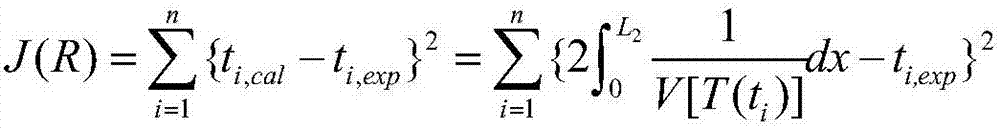Patents
Literature
53 results about "Transient heat transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
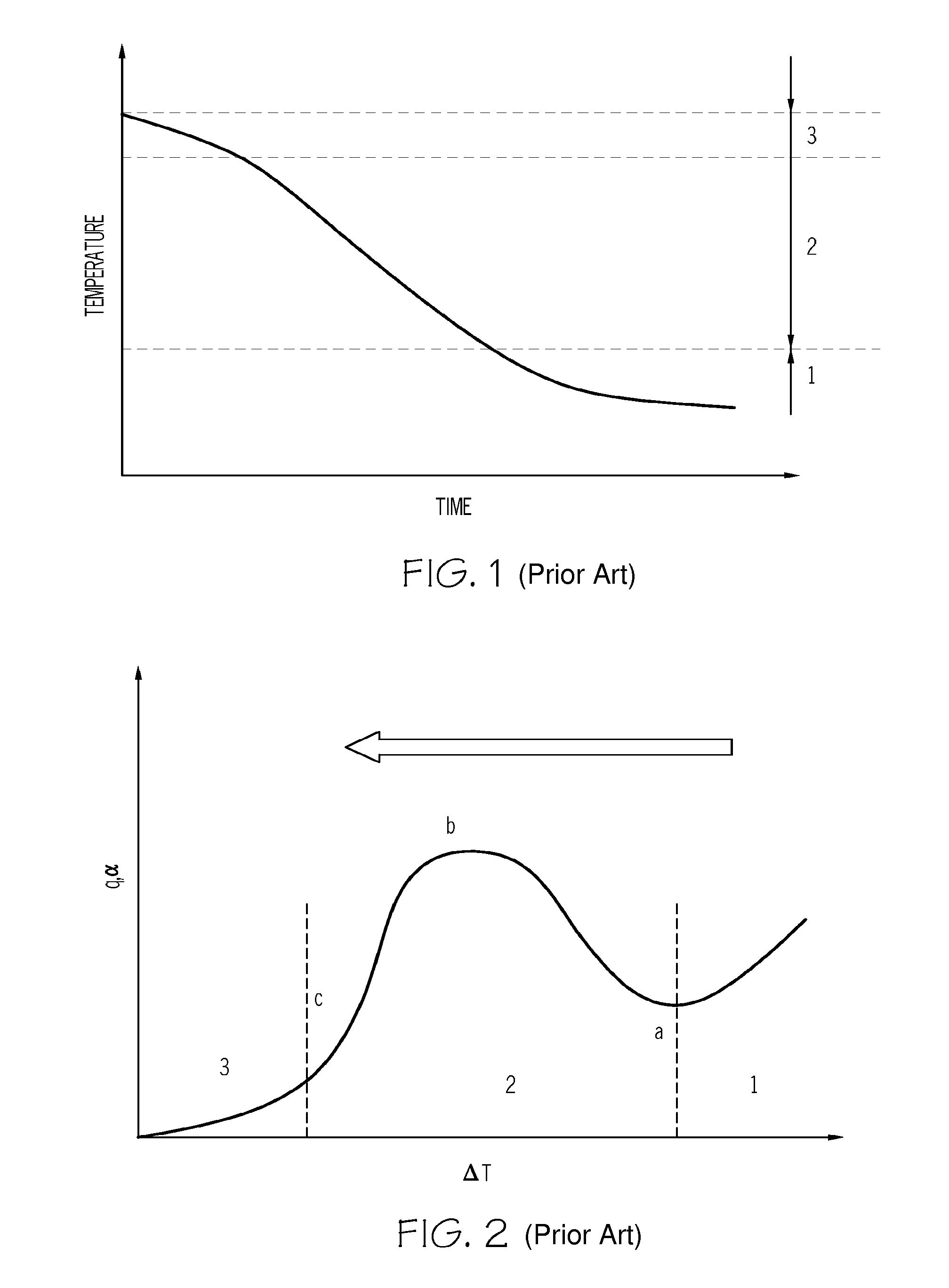
Transient heat transfer is the non-steady state transfer of energy through a medium. The transient state refers to a non-constant flow of energy. This changing rate of heat transfer could be due to fluctuating temperature difference over the medium or changing properties throughout the medium.
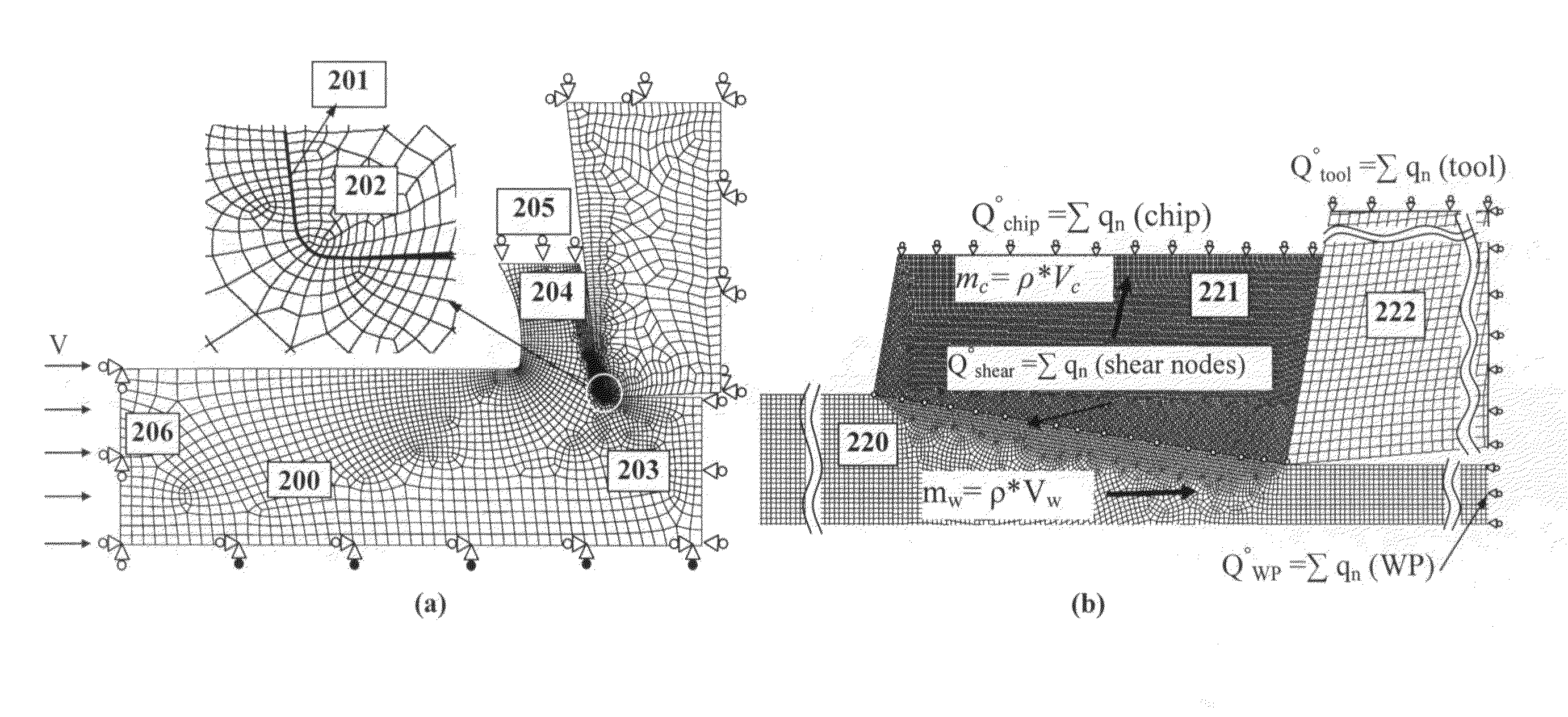
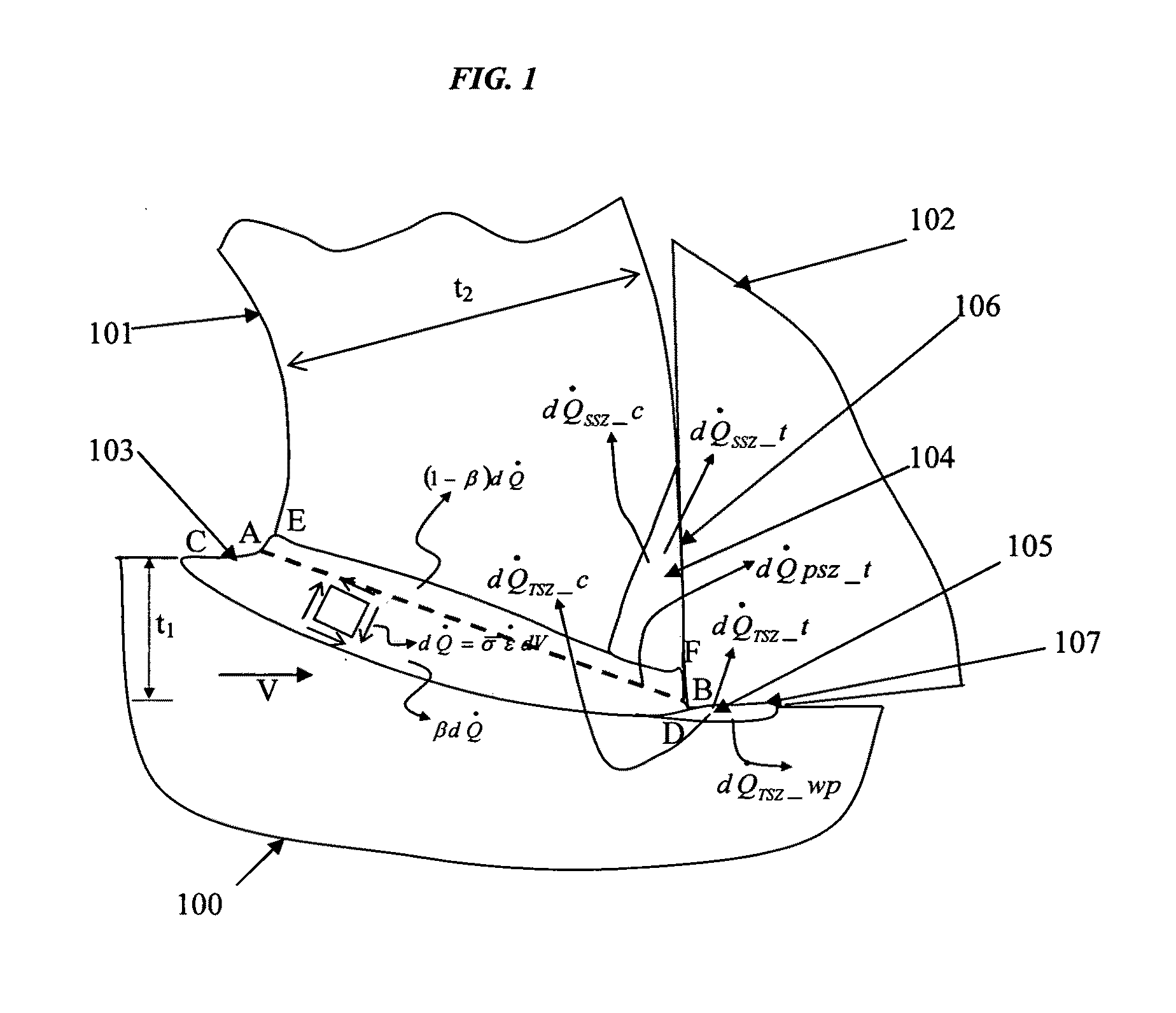
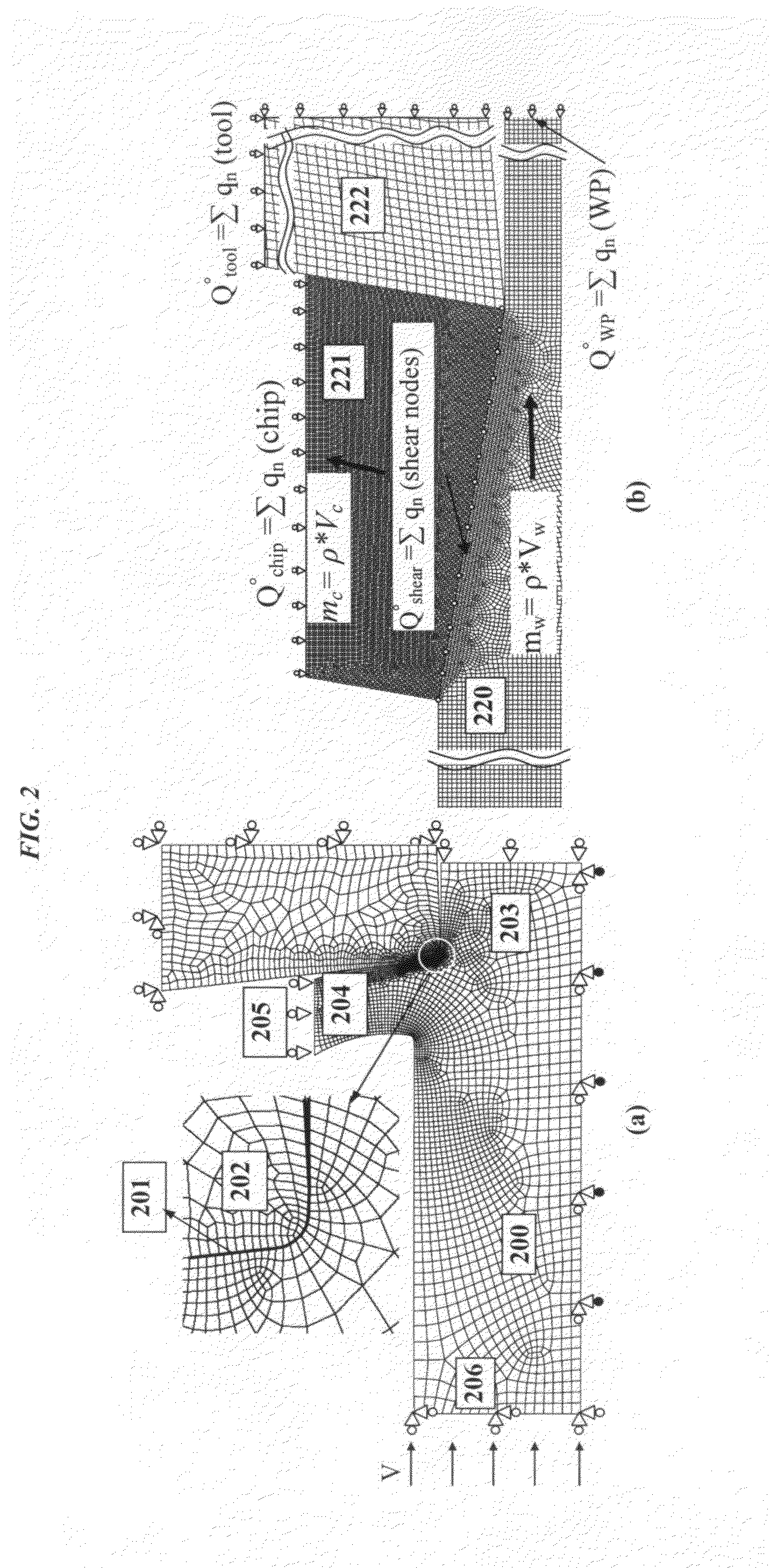
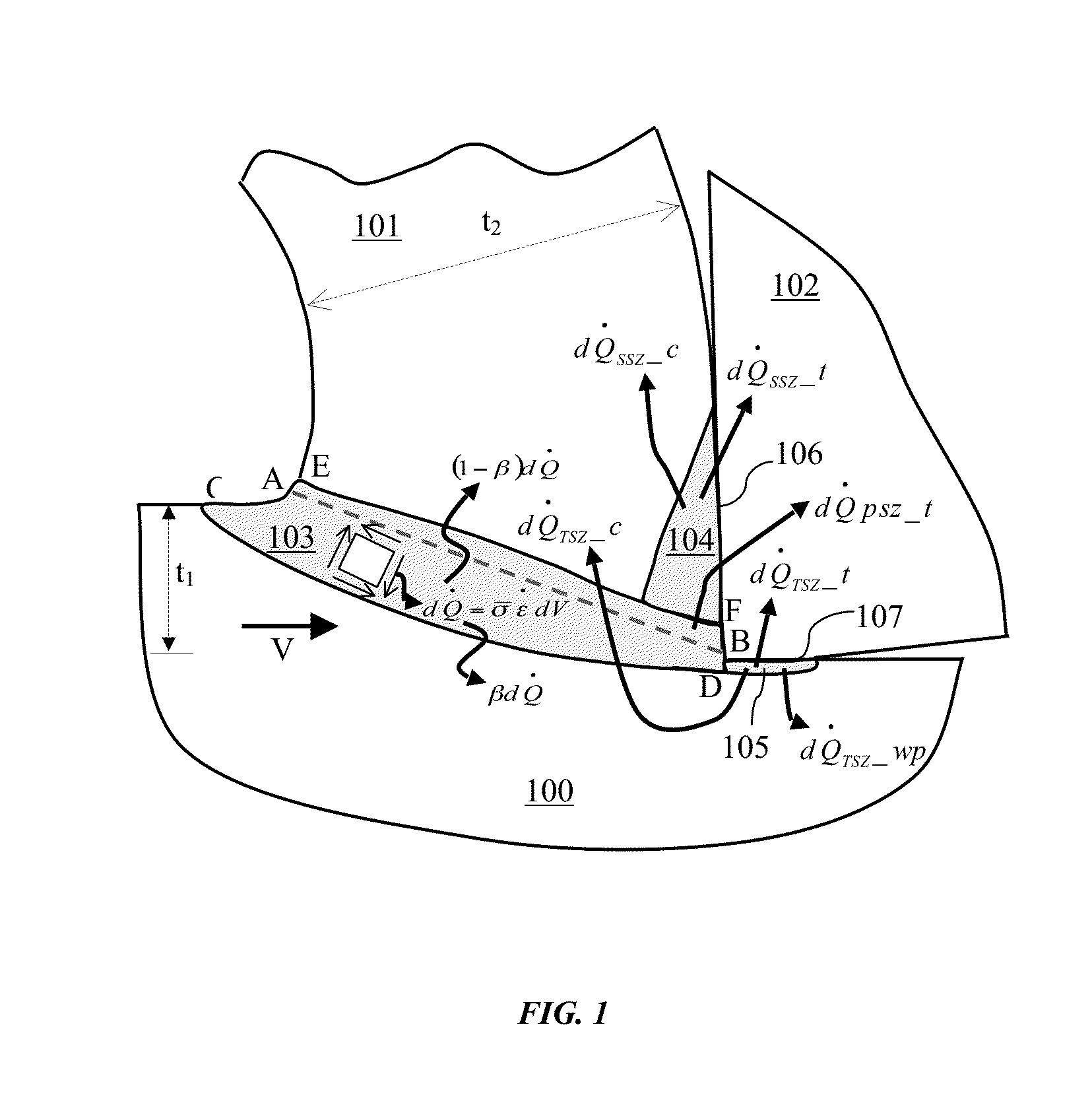
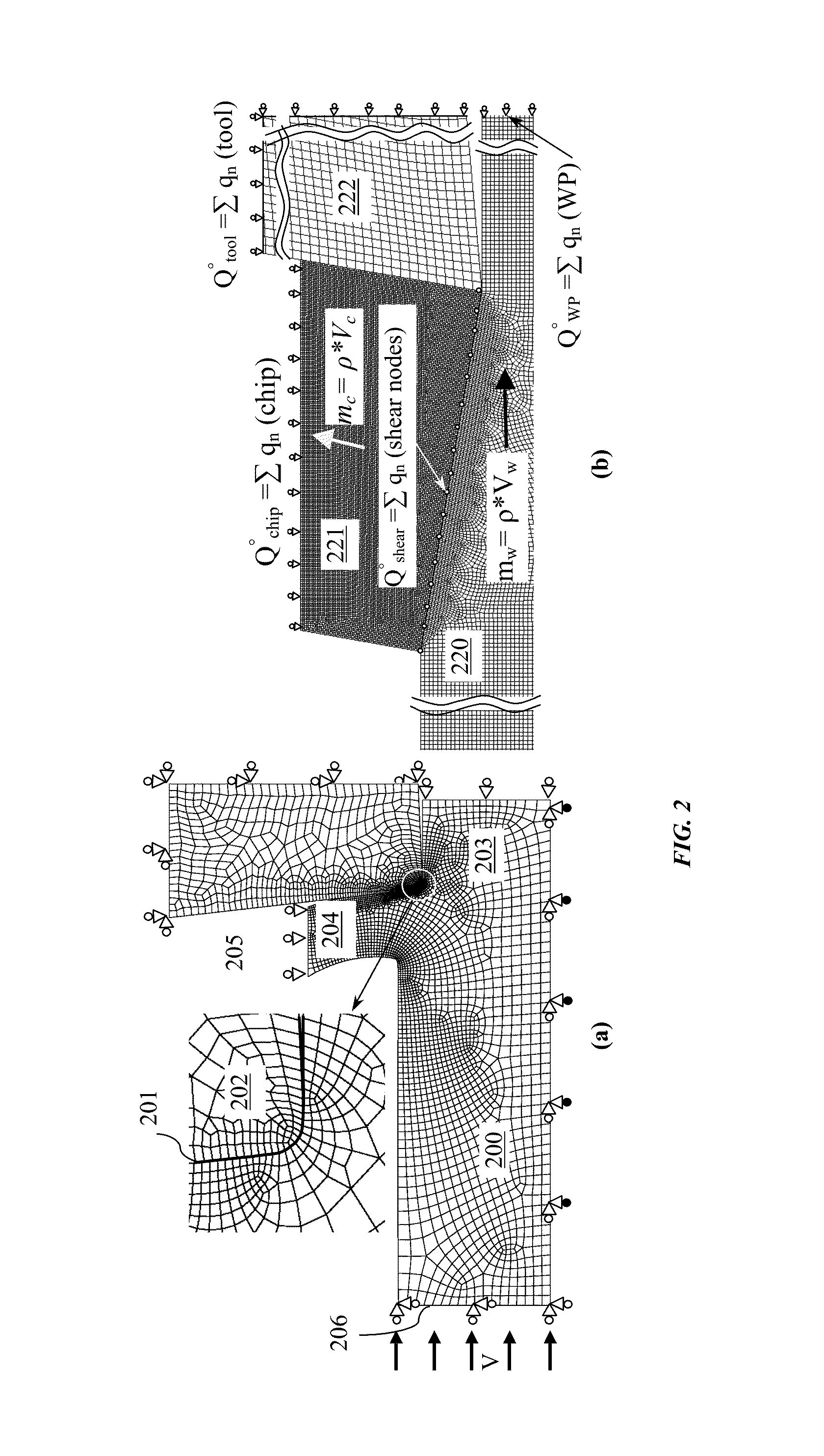
Thermal modeling of an orthogonal machining process
ActiveUS20100174515A1Lower the volumeNo loss of accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationSteady state temperatureElement analysis
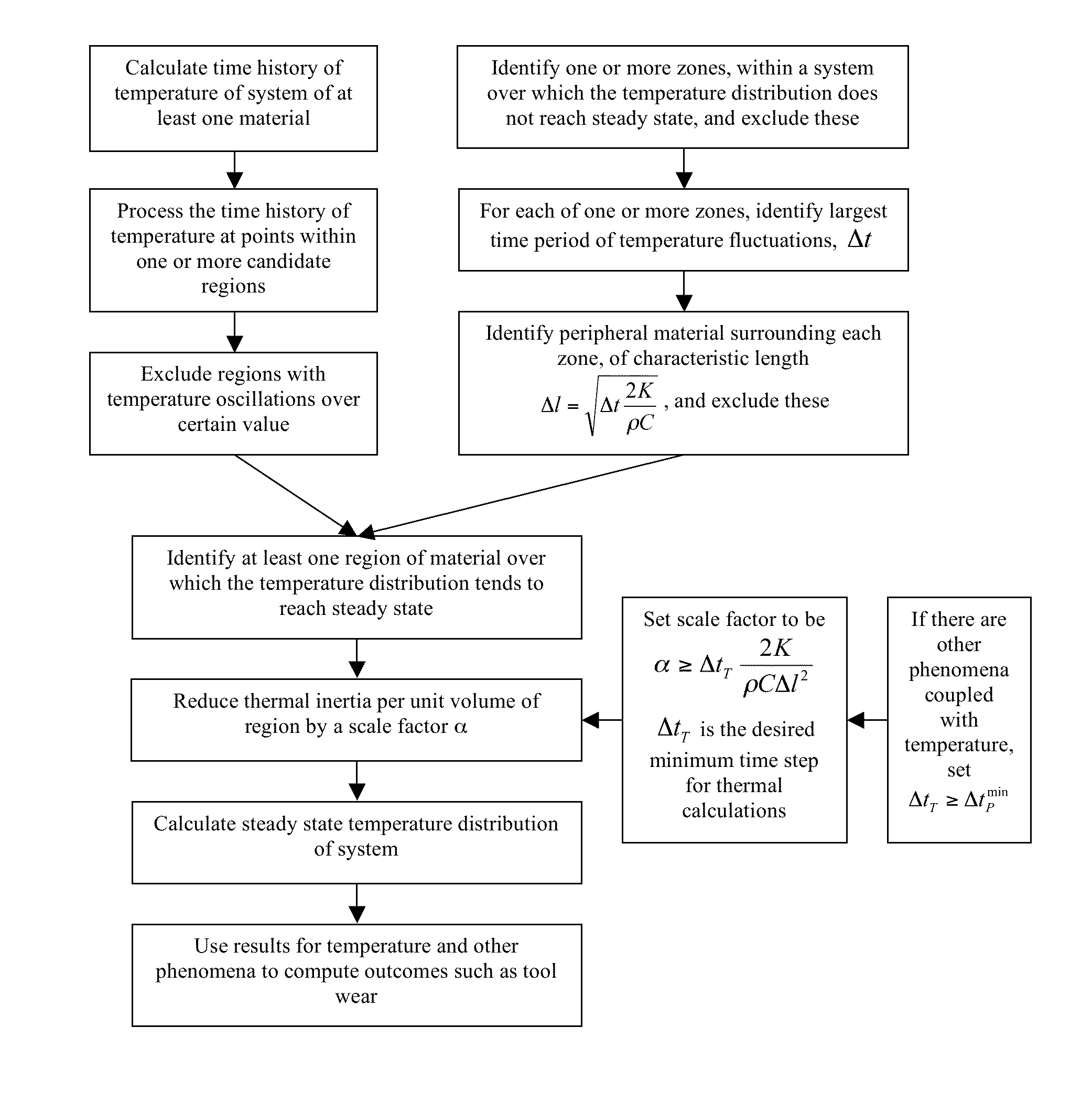
A novel procedure is disclosed, that can be incorporated into Finite Element Analysis (FEA) or other similar analysis techniques, to obtain the steady state temperature distribution in a coupled transient heat transfer analysis rapidly as well as accurately. A scale factor is used to reduce the thermal inertia per unit volume (specific heat capacity) in regions of steady state temperature distribution, thereby hastening the achievement of steady state. An application of this procedure to estimate steady state temperature distributions within cutting tools, and the estimation of cutting tool wear based on the obtained steady state temperature distributions is shown as an example.
