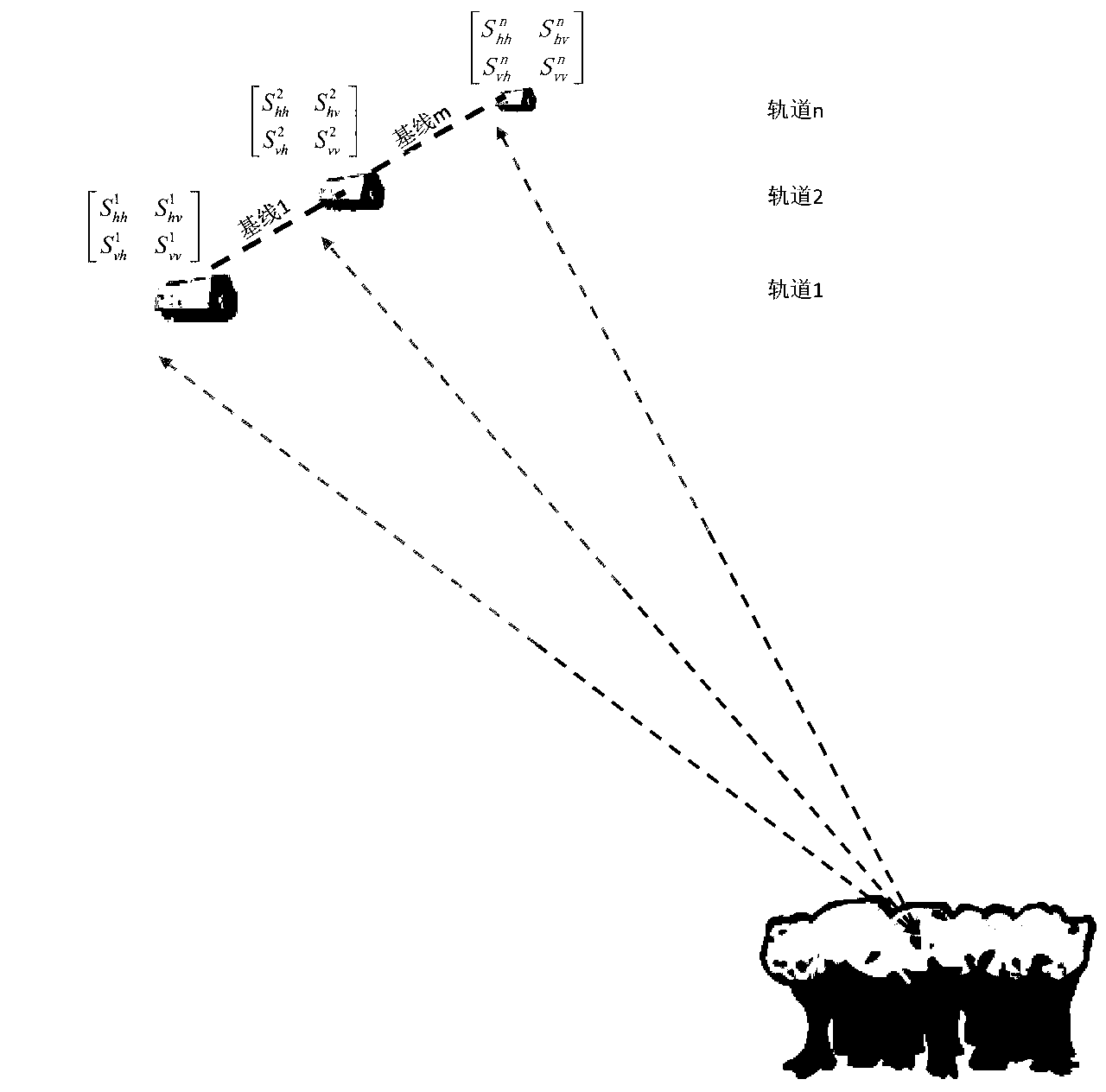
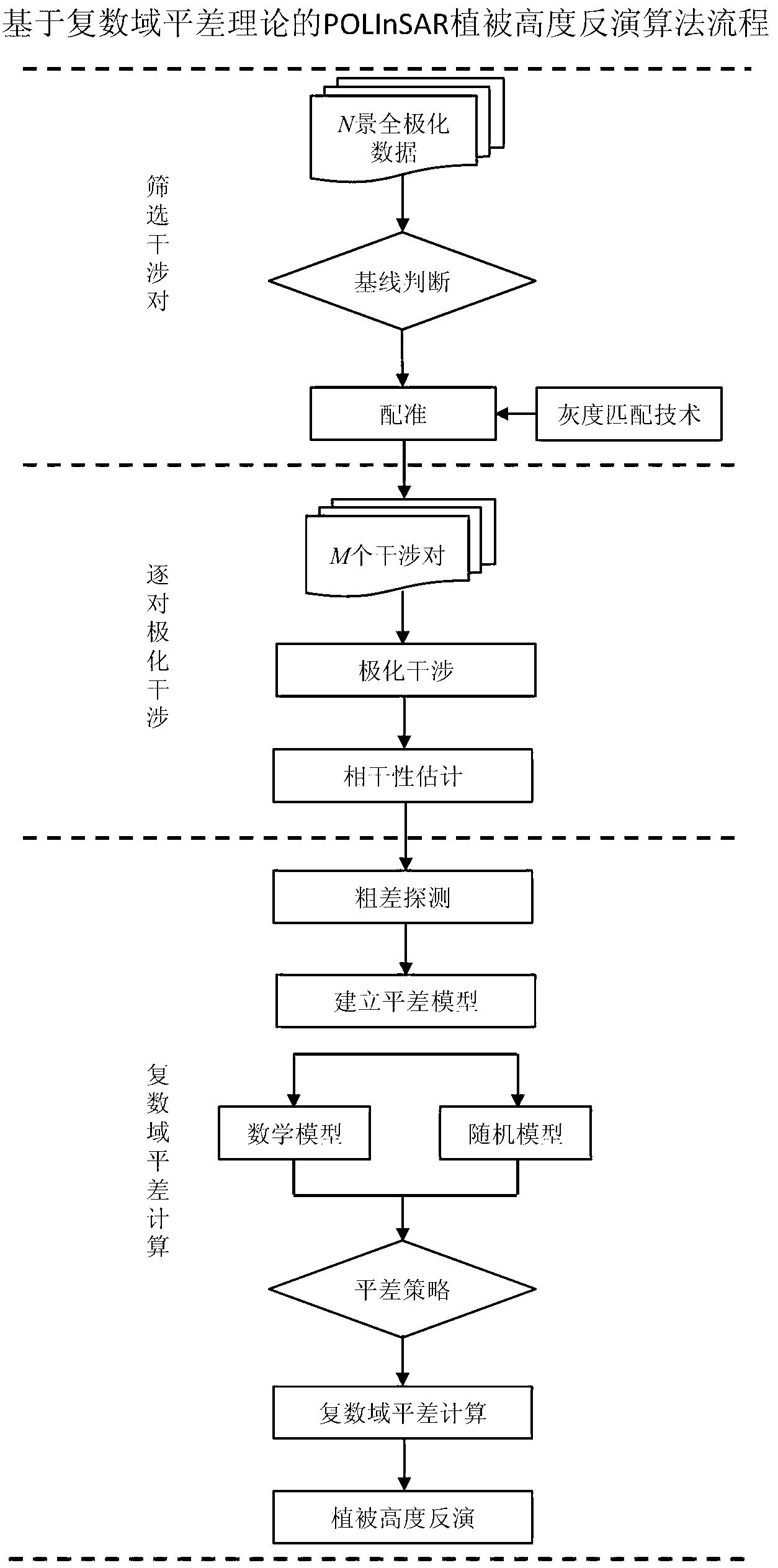
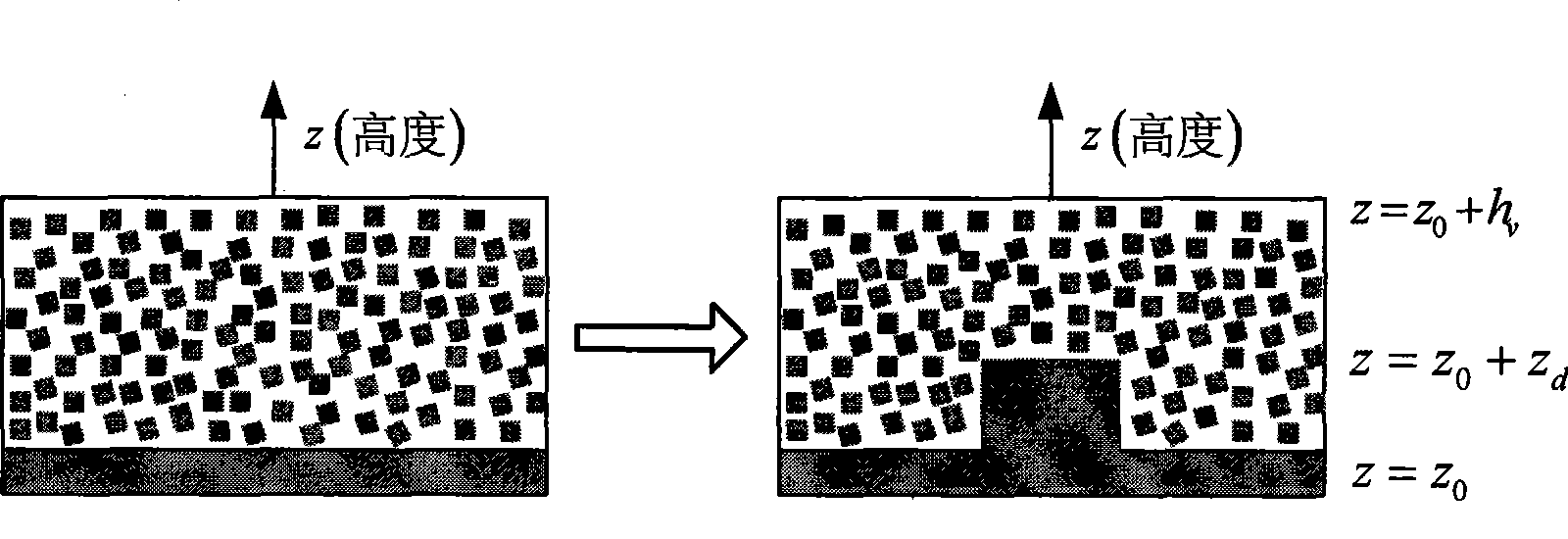
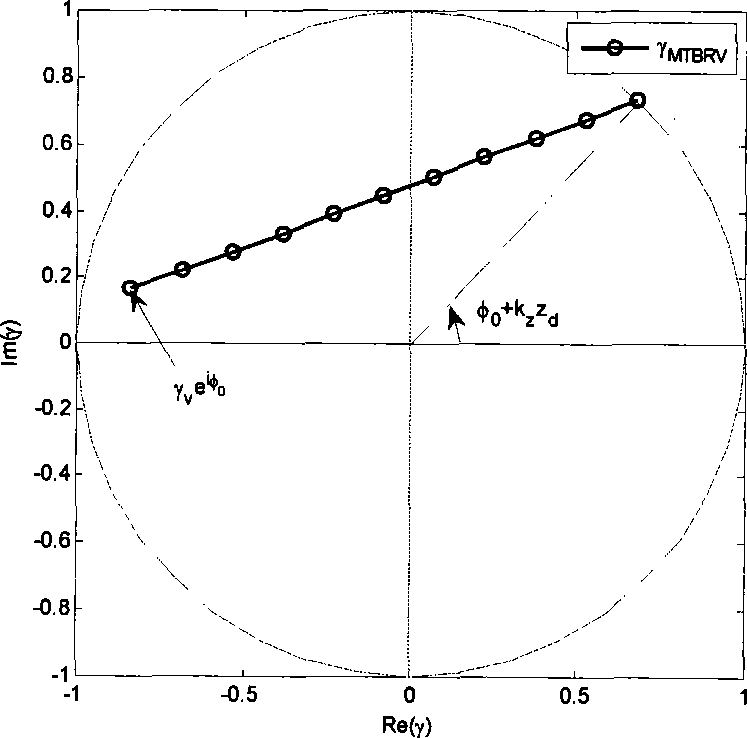
Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interferometry (POLInSAR) vegetation height inversion method based on complex field adjustment theory
ActiveCN103235301AThe principle is intuitiveEasy programmingWave based measurement systemsGeomorphologyVegetation height
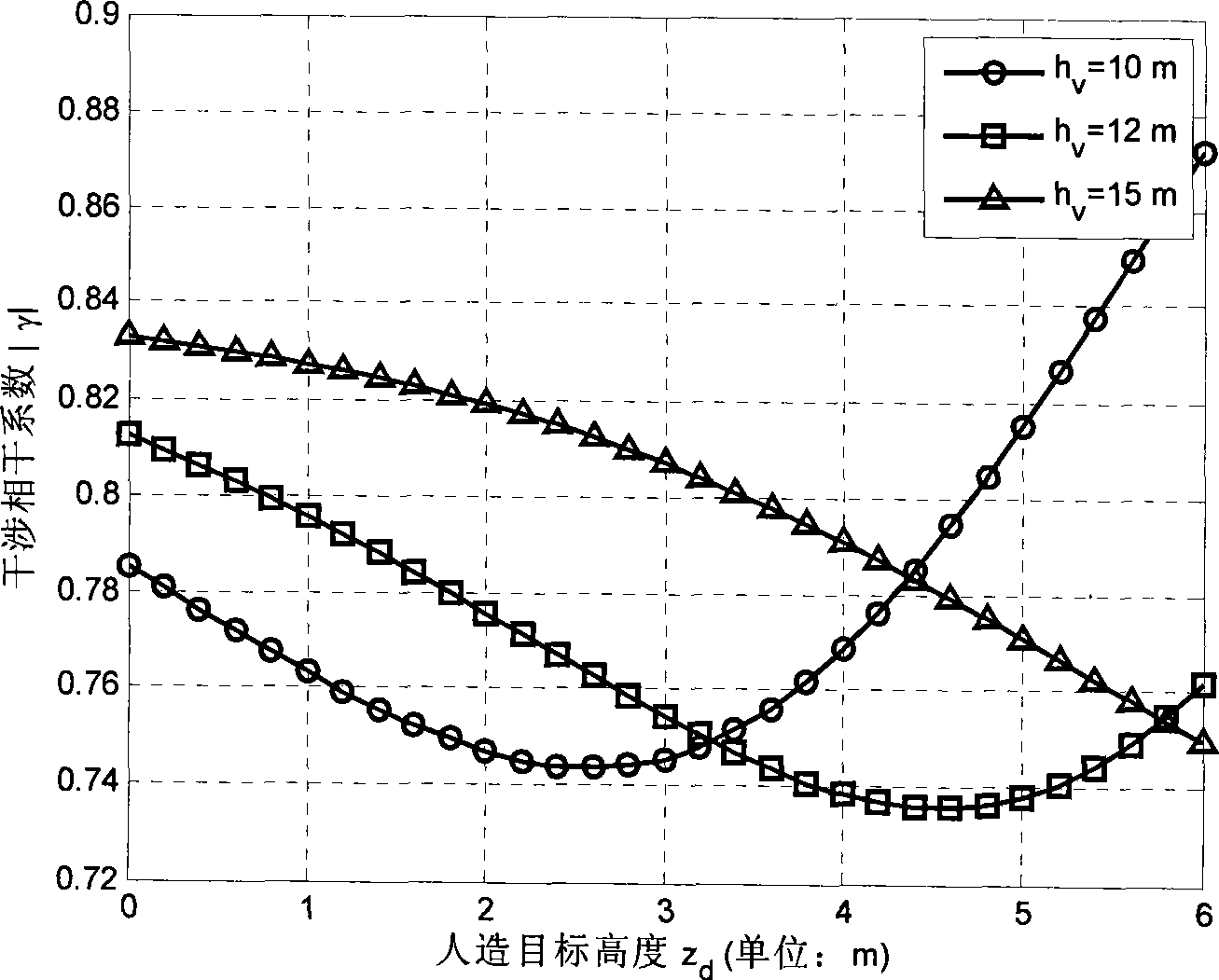
The invention relates to application of microwave remote sensing in the field of forests and discloses a polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interferometry (POLInSAR) vegetation height inversion method based on complex field adjustment theory. The complex field adjustment theory and a physical model for POLInSAR vegetation height inversion are organically combined by the method. The method comprises the following steps of: I, performing registration on obtained complete polarization data of N scenes to obtain M baseline interference pairs; II, performing polarized interference on the M baseline interference pair to obtain M*P interference fringe patterns, and estimating corresponding complex coherences of the M*P interference fringe patterns; and III, working out a vegetation height hv based on complex field adjustment computation. The POLInSAR vegetation height inversion method based on the complex field adjustment theory is visual in principle, is easy to realize programming and extension, is a steady and feasible vegetation height inversion method, and can be widely applied to the POLInSAR technology to measure the vegetation height within a large-scale area and even a global scale.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Portable earth surface roughness measuring instrument
InactiveCN102589487ALow costHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansMeasuring instrumentEngineering
The invention discloses a portable earth surface roughness measuring instrument, comprising a horizontal rotation driving device and a radial moving arm which is connected with the output terminal of the horizontal rotation driving device and can horizontally rotate by taking the output terminal as the center as well as a controller, wherein the radial moving arm is provided with a sliding block which can move along length direction of the radial moving arm; the sliding block is fixedly connected with a distance measuring device and is used for measuring a distance between the sliding block and an upper cushion surface in vertical direction and a distance between the sliding block and a lower cushion surface in the vertical direction; and the controller is used for controlling rotation output of the horizontal rotation driving device, moving of the sliding block on the radial moving arm and starting of the distance measuring device, receiving a measuring result of the distance measuring device, calculating an earth surface roughness result according to a program preset in the distance measuring device and displaying, storing and sending data. The portable earth surface roughness measuring instrument disclosed by the invention has a simple mechanical structure, low cost and high measurement accuracy, is light, handy and portable and can be applied to measurement on the earth surface roughness of the lower cushion surface in agriculture, soil science, weather and climate predication, geology, microwave remote sensing and other fields.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-dimensional radial imaging method for mirror image synthetic aperture
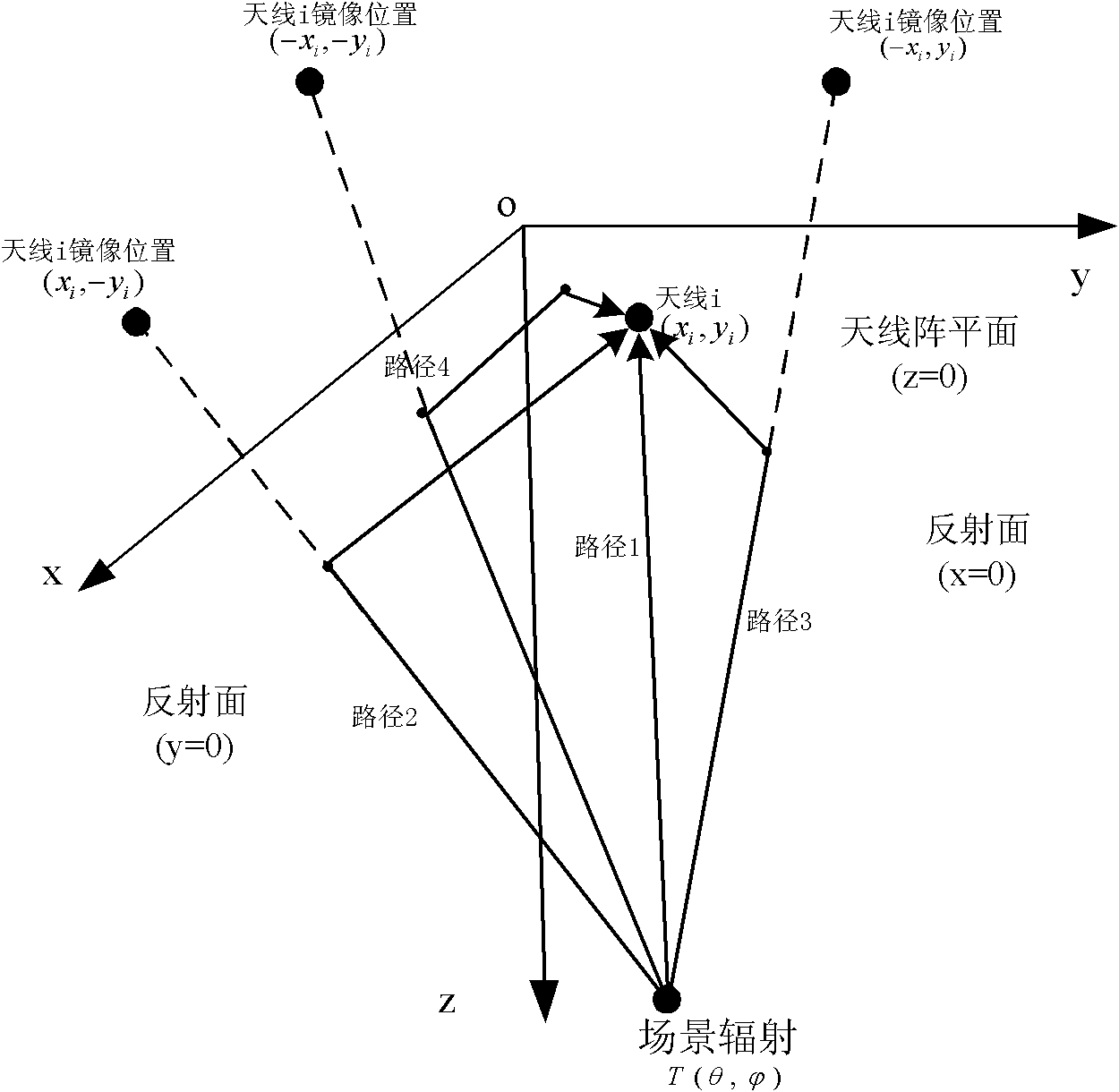
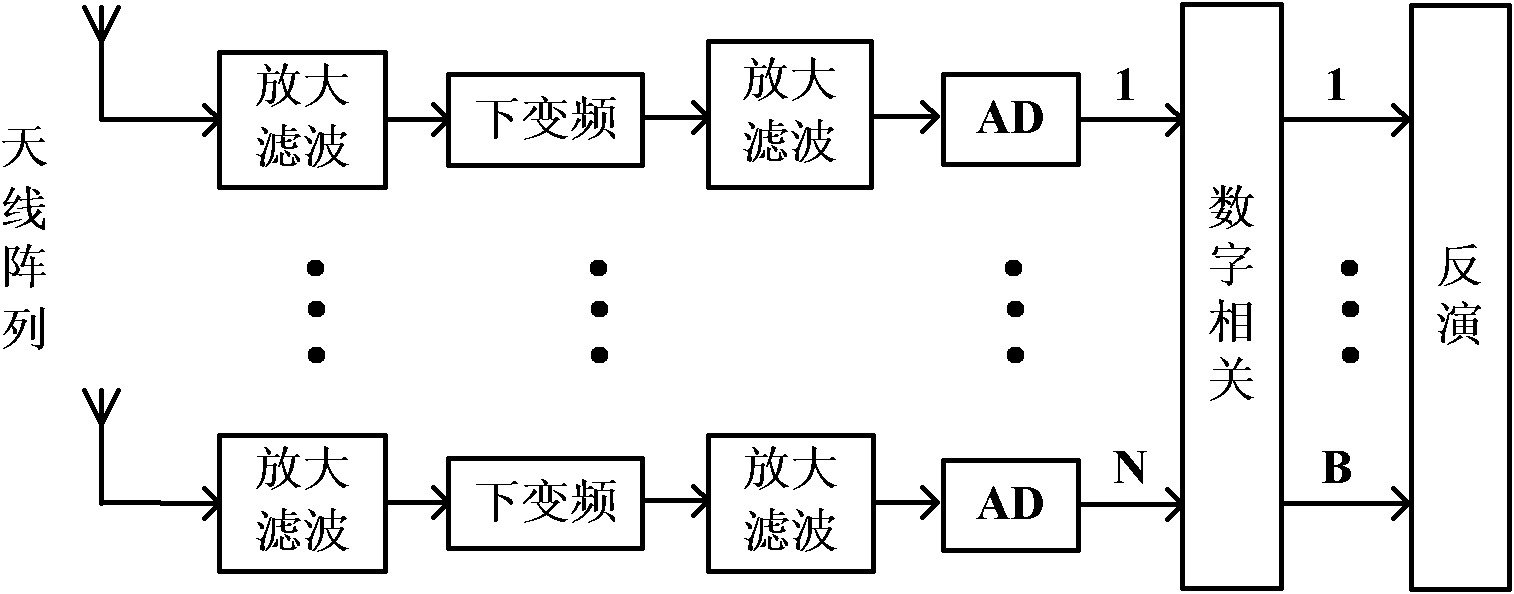
