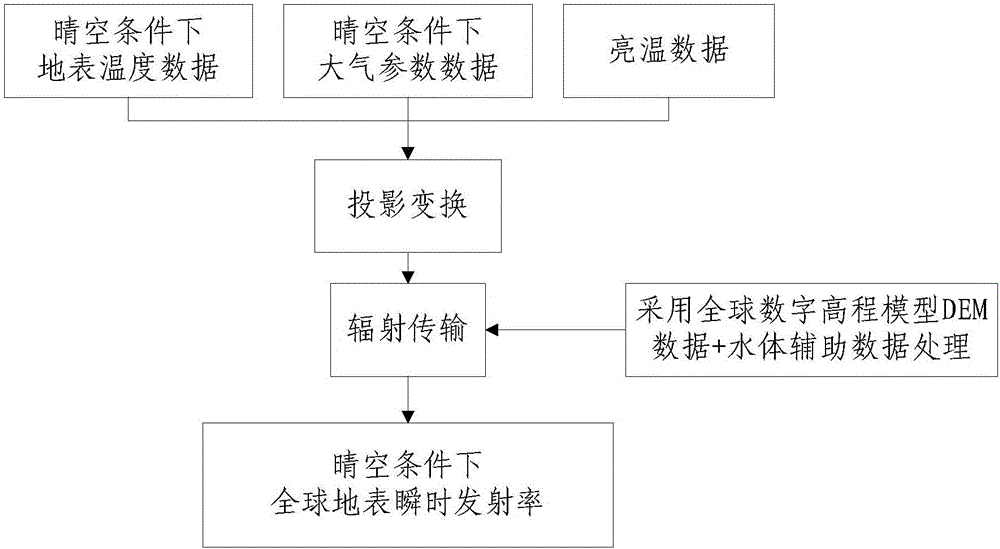
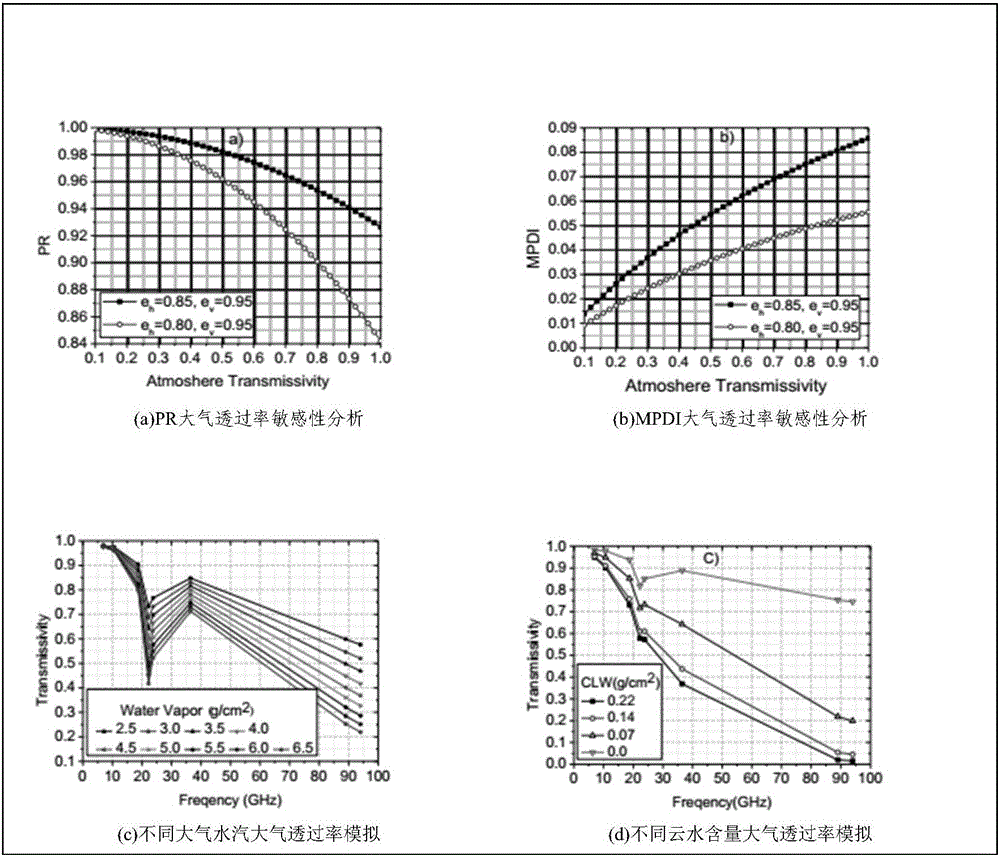
Passive microwave remote sensing instant ground surface emitting rate estimation method and device
A passive microwave remote sensing, surface emissivity technology, applied in the field of remote sensing data geoscience parameter inversion, can solve the problems of land surface parameterization inversion error, difficulty and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] In the first embodiment, the embodiment of the present invention selects two places in China to conduct emissivity estimation tests at 10.7GHz and 18.7GHz. The ground cover in the test area is mainly grassland (southeast of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau) and crops (central China). The tested instantaneous surface emissivity distribution map (time 12-08-2006 ascending orbit), using these two areas to test the emissivity prediction ability of PR and MPDI. The data format is EASE-GRID (Equal-Area Scalable EarthGrid) grid.
[0125] The effective emissivity sampling points for the ascending orbit on August 12, 2008 were 505 and 157 respectively. Both PR and MPDI polarization parameters are used to establish the emissivity prediction equations of formula 4.15 (quadratic polynomial) and 4.16 (multiple / univariate linear regression). The root mean square error (RMSE) of the emissivity obtained by the equation and its horizontal polarization emissivity is shown in Table 1. It can be s...
Embodiment 2
[0134] The second embodiment is the result of calculating the vertical and polarized emissivity of the global surface emissivity at 36.5 GHz by using the above method. The result shows the expected spatial structure. The V polarization is greater than the H polarization, which is in line with the description of the model. The polarization difference in ice-covered areas is large, such as the Antarctic continent and the snow and ice surface of Greenland. This is due to the scattering on the ice and snow surface. The impact of the role. The same phenomenon is also shown in deserts and semi-arid areas. The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has low emissivity in both polarizations, and the same phenomenon also occurs in deserts and semi-arid areas, such as the Sahara Desert and central Australia.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com