Owner:MADHAVAN VISWANATHAN +1
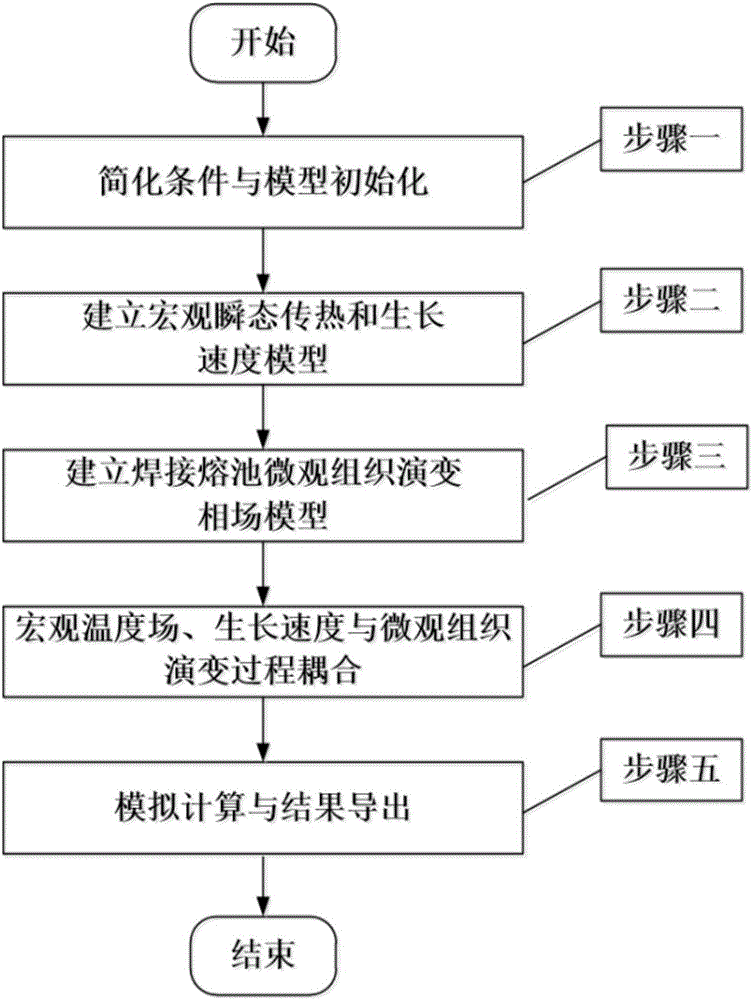
Phase-field method-based microstructure evolution simulation method in welding process in transient state
ActiveCN106407623ASimplify the initialization processDeepen understanding of the evolution processSpecial data processing applicationsMolten stateEngineering
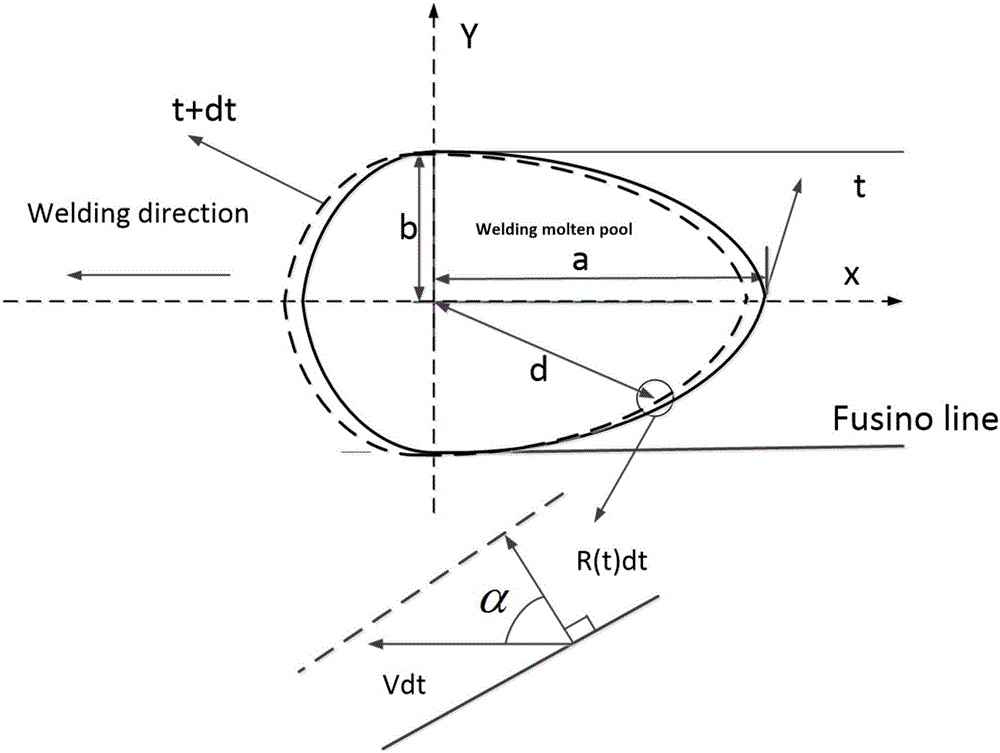
The invention provides a phase-field method-based microstructure evolution simulation method in a welding process in a transient state. The phase-field method-based microstructure evolution simulation method in the welding process in the transient state comprises the following steps of simplifying conditions and initializing a model, building the model according to parameters of a solidification process of a welding pool; building a macro transient heat transfer and growth rate model, wherein the welding pool is regarded to be formed by combining two semi-elliptical spheres, one semi-elliptical sphere is in a molten state and the other semi-elliptical sphere is in a solidified state in the welding process; building the macro transient heat transfer and growth rate model on the basis of hypotheses; building a microstructure evolution model and building a phase-field model of simulating microstructure evolution of the welding pool on the basis of the Ginzburg-Landau theory; and carrying out macro-micro coupling calculation, introducing a transient temperature gradient and a dendrite growth rate into the model, calculating a macro-micro coupled phase-field model and obtaining a microstructure evolution simulation result of the welding pool.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Loose coupling modeling method for fluid-solid coupling heat transfer
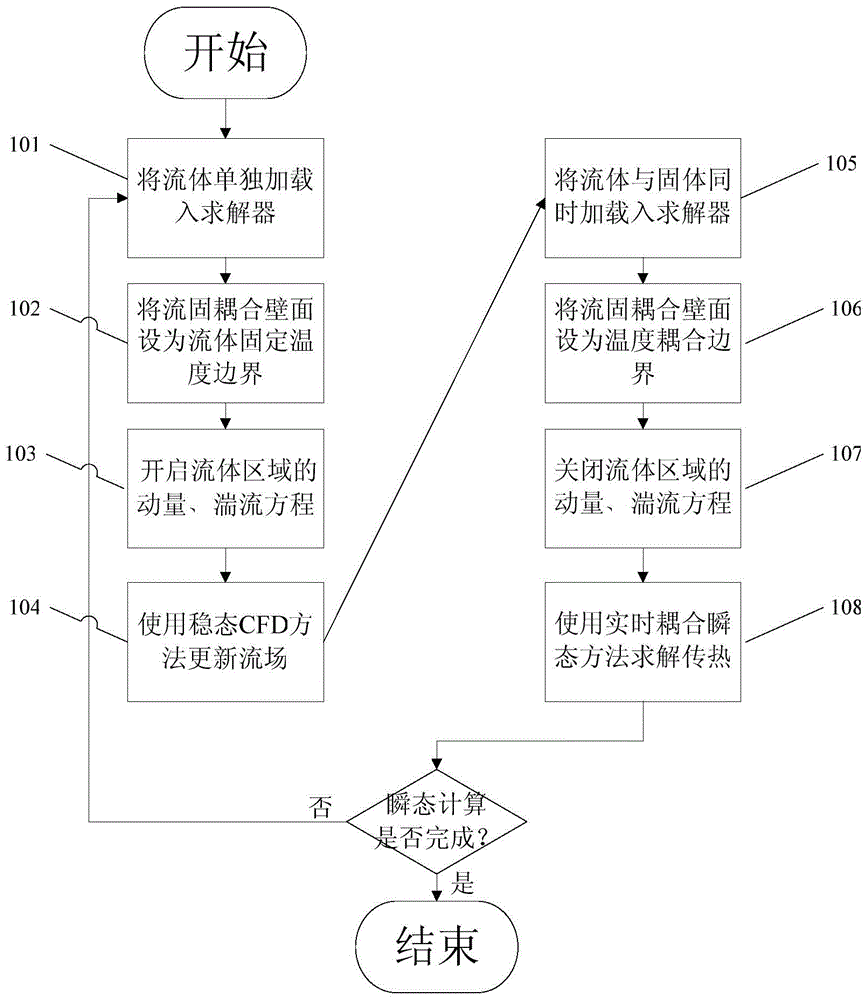
The invention provides a loose coupling modeling method for fluid-solid coupling heat transfer. The loose coupling modeling method is characterized in that the transient change process of a flow filed is ignored, and the global transient heat transfer process is assumed to be performed in a quasi-stable-state flow field. The method comprises the specific calculation procedures that 1, the flow field is updated, wherein only fluid is taken as a solving object, the fluid-solid coupling wall surface is set as a fixed temperature boundary of the fluid, and the flow field is solved through a stable-state CFD algorithm; 2, transient heat transfer is calculated, wherein the fluid and solid are both taken as the solving object, the fluid-solid coupling wall surface is set as a heat transfer coupling boundary, a momentum equation and a turbulent flow equation of the fluid are closed, and transient heat transfer is calculated until the flow field is updated for the next time and / or calculation stops; 3, the first step and the second step are repeated, wherein flow field updating and transient heat transfer calculating are alternately performed until the time arrives at the transient heat transfer termination moment. For the forced-convection heat transfer process of air in a pipe, by comparing the modeling method with a tight coupling calculation result of Fluent commercial software, the absolute error is 1 K or below, the calculation efficiency is improved by one order of magnitude, and the engineering calculation requirement is met.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
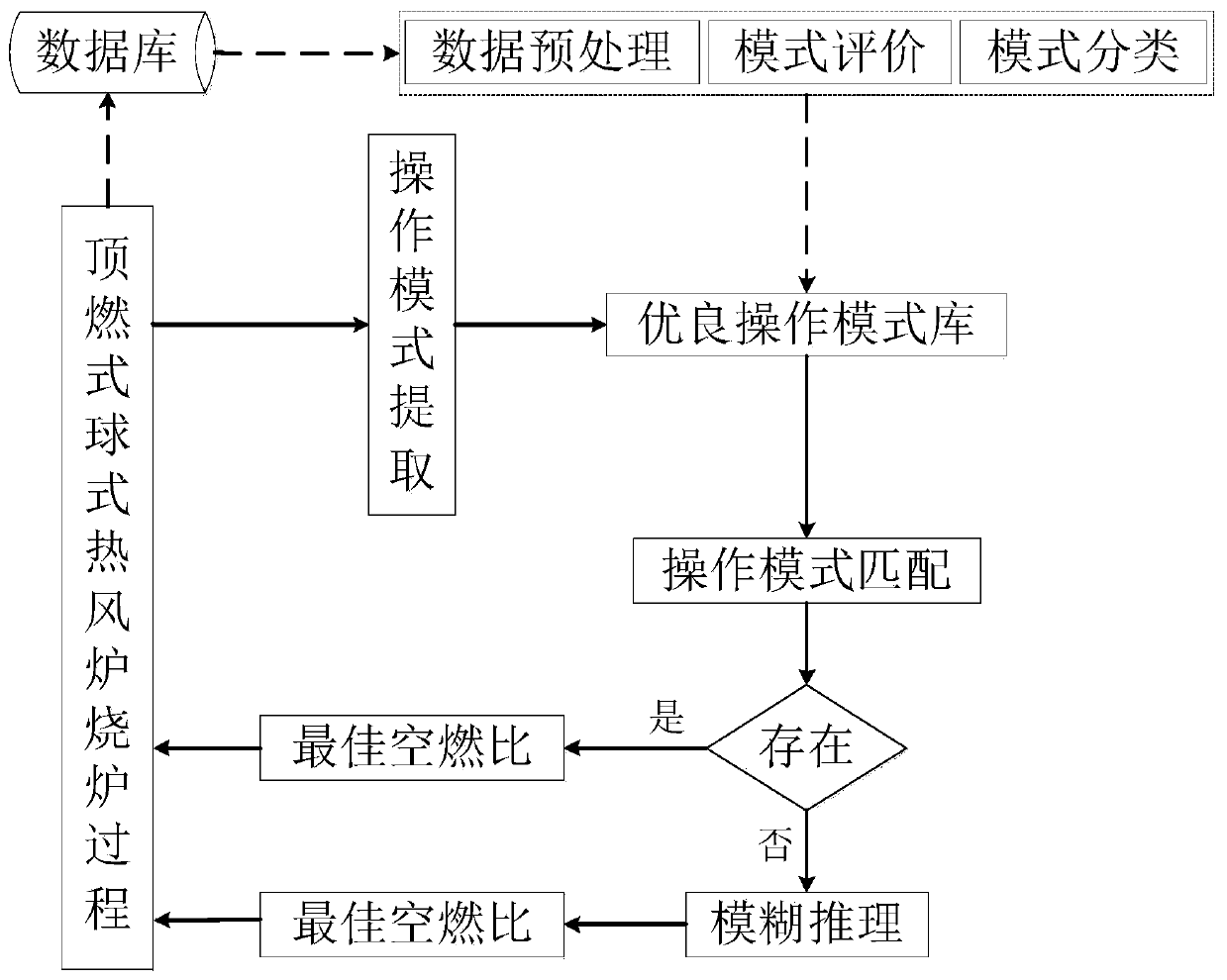
Method and system for ball type hot blast furnace sintering process modeling and energy consumption optimization
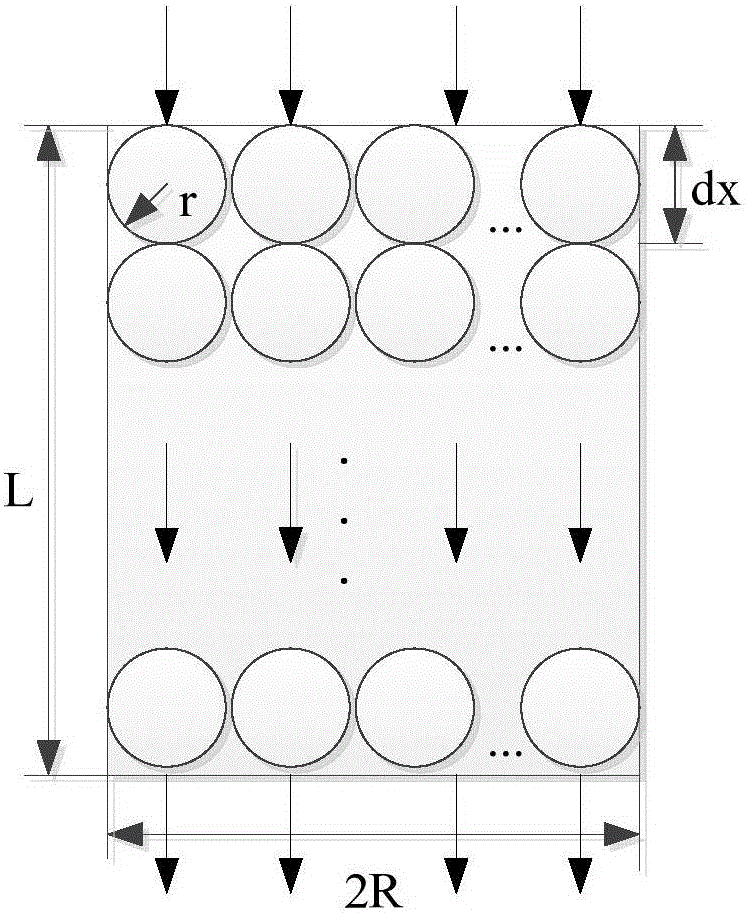
ActiveCN105907906ARealize automatic burning furnaceForecast temperatureSteel manufacturing process aspectsBlast furnace detailsTransient heat transferHot blast
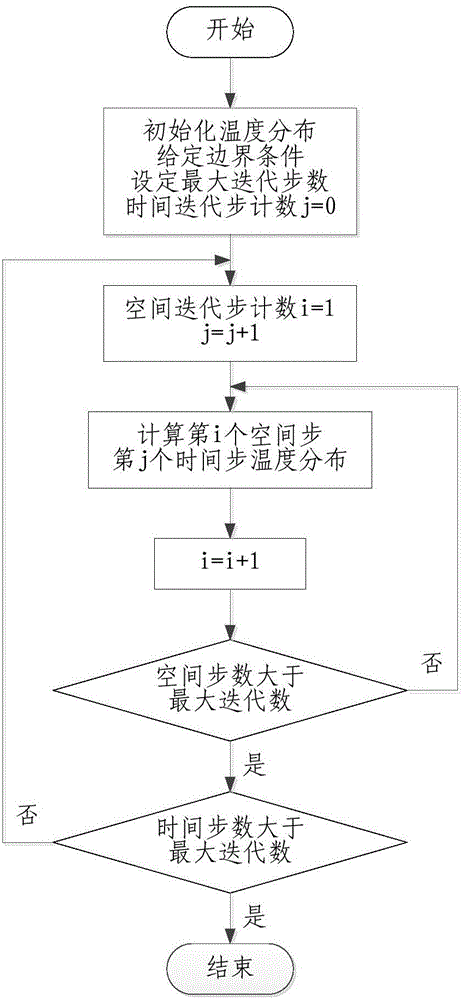
The invention discloses a method and system for ball type hot blast furnace sintering process modeling and energy consumption optimization, and can realize purposes of energy saving and cost reduction. The method includes the steps: S1, according to heat transfer and fluid mechanics principles, establishing a regenerative chamber transient heat transfer model of a hot blast furnace in two stages of furnace sintering and air feeding, and providing boundary conditions and initial conditions for model calculation; S2, calculating the regenerative chamber transient heat transfer model, according to the calculated results of the regenerative chamber transient heat transfer model and with combination of a working system of the hot blast furnace, establishing an optimization model taking the coal gas volume as an optimized target and meeting the dome temperature, the exhaust gas temperature, the hot air flow quantity and temperature, the thermal efficiency and other constraint conditions by a method of time-dividing optimization of the coal gas flow quantity; S3, solving the optimization model, to obtain a change curve of the coal gas flow quantity having minimum energy consumption along with the time; and S4, controlling the coal gas flow quantity of the ball type hot blast furnace sintering process according to the change curve of the coal gas flow quantity along with the time.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Ball type hot blast stove burning process control method and system