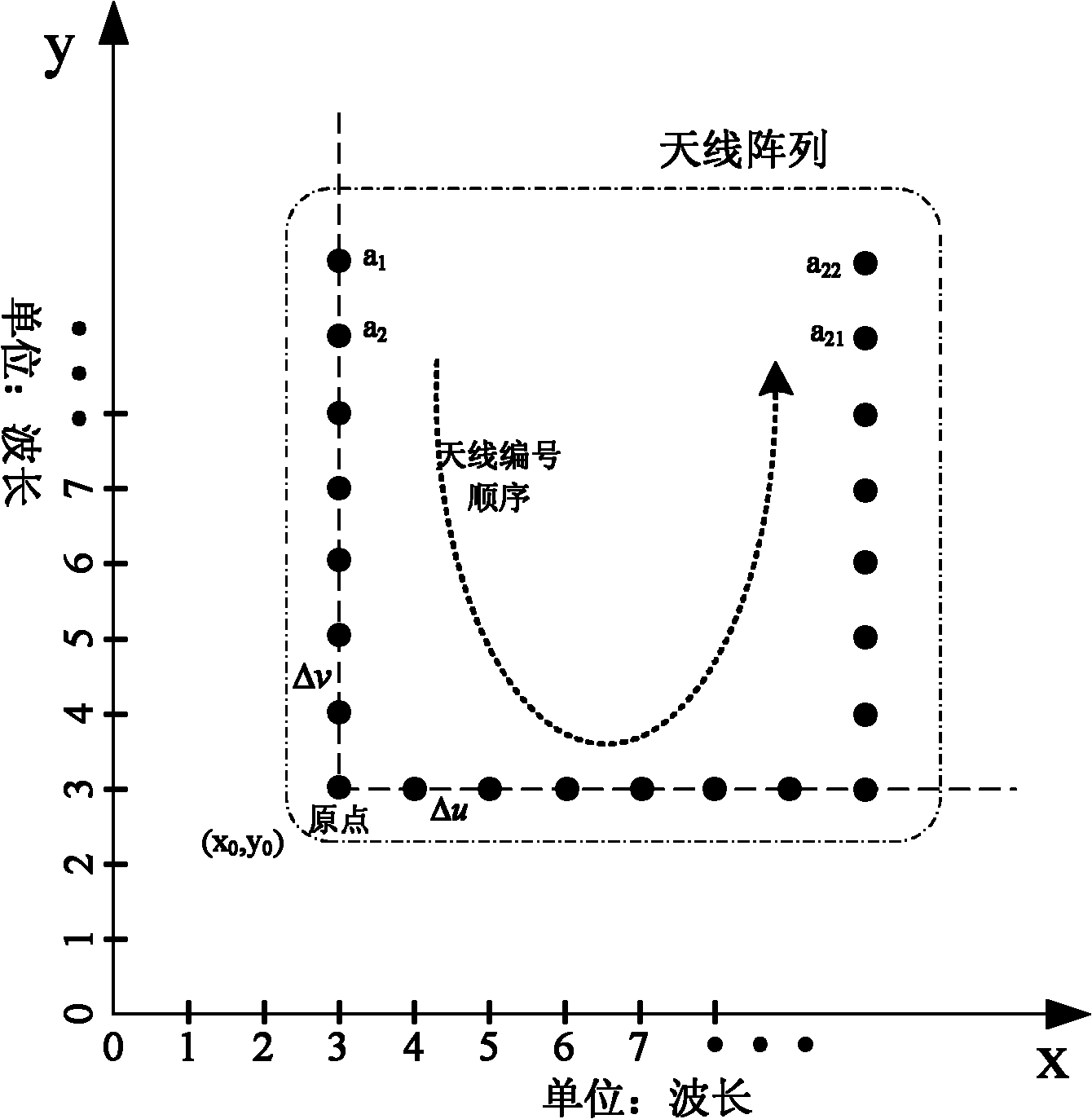
The invention belongs to the technical field of microwave remote sensing and probing, and discloses a two-dimensional radial imaging method. An imaging system consists of an antenna array and two reflecting surfaces. By measuring related output of all antennas, the cosine visibility is solved by solving linear equations associated with the related output and the cosine visibility, and then brightness and temperature distribution of a scene is reestablished by inverse cosine transform. By the imaging method, high system resolution can be obtained by using a small number of antennas and a simple receiver structure.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
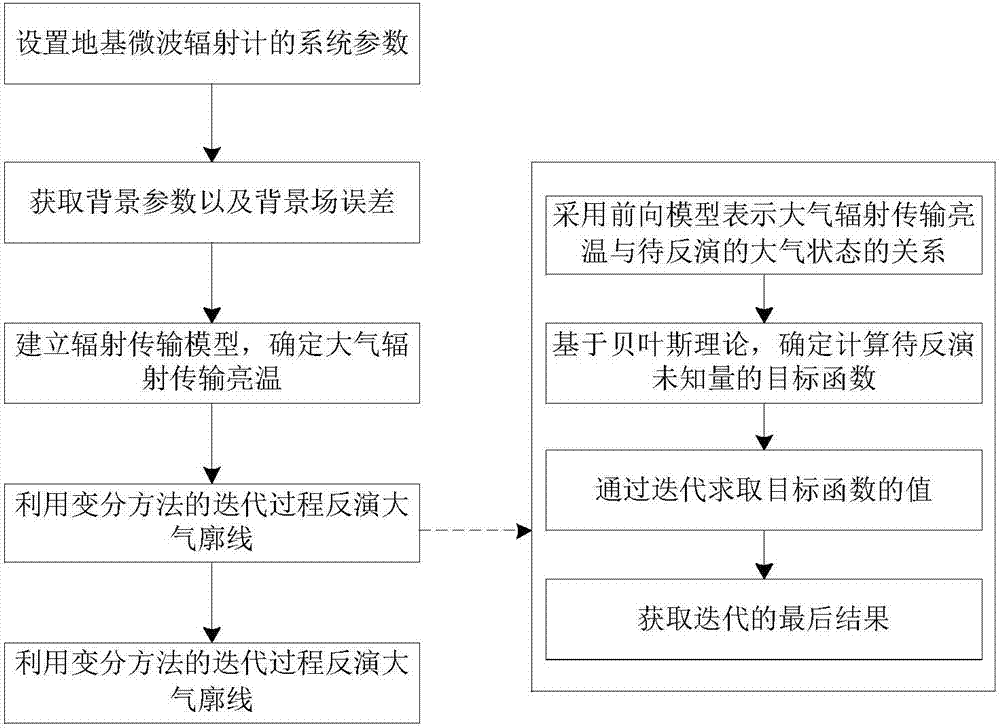
Atmosphere profile inversion method based on foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer
InactiveCN103792538AAdaptableAccurate calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationBrightness temperatureMicrowave radiometer
The invention provides an atmosphere profile inversion method based on a foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, and belongs to the technical field of microwave remote sensing. The atmosphere profile inversion method based on the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer comprises the following steps of setting system parameters of the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, acquiring background parameters and background field errors, establishing a radiation transfer model, determining atmospheric radiation transmission brightness temperature, and inverting an atmosphere profile by using the iterative process of a variational method. Through the utilization of the atmosphere profile inversion method based on the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, the accurately inverted atmosphere profile can be obtained through the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, and the atmosphere profile inversion method is especially suitable for multi-channel radiometers and detection situations of insufficient prior data, enables a large amount of frequency band information provided by the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer to be used completely, and has strong adaptability and small detection errors.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Microwave remote sensing soil moisture monitoring system and method thereof
InactiveCN101865909AReduce volumeReduce weightEarth material testingRadio transmissionData treatmentEarth surface
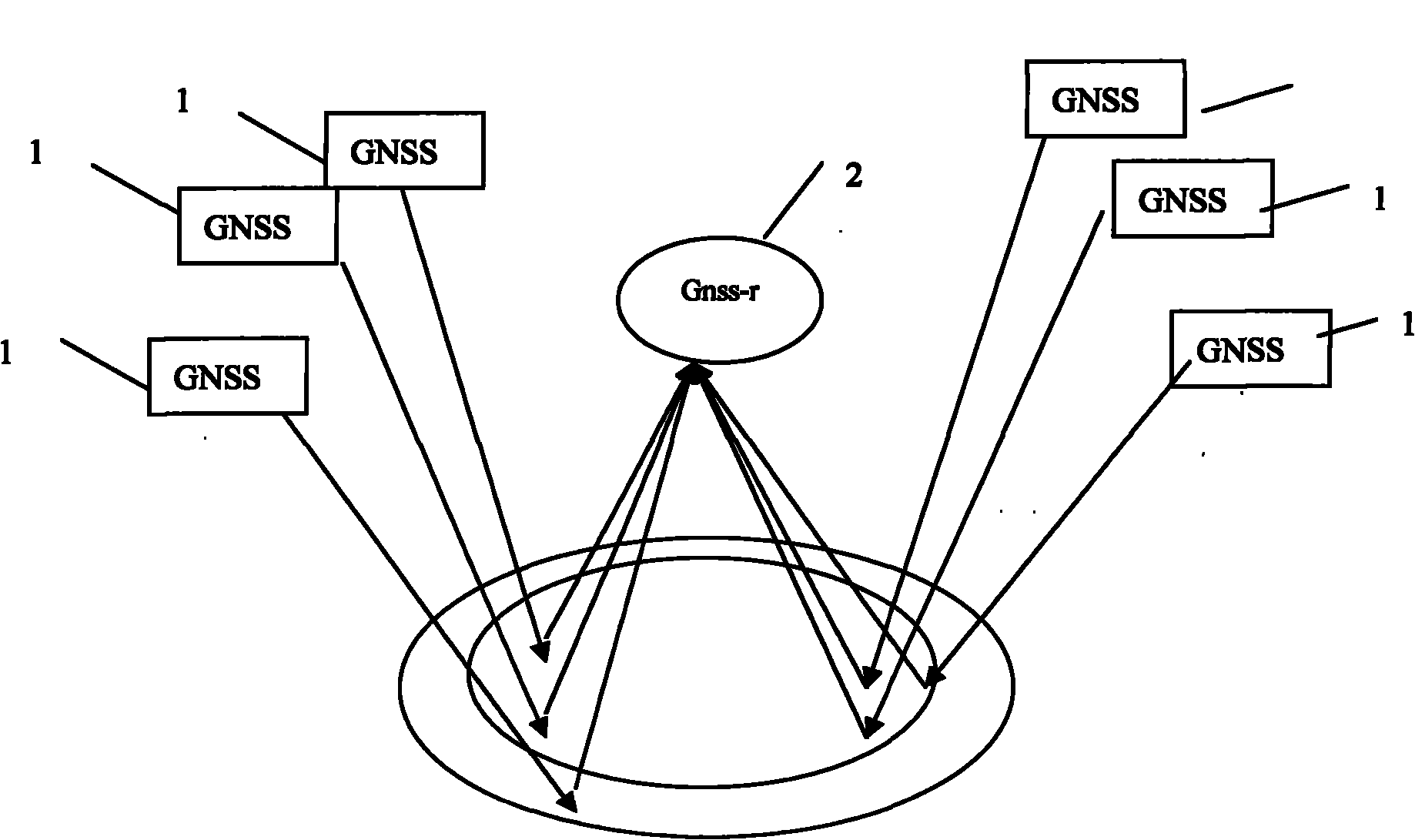
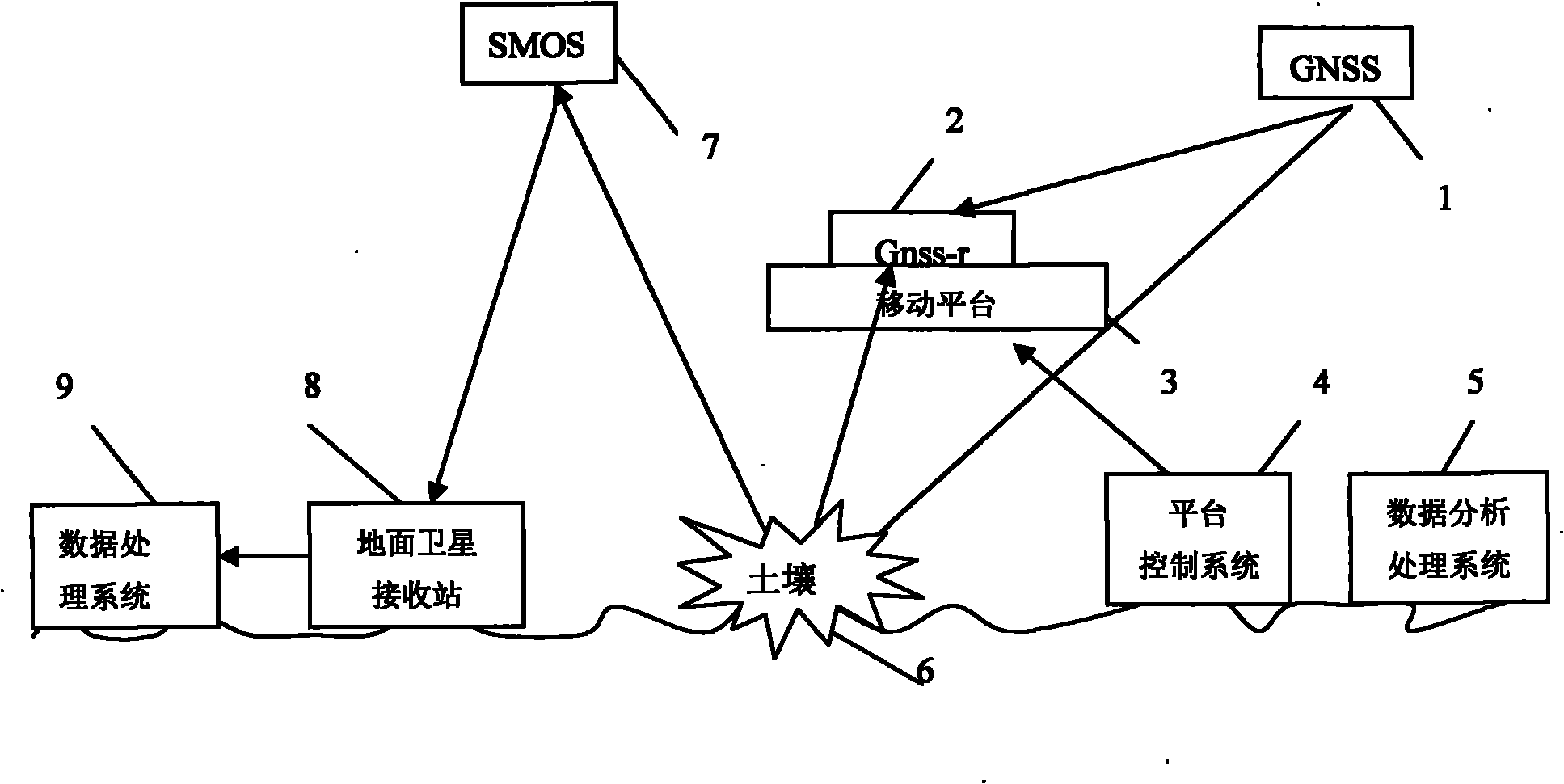
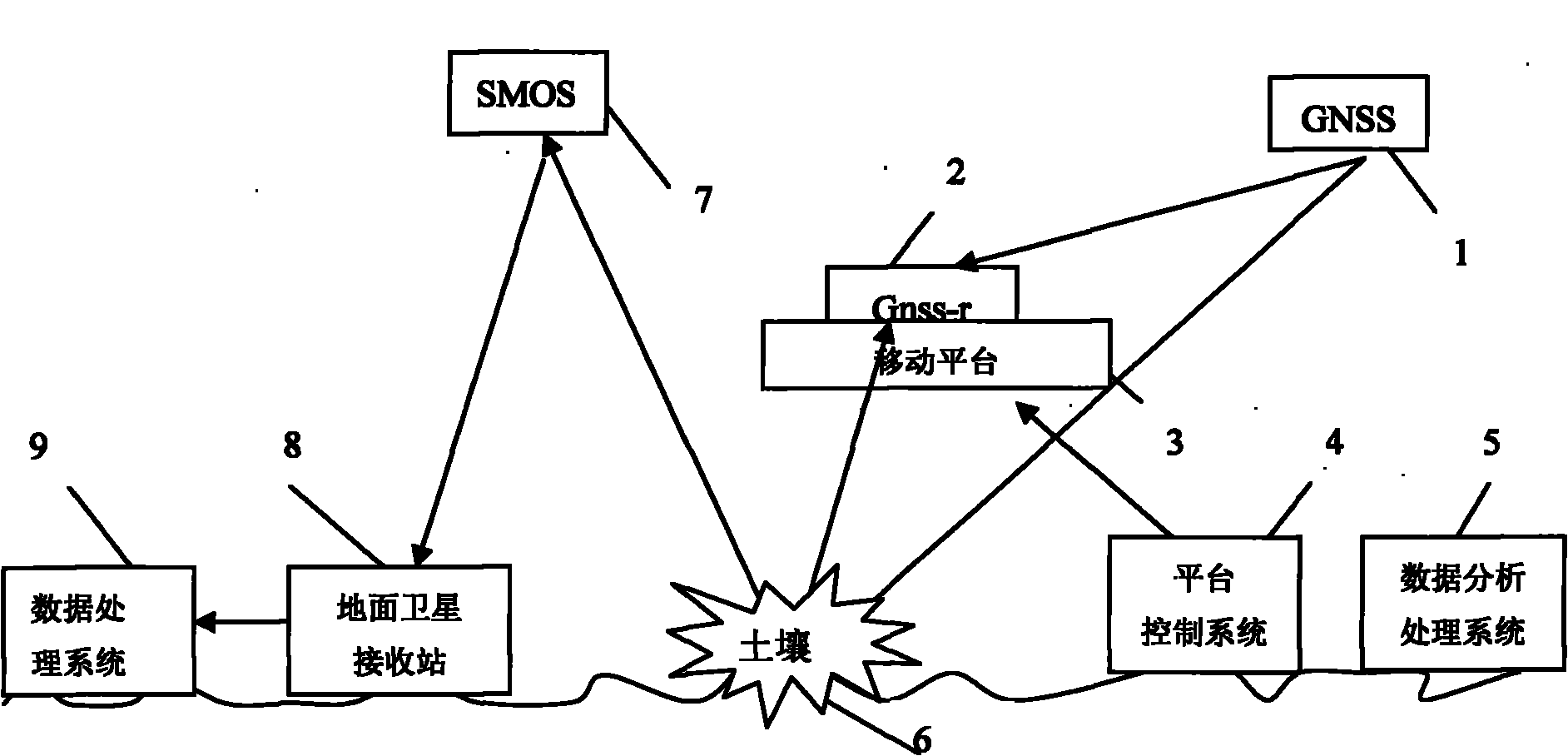
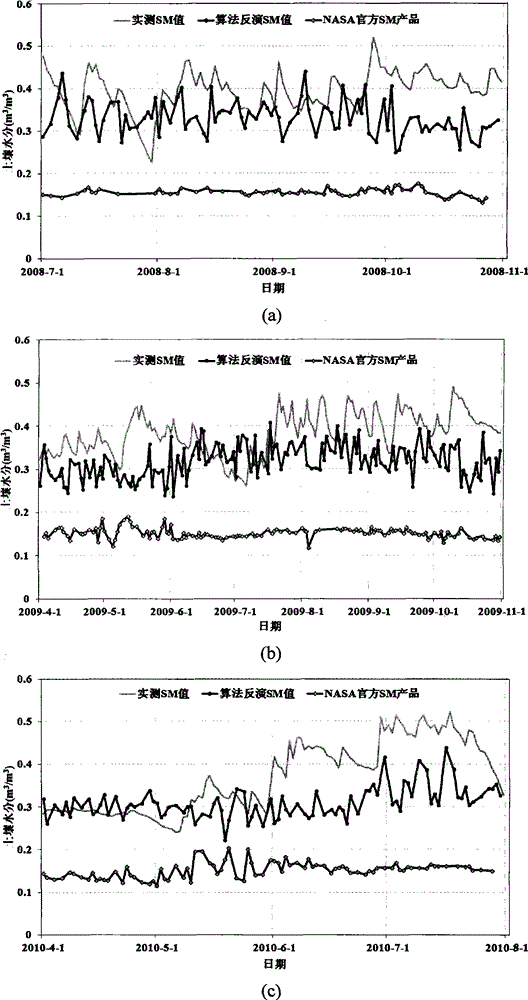
The invention discloses a microwave remote sensing soil moisture monitoring system and a method thereof. The system comprises a soil moisture and ocean salinity (SMOS) satellite, a ground satellite receiving station, a data processing system, a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signal source, a global navigation satellite system-reflection (GNSS-R) receiver, a mobile platform and a platform control system, wherein the SMOS satellite passively receives an L-band microwave signal transmitted by the earth surface, processes the signal through the data processing system and transmits the processed signal to a data analysis processing system; the GNSS-R receiver receives a GNSS direct signal and a forward scattered signal which is reflected by the ground and contains ground object information, and transmits the two signals to the data analysis processing system; and the data analysis processing system performs precision evaluation and inversion algorithm verification on soil moisture information. The ground real-time synchronous data acquired by the GNSS-R receiver is applied to precision evaluation and inversion algorithm verification of an SMOS soil moisture model of a passive microwave sensor so as to realize multi-scale and active and passive combined microwave remote sensing soil moisture monitoring.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
