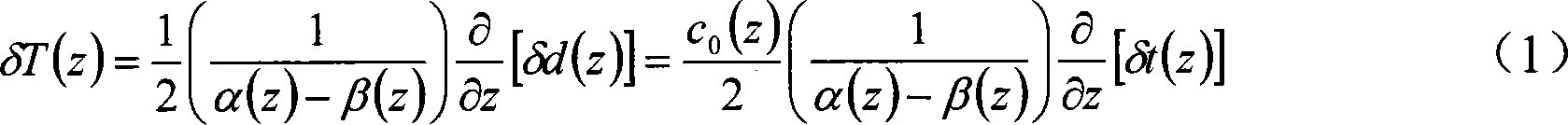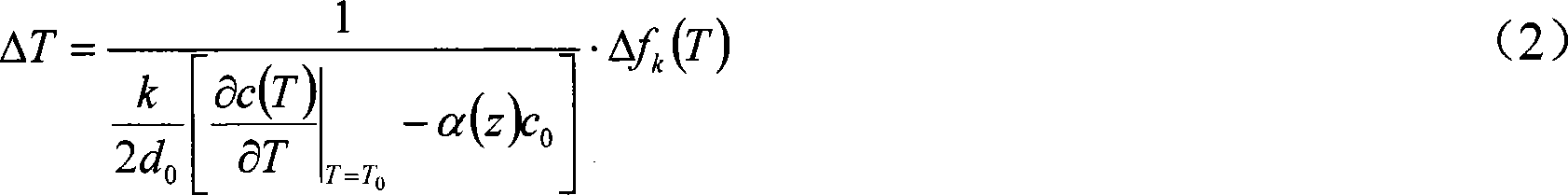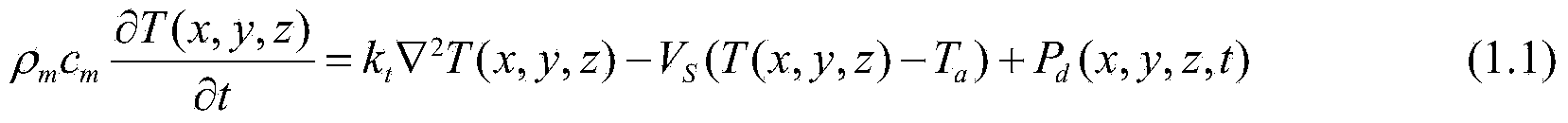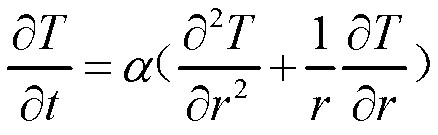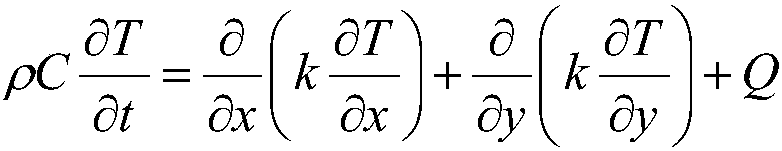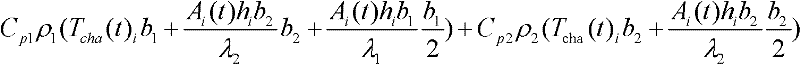Patents
Literature
96 results about "Heat equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics and mathematics, the heat equation is a partial differential equation that describes how the distribution of some quantity (such as heat) evolves over time in a solid medium, as it spontaneously flows from places where it is higher towards places where it is lower. It is a special case of the diffusion equation.
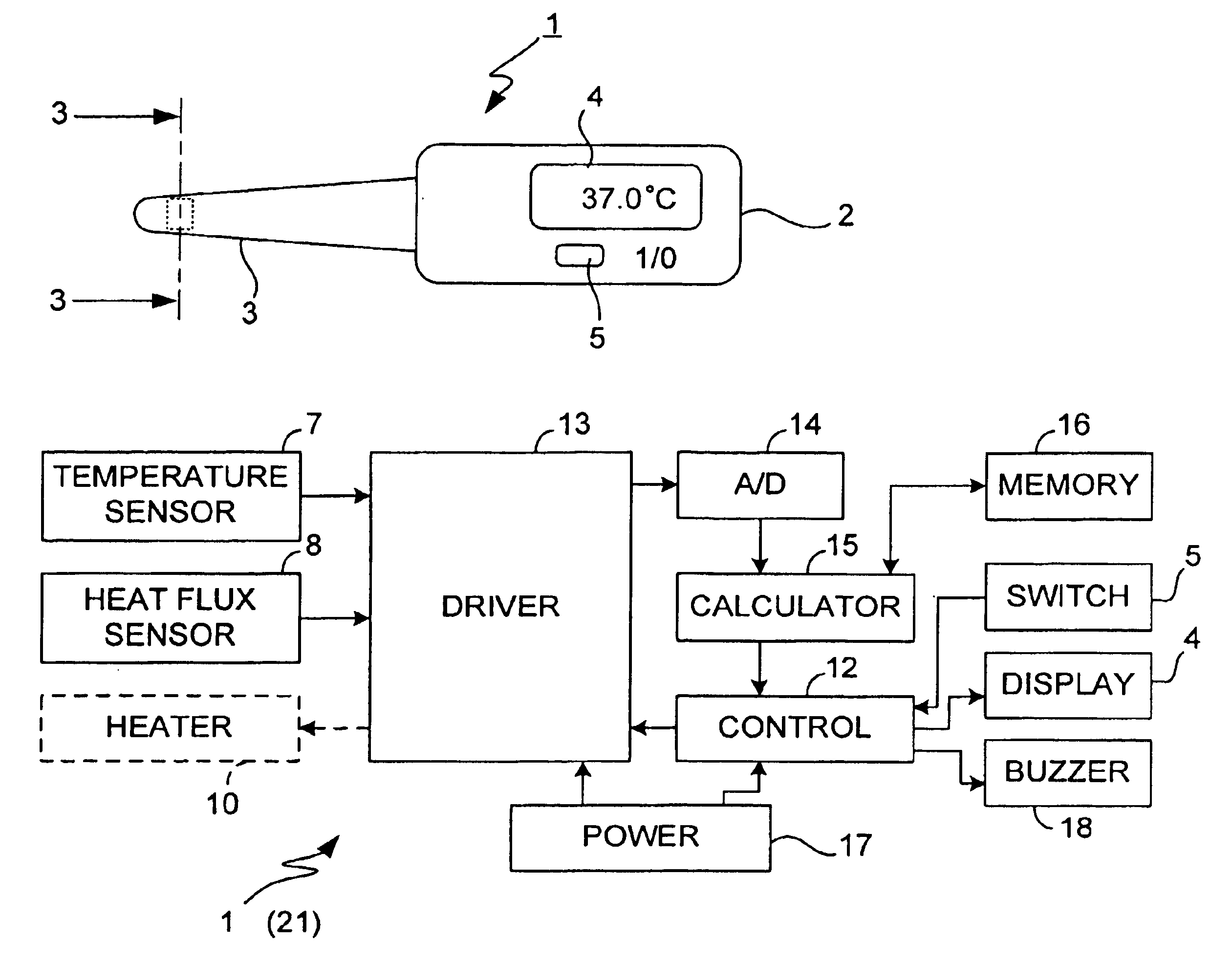
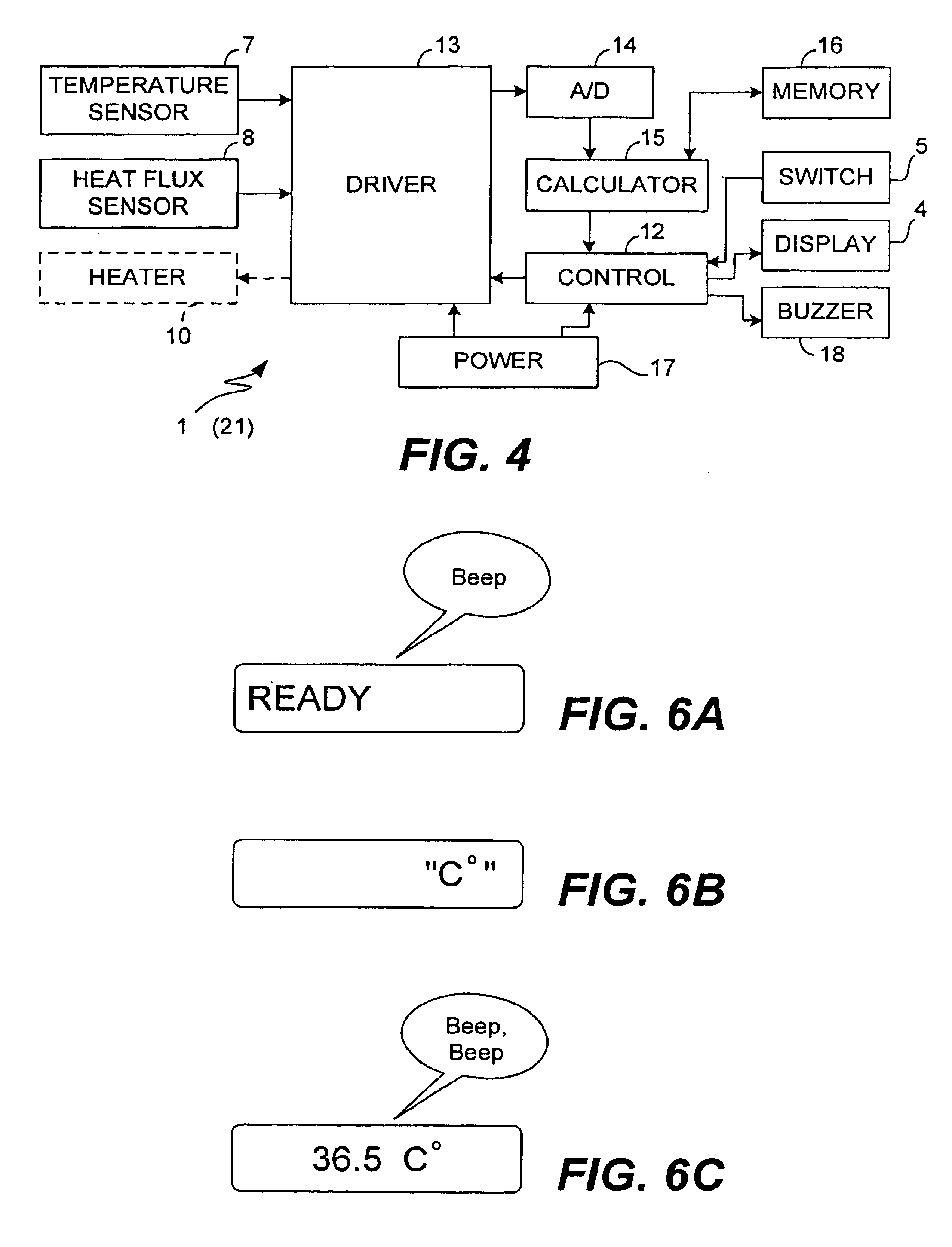
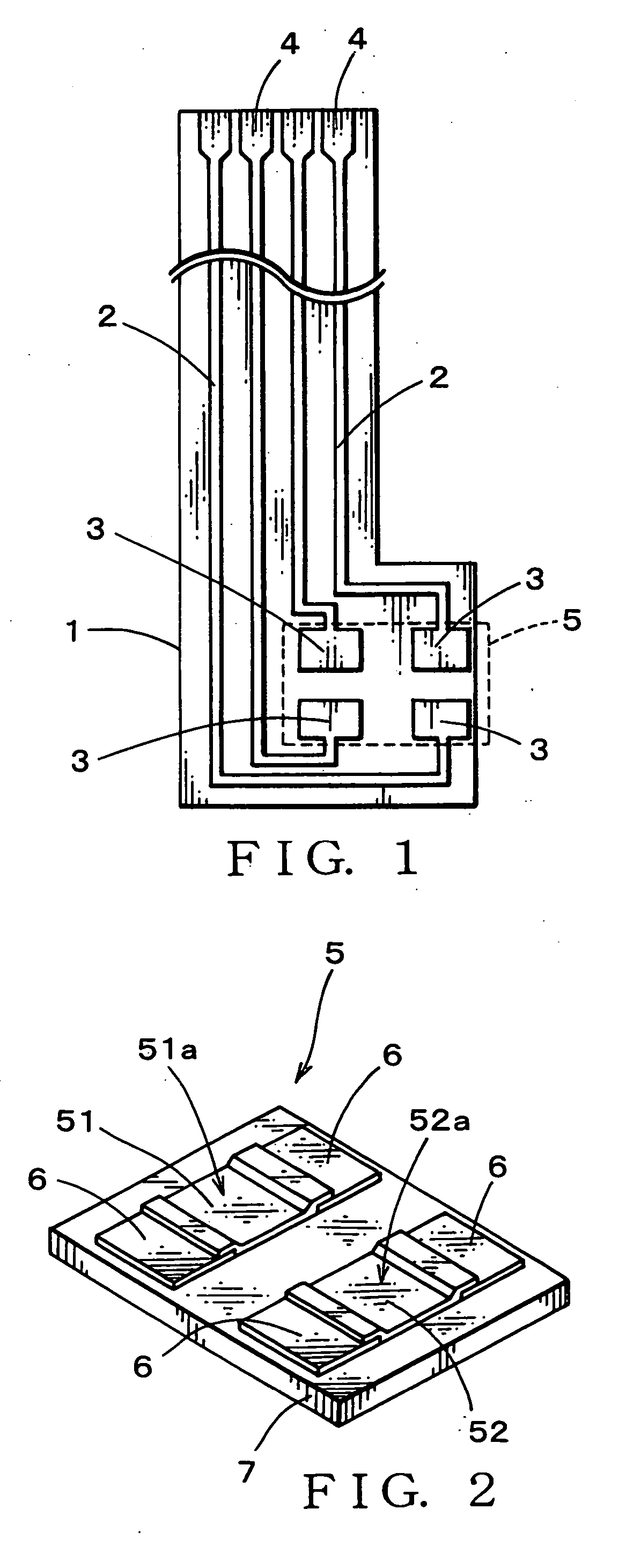
Electronic clinical thermometer
InactiveUS6890096B2Accurately and quickly estimateQuickly and accurately obtainedThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsTwo temperatureEngineering
An electronic clinical thermometer has a probe including a temperature sensor and a heat flux sensor which are controlled to make measurements at specified time intervals. The measured values are used in solving the equation of heat conduction to estimate the temperature of an internal body position. A heater may be included to preheat a body part in order to reduce the time required for measurement. The probe may use two temperature sensors to measure temperatures at two body surface positions through insulating members which are different in thermal conductivity.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
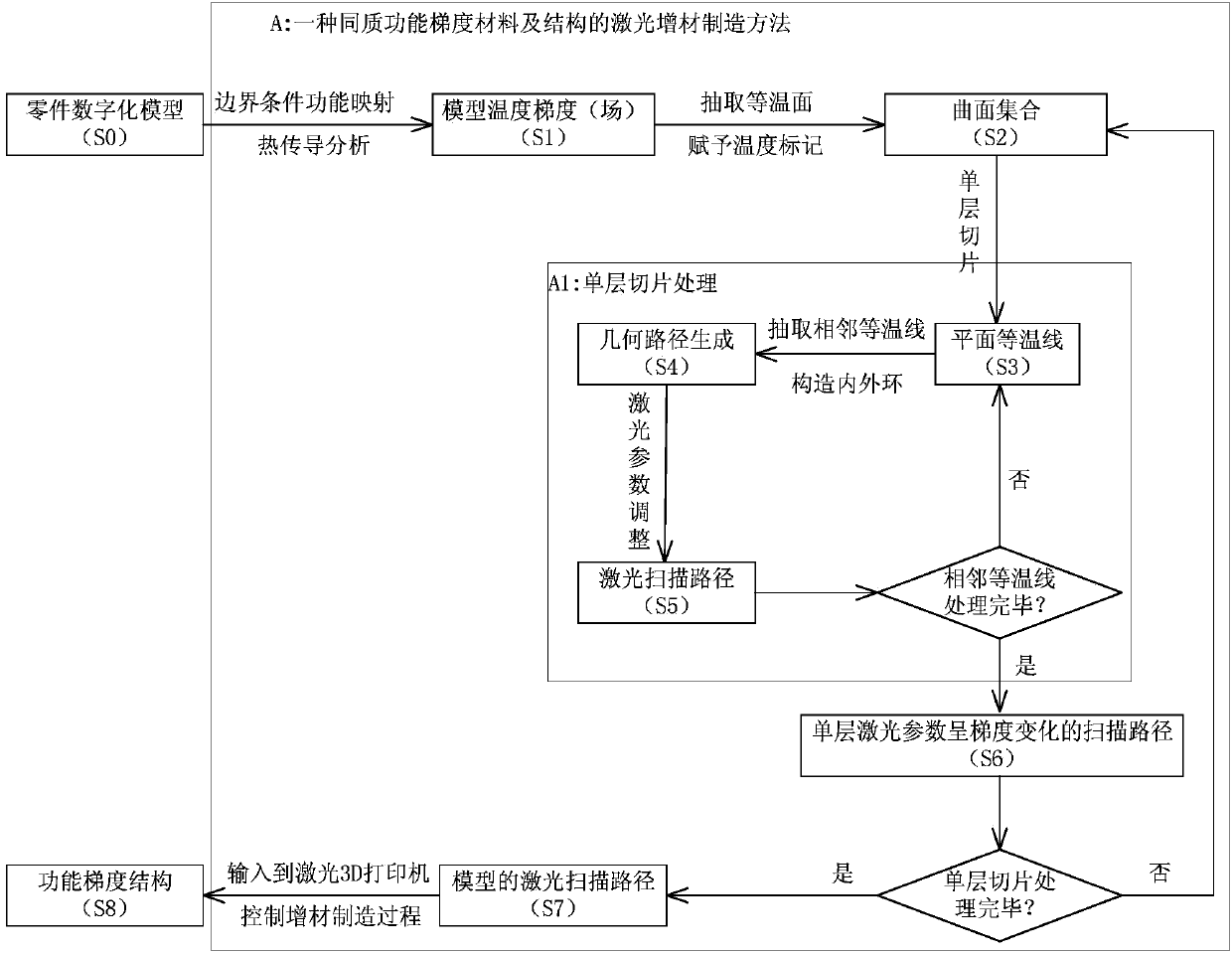
Laser additive manufacturing method for homogeneous functionally graded material and structure
ActiveCN104190930AOvercome functionOvercome structureIncreasing energy efficiencyLaser scanningOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a laser additive manufacturing method for a homogeneous functionally graded material and structure. The method includes the following steps that different functions are mapped into different temperatures which serve as boundary conditions to be exerted on different parts of a three-dimensional model; a three-dimensional finite element method is used for calculating a heat conduction equation of the model, inner temperature graded distribution, namely the temperature field of a model, is obtained, that is a temperature field of the model is obtained; an isothermal surface of the model is extracted, and a curved surface set with different temperature marks is obtained; slicing is conducted on the curved surface set, the intersection outline of each layer and the isothermal surface is obtained, in other words, plane isothermal lines are obtained; slices of each layer are processed, and a scanning route with laser parameters of the single layer in graded variation is obtained; the steps are repeatedly conducted until slicing is completed and a laser scanning route of the model is obtained; the generated laser scanning route is input into a laser 3D printing machine to control the additive manufacturing process, and the homogeneous functionally graded structure is obtained. According to the additive manufacturing method, the fact that the homogeneous functionally graded material and the homogeneous functionally graded structure can be manufactured in an additive mode is achieved, and the fact cannot be achieved through a current laser additive manufacturing method.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
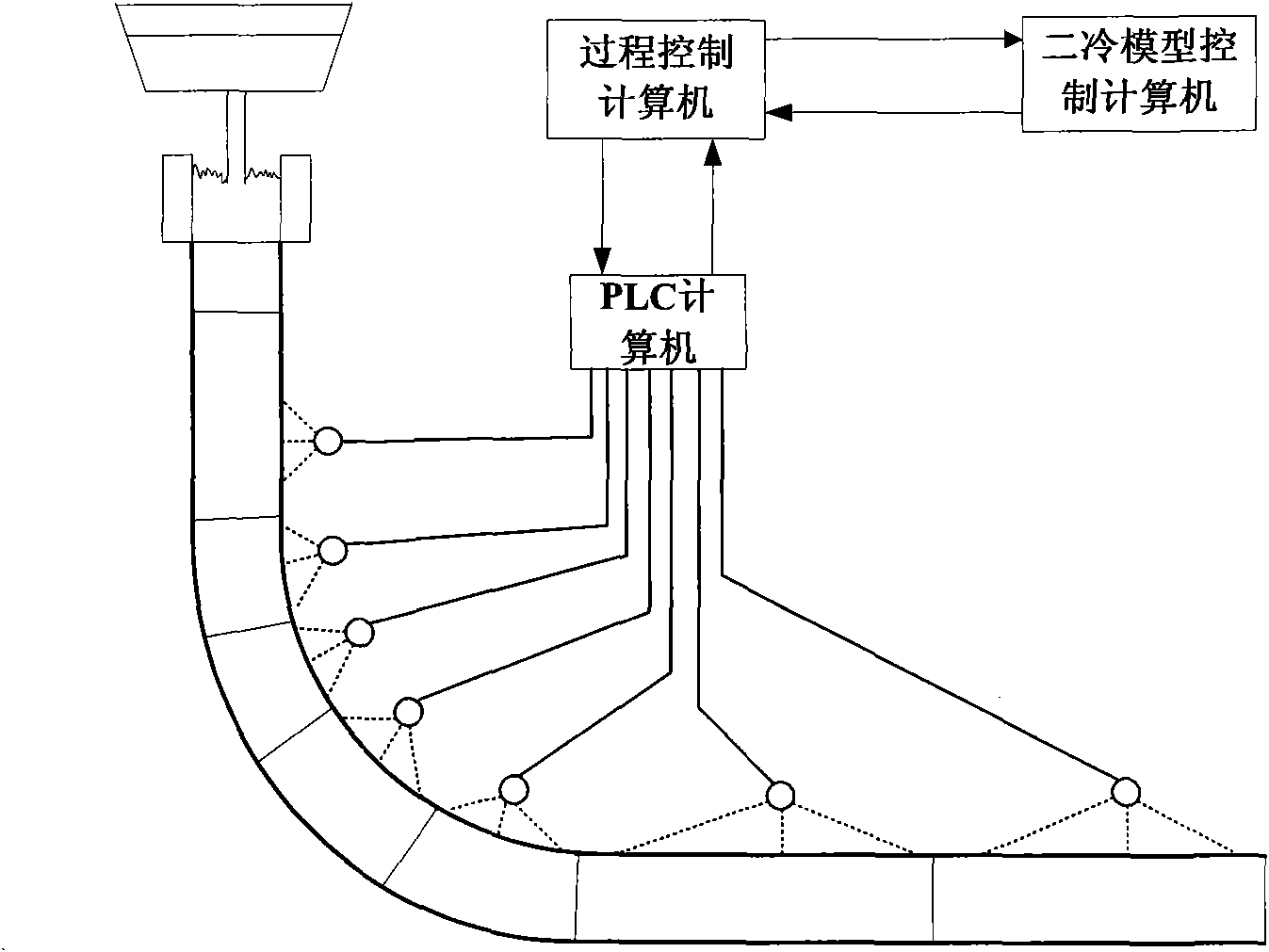
Dynamic secondary cooling control method for slab continuous casting based on double-cooling mode