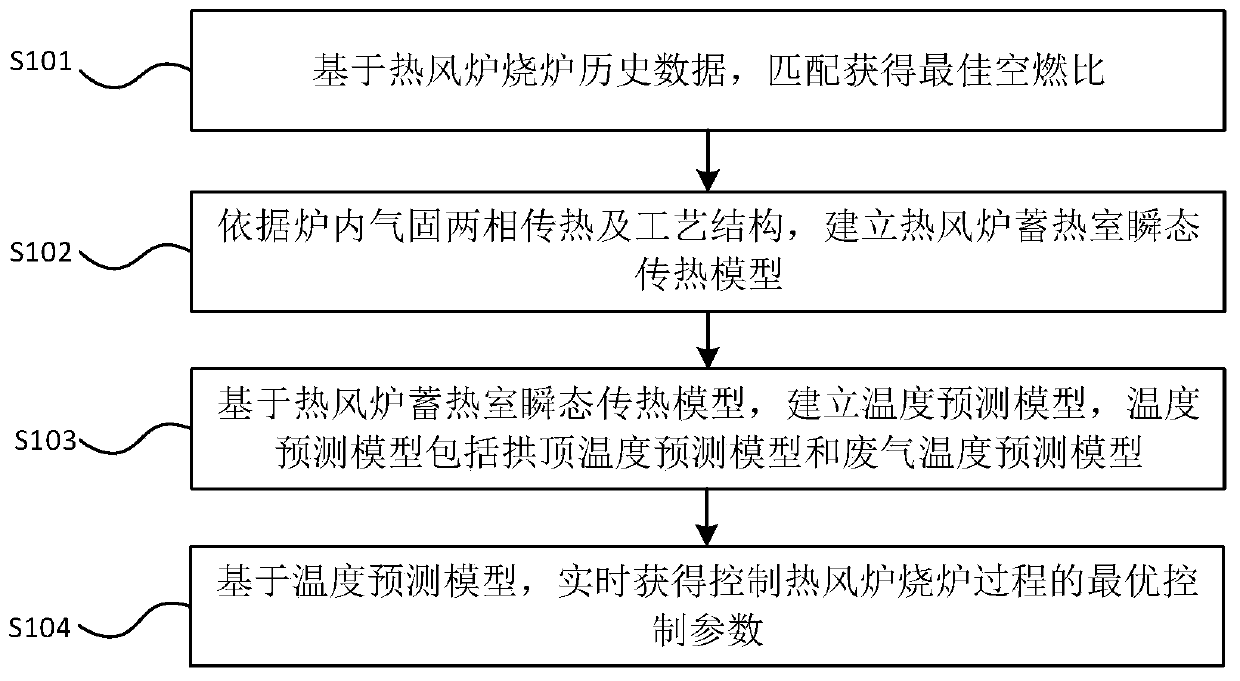
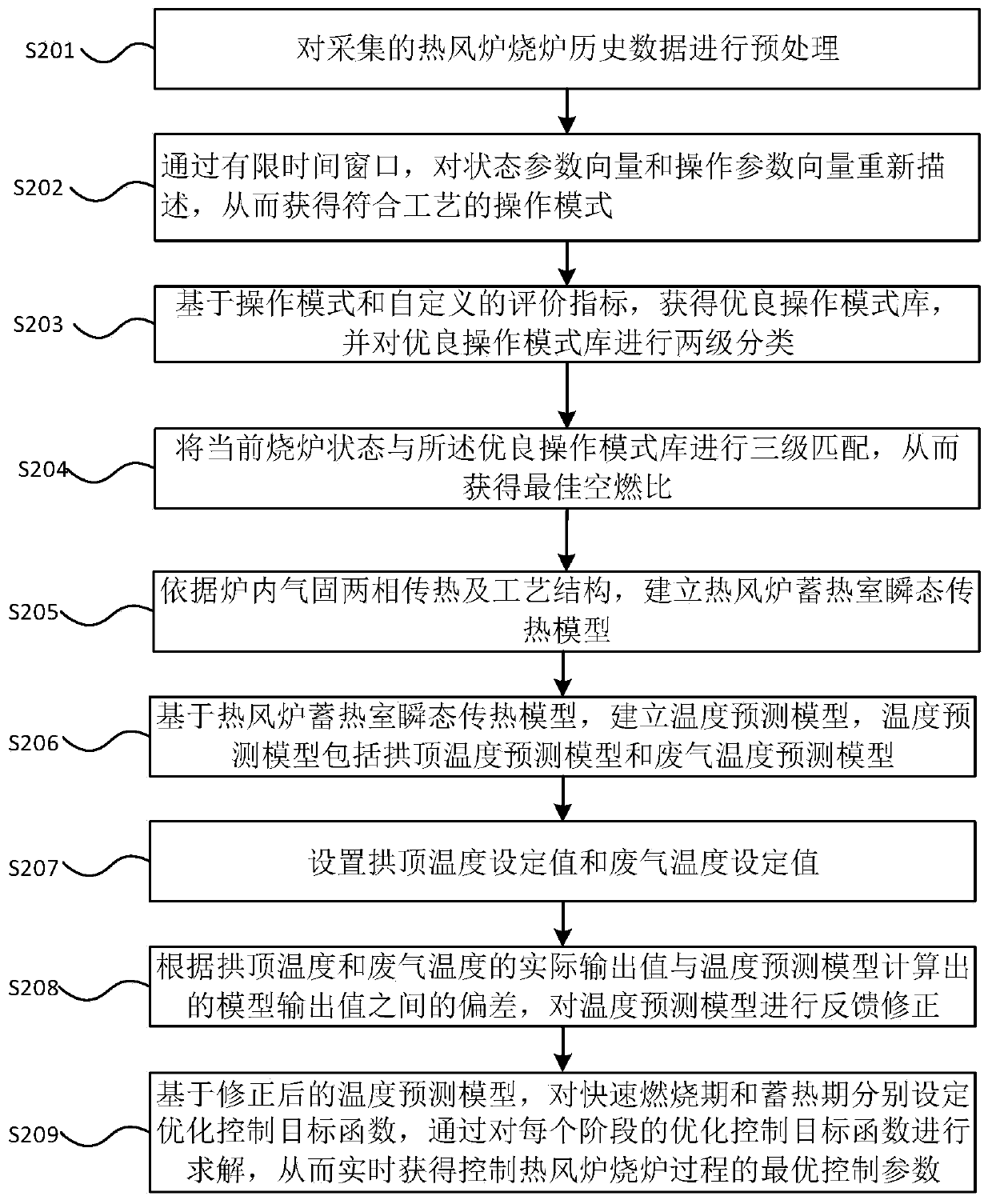
ActiveCN110257577AGood air-fuel ratioOptimal Control ParametersSteel manufacturing process aspectsBlast furnace detailsOptimal controlProcess engineering
The invention discloses a ball type hot blast stove burning process control method and system. The method comprises the steps that the optimal air-fuel ratio is obtained through matching based on hot blast stove burning historical data; a hot blast stove regenerative chamber transient heat transfer model is established according to stove inner gas-solid two-phase heat transfer and a process structure; temperature predicting models are established based on the hot blast stove regenerative chamber transient heat transfer model and include the vault temperature predicting model and the waste gas temperature predicting model; and the optimal control parameters for controlling the hot blast stove burning process are obtained in real time based on the temperature predicting models. The technical problem that the hot blast stove burning process is hard to control precisely in real time in the prior art is solved. By analyzing the ball type hot blast stove burning process, the air-fuel ratio is controlled from the data perspective according to a field process, the coal gas flow rate is controlled form the mechanical perspective, the air-fuel ratio and the coal gas flow rate are caused to reach the optimal values at the same time, in addition, the optimal coal gas flow rate is optimized in real time based on the matched optimal air-fuel ratio, and the hot blast stove burning process can be precisely controlled in real time.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Flow thermal stress turbocharger turbine housing divider wall
InactiveUS20150023788A1Increased durabilityResistance to crackingPump componentsEngine fuctionsTurbochargerTransient heat transfer
The propensity for turbocharger turbine divider wall to crack in the turbine housing is minimized by matching the mass of the divider wall more closely to the transient heat transfer between said divider wall and the exhaust gas flowing past it. This is achieved by providing said divider wall having a cross-sectional shape defined substantially by a Log2 curve.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
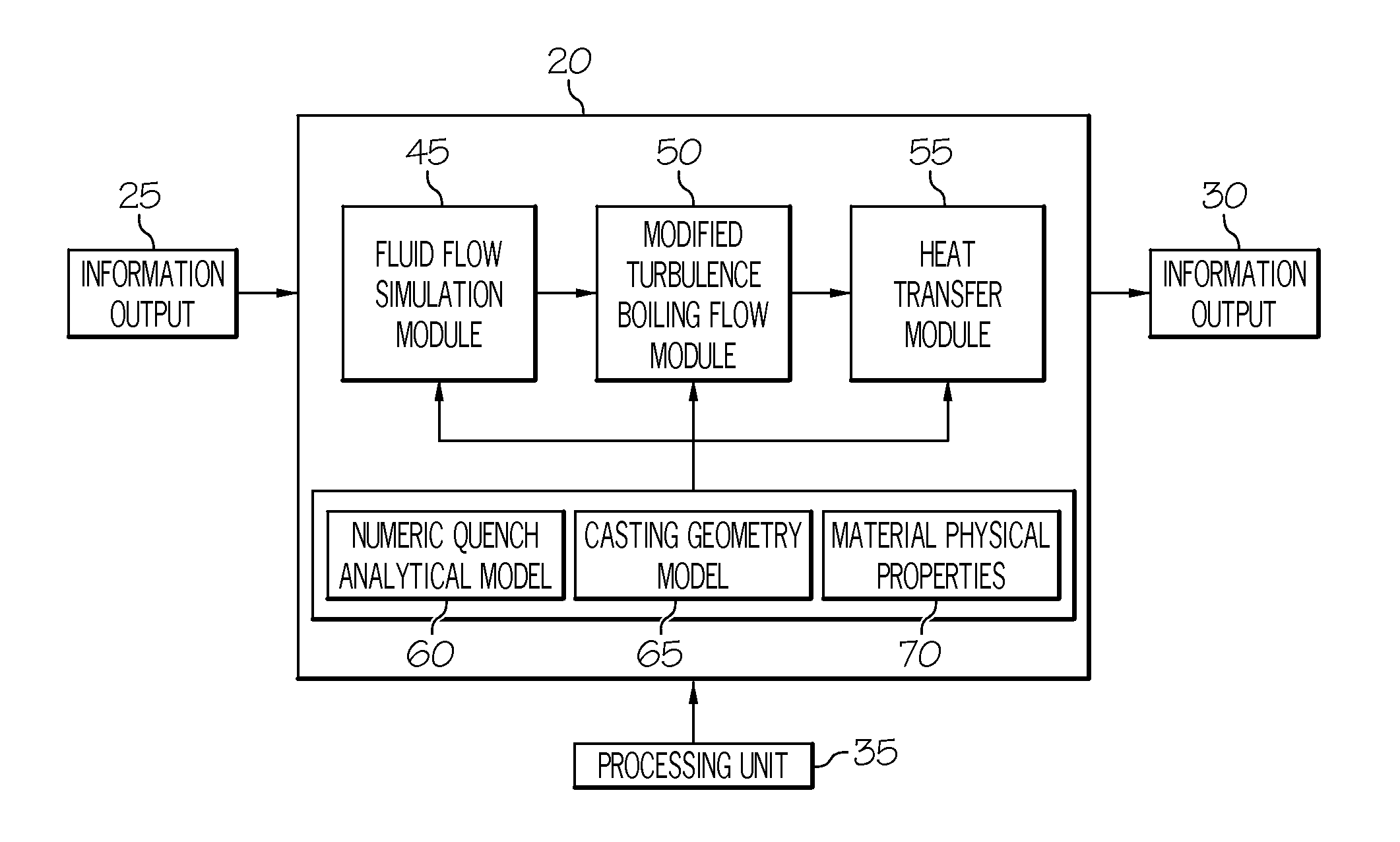
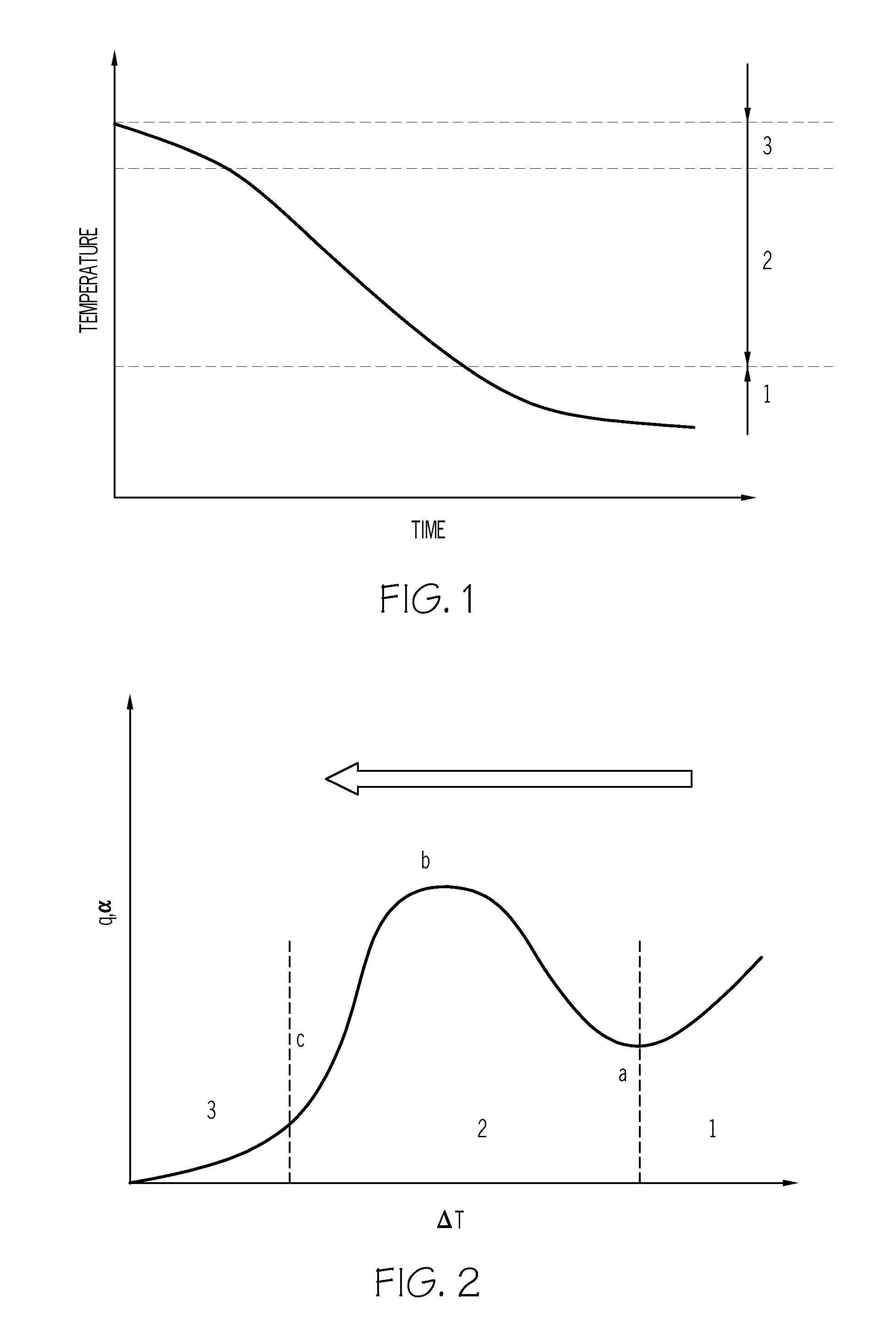
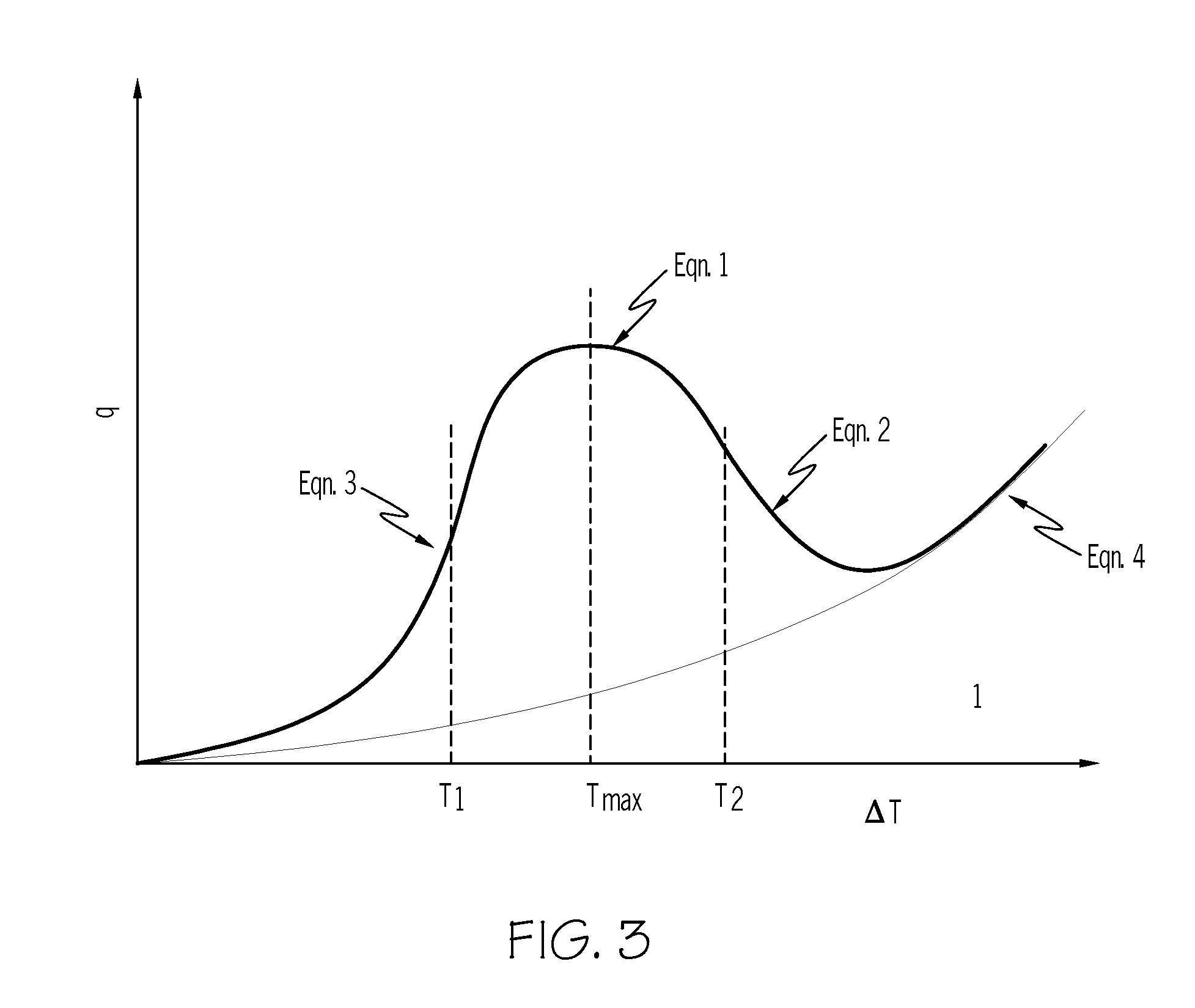
Method for simulating transient heat transfer and temperature distribution of aluminum castings during water quenching
ActiveUS20120041726A1Accurately simulate heat transferAccurate transferDigital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationTransient heat transferQuenching
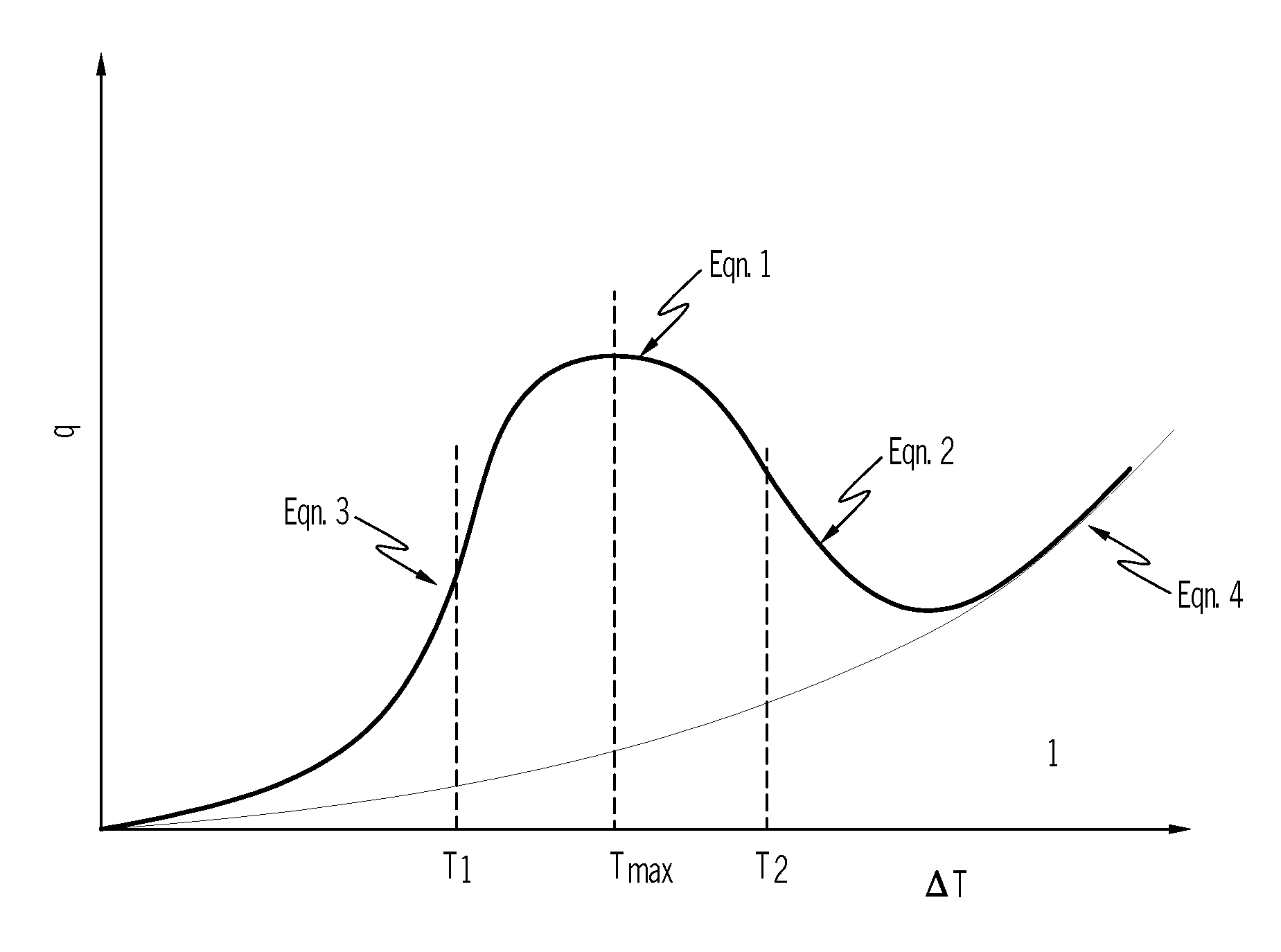
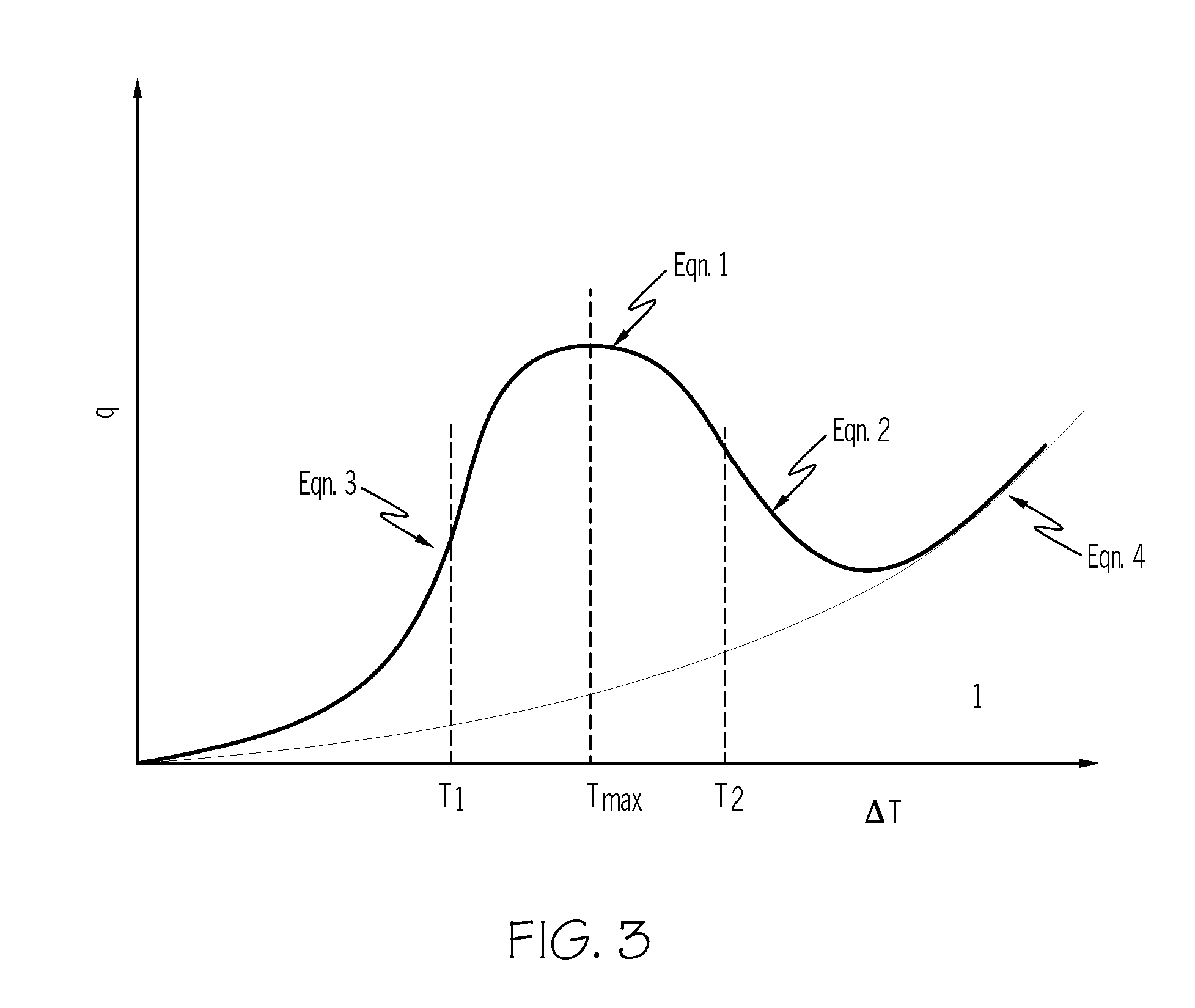
The invention relates to a method for estimating heat transfer during water quench of an aluminum part. The method includes:estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when a temperature of the part is greater than 500° C. usingq=α(ΔT) (1);estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when the temperature of the part is greater than T2 and less than 500° C. usingq=k1ΔTk<sub2>2 < / sub2> (4);estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when the temperature of the part is greater than T1 and less than T2 using a critical point function equation selected from:q=qmax-q0(Tmetal-TmaxT2-T1)2,(3)qn=a0+a1ΔT+a2ΔT2+a3ΔT3+…+anΔTn,(6)q=qmax-(1-4((1-ϕ)(Tmetal-TmaxT2-T1)2),(7)q=qmax-(1-(Tmetal-TmaxT2-T1)2),or(8)q(T1)=q(T2)=ϕqmax;(9)estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when the temperature of the part is less than T1 usingq=c1ΔTc<sub2>2 < / sub2> (5).Systems, methods, and articles to predict transient heat transfer, or temperature distribution, or both of a quenched aluminum casting are also described.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
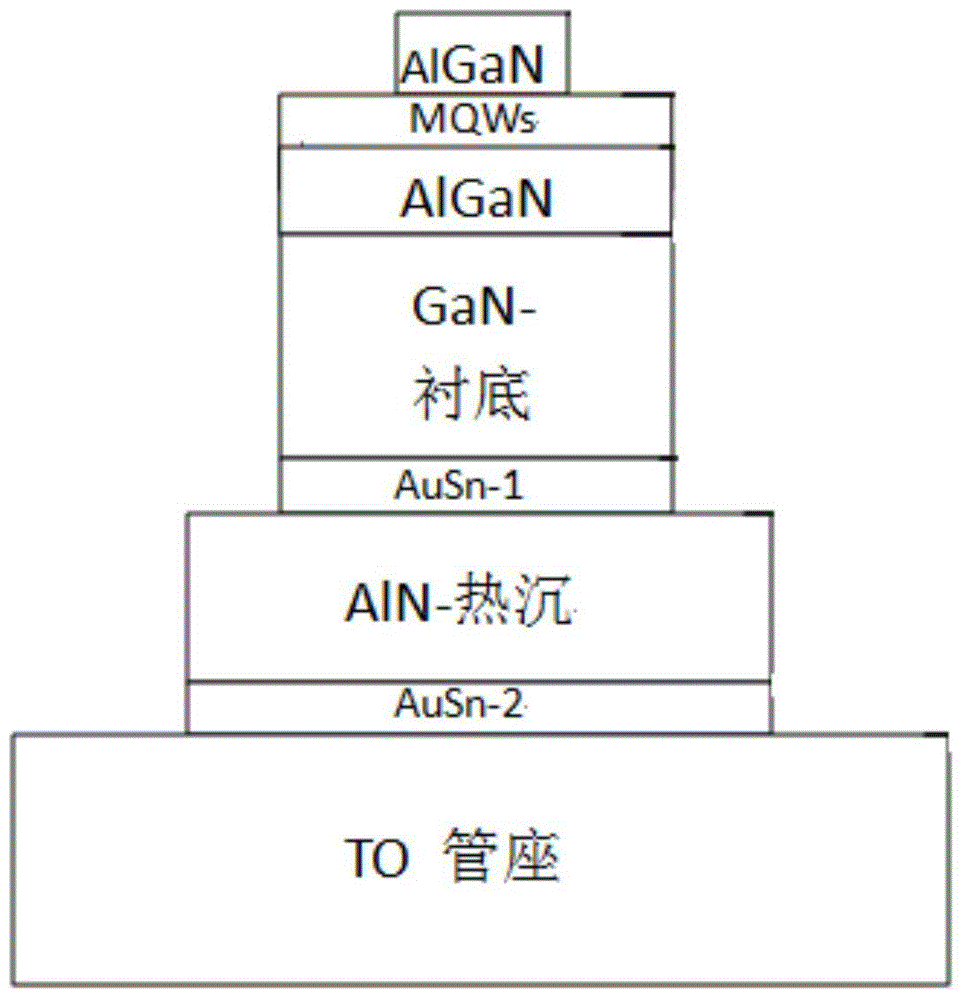
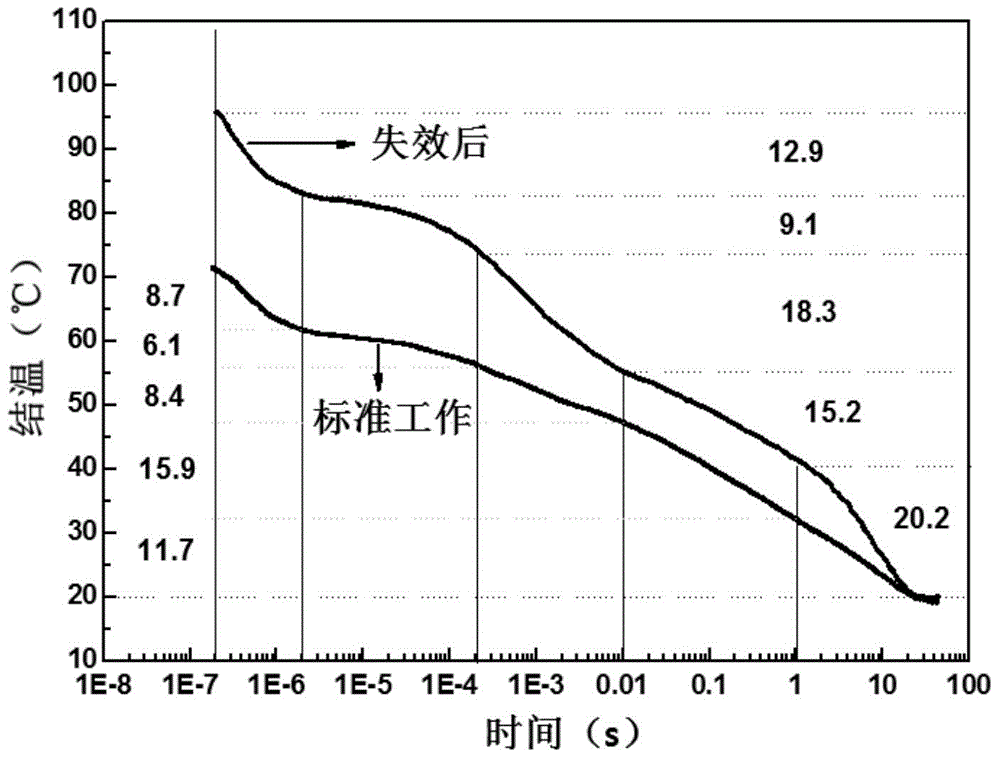
Detection method of semiconductor laser degradation mechanism
InactiveCN105807197AExtend working lifeIndividual semiconductor device testingCooling curveJunction temperature