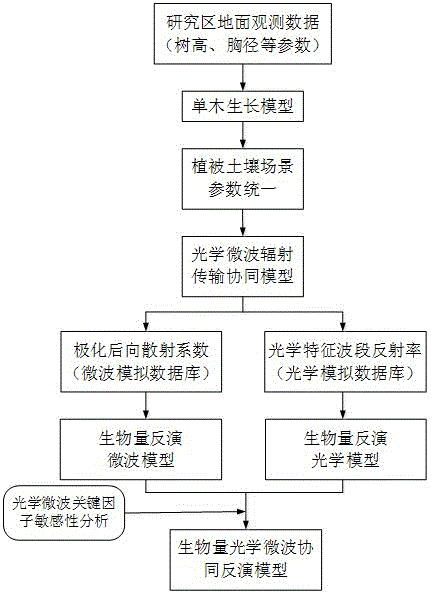
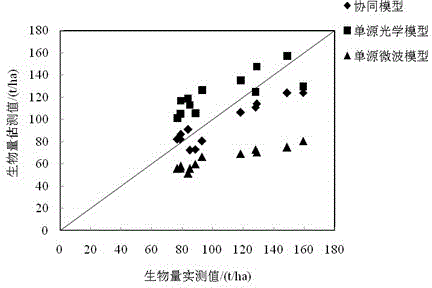
Forest biomass amount retrieval method based on collaboration of optical reflection model and microwave scattering model
ActiveCN104483271AReflect the complementary effectHigh precisionMaterial analysis using microwave meansMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical reflectionGround frost
The invention provides a forest biomass amount retrieval method based on collaboration of an optical reflection model and a microwave scattering model. The forest biomass amount retrieval method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing an optical-microwave radiation transmission collaborative model by comparing the difference between the optical reflection model and the microwave scattering model; 2) establishing an optical bidirectional reflection and microwave back scattering characteristic databank and a corresponding over-ground forest biomass parameter bank of a forest based on an individual growth model and the optical-microwave radiation transmission collaborative model; 3) respectively establishing a unisource optical model and a unisource microwave model for biomass retrieval based on an optical-microwave collaborative simulation databank; 4) through sensitivity analysis on optical and microwave key factors, confirming respective weights of the optical and microwave data in the collaborative model, thereby establishing an optical-microwave collaborative model for AGB retrieval. According to the forest biomass amount retrieval method, optical remote sensing data and microwave remote sensing data are combined, the advantages of the optical remote sensing data and the microwave remote sensing data in biomass retrieval are put into full play sufficiently, and the quantitative retrieval precision of the over-ground frost biomass amount is effectively improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Soil moisture inversion method of mono-frequency microwave radiometer
InactiveCN103149220ANo region dependenciesMoisture content investigation using microwavesLine printerMicrowave radiometer
The invention provides a soil moisture inversion method of a mono-frequency microwave radiometer and belongs to the field of microwave remote sensing. The soil moisture inversion method of the mono-frequency microwave radiometer is neither a multi-parameter simultaneous inversion method, nor an experience regression method, but uses the minimum auxiliary data, and the soil moisture is obtained by the single-parameter inversion method. According to the soil moisture inversion method of the mono-frequency microwave radiometer, the problems existing in the multi-parameter inversion of multiple solutions and huge calculation amount are solved, and the inversion error due to the fact that roughness is set to be a definite value in line printer remover (LPRM) algorithm is also avoided. Meanwhile compared with a science clubs of America (SCA) algorithm which excessively dependent on auxiliary data, the auxiliary data used by the soil moisture inversion method of the mono-frequency microwave radiometer are only soil texture data which are globally and freely shared, and the business application difficulty of the soil moisture inversion is greatly reduced.