The present invention discloses a dynamic secondary cooling control method for slab continuous casting based on a double-cooling mode, which comprises the following steps of: collecting casting process data and indexing target cooling temperatures and ABC parameters of each cooling area; dynamically calculating the heat conduction process of a continuously cast slab in the current period according to a heat conduction equation; calculating the temperature tracking error of each cooling area and calculating the water amount of each cooling area in a second cooling mode by taking the temperature tracking error as a regulation factor; respectively calculating the water amount of each cooling area in a first cooling mode based on the ABC parameters and the current casting speed; determining whether the temperature tracking error exceeds a preset threshold and comparing the water amounts in the two modes to determine the cooling mode and the controlled water amount in the current period; and validating the reasonableness of the controlled water amount, and correcting the controlled water amount to be a preset maximum water amount or minimum water amount if the controlled water amount exceeds the preset maximum water amount or minimum water amount. The invention guarantees the quality stability of the cast blank in secondary cooling process.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
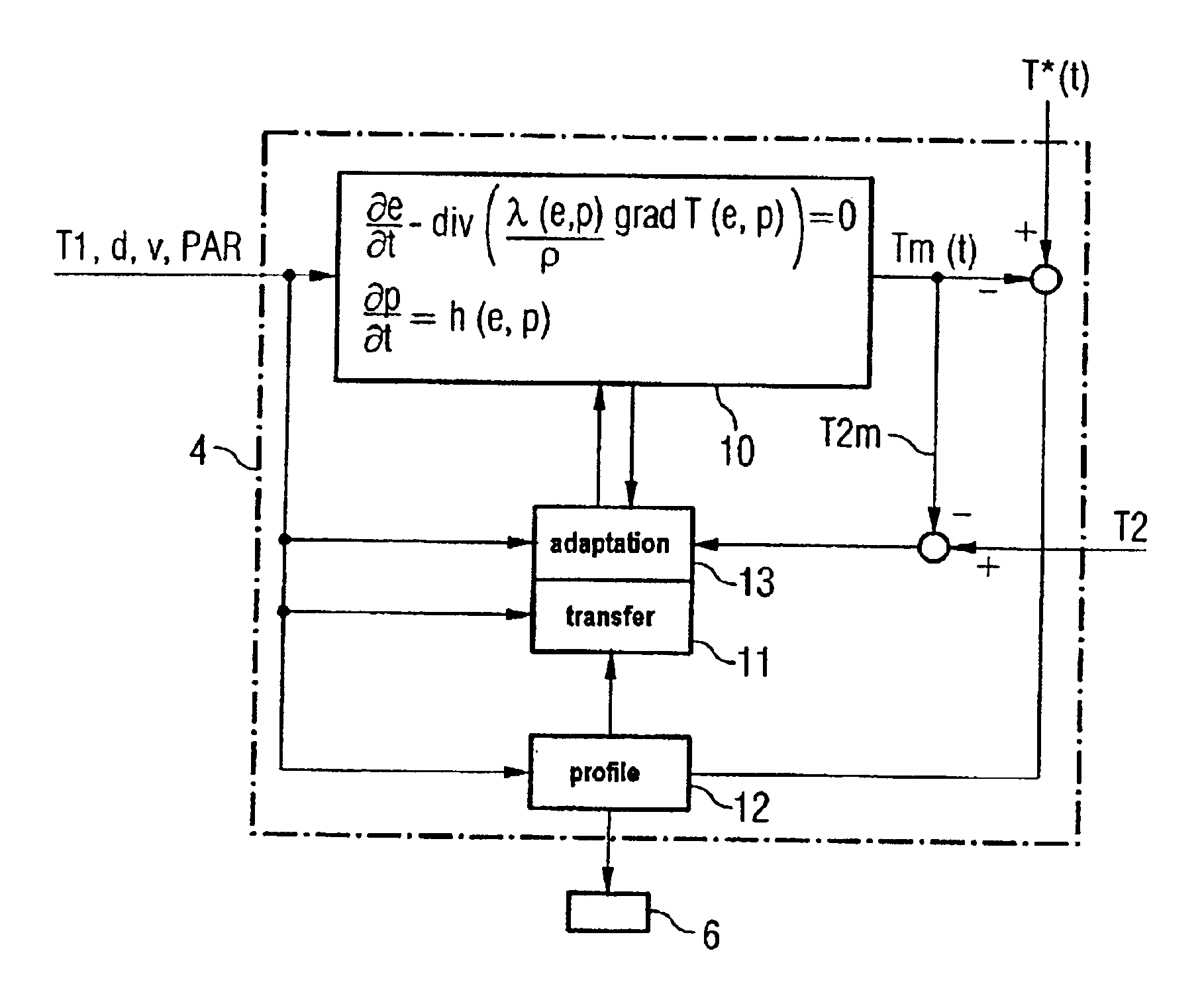
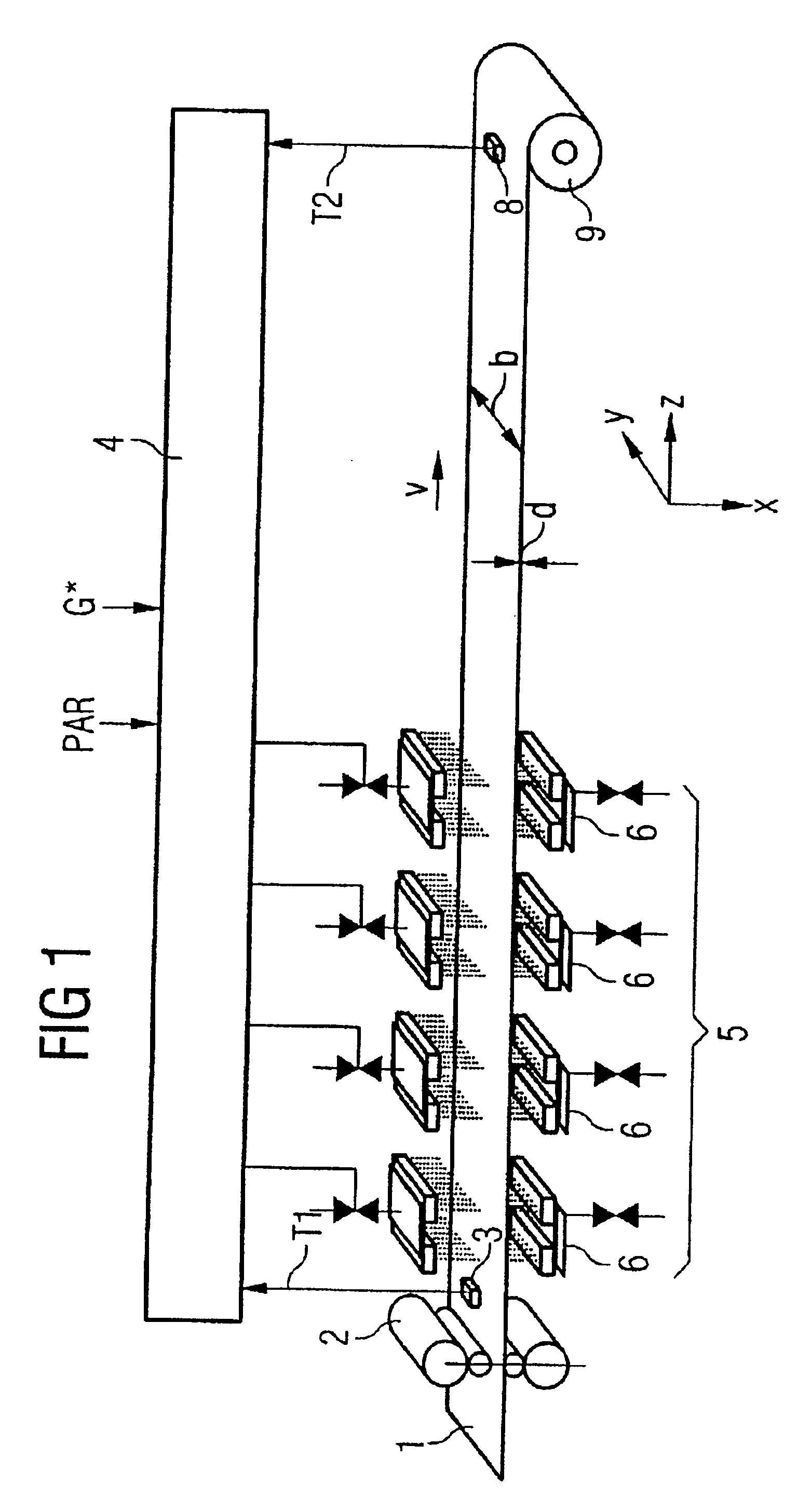
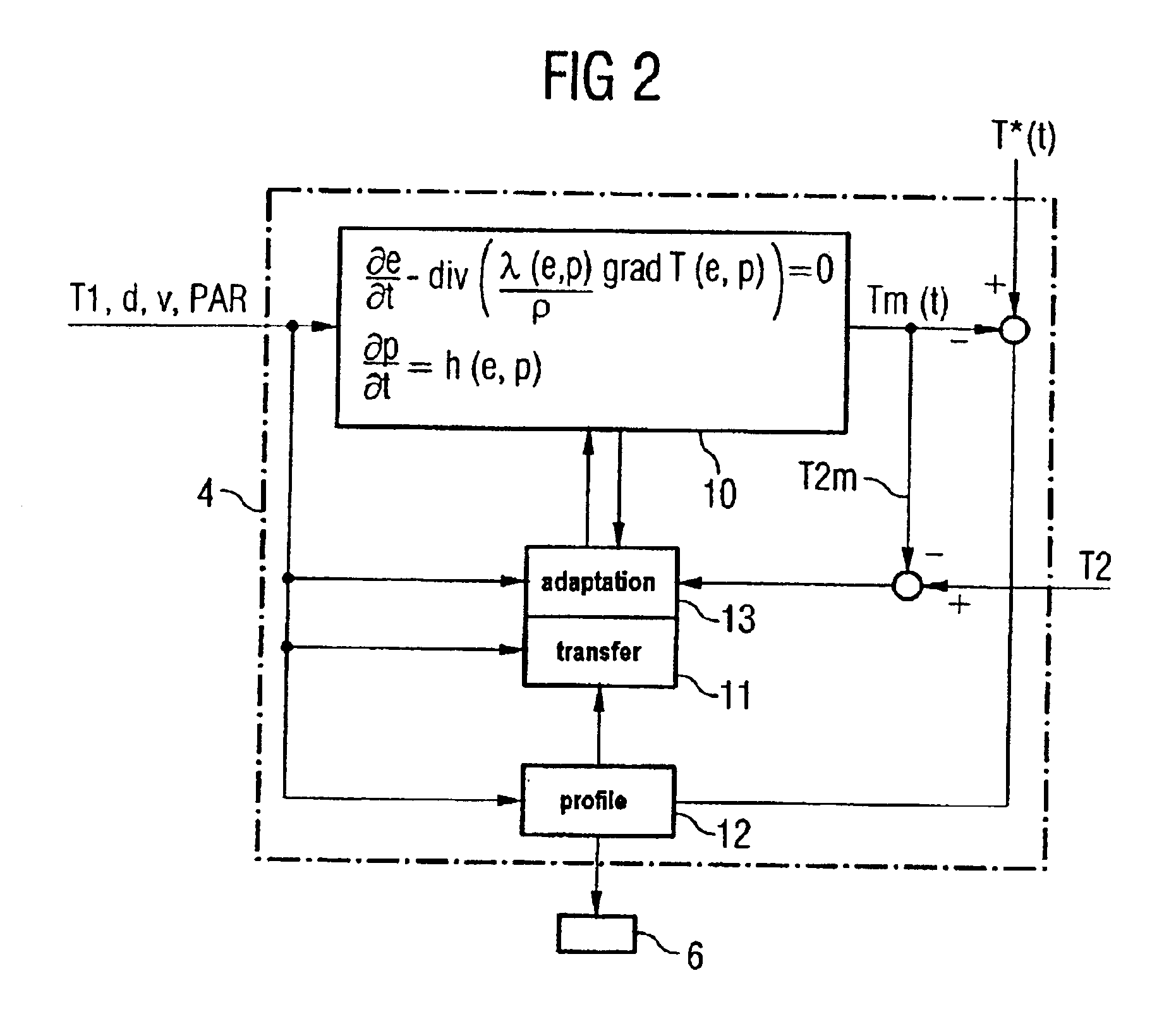
Method for cooling a hot-rolled material and corresponding cooling-line models
InactiveUS6860950B2Temperature control deviceAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesVolumetric Mass DensityLine model
To determine the temperature profile (Tm(t)) of a hot-rolled material (1) in a cooling line (5), a heat conduction equation which takes the following form ∂e∂t-div[λ(e,p)ρ·grad T(e,p)]=0where e is the enthalpy, λ the thermal conductivity, p the degree of phase transformation, ρ the density and T the temperature of the rolled material at the rolled-material location and t is the time, is solved in a cooling-line model (4).
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
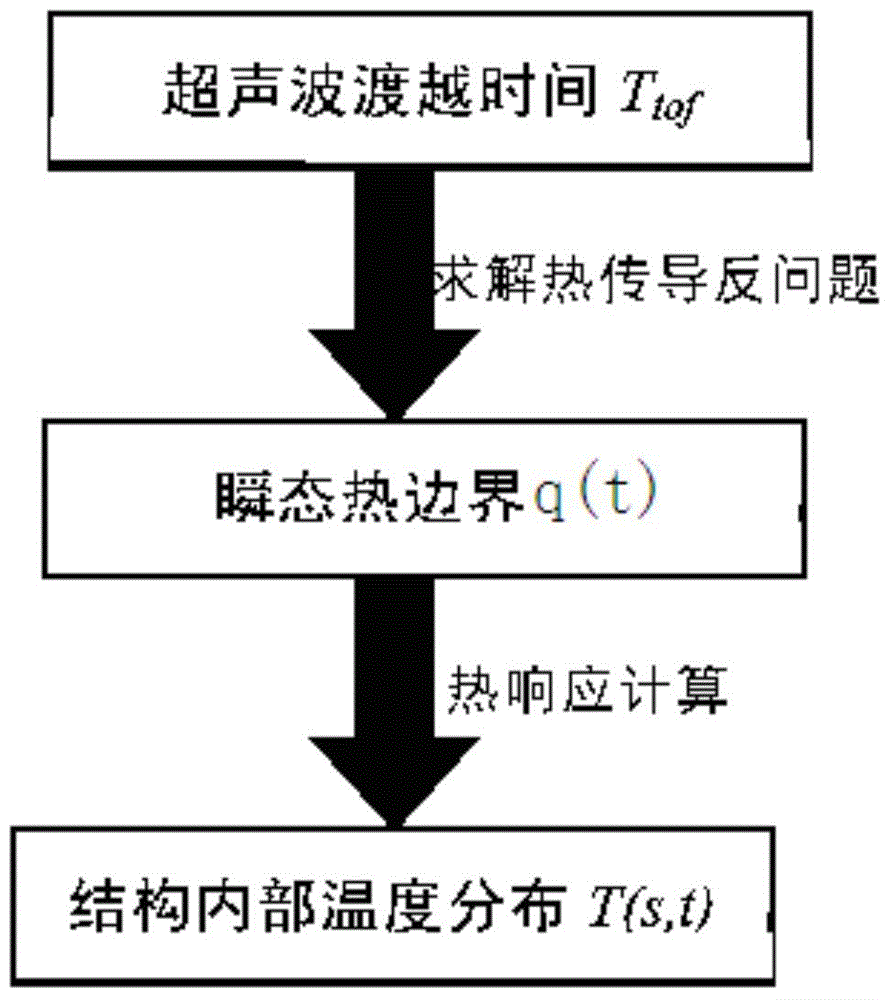
Method for reconstructing nonuniform temperature field inside structure and based on transient-state thermal boundary inversion
ActiveCN104792435AHigh precisionQuick responseThermometers using physical/chemical changesTransient stateSolid structure
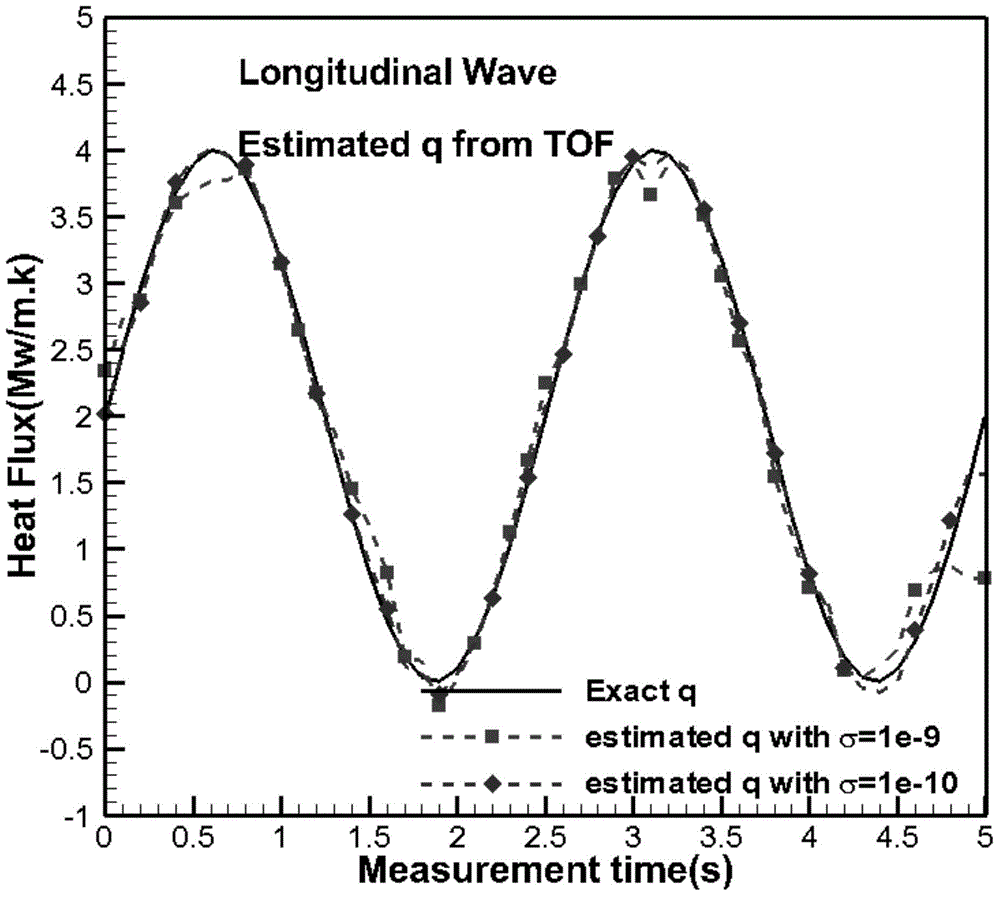
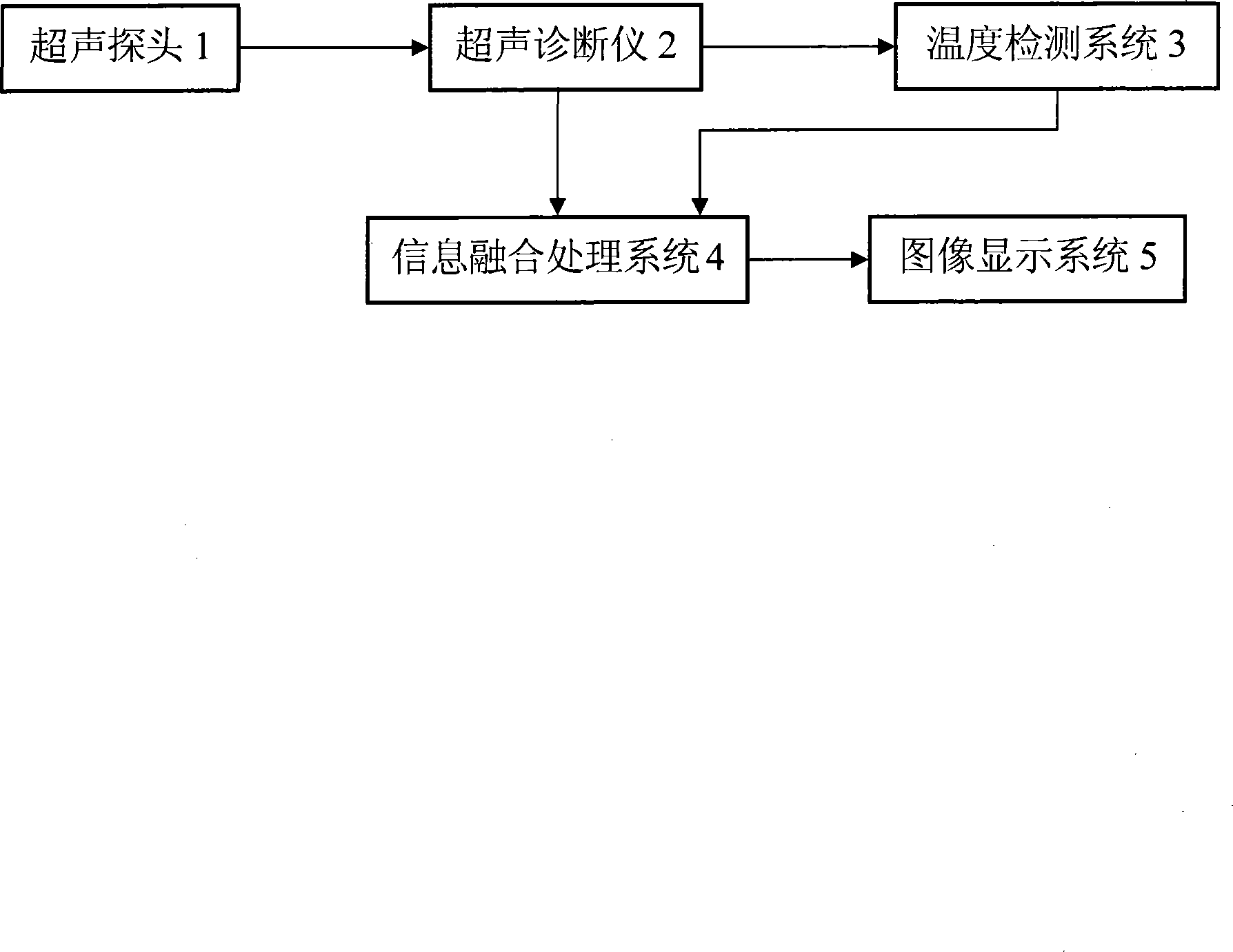
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing a nonuniform temperature field inside structure and based on transient-state thermal boundary inversion. The method includes that on the basis of transition time of ultrasonic pulse echo, transient-state thermal boundary conditions causing temperature change of the structure is inverted; on this basis, non-steady-state temperature distribution inside the structure is reconstructed by solving a thermal conduction equation. Compared with existing ultrasonic temperature measuring methods, the method has the advantages that ultrasonically-detected inside temperature is not acquired directly through transition time and is acquired through inverted transient-state thermal boundary conditions, so that temperature in the method is not a single average value on a transmission path any more but specific temperature distribution, and the method is higher in temperature resolution and higher in stability and can realize realtime and high-accuracy reconstruction of temperature distribution inside solid structure at different moments.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Ultrasonic real time harmless human body temperature-measuring device and temperature-measuring method