The present invention discloses a detection method of a semiconductor laser degradation mechanism. The method comprises the steps of measuring the transient cooling curve of a failed semiconductor laser and the transient cooling curve of a normally working semiconductor laser in a same condition, comparing the two transient cooling curves, and obtaining the degradation mechanism of the failed semiconductor laser. According to the method, the transient heat transfer characteristics of the semiconductor laser is utilized, the transient cooling curve of the laser is obtained through a forward voltage junction temperature measurement method or other methods, then the degradation position of the laser is found through comparing the difference between the transient cooling curve of the failed laser and the transient cooling curve of the normally working laser, the possible failure mechanism of the laser is preliminarily determined according to the magnitude of change, thus the failure reason of the laser is rapidly determined and a solution is rapidly found, and finally the service life of the laser is prolonged.
Owner:杭州增益光电科技有限公司
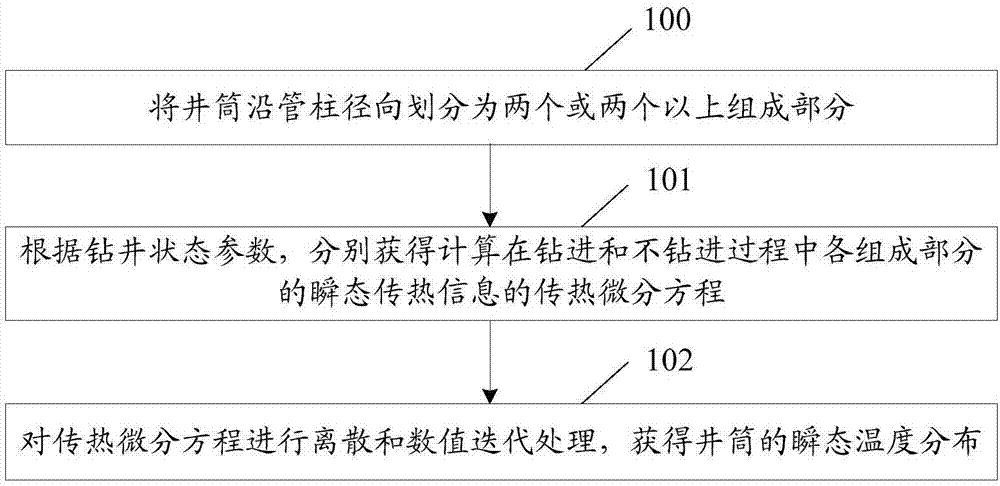
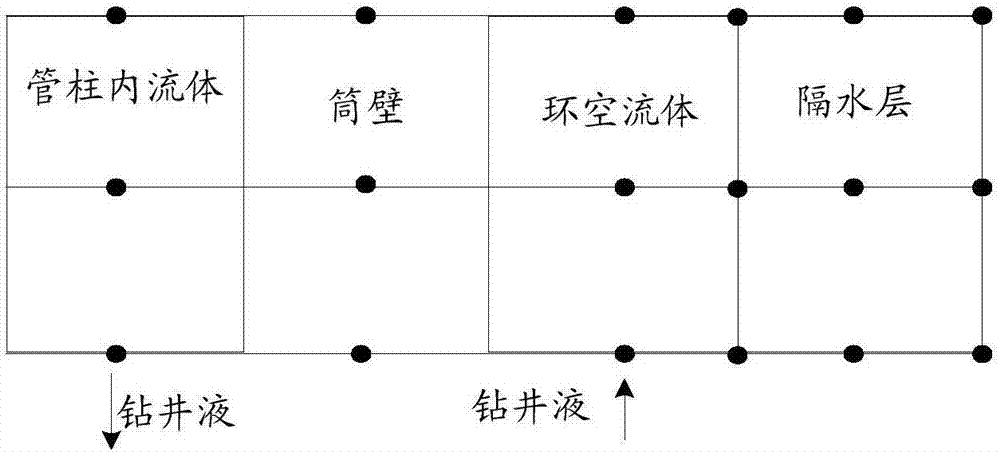
Method and apparatus for obtaining cyclic temperature field
ActiveCN107145705AAchieve acquisitionImprove work efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsState parameterWell drilling
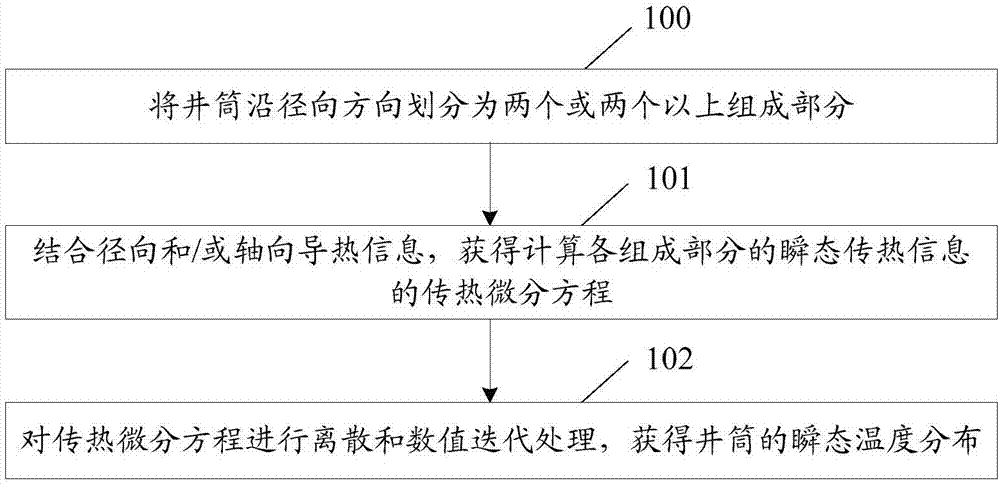
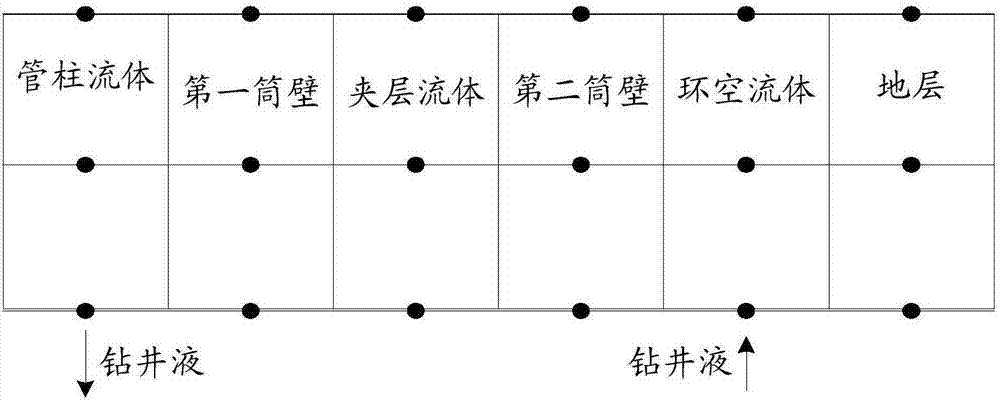
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for obtaining a cyclic temperature field. The method comprises the steps of dividing a shaft into two or more component parts in a radial direction of a pipe column; according to well drilling state parameters, obtaining a heat transfer differential equation for calculating transient heat transfer information of the component parts in drilling and non-drilling processes; and performing discrete and numerical iteration processing on the heat transfer differential equation to obtain transient temperature distribution of the shaft. According to the method and the apparatus, the cyclic temperature field is calculated according to the well drilling state parameters, so that the cyclic temperature field can be obtained in the drilling and non-drilling processes, and the working efficiency of obtaining the cyclic temperature field is improved.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
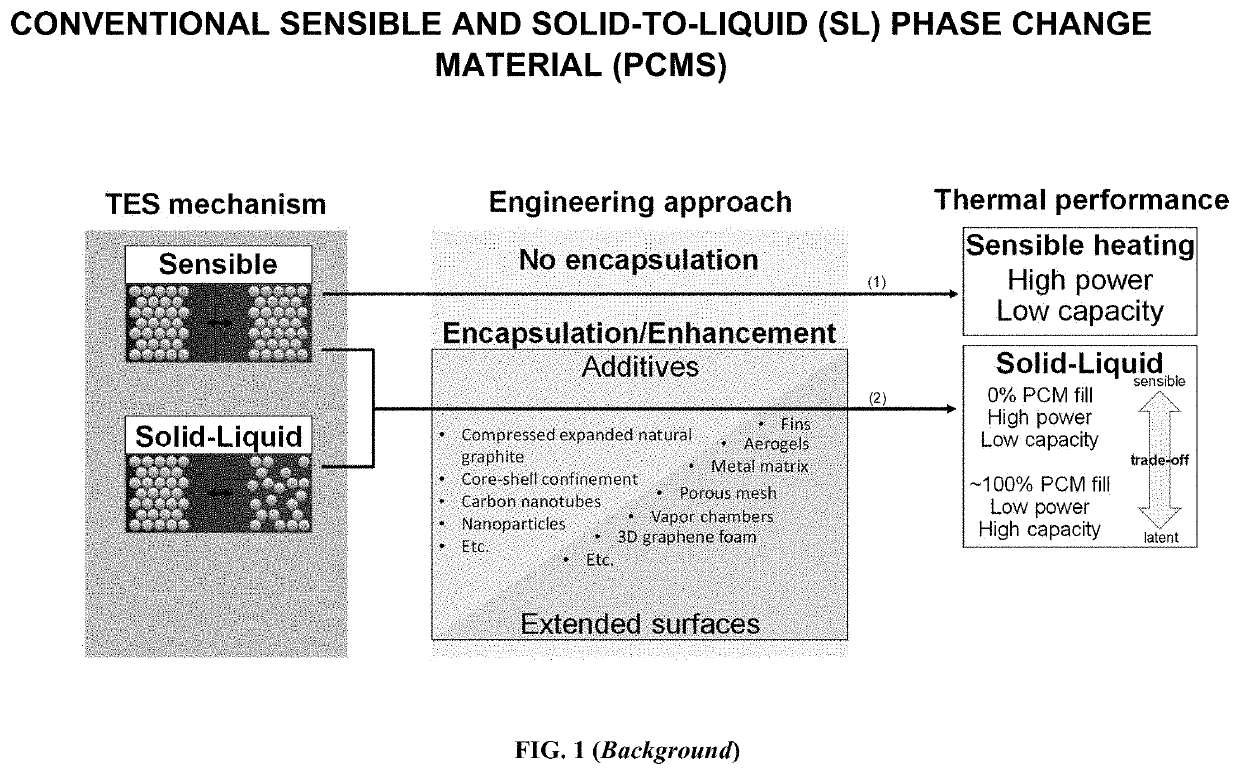
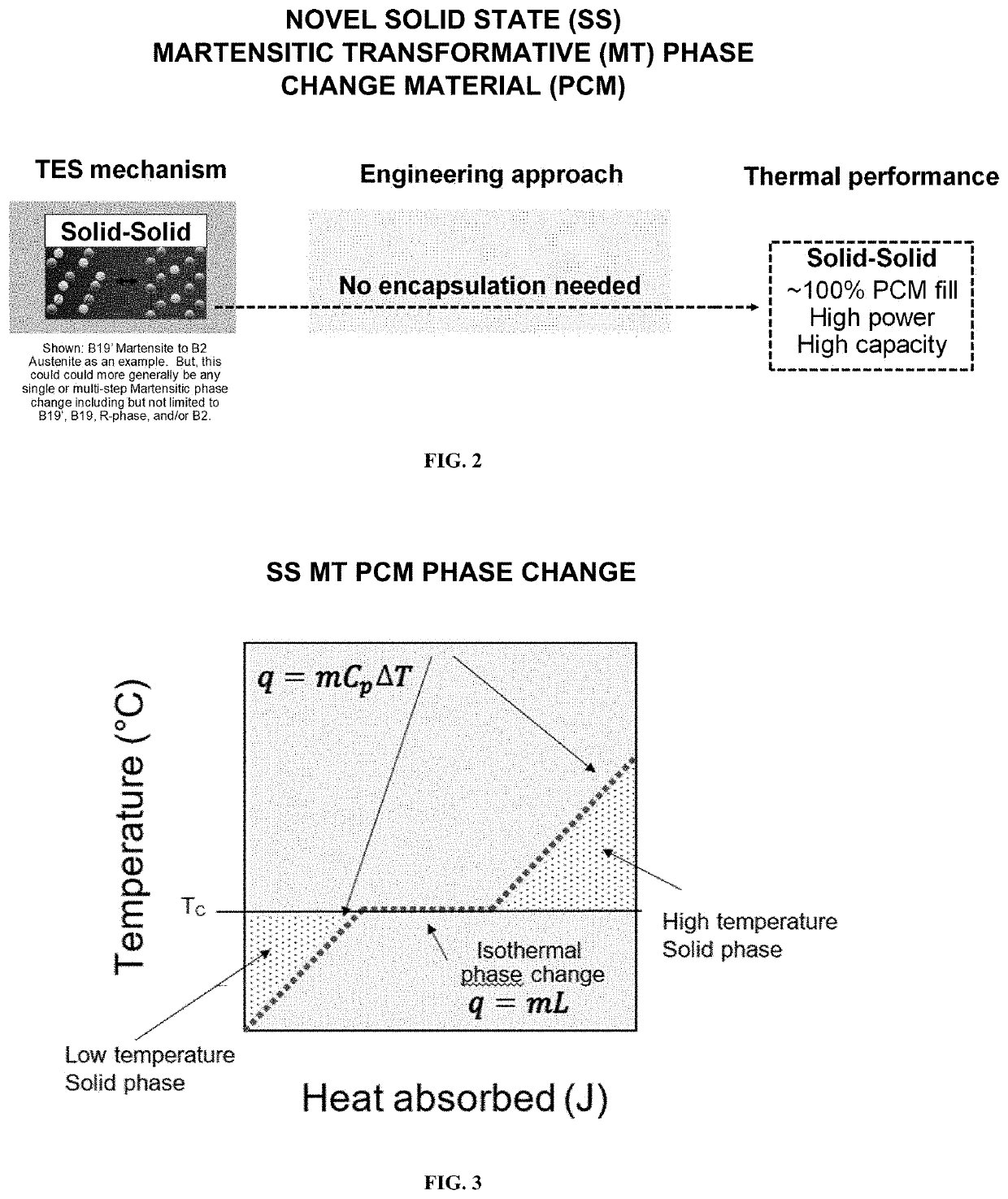
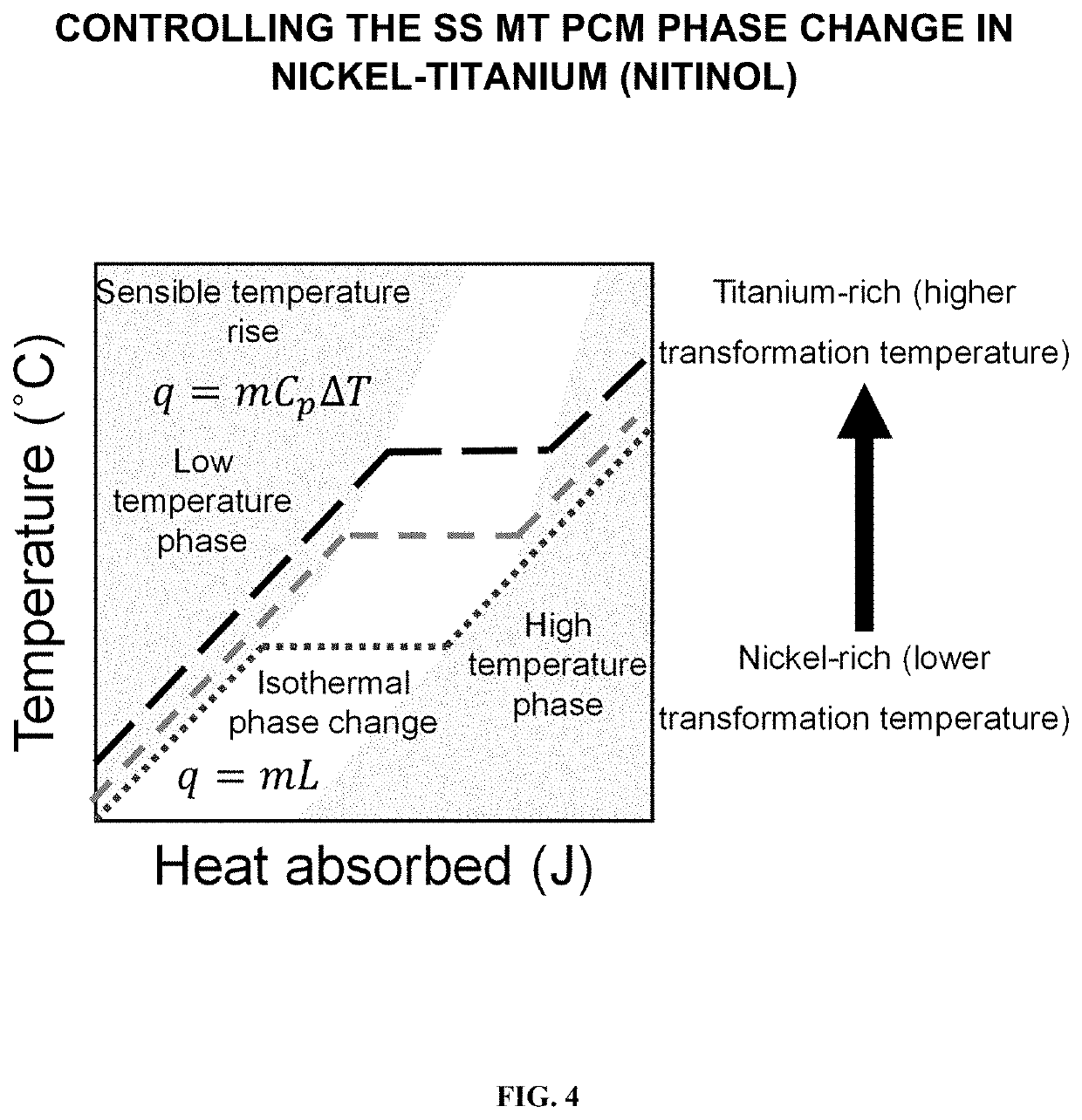
SOLID STATE MARTENSITIC TRANSFORMATION PHASE CHANGE MATERIAL CO'qMPONENTS FOR THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE AND TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSFER SYSTEMS
PendingUS20200407615A1AbilityFast timeHeat storage plantsHeat-exchange elementsThermal energy storageEngineering
A heat exchange component includes a part configured for exchanging thermal energy, the part is formed of at least one solid state Martensitic transformation phase change material which is configured to readily undergo a solid-solid martensitic transformation from one crystalline structure to another different crystalline structure during a change in temperature in the normal and / or anticipated operating temperatures of the heat exchange component. In some embodiments, the system further includes a temporally-evolving external temperature / heat source which changes the temperature and resultant phase of the solid-state phase change material. The temporally-evolving external temperature / heat source may involve a solid conducting material or electronic / photonic component, a fluid, a plasma, and / or a radiation source. The heat exchange component may be configured as a flat plate, tube, finned structure, porous structure, graded structure, cold plate, heat exchanger, condenser, evaporator, or any component generally regarded as a thermal energy storage or heat transfer structure in various embodiments.
Owner:US ARMY COMBAT CAPABILITIES DEV COMMAND ARMY RES LAB
Material high-temperature thermophysical parameter rapid measurement method
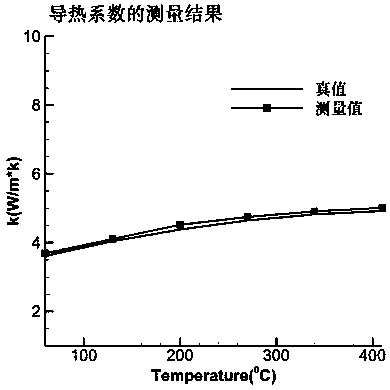
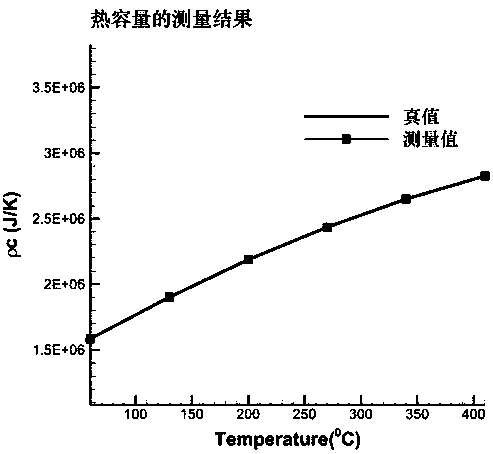
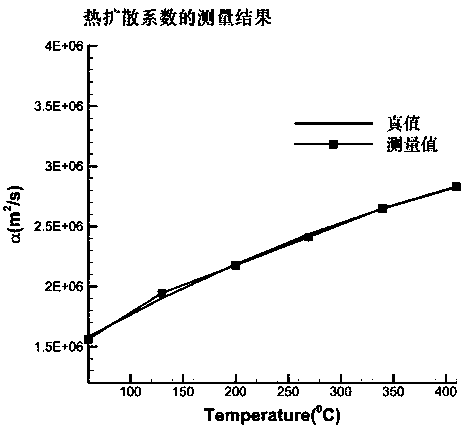
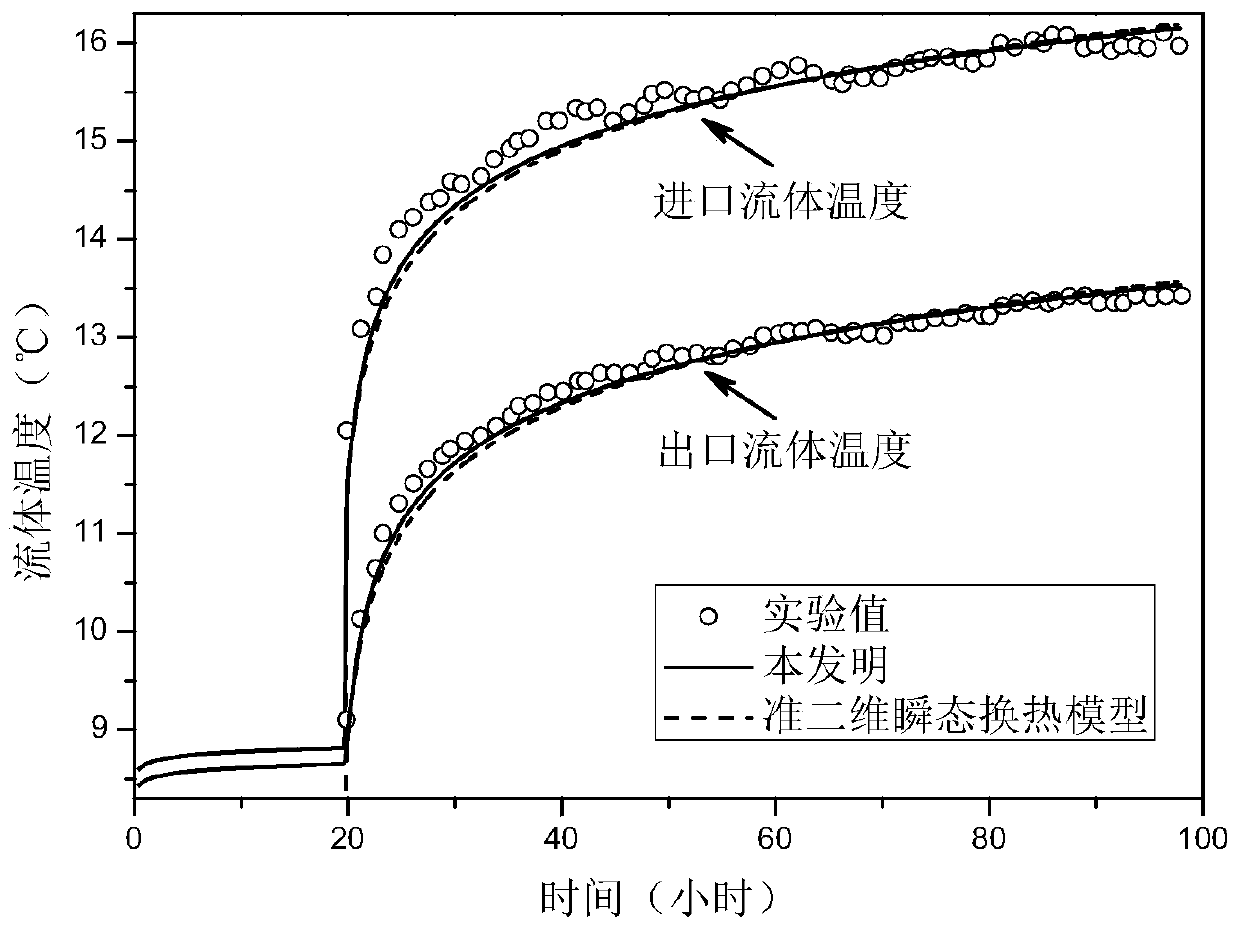
ActiveCN108051472AFast measurementLow costMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentFast measurementThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a material high-temperature thermophysical parameter rapid measurement method which comprises the following steps of according to the material thermophysical parameter-medium temperature-ultrasonic propagation characteristic, adopting an ultrasonic pulse-echo method to acquire an ultrasonic propagation time under the condition of transient heat transfer, inversing materialparameters in a heat transfer equation through the ultrasonic propagation characteristic, and rapidly measuring the thermophysical parameter of a material along with temperature change without loss and contact. By measuring for one time only, the method is capable of acquiring various material thermophysical parameters such as thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity or thermal diffusivity atdifferent temperatures from the room temperature to 400 DEG C, for example, when the temperature of the heating surface of a tested piece is raised to a preset temperature such as 400 DEG C, and has the outstanding advantages of rapid measurement speed, low cost, good universality, large measurement range and the like.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Method for simulating transient heat transfer and temperature distribution of aluminum castings during water quenching