Owner:CENT FOR EARTH OBSERVATION & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Soil moisture monitoring microwave radiometer method
InactiveCN1847832AIncrease dependenceMoisture content investigation using microwavesDielectricMoisture distribution
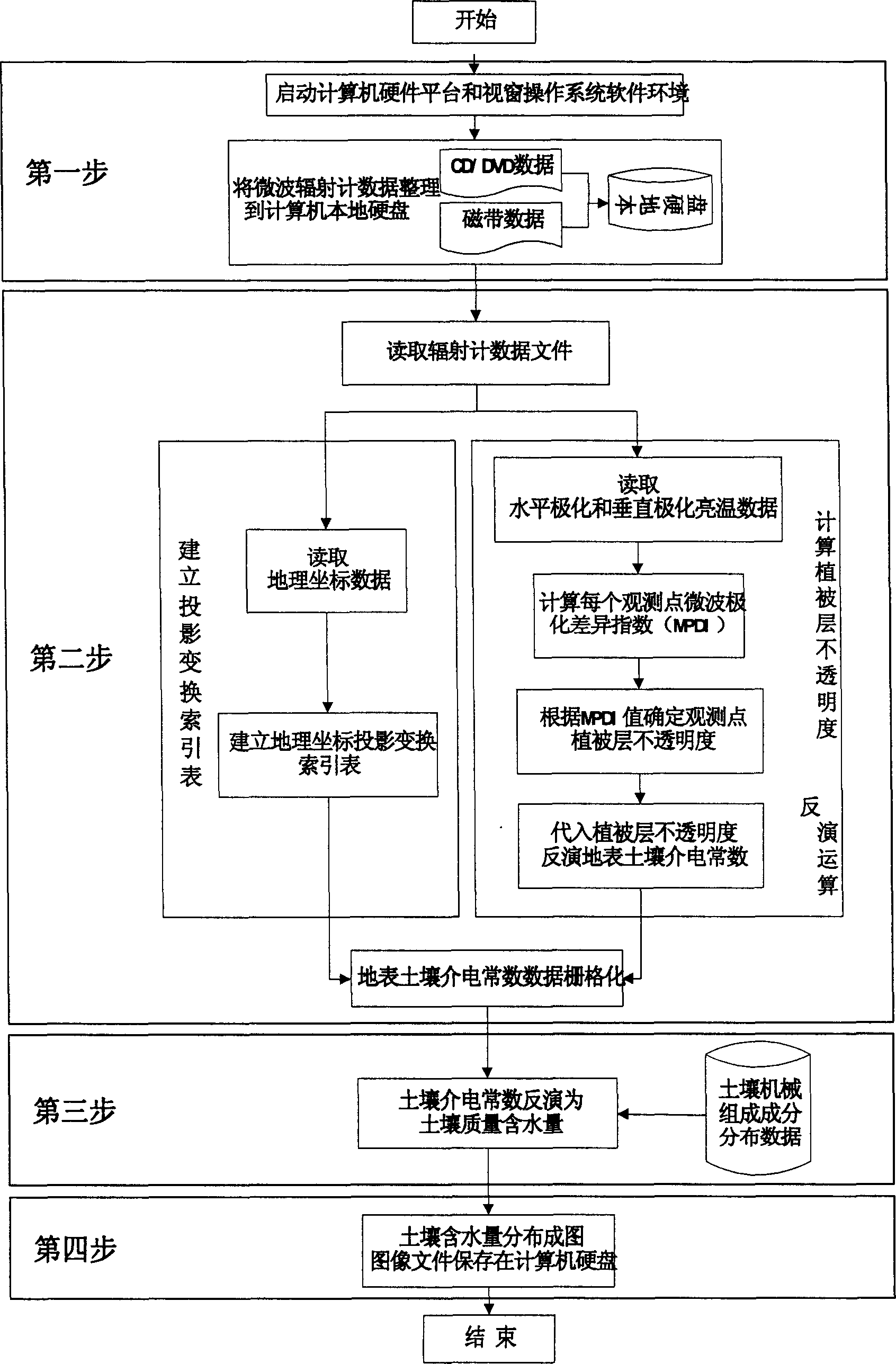
The present invention relates to the application of microwave remote sensing technology, and is especially microwave radiometer method of monitoring soil moisture. The method includes the following steps: 1. preparing operation environment and radiometer data; 2. inverting to obtain field surface dielectric constant of the observed point and forming grids; 3. calculating the soil moisture based on the dielectric constant; and 4. mapping soil moisture distribution and saving as common graph format.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ground vacuum calibration test method of satellite-borne passive microwave remote sensing instrument by use of three calibration sources
InactiveCN102519513AImprove on-orbit quantitative applicationsImprove calibration accuracyThermometer testing/calibrationSensing dataTemperature control
The invention discloses a periodical two-point calibration test method using three calibration sources. By adopting temperature control measures, the passive microwave remote sensing instrument is controlled to be set to work at different working temperatures, and the input / output response curves of the passive microwave remote sensing instrument at different ambient temperatures are obtained; by analyzing the test data, the basic performance parameter and calibration precision of the passive microwave remote sensing instrument working at different temperature conditions are obtained; and therefore, high-precision vacuum microwave calibration test is performed on the ground for the satellite-borne passive microwave remote sensing instrument, and the technical difficulty in the ground vacuum calibration test of the satellite-borne passive microwave remote sensing instrument of our country is solved. The test method has high calibration precision (higher than 1k), estimates the reality of the basic performance of the passive microwave remote sensing instrument, obtains the calibration parameters required by the quantitative application of the on-track remote sensing data of the passive microwave remote sensing instrument, and improves the beneficial effects of the passive microwave remote sensing instrument in on-track quantitative application.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
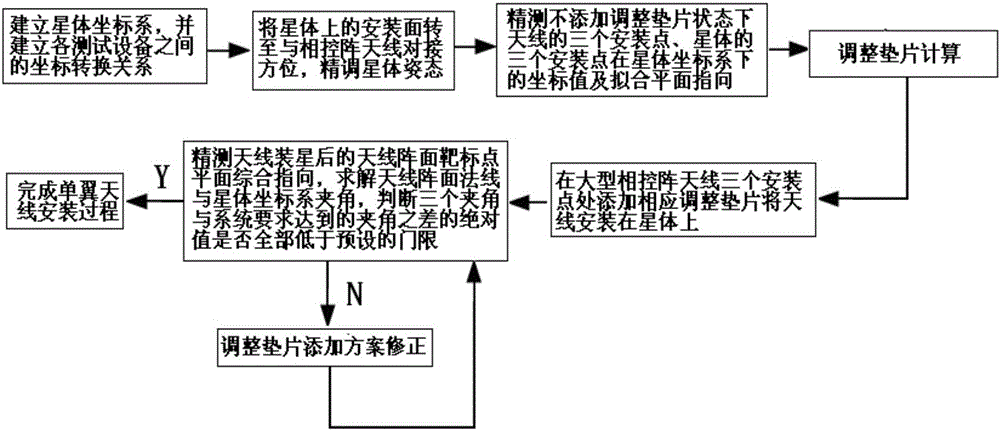
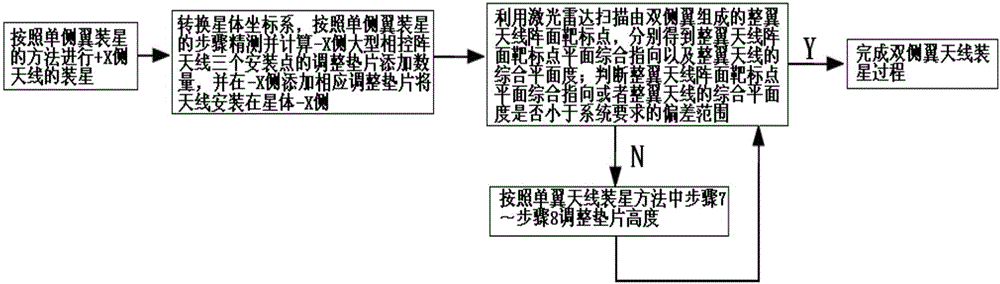
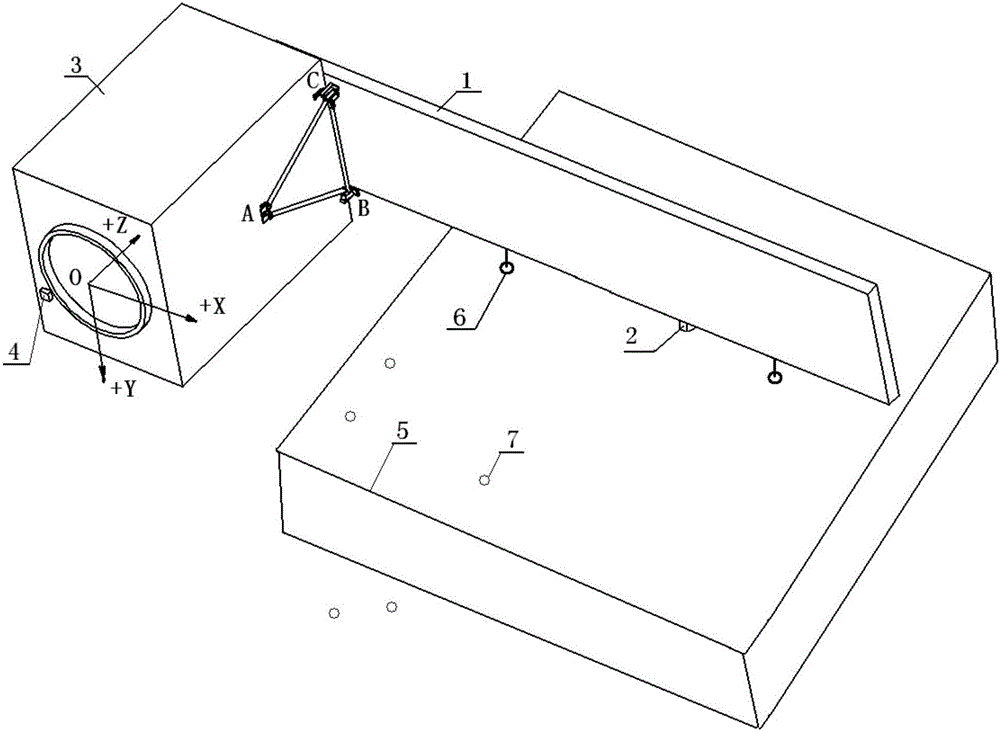
Large phased array antenna accurate installation method based on mathematical modeling
ActiveCN106229605AStrong engineering feasibilityImprove installation efficiencyAntenna supports/mountingsSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a large phased array antenna accurate installation method based on mathematical modeling, is suitable for single-wing or double-wing large phased array antenna accurate installation and adjustment and measurement of large size and high requirement of installation accuracy, and belongs to the field of microwave remote sensing general installation design. The method comprises the steps that (1) a star coordinate system is established; (2) fine adjustment of the star attitude is performed; (3) the coordinates of the installation points on the antenna and the start are measured; (4) a mathematical model is established and a gasket is calculated and adjusted; (5) the gasket is additionally arranged to install the antenna according to the calculation result; and (6) the planar integrated direction is measured and the gasket is corrected. The problems of the influence of repeated trial installation and adjustment of the large phased array antenna on the antenna installation accuracy and efficiency can be avoided so that the method has the advantages that project implementation is high, the installing accuracy can be easily guaranteed, the frequency of installation and adjustment and accurate measurement can be reduced and the installation efficiency can be enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
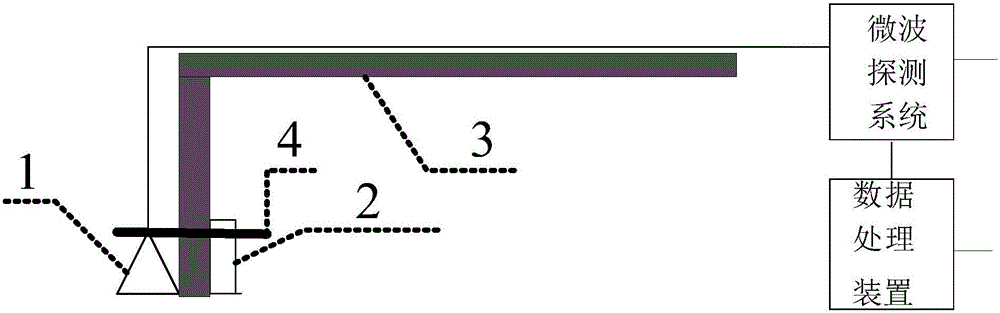
Microwave remote sensing soil moisture monitoring system and monitoring method thereof
InactiveCN106018439ANot limited by observation frequencySimple working modelMoisture content investigation using microwavesEngineeringData treatment