InactiveCN101125088ASolve the difficulty of variable temperature characteristic parametersSolve changing difficultiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringRelational modelBody temperature measure
The present invention relates to an ultrasonic real-time nondestructive body temperature measuring device and the temperature measurement method; the present invention establishes a relationship model of the temperature increment and the echo signal in the time domain or the frequency domain based on that the thermal characteristics of the human tissues and the ultrasound beams which pass through the human tissues thereof have better correlation with the temperature increment on the beam path during the slow change, furthermore, the present invention uses the numerical calculation method (such as, finite element / finite difference method) which is based on the nonlinear medical ultrasonic field to carry out the real-time dynamic calibration of the thermal coefficient of the deep tissue by establishing a Pennes biological heat conduction equation (BHTE) in a human structural model, so as to solve the difficulties that the characteristic parameters of the tissue temperature are too changeable ; the present invention uses the combination method of the numerical calculation and the ultrasonic detection to eliminate the problem of the heat-acoustic lens and adopts the fusion imaging method of the temperature information and the tissue structure information to visually display the temperature distribution and the structure distribution in the body.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
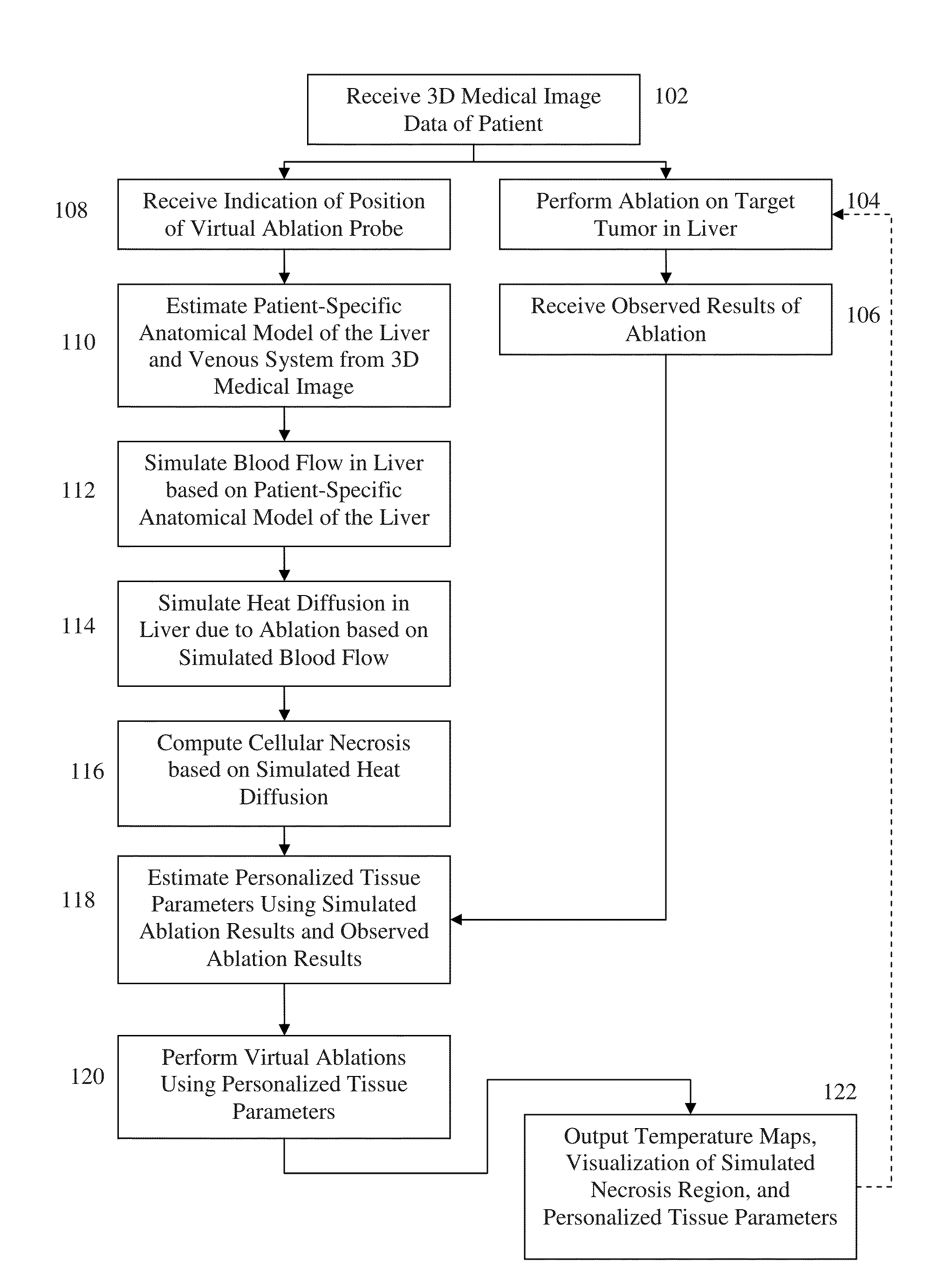
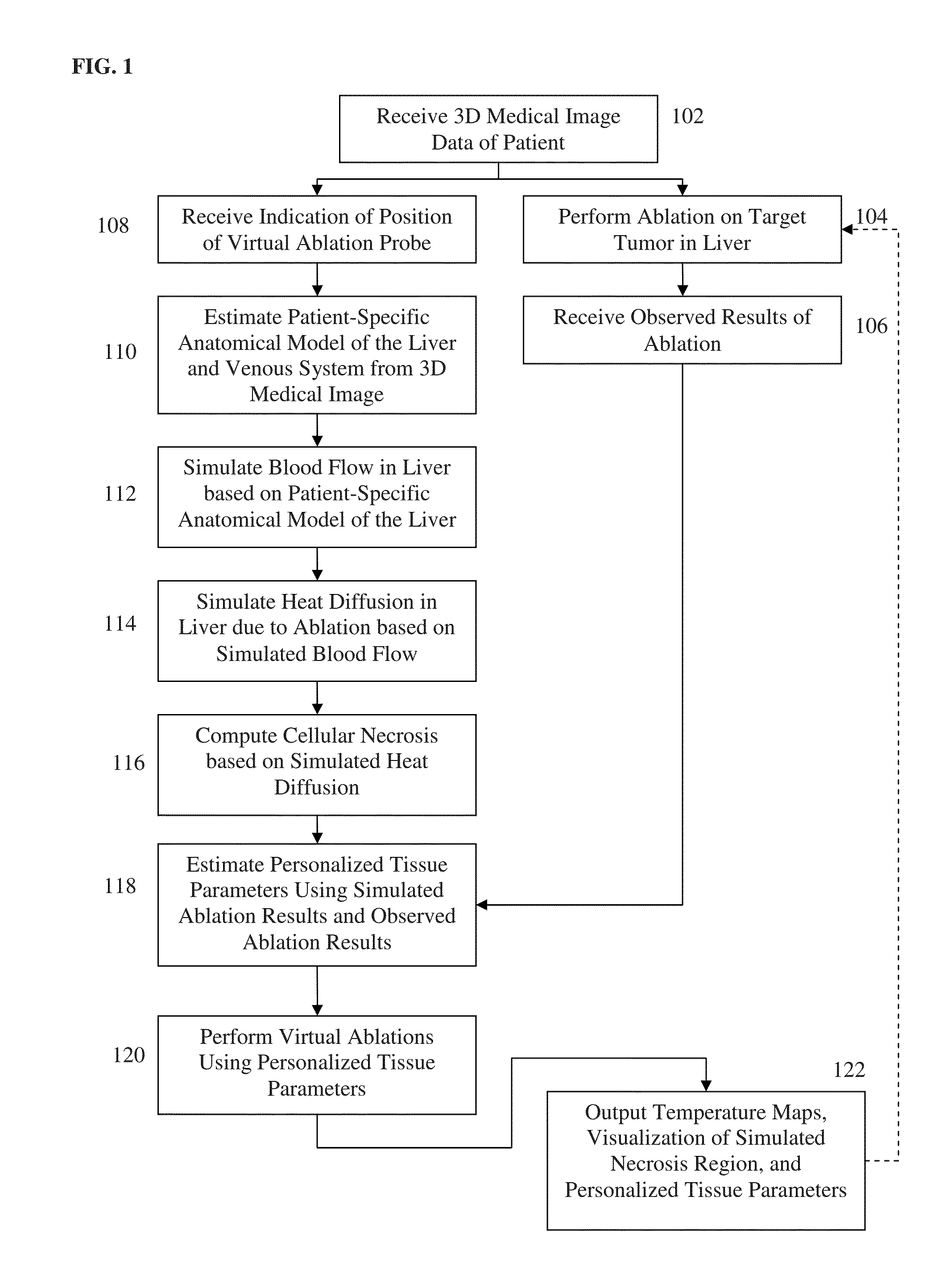
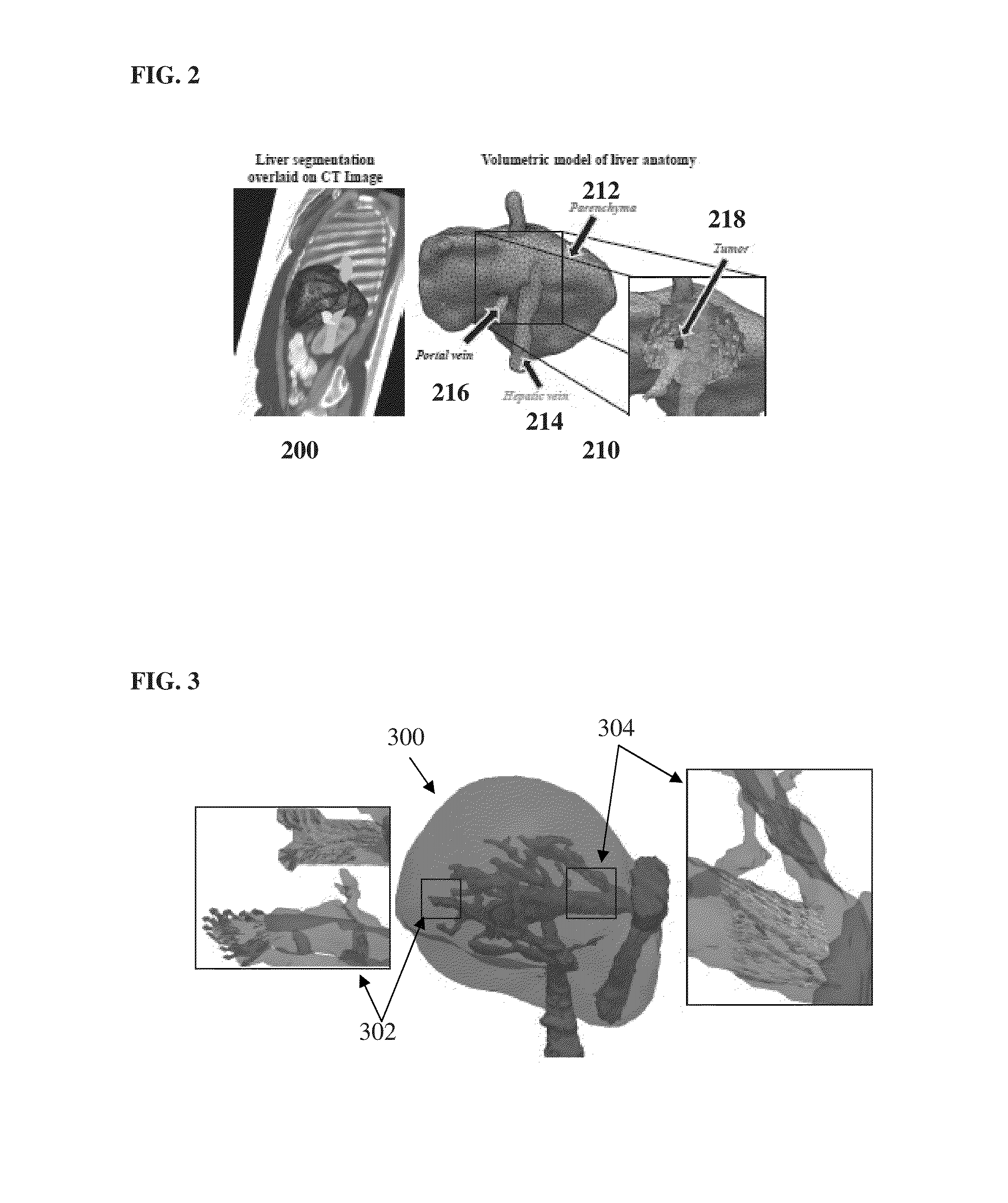
System and Method for Personalized Computation of Tissue Ablation Extent Based on Medical Images
ActiveUS20150242588A1Accurate pre-ablation planningFine stepsMedical simulationRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsPersonalizationBlood flow
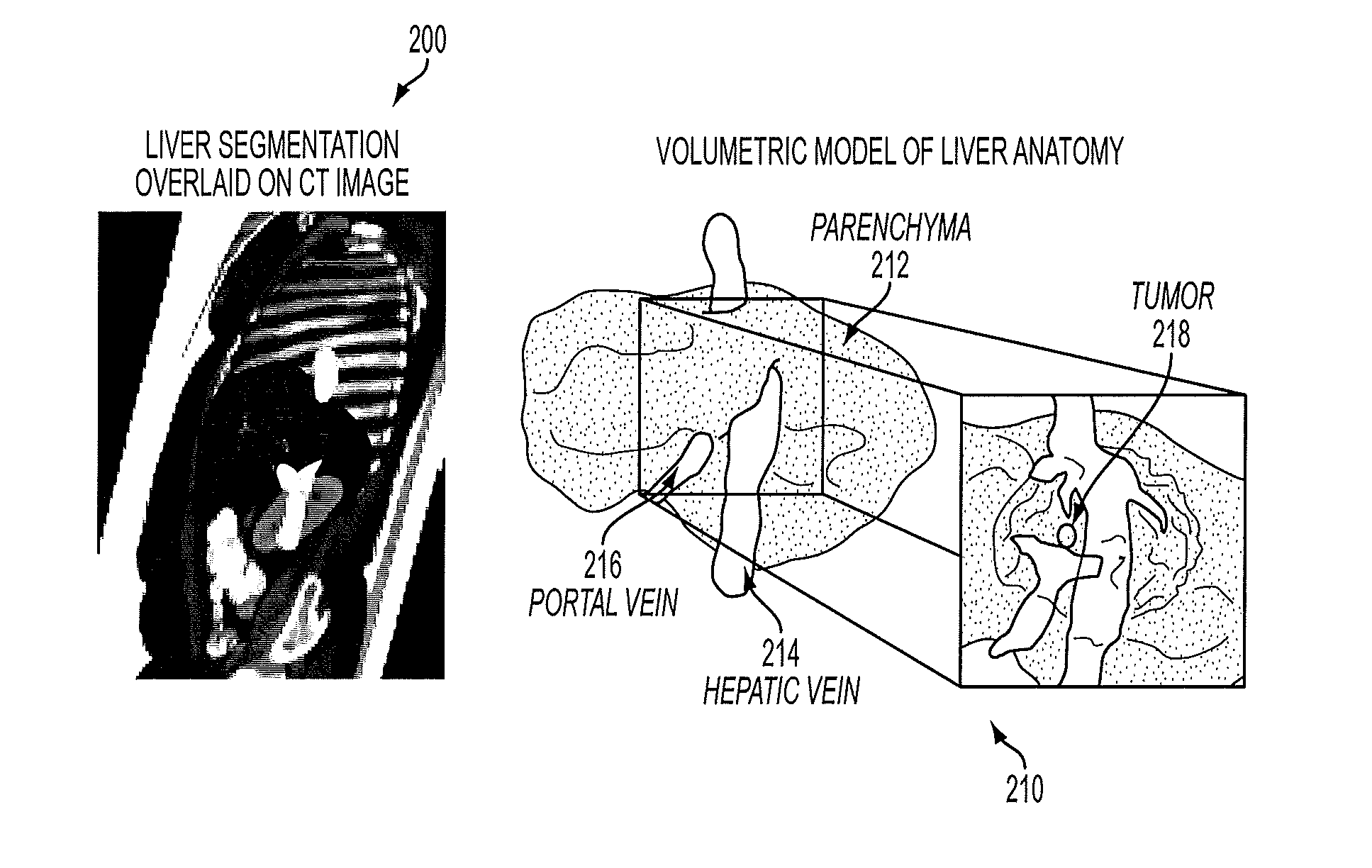
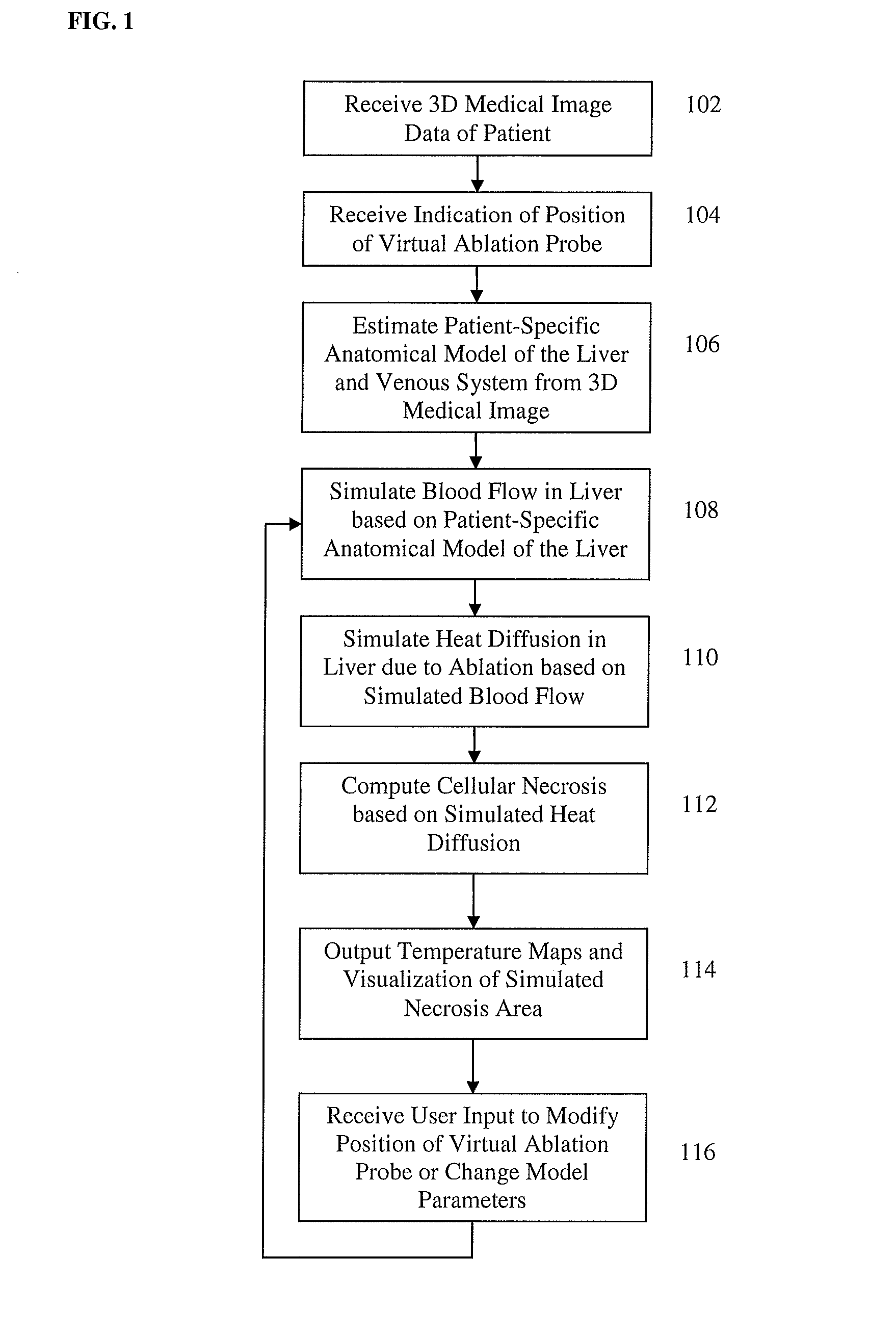
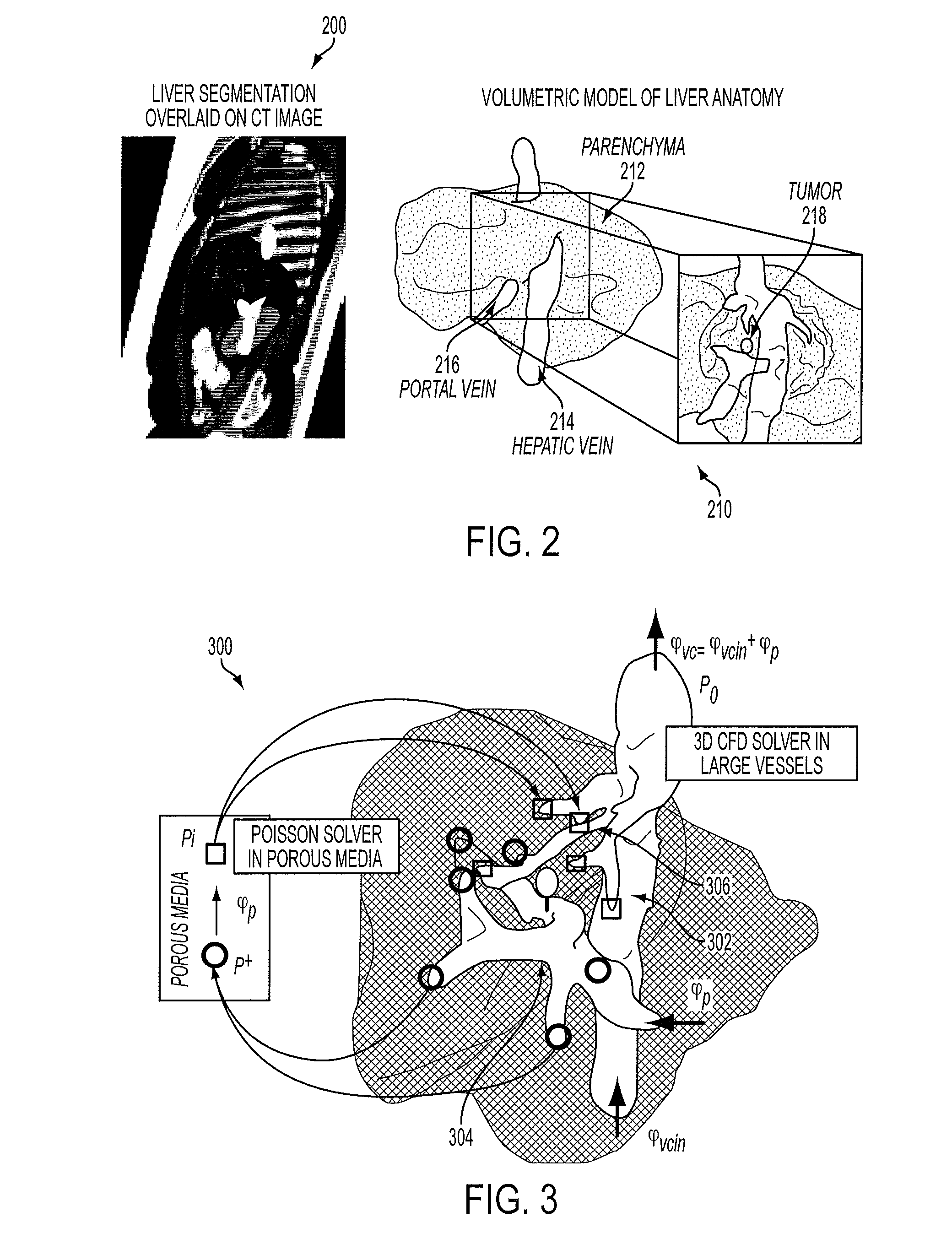
A method and system for personalized computation of tissue ablation extent based on medical images of a patient is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the liver and liver vessels is estimated from medical image data of a patient. Blood flow in the liver and liver vessels is simulated. An ablation simulation is performed that uses a bio-heat model to simulate heat diffusion due to an ablation based on the simulated blood flow and a cellular necrosis model to simulate cellular necrosis in the liver based on the simulated heat diffusion. Personalized tissue parameters of the bio-heat model and the cellular necrosis model are estimated based on observed results of a preliminary ablation procedure. Planning of the ablation procedure is then performed using the personalized bio-heat equation and the cellular necrosis model. The model can be subsequently refined as more ablation observations are obtained.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
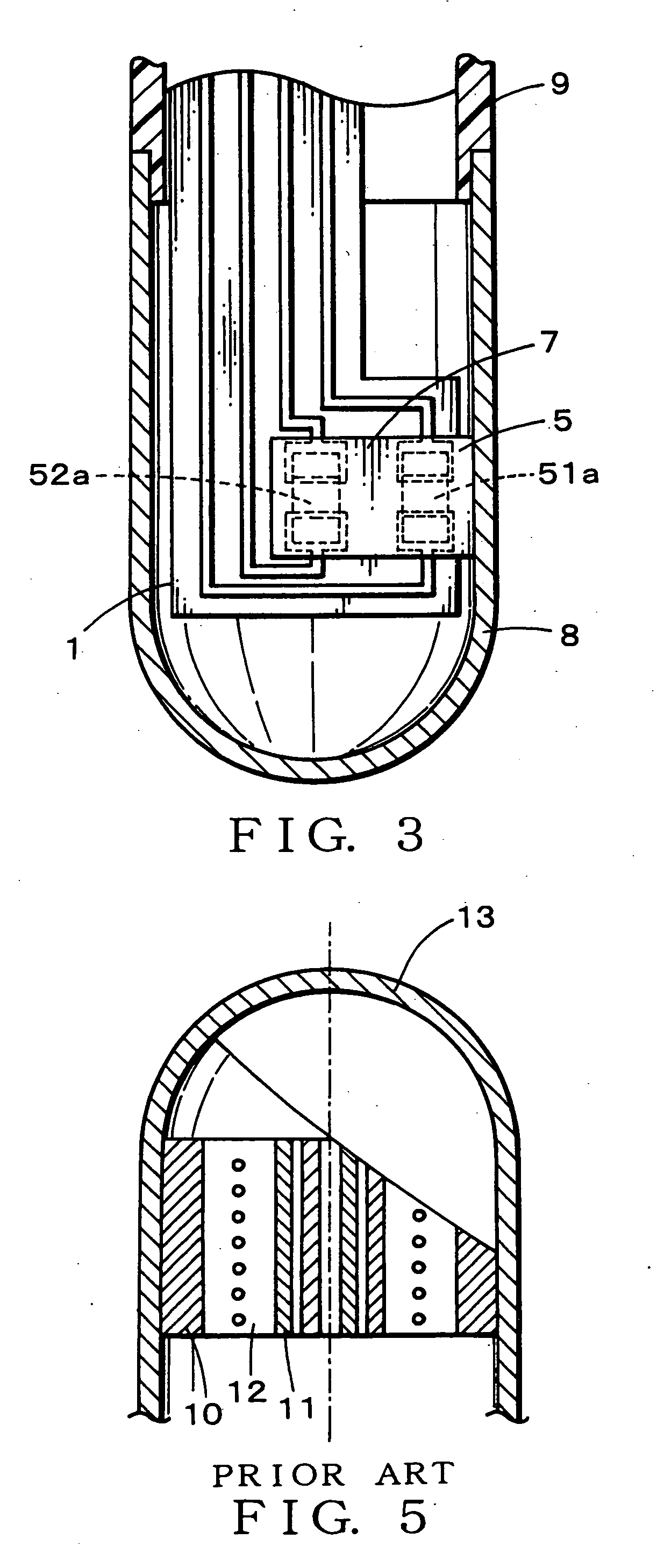
Probe for electronic clinical thermometer
ActiveUS20060209920A1No slack givenImprove production efficiencyThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHuman bodyHeat flux
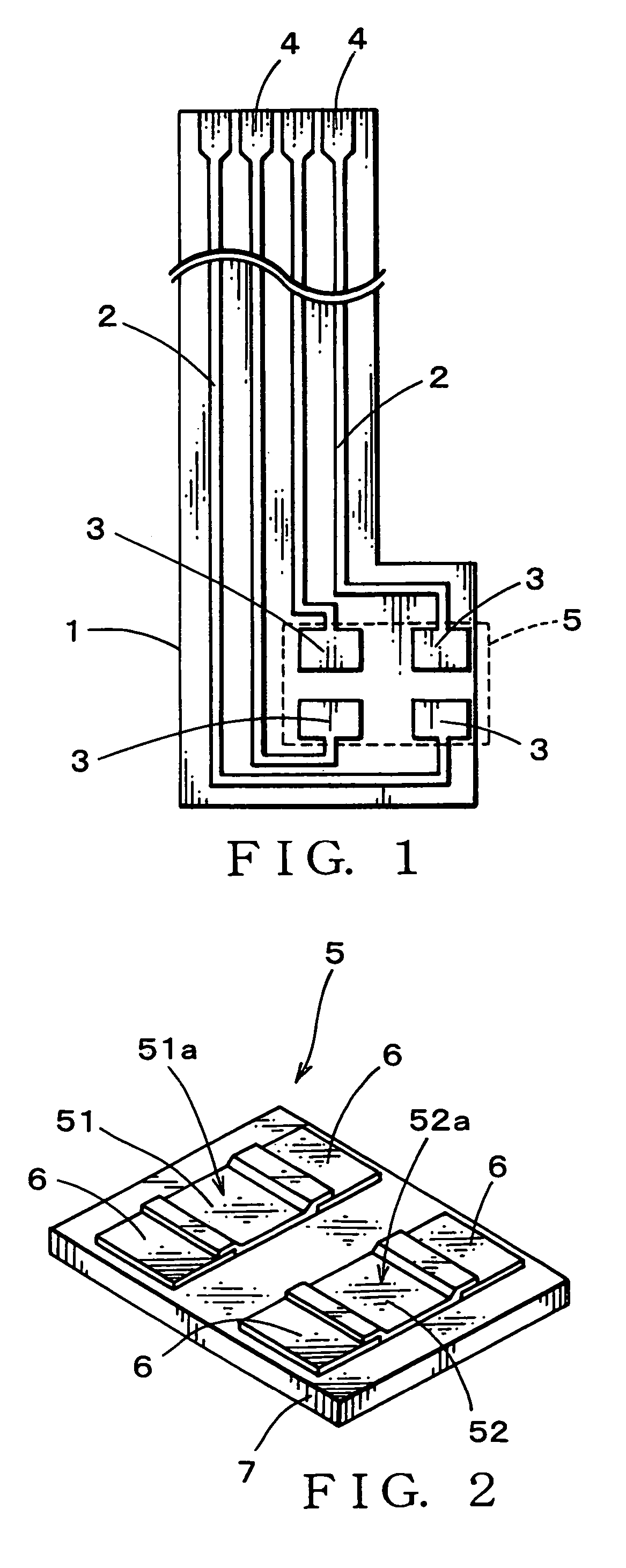
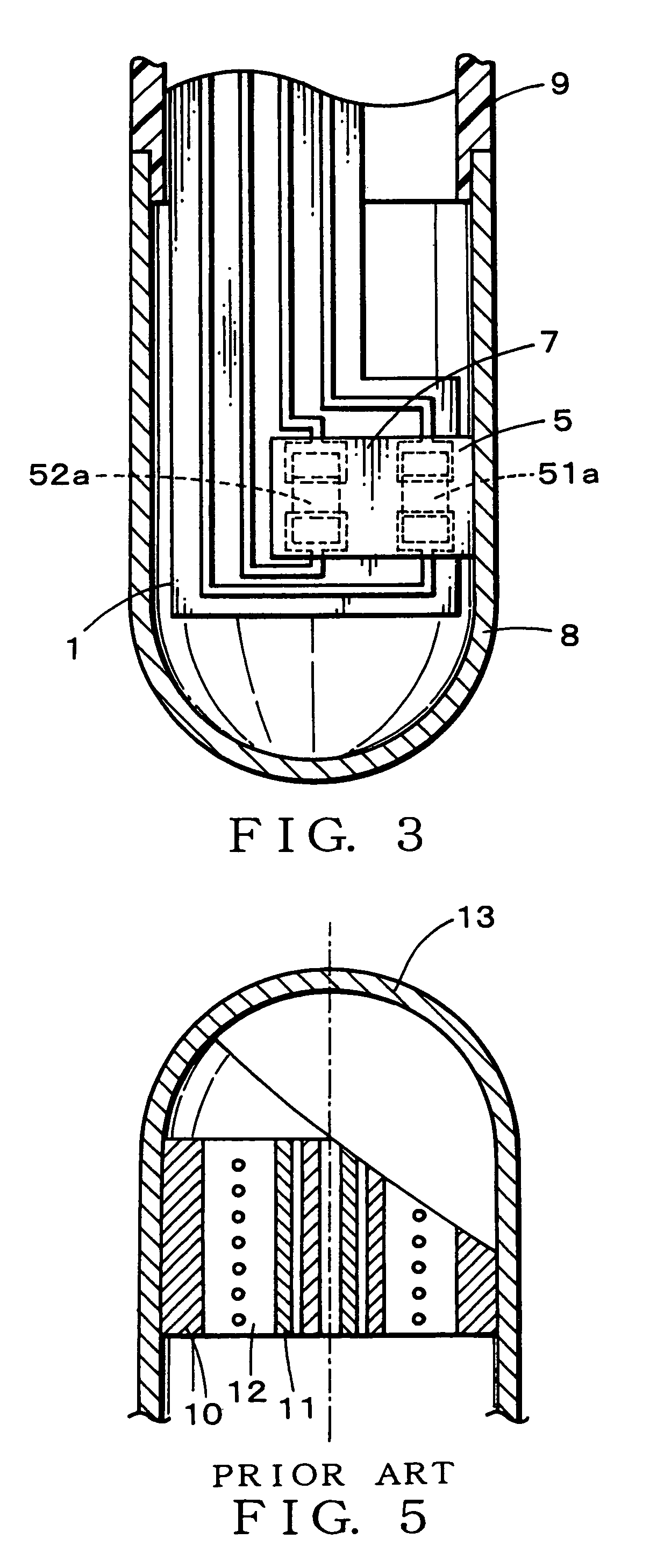