ActiveUS8447574B2Accurate transferDigital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationTransient heat transferQuenching
The invention relates to a method for estimating heat transfer during water quench of an aluminum part. The method includes:estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when a temperature of the part is greater than 500° C. usingq=α(ΔT) (1);estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when the temperature of the part is greater than T2 and less than 500° C. usingq=k1ΔTk<sub2>2< / sub2> (4);estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when the temperature of the part is greater than T1 and less than T2 using a critical point function equation selected from:q=qmax-q0(Tmetal-TmaxT2-T1)2,(3)qn=a0+a1ΔT+a2ΔT2+a3ΔT3+…+anΔTn,(6)q=qmax-(1-4((1-φ)(Tmetal-TmaxT2-T1)2),(7)q=qmax-(1-(Tmetal-TmaxT2-T1)2),or(8)q(T1)=q(T2)=φqmax;(9)estimating the heat transfer of the aluminum part when the temperature of the part is less than T1 usingq=c1ΔTc<sub2>2< / sub2> (5).Systems, methods, and articles to predict transient heat transfer, or temperature distribution, or both of a quenched aluminum casting are also described.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
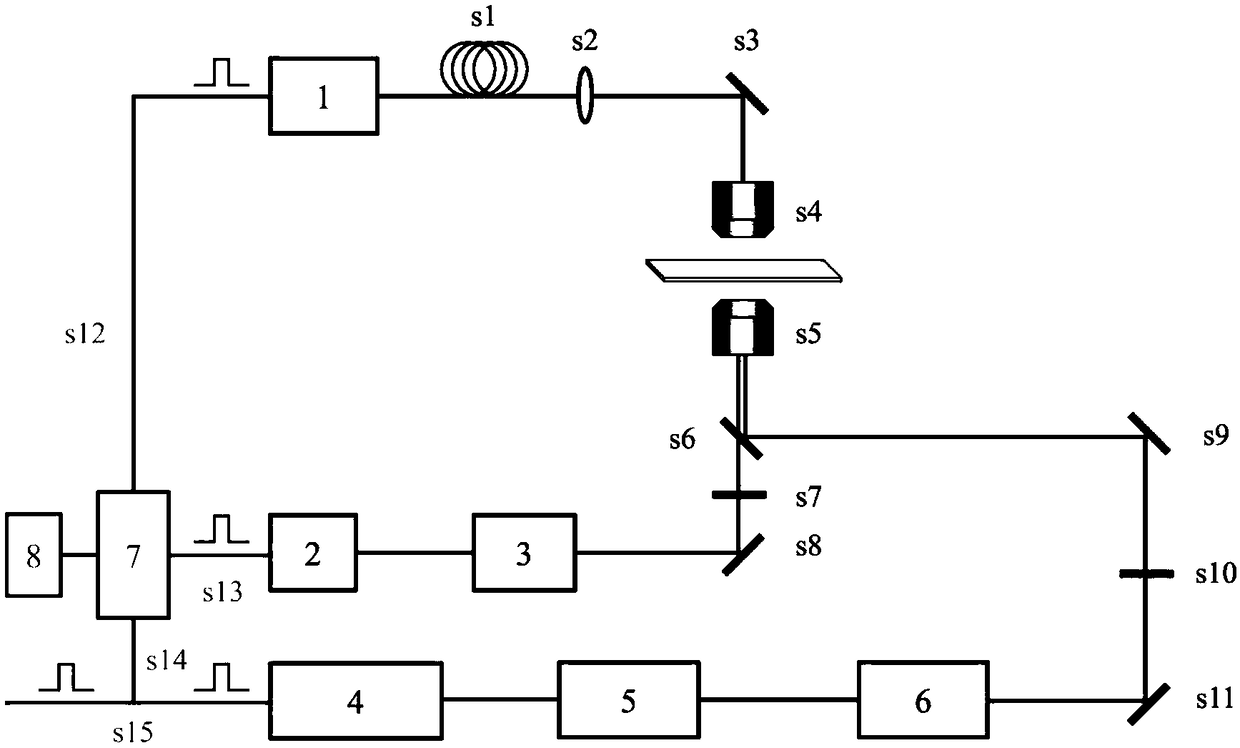
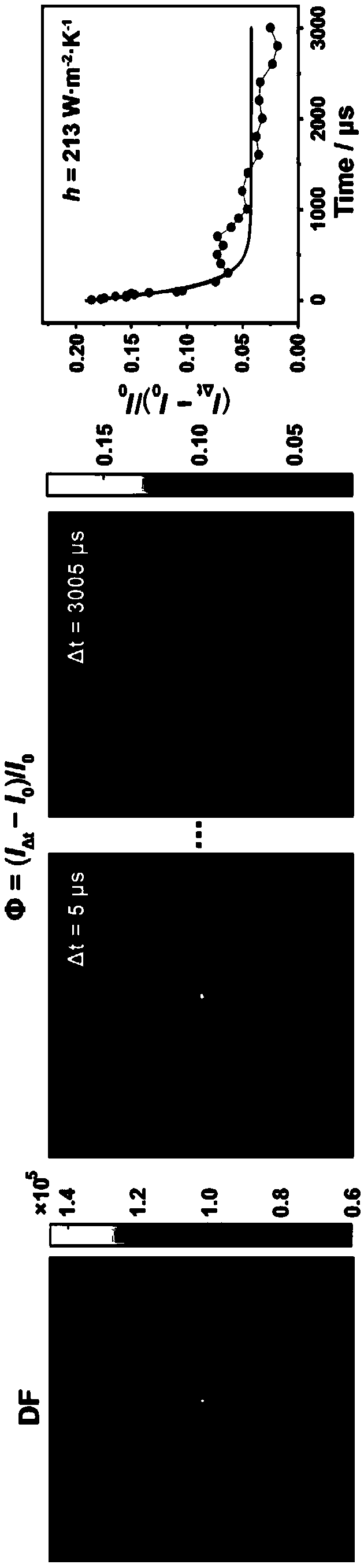
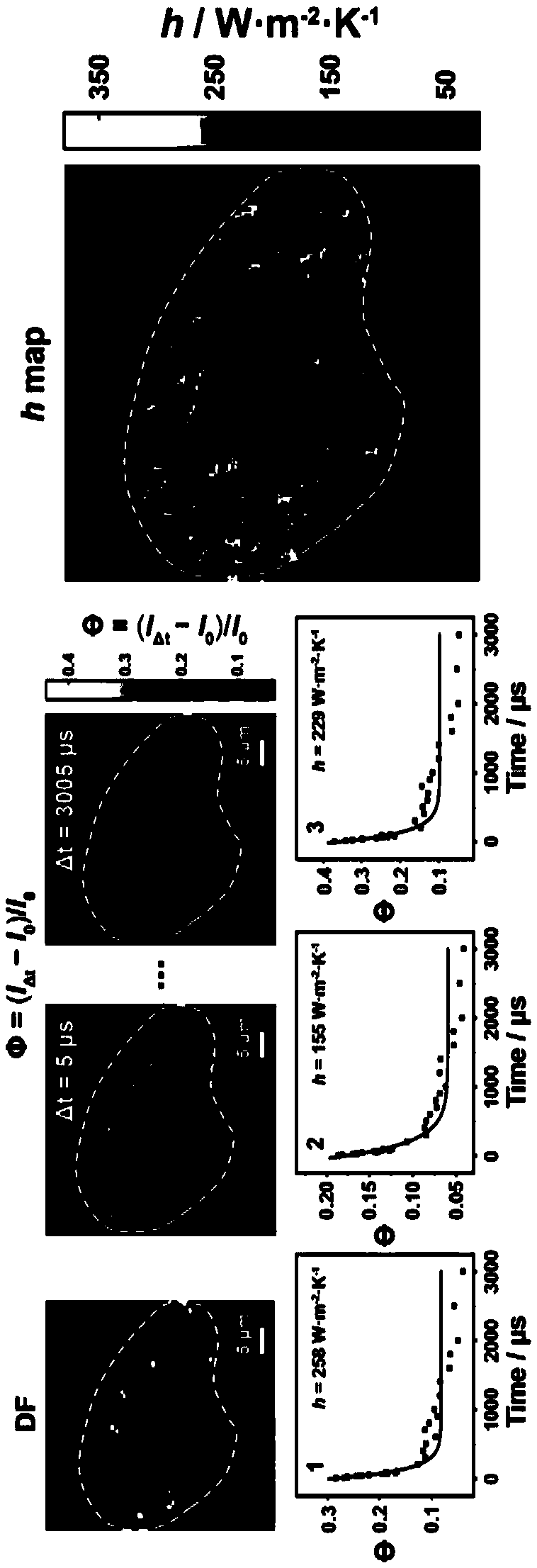
Transient heat transfer microscope and method thereof for micro-area thermal measurement
ActiveCN109444053AScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsCooling curveLiquid medium
The invention discloses a transient heat transfer microscope, which comprises a temperature-sensitive nanometer probe, a nanosecond pulse laser system, a dark field microscope system, an imaging system and a delay generator system, wherein the temperature-sensitive nanometer probe provides a micro-area temperature change signal of a sample to be measured; the nanosecond pulse laser system providesthermal disturbance for the sample to be measured; the dark field microscope system carries out microscopic observation on the temperature-sensitive nanometer probe; the imaging system carries out image information collection processing; the delay generator system provides a delay trigger signal; the delay generator system is separately connected with the imaging system and the nanosecond pulse laser system. The invention also discloses a method for micro-area thermal measurement by the transient heat transfer microscope. The nanosecond pulse laser is used for heating the sample to be measured, then, the delay trigger signal generated by the delay generator system is used for controlling the dark field microscope system and the imaging system to collect the scattering images of the temperature-sensitive nanometer probe at different moments in a cooling process, and finally, the cooling curve of the temperature-sensitive nanometer probe can be obtained to obtain the heat transfer coefficient of a liquid medium around the temperature-sensitive nanometer probe.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Fluid simulation method for target infrared wake characteristics of water scene
ActiveCN105631100AAvoid calculationSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsTransient heat transfer
The invention discloses a fluid simulation method for the target infrared wake characteristics of a water scene. The fluid simulation method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out voxelization on a model in the scene to generate solid particles; 2) adding liquid particles in an area with liquid; 3) for each time frame, carrying out numerical simulation on the mechanical characteristics of the fluid by utilizing SPH; and 4) for each time frame, carrying out numerical simulation and infrared characteristic graph drawing on the thermodynamic characteristics of the fluid by utilizing a transient heat transfer equation. According to the method, the demand for calculating the thermodynamic characteristics in fluid media is solved; the mechanical characteristics and infrared characteristics in the water scene can be simulated truly, and the new-found infrared phenomenon in recent years: the infrared wakes generated by the ship in the sailing process, is successfully simulated under laboratory environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for acquiring well cementation circulating temperature
ActiveCN106934106ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransient heat transferEngineering