The invention relates to a microwave remote sensing soil moisture monitoring system and a monitoring method thereof. The monitoring system comprises a detection arm, a signal receiving antenna and a thermal infrared thermometer carried on the detection arm, a microwave detection system electrically connected with the signal receiving antenna and the thermal infrared thermometer, and a data processing device electrically connected with the microwave detection system. According to the monitoring method, a data analysis treatment system in the data treatment device performs the real-time synchronous treatment according to brightness temperature data acquired by the microwave detection system and physical temperature data on the surface of soil obtained by the thermal infrared thermometer to accurately evaluate soil moisture information. The microwave remote sensing soil moisture monitoring system and the monitoring method thereof provided by the invention obtains soil microwave radiation signals by using a passive way, has a simple working model, high precision, and high efficiency, and is not limited by the observation frequency.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
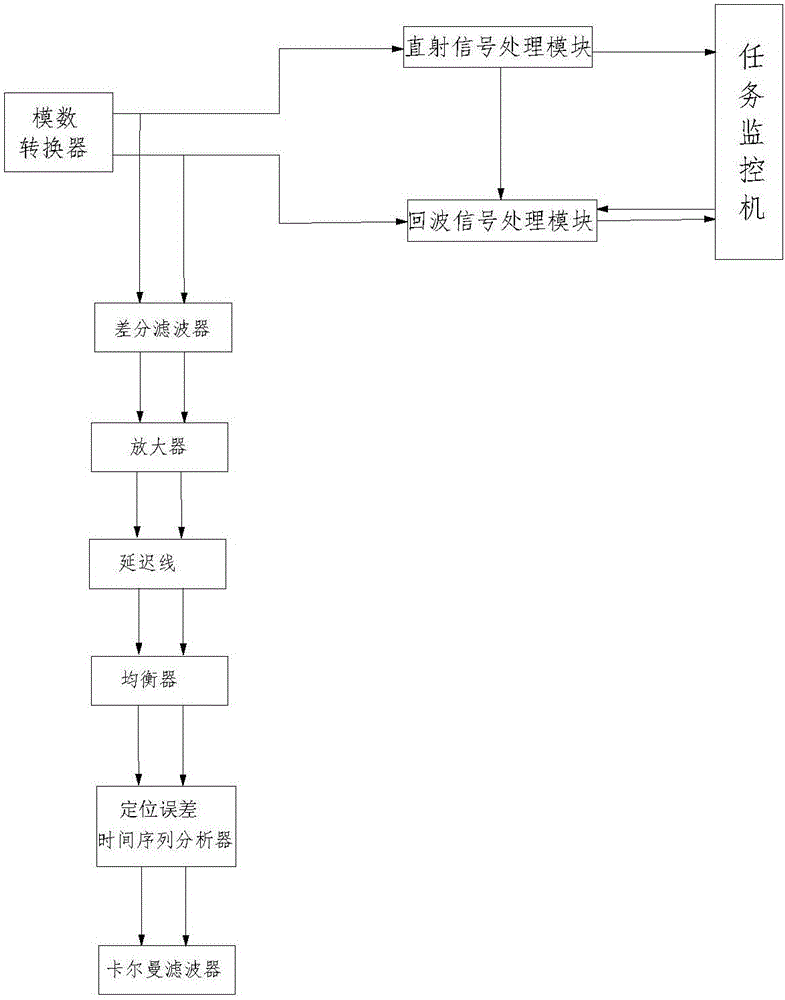
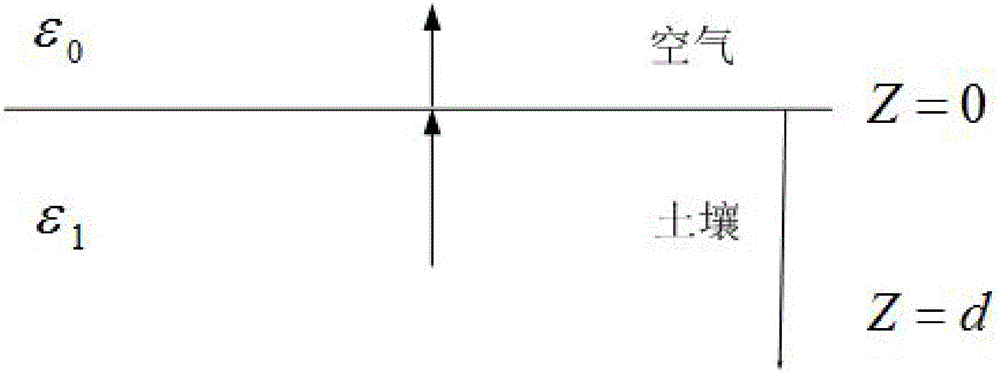
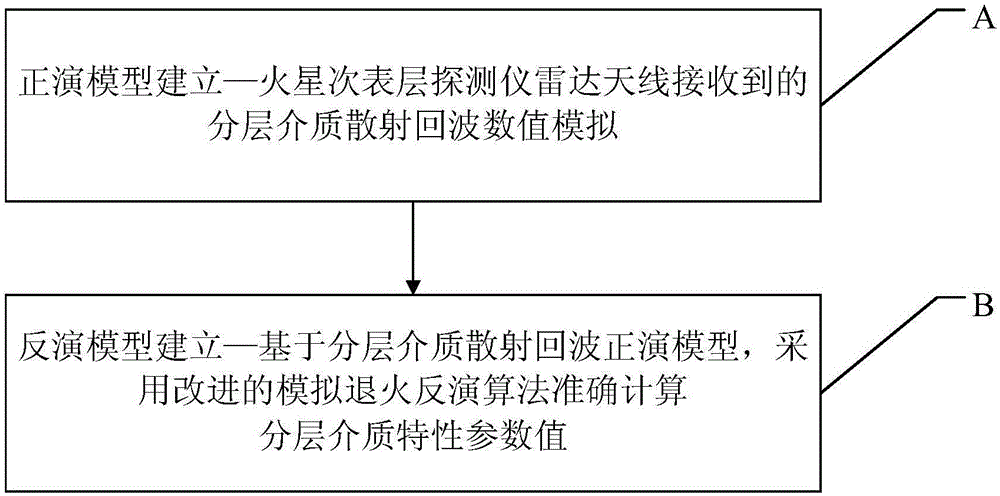
Star subsurface remote sensing detection radar echo simulation and parameter inversion method
InactiveCN105093203AAccurate estimation of electrical characteristic parameter valuesAccurate estimateWave based measurement systemsRough surfaceRadar detection
The invention discloses a star subsurface remote sensing detection radar echo simulation and parameter inversion method based on microwave remote sensing. Scattering echo signals accurately simulating multilayer layered rough surfaces such as the surface and the subsurface and the like of a star are utilized for establishment of a forward model, and according to accurately simulated radar detection echo signals, actually observed radar echo signals are interpreted. According to the established layered medium scattering echo forward model, layered medium characteristic parameters of the star is accurately calculated by use of an improved inversion algorithm.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
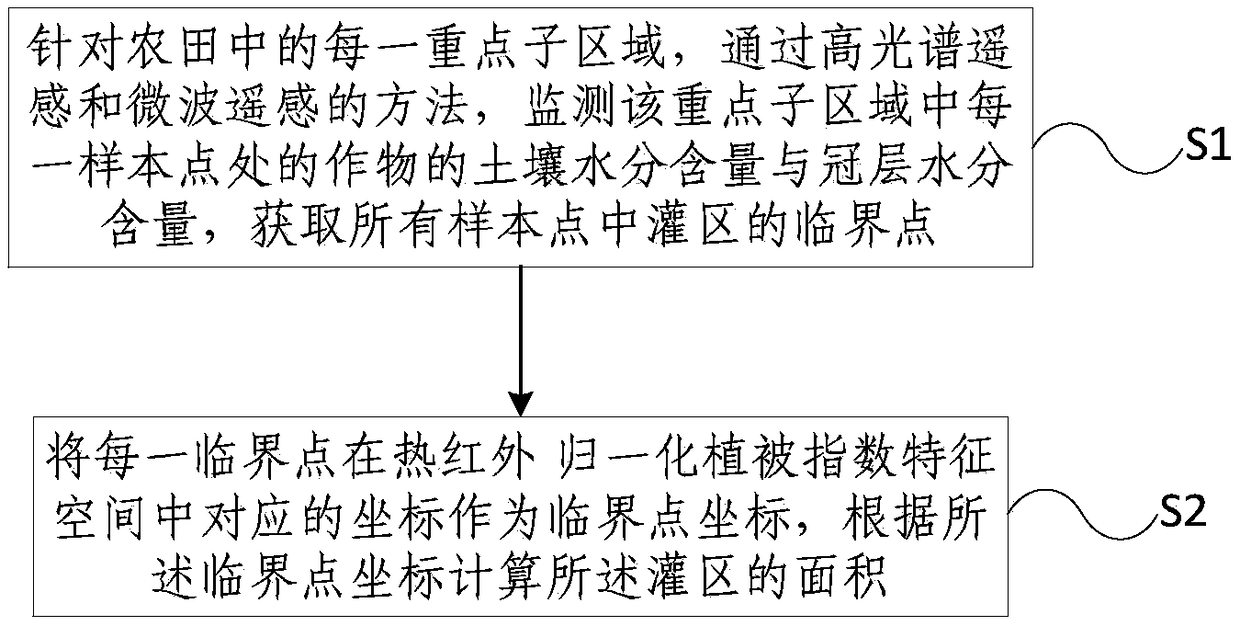
Method and system for farmland irrigation district area remote sensing extraction
ActiveCN108955620AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyColor/spectral properties measurementsMoisture content investigation using microwavesVegetation IndexIrrigation district
The present invention provides a method for farmland irrigation district area remote sensing extraction. The method comprises the steps of: for each key sub area in a farmland, monitoring soil water content and canopy water content of crops at each sampling point in the key sub areas through adoption of a method of a high hyperspectral remote sensing and microwave remote sensing, and obtaining critical points of an irrigation district in all the sampling points; and taking corresponding coordinates of each critical point in a thermal infrared-normalized differential vegetation index feature space as critical point coordinates, and calculating the area of the irrigation district according to the coordinates of the critical points. The method and the system perform remote sensing images to collect data to calculate the normalized differential vegetation index, the soil water content and the canopy water content of the crops to obtain the critical points of the irrigation district in thefarmland and search the coordinate points corresponding to the critical points in the thermal infrared-normalized differential vegetation index feature space so as to divide the range of the irrigation district in the feature space, obtain the area of the irrigation district through calculation of the areas of images elements corresponding to the irrigation district and improve the precision and the efficiency of the irrigation district area extraction method in the farmland.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method for obtaining artificial target information from target parametric inversion model under forest cover
The invention relates to a method for acquiring man-made target information by a target parameter inverse model covered by a forest, which belongs to the field of microwave remote sensing. The method solves the problem that the prior PolInSAR image parameter inversion can only acquire target information of natural scene, and can not acquire man-made target related information. The method can acquire optimized coherent coefficient through performing polarized interfere coherent optimized processing on PolInSAR image data, utilize the known data to establish a scattering model of a man-made target covered by the forest, and acquire related parameters of natural target information and the man-made target information such as vegetation height, extinction coefficient, as well as phase, man-made target height and target amplitude ratio and so on which are related to terrain in the inputted PolInSAR image data through the model. The acquired information can provide basic data for further analysis on a researched area. The method widens the application range of the PolInSAR technology, and can be applied in the fields of forest ecologic parameter detection and man-made target detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Super-resolution reestablishment method for microwave remote sensing image based on SRCNN (Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network)