Providing a probe for an electronic clinical thermometer, which can measure a surface temperature and a deep body temperature of a human body securely in short time, the probe includes a cylindrical housing, a bottomed metal pipe fitted into a top end of the cylindrical housing, and a substrate having two thin-film heat-sensitive elements arranged perpendicularly on an inner wall of the bottomed metal pipe so as to fix one side edge of the substrate tightly on the inner wall. By measuring heat flux between the two thin-film heat-sensitive elements, the surface and the deep body temperatures of the human body can be predicted by applying the measured values into a heat conduction equation without waiting the sensor to reach in heat balance.
Owner:ISHIZUKI ELECTRONICS
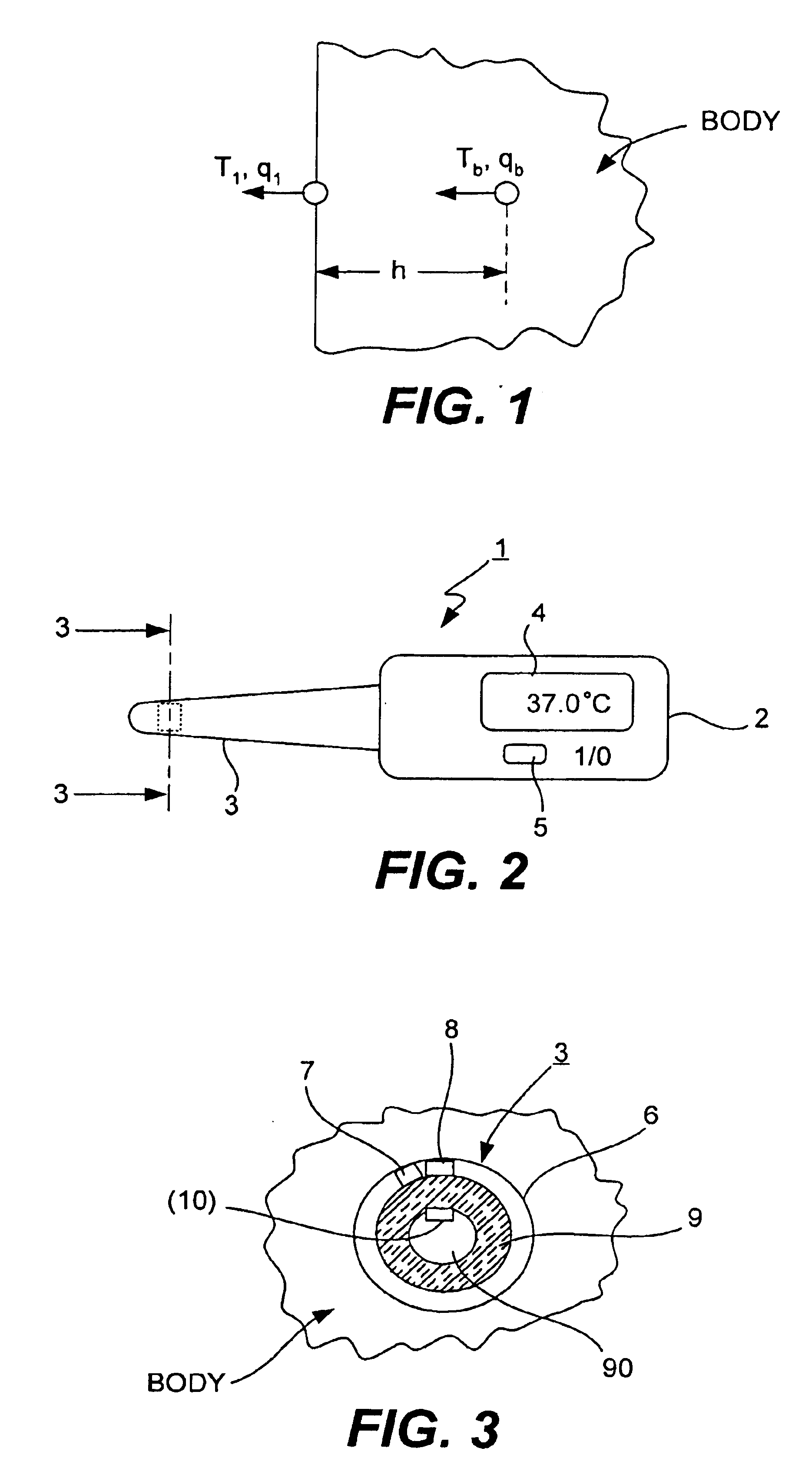
Method and device for obtaining internal heat source information from the surface temperature distribution of living body
InactiveCN1771882AAvoid the question of whether it is reasonableDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReduced modelDisease
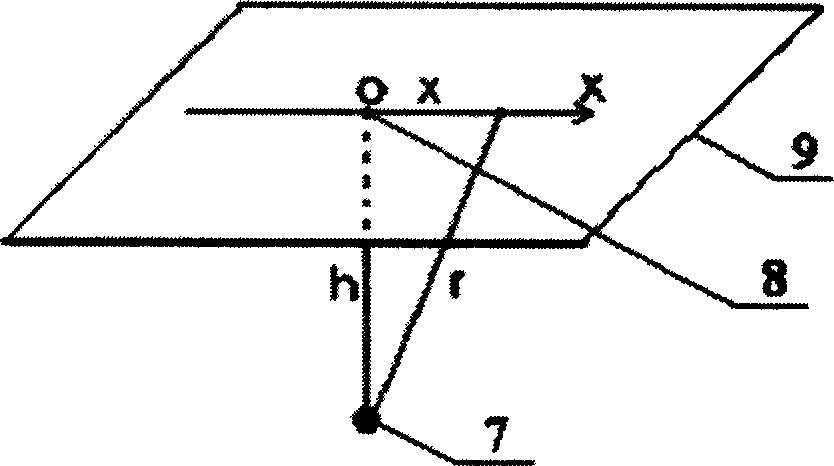
The present invention is method and device for obtaining internal heat source information from the surface temperature distribution of living body. The device consists of three parts: uncooled focal plane infrared detector, interface circuit and computer system. Human body infrared radiation is received with the uncooled focal plane infrared detector and treated with the interface circuit and computer system to obtain temperature distribution data on the body surface. By means of Pennes biothermal conducting equation, properly simplified mold to find out the analytic solution of the equation and corresponding computer software, the depth h and the strength q information of the abnormal intracorporeal heat source may be obtained conveniently and simply based on the temperature distribution data on the body surface. The present invention can provide useful reference for the clinical diagnosis of diseases in imaging science method.
Owner:WUBO SCI TECH WUHAN
Swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method under rainfall infiltration condition
ActiveCN106202980AOvercome deficienciesOvercome defectsInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsSoil mechanicsFluid solid coupling
The invention discloses a swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method under the rainfall infiltration condition. The swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method comprises the following steps: adopting a fluid-solid coupling module and compiling a relevant FISH language program, and realizing the relation of change of the non-saturated region matrix suction, the non-saturated permeability coefficient and the soil strength parameter along with the moisture content in the unsaturated seepage process; then based on the 'humidity stress field theory', according to the similarity of a seepage continuity differential equation and a heat conduction equation, deducing the equivalent conversion relation of a thermodynamic parameter and a seepage parameter, and adopting a thermodynamic module to realize swelling soil swelling deformation process under the humidifying condition. According to the swelling soil humidifying and swelling numerical simulation method, the swelling soil humidifying and swelling whole-process numerical calculation under the rainfall infiltration condition can be effectively and comprehensively realized, so that effective scientific guidance means are provided for engineering design and construction in the high-risk area of the swelling soil engineering disaster, and meanwhile application of the computational soil mechanics to the technical fields of practical engineering construction, geological disaster prevention and control, and the like, is powerfully driven.