The invention discloses a method and a device for acquiring well cementation circulating temperature. The method comprises the steps that a shaft is divided into two or more components in the radial direction; a heat transfer differential equation for calculating transient heat transfer information of all the components is obtained in combination with radial and / or axial heat conduction information; and the heat transfer differential equation is subjected to dispersion and numerical iteration processing to obtain transient temperature distribution of the shaft. According to the embodiment, the well cementation circulating temperature is calculated in combination with the radial and / or axial heat conduction information, and the calculation precision of the well cementation circulating temperature is improved.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
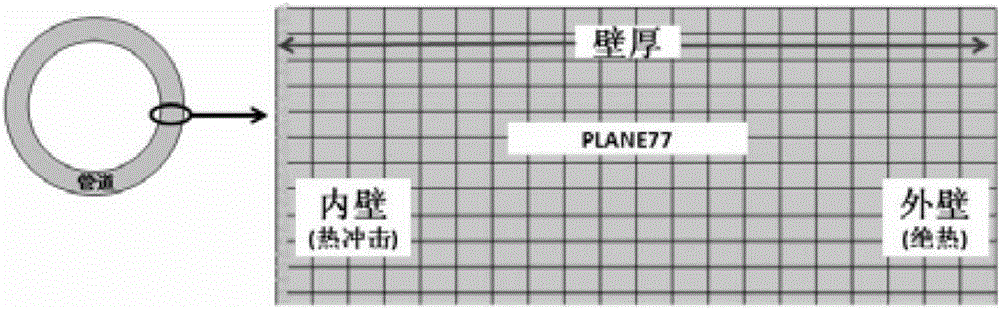
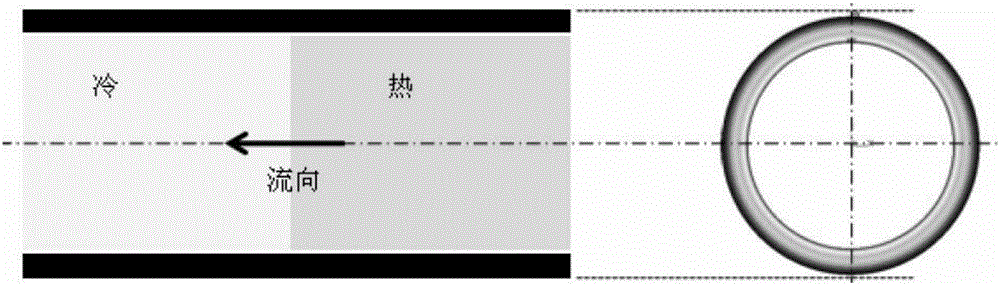
Method and device for measuring inner wall temperature of nuclear power station pipeline
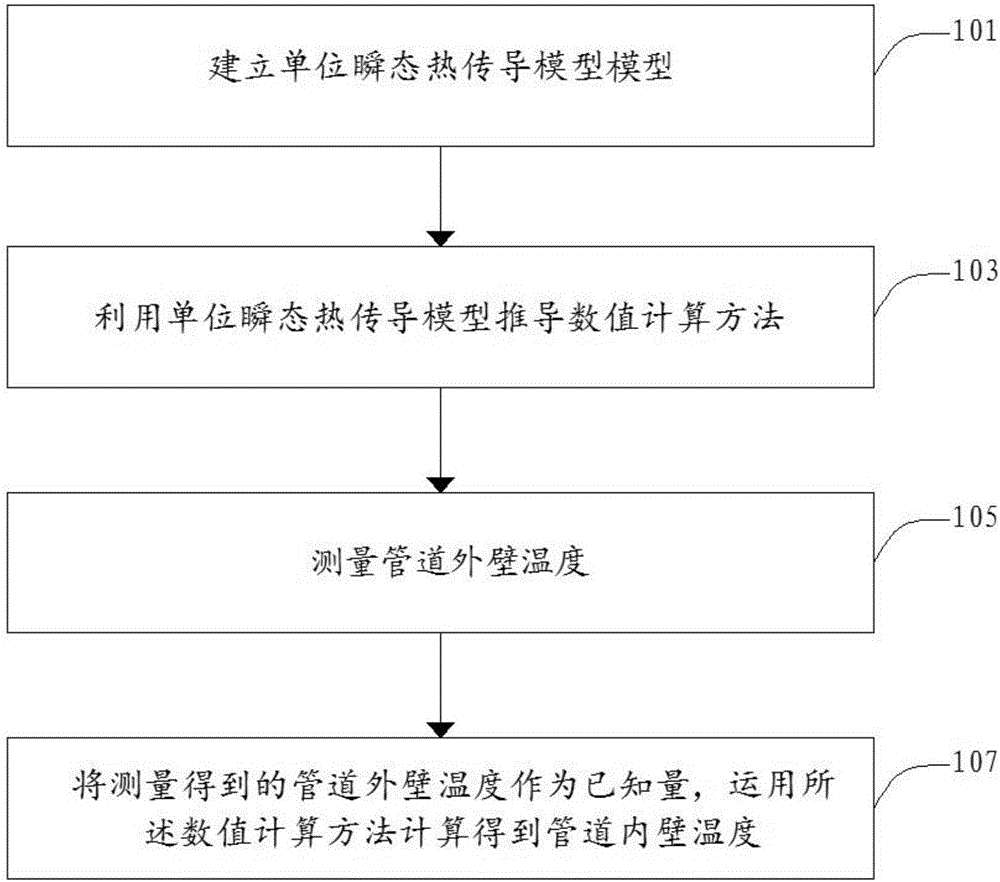
ActiveCN106092351AImprove securityImprove calculation accuracyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansNuclear powerEngineering
The invention discloses a method for measuring the inner wall temperature of a nuclear power station pipeline. The method comprises steps of establishing a unit transient heat transfer model; deriving a numerical computation method using the unit transient heat transfer model; measuring the outer wall temperature of a pipeline; and taking the measured outer wall temperature of the pipeline as a known quantity, and using the numerical computation method to obtain the inner wall temperature of the pipeline. Compared with the prior art, the invention has no requirement of drilling a hole in a tested pipeline, accurately masters temperature distribution information of the inner wall of the pipeline under a precondition that the structure of the primary loop pipeline (containing a radiative fluid) of a nuclear power station is not destroyed, achieves radioactivity containment more effectively, and improves operation security of the nuclear power station. Meanwhile, the outer wall temperature of the pipeline is directly measured instead of the temperature of a fluid in the pipeline, and thus computation of a heat transfer coefficient is omitted, and the computation accuracy of the pipe wall temperature field is obviously improved. In addition, the invention also discloses a device for measuring the inner wall temperature of the nuclear power station pipeline.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
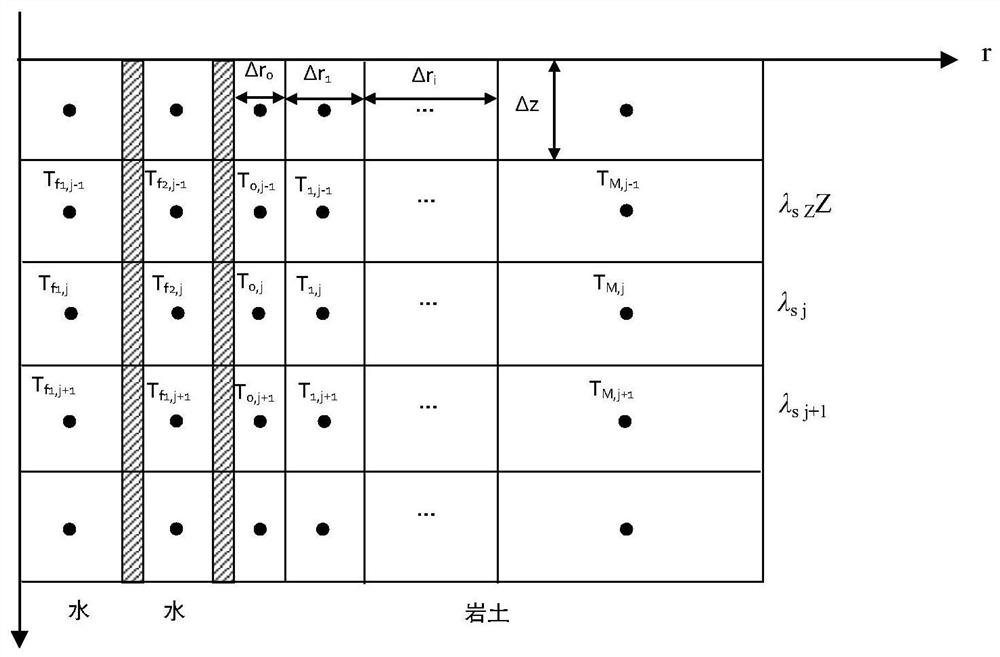
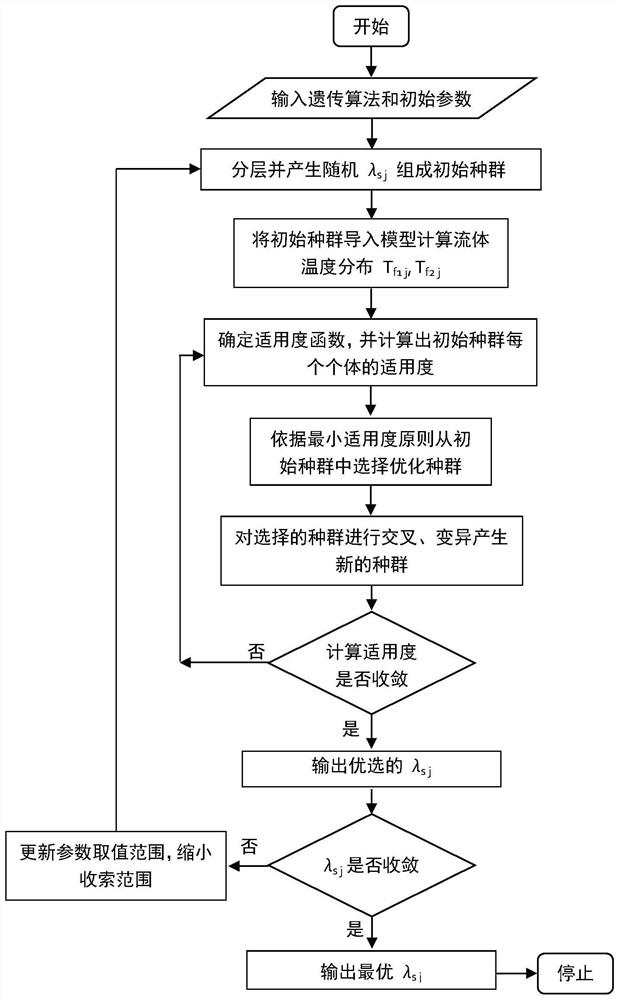
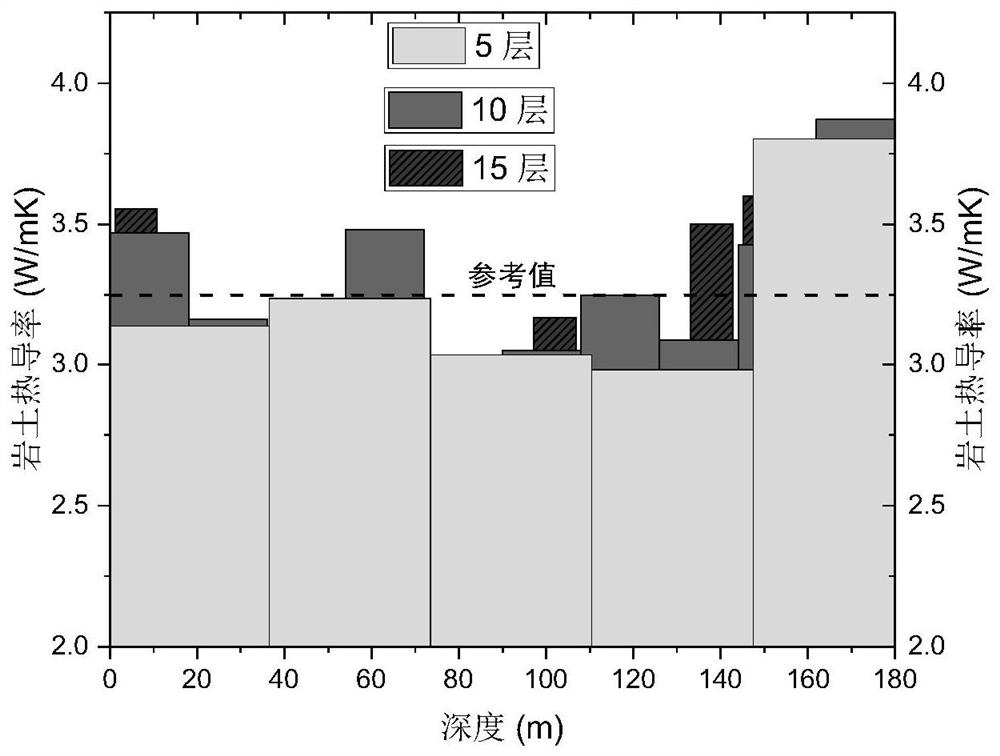
Thermal response testing method for rock-soil thermal conductivity distribution
ActiveCN112632788AImprove reliabilityImprove test accuracyGeothermal energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationThermal response testTransient heat transfer
The invention provides a thermal response testing method for rock-soil thermal conductivity distribution. The method is used for testing the thermal conductivity of rock soil in different underground depth layers. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a multi-dimensional transient heat transfer model of a buried pipe heat exchanger by considering heat transfer in the depth direction of rock soil, simulating a longitudinal temperature distribution curve of fluid in the heat exchanger, then testing temperature distribution data of the fluid at different depths in the heat exchanger through experiments, and finally using a multi-objective optimization algorithm and directly adopting fluid temperature distribution data to predict rock soil thermal conductivity distribution data in multiple spatial layers at the same time. The rock soil thermal conductivity distribution tested by the method has high precision, the problem of poor convergence during layered testing of a traditional method can also be solved, meanwhile, the testing precision is not affected by depth, and the method is wide in applicability and high in testing efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Thermal modeling of an orthogonal machining process
ActiveUS9418185B2Lower the volumeNo loss of accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationSteady state temperatureElement analysis
A novel procedure is disclosed, that can be incorporated into Finite Element Analysis (FEA) or other similar analysis techniques, to obtain the steady state temperature distribution in a coupled transient heat transfer analysis rapidly as well as accurately. A scale factor is used to reduce the thermal inertia per unit volume (specific heat capacity) in regions of steady state temperature distribution, thereby hastening the achievement of steady state. An application of this procedure to estimate steady state temperature distributions within cutting tools, and the estimation of cutting tool wear based on the obtained steady state temperature distributions is shown as an example.