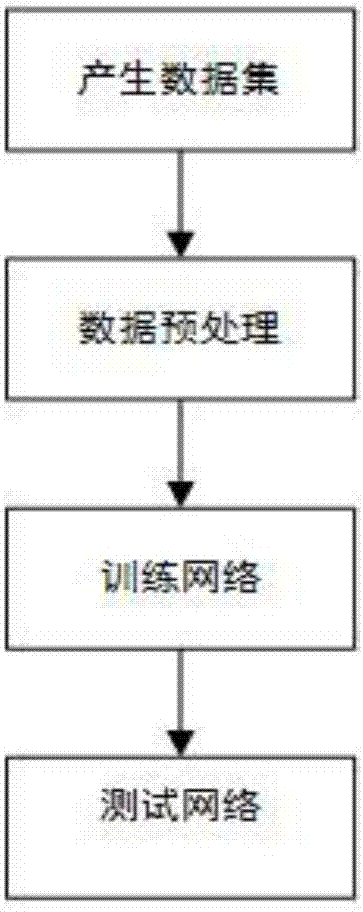
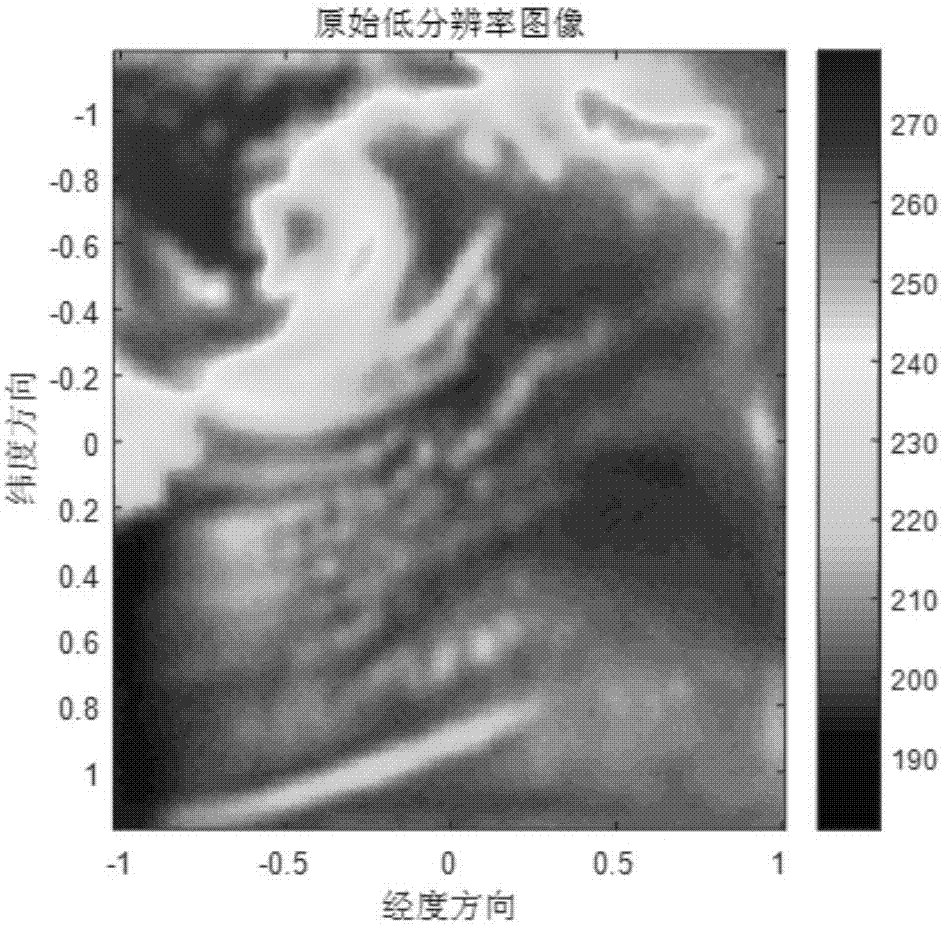
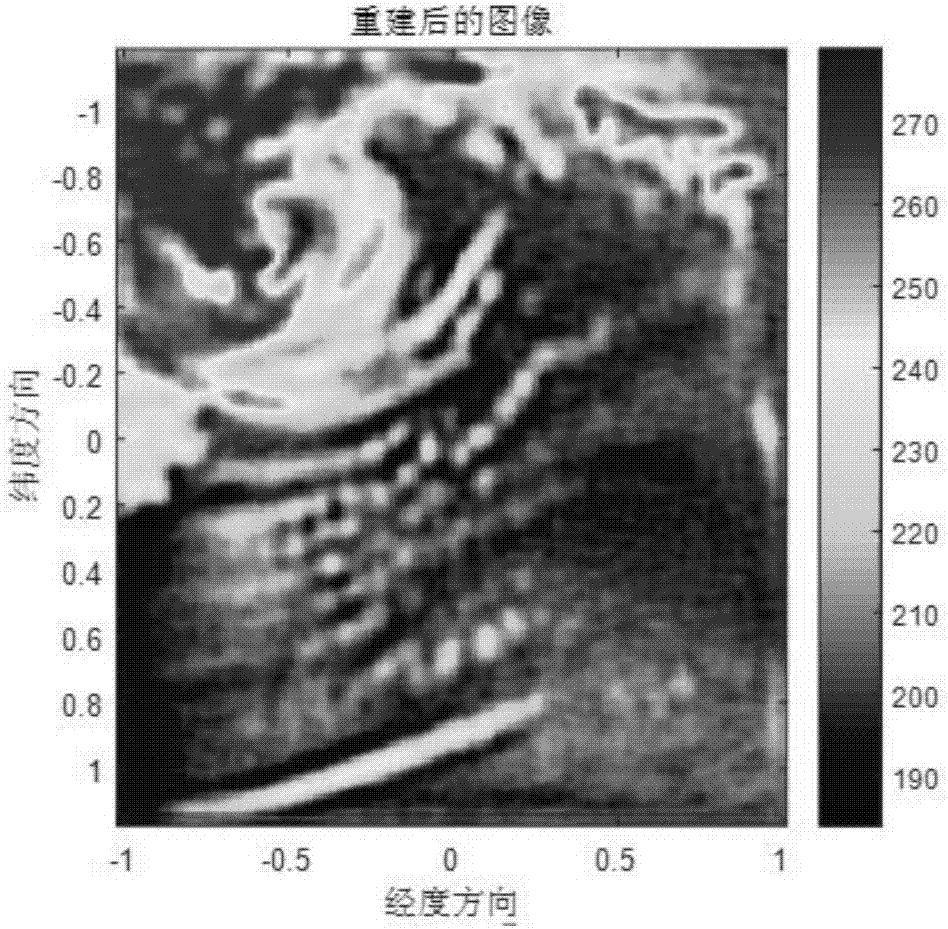
InactiveCN108009989AReduce computational complexityImage enhancementImage analysisComputation complexityData set
The invention discloses a super-resolution reestablishment method for a microwave remote sensing image based on an SRCNN (Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network) and belongs to the technology of microwave remote sensing and detection. The method comprises the steps of firstly simulating a microwave remote sensing flow, and forwardly producing a high-resolution microwave remote sensing imageTB and a low-resolution microwave remote sensing image TA to form a data set; then preprocessing the data set to generate an SRCNN training set; constructing a five-layer depth convolutional neural network based on the SRCNN training set; and finally inputting the to-be-processed low-resolution microwave remote sensing image to the constructed five-layer depth convolutional neural network, wherein the output of a fourth-layer of the depth convolutional neural network is the reestablished high-resolution microwave remote sensing image. With the super-resolution reestablishment method for the microwave remote sensing image based on the SRCNN, the calculation complexity in reestablishment can be effectively reduced, an accurate antenna pattern is not needed, the method is a novel microwave remote sensing image reestablishment method, and a brightness temperature image of an original scene can be efficiently reestablished in real time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ocean internal wave velocity monitoring method
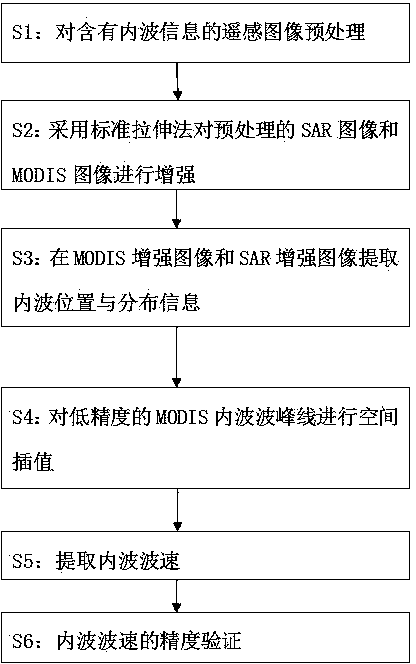
InactiveCN104268848AReduce mistakesImprove extraction accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage extractionData source
The invention relates to an ocean internal wave velocity monitoring method. The method particularly comprises the following steps that S1, remote sensing images comprising internal wave information are preprocessed; S2, a preprocessed SAR image and a preprocessed MODIS image are enhanced through a standard tensile method; S3, the internal wave position and the distribution message are extracted from the enhanced MODIS image and the enhanced SAR image; S4, spatial interpolation is carried out on an MODIS internal wave crest line with low precision; S5, the internal wave velocity is extracted; S6, the precision of the internal wave velocity is verified. The ocean internal wave velocity monitoring method has the advantages that the internal wave velocity is extracted through the satellite microwave remote sensing image and the optical remote sensing image, the extraction precision is high, the cost is low, time and labor are saved, multiple data sources are provided, the spatial distribution of the internal wave velocity within a certain sea area can be obtained, and then research on the aspect of correlation between the internal wave velocity and environmental factors can be expanded.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
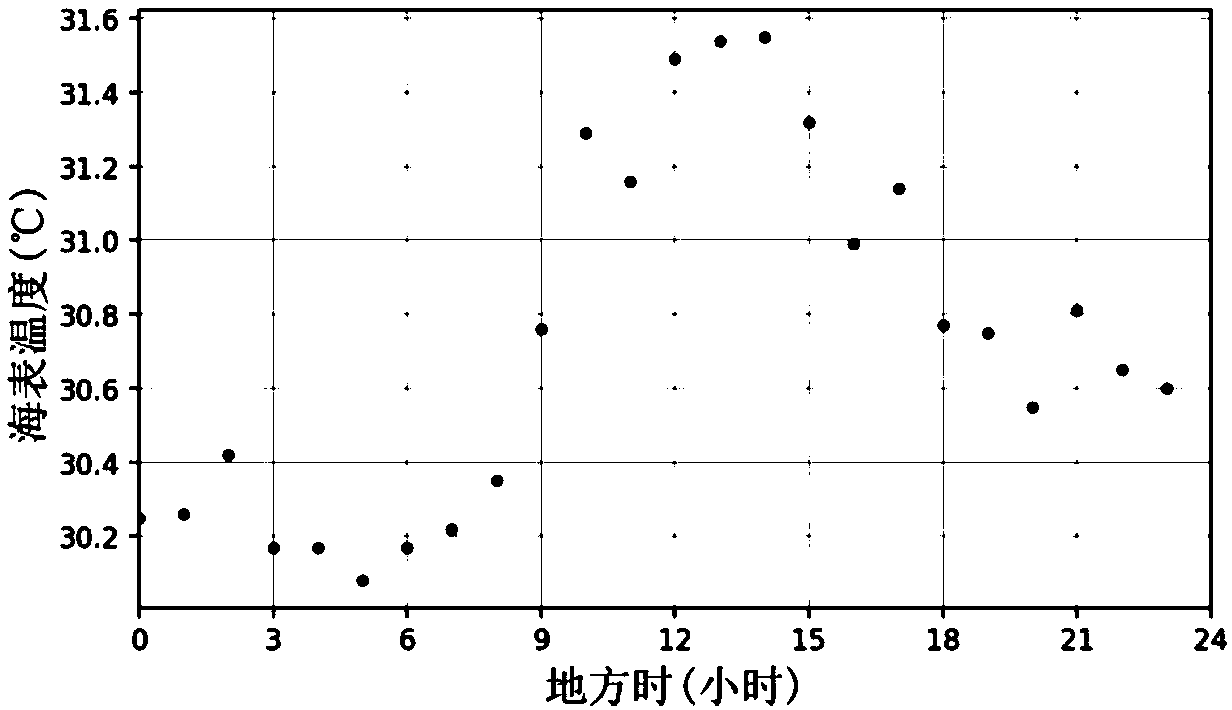
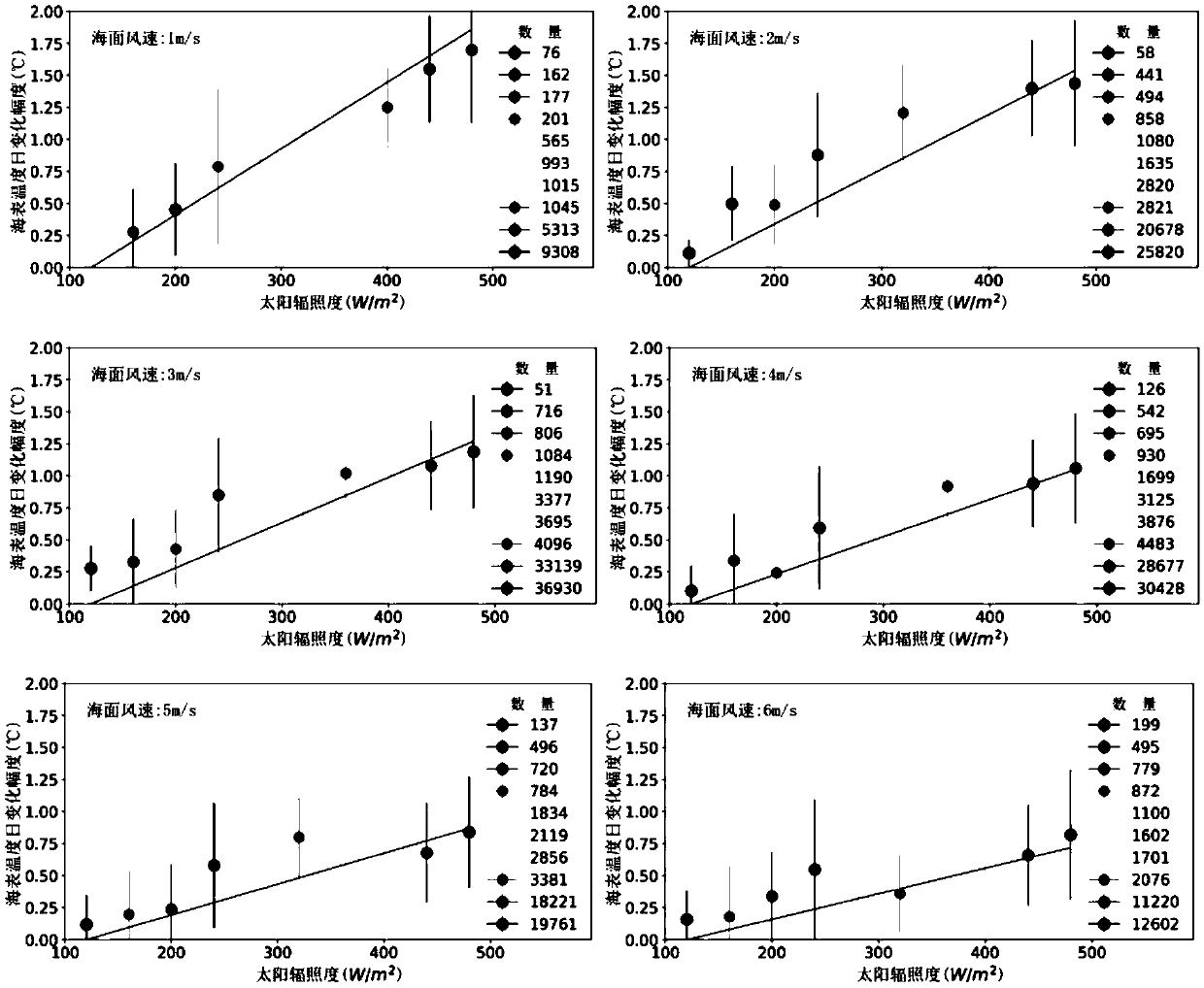
Sea surface temperature fusing method and system
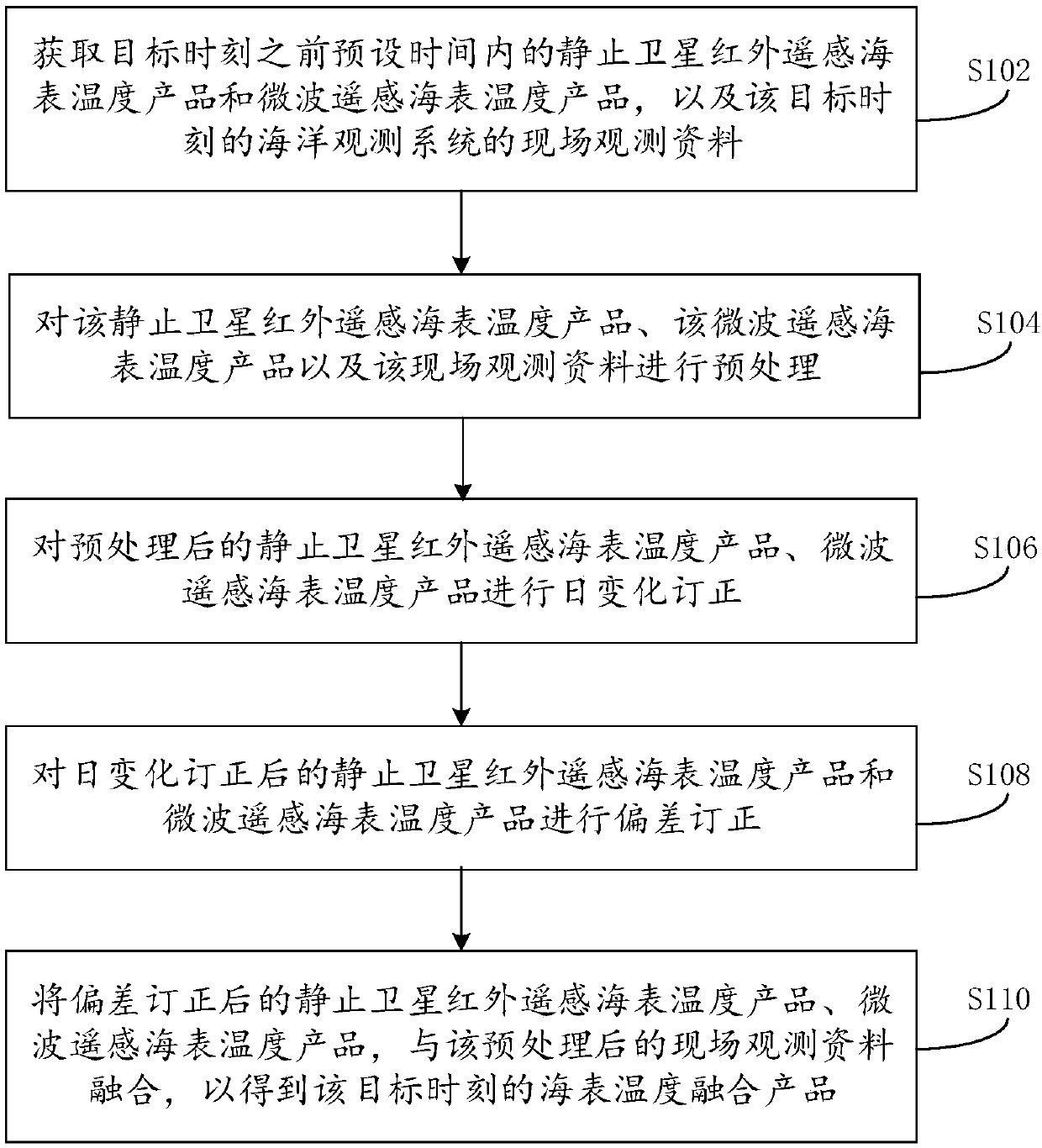
ActiveCN109668635AImprove space coverageImprove spatial resolutionSensing heat from liquidsObservation dataInfrared remote sensing
The invention provides a sea surface temperature fusing method and system, and relates to the technical field of sea information. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring stationary satellite infrared remote sensing and microwave remote sensing sea surface temperature products in preset time before a target moment and on-site observation data of a sea observation system at the target moment; preprocessing the sea surface temperature products and the on-site observation data; carrying out daily change correction on the preprocessed sea surface temperature products; carrying out deviation correction on the stationary satellite infrared remote sensing temperature products and the microwave remote sensing sea surface temperature products subjected to daily change correction; fusingthe stationary satellite infrared remote sensing temperature products and the microwave remote sensing sea surface temperature products subjected to daily change correction with the preprocessed on-site observation data, so as to obtain sea surface temperature fusing products at the target moment. The sea surface temperature fusing method and system of the embodiment of the invention are capable of obtaining the sea surface temperature fusing products with high time-space resolution, high space coverage degree, gradual time level and high accuracy.