Owner:SHANXI PROVINCIAL RES INST OF COMM +1
Modeling method for a metal
ActiveUS20050016712A1Modeling resultSimulator controlCasting safety devicesModel methodFree energies
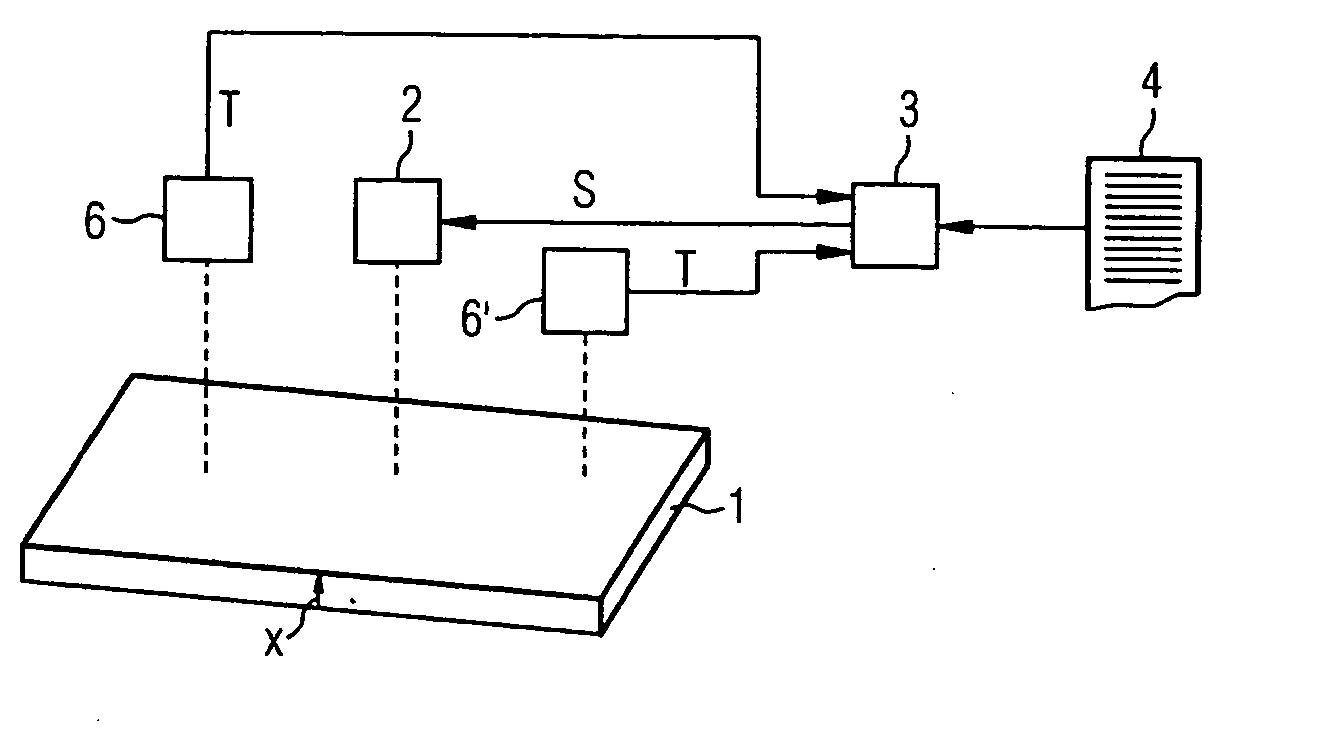
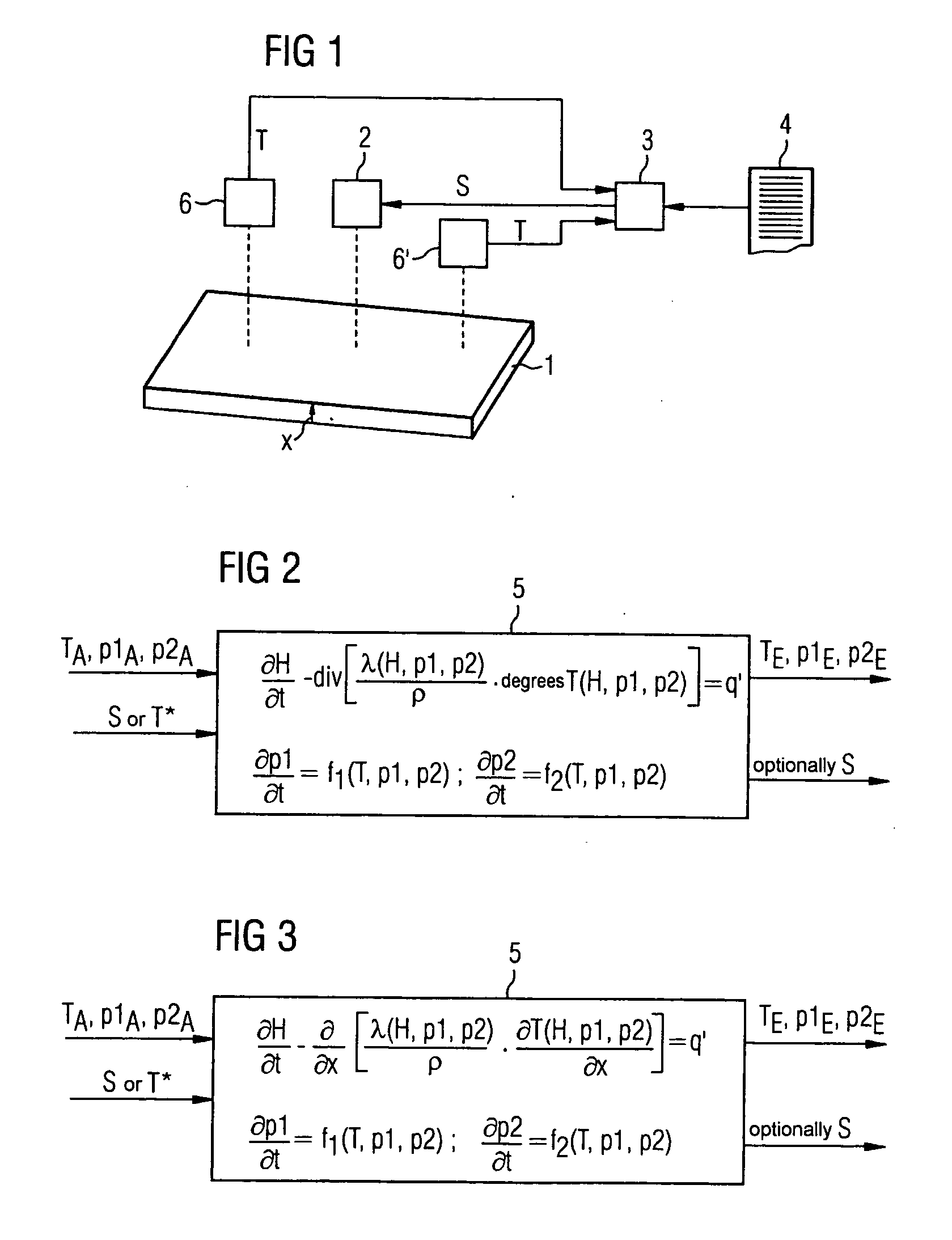
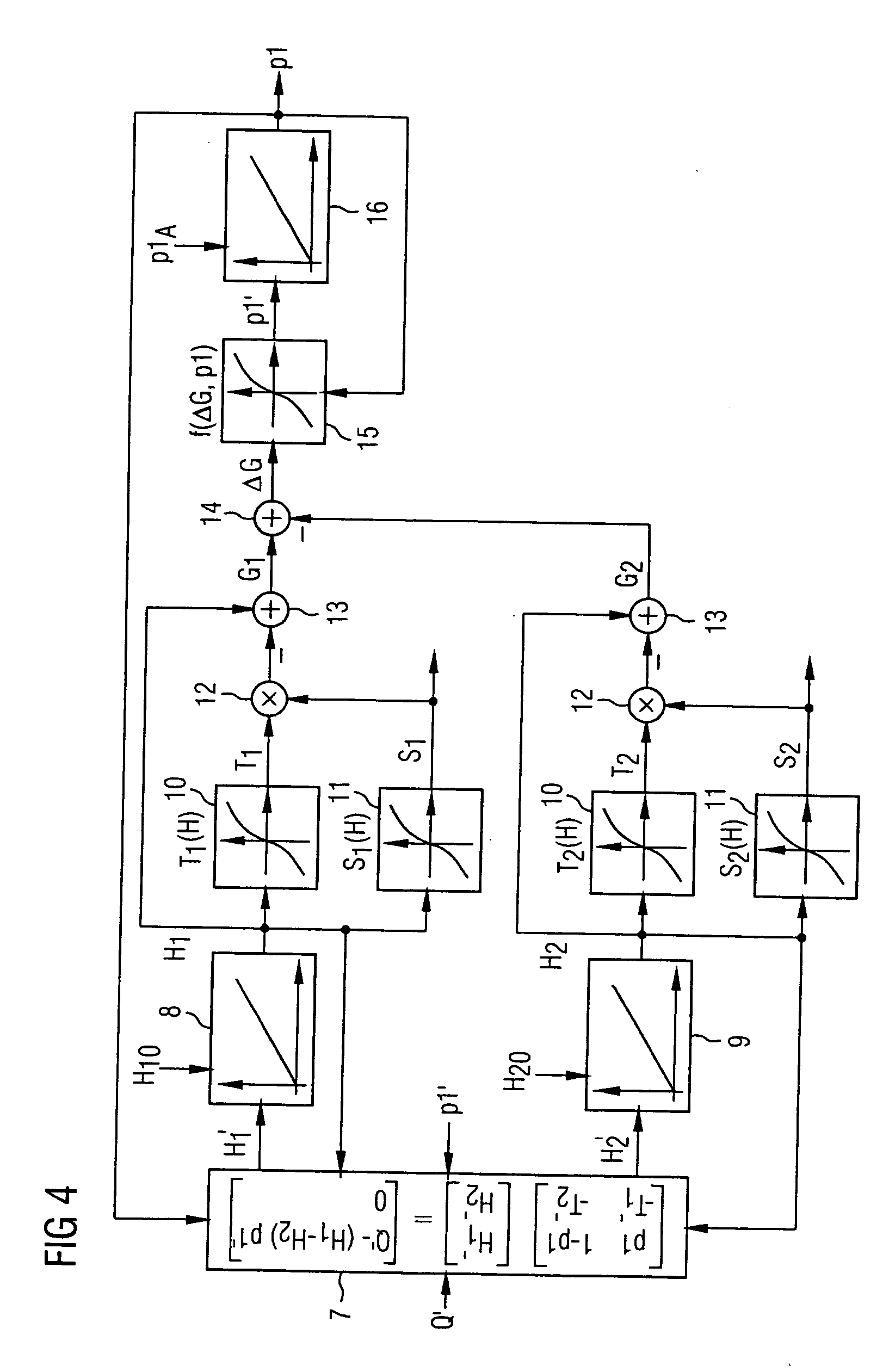
The temperature (T) of a metal (1) can be influenced directly or indirectly by at least one actuator (2) which is actuated in accordance with a control variable (S). The control variable (S) and starting values (TA, p1A, p2A) for a temperature of the metal (1) and phase proportions in which the metal (1) is at least in a first phase or a second phase, respectively, are predetermined for a material model (5). A heat conduction equation and a transformation equation are solved in real time within the material model (5), taking account of these variables (TA, p1A, p2A) , and in this way expected values (TE, p1E, p2E) are determined for these variables. As part of the transformation equation, the Gibbs' free energies (G1, G2) of the phases of the metal (1) are determined, a transformation rate of the metal (1) from the first phase to the second phase is determined therefrom, and the expected proportions (p1E, p2E) are determined from the latter.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
Probe for electronic clinical thermometer
ActiveUS7441950B2No slack givenEasy to insertThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat fluxEngineering
Providing a probe for an electronic clinical thermometer, which can measure a surface temperature and a deep body temperature of a human body securely in short time, the probe includes a cylindrical housing, a bottomed metal pipe fitted into a top end of the cylindrical housing, and a substrate having two thin-film heat-sensitive elements arranged perpendicularly on an inner wall of the bottomed metal pipe so as to fix one side edge of the substrate tightly on the inner wall. By measuring heat flux between the two thin-film heat-sensitive elements, the surface and the deep body temperatures of the human body can be predicted by applying the measured values into a heat conduction equation without waiting the sensor to reach in heat balance.
Owner:ISHIZUKI ELECTRONICS
Library graphic and text information denoising filter based on fractional order calculating equation
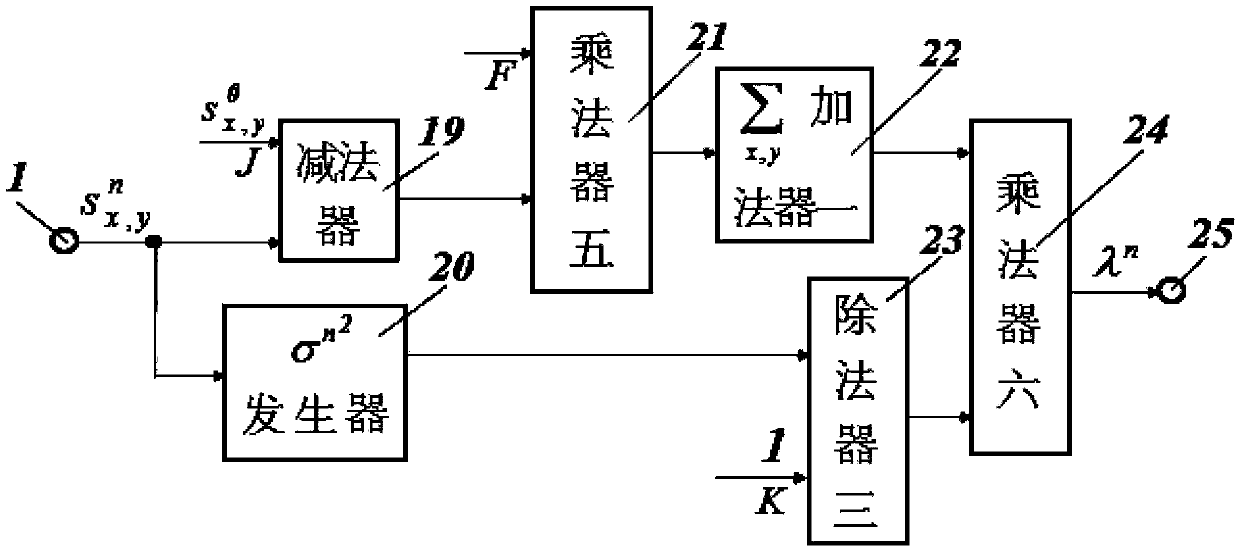
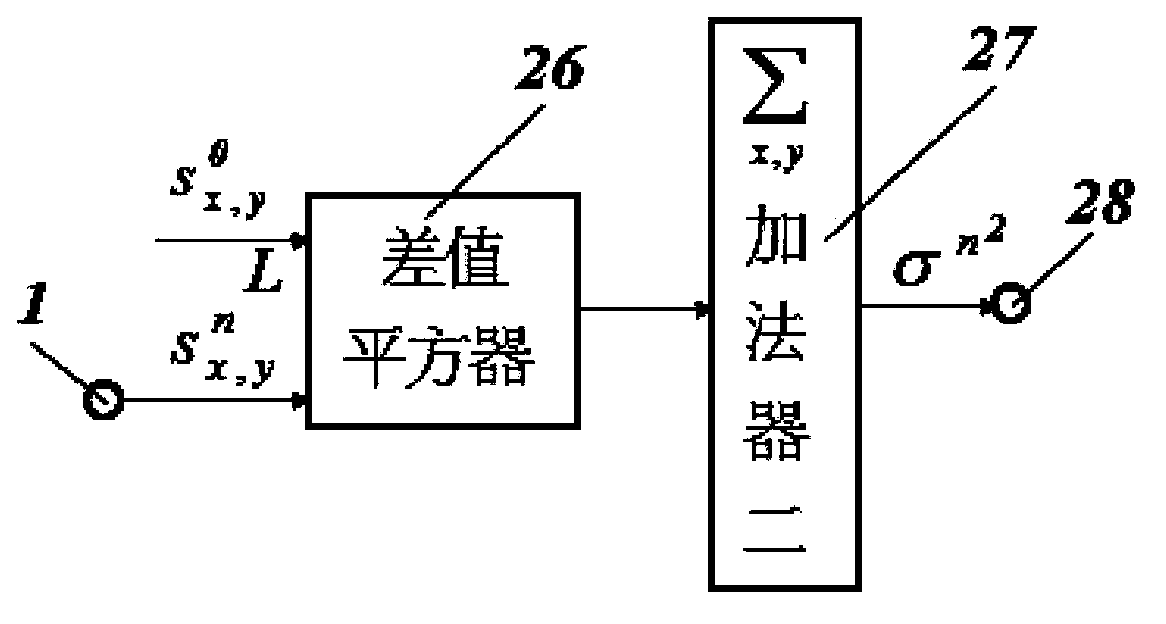
The invention provides a library graphic and text information denoising filter based on a fractional order calculating equation and belongs to the technical field of interdiscipline of applied mathematics, digital image processing and digital circuits. On the basis of a special fractional order thermal conduction equation, fractional order, nonlinear, multi-scale and fast denoising of images is achieved. The related fractional calculus order v1 is not a traditional integer order but a non-integer order which is used in form of fraction or rational fraction in engineering application. The filter comprises a first differentiator, a second differentiator, a third differentiator, a model calculator, a first divider, a second divider, a fourth differentiator, a fifth differentiator, a first adder, a first multiplier, lambda n generator, a second multiplier, a second adder, a third multiplier, a fourth multiplier and a third adder which are in cascade connection. The filter is especially applicable to fast denoising of images rich in complex texture detail features.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
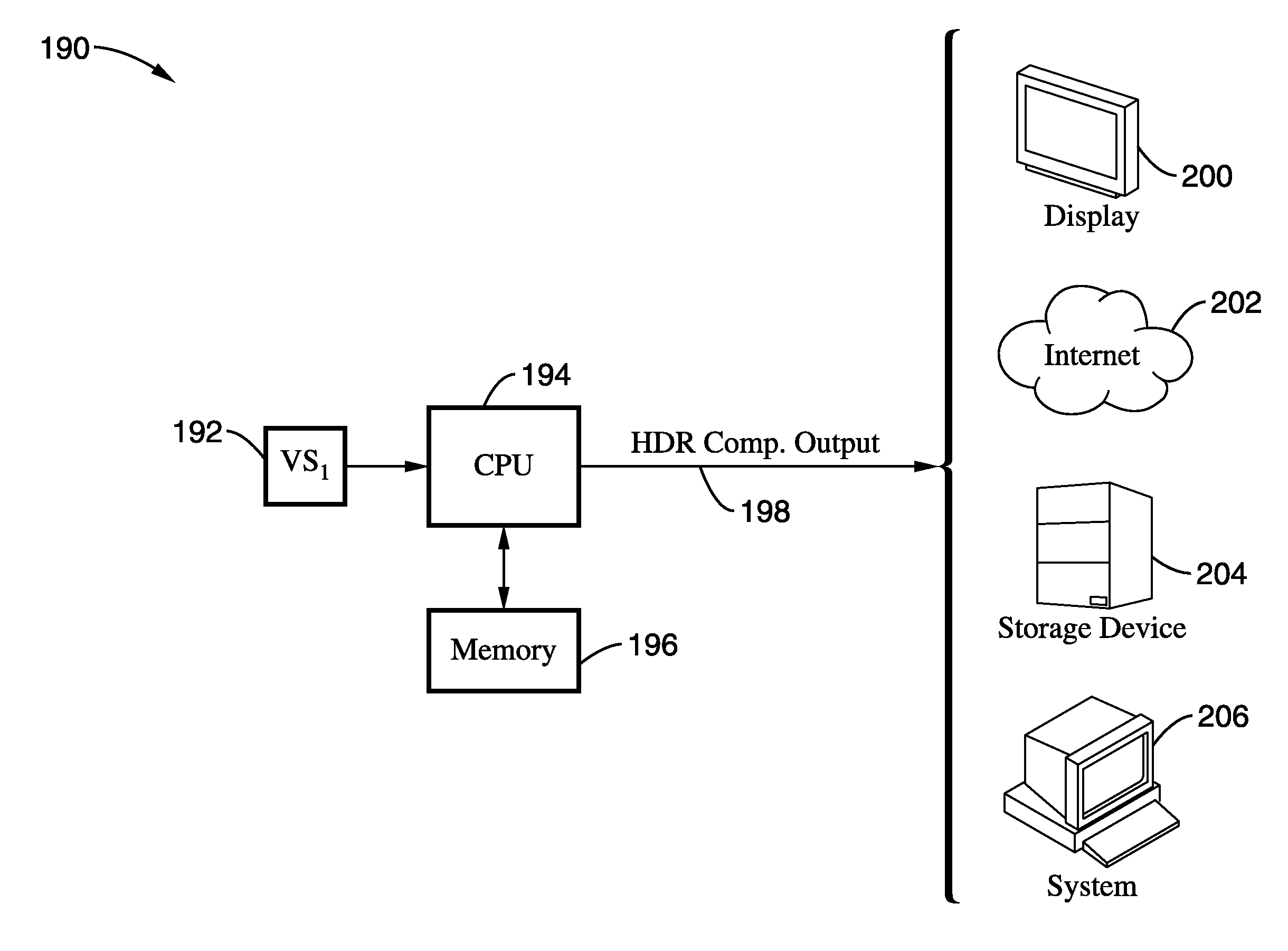
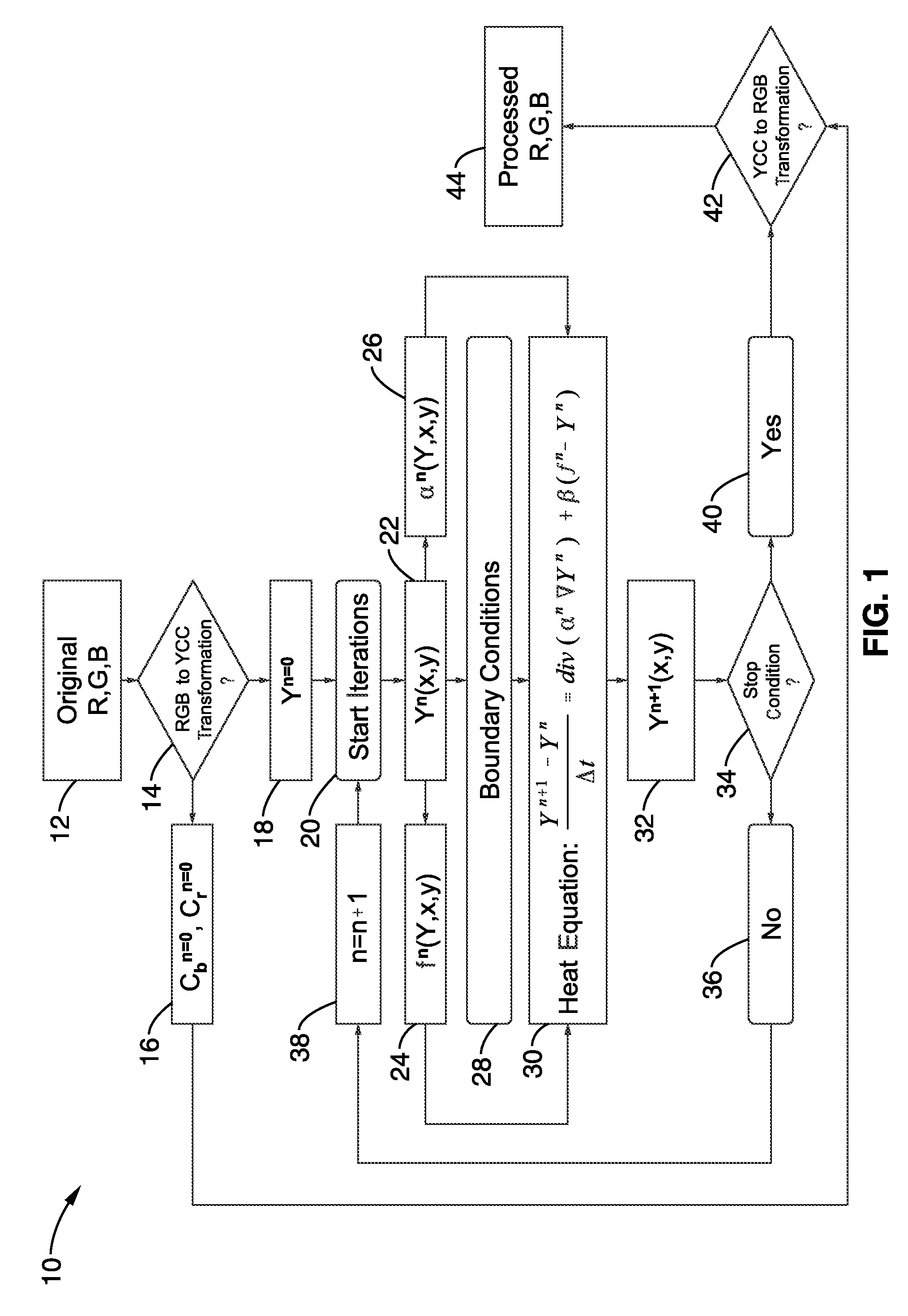
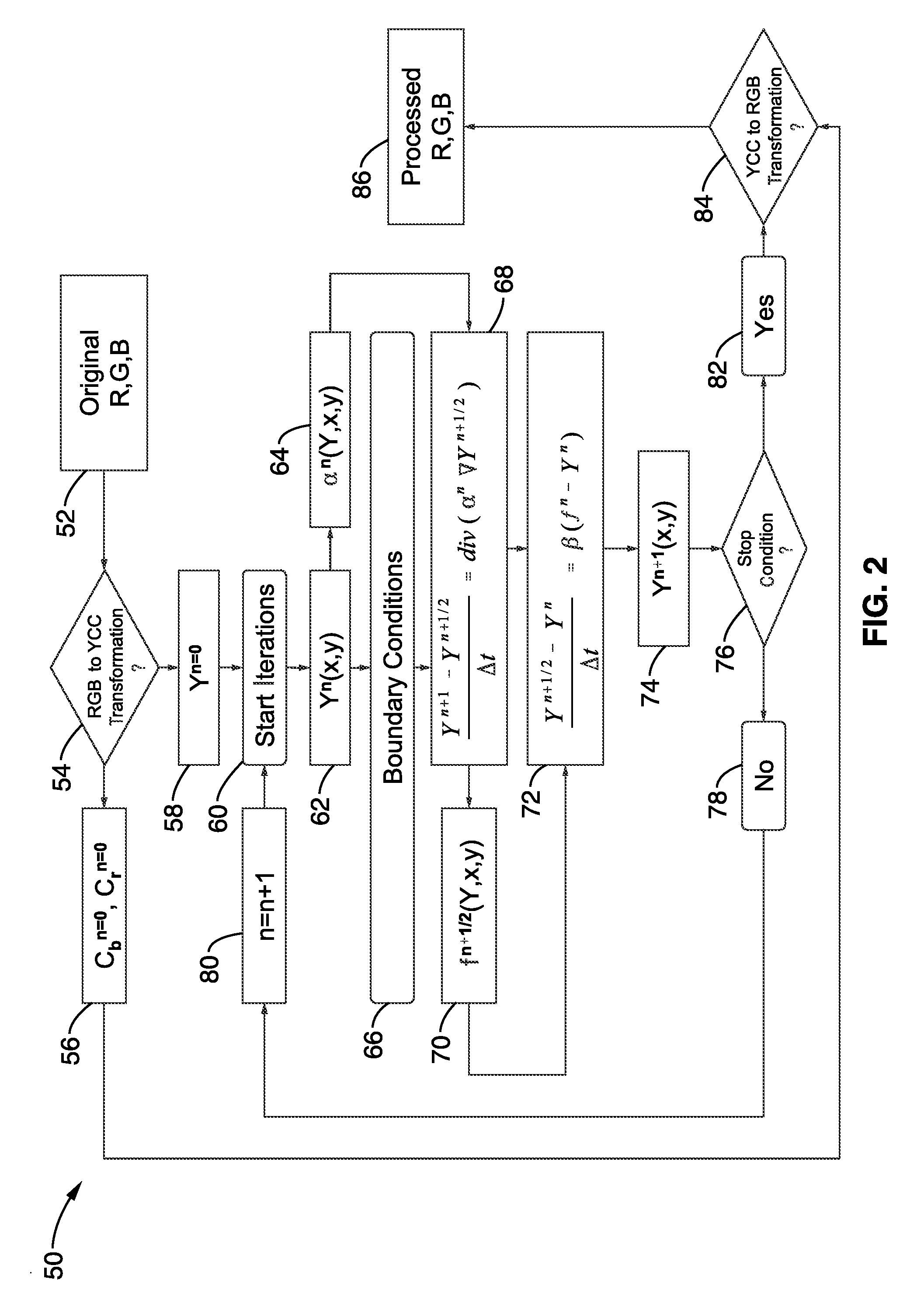
Joint high dynamic range compression and noise reduction
InactiveUS20100238190A1Reduce noiseImprove computing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisSingle processDynamic range compression
A high dynamic range (HDR) compression method and apparatus modeled after the heat equation describing temperature changes in a thin plate. This approach allows combining high dynamic range compression together with noise reduction in a single process, to be performed within the same iteration of the heat equation. Noise reduction is of particular concern while performing HDR compression because brightening of dark areas during high dynamic range compression has the potential to increase noise levels. Performing image processing techniques in combination according to the invention provides enhanced results while lowering the overall processing overhead. This innovation extends the heat equation analogy by adding anisotropic diffusion as an additional term, which allows joint operation of HDR and NR and mitigates noise enhancement within HDR compression during shadow enhancement.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
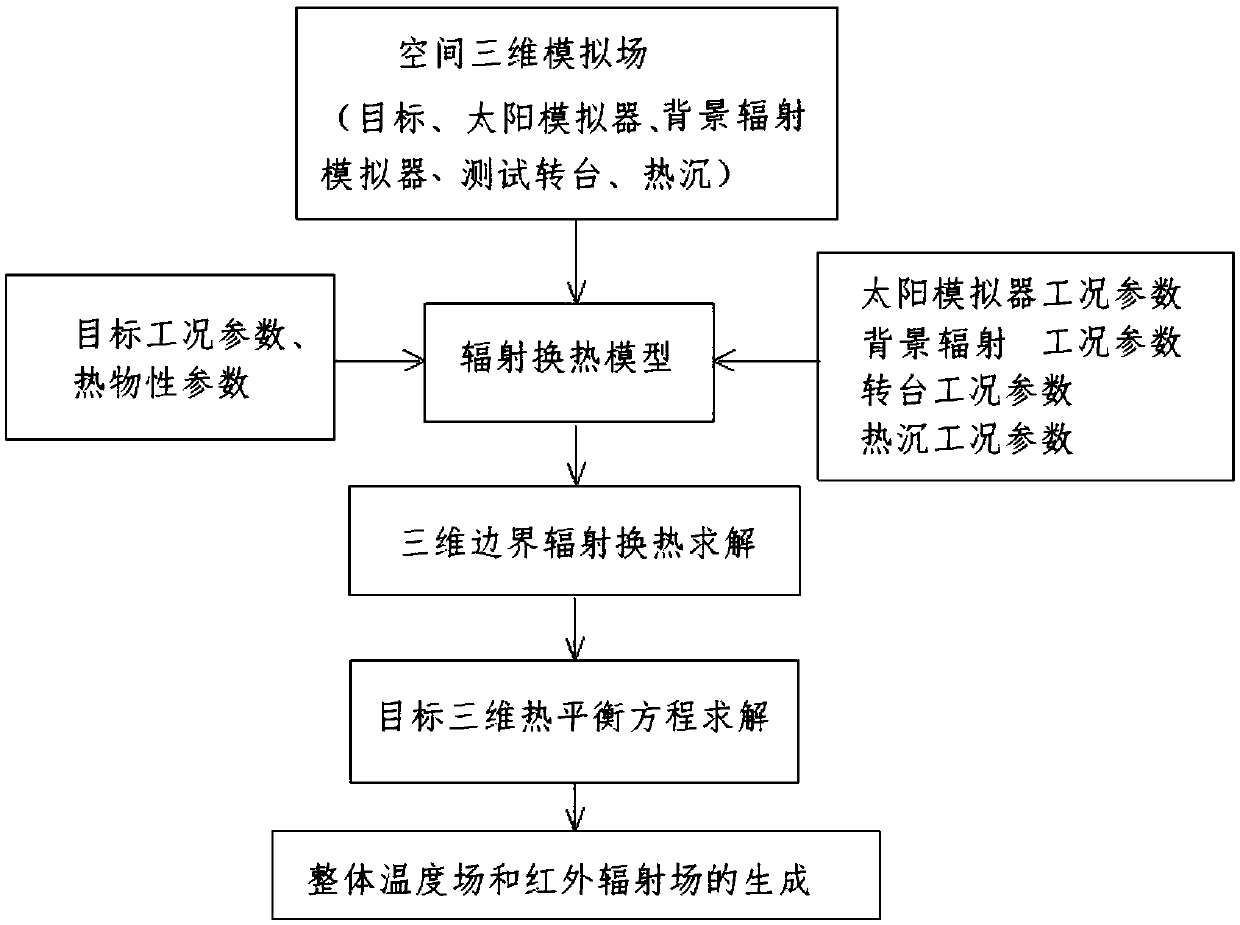
Target heat radiation analyzing method in space environment simulating device
ActiveCN109580698AEnables infrared bolometric analysisMaterial heat developmentThree dimensional simulationRadiation field
The invention relates to a target heat radiation analyzing method in a space environment simulating device. A space three-dimensional simulation scene is firstly established adopting a simulation method, and a heat effect model and a test target is included in the scene; then a heat equation of the test target is established according to determined heat effect model; then a working condition parameter is input, and solution is conducted on the heat equation; and a temperature field and an infrared radiation field of the whole scene are finally generated according to the solved equation. According to the target heat radiation analyzing method in the space environment simulating device, a large spherical vessel, a heat sink, a solar simulator, a background radiation simulator, a test track and device, a rotary table and an observation window simulation scene are adopted, radiation heat transfer analyzing is conducted coupling three-dimensional unsteady state, and thus radiation field with waveband of 30-50 mum can be accurately simulated.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST OF THE LONG MARCH VEHICLE
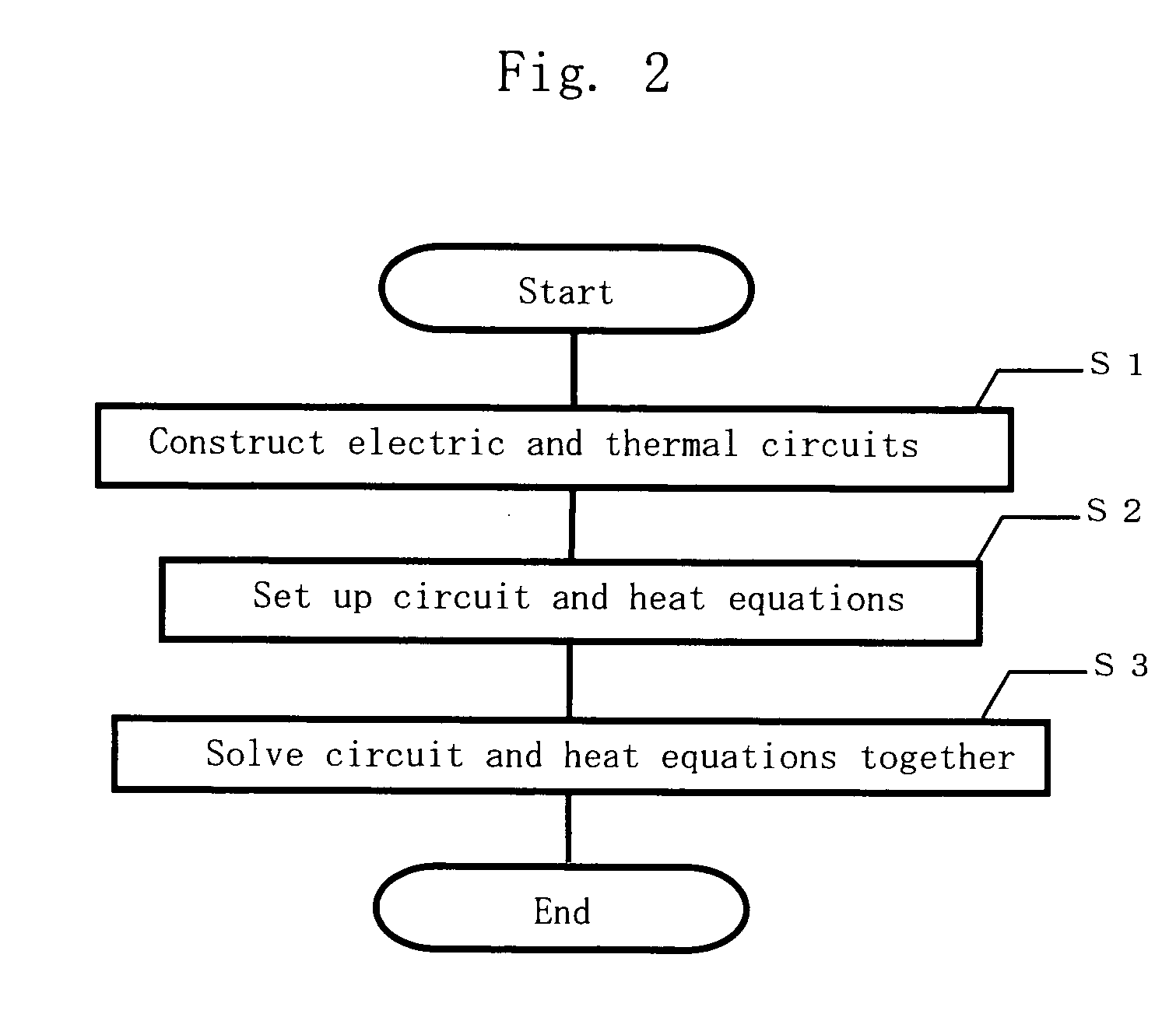
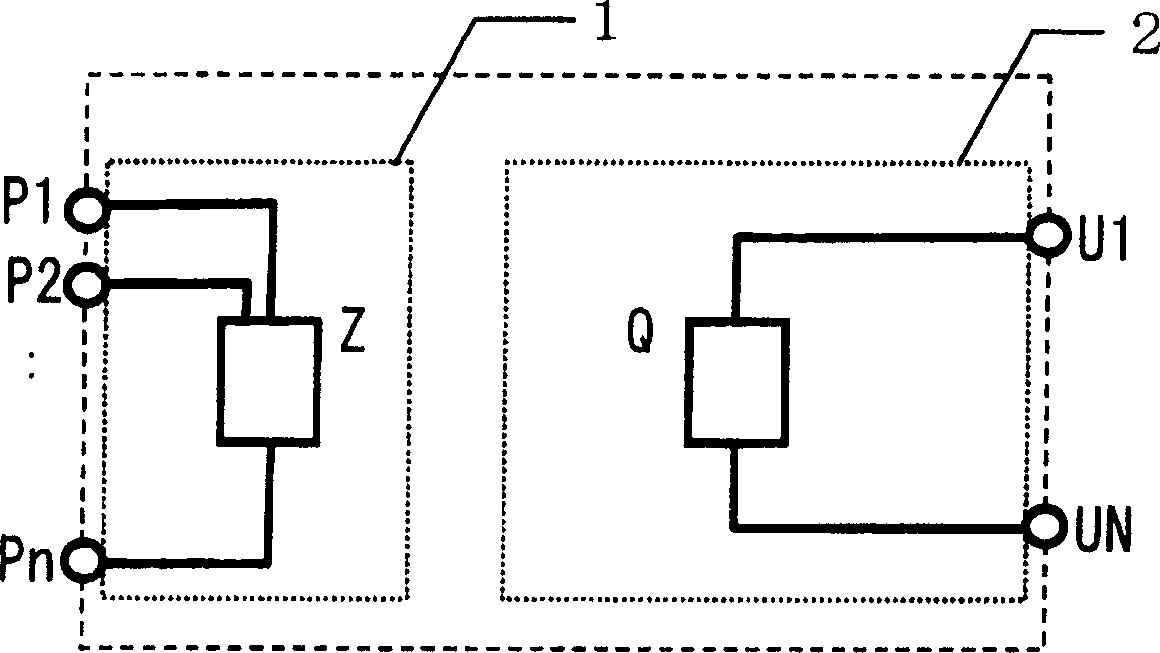
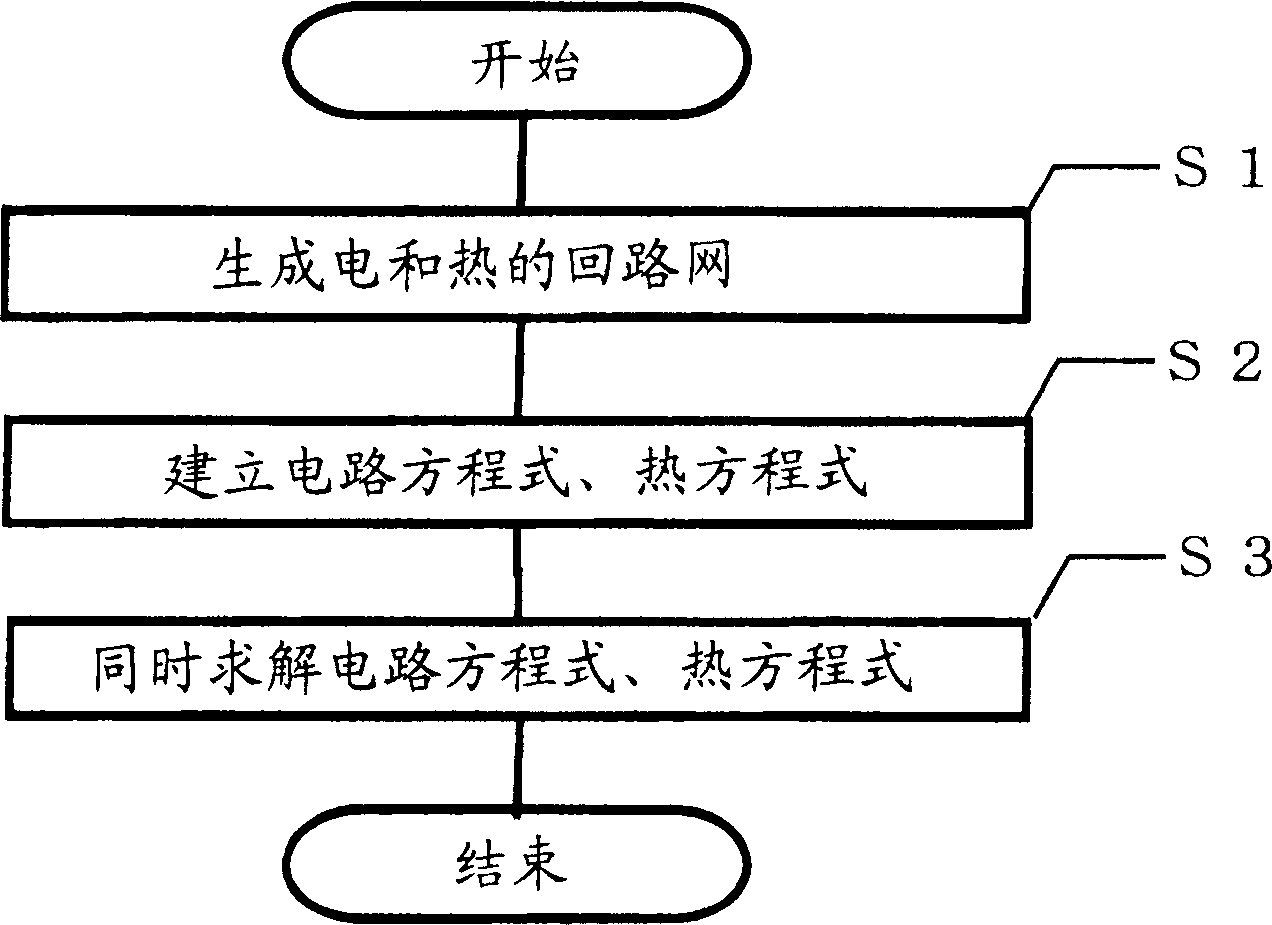
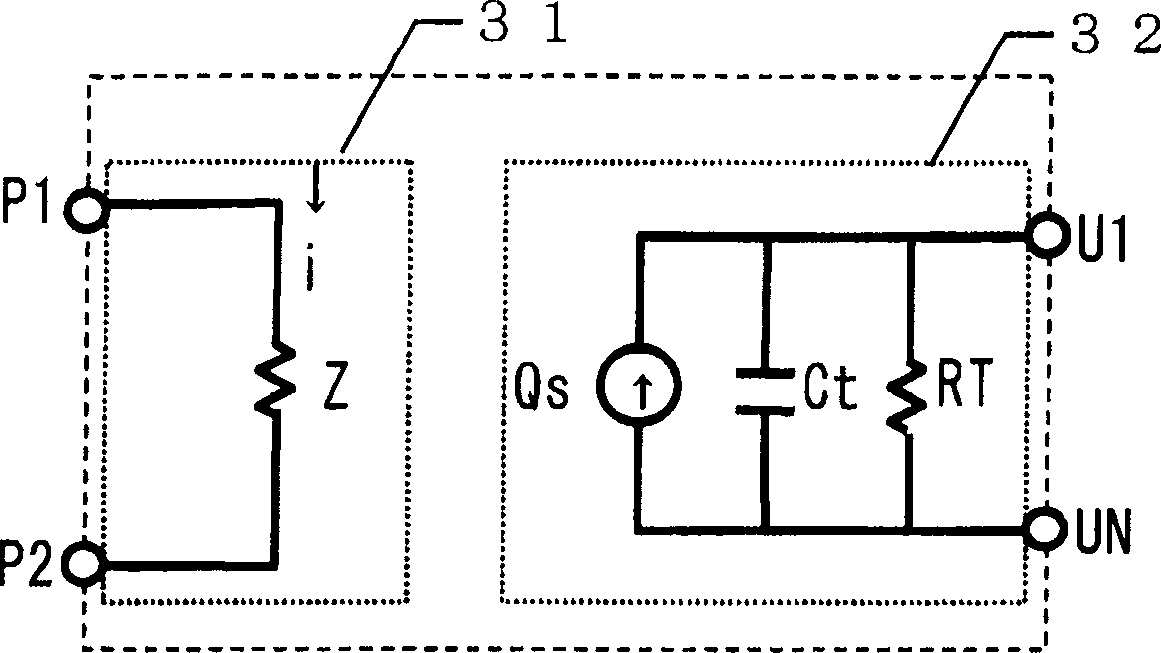
Circuit simulation method, device model, and simulation circuit
InactiveUS20050273309A1High-precision and efficient circuit simulationEffective simulationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer aided designElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
A plurality of elements constituting a semiconductor integrated circuit to be designed are each converted to a device model which merges an electric model exhibiting electric characteristics of the element and a thermal model exhibiting thermal characteristics of the element, and a thermal resistor is inserted between the elements where heat exchange occurs, thereby electric and thermal circuits are formed. Then circuit and heat equations are formulated with respect to the electric and thermal circuits, and then the equations are solved together to acquire electric and thermal characteristics of each element in the circuit. As a result, it becomes possible to achieve high-precision device characteristics which precisely reflect the temperature variation of each element in the circuit during simulation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Microwave passive circuit electromagnetic heat integral analysis method based on time domain spectrum element method