Owner:MADHAVAN VISWANATHAN +1
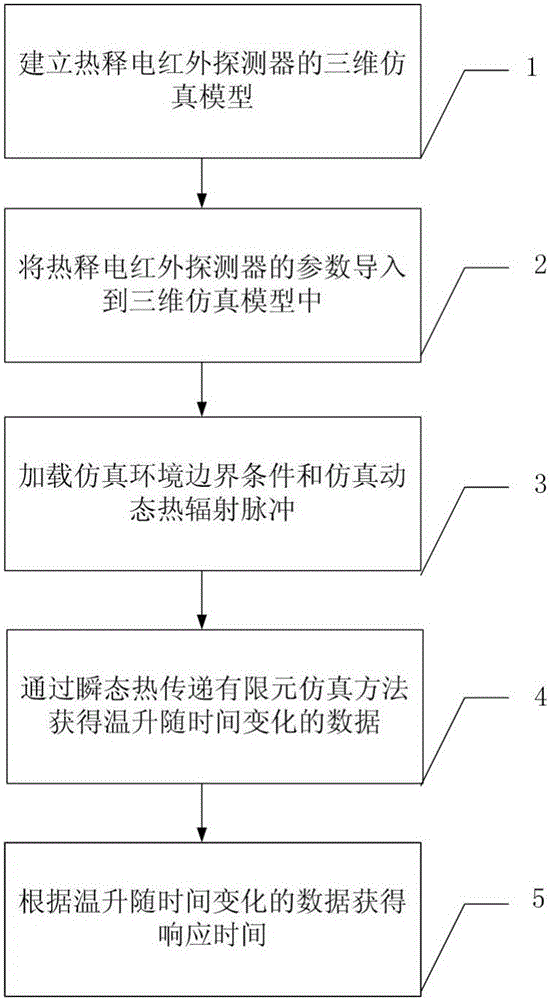
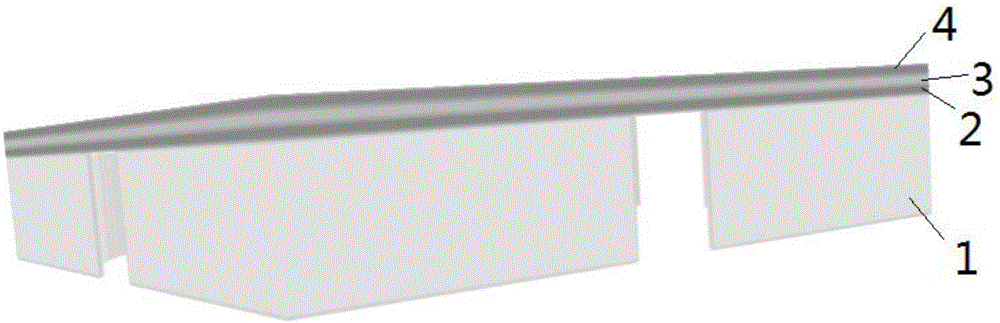
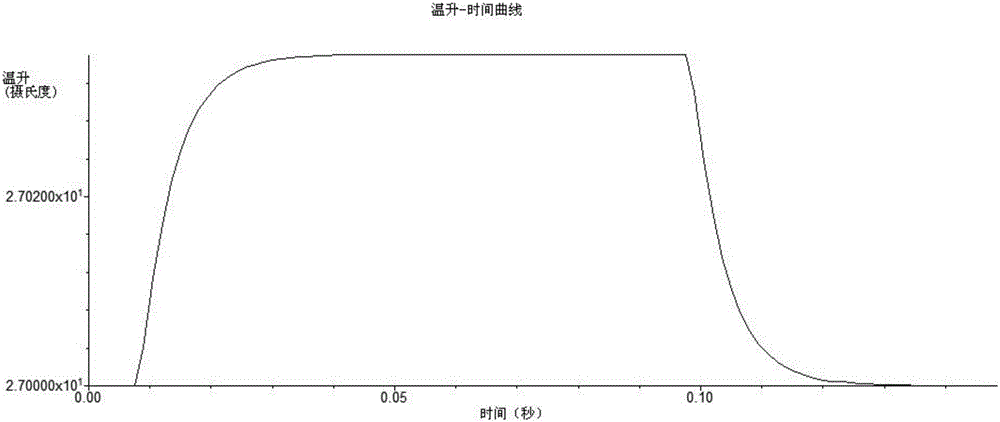
Method for measuring response time of pyroelectric infrared detector
InactiveCN105930560AReduce mistakesImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsThree dimensional simulationDynamic balance
The invention discloses a method for measuring the response time of a pyroelectric infrared detector, and belongs to the technical field of infrared detectors. The method includes: firstly, establishing a three-dimensional simulation model of the pyroelectric infrared detector; then importing a parameter of the pyroelectric infrared detector to be measured into the three-dimensional simulation model; loading an environment boundary condition, and continuously loading simulation dynamic heat radiation pulses on the three-dimensional simulation model till a dynamic balance temperature is achieved after the temperature of the three-dimensional simulation model is stable; acquiring a curve of the three-dimensional simulation model through the transient heat transmission finite element simulation analysis method, wherein the curve uses temperature rise as a vertical coordinate, and uses time as a horizontal coordinate; and using the corresponding time duration from a stable temperature to a dynamic balance temperature in the cure as the response time of the pyroelectric infrared detector. The method can truly simulate the working state of a device, greatly reduce errors due to approximate calculation, and improves the accuracy of measurement.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fluid temperature field analysis method for double-pipe buried pipe heat exchanger
ActiveCN111400893AReduce the number of nodesSmall amount of calculationGeothermal energy generationGeothermal collectorsTransient heat transferField analysis
The invention discloses a fluid temperature field analysis method for a double-pipe buried pipe heat exchanger, and belongs to the technical field of ground source heat pumps. The method comprises thesteps: establishing transient heat transfer equations of an inner pipe fluid and an outer pipe fluid, analyzing radial one-dimensional heat transfer in backfill soil and soil by adopting a compositemedium column heat source model, and respectively establishing a heat transfer model of the double-pipe buried pipe heat exchanger in two flowing directions (inner-in and outer-out: the fluid flows infrom the inner pipe and flows out from the outer pipe; wherein a fluid flows in from the outer pipe and flows out from the inner pipe); based on the established heat transfer model, setting a time step length, equally dividing an inner pipe fluid and an outer pipe fluid into a plurality of nodes along the axial direction respectively, dispersing a heat transfer equation, establishing an algebraicequation of each node, and calculating the temperatures of all nodes at each moment by adopting an iterative method, thereby completing the calculation of fluid temperature fields changing along withdepth and time in two flowing directions. The method has the characteristics of small calculation amount, high precision, wide applicability and the like.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
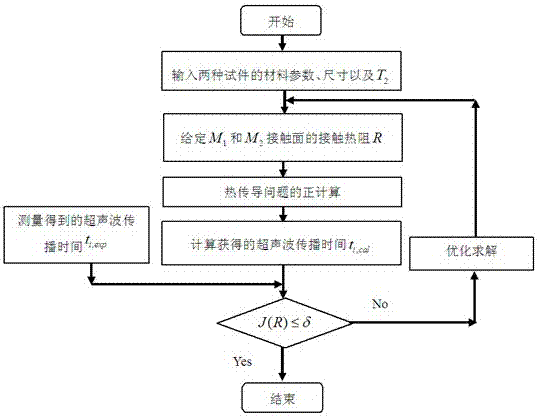
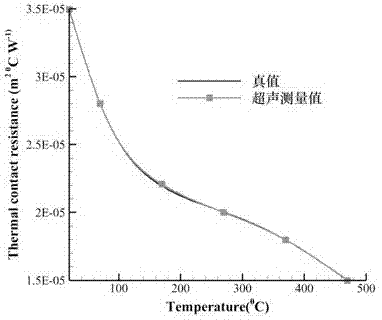
Damage-free quick measurement method of high temperature contact thermal resistance
ActiveCN107966472ALimit distractionsLimit the measurement rangeMaterial heat developmentMeasurement deviceFast measurement
The invention discloses a damage-free quick measurement method of a high temperature contact thermal resistance. According to the medium temperature-ultrasonic propagation characters, ultrasonic propagation time under a transient heat transfer condition is acquired by means of an ultrasonic-echo method, and further the inverse problem of thermo-conduction is subjected to optimization solution, sothat the interface contact thermal resistance parameters, changing with temperature, are measured in a quick, damage-free and non-contact manner. The method only needs simple measurement devices and short measurement period, is free of contact between a sensor and a to-be-tested test piece, so that interference due to the contact between the sensor and the to-be-tested test piece and limitation onmeasurement range due to high temperature resistance of the sensor are avoided.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
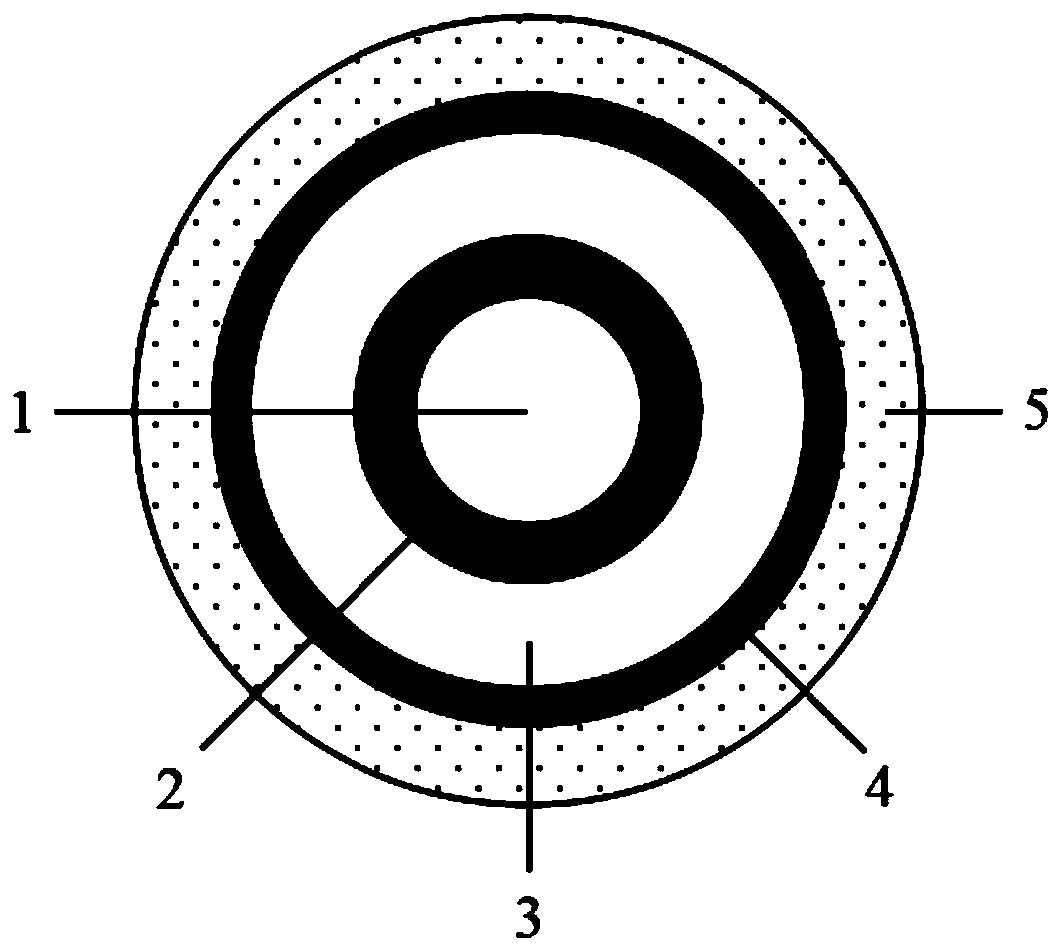
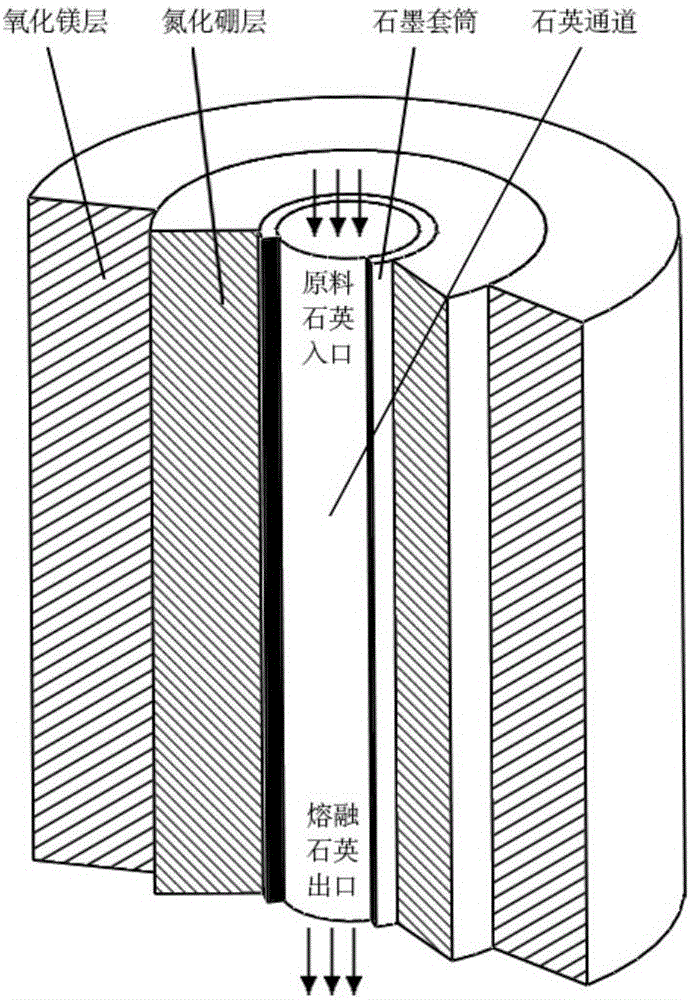
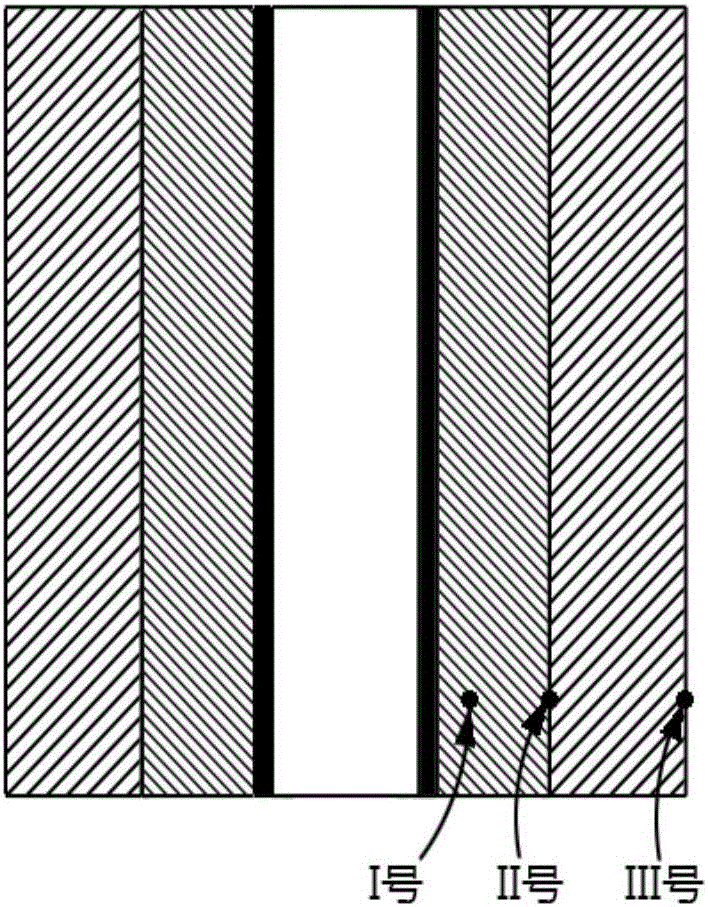
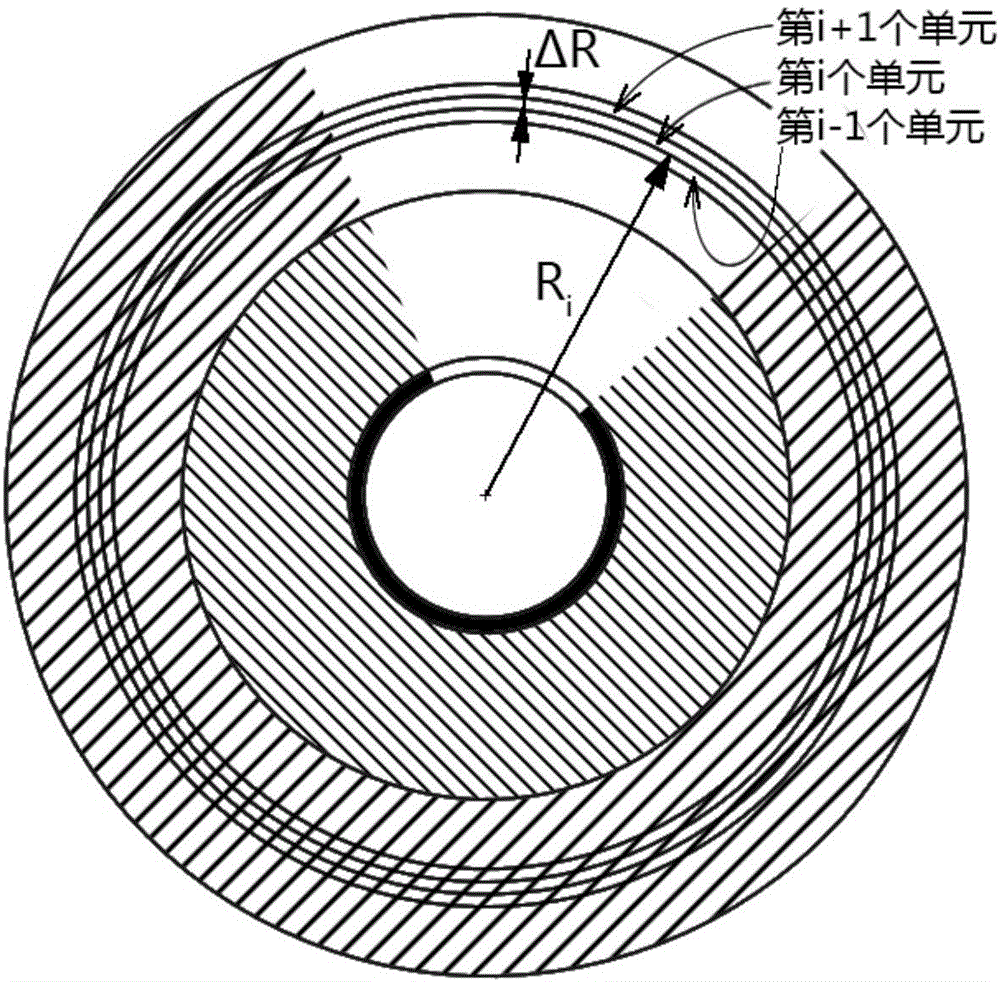
Device and method for measuring temperature of high temperature quartz fusing furnace based on transient heat transfer theory
ActiveCN106225943AAvoid inaccuraciesAchieve accuracyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansTransient heat transferBoron nitride
The invention provides a device and a method for measuring temperature of a high temperature quartz fusing furnace based on a transient heat transfer theory. Three K type thermocouples are arranged in a quartz fusing furnace, wherein the quartz fusing furnace comprises a circular graphite sleeve; a boron nitride layer is wrapped on the graphite sleeve; a magnesium oxide layer is coated on the boron nitride layer; the three K type thermocouples are located in a same plane of the quartz fusing furnace and are distributed along the radial direction of the quartz fusing furnace on the basis of the axis of the graphite sleeve; the three K type thermocouples are connected with a computer through a wire and a signal processing device; the computer is used for calculating the temperature of the quartz fusing furnace according to the temperature measured by the three K type thermocouples. According to the invention, a plurality of K type thermocouples with temperature resistance limit of about 1200 DEG C are adopted for indirectly measuring the high temperature in the quartz fusing furnace, the measuring precision is high and the cost is low.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG RES INST NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
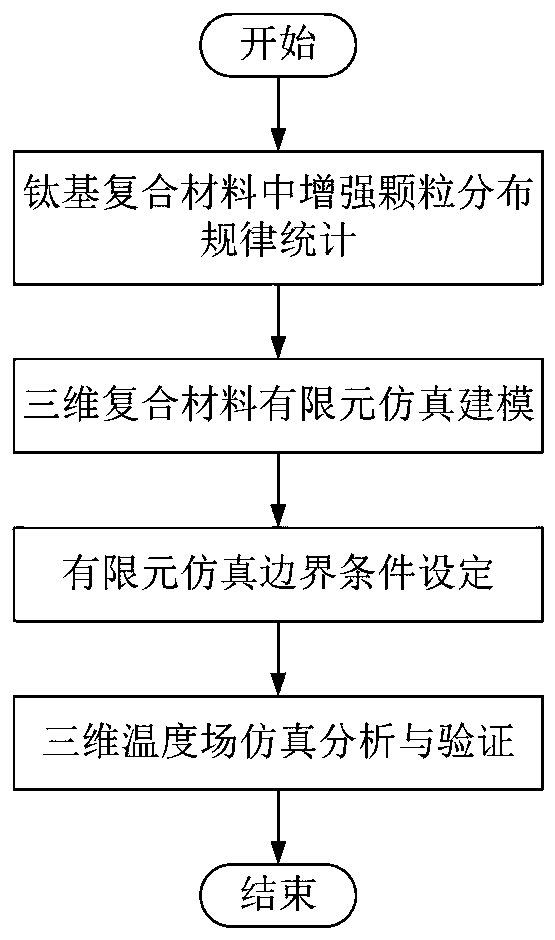
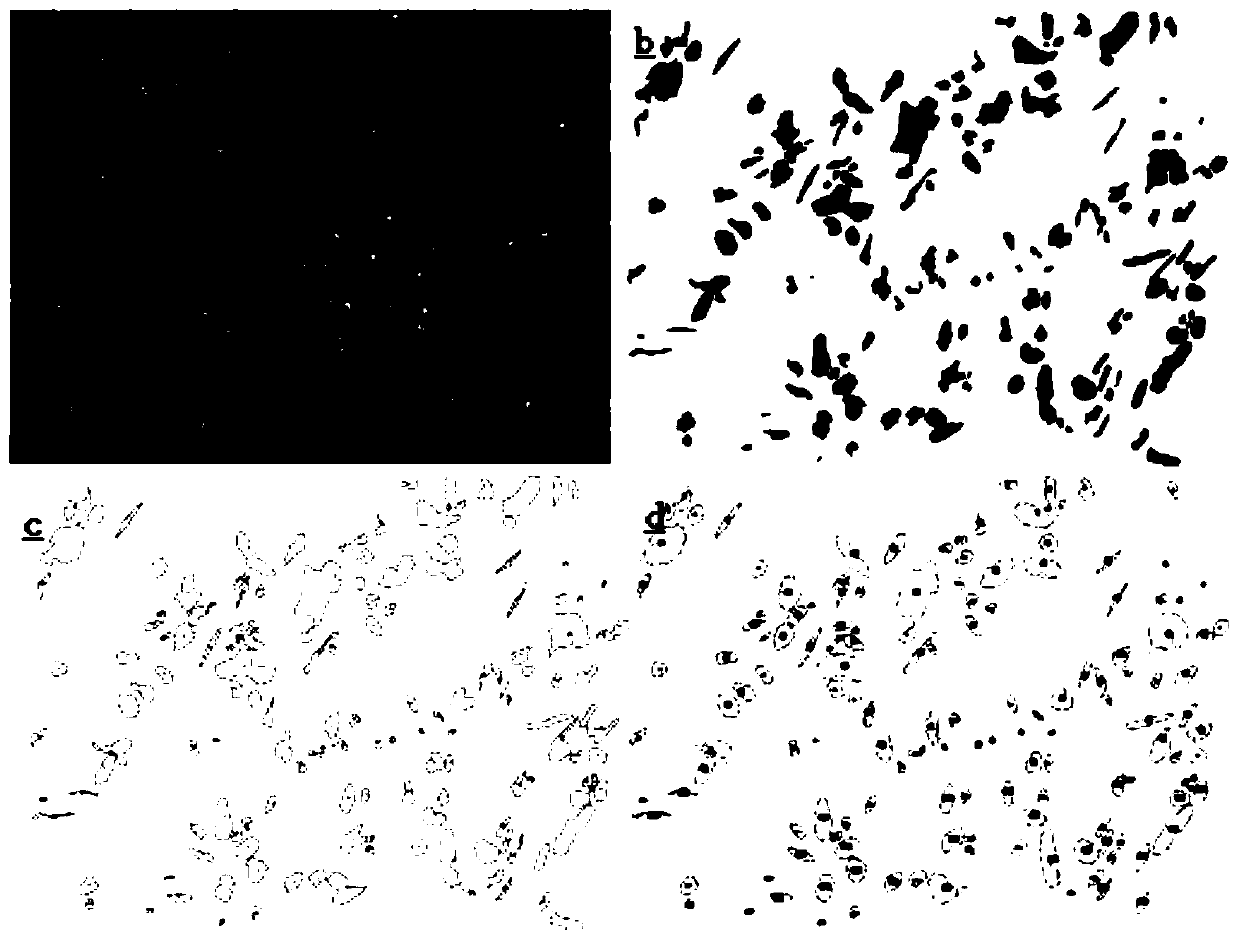
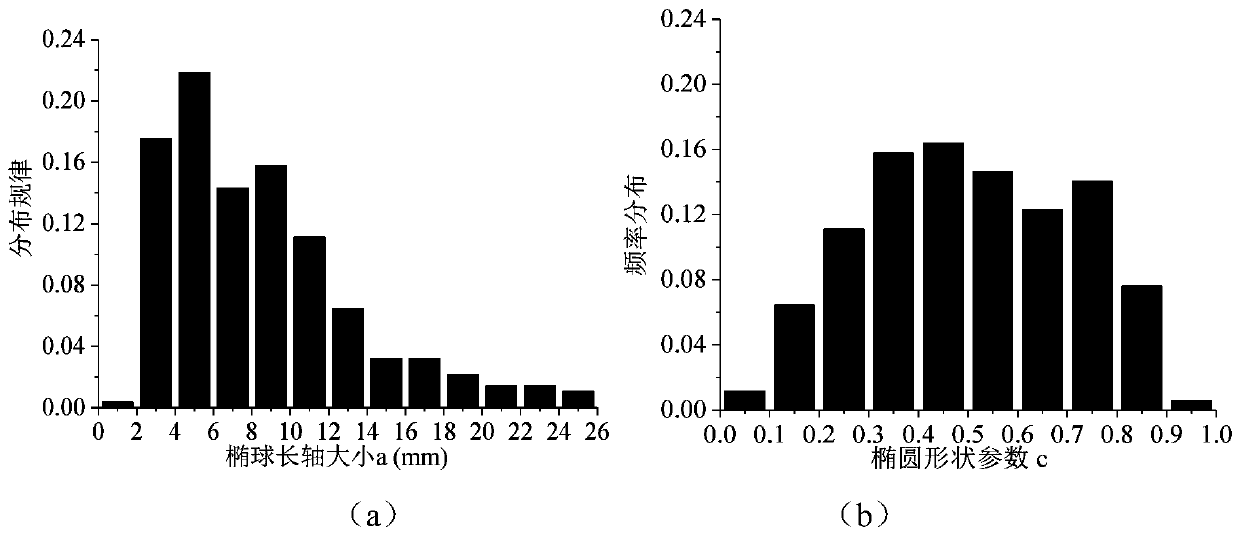
High-speed grinding temperature prediction method for particle reinforced titanium-based composite material
PendingCN110046375AEnhanced TiC shapeSmall sizeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTitanium matrix compositesHigh-speed grinding
The invention provides a high-speed grinding temperature prediction method for particle reinforced titanium-based composite material, which belongs to a transient heat transfer simulation analysis method and comprises the following steps: 1, counting the distribution law of reinforced particles in the particle reinforced titanium-based composite material; 2, performing finite element simulation modeling on the three-dimensional composite material; 3, setting finite element simulation boundary conditions; and 4, performing simulation analysis and verification on the three-dimensional temperature field. The method can predict the grinding temperature of the titanium-based composite material and has the advantages of being higher in accuracy, higher in calculation efficiency and the like compared with an existing method. By means of the method, the high-speed grinding temperature of the particle reinforced titanium-based composite material can be accurately predicted, and basic data and theoretical support are provided for avoiding grinding burn and improving the grinding quality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
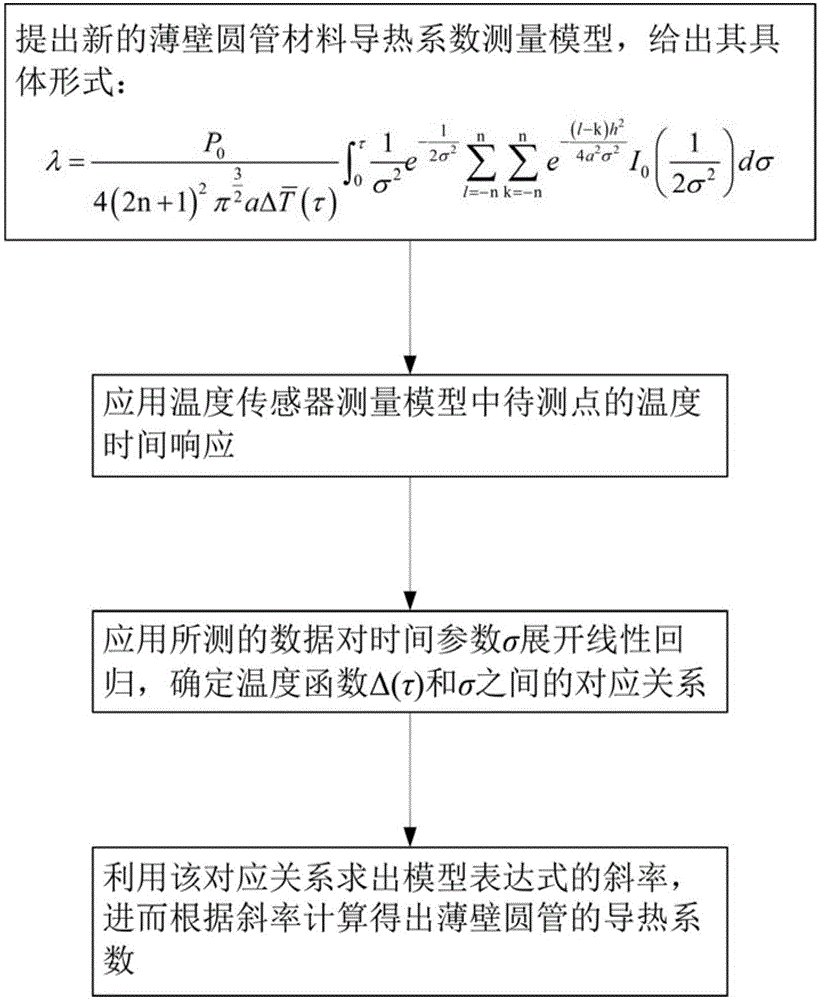
Thin-wall pipe material heat conductivity coefficient calculating method
ActiveCN106226351AUniform thicknessFlat surfaceMaterial heat developmentHot springTransient heat transfer
The invention discloses a thin-wall pipe material heat conductivity coefficient calculating method adopting a transient heat transfer calculation model and belongs to the field of solid-material thermophysical property measurement. The thin-wall pipe material heat conductivity coefficient calculating method includes: putting forward a new thin-wall pipe heat conductivity coefficient calculating model-a Hot Spring model and giving out a concrete formula; measuring to-be-measured temperature points in the model by applying a temperature sensor, and performing fitting on response data of the measured temperature time to acquire a time parameter sigma; determining the formula of the final Hot Spring model and calculating out heat conductivity coefficient of a thin-wall pipe material according to the slope of the formula. Compared with the prior art, the thin-wall pipe material heat conductivity coefficient calculating method has the advantages that reprocessing of the to-be-measured sample is not needed, experiment procedure is simplified, and precision in measuring the heat conductivity coefficient of the to-be-measured sample of the kind is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