Owner:中国人民解放军61741部队
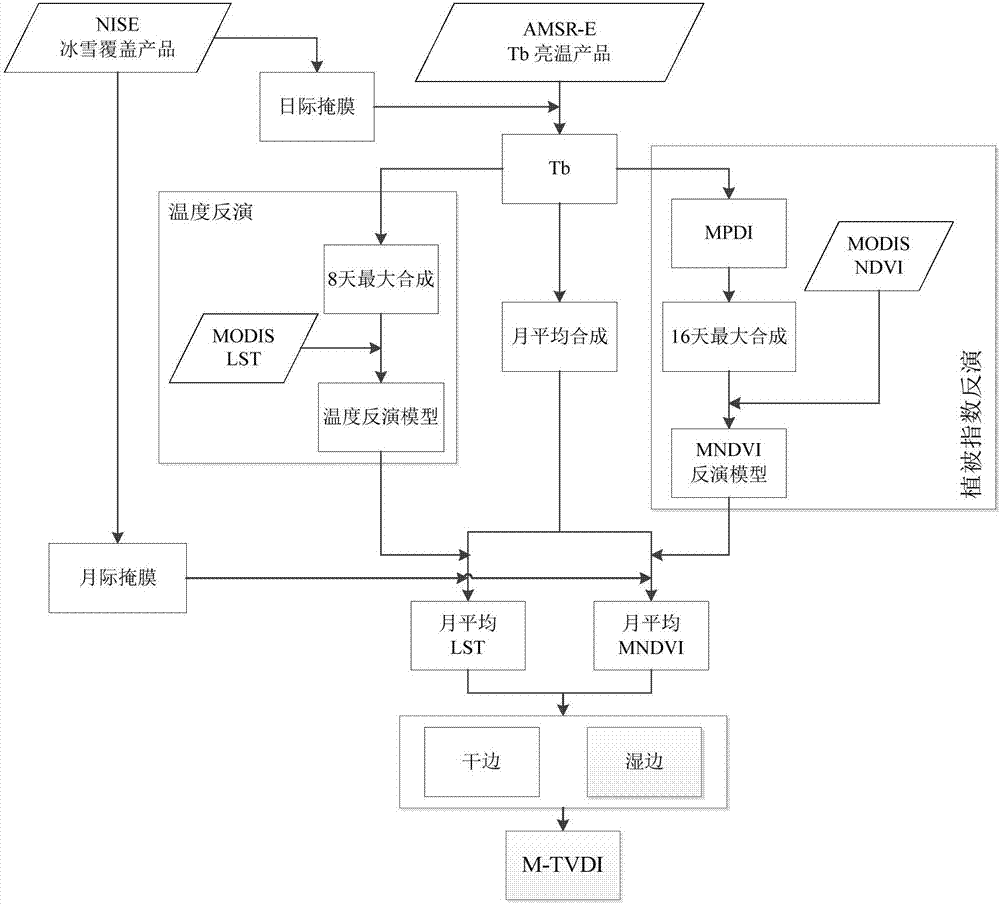
Drought index construction method based on passive microwave remote sensing
InactiveCN106897551AOvercomes vulnerability to weather conditionsInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsInfrared remote sensingVegetation Index
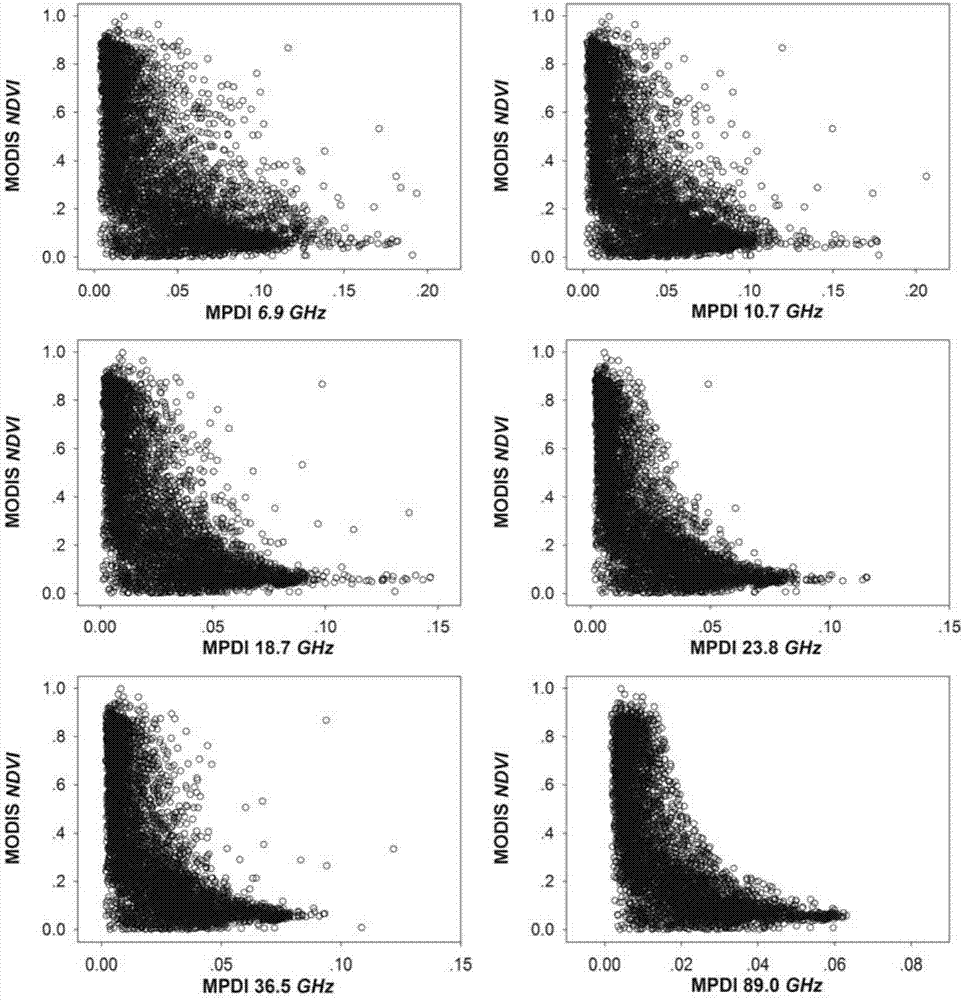
The invention discloses a drought index construction method based on passive microwave remote sensing. The method comprises the specific steps that an inter-diurnal mask and an inter-monthly mask are constructed, and influences of mixed pixels of edges of a glacier, a snow cover and a water body on AMSR-E data during temperature retrieval are eliminated; a land surface temperature retrieval model is constructed through 10.8GHHz and 89.0GHz vertical polarization channel Tb of AMSR-E and used for performing retrieval on land surface temperature, wherein Tb is brightness temperature data of passive microwave remote sensing; a microwave normalized difference vegetation index model is constructed based on a microwave polarization difference index (MPDI); a dry edge equation and a wet edge equation of an MTVDI model are constructed based on the established land surface temperature retrieval model and vegetation index model; and the MTVDI model is established to simulate and monitor drought throughout the country month by month. The method has the advantages that the defect that visible light / near-infrared remote sensing is liable to influences of meteorological conditions is effectively overcome, and a great improvement is made to a TVDI model.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Dual-channel simultaneous transmitting and receiving type Doppler polarization weather radar
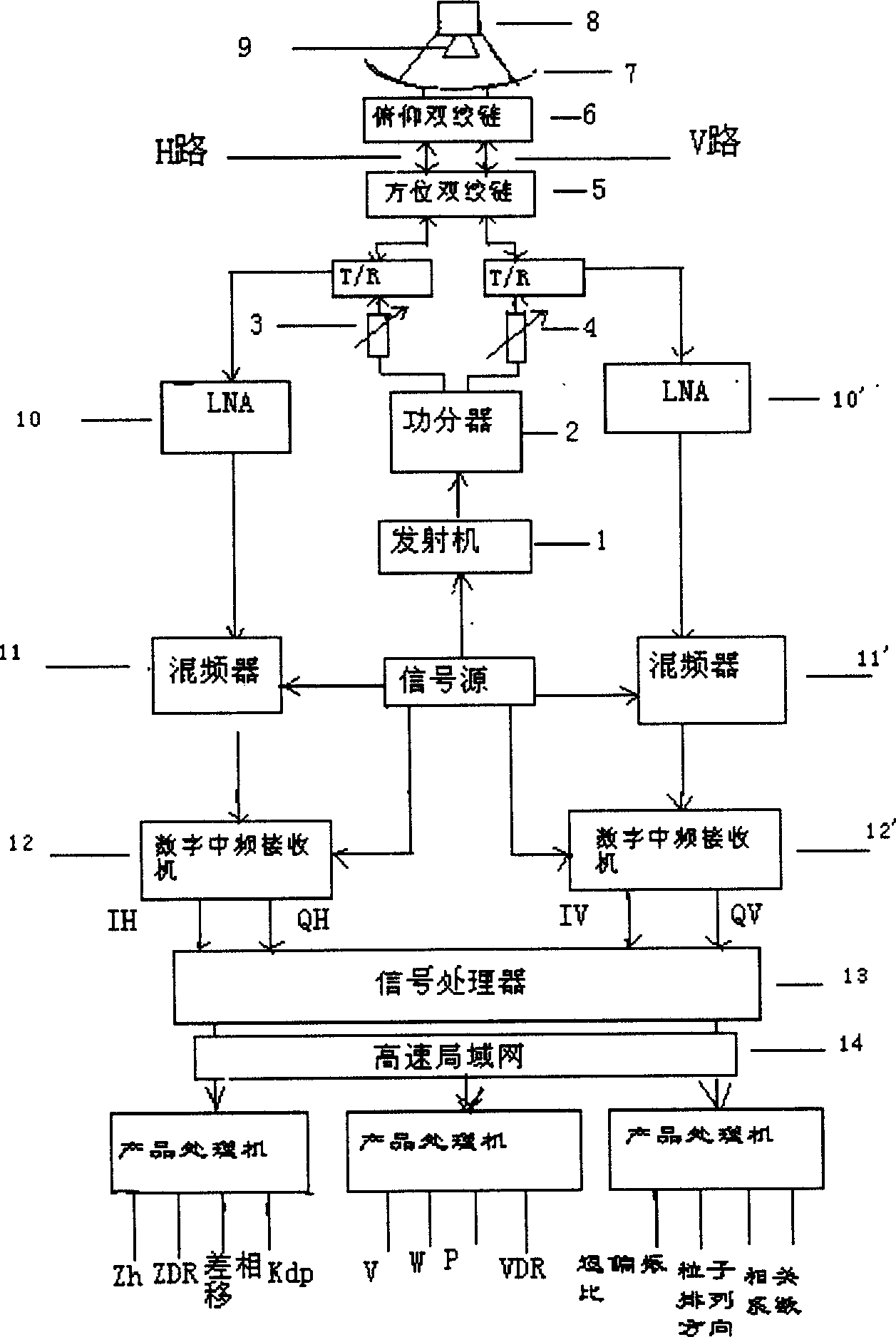
InactiveCN1800876AImprove performanceWide range of usesICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWeather radarTwisted pair
The invention relates to a electronic instrument to detect cloud and precipitation particle in microwave remote sensing and measuring field. Wherein, dividing the large-power microwave signal from a transmitter into two paths to send with azimuth twisted-pair bale and pitch twisted-pair cable to antenna with one path through the phase shifter and another path through the large-power attenuator and emit out with a duplexer and horn; then, driving the horizontal and vertical polarization echo signal formed by back scattering of the target into horizontal and vertical receive channels to mix with preamplifier and mixer into MF signal and send to digital MF receiver and convert into digital signal; finally, sending the signal into signal processor connected to high-speed LAN to transmit information to user. This invention fills up the filed domestic blank and provides a new device for radar weather enterprise and disaster prevention and reduction.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
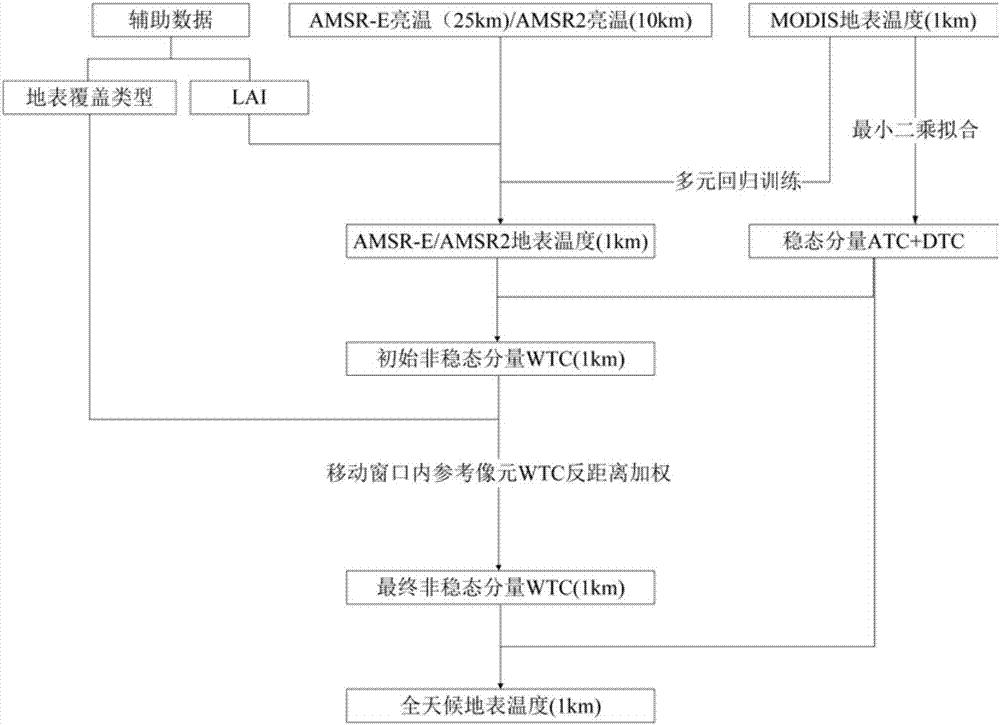
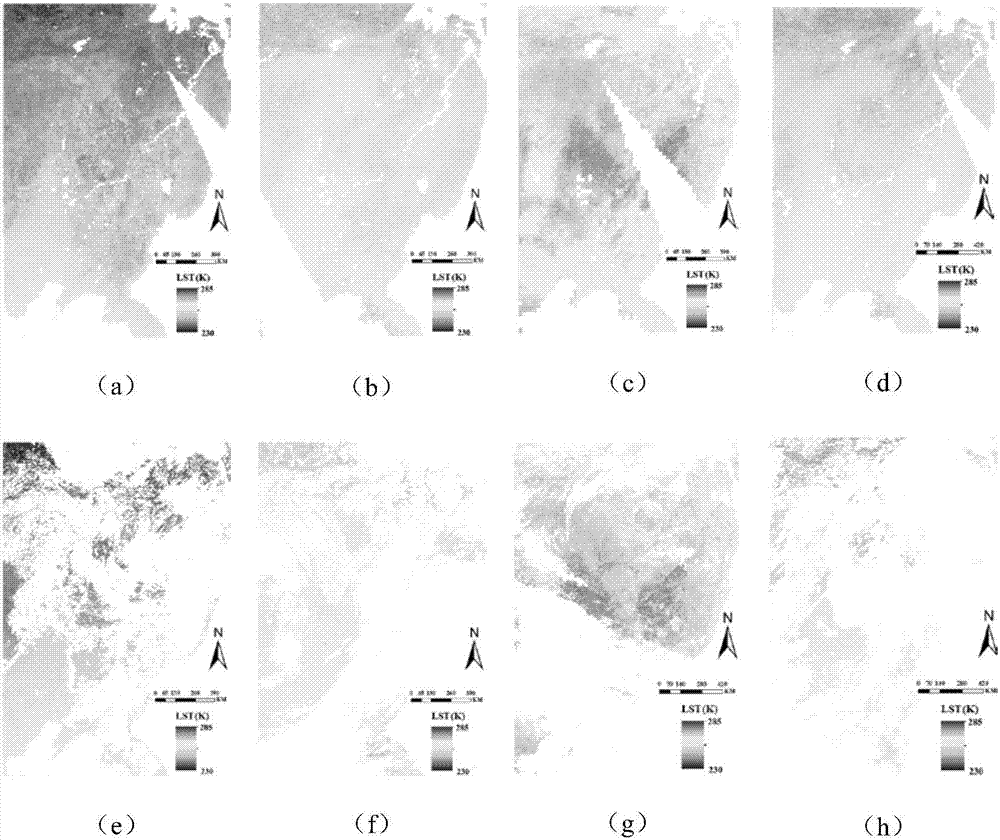
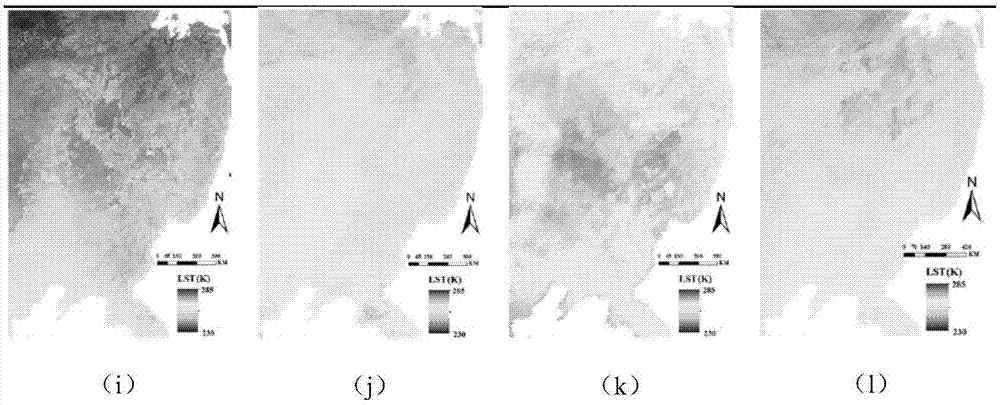
All-weather surface temperature generation method
ActiveCN107576417AMeet quality requirementsHigh precisionRadiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesSpatial correlationBrightness temperature
The invention relates to a surface temperature generation method, in particular to an all-weather surface temperature generation method having a spatial resolution of 1 km. The method of the inventionhas the advantages that the bottleneck of acquiring all-weather surface temperature under the spatial resolution of 1 km traditionally can be broken through; the passive microwave surface temperatureunder the spatial resolution of 1 km is acquired directly from the passive microwave brightness temperature by considering the correlation of temporal and spatial dimensional changes of surface temperature and brightness temperature; from the aspect of decomposing surface temperature-time components, three components of the surface temperature are formed by extracting from both thermal infrared and the passive microwave remote-sensing surface temperature, the components are effectively combined by means of the spatial correlation of the surface temperature, and the integrated all-weather surface temperature under the spatial resolution of 1 km is acquired accordingly. Compared with traditional experiential methods, the method of the invention has the advantages that the method is better in precision, popularization and transplantability, the traditional plaque effect integrated with surface temperature images can be maximally weakened, and image quality can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
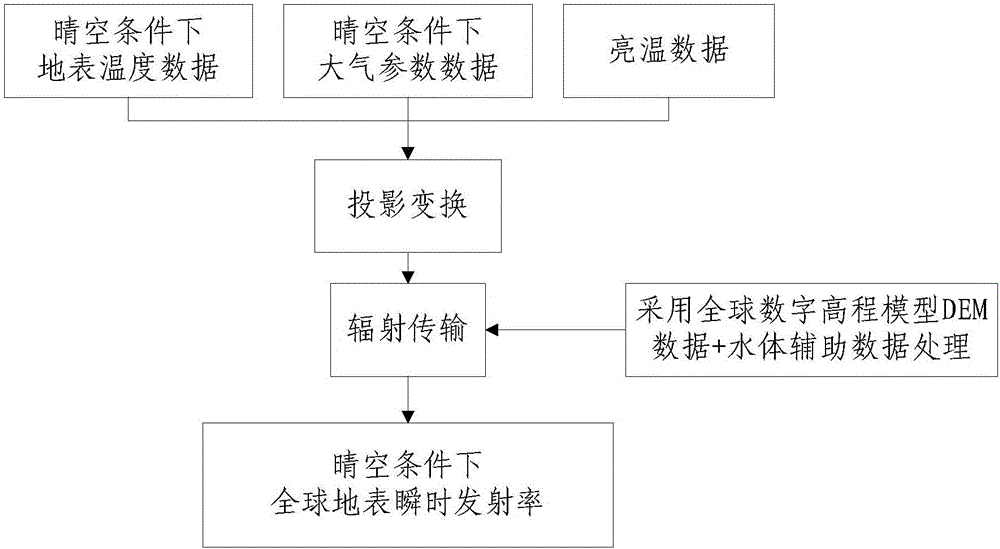
Passive microwave remote sensing instant ground surface emitting rate estimation method and device
ActiveCN106372434AFast data collectionPrecise input parametersSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSpectrographLinear regression