ActiveCN104050307AGood mannersQuickly obtain temperature distributionSpecial data processing applicationsMaxwell's equationsEngineering
The invention discloses a microwave passive circuit electromagnetic heat integral analysis method based on a spectrum element method. According to the method, firstly, a time domain spectrum element method is adopted for solving maxwell's equations, the instantaneous electric field and magnetic field distribution of a circuit under the effect of high-power pulses is worked out, and the electromagnetic loss at the current moment is obtained. If all of the electromagnetic loss inside a mold is converted into heat energy, the obtained heat energy is substituted into a heat conduction equation, and the temperature distribution conditions of each point at the current moment are obtained. Electricity characteristic parameters of materials at a next moment are obtained by utilizing a relational expression of dielectric parameters along with the temperature change, an electromagnetic field equation is calculated again, and the electromagnetic loss is obtained. The operation is repeatedly cycled in such a way until the preset heating time is completed. Through the electromagnetic heat integral analysis, the distribution condition of the temperature inside the mold along the time change when a filter receives the effect of different pulses can be clearly obtained, the modeling is flexible, the subdivision is convenient, formed matrixes have good sparsity, and the solving efficiency is higher.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
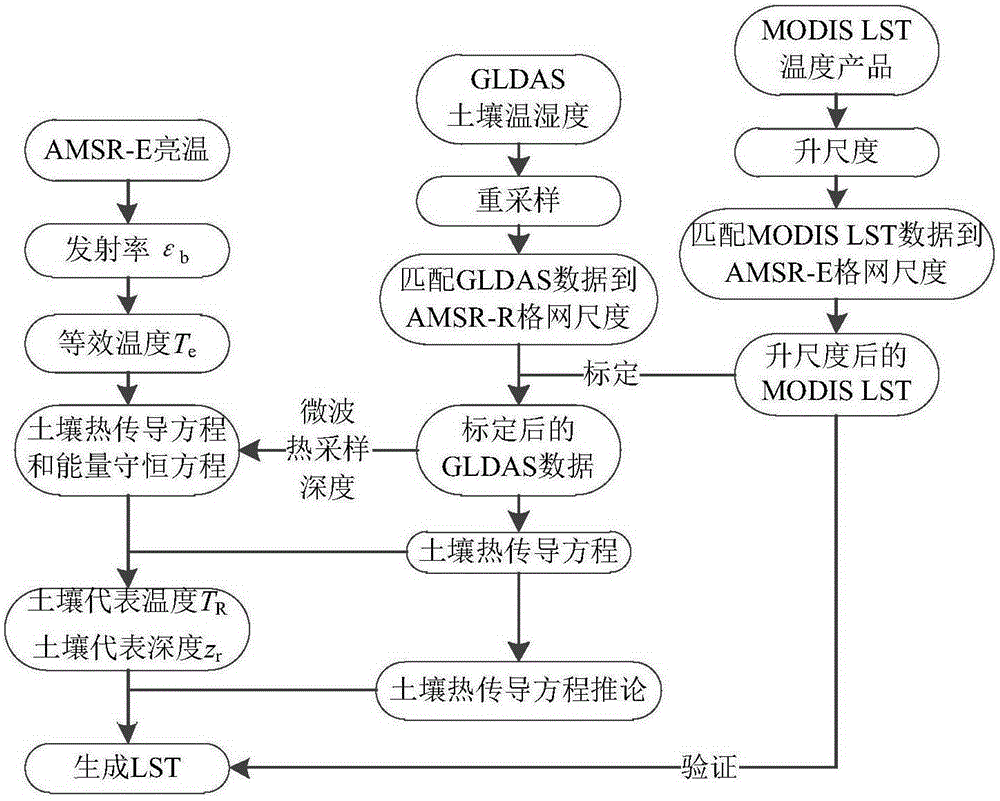
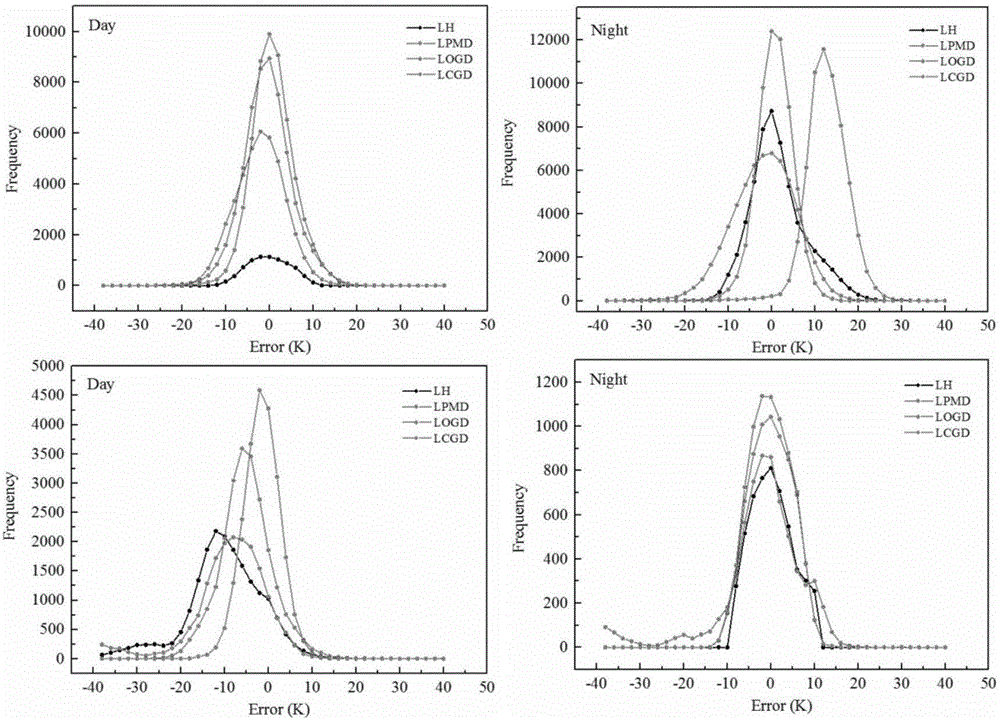
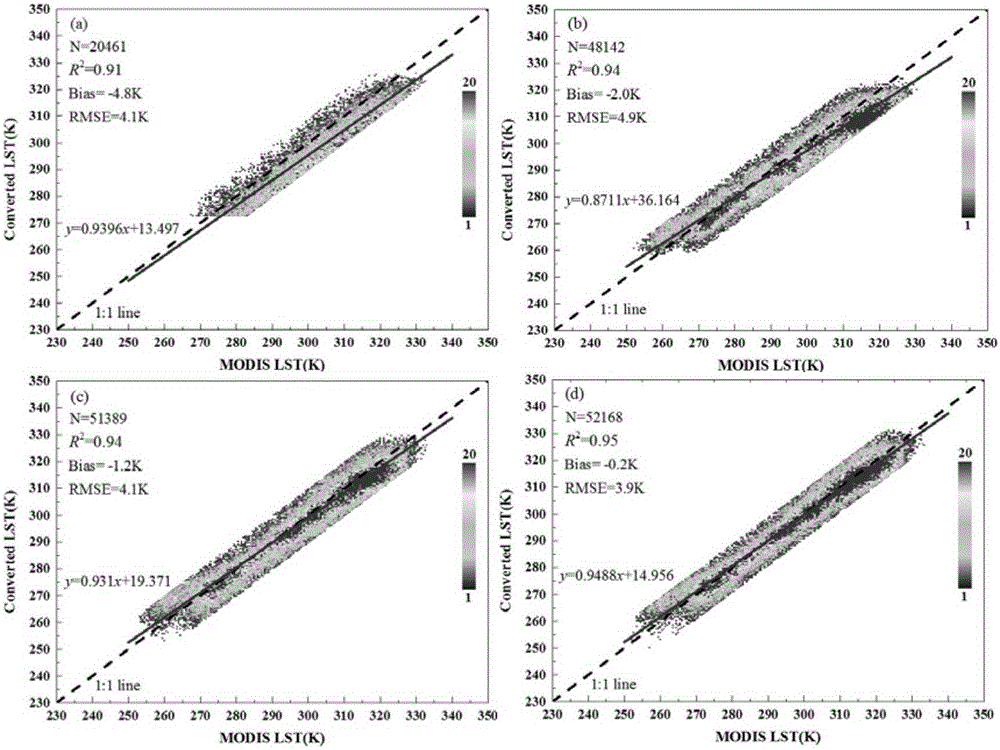
Method for converting microwave remote sensing surface temperature to thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature
ActiveCN105204024AWork around limited usageHigh precisionICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSensing dataThermal infrared remote sensing
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing application, and particularly relates to a method for converting microwave remote sensing surface temperature to thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature. A physical method suitable for a bare-ground area is provided based on a soil heat conduction equation. The method comprises the steps of data preprocessing; GLDAS data calibration; equivalent temperature generation; conversion from microwave remote sensing surface temperature to thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature, wherein land surface temperature which has the same physical significance as thermal infrared remote sensing land surface temperature is generated through passive microwave remote sensing data. The method can be universally applied to existing passive microwave remote sensing inversion land surface temperature algorithms. By the adoption of the method, the precision of the algorithms in inversion of bare-ground area surface temperature is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
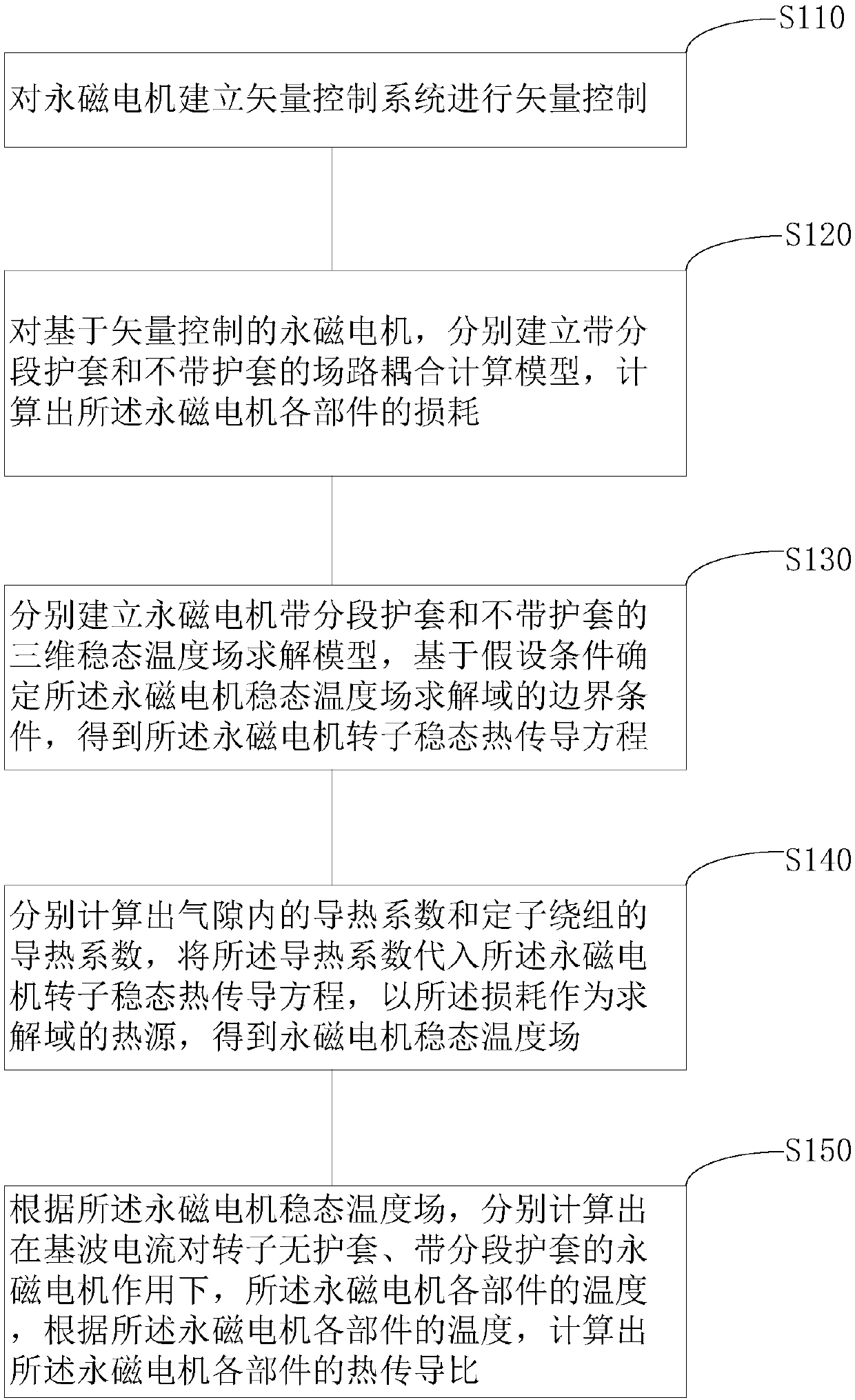
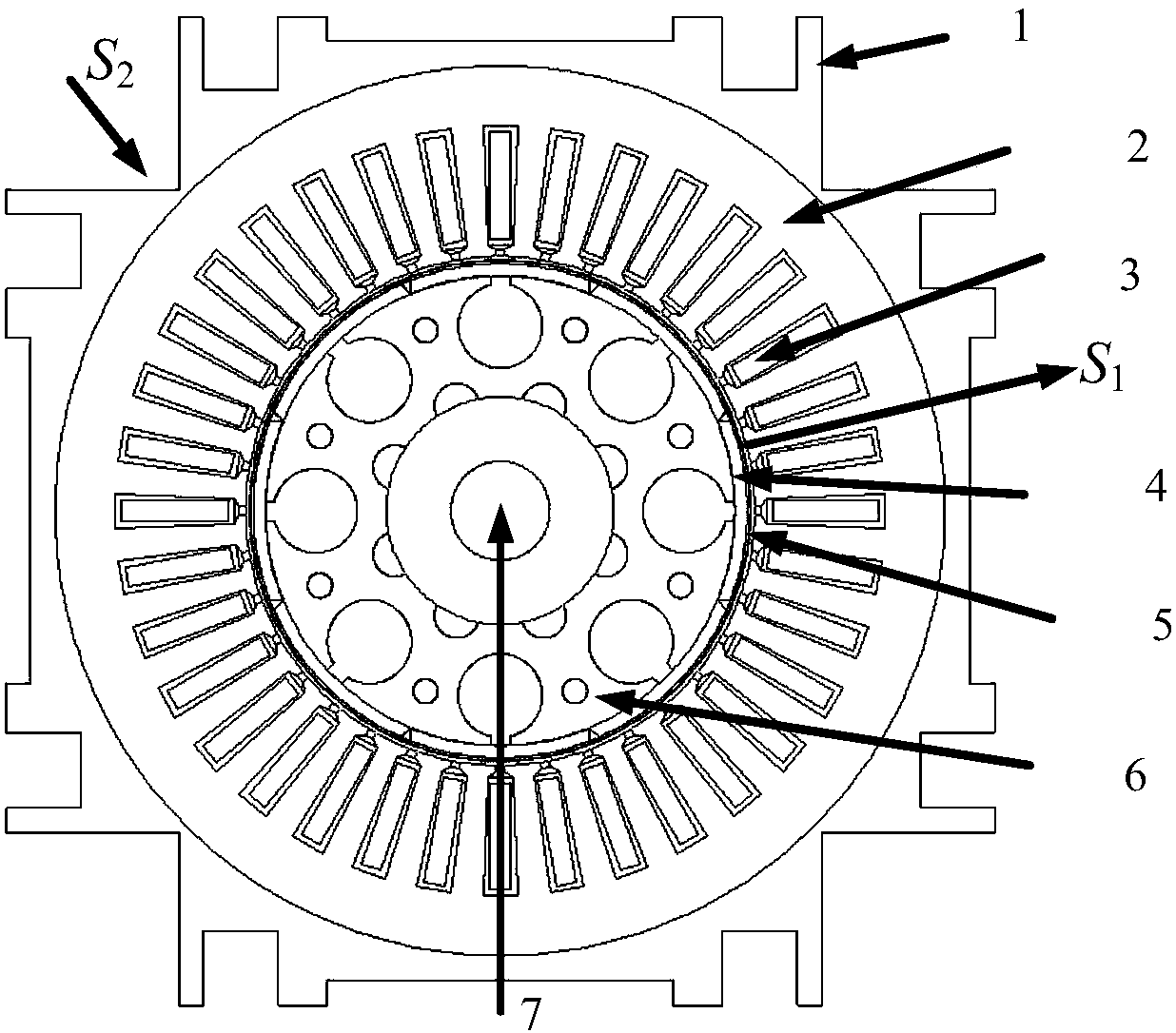
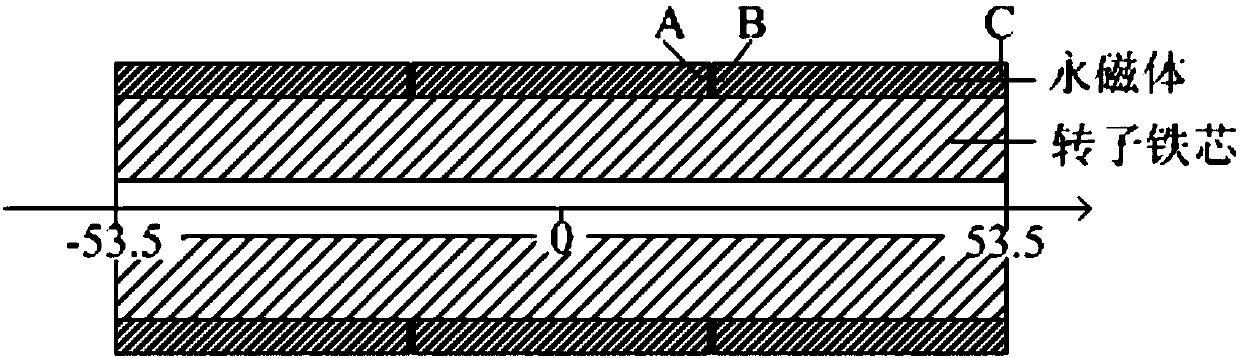
Method for calculating heat transfer ratio based on eddy current loss of rotor segmented sheath of permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN108111079AElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsSteady state temperatureControl vector
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for calculating a heat transfer ratio based on the eddy current loss of a rotor segmented sheath of a permanent magnet motor. The method comprises thefollowing steps: separately establishing a field circuit coupling calculation model with a segmented sheath and a field circuit coupling calculation model without sheath for the permanent magnet motor based on vector control, and calculating the loss of each component; then, separately establishing a three-dimensional steady state temperature field solution model with a segmented sheath and a three-dimensional steady state temperature field solution model without sheath for the permanent magnet motor, determining a boundary condition based on an assumed condition, and obtaining a rotor steadystate heat conduction equation; separately calculating a heat conductivity coefficient in an air gap and the heat conductivity coefficient of a stator winding, substituting the heat conductivity coefficients in the rotor steady state heat conduction equation, and using the loss as the heat source of a solution domain to obtain a steady state temperature field of the permanent magnet motor; and separately calculating the temperature of each component under the action on basic wave current on the permanent magnet motor in which the rotor has no sheath and the permanent magnet motor in which therotor has the segmented sheath, and calculating the heat transfer ratio of each component according to the temperature of each component. The method provided by the invention provides important theoretical basis for the design of an electromagnetic structure of the permanent magnet motor.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
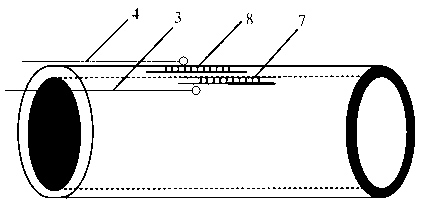
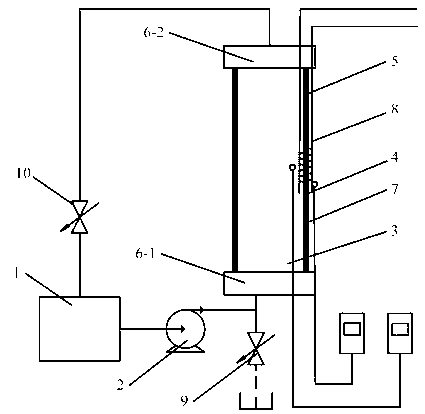
Fiber bragg grating measurement system and method for cylindrical structure thermal diffusivity
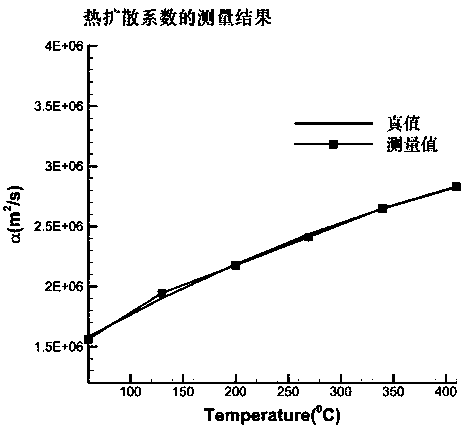
ActiveCN103217454AHigh measurement sensitivityImprove performanceMaterial heat developmentFiberGrating
Belonging to the technical field of measurement, the invention relates to a fiber bragg grating measurement system and a method for cylindrical structure thermal diffusivity. The measurement system comprises a heating water tank (1), a water pump (2), a to-be-measured cylinder (5), a control valve (10), an inner wall thermocouple (3), an outer wall thermocouple (4), an inner wall fiber bragg grating sensor (7), and an outer wall fiber bragg grating sensor (8). The measurement method needs: first measuring the change of a central wavelength of the fiber bragg grating sticked on a structure surface along with temperature, and calculating the functional relationship between temperature and the grating central wavelength; second, heating the cylindrical structure by flowing hot water, and measuring the fiber bragg grating central wavelength change along with time so as to obtain the functional relationship of time and the fiber bragg grating central wavelength; then according to a Fourier's second law and boundary conditions, conducting calculation to obtain a temperature-time function; and finally according to a Fourier's one-dimensional heat conduction equation, calculating the thermal diffusivity of the material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
System And Method For Interactive Patient Specific Simulation Of Radiofrequency Ablation Therapy
ActiveUS20160022369A1Easy to implementAccurately take into accountMedical simulationRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsRadiofrequency ablationBlood flow