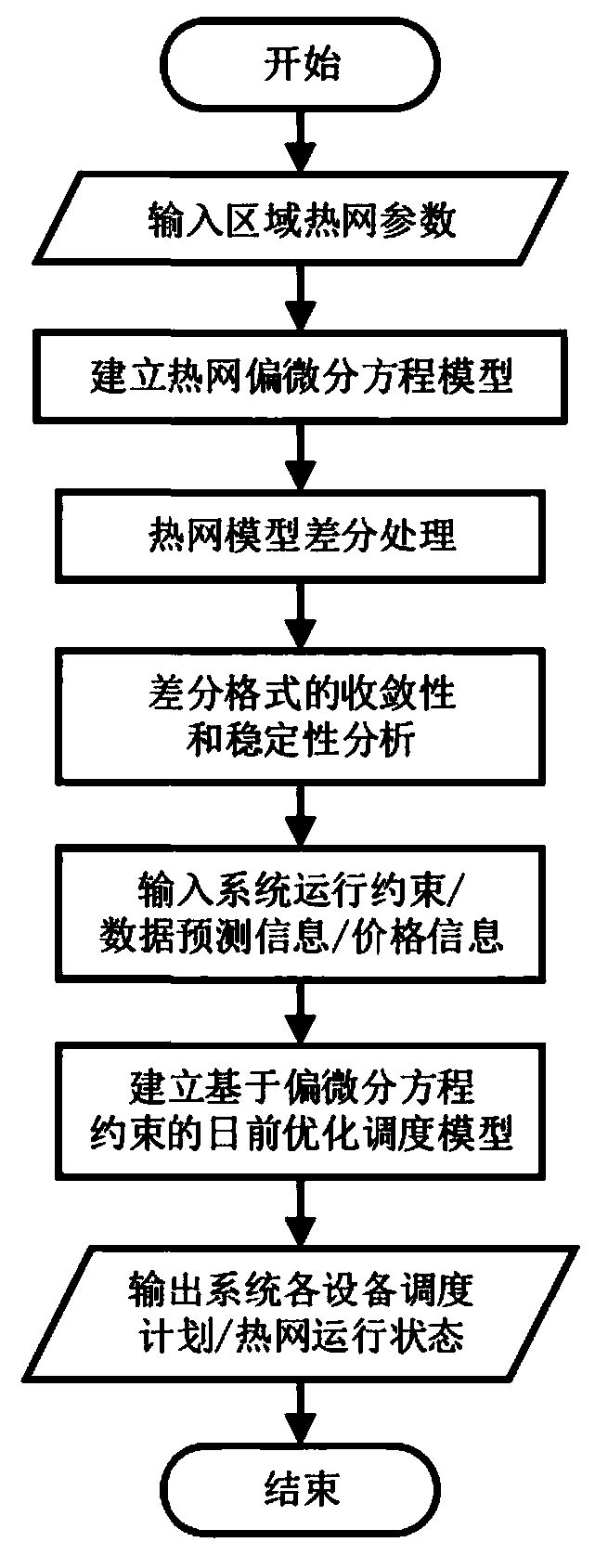
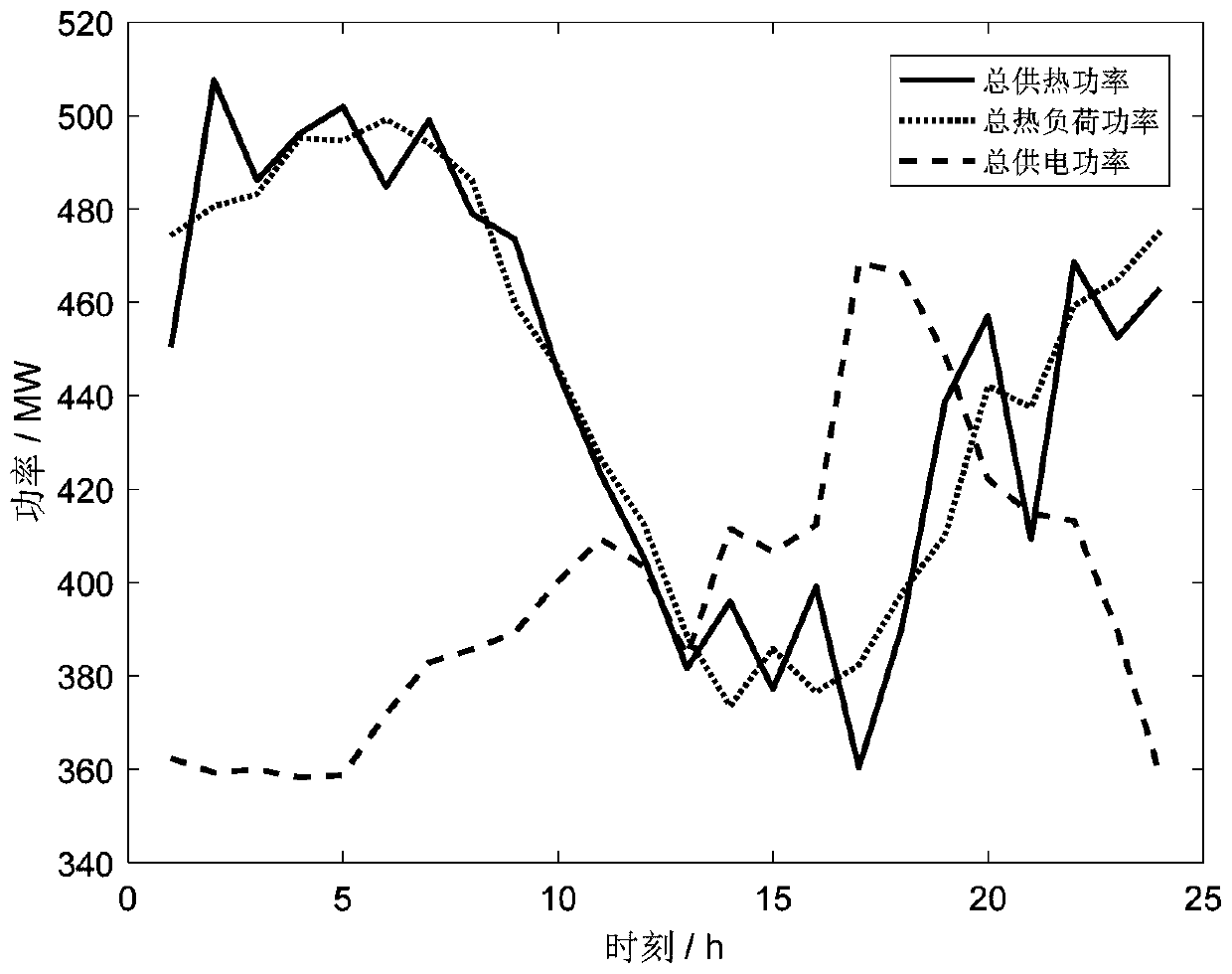
A combined heat and power generation system day-ahead scheduling method based on heat supply network partial differential equation constraint
ActiveCN109726906AImprove economyResourcesComplex mathematical operationsDaily operationAlgebraic equation
The invention discloses a combined heat and power generation system day-ahead scheduling method based on heat supply network partial differential equation constraint. The technical scheme comprises: establishing a partial differential equation model capable of reflecting the transient heat transfer characteristic of a heat supply network based on the first law of thermodynamics; Secondly, carryingout difference processing on the heat supply network partial differential equation, taking an algebraic equation set obtained by difference as a partial constraint condition, and taking the minimum daily operation cost as an objective function to establish a day-ahead optimization scheduling model of the combined heat and power generation system; And finally, according to the heat supply networkpartial differential equation constraint-based combined heat and power generation system day-ahead scheduling model, determining a scheduling plan of each device in the system, a planned power of a connection line and an operation state of the heat supply network. The optimal scheduling method provided by the invention can reflect the real operation state of the heat supply network and improve theoperation economy of the combined heat and power generation system.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMAPNY +1
Mass transfer processes with limited sensible heat exchange
ActiveUS10150051B2Retain heatRelative density is smallLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesDispersed particle separationLatent heat storageMicrobubbles
A process of mass transfer is described which utilizes latent heat transfer with little or sensible heat transfer. In a preferred process microbubbles are used under certain conditions of contact with a liquid phase to ensure highly effective mass transfer between a gaseous and liquid phase with significantly less than expected or little or no sensible heat transfer. The present invention in part provides a means by which the known state of a cold liquid of varying depths can be changed using a hot gas injected via a micro bubble inducing internal mixing without allowing the resultant mixture to reach equilibrium thereby ensuring the transfer process becomes continuous. Thus a process is described wherein at least one gaseous phase is contacted with at least one liquid phase such that the heat ratio of the system (AA) is maintained at an a value of greater than 0.5, and the mass transfer is effected by passing a gaseous phase comprising microbubbles through a liquid phase of thickness no more than 10 cm.
Owner:PERLEMAX LTD
Nuclear power station voltage stabilizer electric heating element arrangement method based on three-dimensional transient heat transfer mechanism
InactiveCN112001068AMitigating Technical Problems in Harsh Work EnvironmentsAvoid layoutDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNuclear powerEngineering
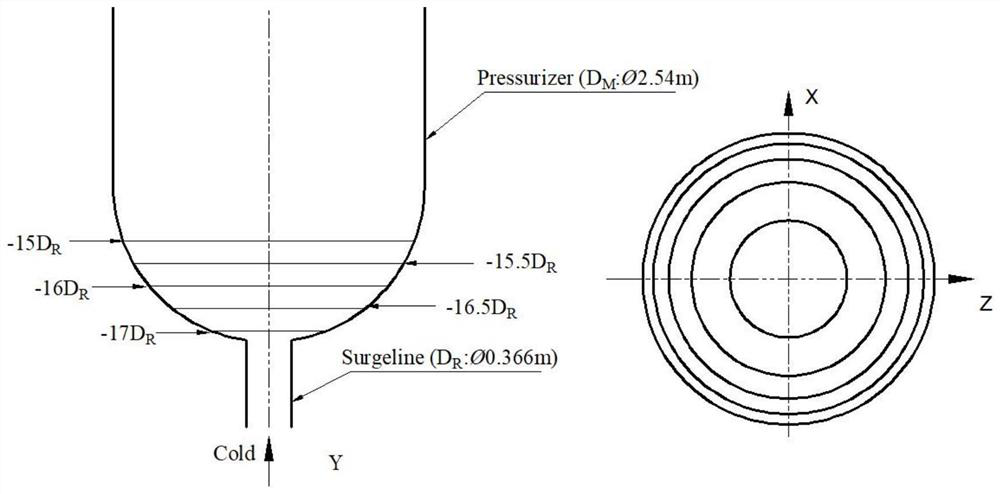
The invention discloses a nuclear power station voltage stabilizer electric heating element arrangement method based on a three-dimensional transient heat transfer mechanism. The method comprises thefollowing steps: firstly, carrying out reasonable three-dimensional modeling and mesh generation on the voltage stabilizer; cFD-based method, an RKE model is combined with a VOF multi-phase flow heattransfer model to carry out numerical simulation on a mixing phenomenon of cold and hot fluids in the voltage stabilizer during positive fluctuation; and finally, carrying out time-mean-square dimensionless and root-mean-square dimensionless processing on a numerical simulation result to represent the average value and fluctuation condition of the speed and the temperature in the mixing process. The accurate range of reasonable arrangement of the electric heating elements in the lower end socket of the voltage stabilizer is obtained by analyzing the fluctuation intensity of the speed and the temperature; according to the method, the flow characteristics and the heat transfer characteristics of the coolant in the wave-in process of the voltage stabilizer are analyzed from the perspective ofnumerical simulation, the accurate range of reasonable arrangement of the electric heating elements in the lower end socket of the voltage stabilizer is obtained, and reference is provided for arrangement optimization of the electric heating elements in actual engineering.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
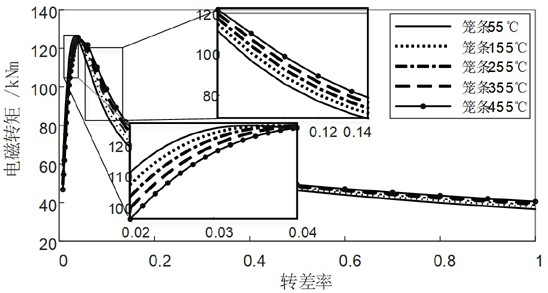
Method for analyzing starting performance of cage type motor
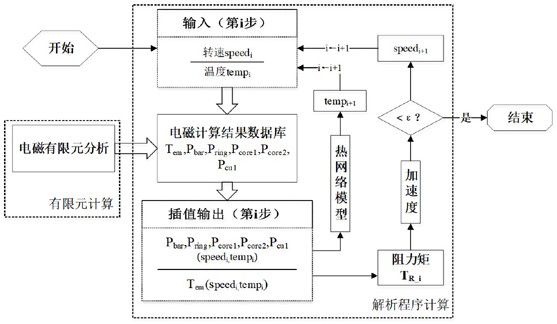
ActiveCN114662365ASave computing resourcesImprove calculation accuracyElectric machinesDesign optimisation/simulationElectric machineryTransient heat transfer
The invention discloses a cage type motor starting performance analysis method, which relates to the field of starting performance calculation, and comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out electromagnetic field finite element modeling and calculation, and establishing a database; s2, carrying out electromagnetic analysis iterative calculation in the starting process; s3, carrying out starting process transient heat transfer calculation; s4, carrying out mechanical calculation in the starting process; s5, performing judgment, if the angular acceleration is calculated and judged to be small enough, ending the calculation if the angular acceleration is small enough, and if the angular acceleration is small enough, performing two-dimensional interpolation from an electromagnetic torque calculation result database by taking the temperature of the next time step obtained in the S3 and the speed of the next time step obtained in the S4 as input, and outputting a result; s7, the steps S3-S6 are repeated until calculation is finished, the problem that pure analytical calculation is poor in reliability is avoided, the problem that the calculation amount is too large due to the fact that a pure transient finite element method is adopted for bidirectional coupling of an electromagnetic field and a temperature field is also avoided, and the method has the outstanding advantages of being high in calculation efficiency and higher in calculation precision.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC MACHINERY
Method for determining transient temperature of air pre-cooled and pre-heated concrete aggregates
ActiveCN105389457ASimplifying Transient Heat Transfer ProblemsSpecial data processing applicationsPorous mediumTransient heat transfer
The invention provides a method for determining the transient temperature of air pre-cooled and pre-heated concrete aggregates. In the process of pre-cooling and pre-heating the aggregates through air, the aggregates are naturally stacked in a storage bin and form a mutual coexistence combination with gaps; therefore, the aggregates in the storage bin and the gaps form a kind of porous medium; a convective heat transfer process of air at the positions of the aggregates in the storage bin and the gaps can be regarded as an unstable-state heat conduction process generated under the action of convective heat transfer at the position of an air inlet section of the porous medium of the aggregates and the gaps; and the unstable-state heat conduction process of the porous medium of the aggregates in the storage bin and the gaps is equivalent to the unstable-state heat conduction process of a three-dimensional cube under the third boundary condition. Because four sides of the storage bin are insulated and only the air inlet section is in the heat transfer process under the third boundary condition, the transient temperature solution of the storage bin, namely the three-dimensional cylinder, can be simplified to the transient heat transfer problem of a one-dimensional infinite plate.
Owner:POWERCHINA XIBEI ENG
Generative design method for special-shaped fuel structure of fast neutron reactor core
PendingCN114662375AAvoid distortionAvoid partitioning processGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAdaptive mesh refinementNuclear engineering
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com