The invention provides a passive microwave remote sensing instant ground surface emitting rate estimation method and device. The method or device comprises a step or a device for calculating the instant ground surface emitting rate under the clear sky condition through simultaneously observing the ground surface data by a satellite-borne passive microwave sensor and a middle-resolution imaging spectrograph, a step or a device for obtaining the horizontal and vertical polarization instant ground surface emitting rate at different frequencies, a step or a device for determining a microwave polarization difference index and the polarization rate according to the same frequency horizontal and vertical polarization according to thebrightening temperature of the same frequency horizontal and vertical polarization, a step or a device for calculating the horizontal emitting rate of the ground surface emitting rate under the cloud covering condition through building a quadratic polynomial and a linear regression equation according to the horizontal polarization emitting rate of the instant ground surface emitting rate, the microwave polarization difference index and the polarization rate. By using the method and the device in the technical scheme, the zoned local blocking test is performed in the global range; the estimation of the ground surface emitting rate under the global cloud layer covering condition is realized; important data basis is provided for the ground surface temperature reversion and atmospheric correction calculation.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for detecting dual-channel SAR moving target based on compressive sensing
ActiveCN105842693AReduce data volumeSatisfy the compressed sensing sparse reconstruction conditionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumOriginal data
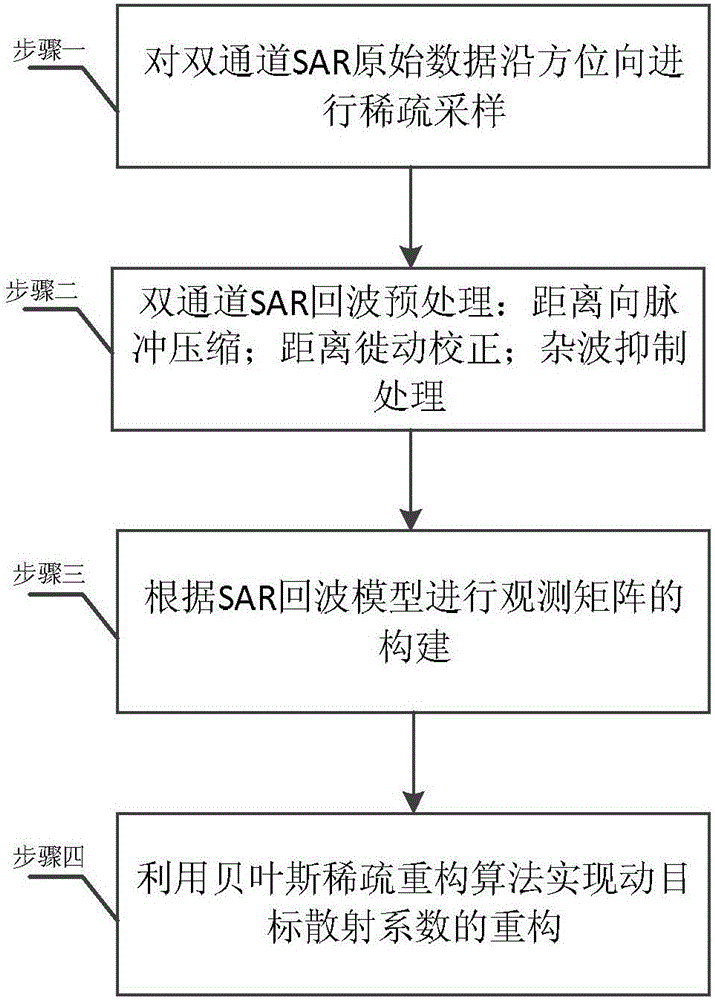
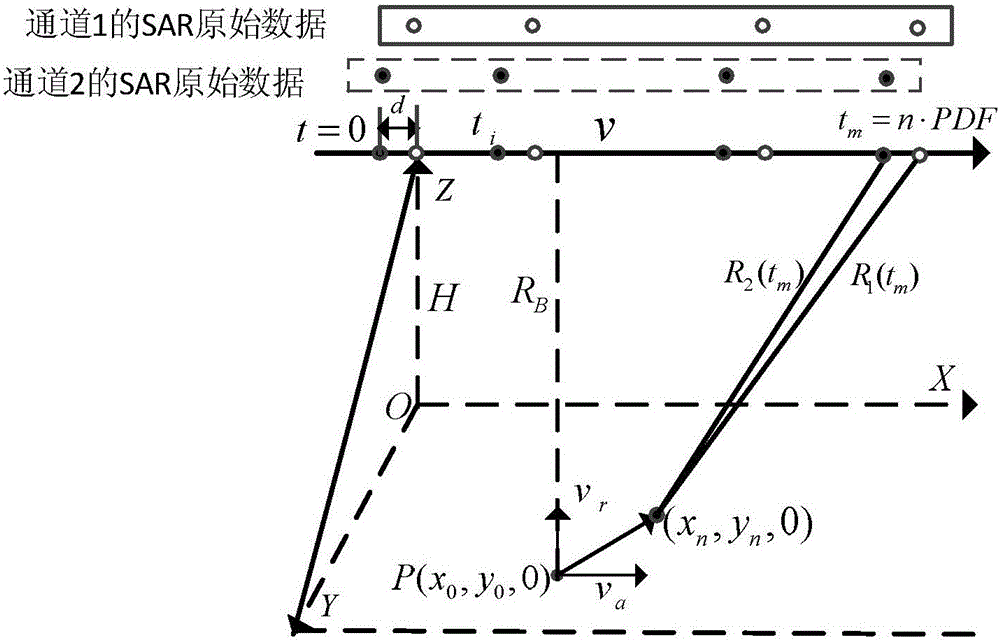
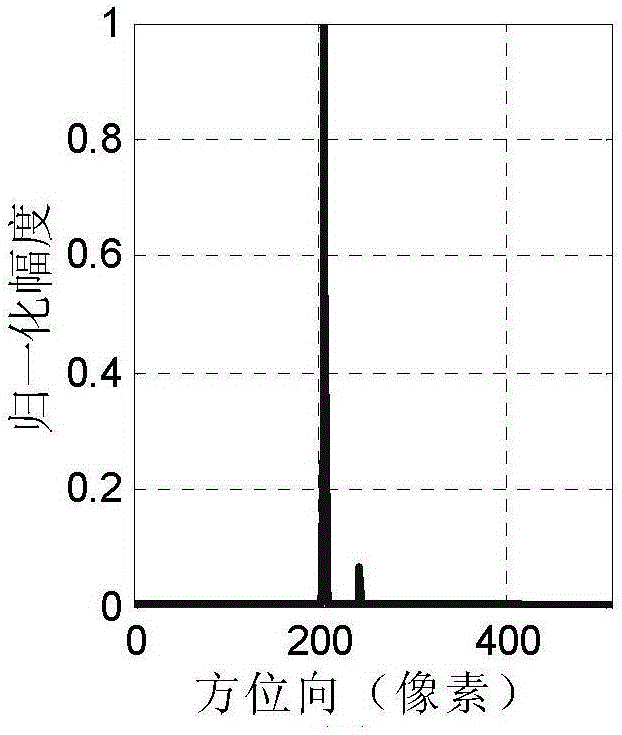
The invention relates to the technical field of microwave remote sensing and especially relates to a method for detecting dual-channel SAR moving target based on compressive sensing. The method solves the following problems: in an SAR-GMTI system in the prior art, due to the widely-spread ground clutter frequency spectrum caused by platform movement, slow moving targets are buried and thus difficult to detect; and large channel number and large data size in the multi-channel SAR system cause a large pressure to data transmission and storage. The method comprises the following steps: 1. sparse sampling of the dual-channel SAR original data in the azimuth direction; 2. pretreatment of dual-channel SAR echoes: range direction pulse compression, distance migration correction, and clutter suppression treatment; 3. pretreatment of dual-channel SAR echoes; and 4. reconstruction of moving target scattering coefficient by means of the Bayes sparse reconstruction algorithm. The method can be applied in technical field of microwave remote sensing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sea fog monitoring method based on multi-source satellite remote sensing data
InactiveCN108761484AImprove monitoring accuracyPosition fixationIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesSensing dataMonitoring methods
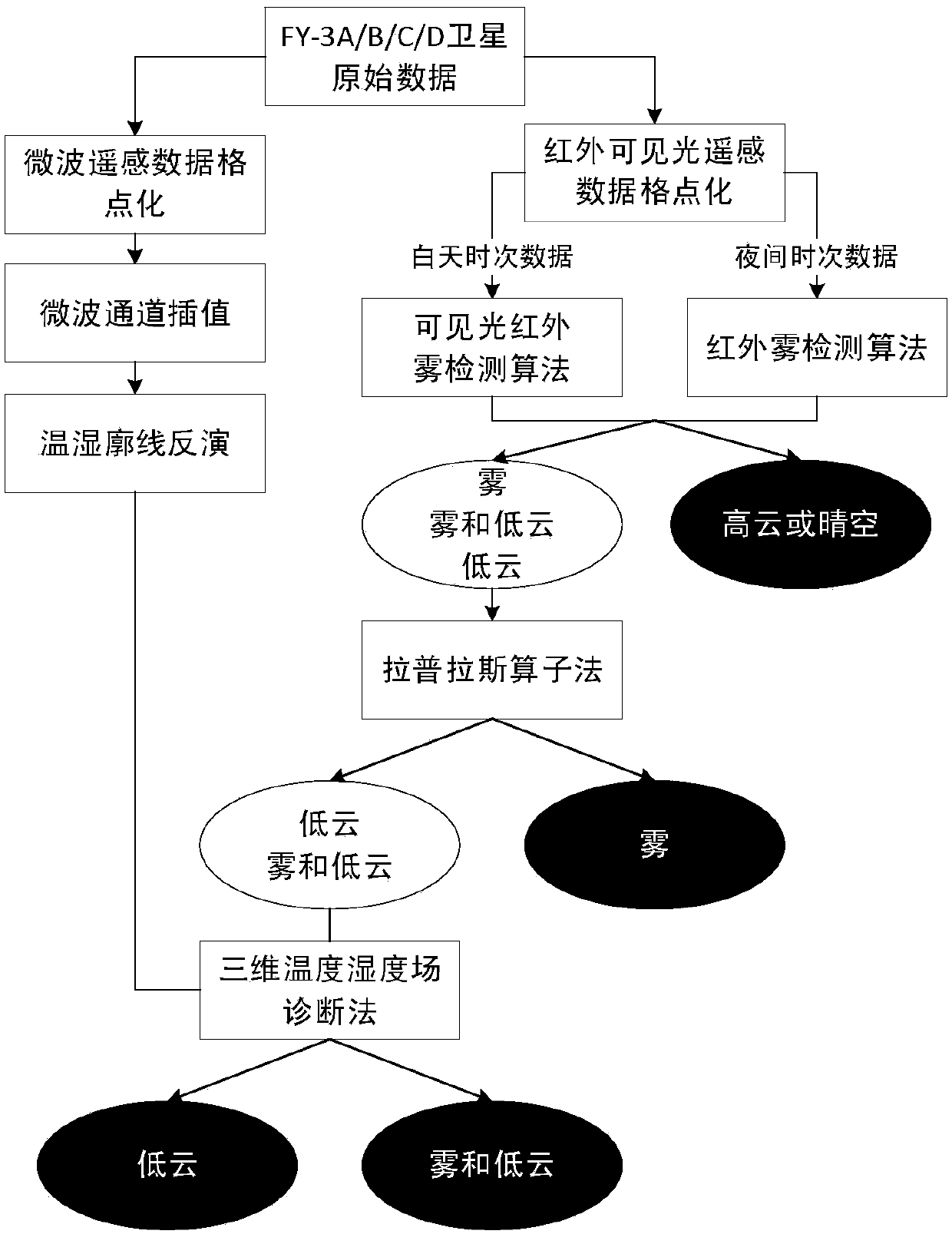
The invention discloses a sea fog monitoring method based on multi-source satellite remote sensing data. Visible light and infrared satellite remote sensing data are used to preliminarily identify a fog and low-cloud mixing area; satellite microwave remote sensing data are used to acquire a temperature and humidity vertical layered structure in the fog and low-cloud mixing area; as the fog and thelow cloud have different large humidity area heights, the heights of the large humidity areas are extracted through the humidity layered structure; and the fog and the low cloud can further be distinguished, and the fog monitoring correctness is effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGSU METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATORY
Active and passive remote sensing data-based rural residential land extraction method
InactiveCN104616015AFully reflect the differenceHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing dataRural settlement
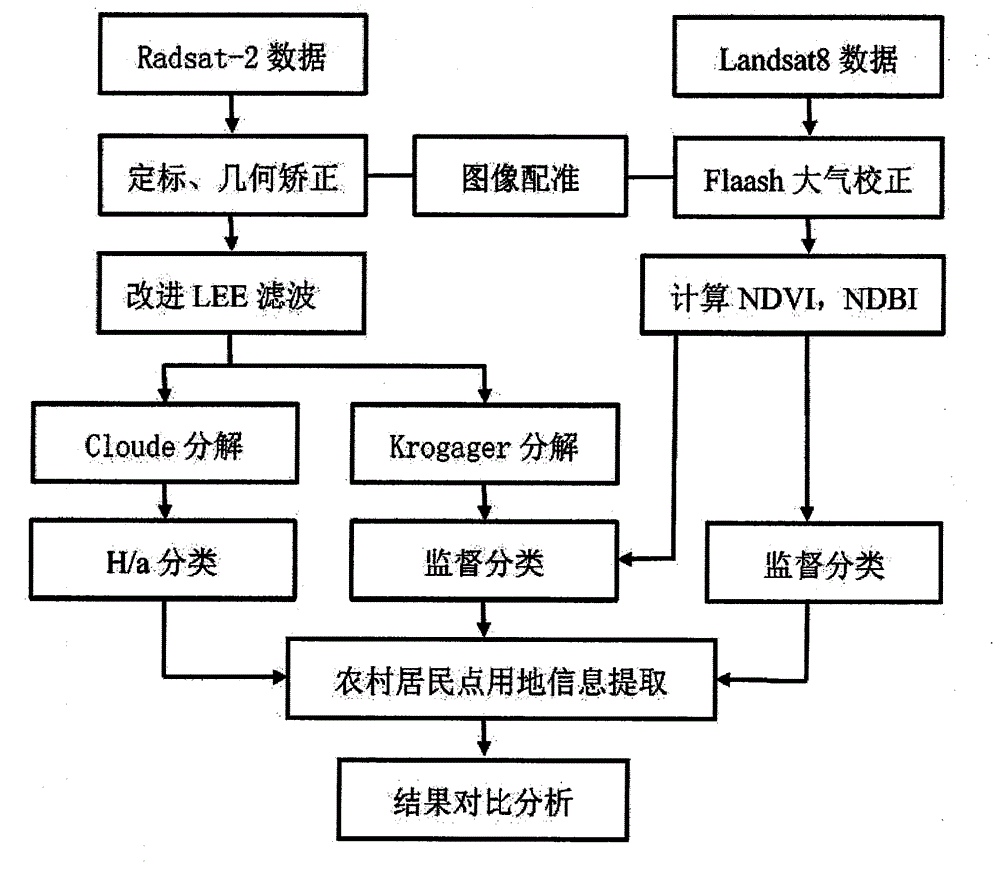
The invention discloses an active and passive remote sensing data-based rural residential land extraction method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring data and preprocessing; (2) calculating a normalized differential vegetation index; (3) calculating a normalized difference build-up index; (4) calculating a POLSAR (Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar) dihedral angle scattering component; (5) performing maximum likelihood classification. According to the method, the optical remote sensing and microwave remote sensing information are comprehensively applied, the difference between ground and an object can be more fully embodied through supplementation of advantages and disadvantages of the two kinds of remote sensing information, and the accuracy for rural residential land extraction is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com