A method and system for interactive patient-specific simulation of liver tumor ablation is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the liver and circulatory system of the liver is estimated from 3D medical image data of a patient. A computational domain is generated from the patient-specific anatomical model of the liver. Blood flow in the liver and the circulatory system of the liver is simulated based on the patient-specific anatomical model. Heat diffusion due to ablation is simulated based on a virtual ablation probe position and the simulated blood flow in the liver and the circulatory system of the liver by solving a bio-heat equation for each node on the level-set representation using a Lattice-Boltzmann method (LBM) implementation. Cellular necrosis in the liver is computed based on the simulated heat diffusion. Visualizations of a computed necrosis region and temperature maps of the liver are generated. A user input is interactively received to modify the position of the virtual ablation probe, the heat diffusion and cellular necrosis is re-simulated based on the user input, and the visualizations of the computed necrosis region and the temperature maps are updated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Circuit simulation method, device model, and simulation circuit
InactiveCN1707486AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A plurality of elements constituting a semiconductor integrated circuit to be designed are each converted to a device model which merges an electric model exhibiting electric characteristics of the element and a thermal model exhibiting thermal characteristics of the element, and a thermal resistor is inserted between the elements where heat exchange occurs, thereby electric and thermal circuits are formed. Then circuit and heat equations are formulated with respect to the electric and thermal circuits, and then the equations are solved together to acquire electric and thermal characteristics of each element in the circuit. As a result, it becomes possible to achieve high-precision device characteristics which precisely reflect the temperature variation of each element in the circuit during simulation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
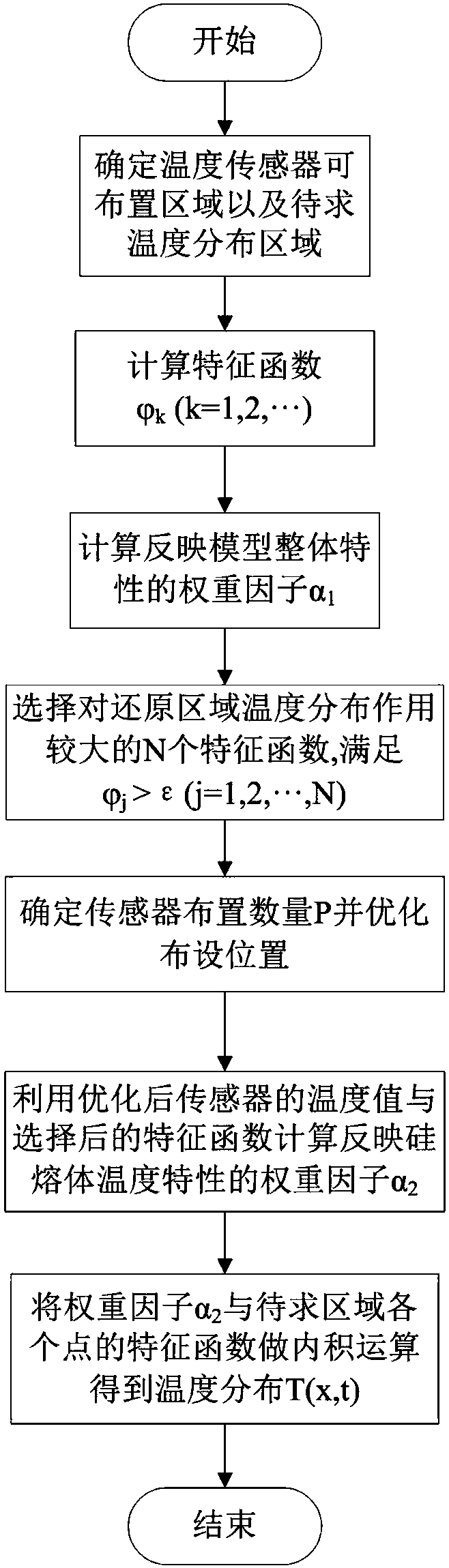
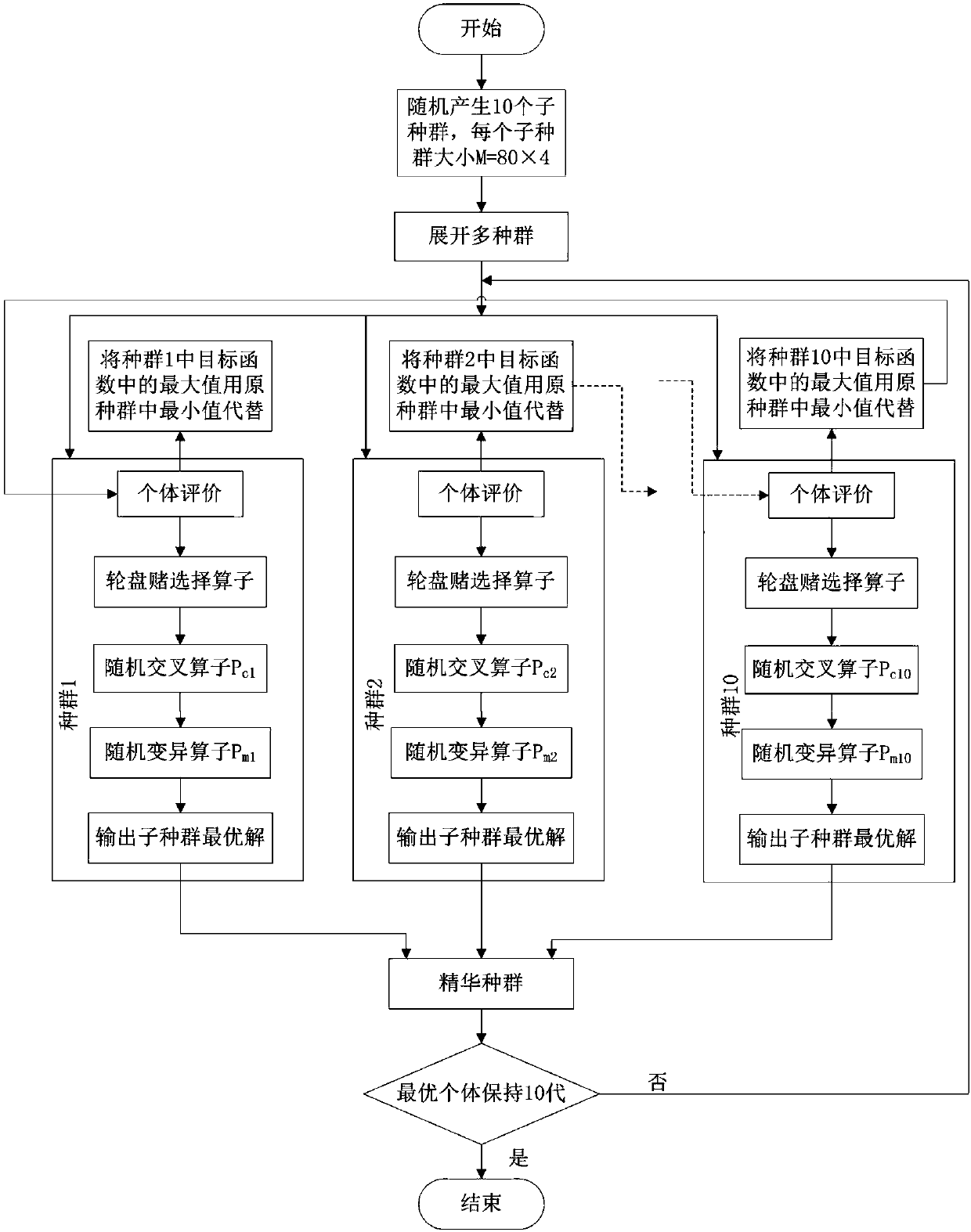
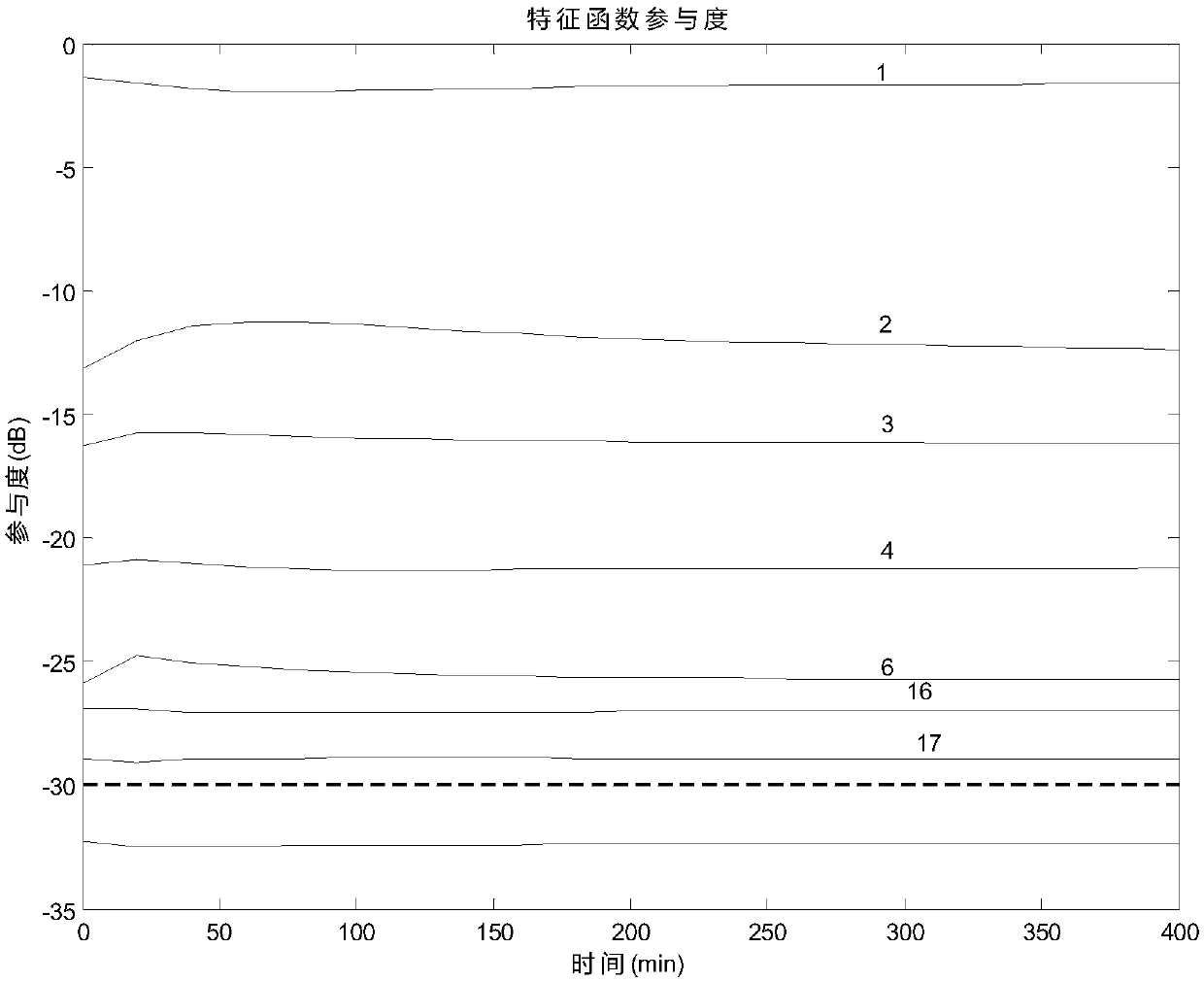
Silicon melt temperature field reconstruction method based on free liquid level temperature measurement value and feature function interpolation
ActiveCN107391789AHigh precisionPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltReconstruction methodSingle crystal
The invention discloses a silicon melt temperature field reconstruction method based on a free liquid level temperature measurement value and a feature function interpolation. The feature value problem of a heat conduction equation is used for analyzing the silicon melt model of the equal-diameter stage of the two-dimensional axial symmetry crystal growth process of a single crystal furnace, and a feature value and a corresponding feature function are obtained by calculation; a threshold scalar function is used for calculating the function of each feature function for an area to be reduced; a scalar value is set as a measuring standard for selecting the feature function; on the basis of a multi-population genetic algorithm, the arrangement position of a temperature sensor measuring point is optimized; finally, the group of temperature measurement values combined on an optimization position and the selected feature function are used for carrying out calculation to obtain a weight factor which reflects he characteristics of a silicon melt area; and an inner product operation is carried out with the feature function of each point in the silicon melt to obtain the temperature distribution of the silicon melt. By use of the method, the influence of a complex structure for an arrangement temperature sensor is reduced, the method is free from a heat conduction physical problem, and expansibility is good.
Owner:XIAN ESWIN MATERIAL TECH CO LTD +1
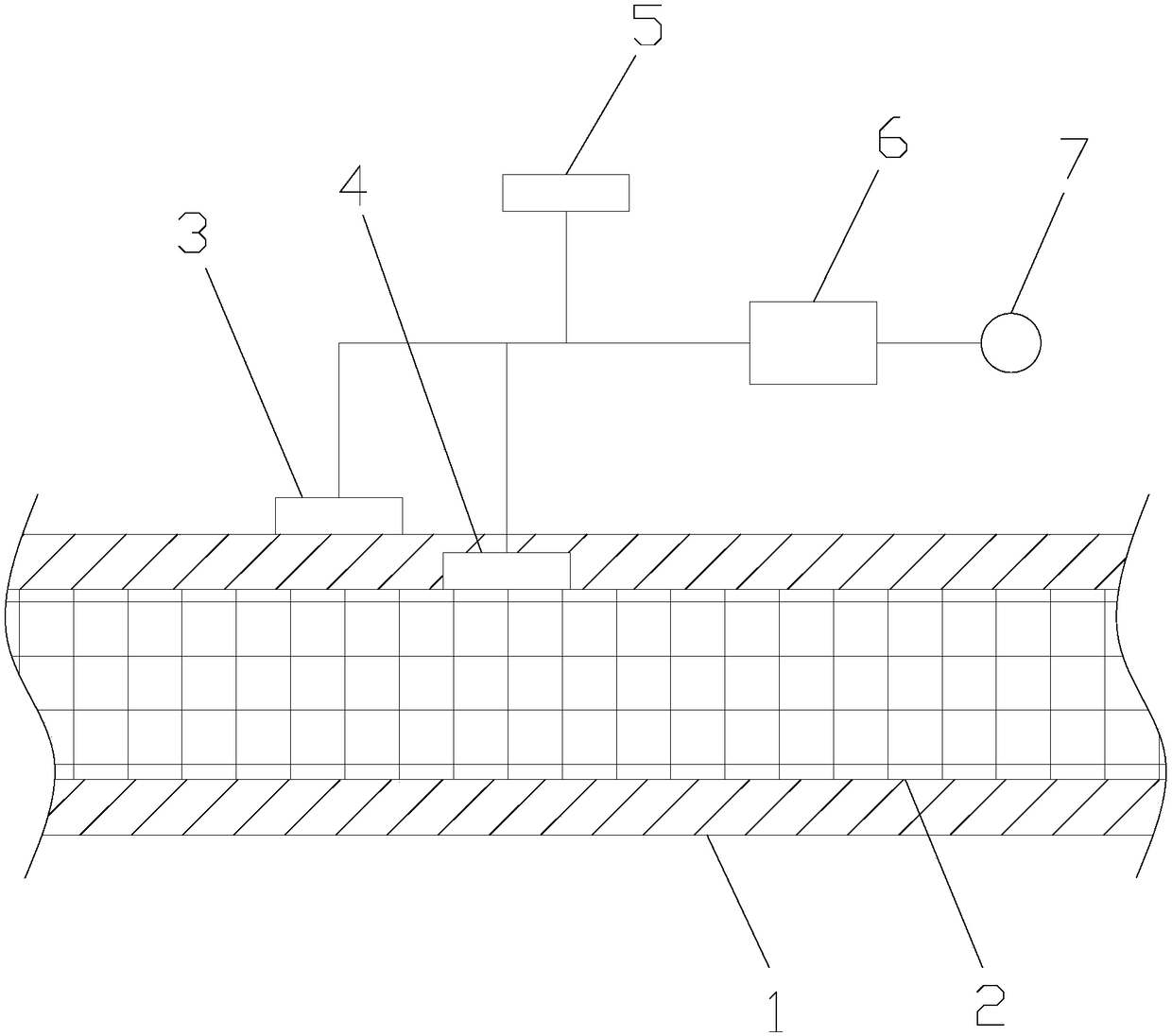
Cable load measurement device and measurement method
ActiveCN108535570ARealize online real-time monitoringEasy to operateElectrical testingElectrical conductorMeasurement device
The invention discloses a cable load measurement device, and relates to the technical field of cable load measurement equipment. The cable load measurement device comprises a temperature probe I, a temperature probe II, a temperature probe III, a controller and an alarm, wherein the temperature probe I is fixed on the surface of an insulating layer; the temperature probe II penetrates through theinsulating layer and is in contact with the surface of a conductor; the temperature probe III is exposed to the air; and the controller is used for computing the temperature and load of the conductor.The invention further discloses a measurement method of the cable load measurement device. The device has the advantages that a relational expression among the working current of the conductor of a cable, the conductor temperature, the temperature of the outer surface of the insulating layer and environment temperature is derived according to the joule law and a heat conduction equation, furtherthe conductor temperature of the cable, the temperature of the outer surface of the insulating layer and the environment temperature are measured, the online real-time measurement of cable load is realized, and the device is convenient to operate, very safe and reliable, simple and efficient.
Owner:陕西协成测试技术有限公司
Dynamic light pressing control method
ActiveCN101168188AReduce negative impactReduce the number of adjustmentsMetal rolling arrangementsLiquid coreSwitching cycle
The invention discloses a controlling method under dynamic light pressure in the continuous casting field. The method is capable of effectively reducing adjusting order number in the light pressure state at the same time when ensuring that the area follows the position of plate blanks and liquid core under light pressure, thereby reducing the disadvantageous effects of the plate blank quality due to frequent adjustment of states under pressure. In every controlling cycle, the method is first based on the equation of heat conduction and calculates the temperature distribution of the continuous casting plate blanks, confirms the solidification rate of each point of the plate blanks, and primarily confirms the state under the current expected light pressure and the time of state switching under pressure. Then according to the peospective casting speed and the bakie temperature of each cut film, when the cut films are produced, the position change of the liquid core point equipped with the appointed solidification rate in the state of under-pressure and in the switching cycle is forecast. At last, based on the forecasting of the peospective position of the liquid core point with appointed solidification rate, relative adjusting strategy under light pressure is adopted.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Welding reverse deformation calculation method
InactiveCN108804725AGuaranteed accuracySmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNonlinear finite element analysisFinite element analyse
The invention discloses a welding reverse deformation calculation method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing two-dimensional geometric models of a temperature field and a deformation field of a to-be-welded workpiece according to a preset reverse deformation and a welding condition; establishing a heat conduction equation and a thermal elastoplastic control equation on the basis of the two-dimensional geometric models, physical performance and mechanical performance of the to-be-welded workpiece and a welding heat source; solving the solid-state heat conduction equationand the thermal elastoplastic equation on the basis of nonlinear finite element analysis software so as to obtain a temperature field and a welding angle deformation in the welding process; and finally determining a welding reverse deformation of the to-be-welded workpiece according to a preset reverse deformation, the welding angle deformation and a deformation target value. Compared with the traditional manners of carrying out analysis by utilizing three-dimensional models, the welding reverse deformation calculation method is capable of reducing the computational complexity of systems and ensuring the correctness of calculation results while obtaining welding reverse deformations of to-be-welded workpieces in an efficient and low-cost manner.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
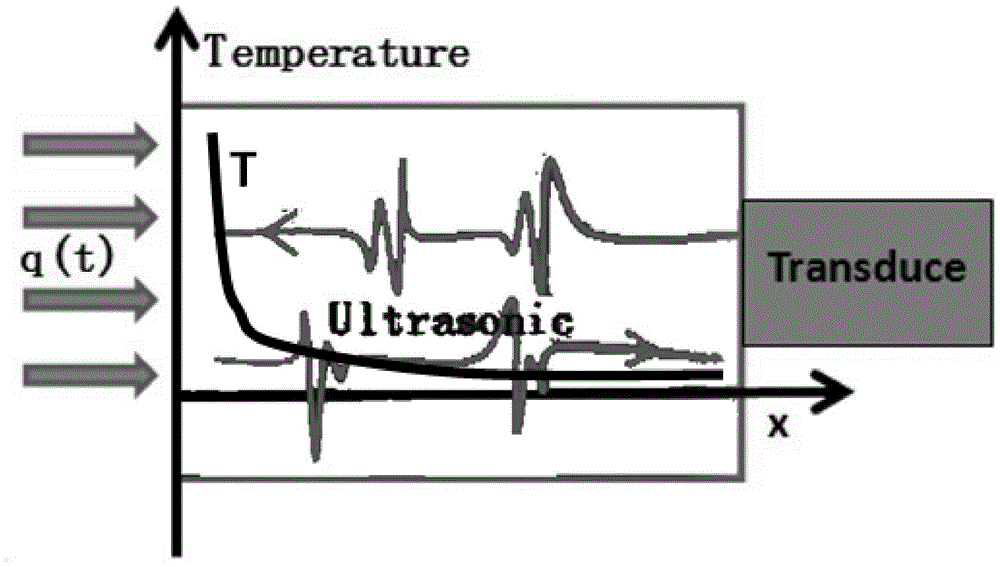
Material high-temperature thermophysical parameter rapid measurement method
ActiveCN108051472AFast measurementLow costMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentFast measurementThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a material high-temperature thermophysical parameter rapid measurement method which comprises the following steps of according to the material thermophysical parameter-medium temperature-ultrasonic propagation characteristic, adopting an ultrasonic pulse-echo method to acquire an ultrasonic propagation time under the condition of transient heat transfer, inversing materialparameters in a heat transfer equation through the ultrasonic propagation characteristic, and rapidly measuring the thermophysical parameter of a material along with temperature change without loss and contact. By measuring for one time only, the method is capable of acquiring various material thermophysical parameters such as thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity or thermal diffusivity atdifferent temperatures from the room temperature to 400 DEG C, for example, when the temperature of the heating surface of a tested piece is raised to a preset temperature such as 400 DEG C, and has the outstanding advantages of rapid measurement speed, low cost, good universality, large measurement range and the like.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Fluid simulation method for target infrared wake characteristics of water scene
ActiveCN105631100AAvoid calculationSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsTransient heat transfer
The invention discloses a fluid simulation method for the target infrared wake characteristics of a water scene. The fluid simulation method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out voxelization on a model in the scene to generate solid particles; 2) adding liquid particles in an area with liquid; 3) for each time frame, carrying out numerical simulation on the mechanical characteristics of the fluid by utilizing SPH; and 4) for each time frame, carrying out numerical simulation and infrared characteristic graph drawing on the thermodynamic characteristics of the fluid by utilizing a transient heat transfer equation. According to the method, the demand for calculating the thermodynamic characteristics in fluid media is solved; the mechanical characteristics and infrared characteristics in the water scene can be simulated truly, and the new-found infrared phenomenon in recent years: the infrared wakes generated by the ship in the sailing process, is successfully simulated under laboratory environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Temperature compensation method for composite material workpiece autoclave forming workpiece
ActiveCN102390121AImprove molding qualitySmall temperature differenceTemperature differenceEngineering
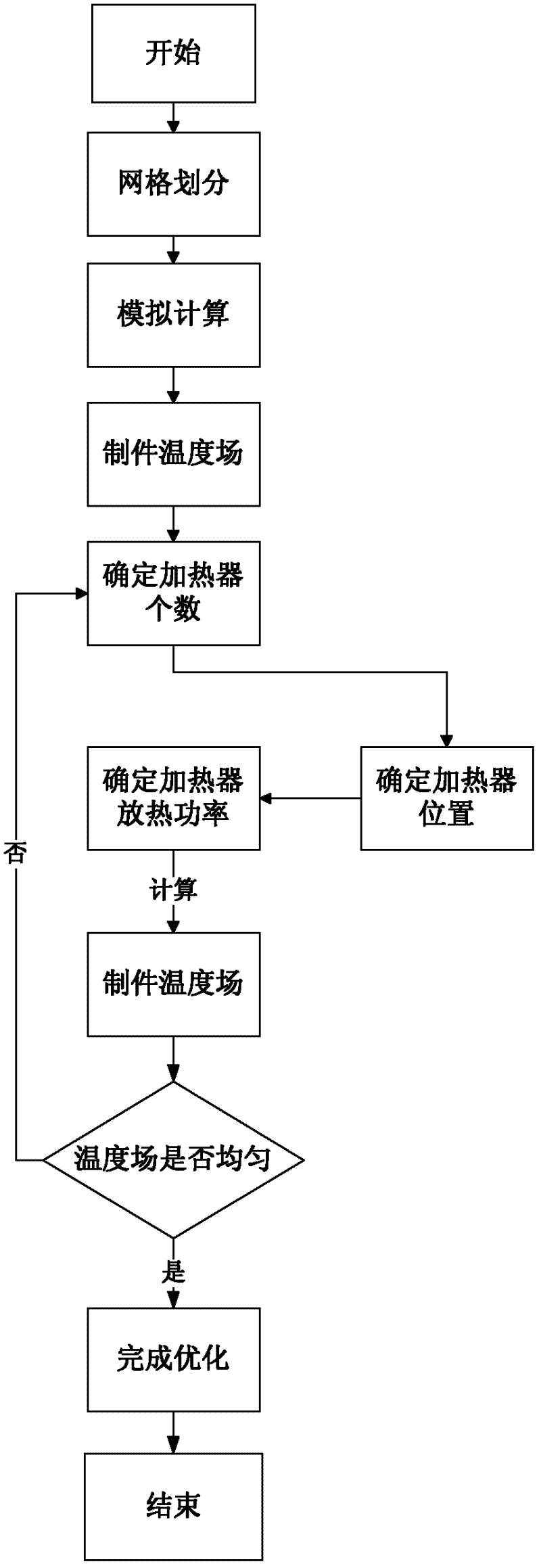
The invention discloses a temperature compensation method for a composite material workpiece autoclave forming workpiece, which utilizes heaters for heating the low-temperature parts of the workpiece to realize temperature compensation and includes steps: simplifying an autoclave model, conducting meshing and simulating the workpiece temperature field in the forming process of the composite material workpiece autoclave by temperature field simulation software; determining the positions of maximum temperature value point and each minimum temperature value point; determining the number and the positions of the heaters; determining the temperature difference value between the maximum temperature value point and each minimum temperature value point; determining the function of heat release rate of each heater; introducing the function of heat release rate of each heater into a three-dimensional heat conduction equation, and conducting analog computation, thus obtaining the optimized temperature field; if the optimized temperature field still can not meet requirements, repeating the last steps until the temperature field of the workpiece meets the requirements. The method can control the temperature difference of the workpiece, ensure the uniformity of the temperature field and lower the production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and device for analyzing heat source intensity and temperature distribution in organism based on point heat source model
The invention discloses a method and a device for analyzing heat source intensity and temperature distribution in an organism based on a point heat source model. The device is composed of an infraredCCD detector, a data acquisition unit and a computer. According to the method and the device provided by the invention, on the basis of a Pennes bioheat conduction equation, an analytic solution of the Pennes equation is obtained through the point heat source model. An organism heat source can be composed of point heat sources which are uniformly distributed; the various point heat sources are subjected to independent heat conduction, so that temperature fields are defined; and a real temperature field is formed by superposing the temperature fields which are formed by the various point heat sources. Surface temperature distribution data of the organism is obtained by virtue of the infrared CCD detector, and based on the surface temperature distribution data, heat source intensity distribution information in the organism is obtained by virtue of a temperature fitting method, so that temperature distribution information in the organism is obtained. According to the heat source intensityand temperature distribution in the organism, functional information which is directly related to metabolism of the organism can be reflected; therefore, objective functional evidences are provided for bio-medical analysis.
Owner:WUBO SCI TECH WUHAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com